Patents
Literature
317results about How to "Adjustable stiffness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
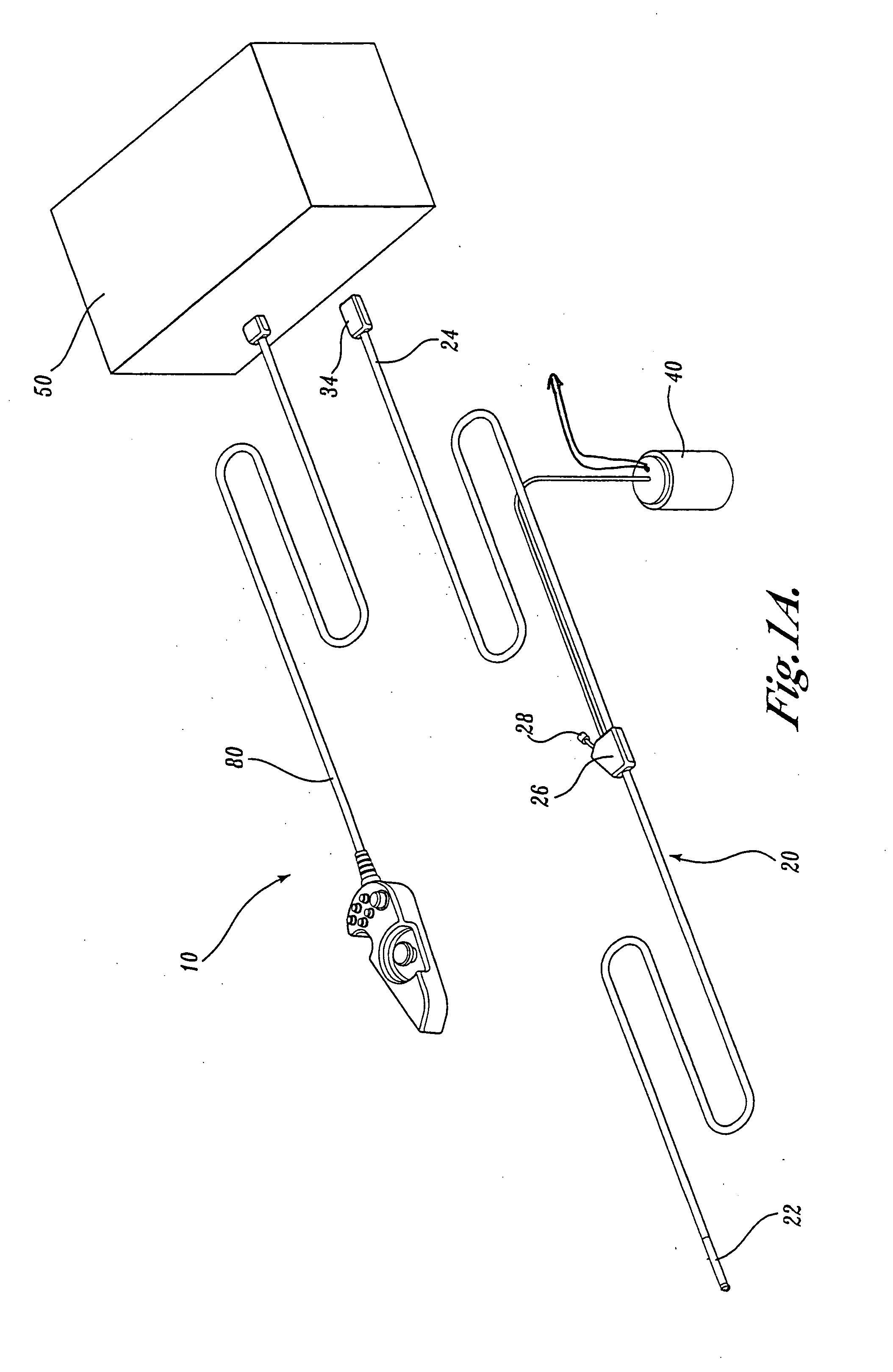
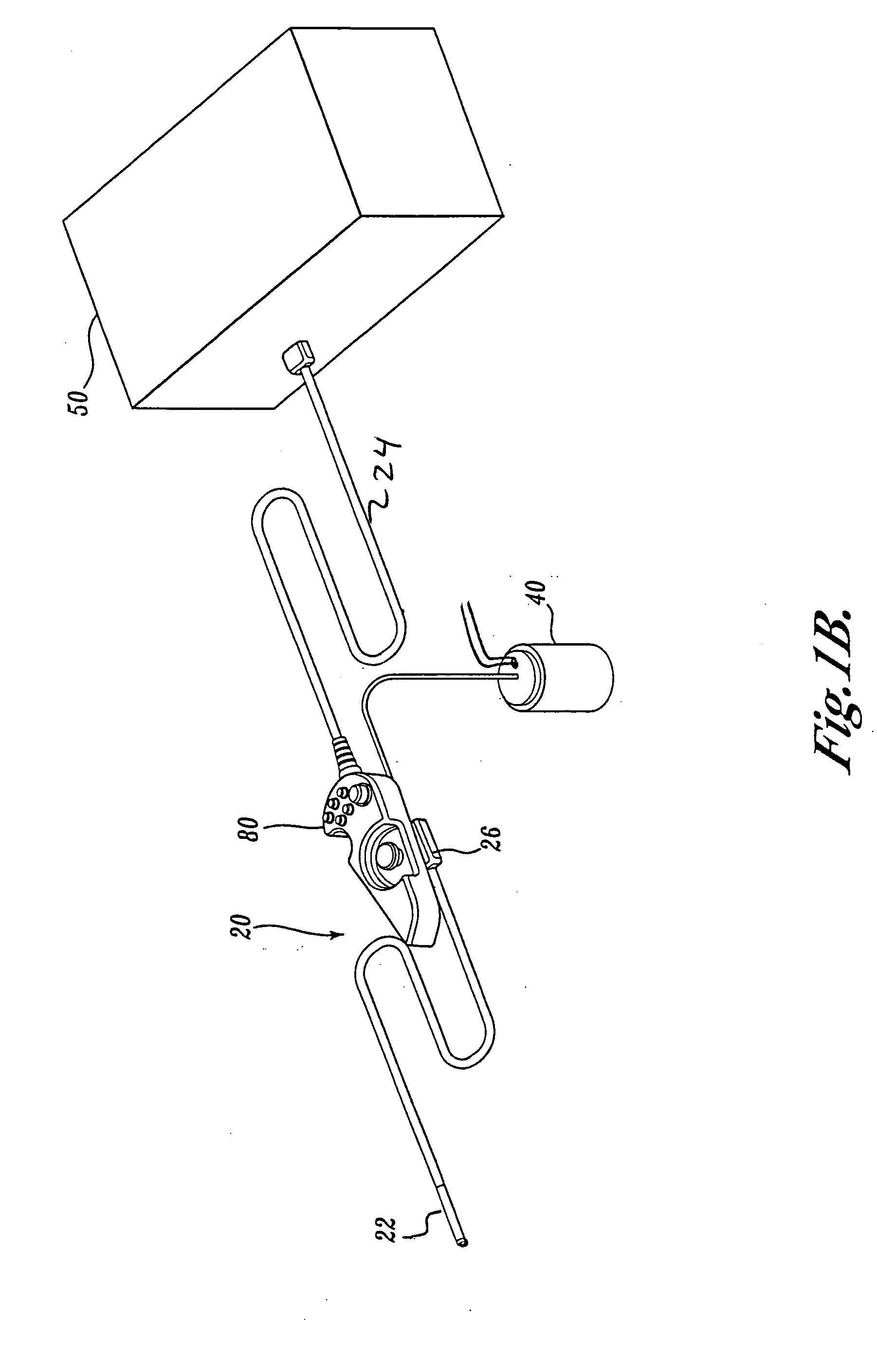
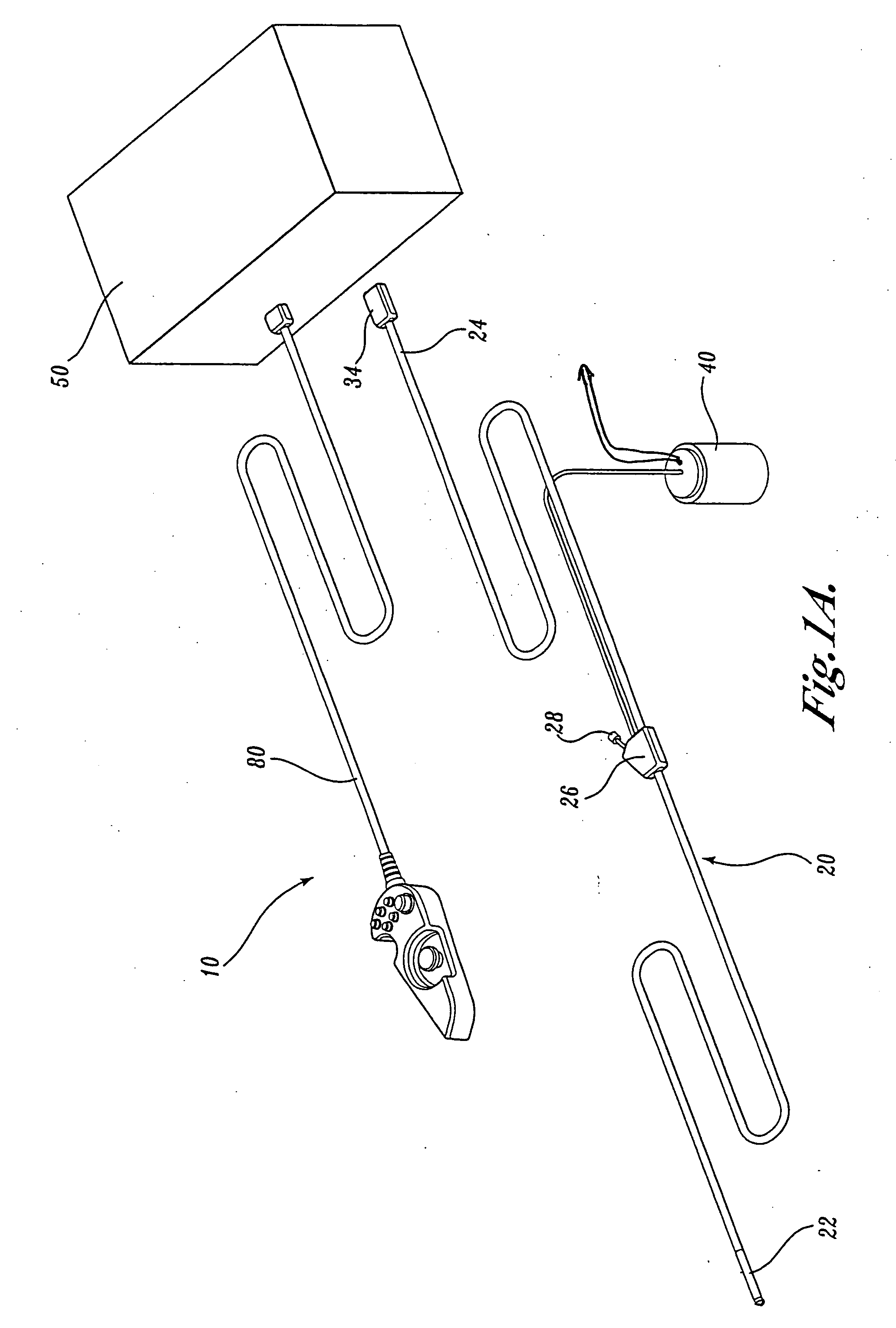
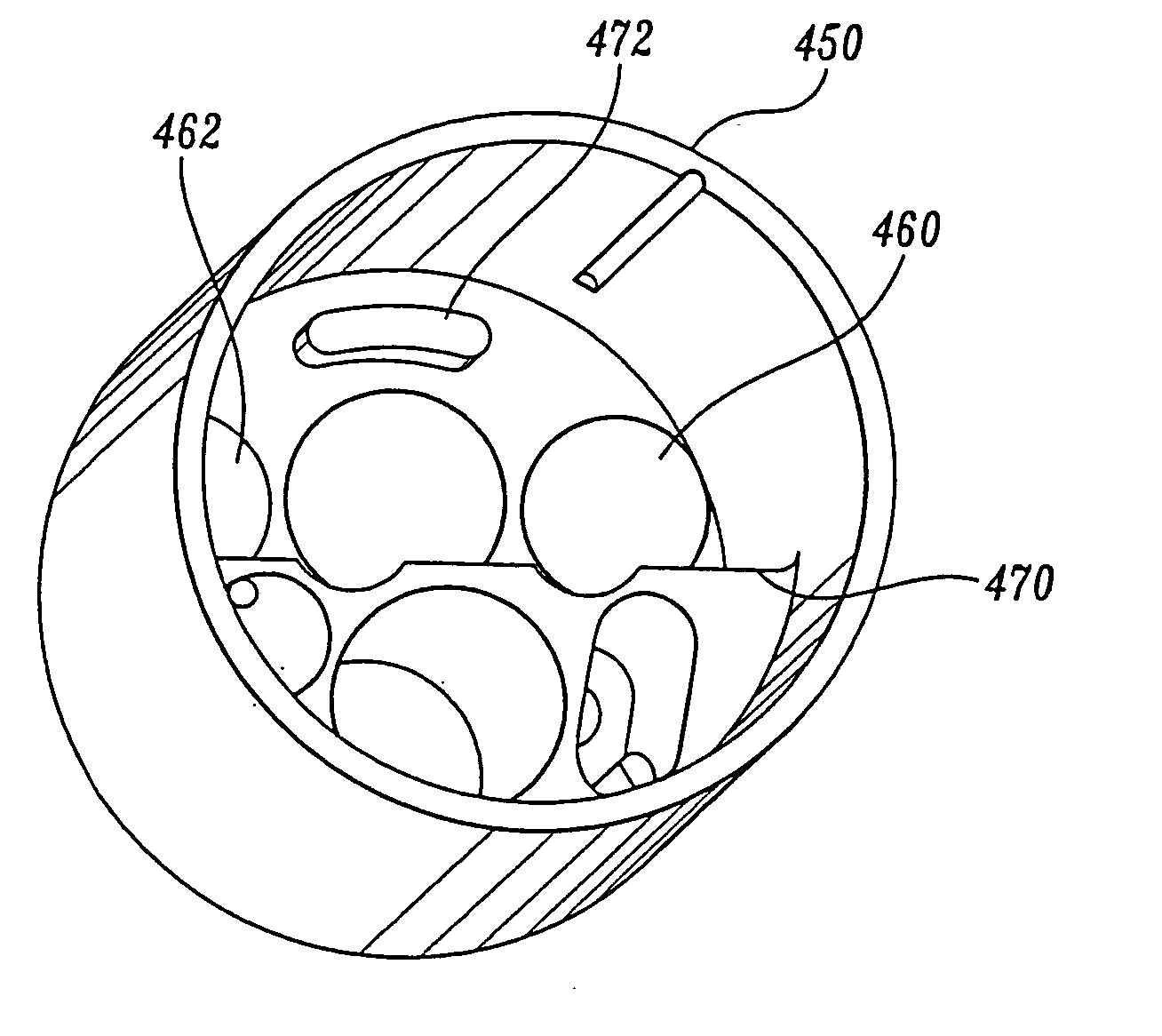
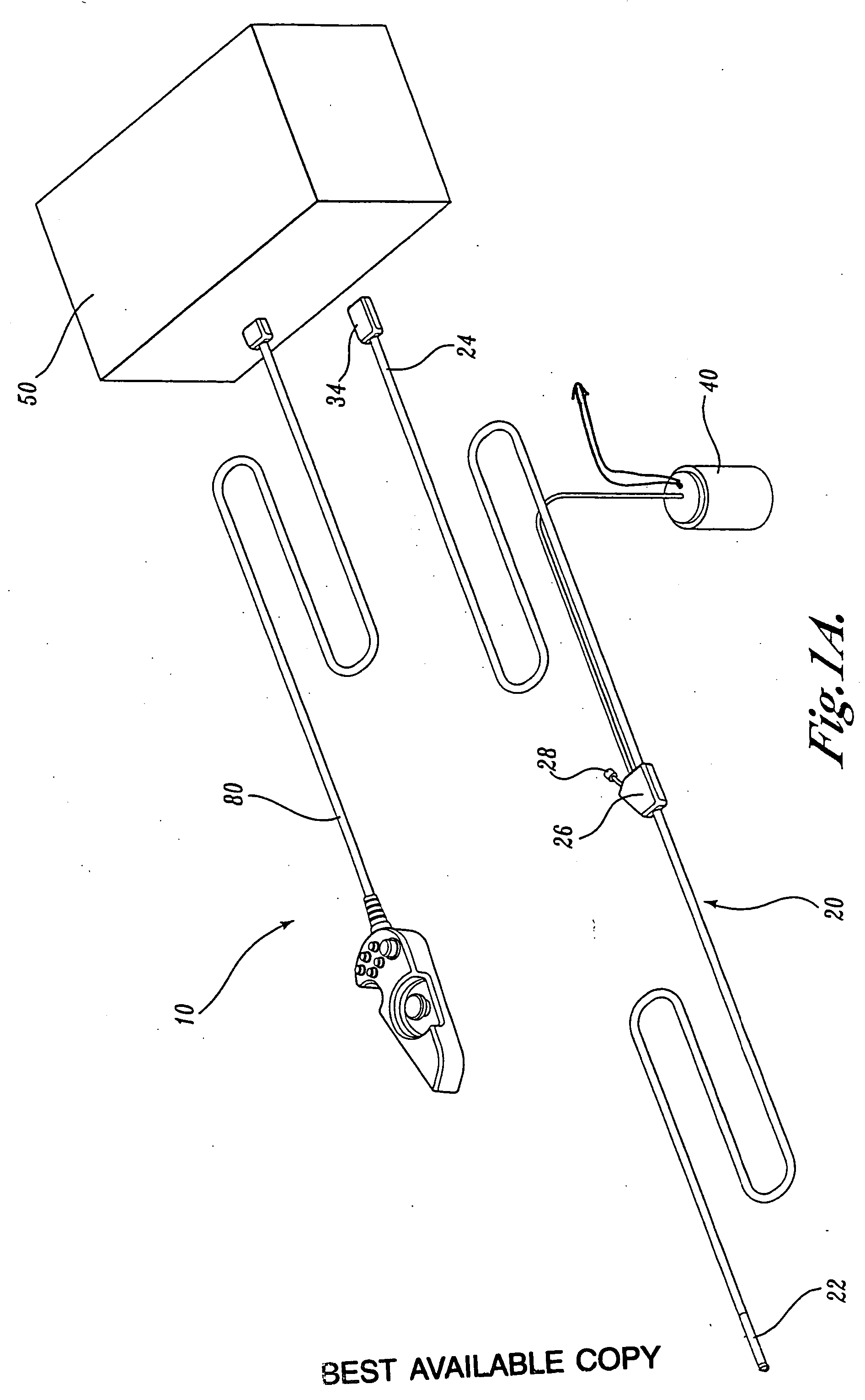
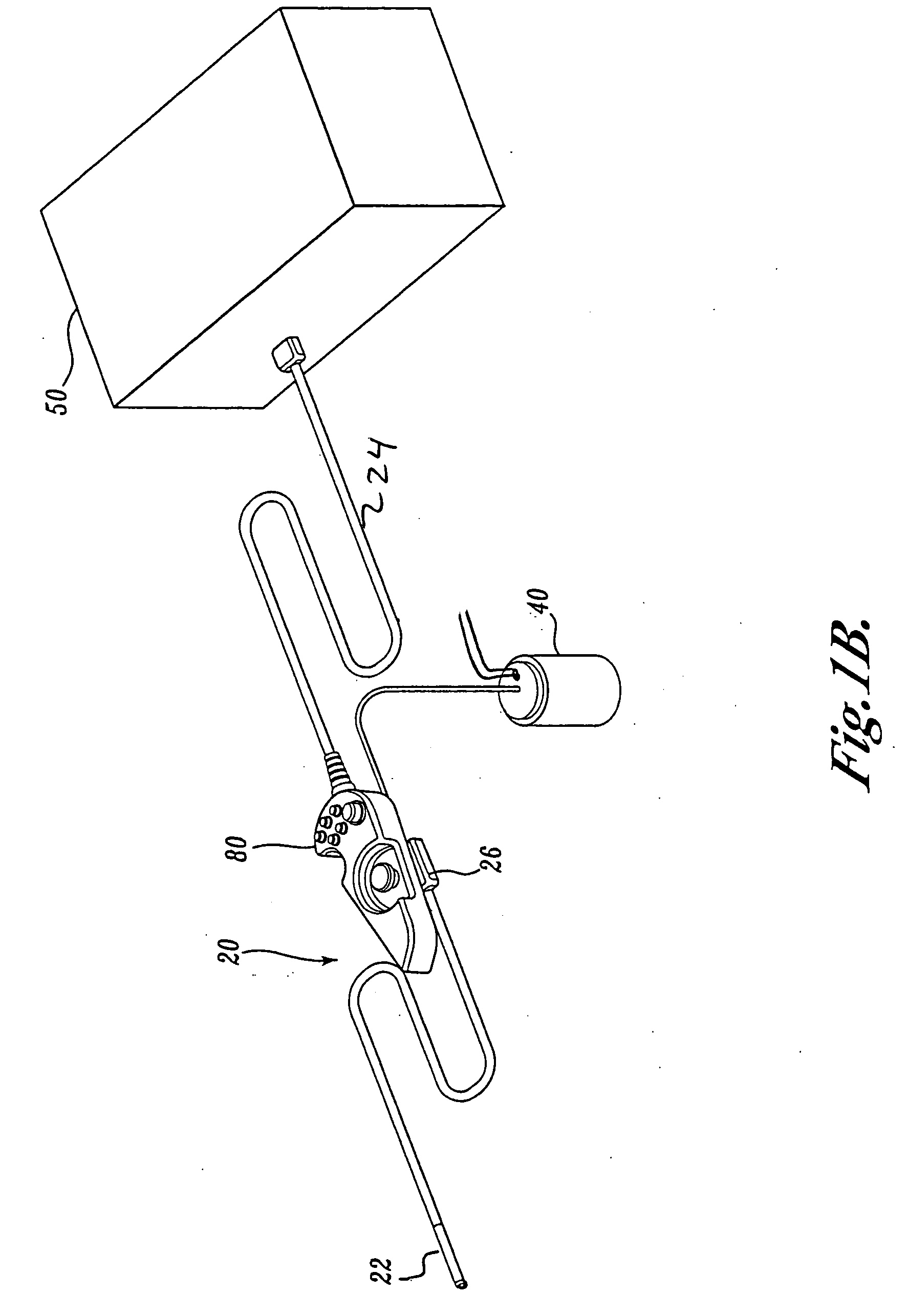
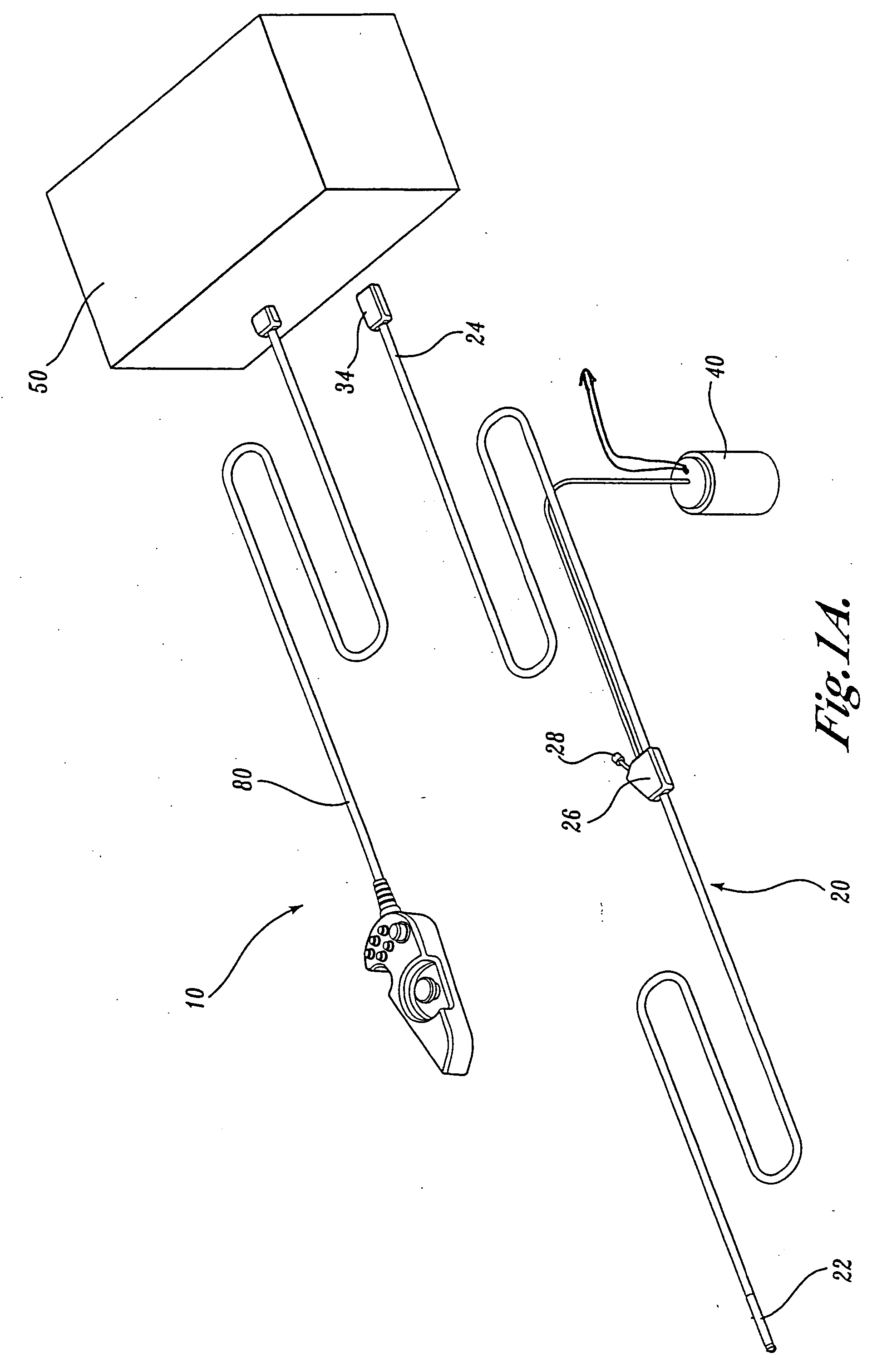
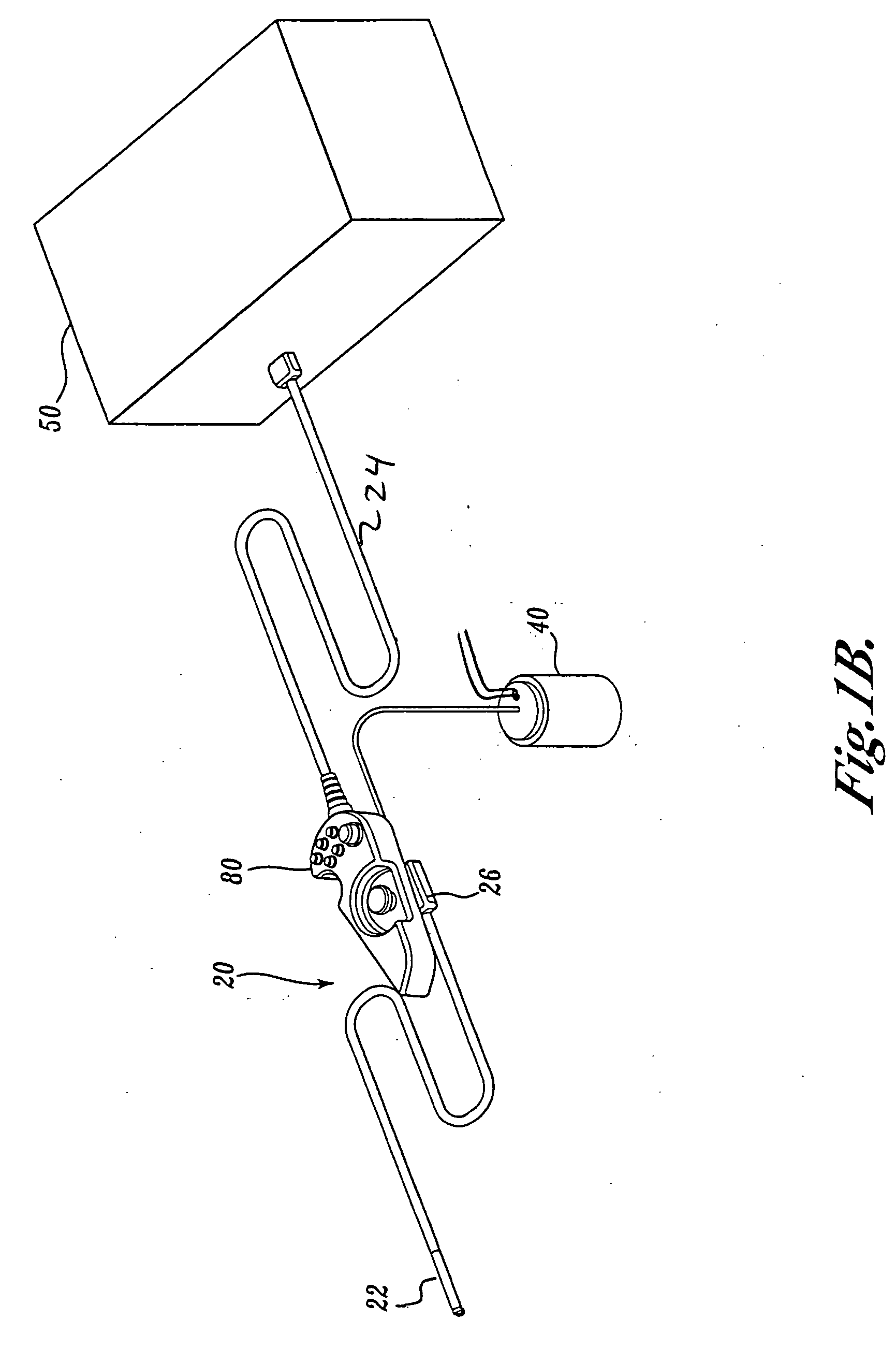
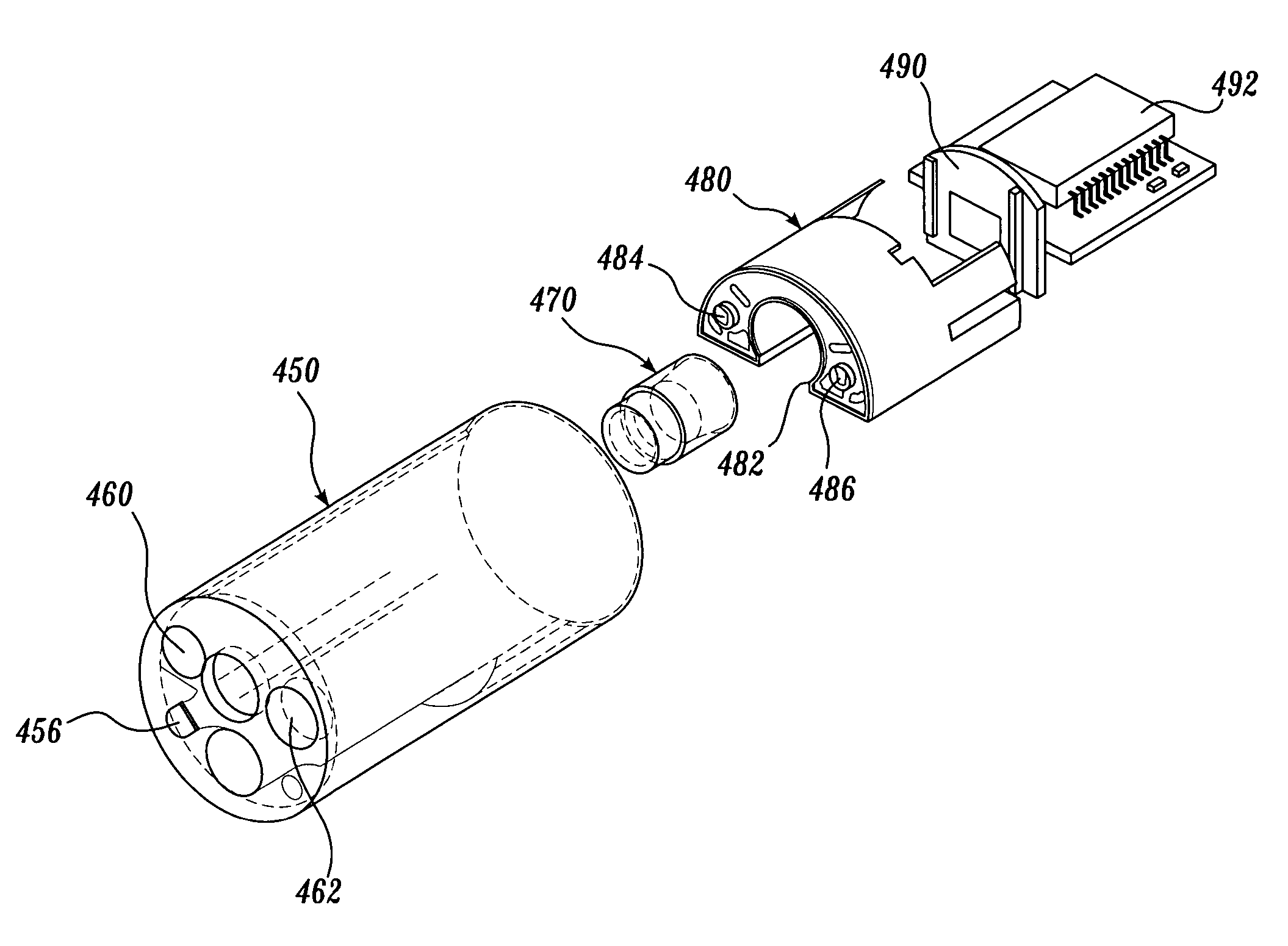
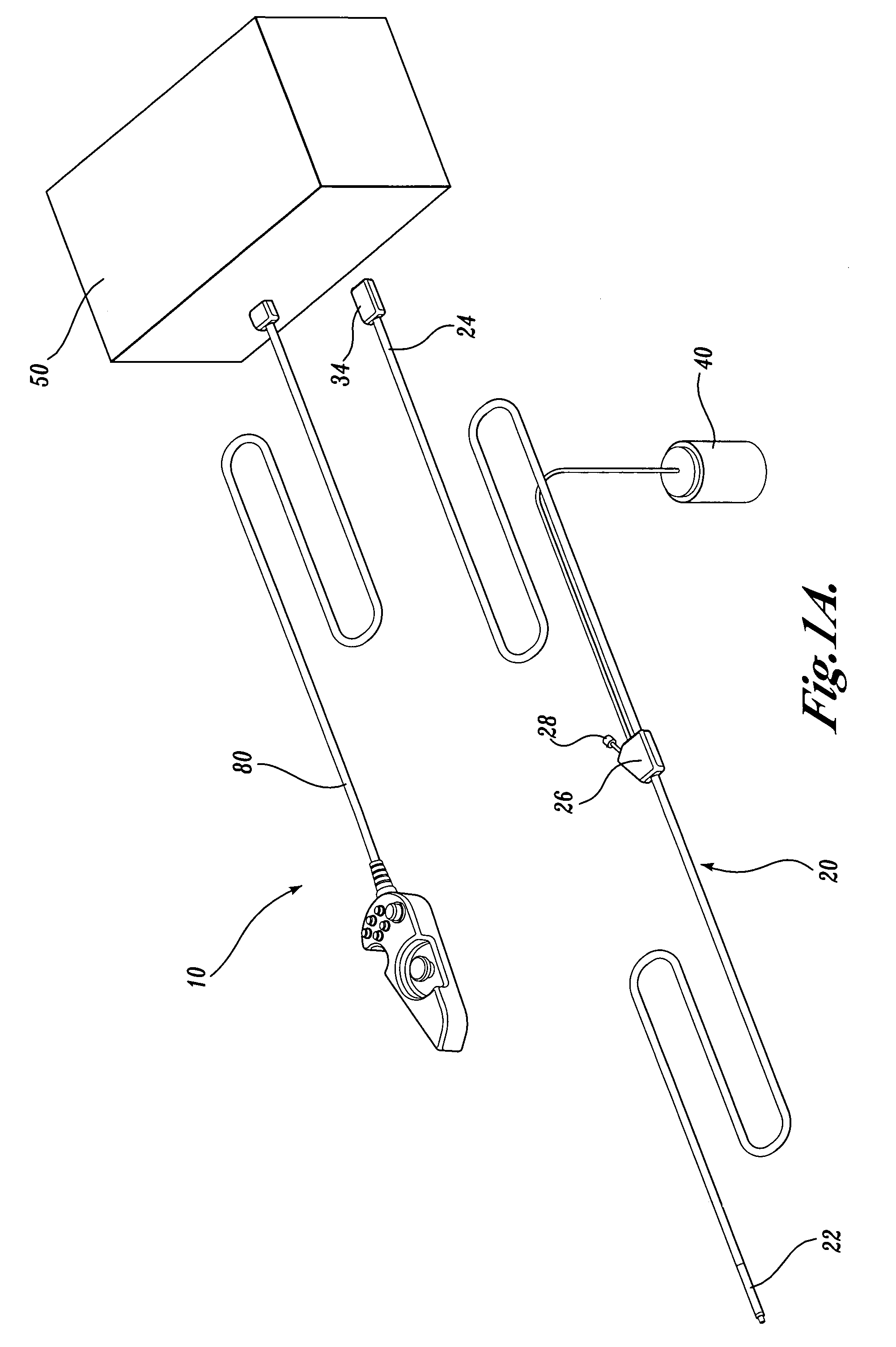
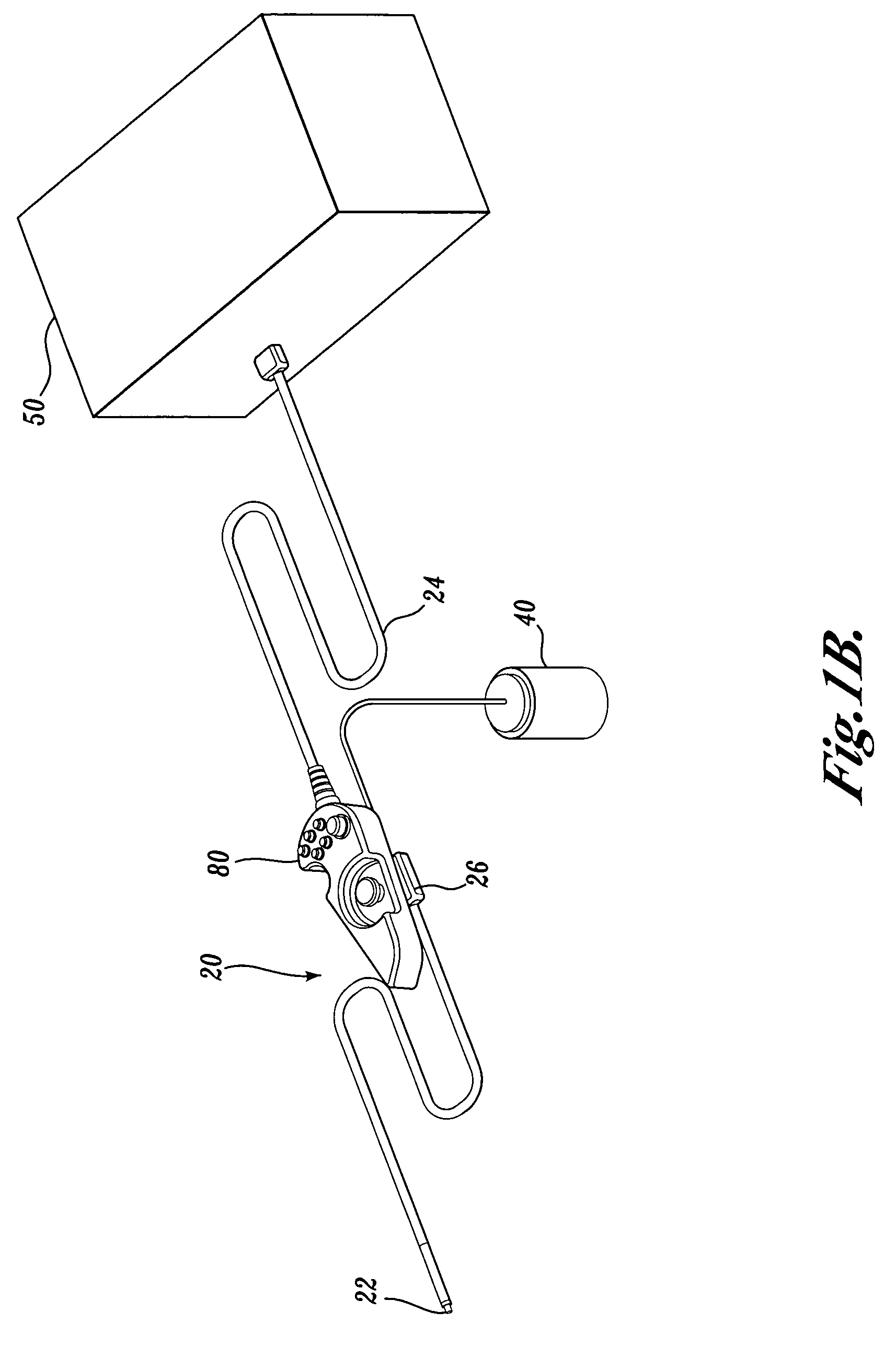
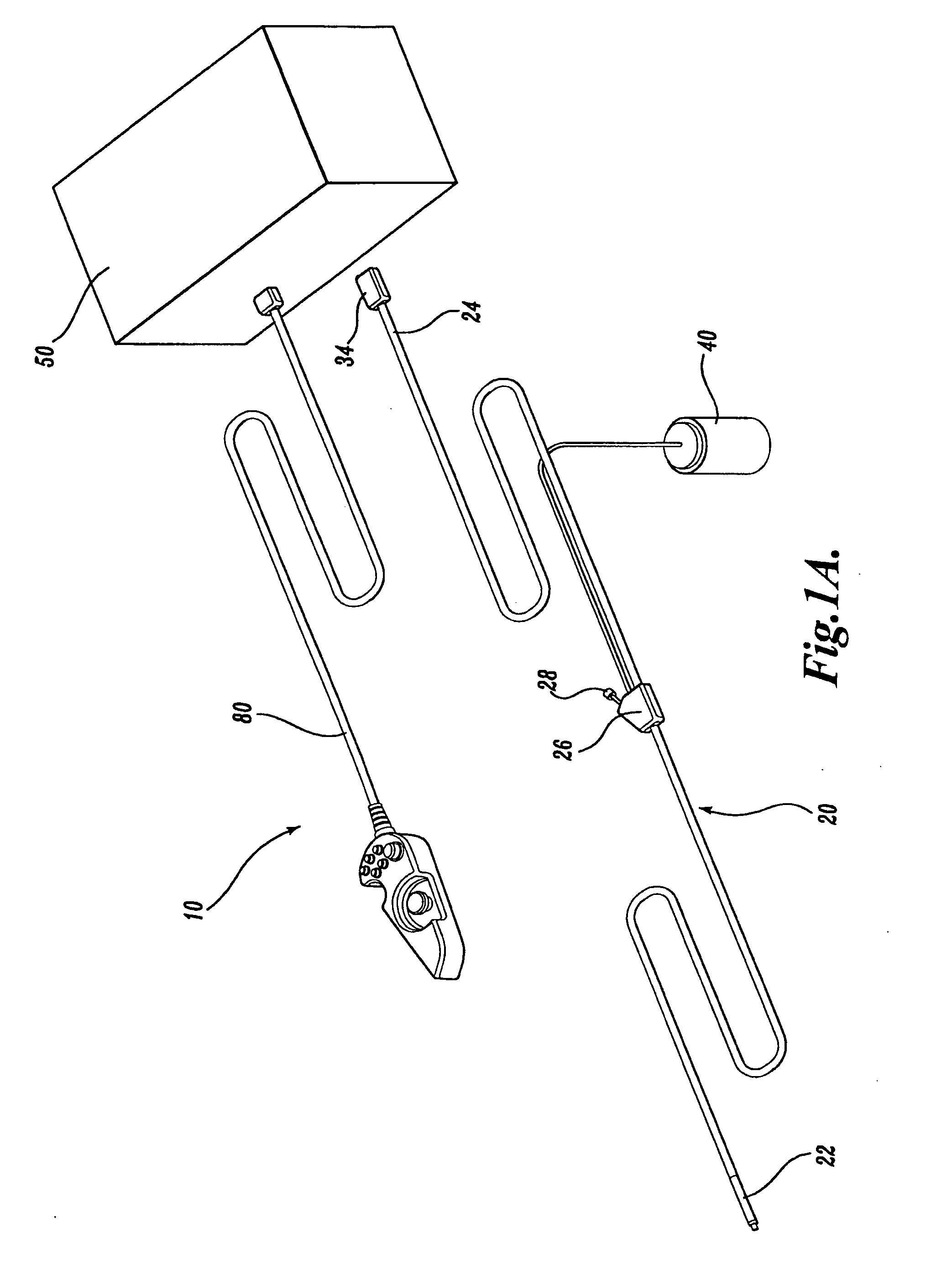
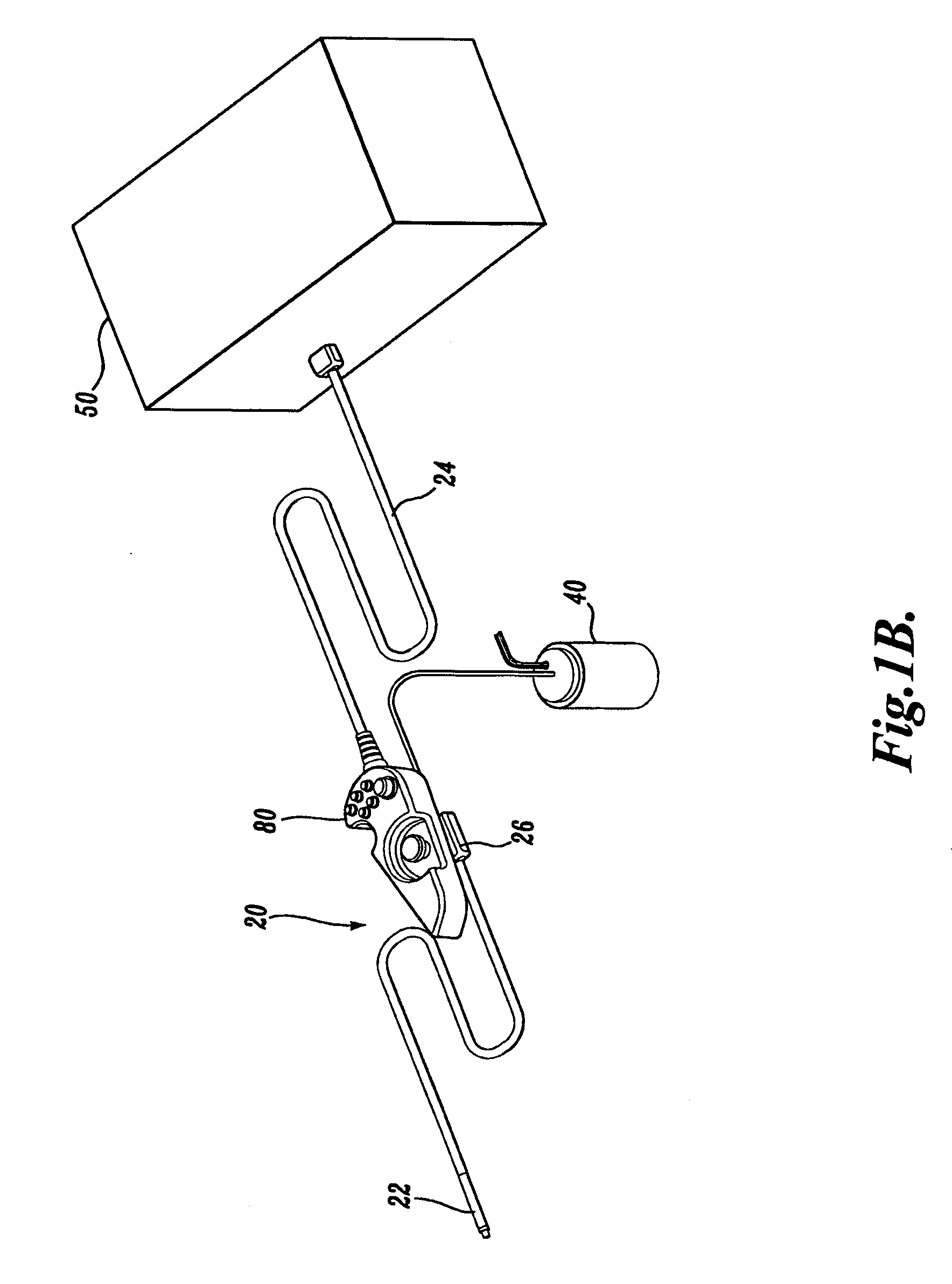
Articulation joint for video endoscope
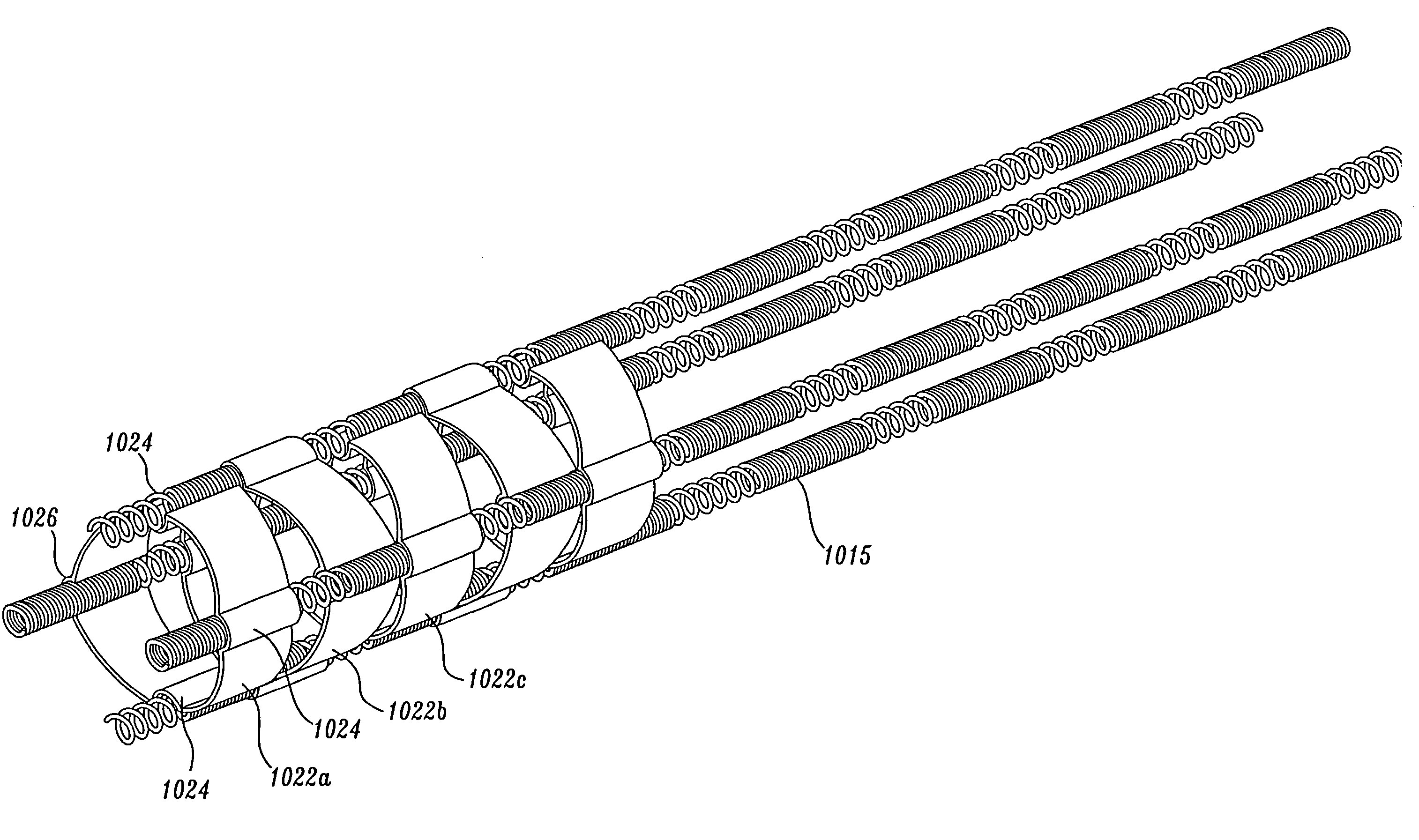
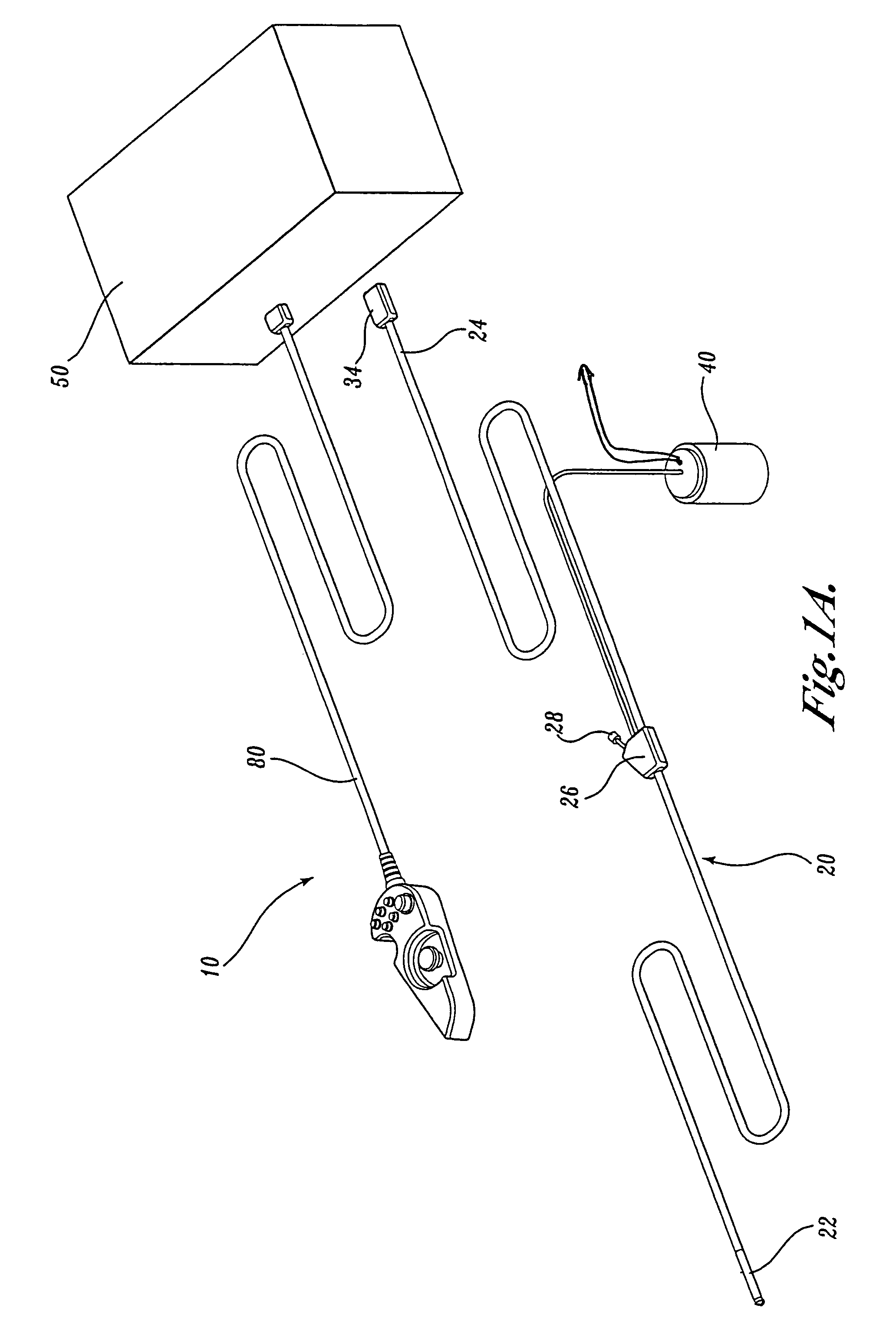
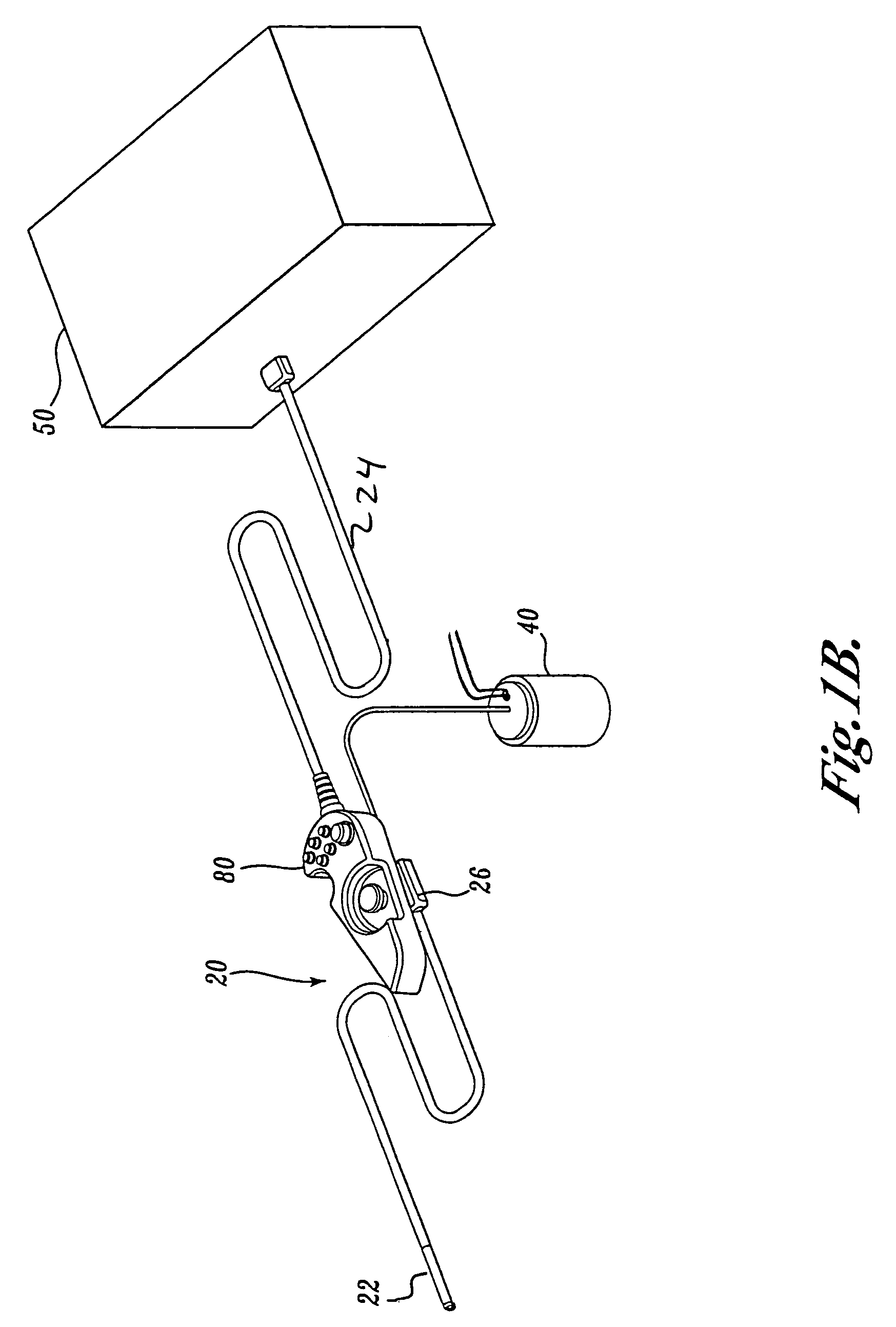
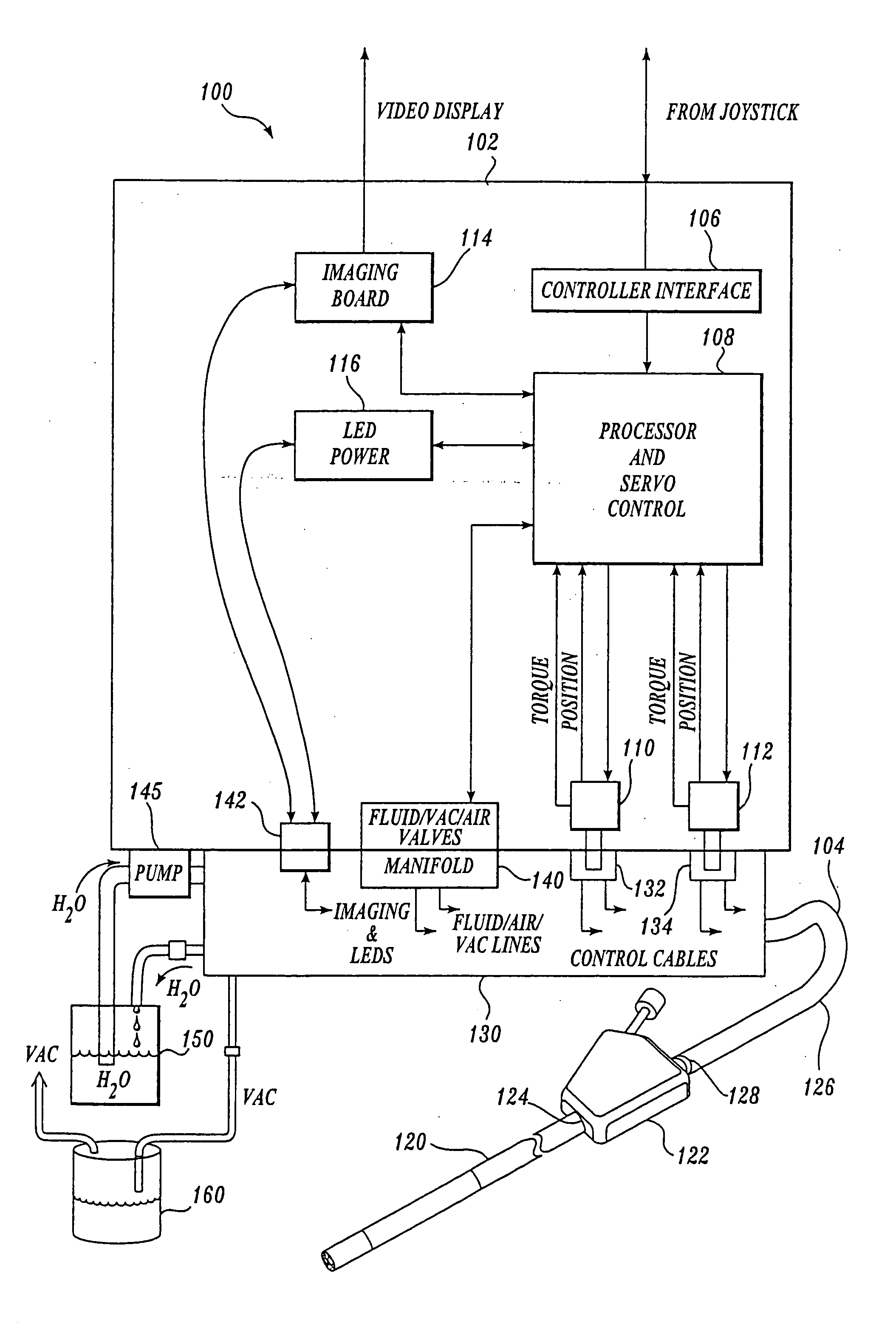
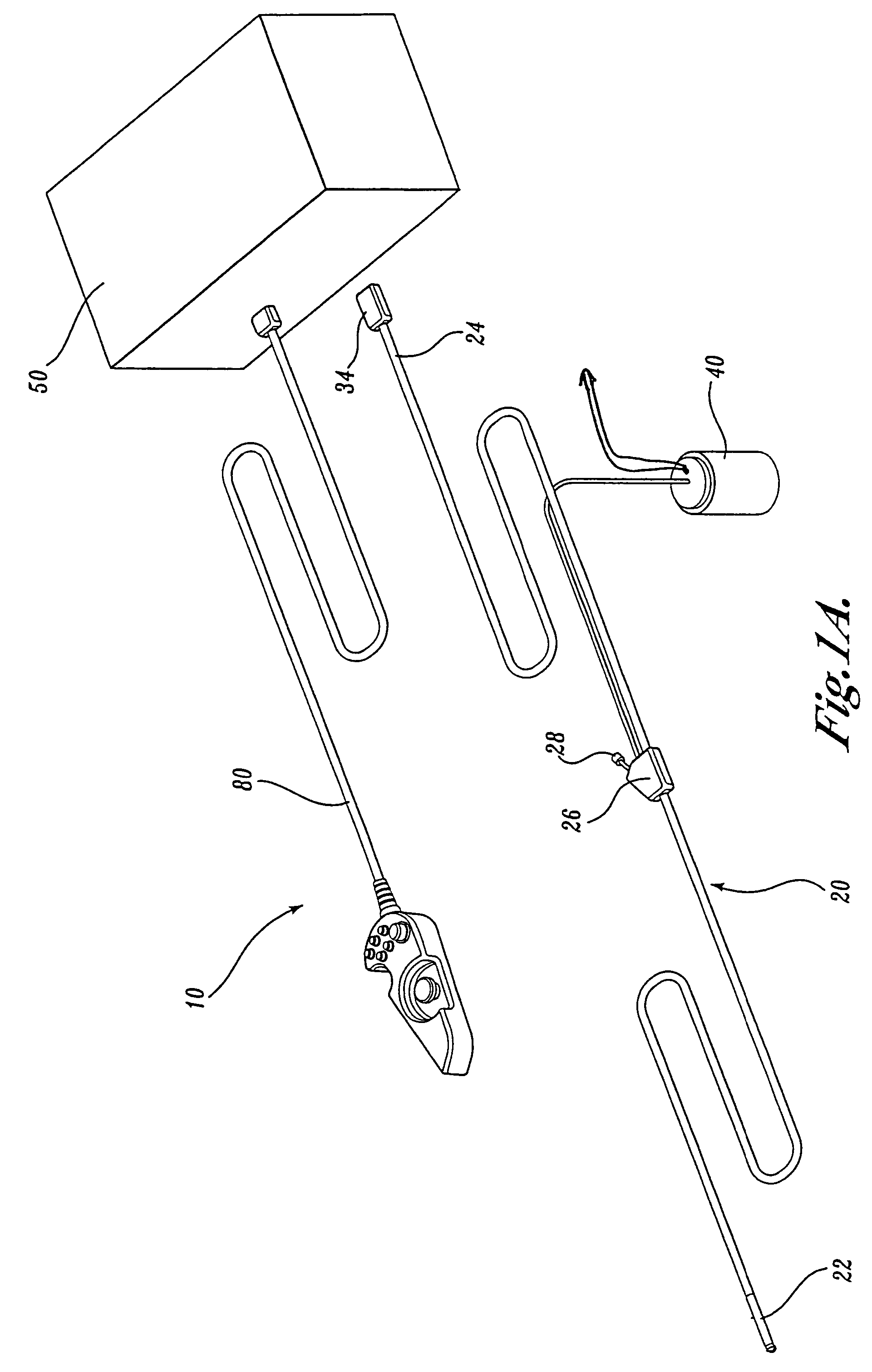
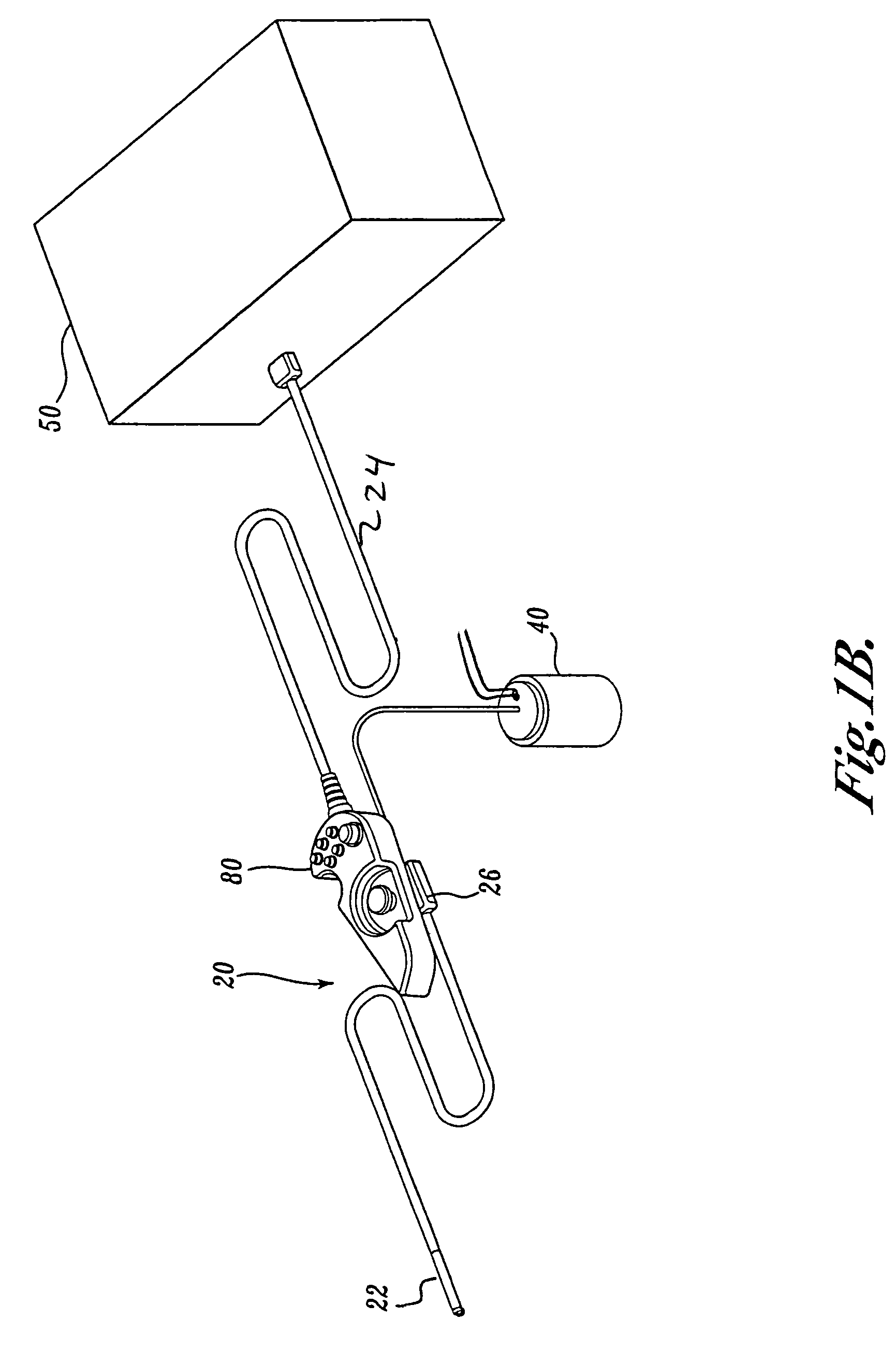
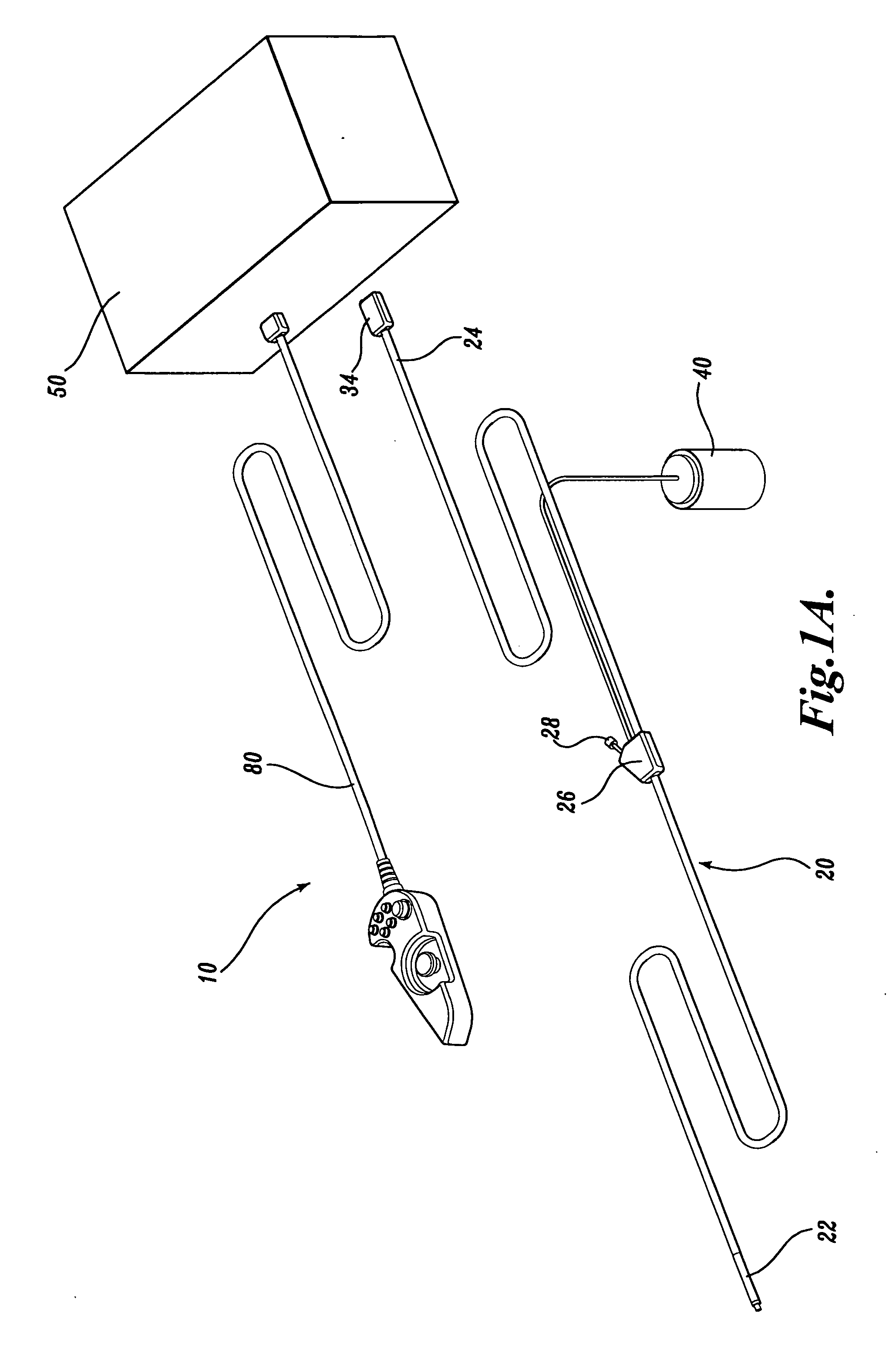
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
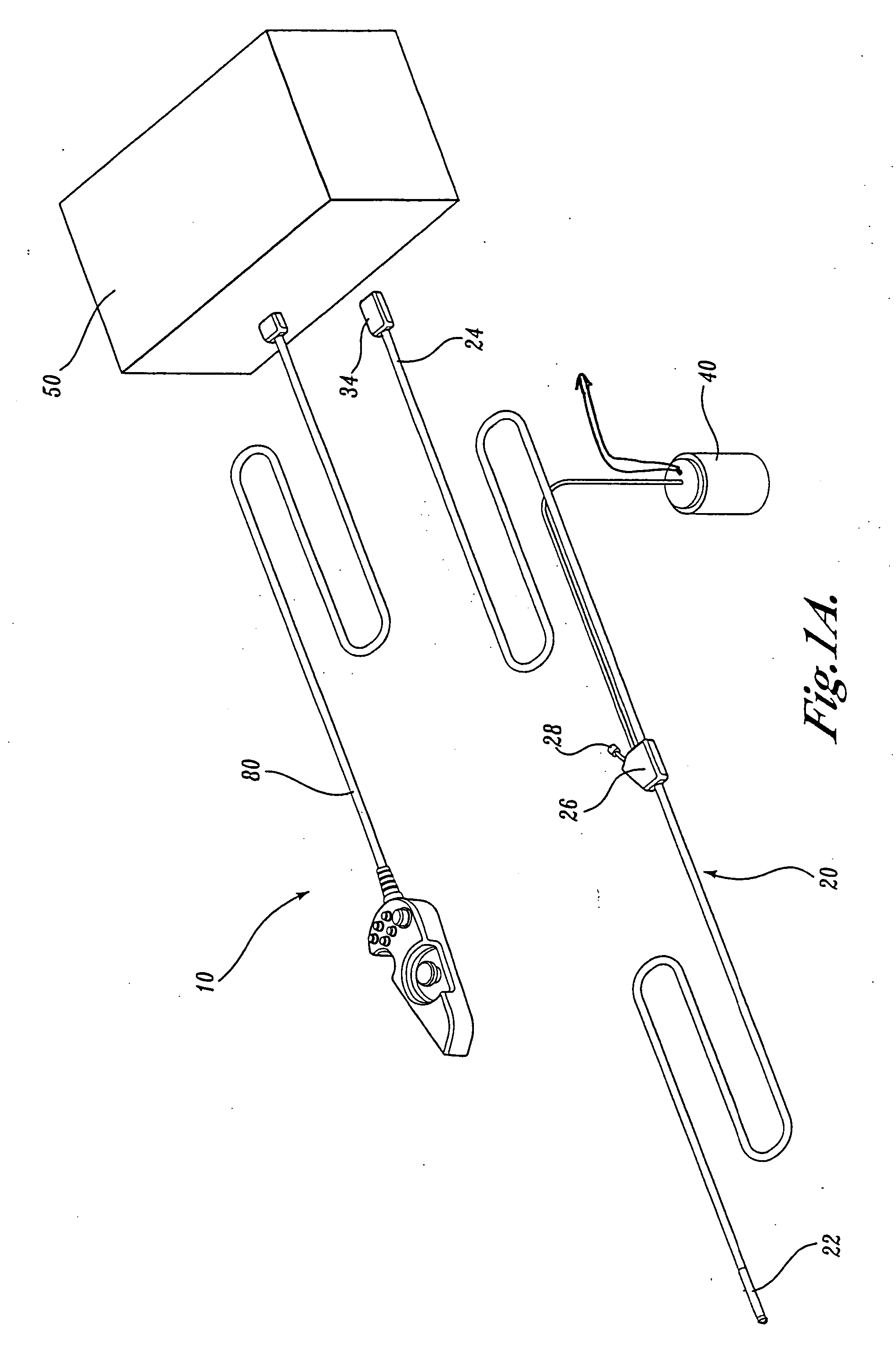
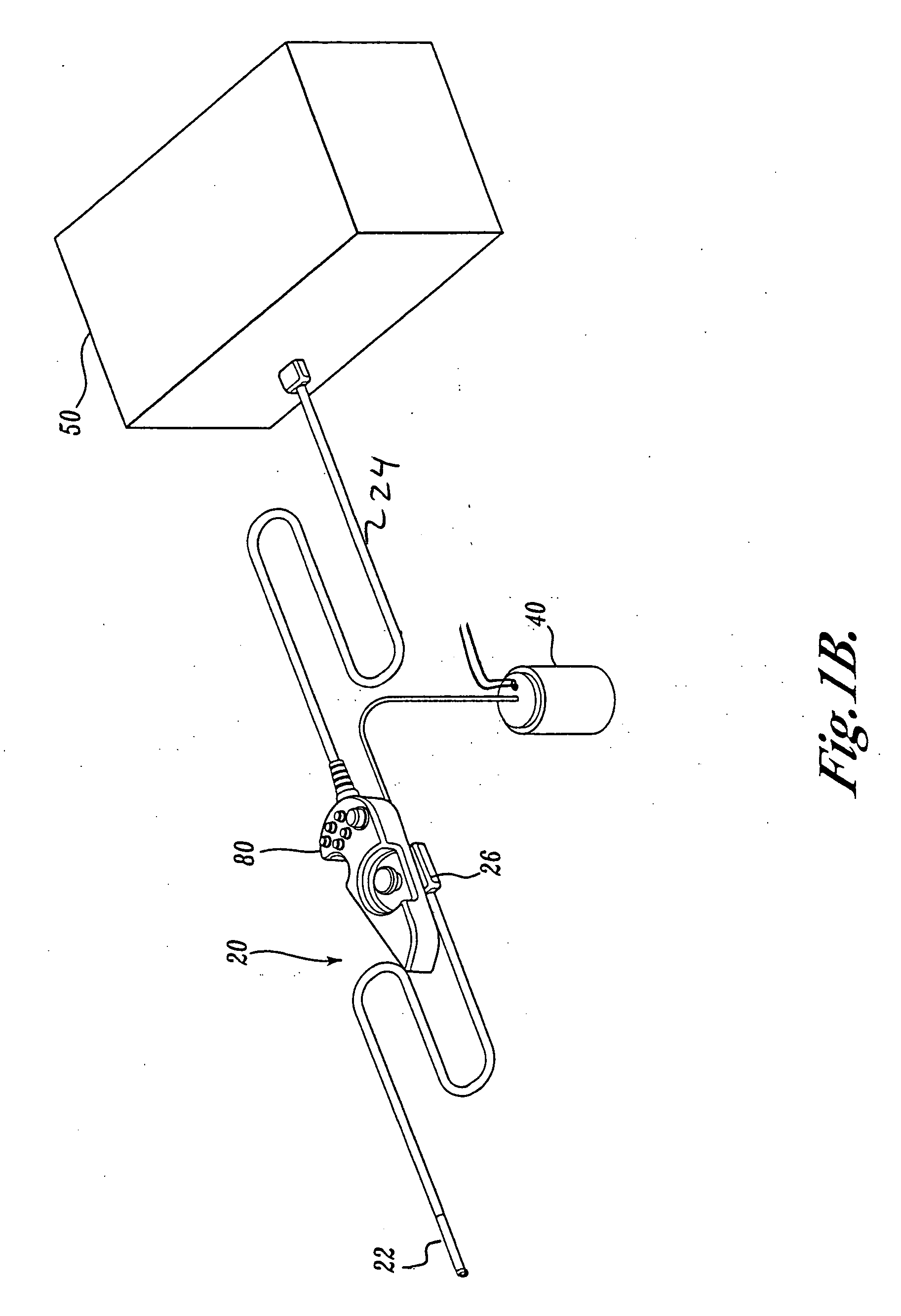
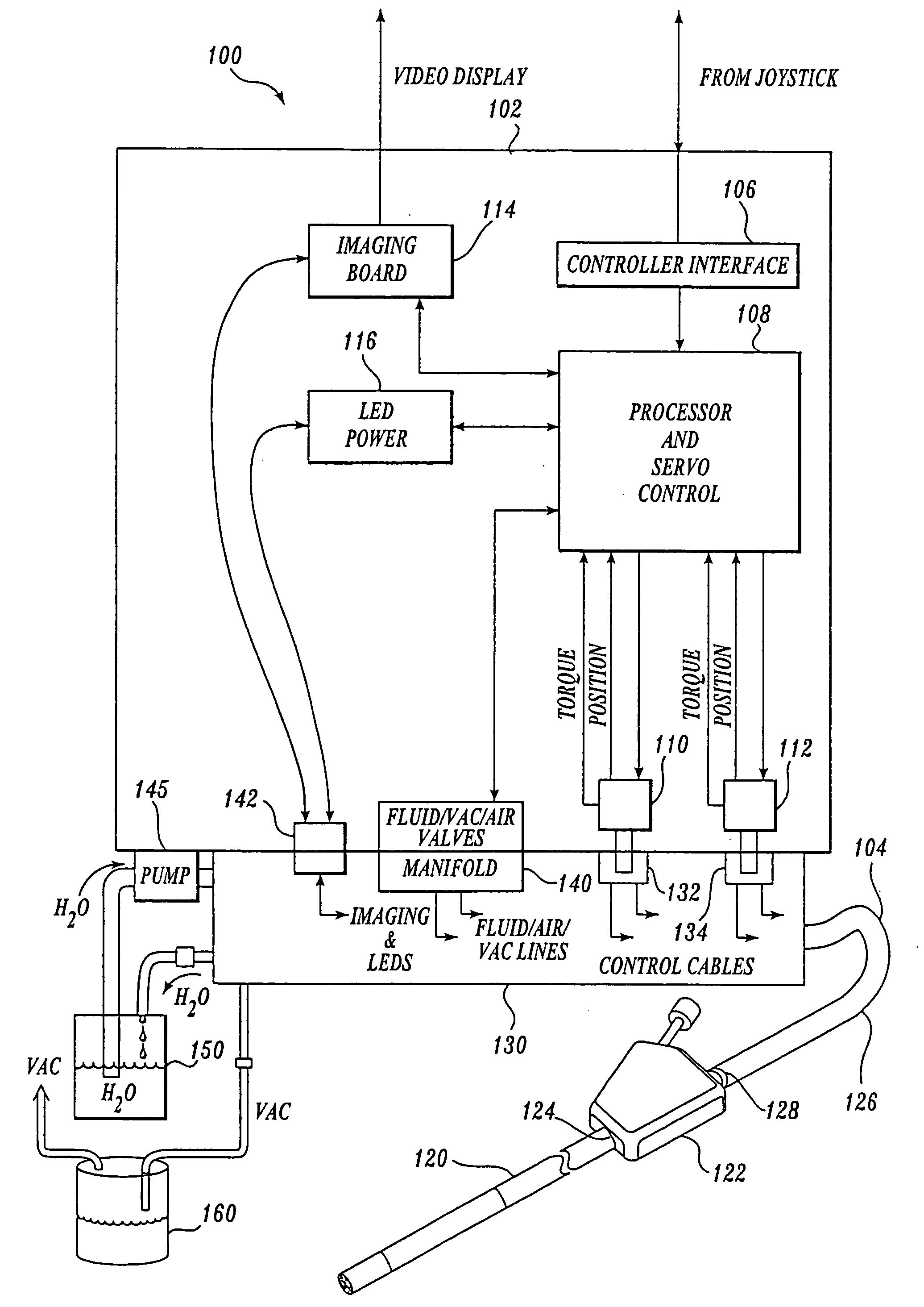
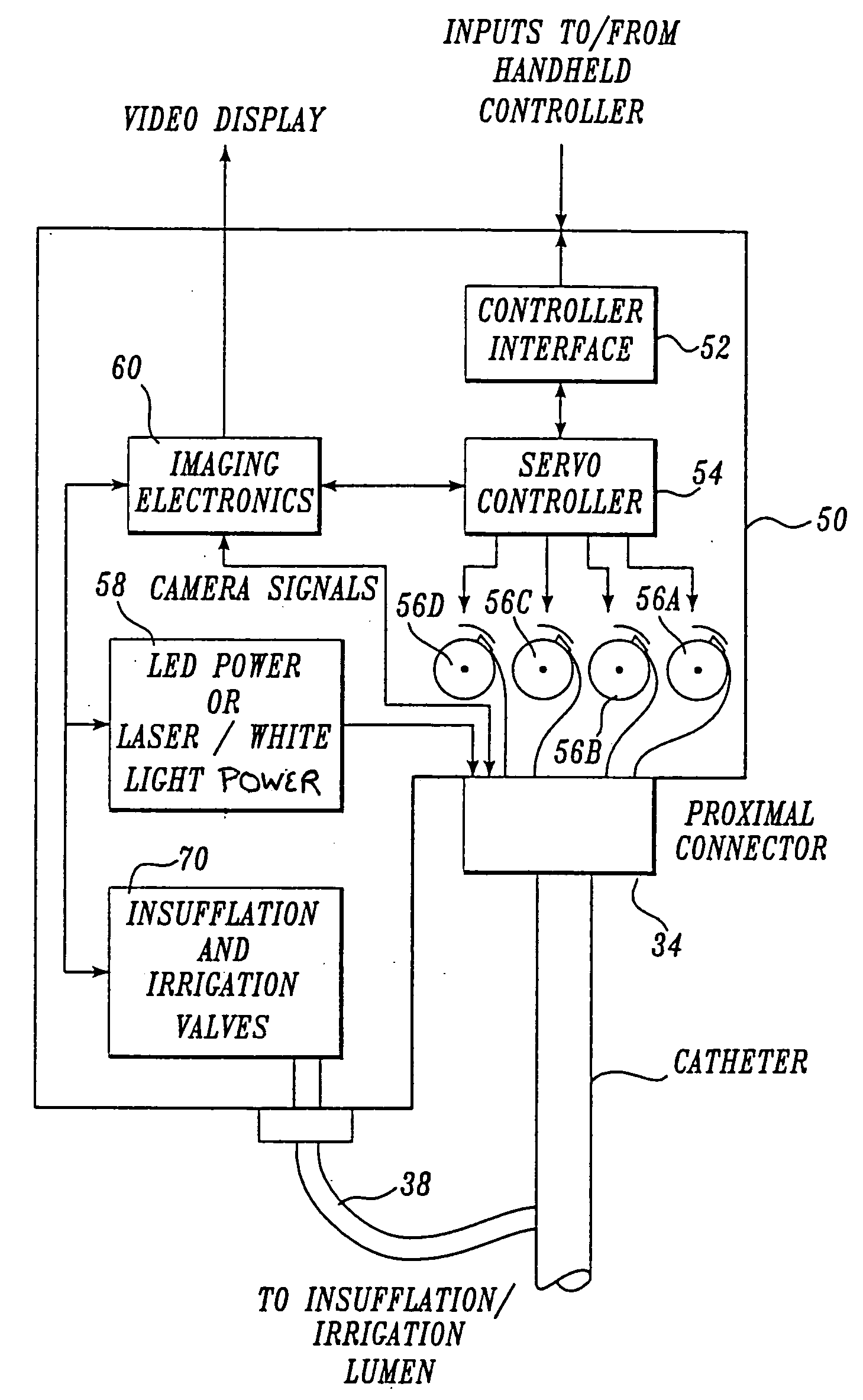
Force feedback control system for video endoscope
