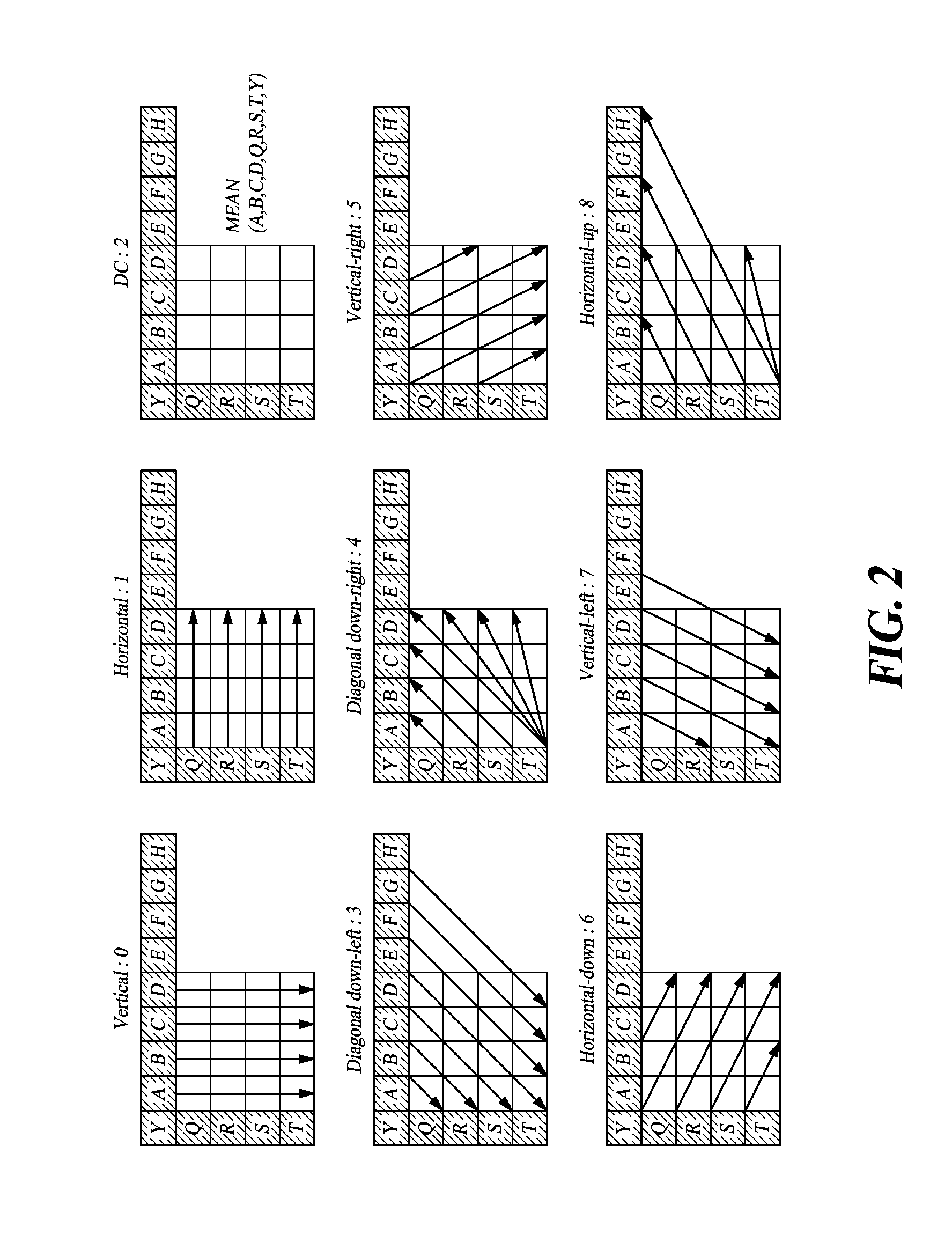
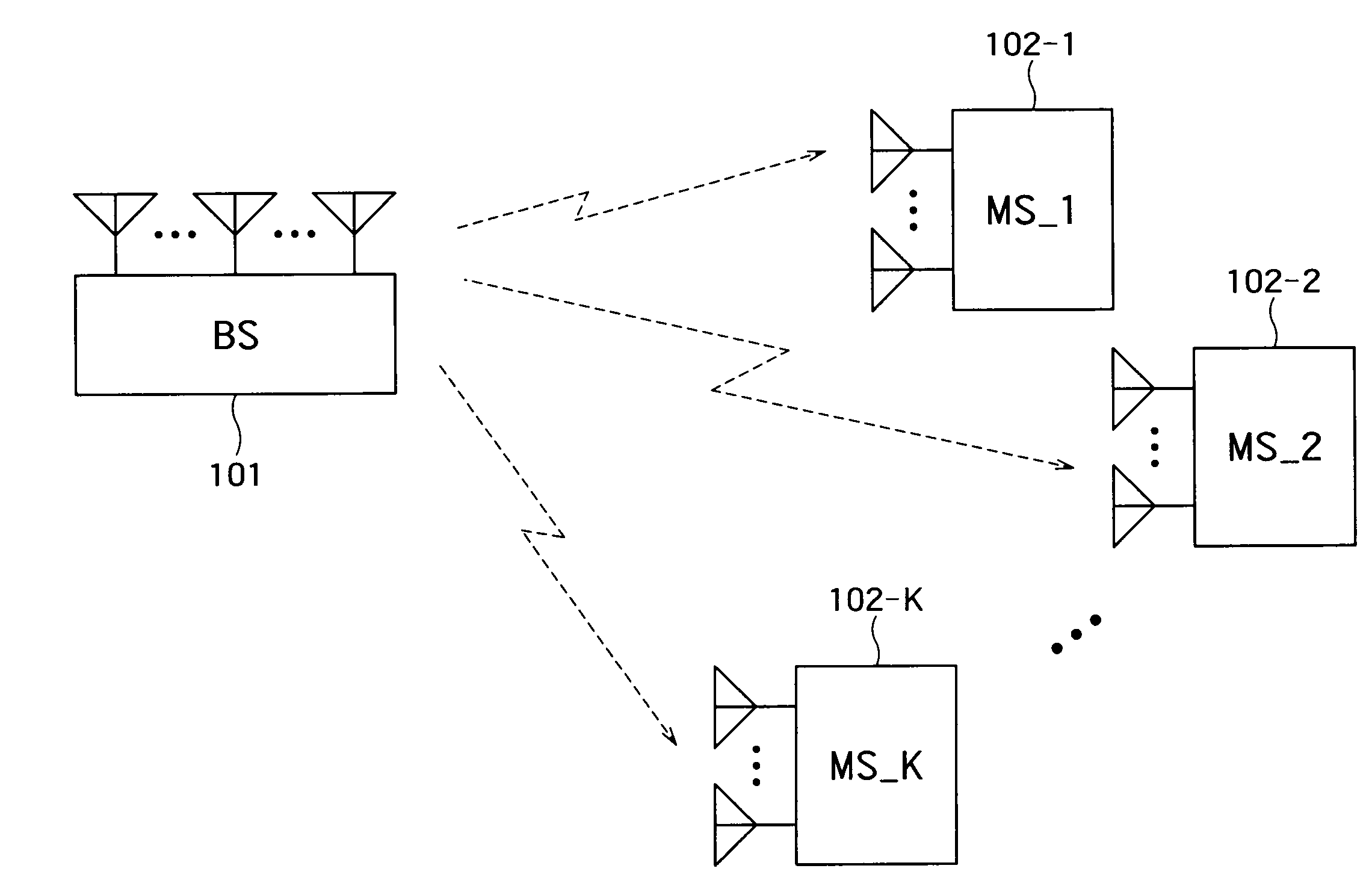
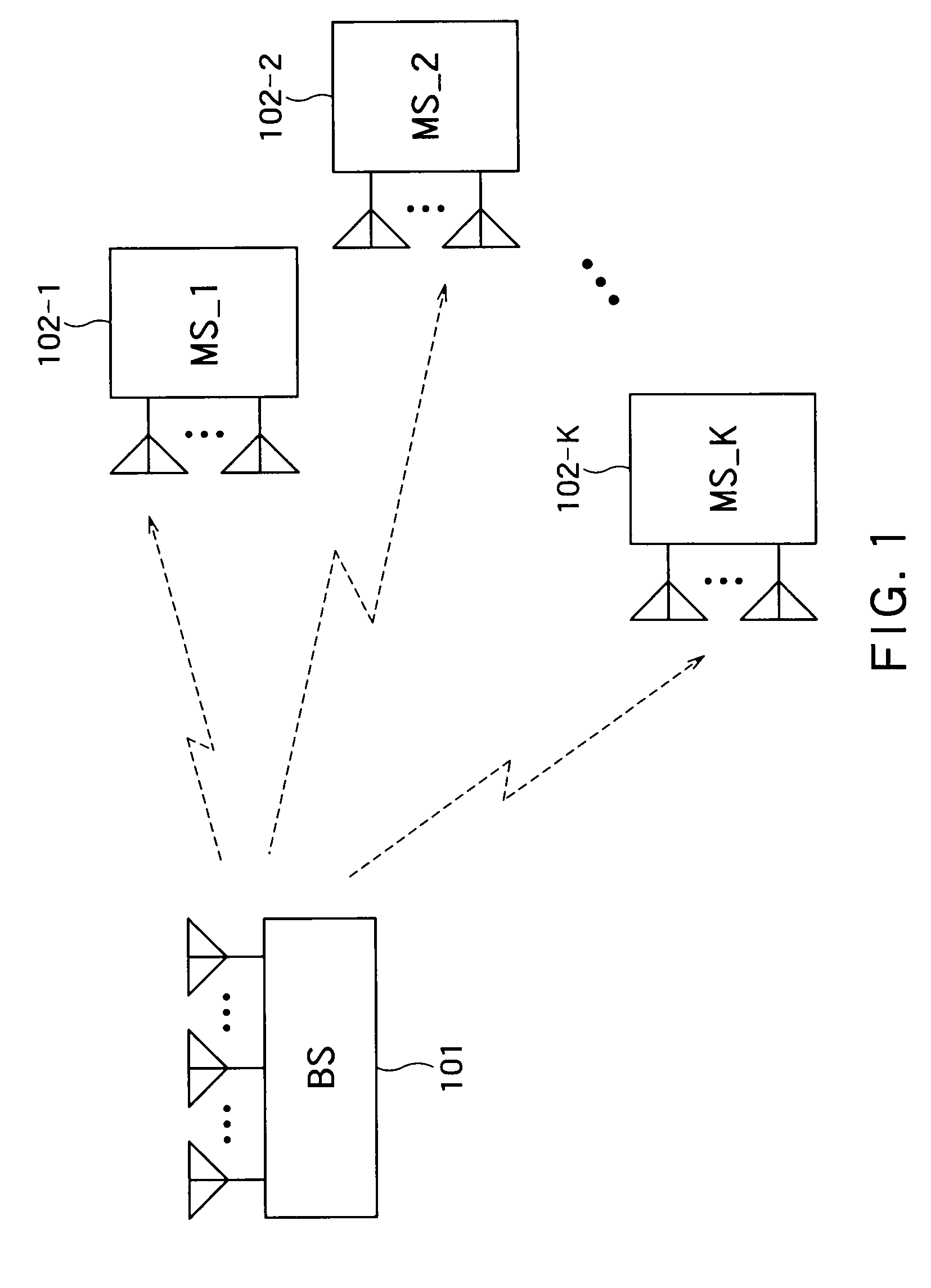
Patents
Literature
269results about How to "High correlation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of producing sustained-release preparation
InactiveUS6267981B1Maintain good propertiesEnhancement of entrapmentPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsEntrapmentBiodegradable polymer
This invention provides a sustained-release preparation comprising a biodegradable polymer metal salt and broactive polypeptide, with enhanced entrapment of the bioactive polypeptides, a suppression of initial burst, and a constant long-term release of the bioactive polypeptides.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
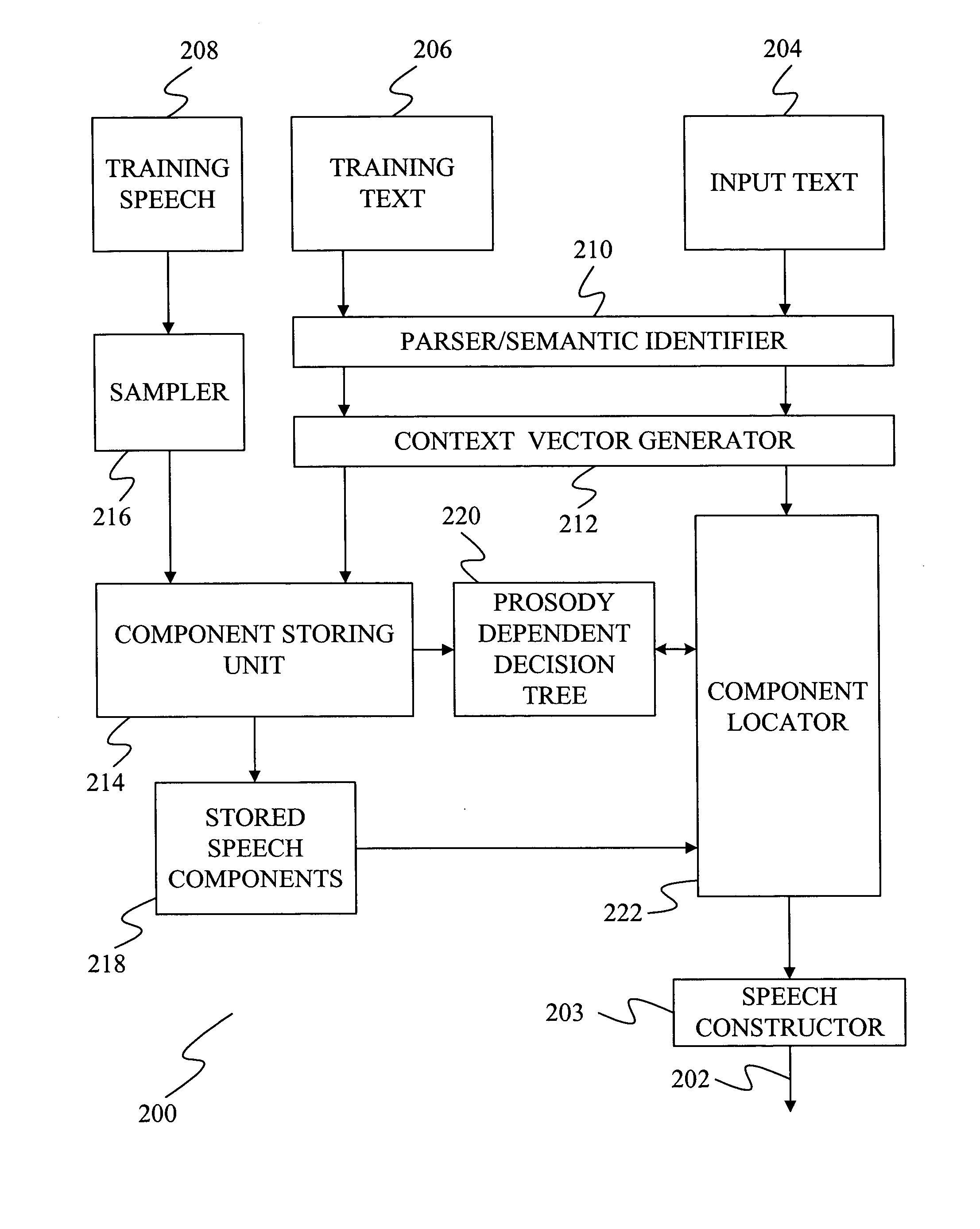
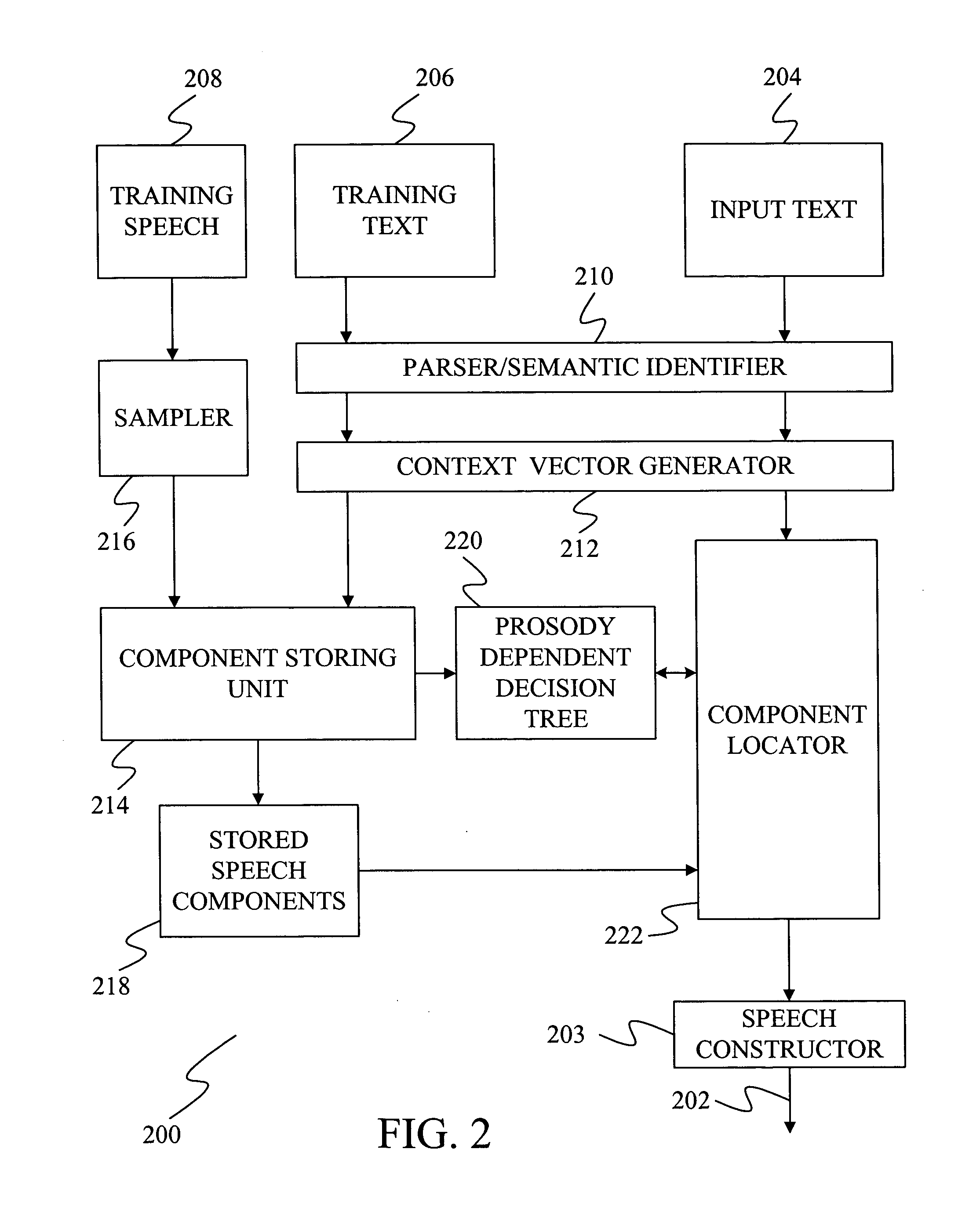
Optimization of an objective measure for estimating mean opinion score of synthesized speech
InactiveUS20050060155A1High correlationImprove relationshipSpeech synthesisMean opinion scoreObjective measurement
A method is provided for optimizing an objective measure used to estimate mean opinion score or naturalness of synthesized speech from a speech synthesizer. The method includes using an objective measure that has components derived directly from textual information used to form synthesized utterances. The objective measure has a high correlation with mean opinion score such that a relationship can be formed between the objective measure and corresponding mean opinion score. The objective measure is altered to provide a different function of textual information derived from the utterances so as to improve the relationship between the scores of the objective measure and subjective ratings of the synthesized utterances.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
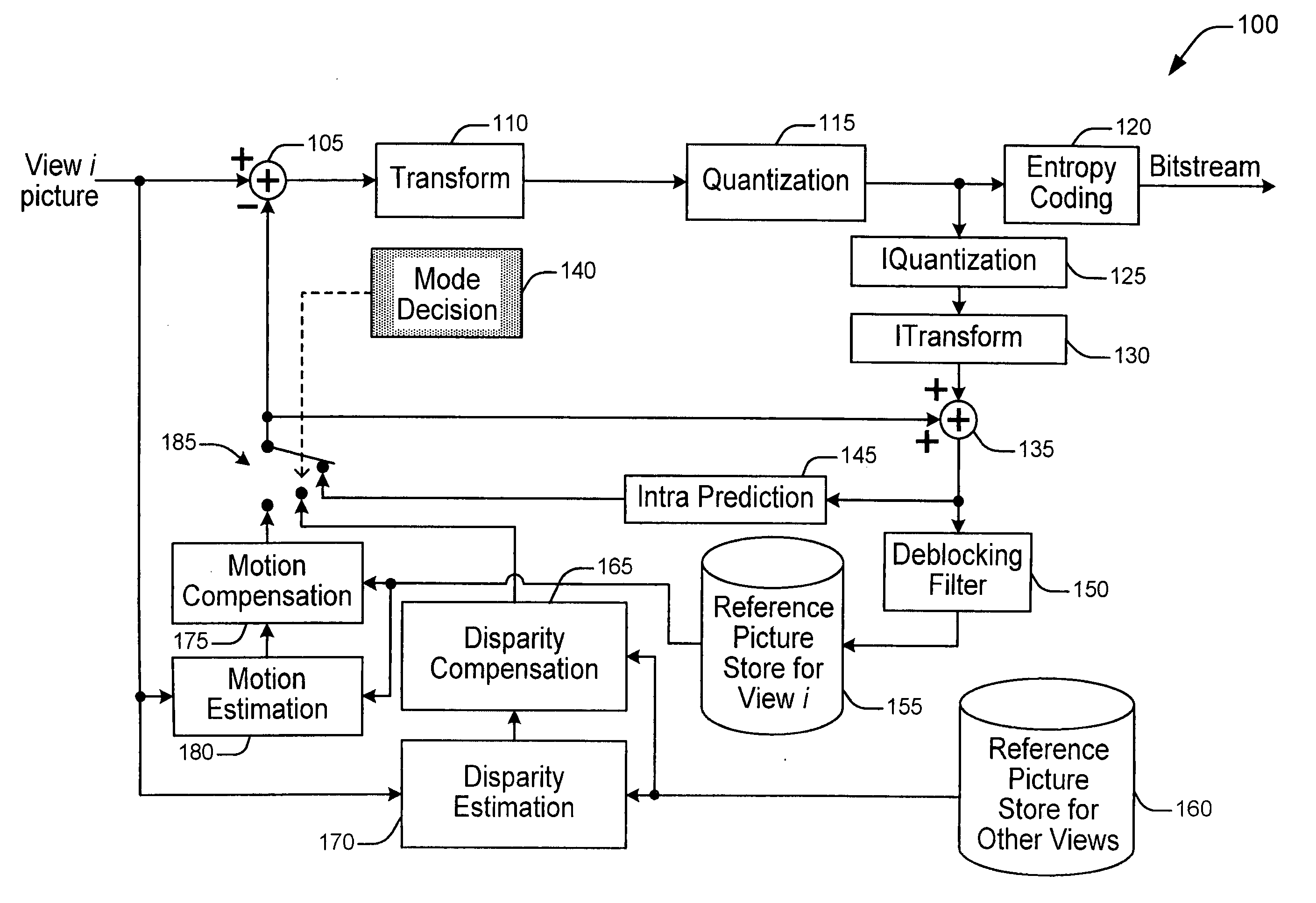
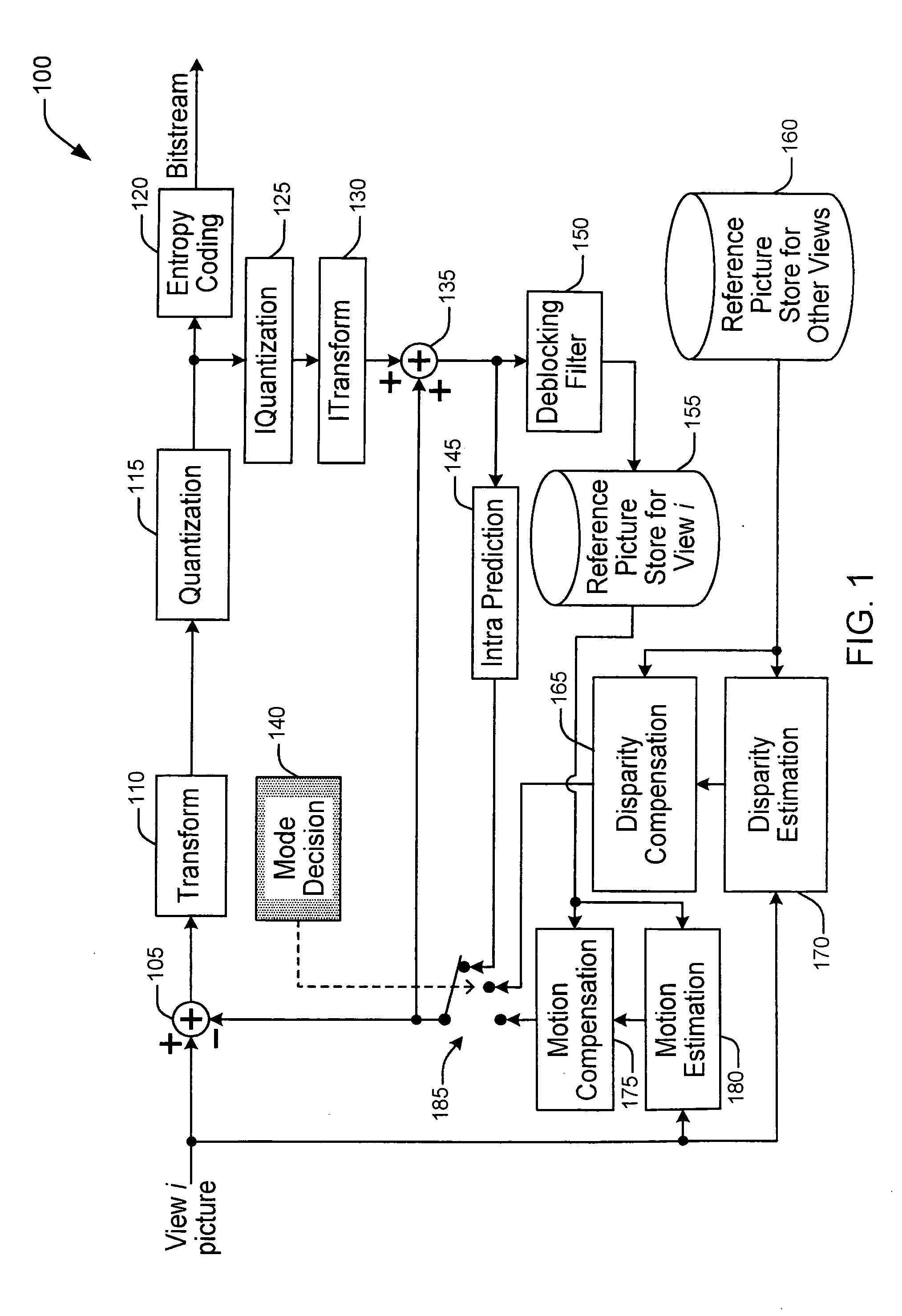
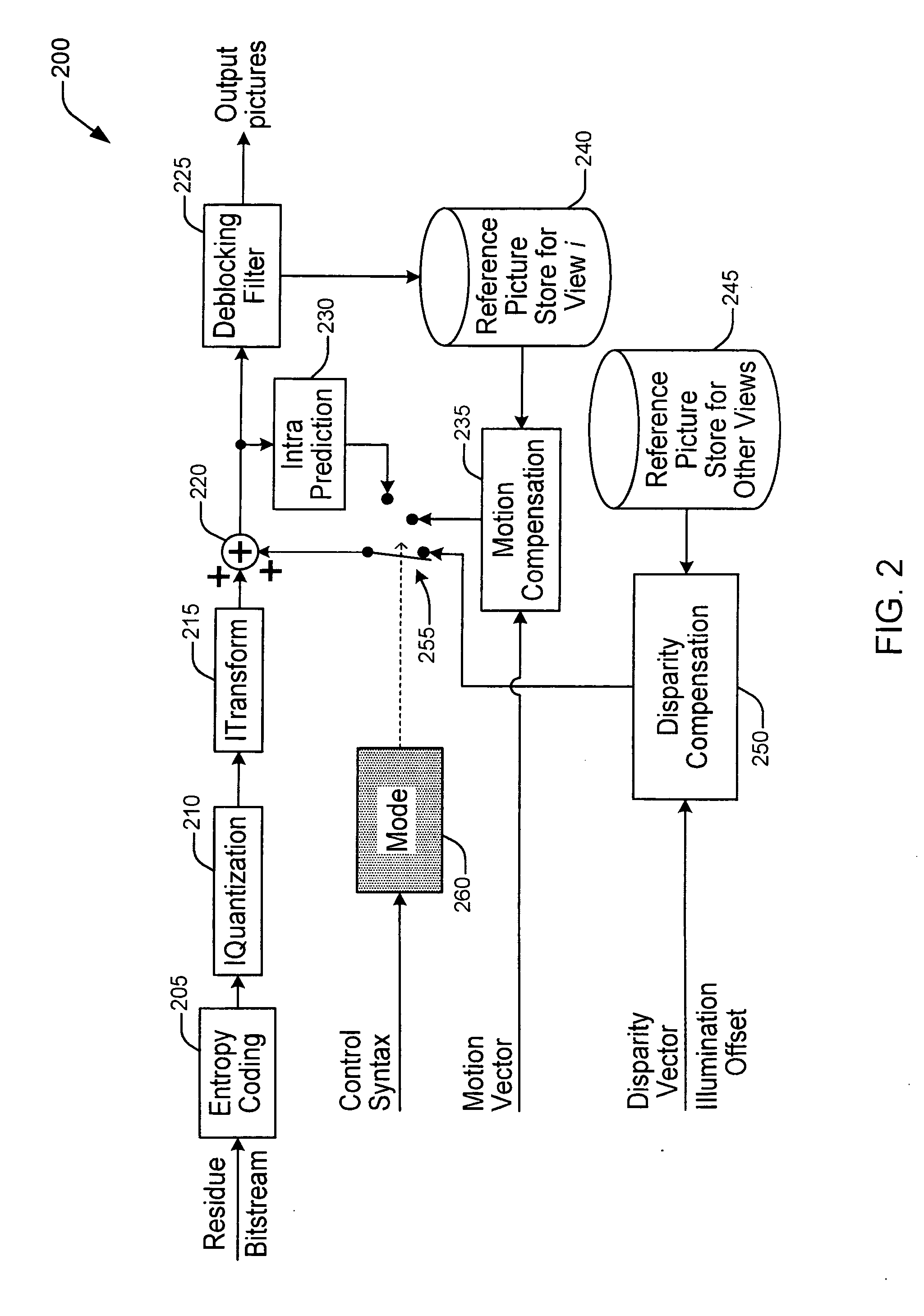
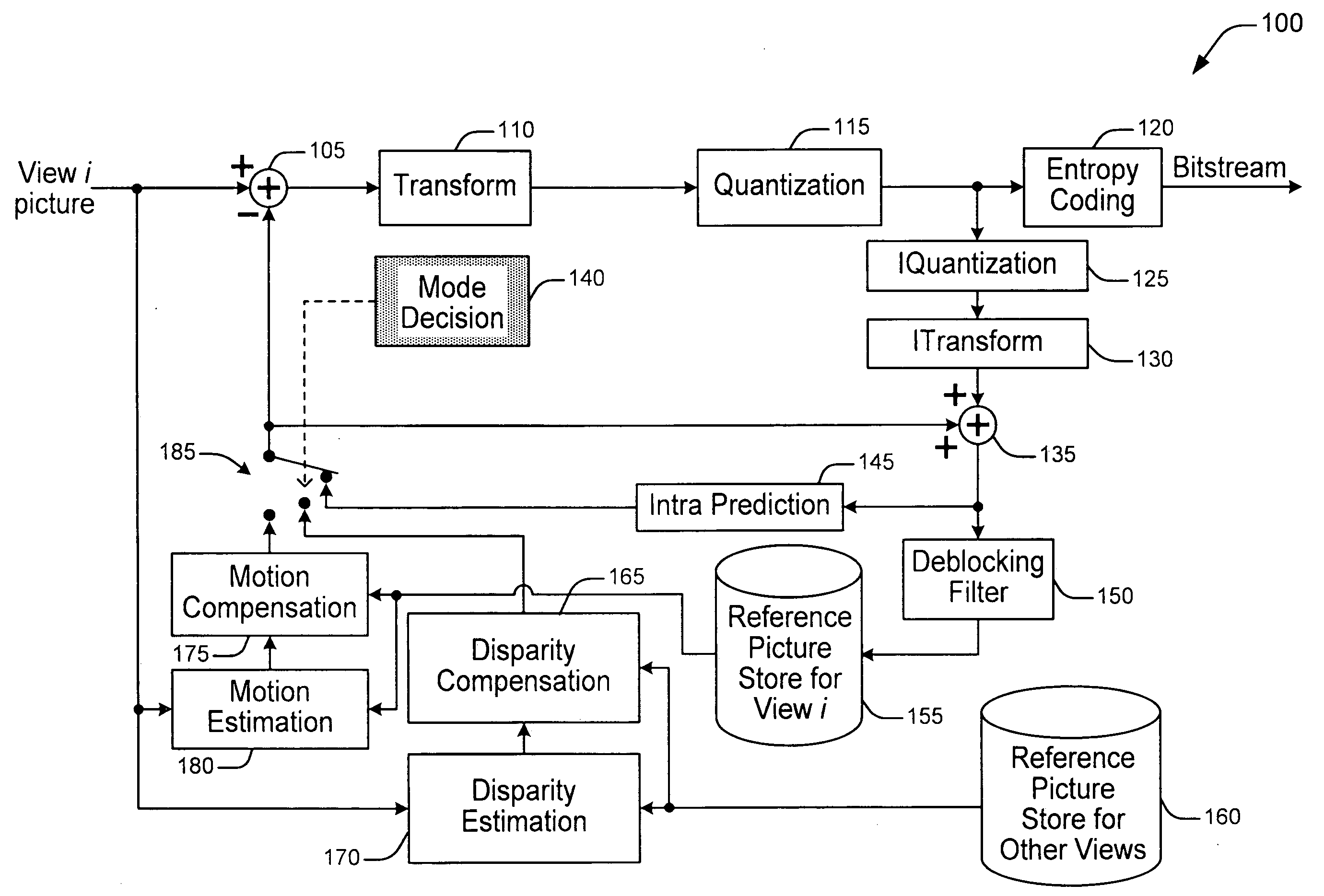
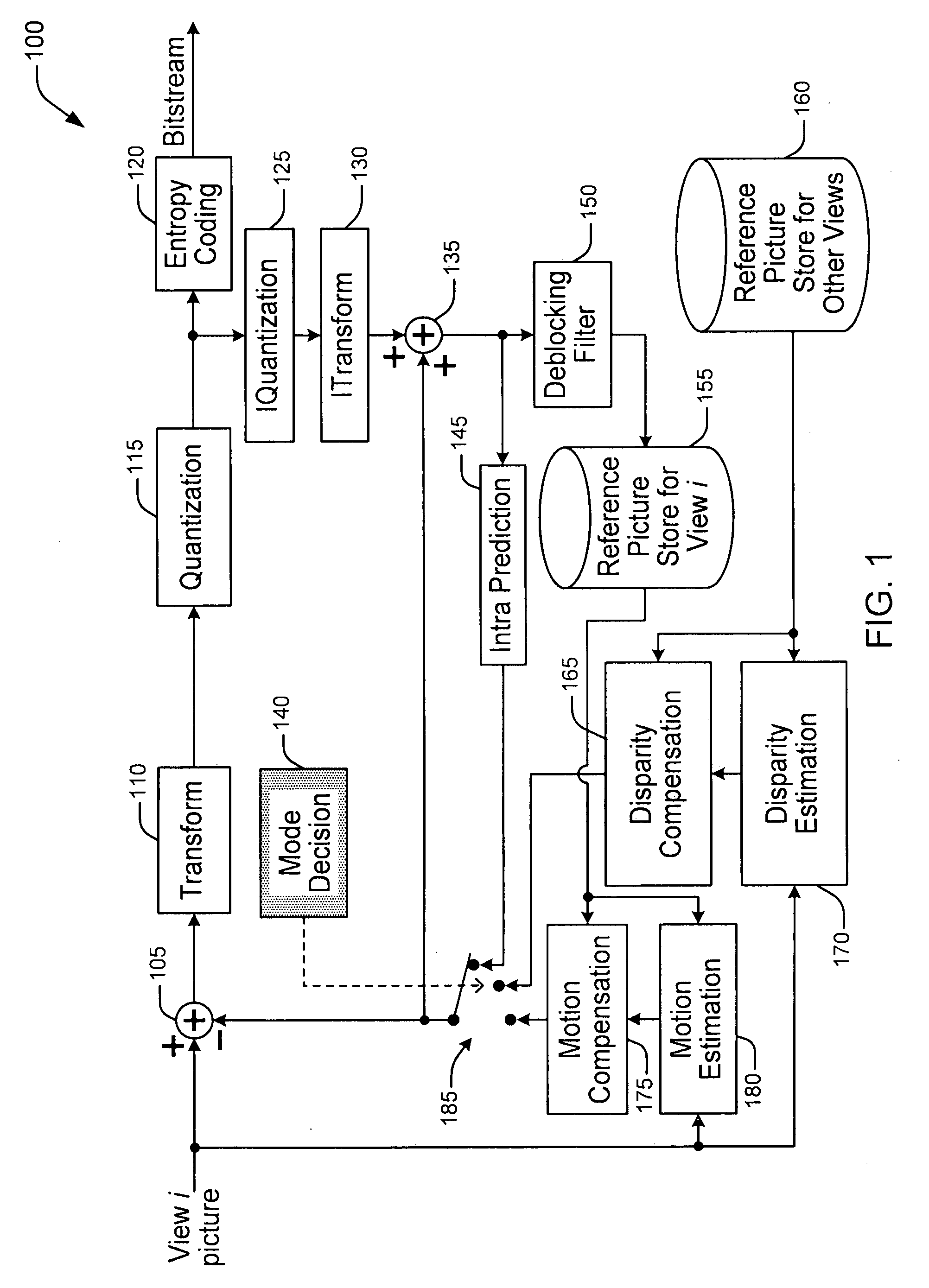
Methods and Apparatuses for Multi-View Video Coding
