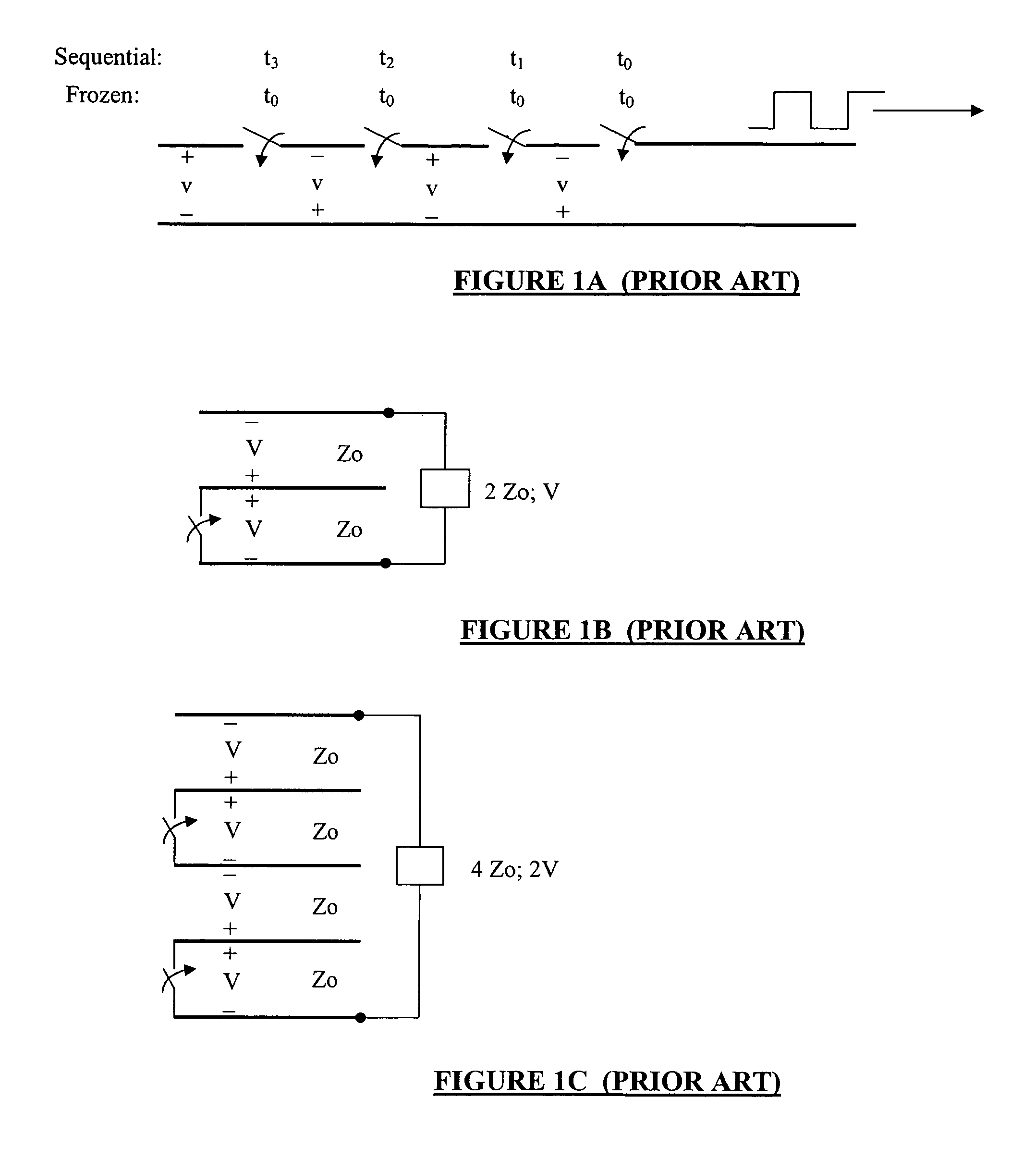
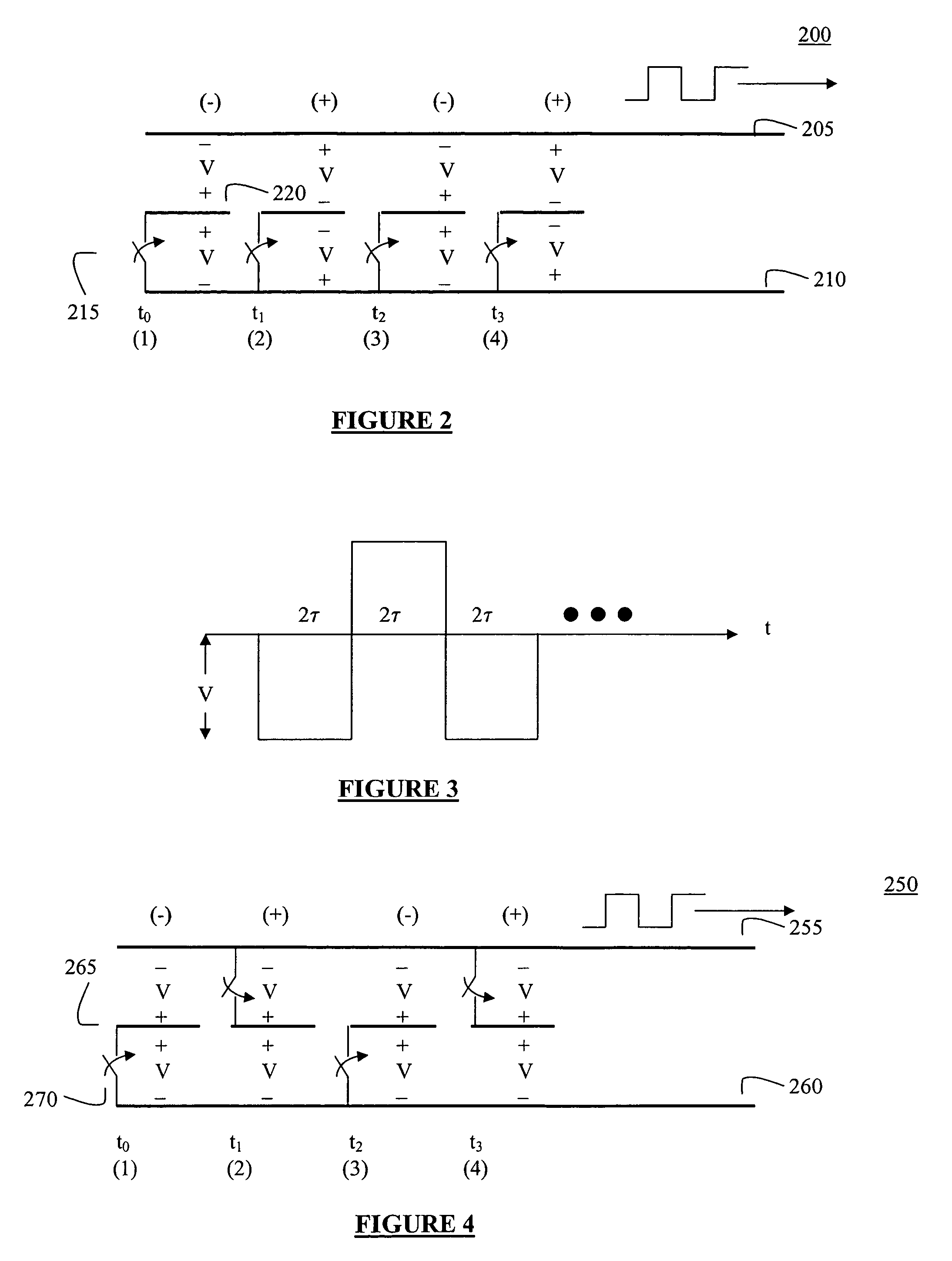
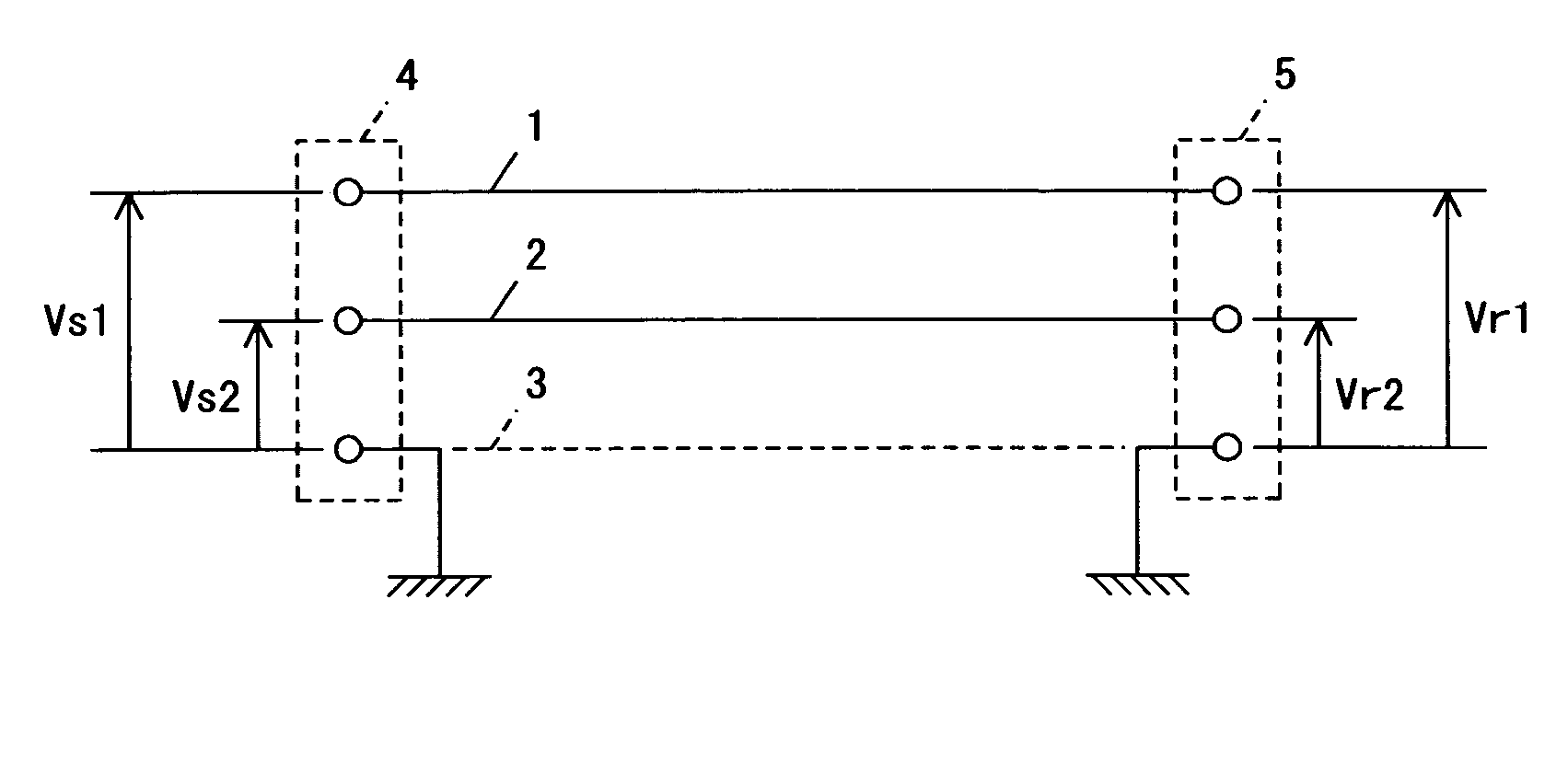
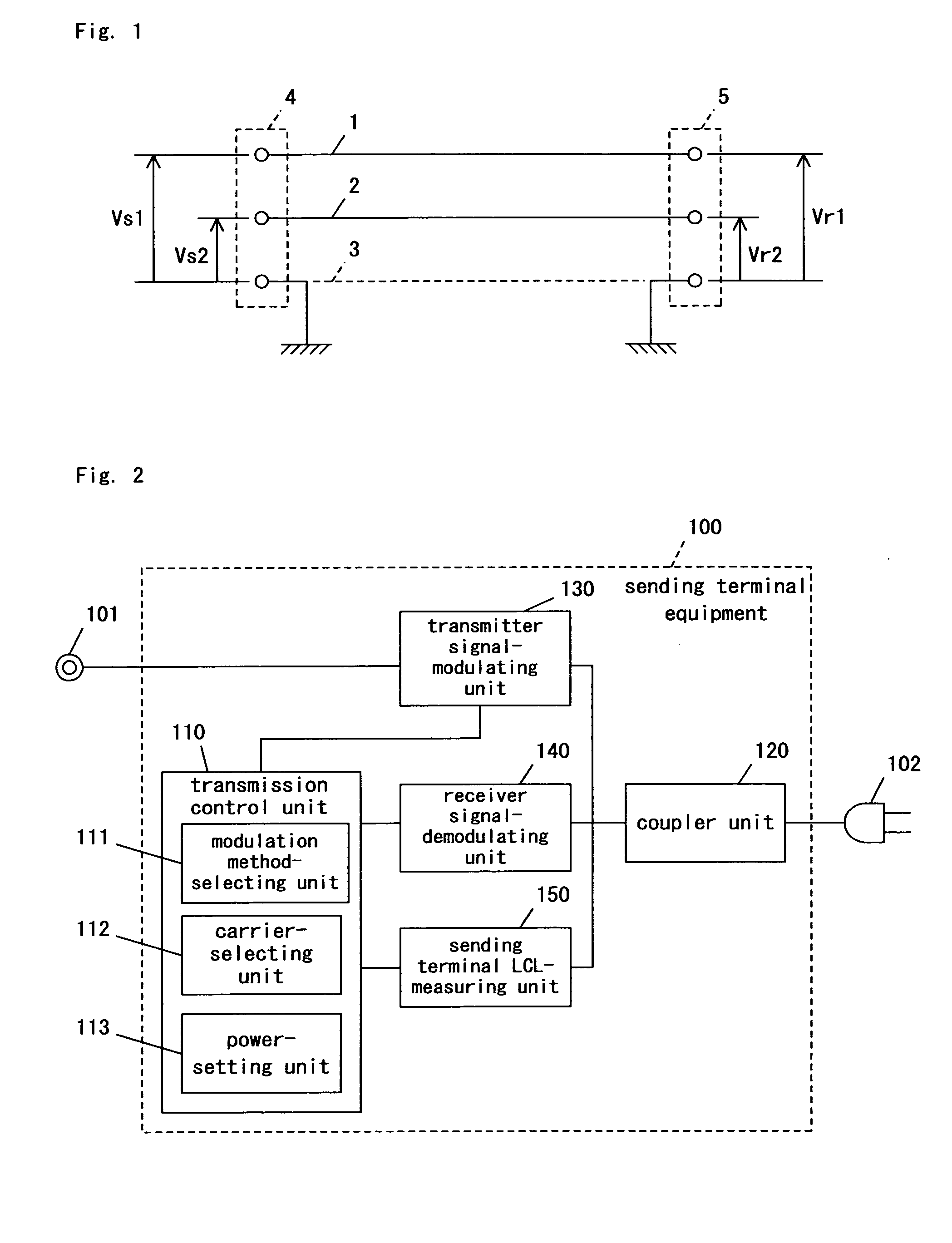
Patents
Literature
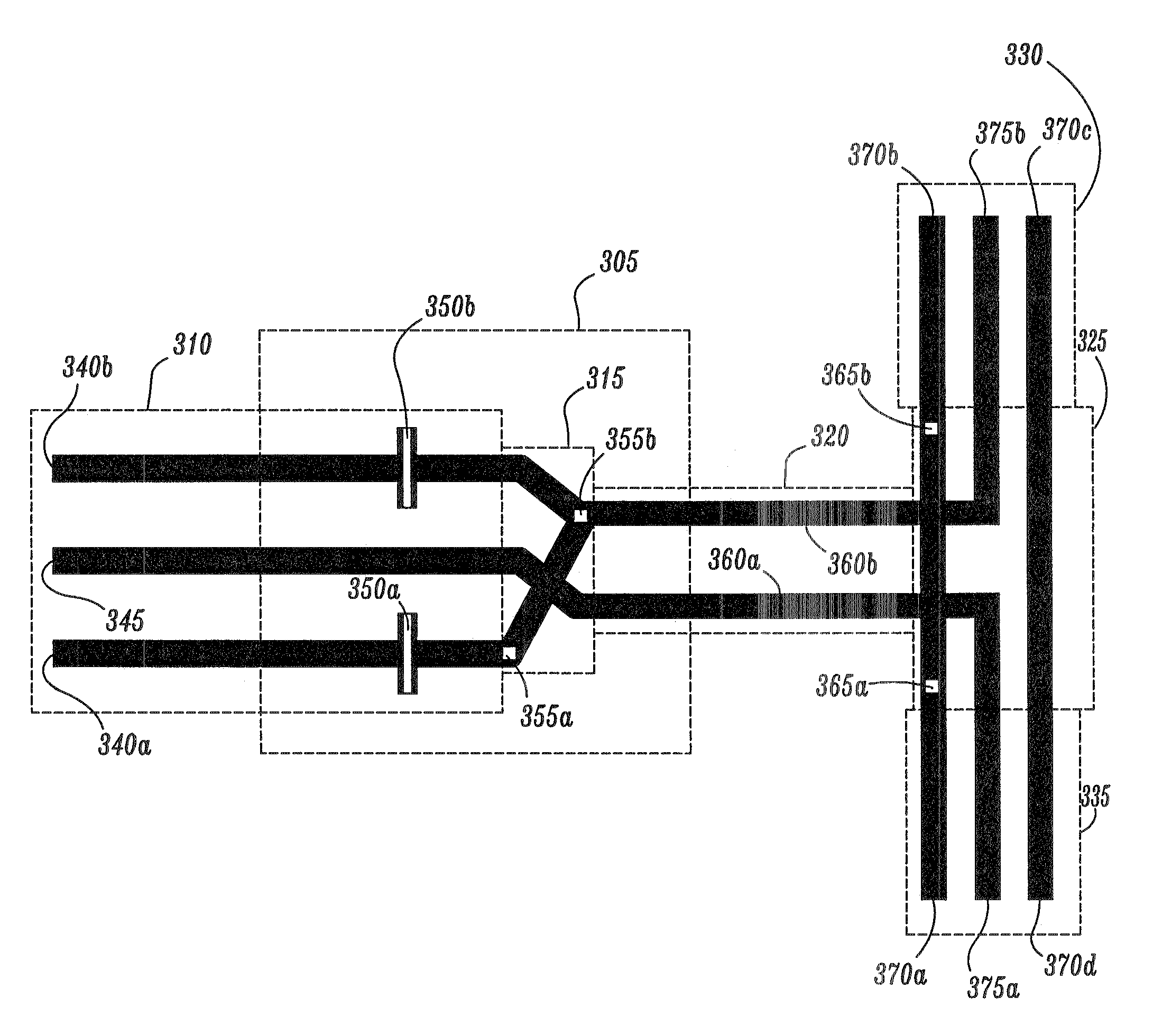
153 results about "Balanced line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
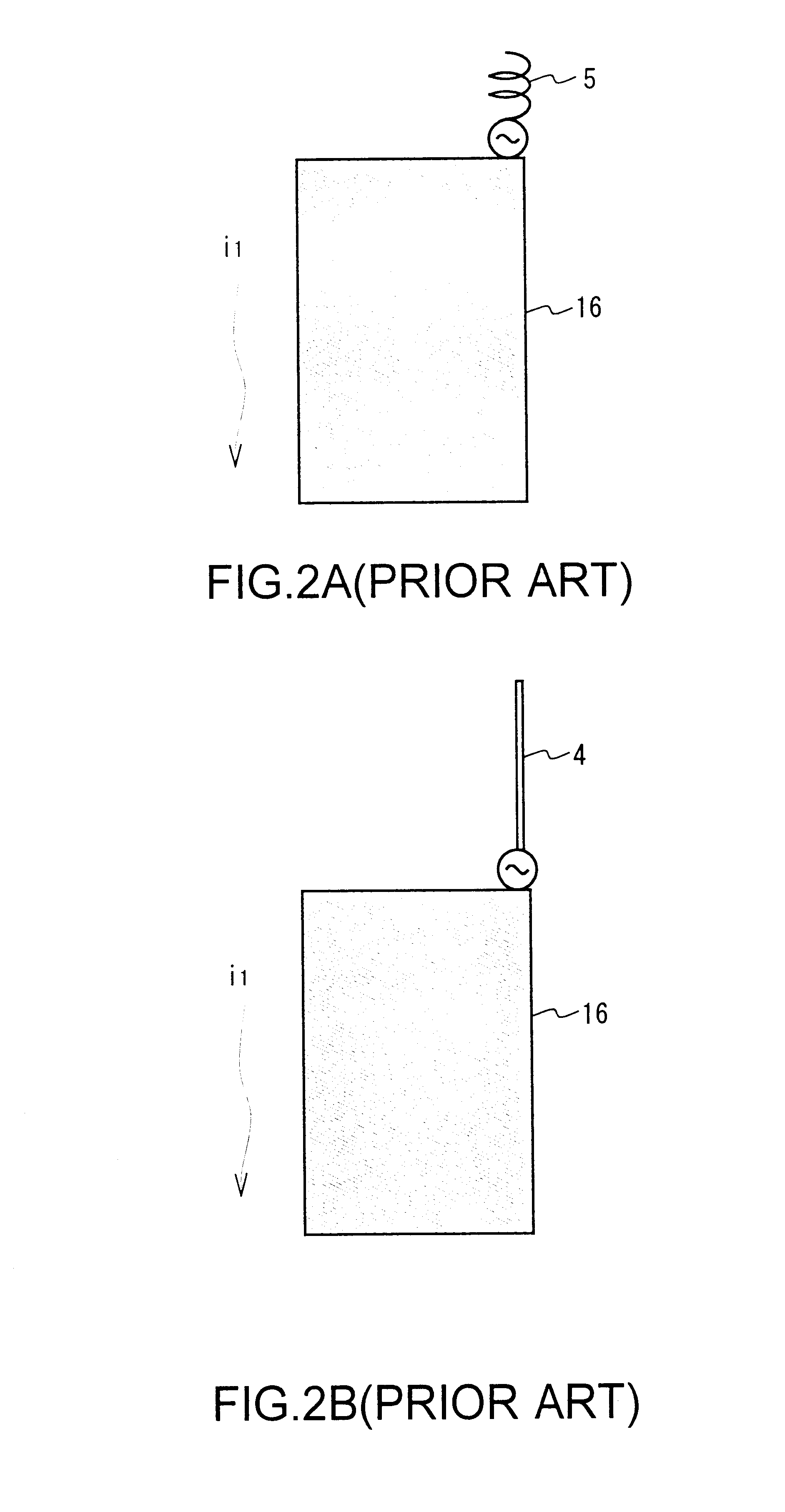
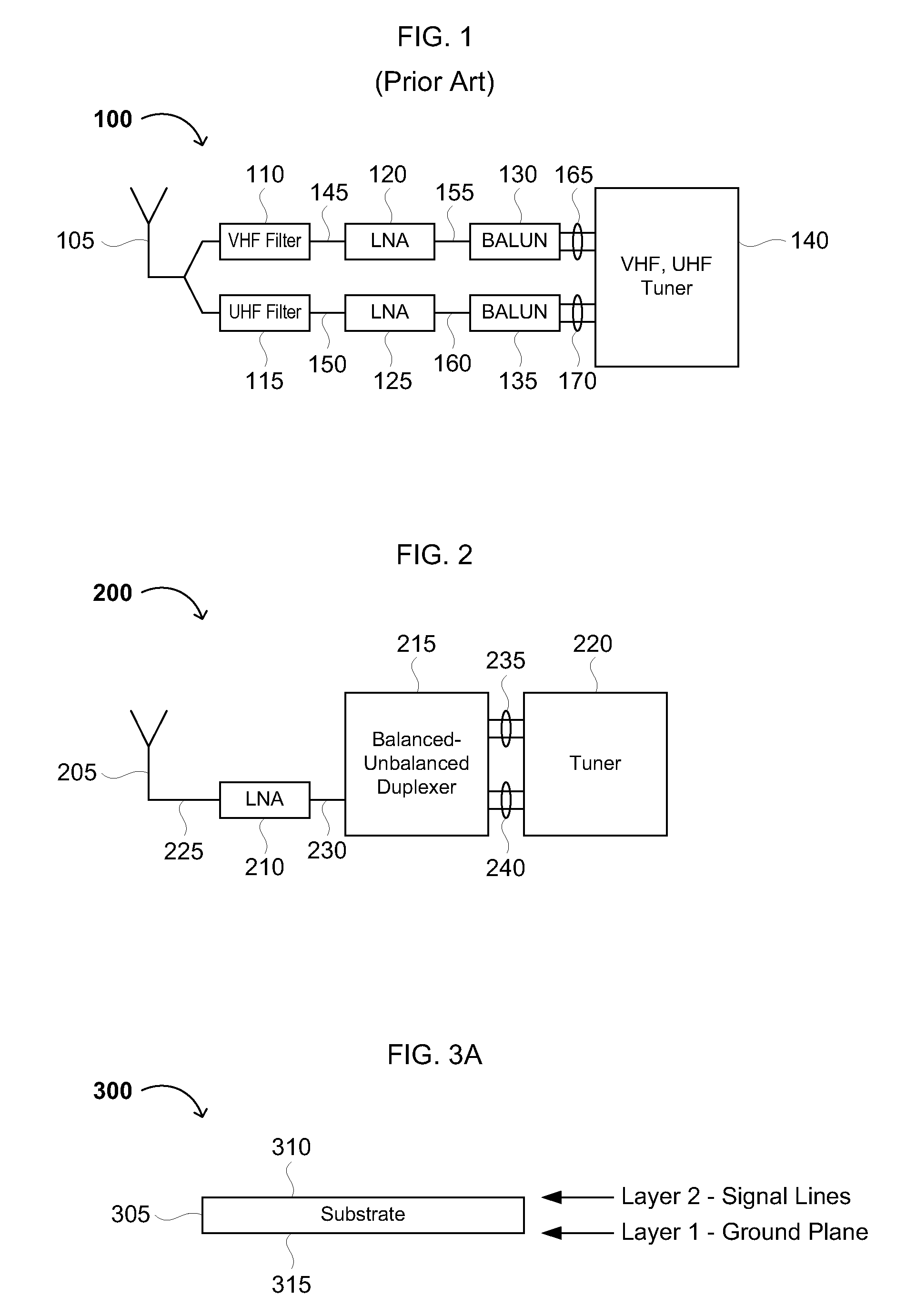
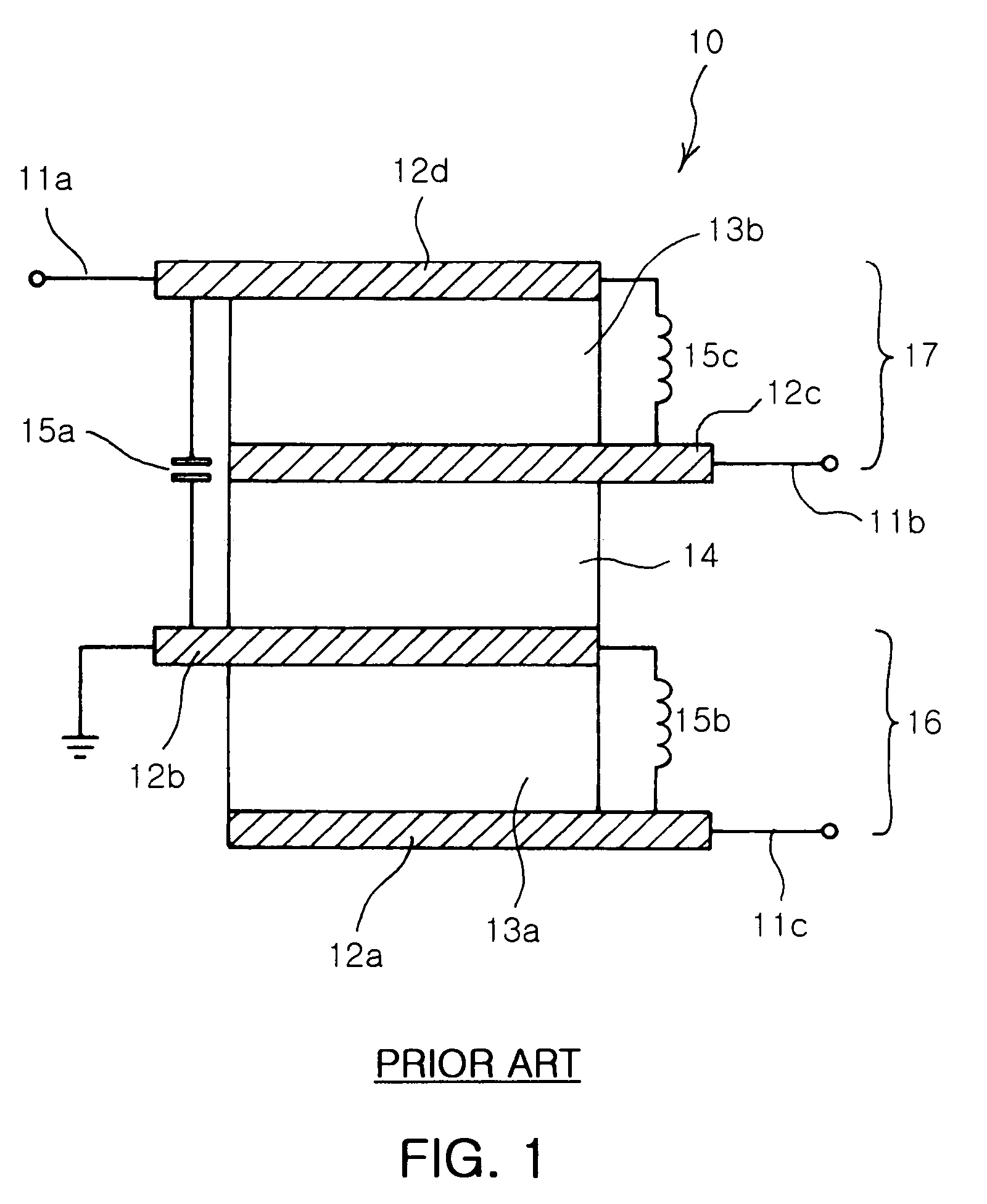
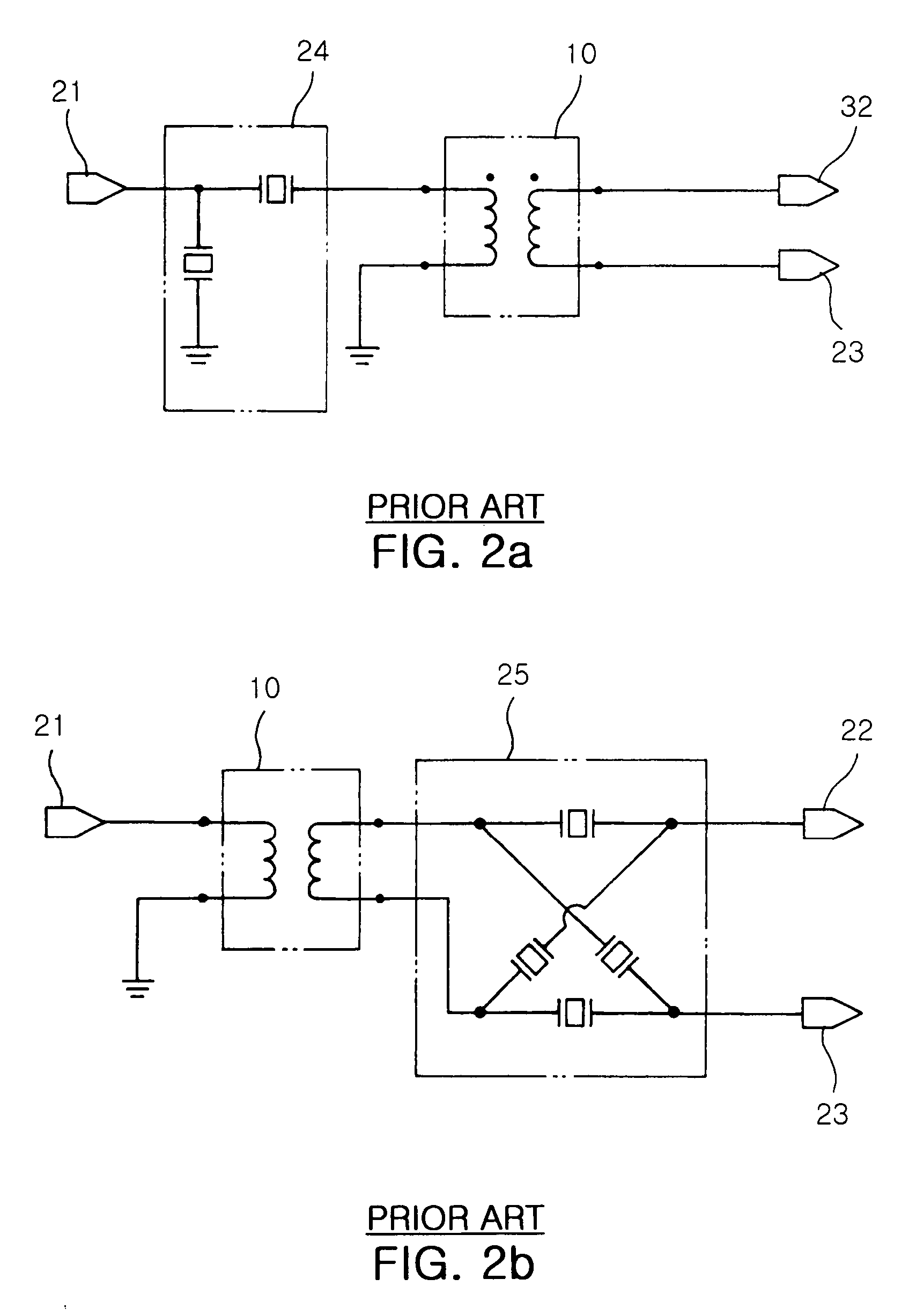
In telecommunications and professional audio, a balanced line or balanced signal pair is a transmission line consisting of two conductors of the same type, each of which have equal impedances along their lengths and equal impedances to ground and to other circuits. The chief advantage of the balanced line format is good rejection of external noise when fed to a differential amplifier. Common forms of balanced line are twin-lead, used for radio frequency signals and twisted pair, used for lower frequencies. They are to be contrasted to unbalanced lines, such as coaxial cable, which is designed to have its return conductor connected to ground, or circuits whose return conductor actually is ground. Balanced and unbalanced circuits can be interconnected using a transformer called a balun.
