Patents
Literature
485 results about "Autocorrelation matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
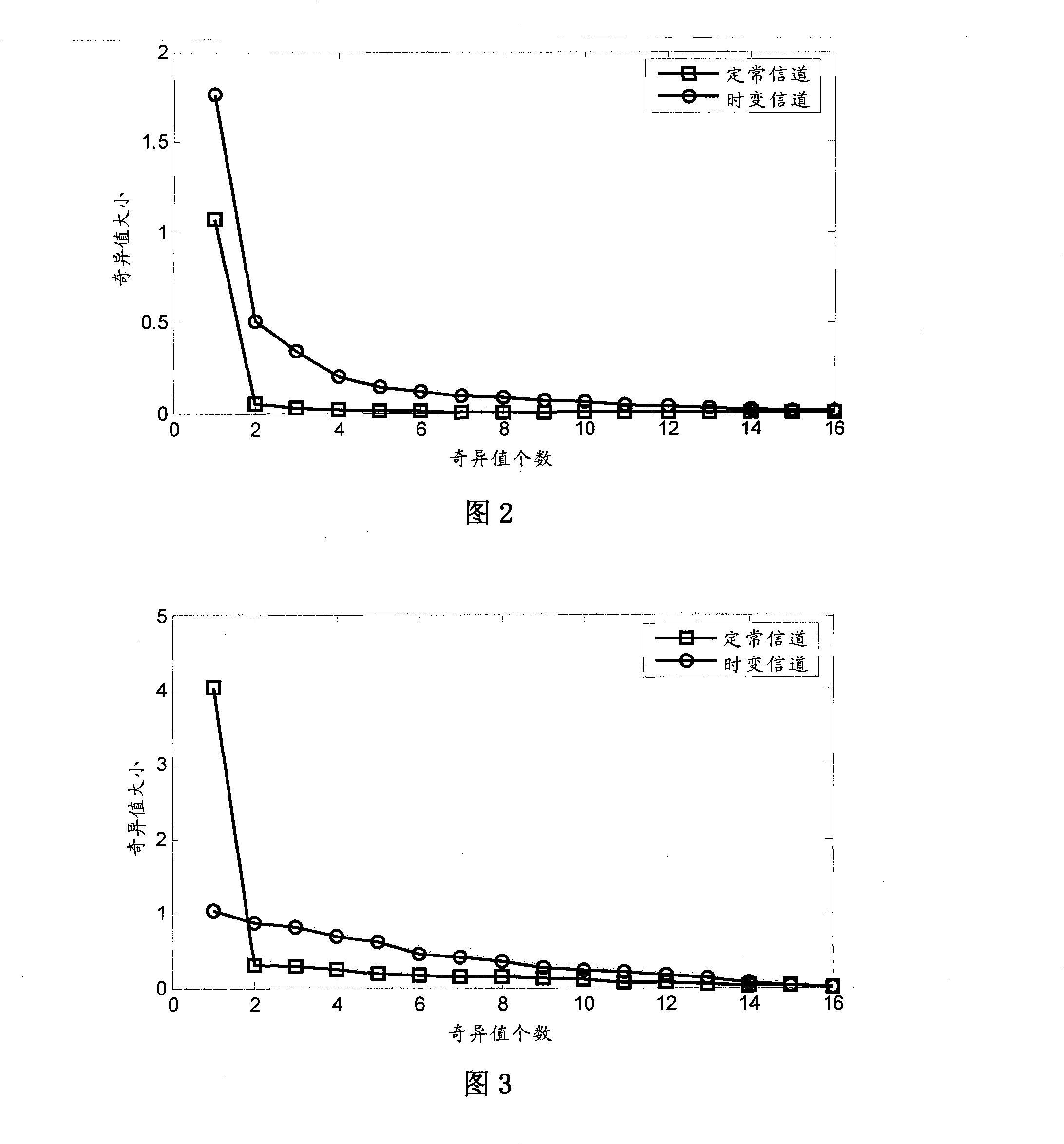
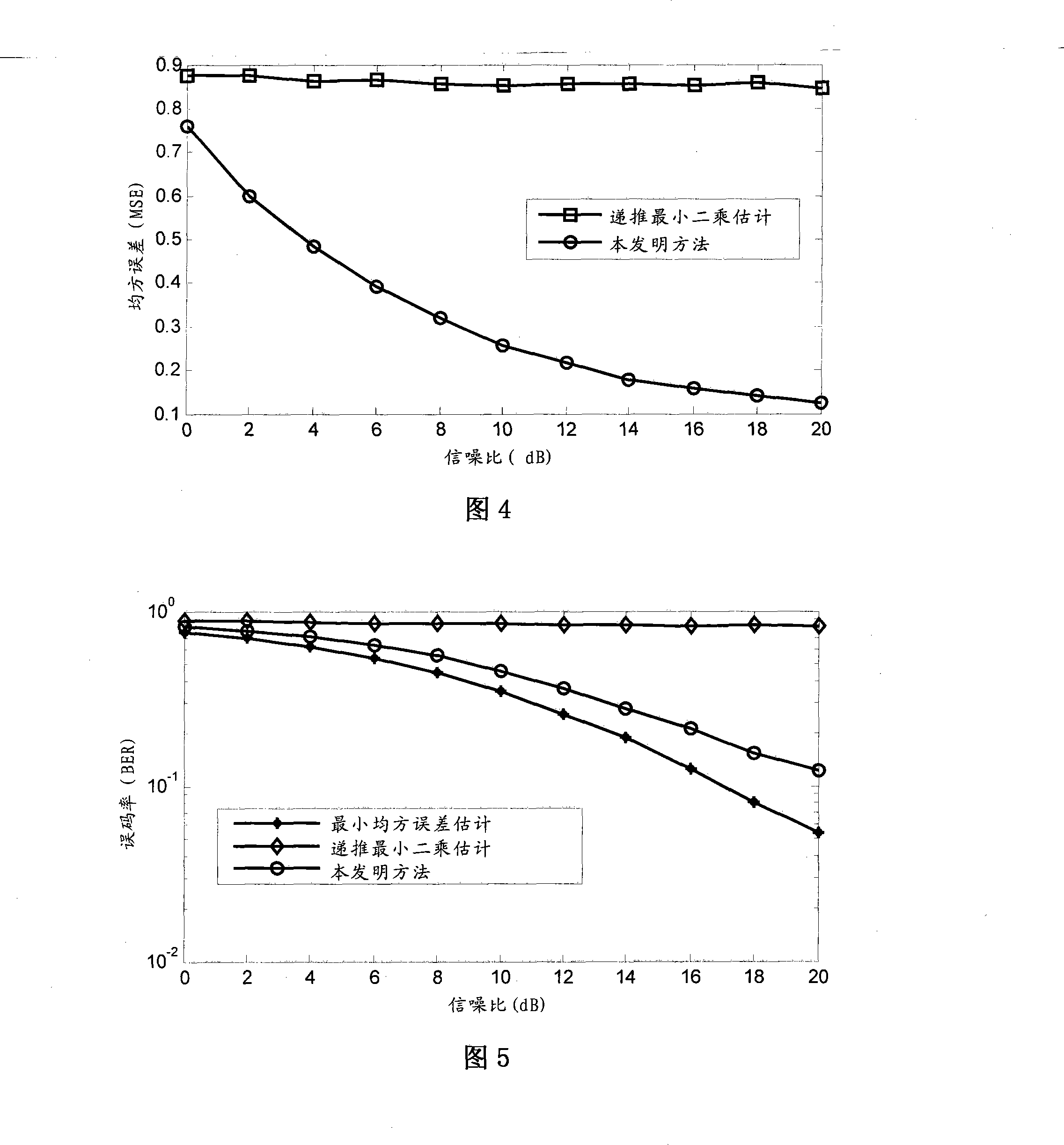
The auto-correlation matrix (also called second moment) of a random vector 𝐗=(X₁,…,Xₙ)ᵀ is an n×n matrix containing as elements the autocorrelations of all pairs of elements of the random vector 𝐗. The autocorrelation matrix is used in various digital signal processing algorithms.
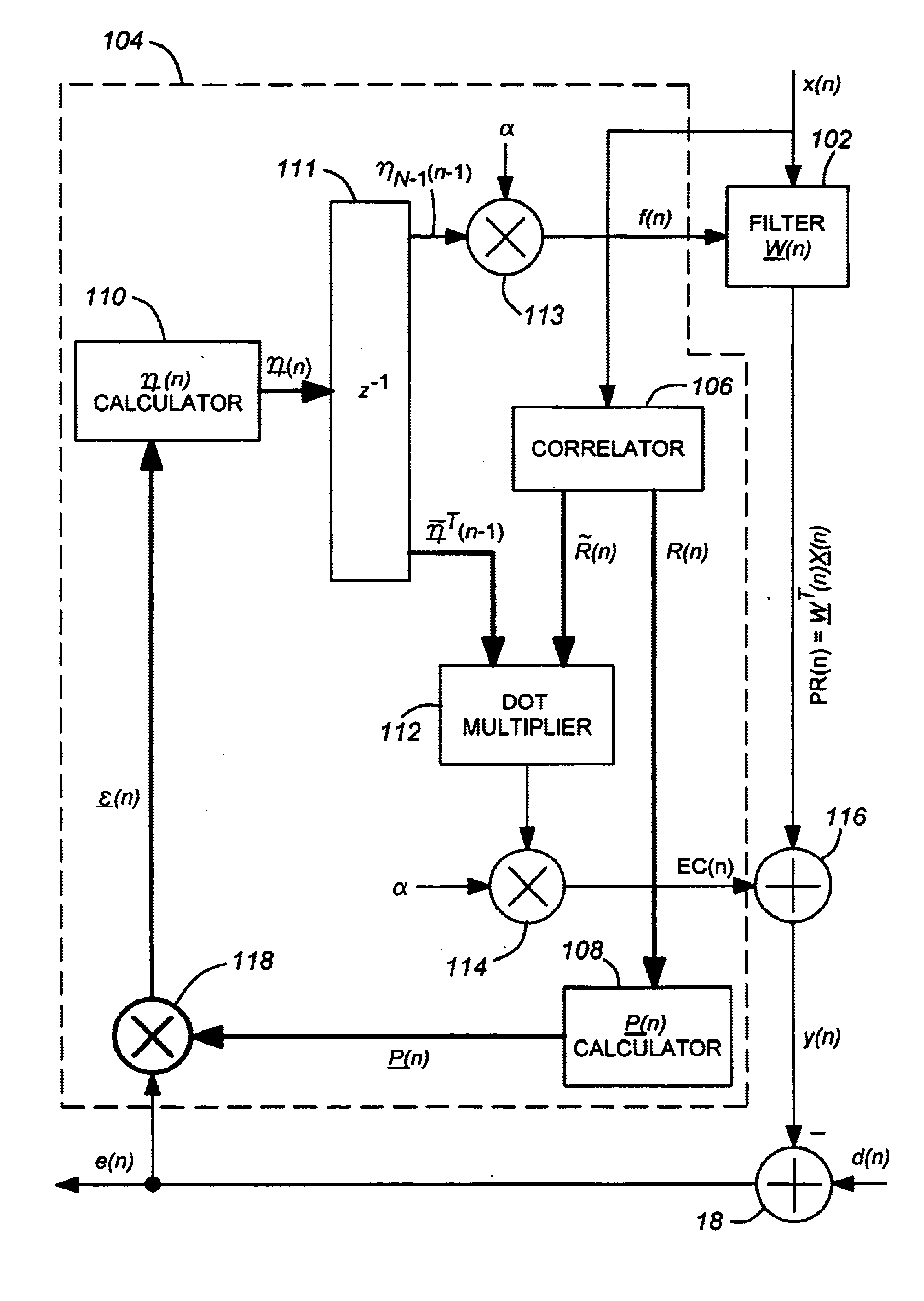
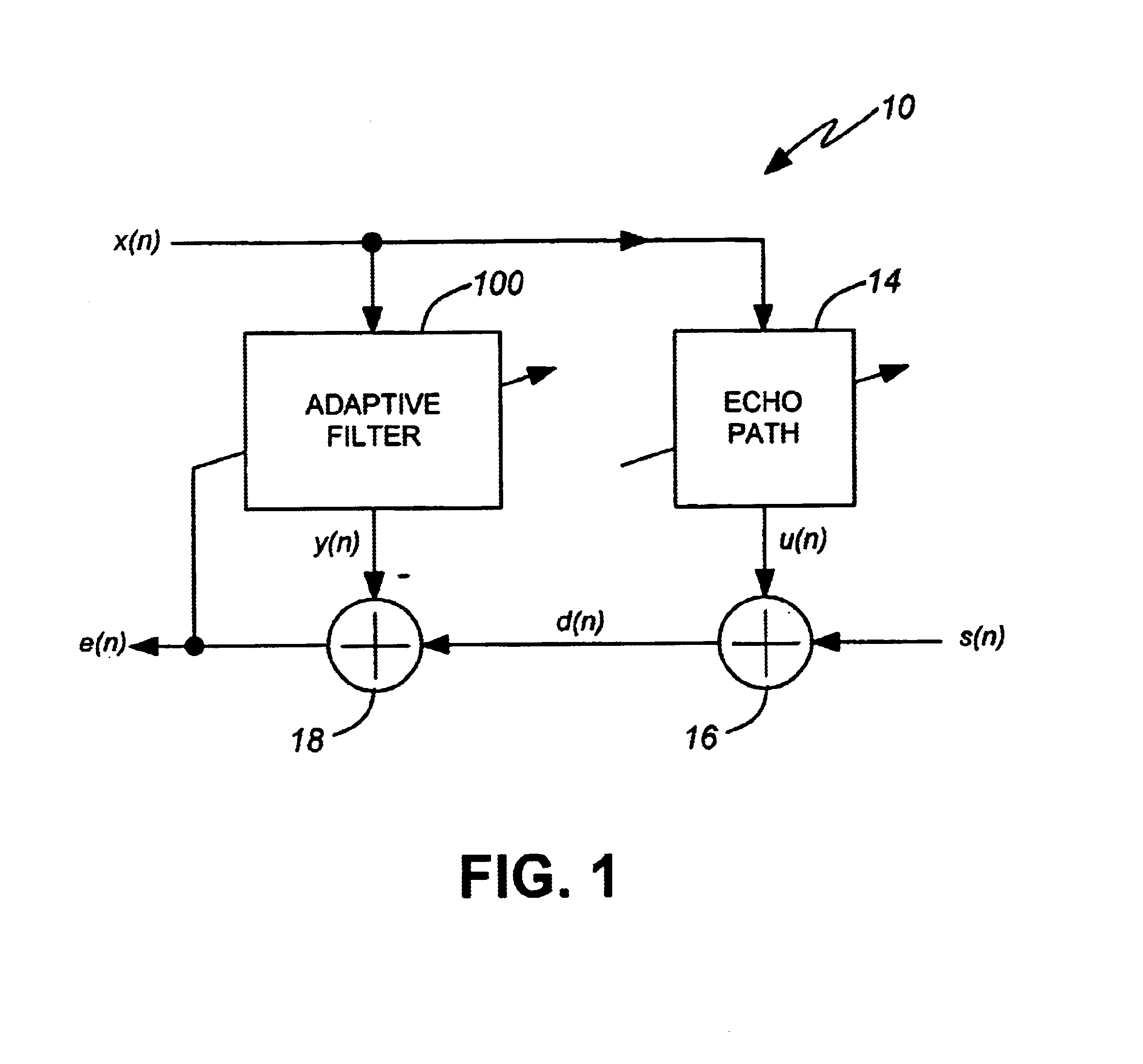
Secondary Path Modeling for Active Noise Control
ActiveUS20080144853A1Noise minimizationSampled-variable control systemsEar treatmentNoise controlMaximum difference
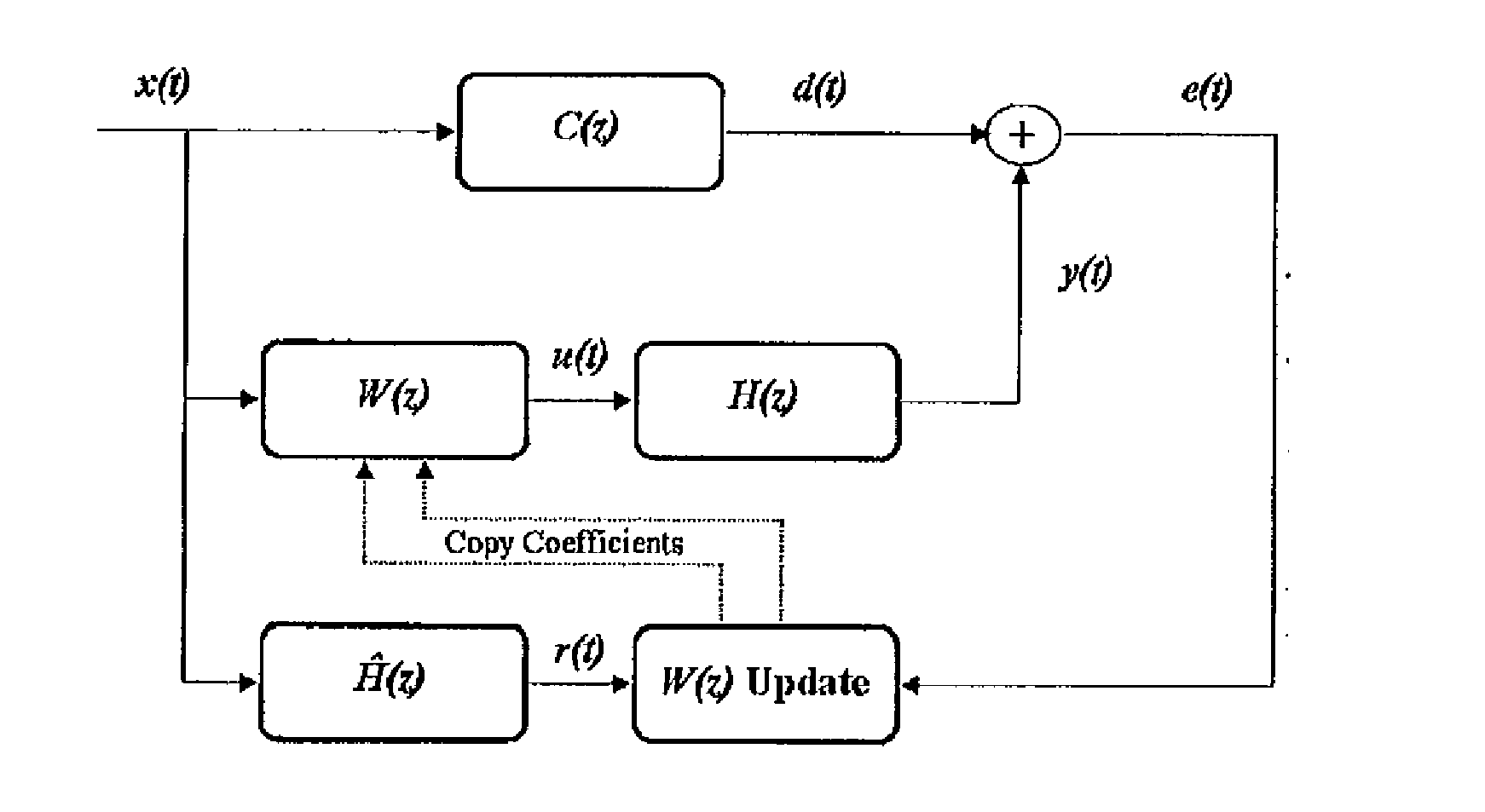
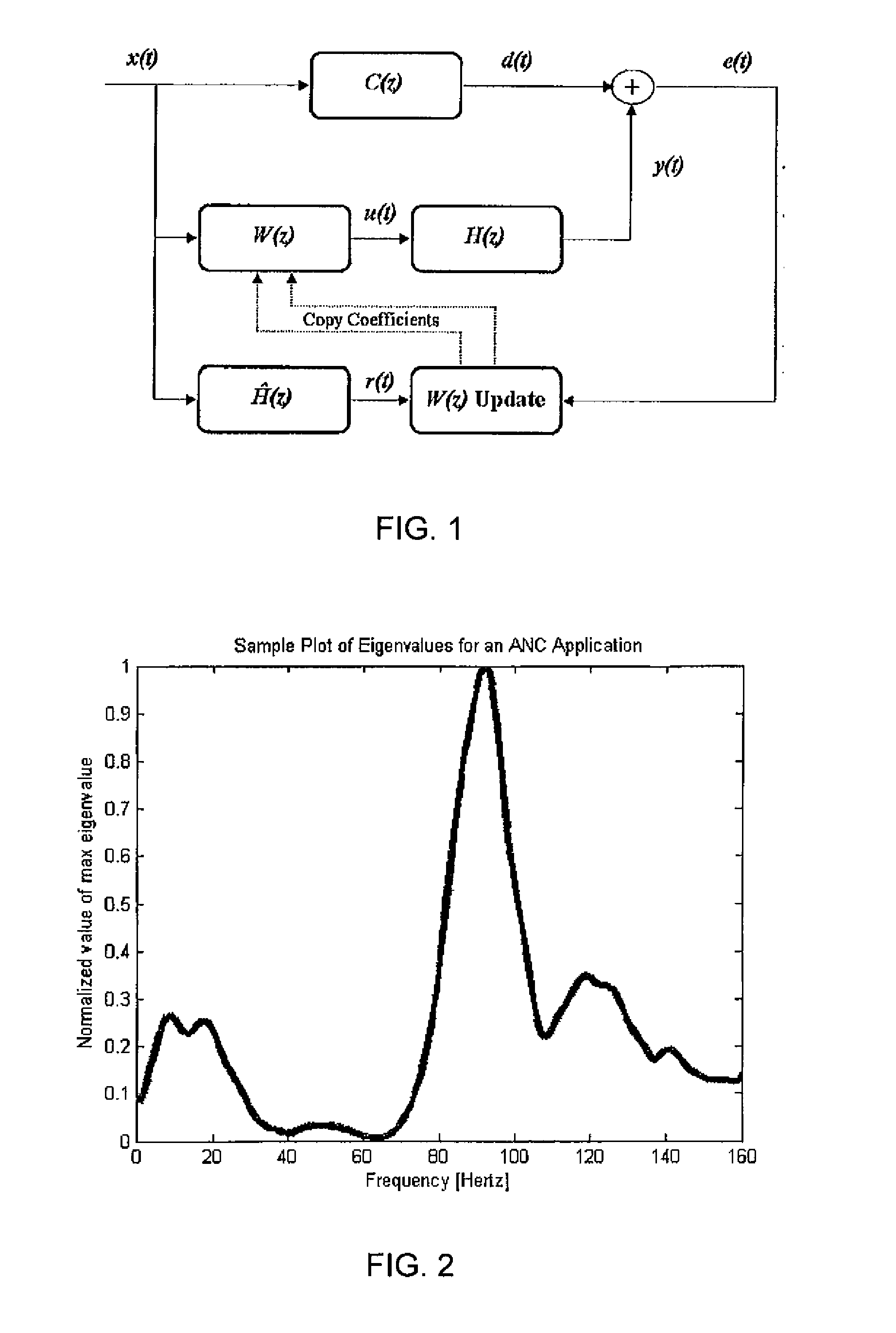
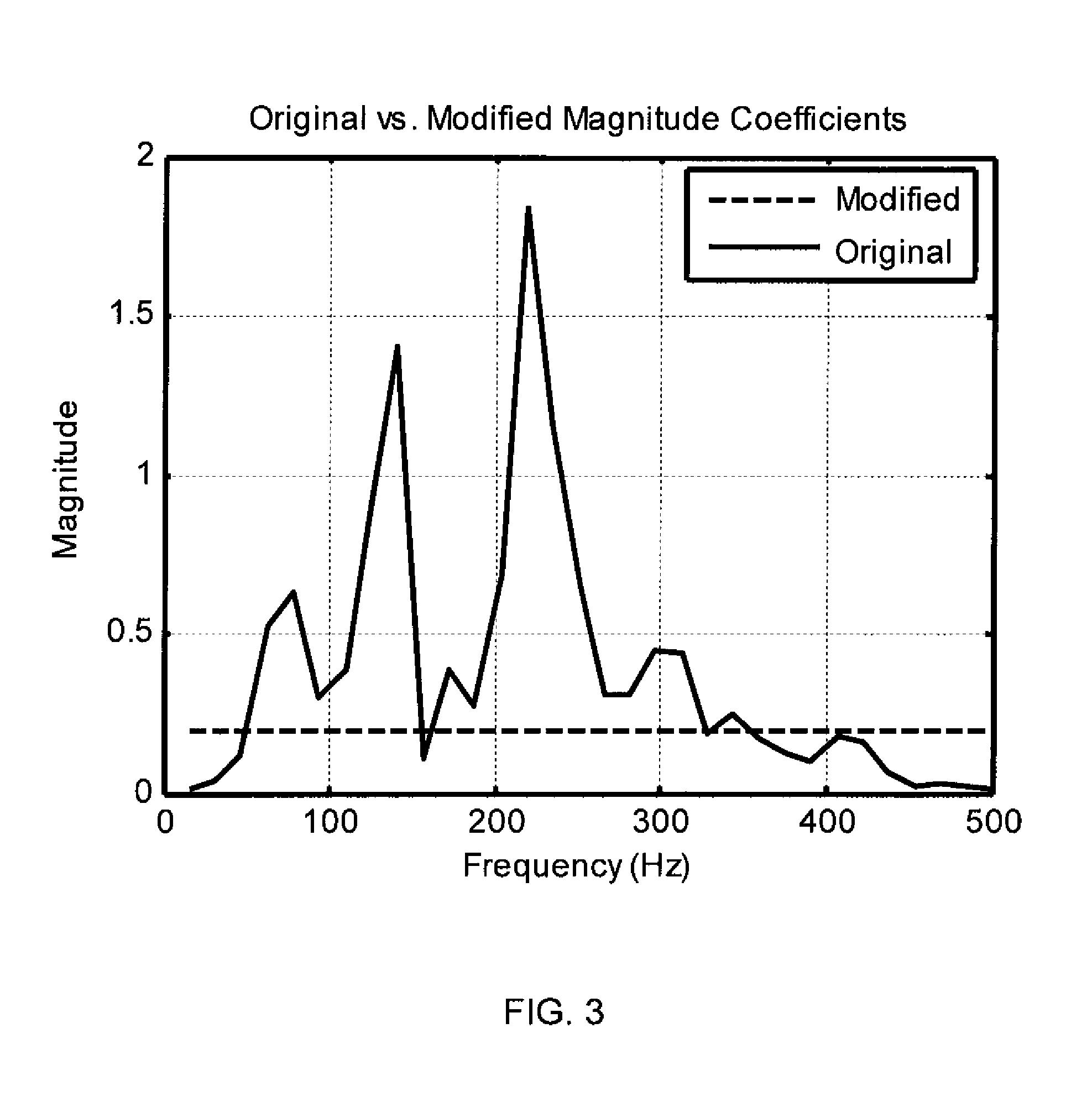
Methods for modeling the secondary path of an ANC system to improve convergence and tracking during noise control operation, and their associated uses are provided. In one aspect, for example, a method for modeling a secondary path for an active noise control system is provided. Such a method may include receiving a reference signal, filtering the reference signal with an initial secondary path model to obtain a filtered reference signal, calculating an autocorrelation matrix from the filtered reference signal, and calculating a plurality of eigenvalues from the autocorrelation matrix. The method may further include calculating a maximum difference between the plurality of eigenvalues and iterating a test model to determine an optimized secondary path model having a plurality of optimized eigenvalues that have a minimized difference that is less than the maximum difference of the plurality of eigenvalues, such that the optimized secondary path model may be utilized in the active noise control system.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Broadband signal DOA estimation method based on co-prime array
ActiveCN106324558AHigh-resolutionEasy to detectDirection findersSparse constraintSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
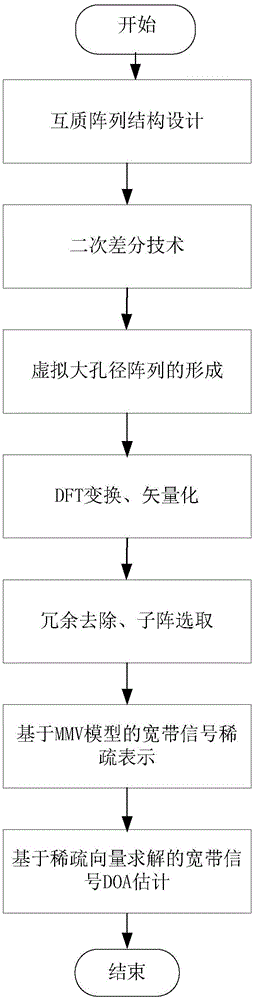
The invention discloses a broadband signal DOA estimation method based on a co-prime array, and the method comprises the steps: S1, designing a co-prime array structure through an antenna; S2, carrying out the sampling and discrete Fourier transform of a broadband signal received by an antenna in the co-prime array, and obtaining a frequency domain signal output model; S3, calculating an autocorrelation matrix of the frequency domain signal output model, carrying out the vectorization of the frequency domain signal output model, and obtaining a new signal model; S4, carrying out the processing of the new signal model, and obtaining a spatial smooth covariance matrix of the broadband signal; Sa5, dividing a space domain grid, constructing a dictionary, carrying out the sparse representation of the spatial smooth covariance matrix through employing the dictionaries of a plurality of frequency points of the broadband signal, and forming a multi-measurement-vector sparse representation model of a plurality of dictionaries of the broadband signal; S6, achieving the arrival direction estimation of the broadband signal in a mode of solving a sparse inverse problem through the joint sparse constraint of the sparse representation coefficients of the plurality of dictionaries. The method can improve the estimation precision of the direction angle of the broadband signal under the condition of low signal to noise ratio, and reduces the direction finding error.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
Stable adaptive filter and method
Stable adaptive filter and method are disclosed. The invention solves a problem of instability associated with Fast Affine Projection adaptive filters caused by error accumulation in an inversion process of an auto-correlation matrix. The Stable FAP uses a simplification of setting a normalized step size close to unity and reduces a problem of the matrix inversion to solving a system of linear equations whose solution coincides with a first column of the inverse auto-correlation matrix. The system of linear equations is then solved by one of descending iterative methods which provide inherent stability of operation due to intrinsic feedback adjustment. As a result, inevitable numerical errors are not accumulated, being corrected as the process goes on. In first and second embodiments of the invention the system of linear equation is solved by steepest descent and conjugate gradient methods respectively. Being immune to numerical errors, the invented method and filter are suitable for various DSP platforms, e.g., 16 and 24 bit fixed-point as well as floating point platform.
