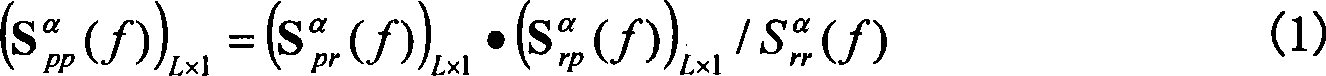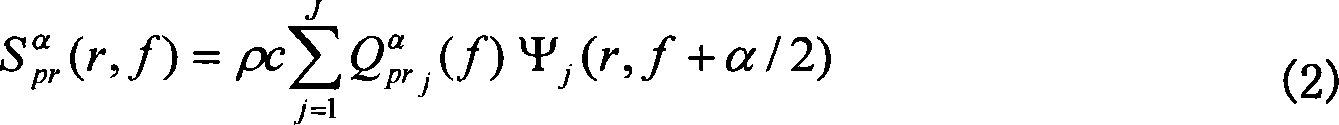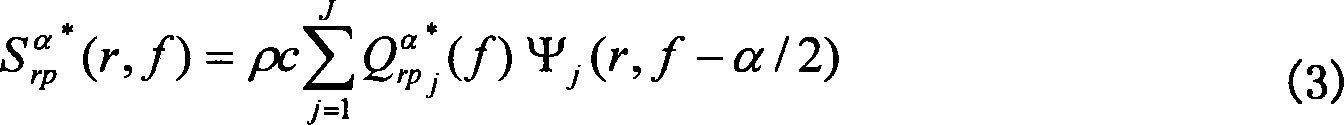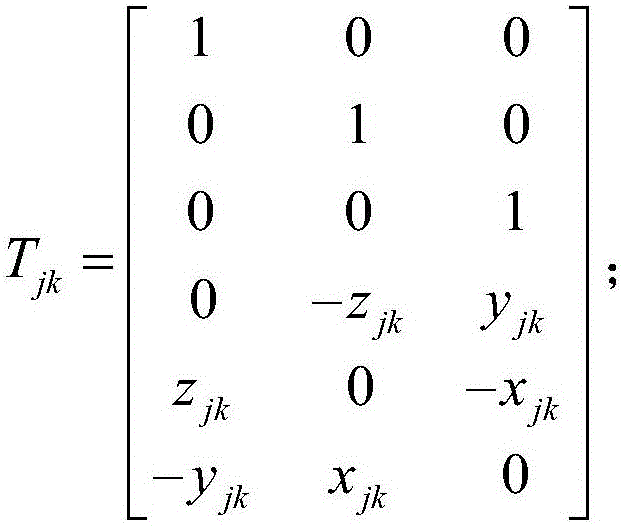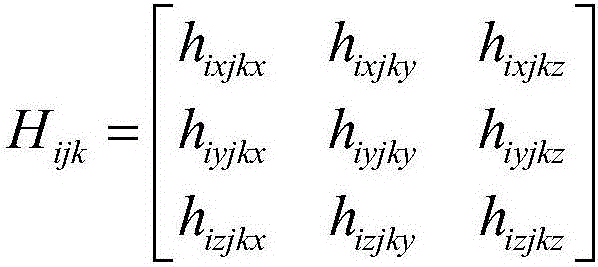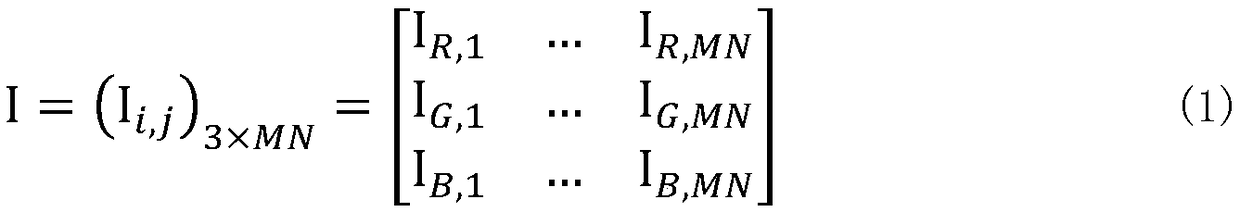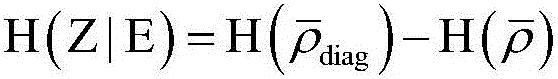Patents
Literature
83 results about "Density matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A density matrix is a matrix that describes the statistical state of a system in quantum mechanics. The probability for any outcome of any well-defined measurement upon a system can be calculated from the density matrix for that system. The extreme points in the set of density matrices are the pure states, which can also be written as state vectors or wavefunctions. Density matrices that are not pure states are mixed states. Any mixed state can be represented as a convex combination of pure states, and so density matrices are helpful for dealing with statistical ensembles of different possible preparations of a quantum system, or situations where a precise preparation is not known, as in quantum statistical mechanics.
Efficient seismic data acquisition with source separation
ActiveUS20090010103A1Minimize crosstalkSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationTime domainFrequency spectrum
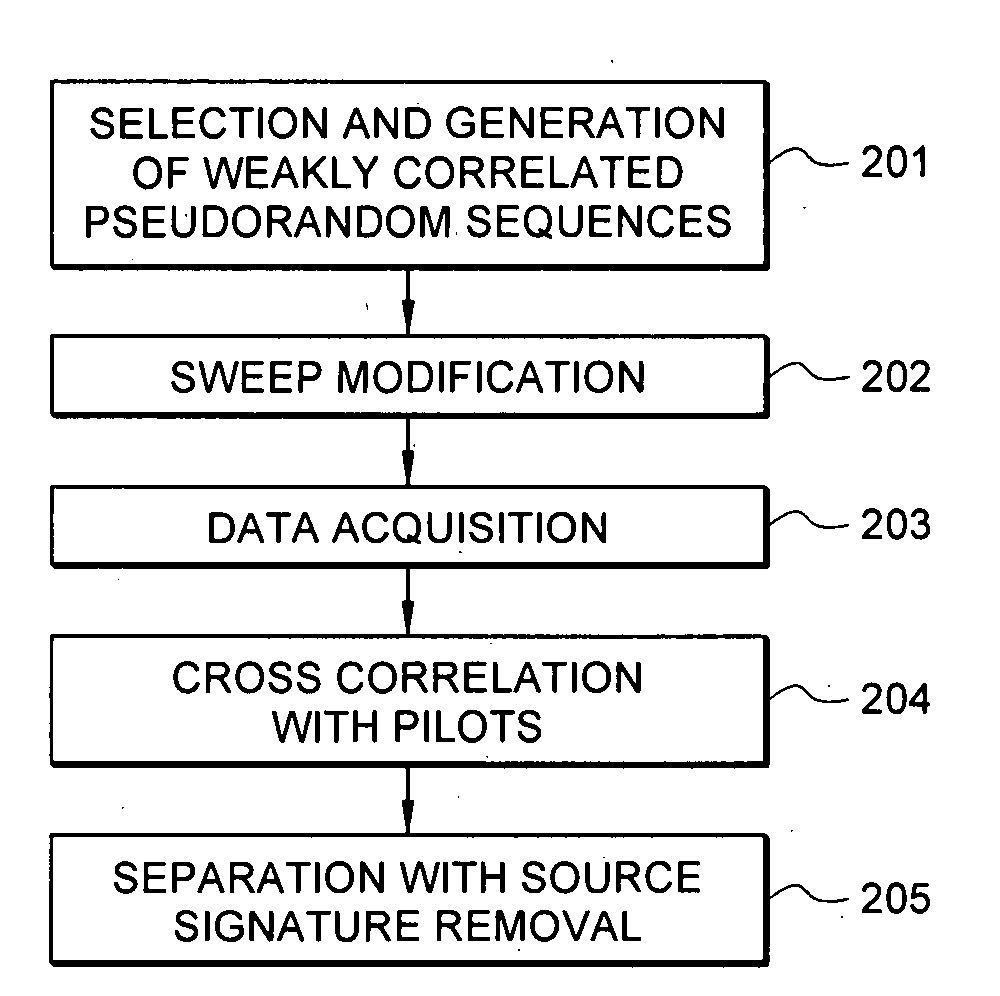
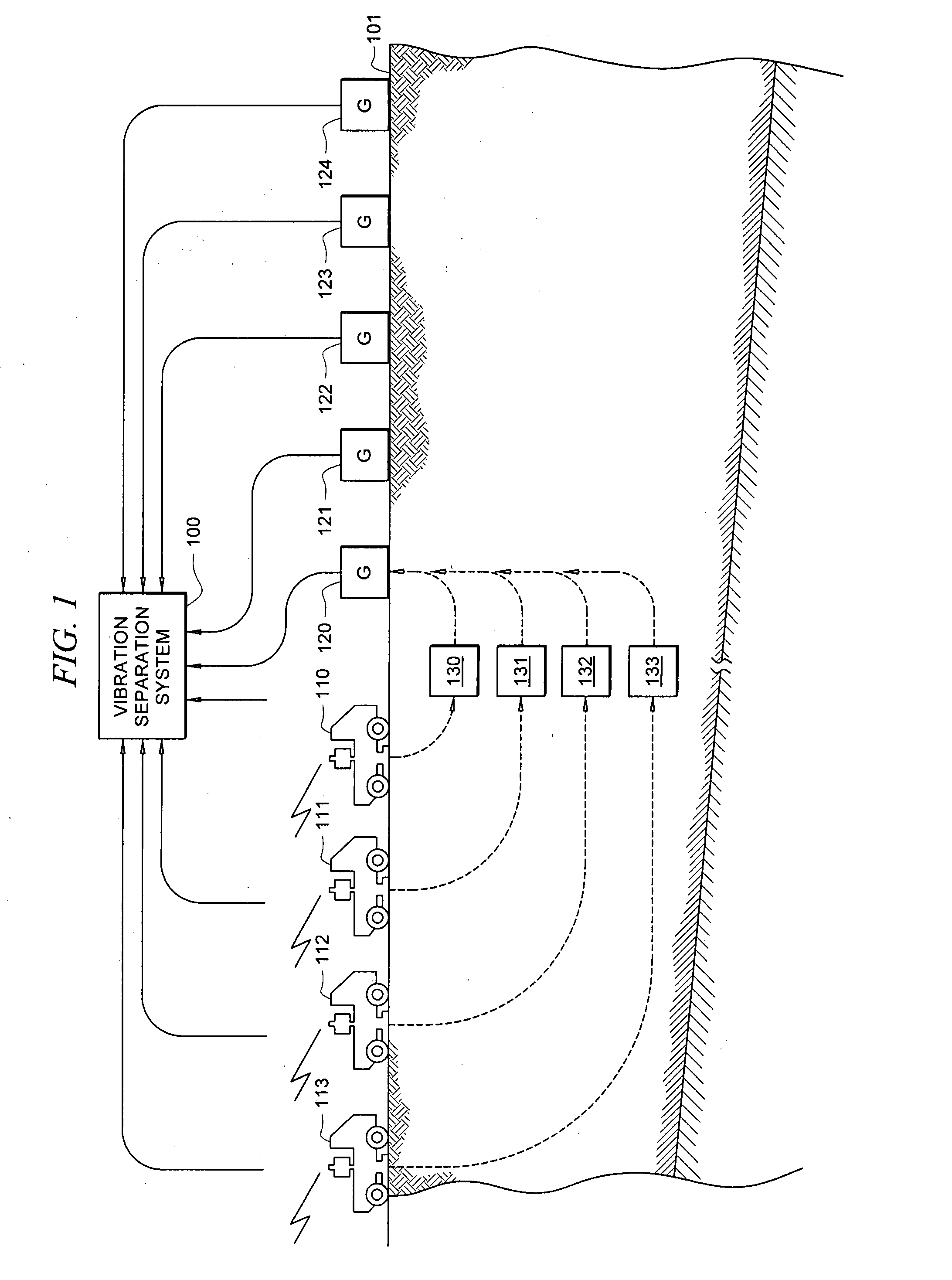
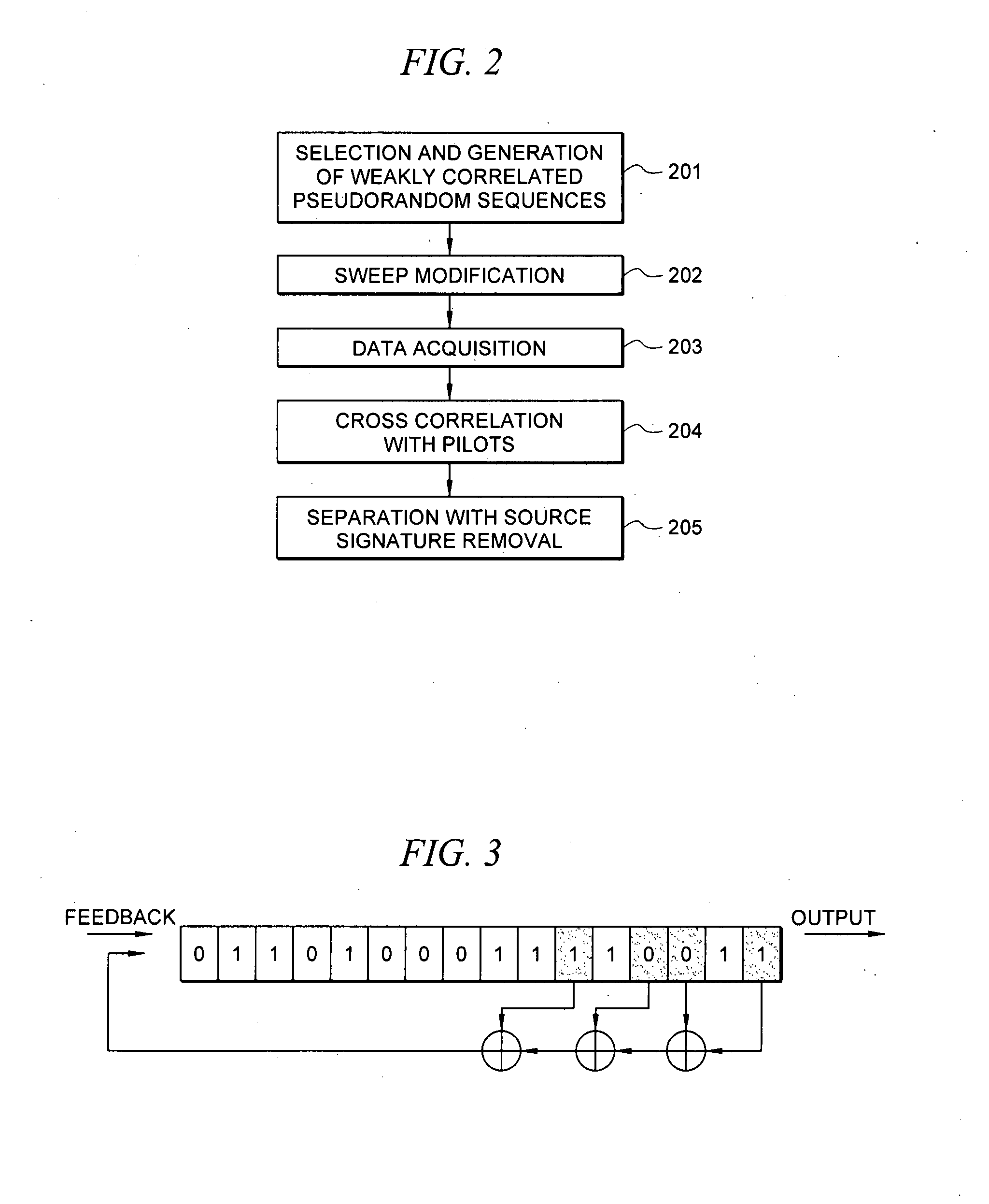
A method for the simultaneous operation of multiple seismic vibrators using unique modified pseudorandom sweeps and recovery of the transmission path response from each vibrator is disclosed. The vibrator sweeps are derived from pseudorandom binary sequences modified to be weakly correlated over a time window of interest, spectrally shaped and amplitude level compressed. Cross-correlation with each pilot signal is used to perform an initial separation of the composite received signal data set. Recordings of the motion of each vibrator are also cross-correlated with each pilot, windowed, and transformed to form a source cross-spectral density matrix in the frequency domain useful for source signature removal and for additional crosstalk-suppression between the separated records. After source signature removal in the frequency domain an inverse transform is applied to produce an estimate of each source-to-receiver earth response in the time domain. The method has application to both land and marine geophysical exploration.
Owner:SERCEL INC
Method for vibration analysis
InactiveUS6779404B1Vibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingSingular value decompositionModal testing
Output-only modal testing of an object. Vibrations are excited in said object and measured by a number of vibration sensitive detectors. From the data of the measurements, a spectral density matrix function is determined. From this density matrix, auto spectral densities for the individual modes are identified performing a decomposition based on the Singular Value Decomposition technique. From the auto spectral densities of the individual modes, natural frequencies and damping ratios for the modes can be estimated, and from the singular vectors of the Singular Value Decomposition, the modes shapes can be estimated.