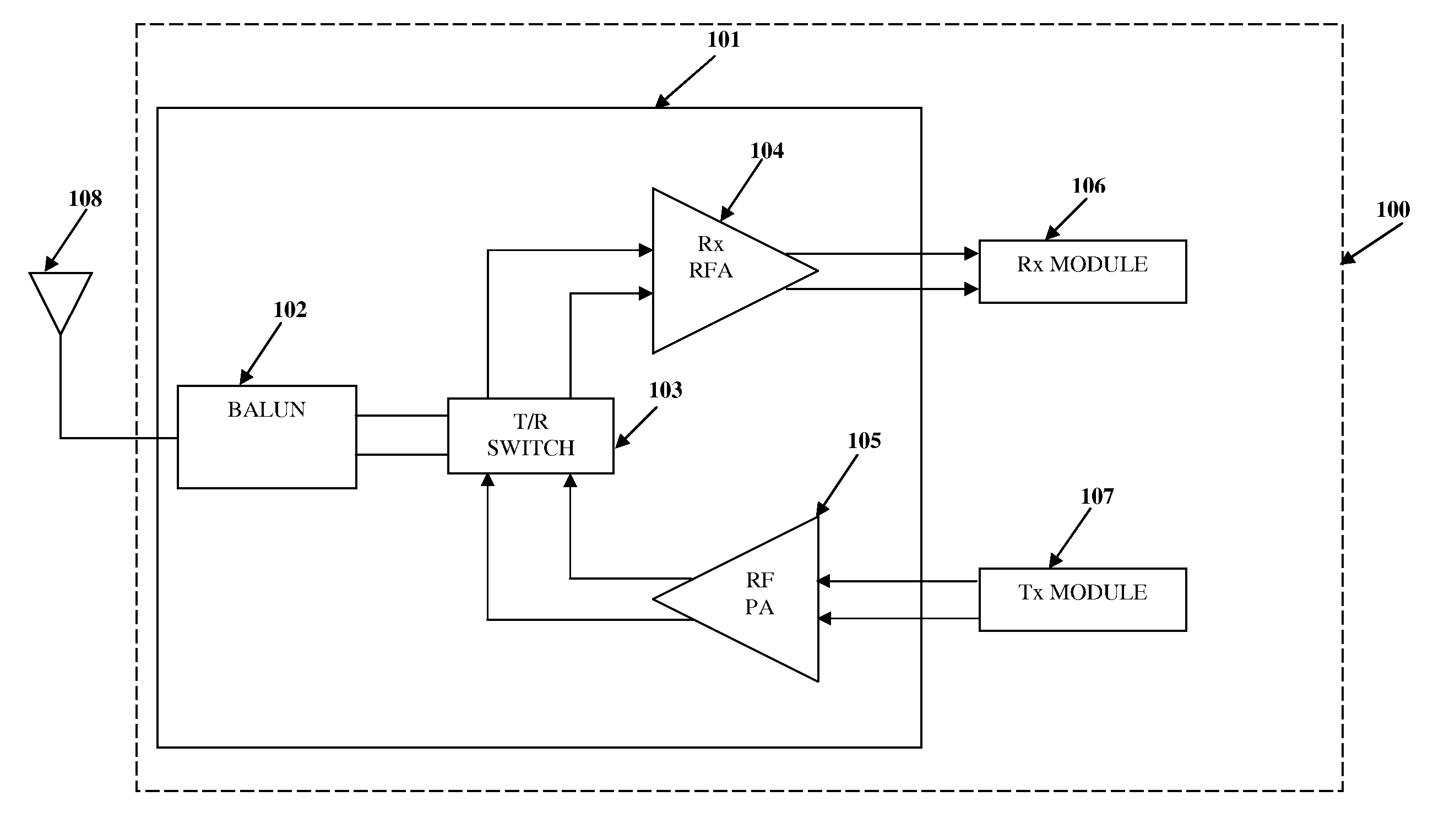
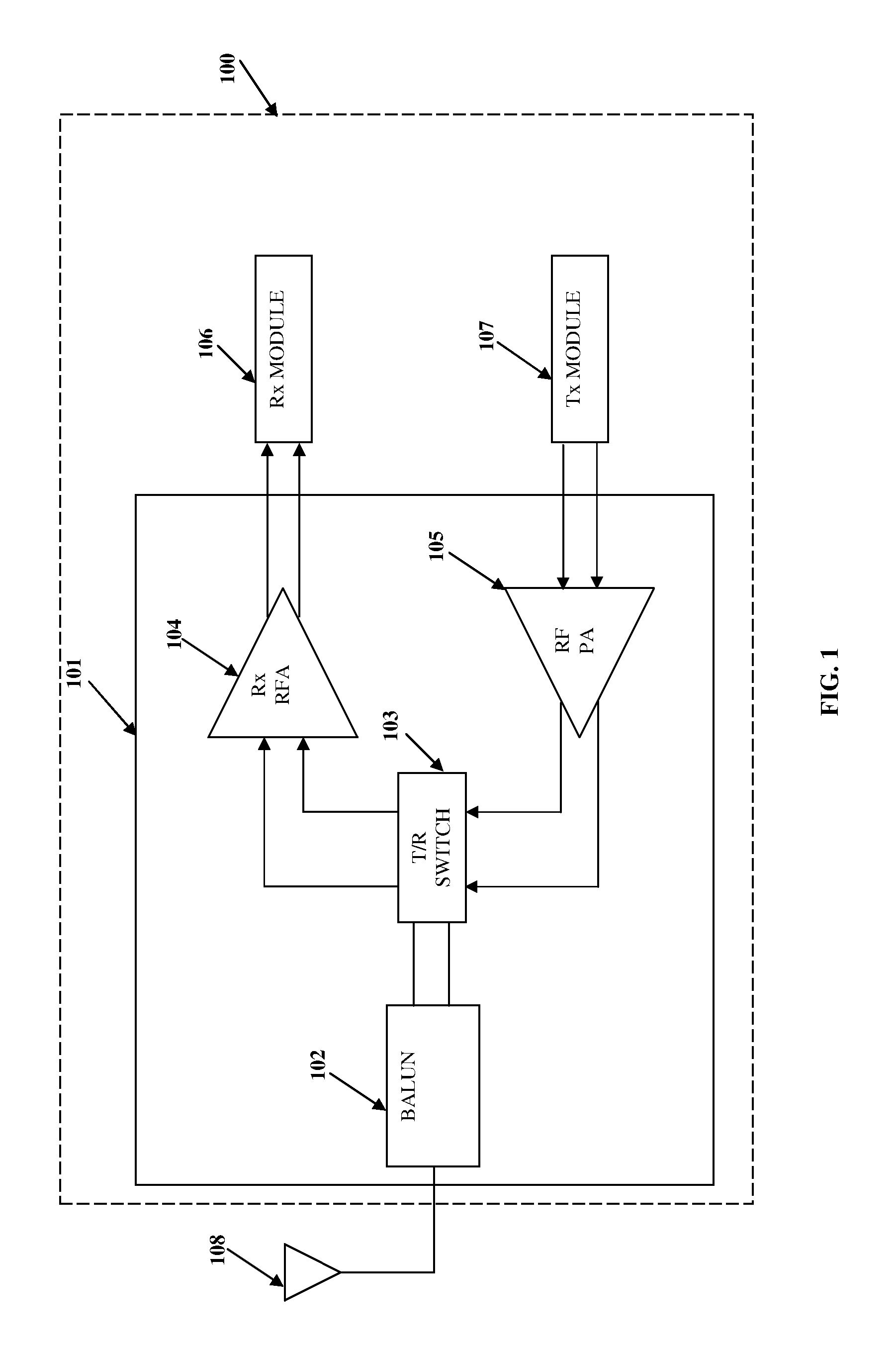
Package filter and combiner network
InactiveUS7283793B1Improve powerImprove efficiencyOne-port networksTransmissionPhase shiftedTransceiver
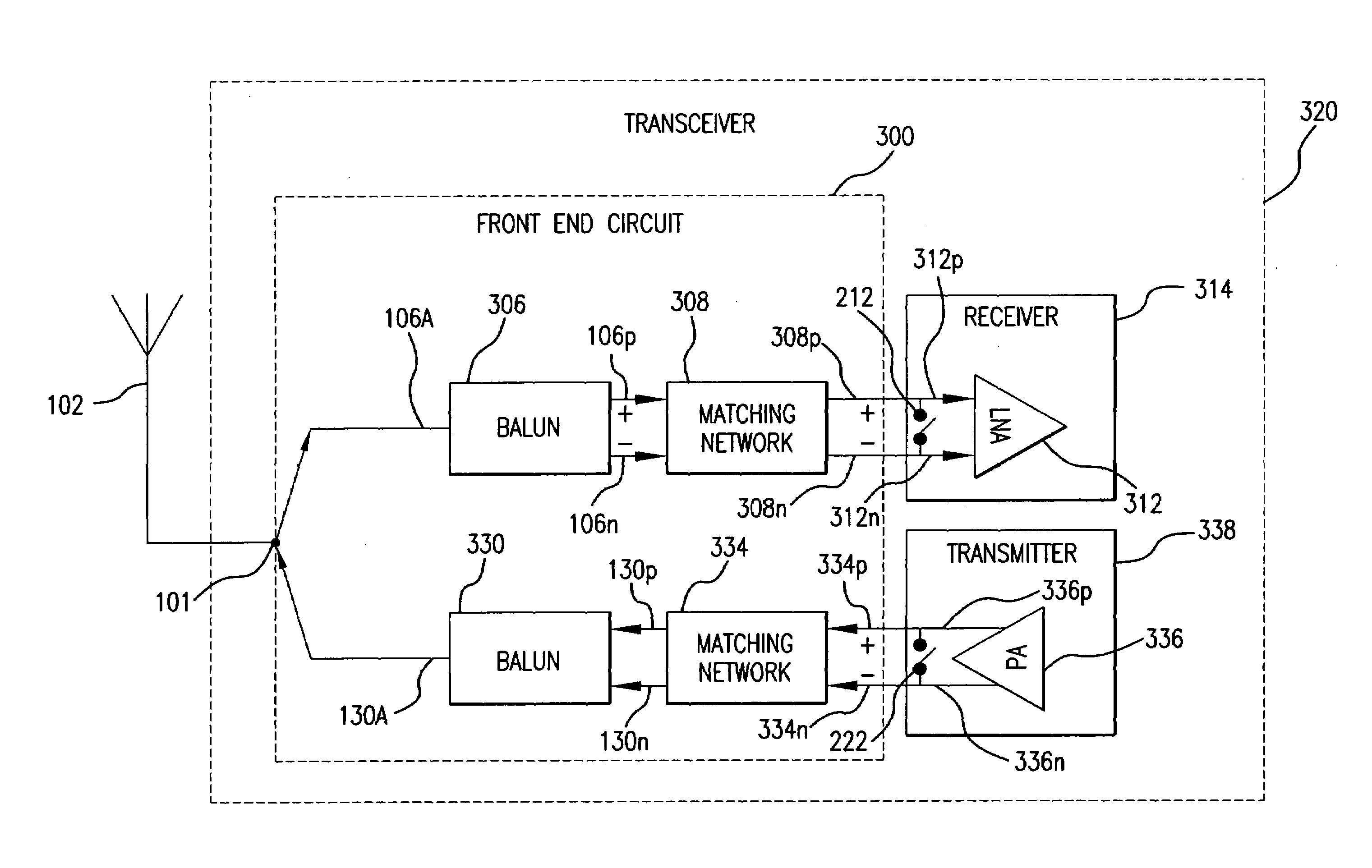
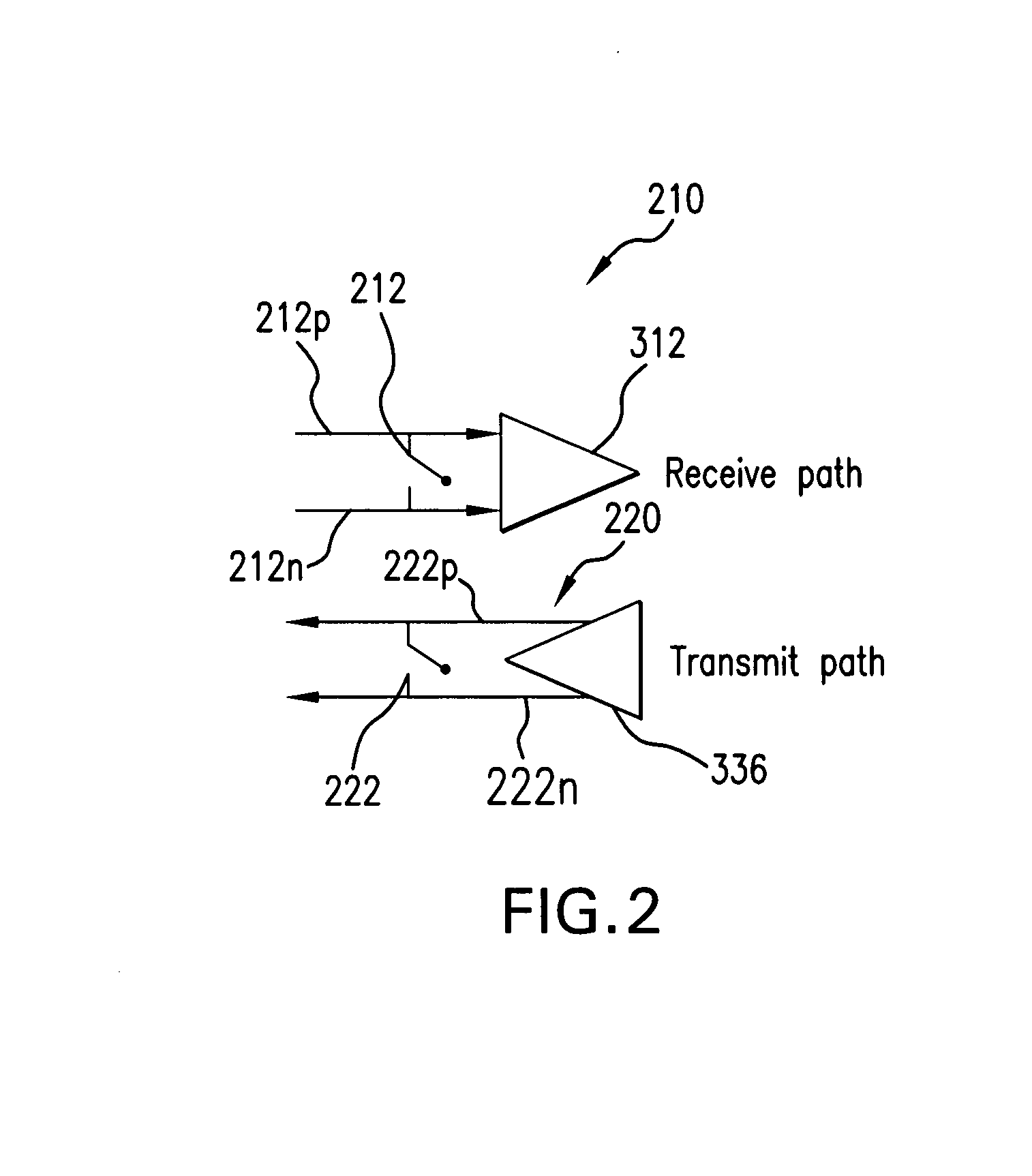
A transceiver front end circuit includes an antenna terminal capable of being coupled to an antenna. A first balun circuit has a single input that is coupled to the antenna terminal, and a pair of balanced outputs coupled to a corresponding pair of balanced receiver inputs. The first balun circuit matches an input impedance of the pair of balanced receiver inputs and substantially phase shifts the input reflection coefficient of the pair of balanced receiver inputs by about 180-degrees. A second balun circuit has a single output coupled to the antenna terminal and a pair of balanced inputs coupled to a corresponding pair of balanced transmitter outputs. The second balun circuit matches an output impedance of the pair of balanced transmitter outputs and substantially phase shifts the output reflection coefficient of the pair of balanced transmitter outputs by about 180-degrees. The first balun circuit and the second balun circuit can be contained within a single package. A first shunt switch can be coupled across the pair of receiver inputs. A second shunt switch can be coupled across the pair of transmitter outputs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
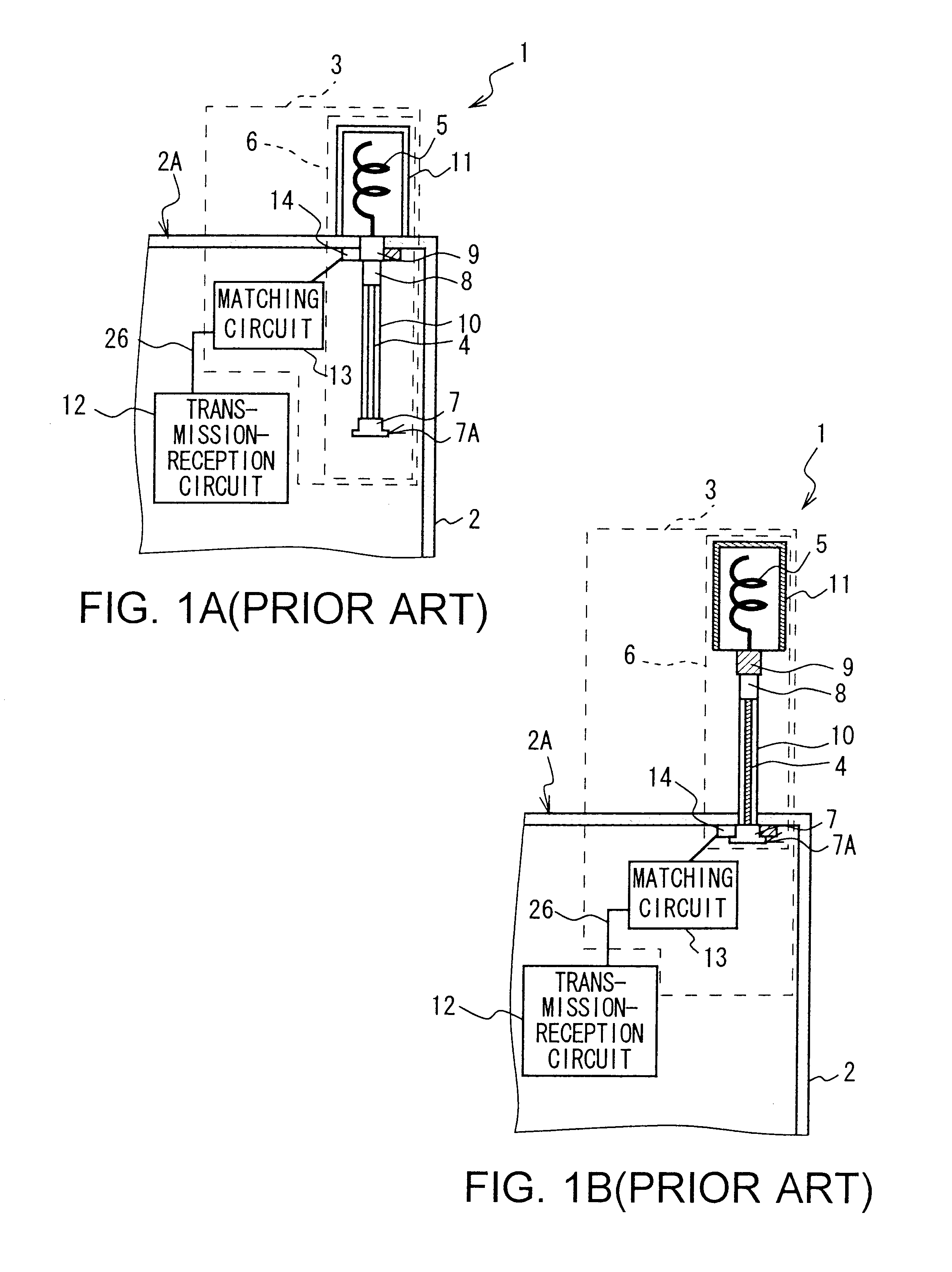
Antenna device and portable radio set
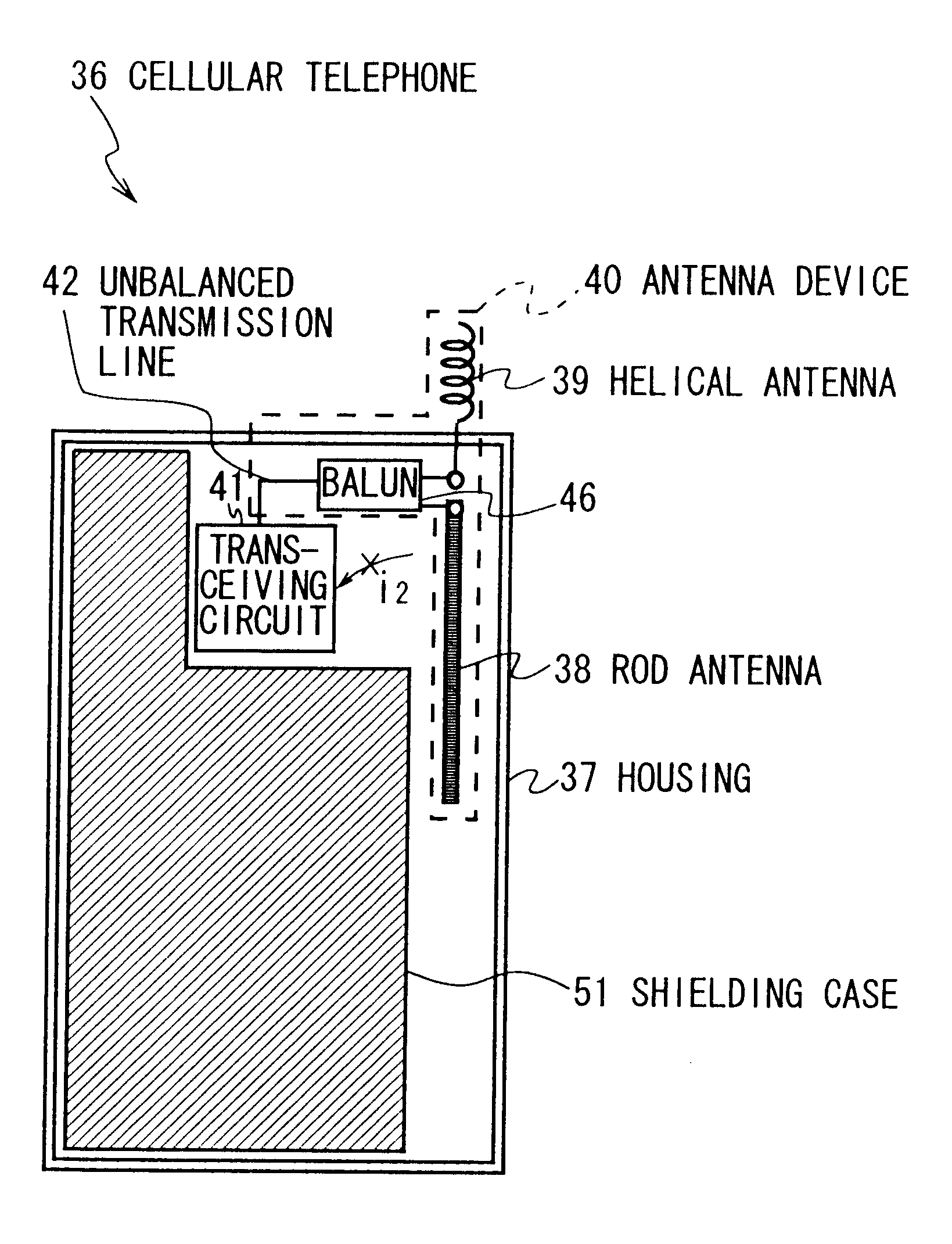
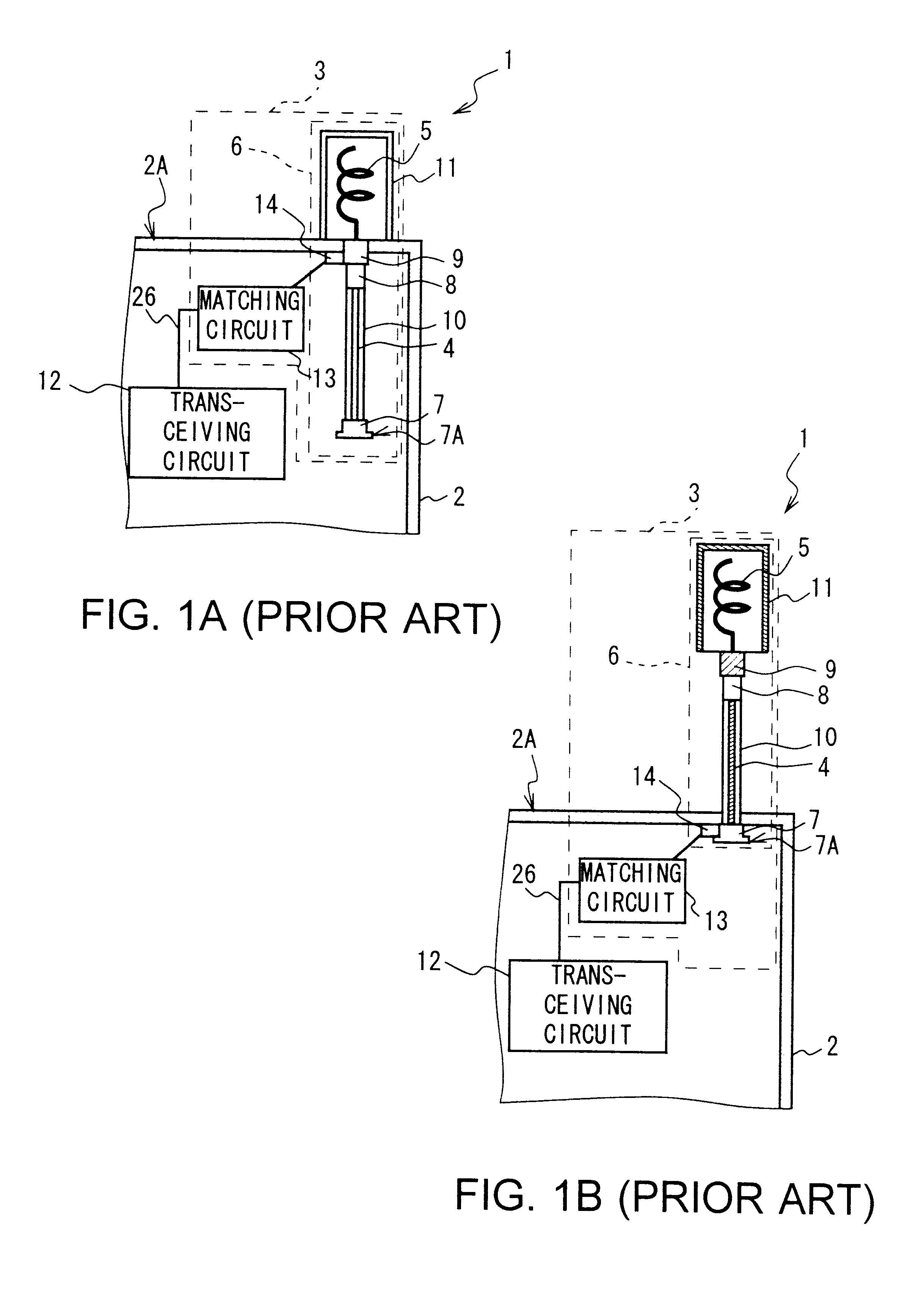
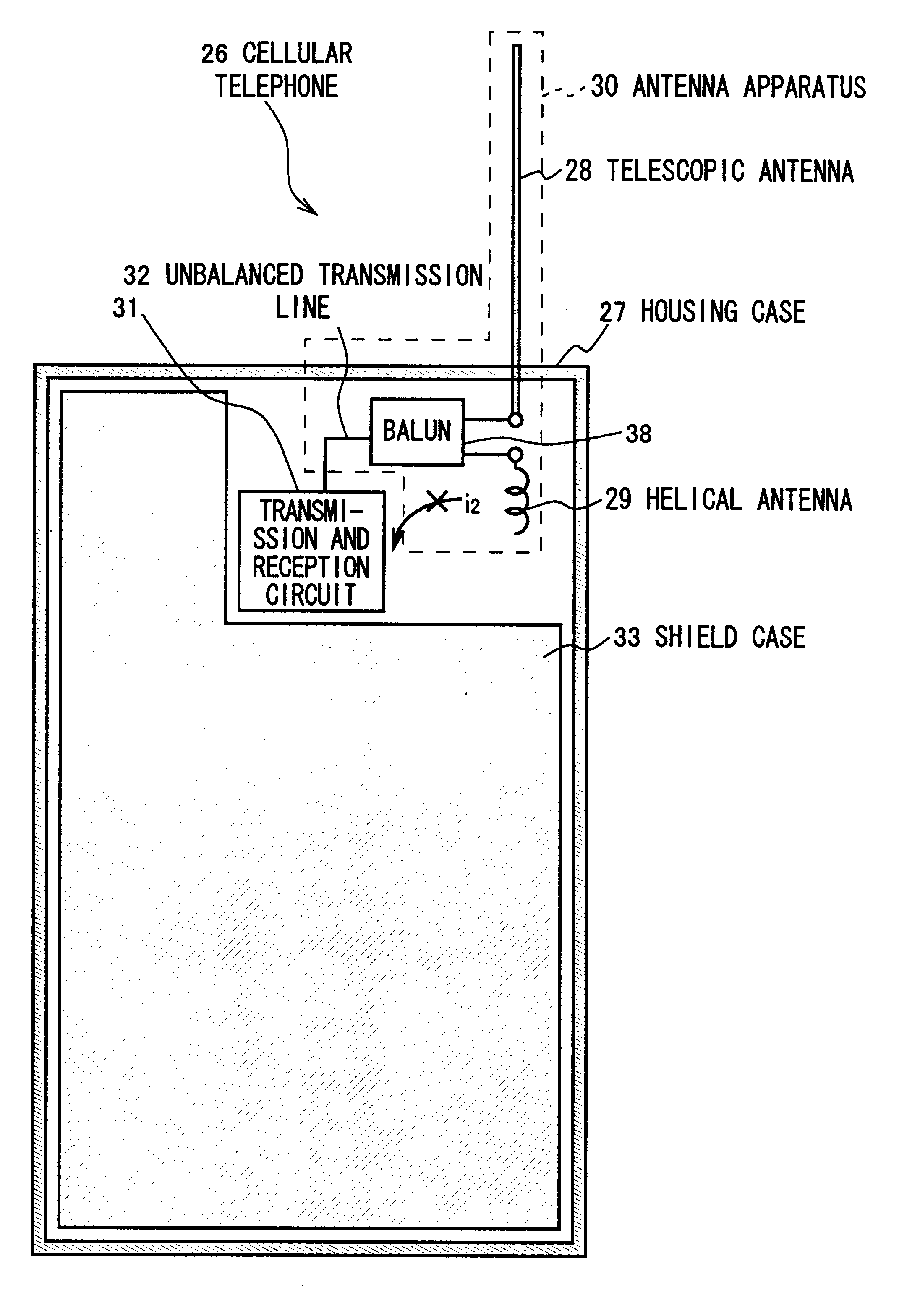
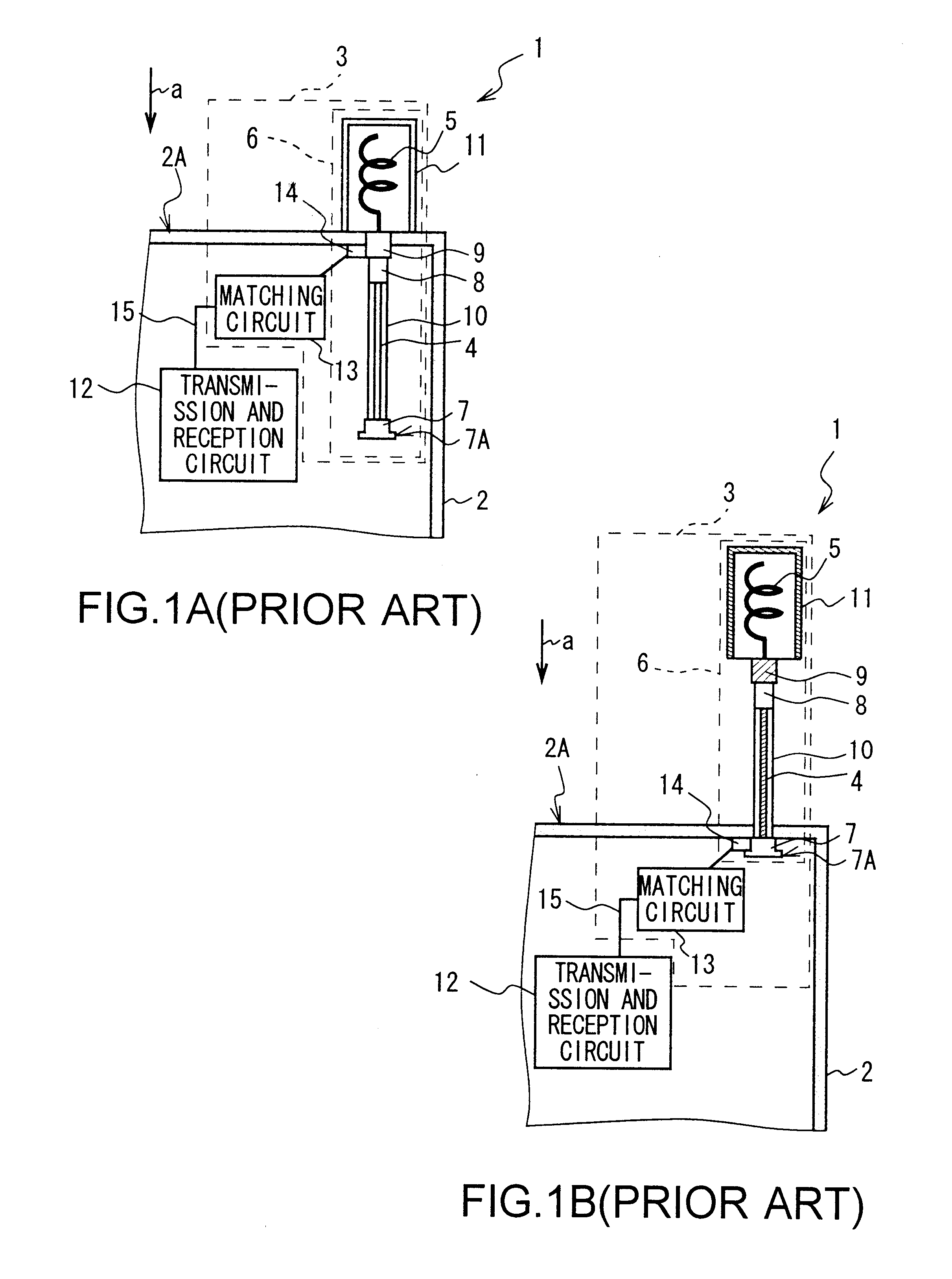
The present invention makes it possible to realize an antenna device and a portable radio set capable of greatly reducing the deterioration of antenna characteristics while used near a human body and greatly reducing the deterioration of communication quality by electrically connecting first and second antenna elements to a balanced-to-unbalanced transform circuit by connection means when a first antenna element is retracted, supplying power to the first and second antenna elements from an unbalanced transmission line through balanced-to-unbalanced transform means to operate the first and second antenna elements as antennas, preventing a leakage current from flowing to a ground member to which the unbalanced transmission line is grounded from the first and second antenna elements through the transmission in accordance with the balanced-to-unbalancecd transform by the balanced-to-unbalanced transform means, and thereby preventing the ground member from operating as an antenna.
Owner:SONY CORP
Antenna apparatus and portable radio set
An antenna that functions as an approximately balanced antenna that is structurally asymmetric but electrically symmetric includes a first antenna element that is extendable and retractable, a second fixed antenna element, an unbalanced transmission line feeding the first and second antenna elements, and a balanced-unbalanced convertor. At a time of extending the first antenna element, the first and second antenna elements are supplied an electric power from the unbalanced transmission line through the balanced-unbalanced convertor, so that the first and second antenna elements cooperate to function as an antenna.
