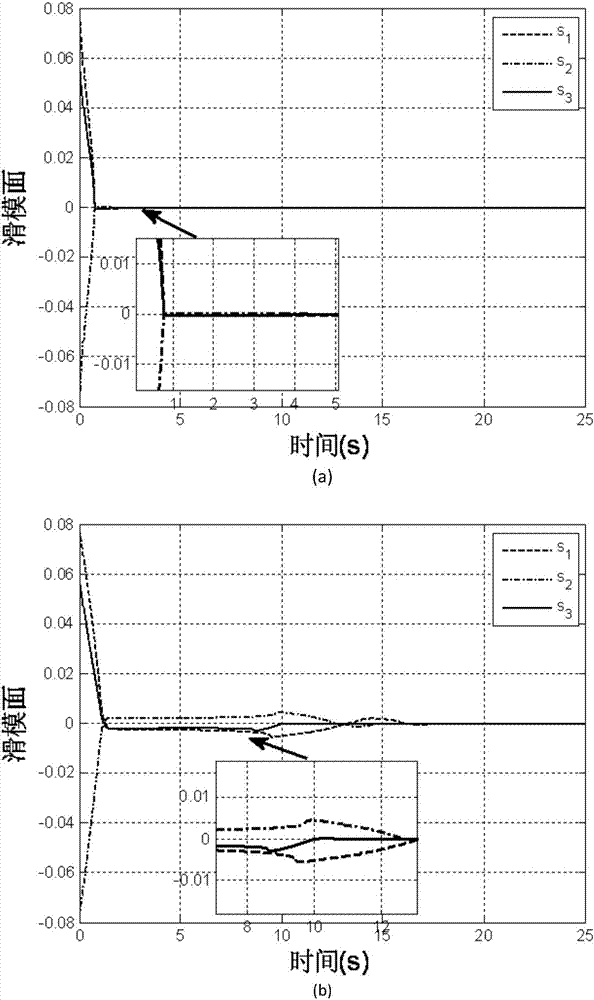
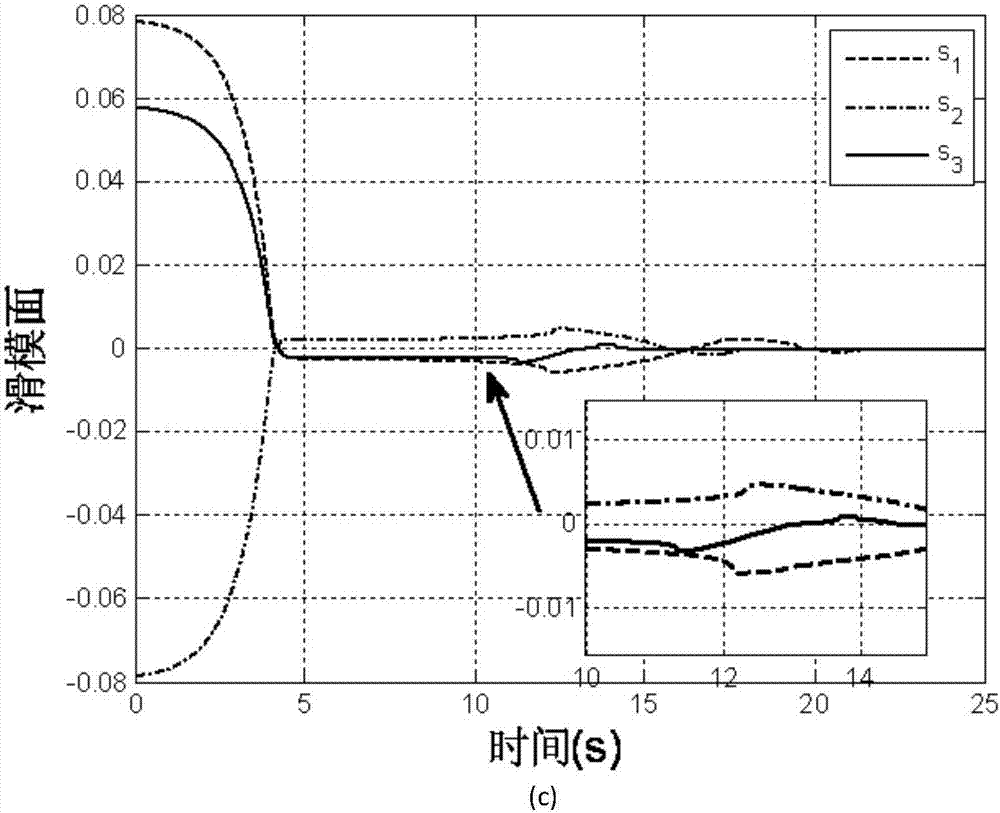
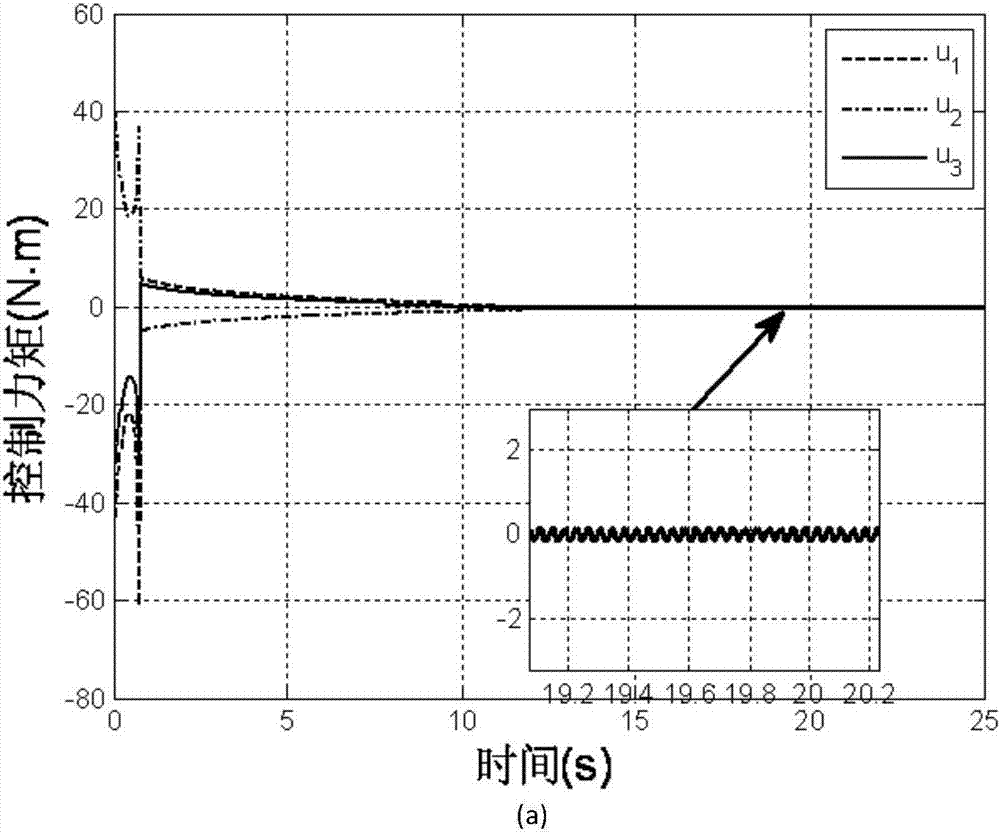
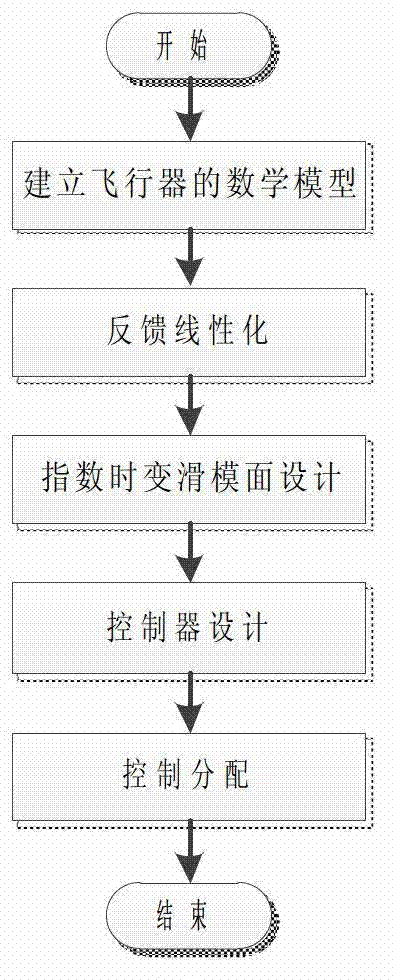
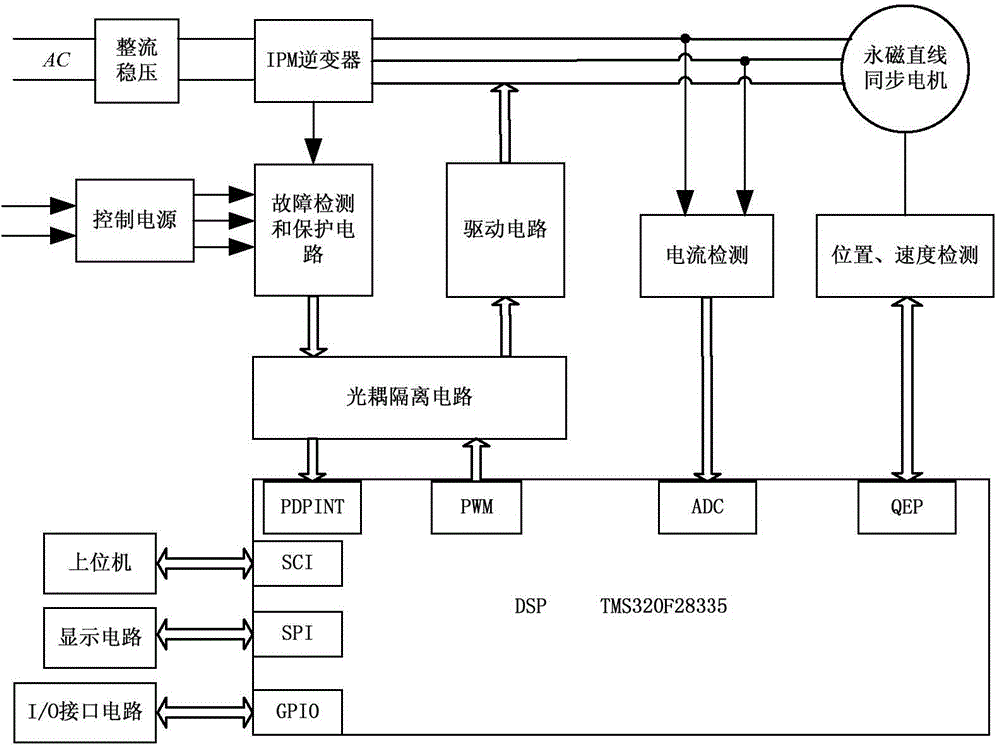
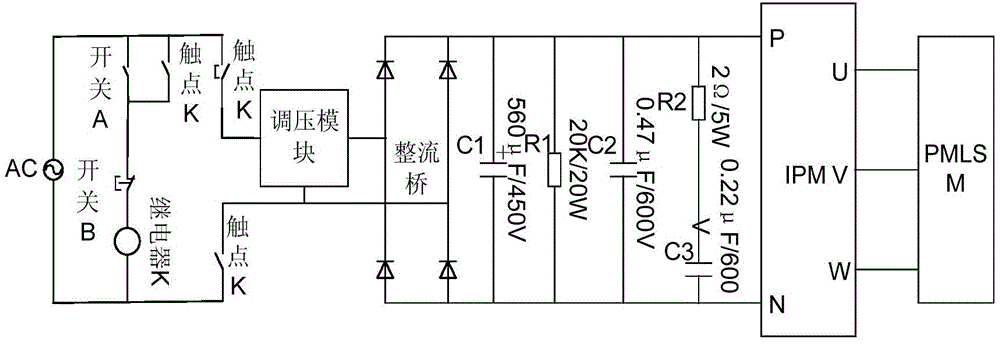
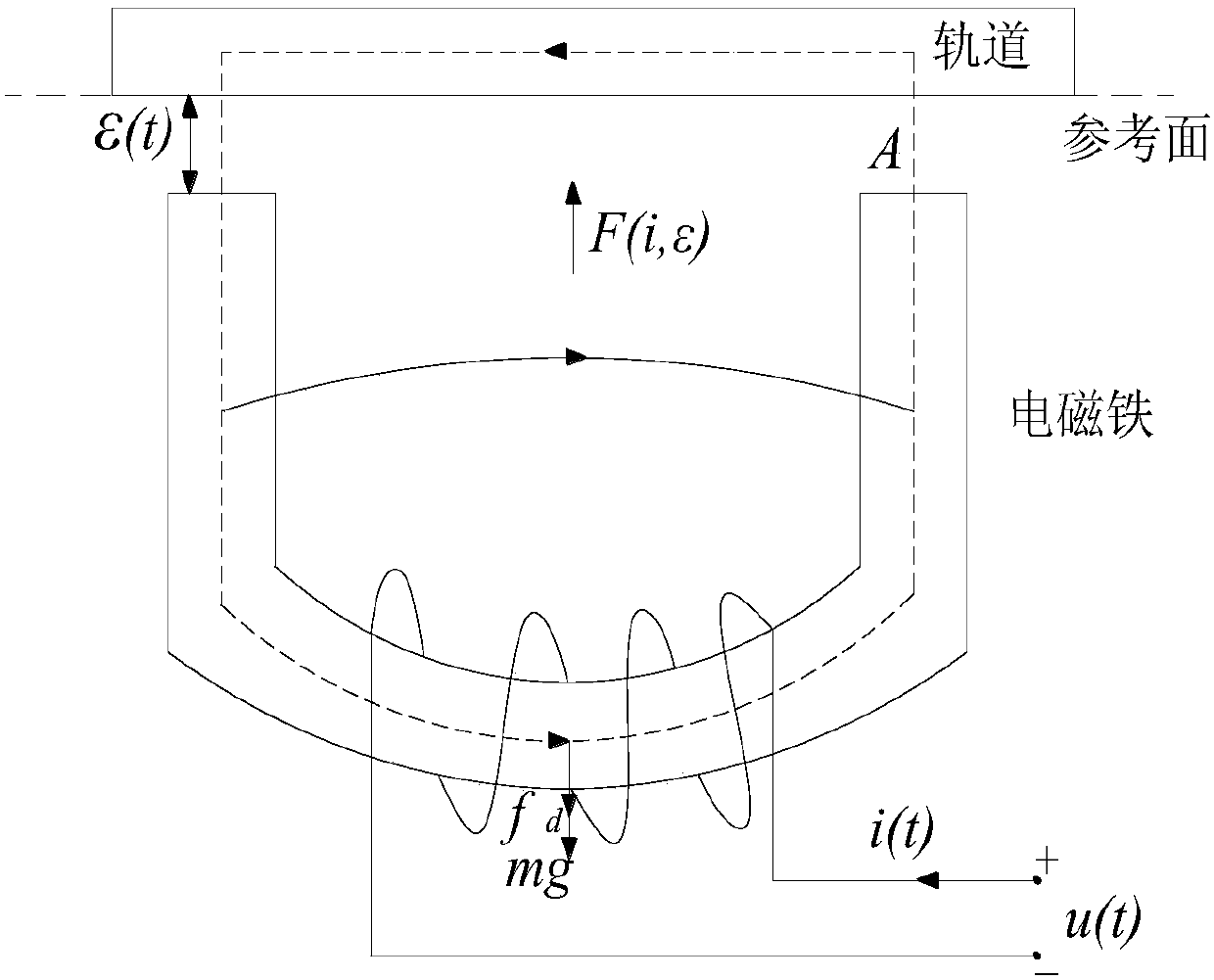
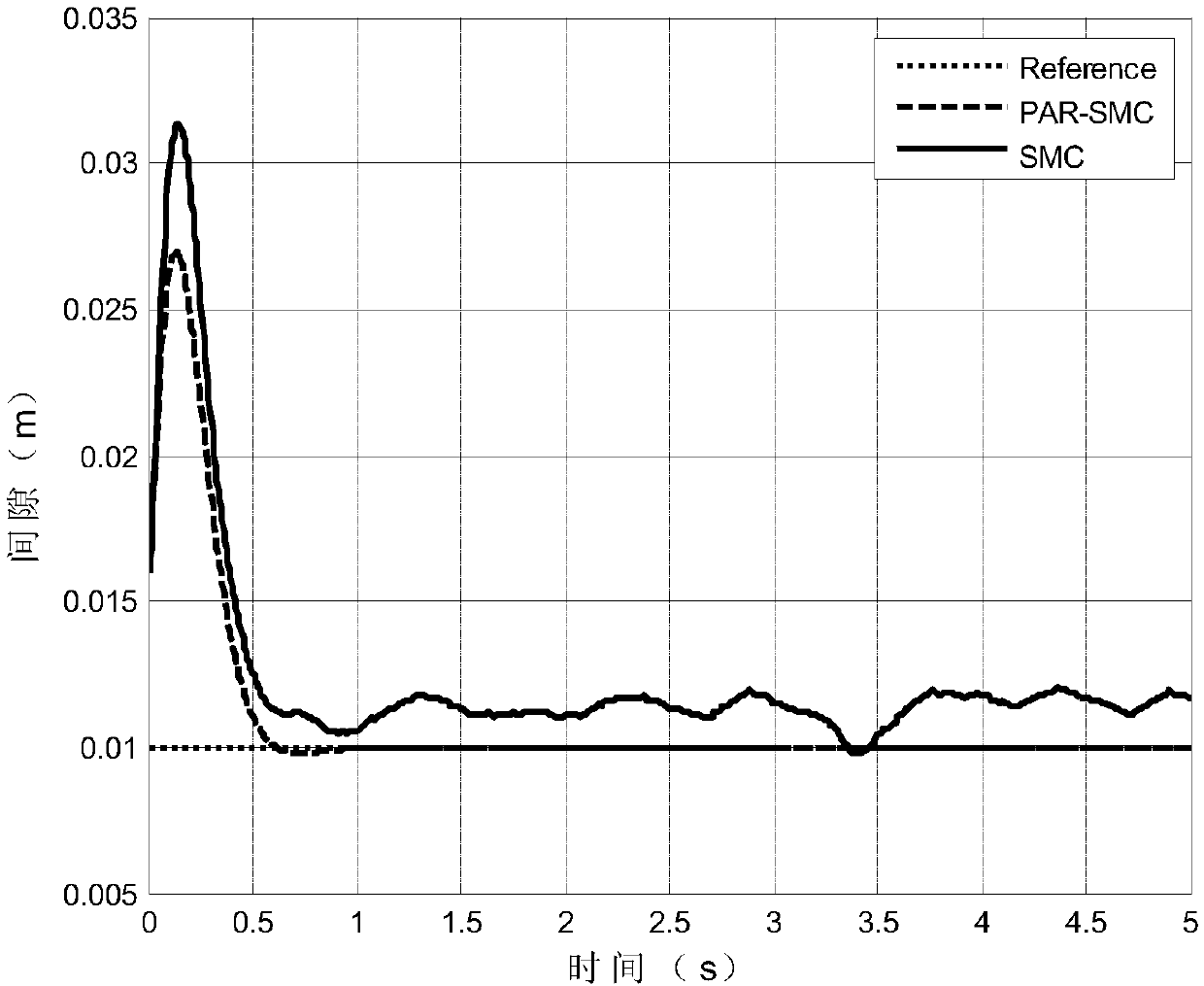
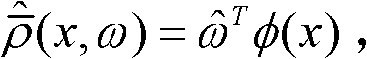Patents
Literature
372results about How to "Reduce buffeting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aircraft limited time adaptive attitude control method based on enhanced index approaching law
ActiveCN107577144AReduce buffetingAttitude controlAdaptive controlTerminal sliding modeSelf adaptive
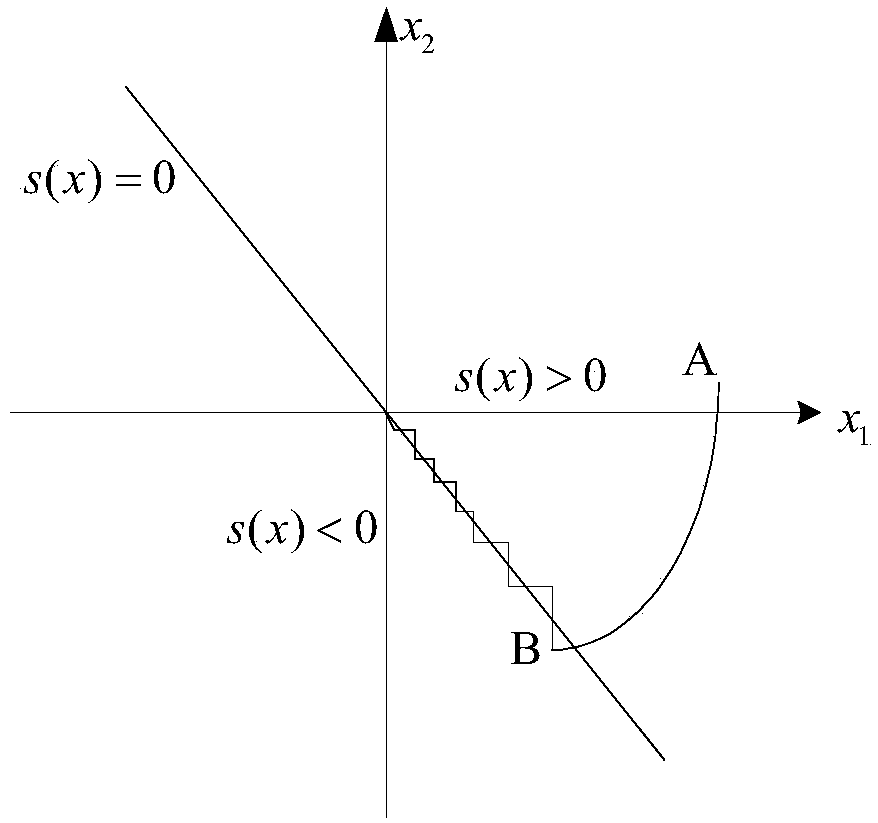
The invention relates to an aircraft limited time adaptive attitude control method based on the enhanced index approaching law, aims to solve an aircraft attitude stabilization problem having concentration uncertainty, utilizes a sliding mode control method based on the enhanced index approaching law and is integrated with adaptive control. A terminal sliding mode surface is designed for guaranteeing limited time convergence of a system, a problem of buffeting is reduced in an actual control system through the enhanced index approaching law, moreover, adaptive control is for adjusting a self characteristic feedback control system according to environment change in an intelligent mode to make the system operates in the optimal state according to certain setting standards. The method is advantaged in that the problem of buffeting of the sliding mode surface and control torque can be reduced, on the condition that the system has uncertainty and interference, limited time consistent boundary control of the system is finally realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
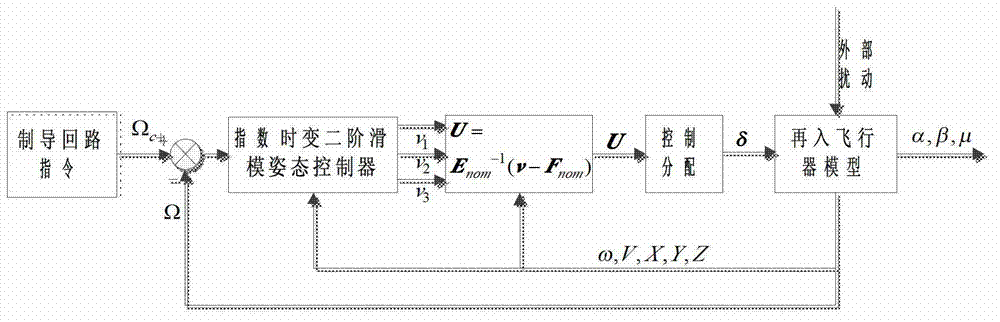
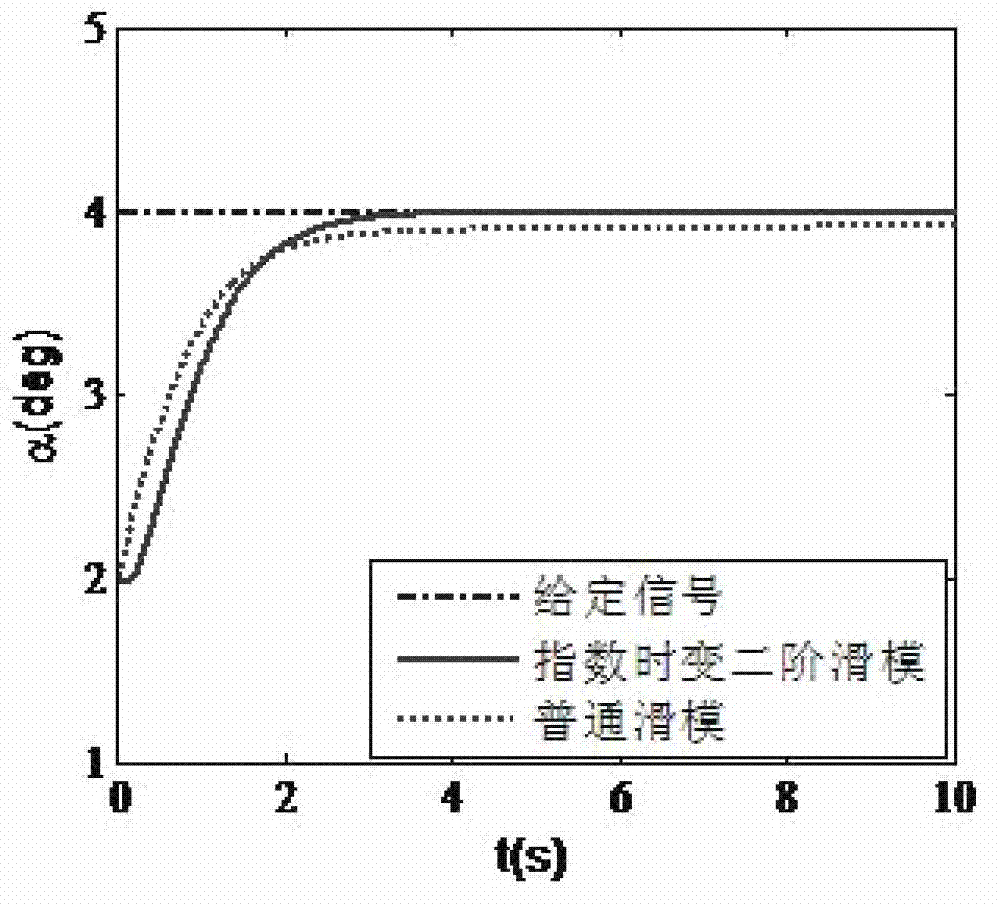
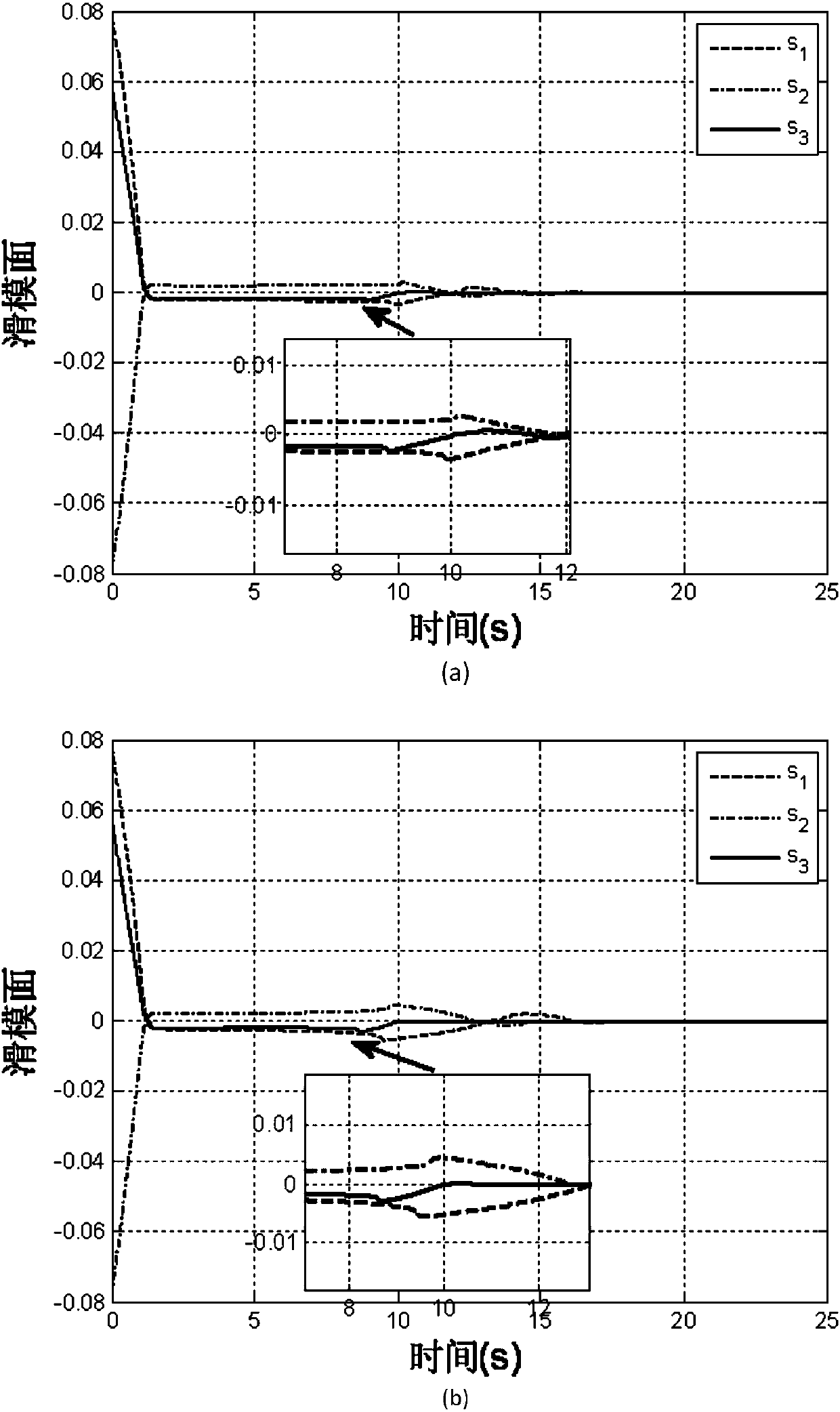
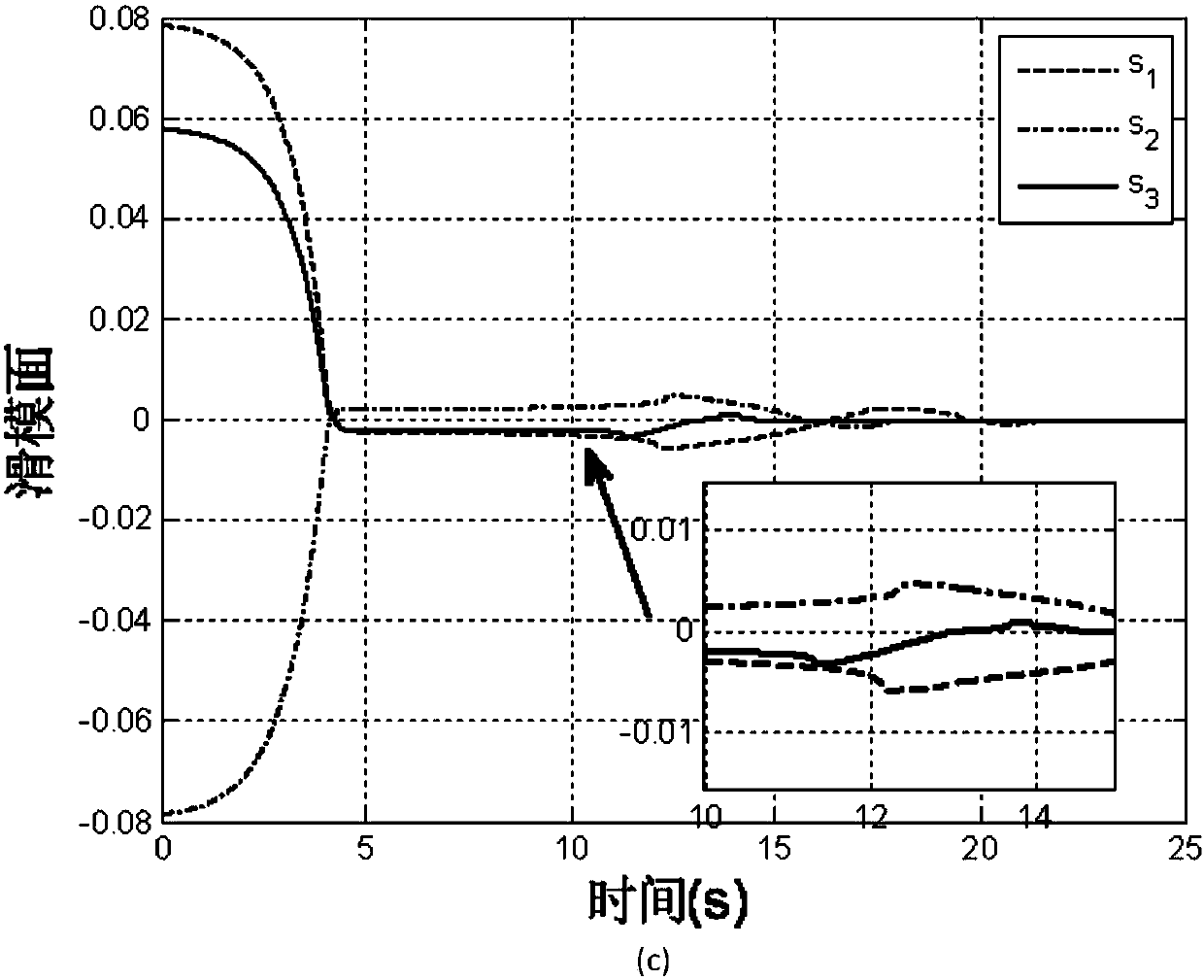
Reentry flying attitude control method based on exponential time-varying second order sliding mode
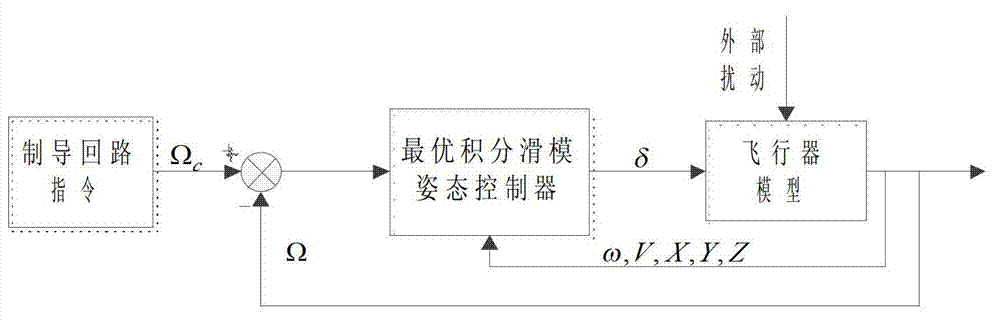
InactiveCN102929151AGuaranteed asymptotic convergenceSolve non-robust problemsAttitude controlAdaptive controlTracking errorAttitude control
The invention relates to a reentry stage aircraft attitude control method based on an exponential time-varying second order sliding mode, belonging to the technical field of aircraft control. According to the reentry stage aircraft attitude control method, a plane symmetric unpowered aircraft model is taken as an object, feedback linearization is carried out on an affine nonlinear system of an aircraft, and the attitude control problem of the aircraft when reentering into the atmospheric layer is studied. The aircraft provides operating force and operating torque only through a pneumatic control surface. A control surface deflection angle signal [delta e delta a delta r]T is given through the designed control law, so that an attitude instruction omega c=[alpha c beta c mu c]T given by a guidance loop can be