Owner:STRUCTURAL VIBRATIONS SOLUTIONS
Reversible arithmetic coding for quantum data compression
A method and structure for encoding / decoding a block of quantum data including removing trailing eigenstates from the block that have eigenvalues below a predetermined limit to retain leading eigenstates that have eigenvalues above the predetermined limit, encoding the remaining quantum bits retained in the block after the removing. The remaining quantum bits can also include a linear superposition of the leading eigenstates. The predetermined limit is based upon a density matrix of the block. This method of encoding produces encoded quantum bits and can further include decoding the encoded quantum bits by reversing the encoding. The decoding reproduces the remaining quantum bits and the encoding completely erases the remaining quantum bits. Further, the invention can include outputting only an encoded or decoded result.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for rebuilding circulation calm sound source by overlapping spherical wave
InactiveCN101251412ABreak through the shape requirementsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound sourcesDensity distribution
The invention relates to a method of reconstructing a circular stable sound source to be measured through spherical wave superposition in the signal reconstruction technical field. Through setting the sound source to be measured, a microphone array and a reference source microphone, the invention synchronously records the acquired reference signal and holographic measuring point sound pressure, obtains a reference phase from the reference signal, obtains the relative phase relation of the holographic measuring point source pressure acquired by the microphone array through the phase relation between the reference signal and the holographic measuring point source pressure, and finally obtains the self-spectrum correlated density matrix of the sound source signal to be measured through the spherical wave basis function reconstruction computing. Through the reconstruction of the sound source signal to be measured on the holographic measurement surface acquired by the microphone array, the method can analyze the sound source to be measure with random shape and obtain the three-dimensional spectrum correlated density distribution of the sound source to be measured. Compared with the traditional method of reconstructing the stable sound source to be measured through spherical wave superposition, the method can be applicable to the circular stable sound source to be measured with breakthrough on the requirements of the shape of the sound source to be measured.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Grid-based spatial multi-scale fast clustering method
ActiveCN108537274AReduce complexityImprove clustering efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeighborhood searchGlobal grid
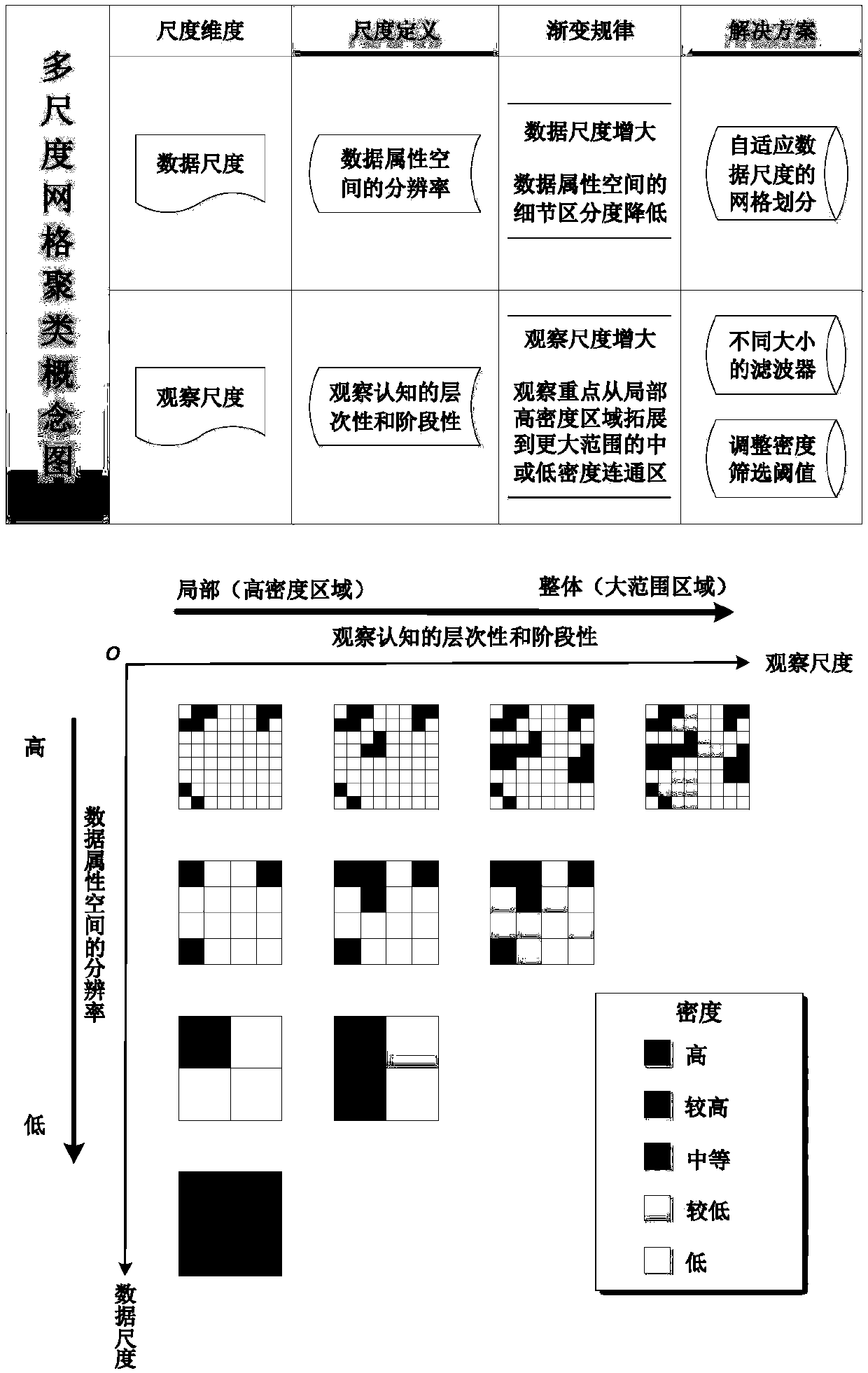
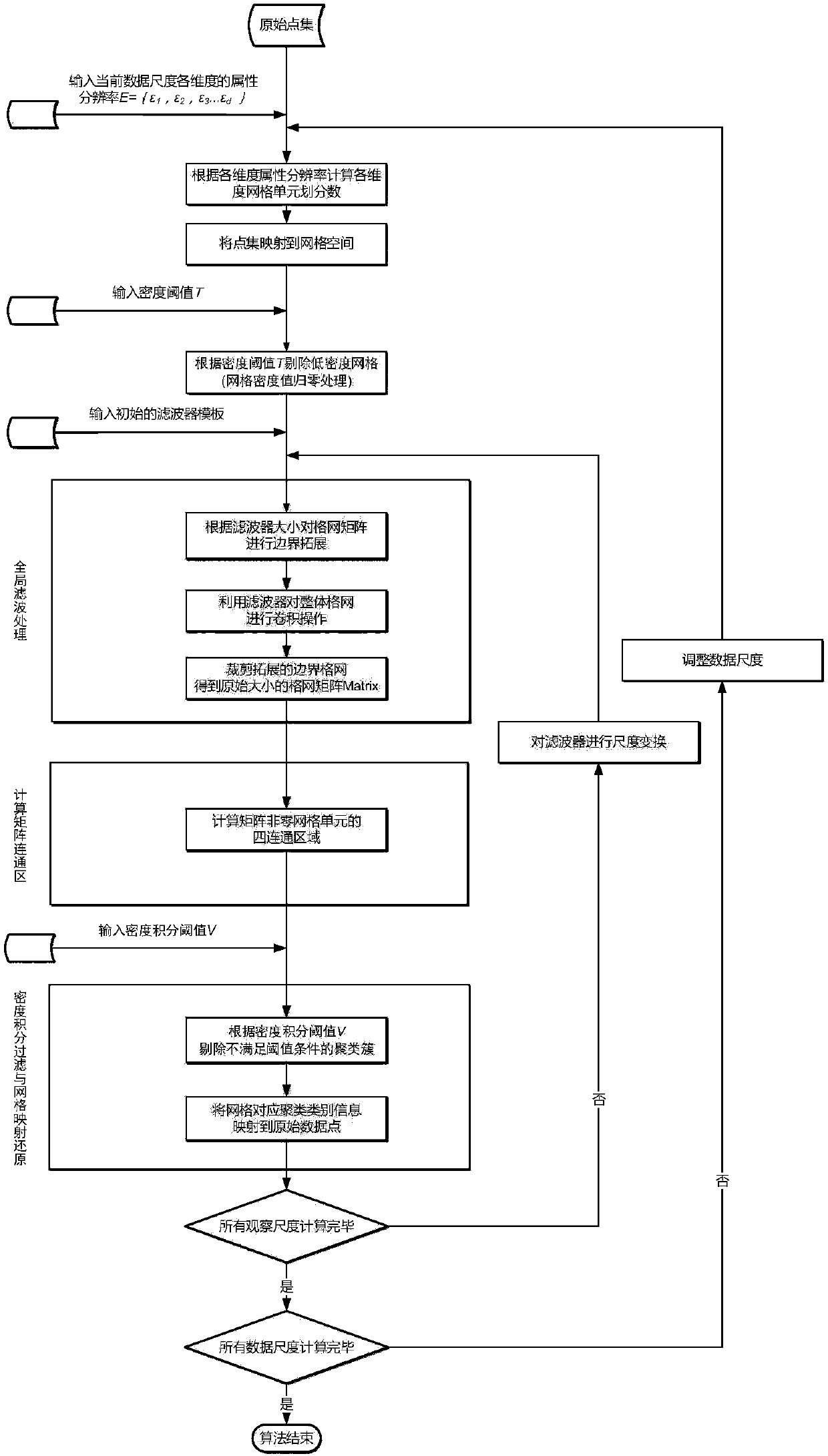
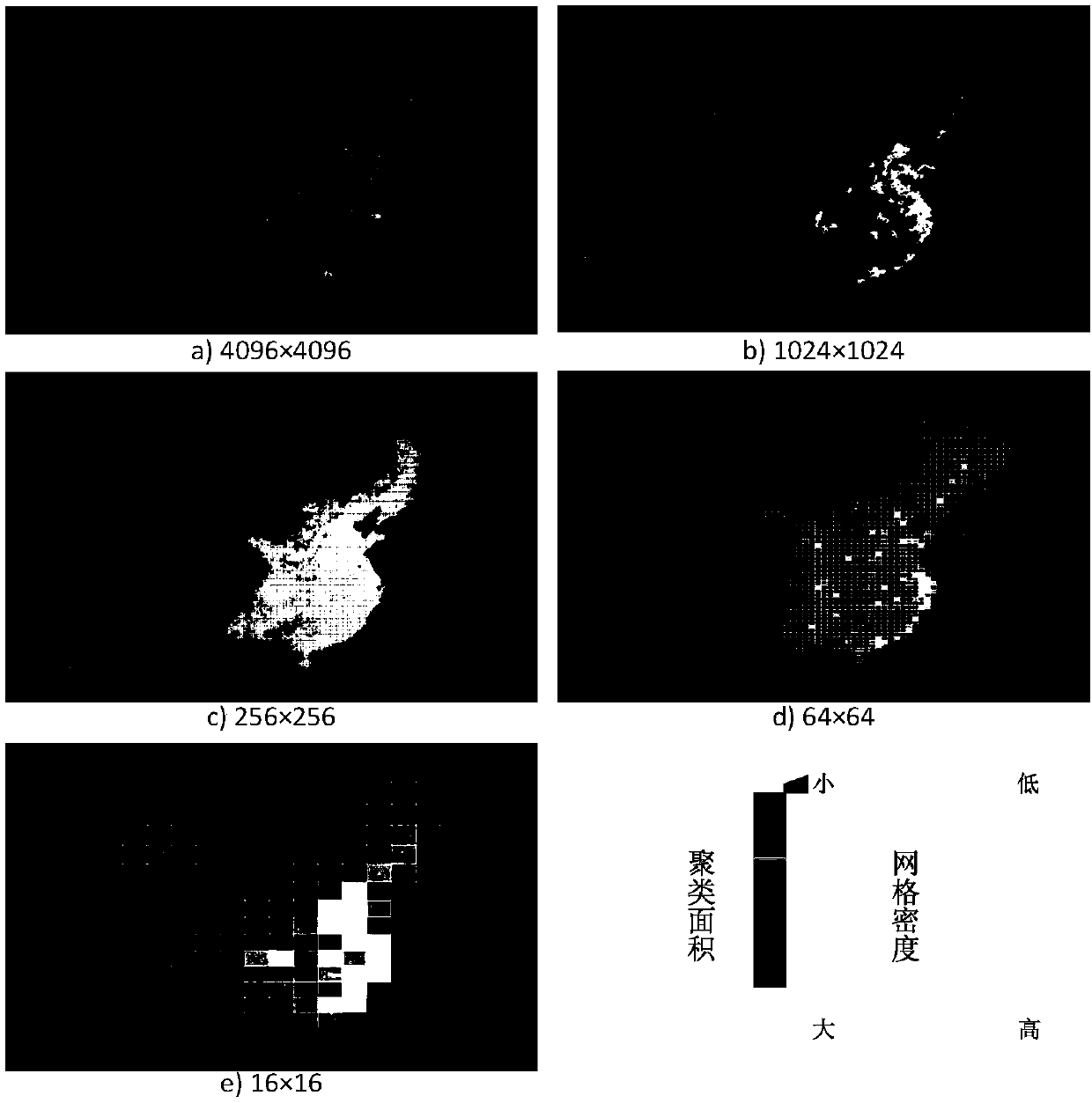
The invention discloses a grid-based spatial multi-scale fast clustering method. The method includes the following steps that: S1, a data scale is selected, the size of grids is determined, gridding is performed on sample data, and the density values of the grids is put into statistics; S2, an initial density threshold is specified, all grids satisfying the threshold condition are reserved, and apreliminary density matrix is obtained; S3, a filter template is specified according to an observation scale, and convolution operation is performed on a global grid space; S4, a connected region is generated through neighborhood search so as to be adopted as a preliminary clustering result, integration operation is performed on the grids, the grid space is mapped onto an original point set, and an original point set clustering result is obtained; S5, the observation scale is adjusted, a transformed new filter is adopted to perform operation in the S3 and S4 on a result matrix again, a clustering result of the next observation scale is obtained; and S6, the data scale is changed, the S1 to S5 are repeated, clustering results under different data scales are obtained. The algorithm of the invention has the advantages of low complexity, high clustering efficiency and high precision, and can meet the requirements of real-time multi-scale clustering and visual analysis of massive point sets.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Content based general steganography analysis method of spatial-domain image
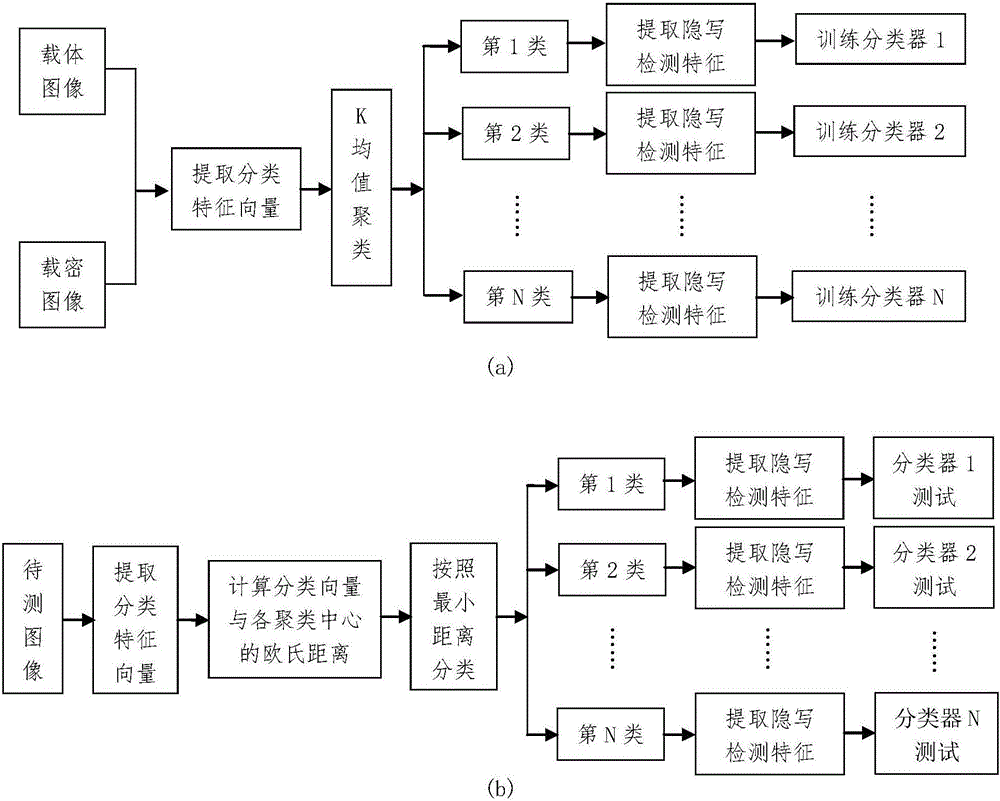
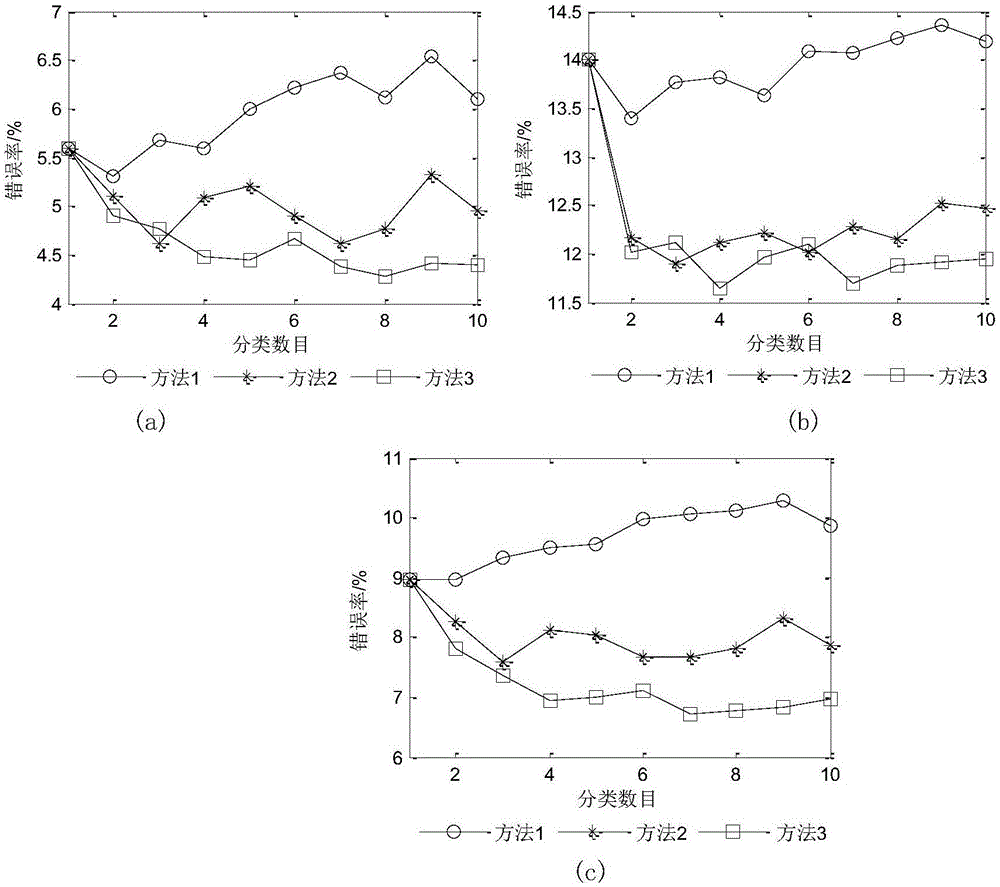
InactiveCN106548445ASteganographic detection feature aggregationGood distinguishabilityImage data processing detailsSteganalysisFeature vector