Owner:SONY CORP
Transmission lines applied to contact free slip rings
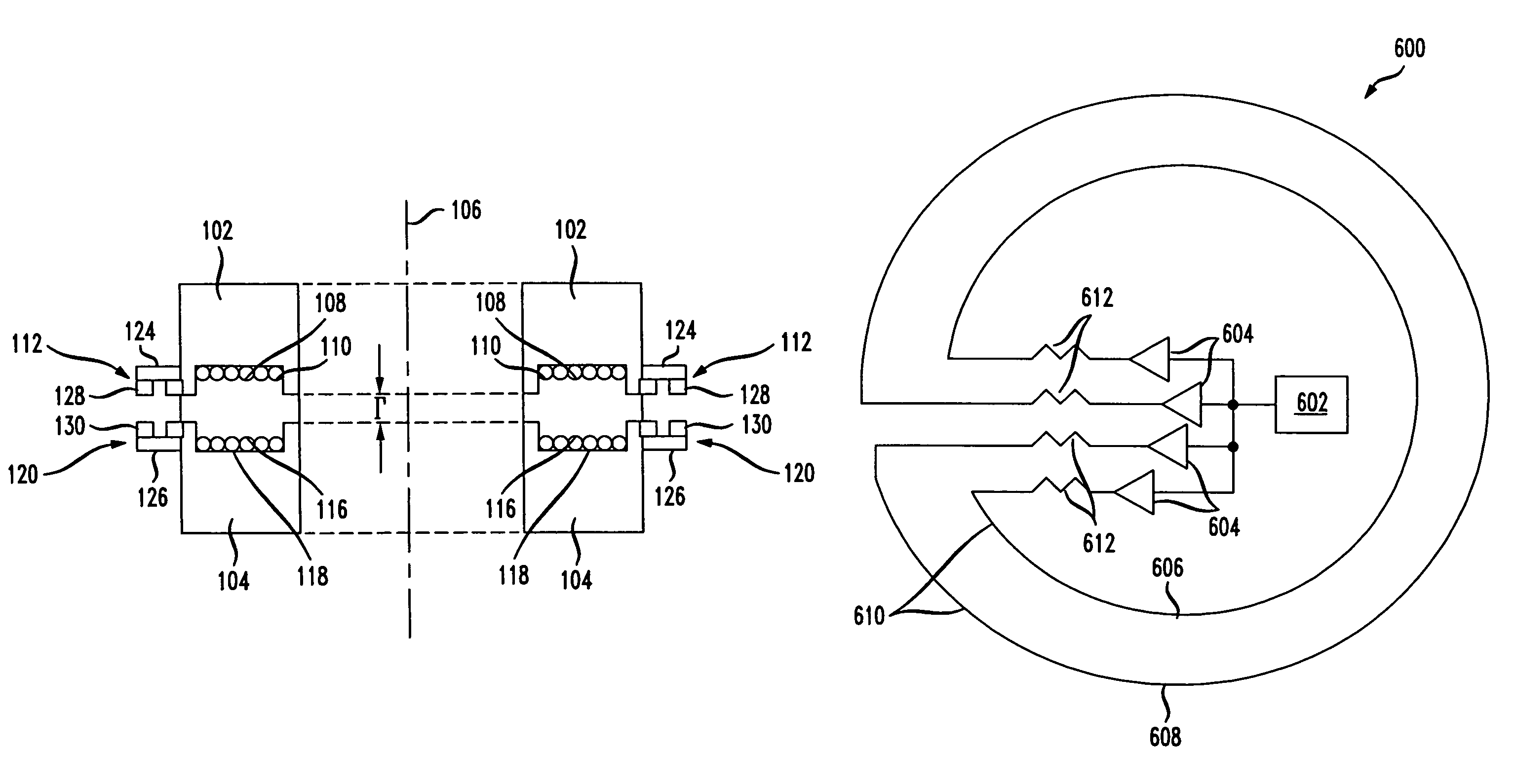
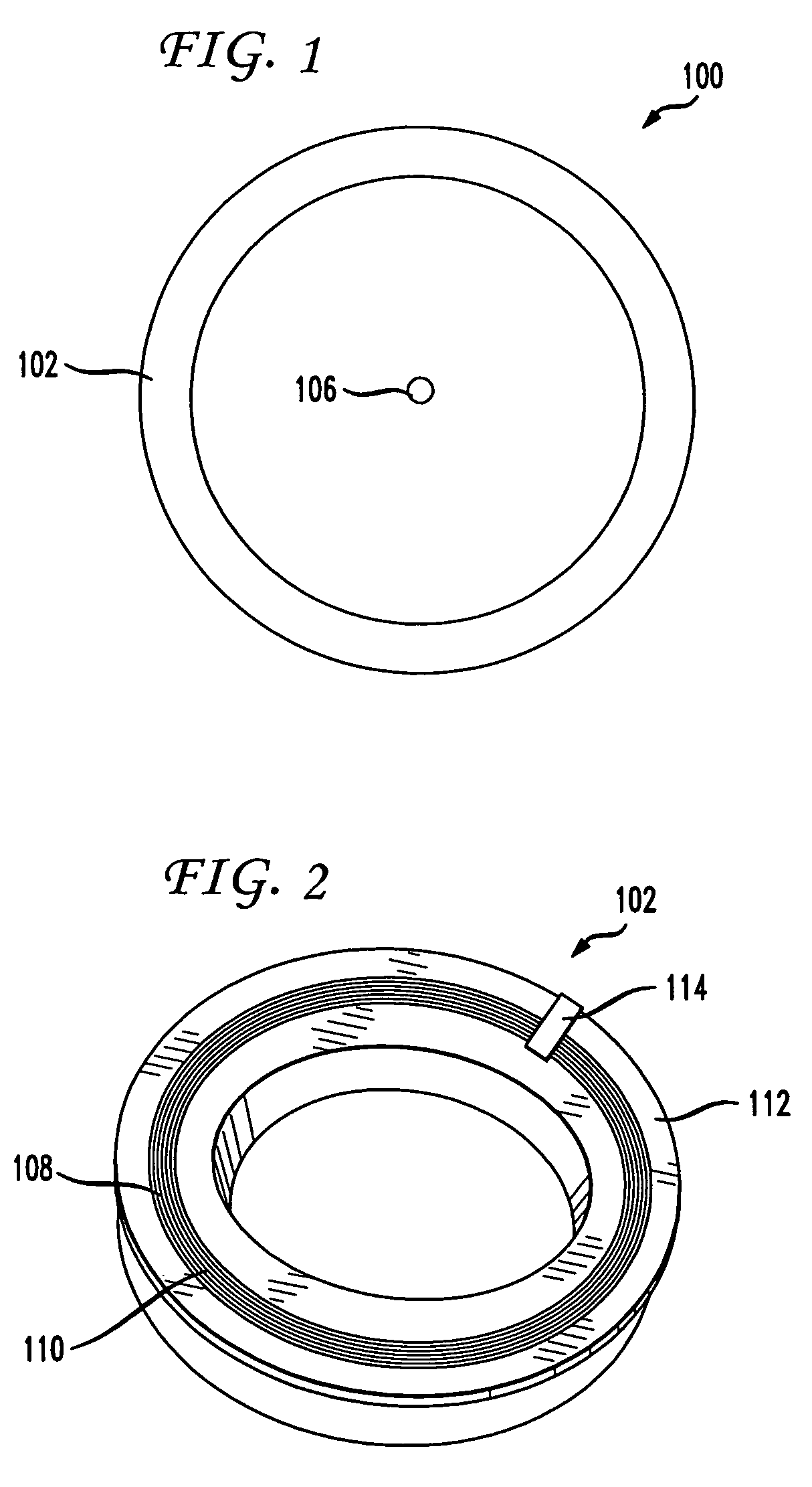
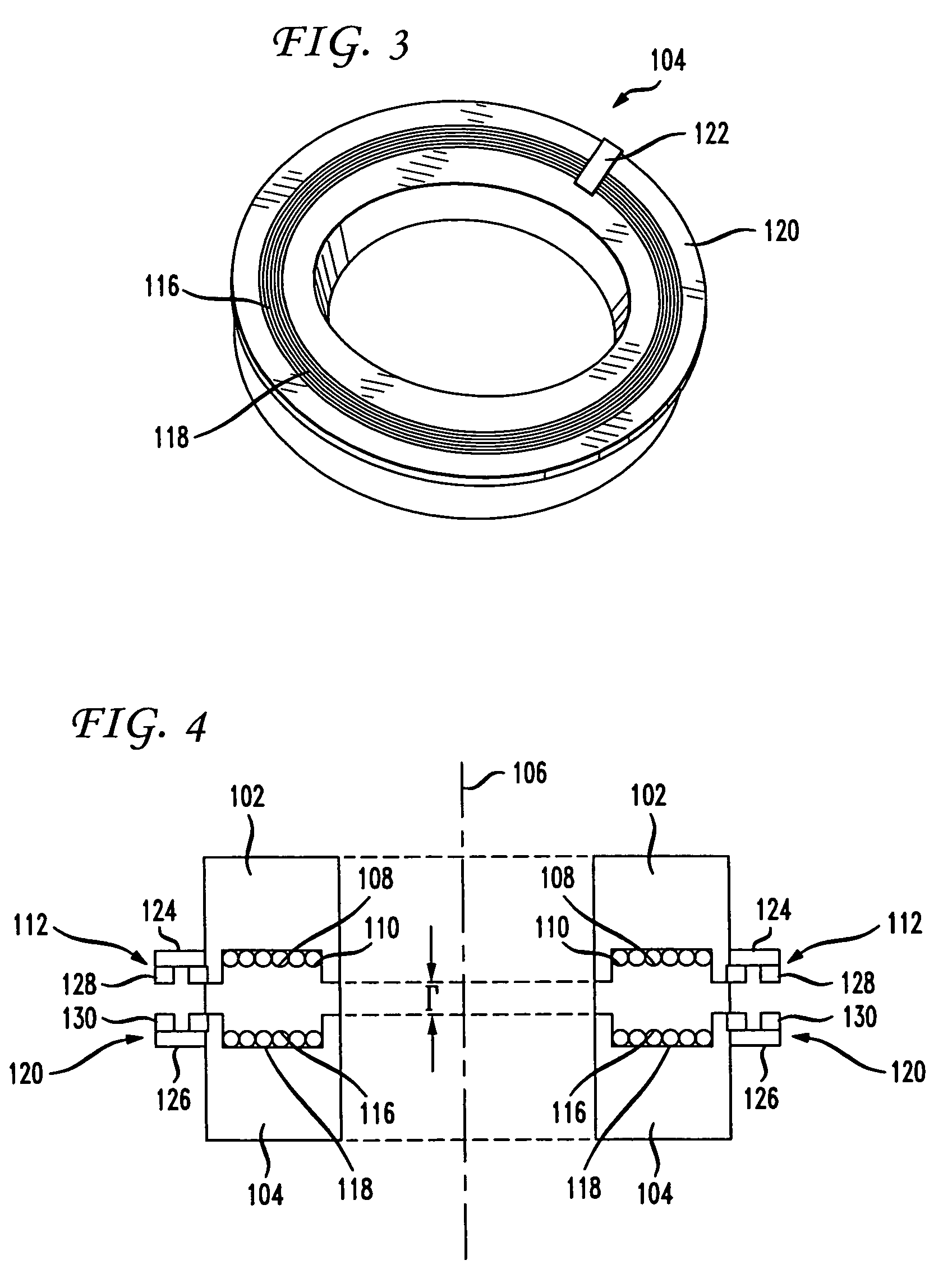
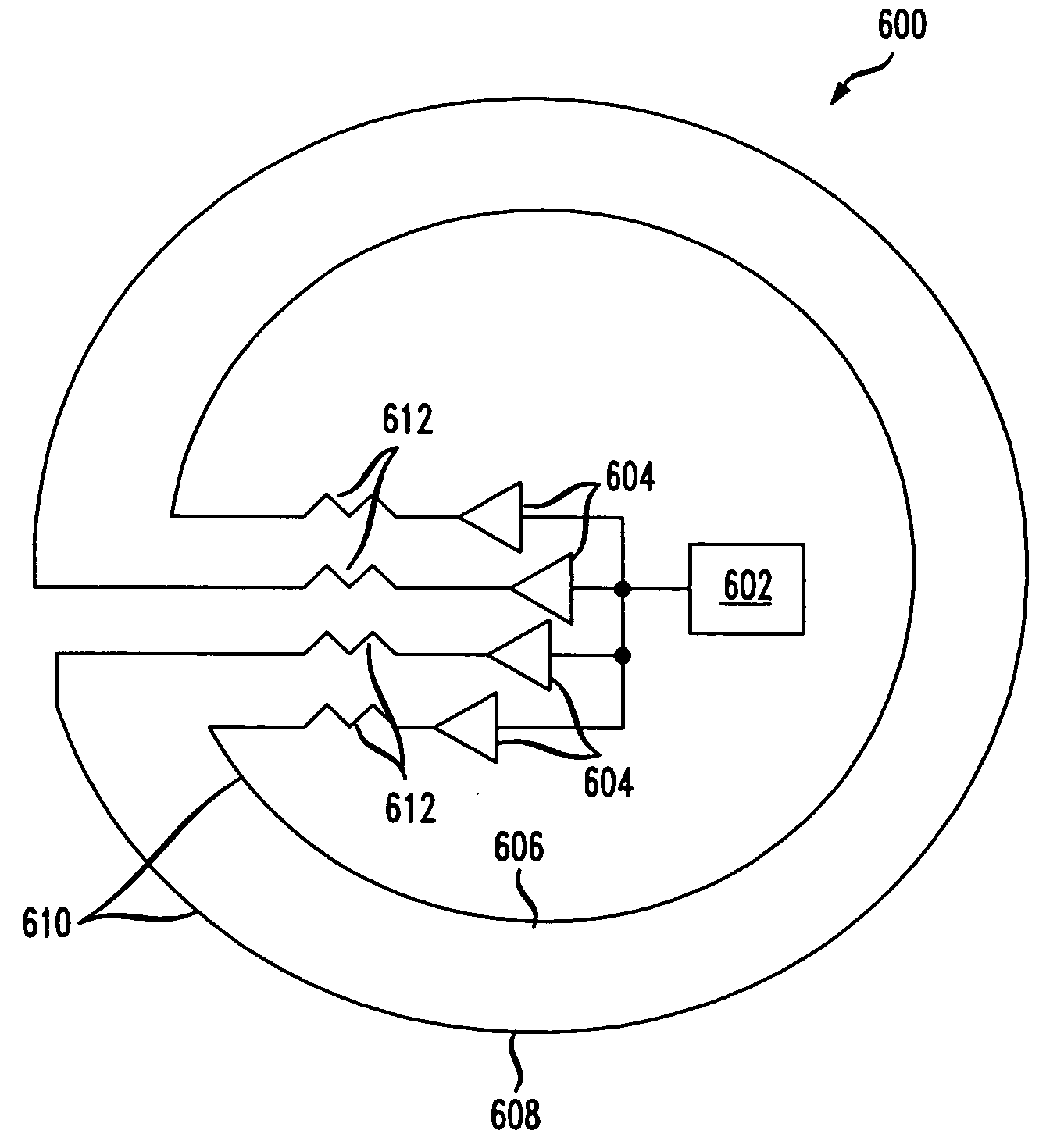
A non-contacting rotary interface has a first core with a first pair of balanced transmission lines coupled to the first core and a second core moveable in relation to the first core with a second pair of balanced transmission lines coupled to the second core and configured to receive signals from the first pair of balanced transmission lines. The first pair of balanced transmission lines has a first transmit wire coupled to a first transceiver at a first end of the first transmit wire, a second transceiver coupled to the first transmit wire at a second end of the first transmit wire, a second transmit wire coupled to a third transceiver at a first end of the second transmit wire, and a fourth transceiver coupled to the second transmit wire at a second end of the second transmit wire. The balanced transmission lines may be electrical traces on a circuit board.
Owner:VOXIS
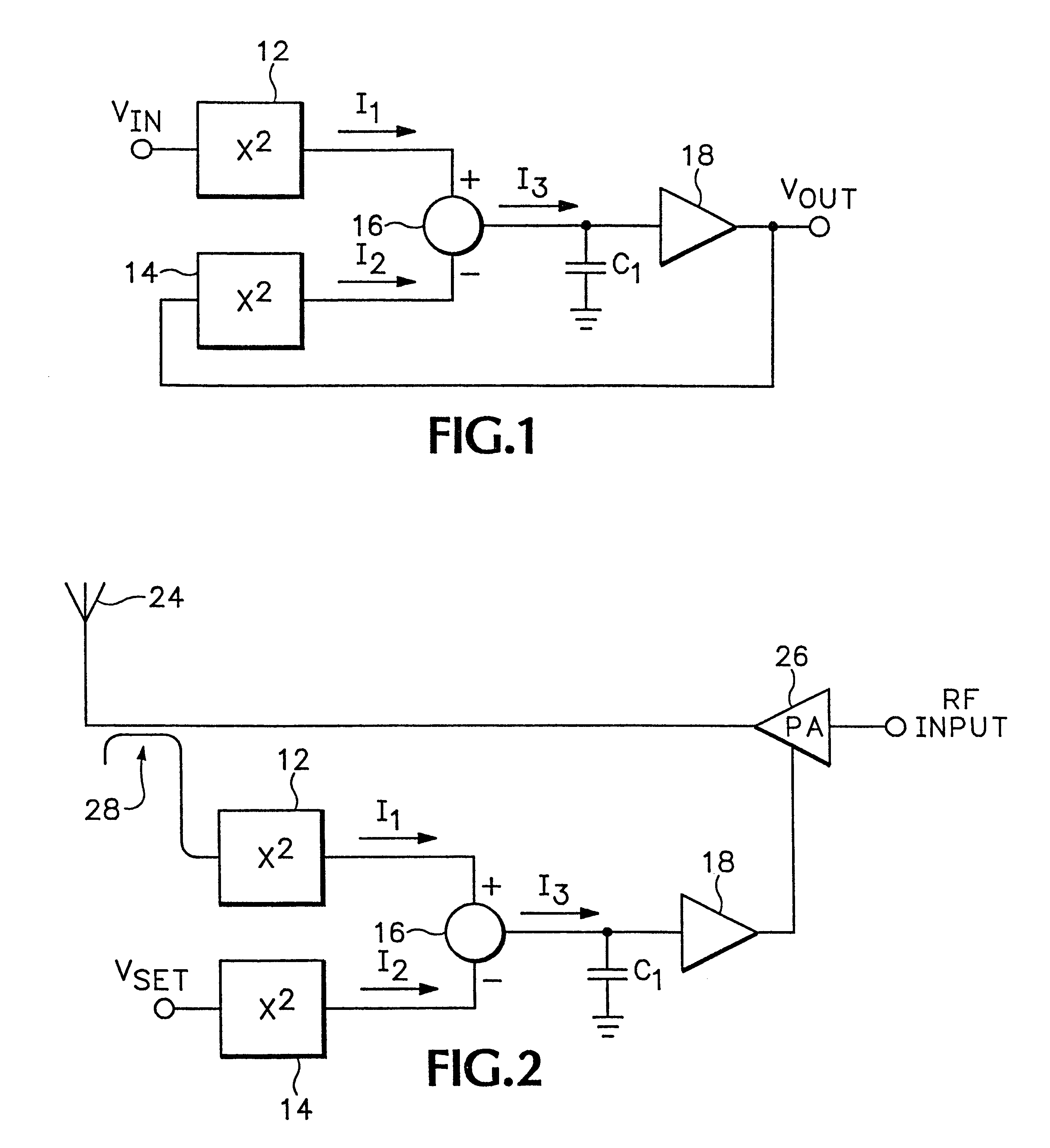
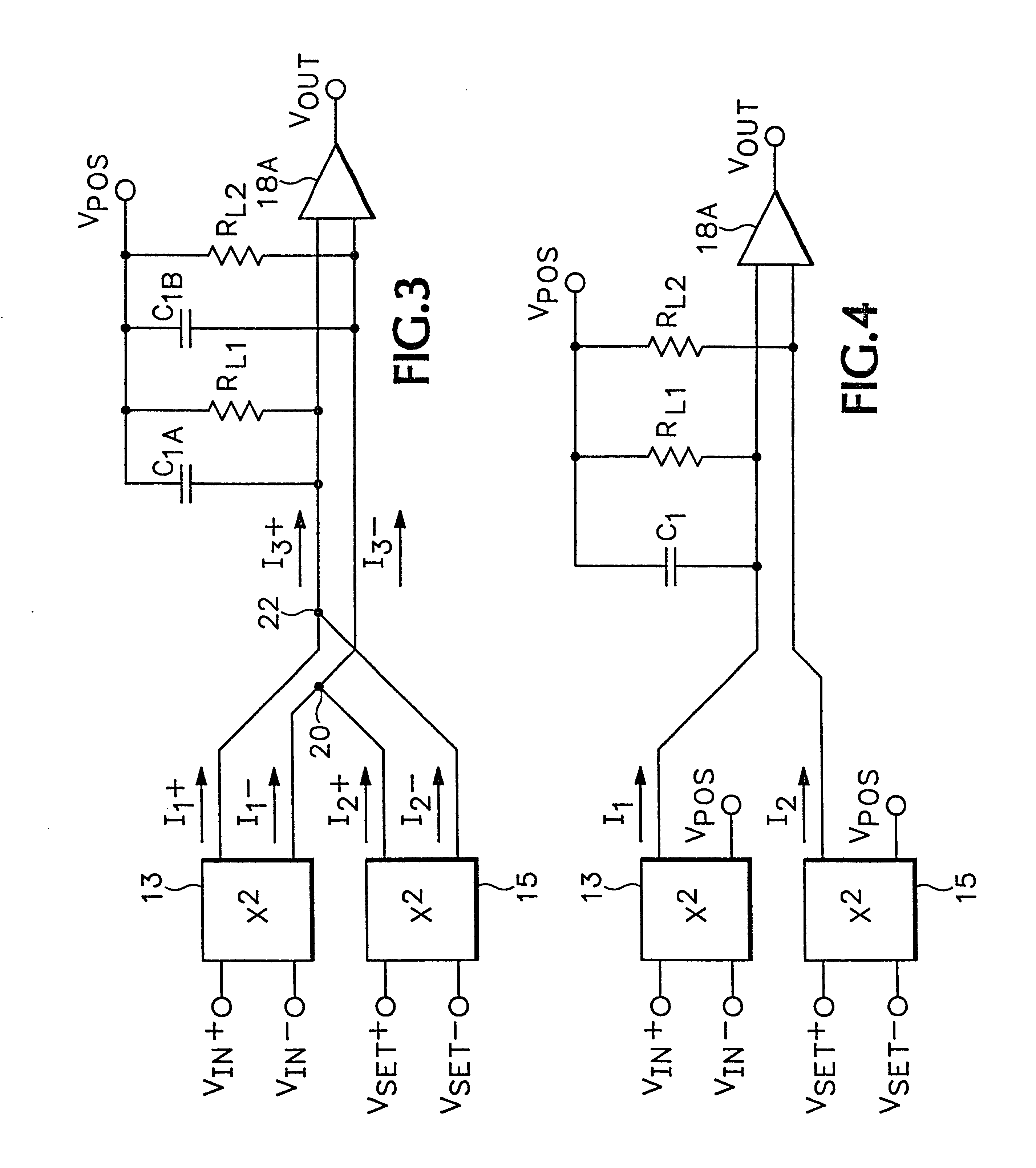
RMS-to-DC converter with balanced multi-tanh triplet squaring cells
InactiveUS6204719B1Accurate square law approximationImprove balanceComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsDigital data processing detailsTransconductanceSet point
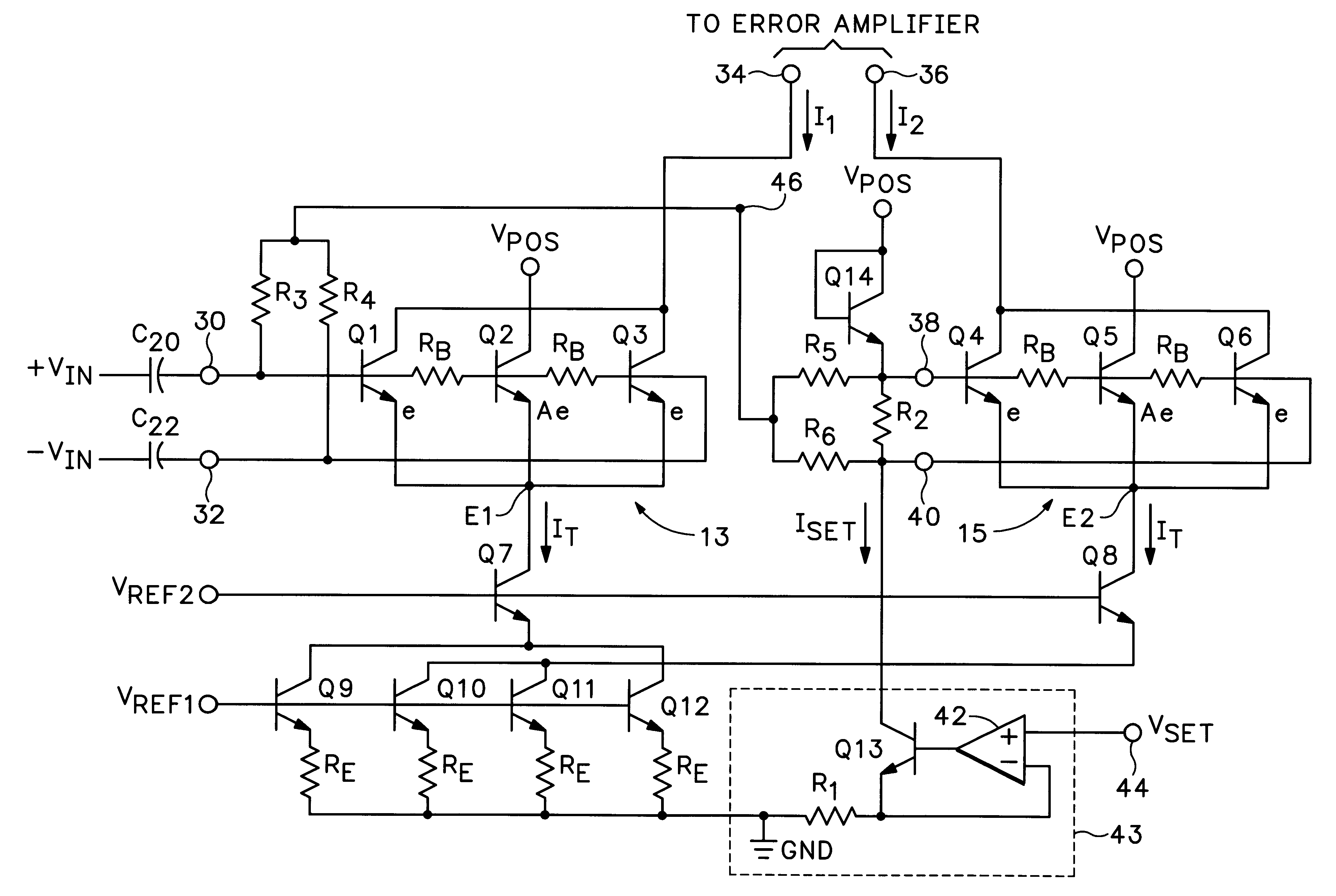
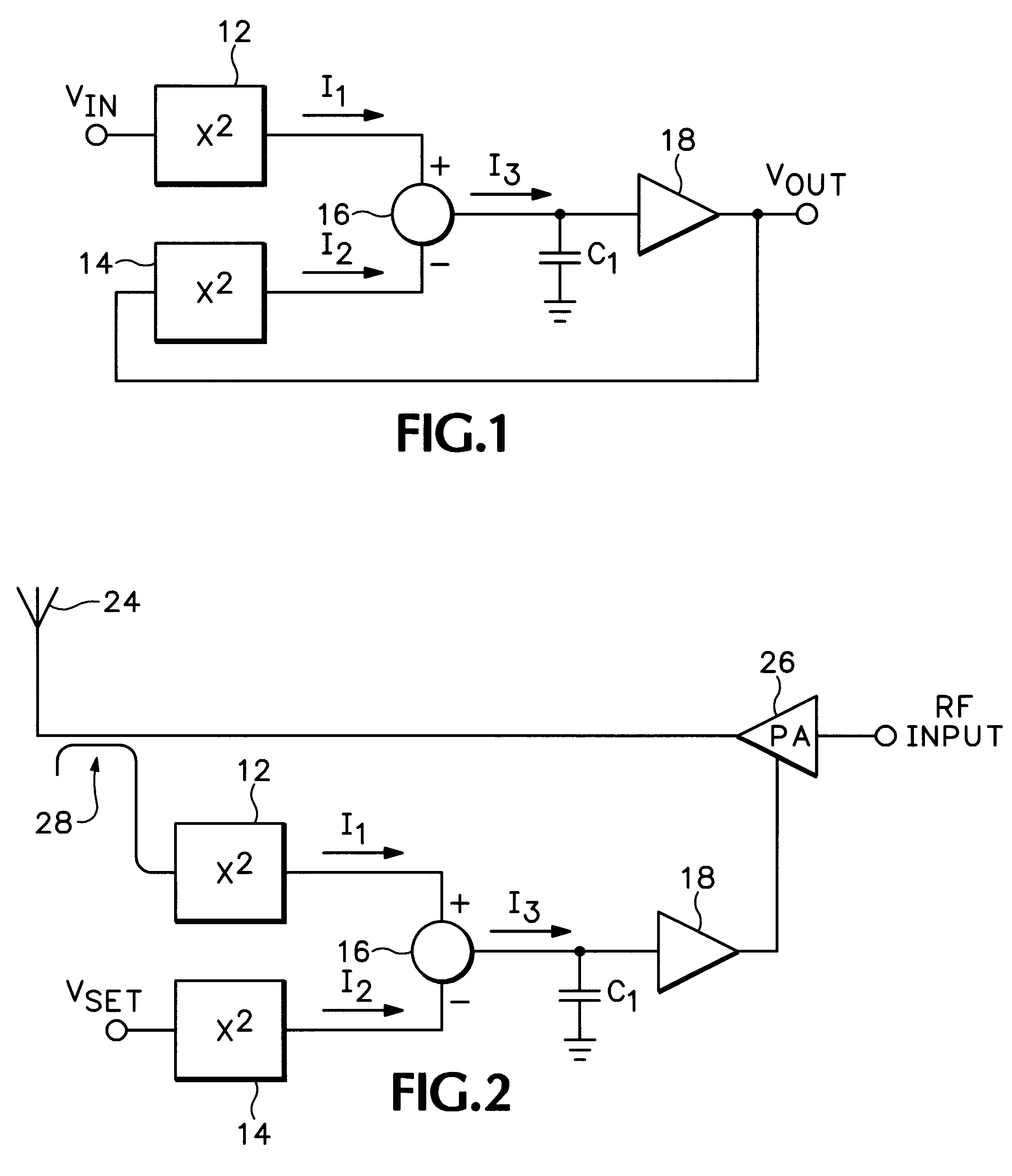
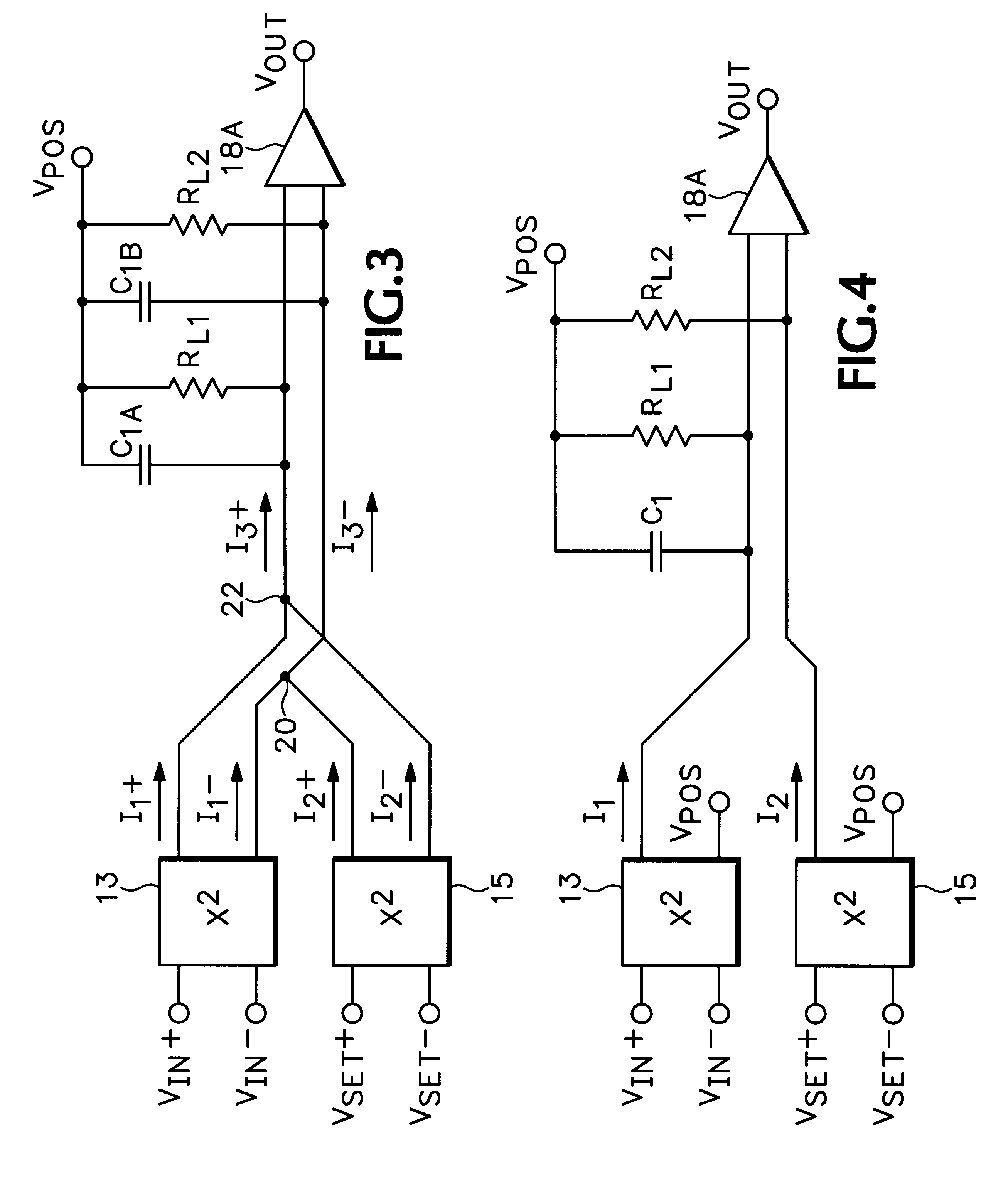
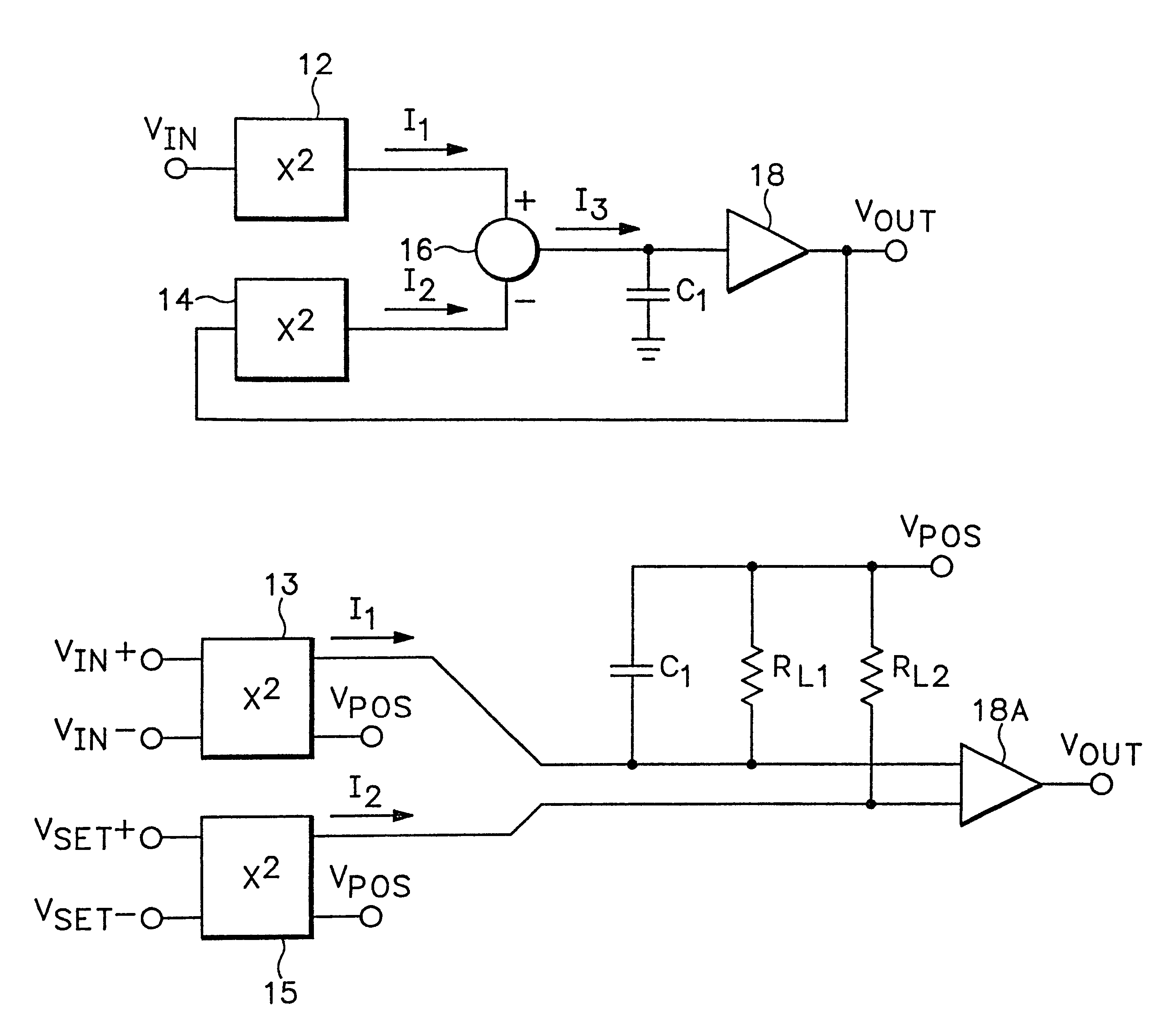
An RMS-to-DC converter implements the difference-of-squares function by utilizing two identical squaring cells operating in opposition to generate two signals. An error amplifier nulls the difference between the signals. When used in a measurement mode, one of the squaring cells receives the signal to be measured, and the output of the error amplifier, which provides a measure of the RMS value of the input signal, is connected to the input of the second squaring cell, thereby closing the feedback loop around the second squaring cell. When used in a control mode, a set-point signal is applied to the second squaring cell, and the output of the error amplifier is used to control a variable-gain device such as a power amplifier which provides the input to the first squaring cell, thereby closing the feedback loop around the first squaring cell. Accurate square law approximation at microwave frequencies can be achieved by implementing the squaring cells as series-connected three-transistor multi-tanh transconductance cells. By using carefully balanced squaring cells and a well-balanced error amplifier, approximation errors are cancelled and accurate RMS measurement is realized at high frequencies. A feedforward bootstrapping feature uses an op amp to balance the voltages at the common nodes of the transconductance squaring cells and also provides a balanced differential input drive to one of the squaring cells. A base current compensation circuit for providing accurate base compensation current to both of the squaring cells prevents errors due to DC offset voltages.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
RMS-to-DC converter with balanced multi-tanh triplet squaring cells
InactiveUS6549057B1Accurate square law approximationImprove balanceComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringTransconductance
An RMS-to-DC converter implements the difference-of-squares function by utilizing two identical squaring cells operating in opposition to generate two signals. An error amplifier nulls the difference between the signals. When used in a measurement mode, one of the squaring cells receives the signal to be measured, and the output of the error amplifier, which provides a measure of the RMS value of the input signal, is connected to the input of the second squaring cell, thereby closing the feedback loop around the second squaring cell. When used in a control mode, a set-point signal is applied to the second squaring cell, and the output of the error amplifier is used to control a variable-gain device such as a power amplifier which provides the input to the first squaring cell, thereby closing the feedback loop around the first squaring cell. Accurate square law approximation at microwave frequencies can be achieved by implementing the squaring cells as series-connected three-transistor multi-tanh transconductance cells. By using carefully balanced squaring cells and a well-balanced error amplifier, approximation errors are cancelled and accurate RMS measurement is realized at high frequencies. A feedforward bootstrapping feature uses an op amp to balance the voltages at the common nodes of the transconductance squaring cells and also provides a balanced differential input drive to one of the squaring cells. A base current compensation circuit for providing accurate base compensation current to both of the squaring cells prevents errors due to DC offset voltages.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Broadband dual polarized antenna unit
ActiveCN101707291AImprove consistencySimple structurePolarised antenna unit combinationsBroadbandLength wave
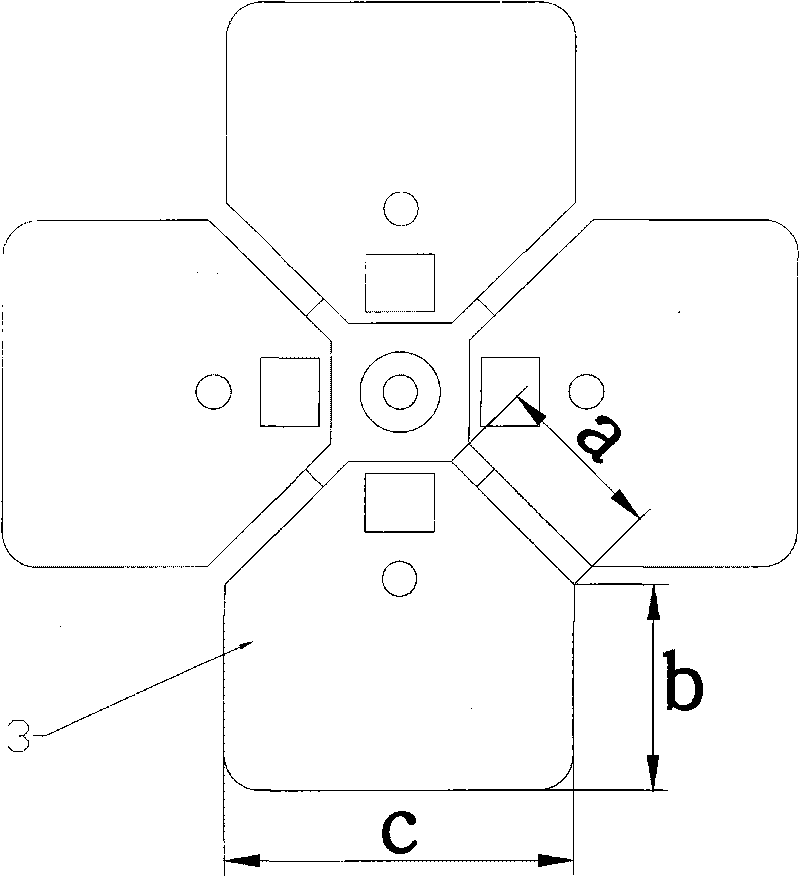
The invention discloses a broadband dual polarized antenna unit, which comprises a radiator and a balanced feeding device, wherein the radiator consists of four radiation fins which are symmetric in pairs and are orthogonally distributed; the balanced feeding device consists of an excitation core wire and a balanced balun; the balanced balun is simultaneously formed into a support of each radiation fin; a symmetric radiation array is as long as a half of wavelength and is as wide as a quarter of the wavelength; each radiation fin further comprises a supporting area and a radiation area which are mutually adjacent; the two short sides and long sides of the radiation area and the two waists of the supporting area form a continuous curve; the ratio of the waist length of the supporting area to the length of the short side of the radiation area to the length of the long side of the radiation area is 1:1:2; and the two waists of each of the two adjacent radiation fins are arranged in parallel and are at an interval less than 0.1 wavelengths. The dual polarized antenna unit is a radiation oscillator which is relatively wider than the broadband and has good indexes, such as a standing-wave ratio and the like in a relatively wider bandwidth.
