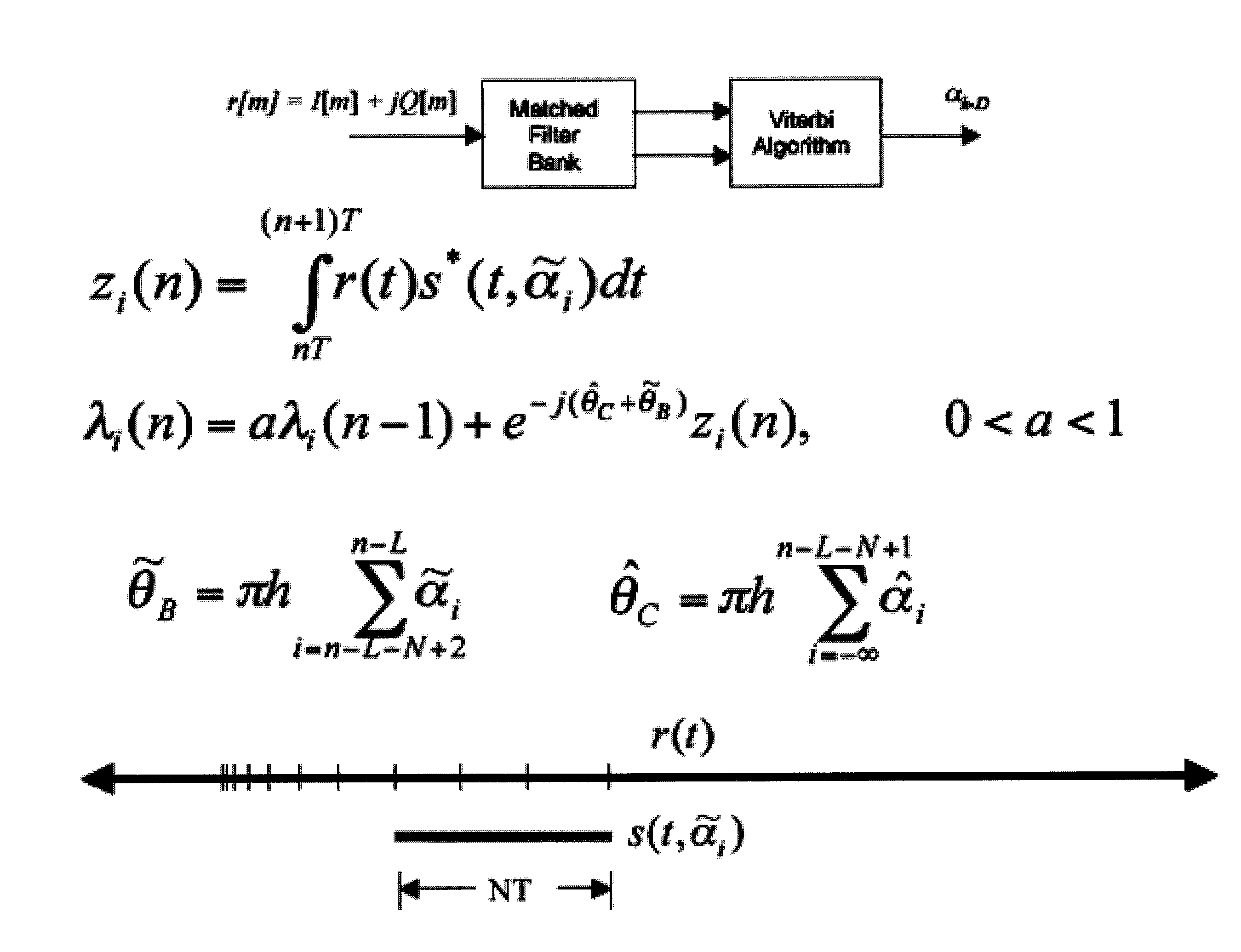Patents
Literature
565 results about "Channel models" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
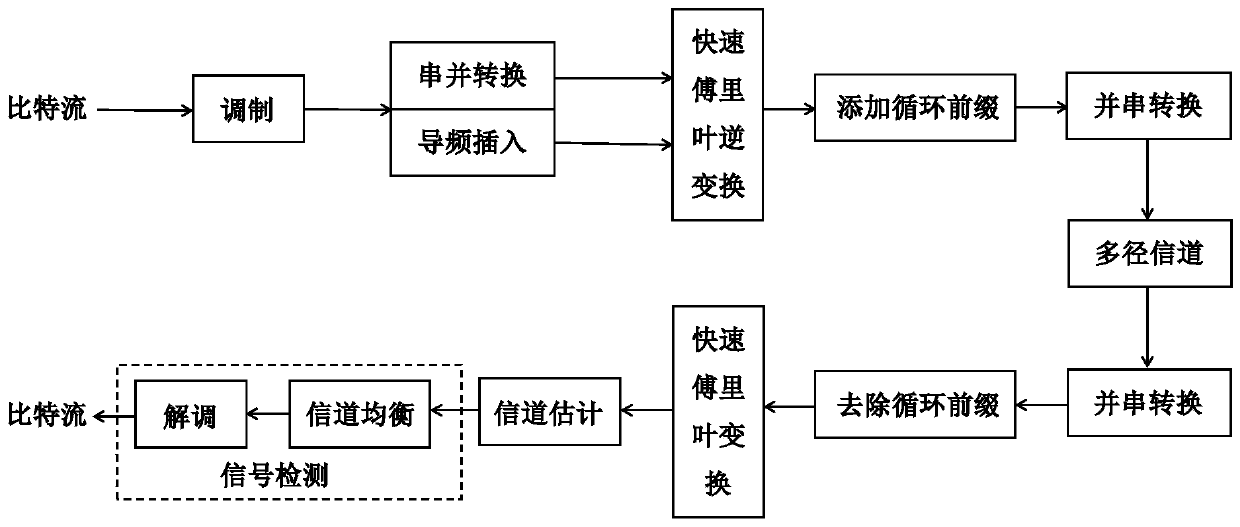
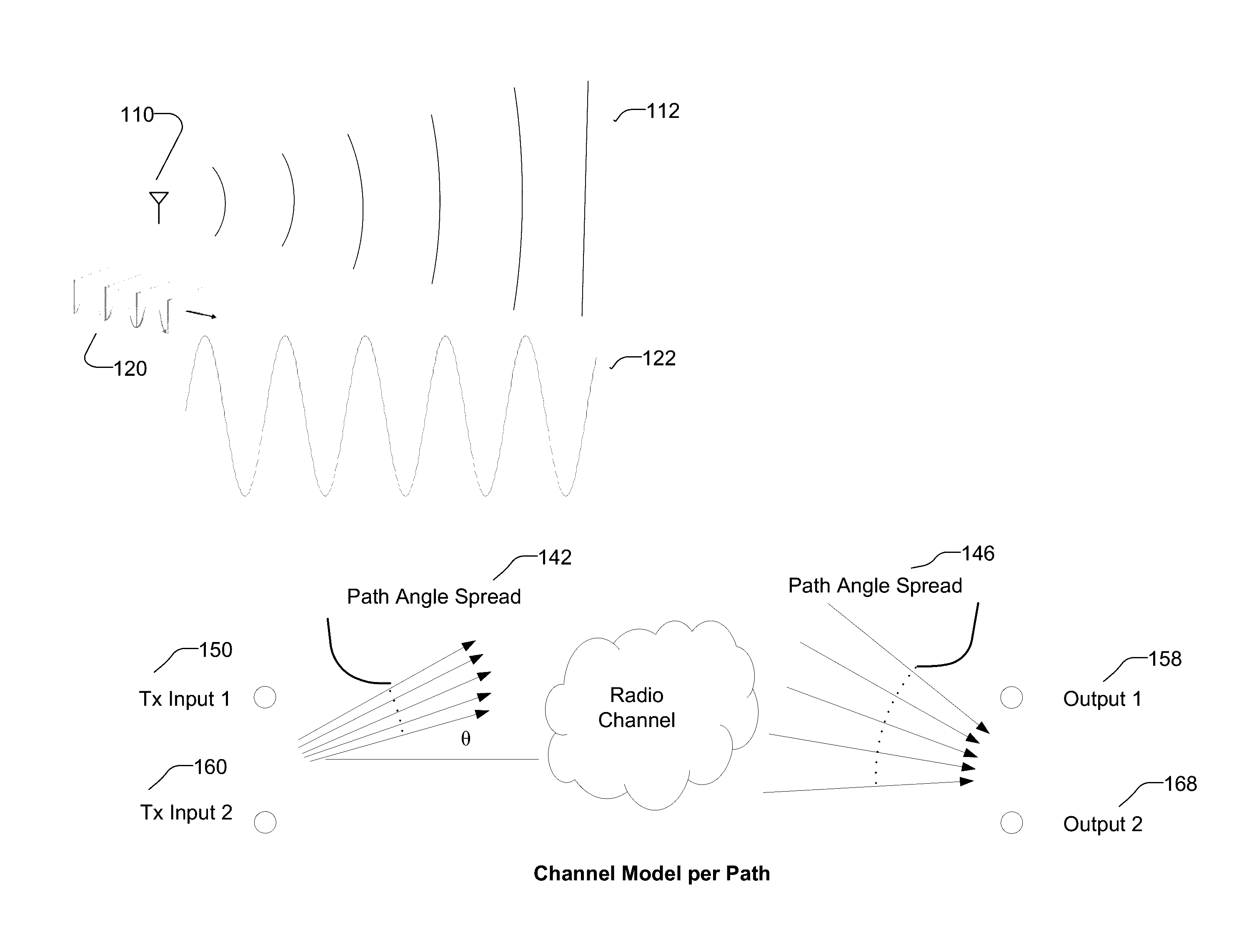
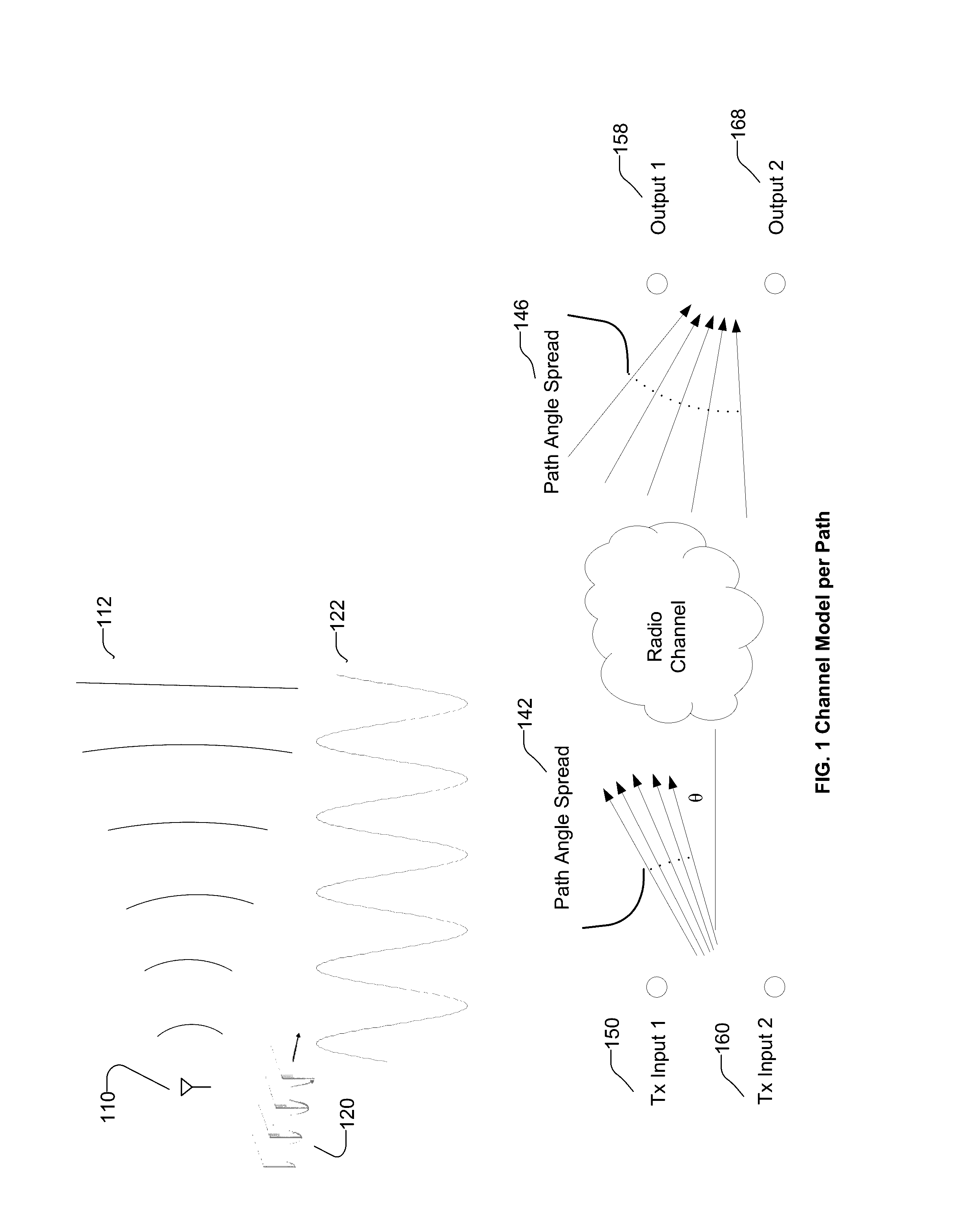
A channel model is an essential piece of a physical layer communication simulation. It is a mathematical representation of the effects of a communication channel through which wireless signals are propagated. The channel model is the impulse response of the channel medium in the time domain or its Fourier transform in the frequency domain.
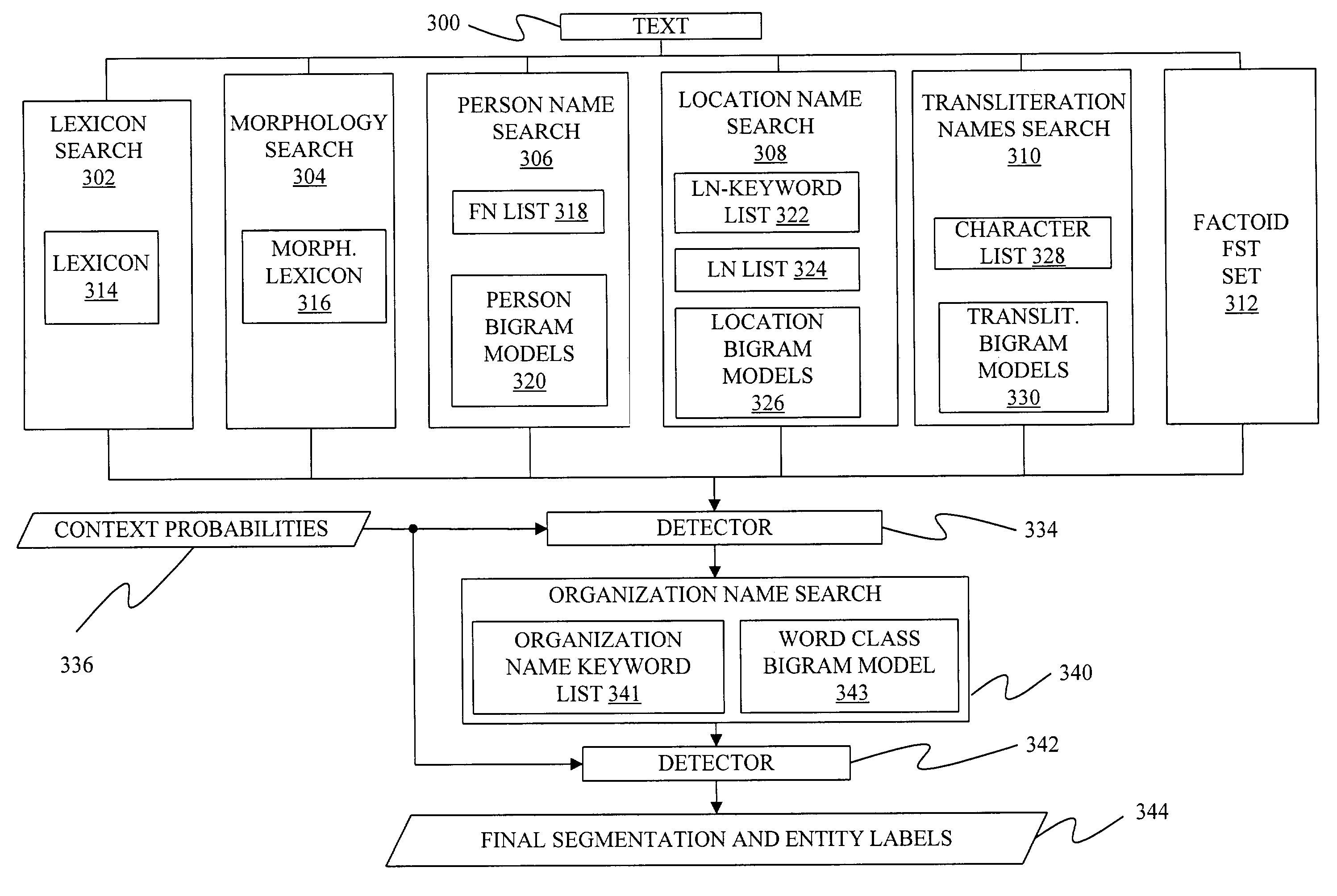
Using source-channel models for word segmentation
A method and apparatus for segmenting text is provided that identifies a sequence of entity types from a sequence of characters and thereby identifies a segmentation for the sequence of characters. Under the invention, the sequence of entity types is identified using probabilistic models that describe the likelihood of a sequence of entities and the likelihood of sequences of characters given particular entities. Under one aspect of the invention, organization name entities are identified from a first sequence of identified entities to form a final sequence of identified entities.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
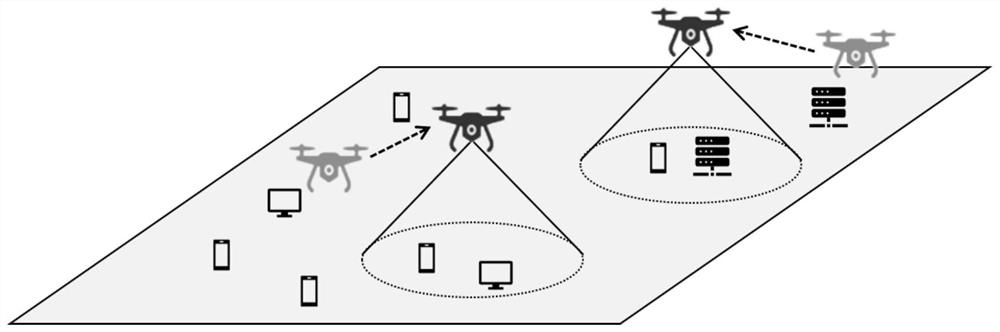
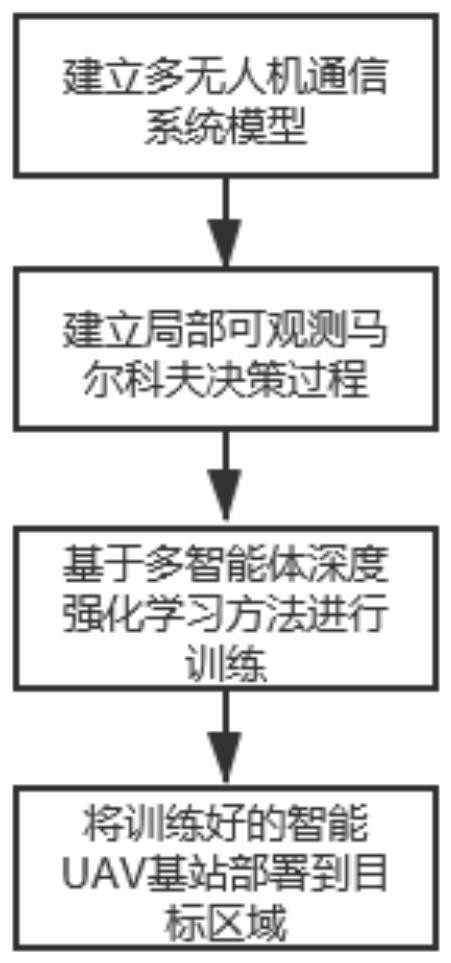
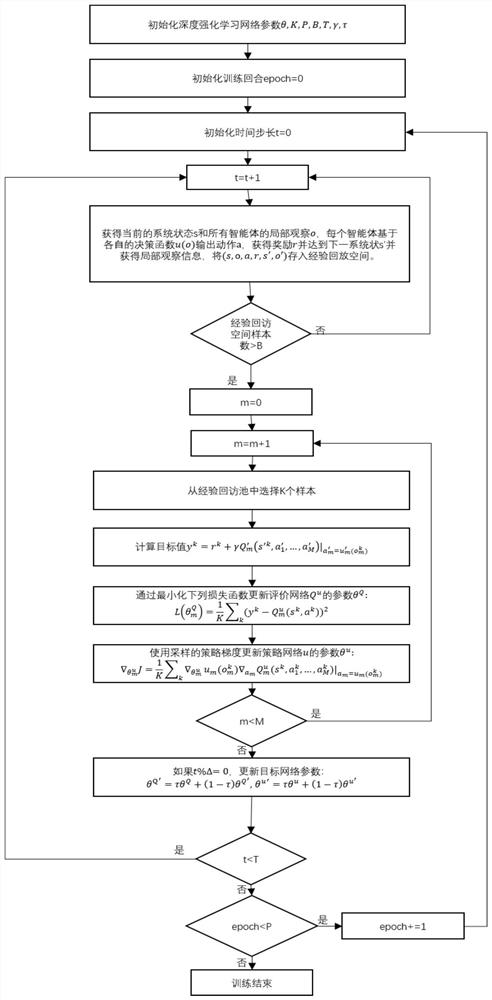
Unmanned aerial vehicle network hovering position optimization method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN111786713AReduce energy consumptionEnsure fairnessRadio transmissionNeural learning methodsSimulationUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle network hovering position optimization method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, modeling a channel model, a coverage model and an energy loss model in an unmanned aerial vehicle to ground communication scene; modeling a throughput maximization problem of the unmanned aerial vehicleto ground communication network into a locally observable Markov decision process; obtaining local observation information and instantaneous rewards through continuous interaction between the unmanned aerial vehicle and the environment, conducting centralized training based on the information to obtain a distributed strategy network; deploying a strategy network in each unmanned aerial vehicle, so that each unmanned aerial vehicle can obtain a moving direction and a moving distance decision based on local observation information of the unmanned aerial vehicle, adjusts the hovering position, and carries out distributed cooperation. In addition, proportional fair scheduling and unmanned aerial vehicle energy consumption loss information are introduced into an instantaneous reward function,the fairness of the unmanned aerial vehicles for ground user services is guaranteed while the throughput is improved, energy consumption loss is reduced, and the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster can adapt to the dynamic environment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
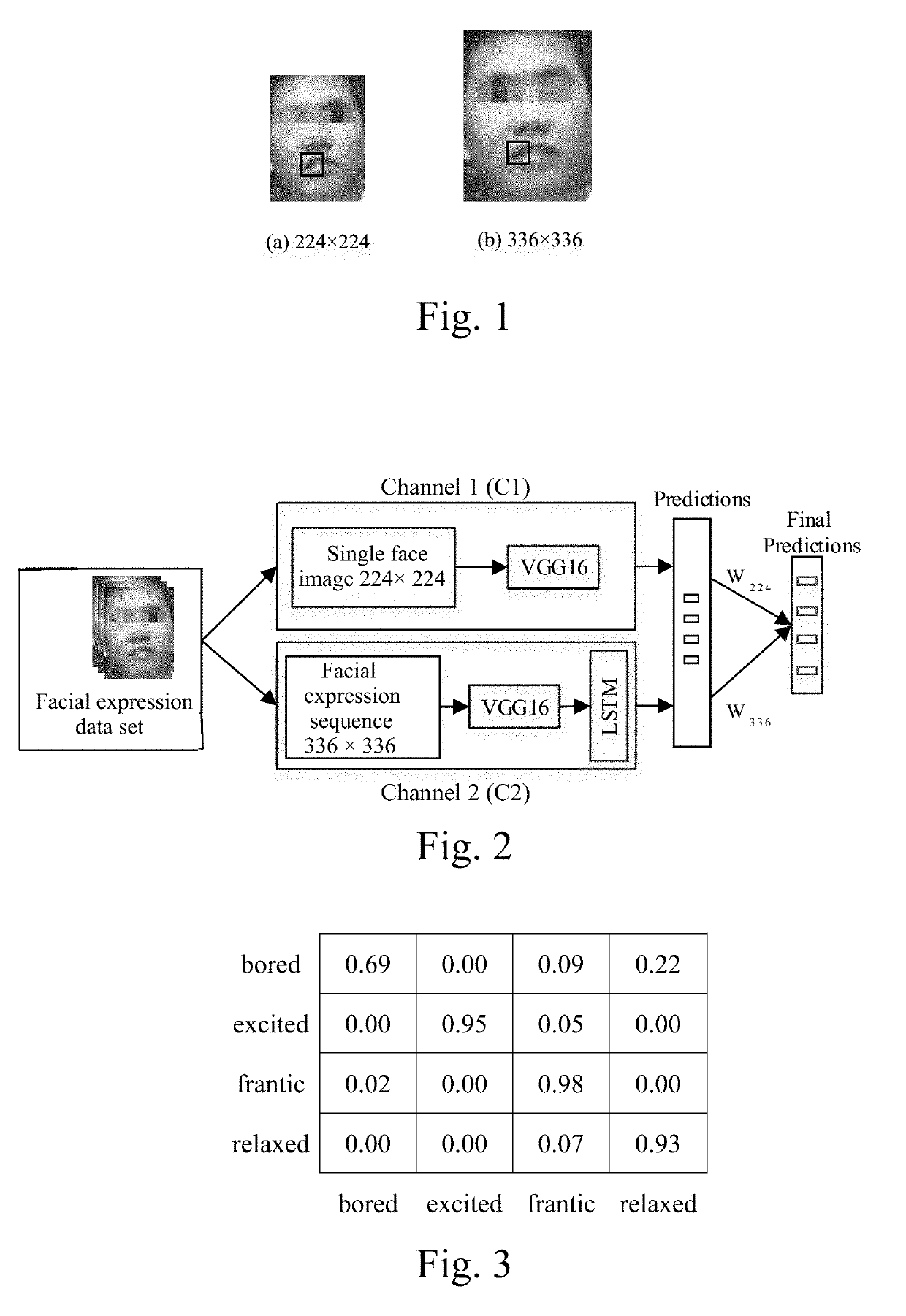
Face emotion recognition method based on dual-stream convolutional neural network
ActiveUS20190311188A1Low accuracyPromote resultsNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsManual extractionChannel network
A face emotion recognition method based on dual-stream convolutional neural network uses a multi-scale face expression recognition network to single frame face images and face sequences to perform learning classification. The method includes constructing a multi-scale face expression recognition network which includes a channel network with a resolution of 224×224 and a channel network with a resolution of 336×336, extracting facial expression characteristics at different resolutions through the recognition network, effectively combining static characteristics of images and dynamic characteristics of expression sequence to perform training and learning, fusing the two channel models, testing and obtaining a classification effect of facial expressions. The present invention fully utilizes the advantages of deep learning, effectively avoids the problems of manual extraction of feature deviations and long time, and makes the method provided by the present invention more adaptable. Moreover, the present invention improves the accuracy and productivity of expression recognition.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
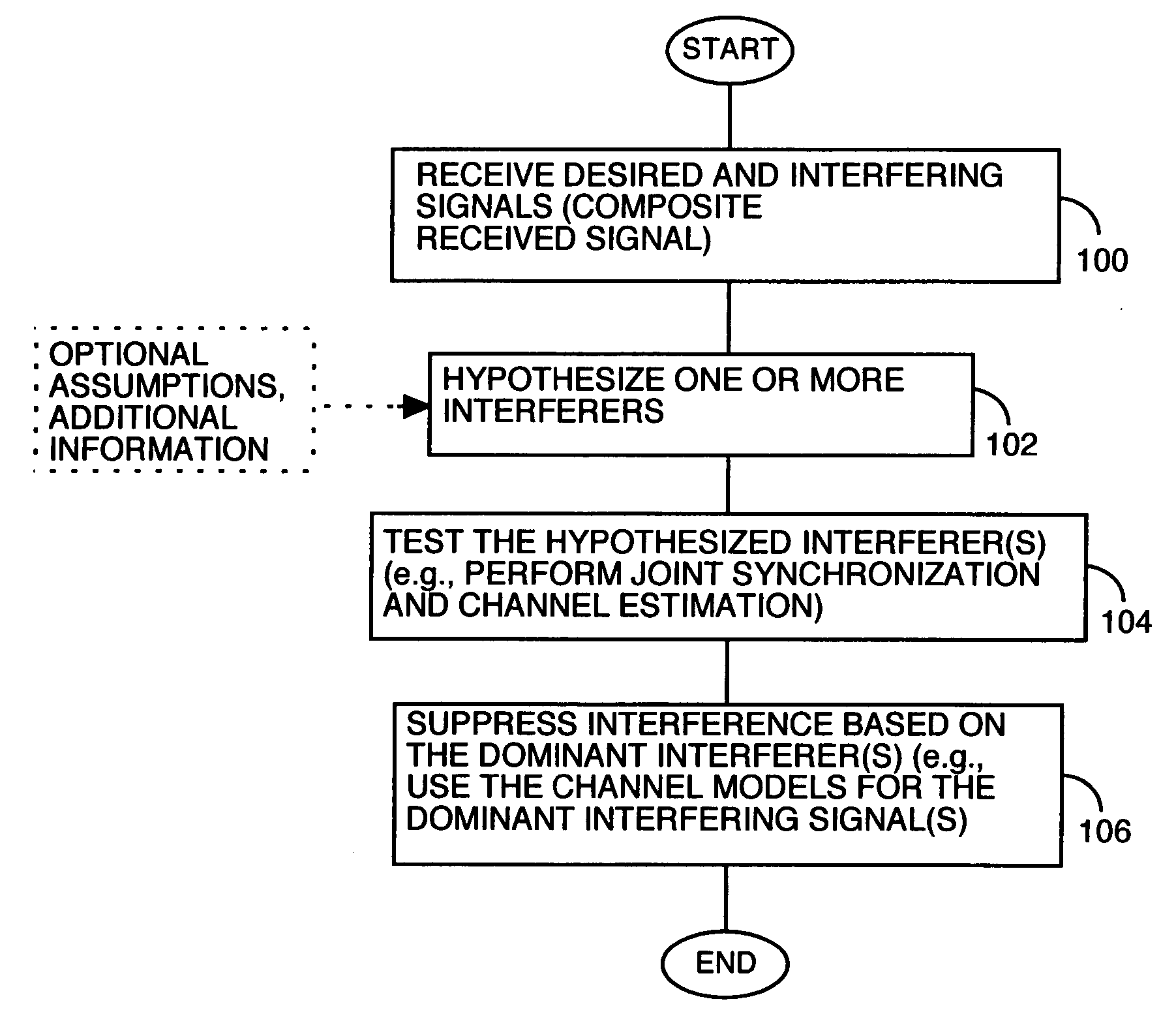
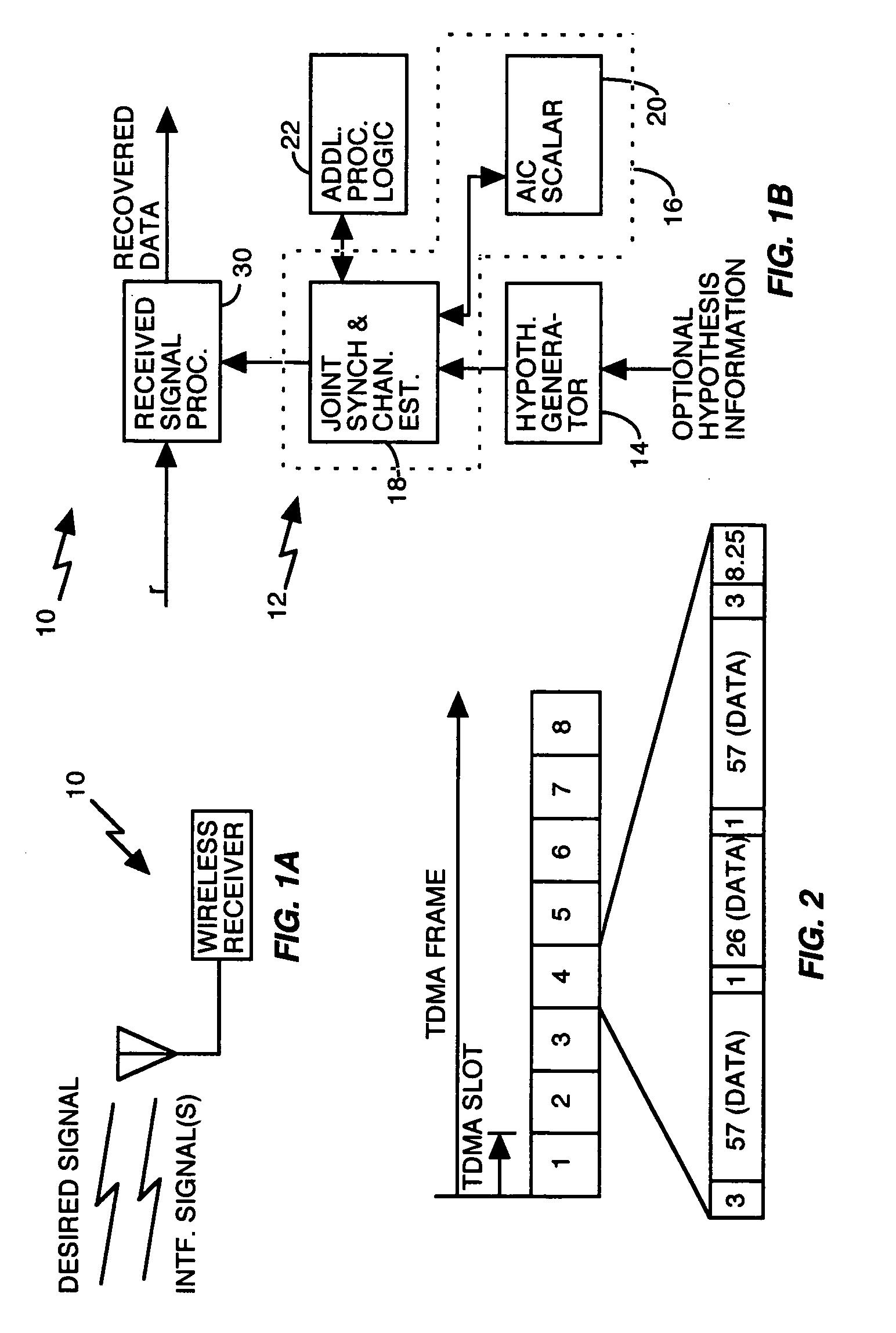
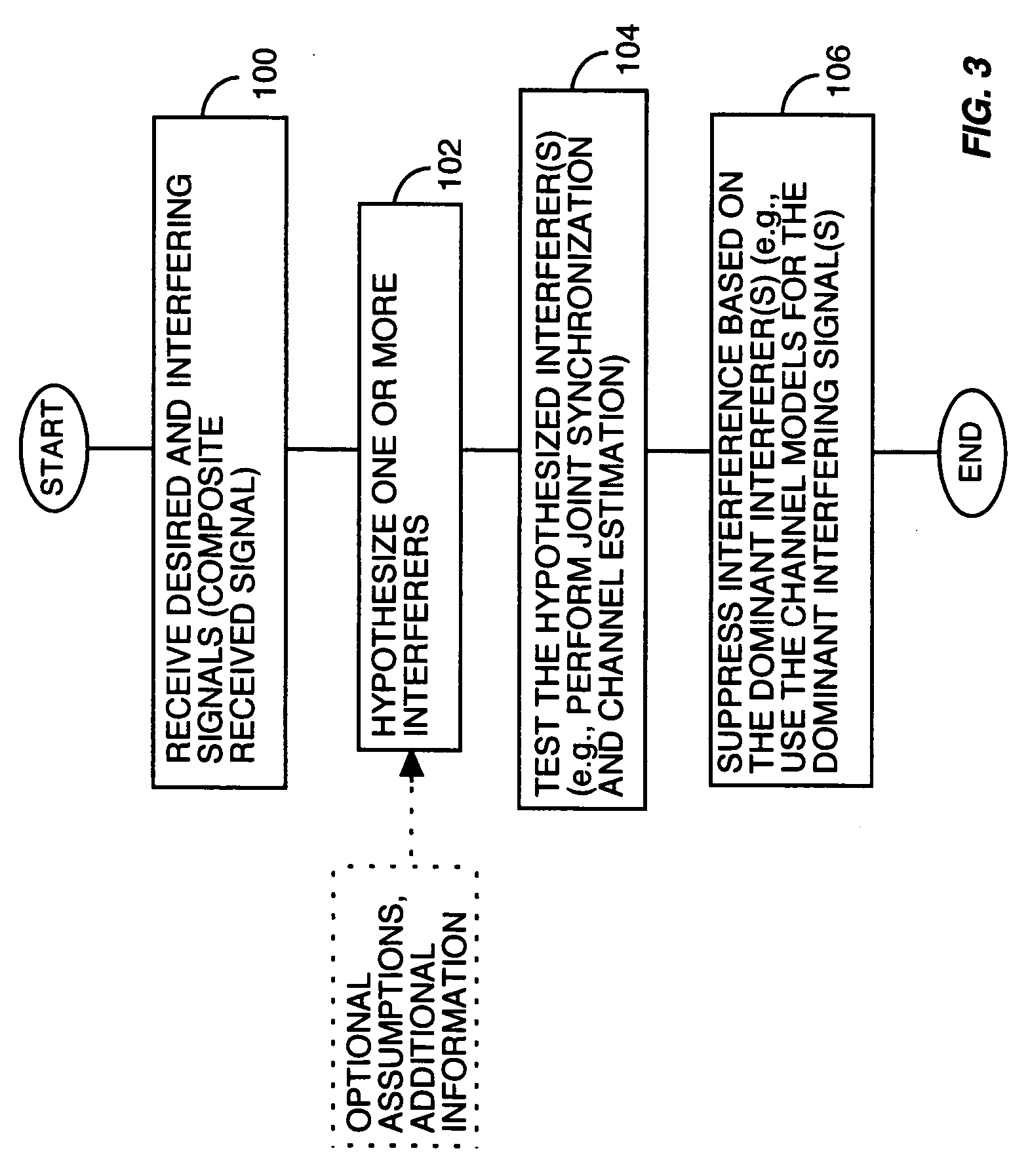
Method and apparatus for multi-user interference determination an rejection
InactiveUS20050095985A1Synchronisation signal speed/phase controlTransmission monitoringMulti user interferenceChannel models
A receiver circuit identifies one or more interfering signals received with a desired signal by generating and evaluating one or more hypothesized interferers. By testing these hypotheses, such as through joint synchronization and channel estimation for the desired signal and the one or more hypothesized interferers, the circuit identifies which hypothesized interferer(s) best correspond to the dominant interfering signal(s) actually received. Channel models thus obtained for the dominant interferer(s) may be used in, for example, generating a whitening filter used in interference suppression, or jointly demodulating the desired and interfering signal(s).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
