Patents
Literature
365results about "Data merging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
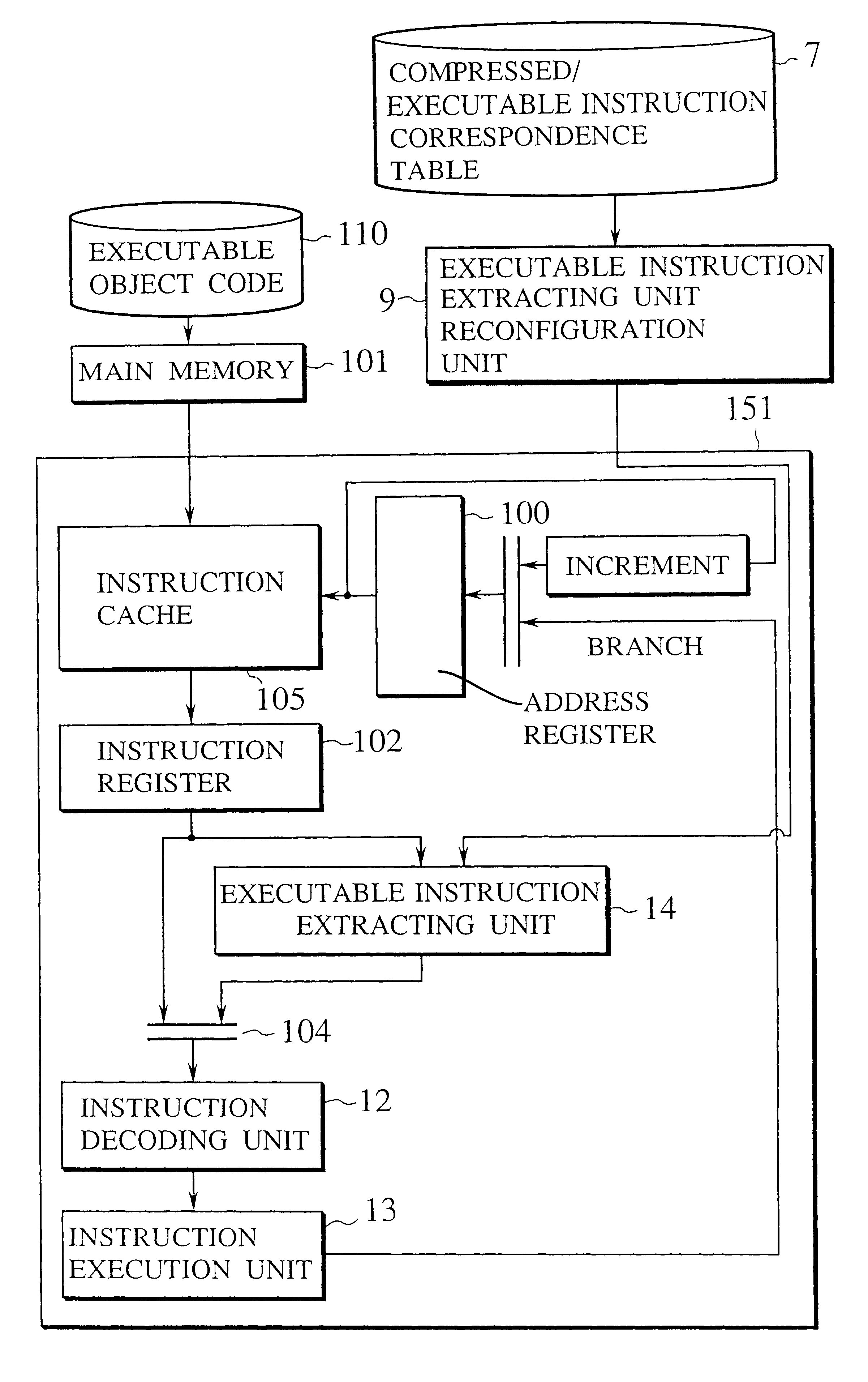
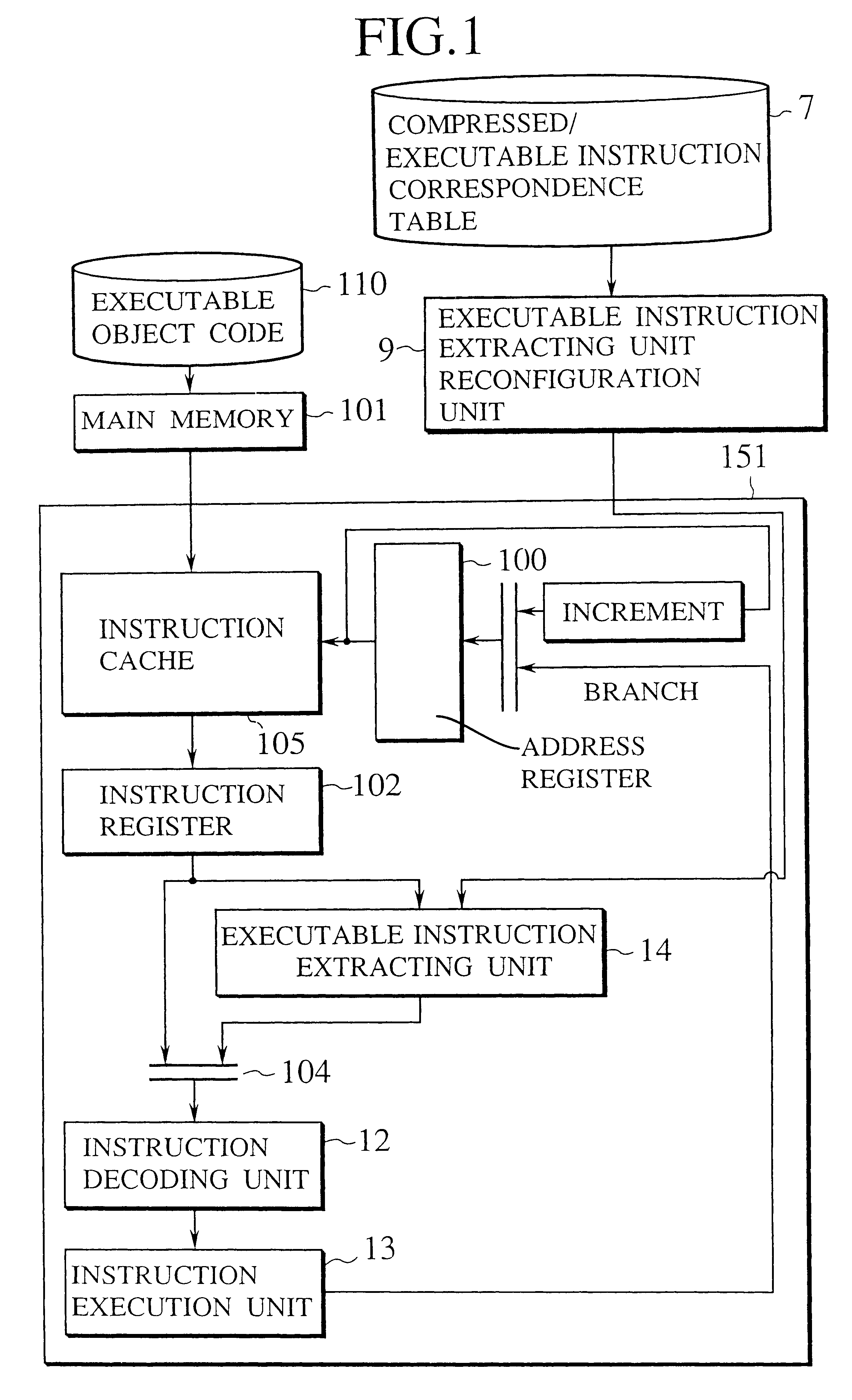
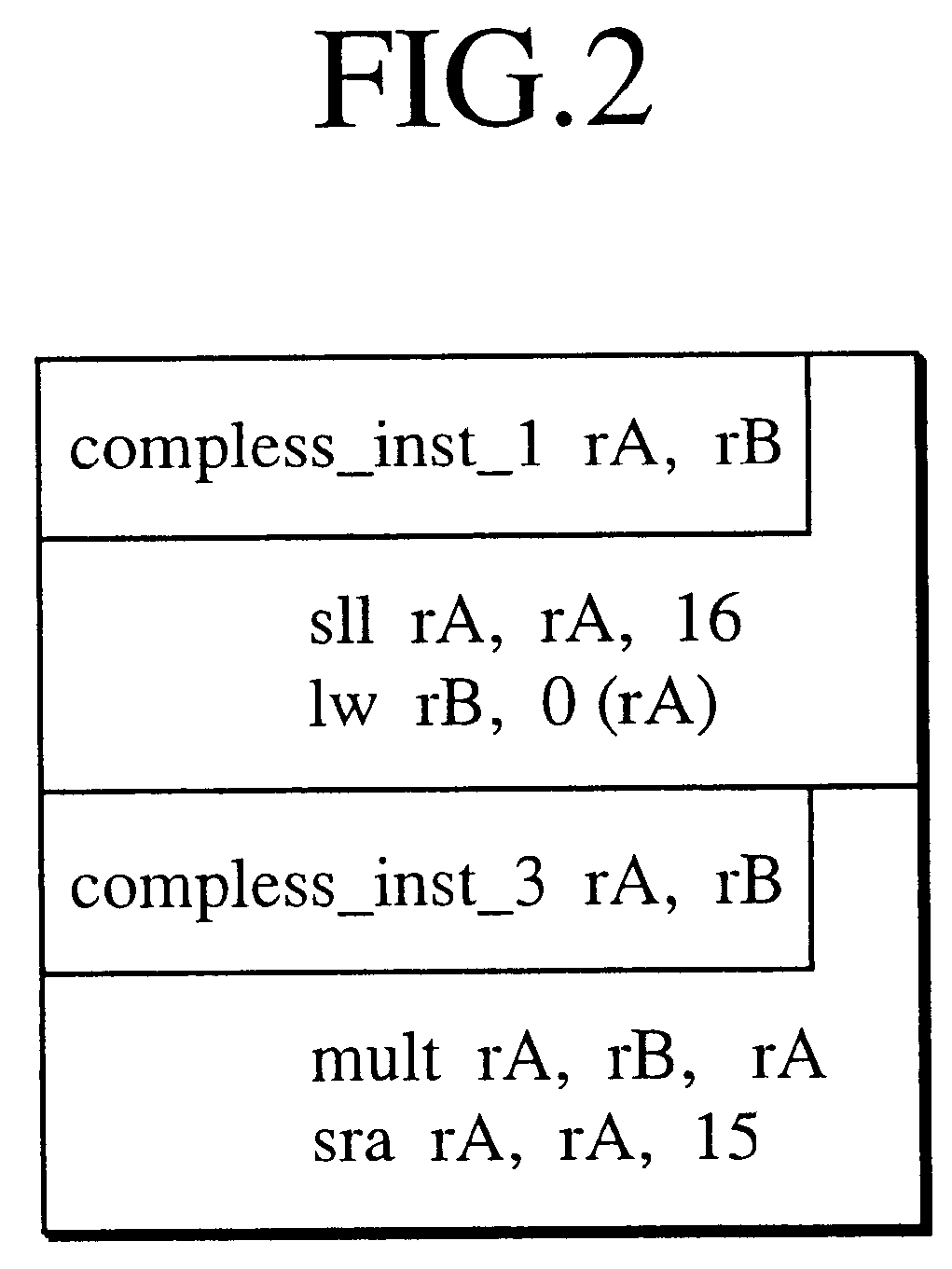
Information processing apparatus provided with an optimized executable instruction extracting unit for extending compressed instructions
InactiveUS6587939B1Reduce the numberData processing applicationsRuntime instruction translationInformation processingInstruction unit
An information processing apparatus is provided with a executable instruction extracting unit which is reconfigured by means of a executable instruction extracting unit reconfiguration unit with reference to a compressed / executable instruction correspondence table optimized for the respective executable program, which has been made up with an compressed instruction. The compressed instruction is extended into the corresponding executable instructions by means of the executable instruction extracting unit as reconfigured.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
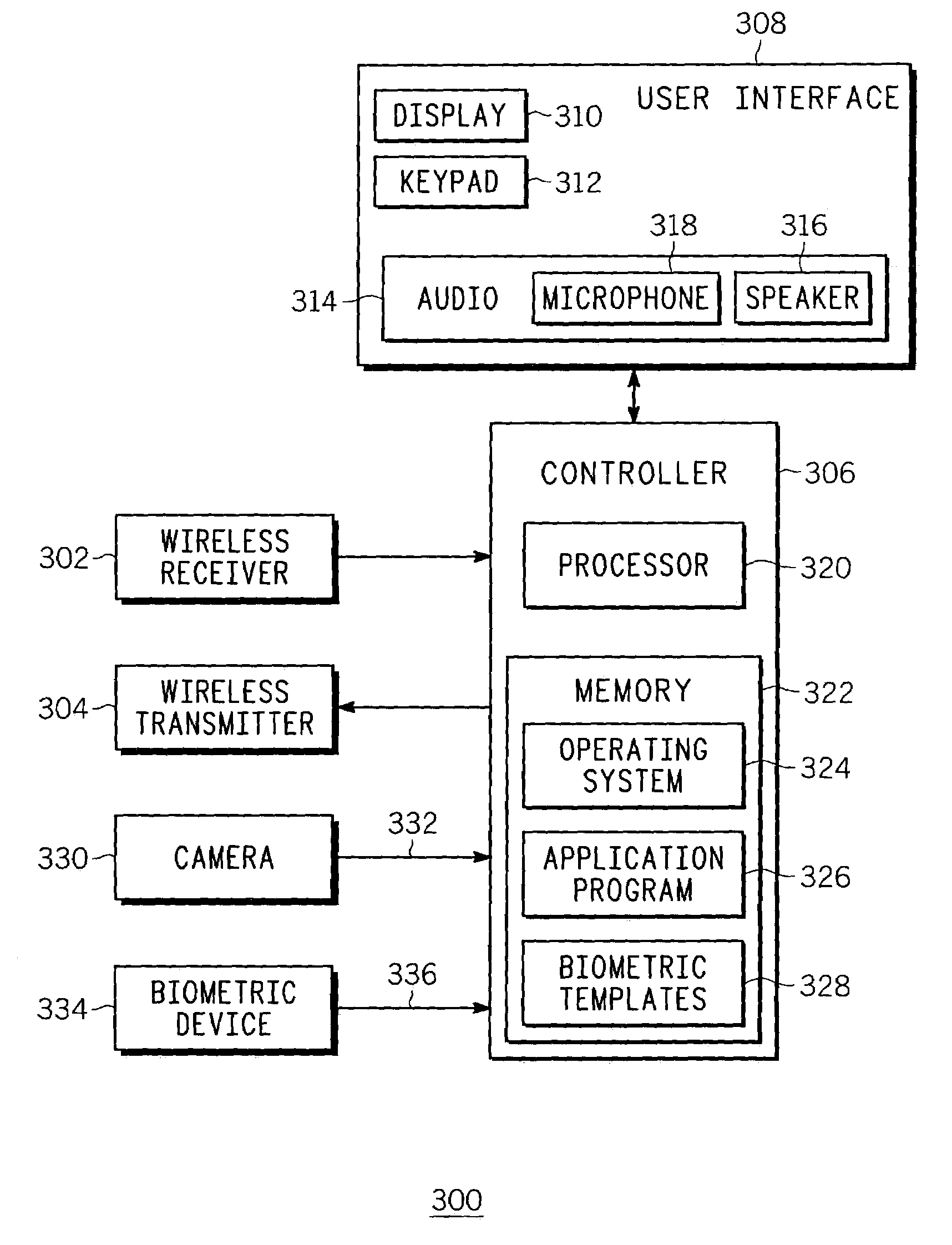
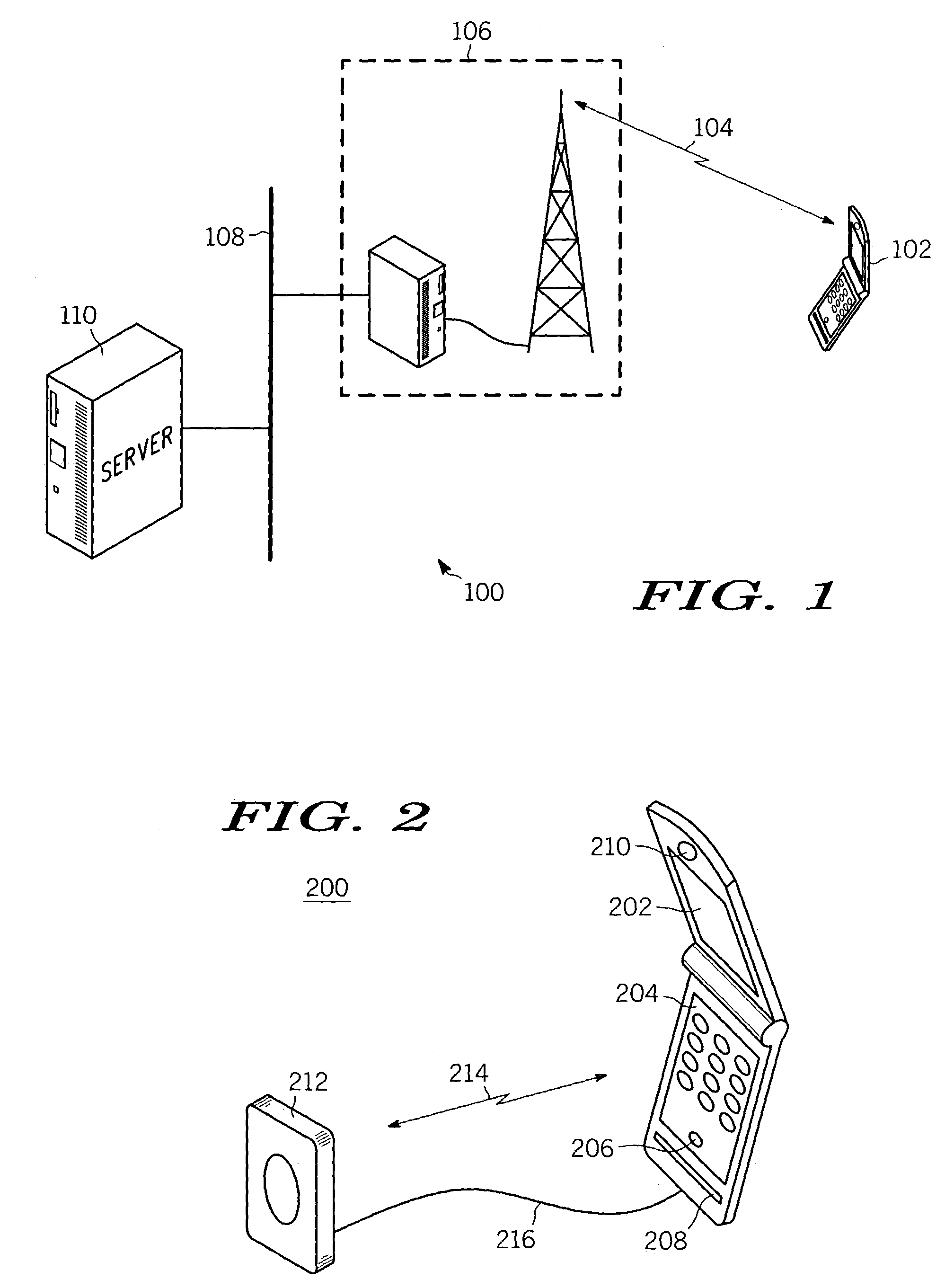
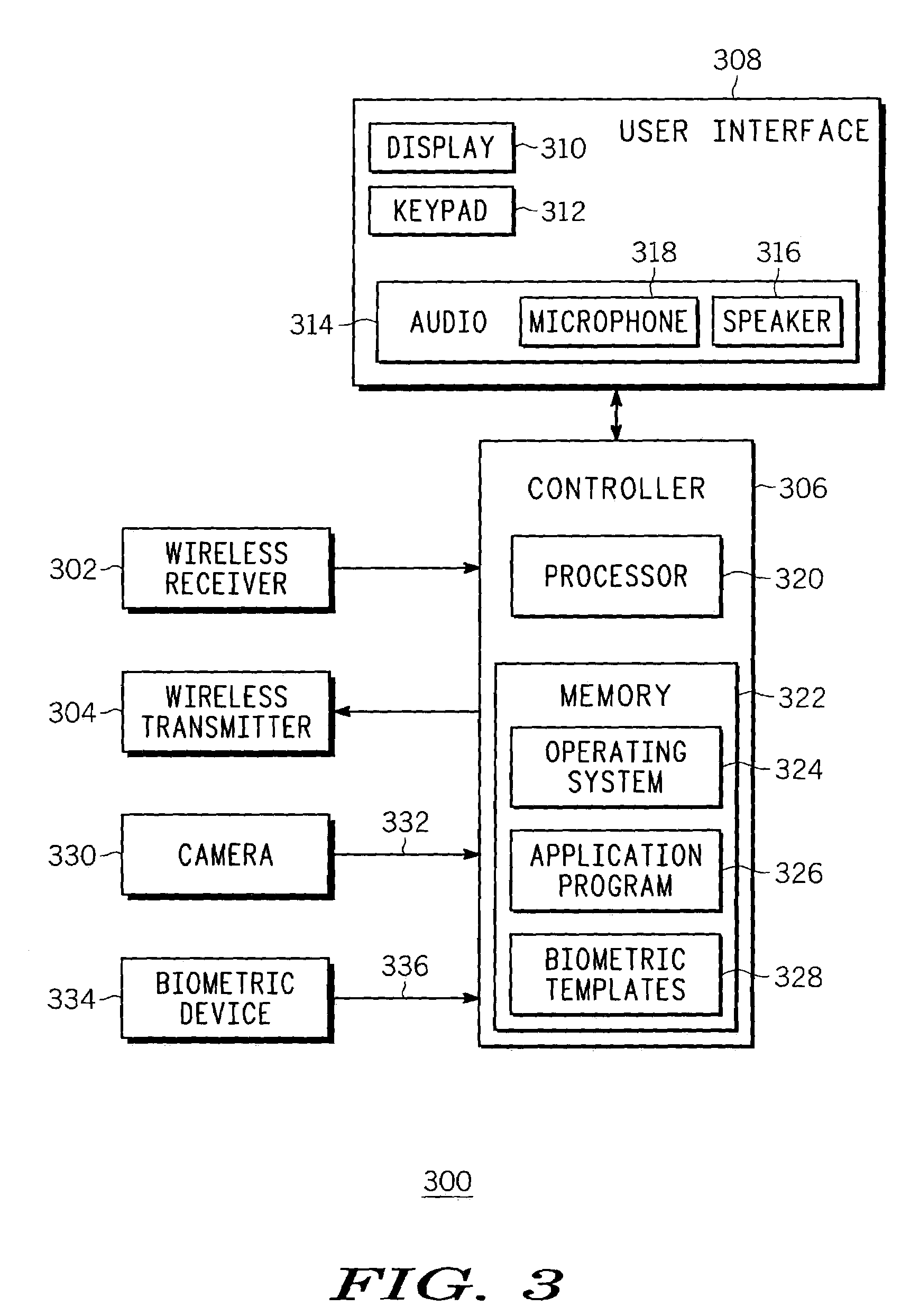
Method and apparatus using biometric sensors for controlling access to a wireless communication device
ActiveUS7088220B2High but convenient level of securityRaise the possibilityElectric signal transmission systemsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionUsabilitySystem usage
A wireless communication device (300) and corresponding system therein uses a plurality of biometric sensors (206, 208, 210) for assessing the identity of a user requesting access to a feature or service provided via the wireless communication device (300). A method comprises collecting (410) a biometric sample from one of the sensors and enabling the feature or service (414) when the sample matches a known sample (412) corresponding to the user. Preferably a sensor will be selected, based on evaluating whether a corresponding predetermined condition exists (406), from a list of the plurality of sensors that is prioritized according to accuracy and ease of use of the sensor.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
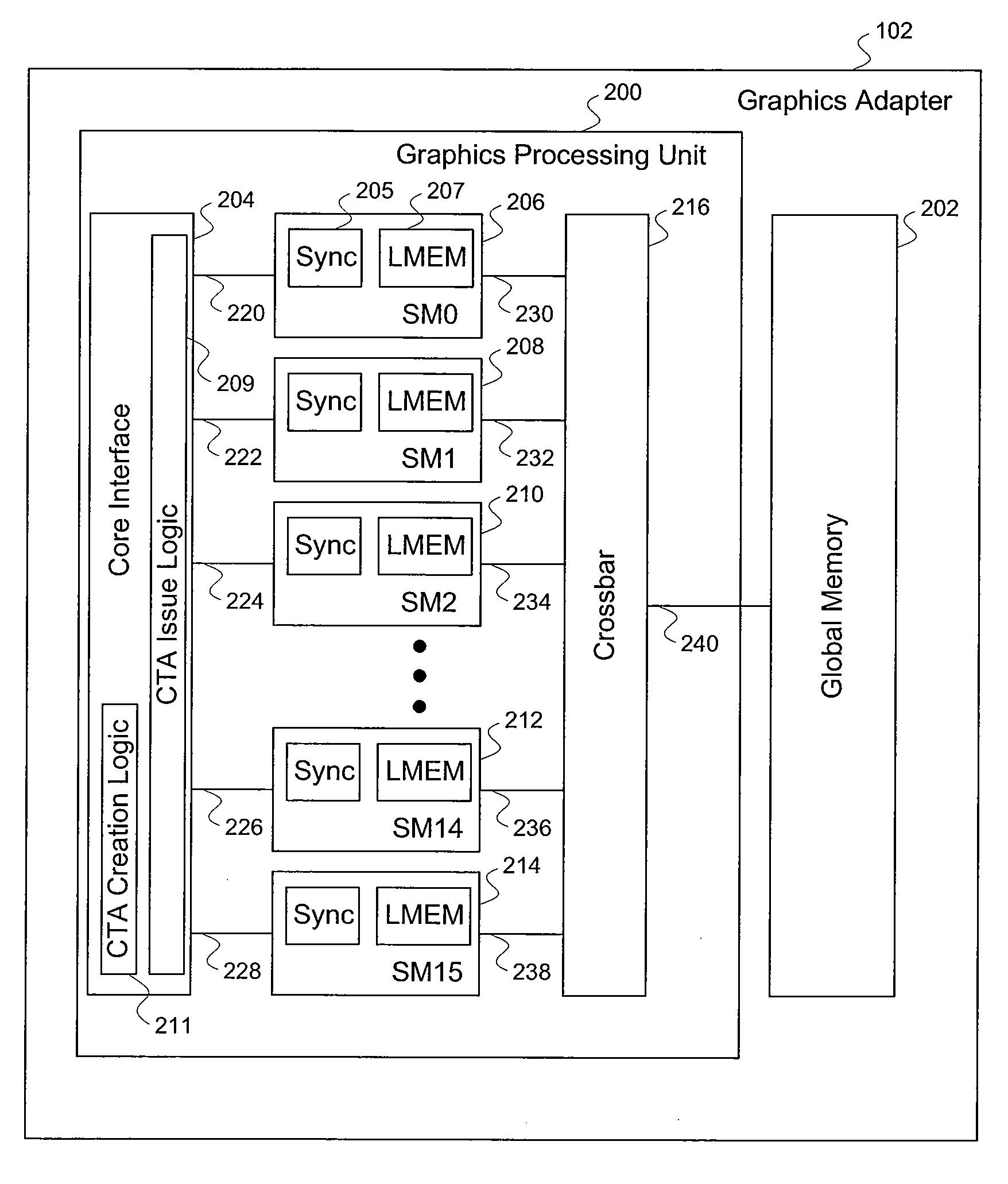
Efficient matrix multiplication on a parallel processing device
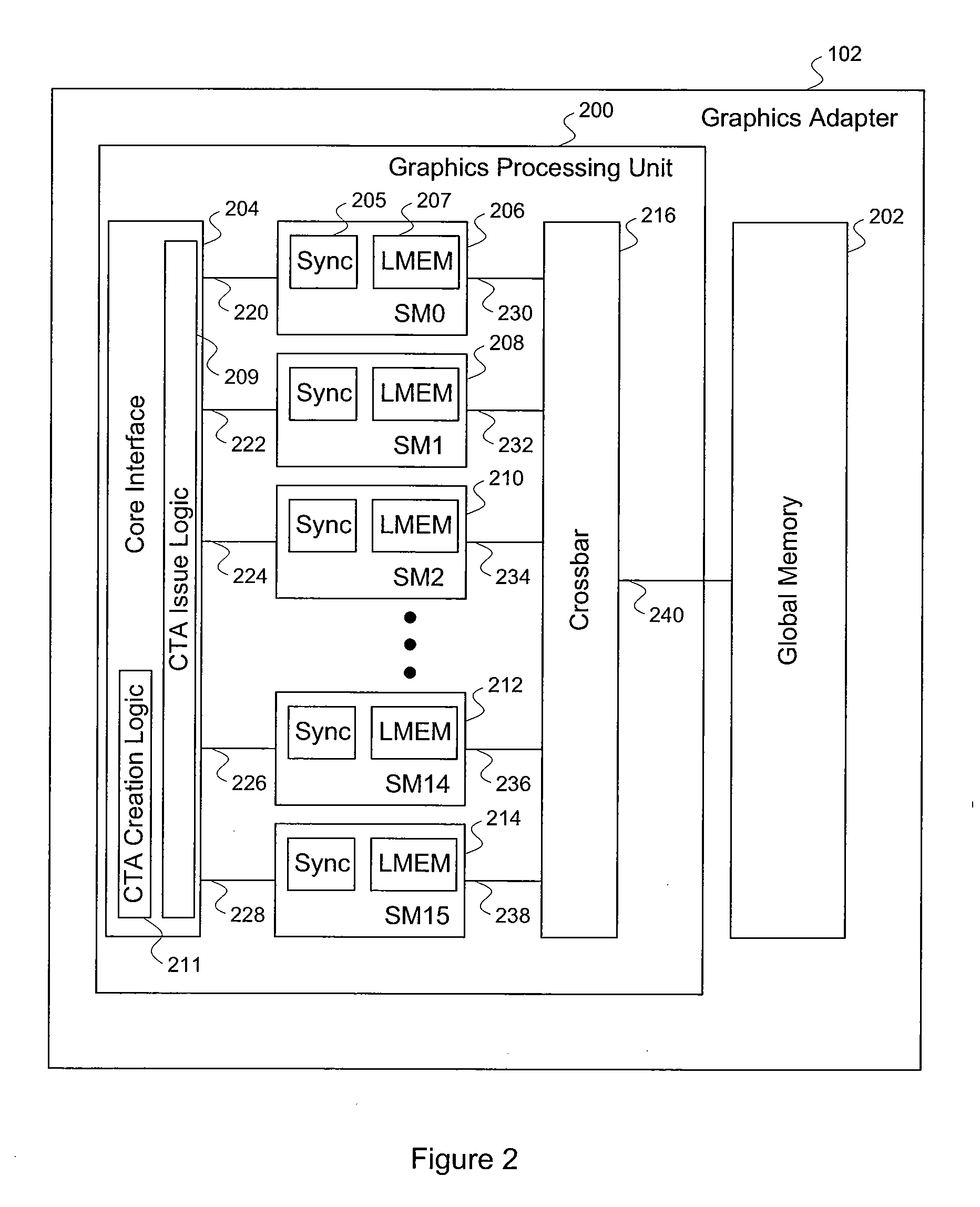
ActiveUS20100325187A1Significant processing efficiencyReduce the number of timesComputation using non-contact making devicesData mergingMulti processorParallel processing
The present invention enables efficient matrix multiplication operations on parallel processing devices. One embodiment is a method for mapping CTAs to result matrix tiles for matrix multiplication operations. Another embodiment is a second method for mapping CTAs to result tiles. Yet other embodiments are methods for mapping the individual threads of a CTA to the elements of a tile for result tile computations, source tile copy operations, and source tile copy and transpose operations. The present invention advantageously enables result matrix elements to be computed on a tile-by-tile basis using multiple CTAs executing concurrently on different streaming multiprocessors, enables source tiles to be copied to local memory to reduce the number accesses from the global memory when computing a result tile, and enables coalesced read operations from the global memory as well as write operations to the local memory without bank conflicts.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Simple MIMO precoding codebook design for a MIMO wireless communications system