effectively tracked, the attitude angle tracking error can be guaranteed to be asymptotically converged, and strong robustness is generated for tremendous environment change, uncertain pneumatic parameters and external disturbance and the like in the reentry process. Meanwhile, the control law in the method only has integral of a switching function, so that the reaching stage of a sliding mode surface is eliminated, the control quantity is enabled to be a continuous signal, the buffeting phenomenon is effectively reduced, and good control accuracy is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Aerial vehicle finite-time adaptive attitude control method based on improved power reaching law
An aerial vehicle finite-time adaptive attitude control method based on an improved power reaching law aims at a problem of aerial vehicle attitude stabilization with concentrated uncertainty. A sliding mode control method based on the improved power reaching law is utilized, and furthermore through adaptive controlling, the aerial vehicle finite-time adaptive attitude control method based on the improved power reaching law is designed. A terminal sliding mode surface is designed for ensuring definite-time convergence of a system. Furthermore through the improved power reaching law, a buffeting problem is reduced in an actual control system. Furthermore the adaptive controlling is used for a feedback control system which intelligently adjusts a self characteristic according to the environment change so that the system can operate in an optimal state according to some preset standards. The invention provides the control method which can reduce the buffeting problem of the sliding mode surface and a control torque and furthermore realizes uniform ultimate boundedness of finite time of the system on the condition that uncertainty and interference exist in the system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Mixed control method based on trace tracking of wheeled mobile robot
ActiveCN104317299AReduce the amount of controlGuaranteed stabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsKinematicsAngular velocity
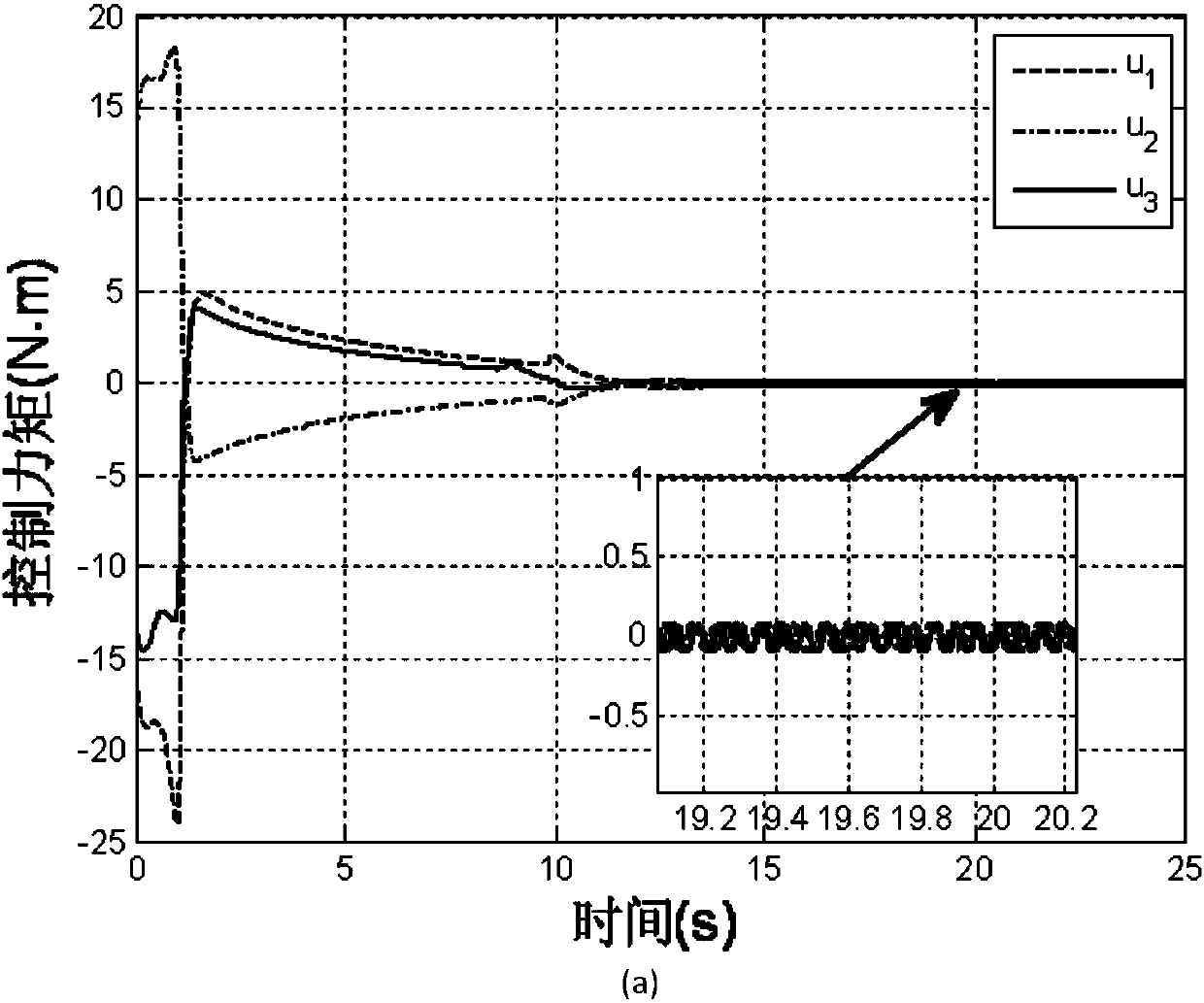
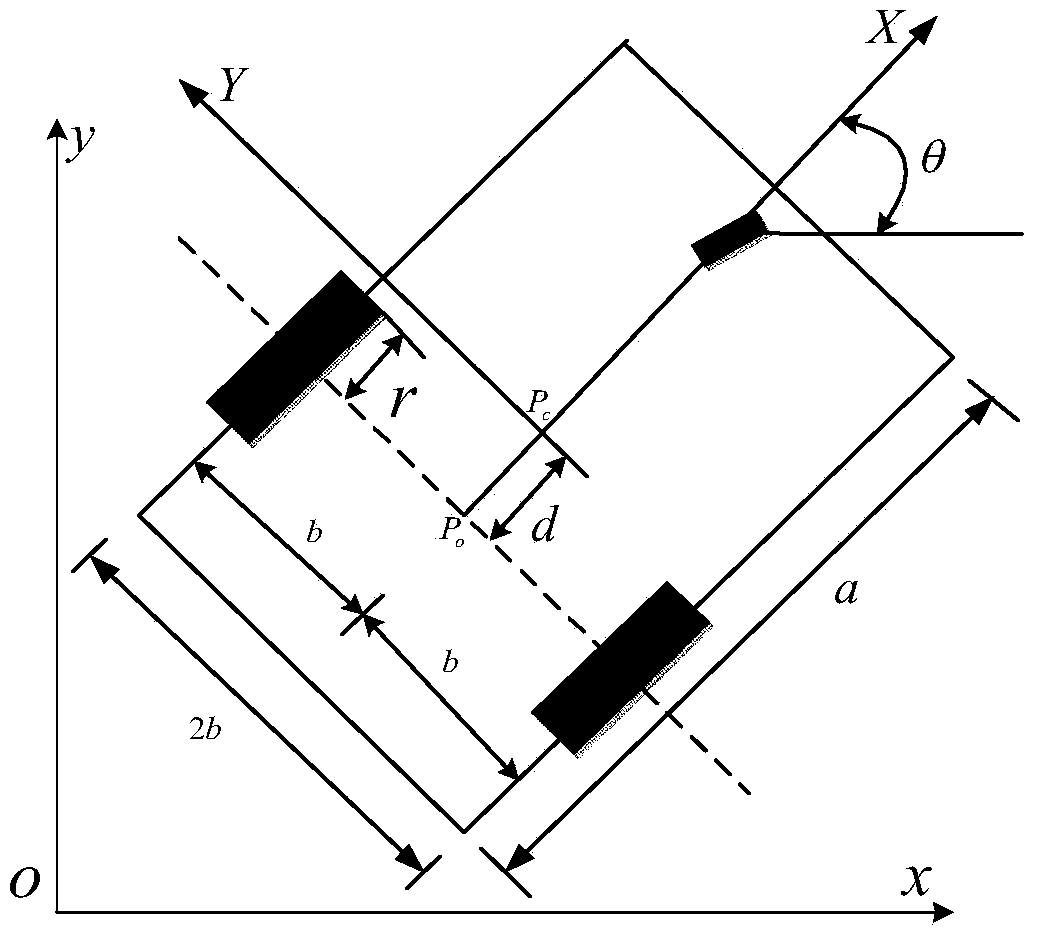
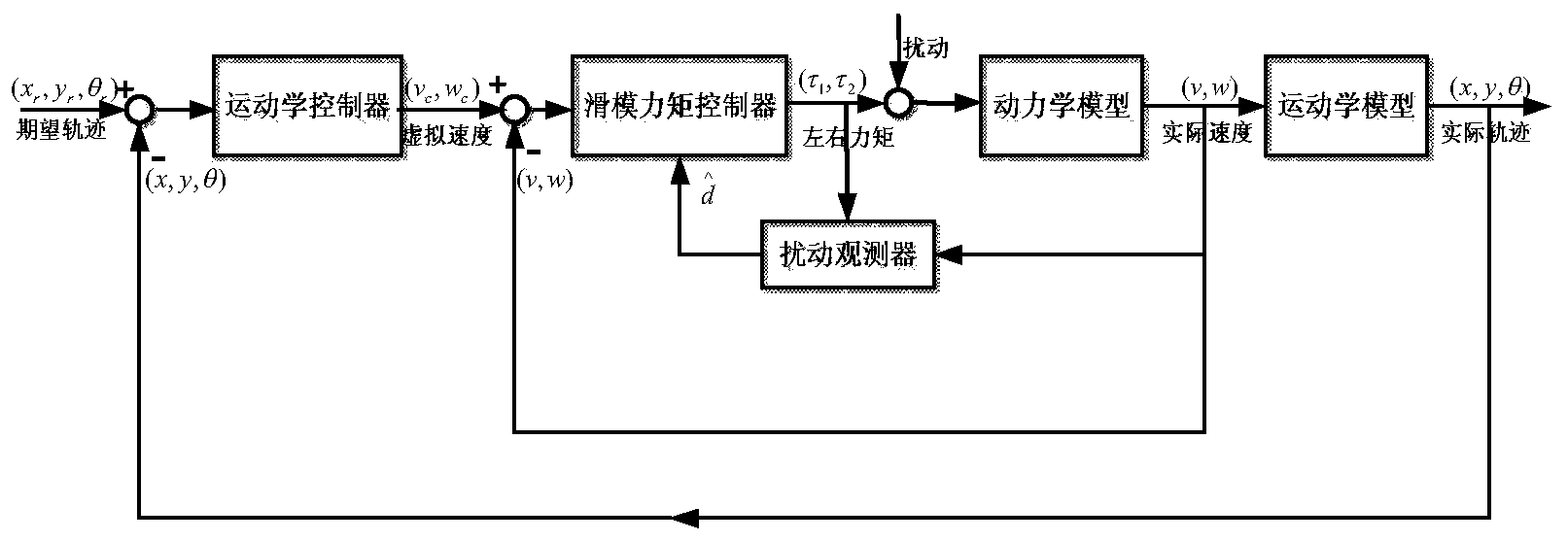
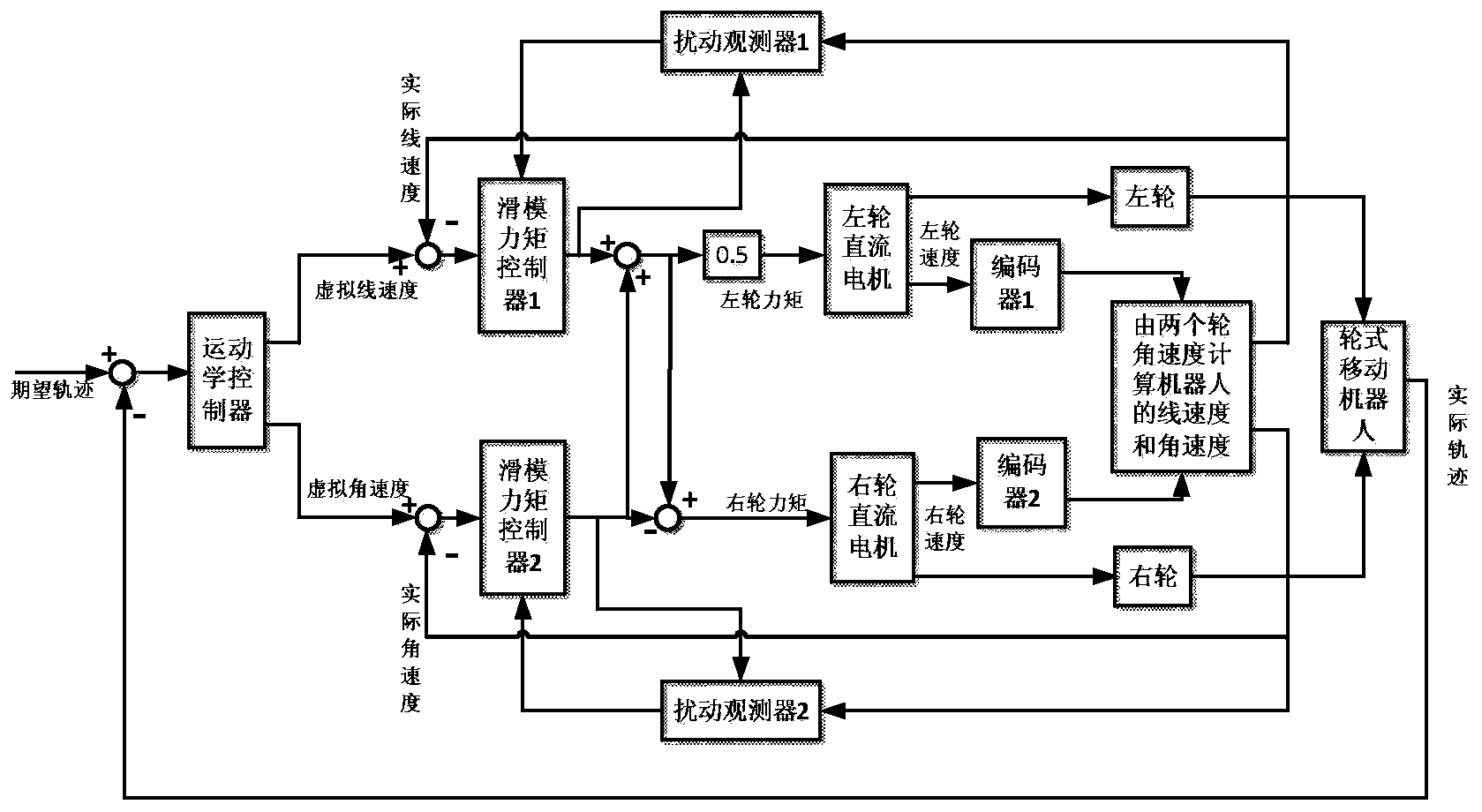
The invention discloses a mixed control method based on trace tracking of a wheeled mobile robot. A kinematic virtual velocity controller, a sliding mode torque controller and a disturbance observer are involved in the mixed control method, wherein the sliding mode torque controller and the disturbance observer are based on dynamics. The virtual velocity controller is used for designing the linear velocity and the angular velocity of the robot; the sliding mode torque controller is used for designing a sliding mode face and a sliding mode control law, and the disturbance observer is used for observation of the external disturbance of a system to reduce the control quantity of the sliding mode controller and is introduced as a feedforward term. By means of the mixed control method, control over the trace tracking of the robot is achieved by the system under the condition that external change and external disturbance happen to a parameter. It is shown upon simulation experiments that by means of the mixed control method, chatter output by sliding mode control and output of the control quantity can be effectively reduced, and good robustness is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
