Patents
Literature
39results about How to "Good kinematic performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
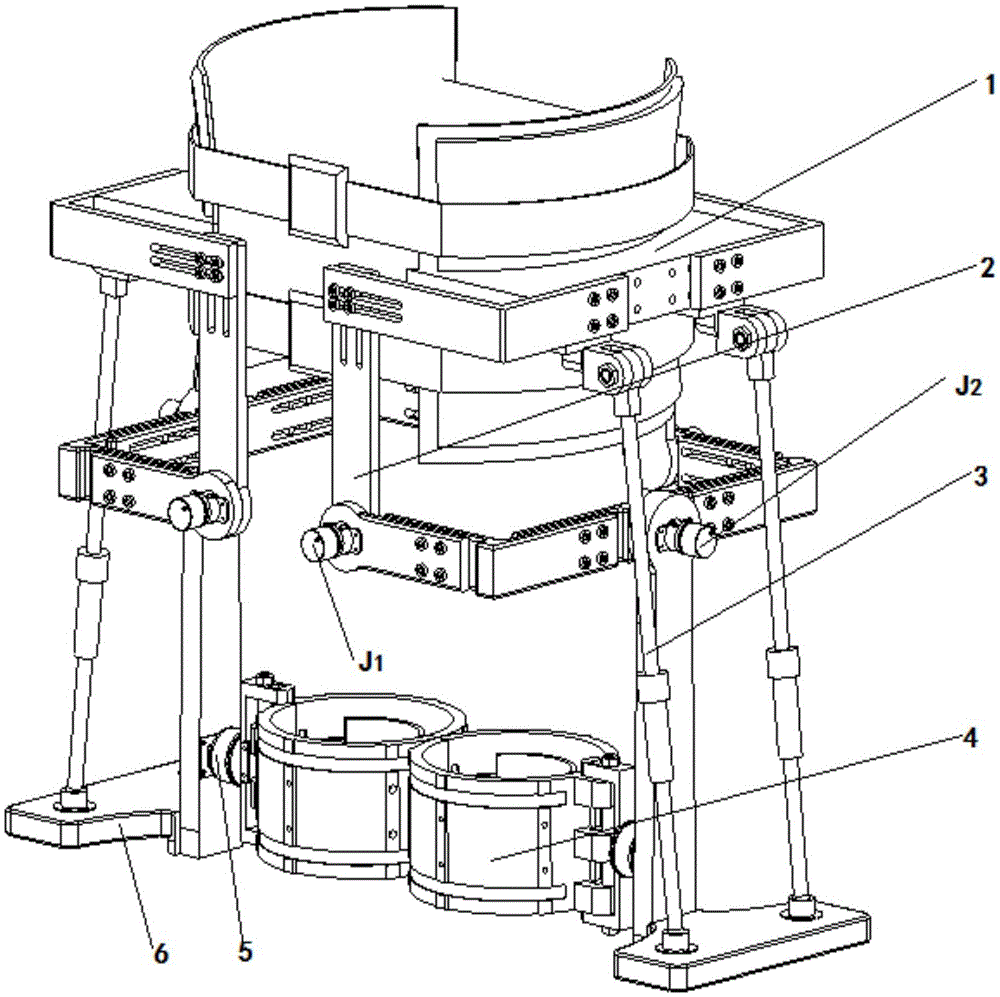
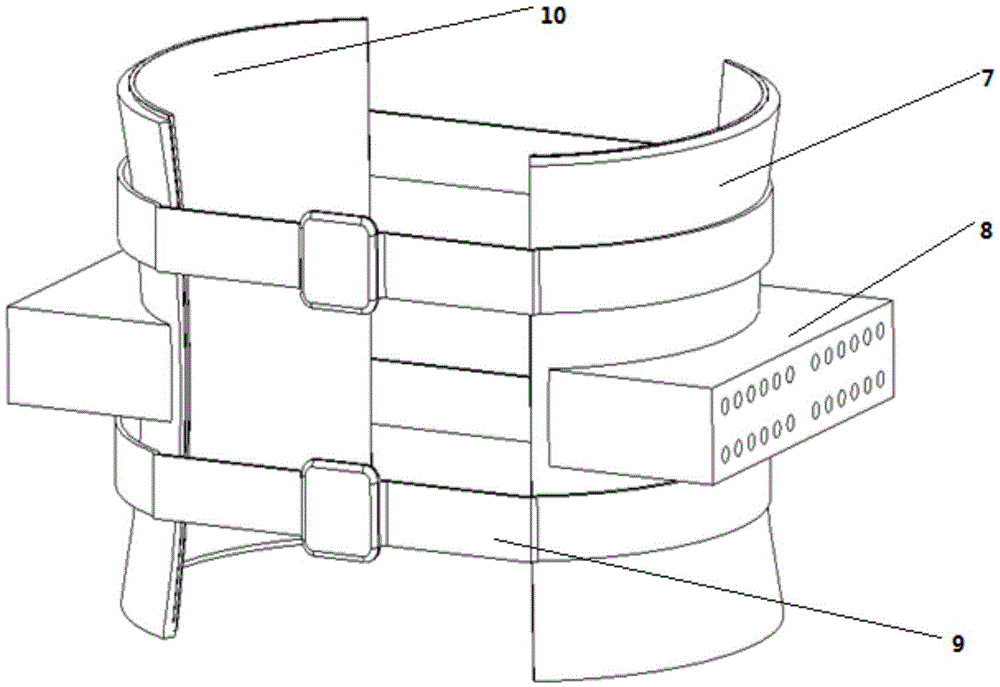
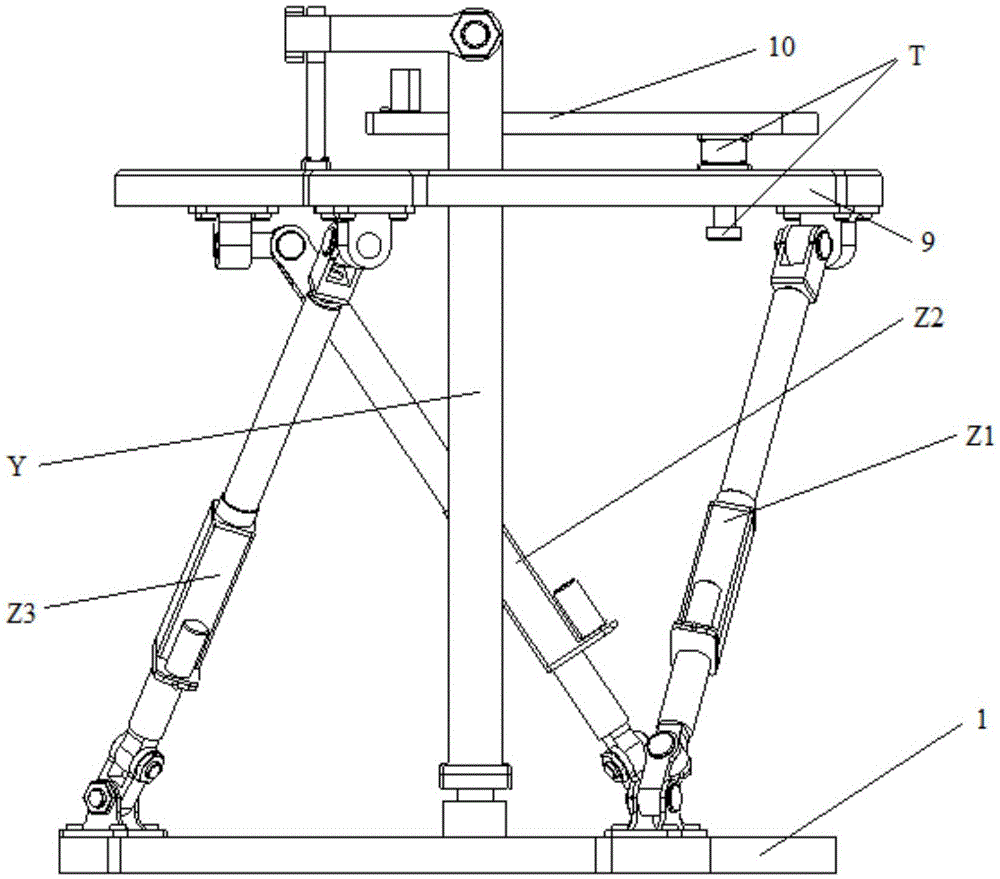
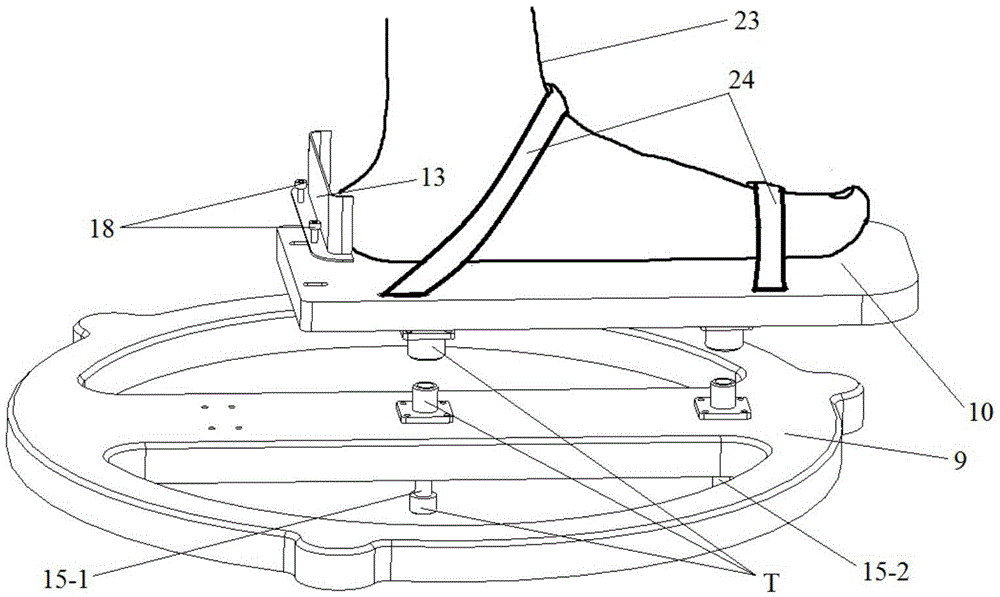
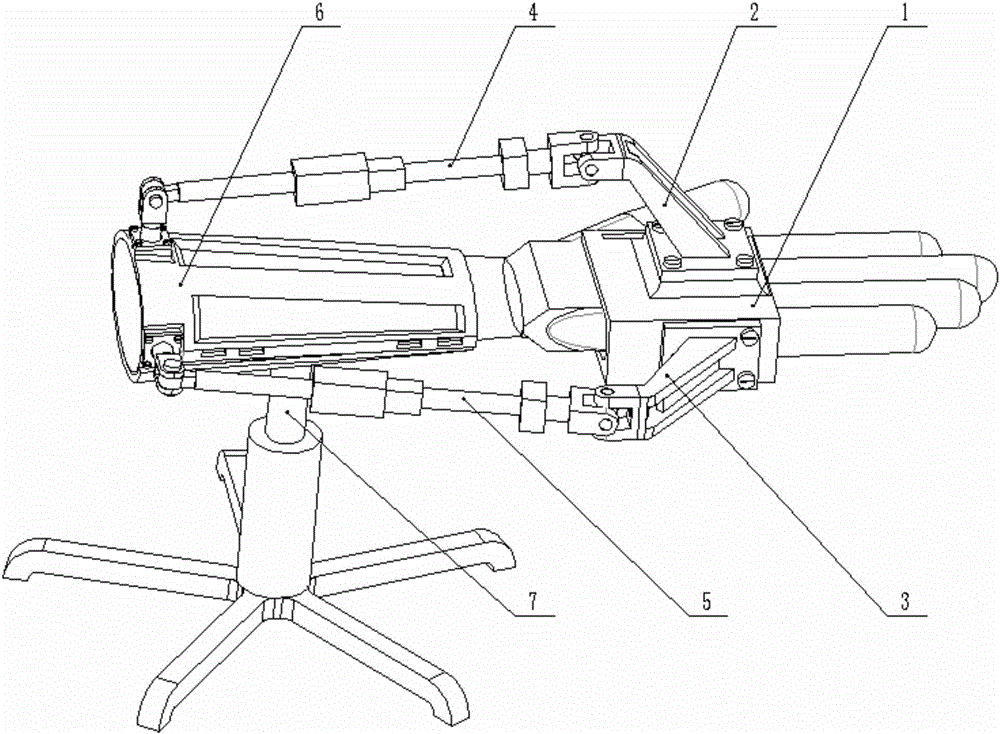
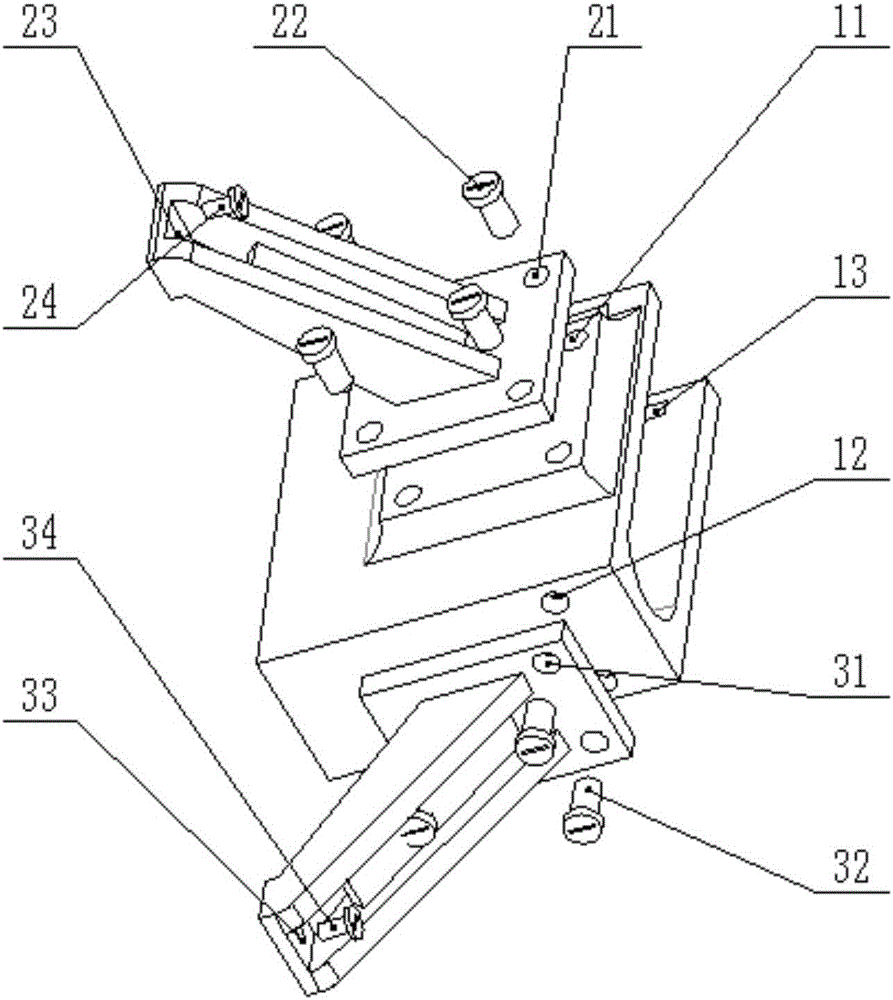
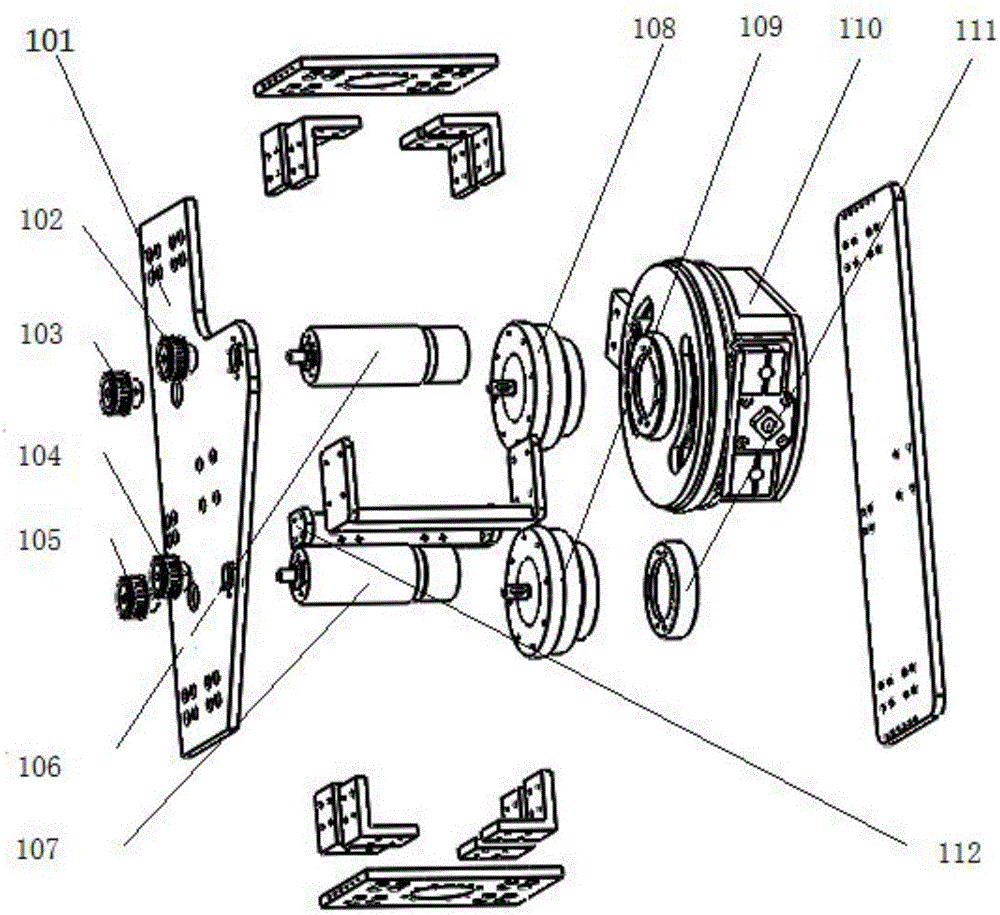
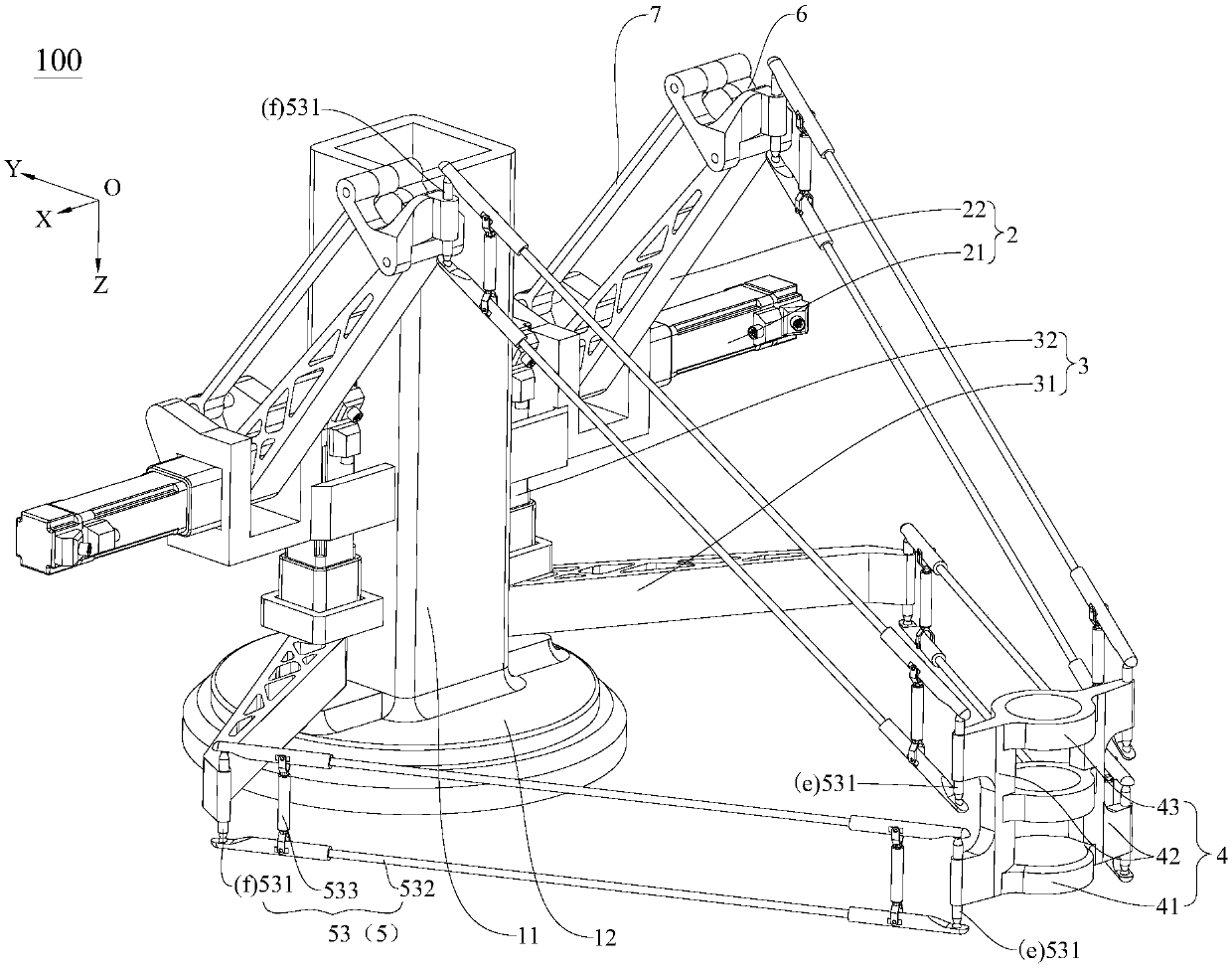
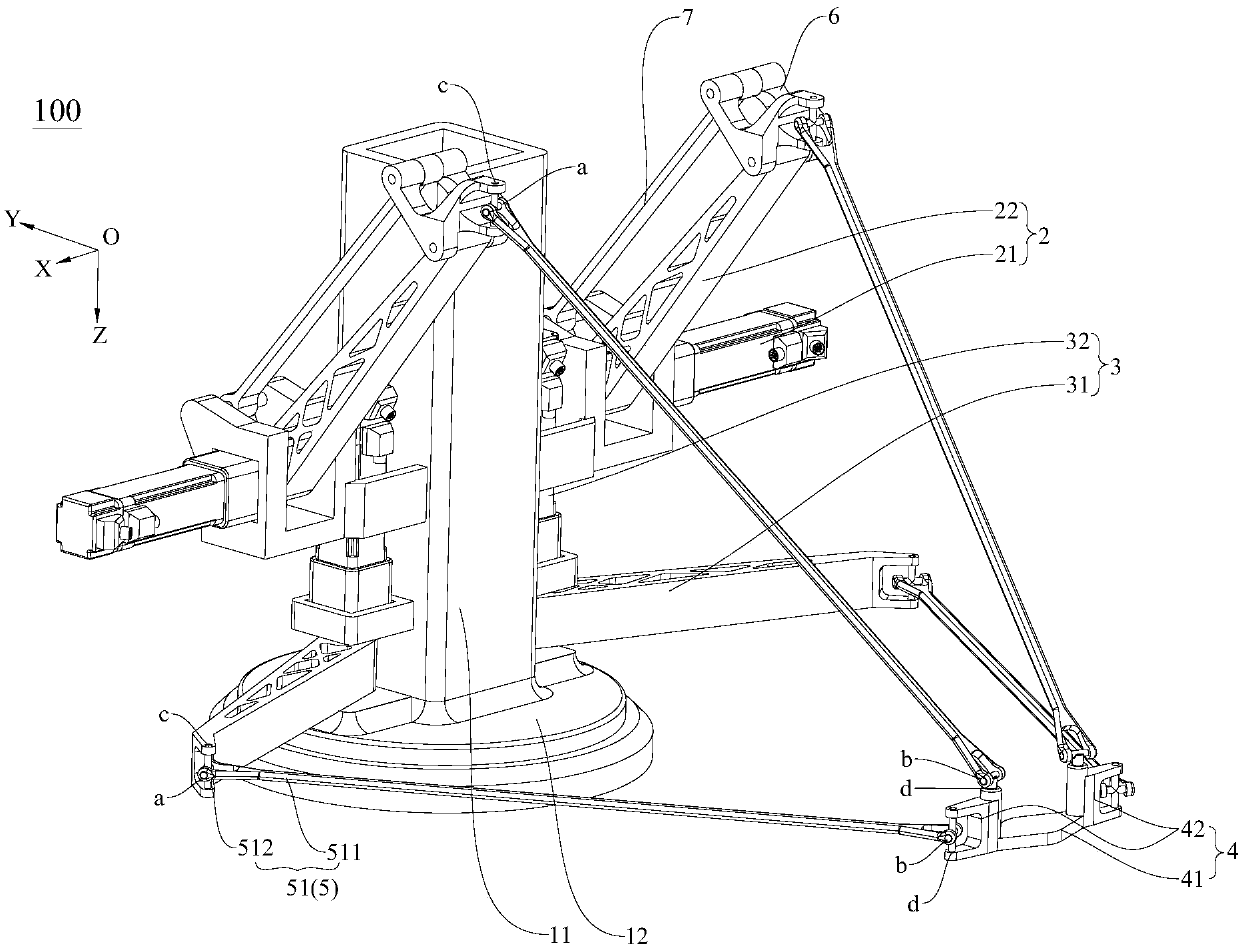
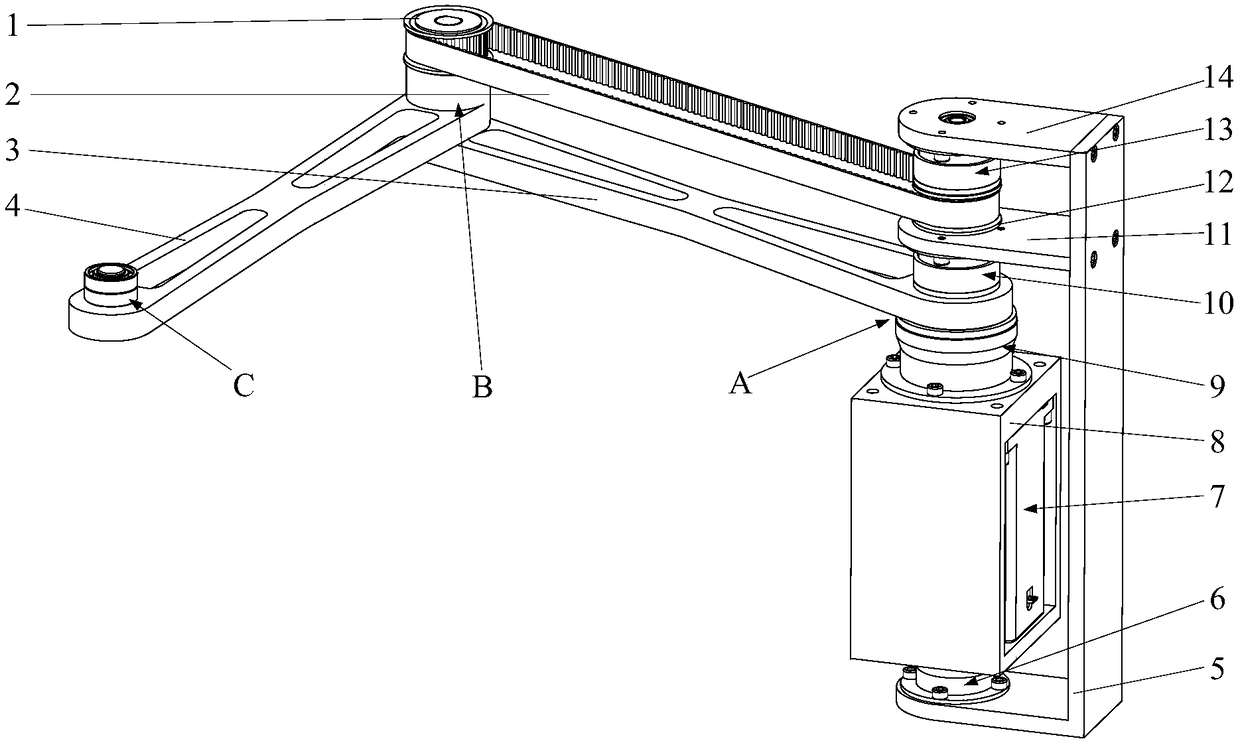
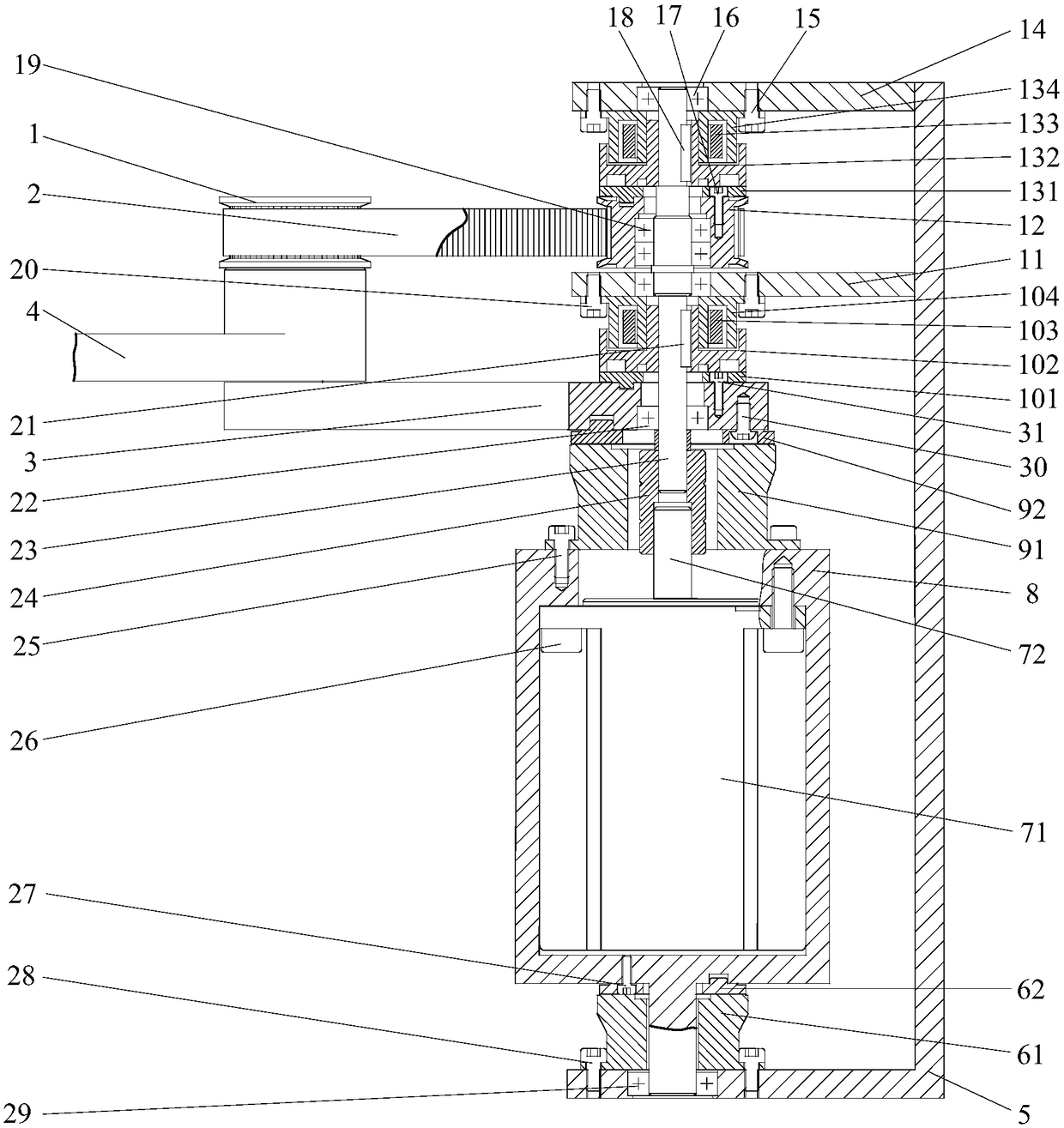
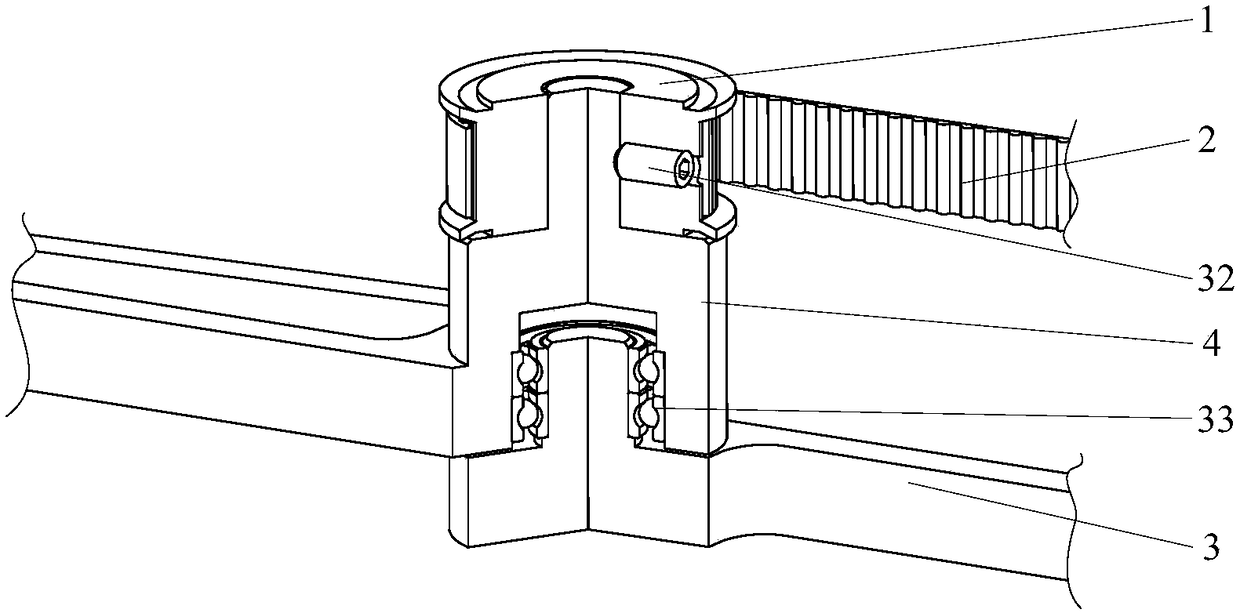
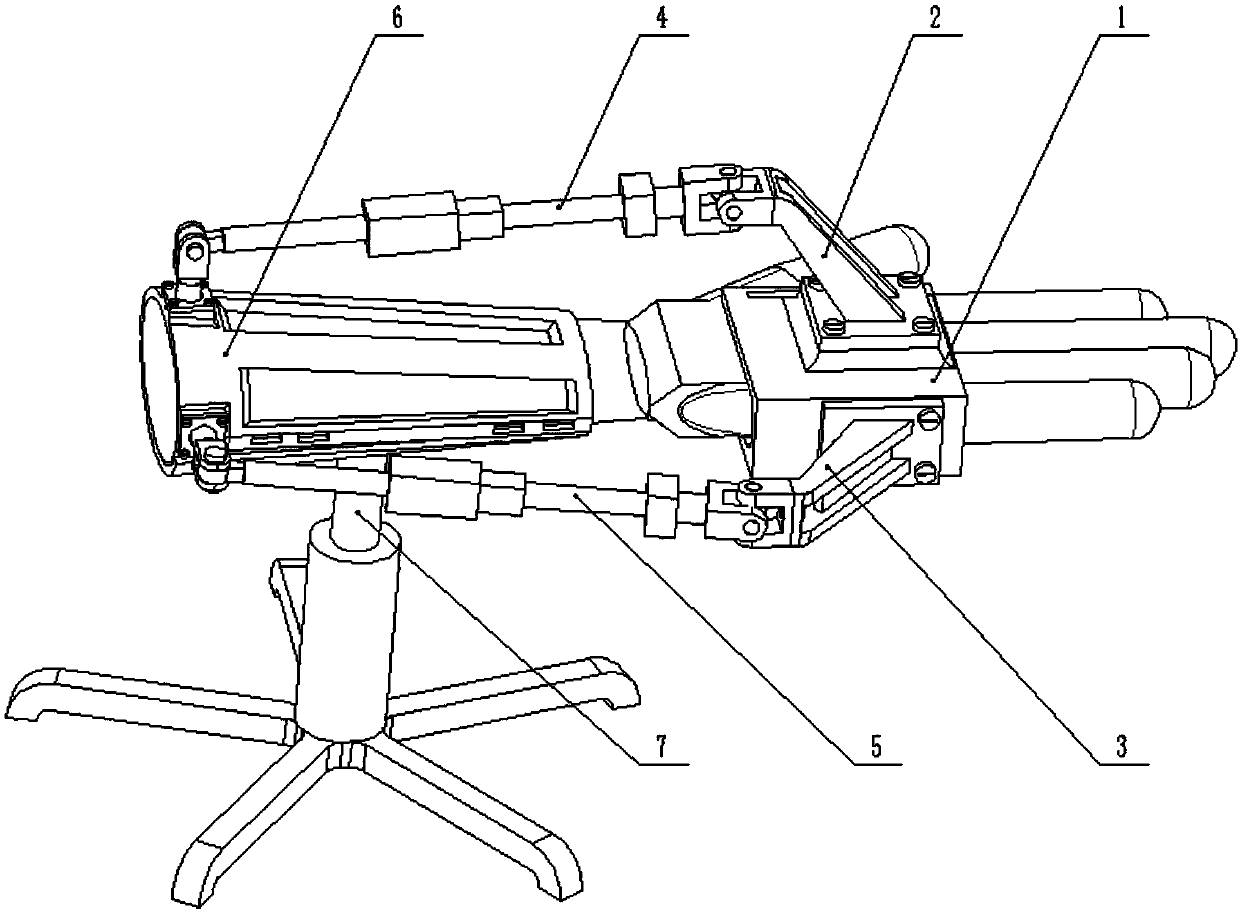
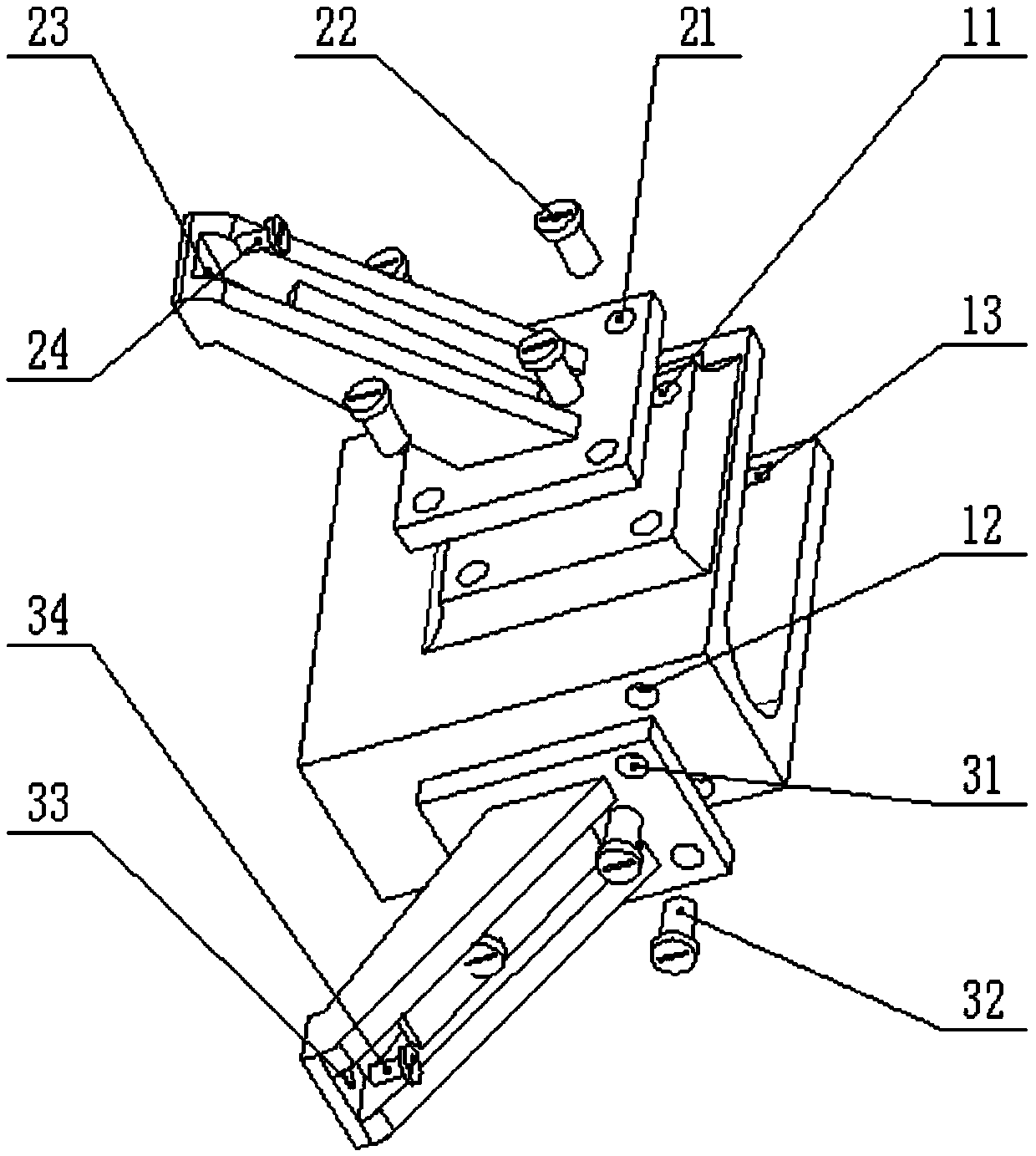
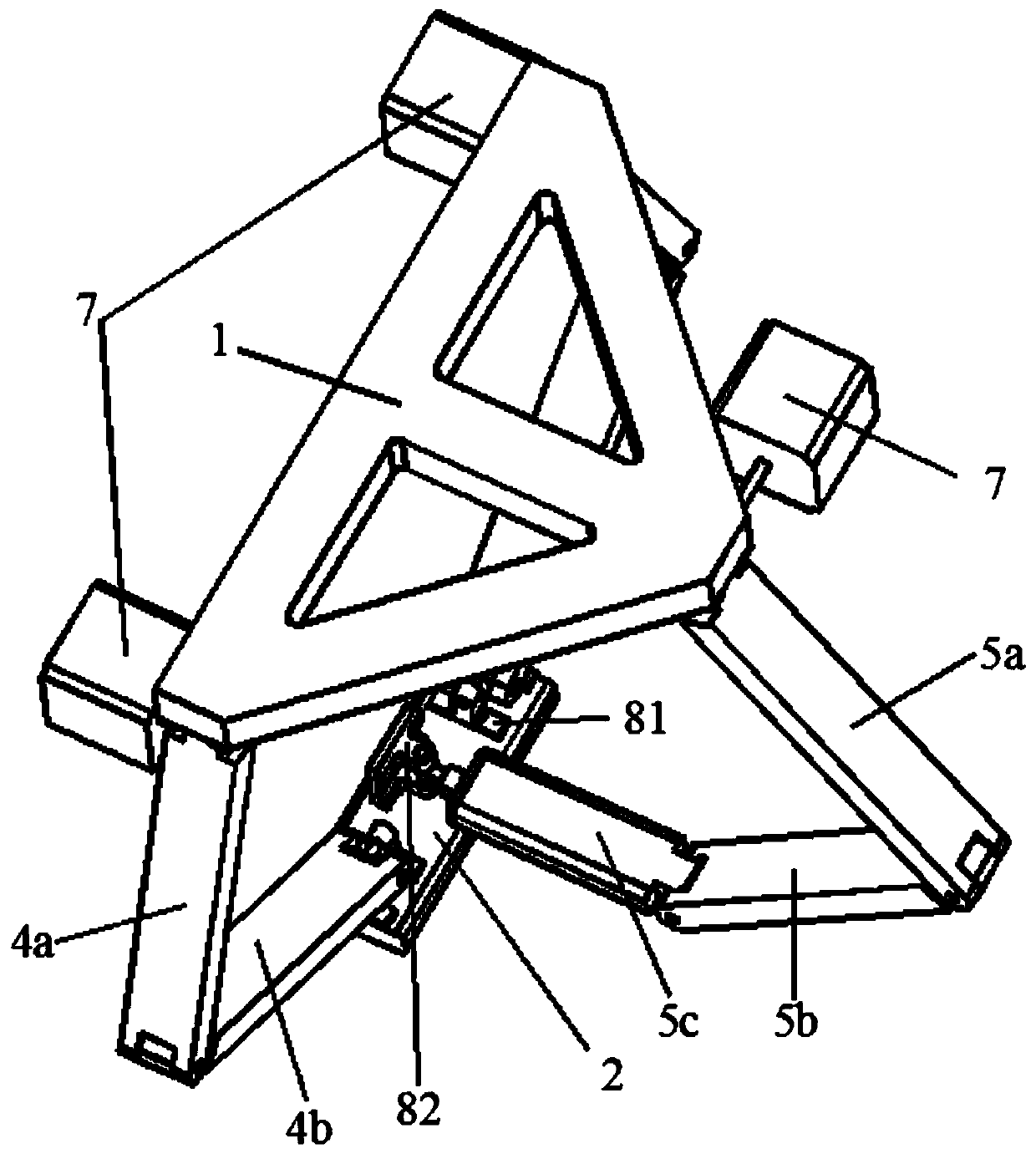
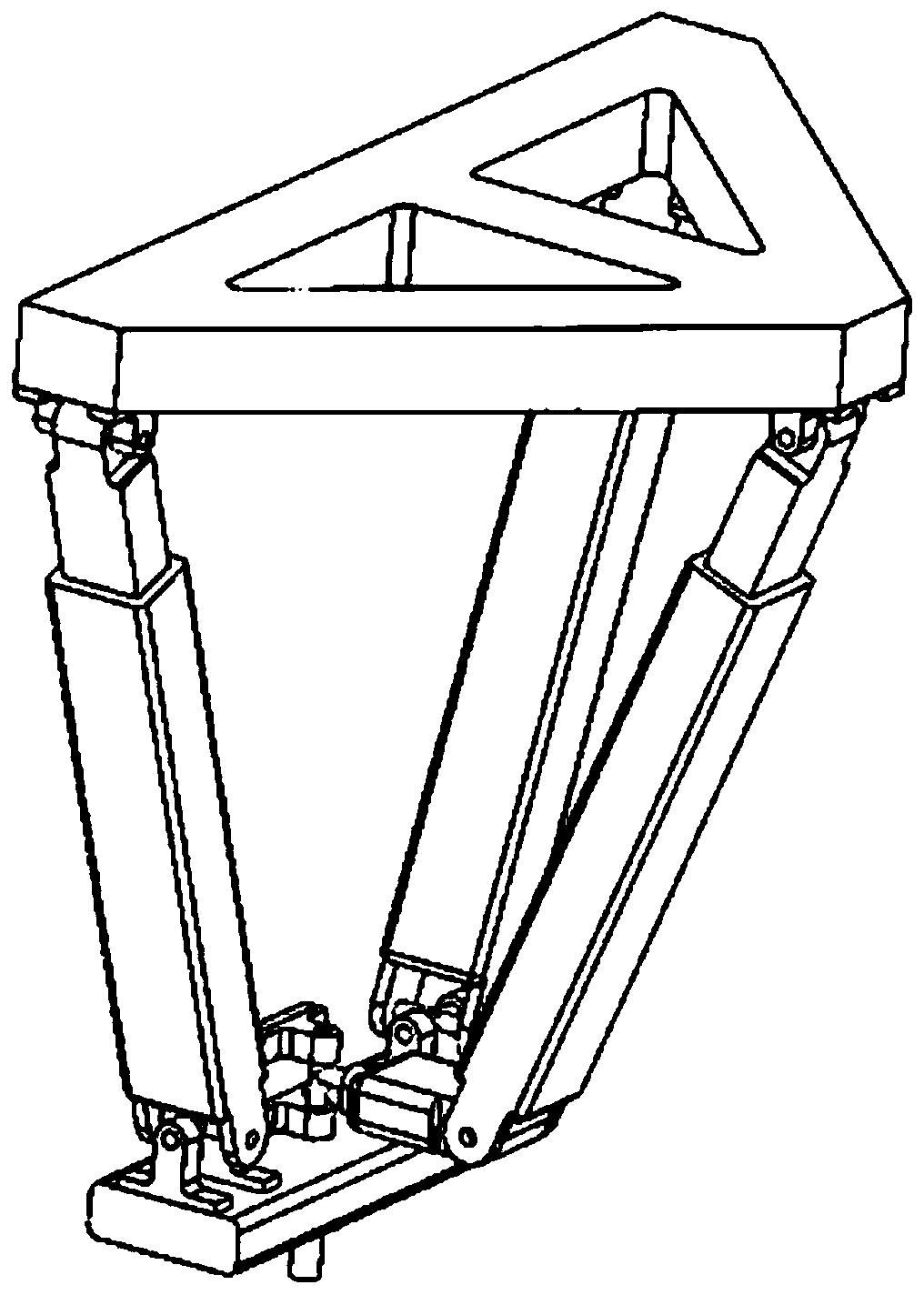
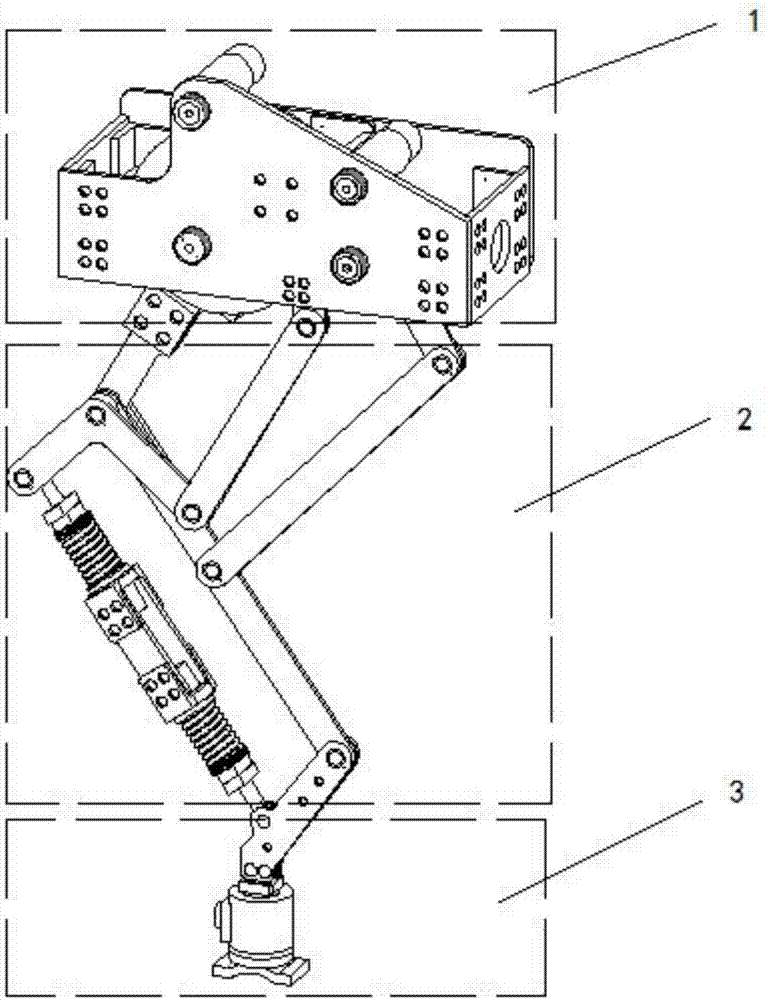
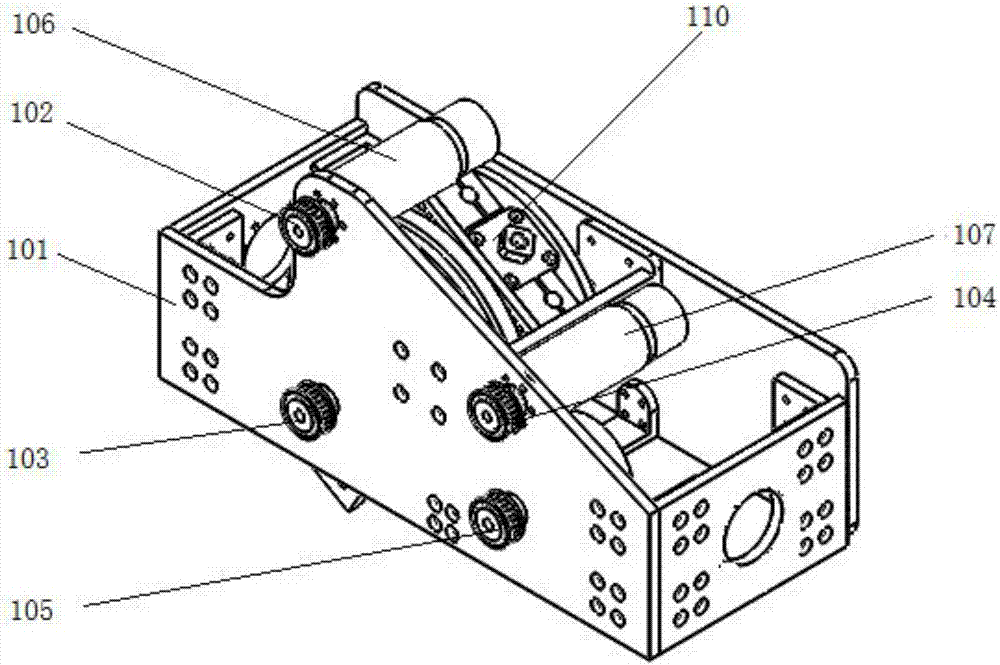
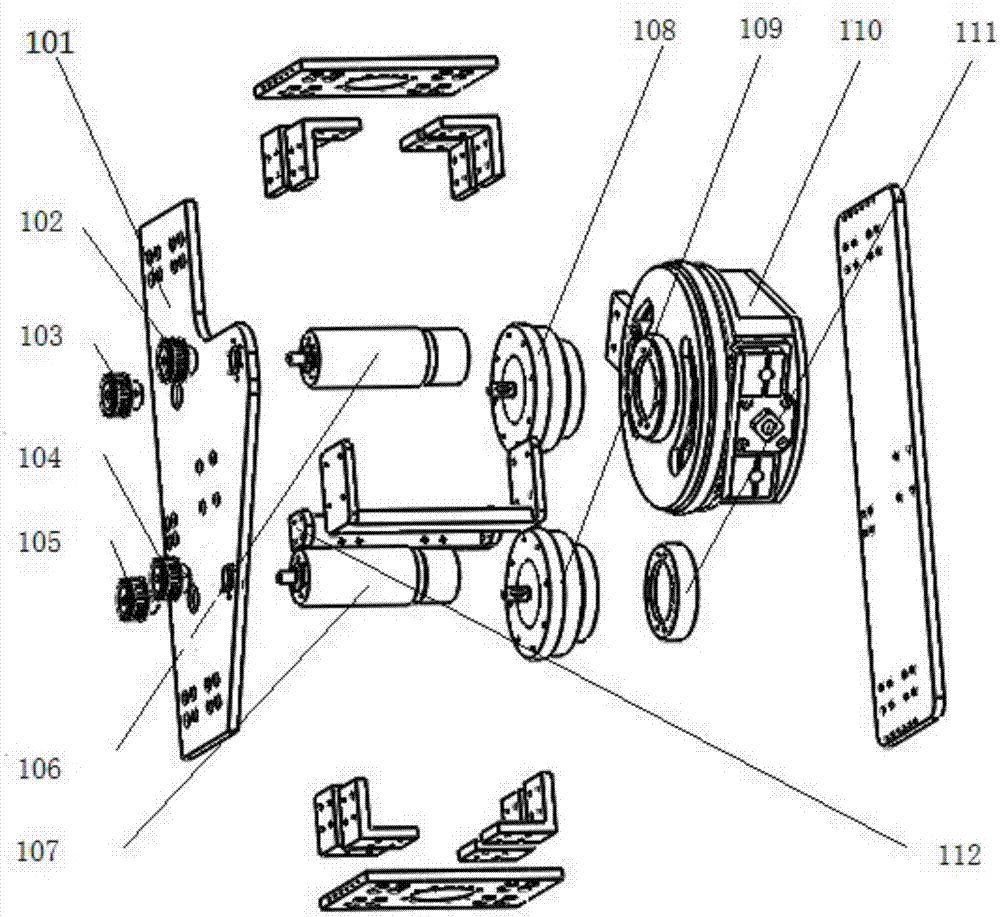
Hip joint boosting device based on parallel mechanisms
InactiveCN105496729AAvoid harmAvoid interferenceChiropractic devicesWalking aidsHip rotationThree degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a hip joint boosting device based on parallel mechanisms. The boosting device comprises a waist support assembly, two constraint assemblies and two execution assemblies; each execution assembly comprises a leg clamping sub assembly, a sensor sub assembly, a fixing plate and two driving branch chain sub assemblies, the driving branch chain sub assemblies are connected with the waist support assembly and the corresponding fixing plates and are UPS branch chains which are symmetrically distributed relative to the front and back of the leg of a person, and each sensor sub assembly is connected with the corresponding leg clamping sub assembly and the corresponding constraint assembly. According to the hip joint boosting device based on the parallel mechanisms, by means of the design of the constraint assemblies and the execution assemblies, three-degree-of-freedom rotation of the device can be achieved, it is guaranteed that the rotation center of the device is overlapped with that of hip joints of different patients, and injuries caused by human-machine interference force is effectively avoided; meanwhile, the structure is simple, and use is convenient.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
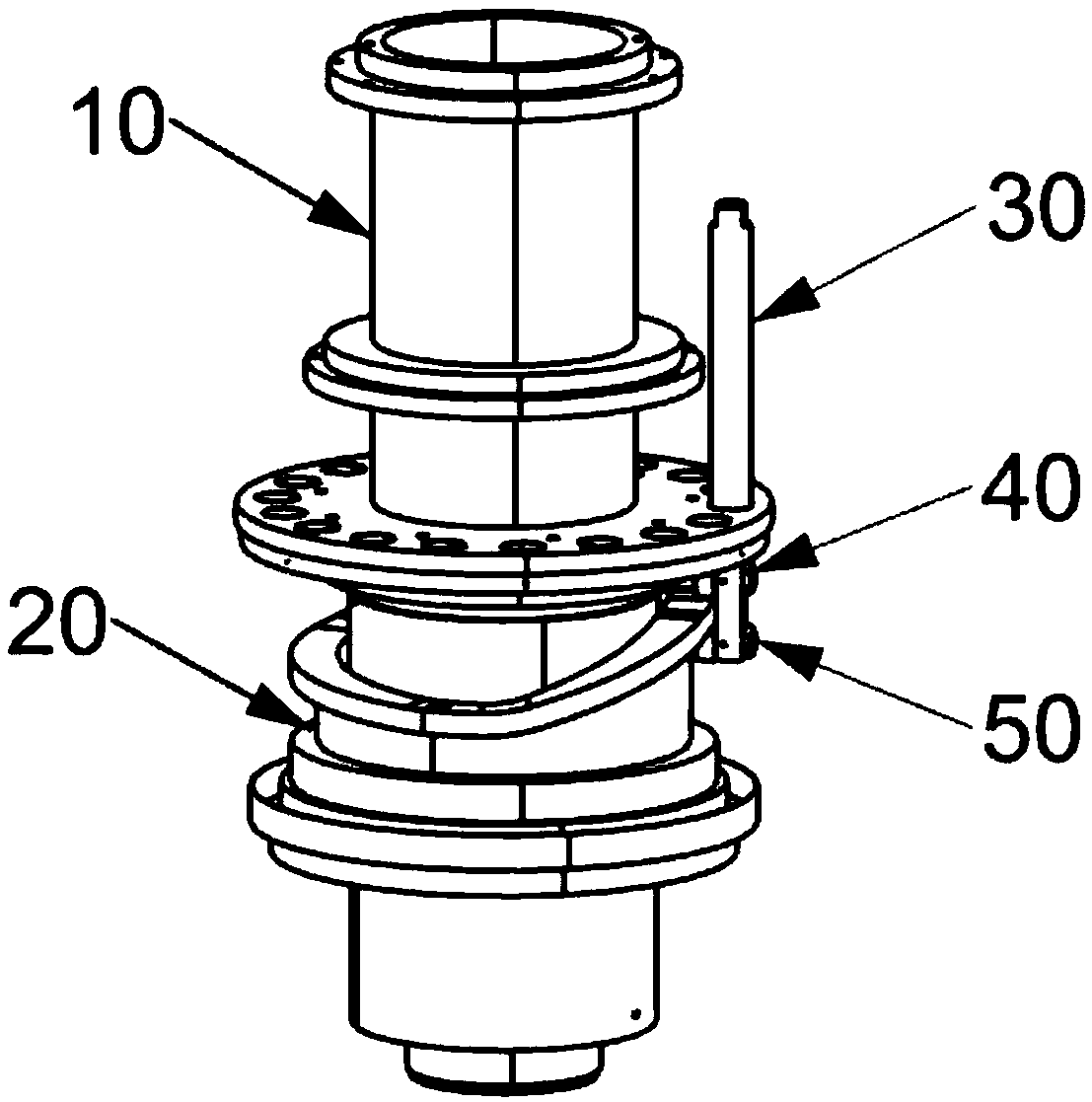
Ankle joint rehabilitation mechanism with driving branch chains arranged obliquely
The invention provides an ankle joint rehabilitation mechanism with driving branch chains arranged obliquely and relates to the field of rehabilitation medicine instruments. The ankle joint rehabilitation mechanism comprises a base, a movable platform, the driving branch chains and a restraining branch chain. The restraining branch chain comprises a lower rotating connecting rod, a first symmetric connecting rod, a second symmetric connecting rod and an upper arc connecting rod, wherein the lower rotating connecting rod is connected with a central shaft of the base through a bearing. The movable platform comprises a foot baffle, an upper platform body, a lower platform body and a connecting piece located between the two platform bodies, wherein the position, relative to the upper platform body, of the feet can be adjusted through the foot baffle and the connecting piece. The driving branch chains comprise the first driving branch chain, the second driving branch chain and the third driving branch chain, and the three driving branch chains are UPS branch chains arranged obliquely with the same oblique angle. By means of the structure, the movable platform can rotate in three mutually orthogonal directions, and meanwhile it can be ensured that the rotating center of the movable platform coincides with the rotating center of the ankles. The ankle joint rehabilitation mechanism is simple, stable in driving and low in cost; in addition, the driving branch chains are arranged obliquely to avoid the singular configuration of the mechanism, and good kinematic performance is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Three-degree-of-freedom mobile decoupling parallel robot mechanism