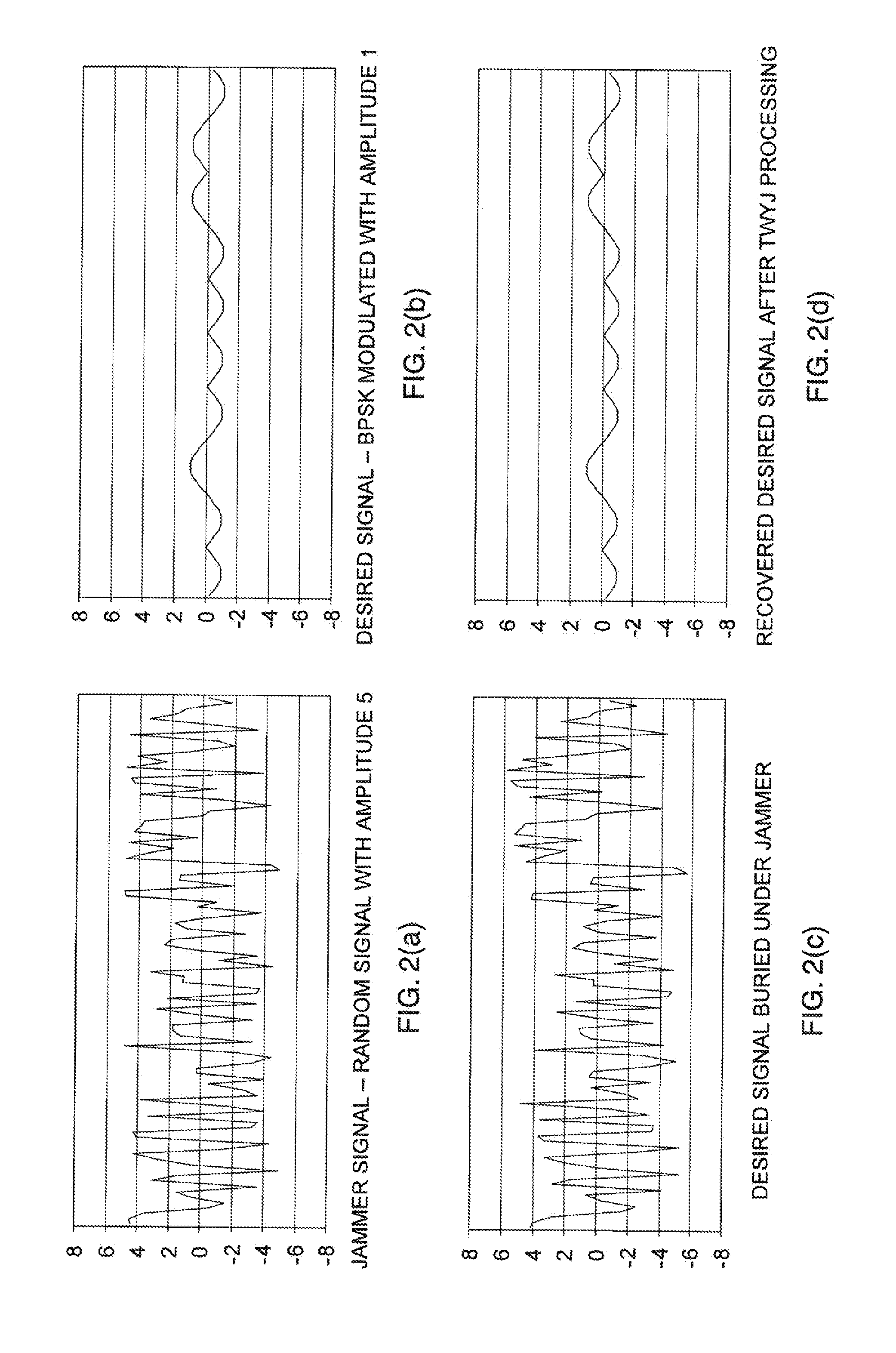
Tactical radio and radio network with electronic countermeasures
A tactical radio includes a radio frequency (RF) processing module having a receiving component path and a transmitting component path. A signal processing module coupled to the RF processing module includes a jammer detection stage for identifying a type of jamming signal on a channel over which communications signals are received simultaneously. A jammer model stage in the signal processing module produces a waveform model for the jamming signal, and a channel model stage replicates propagation conditions on the channel and produces a corresponding cancellation signal. The cancellation signal is coupled at such a level into the receiving component path so as to cancel the jamming signal from received communications signals at the front end of the radio. Any residual jamming signals may then be removed by a secondary jamming cancellation stage operating at baseband.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
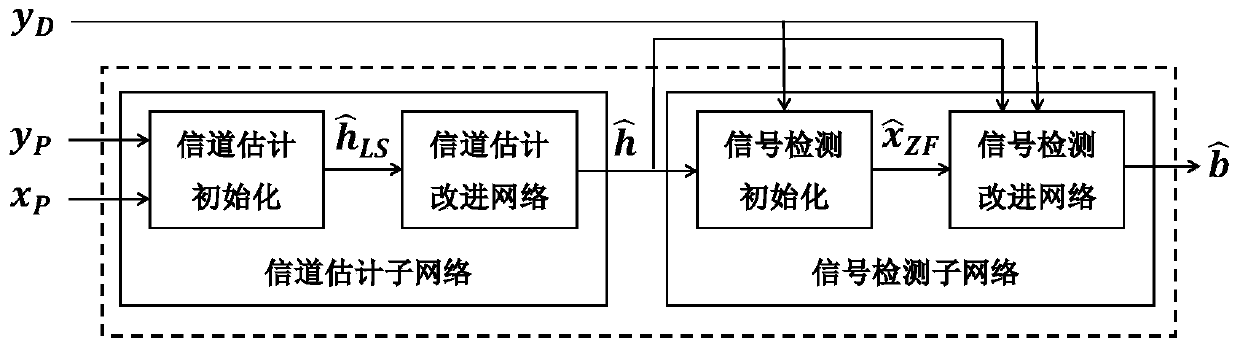
OFDM channel estimation and signal detection method based on deep learning
ActiveCN111404849AEffectively reflect nonlinear characteristicsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksNeural architecturesAlgorithmUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses an OFDM channel estimation and signal detection method based on deep learning, and belongs to the field of unmanned aerial vehicle measurement and control communication. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, generating a sample database of an OFDM multipath channel model matrix in a complex environment based on an existing No-WSSUS channel model; then, constructing a neural network comprising a channel estimation sub-network and a signal detection sub-network, and training the neural network by utilizing the data sample of the multipath channel model matrix; finally, applying the trained neural network to the OFDM data link system of the unmanned aerial vehicle in a complex environment in an off-line mode, and detecting signals while a channel is estimated. According to the method, a large-data-volume channel sample set capable of reflecting OFDM channel characteristics in a complex environment is generated, so that the whole network can effectivelyreflect nonlinear characteristics of a wireless channel and a transmission signal.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
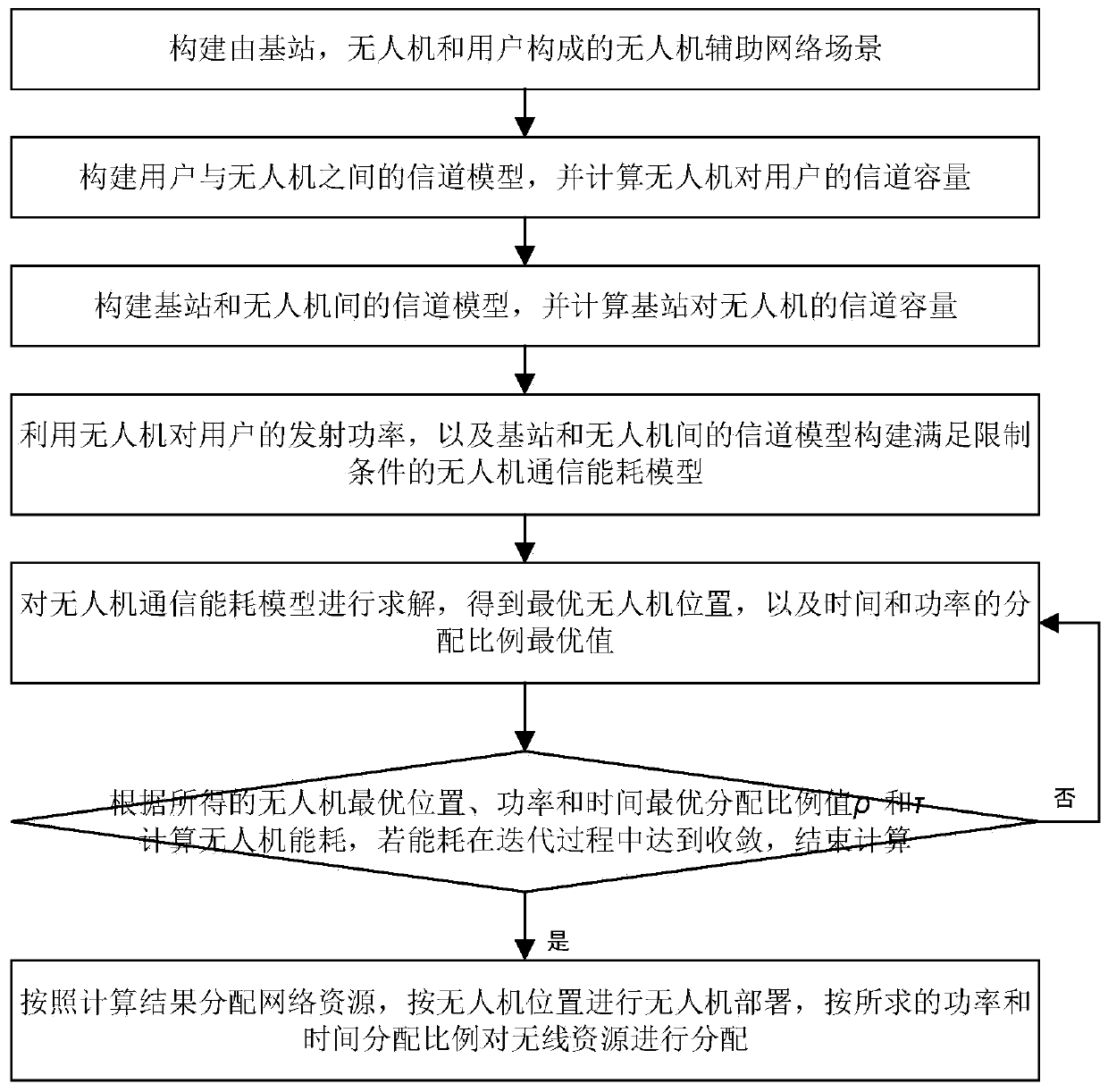
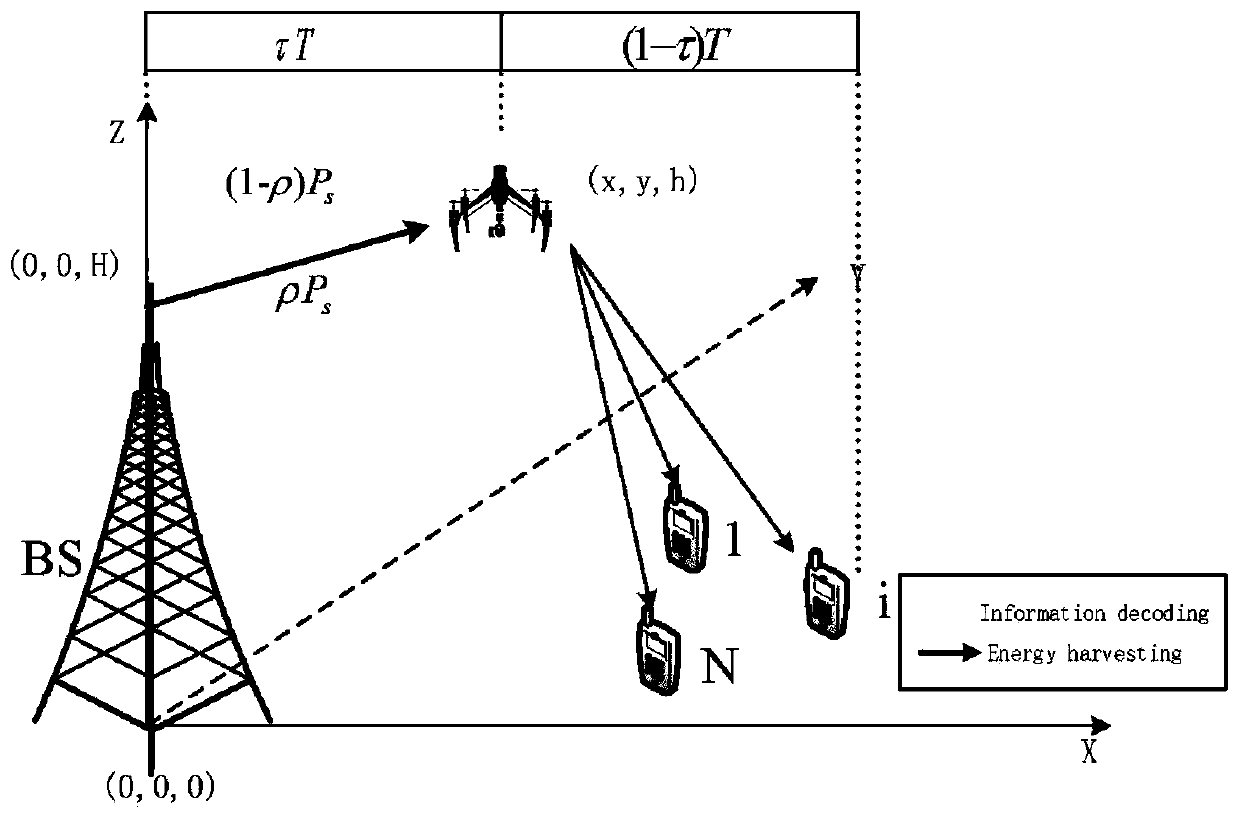
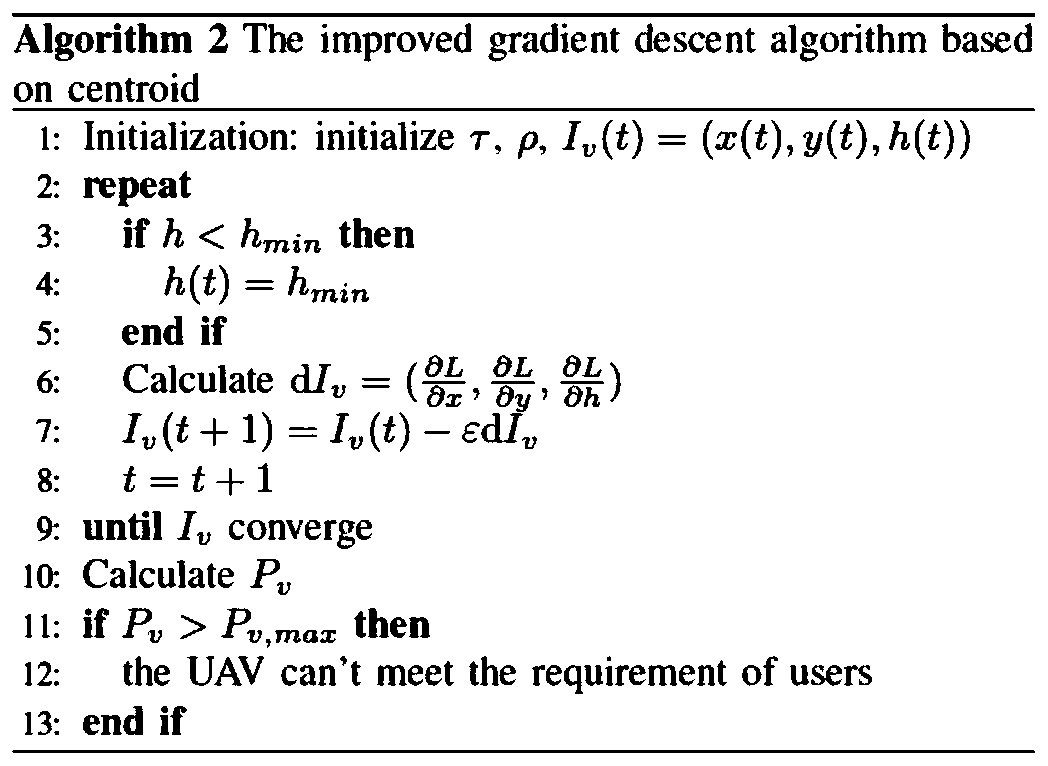
Resource allocation method in unmanned aerial vehicle auxiliary network based on wireless energy transmission
ActiveCN110958619AReduce consumptionMeeting Data Rate NeedsPower managementRadio transmissionResource assignmentSimulation
The invention discloses a resource allocation method in an unmanned aerial vehicle auxiliary network based on wireless energy transmission, and belongs to the field of mobile communication. The methodcomprises firstly, constructing an unmanned aerial vehicle auxiliary network scene composed of a base station, an unmanned aerial vehicle and a user; then separately constructing channel models and channel capacities between the user and the unmanned aerial vehicle and between the base station and the unmanned aerial vehicle; uing the transmitting power of the unmanned aerial vehicle to the userand the channel model between the base station and the unmanned aerial vehicle to construct and solve an unmanned aerial vehicle communication energy consumption model meeting a limiting condition, introducing a centroid concept to optimize the position of the unmanned aerial vehicle under the condition that a time distribution proportion and a power distribution proportion are given, continuously optimizing the time distribution proportion and the power distribution proportion under the condition that the position of the unmanned aerial vehicle is given, and alternately optimizing an optimalsolution; and deploying the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the optimal position of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and allocating wireless resources according to the solved optimal power and timedistribution proportion. According to the invention, the wireless energy is collected to the maximum extent while the requirement of user data rate is met, and the energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Massive MIMO array emulation
ActiveUS20170019154A1Spatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringCross correlation matrixEngineering
The disclosed technology relates to systems and methods for emulating a massive MIMO beamforming antenna array of arbitrary size—a channel model between a transmitter and a receiver, with one or more signal paths having respective amplitudes, angles of arrival, angle spreads, and delays. The disclosed technology includes defining a complete channel model H, calculating the correlation matrix for the channel, grouping the base antenna elements of the antenna array by combinations of signal and polarization, and calculating observed beamforming power of each group of the base elements, by applying a cross-correlation matrix to determine observed power signals and delay of each signal at each remote antenna element of the user equipment. Emulation includes supplying cross-correlated signals to remote antenna elements of user equipment during a RF test of the user equipment. Disclosed technology includes a channel emulator that generates output streams for testing user equipment for multiple users.