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for establishing a precoding codebook for a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) wireless communication system. The precoding codebook includes a plurality of codebook entries. Each codebook entry includes four sets of vectors for four respective corresponding transmission ranks. The vectors may be predetermined, or generated from source unitary matrices. In addition, the codebook is fully nested.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
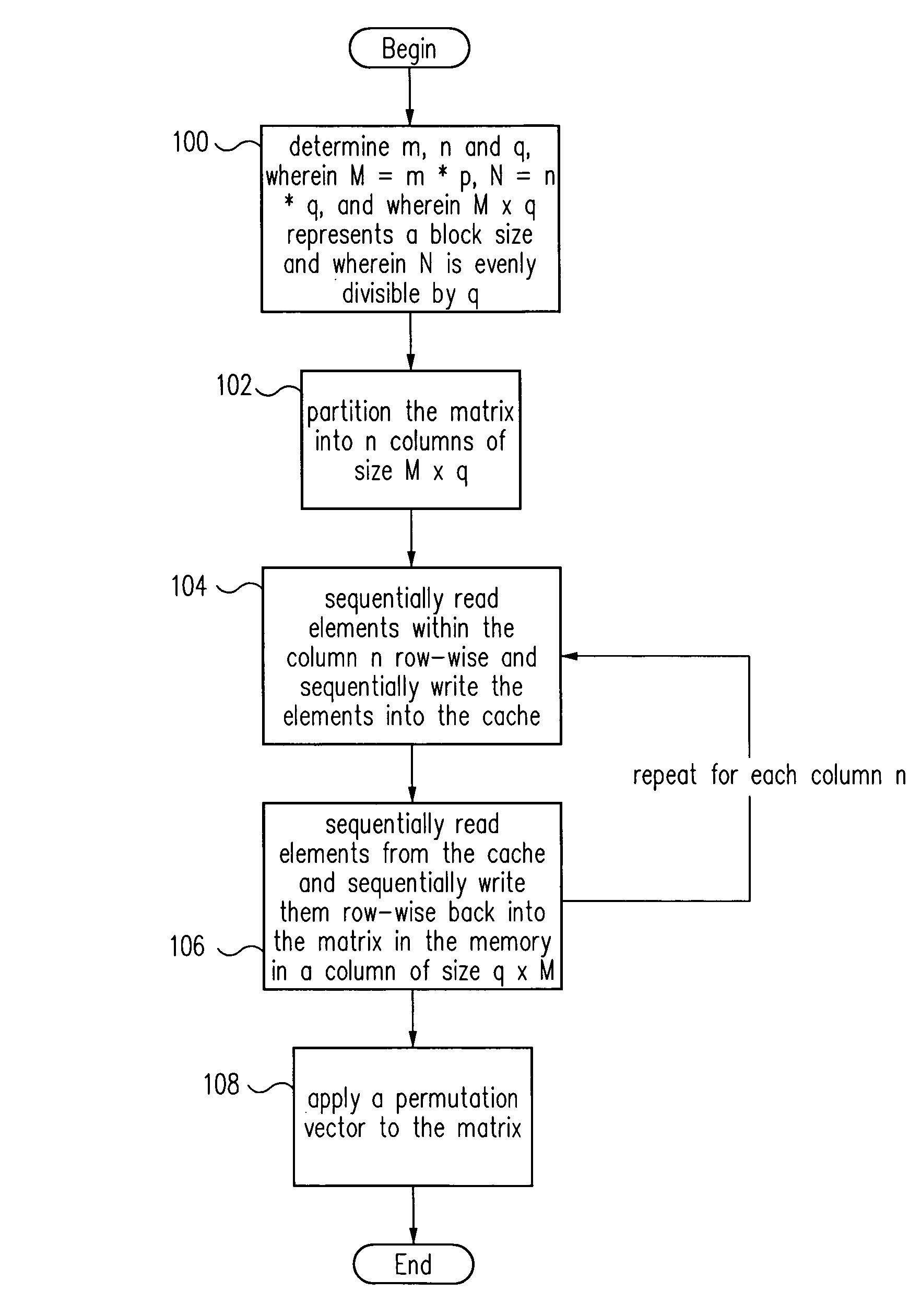
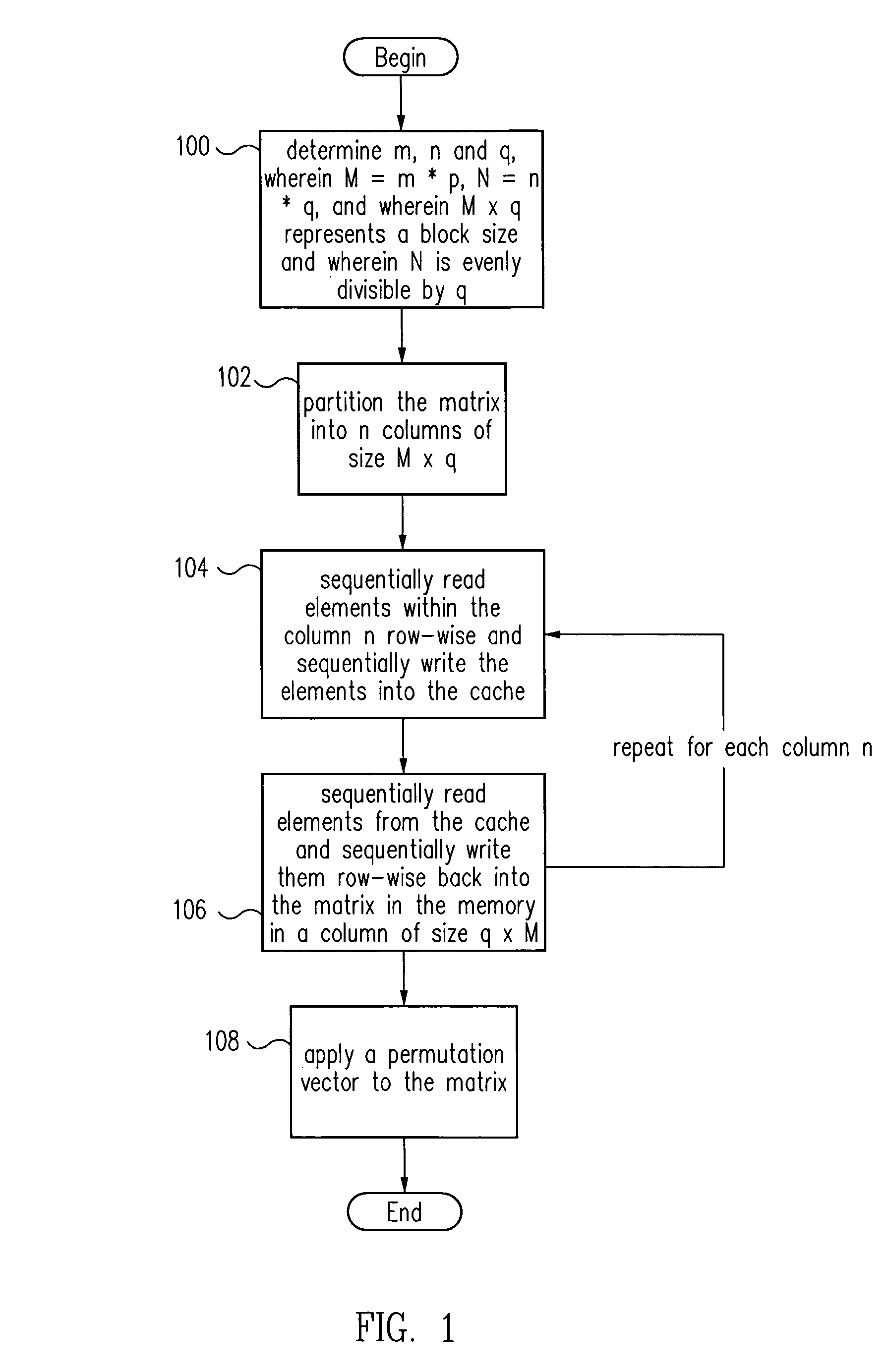
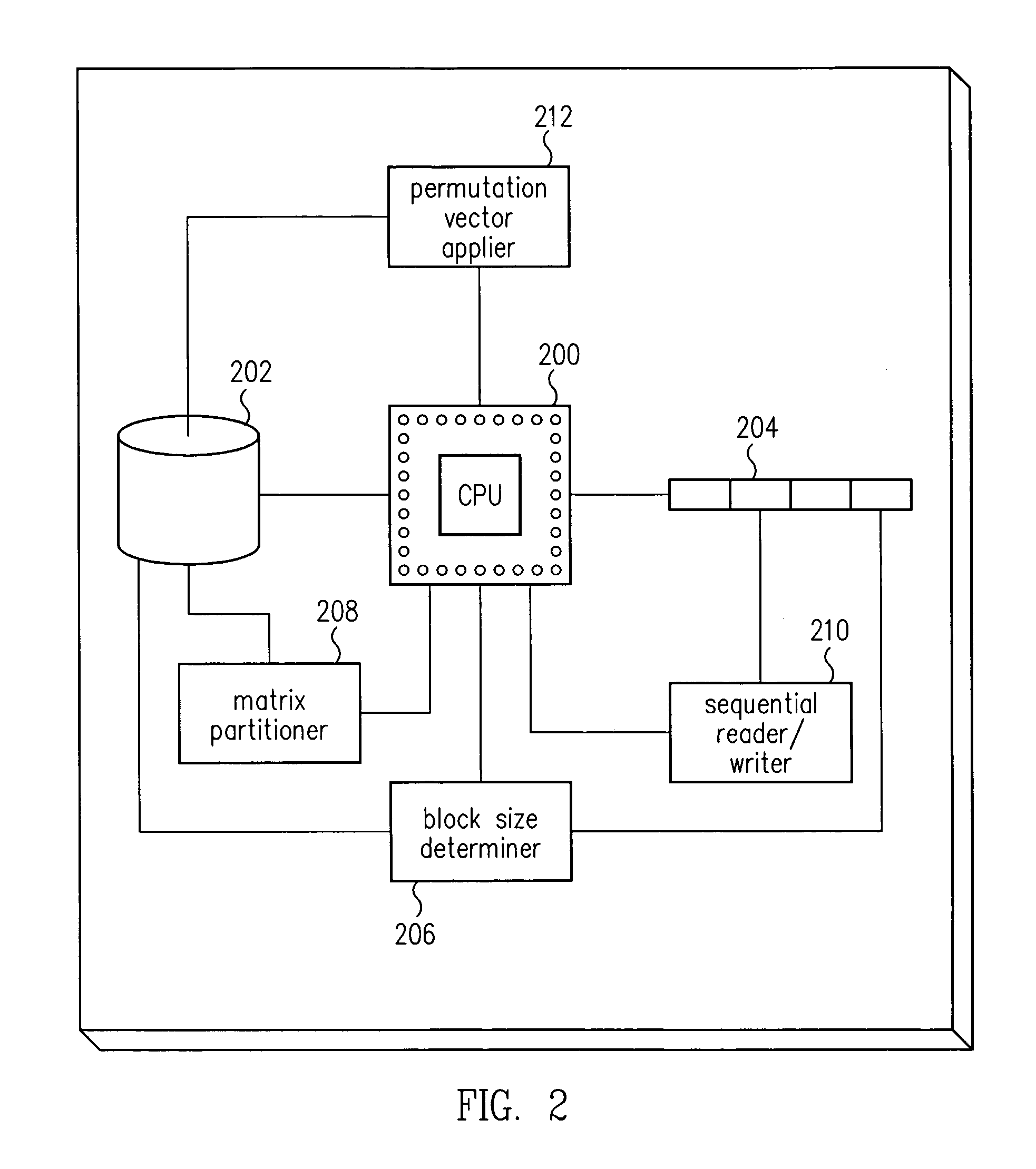
Matrix transposition in a computer system
ActiveUS7031994B2Improves speed and parallelabilityEasy transpositionHandling data according to predetermined rulesGeneral purpose stored program computerAlgorithmComputerized system
Improved transposition of a matrix in a computer system may be accomplished while utilizing at most a single permutation vector. This greatly improves the speed and parallelability of the transpose operation. For a standard rectangular matrix having M rows and N columns and a size M×N, first n and q are determined, wherein N=n*q, and wherein M×q represents a block size and wherein N is evenly divisible by p. Then, the matrix is partitioned into n columns of size M×q. Then for each column n, elements are sequentially read within the column row-wise and sequentially written into a cache, then sequentially read from the cache and sequentially written row-wise back into the matrix in a memory in a column of size q×M. A permutation vector may then be applied to the matrix to arrive at the transpose. This method may be modified for special cases, such as square matrices, to further improve efficiency.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
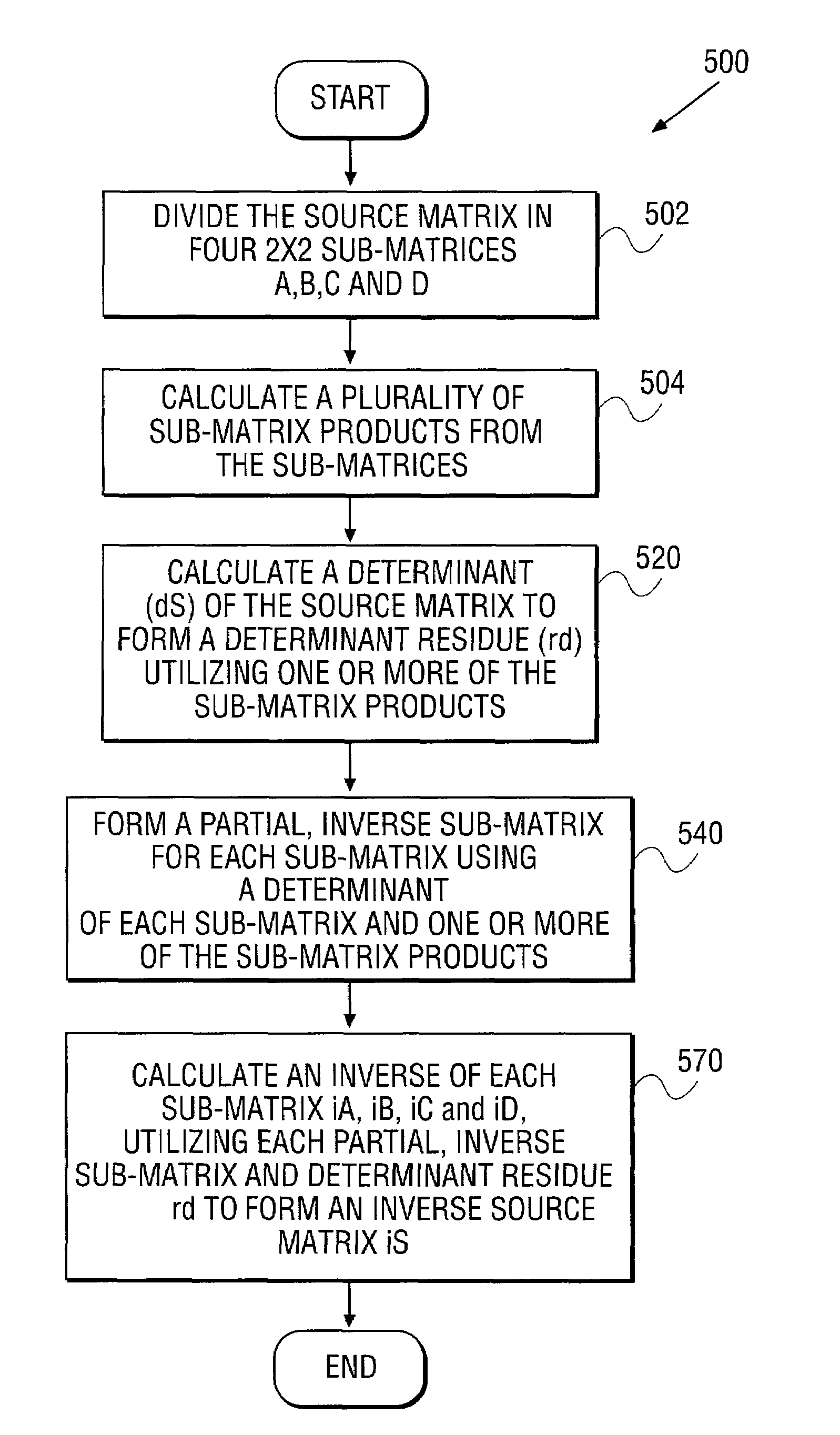
Apparatus and method for inverting a 4x4 matrix
An apparatus and method for inverting a 4×4 source matrix. A source matrix is divided into four 2×2 sub-matrices. A plurality of sub-matrix products are subsequently calculated from the sub-matrices. Next, a determinant of the source matrix is calculated to form a determinant residue utilizing the previously computed sub-matrix products. Calculation of partial inverse for each sub-matrix is next performed, using the sub-matrix products and determinants of the sub-matrices. Finally, an inverse of each sub-matrix is calculated, utilizing the partial inverse sub-matrices and the determinant residue to form an inverse of the 4×4 source matrix. The article allows processors to store two floating-point elements within a Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) register. Accordingly, a sub-matrix is represented using two SIMD registers, resulting in improved computational locality and efficiency. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
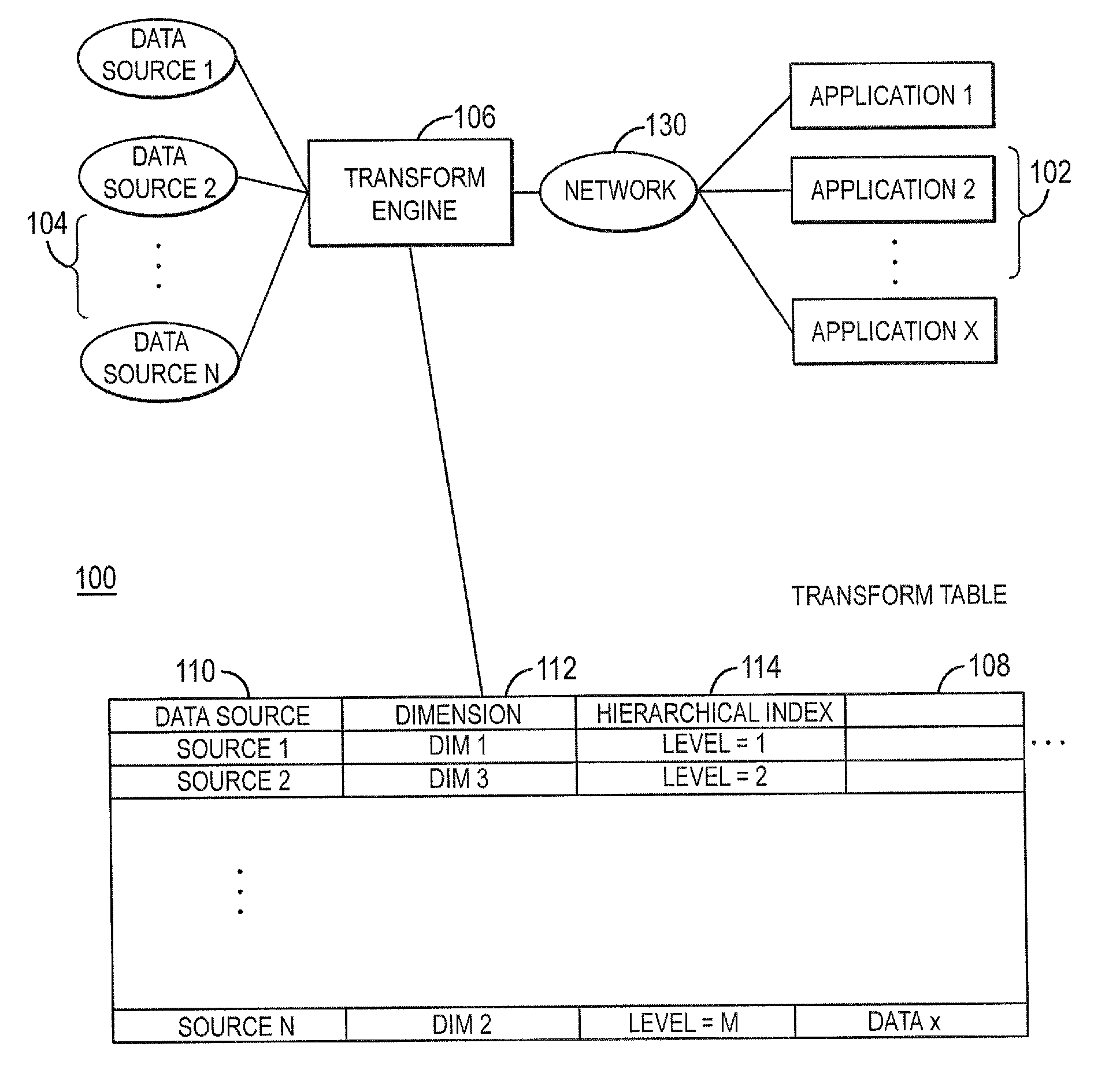
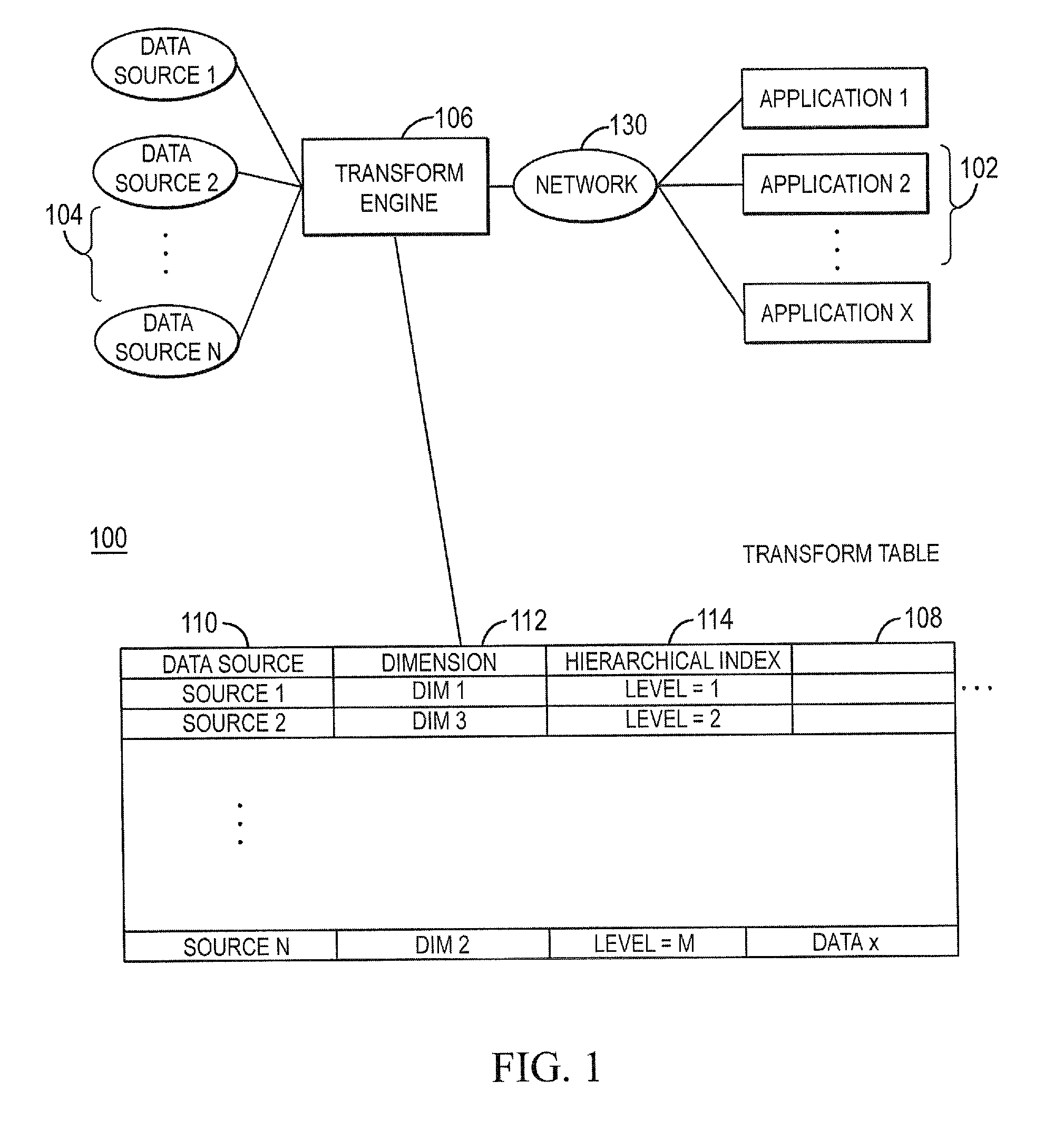
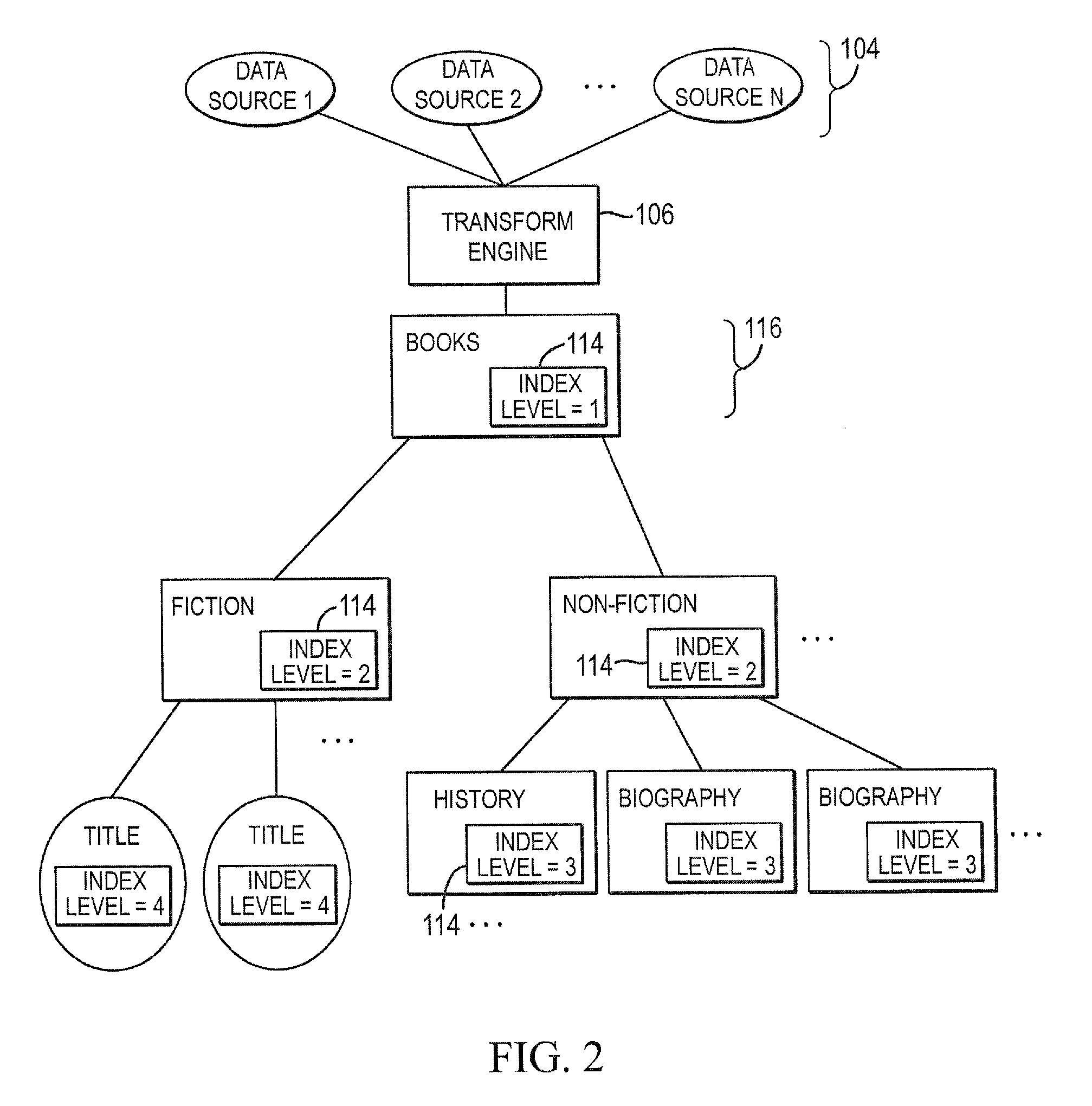
Systems and methods for hierarchical aggregation of multi-dimensional data sources
ActiveUS20100057700A1Multi-dimensional databasesSpecial data processing applicationsData sourceMultidimensional data
Embodiments relate to systems and methods for the hierarchical aggregation of multi-dimensional data sources. A set of applications such as online analytical processing (OLAP) applications can access the combined data of a set of multi-dimensional data sources via a transform engine. The set of data sources can be configured with diverse dimensions and associated data, which in general do not reflect a strictly hierarchical structure. In embodiments, the transform engine can combine or aggregate the set of data sources using common dimensions or data points, and build an index into a transform table reflecting the hierarchical level of dimension from each data source in a combined hierarchical mapping. An OLAP or other application can therefore perform searches, sorts, and / or other operations on the combined hierarchical mapping based on the resulting ordering of data, even when the original multi-dimensional data sources do not contain an explicit common hierarchy.