InactiveCN102699907AReverse solution is simpleSimplify trajectory planningProgramme-controlled manipulatorThree degrees of freedomEngineering
A three-degree-of-freedom mobile decoupling parallel robot mechanism is mainly composed of a fixed platform, a movable platform and three branches for connecting the two platforms. One end of a connecting rod of the first branch is connected with the fixed platform through a rotating pair, the other end of the connecting rod is connected with the other connecting rod through the rotating pair, the other end of the other connecting rod is connected with one end of a third connecting rod through a movable pair, and the other end of the third connecting rod is connected with the movable platform through the movable pair; one end of a connecting rod of the second branch is connected with the movable platform through the rotating pair, the other end of the connecting rod is connected with the other connecting rod through the rotating pair, and the other end of the other connecting rod is connected with the fixed platform through a cylinder pair; one connecting rod of the third branch is connected with the fixed platform through the movable pair, the other end of the connecting rod is connected with the other connecting rod through the movable pair, and the other end of the other connecting rod is connected with the movable platform through the movable pair. The three-degree-of-freedom mobile decoupling parallel robot mechanism has the advantages of being large in working space, simple in manufacturing and mounting, completely decoupled in moving, easy to control and the like.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
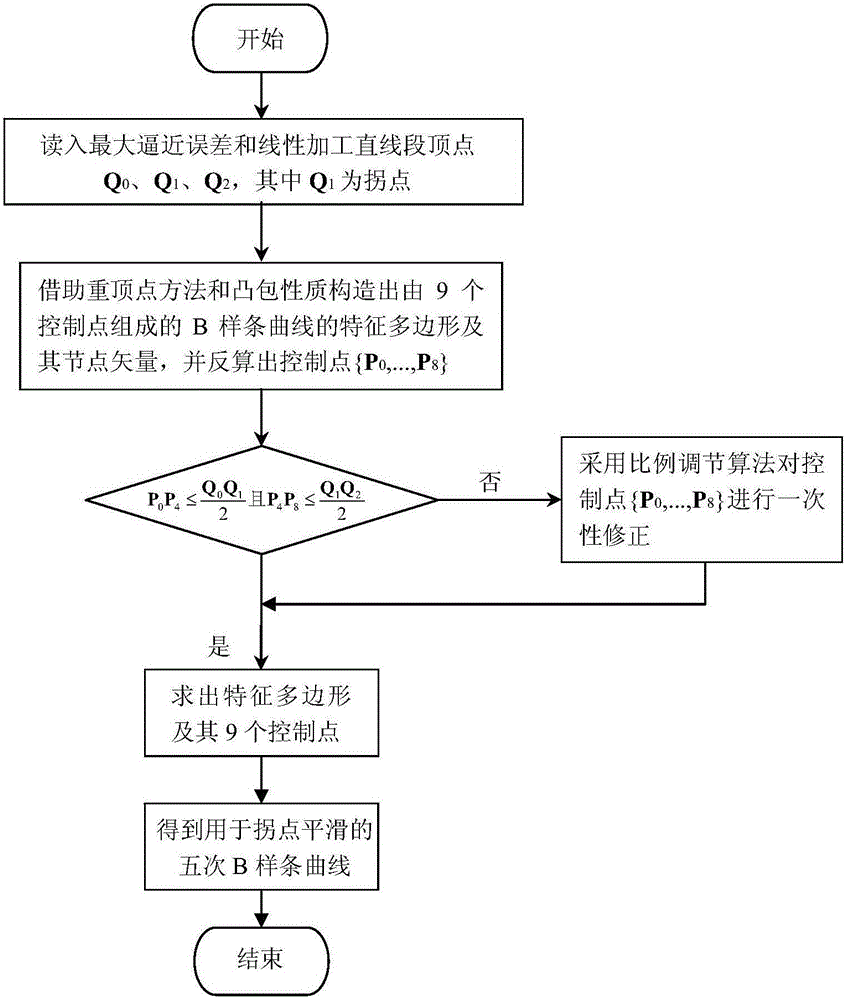
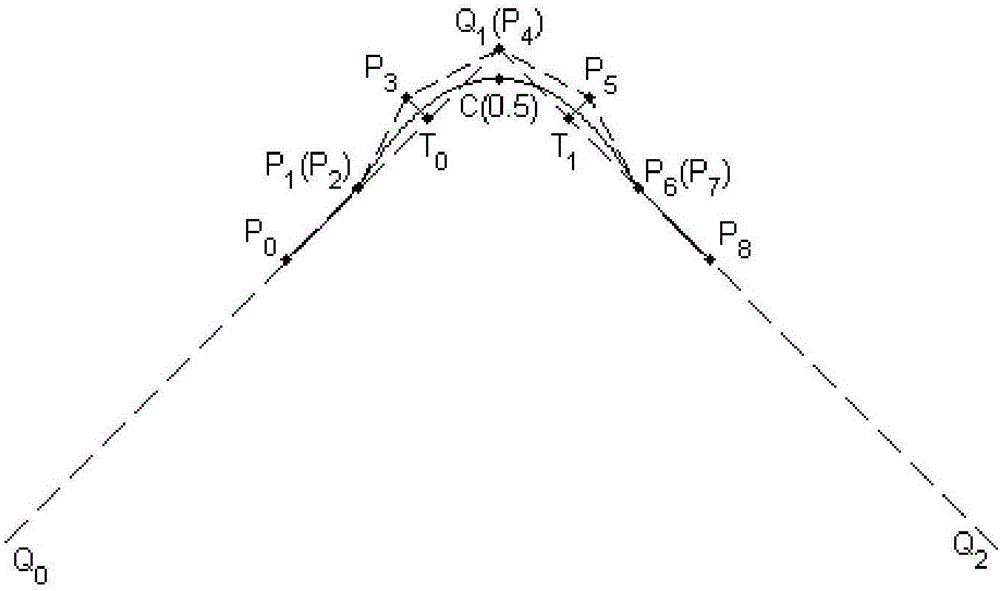
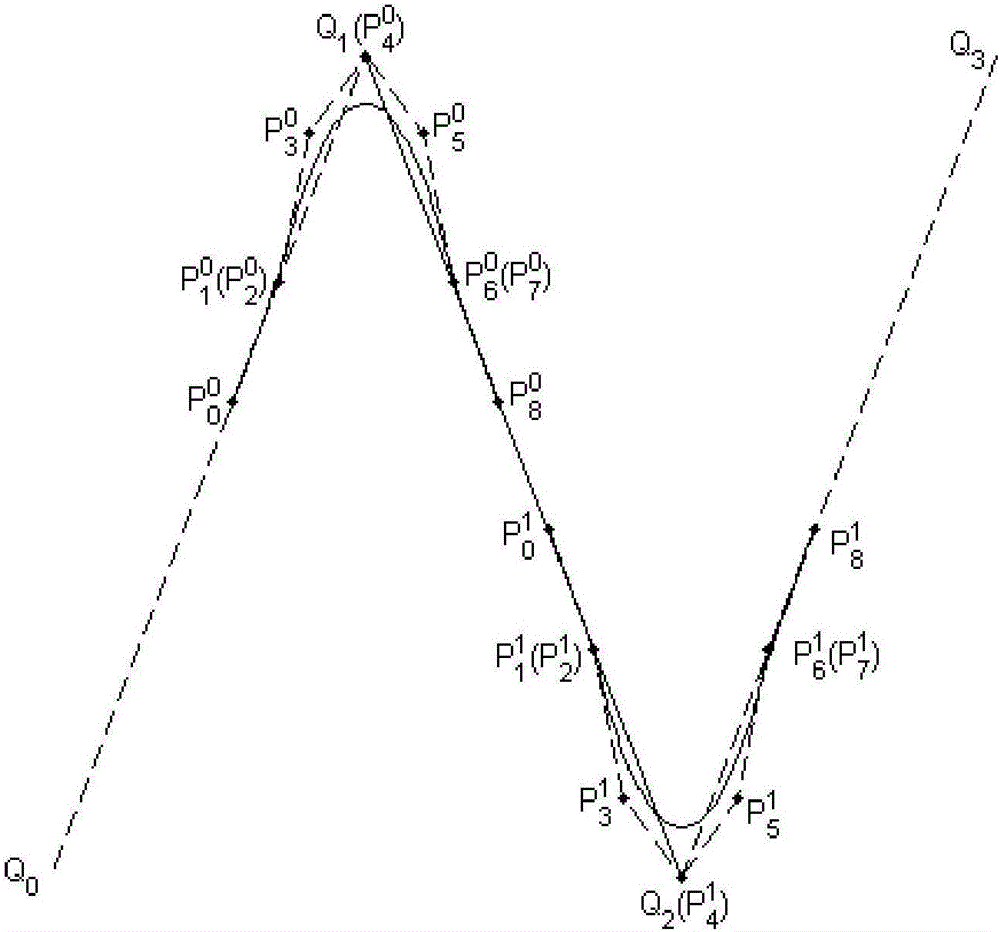
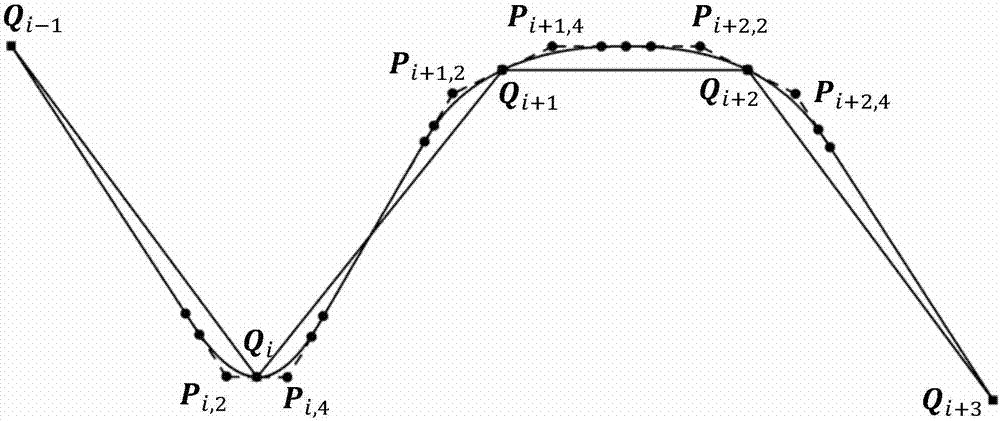
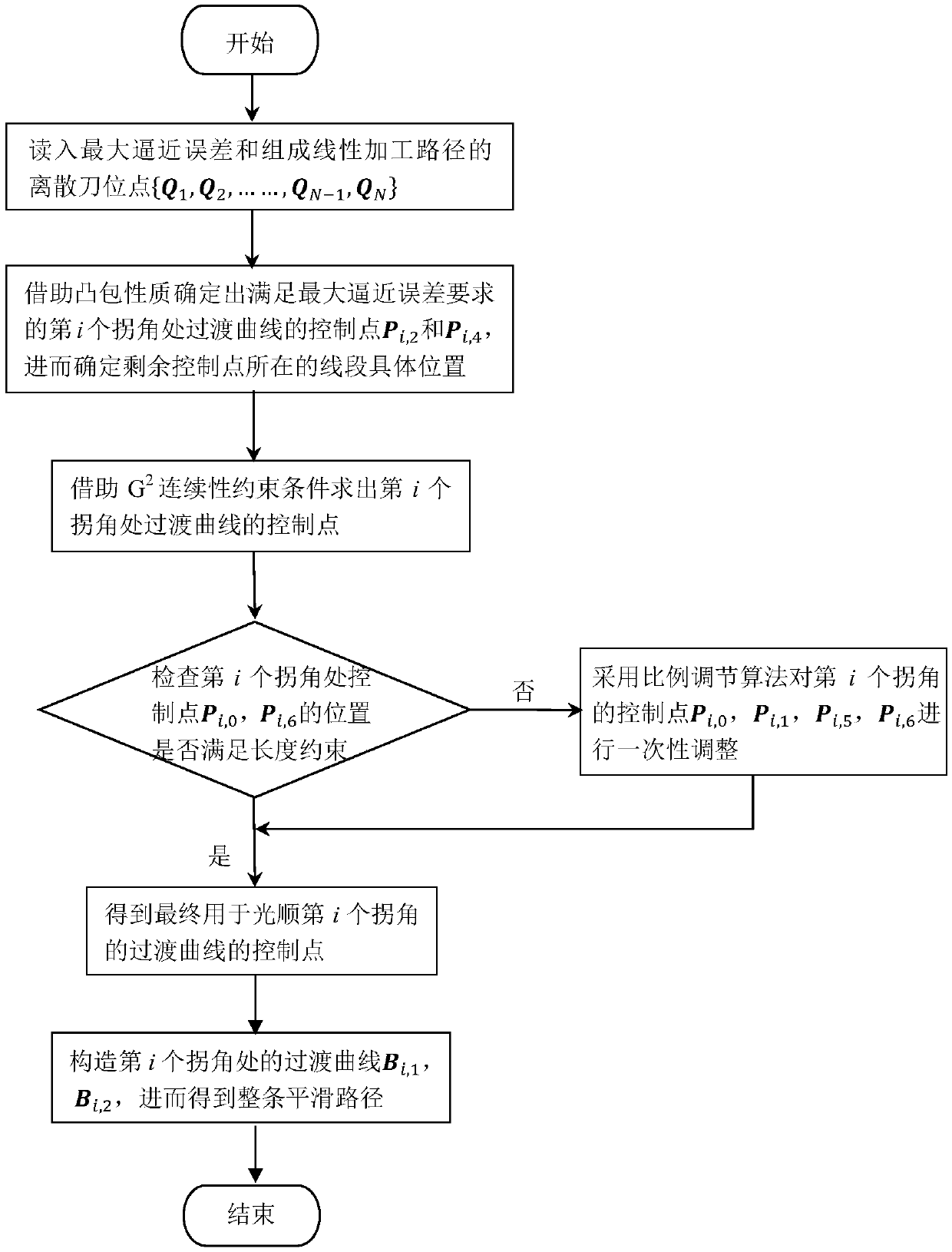
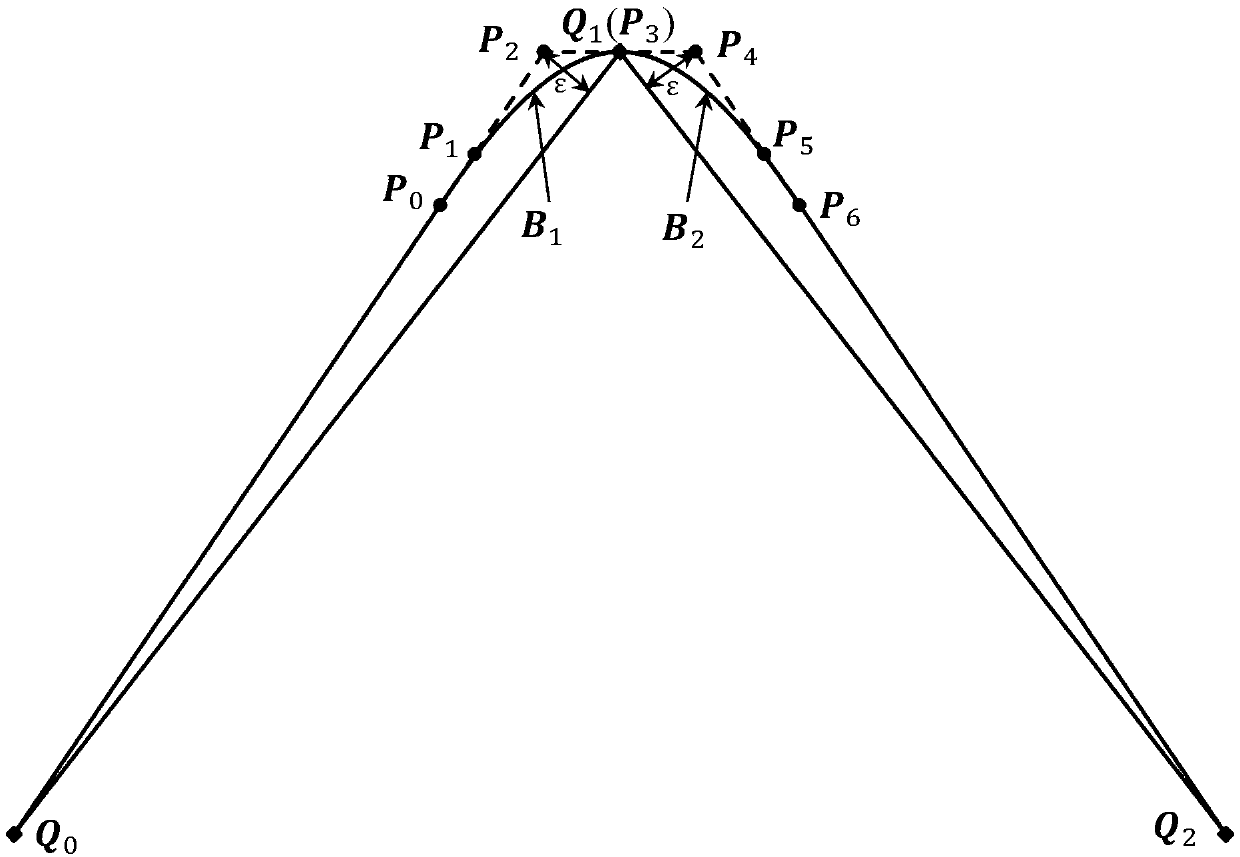
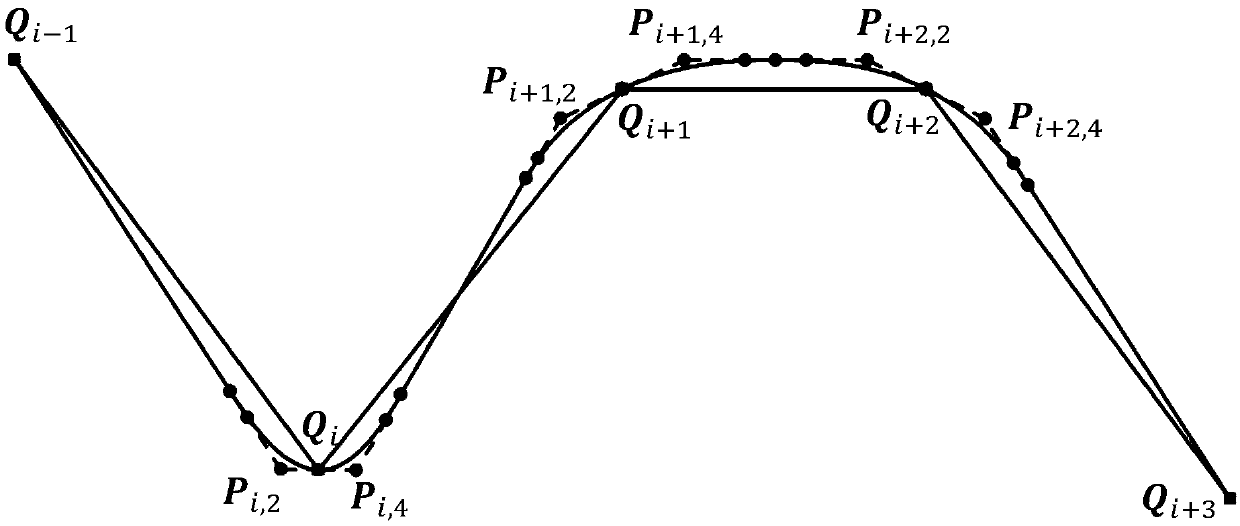
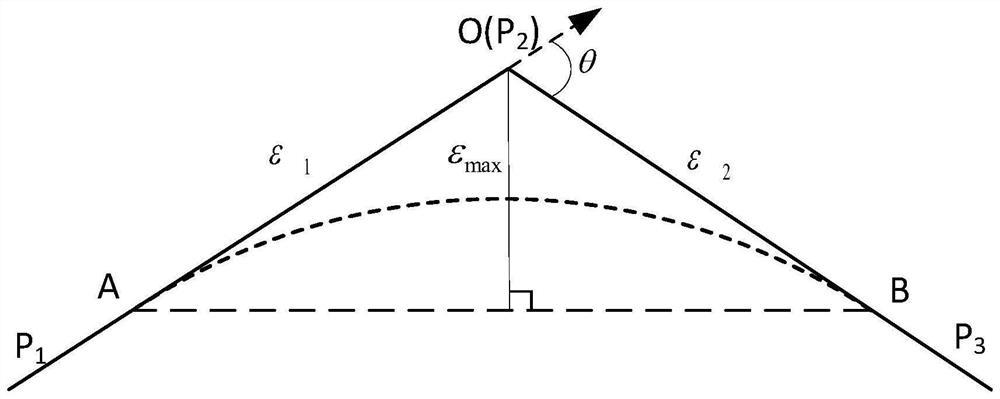
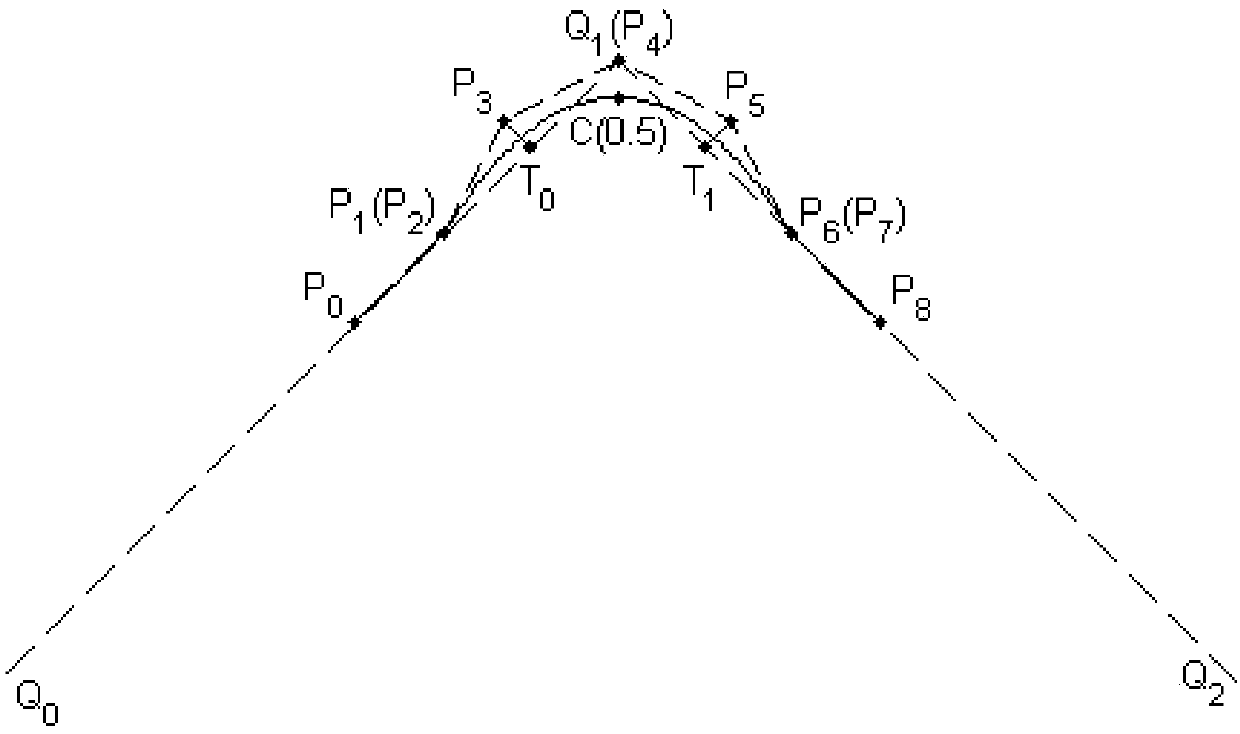
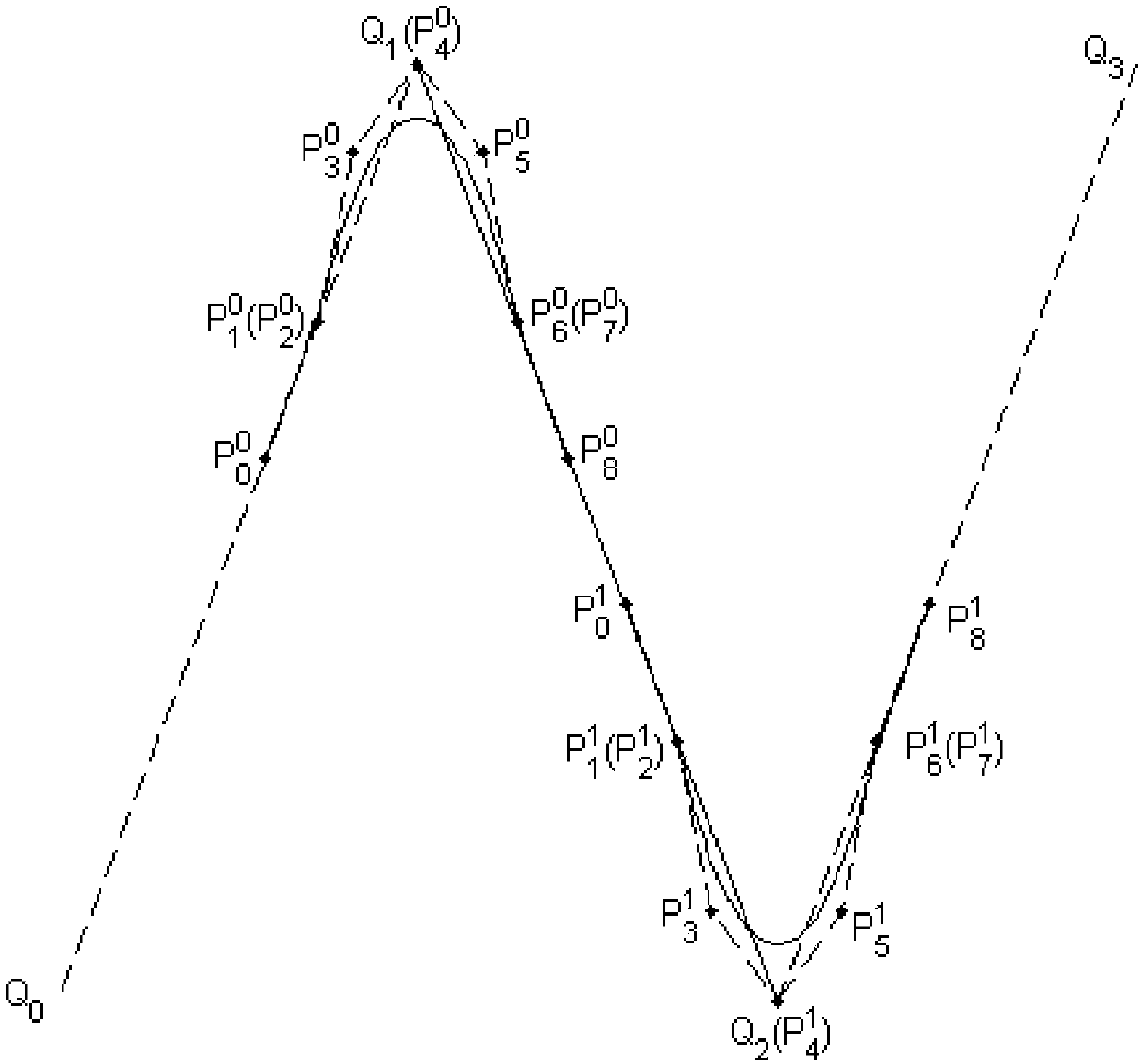
Method for smoothing inflection point of discrete processing path
ActiveCN105955194AIncrease the radius of curvatureGood kinematic performanceNumerical controlComputational scienceNumerical control
The invention relates to a method for smoothing an inflection point of a discrete processing path, and belongs to the field of high-speed high-performance numerical control processing. The method is characterized in that an externally tangent quintic B-spline curve with 9 control points is adopted to carry out smoothing processing on the inflection point of the discrete processing path, and problems of low speed and easy fluctuation in conventional discrete path inflection point processing are solved. The method comprises the steps of firstly constructing concrete forms of a characteristic polygon of a B-spline curve formed by the 9 control points and a node vector of the characteristic polygon with the aid of a vertex overlapping method and a convex-hull property, and back calculating the control points under the constraint of approximating to an error allowance value; then carrying out one-time correction on the control point by adopting a proportion regulating algorithm based on a length constraint of a transition section; and finally, and acquiring a quintic B-spline curve for inflection point smoothing according to the acquired characteristic polygon and the node vector. The method provided by the invention can enable the smoothed path to reach G1 continuity, and the smoothed curve has a greater curvature radius at the inflection point under the same error approximating condition compared with an internally tangent method.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
