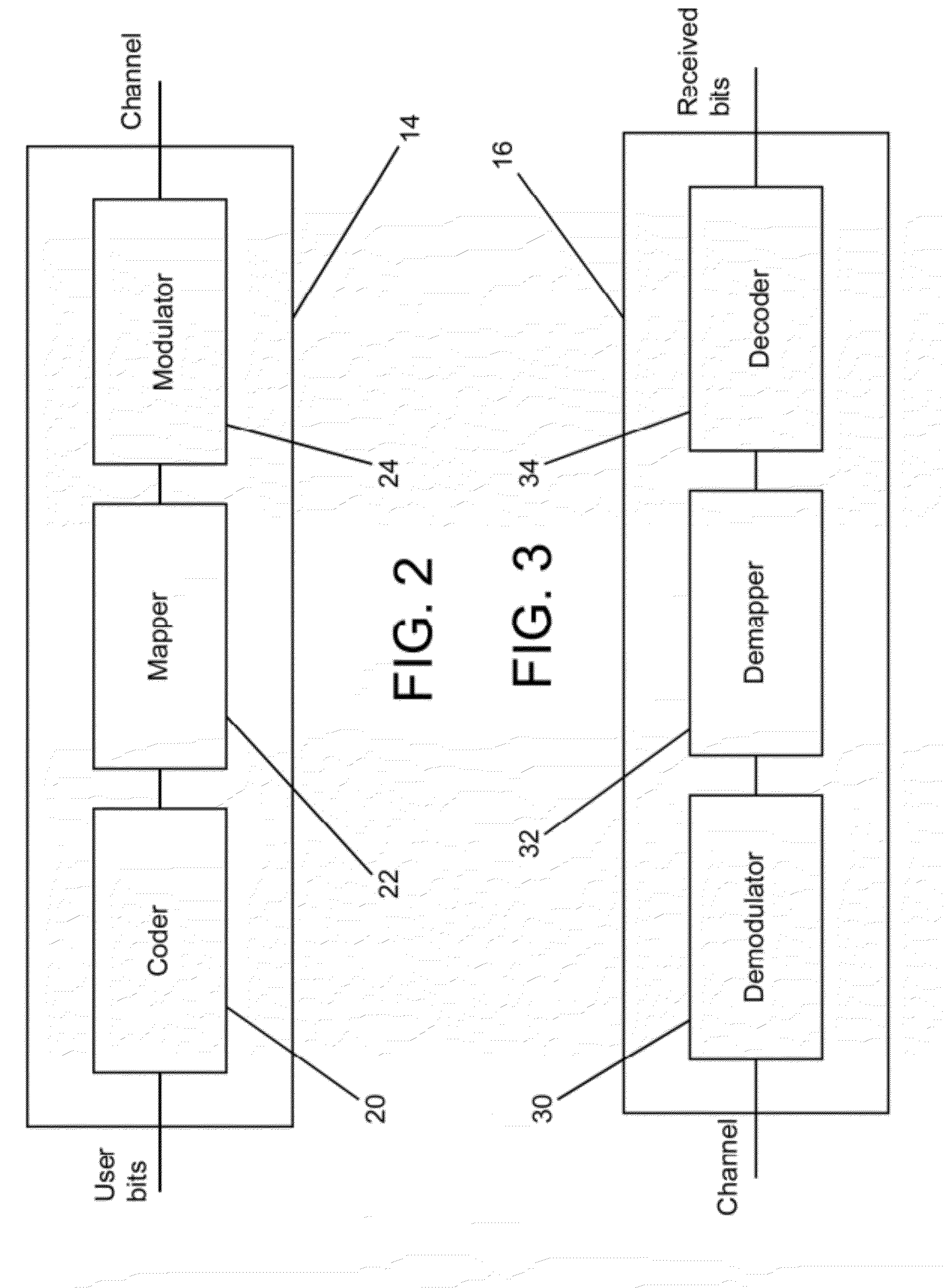
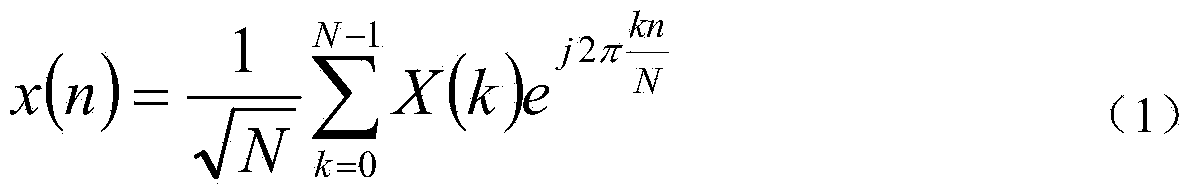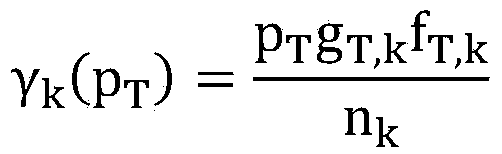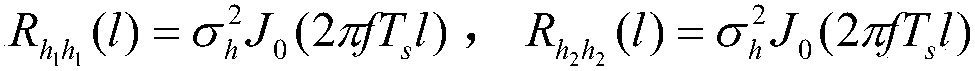Patents
Literature
143 results about "Rayleigh fading" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
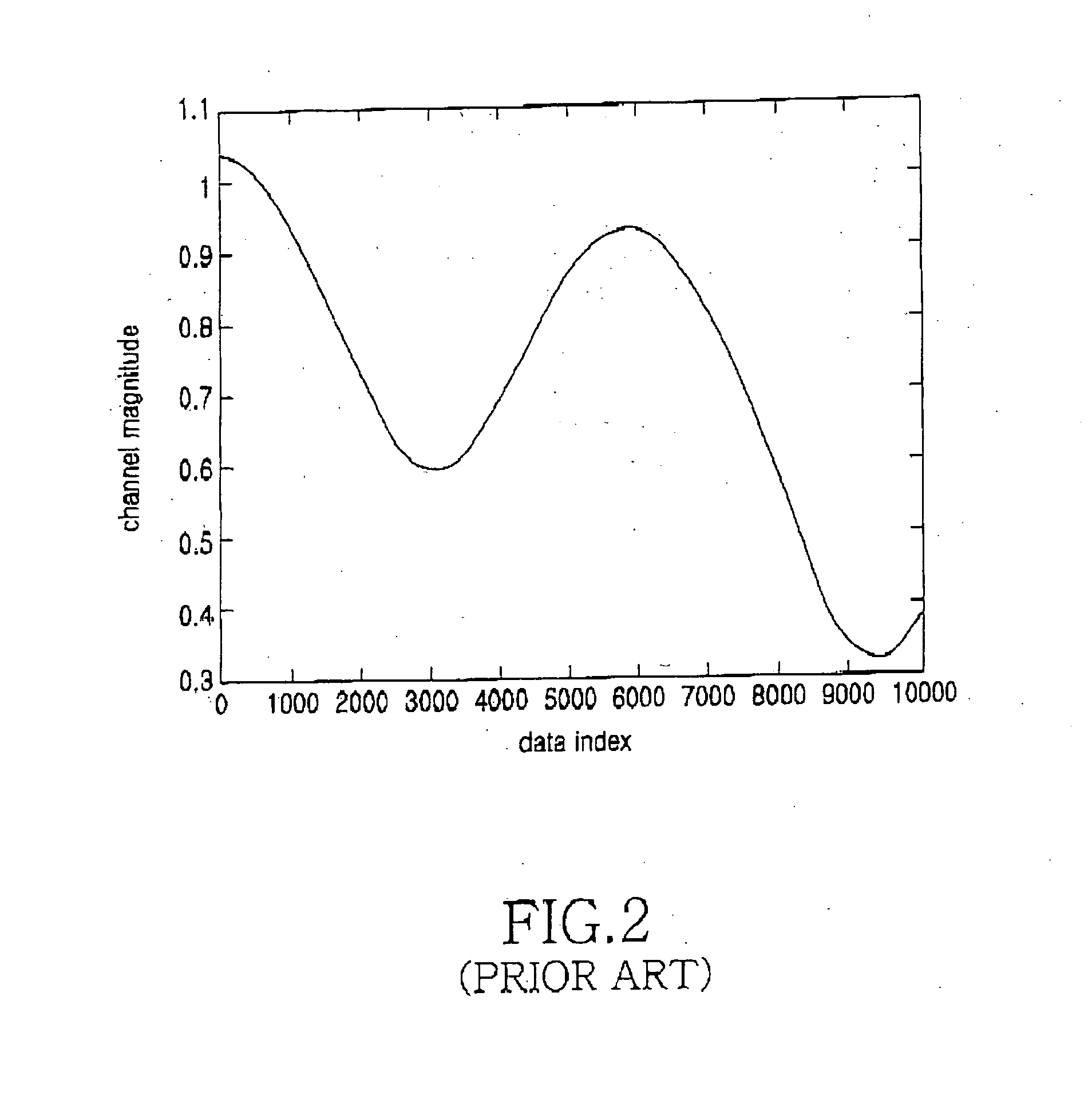
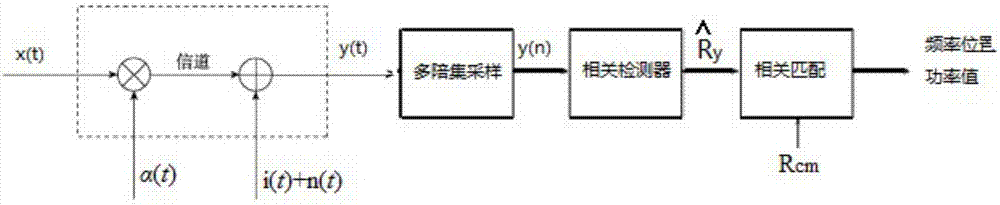
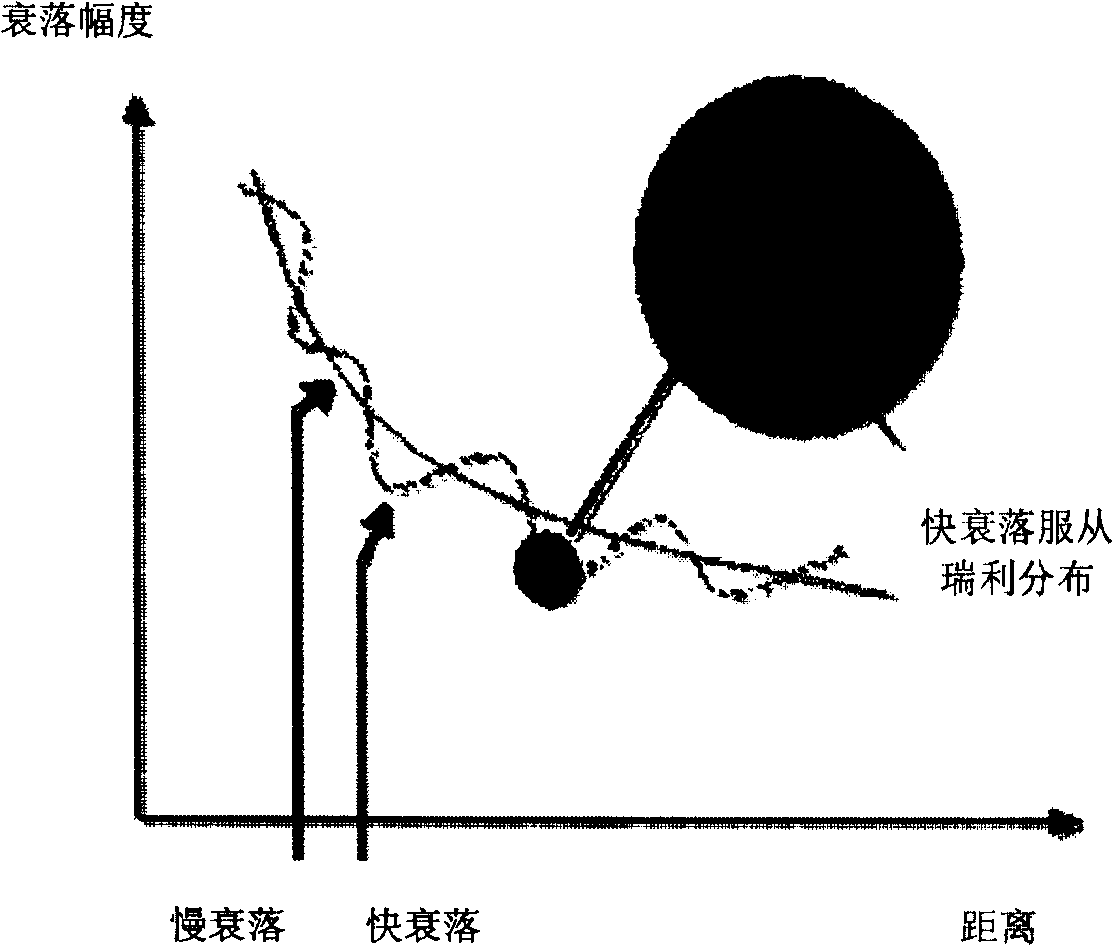
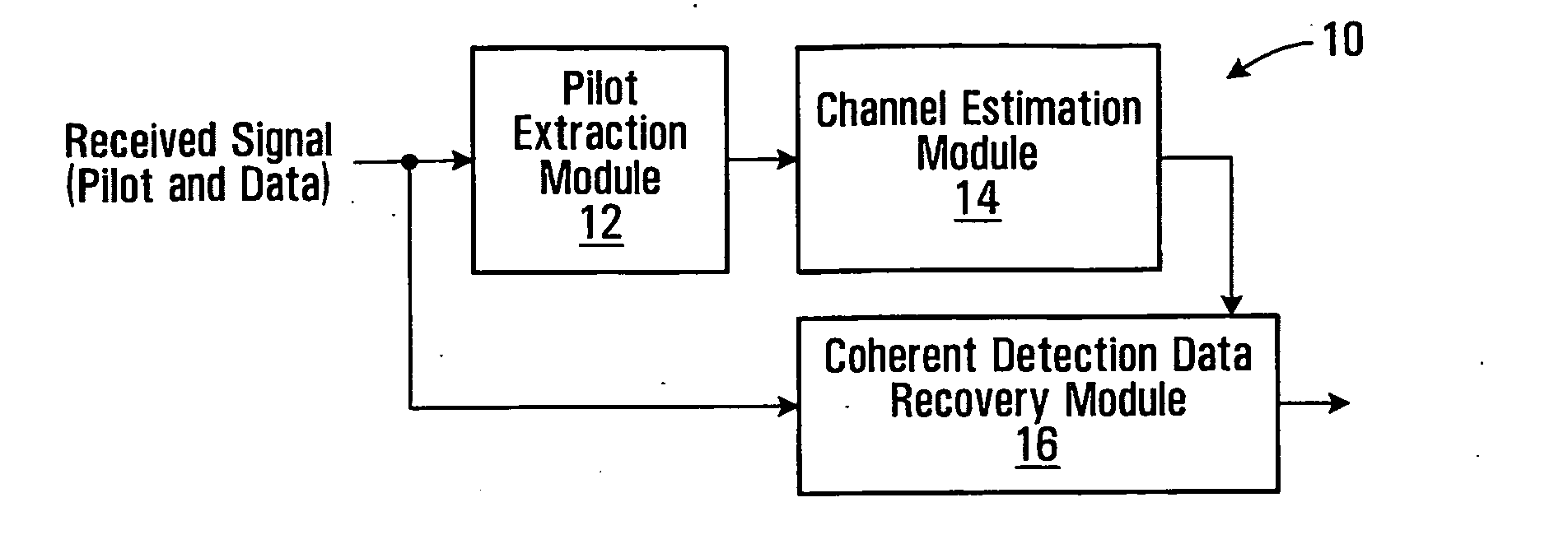
Rayleigh fading is a statistical model for the effect of a propagation environment on a radio signal, such as that used by wireless devices. Rayleigh fading models assume that the magnitude of a signal that has passed through such a transmission medium (also called a communication channel) will vary randomly, or fade, according to a Rayleigh distribution — the radial component of the sum of two uncorrelated Gaussian random variables.
