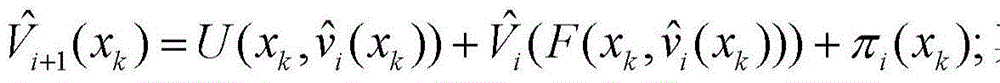Patents
Literature
238 results about "Approximation error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The approximation error in some data is the discrepancy between an exact value and some approximation to it. An approximation error can occur because...
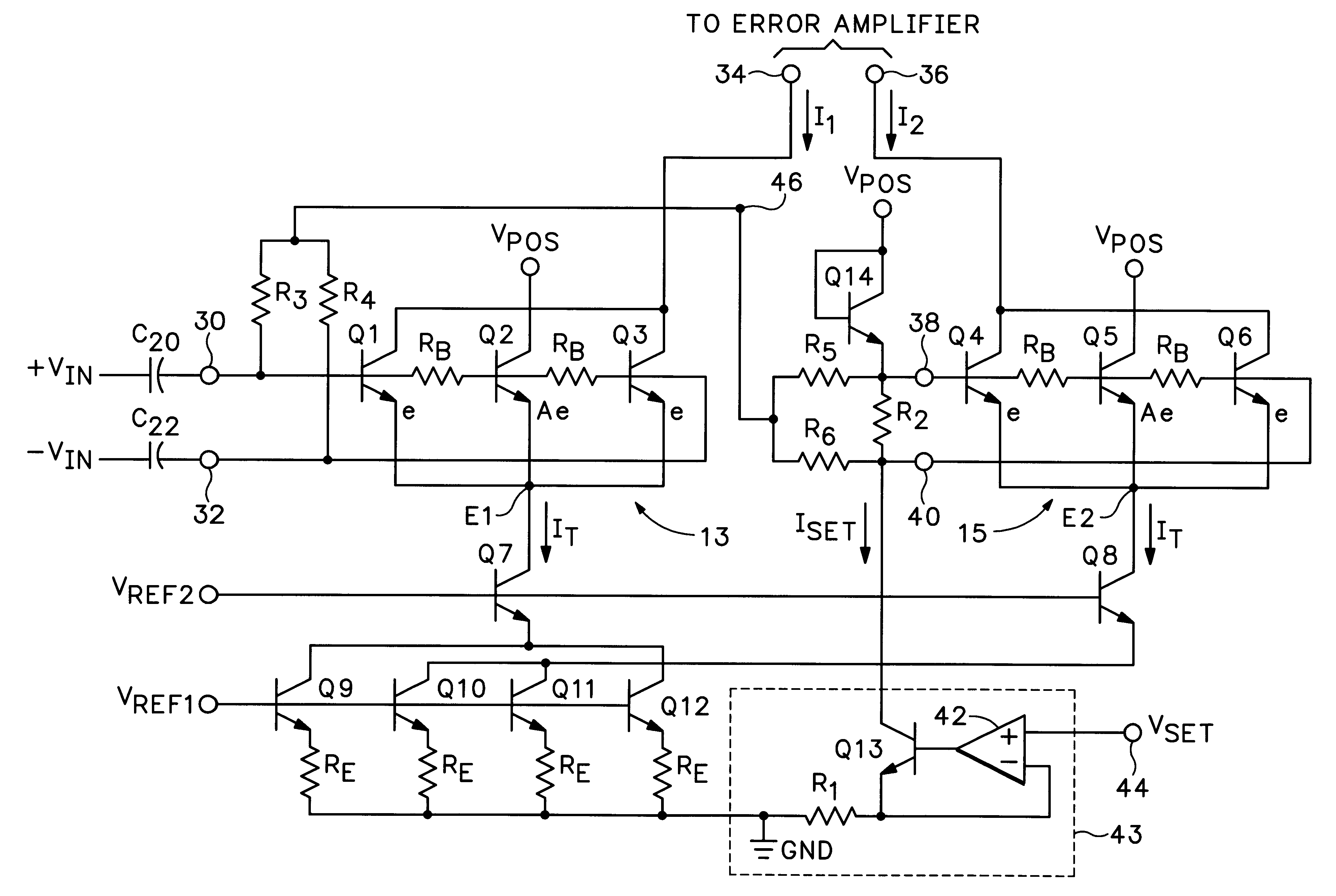
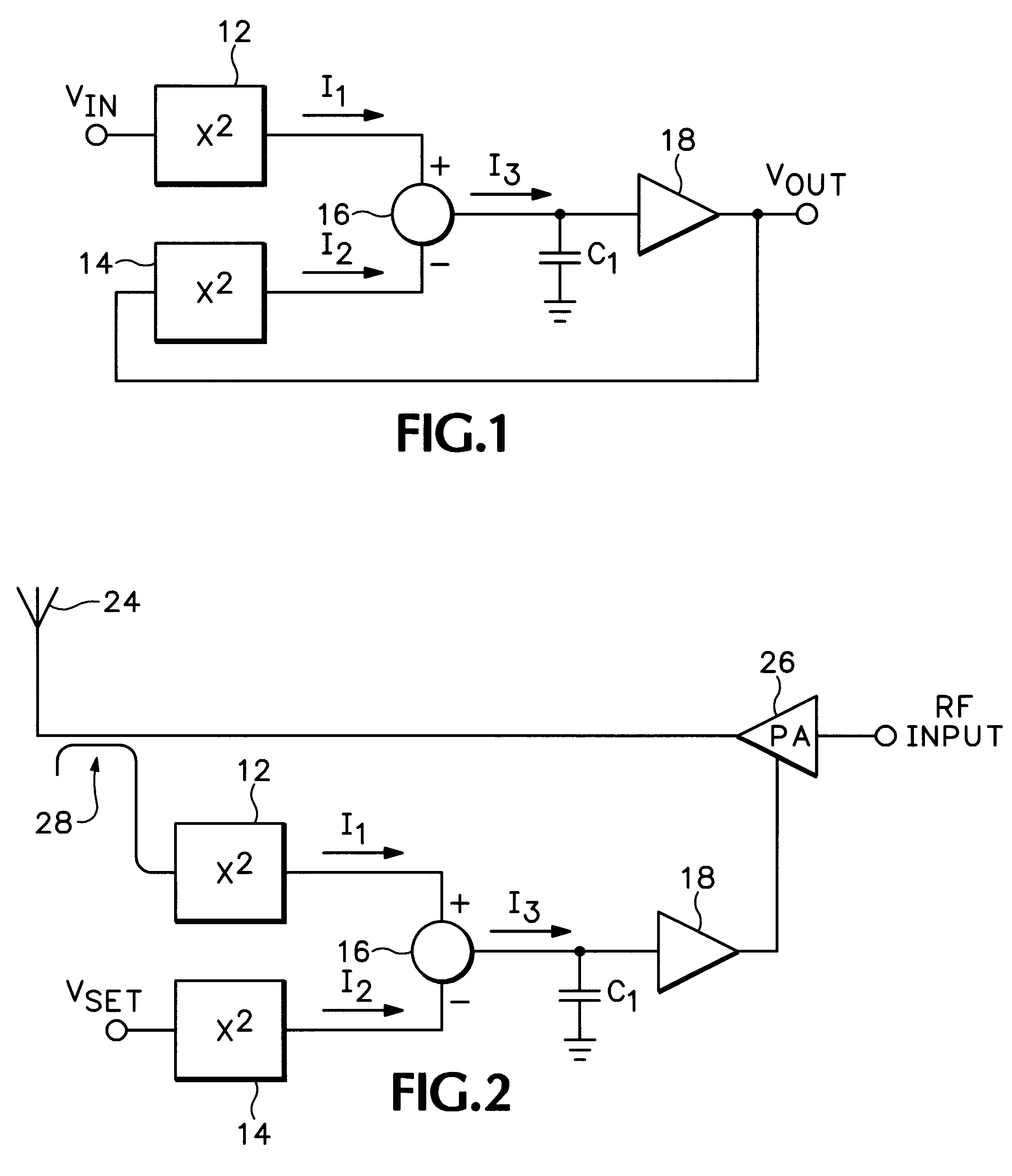
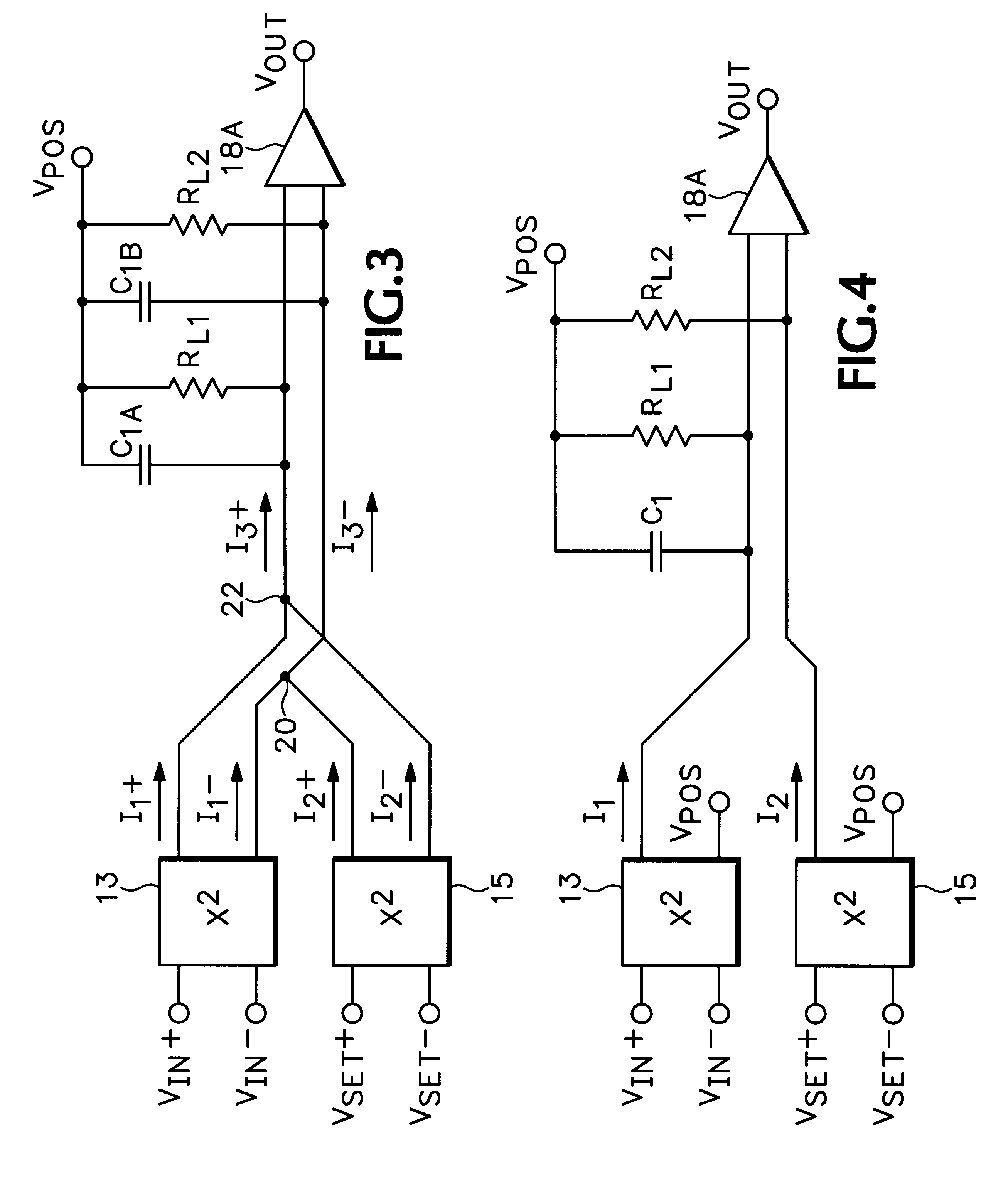
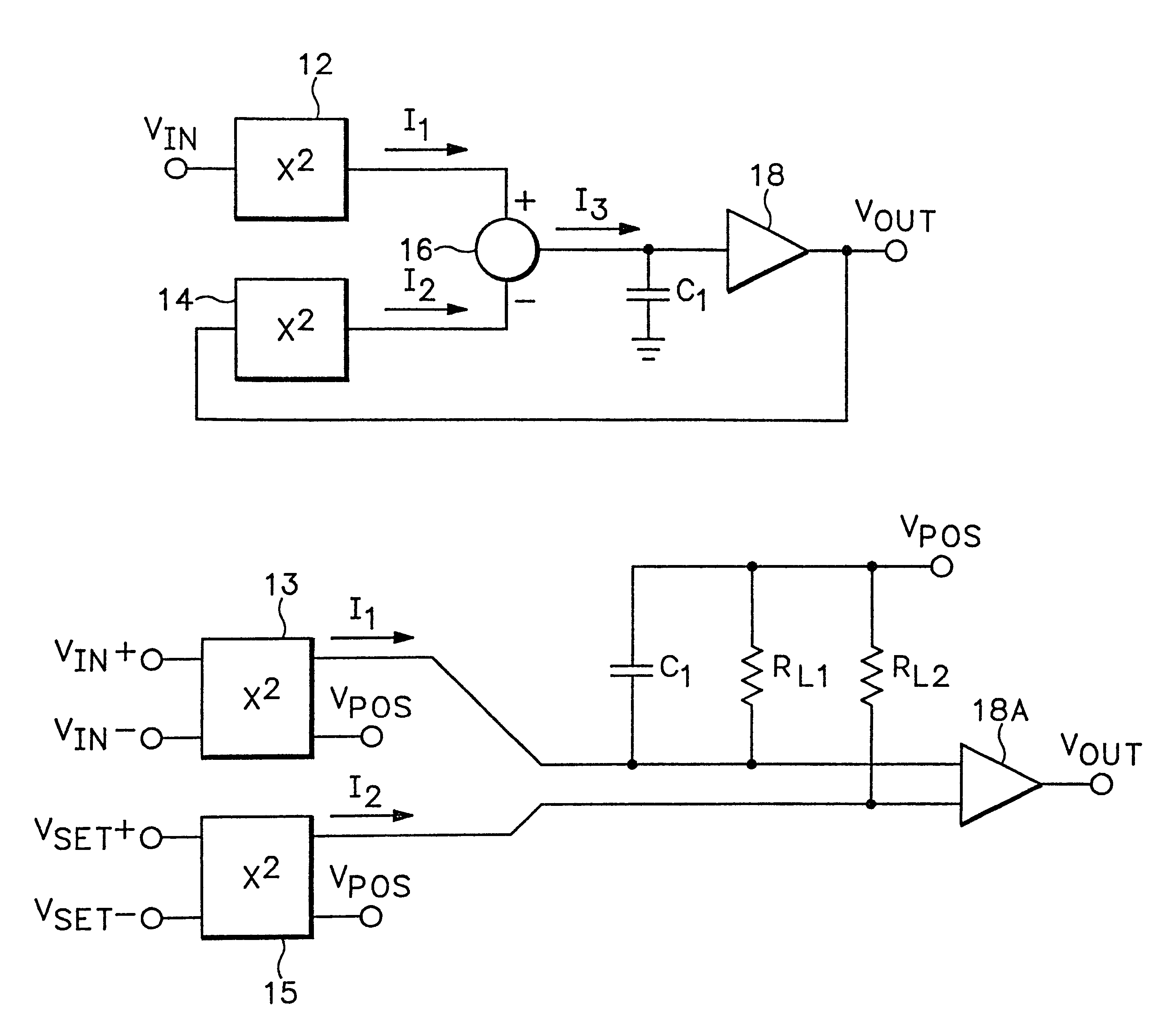
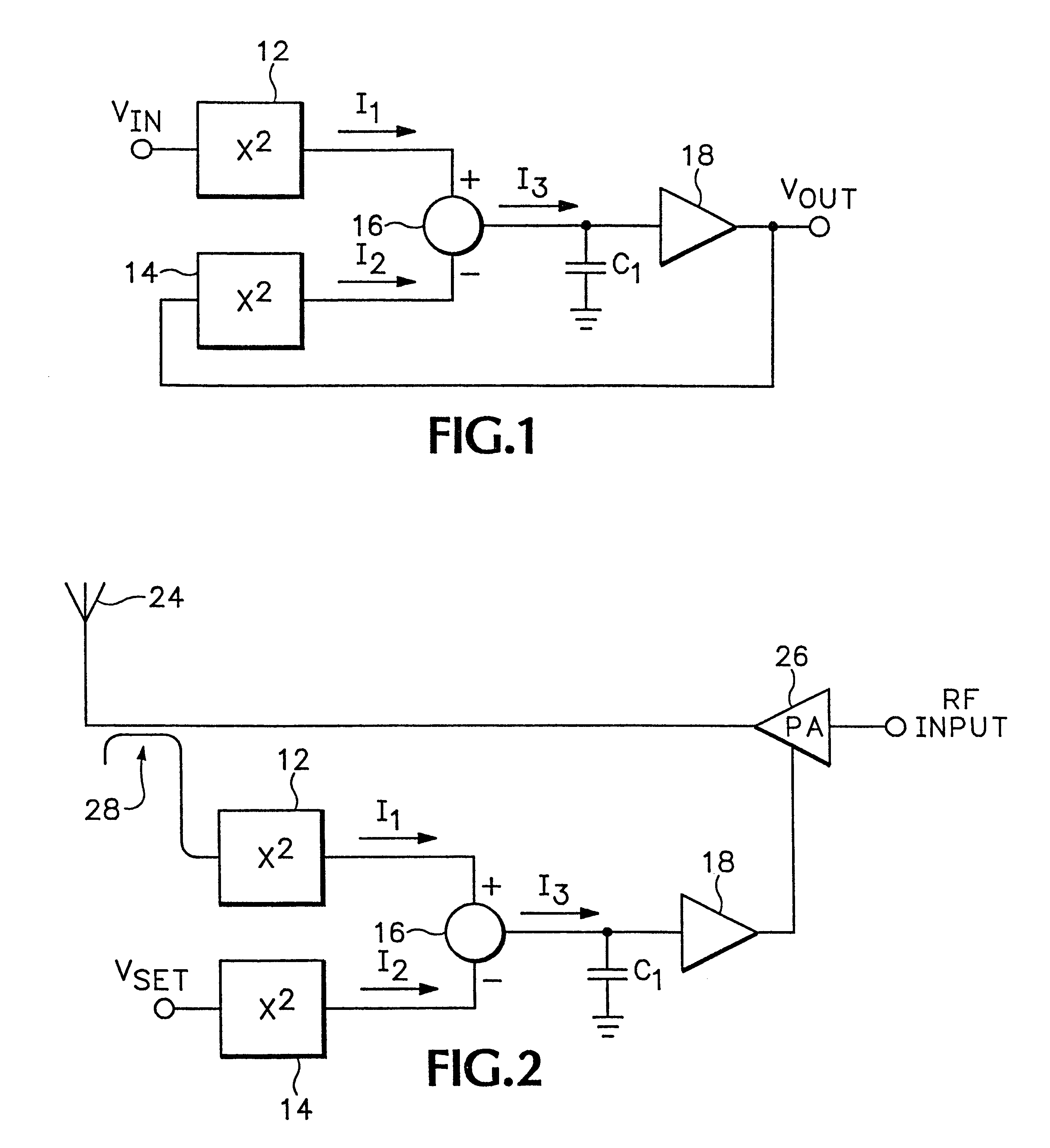
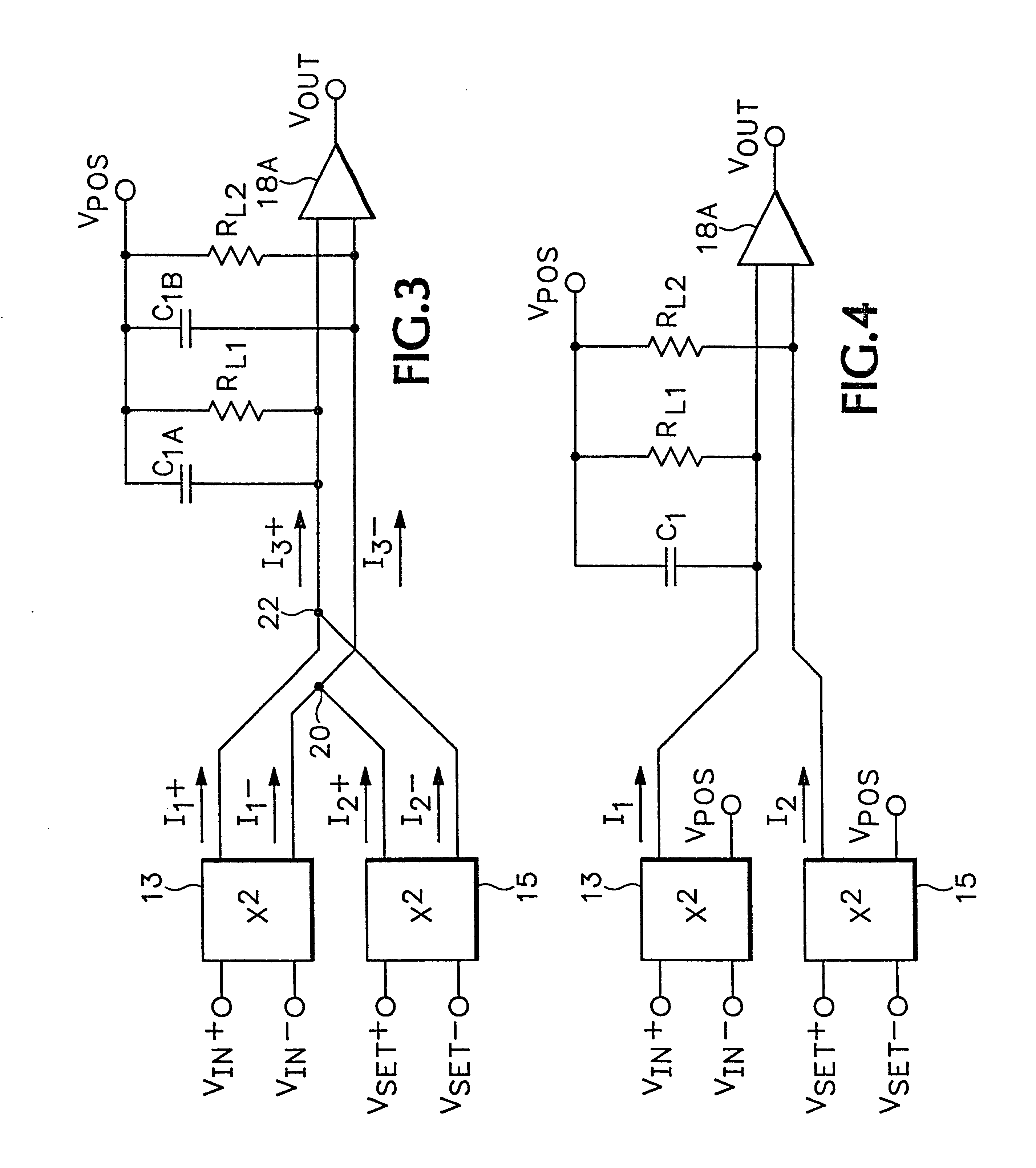
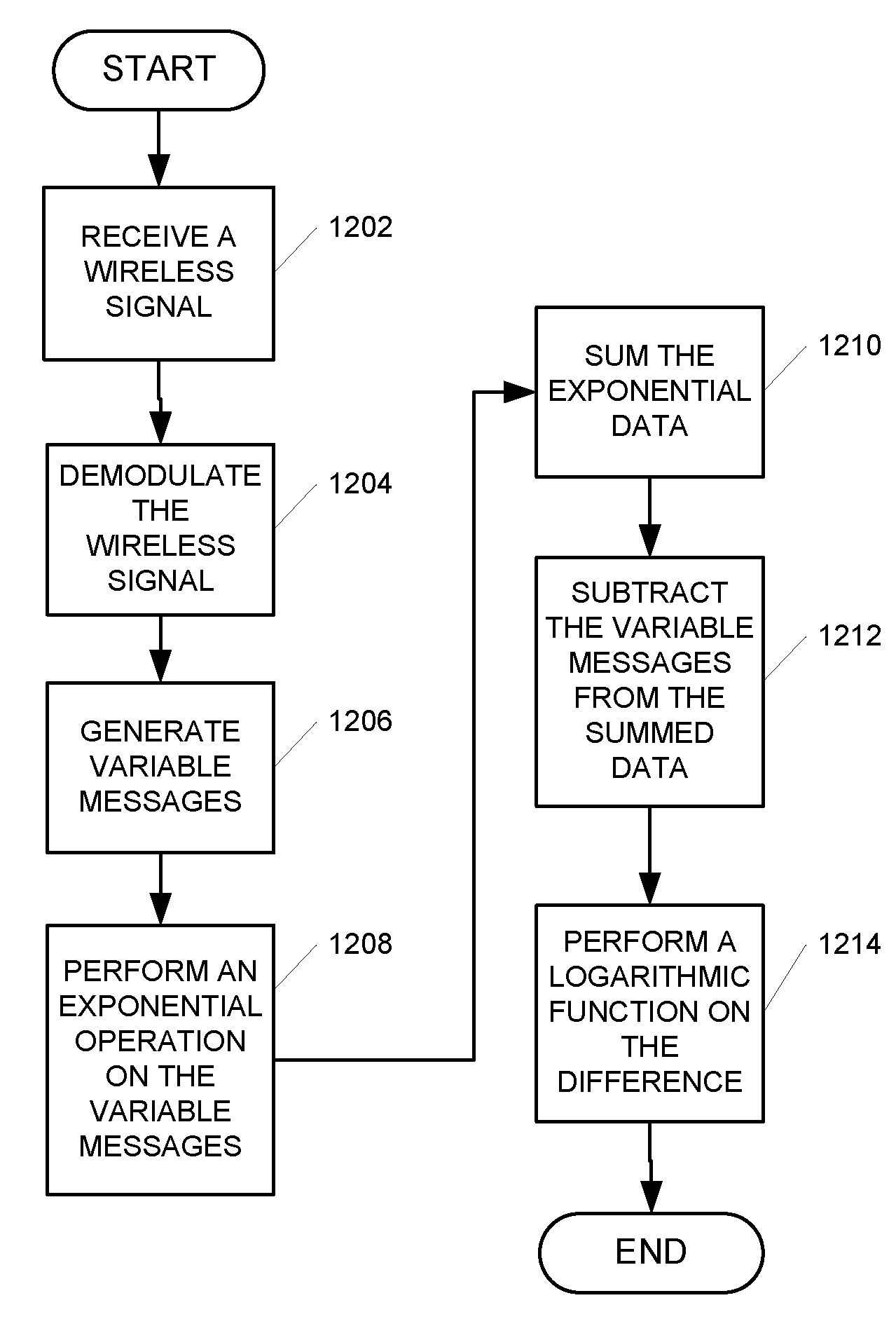
RMS-to-DC converter with balanced multi-tanh triplet squaring cells
InactiveUS6204719B1Accurate square law approximationImprove balanceComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsDigital data processing detailsTransconductanceSet point
An RMS-to-DC converter implements the difference-of-squares function by utilizing two identical squaring cells operating in opposition to generate two signals. An error amplifier nulls the difference between the signals. When used in a measurement mode, one of the squaring cells receives the signal to be measured, and the output of the error amplifier, which provides a measure of the RMS value of the input signal, is connected to the input of the second squaring cell, thereby closing the feedback loop around the second squaring cell. When used in a control mode, a set-point signal is applied to the second squaring cell, and the output of the error amplifier is used to control a variable-gain device such as a power amplifier which provides the input to the first squaring cell, thereby closing the feedback loop around the first squaring cell. Accurate square law approximation at microwave frequencies can be achieved by implementing the squaring cells as series-connected three-transistor multi-tanh transconductance cells. By using carefully balanced squaring cells and a well-balanced error amplifier, approximation errors are cancelled and accurate RMS measurement is realized at high frequencies. A feedforward bootstrapping feature uses an op amp to balance the voltages at the common nodes of the transconductance squaring cells and also provides a balanced differential input drive to one of the squaring cells. A base current compensation circuit for providing accurate base compensation current to both of the squaring cells prevents errors due to DC offset voltages.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
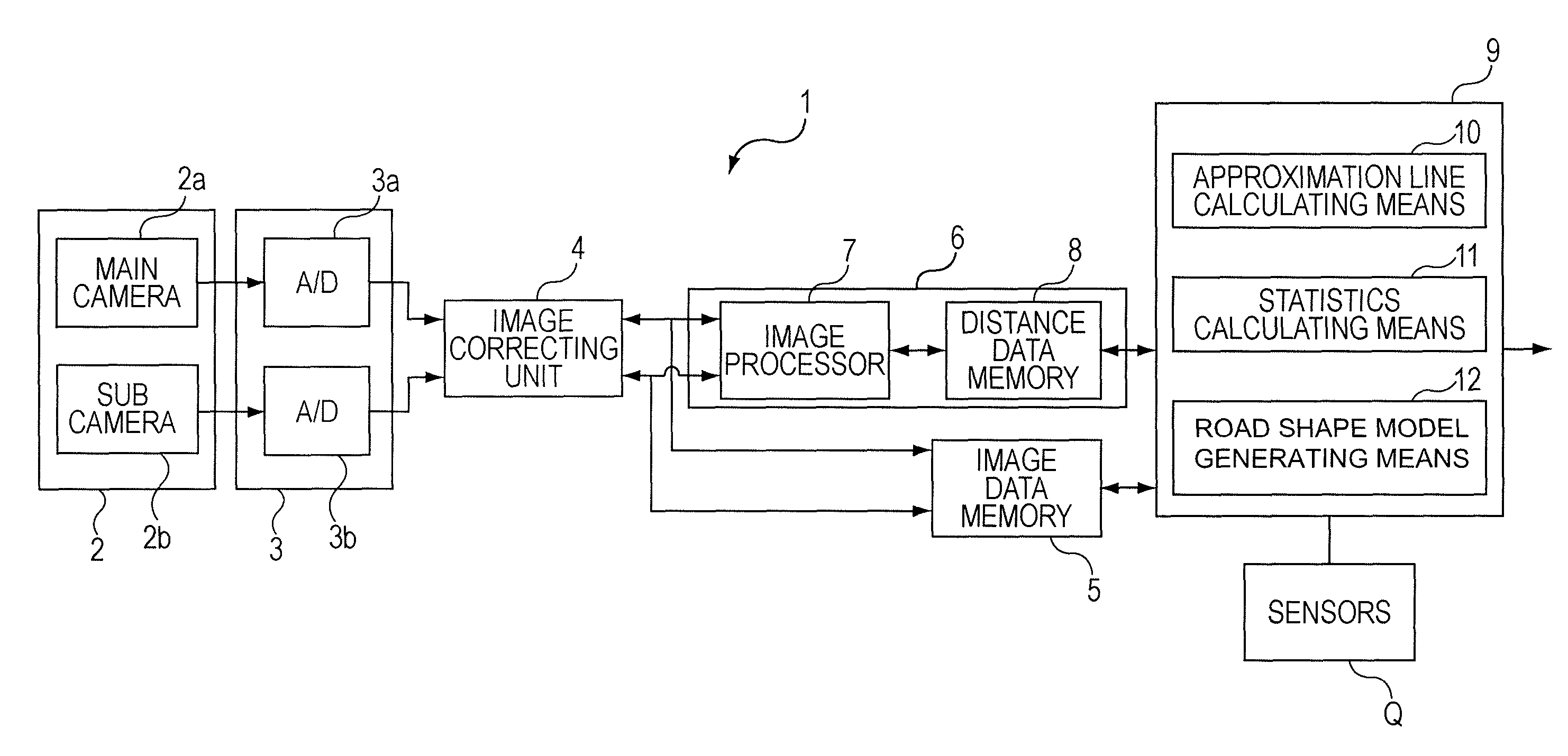
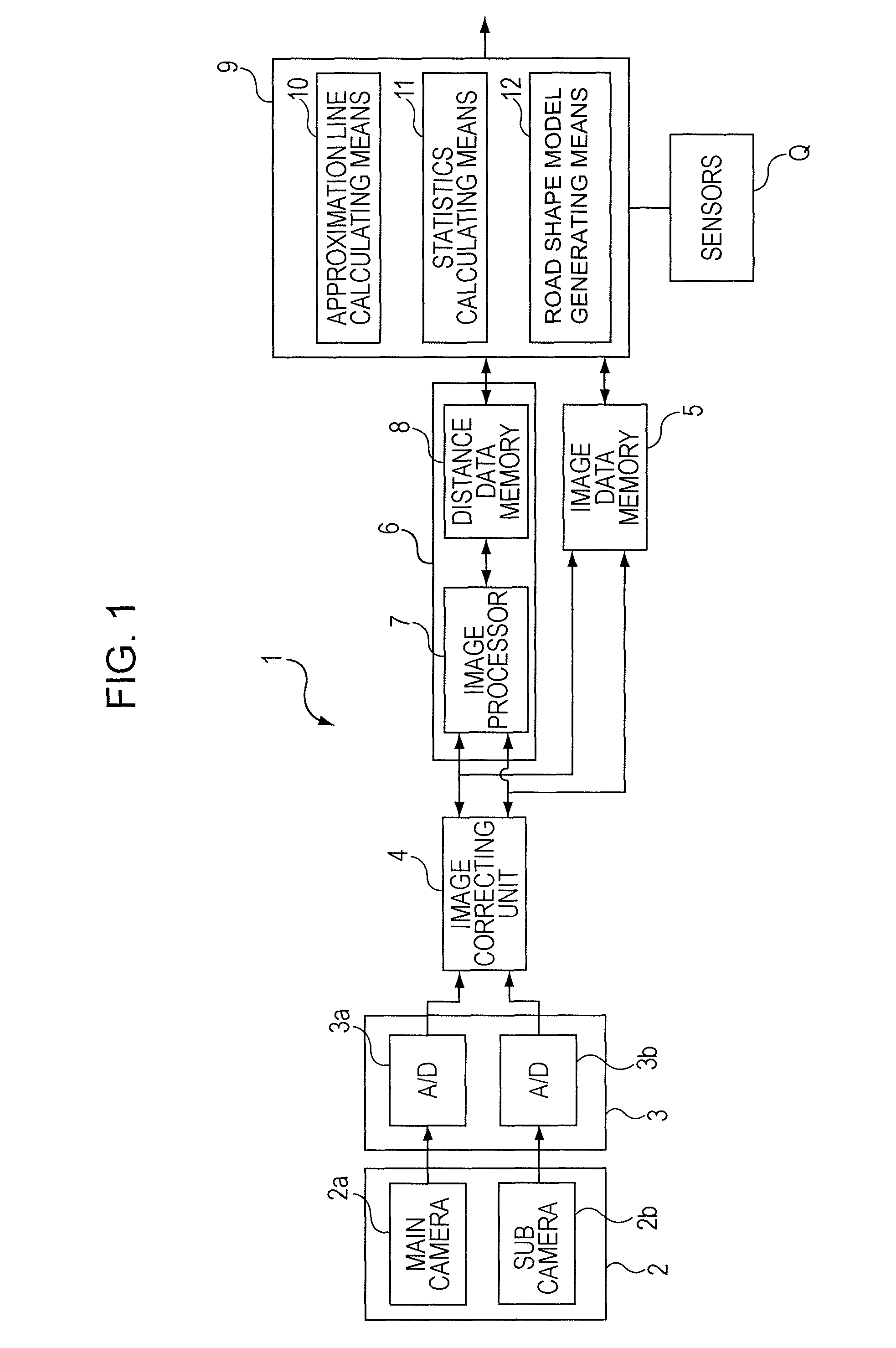
Road shape recognition device
ActiveUS20100299109A1Way accurateGenerate accuratelyControlling traffic signalsImage enhancementAlgorithmIdentification device
A road shape recognition device includes: distance and height detecting means for detecting distance data having a distance and height in real space regarding a road surface where a vehicle is traveling at multiple mutually different points; approximation line calculating means for dividing the plurality of distance data into near and far groups as viewed from the vehicle to calculate an approximation line of the distance data for each group each time the distance data of the boundary portion between the two groups is transferred from one of the groups to the other; statistics calculating means for calculating statistics from the corresponding approximation line for each group where the distance data is transferred; and road shape model generating means for selecting one out of combinations of the approximation lines to generate a road shape model using the selected combination.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
RMS-to-DC converter with balanced multi-tanh triplet squaring cells
InactiveUS6549057B1Accurate square law approximationImprove balanceComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringTransconductance
An RMS-to-DC converter implements the difference-of-squares function by utilizing two identical squaring cells operating in opposition to generate two signals. An error amplifier nulls the difference between the signals. When used in a measurement mode, one of the squaring cells receives the signal to be measured, and the output of the error amplifier, which provides a measure of the RMS value of the input signal, is connected to the input of the second squaring cell, thereby closing the feedback loop around the second squaring cell. When used in a control mode, a set-point signal is applied to the second squaring cell, and the output of the error amplifier is used to control a variable-gain device such as a power amplifier which provides the input to the first squaring cell, thereby closing the feedback loop around the first squaring cell. Accurate square law approximation at microwave frequencies can be achieved by implementing the squaring cells as series-connected three-transistor multi-tanh transconductance cells. By using carefully balanced squaring cells and a well-balanced error amplifier, approximation errors are cancelled and accurate RMS measurement is realized at high frequencies. A feedforward bootstrapping feature uses an op amp to balance the voltages at the common nodes of the transconductance squaring cells and also provides a balanced differential input drive to one of the squaring cells. A base current compensation circuit for providing accurate base compensation current to both of the squaring cells prevents errors due to DC offset voltages.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
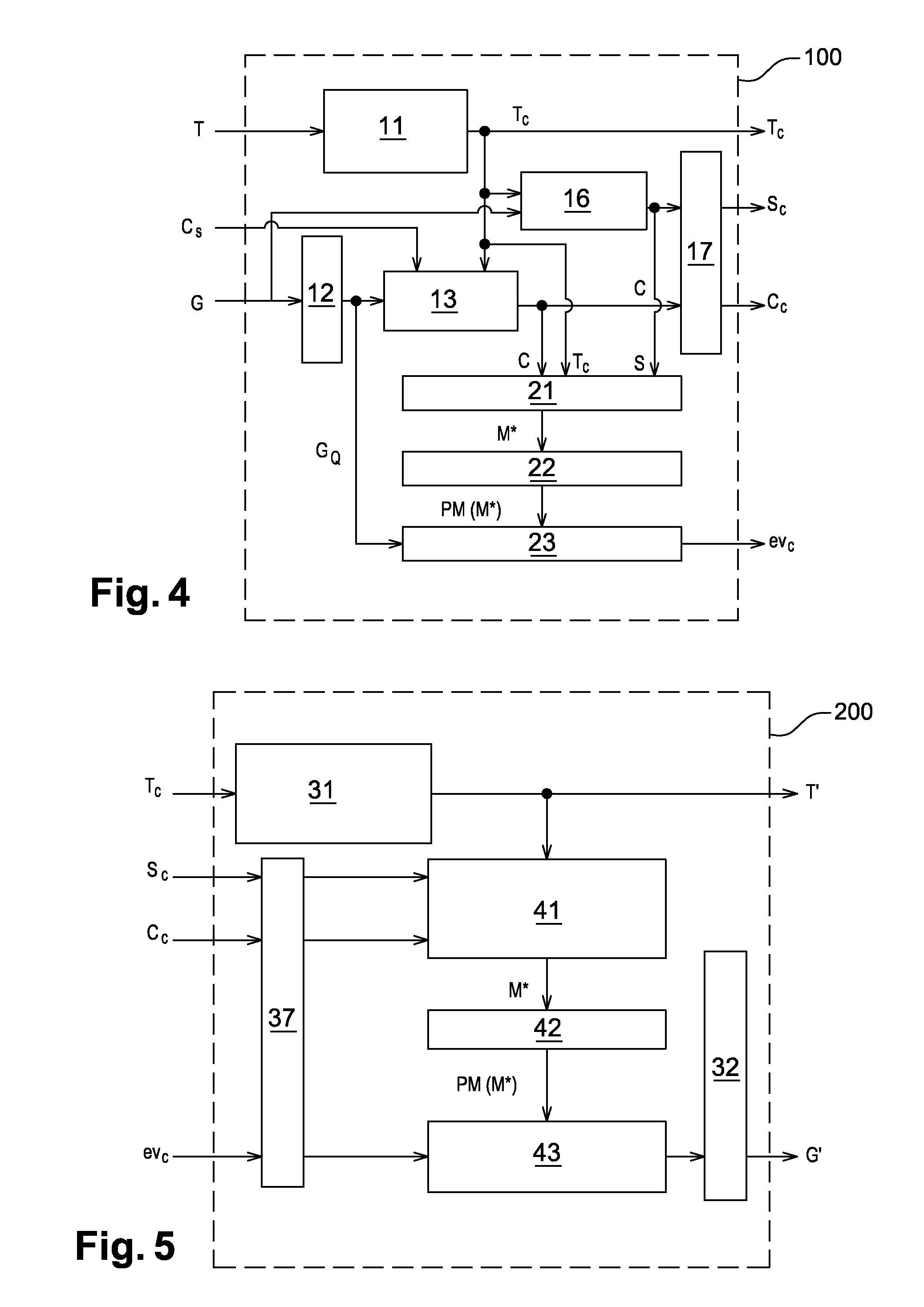
Method for compressing/decompressing a three-dimensional mesh
ActiveUS9064311B2Lower the volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingAlgorithmLevel of detail
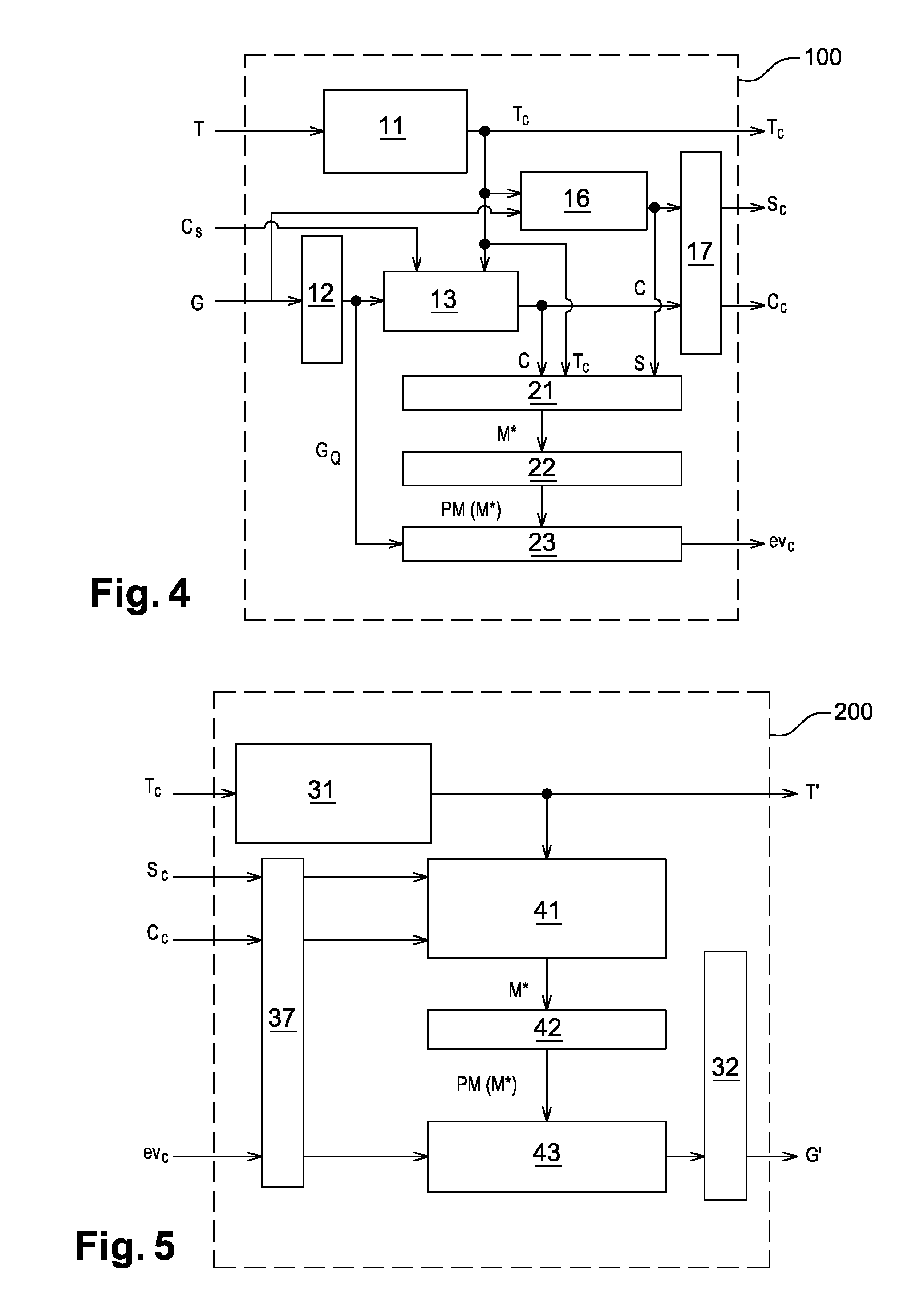
The method for encoding / decoding three-dimensional meshes of dots or vertices connected in the form of facets delimited by edges; the mesh M is defined by connectivity data T and geometry data G includes the steps of:lossless encoding of the connectivity data T into encoded connectivity data Tc,iteratively generating a progressive mesh hierarchy, i.e. a set of meshes with progressive levels of detail, PM(M*),generating a piecewise smooth approximation M* of the original mesh M, from the mesh connectivity T; this smooth approximation M* being described as follows:a. compressed connectivity data Tc;b. a small number N of control dots andc. a number of indexes S of edges called protruding edges of the mesh M, identified beforehand,using the progressive mesh hierarchy PM(M*) to calculate a prediction of approximation errors in M* compared with the original mesh M.
Owner:FITTINGBOX
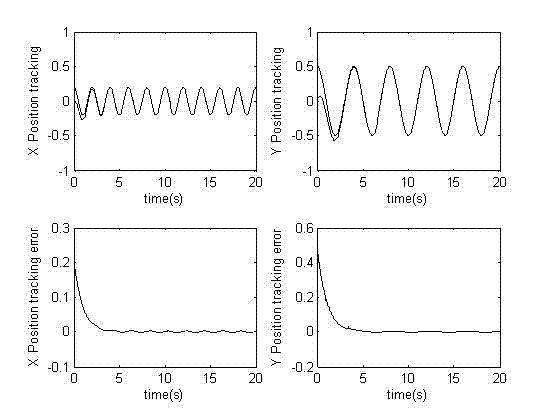
Distributed adaptive-neural-network continuous tracking control method of multi-robot system
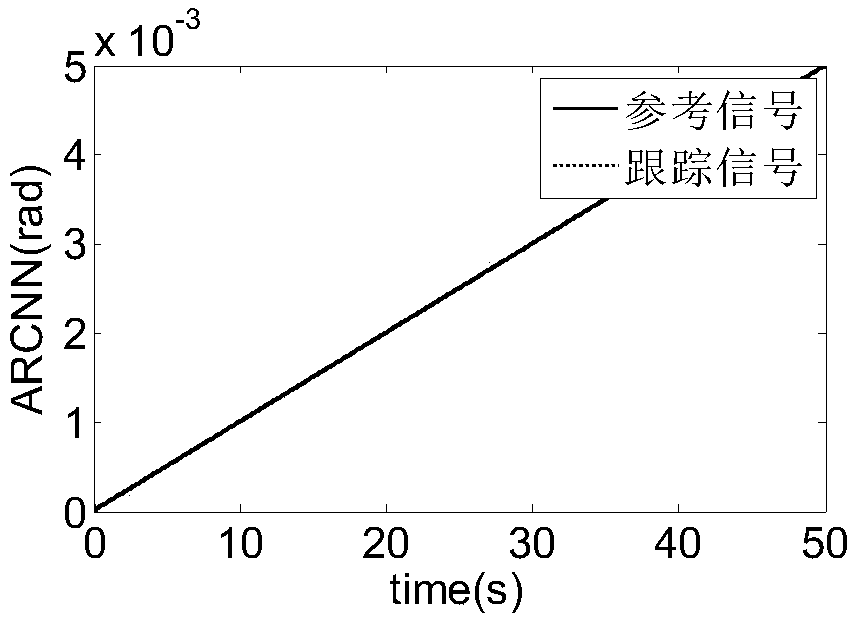
ActiveCN104865829AObservation error is boundedImprove robustnessAdaptive controlRobotic systemsMultirobot systems
The invention, which belongs to the robot system control field, relates to a distributed adaptive-neural-network continuous tracking control method of a multi-robot system. According to the existing coordinated tracking and controlling method of the multi-robot system, problems of parameter uncertainty and external interference existence in the multi-robot system exist. The provided method comprises: under the circumstances that only parts of followers can obtain dynamic navigator state information, a distributed observer design is implemented with limitation of communication tine delay existence, so that all followers can obtain the dynamic navigator state information; and with consideration of the parameter uncertainty and external interference existence in the system, controlling is carried out by using a distributed adaptive tracking control expression designed based on two neural networks, so that the approximate error is close to zero. In addition, the control algorithm of the distributed adaptive tracking control expression is in a continuous control mode, no buffet is caused at the system and the great practical application value is created. Besides, validity of the control algorithm is verified by the simulation experiment.