ActiveUS20090010323A1High correlationLess bitColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingComputer graphics (images)
There are provided methods and apparatus for multi-view video coding. A video encoder includes an encoder for encoding a block in a picture by choosing between temporal prediction and cross-view prediction to enable a prediction for the block. The picture is one of a set of pictures corresponding to multi-view video content and having different view points with respect to a same or similar scene. The picture represents one of the different view points. A high-level syntax is used to indicate the use of cross-view prediction for the block.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
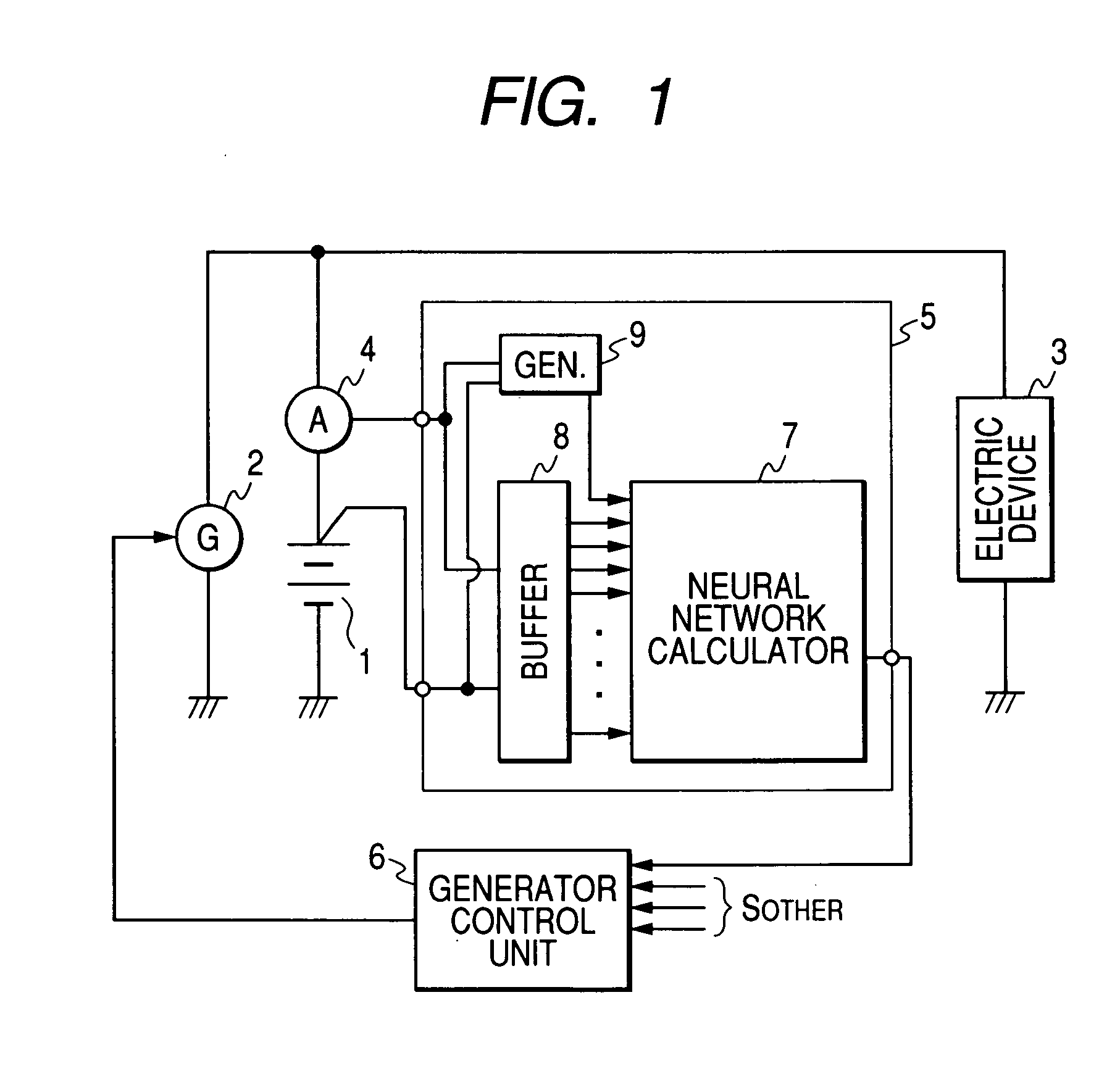
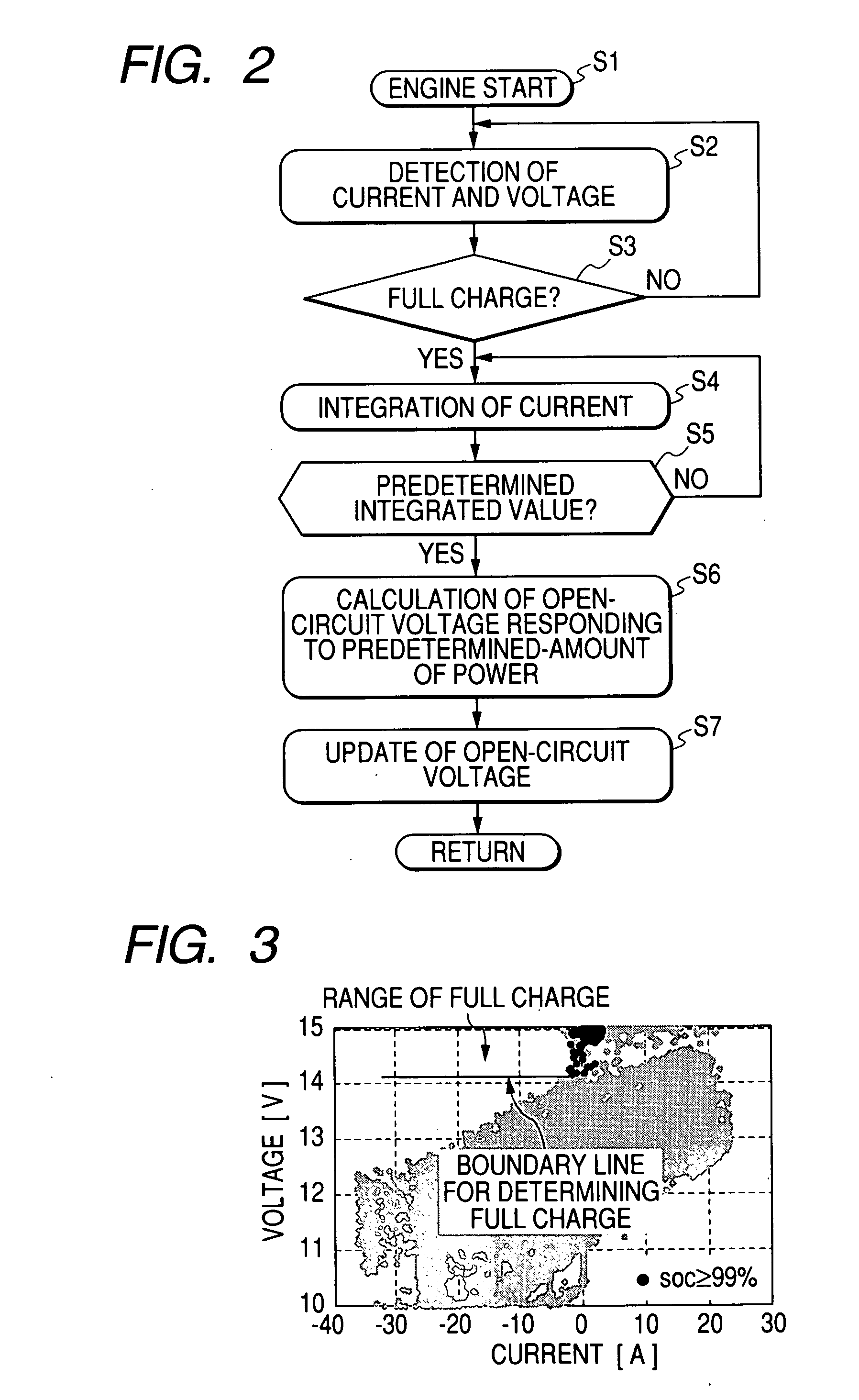
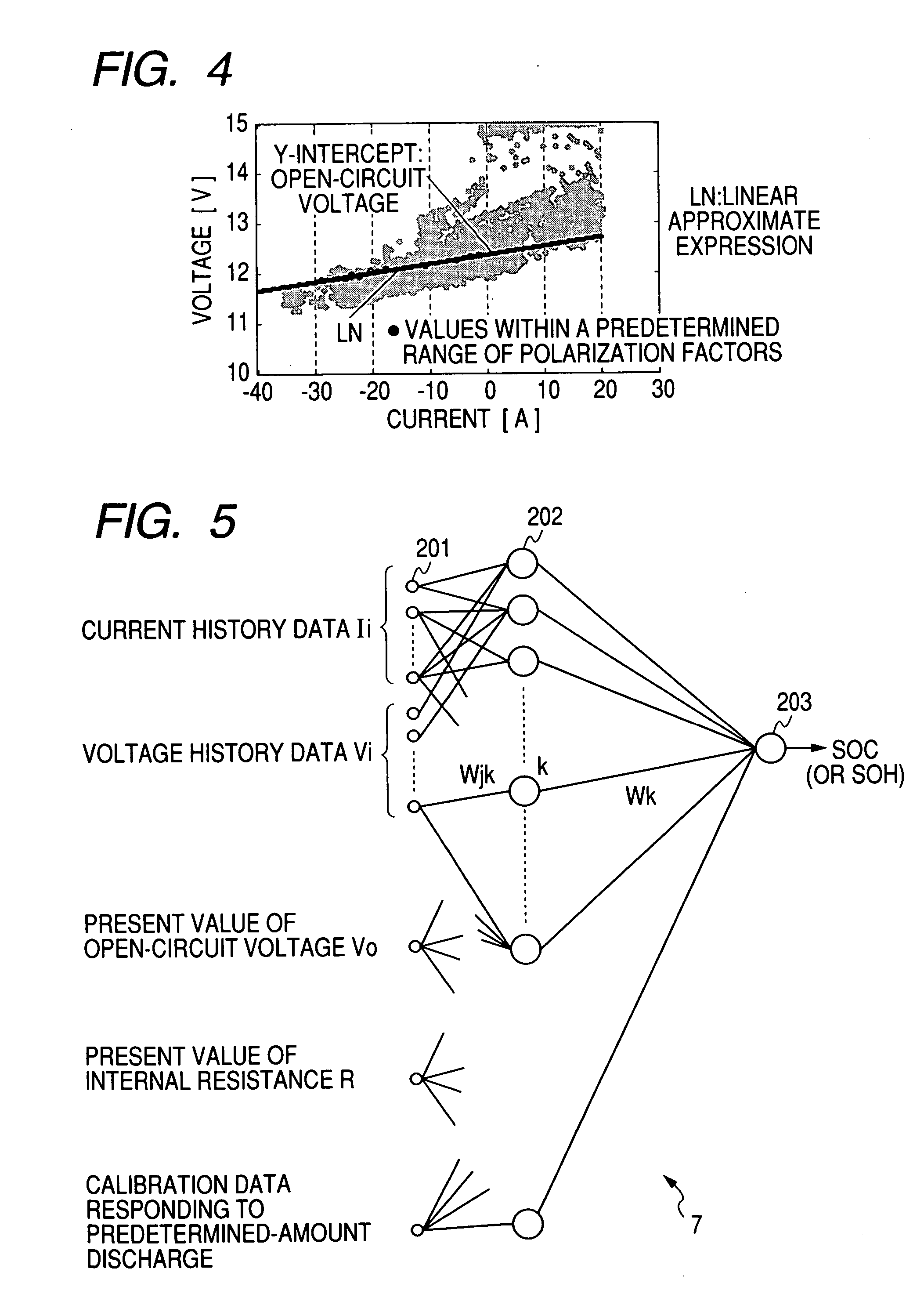
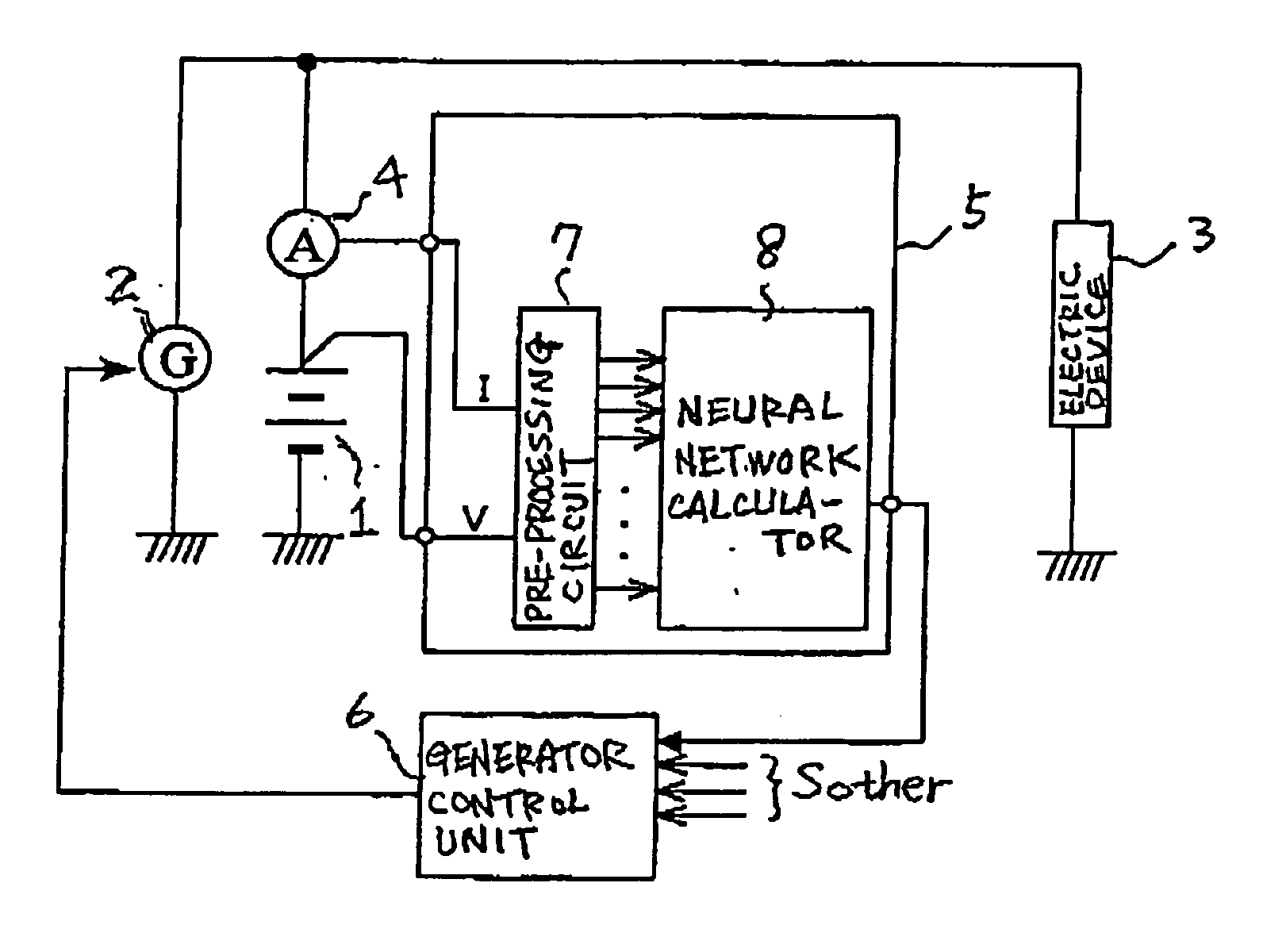
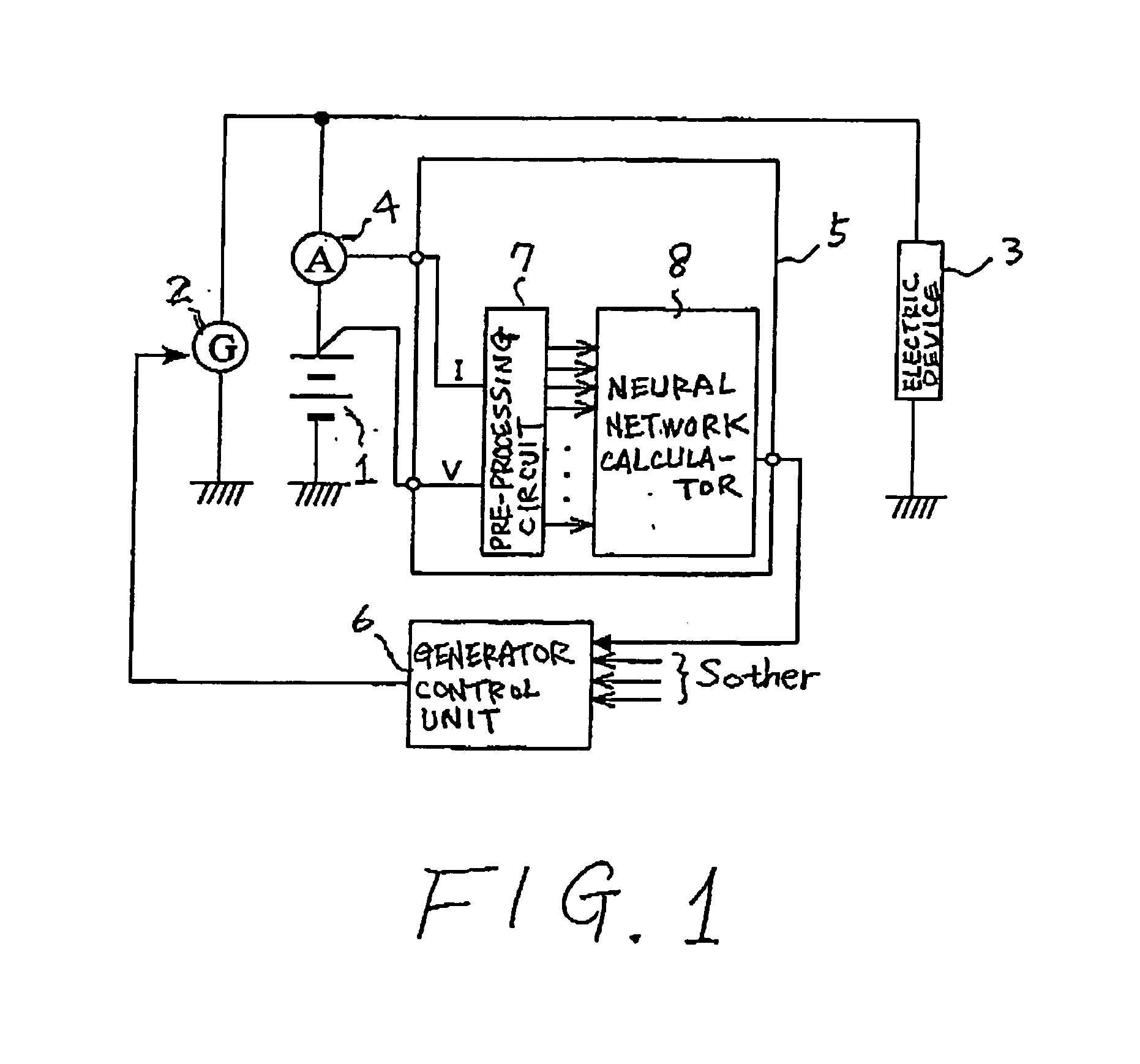
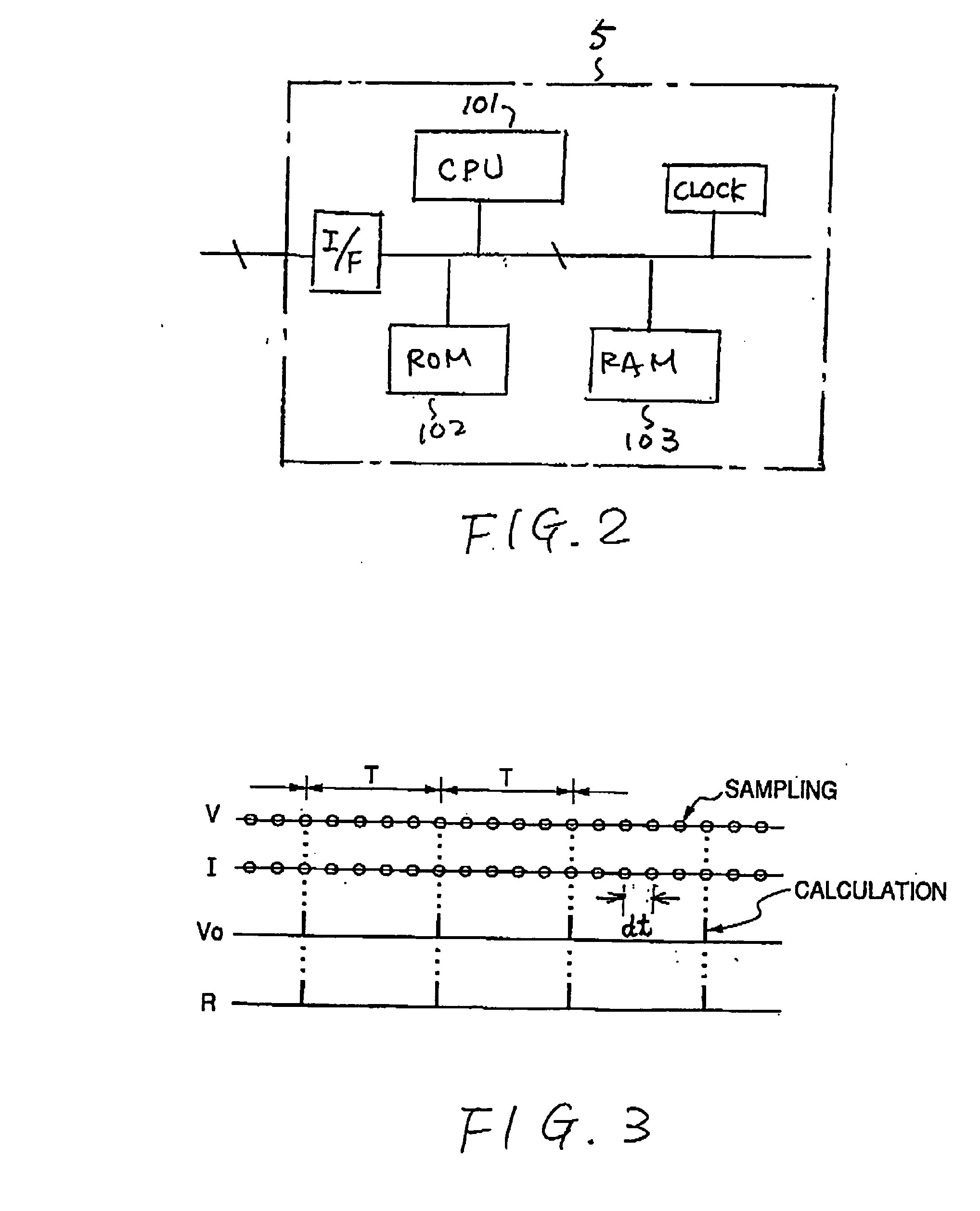
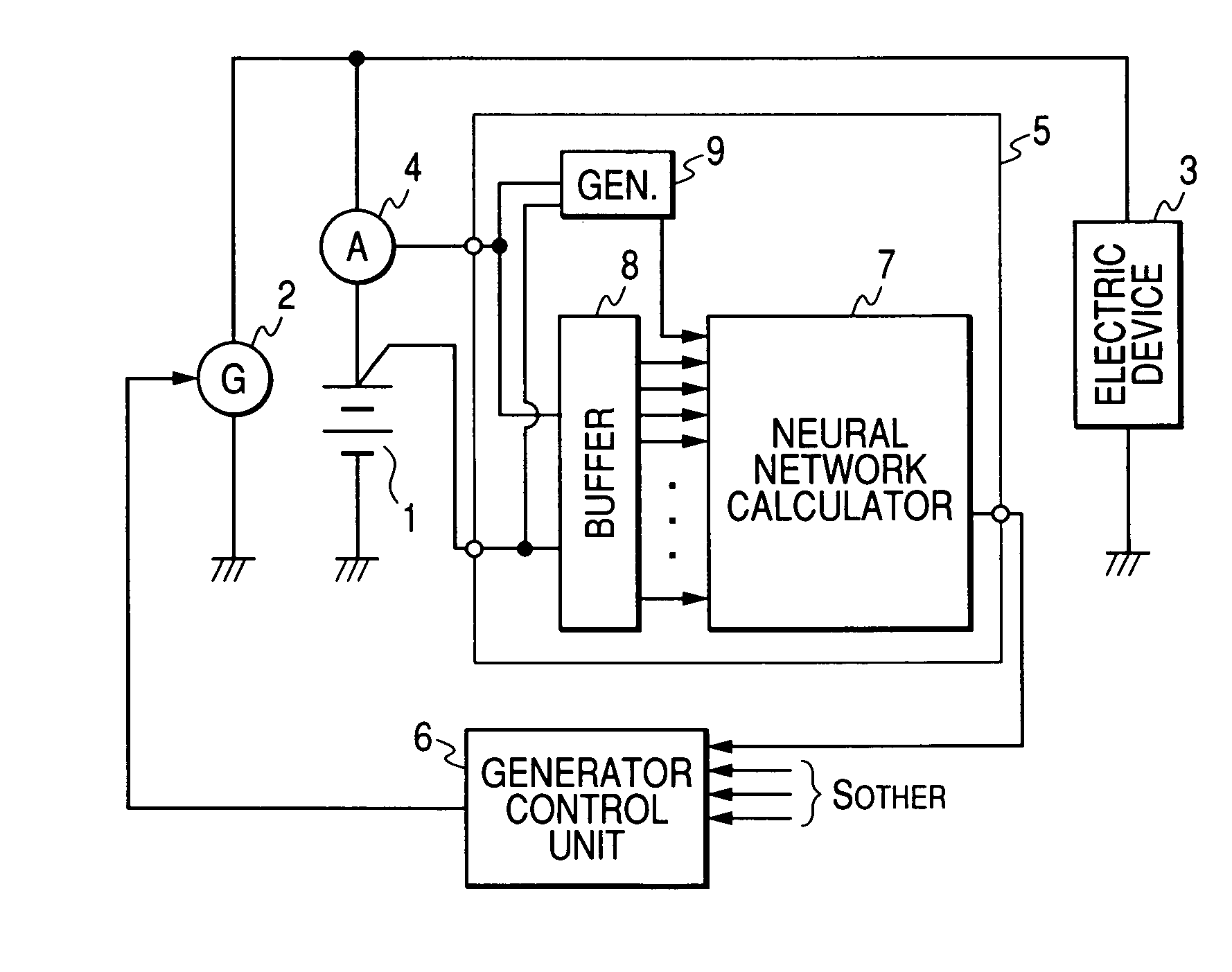
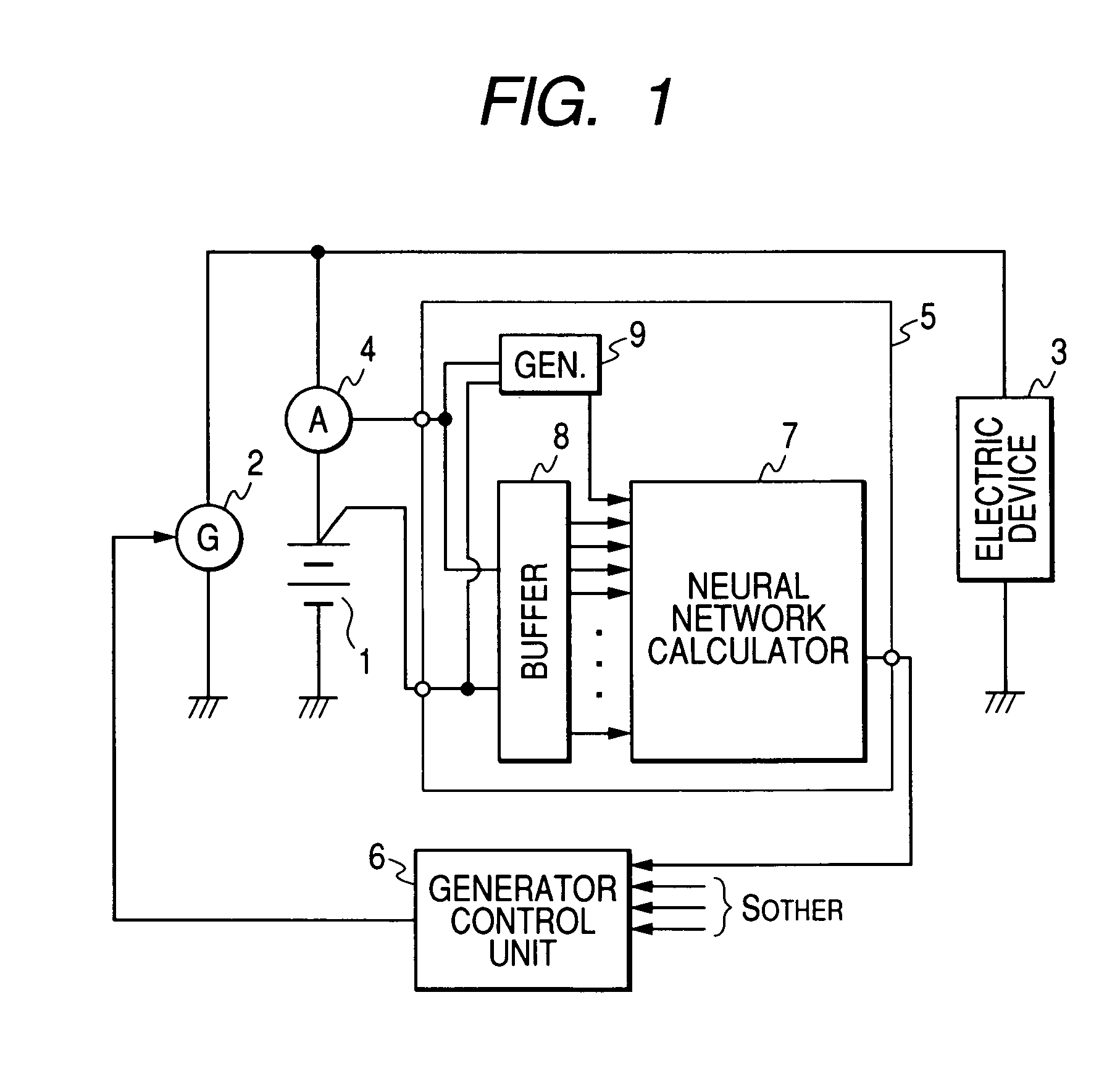
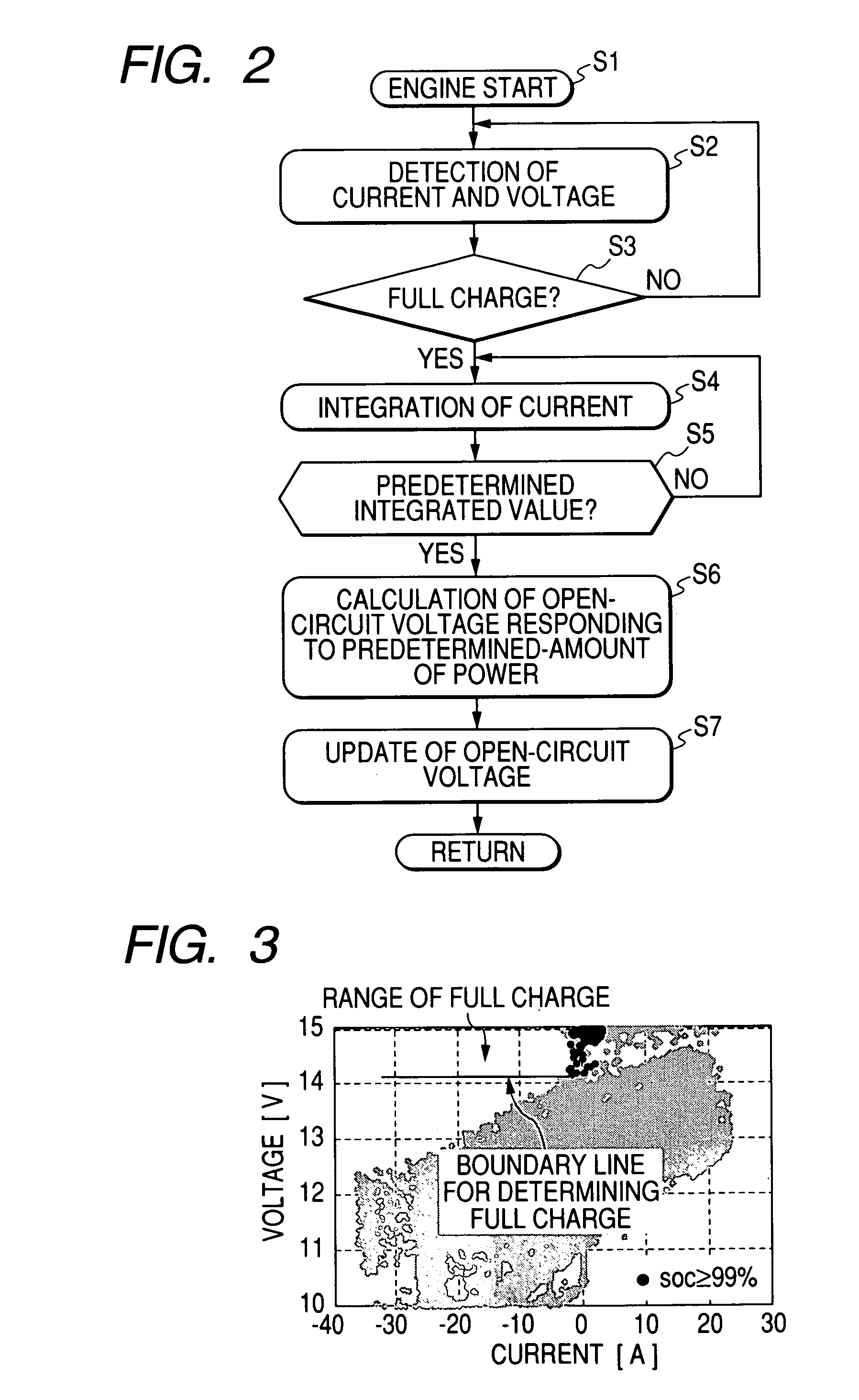
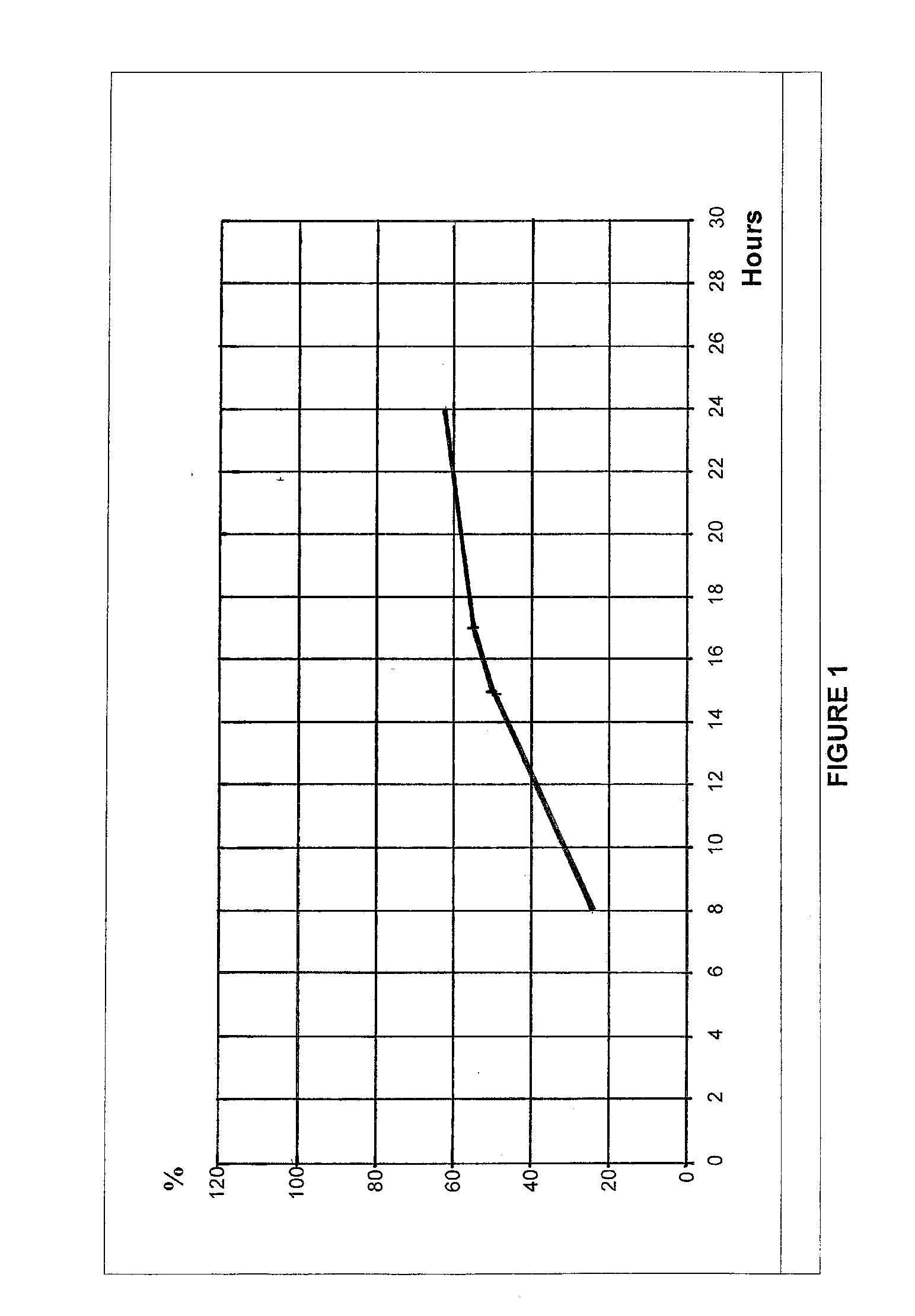
Method and apparatus for detecting charged state of secondary battery based on neural network calculation
InactiveUS20060181245A1Improve accuracyAccurate calculationBatteries circuit arrangementsLighting and heating apparatusBattery state of chargeEngineering
A neural network type of apparatus is provided to detect an internal state of a secondary battery implemented in a battery system. The apparatus comprises a detecting unit, producing unit and estimating unit. The detecting unit detects electric signals indicating an operating state of the battery. The producing unit produces, using the electric signals, an input parameter required for estimating the internal state of the battery. The input parameter reflects calibration of a present charged state of the battery which is attributable to at least one of a present degraded state of the battery and a difference in types of the battery. The estimating unit estimates an output parameter indicating the charged state of the battery by applying the input parameter to neural network calculation.