System and method for accurately predicting signal to interference and noise ratio to improve communications system performance
InactiveUS6426971B1Energy efficient ICTError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFinite impulse responseEngineering
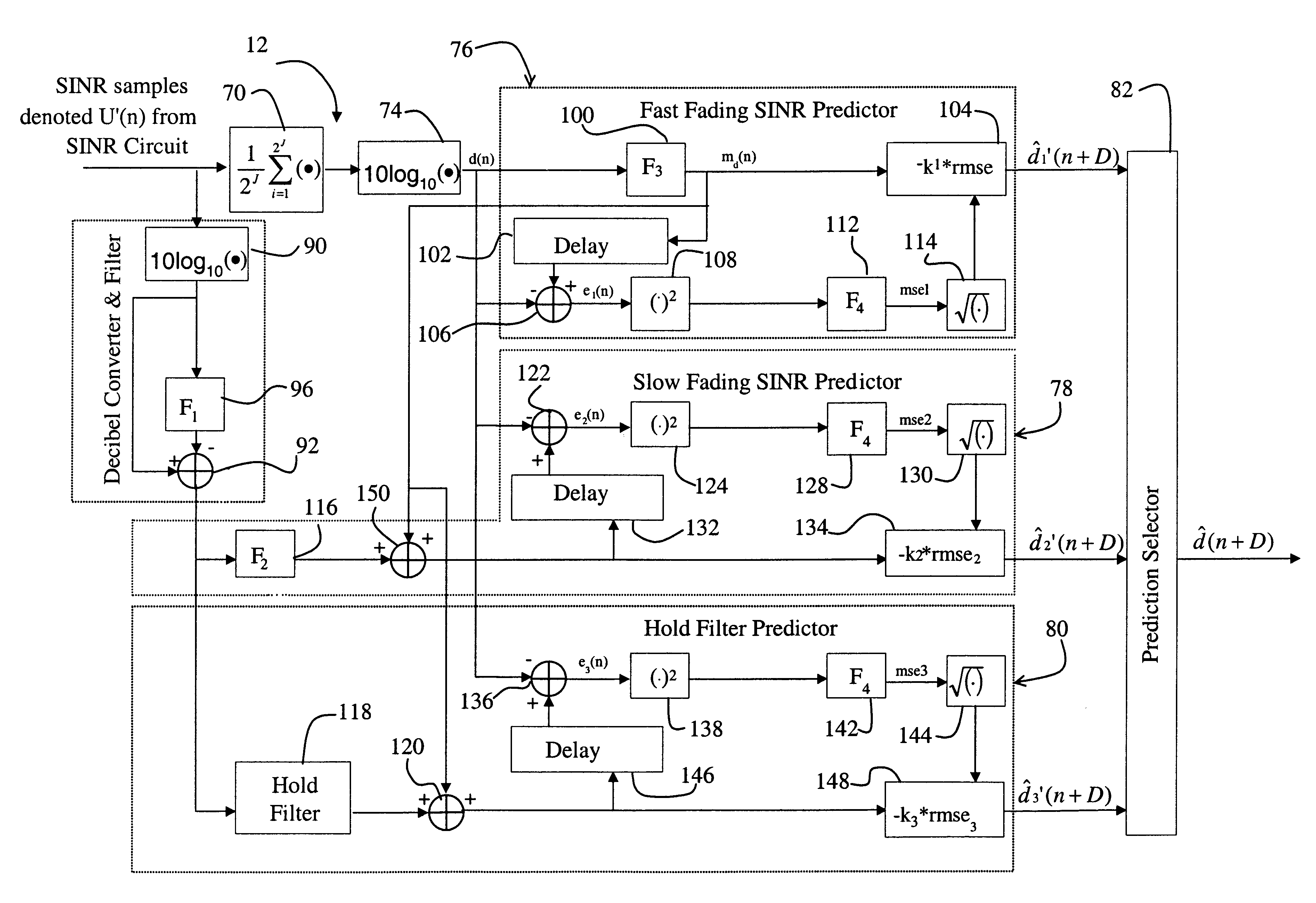
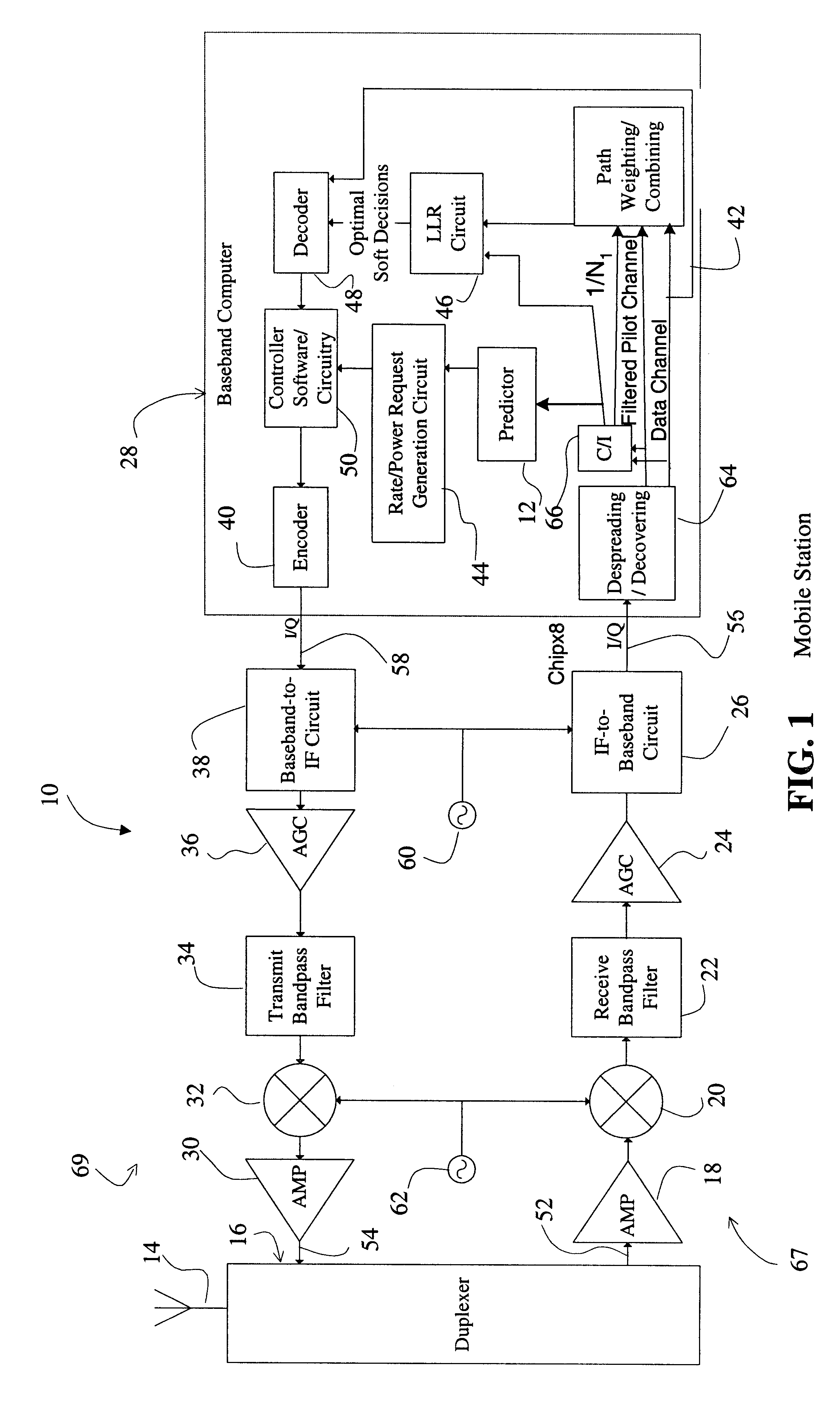
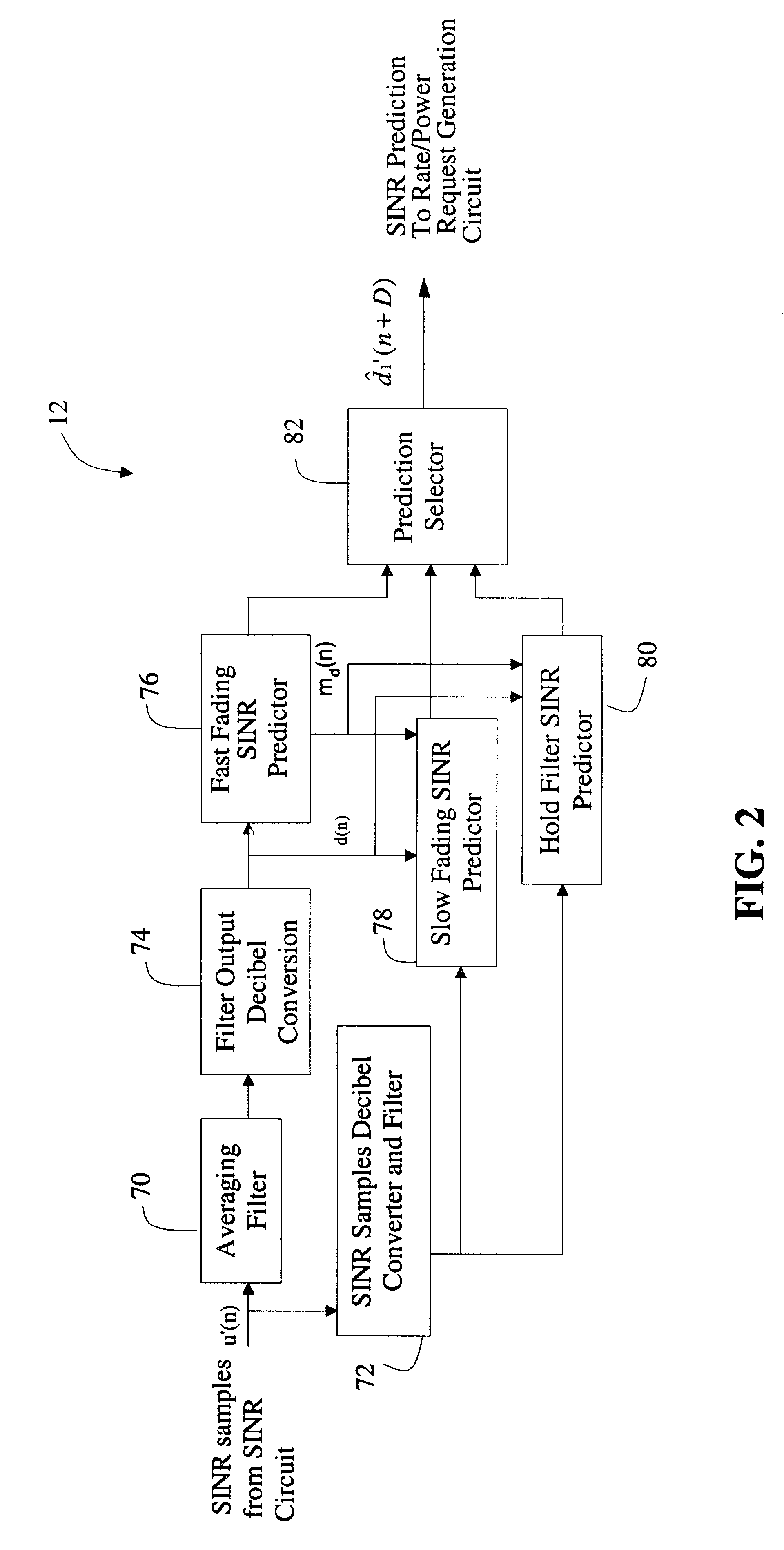
A system for providing an accurate prediction of a signal-to-interference noise ratio is described. The system includes a first circuit for receiving a signal transmitted across a channel via an external transmitter. A second circuit generates a sequence of estimates of signal-to-interference noise ratio based on the received signal. A third circuit determines a relationship between elements of the sequence of estimates. A fourth circuit employs the relationship to provide a signal-to-interference noise ratio prediction for a subsequently received signal. In the illustrative embodiment, the inventive system further includes a circuit for generating a data rate request message based on the signal-to-noise ratio prediction. A special transmitter transmits the data rate request message to the external transmitter. In the specific embodiment, the relationship between elements of the sequence of estimates is based on an average of the elements of the sequence of estimates. The third circuit includes a bank of filters for computing the average. The bank of filters includes finite impulse response filters. Coefficients of the transfer functions associated with each filter in the bank of filters are tailored for different fading environments. The different fading environments include different Rayleigh fading environments, one environment associated with a rapidly moving system, a second environment associated with a slow moving system, and a third system associated with a system moving at a medium velocity. A selection circuit is connected to each of the filter banks and selects an output from one of the filters in the filter bank. The selected output is associated with a filter having a transfer function most suitable to a current fading environment.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