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
Bayesian Geolocation and Parameter Estimation by Retaining Channel and State Information
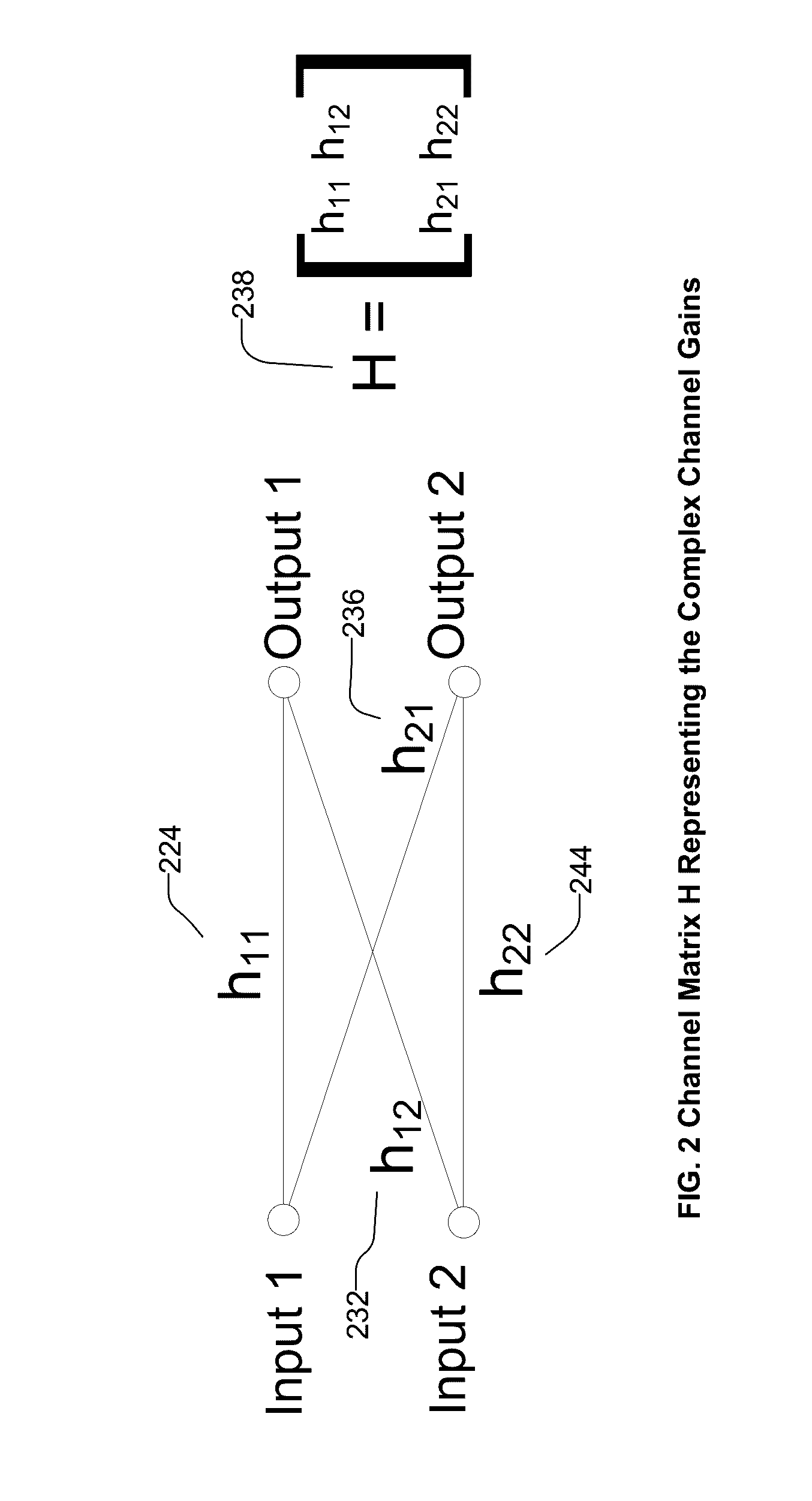
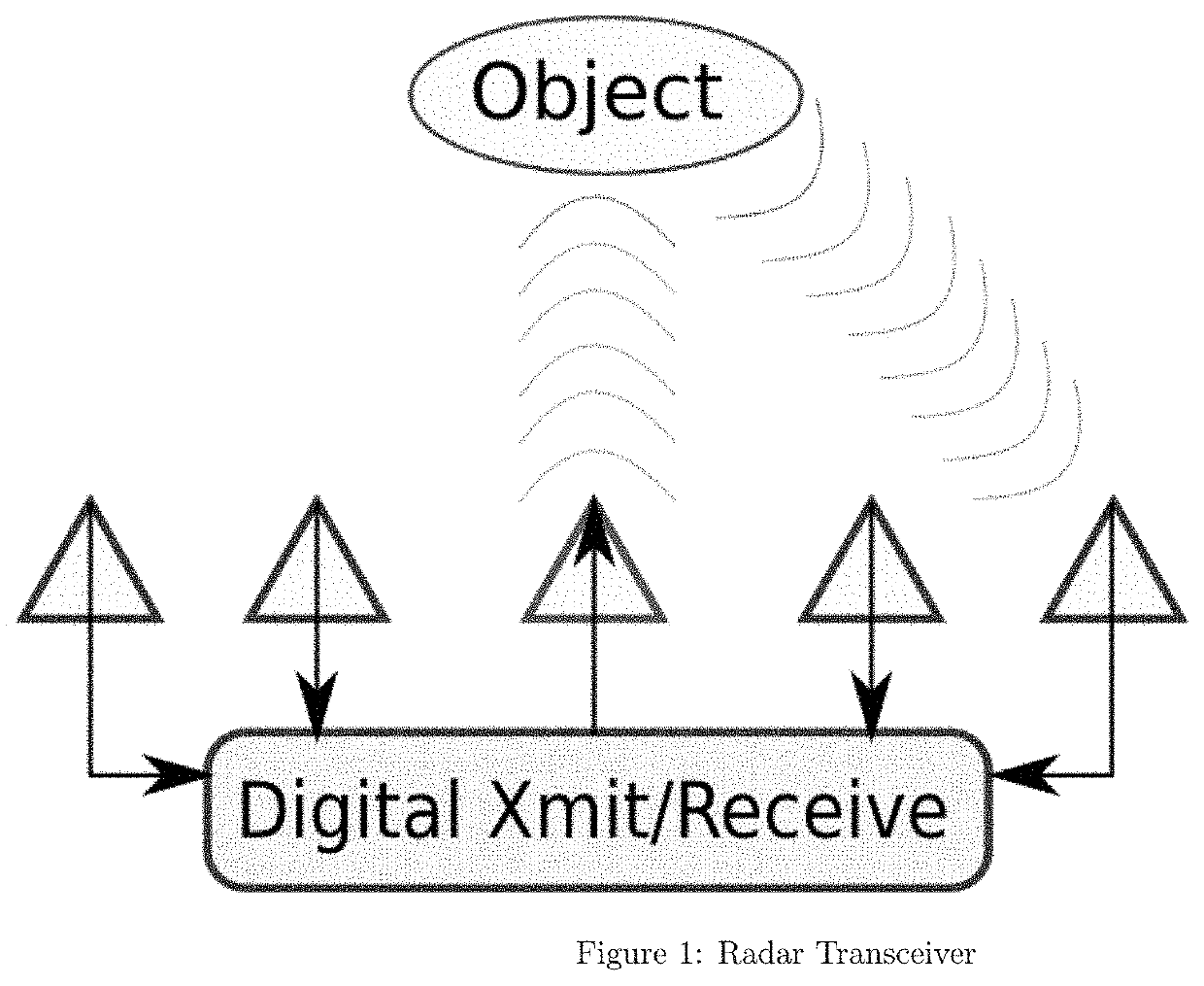
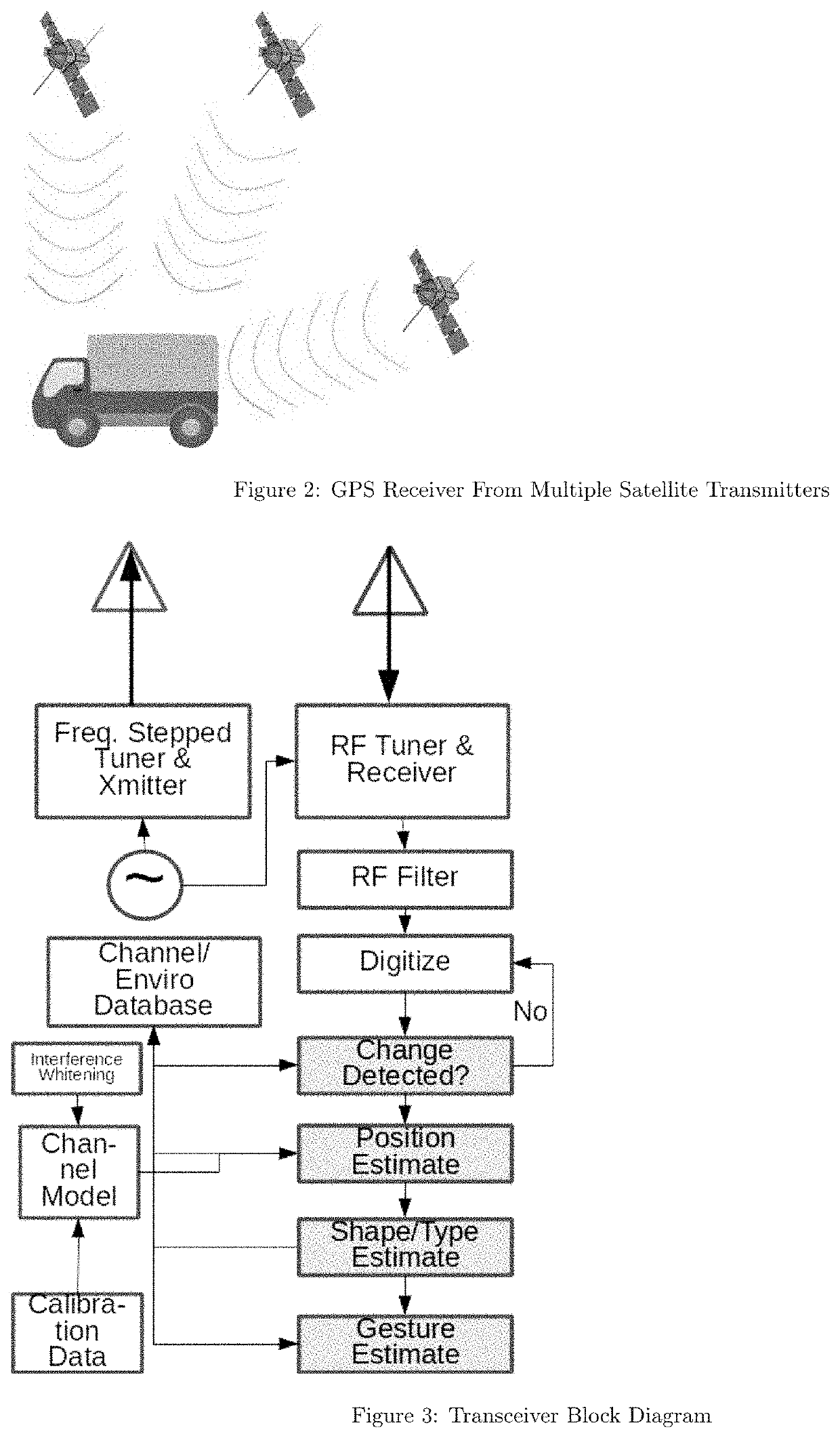
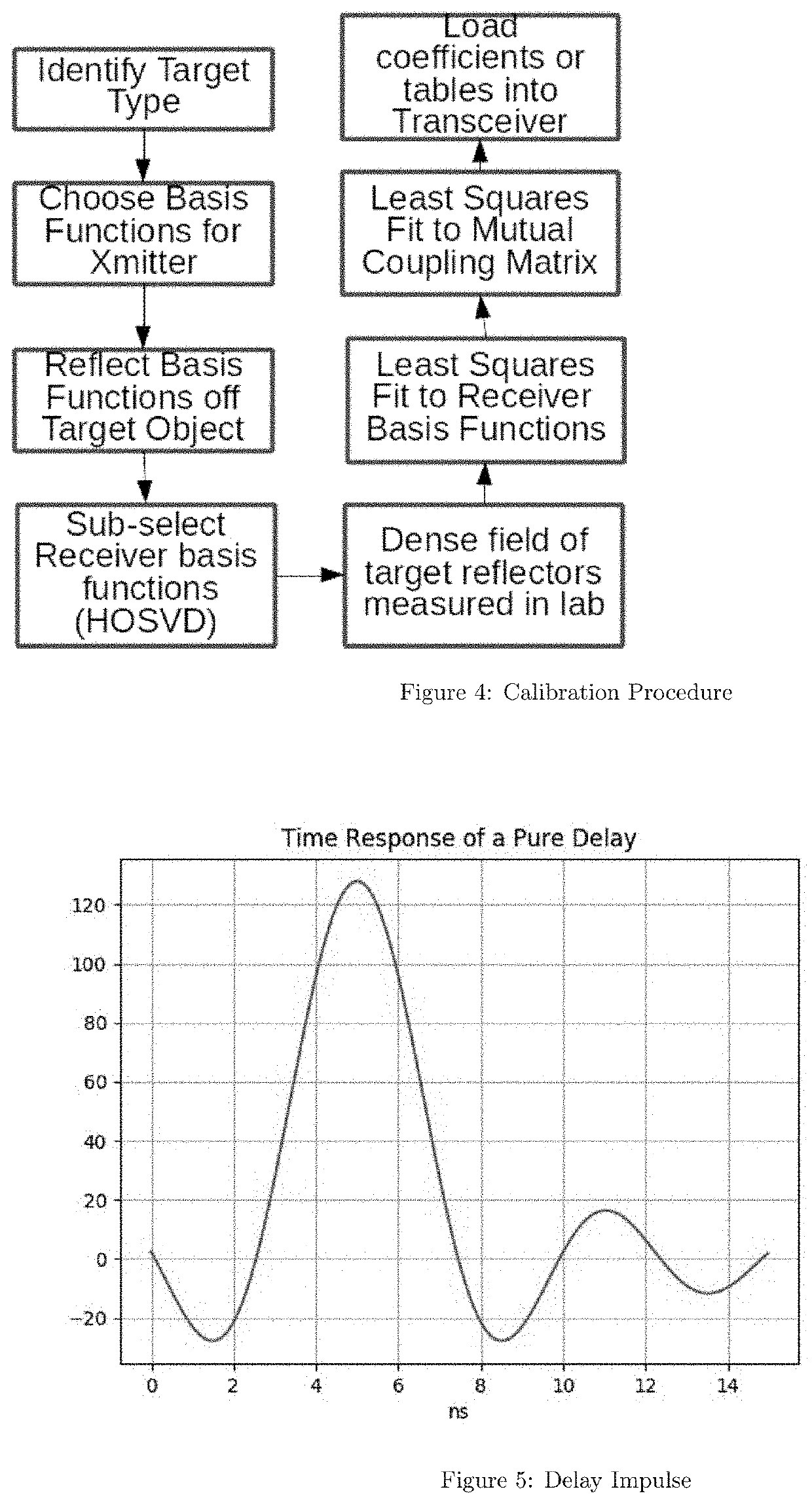
There is provided a method of parameter estimation in a multi-channel signal environment where a plurality of receive antennas receive signals from one or more transmitters that transmit a signal or wave that is reflected from one or more targets, or receive antennas that receive directly from the transmitters, whose received signals are processed over multiple frequencies or channels by a digital receiver. The method comprises (a) calibrating before the operation of the digital receiver to determine the free parameters of a mathematical model of a channel either as the channel model parameters or in the form of tabulated data; (b) calibrating during the operation of the digital receiver to determine the channel model; (c) comparing received antennas array voltages to an analytic or table driven channel model from a calibrated template without only relying on information lossy intermediate steps such as delay time of arrival or angle of arrival measurements; (d) creating a statistical likelihood function modeling receiver noise to determine model channel parameters or prior channel uncertainty; (e) saving target reflector / emitter parameters to be reused for dynamic tracking; and (f) using Bayesian particle filtering or Maximum Likelihood Methods to update mixture models for the unknown parameters.
Owner:MOVANO INC
Near space dynamic plasma sheath channel modeling and simulating method
ActiveCN104378170AGuaranteed feasibilityAvoiding undetectable problemsTransmission monitoringRegular patternChannel parameter
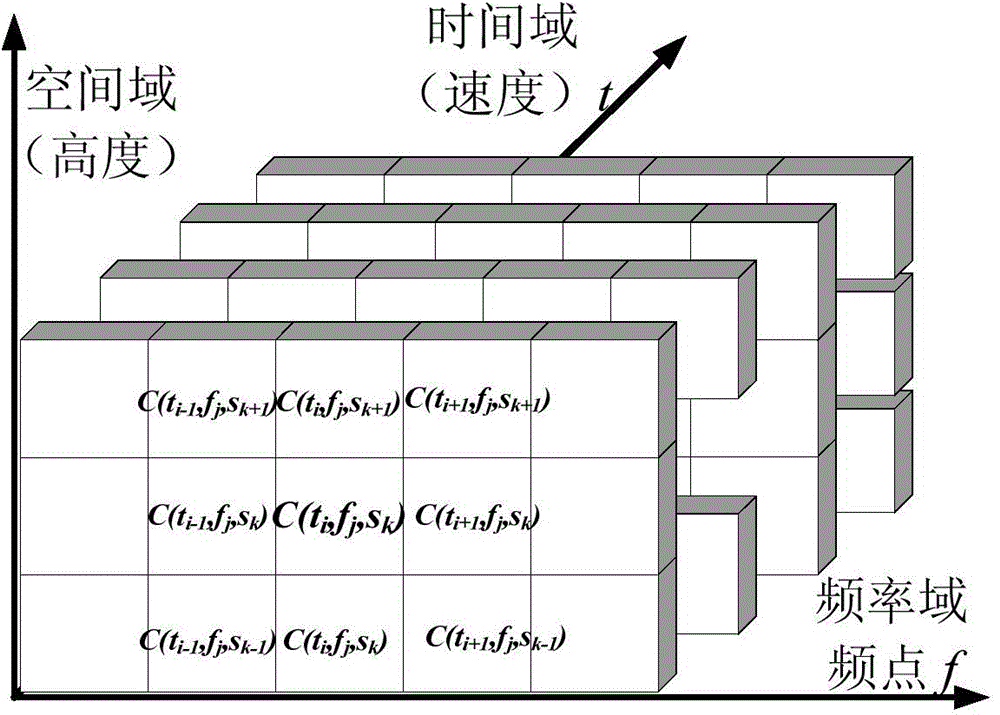
The invention discloses a near space dynamic plasma sheath channel modeling and simulating method. The method comprises the steps that channel resources are partitioned according to large-scale space-time-frequency characteristics to construct a large-scale space-time-frequency channel resource matrix, wherein the height corresponds to large-scale space domain characteristics, the speed corresponds to large-scale time domain characteristics, and frequency points correspond to large-scale frequency domain characteristics; for all channel resource matrixes, dynamic small-scale channel parameters are obtained; small-scale channel model simulating is achieved according to given small-scale channel parameters; large-scale channel model simulating is achieved by repeating small-scale channel models at multiple states on a near space flight path. The method is suitable for channel modeling under different dynamic rules, random-amplitude phase probability density distribution which may occurs under a plasma sheath is simulated, and channel modeling feasibility is guaranteed; the method is suitable for near space aircraft plasma sheath channel modeling and spaceflight reentry-return spacecraft plasma sheath channel modeling.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for channel estimation using iterative estimation and detection
InactiveUS7139336B2Improve wireless performanceFast convergenceTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksTime domainAlgorithm
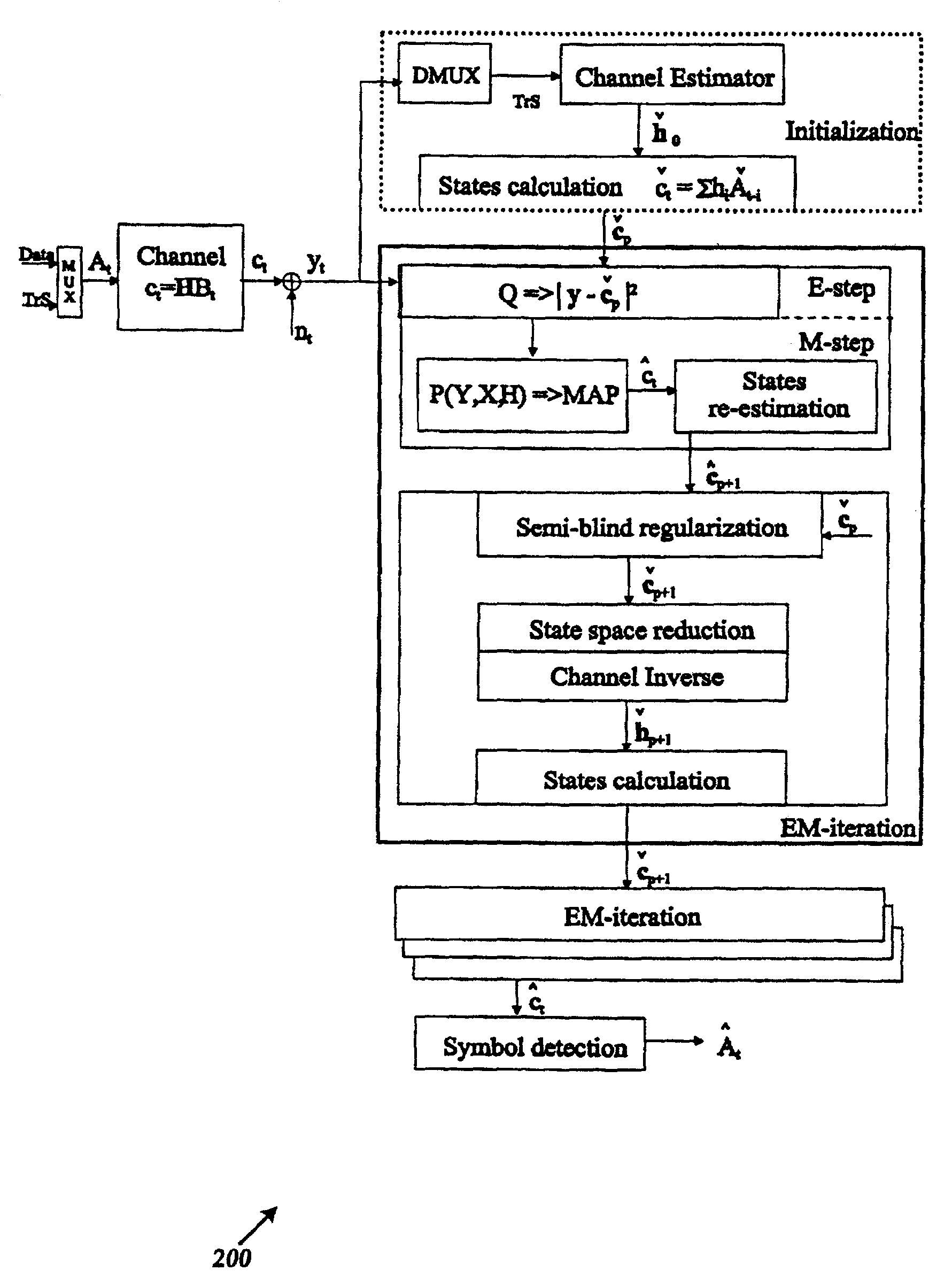
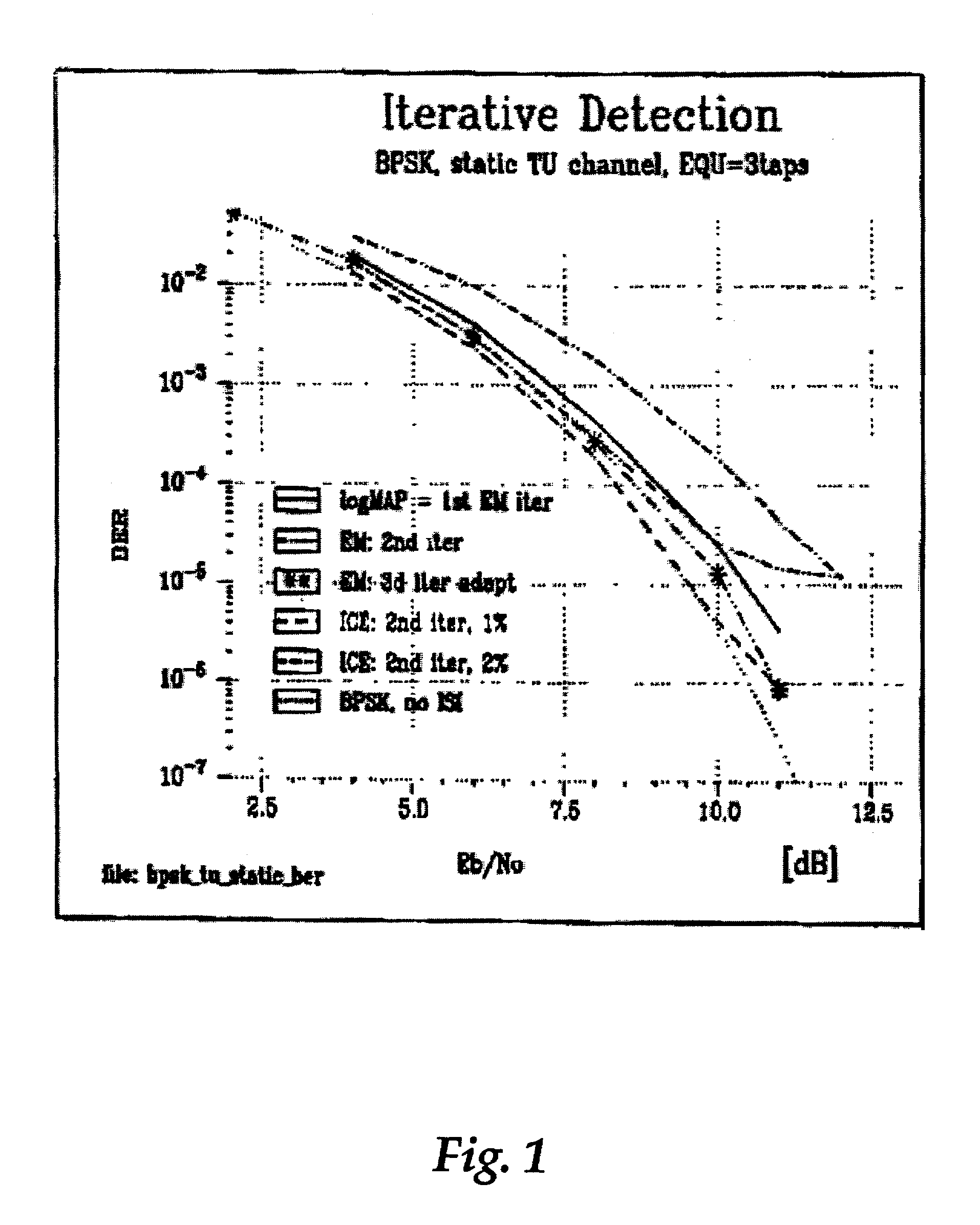
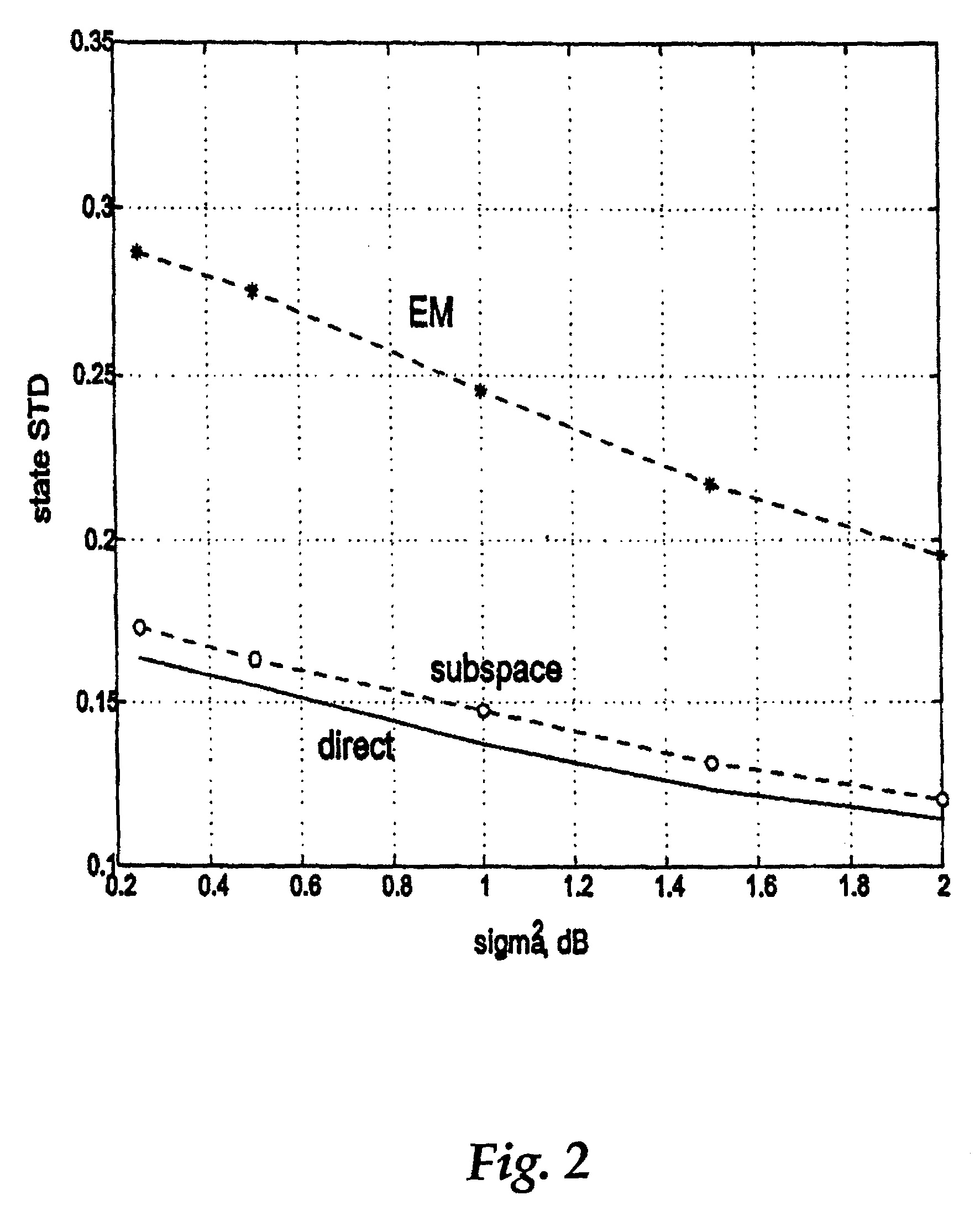
A method and system are directed to enabling a detector to perform relatively accurate channel estimates on blocks of data that include relatively short training sequences in wireless communication signals. Channel re-estimation is performed by transferring the estimation calculations from the time domain into a channel state domain. In one embodiment, information obtained from known training sequences and unknown data may be combined to generate an initial channel estimate. An embodiment of a new recursive Expectation Maximization (EM) process generally i) initializes the EM process with the initial channel estimate; ii) determines updates for the channel estimates; iii) produces a reduced observation vector; iv) generates a special sequence of channel states; v) rearranges each channel state estimate in the reduced observation vector; vi) generates a low-dimensional channel model matrix inversion based on the generated special sequence of channel states; and vii) generates channel estimates based on the generated matrix inversion.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Modeling method based on three-dimensional spatial domain multi-antenna MIMO (Multiple input and multiple output) statistical channel
ActiveCN103747456AImprove researchBroaden applicationSpatial transmit diversityNetwork planningMulti inputAlgorithm
The invention discloses a modeling method specific to an indoor 3D (Three-Dimensional) spatial statistical channel. The modeling method can be applied to a distributed multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) system. When a base station (BS) is designed with a directional antenna, important space-time channel parameters such as Doppler Power Spectrum (DS), space-time correlation and channel capacity are concluded by taking a Poda signal at an MS (Mobile Station) end as a basis; space-time model parameters and the mechanism relationship among included angles of directional antenna main lobes are resolved by using channel space-time feature parameters; meanwhile, the system transmission performance of an MIMO multi-antenna linear array and a circular array under a 3D spatial statistical channel model is researched, so that accurate, flexible diverse channel models are provided for an MIMO multi-antenna space-time processing algorithm and a simulation wireless communication system, and the research of the spatial statistical channel model is expanded.