Owner:DENSO CORP +2
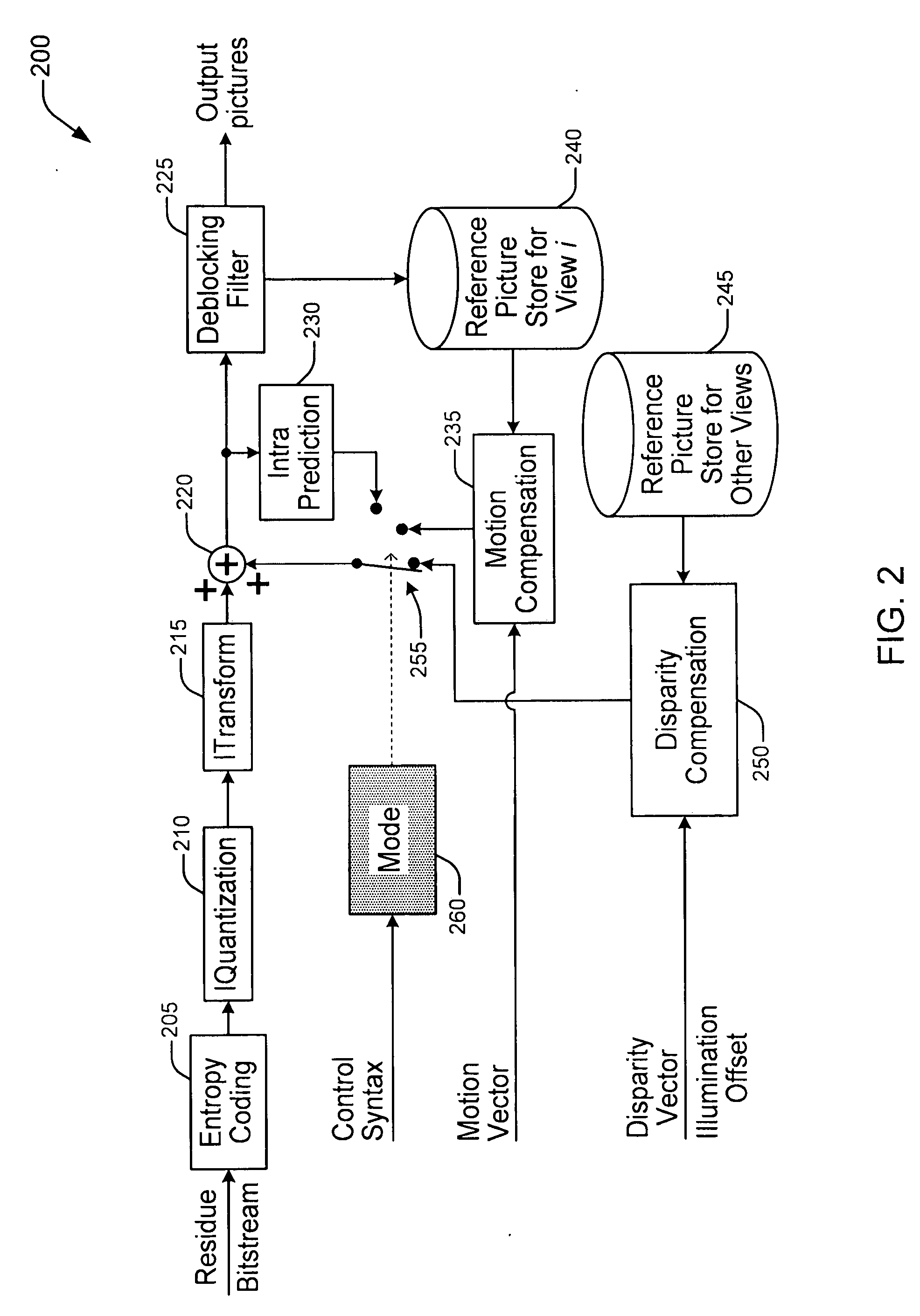
Methods and Apparatus for Multi-View Video Coding
ActiveUS20090168874A1High correlationLess bitColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingComputer graphics (images)
There are provided methods and apparatus for multi-view video coding. A video encoder includes an encoder for encoding a block in a picture by choosing between temporal prediction and cross-view prediction to enable a prediction for the block. The picture is one of a set of pictures corresponding to multi-view video content and having different view points with respect to a same or similar scene. The picture represents one of the different view points. A high-level syntax is used to indicate the use of cross-view prediction for the block.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Security system with maskable motion detection and camera with an adjustable field of view
InactiveUS6727938B1Strong correlation and repeatabilityHigh correlationColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsSafe systemMotion detector
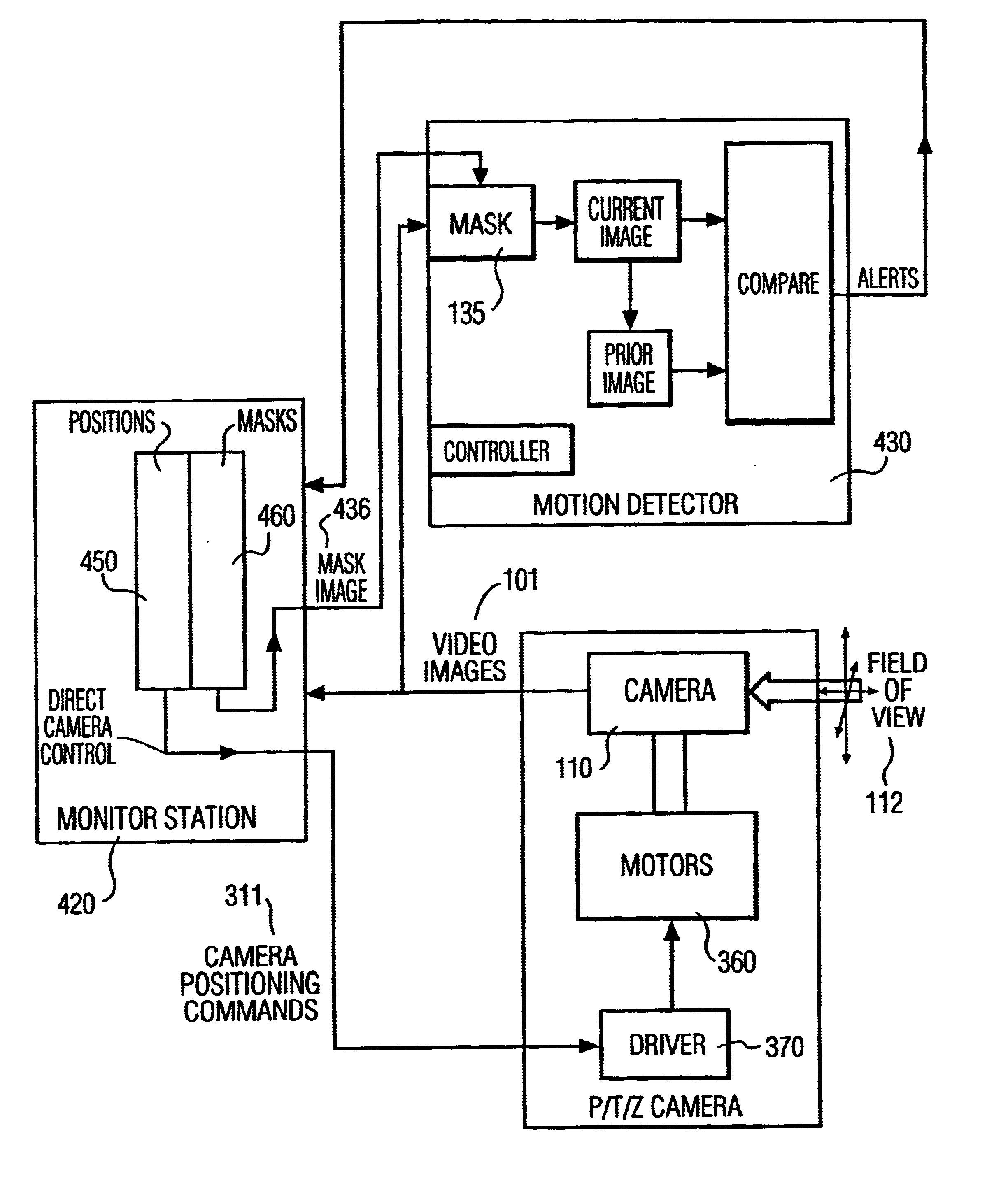
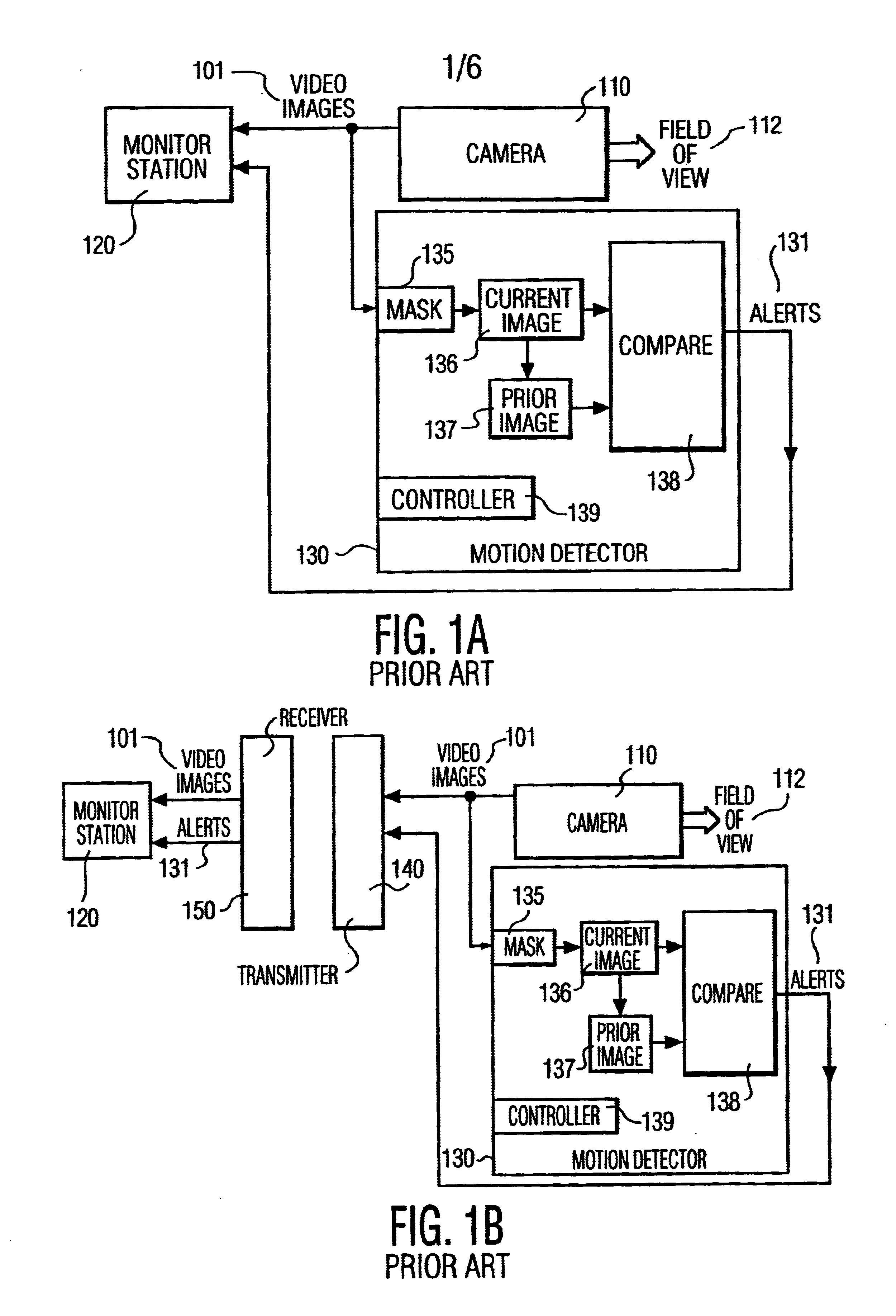
A security system with a Pan / Tilt / Zoom Camera and maskable motion detection is disclosed. At selected fields of view of the P / T / Z camera, masks are created to mask, from motion detection, select sub-areas within the selected field of view. The mask created for the selected view may be saved in memory. The saved mask may be recalled and reapplied to the motion detector whenever the P / T / Z camera is repositioned to the field of view corresponding to the saved mask. The commands required to reposition the camera to each selected field of view may also be saved. The mask and repositioning commands can be associated with each other, so that selecting a target view corresponds to selecting the commands to position the camera to that view, as well as the mask to be applied for this view.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NORTH AMERICA +1
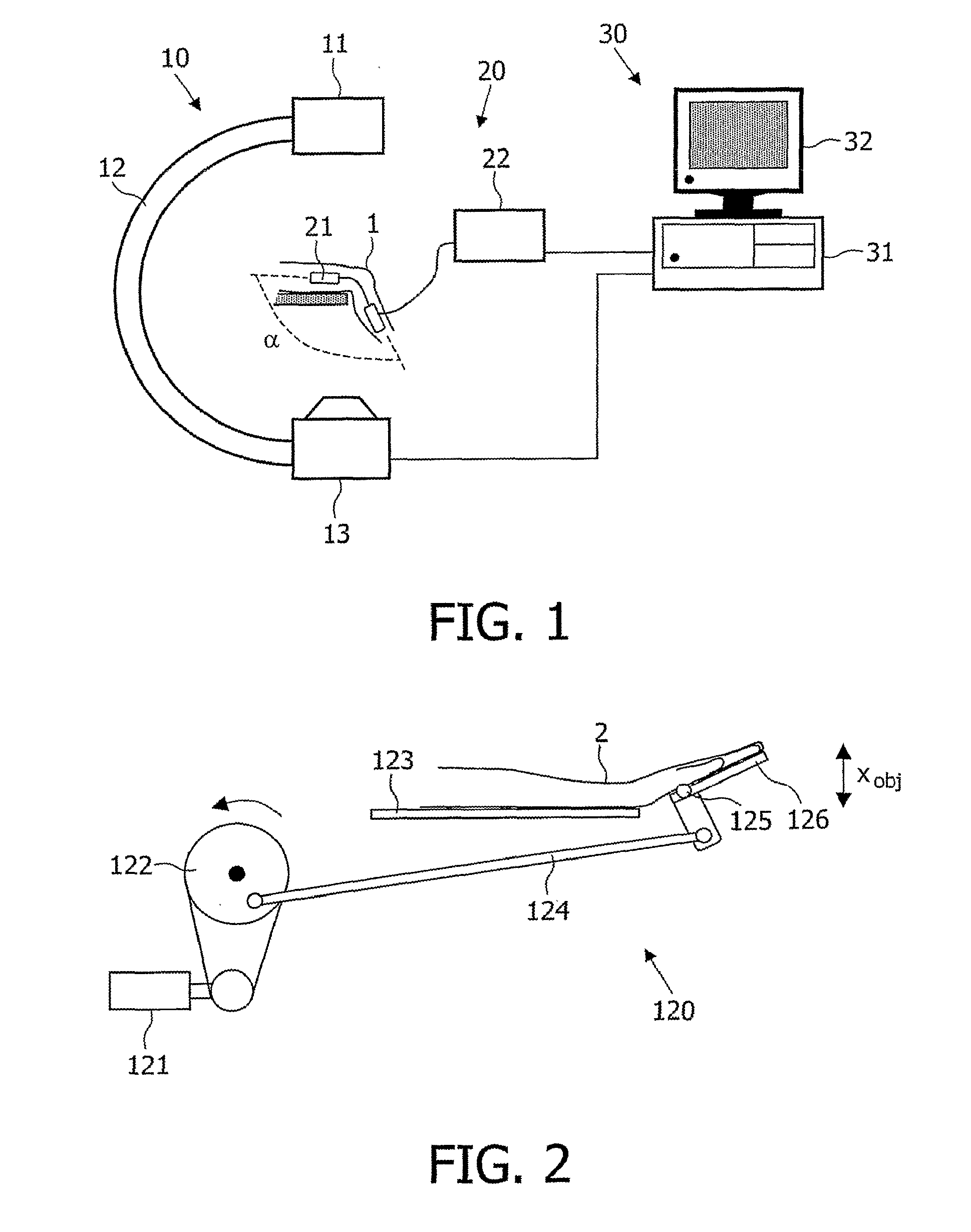
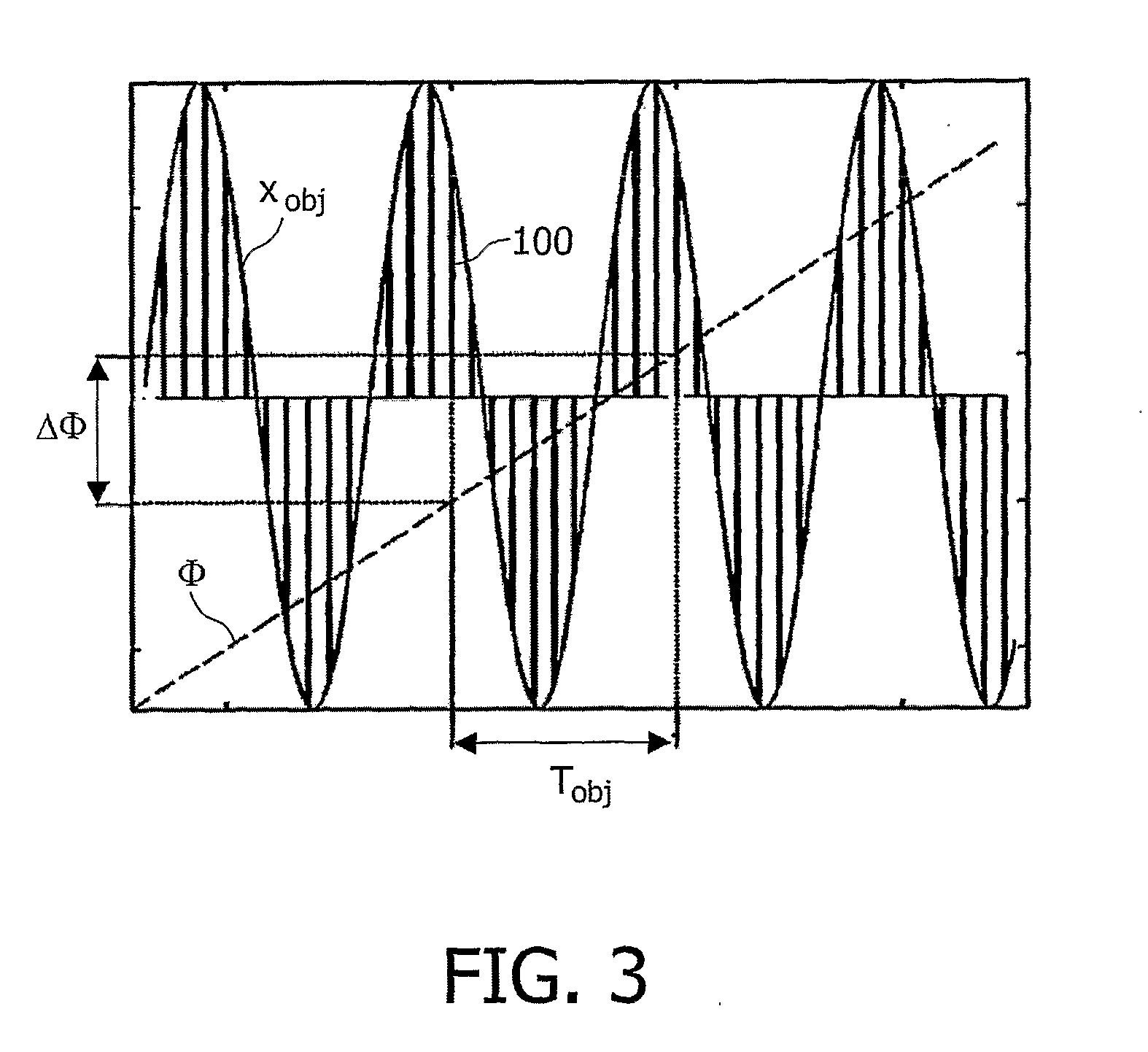
System For The Three-Dimensional Imaging Of A Moving Joint
InactiveUS20080094396A1Highly informativeHigh analysisReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognition3d imageX-ray
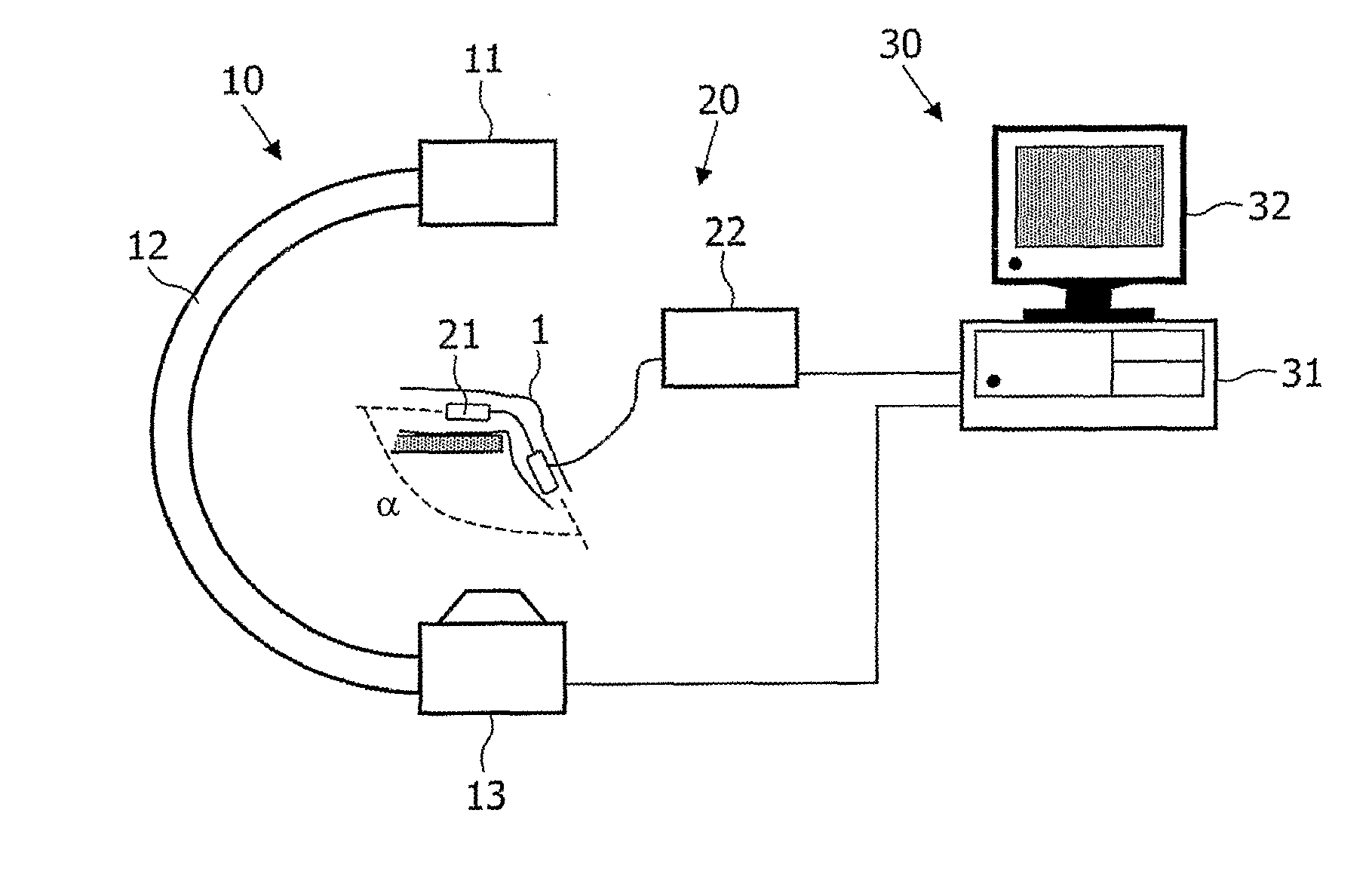
The invention relates to a system and a method for the generation of 3D images of a moving joint (1). A rotational X-ray device (10) generates projections of said joint from different directions while the simultaneous periodic movement of the joint (1) is recorded by a monitoring device (20). The generated X-ray projections are then classified according to the phase of joint movement to which they belong, and 3D images are reconstructed from X-ray projections of each class. Thus a 3D movie of the joint movement can be produced and shown on a monitor. The monitoring device (20) may particularly be realized by an apparatus that allows the forced movement of the joint (1) in synchronization with the generation of X-ray projections.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
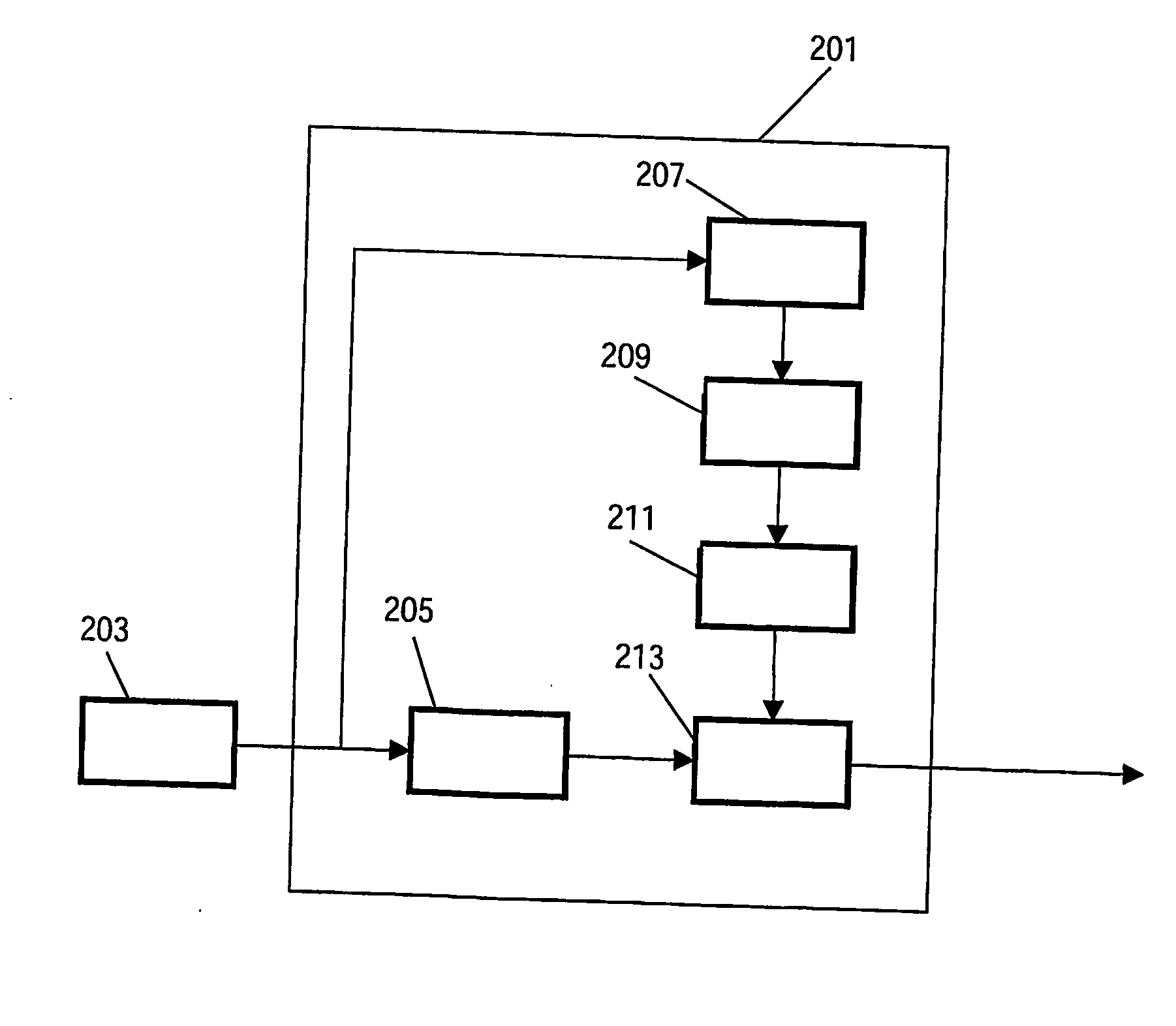
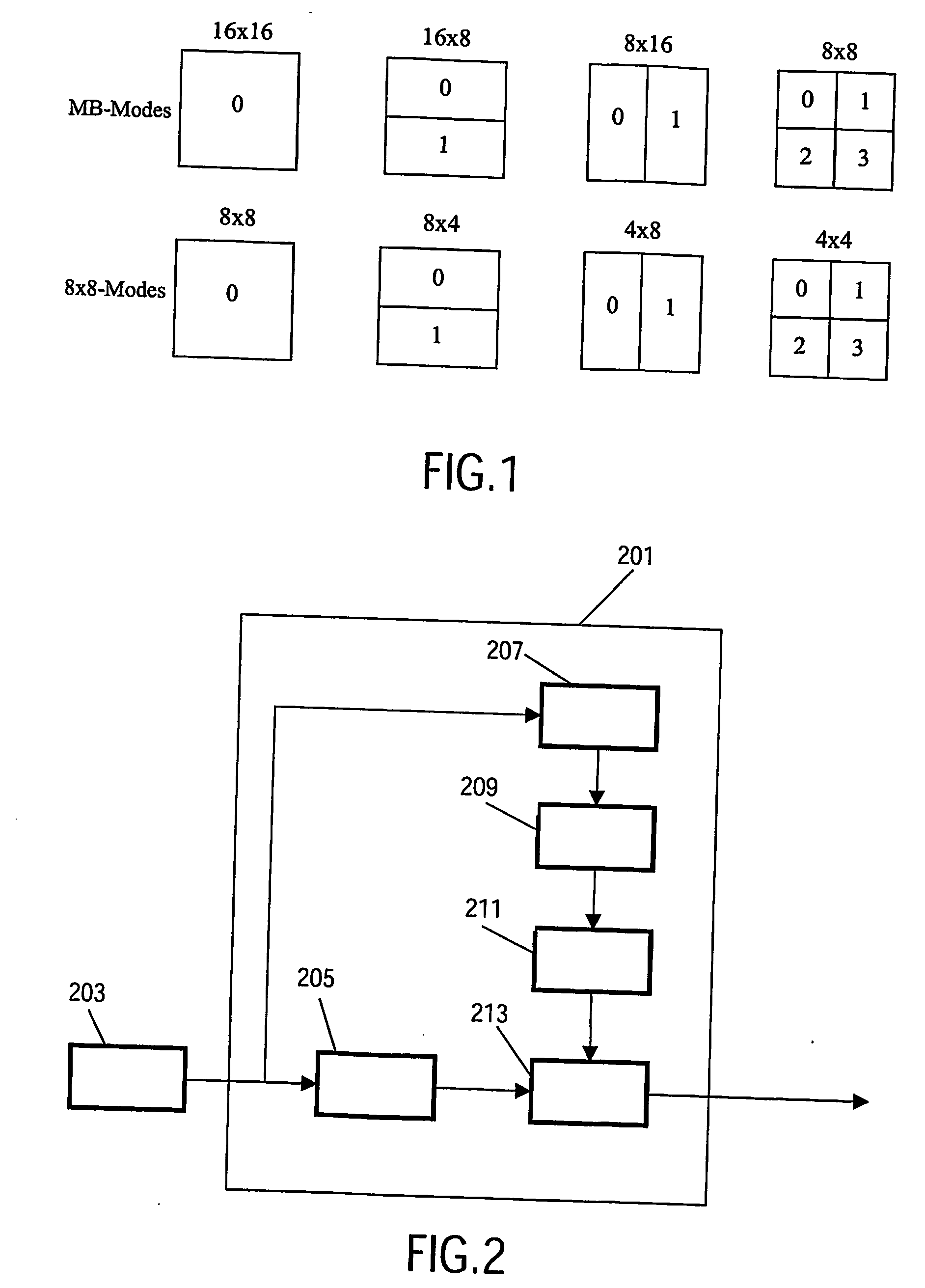
Video encoding
InactiveUS20060165163A1Improve performanceReduce lossesColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo encoding
The invention relates to a video encoder (201) for encoding a video signal. The video encoder comprises a segmentation processor (207) which divides the picture into picture regions. Preferably, picture regions having a high degree of flatness or uniformity are determined in this way. A characteristics processor (209) determine a spatial frequency characteristic for each picture region, and a coding controller (211) selects an encoding block size, such as a prediction block size for motion estimation, in response to the spatial frequency characteristic. An encode processor (213) encodes the picture using the selected encoding block size. Specifically, increasing block sizes are selected for increasing degrees of uniformity or flatness indicated by the spatial frequency characteristic. Thereby, an increasing proportion of high frequency components and a consistent choice of encoding block sizes are maintained, and thus the coding artefacts from many encoders having variable prediction block sizes is reduced. The invention is particularly suitable for H.264 and similar encoders.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for providing identification