Owner:CIENA
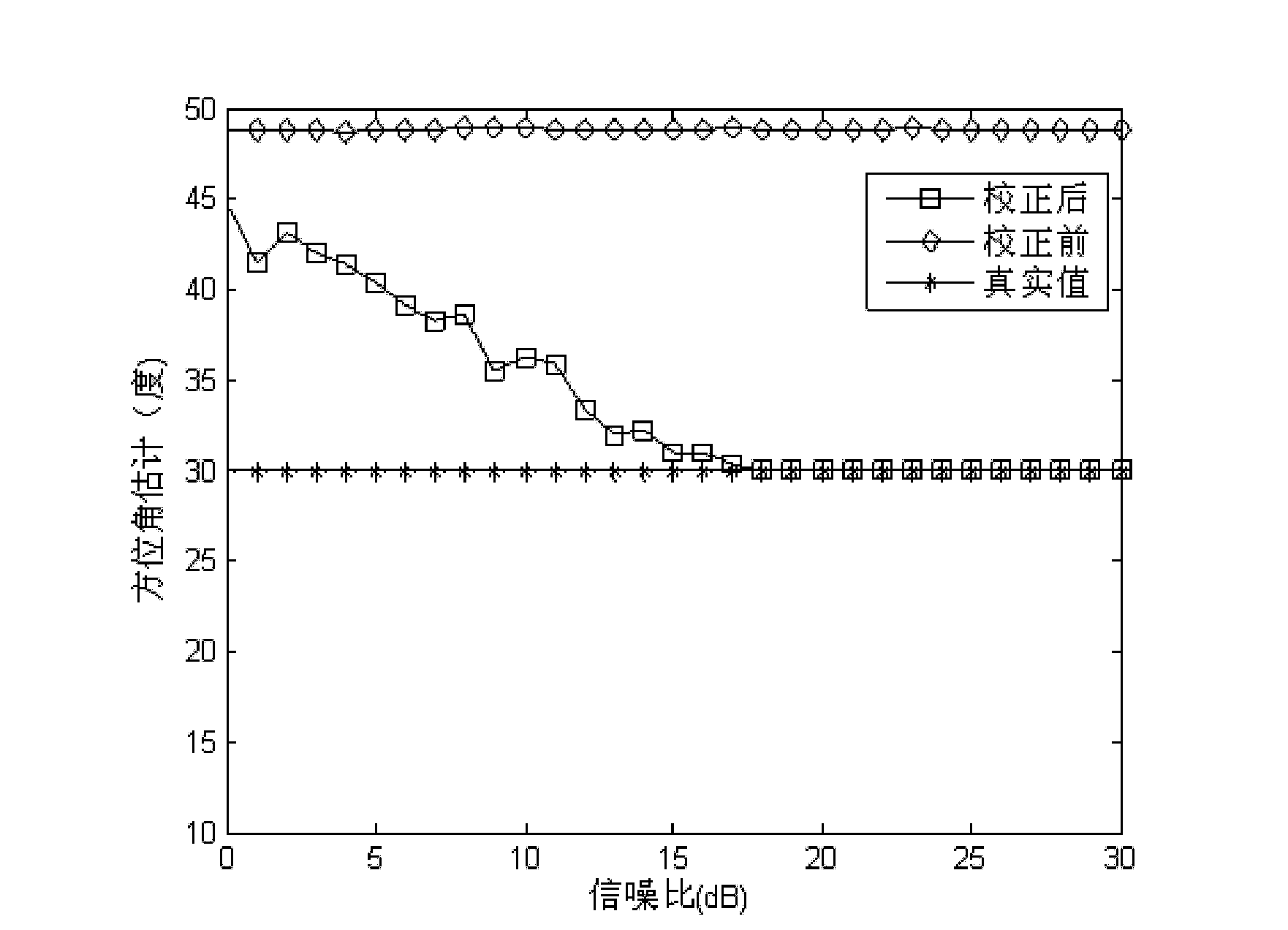
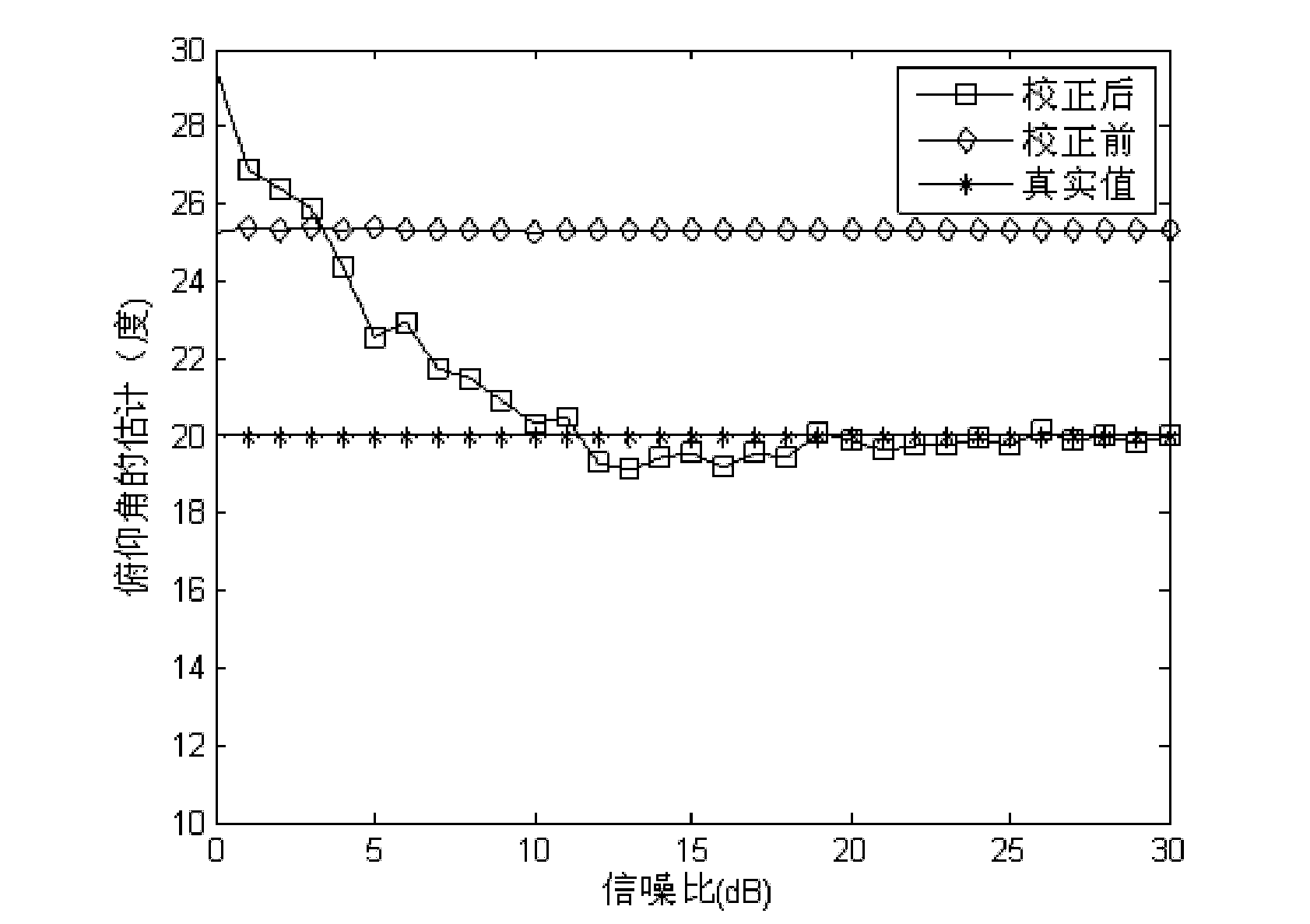
Method for self-correction of array error of multi-input multi-output radar system
ActiveCN101251597AHigh Target Angle Estimation AccuracyEffective correctionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputRadar systems
The invention discloses a self-correction method of a multi-input multi-output radar system array error, relating to the radar technical field. The method aims to carry out self correction of the reliant amplitude and phase error of a receiving array azimuth on the premise that the transmitting array of a multi-input multi-output radar system. The implementation process of the method is as follows: firstly, by means of the two corrected transmitting array elements of the multi-input multi-output radar system, orthogonal signals are transmitted; then, the echo signals of the transmitting array elements are separated by means of the orthogonality of transmitting signal through adopting a matched filtering method; an auto correlation matrix and a cross correlation matrix are established by means of the echo signals; a real guide vector and a target angle of an array are estimated by means of a rotary invariant subspace method; finally, by means of the real guide vector and the target angle of the array obtained through estimation, the array azimuth reliant amplitude and phase error can be corrected. The self-correction method can be used in the array error correction field of a multichannel radar system.
Owner:XIAN CETC XIDIAN UNIV RADAR TECH COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION INST CO LTD
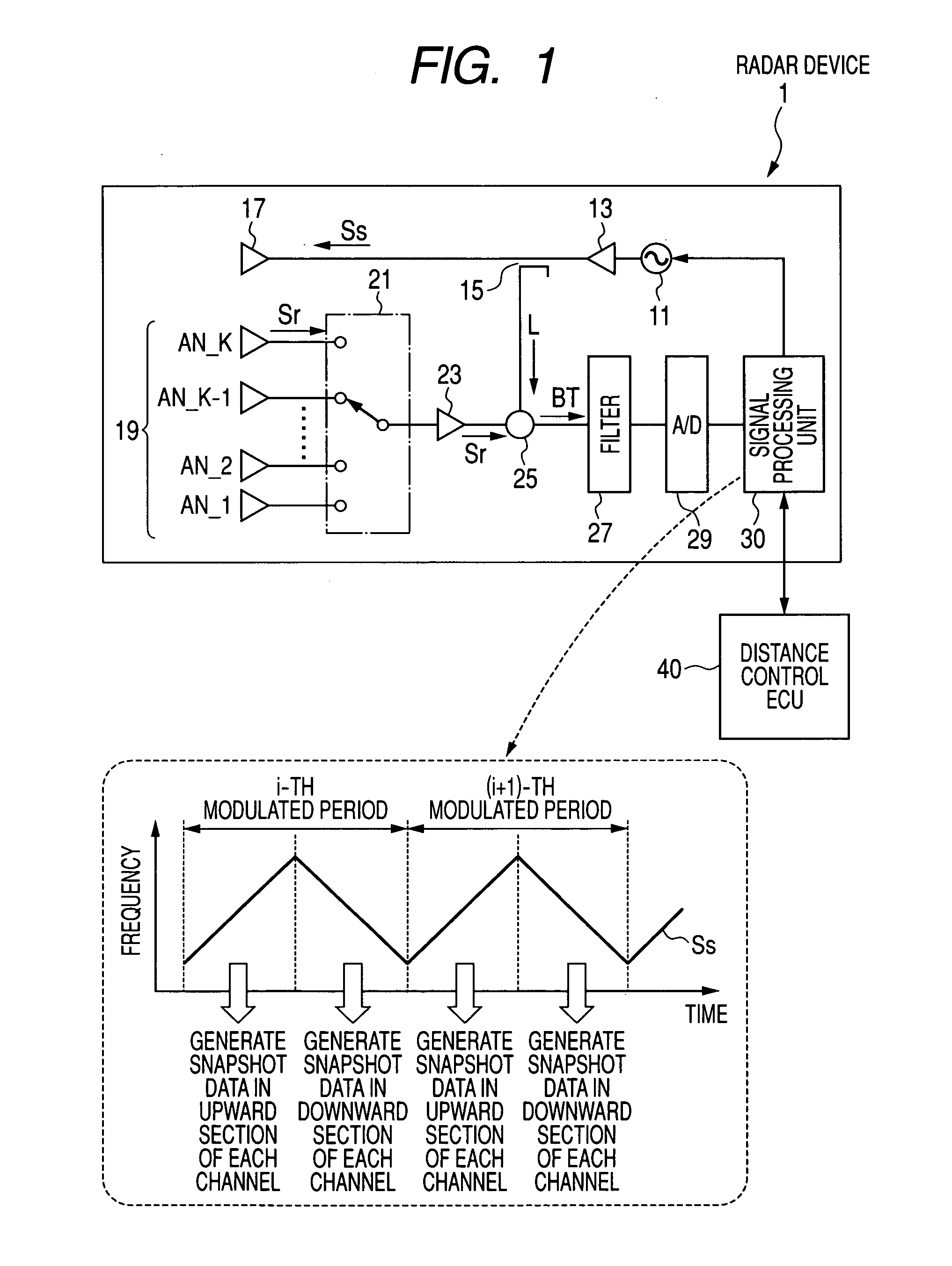
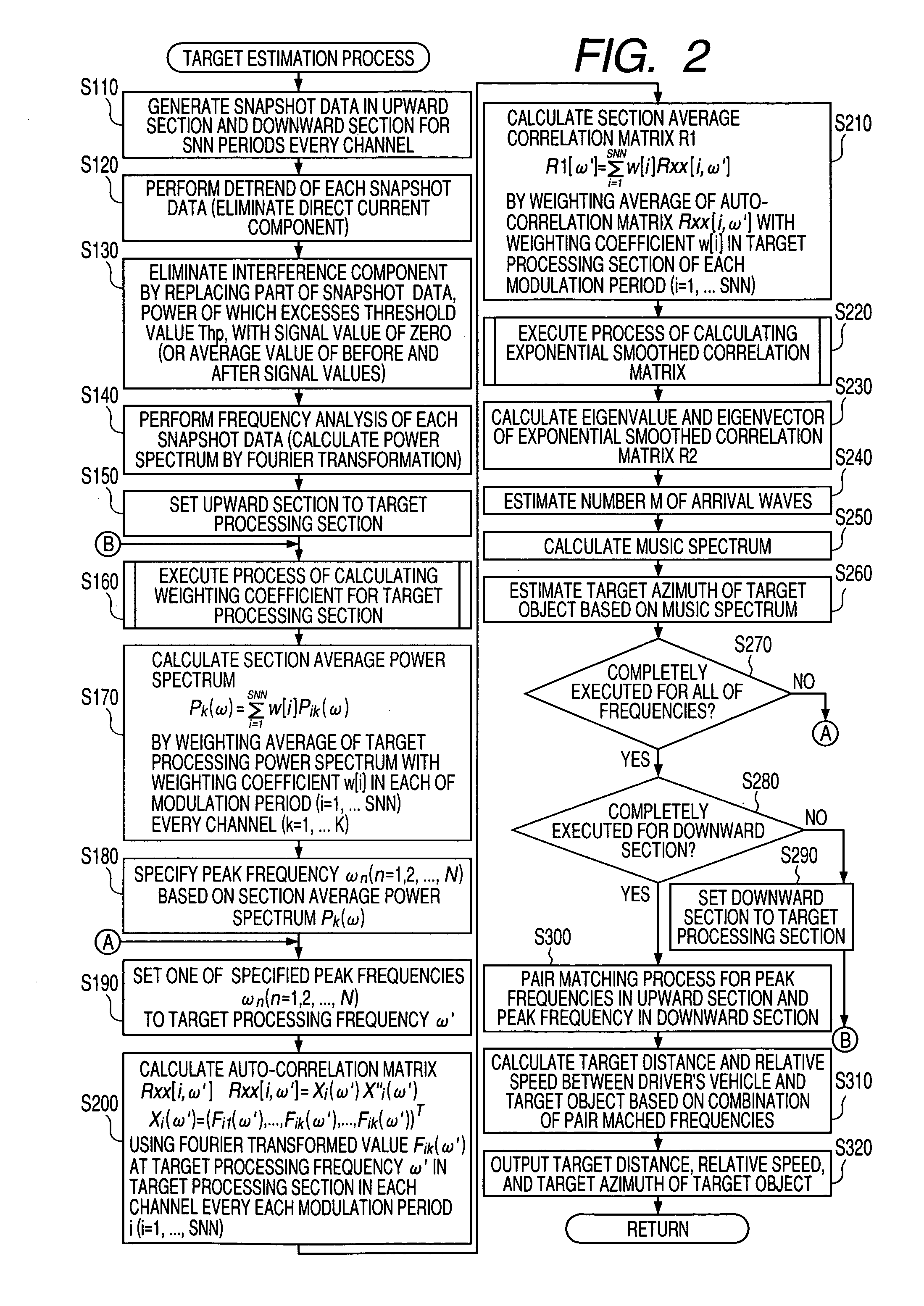
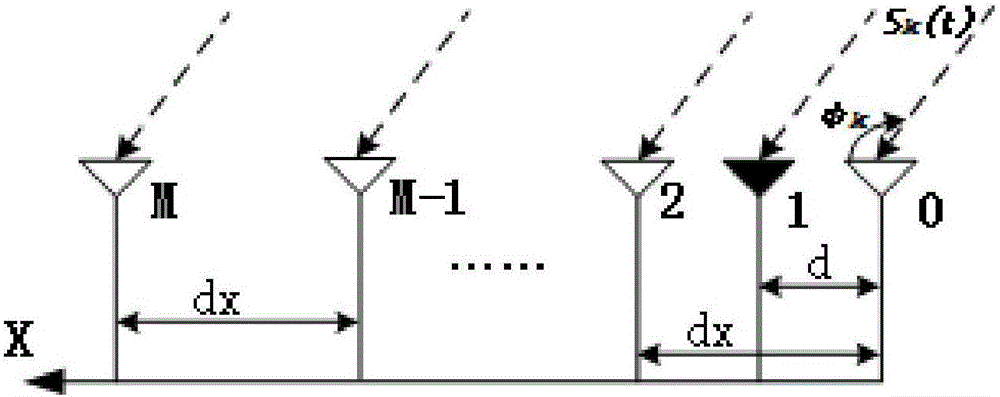
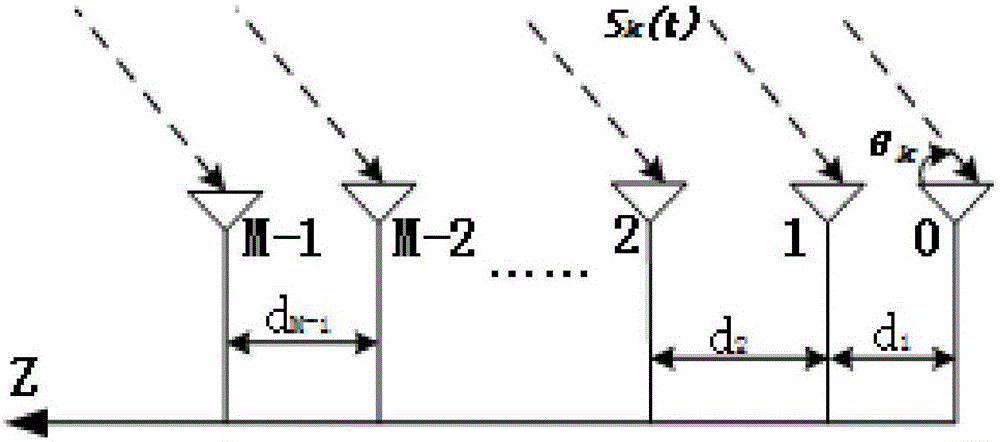
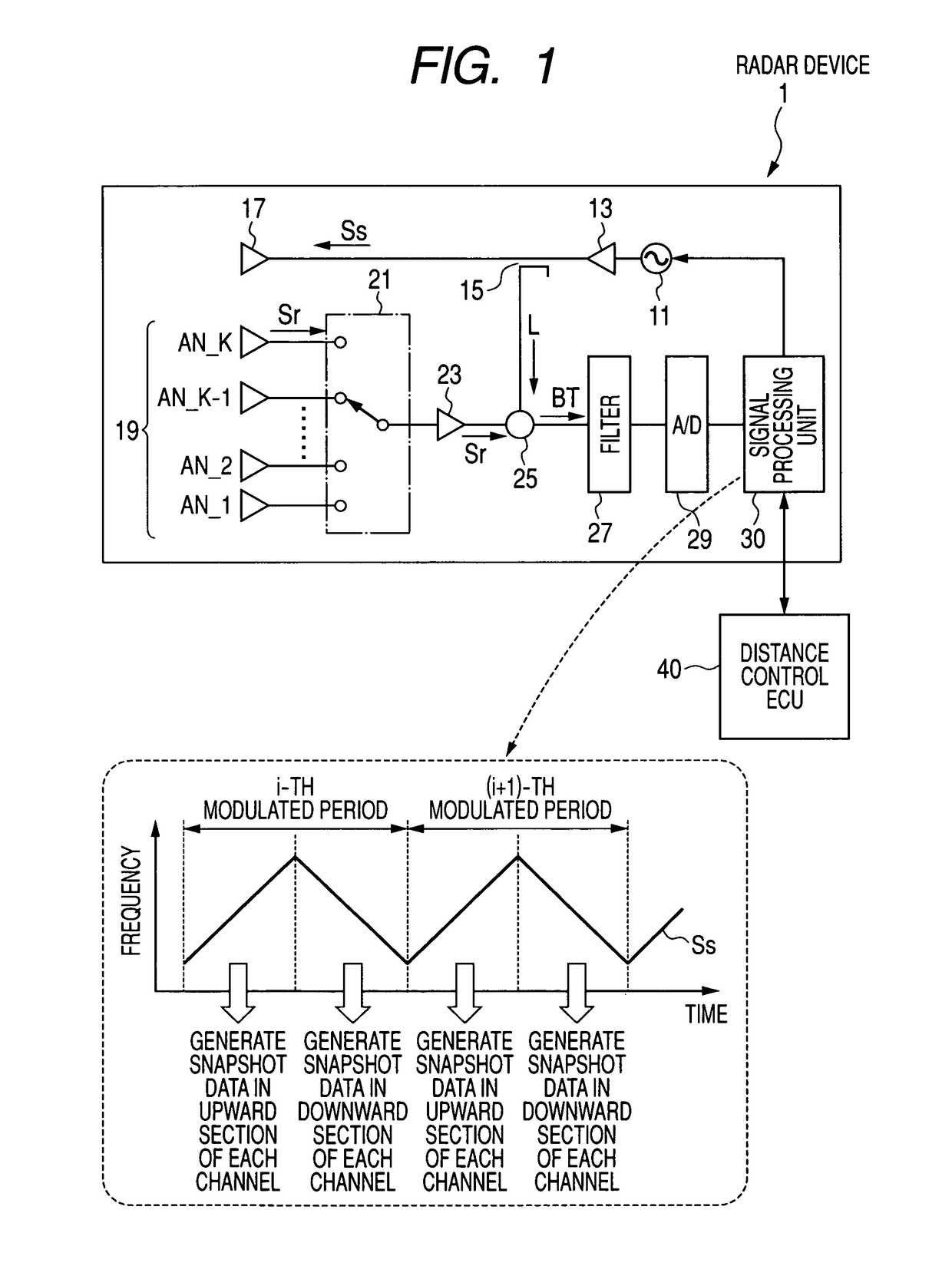
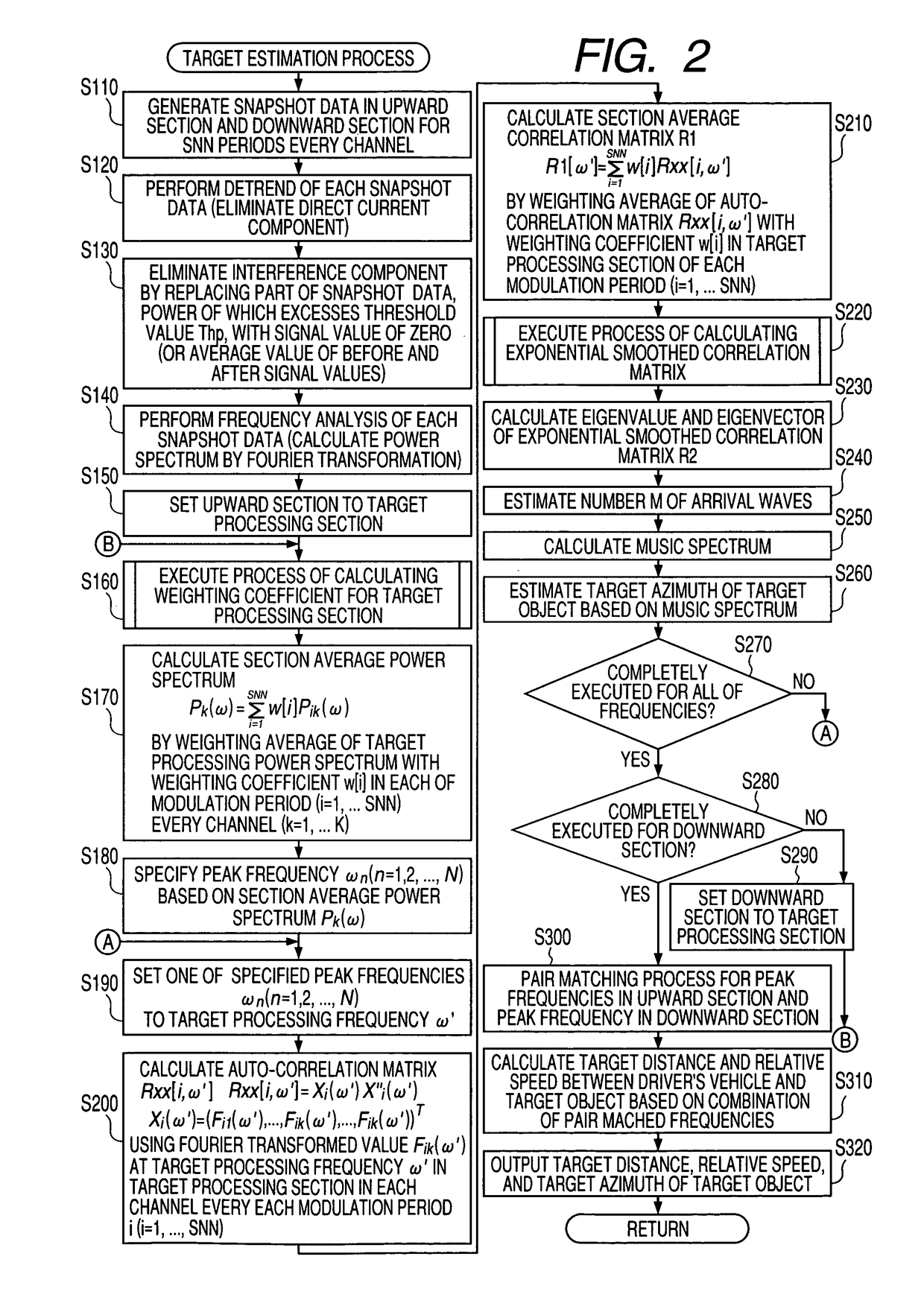
Radar device
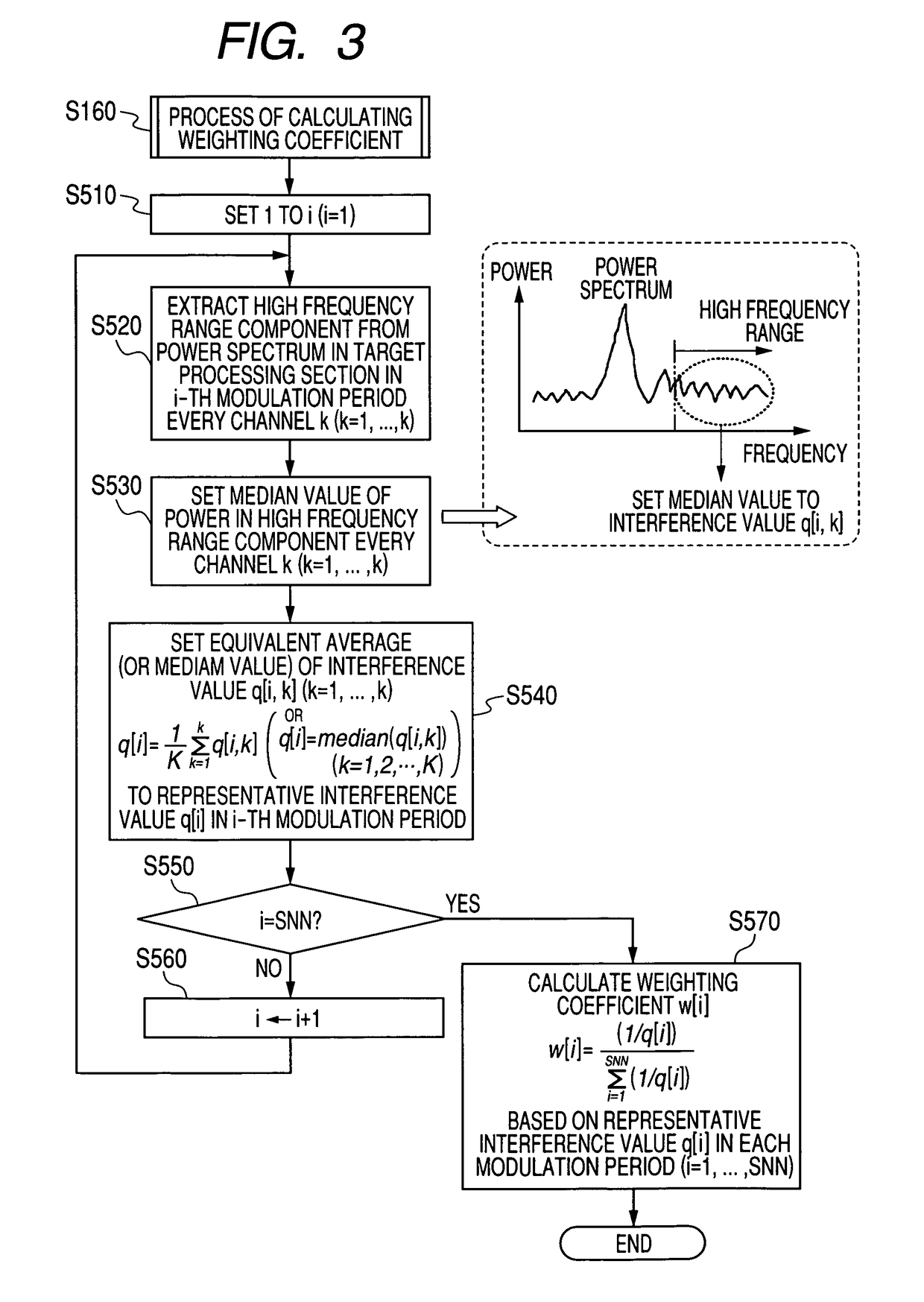
ActiveUS20100073216A1Improve accuracyConvenient and accurateMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMixed noiseSignal classification
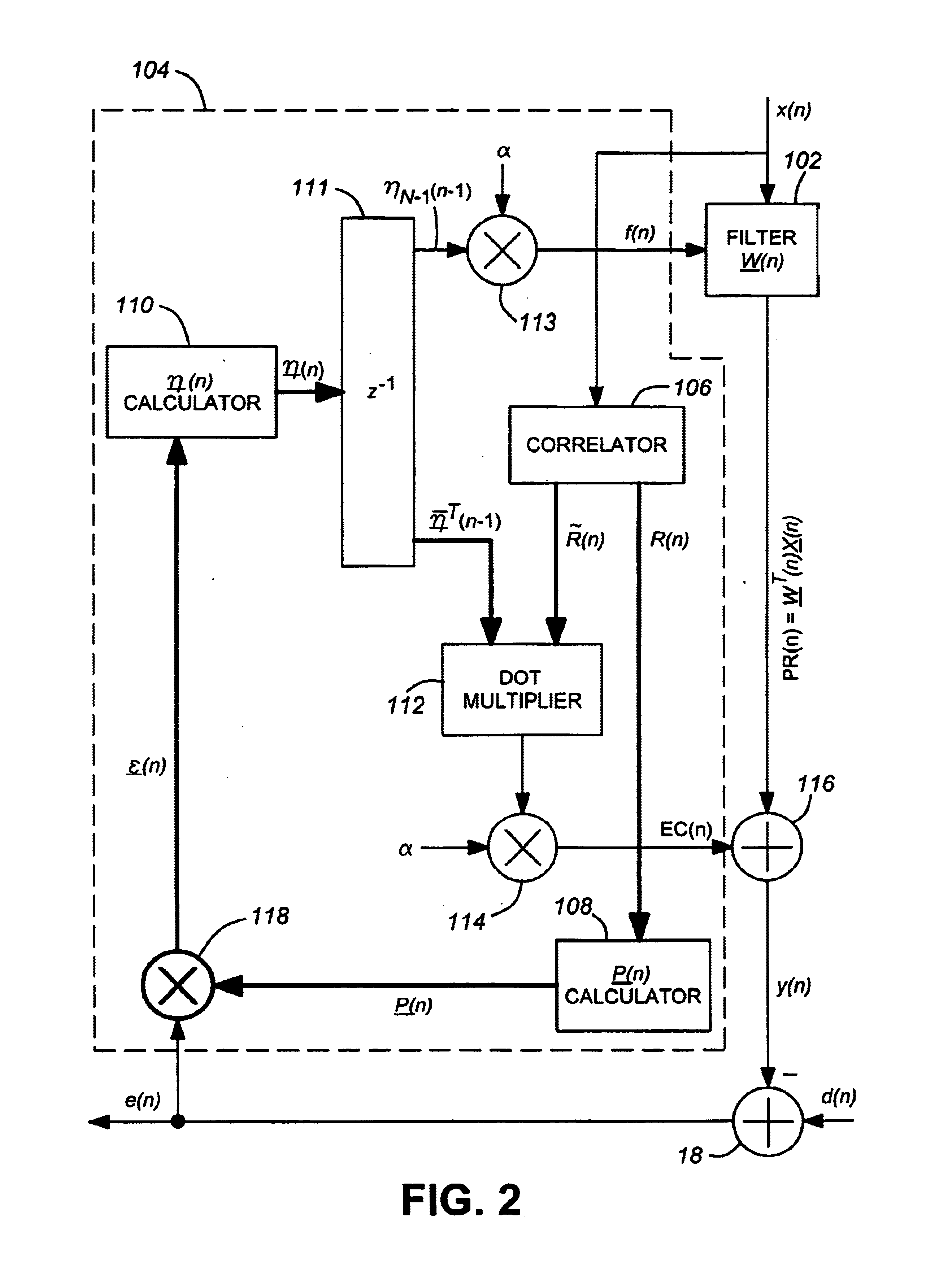
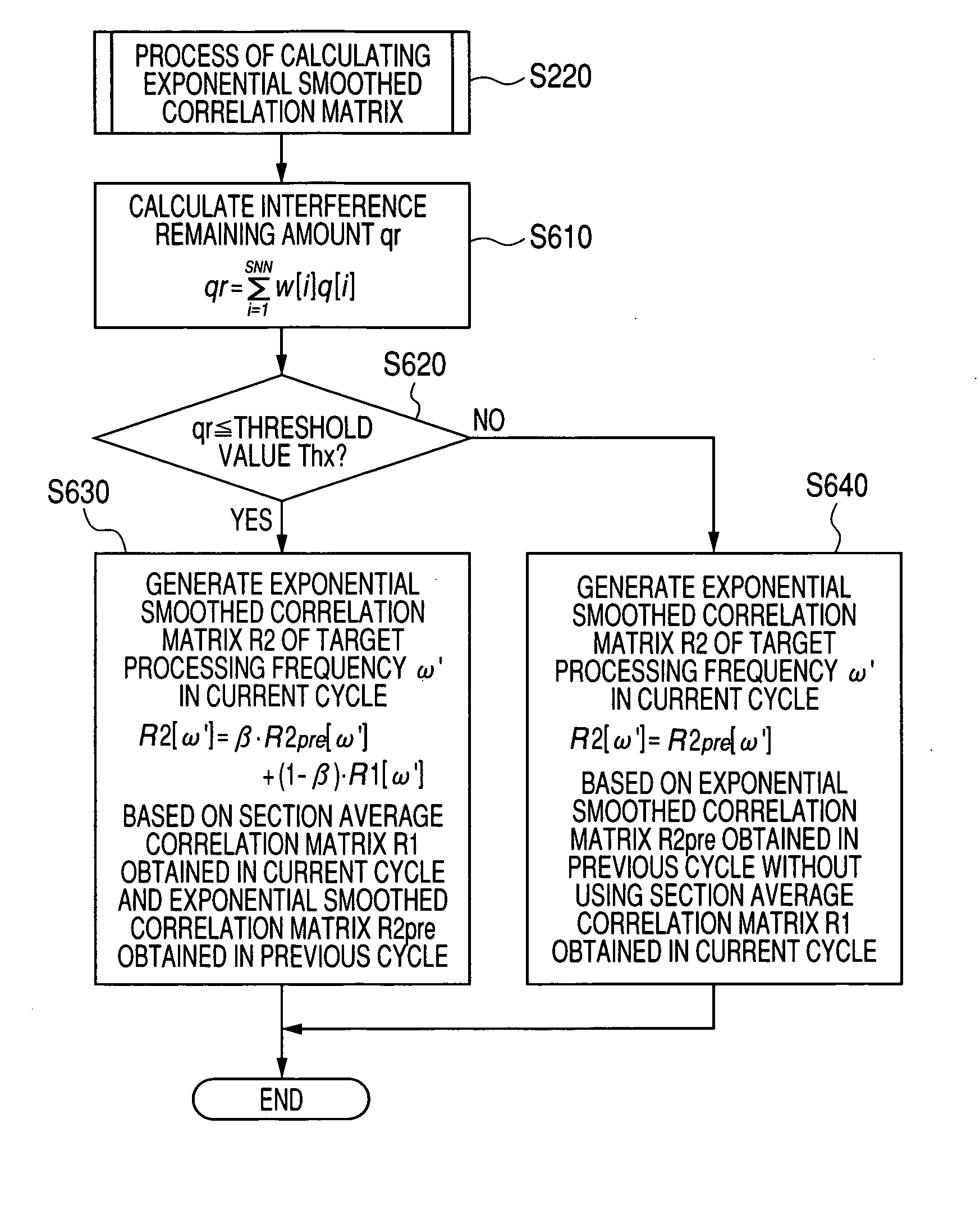
A FMCW-type radar device generates snapshot data from a beat signal that represents a received condition of the radar device every modulation period. Auto-correlation matrices generated by the snapshot data every modulation period are averaged every set of plural periods. The radar device calculates the target azimuth of a target object such as a preceding vehicle based on the averaged auto-correlation matrix based on MUSIC (MUltiple SIgnal Classification) method. This averaging is performed by weighting average based on an amount of mixed noise (or an interference amount) contained in the snapshot data in each modulation period. A weighting coefficient to be applied to the auto-correlation matrix in each modulation period is set to a value corresponding to the amount of mixed noise, namely, the interference amount of this modulation period. The weighting coefficient becomes large when the interference amount is small, and on the other hand, becomes small when it is large.