Owner:RED HAT
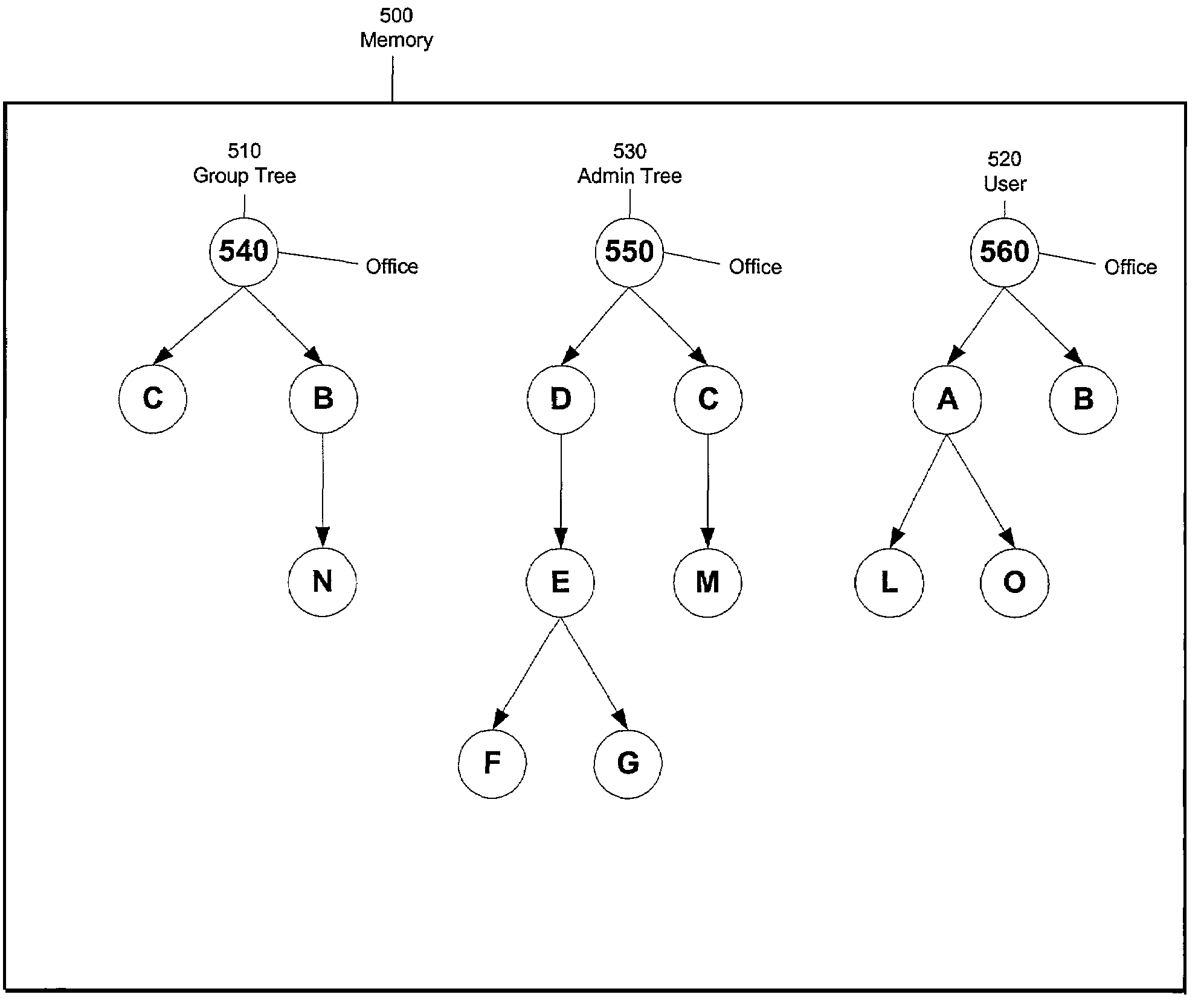
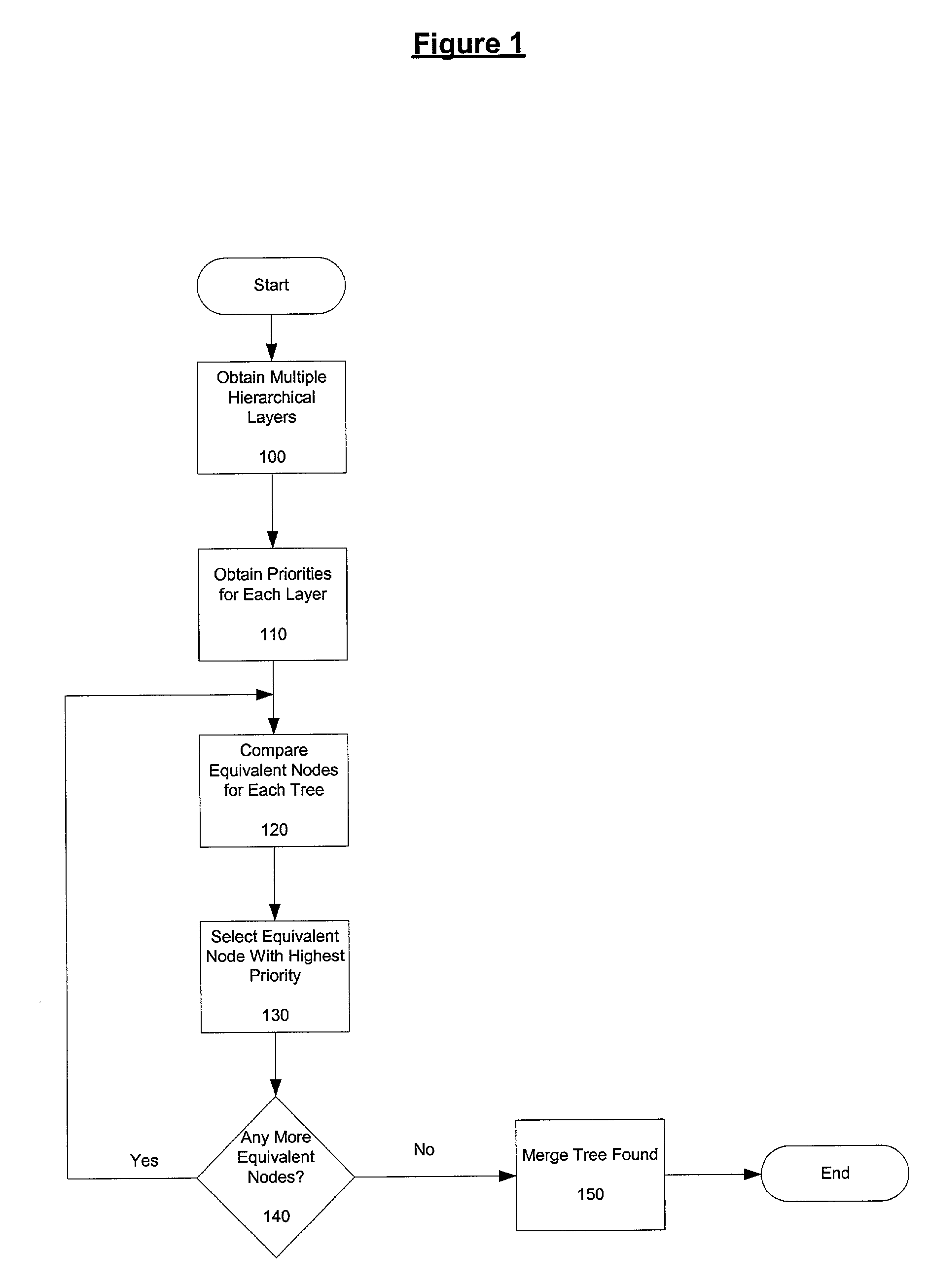
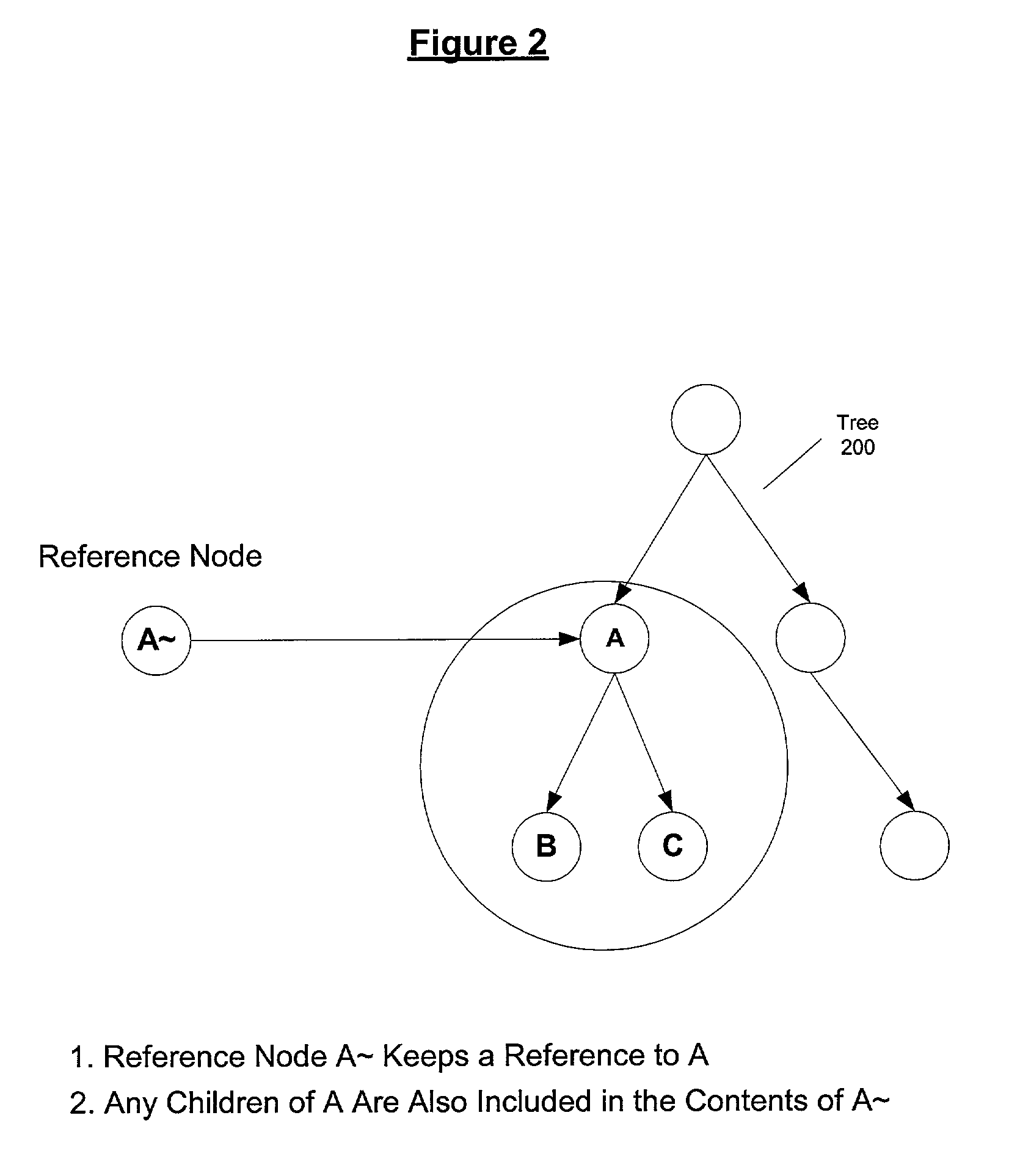
Method and apparatus for runtime merging of hierarchical trees
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a method and apparatus for a runtime merging system of hierarchical trees with a reference node implementation. According to one or more embodiments of the present invention, a reference node is implemented which holds a reference to a node in a DOM tree active in memory. The reference node class allows adding nodes to the merged tree without having to make a clone of the node, which is an expensive operation. In one embodiment, if a particular node is not present below a certain level of the tree in any layer except a unique layer, it renders visiting the children of that node unnecessary. A reference is kept to the node in the memory.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
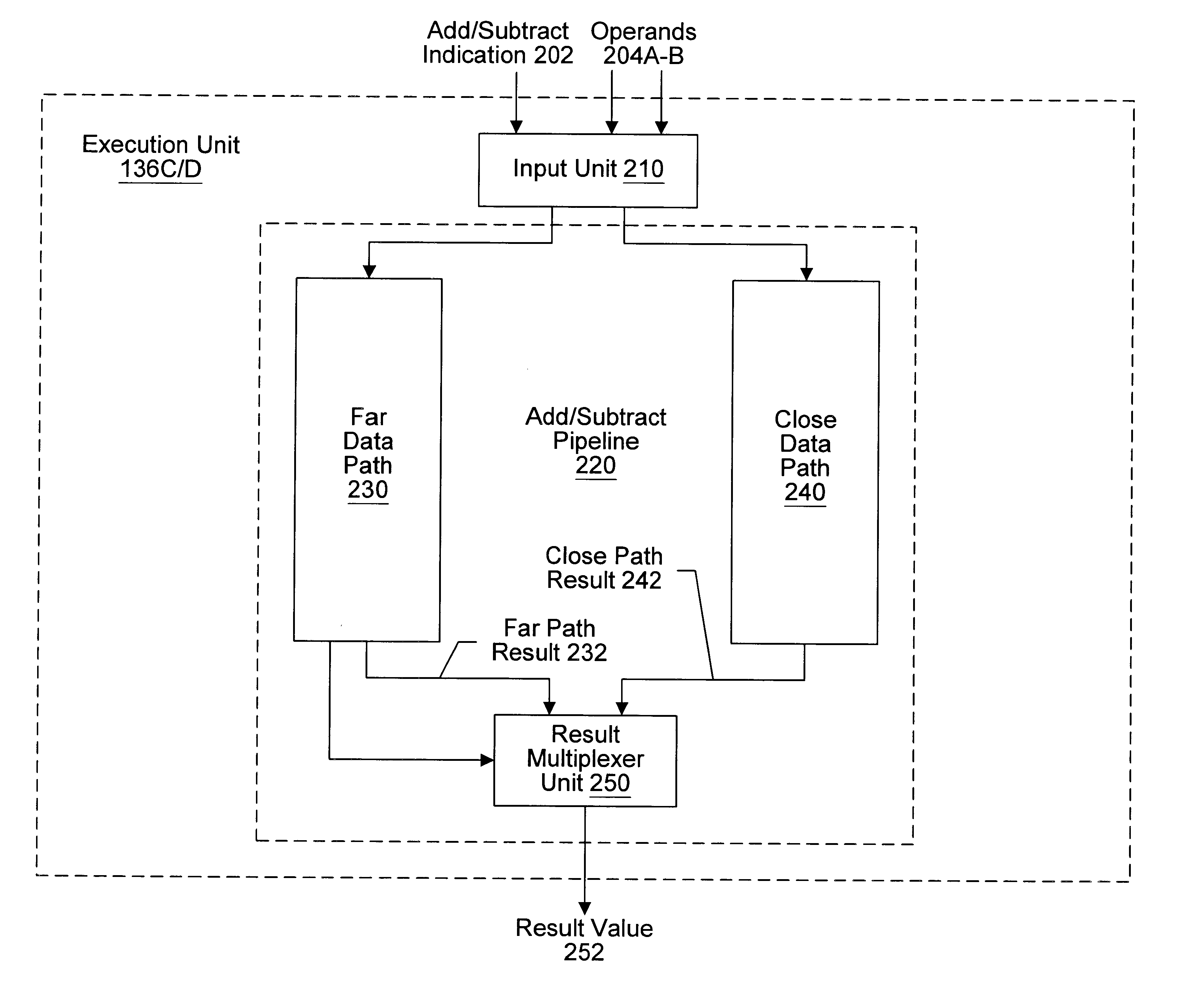
Floating point addition pipeline including extreme value, comparison and accumulate functions
InactiveUS6397239B2Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesPathPingExecution unit
A multimedia execution unit configured to perform vectored floating point and integer instructions. The execution unit may include an add / subtract pipeline having far and close data paths. The far path is configured to handle effective addition operations and effective subtraction operations for operands having an absolute exponent difference greater than one. The close path is configured to handle effective subtraction operations for operands having an absolute exponent difference less than or equal to one. The close path is configured to generate two output values, wherein one output value is the first input operand plus an inverted version of the second input operand, while the second output value is equal to the first output value plus one. Selection of the first or second output value in the close path effectuates the round-to-nearest operation for the output of the adder.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
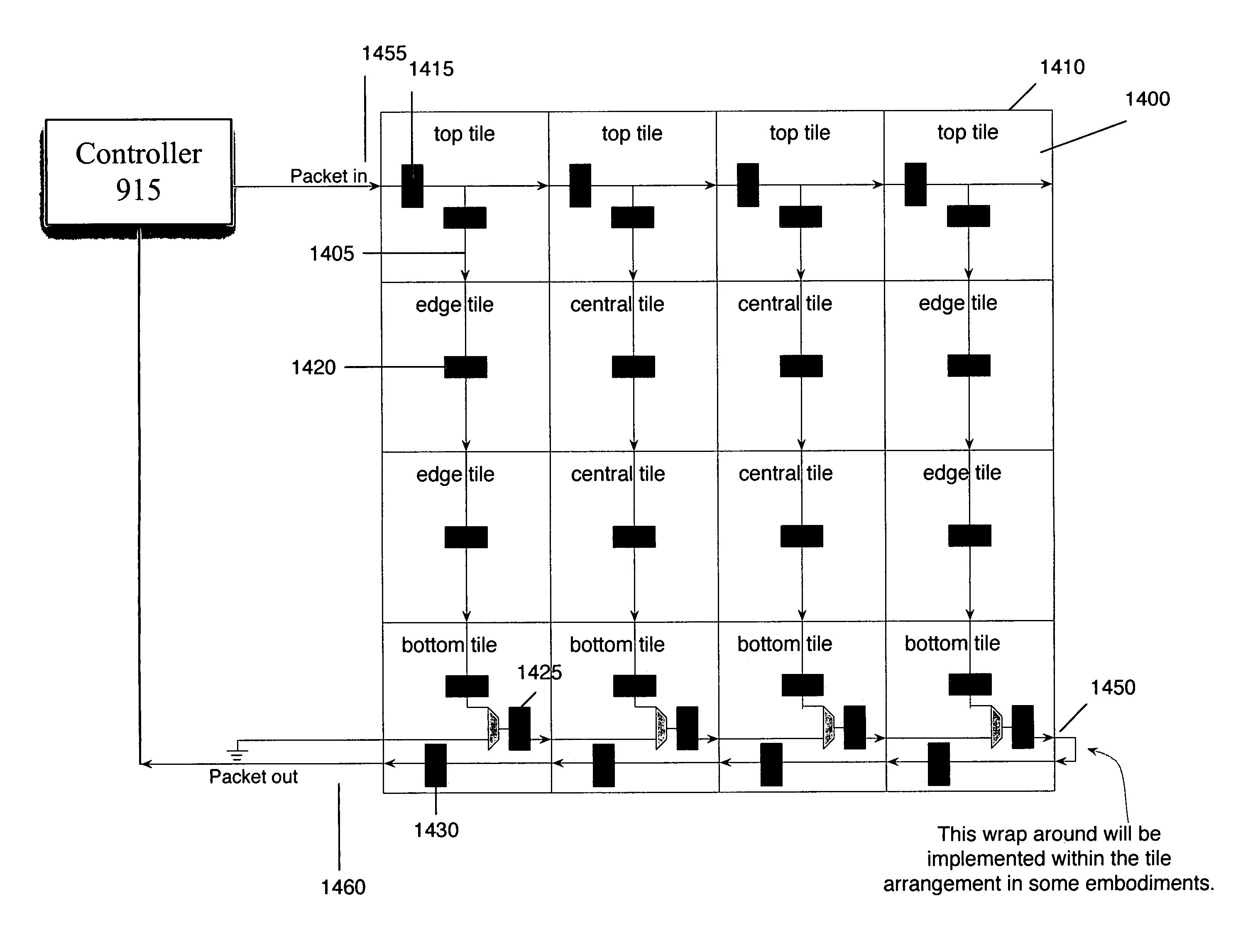
Configurable IC with packet switch configuration network
ActiveUS7375550B1Quick configurationEasy to operateSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsIntegrated circuitPacket switch
Some embodiments of the invention provide configurable integrated circuit (IC) that includes several configurable circuits that are conceptually in tiles. The IC also includes a first data network for passing data between the configurable circuits. The IC further includes a second packet-switch network for receiving packets of data from the outside of the configurable IC and switchably routing each packet to at least one destination tile. In some embodiments, the second packet-switch network supplies data from the tiles that the configurable circuits output in response to data packets received from outside of the configurable IC. Also, in some embodiments, a particular packet that is for a particular resource in a particular tile includes a fist address that identifies the particular configurable tile from the plurality of configurable tiles, and then a second address that identifies the particular resource within the particular configurable tile.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
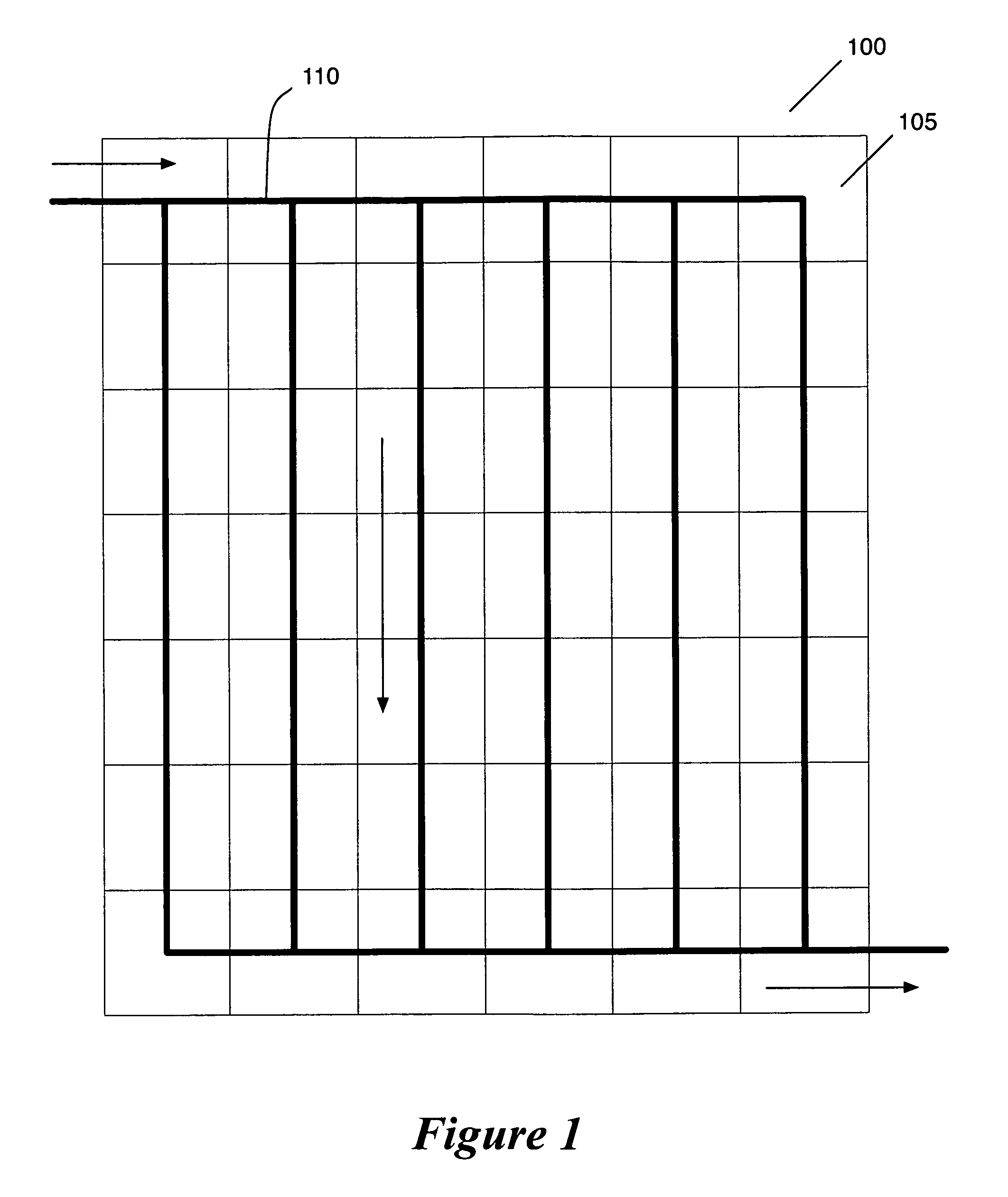
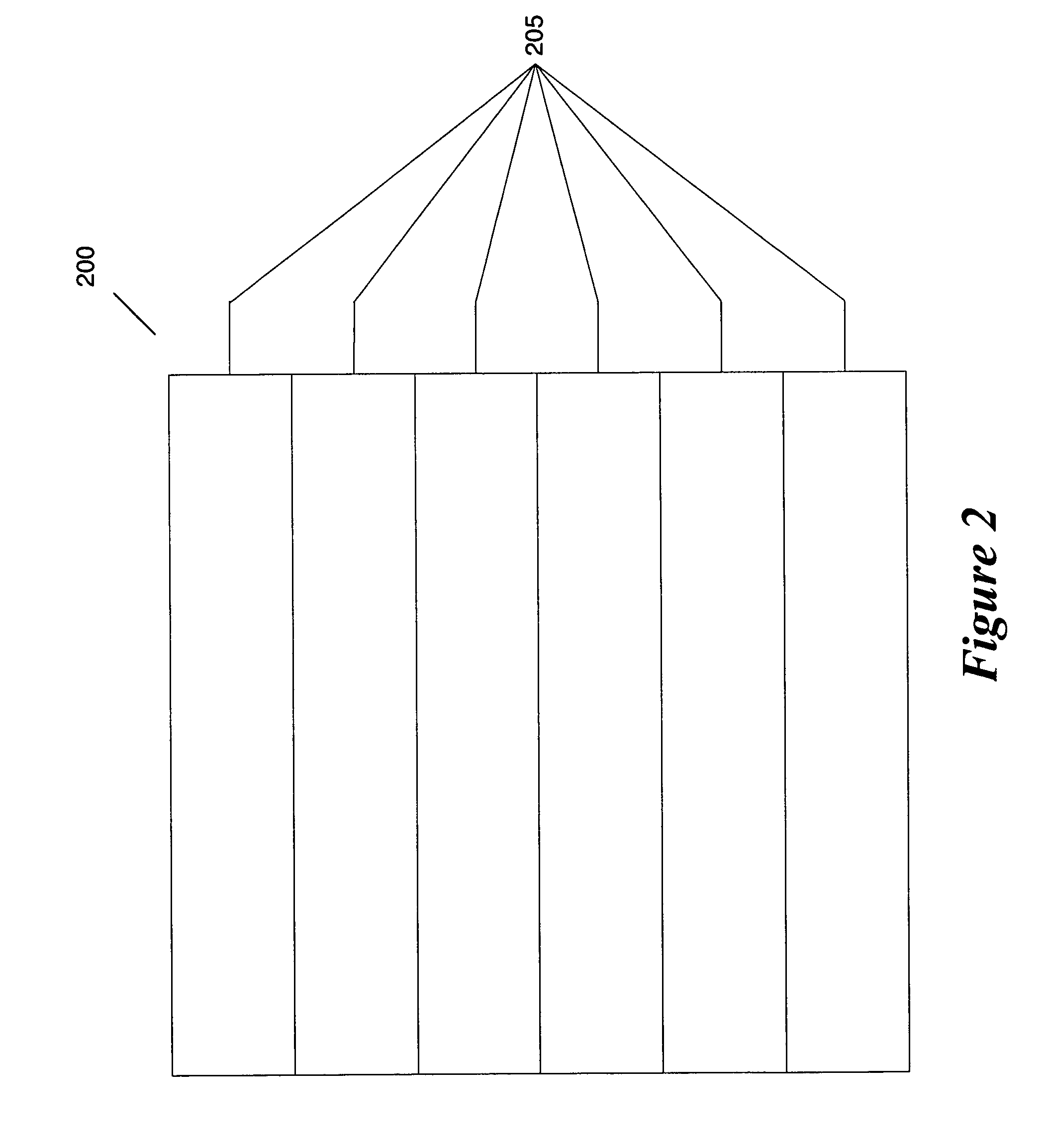
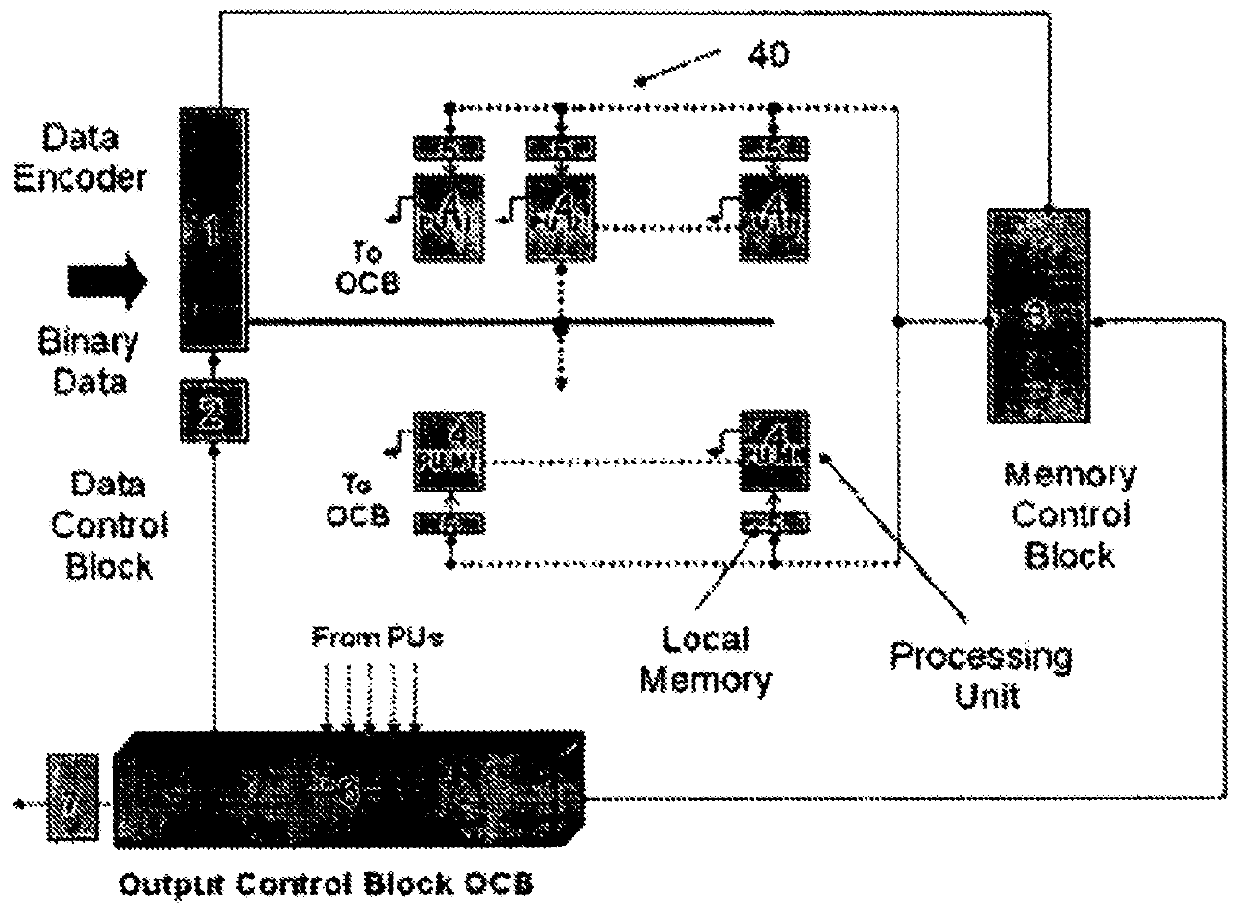
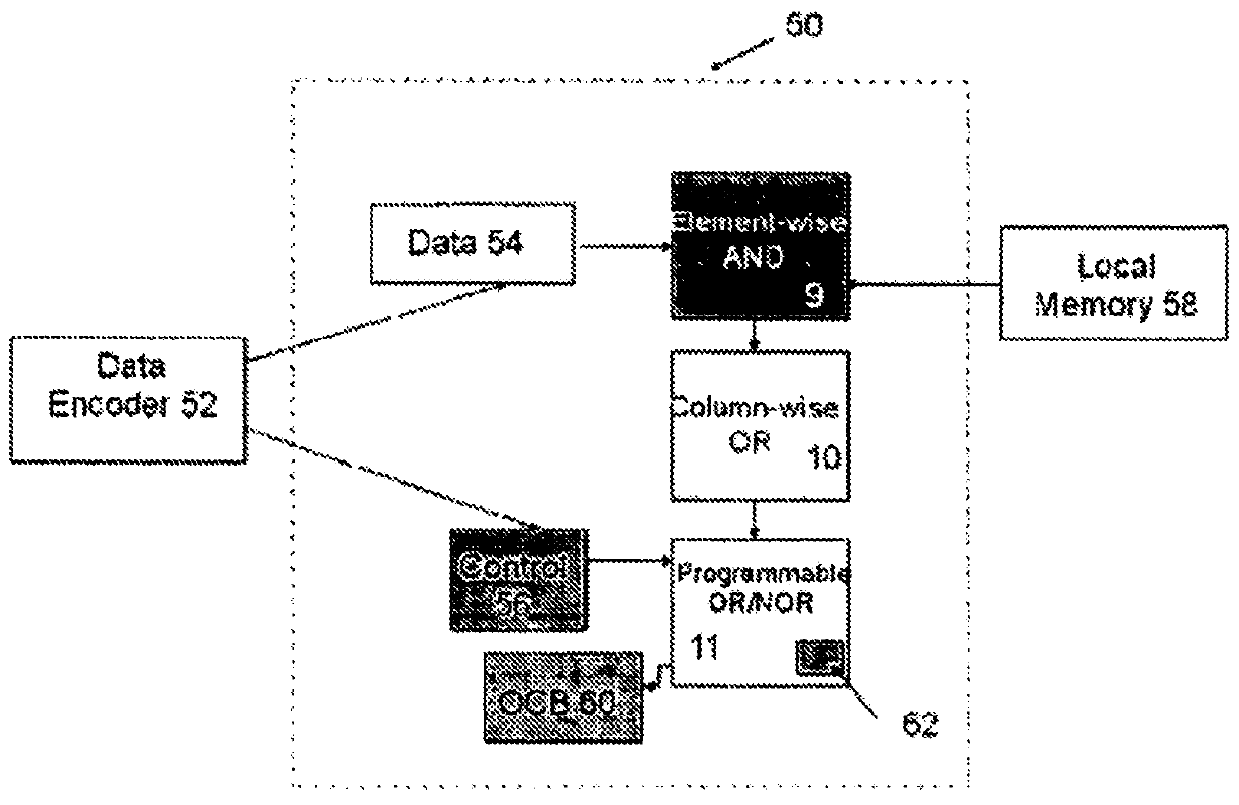
Programmable matrix processor
