Patents
Literature
780results about "Runtime instruction translation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
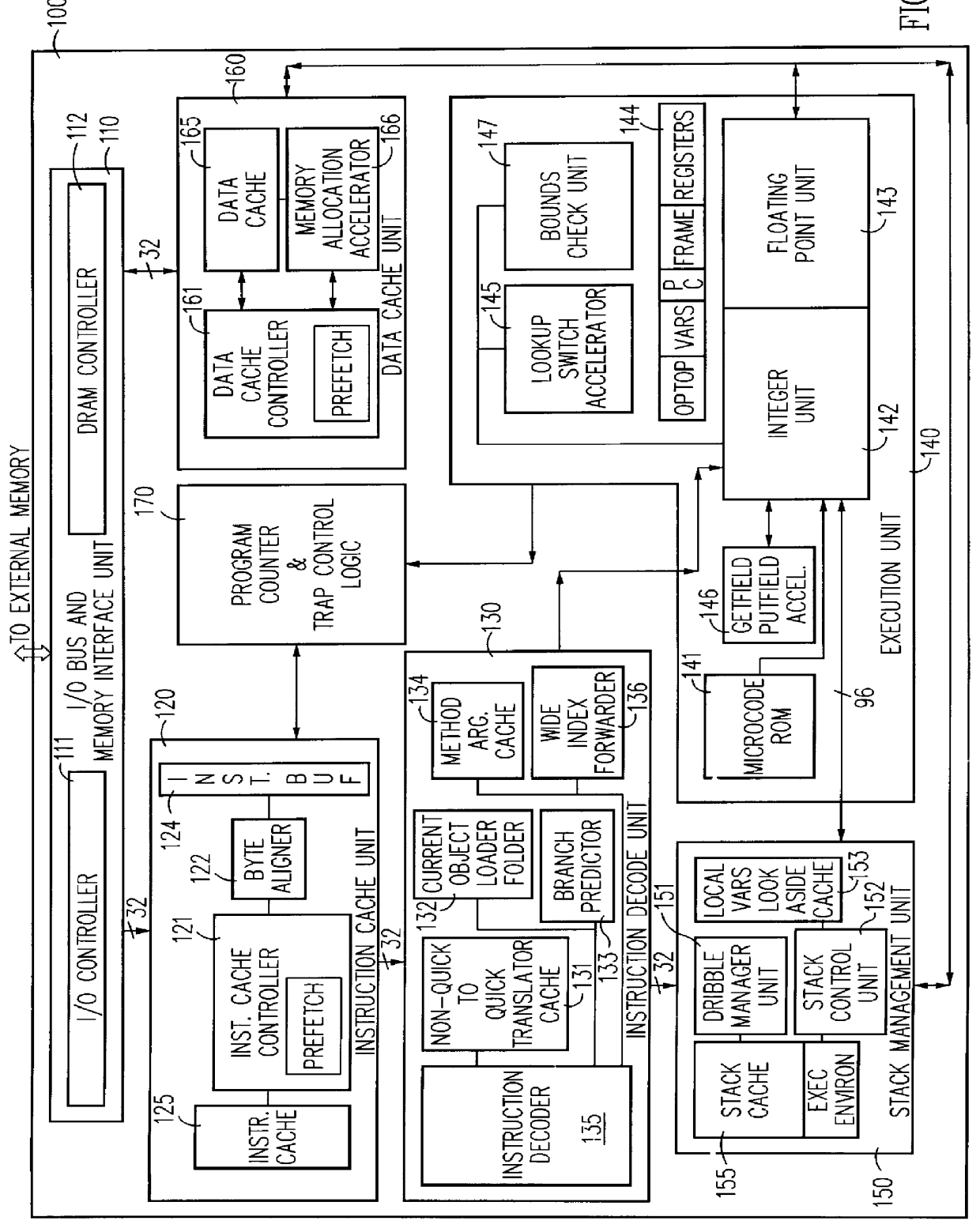
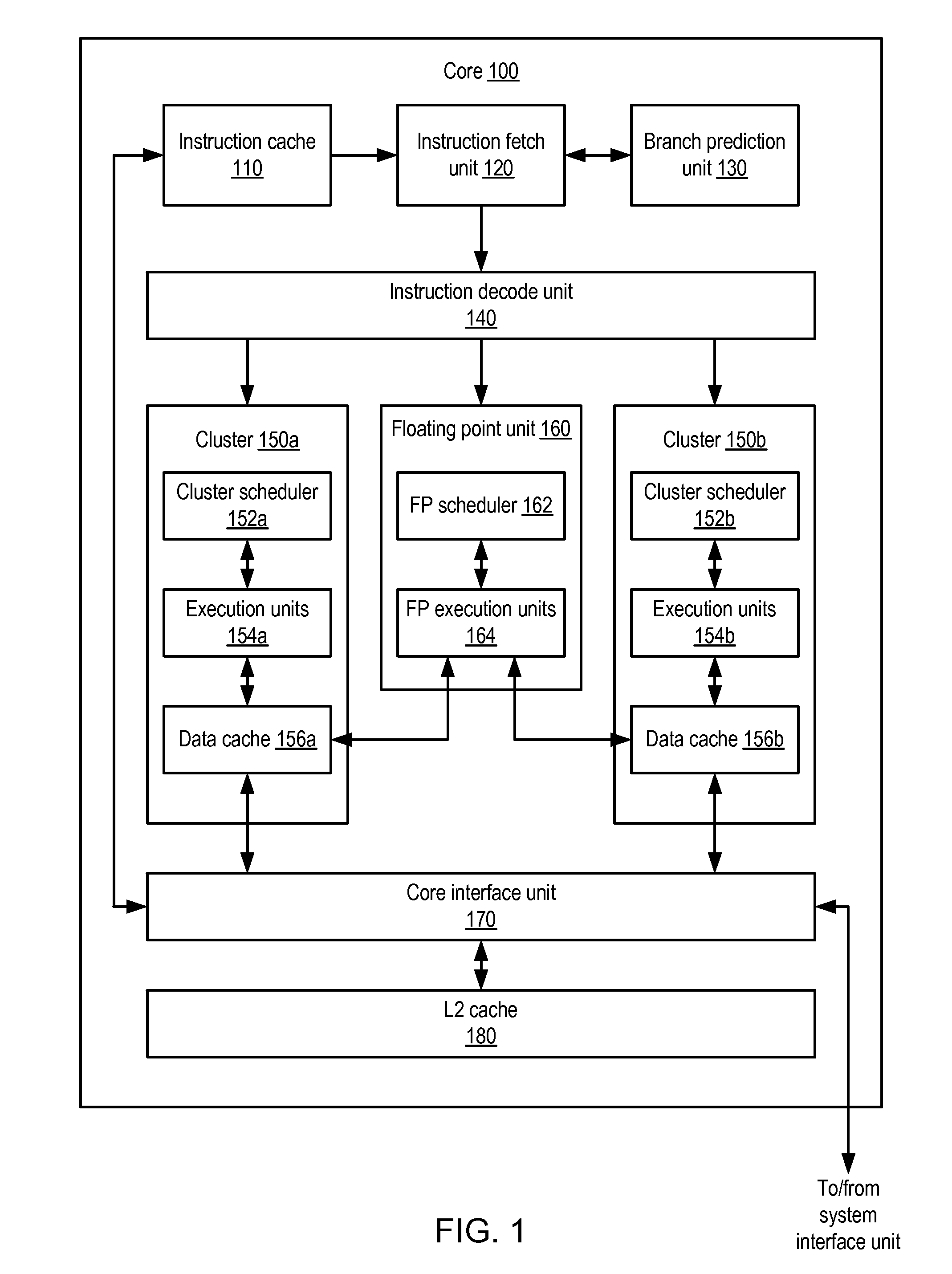
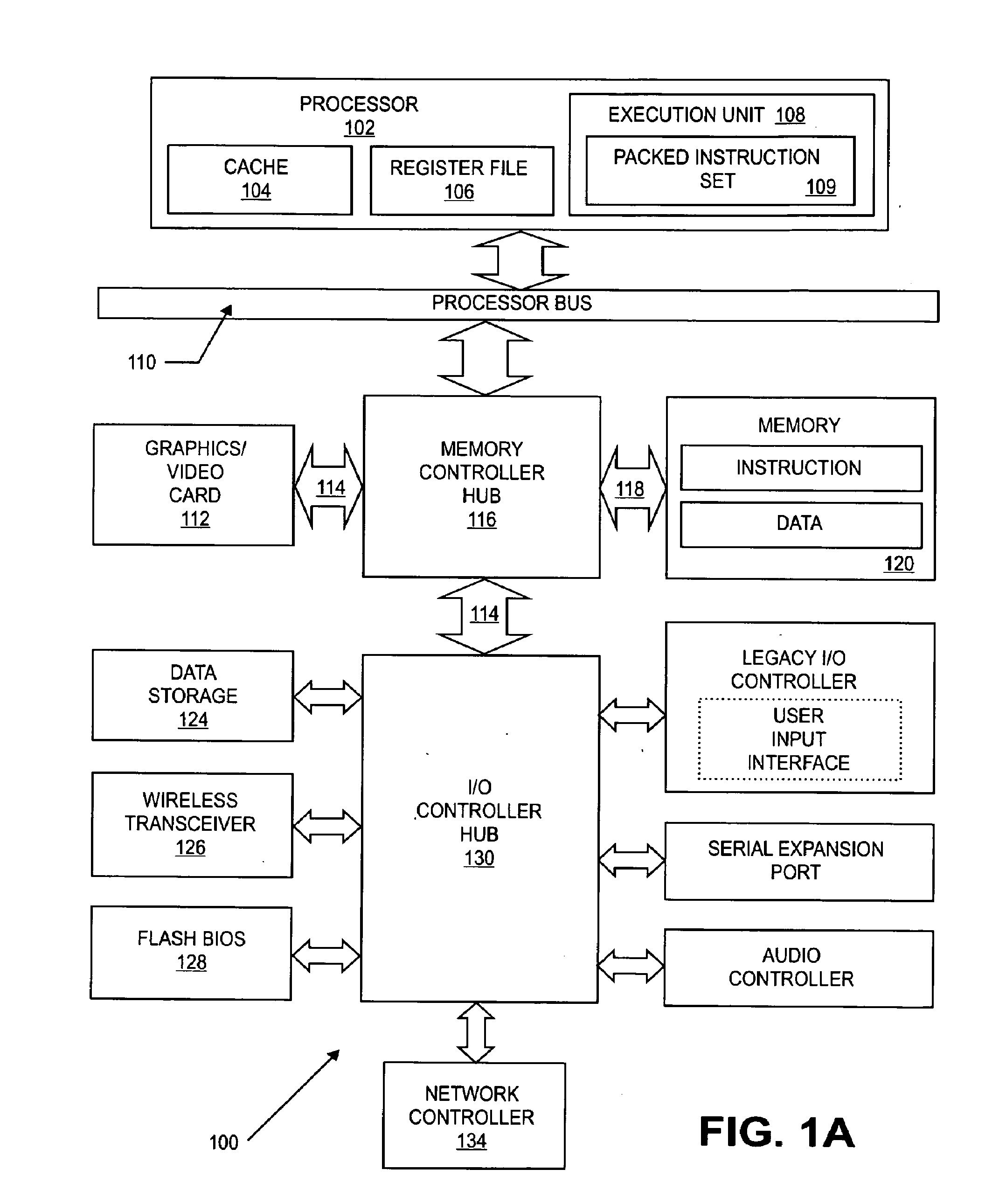
Hardware virtual machine instruction processor
InactiveUS6021469AProhibitive expenseLow costMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTThe InternetCellular telephone
A hardware virtual machine instruction processor directly executes virtual machine instructions that are processor architecture independent. The hardware processor has high performance; is low cost; and exhibits low power consumption. The hardware processor is well suited for portable applications. These applications include, for example, an Internet chip for network appliances, a cellular telephone processor, other telecommunications integrated circuits, or other low-power, low-cost applications such as embedded processors, and portable devices.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
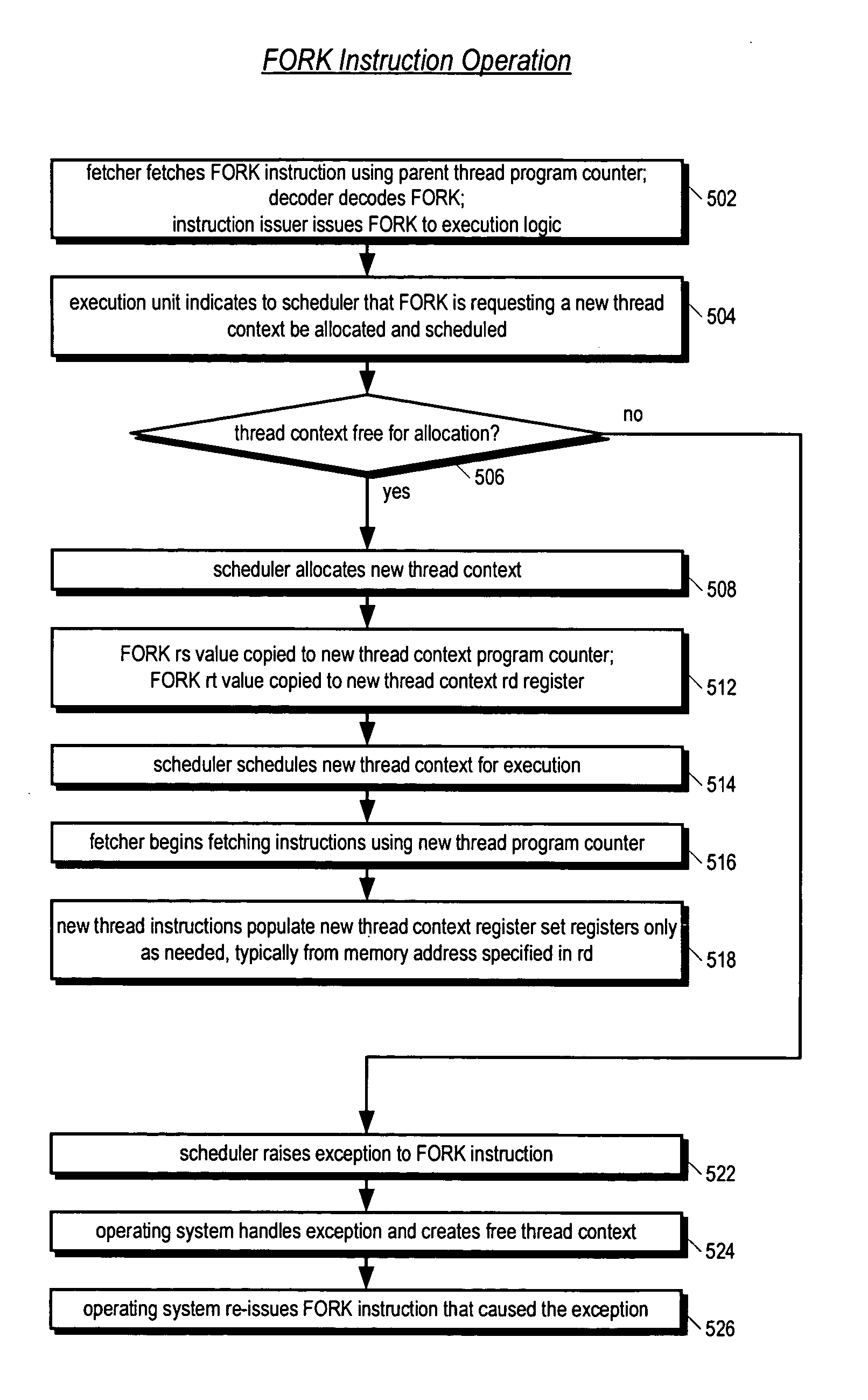
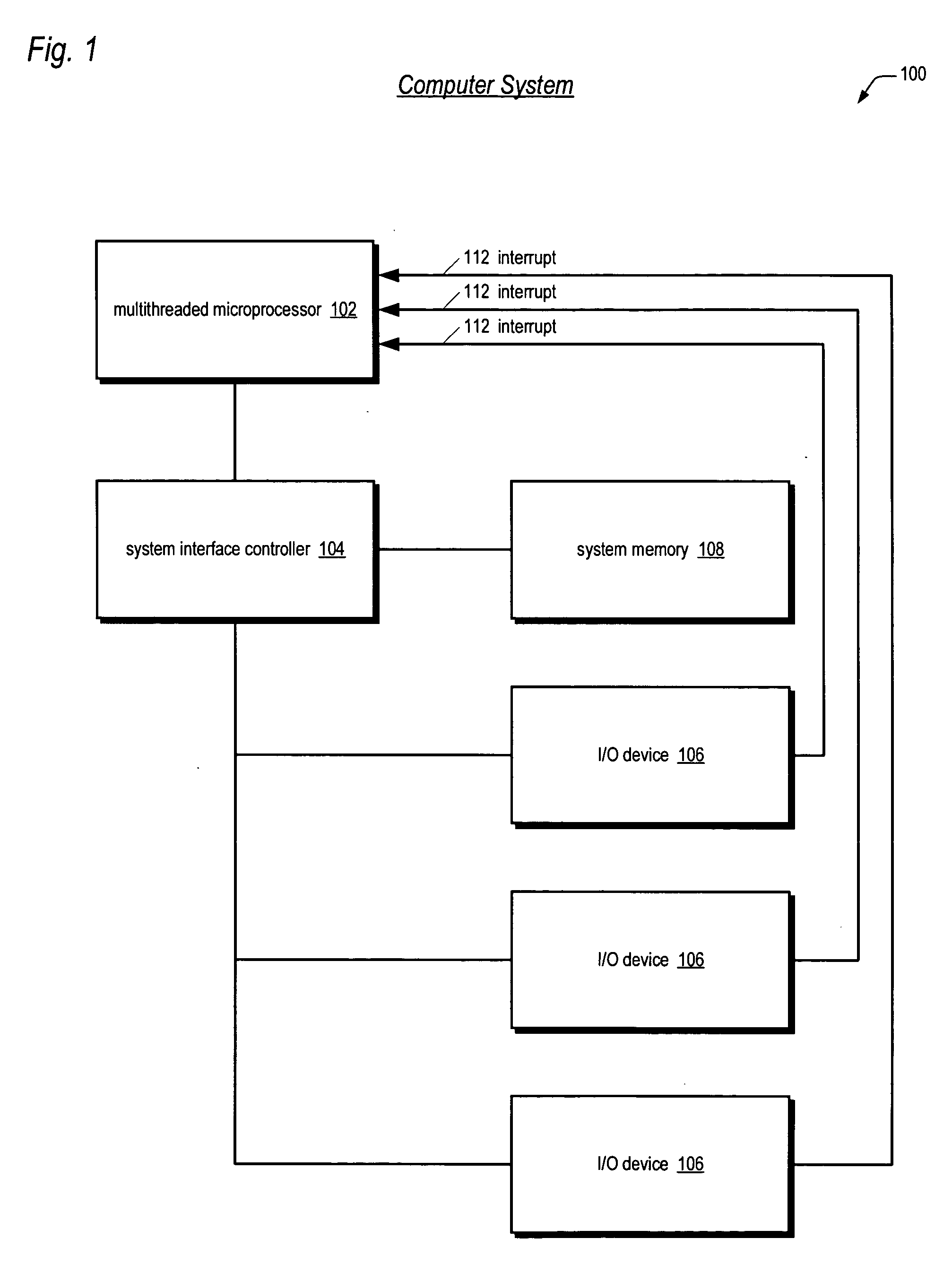
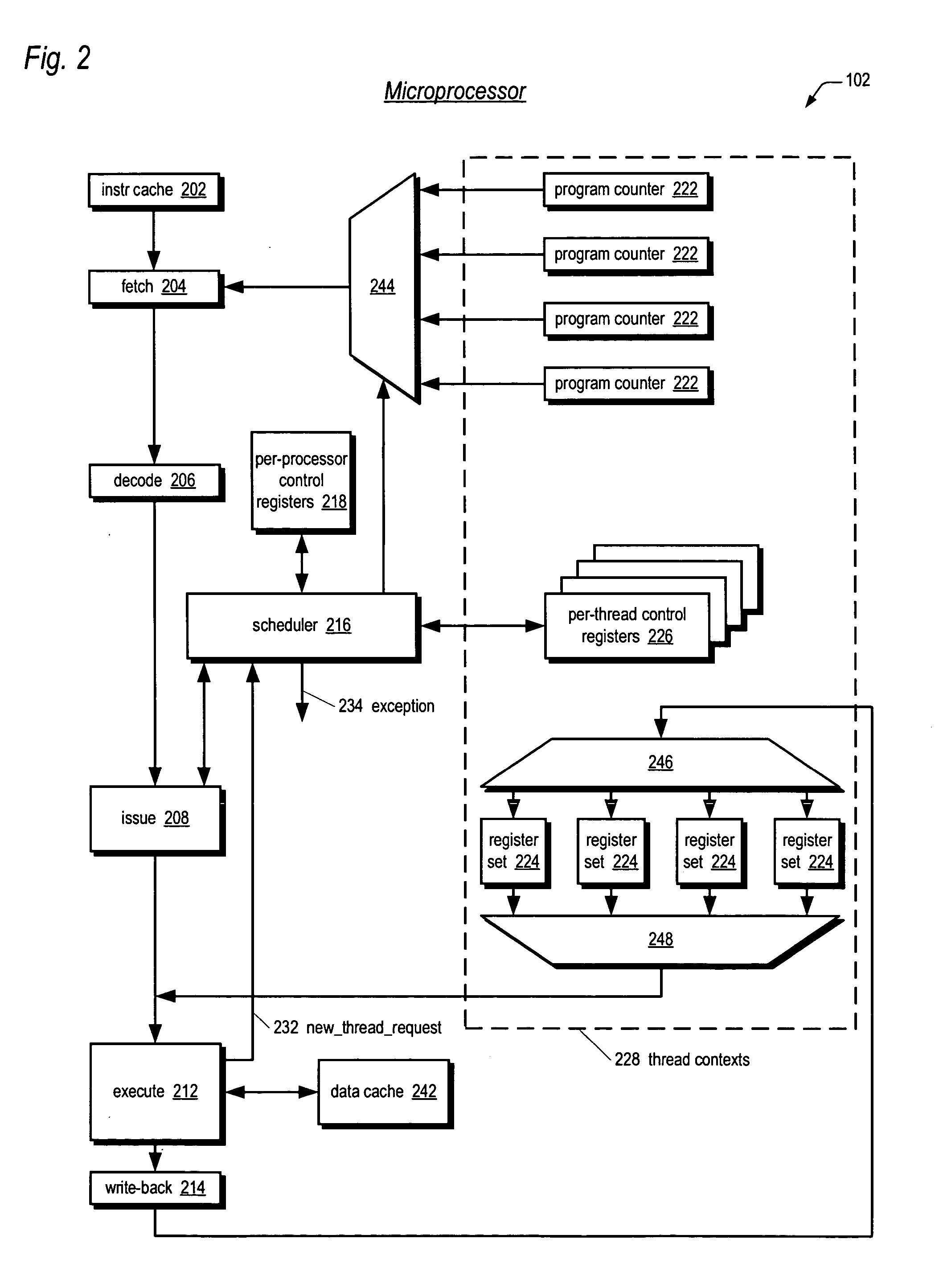
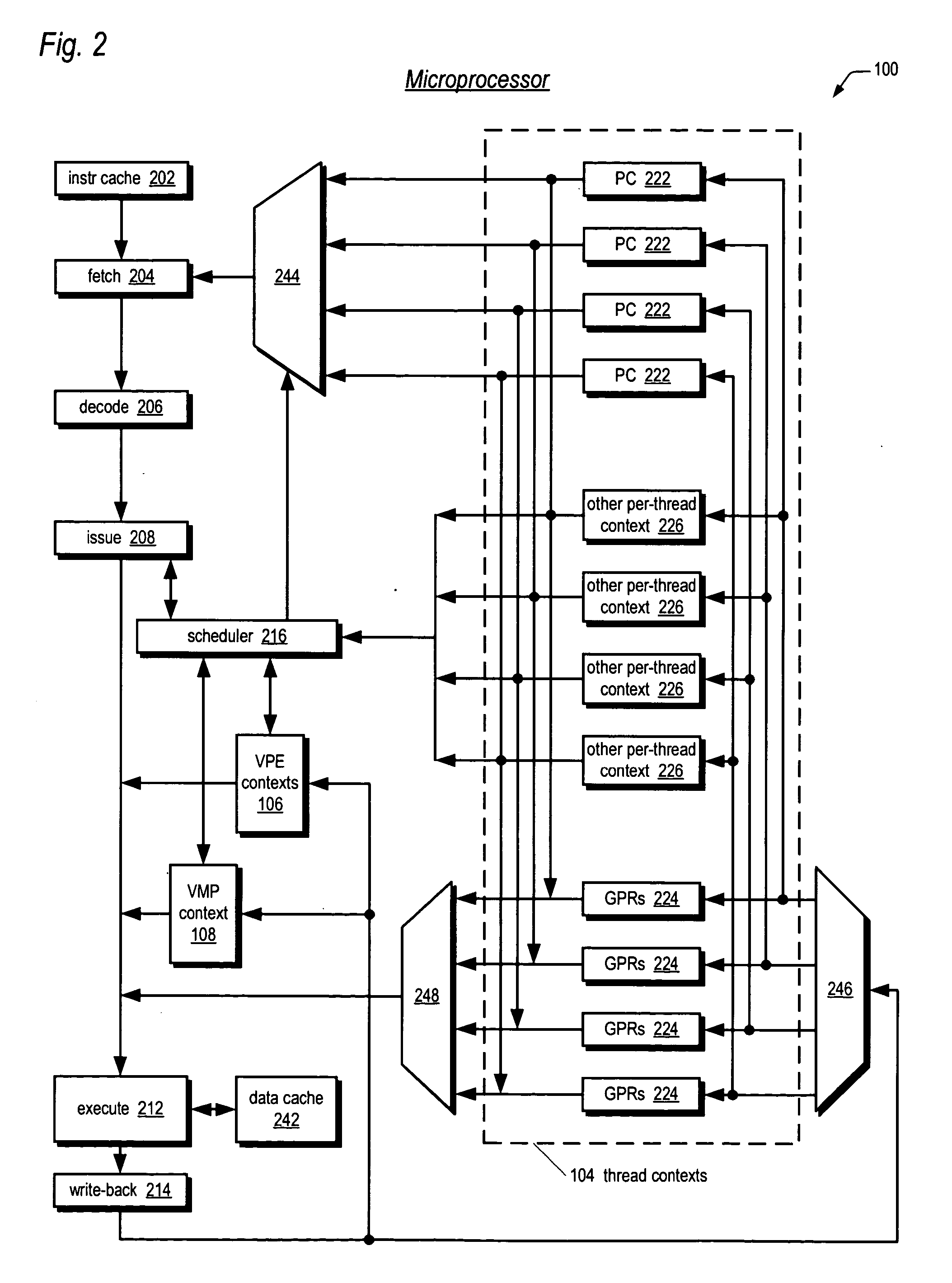
Apparatus, method, and instruction for initiation of concurrent instruction streams in a multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS20050120194A1Reduce overheadAvoid wasting energyProgram initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringGeneral purposeComputer architecture
A fork instruction for execution on a multithreaded microprocessor and occupying a single instruction issue slot is disclosed. The fork instruction, executing in a parent thread, includes a first operand specifying the initial instruction address of a new thread and a second operand. The microprocessor executes the fork instruction by allocating context for the new thread, copying the first operand to a program counter of the new thread context, copying the second operand to a register of the new thread context, and scheduling the new thread for execution. If no new thread context is free for allocation, the microprocessor raises an exception to the fork instruction. The fork instruction is efficient because it does not copy the parent thread general purpose registers to the new thread. The second operand is typically used as a pointer to a data structure in memory containing initial general purpose register set values for the new thread.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