InactiveUS20050258238A1High correlationReduce correlationElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisIdentification deviceData mining
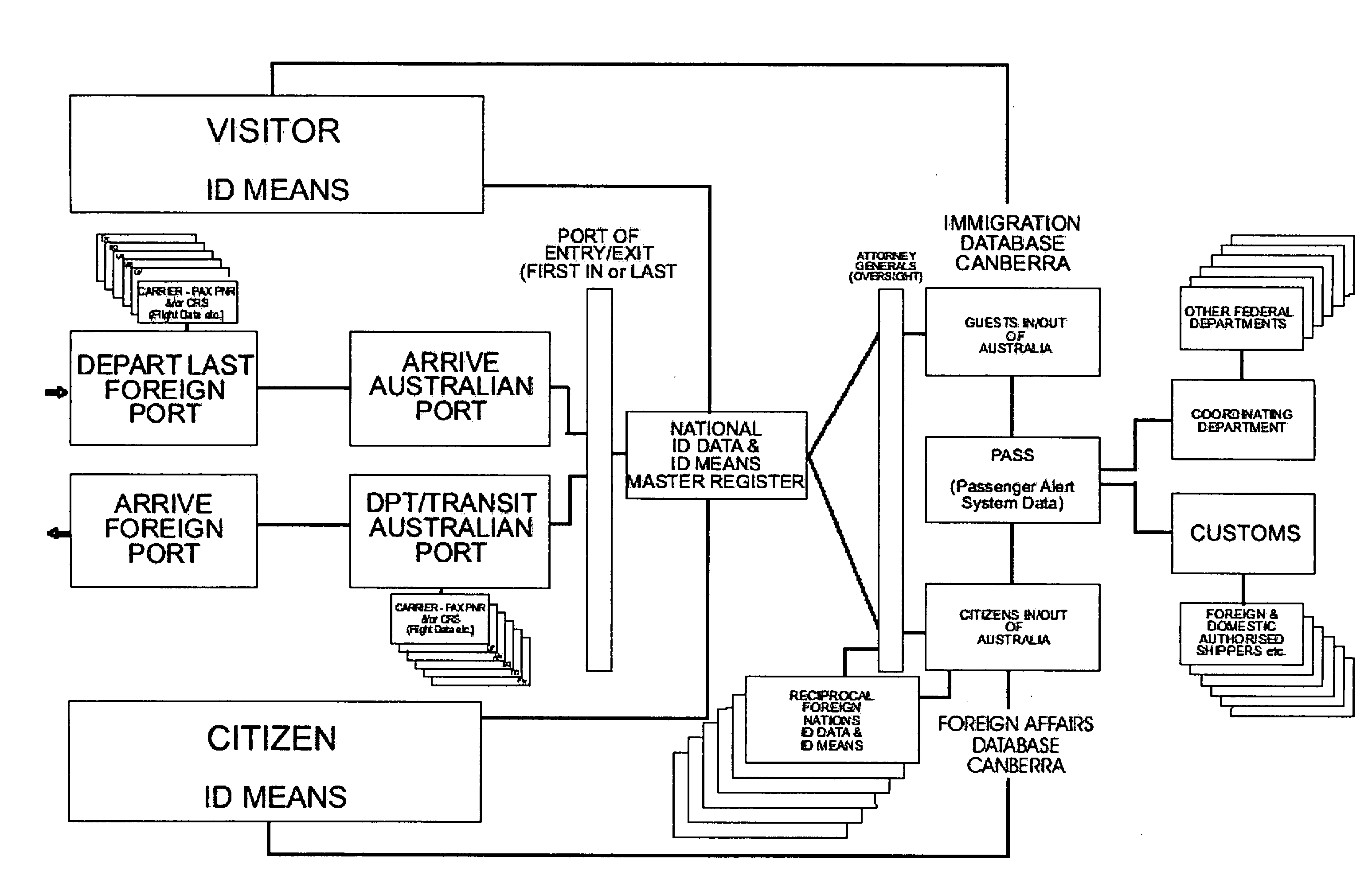
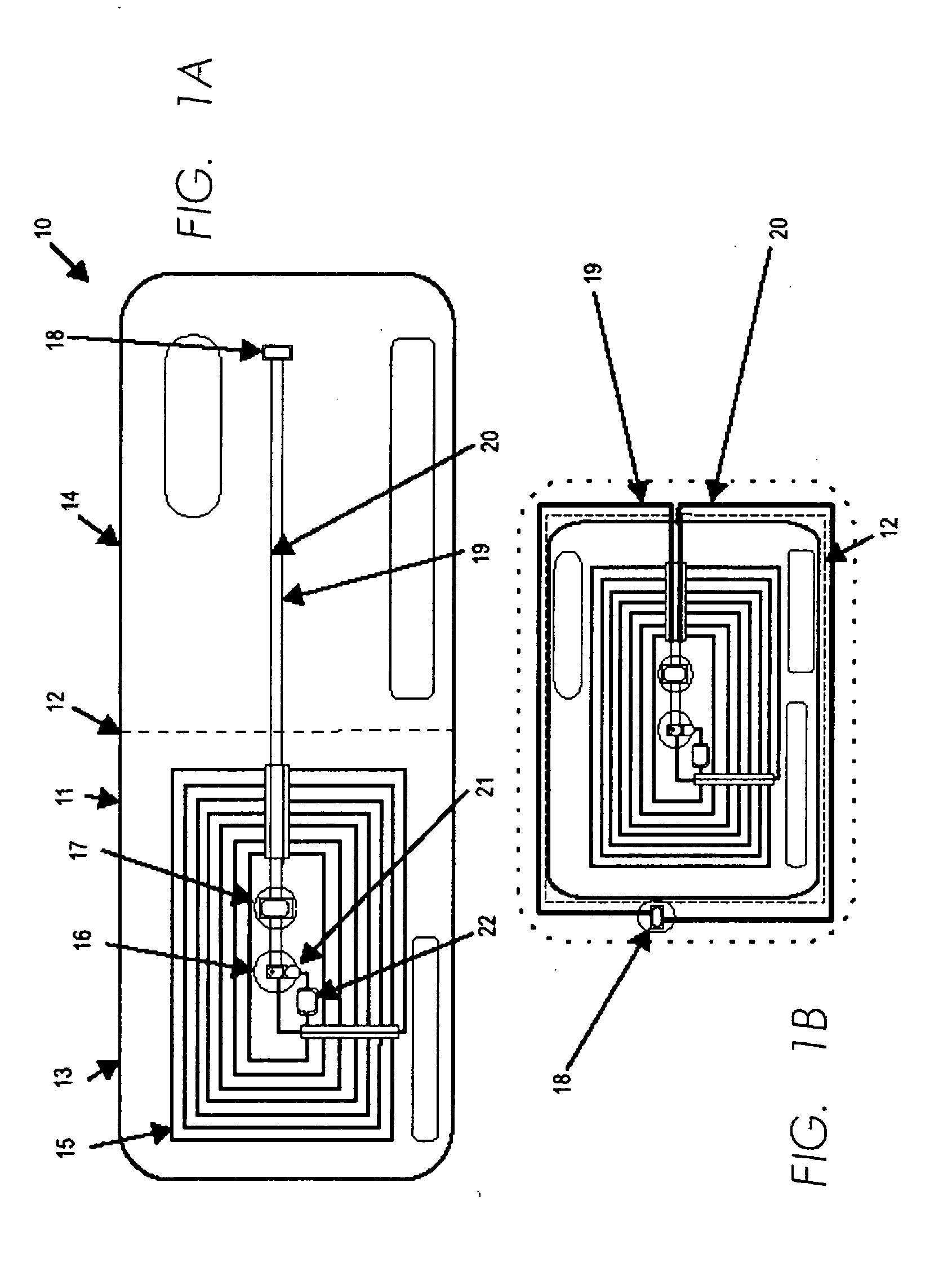
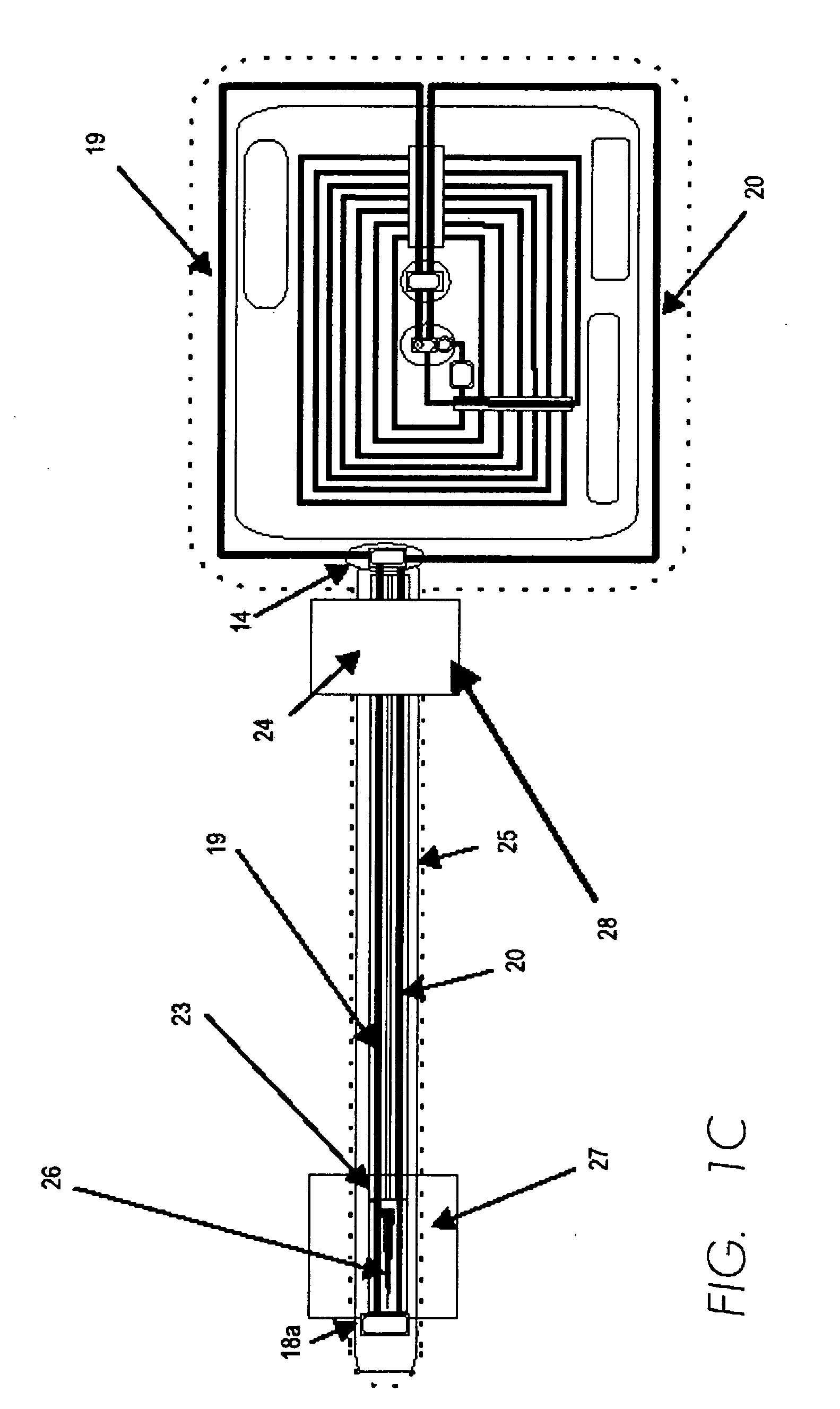
A method of providing identification of an entity includes maintaining a database of identification data specific to the appearance and condition of entities, providing a unique description for each entity enabling access to the entity's identification data in the database, providing identification means adapted for portage with the entity and containing the unique description and maintaining secondary databases containing the entity's identification data as acquired from prior encounters so that multiple comparisons can be made to assure that the individual bearing the identification means is the same individual to whom the identification means were issued.
Owner:NEOTEC HLDG LTD
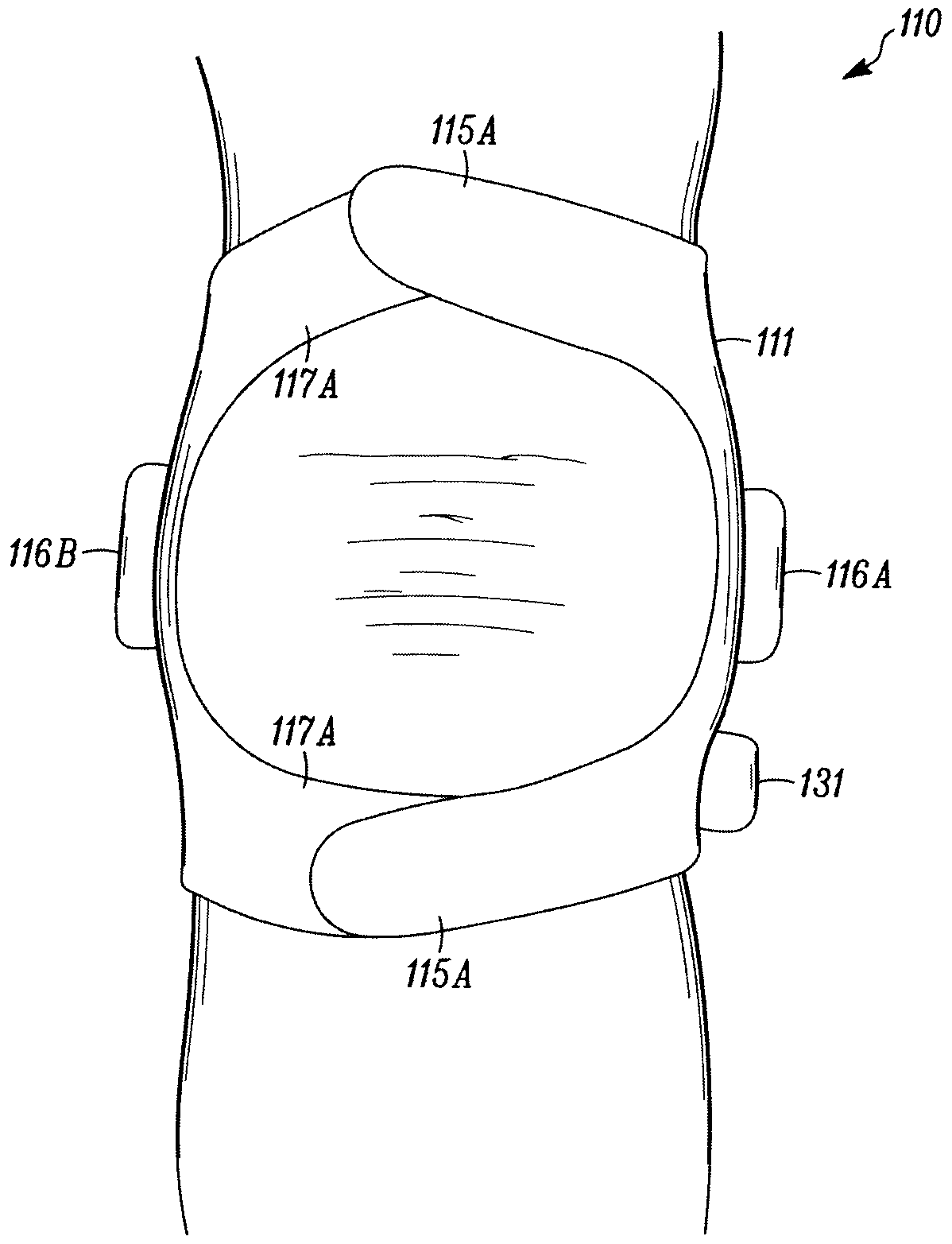
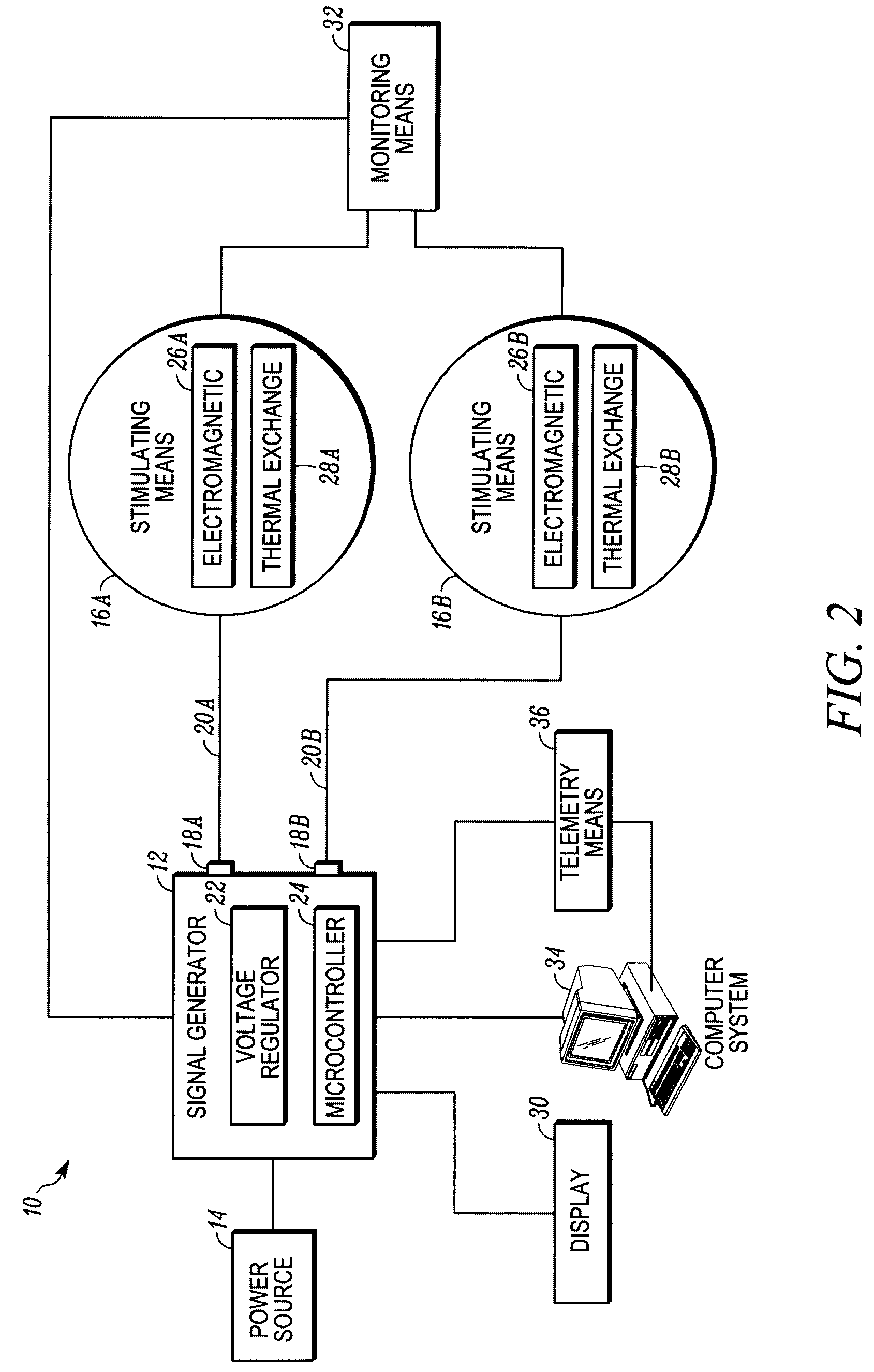
Stimulation Device for Treating Osteoarthritis
ActiveUS20080288035A1Relieve painExtended range of motionElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsTherapeutic treatmentPhysical therapy
A device for providing therapeutic treatment to a body part such as a joint to promote healing of the body part comprises a signal generator for generating a pulsed electromagnetic field based upon a selected treatment mode, a controller for storing the treatment mode and communicating the treatment mode to the signal generator, a heat source configured to provide thermal therapy to the body part, and monitoring means for monitoring the electromagnetic field generated by the electromagnetic stimulating means. The device may also include telemetry means in communication with the monitoring means for remotely accessing the controller to modify the treatment mode. The device can also be disposable.
Owner:ORTHOCOR MEDICAL
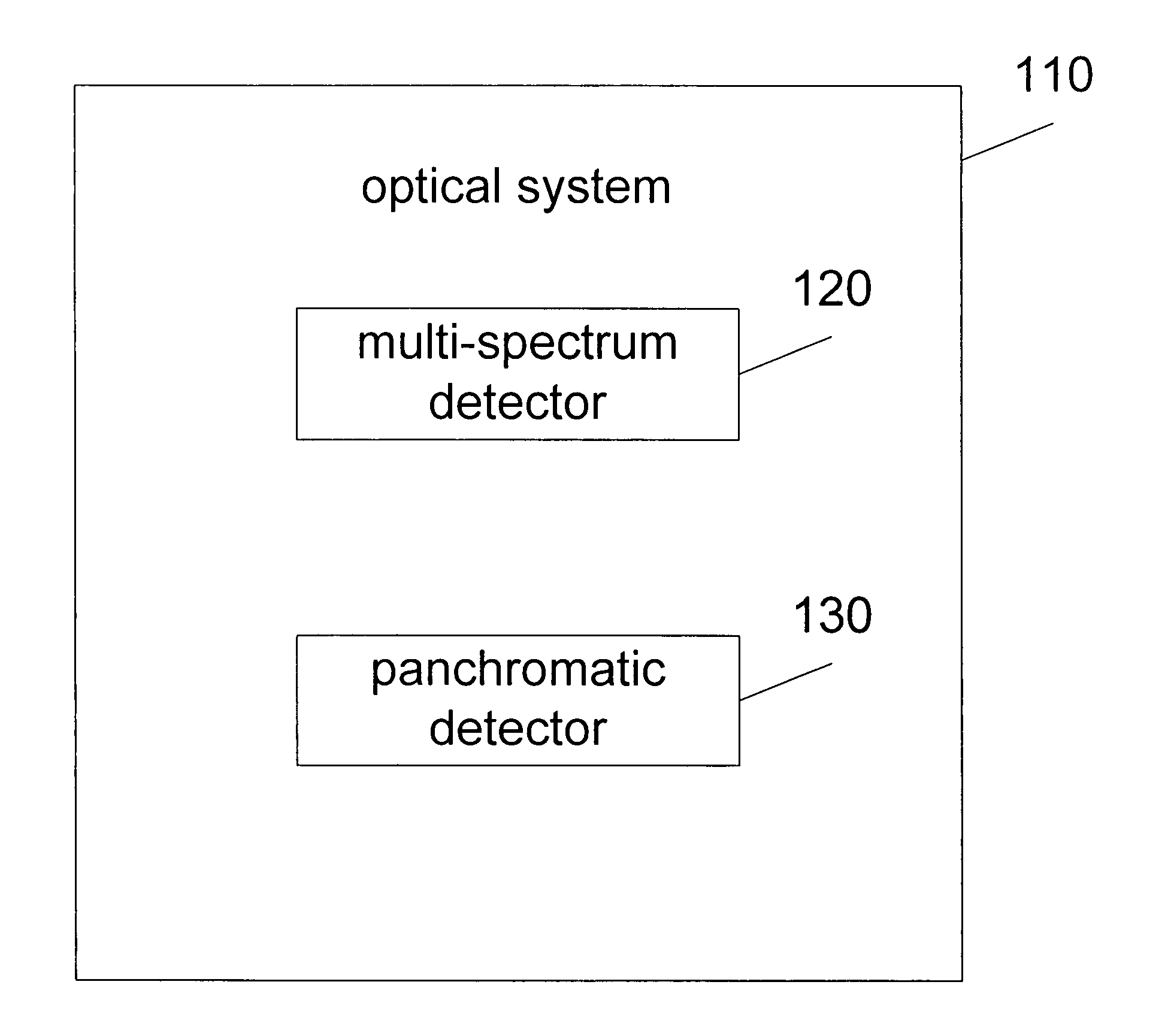
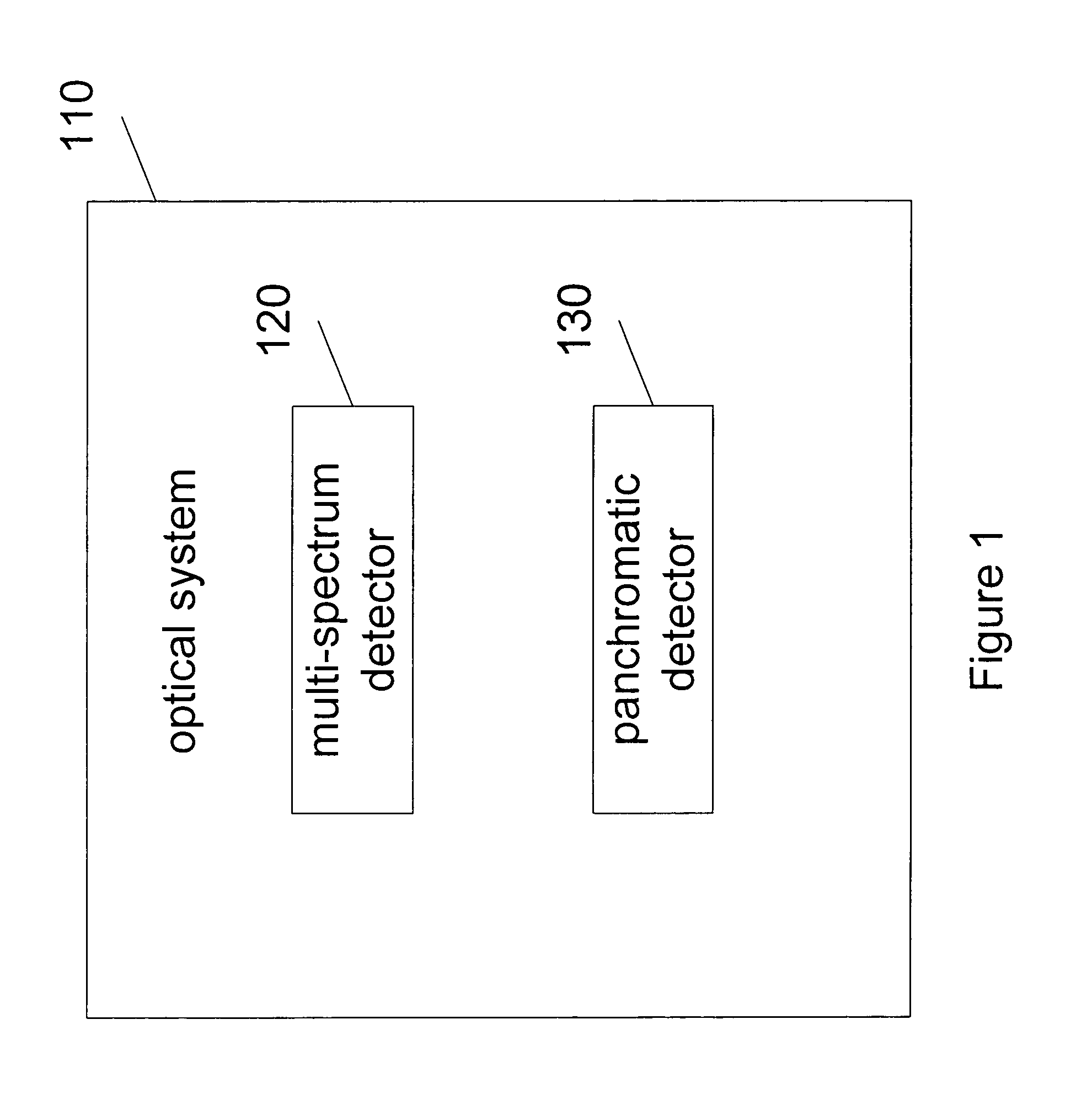
Synthetic panchromatic imagery method and system
ActiveUS7298922B1Quality improvementHigh imagingImage enhancementImage analysisMultispectral imageSpectral weight
Method and system for generating synthetic panchromatic imagery. A method for making a multi-spectral image includes capturing a panchromatic image of an imaging target. Additionally, the method includes capturing at least a first spectral image of the imaging target in a first spectral bandwidth, and capturing at least a second spectral image of the imaging target in a second spectral bandwidth. Also, the method includes determining at least a first spectral weight and a second spectral weight for the first spectral image and the second spectral image respectively. Additionally, the method includes generating a synthetic panchromatic image, determining a registration offset between the synthetic panchromatic image and the captured panchromatic image, warping the first spectral image and the second spectral image, and generating a multi-spectral image.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
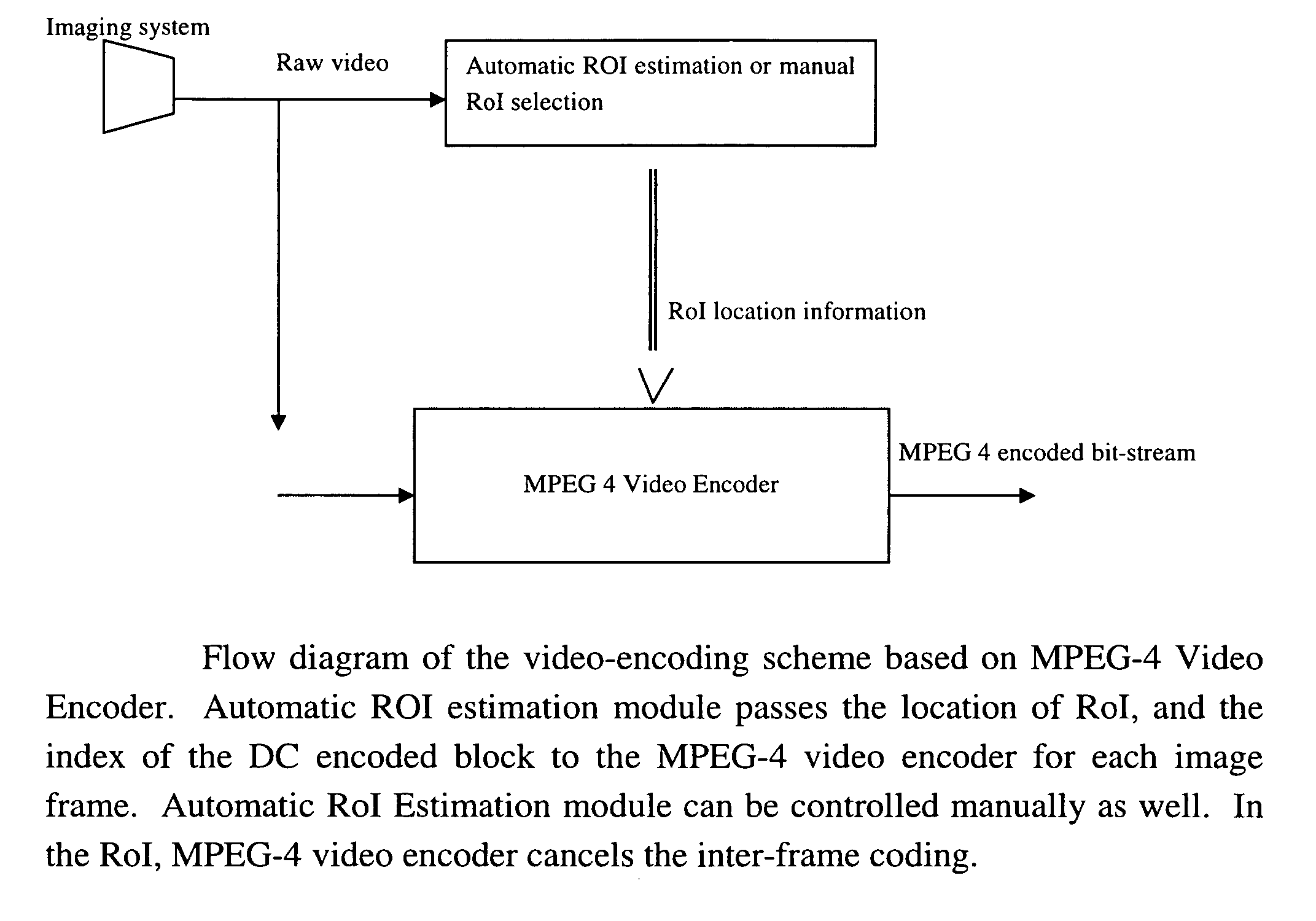
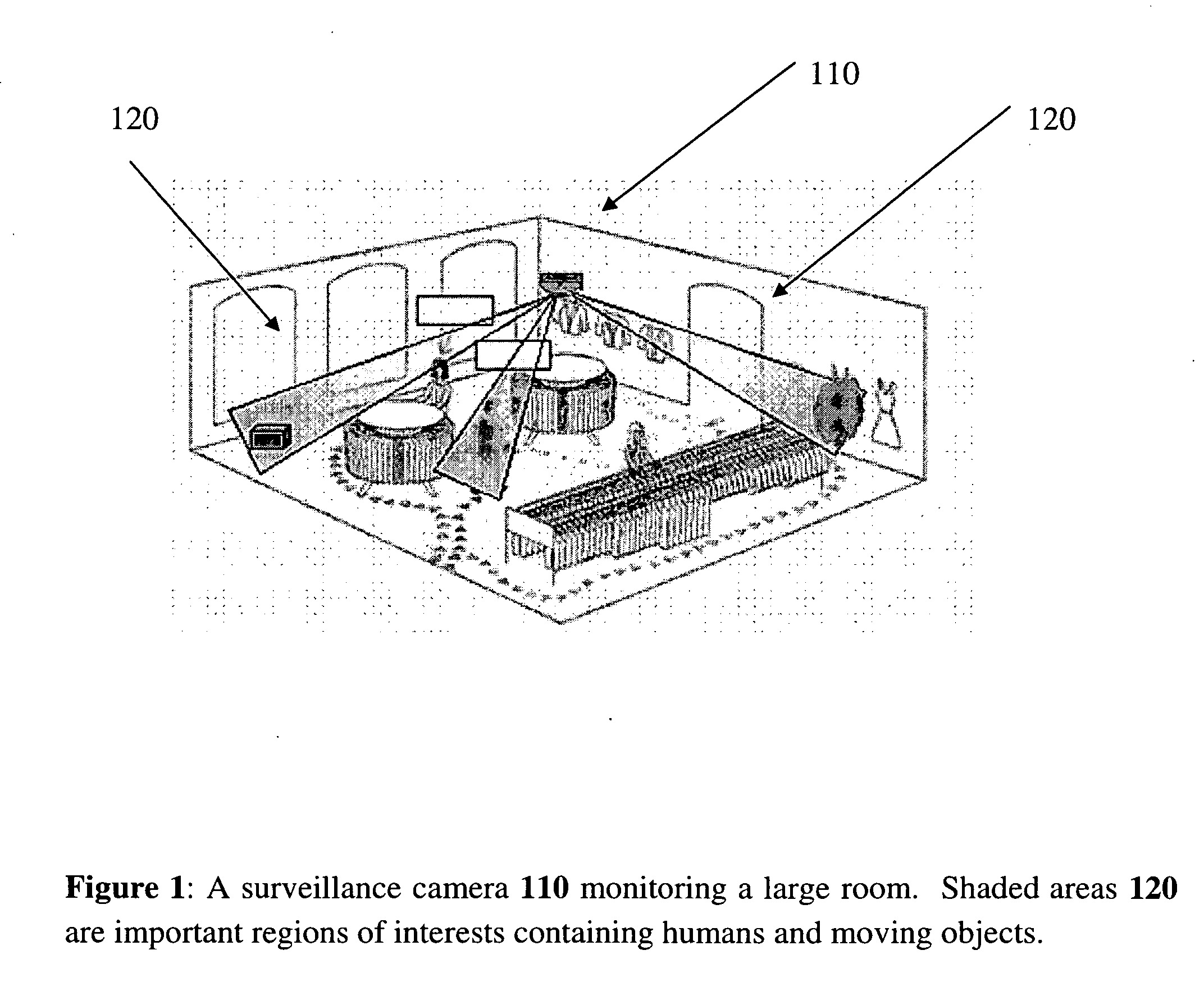
Region-sensitive compression of digital video
InactiveUS20060062478A1Reduce data volumeDegrade content of imageTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital videoSide information
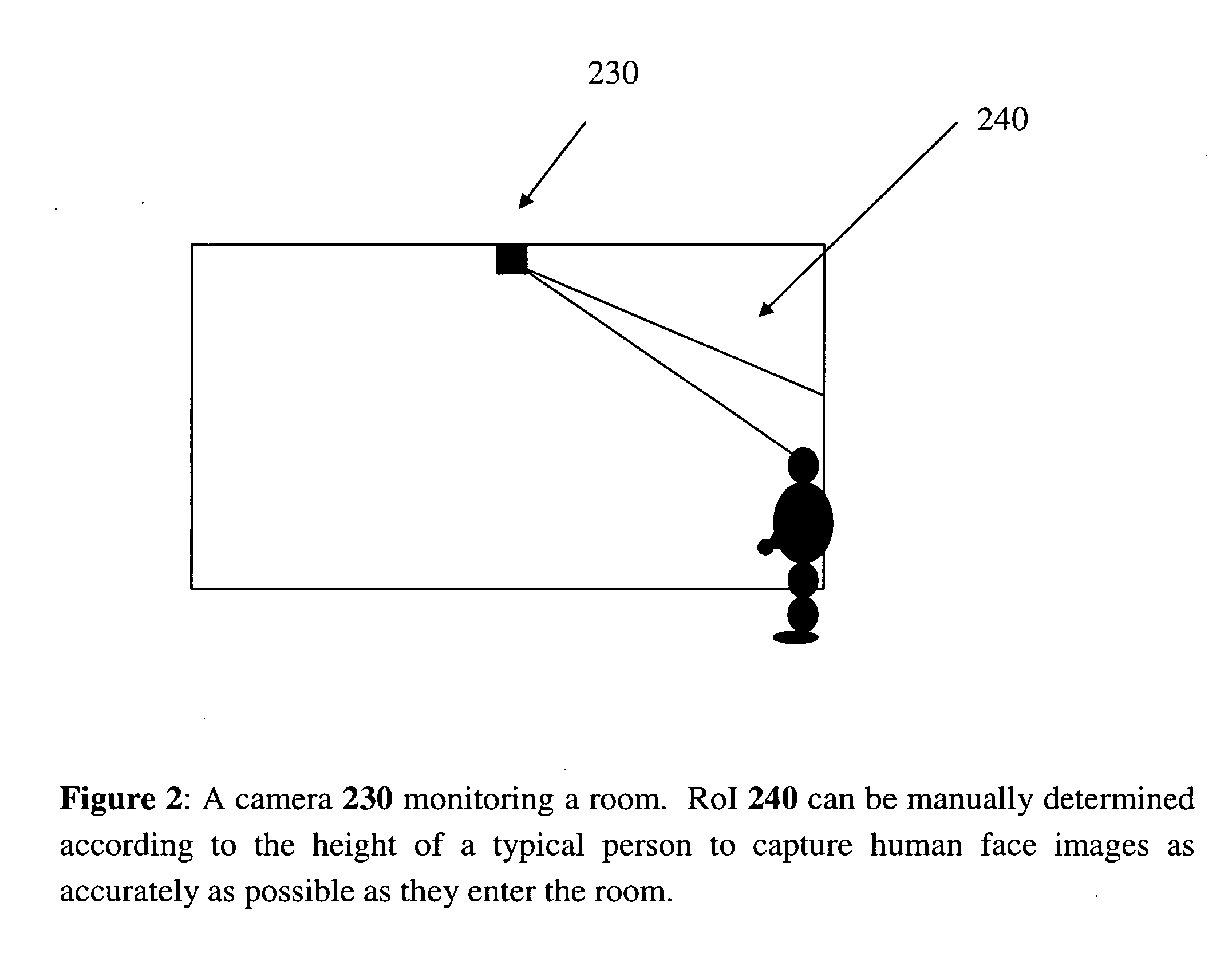
A video coding method for surveillance videos allowing some regions of the scene to be encoded in an almost lossless manner. Such Regions of Interest (RoI) can be determined a priori or they can be automatically determined in real-time by an intelligent system. The user can set high priority in such regions a priori or the intelligent video analysis algorithm can automatically assign some windows a higher priority compared to the rest of the video. In a preferred embodiment, this can be achieved by canceling the motion estimation and compensation operations, and then decreasing the size of the quantization levels during the encoding process in the RoI. The present inventions can produce MPEG compatible bit-streams without sending any side information specifying the RoI.