ActiveUS20050119527A1Reduce coefficient of frictionImprove device performanceSurgeryEndoscopesFluidicsControl system
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Articulation joint for video endoscope
ActiveUS20050131279A1Reduce coefficient of frictionImprove device performanceSurgeryEndoscopesFluidicsEngineering
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
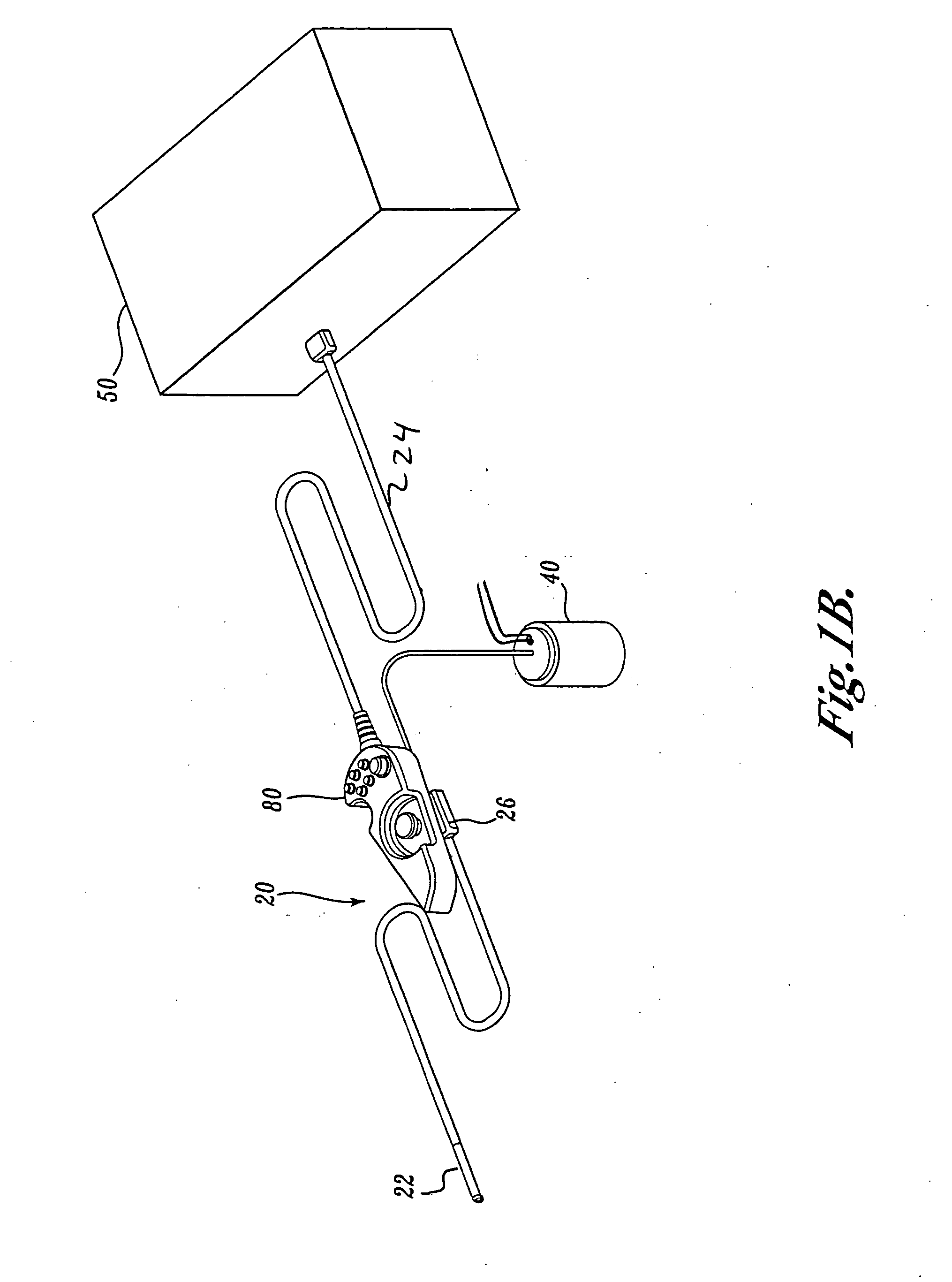
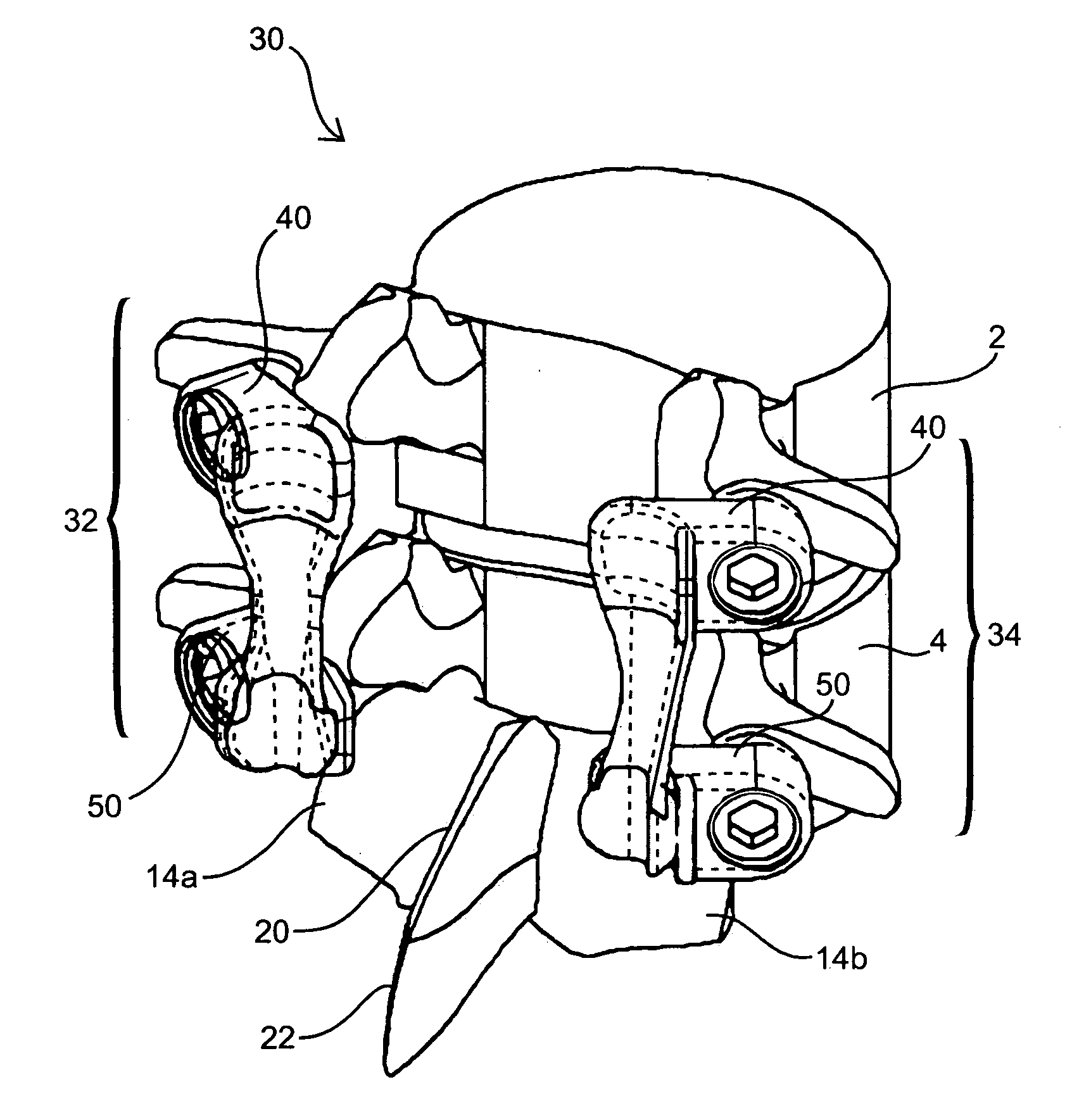
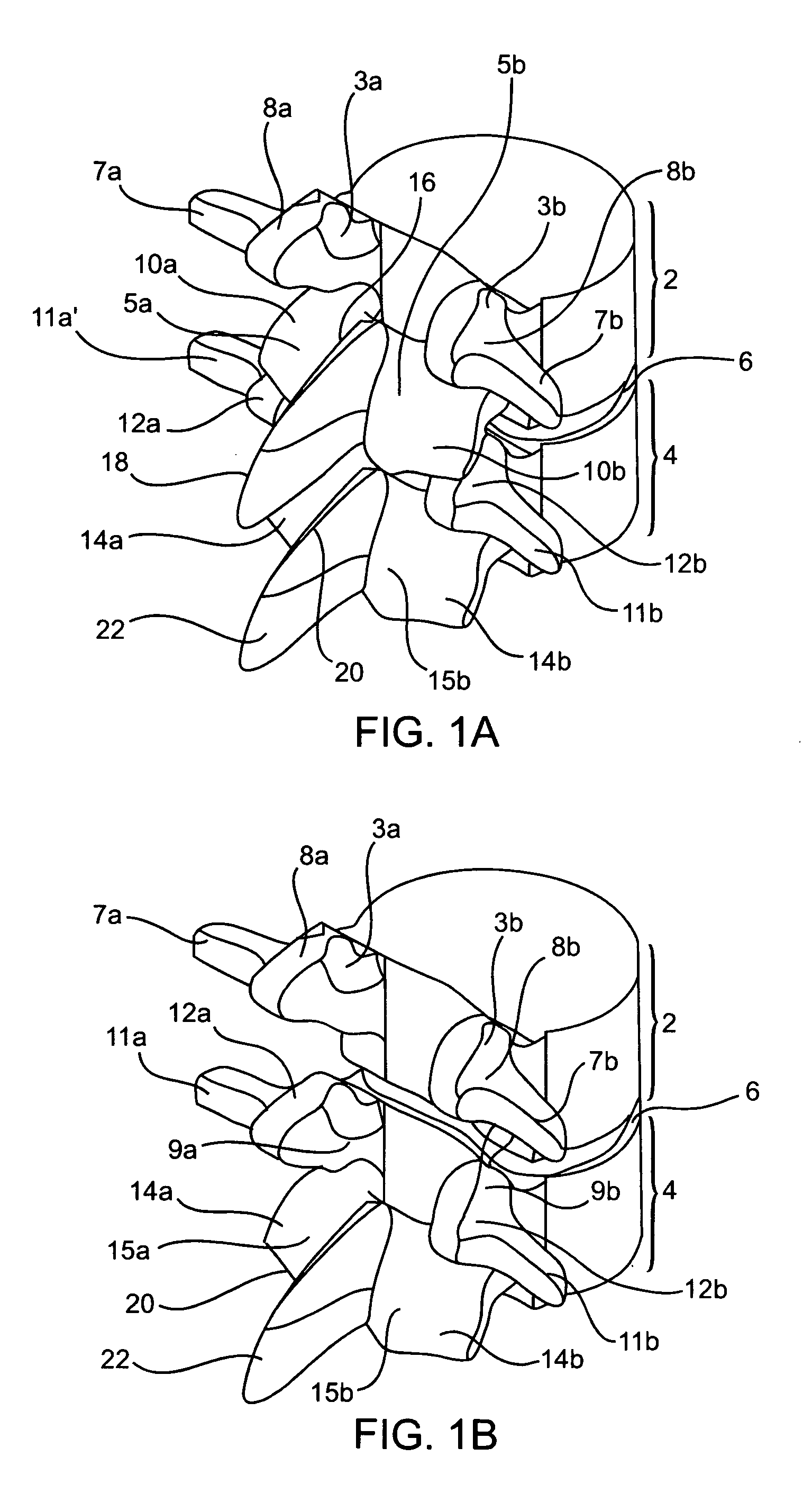
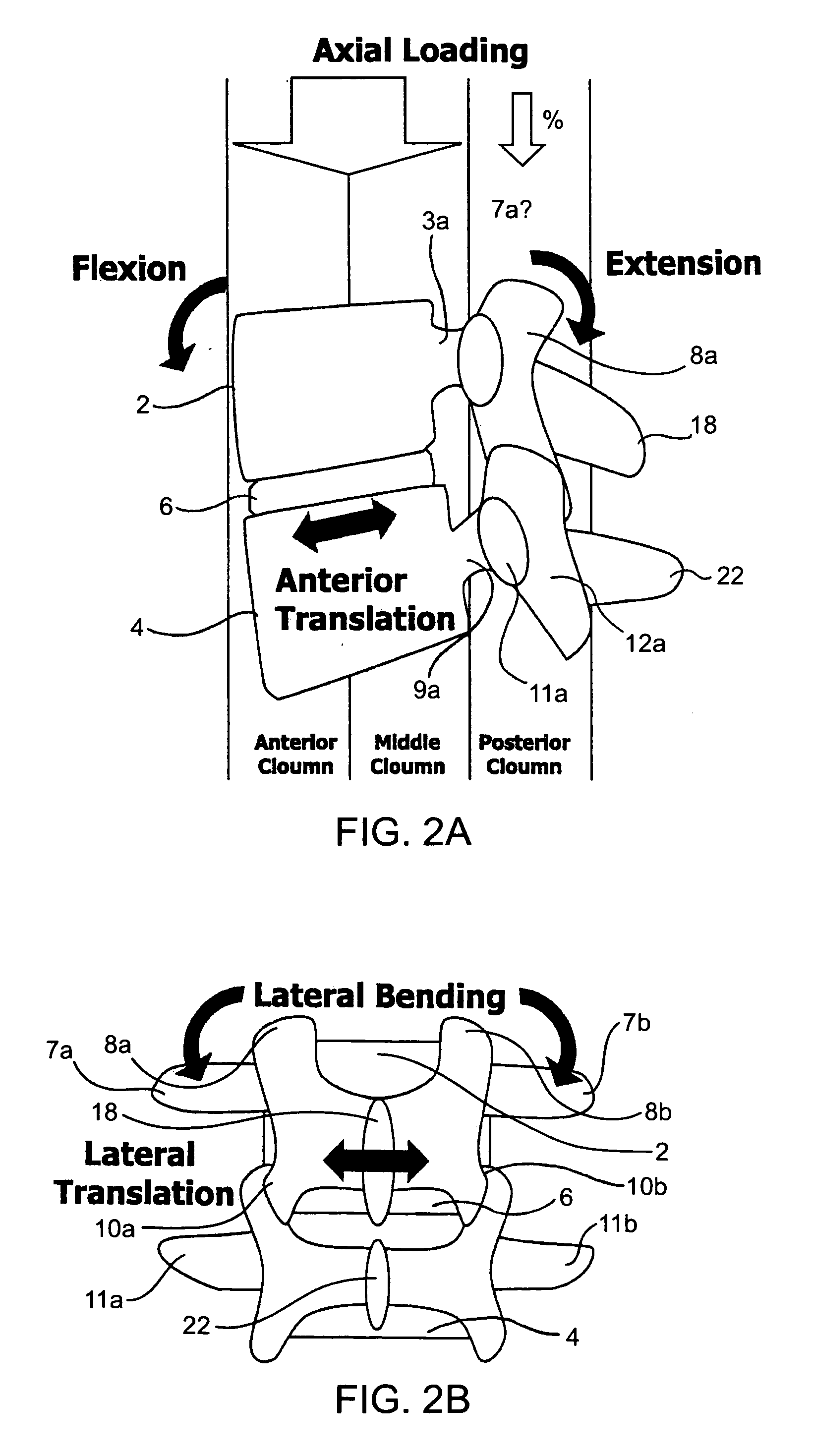
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
ActiveUS20060084982A1Length , stiffness and shape of be adjustableStabilizing spineInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsVertebraSpinal locomotion
Systems and devices for dynamically stabilizing the spine are provided. The systems include a superior component for attachment to a superior vertebra of a spinal motion segment and an inferior component for attachment to an inferior vertebral of a spinal motion segment. The interconnection between the two components enables the spinal motion segment to move in a manner that mimics the natural motion of the spinal motion segment. Methods are also provided for stabilizing the spine and for implanting the subject systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Imaging system for video endoscope