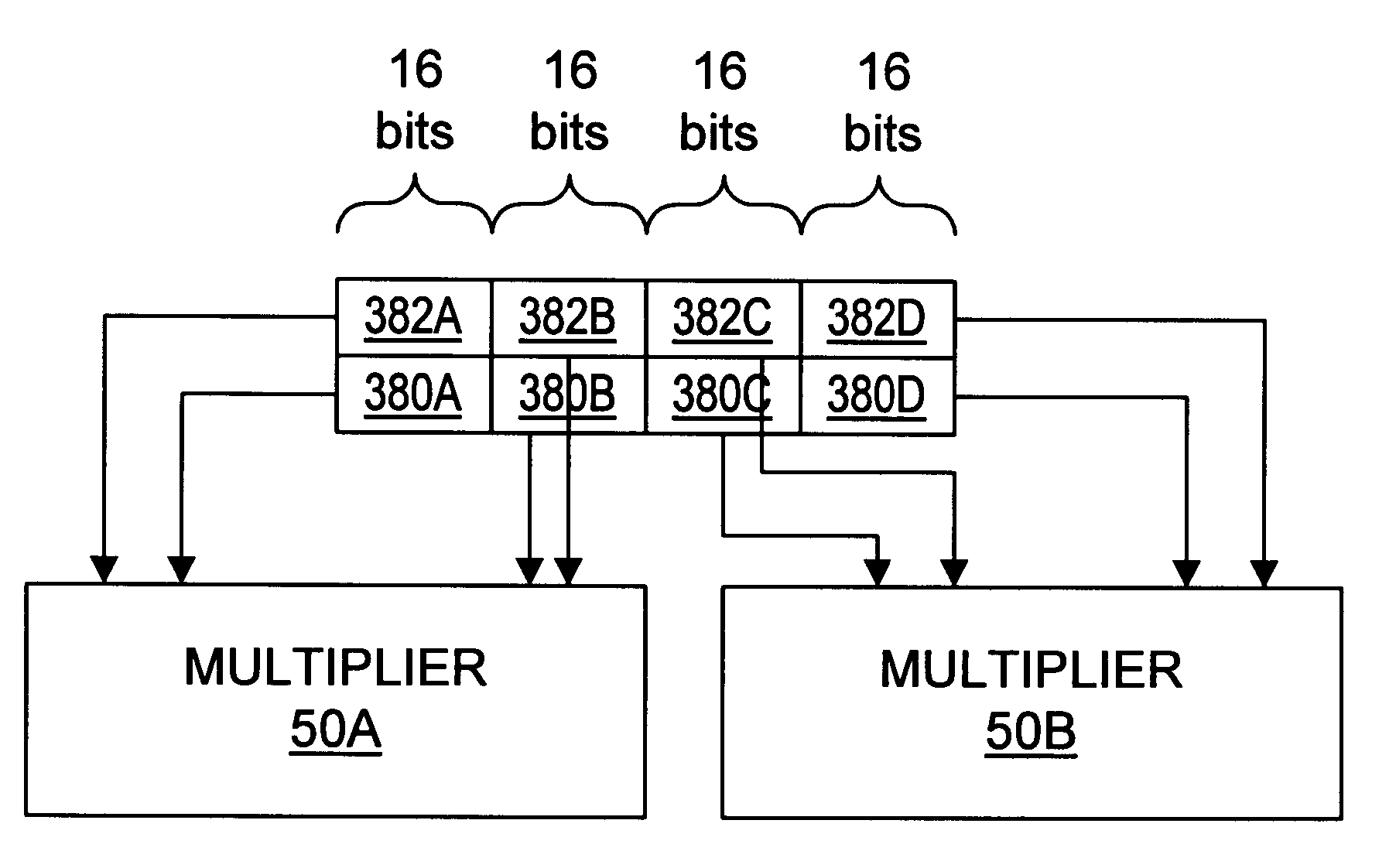
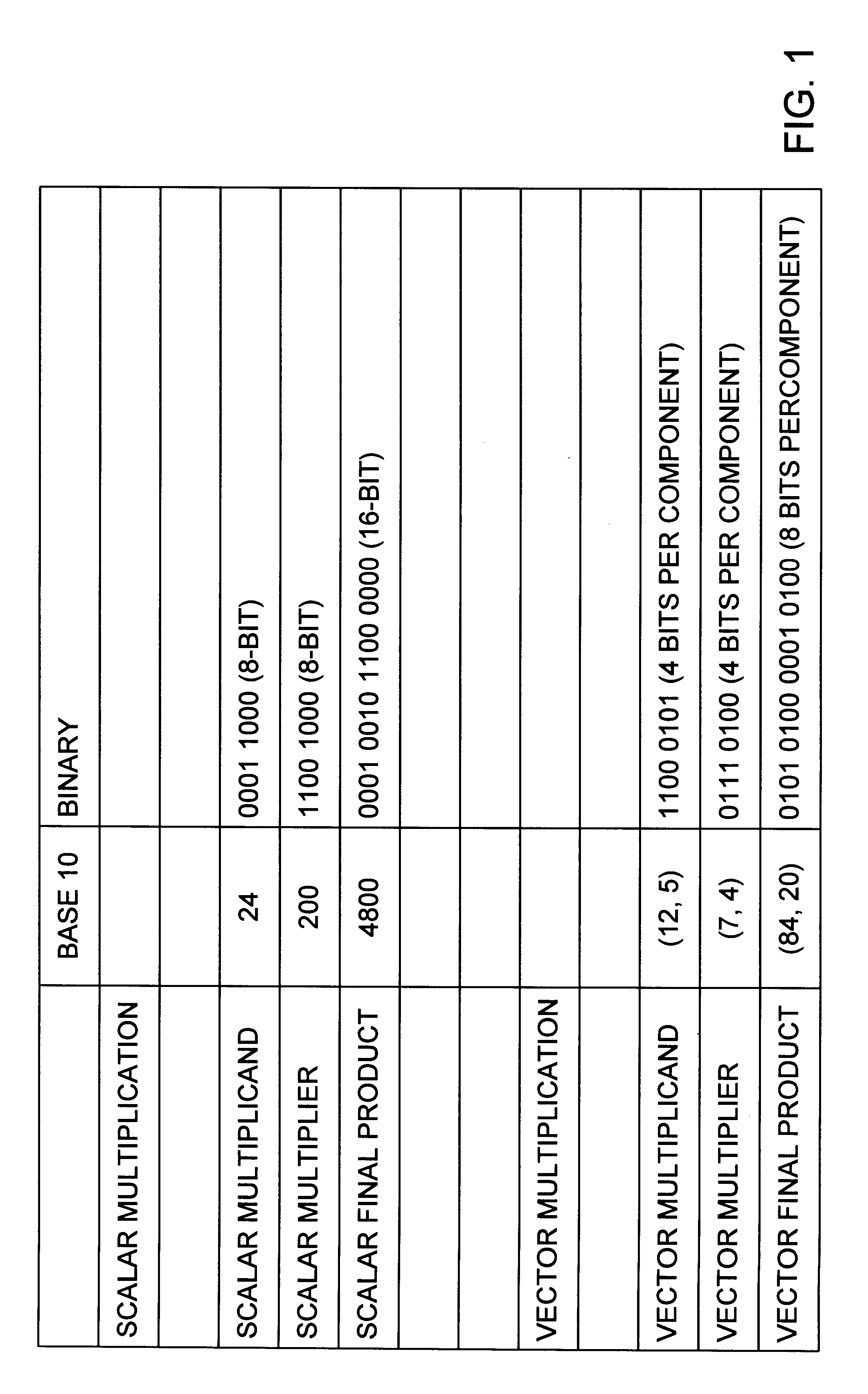
Method and apparatus for multi-function arithmetic
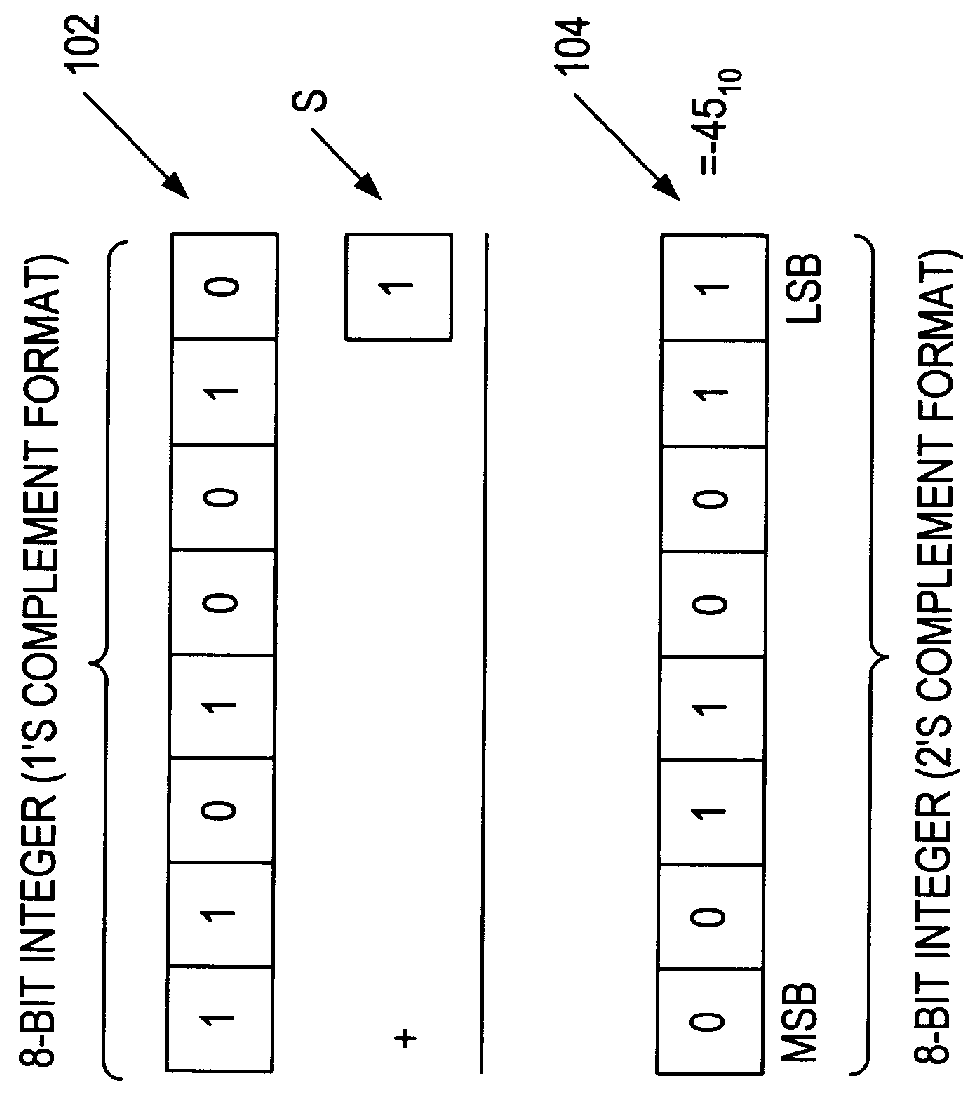
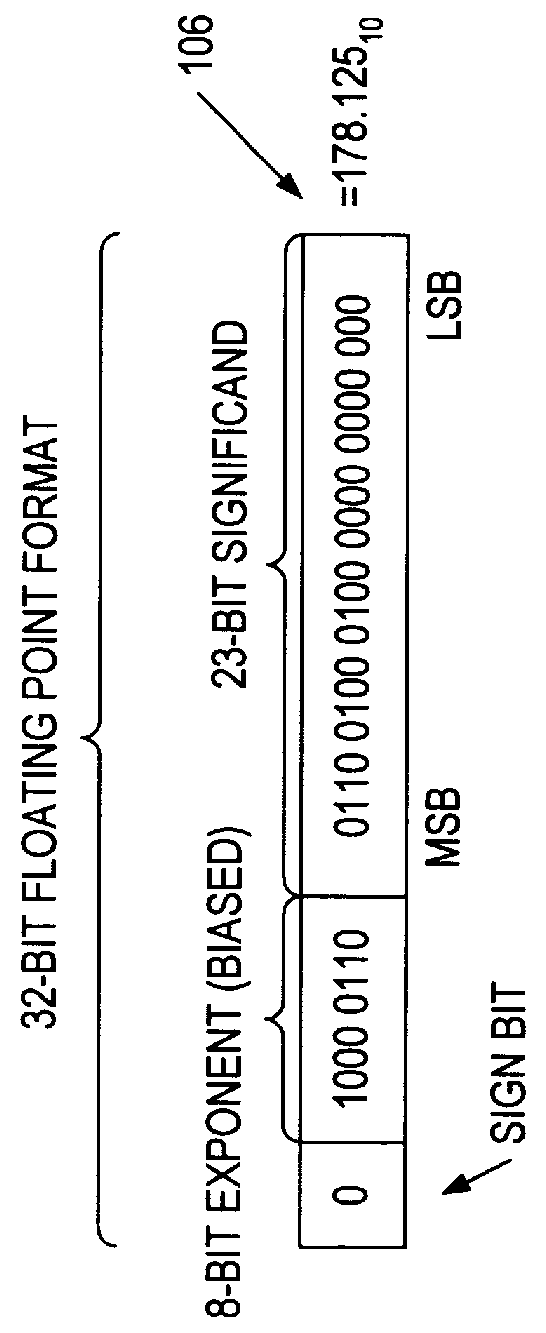
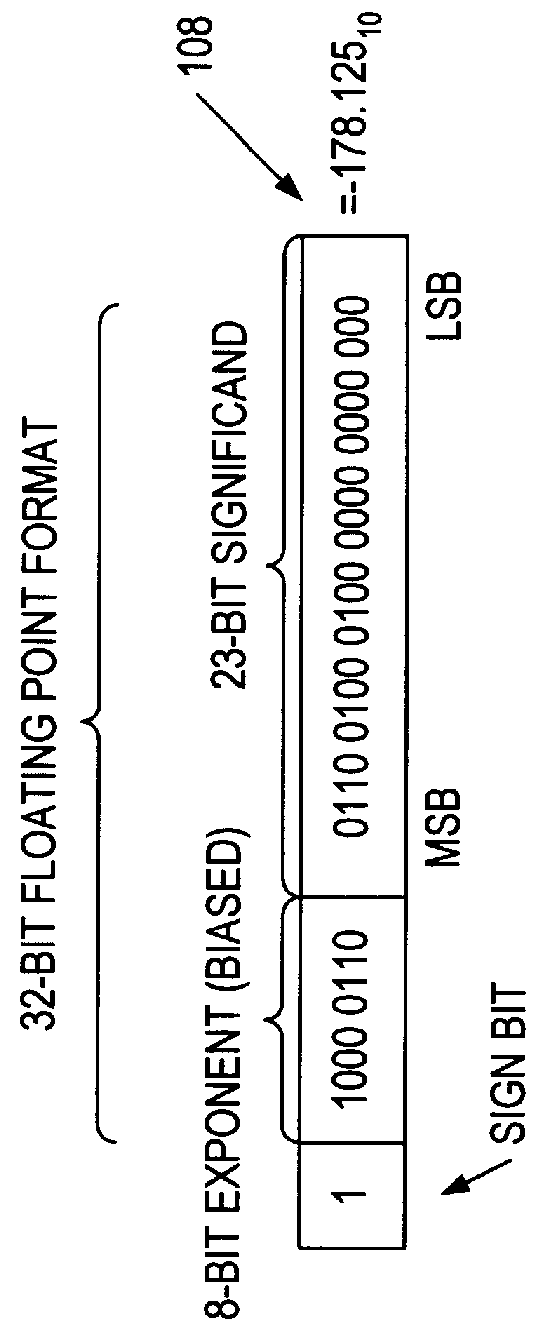
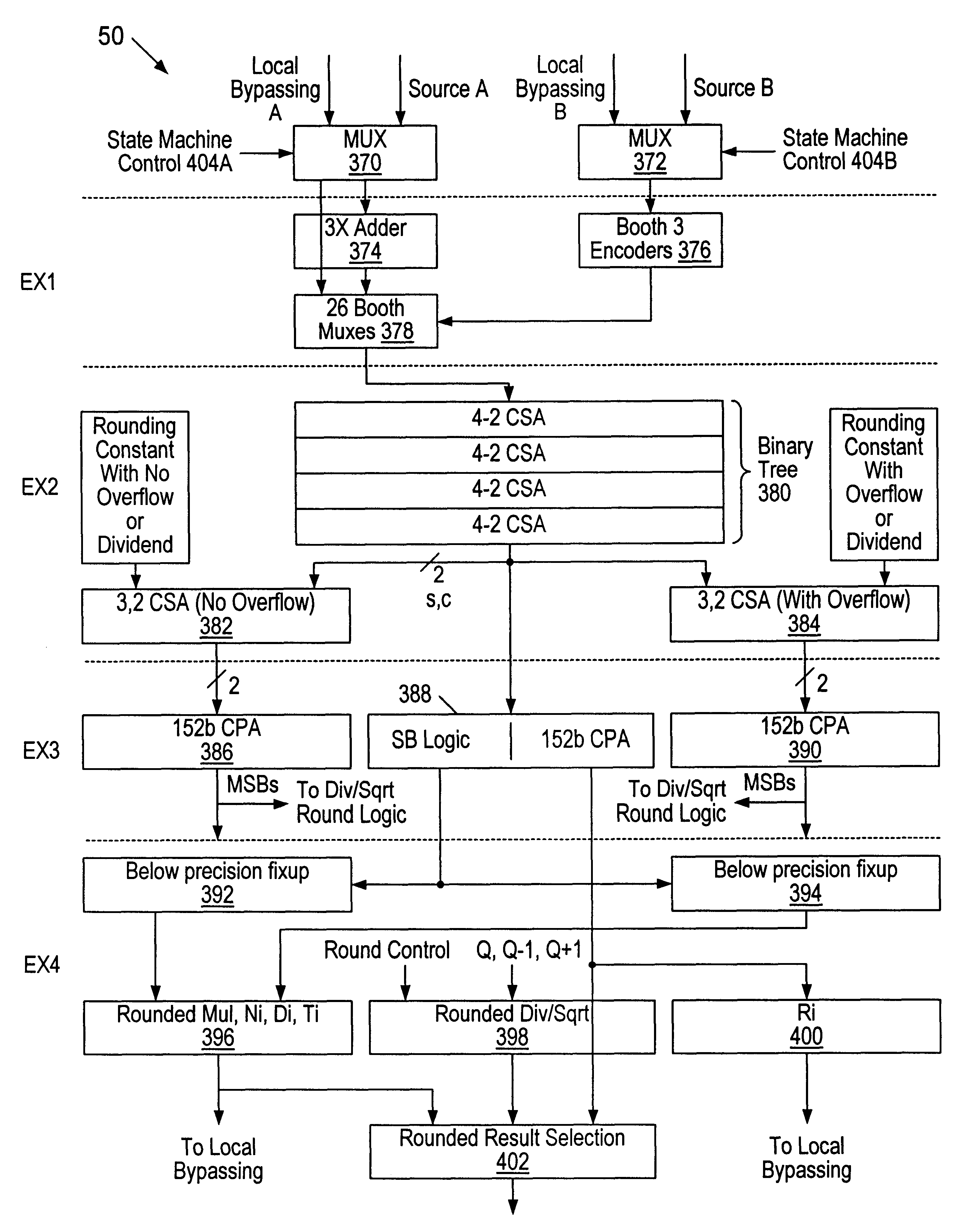
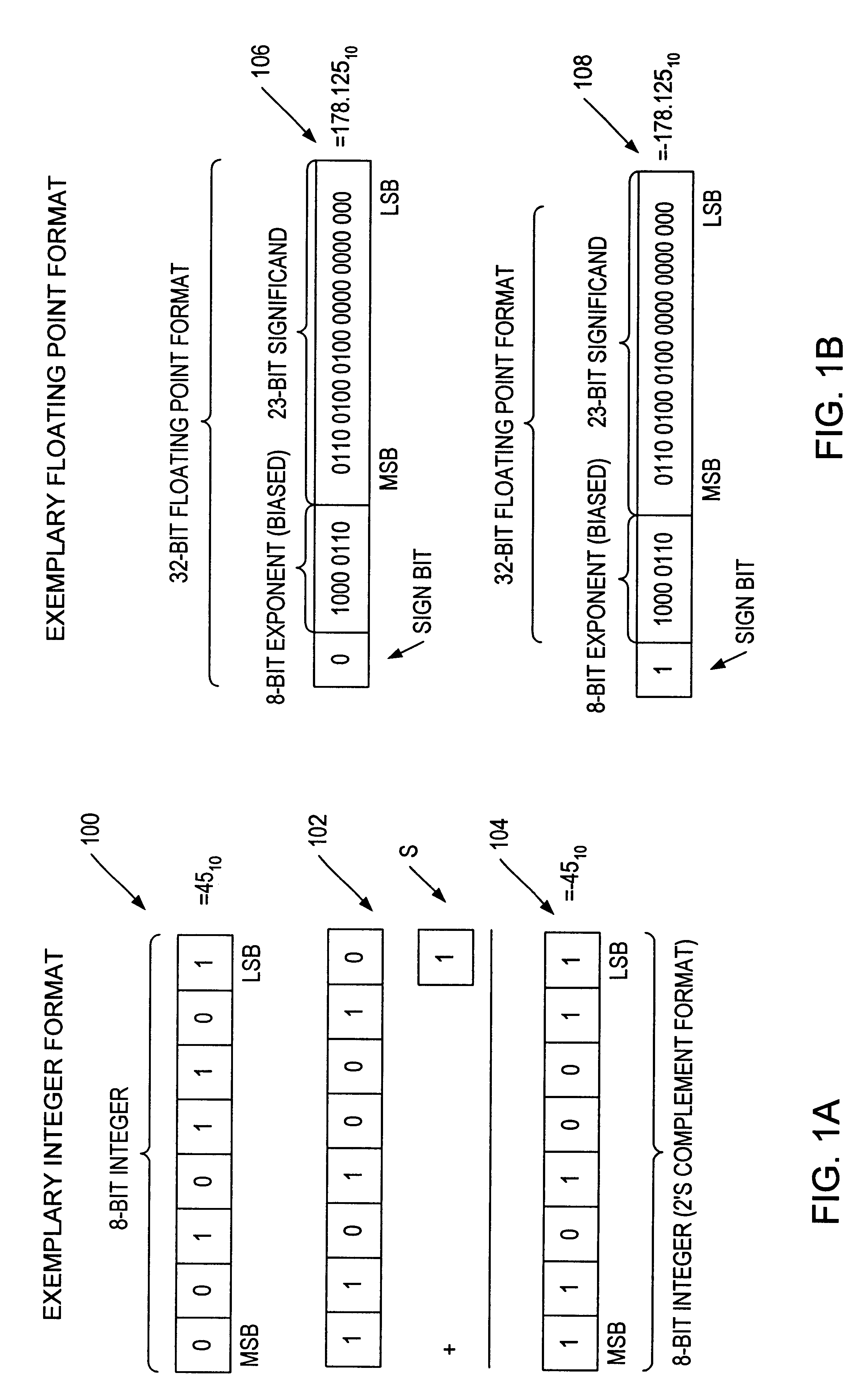
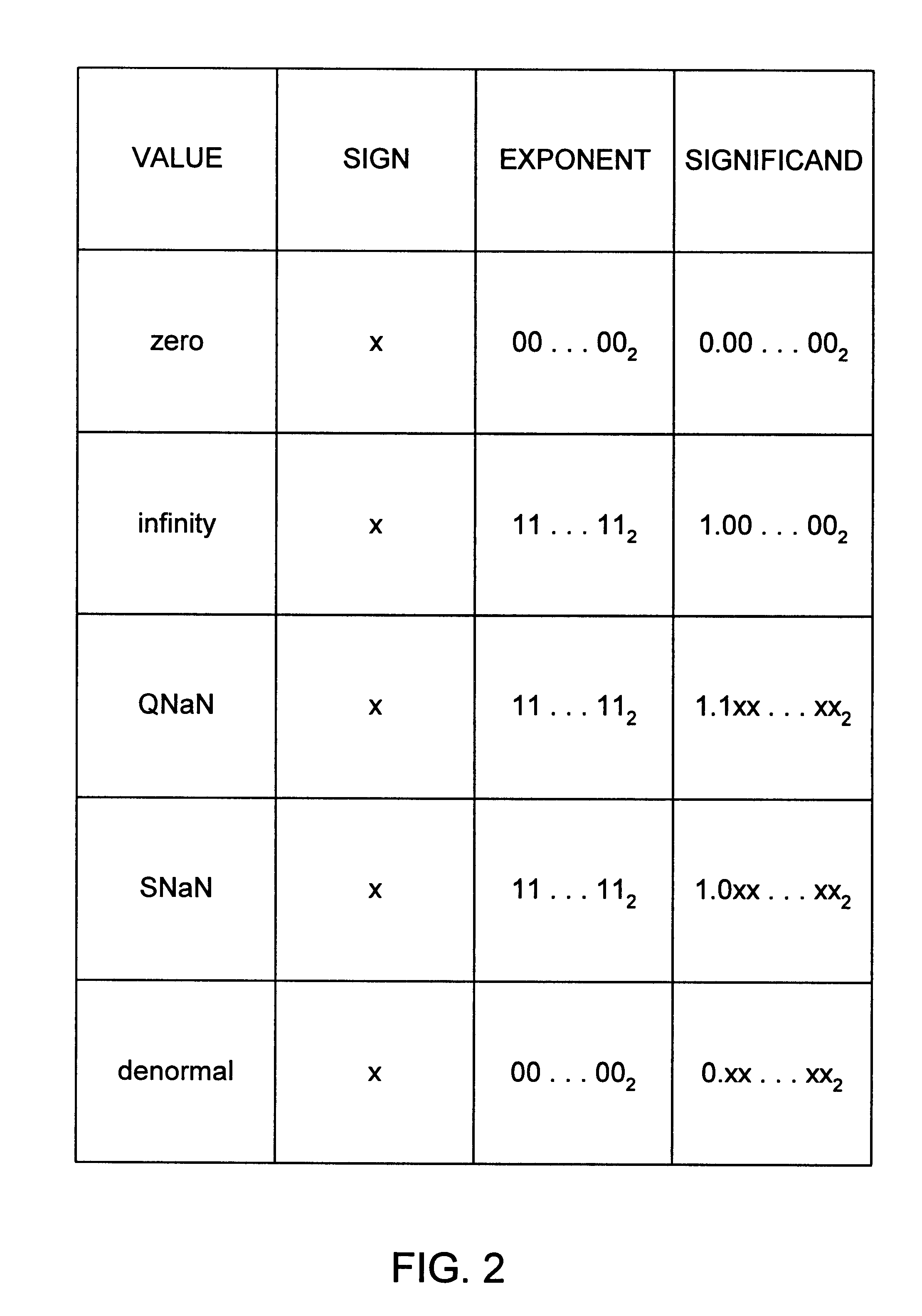
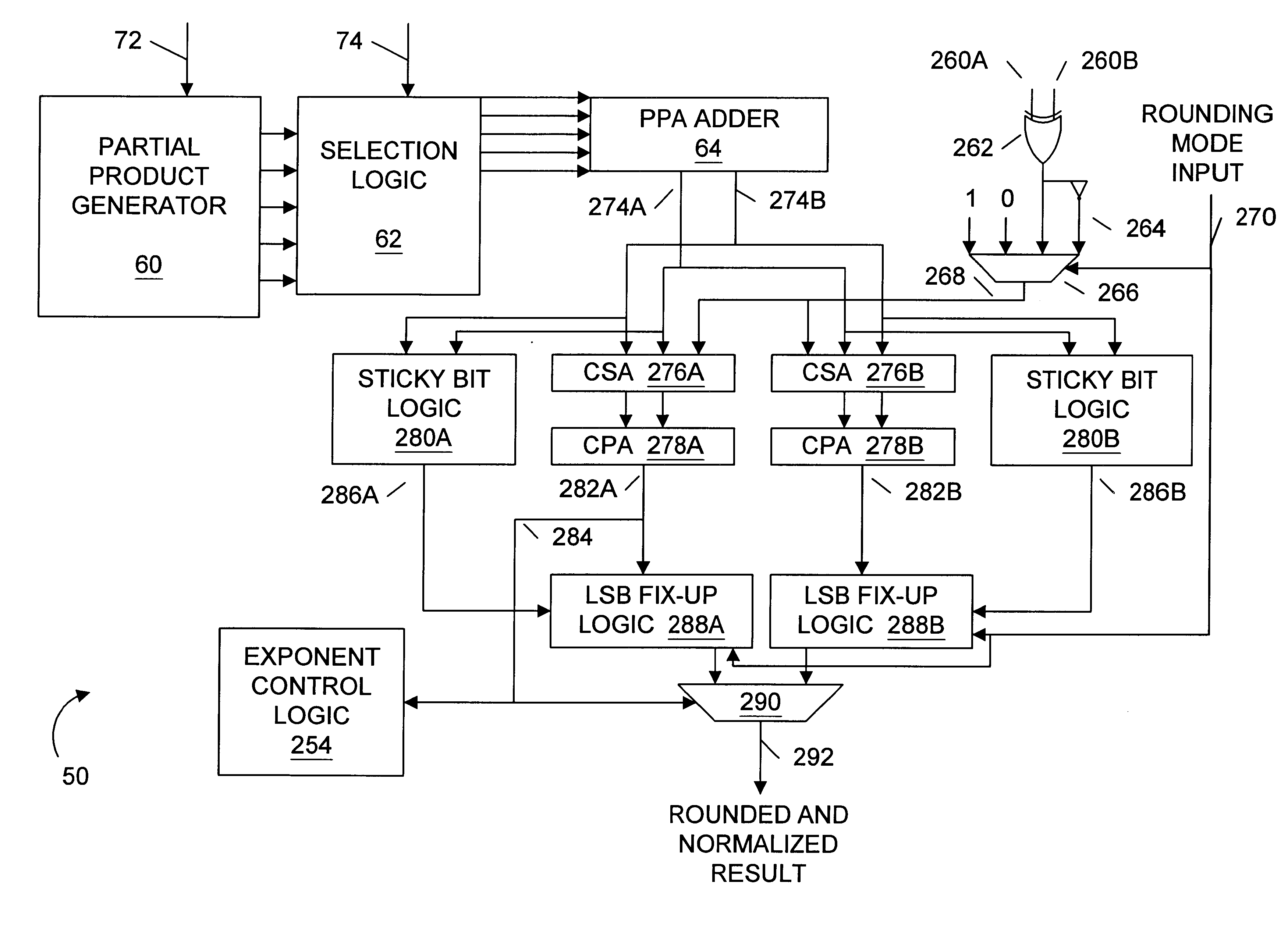
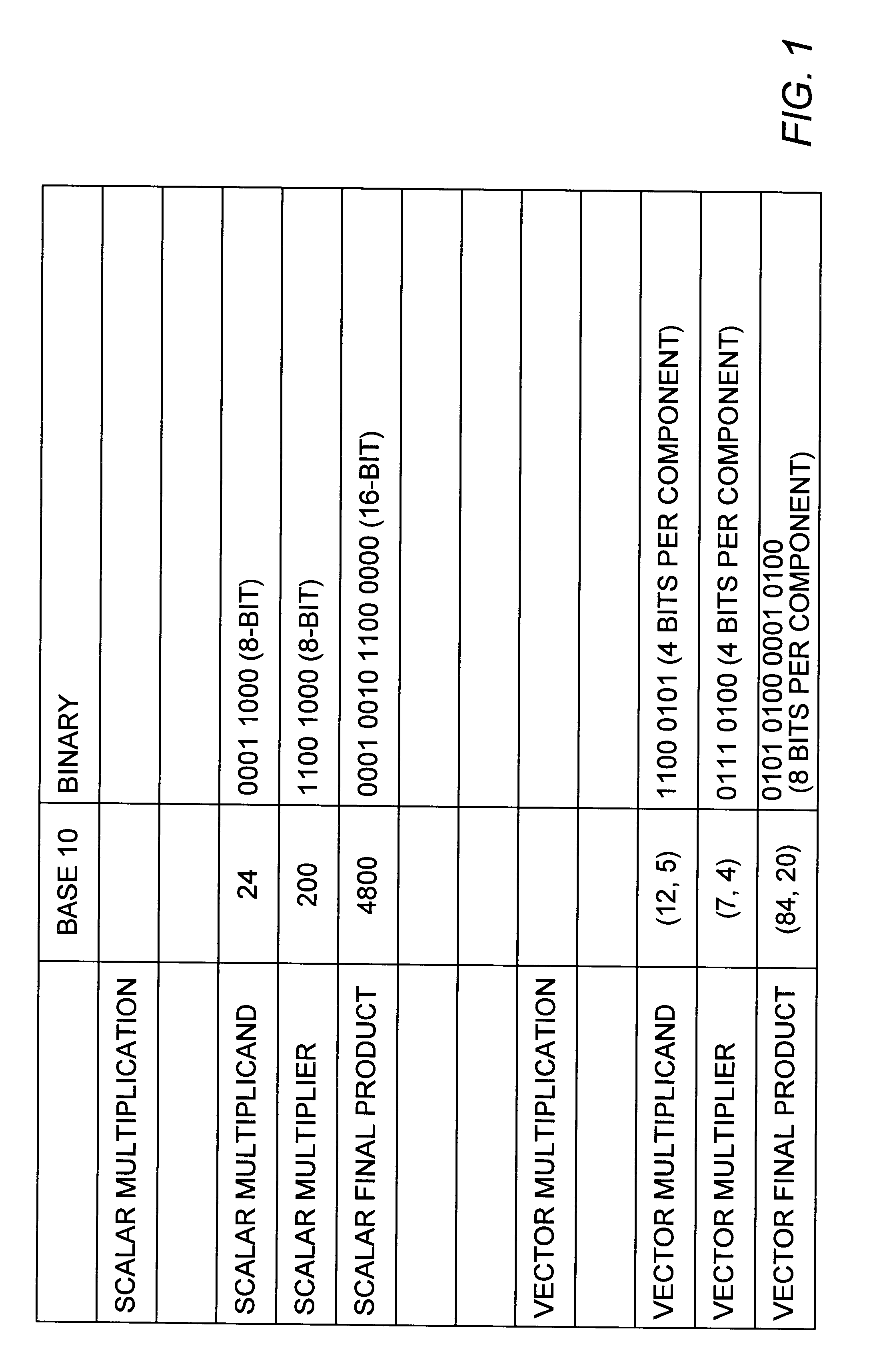
InactiveUS6223198B1Runtime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesConstant powerRounding
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated and used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur. The multiplier may also be configured to perform iterative calculations to evaluate constant powers of an operand. Intermediate products that are formed may be rounded and normalized in two paths and then compressed and stored for use in the next iteration. An adjustment constant may also be added to increase the frequency of exactly rounded results.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Computing System with Transactional Memory Using Millicode Assists
InactiveUS20080288819A1FasterSolve excessive overheadRuntime instruction translationDigital computer detailsProcess memoryTransactional memory
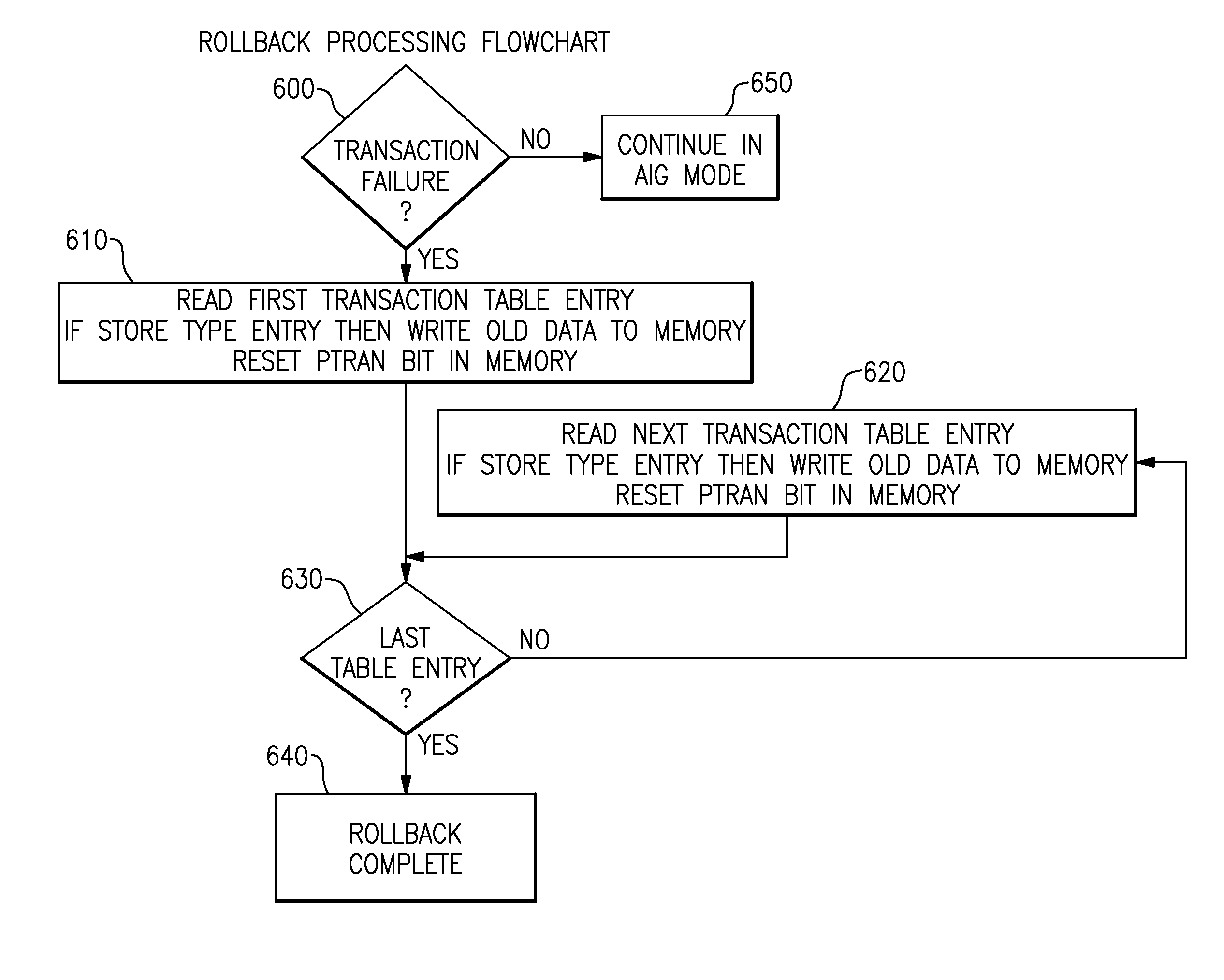
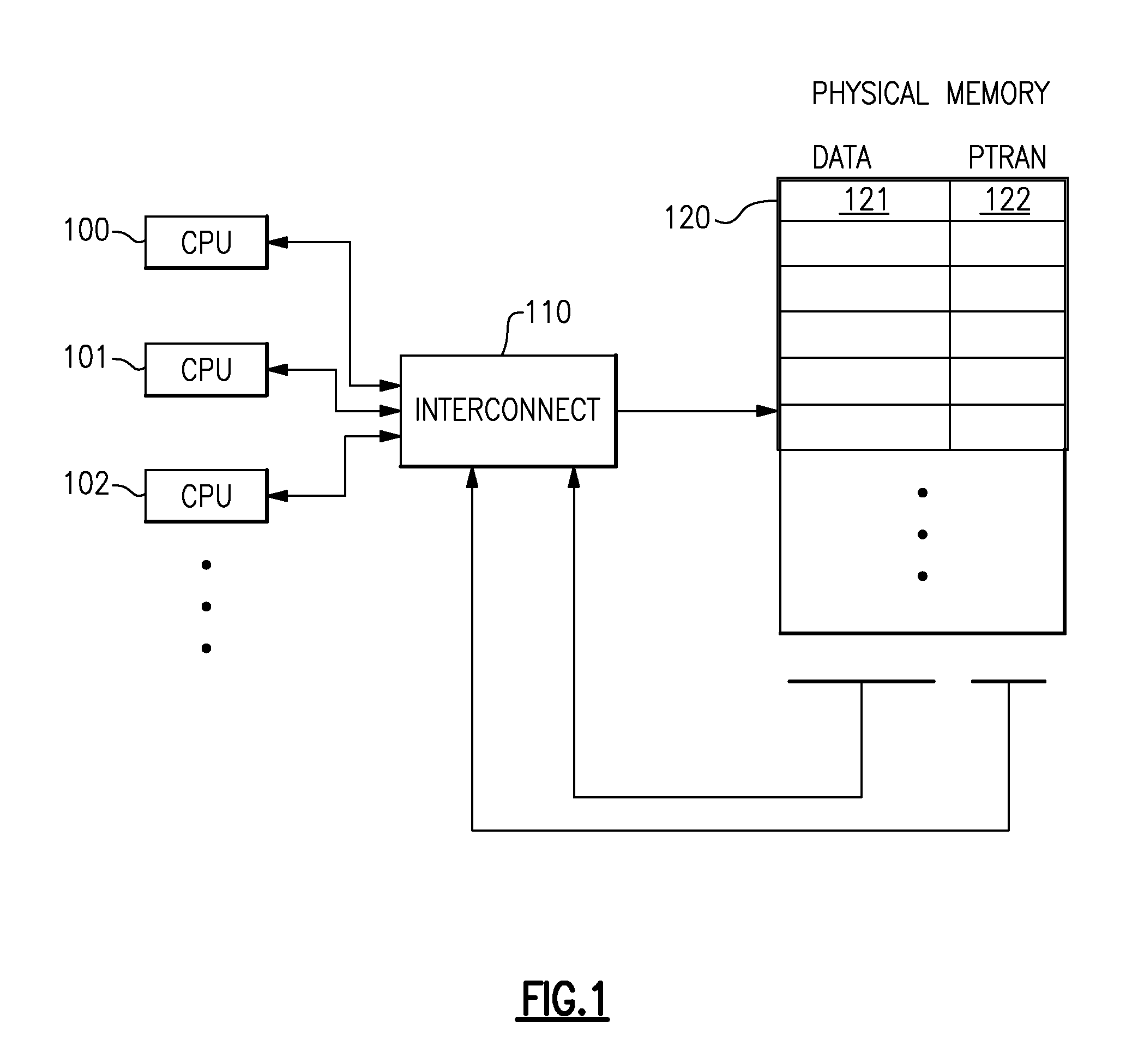
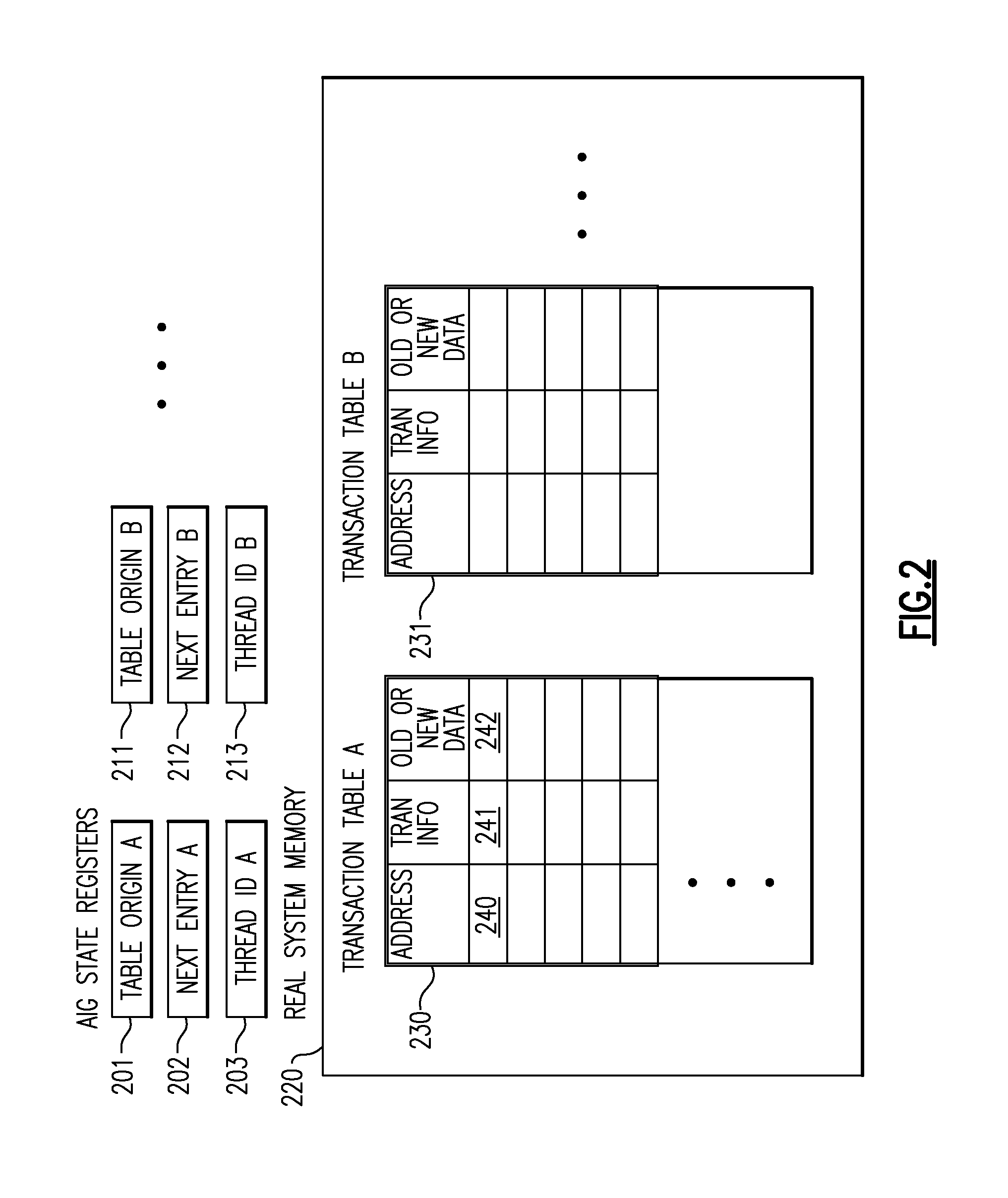
A computing system processes memory transactions for parallel processing of multiple threads of execution with millicode assists. The computing system transactional memory support provides a Transaction Table in memory and a method of fast detection of potential conflicts between multiple transactions. Special instructions may mark the boundaries of a transaction and identify memory locations applicable to a transaction. A ‘private to transaction’ (PTRAN) tag, directly addressable as part of the main data storage memory location, enables a quick detection of potential conflicts with other transactions that are concurrently executing on another thread of said computing system. The tag indicates whether (or not) a data entry in memory is part of a speculative memory state of an uncommitted transaction that is currently active in the system. Program millicode provides transactional memory functions including creating and updating transaction tables, committing transactions and controlling the rollback of transactions which fail.