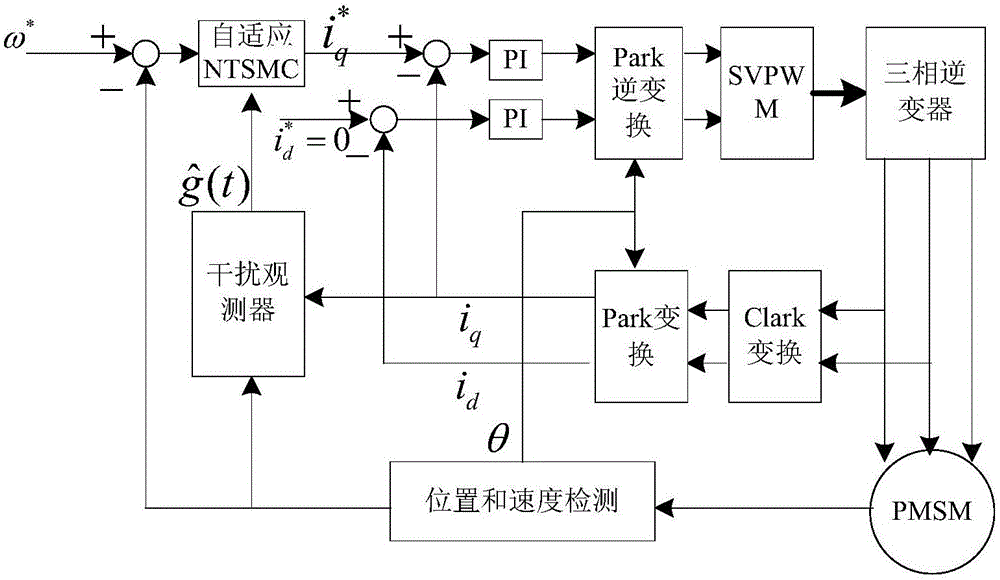
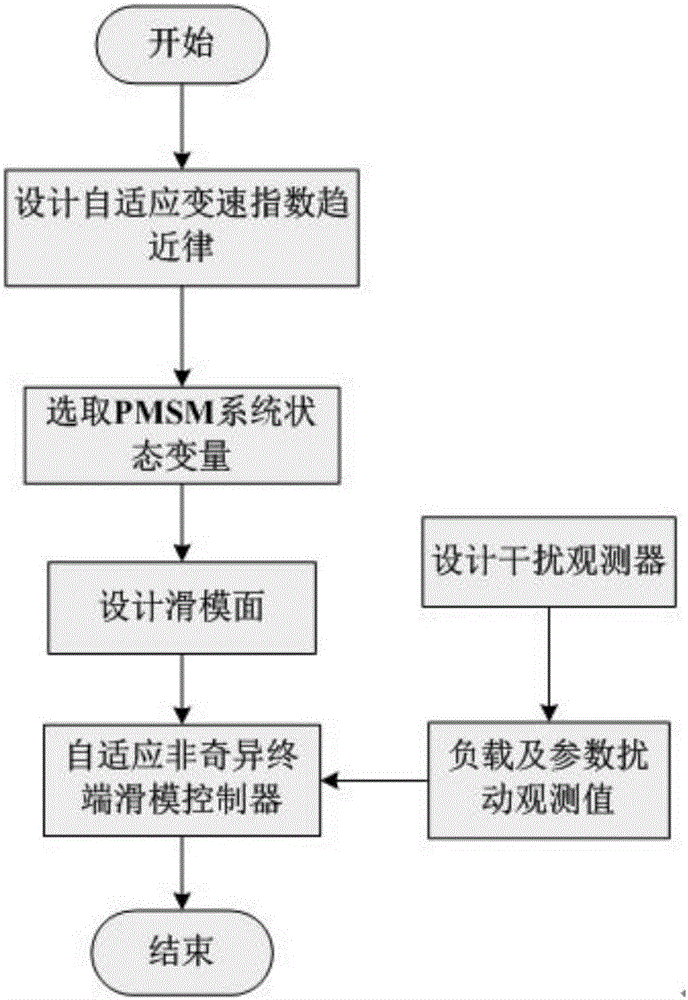
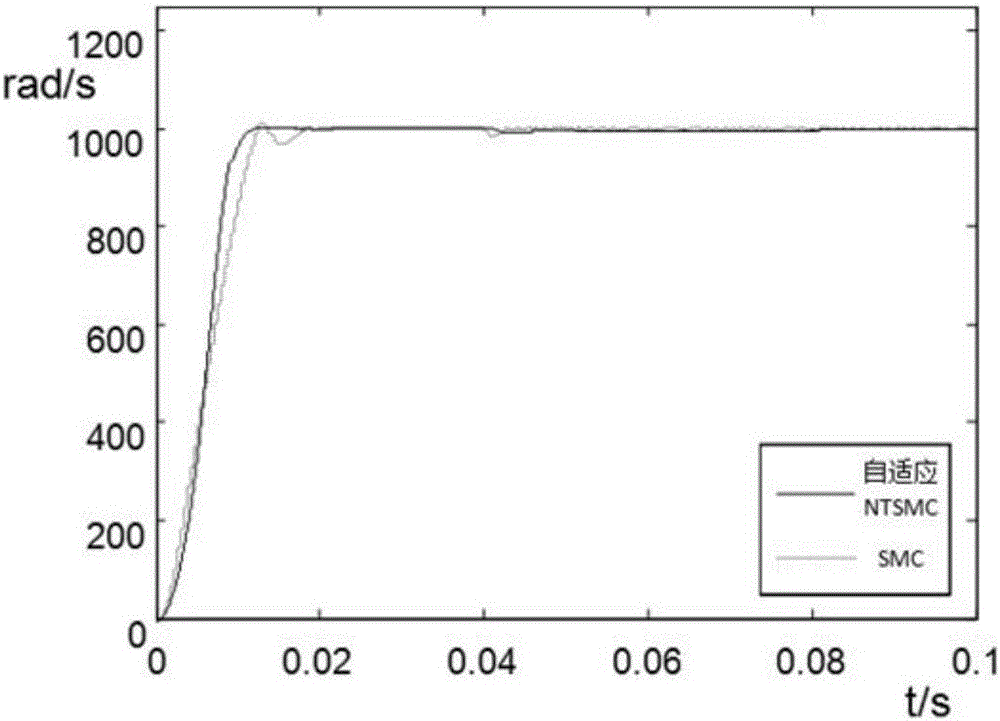
Adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding model control method for permanent magnet synchronous motors on basis of disturbance observers
InactiveCN106788044AImprove global fast convergenceShorten the timeElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorControl system
The invention relates to an adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding model control method for permanent magnet synchronous motors on the basis of disturbance observers. An adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding model controller is introduced into speed loops of vector control systems for the permanent magnet synchronous motors. The adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding model control method is characterized in that an adaptive variable-speed exponential approach law is proposed, first-order norms of state variables are introduced into the approach law, index approach speeds and constant approach speeds are adaptively adjusted according to the distances from the state variables to balance points, accordingly, the approach time can be shortened, and system buffeting can be weakened; the disturbance observers are designed for solving the problems of external disturbance of existing systems and load perturbation, and observation values are fed into designs of the sliding mode controllers. Rotational speeds can be quickly tracked when the systems are disturbed or load fluctuates, accordingly, overshoot and steady-state static difference of the systems can be reduced, and the robustness of the systems can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
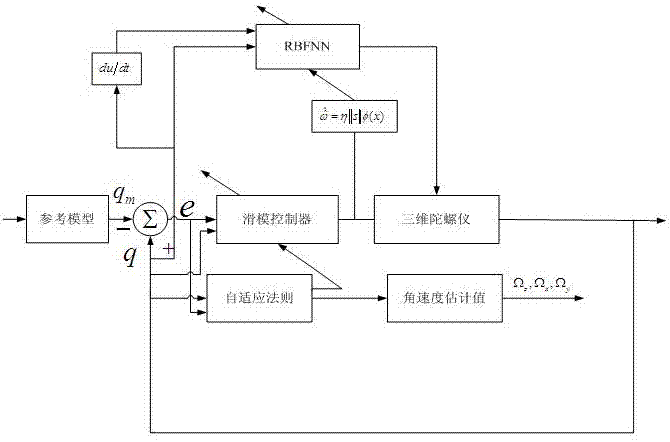
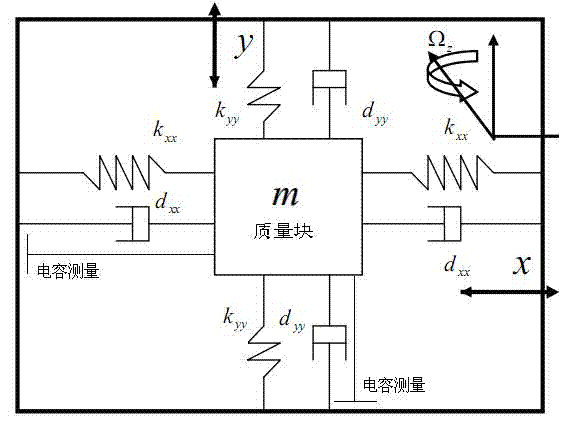
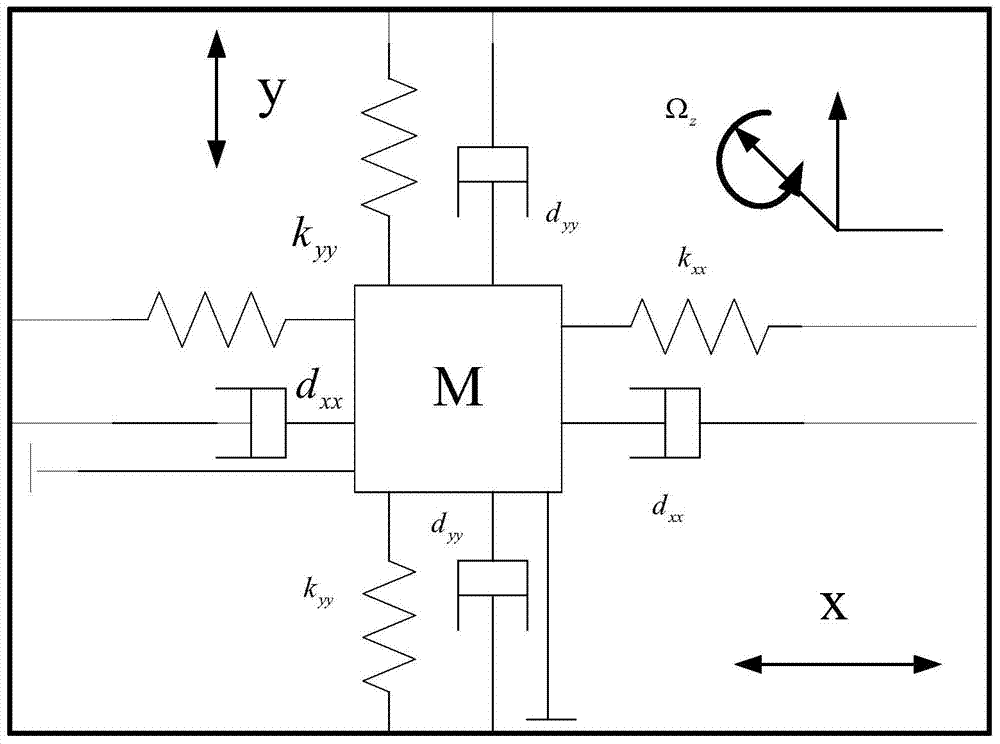
Adaptive control system based on radial basis function (RBF) neural network sliding mode control for micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) gyroscope
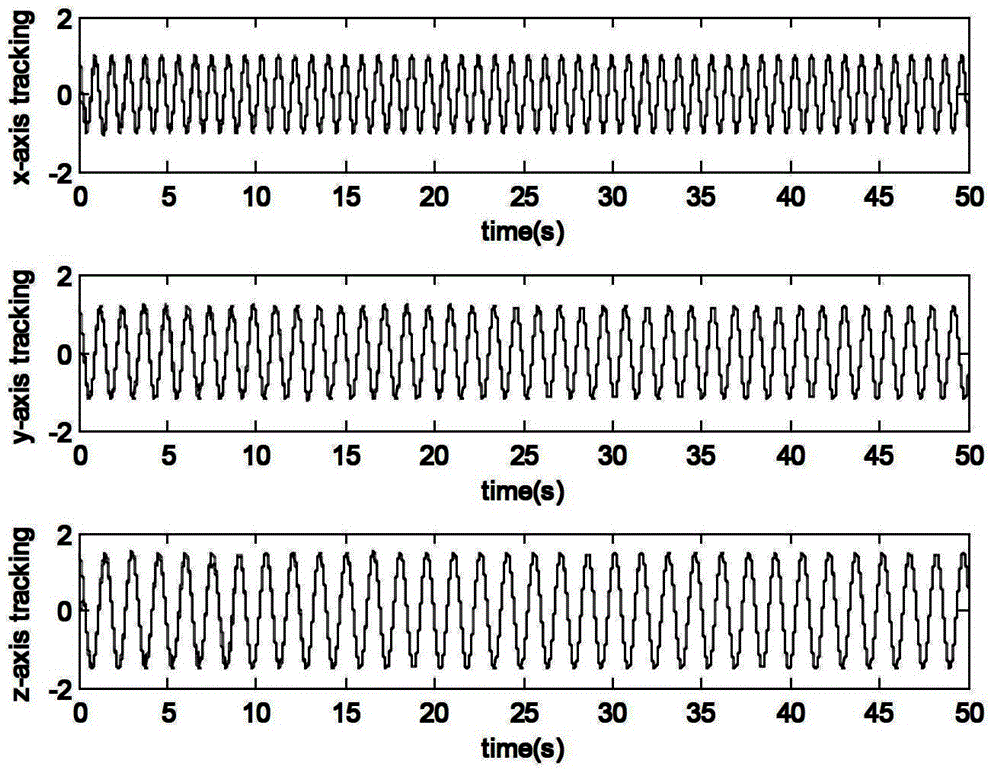
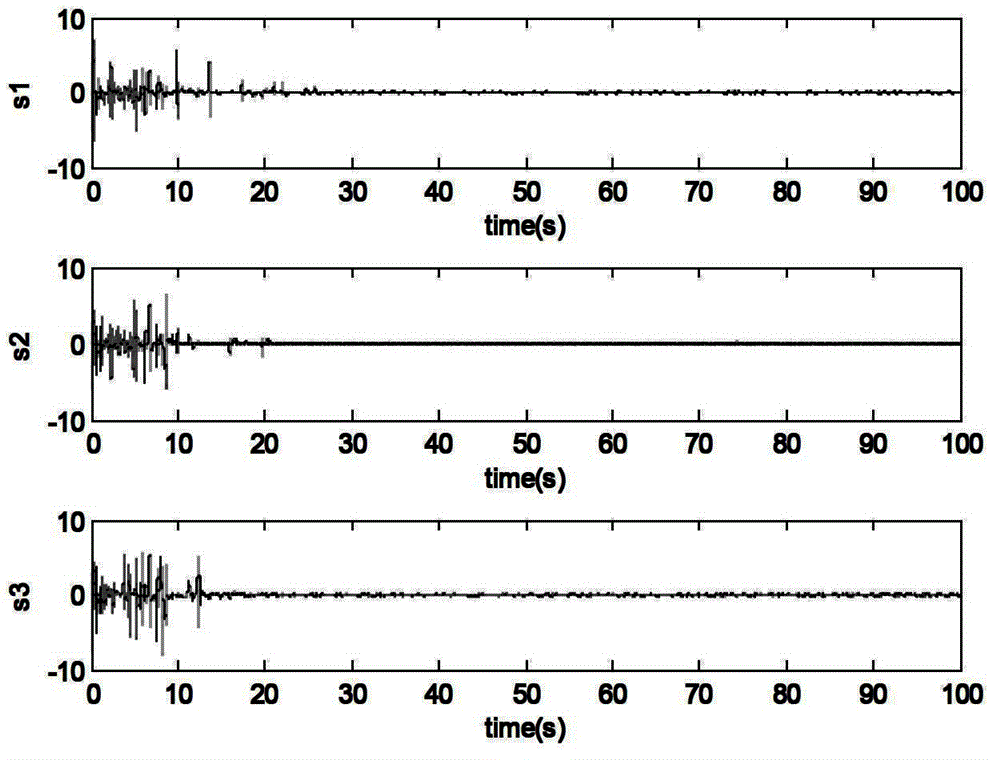
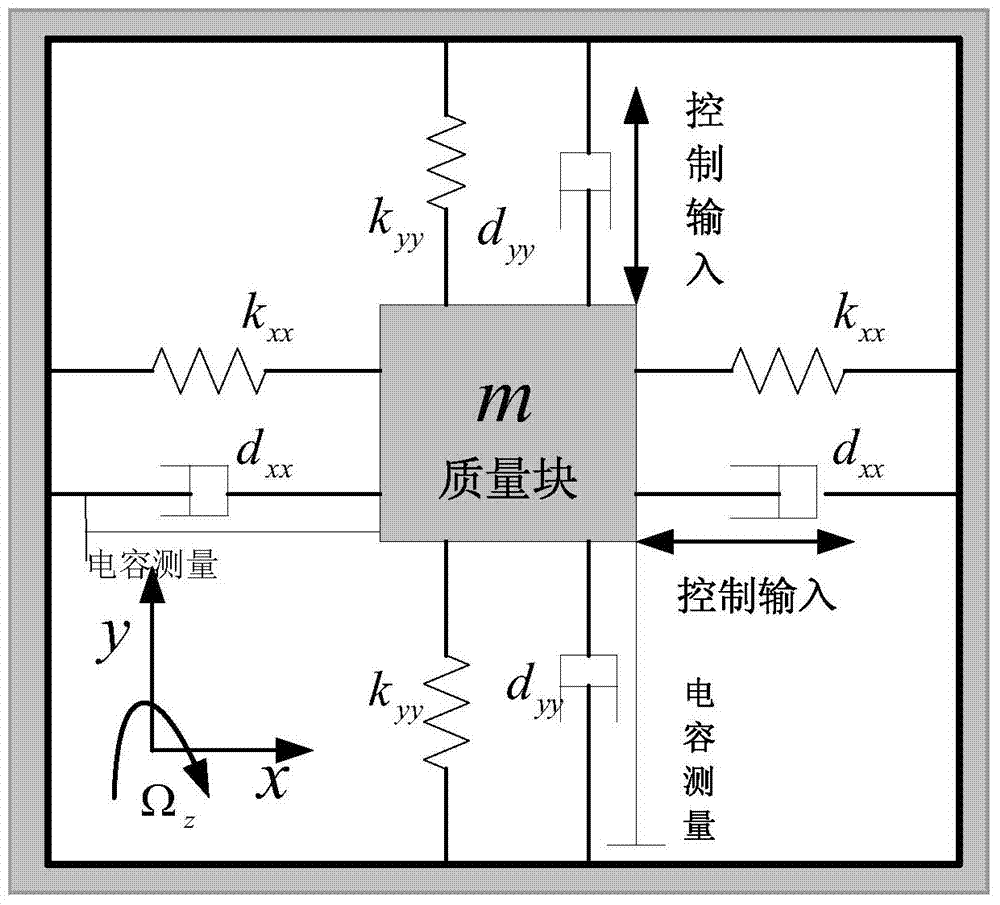
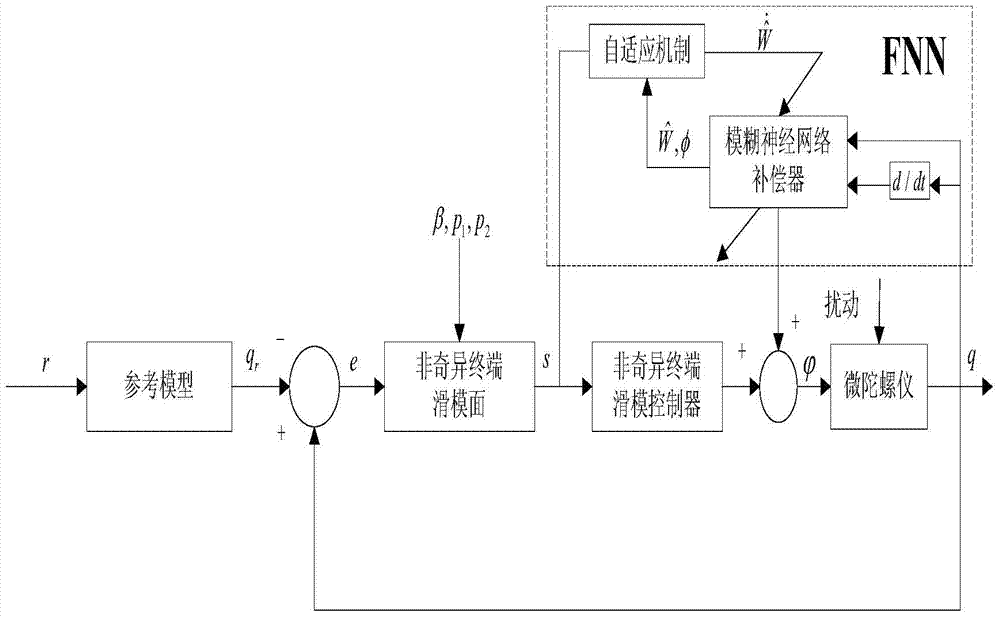