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Interface for video endoscope system
InactiveUS20050222499A1Reduce coefficient of frictionImprove device performanceSurgeryEndoscopesFluidicsEngineering
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Video endoscope
InactiveUS20050197536A1Reduce coefficient of frictionImprove device performanceSurgeryEndoscopesFluidicsEngineering
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
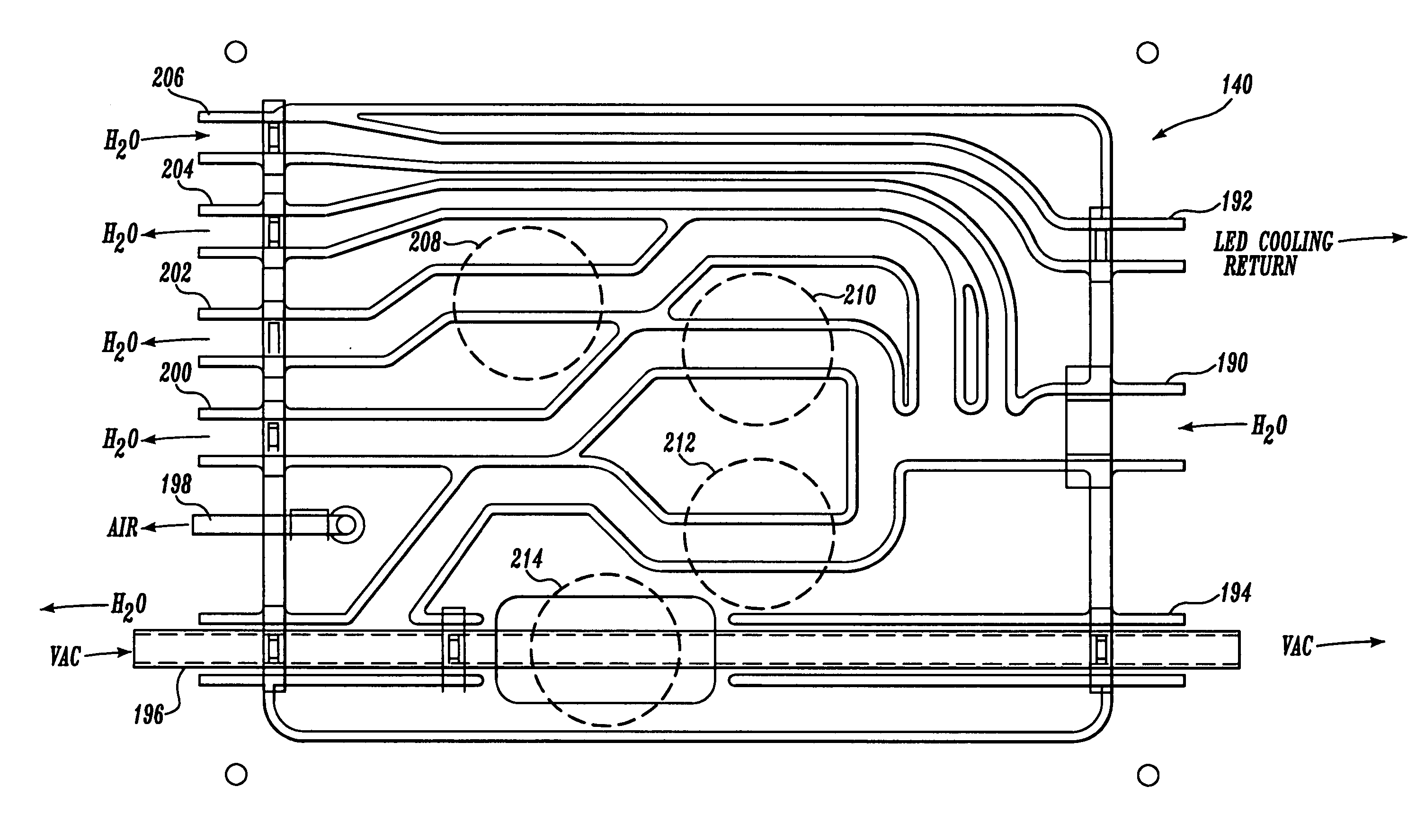
Endoscope with actively cooled illumination sources
ActiveUS7413543B2Inexpensive and easy to assembleRemove heatSurgeryEndoscopesHydrophilic coatingActive cooling
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Direct drive instruments and methods of use
ActiveUS20080221391A1Limited stiffnessAdjustable stiffnessSuture equipmentsCannulasDistal portionUser input
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Video endoscope
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Fluid manifold for endoscope system
InactiveUS20050245789A1Reduce coefficient of frictionImprove device performanceServomotor componentsSurgeryFluidicsActuator