Owner:IBM CORP
Token based power control mechanism
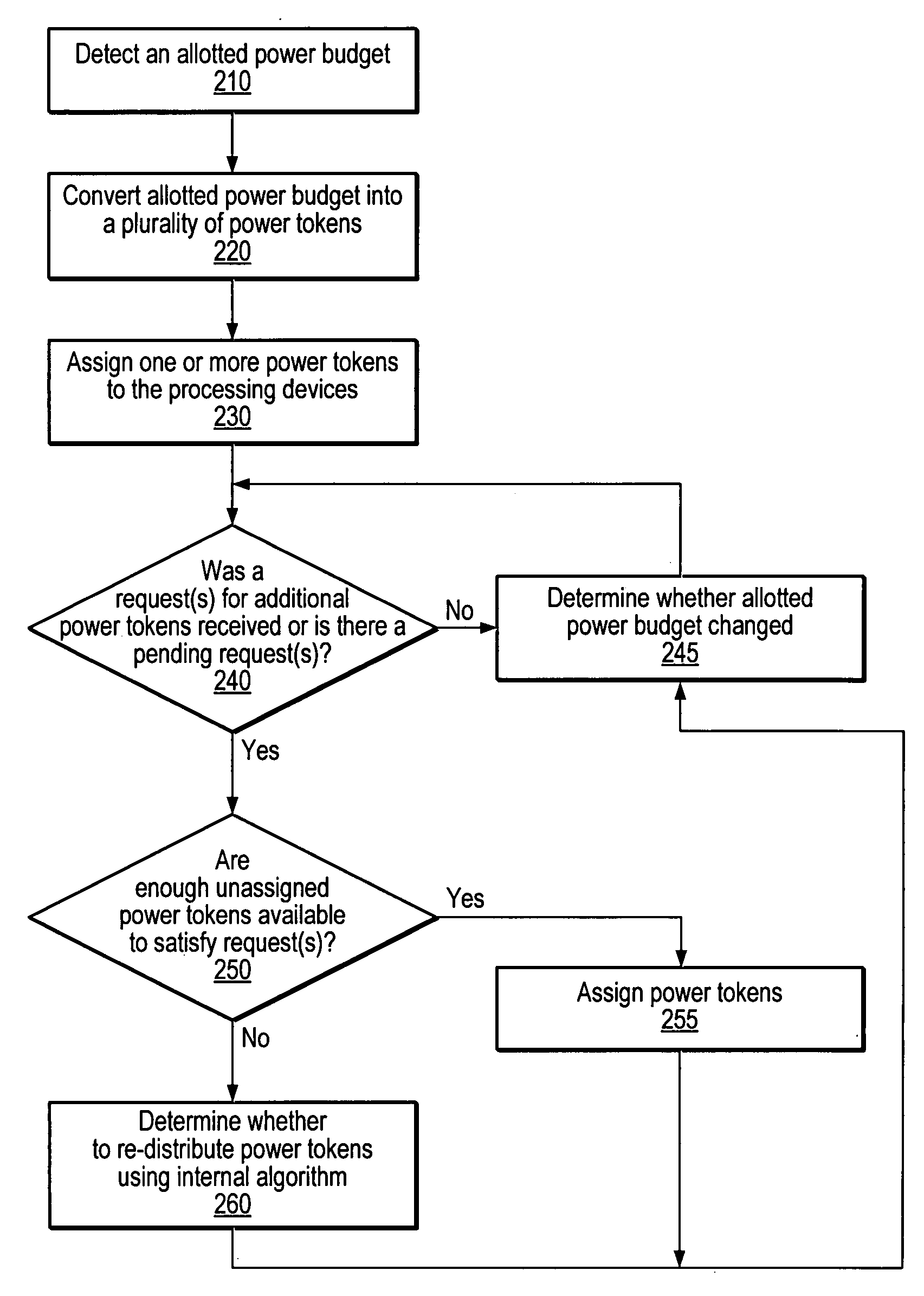
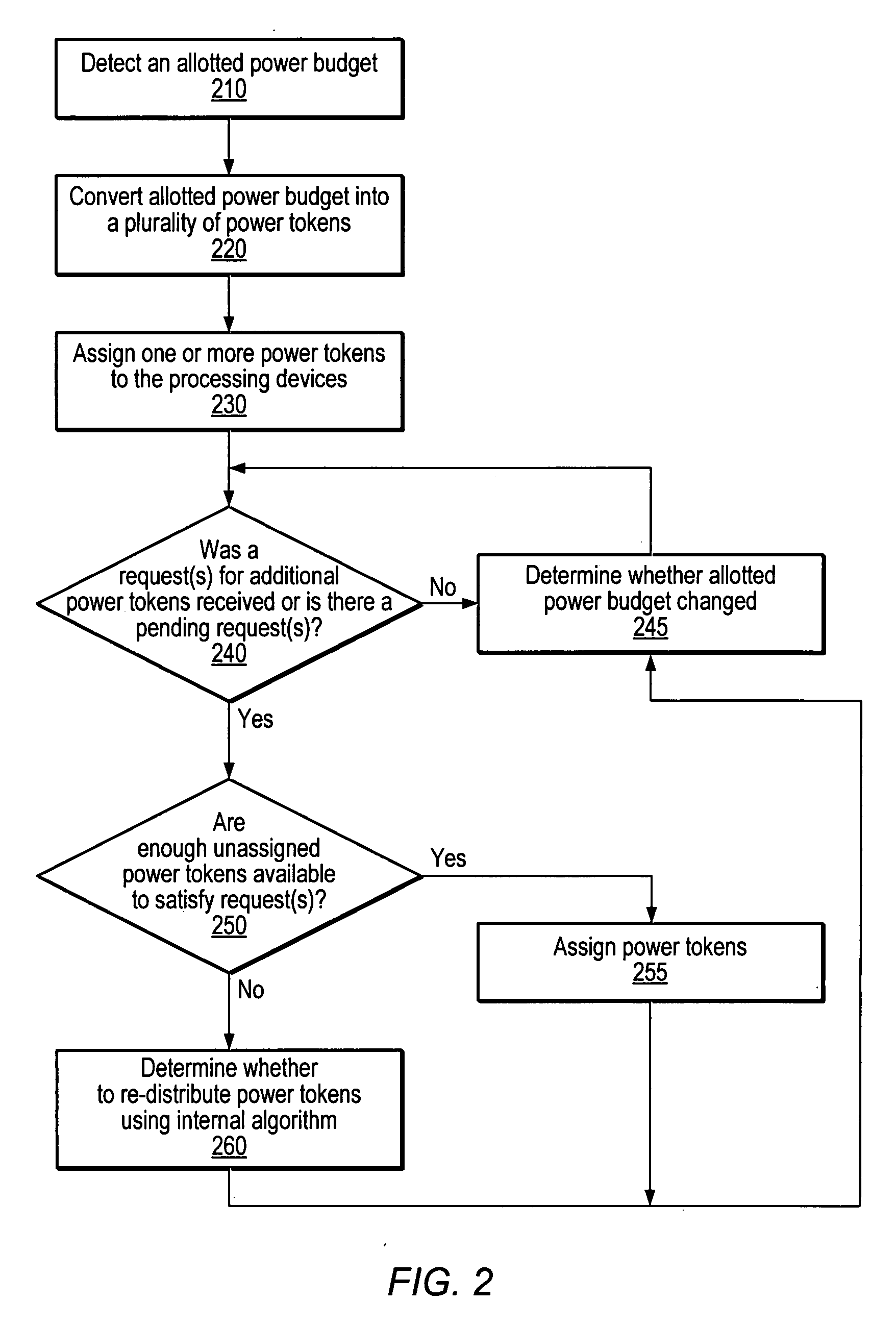
A token-based power control mechanism for an apparatus including a power controller and a plurality of processing devices. The power controller may detect a power budget allotted for the apparatus. The power controller may convert the allotted power budget into a plurality of power tokens, each power token being a portion of the allotted power budget. The power controller may then assign one or more of the plurality of power tokens to each of the processing devices. The assigned power tokens may determine the power allotted for each of the processing devices. The power controller may receive one or more requests from the plurality of processing devices for one or more additional power tokens. In response to receiving the requests, the power controller may determine whether to change the distribution of power tokens among the processing devices.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
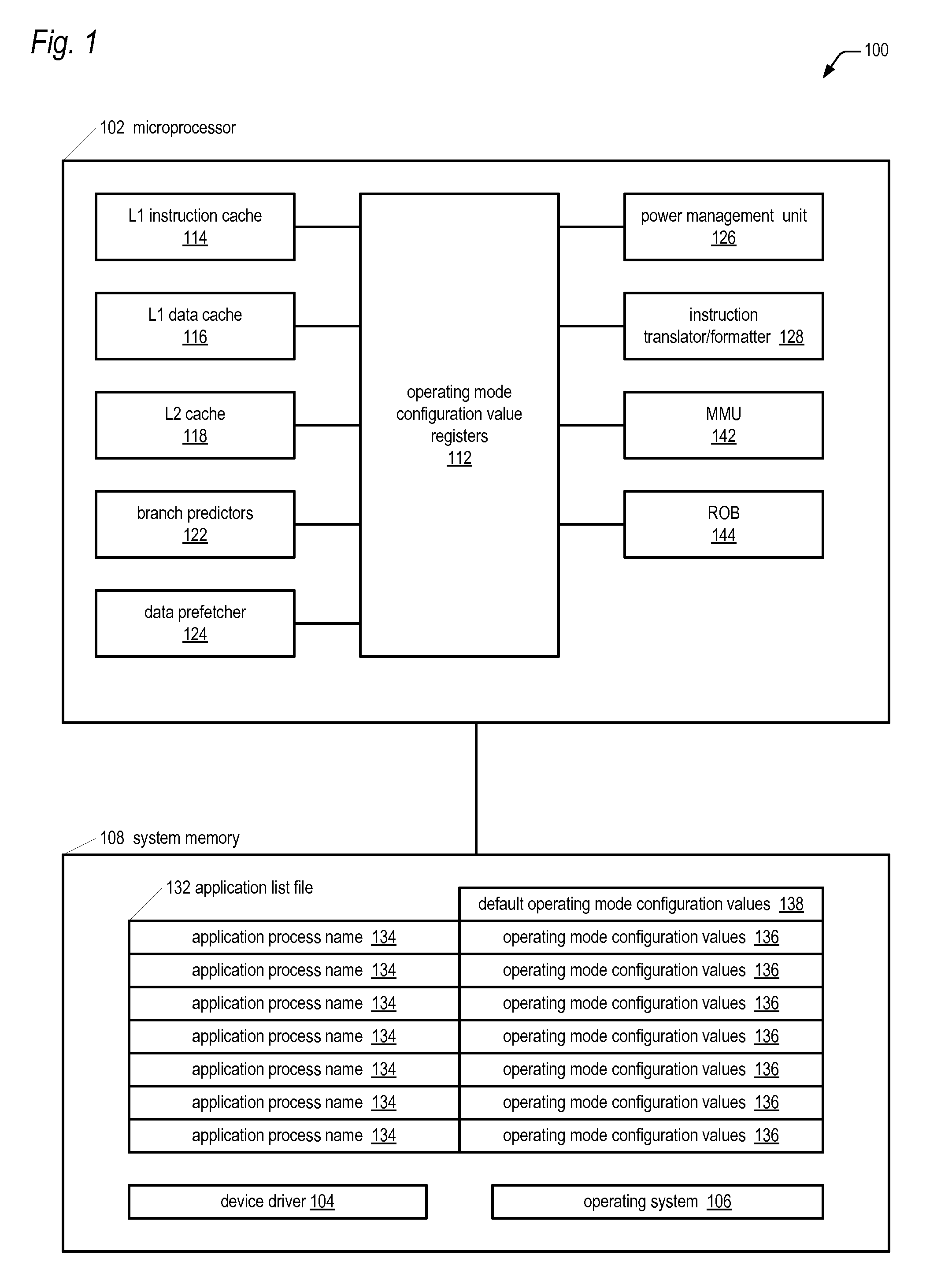
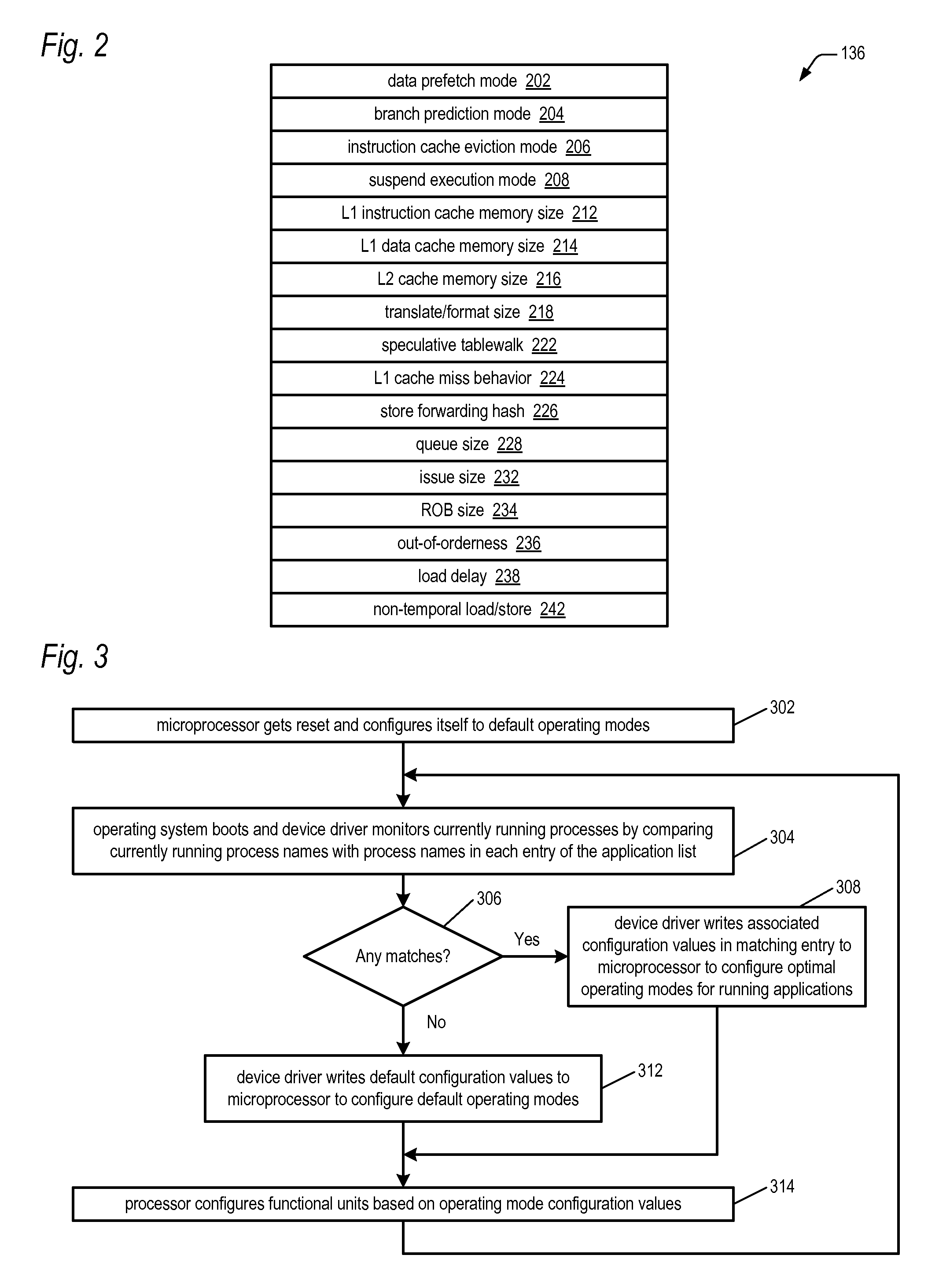
Microprocessor with multiple operating modes dynamically configurable by a device driver based on currently running applications
ActiveUS20100011198A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionRuntime instruction translationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationBranch target address cacheApplication software
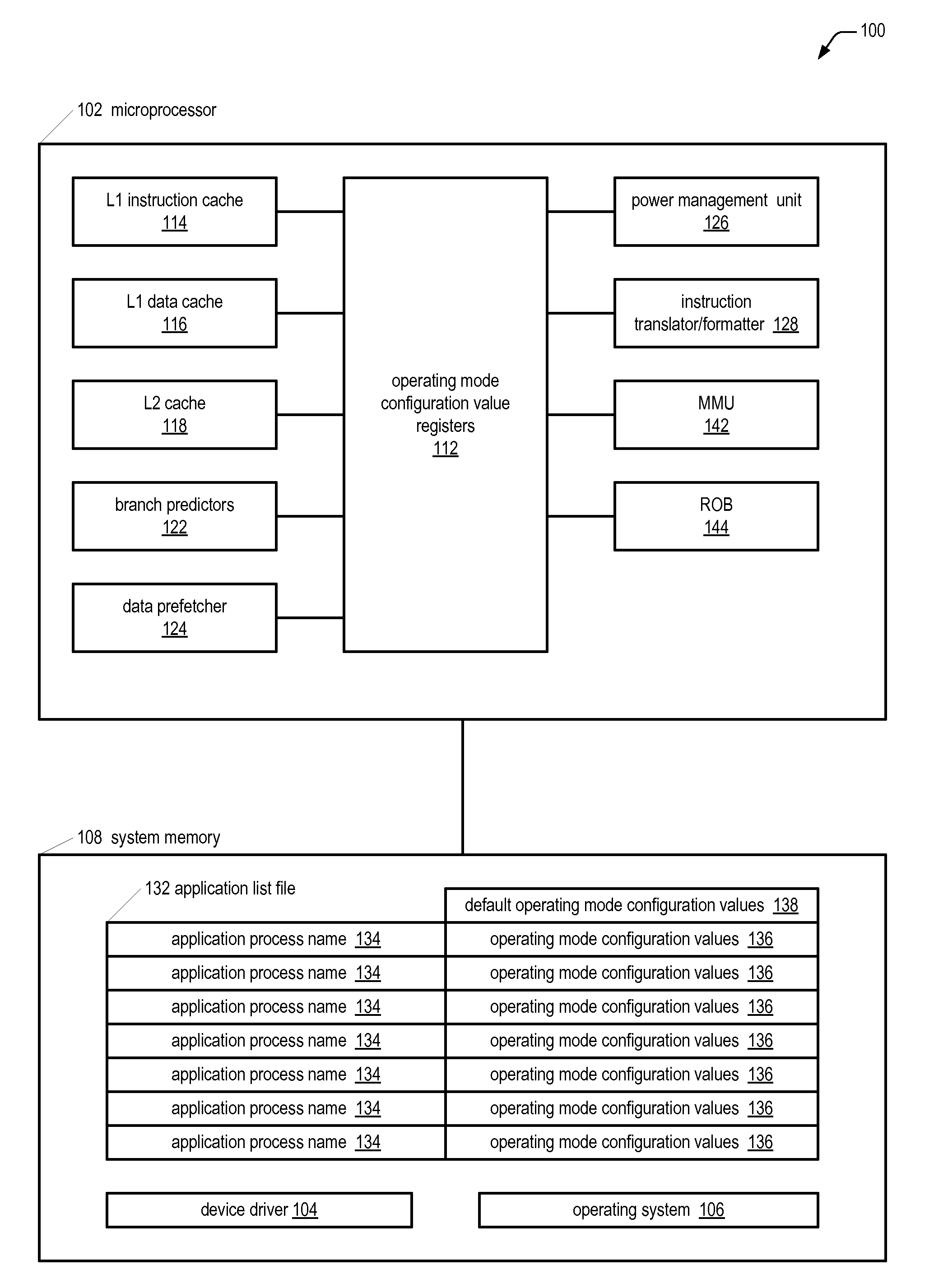
A computing system includes a microprocessor that receives values for configuring operating modes thereof. A device driver monitors which software applications currently running on the microprocessor are in a predetermined list and responsively dynamically writes the values to the microprocessor to configure its operating modes. Examples of the operating modes the device driver may configure relate to the following: data prefetching; branch prediction; instruction cache eviction; instruction execution suspension; sizes of cache memories, reorder buffer, store / load / fill queues; hashing algorithms related to data forwarding and branch target address cache indexing; number of instruction translation, formatting, and issuing per clock cycle; load delay mechanism; speculative page tablewalks; instruction merging; out-of-order execution extent; caching of non-temporal hinted data; and serial or parallel access of an L2 cache and processor bus in response to an instruction cache miss.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
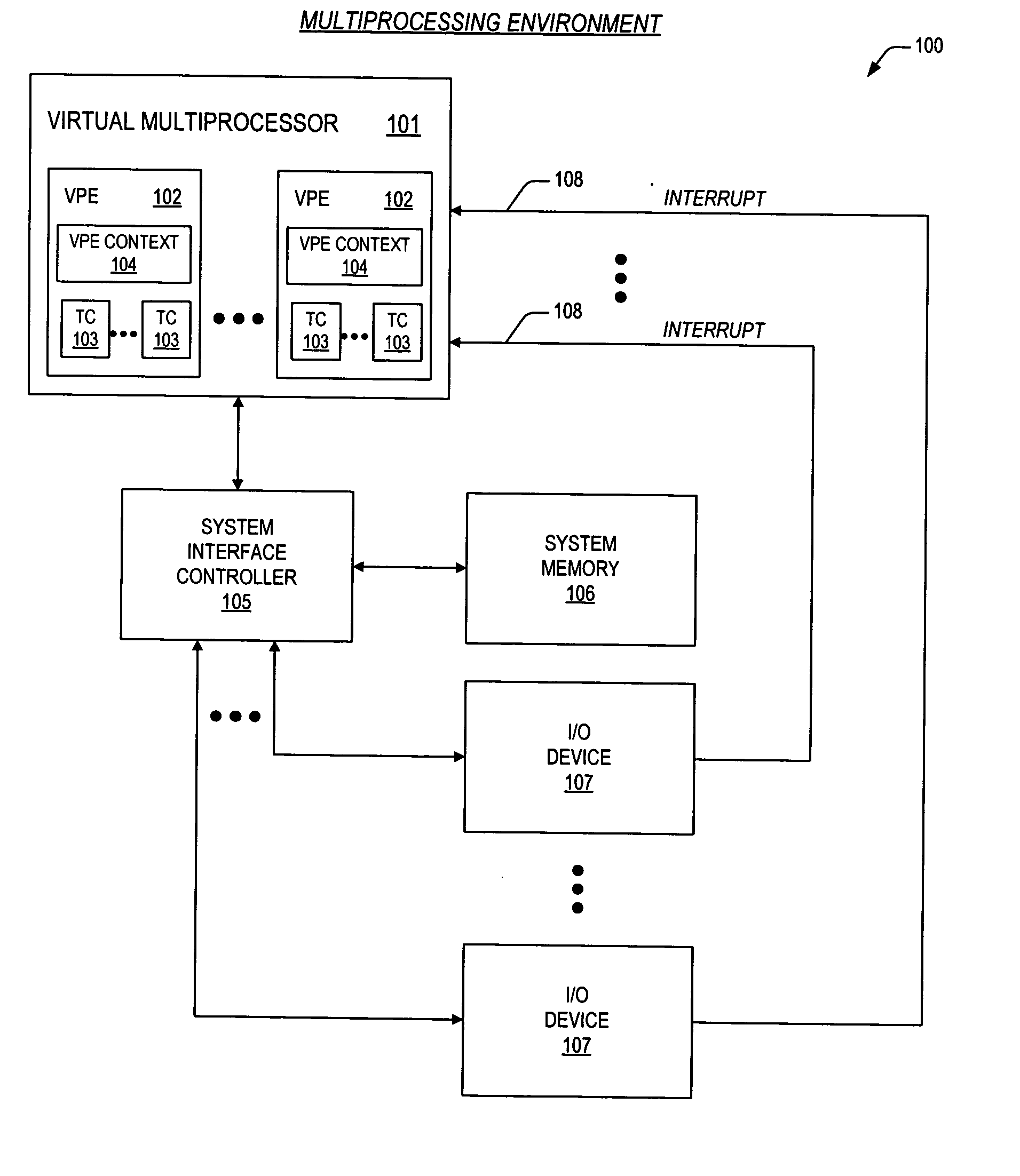
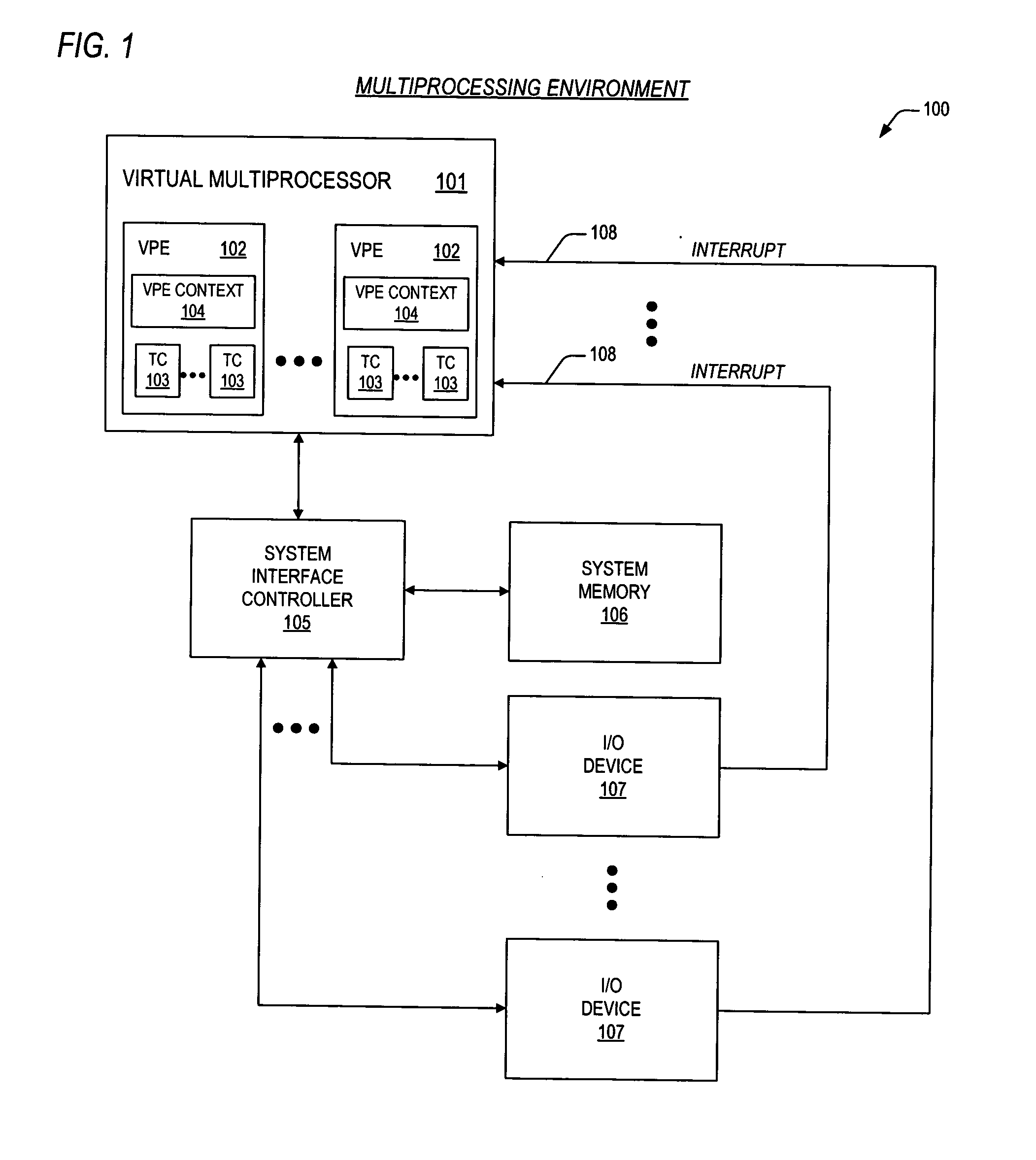
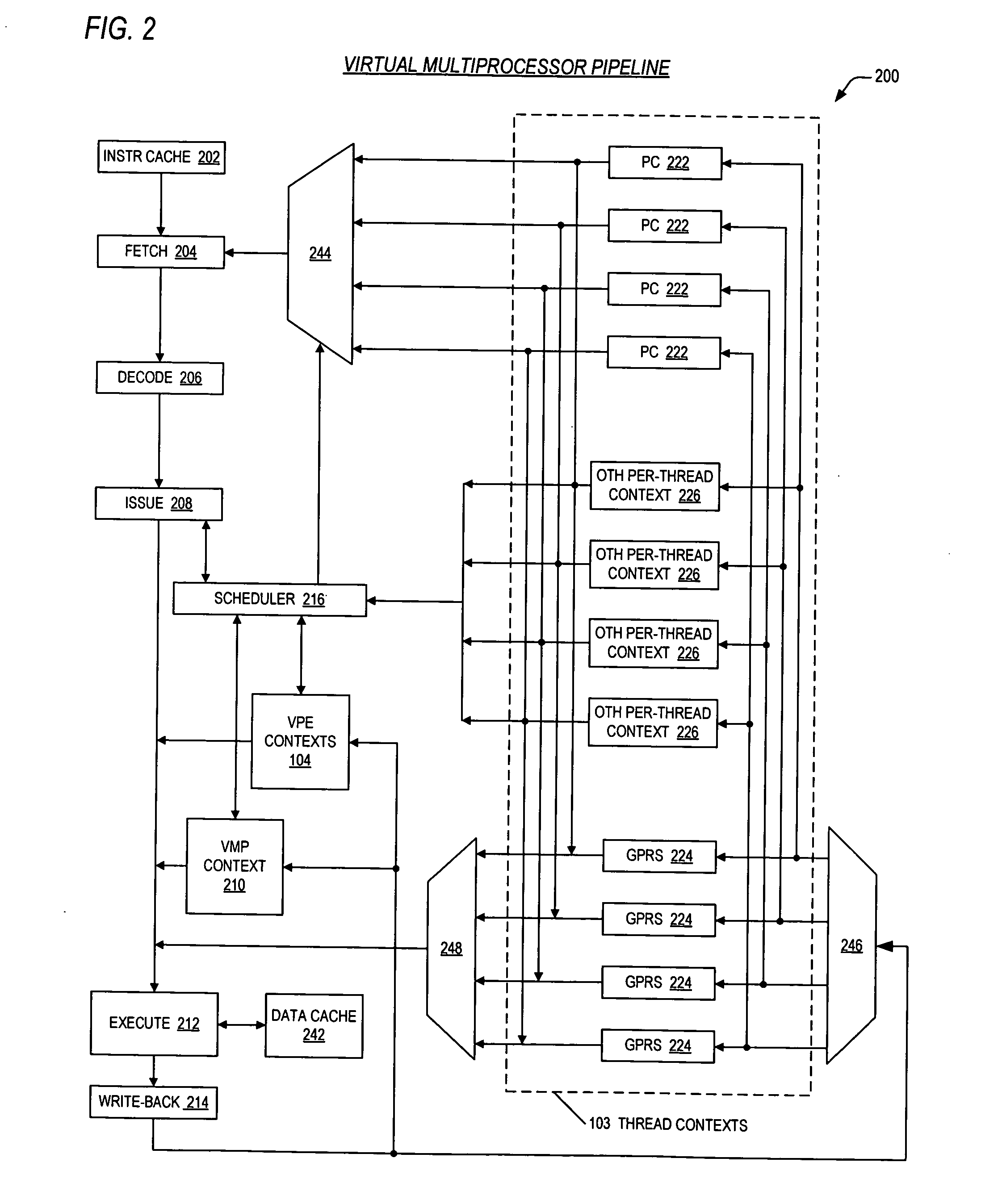
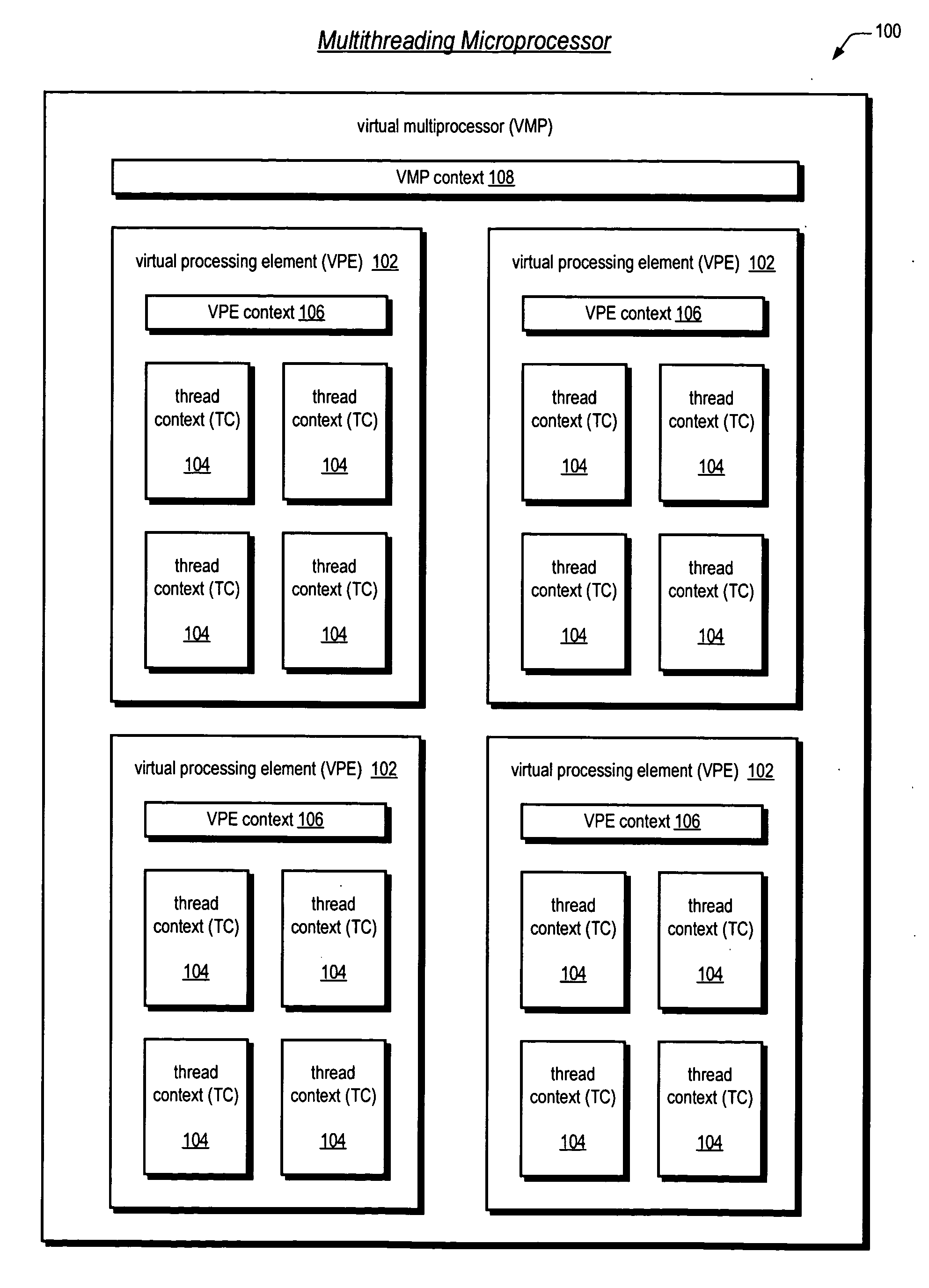
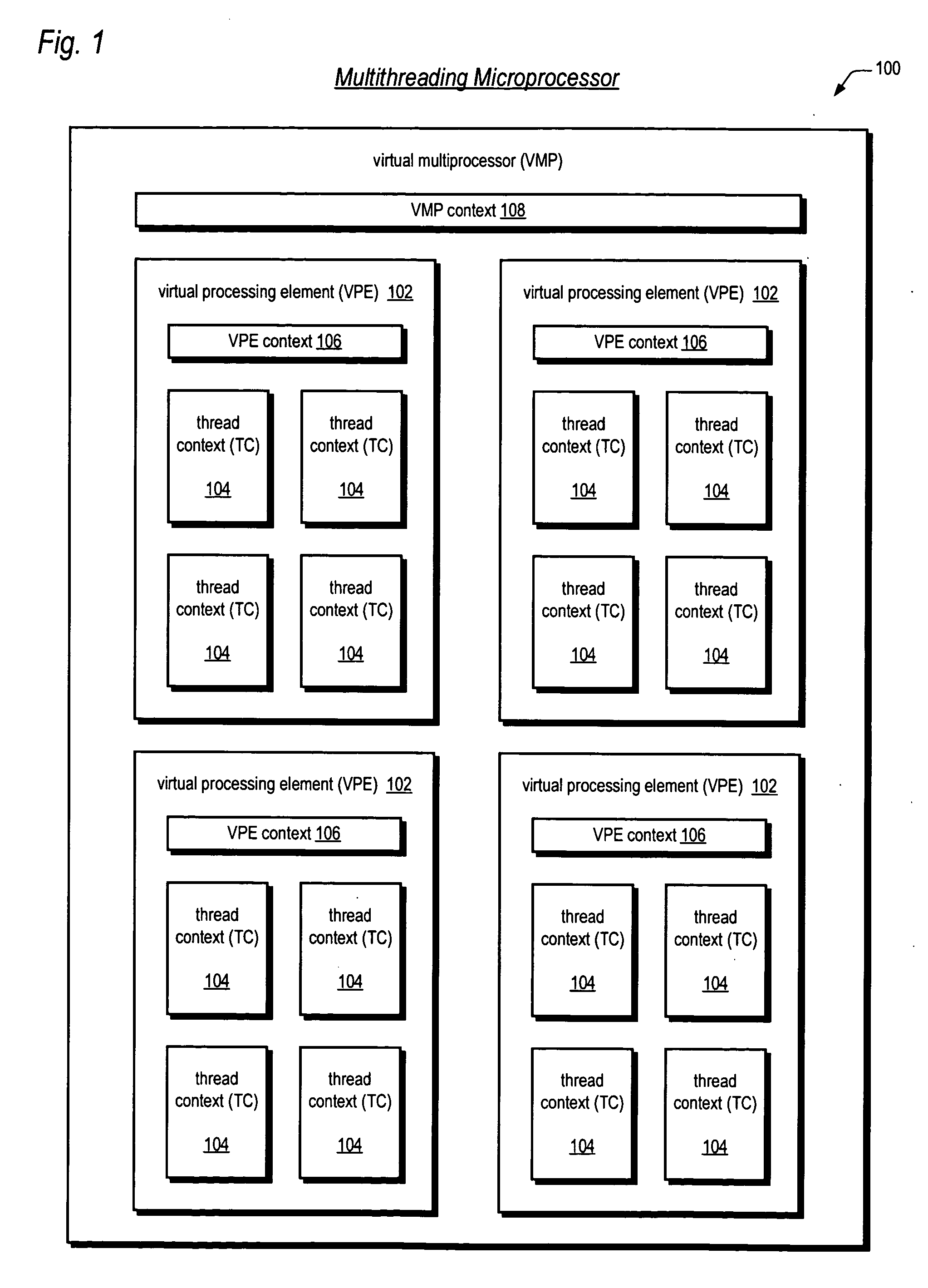
Mechanisms for dynamic configuration of virtual processor resources
ActiveUS20050125629A1Program initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringMulti processorProcessing element
Mechanisms for dynamically configuring the resources of a virtual multiprocessor are provided. The invention contemplates provision of an apparatus to configure resources for one or more virtual processing elements in a virtual multiprocessor. The apparatus includes a virtual multiprocessor context, one or more virtual processing element contexts, and configuration logic. The virtual multiprocessor context, prescribes the resources, and controls a configuration state of the virtual multiprocessor. The one or more virtual processing element contexts each exclusively correspond to one of the one or more virtual processing elements. The one or more virtual processing element contexts each have first logic, for prescribing whether the one of the one or more virtual processing elements is permitted to configure the resources; and second logic, for prescribing a subset of the resources that is allocated to said one of the one or more virtual processing elements. The configuration logic is coupled to the virtual multiprocessor context and the one or more virtual processing element contexts. The configuration logic detects whether the one of the one or more virtual processing elements is permitted to configure the resources, updates the virtual multiprocessor context to direct that the virtual multiprocessor enter the configuration state, and configures the resources by updating a prescribed virtual processing element context.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