Owner:南京洛仑通讯科技有限公司
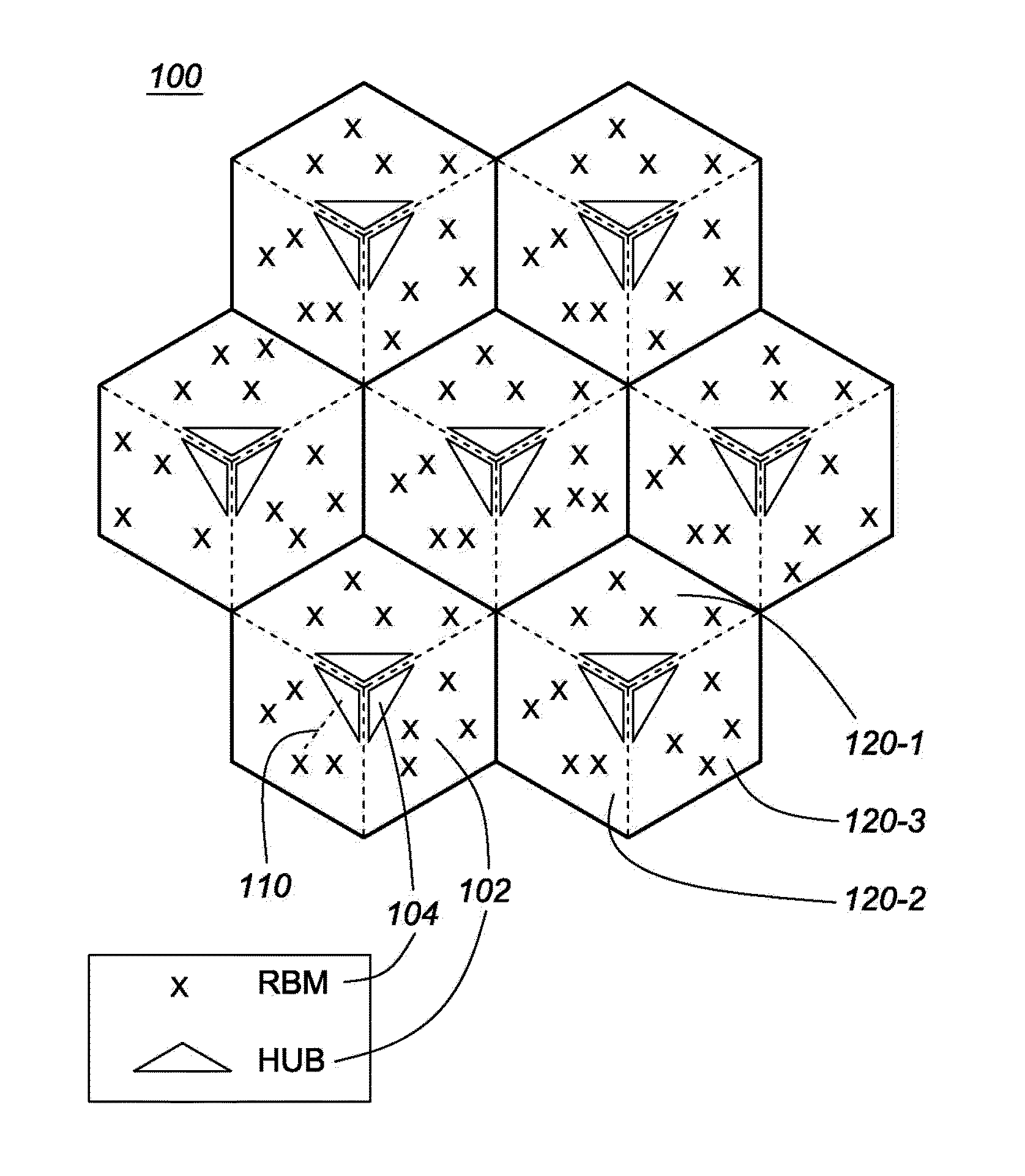
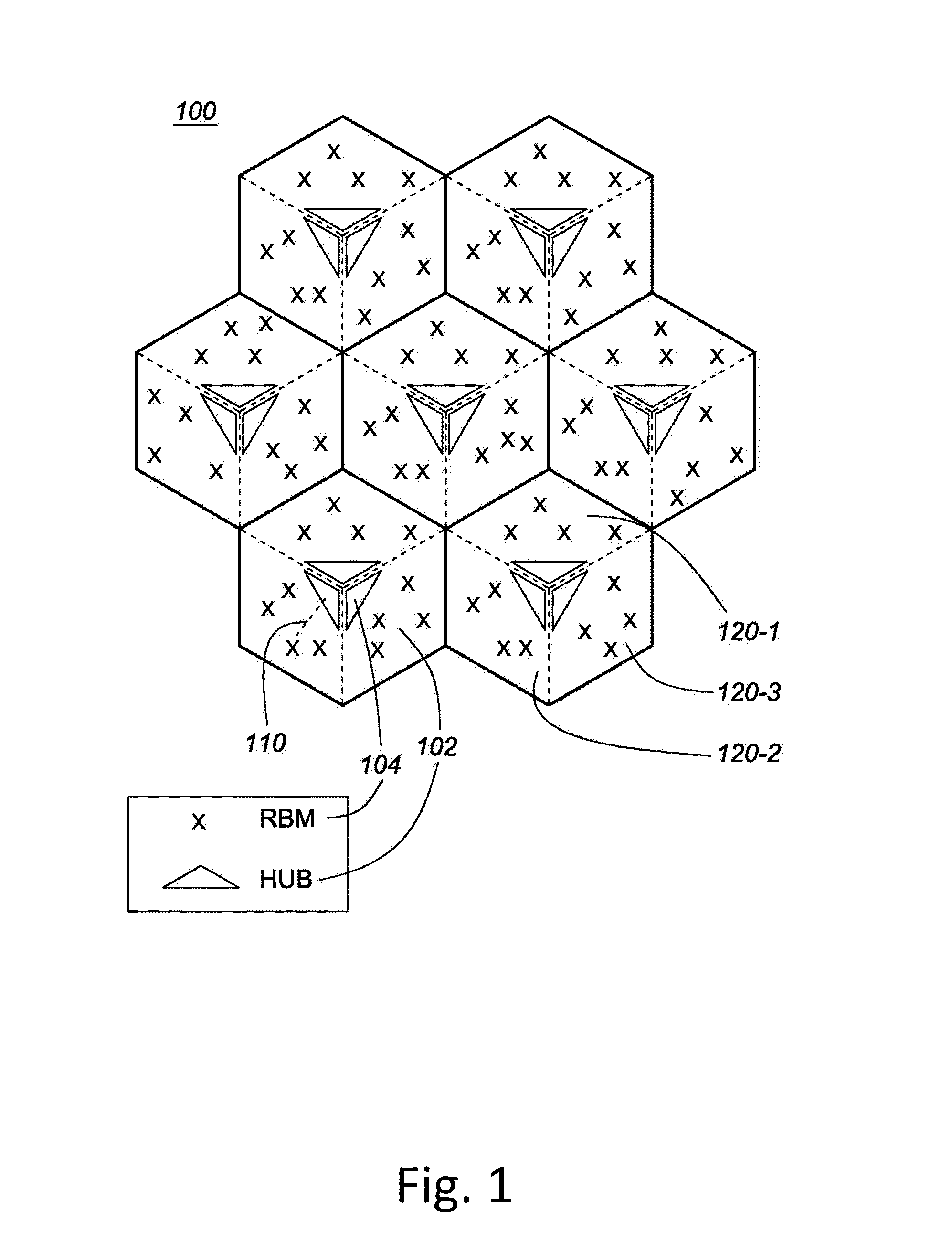
Method and system for network planning in fixed wireless backhaul networks
ActiveUS20160269911A1Eliminate, orReduce disadvantagesNetwork topologiesNetwork planningTerrainSystems design
Systems and methods are disclosed for networking planning for fixed backhaul networks comprising a plurality of hubs, each serving one or more RBMs. The method comprises one or more of terrain pathloss (PL) and antenna gain prediction; network design comprising site association, hub dimensioning and pointing; and optimization of small cell (SC) deployment. PL prediction is based on correlation of user input parameters with reference use cases for channel models for each of downtown, urban, and suburban deployment scenarios. Rapid and effective network planning is achieved with limited input data, even in the absence of high resolution digital maps or building polygons, by selecting the channel model having a highest correlation with available environmental parameters. Optimization of network topology design, system design, and SC deployment, with both access link and backhaul link evaluation, is based on optimization of a sum-utility function across all links for feasible SC site locations.
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
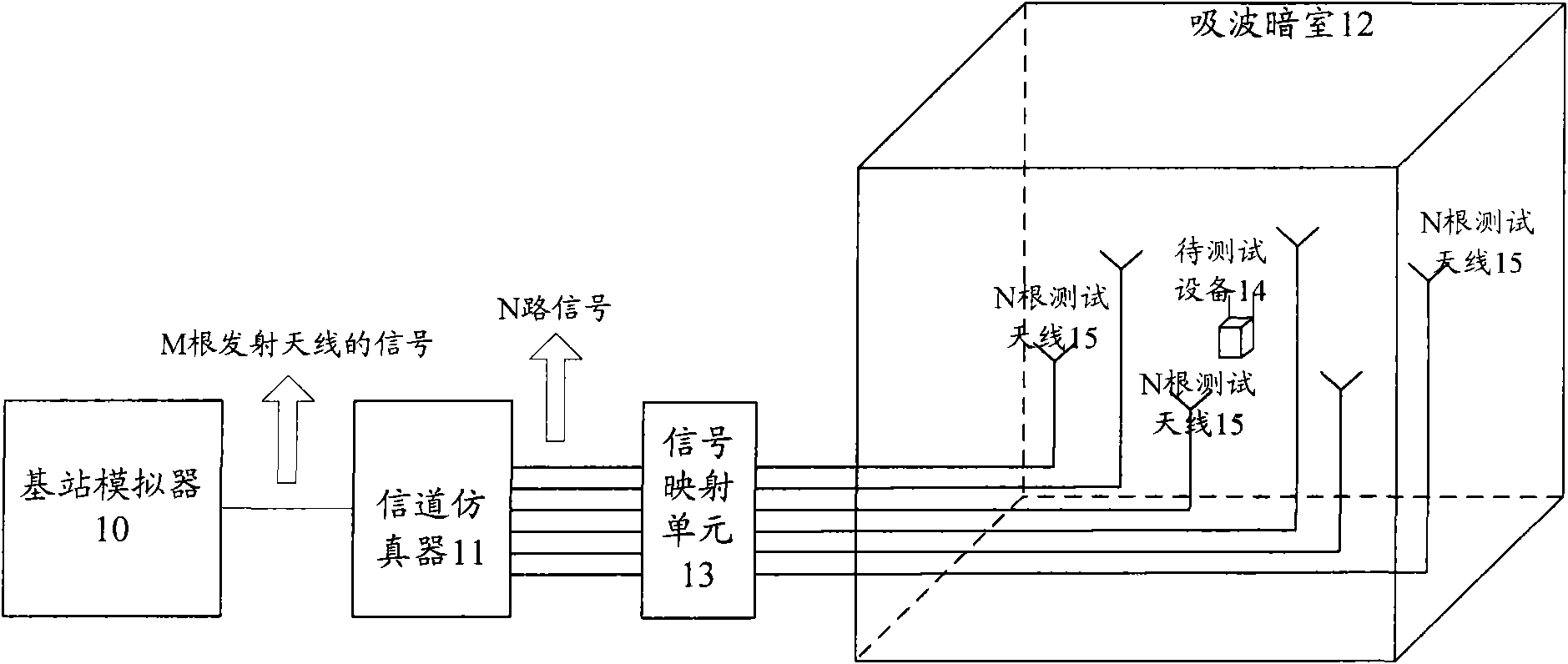
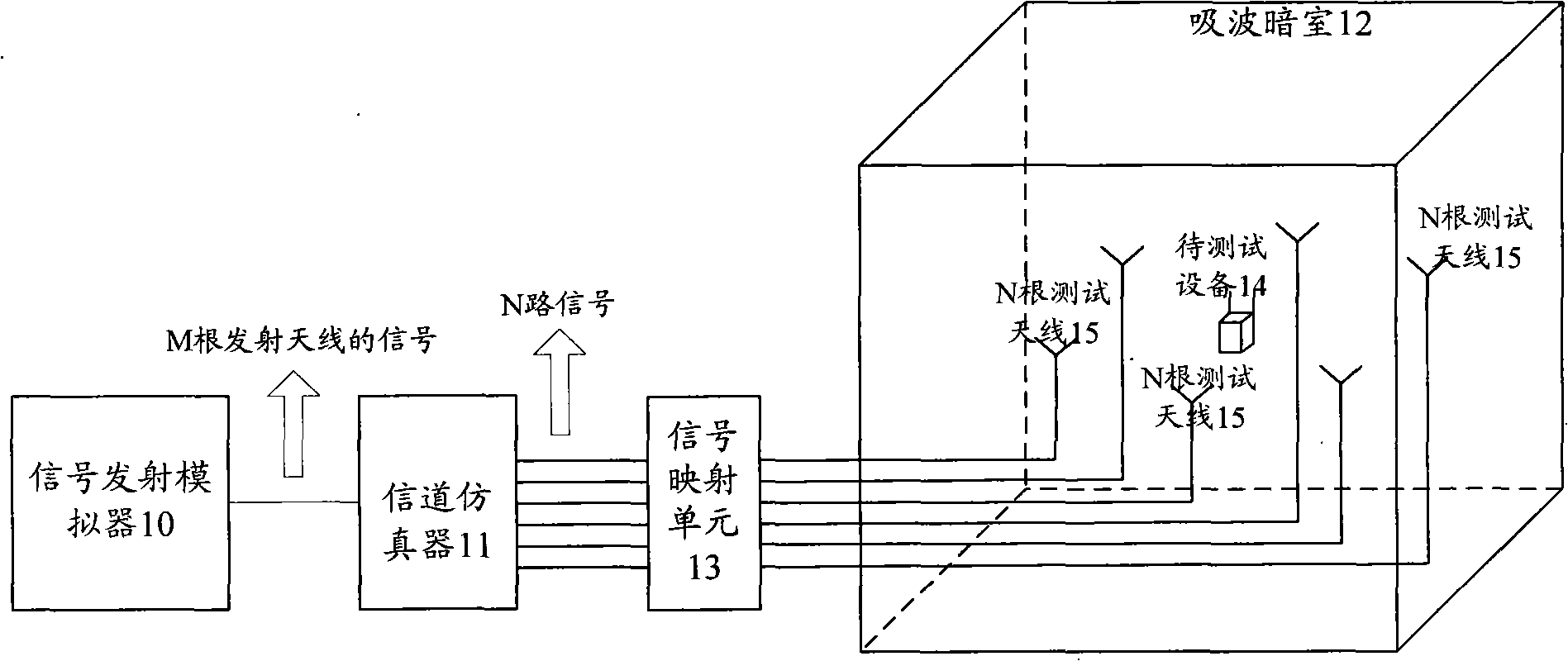
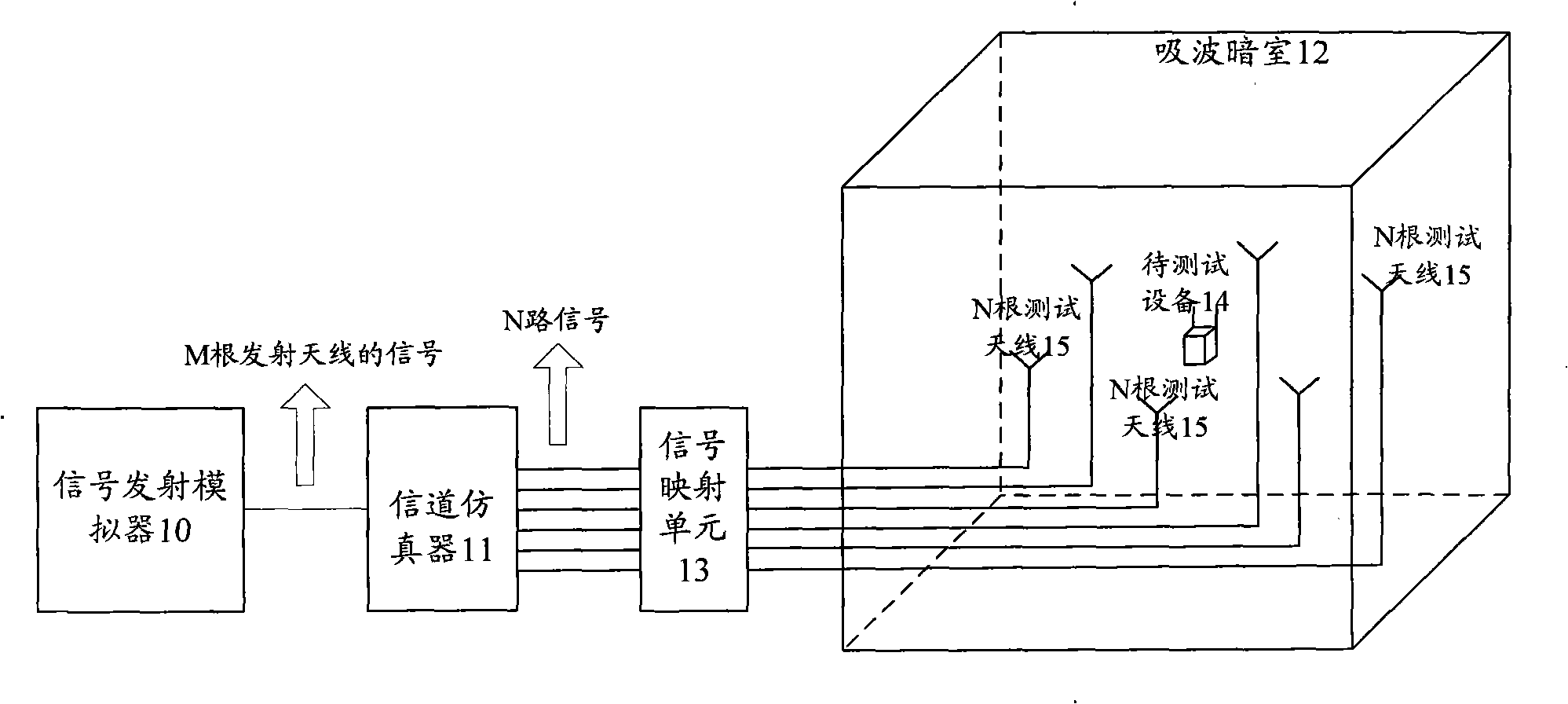
Space radio-frequency performance test method and system in multi-antenna system
InactiveCN102148648AEasy to testEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringReference testEngineering
The invention discloses a space radio-frequency performance test method and a system in a multi-antenna system. More than two antennas are arranged on a dark absorbing chamber; a base station simulator is controlled to send a reference test signal to a device to be tested through a channel simulator and an antenna; when the reference test signal is determined to not satisfy set requirements, the reference test signal is adjusted until the set requirements are satisfied; corresponding test cases are determined according to different channel models; signal simulation is implemented by a channel emulator on the test signal outputted by the base station simulator, and then the test signal is sent to the device to be tested through the antenna; each radio-frequency performance of the device to be tested after the receiving of the test signal is tested according to the radio-frequency performance test items corresponding to the test cases; and when all the radio-frequency performances reach the standard, the space radio-frequency performance reaches the standard. The invention also discloses a space radio-frequency performance test system in the multi-antenna system. The invention is simple to realize and has lower cost.
Owner:李翠梅
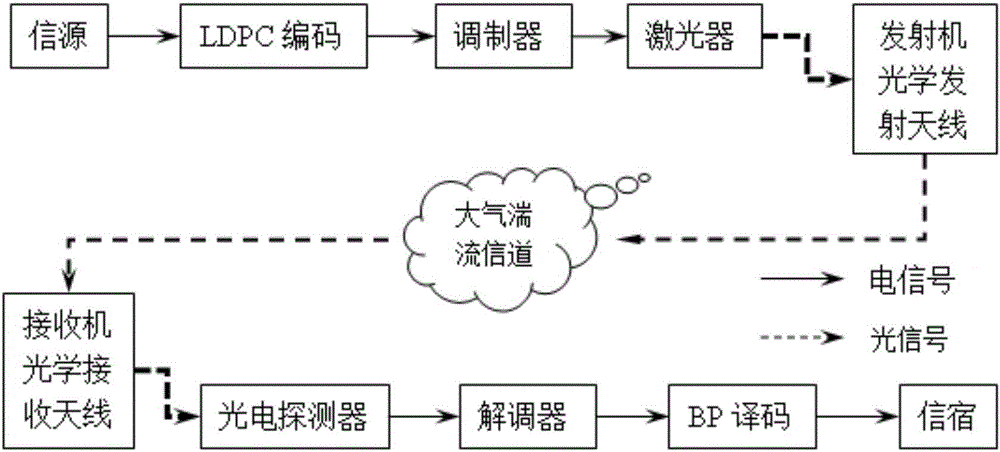
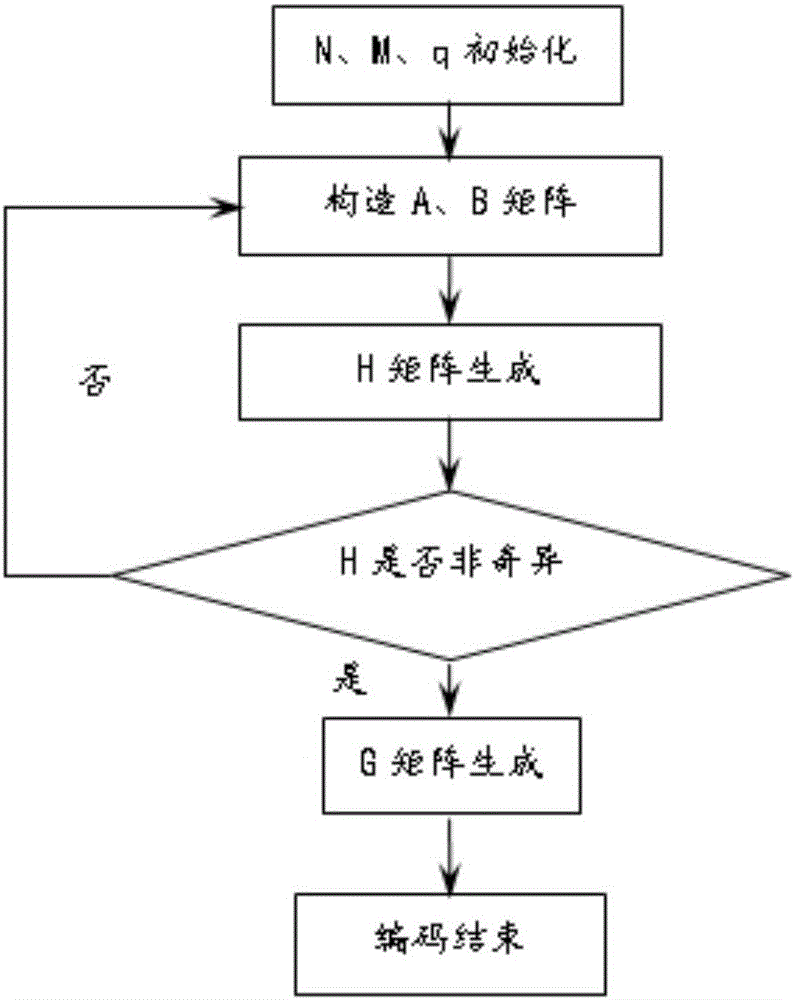
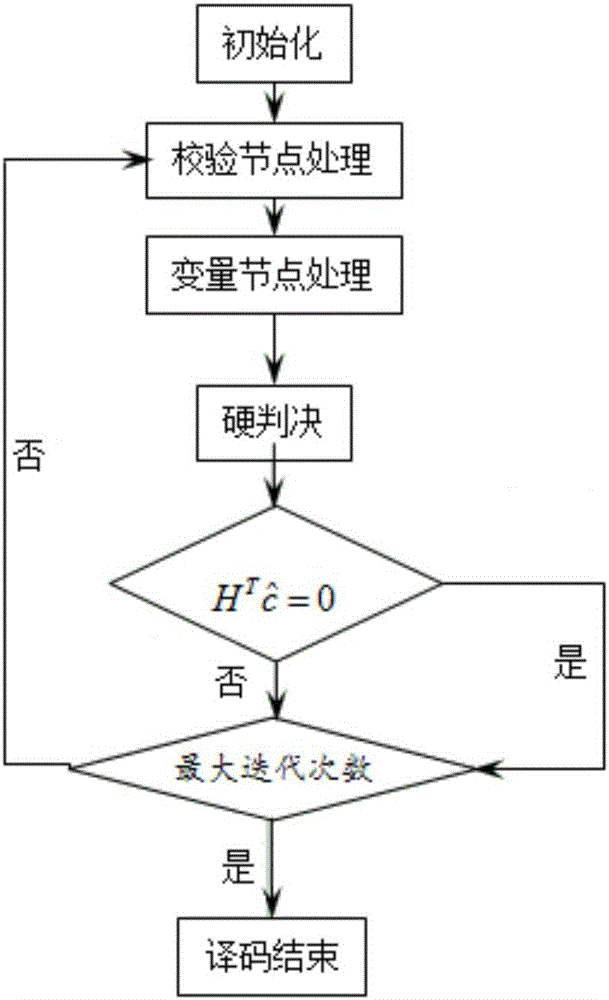
Free space optical communication method and system based on LDPC code
ActiveCN106685527AImprove performanceMeet the requirements of multiple scattering mechanismsError preventionClose-range type systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Communications system
The invention provides a free space optical communication method and system based on an LDPC code. The method and system aim at a problem that the error rate, communication distance and communication bandwidth of a system are affected by the flicker and light beam drift and extension caused by atmosphere turbulence and the reduction of signal to noise ratio of a receiving end in laser communication. The method comprises the steps: firstly proposing a logarithmic normal distribution channel model under weak turbulence and a K-distribution channel model under strong turbulence according to the characteristics of atmosphere turbulence channels; secondly constructing an irregular QC-LDPC code on the basis of the proposed channel models; finally deducing an LLR probability density function, and carrying out the decoding through an LLR-BP algorithm. A confidence decoding BP result indicates the error rate of the system remarkably decreases along with the increase of signal to noise ratio. An experiment indicates that the method and system can effectively reduce the performance of an FSO system.