A matrix processor and processing method, the processor including a data encoder for receiving an input data stream; a data controller coupled to the data encoder for arranging the input data in an operand matrix, at least one processing unit for processing the data in matrix form by Boolean matrix-matrix multiplication with a selected operator matrix, and an output control module coupled to the processing unit for outputting desired results therefrom.
Owner:RUSNANO
Sparse Matrix-Vector Multiplication on Graphics Processor Units
InactiveUS20110078226A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsGraphicsMatrix multiplication
Techniques for optimizing sparse matrix-vector multiplication (SpMV) on a graphics processing unit (GPU) are provided. The techniques include receiving a sparse matrix-vector multiplication, analyzing the sparse matrix-vector multiplication to identify one or more optimizations, wherein analyzing the sparse matrix-vector multiplication to identify one or more optimizations comprises analyzing a non-zero pattern for one or more optimizations and determining whether the sparse matrix-vector multiplication is to be reused across computation, optimizing the sparse matrix-vector multiplication, wherein optimizing the sparse matrix-vector multiplication comprises optimizing global memory access, optimizing shared memory access and exploiting reuse and parallelism, and outputting an optimized sparse matrix-vector multiplication.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for sorting and distributing data among a plurality of nodes
ActiveUS7293024B2Improve economyTransparent operationData processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationData setTheoretical computer science
A method for distributing and sorting data among a plurality of nodes is described herein. After receiving a portion of a data set (e.g., a database), each node sorts its portion and estimates a partitioning of the sorted dataset among the nodes based in part on its own sorted data portion. Each node then provides a representation of its estimated partition to a master node. The master node, using the provided estimated partitions, determines a tentative partitioning and submits the tentative partitioning to each node. Each node then determines the effect the tentative partitioning using its data portion. If the effect is acceptable for each node, the tentative partitioning plan is used to partition the data. Otherwise, the tentative partitioning plan is repeatedly revised by the master node and considered by the nodes having data portions until an acceptable or optimum partitioning is determined. Each node then distributes data from its data portion that falls outside the partition assigned to the node to the appropriate node. Upon receipt of this data, each node can perform a merge sort to add the received data to the previously sorted data portion at the node.
Owner:LEXISNEXIS RISK DATA MANAGEMENT
Reversible arithmetic coding for quantum data compression
A method and structure for encoding / decoding a block of quantum data including removing trailing eigenstates from the block that have eigenvalues below a predetermined limit to retain leading eigenstates that have eigenvalues above the predetermined limit, encoding the remaining quantum bits retained in the block after the removing. The remaining quantum bits can also include a linear superposition of the leading eigenstates. The predetermined limit is based upon a density matrix of the block. This method of encoding produces encoded quantum bits and can further include decoding the encoded quantum bits by reversing the encoding. The decoding reproduces the remaining quantum bits and the encoding completely erases the remaining quantum bits. Further, the invention can include outputting only an encoded or decoded result.