Owner:DENSO CORP
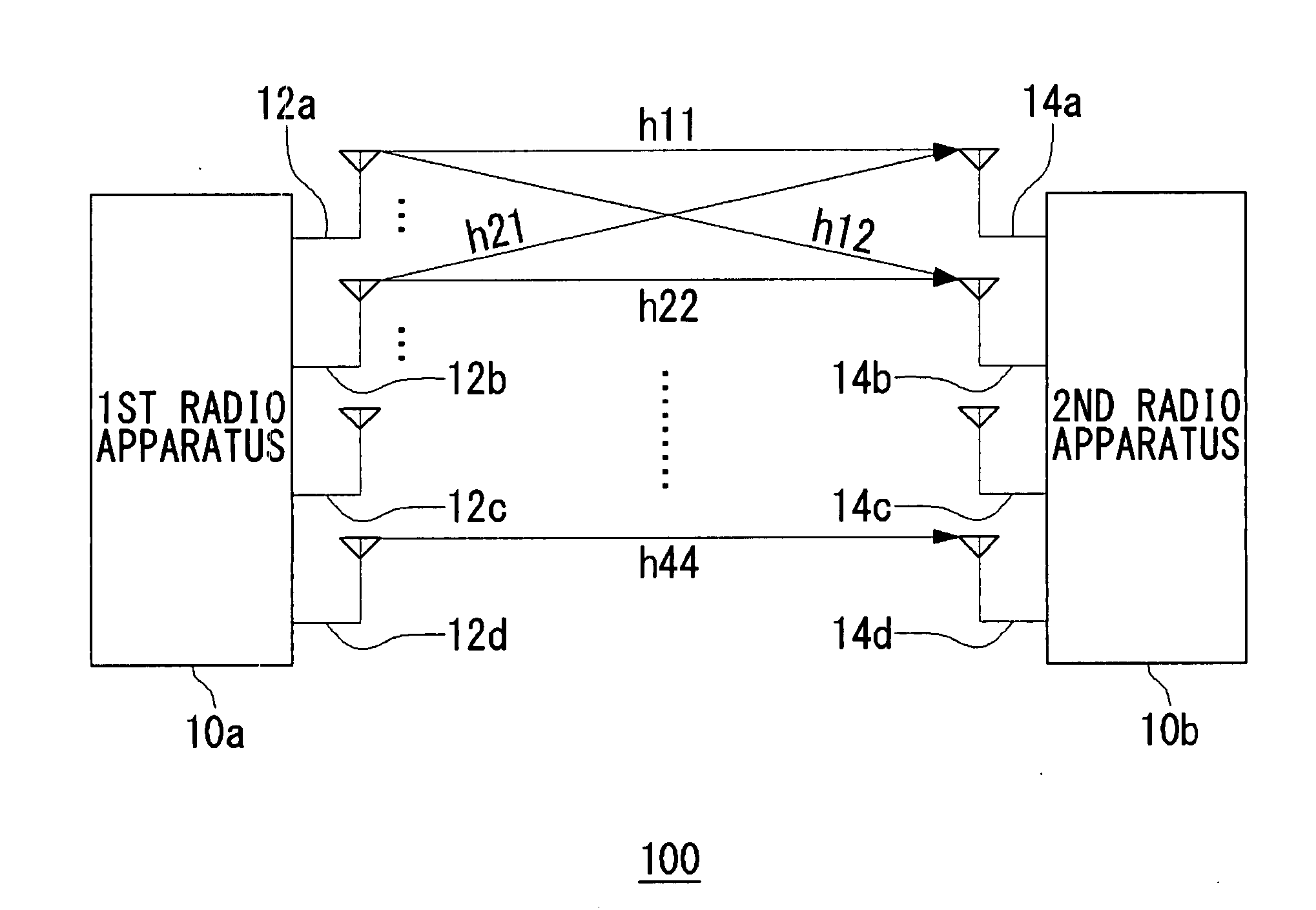
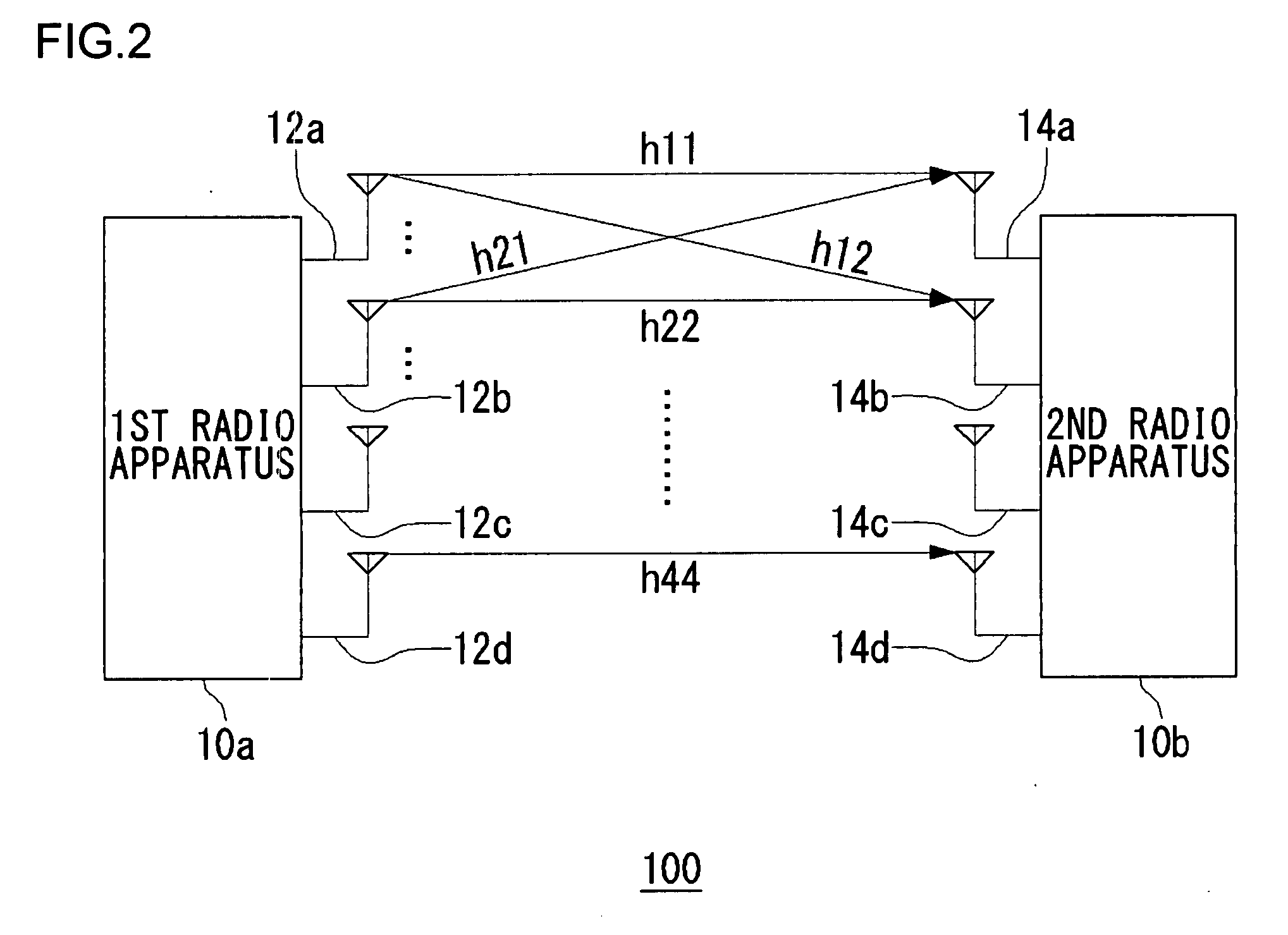
Method for deriving weight vectors to be used at the time of transmitting signals from a plurality of antennas, and transmitting apparatus and communication system utilizing said method
ActiveUS20070280367A1Frequency-division multiplexDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemCarrier signal
A plurality of antennas transmit multicarrier signals composed of a plurality of streams. An IF unit acquires, per carrier, a channel matrix having elements the number of which is determined by the number of a plurality of transmitting antennas and the number of a plurality of receiving antennas provided in a receiving apparatus. A baseband processing unit includes a means which derives a common autocorrelation matrix for the channel matrix acquired per carrier and a means which derives a steering matrix by eigenvalue-decomposing the derived common autocorrelation matrix. The baseband processing unit derives, per carrier, weight vectors for a plurality of streams in a manner such that an orthonormalization is performed respectively on matrices obtained by operating the derived steering matrix on the channel matrix per carrier.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
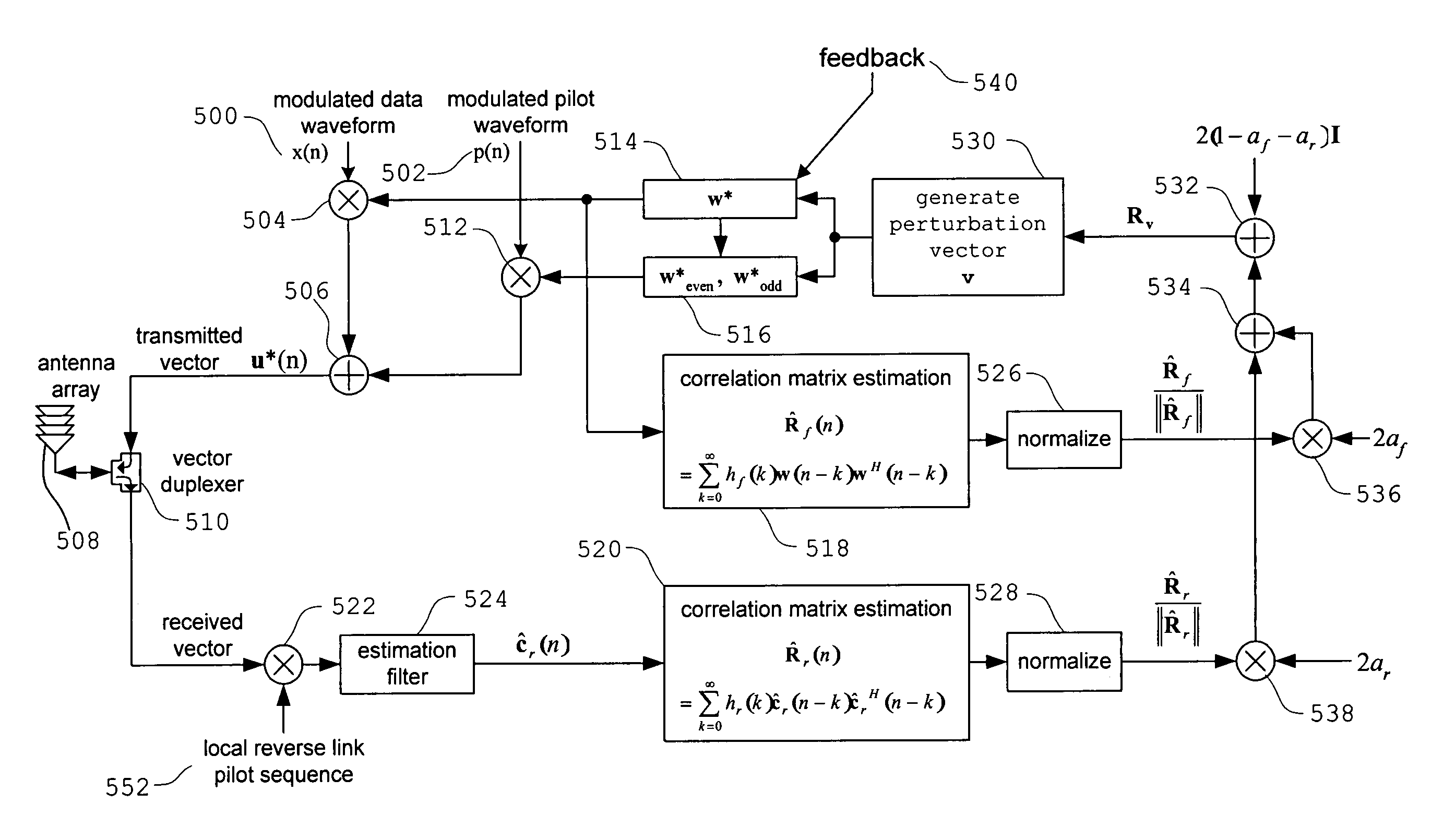
Method and apparatus for improving transmit antenna weight tracking using channel correlations in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS7236538B1Improves weight vector trackingDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPhase correlationGradient estimation
A novel method and apparatus for improving transmit antenna weight tracking using channel vector element to element correlations in a wireless communication system is disclosed. The present channel autocorrelation tracking technique utilizes the observation that tracking can be improved when a channel gain vector contains correlated elements. In a first embodiment of the autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention extracts a coarse gradient estimate by utilizing a perturbation vector autocorrelation matrix estimate and a perturbation autocorrelation matrix to update TxAA weight vectors accordingly. In a second embodiment of the channel autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention extracts a coarse gradient estimate by utilizing eigendecompositions, perturbation vector autocorrelation matrix estimates, and perturbation autocorrelation matrices to update TxAA weight vectors accordingly. In a third embodiment of the channel autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention reduces the phase change that can occur at receivers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Estimating method of direction of arrival of bistatic MIMO (Multi-Input Multi-Output) radar based on circular array
InactiveCN102707264AReduce computationQuick calculationWave based measurement systemsMulti inputAngle of departure
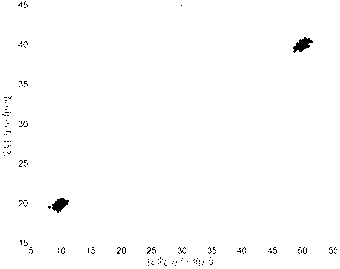
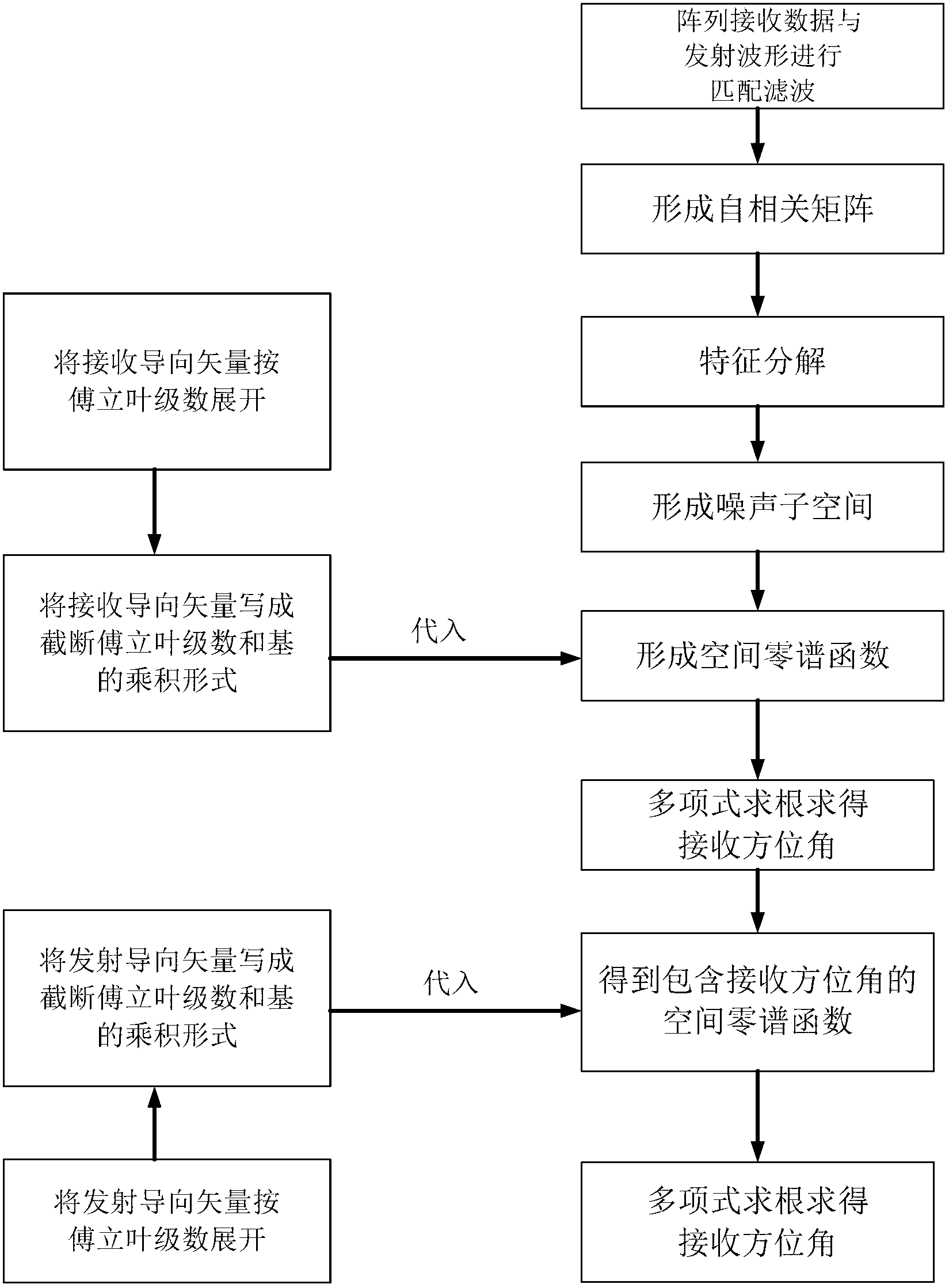
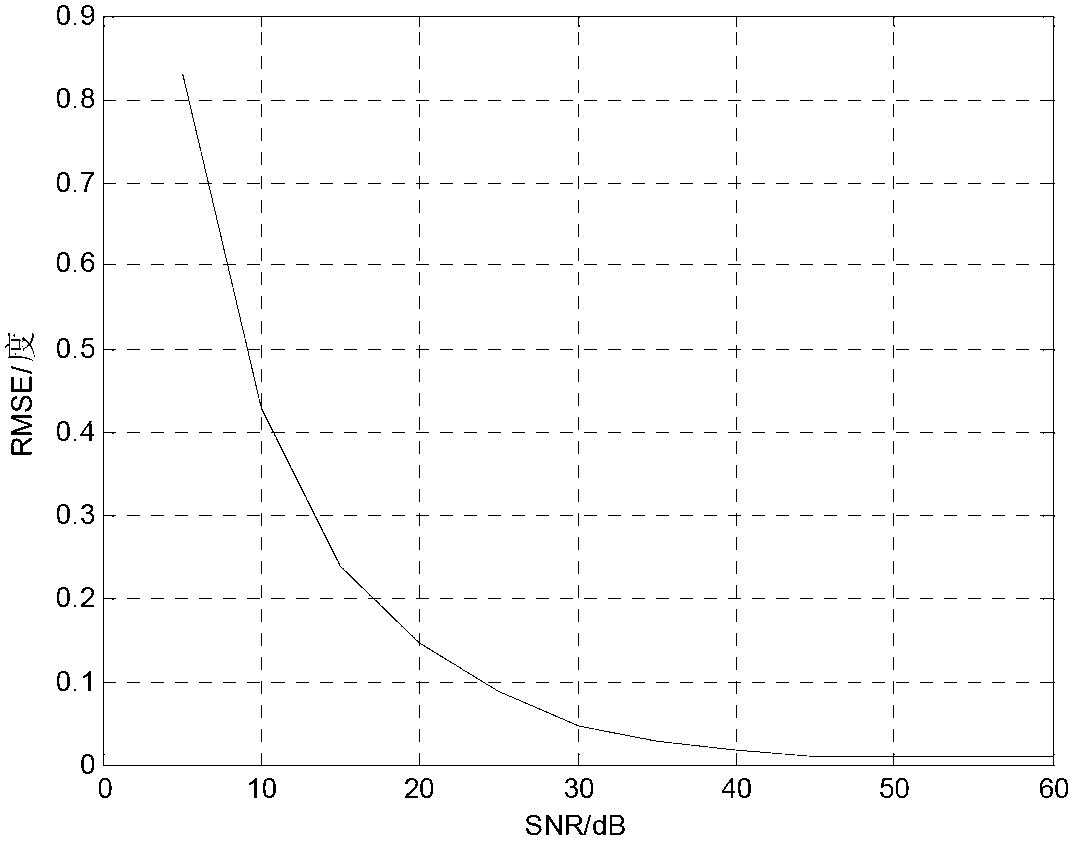
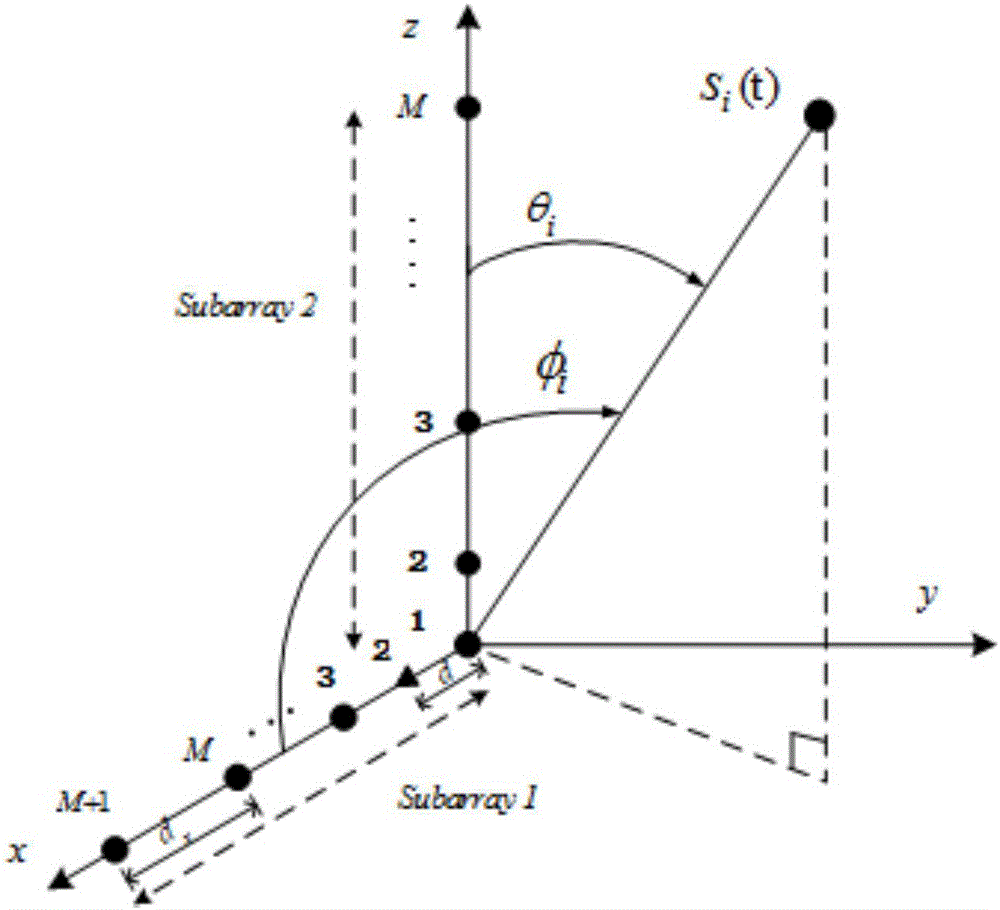
The invention discloses an estimating method of direction of arrival of a bistatic MIMO (Multi-Input Multi-Output) radar based on a circular array, and mainly solves the problems that in the prior art, calculation is large and the direction of arrival of the circular array cannot be estimated. The realizing process comprises the steps of: 1, obtaining a cut-off Fourier coefficient of a steering vector of the array, and replacing the steering vector by the product of the Fourier coefficient and a base; 2, performing matched filtering for received data by the array to form an autocorrelation matrix and performing characteristic-decomposition for the matrix; 3, selecting a characteristic vector to form a noise sub space and obtaining a spatial zero-spectral function; 4, introducing the steering vector received to the spatial zero-spectral function, and solving an acceptance angle by polynomial rooting; and 5, introducing the acceptance angle received to the spatial zero-spectral function and solving an angle of departure by polynomial rooting. According to the estimating method of direction of arrival of the bistatic MIMO radar based on the circular array, the polynomial rooting method can be adopted to estimate the direction of arrival of the manifold MIMO radar of the circular array, spectrum peak search is avoided, calculation is low, and the estimating method of direction of arrival of the bistatic MIMO radar based on the circular array can be applied to estimating the direction of arrival of the bistatic MIMO radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
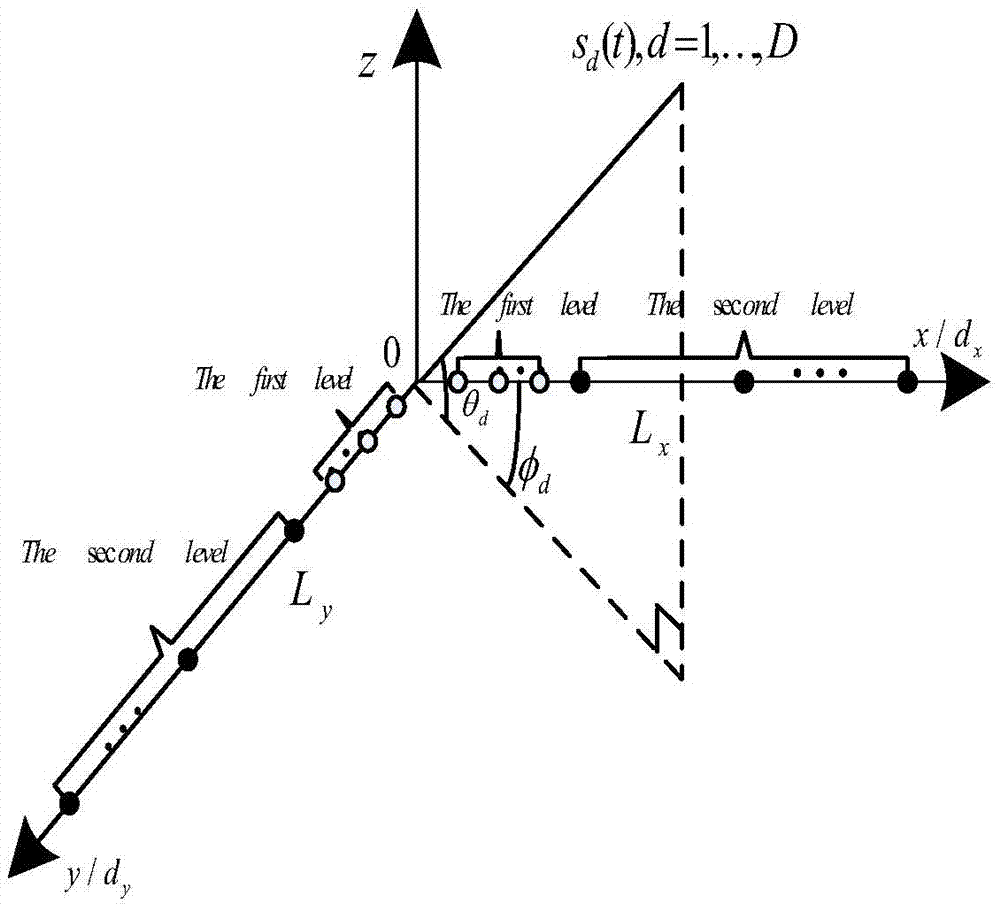
Sparse L-shaped array and two-dimensional DOA estimation method thereof
InactiveCN106054123ASmall amount of calculationThe parameters are accurateRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsCross correlation matrixDecomposition
The invention discloses a sparse L-shaped array and a two-dimensional DOA estimation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of wireless mobile communication. The sparse L-shaped array comprises a first subarray formed by a sparse uniform linear array, the array element space of which is equal to the wavelength, and an auxiliary array element, and a second subarray formed by an arbitrary sparse linear array, the minimum array element space of which is smaller than or equal to a half wavelength. The shared array element of the two linear arrays is a reference array element, and the distance between the auxiliary array element and the reference array element is the half wavelength. The two-dimensional DOA estimation method is characterized by, to begin with, calculating an autocorrelation matrix according to received data of the second subarray, carrying out characteristic decomposition on the autocorrelation matrix and then, estimating a corresponding second angle, and carrying out calculation to obtain an information source autocorrelation matrix based on the second angle; and obtaining an array manifold matrix of the first subarray according to a cross-correlation matrix of the received data of the two subarrays and the information source autocorrelation matrix, thereby finishing estimation of a first angle corresponding to the first subarray, and obtaining the two-dimensional DOA. Complexity is low, and DOA estimation precision is high.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Radar device