Owner:武汉全信通通信工程有限公司
Rapid identification of transmission media channel characteristics
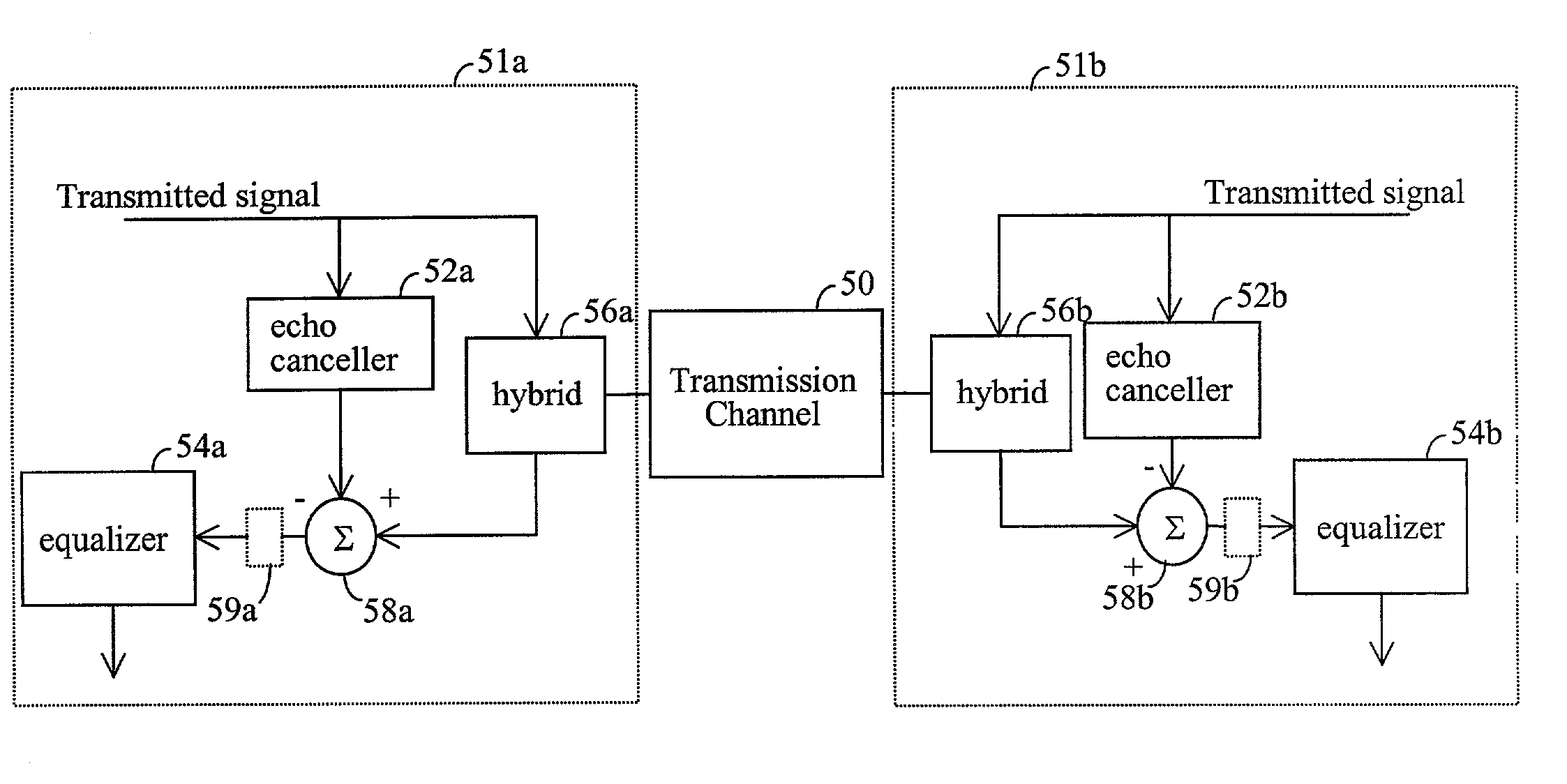
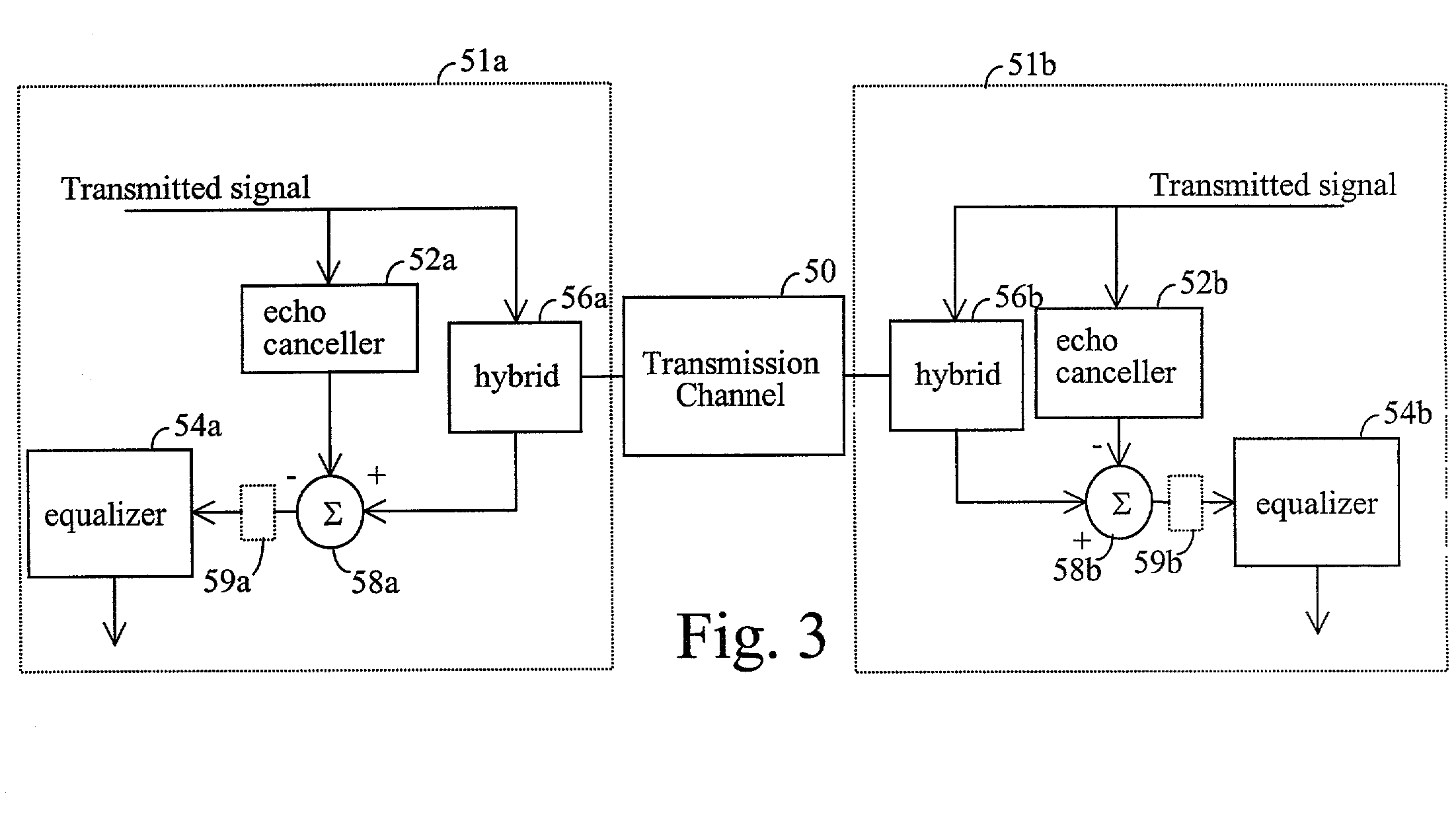
InactiveUS20020181567A1Compensates for and reduces effectReduce eliminate effectMultiple-port networksTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsCommunications systemMean square
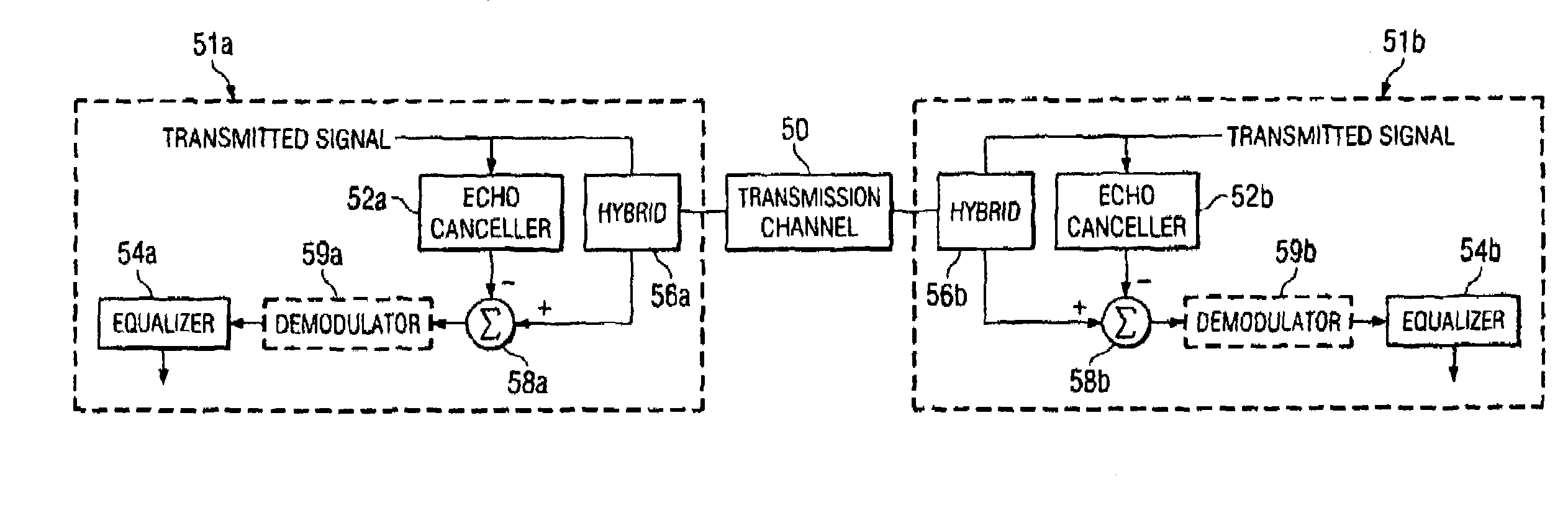
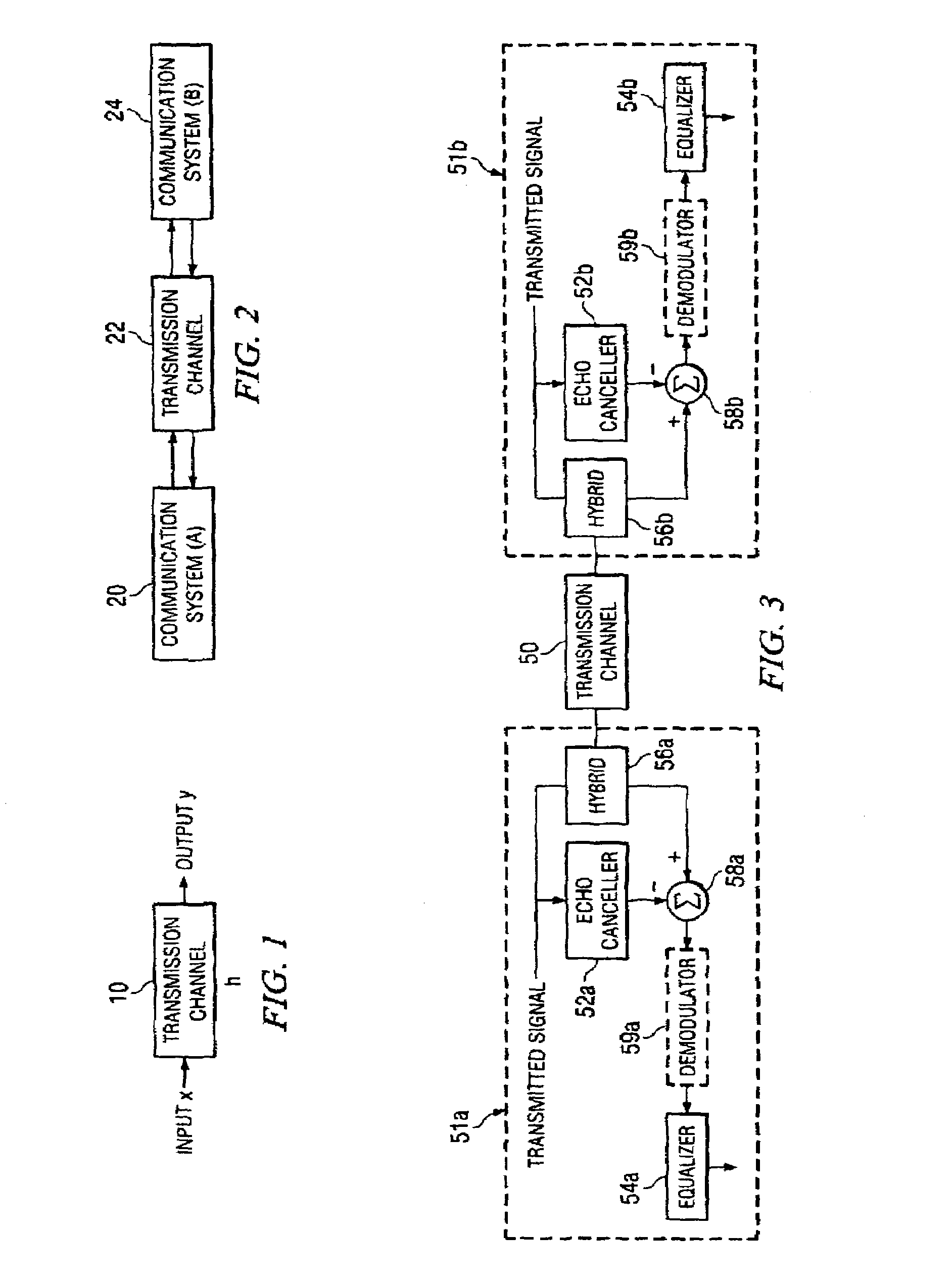
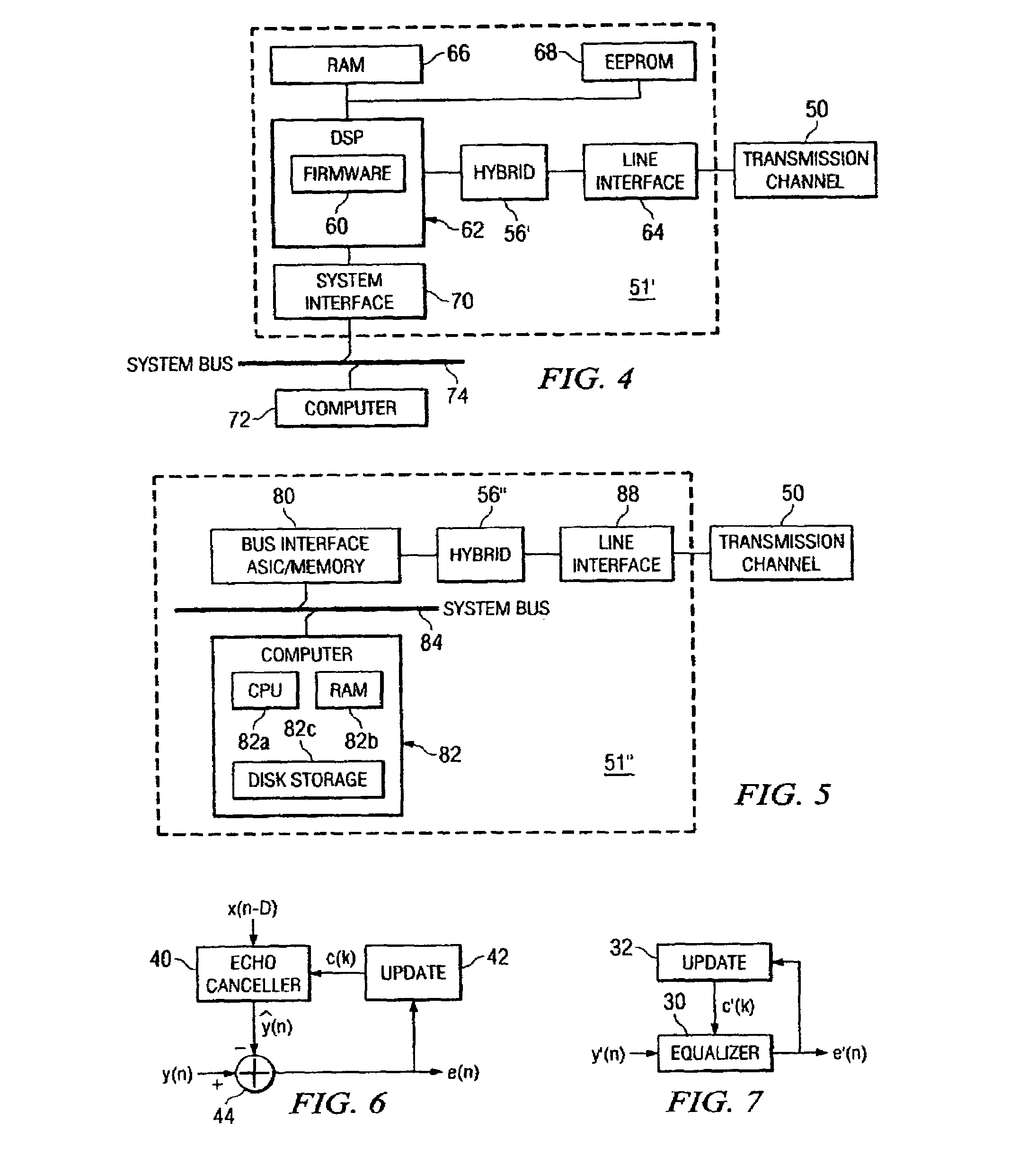
Rapid identification and modeling of transmission media channel characteristics of a communications system using a correlation based technique. The technique provides a known training sequence used to generate a known quantity that operates on an observed or measured received signal, which is a function of the training sequence and the channel's impulse response, to give an estimate of the model of the channel. The technique decouples the training sequence from the observed or measured output, leaving the estimated impulse response. The impulse response of the transmission media channel is rapidly computed and processed to set the initial values of filter coefficients, for example, an echo canceller and an equalizer, in the communications system. Once the coefficients are initialized, if needed, a standard technique, such as least mean square (LMS) correlation, can be used to fine-tune the coefficients to converge on or model the transmission media channel's characteristics.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Joint estimation method of high-precision wireless channel parameterized model
InactiveCN101588328AImprove resolution accuracyBaseband system detailsNegative feedbackCommunications system
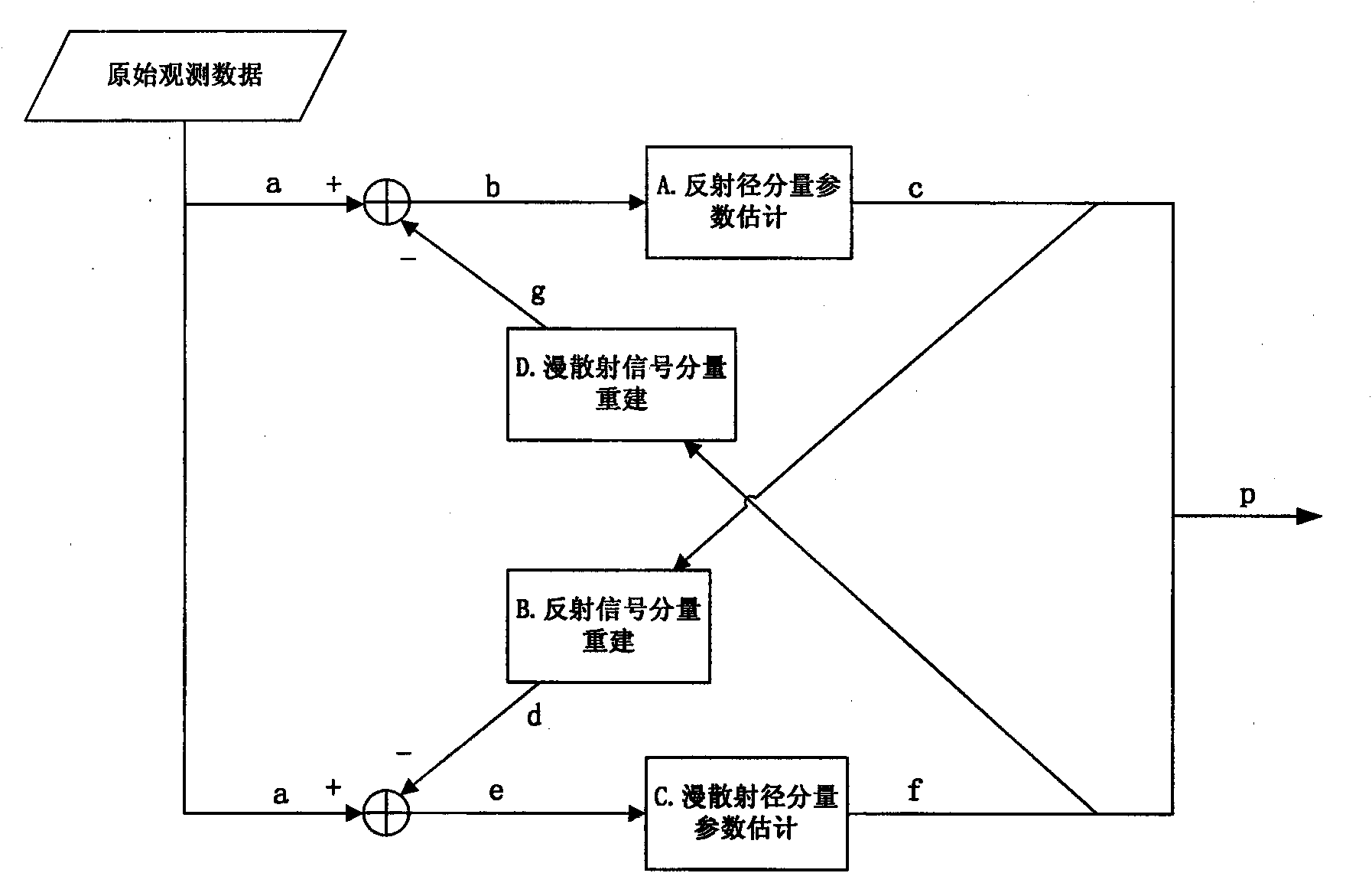
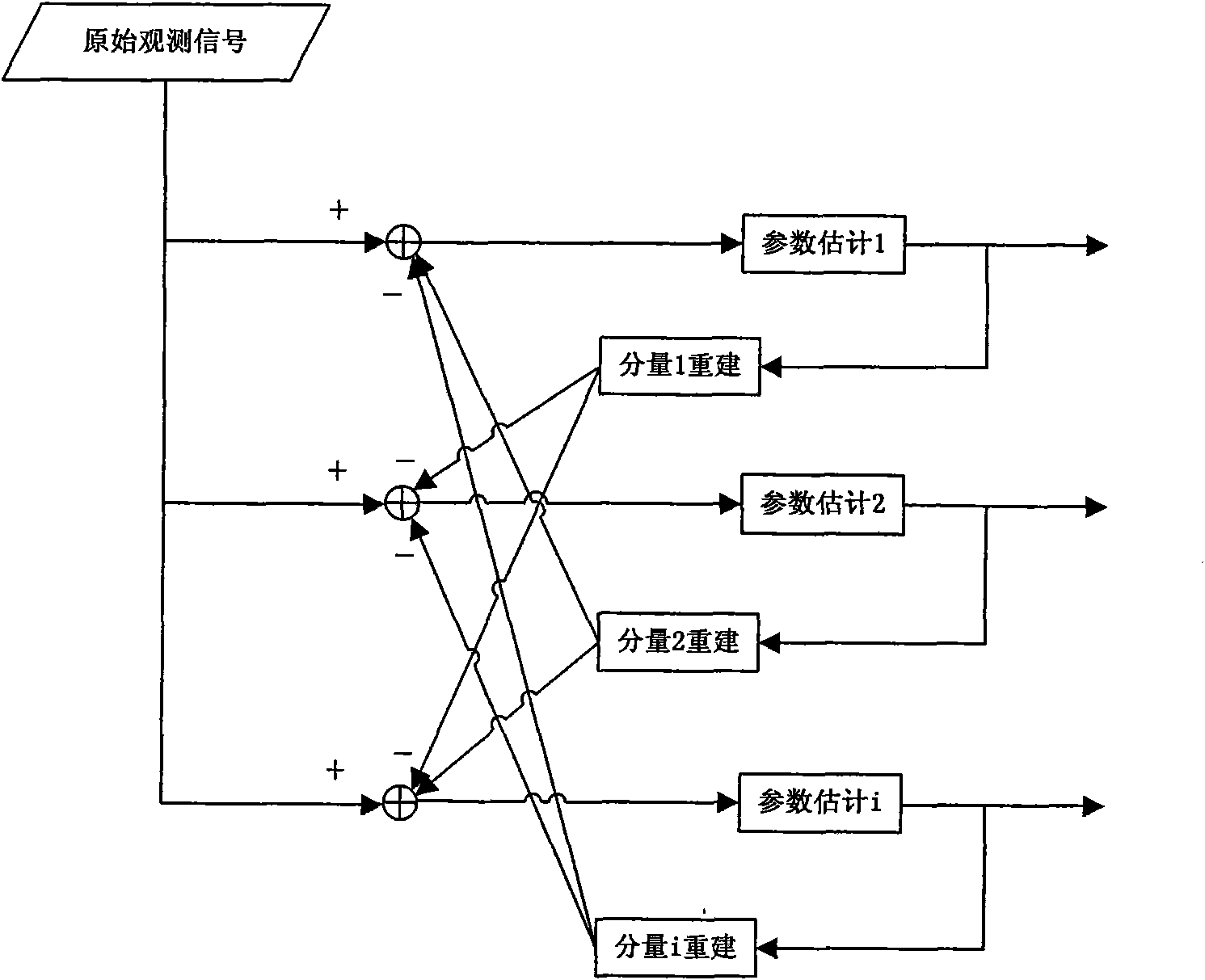
The invention provides a joint estimation method of high-precision wireless channel parameterized model, comprising the following steps: reflecting radial component parameter estimation, diffusing radial component parameter estimation, reflecting signal component reestablishment, and diffusing signal component reestablishment. The output of reflecting radial component parameter estimation is negatively fed back to the input of diffusing radial component parameter estimation by reflecting signal component reestablishment; the output of diffusing radial component parameter estimation is negatively fed back to the input of reflecting radial component parameter estimation by diffusing signal component reestablishment; and the output terminals of two parameter estimators self-consistently estimate each parameter of independent components of channel models by such 'butterfly negative feedback' cross iteration mechanism to increase the resolving precision and wideband wireless channel parameterized model. The invention is capable of being applied to the high-precision channel test and modelling of wideband wireless communication systems and digital broadcasting systems, such as WIMAX, LTE, B3G, 4G, UWB and DVB.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
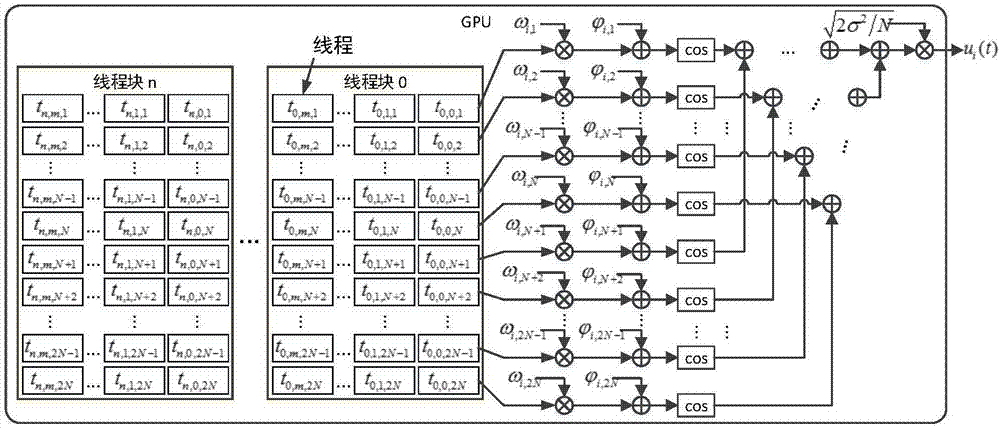
Large-scale UAV relay network channel simulation device and GPU real-time simulation method
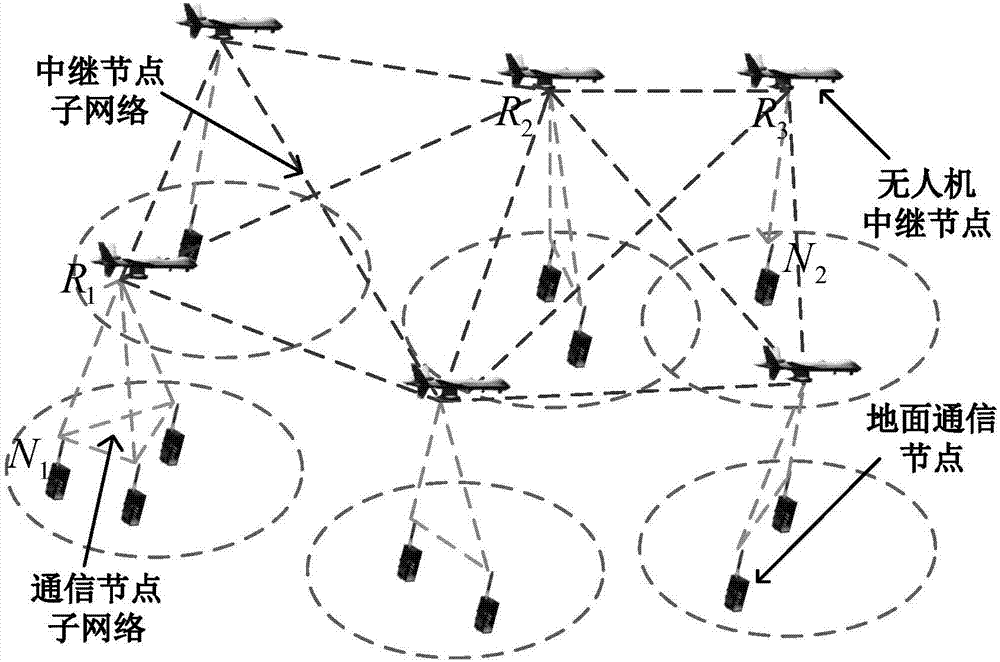
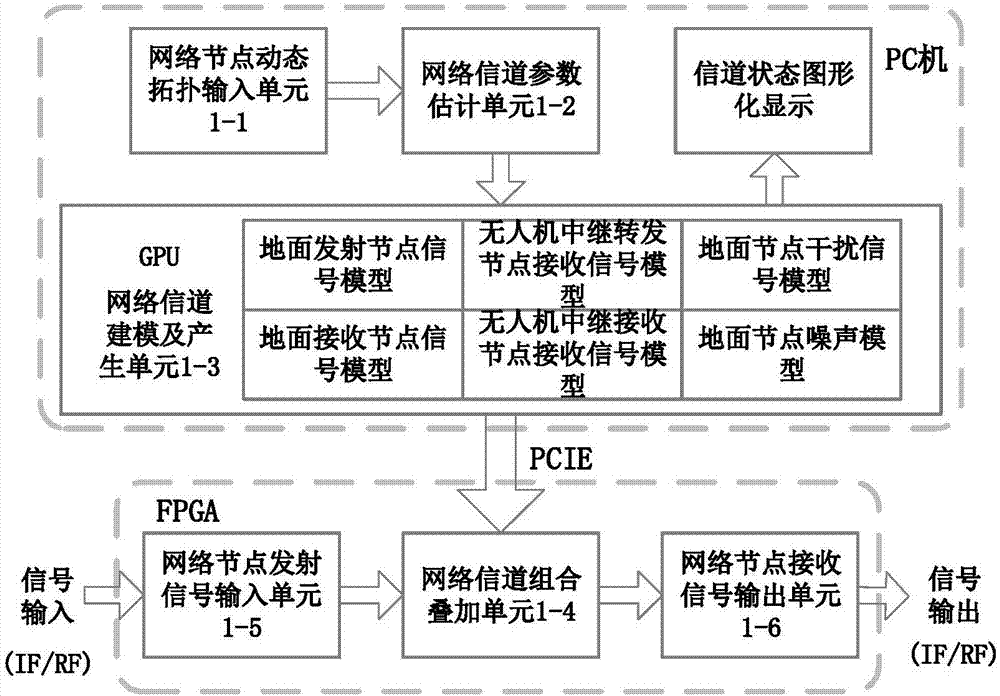
ActiveCN107579789ASupport dynamic adjustmentSimplify complexityTransmission monitoringNetwork sizeReal-time simulation
The invention discloses a large-scale UAV relay network channel simulation device and a GPU real-time simulation method. The large-scale UAV relay network channel simulation device includes a networknode dynamic topology parameter input unit, a network channel parameter estimation unit, a network channel modeling and generating unit, a network channel combination superposition unit, a network node transmitting signal input unit and a network node receiving signal output unit. The simulation system is flexible and general, and supports the dynamic adjustment of the network size and topology structure; the signal, interference and noise of each relay link are modeled using the equivalent method, the complexity of system simulation is greatly simplified; and for different communication scenes, different nodes are supported to adopt different channel models and updated in real time, the mutual interference between network nodes are considered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Antenna testing system and antenna testing method
InactiveCN102136873AEasy to testLow costSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringTest channelEngineering
The invention discloses an antenna testing system which comprises a signal transmission simulator, a channel simulator and a wave absorbing chamber, wherein at least two antennas are arranged in the wave absorbing chamber, the antennas are connected with the signal transmission simulator through the channel simulator and used for providing at least two paths of transmitting signals to equipment to be tested; the two antennas are positioned on a spherical surface taking the position of the equipment to be tested as the centre of sphere. Simultaneously, the invention also discloses an antenna testing method on the basis of the testing system. More than one testing channel model are arranged in the signal transmission simulator. A channel model is selected from the channel models, a wireless signal is transmitted according to the selected channel model and simulated by the channel simulator, and then the simulated wireless signal is transmitted through the antennas in the wave absorbing chamber; and the equipment to be tested which is arranged in the wave absorbing chamber receives the transmission signals of all the antennas, processes the signals and outputs the processing result. The antenna testing system and the testing method are easy to realize and have lower cost.