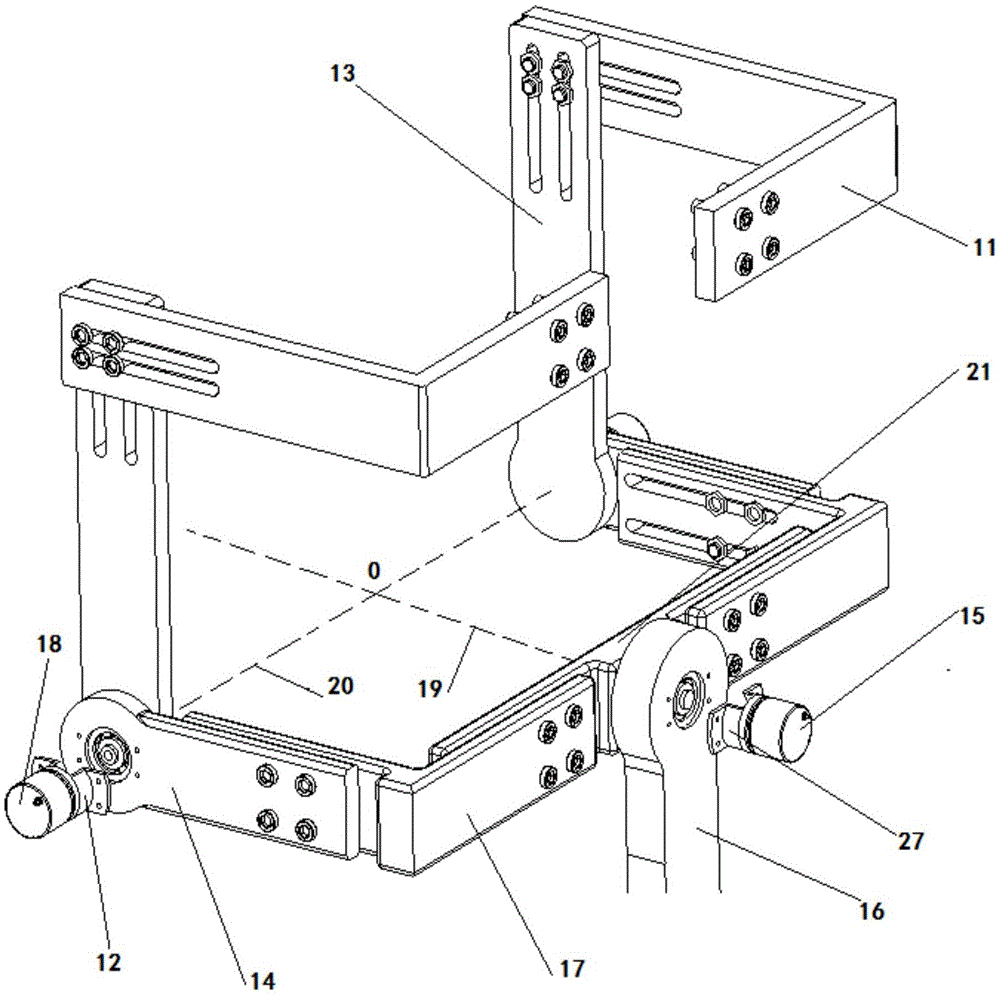
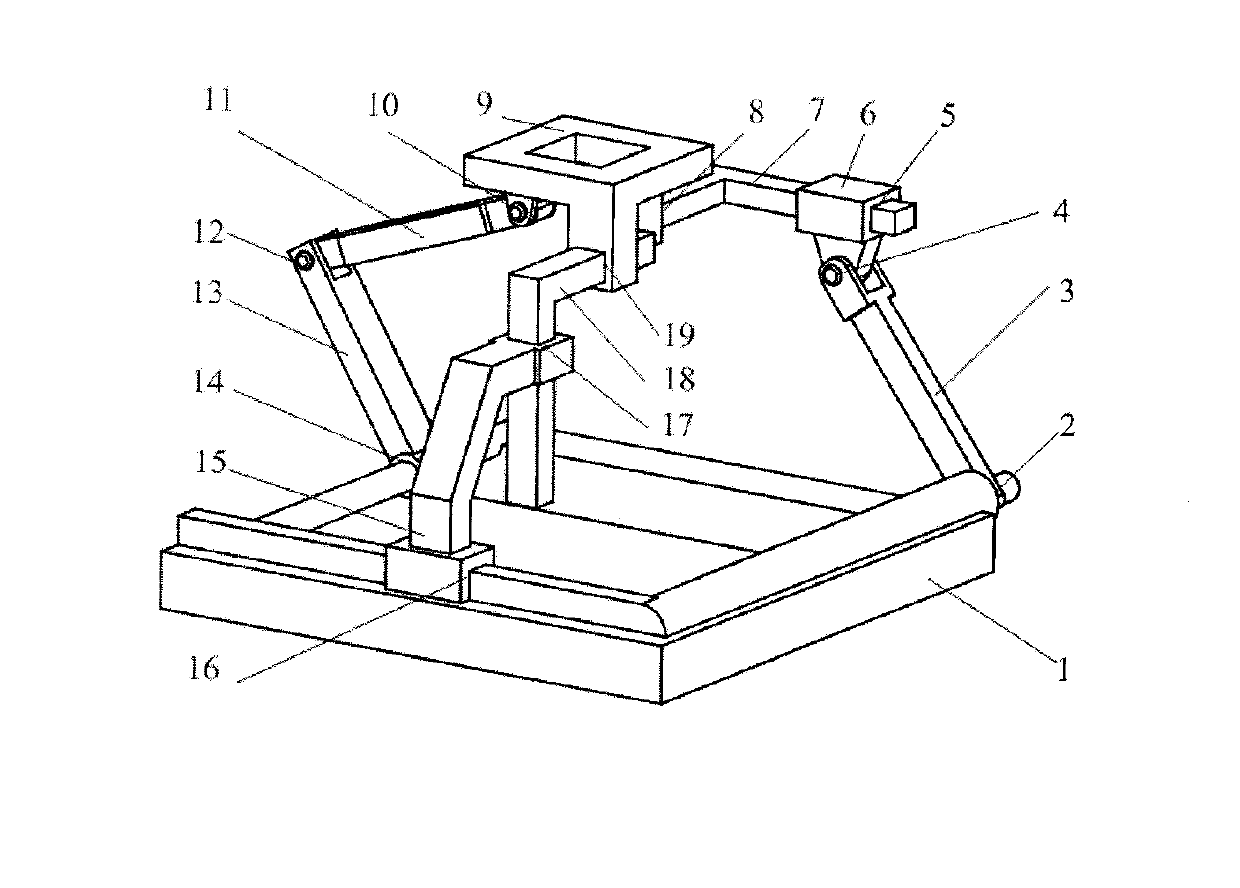
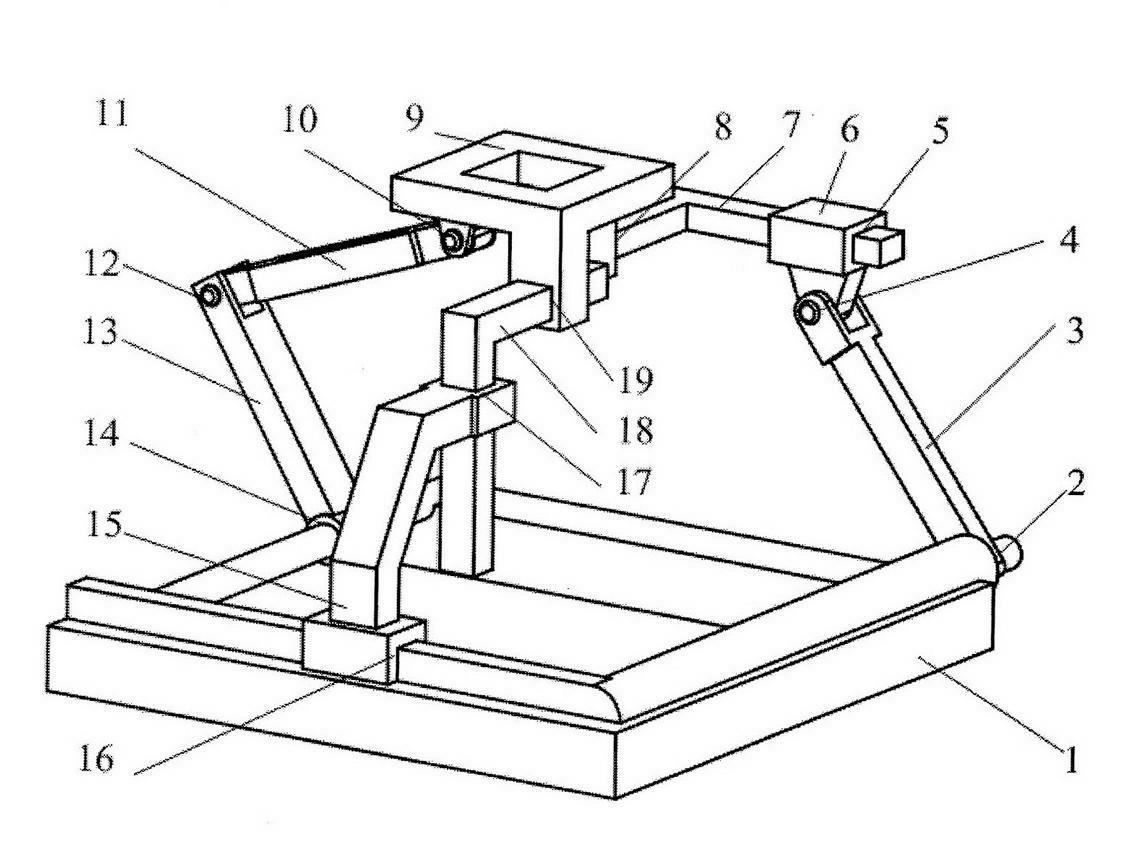
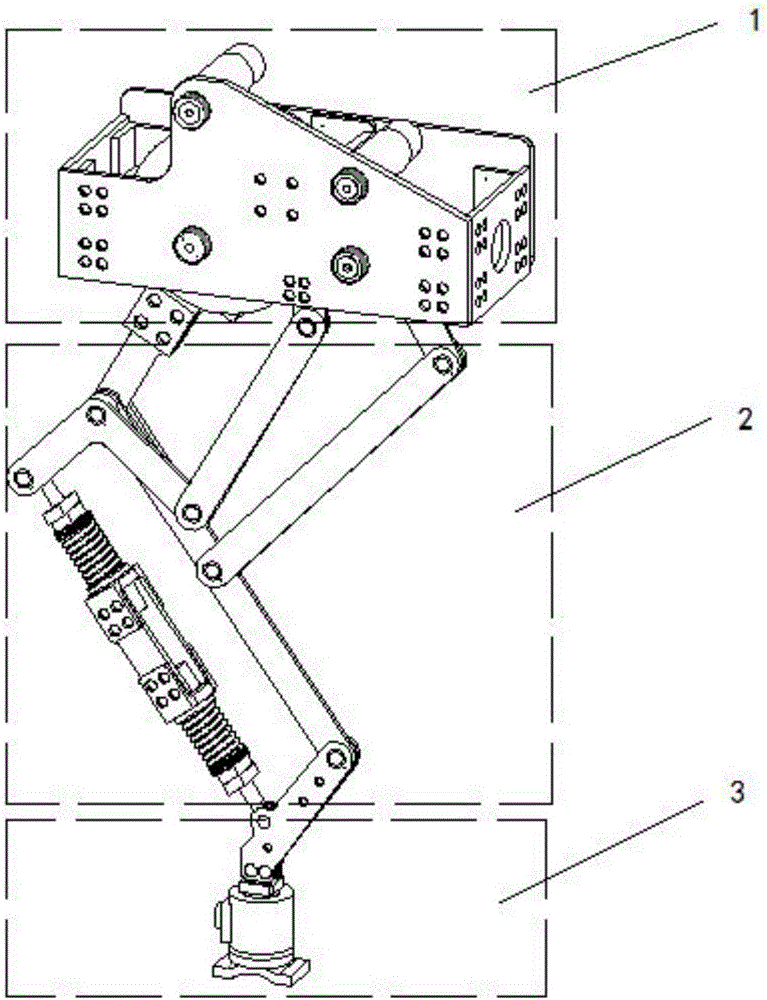
Parallel wrist joint rehabilitation training device based on self-adaptation
InactiveCN106726353ASimple structureCompact installationChiropractic devicesWrist jointsRehabilitation exercise
The invention discloses a parallel wrist joint rehabilitation training device based on self-adaptation and relates to the field of rehabilitation medical instruments. The parallel wrist joint rehabilitation training device adopts a parallel structure and has two rotation freedom degrees after a user wears the device. The parallel wrist joint rehabilitation training device comprises a hand support rack, a top support, a lateral support, a first branch chain, a second branch chain, a forearm support rack and a forearm support. The parallel wrist joint rehabilitation training device has the advantages that the device has six freedom degrees, two generalized rotation freedom degrees of the wrist joint limit the four freedom degrees of the device when the user wears the device, the device only has the two generalized rotation freedom degrees of the wrist joint after the user wears the whole device, the rotation center of the whole device constantly coincides with the rotation center of the wrist joint of a human body after the user wears the device, the man-machine compatibility problem is solved, and good comfortableness is achieved; unnecessary interference during training can be avoided, the requirements of wrist joint rehabilitation exercises can be satisfied completely, and the device is simple and compact in structure, convenient to use, stable to drive and low in manufacturing cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Flexible leg structure with plane five-rod mechanism
The invention discloses a flexible leg structure with a plane five-rod mechanism. The flexible leg structure is characterized by comprising a pitching drive joint, a foot tip and a connecting rod mechanism. The pitching drive joint comprises a variable stiffness driving flexible joint, a drive motor, two harmonic reducers, a supporting frame, a synchronous pulley and a synchronous belt. The foot tip comprises a three-dimensional mechanical sensor, a three-dimensional mechanical sensor support and a foot arch. The bottom of the three-dimensional mechanical sensor is connected with the three-dimensional mechanical sensor support. The bottom of the three-dimensional mechanical sensor support is connected with the foot arch. The connecting rod mechanism comprises ten hinge points (A), (B), (C), (D), (E), (F), (G), (H), (R) and (I). Connecting rods are hinged to a conventional four-rod mechanism, a four-rod mechanism with a spring rod and a plane pentagon five-rod mechanism through the ten hinge points. The hinge points (A), (R) and (I) are used for fixing the connecting rod mechanism to the pitching drive joint.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
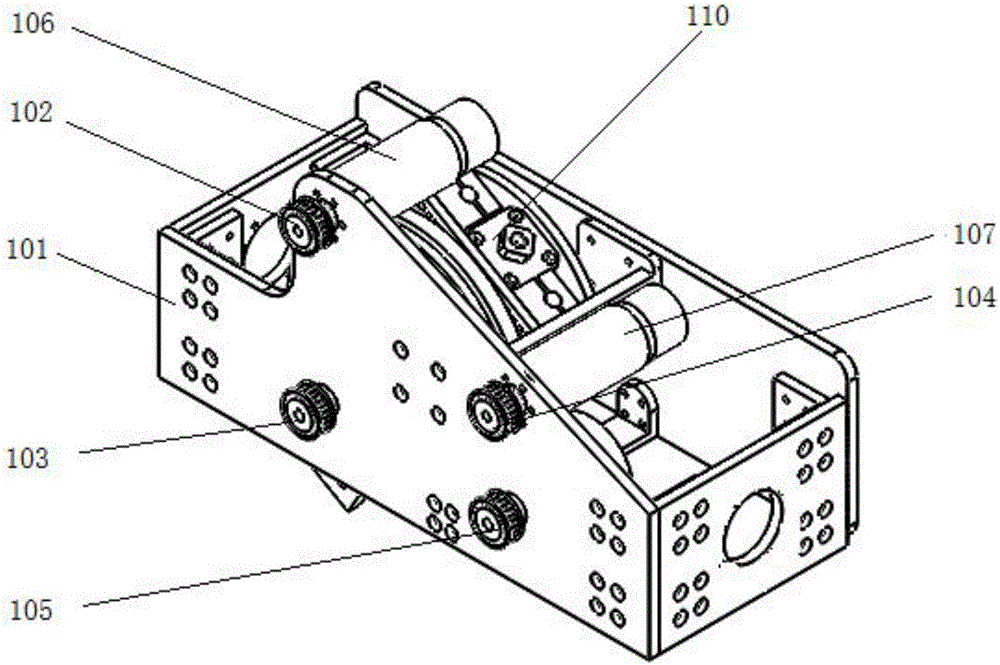
Macro/micro driven two-degree-of-freedom high-acceleration high-precision parallel positioning system