ActiveUS7907083B2Improve accuracyConvenient and accurateMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMixed noiseRadar
A FMCW-type radar device generates snapshot data from a beat signal that represents a received condition of the radar device every modulation period. Auto-correlation matrices generated by the snapshot data every modulation period are averaged every set of plural periods. The radar device calculates the target azimuth of a target object such as a preceding vehicle based on the averaged auto-correlation matrix based on MUSIC (MUltiple SIgnal Classification) method. This averaging is performed by weighting average based on an amount of mixed noise (or an interference amount) contained in the snapshot data in each modulation period. A weighting coefficient to be applied to the auto-correlation matrix in each modulation period is set to a value corresponding to the amount of mixed noise, namely, the interference amount of this modulation period. The weighting coefficient becomes large when the interference amount is small, and on the other hand, becomes small when it is large.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Nested L-shaped antenna array structure and direction of arrival estimation method thereof
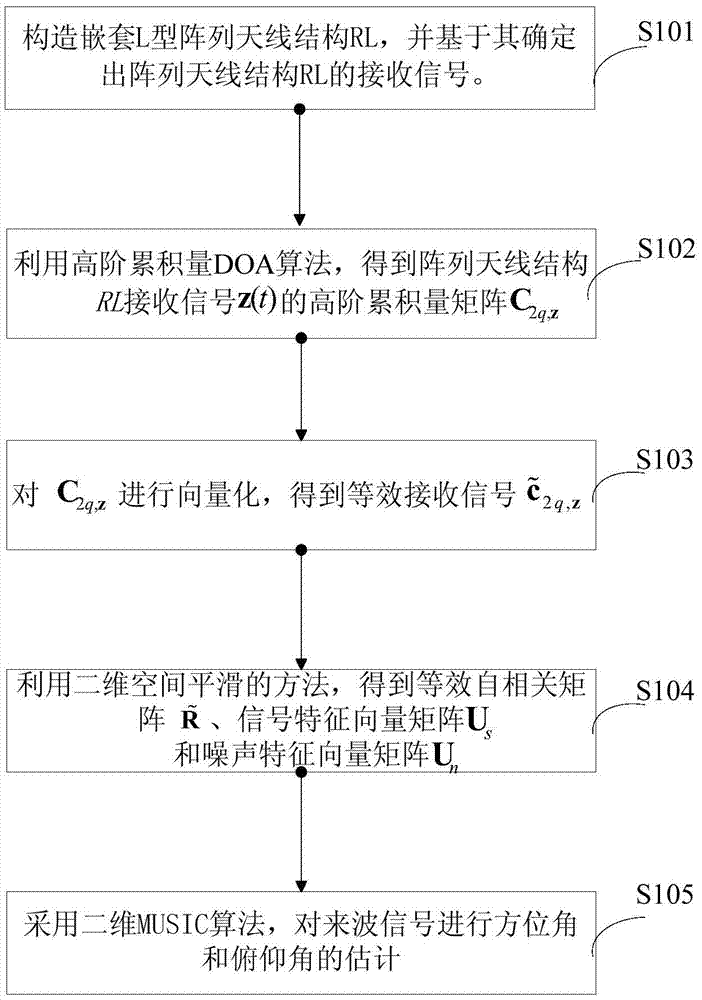
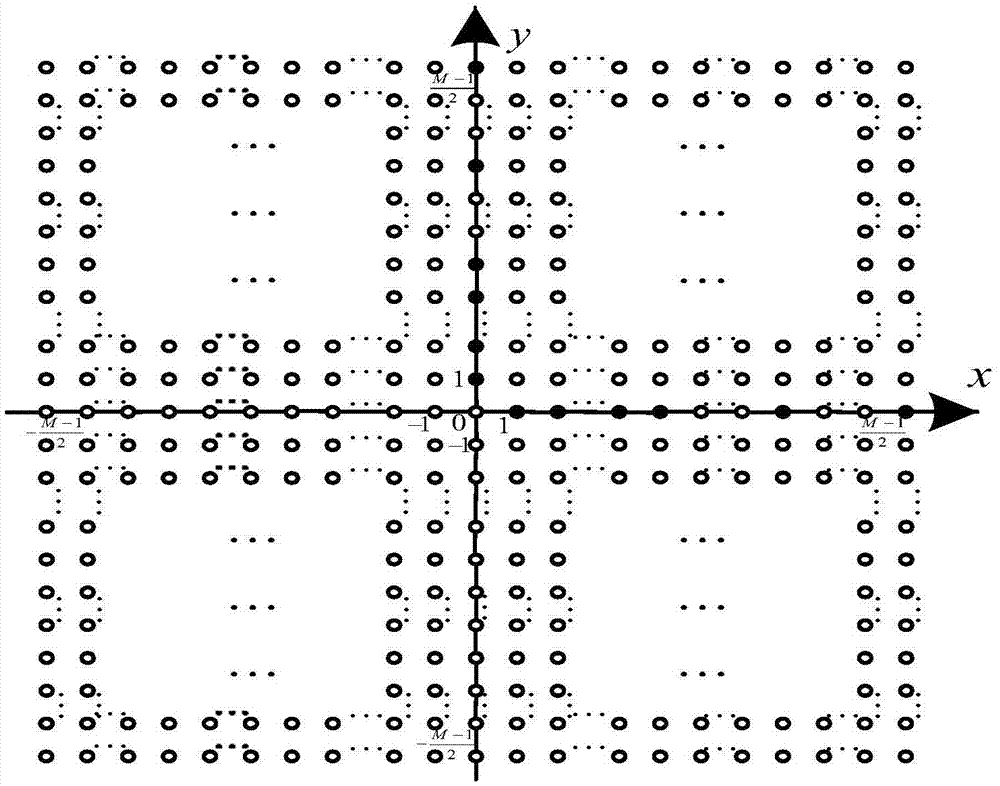
InactiveCN105445696ASimple structureEasy to implementRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFeature vectorDecomposition
The invention relates to a nested L-shaped antenna array structure and a direction of arrival estimation method thereof. The direction of arrival estimation method includes the following steps that: a nested L-shaped antenna array structure is constructed, and the received signals of a physical array antenna structure is determined based on the nested L-shaped antenna array structure; the high-order cumulant matrix of the received signals of the physical array antenna structure is obtained through using a high-order cumulant DOA algorithm; vectorization calculation is performed on the high-order cumulant matrix, so that a vectorized high-order cumulant matrix can be obtained, and the information of maximum continuous virtual square matrixes is extracted, and equivalent received signals can be obtained; two-dimensional spatial smoothing processing is performed on the equivalent received signals, so that an equivalent autocorrelation matrix can be obtained, eigenvalue decomposition is performed on the equivalent autocorrelation matrix, so that a signal feature vector matrix and a noise feature vector matrix can be obtained; and the signal feature vector matrix and the noise feature vector matrix are utilized to construct a spectral peak searching relational expression, and direction of arrival estimation is carried out, and the estimated value of the direction of arrival of the received signals is obtained. According to the nested L-shaped antenna array structure and the direction of arrival estimation method thereof adopted, a larger effective aperture can be realized when few array elements are adopted, and direction of arrival estimation precision can be improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
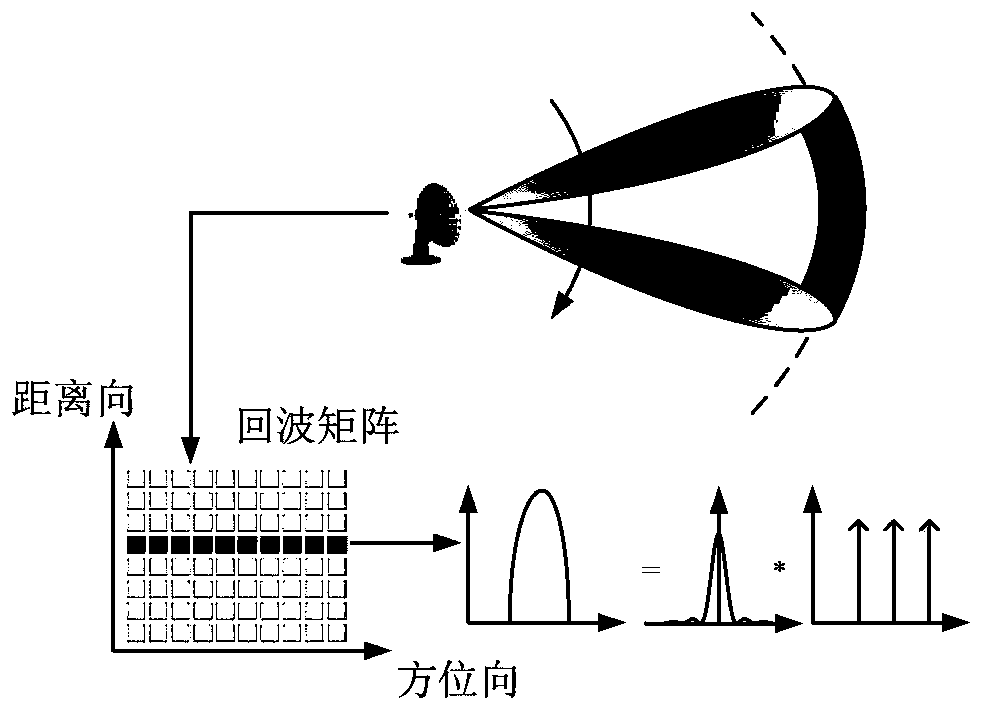
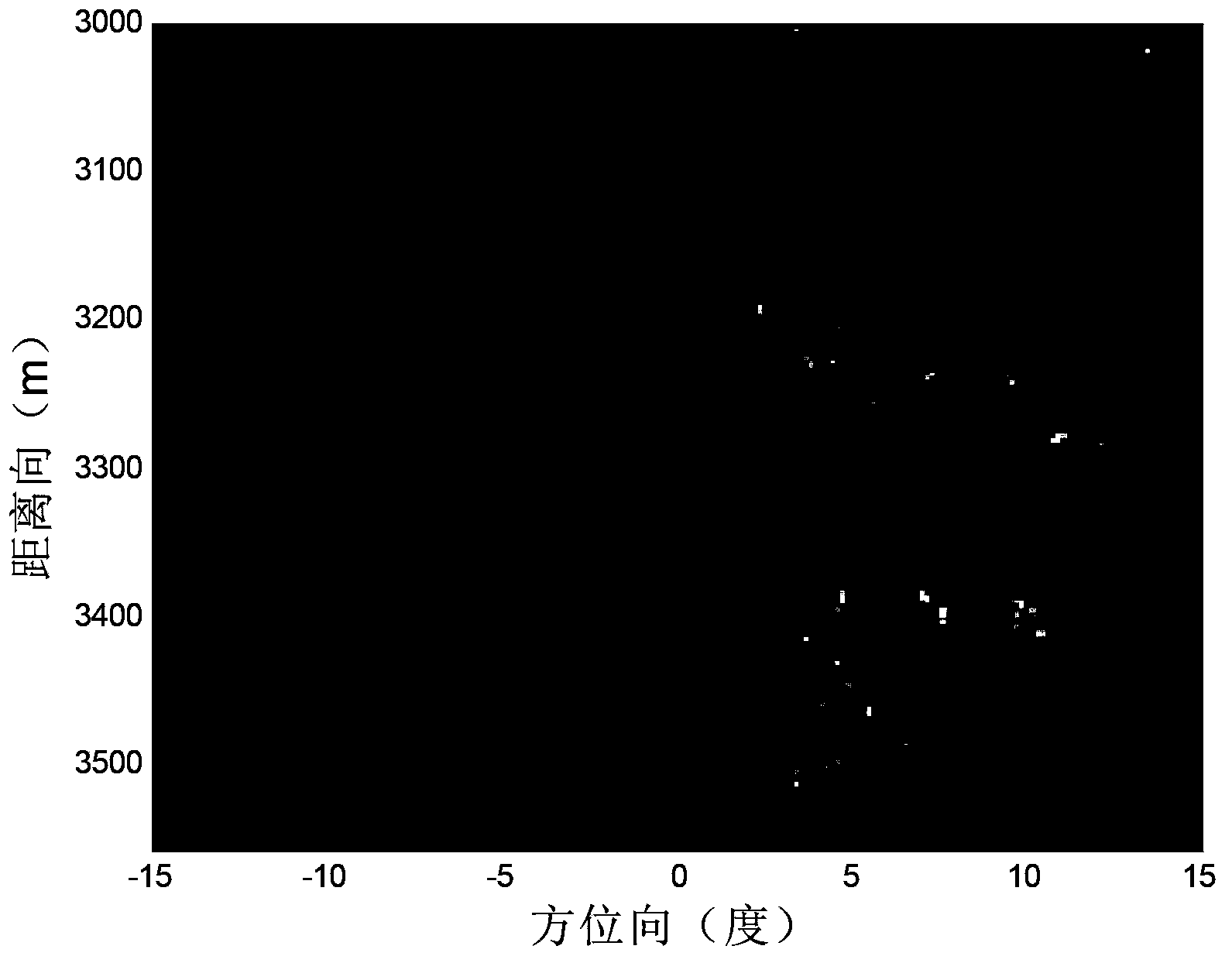
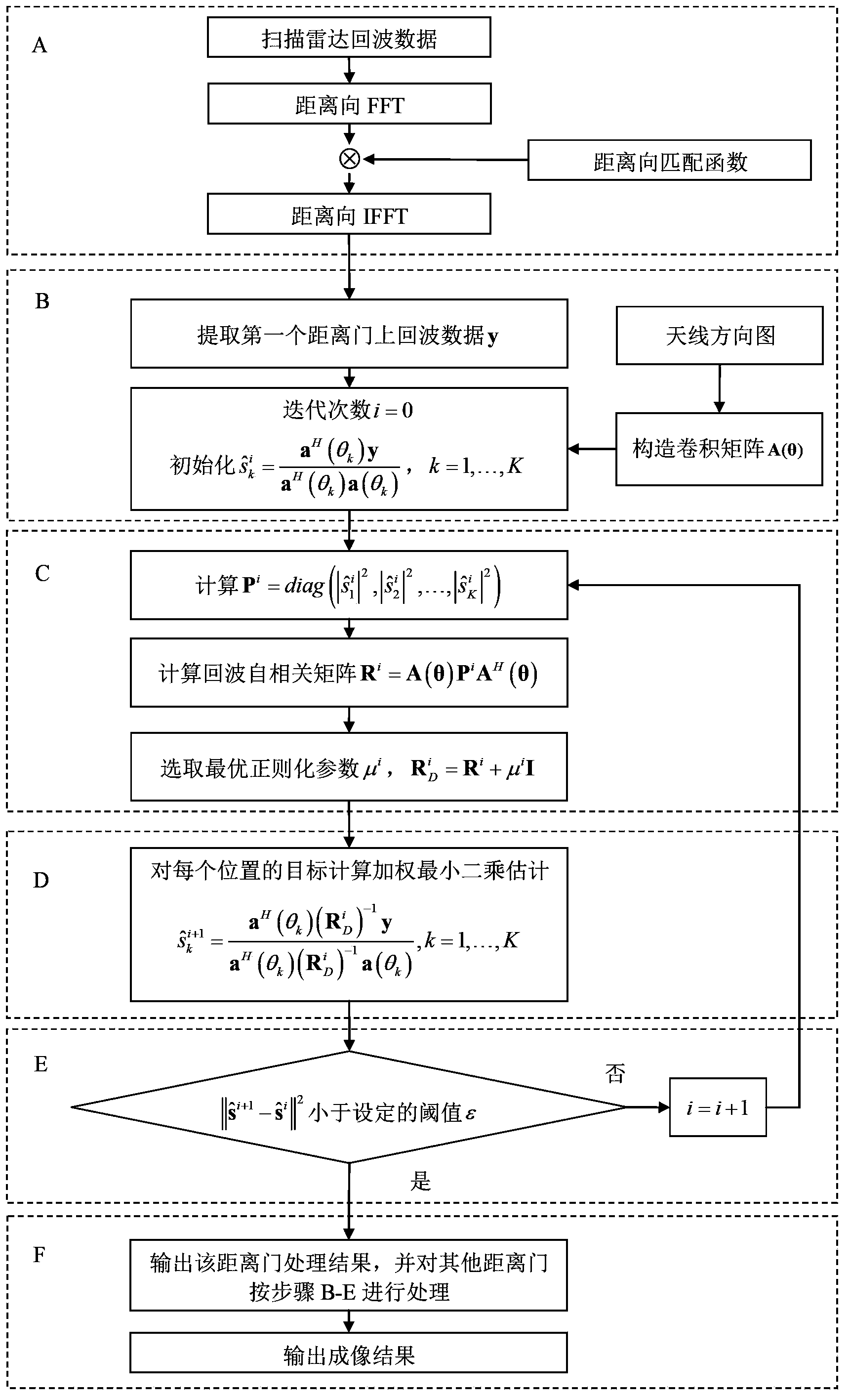
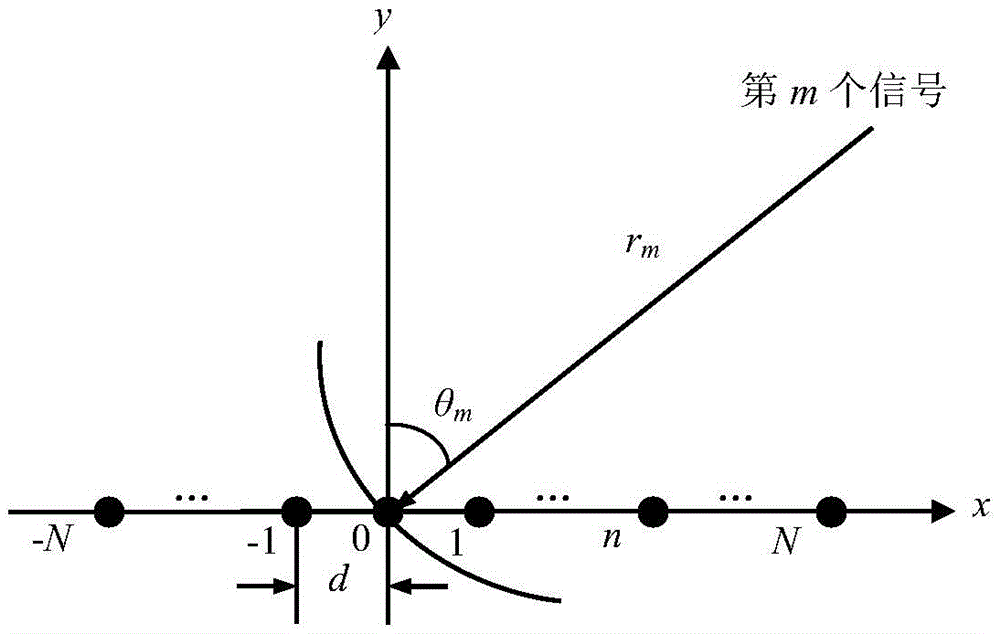
Scanning radar super-resolution imaging method
ActiveCN103412305AReduce signal to noise ratioImprove robustnessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Radar imaging
The invention discloses a scanning radar super-resolution imaging method. The method comprises the following steps of: performing distance-to-pulse compression; constructing a convolution matrix; initializing the convolution matrix; calculating an echo autocorrelation matrix; regularizing the echo autocorrelation matrix; performing orientation-to-parameter estimation; judging whether iteration is performed until a convergence state appears; and outputting super-resolution imaging results. According to the scanning radar super-resolution imaging method, an orientation-to-echo spectrum estimation model is constructed according to a radar antenna scanning process; a scanning radar imaging problem is converted into a parameter estimation problem; and amplitude and orientation estimation is performed on a site through an iteration self-adaptive method. Compared with an existing method, the scanning radar super-resolution imaging method can be applicable to low signal-to-noise ratio and has high robustness; and at the same time, with the scanning radar super-resolution imaging method adopted, robust imaging results can be obtained with a single times of scanning.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
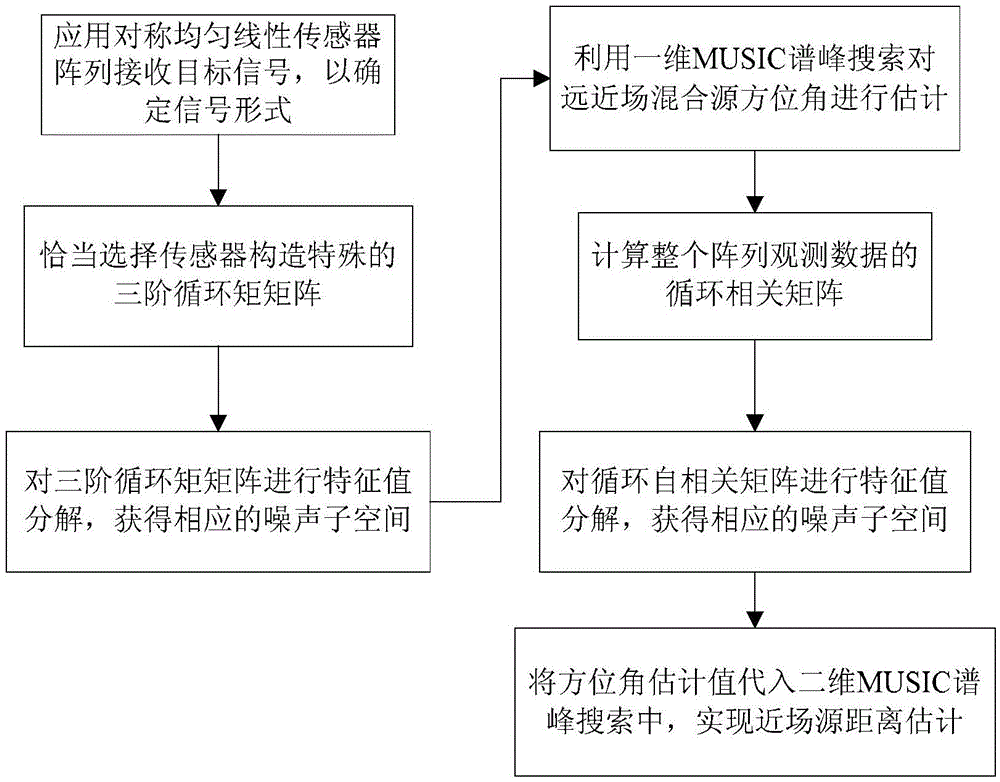
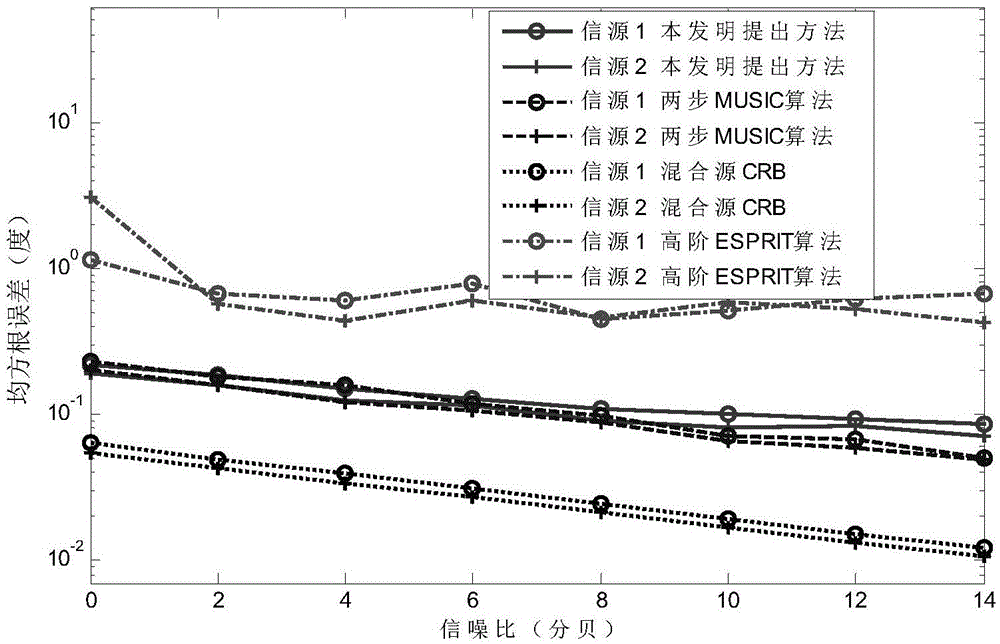
Multi-objective near-and-far field mixed source positioning method
ActiveCN105589056AReduce usageReduce computational complexityPosition fixationSensor arrayComputation complexity