Owner:ZTE CORP
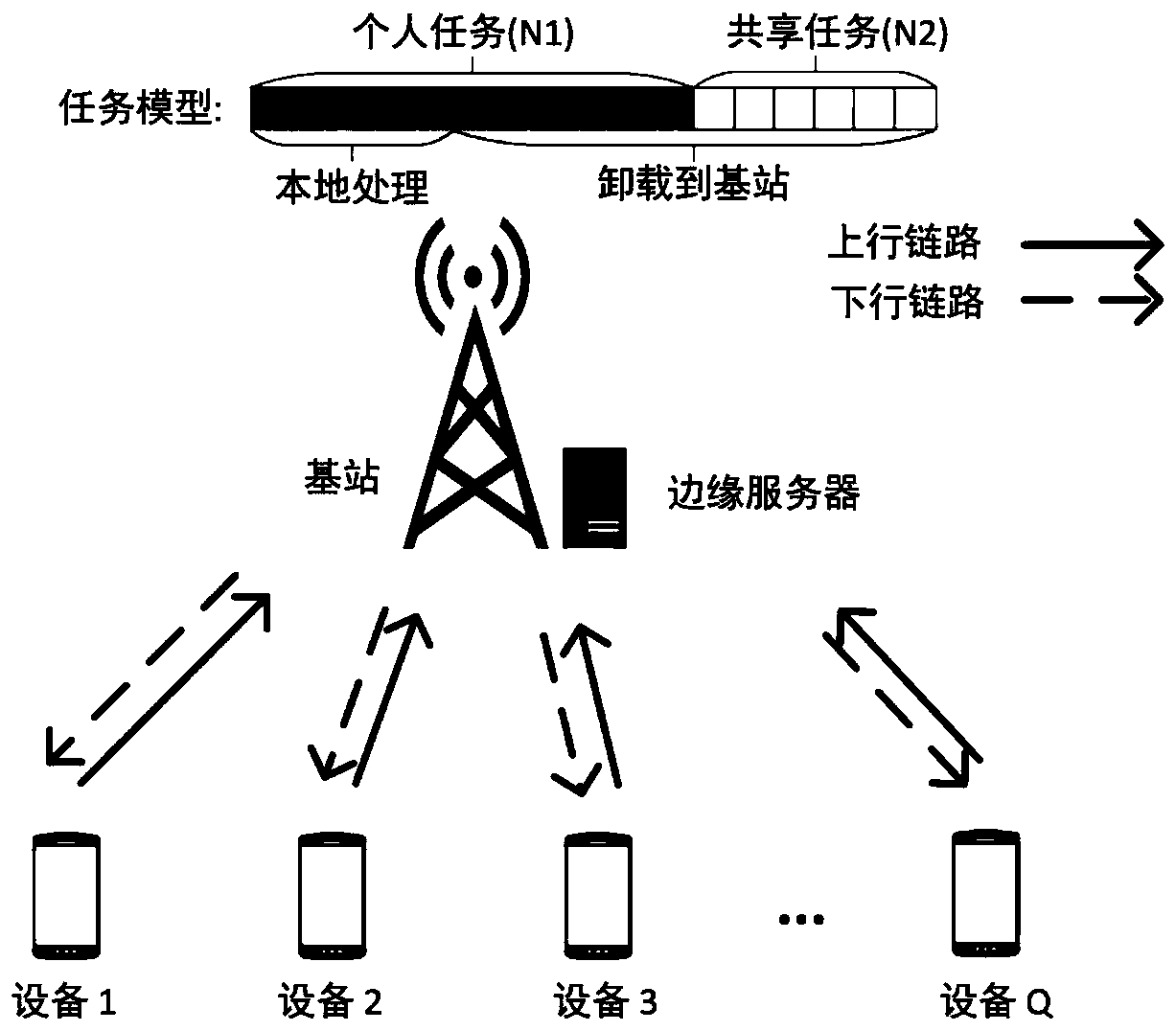
Multi-user multi-task unloading method based on mobile edge computing
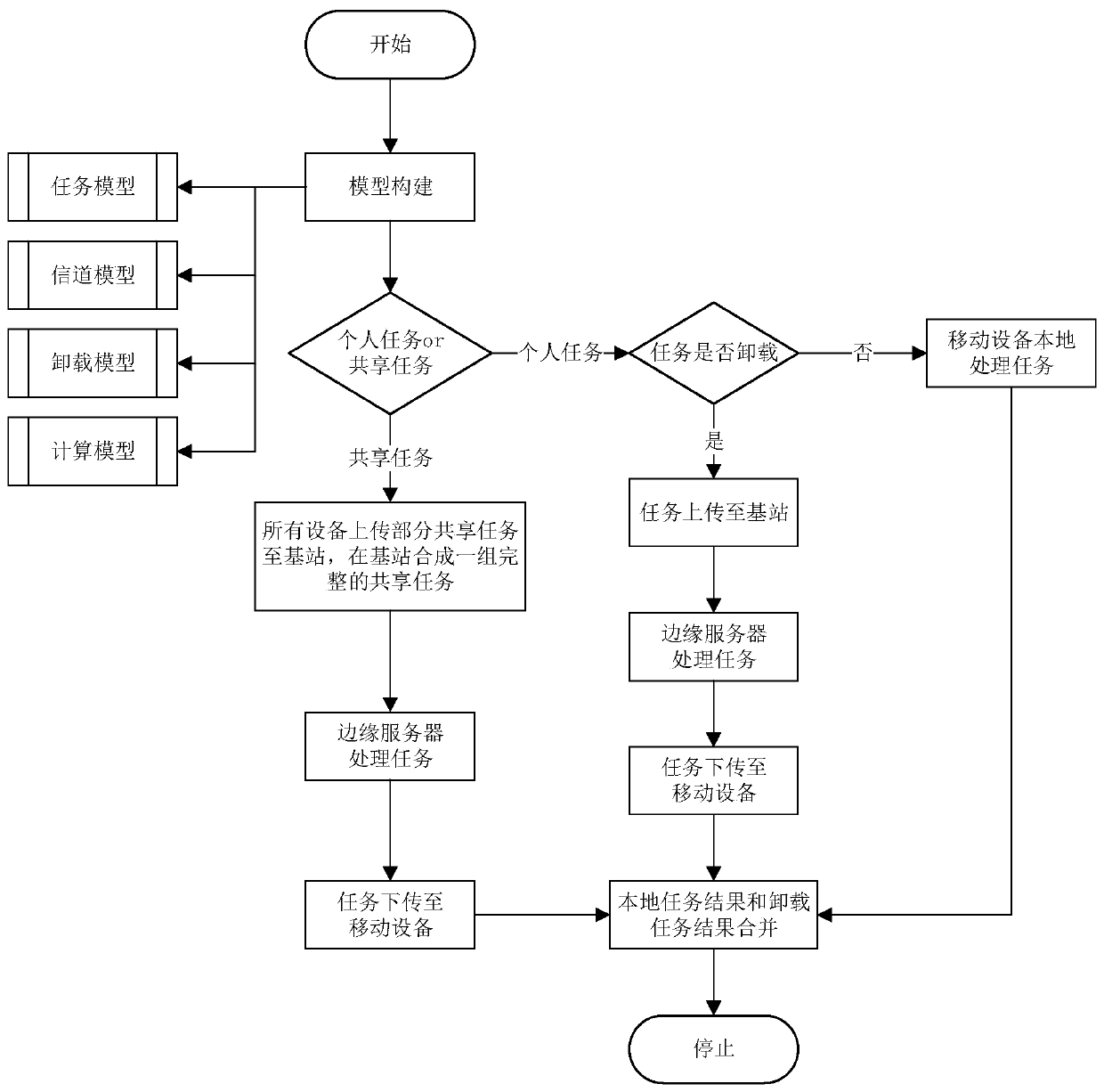
ActiveCN111148134AReduce latencySmooth experienceWireless communicationEdge serverComputational model
The invention discloses a multi-user and multi-task unloading method based on mobile edge computing, and the method comprises the steps: 1, a multi-user and multi-task scene model is built based on mobile edge computing, and the multi-user and multi-task scene model comprises a system model and a module model; the module model comprises a task model, a channel model, a task unloading model and a computing model of a local and edge server of the mobile equipment; 2, the tasks are unloaded according to task categories and task unloading strategies, wherein the task categories include personal tasks and shared tasks, and the task unloading strategies are obtained by solving with the optimal task processing time delay as the target. By adopting the method, the time delay optimization of the joint processing of the user and the edge server can be realized through mobile edge calculation under the conditions of multiple users and multiple tasks with shared tasks and inseparable tasks.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Wireless performance testing system for wireless equipment
InactiveCN106255143AReliable test environmentThe test data is reliableNetwork topologiesUltrasound attenuationTerminal equipment
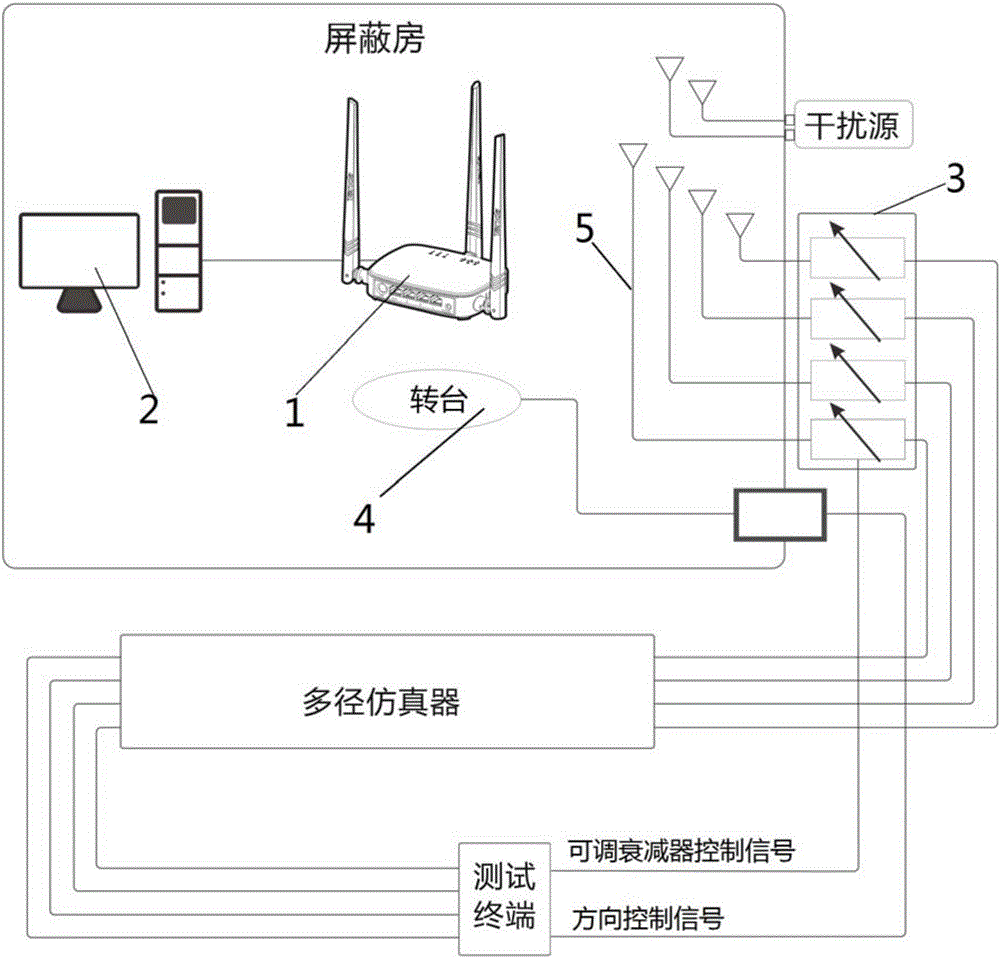
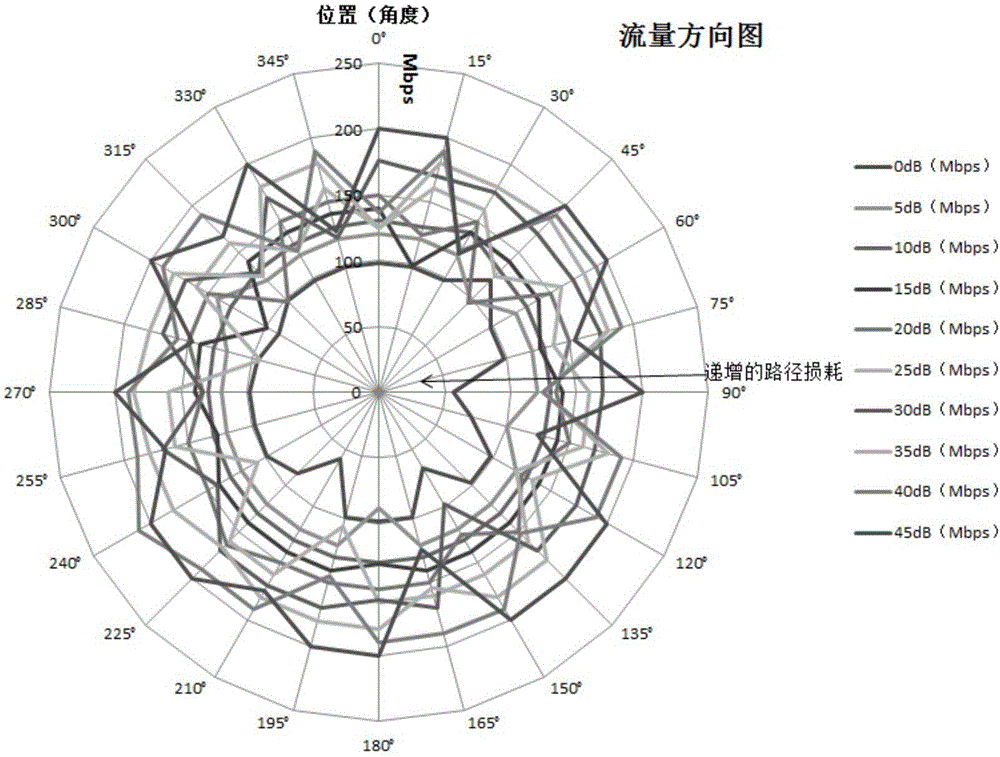
The invention provides a wireless performance testing system for wireless equipment, belonging to the technical field of wireless performance testing. The wireless performance testing system disclosed by the invention comprises a shielded room, a direction control device, terminal equipment, wireless equipment and a testing antenna; the direction control device, the terminal equipment, the wireless equipment and the testing antenna are arranged in the shielded room; the direction control device can control the direction of the wireless equipment; the terminal equipment is connected with the wireless equipment; the wireless performance testing system further comprises a testing terminal, a multi-path simulator and an adjustable attenuator; one end of the adjustable attenuator is connected with the testing antenna; the other end of the adjustable attenuator is connected with the output end of the multi-path simulator; and the testing terminal is respectively connected with the input end of the multi-path simulator, the adjustable attenuator and the direction control device. The wireless performance testing system disclosed by the invention has the benefits that: a testing environment is steady and reliable; testing data can be repetitive, steady and reliable; the throughput capacities and the whole directionality in an interference-free environment, an interference environment and a practical environment, at different angles and under different attenuations can be tested; and channel models at different angles and the throughput capacities under a multi-path effect can be tested.
Owner:SHENZHEN JIXIANG TENGDA TECH
Non-stationary V2V MIMO channel modeling method based on geometry
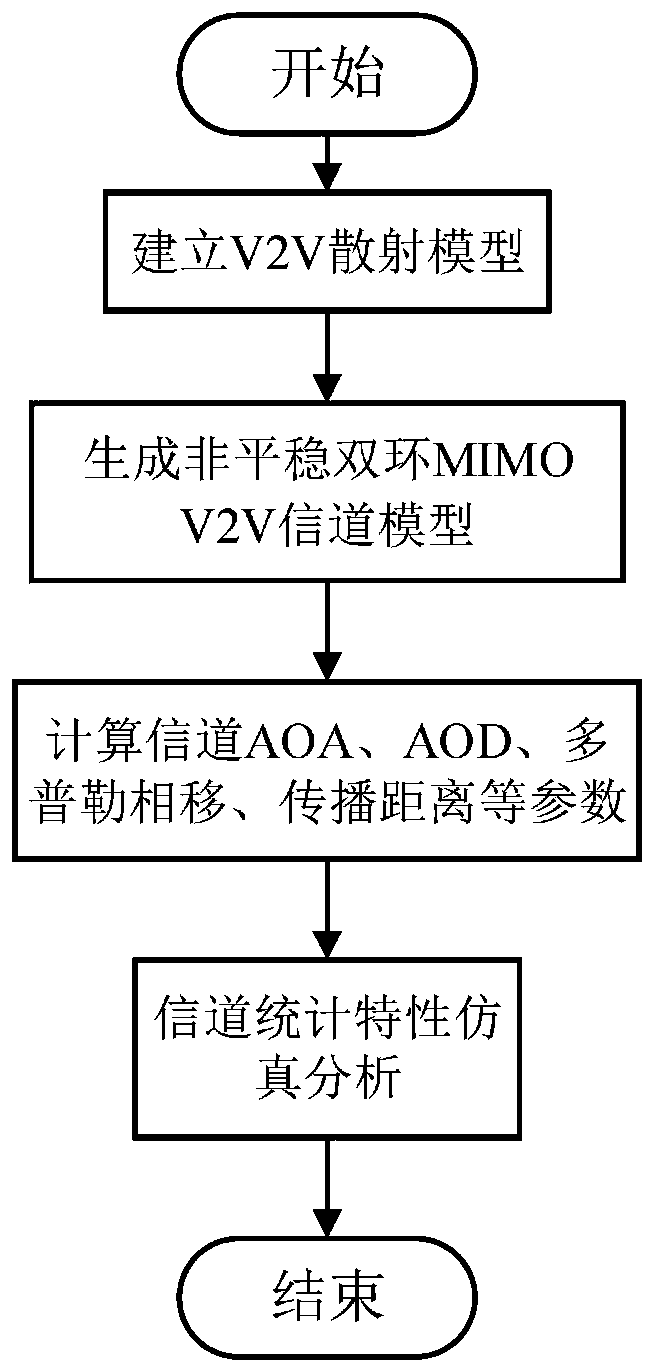
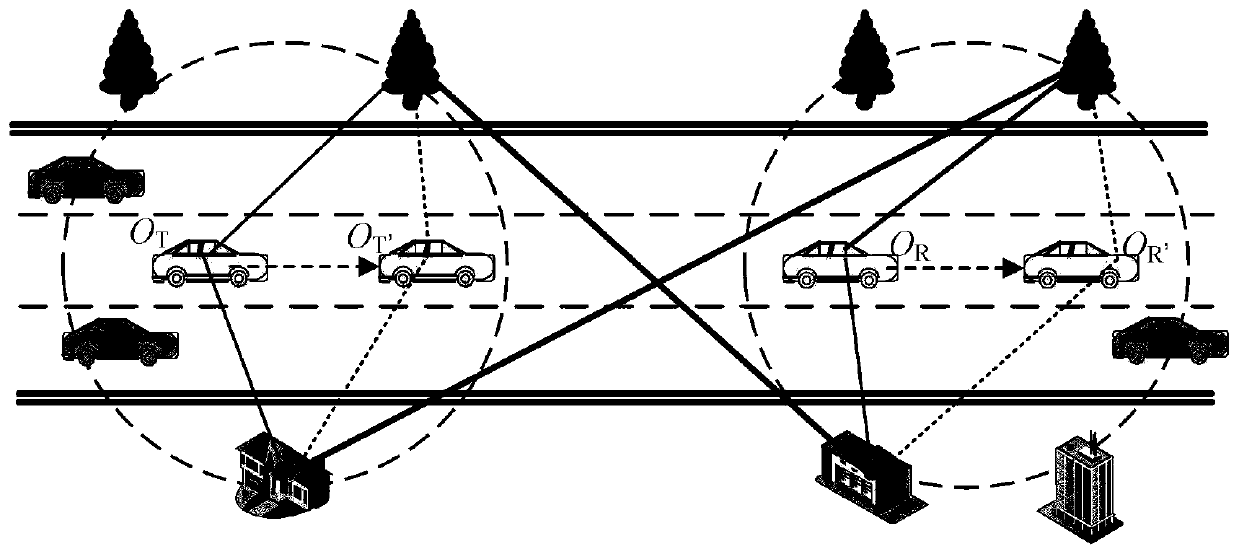
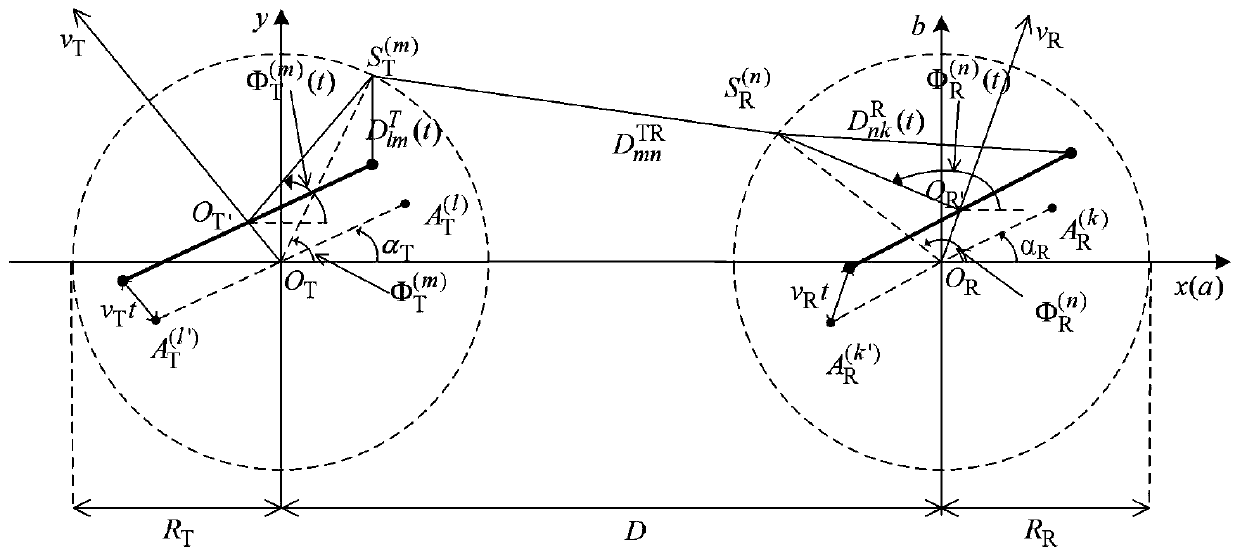
InactiveCN111314001ARich modeling methodsParticular environment based servicesVehicle-to-vehicle communicationChannel impulse responsePhase shifted
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Large-scale MIMO system CSI feedback method based on long-short-term attention mechanism
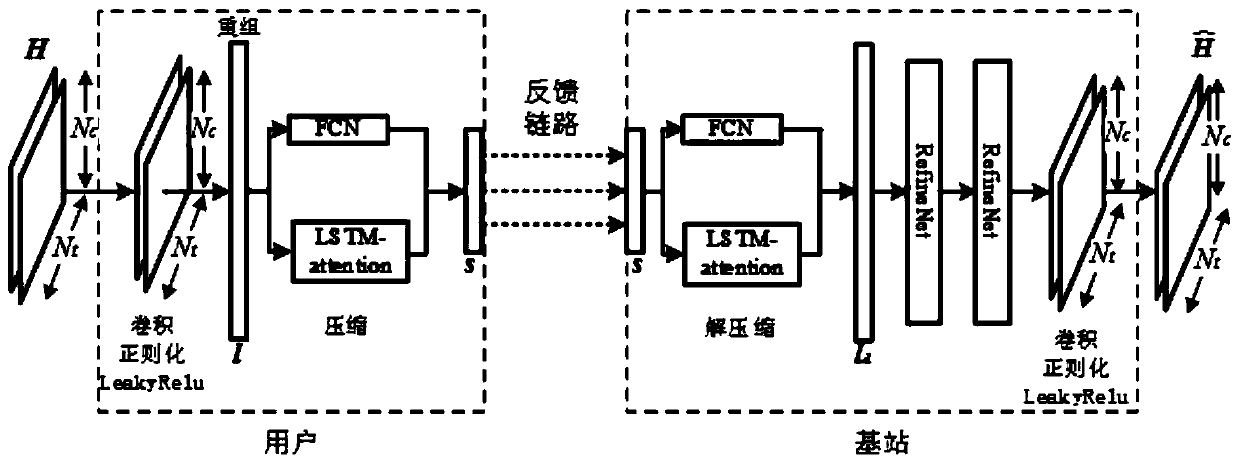
ActiveCN110912598AAvoid iterative calculationsReduce computational complexitySpatial transmit diversityNeural architecturesAlgorithmDescent algorithm
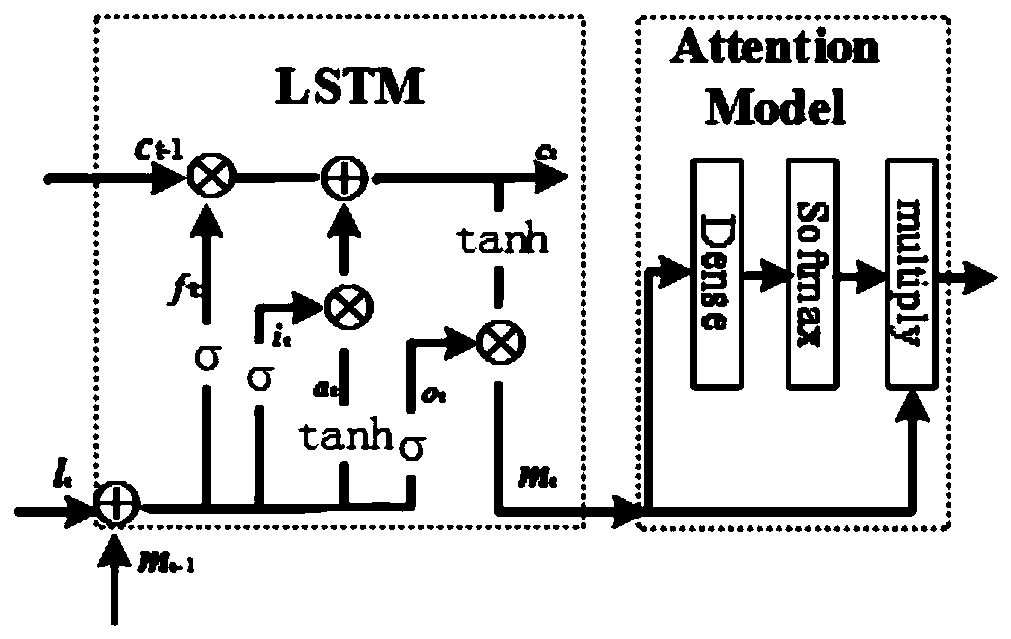
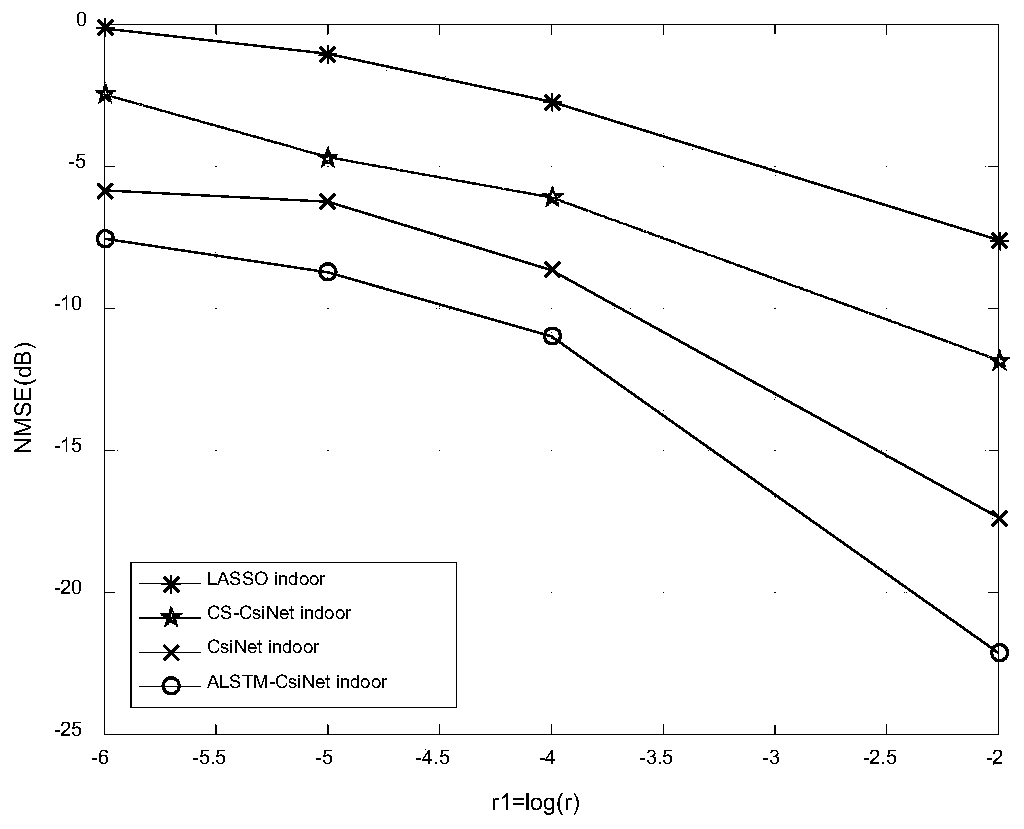
The invention provides a large-scale MIMO system CSI feedback method based on a long-short-term attention mechanism. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, generating sample data of a space-frequency domain channel matrix by using a COST 2100 channel model, and preprocessing the sample data through discrete Fourier transform and truncation operation to obtain a training set and a testset; secondly, establishing an ALSTM-CsiNet channel state information feedback reconstruction model by utilizing an LSTM and an attention mechanism; inputting the training set into an ALSTM-CsiNet channel state information feedback reconstruction model, and performing iterative training on the model by adopting a mean square error and an adaptive estimation gradient descent algorithm to obtain anoptimized ALSTM-CsiNet model; and finally, directly inputting the test set into the ALSTM-CsiNet model to carry out channel state information reconstruction. According to the invention, the LSTM is used to learn the time correlation of the channel, and the attention mechanism is used to perceive the local information and the automatic weighting feature information, so that the channel feedback precision is improved.