Owner:IBM CORP
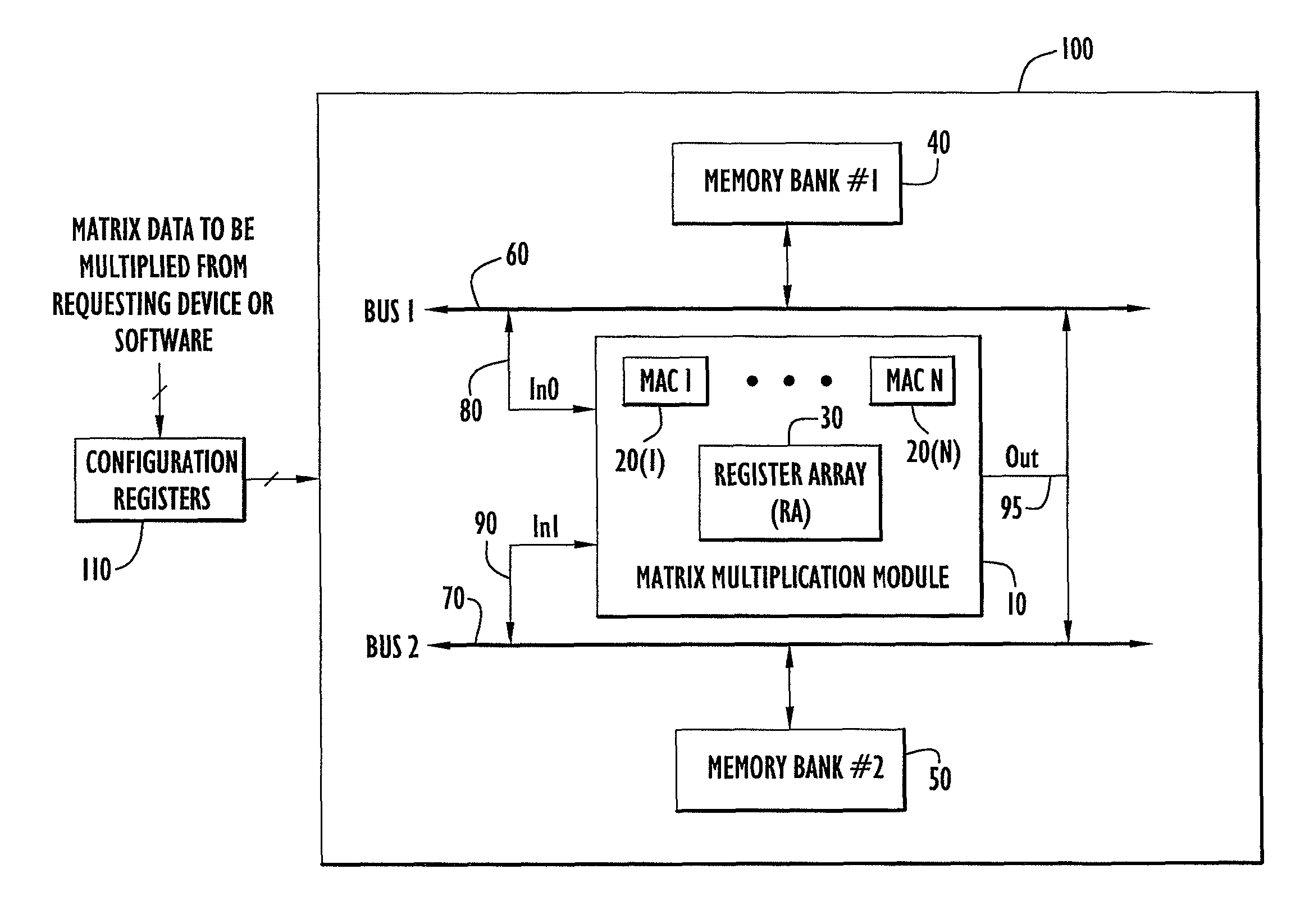
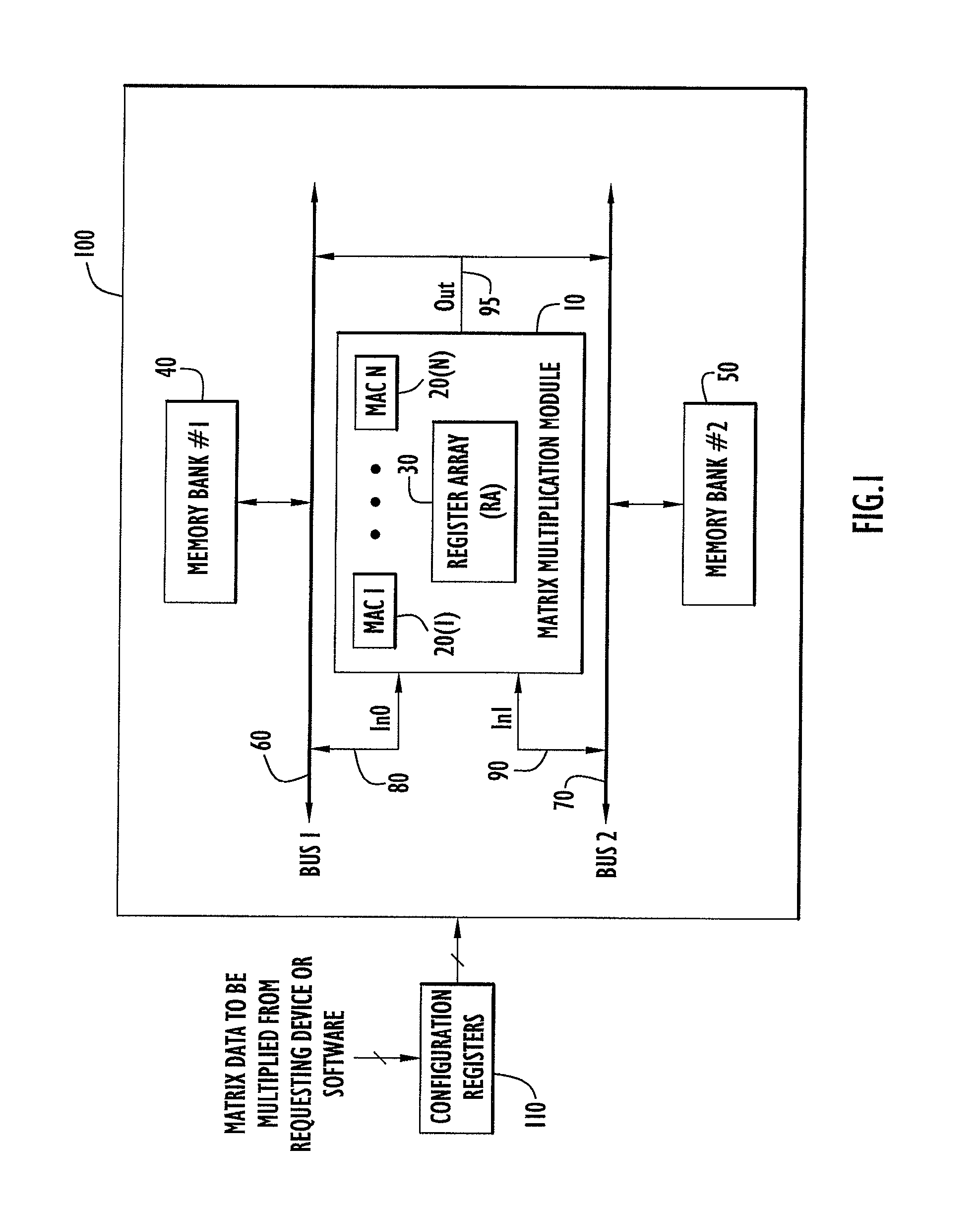
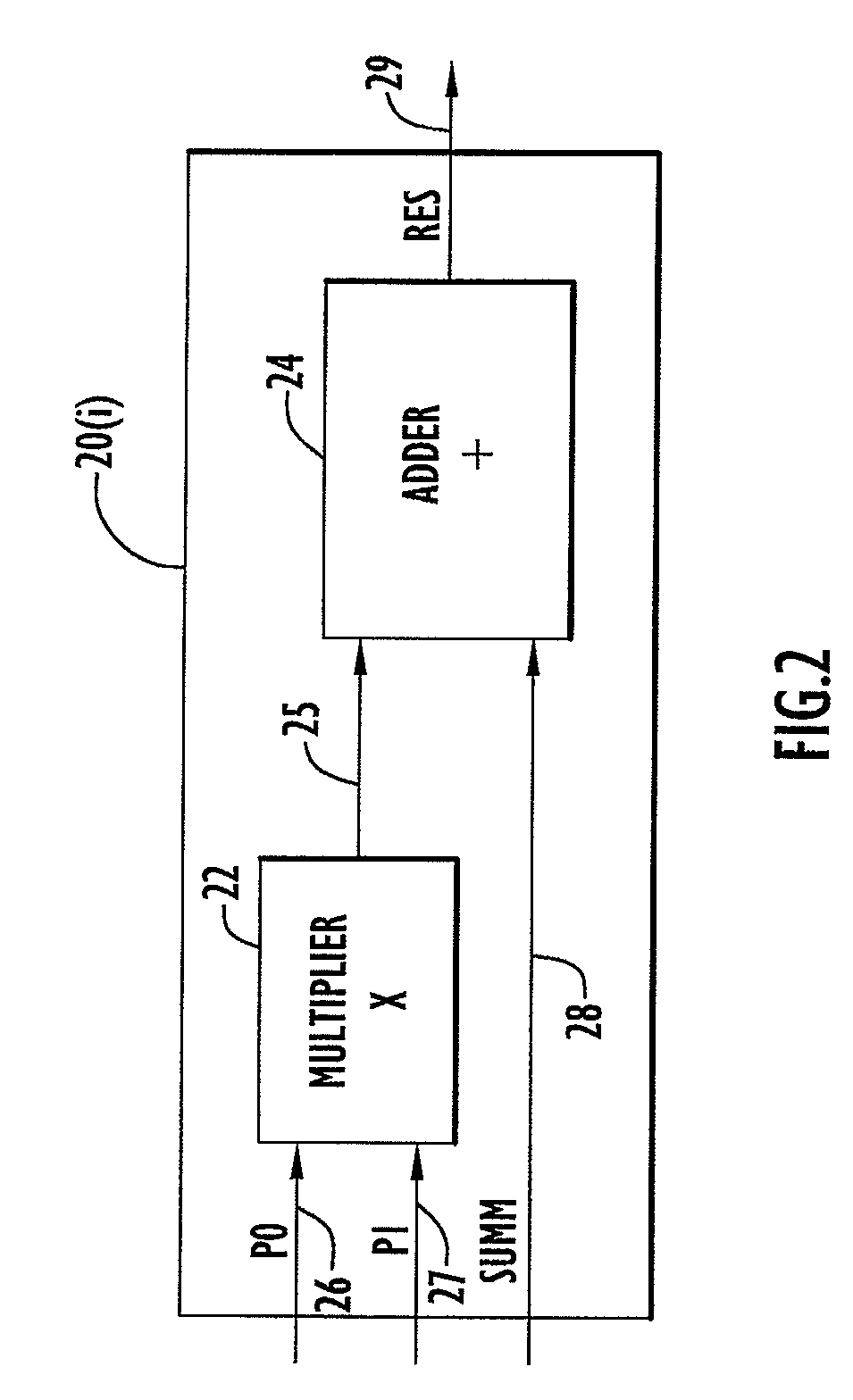
High speed and efficient matrix multiplication hardware module
ActiveUS8051124B2Computation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlClock rateComputer module
A matrix multiplication module and matrix multiplication method are provided that use a variable number of multiplier-accumulator units based on the amount of data elements of the matrices are available or needed for processing at a particular point or stage in the computation process. As more data elements become available or are needed, more multiplier-accumulator units are used to perform the necessary multiplication and addition operations. To multiply an N×M matrix by an M×N matrix, the total (maximum) number of used MAC units is “2*N−1”. The number of MAC units used starts with one (1) and increases by two at each computation stage, that is, at the beginning of reading of data elements for each new row of the first matrix. The sequence of the number of MAC units is {1, 3, 5, . . . , 2*N−1} for computation stages each of which corresponds to reading of data elements for each new row of the left hand matrix, also called the first matrix. For the multiplication of two 8×8 matrices, the performance is 16 floating point operations per clock cycle. For an FPGA running at 100 MHz, the performance is 1.6 Giga floating point operations per second. The performance increases with the increase of the clock frequency and the use of larger matrices when FPGA resources permit. Very large matrices are partitioned into smaller blocks to fit in the FPGA resources. Results from the multiplication of sub-matrices are combined to form the final result of the large matrices.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
System and method for successive matrix transposes
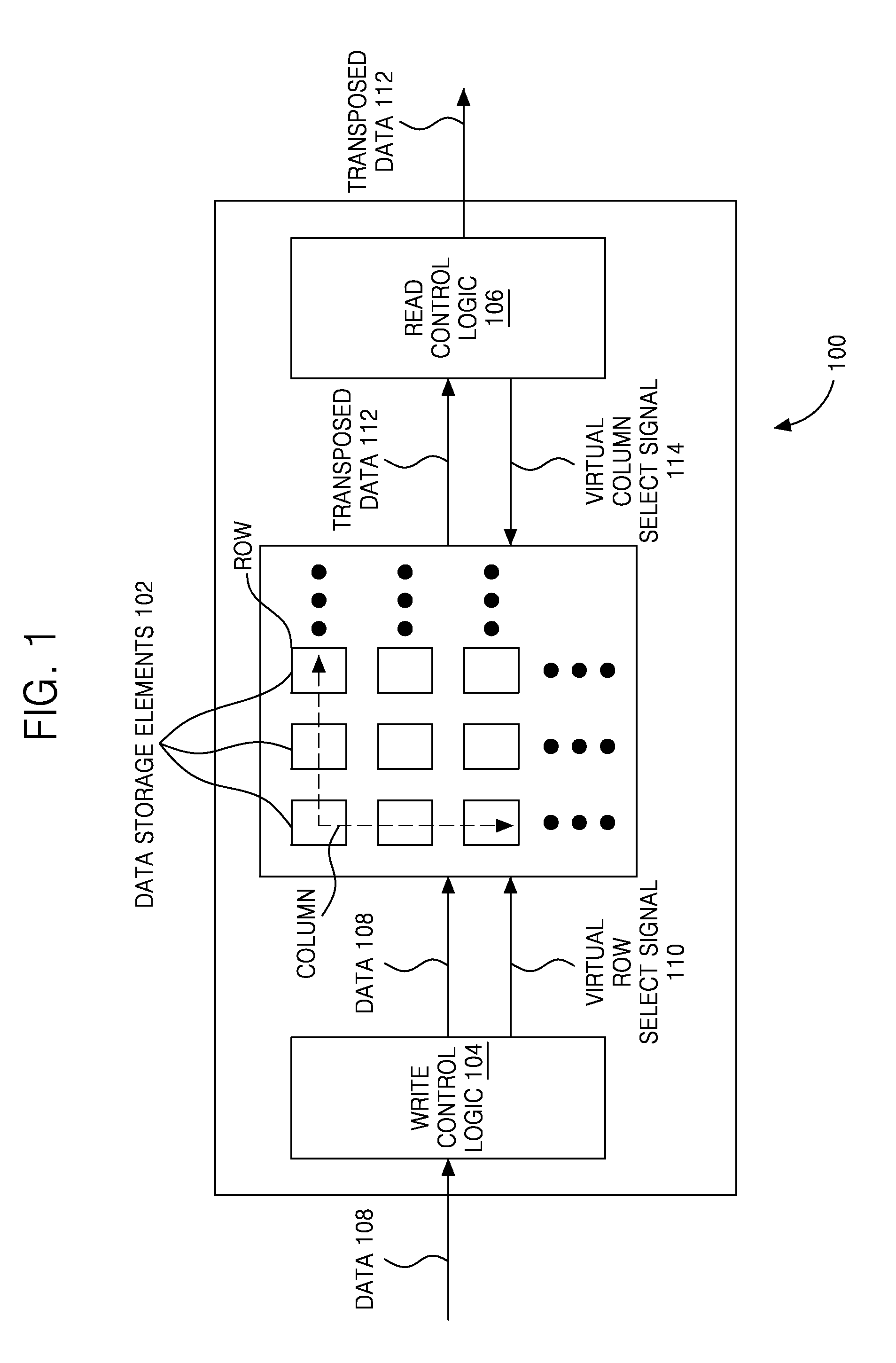
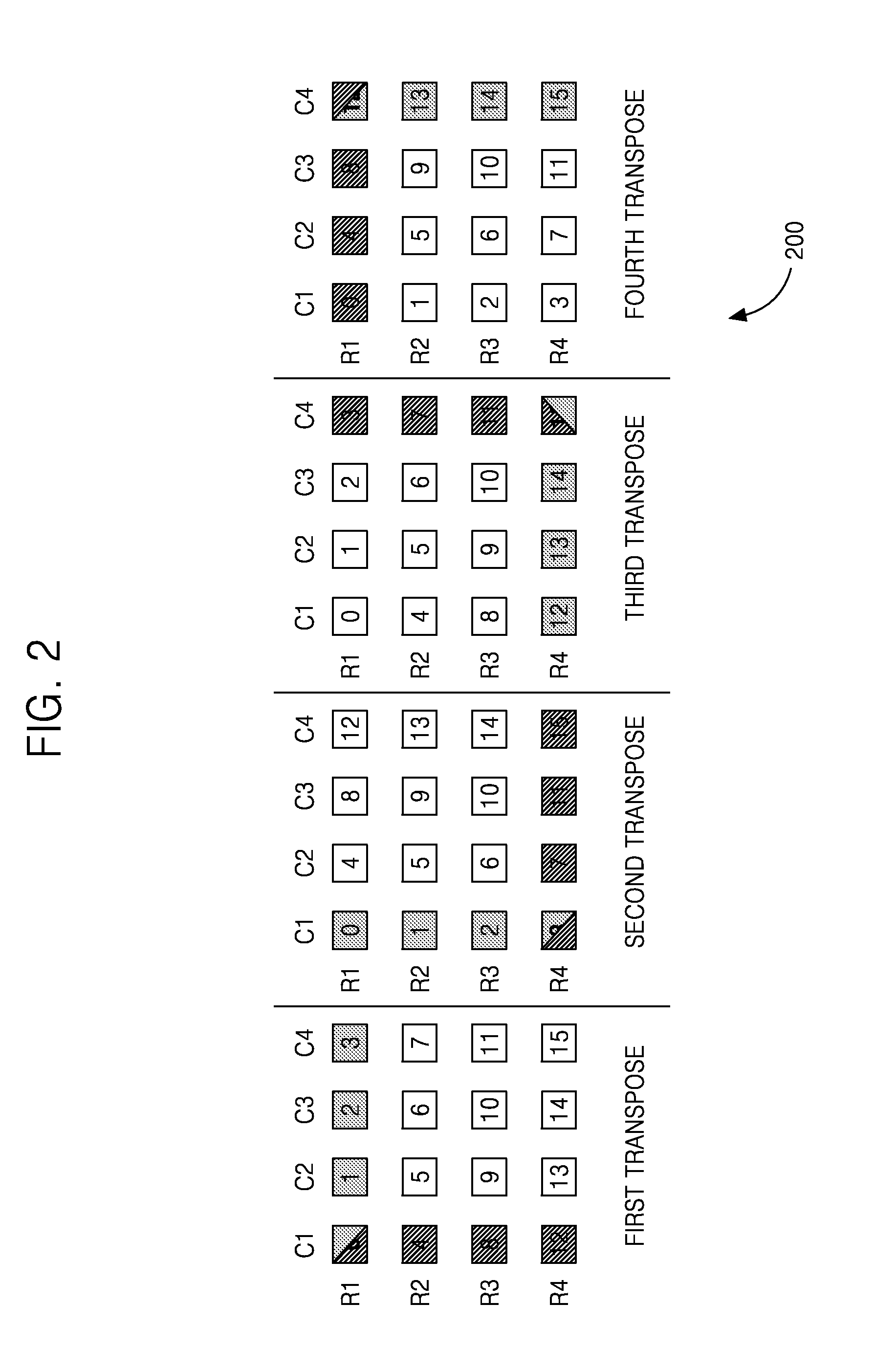
InactiveUS20110264723A1Handling data according to predetermined rulesData mergingComputer architectureTranspose
A system and method for successively transposing a matrix is disclosed. The device includes a plurality of data storage elements arranged as a two dimensional (2D) structure including X rows and Y columns. The device further includes write control logic coupled to the input of plurality of data storage elements for writing data in at least one virtual row. The device also includes read control logic coupled to the output of the plurality of data storage elements for reading the data from at least one virtual column, where the data write to the at least one virtual row and the data read from the at least one virtual column are performed substantially simultaneously during each cycle of operation such that the 2D structure is transposed successively with zero cycle delay between successive transposes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Addition of new images to an image database by clustering according to date/time and image content and representative image comparison
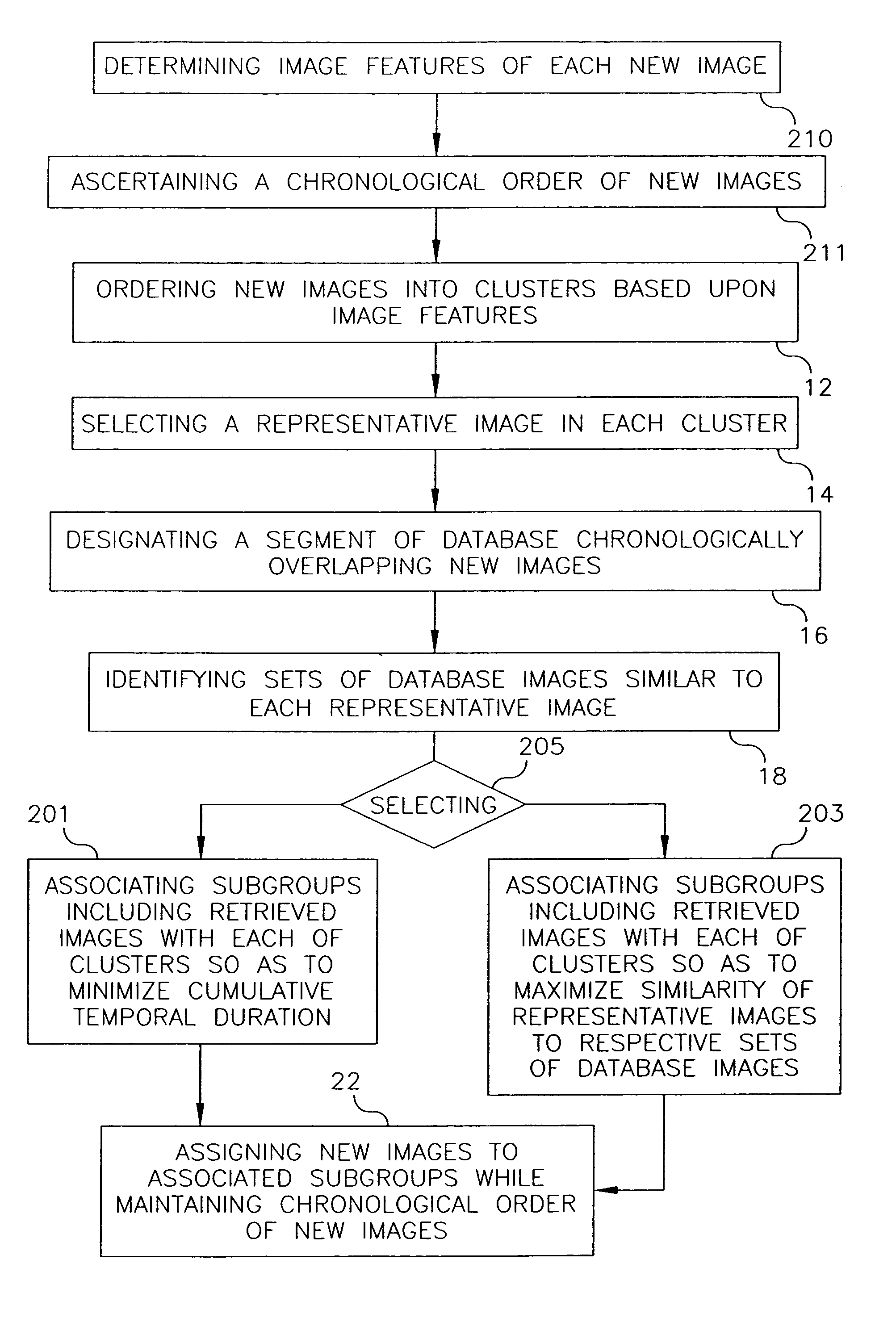
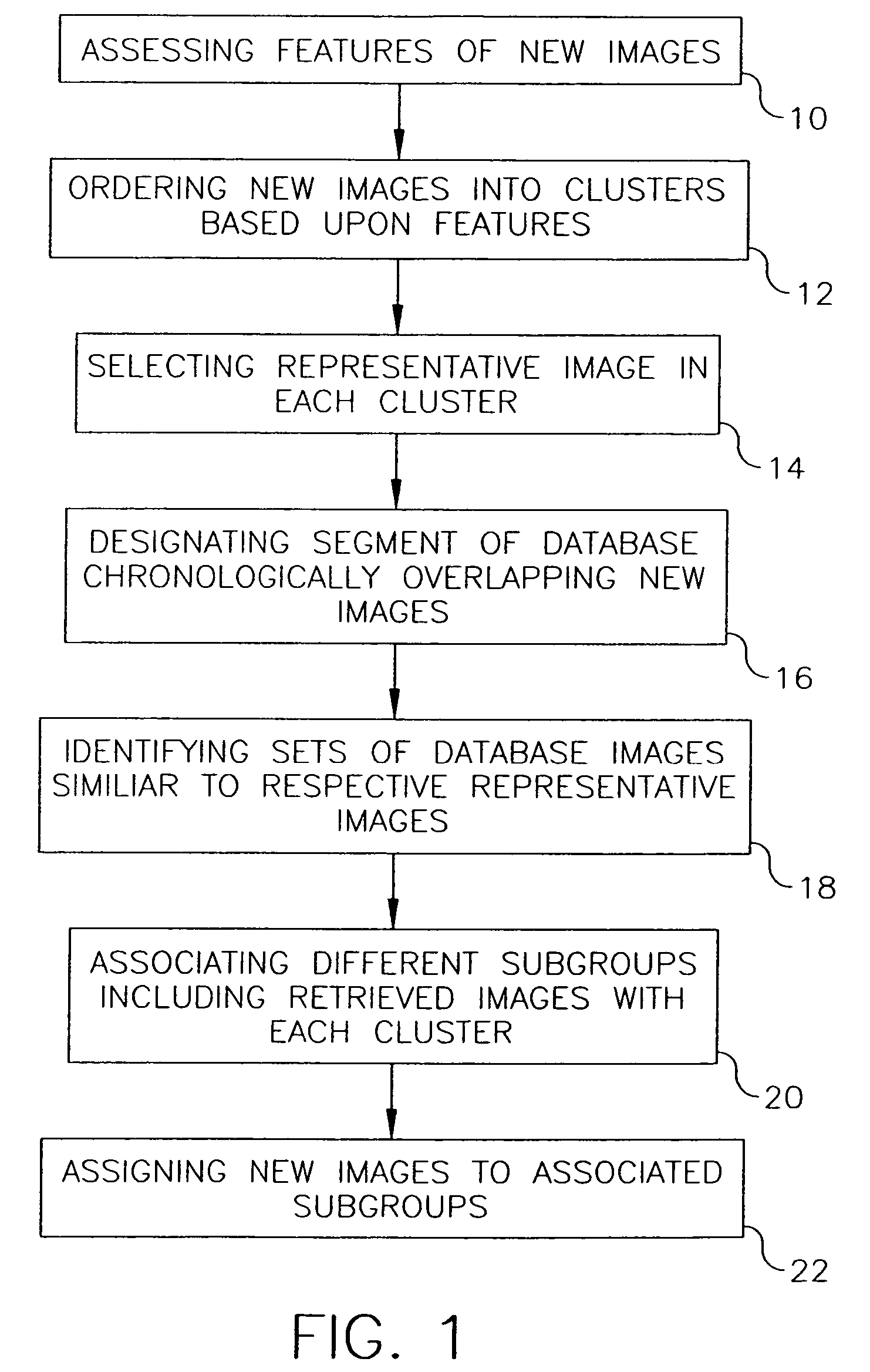
InactiveUS7831599B2Character and pattern recognitionMetadata still image retrievalImaging FeatureChronological time
A database has chronologically ordered images classified into event groups based upon a time difference threshold, and into subgroups based upon a similarity measure. In a method and system for combining new images into such a database, new images are ordered into clusters based upon assessed image features. A representative image is selected in each cluster. A database segment chronologically overlapping the new images is designated and a set of database images similar to each representative image are identified in the segment. Different subgroups including one or more retrieved images are associated with each cluster to provide matched subgroups. The new images are assigned to matched subgroups associated with respective clusters.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Coordination of event logging operations and log management
InactiveUS20130073532A1Well formedProgram synchronisationError detection/correctionSingle processOperational system
A plurality of log processes are synchronized. Each is independently performed in parallel with one another, into a single set of log files. A line buffering mechanism of an operating system (OS) of the computing environment forecloses interleaving of the log processes. Log management operations are concurrently performed by a single process protected by a file-system lock of the OS. The log management operations include at least one of a log compression, log retention, and log rotation operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
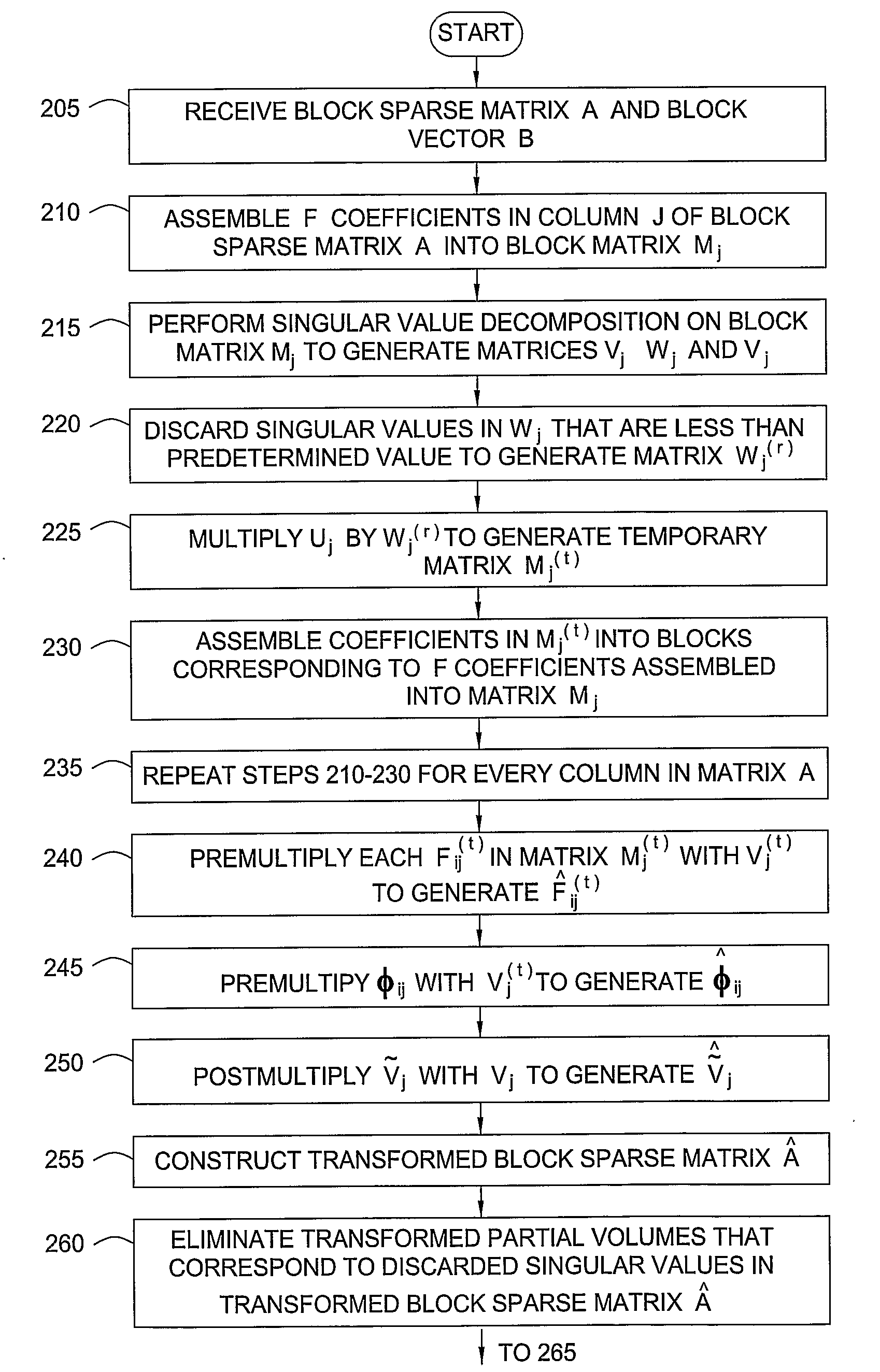
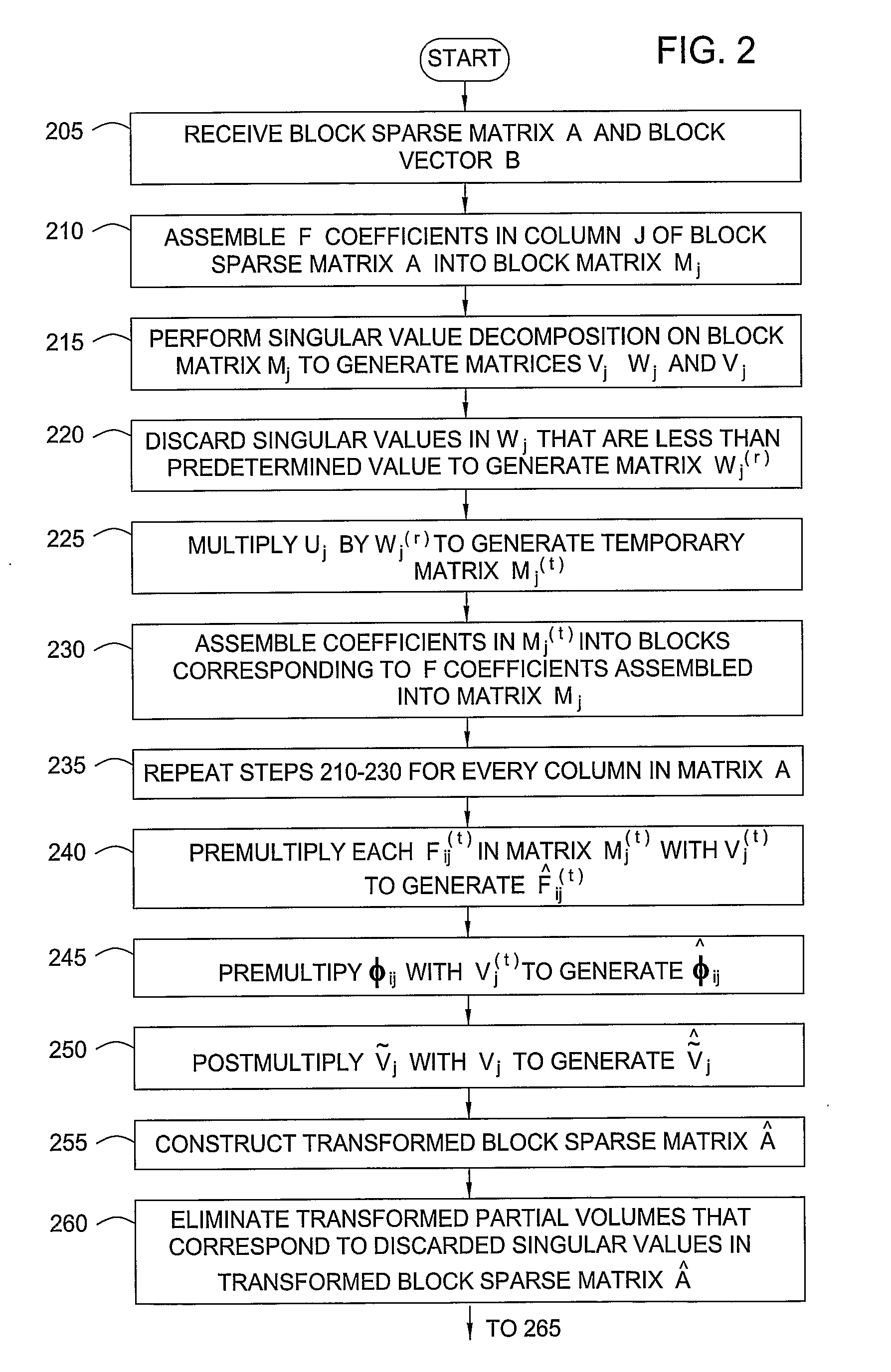
Method For Solving Implicit Reservoir Simulation Matrix
A method for solving a matrix equation AX=B, wherein A represents a block sparse matrix, B represents a right hand side block vector and X represents a solution block vector. In one embodiment, the method includes receiving the block sparse matrix and the right hand side block vector, constructing a reduced transformed block sparse matrix from the block sparse matrix, constructing a reduced transformed residual block vector from the block sparse matrix and the right hand side block vector, and solving for the solution block vector using the reduced transformed block sparse matrix and the reduced transformed residual block vector.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Software implementation of matrix inversion in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20100293210A1Efficient executionDigital computer detailsProgram controlCommunications systemCommunication device