Owner:GRANDEYE
Automated user evaluation and lifecycle management for digital products, services and content
Owner:AUTOLYTICS
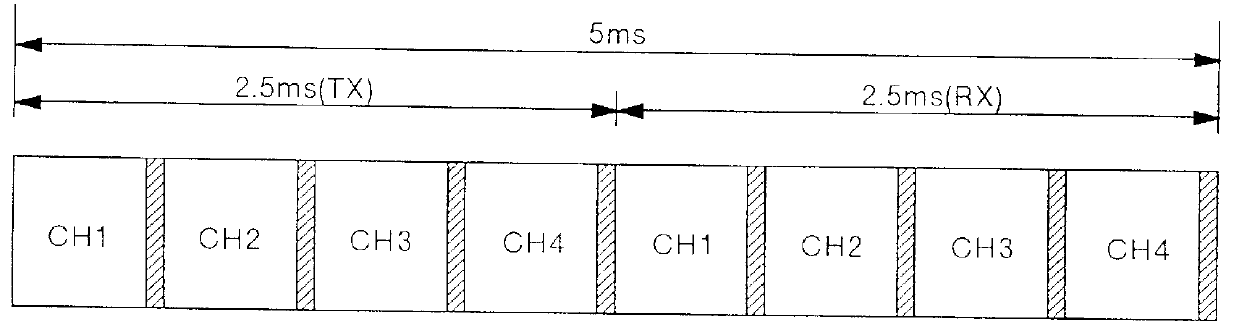
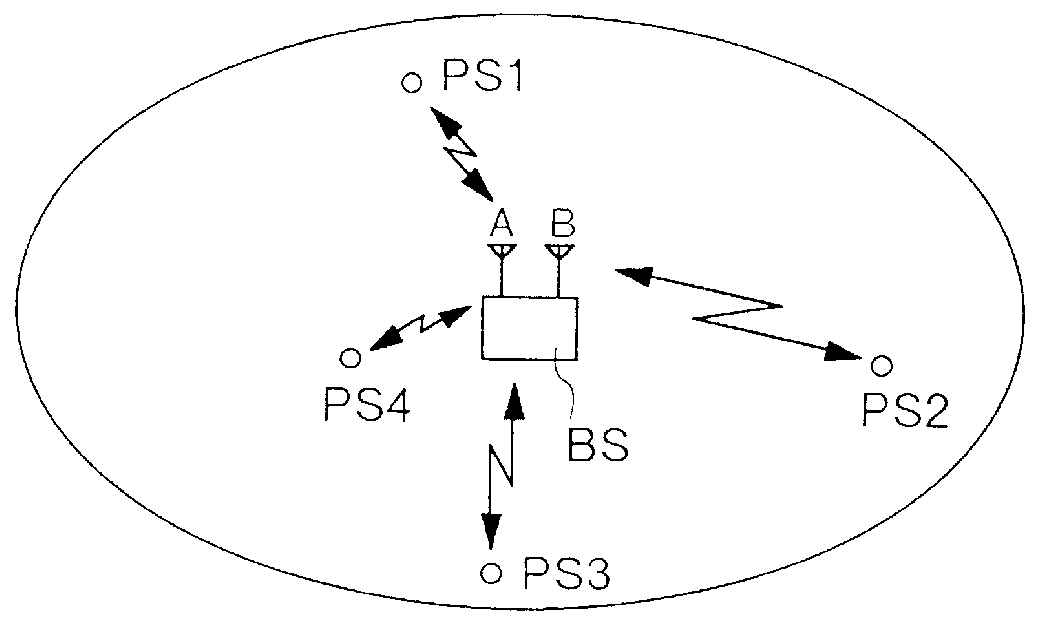
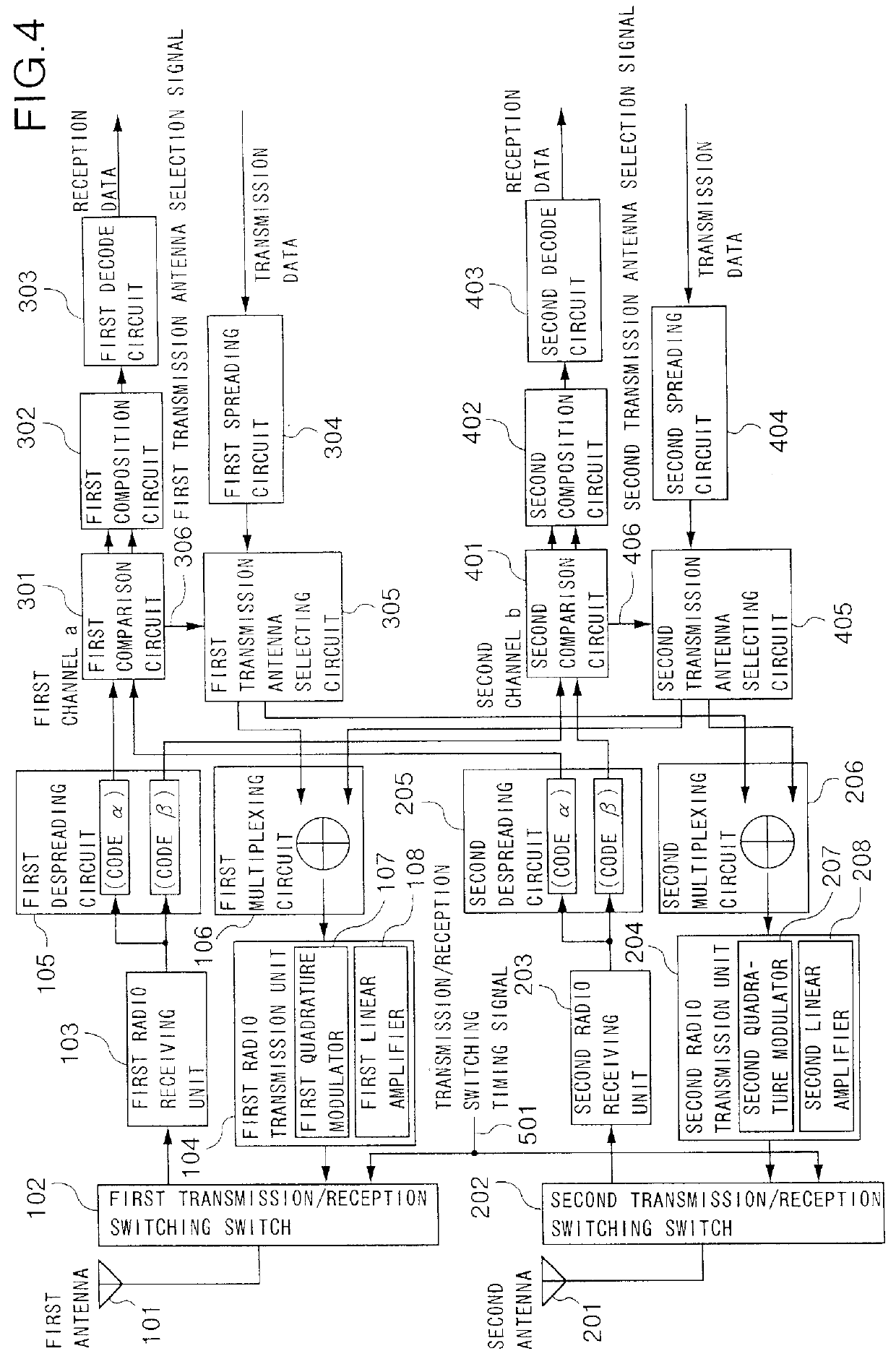
Transmission diversity for a CDMA/TDD mobile telecommunication system
InactiveUSRE36591E1Improve communication qualityExcellent stateSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexingEngineering
In a base station which has a plurality of antennas, each of a plurality of comparison circuits operates to compare correlation levels, which are obtained by despreading received signals for a plurality of channels, with each other with respect to the antennas. Each of a plurality of transmission antenna selecting circuits operates to determine from which antenna a transmission signal is to be transmitted for every channel. Each of a plurality of multiplexing circuits operates to multiplex the transmission signals of the individual channels, which are spread, for every antenna. As a result, on the basis of the result of the comparison of the correlation levels with respect to the antennas, a transmission antenna is selected for every channel, and the signals of the channels that are to be transmitted by a given antenna are multiplexed, whereby the base station achieves transmission diversity.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
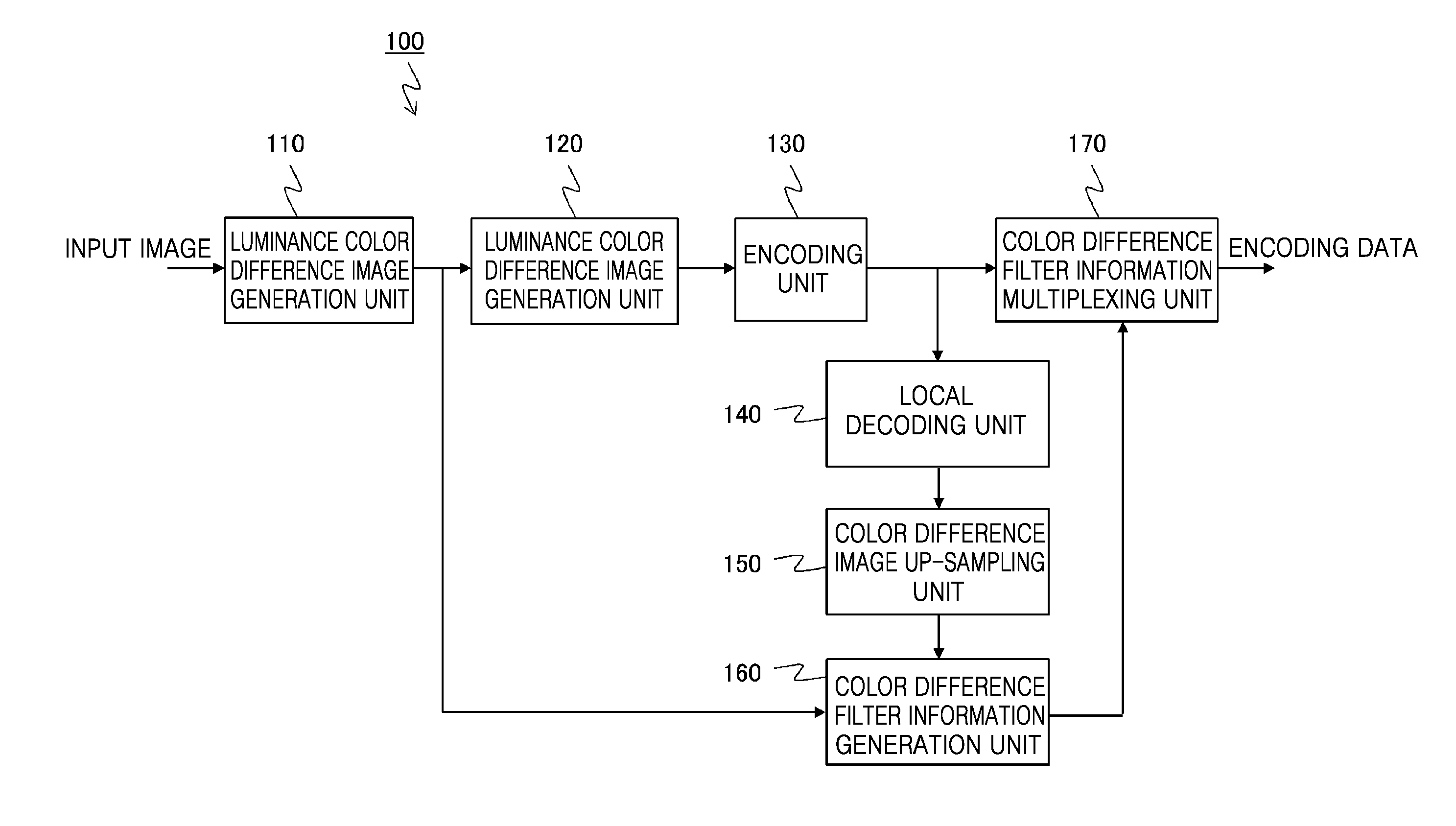
Method, apparatus, and program for encoding image, method, apparatus, and program for decoding image, and image processing system
ActiveUS20150189329A1Error minimizationReduce noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionImaging processing
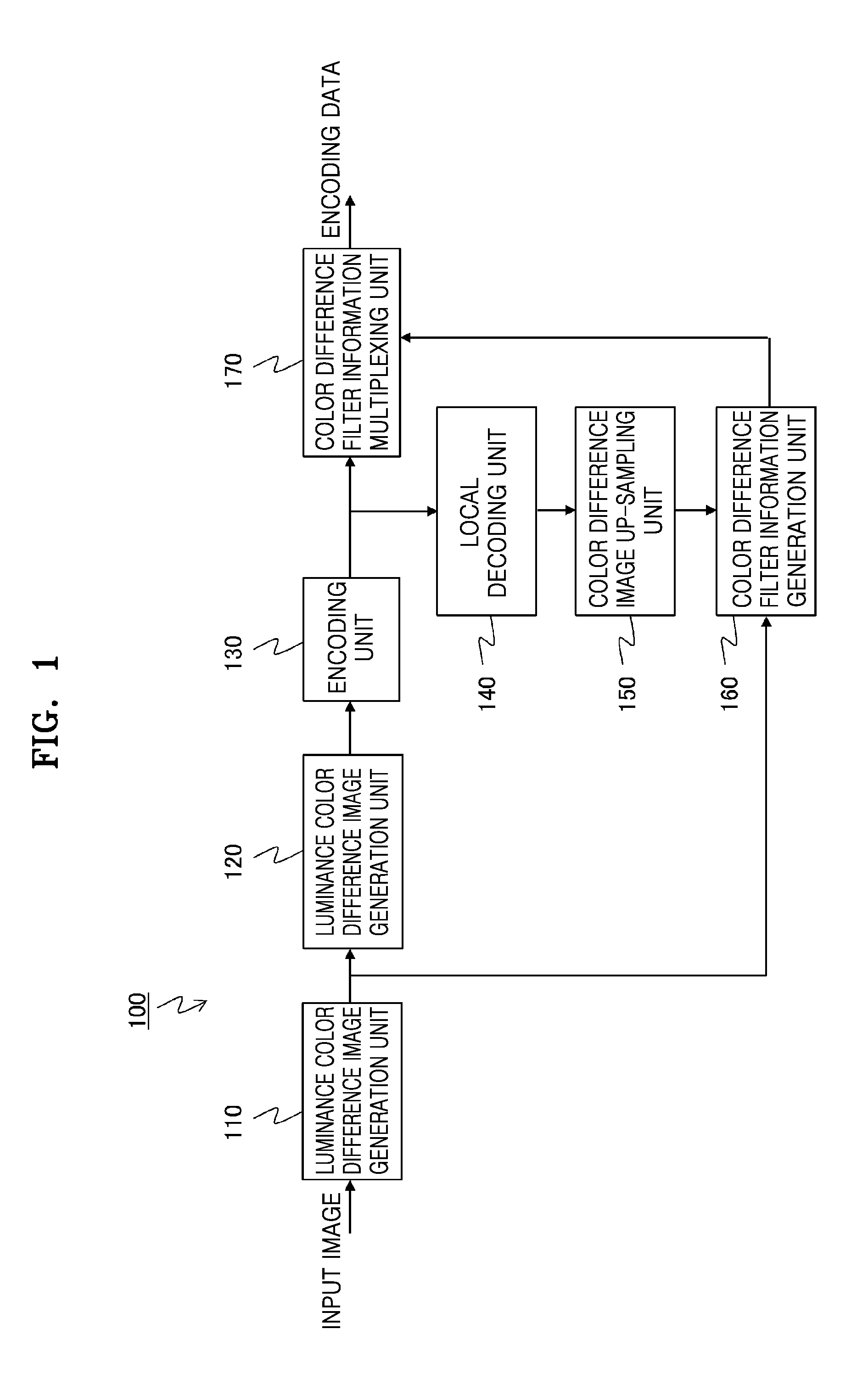
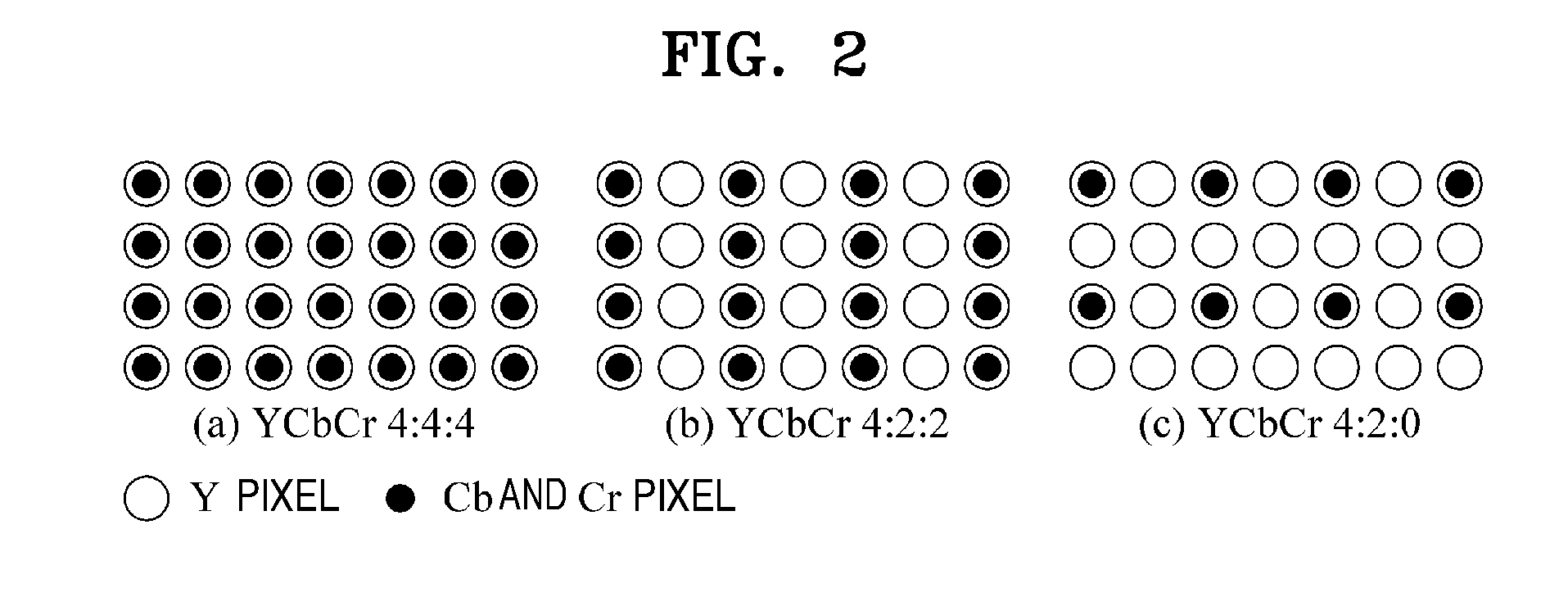
Provided is an image encoding device including an encoding unit that encodes a down-sampling image obtained by performing down-sampling of a color difference signal; a decoding unit that decodes the encoded encoding image; and a filter information generation unit that performs up-sampling of a color difference signal of the decoded decoding image, filters the color difference signal of the decoded image by using the up-sampled color difference signal of the decoded image and a luminance signal as reference signals, and acquires filter information related to the filtering.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Encoding/decoding method and device for high-resolution moving images
ActiveUS20120201300A1Reduced block distortionReduce the number of timesColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo encoding
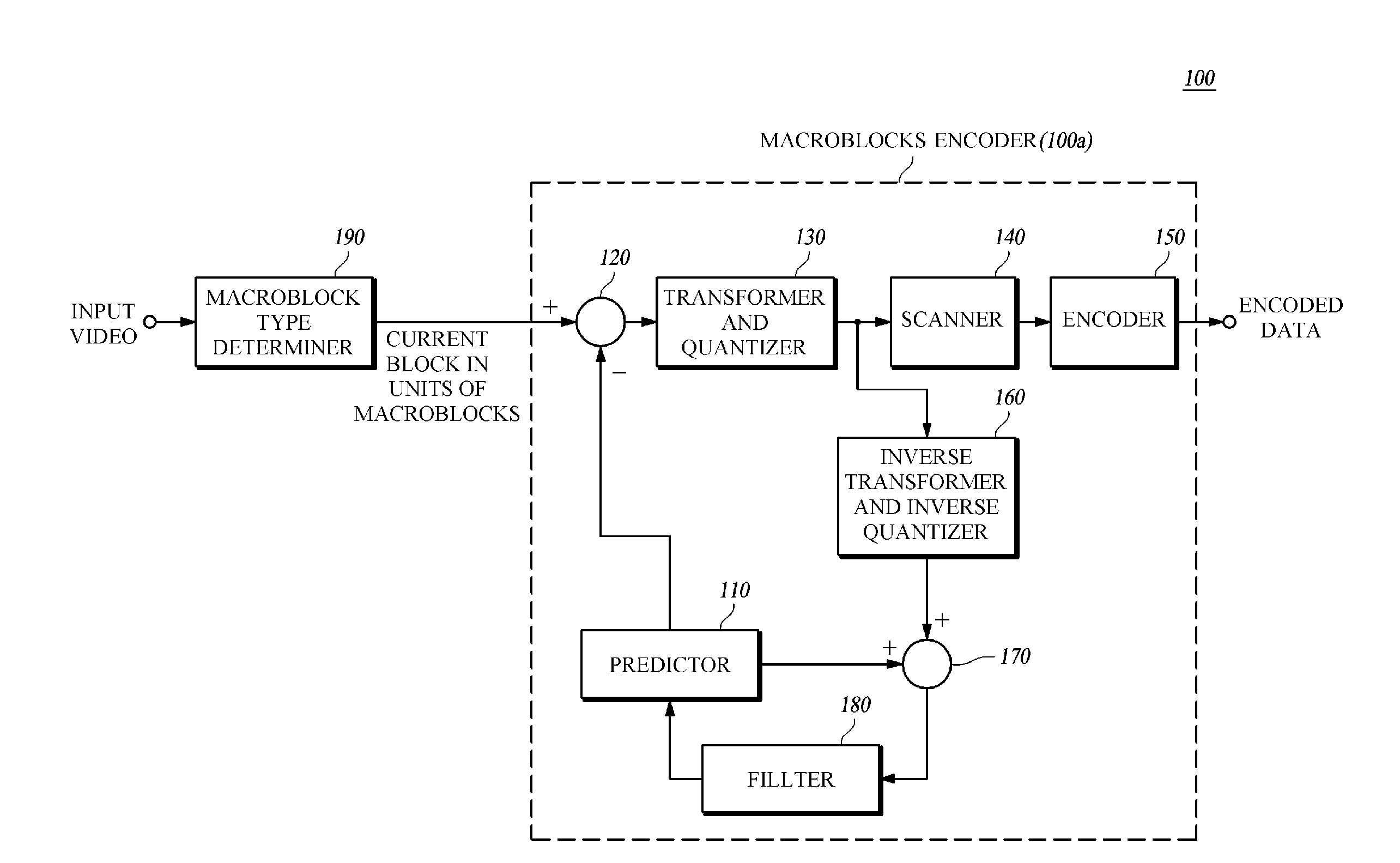
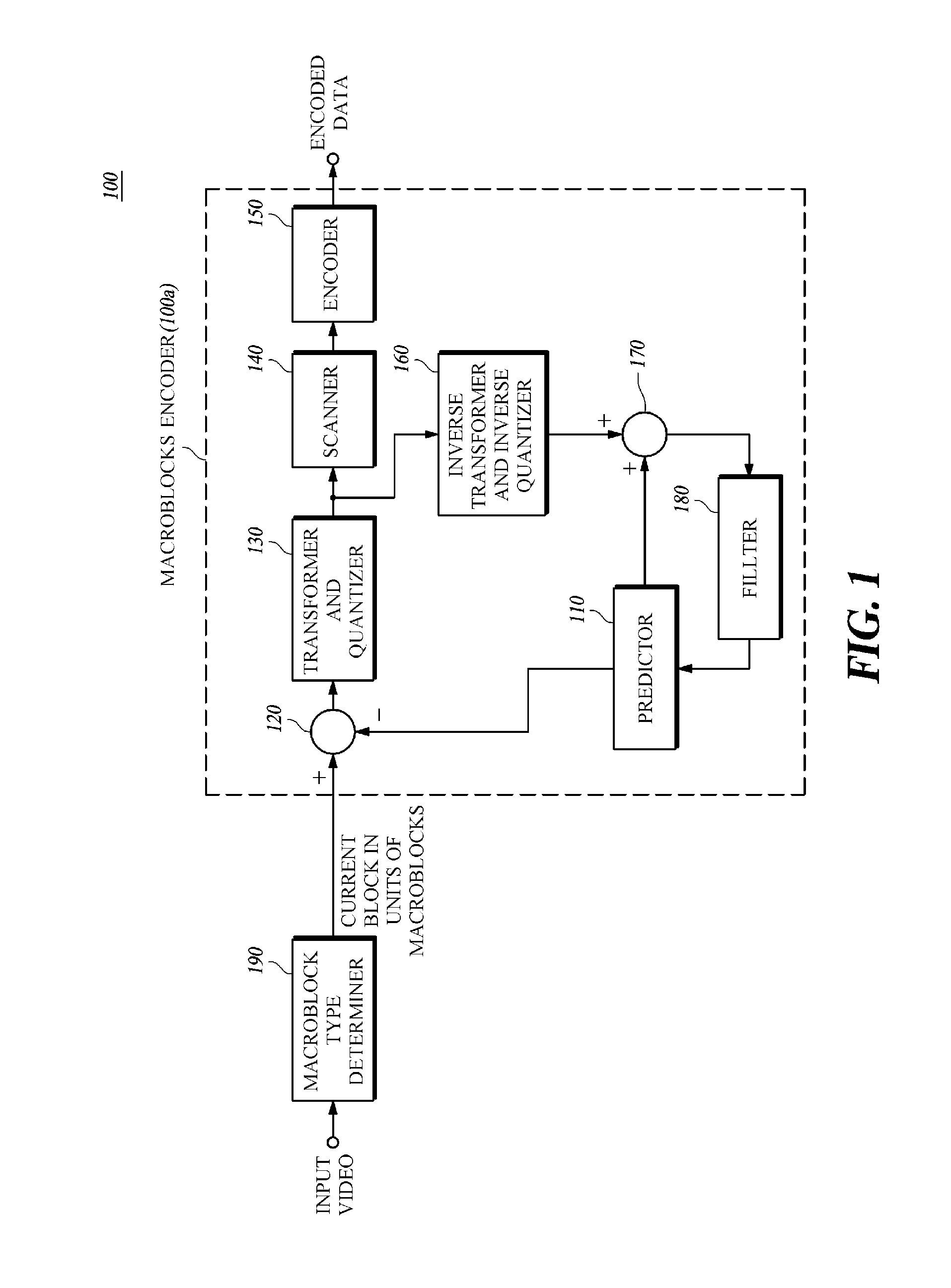
Disclosed is a high-resolution video encoding / decoding method and apparatus. The video encoding method includes: predicting a current block to generate a predicted block, subtracting the predicted block from the current block to generate a residual block, determining a transform and quantization type according to the block type of the current block; transforming and quantizing the residual block according to the determined transform and quantization type; and encoding the transformed and quantized residual block. According to the video encoding / decoding method and apparatus, not only the encoding efficiency can be improved because it enables an encoding using a high correlation between temporally / spatially adjacent pixels appearing in a video, but the compression efficiency can also be improved by reducing block distortion.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
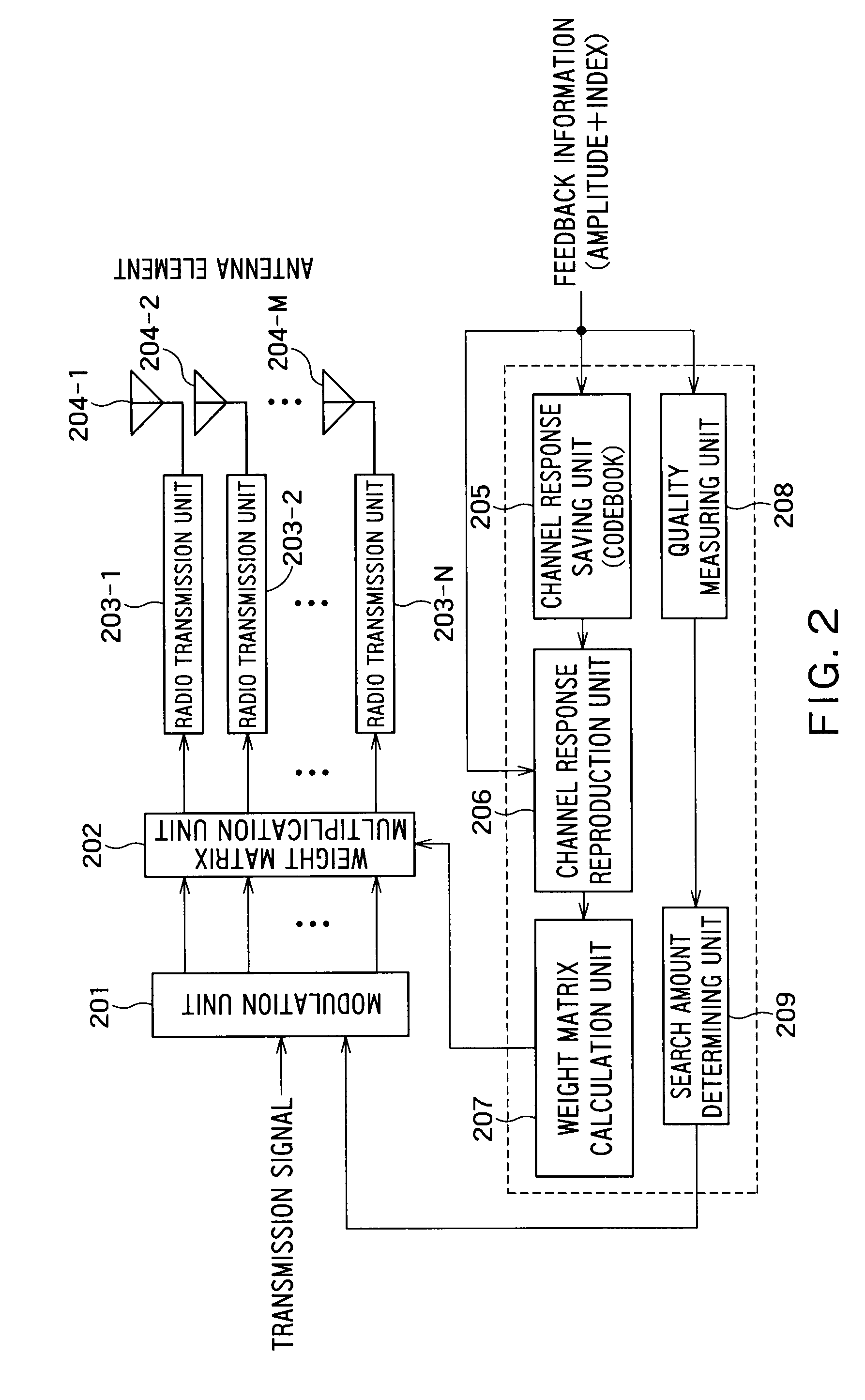
Terminal apparatus, base station, radio communication method and program storage medium
InactiveUS20090154411A1High correlationRadio transmissionChannel estimationTerminal equipmentComputer science
A terminal apparatus includes: a reception unit configured to receive a signal from a base station; a channel estimation unit configured to estimate a state of a channel based on a received signal; a storage configured to store a codebook including channel state values; an index of search number acquisition unit configured to acquire index of search number of candidates to be selected from among the channel state values for a correlation calculation with the estimated state value; a candidate selecting unit configured to select candidates for which the correlation calculation should be performed from among the channel state values according to the index of search number; a correlation calculation unit configured to calculate a correlation between the estimated state value and each of selected candidates; a selection unit configured to select a candidate having a highest correlation value; and a reporting unit configured to report a selected candidate to the base station.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
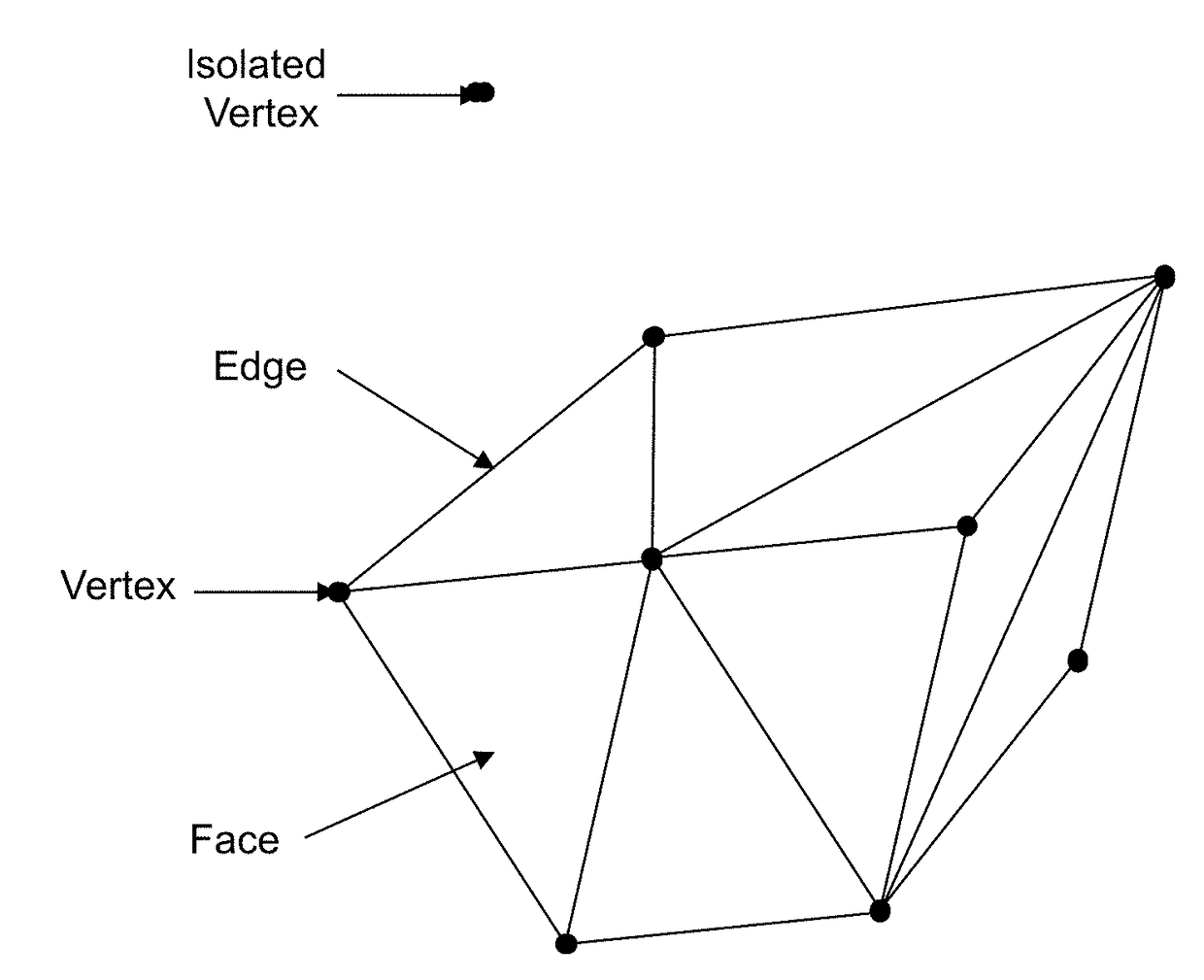
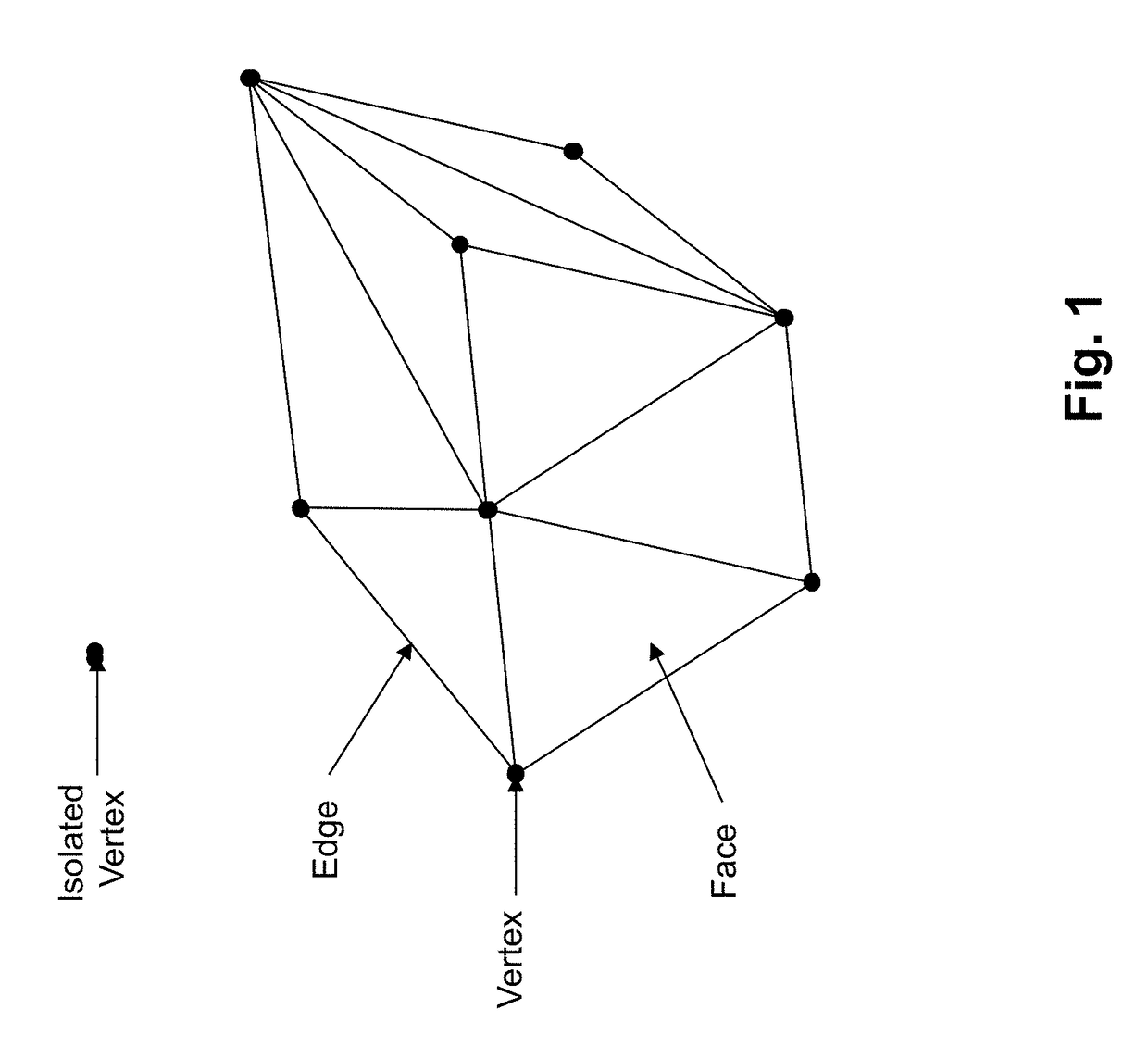
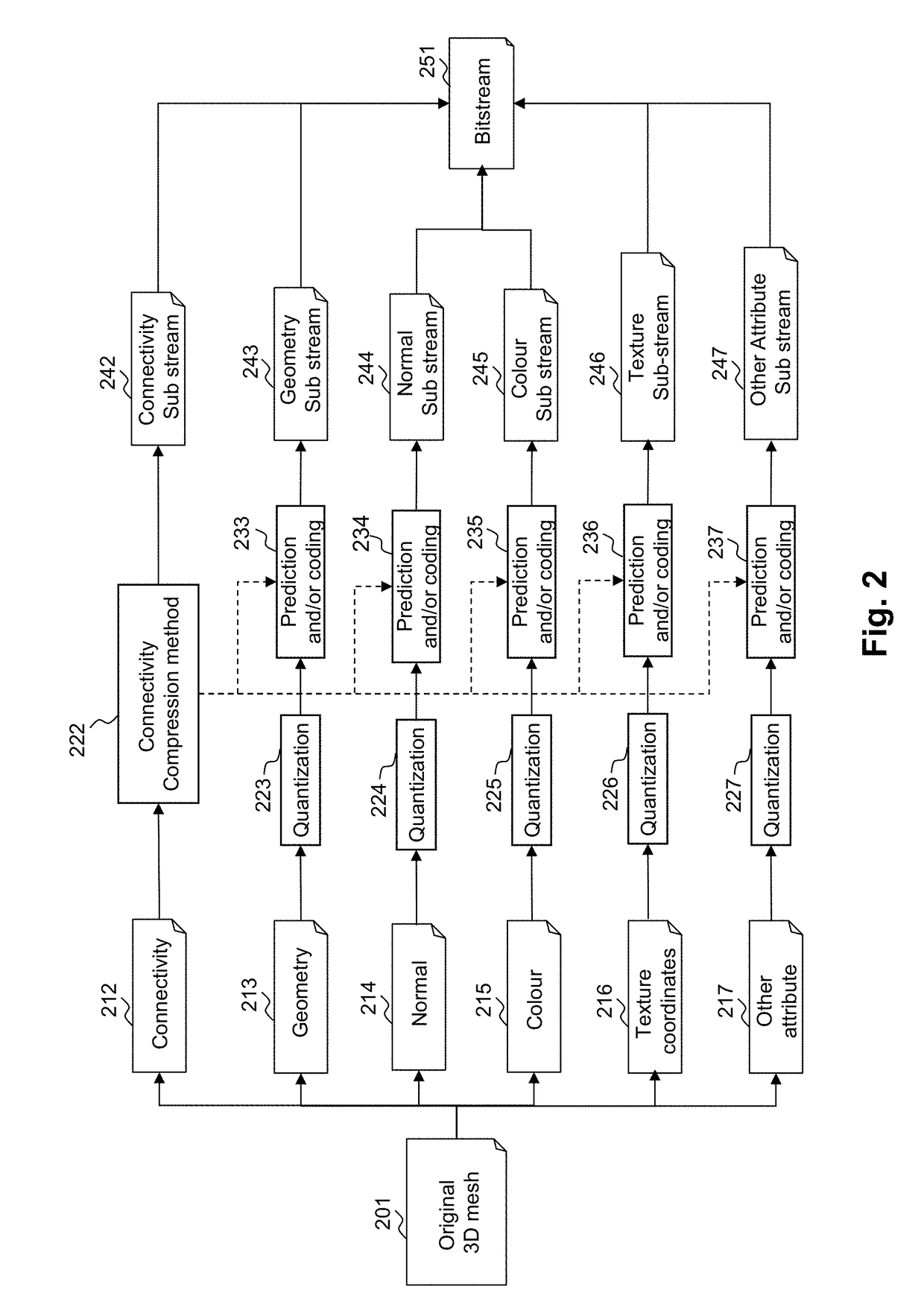
Attribute mapping to encode and decode 3D models