Owner:成都川哈工机器人及智能装备产业技术研究院有限公司
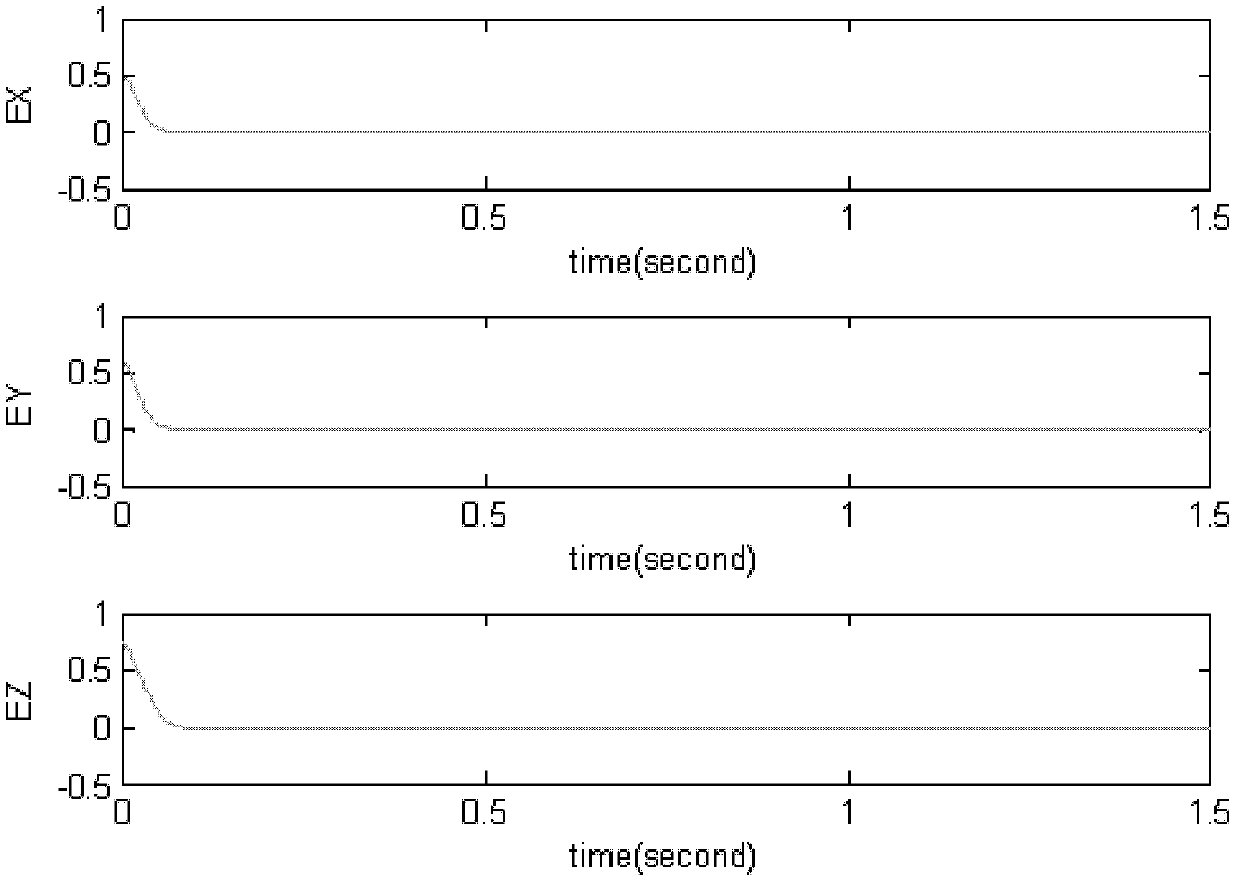
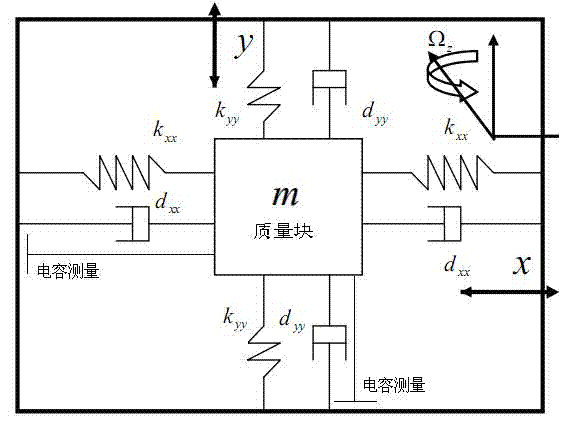
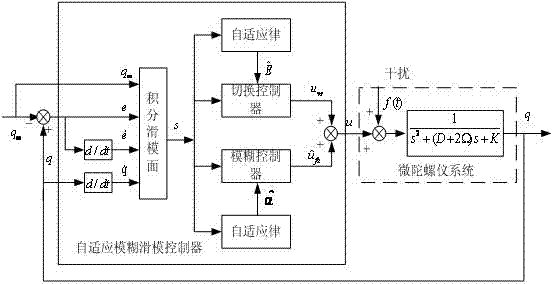
Micro-gyroscope tracking control method based on adaptive fuzzy sliding mode
The invention discloses a micro-gyroscope tracking control method based on an adaptive fuzzy sliding mode. The method comprises the following steps of: designing a control law according to the linear feedback technology and a micro-gyroscope dynamic equation; adding the sliding mode control to the control law based on the method to obtain a sliding mode control law; approaching to a practical system with a fuzzy system to obtain a fuzzy sliding mode control law; and determining an adaptive law of parameters based on the method. As the fuzzy approaching error is greater than or equal to the least approaching error, a parameter in the control law is selected as the absolute value of the approaching error plus a constant greater than 0, thus the unconditional stability of the system is ensured, the system response is accelerated and the system buffeting is reduced. Through the invention, the problems that the control accuracy of a traditional micro-gyroscope control system is relatively low due to the influence of environment change as the parameter variation is not considered and the like are solved, the micro-gyroscope can be effectively and reliably controlled in the case of uncertain parameters caused by the manufacturing error or unknown and existing environmental interference, and the overall stability of the system is ensured.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
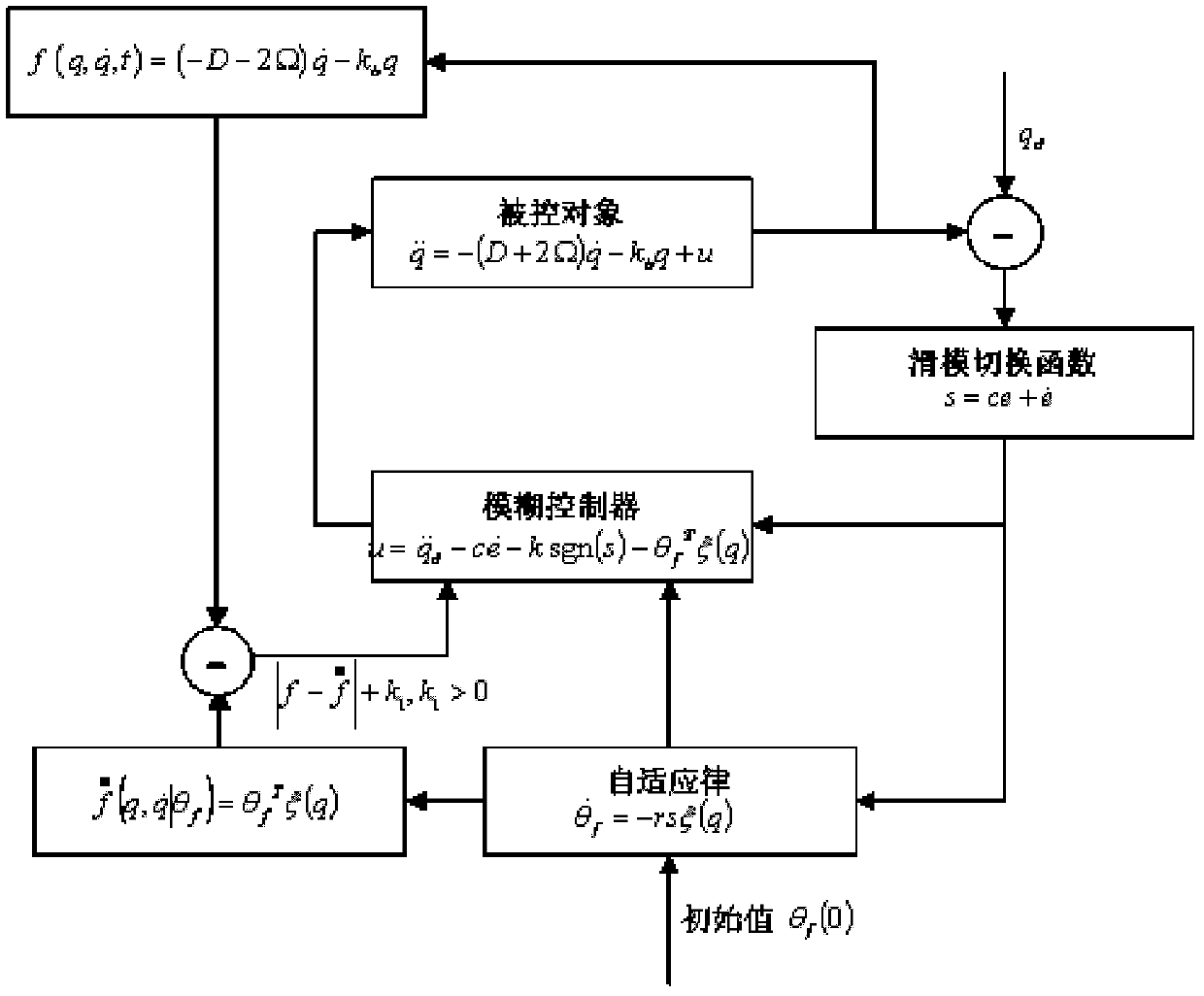
Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller for micro gyroscope
InactiveCN102508434AGuaranteed global asymptotic stabilityCompensate for manufacturing errorsAdaptive controlReference modelGyroscope
The invention discloses an adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller for a micro gyroscope, which is characterized by comprising an adaptive fuzzy control system based on a reference module, and a switching control system. In the adaptive fuzzy control system, a sliding mode surface is used as the input of the fuzzy controller, and the weight is automatically adjusted by a dynamic adaptive law so as to realize fuzzy approximation to an equivalent control law. The adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller for the micro gyroscope of the invention has the following benefits that: when the system is in a steady state, the dynamic performance of the micro gyroscope is an ideal mode, and the manufacturing error and the environment interference are compensated; an adaptive algorithm designed based on a Lyapunov method can ensure the global asymptotic stability of the whole closed-loop system; and with adaptive adjustment on the upper bound of the approximation error, buffeting is reduced obviously.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
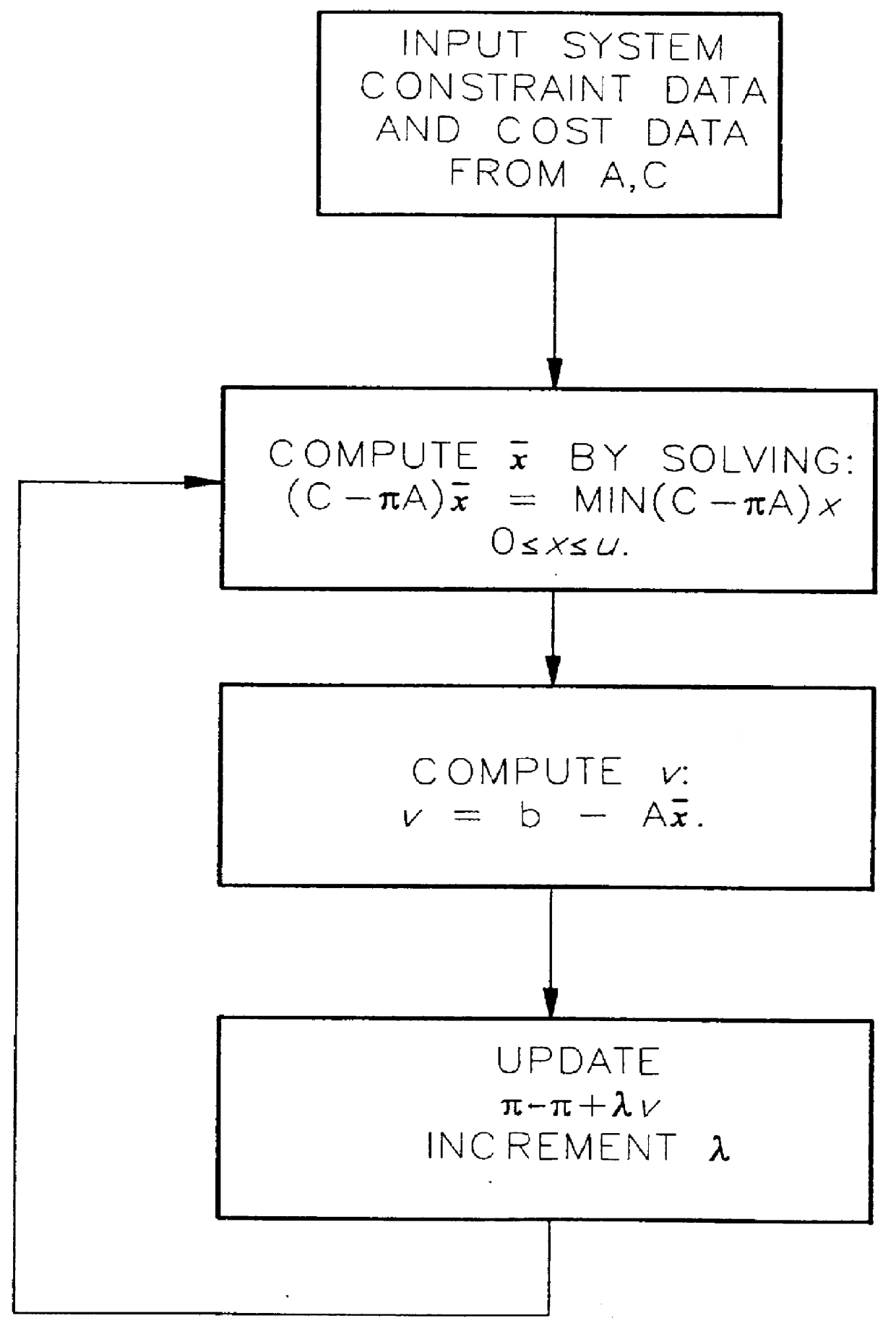
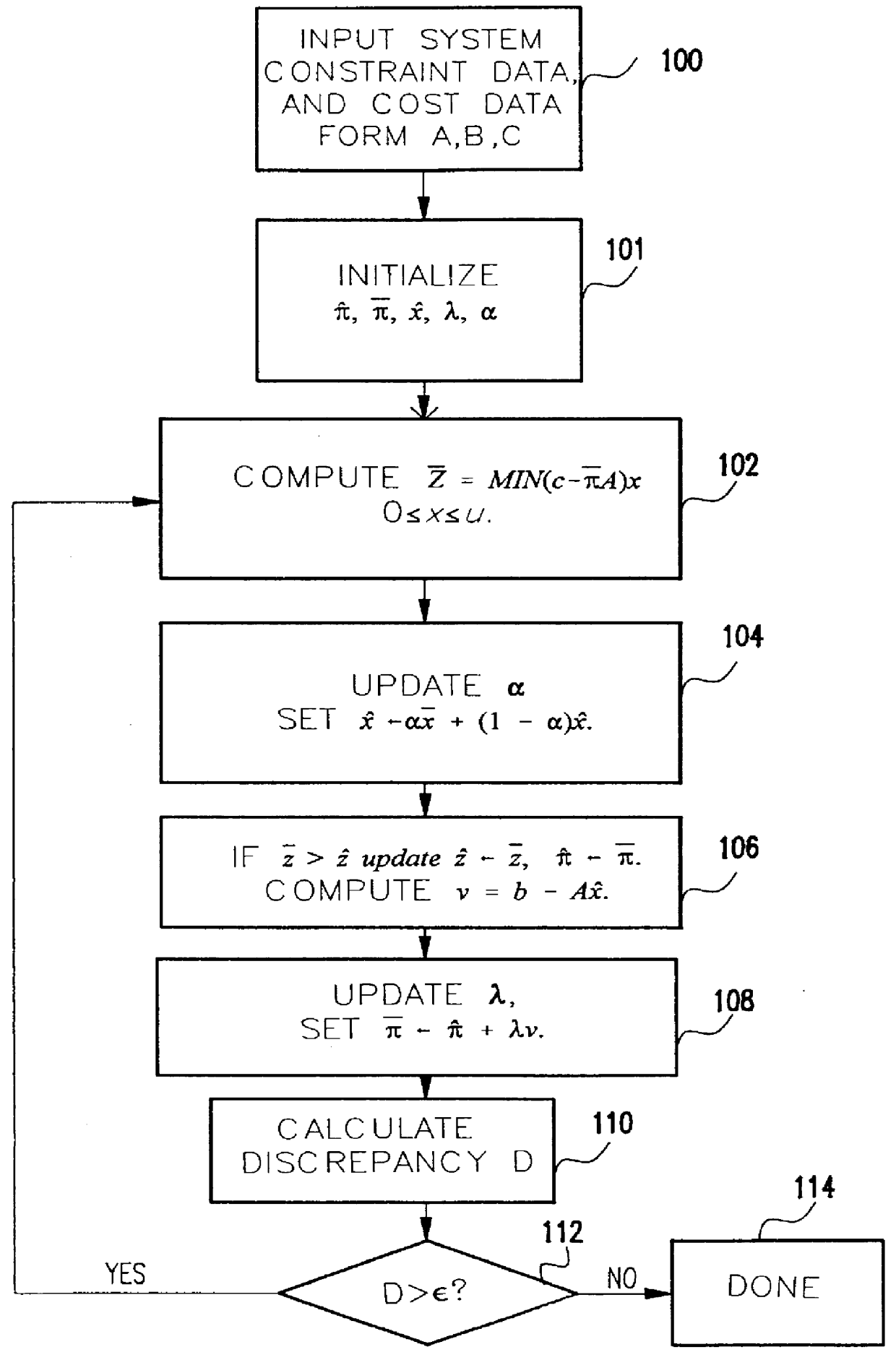
Approximation method for efficient resource allocation
InactiveUS6035277AComputationally efficientComputationally fastResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmOptimal control
A method for finding fast approximations to an optimal operational state of a physical system, using an iterative procedure for converging to a solution of a Linear Program and yielding, in addition to a lower bound for an optimal cost and an approximation to the dual variables, a value representing an optimal allocation of system resources.
Owner:IBM CORP
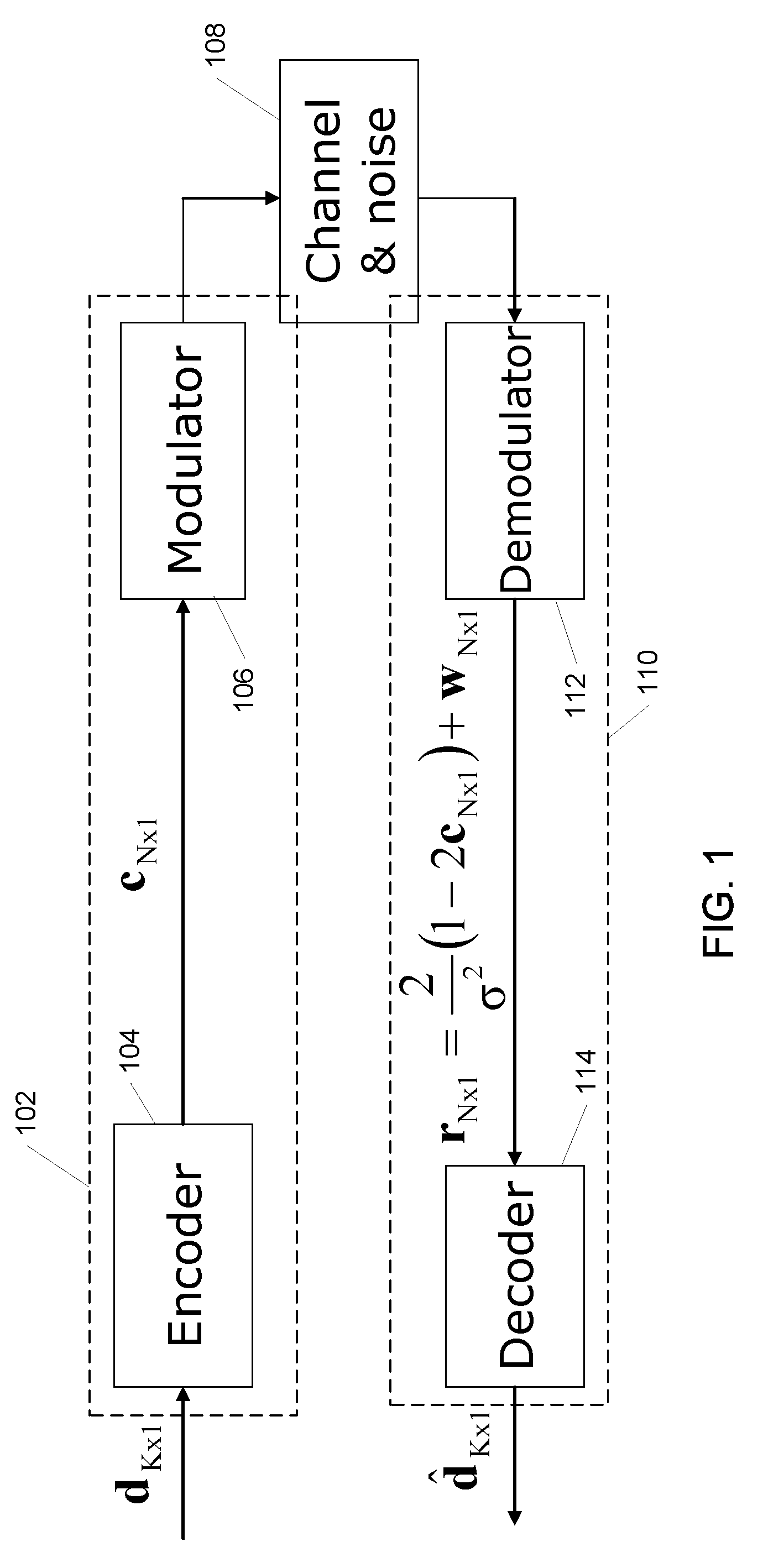
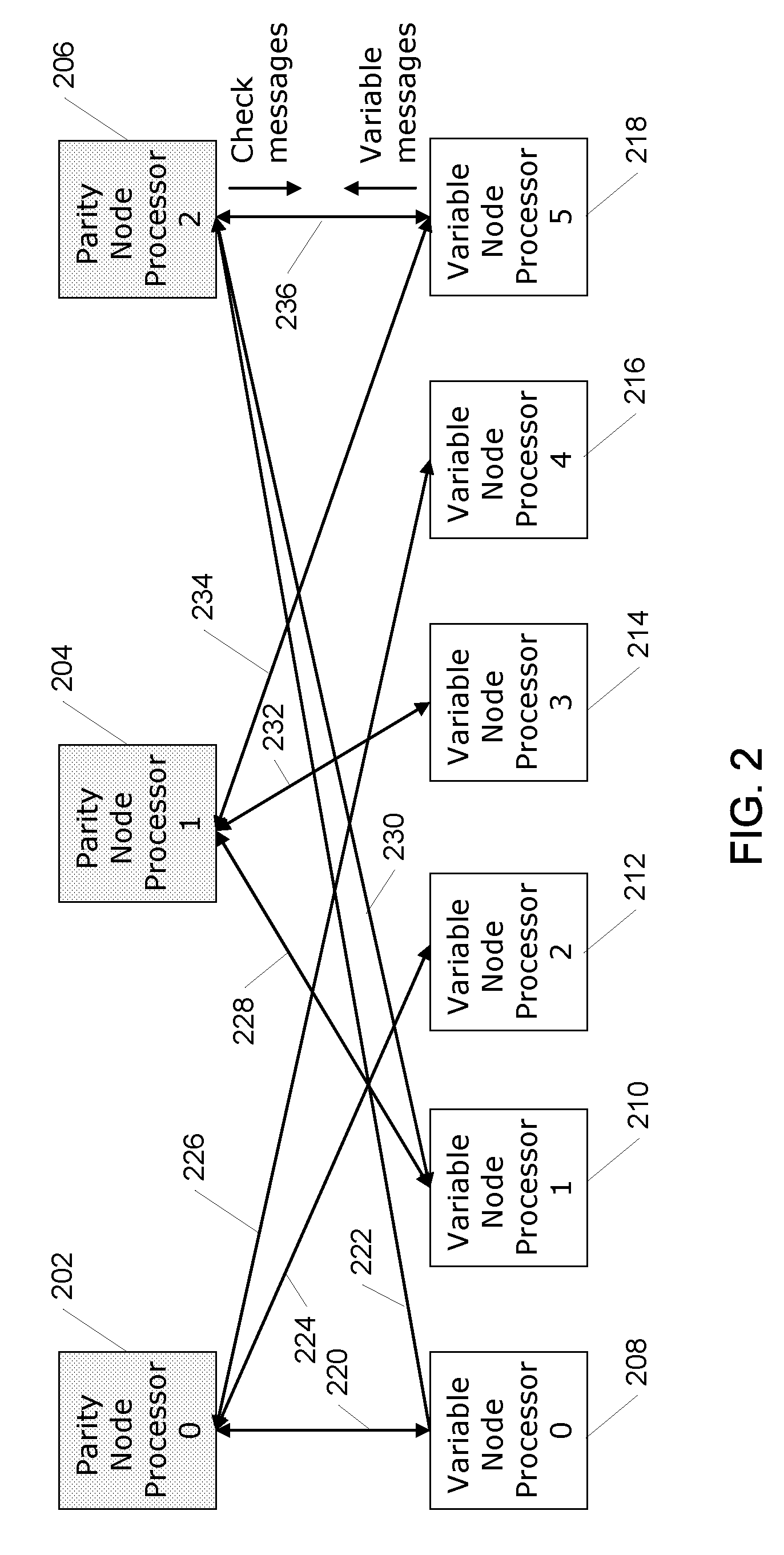
Systems and methods for reduced complexity LDPC decoding
InactiveUS7895500B2Reduce complexityReduce approximation errorCode conversionCoding detailsRound complexityLow density
Systems and methods for generating check node updates in the decoding of low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes use new approximations in order to reduce the complexity of implementing a LDPC decoder, while maintaining accuracy. The new approximations approximate the standard sum-product algorithm (SPA), and can reduce the approximation error of min-sum algorithm (MSA) and have almost the same performance as sum-product algorithm (SPA) under both floating precision operation and fixed-point operation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
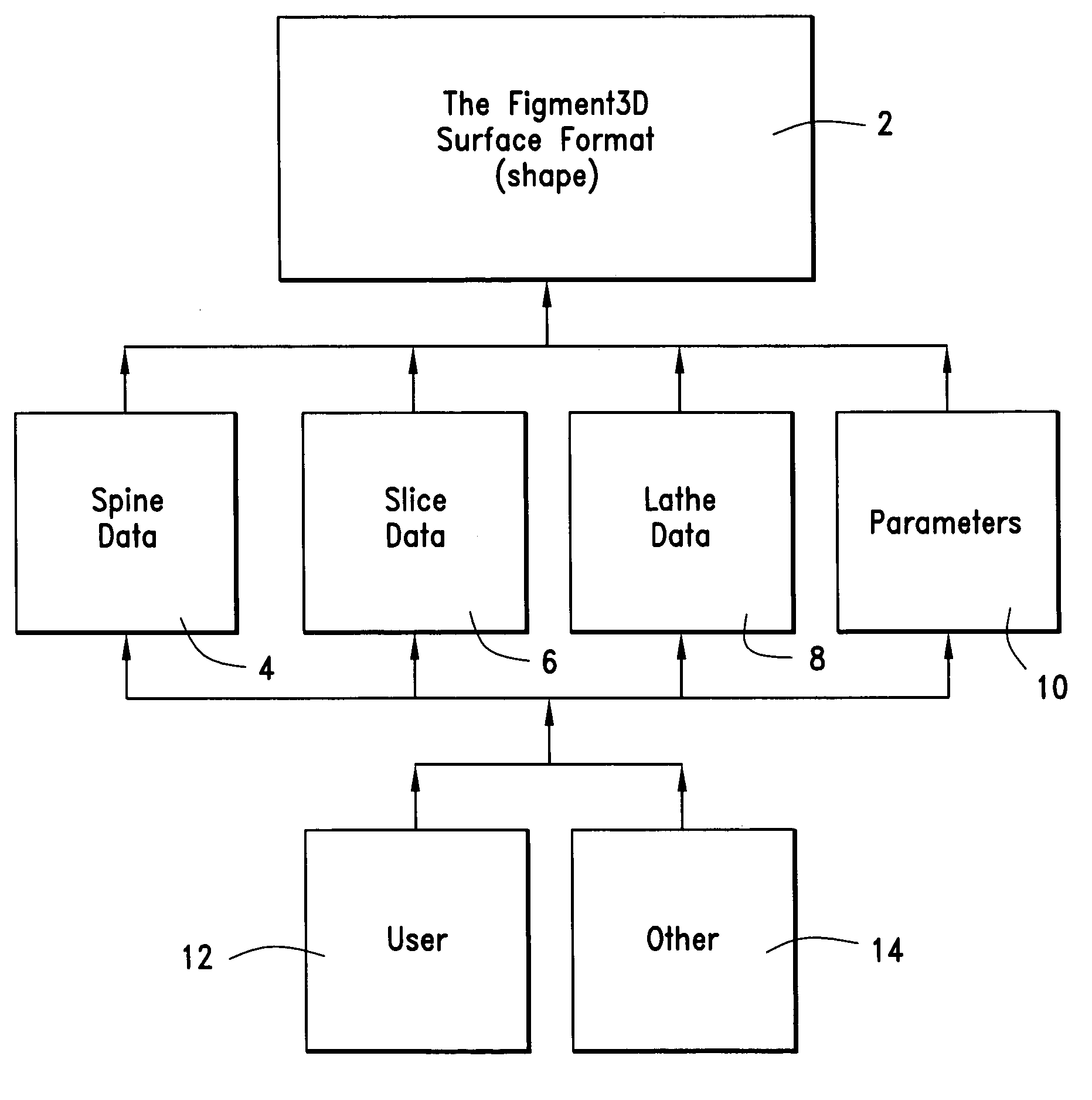
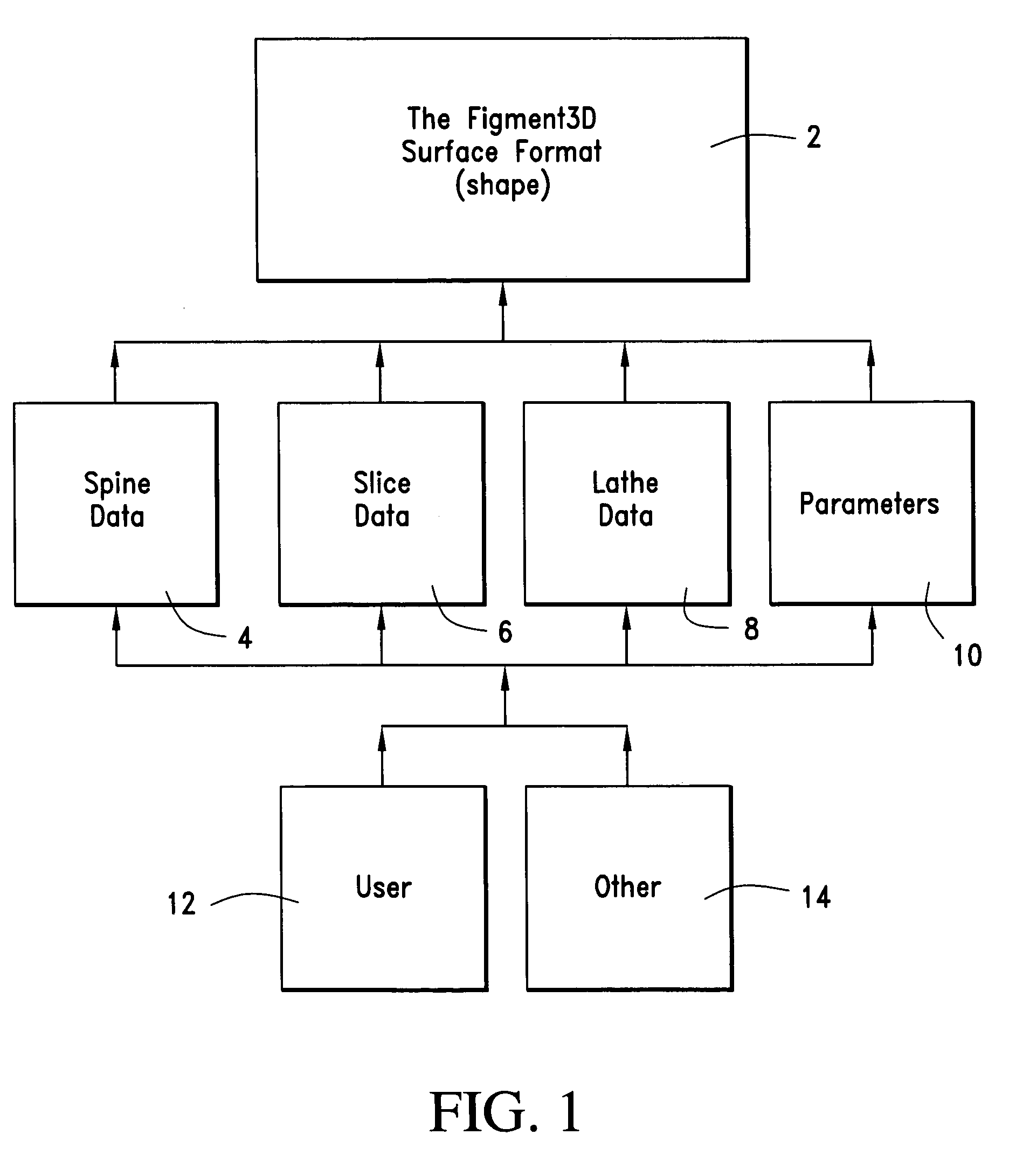
Apparatus and method for generating 3D images
InactiveUS7173622B1Method is fastAccurate assessmentDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsTerrainBrick
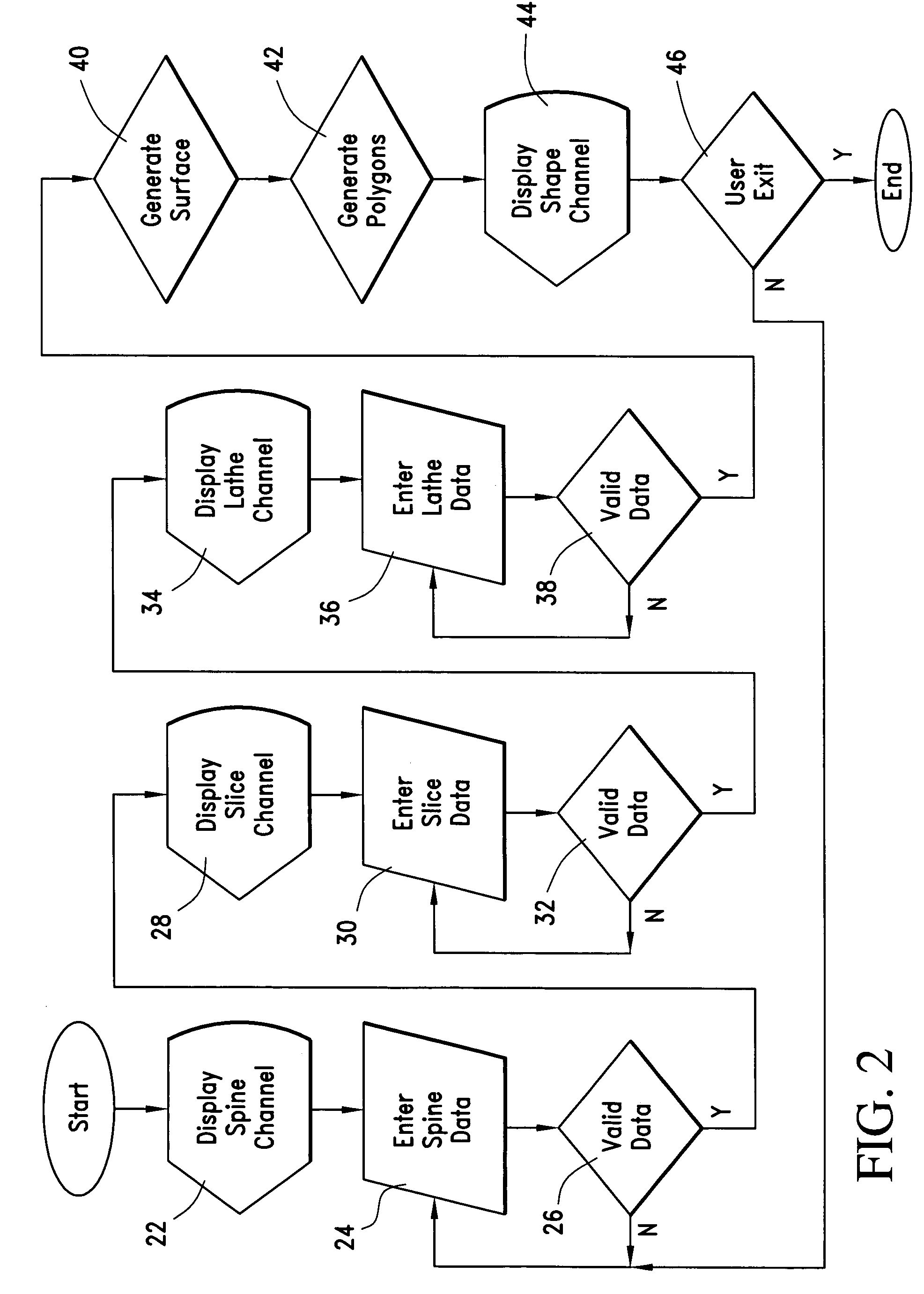
A method of representing n-dimensional parametric surfaces (animated shapes) is provided that expresses all shapes in a consistent manner to reduce storage requirements, support deformation and simplify interaction between shapes. The method, a version of sweeps, represents shapes using a unique combination of three discrete types of (piecewise polynomial) curves: spine (sweeping) curves, slice (section) curves, and lathe (plane) curves, which are combined to create surfaces. The curves required to make simple 3D primitives (i.e. torus, sphere, cube and pyramid) are themselves simple 2D primitives (i.e. line, circle, square, triangle). The storage size of this system's shapes is exponentially smaller than the size of polygonal versions of the same shapes (as a function of the number of polygons). Complex models can be broken into multiple shapes, which are arranged in a tree hierarchy. The shapes of this invention can be tiled with other shapes of this invention (i.e. a row of smokestacks made of bricks). The shapes of this invention can smoothly travel on other shapes of this invention (i.e. a football rolling over arbitrary terrain). This invention supports fast, intuitive creation of shapes such as hand-drawn shapes. This invention is a closed system, providing a suite of operations that can occur in arbitrary order sans approximation errors. When scenes are constructed of parametric building blocks, each represented with the same universal formula, a suite of advanced operations becomes available, providing support critical to advanced software simulations.