The invention provides a content based general steganography analysis method of a spatial-domain image, belongs to the technical field of information safety, and aims at describing the content complexity of the image reasonably, improving features of steganography detection effectively, and improving the accuracy of spatial-domain steganography analysis substantially on the premise that low operand is ensured. The method comprises the steps that 1) a characteristic vector of image content classification is obtained; 2) a K-means clustering algorithm is used divide a training sample into non-intersected classes; 3) a second-order joint probability density matrix in the corresponding vertical direction is calculated and serves as a characteristic vector of steganography detection; 4) classifier models of different types are obtained; 5) an image to be detected is given, the classification characteristic vector is calculated according to the step 1), the image to-be-detected is attributed to a corresponding class according to Euclidean distances from the image to different clustering centers, and characteristics of steganography detection are extracted according to the step 3); and 6) whether the image includes hidden information is determined. The steganography analysis method is mainly applied to image processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
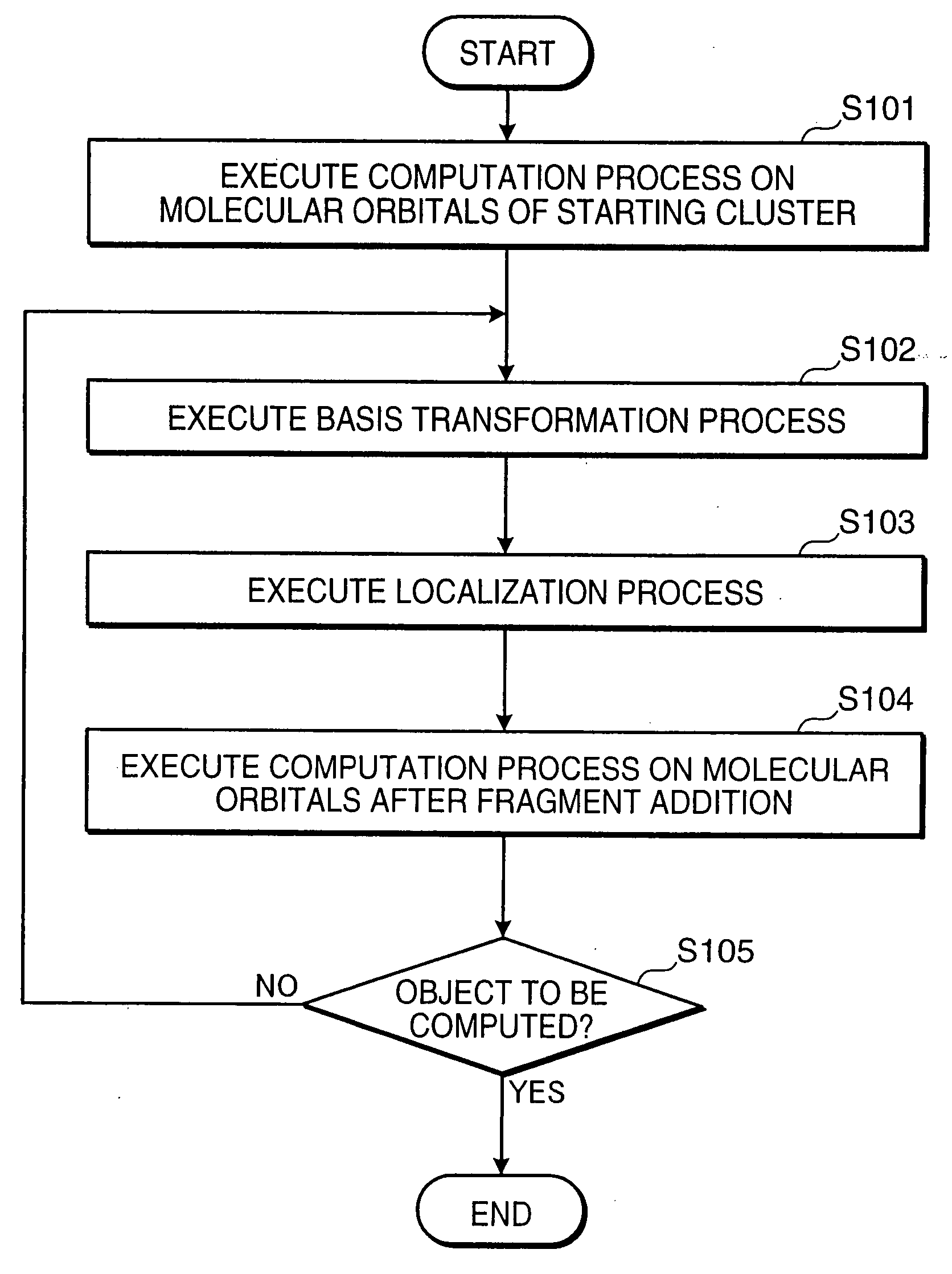
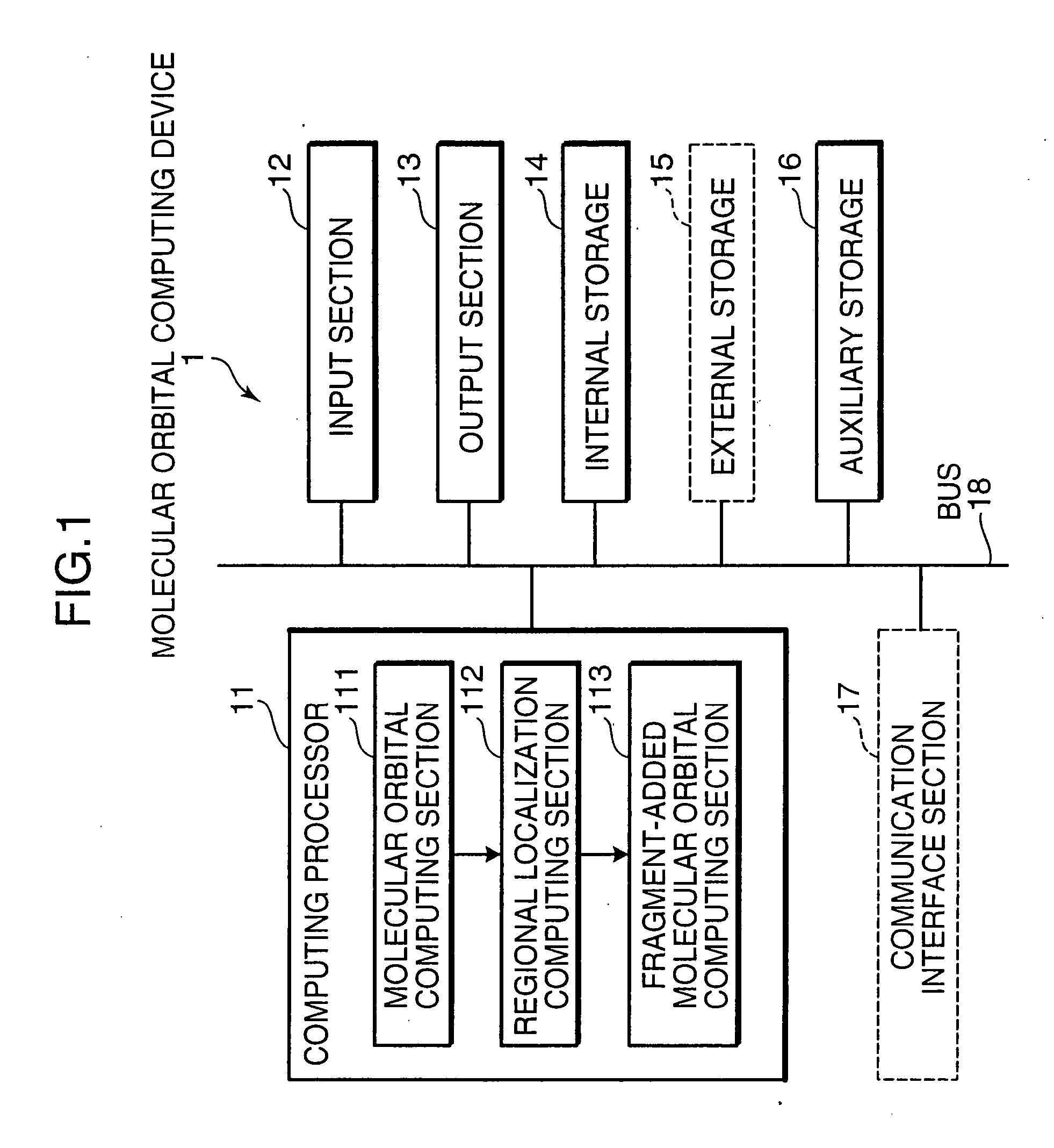
Molecular Orbital Computing Device for Elongation Method
InactiveUS20080059549A1Eliminate needHigh speed machiningAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputational theoretical chemistryAtomic orbitalElectronic states
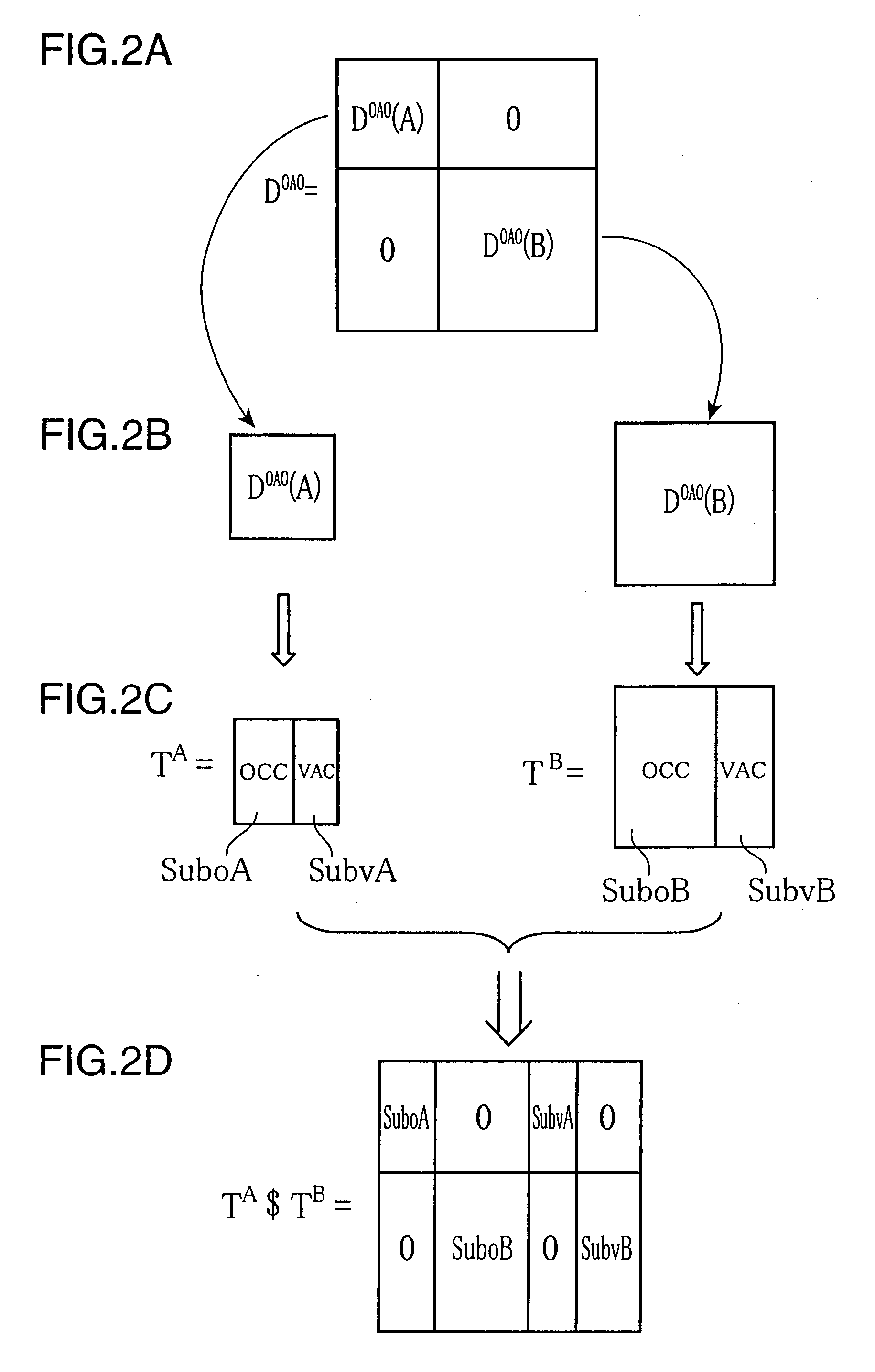
A molecular orbital computing device, method, program, and a recording medium recorded with the program, capable of computing electronic states at a high speed by an elongation method, are provided. A molecular orbital computing device (1) for determining molecular electronic states by the elongation method implements a localization process of transforming a canonical molecular orbital by an atomic orbital basis into a regional localized molecular orbital by using the formulas expressed by: YCMORLMO=CROCML+U CAORLMO=CAOCMOYCMORLMO where YCMORLMO is a transformation matrix for transforming into a regional localized molecular orbital by a canonical molecular orbital basis, CROCMO+ is a transpose matrix of a matrix representing a canonical molecular orbital by a regional atomic orbital basis, U is a transformation matrix for erasing elements in an off-diagonal block in a density matrix DRO by the regional atomic orbital basis by a Jacobi method, CAORLMO is a matrix representing a regional localized molecular orbital by the atomic orbital basis, and CAOCMO is a matrix representing the canonical molecular orbital by the atomic orbital basis.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
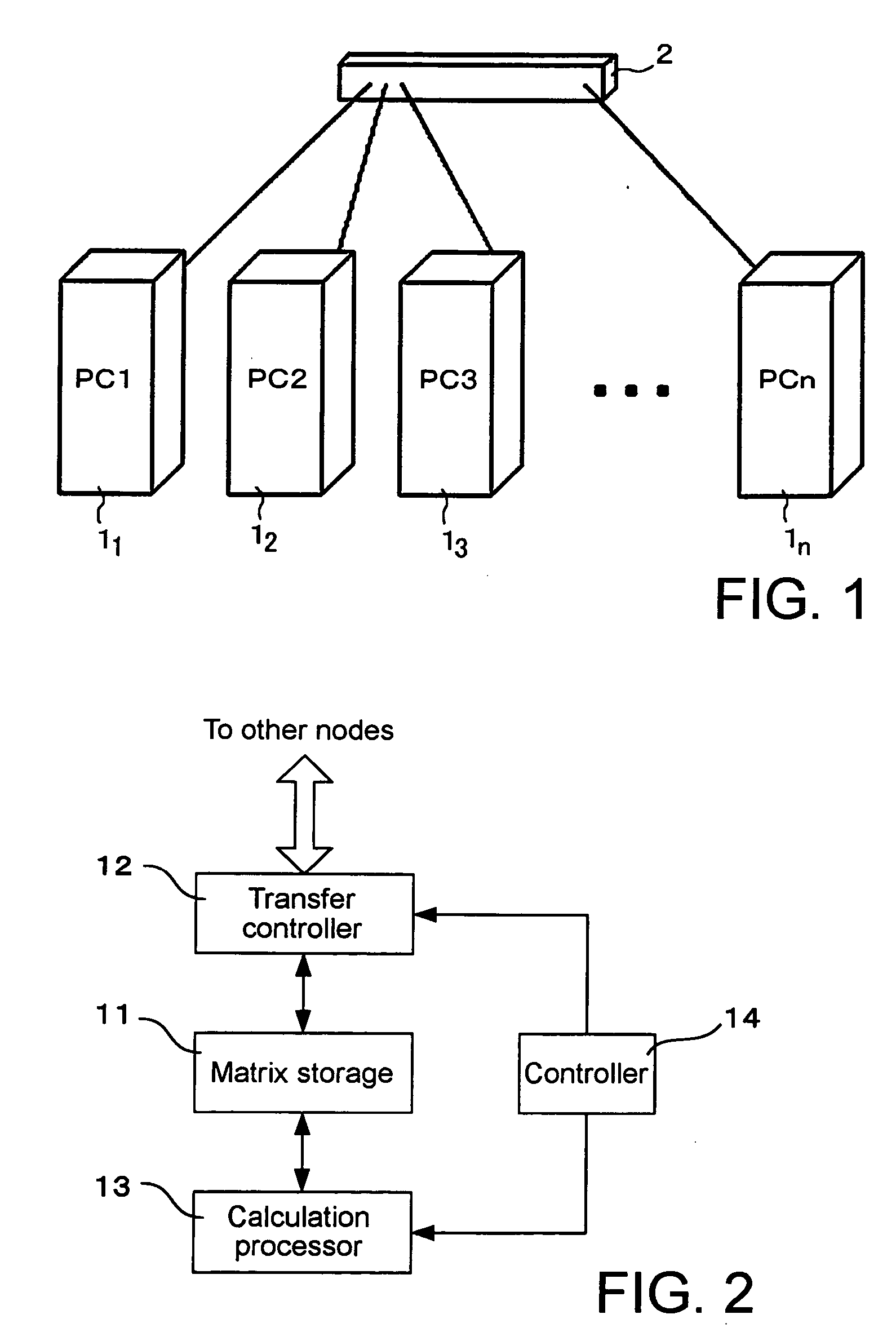
Parallel calculation method and device
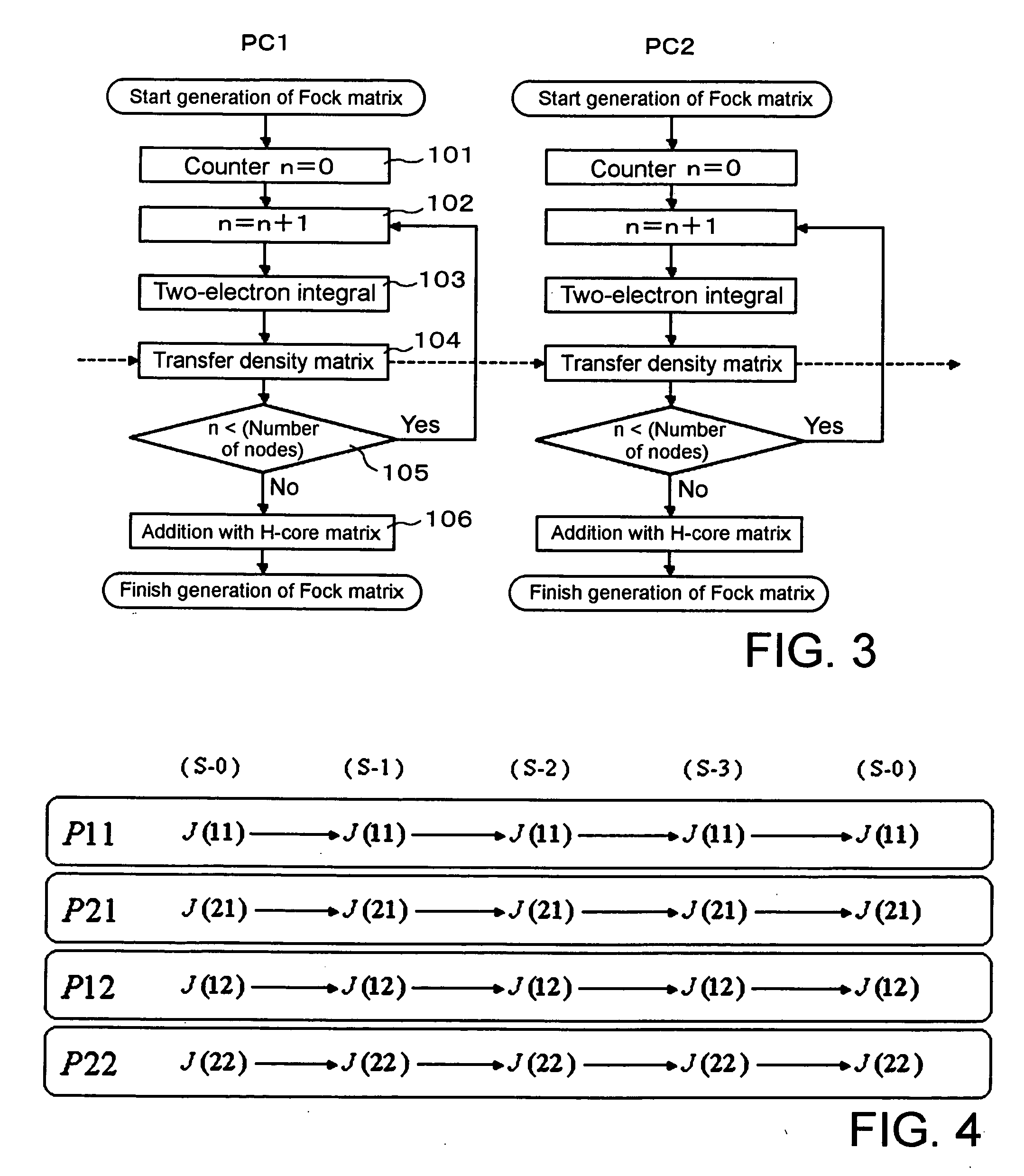
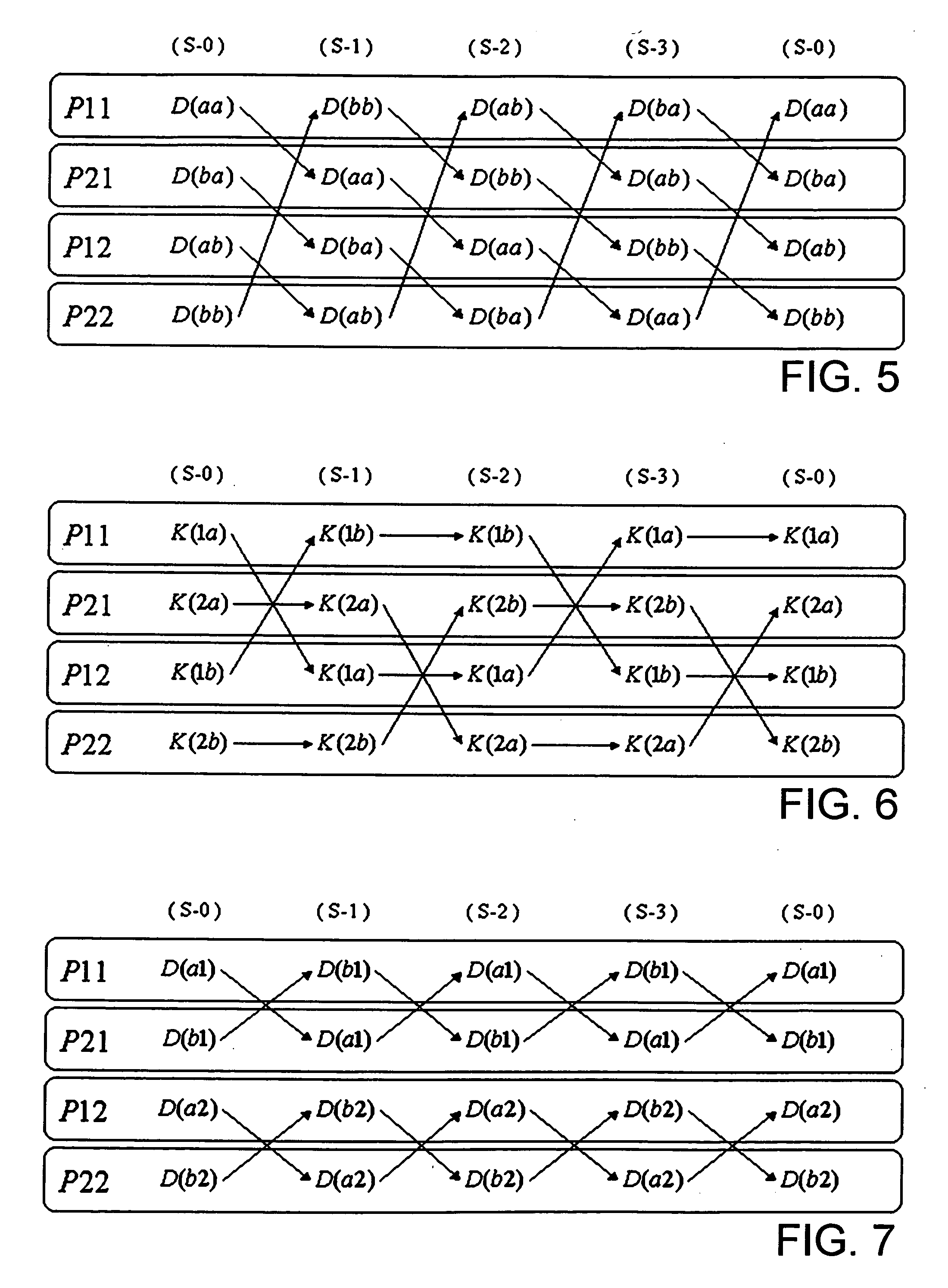
InactiveUS20060271301A1Reduce the amount of calculationExpand the working areaAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingDistributed memoryComputer cluster
A method for executing calculation of the Hartree-Fock method in a molecular orbital method by a distributed memory parallel computing system includes the steps of: using a computer cluster made up of a plurality of computers; dividing a density matrix into multiple density submatrixes and distributing them to the individual computers and storing therein; and executing calculation processes such as twoelectron integration or the like relating to density submatrixes in each computer while sequentially transferring the multiple density submatrixes between the multiple computers.
Owner:NEC SOLUTION INNOVATORS LTD
Feature extraction method for automatic recognition of identity through electrocardiosignal
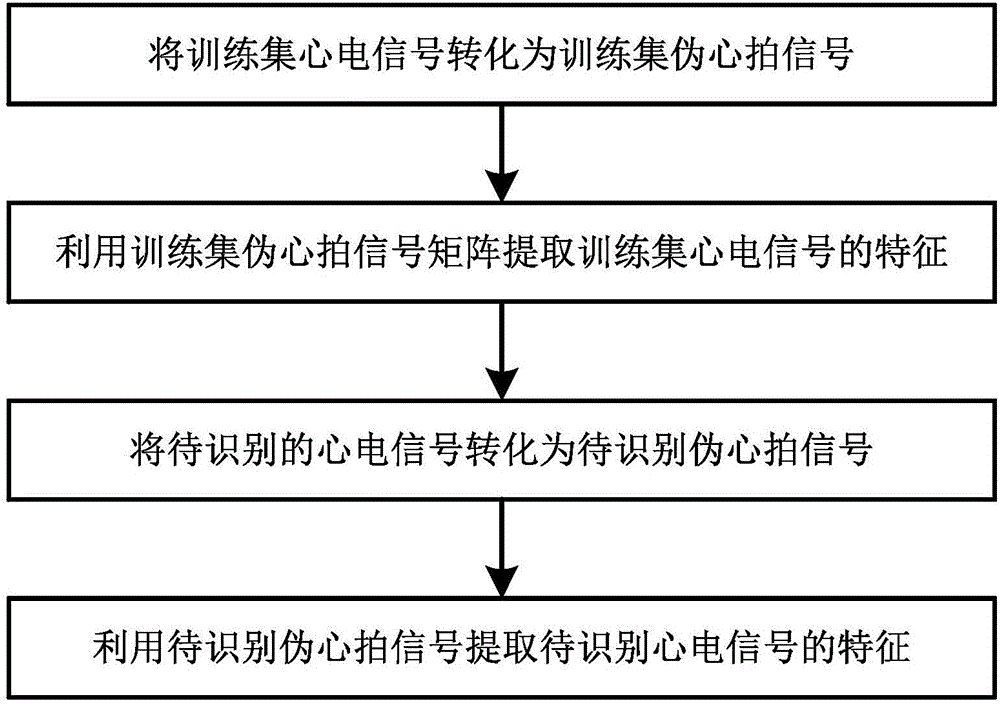
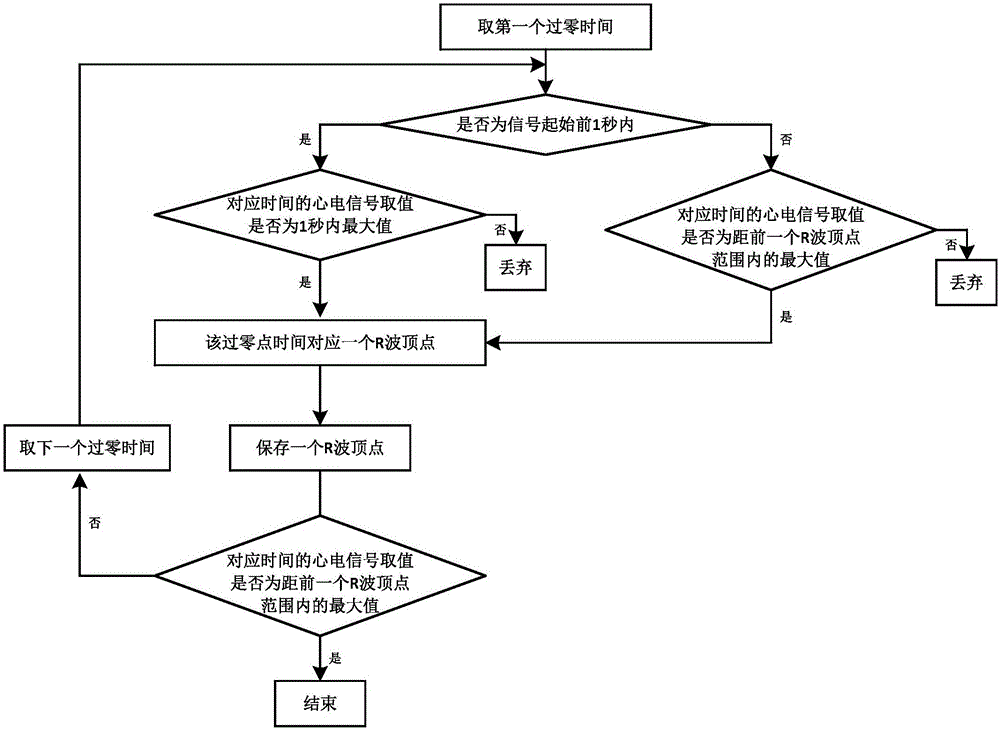
ActiveCN106485213AImprove recognition accuracyReduce signal acquisition timePerson identificationPhysiological signal biometric patternsTime domainEcg signal
The invention discloses a feature extraction method for the automatic recognition of identity through an electrocardiosignal, and the method comprises the steps: (1), enabling a training set electrocardiosignal to be converted into a training set pseudo cardiac beat signal, removing the noise in the training set electrocardiosignal, searching the second-order differential zero point of the training set electrocardiosignal, detecting an R wave of the training set electrocardiosignal, and forming a training set pseudo cardiac beat signal matrix through segmenting; (2), extracting the features of the training set electrocardiosignal through employing the training set pseudo cardiac beat signal matrix: calculating the power spectrum density matrix and autocorrelation matrix of the training set pseudo cardiac beat signal matrix, and carrying out the fusion of training set transform domain features and training set time domain features; (3), converting a to-be-recognized electrocardiosignal into a to-be-recognized pseudo cardiac beat signal; (4), extracting the features of the to-be-recognized electrocardiosignal through the to-be-recognized pseudo cardiac beat signal. The method effectively reduces the signal collection time needed by the identity recognition, improves the recognition accuracy, and reduces the calculation cost.