The invention discloses an adaptive control system based on a radial basis function (RBF) neural network sliding mode control for a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) gyroscope, and the system comprises a gyroscope and a control circuit, wherein the control circuit comprises a sliding mode controller and an RBF neural network; the difference of displacement of the three-axis gyroscope in the directions of three coordinate axes x, y and z and displacement of a reference model is taken as the input of the sliding mode controller. In the adaptive control system, an adaptive sliding mode control method is applied in controlling the gyroscope, so as to improve the stability and reliability of the system; and the RBF neural network is adopted to carry out adaptive learning on upper boundary of uncertain interference, thus reducing the influence of measurement error and external interference, effectively lowering the occurrence of buffeting, and achieving a better control effect.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
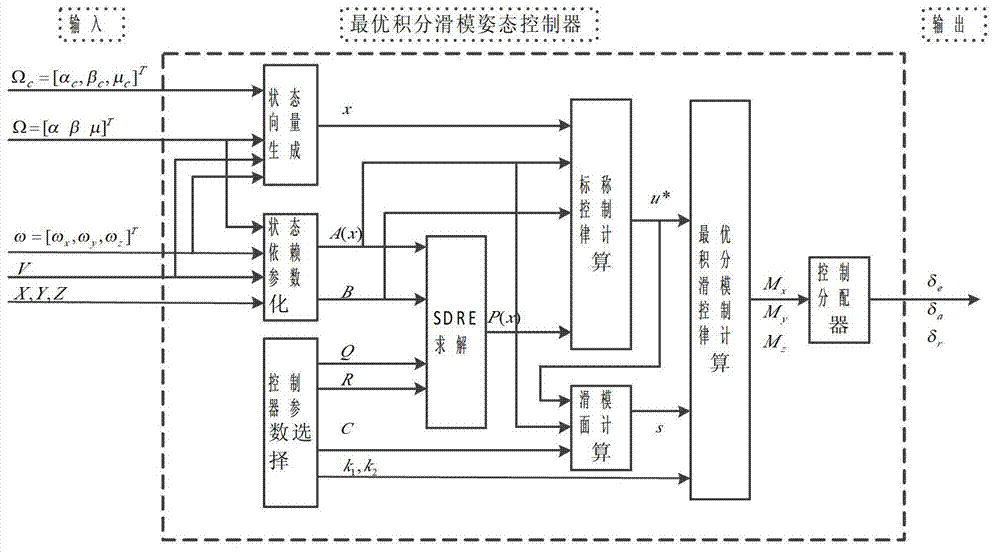
Optical-integral sliding-mode attitude control method of reentry vehicle and controller
InactiveCN102862686APreserve nonlinearityCompromise dynamic performanceGround installationsRiccati equationState dependent
The invention relates to an optical integral sliding-mode attitude control method of a reentry vehicle and a controller, and belongs to the technical field of vehicle control. The optical-integral sliding-mode attitude control method comprises the following steps of: firstly designing an SDRE (State-dependent Riccati Equation) nominal attitude control law according to a nominal model of the vehicle, and enabling the performance of a nominal system to meet the proposed optimal indexes; then considering the uncertainty of the system, designing an integral sliding-mode control law on the basis of the SDRE nominal attitude control law, enabling the system to have robustness while meeting the performance index requirement; and in order to weaken the buffeting, introducing a design idea of a second-order sliding mode and enabling the output of the controller to be smoother. The attitude controller designed by the invention not only can guarantee the expected indexes, but also has better robustness.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
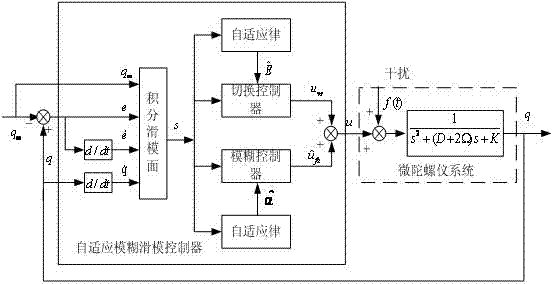
Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller for micro gyroscope
InactiveCN102508434AGuaranteed global asymptotic stabilityCompensate for manufacturing errorsAdaptive controlReference modelGyroscope
The invention discloses an adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller for a micro gyroscope, which is characterized by comprising an adaptive fuzzy control system based on a reference module, and a switching control system. In the adaptive fuzzy control system, a sliding mode surface is used as the input of the fuzzy controller, and the weight is automatically adjusted by a dynamic adaptive law so as to realize fuzzy approximation to an equivalent control law. The adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller for the micro gyroscope of the invention has the following benefits that: when the system is in a steady state, the dynamic performance of the micro gyroscope is an ideal mode, and the manufacturing error and the environment interference are compensated; an adaptive algorithm designed based on a Lyapunov method can ensure the global asymptotic stability of the whole closed-loop system; and with adaptive adjustment on the upper bound of the approximation error, buffeting is reduced obviously.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