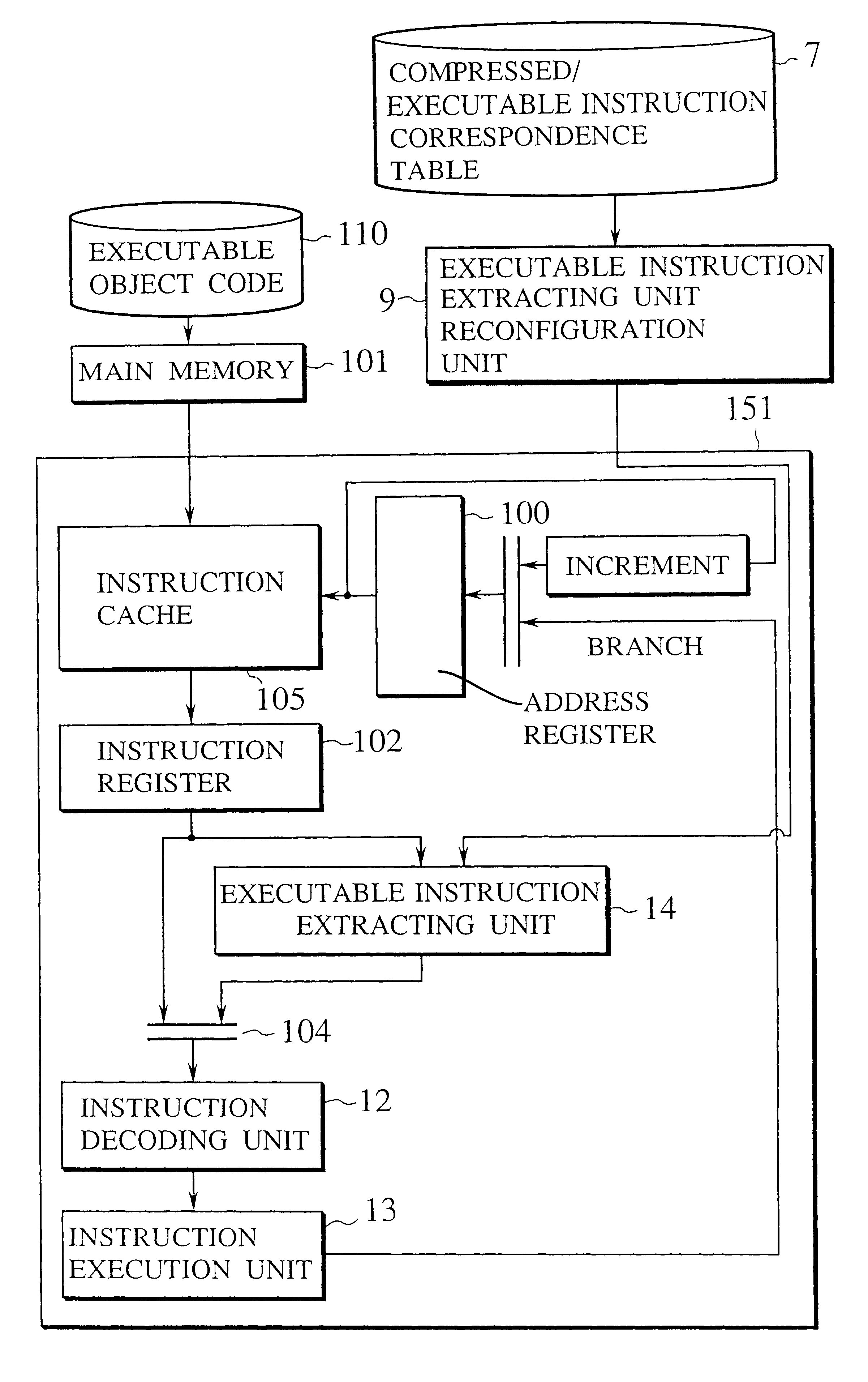
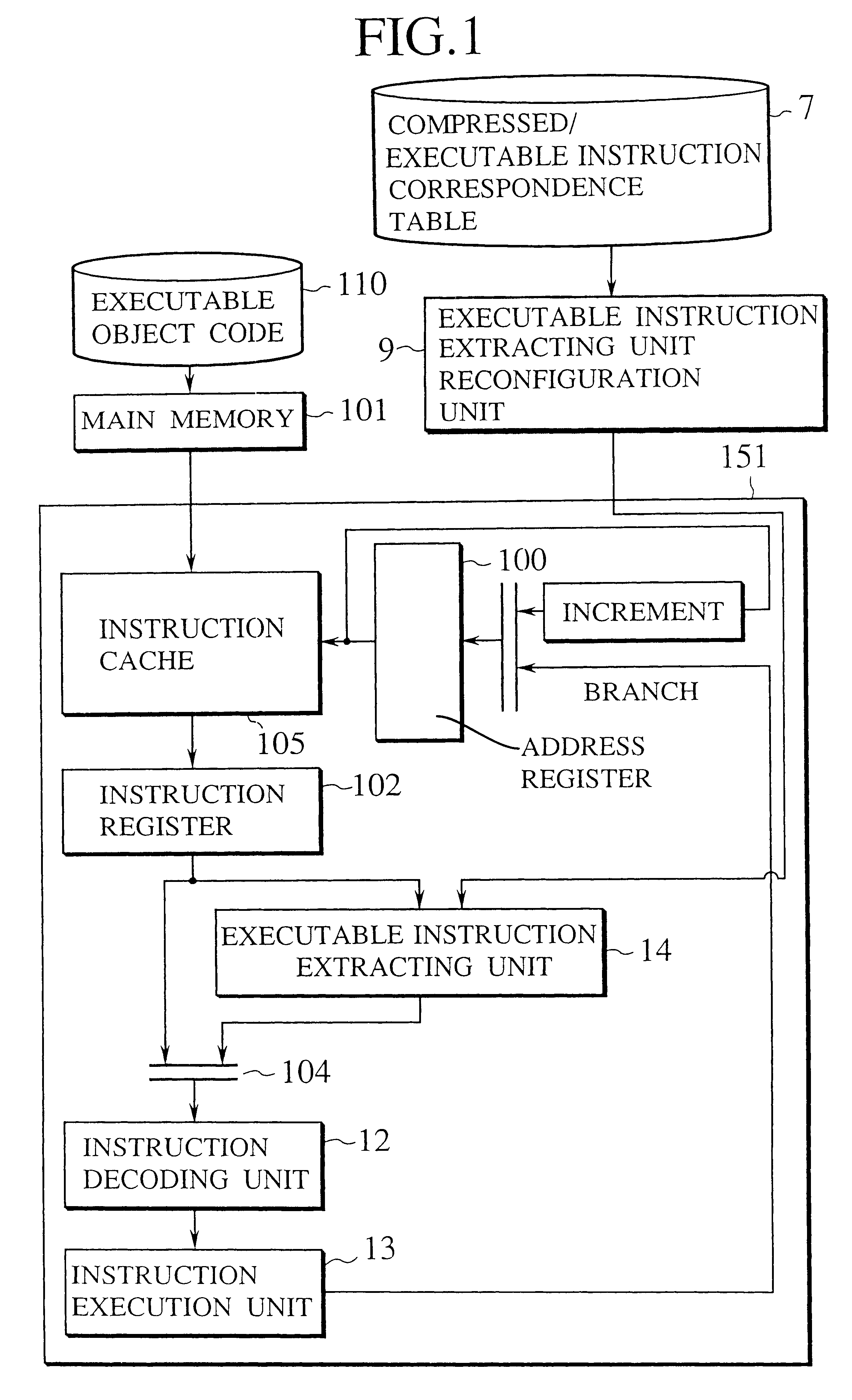
Information processing apparatus provided with an optimized executable instruction extracting unit for extending compressed instructions
InactiveUS6587939B1Reduce the numberData processing applicationsRuntime instruction translationInformation processingInstruction unit
An information processing apparatus is provided with a executable instruction extracting unit which is reconfigured by means of a executable instruction extracting unit reconfiguration unit with reference to a compressed / executable instruction correspondence table optimized for the respective executable program, which has been made up with an compressed instruction. The compressed instruction is extended into the corresponding executable instructions by means of the executable instruction extracting unit as reconfigured.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for performing multiple types of multiplication including signed and unsigned multiplication
InactiveUS6144980ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesControl signalOperand
A multiplier capable of performing both signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured for use in a microprocessor and may include a partial product generator, a selection logic unit, and an adder. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. The multiplier is also configured to receive a first control signal indicative of whether signed or unsigned multiplication is to be performed and a second control signal indicative of whether vector multiplication is to be performed. The multiplier is configured to calculate an effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands based upon each operand's most significant bit and the control signal. The effective signs may then be used by the partial product generation unit and the selection logic to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, the adder is configured to sum them and output the results, which may be signed or unsigned. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier is configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Shared FP and SIMD 3D multiplier
InactiveUS6490607B1Computations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationComputerized systemTheoretical computer science
A multiplier configured to perform multiplication of both scalar floating point values (XxY) and packed floating point values (i.e., X1xY1 and X2xY2). In addition, the multiplier may be configured to calculate XxY-Z. The multiplier comprises selection logic for selecting source operands, a partial product generator, an adder tree, and two or more adders configured to sum the results from the adder tree to achieve a final result. The multiplier may also be configured to perform iterative multiplication operations to implement such arithmetical operations such as division and square root. The multiplier may be configured to generate two versions of the final result, one assuming there is an overflow, and another assuming there is not an overflow. A computer system and method for performing multiplication are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Method and apparatus for rounding and normalizing results within a multiplier
InactiveUS6269384B1Computations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Integrated mechanism for suspension and deallocation of computational threads of execution in a processor
ActiveUS20050125795A1Valuable opcode spaceLittle overheadProgram initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringOperandProgram Thread