Owner:烽想(山东)医疗科技有限公司
Dynamic calibration method for high-frequency force balance
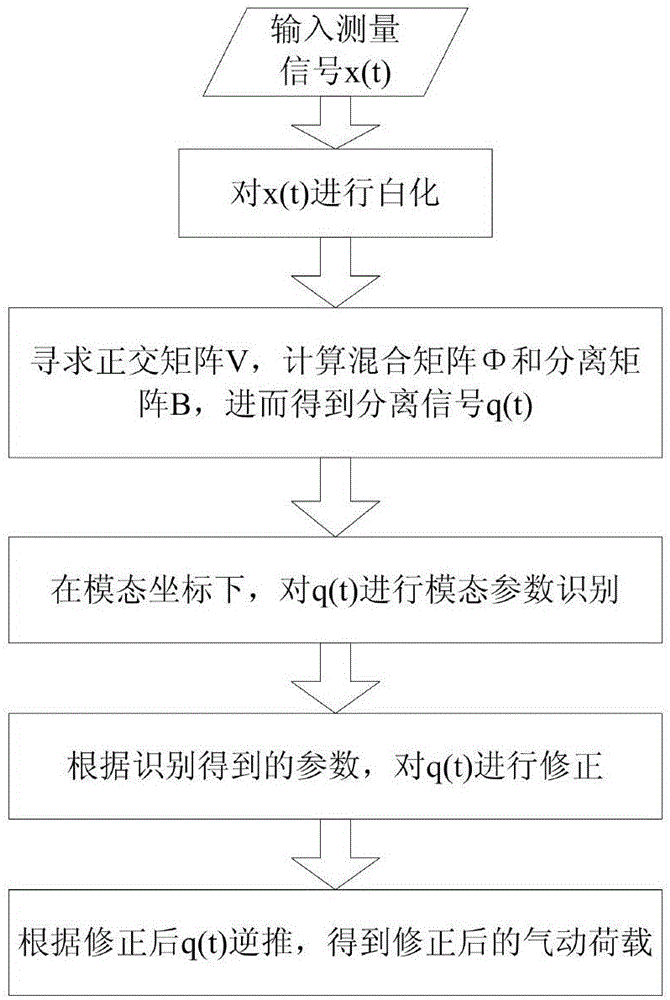
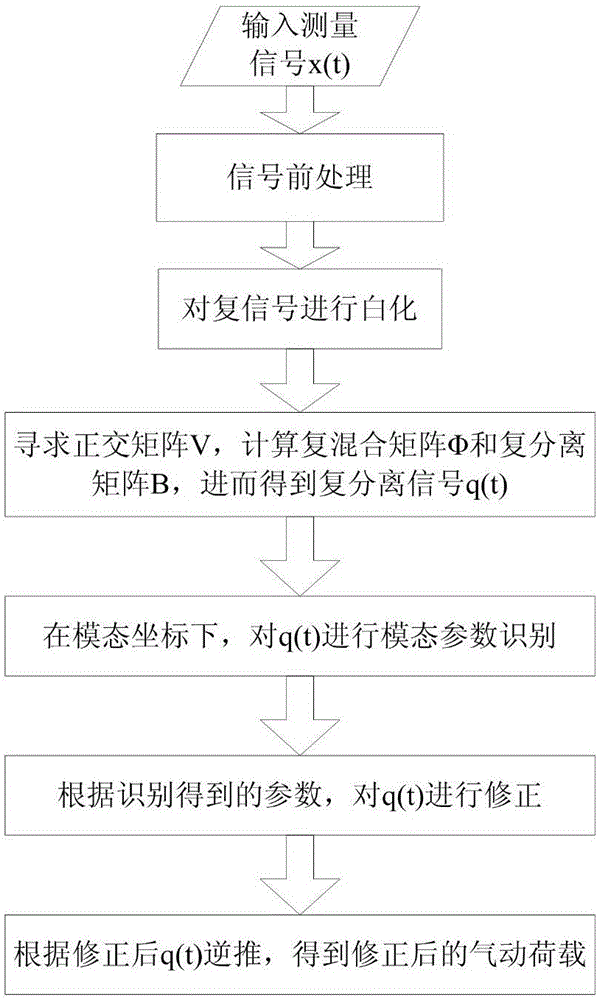
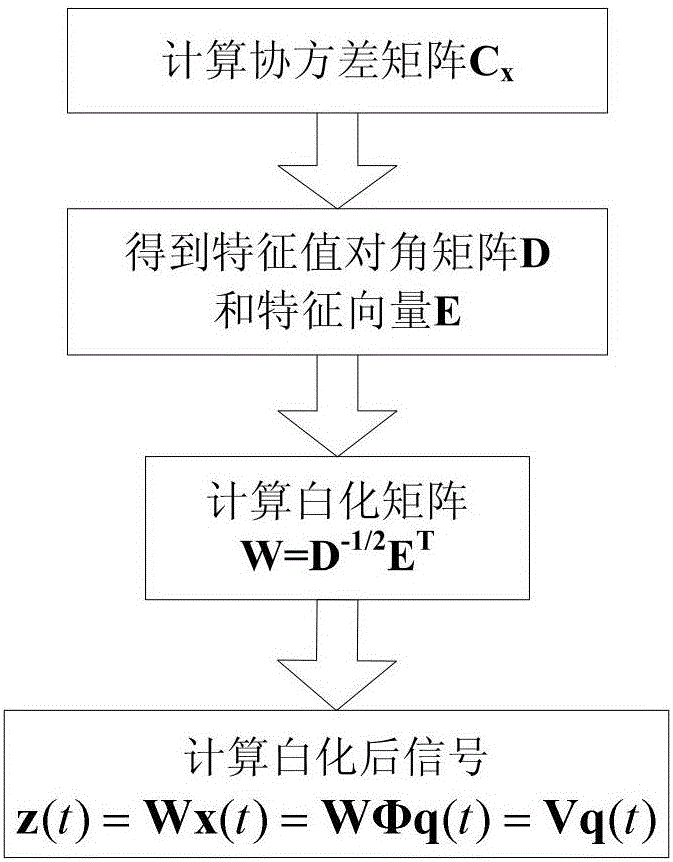
ActiveCN106709460ASimple test stepsEfficient separationAerodynamic testingCharacter and pattern recognitionCurve fittingParametric identification
The invention discloses a dynamic calibration method for a high-frequency force balance, which comprises the steps of performing whitening on a measurement signal x(t) to acquire a whitened signal z(t); seeking an orthogonal matrix V, enabling the whitened signal z(t) to equal to Vq(t), and thus acquiring a separated signal q(t); performing natural frequency and modal damping ratio recognition on the separated signal in modal coordinates; correcting the separated signal according to recognized parameters; and inversely deducing according to the separated signal to acquire a corrected pneumatic load. According to the invention, separation is performed on a coupling signal, and for independent components acquired by separation, natural frequency and modal damping ratio recognition is performed on the separated signals one by one by adopting a curve fitting method through combining aerodynamic characteristics, so that a dynamic amplification effect of a modal coupling system is corrected and eliminated, a real aerodynamic load spectrum density matrix is acquired finally, the reliability of parameter recognition and corresponding HFFB (High-Frequency Force Balance) dynamic signal calibration can be improved to the maximum extent, and an important basis is laid for subsequent accurate estimation for high-rise building prototype wind-induced responses.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Modal analysis method and device of driving belt
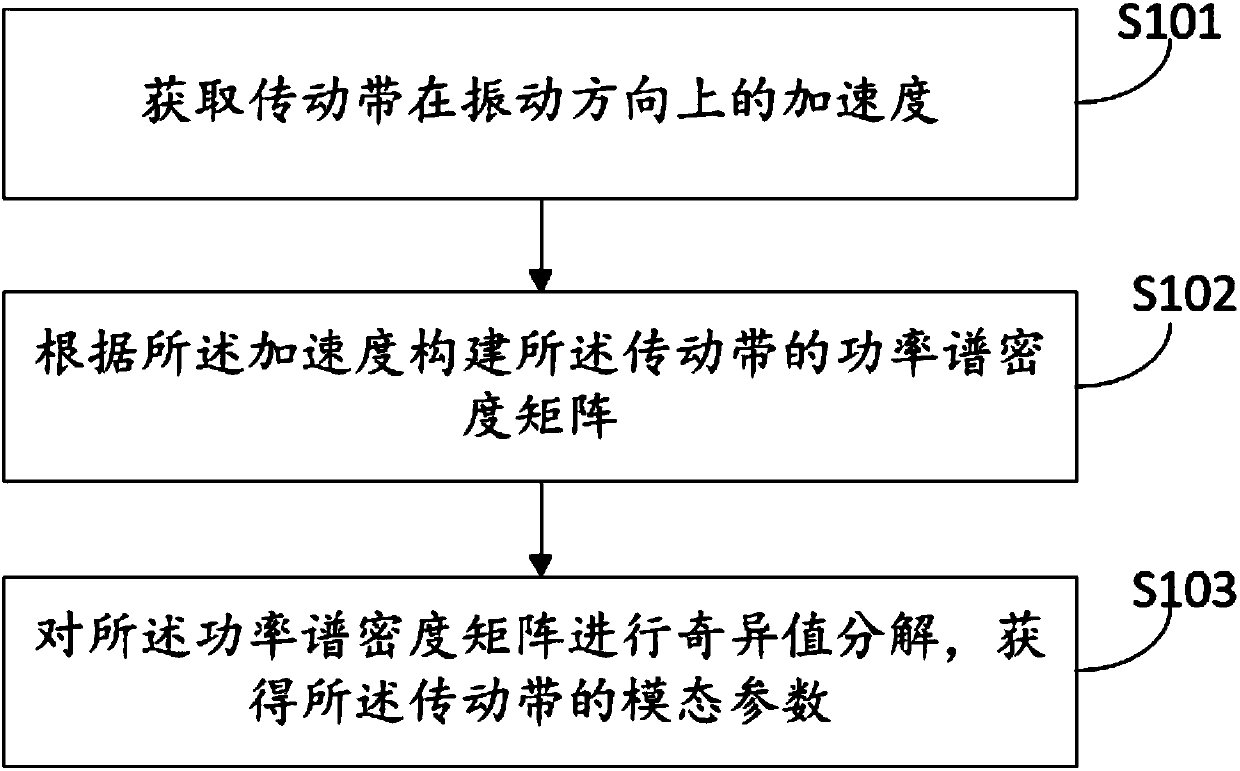
InactiveCN107782547AModal analysis is accurateGood for dynamic structure designMachine part testingSingle degree of freedomSingular value decomposition method
The invention discloses a modal analysis method and device of a driving belt. The modal analysis method and device are used for solving the technical problem that according to a peak value detection method, the vibration types and the damping ratios of all modals of the driving belt cannot be measured, and therefore complete modal parameters of the driving belt cannot be obtained, which is not beneficial to modal analysis of the driving belt. By ceaselessly obtaining acceleration signals of the driving belt in the vibration direction, characteristics when the driving belt is vibrated can be obtained, a power spectrum density matrix is constructed through the acceleration signals, according to a singular value decomposition method, the power spectrum density matrix is decomposed into a series of power spectrum density functions of a single-degree-of-freedom system, the modal parameters of the vibration types, the damping ratios and the like of the driving belt can be obtained so that the modal analysis of the driving belt can be more accurate, which is beneficial to dynamic structural design of the driving belt and fault diagnosis in the running process.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
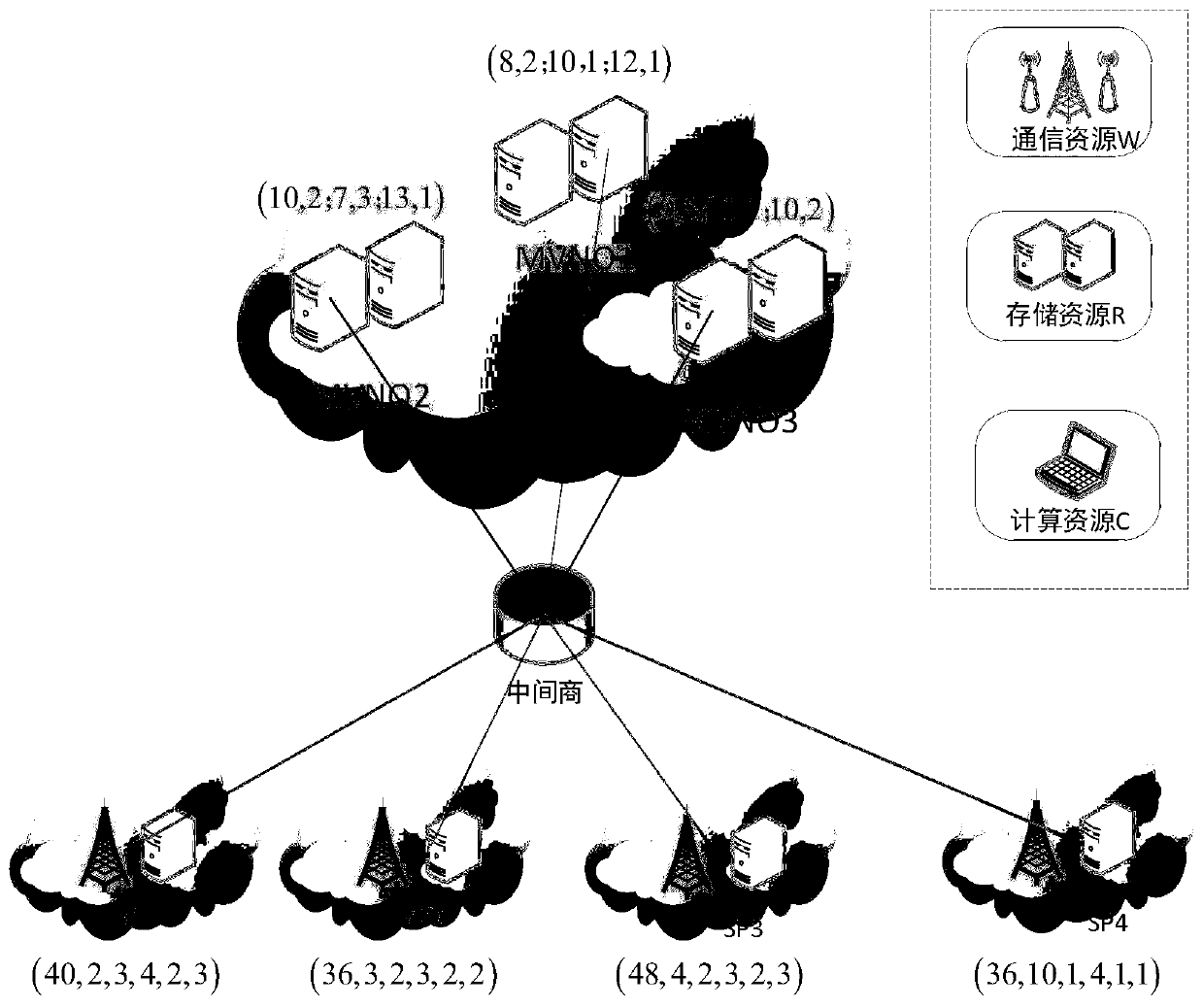
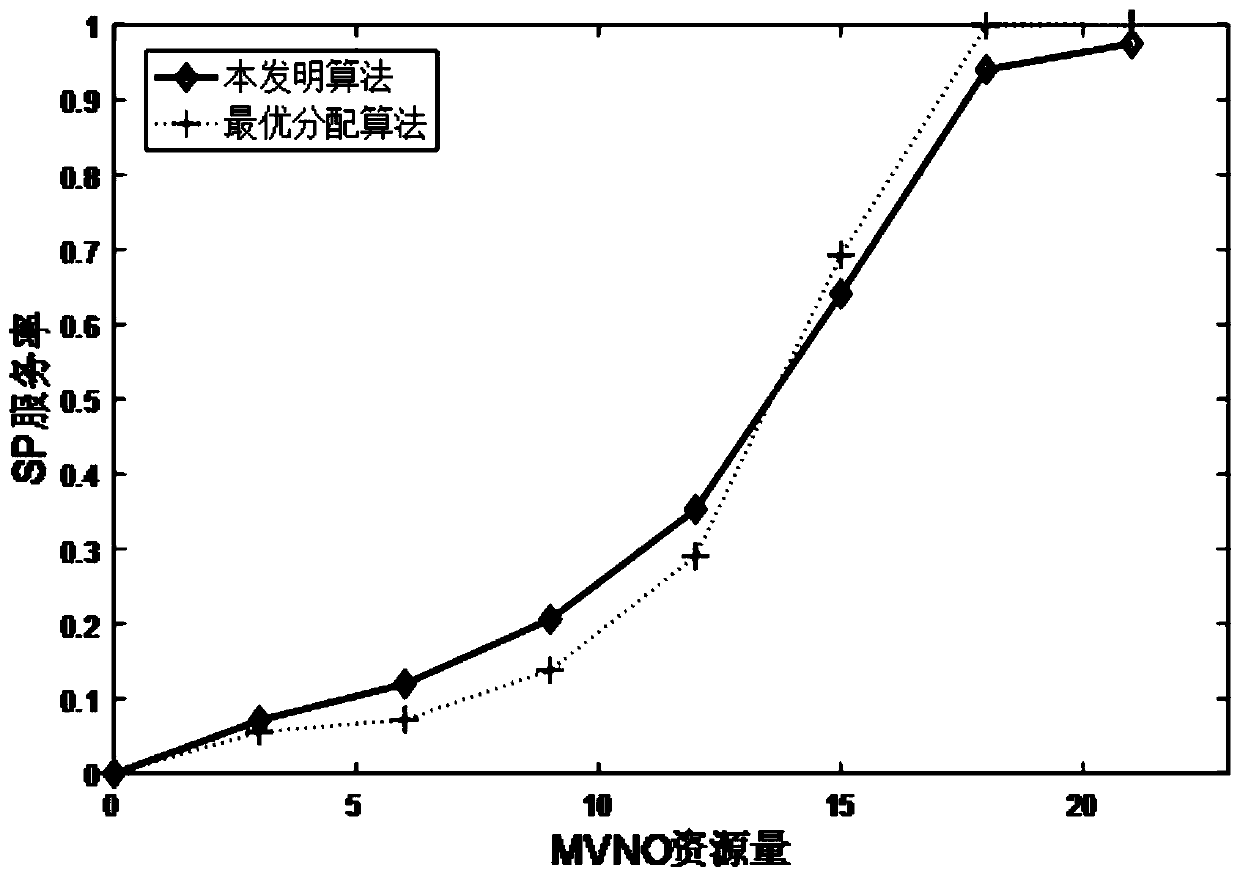
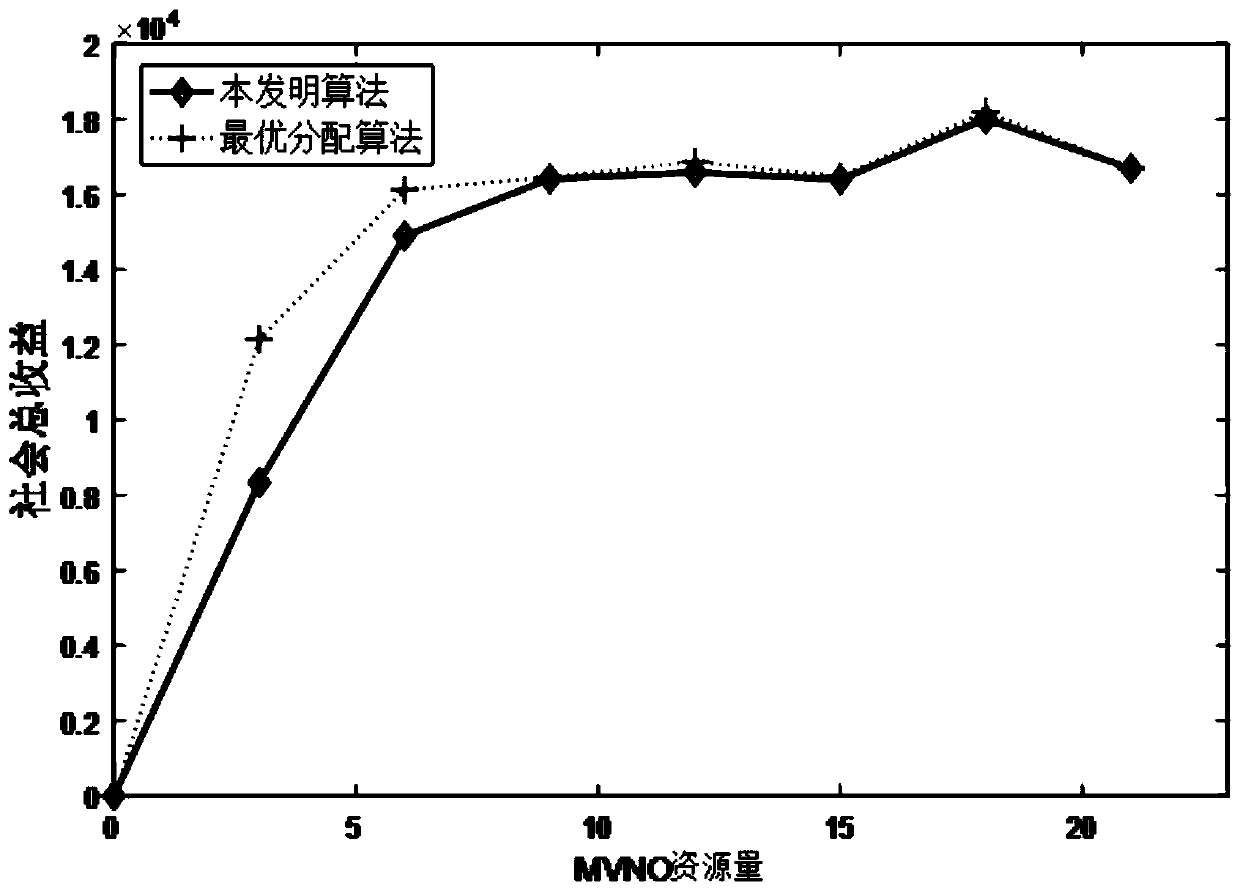
Online combined resource allocation and payment method based on bilateral auction
The invention discloses an online combined resource allocation and payment method based on bilateral auction. The method comprises the steps that each buyer (SP) provides quotation information; each seller (MVNO) provides offer information; an auctioneer (the intermediary) calculates a bidding density function and constructs a joint bidding density matrix, and a bidding density sorting vector is obtained through ascending order or descending order arrangement; whether the resources owned by the seller associated with each element completely meet the resources applied by the buyer or not is sequentially judged, and if yes, the corresponding seller and the buyer are taken as a bidding winning mechanism; then, based on the critical minimum bidding density as a reference, a to-be-charged fee qm of each bid winning seller is determined; a to-be-paid fee pn of each bid winning buyer is determined based on the critical maximum bidding density; and finally the buyers and the sellers corresponding to the pn>=qm are selected for matching to realize resource allocation. The method has the advantages that the distribution waiting time can be remarkably shortened, the sum of benefits of three parties is maximized, the convergence speed is high, the complexity is low, and implementation is easy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
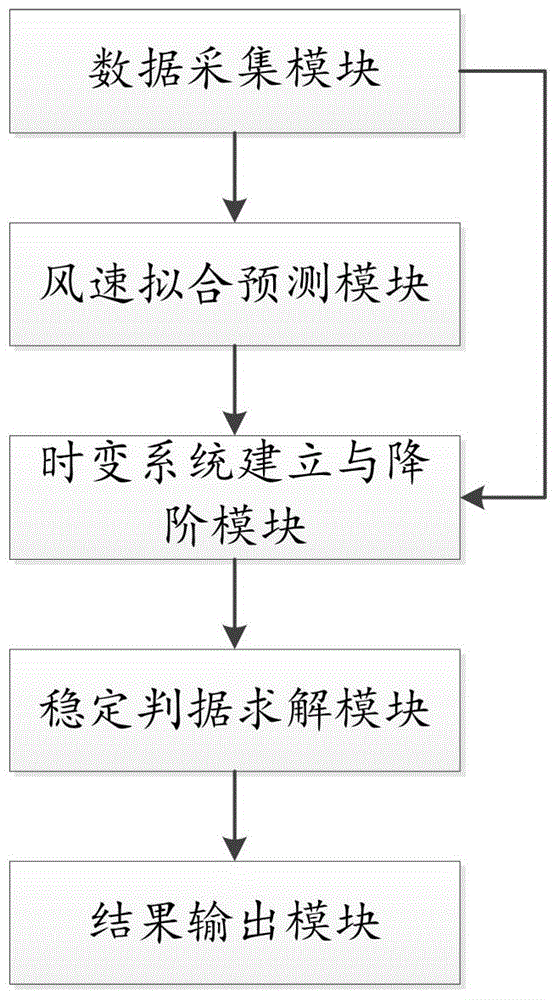
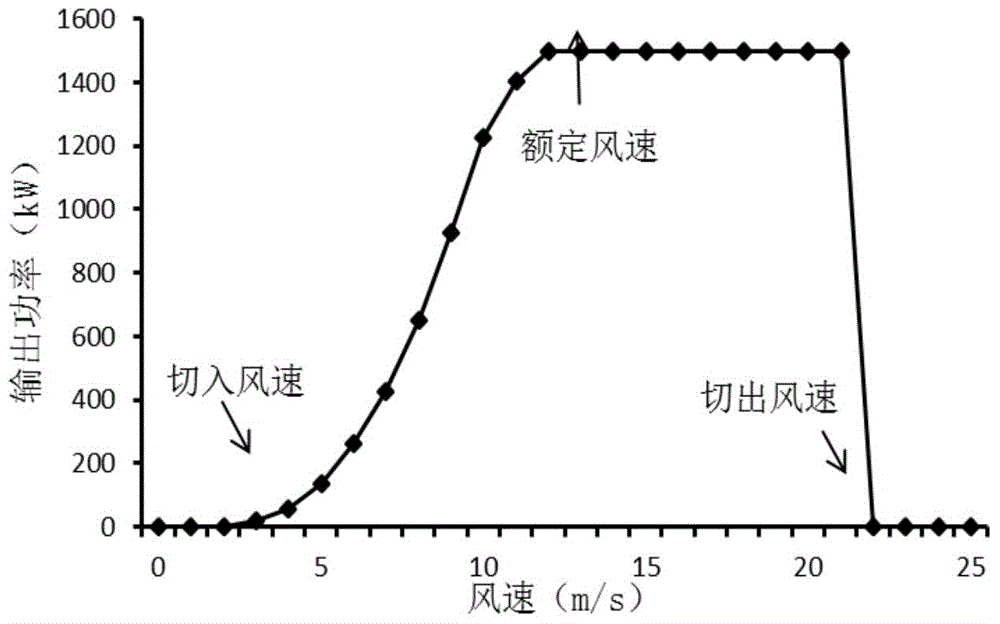
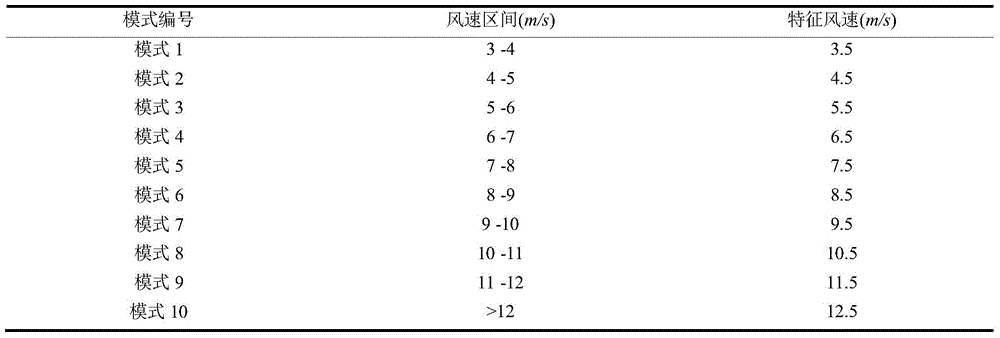
Stability analysis system and method of time-varying power system
ActiveCN104680017ASolve the difficult problem of variable stabilitySolve the problem that the stability is not easy to judgeClimate change adaptationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectric power systemSlope stability analysis
The invention discloses a stability analysis system and method of a time-varying power system. The system comprises a data acqusition module, a wind velocity fitting prediction module, a time-varying system establishment and order reduction module, a stability criterion solving module and a result output module, wherein the data acqusition module is used for acquiring data; the wind velocity fitting prediction module is used for performing fitting prediction on conditional wind velocity trend in short time, sectioning the wind velocity and calculating a conditional characteristic wind velocity probability density matrix of each section according to a fitting model; the time-varying system establishment and order reduction module is used for establishing a continuous markov time-varying power system model considering a wind velocity random characteristic and reducing order of the system; the stability criterion solving module is used for solving whether the system is stable by using a feasibility problem solving method in a linear matrix inequality. Through the stability analysis system and method of the time-varying power system, the problem that the stability of the time-varying power system is difficult to distinguish caused by the wind velocity random characteristic in case of fan connection can be effectively solved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Random data-based power system small disturbance stability analysis online identification method
InactiveCN109510217AEasy to calculateAdaptablePower oscillations reduction/preventionSingular value decompositionWide area
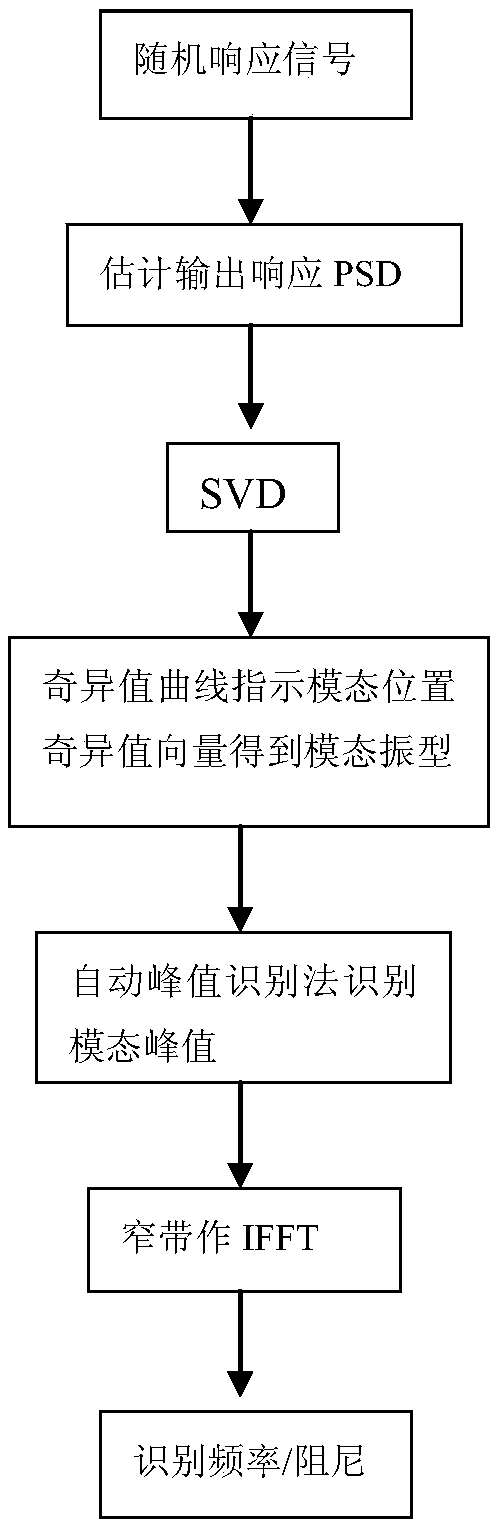
The invention relates to a random data-based power system small disturbance stability analysis online identification method and belongs to the technical field of power system operation and maintenance. The method includes the following steps that: step 1, the output power spectral density matrix of a power system small interference state space model is established; step 2, singular value decomposition is performed on the output power spectral density matrix; step 3, automatic peak identification is performed; and step 4, system modal parameter identification is performed. According to the random data-based power system small disturbance stability analysis online identification method of the invention, with active power adopted as output, singular value decomposition is performed on power spectral density, an automatic peak selection method is adopted to obtain related modal parameters such as frequency and damping, and therefore, accuracy loss caused by the introduction of MAC criteriaand the least squares method to an FDD method can be avoided, the calculation efficiency of FDD modal parameters is greatly improved, and the problem that single channel signals cannot correctly identify a plurality of oscillation modes can be solved; and wide-area measurement information is utilized to identify modal parameters online, and the influence of dimension disasters can be avoided. Themethod has the advantages of simple calculation, high adaptability, and high practical application value.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY +1
Automobile six-degrees-of-freedom wheel center force test and vibration noise contribution rate calculation method
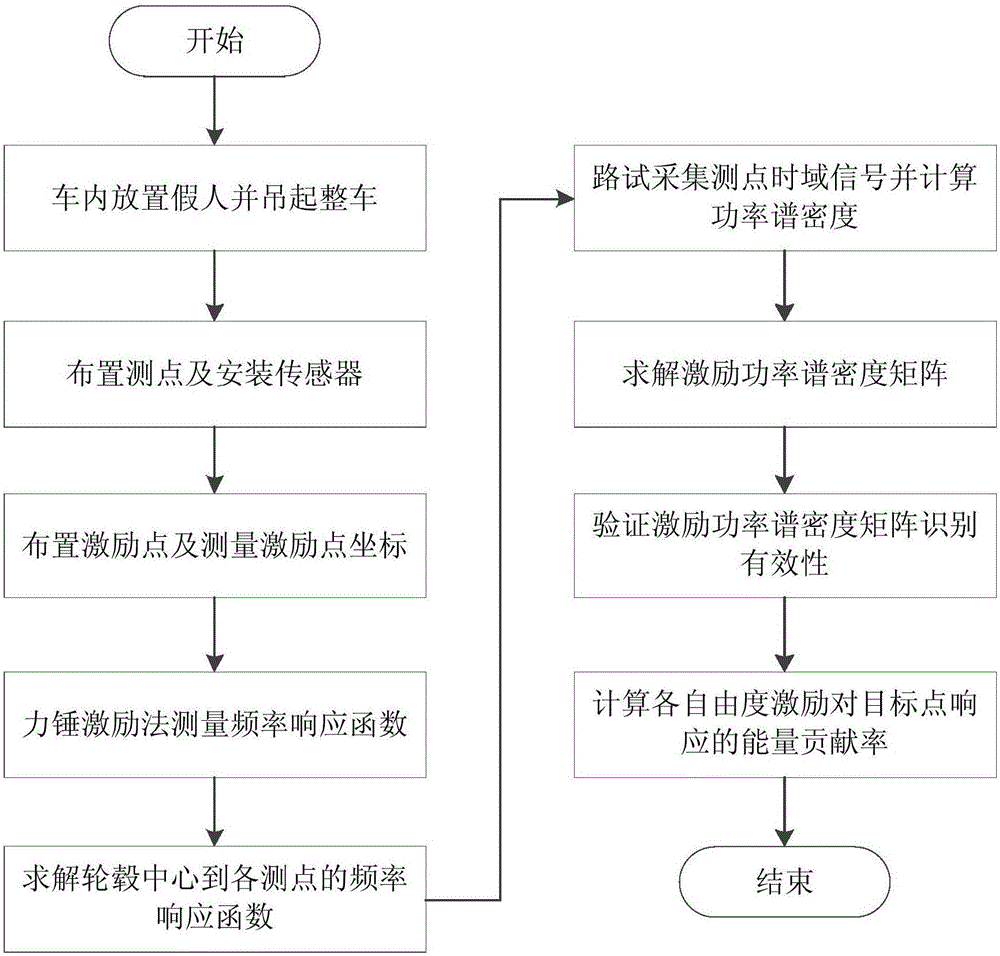