A digital signal processor is provided in a wireless communication device, wherein the processor comprises a vector unit, first and second registers coupled to and accessible by the vector unit; and an instruction set configured to perform matrix inversion of a matrix of channel values by coordinate rotation digital computer instructions using the vector unit and the first and second registers.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for predicting multi-variable outcomes
InactiveUS7191106B2Eliminates artifactual inferenceReduce random noiseMedical simulationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAlgorithmSystems approaches
Systems methods and recordable media for predicting multi-variable outcomes based on multi-variable inputs. Additionally, the models described can be used to predict the multi-variable inputs themselves, based on the multi-variable inputs, providing a smoothing function, acting as a noise filter. Both multi-variable inputs and multi-variable outputs may be simultaneously predicted, based upon the multi-variable inputs. The models find a critical subset of data points, or “tent poles” to optimally model all outcome variables simultaneously to leverage communalities among outcomes.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
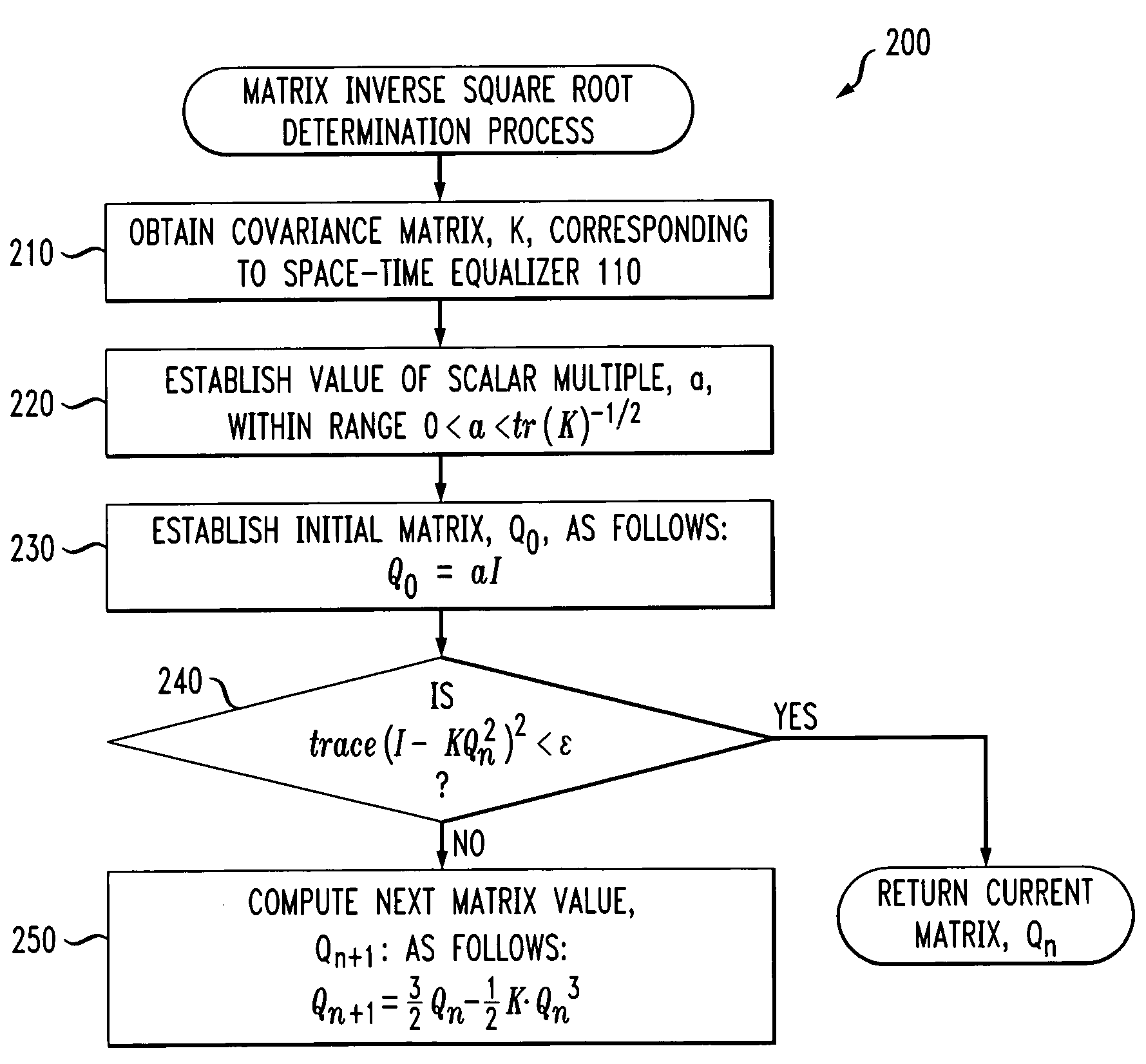
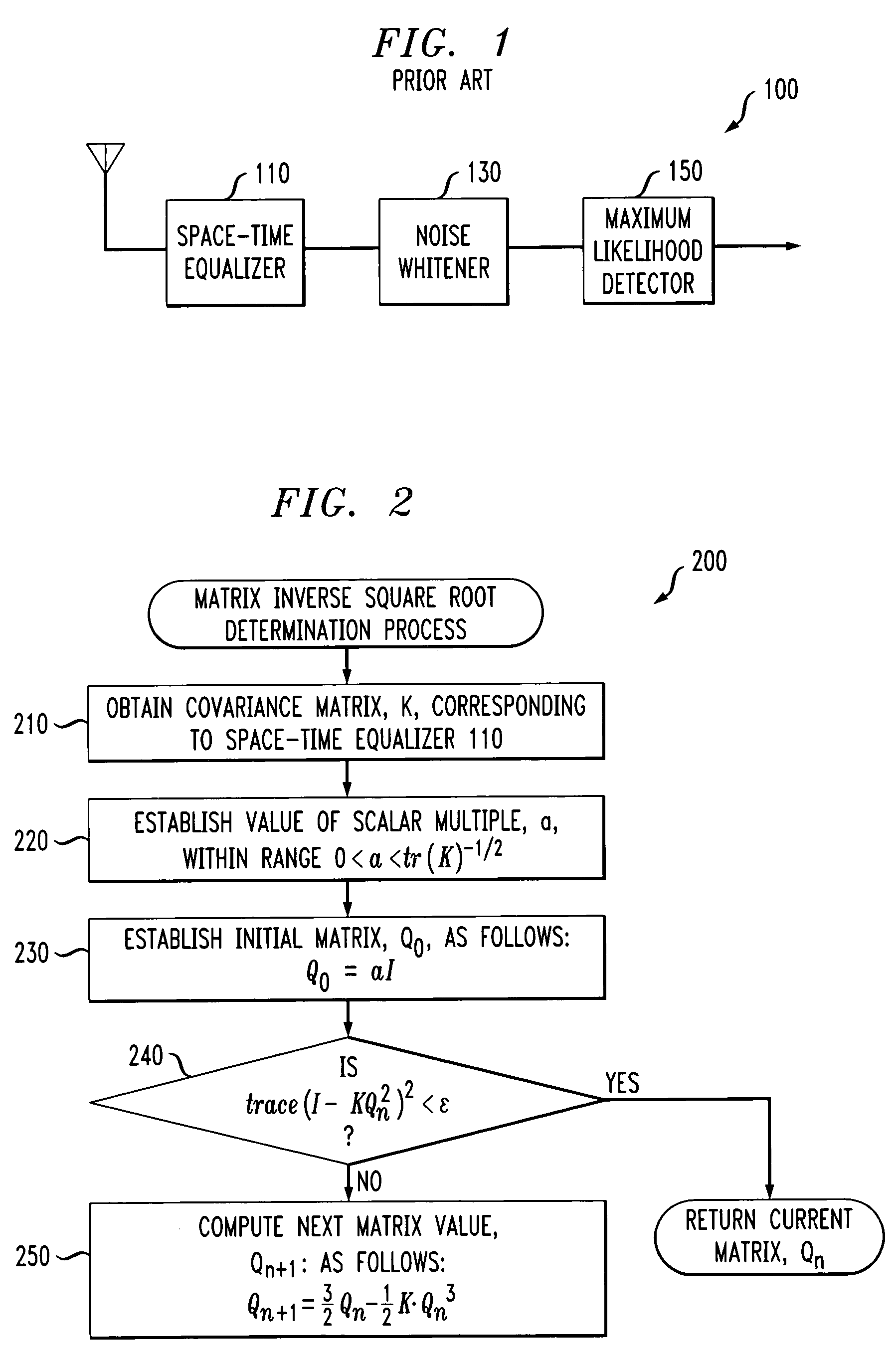
Method and apparatus for determining an inverse square root of a given positive-definite hermitian matrix
Generally, a method and apparatus are provided for computing a matrix inverse square root of a given positive-definite Hermitian matrix, K. The disclosed technique for computing an inverse square root of a matrix may be implemented, for example, by the noise whitener of a MIMO receiver. Conventional noise whitening algorithms whiten a non-white vector, X, by applying a matrix, Q, to X, such that the resulting vector, Y, equal to Q·X, is a white vector. Thus, the noise whitening algorithms attempt to identify a matrix, Q, that when multiplied by the non-white vector, will convert the vector to a white vector. The disclosed iterative algorithm determines the matrix, Q, given the covariance matrix, K. The disclosed matrix inverse square root determination process initially establishes an initial matrix, Q0, by multiplying an identity matrix by a scalar value and then continues to iterate and compute another value of the matrix, Qn+1, until a convergence threshold is satisfied. The disclosed iterative algorithm only requires multiplication and addition operations and allows incremental updates when the covariance matrix, K, changes.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS +1
Method and structure for improving processing efficiency in parallel processing machines for rectangular and triangular matrix routines
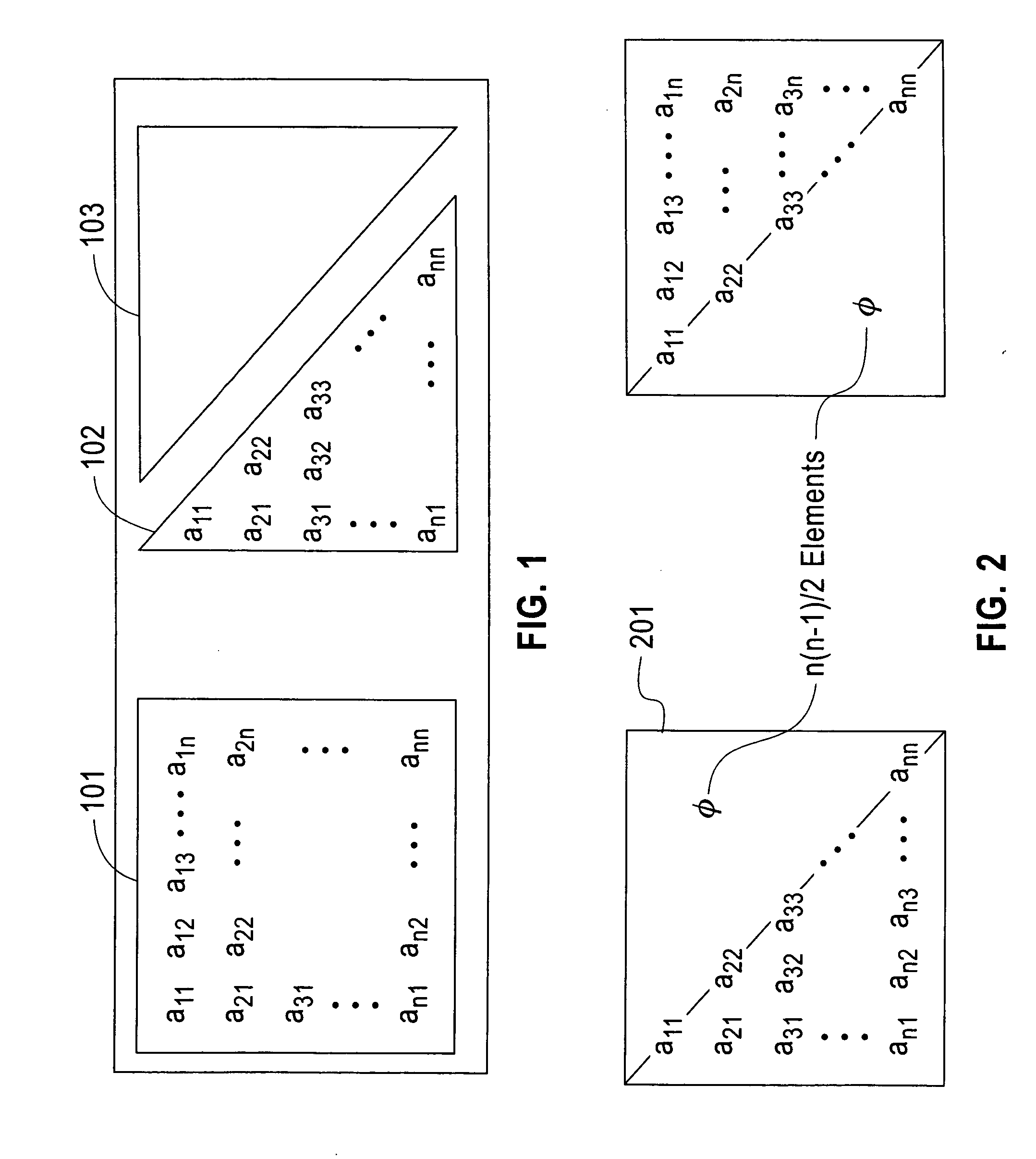
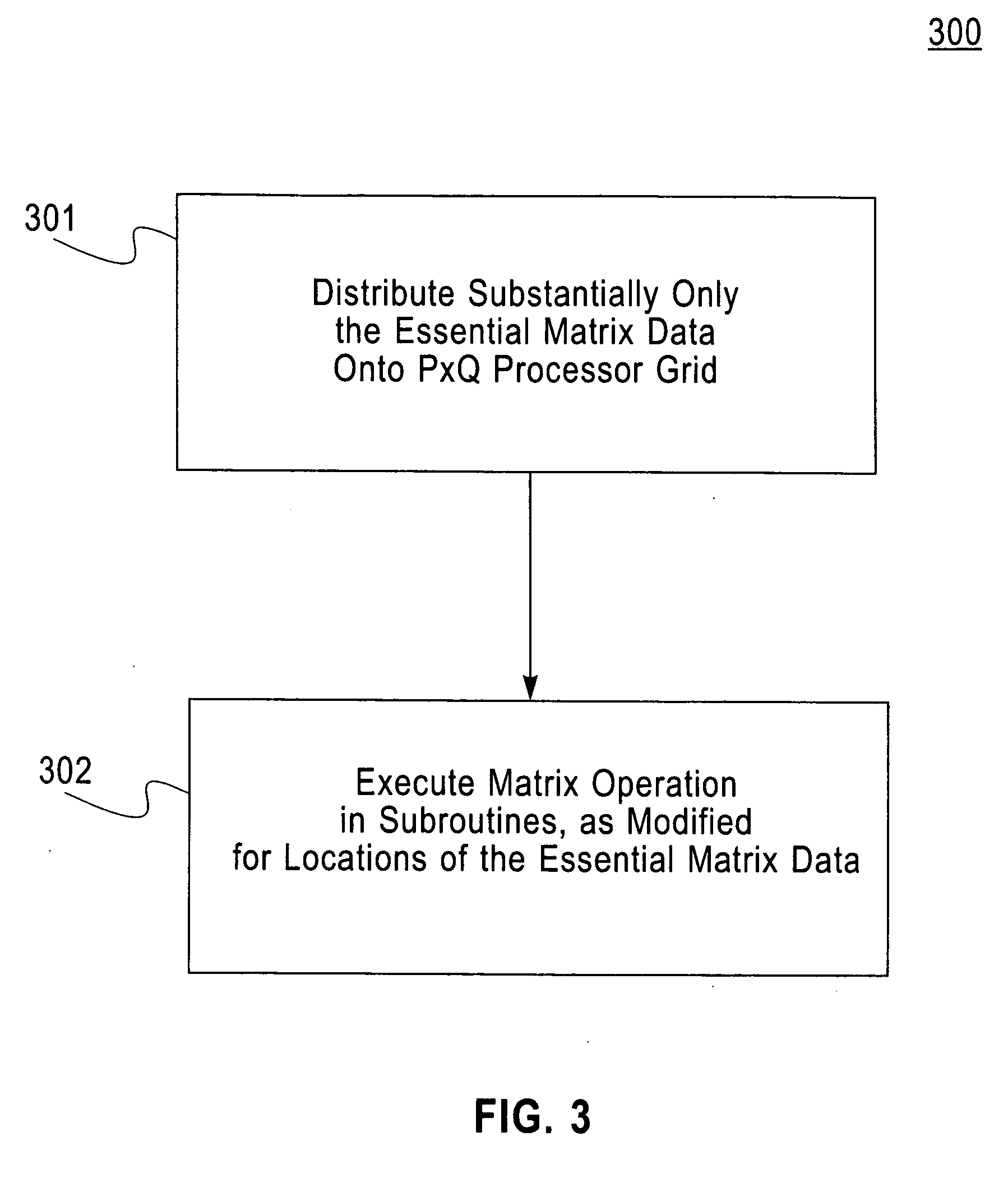
InactiveUS20060265445A1Reduce storageImprove efficiencyData mergingComplex mathematical operationsDistributed memoryData preparation
A computerized method (and structure) of linear algebra processing on a computer having a plurality of processors for parallel processing, includes, for a matrix having elements originally stored in a memory in a rectangular matrix AR or especially of one of a triangular matrix AT format and a symmetric matrix AS format, distributing data of the rectangular AR or triangular or symmetric matrix (AT, AS) from the memory to the plurality of processors in such a manner that keeps all submatrices of AR or substantially only essential data of the triangular matrix AT or symmetric matrix AS is represented in the distributed memories of the processors as contiguous atomic units for the processing. The linear algebra processing done on the processors with distributed memories requires that submatrices be sent and received as contiguous atomic units based on the prescribed block cyclic data layouts of the linear algebra processing. This computerized method (and structure) defines all of its submatrices as these contiguous atomic units, thereby avoiding extra data preparation before each send and after each receive. The essential data or AT or AS is that data of the triangular or symmetric matrix that is minimally necessary for maintaining the full information content of the triangular AT or symmetric matrix AS.
Owner:IBM CORP
Digital mask-forming film and method of use
ActiveUS7226709B1Improve efficiencyDiffusion transfer processesPhotography auxillary processesPolymer chemistryPolymer
A masking film has a unique polymeric binder in the imageable layer that enables the imaged film to be readily solubilized in non-chlorinated developers when it is used to form a relief image in a radiation-sensitive element, such as a UV-sensitive flexographic printing plate precursor. The polymeric binders in the imageable layer are resins that can be dissolved or dispersed in cyclohexane at 10% solids at 23° C. within 24 hours.