Owner:TONGYU COMM INC
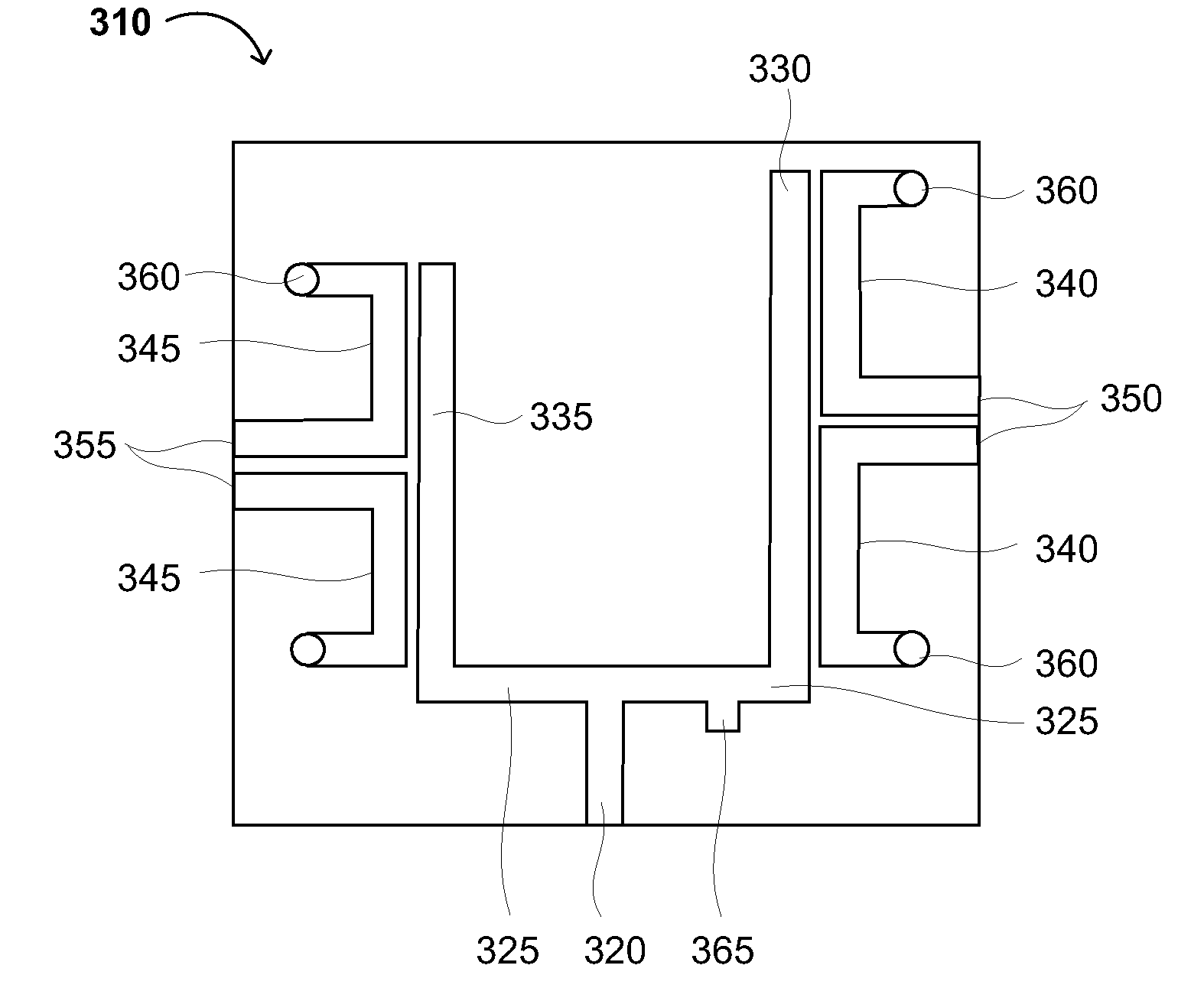
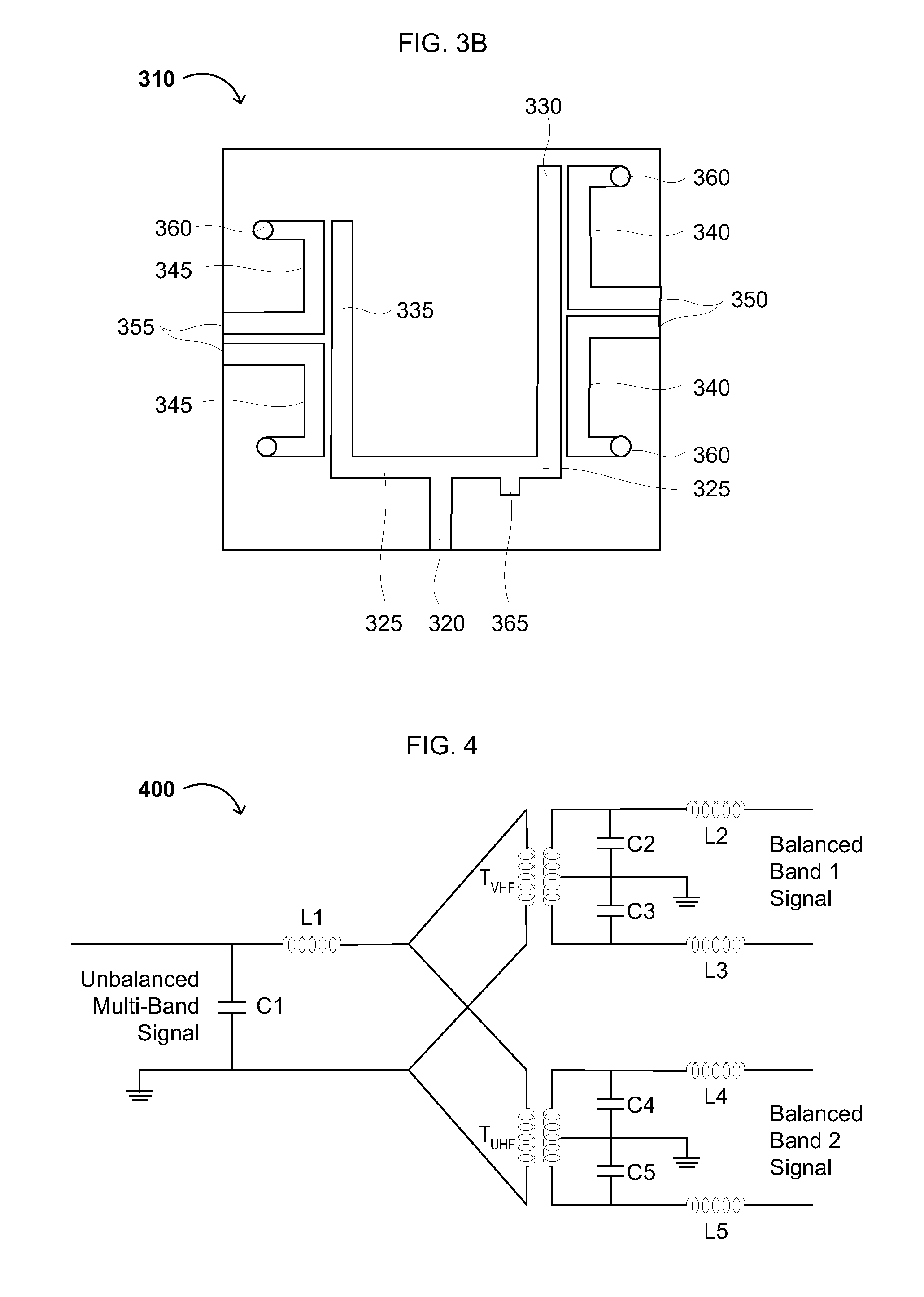
Integrated Balanced-Unbalanced Duplexer
InactiveUS20080224791A1Increase costAdd dimensionMultiple-port networksOne-port networksElectromagnetic couplingMulti band
Circuitry, architectures, devices and systems for multi-band radio communications using a balanced-unbalanced duplexer. An integrated balanced-unbalanced duplexer for multi-band communications may include an unbalanced multi-band port; a first balanced single-band port; a second balanced single-band port; a first unbalanced coupling arm conductively coupled to the unbalanced multi-band port; a second unbalanced coupling arm conductively coupled to the unbalanced multi-band port; a first pair of balanced coupling arms conductively coupled to the first balanced single-band port and electromagnetically coupled to the first unbalanced coupling arm; and a second pair of balanced coupling arms conductively coupled to the second balanced single-band port and electromagnetically coupled to the second unbalanced coupling arm. The architectures and / or systems generally include components embodying one or more of the concepts disclosed herein.
Owner:MARVELL INT LTD
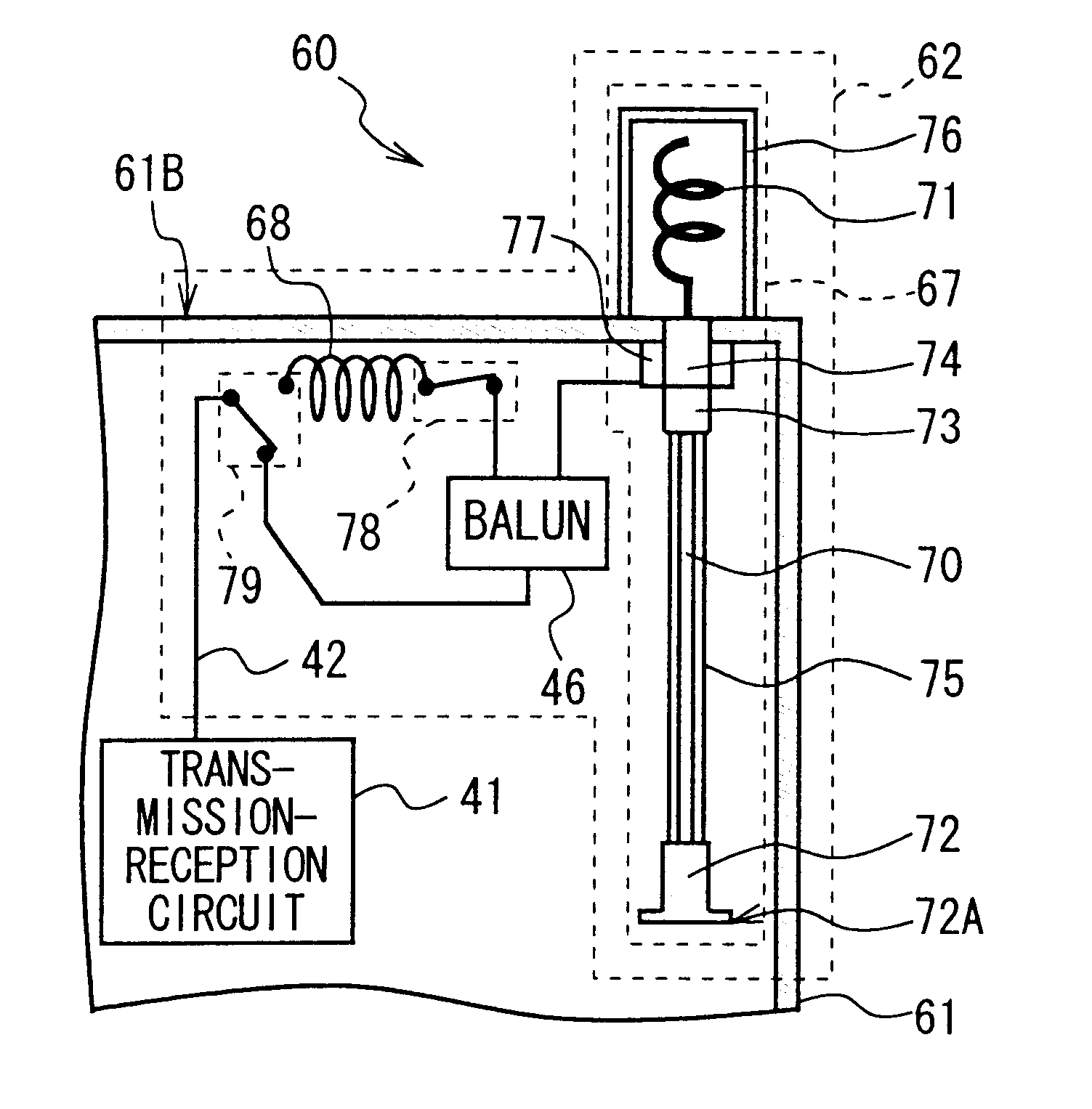
Antenna device and portable radio set
InactiveUS6362793B1Multiple-port networksSpatial transmit diversityCommunication qualityDrain current
An antenna in which first and second antenna elements are selected by a switching apparatus so that the first and the second antenna elements are connected to an unbalanced transmission line via a balancing-unbalancing transmission line or only the first antenna element is connected to the unbalanced transmission line. The unbalanced transmission line supplies power via a balanced-to-unbalanced transformation apparatus to the first and the second antenna elements, so as to operate as an antenna, at which time, balanced-to-unbalanced transformation action of the balanced-to-unbalanced transformation apparatus prevents leakage current from flowing from the first or the second antenna element to the unbalanced transmission line and prevents a ground element on which the unbalanced transmission line is grounded from operating as an antenna. This reduces deterioration of antenna characteristics in the vicinity of a human body, so that an antenna device and portable radio set which can sizably reduce deterioration of communication quality can be realized.
Owner:SONY CORP
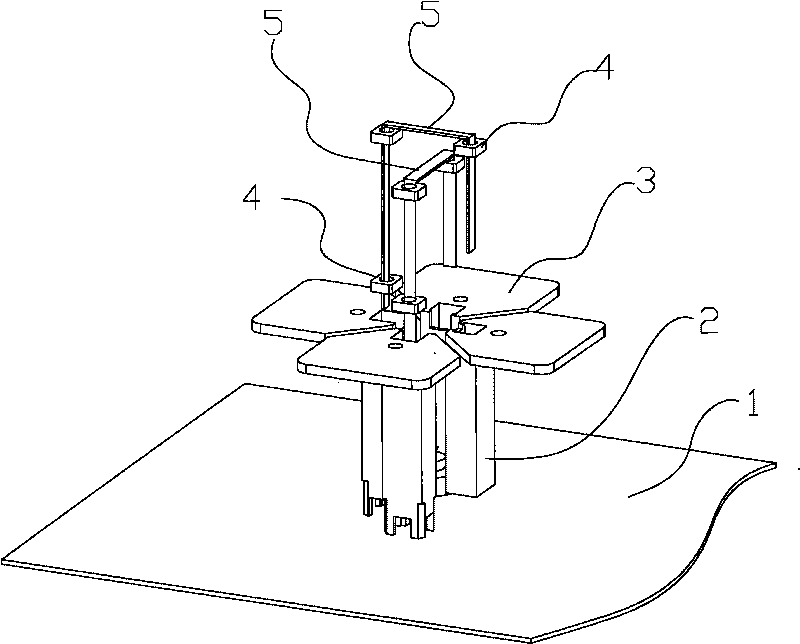
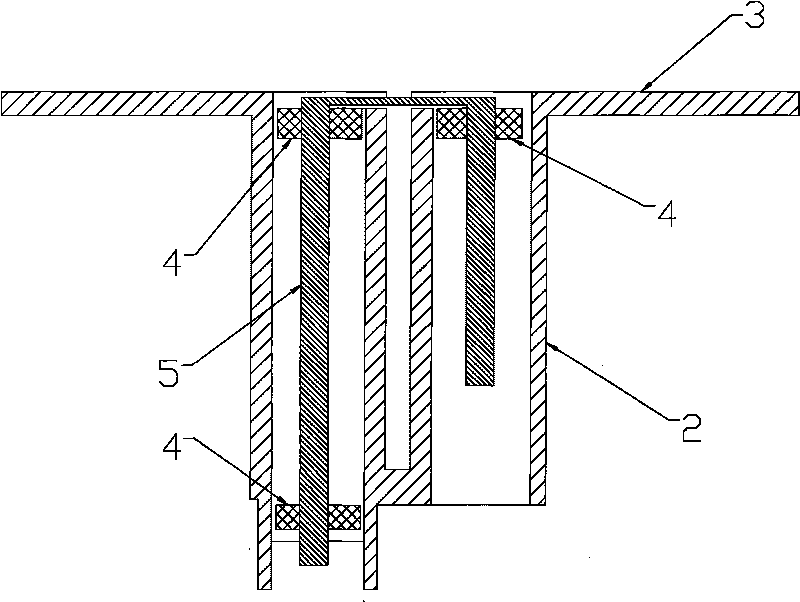
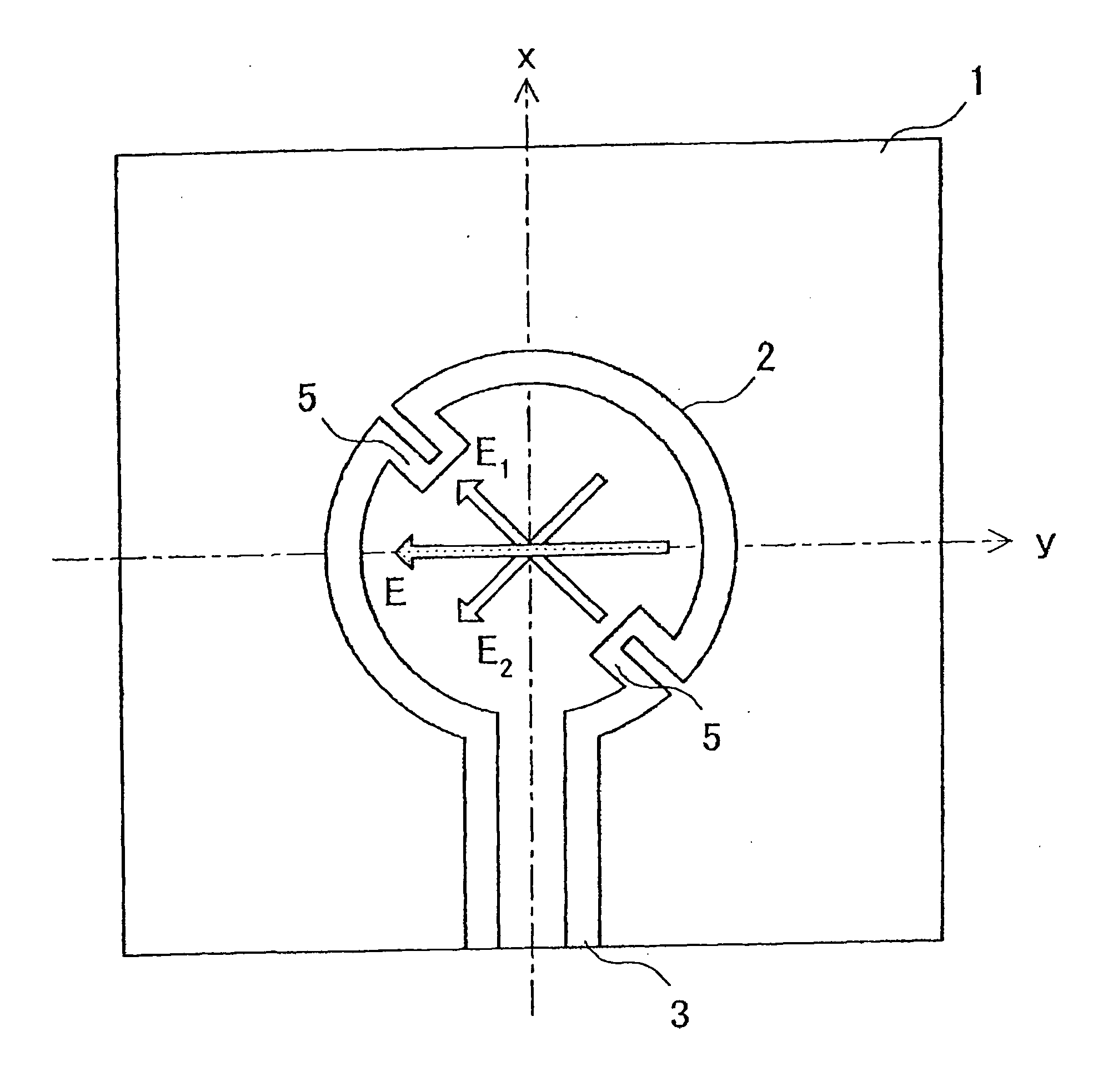
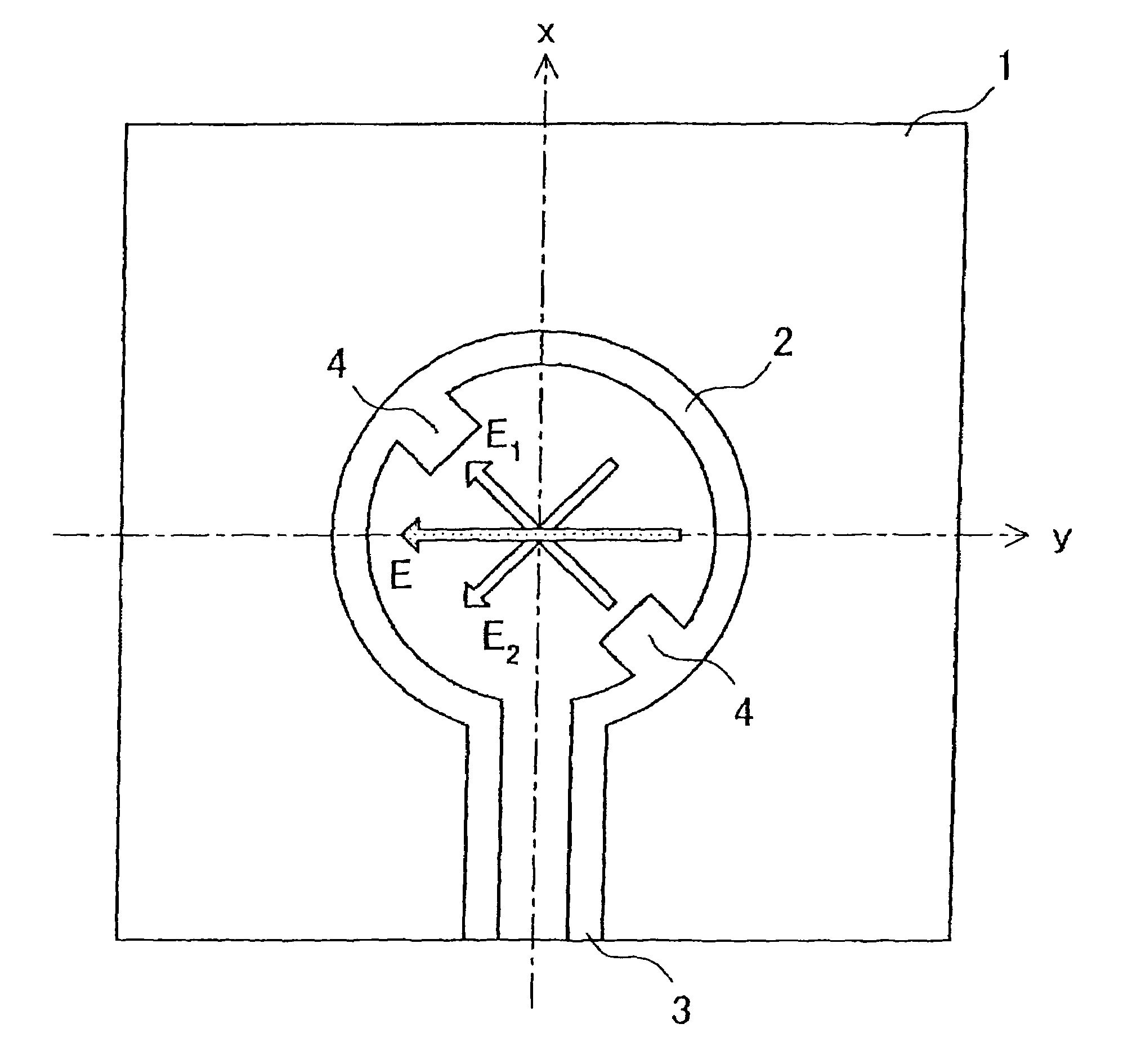
Circularly polarized antenna and rectenna using this antenna
InactiveUS20050259030A1Simple structureImprove productivityResonant long antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectricCircularly polarized antenna
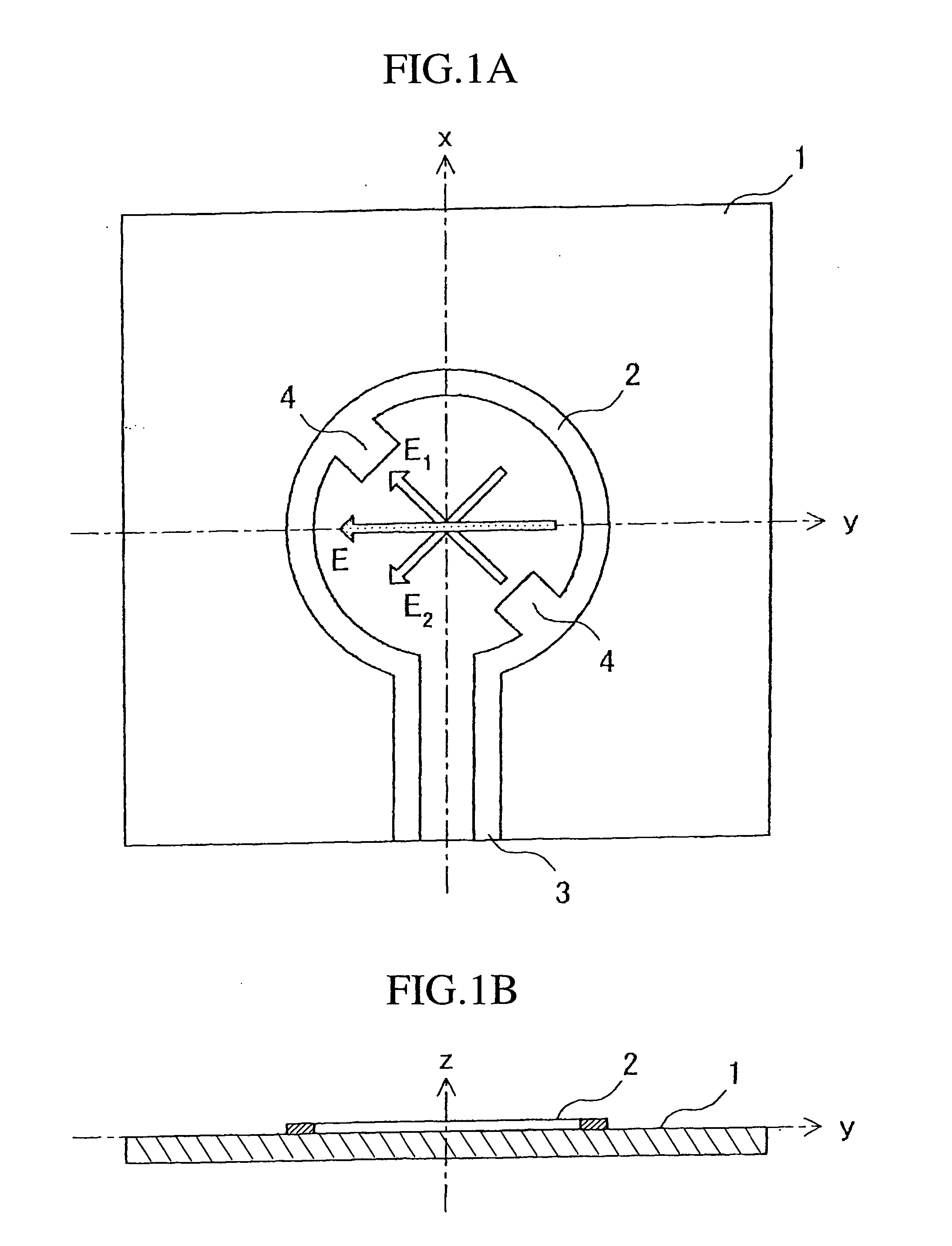
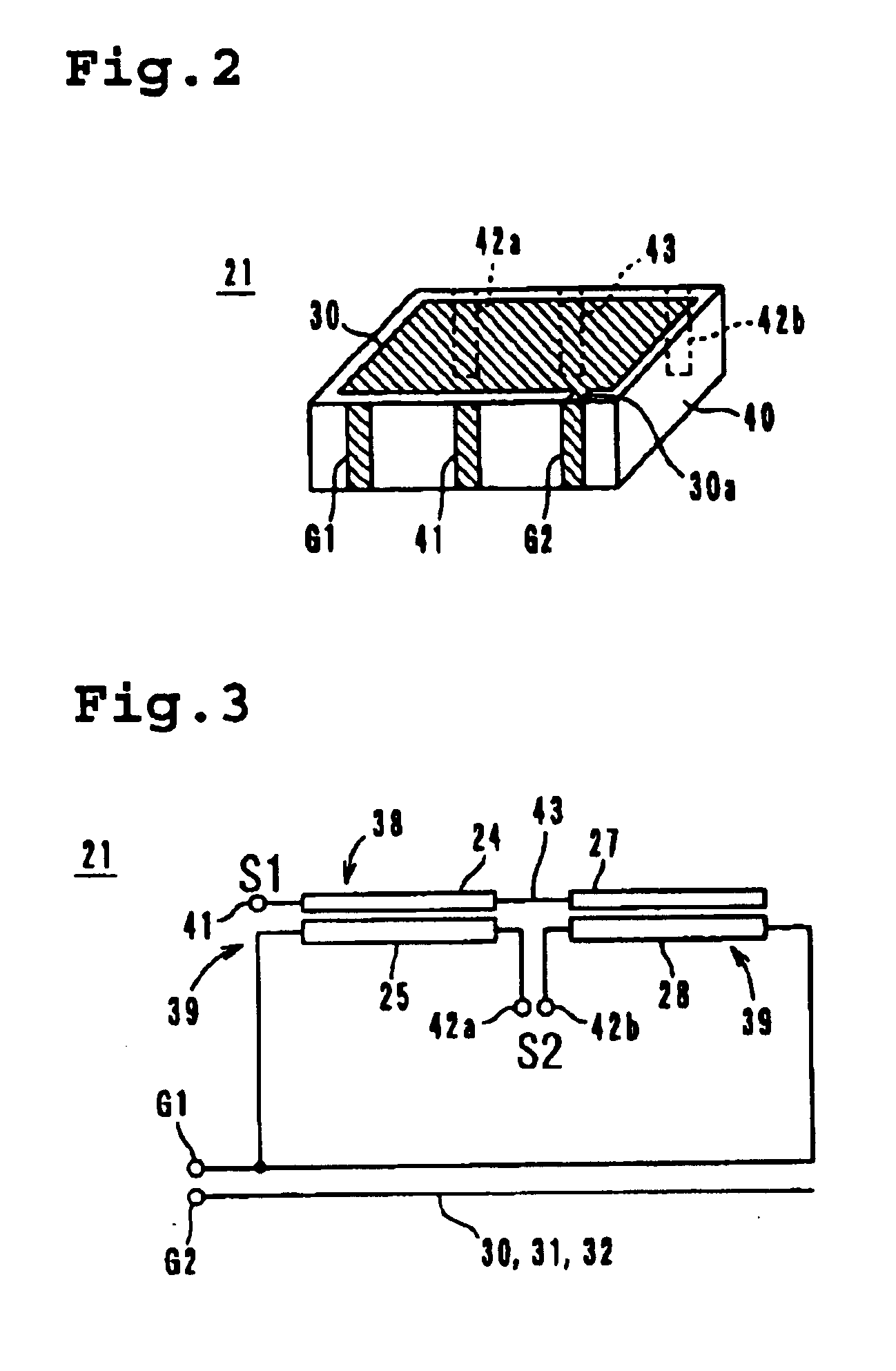
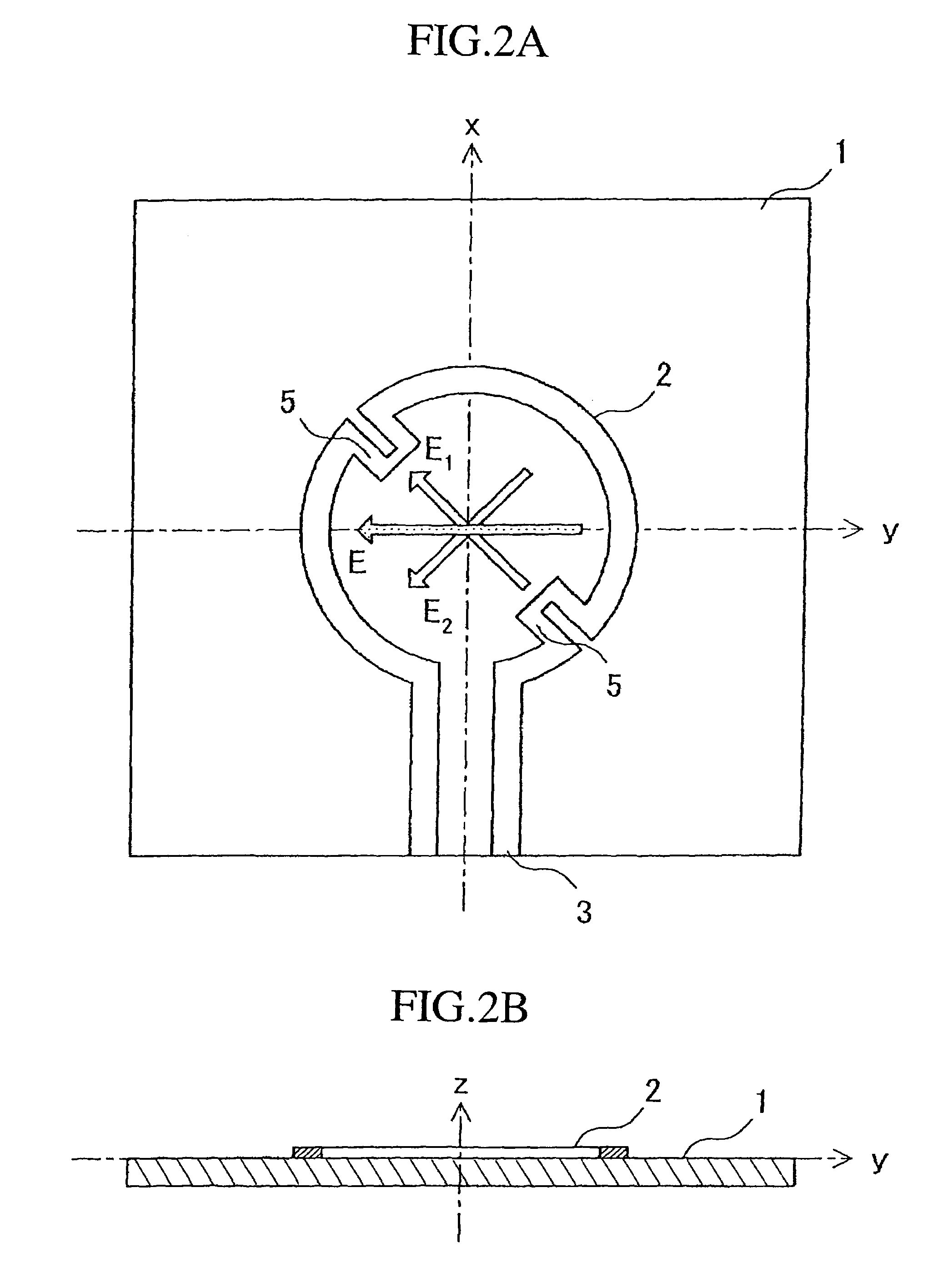
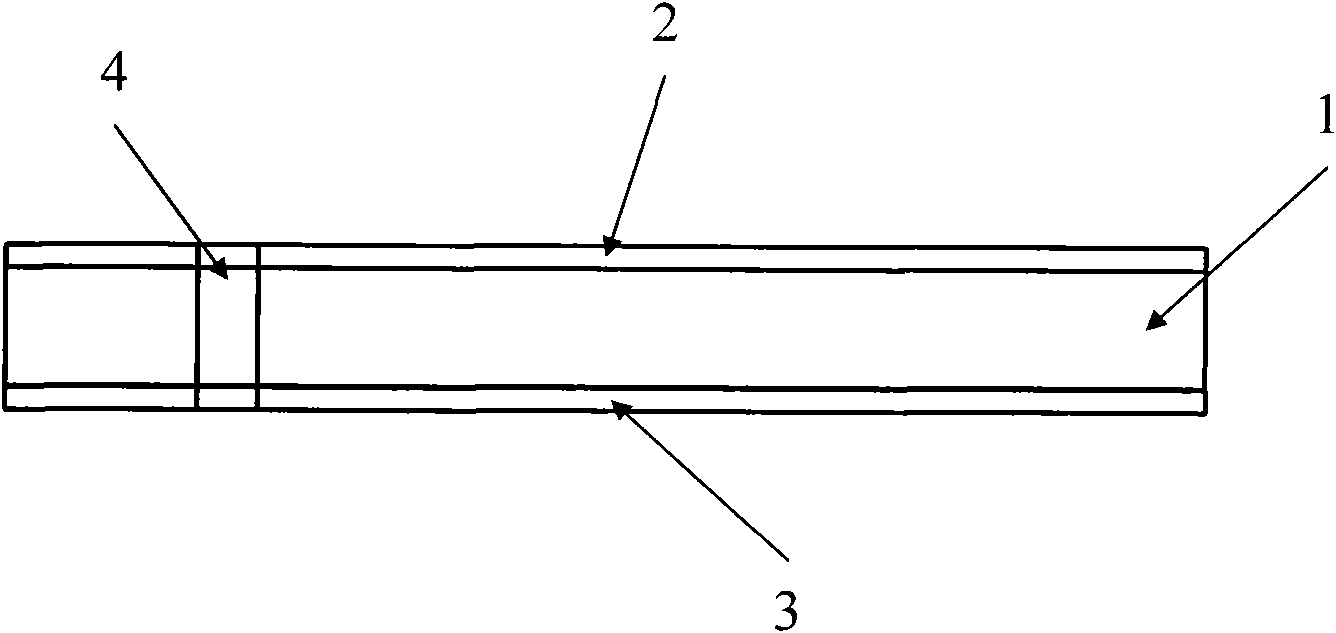
A loop antenna unit (2), a balanced line (3), and two perturbation elements (4) are formed on a dielectric board (1) by using manufacturing methods, such as printing and etching. The loop antenna unit (2) is formed along the circumference of a circle, and is connected to the balanced line (3). Each of the two perturbation elements (4) is a member in the shape of a tooth which is inclined 45 degrees against a direction of feeding of power via the balanced line (3) and which is projecting from the loop antenna unit (2) in an inward direction toward the center of the loop antenna unit (2). The two perturbation elements (4) are arranged at two opposite points in the loop antenna unit (2) so that they are opposite to each other.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Laminated balun transformer