The invention discloses an automobile six-degrees-of-freedom wheel center force test and vibration noise contribution rate calculation method. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a coordinate system; arranging measurement points and installing sensors; arranging excitation points and measuring the coordinates of the excitation points; measuring a frequency response function; solving a frequency response function matrix from the center of a wheel hub to a response point; solving a frequency response function vector from the center of the wheel hub to a target point; carrying out road test; solving an excitation power spectrum density matrix; verifying the identification effectiveness of the excitation power spectrum density matrix; and calculating the energy contribution rate of each degree of freedom to the response of the target point. Compared with the prior art, the method of the invention has the following advantages: (1) as the excitation force and excitation torque of the road to automobiles can be considered simultaneously, error caused due to neglect of excitation torque in the prior art is eliminated; and (2) as the energy contribution rate of the wheel center force at each of the six correlated degrees of freedom to the vibration noise of automobiles can be calculated, error caused by an ordinary coherence coefficient method or a multiple correlation coefficient method is avoided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
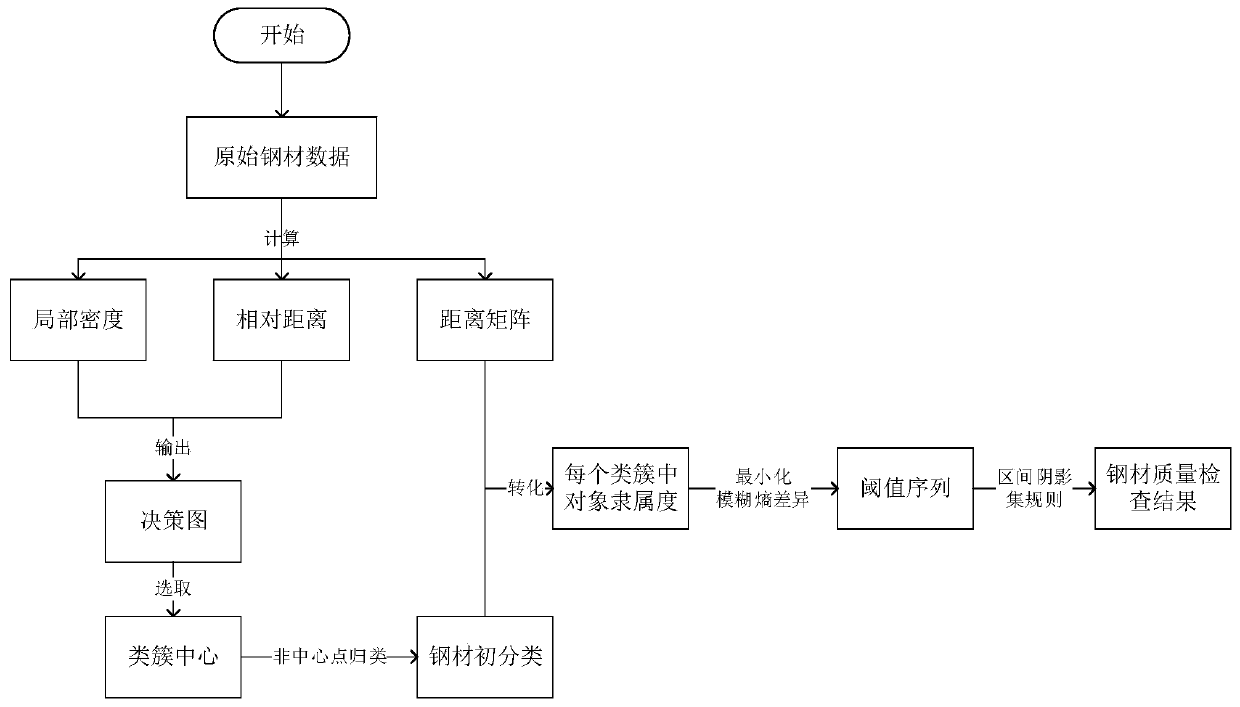
Steel quality detection method based on interval shadow set and density peak clustering
ActiveCN109858544AImprove work efficiencyHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionData setDistance matrix
The invention belongs to the field of steel quality testing, and particularly relates to a steel quality detection method based on an interval shadow set and density peak clustering. The method comprises the steps of acquiring an original steel data set, and calculating a distance matrix of the original steel data set through an Euclidean distance formula; obtaining a local density matrix and a relative distance matrix through a calculation formula in density peak clustering; outputting a decision diagram of a data set in density peak clustering, selecting m clustering centers, and classifyingnon-clustering centers to obtain m class clusters; calculating a membership value of each object in the m class clusters; determining an optimal threshold sequence of m class clusters by minimizing fuzzy entropy difference; and based on the optimal threshold sequence, performing three-way classification on non-central objects in the m class clusters by adopting a classification rule according tomembership values of the non-central objects by adopting an interval shadow set, thereby determining a quality detection result of each object, namely, obtaining a quality detection result of the original steel data set. According to the invention, the quality of steel can be effectively and rapidly detected.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for predicting crude oil density by infrared spectroscopy
ActiveCN103134763AImprove production conditionsColor/spectral properties measurementsLuminosityLength wave
A method for predicting crude oil density by infrared spectroscopy comprises the following steps: (1) collecting various crude oil samples, determining the densities of the crude oil samples by a standard method, establishing a crude oil density matrix Y; (2) determining infrared spectra of the collected various crude oil samples at different temperatures, performing first-order or second order differential processing, establishing a three dimensional spectrum matrix X (I*J*K) based on absorbances at characteristic spectrum zones of 650-1810 cm-1 and 2750-3100 cm-1, wherein I is the number of the crude oil samples, J is the wavelength point number of the characteristic spectrum zones, and K is the temperature change value, establishing a correction model with the crude oil density matrix established by the standard method by using a multidimensional partial least squares method; (3) determining the infrared spectra of a crude oil sample to be determined at different temperatures under a same condition as the collected crude oil samples, performing first-order or second order differential processing, establishing a three dimensional spectrum matrix Xun based on absorbances at characteristic spectrum zones of 650-1810 cm-1 and 2750-3100 cm-1, substituting Xun into the correction model established in step (2) to obtain the density of the crude oil sample to be determined. The method is rapid in analysis speed, high in testing accuracy, and good in repeatability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Time-varying electric power system self-adaption control method and device
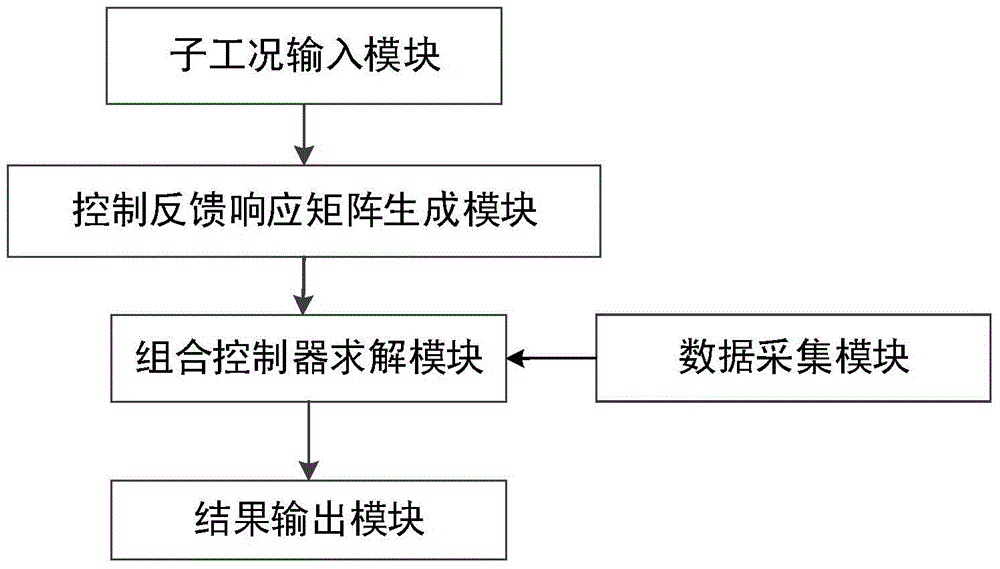
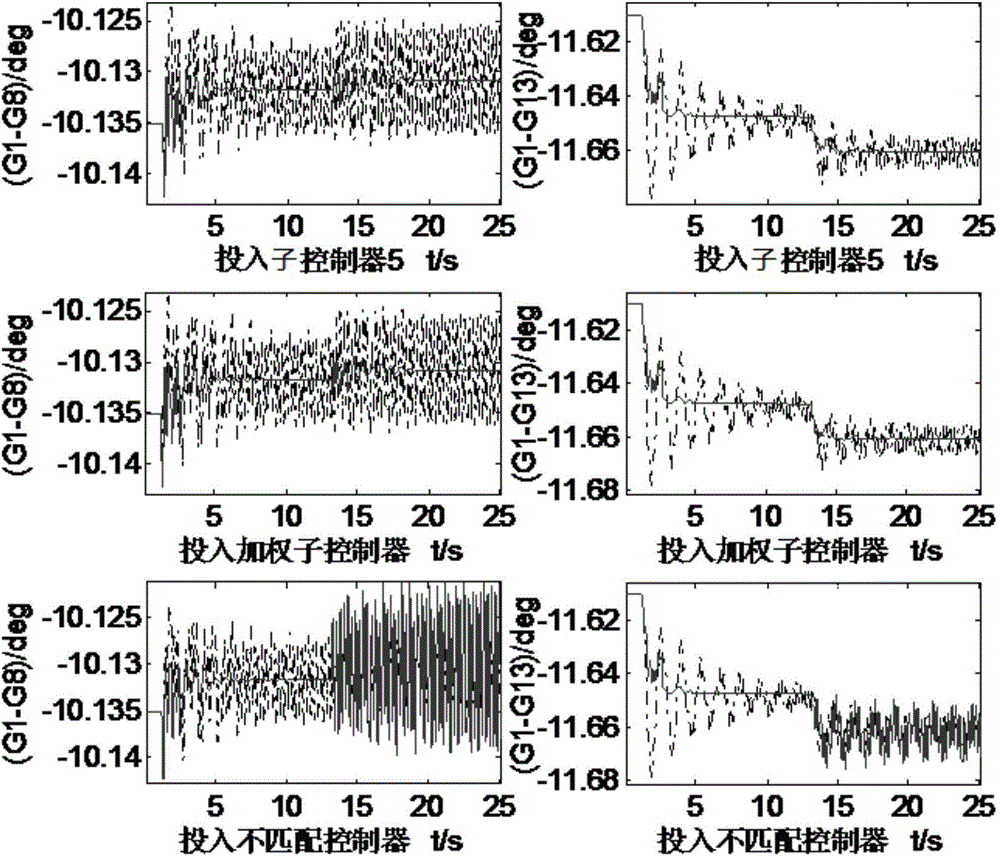
The invention relates to a time-varying electric power system self-adaption control method and a device. The device comprises a data acquisition module, a sub working condition input module, a control feedback response matrix generation module, a combination controller solution module and a result output module, wherein the data acquisition module is used for acquiring time-varying electric power system network structure parameters, generator frequency in the system and power angles; the sub working condition input module is used for acquiring different sub working condition information of the time-varying electric power system, and state transition probability density matrixes under different sub working conditions; the control feedback response matrix generation module is used for confirming control feedback response matrixes corresponding to different sub working conditions of the system; the combination controller solution module is used for confirming a system combination controller; the result output module is used for outputting the system combination controller. Through the application of the method and the device provided by the invention, the problem that a stuck fault set cannot be reasonably matched with the current working condition of the time-varying electric power system can be solved, and the impact caused on the time-varying electric power system when the controller is switched is avoided.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Current-voltage mapping construction method based on adjacent stimulus measurement model
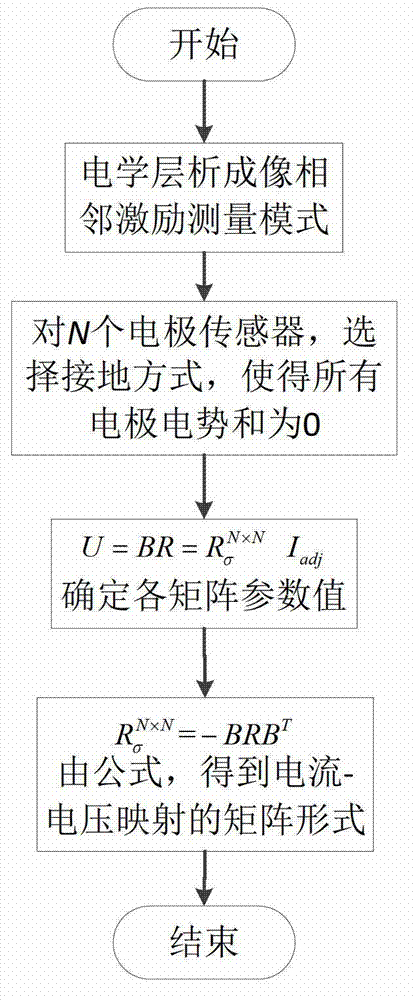
ActiveCN103163404AElectrical testingSpecial data processing applicationsGeomorphologyCurrent voltage
The invention relates to a current-voltage mapping construction method based on an adjacent stimulus measurement model. The current-voltage mapping construction method based on the adjacent stimulus measurement model aims at the adjacent stimulus measurement model of a sensor which is provided with N electrodes in electrical tomography, utilizes a formula which is reduced by calculating parameters such as an impedance matrix and an electric current density matrix to uniquely calculate a current-voltage matrix and to construct current-voltage mapping based on the adjacent stimulus measurement model. The invention provides the current-voltage mapping construction method based on the adjacent stimulus measurement model. The current-voltage mapping construction method based on the adjacent stimulus measurement model can be applied to a direct reconstruction algorithm in an electrical tomography field, provides direct physical significance of the current-voltage mapping, does not relate to matrix inversion and is easy to operate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Automatic cell counting method based on dynamic learning for microscope
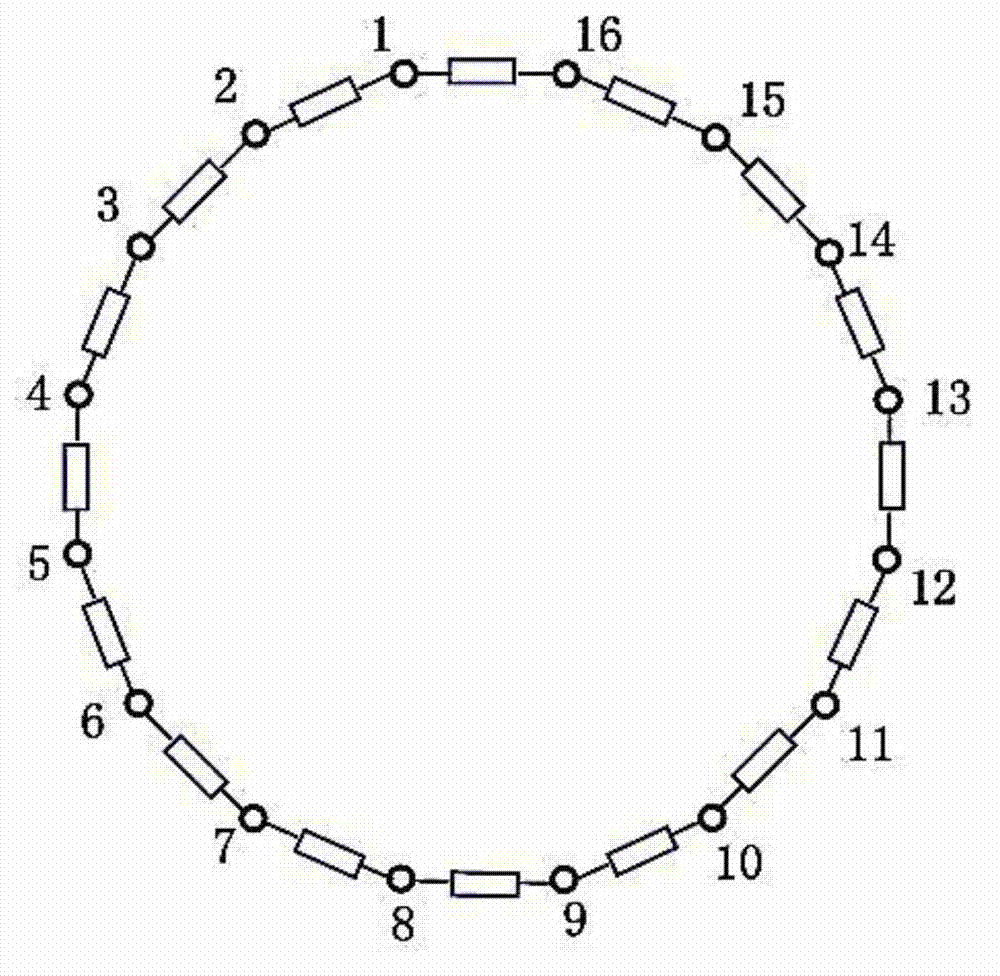
ActiveCN110516584AThe realization principle is simpleSolve the sticky counting problemImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorAlgorithm
The invention discloses an automatic cell counting method based on dynamic learning for a microscope, and the method comprises the steps: learning the mapping relation between the pixel-level featuresof cells and a distribution function, and obtaining the distribution result of a new cell image at the pixel level; the method comprises the steps that firstly, manually labeling cells and a background of a to-be-recognized image, each cell is represented by a point, and a labeled area with the point as the center point is obtained; then constructing a density function, acting on the marking areaof each cell, and obtaining a corresponding density matrix by taking the marking point as the center; wherein the size of each element value in the density matrix represents the density distributionof the cells in units of pixels, and summing the elements of the whole matrix to obtain the total number of the cells. By establishing the model and learning the relationship between the feature vector of each pixel point in the original image and the corresponding element value in the density matrix, the mapping from the features to the density can be determined, so that the estimation result ofthe cell quantity can be obtained according to the mapping relationship.