Owner:MIRACLON CORP
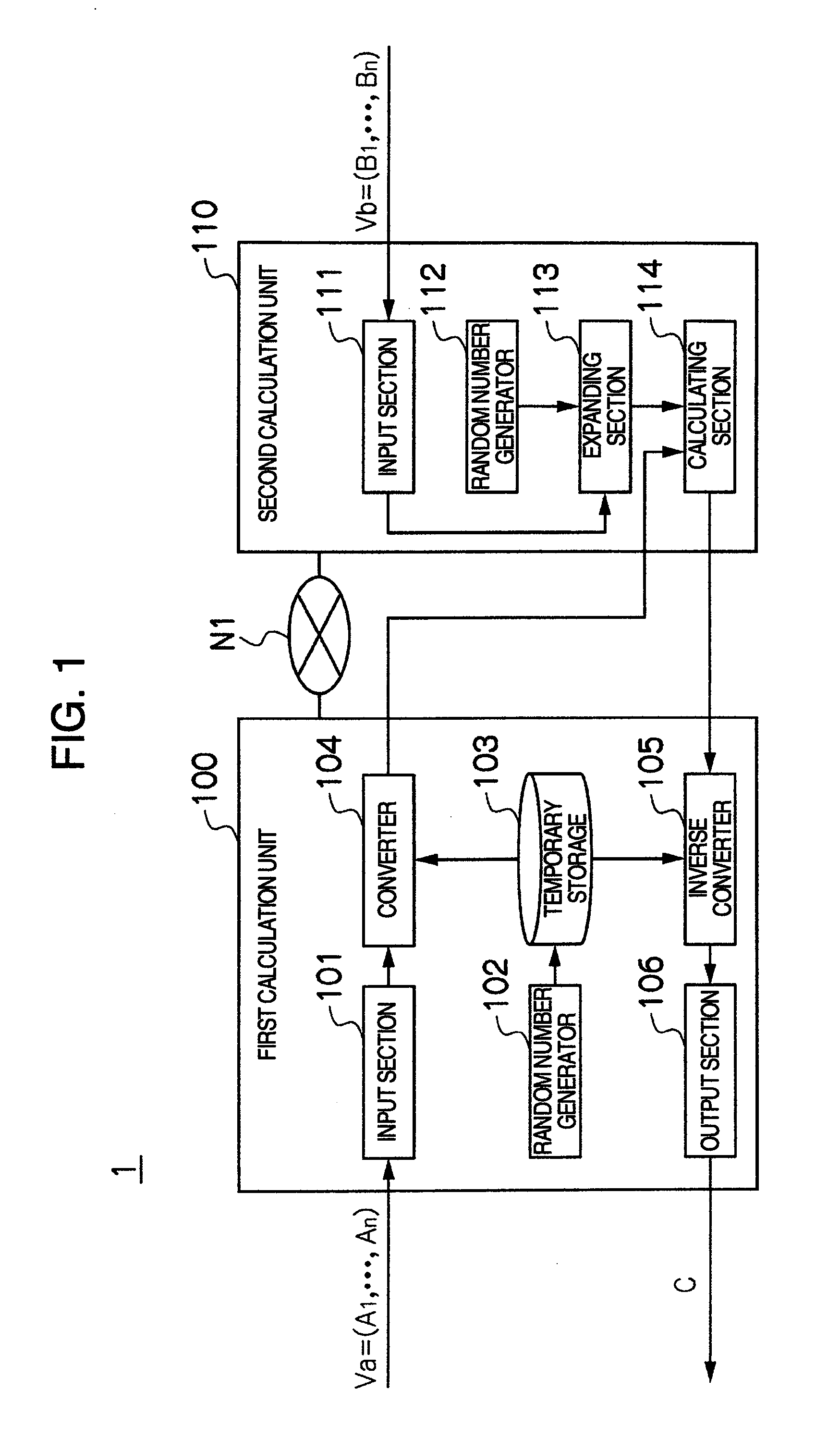
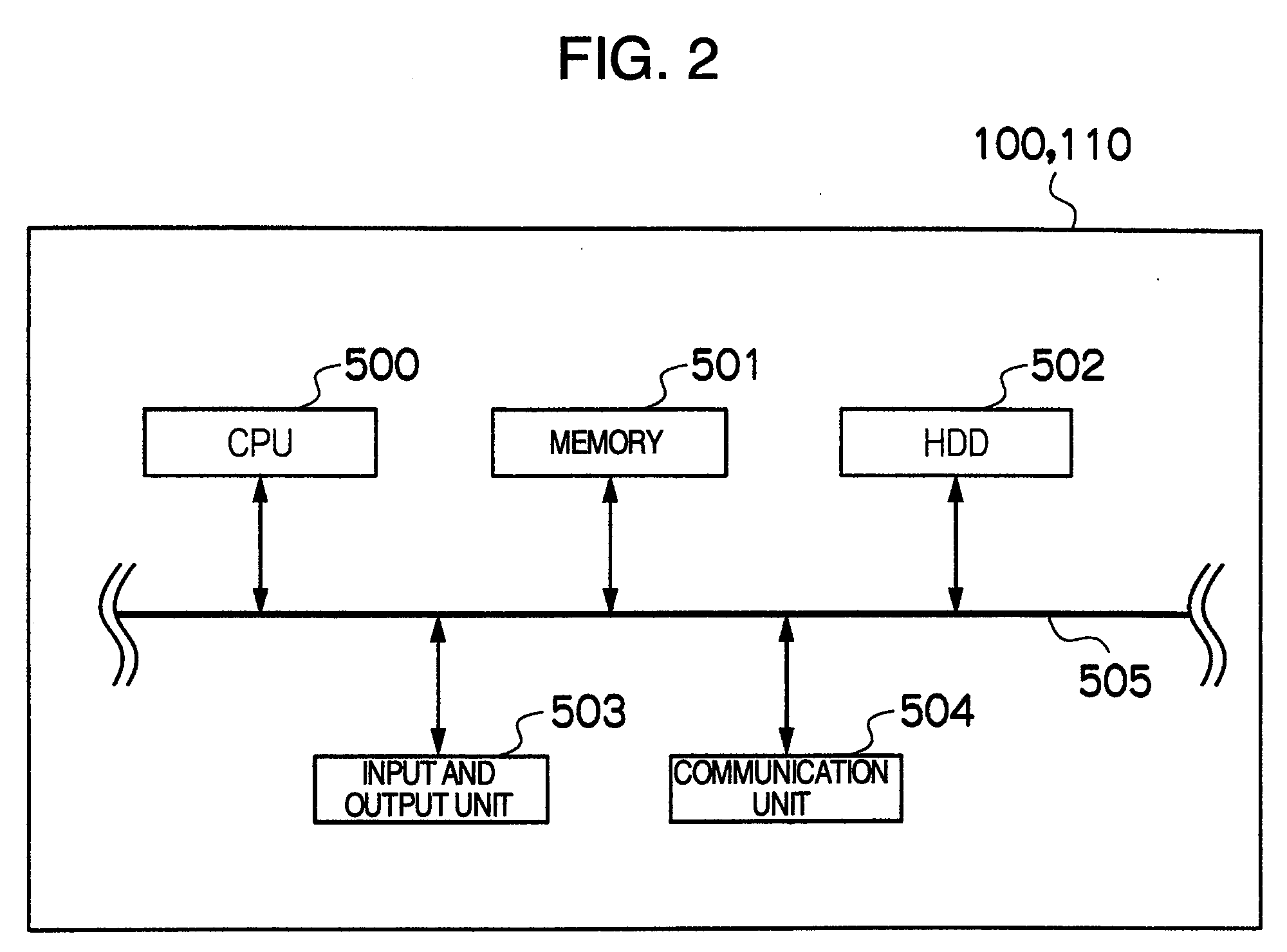
Privacy-preserving scalar product calculation system, privacy-preserving scalar product calculation method and cryptographic key sharing system
InactiveUS20090279694A1Calculation cost is highReduce computing costKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsScalar ValuePrivacy preserving
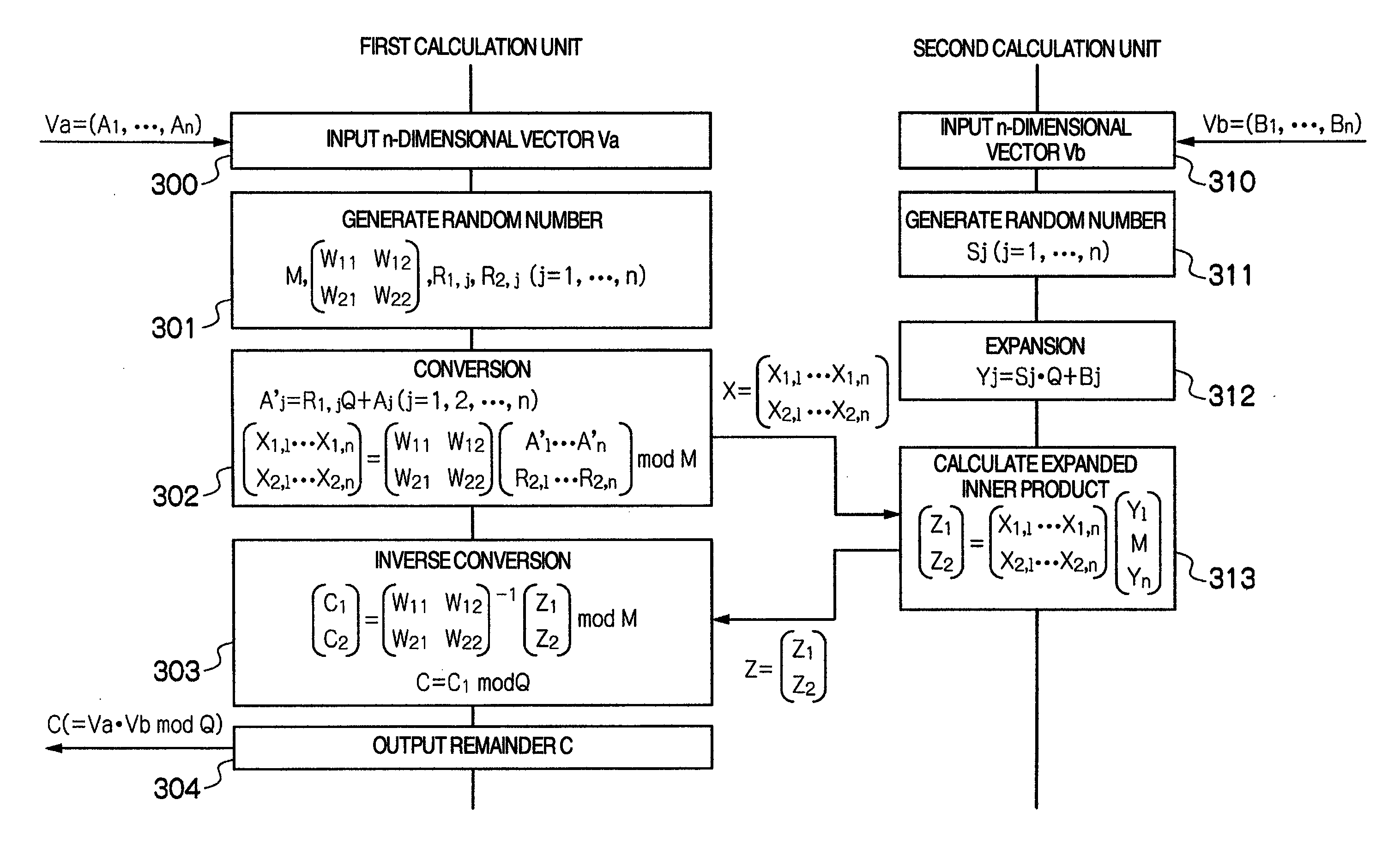
A privacy-preserving scalar product calculation system is provided. A first unit linearly transforms an n-dimensional vector Va into an n-dimensional vector based on a scalar value based on a random number Wi and a random number Rj to calculate a remainder by dividing each element of the linearly transformed n-dimensional vector by a random number Mi, and transmits an n-dimensional converted vector X including each of the remainders as its element to the second unit, the second unit calculates an inner product value Z based on the received n-dimensional converted vector X and an n-dimensional vector Vb, and transmits the inner product value Z to the first unit, and the first unit further calculates, based on a reciprocal of the scalar value and the receive inner product value, a scalar value and which calculates a remainder by dividing the scalar value by the random number Mi.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
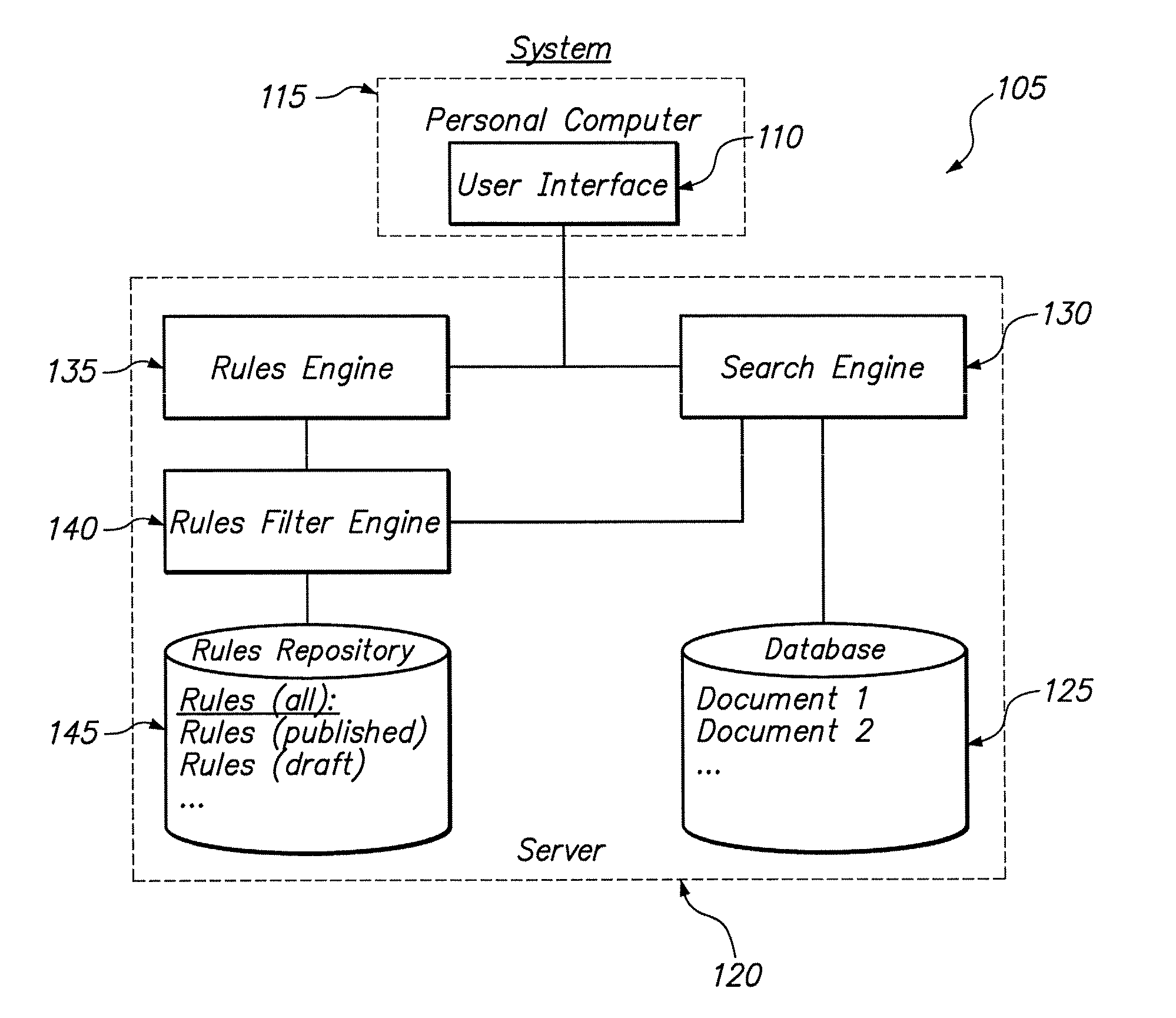
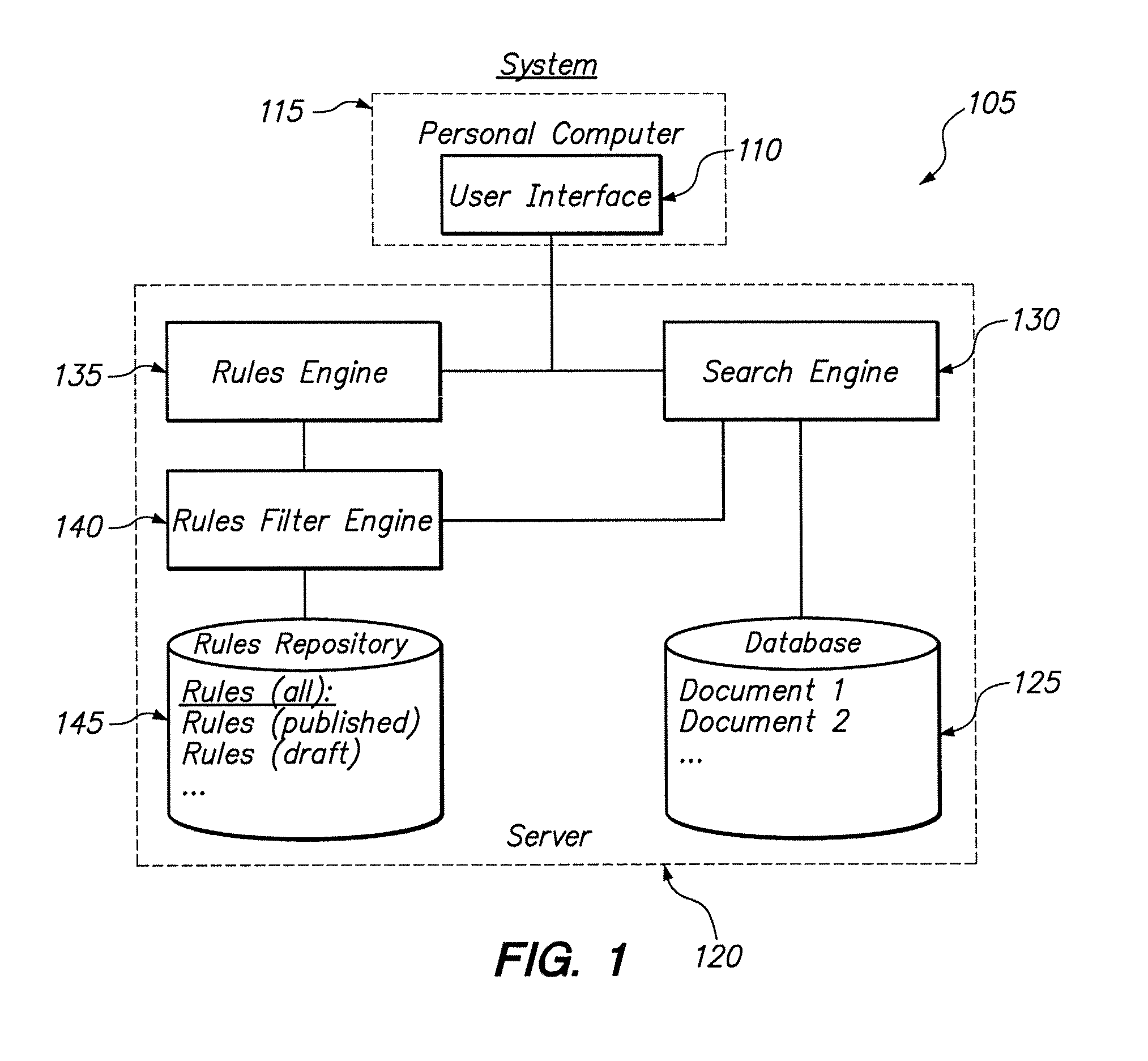
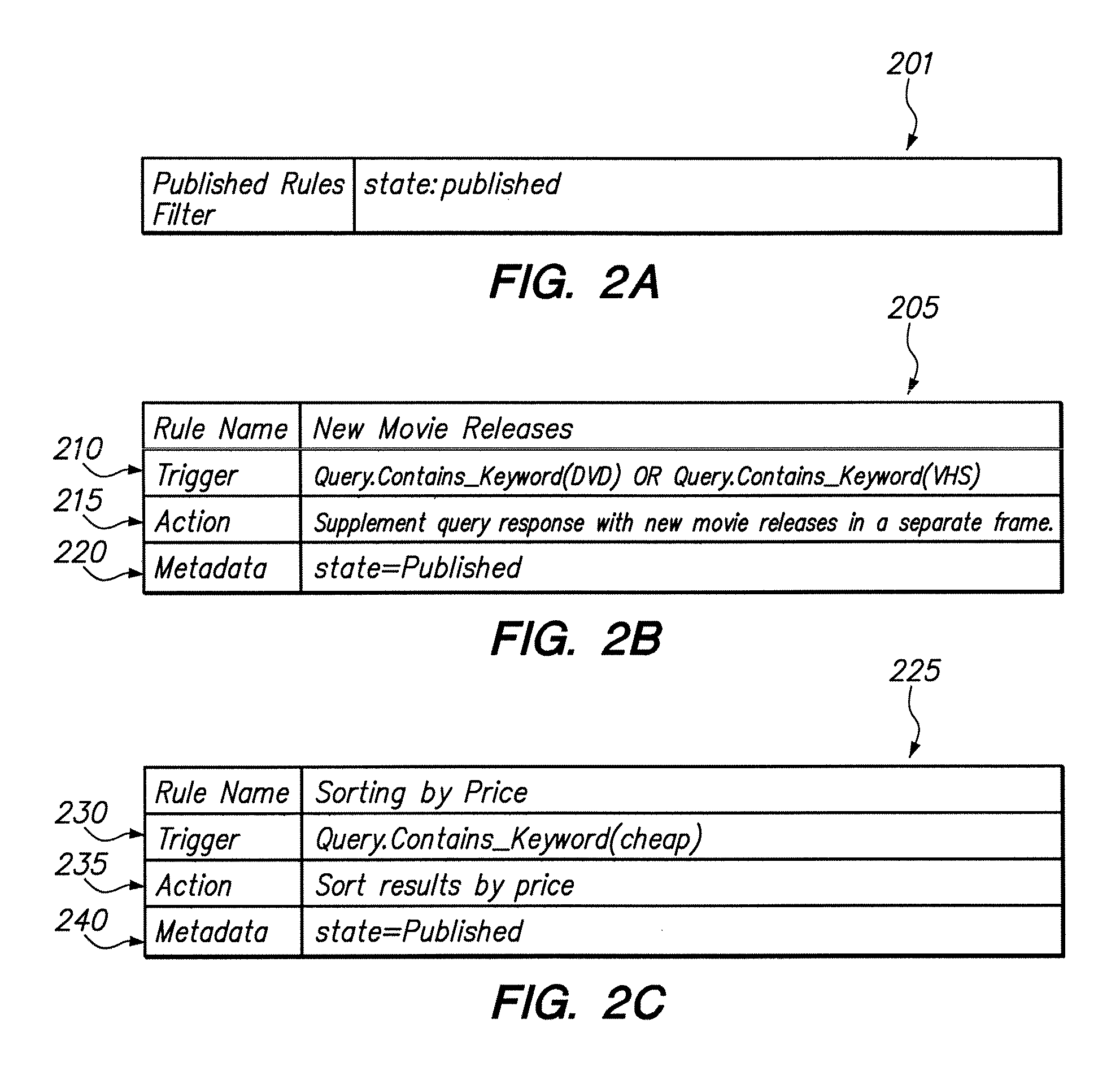
System and method for filtering rules for manipulating search results in a hierarchical search and navigation system
ActiveUS7856434B2Web data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsFiltering rulesNavigation system
A method is disclosed for modifying the results of a search performed in a collection of items by a search and navigation system. The method includes receiving a query from a user interface and determining a navigation state, defined by expressions of attribute-value pairs, based on the received query. The user interface accepts both selecting and deselecting of any of the attribute-value pairs in an expression corresponding to a navigation state to obtain an expression corresponding to a different navigation state, and each selection and deselection forms a new query. The method further includes retrieving, from the collection, items associated with the navigation state to form a set of unmodified search results, the set of unmodified search results having an arrangement for presentation to the user. A rule filter that includes a metadata expression is applied to a set of rules, each rule having a trigger, an action, and metadata. The application of the rule filter to the set of rules includes evaluating the metadata expression of the rule filter based on the metadata of each rule and passing rules for which the metadata expression of the rule filter evaluates as logical true. The trigger of each rule passed by the rule filter is evaluated, and the action of each rule for which the trigger of the rule evaluates as logical true is executed to modify the unmodified search results to form modified search results.