A laminated balun transformer includes first line elements which are connected in series through a relay terminal, to constitute an unbalanced transmission line. Other line elements each constitute a balanced transmission lines. Strip lines are electromagnetically coupled to constitute a coupler. Similarly, other line elements are electromagnetically coupled to constitute a coupler. A ground terminal is connected to the balanced transmission lines, which are constituted by a pair of the line elements. Meanwhile, a shield terminal is connected to leading portions of shield electrodes. These two terminals are electrically independent of each other.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Level shifter with balanced rise and fall times
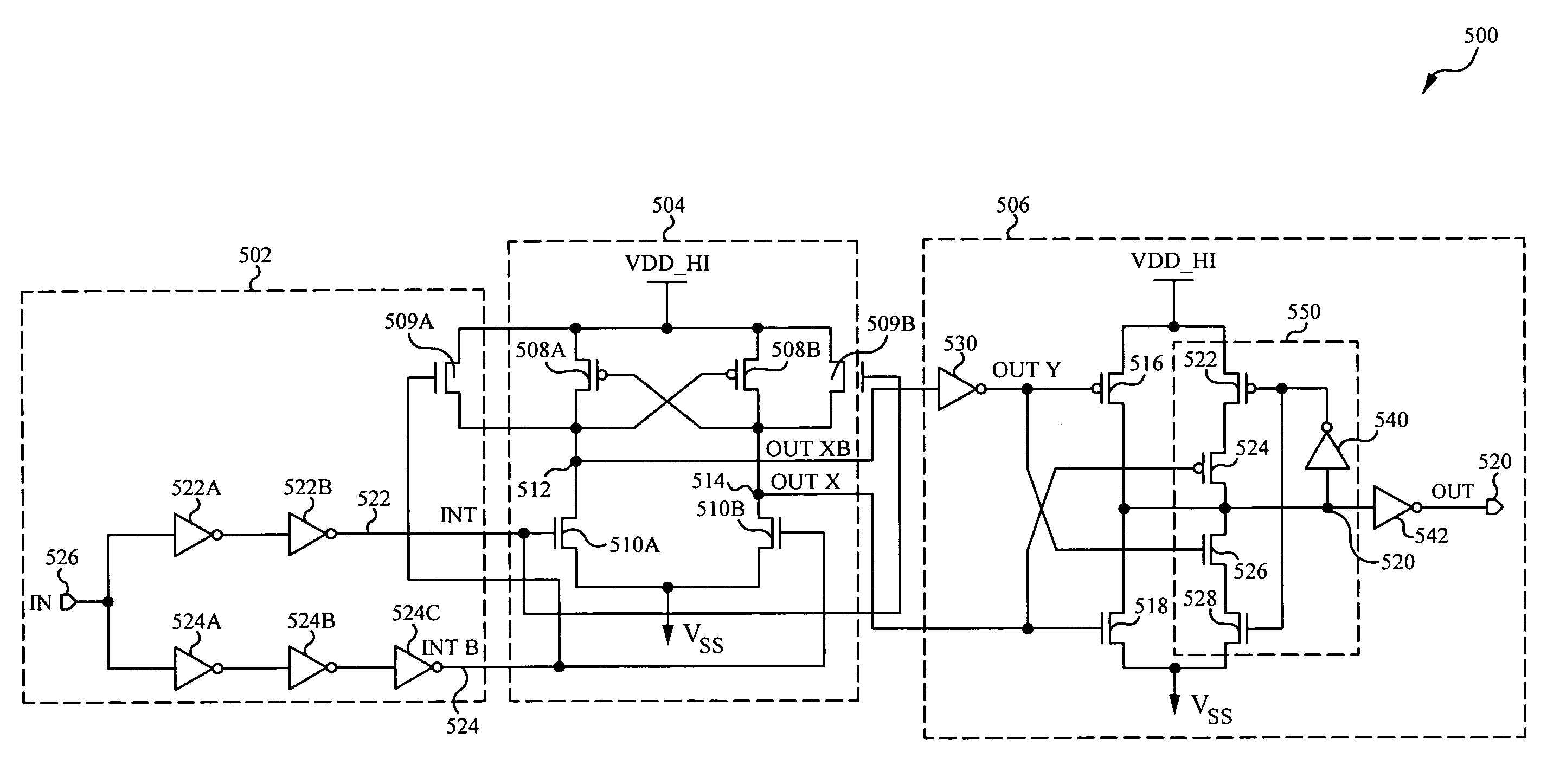
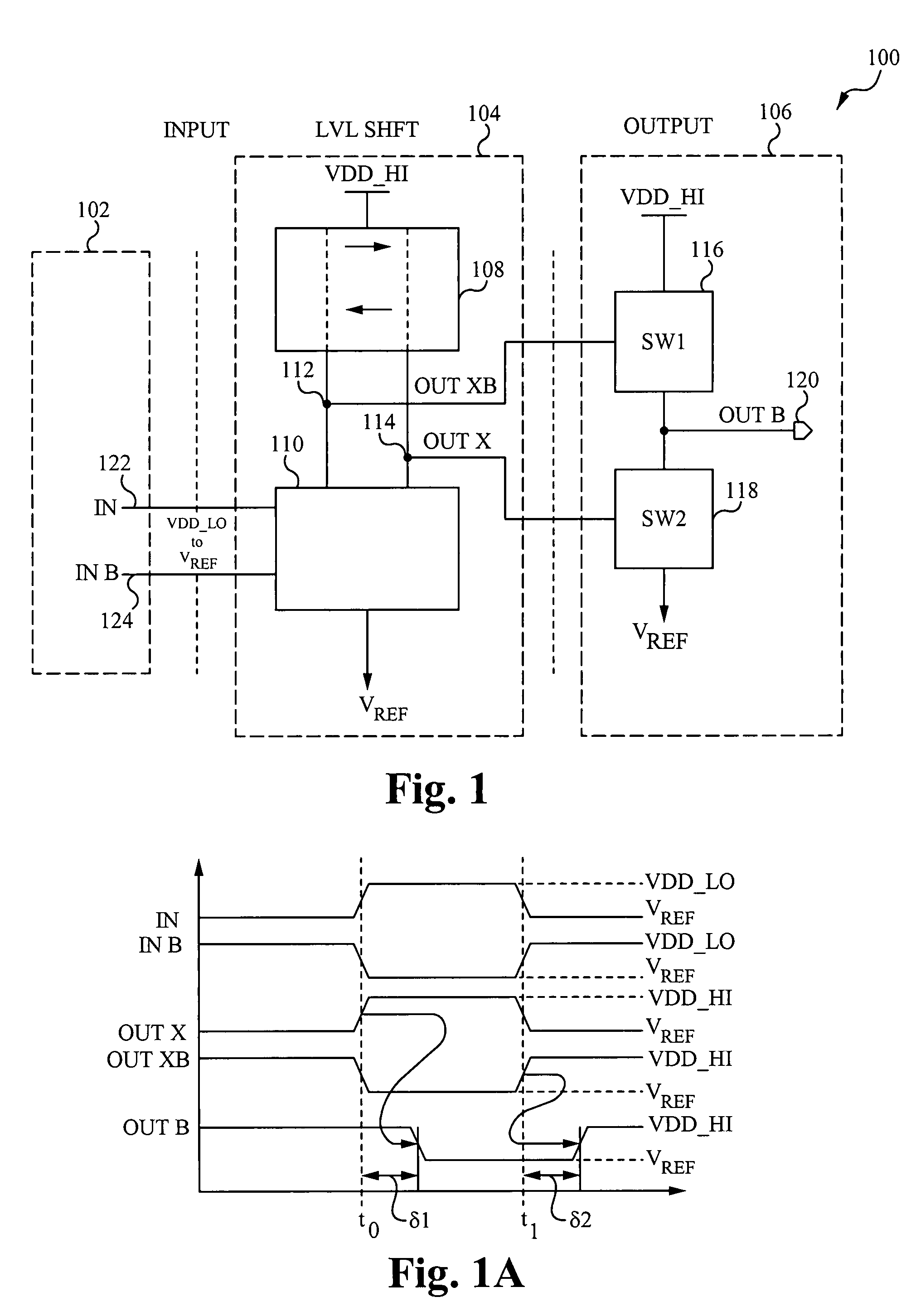
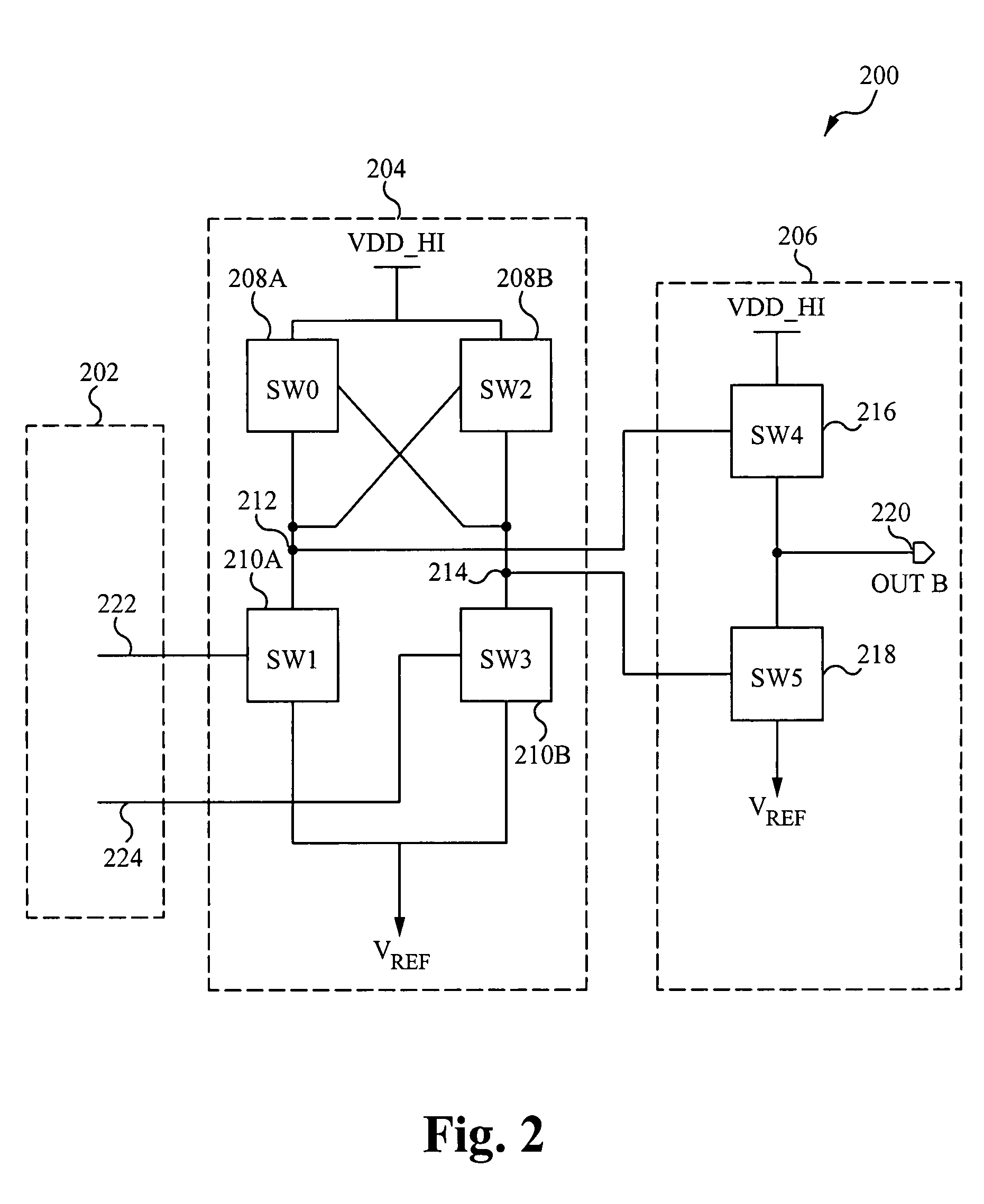
A level shifting circuit can include a shift stage that latches first and second internal nodes to opposite shifted logic potentials in response to different transitions at an input signal node. The input signal node can vary between non-shifted logic potentials. An output stage can enable a first controllable impedance path coupled between an output node and a first shifted power supply node in response to a first type transition at the first internal node, and can enable a second controllable impedance path coupled between the output node and a second shifted power supply node in response to the first type transition at the second internal node.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
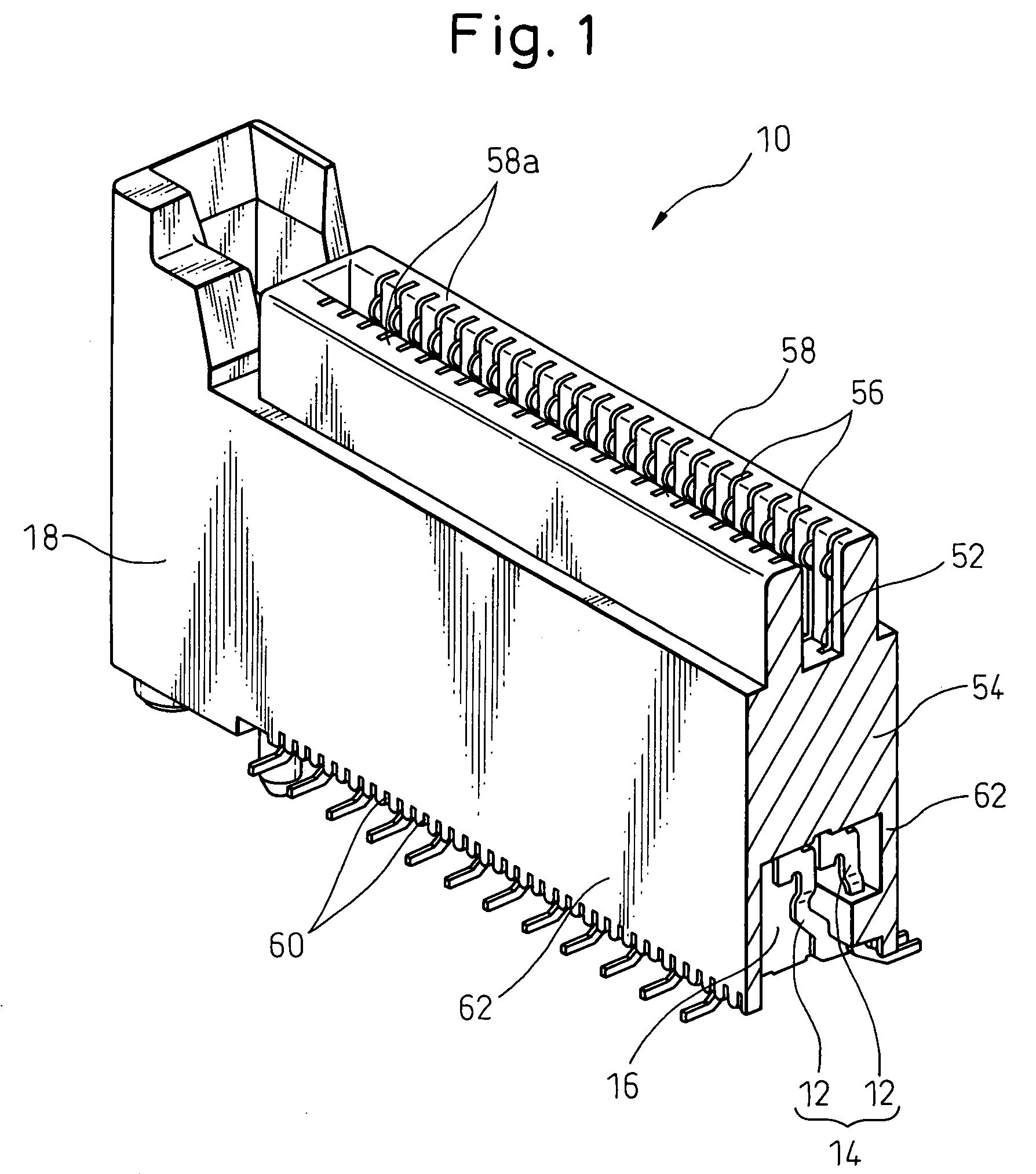
Cable connector for balanced transmission
InactiveUS20060270271A1Increase speedImprove featuresElectrically conductive connectionsElectric discharge tubesStructural engineeringElectric cables
A cable connector for balanced transmission is disclosed. A spacer member is attached to a contact assembly body in the cable connector for balanced transmission, a first signal wire connecting part of a first signal contact member is inserted into a first groove of the spacer member, a second signal wire connecting part of a second signal contact member is inserted into a second groove of the spacer member, and a ground contact member is inserted in a slit of the spacer member, so that their positions are decided. A cable for balanced transmission includes plural pairs of wires, and a first signal wire of the pair of wires is soldered to the first signal connecting part, a second signal wire thereof is soldered to the second signal connecting part, and a drain wire thereof is soldered to a drain wire connecting part of the ground contact member.
Owner:FUJITSU COMPONENENT LTD
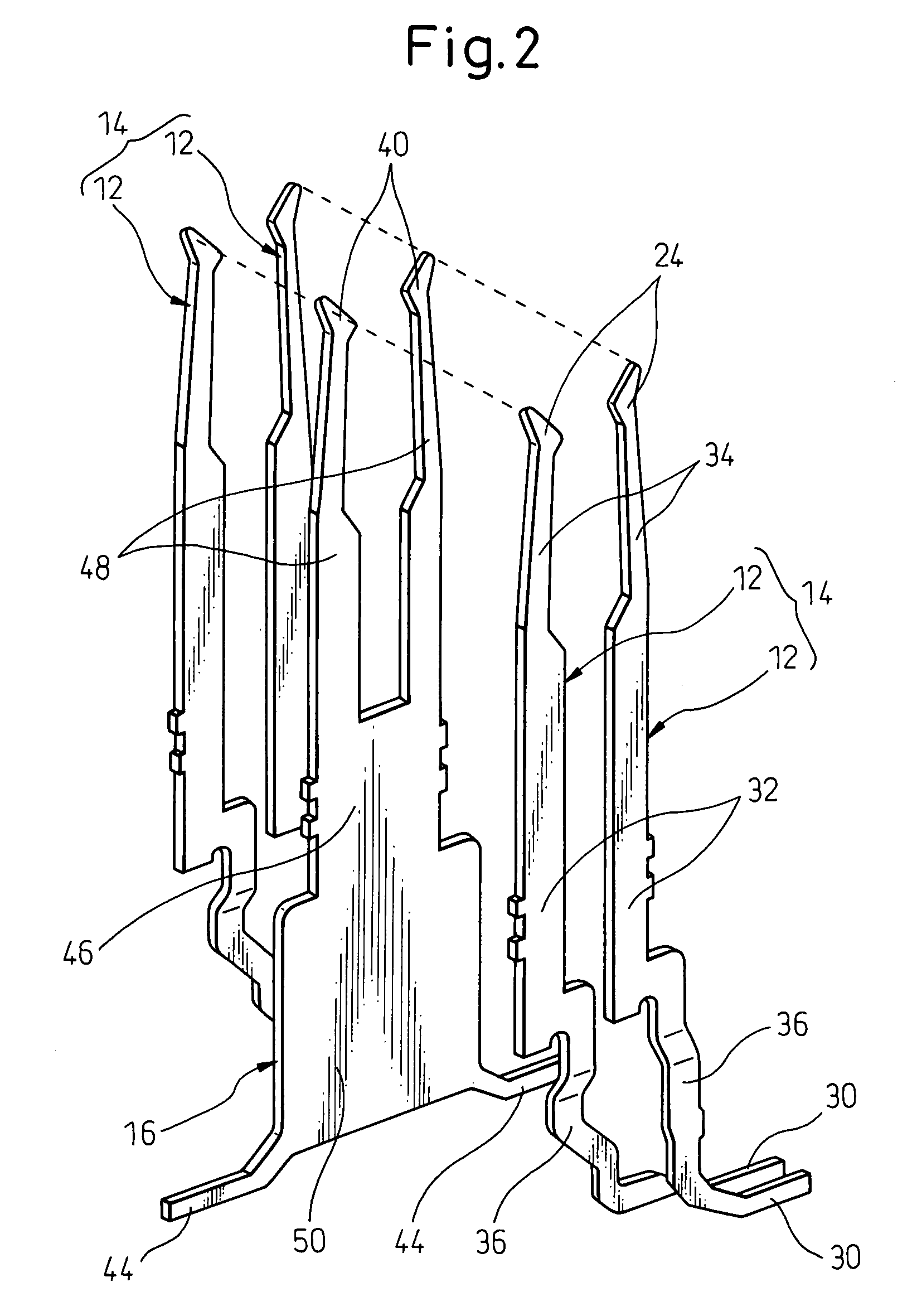
High speed transmission connector
InactiveUS7604510B2Reduce the differenceConductor pattern on a circuit board can be simplifiedElectrically conductive connectionsIncorrect coupling preventionElectrical conductorMechanical engineering
A high speed transmission connector including several signal contact pairs arranged in a parallel array, each including a pair of signal contacts constituting a balanced transmission line; several ground contacts, each being arranged between two signal contact pairs arranged in the parallel array; and an electro-insulating body supporting the signal contact pairs and the ground contacts. Each signal contact is provided with a contacting section at one longitudinal end for conductive contact with a corresponding signal contact of a counterpart connector, a board connecting section at another longitudinal end for connection with a conductor on a circuit board, and an attaching section between the contacting section and the board connecting section for an attachment to the body. All of the board connecting sections of the signal contacts are disposed along a first lateral surface of the body. The signal contacts of the signal contact pairs are individually covered, at least partially, by materials having dielectric constants different from each other, in certain regions defined between board connecting sections and attaching sections.