Owner:FIGMENT3D ENTERPRISES
Anomaly Diagnosis System and Anomaly Diagnosis Method
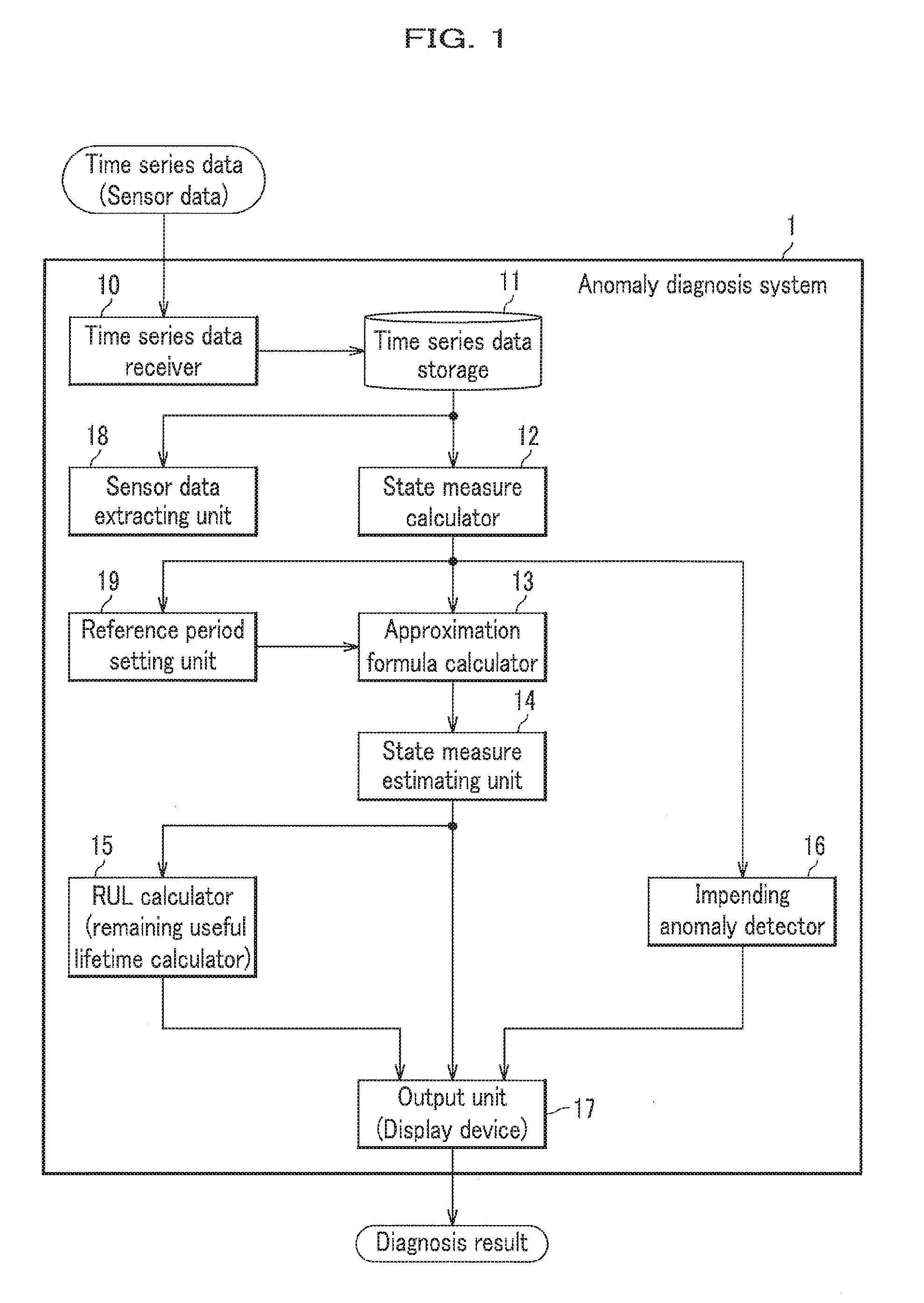
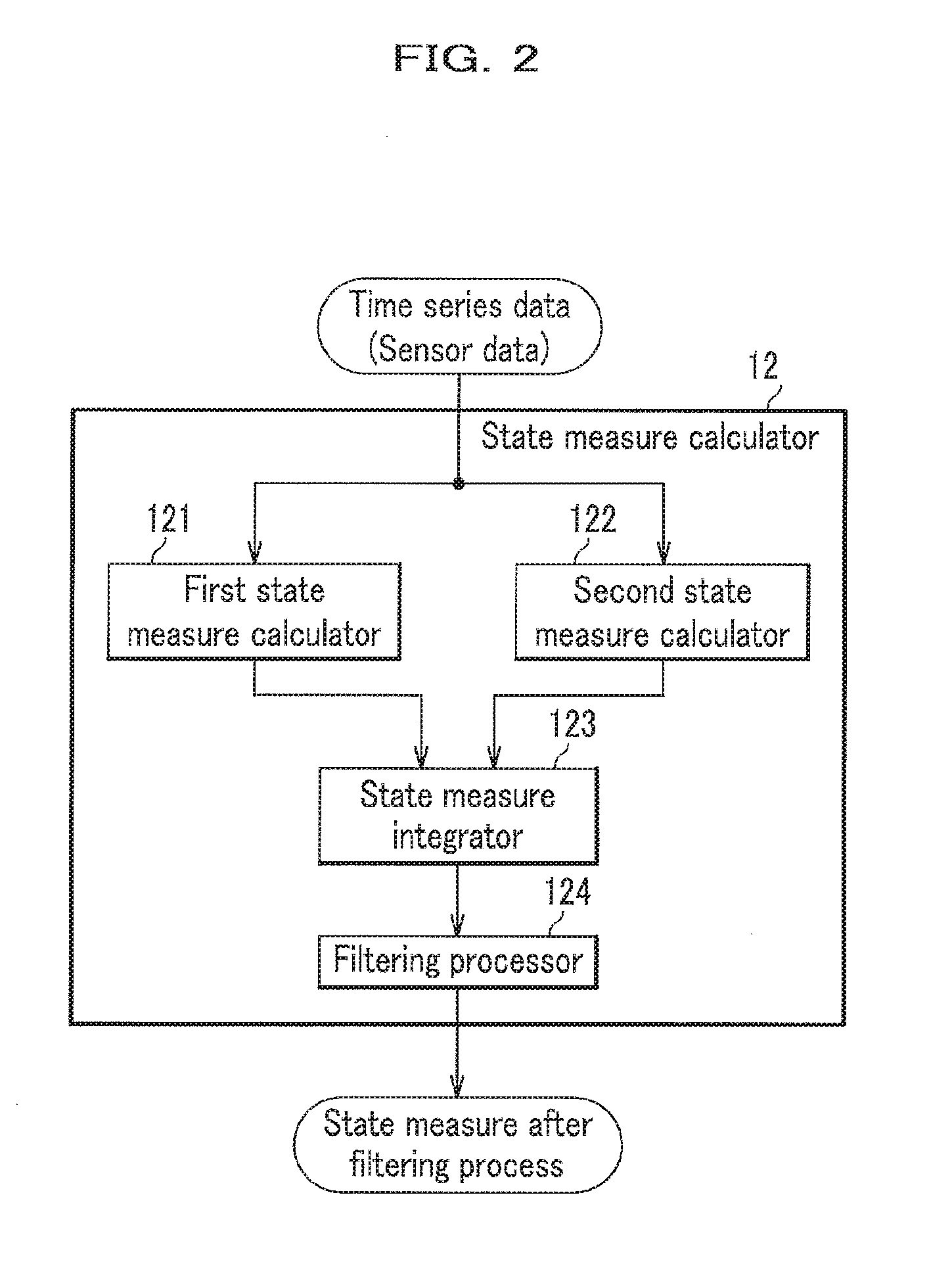
The anomaly diagnosis system includes the state measure calculator acquiring sensor data from sensors in a machine facility as time series data; an approximation formula calculator calculating a state measure being an index indicating a state of the machine facility, such as anomaly and a performance by a statistical method in which the time series data is used as learned data; and a state measure estimating unit estimating the state measures until future time using the approximation formula. Whenever the latest time series data is acquired, the reference period in which the time series data corresponding to the state measure referred to calculate the approximation formula by the reference period setting unit, is successively extended by addition of time when the latest time series data is acquired. The approximation formula calculator calculates the approximation formula using the state measure of the time series data acquired in the reference period.
Owner:HIATACHI POWER SOLUTIONS CO LTD
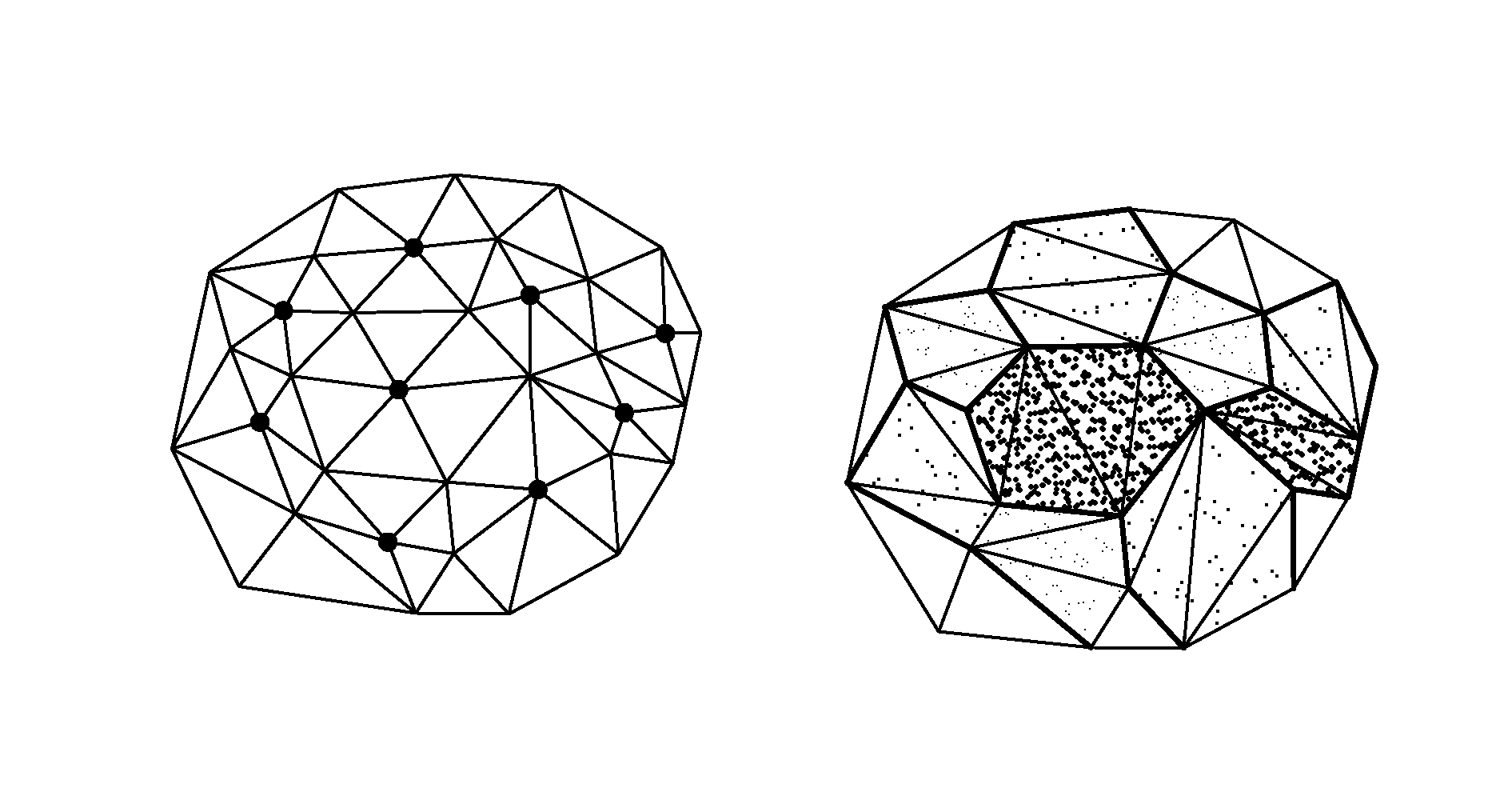
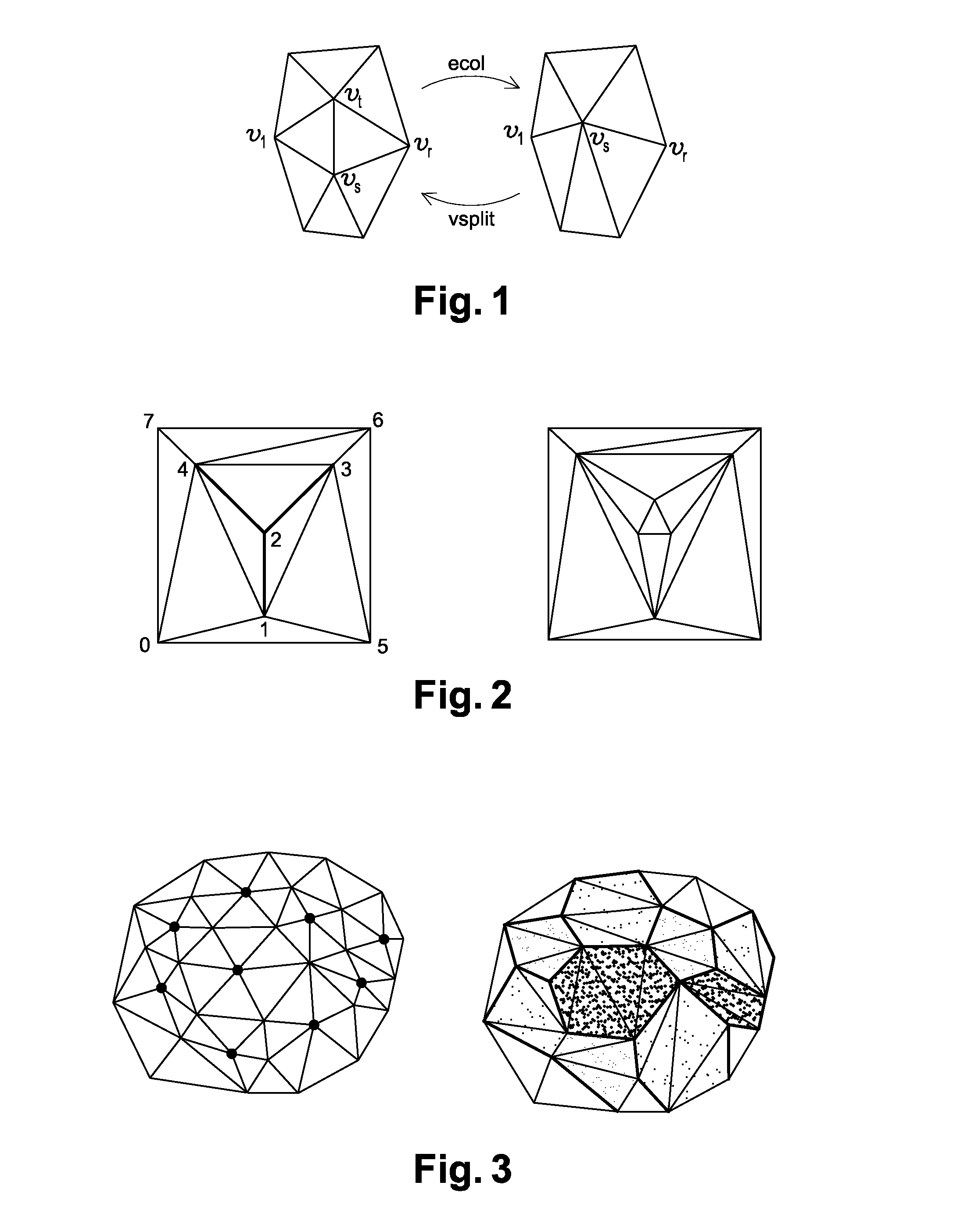
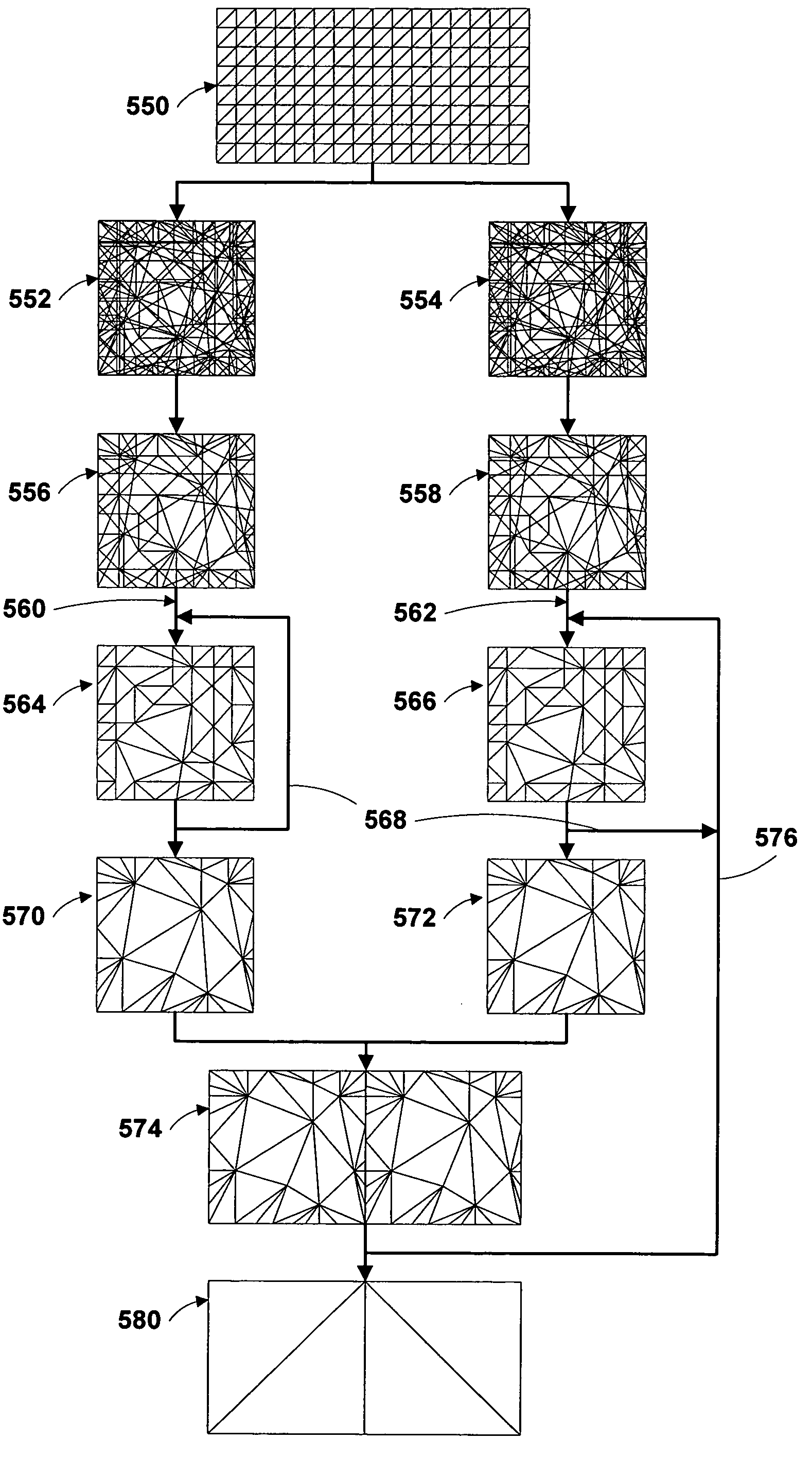
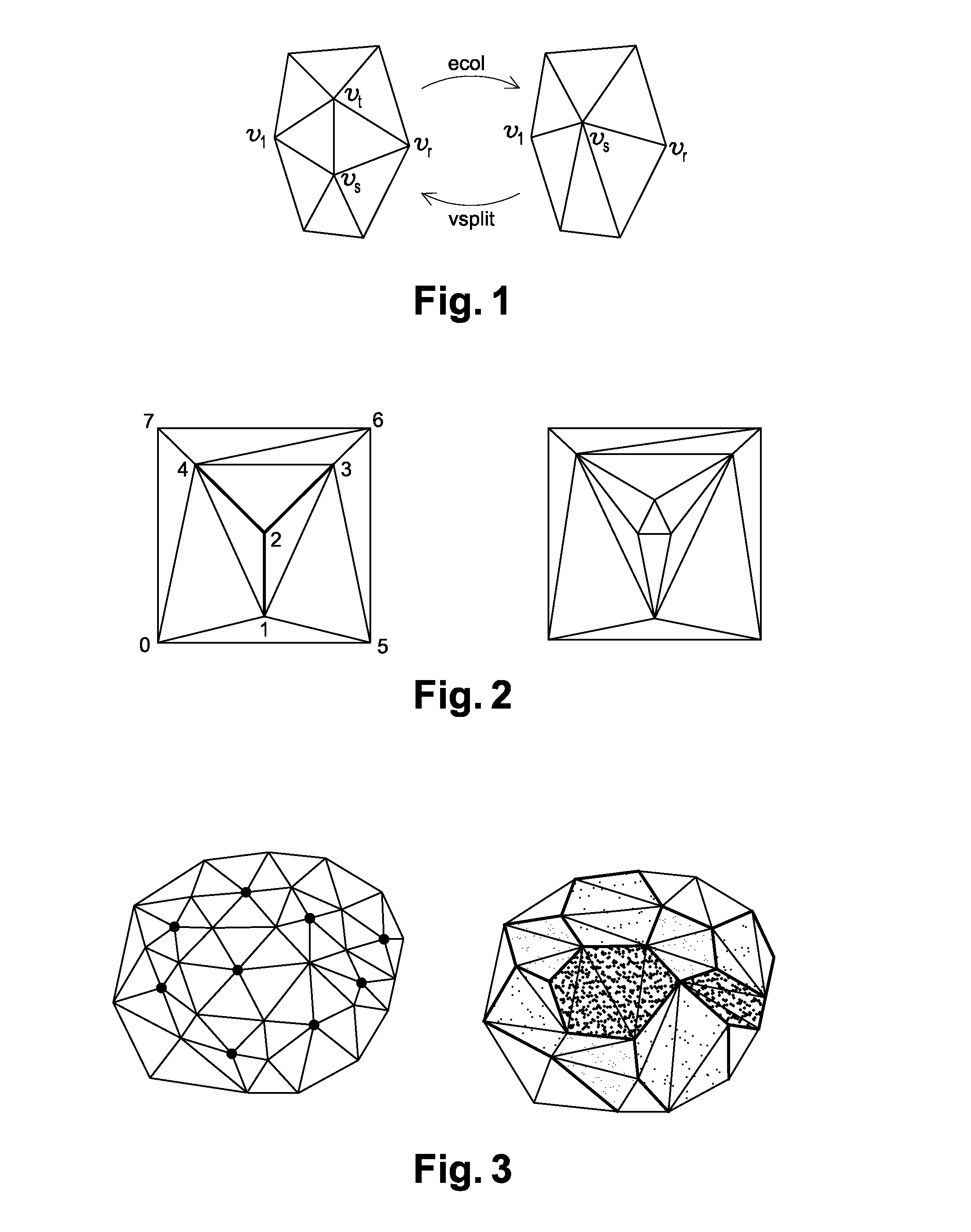
Regional progressive meshes
A regional progressive mesh provides support for real-time rendering of large-scale surfaces with locally adapting surface geometric complexity according to changing view parameters. The regional progressive mesh is constructed by subdividing an initial detailed mesh one or more times into multiple sub-regions as an iterative or recursive process. Each sub-region is separately simplified, and the localized transformations recorded in separate segments in a sequence of mesh refinement transformations that form the progressive mesh representation. The resulting regionalized organization of mesh refinement transformations reduces the working set of memory pages containing progressive mesh data needed for real-time view-dependent adaptation and rendering of the mesh surface. An exact approximate error measurement of a vertex split transformation also is defined as the maximum height deviation at enumerated vertices in the open neighborhood of the transformation relative to a regular triangulation of grid points, where the enumerated vertices include the grid points internal to the faces adjacent the split vertex and the grid line crossings internal to edges adjacent the split vertex.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
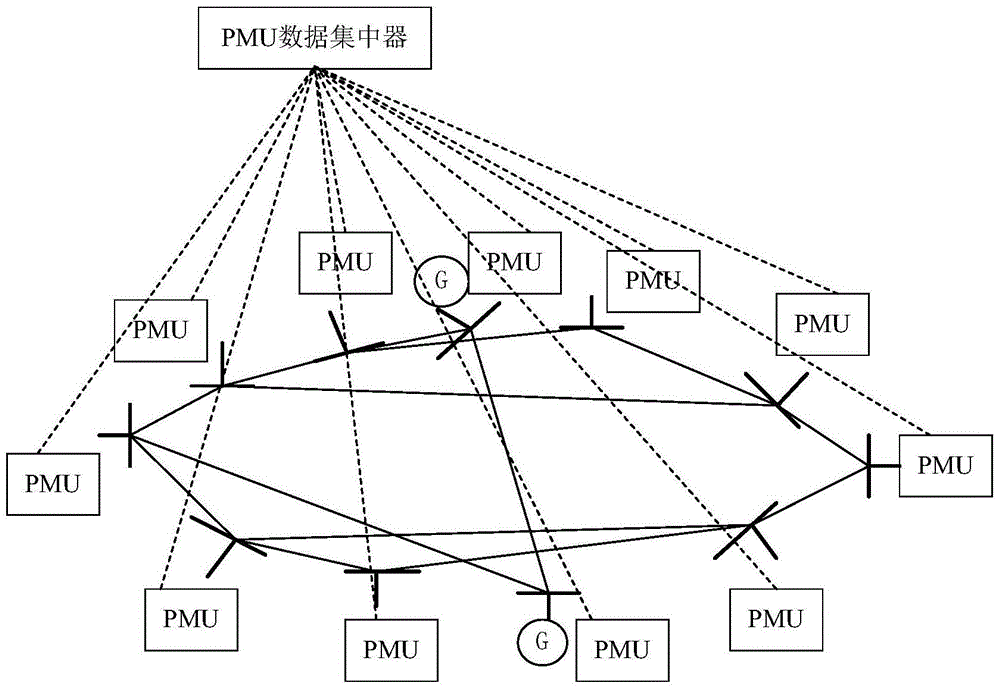
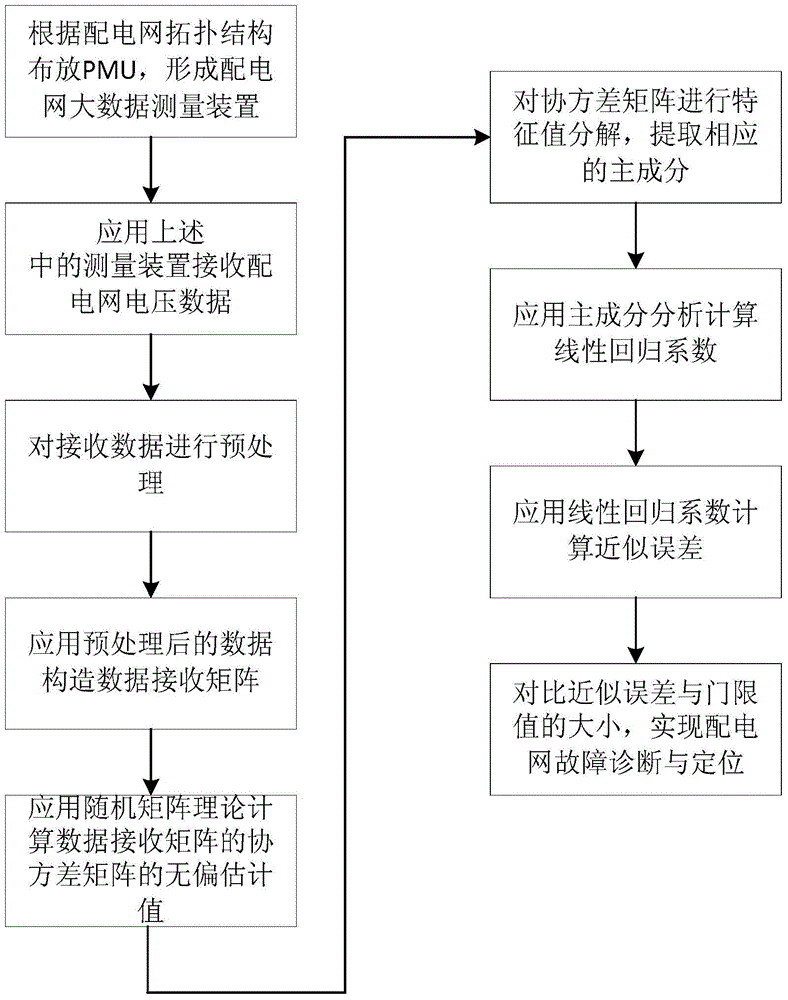
Big data fault detection and positioning method for power distribution network
ActiveCN105699804AOvercoming the problem of large estimation biasImprove applicabilityFault location by conductor typesSystems intergating technologiesPrincipal component analysisSmart grid
The invention provides a big data fault detection and positioning method for a power distribution network, and belongs to the field of intelligent power grids. The method comprises the steps: receiving voltage sampling data of the power distribution network through employing PMUs (Phasor Measurement Units); carrying out the preprocessing of voltages received by all PMUs, and constructing a receiving matrix; obtaining an unbiased estimated value of a receiving data covariance matrix through employing a random matrix theory; carrying out the eigenvalue decomposition of the covariance matrix, and obtaining a corresponding principal component; calculating a linear regression coefficient through employing PCA (Principal Component Analysis); comparing a relative approximation error and a threshold value, and achieving the fault detection and positioning of the power distribution network. The method provided by the invention solves a problem that the conventional covariance matrix estimation is biased under the measurement of a plurality of PMUs, and can achieve the real-time fault detection and positioning of the power distribution network.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Automatic trademark application success rate analysis method and system based on artificial intelligence
ActiveCN106844551AIncrease success rateData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmArtificial general intelligence
The invention provides an automatic trademark application success rate analysis method and system based on artificial intelligence. The method comprises the steps that 1, whether or not a to-be-applied trademark belongs to content specified by prohibitive terms of trademark application is judged on the basis of artificial intelligence querying, and the approximation degree is calculated, wherein the approximation degree is the probability Pjz; 2, the approximation degree between the to-be-applied trademark and an existing trademark is judged on the basis of artificial intelligence retrieval, wherein the approximation degree of the existing trademark is the probability Pjs; 3, the trademark application passing probability P is calculated through the formula P=(1-Pjz)+(1-Pjs). According to the method, success rate analysis before trademark application is conducted through an artificial intelligence technique, and therefore the trademark application success probability can be significantly increased.
Owner:全民互联科技(天津)有限公司
Regional progressive meshes