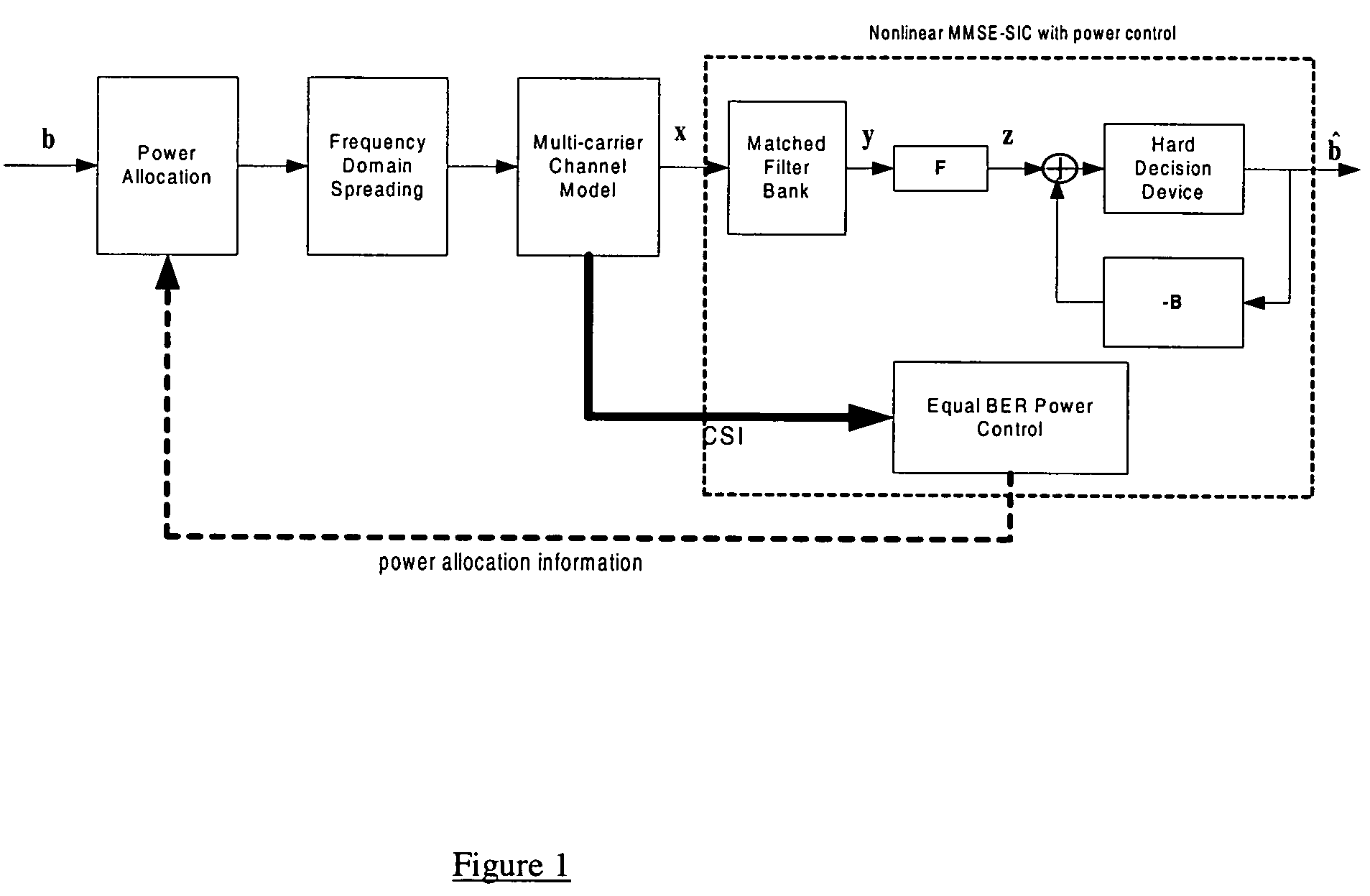
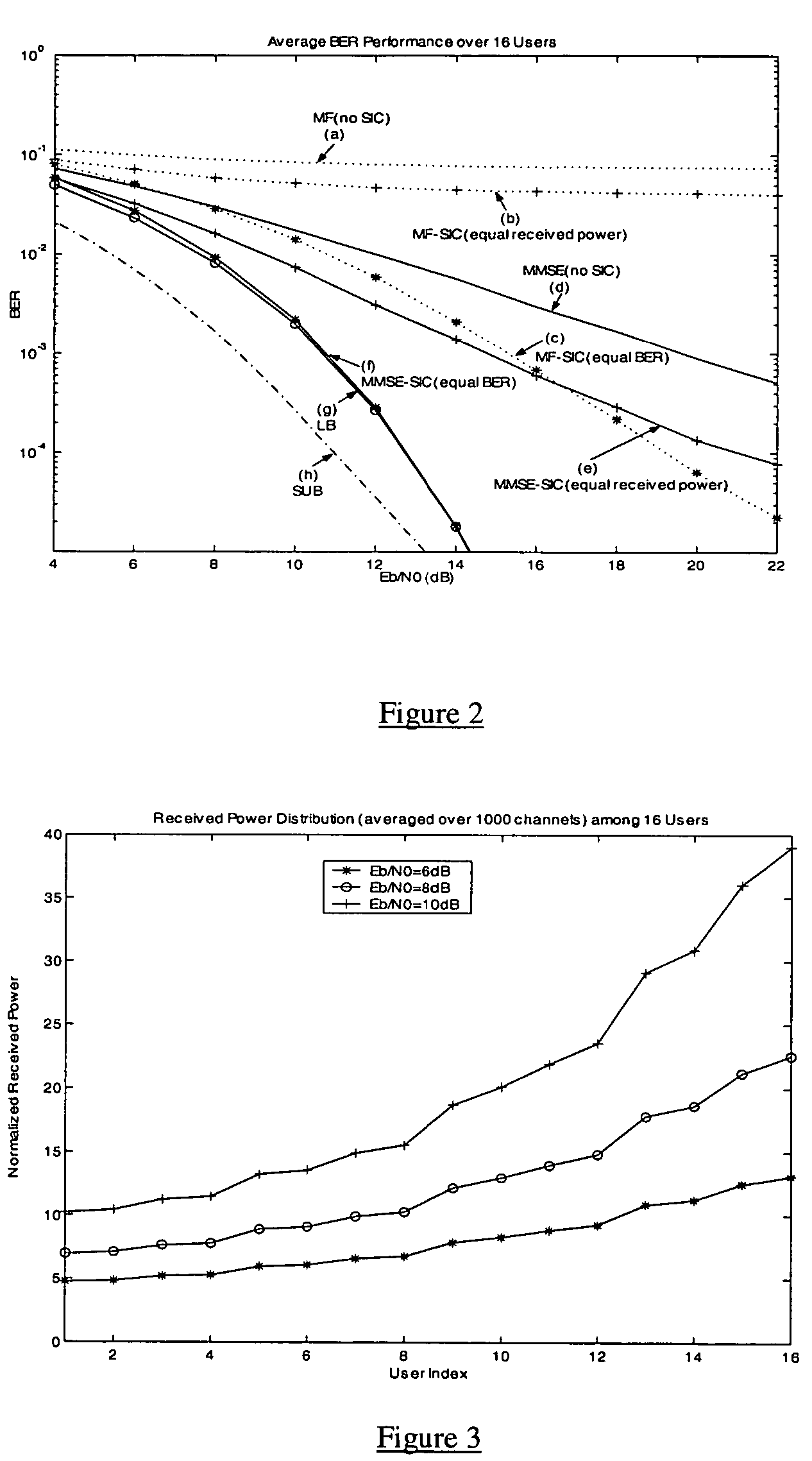
Equal BER power control for uplink MC-CDMA with MMSE successive interference cancellation
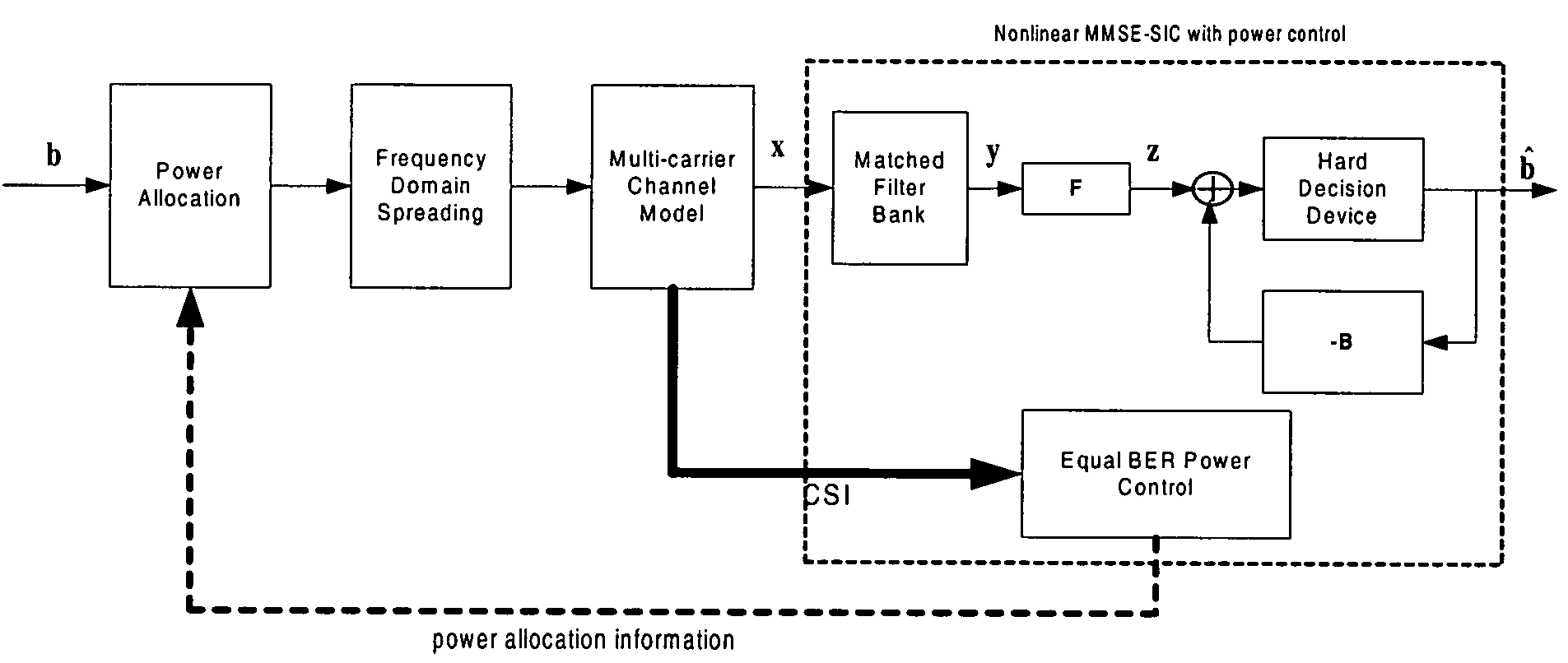
ActiveUS7620096B2Maximize SIRsImprove efficiencyPower managementEnergy efficient ICTEngineeringPower control
For a given decision order, MMSE successive interference cancellation (MMSE-SIC) can simultaneously maximize SIRs of all users. To further increase its efficiency, a power control (PC) algorithm, under equal BER criterion, is disclosed for uplink MC-CDMA. In frequency-selective Rayleigh fading channels, the MMSE-SIC integrated with the equal BER PC suppresses multiple access interference (MAI) effectively, resulting in a performance very close to the single user bound (SUB).
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
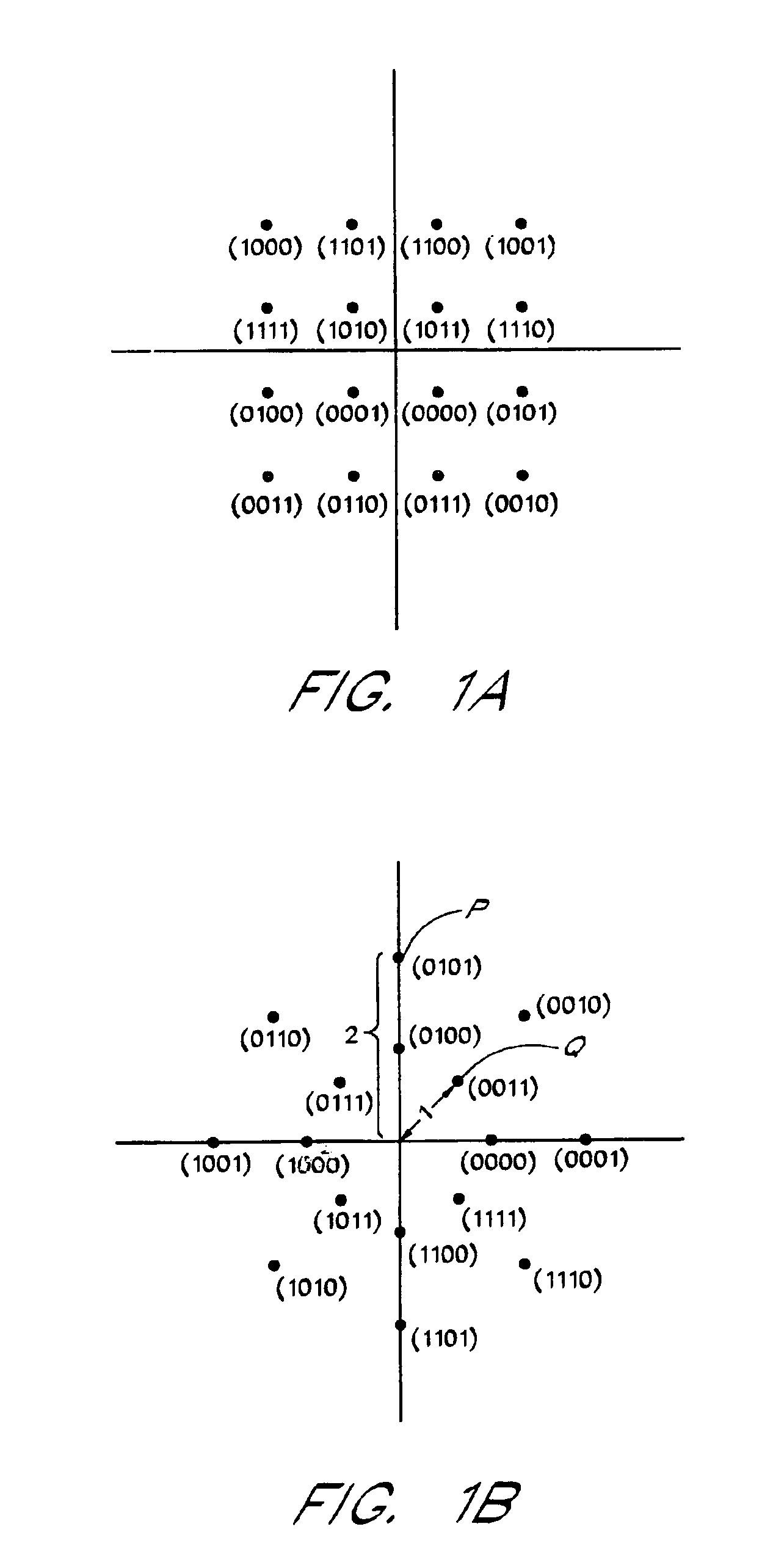
Methods and apparatuses for signaling with geometric constellations in a raleigh fading channel
ActiveUS20120147983A1Present inventionEliminate gapsSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationCriteria allocationCommunications systemEngineering
Communication systems are described that use signal constellations, which have unequally spaced (i.e. ‘geometrically’ shaped) points. In many embodiments, the communication systems use specific geometric constellations that are capacity optimized at a specific SNR, over the Raleigh fading channel. In addition, ranges within which the constellation points of a capacity optimized constellation can be perturbed and are still likely to achieve a given percentage of the optimal capacity increase compared to a constellation that maximizes dmin, are also described. Capacity measures that are used in the selection of the location of constellation points include, but are not limited to, parallel decode (PD) capacity and joint capacity.