A yield instruction for execution in a multithreaded microprocessor is disclosed. The yield instruction includes an operand. If the operand is zero the microprocessor terminates the program thread including the yield instruction. If the operand is −1 the microprocessor unconditionally reschedules the program thread. If the operand is a positive integer the microprocessor views the operand as a bit vector specifying one or more yield qualifier inputs, such as interrupt signals, and conditionally reschedules the thread based on the qualifier inputs and bit vector values. The microprocessor also includes a mask register that specifies a bit vector of the qualifier inputs. If the operand specifies a qualifier input not also specified in the mask register, an exception to the instruction is raised. The instruction returns a value specifying the values of the qualifier inputs qualified by the mask register value.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Method and apparatus for simultaneously multiplying two or more independent pairs of operands and calculating a rounded products
InactiveUS6038583ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
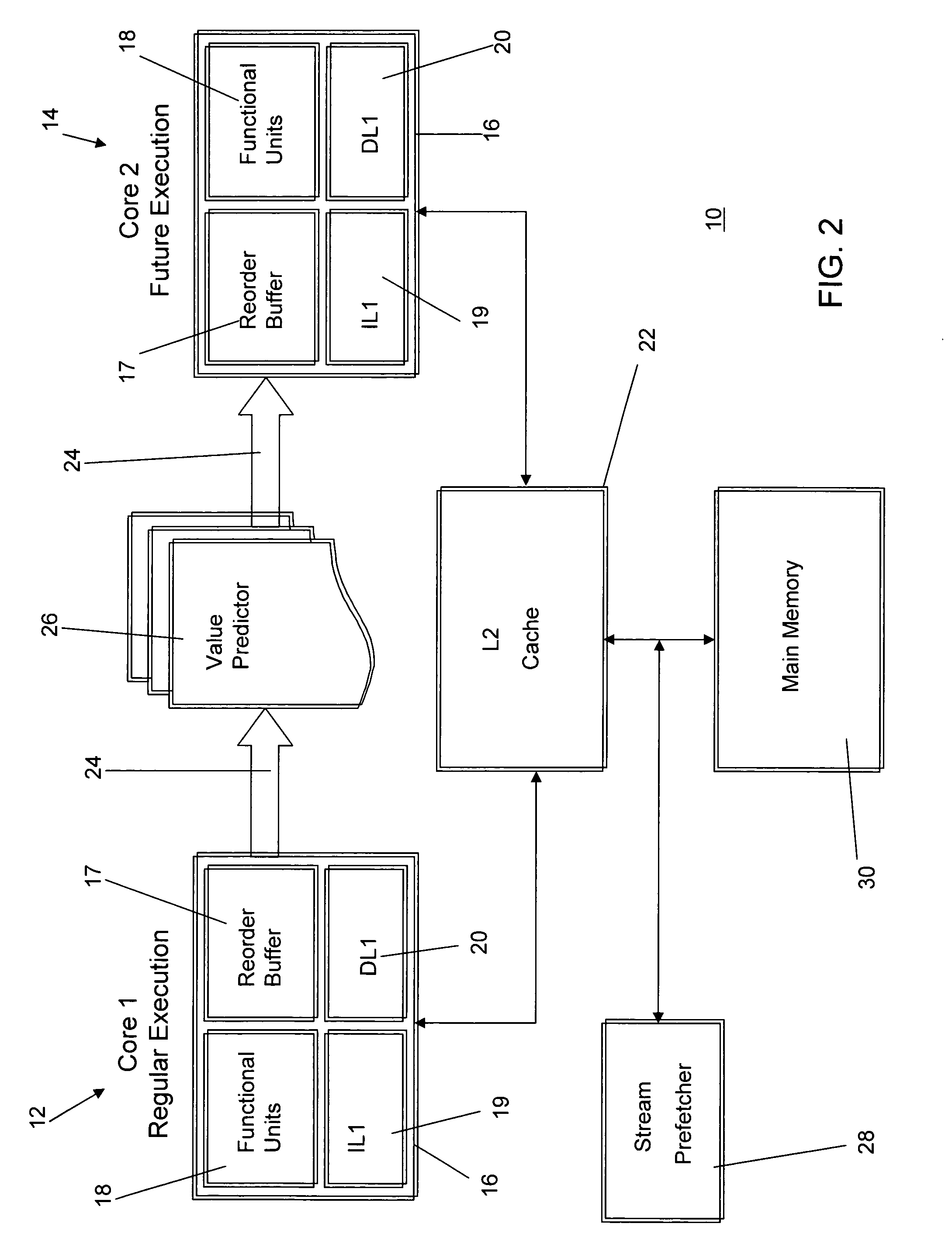
Future execution prefetching technique and architecture
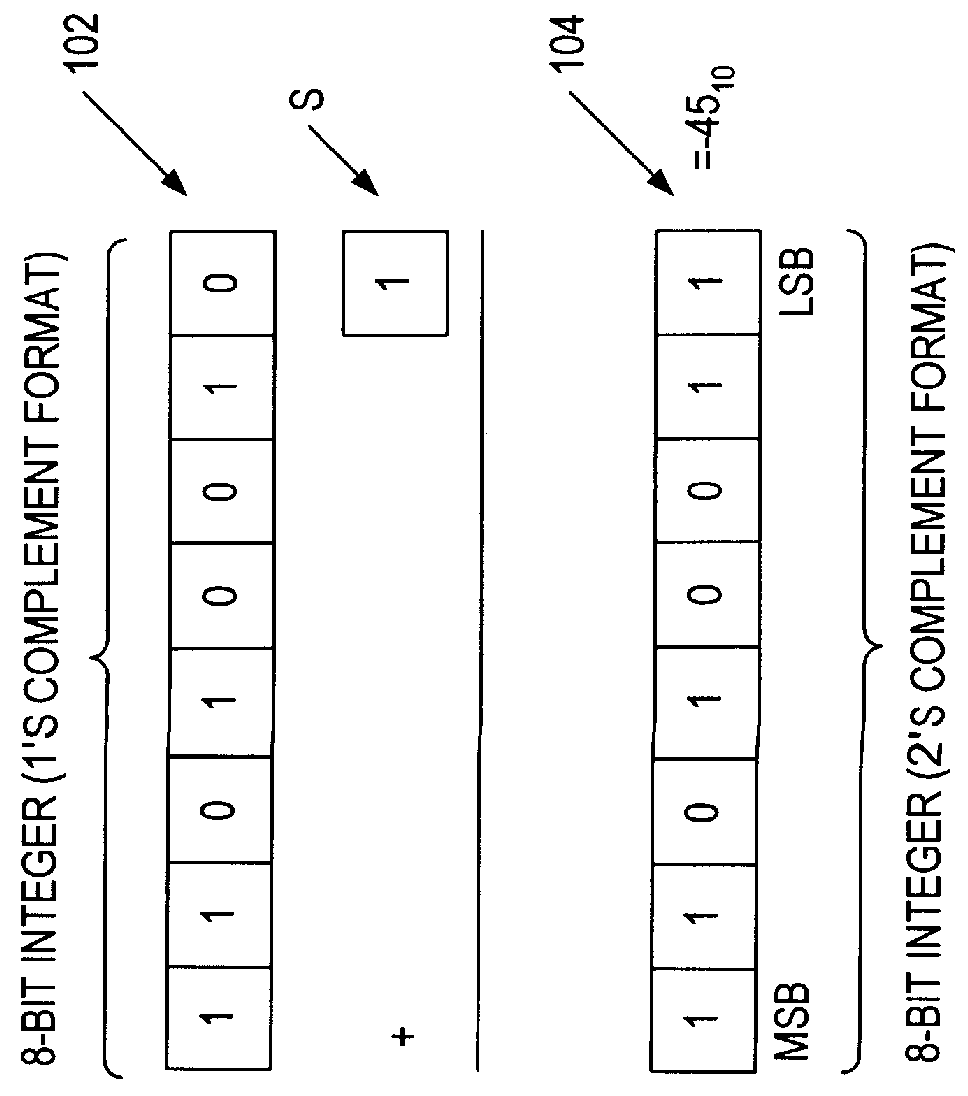
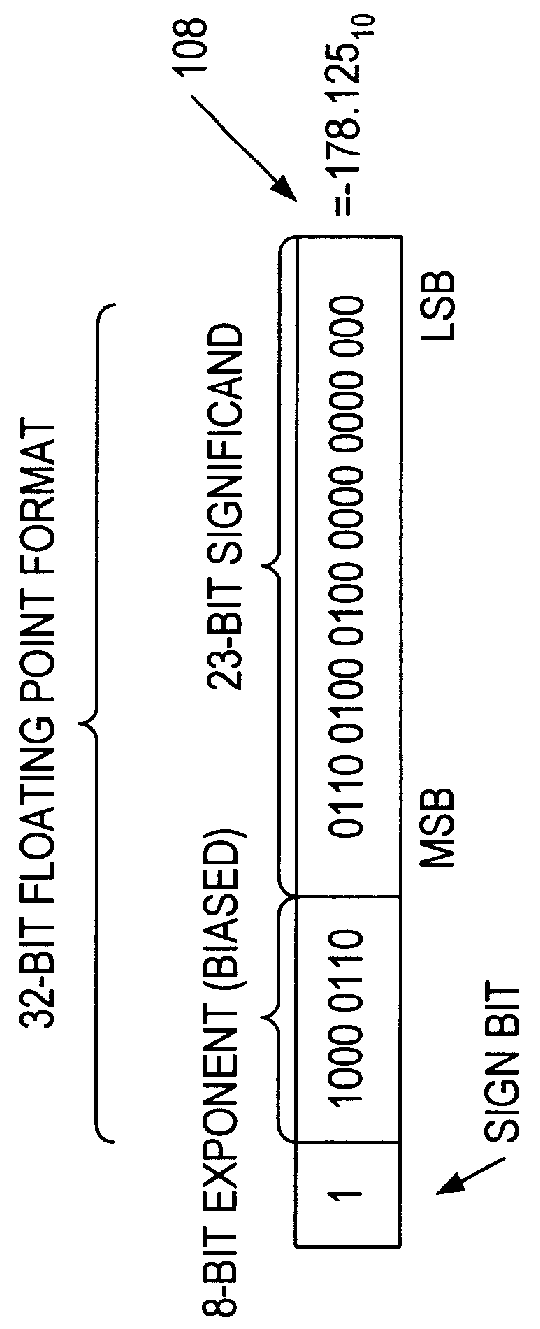
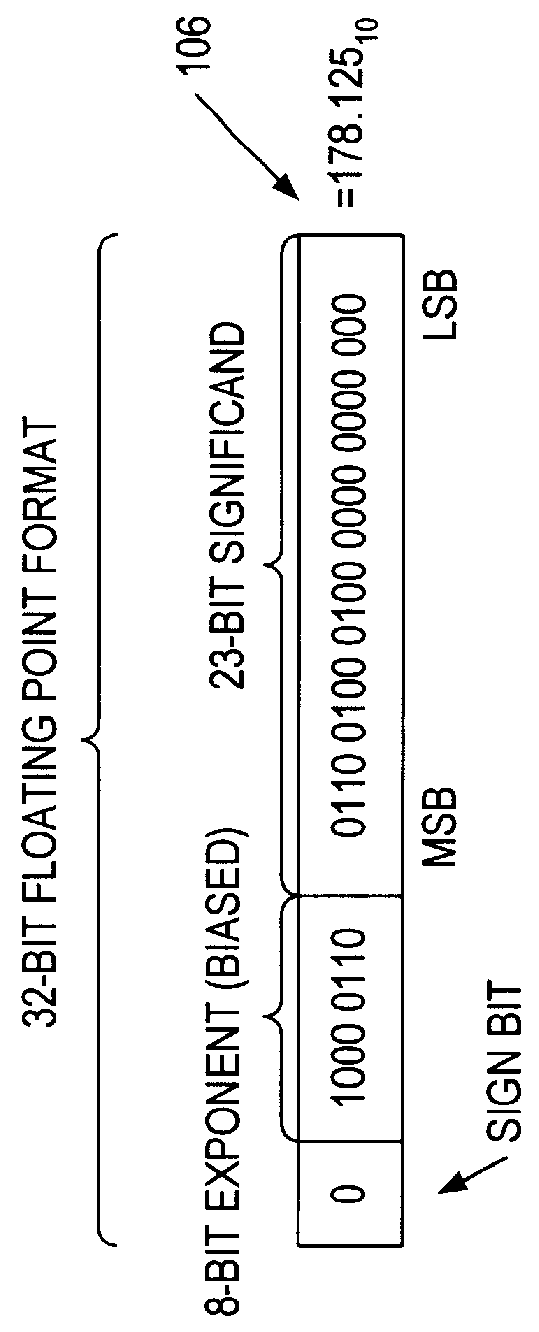
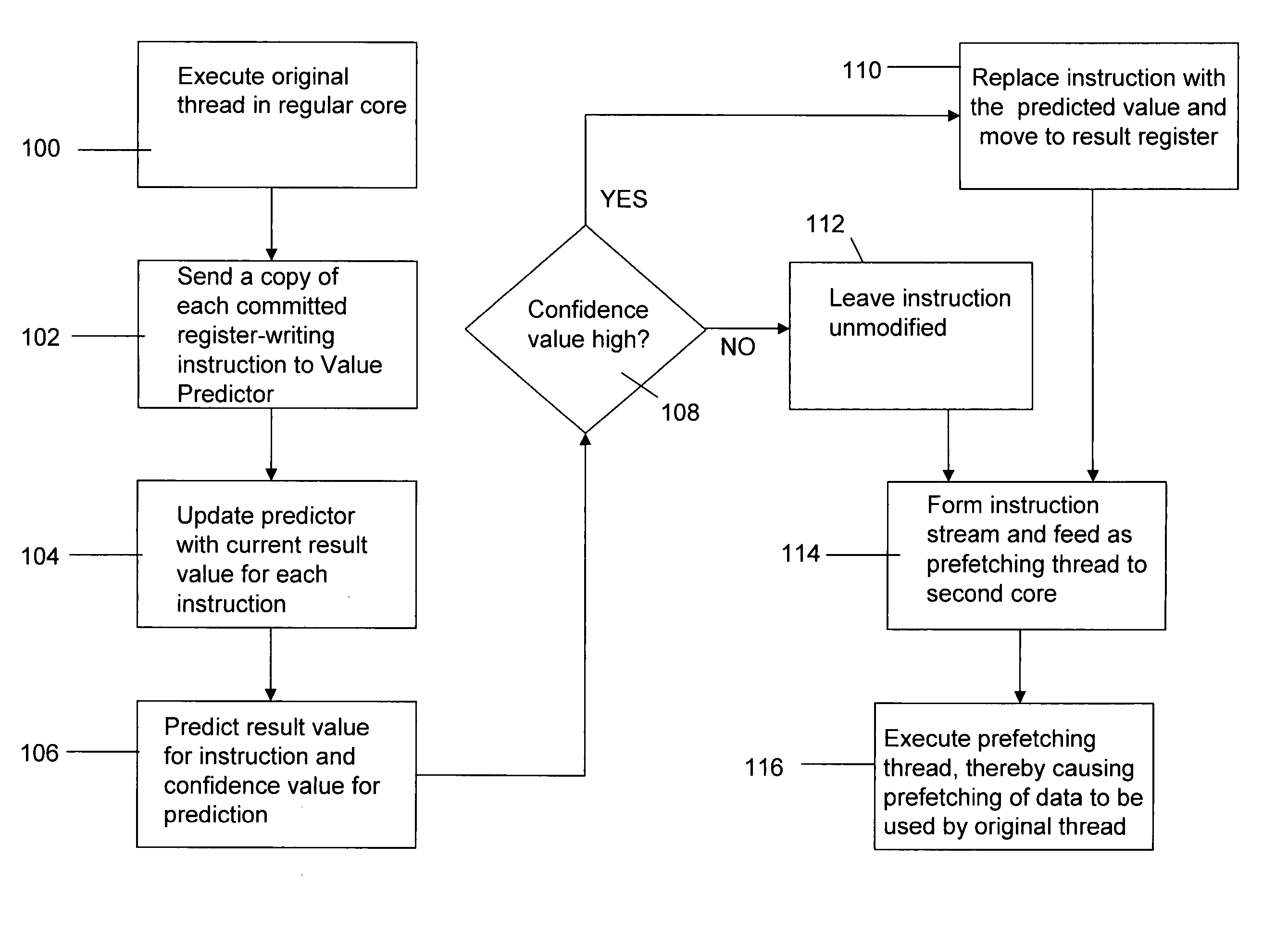
ActiveUS20070174555A1Lower performance requirementsIncreased complexityRuntime instruction translationMemory systemsAccess timeTerm memory
A prefetching technique referred to as future execution (FE) dynamically creates a prefetching thread for each active thread in a processor by simply sending a copy of all committed, register-writing instructions in a primary thread to an otherwise idle processor. On the way to the second processor, a value predictor replaces each predictable instruction with a load immediate instruction, where the immediate is the predicted result that the instruction is likely to produce during its nth next dynamic execution. Executing this modified instruction stream (i.e., the prefetching thread) in another processor allows computation of the future results of the instructions that are not directly predictable. This causes the issuance of prefetches into the shared memory hierarchy, thereby reducing the primary thread's memory access time and speeding up the primary thread's execution.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
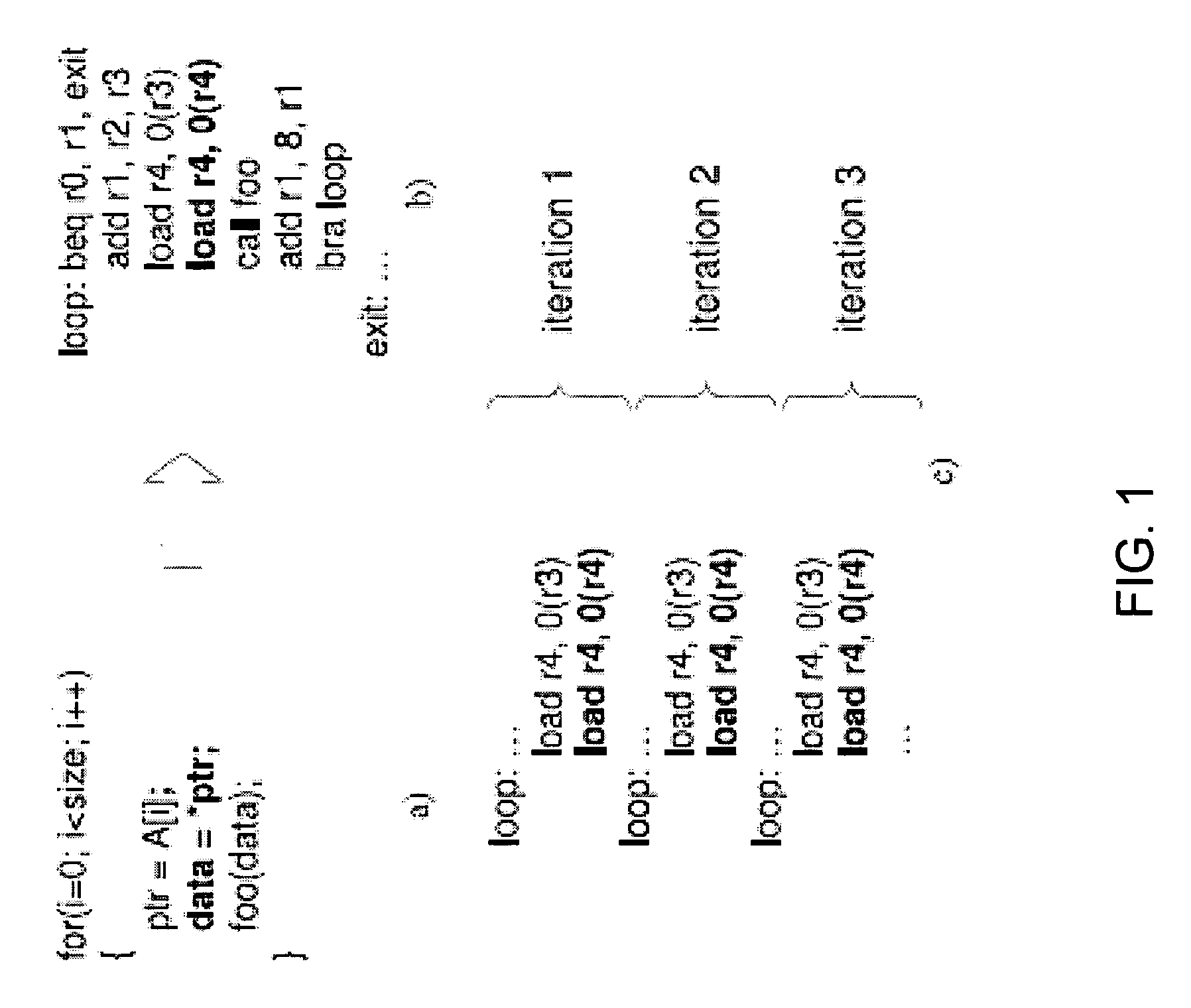
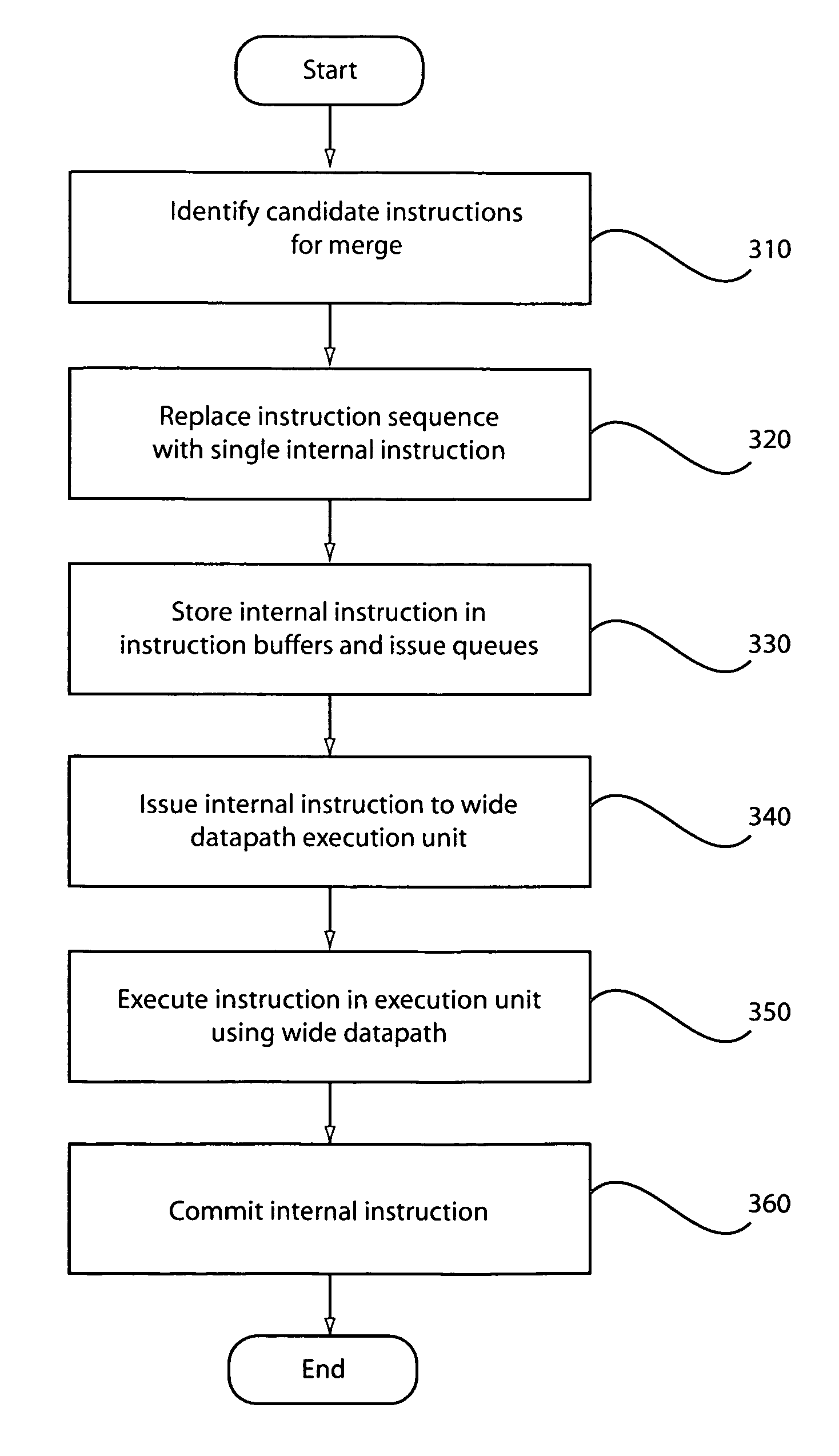
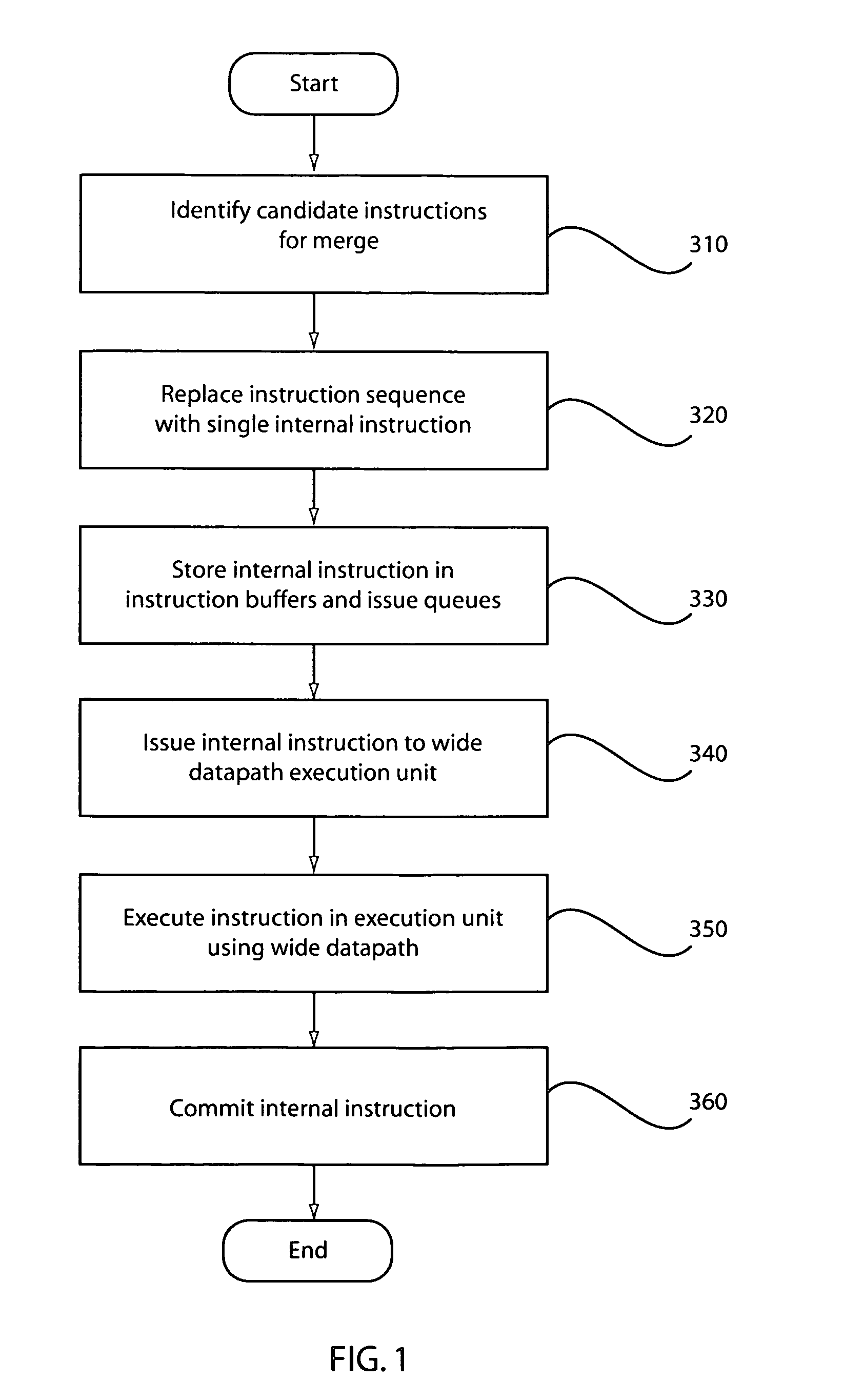
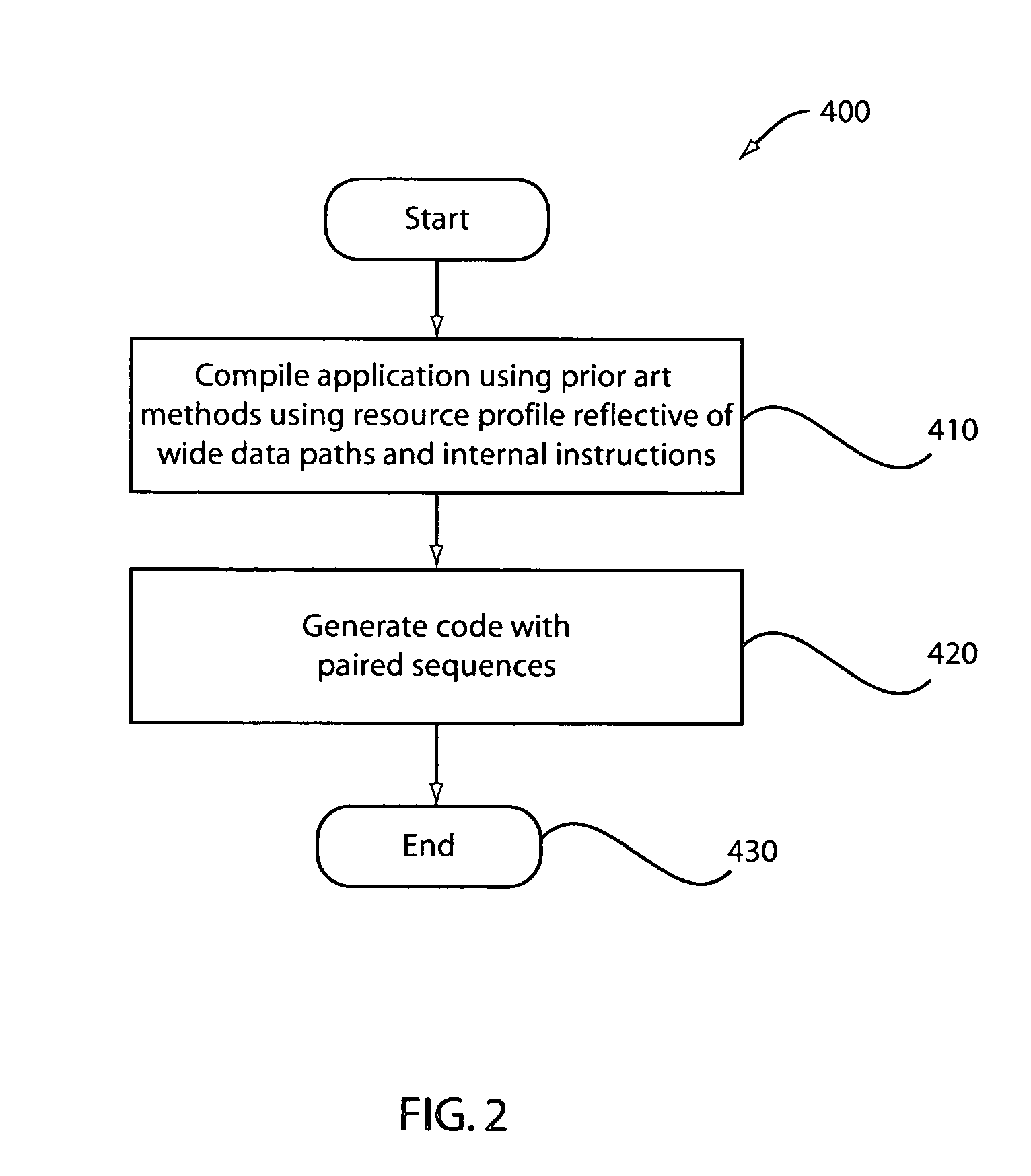
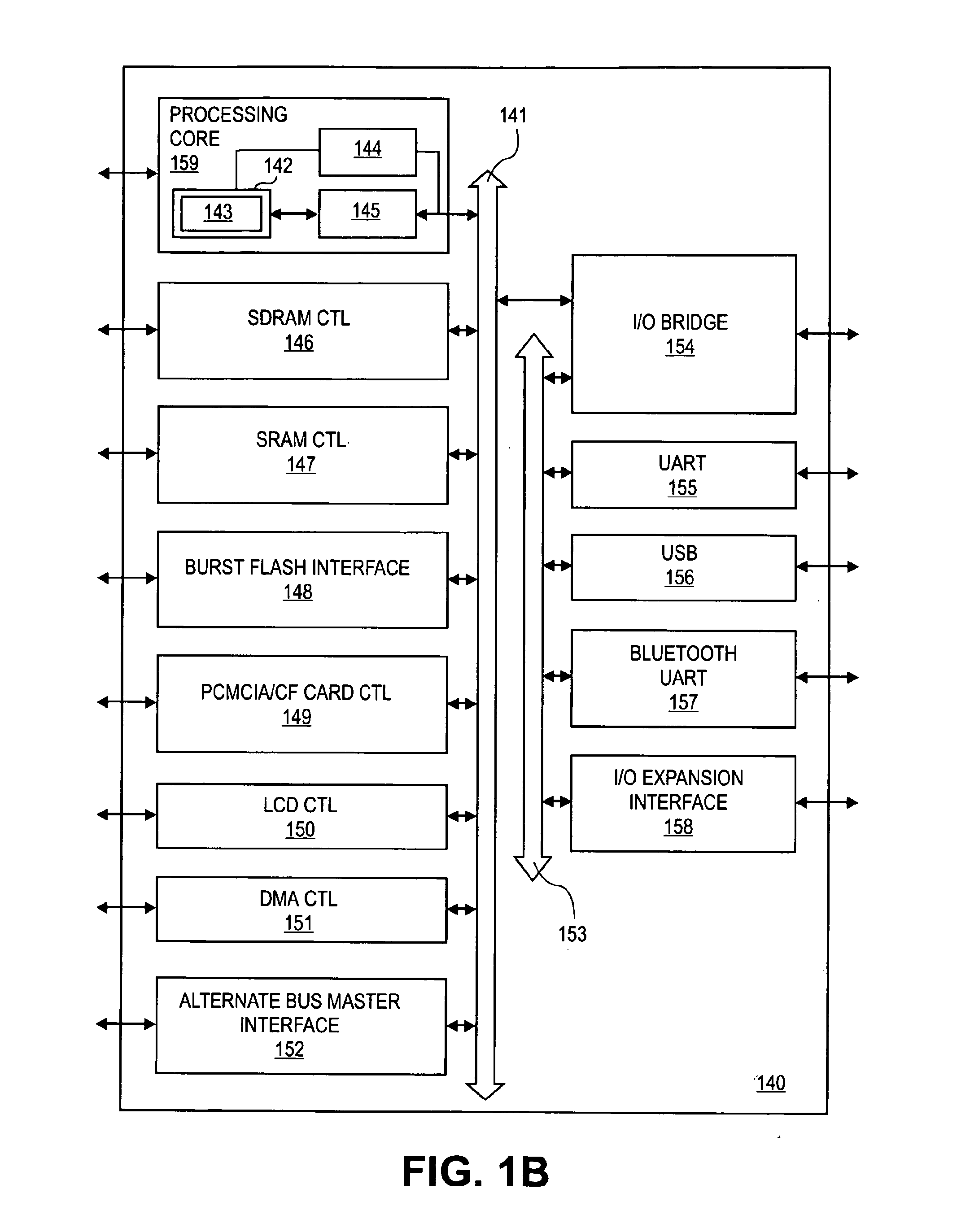
Method and apparatus for the dynamic creation of instructions utilizing a wide datapath
ActiveUS20070260855A1Maintain compatibilityImprove performanceRegister arrangementsInstruction analysisInstruction memoryExecution unit
A processing system and method includes a predecoder configured to identify instructions that are combinable. Instruction storage is configured to merge instructions that are combinable by replacing the combinable instructions with a wide data internal instruction for execution. An instruction execution unit is configured to execute the internal instruction on a wide datapath.
Owner:IBM CORP
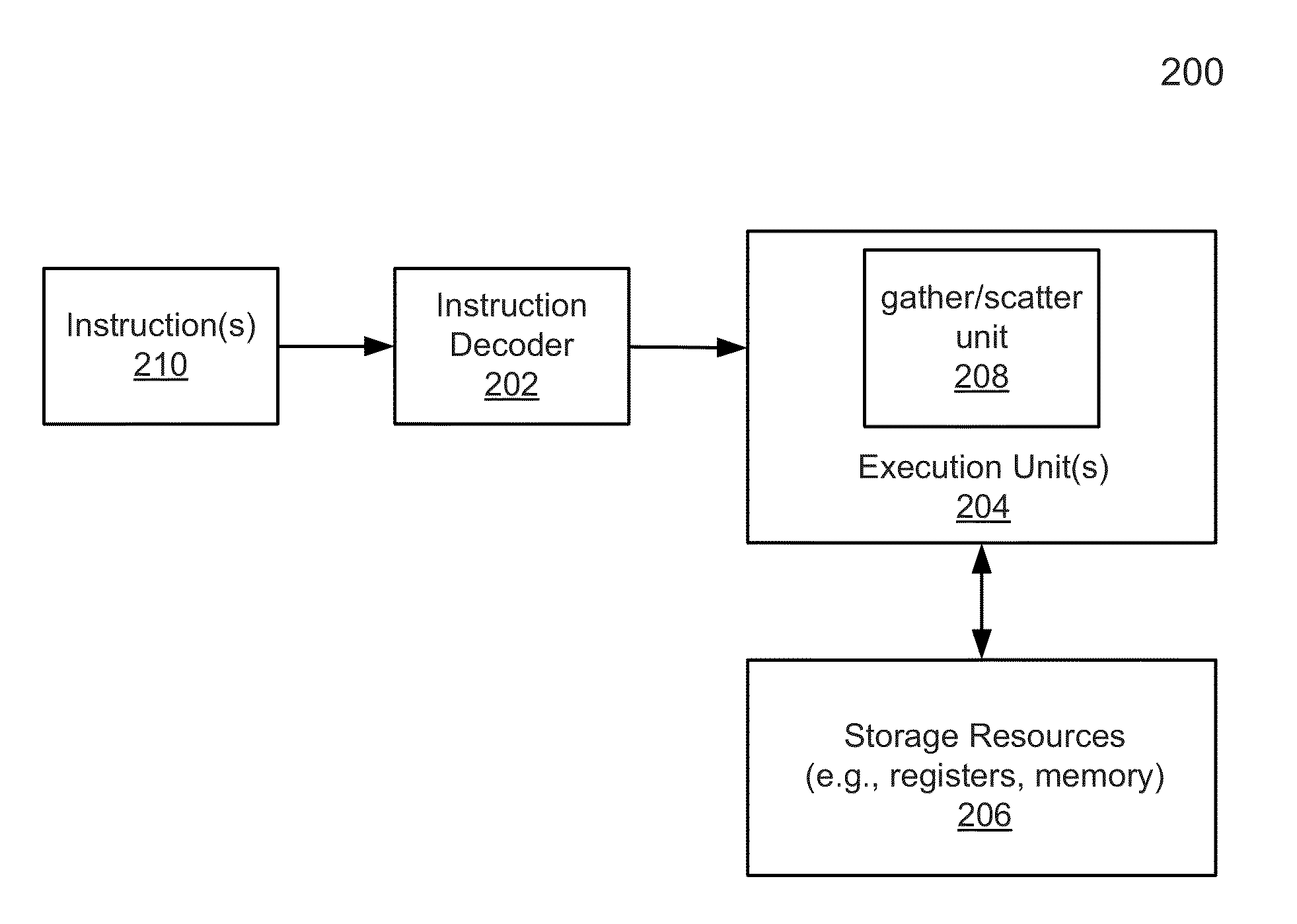
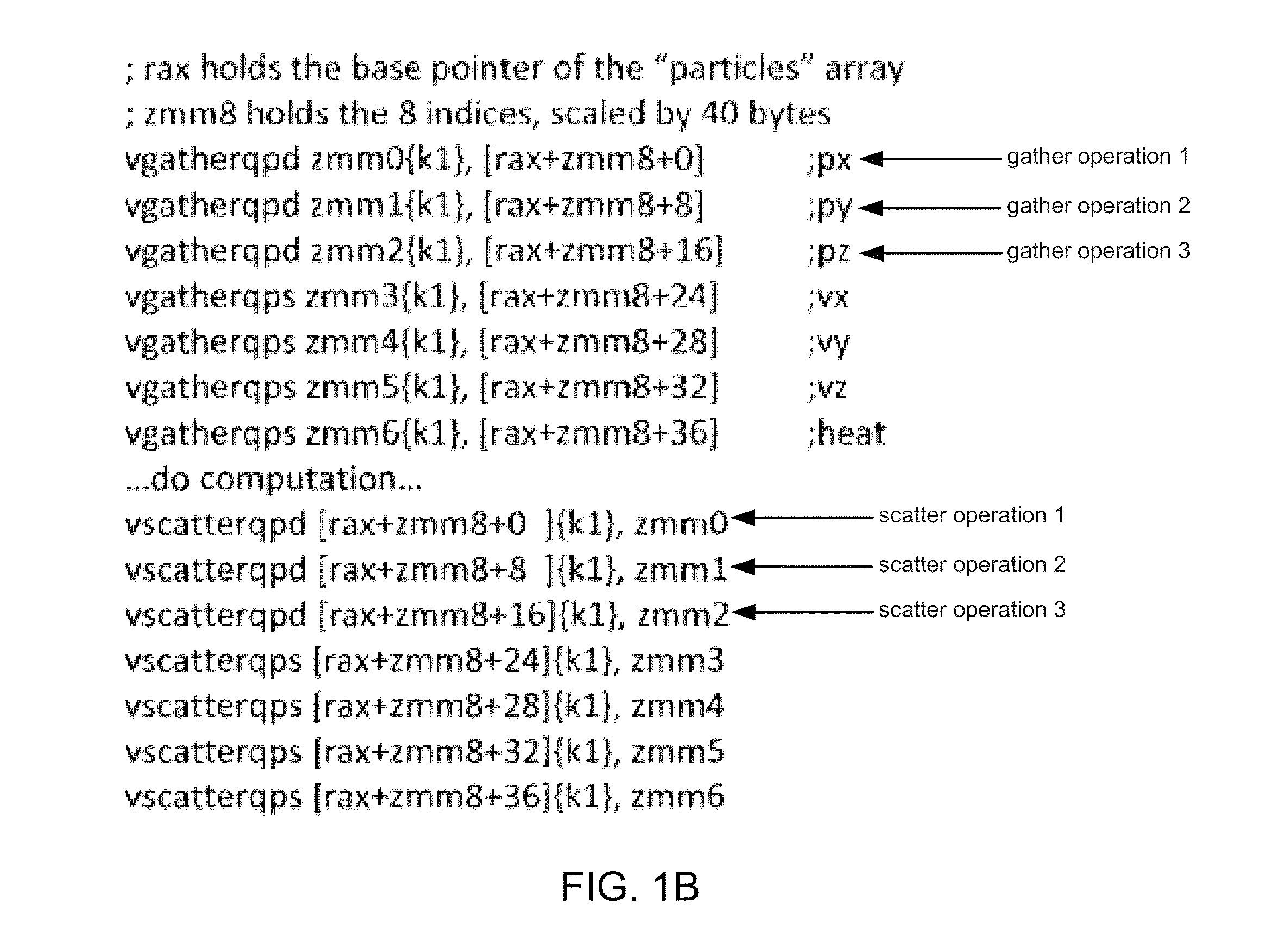
Coalescing adjacent gather/scatter operations
ActiveUS20140181464A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsMemory addressExecution unit
According to one embodiment, a processor includes an instruction decoder to decode a first instruction to gather data elements from memory, the first instruction having a first operand specifying a first storage location and a second operand specifying a first memory address storing a plurality of data elements. The processor further includes an execution unit coupled to the instruction decoder, in response to the first instruction, to read contiguous a first and a second of the data elements from a memory location based on the first memory address indicated by the second operand, and to store the first data element in a first entry of the first storage location and a second data element in a second entry of a second storage location corresponding to the first entry of the first storage location.