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
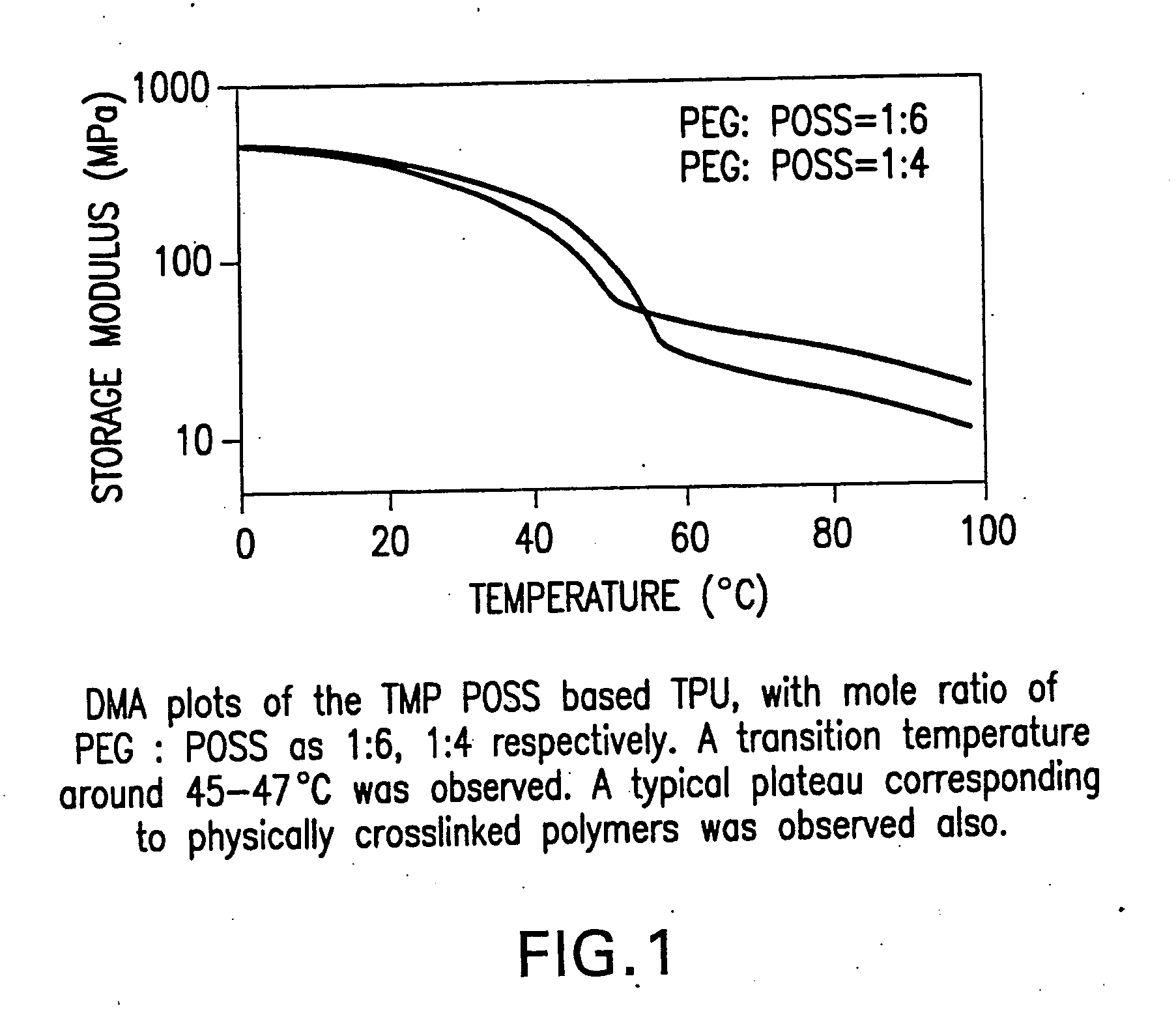
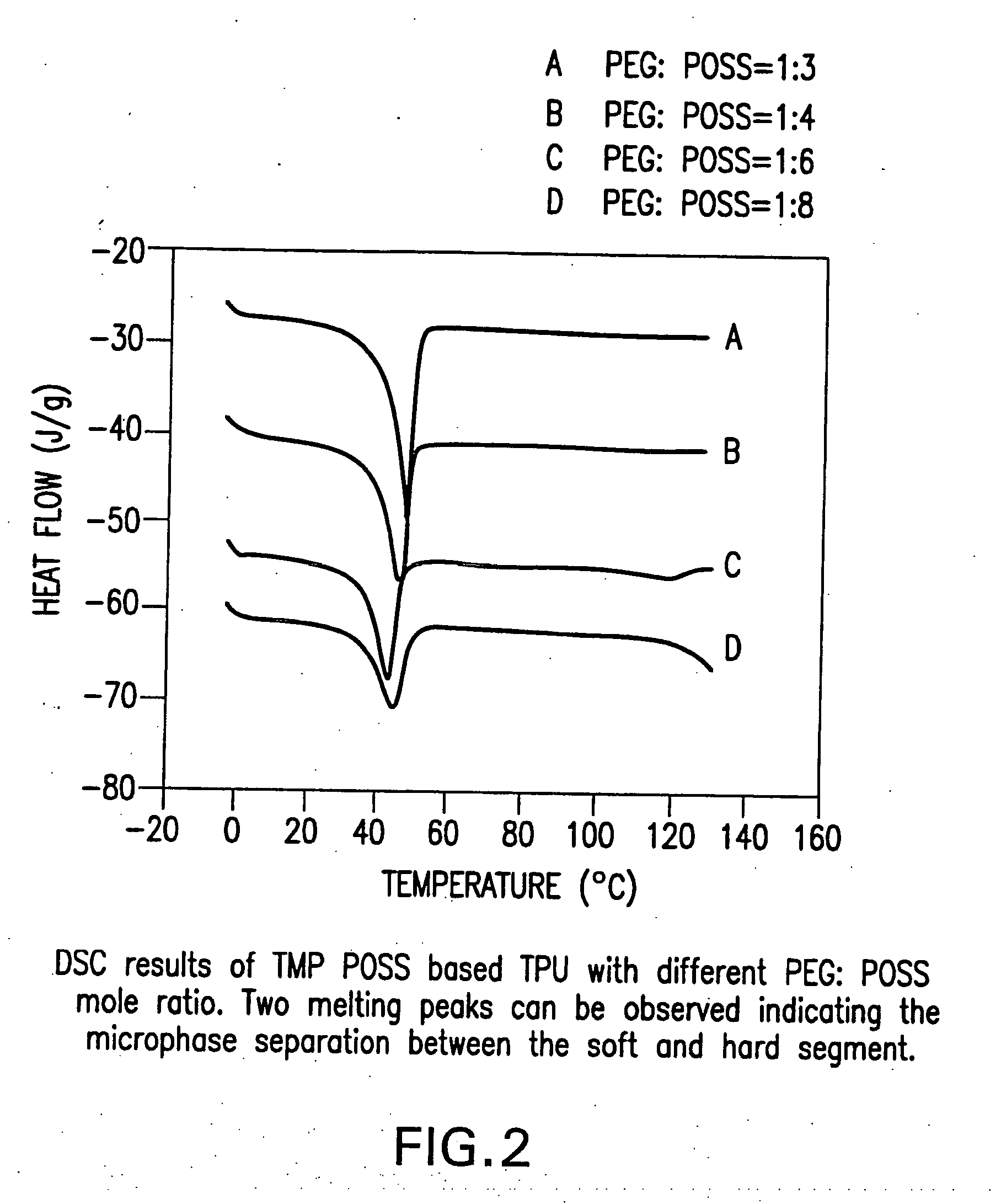
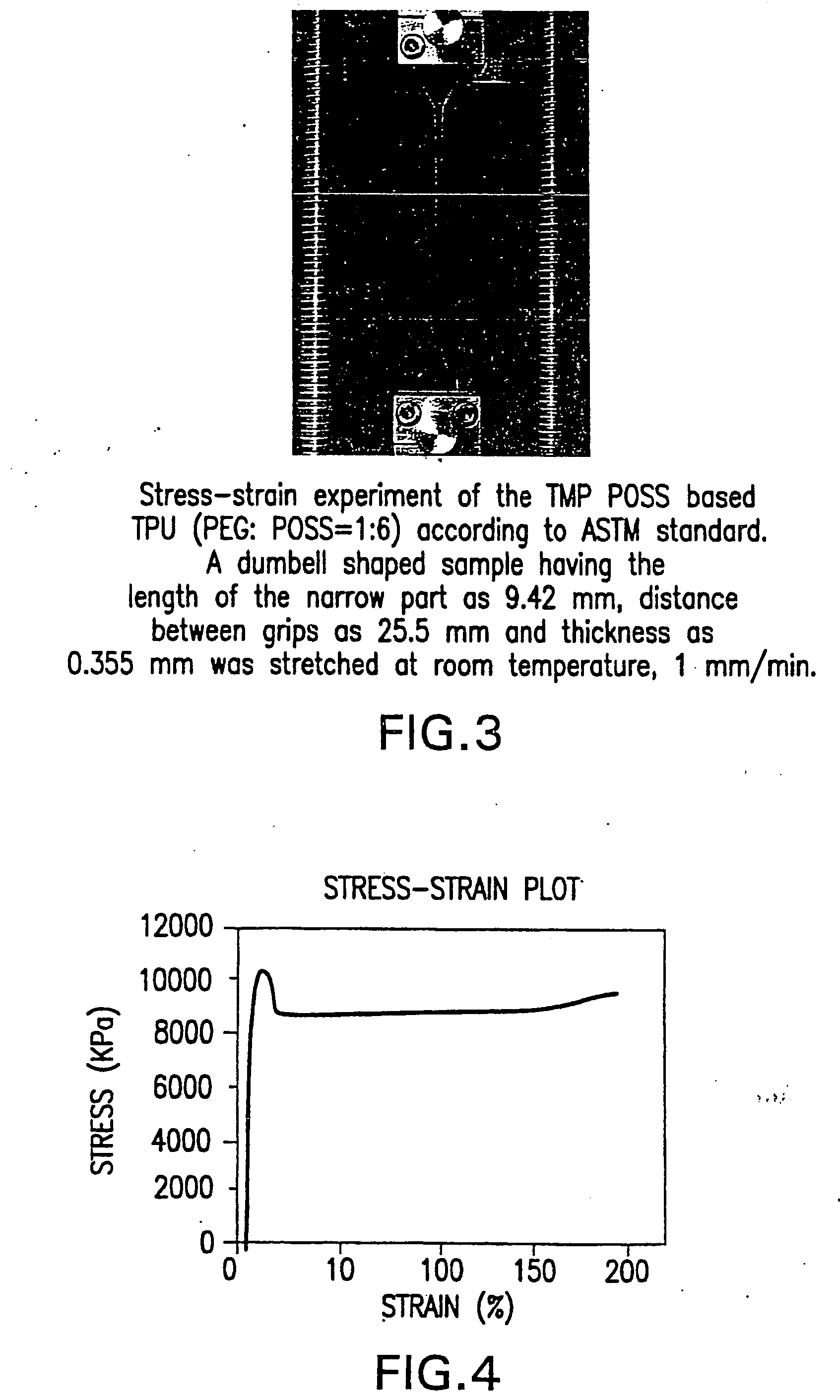
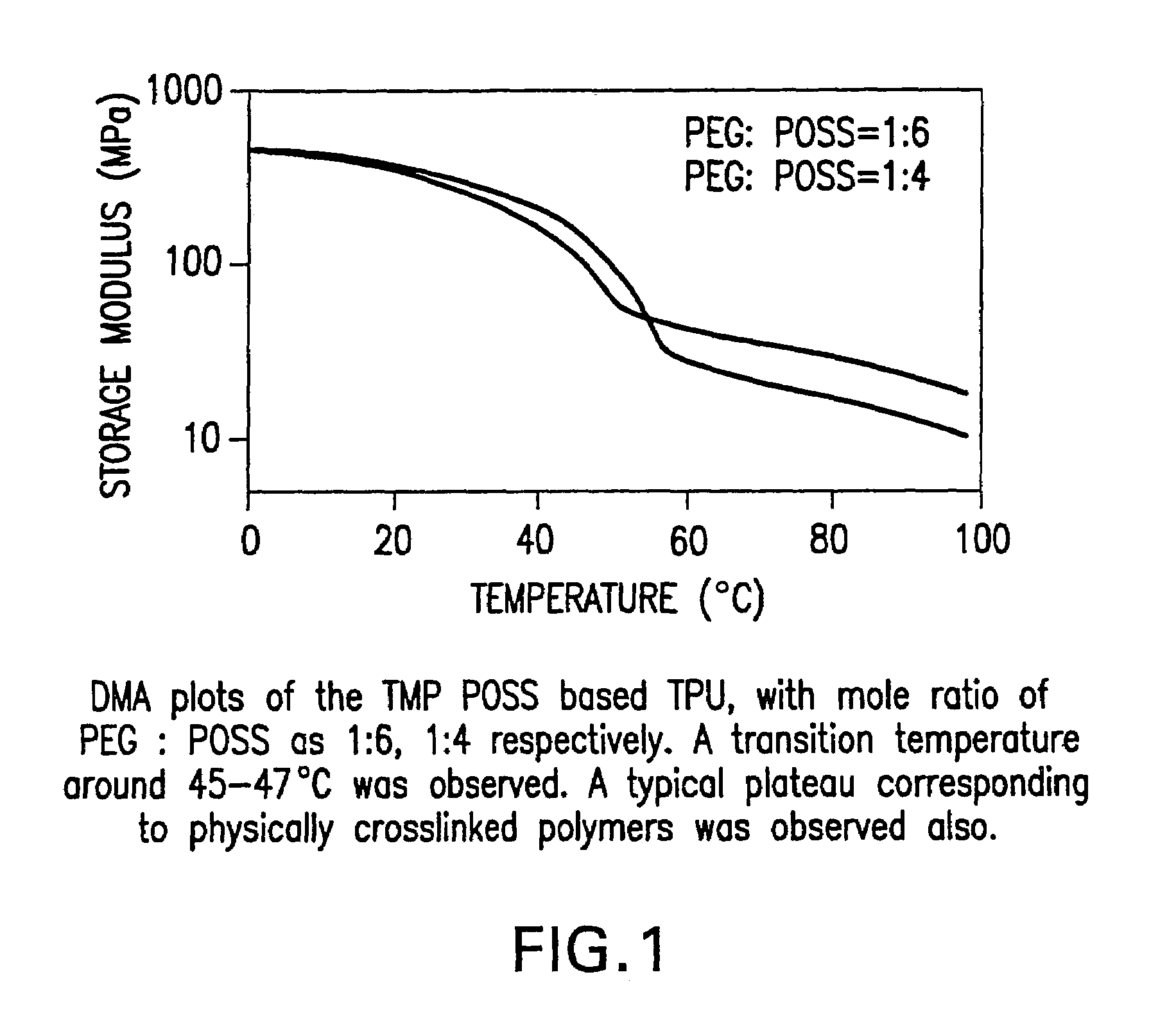
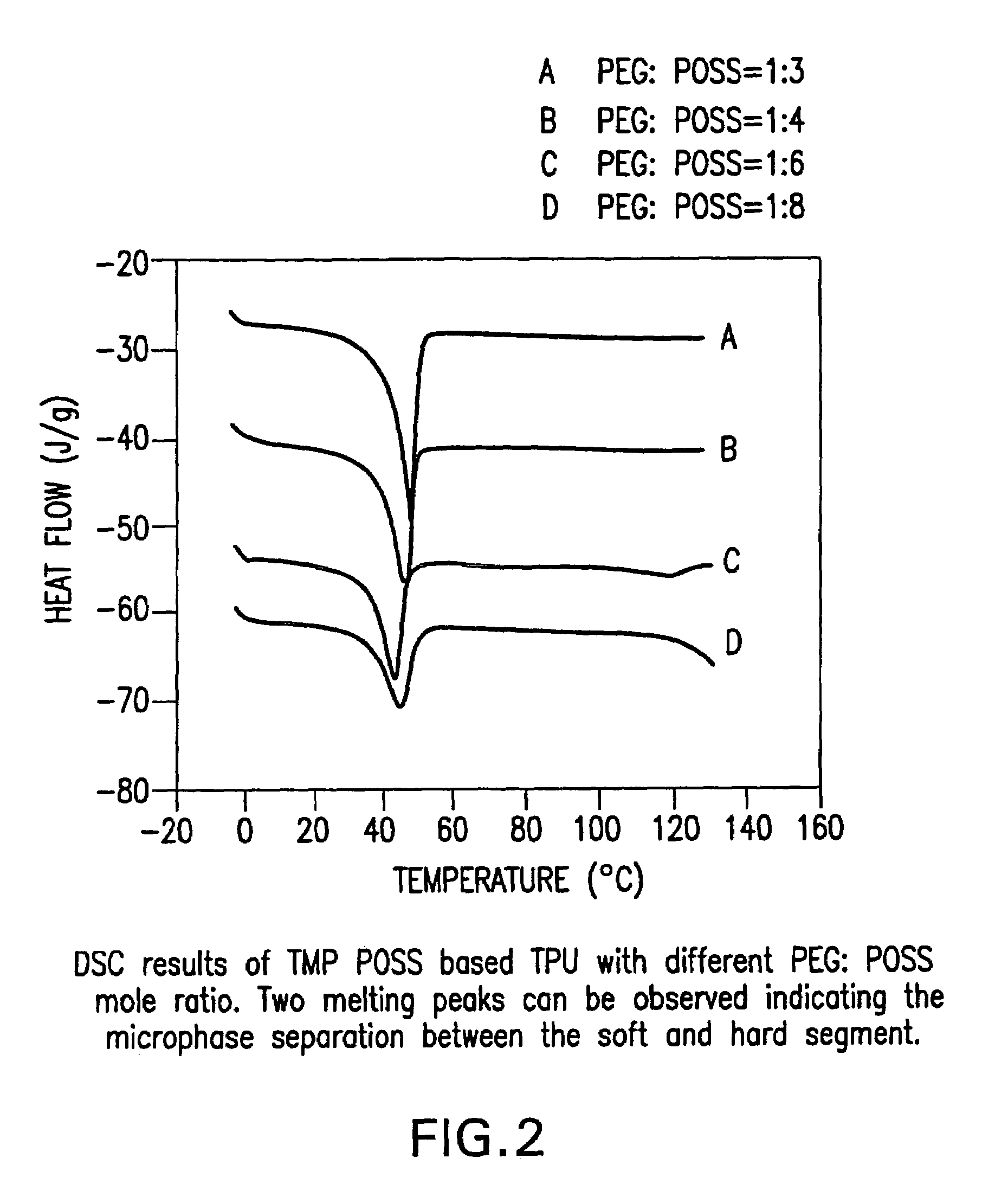
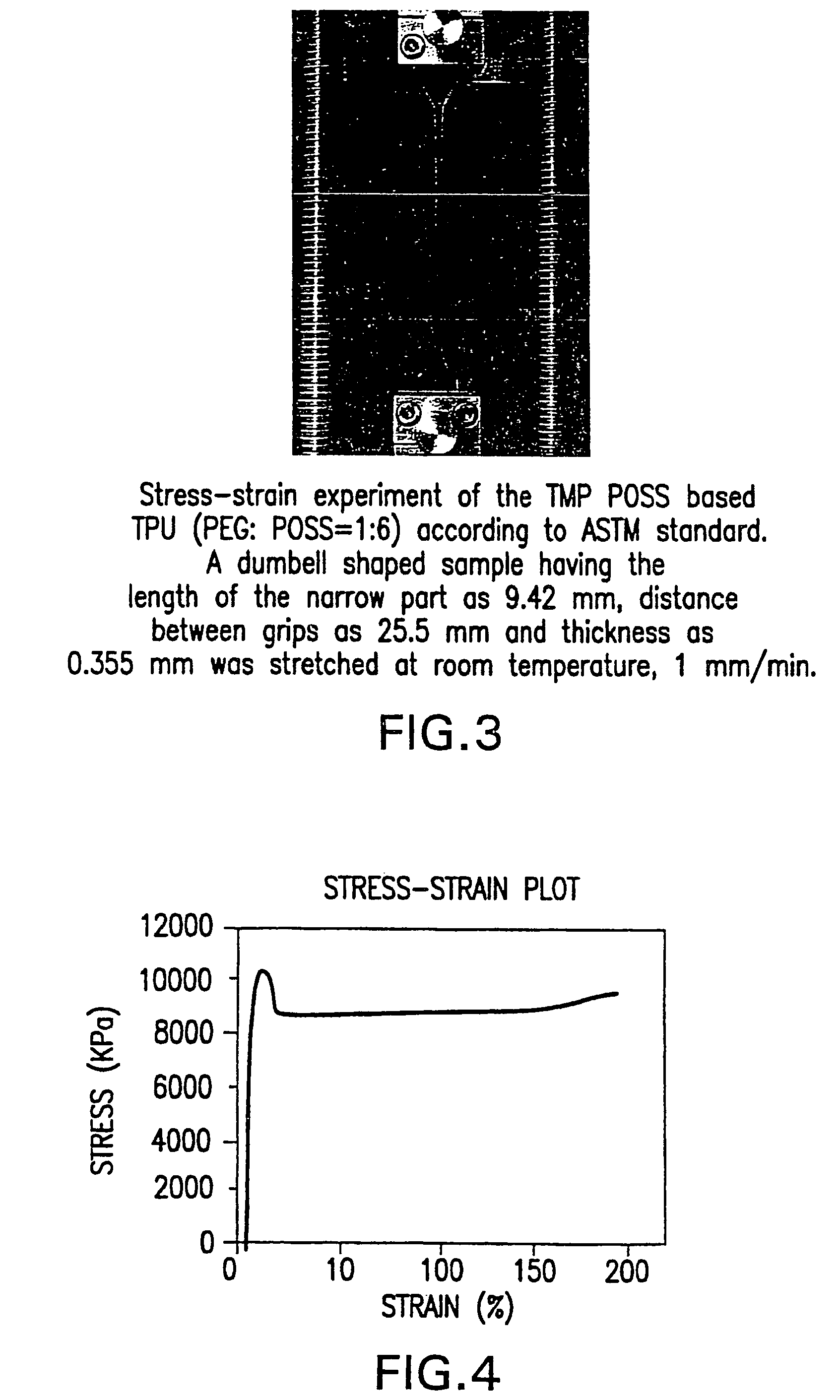
Shape memory polymers based on semicrystalline thermoplastic polyurethanes bearing nanostructured hard segments
InactiveUS20050245719A1Sharp and tunable transition temperatureAbove melting pointPolymer scienceAdhesive
Thermoplastic polyurethanes having an alternating sequence of hard and soft segments in which a nanostructured polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane diol is used as a chain extender to form a crystalline hard segment constituting SMPs. The polyurethanes are formed by reacting a polyol, a chain extender dihydroxyl-terminated polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane and a diisocyanate. The polyurethanes have multiple applications including for example, implants for human health care, drug delivery matrices, superabsorbant hydrogels, coatings, adhesives, temperature and moisture sensors, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Prosthetic foot with energy transfer including variable orifice