Owner:CONSTELLATION DESIGNS LLC
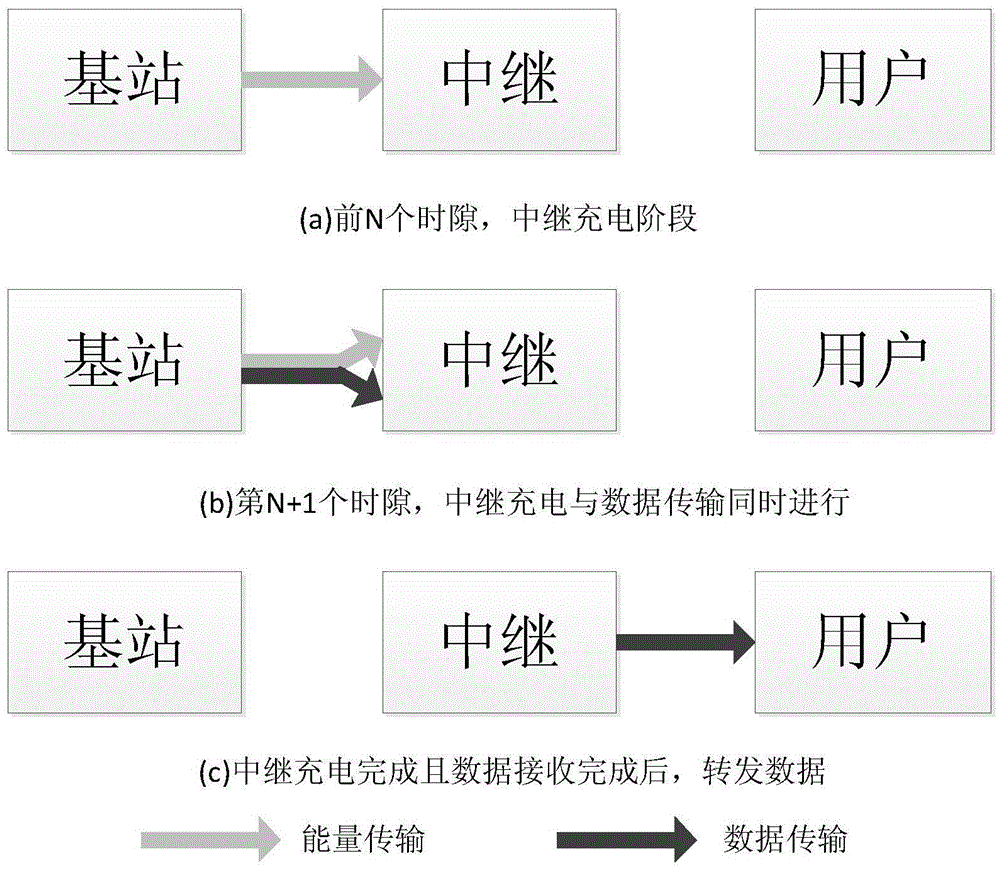
Wireless relay communication system SWIPT (Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer) method
ActiveCN105610485ASave time resourcesSave energy resourcesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerCommunications systemPower factor
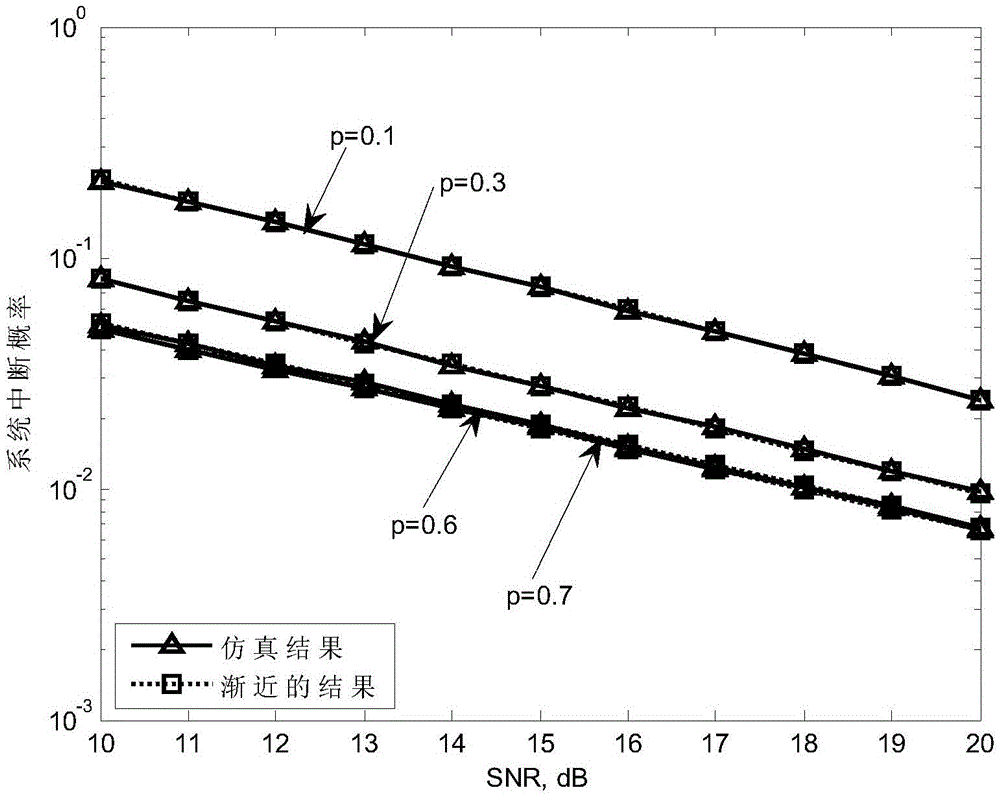
The invention discloses a wireless relay communication system SWIPT (Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer) method. The time and power distribution scheme of a wireless power supply relay communication system under the requirements of certain service quality and interrupt performance saves the time and energy resources, and is suitable for wireless communication. When the system is in operation, a transmitting end transmits energy and signals to a relay network. After given time, the relay network decodes the received signals and transmits the signals to a receiving end through employing a part of received energy. Through a derived system interrupt probability progressive expression and a simulation result in a flat Rayleigh fading channel, the method designs the distribution of time and power factors. The method can remarkably save the time and energy resources.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
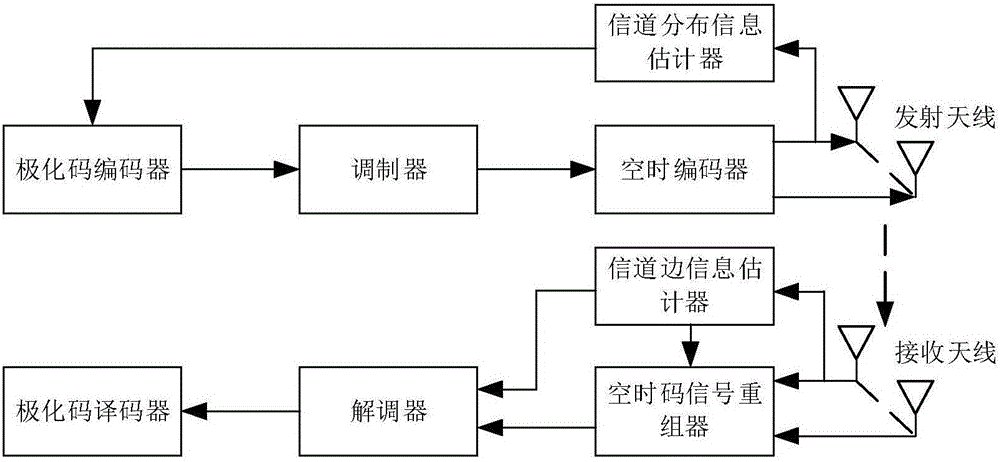
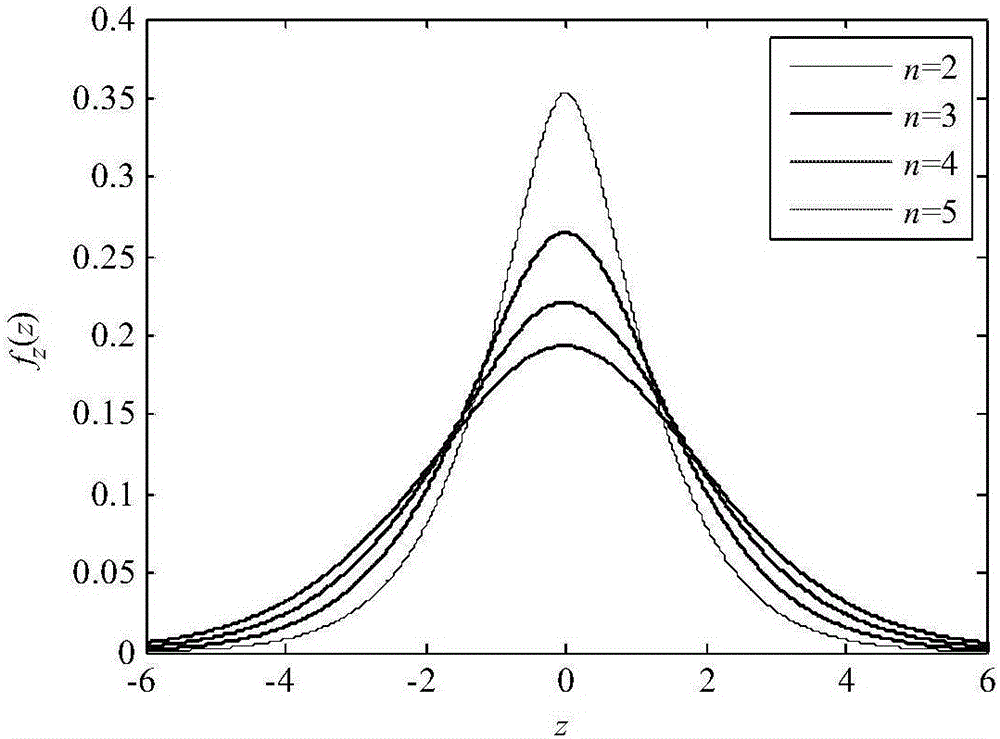
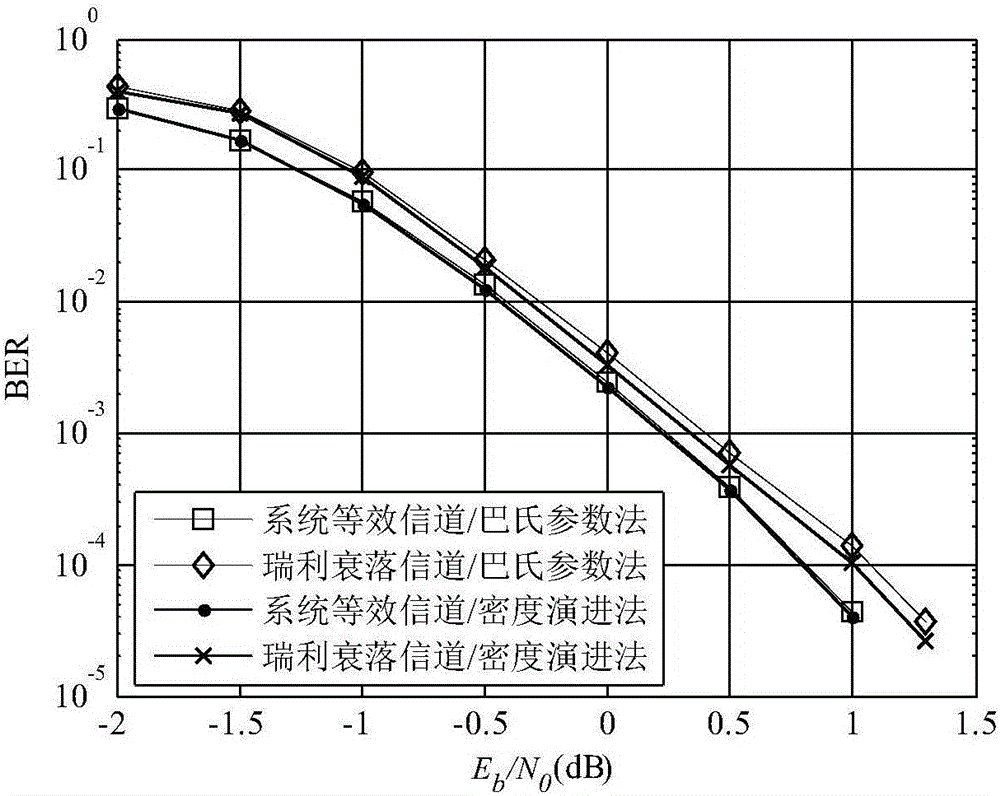
Polarization code cascade space-time code system and cascade polarization code coding method thereof
ActiveCN105897379AImprove bit error rate performanceObvious advantagesError correction/detection using linear codesError prevention/detection by diversity receptionComputer hardwareChannel state information
The present invention provides a polarization code cascade space-time code system and a cascade polarization code coding method thereof. The polarization code cascade space-time code system comprises the following steps that S1 a channel distribution information estimated value of a sending terminal is sent to a polarization code coder, the space-time code coding is carried out on a generated polarization code after modulation, and then the polarization code is sent to an MIMO channel; S2 a signal passes the MIMO channel and then is received by a reception antenna of a reception terminal, and then a space-time code signal reformer reforms the received signal according to a channel side information estimator of the reception terminal; S3 the demodulation and decoding operations are carried out according to the reformed signal and the channel side information of the reception terminal to obtain the original source bit. The present invention provides the reasonable polarization code cascade space-time code system, and according to the analysis in a Rayleigh fading MIMO antenna, each polarization code word equalizes the polarization code cascade space-time code system as a single transmission channel, and the channel gain and addition noise distribution of the equivalent channels is given out.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
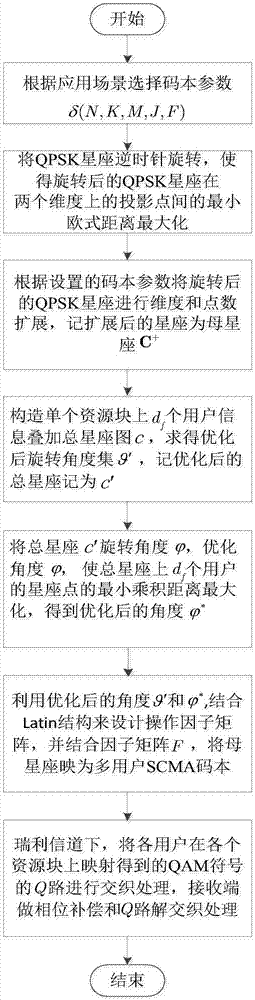
SCMA optimization codebook design method
ActiveCN107276960AImprove noiseImprove interferenceForward error control useMultiple carrier systemsResource blockSymbol of a differential operator
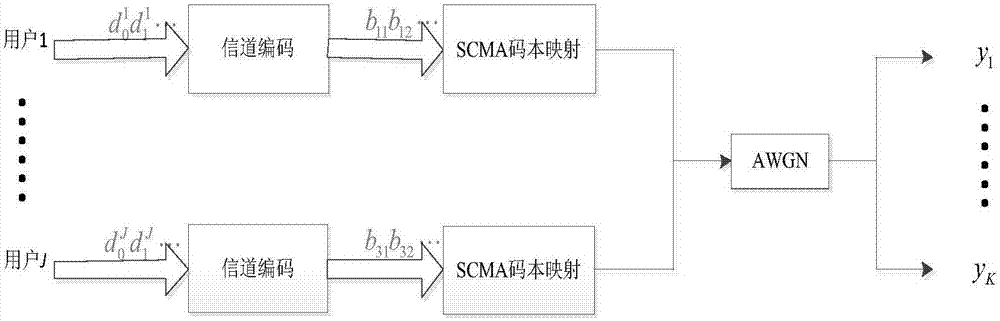
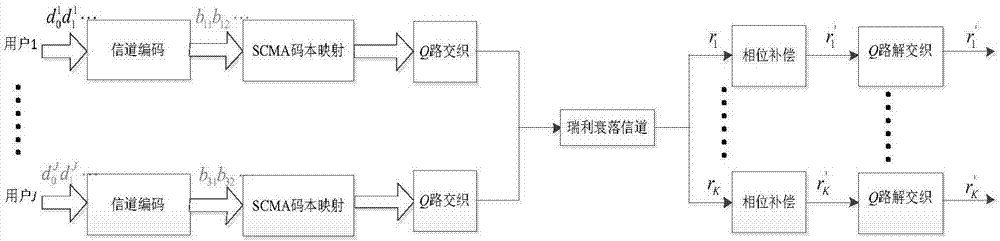
Disclosed is an SCMA (Sparse Code Multiple Access) optimization codebook design method, comprising the following steps: firstly, setting an SCMA codebook parameter; secondly, rotating a QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) constellation an angle anticlockwise to maximize the minimum Euclidean distance between projection constellation points of QPSK on two dimensions; thirdly, performing dimensional and point extension on C to obtain a mother constellation C+, and then rotating the C+ to construct a total constellation map c of df users on a single resource block to maximize the minimum Euclidean distance between the users; fourthly, rotating the total constellation anticlockwise to maximize the minimum product distance of each user on the resource block, and then mapping the mother constellation C+ to an SCMA codebook of multiple users with the use of the optimized rotating angle and in combination with a factor matrix F; and finally, in a Rayleigh fading channel, interweaving Q channels of QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) symbols, obtained by mapping on each resource block, of the users. The SCMA codebook designed by the method has good capability of resisting noise, interference and fading.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Dual-path static baseband channel simulating device and method
InactiveCN105049142ASimple structureImprove scalabilityTransmission monitoringChannel parameterControl signal
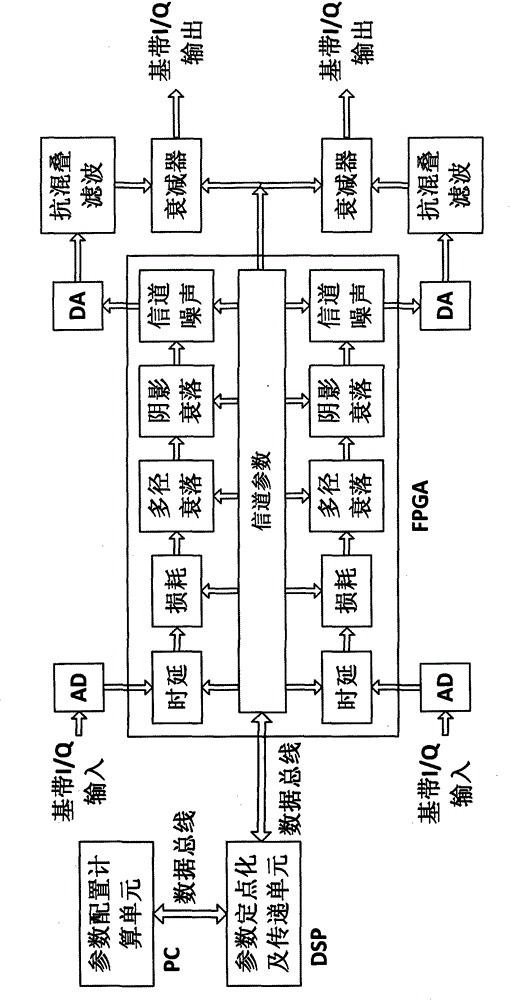
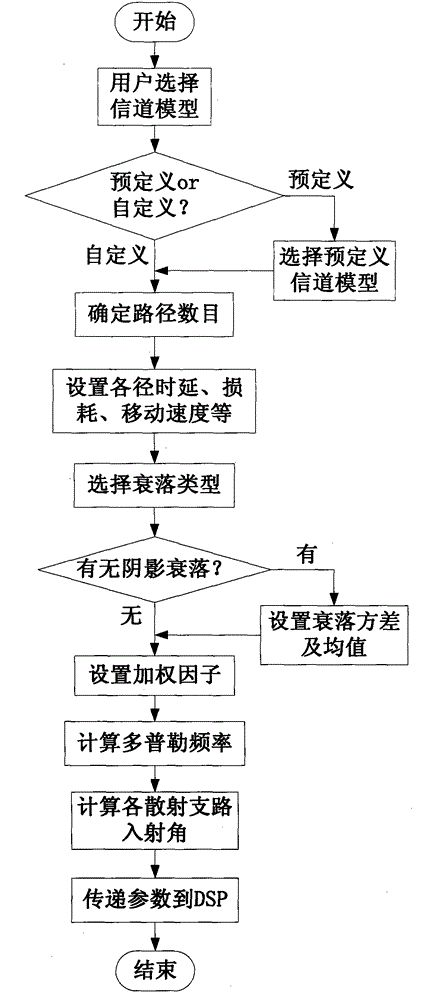
This invention provides a dual-path static baseband channel simulating device and method, which are applicable to a variety of communication scenarios. A channel model of each channel is selected by a user, and channel parameters are set and calculated; the channel parameters are subjected to fixed-point processing by a DSP (Digital Signal Processor), and the fixed-point parameters are transmitted into an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) through an EMIF; multipath fading, shadow fading and Gaussian noise are superposed on the dual-path digital baseband signals collected by an AD in the FPGA, wherein the type of the multipath fading includes constant fading, pure Doppler fading, Rayleigh fading, Rician fading and the like; the shadow fading follows lognormal distribution; at last, an analog signal is output by a DA, and signal conditioning is performed on the analog signal, wherein the signal conditioning mainly comprises eliminating mirror components of the signal and controlling signal attenuation. The channel simulating device and method provided by the invention have the advantages of being various in fading types, simple in operation and the like.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Method and apparatus relating to radio communication
InactiveUS20010041537A1Easy to useExpand coverageError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorRadio transmission for post communicationCellular radioCommunications system
The present invention pertains to the field of methods and apparatuses relating to radio communication; and in particular to the part of this field that concerns cellular radio communication. The present invention addresses mainly the problem of improving reliability and communication quality in a cellular radio communication system (1). According to the invention, it is determined whether one of an uplink (25) or a downlink (25) of a radio channel (23) is subject to a Rayleigh fading dip. If it is determined that one of the uplink (25) or the downlink (27) is subject to a Rayleigh fading dip, it is then determined whether it is necessary to execute a countermeasure in order to avoid the negative influences of Rayleigh fading on the channel (23). The invention is not limited to improving conditions on one channel but may be employed to any number of channels used for communications in the cellular radio communication system (1).