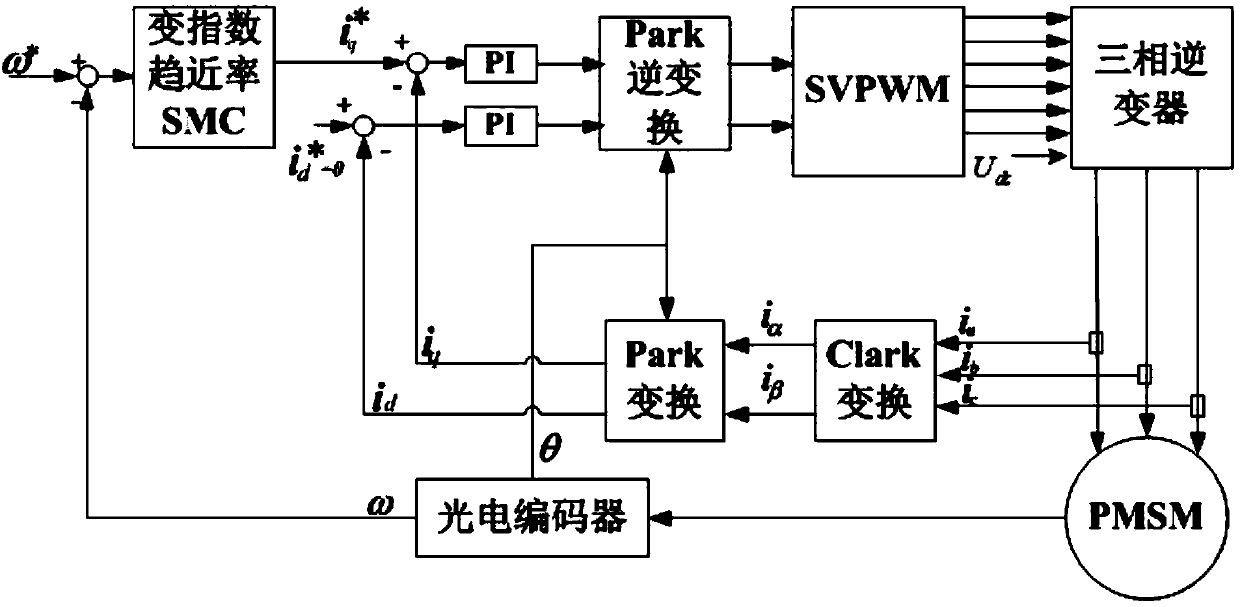
Permanent magnet synchronous motor control method
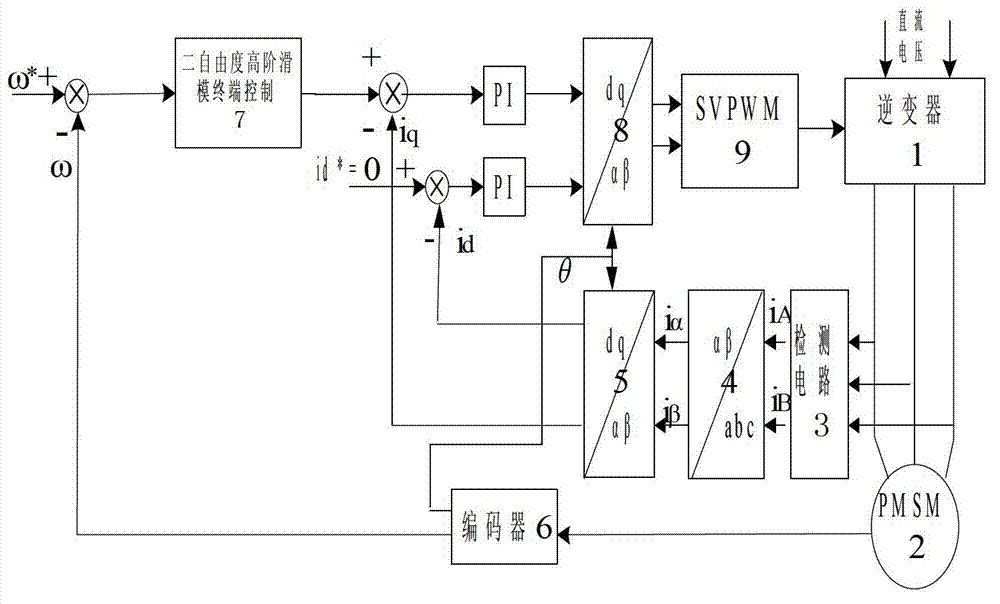
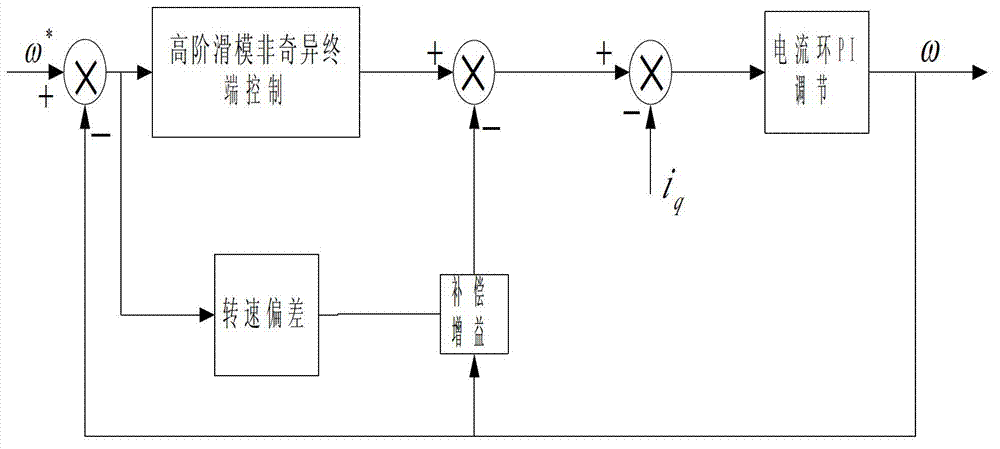
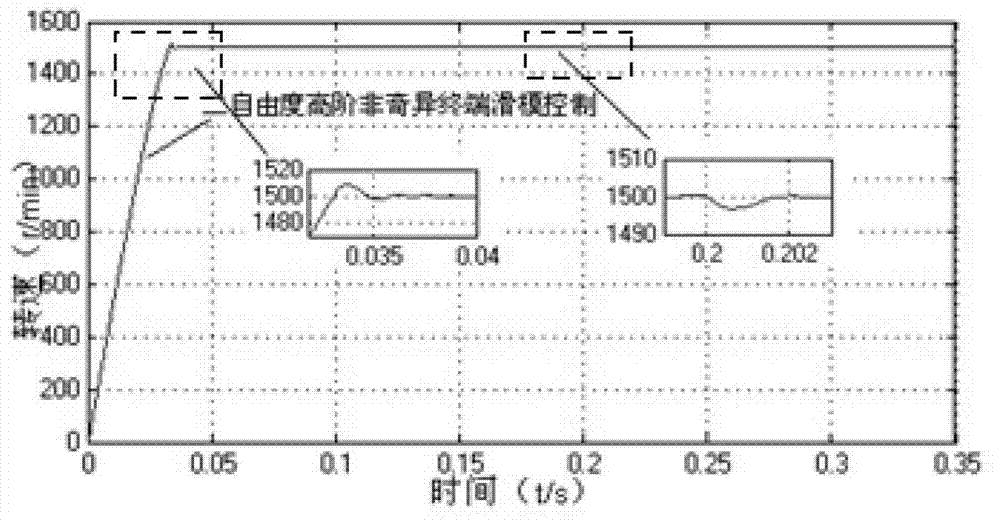
InactiveCN102969968AReduce buffetingHigh control precisionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl systemPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor control method in which a vector control system is used. The vector control system comprises an outer speed ring and an inner current ring, and a PI (proportional-integral) controller of a rotating speed ring is replaced with a two-DOF (degree of freedom) higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller; the input of the two-DOF higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is the difference between the given rotating speed w* of a motor and the actual feedback rotating speed w* of the motor; the error between the given rotating speed and the feedback rotating speed is judged, when the error of the rotating speed is less than Xi, an output exciting current iq* is calculated by a simple higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller; when the error of the rotating speed is greater than Xi, the output of the two-DOF higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is an output iq* controlled by a higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode and the sum of the output and compensation gain of the higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode; and the size of Xi can be set according to actual situations and needs. According to the method, the system control accuracy is improved and the rapid convergence of the rotating speed of the motor is realized; and the method has strong robustness on load disturbances.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
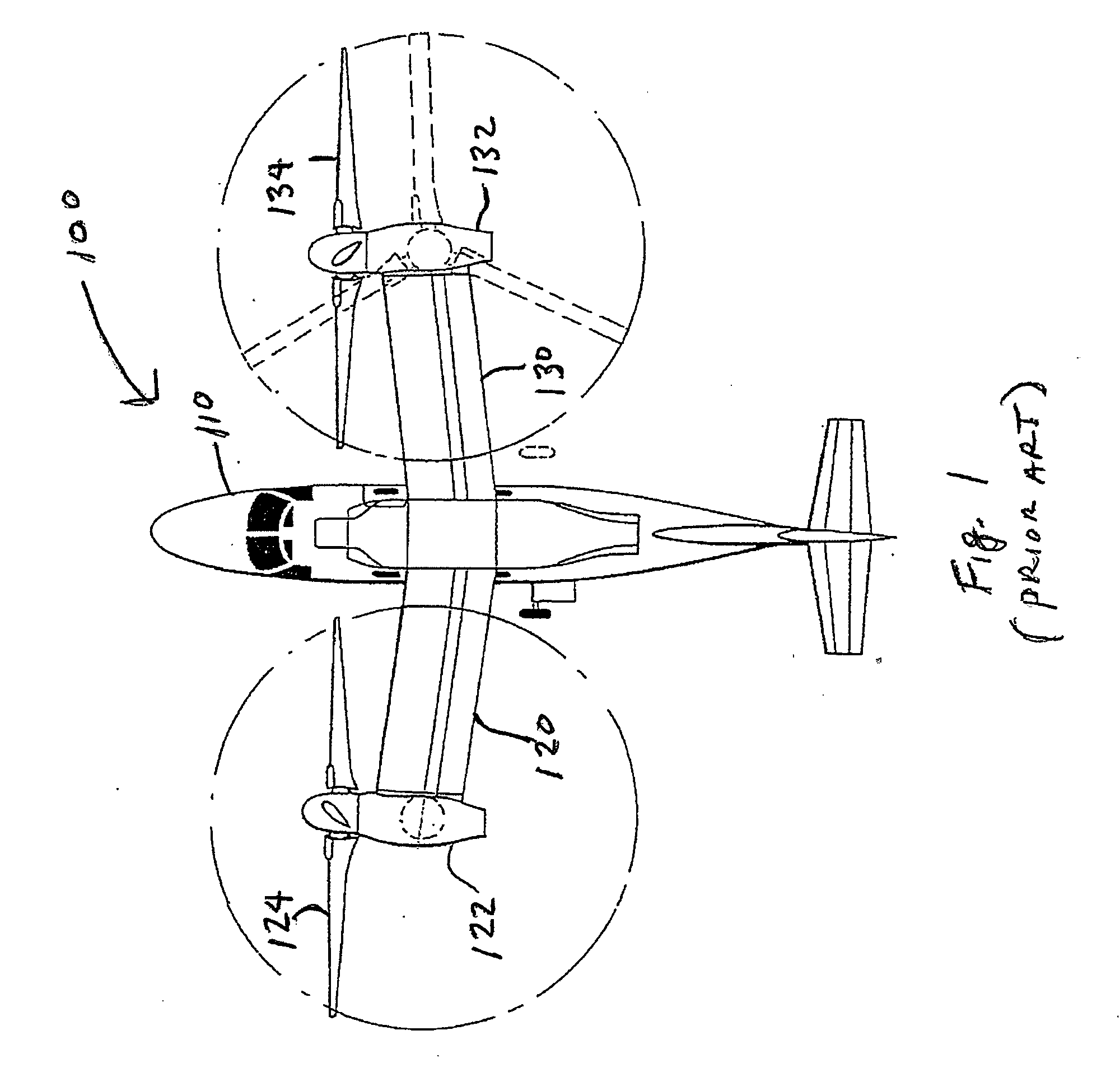
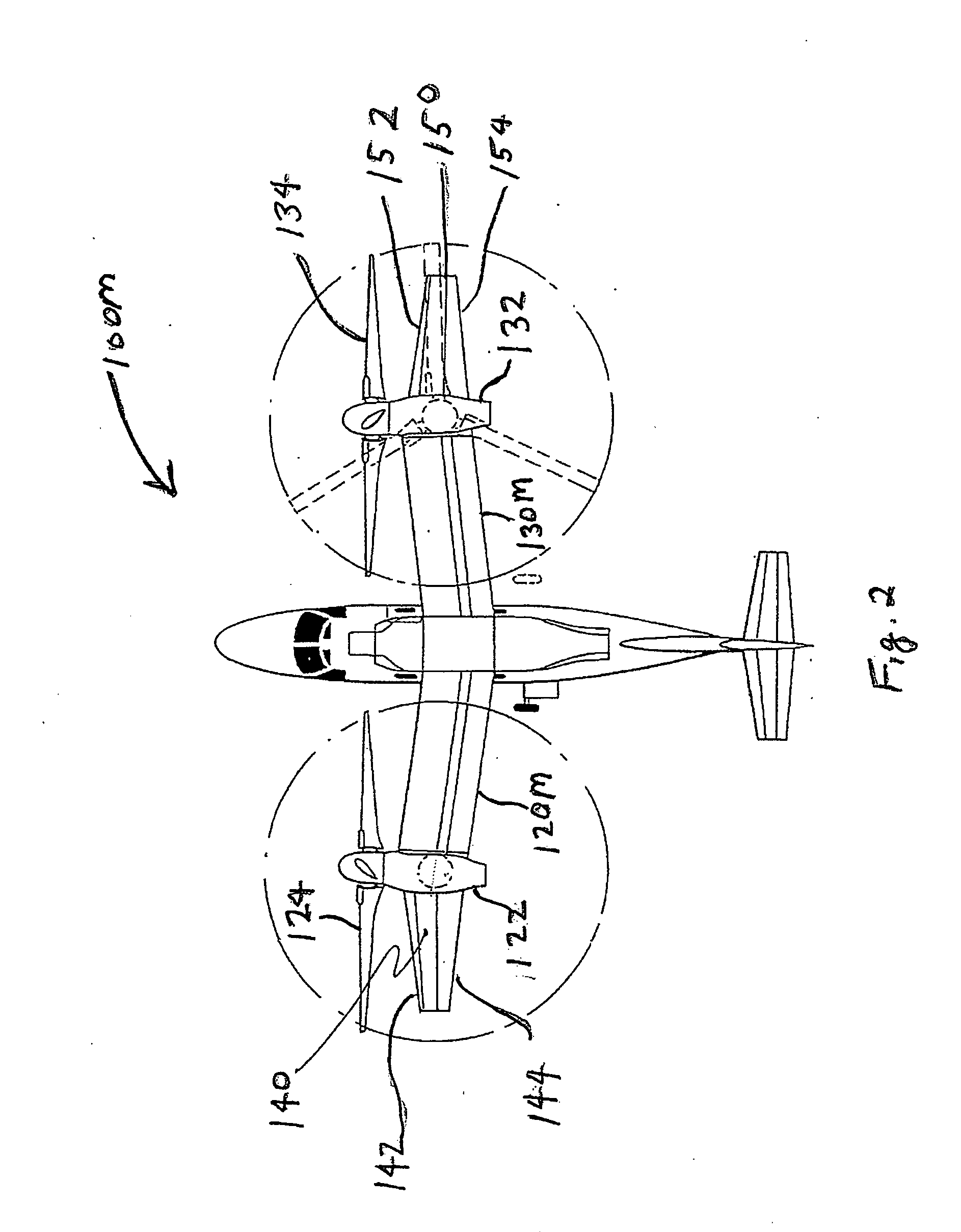
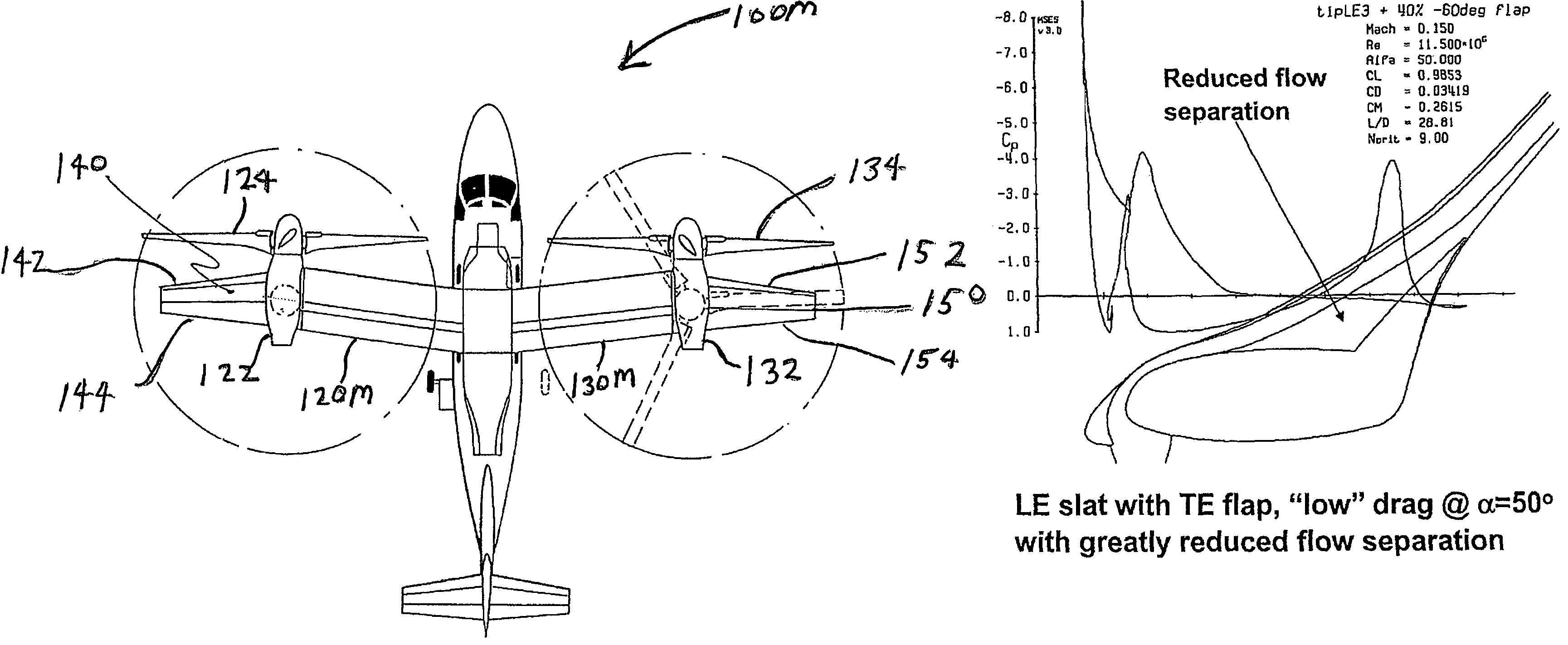
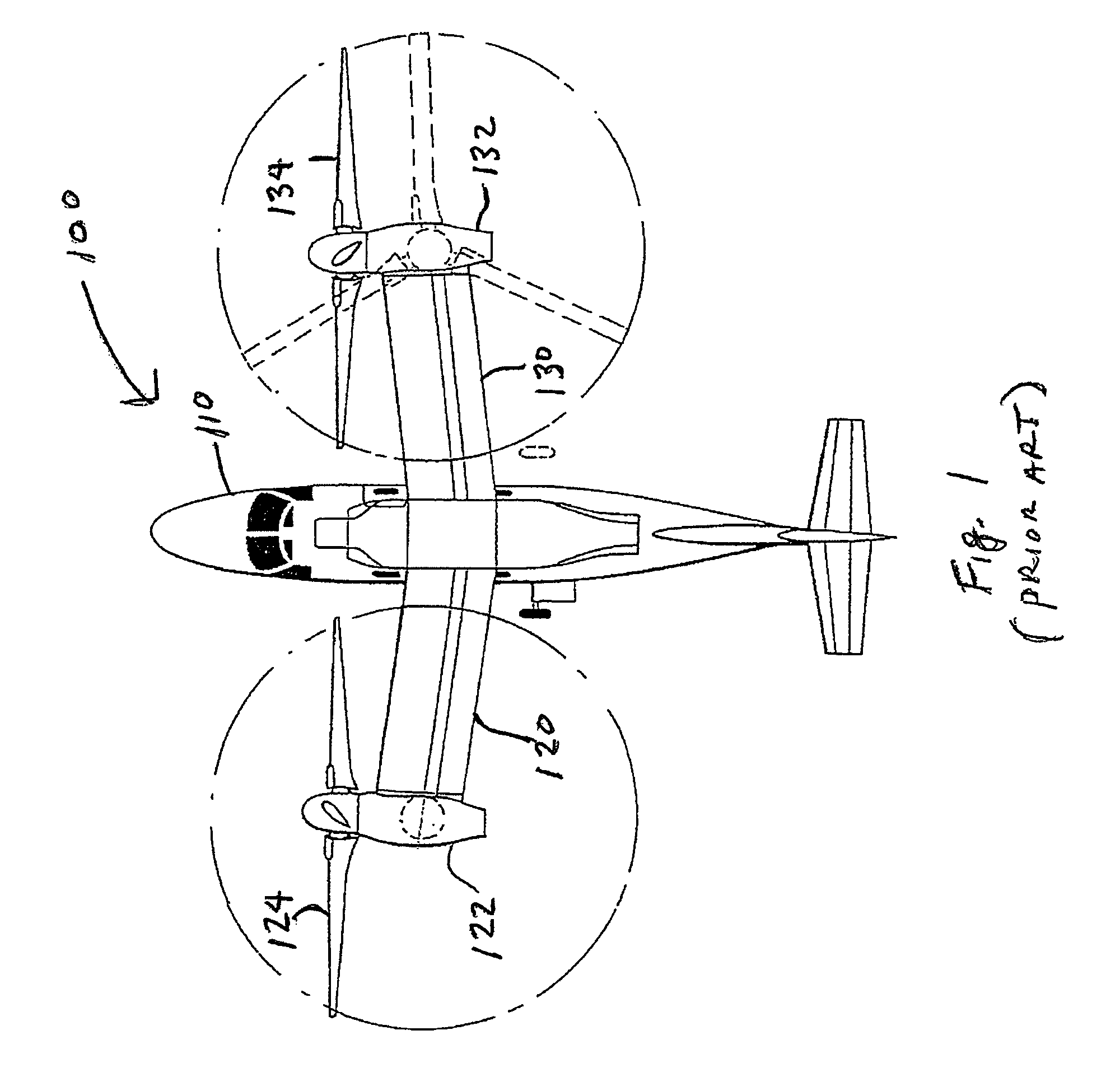
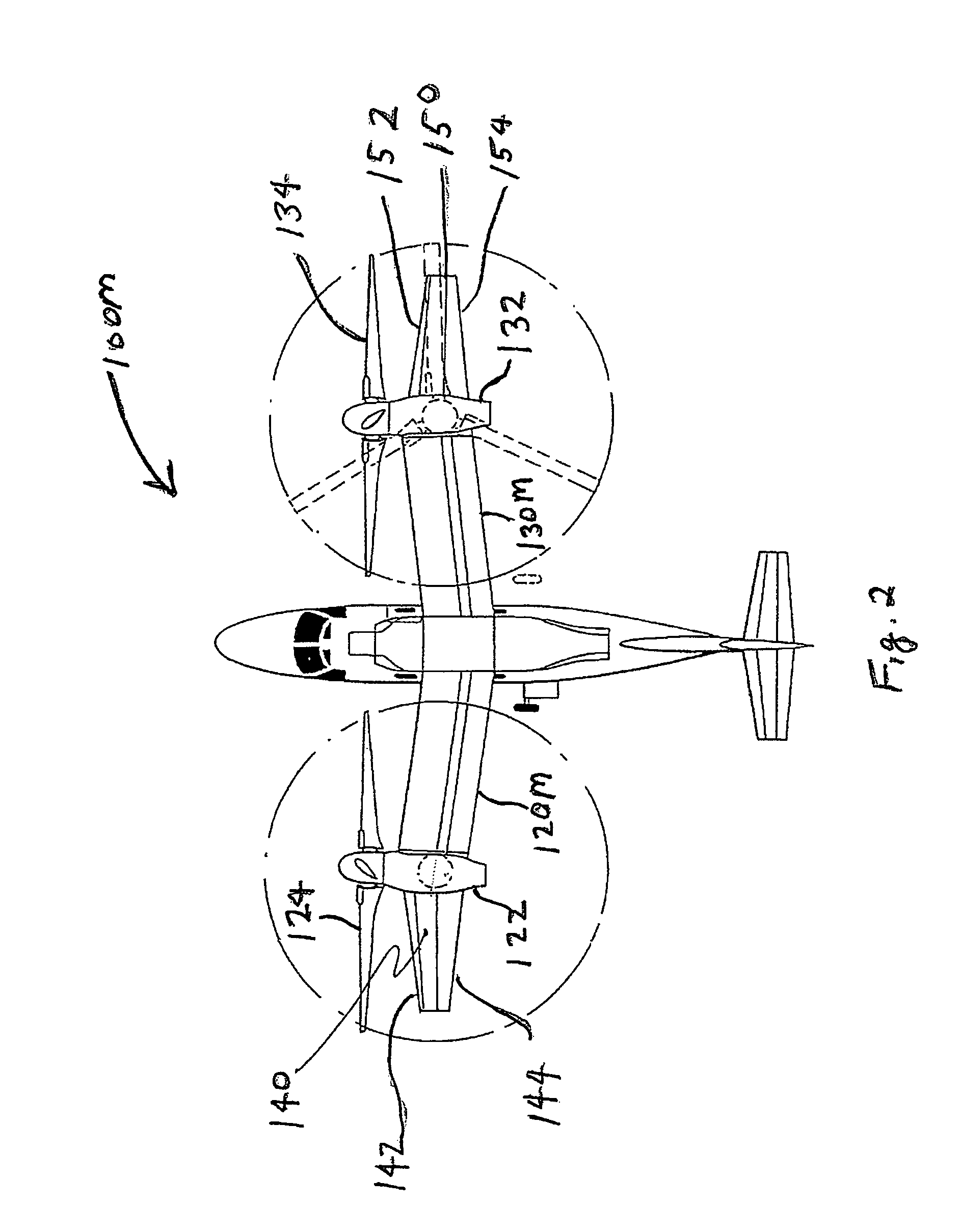
Tilt outboard wing for tilt rotor aircraft
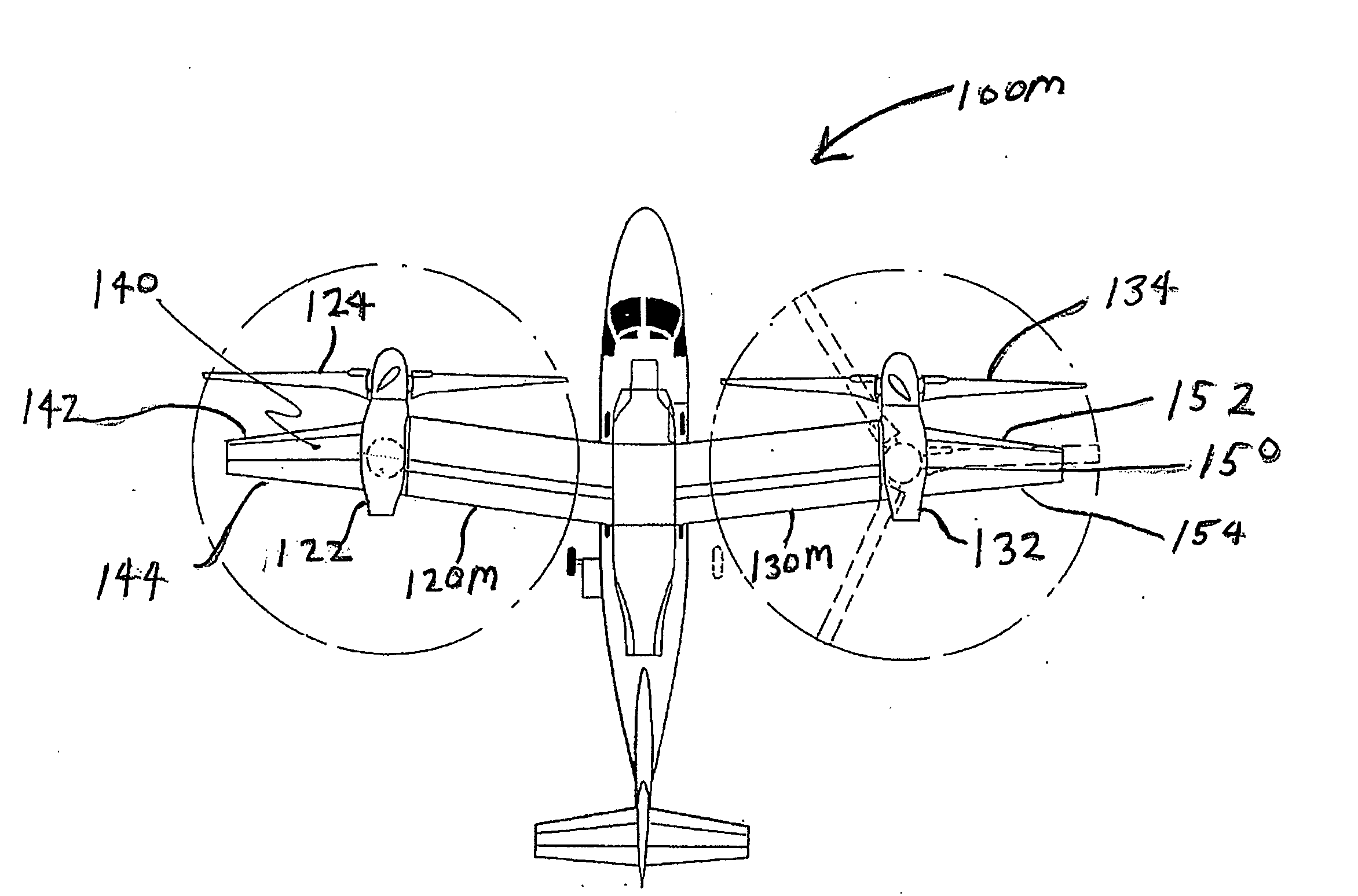
ActiveUS20090266942A1Increase in aircraft performanceImprove flight performanceAircraft navigation controlWing adjustmentsLeading-edge slatsAirplane
Tilt-rotor aircraft experience increased efficiency and fuel economy by including wing extensions outboard of the tilting nacelles. Stall and buffeting during conversion from rotor-born hover to wing-born forward flight are reduced to an acceptable level using wide chord flaps deflected upwards by at least 15-20°, preferably in combination with leading edge slats. The outboard wing or wing portion is preferably has a span at least 25-40% of a span of the inboard section, and a total surface area at least 10-20% the total surface area of the corresponding inboard section.