Owner:ORACLE OTC SUBSIDIARY LLC
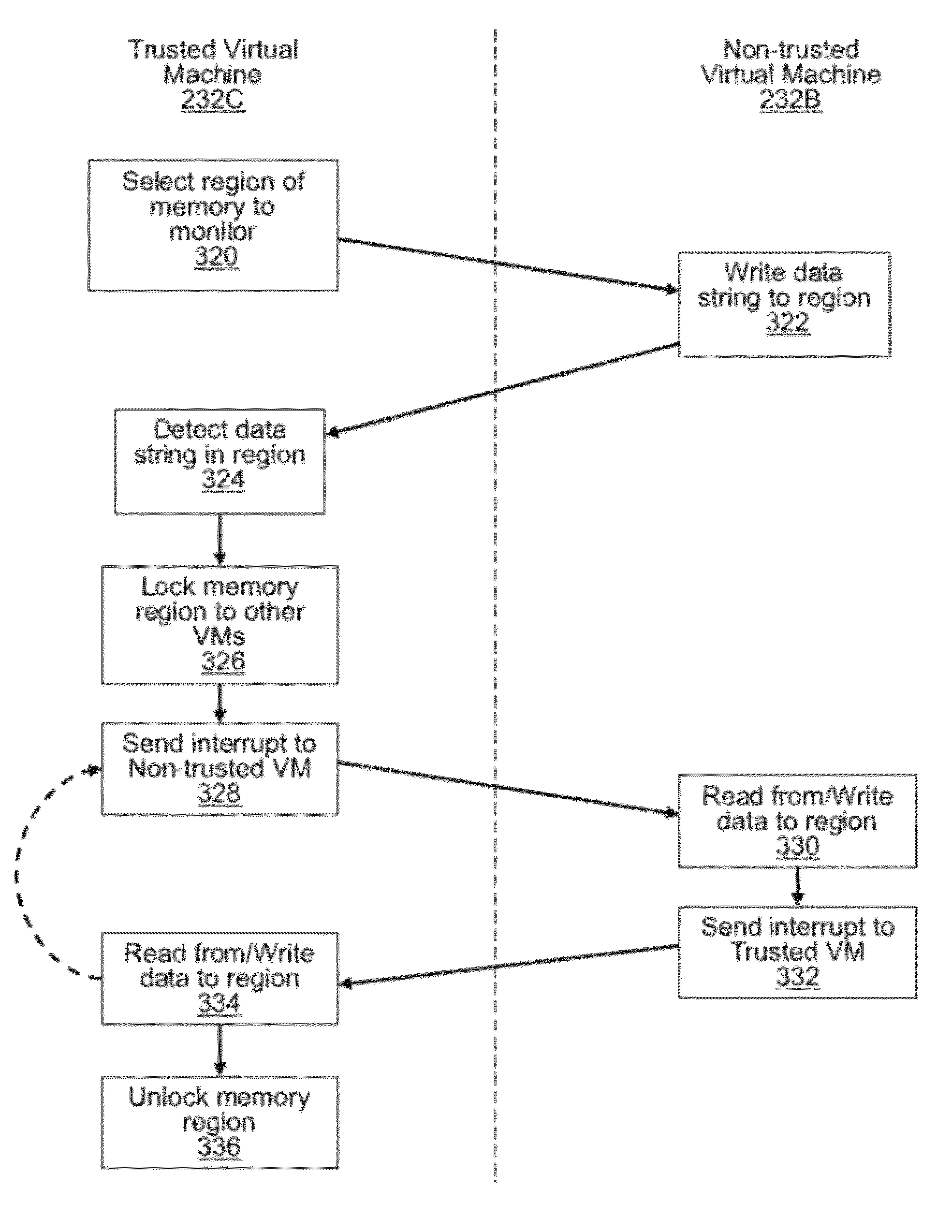
Redirection of information from secure virtual machines to unsecure virtual machines
ActiveUS8869300B2Unauthorized memory use protectionAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsApplication softwareUniform resource locator
The present invention is directed towards methods and systems for redirecting an access request to an unsecure virtual machine. A computing device may execute a hypervisor hosting a secure virtual machine and an unsecure virtual machine. A control virtual machine, hosted by a hypervisor executing on the computing device, may intercept a request to access an unsecure resource. The unsecure resource may include one of: a file, an application and an uniform resource locator (URL). The control virtual machine may further determine that the request originates from a secure virtual machine executing on the computing device. The control virtual machine may redirect, responsive to the determination, the request to an unsecure virtual machine executing on the computing device, whereupon the unsecure virtual machine may provide access to the requested unsecure resource.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
System for Generating a Multi-Modality Imaging Examination Report
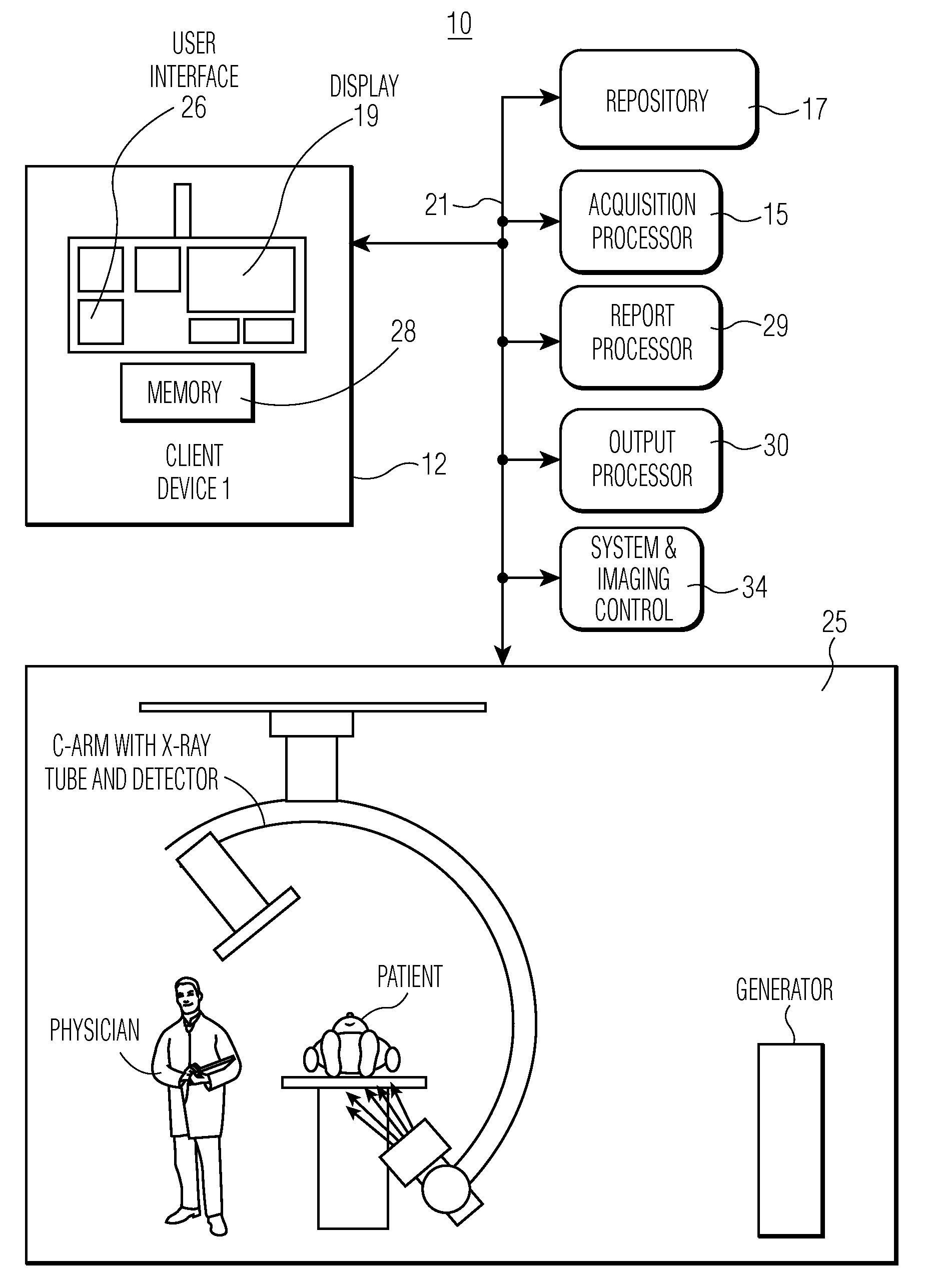
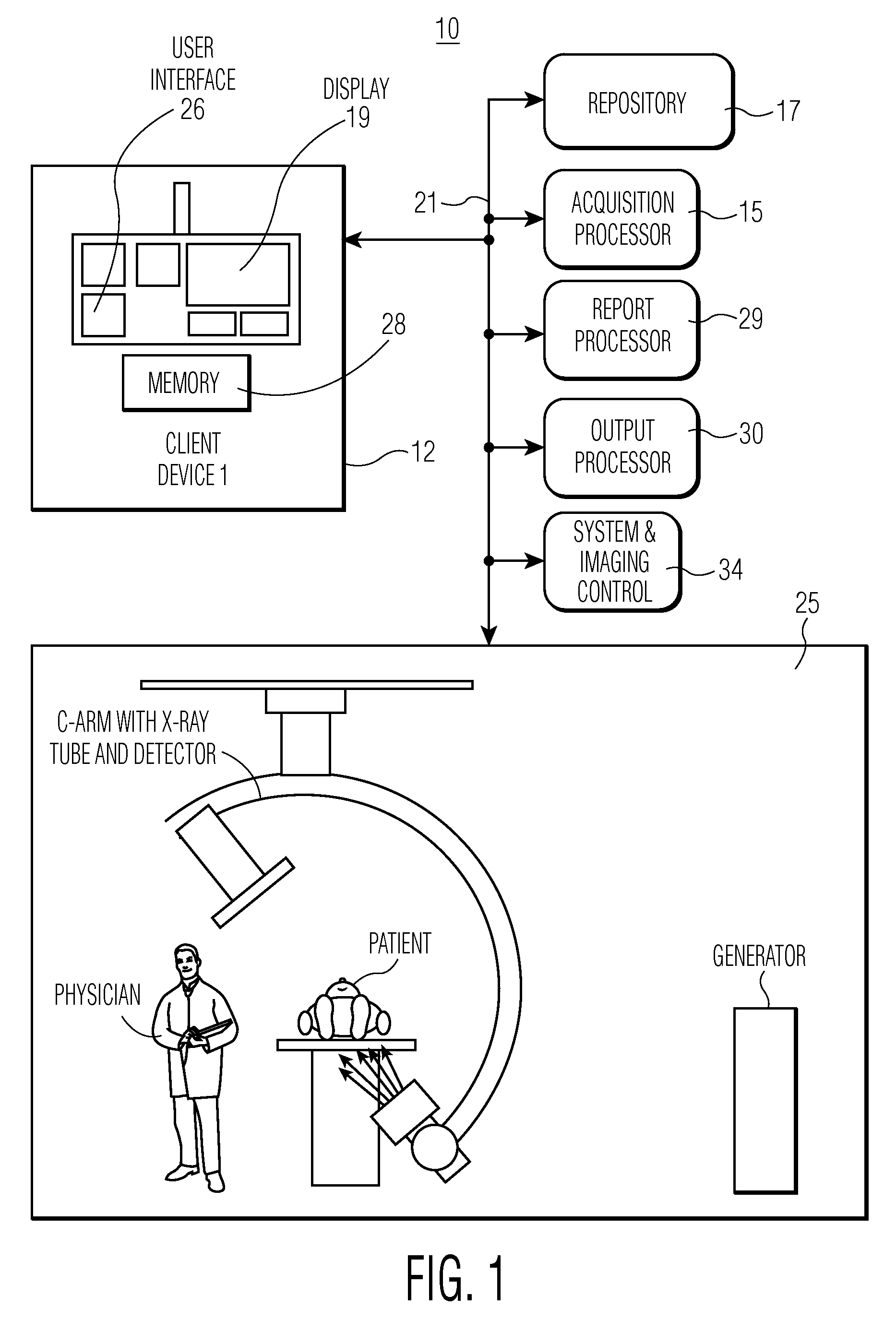
InactiveUS20100099974A1Data processing applicationsMedical report generationImaging modalitiesData field
A system processes medical report data associated with different types of imaging modality devices to provide a composite examination report. An acquisition processor in the system acquires multi-modality medical imaging examination report data for examinations performed on a patient by different types of imaging modality device. A report processor processes acquired multi-modality medical imaging examination report data items by, in response to predetermined selection riles, selecting between individual data items in the acquired multi-modality medical imaging examination report data items to provide a single individual data item for incorporation in a composite report. The report processor maps individual data items including the single individual data item in the acquired multi-modality medical imaging examination report data items to corresponding data fields in a composite report data structure in memory in response to predetermined mapping information. An output processor outputs data representing the composite report to a destination device.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
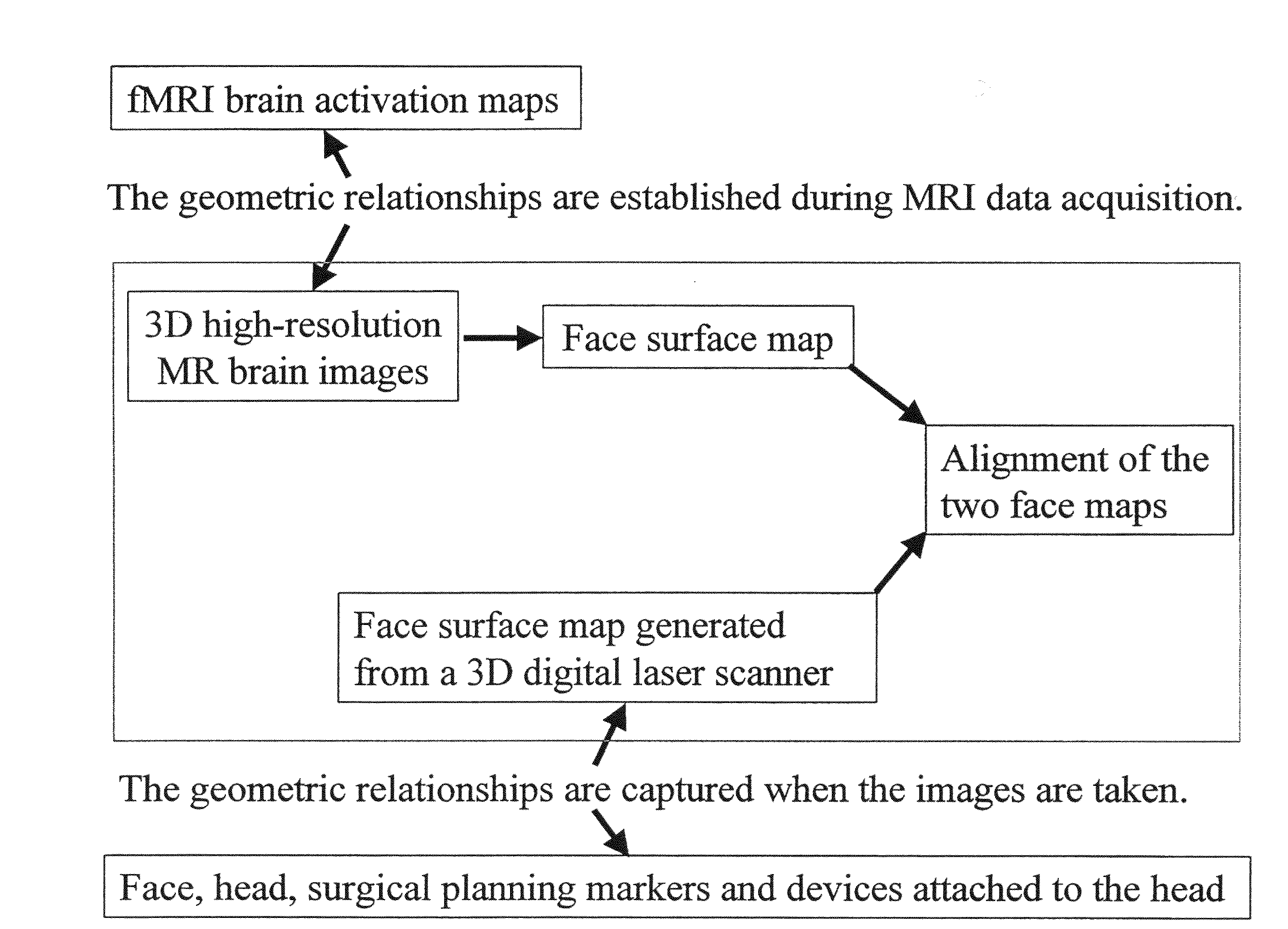
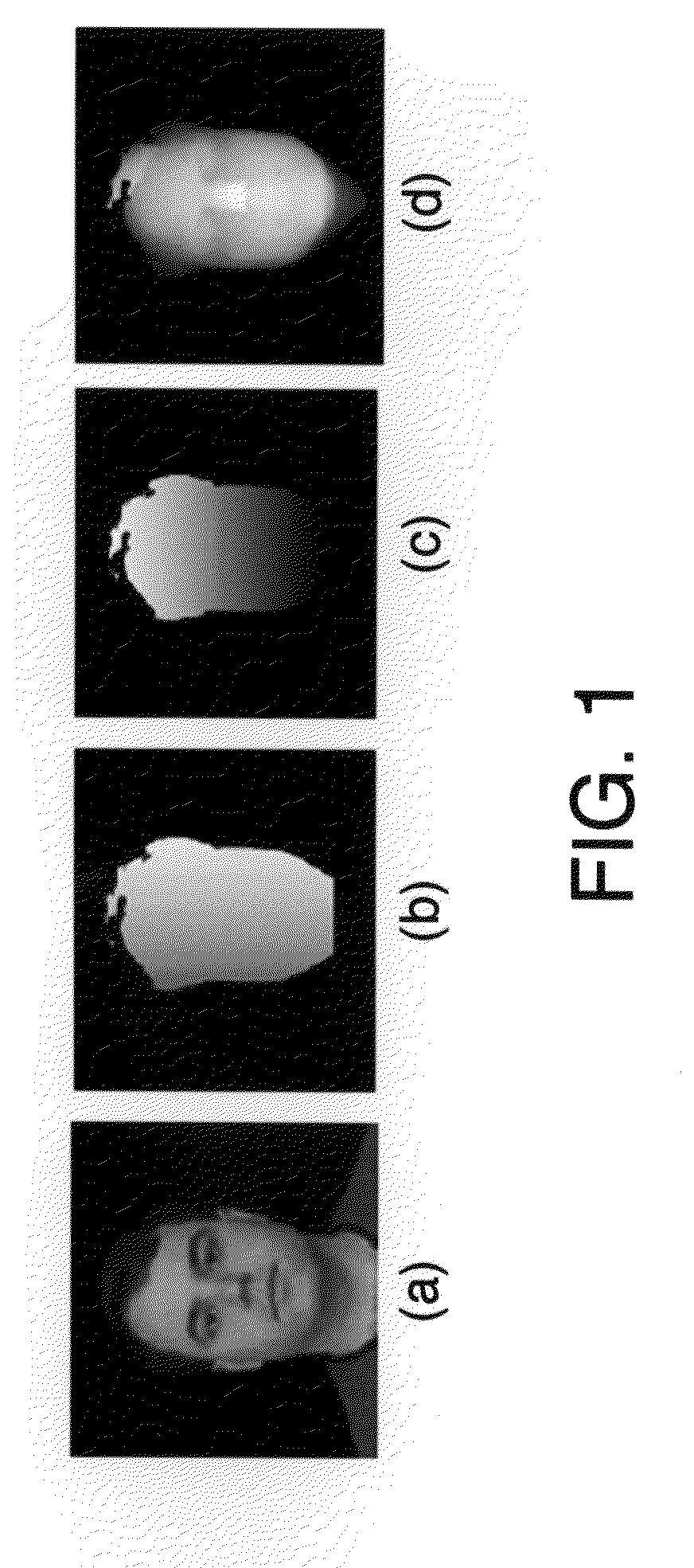
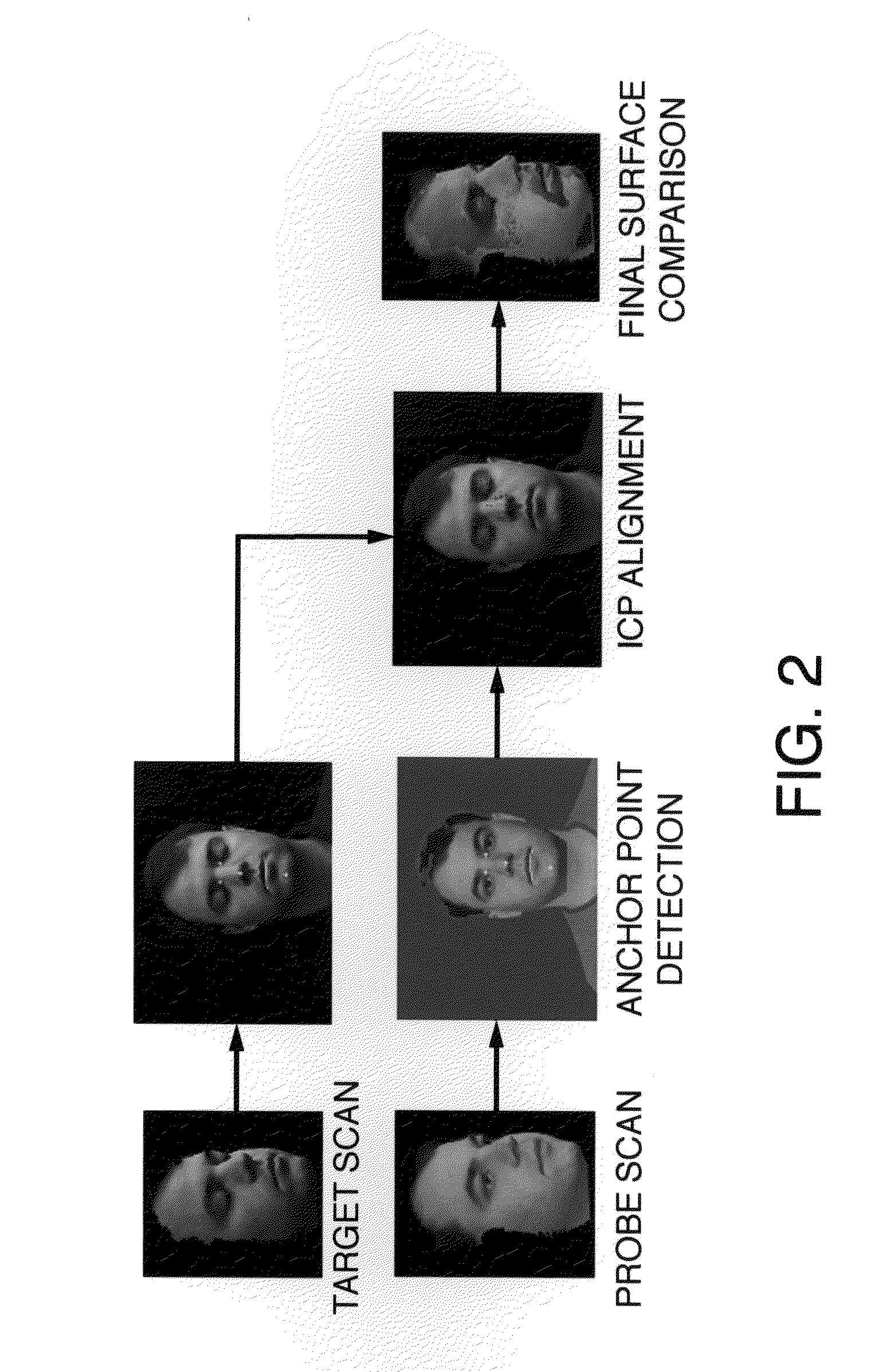
Automatic Methods for Combining Human Facial Information with 3D Magnetic Resonance Brain Images
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for provided fused images of external and internal body scans by fusing data generated from color external laser scans with internal magnetic resonance (MR) images. In particular, the present inventions relate to software for fusing and displaying images produced by fusing color 2.5D laser scans of the human face with 3D magnetic resonance (MR) brain images. Further, these fused images may be used for clinical and research applications, such as in methods for neurosurgical planning procedures.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
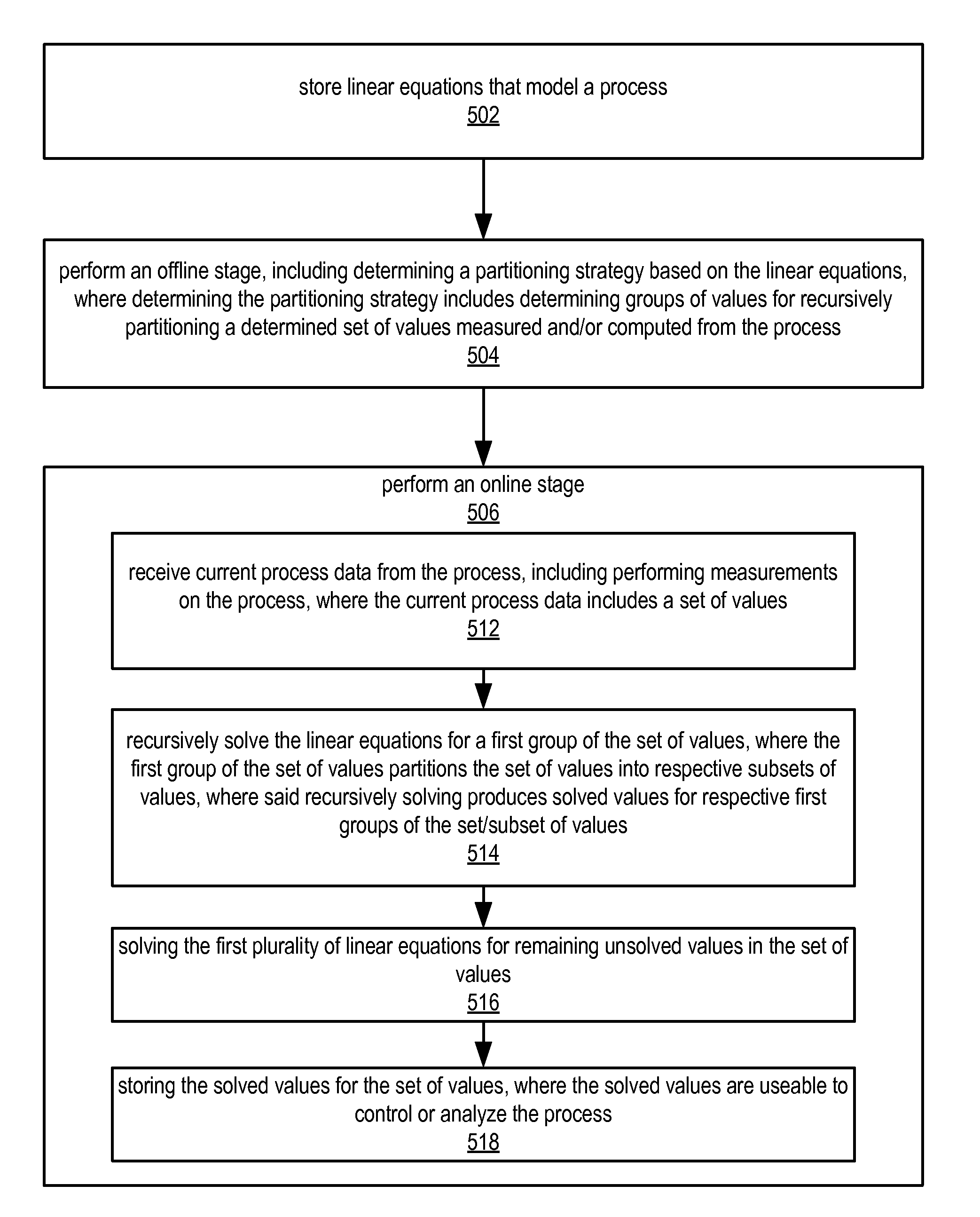
Controlling or Analyzing a Process by Solving A System of Linear Equations in Real-Time
ActiveUS20090292511A1Computation using non-contact making devicesComputation using non-denominational number representationTime systemRecursion
System and method for controlling / analyzing a process by solving a system of linear equations in real-time. Linear equations that model the process are stored. In an off-line stage a partitioning strategy is determined based on the linear equations, including determining groups of values for recursively partitioning a set of values measured and / or computed from the process. In an on-line stage: current process data are received from the process, including measurements from the process, and composing a set of values; the linear equations are recursively solved for a first group of the set, where the first group partitions the set into respective subsets of values, and where the recursively solving produces solved values for respective first groups of the set / subset of values; the linear equations are solved for remaining unsolved values in the set, thereby producing solved values for the set, which are stored and are useable to control / analyze the process.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Popular searches
Specific program execution arrangements Memory systems Computation using denominational number representation Eavesdropping prevention circuits User identity/authority verification Digital data authentication Individual entry/exit registers Alarms Programme control Telemetry/telecontrol selection arrangements
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com