Owner:杭州图谱光电科技有限公司
Data Display System and Method
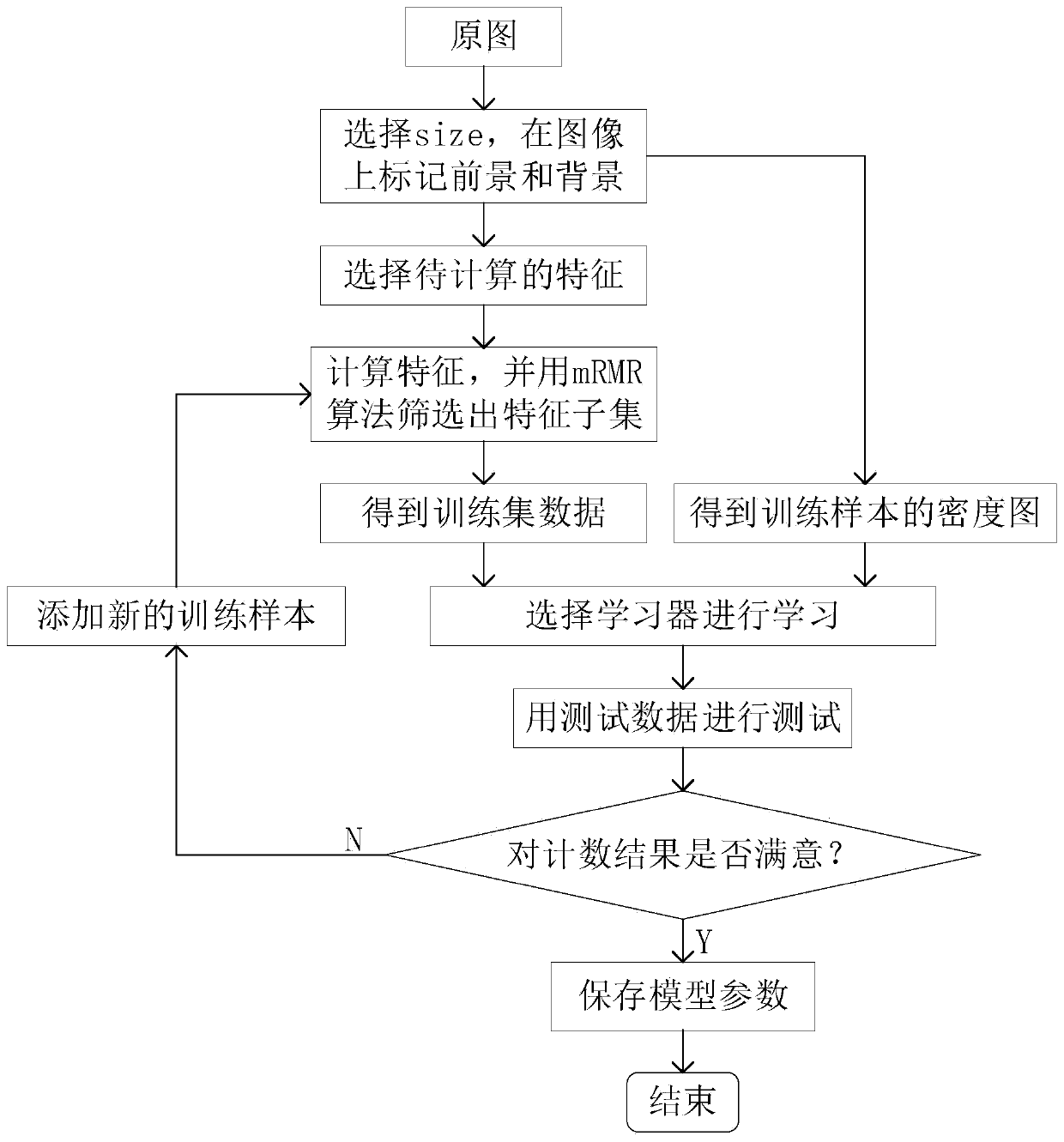
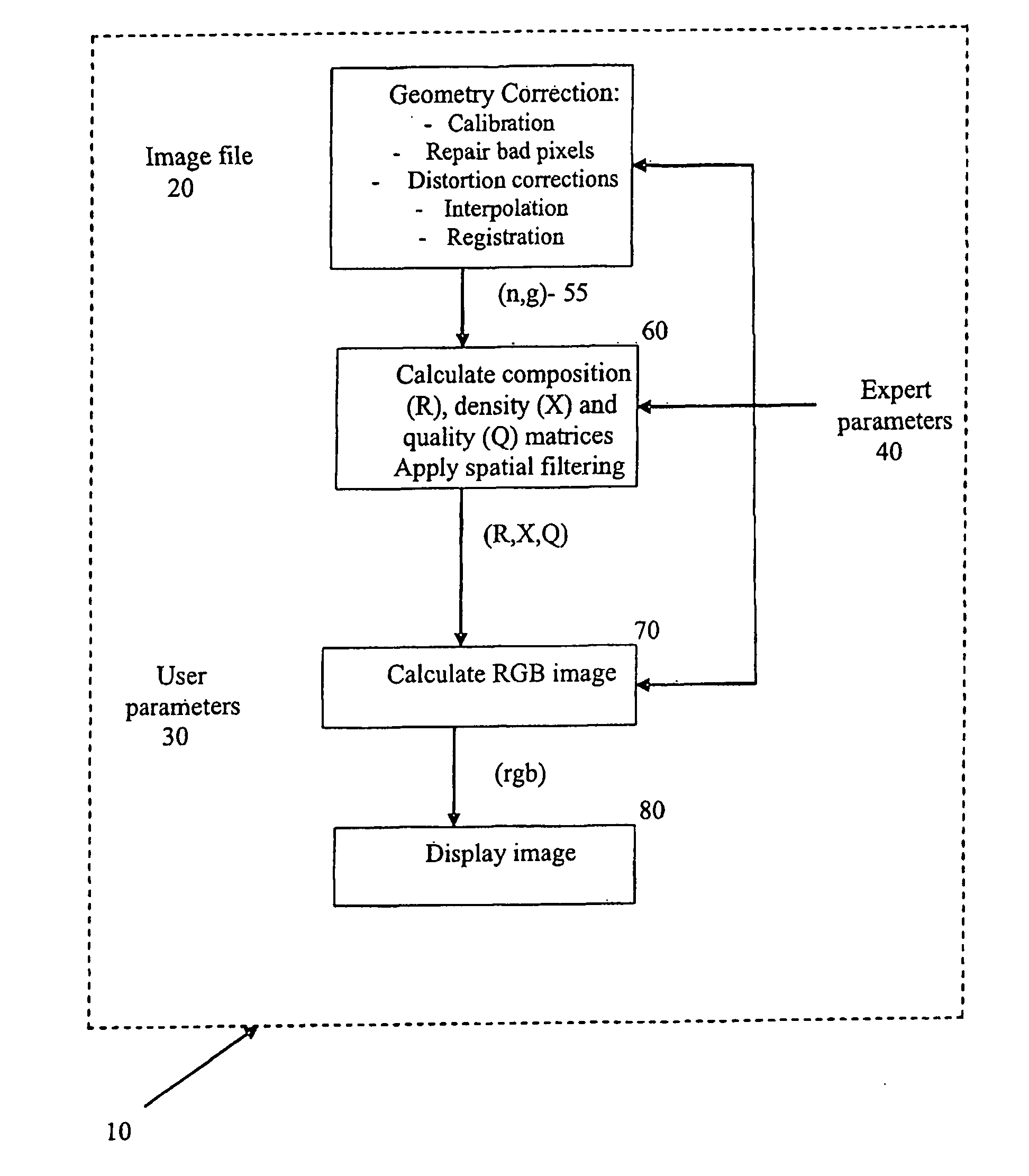
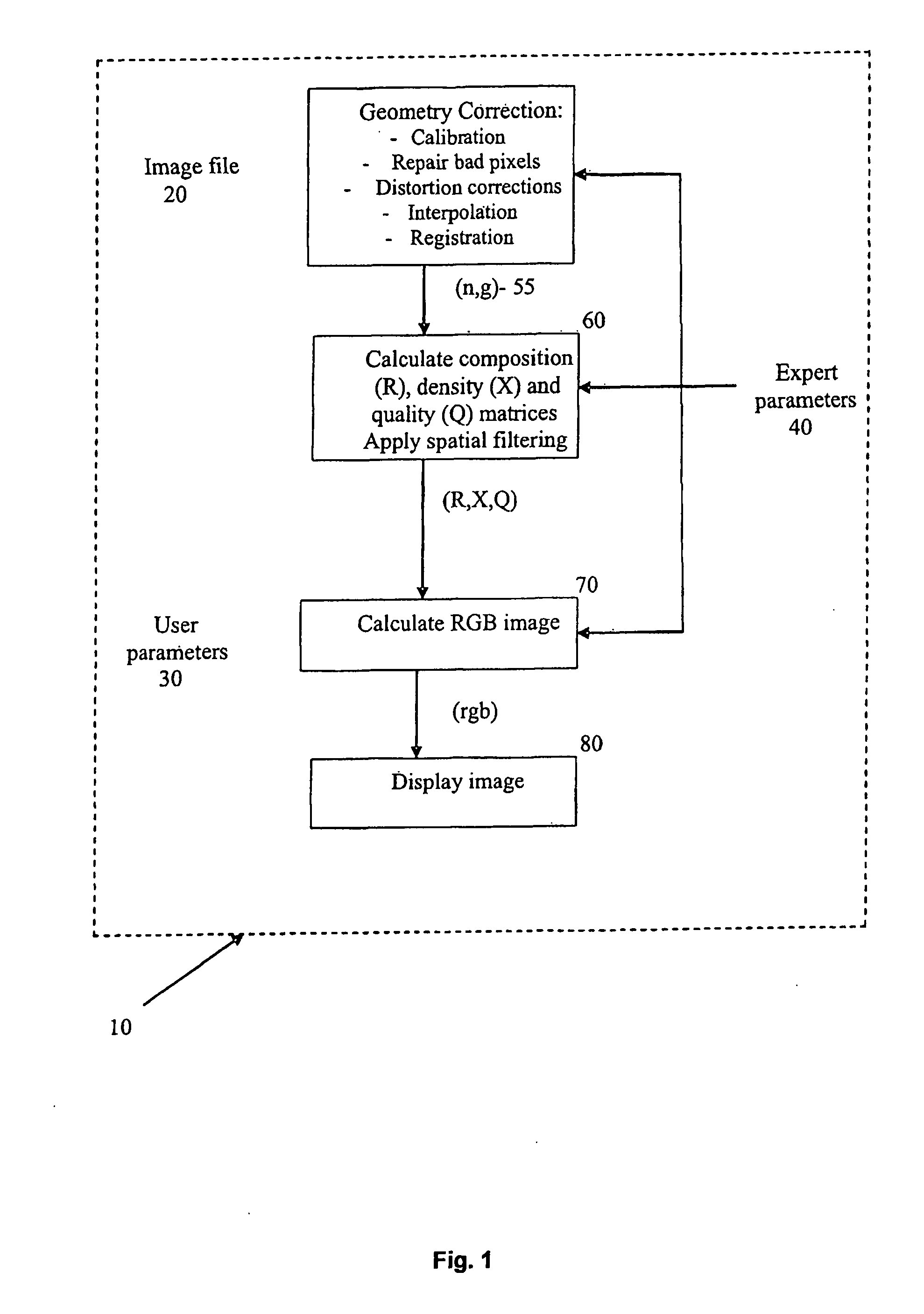
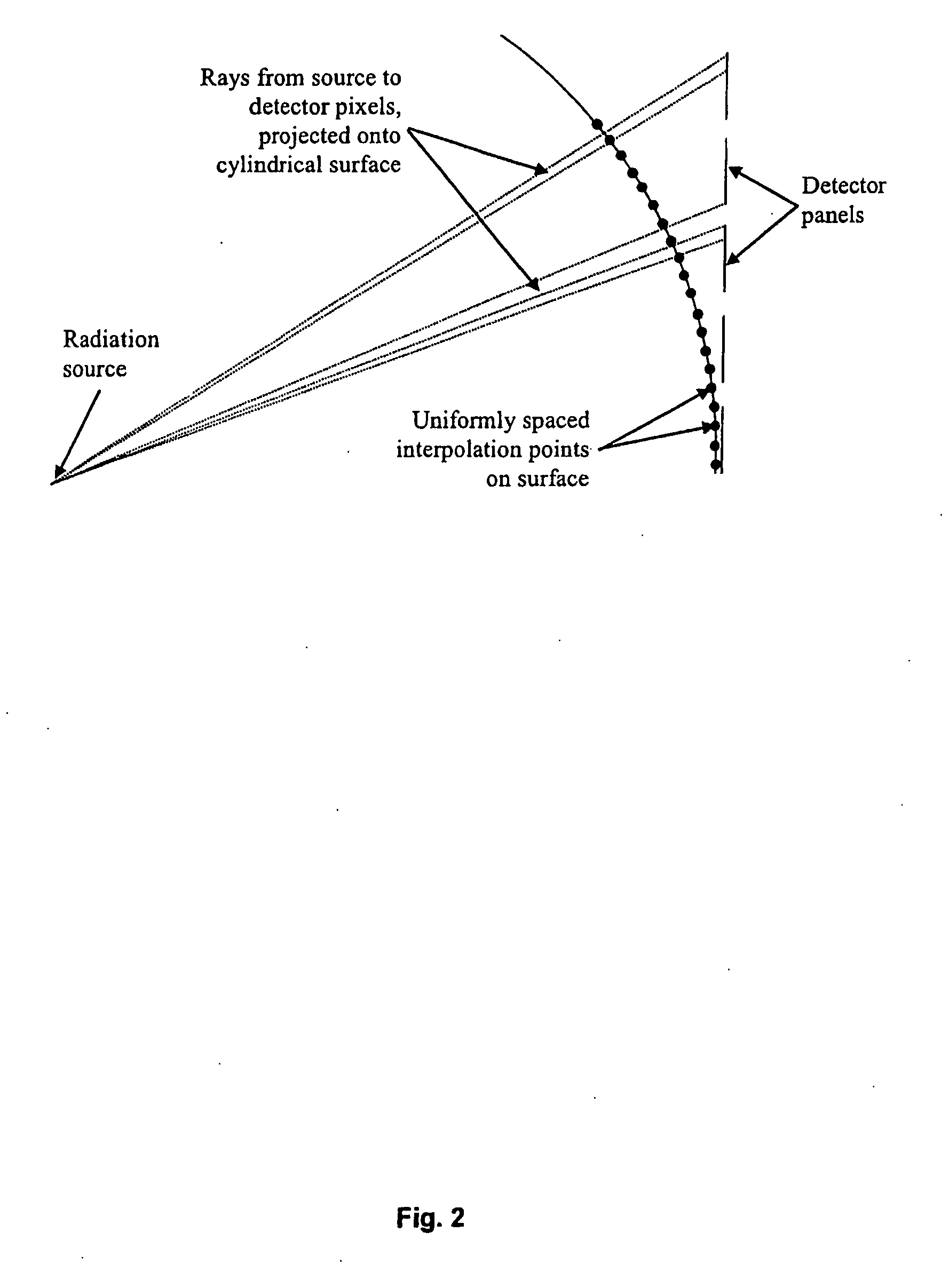
InactiveUS20080135773A1Minimize geometric distortionIncreasing statistical noiseMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsGamma ray attenuationData display
A method for processing transmission data from neutron and gamma-ray radiation to form an image, the neutron and gamma-ray radiation having traversed through an object and representing a measure of neutron attenuation and gamma-ray attenuation introduced by the object, comprising forming a neutron mass attenuation matrix ‘n’ and gamma-ray mass attenuation matrix ‘g’ from the measure of neutron attenuation and gamma-ray attenuation respectively; calculating a composition matrix R whose elements Rij are defined as a function of elements nij from ‘n’ and the corresponding elements gij from ‘g’, R representing an average composition of material between a source which generated the radiation and a point (i,j); calculating a density matrix X whose elements Xij are defined as a function of the elements nij from ‘n’ and the corresponding elements gij from ‘g’, X representing an approximate amount of material between the radiation source and the point (i,j); calculating a quality matrix Q as a function of the elements nij from the ‘n’ and the elements gij from ‘g’, Q representing a measure of the reliability of the elements of Rij; and forming an image for display; wherein the image contains information from R, X and Q.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method for color standardization of pathological image based on low rank embedded non-negative matrix decomposition
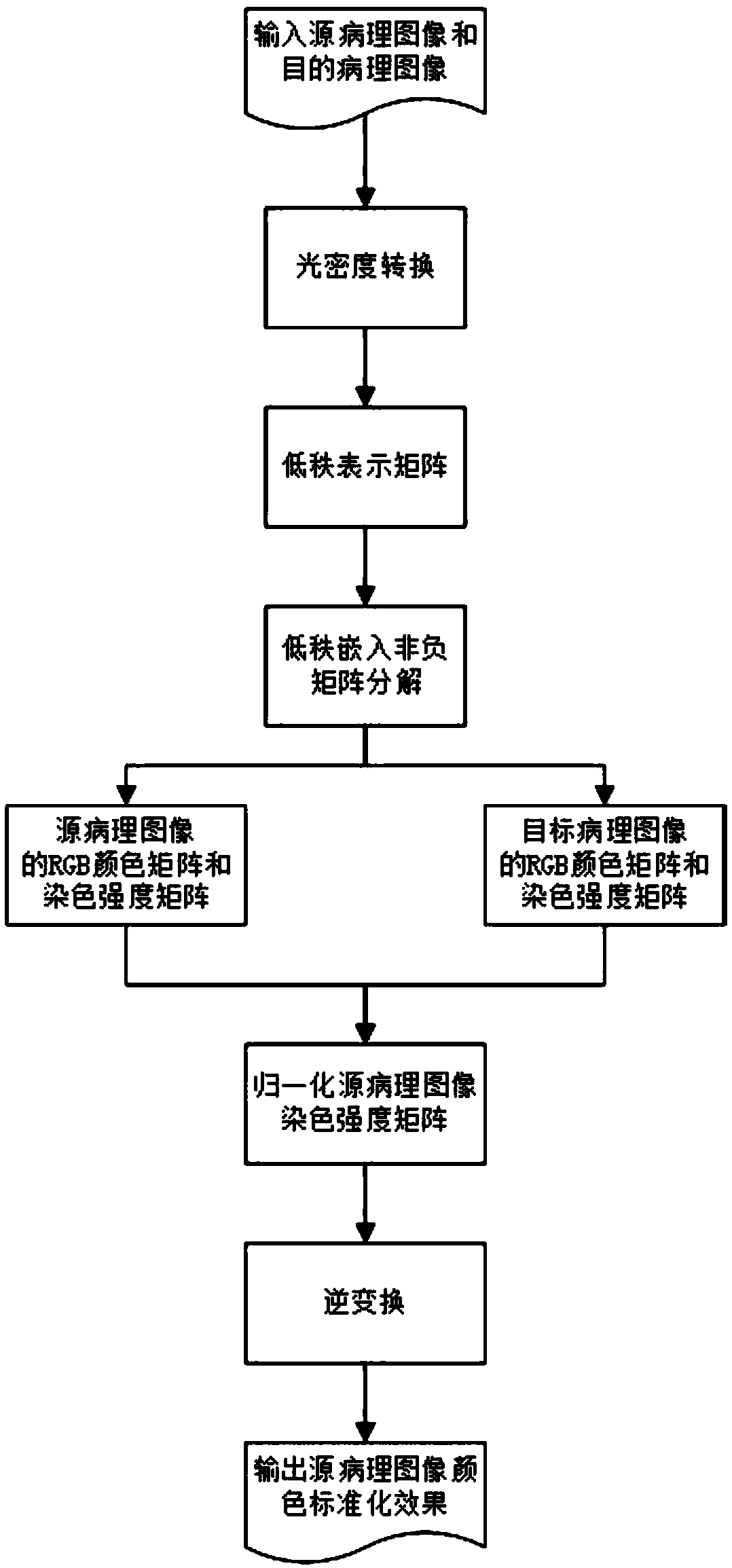
ActiveCN109345601AEfficient color standardizationCalculation speedImage enhancementImage analysisMatrix decompositionStaining
The invention discloses a method for color standardization of pathological image based on low rank embedded non-negative matrix decomposition, the data of two pathological images are expressed in theform of observation matrix, which are converted into optical density, the low rank representation matrices of the source optical density matrix and the target optical density matrix are solved respectively, the corresponding optical density matrix is decomposed into an RGB color matrix of each dyeing component and an intensity matrix of each pixel under each dyeing component, At last, that image is convert to RGB form, so as to achieve the color standardization from the source pathological image to the target pathological image, the invention can be used for color standardization of pathological images and improvement of visualization effect, Avoiding the color inconsistency of pathological images caused by different pathological scanners, different laboratory staining methods and different staining ratio has important significance for pathological image imaging, staining separation and intelligent pathological image analysis, and has broad market prospects and application value.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Mileage signboard automatic recognition method for road video routing inspection
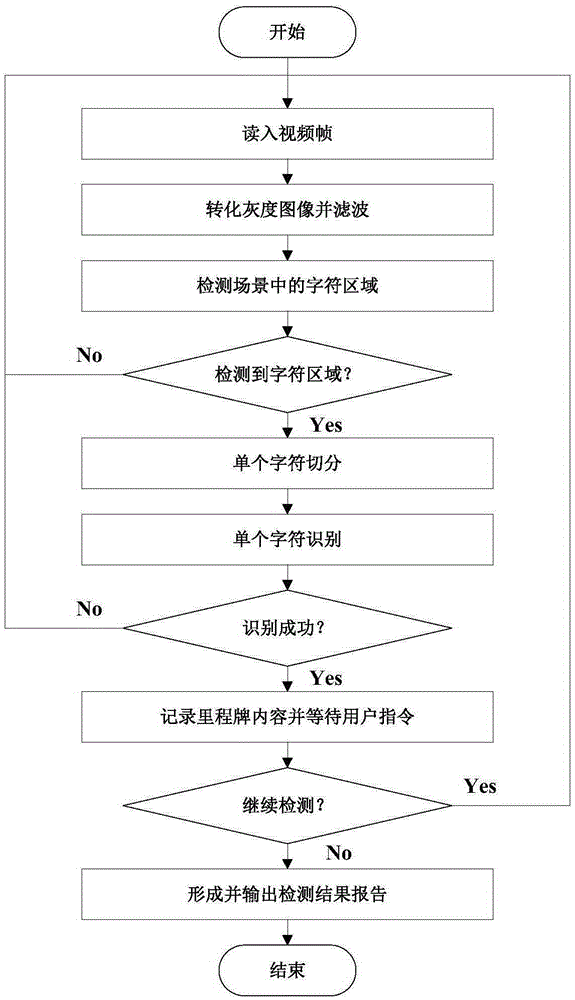
ActiveCN105279488AImprove recognition efficiencyImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionPositive sampleFeature vector
The invention discloses a mileage signboard automatic recognition method for road video routing inspection. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining video data, and converting the video data into a frame image; using a rectangular frame to select a mileage signboard for dividing the frame image into a positive sample region and a negative sample region, and performing positive and negative sample correction; extracting gradient histogram feature operators of corrected positive and negative samples, and training classification models from feature vectors; outputting a grayscale image of a probability density matrix; calculating a frame image to be tested to perform global binaryzation on a threshold; performing global binaryzation on the output probability density matrix grayscale image to find the maximum connected domain; cutting the corresponding maximum connected domain region ROI in the frame image to be tested; dividing the mileage signboard, and extracting the character region of the mileage signboard; and using wavelet packet texture features and combining a vector machine classifier for performing mileage signboard character recognition. The mileage signboard automatic recognition method has the advantages that the recognition efficiency is high; the accuracy is high; the influence by geographical factors and environment factors is avoided; and the existing hardware equipment is used, so that the cost is low.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Real-time voltage control method for distributed expandable quantum deep width learning