Owner:KAREM ABE
MEMS gyroscope robust self-adaptation control method based on neural network upper bound learning
InactiveCN104281056ACompensate for manufacturing errorsCompensate for interferenceAdaptive controlVibration amplitudeGyroscope
The invention discloses an MEMS gyroscope robust self-adaptation control method based on neural network upper bound learning. The method includes the following steps that an ideal kinetic model and an MEMS gyroscope kinetic model are established, a sliding mode function is designed, a control law is obtained based on the sliding mode function, and an RBF neural network upper bound estimated value is used as a gain of a robust item on the basis of the control law together with a feedback item and the robust item; a parameter self-adaptation law and a network weight self-adaptation law are designed based on a Lyapunov method. According to the MEMS gyroscope robust self-adaptation control method based on neural network upper bound learning, the feedback item is added in the control law, the two-shaft vibration trajectory tracking speed and the parameter estimation speed of an MEMS gyroscope are greatly increased, and the vibration amplitude is decreased; the robust item based on RBF neural network upper bound learning is added in the control law, the buffeting problem caused by large external disturbance and fluctuation and the problem that the dynamic characteristics are changed worse are solved, the uncertainty of a structural formula and the uncertainty of a non-structured formula are eliminated, and therefore the robustness of the system is further improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
PMSM control method and system based on sliding mode observation
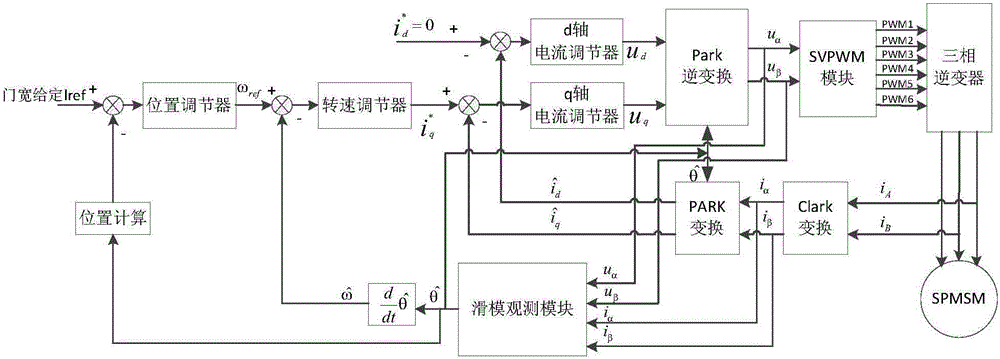
ActiveCN105827168AImprove responsivenessImprove stabilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorReference current
The invention discloses a PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor) control method and system. The PMSM control method and system are characterized in that a sliding mode observer for a load torque is designed in a PMSM vector control; compensation is performed by means of integration with slide mode control of a speed ring; redesign is performed on a speed controller; and at the same time, a relatively stable q-axis reference current can be obtained so that relatively ideal rotating speed and torque can be obtained. The PMSM control method and system can quickly and effectively adjust various input and output parameters of the PMSM when the system is interfered, and has the advantages of being high in the dynamic response speed and the robustness, and improving the control accuracy and operational reliability of the PMSM.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
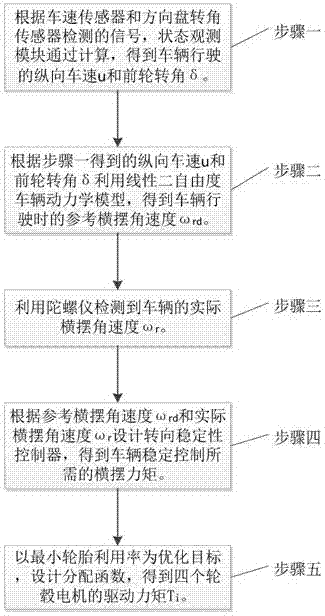
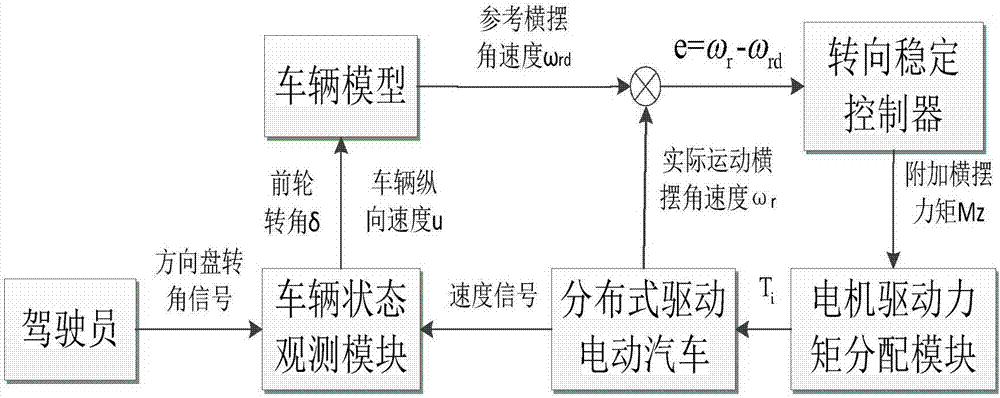
Method for controlling steering stability of distributed-drive electric vehicle
InactiveCN107415939AReduce buffetingShorten convergence timeSpeed controllerElectric devicesVehicle dynamicsGyroscope
The invention discloses a method for controlling steering stability of a distributed-drive electric vehicle. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1: according to signals detected by a vehicle speed sensor and a steering wheel angle sensor, obtaining a longitudinal vehicle speed u and a forewheel steering angle delta of a running vehicle through calculation of a state observation module; step 2: according to the longitudinal vehicle speed u and the forewheel steering angle delta obtained in the step 1, and obtaining a reference yaw rate omega rd of the running vehicle by a linear two-degree-of-freedom vehicle dynamic model; step 3: detecting an actual yaw rate omega r of the vehicle by using a gyroscope; step 4: according to the reference yaw rate omega rd and the actual yaw rate omega r, designing a steering stability controller and obtaining a yaw moment required by the steering stability control of the vehicle; and step 5: using the minimum tire utilization rate as an optimization objective, designing a distribution function and obtaining a driving torque Ti of four wheel hub motors. The phenomenon of ''chattering'' of a system is effectively suppressed, robustness is improved, and the steering stability of the distributed-drive electric vehicle is well controlled.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Tilt outboard wing for tilt rotor aircraft
ActiveUS7802754B2Little and no reduction in positive contributionHigh aspect ratioAircraft navigation controlWing adjustmentsRotary wingLeading-edge slats
Tilt-rotor aircraft experience increased efficiency and fuel economy by including wing extensions outboard of the tilting nacelles. Stall and buffeting during conversion from rotor-born hover to wing-born forward flight are reduced to an acceptable level using wide chord flaps deflected upwards by at least 15-20°, preferably in combination with leading edge slats. The outboard wing or wing portion preferably has a span at least 25-40% of a span of the inboard section, and a total surface area at least 10-20% the total surface area of the corresponding inboard section.
Owner:KAREM ABE
Sliding-mode variable structure control method of variable exponential coefficient reaching law of permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN106549616AIncrease approach speedReduce buffetingElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlState variableControl system
The invention discloses a sliding-mode variable structure control method of a variable exponential coefficient reaching law of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: aiming at the requirements of a control system of a high-performance permanent magnet synchronous motor, a variable exponential function term formula is introduced on the basis of a conventional exponential reaching law; the formula takes a first-order norm of systematic state variables as an exponent of exponential functions, adaptively adjusts the reaching speed of a variable exponent term and a variable speed term according to the distance between the system and a sliding-mode surface, and is helpful to increase the dynamic response speed of the system; the systematic state variables are associated by taking the first-order norm of the systematic state variables as the exponent of the functions; and an s function is introduced to replace a symbolic function for further suppressing system chattering. Therefore, the sliding-mode variable structure control method of the permanent magnet synchronous motor using the variable exponential coefficient reaching law is provided. Compared with an integral-type sliding-mode variable structure control method, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively increasing the dynamic characteristics and steady state characteristics of the system as well as increasing the robustness of the system.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Permanent magnet synchronous motor control method based on second-order terminal slip form
ActiveCN109560736ADecrease the value of switching gainSolve the problem of excessive speed changeElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlVoltage vectorLoad torque
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor control method based on a second-order terminal slip form. The method comprises the following steps that: S1: under a rotator coordinate system, obtaining dq shaft current id and iq; S2: obtaining a q shaft current given value iq'; S3: obtaining a load torque observation value; S4: after compensation, obtaining a q haft current given value iq<*>; S5: obtaining input voltage u[Alpha] and u[Beta] under an [Alpha] [Beta] coordinate system; and S6: adopting a space voltage vector pulse width modulation technology to convert the u[Alpha]and the u[Beta] obtained in S5 into an on-off signal used for controlling a three-phase inverter power device, and finally, driving the permanent magnet synchronous motor to operate. By use of the method, a current loop controller adopts a dead-beat controller, a speed loop adopts a two-order terminal slip form controller to realize the high-accuracy control of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, and therefore, the problem that the speed change range of the permanent magnet synchronous motor with small rotational inertia is large during load mutation or given revolving speed mutation can be solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Adaptive second-order terminal sliding-mode control system and method of permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
InactiveCN104917436ALimitations of Overcoming Uncertainty Bounds to DetermineOvercome limitationsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsRobustificationControl system
The invention relates to an adaptive second-order terminal sliding-mode control system and method. On the basis of comparison of a given speed signal and a feedback speed signal of a servo system of a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor, an error amount is obtained; a terminal sliding mode surface is designed based on the error amount and a super-coiling algorithm controlled by the second-order sliding mode is used for realizing the input of a speed controller; and an adaptive control way is introduced to carry out dynamic adjustment on a control gain of the super-coiling algorithm. Therefore, the rapid response of the system is realized; and the system robustness is improved. With the control method, the system can have the high robustness and the system buffeting can be weakened effectively.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Power-reaching-law-based sliding-mode controlled magnetic suspension train system control method
The invention relates to a power-reaching-law-based sliding-mode controlled magnetic suspension train system control method. Based on a single magnet structure magnetic suspension system model, and onthe basis of performing linearization on the input and output relation, the power-reaching-law-based sliding-mode controlled magnetic suspension train system control method analyzes the control relation of the application of sliding-mode control of the power reaching law in the single magnet structure magnetic suspension system, and utilizes a Lyapunov stability theory to analyze the stability ofthe method. The Matlab simulation result shows that compared with traditional sliding-mode control, the sliding-mode control of the power reaching law has better control performance, and has the advantages of significantly weakening buffeting, being smaller in the positional signal error, being better in dynamic characteristic, and being higher in robustness.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Whole-speed range control method of position sensor of elevator door motor
InactiveCN104601072AImprove anti-interference abilityLow costElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPower flowLow speed
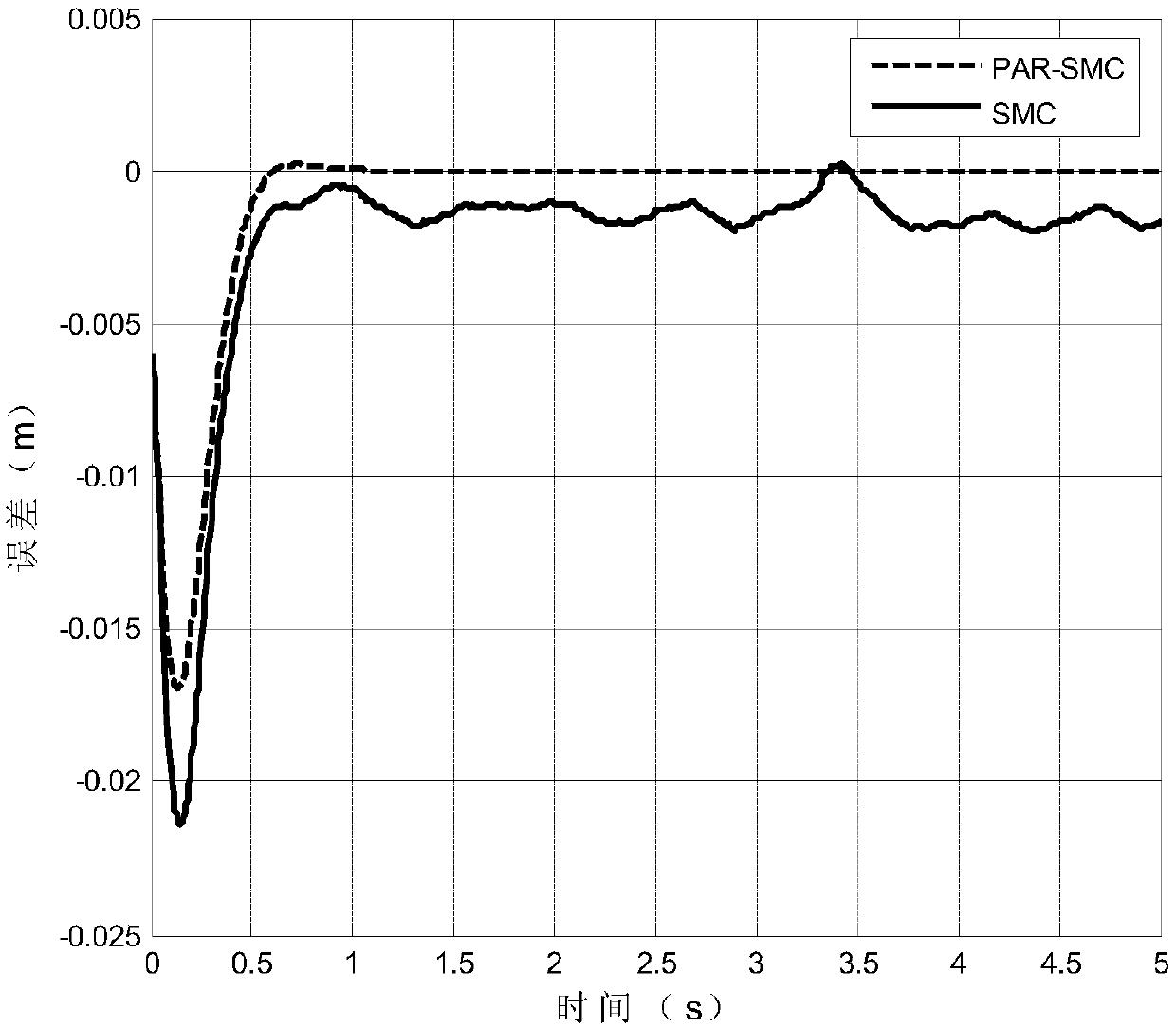
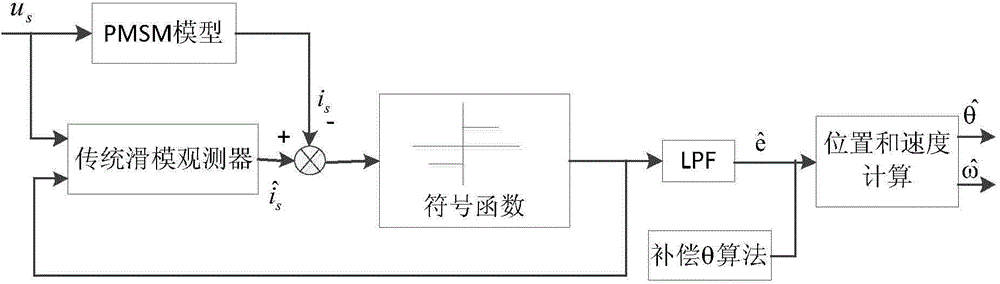
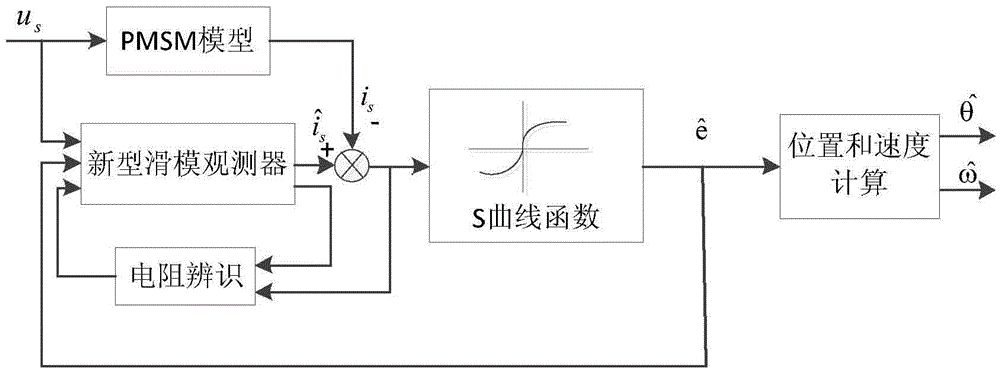
The invention discloses a whole-speed range control method of a position sensor of an elevator door motor. The method comprises the steps of injecting high-frequency pulse-vibrating current signals in an estimation coordinate system through a current closed-loop control in a scope of zero speed and under-speed, extracting information relevant to position errors to track the position and low-speed rotating speed of a rotor of the elevator door motor, and then using a variable gain S curve function and a novel sliding-mode observer to realize no sensor control in the high-speed scope. By adopting a weighting algorithm to complete smooth switching between low and high speed scopes. According to the no-sensor control in the whole speed scope of the door motor can be realized finally, and the mounting difficulty of the process installation of the door-motor system can be reduced; furthermore, the method has the advantages of wide scope of application, strong capacity of resisting disturbance, low cost and the like.
