Automatic cell counting method based on dynamic learning for microscope
A dynamic learning and automatic counting technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of reducing the learning effect of the model, under-fitting learning, slow program running, etc., achieving the effect of simple implementation principle, ensuring counting accuracy, and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046]The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be understood that these examples are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. In the following examples, the operating methods without specific conditions are generally in accordance with conventional conditions, or in accordance with the conditions suggested by the manufacturer.
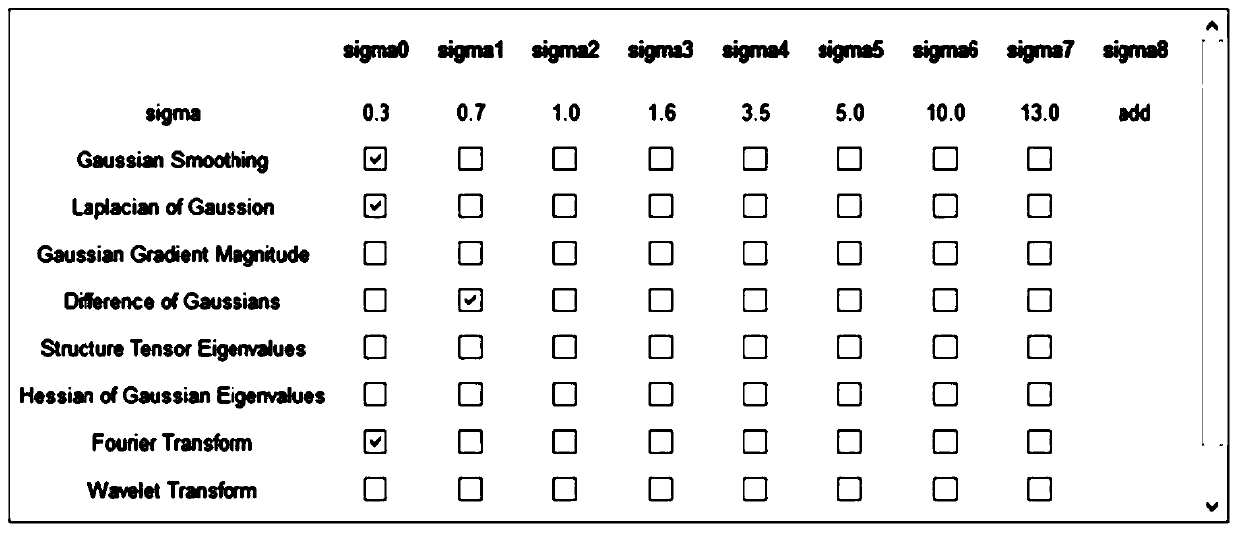
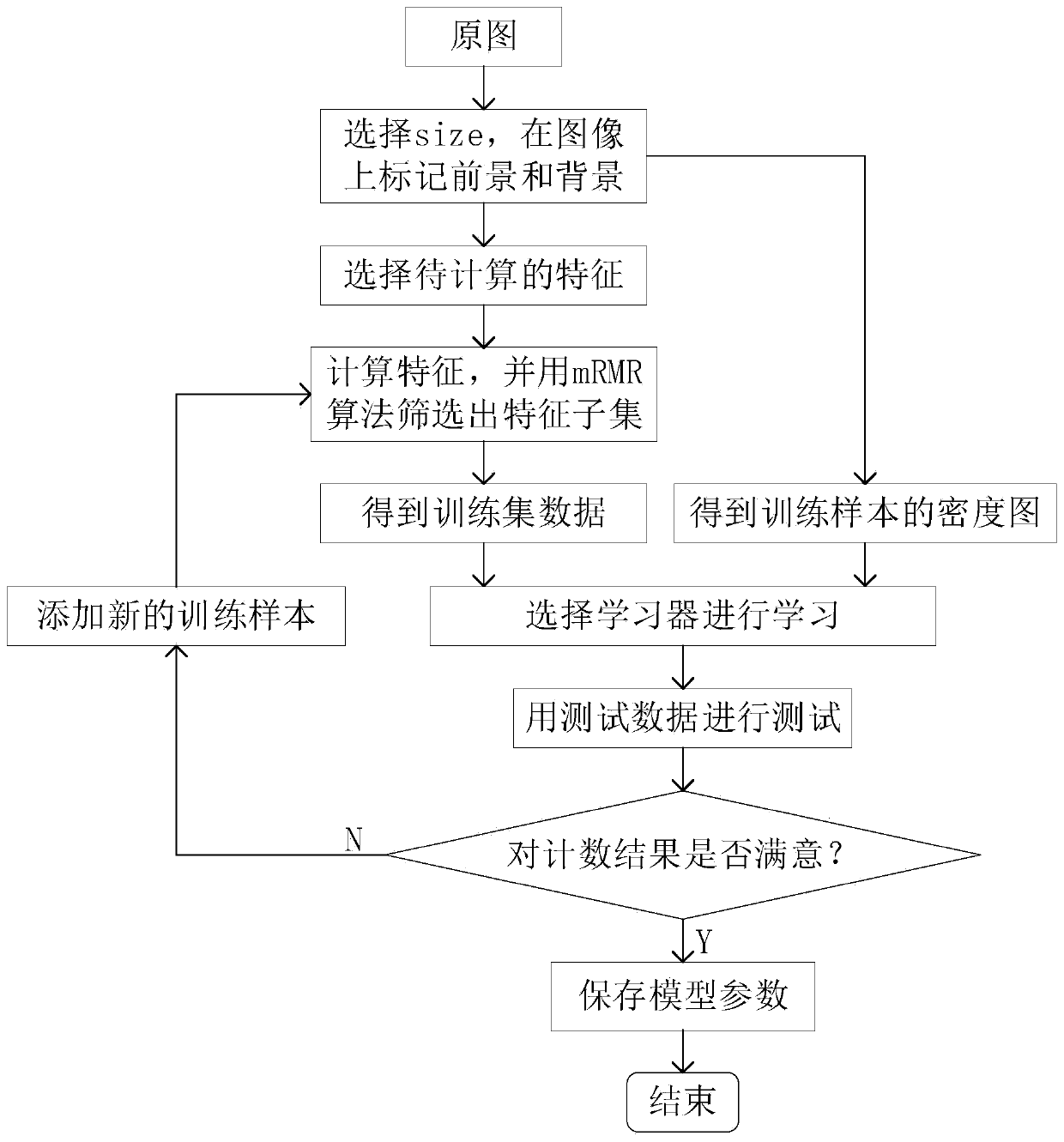
[0047] The modeling process of the automatic cell counting method based on dynamic learning for the microscope of this embodiment is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific steps include:
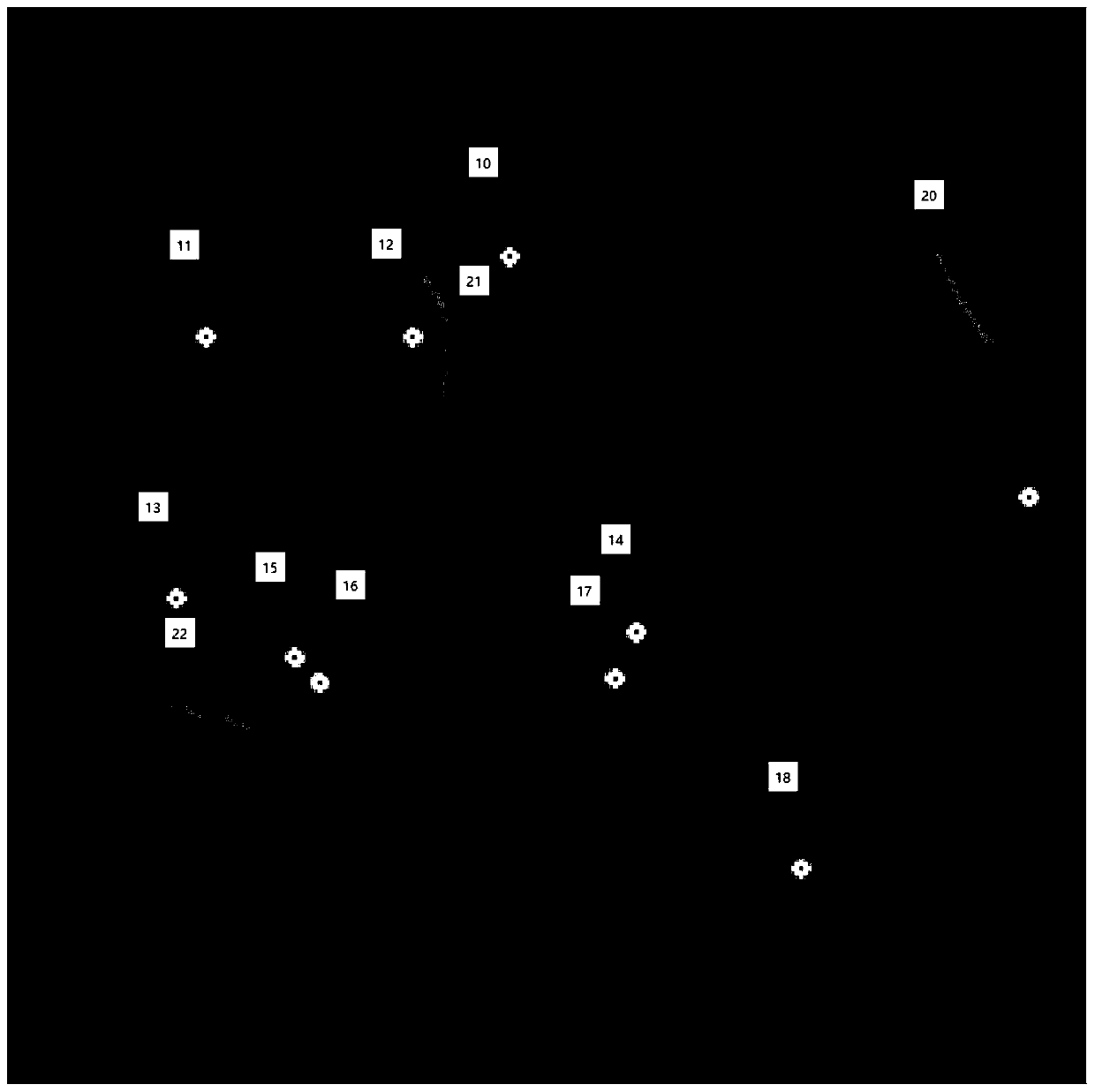
[0048] (1) if figure 2 As shown in , the user manually marks the cells to be counted (foreground) and background pixels (background) in the training image (original image) as training samples, and defines the true density function, specifically:
[0049] (1-A) The set of marker points of the cell...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com