The invention provides a multi-target near-and-far field mixed source positioning method and belongs to the field of the array signal processing technology. According to the method, firstly, a symmetric and homogeneous linear sensor array is arranged to receive a target signal, and then the observation signal form of a near-and-far field mixed source is determined. Secondly, a special third-order cyclic matrix is constructed based on the output of a properly selected sensor, and a direction matrix thereof only contains the azimuth information of a far-field source and the azimuth information of a near-field source. Thirdly, the eigenvalue of the third-order cyclic matrix is decomposed, so that a corresponding noise sub-space is obtained. Fourthly, a cyclic autocorrelation matrix based on the observation data of the entire matrix is calculated, and the eigenvalue of the cyclic autocorrelation matrix is decomposed. In this way, a corresponding noise sub-space is obtained. Fifthly, an already estimated azimuth is substituted to the two-dimensional MUSIC spectrum peak searching process, so that the estimation on the distance of the near-field source is realized. The application of four-order cumulants is avoided, and the calculation complexity of the algorithm is effectively reduced. The operation time of the algorithm is shortened. Meanwhile, the cyclic steady interference and the steady background noise are effectively suppressed. Moreover, the extra parameter matching process is avoided.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
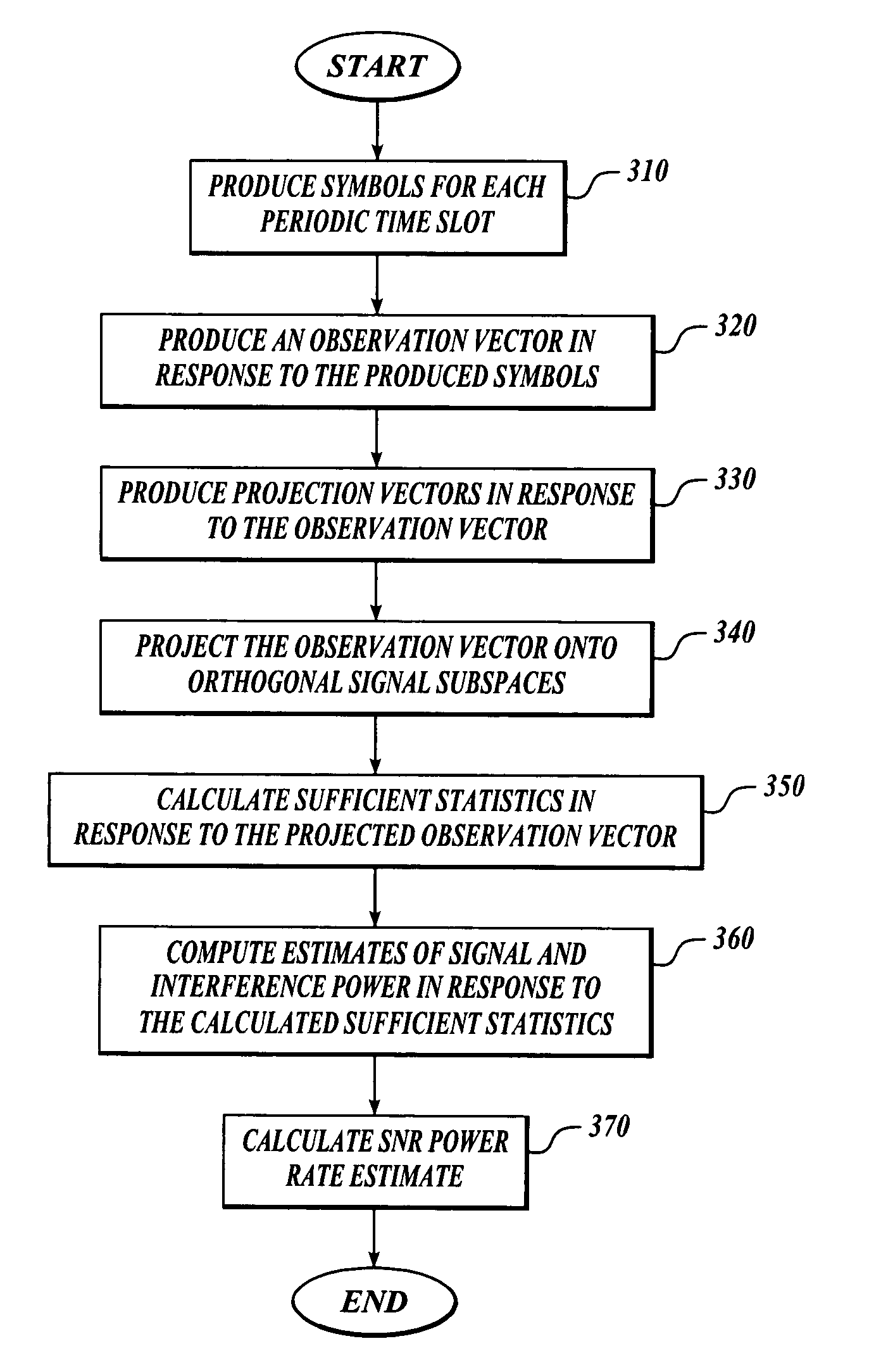
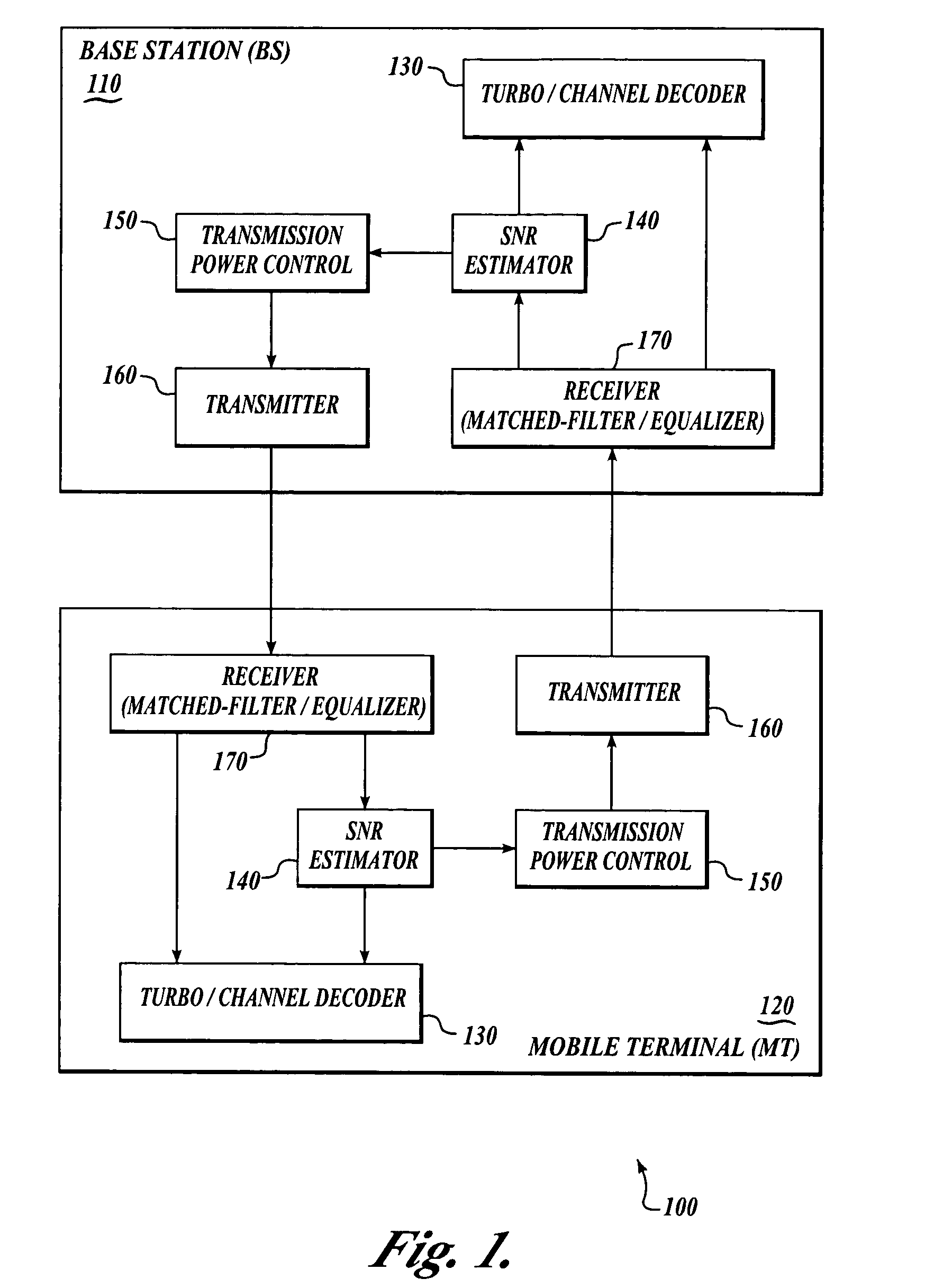
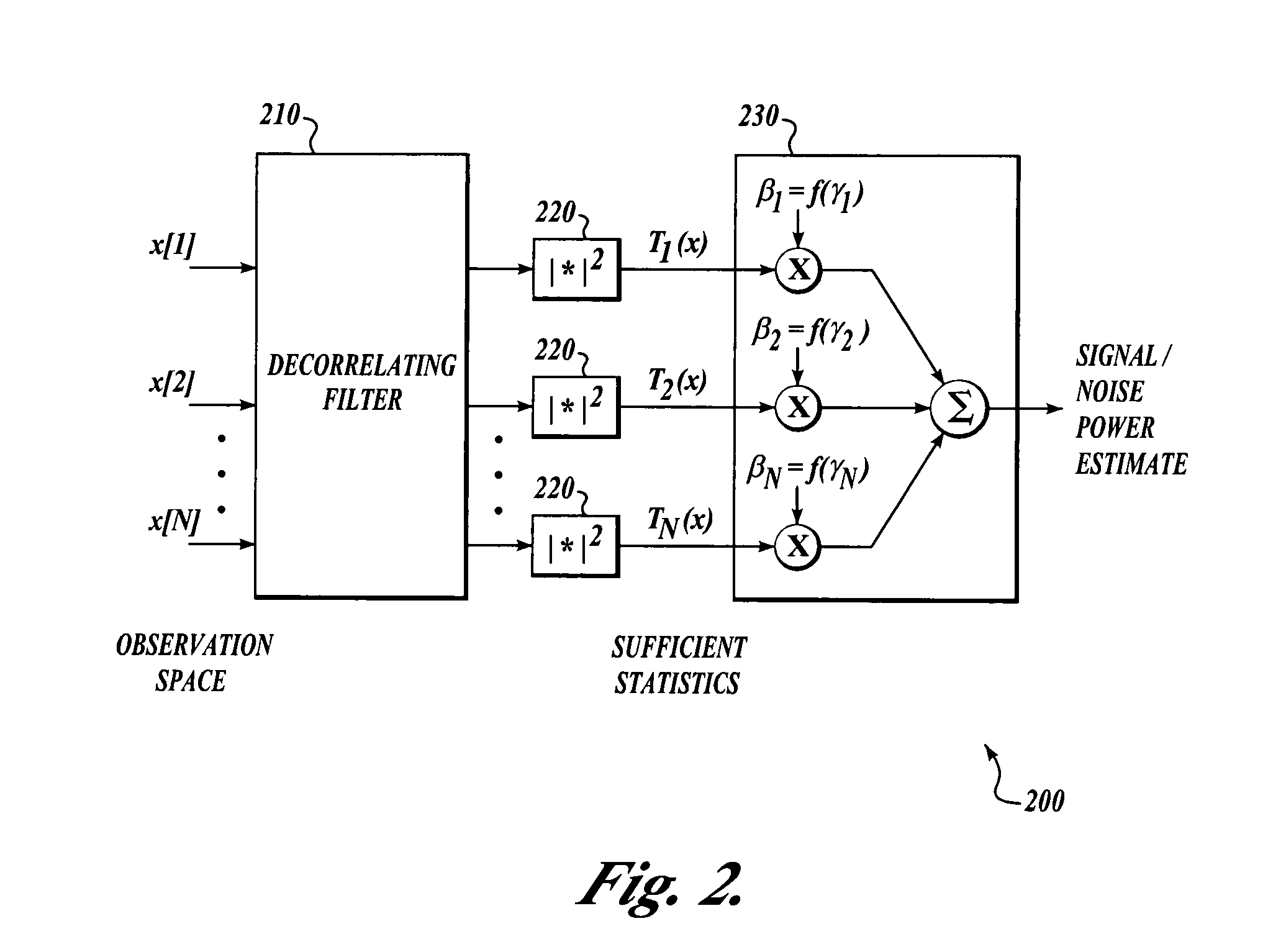
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) estimator in wireless fading channels
ActiveUS7006800B1Receivers monitoringAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCode division multiple accessThird generation
A signal-to-noise estimator is provided for estimating the signal-to-noise ratio in wireless fading channels. The estimator can be applied to likelihood ratio estimation of turbo decoders in third generation wide-band code division multiple access (WCDMA) systems. Time-multiplexed samples of pilot symbols from a wireless receiver are supplied to the estimator to obtain individual estimates of signal power and / or noise power. The estimator uses a de-correlating filter in which the coefficients are known functions (such as eigen-vectors) of the auto-correlation matrix for a wireless channel. The decorrelating filter is used by the estimator to map an observation vector into a set of statistically independent samples. The energy of each vector component is computed individually and combined to produce an aggregate sum for the vector. The aggregate sum can be subtracted from the pilot tone power in order to produce an estimate of noise power.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
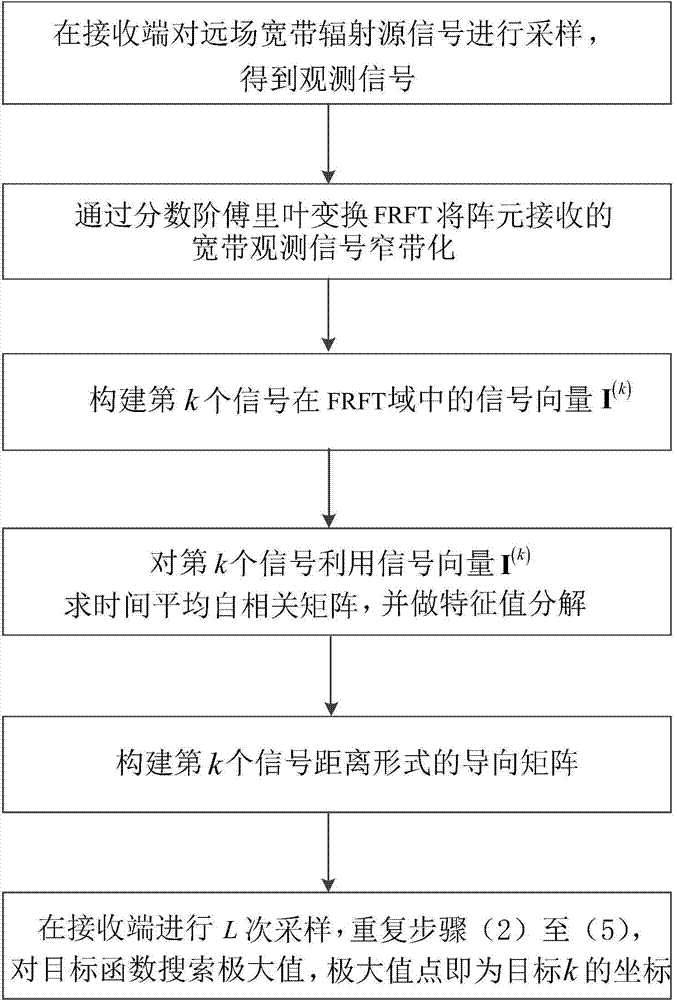
Airborne single-station passive positioning method for multiple broadband targets
ActiveCN104515971AOvercoming the disadvantage of difficult estimationImprove adaptabilityPosition fixationDecompositionArray element
The invention discloses an airborne single-station passive positioning method for multiple broadband targets and mainly solves the problem that multiple broadband radiation source targets cannot be subjected to single-station passive positioning in the prior art. The method comprises the following implementation steps: (1) sampling a far-field broadband radiation source signal at the receiving end to obtain an observation signal; (2) performing band narrowing on a broadband observation signal received by an array element through FRFT; (3) building a signal vector I(k) of a k-th signal in an FRFT domain; (4) obtaining a time average autocorrelation matrix for the k-th signal by utilizing the signal vector I(K), and performing eigen value decomposition; (5) building a guide matrix in a distance form of the k-th signal; (6) performing sampling at the receiving end for L times, repeatedly executing the steps of (2) to (5), and searching a target function for a maximum value, wherein (xk,yk,zk) corresponding to a maximum value point serves as the coordinates of a target k. According to the airborne single-station passive positioning method for the multiple broadband targets, the multiple broadband radiation source targets can be subjected to single-station passive positioning. The method can be used for detecting and reconnoitering an unmanned flight platform and a manned flight platform.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
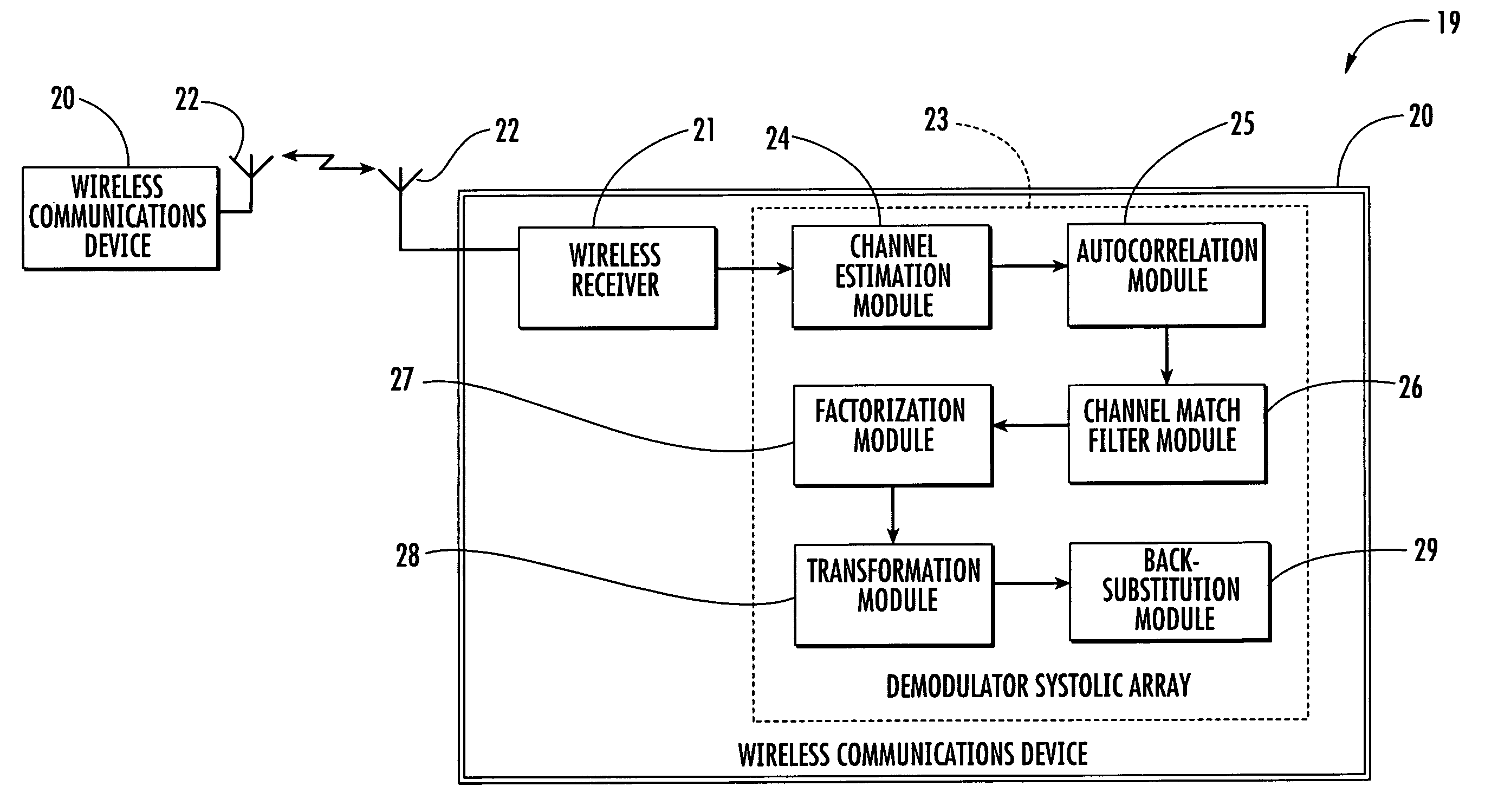
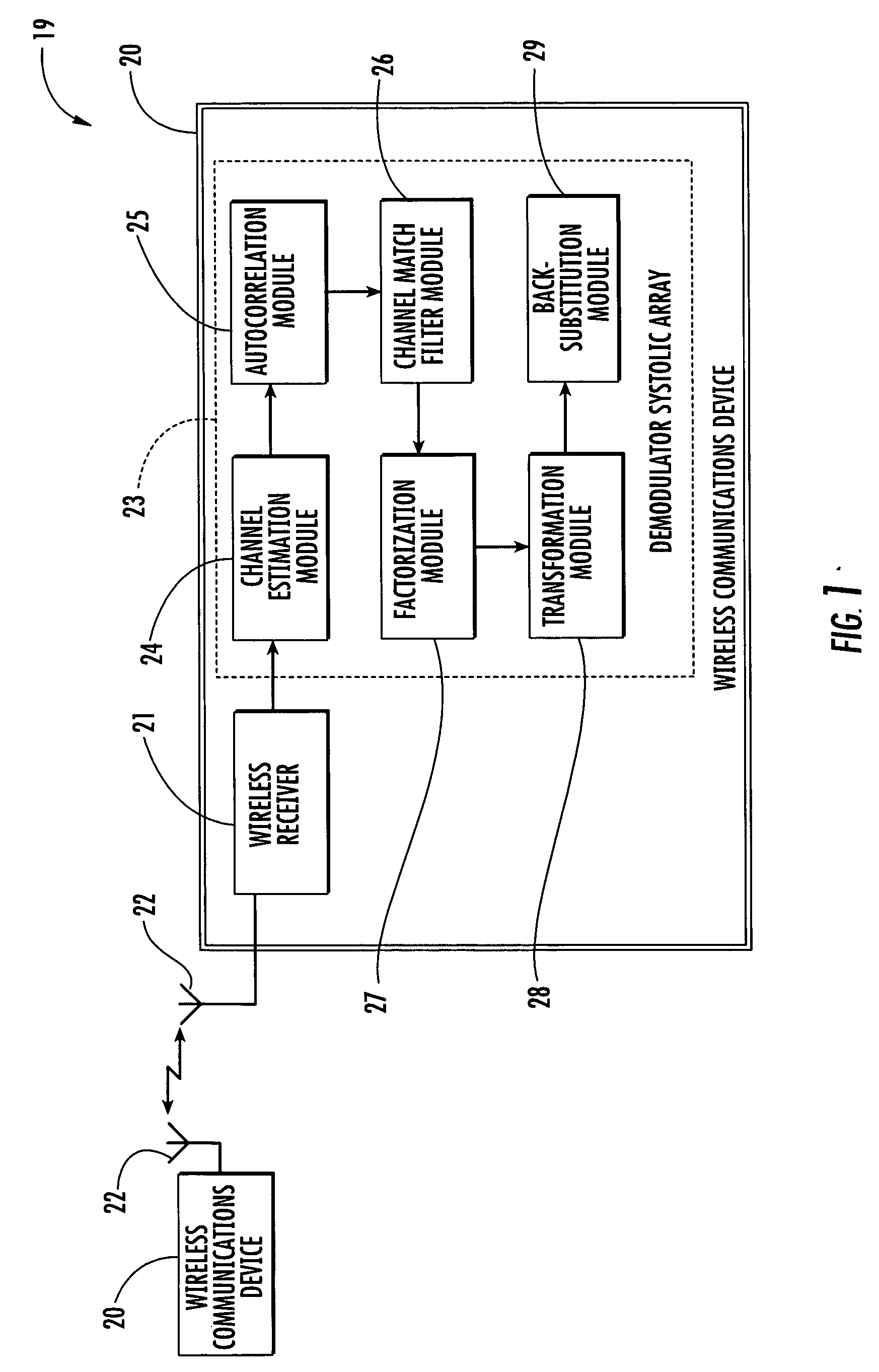
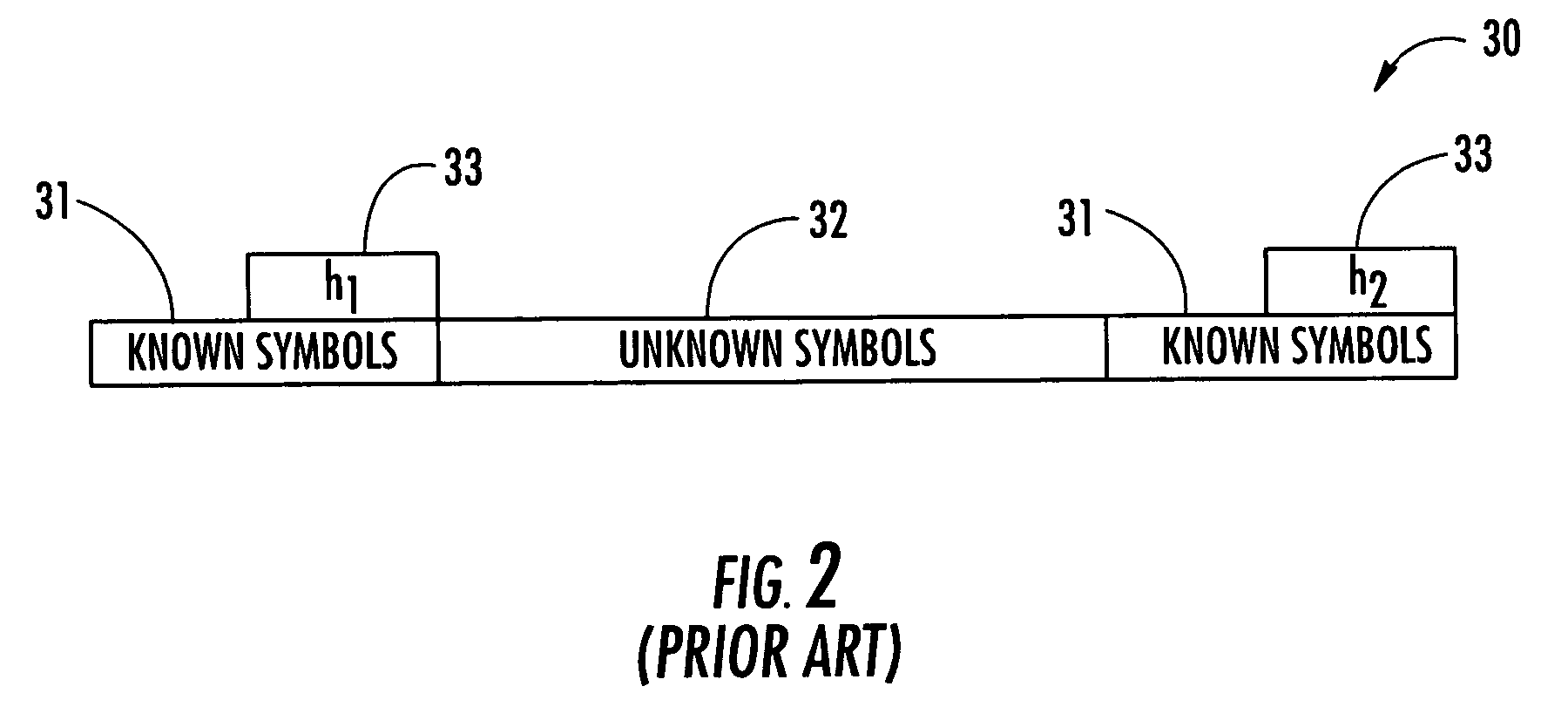
Wireless communications device performing block equalization based upon prior, current and/or future autocorrelation matrix estimates and related methods
ActiveUS20060176941A1Block equalizationBlock methodMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEqualizationComputer science
A wireless communications device may include a wireless receiver for receiving signals comprising alternating known and unknown symbol portions, and a demodulator connected thereto. The demodulator may include: a channel estimation module for generating respective channel estimates for a prior unknown symbol portion(s), current unknown symbol portion and for future unknown symbol portion(s); an autocorrelation module for generating autocorrelation matrices for the prior, current and future unknown symbol portions; a channel match filter module for generating respective channel matching coefficients for the prior and current / future unknown symbol portions; a factorization module for dividing the autocorrelation matrices into respective upper and lower autocorrelation matrices; a transformation module for transforming the channel matching coefficients into upper and lower channel matching coefficients; and a back-substitution module for determining the current unknown symbol portion based upon the upper and lower autocorrelation matrices and channel matching coefficients for the current and prior / future unknown symbol portions.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
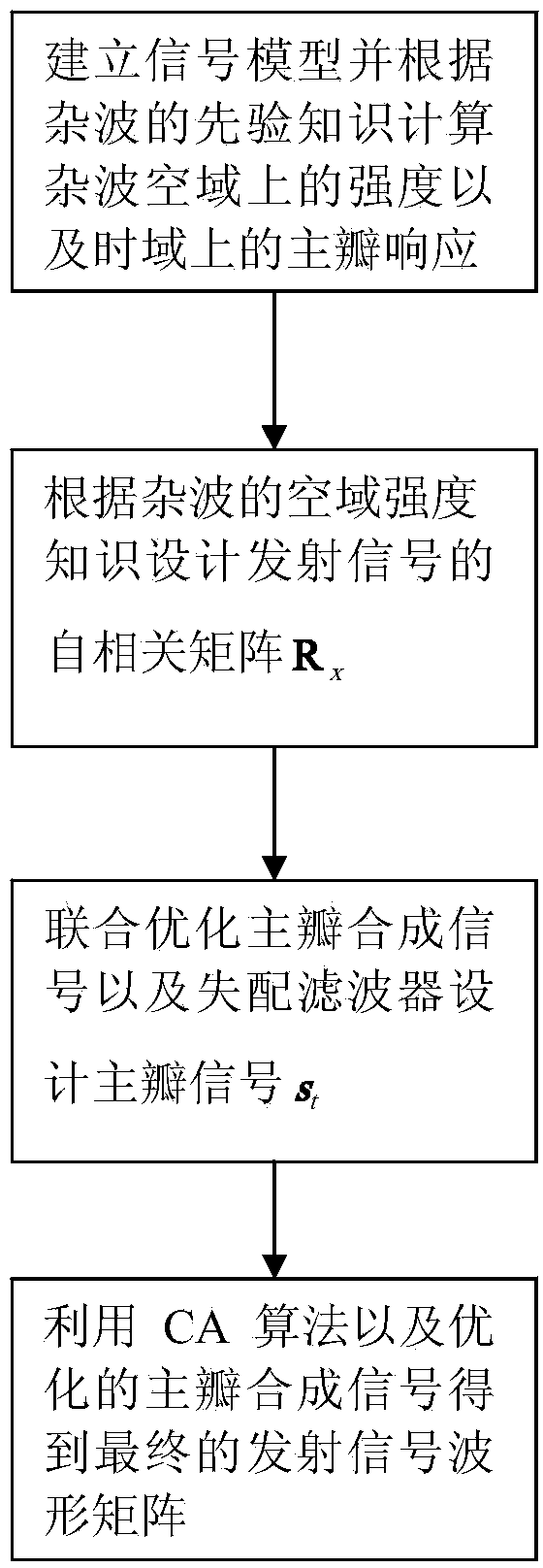
Method for hierarchically designing transmission waveforms of MIMI (multiple input multiple output) radar for detecting targets in clutter
ActiveCN103969633AAchieve inhibitionImprove the performance of detecting objectsWave based measurement systemsTime domainRadar