Owner:宁波申菱机电科技股份有限公司
Terminal sliding mode manipulator trajectory tracking method based on fractional order power reaching law
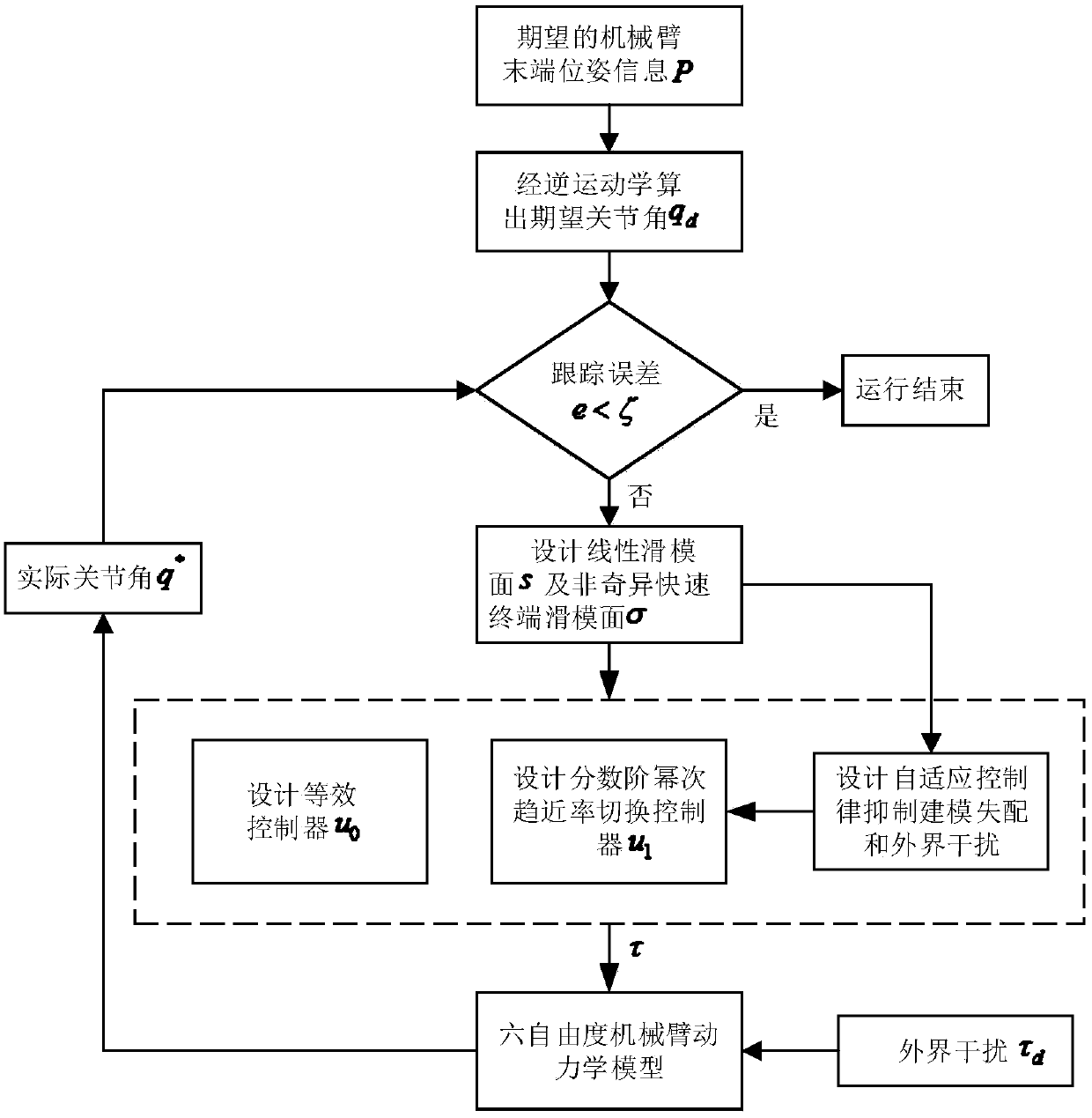
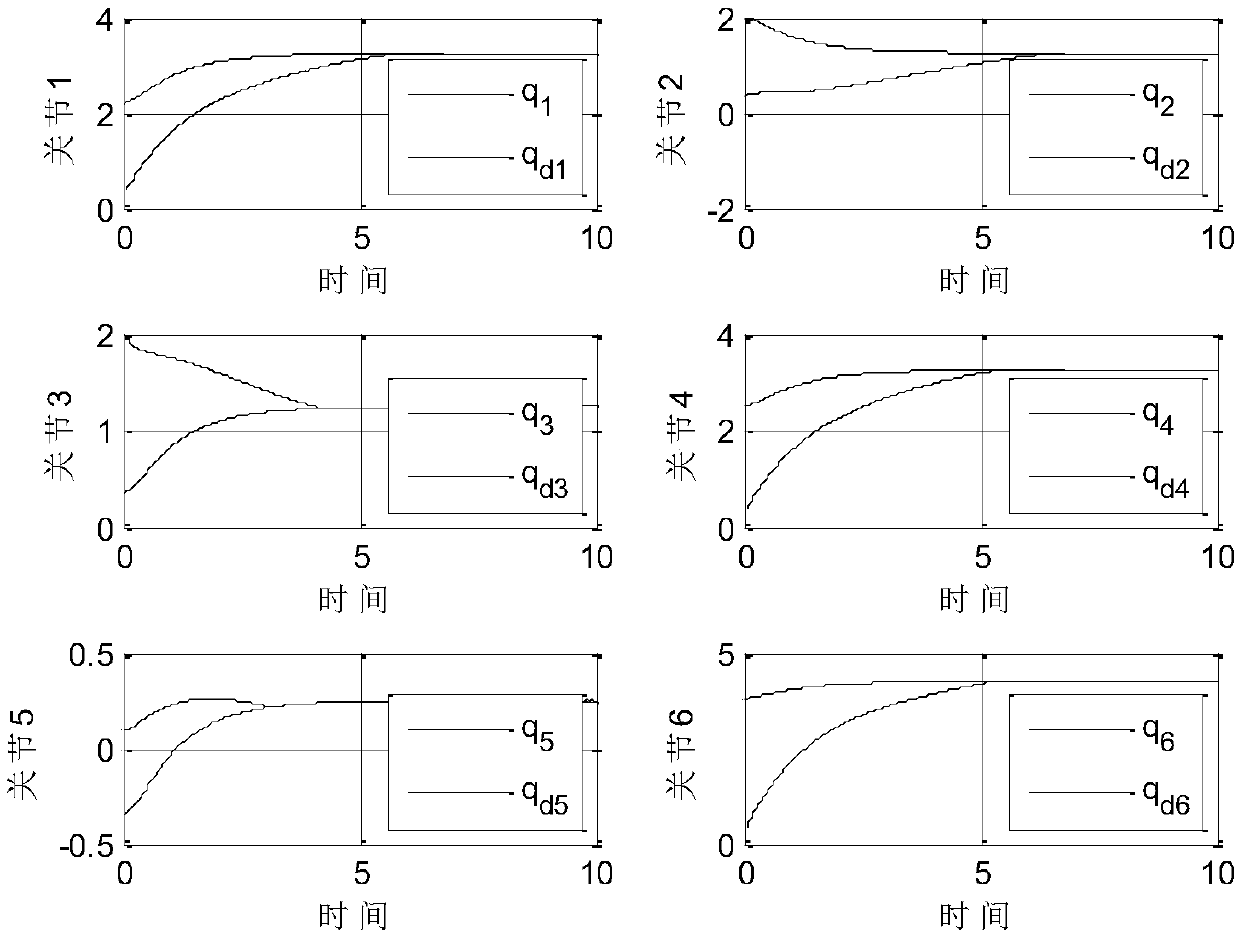
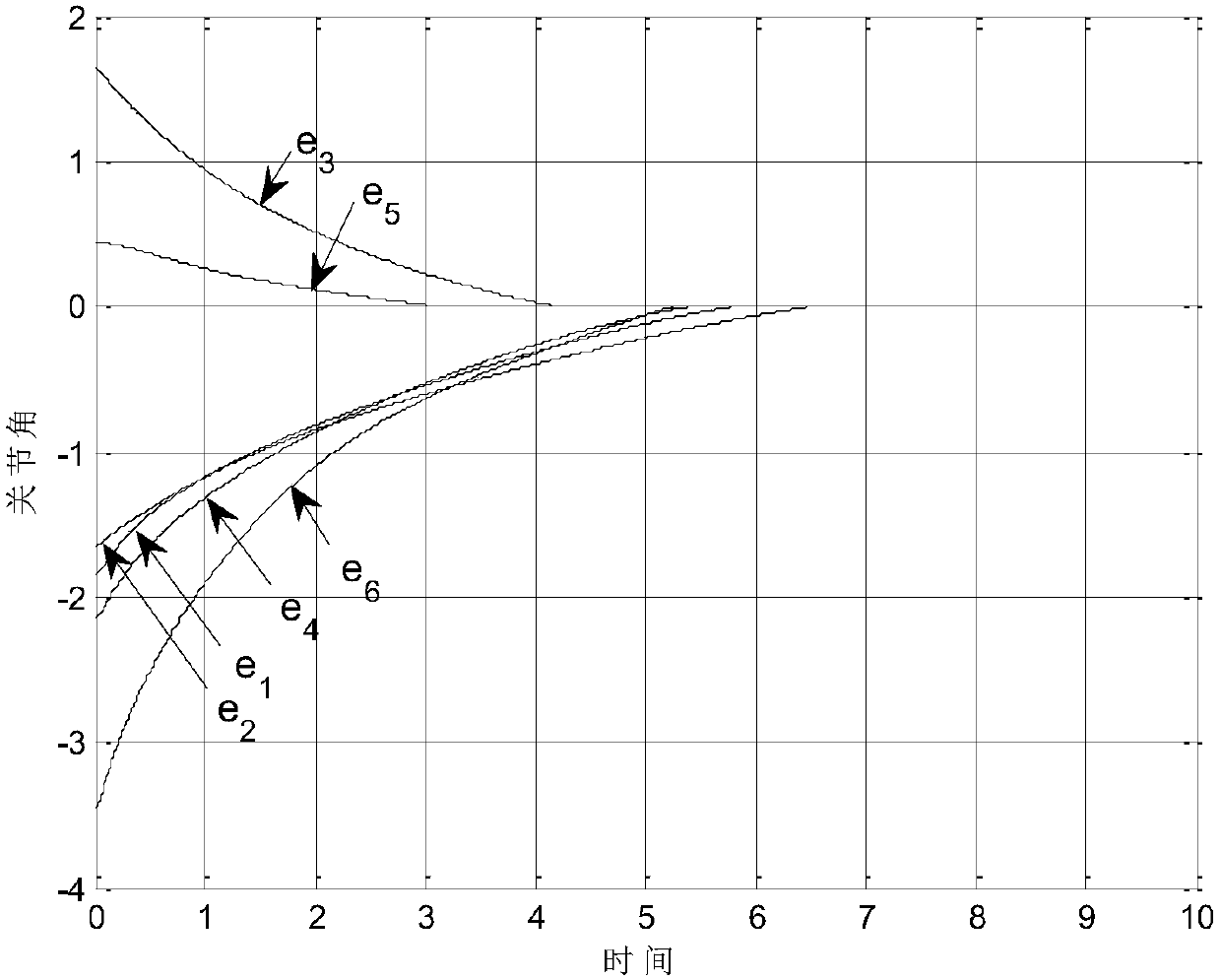
The invention discloses a terminal sliding mode manipulator trajectory tracking method based on fractional order power reaching law. By designing adaptive rate to an upper bound of uncertainty and switching control of fractional order powder reaching, system state may be converged more quickly to a sliding mode surface; through sliding mode characteristics of a nonsingular quick terminal sliding mode surface, the system state is converged more quickly to a balance point within limited time, namely, a tracking error is converged to 0; therefore, tracking an expected joint angular trajectory isachieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
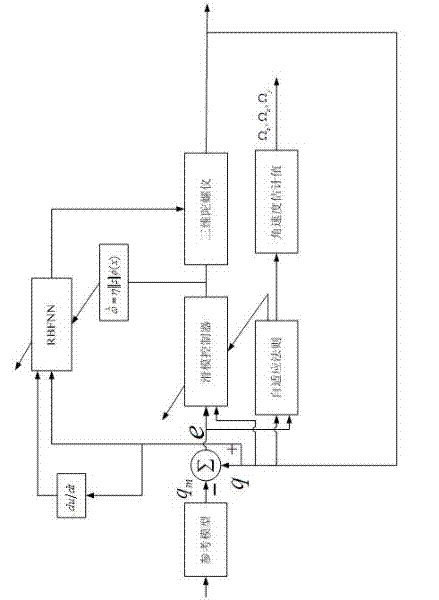
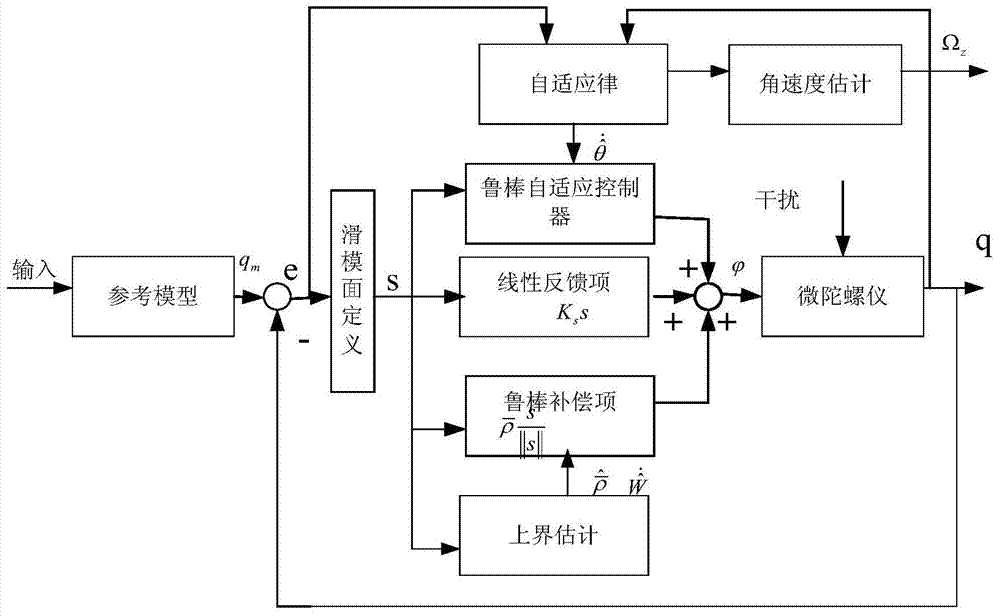
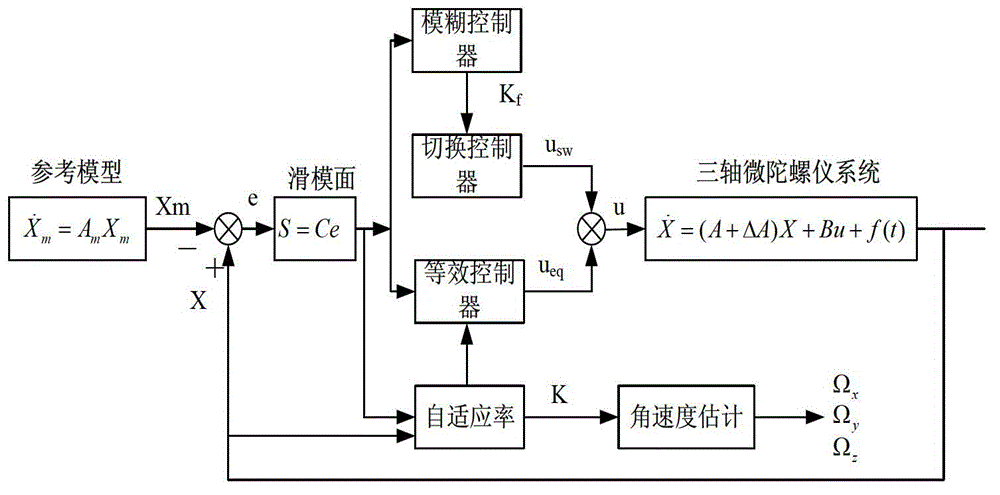
Angular velocity estimation based self-adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control method for micro gyroscope
InactiveCN103336435AReduce in quantityGuaranteed global asymptotic stabilityAdaptive controlGyroscopeControl system
The invention provides an angular velocity estimation based self-adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control method, applies the self-adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control method to a micro three-axis gyroscope control system, and can realize the trajectory tracking control and parameter estimation of a micro gyroscope system. According to the self-adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control method, a controller is designed on the basis the state-space equation of a micro gyroscope. Firstly, on the basis of the sliding mode controller, a novel self-adaptive identification method is designed, and the angular velocity of the micro gyroscope and the estimated valves of other systematic parameters are updated on line and in real time; besides, a fixed gain in a sliding mode control toggle item is adjusted by virtue of a self-adaptive fuzzy system, and fuzzy approximation is performed to the upper bound of the fixed gain, so that a chattering phenomenon arising in sliding mode control can be reduced. Through the adoption of the self-adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control method, a favorable tracking performance can be obtained, and the self-adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control method has robustness in parameter variation and external disturbance.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Self-adaption fuzzy neural compensating nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method of micro gyroscope
InactiveCN104122794AEnsuring Global Asymptotic StabilityImprove robustnessAdaptive controlLyapunov stabilityGyroscope
The invention discloses a self-adaption fuzzy neural compensating nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method of a micro gyroscope. The method mainly involves a nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller and a fuzzy neural network compensating controller; the designed nonsingular terminal sliding mode enables that a system can reach a sliding mode surface and a balance point within a limited time from any initial state, and therefore, the convergence rate and steady stacking precision of the system are improved; meanwhile, the fuzzy neural network compensates the parametric modeling error of the micro gyroscope and outside disturbance effect on line, in order to improve the tracking performance; the fuzzy neural network is practiced on line, the self-adaption learning algorithm of weight of the fuzzy neural is on the basis of the lyapunov stability theorem, which ensures the tracking performance and the stability of the whole control system. The simulation result shows that the method is able to improve the problem of trace tracking of the micro gyroscope and can also effectively inhibit the parameter uncertainty and the influence from the outside disturbance, and as a result, the robust tracking can be realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Transverse waveguide
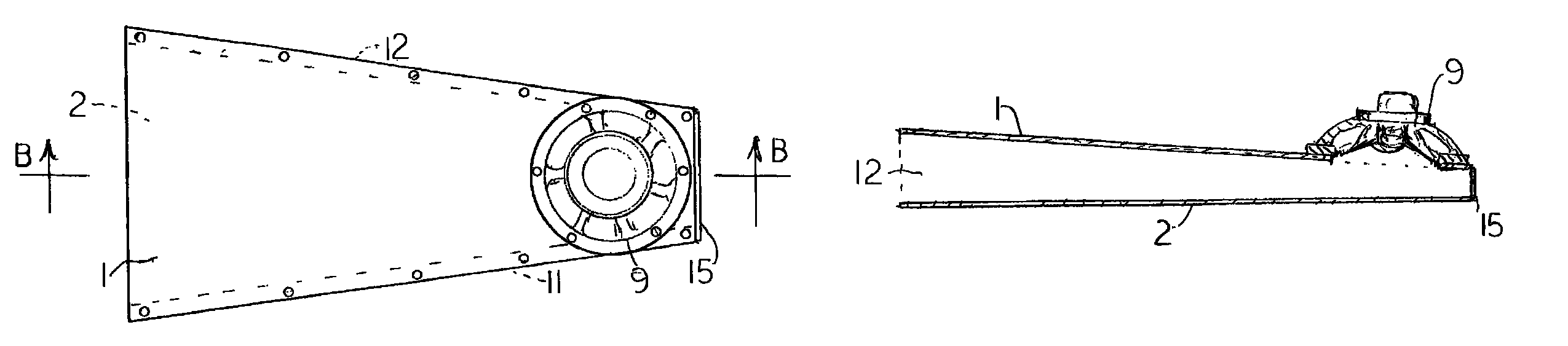
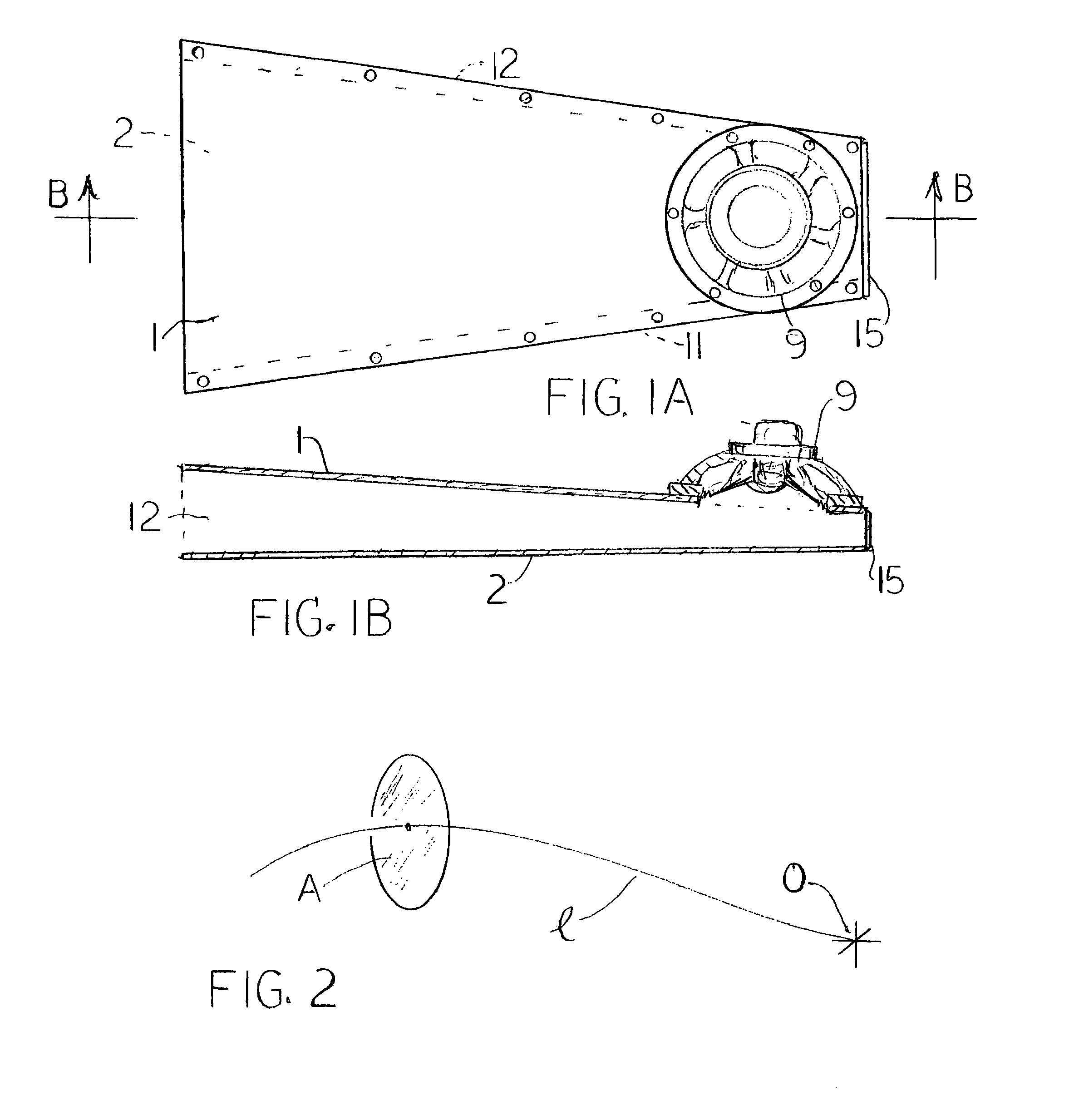
InactiveUS8066095B1Reduce buffetingHeat dissipationFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringAcoustic wave
A compact bass speaker cabinet uses a long, narrow, tapered waveguide that acts as does a small radial portion of the air outside a large pulsating sphere, and has the same bass response as the large pulsating sphere. The smaller end is closed and the longer end is open. In one embodiment the inside of the waveguide is a rectangle about an inch thick and substantially as wide as the speaker or speakers that are mounted on the wider surface close to or slightly overlapping the closed end; and the inside surfaces are tapered so that they meet at a point which lies beyond the closed end by a distance equal to the radian wavelength of the longest sound wave that is to be produced.