A prosthetic foot device with variable stiffness response includes a variable energy transfer mechanism or variable resistance cell disposed between first and second foot members to transfer a variable amount of energy from the second member to the first member during use. The energy transfer mechanism or variable resistance cell includes a variable orifice with variable size to variably resist flow of fluid therethrough, and thus variably transfers energy between the first and second members to vary stiffness of the prosthetic foot device.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
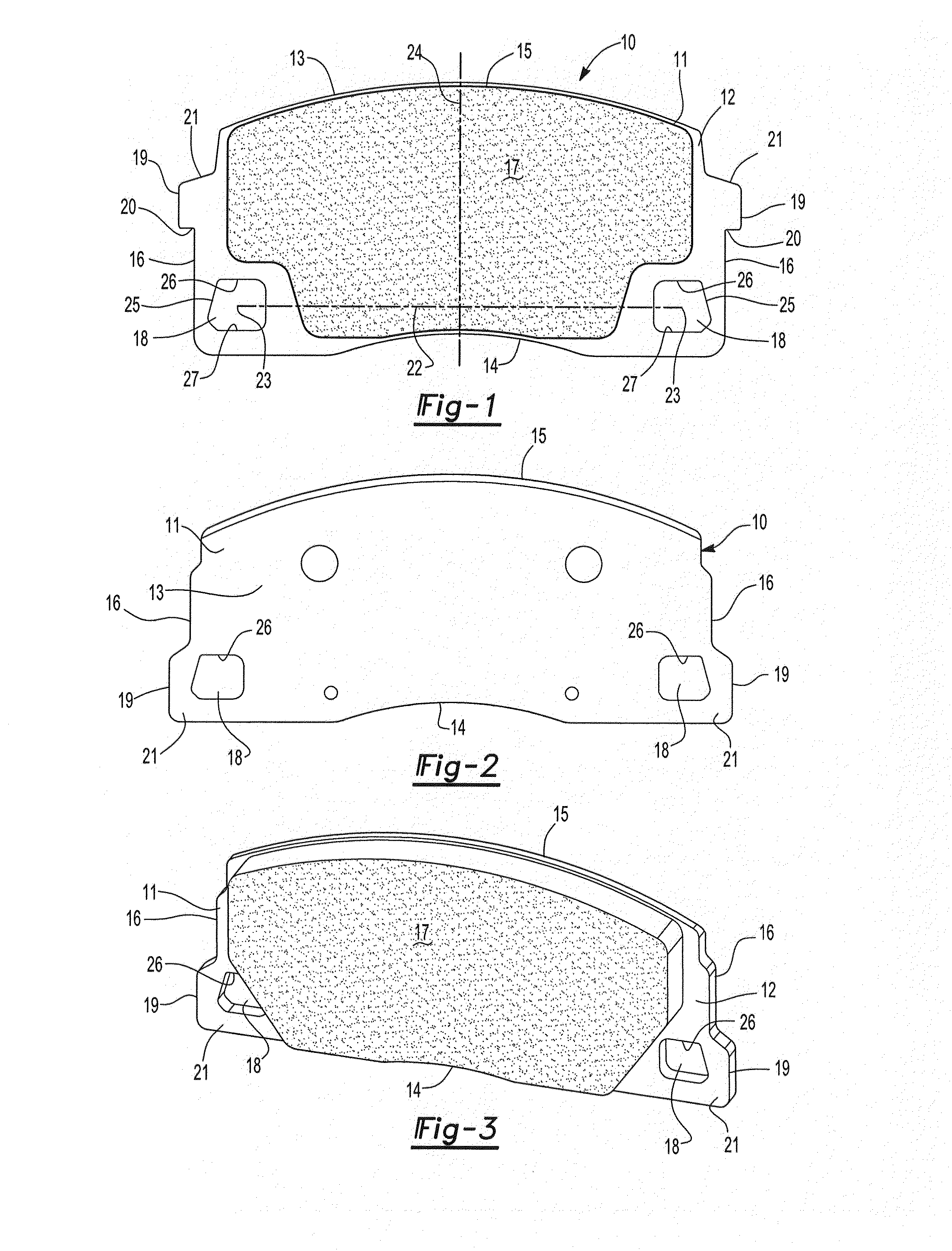
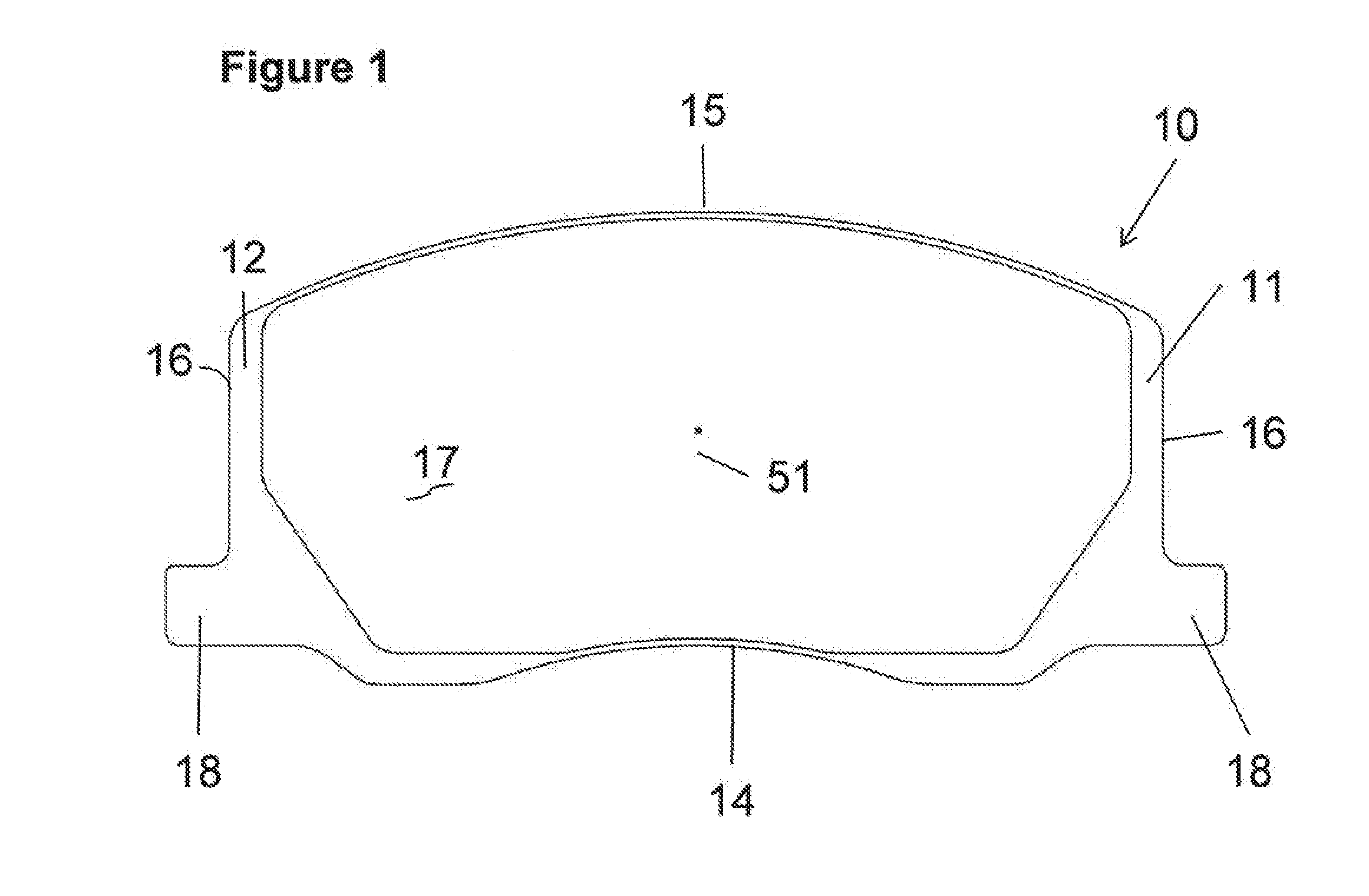
Brake systems, caliper assemblies and pads incorporating differential abutments
InactiveUS20120043168A1Transmission of forceImprove NVH performanceMechanically actuated brakesBraking membersPush pullEngineering
The present invention is directed to a unique solution for caliper assemblies, brake pads utilized in such caliper assemblies, support structures utilized in caliper assemblies and disc brake systems containing such caliper assemblies which utilize push pull or pull push abutment designs.