A regional progressive mesh provides support for real-time rendering of large-scale surfaces with locally adapting surface geometric complexity according to changing view parameters. The regional progressive mesh is constructed by subdividing an initial detailed mesh one or more times into multiple sub-regions as an iterative or recursive process. Each sub-region is separately simplified, and the localized transformations recorded in separate segments in a sequence of mesh refinement transformations that form the progressive mesh representation. The resulting regionalized organization of mesh refinement transformations reduces the working set of memory pages containing progressive mesh data needed for real-time view-dependent adaptation and rendering of the mesh surface. An exact approximate error measurement of a vertex split transformation also is defined as the maximum height deviation at enumerated vertices in the open neighborhood of the transformation relative to a regular triangulation of grid points, where the enumerated vertices include the grid points internal to the faces adjacent the split vertex and the grid line crossings internal to edges adjacent the split vertex.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for compressing/decompressing a three-dimensional mesh
ActiveUS20130114910A1Lower the volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The method for encoding / decoding three-dimensional meshes of dots or vertices connected in the form of facets delimited by edges; the mesh M is defined by connectivity data T and geometry data G includes the steps of:lossless encoding of the connectivity data T into encoded connectivity data Tc,iteratively generating a progressive mesh hierarchy, i.e. a set of meshes with progressive levels of detail, PM (M*),generating a piecewise smooth approximation M* of the original mesh M, from the mesh connectivity T; this smooth approximation M* being described as follows:a. compressed connectivity data Tc;b. a small number N of control dots andc. a number of indexes S of edges called protruding edges of the mesh M, identified beforehand,using the progressive mesh hierarchy PM(M*) to calculate a prediction of approximation errors in M* compared with the original mesh M.
Owner:FITTINGBOX
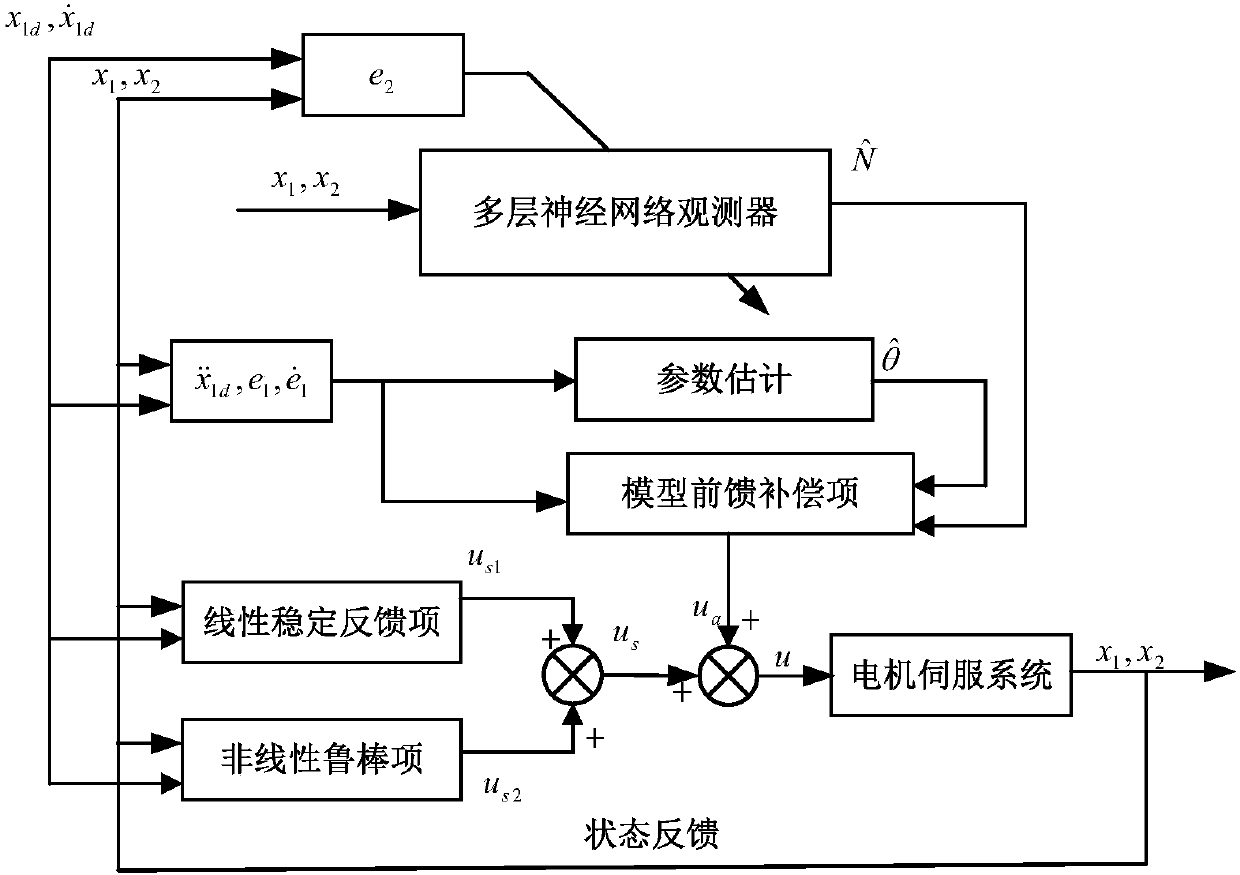
Multilayer neural network-based motor position servo system friction compensation control method
ActiveCN107561935ASolve uncertain nonlinear problems such as nonlinear frictionImprove tracking accuracyAdaptive controlObserver basedControl theory
The present invention discloses a multilayer neural network-based motor position servo system friction compensation control method and belongs to the electromechanical servo control field. According to the friction compensation control method, a neural network and the idea of adaptive robust control are combined, so that a multilayer neural network observer-based adaptive robust controller is designed; and a multilayer neural network is adopted to compensate complex uncertain items in nonlinear friction, and at the same time, an adaptive robust controller is designed to estimate uncertain parameters in a system and compensate external disturbances and the approximation errors of the neural network. With the control method designed by the invention adopted, the nonlinear friction problem ofa motor servo system can be solved, and the excellent tracking performance of the motor servo system can be ensured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Curved path approximation in vehicle guidance systems and methods
ActiveUS9804603B1Prevent overfittingAutonomous decision making processPosition/course control in two dimensionsGuidance systemIn vehicle
Improved vehicle guidance systems and methods are provided. A generated guidance curve approximates a vehicle trajectory path comprising a set of two-dimensional reference points. The guidance curve is based on a summed and weighted radial basis functions. Weighting is associated with coefficients calculated using linear least-squares regression to minimize approximation error between the guidance curve and the vehicle trajectory path. Guidance instructions are based, at least in part, on a nearest location point, and a tangent direction and curvature of the guidance curve at the nearest location point. The controller autonomously guides the vehicle along the guidance curve. The basis functions can have a cardinality less than a cardinality of the reference points. A distorting effect at the path ends can be minimized by augmenting the path ends of the vehicle trajectory path. Irregular reference point spacing can be mitigated using regularization techniques.
Owner:LEADER TECH
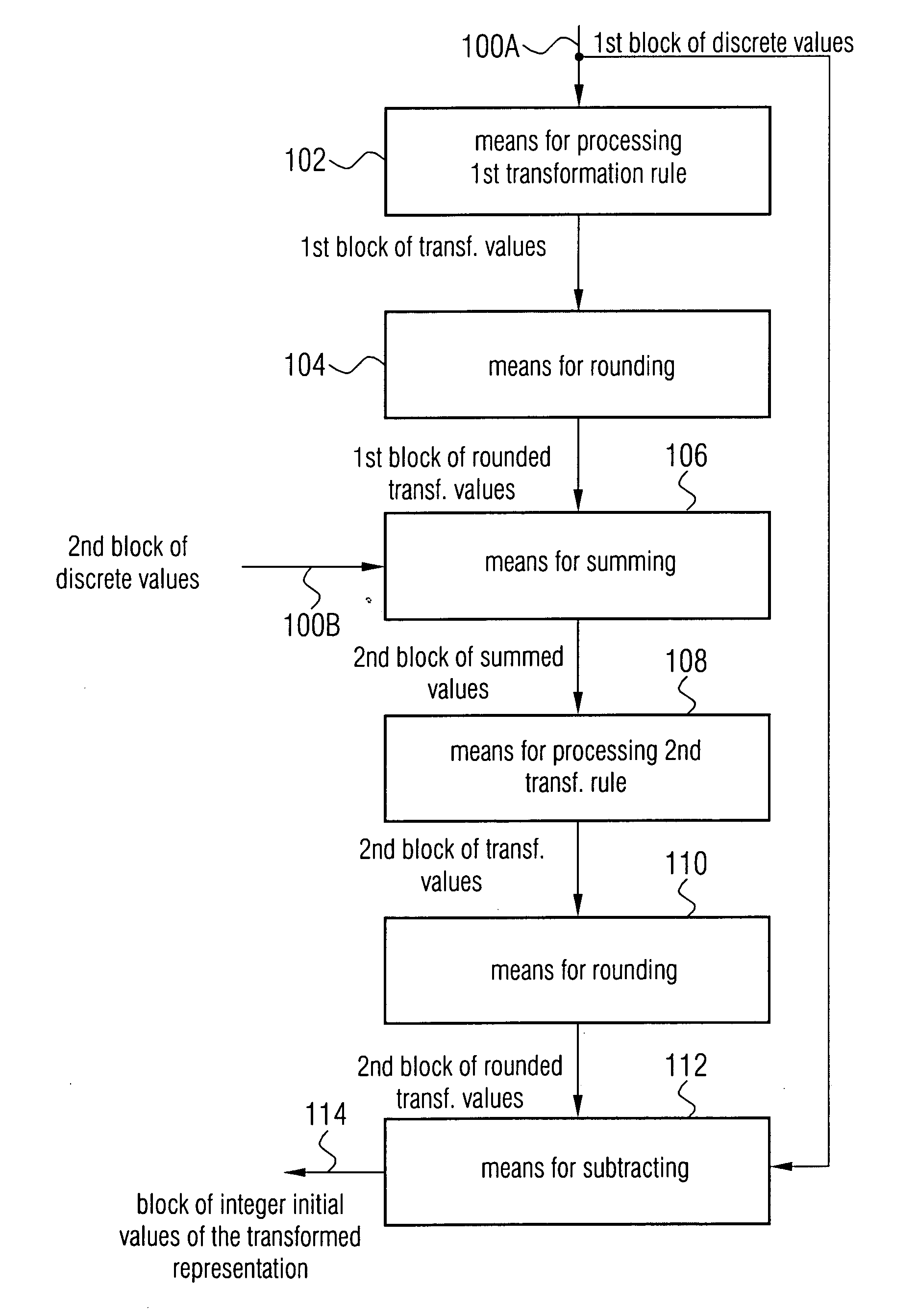
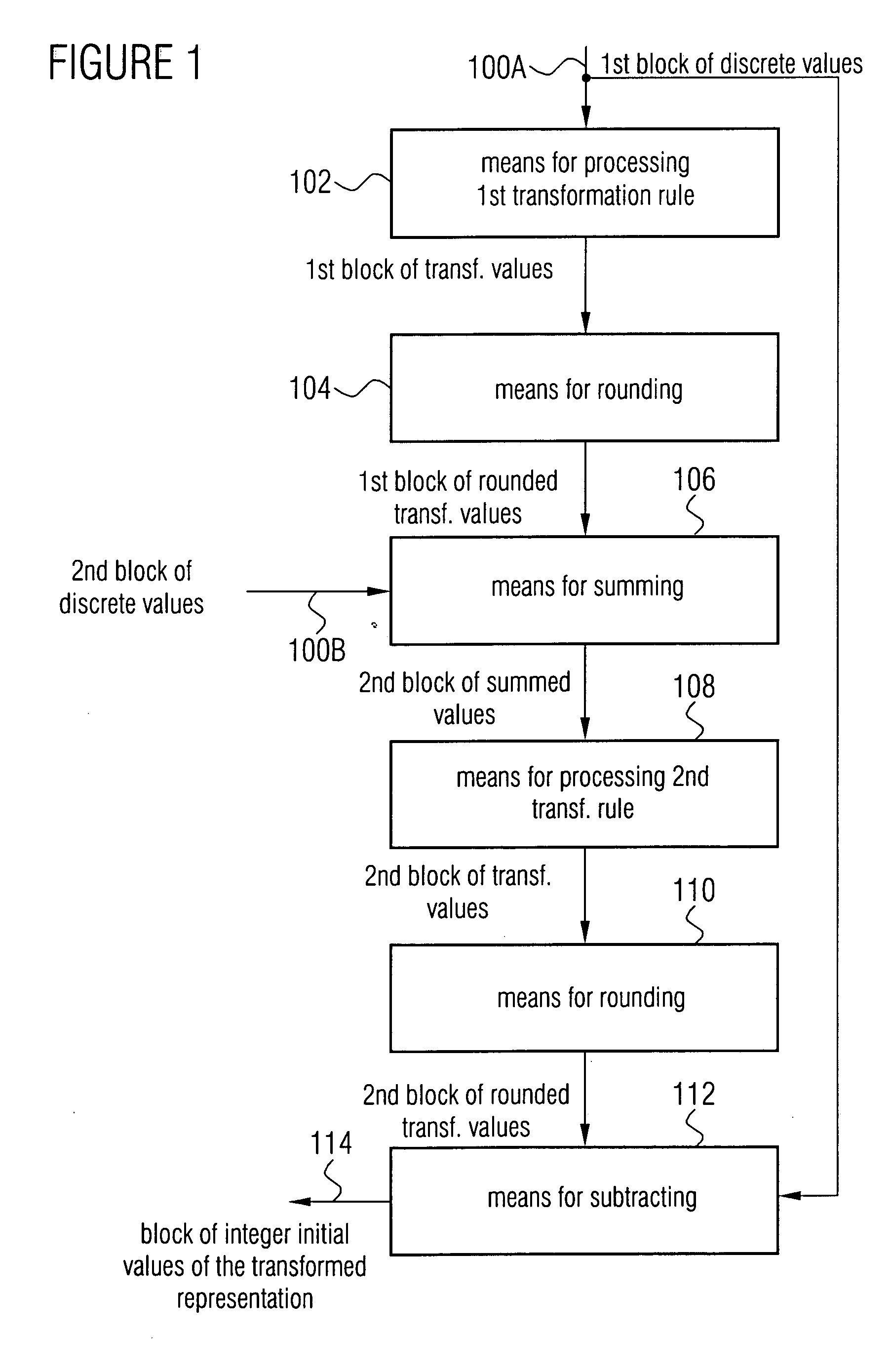
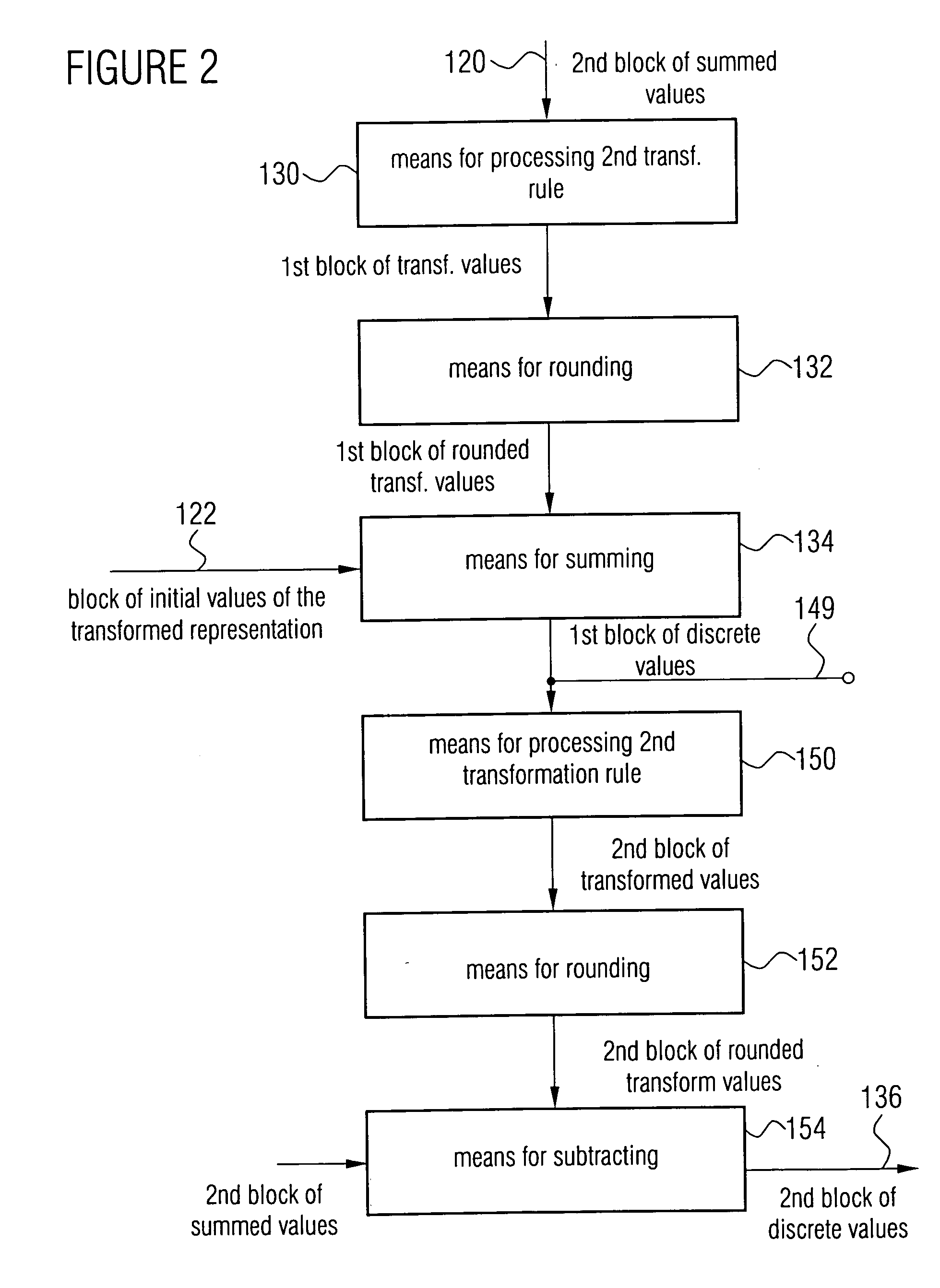
Apparatus and method for conversion into a transformed representation or for inverse conversion of the transformed representation
ActiveUS20060115171A1Fast algorithmSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityMulti dimensional