Owner:HIGHBRIDGE PRINCIPAL STRATEGIES LLC AS COLLATERAL AGENT
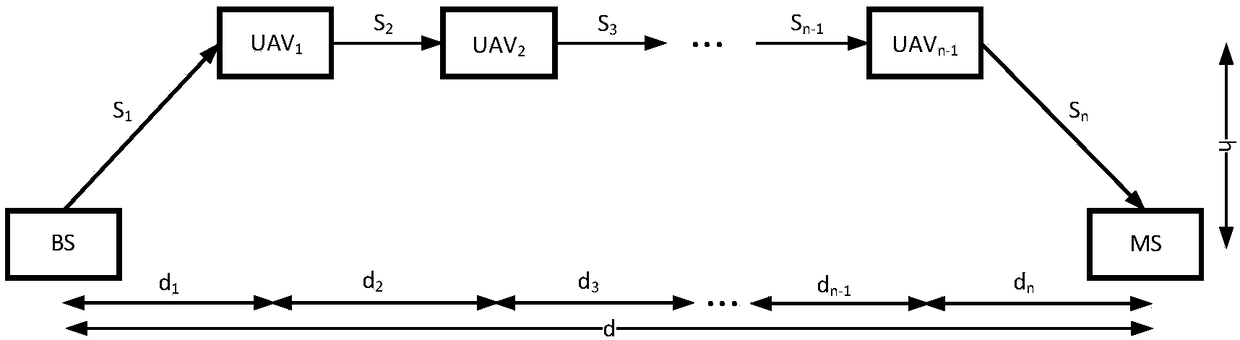
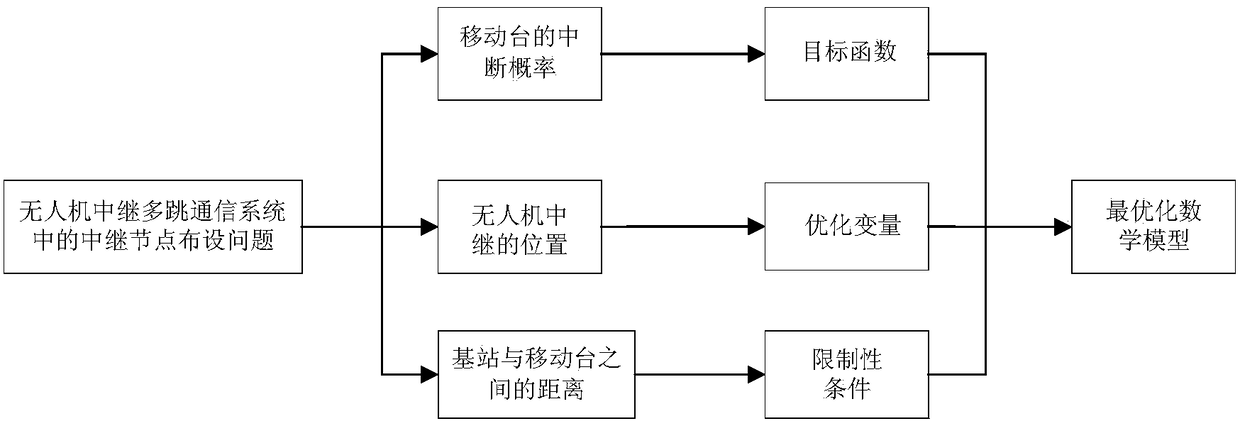
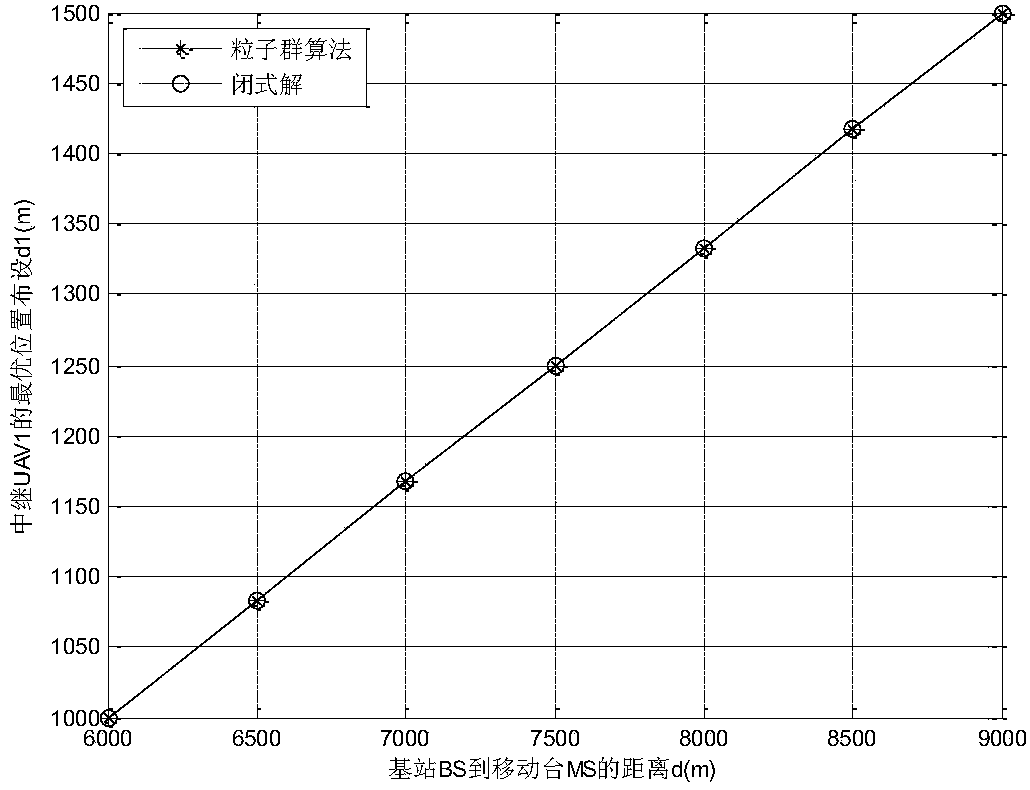
Relay node distribution method in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) relay multi-hop communication system
InactiveCN108156613AClosed-form solutionReduce computational complexityInternal combustion piston enginesRadio transmissionComputation complexityMathematical model
The invention discloses a relay node distribution method in an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) relay multi-hop communication system, and provides a UAV relay position distribution method based on an outage probability minimum criterion under a Rayleigh fading channel. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, building a target function by using the outage probability of a mobile station, and building a limiting condition according to the distance between a base station and the mobile station in order to transform a UAV relay distribution problem into an optimal mathematic model; secondly, simplifying the target function of an optimal model by means of the monotonicity of an exponential function and the hypothesis of a relation between the distance from the relay UAV to the base station and the height of the relay UAV; and lastly, solving a convex optimization problem by using a conventional KKT (Karush-Kuhn-Tucker) optimizing condition to obtain a closed-form solution of a bestUAV position. Thus, the calculation complexity is lowered under the condition of keeping the calculation accuracy, and a good engineering reference is provided for the design and optimization of a UAVrelay communication system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
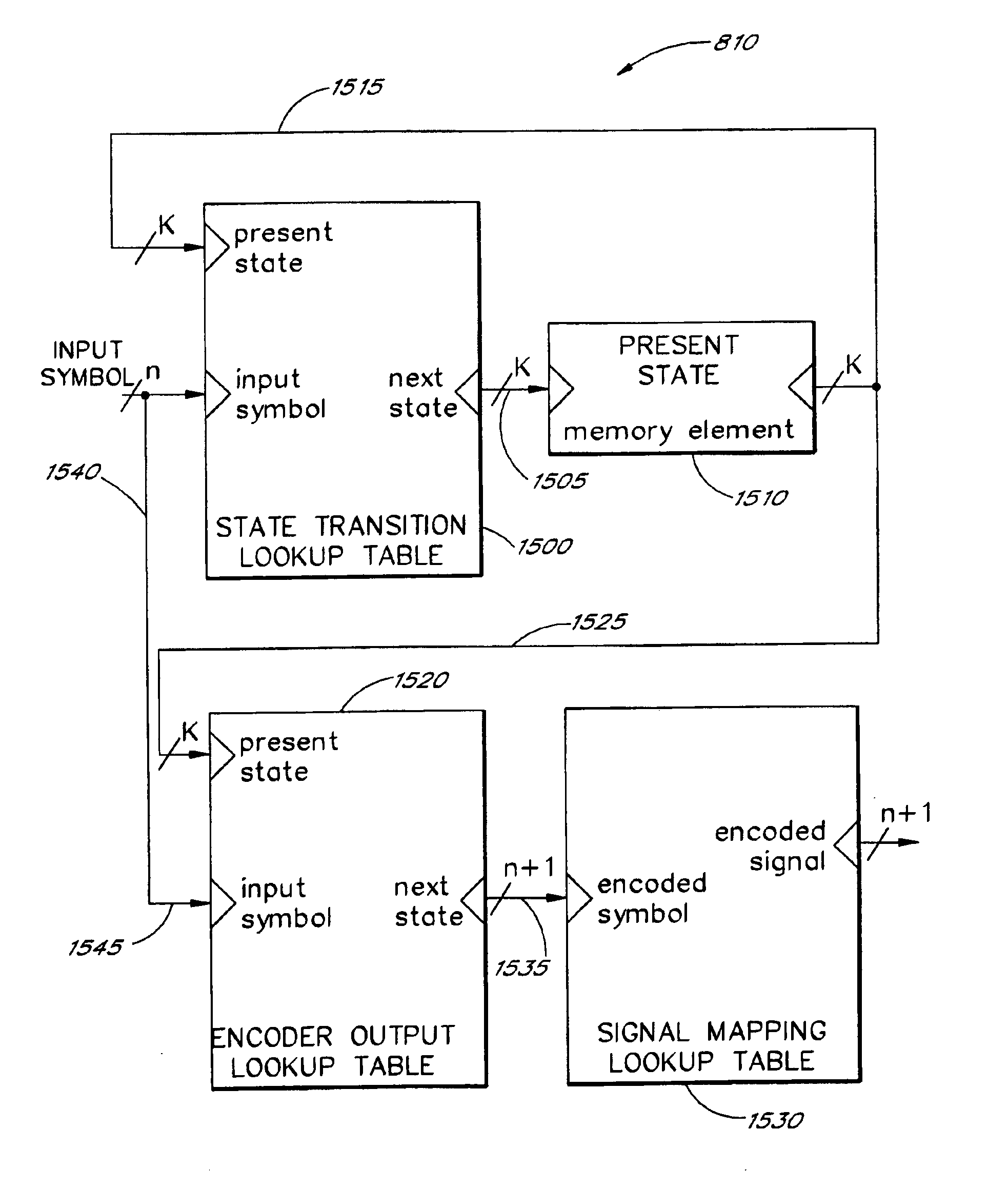
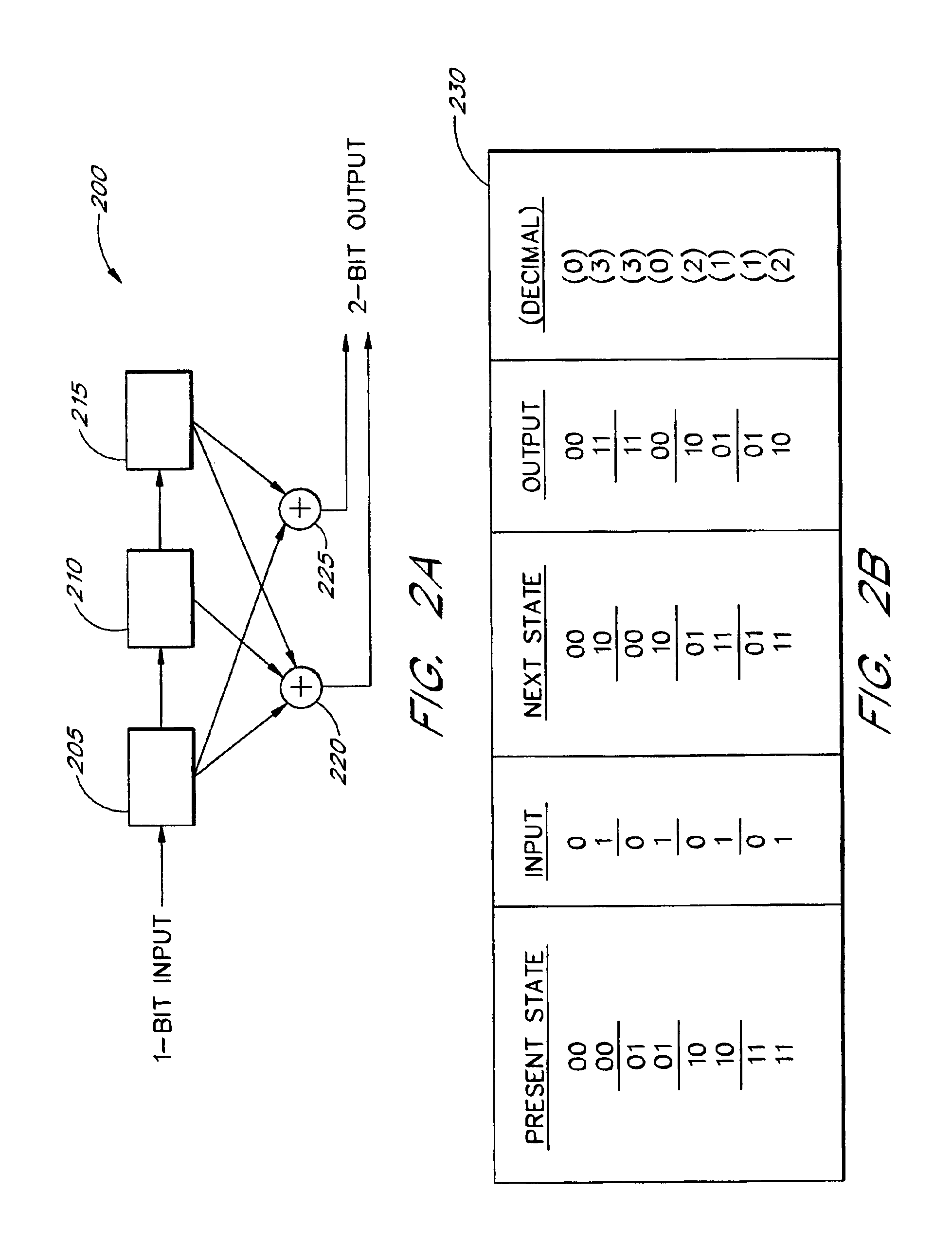
Cyclic trellis coded modulation
InactiveUS6889356B1Increase the minimum Euclidean distanceData representation error detection/correctionError correction/detection using concatenated codesShift registerTheoretical computer science
A universal method of trellis encoding signals mapped according to any signal constellation format involves constructing an encoder output table and a state transition table. The encoder output table defines the output symbol of an encoder given the input symbol and the present state of the encoder, while the state transition table defines the next state of the encoder given the present state of the encoder and the input applied to the encoder. The output table and the next state table are constructed with the objective of providing maximal distances between the branches of the trellis diagram without any regards for the shift register implementation of the code. Cyclic trellis-coded modulation is an example of such codes without feed-forward or feed-back shift register implementations, and with equal or better performance than “optimal” shift register trellis codes with 16 states or less. The cyclic trellis codes for both AWGN and Rayleigh fading applications can be constructed for any signal constellation without resorting to exhaustive searches.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
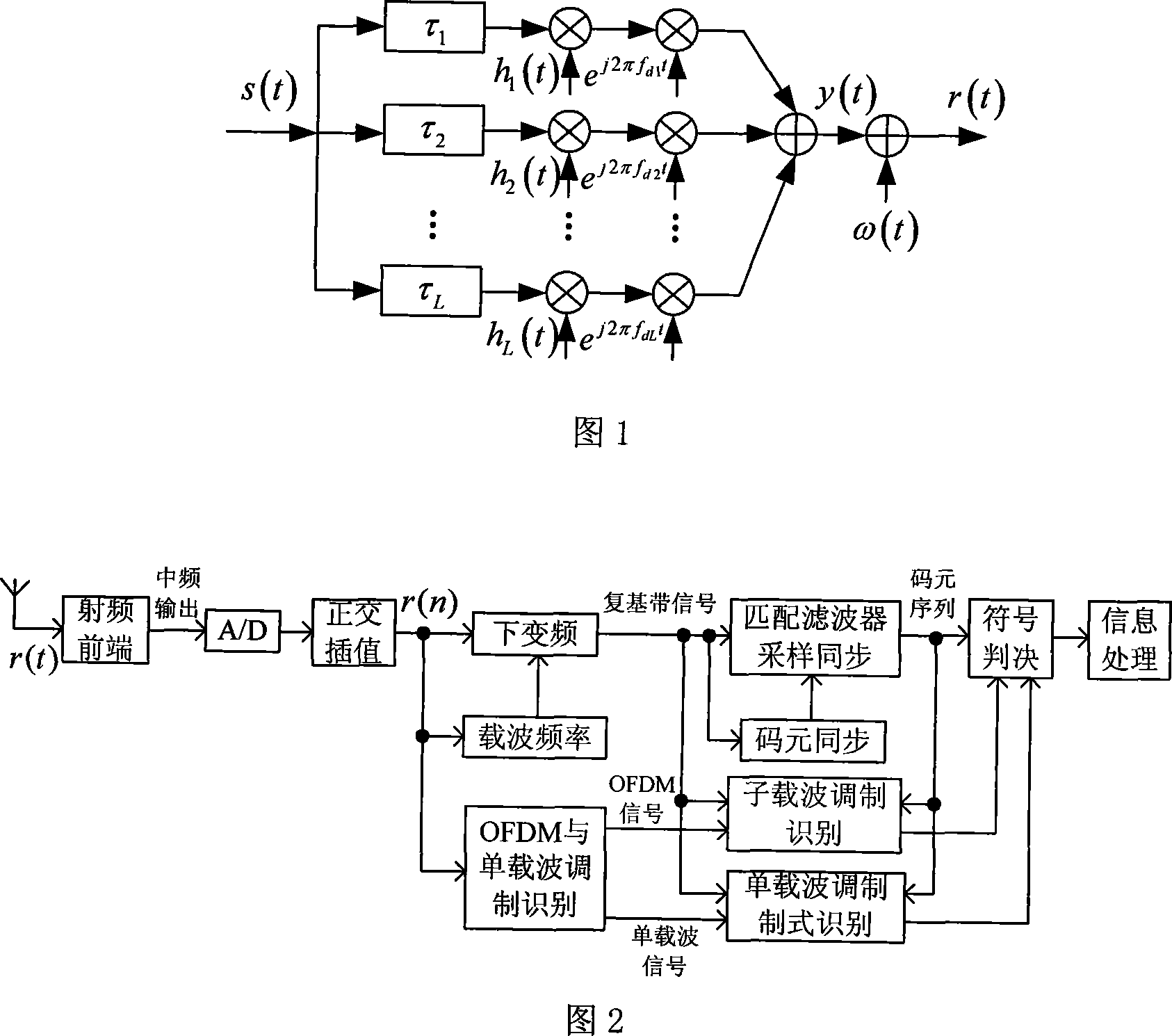
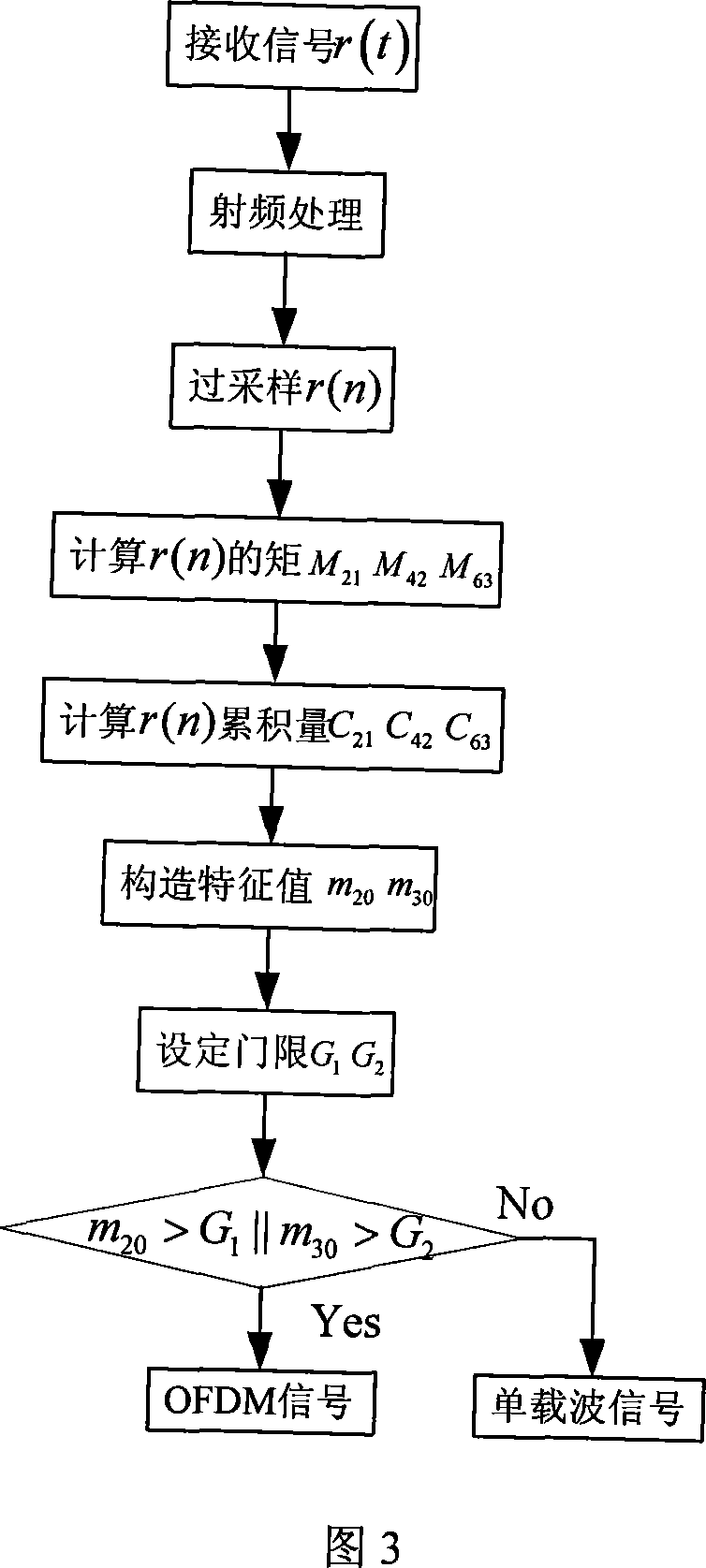
Method for identifying OFDM modulation system of multi-path Rayleigh fast fading channel
InactiveCN101083649AImprove recognition rateReduce complexityMulti-frequency code systemsRound complexityHigh probability