Owner:INTEL CORP
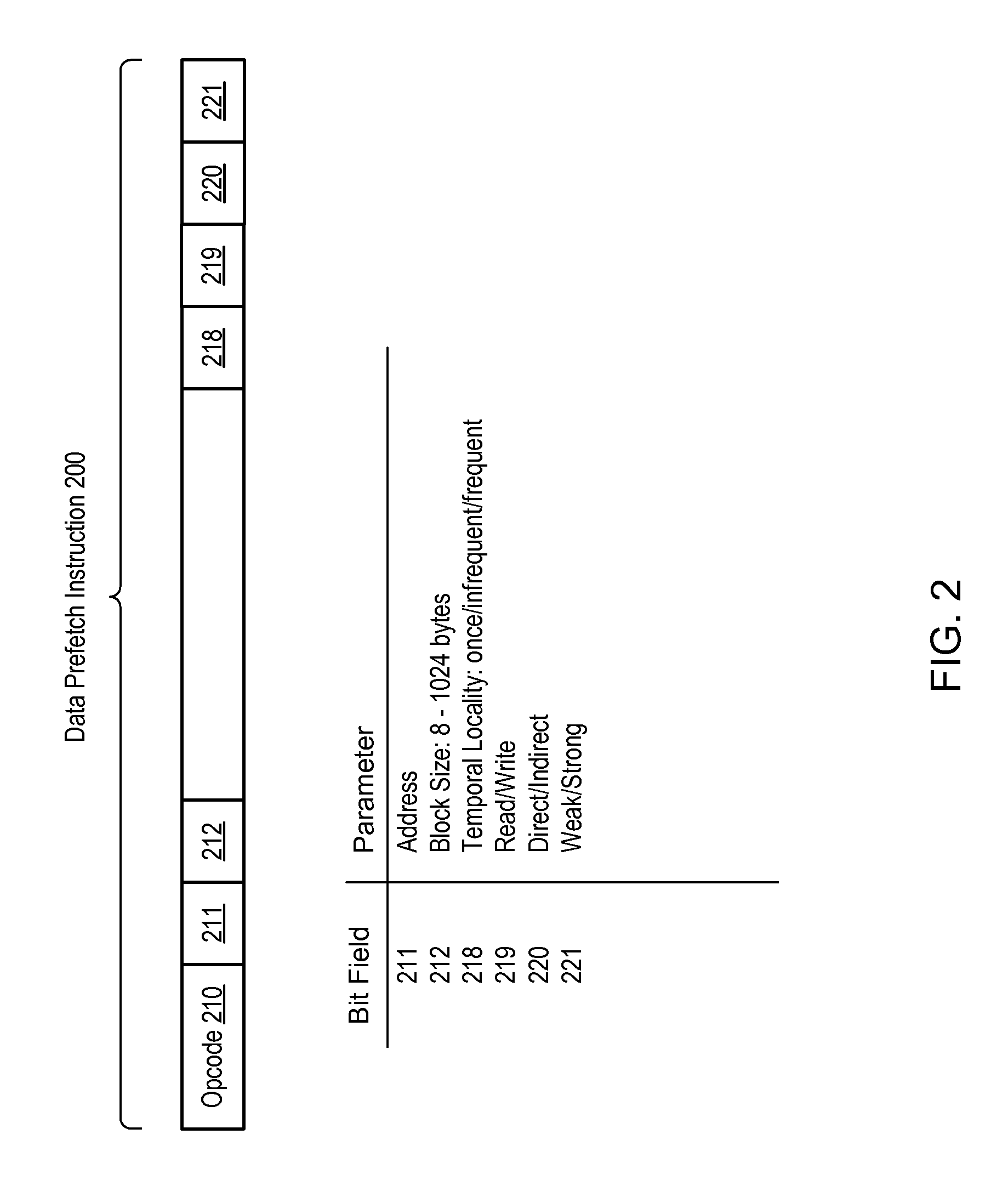
Prefetch instruction extensions
ActiveUS20090138661A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRuntime instruction translationMemory addressComputerized system
A computer system and method. In one embodiment, a computer system comprises a processor and a cache memory. The processor executes a prefetch instruction to prefetch a block of data words into the cache memory. In one embodiment, the cache memory comprises a plurality of cache levels. The processor selects one of the cache levels based on a value of a prefetch instruction parameter indicating the temporal locality of data to be prefetched. In a further embodiment, individual words are prefetched from non-contiguous memory addresses. A single execution of the prefetch instruction allows the processor to prefetch multiple blocks into the cache memory. The number of data words in each block, the number of blocks, an address interval between each data word of each block, and an address interval between each block to be prefetched are indicated by parameters of the prefetch instruction.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and apparatus for achieving higher frequencies of exactly rounded results
InactiveUS6134574ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesBinary multiplierOperand
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
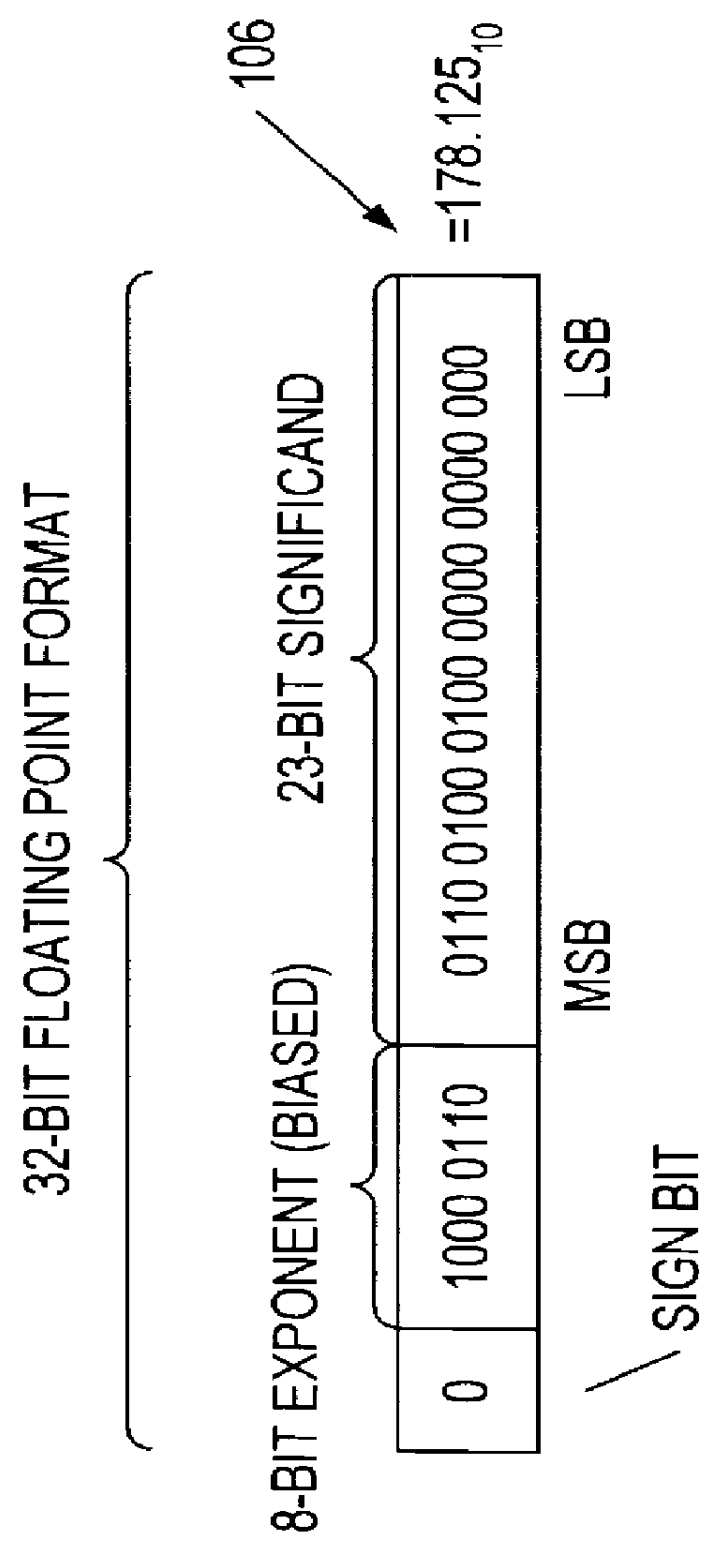
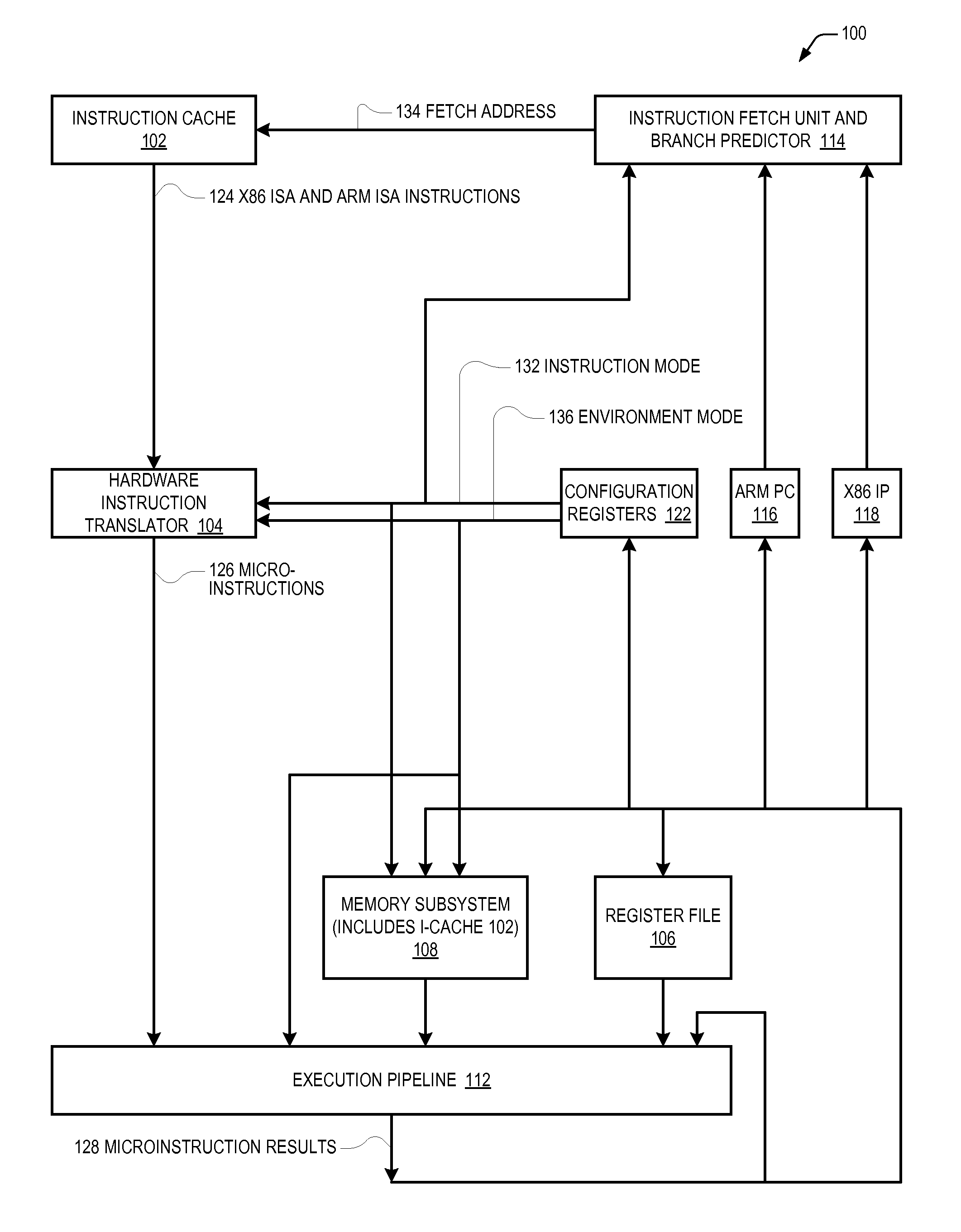
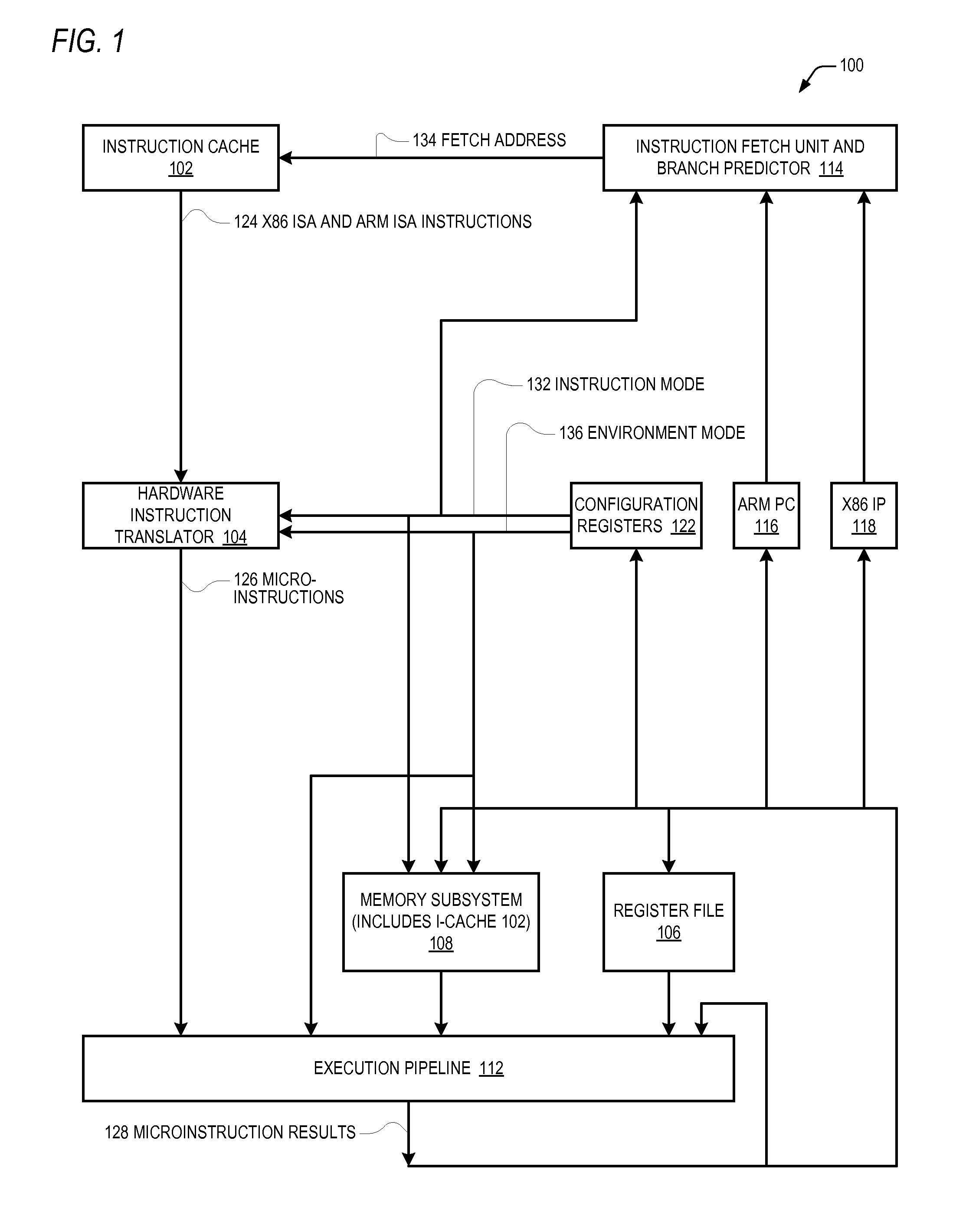
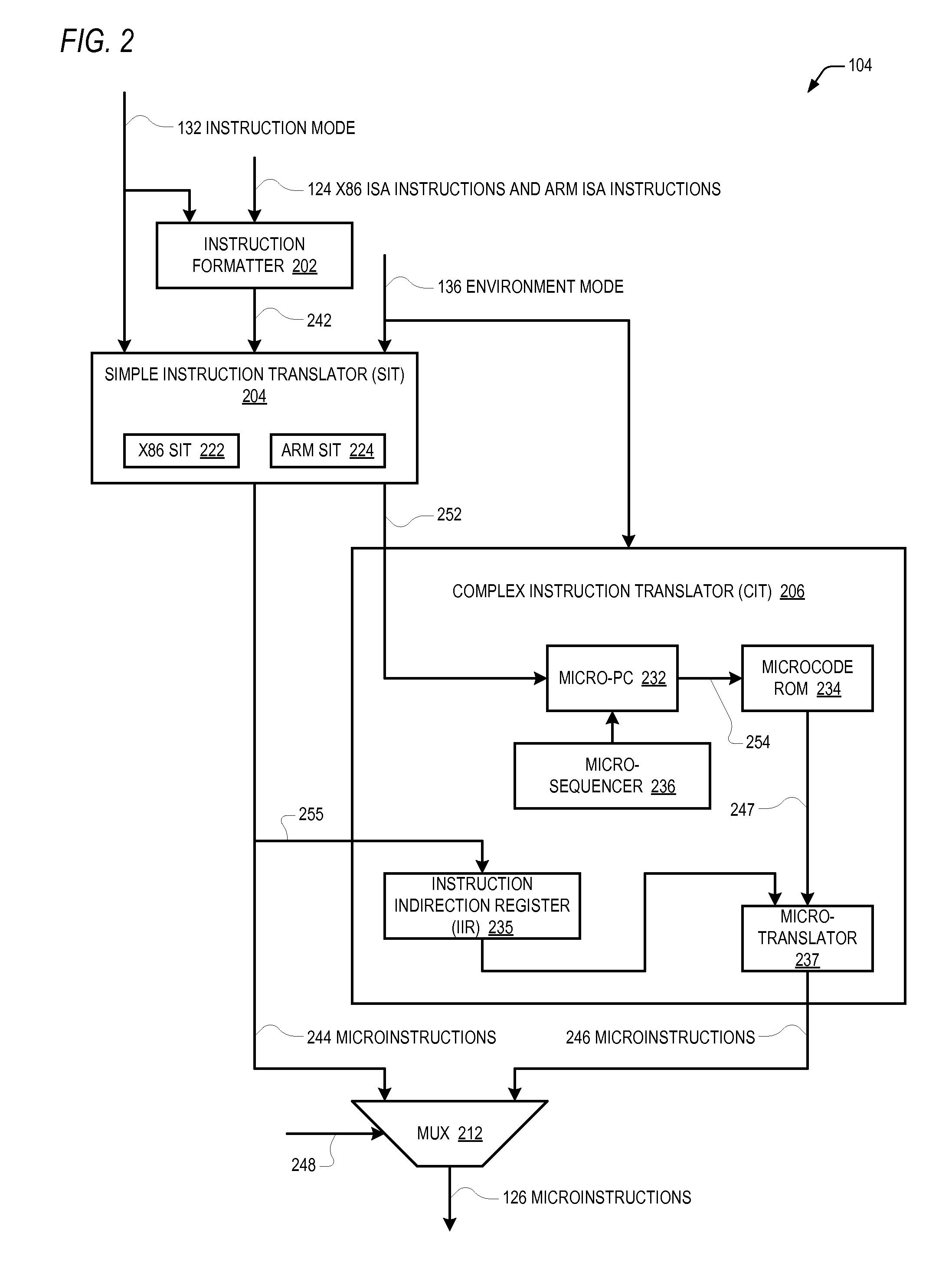
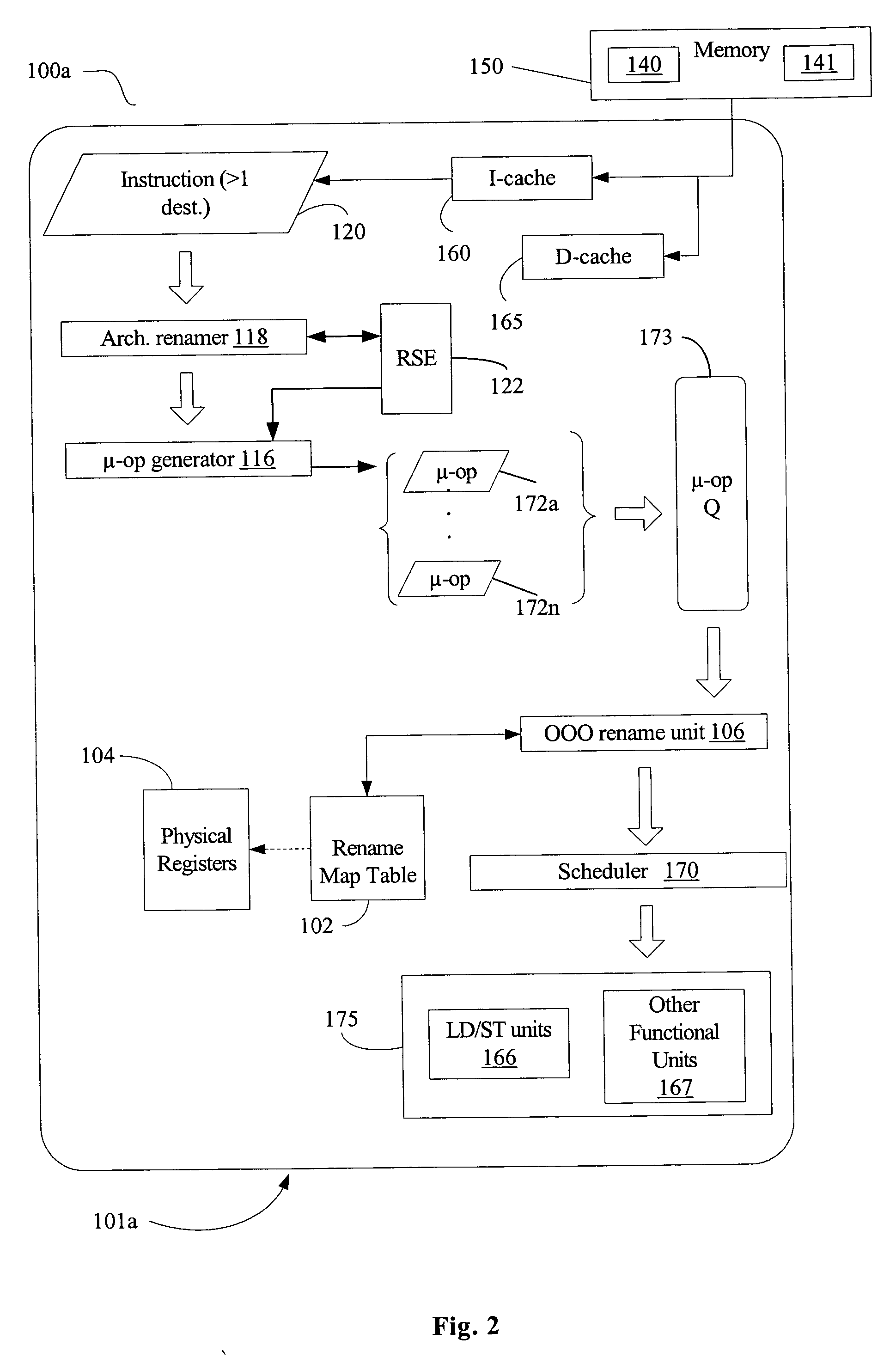
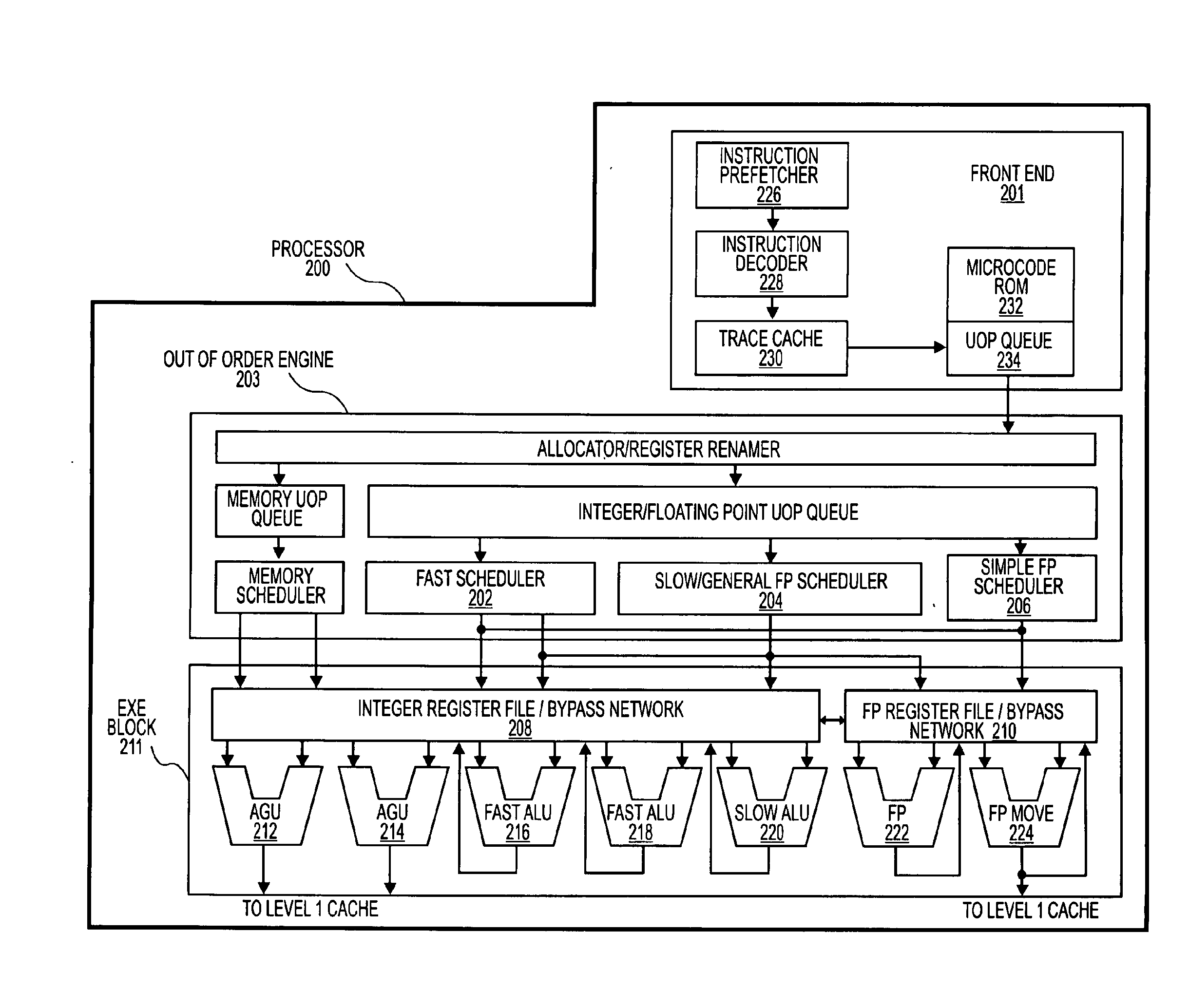
Microprocessor that performs x86 isa and arm isa machine language program instructions by hardware translation into microinstructions executed by common execution pipeline
ActiveUS20120260067A1Instruction analysisRuntime instruction translationComputer architectureProgram instruction
A microprocessor includes a hardware instruction translator that translates x86 ISA and ARM ISA machine language program instructions into microinstructions, which are encoded in a distinct manner from the x86 and ARM instructions. An execution pipeline executes the microinstructions to generate x86 / ARM-defined results. The microinstructions are distinct from the results generated by the execution of the microinstructions by the execution pipeline. The translator directly provides the microinstructions to the execution pipeline for execution. Each time the microprocessor performs one of the x86 ISA and ARM ISA instructions, the translator translates it into the microinstructions. An indicator indicates either x86 or ARM as a boot ISA. After reset, the microprocessor initializes its architectural state, fetches its first instructions from a reset address, and translates them all as defined by the boot ISA. An instruction cache caches the x86 and ARM instructions and provides them to the translator.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Integrated circuit with CPU and FPGA for reserved instructions execution with configuration diagnosis
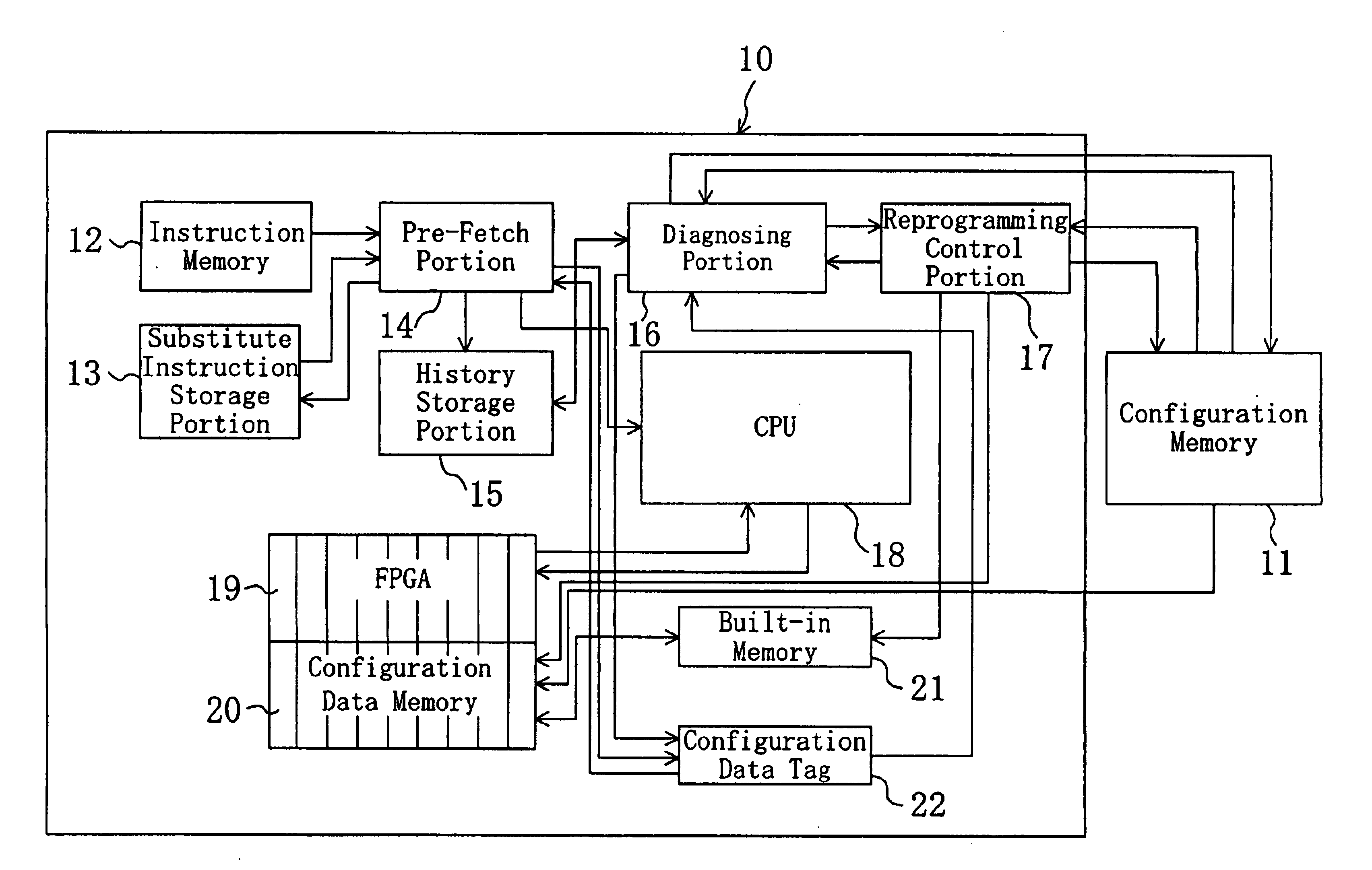
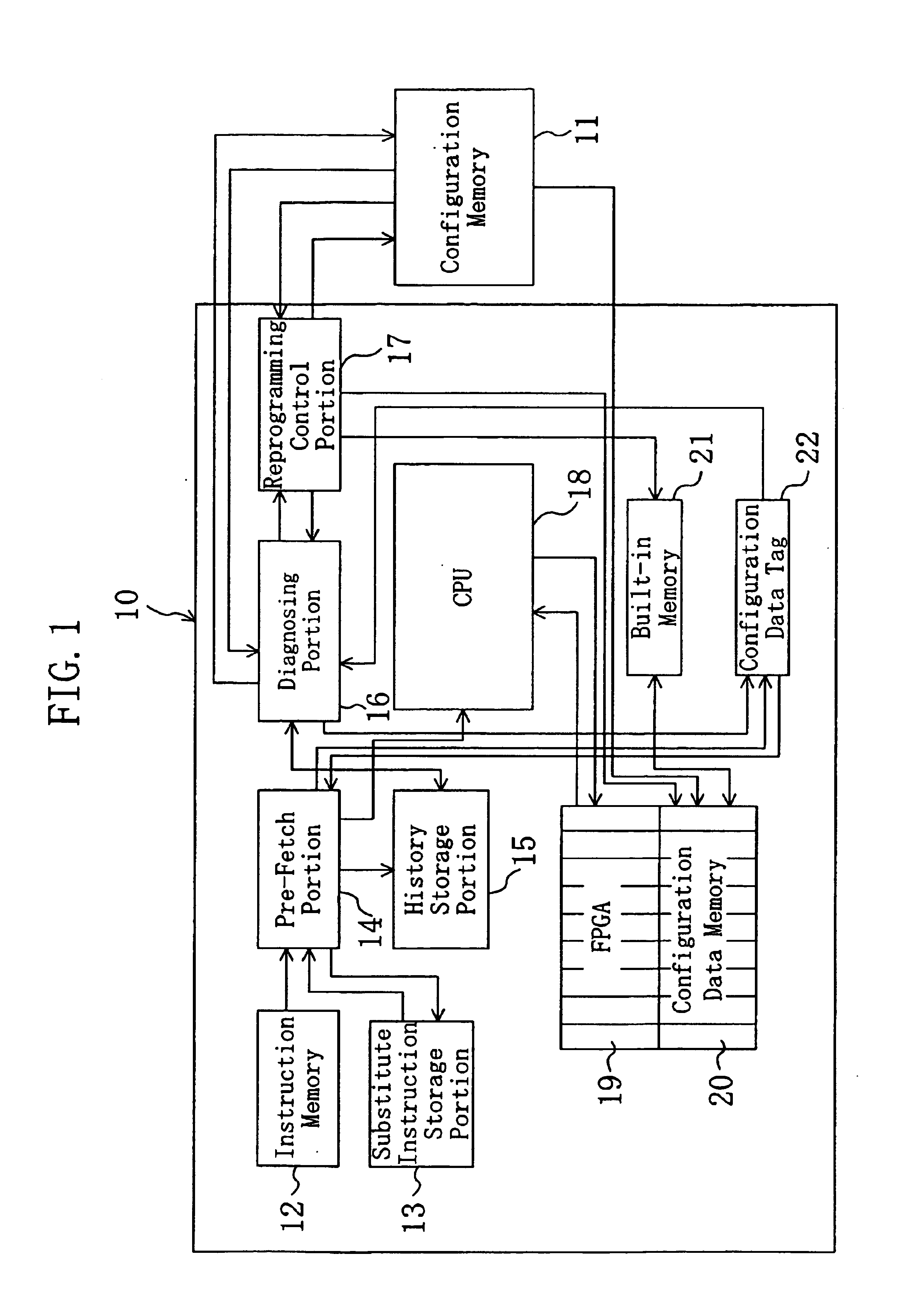
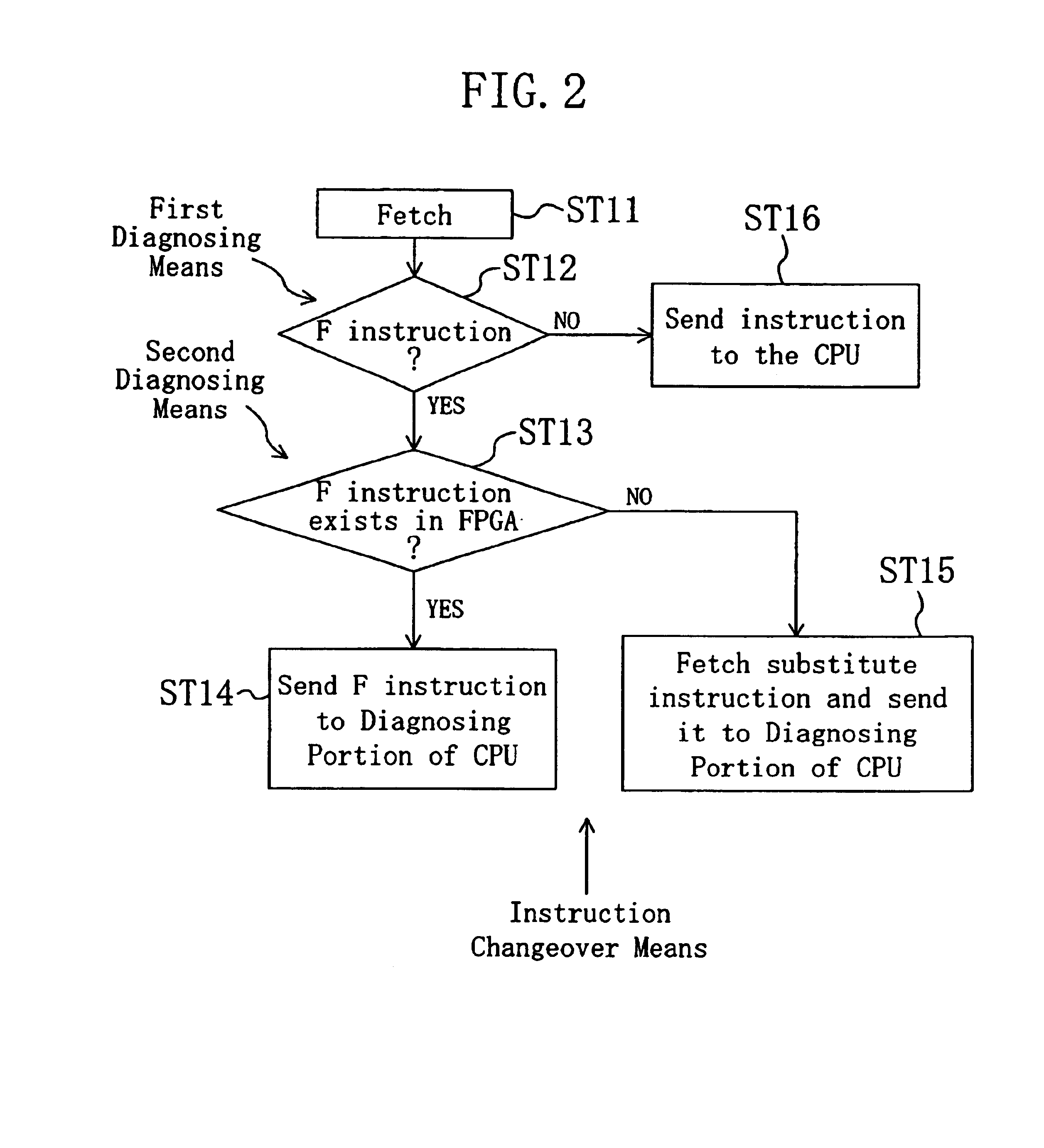
InactiveUS6901502B2Easy to processReduce frequency of useError detection/correctionRuntime instruction translationInstruction memoryComputer architecture