Owner:AKEBONO CORP (NORTH AMERICA)
Femoral sleeve for hip resurfacing
InactiveUS20080262626A1Maximizes retentionMinimize installation difficultyAnkle jointsJoint implantsRight femoral headCoxal joint
A hip resurfacing femoral prosthesis has a sleeve component with an internal bore adapted to receive a femoral head and a partially conical outer surface. The sleeve is for use with a mating partial ball component shaped to conform to an acetabular socket. The sleeve is slotted or segmented to enhance the engagement with the femoral head. The partial ball component may be translated proximally and distally to reposition the outer surface by selecting sleeves with varying geometries.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Prosthetic foot with energy transfer
A prosthetic foot device with variable stiffness response includes a variable energy transfer mechanism disposed between first and second foot members to transfer a variable amount of energy between the members during use. A chamber is associated with one of the first and second foot members, and a piston is associated with another of the first and second foot members and is movable in the chamber. At least one aperture is formed between the piston and the chamber. A variable viscosity fluid is disposed in the chamber and displaceable through the at least one aperture between the piston and the chamber to allow fluid to flow within the chamber between opposite sides of the piston. The variable viscosity fluid has a viscosity that is variable to vary an ability of the variable viscosity fluid to flow through the at least one aperture.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
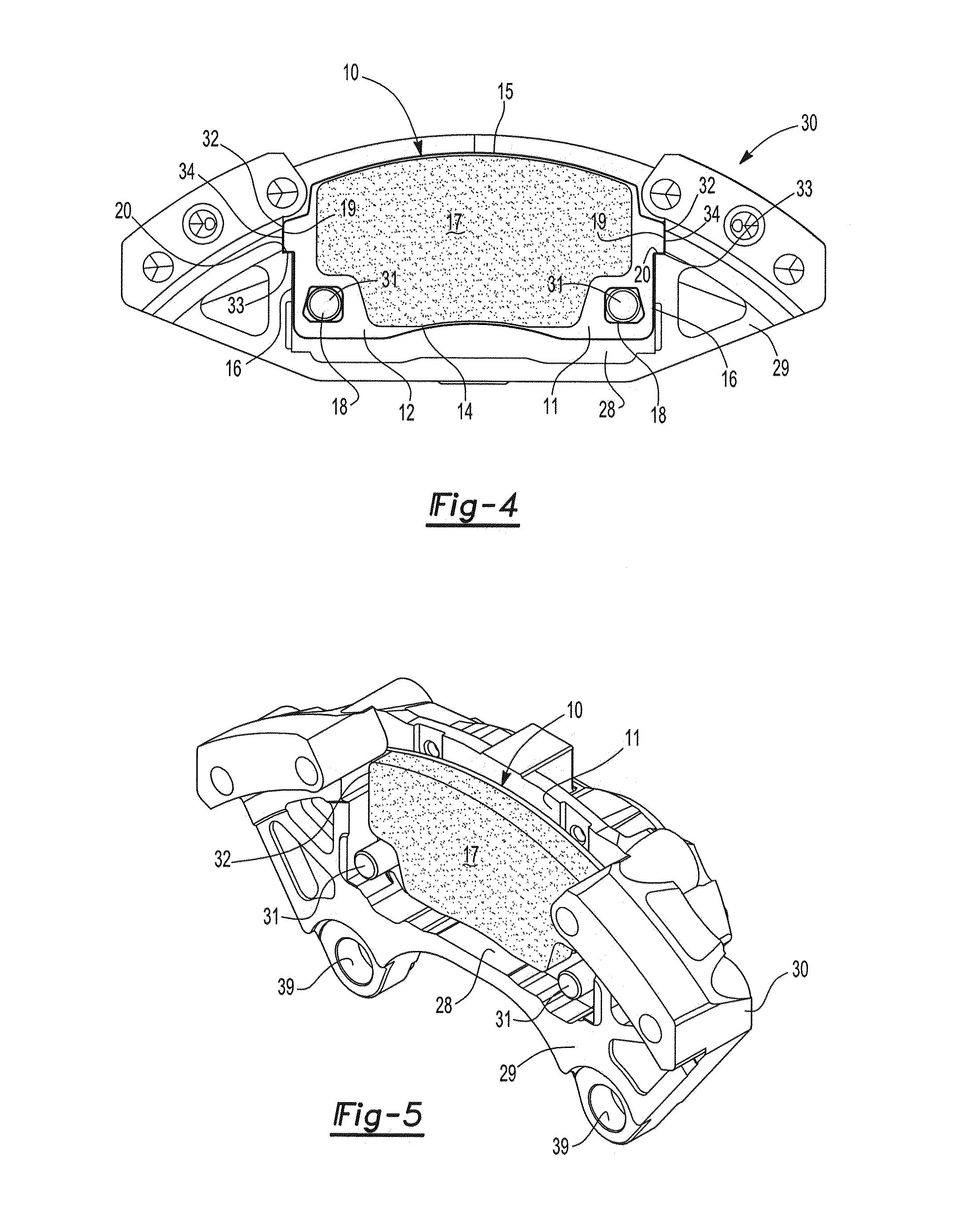
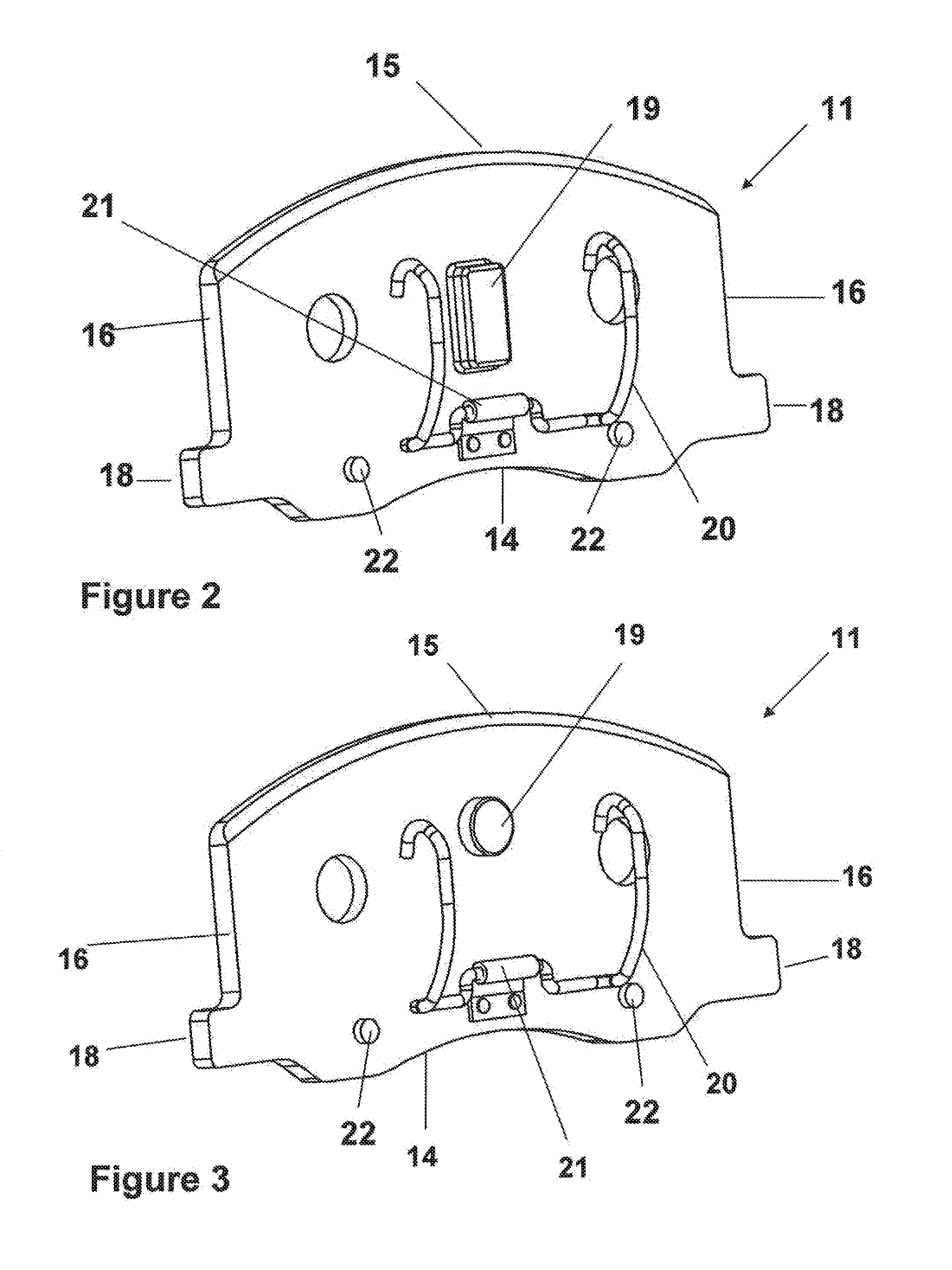
Caliper assembly for disc brake system
InactiveUS20120085597A1Improve NVH performanceImprove component performanceMechanically actuated brakesSlack adjustersEngineeringCalipers
A caliper assembly comprising: a brake pad comprising a carrier plate having two opposing faces and a top edge a bottom edge and two opposing side edges, wherein on one face is friction material and on the opposing face is a projection adapted to seat in a matched hole or recess in a caliper body, the two opposing side edges each having an ear which is adapted to seat in pad locator indentations in a support structure; a support structure comprising a recess for housing at least one brake pad and at least two pad locator indentations adapted for receiving the ears located on the two opposing sides of the brake pad and at least two caliper body locator indentations for seating two ears defined by the caliper body; and a caliper body having a hole or recess adapted for seating the projection on the opposing face of the brake pad and having two ears on each opposing side which are adapted to seat in the caliper body locator indentations of the support structure; wherein the ears of the brake pad are seated in the pad locator indentations of the support structure, the projection on the opposing face of the brake pad is seated in the hole or recess located in the caliper body, and a clip which engages the opposing face of the brake pad and the caliper body and holds the brake pad in position with respect to the caliper body and the ears of the caliper body are seated in the caliper body locator indentations in the support structure.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Magnetic flowing deformation elastomer frequency shift type attenuator and control method
InactiveCN1948781AAdjust the natural frequencyAdjust stiffnessNon-rotating vibration suppressionElastomerMagnetic current
The inventive vibration absorber comprises an execution unit, a control unit and a sensor. The execution unit consists of a magnetic inductor, a coil, a magnetic rheological elastic body, a vibration-absorbing mass block and a base. The above magnetic inductor consists of inner and outer sleeves, or a U-shaped iron-core and an armature or top and bottom plates and a column iron-core. Between inner and outer sleeves, the U-shaped iron-core and the armature or the top and bottom plates are filled the magnetic rheological elastic bodies. By regulating the voltage on the coil, the rigidity and the elasticity of the magnetic rheological elastic body are regulated to make its vibration frequency change, so as to make the vibration frequency of the vibration absorber execution unit is the same as that of the vibration-damping object.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
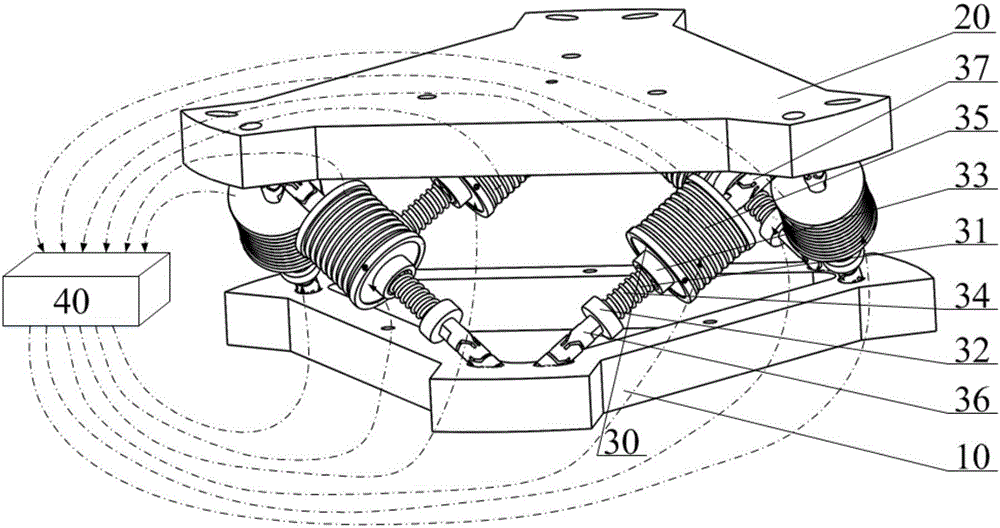
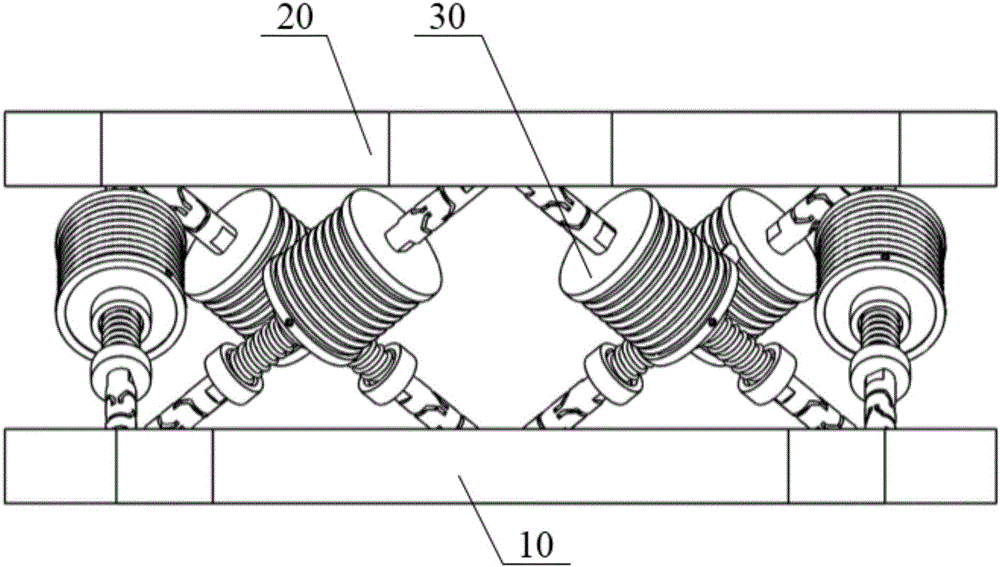
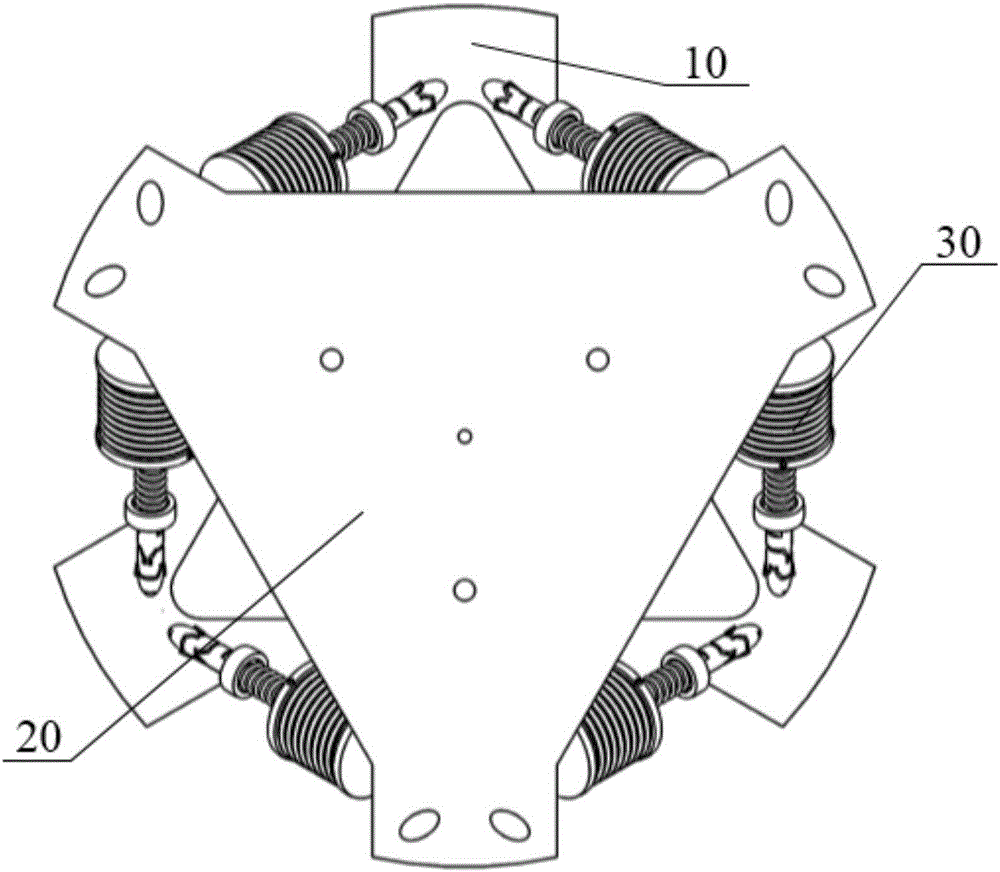
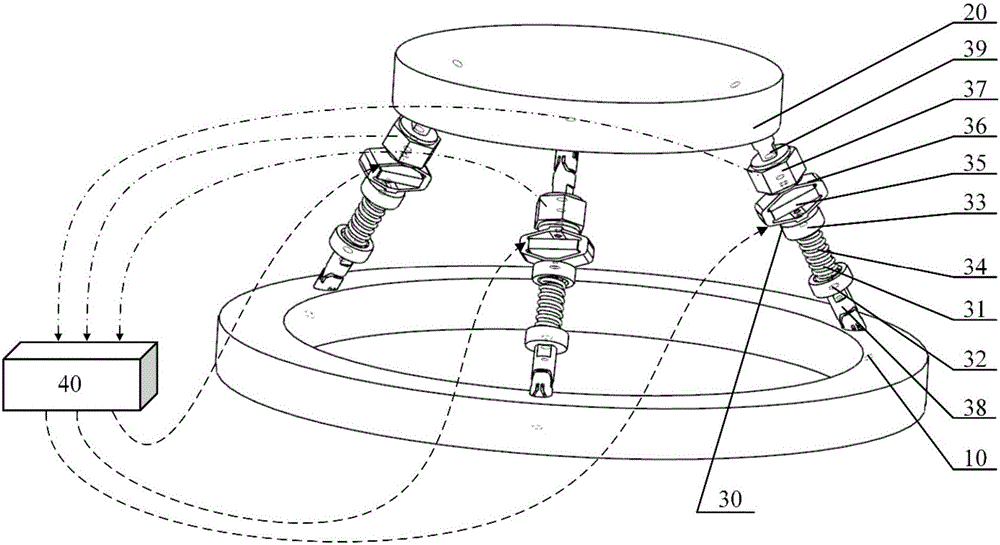
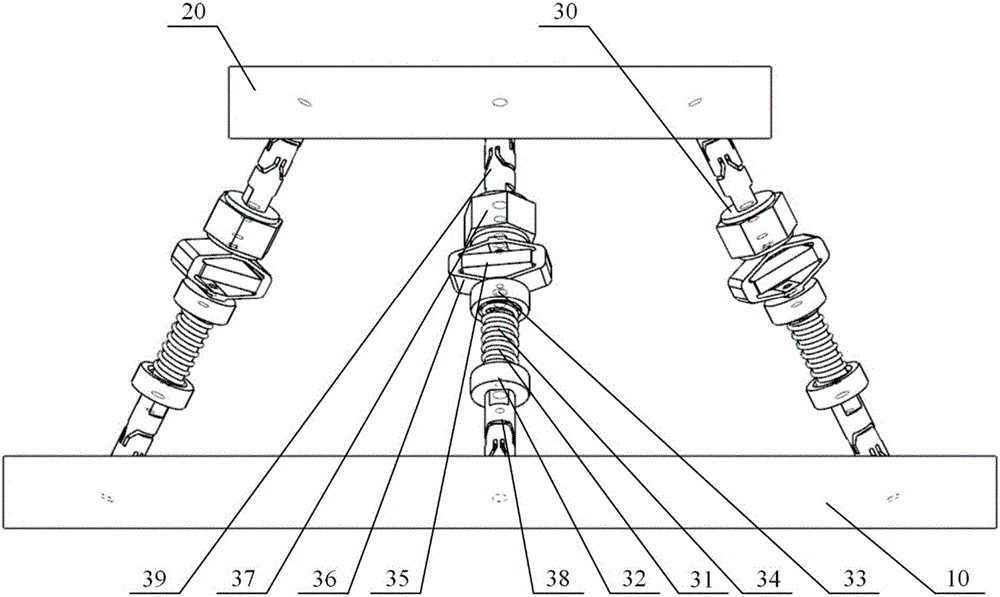
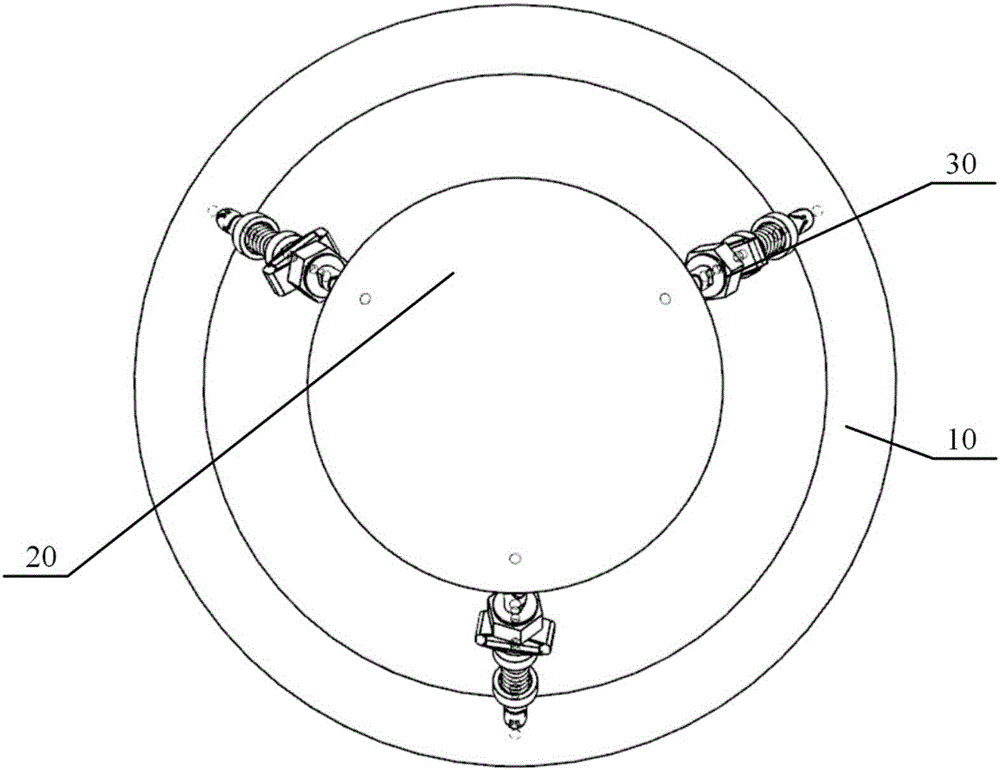
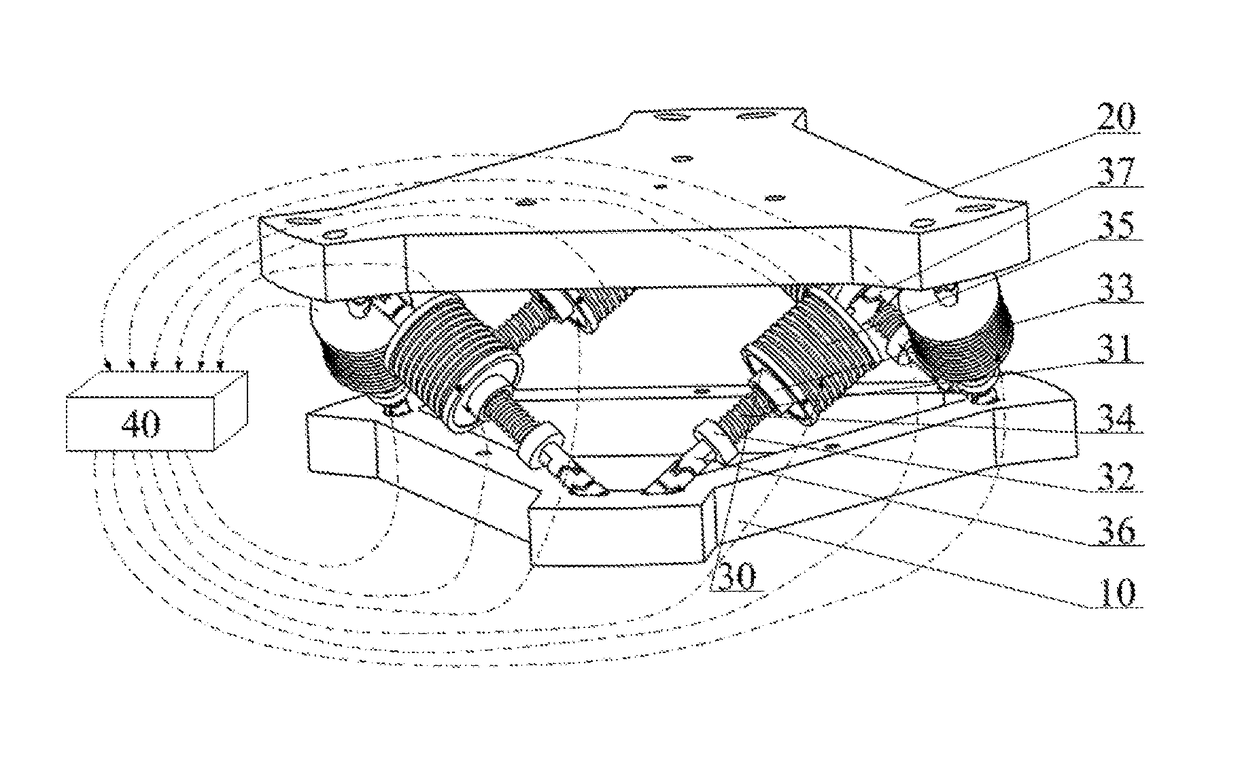
Six-degree-of-freedom micro vibration abatement platform and control method thereof
ActiveCN106286692AChange the stiffnessChange propertiesProgramme controlSpringsControl mannerSingle degree of freedom
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three degree of freedom micro-vibration suppression platform and control method thereof
ActiveCN105909725AReduce computationSimple Feedback Control StructureControllers with particular characteristicsVibration suppression adjustmentsControl signalControl manner
The invention provides a three degree of freedom micro-vibration suppression platform and a control method thereof, belongs to vibration isolation and suppression devices, and solves problems of complicated structure and complex control method of a prior active-passive composite vibration isolation structure. The platform provided by the invention includes a base platform, a load platform, three sets of single degree of freedom active-passive composite vibration isolation assemblies which are totally identical and a controller. The upper end and the lower end of each single degree of freedom active-passive composite vibration isolation assembly are connected with the load platform and the base platform. The control method provided by the invention includes calculating logic axis translation signals, calculating logic axis control signals, calculating physical axis real time control signals and transmission steps. The platform provided by the invention is simple in structure, adjustable in rigidity, is capable of suppressing and isolating three degree of freedom microvibration in rotation directions of an X axis and a Y axis and a translation direction of a Z axis and is suitable for different occasions. Microvibration of different frequency bands can be dampened effectively and reliable guarantee can be provided for precision machining and measurement equipment in a microvibration environment.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Six-degree-of-freedom micro vibration suppression platform and control method thereof
ActiveUS9777793B1Low dynamic stiffnessNatural frequency can be reducedProgramme controlSpringsSingle degree of freedomControl signal