Owner:BROMER NICHOLAS SHEPPARD
Four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on nonsingular terminal sliding mode
ActiveCN107479370ASuppress external interferenceAvoid singularity problemsAdaptive controlProcess systemsFinite time
A four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on a nonsingular terminal sliding mode is provided; the method aims at a four-rotor unmanned plane system with inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences; according to the four-rotor unmanned plane dynamic system, a nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method is employed, and self-adaptive control is combined, thus designing the four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on the nonsingular terminal sliding mode; the nonsingular terminal sliding mode is designed so as to ensure the system finite time convergence features, thus preventing singularity problems existing in terminal sliding mode control, and effectively weakening jittering problems; in addition, the self-adaptive control is used for processing system inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences; the method can remove the sliding mode surface singularity problems, and can effectively prevent and compensate the system inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences, thus ensuring the system finite time convergence features.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode
ActiveCN107479371AAvoid singularity problemsReduce buffetingAdaptive controlProcess systemsFinite time
A four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on a fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode is provided; the method aims at a four-rotor unmanned plane system with inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences; according to the four-rotor unmanned plane dynamic system, a fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method is employed, and self-adaptive control is combined, thus designing the four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on the fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode; the fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode is designed so as to ensure the system finite time convergence features and fast convergence speed, thus preventing singularity problems existing in terminal sliding mode control, and effectively weakening jittering problems; in addition, the self-adaptive control is used for processing system inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences; the method can remove the sliding mode surface singularity problems, and can effectively prevent and compensate the system inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences, thus ensuring the system finite time convergence features.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Control method for changing structure of underwater hiding-machine space based on recursion fuzzy neural network
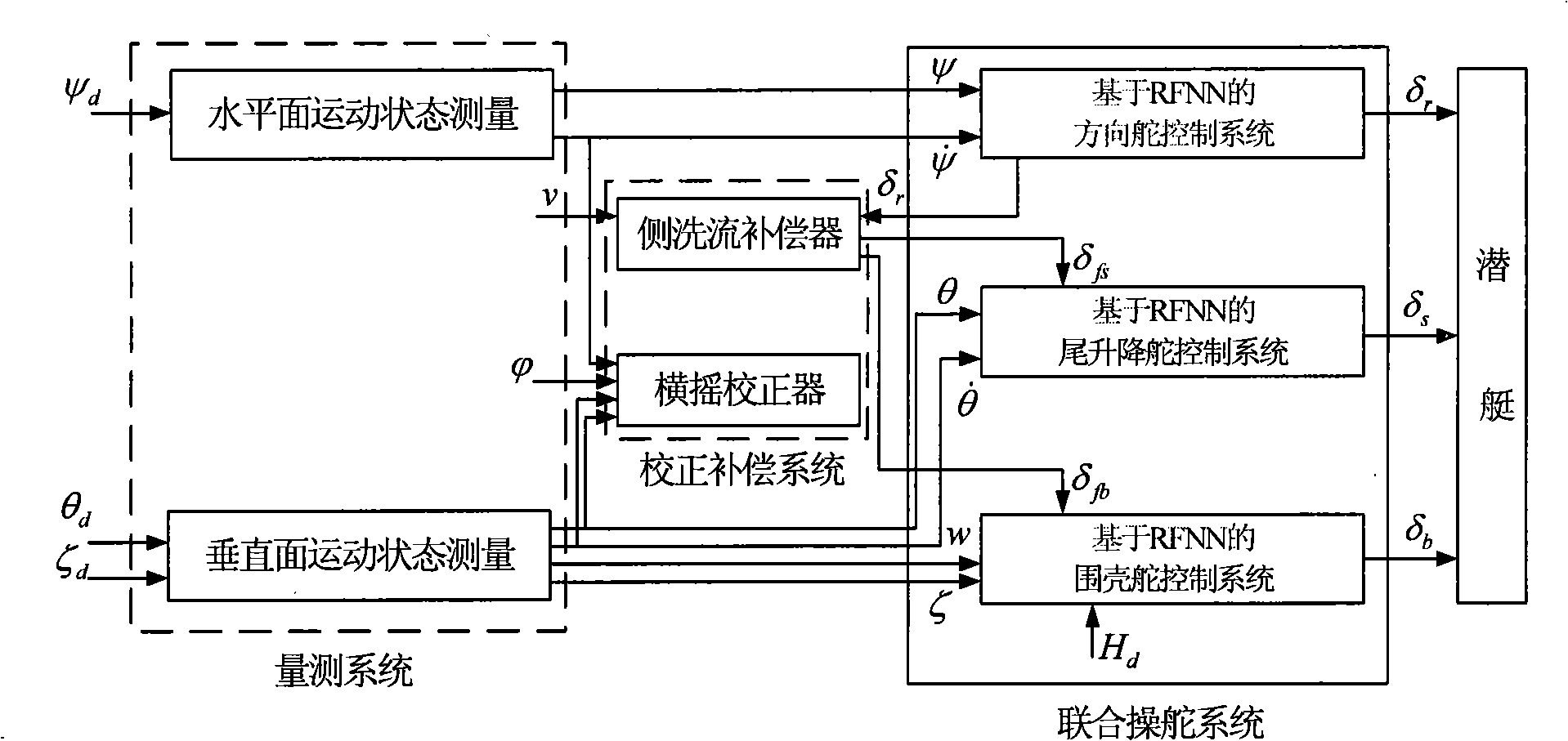
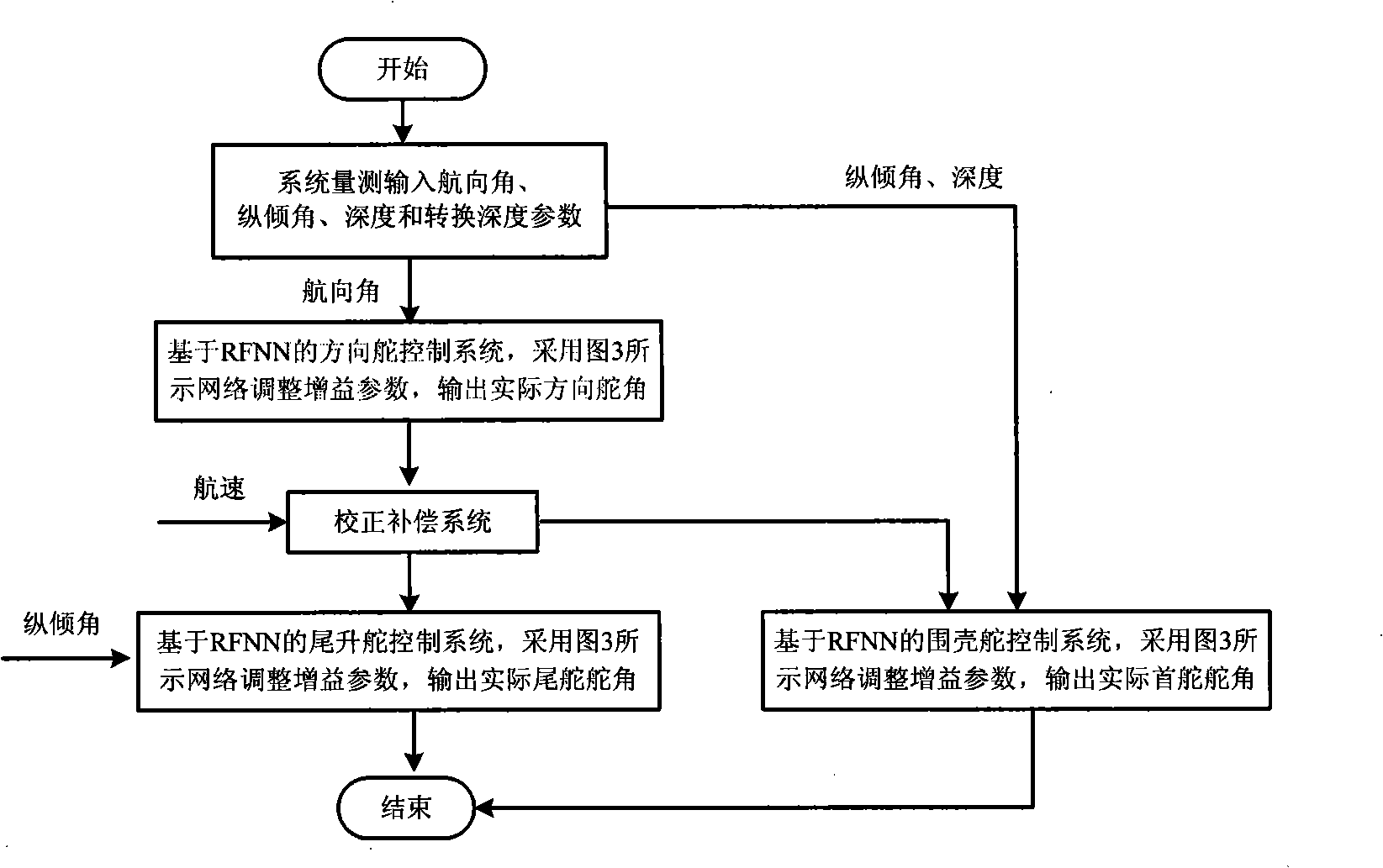
InactiveCN101256409ATo achieve the coupling effectSimplify complexityAttitude controlUnderwater vesselsControl systemRudder
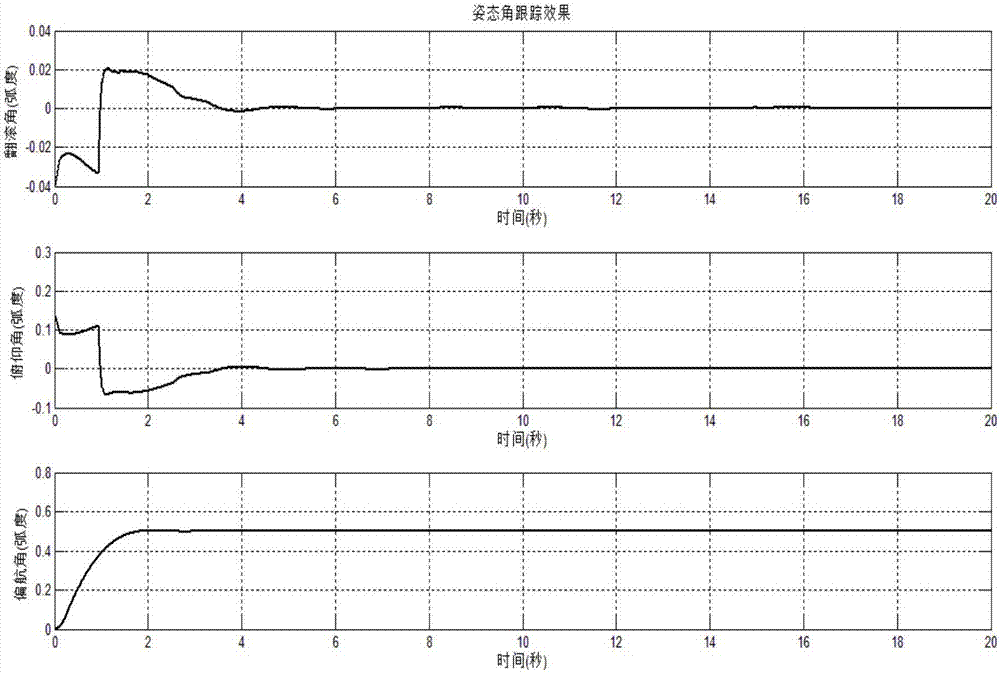
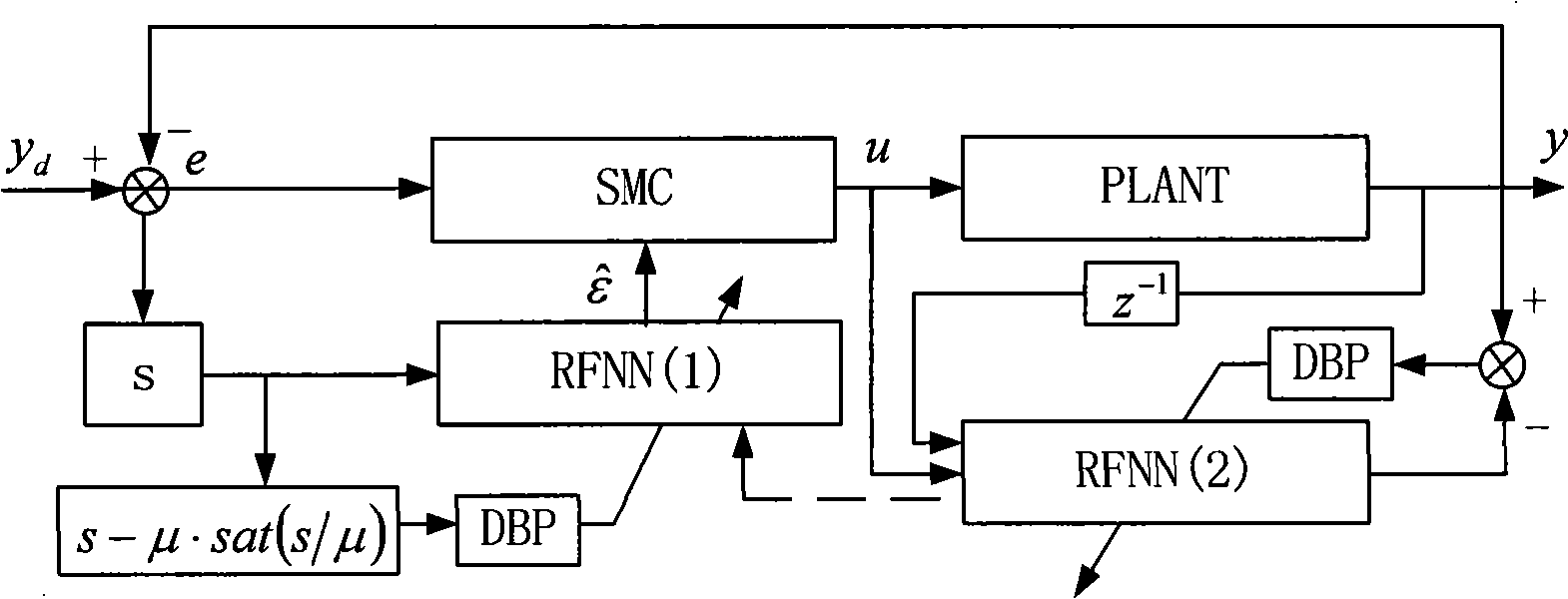
The invention provides an underwater vehicle space variable structure control method based on a recurrent fuzzy neural network. A RFNN-based rudder control system, a RFNN-based envelope rudder control system and a RFNN-based tail elevating rudder control system are designed, and combined together to form a united control system for underwater vehicle space motion. In this invention, the RFNN-based rudder control system, the RFNN-based envelope rudder control system and the RFNN-based tail elevating rudder control system are designed, and further combined to compose a united control system for underwater vehicle space motion, since the RFNN can make real-time adjustment of a controller gain epsilon, according to uncertain items of the system, the system not only has good dynamic property, but also effectively lowers buffeting and improves the robustness of an underwater vehicle automatic rudder control system.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Nonlinear robust control method with finite-time convergence capacity for unmanned helicopter attitude error
ActiveCN104950901ASimple control processReduce chatteringAttitude controlTracking errorAttitude control
The invention belongs to the field of flight control of a small-scale single-rotor unmanned helicopter and aims to realize finite-time convergence for unmanned helicopter attitude tracking control. Therefore, the technical scheme is that a nonlinear robust control method with the finite-time convergence capacity for an unmanned helicopter attitude error comprises the following steps: 1, a small-scale unmanned helicopter dynamic model is determined; 2, small-scale unmanned helicopter attitude control is defined as follows: eta d(t)=[phi d(t), theta d(t), psi d(t)]<T>, wherein T is a given reference vector of an attitude angle, phi d(t), theta d(t) and psi d(t) are a given roll angle, a given pitch angle and a given yaw angle, and the relationship and relevant parameters are shown in the specification. For writing convenience, the variables do not carry the time t, and for example, eta d(t) is directly written as eta d; the attitude tracking error is defined as follows: e= eta d-eta. The method mainly applies to flight control of the small-scale single-rotor unmanned helicopter.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Fractional-order adaptive inverse fuzzy sliding mode control method for microgyroscope
ActiveCN107831655AGuaranteed stabilityRealize online adjustmentAdaptive controlLyapunov stabilityDynamic equation
The invention discloses a fractional-order adaptive inverse fuzzy sliding mode control method for a microgyroscope. The method comprises a step of establishing a dimensionless dynamic equation mathematical model and a reference trajectory model of a microgyroscope system, and a step of constructing an inversion adaption fuzzy sliding mode controller based on a fractional order. According to the method, the real-time tracing of a target by the microgyroscope can be achieved, the robustness of the system is increased, and good performance still can be maintained under the condition of external interference. A fractional order adaptive law is designed based on a fractional order sliding mode surface, a self-adaptive identification method is designed based on a Lyapunov stability criterion, various unknown system parameters of the microgyroscope is estimated in an online way in real time, compared with an integer order, adjustable items are added, and a control effect and a parameter estimation effect are improved. A fuzzy system approaches upper bound values of a parameter uncertainty and an external disturbance total number, through the fuzzy approximation of the upper bound values,switching terms in the sliding mode controller can be continuous, and buffeting can be greatly reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
MEMS(Micro-electromechanical System) gyroscope sliding mode control method based on disturbance observer
ActiveCN107607101AReduce buffetingModified weight coefficientSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAdaptive controlGyroscopeWeight coefficient
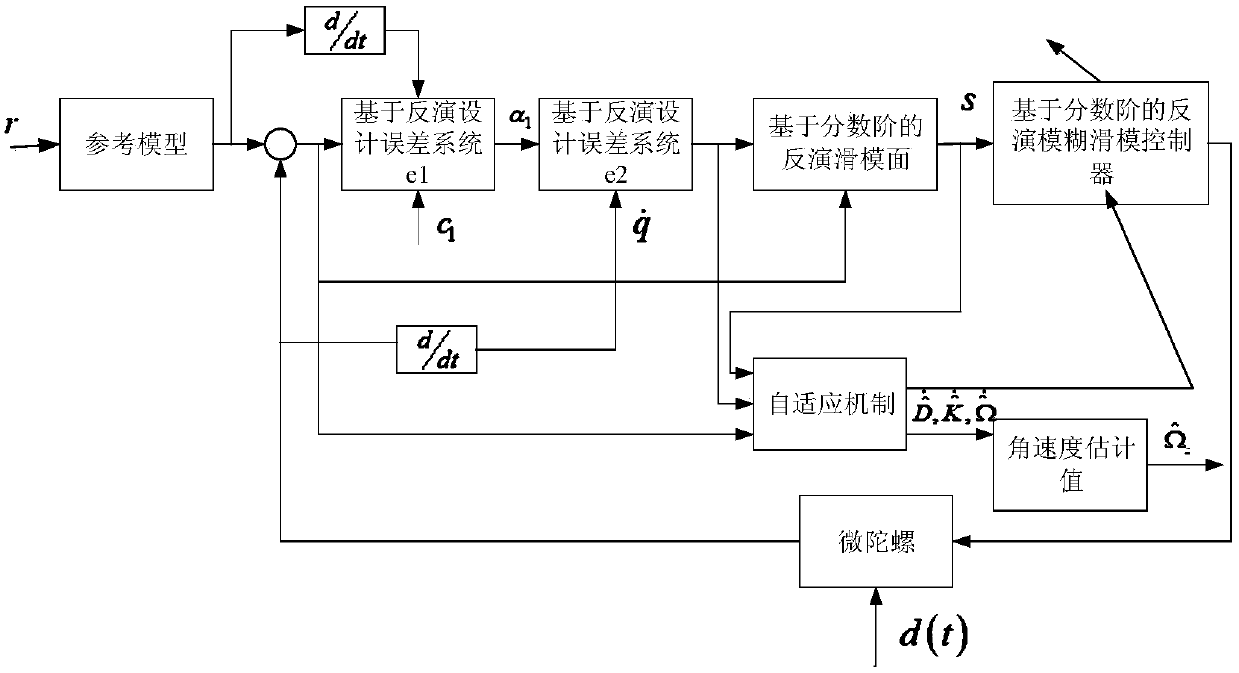
The invention discloses an MEMS (Micro-electromechanical System) gyroscope sliding mode control method based on a disturbance observer, which is used for solving the technical problem of poor practicability of the existing MEMS gyroscope sliding mode control method. According to the technical scheme, the steps are as follows: designing a disturbance observer firstly, estimating and compensating disturbance in sliding mode control, thereby reducing buffeting; meanwhile, according to the prediction error and the tracking error of a neutral network, designing the combined self-adaptive rule of aneural network weight, and correcting the weight coefficient of the neural network, thereby realizing the effective dynamic estimation of unknown dynamics. According to the method, the effective dynamic estimation of unknown dynamics can be realized by designing the combined self-adaptive rule of the neural network weight and correcting the weight coefficient of the neutral network. In combinationwith the sliding mode control theory, the feed-forward compensation of the unknown dynamics of an MEMS gyroscope can be realized, and further, the control precision of the MEMS gyroscope can be improved. The disturbance observer is designed for estimating and compensating the external disturbance and effectively reducing the buffeting of a sliding mode, and is good in practicability.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +2
Micro-gyroscope fractional order self-adaptive fuzzy neural inversion terminal sliding mode control method
The invention discloses a micro-gyroscope fractional order self-adaptive fuzzy neural inversion terminal sliding mode control method. The method includes the steps of establishing a dimensionless kinetic equation mathematical model and a reference trajectory model of a micro-gyroscope system, and establishing a fractional-order-based inversion terminal sliding mode controller. By means of the method, a micro-gyroscope can track a target in real time, so that errors are converged to zero within limited time; the robustness of the system is enhanced, and good performance is still kept under thecondition that external interference exists; a fractional order adaptive law is designed according to a fractional order terminal sliding mode surface, a self-adaptive identification method is designed on the basis of a Lyapunov stability criterion, and various unknown system parameters of the micro-gyroscope are estimated online in real time; compared with an integer order, adjustable items are added, so that the control effect and the parameter estimation effect are improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com