ActiveCN1731082AIncrease stiffnessIncrease load capacityUsing optical meansMechanical measuring arrangementsTwo degrees of freedomLinkage concept
The invention relates to a parallel orientating system with two free degree, high acceleration, high precision and macro / micro dual driven. The mutually perpendicular X-shaft liner driven apparatus 2 and Y-shaft liner driven apparatus are fixed on the base 1; the X-shaft liner driven apparatus 2 is fastened with X-shaft moving platform assembly 8; the Y-shaft liner driven apparatus 3 is fastened with Y-shaft moving platform assembly 9; the X-shaft parallel linkage 12 is hinged between X-shaft moving platform assembly 8 and X-shaft end platform 10; the Y-shaft parallel linkage 13 is hinged between Y-shaft moving platform assembly 9 and Y-shaft end platform 11; the X-shaft end platform 10 and the Y-shaft end platform 11 are fastened with the end output platform 15.
Owner:CHANGZHOU MINGSEAL ROBOT TECH CO LTD
Four-freedom-degree cylindrical coordinate parallel robot
ActiveCN109531556ACompact structureFlexible movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsEngineering
The invention discloses a four-freedom-degree cylindrical coordinate parallel robot. A reference plane is defined by a stand column, and two X-axis drive devices and two Z-axis drive devices are symmetric about the reference plane. A tail end support is hinged to each X-axis driving arm, and a parallelogram mechanism is formed by the stand column, each X-axis driving arm, the corresponding tail end support and a reinforcement rod. One ends of four sub branch chains are connected with a moving platform, and the other ends of the four sub branch chains are connected with the two tail end supports and two Z-axis driving arms. The four sub branch chains are single rods, and the two ends of each sub branch chain are connected through a hooke joint. Or the four sub branch chains are parallelogram composite chains. Each composite chain comprises two shaft rods and two chain rods, one of the two shaft rods in each composite chain is arranged on the moving platform, and the other of the two shaft rods in each composite chain is arranged on the corresponding tail end support or Z-axis driving arm. The four-freedom-degree cylindrical coordinate parallel robot is compact in structure, flexiblein motion and excellent in kinematics performance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Two-degree-of-freedom decoupling parallel mechanism with mixed movement
InactiveCN103072134AReverse solution is simpleEasy to controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorLarge fixed membersDegrees of freedomEngineering
The invention discloses a two-degree-of-freedom decoupling parallel mechanism with mixed movement. The two-degree-of-freedom decoupling parallel mechanism mainly comprises a movable platform, a fixed platform and two branches, wherein the branches connect the platforms in such a manner that one end of a first branch is connected with the fixed platform through a movable pair; the movable pair is connected with a rotating pair through a connecting rod; the rotating pair is connected with another rotating pair through a connecting rod; the rotating pair is connected with the movable platform; one end of a second branch is connected with the fixed platform through the movable pair, and the other end of the second branch is connected with the movable platform through the rotating pair; the movable pair is connected with the rotating pair through a connecting rod; and the other end of the branch is connected with the movable platform through the rotating pair. The two-degree-of-freedom decoupling parallel mechanism has the advantages of large working space, simple structure, low cost, easiness in controlling, and the like.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