For converting first and second blocks of discrete values into a transformed representation, the first block is transformed according to a first transformation rule and then rounded. Then, the rounded transformed values are summed with the second block of original discrete values, to then process the summation result according to a second transformation rule. The output values of the transformation via the second transformation rule are again rounded and then subtracted from the original discrete values of the first block of discrete values to obtain a block of integer output values of the transformed representation. By this multi-dimensional lifting scheme, a lossless integer transformation is obtained, which can be reversed by applying the same transformation rule, but with different signs in summation and subtraction, respectively, so that an inverse integer transformation can also be obtained. Compared to a separation of a transformation in rotations, on the one hand, a significantly reduced computing complexity is achieved and, on the other hand, an accumulation of approximation errors is prevented.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
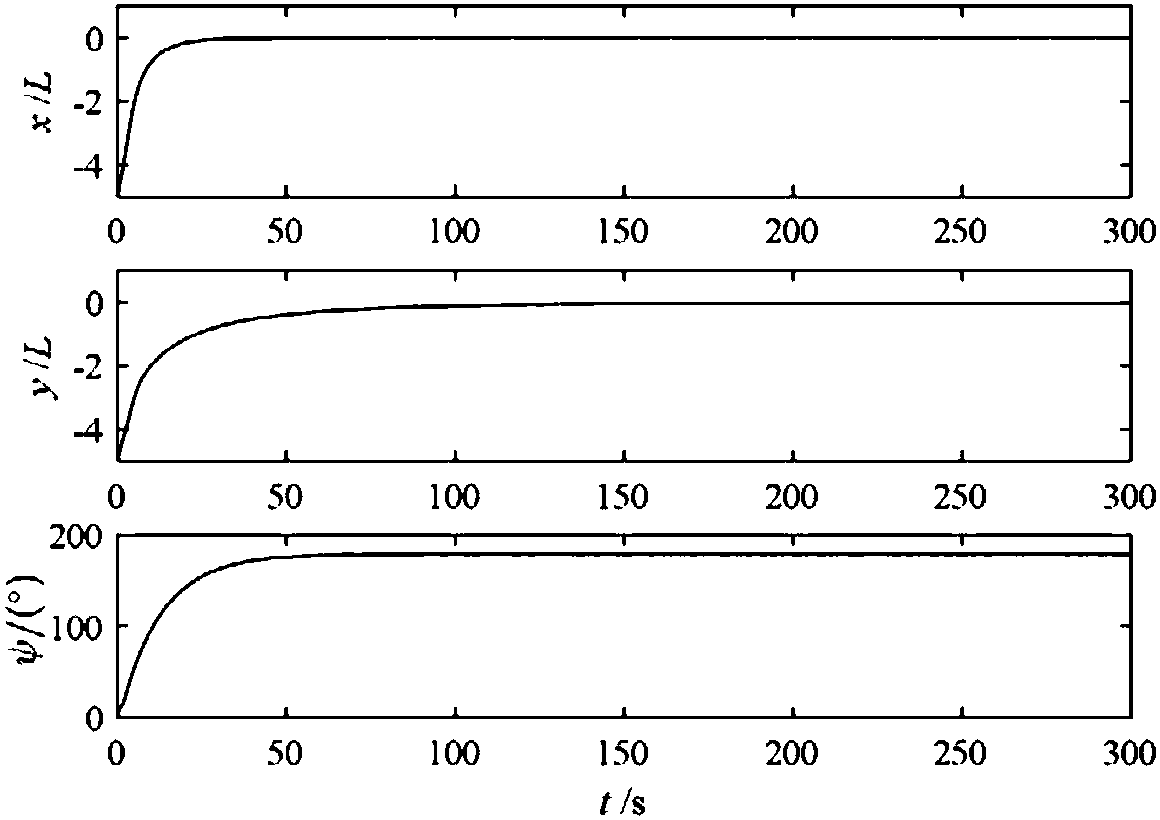
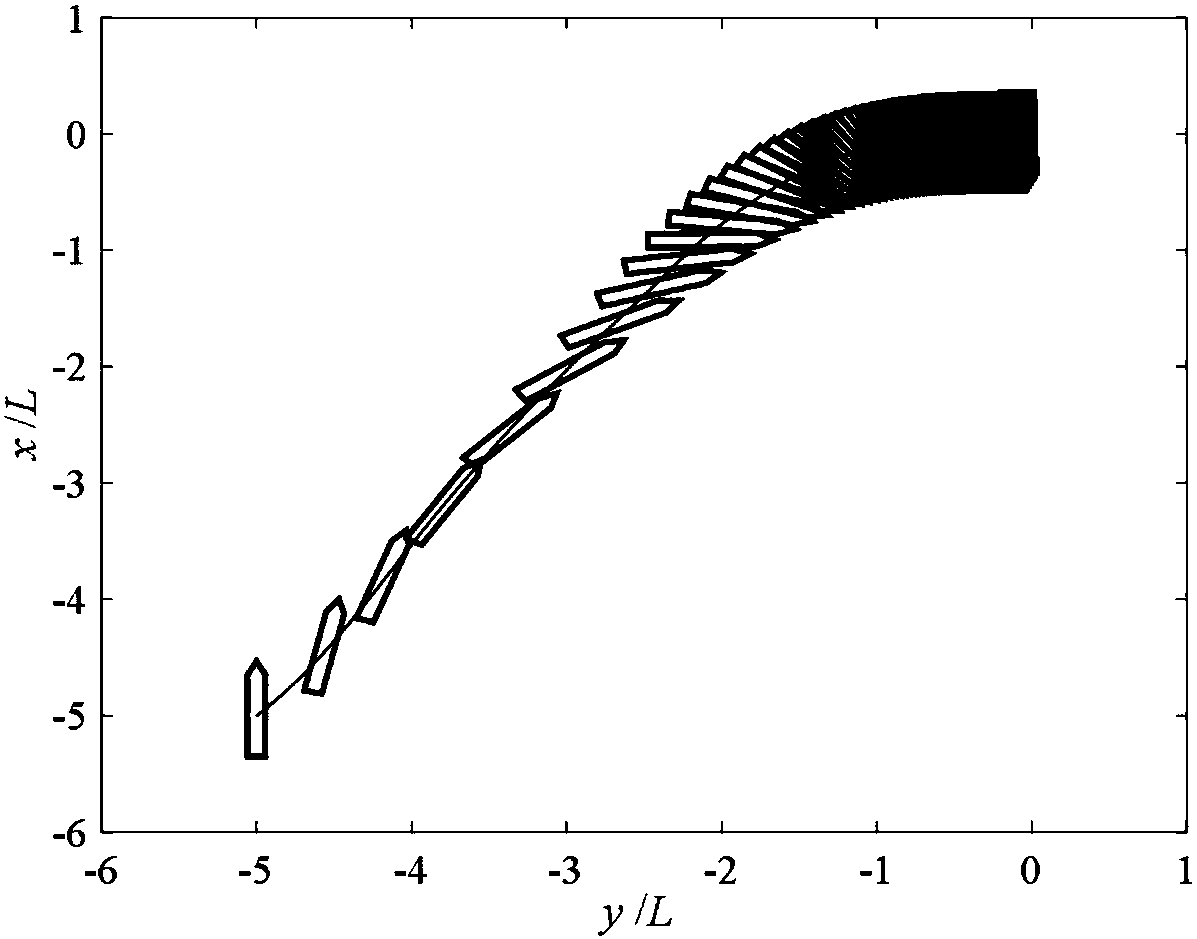
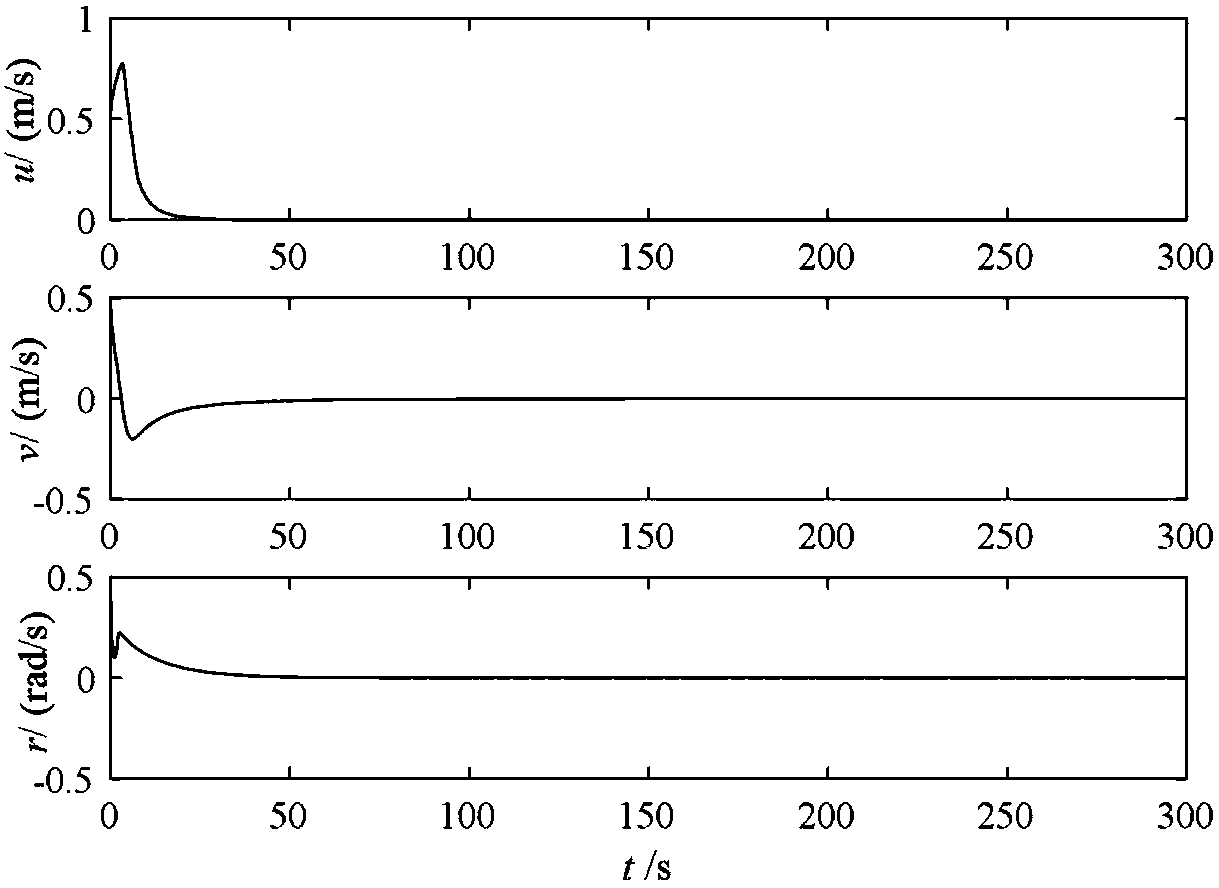
Trajectory planning method, trajectory planning system and trajectory planning and control system
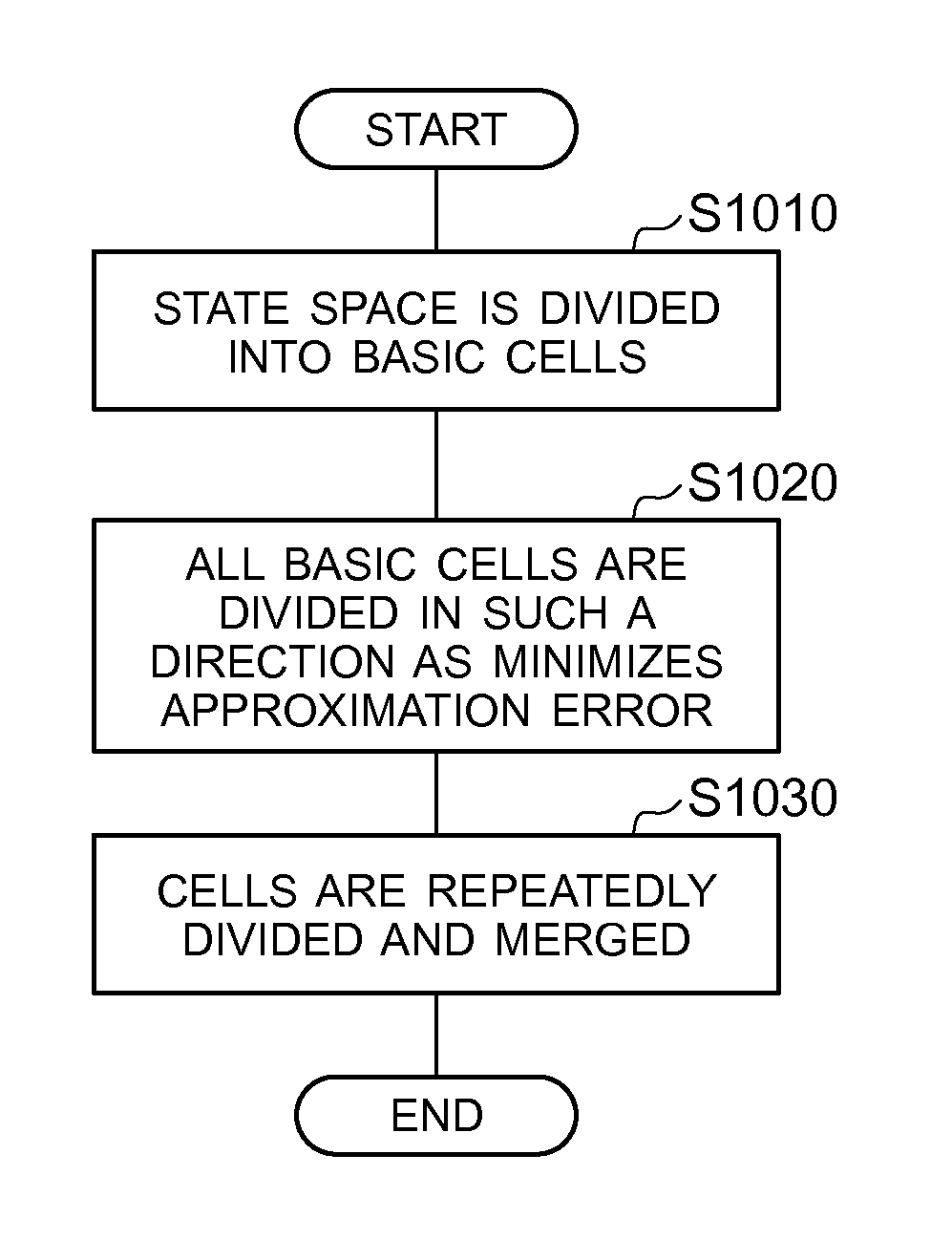
ActiveUS8825207B2Error minimizationLow costProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemState space
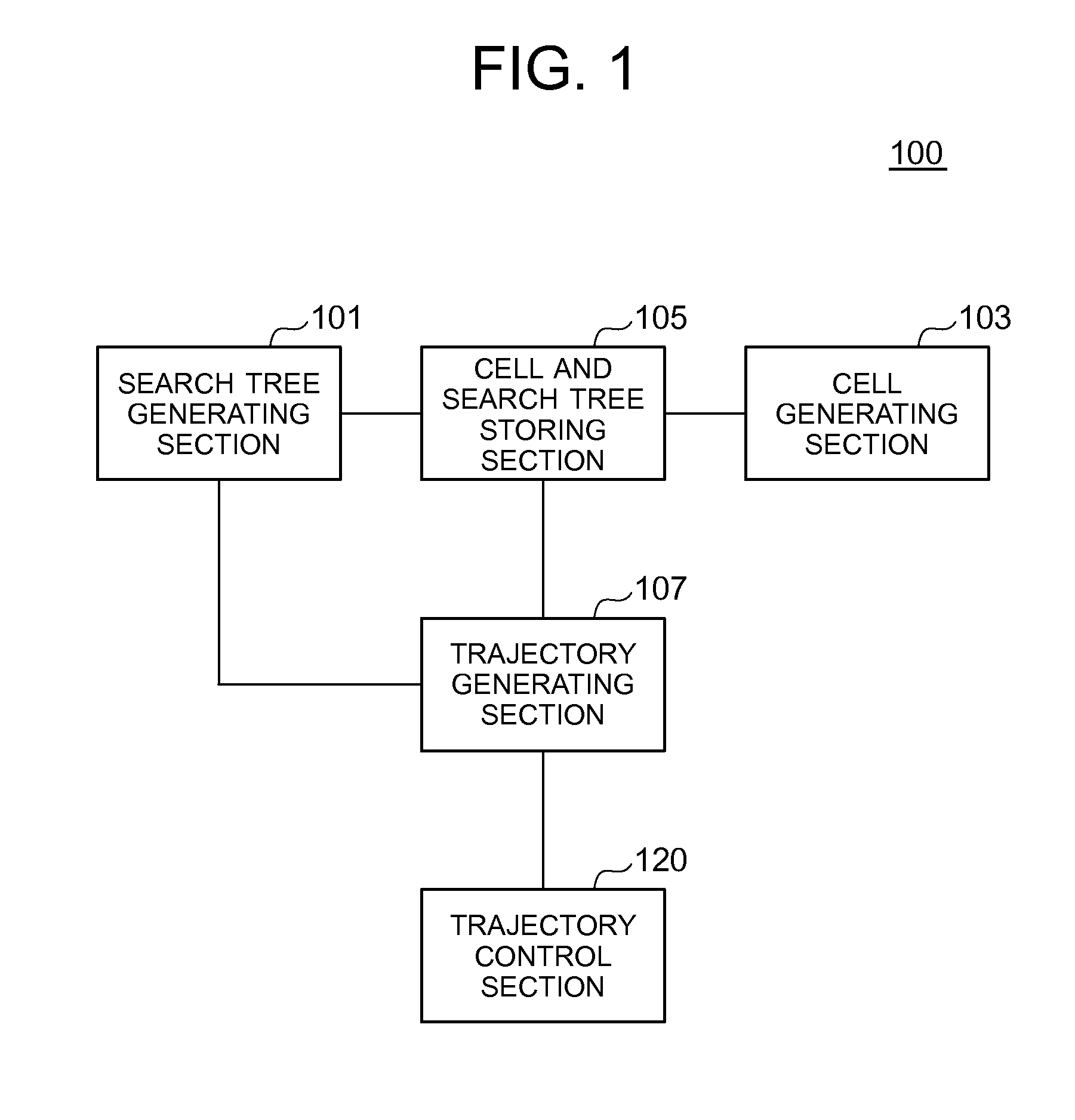
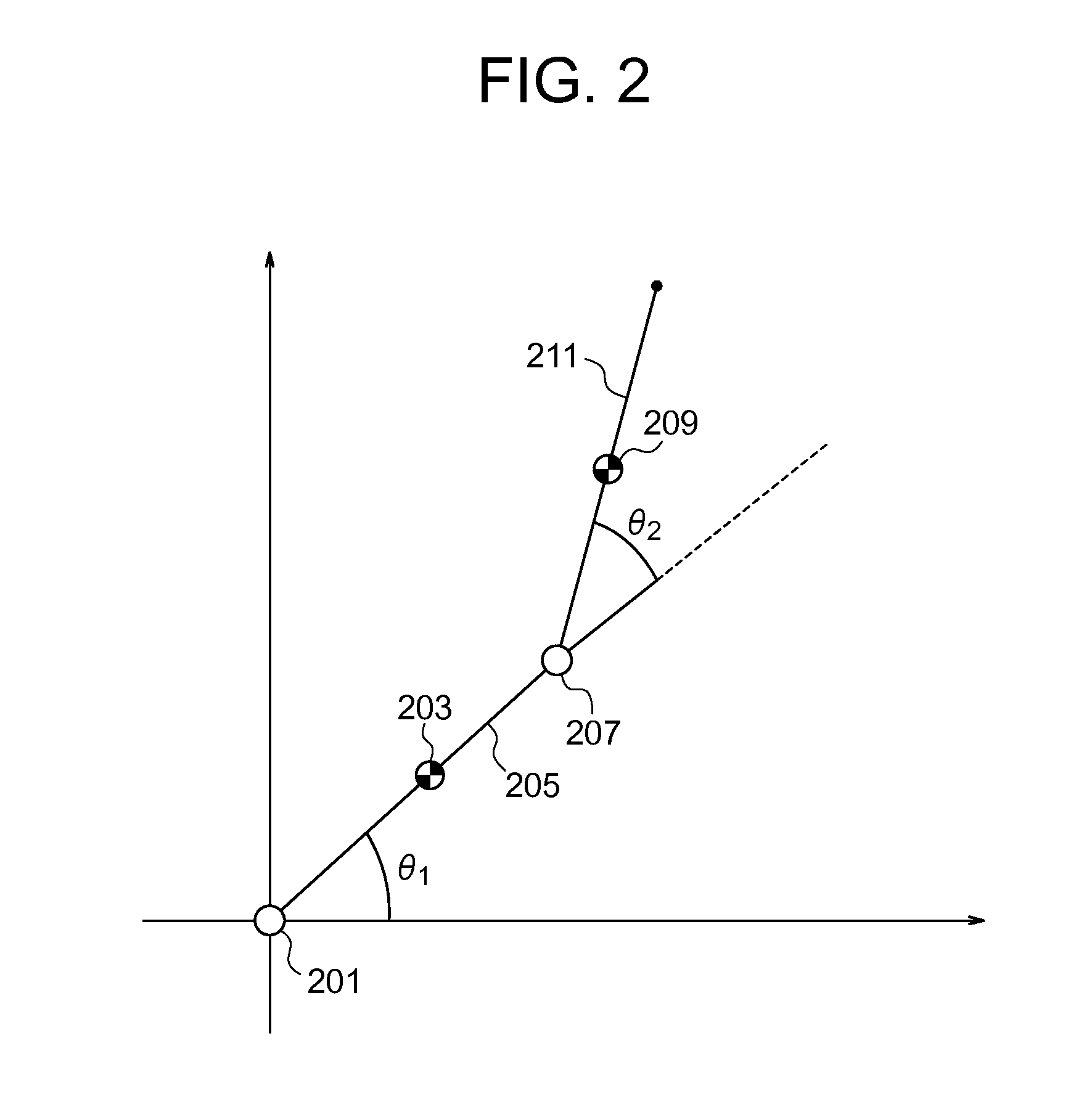
A trajectory planning method according to the present invention is one for obtaining a trajectory for controlling a state of an object toward a goal state by a trajectory planning system. The method includes the steps of dividing, by a cell generating section for dividing a state space of the object into cells, the state space into cells in such a way that approximation error due to discretization is minimized for a predetermined number of cells; generating, by a search tree generating section, a search tree which corresponds to state transition of the object in such a way that each cell does not contain more than one of nodes of branches of the search tree; and determining, by a trajectory generating section, a path from the current state to the goal state of the object using the search tree.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Texture morphing process provided by the preferred embodiment of the present invention
InactiveUS6906732B1Simplify and reduce computationFast and efficientCathode-ray tube indicatorsAnimationMorphingComputational science
A fast, texture morphing algorithm for real-time computer simulation and video games dynamically generates objects “on the fly” by simplifying and reducing the computational load required for a texture morphing / blending process. Incremental interpolation techniques compute a morph parameter based on previous value and morph change rate. Precomputed initial and incremental morph parameter values for each texel component are applied during real-time morphing procedures using integer arithmetic. Approximation errors are reduced by incrementing / decrementing by an extra integer value when the number of morph iterations is a multiple of a frame counter. The frame counter avoids over-runs, and the morphing procedure is “snapped” the texel value to the precise texture target value to prevent under-runs and corresponding artifacts. Interlacing (applying interpolation to a subset of the texels each frame) significantly reduces computational load without introducing significant image artifacts. The morph texture buffer data structure is initially decomposed off-line to reduce the number of real-time calculations required to manipulate texel component data.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Self-adaptive neural network automatic berthing control method and equipment for underactuated ship and medium
ActiveCN108563130ARealize automatic berthing controlReduce conservatismAdaptive controlModel dynamicsSelf adaptive
The invention provides a self-adaptive neural network automatic berthing control method for an underactuated ship. According to the method, an additional control method is adopted for solving the difficulty of design of an underactuated controller; uncertain ship model dynamic parameters and unknown disturbance vectors are reconstructed by utilizing a neutral network self-adaptive method of navigation dynamic depth information, the neutral network weight, approximate error and disturbance quantity are taken as complex uncertain parameters to be estimated on line, the problem that since disturbance and approximate error are separated to be processed, the unknown disturbance input cannot directly approach and the coupling property to the system is neglected is solved, the uncertain couplingproperty is considered, also the design conservatism is reduced, and also the system computation load is reduced; the input saturation of rudder and paddle executors are considered in the controller,and dynamic technology and minimum study parameter methods are introduced, so that the provided control method is more convenient, and the engineer is easy to realize.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
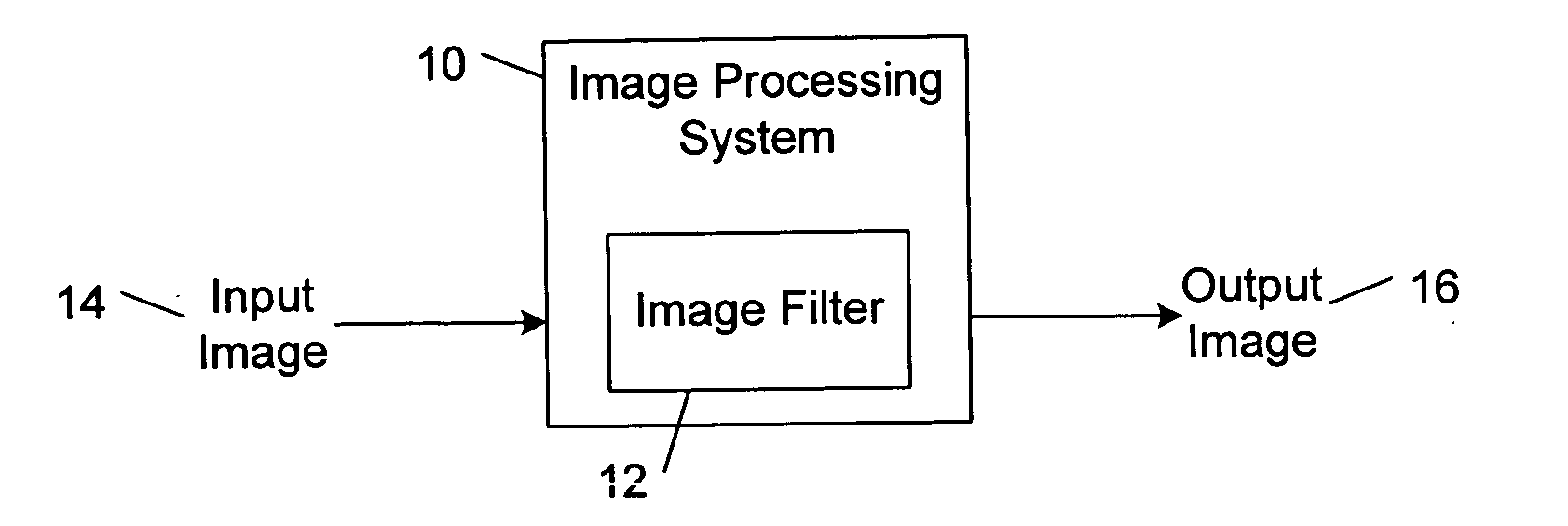
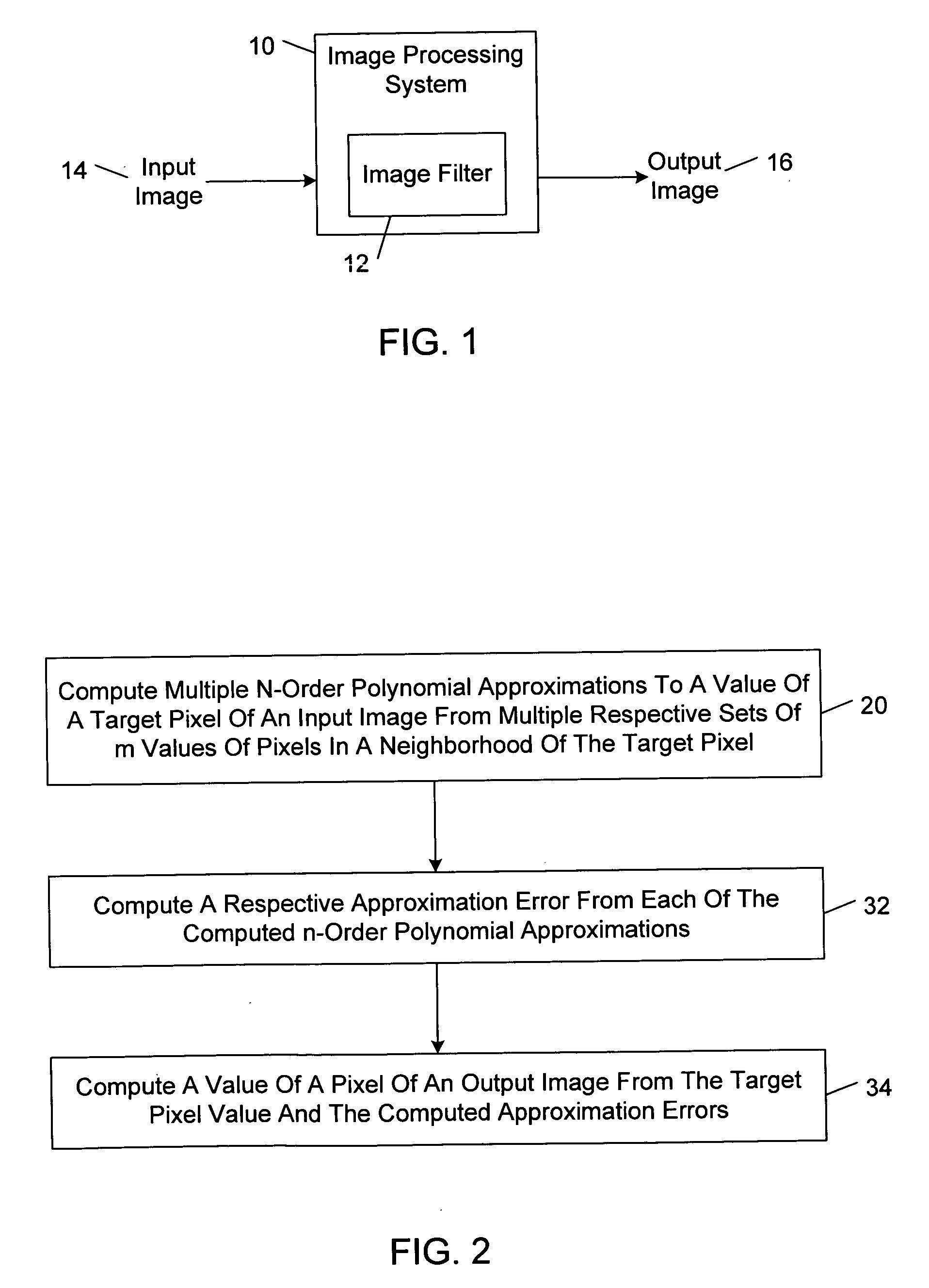
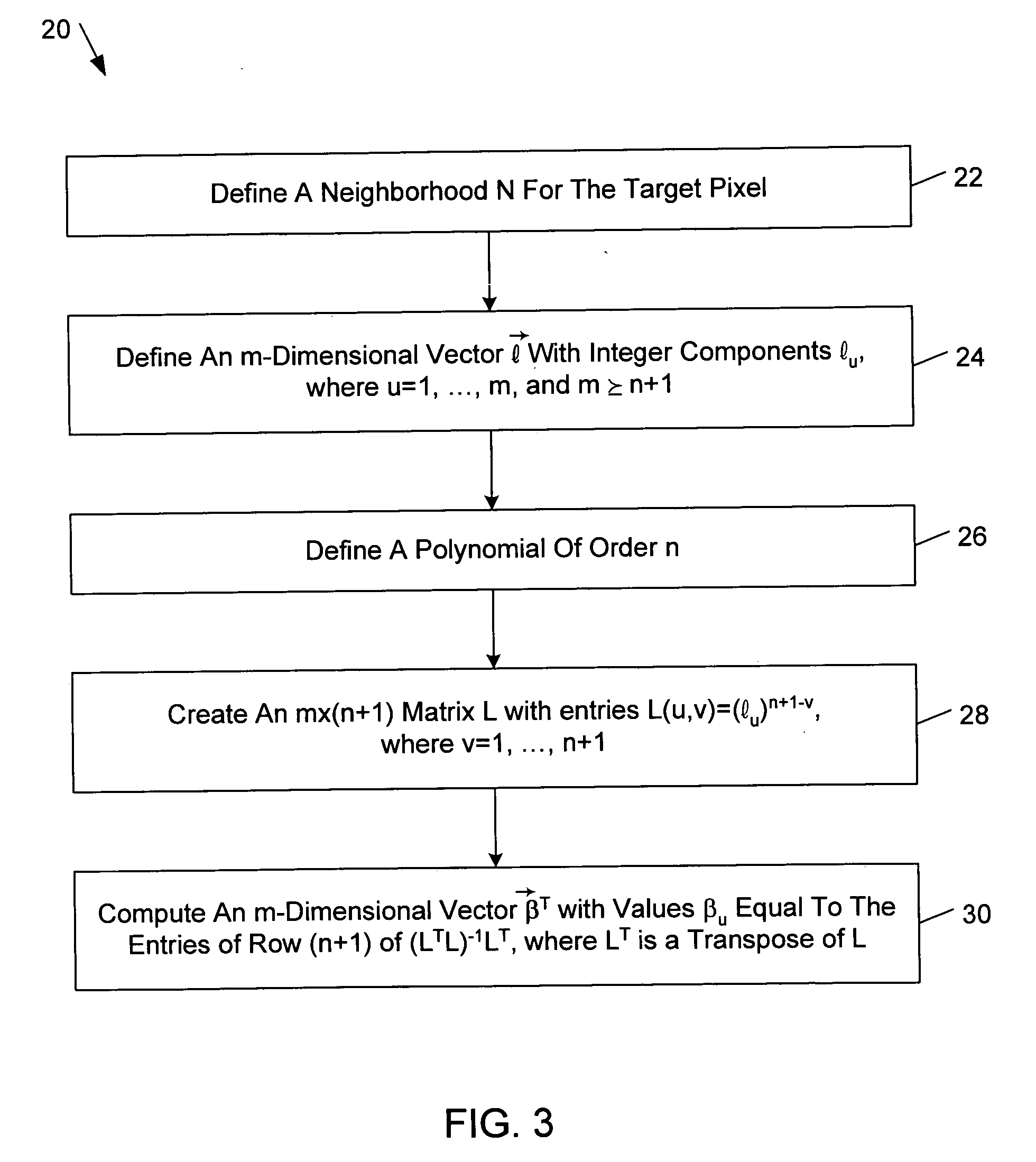
Polynomial approximation based image filter methods, systems, and machine-readable media
Polynomial approximation based image filter methods, systems, and machine-readable media are described. In one aspect, multiple n-order polynomial approximations to a value of a target pixel of an input image are computed from multiple respective sets of m values of pixels in a neighborhood of the target pixel, wherein n≧0 and m≧n+1. A respective approximation error is computed from each of the computed n-order polynomial approximations. A value of a pixel of an output image is computed from the target pixel value and the computed approximation errors.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