Owner:FUJITSU COMPONENENT LTD
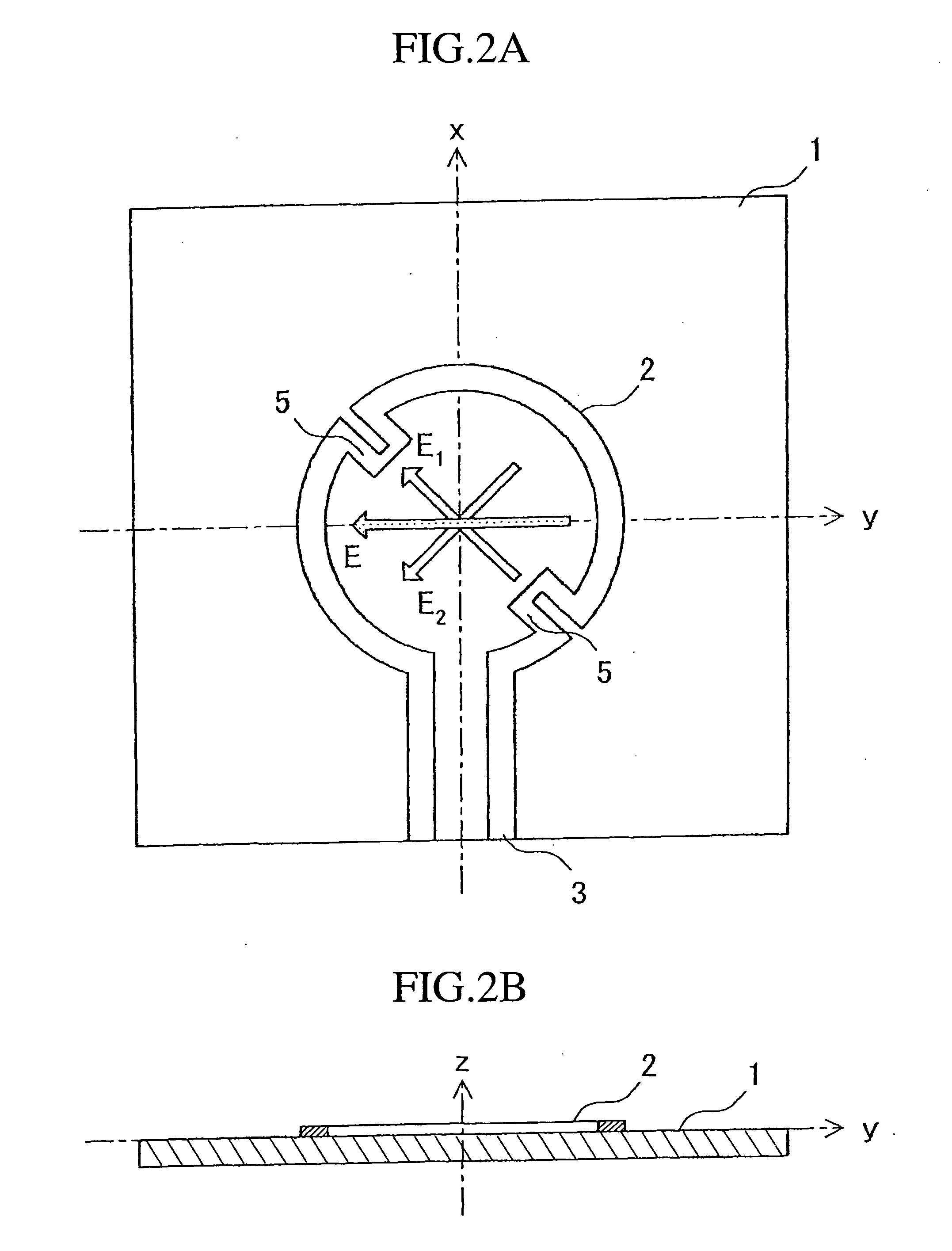
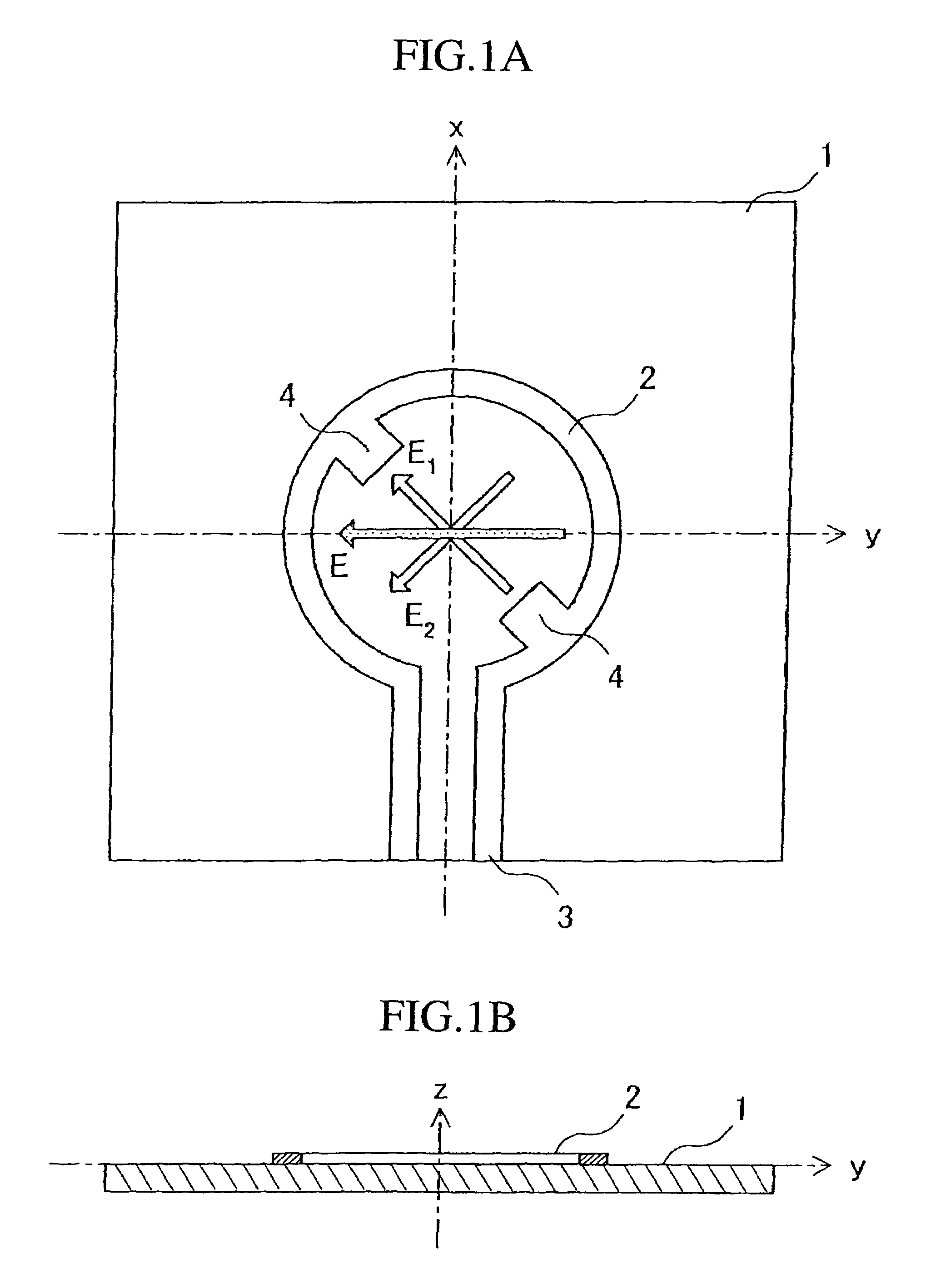
Circularly polarized antenna and rectenna using this antenna
InactiveUS7079080B2Simple structureImprove productivityResonant long antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectricCircularly polarized antenna
A loop antenna unit (2), a balanced line (3), and two perturbation elements (4) are formed on a dielectric board (1) by using manufacturing methods, such as printing and etching. The loop antenna unit (2) is formed along the circumference of a circle, and is connected to the balanced line (3). Each of the two perturbation elements (4) is a member in the shape of a tooth which is inclined 45 degrees against a direction of feeding of power via the balanced line (3) and which is projecting from the loop antenna unit (2) in an inward direction toward the center of the loop antenna unit (2). The two perturbation elements (4) are arranged at two opposite points in the loop antenna unit (2) so that they are opposite to each other.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Ultra-broadband integrated balun
Owner:IBM CORP
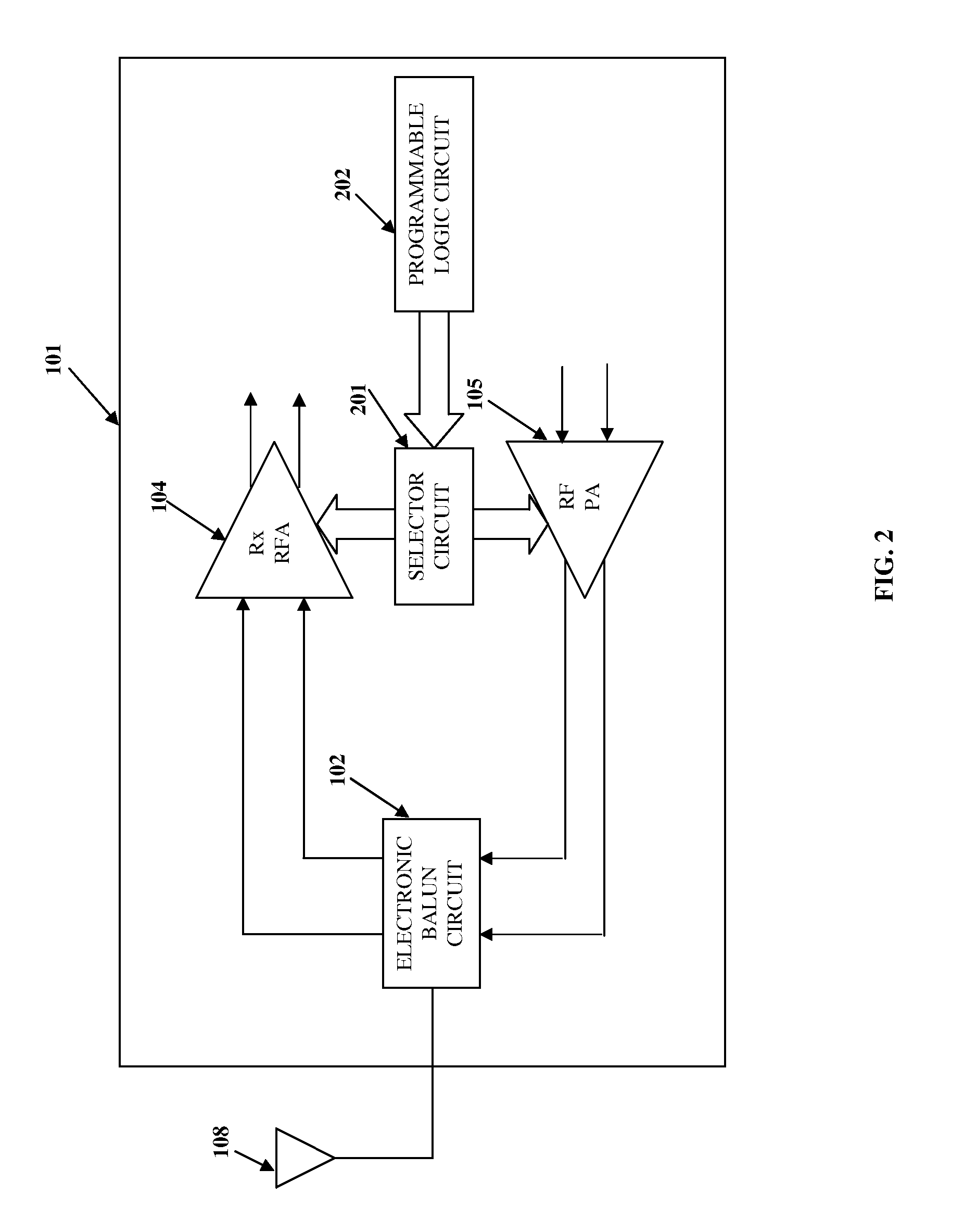
Integrated Radio Frequency Front-end Circuit
ActiveUS20110319042A1Reduce chip areaReduce energy consumptionAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransmissionRF front endAudio power amplifier
An integrated RF front-end circuit comprising a balun, a receiver amplifier, a power amplifier, and a selector circuit is provided. The balun comprises a center-tapped inductor having a first node, a center-tap switchlessly coupled to a fixed voltage, and a second node. The balun receives a single-ended signal through the first node to produce a differential signal at the first and second nodes. The differential signal is provided to balanced input lines of the receiver amplifier. Balanced output lines of the power amplifier provide a differential signal to the first and second nodes. The balun converts the differential signal to a single-ended signal. The single-ended signal is available at the first node of the center-tapped inductor. The selector circuit activates the receiver amplifier and deactivates the power amplifier, and vice versa. The power amplifier may comprise only a single-ended output line connected to either the first or the second node.
Owner:LTIMINDTREE LTD
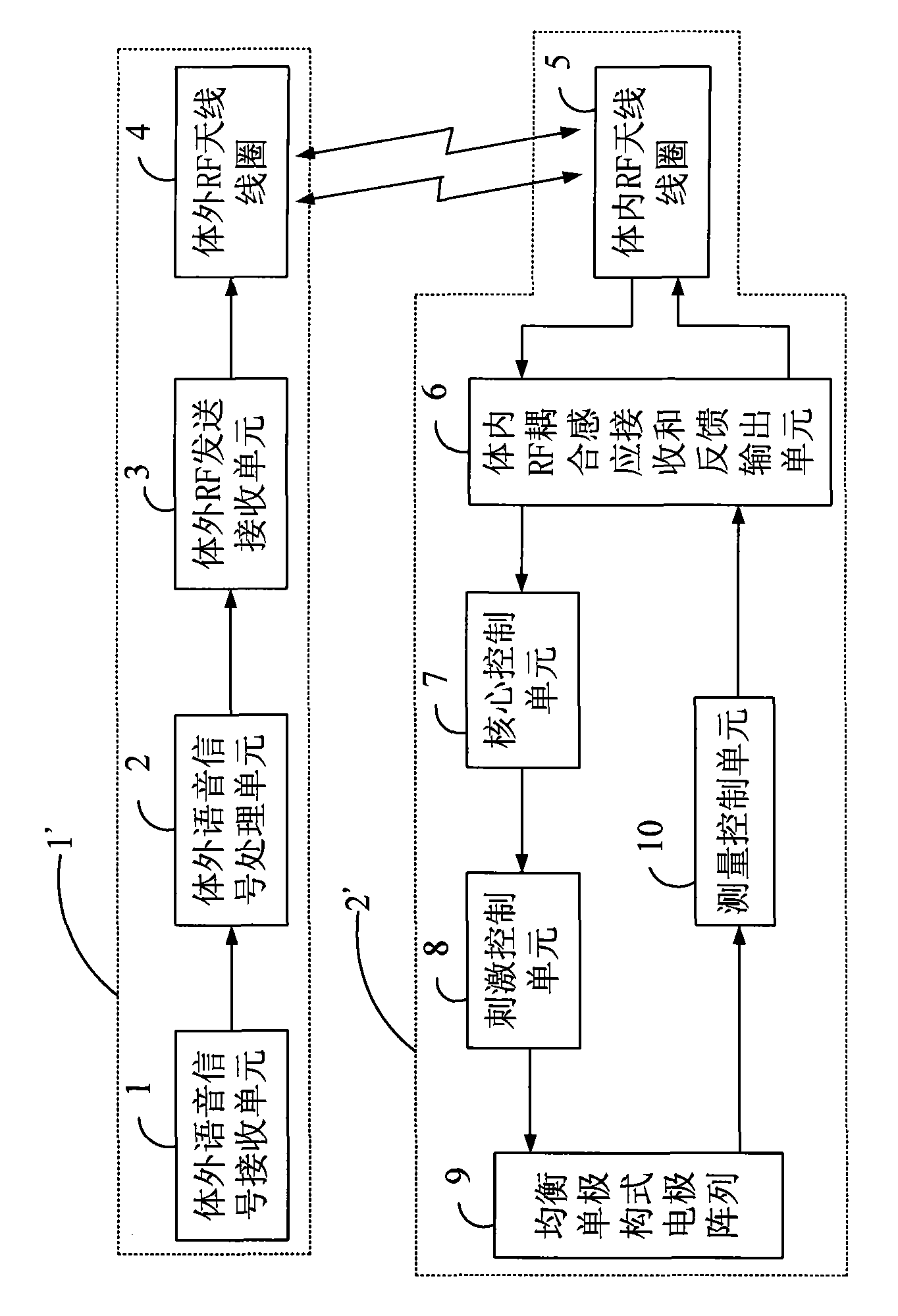
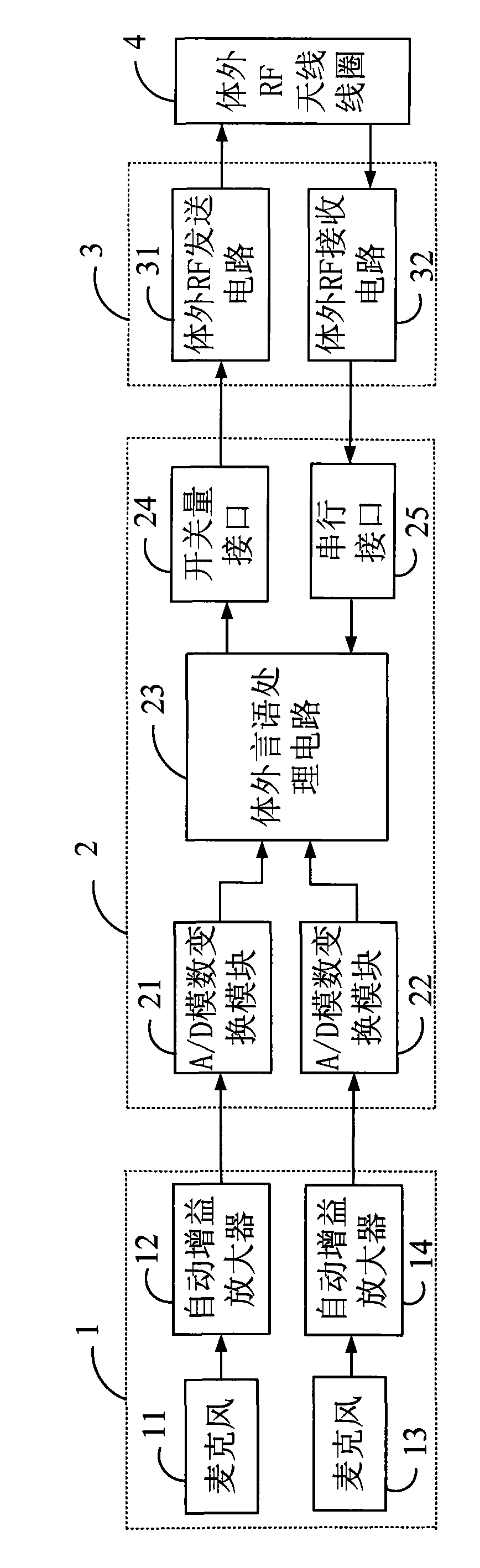
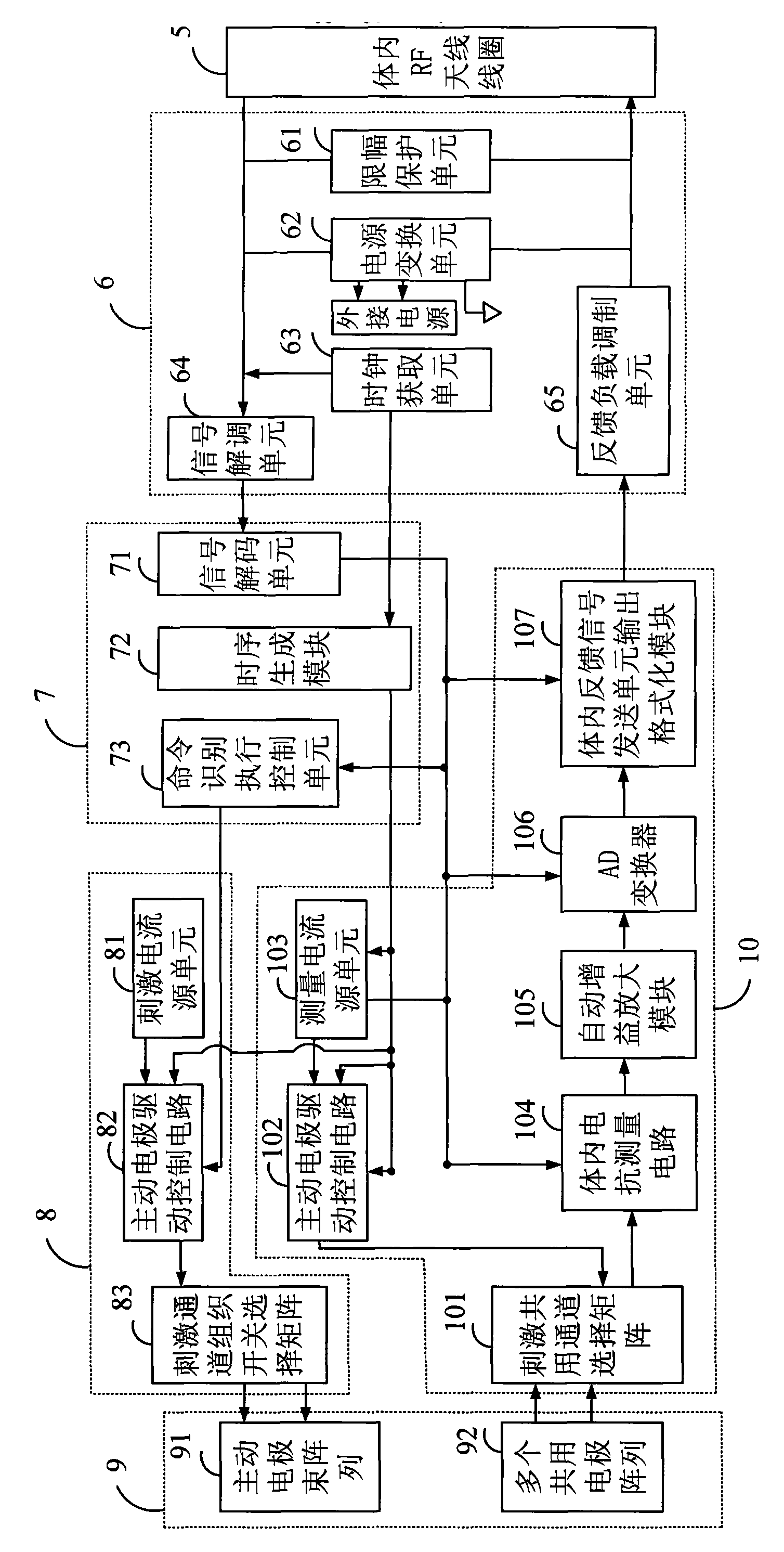
Balanced single-polar component type multi-channel cochlear implant system with detection feedback function
InactiveCN101874913AAdapt to useBalanced stimulusEar treatmentArtificial respirationRadio frequencyElectrode array
The invention provides a balanced single-polar component type multi-channel cochlear implant system with a detection feedback function, which comprises an external device and an internal device which are connected in a radio frequency (RF) coupling induction way, wherein the radio coupling induction way is realized by a radio proximity coupling and feedback load modulation circuit; the internal device comprises a balanced single-polar component type electrode array, a stimulus control unit, a core control unit, an internal RF coupling induction receiving and feedback output unit and a measurement control unit, wherein the balanced single-polar component type electrode array consists of an active electrode beam array used for stimulating cochlear nerves, and a plurality of common electrodearrays used for feeding measurement current signals back from the internal device to the external device; and the stimulus control unit, the core control unit, the internal RF coupling induction receiving and feedback output unit and the measurement control unit are connected with the balanced single-polar component type electrode array and are integrated on an integrated circuit chip by a binary-coded decimal (BCD) process. Through the technical scheme provided by the invention, the aims of once careful mounting, adaptive adjustment and long-term high-quality use can be fulfilled.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALING ARTIFICIAL EAR MEDICAL TECH +1
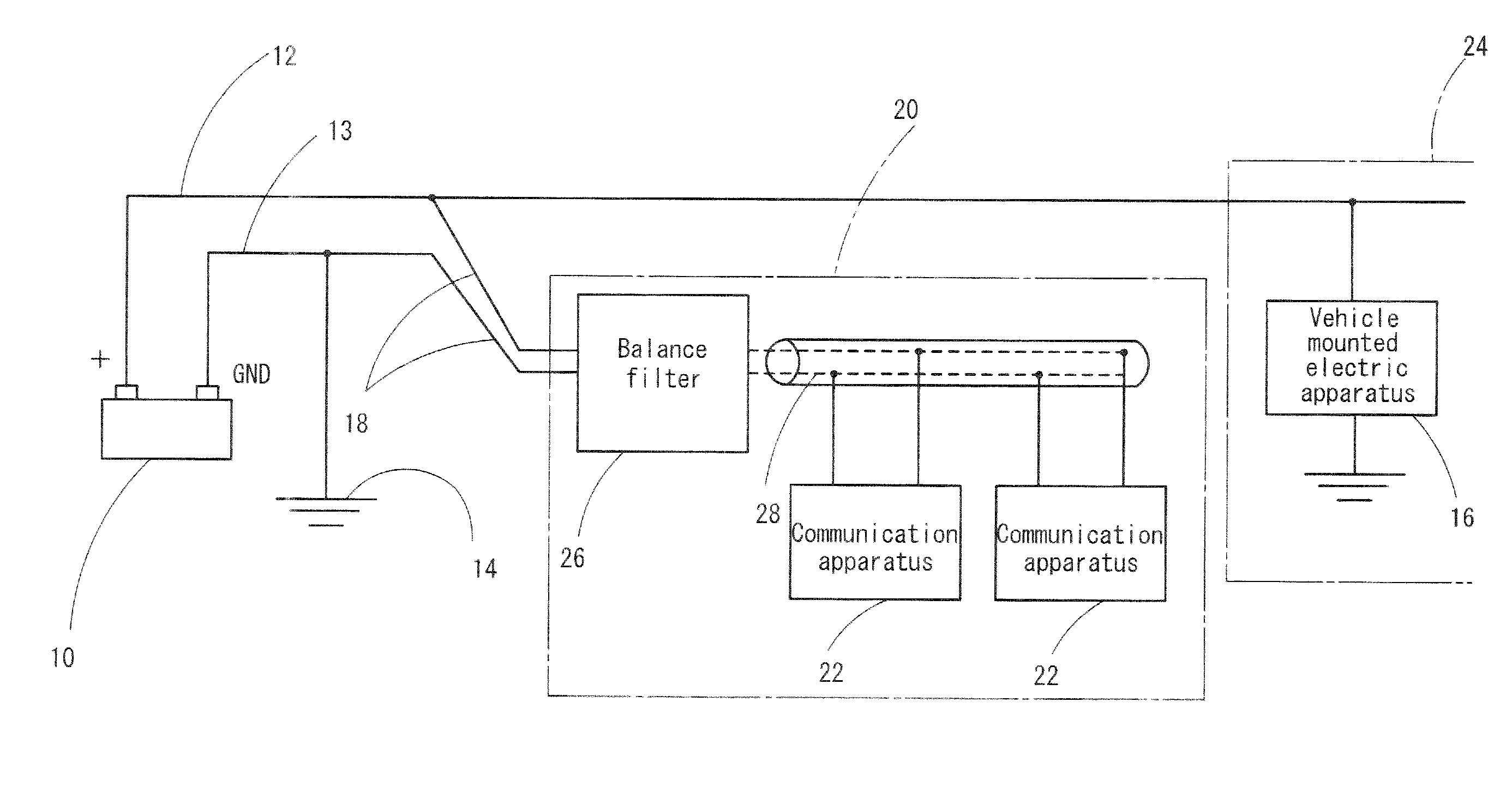
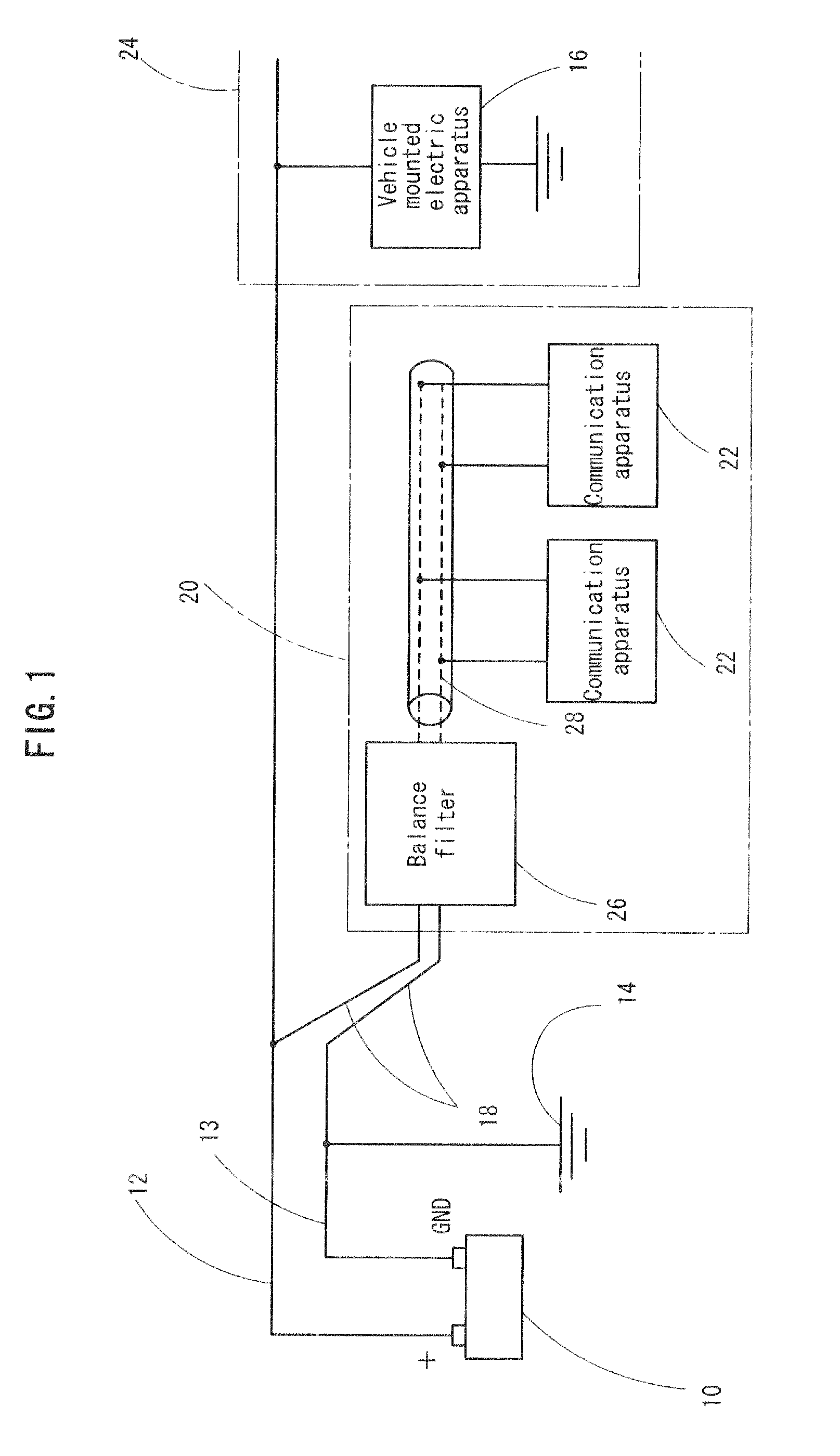
Power line communication system
InactiveUS20100111201A1Stable communicationQuality improvementDc network circuit arrangementsElectric devicesCommunications systemEngineering
A power line communication system which enables high quality communication, utilizing a pair of power lines 12, 13 connected to a vehicle mounted battery 10, has a pair of communication lines 18 connected to a pair of power lines 12, 13, respectively, to communicate a high frequency signal of 1 MHz or more. This system has a balance filter 26 which is interposed between each of the communication lines 18 and a vehicle mounted communication apparatus 22, the filter 26, a circuit configuration of which is formed in balance type. The communication system also has a pair of electrically balanced lines 28 which are connected between the balance liter 26 and each of the communication apparatuses 22 and are power-fed from the battery 10, for performing communication between the communication apparatuses 22.