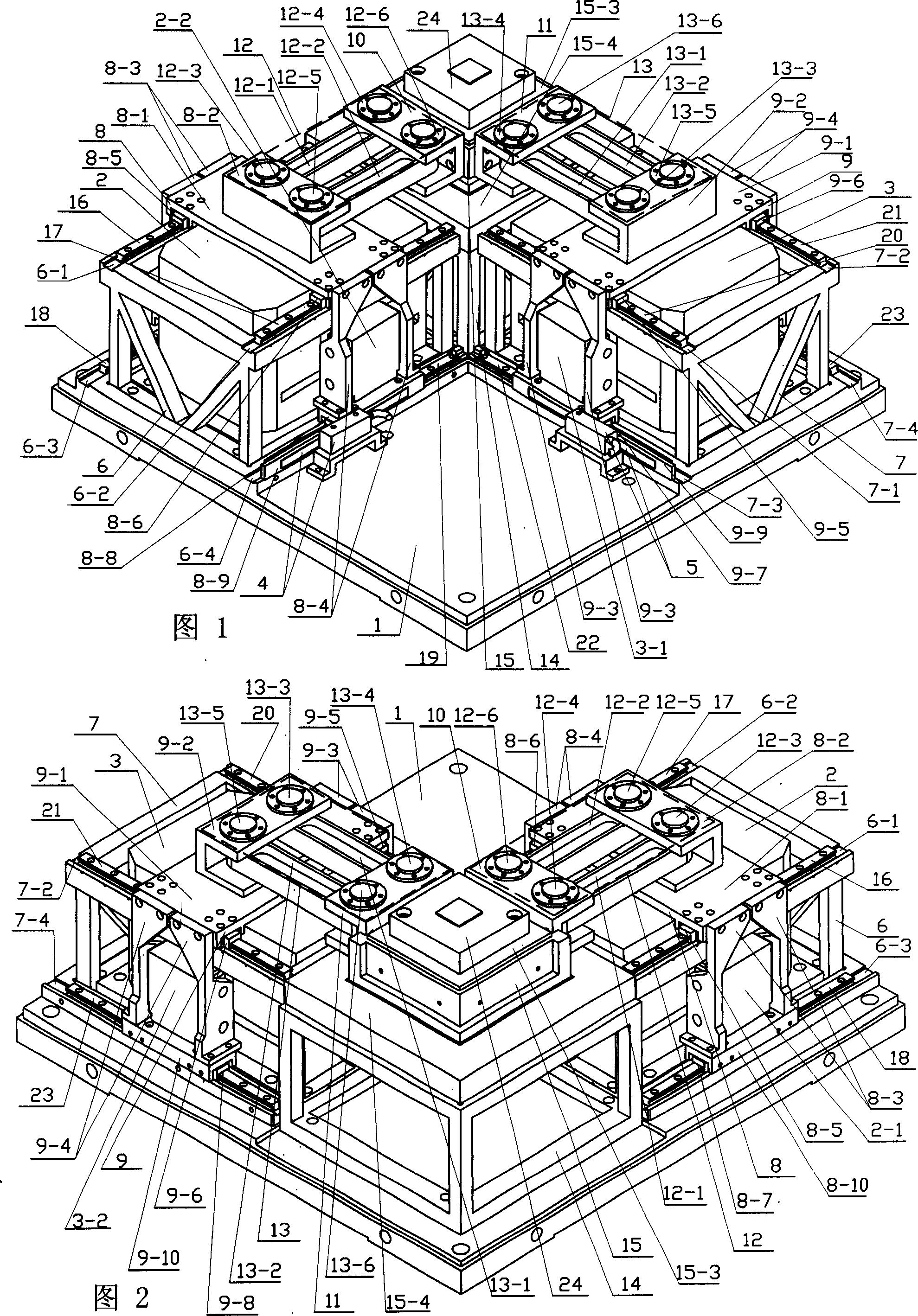
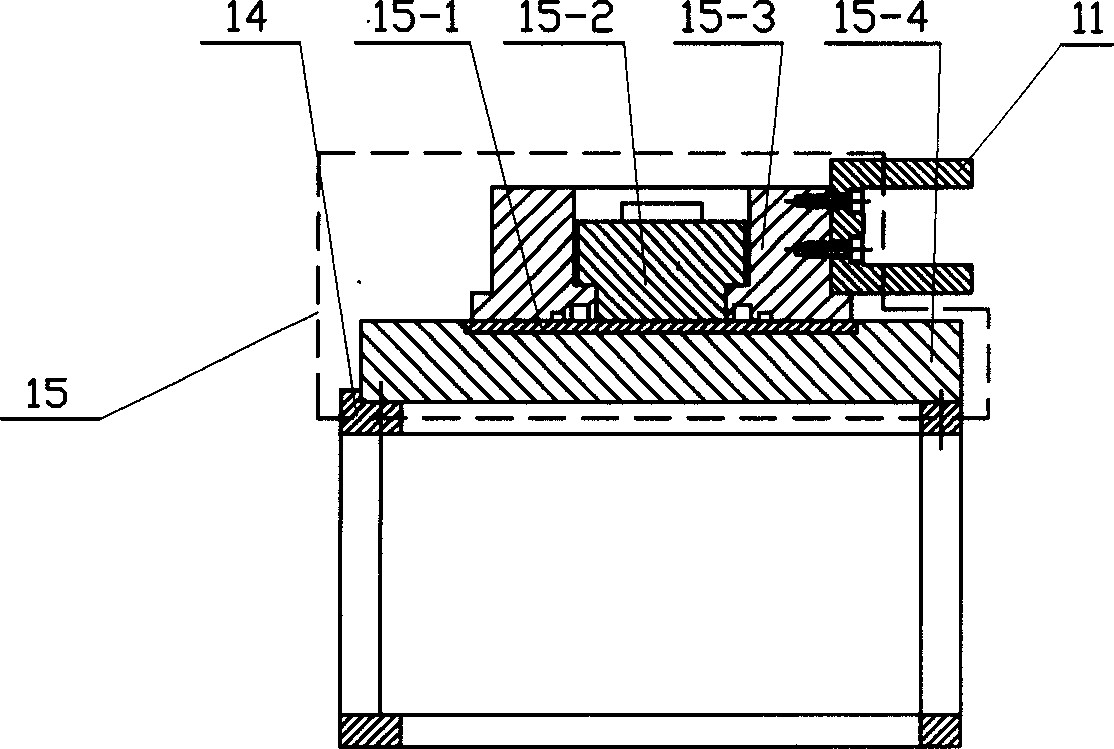
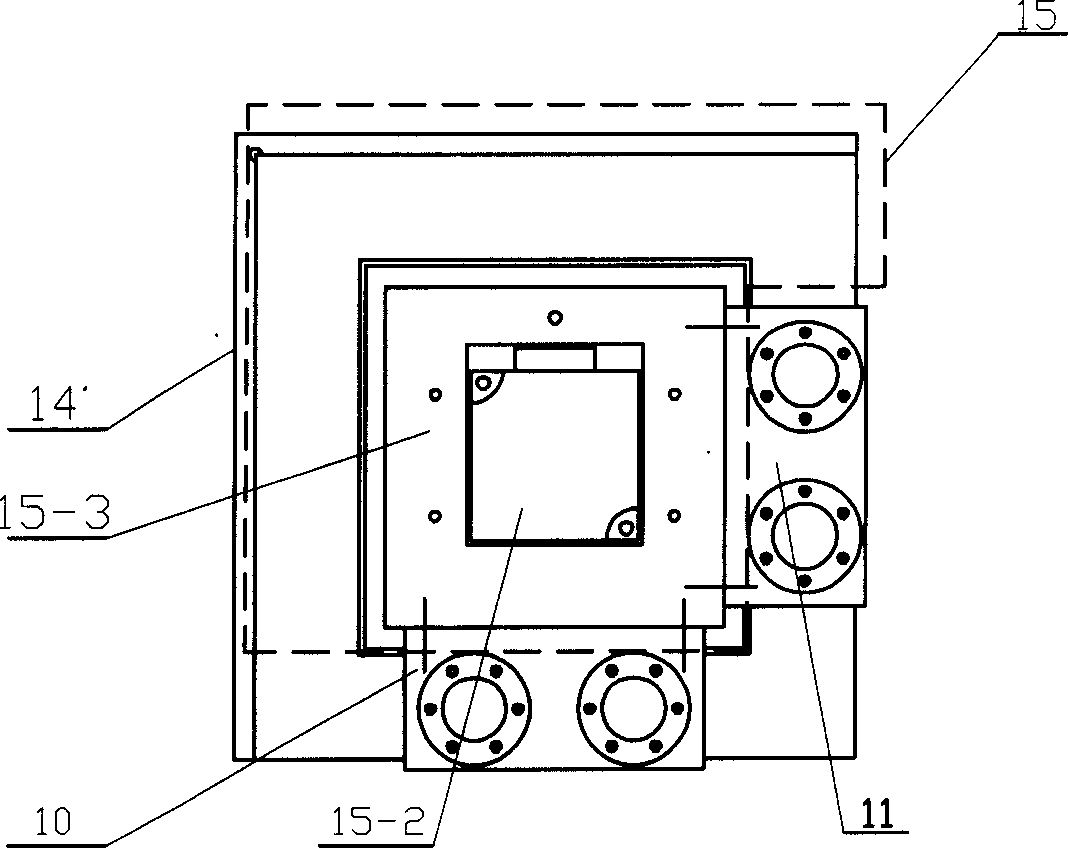
Large-stroke high-rigidity series-parallel hybrid machine tool with reconfigurable characteristic
ActiveCN107443173AHave controlHigh attitude adjustment abilityFeeding apparatusLarge fixed membersControl engineeringProcess engineering
The invention relates to a large-stroke high-rigidity series-parallel hybrid machine tool with the reconfigurable characteristic. The large-stroke high-rigidity series-parallel hybrid machine tool comprises a fixed working table, an X-direction movement unit, a Y-direction movement unit, a lifting adjusting device, three driving branches with same structures, a movable platform and a main shaft head. A special clamp is installed on the fixed working table, and the X-direction movement unit and the Y-direction movement unit are each composed of a rack and a servo driving unit. The lifting adjusting device comprises three passive branches with the same structures and a middle active branch, the structure dip angle of a parallel structure can be adjusted, and the parallel structure has the reconfigurable characteristic. The three driving branches with the same structures are connected with the lifting adjusting device and the movable platform, and one-dimensional movement and two-dimensional movement can be achieved through the space closed loop parallel mechanism. The large-stroke high-rigidity series-parallel hybrid machine tool has the beneficial effects of good structural symmetry, high rigidity, large working space, high posture capacity, good in dynamic performance and the like; meanwhile, the beneficial effects of a series machine tool and a parallel machine tool are achieved at the same time; and the large-stroke high-rigidity series-parallel hybrid machine tool can be used for five-axis machining of large heterogeneous part complex surfaces.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
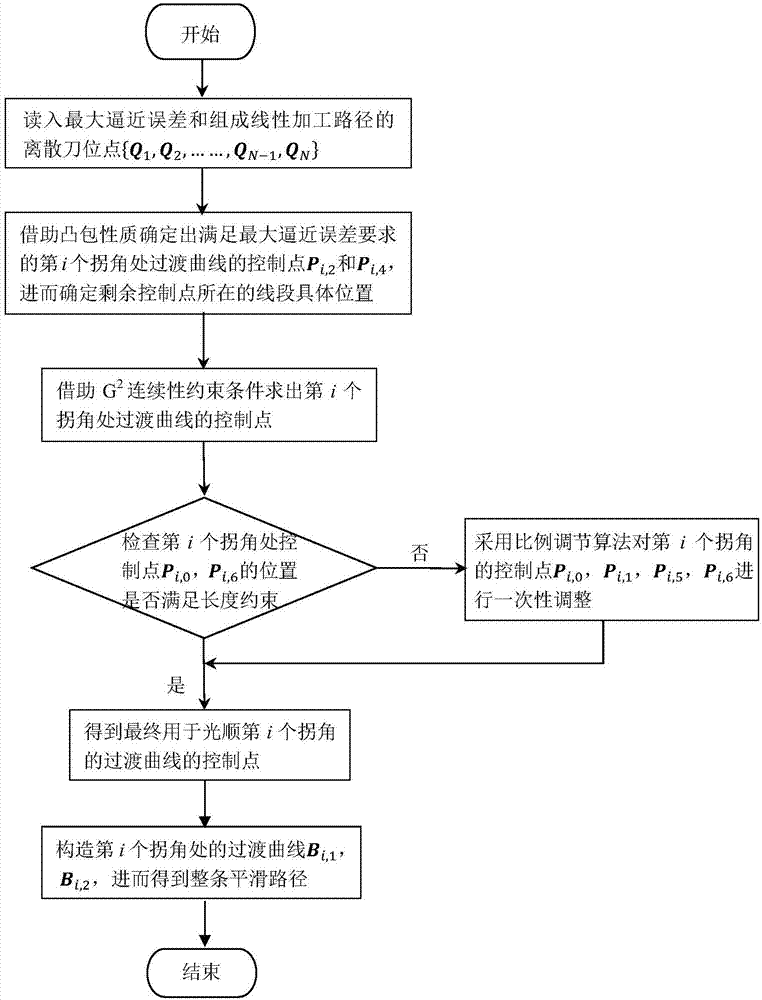
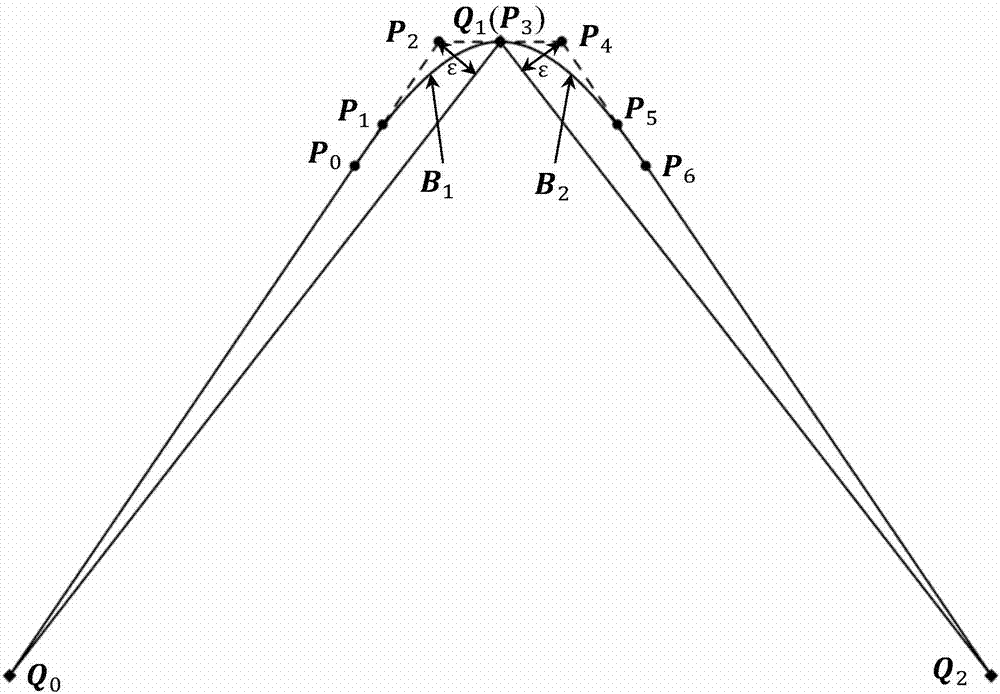
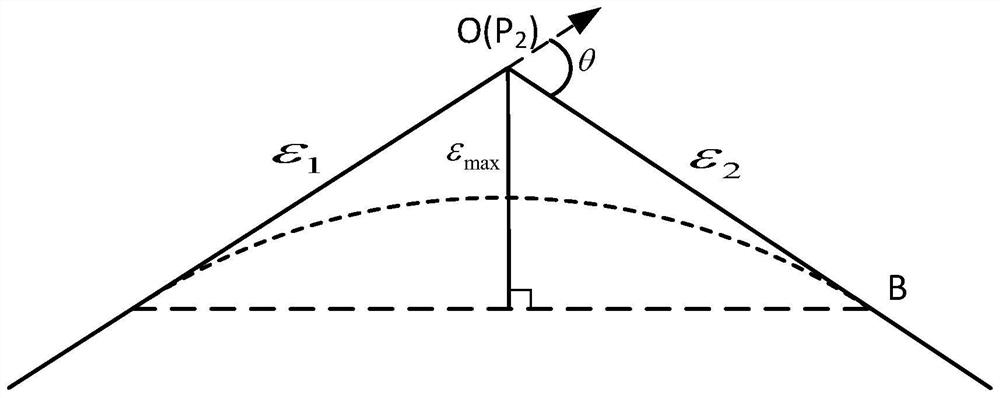
Local smoothing method having controllable errors and capable of passing predetermined cutter location points of scattering processing path
ActiveCN107255998AAccurate responseGood kinematic performanceProgramme controlComputer controlCutter locationParallel computing
The invention discloses a local smoothing method having controllable errors and capable of passing predetermined cutter location points of a scattering processing path, and belongs to the high speed high precision numerical control processing field. Every corner of the scattering processing path adopts two cubic Bezier curves to be used as transition curves for the smoothing processing, and problems of routine scattering path processing such as low precision and easy speed fluctuation are solved. The concrete position of the control point of the transition curve satisfying a maximum approximation error requirement on a line segment is determined with help of convex hull property. Under conditions of G2 continuity restriction and line segment length restriction, the inverse computation of the control point of the transition curve is carried out. According to the acquired control point, a dual-cubic Bezier curve used for the path smoothing is finally acquired. By adopting the local smoothing method, the G2 continuity of the path after the smoothing is achieved, and by comparing with other path smoothing algorithms, processing precision is guaranteed, and the method can pass the cutter location points used to form the scattering processing path.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