A six-degree-of-freedom micro vibration suppression platform includes a basic platform, a load platform, six sets of single-degree-of-freedom active and passive composite vibration isolation devices that are exactly the same and a controller. Upper and lower ends of each set of single-degree-of-freedom active and passive composite vibration isolation devices are connected with the load platform and the basic platform, respectively. A control method includes: calculating a logical axis signal, calculating a logical axis control signal, calculating physical axis real-time control signals and a transfer step.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Shape memory polymers based on semicrystalline thermoplastic polyurethanes bearing nanostructured hard segments
InactiveUS7524914B2Above the melting point of the POSS domainsAdjustable stiffnessPolymer scienceAdhesive
Thermoplastic polyurethanes having an alternating sequence of hard and soft segments in which a nanostructured polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane diol is used as a chain extender to form a crystalline hard segment constituting SMPs. The polyurethanes are formed by reacting a polyol, a chain extender dihydroxyl-terminated polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane and a diisocyanate. The polyurethanes have multiple applications including for example, implants for human health care, drug delivery matrices, superabsorbant hydrogels, coatings, adhesives, temperature and moisture sensors, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Force feedback control system for video endoscope
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Suspended operator platform
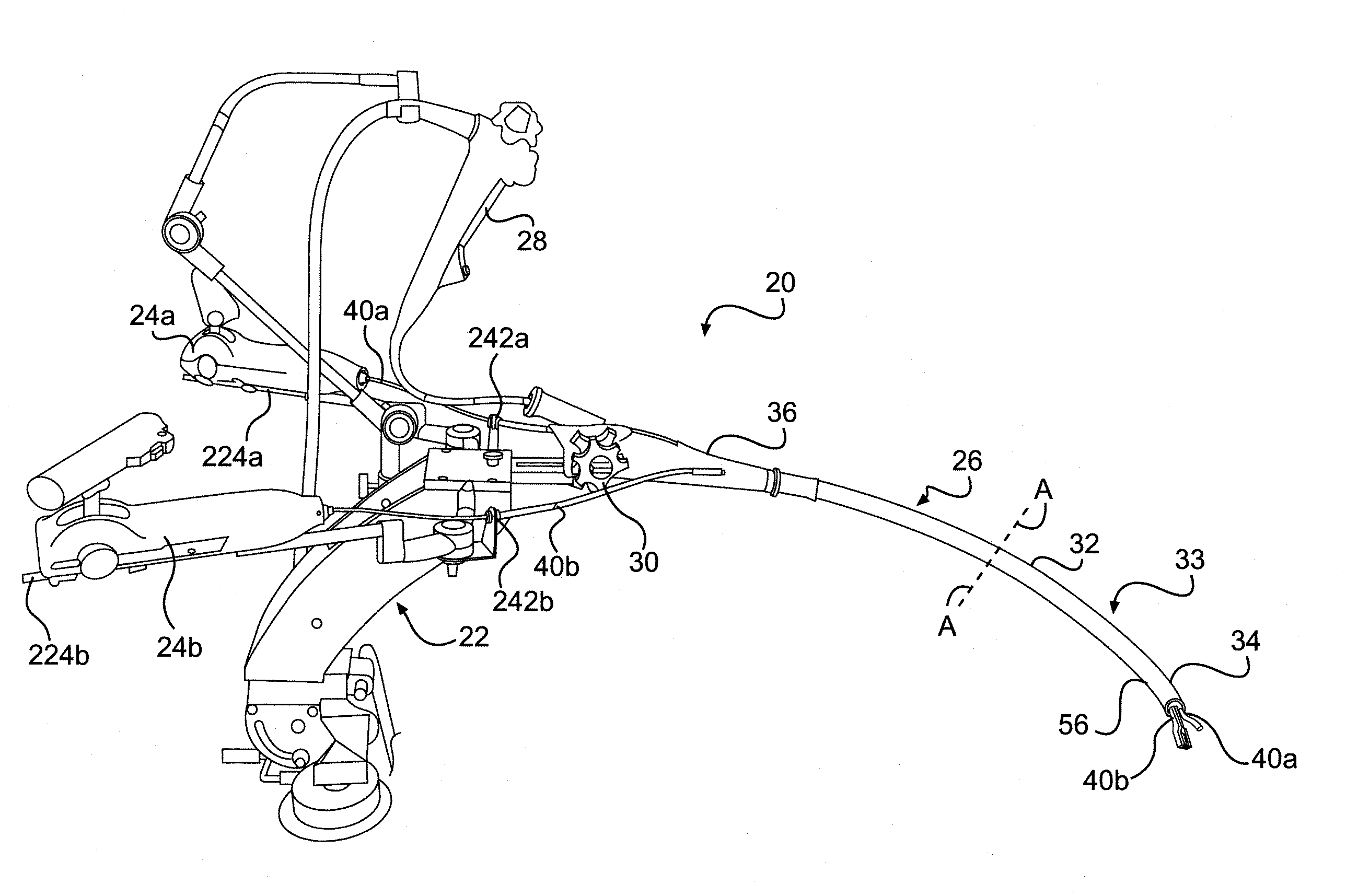
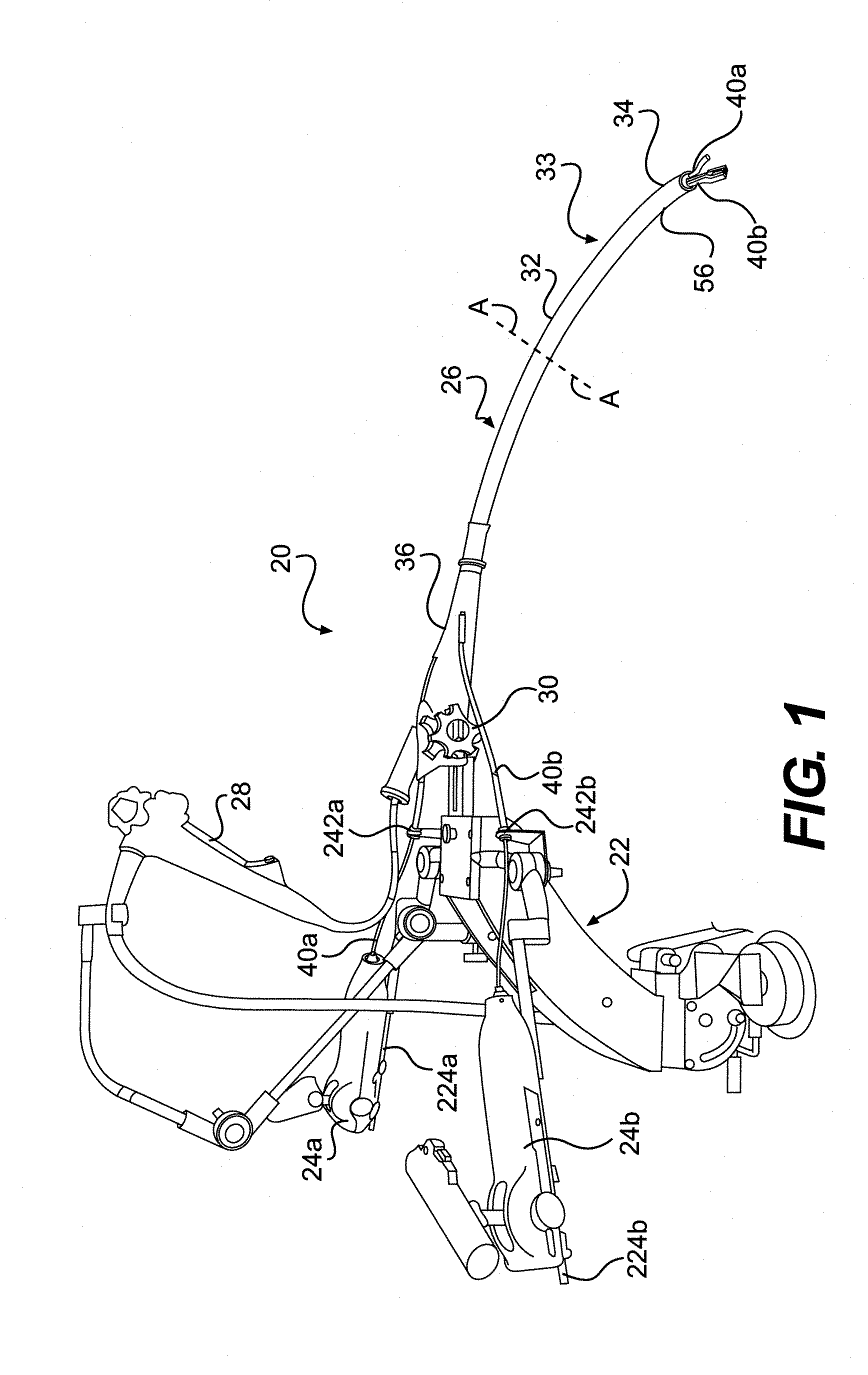
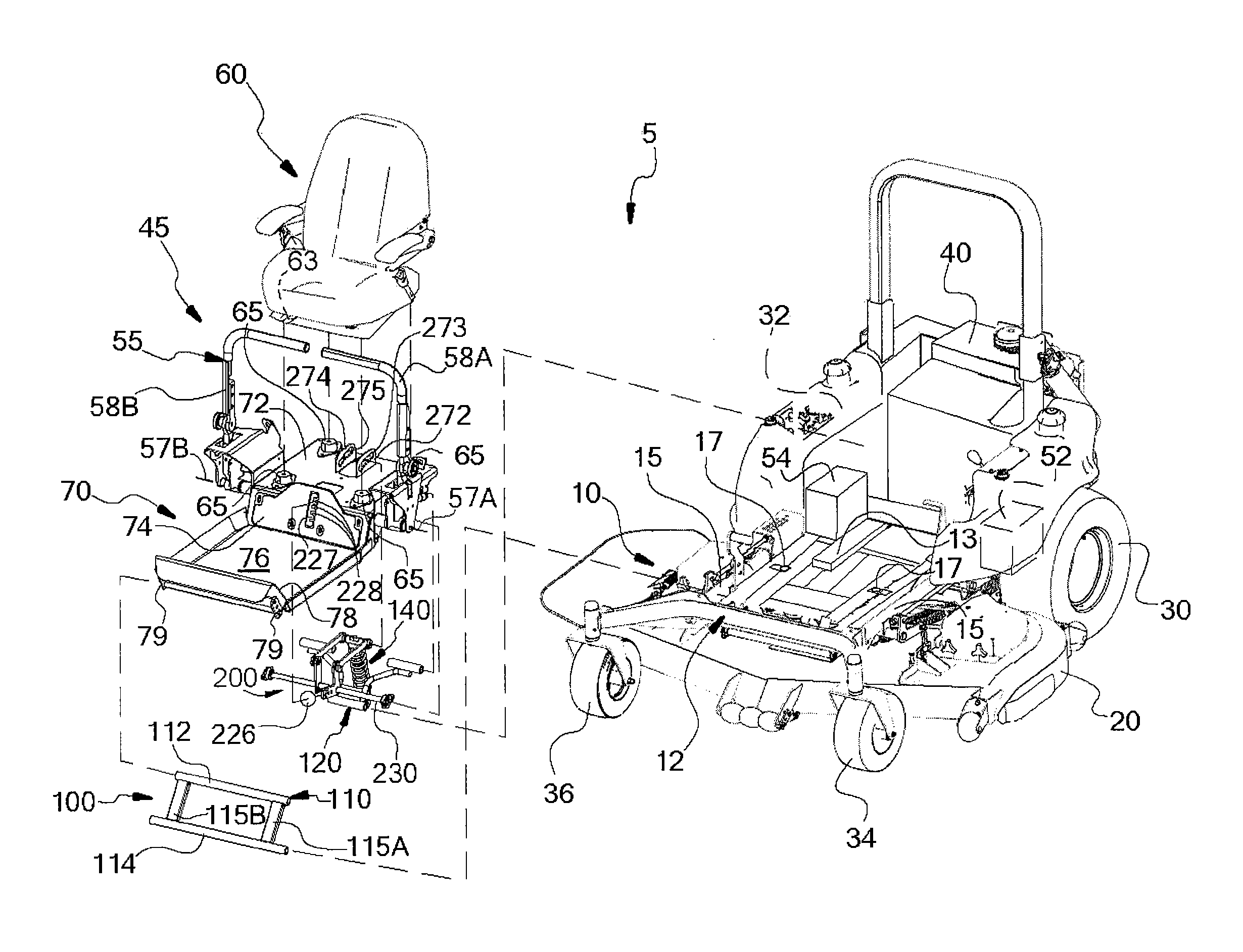
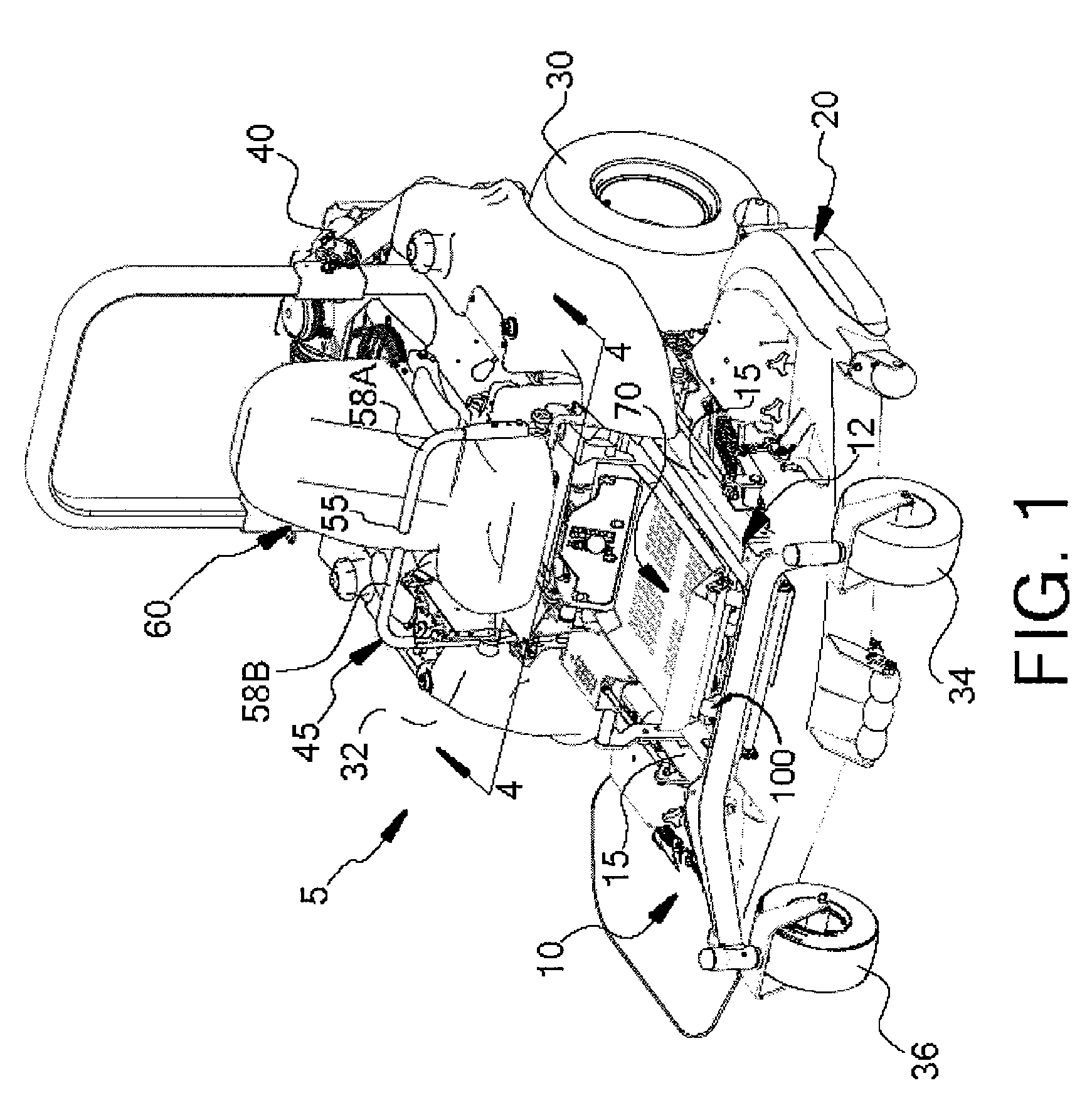
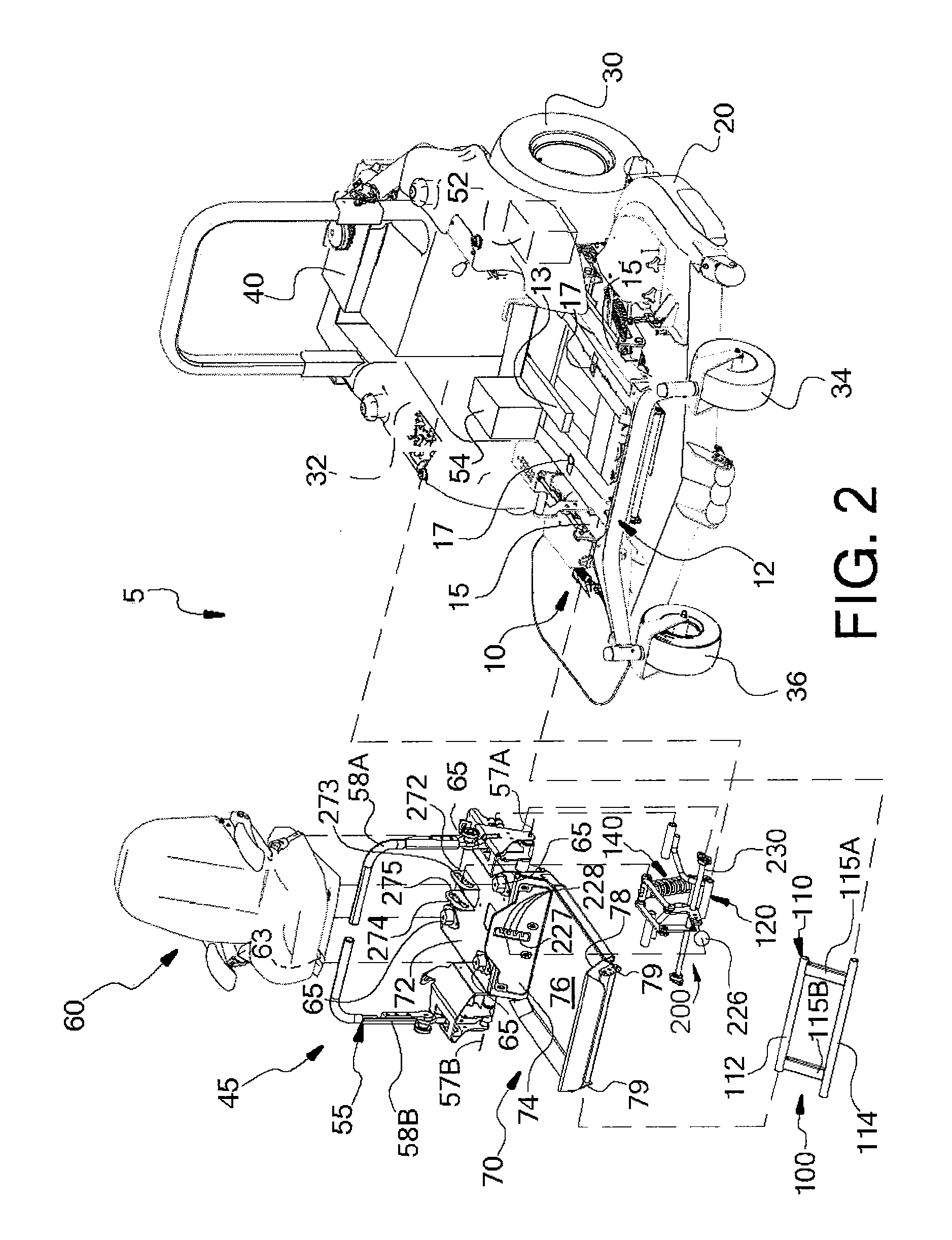
ActiveUS20110277433A1Improve stateAdjustable stiffnessMowersVehicle mounted steering controlsTerrainLawn mower
A suspended operator platform for use with a ride-on lawnmower or the like is connected to a rigid chassis of the ride-on lawnmower by a suspension system that has a parallelogram linkage. The operator platform supports an entire body of the operator and isolation mounts connect a seat assembly to the operator platform. Steering controls of the ride-on lawnmower are connected to the operator platform so that the steering controls move with the operator platform and are suspended and / or isolated from the chassis. The suspension system includes a course-stiffness adjuster and a fine-stiffness adjuster that for adjusting suspension stiffness to correspond to a particular operator and / or terrain.
Owner:METALCRAFT OF MAYVILLE
Fluid manifold for endoscope system
A video endoscope system includes a reusable control cabinet and an endoscope that is connectable thereto. The endoscope may be used with a single patient and then disposed. The endoscope includes an illumination mechanism, an image sensor, and an elongate shaft having one or more lumens located therein. An articulation joint at the distal end of the endoscope allows the distal end to be oriented by the actuators in the control cabinet or actuators in a control handle of the endoscope. Fluidics, electrical, navigation, image, display and data entry controls are integrated into the system along with other accessories.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
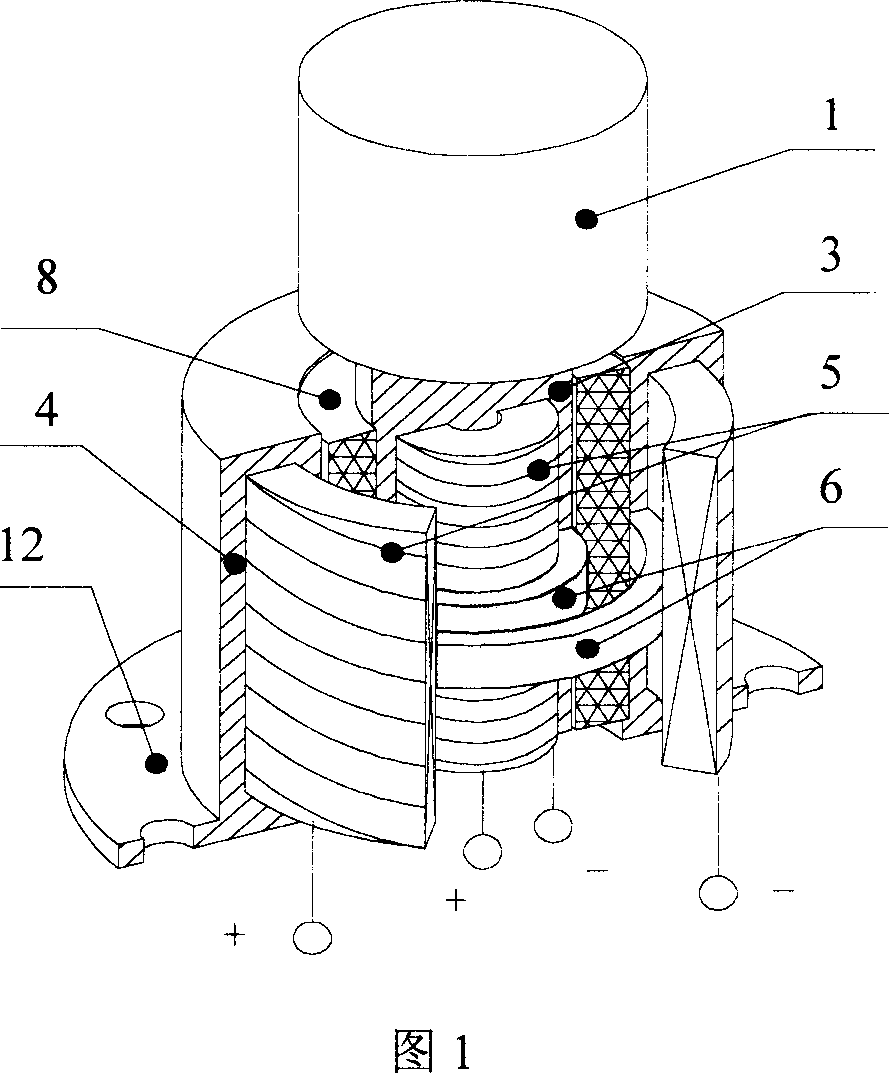
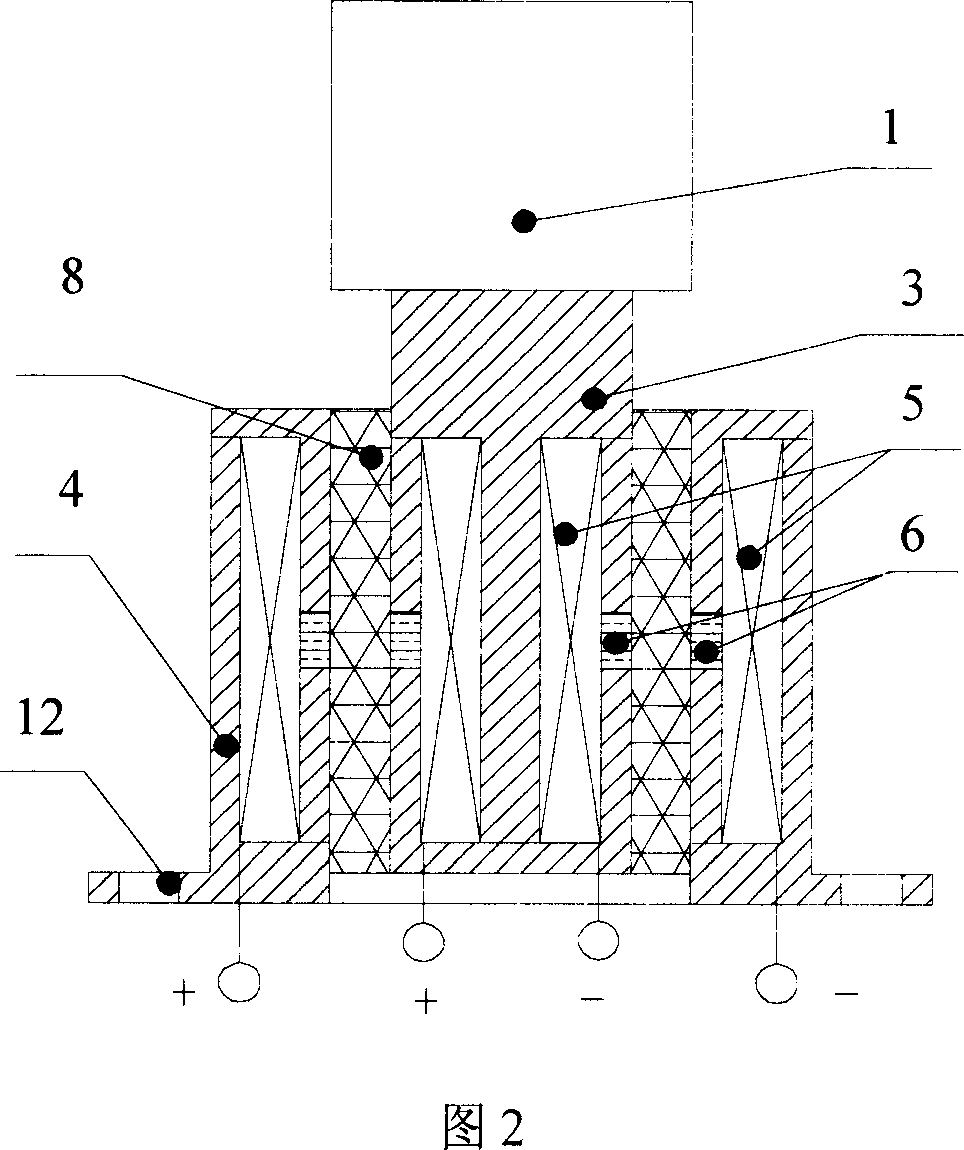
Variable rigidity shock insulation integral intelligent support seat
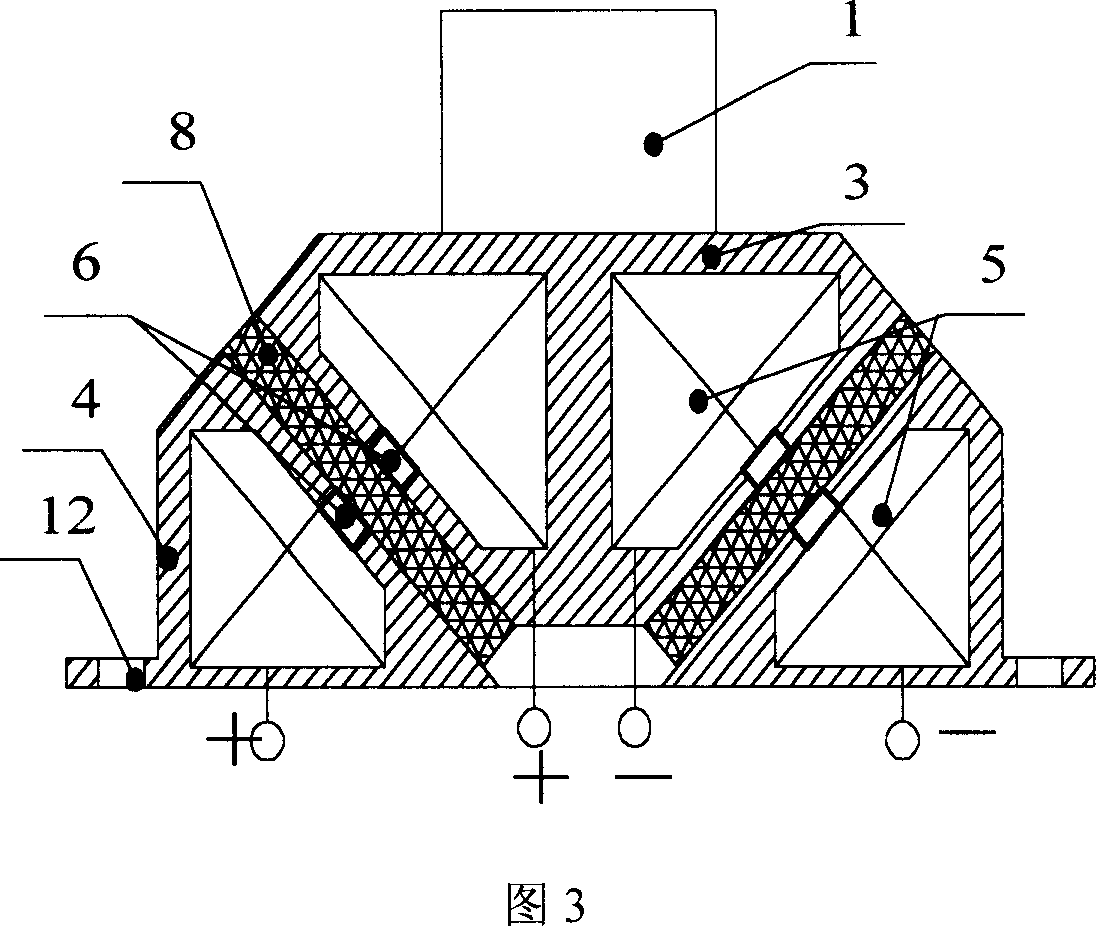
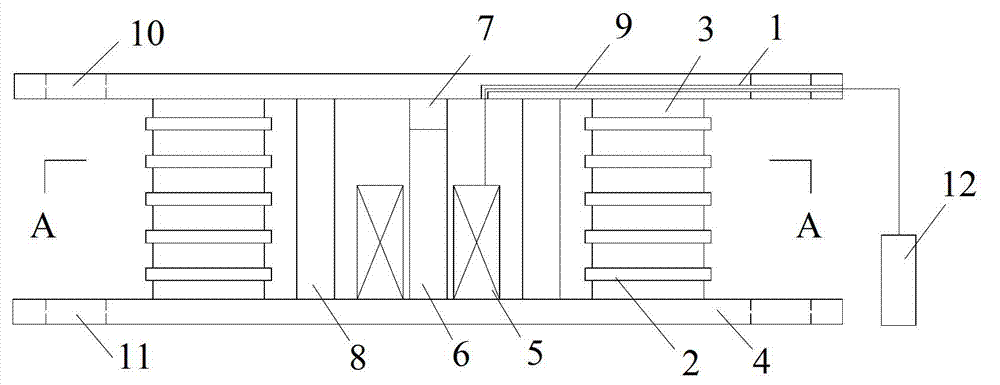
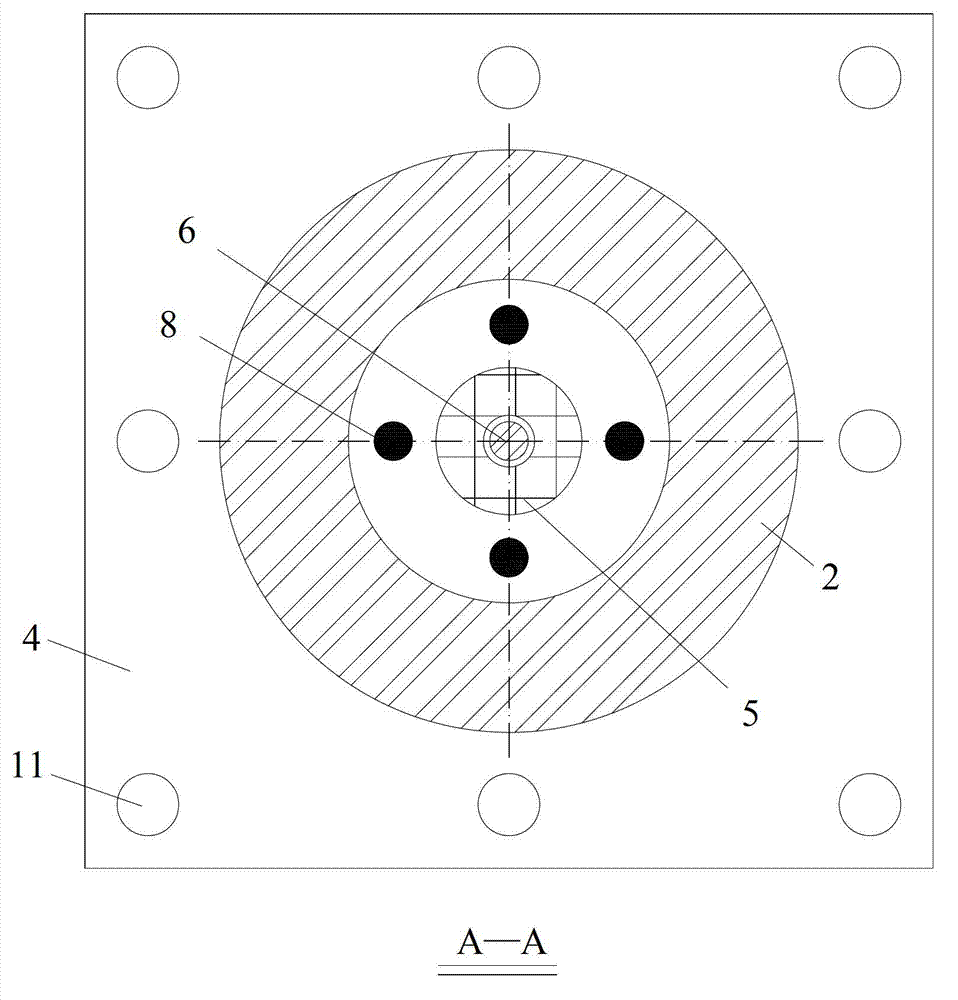
InactiveCN102733483ASolve the problem that the stiffness can only be adjusted larger but not smallerAvoid destructionShock proofingEngineeringMagnetorheological elastomer
The invention relates to a variable rigidity shock insulation integral intelligent support seat and belongs to the technical field of building structure shock absorption. The variable rigidity shock insulation integral intelligent support seat is characterized by comprising an upper connecting plate (1), a lower connecting plate (4), a magnetic conduction steel plate (2), a magnetorheological elastic body (3), an excitation coil (5), a magnetic conduction iron core (6), a polymer matrix composite permanent magnet material (7), a lead core (8), a conducting wire passage (9), an upper connecting screw bolt hole (10), a lower connecting screw bolt hole (11) and a driving power supply (12), wherein the a magnetorheological elastic body (3) and the magnetic conduction steel plate (2) are in a circular ring shape or a square ring shape, the excitation coil (5) and the magnetic conduction iron core (6) are arranged inside a support seat, and the polymer matrix composite permanent magnet material (7) provides a bias magnetic field for a closed magnetic circuit. The variable rigidity shock insulation integral intelligent support seat has the effects and benefits that the shock insulation and the variable rigidity are integrated, the structure is simple, the anti-interference performance is high, the two-way rigidity regulation can be realized, different horizontal rigidities can be provided for the structure according to different quake waves, and the destroy of earthquake disasters on building structures and bridge structures is effectively reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
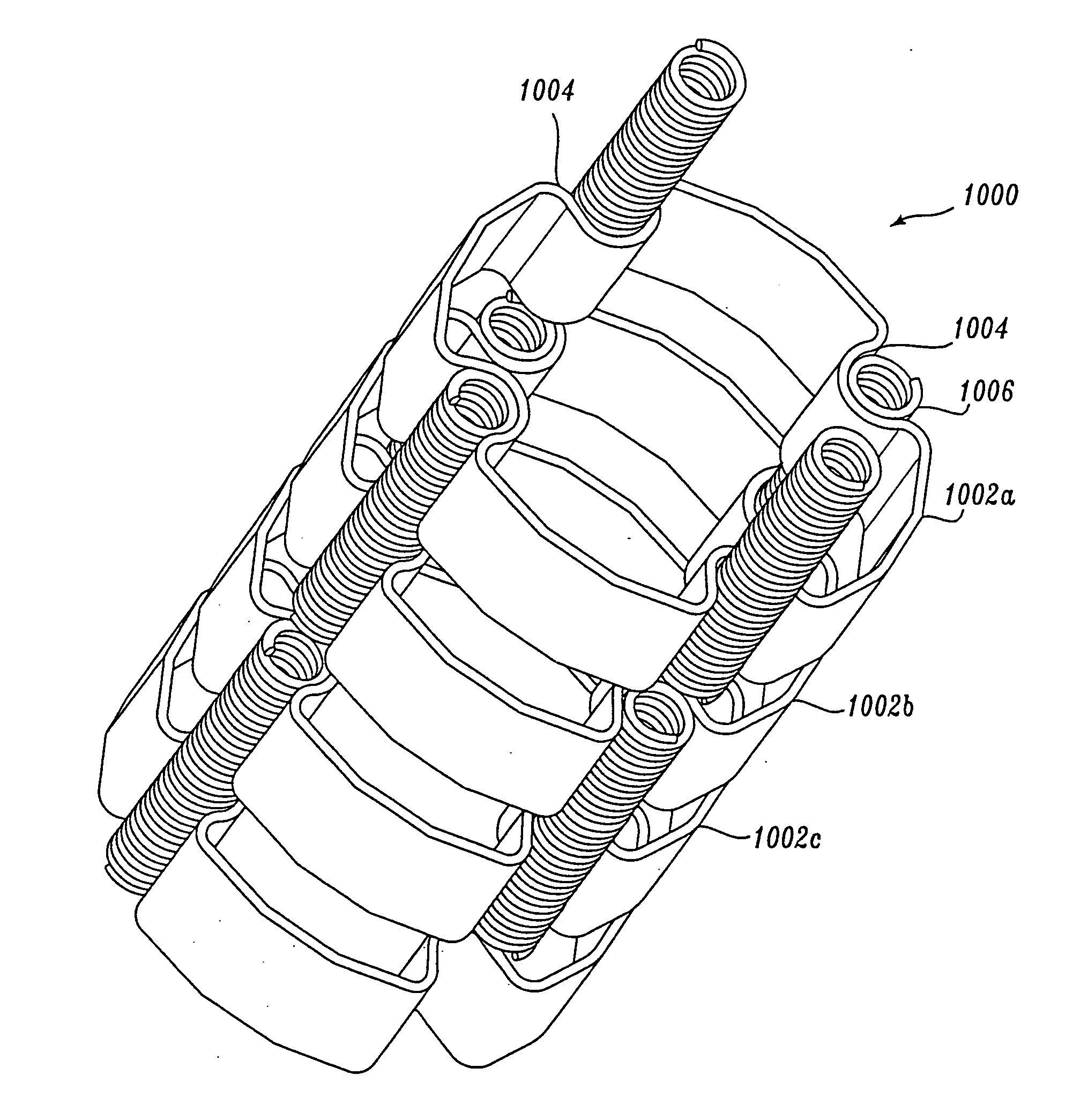
Adjustment method for dynamic stiffness of rubber joint with liquid damping, and rubber joint
ActiveCN102644693AAdjustable stiffnessMeet operational requirementsSpringsShock absorbersDynamic stiffnessClassical mechanics
An adjustment method for the dynamic stiffness of a rubber joint with liquid damping, and the rubber joint, and the rubber joint comprises metal outer sleeves, a rubber joint body, a throttling channel adjustment device and other parts, wherein the specific structure is as follows: proper holes are arranged on the outer surface of the rubber joint body and pressed-installed with the metal outer sleeves on the outer surfaces thereof to form closed cavities, the cavities are arranged in the relative movement directions of the mandrel and the outer sleeve of the rubber joint body, and symmetrically distributed at the both sides of the axis of the rubber joint body, and the two cavities are connected via a throttling channel; and in this way, when the mandrel and the outer sleeve of the rubber joint perform a relative movement, the volume of one side of each of the cavities at the both sides of the mandrel is reduced, and the volume of the other side is increased, so that a liquid damping medium at the side with the reduced volume flows to the side with the increased volume via pores, and the liquid damping medium generates a damping force while passing through the throttling channel due to damping action. The size of the throttling channel can be changed via the adjustment device, so as to achieve the purposes of adjusting the damping force and obtaining the needed dynamic stiffness.