The invention belongs to the field of radar technologies, relates to designs for transmission waveforms of centralized MIMO (multiple input multiple output) radar, and discloses a method for hierarchically designing transmission waveforms of MIMO radar for detecting targets in clutter. The method includes steps of 1, building an MIMO radar signal model and acquiring the intensity of the clutter in a space domain and mainlobe response priori knowledge in a time domain; 2, designing autocorrelation matrixes Rx of transmission signals on the basis of intensity priori knowledge of the clutter in the space domain; 3, combining each optimal mainlobe synthesized signal (MSS) with a mismatched filter to suppress mainlob clutter signals; 4, designing transmission waveform matrixes under constant-modulus conditional constraints. The method has the advantages that the clutter suppression performance can be improved, and accordingly the radar can be used for detecting the targets in the heavy clutter.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method to improve the channel estimate in broadband simo/mimo cellular radio networks during abrupt interference variations
InactiveCN101056286ASpatial transmit diversityData switching by path configurationTime domainCellular radio
The invention relates to multi signalpath response which is evaluated in the way of MIMO of a wireless receiver used in broadband honeycomb radio net. Relativity of interference covariance matrix is calculated at each new symbol and compared with a threshold to determine whether interference has significant change. A first event is mainly for reinitialization of the interference covariance matrix, or actual value is used for renewing operation average value of the interference covariance matrix. The renewing or reinitialization interference covariance matrix and emission autocorrelative matrix of pilot sequence (storing in a receiver) are used in front of channel matrix for downward rank to submit evaluation to mode filtering so as to whiten evaluated singalpath matrix. The premier space and / or time correlation is reintroduced to downward rank channel matrix. The channel matrix is first evaluated in dispersed time domain, and then is submitted to DFT used for changing of a whole bandwidth, which can be used correctly by the receiver.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS ITAL
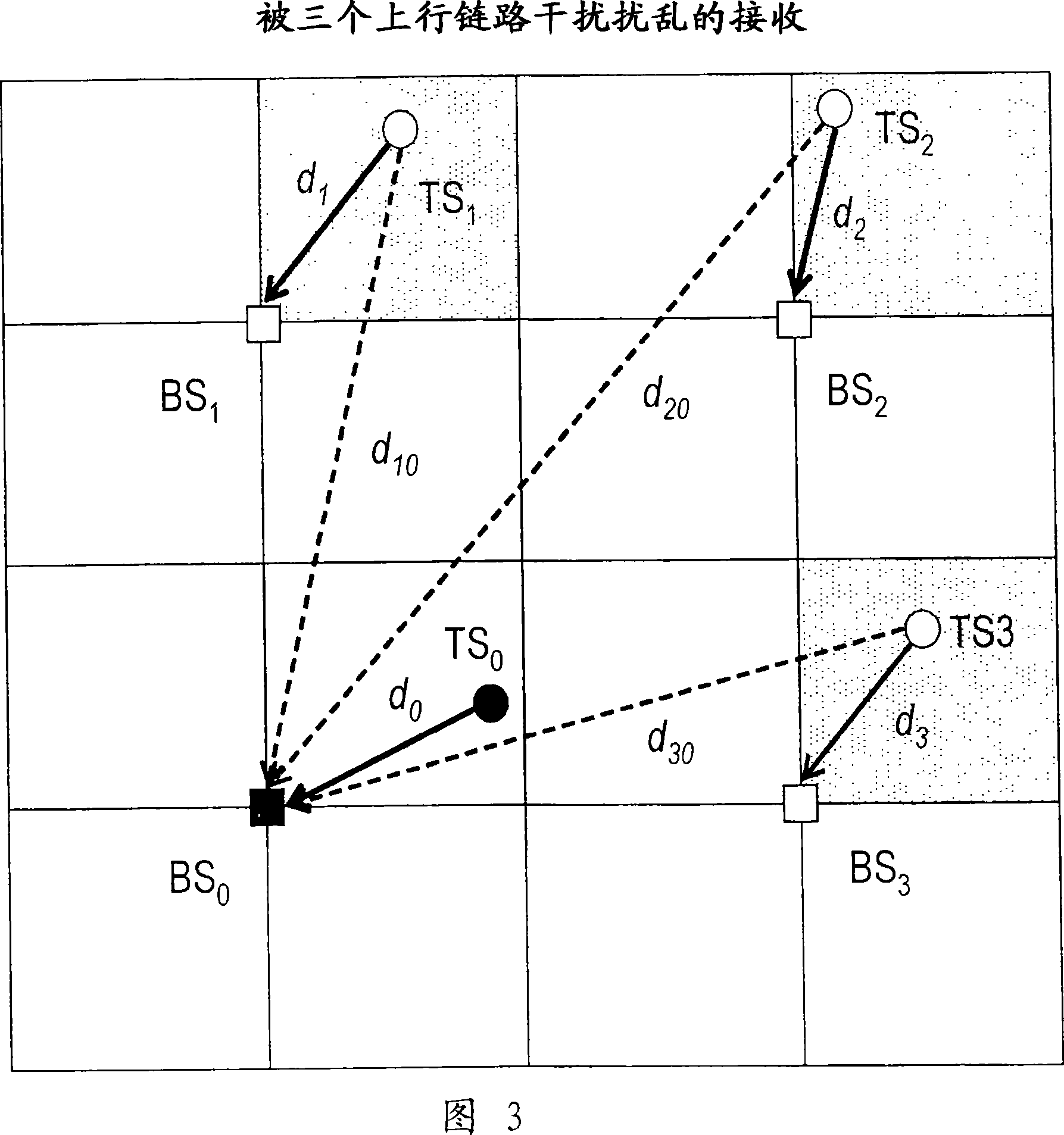
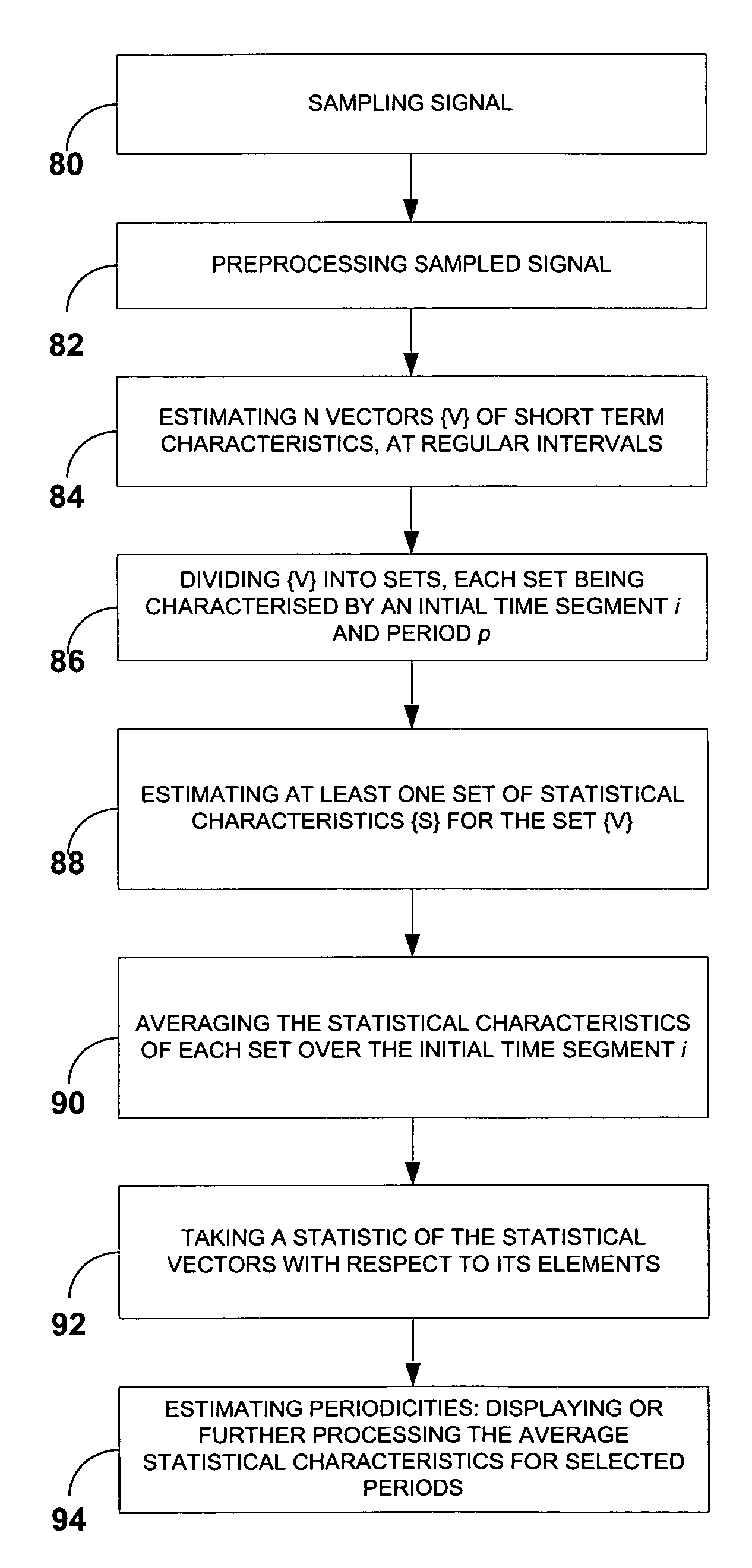
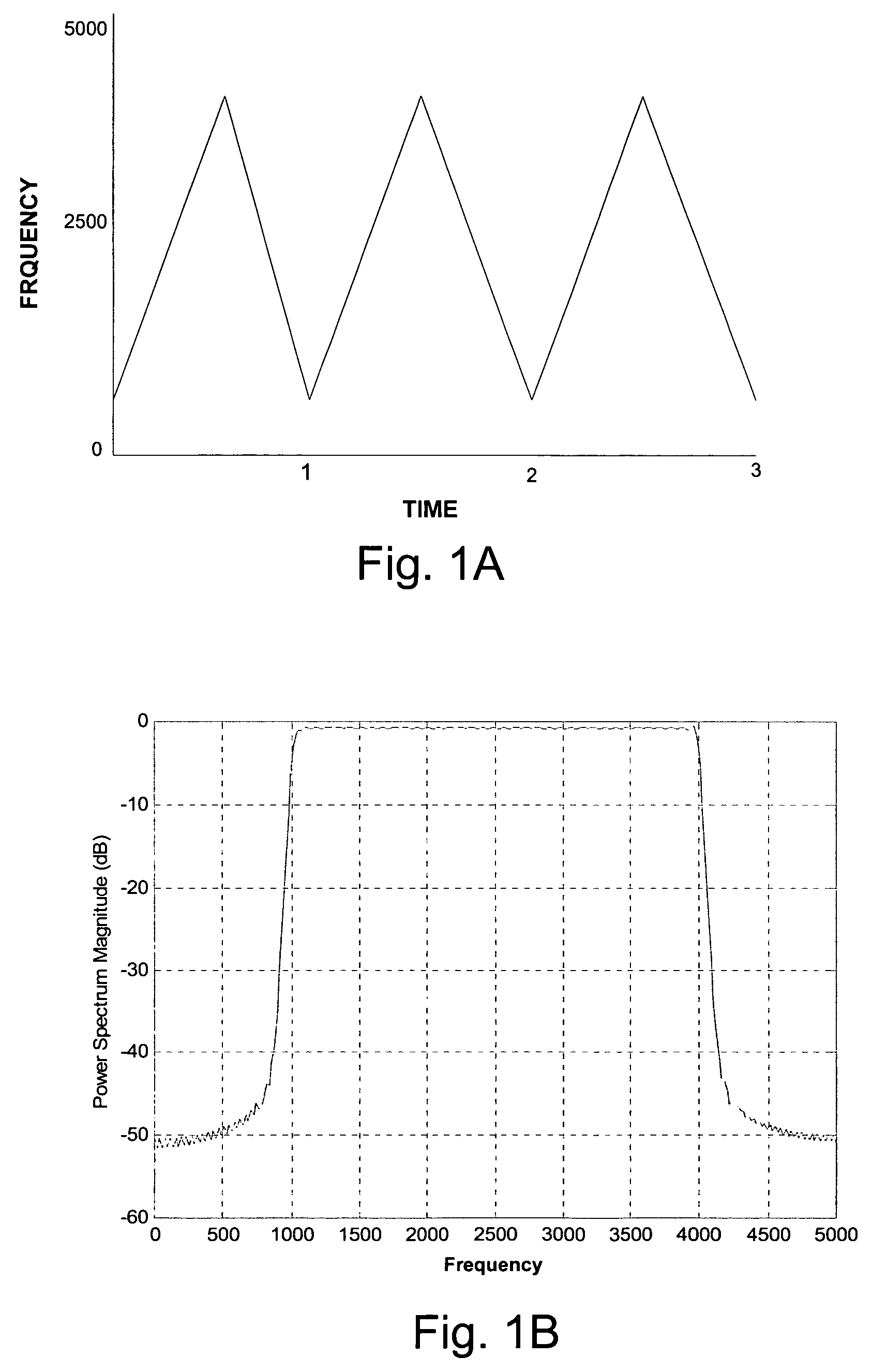
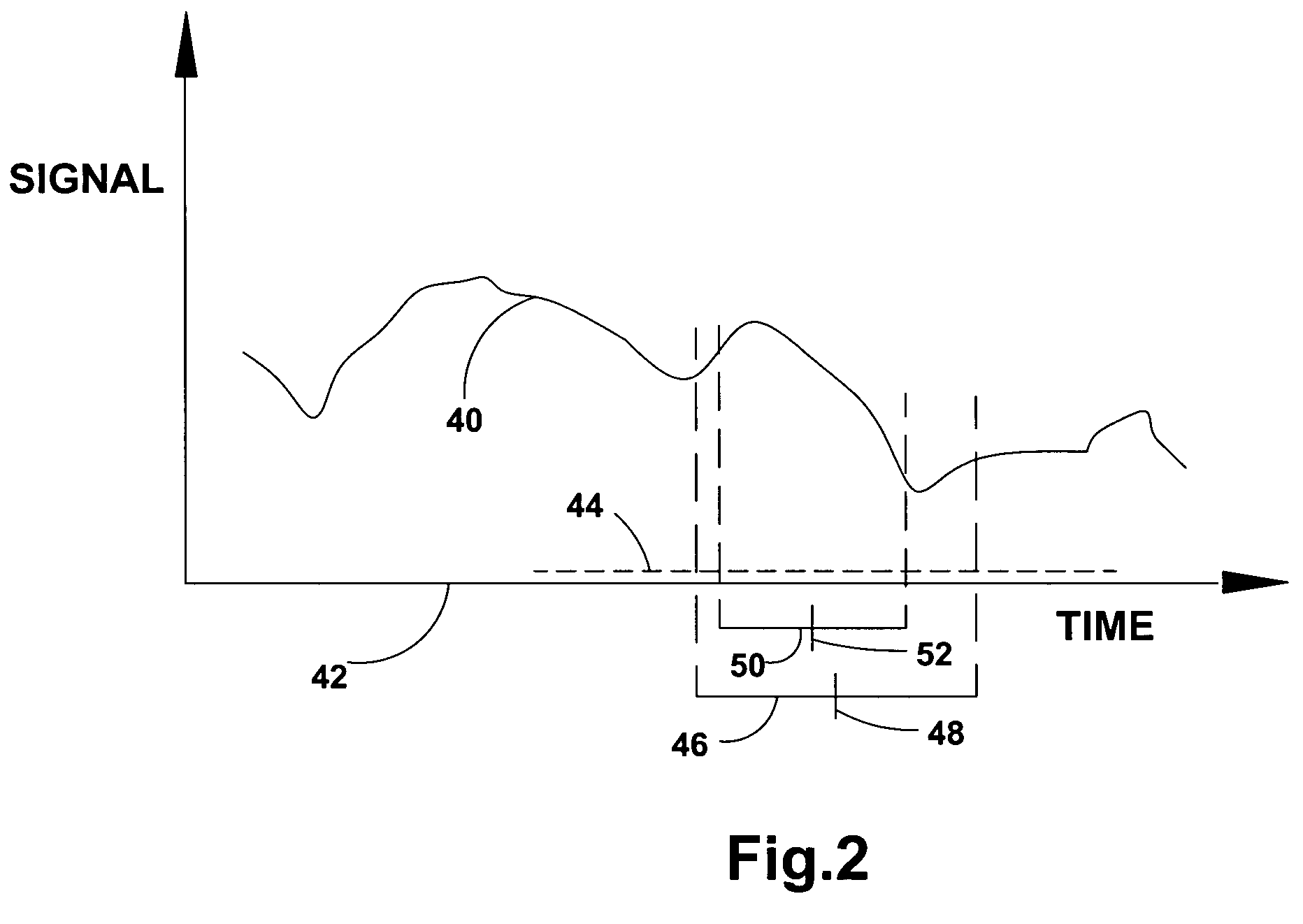
System for detection and estimation of periodic patterns in a noisy signal
Owner:TROYANSKY LIDROR +1
Limited feedback method for multi-antenna system
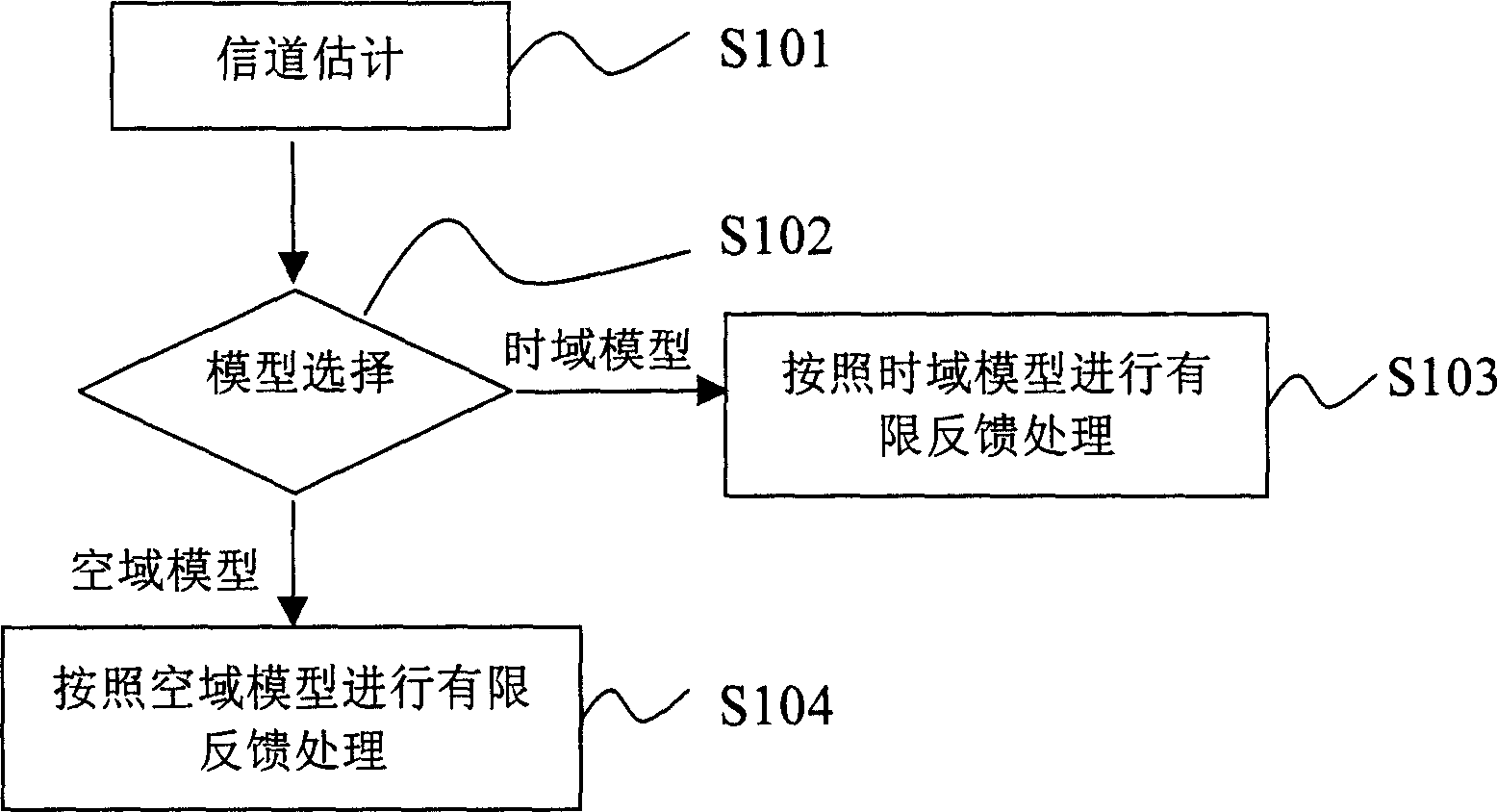
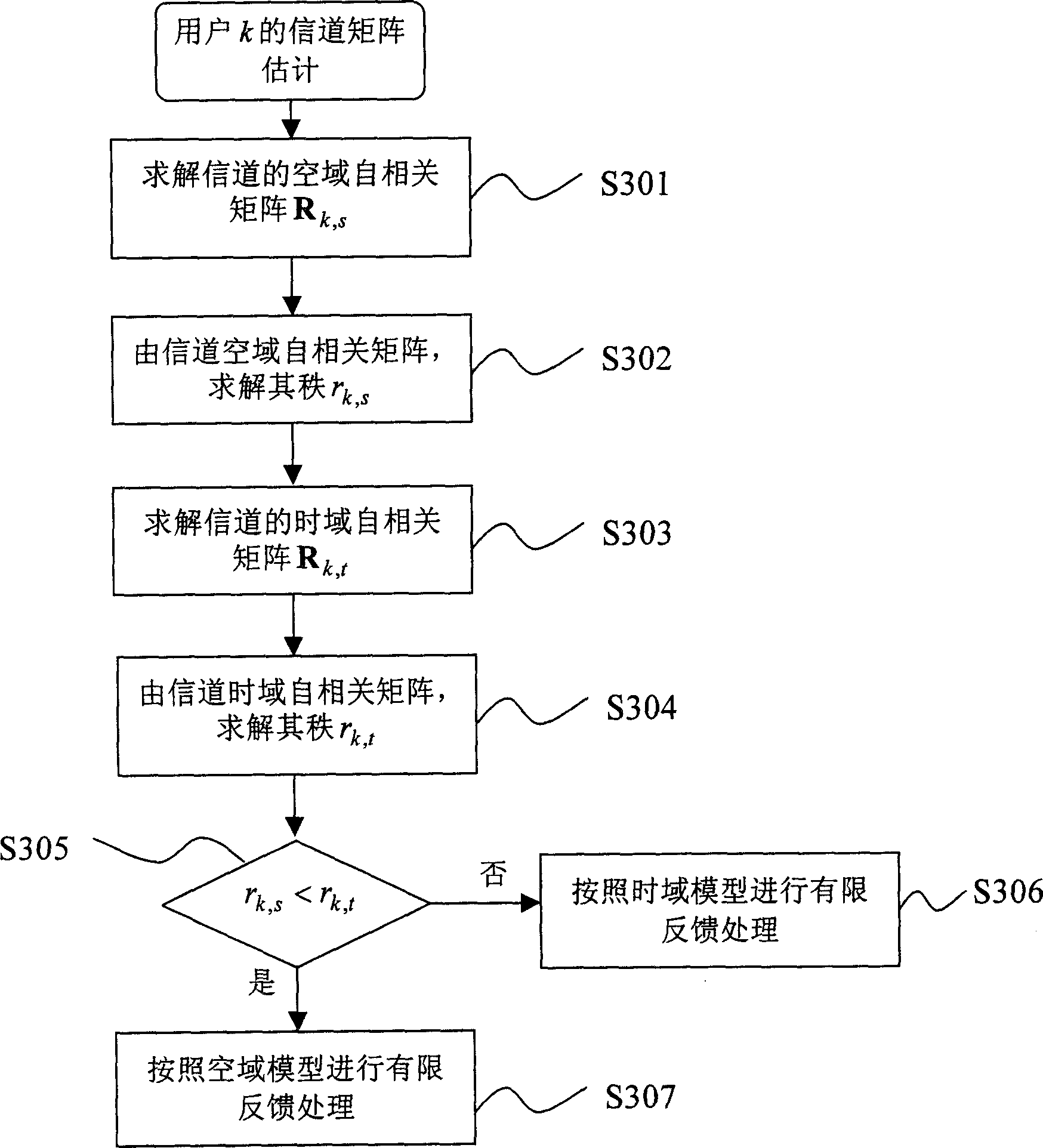
InactiveCN1841985AKeep the main componentsRealize Limited Feedback TransmissionCode division multiplexRadio transmissionTime domainWavelet transform
The invention discloses a limit feedback method in the multi-antenna system, which comprises the following steps: estimating the channel matrix from the received signal, computing the empty region autocorrelation matrix and the rank of the empty region autocorrelation matrix by the channel matrix, computing the time region autocorrelation matrix and the rank of the time region autocorrelation matrix by the channel matrix, if the rank of the empty region autocorrelation matrix is less than the rank of the time region autocorrelation matrix, it uses the column of the channel matrix to do wavelet converting to obtain the limit feedback output; if the rank of the empty region autocorrelation matrix is more than the rank of the time region autocorrelation matrix, it uses the line of the channel matrix to do wavelet converting to obtain the limit feedback output.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
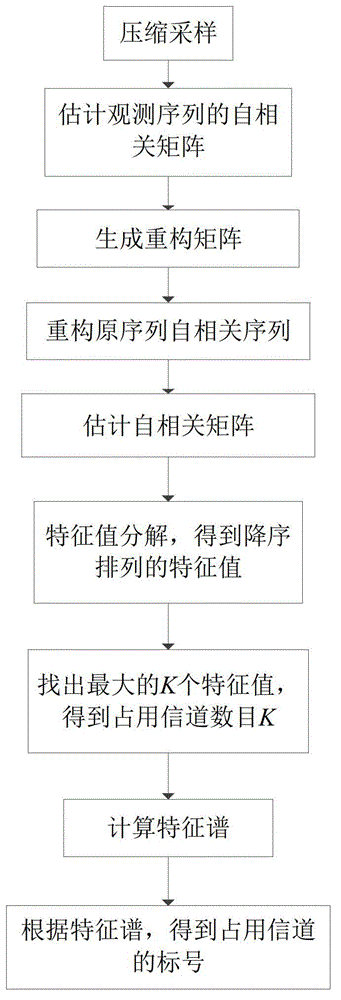
Compressed spectrum sensing method based on autocorrelation matrix reconstitution
InactiveCN102946288ADownsamplingSave storage spaceTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSignal classification
The invention provides a compressed spectrum sensing method based on autocorrelation matrix reconstitution and mainly solves the problem that an existing sensing algorithm is high in sampling speed and large computation overhead. The compressed spectrum sensing method comprises that a secondary user obtains an observation sequence of a frequency spectrum environment through compressed sensing and obtains an autocorrelation matrix estimated value of Nyquist sampling by utilizing autocorrelation vector quantity of a autocorrelation matrix reconstitution Nyquist sample sequence of the observation sequence; a multi-signal classification MUSIC algorithm is adopted to obtain an estimated value of occupied channel number according to a characteristic value of the autocorrelation matrix estimated value; a characteristic spectrum is constructed according to the characteristic value and the estimated value of the occupied channel number, spectral amplitude values corresponding to characteristics of channels are added to obtain a sum, and mark numbers of the occupied channels are judged. By means of the compressed spectrum sensing method, the sampling speed of a secondary user receiving machine can be reduced, algorithm complexity at the reconstitution end is low, and spectral amplitude occupying situation in a cognitive radio system can be judged quickly.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
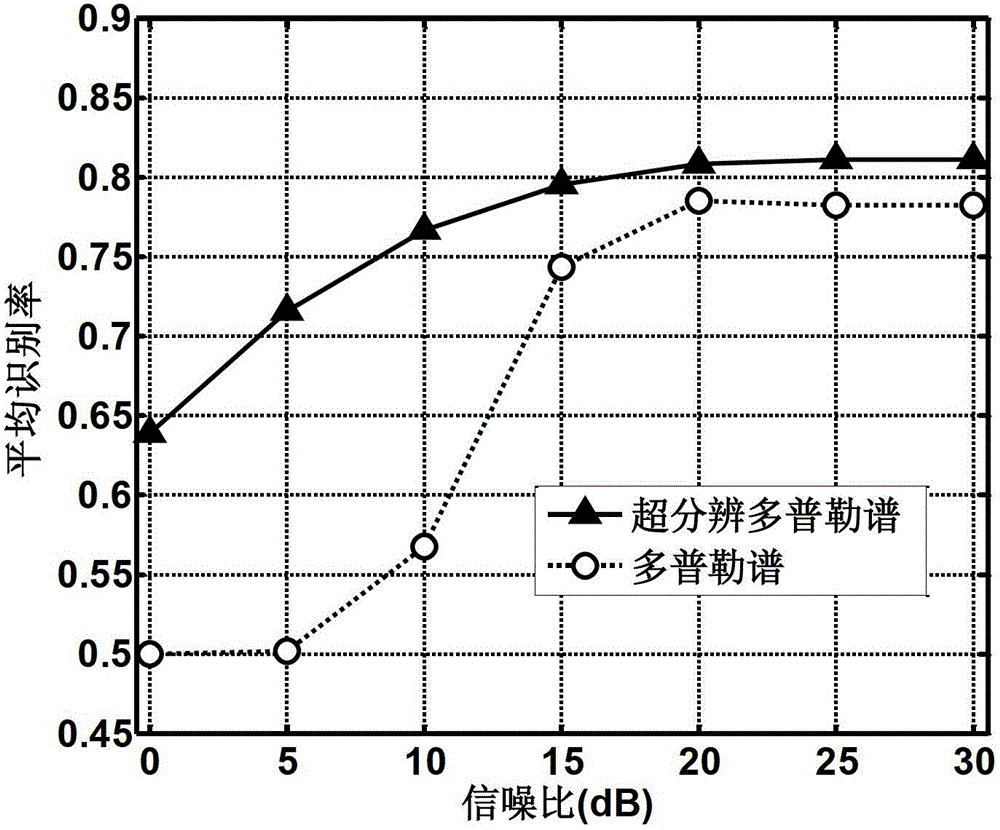
Method for steadily classifying ground moving target based on super-resolution Doppler spectrum
InactiveCN102721952AEasy to keepAdaptive clutterWave based measurement systemsMobile vehicleImage resolution
The invention discloses a method for steadily classifying a ground moving target based on super-resolution Doppler spectrum, and mainly solves the problem that the classification performance is low because the signal structure is influenced during clutter reduction, the resolution ratio is low under short residence time and the noise cannot be suppressed in the conventional similar method. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating a short-time echo signal Doppler spectrum, and estimating the noise energy in the signal by utilizing the short-time echo signal Doppler spectrum; estimating a clutter autocorrelation matrix by utilizing a target approach distance unit; establishing a Fourier-based dictionary matrix, and solving the l1 norm optimization problem to obtain a super-resolution Doppler spectrum of a target; extracting characteristics of the super-resolution Doppler spectrum of the target; and classifying the extracted characteristics by using a classifier. By the method, the resolution ratio of the Doppler spectrum of the target is improved, the signal structure can be kept during adaptive clutter reduction, and the noise in the signal is suppressed; and moreover, the classification performance is improved, the noise robustness is obtained, and the method can be used for classifying moving vehicle targets with maneuvering parts.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