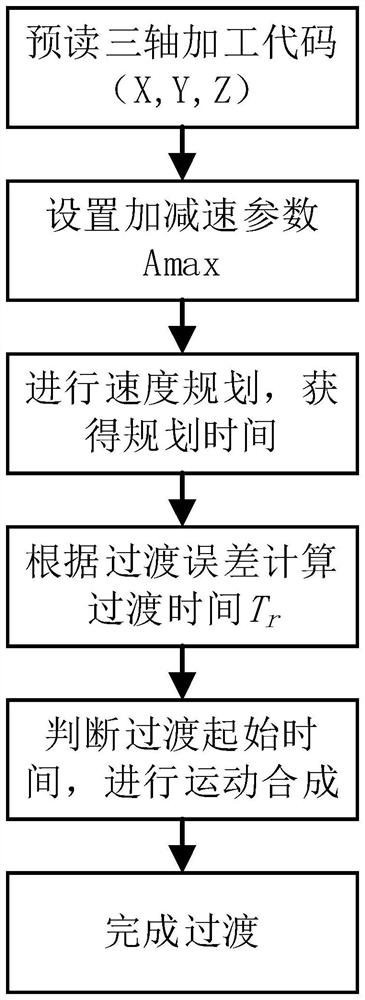
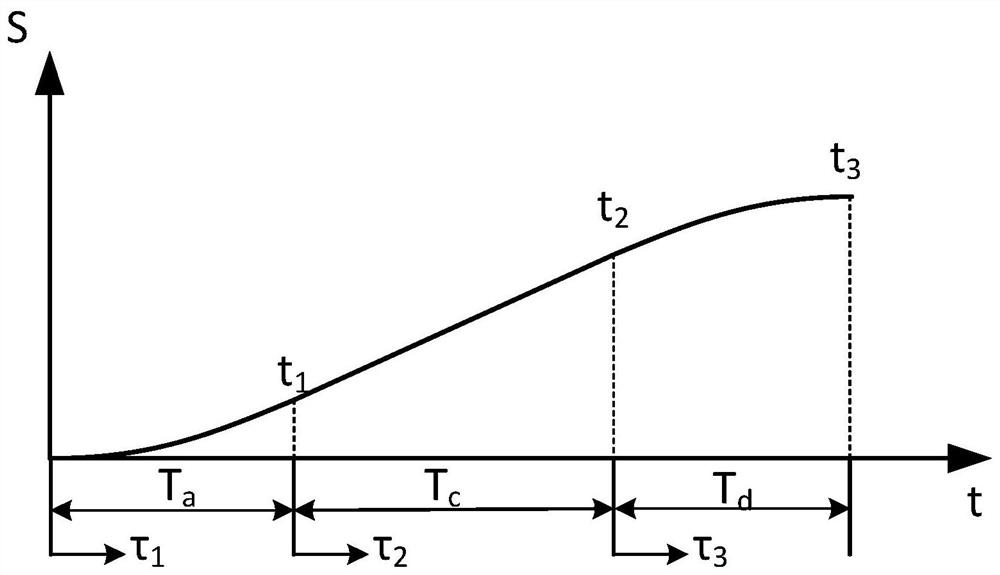
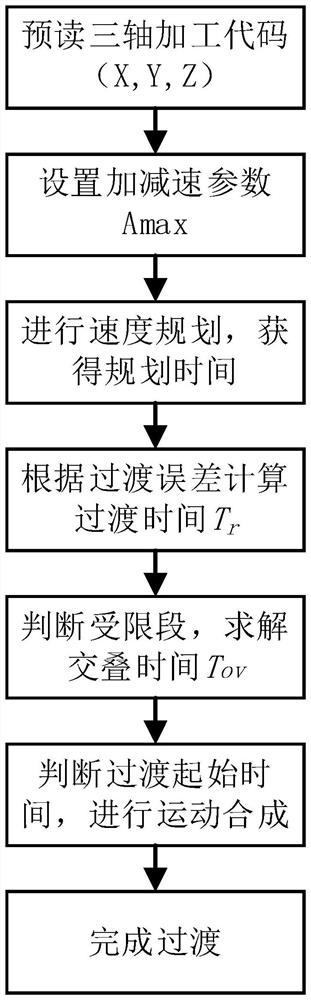
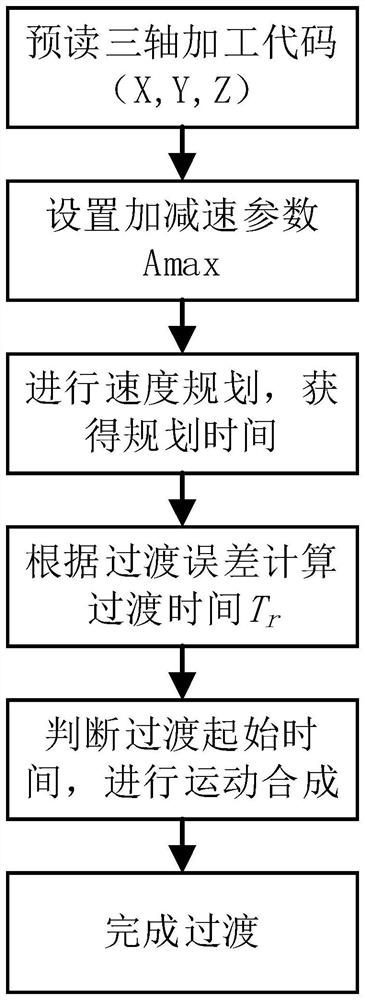
Three-axis micro-line segment direct speed transition method based on trigonometric function acceleration and deceleration control
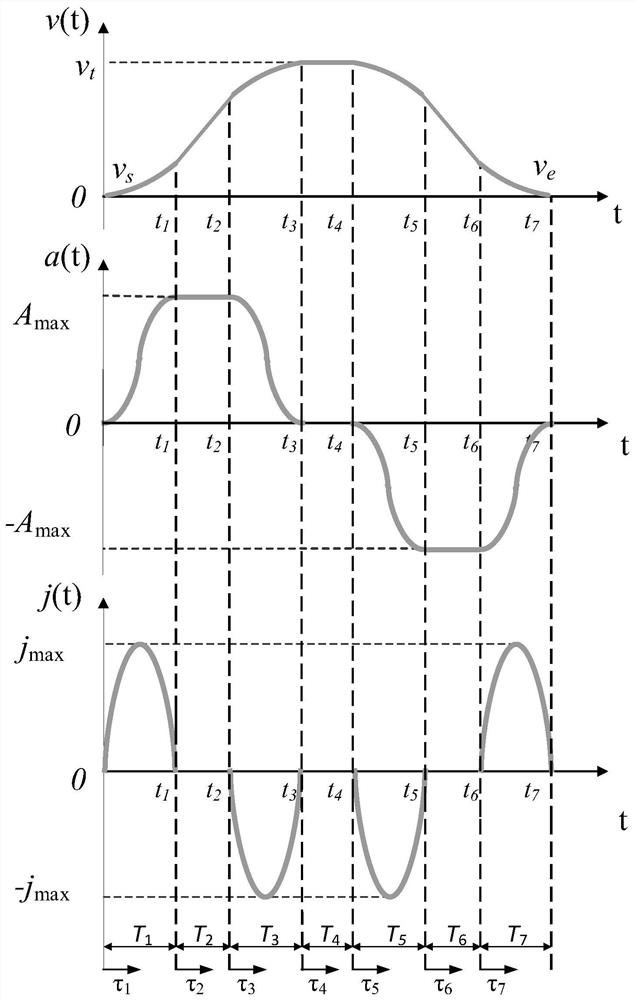
ActiveCN111966047AImprove continuity of motionReduce complexityNumerical controlTransition lineControl theory
The invention discloses a three-axis micro-line segment direct speed transition method based on trigonometric function acceleration and deceleration control. The method comprises the steps of obtaining the length of each micro-line segment and the rotation angle between any two adjacent micro-line segments through machining code point position coordinates; establishing a trigonometric function acceleration and deceleration model for two adjacent micro line segments of which the rotation angle is than 0 degree to obtain interpolation speed functions and interpolation displacement functions of the acceleration segments, the constant speed segments and the deceleration segments of the corresponding micro line segments; carrying out speed planning to determine interpolation time of each segment; setting the maximum transition error of two adjacent micro-line segments, solving the maximum transition line segment length, and setting the transition line segment lengths of the two micro-line segments to be equal and less than or equal to the minimum value of the first micro-line segment deceleration segment length and the second micro-line segment acceleration segment length; determining atransition starting moment according to the transition line segment length; calculating transition time through an interpolation displacement function; and synthesizing the motions of the transitionline segments of two adjacent micro-line segments to obtain a transition path. According to the method, the complexity of an algorithm is reduced, and meanwhile, the corner machining efficiency is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
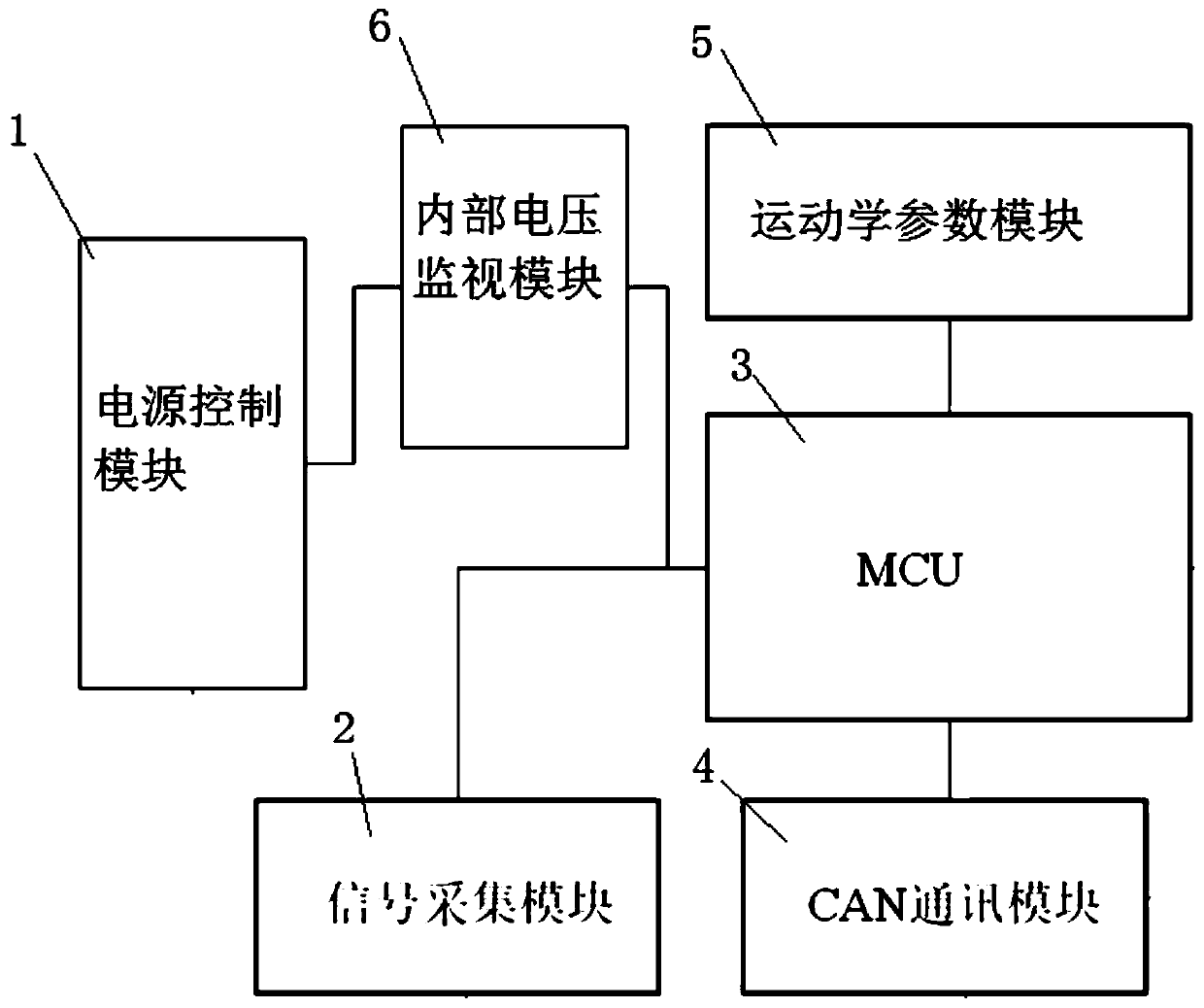
Two-wheeled hub motor driven pure electric vehicle controller and control method
ActiveCN110466361AGood kinematic performanceGood torque vectoringSpeed controllerElectric devicesDriver/operatorEnergy recovery
The invention discloses a two-wheeled hub motor driven pure electric vehicle controller. A signal collecting module of the pure electric vehicle controller is used for collecting an electronic shiftersignal, a hub motor differential torque control switch signal, an accelerator pedal status signal, a brake pedal status signal and a brake pedal opening signal; a CAN communication module is used forsending wheel speed signals of all wheels, a steering wheel angle signal, a vehicle speed signal, a power battery SOC value, a ABS trigger signal and a battery management system working state signalto an MCU; a kinematics parameter module is used for sending a yaw angle velocity signal and a three-axis vehicle acceleration signal required by the differential torque control to the MCU; and identification of driving intention of a driver, controlling of differential torque yawing moment, controlling of driving and skid resistance and controlling of braking energy recovery are conducted by theMCU. According to the two-wheeled hub motor driven pure electric vehicle controller, the control conditions of a hub motor can be met, and the differential torque control advantages are reflected.