Owner:ZHUZHOU TIMES NEW MATERIALS TECH
Method for Chassis Control of a Motor Vehicle, and Device for the Performance Thereof
ActiveUS20120055745A1Increase stiffnessAdjust stiffnessSpringsResilient suspensionsCompressive loadMotorized vehicle
In a method for chassis control of a motor vehicle which has at least one wheel suspension, a vehicle body, and a shock absorber having a rebound stage, whose stiffness is adjustable, and a compression stage, whose stiffness is adjustable, the stiffness of the compression stage is changed for a compressive load of the shock absorber generated by a specific vehicle body movement, and the stiffness of the rebound stage is additionally changed for a subsequently following tensile load of the shock absorber generated by the specific vehicle body movement, or the stiffness of the rebound stage is changed for a tensile load of the shock absorber generated by a specific vehicle body movement, and the stiffness of the compression stage is additionally changed for a subsequently following compressive load of the shock absorber generated by the specific vehicle body movement.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
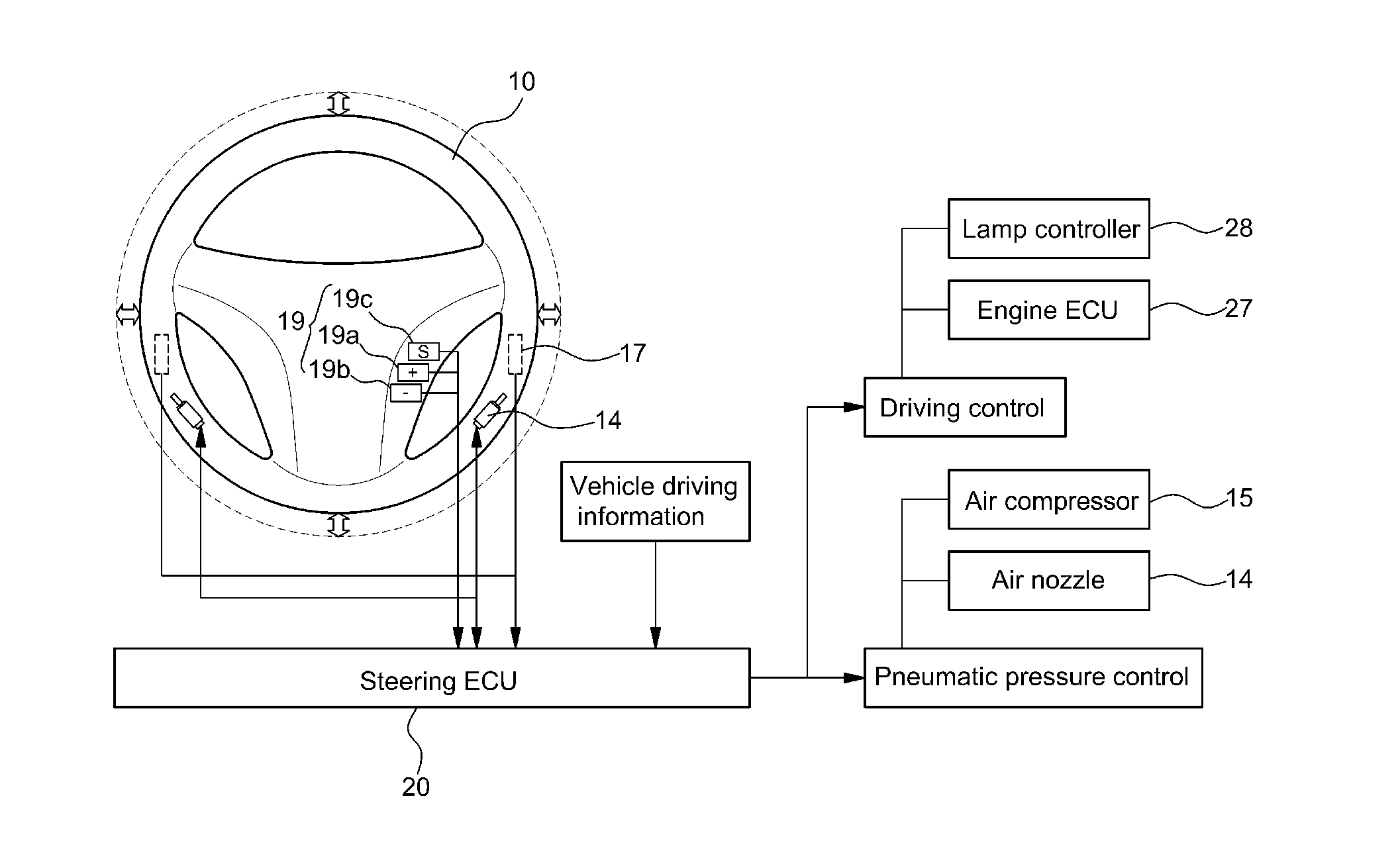
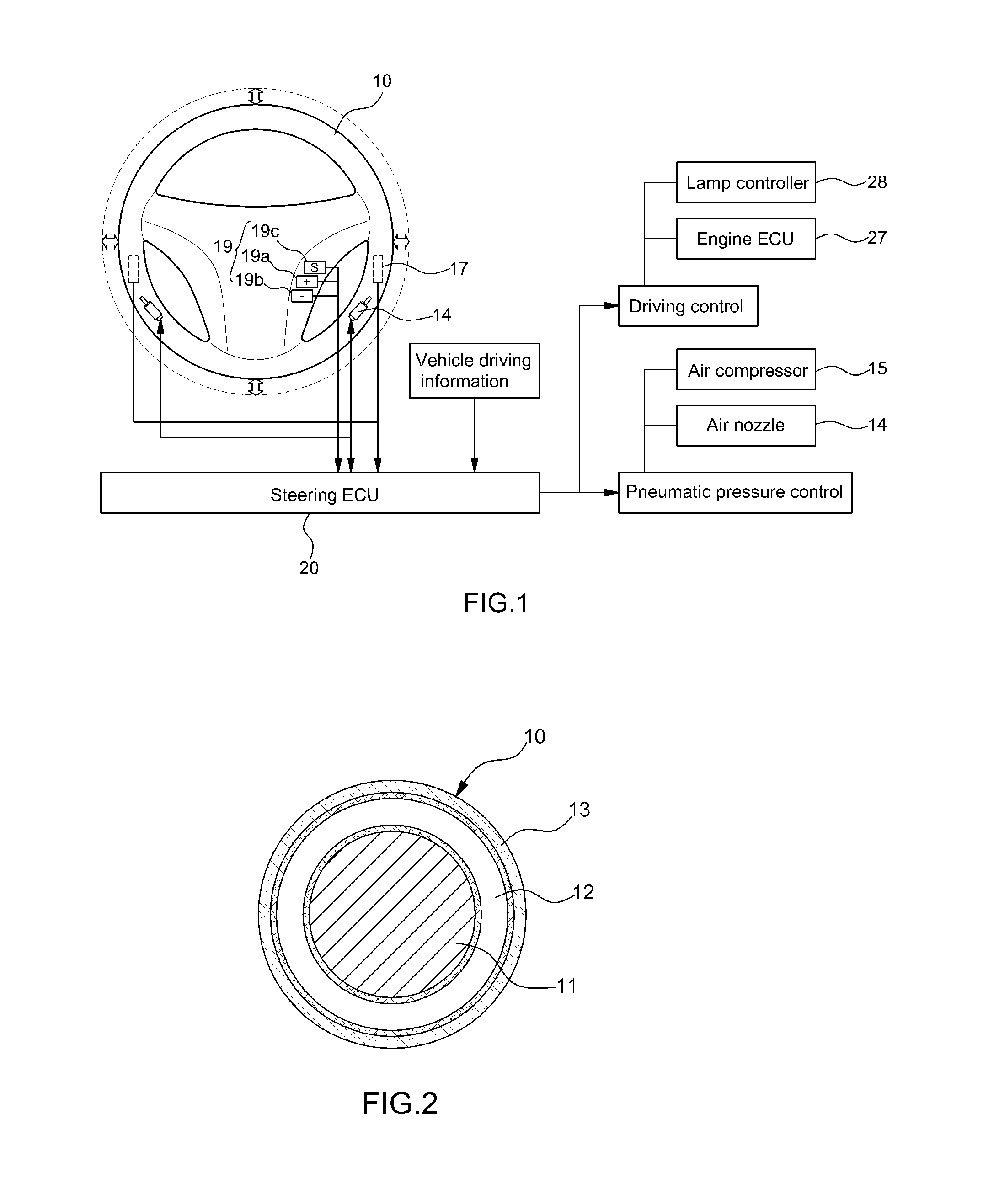
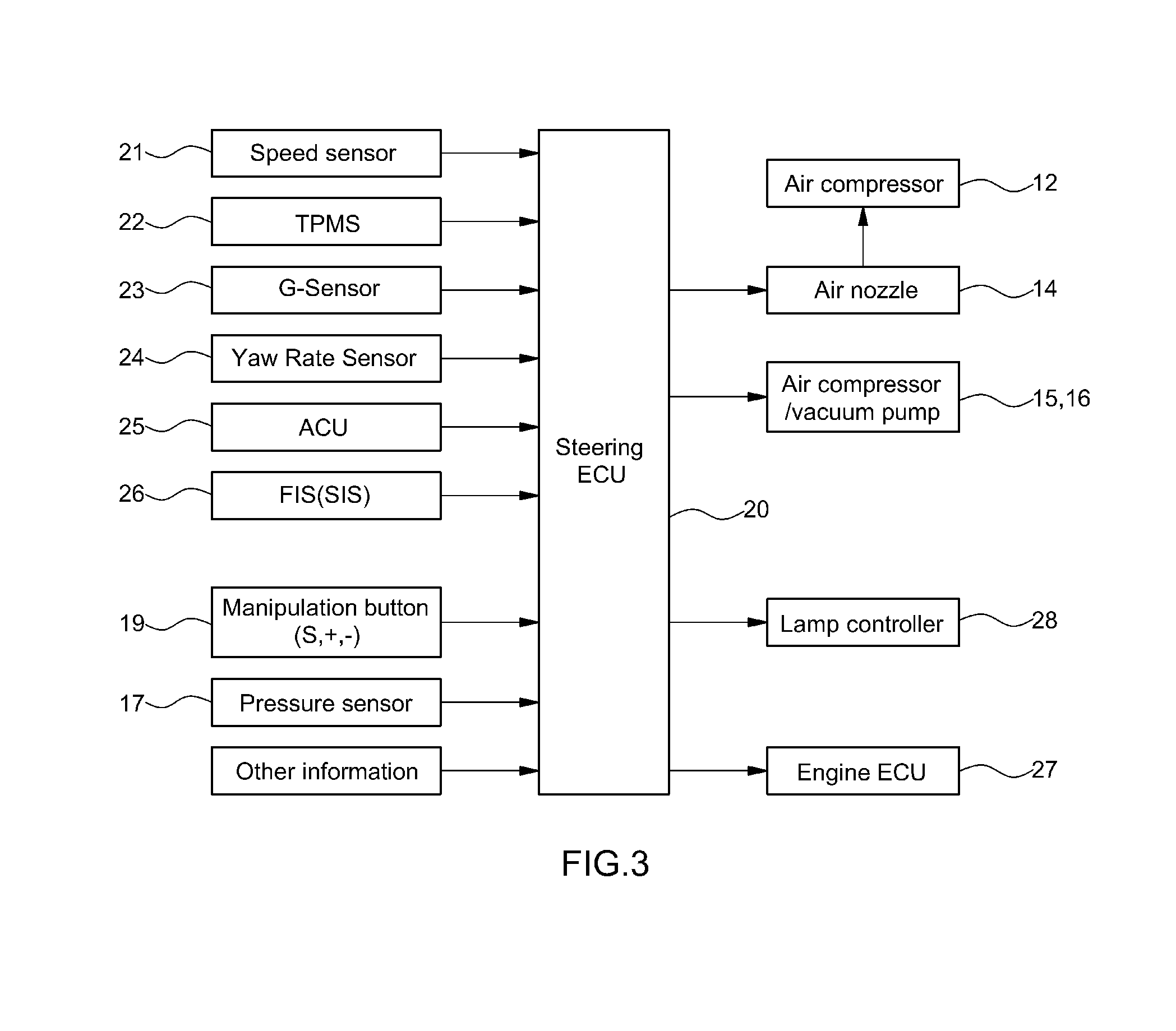
Steering wheel apparatus for adjusting stiffness and receiving pressure and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20150032334A1Improve security featuresAdjustable stiffnessSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering wheelEngineering
A steering wheel apparatus for adjusting stiffness and receiving a pressure is provided. The apparatus includes a rim having a ring-shaped frame structure and an air container disposed around an outer surface of the rim. An outer sheath covers an outer surface of the air container and an air nozzle is connected to an inside of the air container. A pressure sensor is mounted to the rim to detect a pressure by which the steering wheel apparatus is gripped and an air compressor and a vacuum pump are connected to the air nozzle. A steering controller analyzes signals input from sensors to maintain an air pressure of the air container and operate the air compressor or the vacuum pump when present condition information is satisfied. An engine controller analyzes a signal input from the pressure sensor and when the signal corresponds to a predetermined pressure or greater decelerate the vehicle.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
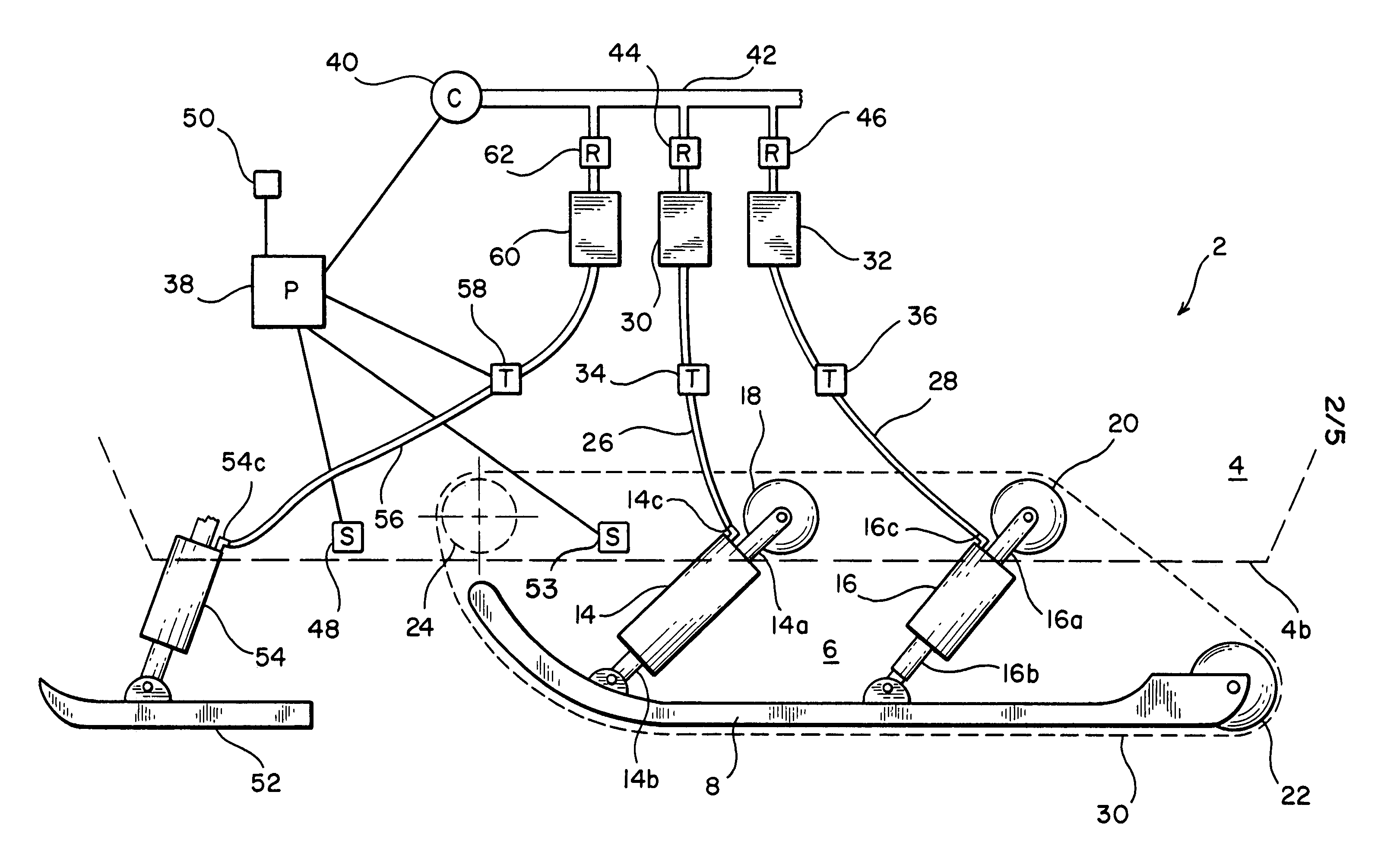
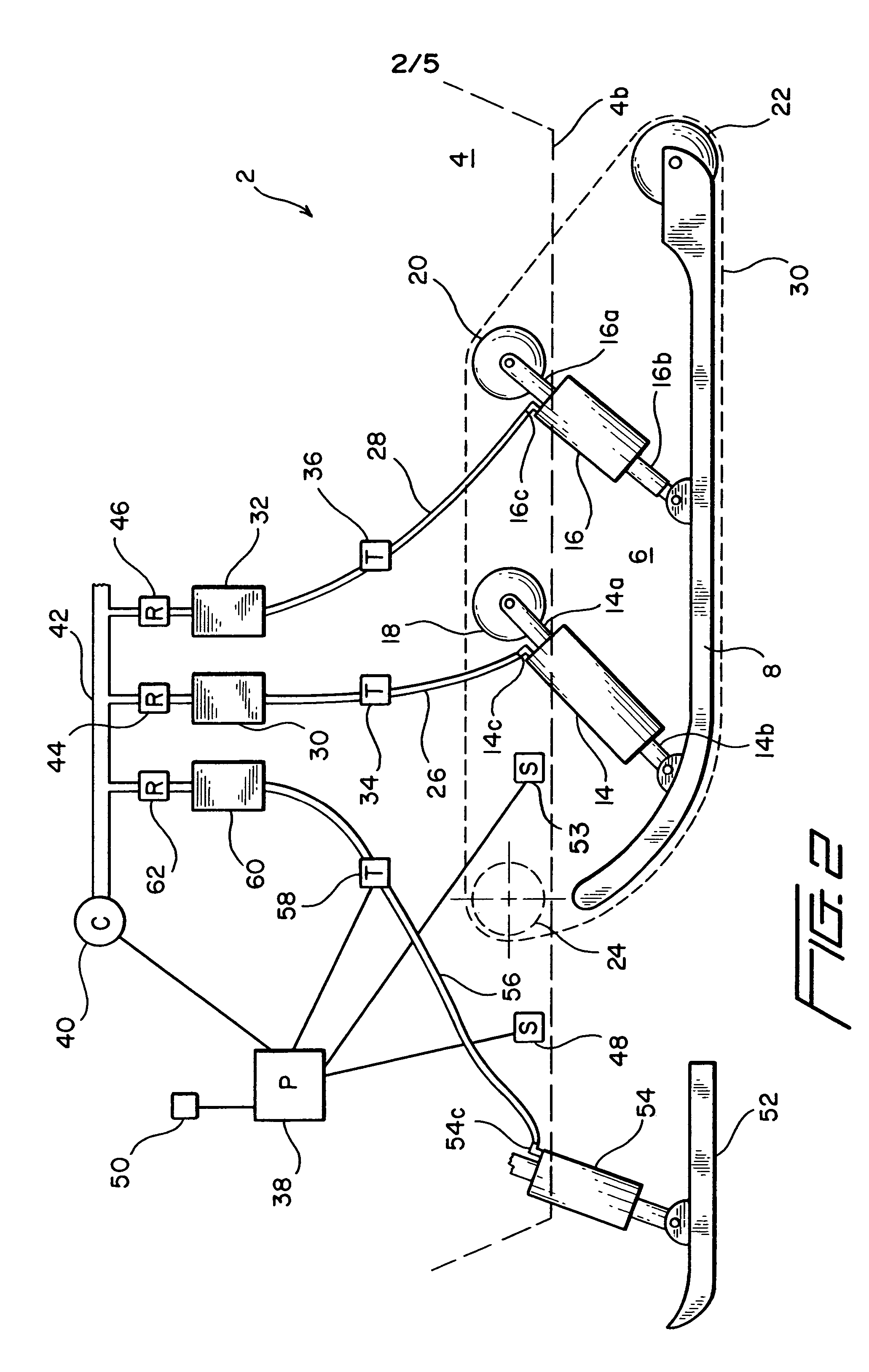
Snowmobile suspension system
InactiveUS7322435B2Adjustable stiffnessVehicle cleaning apparatusLoading/unloading vehicle arrangmentEngineeringSnow
To enable a rider to control in real time the type of ride he desires, a snowmobile is equipped with a suspension system that includes at least one fluid actuated device which can be adjusted in real time to control the relative distance between the body of the snowmobile onto which the rider sits and the frame, or the slide tracks about which the drive belt is mounted. By setting a constant predetermined desirable distance between the body and the slide tracks, or the frame, of the snowmobile, an optimal cushioned ride for the rider is obtained. The control of the fluid actuated device(s) may be effected at any time manually by the rider, or be effected by a feedback system. The snowmobile is also equipped with an ABS system for enhancing the traction of the drive belt on snow and therefore the control of the snowmobile by the rider.
Owner:LILLBACKA JETAIR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com