A semiconductor integrated circuits can send and receive signals to and form a configuration memory. The semiconductor integrated circuits is provided therein wiht an instruction memory, an instruction storage portion that stores reserved instructions as F instructions, and stores the substantially equivalent processing contents to the F instructions as substitute instructions for processing by the CPU, a pre-fetch portion, a history storage portion, a diagnosing portion for diagnosing the types of instructions, a reprogramming control portion for reprogramming the instructions, a CPU, an FPGA, a configuration data memory, a built-in memory, and a configuration data tag. When the configuration data of the F instruction does not exist in the FPGA, the substantially equivalent processing by FPGA is executed by the CPU by making use of the substitute instructions.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
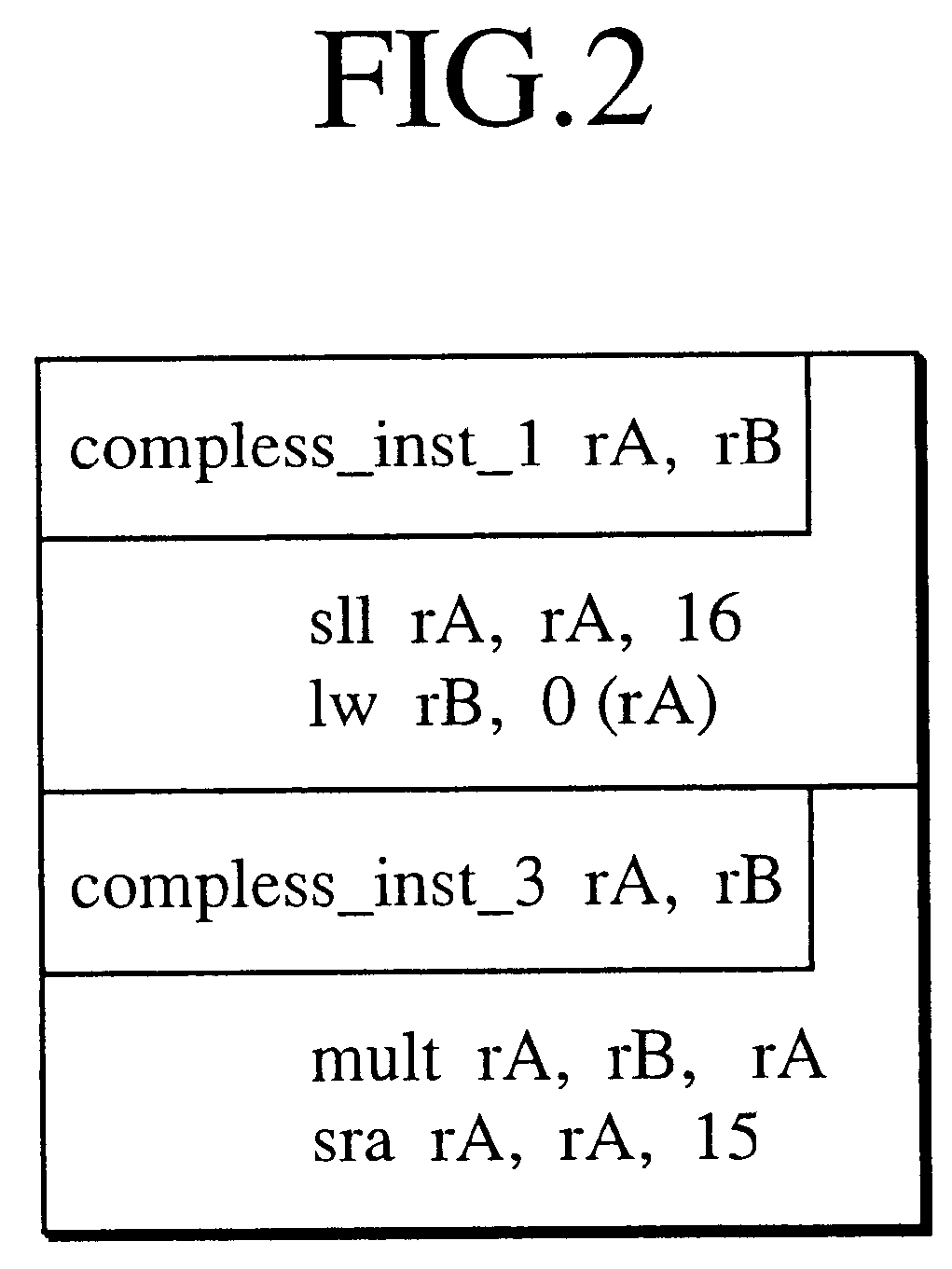
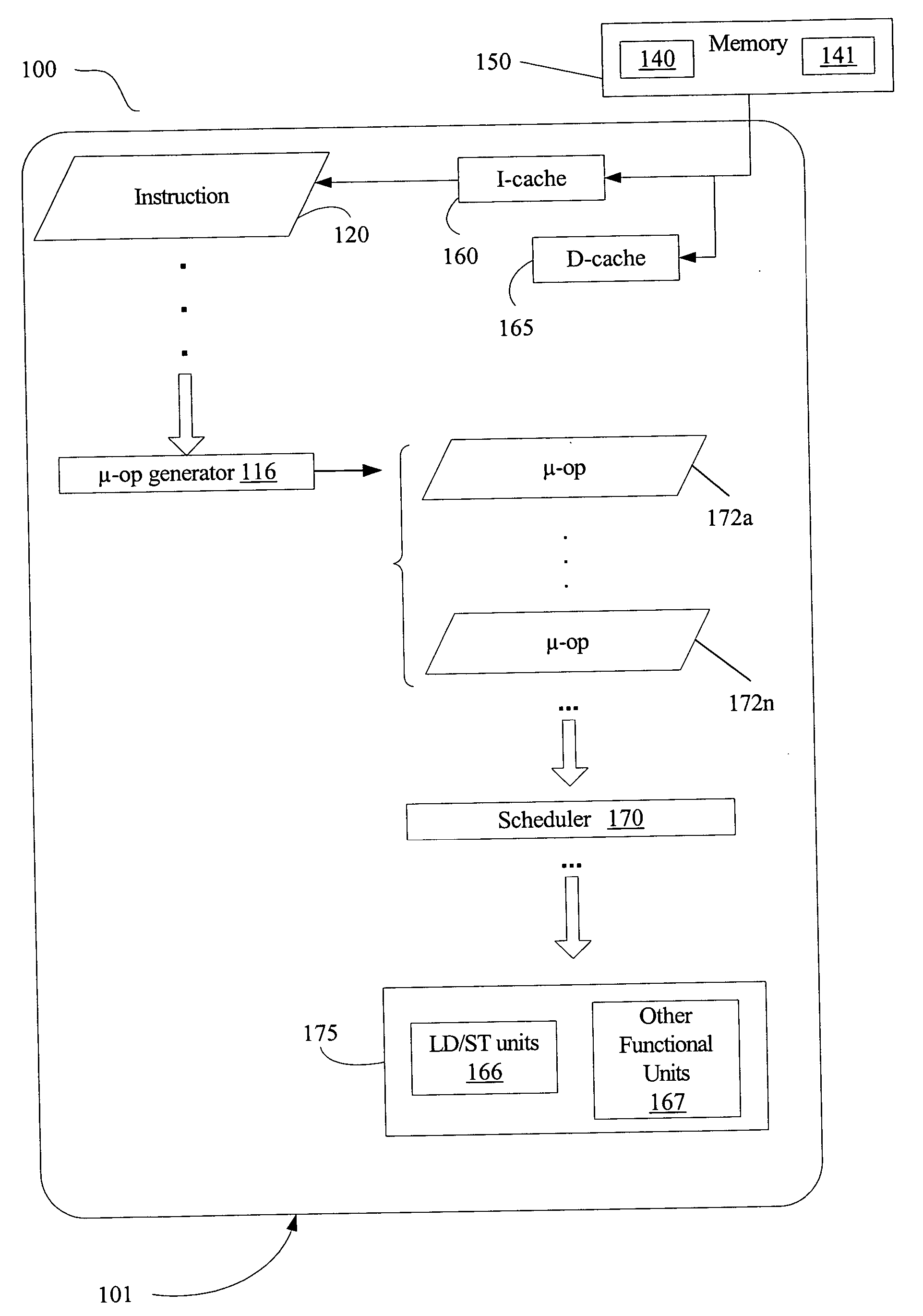
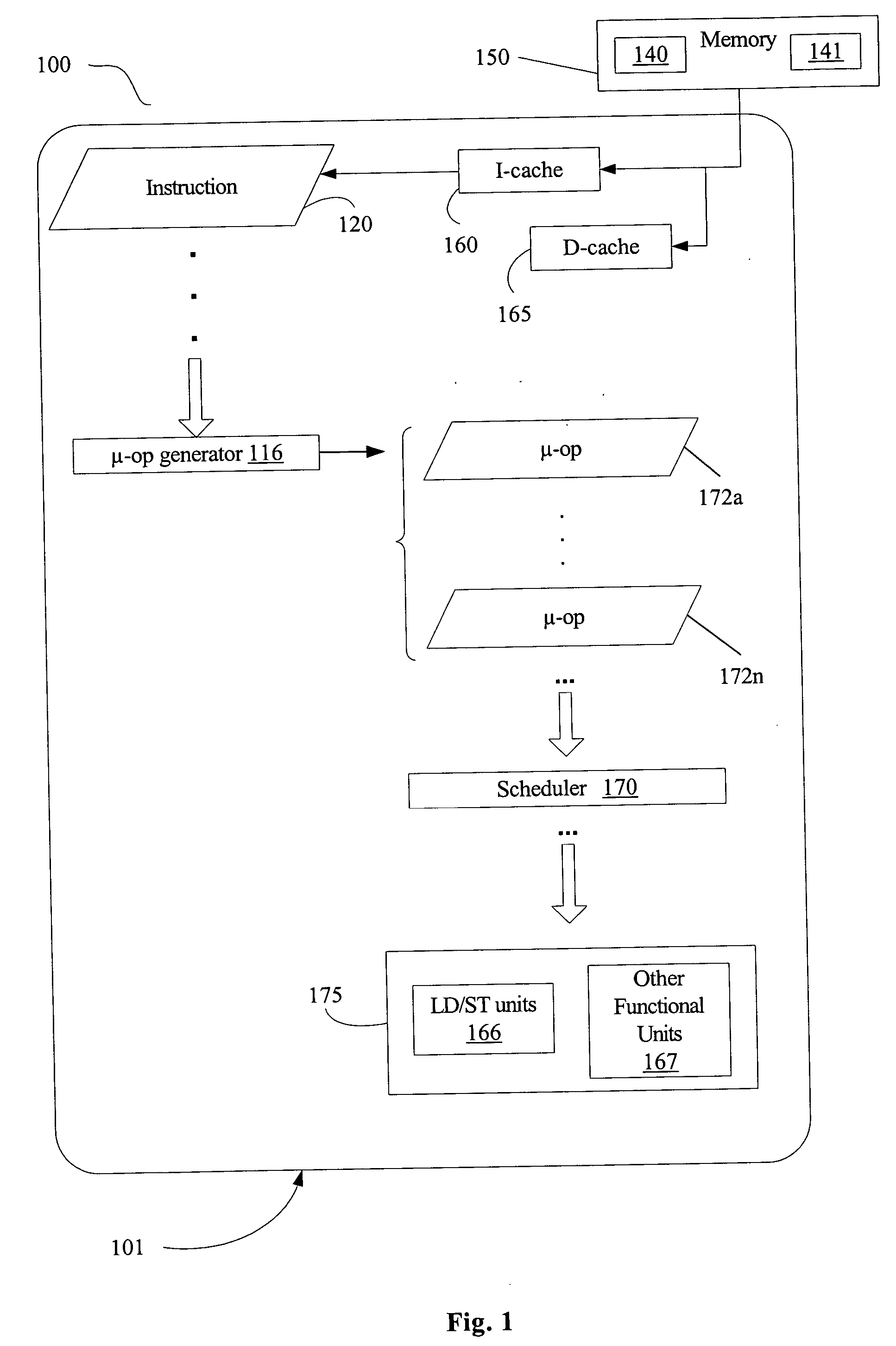
Method and system for compressing program code and interpreting compressed program code
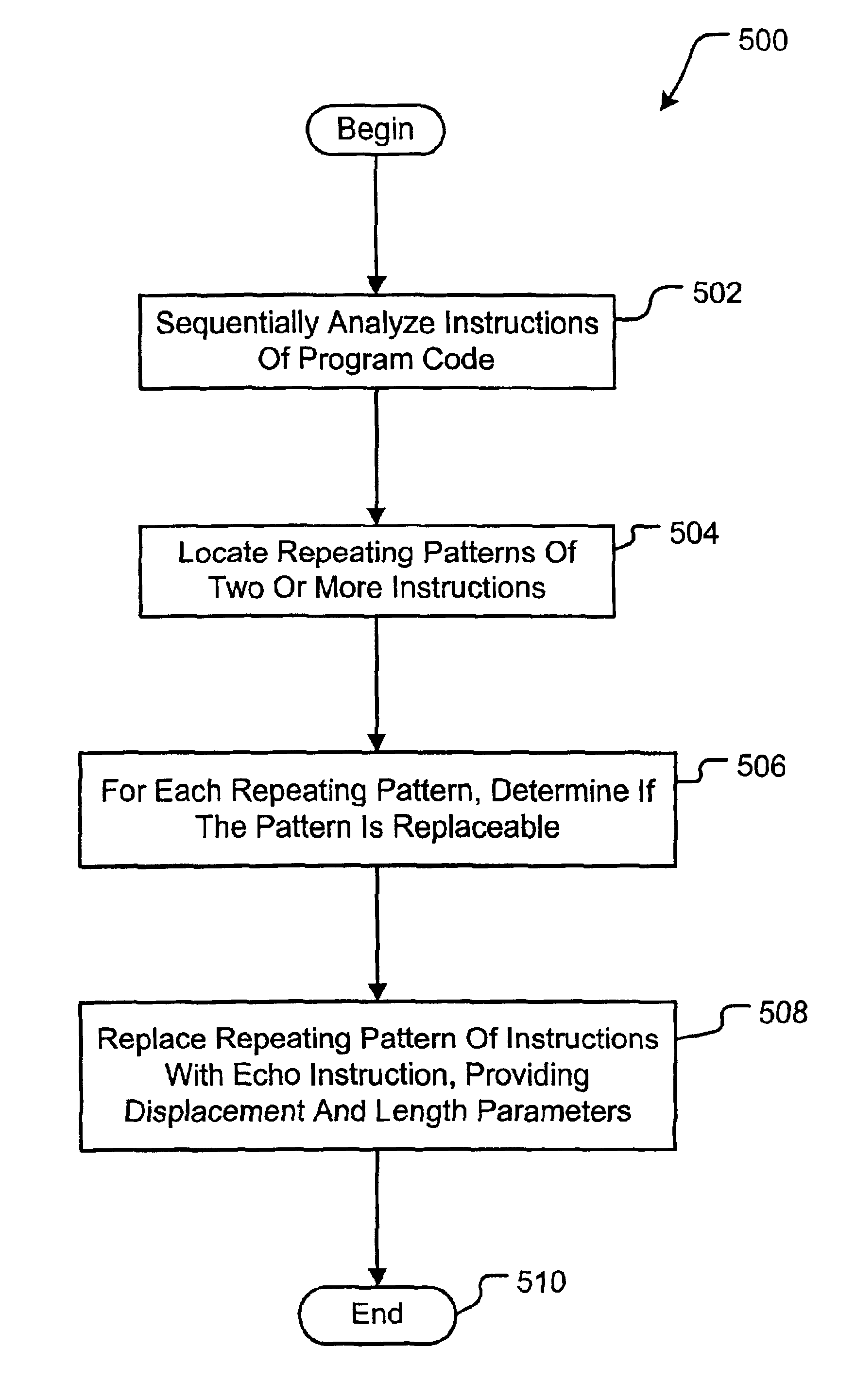
ActiveUS6907598B2Small sizeReduce in quantityRuntime instruction translationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram codeInstruction stream
A computer system and method for compressing an instruction stream and executing the compressed instruction stream without decompression. The invention utilizes a new pointer instruction, i.e., an “Echo” instruction that is used to replace repeated instructions or sequences of instructions, also referred to as phrases. Replacing subsequent, repeated phrases with the Echo instruction reduces the size of the instruction stream, i.e., compresses the instruction stream. The Echo instruction generally identifies at least one literal instruction appearing before the Echo instruction and further identifies the number of instructions appearing before the Echo instruction to be repeated. No additional delimiters are necessary, e.g., no End Echo instructions are required. Omitting the End Echo instruction allows for overlapping phrases without the need for two Echo instructions. Reducing the number of instructions used significantly increases compression.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
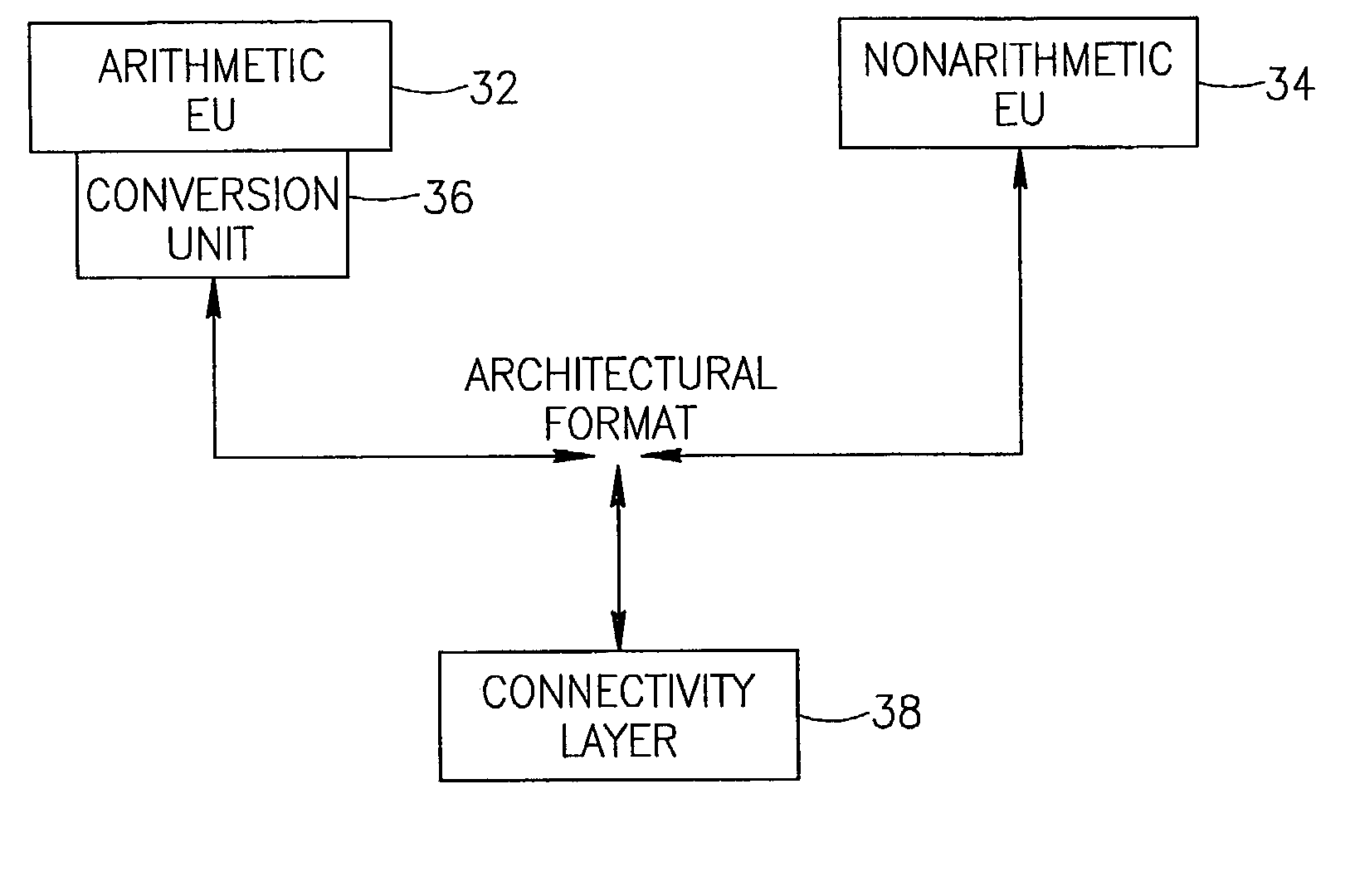
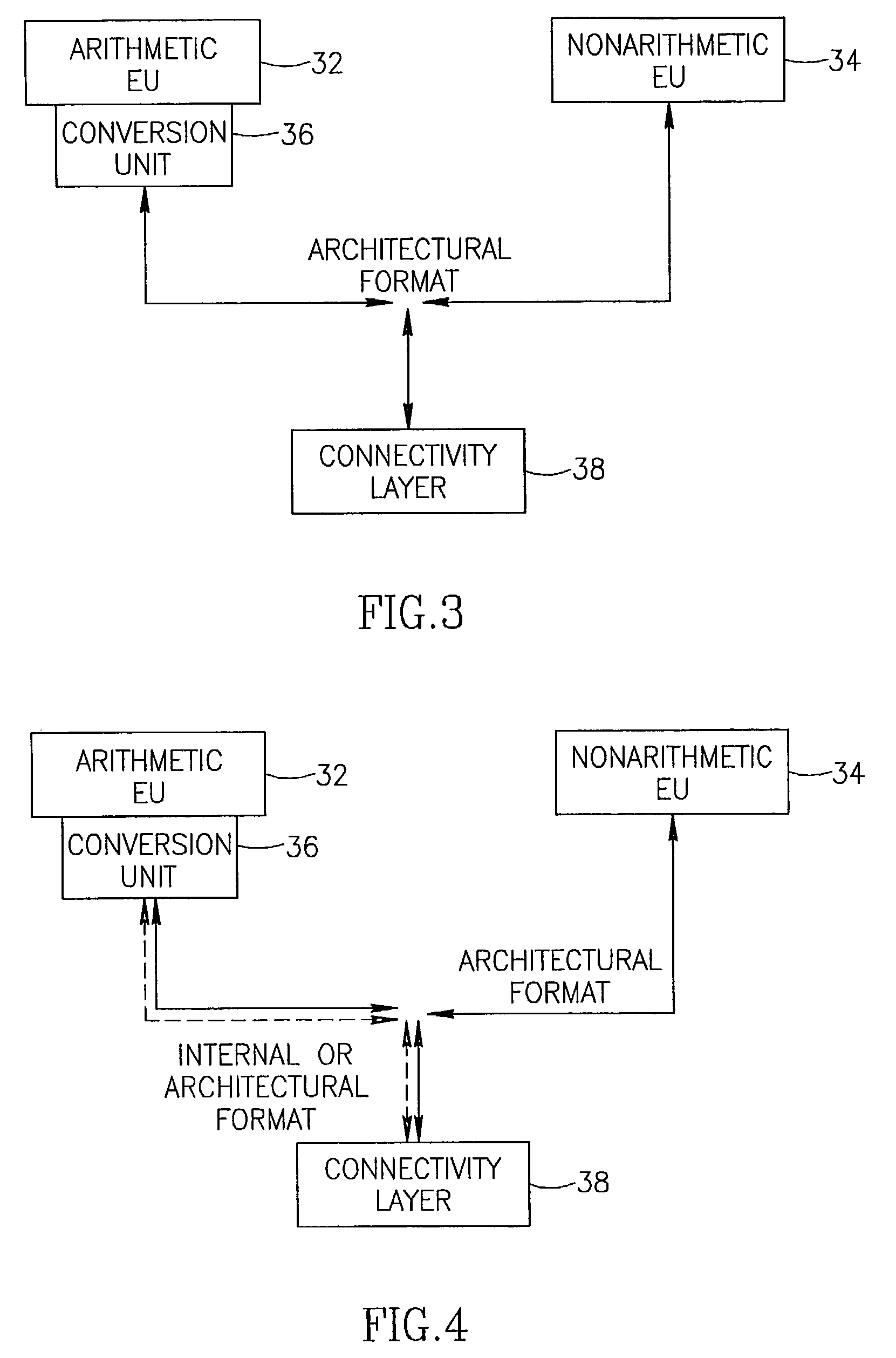
System and method of converting data formats and communicating between execution units
InactiveUS7430656B2Runtime instruction translationDigital computer detailsComputer architectureData transformation
A method and system including transmitting data in an architectural format between execution units in a multi-type instruction set architecture and converting data received in the architectural format to an internal format and data output in the internal format to the architectural format based on an operation code and a data type of a microinstruction.
Owner:INTEL CORP
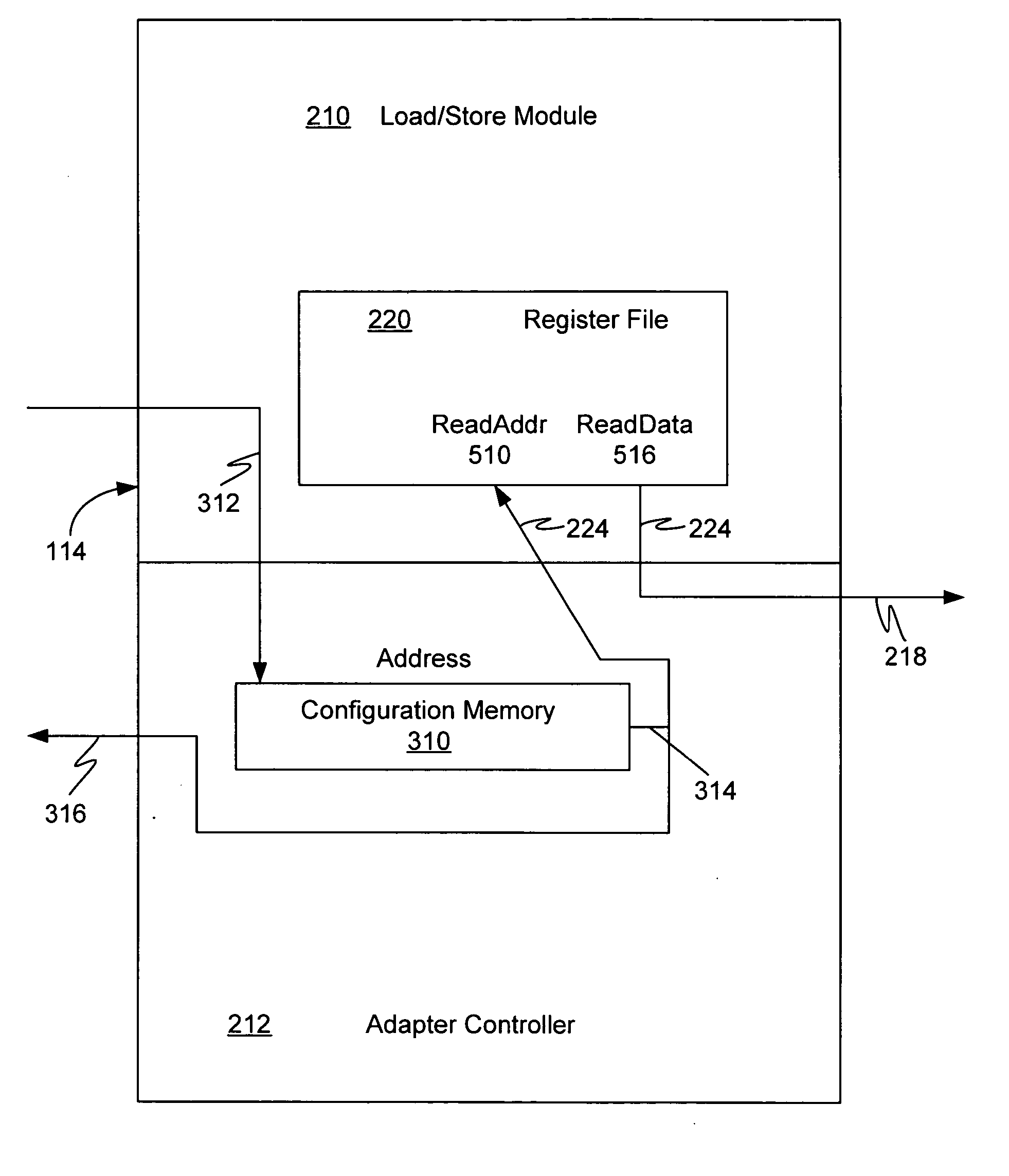
Extension adapter
ActiveUS20040193852A1Runtime instruction translationDigital computer detailsProgrammable logic deviceComputer science
A processor system. The processor system comprises a processor having a first set of instructions associated therewith. The processor system also comprises a programmable logic device and an extension adapter coupled to the processor and the programmable logic device. The extension adapter allows the programmable logic device to implement a second set of reconfigurable instructions for the processor.