Owner:DONGFENG MOTOR CORP HUBEI
Six-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism containing redundant drive
PendingCN108858144AGood kinematic performanceExtended swing rangeProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsUniversal joint
The invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism containing redundant drive. The six-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism comprises two Delta parallel mechanism bodies sharing one static platform, movable platforms of the two Delta parallel mechanism bodies are parallel up and down, movement branch chains of the two Delta parallel mechanism bodies are uniformly staggered, a redundant driving motor with a vertical and downward output shaft is installed in the center of a movable platform of the Delta parallel mechanism body at the upper portion, and a movable ball which formsa spherical hinge structure with a movable platform of the Delta parallel mechanism body at the lower portion is installed in the center of the movable platform of the Delta parallel mechanism body atthe lower portion; a rotary rod fixedly connected with the movable ball is arranged above the movable ball, a tail paw fixedly connected with the movable ball is arranged below the movable ball, andan output shaft of the redundant driving motor is connected with the rotary rod through a universal joint. By means of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism, six-degree-of-freedom movement of the tail paw in the space can be achieved, the rotation range of the rotary rod around its own axis is expanded, and the kinematics performance of the mechanism is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Belt-driven variable-drive kinematic chain and parallel robot with same
InactiveCN108115654ALighten the system massDo not change the dynamic performance advantageProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematic chainMass distribution
The invention relates to a belt-driven variable-drive kinematic chain and parallel robot with the same. The kinematic chain comprises a supporting module, a driving module, a drive switching device, two-stage rods and a belt transmission system. The driving module comprises a servo motor, a center shaft and a motor cover, the drive switching device comprises an electromagnetic clutch and an electromagnetic brake, the two-stage rods are sequentially connected outwards from a driving end through a rotating pair, and the belt transmission system is connected with the driving module and a two-stage rod rotating joint. By switching of electrification states of the electromagnetic clutch or the electromagnetic brake, acting positions of a driving torque and a reaction torque are changed, configuration modes of driving and driven rods and the joint are changed, and three driving modes can be realized by a single kinematic chain. By introduction of the belt transmission system and the drive switching device to a traditional kinematic chain, mechanism mass distribution is slightly changed; by the kinematic chain, variable-drive parallel robots in various configurations can be formed, and mechanism performances are improved through drive variation under the condition that mechanism configuration and size are unchanged.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
An Adaptive Parallel Wrist Joint Rehabilitation Training Device
InactiveCN106726353BMeet rehabilitation sports needsSimple structureChiropractic devicesHuman bodyMan machine
The invention discloses a parallel wrist joint rehabilitation training device based on self-adaptation and relates to the field of rehabilitation medical instruments. The parallel wrist joint rehabilitation training device adopts a parallel structure and has two rotation freedom degrees after a user wears the device. The parallel wrist joint rehabilitation training device comprises a hand support rack, a top support, a lateral support, a first branch chain, a second branch chain, a forearm support rack and a forearm support. The parallel wrist joint rehabilitation training device has the advantages that the device has six freedom degrees, two generalized rotation freedom degrees of the wrist joint limit the four freedom degrees of the device when the user wears the device, the device only has the two generalized rotation freedom degrees of the wrist joint after the user wears the whole device, the rotation center of the whole device constantly coincides with the rotation center of the wrist joint of a human body after the user wears the device, the man-machine compatibility problem is solved, and good comfortableness is achieved; unnecessary interference during training can be avoided, the requirements of wrist joint rehabilitation exercises can be satisfied completely, and the device is simple and compact in structure, convenient to use, stable to drive and low in manufacturing cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
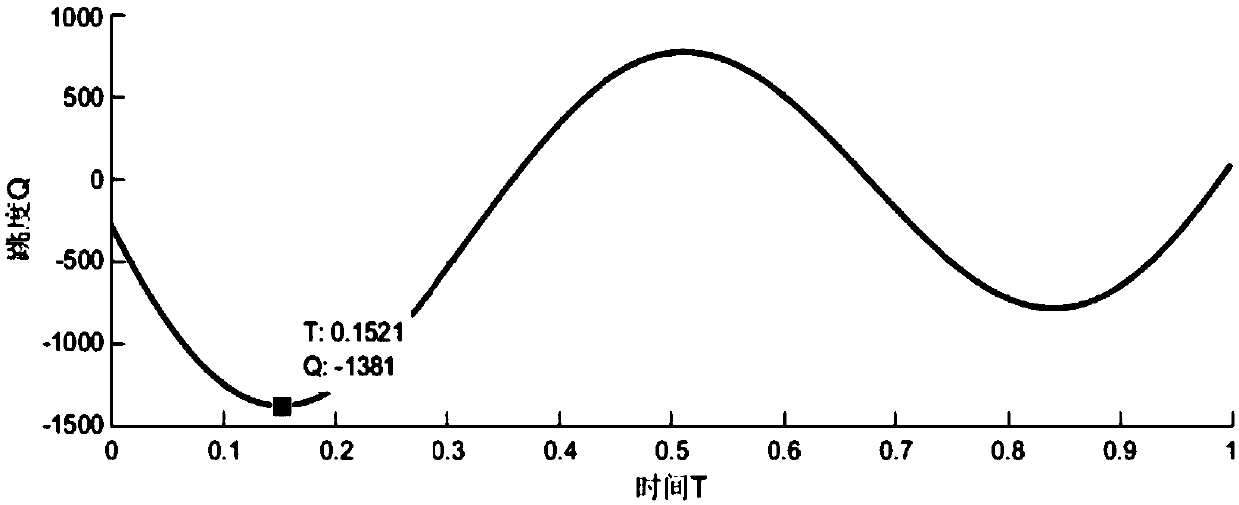
Cam curve design method based on k-order harmonic function
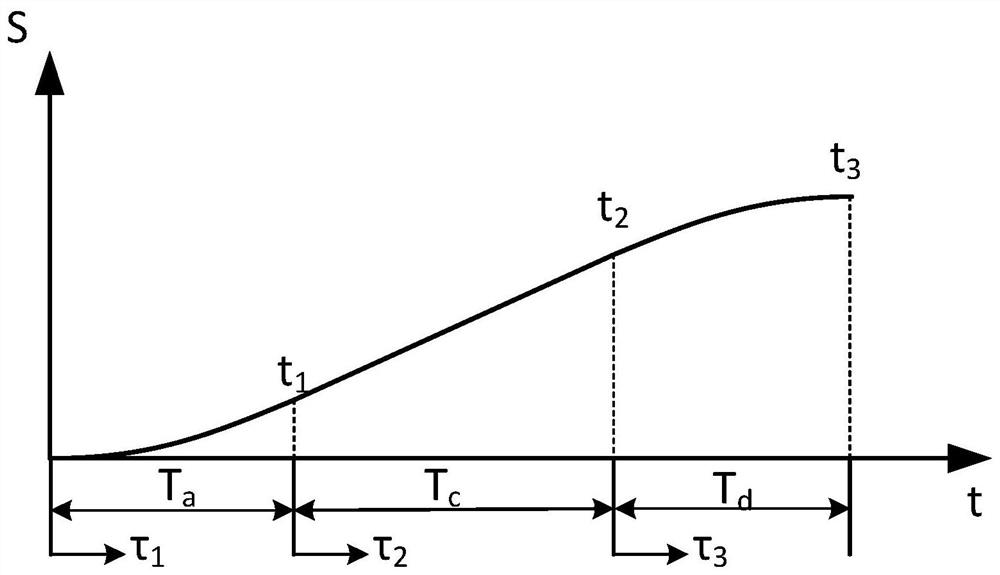
ActiveCN108629067AGuaranteed continuitySmall fluctuationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCurve fittingEngineering
The present invention provides a cam curve design method based on the k-order harmonic function, and belongs to the technical field of cam design, in order to solve the problem that the mechanism is fluctuate and cannot be applicable to the high speed occasion due to that some characteristic parameter curves among the existing harmonic cam curves are close to infinity at the end point. The methodcomprises: obtaining key point data determined by the cam for realizing the function; making the key point data to be dimensionless to obtain the dimensionless time T and the dimensionless displacement S; writing a cam curve fitting program to obtain a first cam curve expression based on the k-order harmonic function, and adding the first cam curve expression to a local control point; and after the solution, transforming the first cam curve expression to obtain a second cam curve expression, combining the first two expressions to obtain a final cam curve expression, determining the order of k,adding the final cam curve expression to the local control point, and obtaining an optimized cam curve. The method provided by the present invention is used in the design of cam curves.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Local smoothing method for discrete machining path with controllable error and passing a given tool position
ActiveCN107255998BAccurate responseGood kinematic performanceProgramme controlComputer controlCutter locationKnickpoint
The invention discloses a local smoothing method having controllable errors and capable of passing predetermined cutter location points of a scattering processing path, and belongs to the high speed high precision numerical control processing field. Every corner of the scattering processing path adopts two cubic Bezier curves to be used as transition curves for the smoothing processing, and problems of routine scattering path processing such as low precision and easy speed fluctuation are solved. The concrete position of the control point of the transition curve satisfying a maximum approximation error requirement on a line segment is determined with help of convex hull property. Under conditions of G2 continuity restriction and line segment length restriction, the inverse computation of the control point of the transition curve is carried out. According to the acquired control point, a dual-cubic Bezier curve used for the path smoothing is finally acquired. By adopting the local smoothing method, the G2 continuity of the path after the smoothing is achieved, and by comparing with other path smoothing algorithms, processing precision is guaranteed, and the method can pass the cutter location points used to form the scattering processing path.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
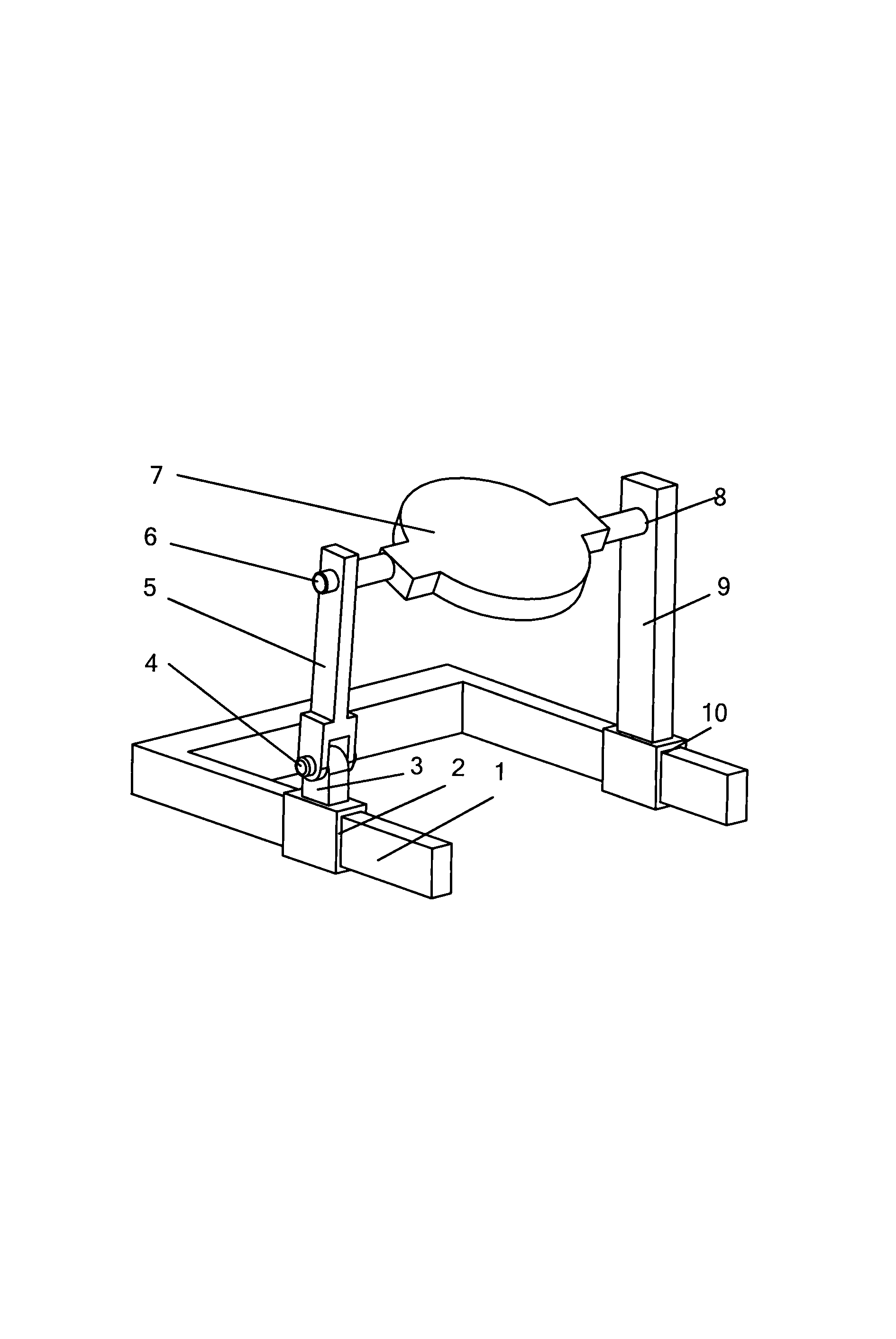
PC board mounting mechanism
PendingCN113374273AGood kinematic performanceReduce complexityBuilding material handlingKinematic chainMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a PC board mounting mechanism. The PC board mounting mechanism comprises a rack, a movable arm, a push rod, a pull rod, a supporting arm, a PC board frame, a movable arm oil cylinder and a push rod oil cylinder, the movable arm is connected with the rack through a rotating pair, and the movable arm can rotate relative to the rack under driving of the movable arm oil cylinder; the push rod is connected with the rack through the rotating pair, and the push rod can rotate relative to the rack under the driving of the push rod oil cylinder; the movable arm, the push rod, the pull rod and the supporting arm form a plane four-rod kinematic chain and form a parallelogram structure; the PC board frame is mounted on the supporting arm through the rotating pair; and in the lifting process of the movable arm, if the push rod oil cylinder does not work, the supporting arm keeps translational motion, that is, the PC board frame mounted on the supporting arm keeps translational lifting, the kinematics performance of existing PC board mounting equipment is effectively improved, and the mechanism coupling degree and the complexity of a hydraulic system are reduced. The PC board mounting mechanism is very suitable for carrying and mounting indoor partition PC boards.
Owner:SHANDONG TIANYI MACHINERY
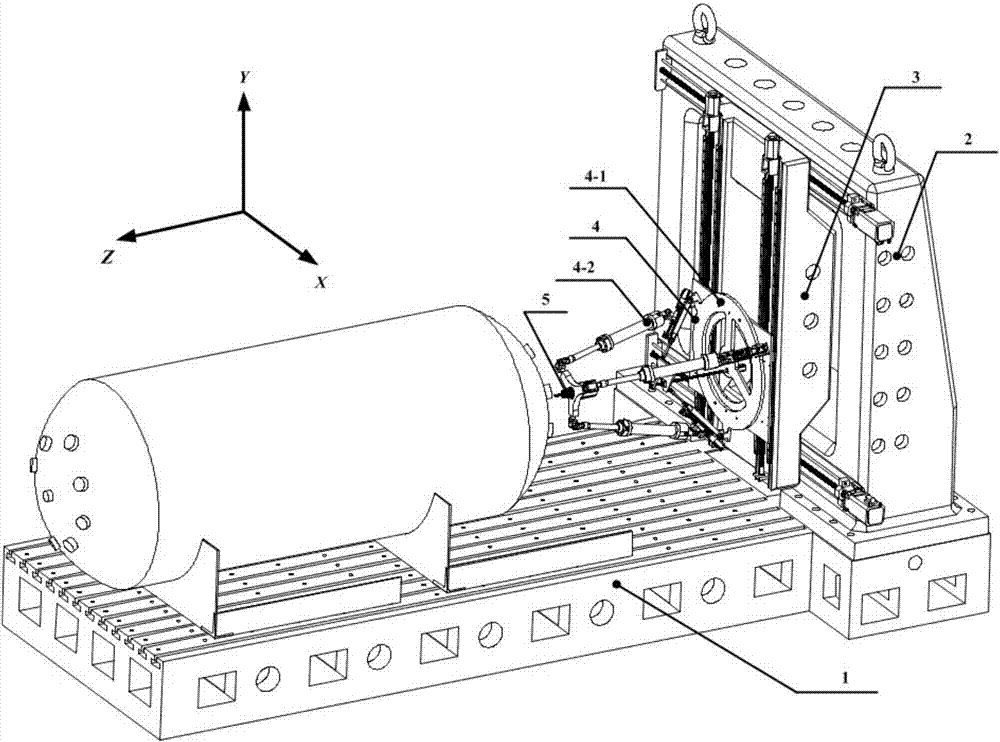
Three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism without accompanying movement
ActiveCN110815187AStrong carrying capacityGood kinematic performanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism without accompanying movement. The three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism without accompanying movement comprises a static platform and a movable platform, wherein the static platform is fixedly arranged on an external device, and the movable platform is connected with the static platform through a flexible driving chain. Theflexible driving chain comprises two arranged symmetrically three-joint movable assemblies, a four-joint movable assembly and a plurality of rotary driving assemblies, wherein the upper ends of the three joint movable assemblies are rotationally connected with the static platform, and the lower ends of the three joint movable assemblies are movably connected with the movable platform; and the upper end of the four-joint movable assembly is rotationally connected with the static platform, and the lower end of the four-joint movable assembly is movably connected with the movable platform; and the three-joint movable assemblies and the four-joint movable assembly are located on the same straight line with the movable connection of the movable platform. According to the three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism without accompanying movement, the movable platform has two rotational degrees of freedom and one translational degree of freedom in space, accompanying movement does not exist, good kinematic performance is achieved, motion decoupling of all degrees of freedom is achieved, and the design of a controller is convenient to achieve.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Cam Curve Design Method Based on k-order Harmonic Function