Encoding and decoding of property data, such as colour values, associated with vertices forming 3D objects. From an analysis of connectivity data, a spiral-like scanning path of the vertices within the 3D model is obtained. The colour values are mapped to a 2D image, each attribute value to a pixel. Next, the mapped 2D image is encoded. To increase redundancies in the 2D image, the spiral-like path is split into path segments, each forming a turn in the spiral; each path segment is assigned to a respective line of the 2D image; and the colour values of each path segment are mapped, in the same order, to the respective line of the 2D image. Successive lines in the 2D image thus contain the colour values of neighbouring vertices in the 3D object, and a better encoding can be achieved.
Owner:CANON KK
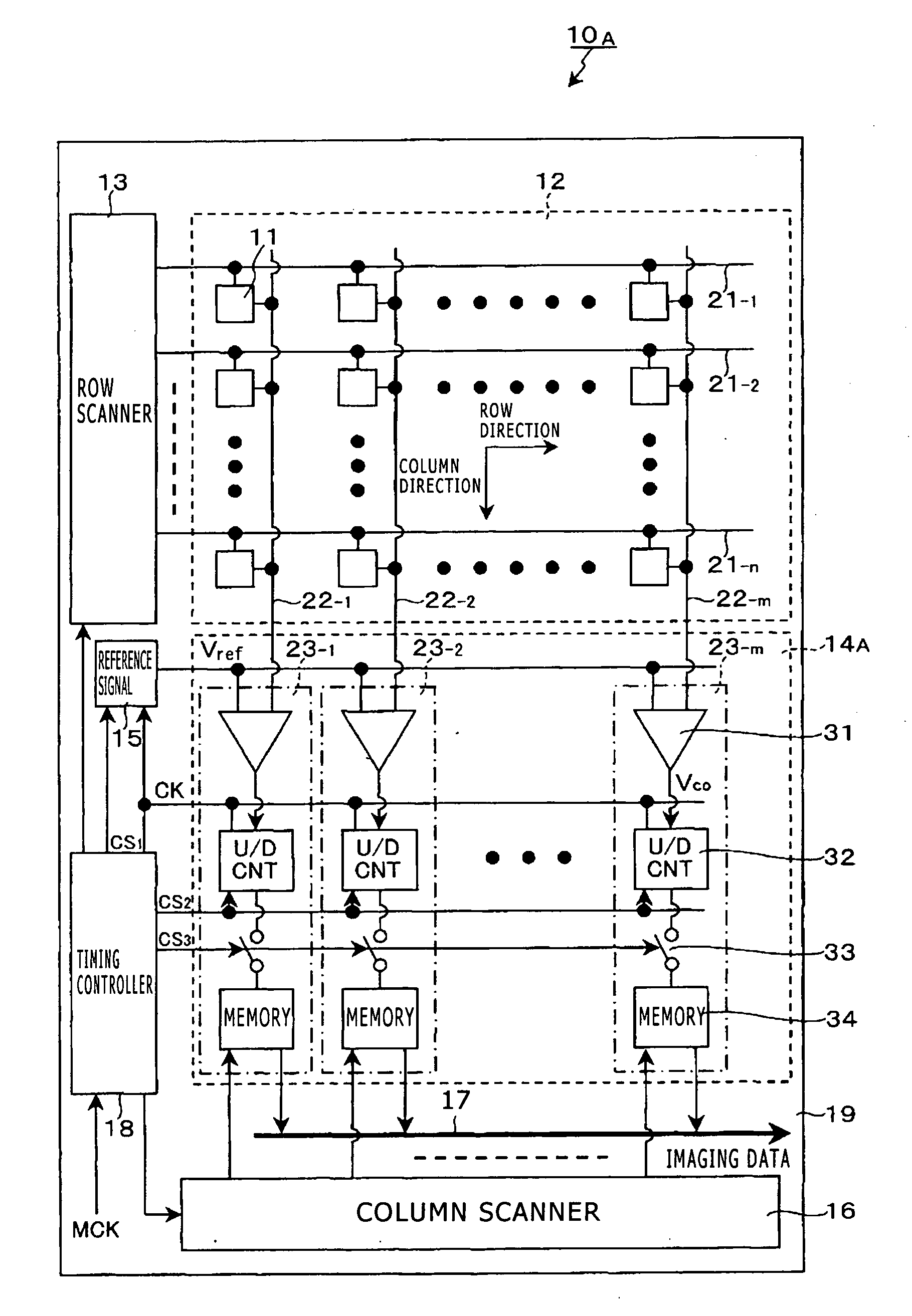
Solid-state imaging device, method for driving solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20120026370A1Remove differenceNarrow range of input voltageTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsVoltage converterCharge voltage
Disclosed herein is a solid-state imaging device, including: a pixel array unit configured to be formed by two-dimensionally arranging unit pixels each having a photoelectric converter, a charge-voltage converter, a reset transistor to set the charge-voltage converter to a predetermined potential, and an amplification transistor to read out a signal converted by the charge-voltage converter; a signal processor configured to process a signal output from the unit pixel by using a reference voltage; and a setter configured to set a reset level obtained from a second unit pixel from which a signal level has been already read out as the reference voltage of the signal processor before readout of a signal level based on a signal charge accumulated or retained in the charge-voltage converter from a first unit pixel.
Owner:SONY CORP
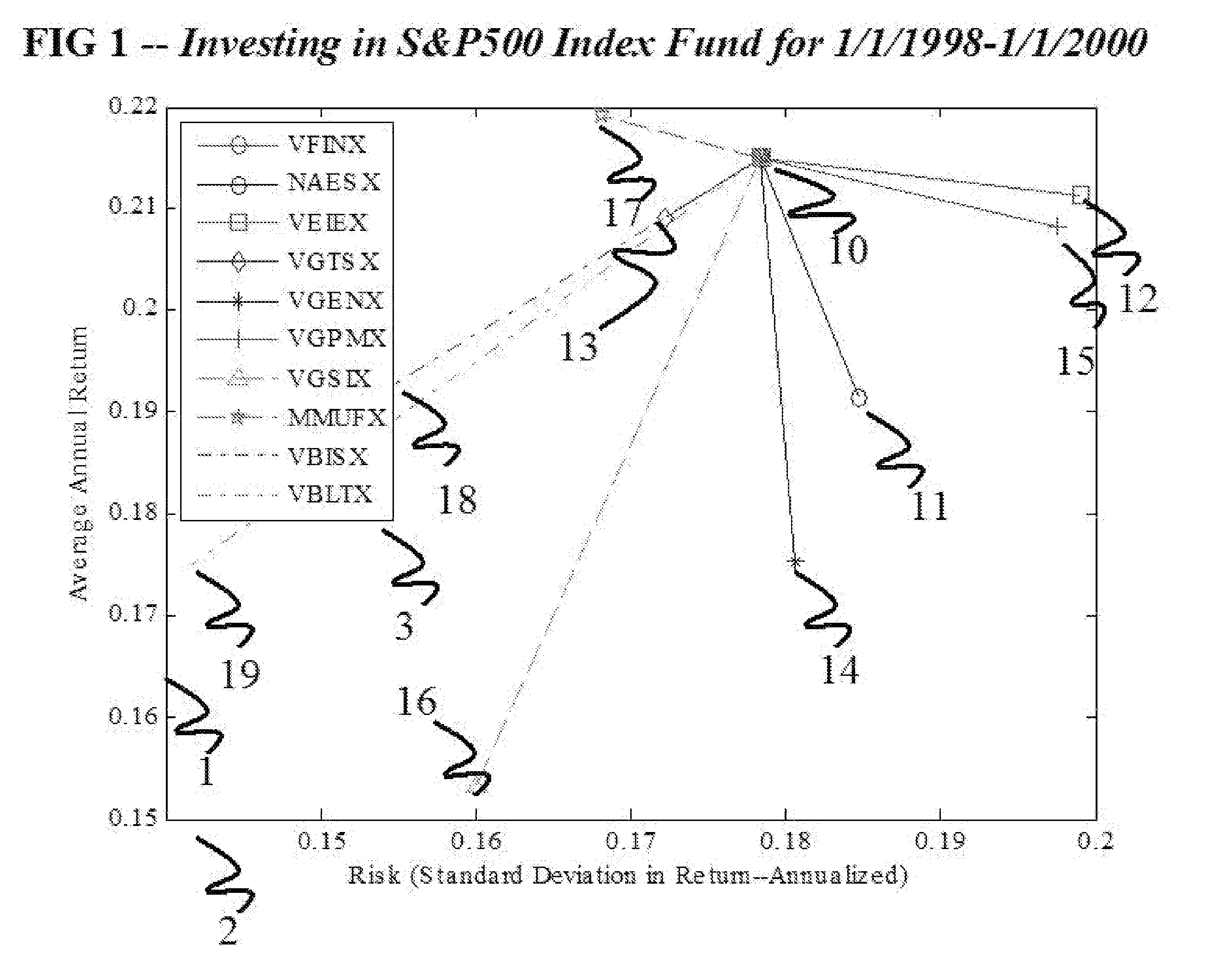
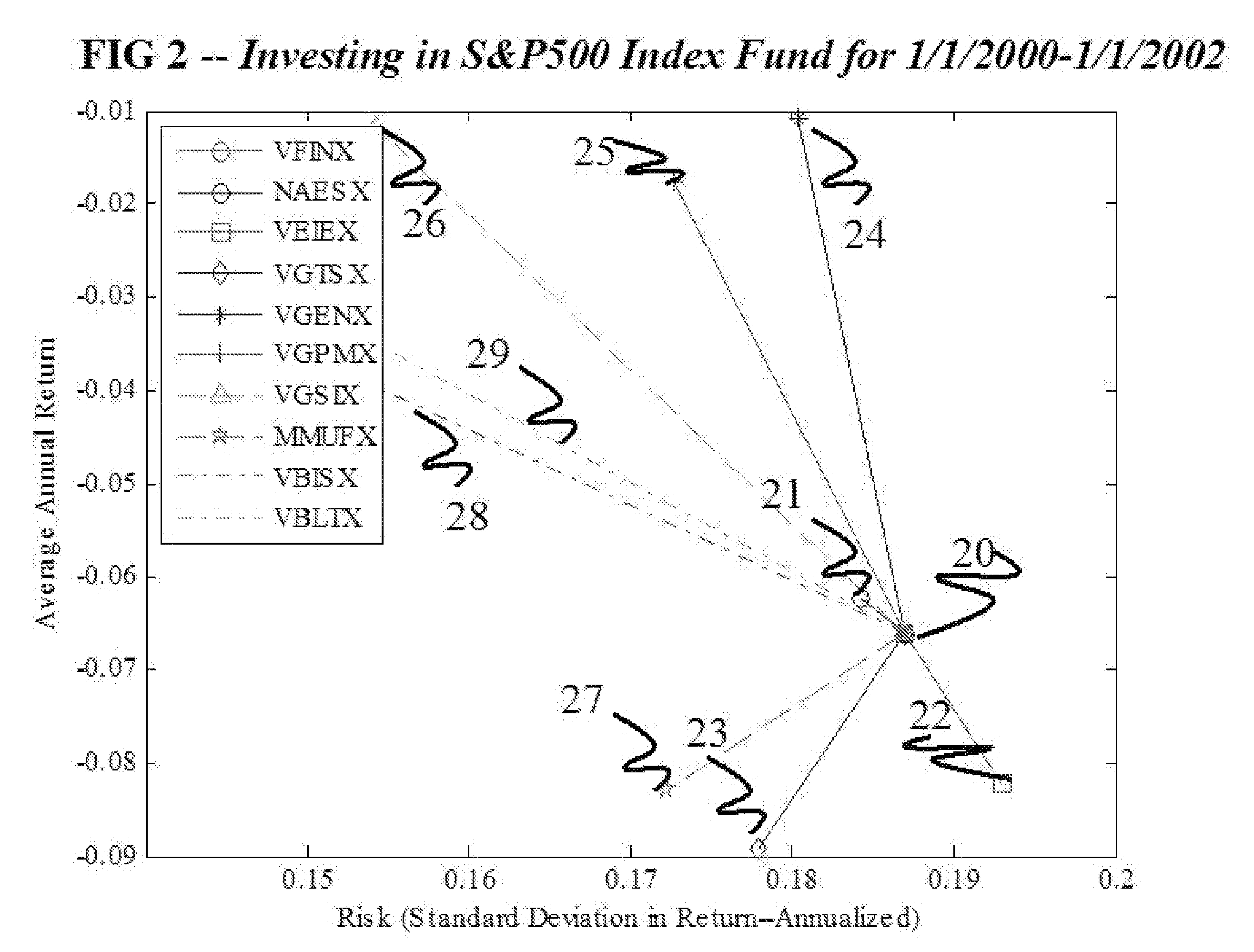
Method and apparatus for characterizing the key properties and analyzing the future performance of an investment portfolio
InactiveUS20100235299A1Reduce diversificationIncrease diversityDrawing from basic elementsFinanceDiagnostic informationData science
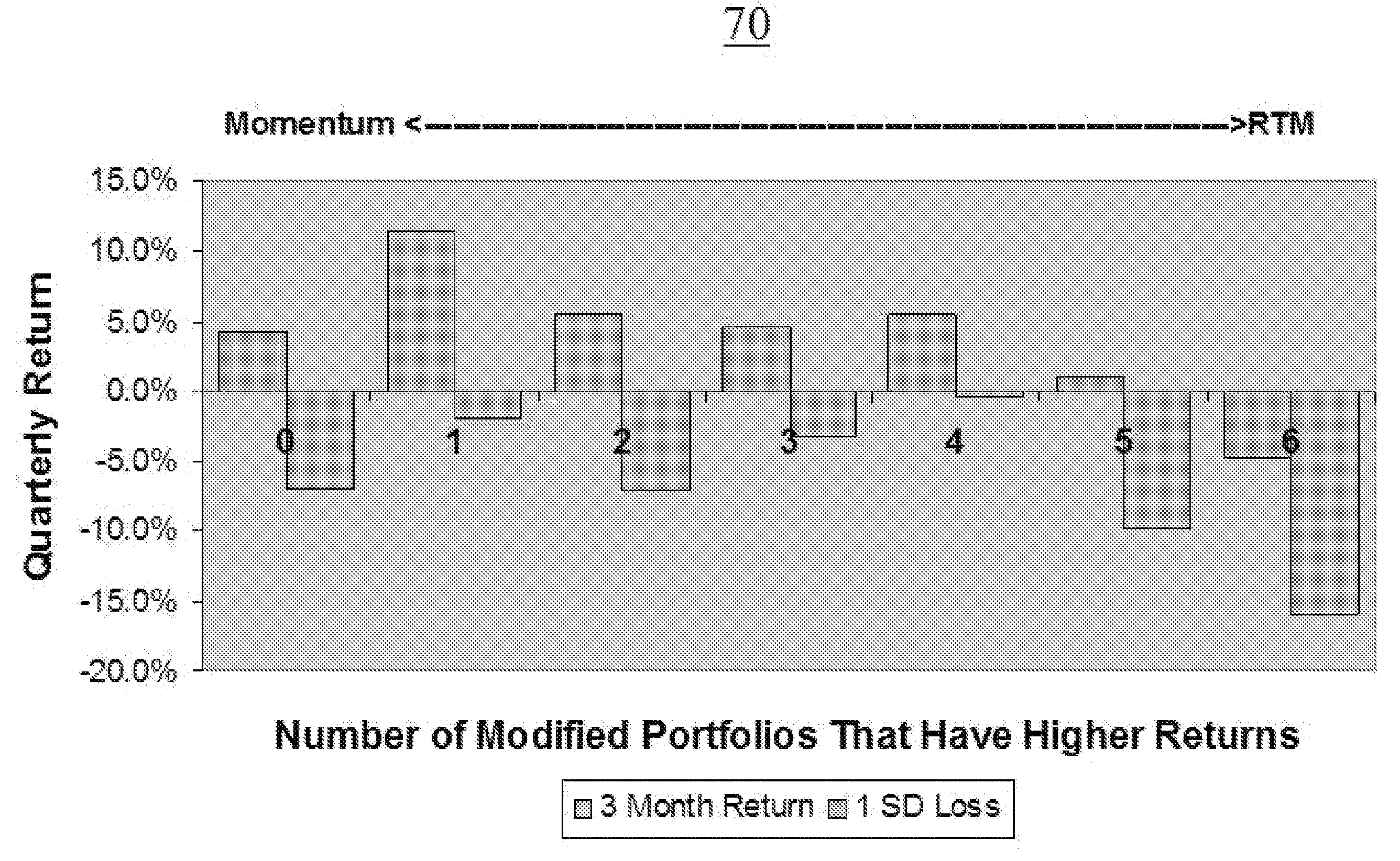
Prognostic and diagnostic information is determined about an investment portfolio through perturbing the investment portfolio with allocations to other sectors and reviewing the performance of the perturbed investment portfolios using historical data, and combining that with other factors. Relationships between one's investment portfolio and other assets, rights or liabilities can be identified by creating several modified portfolios each of which comprise a mix of the original investment portfolio and one or more of the other assets, rights or liabilities. The performance of these modified portfolios, as compared to the original portfolio over a historical period, indicates the correlation (or lack thereof) between these other assets, rights or liabilities and one's investment portfolio. By identifying these correlations, one can then take any desired action to modify one's portfolio to obtain the desired results.
Owner:CONSIDINE GEOFF
Method and apparatus for detecting charged state of secondary battery based on neural network calculation
InactiveUS20060276980A1Less-delay of calculationImprove accuracySparking plugsBatteries circuit arrangementsBattery state of chargeEngineering
An apparatus and method of neural network type are provided to detect an internal state of a secondary battery implemented in a battery system. Electric signals indicating an operating state of the battery is detected and, using the electric signals, information indicating the internal state of the battery is calculated on the basis of neural network calculation, in which the information reflects a reduction in an effect of polarization of the secondary battery. Using the electric signals, input parameters required for calculating the internal state of the battery is calculated. The input parameters may include, as one input parameter, a polarization-related quantity to correct the effect of the polarization in an output parameter (such as SOC and / or SOH) from the neural network. Further, the input parameters may include, as one input parameter, a functional value already subjected to the correction for correcting the effect of the polarization.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +2
Method and apparatus for detecting charged state of secondary battery based on neural network calculation
InactiveUS7554296B2Accurate calculationImprove accuracyBatteries circuit arrangementsLighting and heating apparatusBattery state of chargeElectrical battery
Owner:DENSO CORP +2
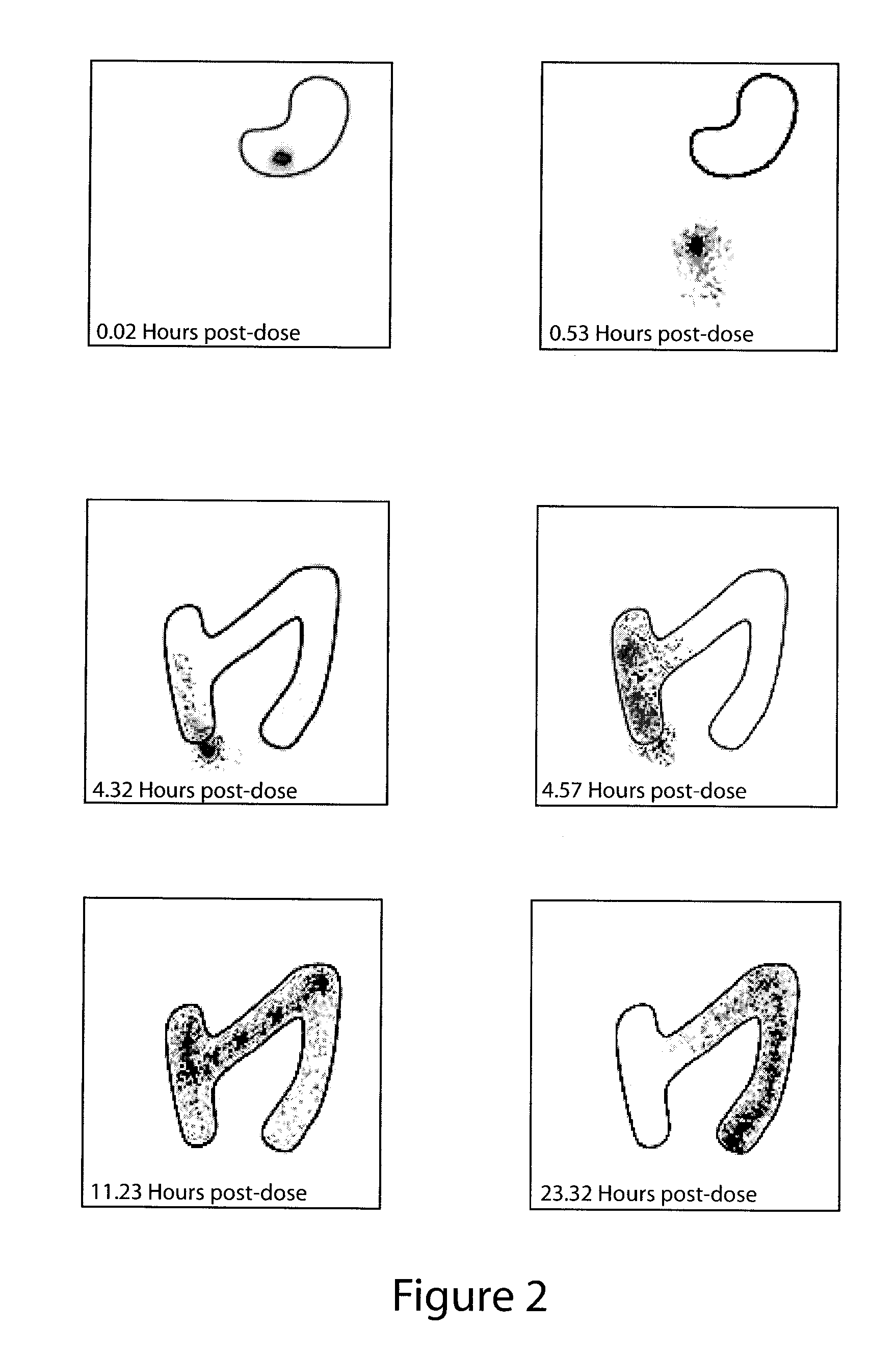
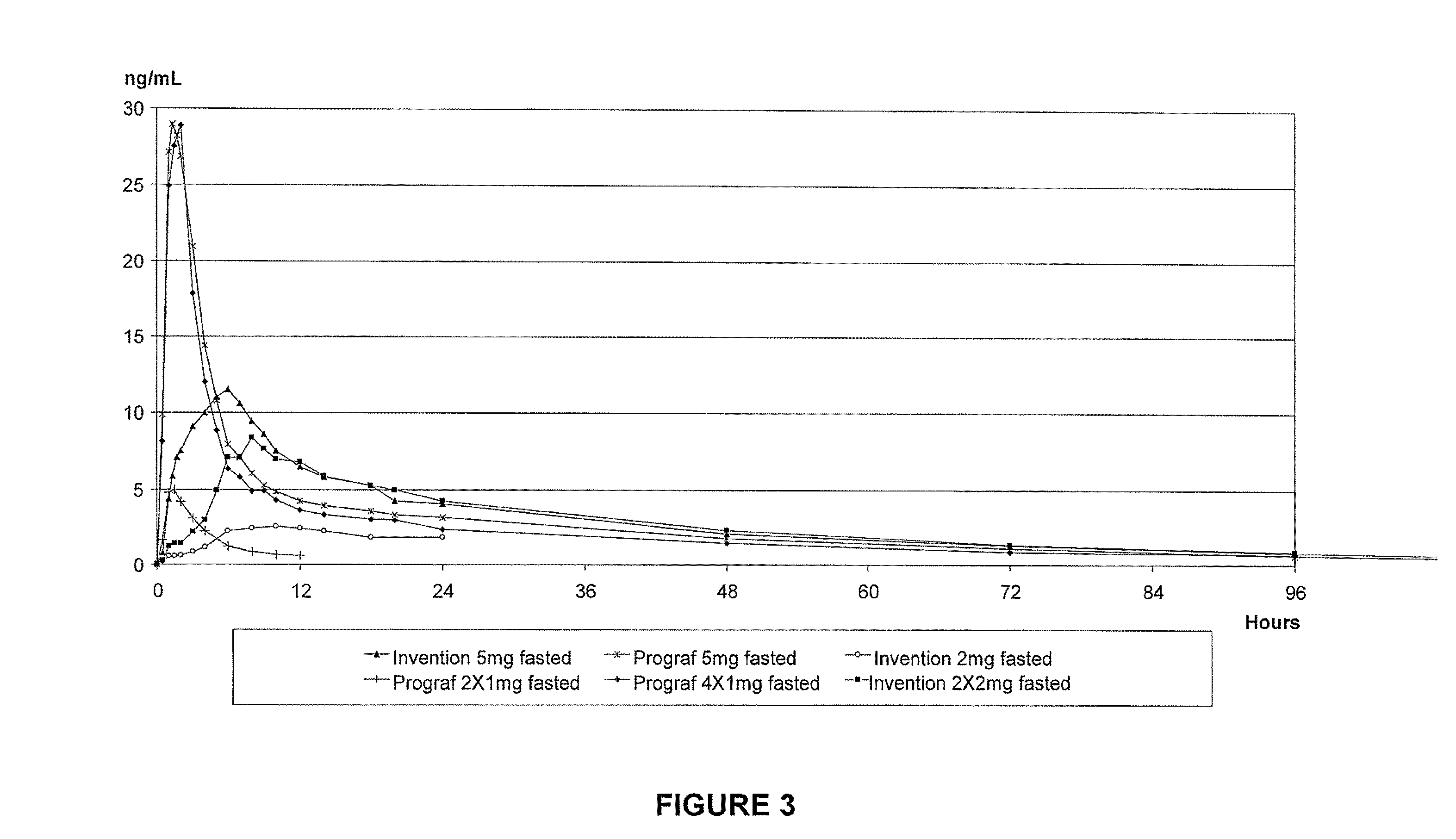
Tacrolimus for improved treatment of transplant patients
ActiveUS20100105717A1Improve bioavailabilityReduce riskBiocideOrganic chemistryTherapeutic effectIn vivo
An extended release oral dosage form comprising as active substance tacrolimus or a pharmaceutically active analogue thereof for a once daily immunosuppressive treatment of a patient in need thereof, preferable a kidney or liver transplant patient. The dosage form releases the active substance over an extended period of time. It also provides improved pharmacokinetic parameters due to an extended and constant in vivo release including substantial decreased peak concentrations, despite increased bioavailability, substantial extended times for maximal concentration, and higher minimal concentrations when compared with conventional immediate release dosage forms and a recent modified release tacrolimus dosage form.