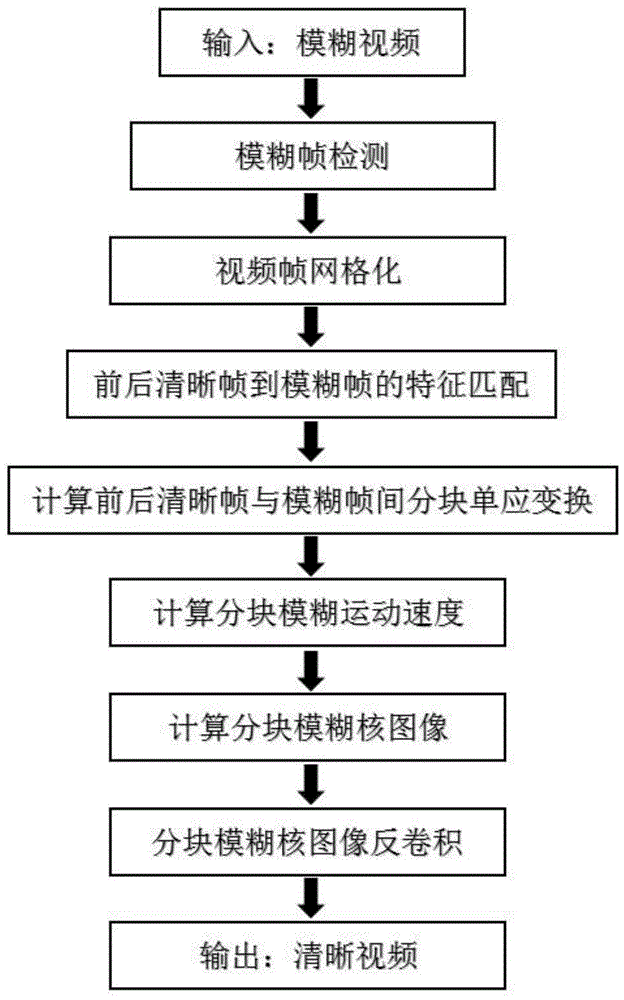
Block-blur-kernel-set-based heterogeneous video blind deblurring method
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of video processing, relates to a block-blur-kernel-set-based heterogeneous video blind deblurring method. The method comprises the following steps: detecting a blurred frame according to a gradient size of a video frame image; calculating block homograph according to feature matching of a clear frame and a blurred frame; carrying out discrete sampling of the block homograph to realize blurring approximation motion and calculating a velocity parameter of the blurring motion based on approximation error optimization; according to the blurring motion velocity, obtaining burring kernels corresponding to all blocks and calculating clear blocks by using deconvolution; and splicing the clear blocks to obtain a clear frame image, thereby removing blurred frames. Compared with the prior method, the provided method is characterized in that a blurring motion of a video frame is described by using a plurality of blur kernels; no initial value needs to be set during calculation, thereby enhancing the robustness; heterogeneous video blurring processing becomes efficient; requirements on the clear area of the video are low; and the application range is widened.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
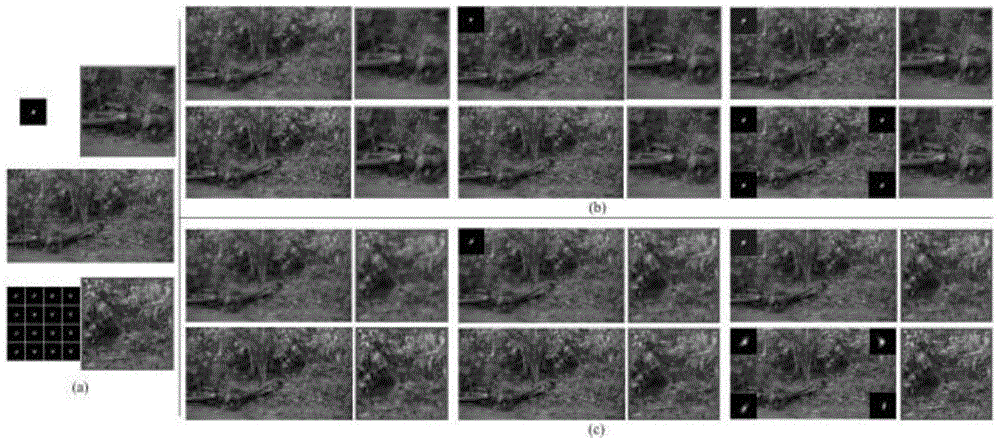
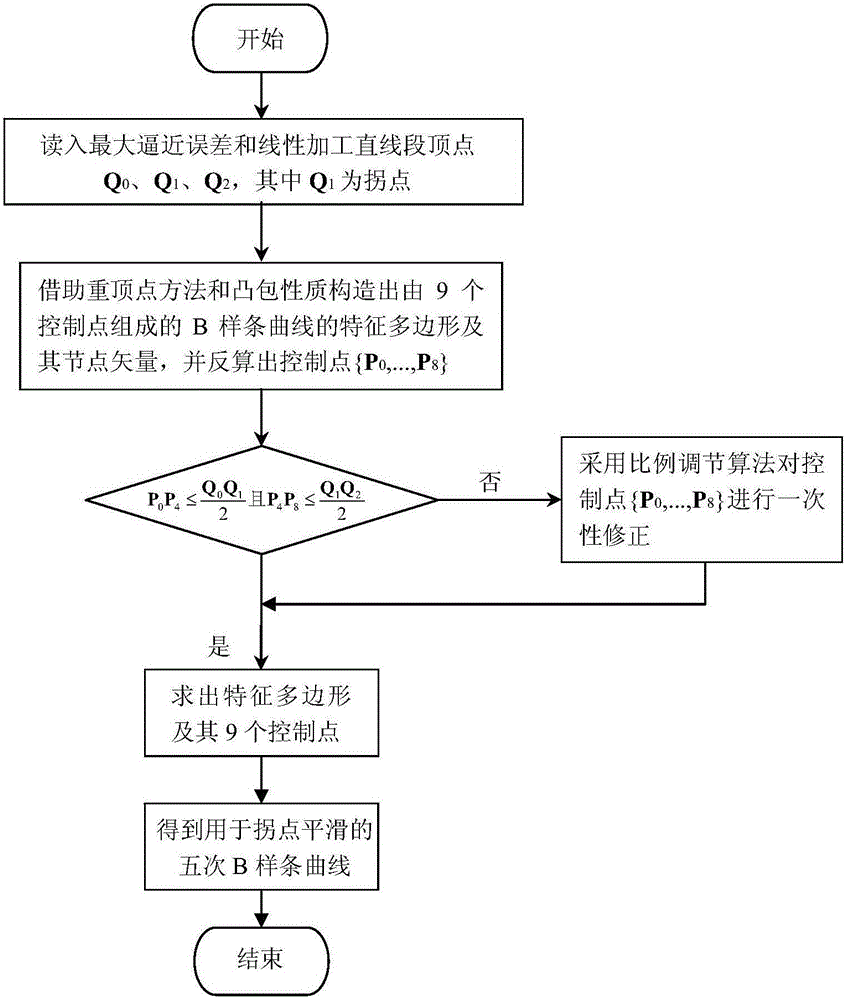
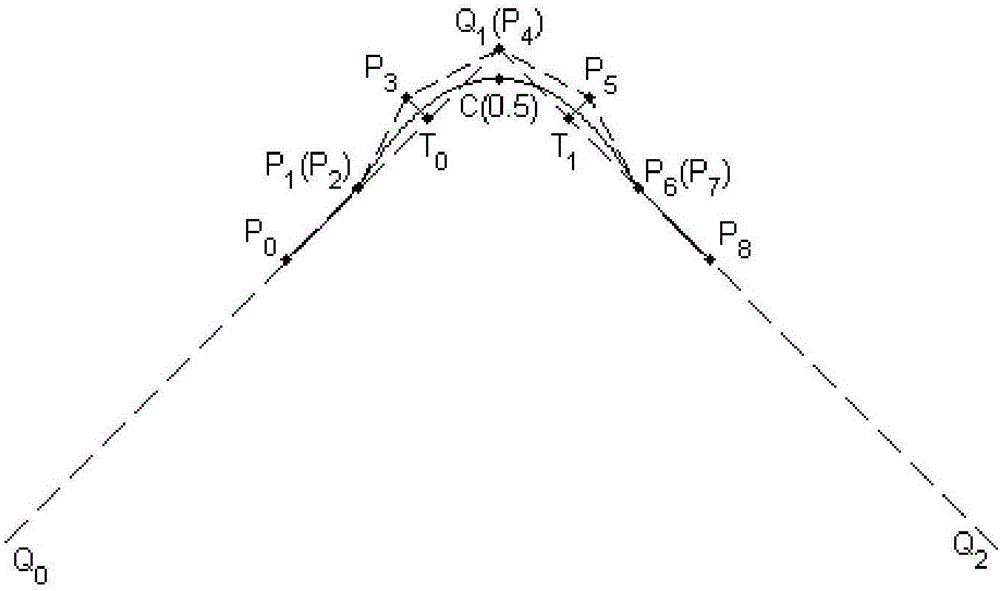
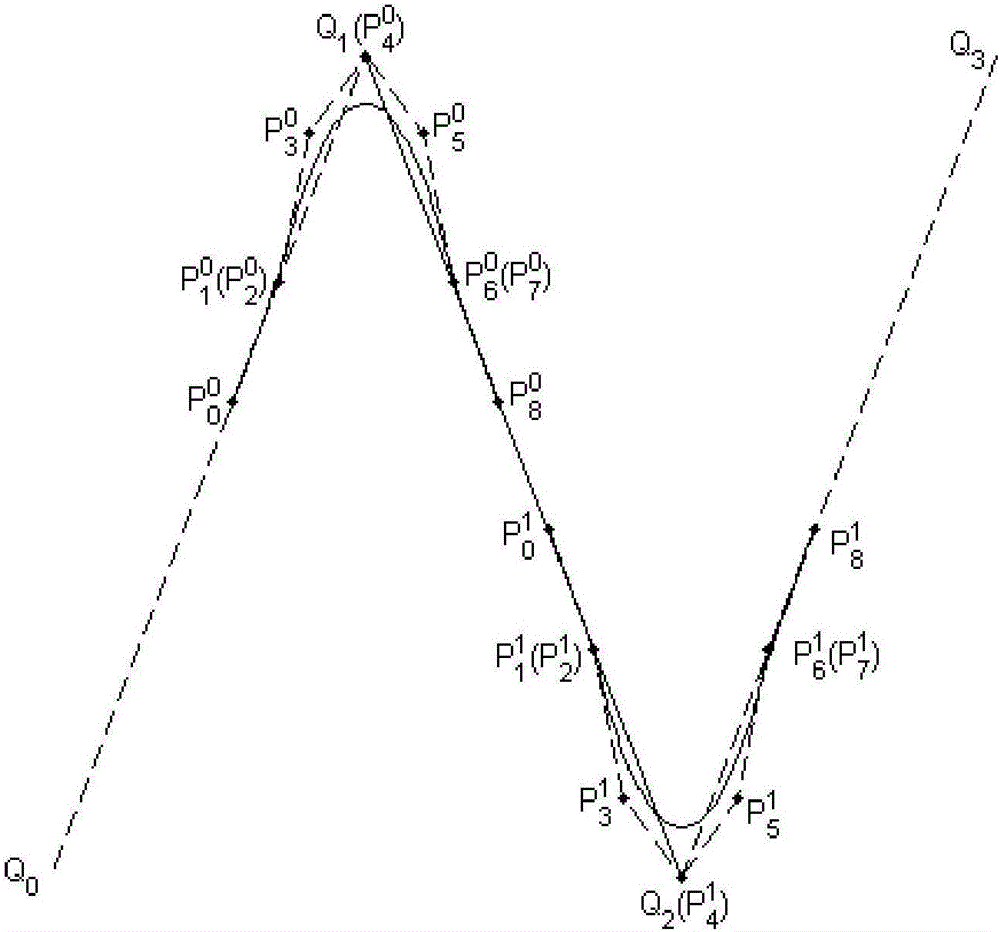
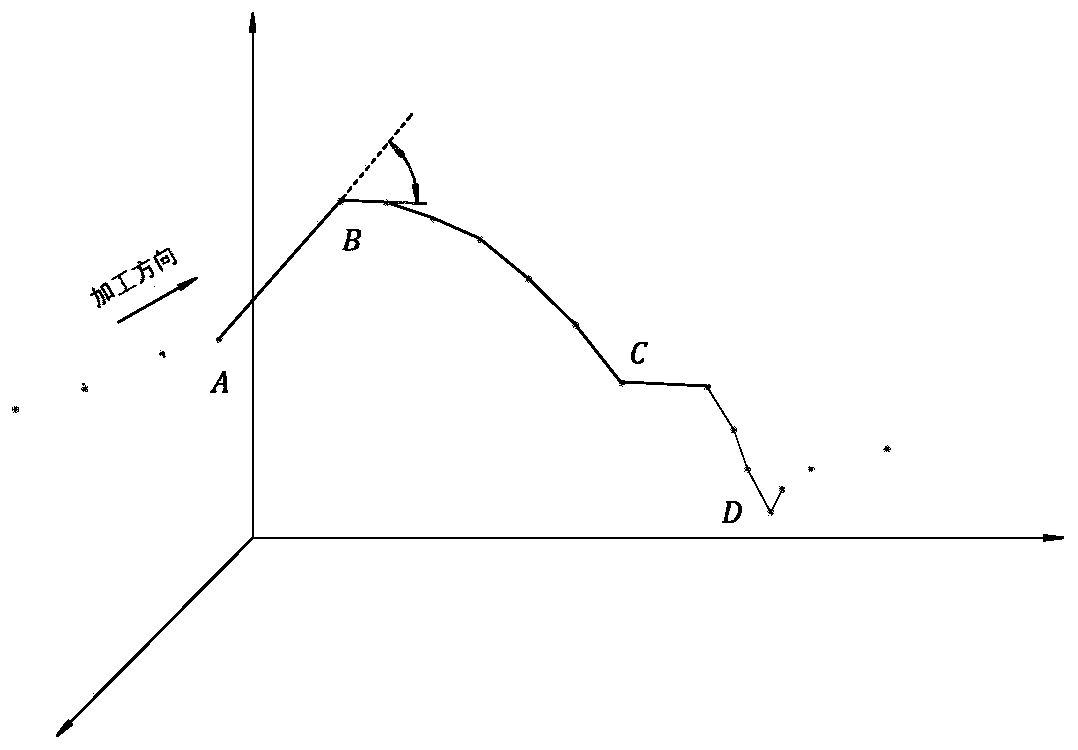
Method for smoothing inflection point of discrete processing path
ActiveCN105955194AIncrease the radius of curvatureGood kinematic performanceNumerical controlComputational scienceNumerical control
The invention relates to a method for smoothing an inflection point of a discrete processing path, and belongs to the field of high-speed high-performance numerical control processing. The method is characterized in that an externally tangent quintic B-spline curve with 9 control points is adopted to carry out smoothing processing on the inflection point of the discrete processing path, and problems of low speed and easy fluctuation in conventional discrete path inflection point processing are solved. The method comprises the steps of firstly constructing concrete forms of a characteristic polygon of a B-spline curve formed by the 9 control points and a node vector of the characteristic polygon with the aid of a vertex overlapping method and a convex-hull property, and back calculating the control points under the constraint of approximating to an error allowance value; then carrying out one-time correction on the control point by adopting a proportion regulating algorithm based on a length constraint of a transition section; and finally, and acquiring a quintic B-spline curve for inflection point smoothing according to the acquired characteristic polygon and the node vector. The method provided by the invention can enable the smoothed path to reach G1 continuity, and the smoothed curve has a greater curvature radius at the inflection point under the same error approximating condition compared with an internally tangent method.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
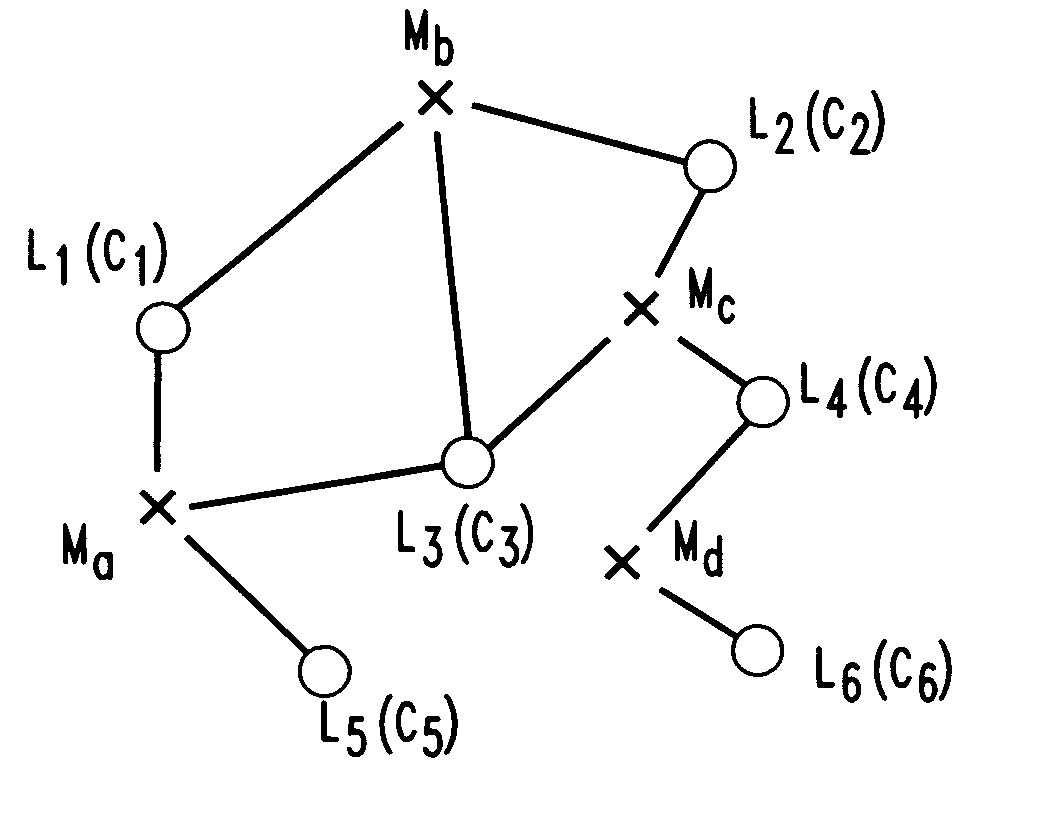
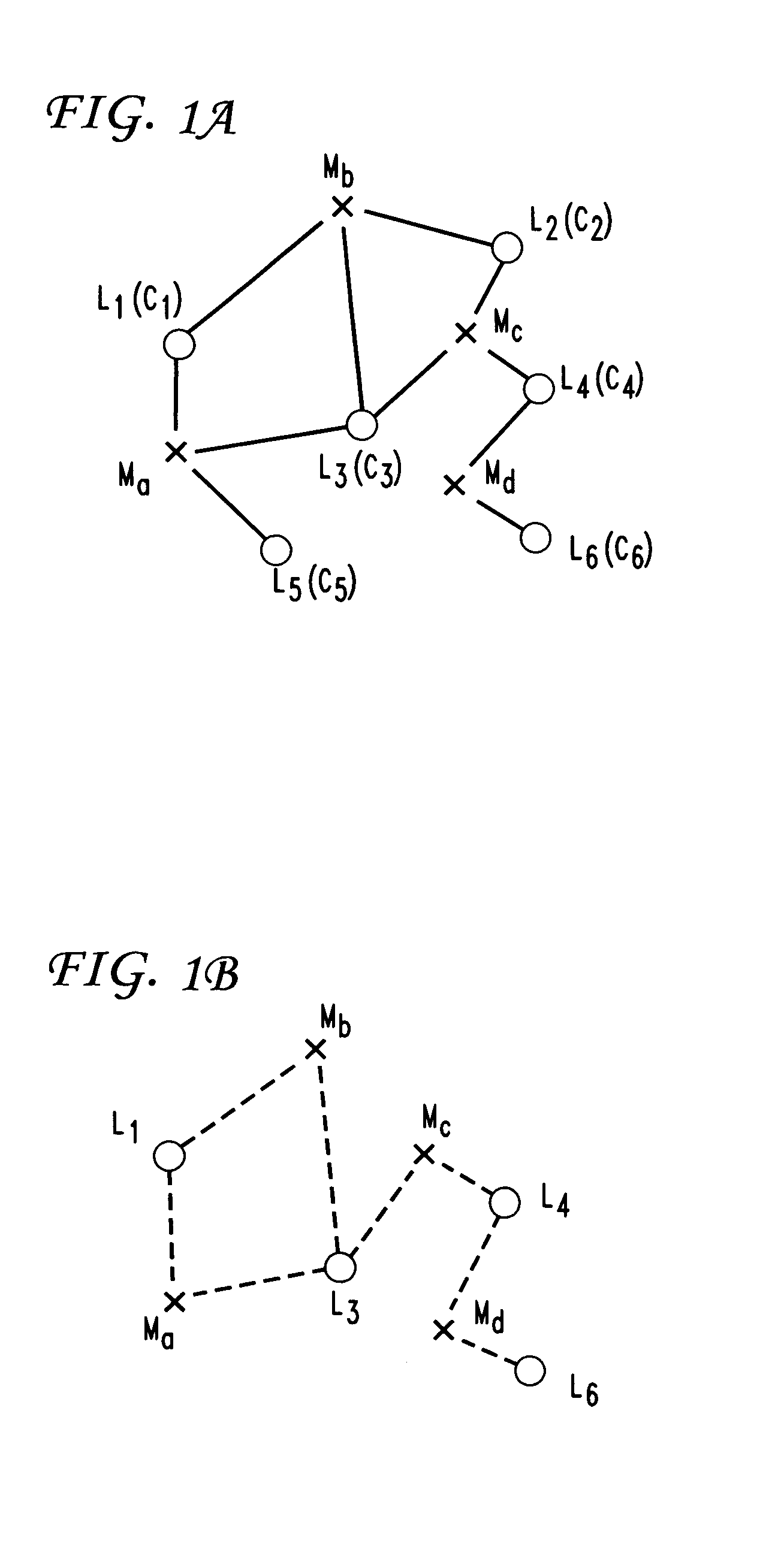
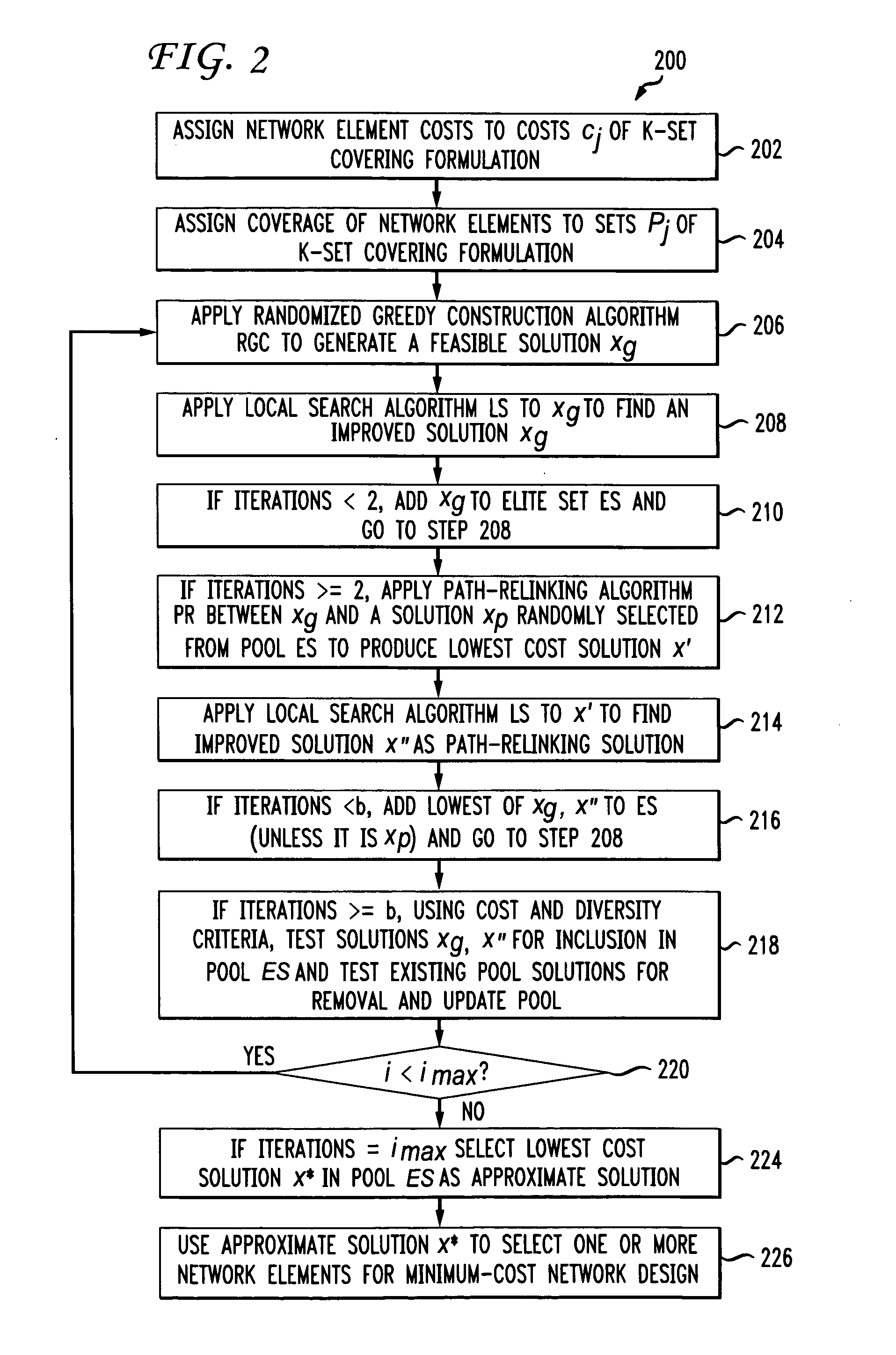
Networks with redundant points of presence using approximation methods and systems
Minimum cost networks, such as cellular networks, able to supply k-fold coverage to users, are obtained by defining potential network elements having cost and coverage parameters, and selecting from these available network elements using an iterative approximation method or system that first constructs a k-set coverage formulation incorporating the cost and coverage parameters of the available network elements, and then finds an optimal solution to the k-set coverage formulation using applications of GRASP (greedy randomized adaptive search procedure) and path-relinking heuristics. In one version, GRASP and path-relinking start from a random choice of a network element and build feasible solutions using greedy construction, local search and path-relinking heuristics that are iteratively applied to find an approximate solution. In a second version, a Lagrangian relaxation formulation of the k-set coverage formulation is solved with iterative subgradient optimization methods, and a Lagrangian heuristic that finds a feasible solution at each iteration of the subgradient optimization method, to modify the subgradient optimization and find an approximate feasible solution. The Lagrangian heuristic may be a greedy construction heuristic applied at each iteration of the subgradient optimization method, or may be a GRASP with path-relinking heuristic applied at each iteration of the subgradient optimization method to find an approximate feasible solution. The approximate solutions to the k-set coverage formulation are then used to select at least some of the potential network elements for use in a minimum cost network. The method and system may be software or hardware implementations of conventional computer equipment enabling good approximate solutions to be obtained in reasonable times.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
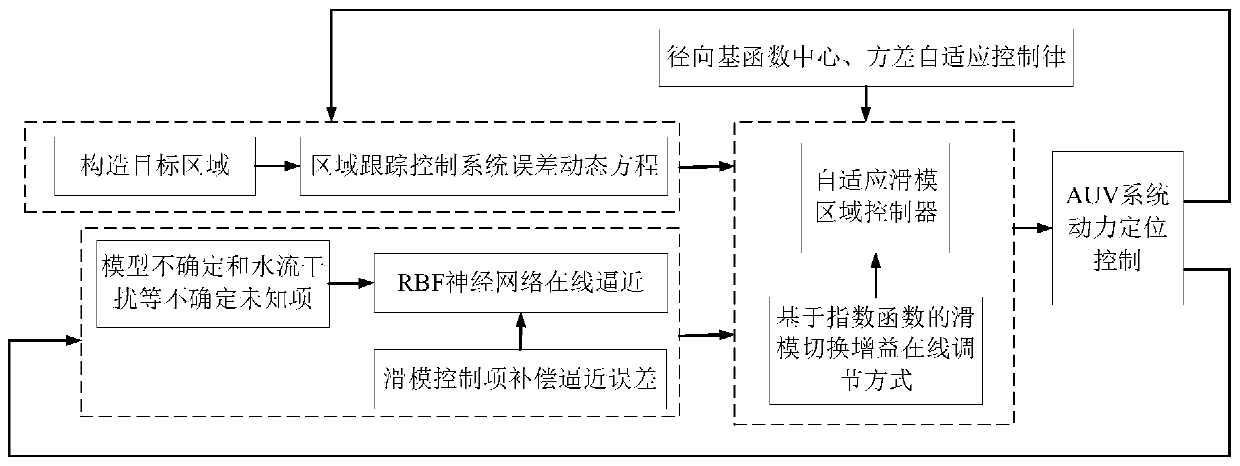