ActiveCN108629067BGuaranteed continuityImprove conductivityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringComputational physics
The invention relates to a cam curve design method based on a k-order harmonic function, which belongs to the technical field of cam design. The invention aims to solve the problem that the existing harmonic cam curve is unsuitable for high-speed occasions due to mechanism fluctuations caused by some characteristic parameter curves approaching infinity at the endpoints. It includes: obtaining the key point data determined by the cam to realize the function; dimensionless the key point data to obtain the dimensionless time T and dimensionless displacement S; writing the cam curve fitting program to obtain the k-order harmonic function Add local control points to the first cam curve expression; after solving, deform to obtain the second cam curve expression, then combine the first two expressions to obtain the final cam curve expression, determine the order of k, and add local control points, An optimized cam profile is obtained. The invention is used in the design of cam curves.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cycloid type scanning measurement trajectory planning method and system for free-form surface
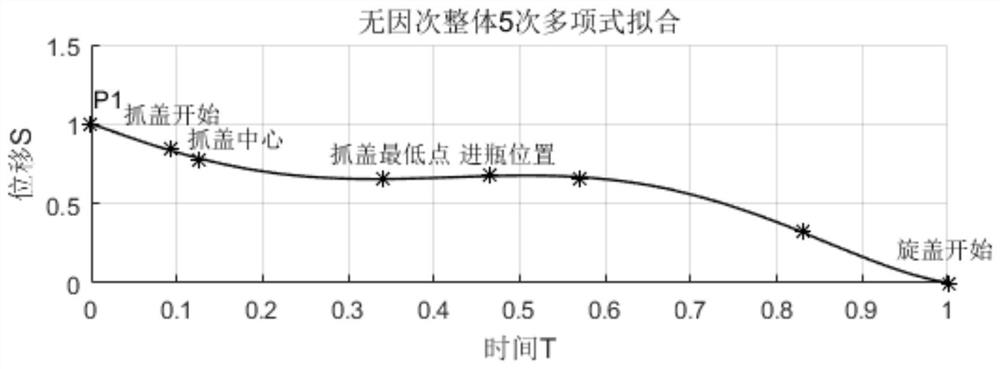
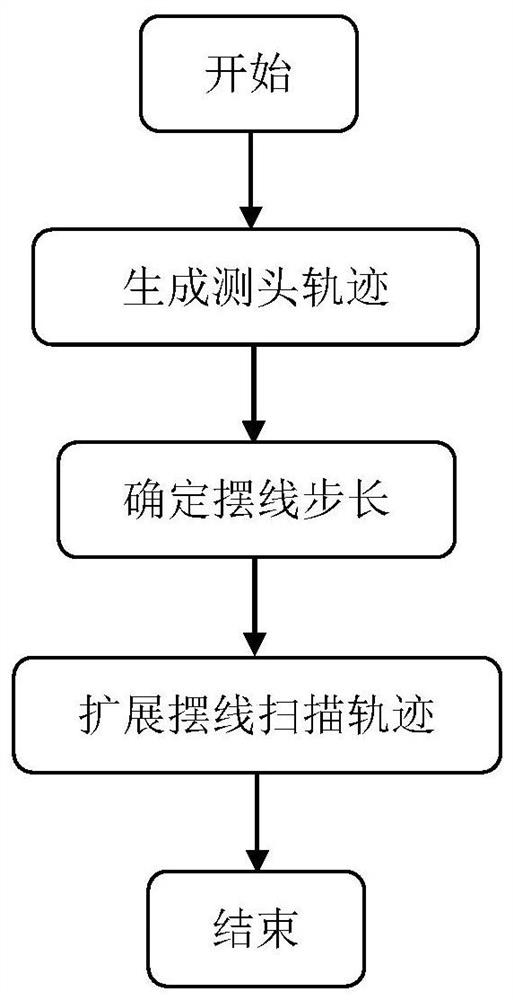
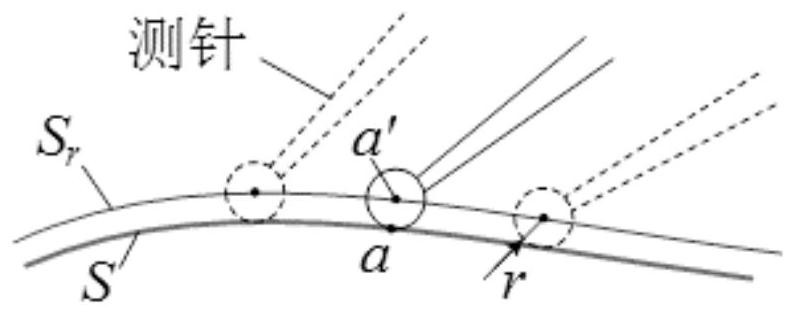
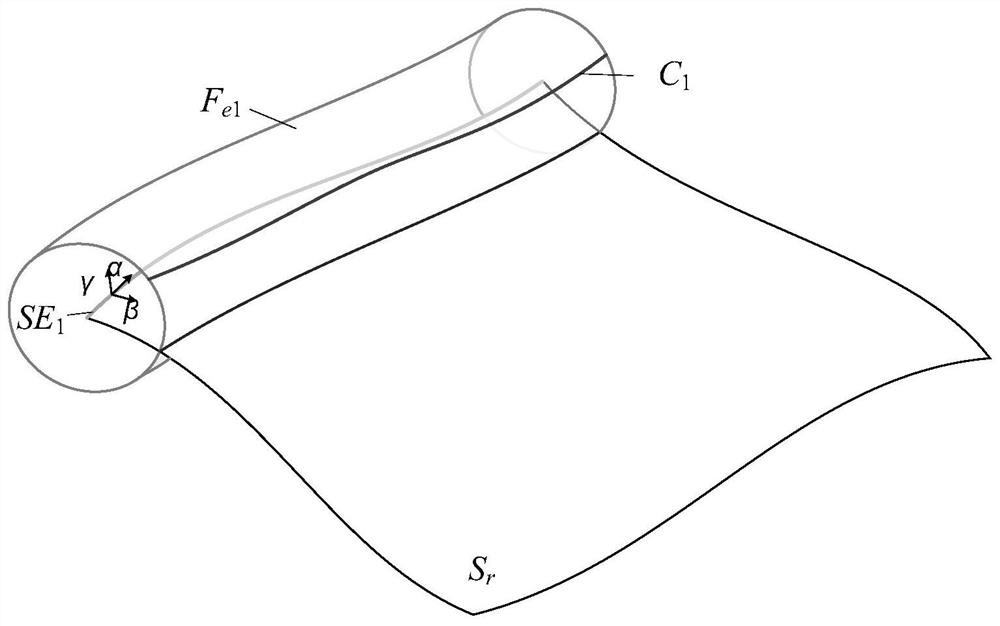
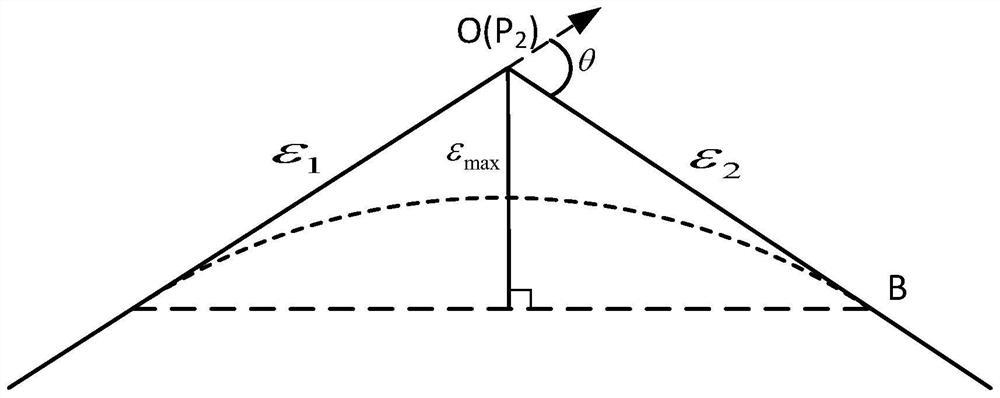
ActiveCN112859736ALow exercise loadGood kinematic performanceNumerical controlRotational axisContinuous measurement
The invention discloses a cycloid type scanning measurement trajectory planning method and system for a free-form surface, belongs to the field of five-axis continuous measurement of the free-form surface, and aims to improve the dynamic performance of a machine by avoiding frequent acceleration and deceleration of a rotating shaft of a measuring head so as to improve the measurement efficiency. The method comprises a measuring head track curve generation step, a cycloid step length determination step and a cycloid scanning track expansion step. According to the invention, in the scanning measurement process, the C axis can be always kept in the same rotation direction, the constant angular velocity can be kept when necessary, vibration caused by sudden change of the rotation direction of the C axis is avoided, the dynamic performance of a measuring machine is remarkably improved, the track length of a measuring head can be remarkably shortened, the motion amount of a linear axis is reduced, and the measurement efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A flexible leg structure of a planar five-bar mechanism
The invention discloses a flexible leg structure with a plane five-rod mechanism. The flexible leg structure is characterized by comprising a pitching drive joint, a foot tip and a connecting rod mechanism. The pitching drive joint comprises a variable stiffness driving flexible joint, a drive motor, two harmonic reducers, a supporting frame, a synchronous pulley and a synchronous belt. The foot tip comprises a three-dimensional mechanical sensor, a three-dimensional mechanical sensor support and a foot arch. The bottom of the three-dimensional mechanical sensor is connected with the three-dimensional mechanical sensor support. The bottom of the three-dimensional mechanical sensor support is connected with the foot arch. The connecting rod mechanism comprises ten hinge points (A), (B), (C), (D), (E), (F), (G), (H), (R) and (I). Connecting rods are hinged to a conventional four-rod mechanism, a four-rod mechanism with a spring rod and a plane pentagon five-rod mechanism through the ten hinge points. The hinge points (A), (R) and (I) are used for fixing the connecting rod mechanism to the pitching drive joint.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Direct speed transition fairing method based on trigonometric function acceleration and deceleration control
The invention discloses a direct speed transition fairing method based on trigonometric function acceleration and deceleration control. The method comprises the following steps that a processing code point position coordinate is read, an original processing path is set to be composed of micro line segments connected by continuous point positions, and the length of the micro line segments and an included angle between the adjacent micro line segments are calculated according to point position coordinates; the machining process of each micro line segment is divided into a plurality of segments according to an acceleration function, transition stages of corners of two adjacent micro line segments are located in a deceleration stage of the previous micro line segment and an acceleration stage of the next micro line segment, sin(2x) is adopted as a basis function of jerk to establish an acceleration and deceleration model, and the maximum acceleration and acceleration and deceleration parameters are set; and according to the maximum allowable machining error, the overlapping mixing transition time and the transition starting time of the micro-line segment corner are solved, motion synthesis is carried out, and therefore the machining path after fairing optimization is obtained. The method is advantaged in that one-step transition can be achieved, smooth transition of three-axis motion inflection points can be achieved under the condition that high motion continuity is guaranteed, and high-order continuity of motion in the machining process is guaranteed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Input-output complete decoupling three-freedom-degree moving parallel robot mechanism
InactiveCN102825595BSimple structureEasy processing and assemblyProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl theoryMachine tool
An input-output complete decoupling three-freedom-degree moving parallel robot mechanism comprises a fixed platform, a movable platform and three branches for connecting the fixed platform and the movable platform. The first branch and the third branch are composed of three moving pairs and two connecting rods. The third branch is composed of five rotating pairs and four connecting rods. The input-output complete decoupling three-freedom-degree moving parallel robot mechanism is simple in structure, easy to control, high in flexibility, low in cumulative error, fast in response, large in operation space and high in bearing capacity, is widely applicable to parallel machine tools, walking machines, parallel pressing machines, error compensators, high-precision electronic element encapsulation, food, packing and medical industries, and realizes complete decoupling of three motions of the movable platform.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
A Knee Point Smoothing Method for Discrete Machining Paths
ActiveCN105955194BIncrease the radius of curvatureGood kinematic performanceNumerical controlNumerical controlComputational science
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Three-degree-of-freedom mobile decoupling parallel robot mechanism
InactiveCN102699907BReverse solution is simpleSimplify trajectory planningProgramme-controlled manipulatorThree degrees of freedomEngineering
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Direct speed transition method of three-axis micro-line segment based on trigonometric function acceleration and deceleration control
ActiveCN111966047BImprove continuity of motionReduce complexityNumerical controlTriangular functionCode point
The invention discloses a three-axis micro-line segment direct speed transition method based on trigonometric function acceleration and deceleration control. The length of each micro-line segment and the rotation angle between any two adjacent micro-line segments are obtained from the point coordinates of the processing code; for the rotation angle greater than 0° Establish the trigonometric function acceleration and deceleration model to obtain the interpolation velocity function and interpolation displacement function of the acceleration section, constant velocity section and deceleration section corresponding to the microline section; carry out speed planning to determine the interpolation time of each section; set the phase The maximum transition error of two adjacent micro-segments, solve the maximum transition line segment length, assuming that the transition line lengths of the two are equal, and ≤ the minimum value of the length of the deceleration segment of the first micro-segment and the length of the acceleration segment of the second micro-segment; determined by the length of the transition line segment Transition start time; transition time is calculated by interpolating the displacement function; transition path is obtained by synthesizing the motions of the transition line segments of two adjacent micro-line segments. The invention reduces the complexity of the algorithm and improves the processing efficiency at the corner.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
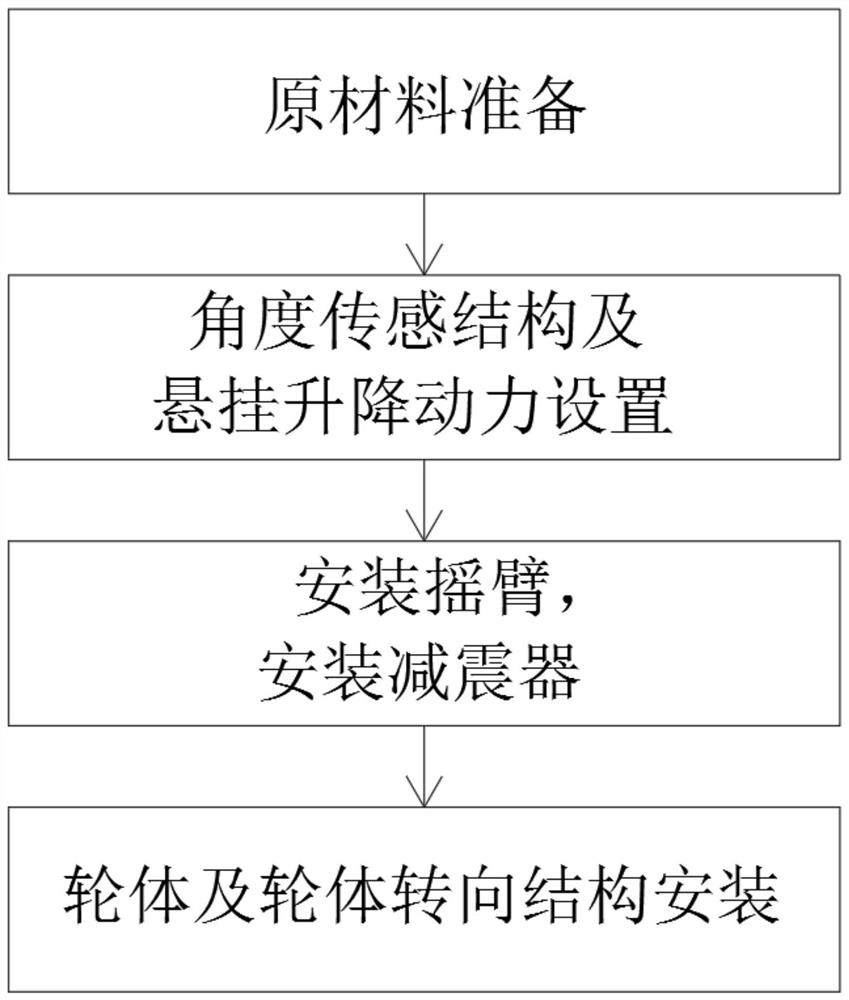
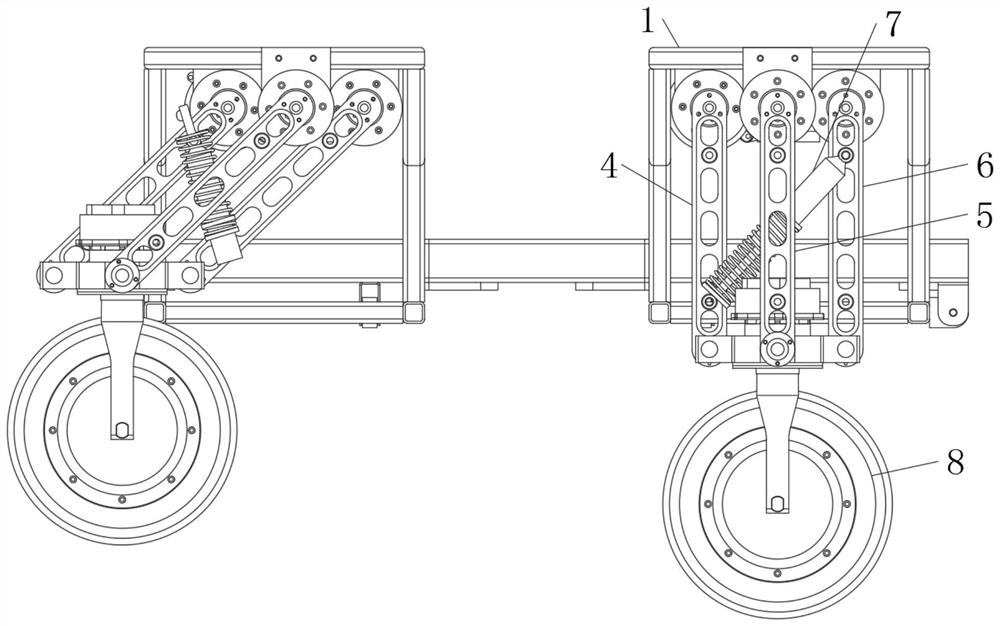
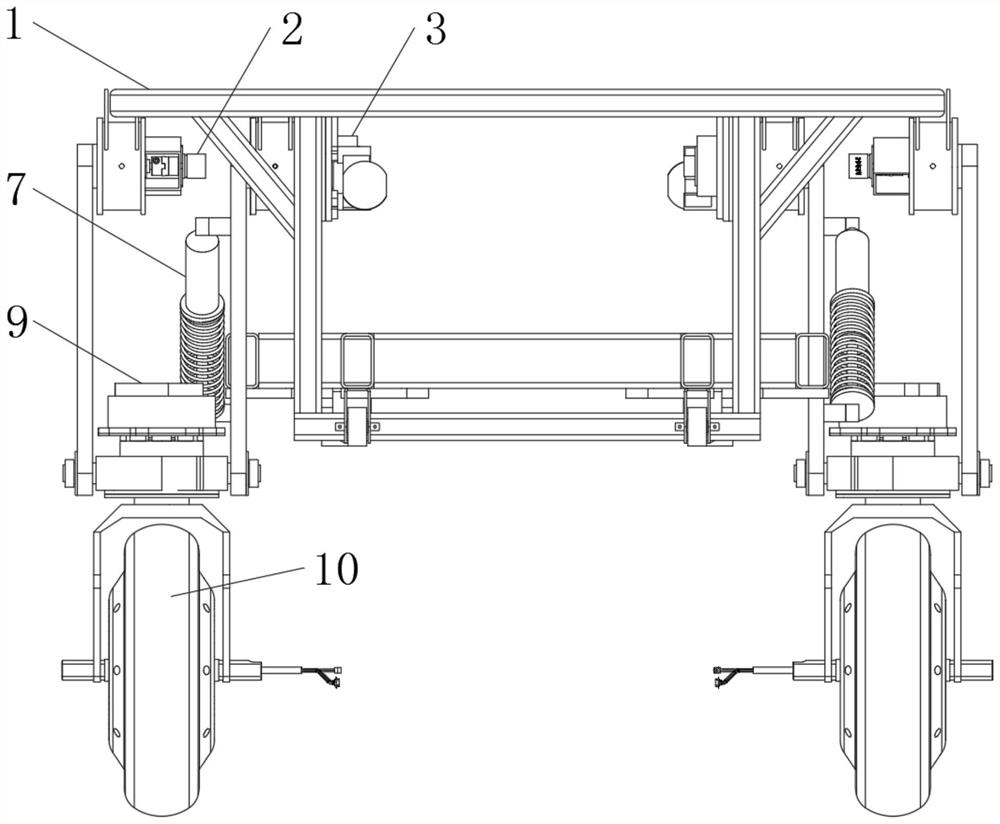
Design method of full-dynamic mobile robot chassis with self-adaptive adjustment function
InactiveCN112896377AWith adaptive adjustment functionAdjustable stiffnessResilient suspensionsVehiclesVehicle frameElectric machinery
The invention relates to the technical field of robot design, and discloses a full-dynamic mobile robot chassis design method with a self-adaptive adjustment function. The method comprises the steps: raw material preparation, angle sensing structure and suspension lifting power arrangement, rocker arm installation, damper installation and wheel body and wheel body steering structure installation and design. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) preparing raw materials, wherein a certain amount of frame bodies, angle sensors, suspension lifting motors, rocker arms, shock absorbers, tires, hub motors and tire steering motors are prepared. According to the universal self-adaptive robot chassis design method, the rigidity of the robot chassis is adjustable; meanwhile, the height of the chassis is adjustable, self-adaptive adjustment can be conducted according to different road conditions, and the chassis can automatically and intelligently adapt to various road conditions; and the suspension structure has the characteristics of being compact, light in weight and relatively low in price, is more suitable for the field of mobile robots, and can bring better use prospects in practical application.
Owner:苏州需要智能技术有限公司
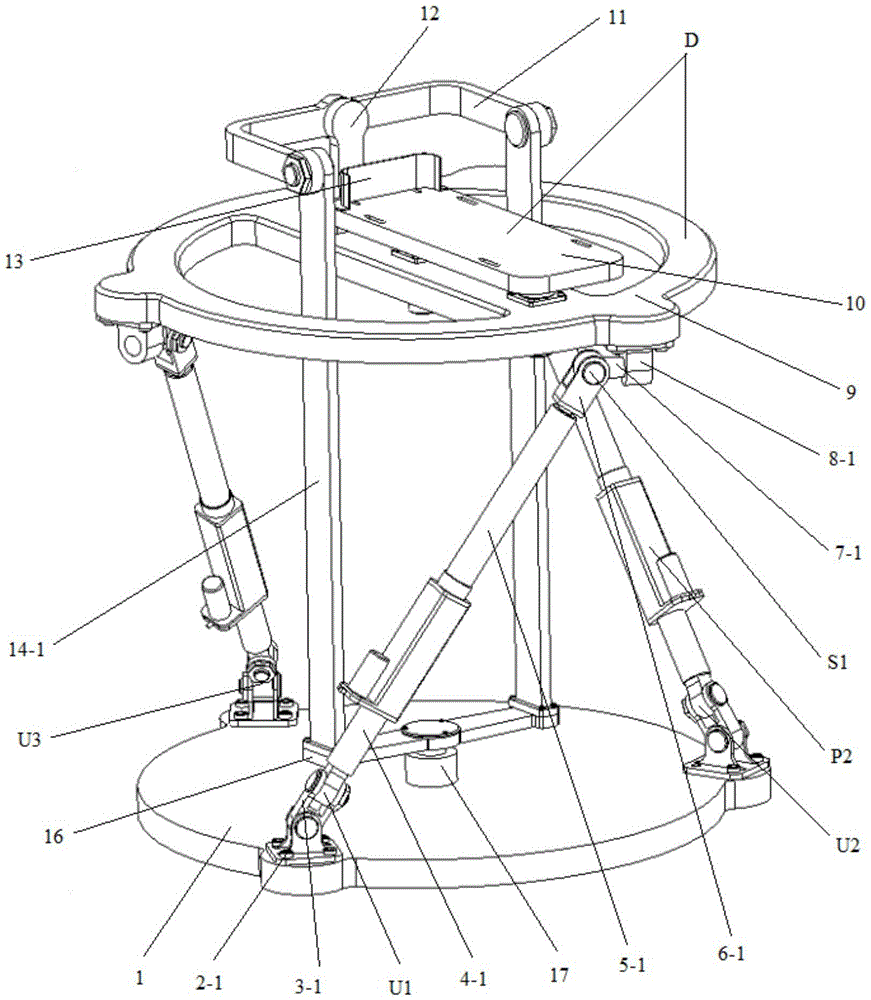
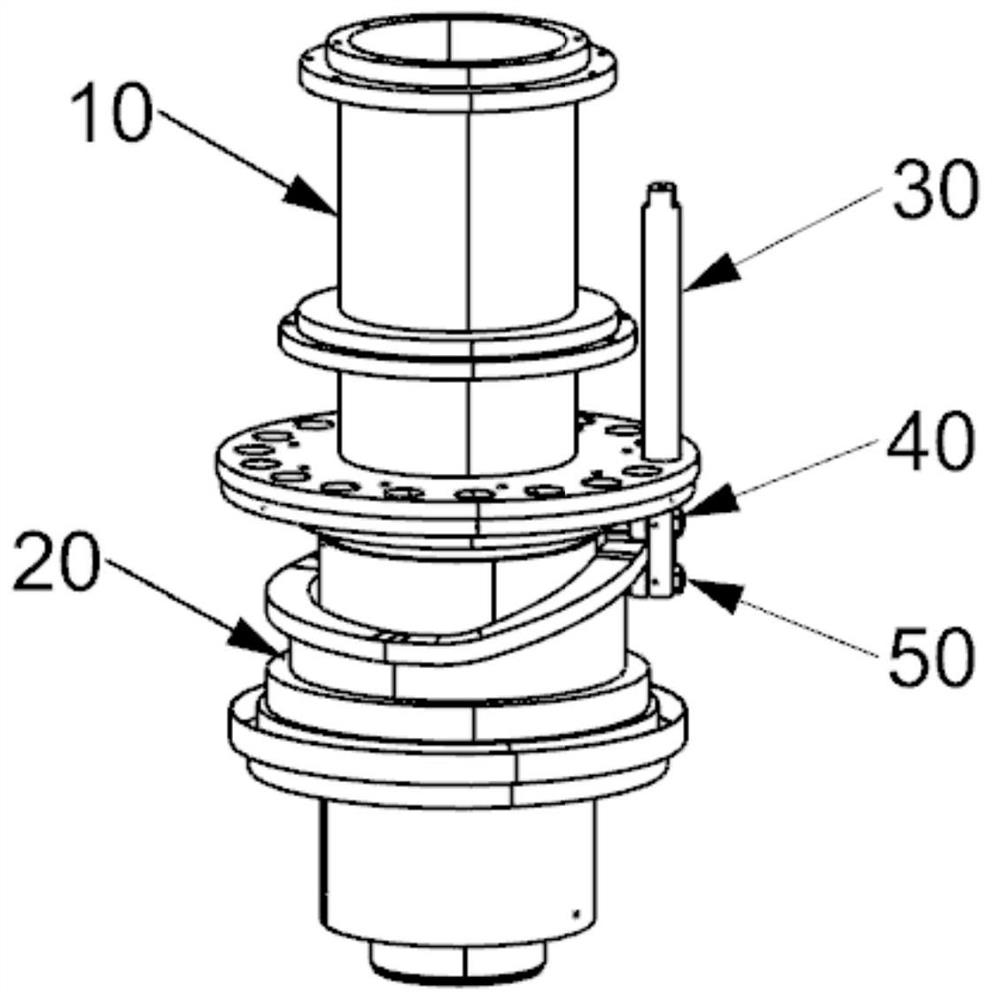
A six-degree-of-freedom self-adaptive wrist joint rehabilitation device
InactiveCN106109165BFix compatibility issuesGuaranteed dynamic coincidenceChiropractic devicesRotary stageRotational freedom
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com