Using expressions of cumulant in second, fourth, and sixth orders of signal of passing through multipath Rayleigh fast fading channel (MRFFC), the method carries out combination in order to counteract the influence of multipath Rayleigh fading and Doppler shift. Concrete process includes steps: after mixing, oversampling, and orthogonal interpolating signals received, receiver obtains orthogonal plural sequence in mid frequency; calculating cumulant in second, fourth, and sixth orders; combining cumulant in fourth and second orders as well as sixth and second orders so as to obtain two types of eigenvalue; setting up threshold of the eigenvalue, comparing the two types of eigenvalue to the threshold so as to identify OFDM signal and single carrier signal. Comparing prior art, the invention possesses advantages of high probability of identification, low complexity, suitable to processing in real time. The invention is applicable to identifying OFDM modulation format in mid frequency.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Recognition method of M-ary orthogonal amplitude modulation
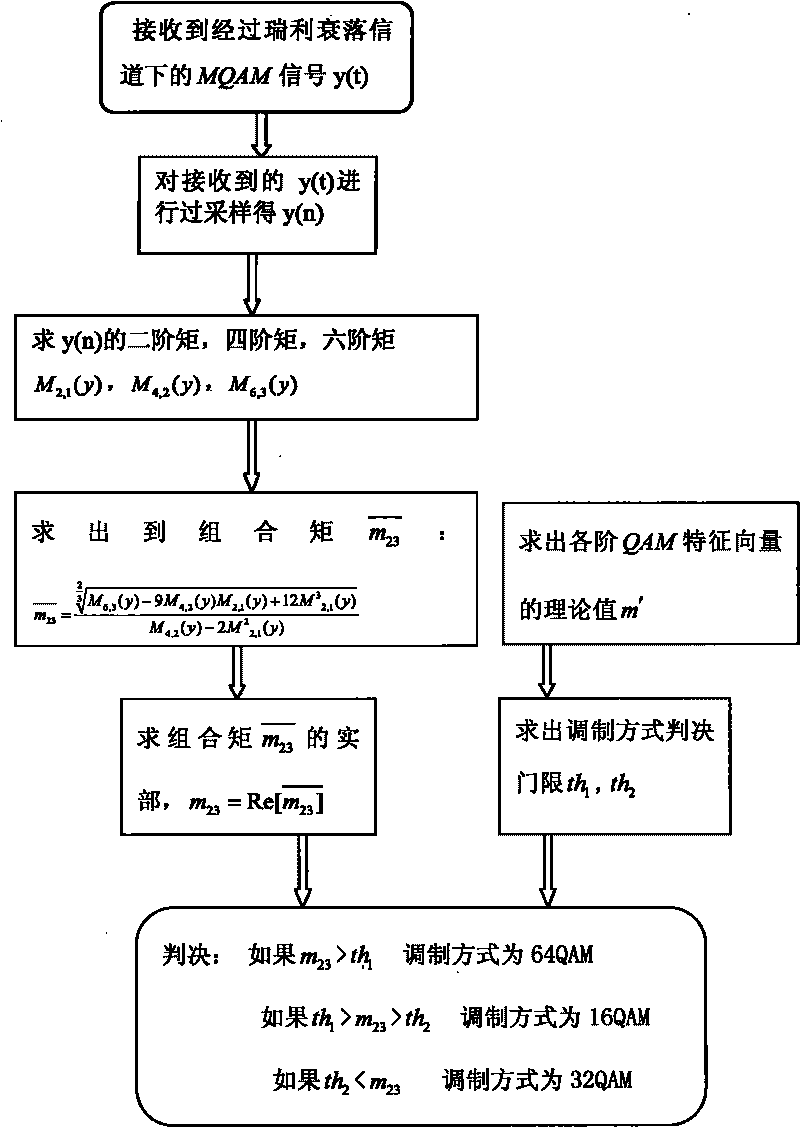
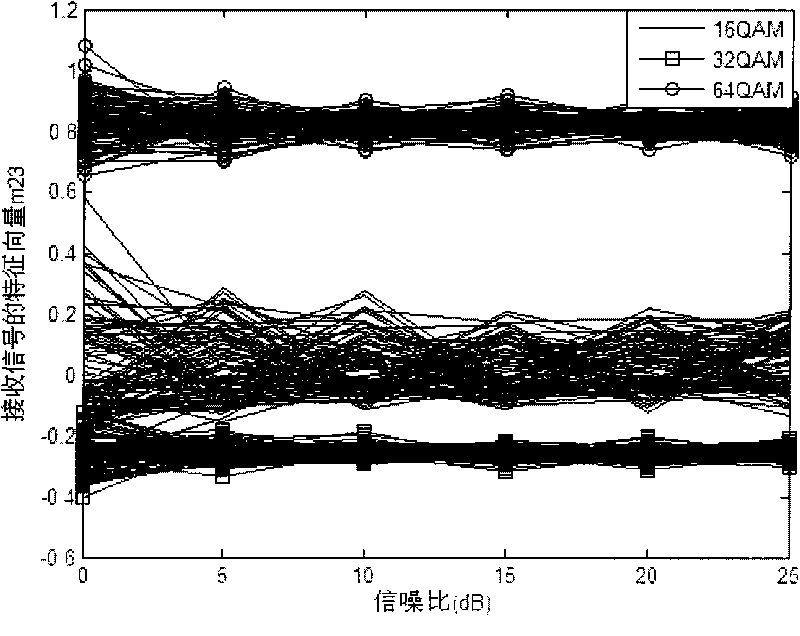
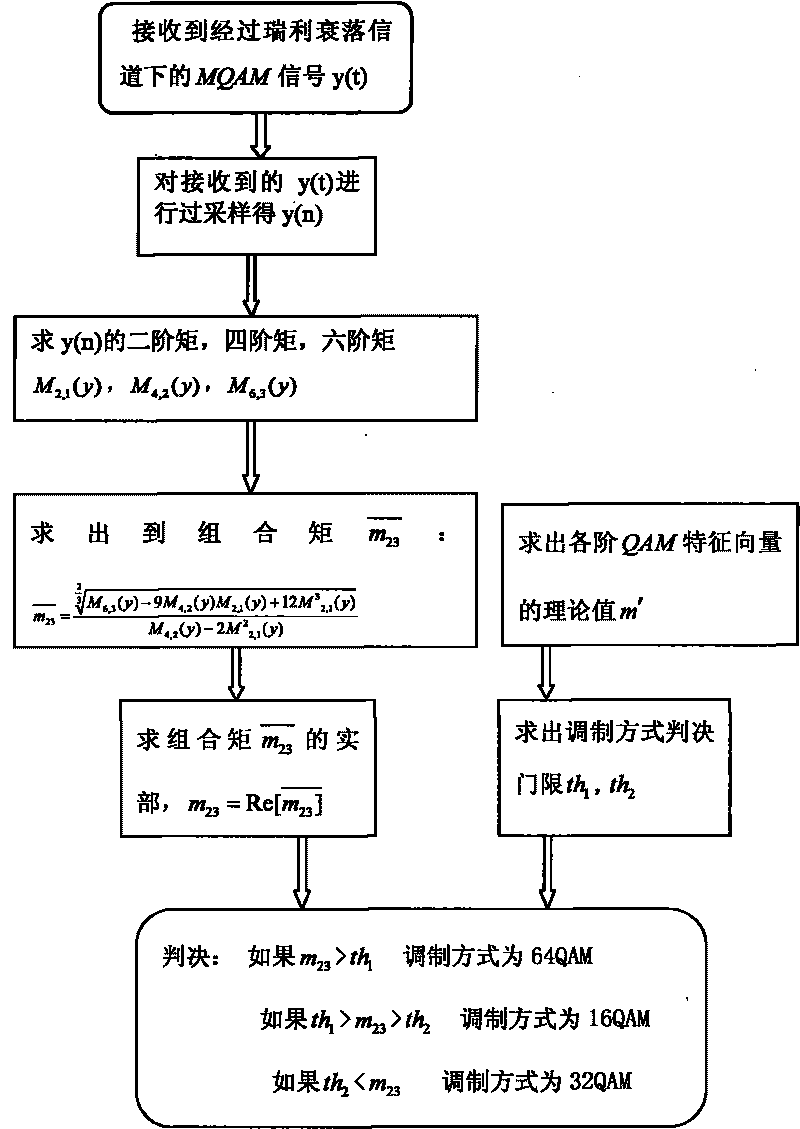
InactiveCN101753515AOmit estimating SNRReduce computationMultiple carrier systemsFeature vectorSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a recognition method of M-ary orthogonal amplitude modulation, which is mainly used for solving the problems of complicated computational complexity and low recognition rate of the existing recognition way of MQAM within-class signal modulation. The implementation process is as follows: firstly carrying out over-sampling on received signals y(t) for obtaining a sampling sequence y(n), thereby changing continuous signals to discrete signals; calculating values of two-order moment, four-order moment and six-order moment of a received sampling signal y(n); utilizing the values of the two-order moment, the four-order moment and the six-order moment for calculating the combined moment m23; taking a solid part of the combined moment m23 as a feature vector m23 of the received sampled signal; calculating theoretical values m' of the QAM feature vectors of all the orders; calculating the decision threshold of the modulation way through the theoretical values m' of the QAM feature vectors of all the orders; and determining the modulation way of the received signals according to the feature vector m23 of the received sampling signal and the decision threshold of the modulation way. The recognition rate of the method for recognizing the MQAM within-class signals under the environment of a Rayleigh fading channel and low signal to noise ratio can achieve 100% above 5dB, thereby being higher than the existing other methods.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
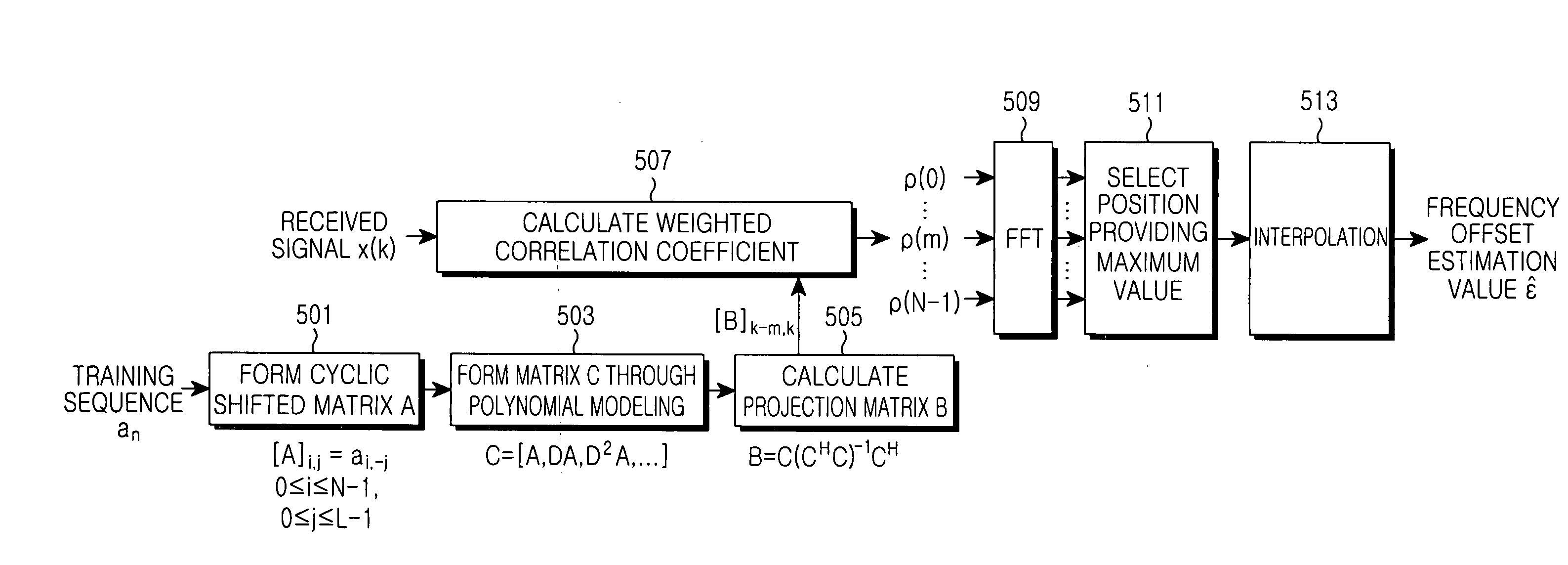
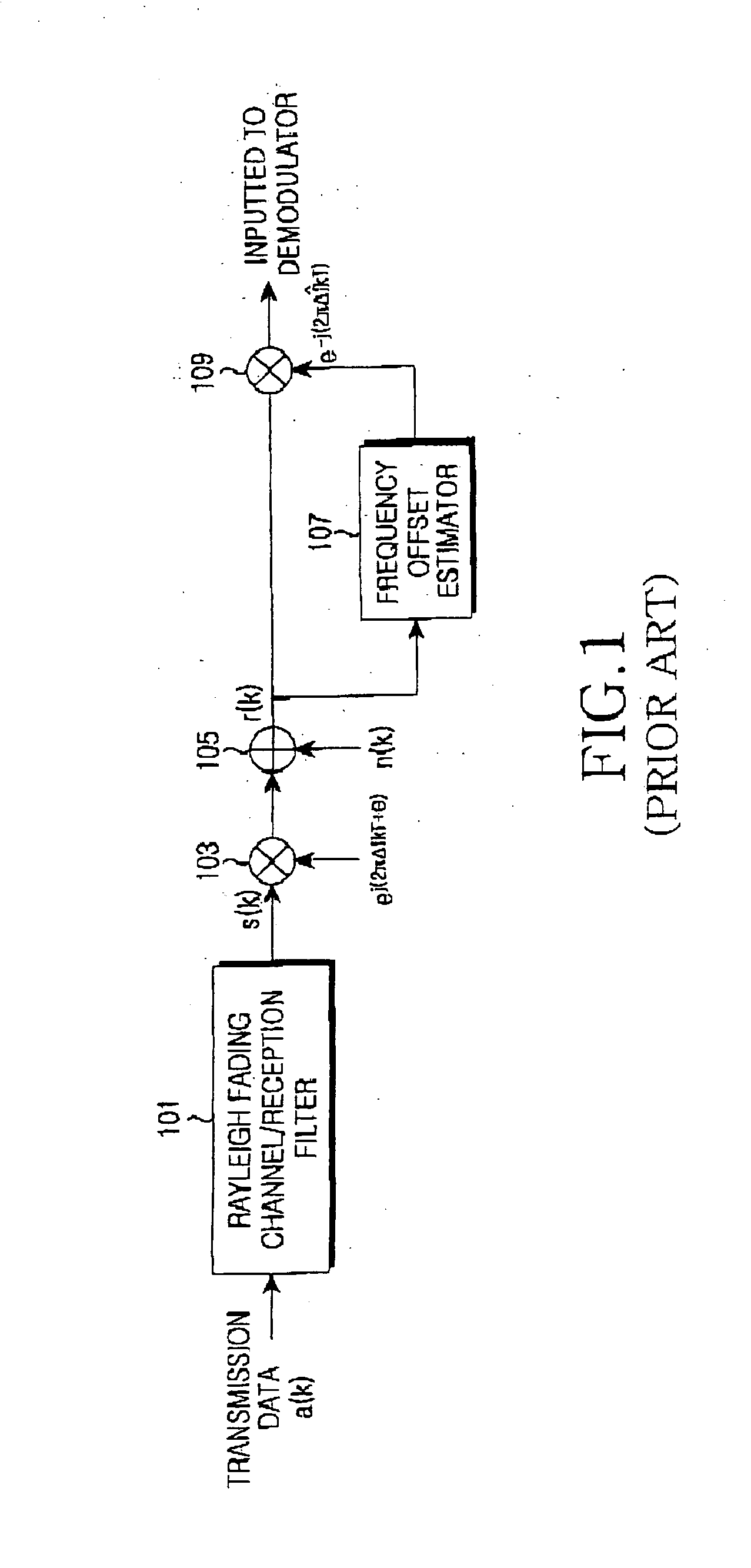
Method for estimating maximum likelihood frequency offset in mobile communication system in fast rayleigh fading channel environment
InactiveUS20060018412A1Constant estimation performanceFrequency offset can be largeError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemEngineering
Disclosed is a method for estimating a frequency offset in a mobile communication system that divides a predetermined frequency band by a time division scheme to transmit data signals or divides an entire frequency band into a plurality of sub-frequency bands to transmit the data signals. The method includes the steps of modeling a fast fading channel by one of a linear equation and a polynomial equation; and applying the model to a variable for the channel after performing the modeling and estimating the channel and the frequency offset based on a joint maximum likelihood using a training sequence.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
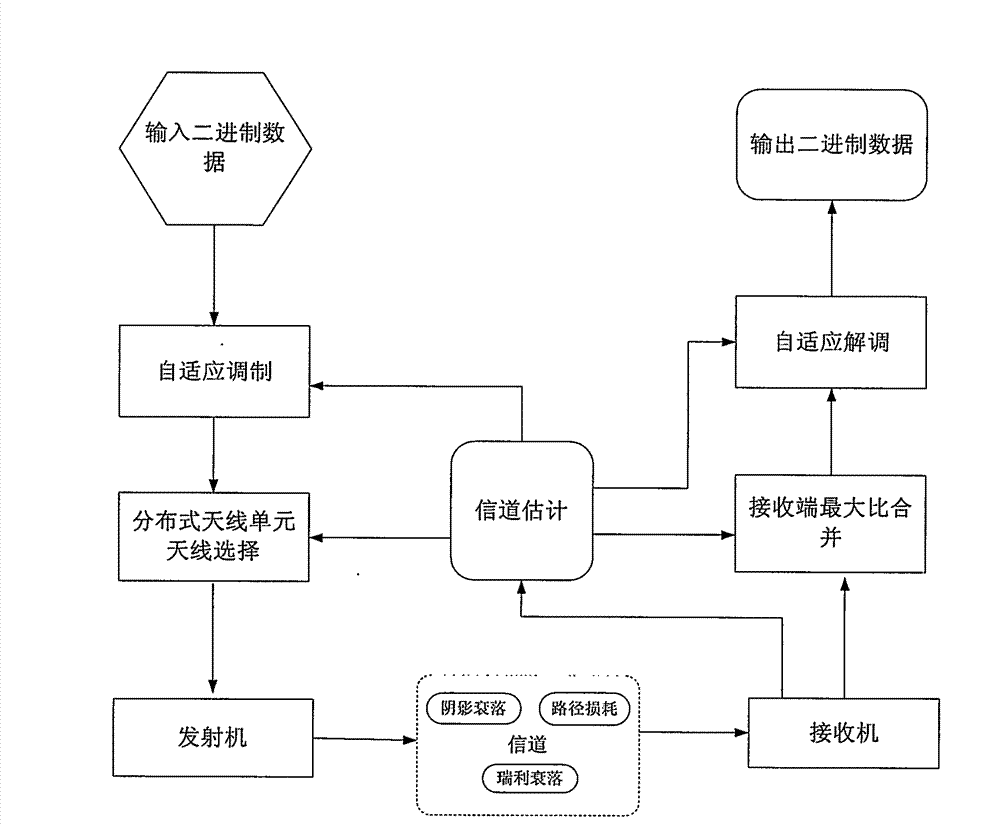
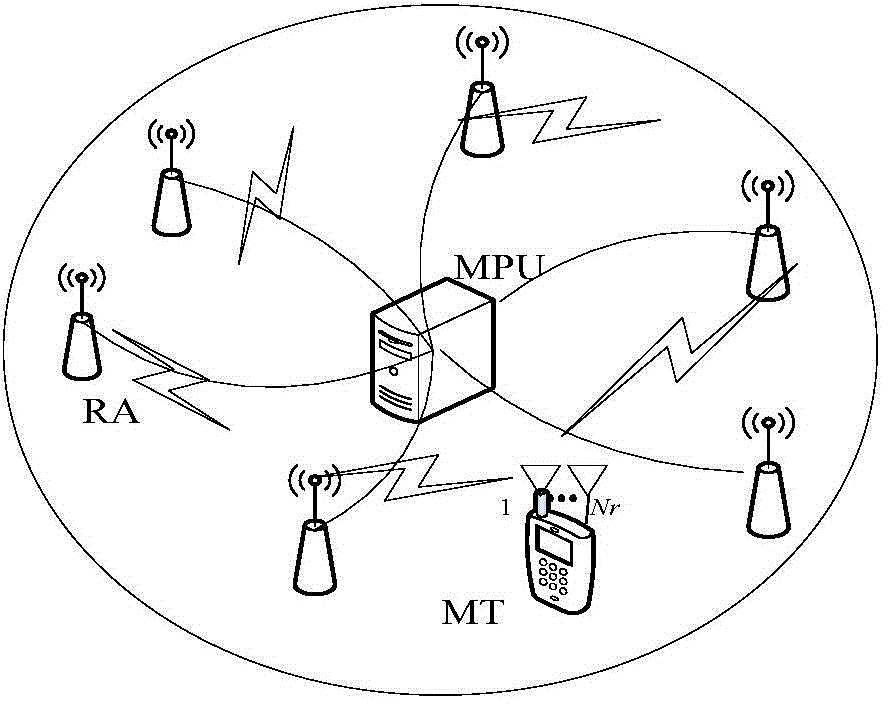
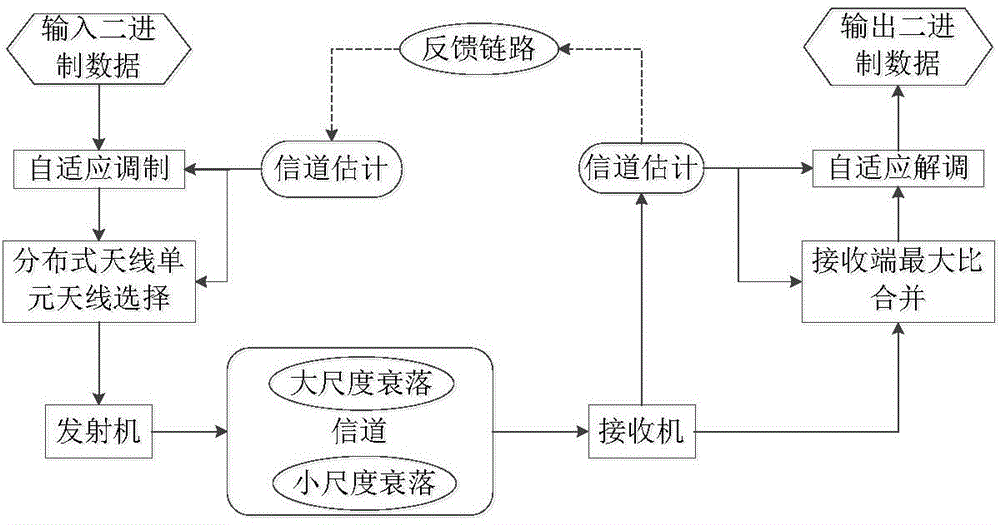
Adaptive modulation method for distributed multi-antenna system
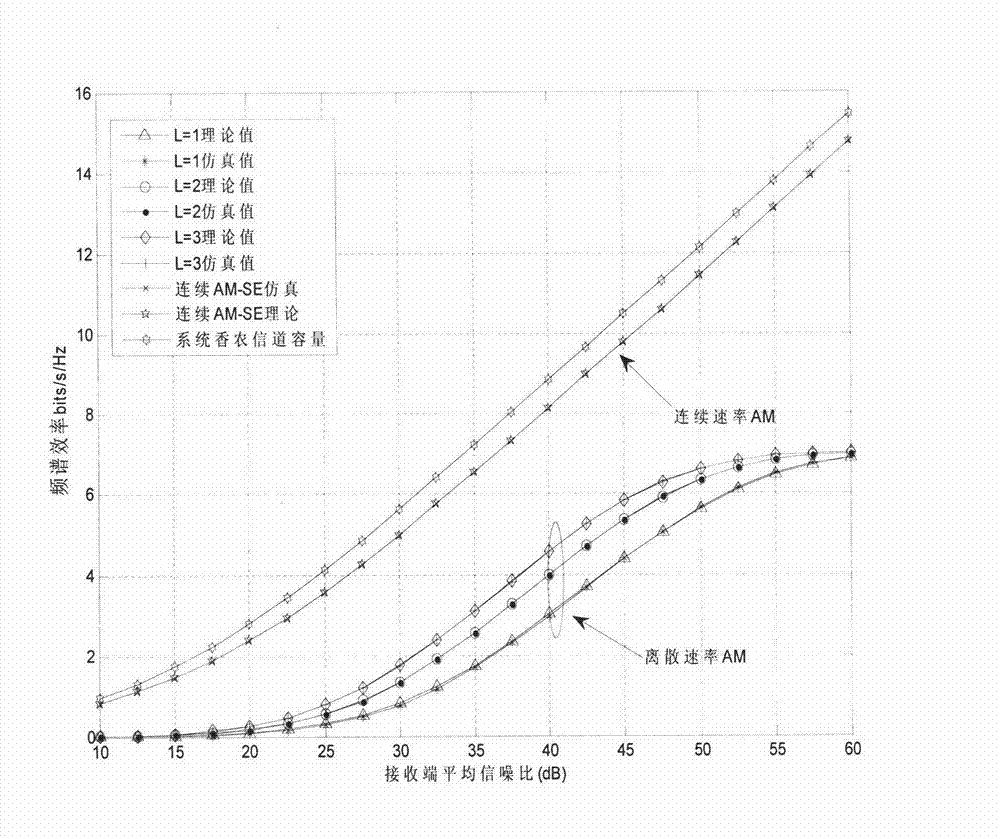
InactiveCN102833046AImprove spectral efficiencyVerify validityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionFrequency spectrumMATLAB
The invention relates to an adaptive modulation (AM) method design and performance evaluation for a wireless distributed multi-antenna system (DAS). Under the constraint condition of a target bit error rate (BER), the system frequency spectrum efficiency is maximized to respectively design two AM schemes of a discrete rate and a continuous rate. By aiming at the discrete rate AM, an adaptive switching threshold based on precise BER is provided. Compared with the traditional AM based on an approximate threshold, the AM method disclosed by the invention can obtain high frequency spectrum efficiency. A channel model comprising path loss, shadow fading and Rayleigh fading is designed by considering the practical situation of DAS. On the basis, the computation expression of a continuous rate AM frequency spectrum efficiency, a discrete rate AM frequency spectrum efficiency and the average BER is given so as to provide an effective method for system performance evaluation. An Matlab (matrix laboratory) simulation platform shows that the designed AM method can satisfy the target BER requirement, and the continuous rate AM method is better than a discrete rate AM method. In addition, due to the providing of an improved threshold, the discrete rate AM can be used for realizing the high frequency spectrum efficiency if being compared with the traditional AM method. In addition, the provided frequency spectrum efficiency has good consistency with the average BER calculation and simulation, and the system performance can be effectively evaluated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
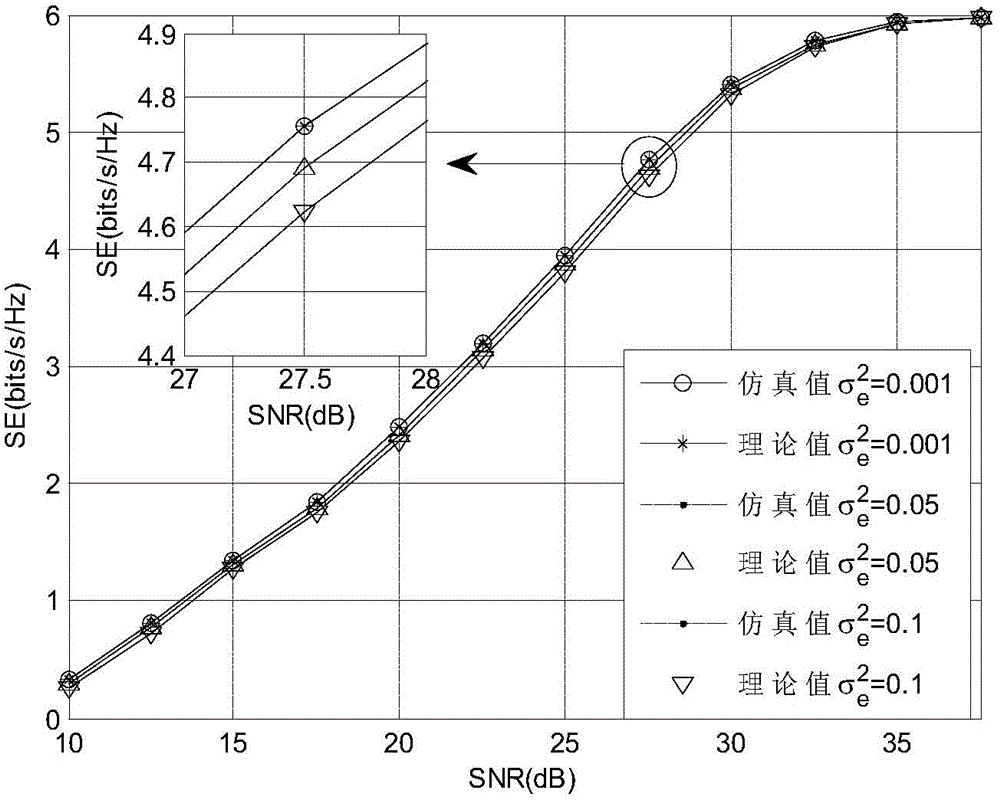
Incomplete CSI (Channel State Information)-based distributed antenna system adaptive modulation method
InactiveCN104702557AMeet target BER requirementsIncrease effective transmission efficiencySpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsFrequency spectrumQam modulation
The invention discloses an incomplete CSI (Channel State Information)-based distributed antenna system adaptive modulation method. A distributed antenna system model is constructed by using multiple remote transmitting antennas, a Rayleigh fading channel model is constructed, channel estimation is performed on small-size fading of the Rayleigh fading channel model to obtain an estimated signal-noise ratio between the remote antennas and an MT (Mobile Terminal); by using an antenna selection technology, the remote transmitting antenna with the maximum estimated signal-noise ratio is selected to perform signal transmission; an adaptive modulation method and adaptive switching threshold setting are designed according to maximum