Owner:XILINX INC
Multiple mode power throttle mechanism
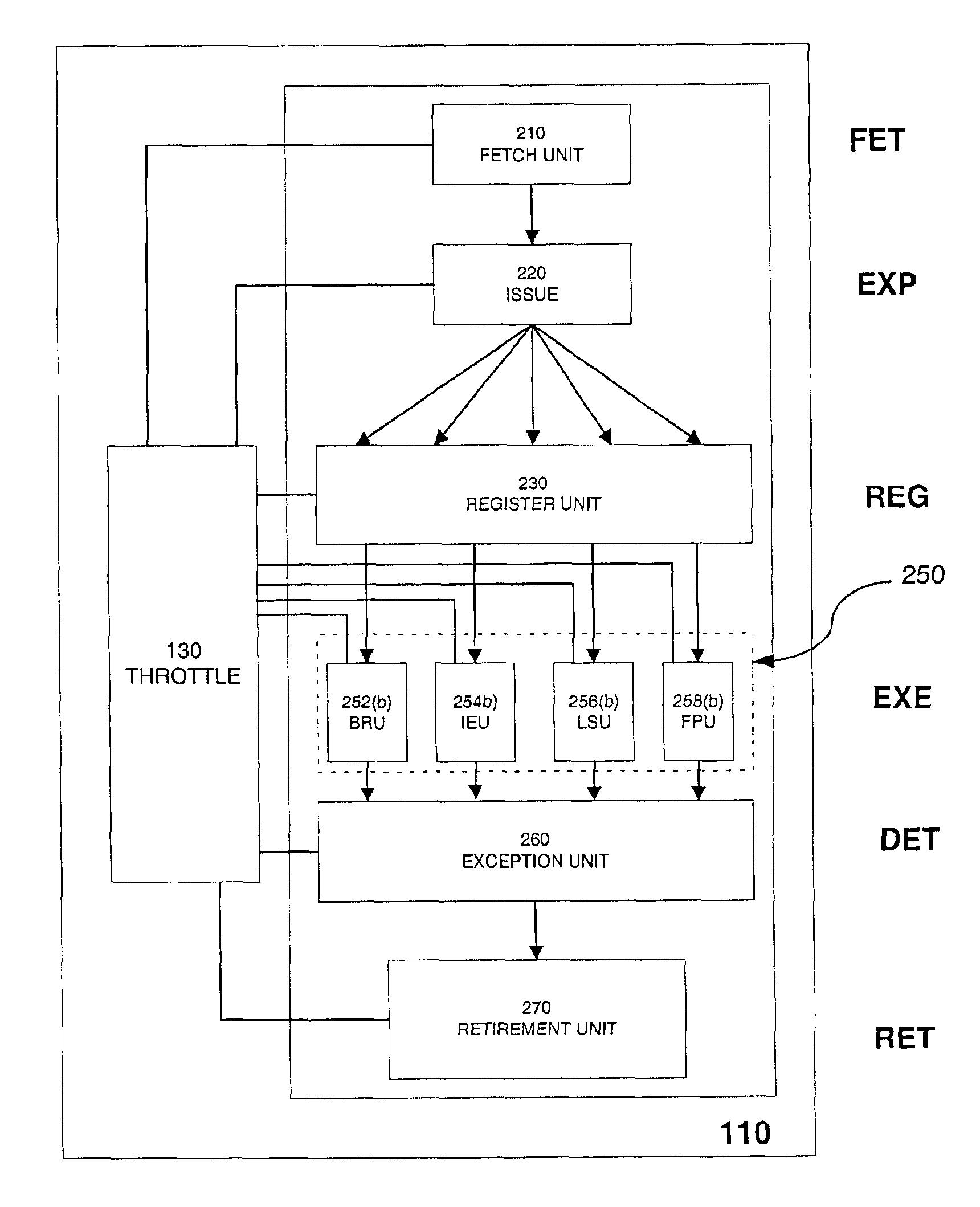
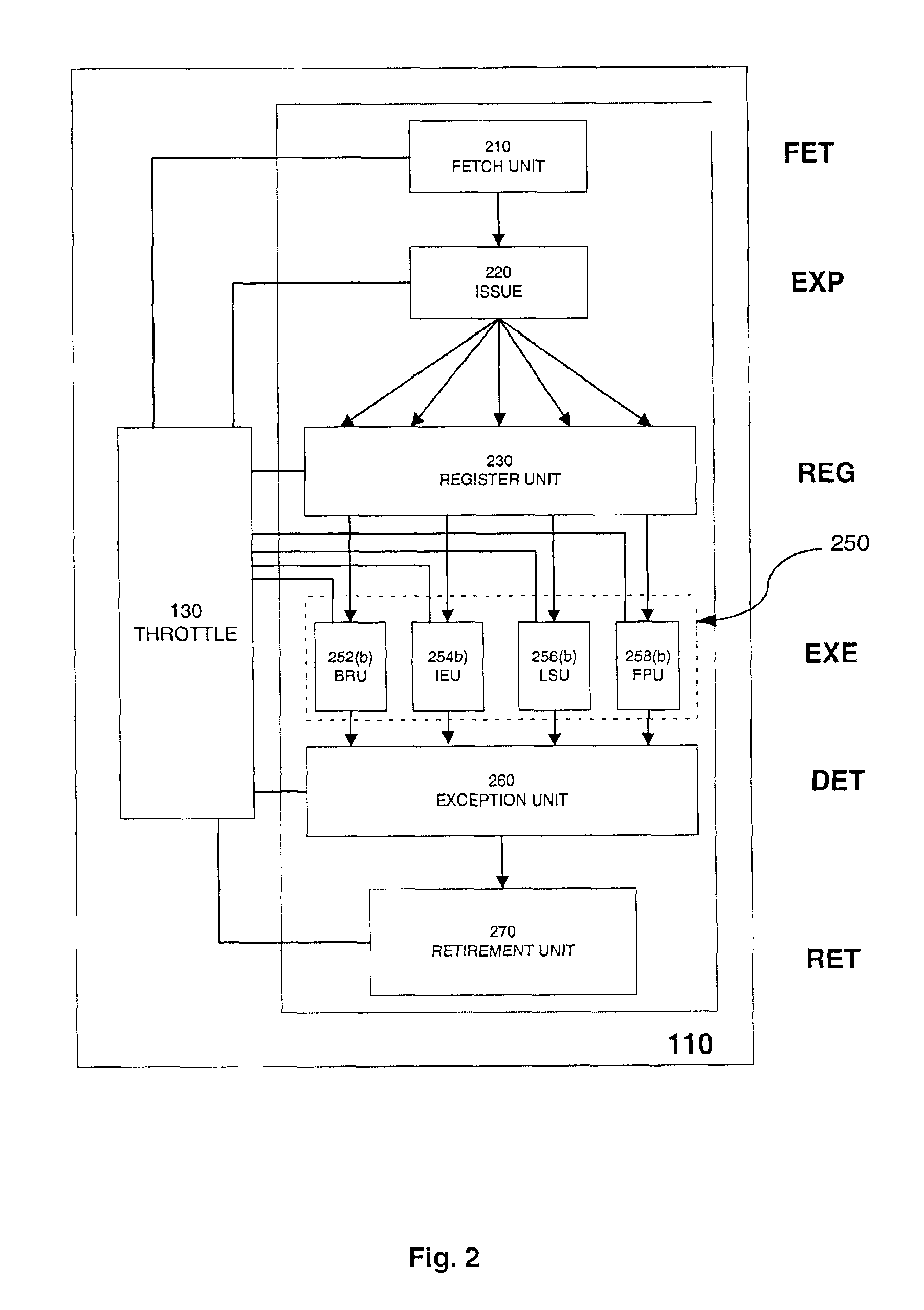
InactiveUS6931559B2Controlling the power dissipation of a processorEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringThrottle
A processor includes a digital throttle to monitor the activity of various units of the processor's instruction execution pipeline, and to determine a power state for the processor from the monitored activity. One of two or more power control mechanisms is engaged, responsive to the power state of the processor reaching a threshold.
Owner:INTEL CORP
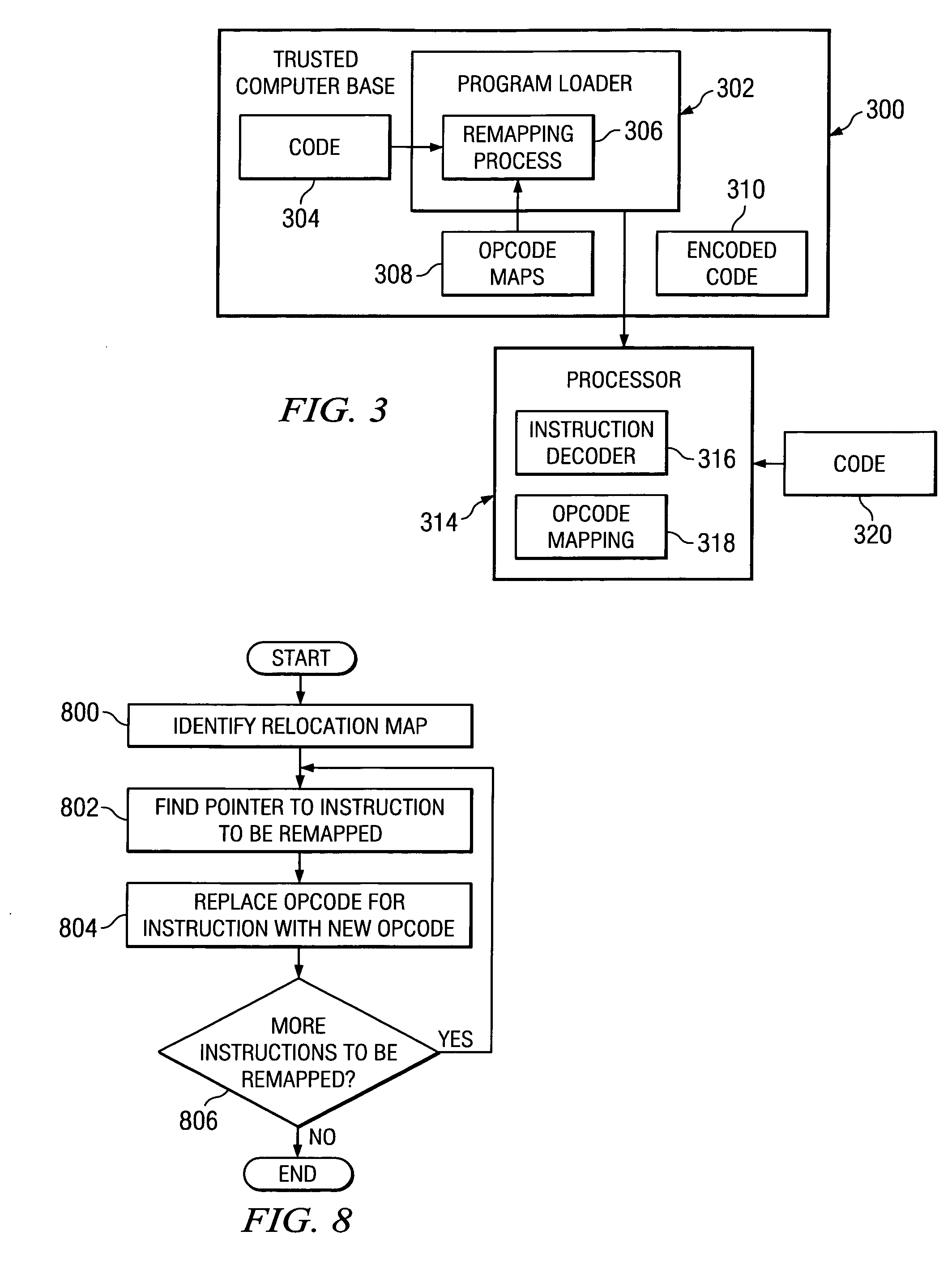
Method and apparatus to prevent vulnerability to virus and worm attacks through instruction remapping
InactiveUS20050188171A1Memory loss protectionInstruction analysisProcessing InstructionInstruction unit
A method, apparatus, and computer instructions for processing instructions by a processing unit. An instruction set is dynamically set for the processing unit using a selected instruction map. The selected instruction map is selected as one being different from a normal instruction map for the processing unit. The instructions are processed at the processor using the instruction set. A set of authorized instructions are encoded using the selected instruction map.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
Apparatus, method, and instruction for software management of multiple computational contexts in a multithreaded microprocessor
A multithreading microprocessor is disclosed. The microprocessor includes a plurality of thread contexts. The microprocessor provides instructions that enable a thread context issuing the instructions to move a value between itself and a target thread context distinct from the issuing thread context independent of cooperation from the target thread context. The instructions employ an operand to specify the target thread context. In one embodiment, the microprocessor is also a virtual multiprocessor including a plurality of virtual processing elements. Each virtual processing element includes a plurality of thread contexts. The instructions also employ a second operand to specify the target virtual processing element.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Method and apparatus for predication using micro-operations
InactiveUS20050081017A1Instruction analysisRuntime instruction translationTemporary variableMicro-operation
Disclosed are an apparatus, system, and method for implementing predicated instructions using micro-operations. A micro-code engine receives an instruction, decomposes the instruction, and generates a plurality of micro-operations to implement the instruction. Each of the decomposed micro-operations indicates a single destination register. For predicated instructions, the decomposed micro-operations include “conditional move” micro-operations to select between two potential output values. Except in the case that one of the potential output values is a constant, the decomposed micro-operations for a predicated instruction also include an append instruction that saves the incoming value of a destination register in a temporary variable. For at least one embodiment, the qualifying predicate for a predicated instruction is appended to the incoming value stored in the temporary register.
Owner:INTEL CORP
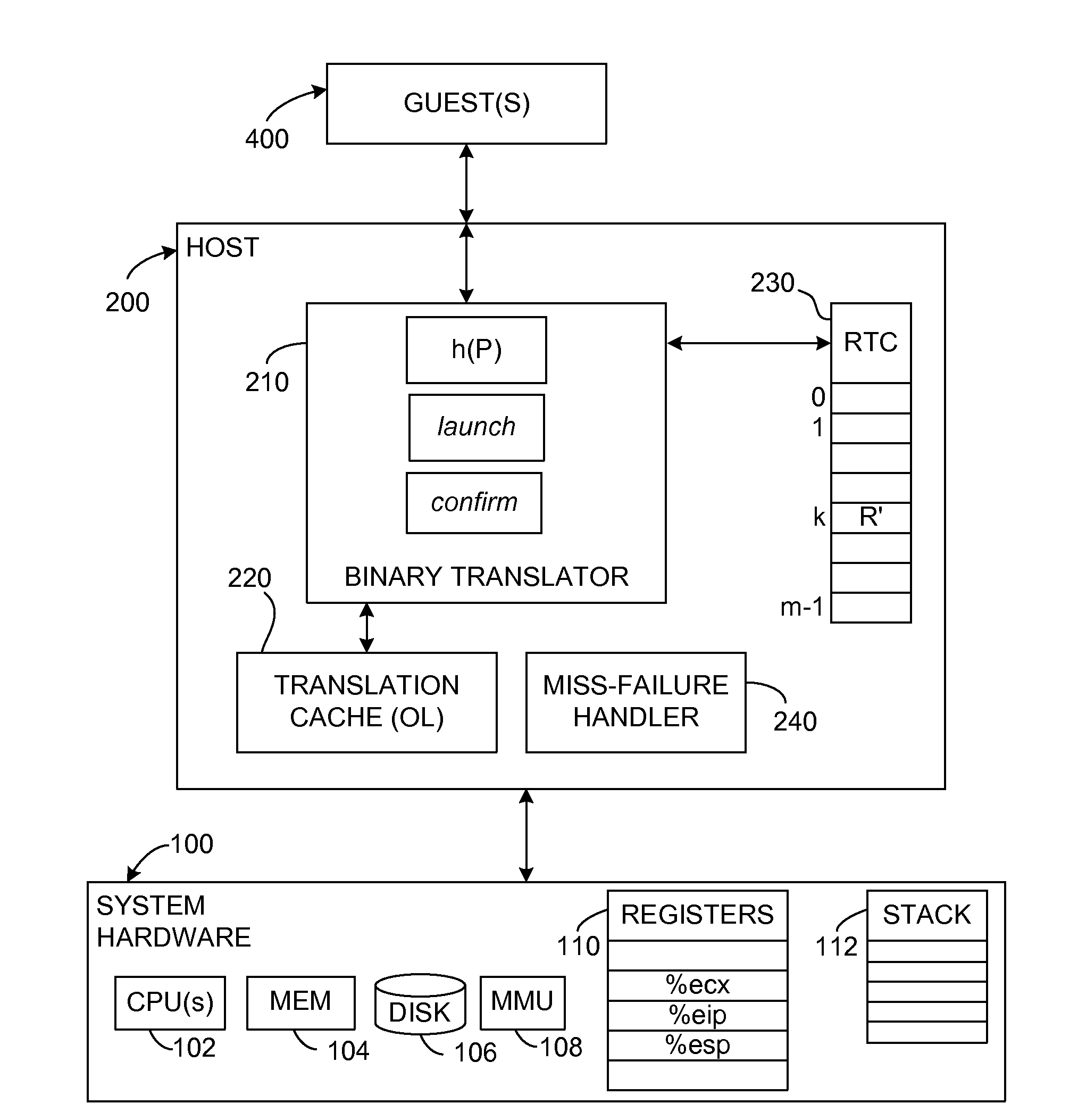
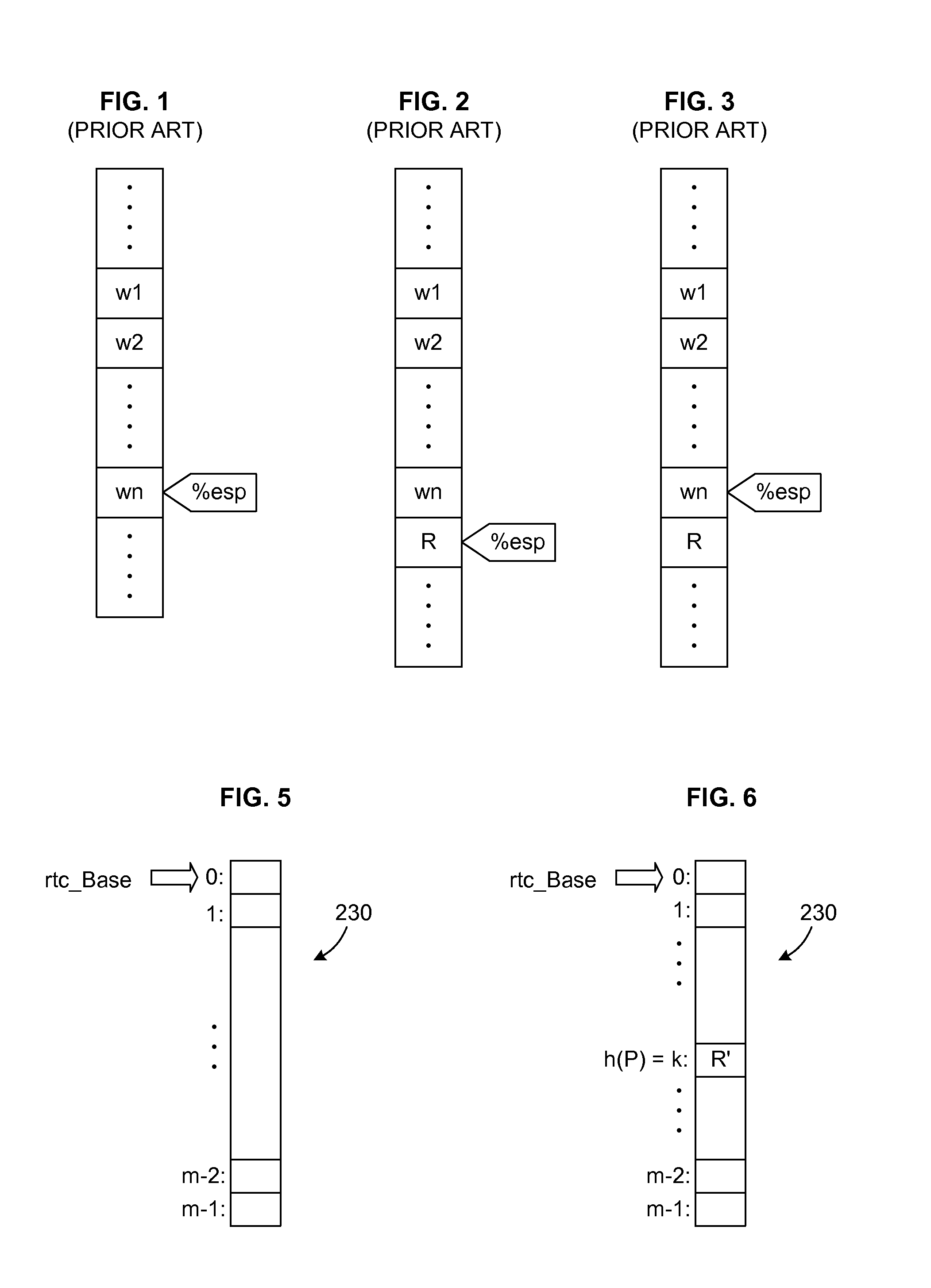
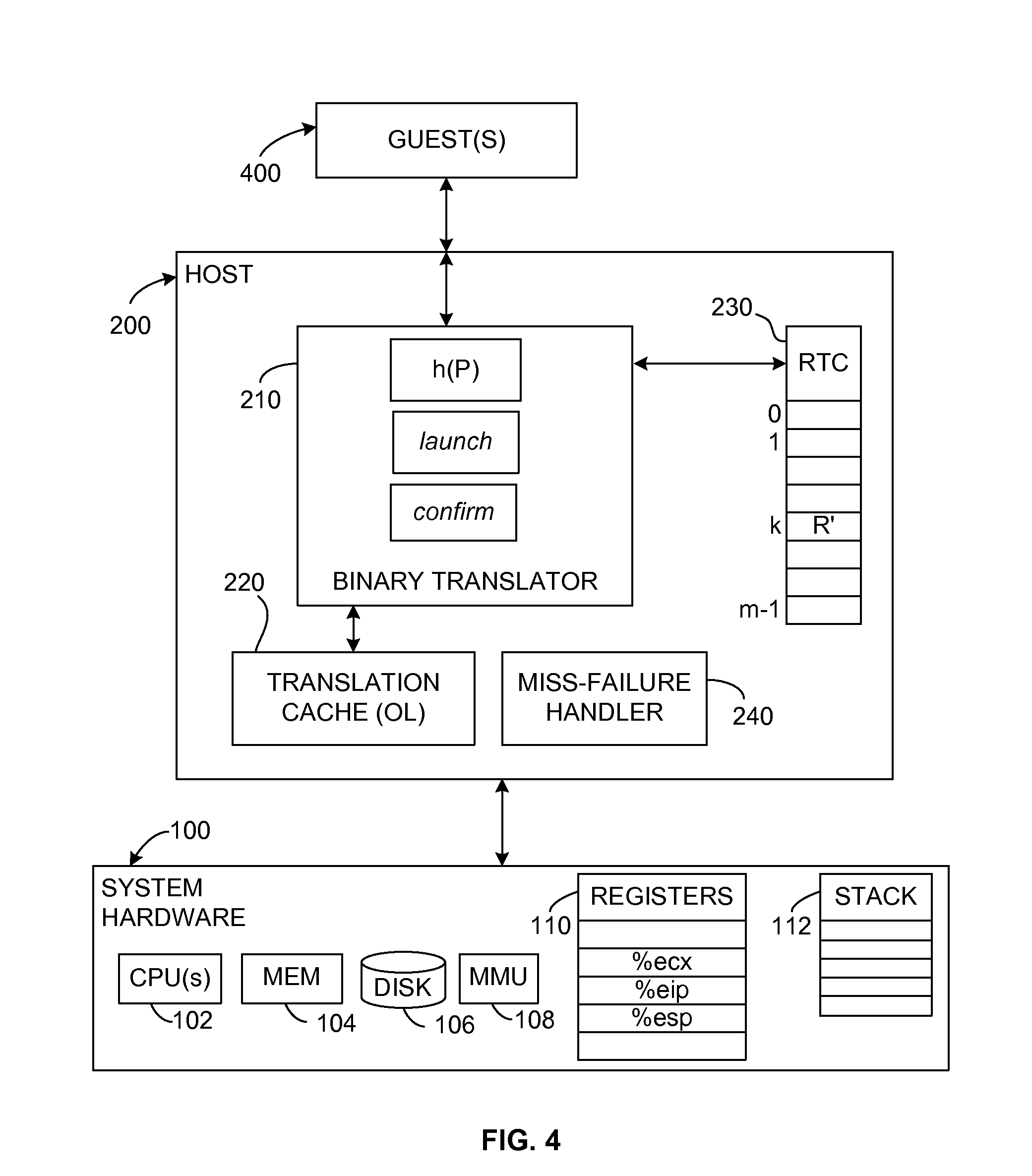
Prediction Mechanism for Subroutine Returns in Binary Translation Sub-Systems of Computers
Owner:VMWARE INC
Instruction and logic for processing text strings
ActiveUS20110246751A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationProgram control using stored programsProgramming languageOperand
Method, apparatus, and program means for performing a string comparison operation. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes execution resources to execute a first instruction. In response to the first instruction, said execution resources store a result of a comparison between each data element of a first and second operand corresponding to a first and second text string, respectively.
Owner:INTEL CORP
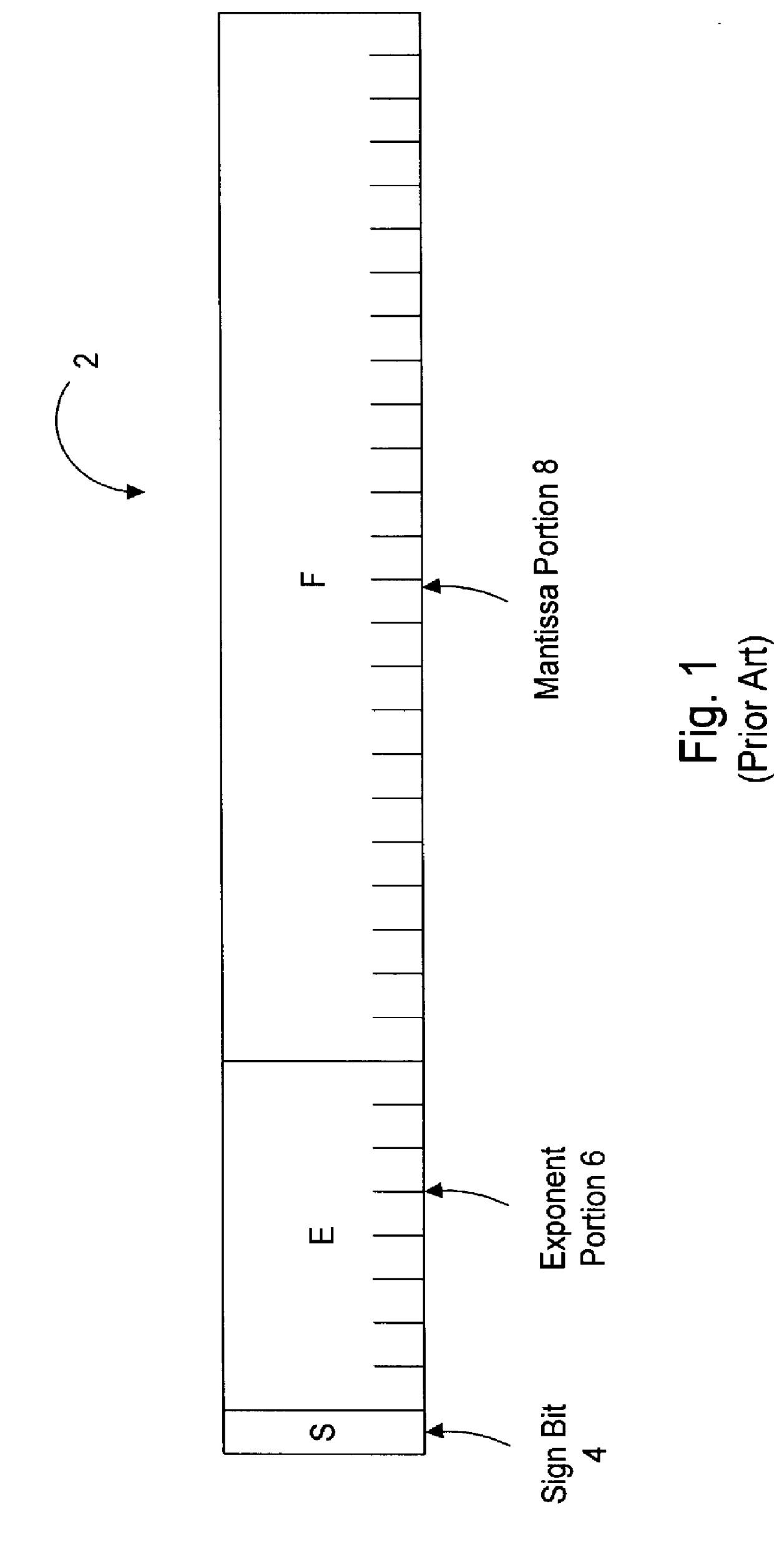
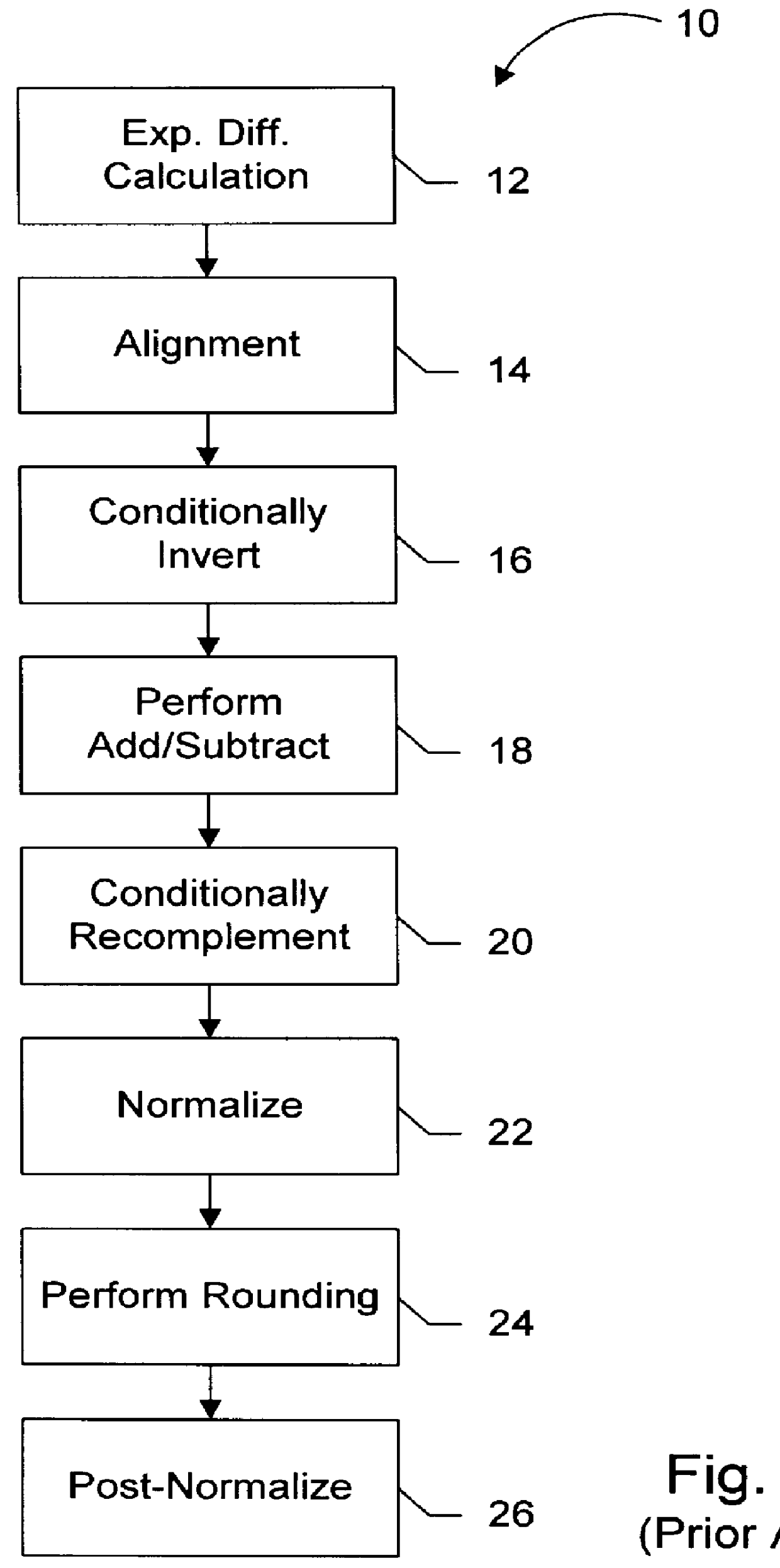
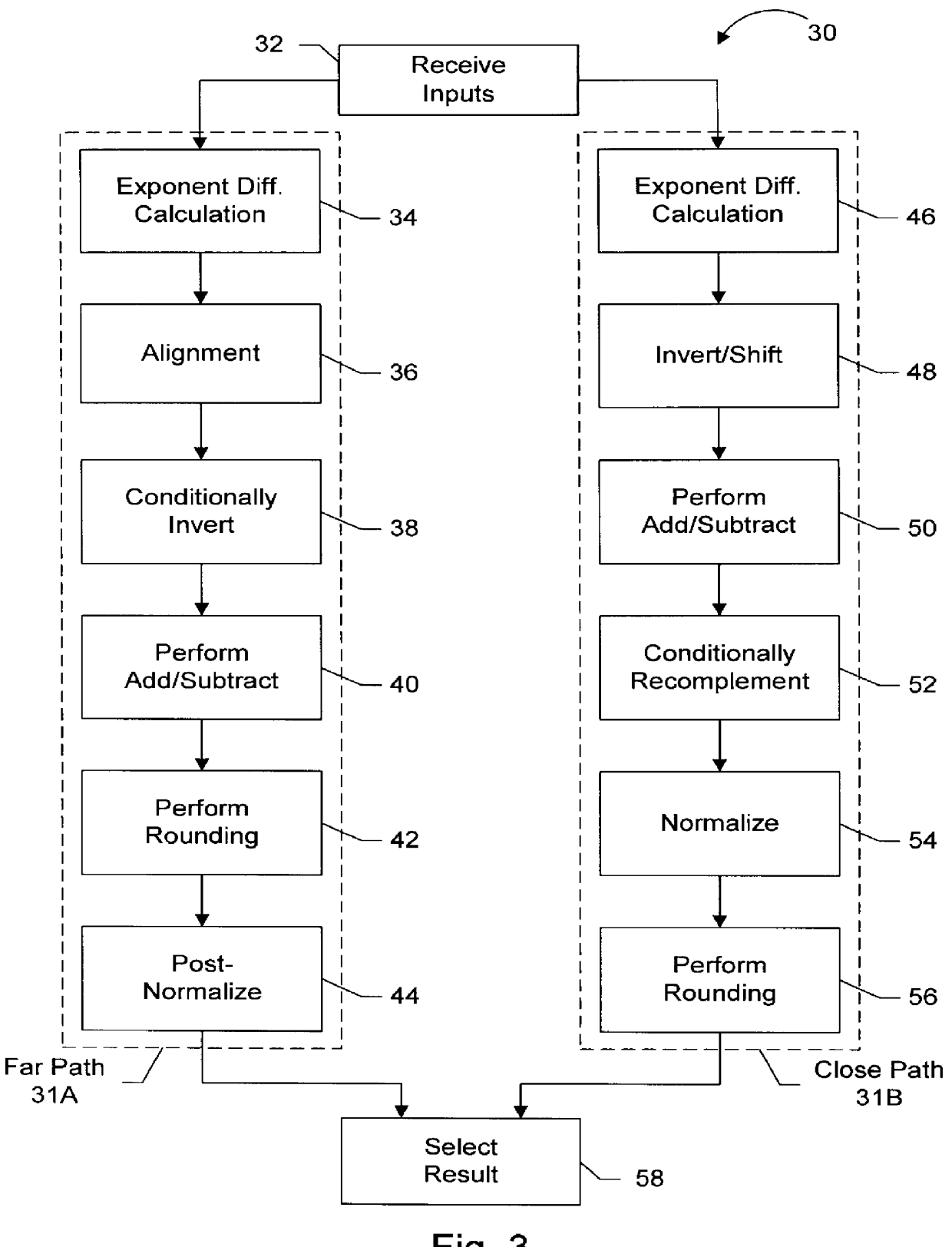
Floating point arithmetic unit including an efficient close data path
InactiveUS6094668AComputations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationMultiplexerExecution unit
An execution unit configured to execute vectored floating point and integer instructions. The execution unit may include an add / subtract pipeline having far and close data paths. The far data path is configured to handle effective addition operations, as well as effective subtraction operations for operands having an absolute exponent difference greater than one. The close data path is configured to handle effective subtraction operations for operands having an absolute exponent difference less than or equal to one. The close data path includes an adder unit configured to generate a first and second output value. The first output value is equal to the first input operand plus an inverted version of the second input operand, while the second output value is equal to the first output value plus one. The two output values are conveyed to a multiplexer unit, which selects one of the output values as a preliminary subtraction result based on a final selection signal received from a selection unit. The selection unit generates the final selection signal from a plurality of preliminary selection signals based on the carry in signal to the most significant bit of the first adder output value. Selection of the first or second output value in the close data path effectuates the round-to-nearest operation.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Popular searches
Program loading/initiating Execution paradigms Energy efficient computing Software simulation/interpretation/emulation Interprogram communication Concurrent instruction execution Specific program execution arrangements Computation using denominational number representation Complex mathematical operations Redundant operation error correction
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com