Owner:ZHONGYUAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Wireless communication node connections
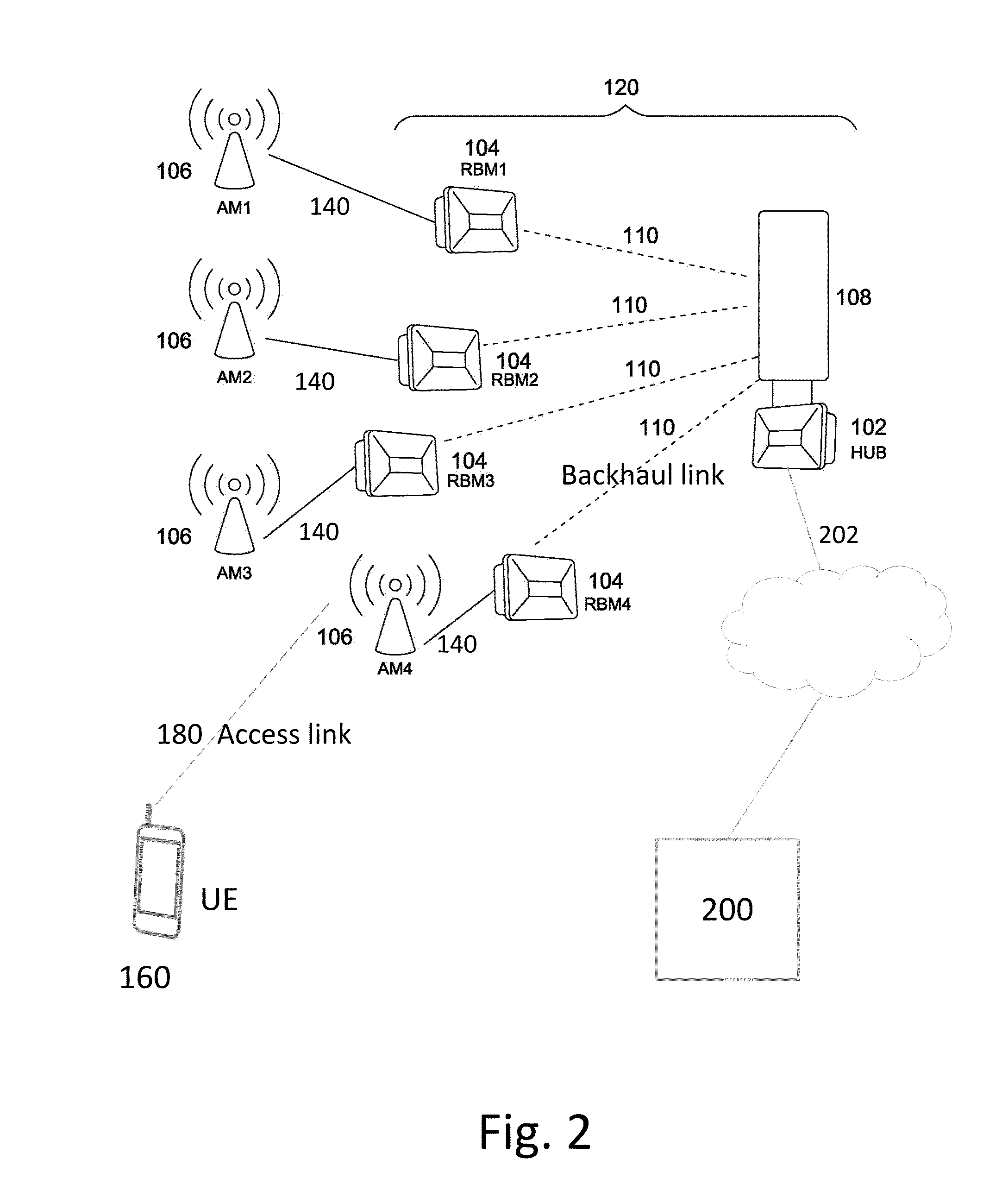
ActiveUS20120087450A1Simple methodReliable and reliableTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringTelecommunicationsEngineering
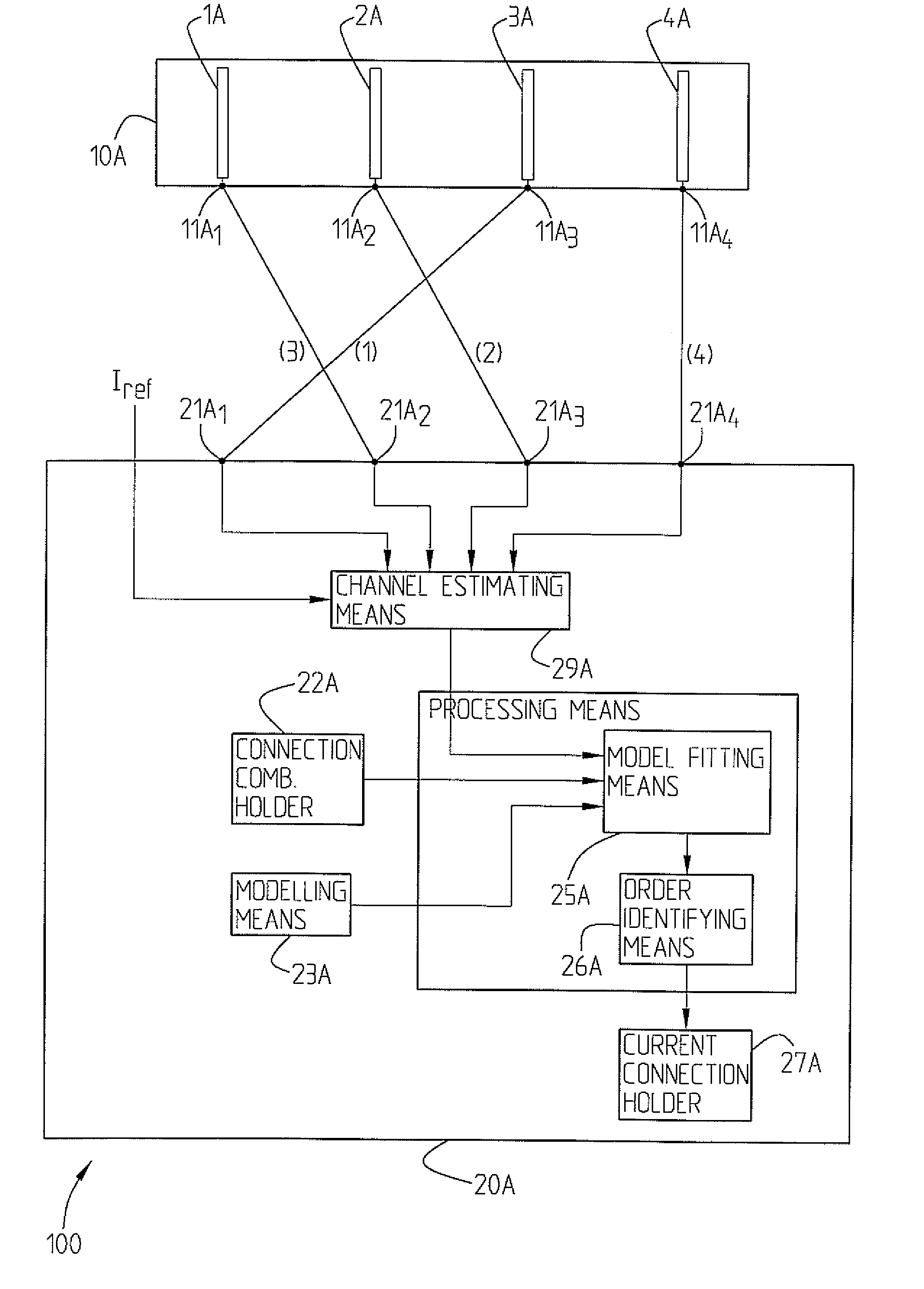
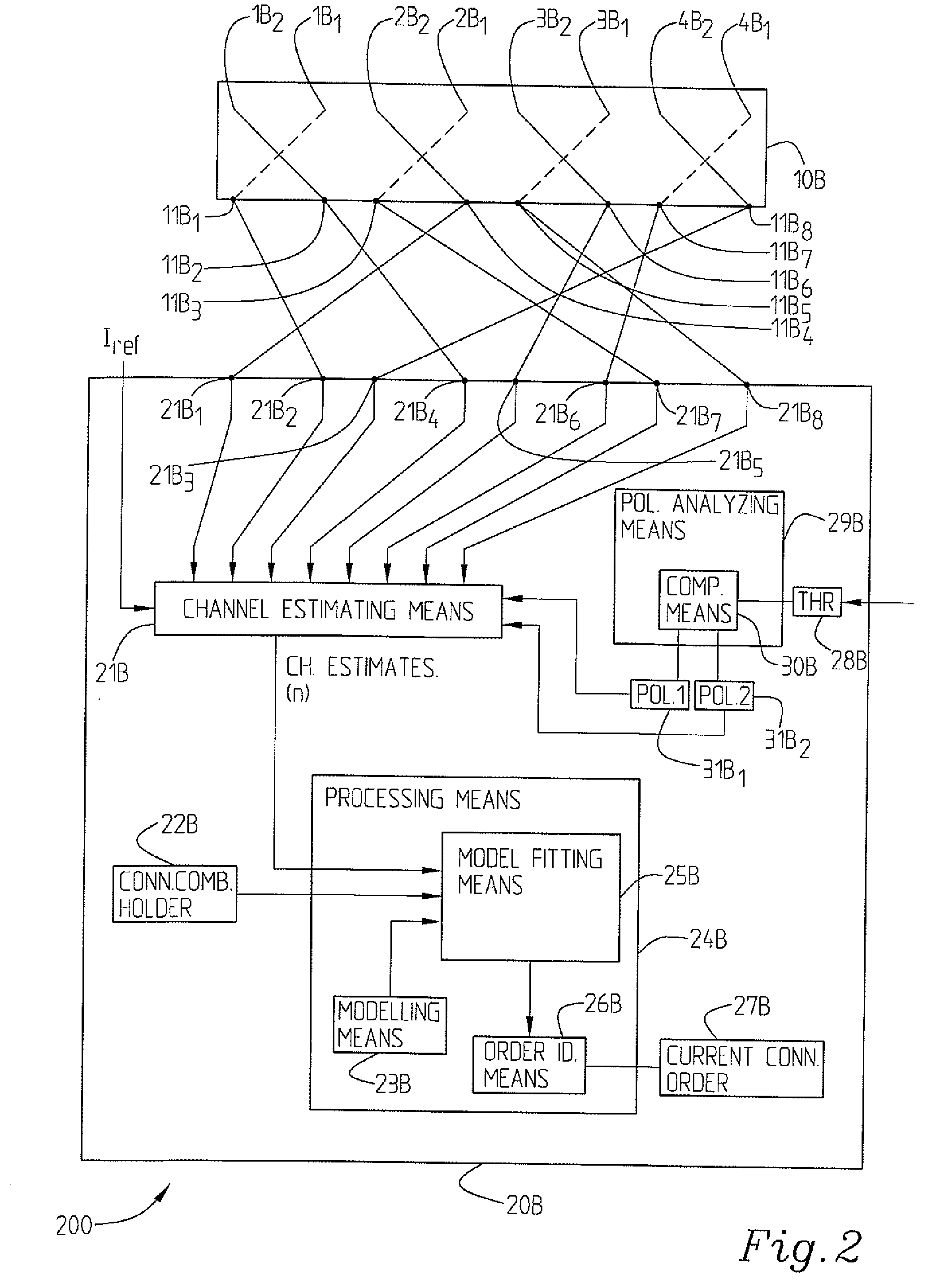
The present invention relates to a wireless communication node (20A) adapted to via feeder ports be connected to antenna ports. It comprises signal handling and estimating means (21A) adapted to collect signals from a mobile station and to generate a plurality of channel estimates, connection combination information holding means (22A) adapted to hold information about all possible feeder port-antenna port connections, processing means (24A) comprising channel modelling means (23A) adapted to provide a channel model for the received signals. If further comprises channel model fitting means (25A) adapted to compare the channel model with the channel estimates for a plurality of permutations obtained by the connection combination information and order identifying means (26A) adapted to identify the feeder port connection order corresponding to the permutation order giving the best fit between channel model and channel estimates, hence allowing identification of the order in which the feeder ports actually are connected to the antenna ports.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
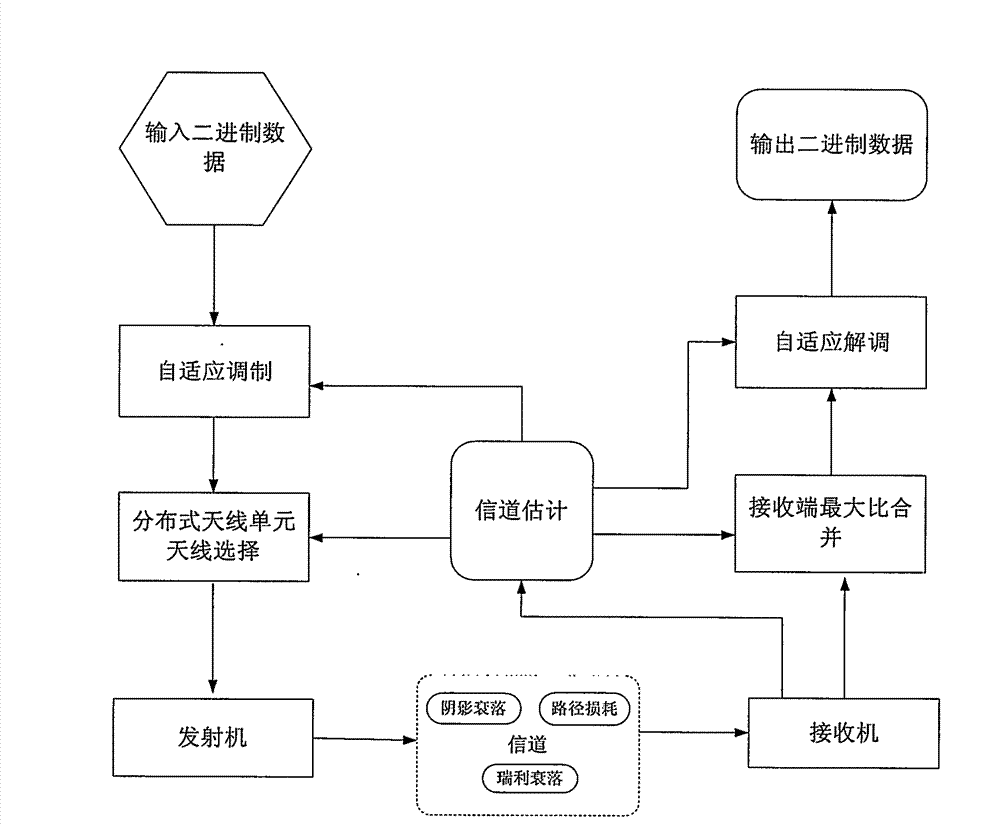
Adaptive modulation method for distributed multi-antenna system
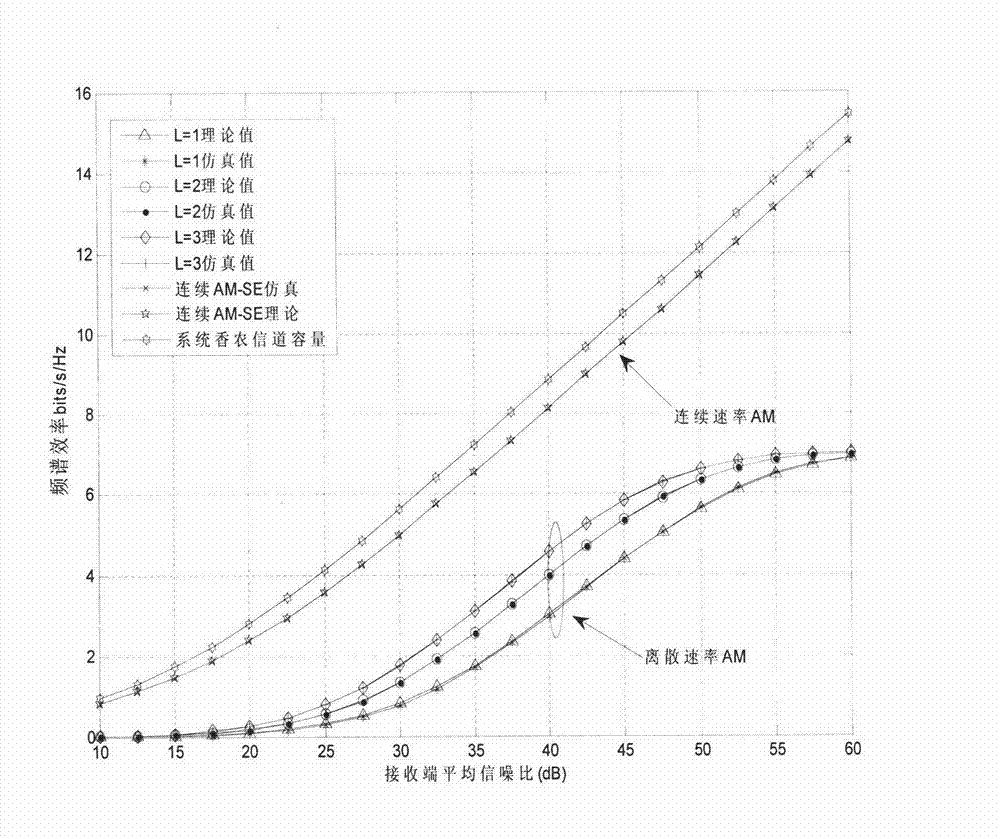
InactiveCN102833046AImprove spectral efficiencyVerify validityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionFrequency spectrumMATLAB
The invention relates to an adaptive modulation (AM) method design and performance evaluation for a wireless distributed multi-antenna system (DAS). Under the constraint condition of a target bit error rate (BER), the system frequency spectrum efficiency is maximized to respectively design two AM schemes of a discrete rate and a continuous rate. By aiming at the discrete rate AM, an adaptive switching threshold based on precise BER is provided. Compared with the traditional AM based on an approximate threshold, the AM method disclosed by the invention can obtain high frequency spectrum efficiency. A channel model comprising path loss, shadow fading and Rayleigh fading is designed by considering the practical situation of DAS. On the basis, the computation expression of a continuous rate AM frequency spectrum efficiency, a discrete rate AM frequency spectrum efficiency and the average BER is given so as to provide an effective method for system performance evaluation. An Matlab (matrix laboratory) simulation platform shows that the designed AM method can satisfy the target BER requirement, and the continuous rate AM method is better than a discrete rate AM method. In addition, due to the providing of an improved threshold, the discrete rate AM can be used for realizing the high frequency spectrum efficiency if being compared with the traditional AM method. In addition, the provided frequency spectrum efficiency has good consistency with the average BER calculation and simulation, and the system performance can be effectively evaluated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Rapid identification of transmission media channel characteristics
InactiveUS7133442B2Quick identificationEliminate damageTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsMultiple-port networksCommunications systemAlgorithm
Rapid identification and modeling of transmission media channel characteristics of a communications system using a correlation based technique. The technique provides a known training sequence used to generate a known quantity that operates on an observed or measured received signal, which is a function of the training sequence and the channel's impulse response, to give an estimate of the model of the channel. The technique decouples the training sequence from the observed or measured output, leaving the estimated impulse response. The impulse response of the transmission media channel is rapidly computed and processed to set the initial values of filter coefficients, for example, an echo canceller and an equalizer, in the communications system. Once the coefficients are initialized, if needed, a standard technique, such as least mean square (LMS) correlation, can be used to fine-tune the coefficients to converge on or model the transmission media channel's characteristics.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Multi-symbol noncoherent CPM detector
InactiveUS20060291592A1Improve performanceMinimal lengthAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsRound complexityEngineering
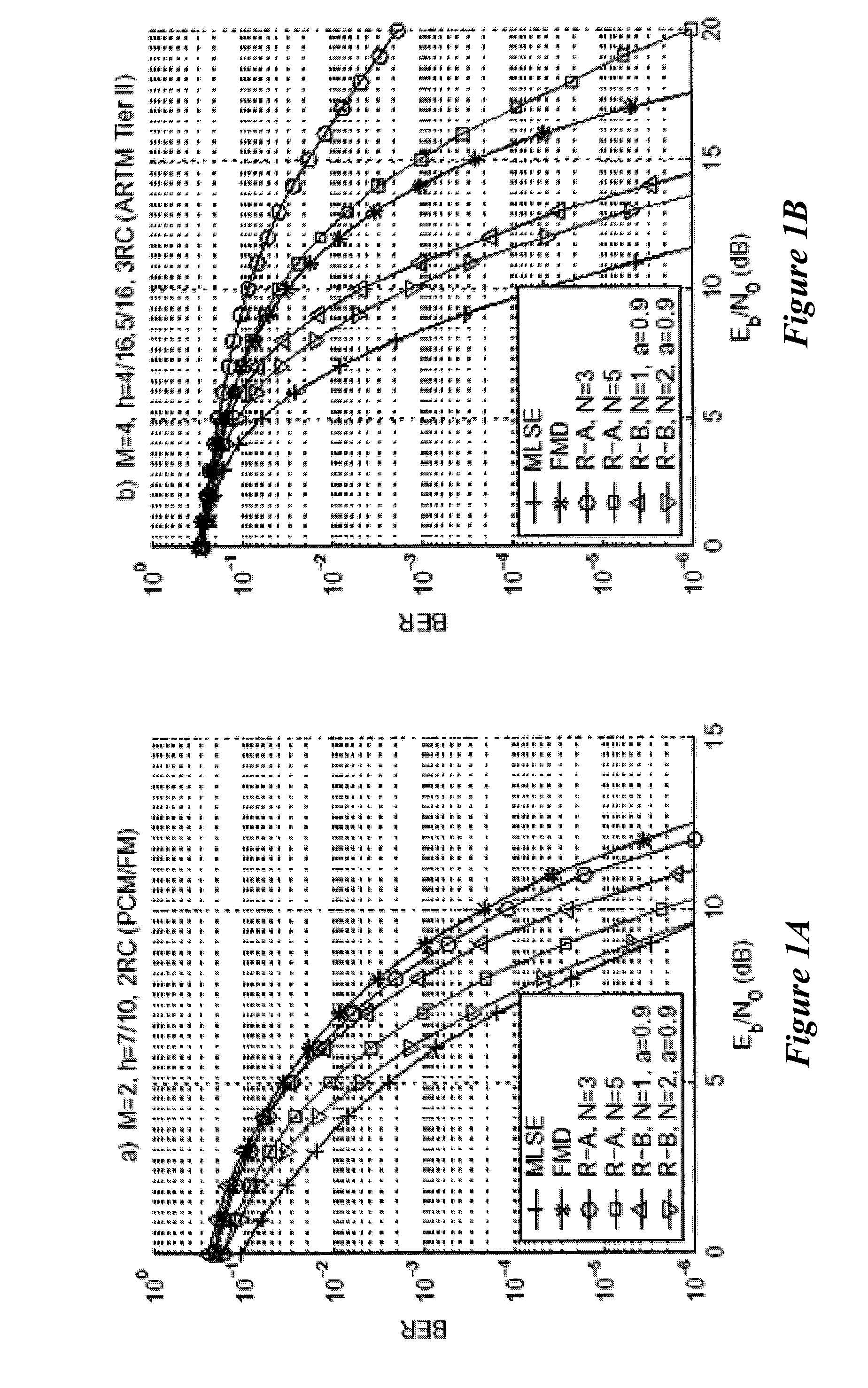
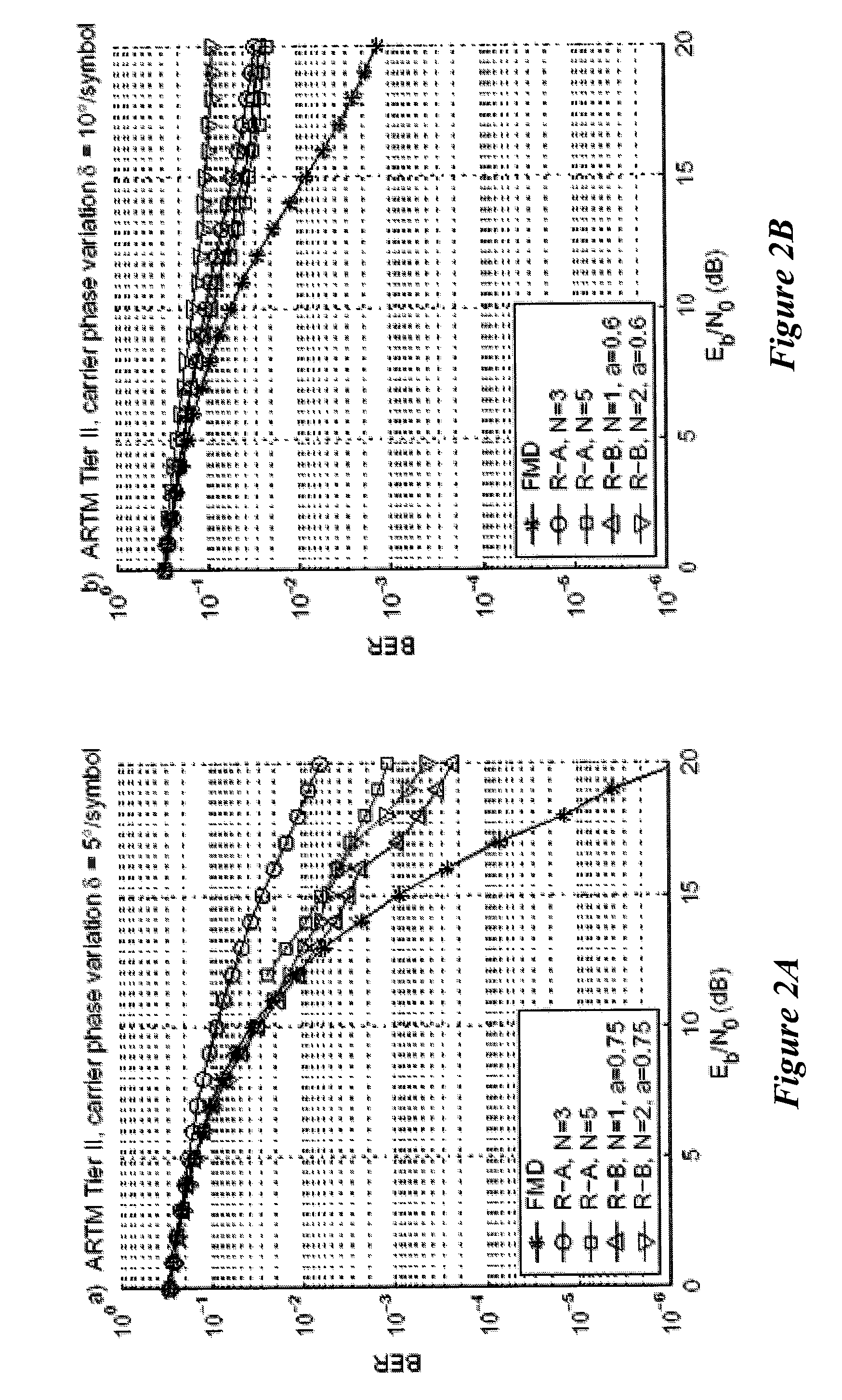
Three receivers are presented for the general case of noncoherent detection of multi-h continuous phase modulation. All three receivers yield performance gains using multi-symbol observations. The first is an existing receiver which has previously been applied to PCM / FM and is now applied to the Advanced Range Telemetry Tier II waveform. The second and third receivers are presented for the first time in this paper. The existing noncoherent receiver is found to perform poorly (and with high complexity) for the Advanced Range Telemetry Tier II case. For single-symbol observations, the new receivers outperform conventional FM demodulation for both telemetry waveforms, and for multi-symbol observation lengths their performance approaches that of the optimal coherent receiver. The performance is evaluated using computer simulations. Receiver performance is also evaluated using a simple channel model with varying carrier phase. The traditional FM demodulator approach is found to outperform all three receivers as channel conditions worsen.