Owner:SMK CORP +1
Method for Bit-Error Rate Testing of Resistance-based RAM Cells Using a Reflected Signal
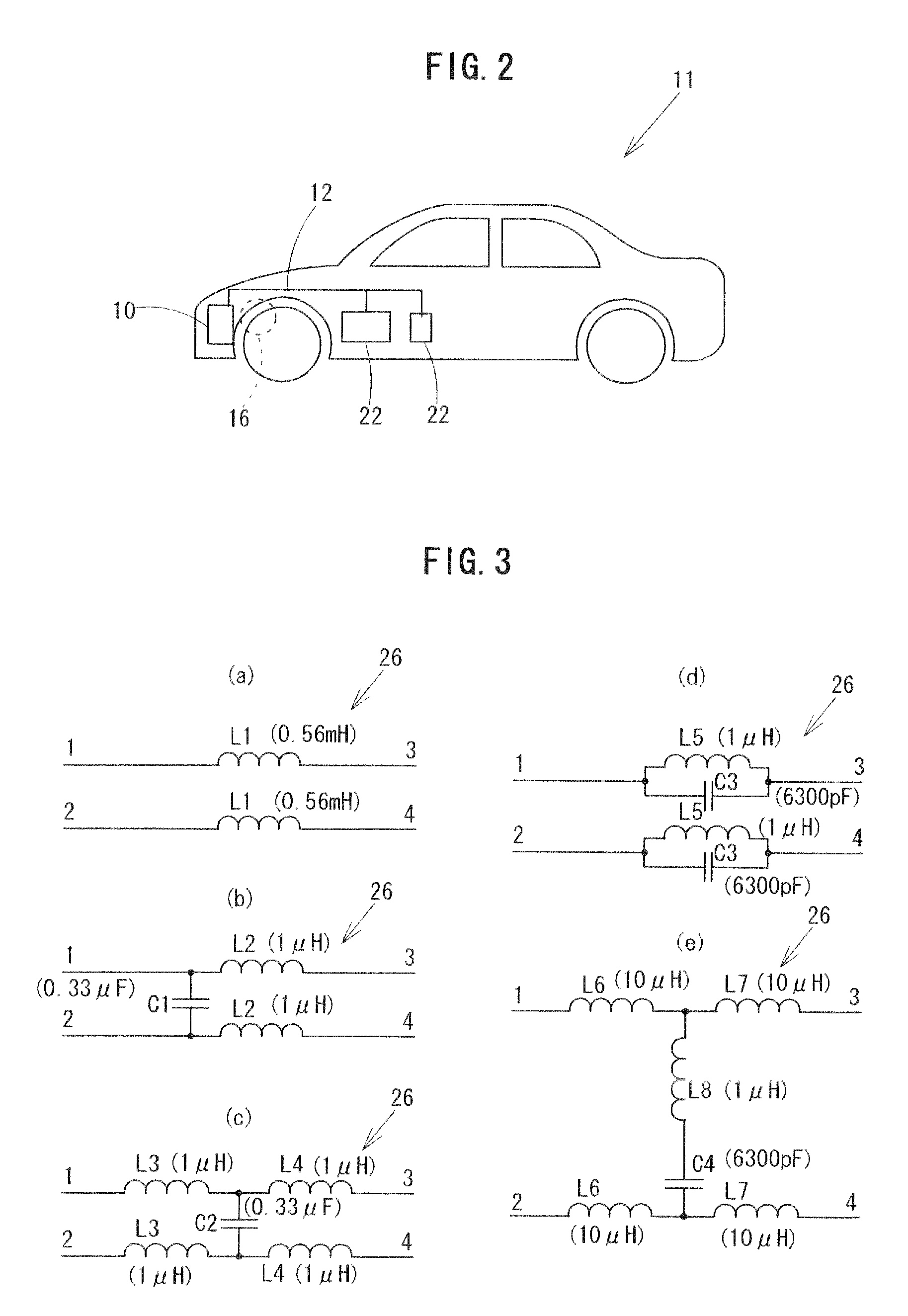
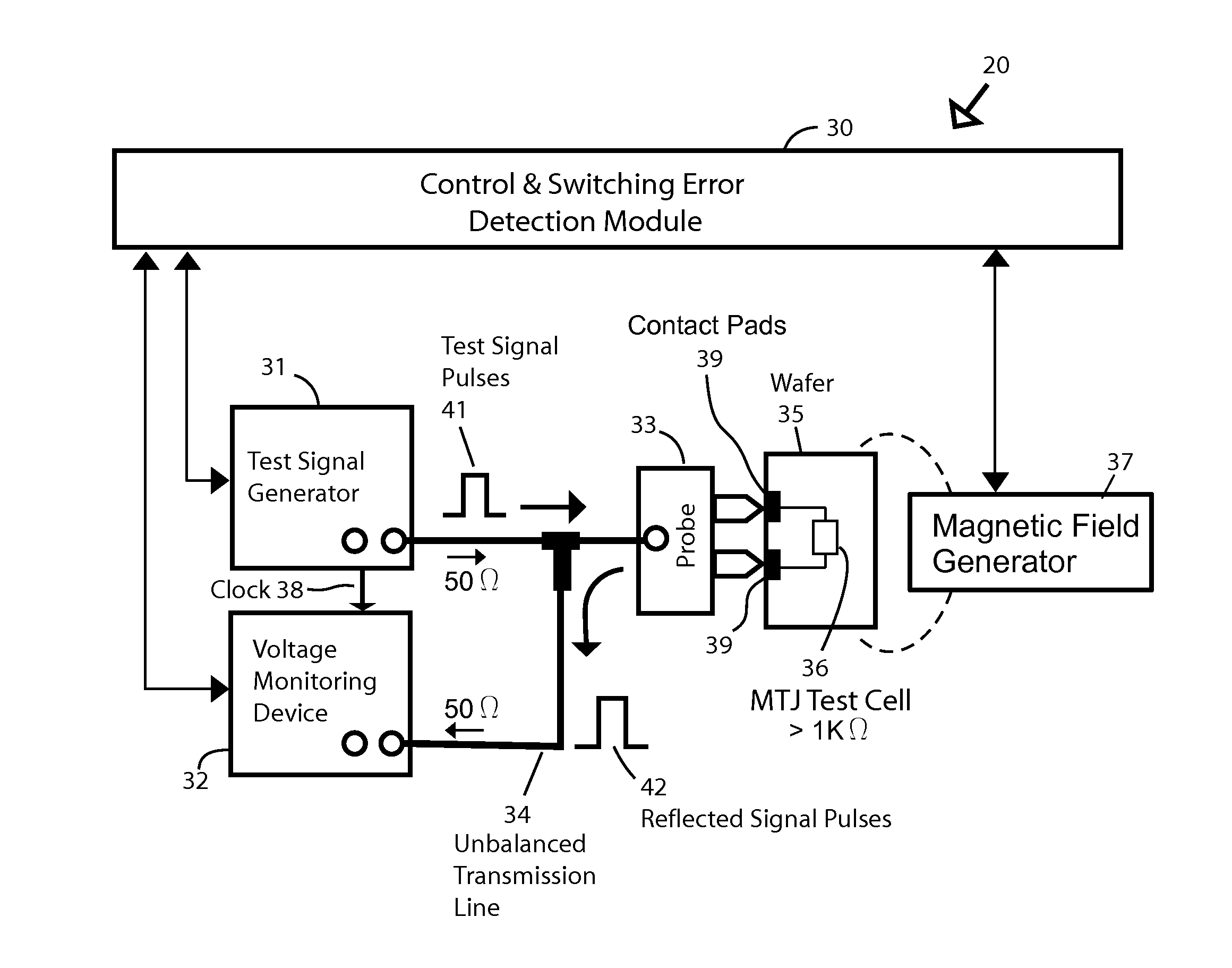
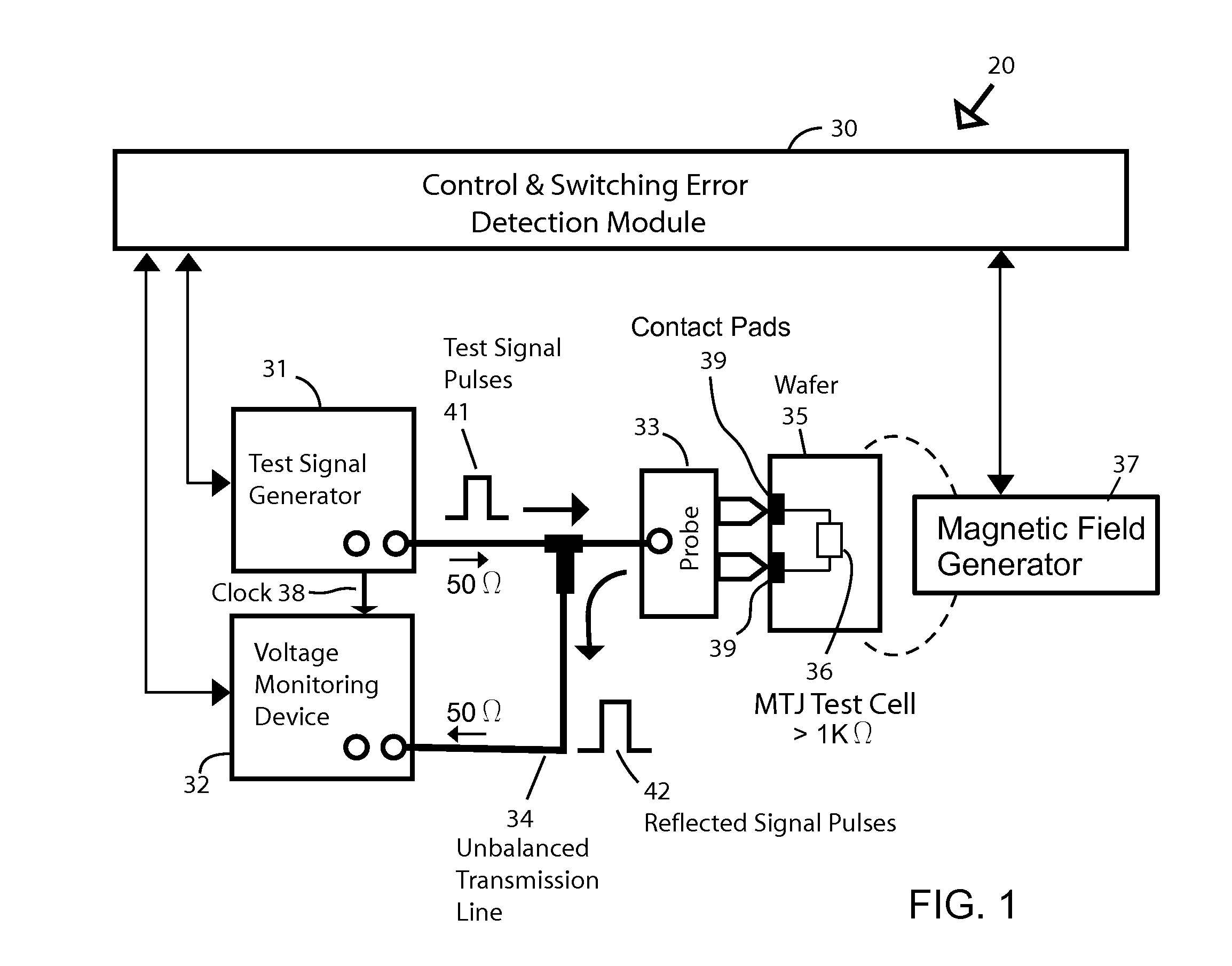
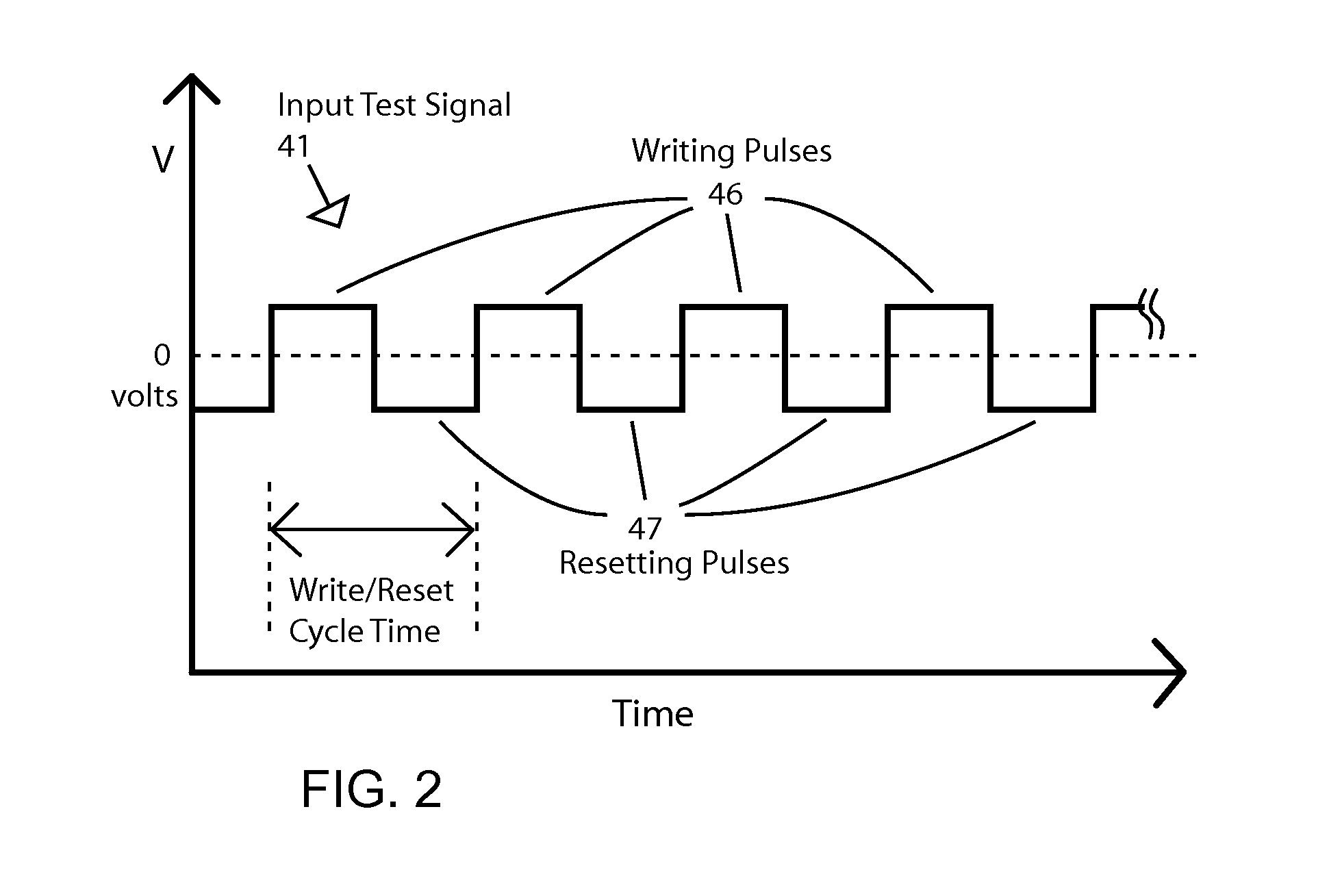
A testing method is described for performing a fast bit-error rate (BER) measurement on resistance-based RAM cells, such MTJ cells, at the wafer or chip level. Embodiments use one or more specially designed test memory cells fabricated with direct electrical connections between the two electrodes of the cell and external contact pads (or points) on the surface of the wafer (or chip). In the test setup the memory cell is connected an impedance mismatched transmission line through a probe for un-buffered, fast switching of the cell between the high and low resistance states without the need for CMOS logic to select and drive the cell. The unbalanced transmission line is used generate signal reflections from the cell that are a function of the resistance state. The reflected signal is used to detect whether the test cell has switched as expected.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Signal Equalizer for Balanced Transmission Line-Based Video Switching
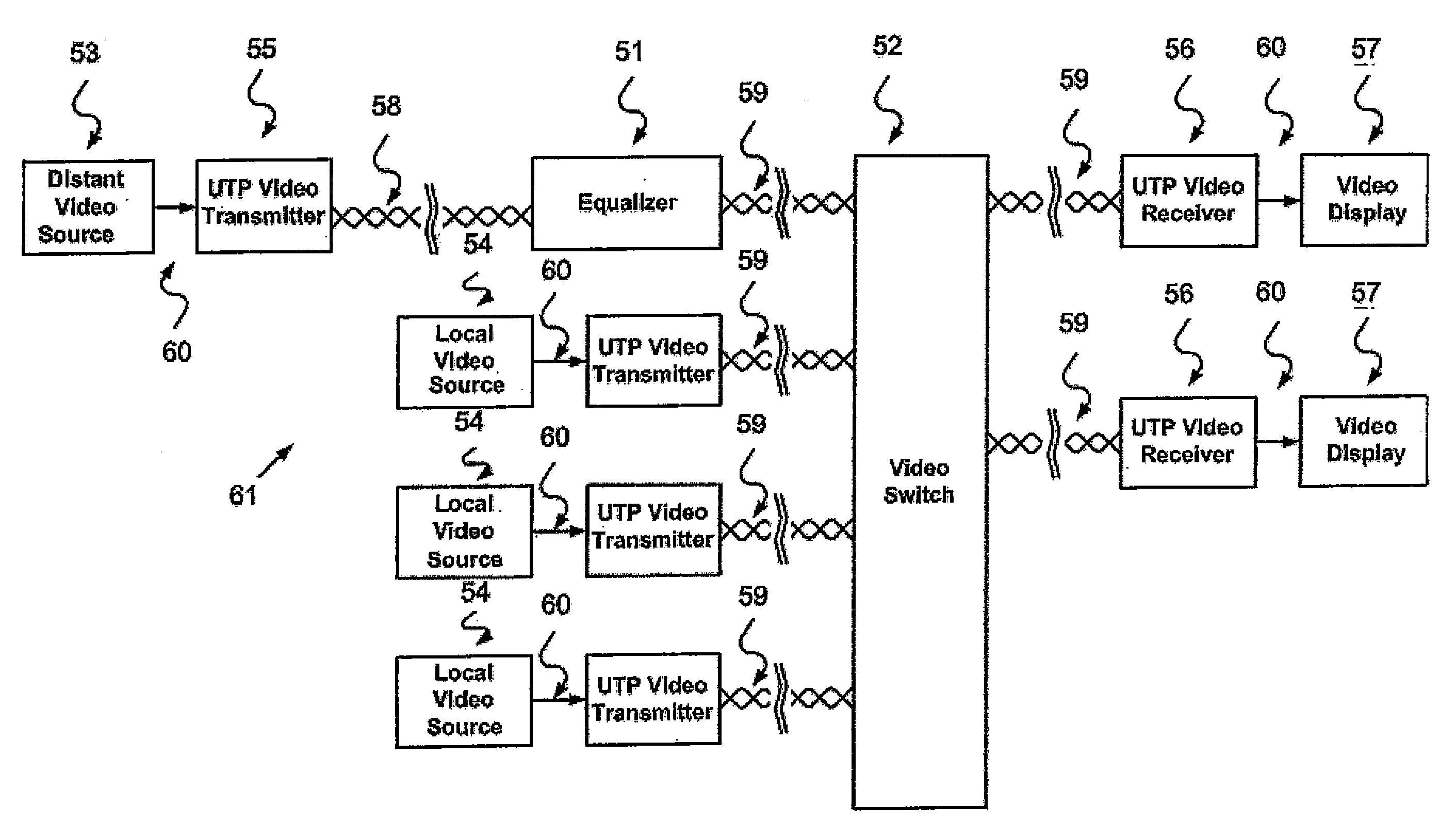
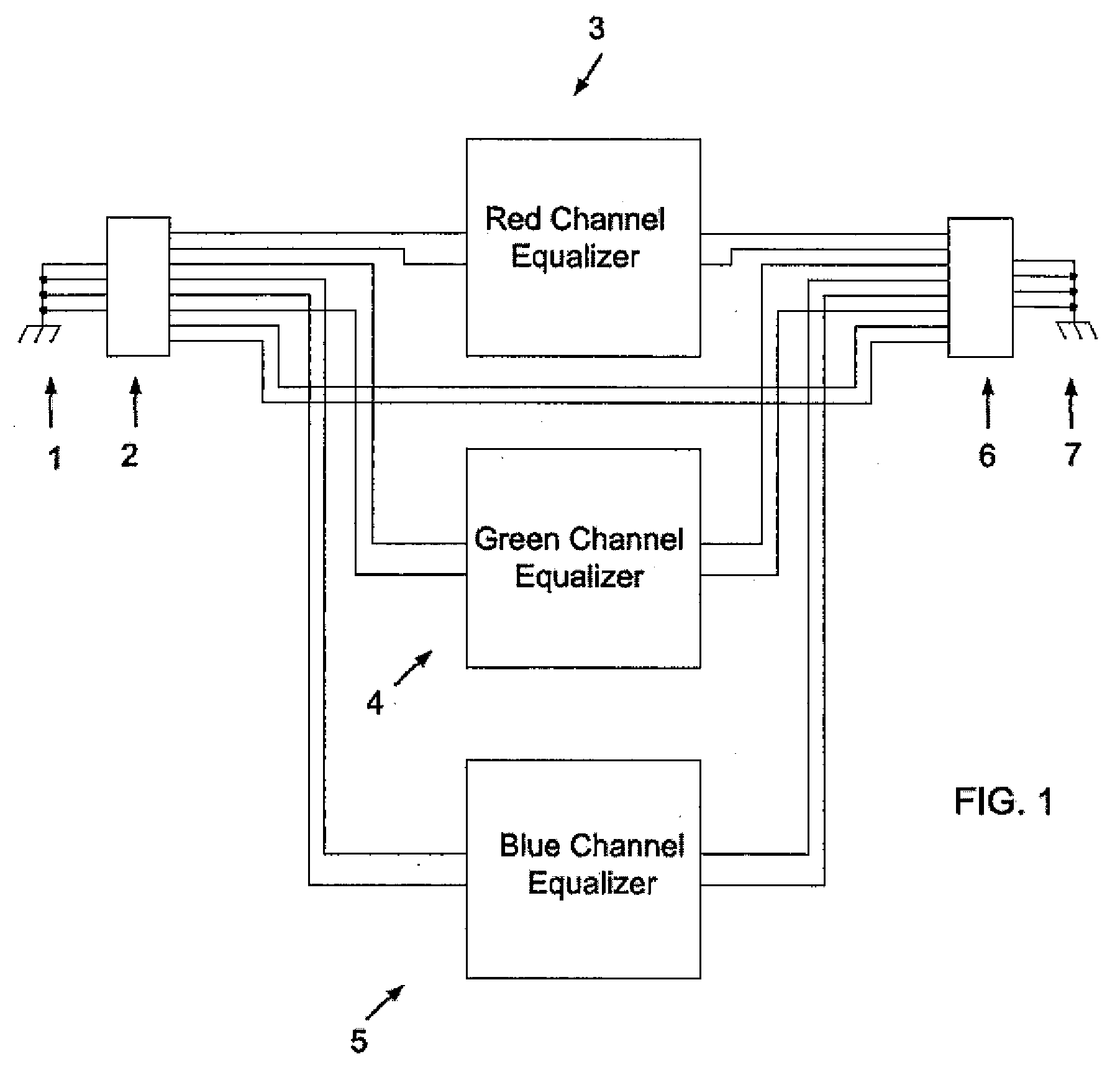
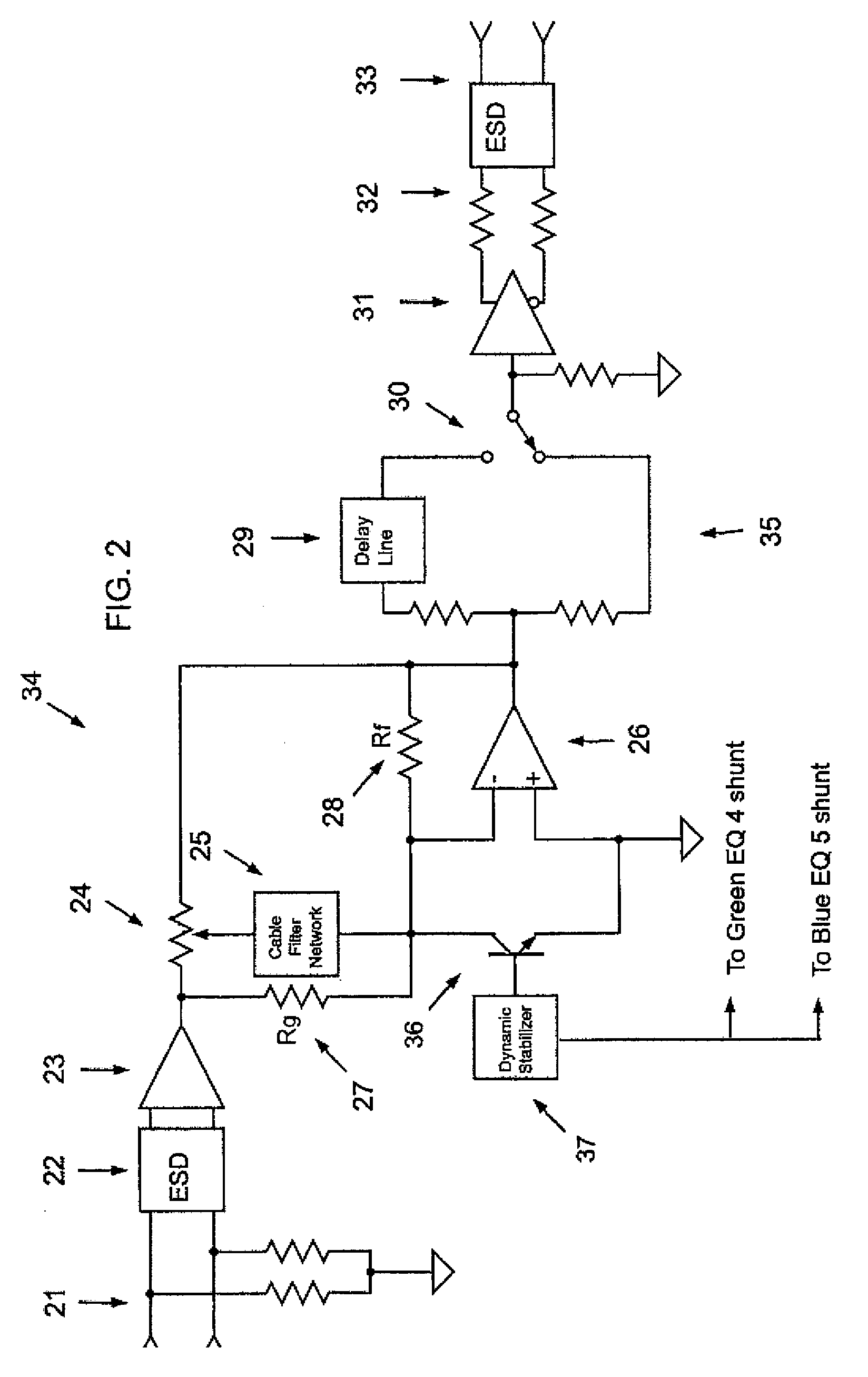
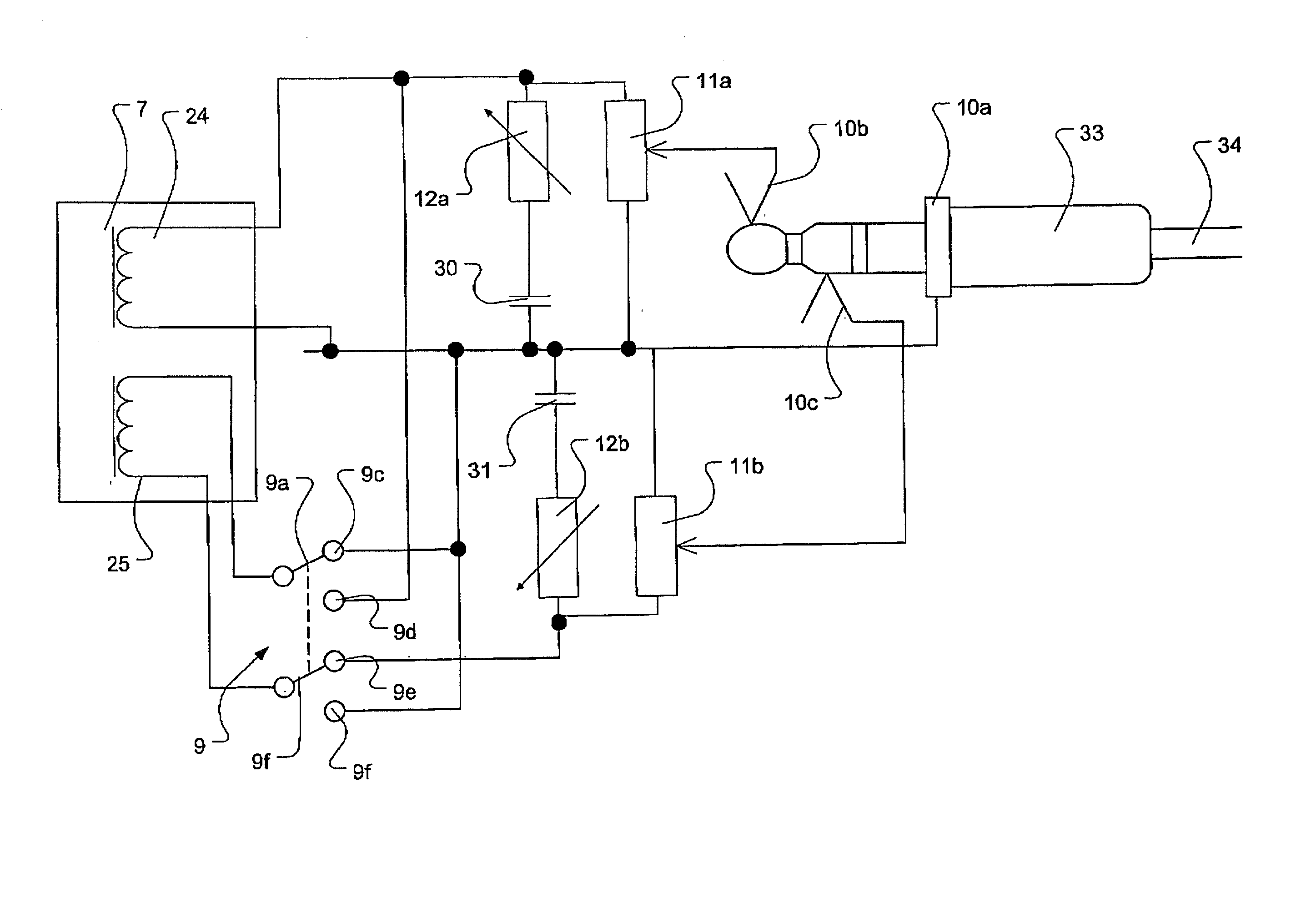
InactiveUS20080186407A1Promote lowerReduce decreaseTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsCable transmissionResistor
A method of equalizing signals from a plurality of balanced transmission line cables having different lengths includes providing a first cable having a first length and a second cable having a second length, the first cable coupled to a variable resistor. A first signal is transmitted along the first cable to the variable resistor such that the first signal is attenuated to assume a first frequency domain characteristic. A second signal is transmitted along the second cable such that the second signal is attenuated to assume a second frequency domain characteristic. A voltage of the first signal is divided in the variable resistor such that the first signal assumes substantially the second frequency domain characteristic. The first signal having the second frequency domain characteristic is outputted.
Owner:MAGENTA RES
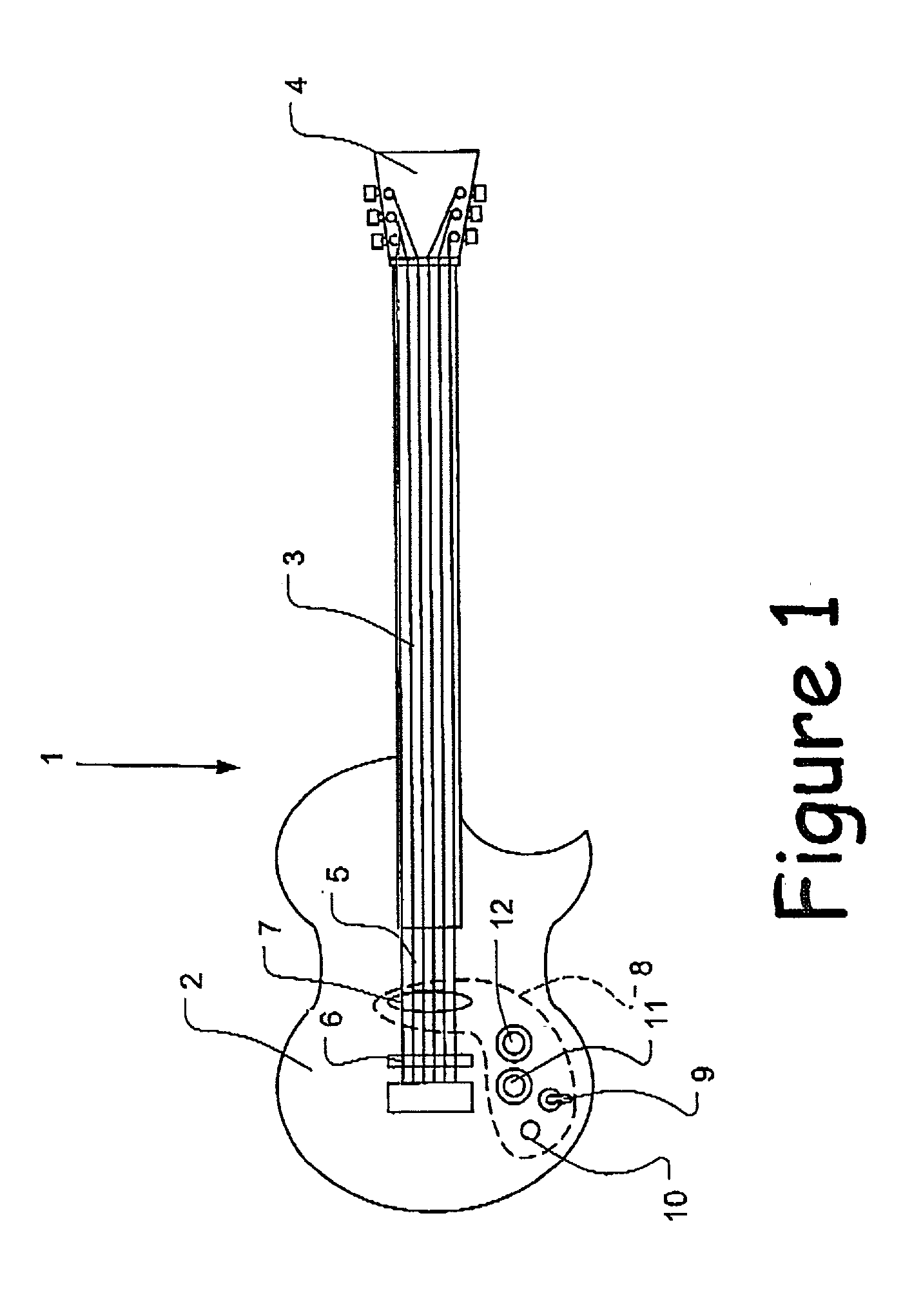
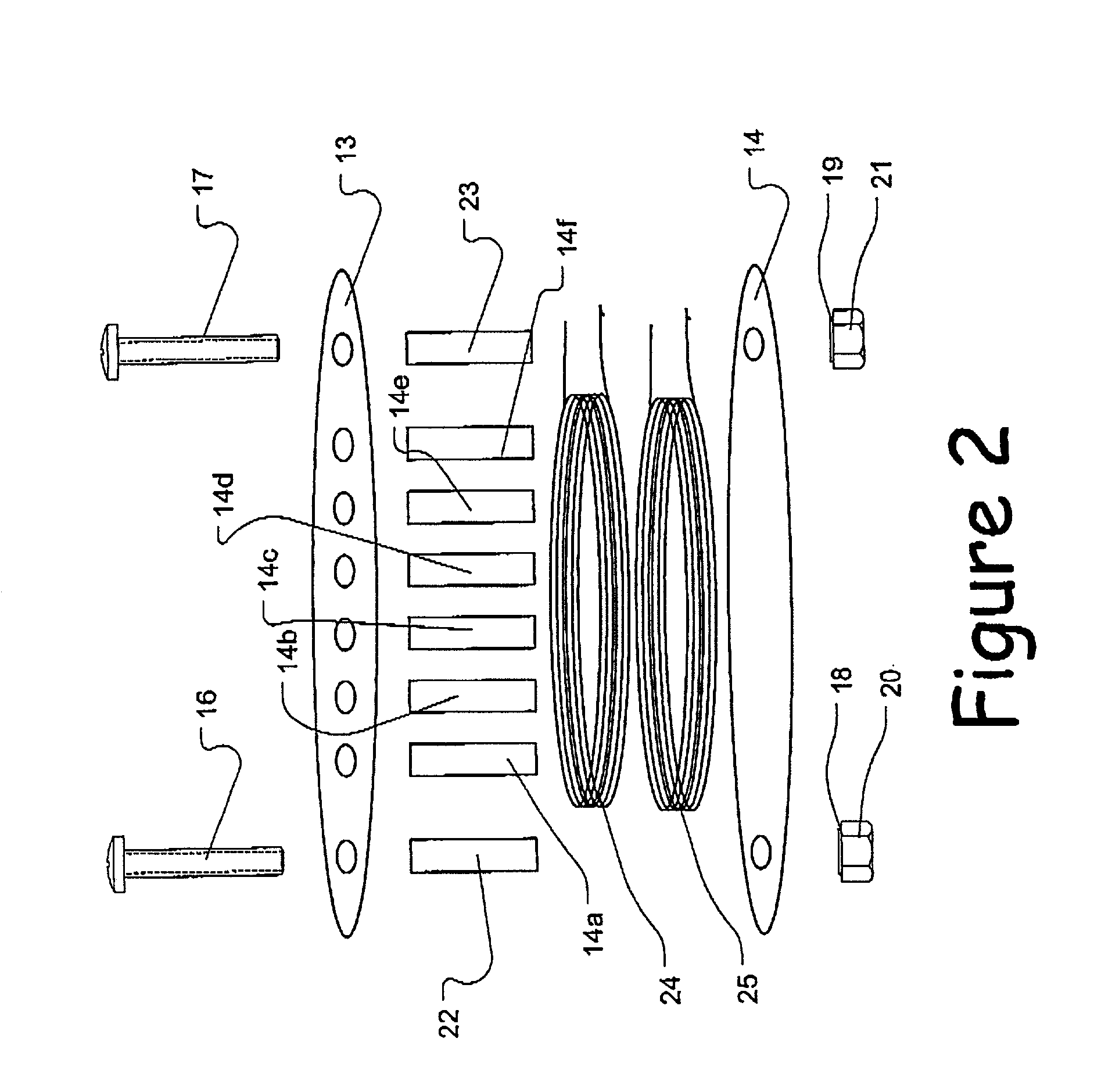
Balanced pickup for stringed instruments
A balanced pickup for a stringed instrument comprises first and second windings wound in opposite senses from a common point. A switch may be provided for configuring the pickup for both balanced and single-ended output. Also, a balanced lead incorporating a balun is described.