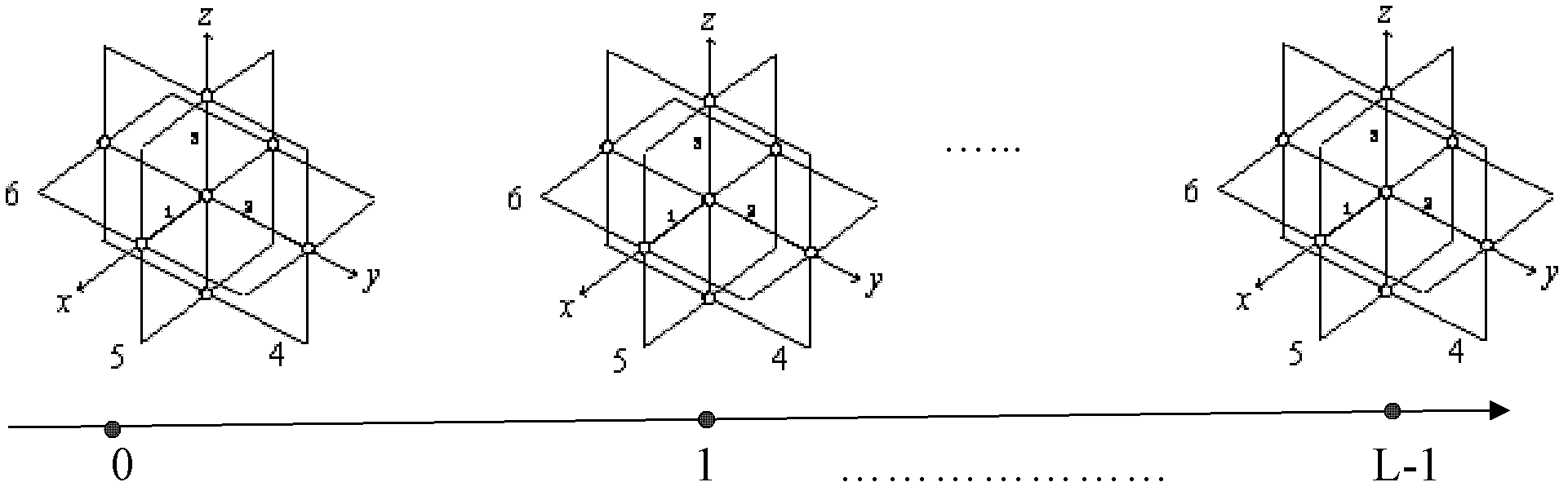
Electromagnetic vector sensor array amplitude and phase error self-correcting method based on array rotation
InactiveCN103135083AImprove calculation accuracyCalculation is simple and fastElectrical measurementsArray elementCorrection method
The invention discloses an electromagnetic vector sensor array amplitude and phase error self-correcting method based on array rotation. The method includes: an electromagnetic vector sensor with amplitude and phase errors is used as a receiving array and installed on a rotation device to receive a transverse electromagnetic wave calibration source signal, two groups of sampling data of an array output signal are received before the array rotates and after the array rotates 90 degrees around a z axis in clockwise mode, a sampling signal autocorrelation matrix formed by the two groups of sampling data is calculated, characteristic decomposition is performed on the sampling signal autocorrelation matrix to obtain signal guiding vector estimation values before and after rotation of an array and estimate an amplitude and phase error matrix, and an array element to be corrected receives an inverse matrix of a data premultiplication amplitude and phase error matrix so as to achieve correction of amplitude and phase errors. The electromagnetic vector sensor array amplitude and phase error self-correcting method based on the array rotation can estimate amplitude errors and signal arrival angles of the signal of the electromagnetic vector sensor, has high parameter estimation accuracy, does not need iterative operation, and is small in calculated amount.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
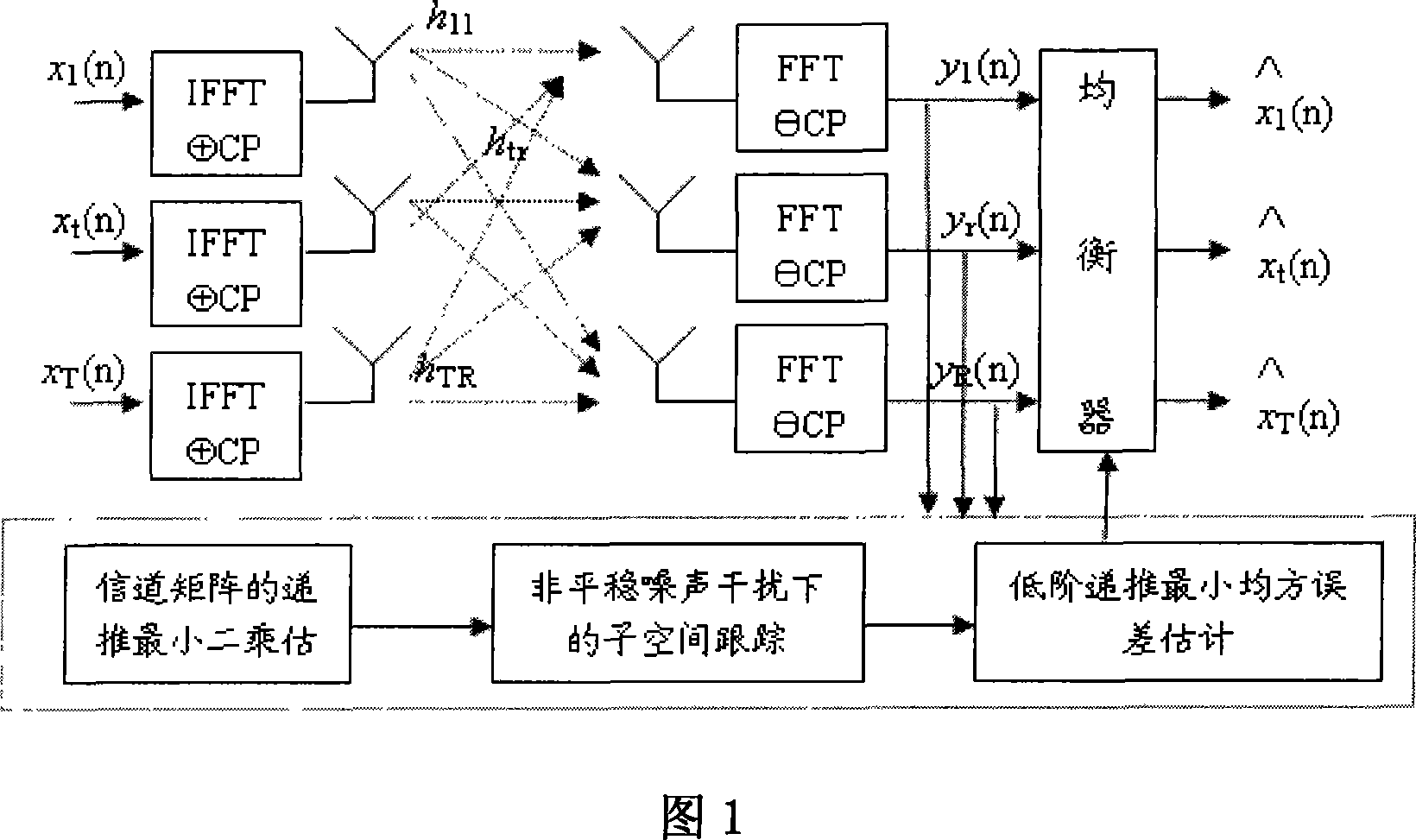
Low-level recursion minimum mean-square error evaluation of MIMO-OFDM channel
InactiveCN101222458AReduce computational complexityEfficient use ofBaseband system detailsComputation complexityThird generation
The invention discloses a low-order recurrence least mean square error estimation for an MIMO-OPDM channel, which relates to the wireless transmission technical field. After a pilot frequency is used to insert in to obtain a recurrence least square estimation of a time-varying channel fading, the channel fading is decomposed into a signal subspace and a noise subspace by adopting a subspace tracking method of being capable of tracking singular values and singular vectors under the non-stationary complicated noise, then an order-reduction is made according to the quantity of main singular values to obtain an auto-correlation matrix of the channel fading, and a least mean square error estimation with higher precision is obtained through the recurrence. The invention has the characteristics of having computation complexity of decreasing algorithm, higher estimation accuracy as well as good robustness and applicability, and being capable of providing channel estimation and self-adaptive equalization proposals of systems such as third generation (3G) cell mobile communication, beyond third generation (B3G) cell mobile communication, fourth generation (4G) cell mobile communication and digital TVs, wireless local area networks (WLAN), wireless wide area networks (WWAN) and so on, with an important theoretical evidence and a concrete realization method and so on.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
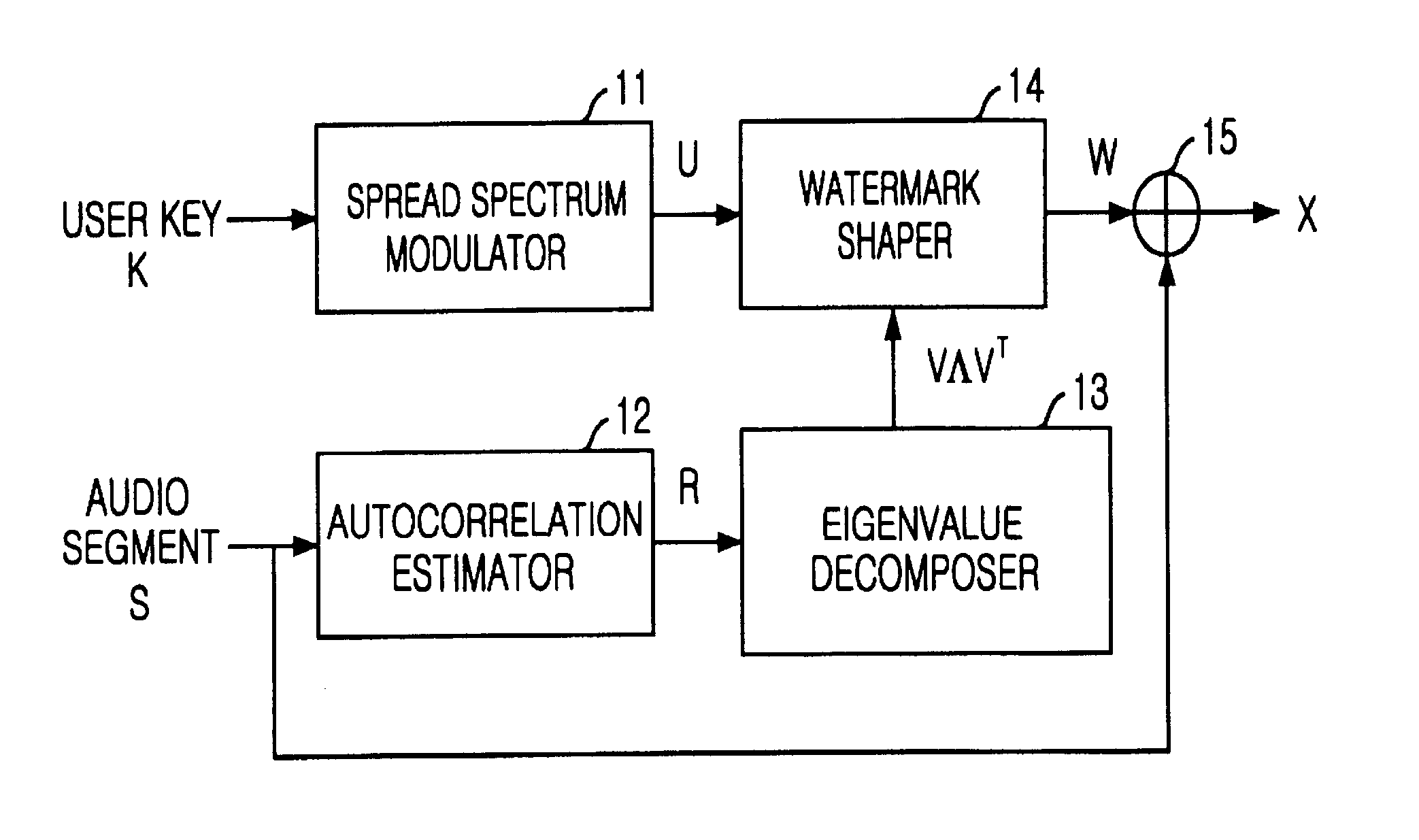
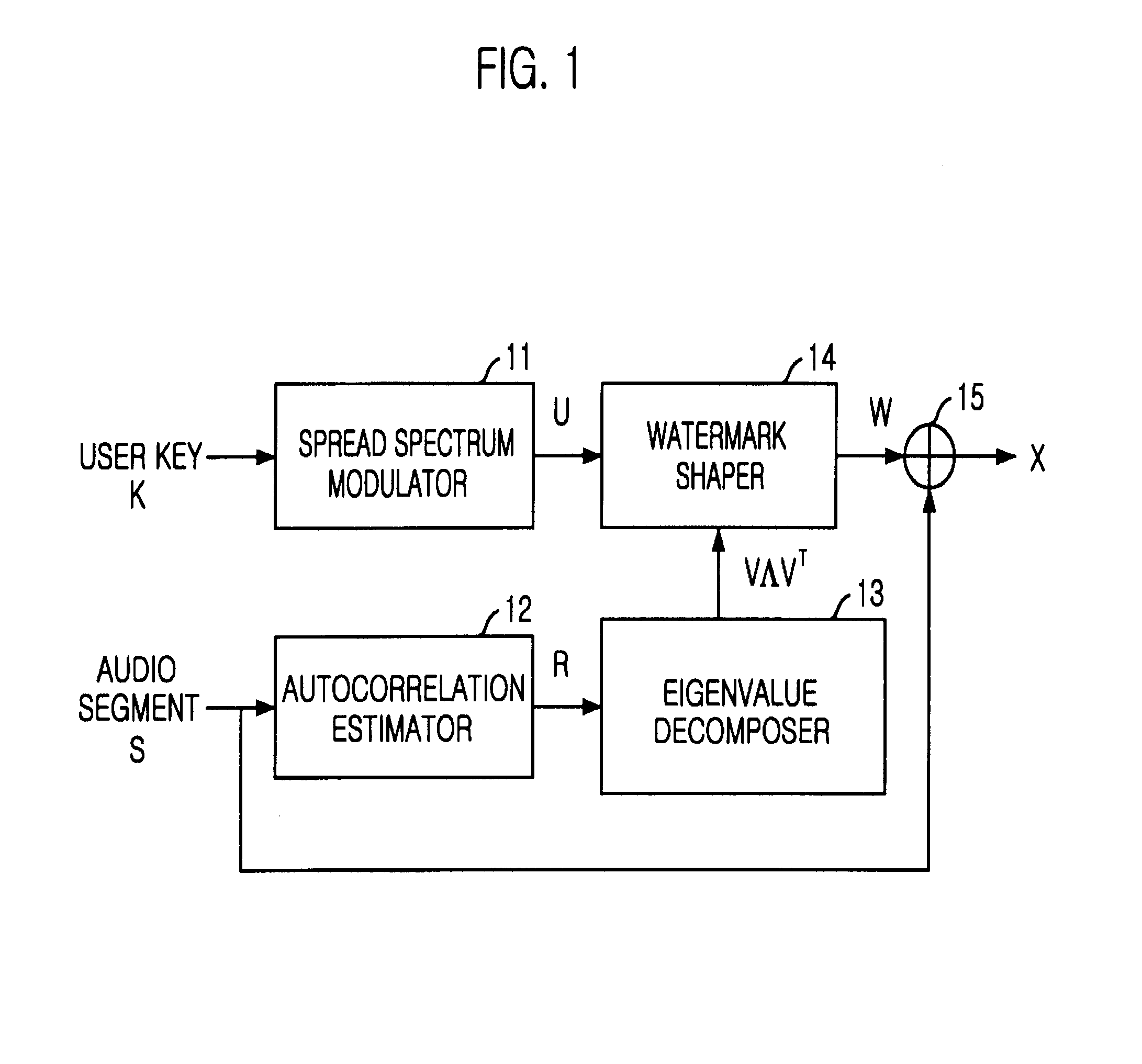
Apparatus and method for inserting and detecting watermark based on stochastic model
InactiveUS6853676B2Reduce distractionsUser identity/authority verificationRecord information storageFeature vectorComputer science
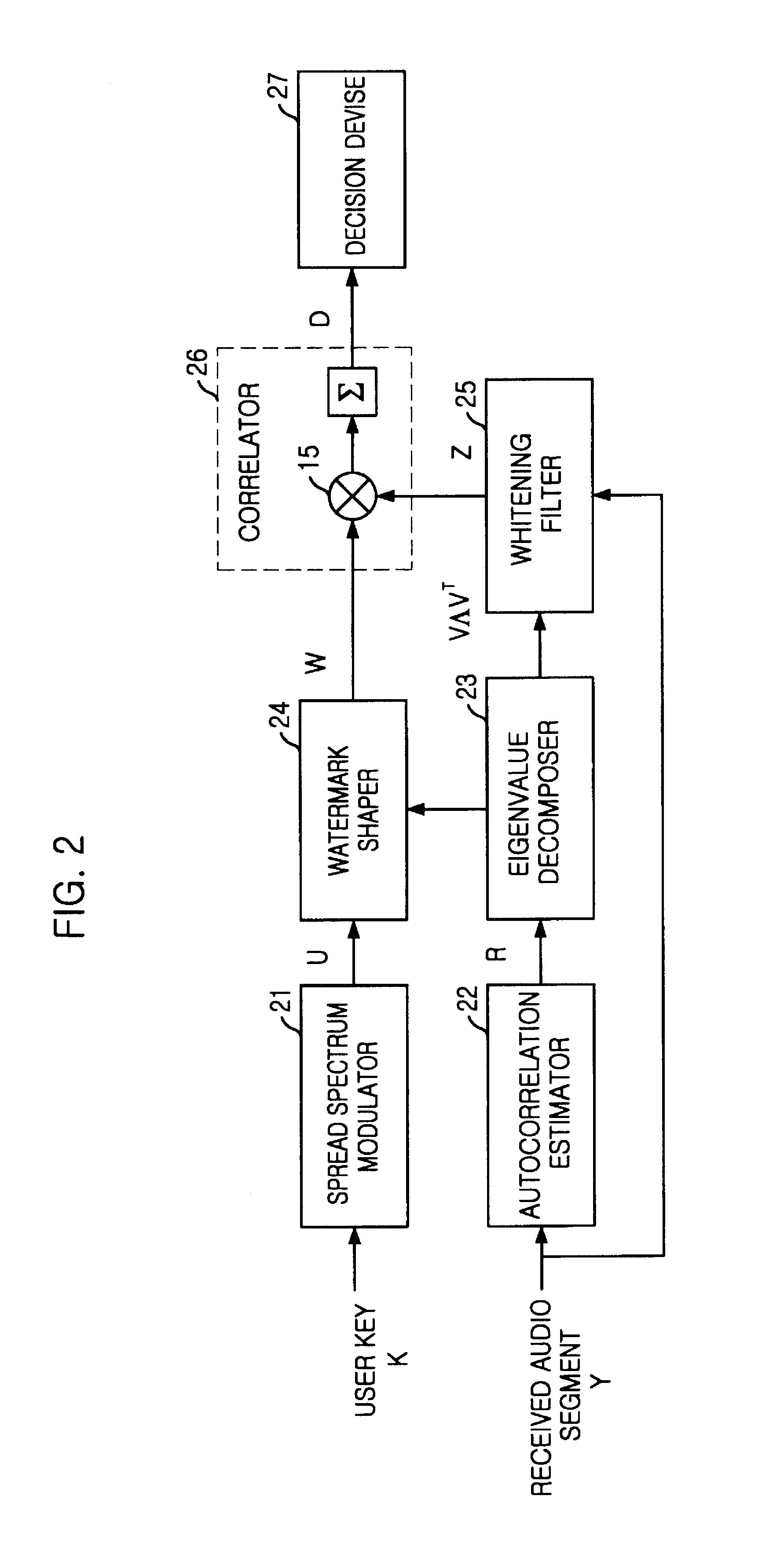
A method for inserting and detecting a watermark based on a stochastic model is disclosed. The apparatus for inserting a watermark based on a stochastic model, includes: a generator for generating a spread spectrum signal by using a user key from outside; an estimator for estimating an autocorrelation matrix of an original signal from outside as an object for inserting a watermark; an eigenvalue decomposer for decomposing the autocorrelation matrix to an eigenvector matrix and an eigenvalue matrix; a watermark shaper for shaping a watermark from the spread spectrum signal in reference to both the eigenvector matrix and the eigenvalue matrix; and an adder for adding the watermark to the original signal.
Owner:KT CORP
Nonlinear phase noise compensation method and system in coherent optical fiber communication system
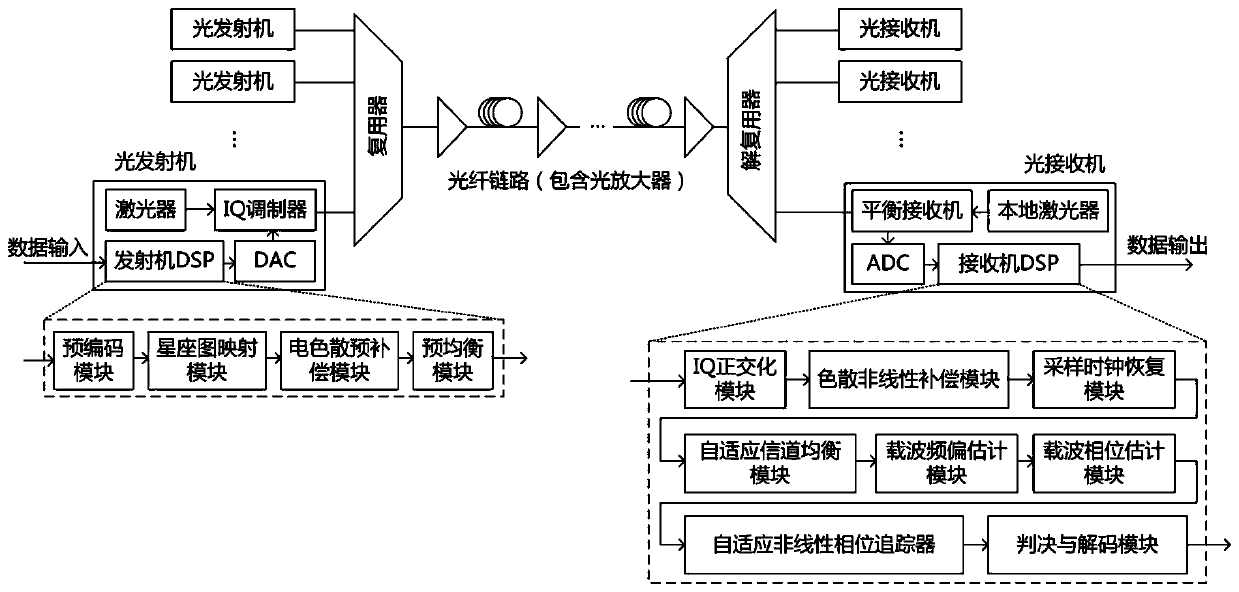
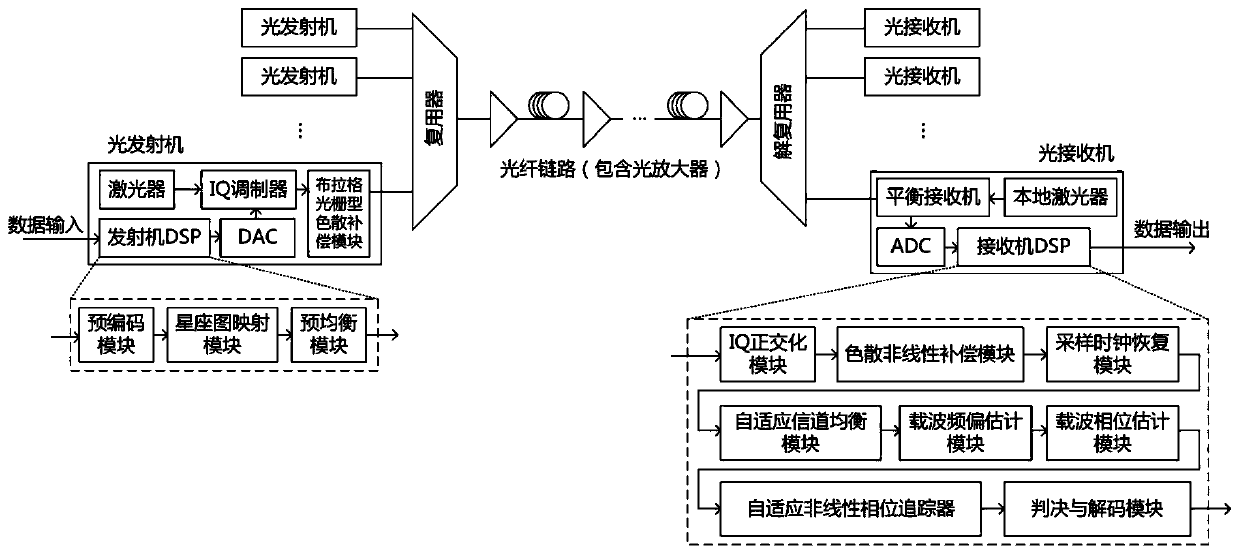
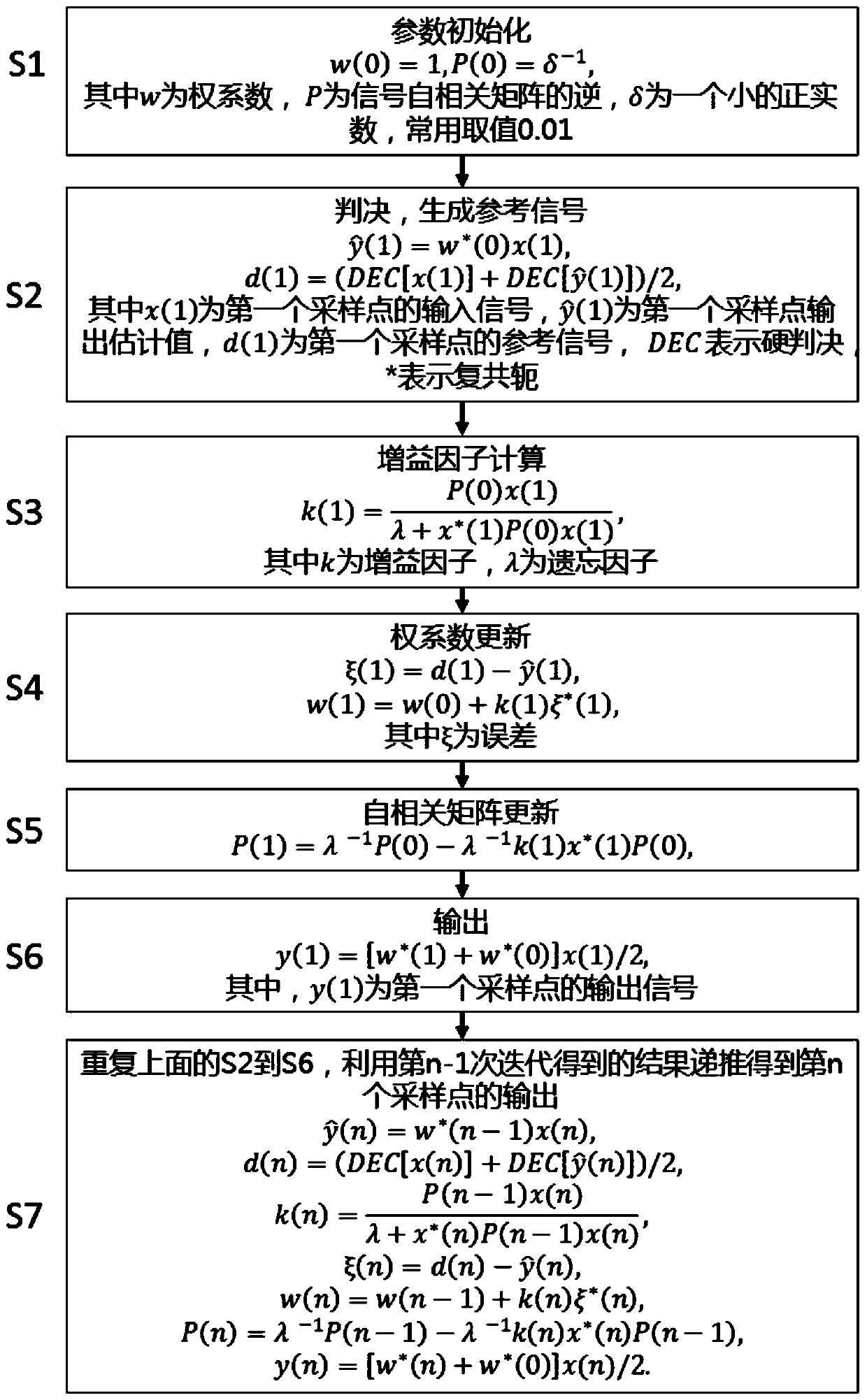
ActiveCN111010239ACross Phase Modulation SuppressionReduce computational complexityElectromagnetic receiversComputation complexitySoftware engineering
The invention discloses a nonlinear phase noise compensation method and a system in a coherent optical fiber communication system. Signals enter the optical fiber from the transmitting end through themultiplexer and are transmitted to the receiving end. After coherent receiving and ADC sampling, the signals enter a receiving end DSP, wherein the receiving end DSP comprises IQ orthogonalization, dispersion nonlinear compensation, sampling clock recovery, self-adaptive channel equalization, carrier frequency offset estimation, carrier phase estimation and self-adaptive nonlinear phase tracking;initializing parameters of the adaptive nonlinear phase tracking; judging the input signal to generate a reference signal; calculating a gain factor corresponding to the sampling point according to the reference signal; updating the weight coefficient and the autocorrelation matrix of the input signal according to the gain factor so as to generate an output signal; repeating the above steps, andobtaining the output of the nth iteration through the data recursion of the (n-1) th iteration. The method does not need extra optical devices, is suitable for any system structure and modulation mode, and the DSP algorithm of the receiving end is low in calculation complexity.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