ActiveCN112564118ALighten the computational burdenLower requirementData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionDistributed structureElectric power system
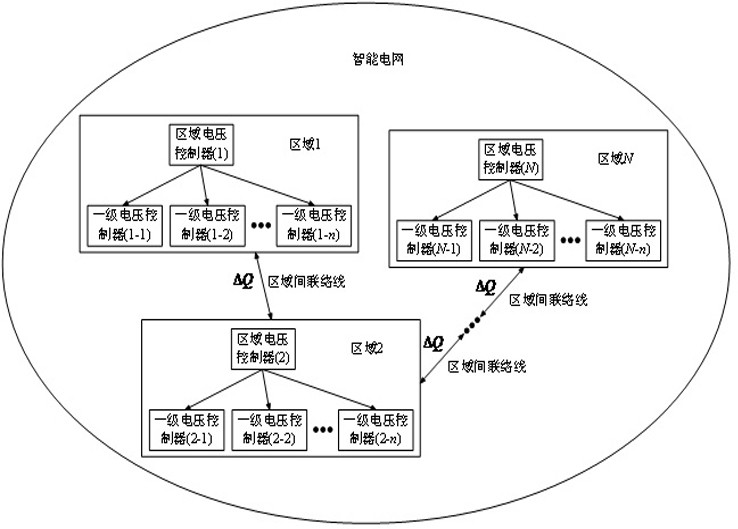
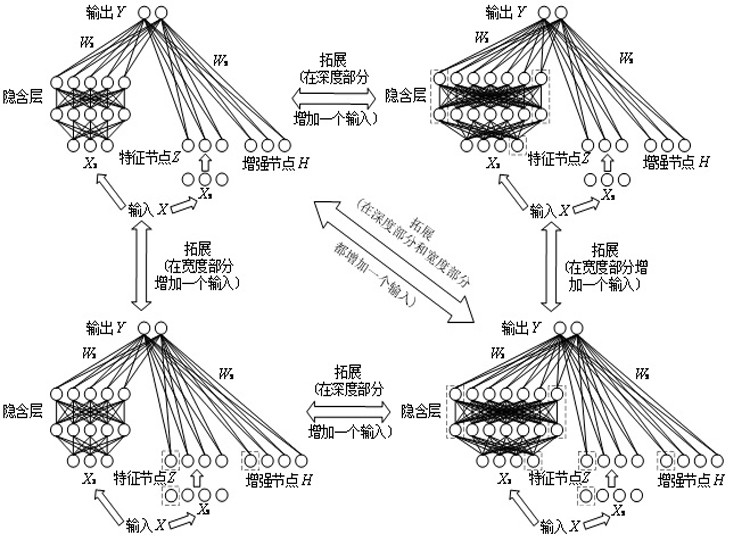
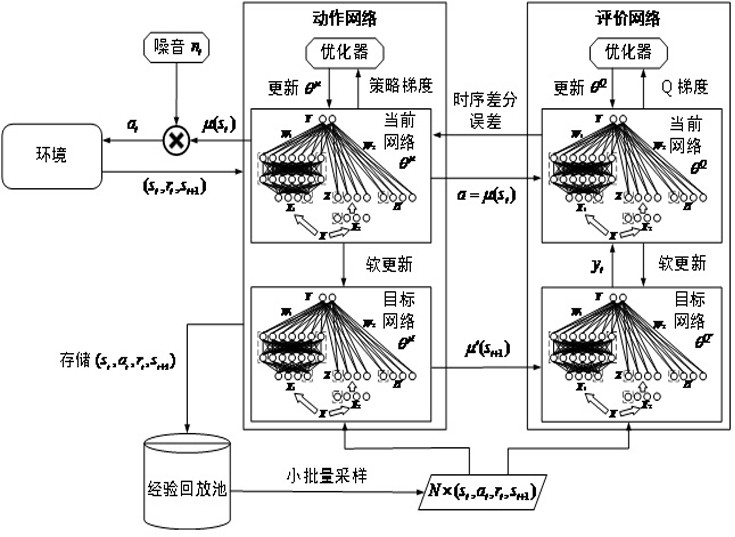
The invention provides a real-time voltage control method for distributed expandable quantum deep width learning. According to the method, a distributed structure and an expandable quantum depth-widthlearning method are combined for voltage control of a power system. Firstly, the proposed method combines the ideas of deep learning and width learning, introduces a density matrix in quantum mechanics, and proposes an expandable quantum deep-width neural network. Secondly, according to the method, four networks of a depth deterministic strategy gradient method structure are fitted by using an expandable quantum deep width neural network, and an expandable quantum deep width learning method is provided. And finally, the voltage of the power system is controlled in real time through a distributed structure. According to the method, real-time global optimal control of the voltage of the power system can be achieved, on the basis of guaranteeing the control precision, the calculation burdenof a controller is relieved, the calculation process is accelerated, the requirement of the voltage control process for the reliability of the communication technology is lowered, and the privacy of power system information of all regions is kept.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
System and method for solving 3sat using a quantum computer
A method for solving the NP complete problem 3SAT and other computational problems which can be reduced to it. Quantum mechanical operations are performed on a finite number of quantum mechanical bits, or “qubits,” in such a way as to concentrate probability in states which solve a given 3SAT problem, provided they exist. Concentration of probability is achieved by generalizing the traditional, reversible model of quantum computation to include irreversible operations mapping one density matrix to another.
Owner:WALTERS ZACHARY B
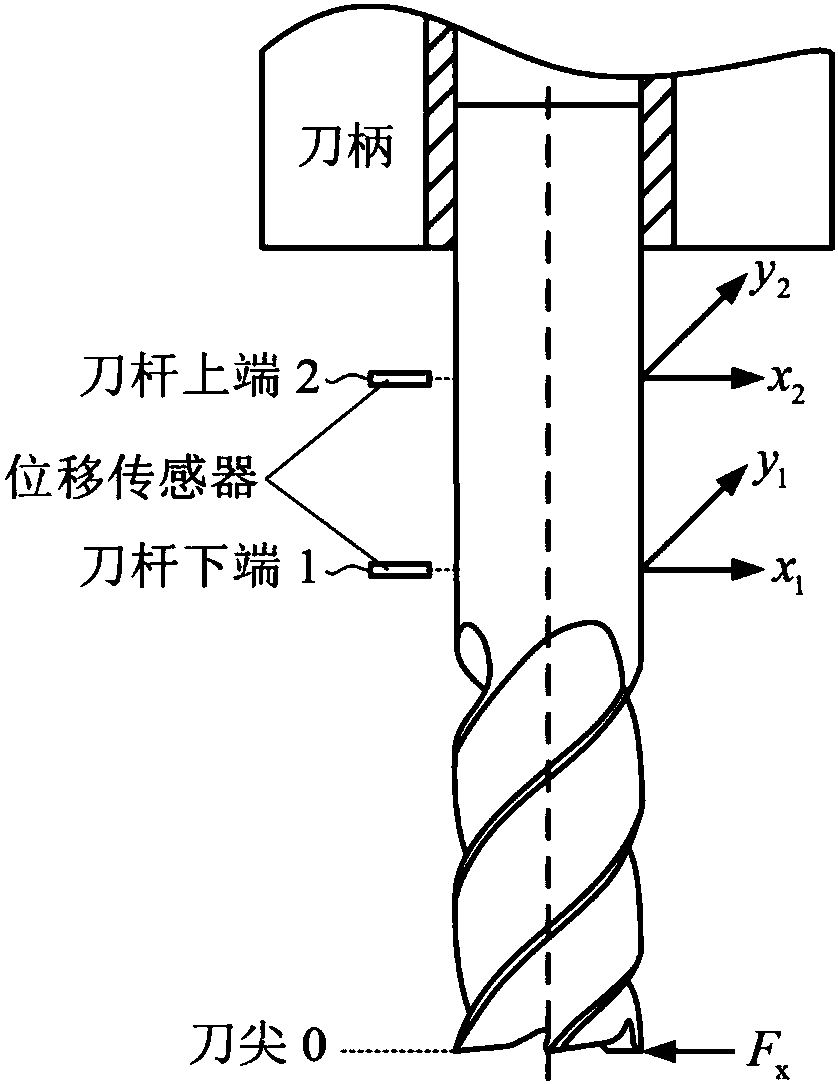
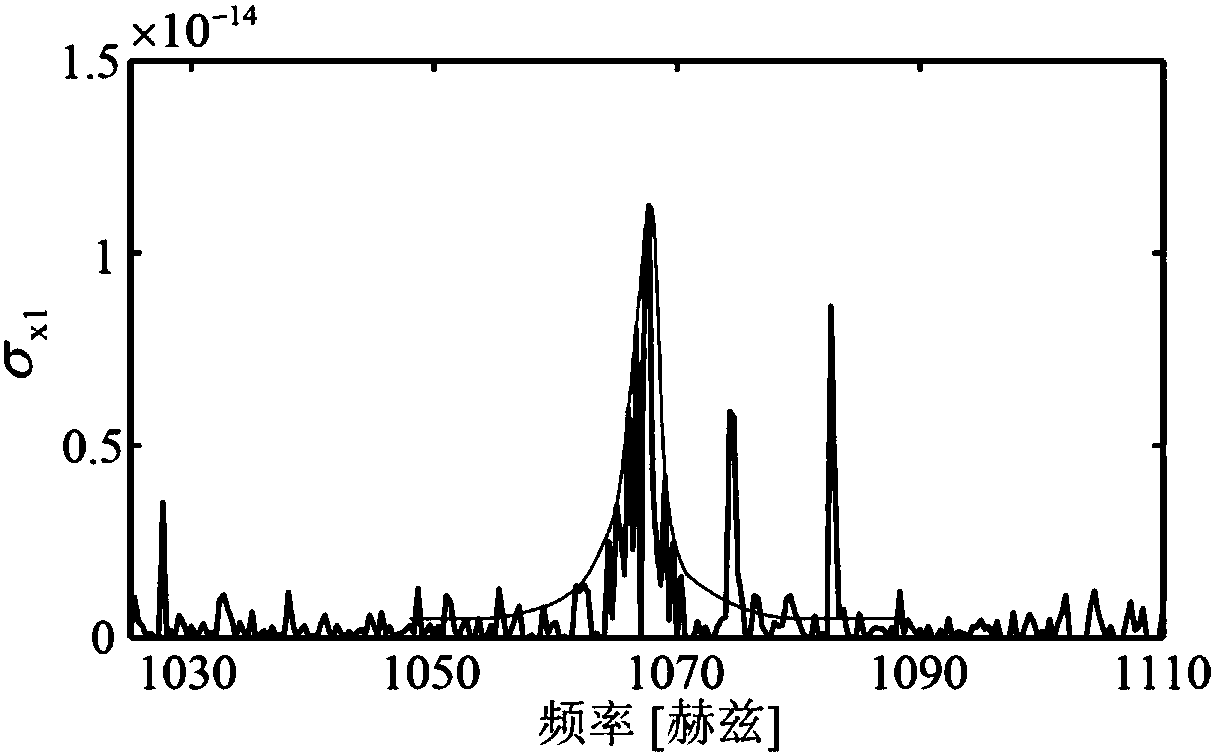
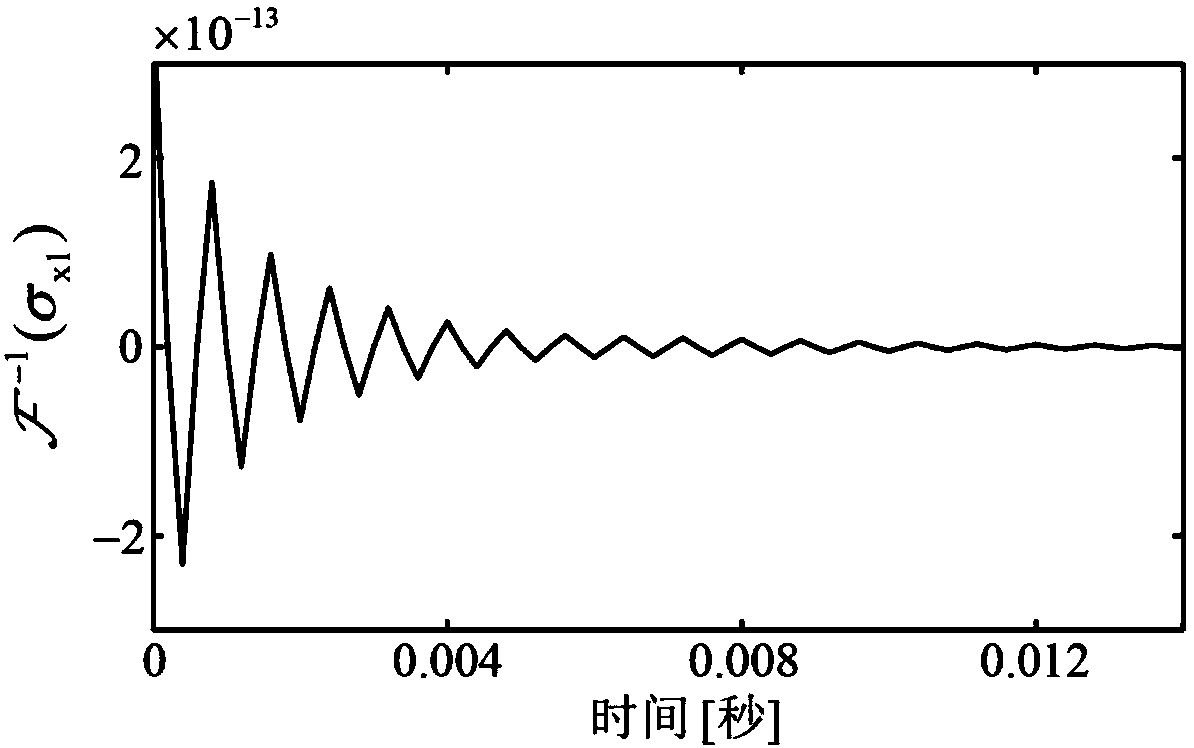
Milling process damping calibration method based on operating modal analysis
The invention discloses a milling process damping calibration method based on operating model analysis, and is used for solving the technical problem of poor practicability of an existing milling process damping calibration method. The technical scheme includes the following steps: first obtaining cutter-machine tool system model parameters; then carrying out a no-flutter-stable milling experiment, and measuring vibration signals in an upper position and a lower position in x and y directions of a milling cutter bar; and determining a power spectrum density matrix of the measured vibration signals at each frequency point, performing singular value decomposition on the matrix, then removing characteristic values corresponding to periodic cutting force, performing inverse Fourier transform on the corresponding larger characteristic values, and extracting an average damping coefficient on peak and valley values of an inverse transformation result. After the average damping coefficient is obtained, first cutting force and tool nose frequency response are utilized to obtain a too nose position vibration amplitude value, then the vibration amplitude value together with the average process damping coefficient is substituted into energy balance relational expressions established in the x and y directions, a milling process damping coefficient is calibrated, and he practicability is good.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
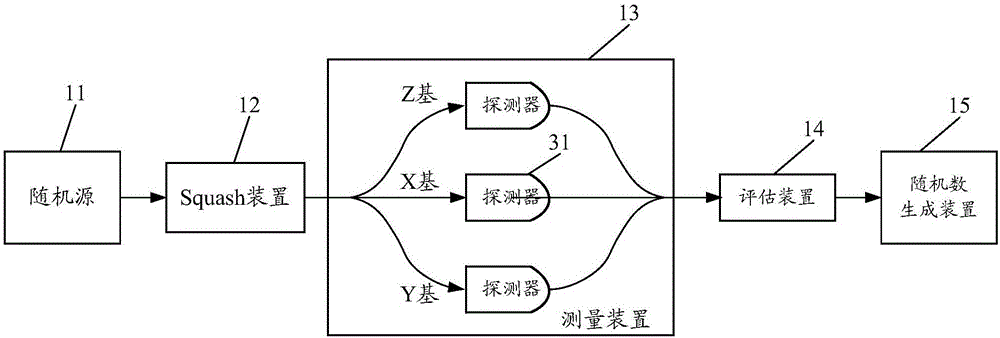
Quantum random number generator and quantum random number generation method
ActiveCN106708470AGuaranteed normal outputRandom number generatorsMeasurement deviceCompression device