Owner:VELOXIS PHARM INC
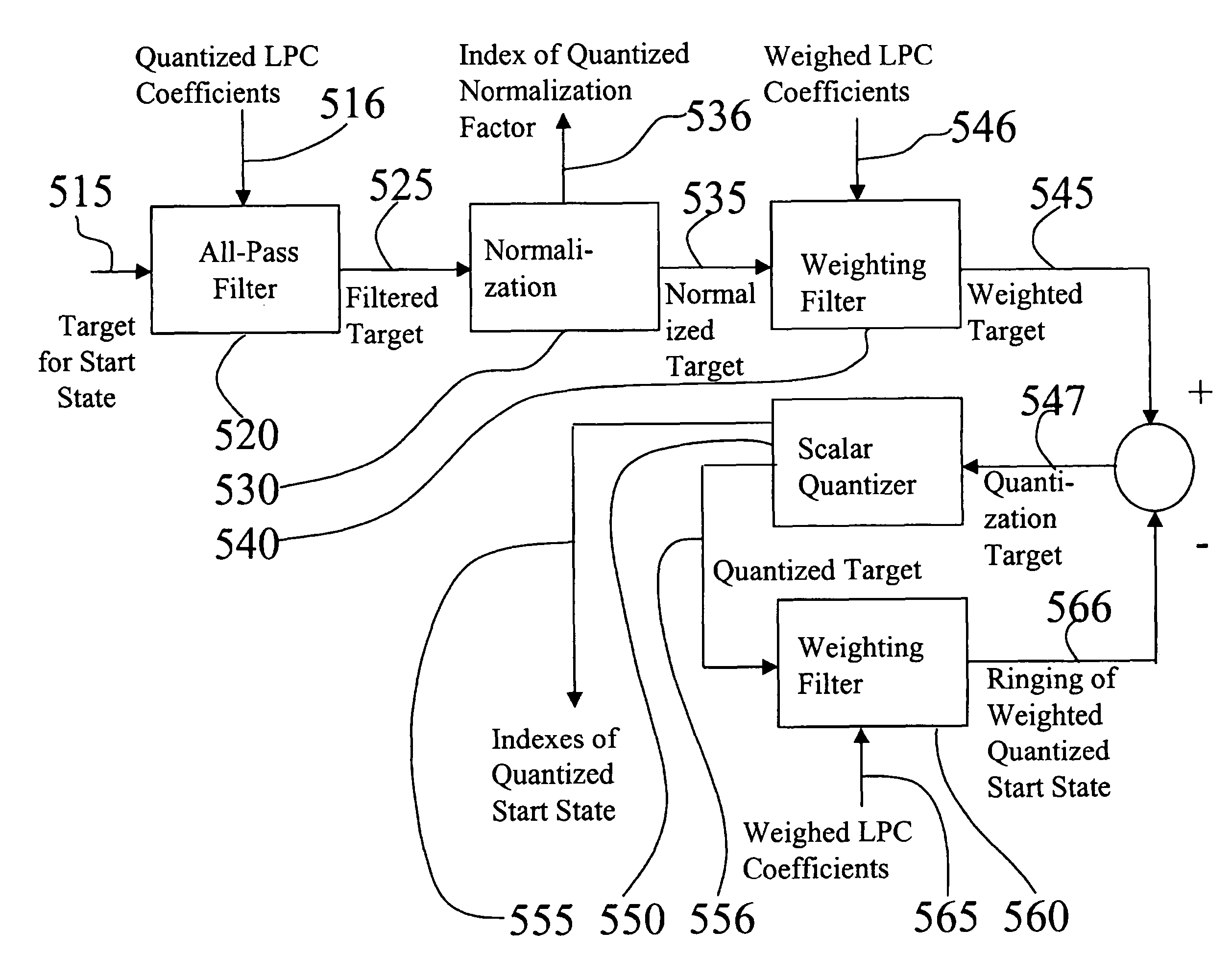
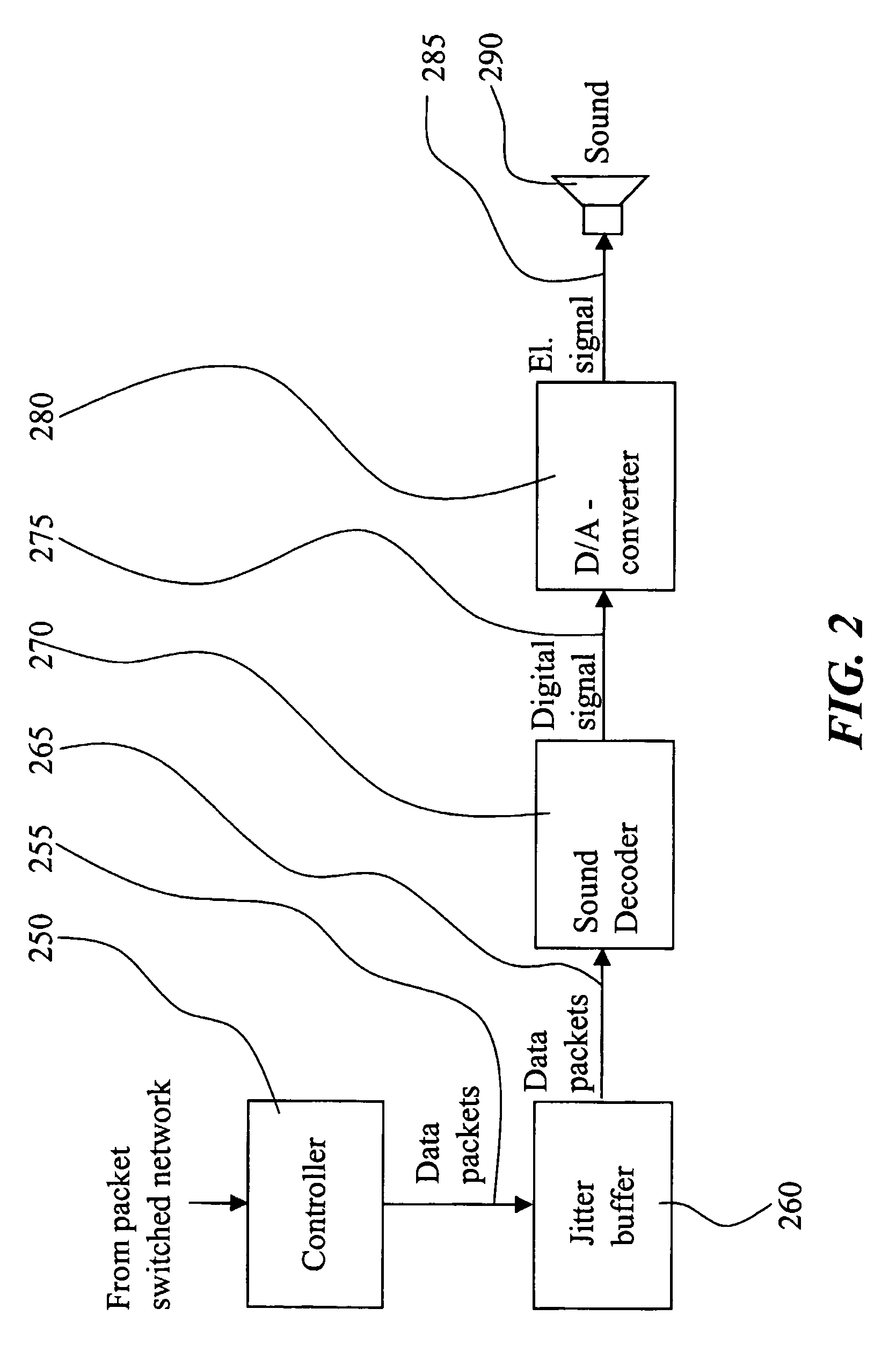
Low bit rate codec
ActiveUS7895046B2Robust to packet lossPoor approximationSpeech analysisComputer hardwarePacket switched
The present invention relates to improvements of predictive encoding / decoding operations performed on a signal which is transmitted over a packet switched network. The signal is encoded on a block by block basis in such way that a block A-B is predictive encoded independently of any preceding blocks. A start state (715) located somewhere between the end boundaries A and B of the block is encoded using any applicable coding method. Both block parts surrounding the start state is then predictive encoded based on the start state and in opposite directions with respect to each other, thereby resulting in a full encoded representation (745) of the block A-B. At the decoding end, corresponding decoding operations are performed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
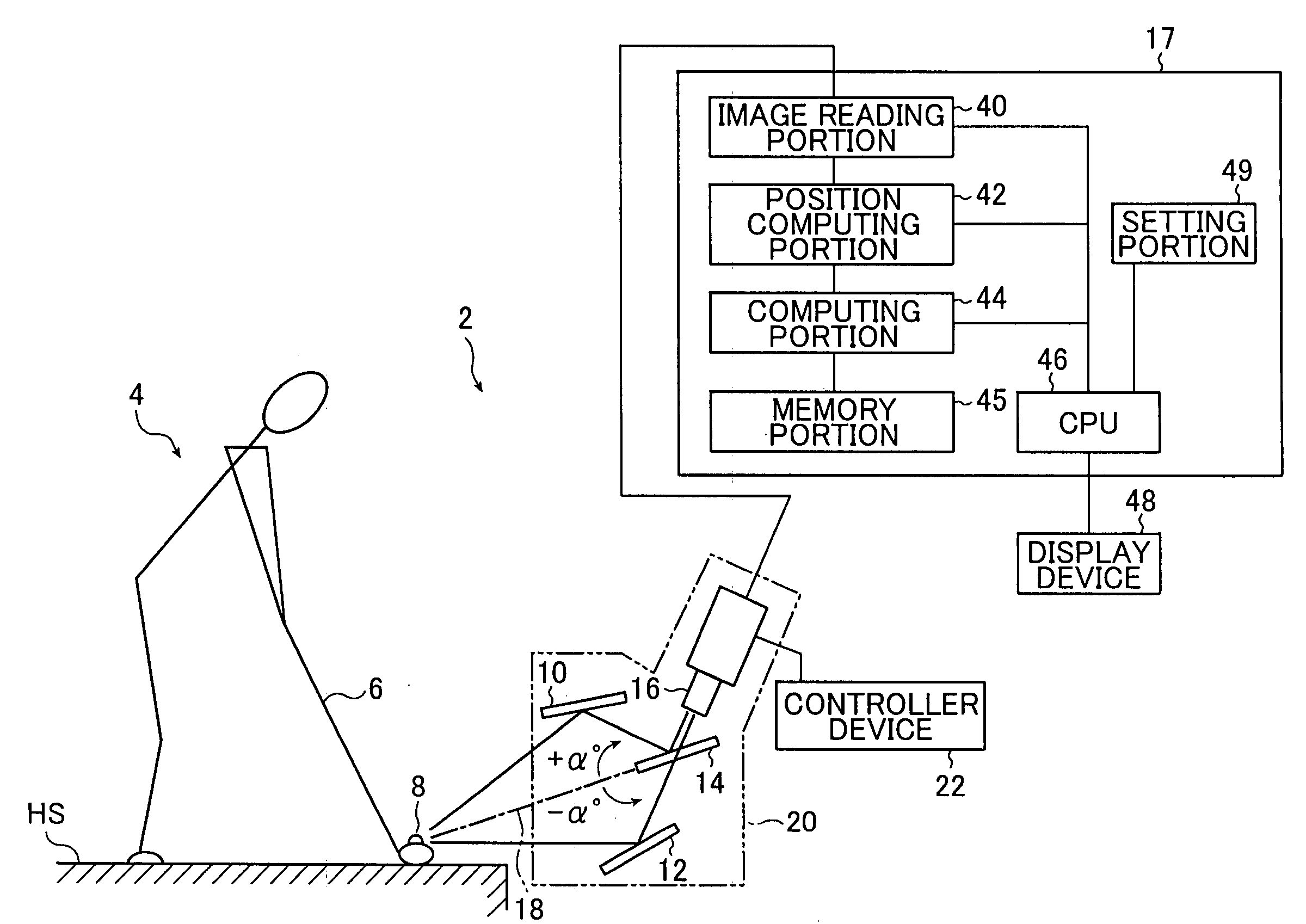
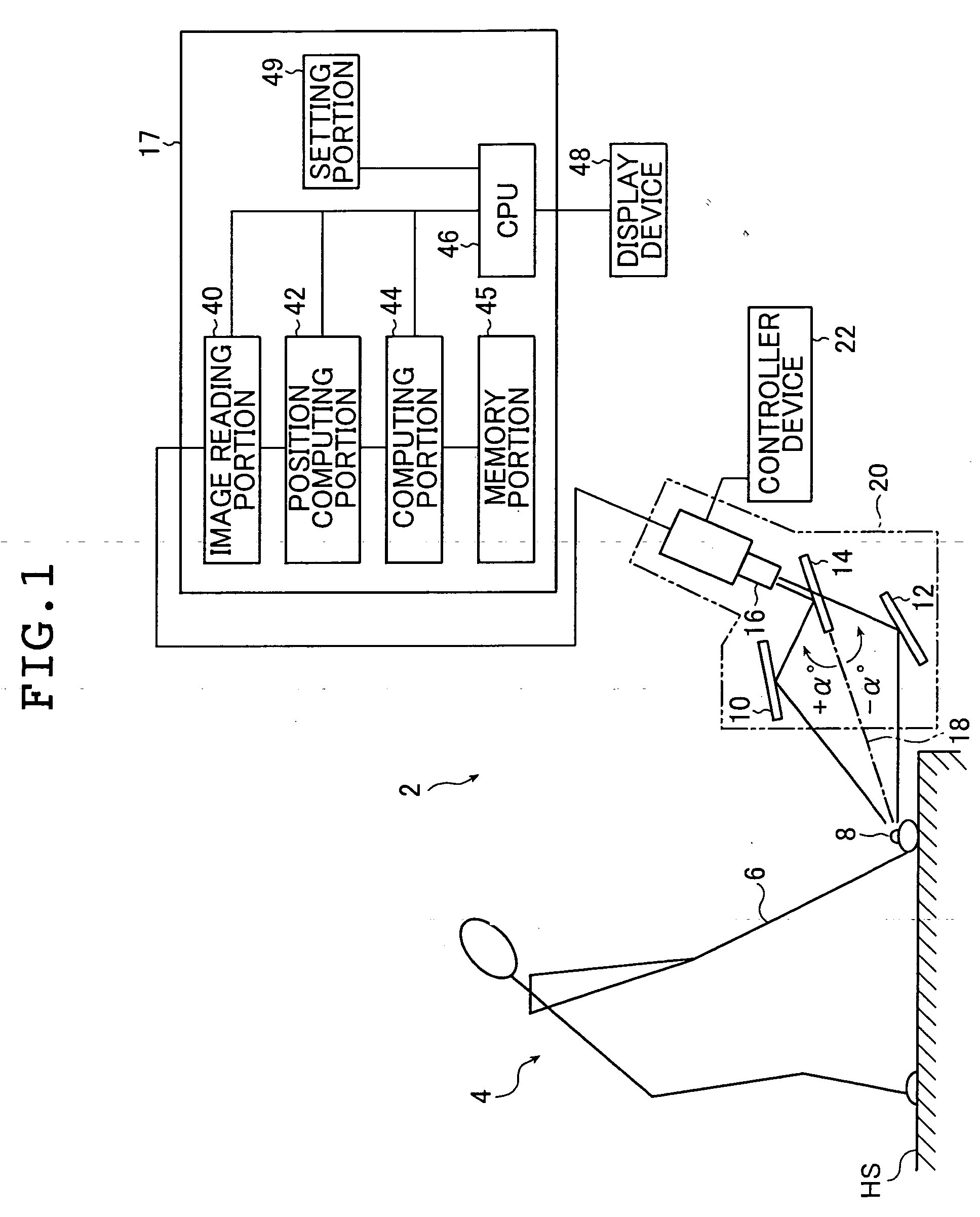
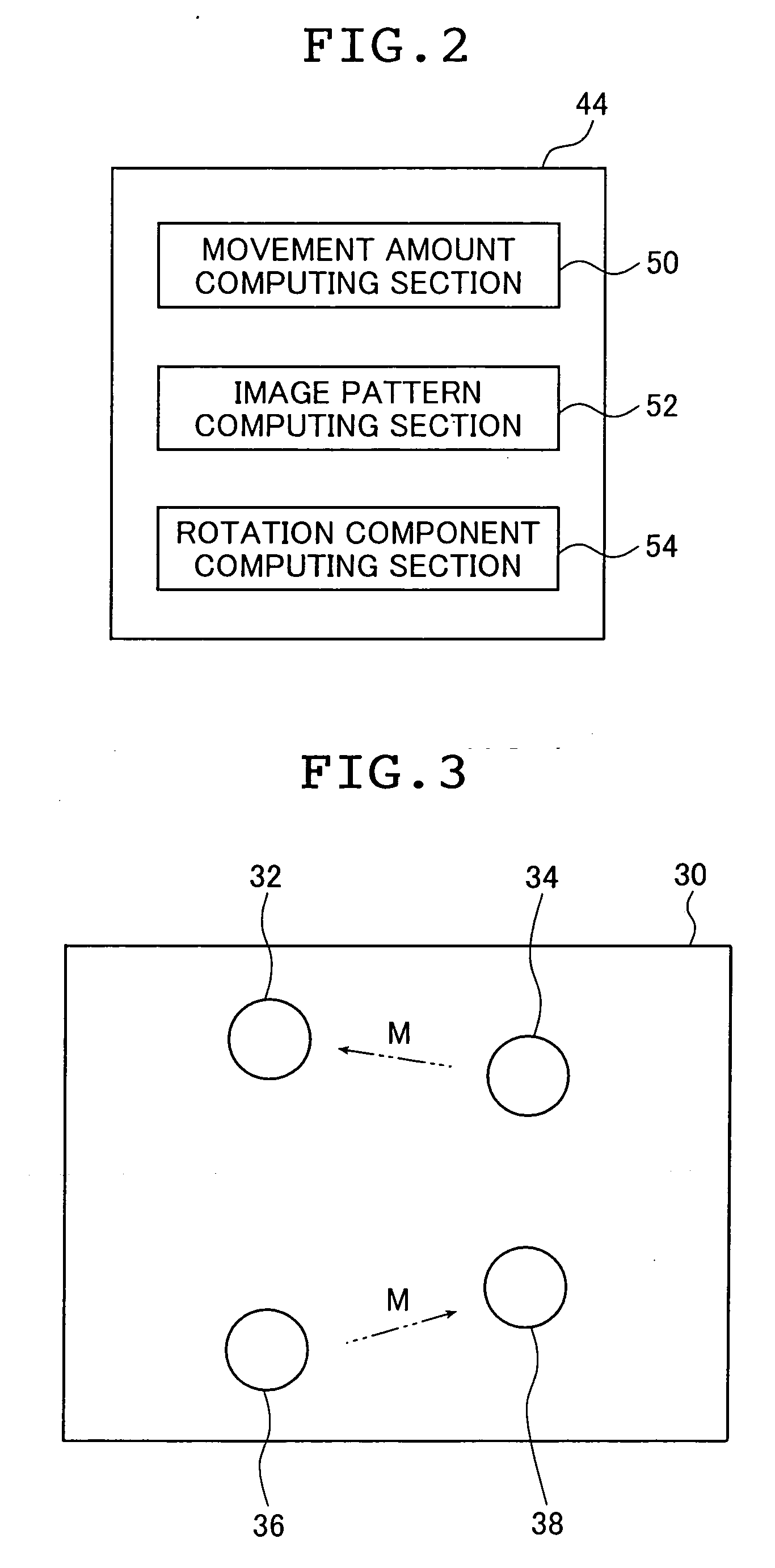
Apparatus and method of measuring the flying behavior of a flying body
InactiveUS20050233816A1Improve accuracyReduce measurementImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Flight behaviour
A measuring apparatus of a flying behavior of a spherical flying body has: a recording portion that optically records the flying body during flight with a predetermined interval of time, to obtain a first image and a second image of the fling body; image information computing portion that detects a first outline region of the flying body in the first image of the flying body and a second outline region of the flying body from the second image of the flying body, and finds first image information from the first image of the flying body in at least a portion of the first outline region and second image information from the second image of the flying body in the second outline region; and rotation amount computing portion that maps the first image information to a surface of a first virtual spherical body, the second image information to a surface of a second virtual spherical body, and computes a rotation amount that is used for rotation processing when the rotation processing is performed on the first virtual spherical body to obtain a highest correlation between the first image information and the second image information.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA NAT UNIV +1
Face recognition apparatus and face recognition method
ActiveUS8116534B2Increase probabilityHigh correlationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionRadiology
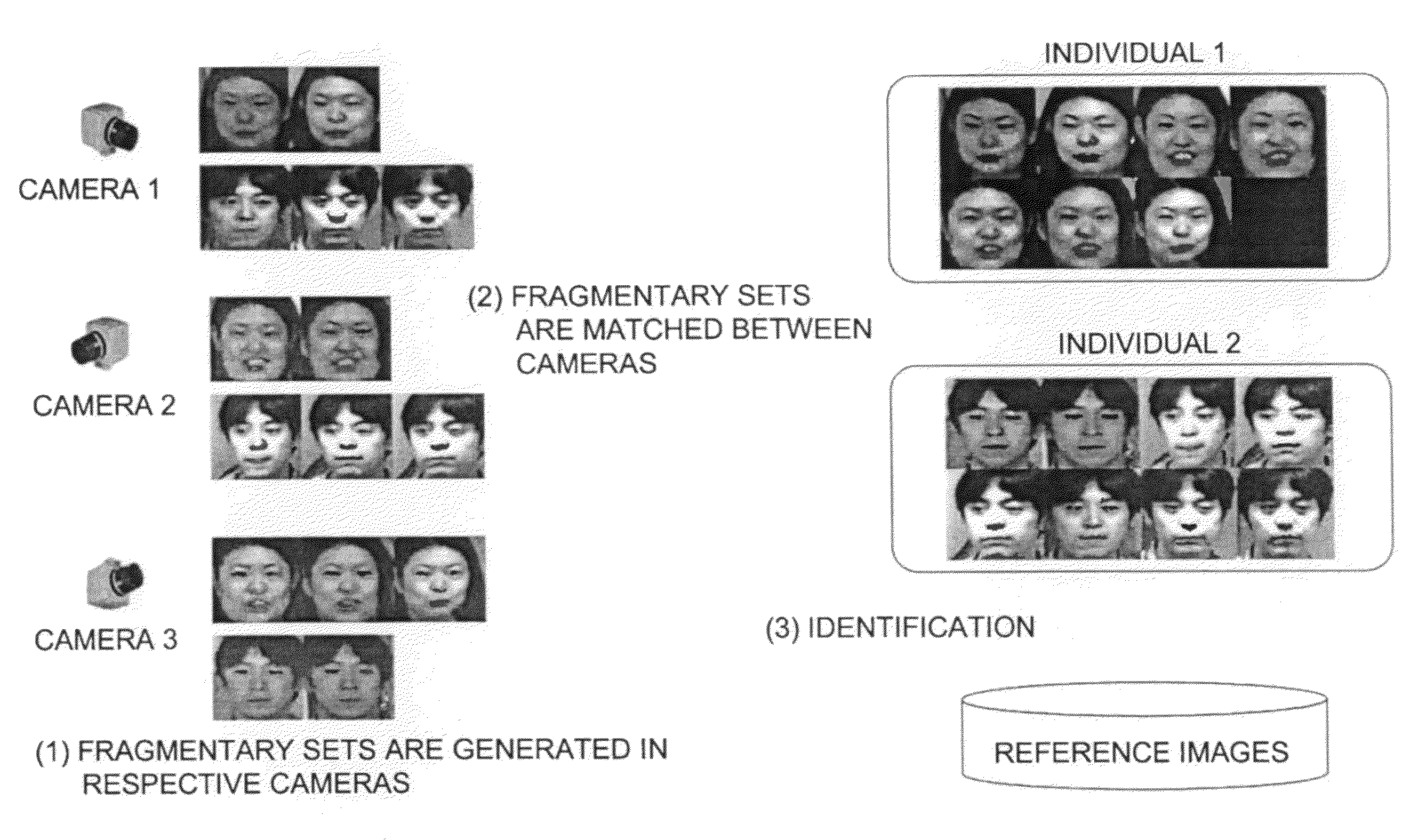
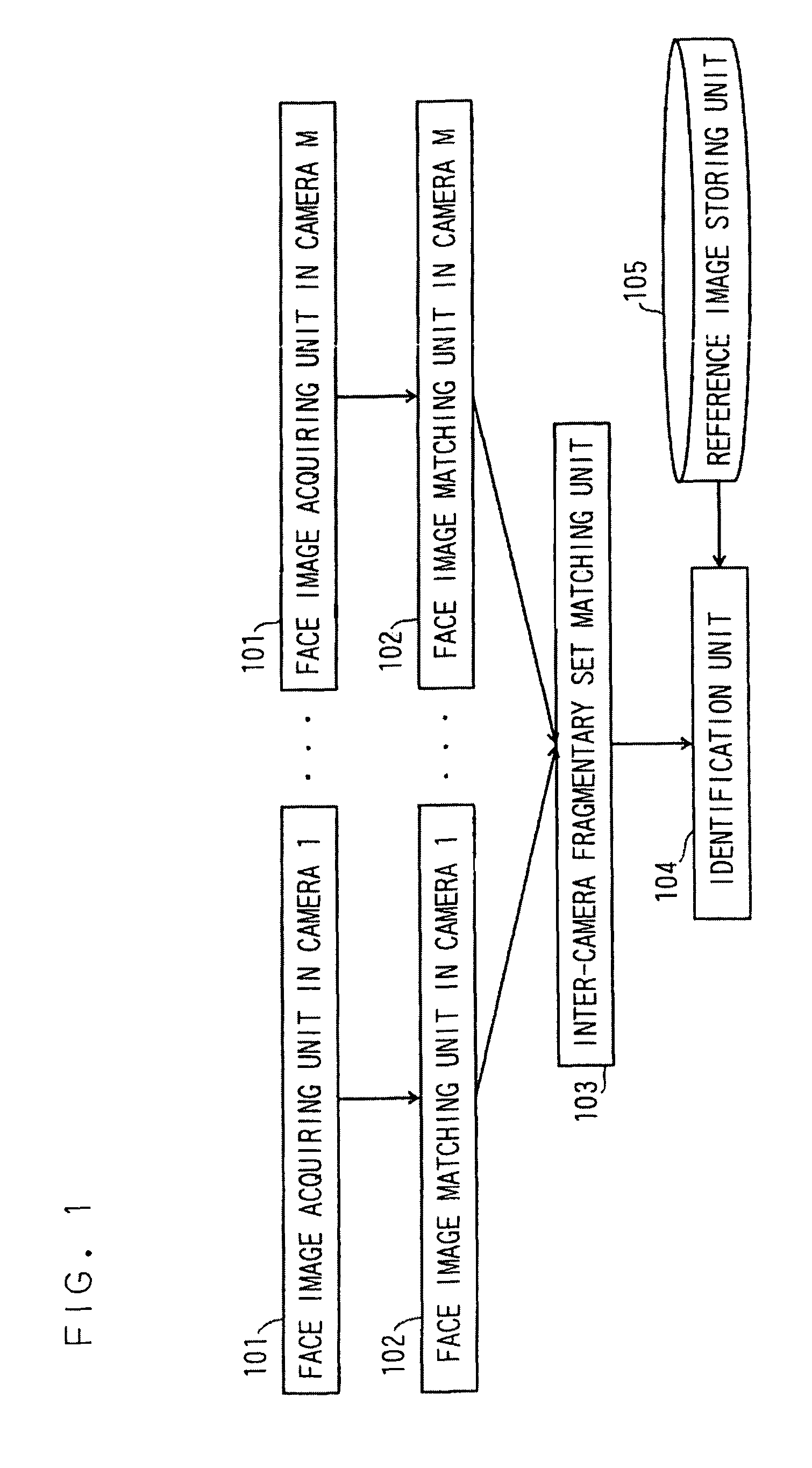
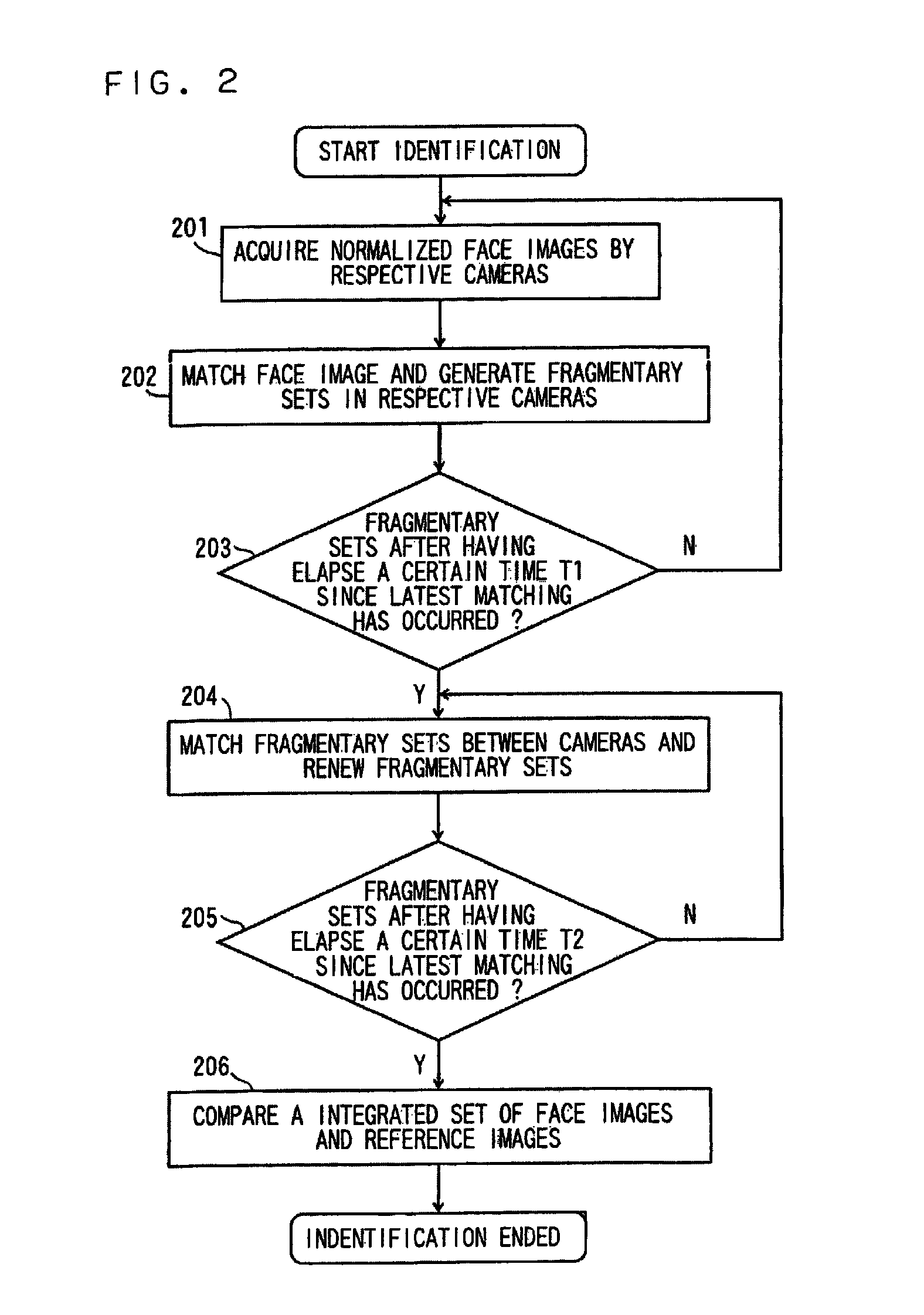
A face recognition apparatus includes an image sequence acquiring unit, a face image acquiring unit, an intra-sequence classifying unit, an inter-sequence classifying unit, an identification unit, and a reference image storing unit. A plurality of cameras are attached in a corridor for monitoring one place with these cameras, so that when a plurality of moving people pass through, identification is performed for each moving people. Face images are classified into fragmental face image sets, and the fragmental face image sets are classified into integrated sets to achieve the identification.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
System and methods for detecting bots real-time
ActiveUS20180234447A1AccuracyHigh correlationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalSocial mediaLag
Bots are detected real-time by correlating activity between users using a lag-sensitive hashing technique that captures warping-invariant correlation. Correlated users groups in social media may be found that represent bot behavior with thousands of bot accounts detected in a couple of hours.