Owner:QUASONIX
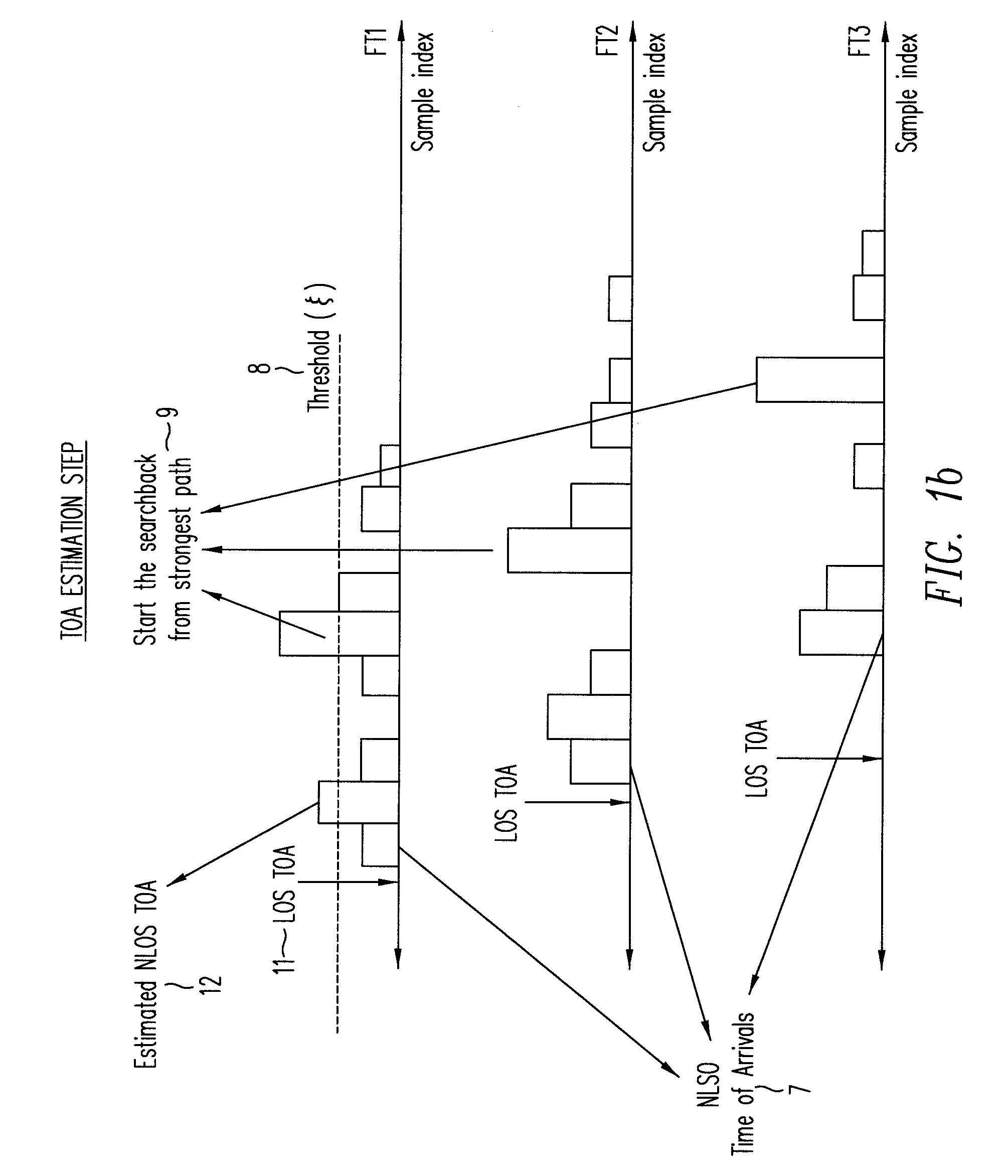
Line-of-sight (LOS) or non-LOS (NLOS) identification method using multipath channel statistics
Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) identification and mitigation are carried out in a wireless positioning system based on channel statistics derived from multipath components of a received signal. The statistics may be based on the kurtosis, the mean excess delay spread, or the root mean square delay spread. The results are justified using IEEE 802.15.4a ultrawideband channel models. Amplitude and delay statistics based on the IEEE models are shown to be log-normal random variables. A joint likelihood ratio test is presented for the LOS and NLOS identification.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
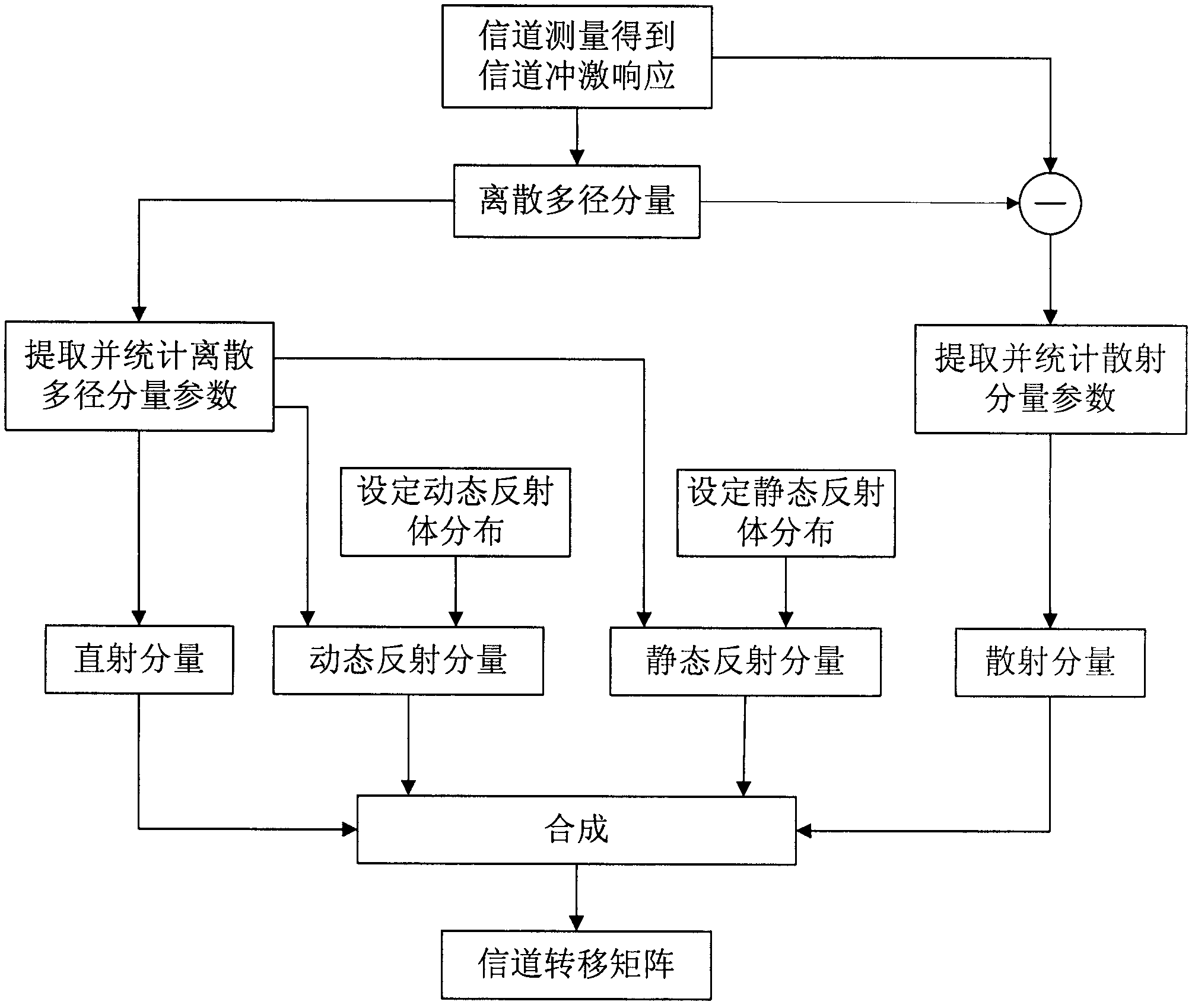
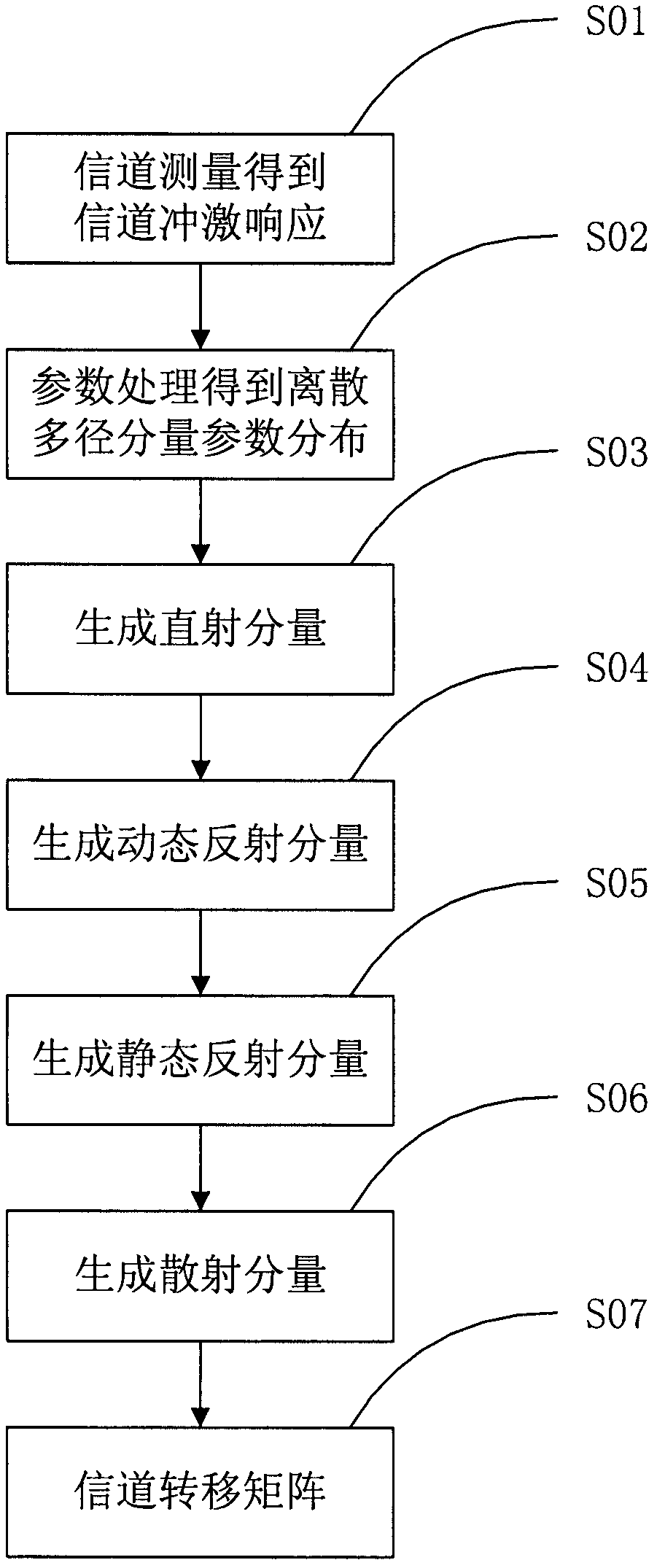
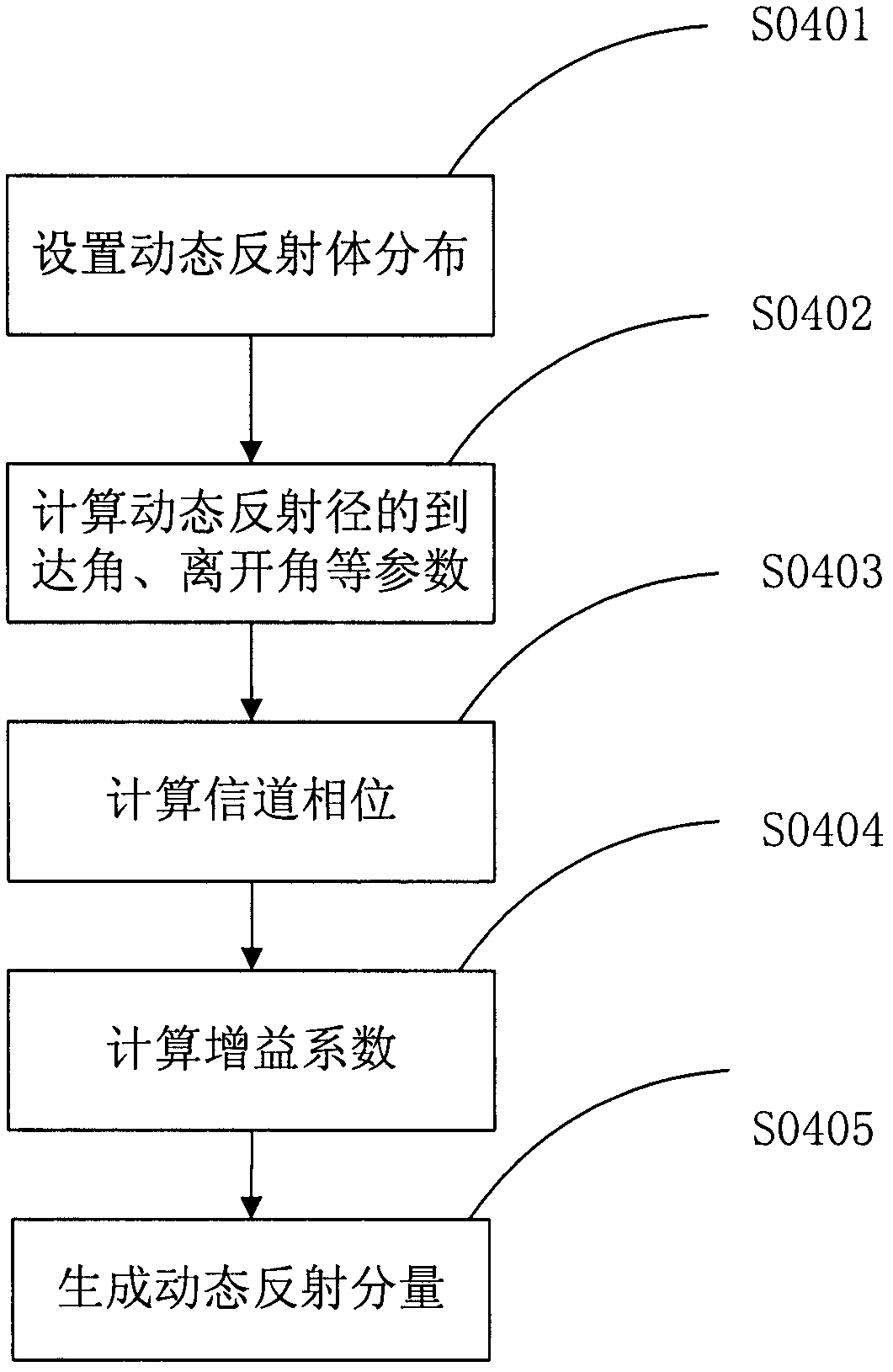
Broadband wireless multi-input multi-output (MIMO) channel modeling method for vehicle-to-vehicle communication
The invention discloses a broadband wireless multi-input multi-output (MIMO) channel modeling method for vehicle-to-vehicle communication. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring a channel to obtain channel impulse response; according to the channel impulse response, extracting a discrete multi-path component and counting the distribution of parameters of the discrete multi-path component; judging whether a collineation component exists, if so, acquiring the collineation component according to a geometrical relationship, otherwise, setting the collineation component as 0; according to vehicle density and statistical distribution of dynamic and static reflectors, setting a reflection environment, and respectively acquiring dynamic and static reflection components according to a processing result of channel measurement data; subtracting the discrete multi-path component from the channel impulse response to obtain a remainder, estimating scattering component parameters according to the remainder, and counting the distribution of the scattering component parameters to obtain a scattering component; and superposing the four components to obtain a channel transfer matrix so as to finish channel modeling. The method has the advantages that: on the basis of the non-stationarity and time-varying performance of a vehicle-to-vehicle communication environment, a channel model is established by taking influence of the dynamic reflection component into full consideration and using other components, and the channel model can be approximate to an actual channel.
Owner:武穆清
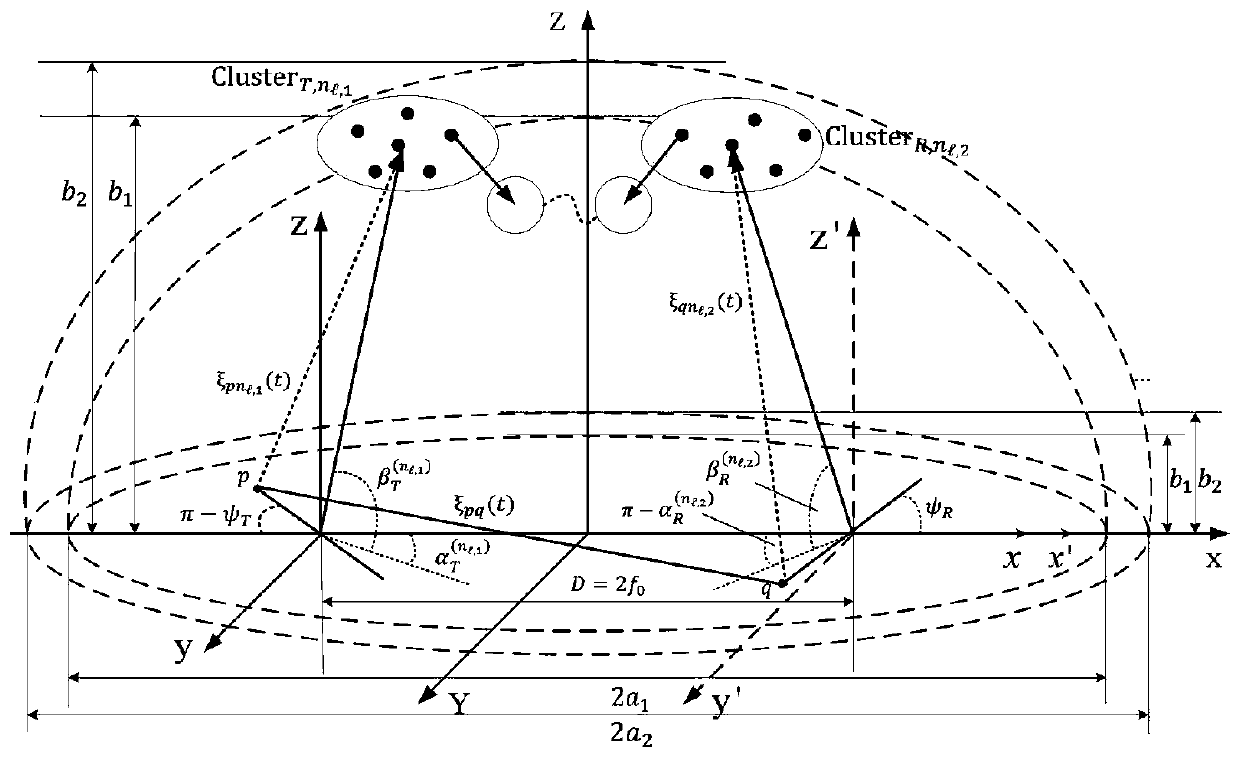
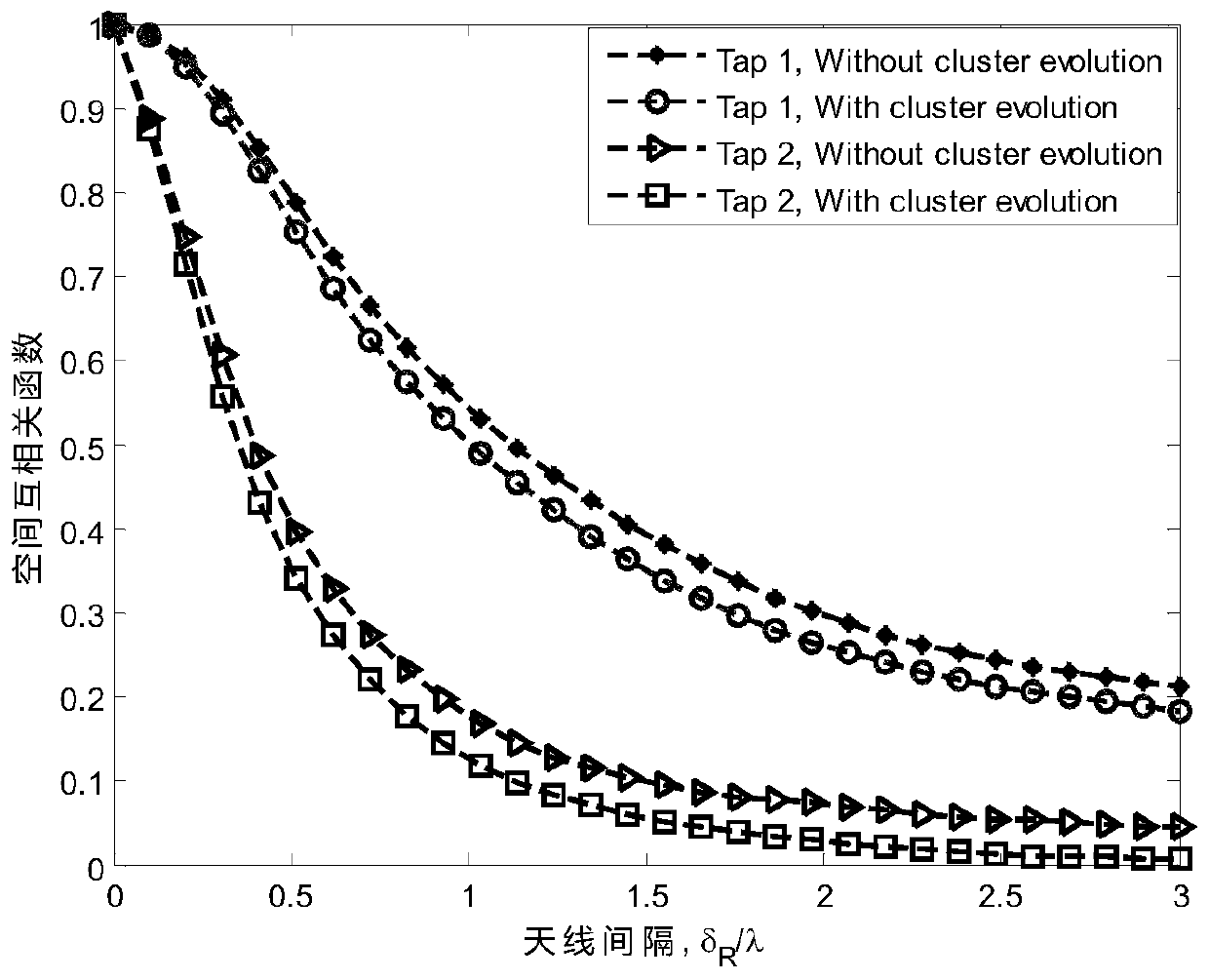
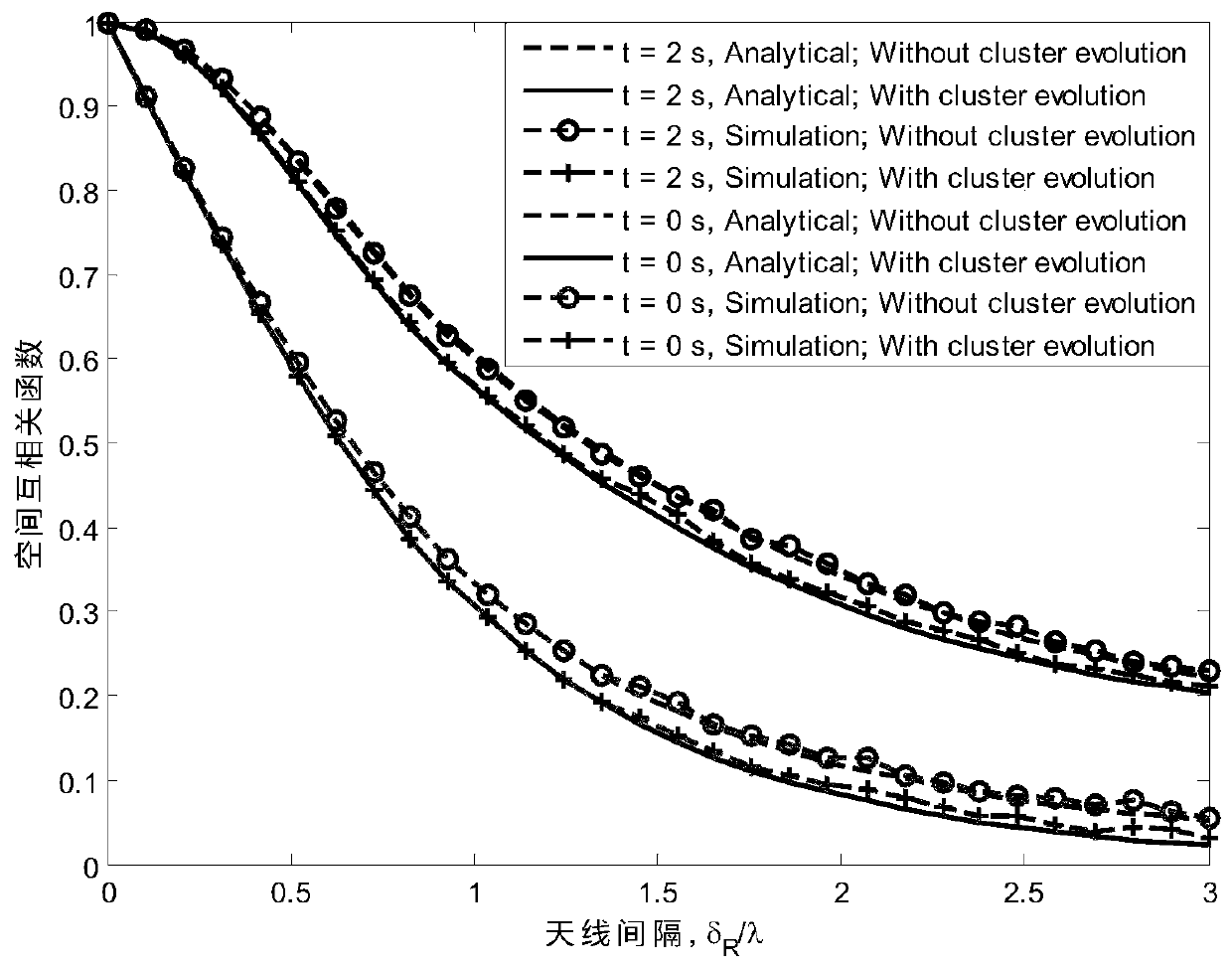
Double-cluster geometric channel modeling method based on three-dimensional space
ActiveCN111245480AImprove performanceParticular environment based servicesVehicle-to-vehicle communicationCommunications systemChannel impulse response
The invention discloses a double-cluster geometric channel modeling method based on a three-dimensional space. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, building a large-scale MIMO V2V channel model based on a geometric relation in a confocal semi-ellipsoid scattering scene; secondly, using the concept of clusters to describe scatterers, wherein many scatterers exist in the clusters, andthe clusters are randomly distributed on the semi-ellipsoidal surface; supposing that the number of the scatterers in the clusters approaches infinity, and respectively expressing the continuous random variables alphaT<nl,1>, betaT<nl,1>, alphaR<nl,2> and betaR<nl,2> by discrete variables alphaT<l,1>, betaT<l,1>, alphaR<l,2> and betaR<l,2>; then, introducing a birth and death algorithm to simulatedisappearance and evolution of the clusters on a time axis and an array axis; and finally, deducing the statistical characteristics of the proposed channel model according to the complex channel impulse response. The performance of the communication system of the V2V in the semi-ellipsoidal environment is improved by calculating the geometric statistical characteristics of the three-dimensional double-cluster semi-ellipsoidal body.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com