The invention provides a quantum random number generator and a quantum random number generation method. The method comprises the following steps of: converting quantum states sent by a random source into two-dimensional quantum states by a compression device and sending the two-dimensional quantum states to a measurement device; randomly using a group of measurement basics in three preset groups of measurement basics to measure the received two-dimensional quantum states by the measurement device according to a preset measurement probability, so as to obtain a measurement result and send the measurement result to an assessment device; taking the measurement result obtained by using random number measurement basics as an initial random number by the assessment device, estimating an average density matrix of each quantum state sent by the random source according to the received measurement result, and calculating randomness of the initial random number according to the average density matrix; and carrying out privacy amplification according to the calculated randomness of the initial random number, so as to obtain a final random number. By applying the quantum random number generation method, the quantum random number generator for the self-detection of the source is realized under a condition that the source is free of assumption, so as to generate required quantum random numbers.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
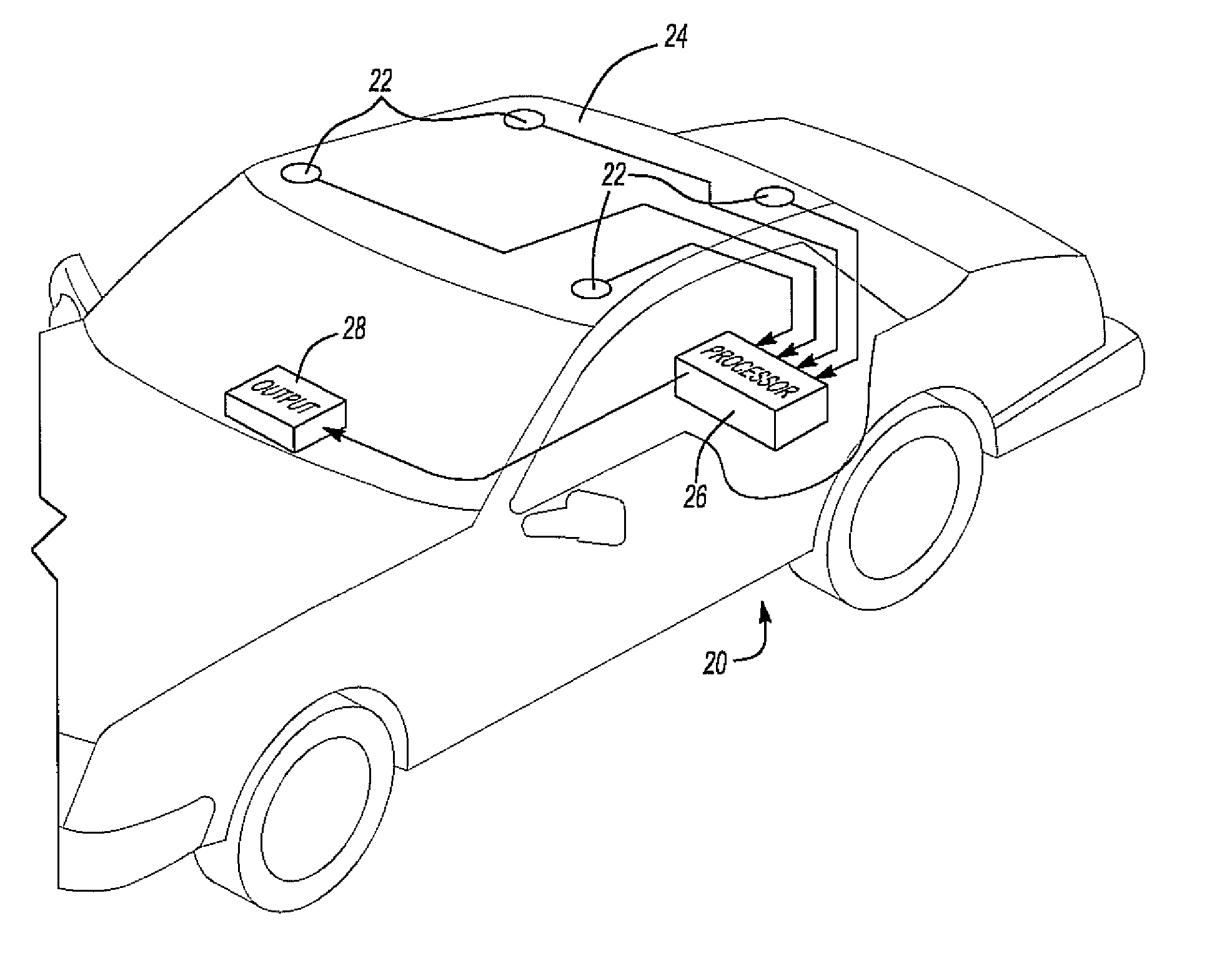
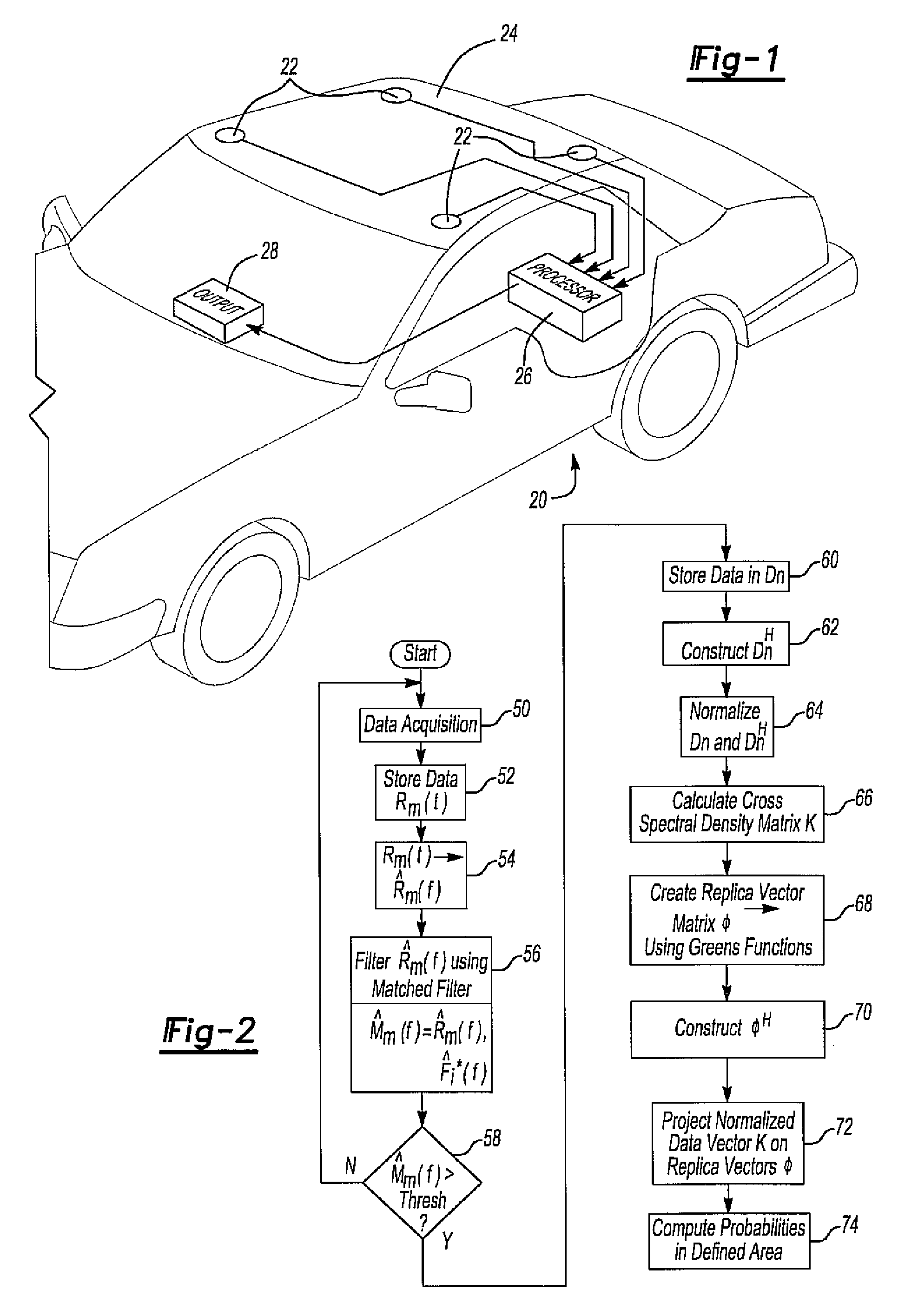
Method and system for locating a wave source within a defined area
InactiveUS7969821B2Position fixationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic finder detailsSound sourcesPosition dependent
A method and system for locating a sound source within a defined area in which the sound data is collected with a plurality of spaced apart microphones. The sound data received by the microphones is processed to form a cross spectral density matrix containing vectors of cross correlations and auto correlations of the sound data. A replica vector matrix containing sound data from at least one test sound at a plurality of predetermined locations within the defined area is then constructed. The sound data vectors in the cross spectral density matrix are then projected on the replica vectors in the replica vector matrix to obtain a probability of the location of the sound source at each predetermined location within the defined area. These probabilities form a distribution within the defined area in which the largest probability distribution correlates with the location of the sound source.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
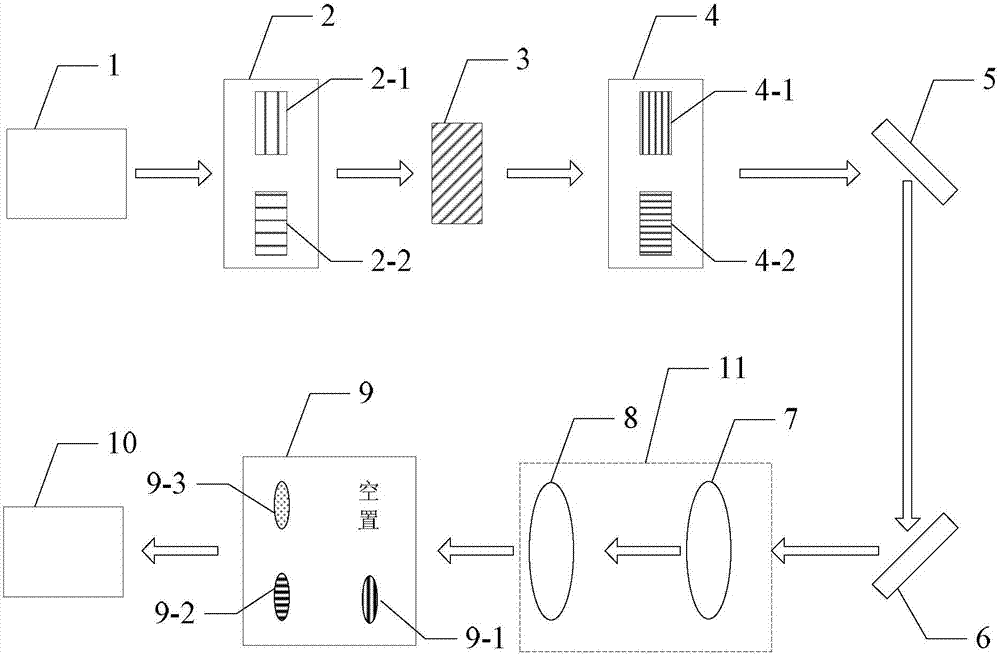
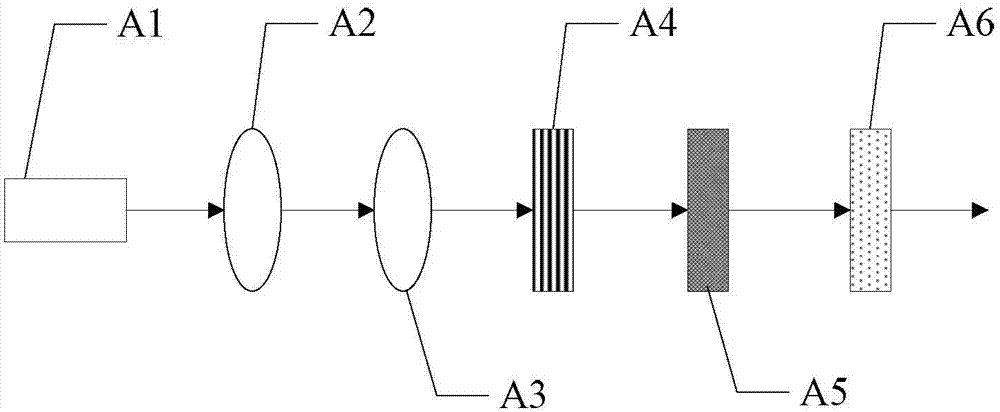
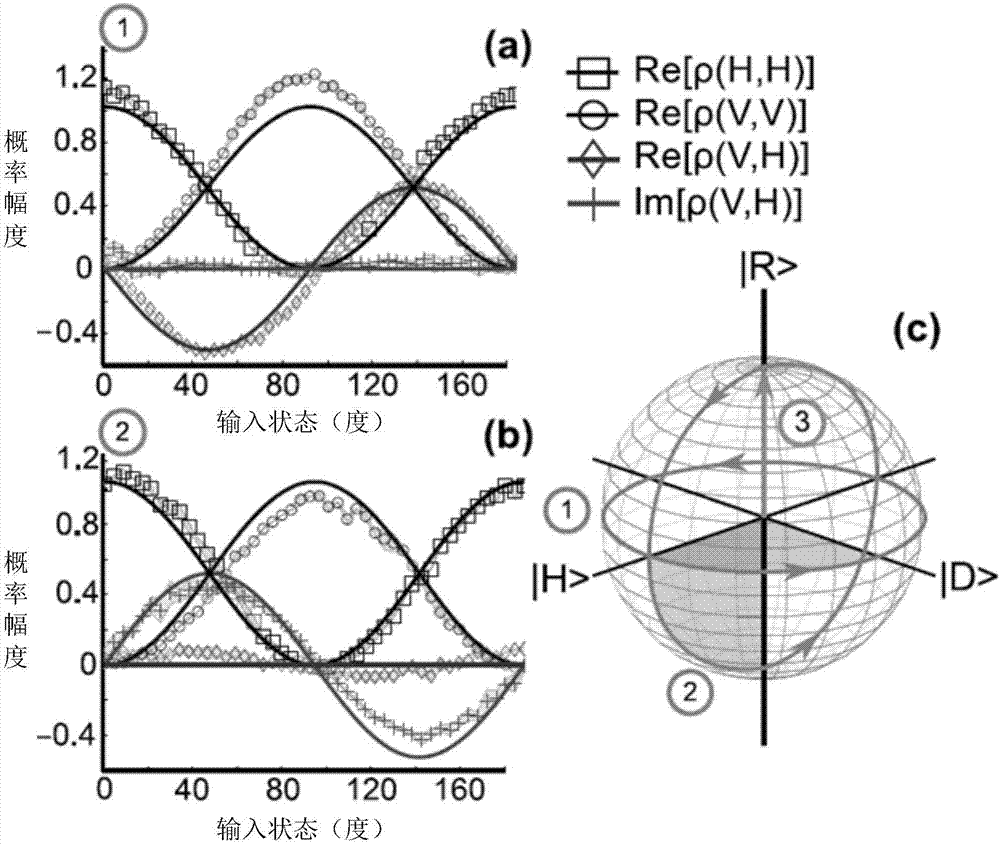
Device and method for directly measuring photon polarization density matrix
A device and a method for directly measuring a photon polarization density matrix relate to a technology for directly measuring a photon polarization density matrix, and are disclosed in order to solve the problem that the quantum tomography fails to provide a method for directly getting the coherence in quantum physics. A to-be-measured signal enters a first state converter. The to-be-measured signal after conversion by the first state converter enters a diagonal polarization dependent displacement crystal. The to-be-measured signal after conversion by the diagonal polarization dependent displacement crystal enters a second state converter. The to-be-measured signal after conversion by the second state converter enters an imaging system. The to-be-measured signal output by the imaging system enters a third state converter. The to-be-measured signal after conversion by the third state converter is received by a CCD camera. The beneficial effects are as follows: the measuring method only needs three times of measurement of two substrates to determine arbitrarily selected density matrix elements without considering the system dimension (d), and is a very attractive and effective method to replace the tomography to detect the potential mixed state locally.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
Quantum state filter and a related method
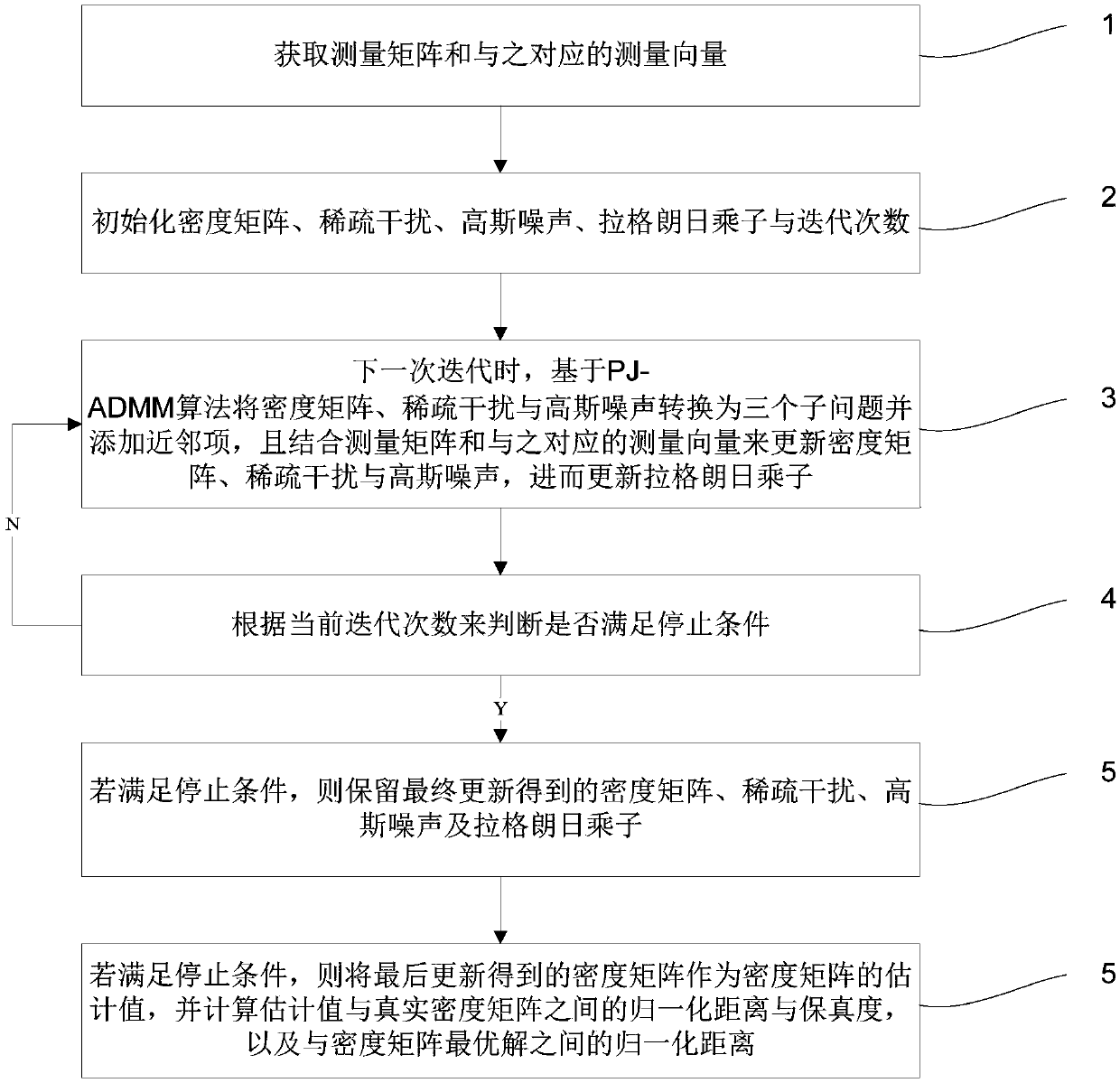
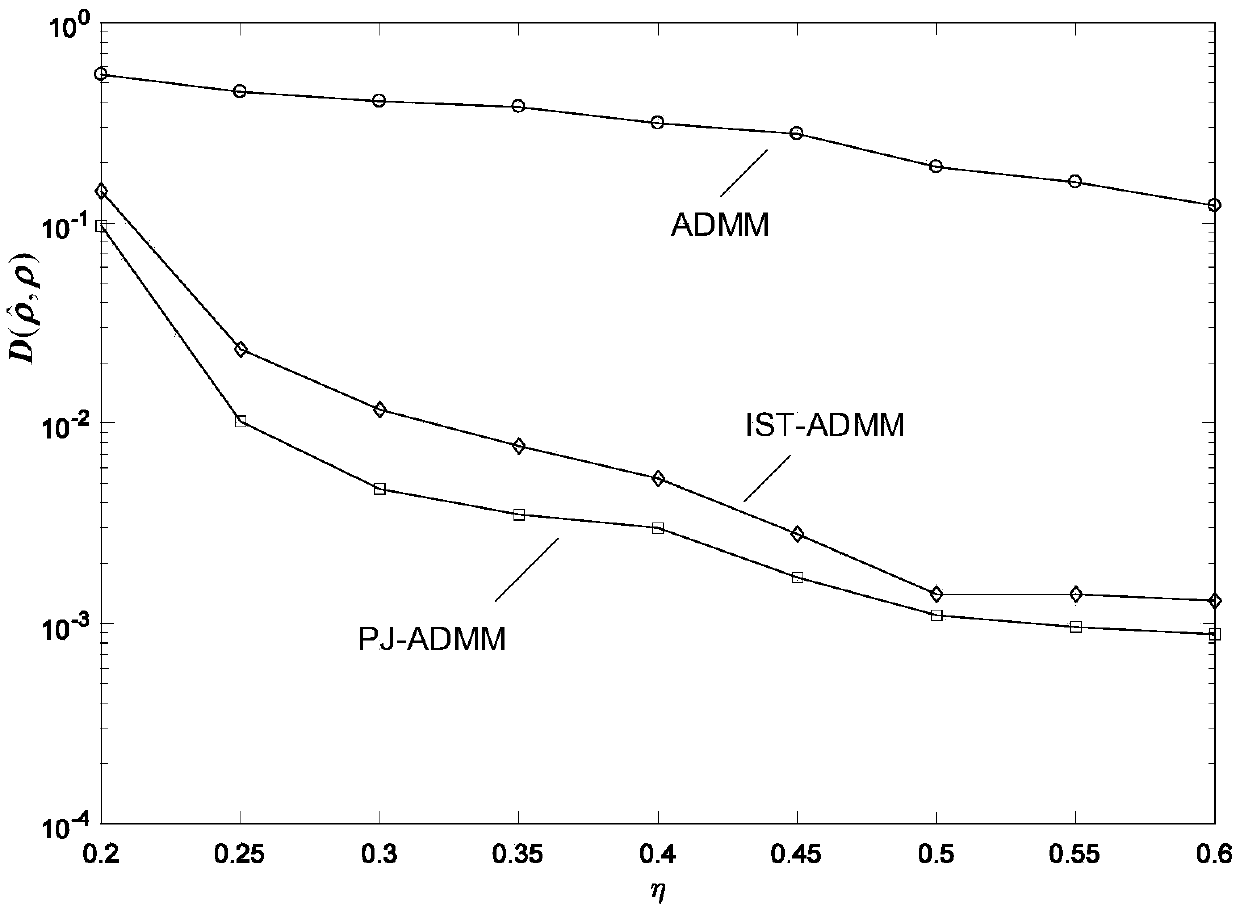
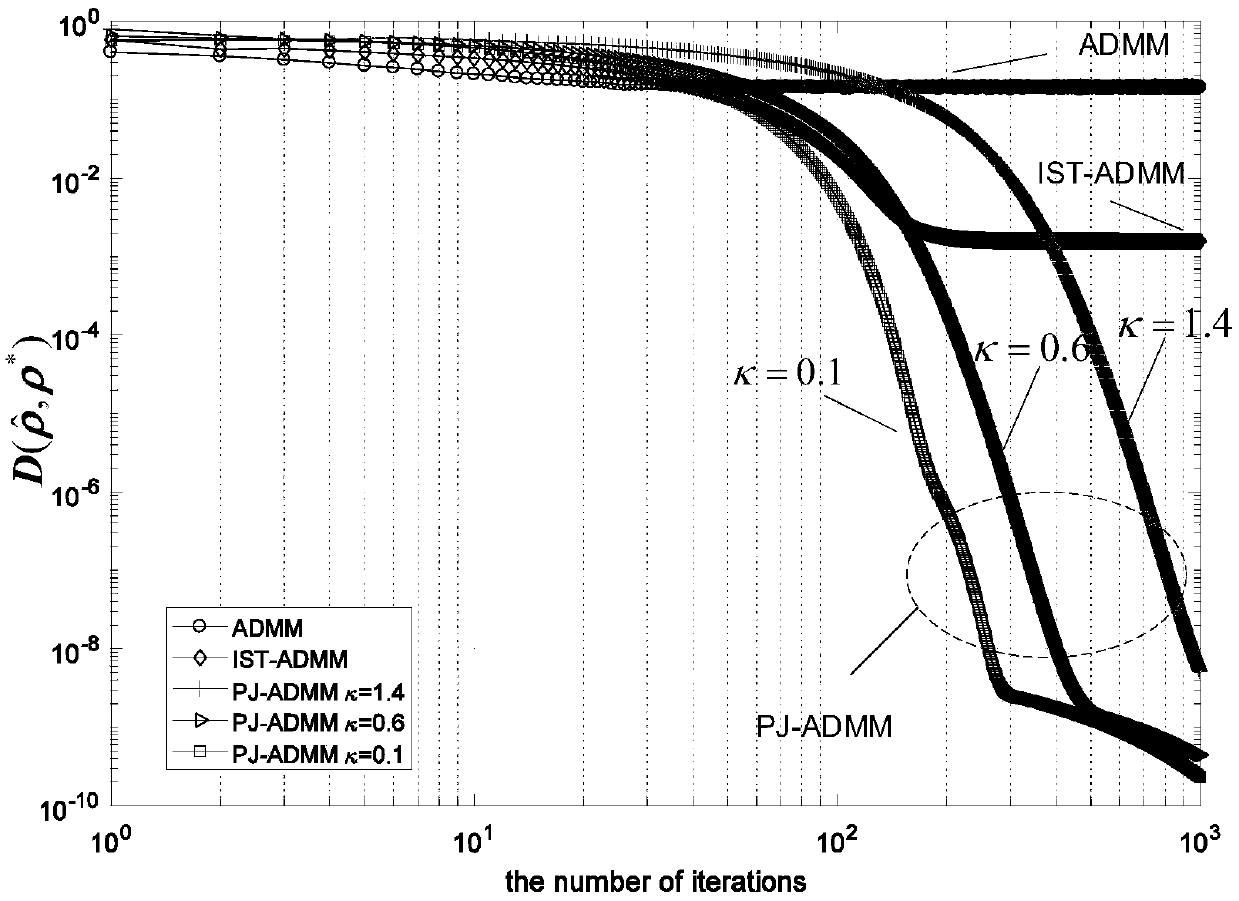
InactiveCN109004916AExact solutionAvoid massive matrix operationsAdaptive networkRound complexityNear neighbor
The invention discloses a quantum state filter and a related method. The proximal Jacobian ADMM algorithm is applied to the reconstruction of high qubit states based on squeezed sensing to ensure thatthe reconstructed density matrix satisfies the constraint of quantum states. The algorithm can find more accurate solutions more quickly. The algorithm adds a nearest neighbor term to each sub-problem to obtain a closed-form solution, avoids large-scale matrix operation and greatly reduces the computational complexity. At the same time, the Lagrangian multiplier is updated with adjustable step size to accelerate the convergence rate, and the conditions satisfying the convergence of the algorithm are given to provide a basis for the parameter selection. The filter can realize the simultaneousestimation of the quantum state with state sparse disturbance and Gaussian noise and its sparse disturbance and Gaussian noise with high precision.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com