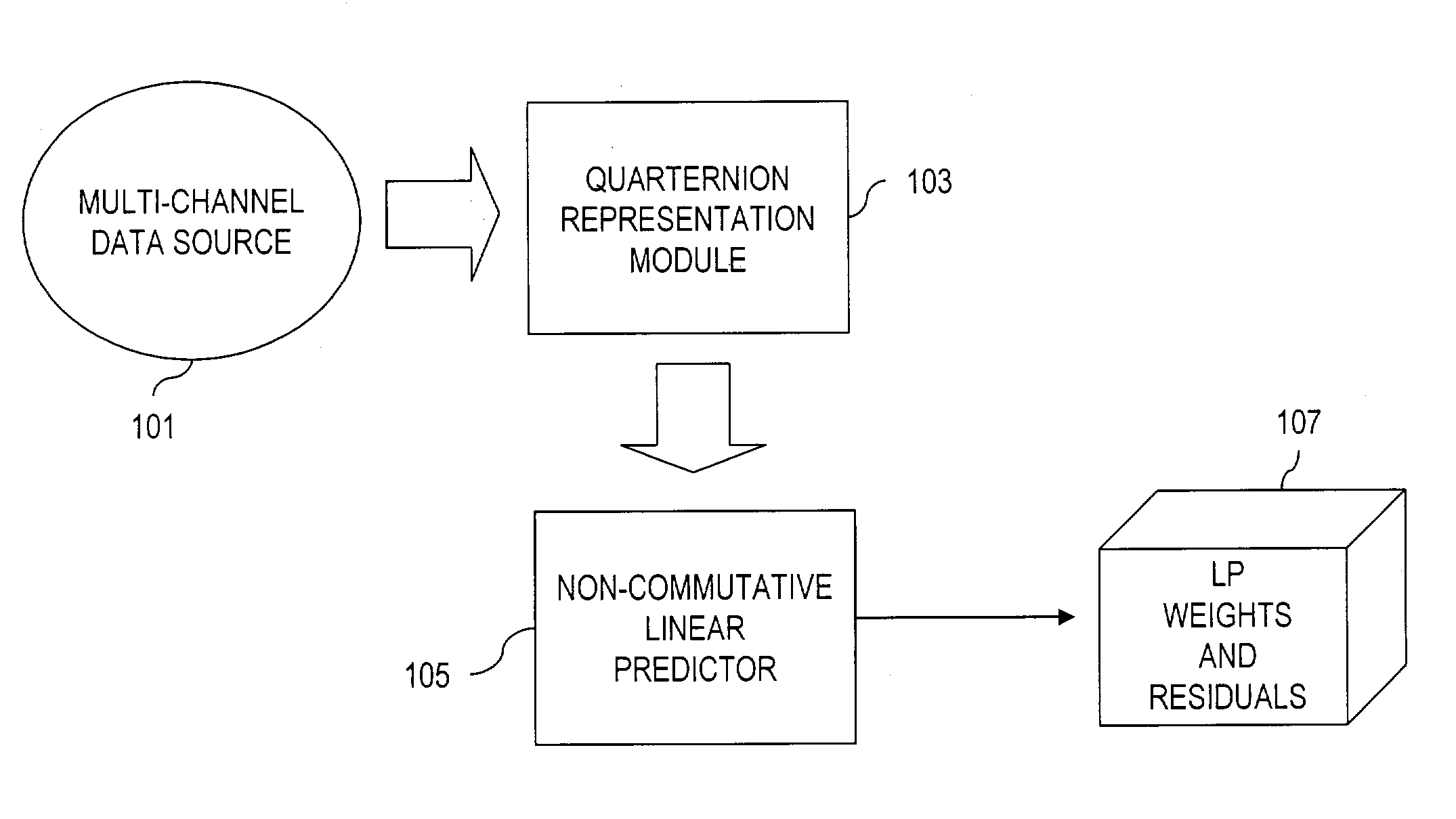
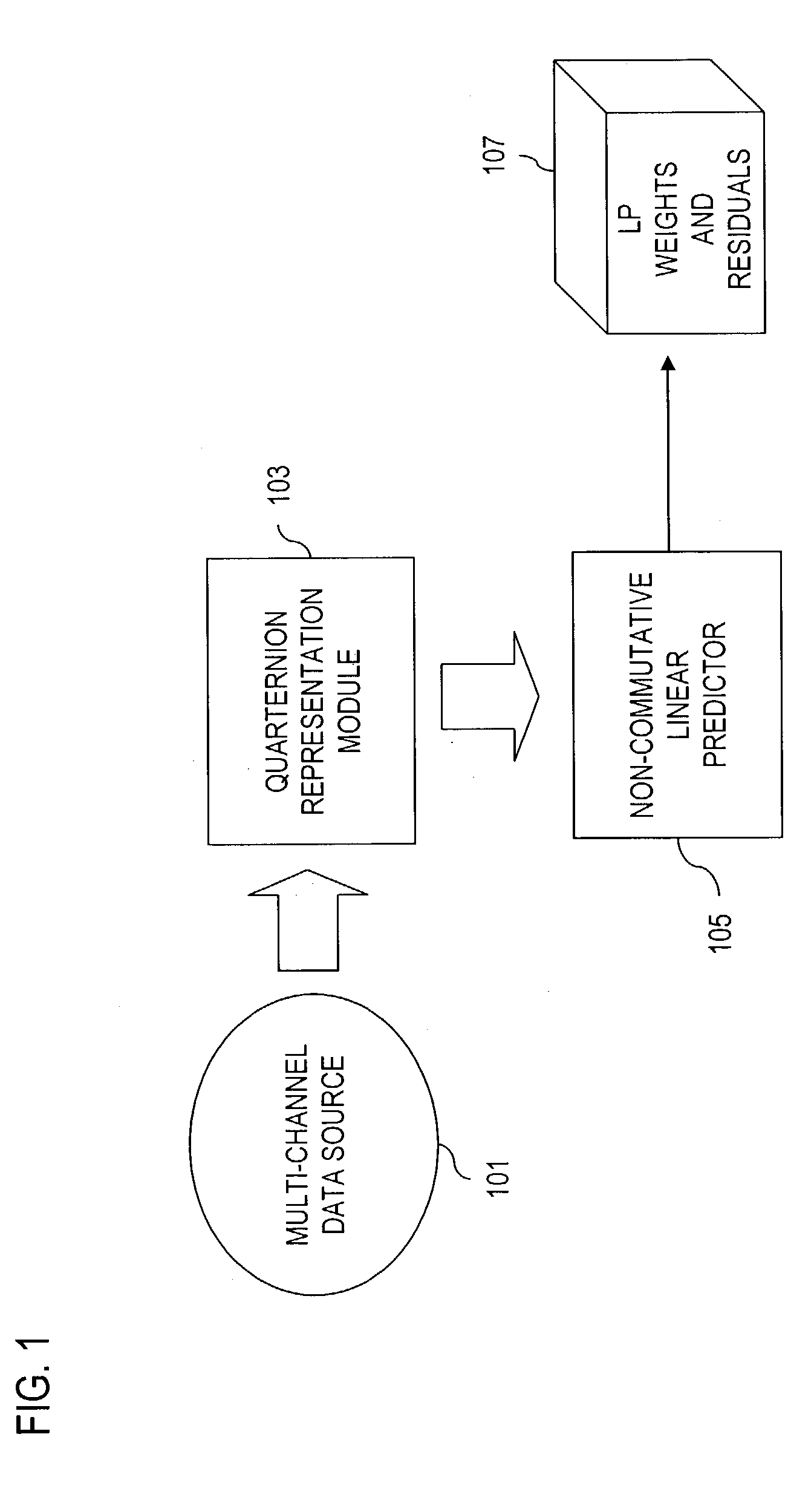
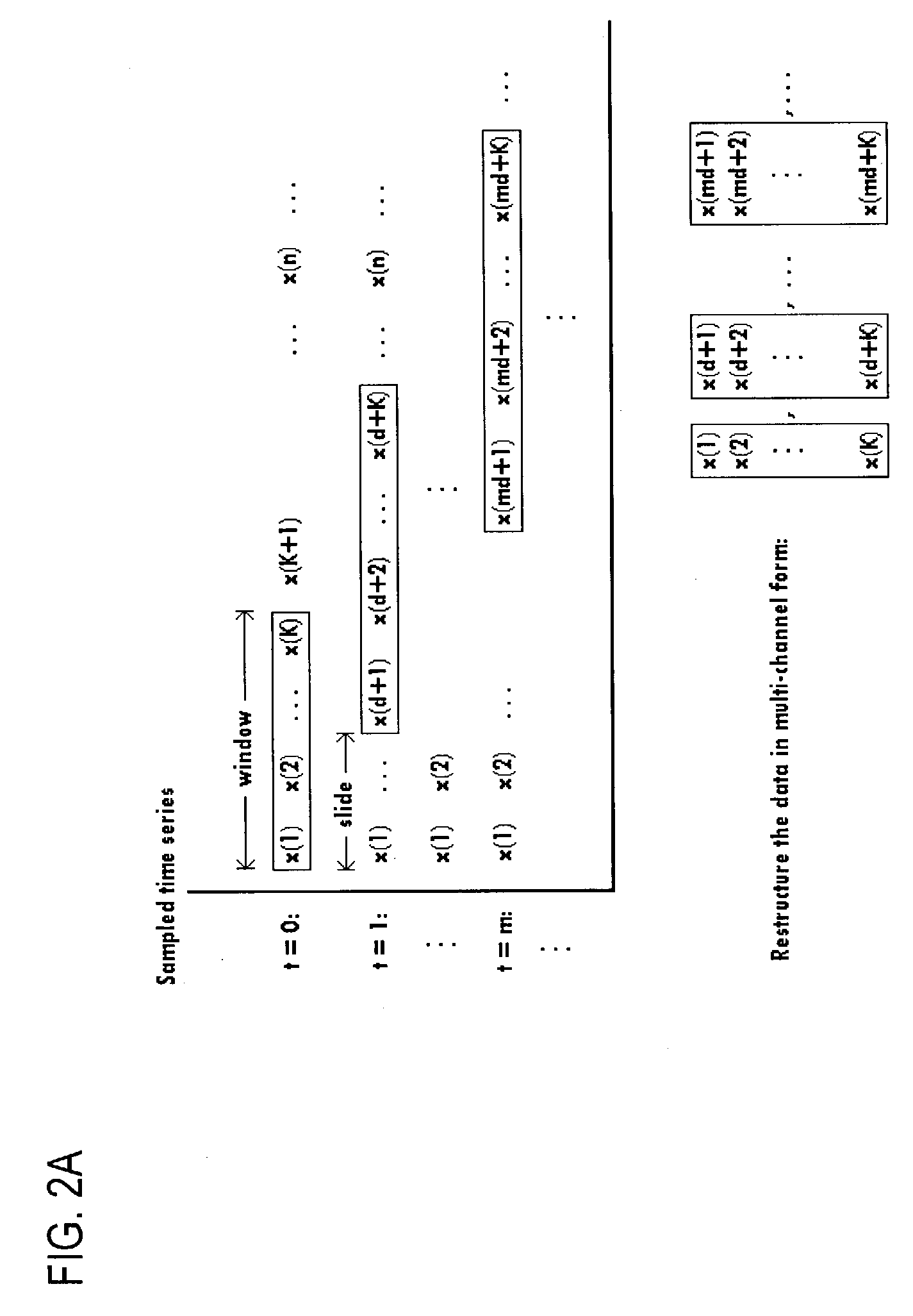
Signal processing of multi-channel data
InactiveUS7243064B2High correlationEffective approachColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionQuaternionMulti dimensional data
An approach for providing non-commutative approaches to signal processing. Quaternions are used to represent multi-dimensional data (e.g., three- and four-dimensional data). Additionally, a linear predictive coding scheme (e.g., based on the Levinson algorithm) that can be applied to wide class of signals in which the autocorrelation matrices are not invertible and in which the underlying arithmetic is not commutative. That is, the linear predictive coding scheme multi-channel can handle singular autocorrelations, both in the commutative and non-commutative cases. This approach also utilizes random path modules to replace the statistical basis of linear prediction.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
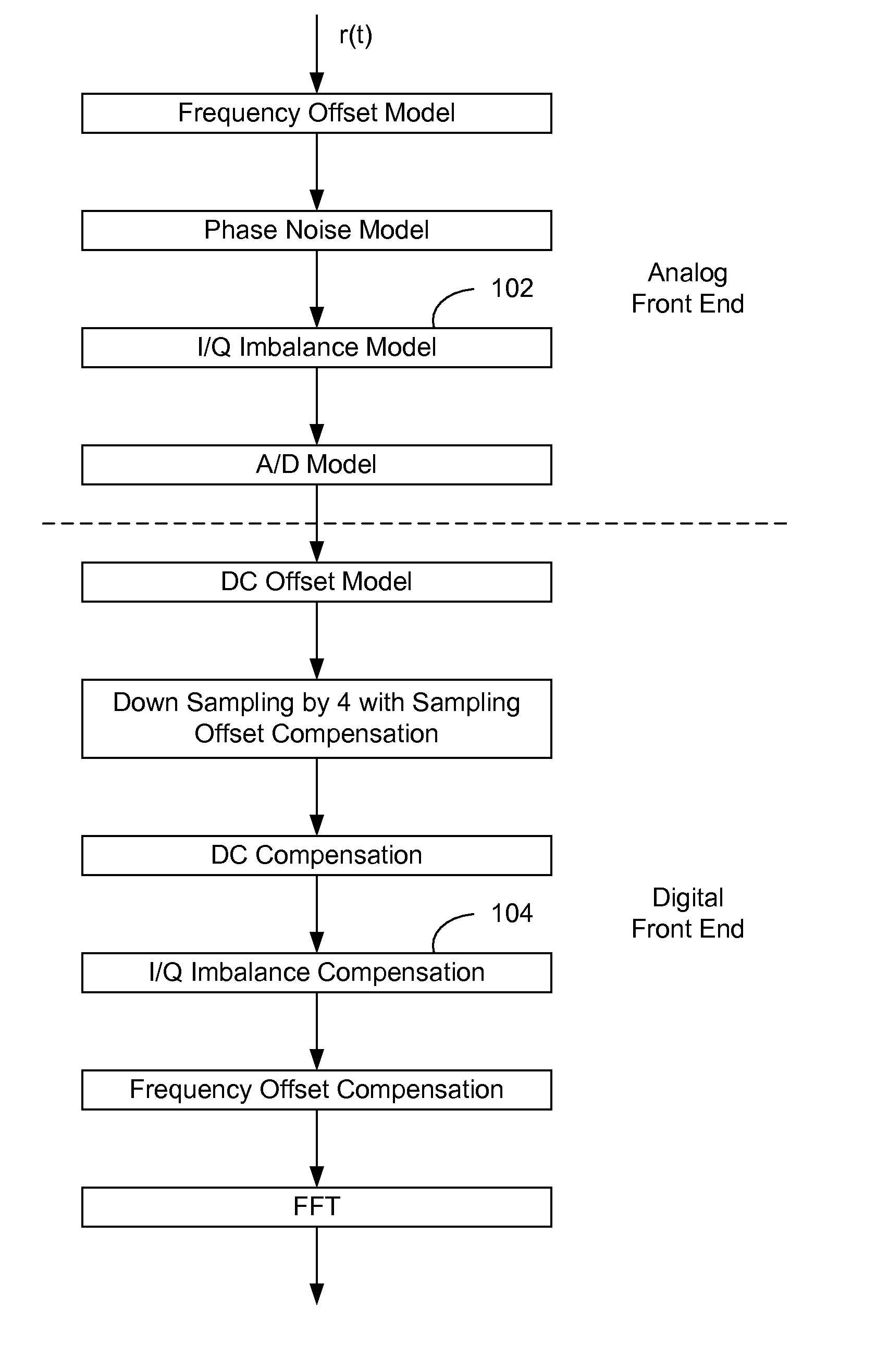
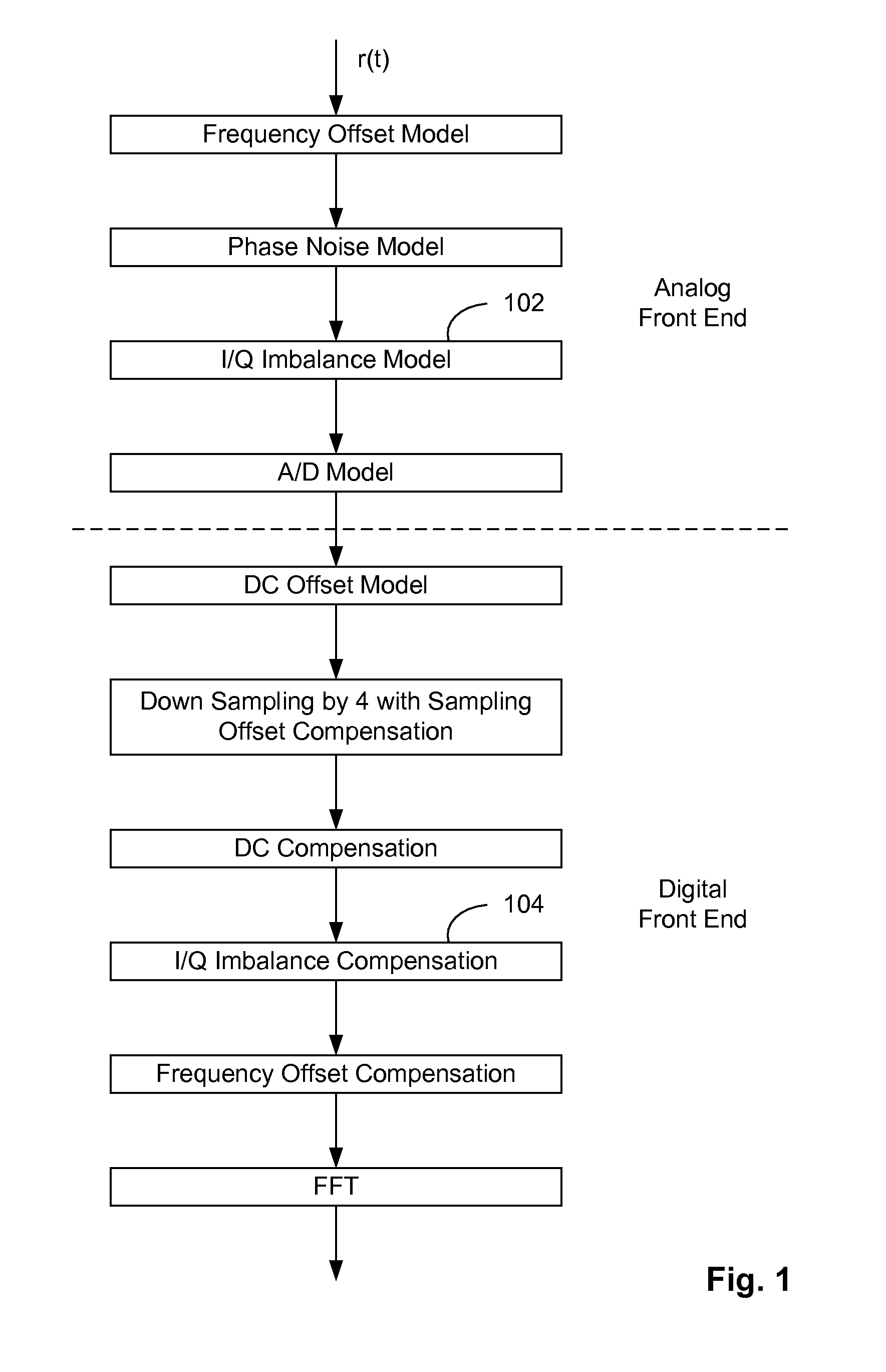
Methods for Compensating for I/Q Imbalance in OFDM Systems
InactiveUS20090122918A1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCarrier regulationPhase imbalanceEngineering
The present invention relates to methods for demodulating orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulated signals. In particular, this invention relates to methods for in-phase (I) and quadrature phase (Q) imbalance compensation in OFDM systems. For example, the present invention relates to methods for calculating an IQ imbalance compensated signal from a received signal, comprising the steps of: removing DC from the received signal; calculating an autocorrelation matrix of IQ signal vector of the received signal; estimating IQ imbalance compensation values, K1 and K2, as a function of an amplitude imbalance, g, and a phase imbalance, θ; and calculating an IQ compensated signal as a function of the estimated K1 and K2.
Owner:AUGUSTA TECHNOLOGIE
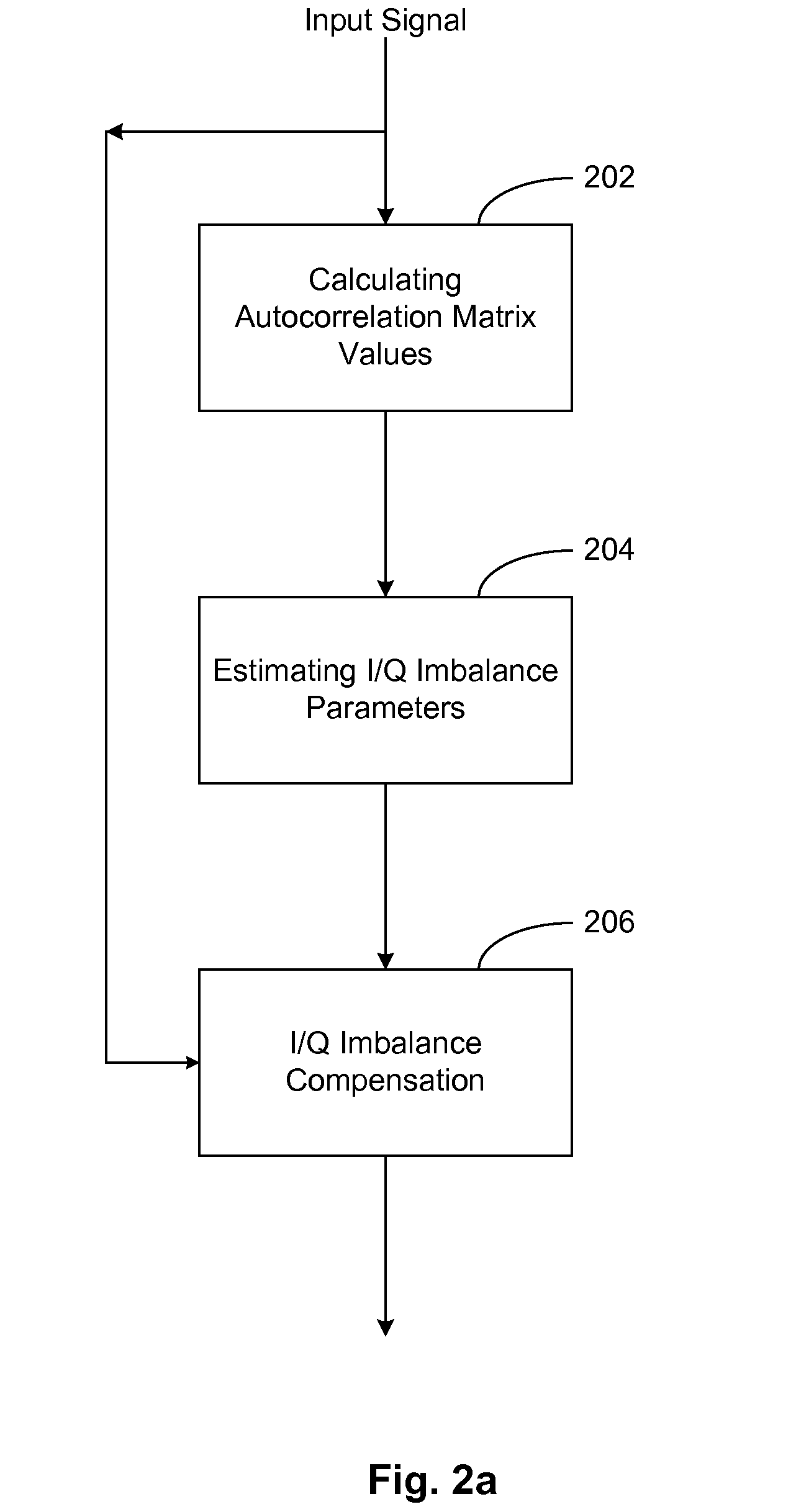
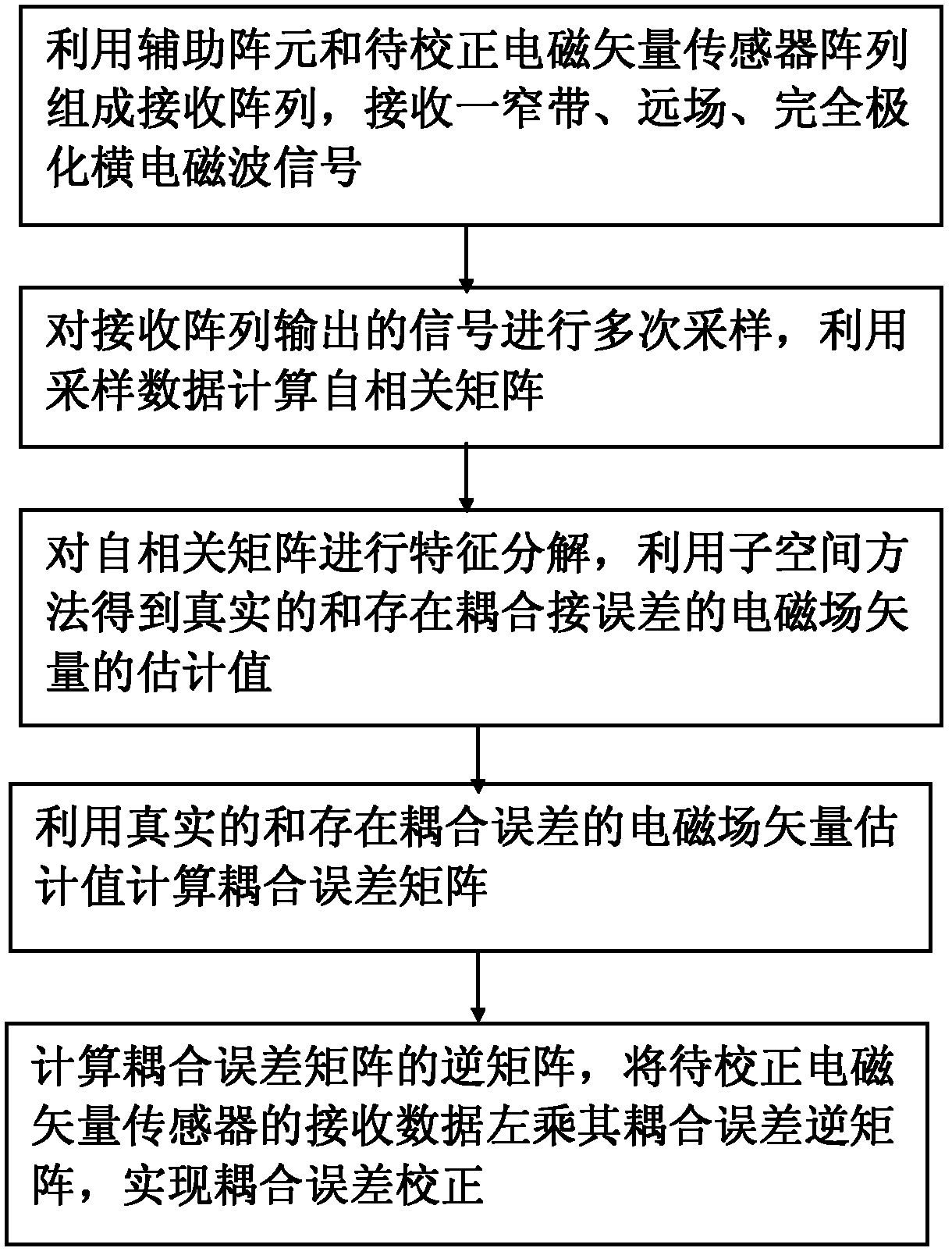
Method for self-correcting coupling error of electromagnetic vector sensor array
InactiveCN102401888ASimplify the solution processSmall amount of calculationElectrical measurementsCouplingComputational physics
The invention discloses a method for self-correcting a coupling error of an electromagnetic vector sensor array. According to the method, an ideal electromagnetic vector sensor is additionally arranged to be used as an auxiliary array element and forms a receiving array with the electromagnetic vector sensor array to be corrected, the receiving array receives the completely polarized transverse electromagnetic wave signal data of a far field, the autocorrelation matrix of the sample data is calculated, the real electromagnetic field vector and electromagnetic vector having errors of the signal are estimated through a subspace method, the obtained estimated value of the real electromagnetic field vector and the estimated value of the electromagnetic field vector having errors are used to estimate the coupling error variance, the coupling error matrix is constructed according to the coupling error variance and the inverse matrix is calculated, and the data received by the electromagnetic vector sensor to be corrected are pre-multiplied by the inverse matrix of the coupling error matrix so as to correct the coupling error. The method disclosed by the invention has a simple solving process and small calculated amount, the real electromagnetic filed vector and the electromagnetic field vector having coupling errors of the signal can be estimated, and higher coupling error estimation accuracy can be achieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-antenna joint optimization clutter suppression method based on fractional time delay estimation
ActiveCN105527610AEasy to detectImprove the clutter rejection ratioWave based measurement systemsDecompositionTime delays
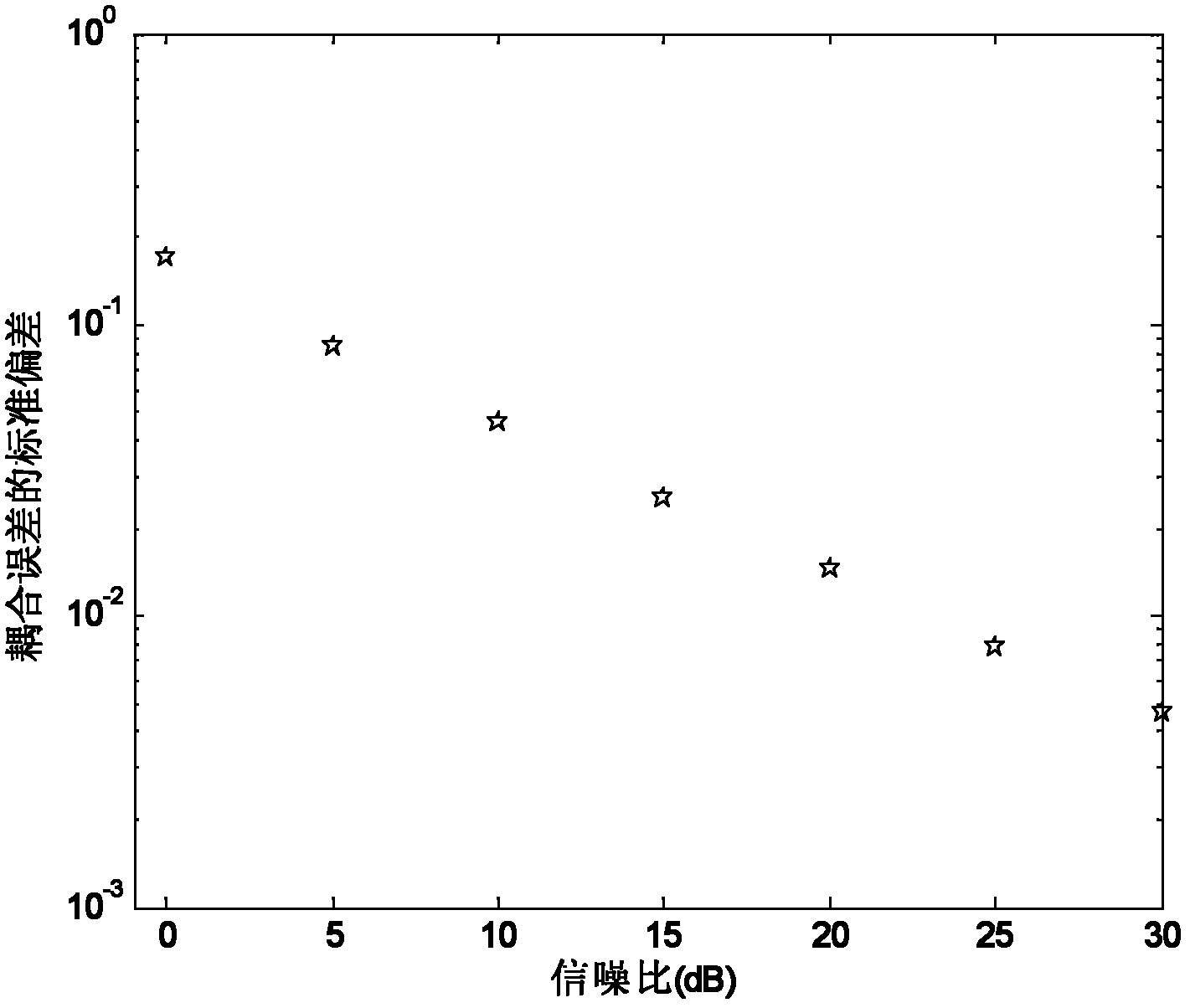
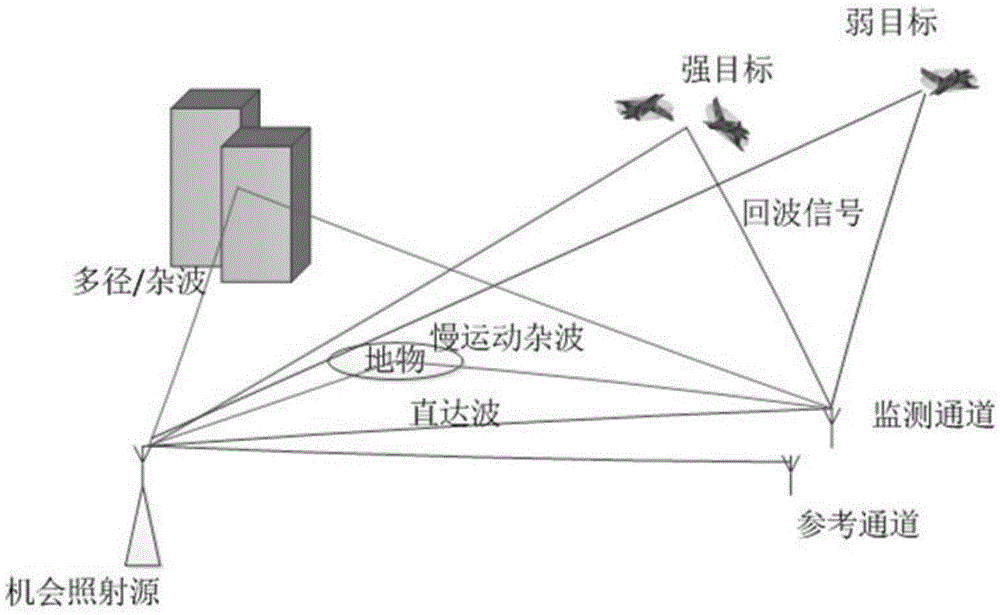
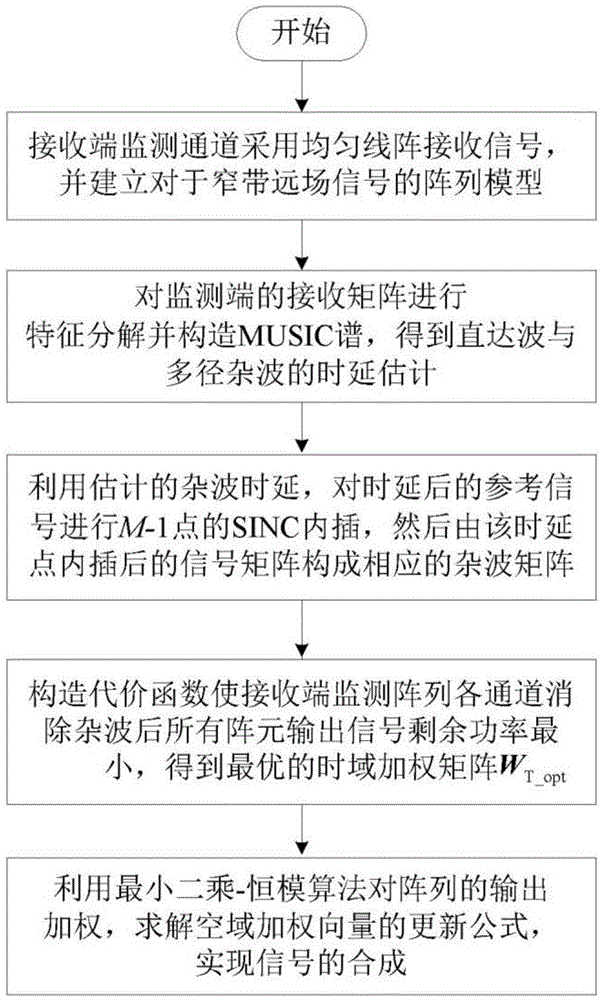
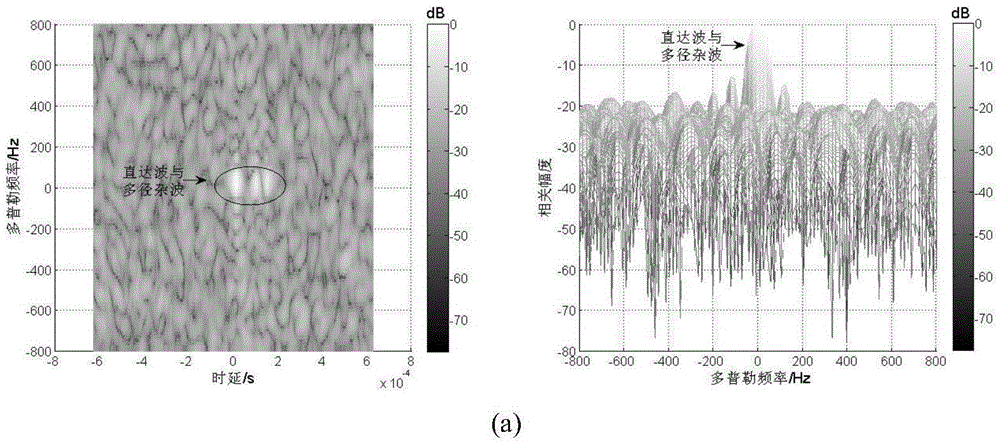
The present invention relates to a multi-antenna joint optimization clutter suppression method based on fractional time delay estimation. A receiving end monitoring channel receives a signal by using a uniform linear array, and a signal array model is established; the self-correlation matrix of an array model matrix is subjected to feature decomposition, a MUSIC spectrum is constructed, and the time delay estimation of a direct wave and a multipath clutter is obtained; the time delay signal after time delay is subjected to SINC function interpolation, and a corresponding clutter matrix is constructed; through constructing a cost function, an optimal time-domain weighting matrix WT_opt is obtained; the output of the array is weighted by using a least squares-constant modulus algorithm, a spatial weighting vector ws is solved, and the signal combination and output are carried out. According to the method, the time domain and spatial domain information of the signal are fully dug, the correlation of the signals in different array elements is monitored by using a receiving end, through the least squares-constant modulus algorithm, the noise and residual clutter outside a target echo coming direction are subjected to attenuation, the clutter rejection ratio of the output signal is raised, and the detection performance of a weak object can be improved at the same time.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com