Owner:PETHERICK JOHN ELLIOT
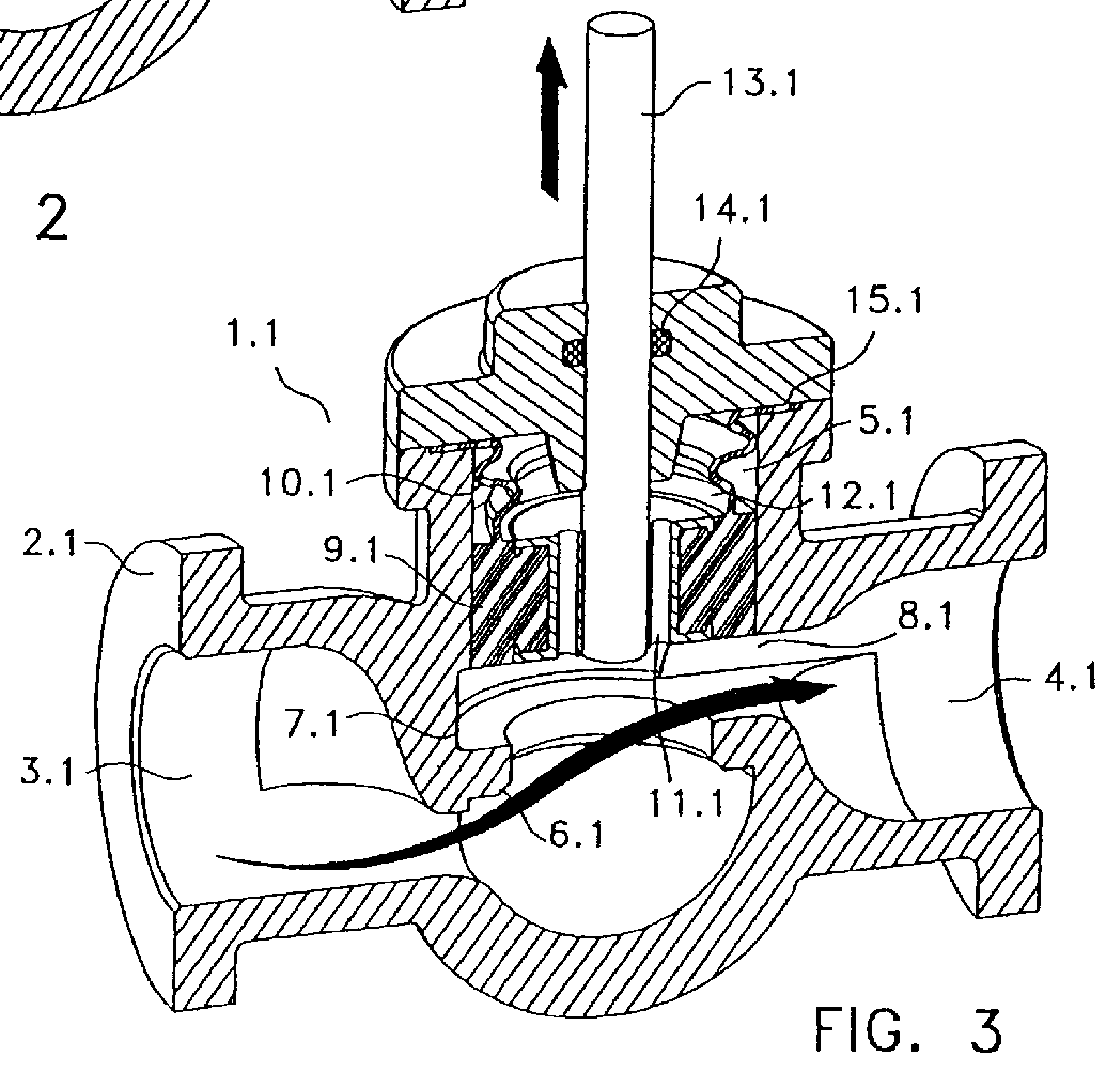
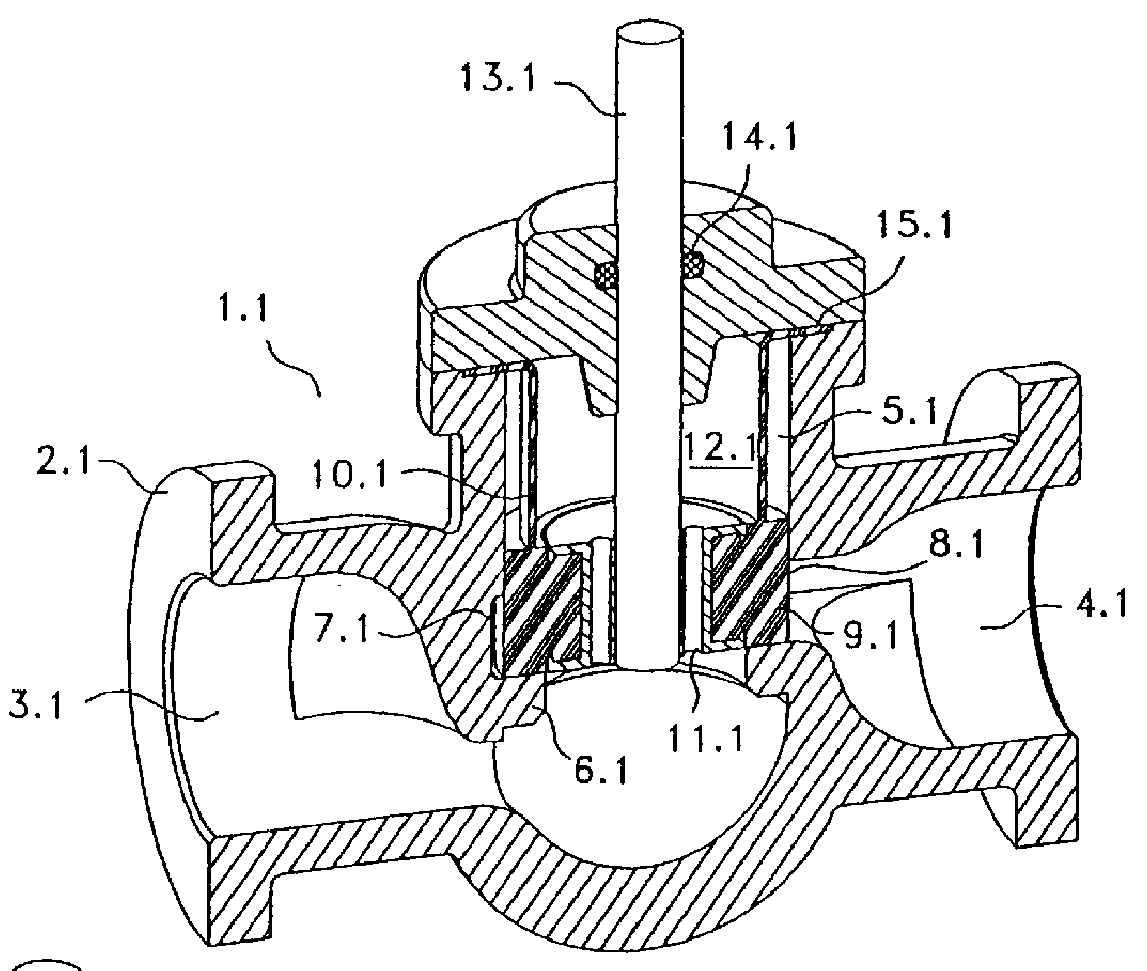
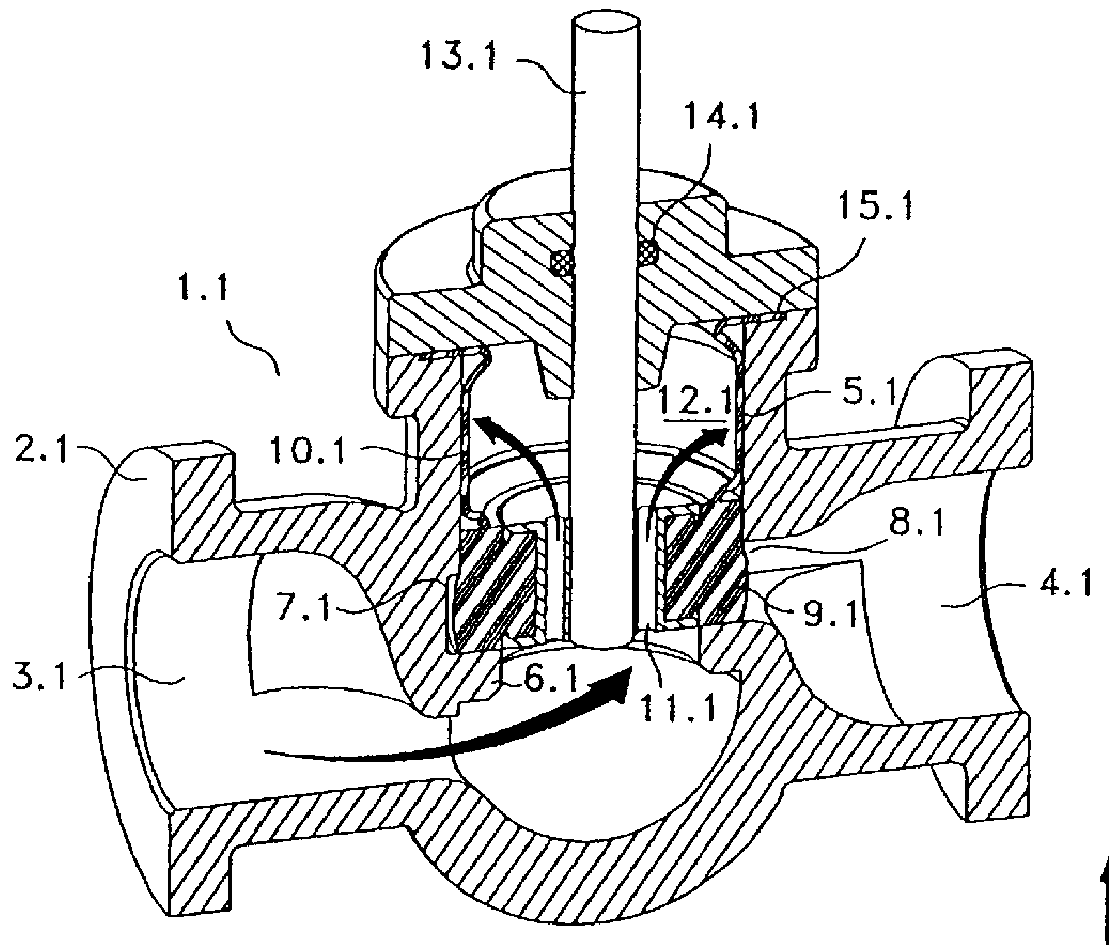
Balanced valve operated by the axial driving of a stem displacing a special elastomeric sealing body
A balanced valve for flows operated by the axial driving of a stem which commands a sealing body liable to axially slip between an opened position far from the valve seat and a closed seal in contact with the valve s eat. The valve basically consists in a valve body having an inlet opening for the flow with a valve seat at the bottom. The valve body also has an opening for the flow outlet oriented in a substantially cross-section way to the flow inlet. Between the inlet and outlet of flow there is a cylindrical cavity with a ring-shaped broadening in the zone communicating with the flow outlet above the valve seat. There is an elastomeric sealing body located inside the cylindrical cavity, which is mainly made up of a relatively solid sealing end, with a slightly greater height than the height of the ring-shaped broadening of the cylindrical activity. This sealing end is provided with one or more axial passes or holes, an d its also has a coaxial zone of radial seal located in the section of upper base of said sealing end, which consists of a circular groove in "V" section at the lower face of the sealing end near its periphery defining a perimetric lug. A variant of the valve considers a cylindrical elastomeric wall topping out the sealing end, which consists of an upper extension of the same sealing end, and topping in its other end in a radial edge withheld in the valve body. This elastomeric cylindrical wall may have one or more reinforcing rings conformed in its mantle and axially arranged.
Owner:PEREZ C SERGIO
Ultra-broadband integrated balun
An ultra-broadband balun is provided. The balun comprises: a first unbalanced transmission line comprising a first ground trace and a signal trace; and a balanced transmission line comprising a first and second signal trace, wherein the first signal trace of the balanced transmission line is connected to the first ground trace of the first unbalanced transmission line and the second signal trace of the balanced transmission line is connected to the signal trace of the first unbalanced transmission line, wherein a first capacitor is disposed in series with one of the first ground trace of the first unbalanced transmission line and the first signal trace of the balanced transmission line.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wideband Yagi aerial for half-mould substrate integrated waveguide feed
InactiveCN101656351AWith broadband characteristicsMeet the requirements of broadband microwave and millimeter wave communication systemsRadiating elements structural formsMetal coatingPhase difference
The invention discloses a wideband Yagi aerial for half-mould substrate integrated waveguide feed, comprising a dielectric substrate which is provided with a metal coating on both sides. The structurecomprises a half-mould substrate integrated waveguide, a Yagi aerial, a micro-strip gradual-change transition wire and a 50 Ohm micro-strip output wire. The half-mould substrate integrated waveguidecomprises a metallic through hole, an upper metal coating and a lower metal coating. The Yagi aerial comprises a wave director, a cross feed source matrix of upper and lower surfaces, and parallel wires. For measuring conveniently, the micro-strip gradual-change transition wire is connected between the half-mould substrate integrated waveguide and the 50 Ohm micro-strip output wire. The half-mouldsubstrate integrated waveguide structure is used as the feeding structure of aerial, so the 180 DEG balanced line structure with a current phase difference of upper and lower metal surfaces is formedand can be directly connected to the Yagi aerial. For improving the plus, four wave directors are used to form a printed antenna structure, with wideband, high plus, low cost and low outline.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and apparatus for digital synthesis of microwaves through balanced transmission line structures
InactiveUS7518464B2Quality improvementHigh controlTransmission control/equlisationPulse generation by opto-electronic devicesMicrowaveElectrical conductor
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
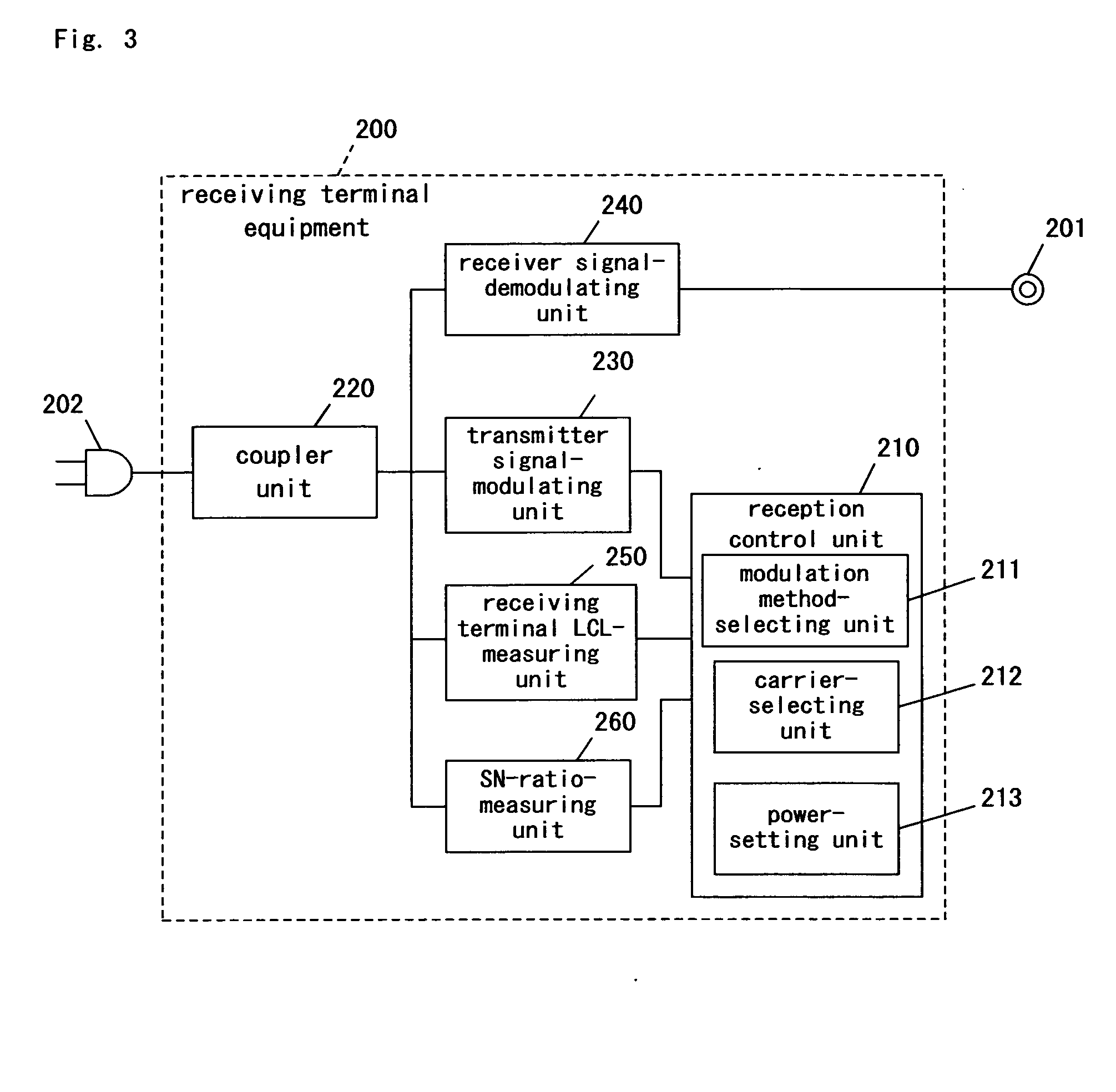
Multicarrier communication method and system, and communication apparatus incorporated therein
ActiveUS20050078803A1Suppress unwanted radiated emissionGreat multivaluesEnergy efficient ICTError preventionCarrier signalEngineering
In a multicarrier communication using a balanced transmission line such as a power line, a multicarrier communication method operable to select carriers on the basis of an SN-ratio and balancing of the transmission line is provided. Available carriers are selected in accordance with the balancing of the balanced transmission line, in which the balancing is measured at either a sending terminal or a receiving terminal or alternatively at both of them, and the SN-ratio measured between the sending terminal and the receiving terminal. More specifically, any frequency domain having poor balancing and a poor SN-ratio is treated as a non-carrier-employing domain, and consequently the available carriers are selected at other frequency domains. In addition, a modulation method having the greatest permissible multivalue is selected for each of the carriers. The carriers are selected in light of the SN-ratio and balancing, or alternatively in highest-to-lowest order of frequency. Transmission power is controlled for each of the carriers to suppress radiated emission. The SN-ratio and balancing are measured at predetermined time intervals to renew the selection of the carriers and the selection of the modulation methods.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
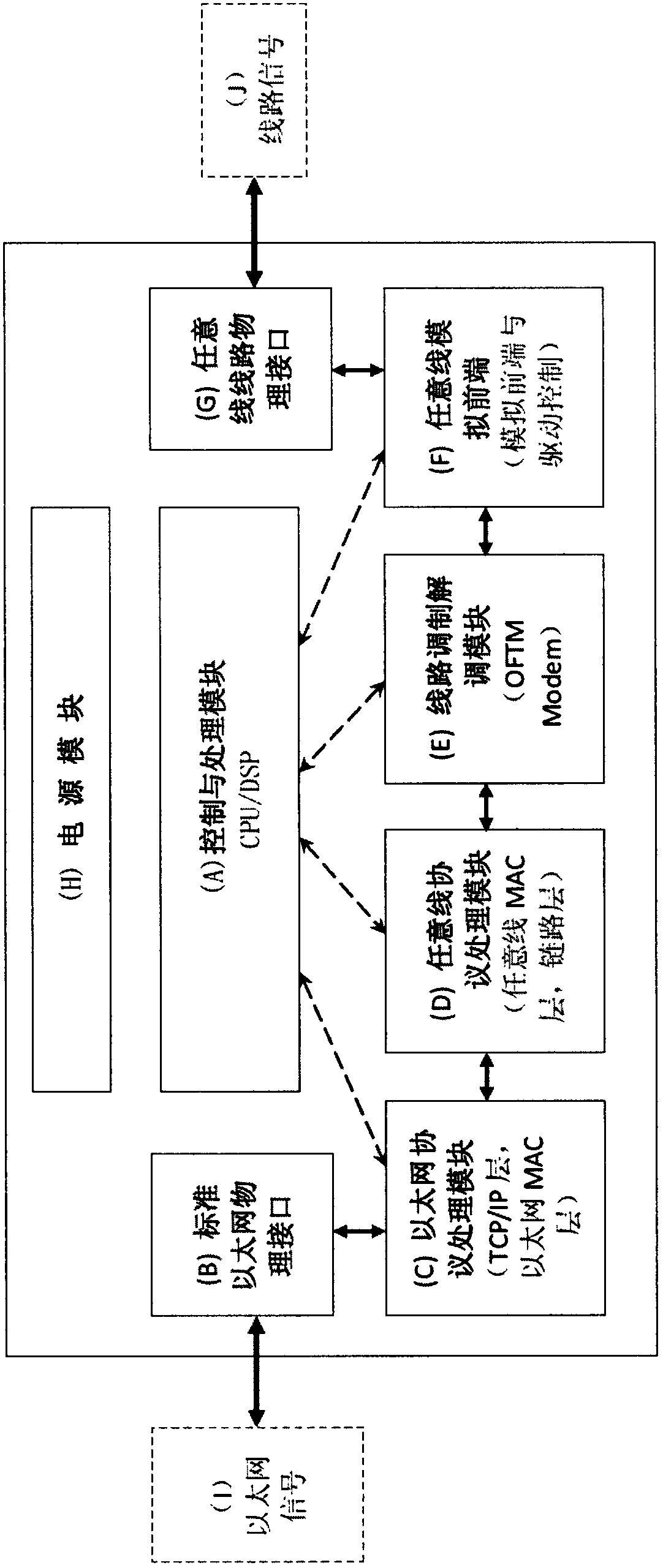
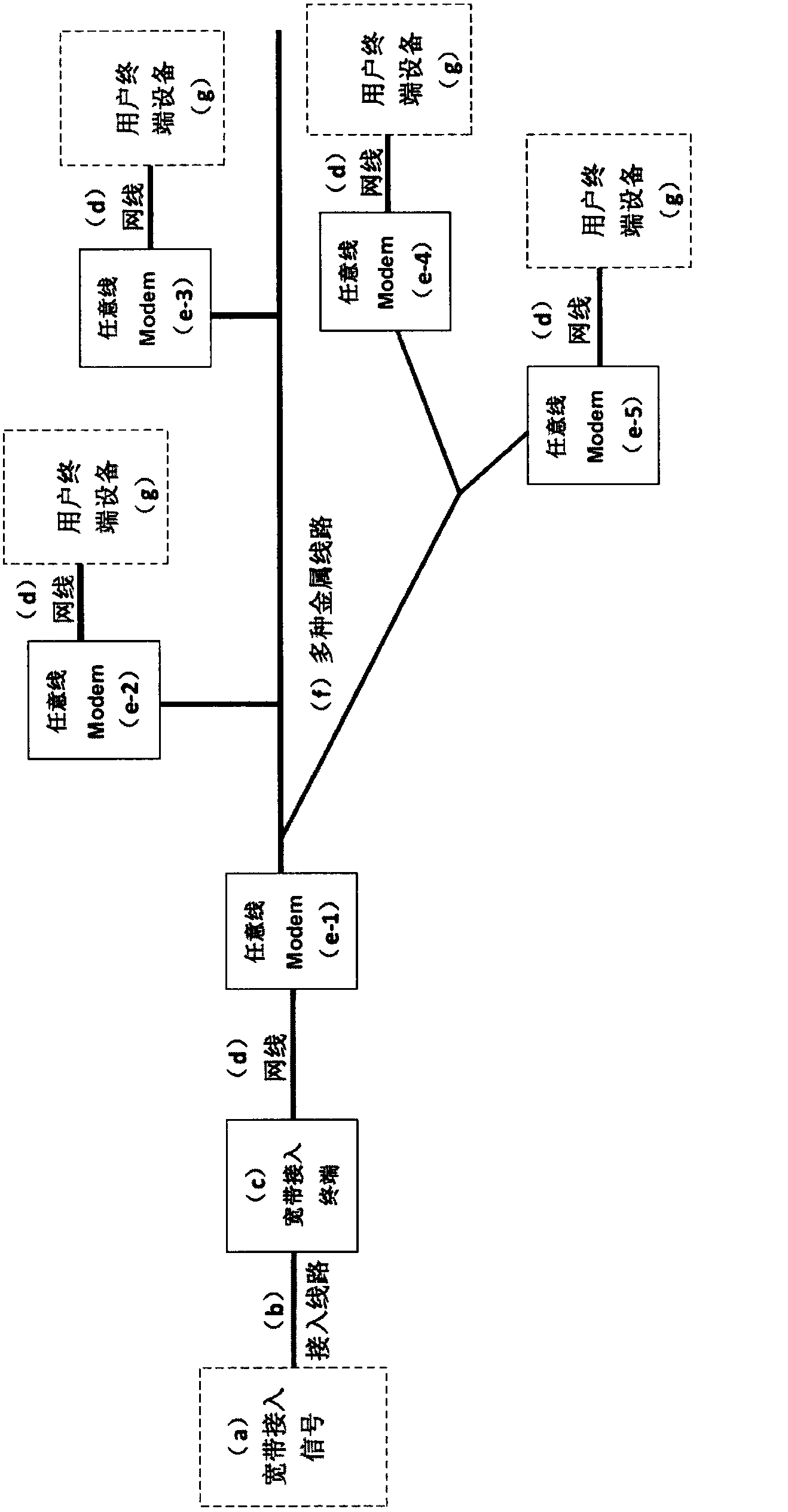
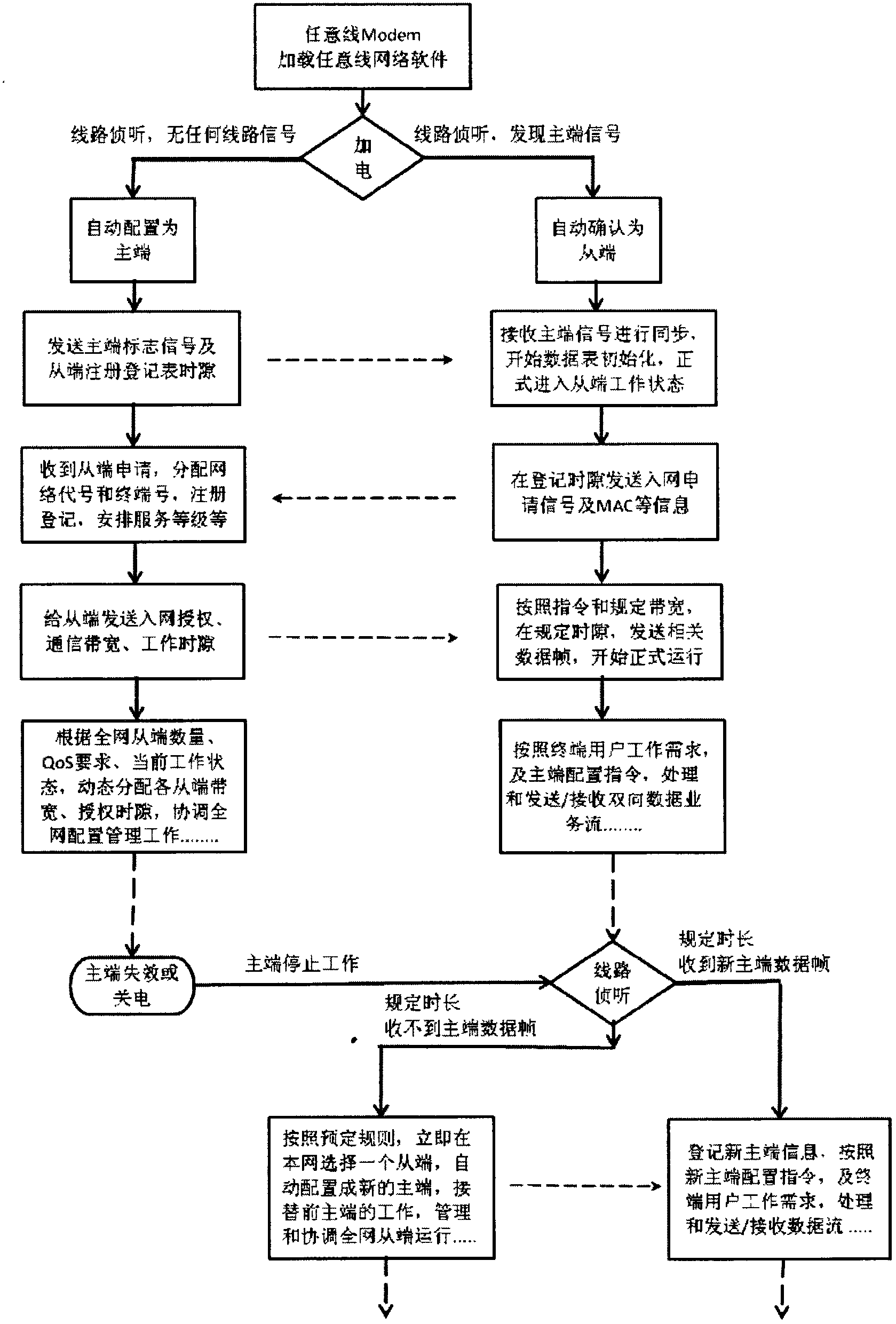
Free-throw line Modem and bus type multi-medium multi-point networking broadband network thereof
InactiveCN102710475AReduce construction costsEasy to buildData switching by path configurationProtocol processingEthernet protocol
The invention discloses a free line Modem which is characterized by comprising one or any combination of a telephone line, a coaxial line, a network line, a twisted-pair and a balanced line. The free line Modem comprises a controlling and processing module (A), a power supply module (H), a standard Ethernet physical interface (B), an Ethernet protocol processing module (C), an any line protocol processing module (D), a line modulation / demodulation module (E), an any line simulation front end module (F) and an any line physical interface (G). A bus type multi-medium multi-point networking broadband network constructed by using the any line Modems comprises at least two any line Modems and multiple kinds of line passive branch networks (f) and is connected with an external device through the network line, wherein the external device is a user terminal device (g) or broadband access terminal (c), and topological structures of the line passive branch networks (f) are chain-shaped, star-shaped, tree-shaped topological structures or mixed topological structures.
Owner:MIANYANG NETOP TELECOM EQUIP
Transmission Lines Applied to Contact Free Slip Rings
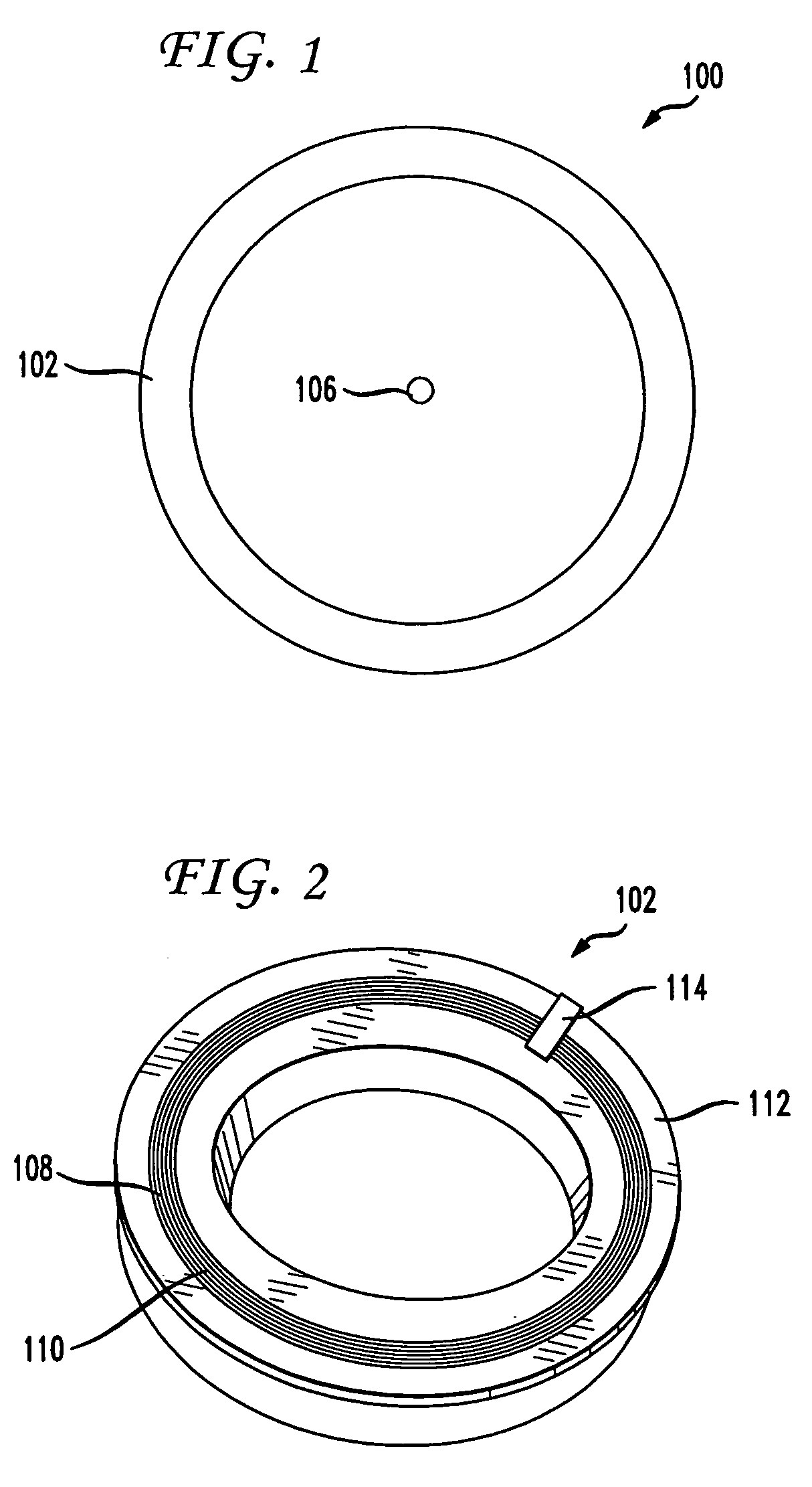
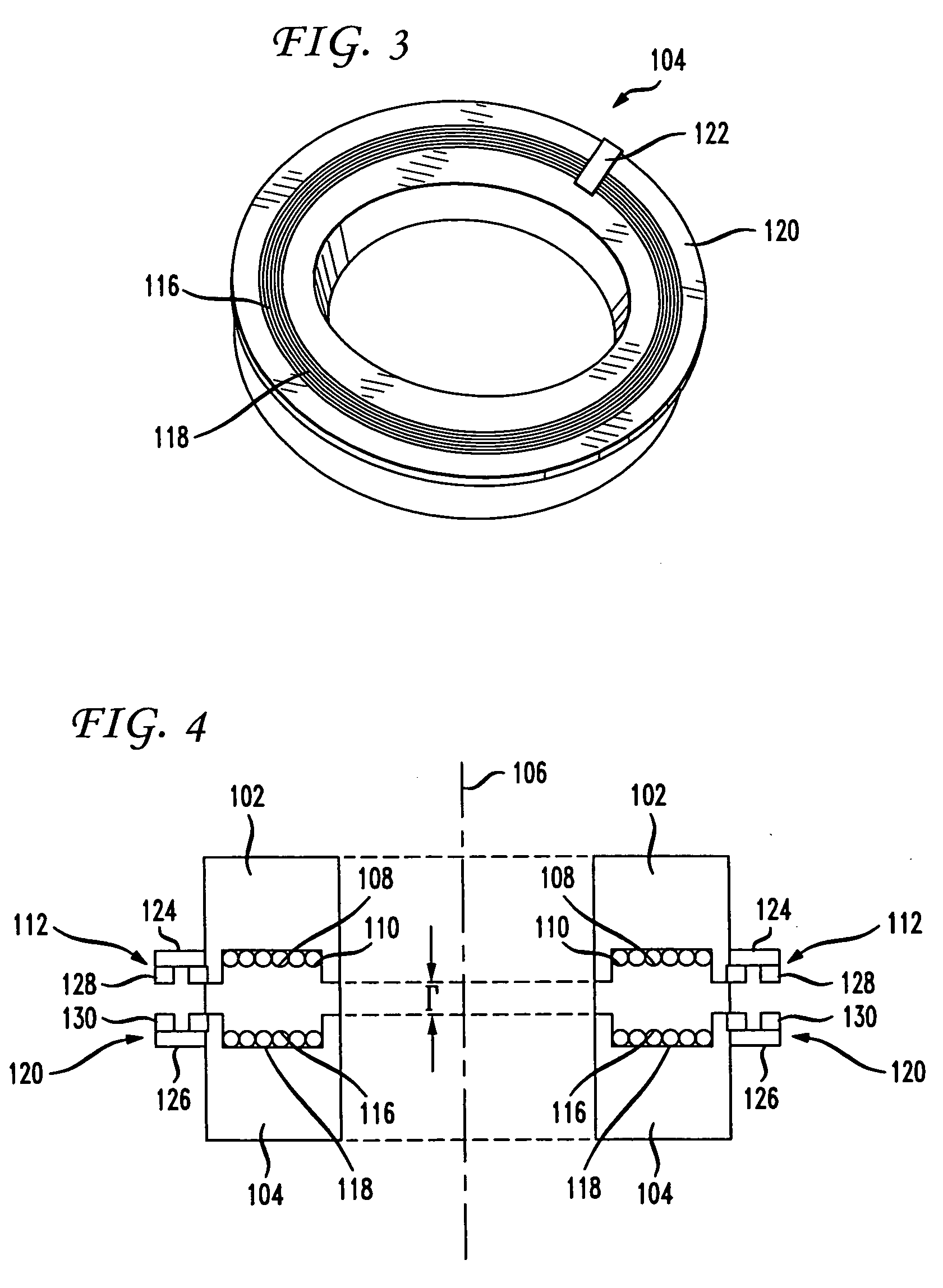
A non-contacting rotary interface has a first core with a first pair of balanced transmission lines coupled to the first core and a second core moveable in relation to the first core with a second pair of balanced transmission lines coupled to the second core and configured to receive signals from the first pair of balanced transmission lines. The first pair of balanced transmission lines has a first transmit wire coupled to a first transceiver at a first end of the first transmit wire, a second transceiver coupled to the first transmit wire at a second end of the first transmit wire, a second transmit wire coupled to a third transceiver at a first end of the second transmit wire, and a fourth transceiver coupled to the second transmit wire at a second end of the second transmit wire. The balanced transmission lines may be electrical traces on a circuit board.
Owner:VOXIS
Film bulk-acoustic resonator filter having unbalanced-balanced input/output structure
An FBAR filter includes a wafer, a filter circuit unit and a balun circuit unit. The filter circuit unit includes a plurality of FBAR resonators formed on a predetermined region on a top of the wafer. The balun circuit unit includes a plurality of metal layers electrically connected to each other to implement a balun circuit and a plurality of dielectric layers each placed between the plurality of metal layers. The balun circuit unit is electrically connected to the filter circuit unit on a predetermined region of the wafer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com