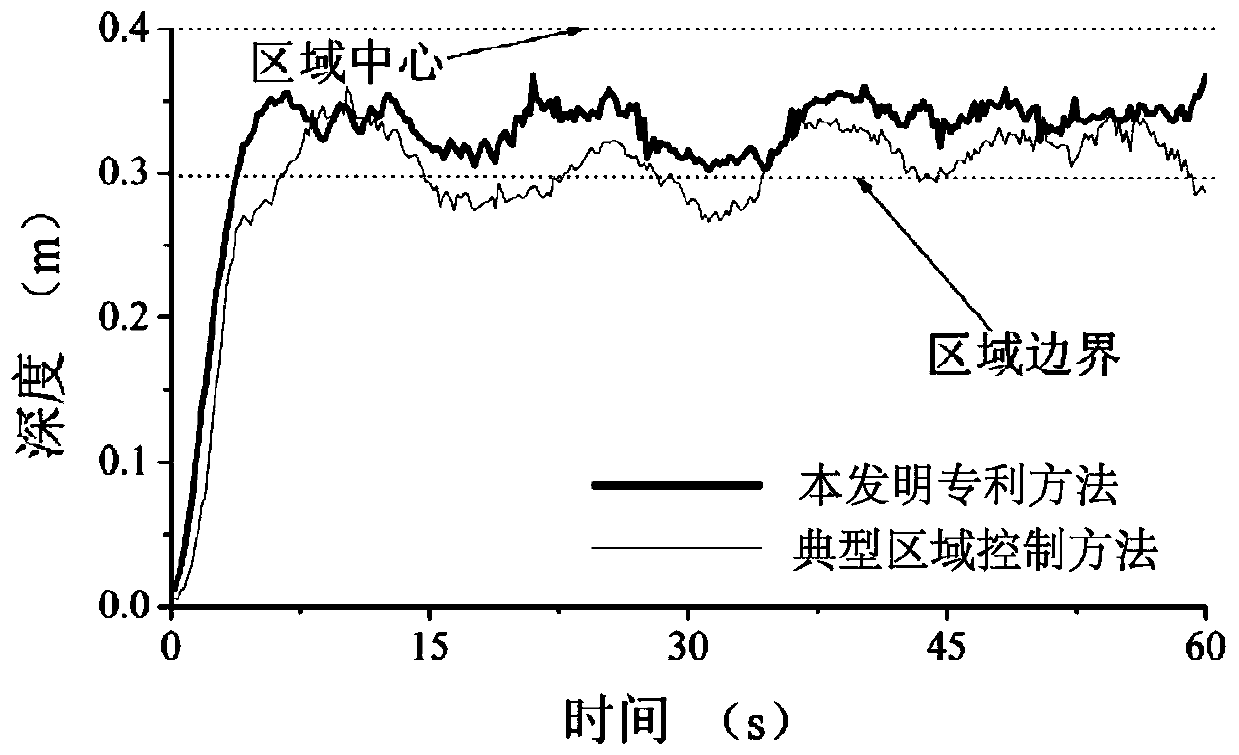
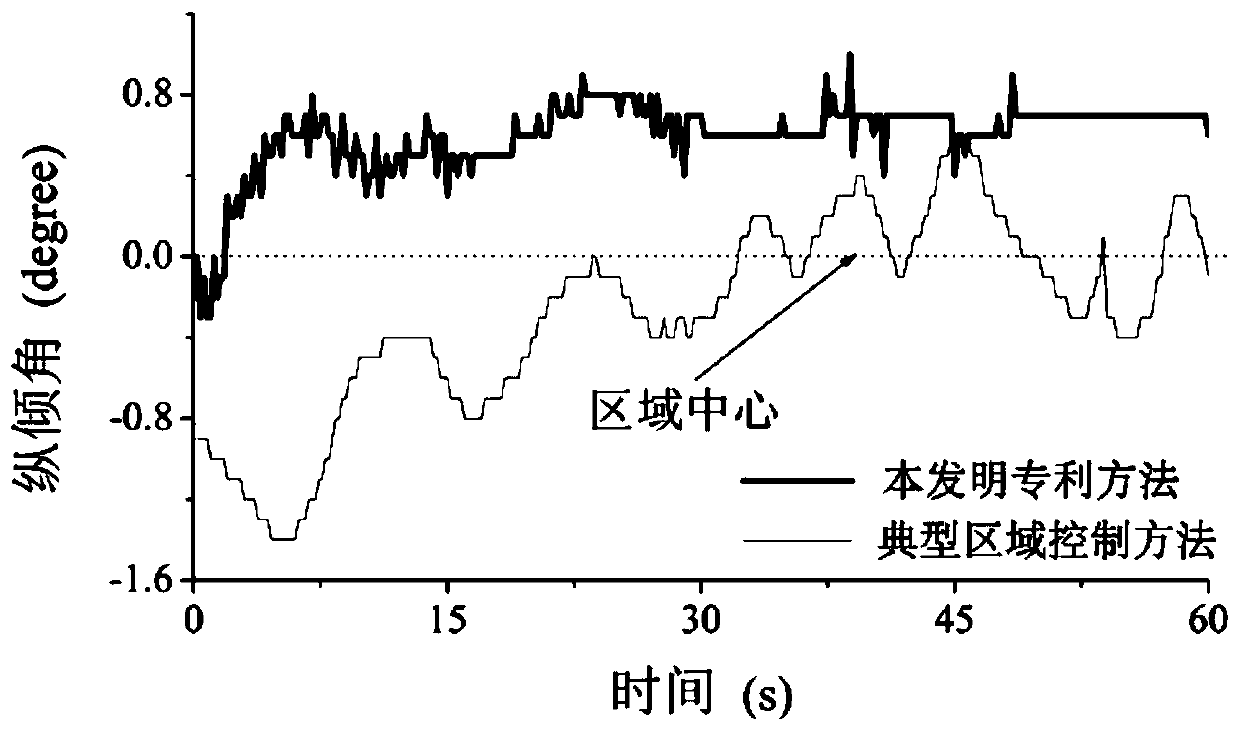
Underwater robot self-adaptive regional dynamic positioning control method based on RBF neural network
ActiveCN110597069AGuaranteed convergenceThere will be no frequent forward and reverse switchingAdaptive controlDynamic equationPosition control
The invention relates to an underwater robot self-adaptive regional dynamic positioning control method based on a RBF neural network. The underwater robot self-adaptive regional dynamic positioning control method belongs to the field of underwater robot dynamic positioning control. The underwater robot self-adaptive regional dynamic positioning control method comprises the steps of: establishing asix-degree-of-freedom spatial motion model of an AUV, and constructing a target region and an region control system error dynamic equation; adopting the RBF neural network to carry out online approximation on an unknown vector, and adopting a sliding mode control item to compensate for an approximation error; performing online adjustment on network weight, a radial basis function center and variance; adopting a sliding mode switching gain online adjustment mode based on an exponential to avoid high-frequency buffeting of a control system caused by overlarge sliding mode switching gain; and performing dynamic positioning control on the AUV by means of a neural sliding mode region controller, so that the position and attitude vectors eta are converged into the target region. The underwaterrobot self-adaptive regional dynamic positioning control method solves the AUV dynamic positioning control problem under the influence of factors such as external interference and measurement precision of an underwater sensor, improves the dynamic positioning precision, and can still be quickly converged into the target region when the properties of the AUV change.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Machining method based on Bezier curve corner smooth transition algorithm
ActiveCN111061213ASolve the feed rateError controllableNumerical controlManufacturing computing systemsAlgorithmEngineering
The invention discloses a machining method based on a Bezier curve corner smooth transition algorithm. The machining method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring discrete data points of the tracks of small line segments by using CAD / CAM software; secondly, reading in three data points, marking a middle point as an inflection point, and calculating the length, the rotation angle and theunit direction vector of micro line segments on the two sides of the inflection point; thirdly, constructing different corner arc transition vector models with G2 continuous characteristics accordingto the value range of the central angle; fourthly, calculating a transition error and a curvature extreme value, determining the positions of transfer points on the two sides of the corner and the length of a transition section according to a preset approximate error constraint and a maximum curvature limit, and substituting the positions and the length into the model to solve a transition curve,thus completing smooth transition of one corner; and fifthly, repeatedly reading in data points, sequentially finishing smooth transition of all corners, and outputting a processing path for realizing smooth connection between small line segments by adopting the transition curves.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
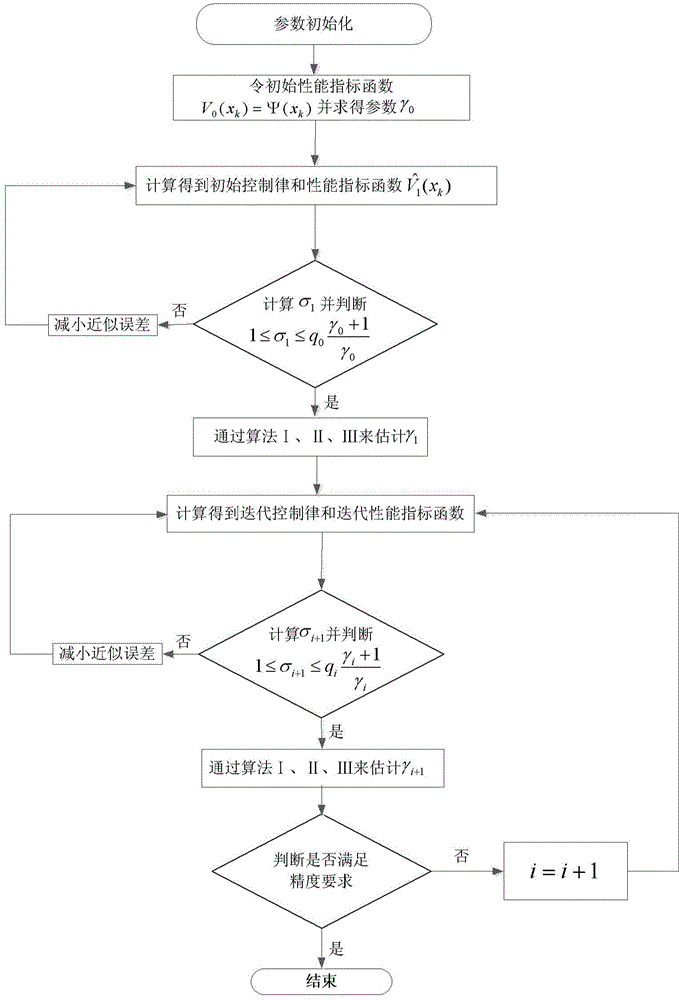
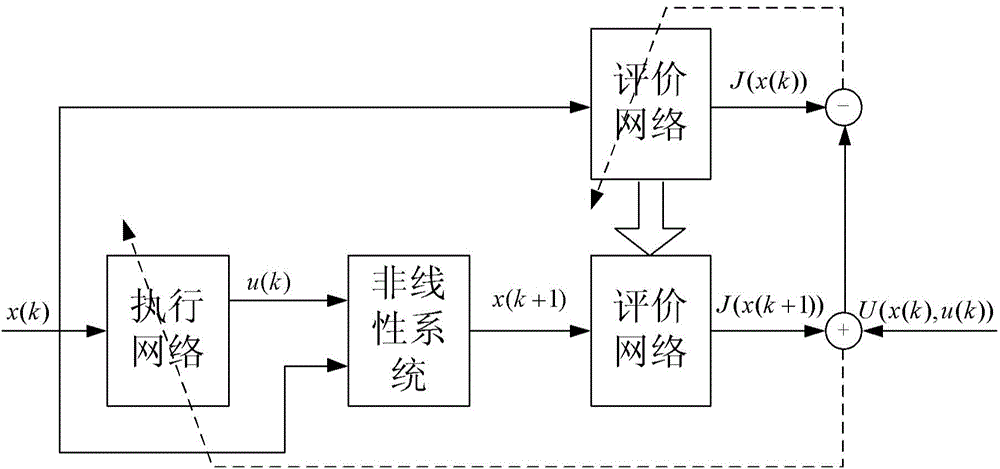
Non-linear system adaptive optimal control method based on variable error
InactiveCN104834221AGuaranteed convergenceGuaranteed stabilityAdaptive controlNerve networkSimulation
The invention discloses a variable error non-linear adaptive control method; a proper approximation error is introduced to approach a performance index function and a strategy control function, so the index function can finally realize uniform convergence. The method combines with a nerve network; because of excellent approach performance of the nerve network, and evaluate network and strategy network approximation errors can be simultaneously adjusted, so finally the performance index function can be converged into a neighborhood of an optimal evaluate function.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and methods for providing signal-specialized parametrization
InactiveUS7071936B2Minimize signalingImprove textureCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingPattern recognitionImage resolution
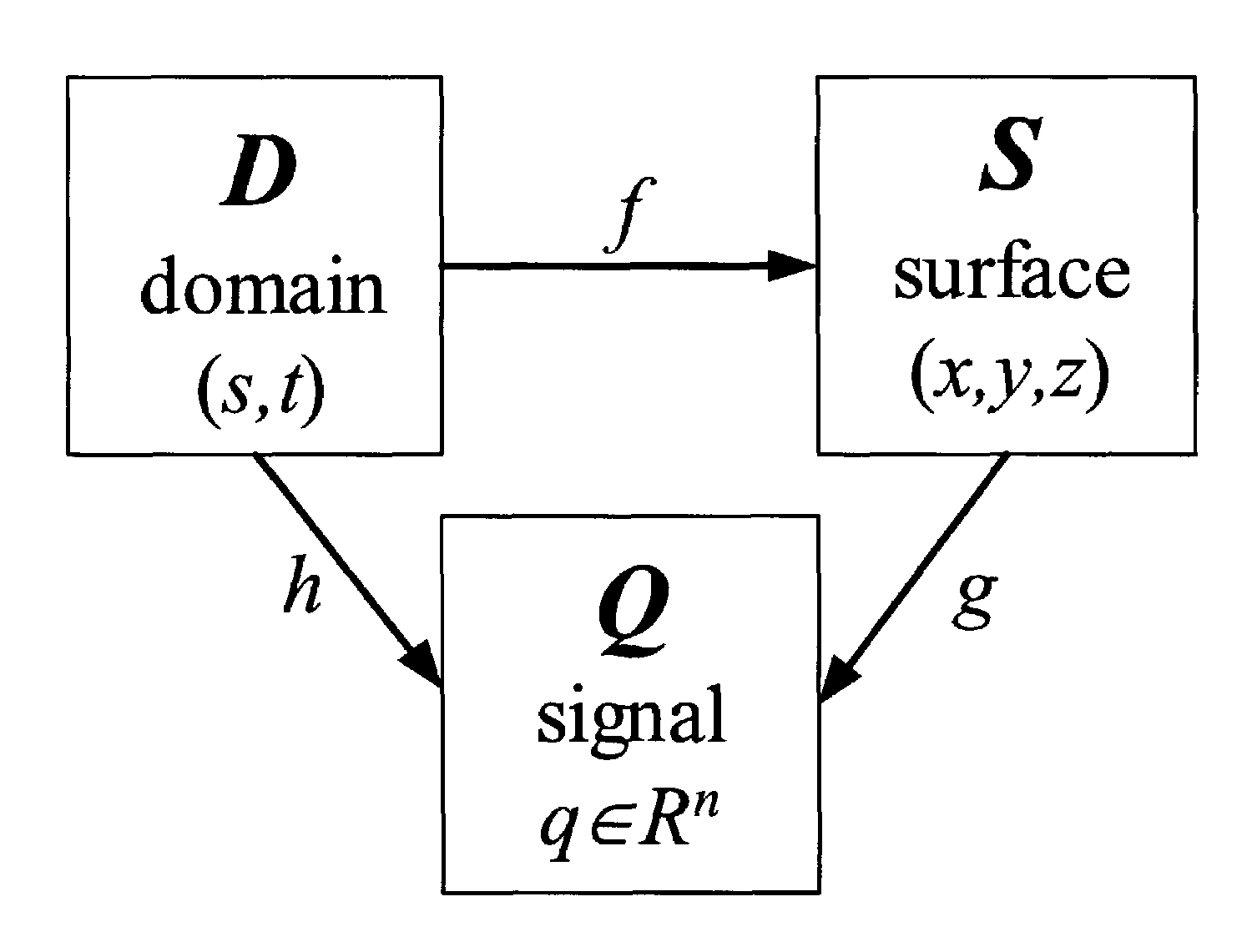
Systems and methods are provided for optimizing a parametrization scheme in accordance with information about the surface signal. A surface parametrization is created to store a given surface signal into a texture image. The signal-specialized metric of the invention minimizes signal approximation error, i.e., the difference between the original surface signal and its reconstruction from the sampled texture. A signal-stretch parametrization metric is derived based on a Taylor expansion of signal error. For fast evaluation, the metric of the invention is pre-integrated over the surface as a metric tensor. The resulting parametrizations have increased texture resolution in surface regions with greater signal detail. Compared to traditional geometric parametrizations, the number of texture samples can often be reduced by a significant factor for a desired signal accuracy.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com