Owner:STC UNM
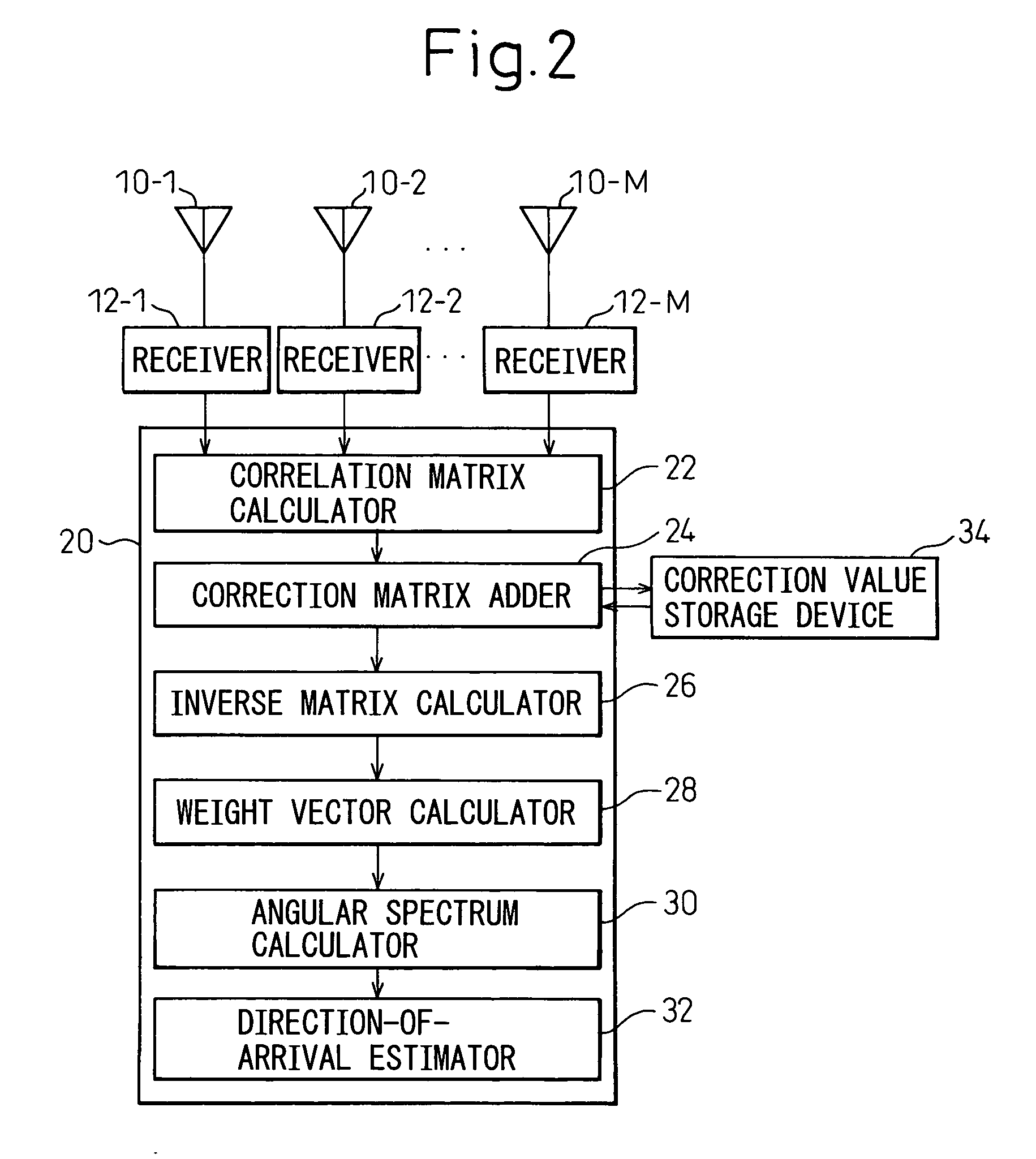
Apparatus and method for estimating direction of arrival of radio wave
InactiveUS20060208947A1Shorten the estimated timeImprove estimation accuracyMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesPosition fixationPeak valueAntenna element
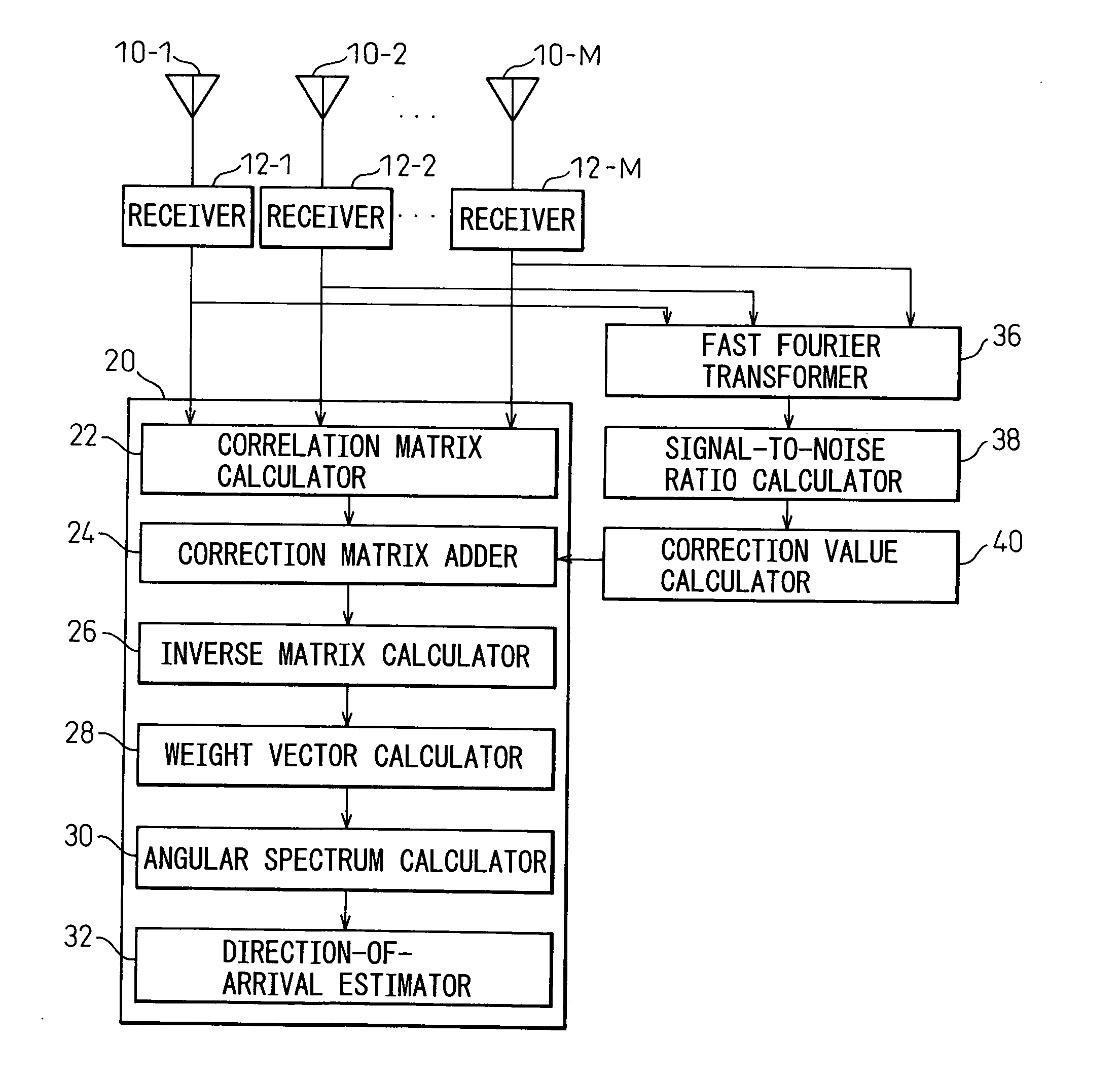
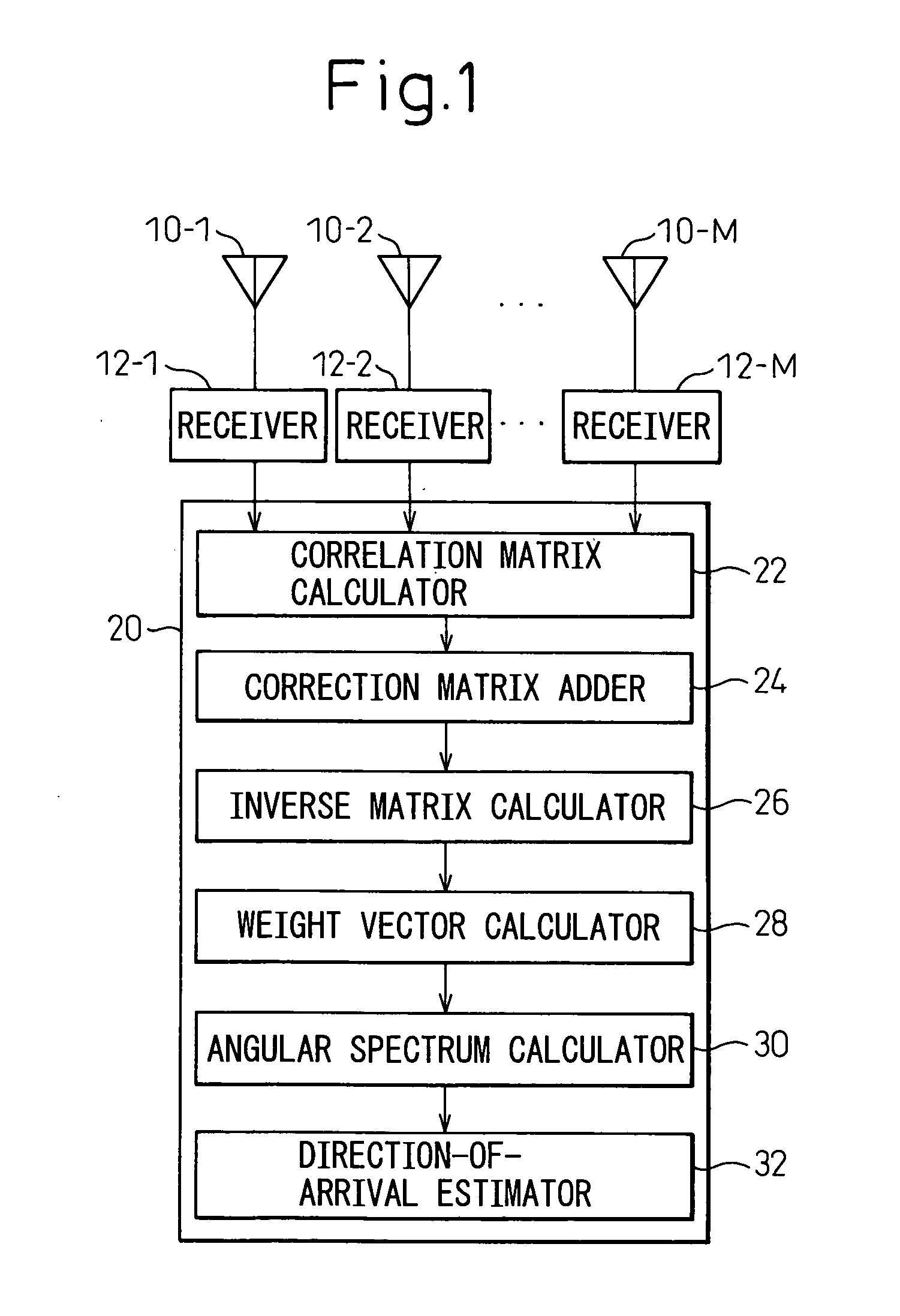
A radio wave direction-of-arrival estimation apparatus and method that can estimate, at high speed and with good accuracy, the direction of arrival of a plurality of incoming waves having high correlation. The radio wave direction-of-arrival estimation apparatus includes: an array antenna constructed from a plurality of antenna elements; a receiver for receiving an incoming wave via each of the antenna elements; a correlation matrix calculator for calculating a correlation matrix from each received signal; a correction matrix adder for adding a correction matrix having a suitable correction value only at a specific matrix element to the calculated correlation matrix; an inverse matrix calculator for calculating the inverse matrix of the correlation matrix to which the correction matrix has been added; a weight vector calculator for calculating a weight vector based on the calculated inverse matrix; an angular spectrum calculator for calculating an angular spectrum by using the calculated weight vector; and a direction-of-arrival estimator for estimating the direction of arrival of the incoming wave from the peak waveform of the calculated angular spectrum.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD +1
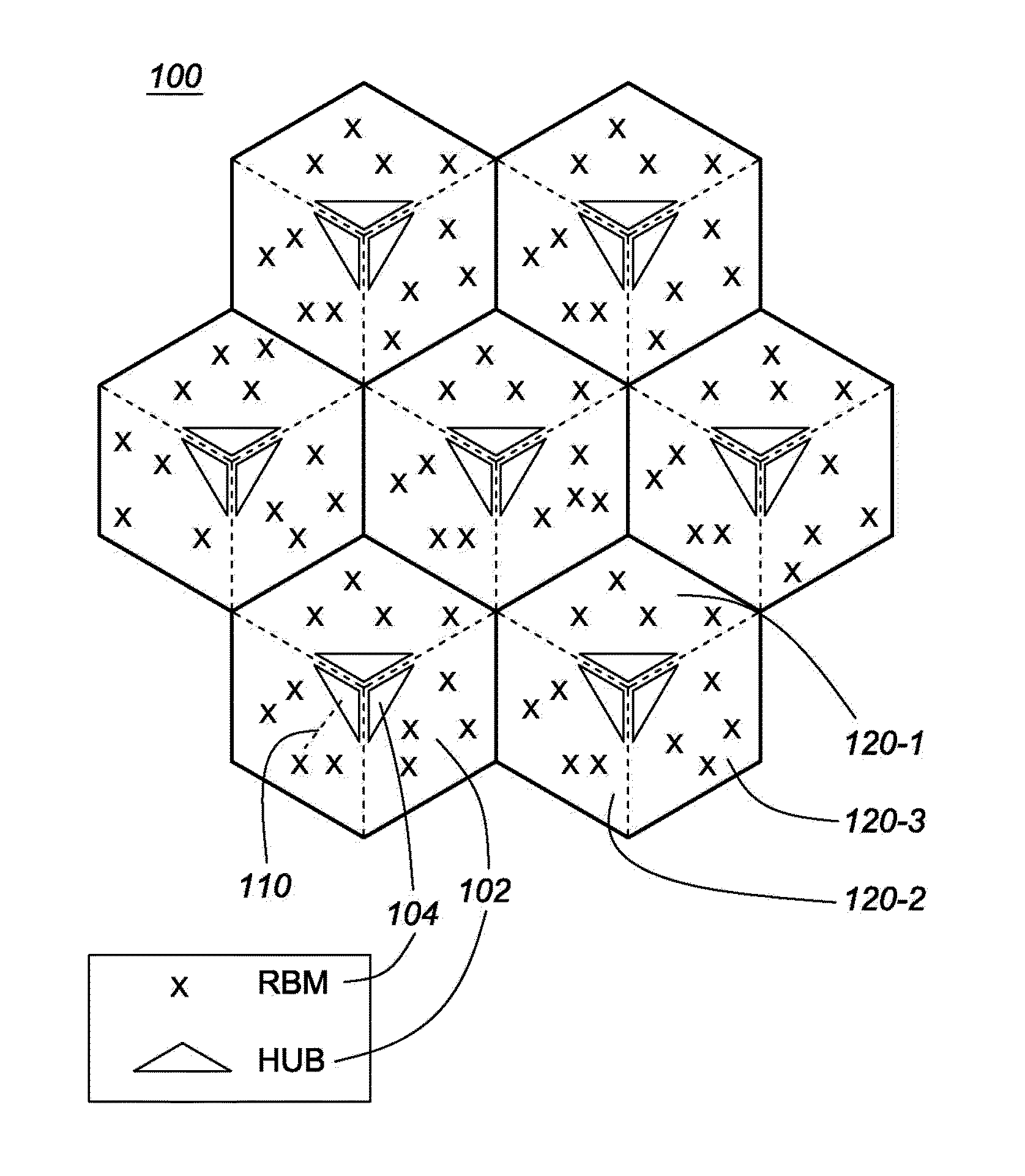
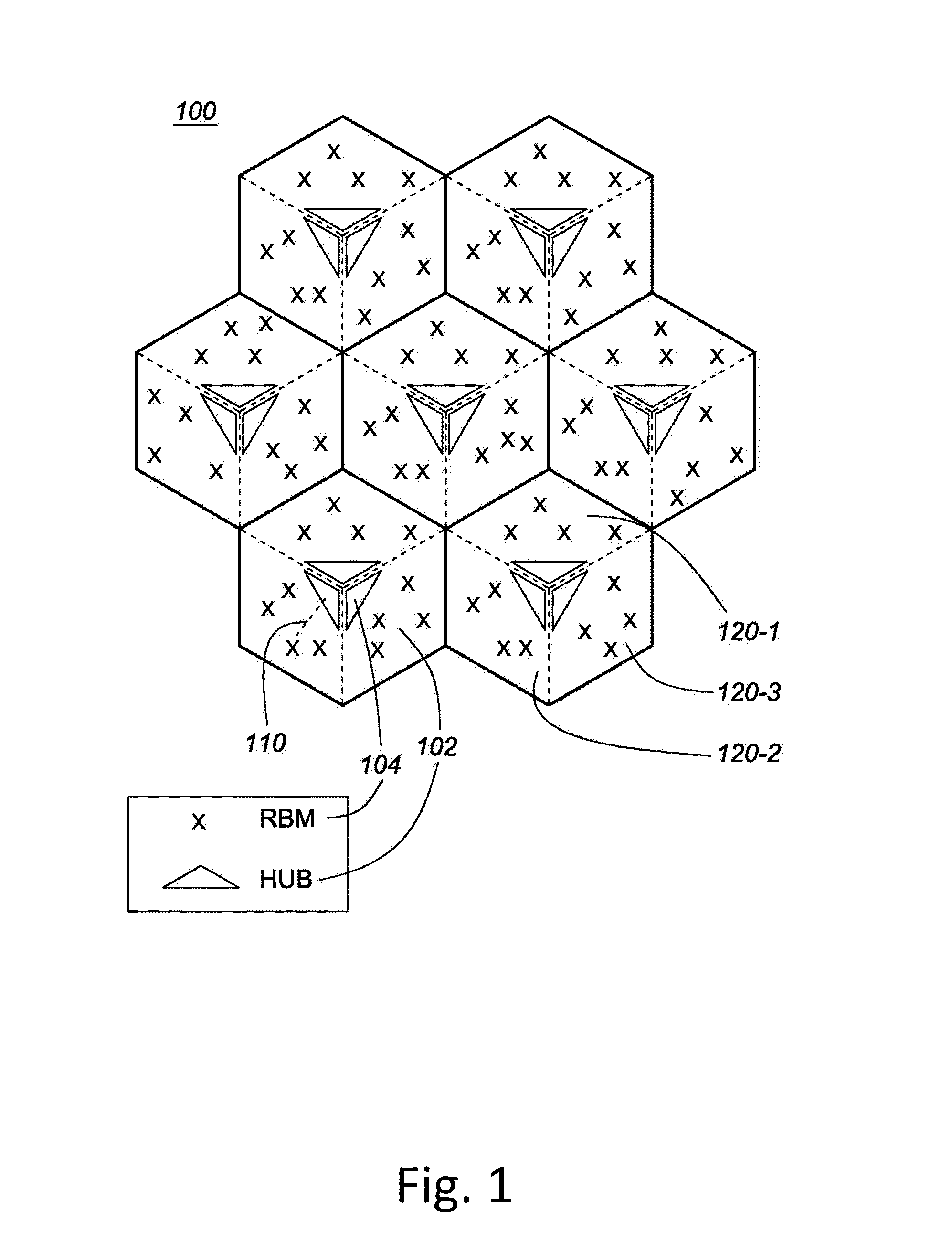
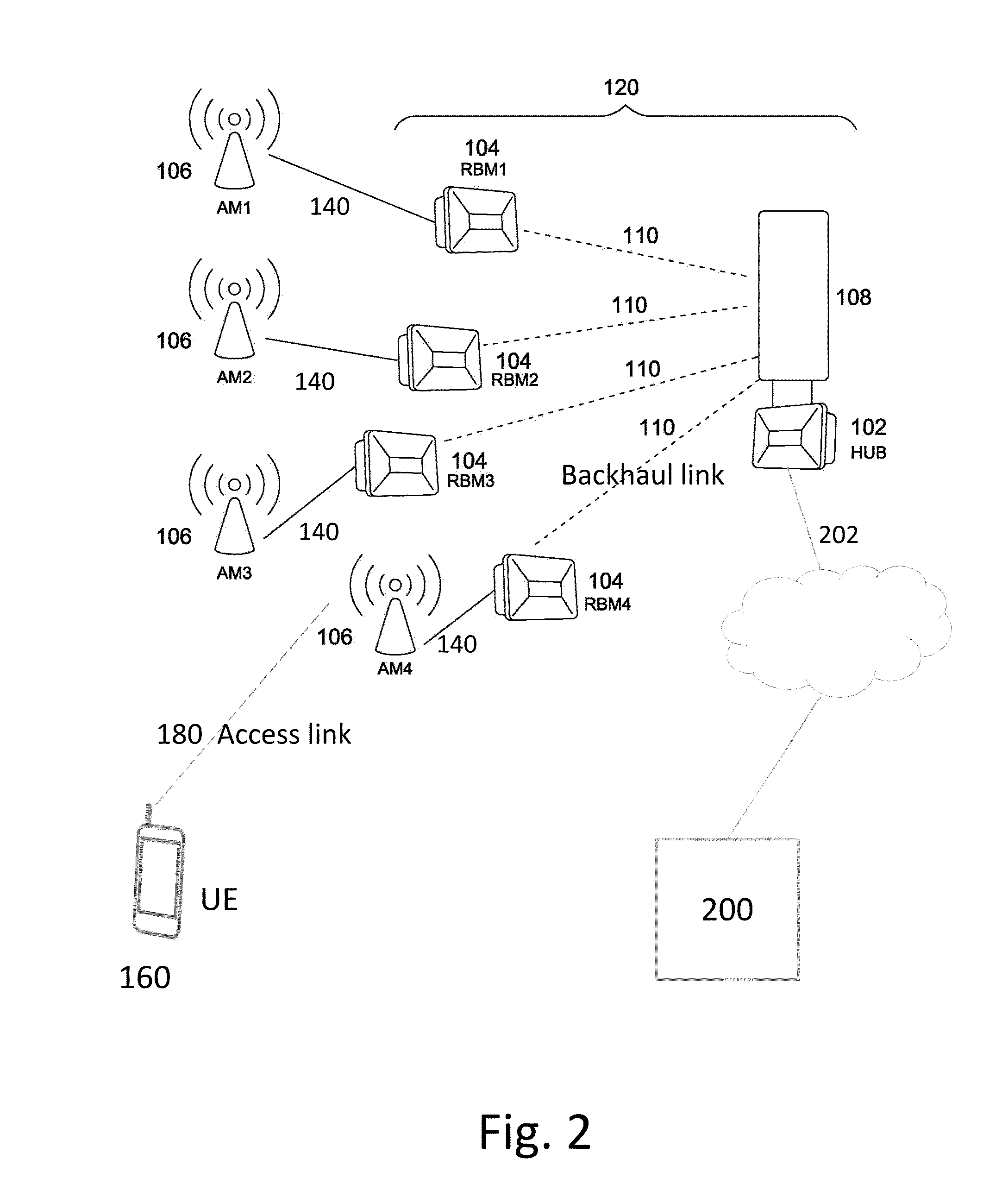
Method and system for network planning in fixed wireless backhaul networks
ActiveUS20160269911A1Eliminate, orReduce disadvantagesNetwork topologiesNetwork planningTerrainSystems design
Systems and methods are disclosed for networking planning for fixed backhaul networks comprising a plurality of hubs, each serving one or more RBMs. The method comprises one or more of terrain pathloss (PL) and antenna gain prediction; network design comprising site association, hub dimensioning and pointing; and optimization of small cell (SC) deployment. PL prediction is based on correlation of user input parameters with reference use cases for channel models for each of downtown, urban, and suburban deployment scenarios. Rapid and effective network planning is achieved with limited input data, even in the absence of high resolution digital maps or building polygons, by selecting the channel model having a highest correlation with available environmental parameters. Optimization of network topology design, system design, and SC deployment, with both access link and backhaul link evaluation, is based on optimization of a sum-utility function across all links for feasible SC site locations.
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
Ultrasonic strain imaging device with selectable cost-function
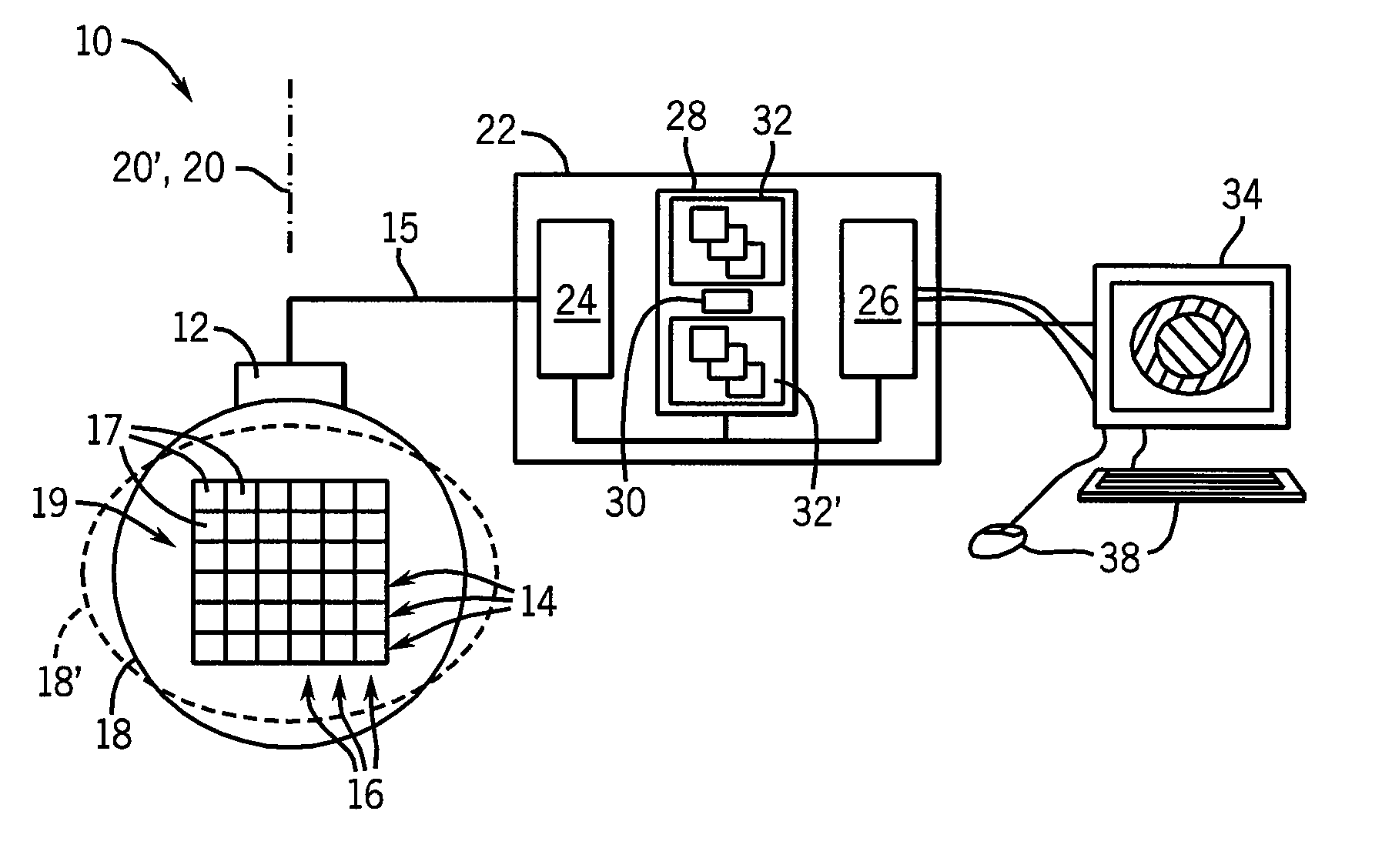
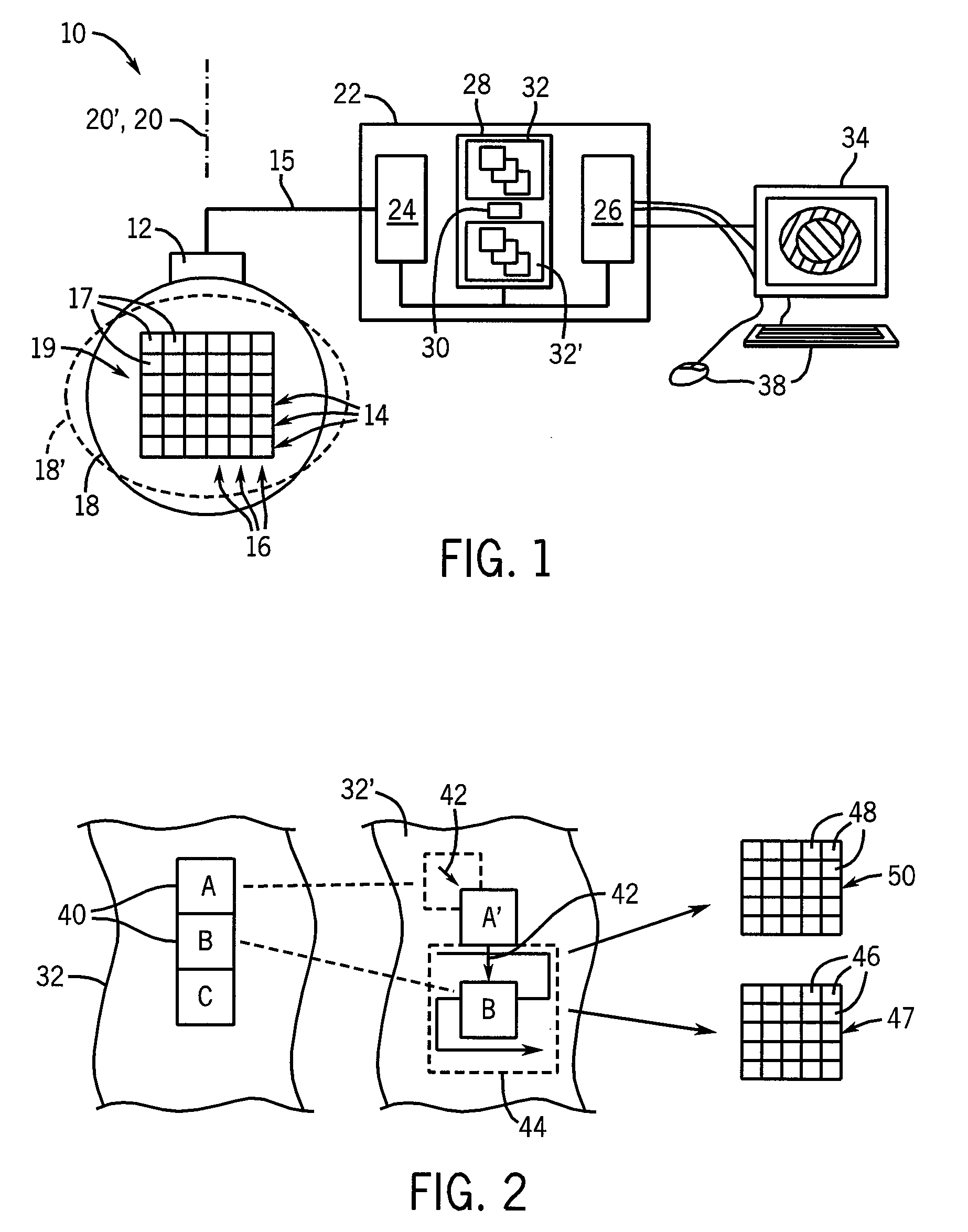
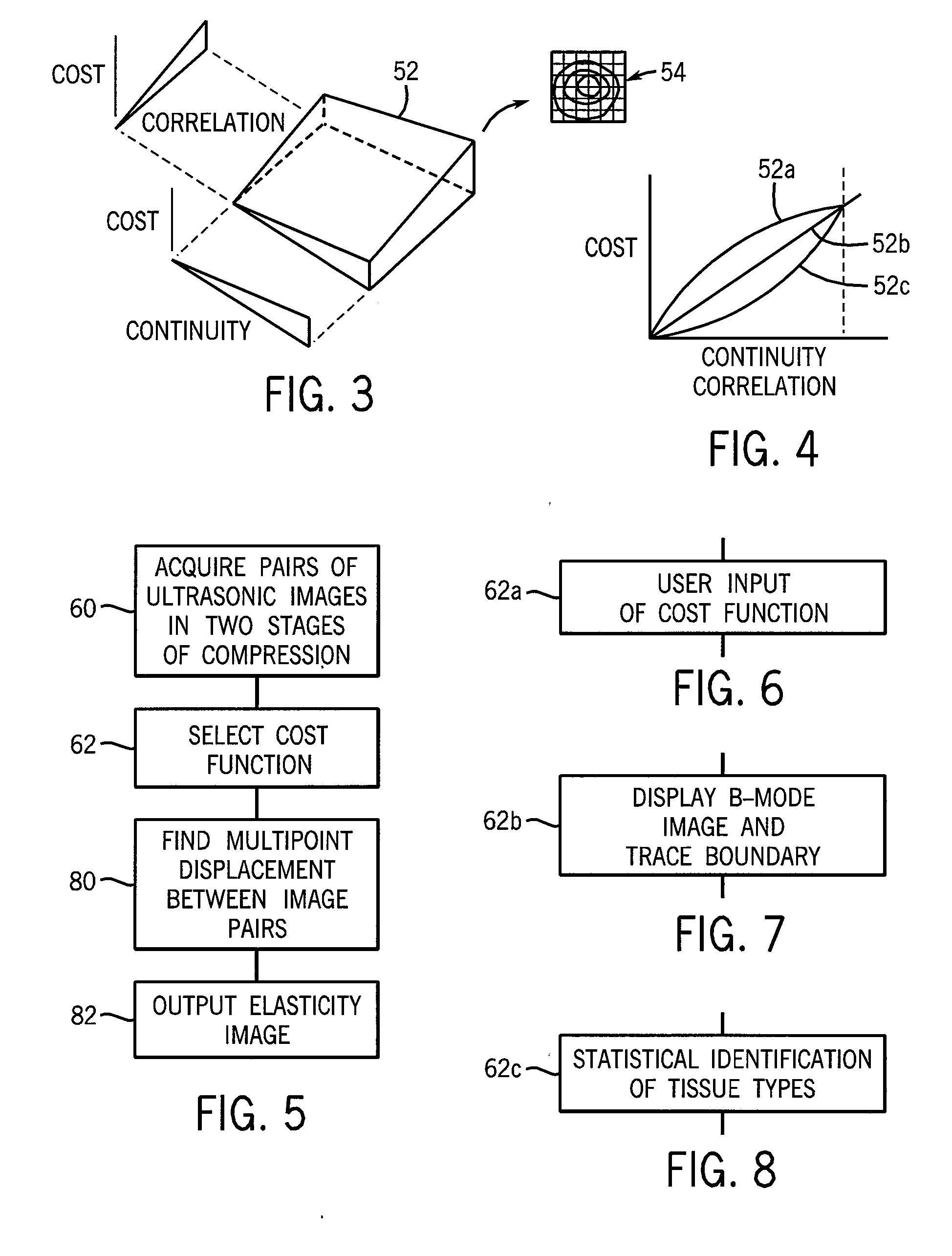
ActiveUS20100106018A1Enhance the imageInherent tensionOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsPre deformationTissues types
An elasticity measuring system determines tissue displacement between a pre-deformation and post-deformation image by a matching process using a cost function accepting as its arguments continuity of the tissue motion and correlation of the tissue in making the block matching. The invention allows the selection among different cost functions for different imaging situations or tissue types, to provide improved displacement calculations using a priori knowledge about the tissue and structure of tissue interfaces or information derived during the scanning process.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com