average spectral efficiency; adaptive modulation switching threshold is calculated by using a BER (Bit Error Rate) formula of a precise M-QAM (Mulriple Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) modulation mode under an additive white Gaussian noise channel; average effective transmission efficiency SE and average bit error rate BER are calculated by using an integral transformation formula and a numerical analysis method. The adaptive modulation method and the adaptive switching threshold guarantee that the SE of the system is improved by meeting the requirement of a target BER.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Broadband spectrum sensing method based on spectrum characteristics
ActiveCN107517089AImprove anti-interference abilityEasy to detectTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumResource utilization
The invention discloses a broadband spectrum sensing method based on spectrum characteristics, and belongs to the field of spectrum sensing of cognitive radios. According to the method, by signal spectrum characteristic detection the frequency band occupied by a master user is detected, and power level is estimated. According to the characteristic of low practical use ratio of spectrum resources, possible frequency positions and corresponding power value level are estimated, a Rayleigh fading channel model is added to an original model without a fading channel to solve the Rayleigh fading channel, a WOMP (weighted orthogonal matching pursuit) algorithm serves as a signal reconstruction algorithm for estimating the signal power value level and frequency occupation by the aid of technology based on the spectrum characteristics.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for identifying OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing)-based distorted communication signals under QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation)
InactiveCN104079524ASimple structureReduce the number of iterationsMultiple carrier systemsQam modulationSymbol of a differential operator
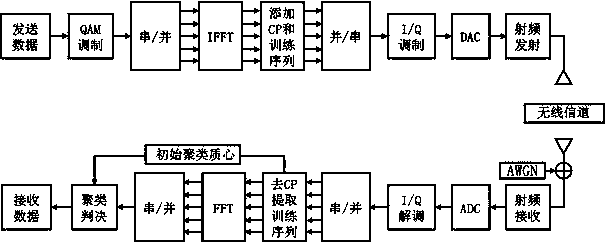
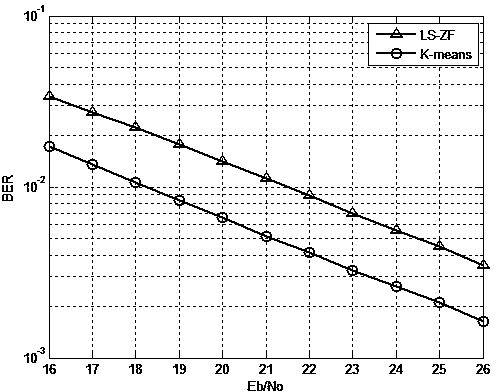
The invention discloses a method for identifying OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing)-based distorted communication signals under QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation). The method comprises steps of training symbol addition at a sending end and distinguishing of distorted signals at a receiving end. According to the method, the structure of a receiver under a flat Rayleigh fading channel is simplified, the receiver is not required to use channel estimation and channel equalization modules, improvement of initial cluster centroids is performed on the conventional k-means clustering algorithm by using pilot signals which are then applied to distinguishing and identifying of the distorted communication signals, so that the method has the characteristics of few iteration times, small calculated amount and the like, and has better distinguishing and identifying performance on signal phase distortion and amplitude distortion.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Systematic simulation method and apparatus for wireless communication system
InactiveCN101335967AImprove simulation time efficiencyShorten the development cycleRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringCommunications systemBiological activation
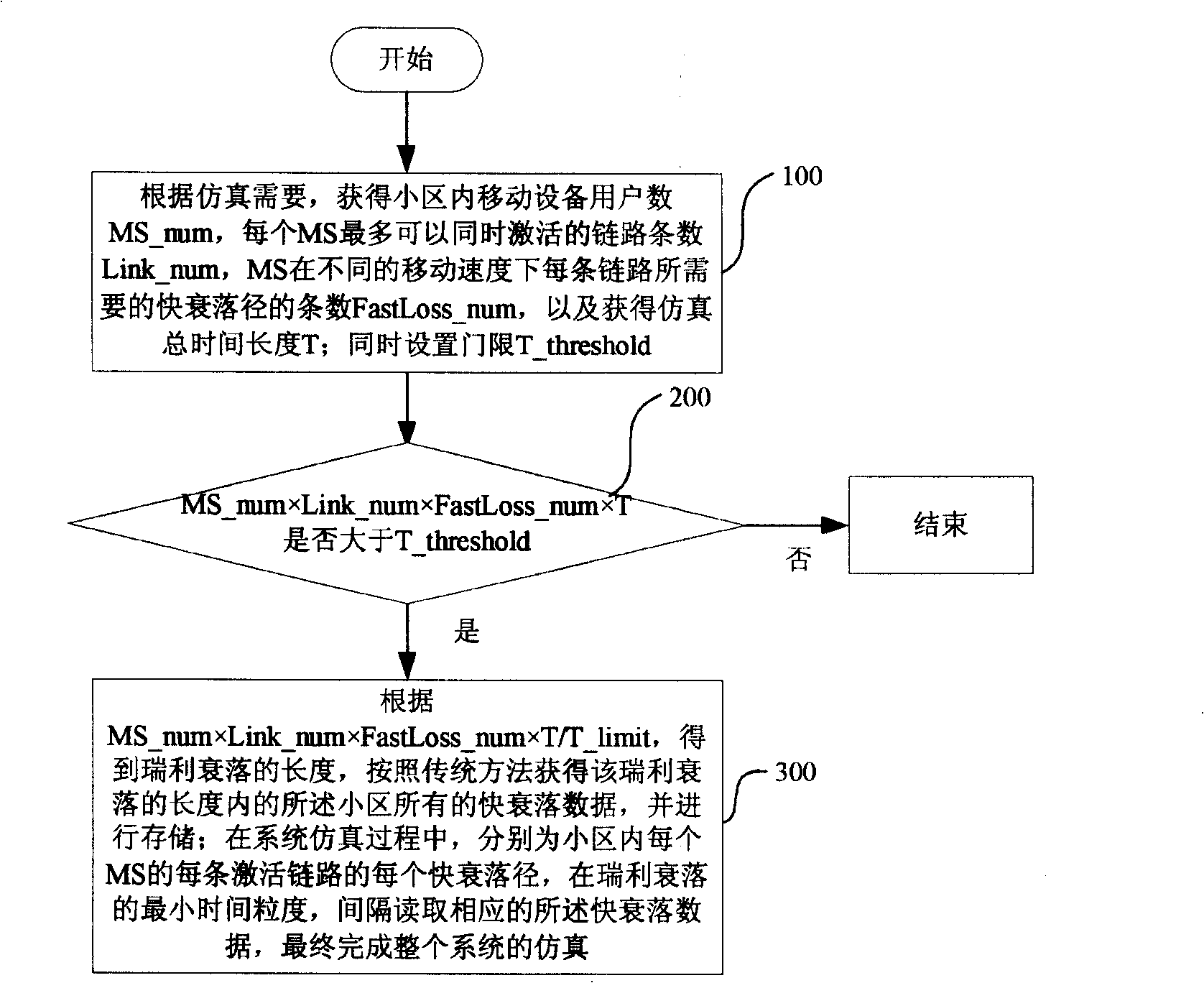
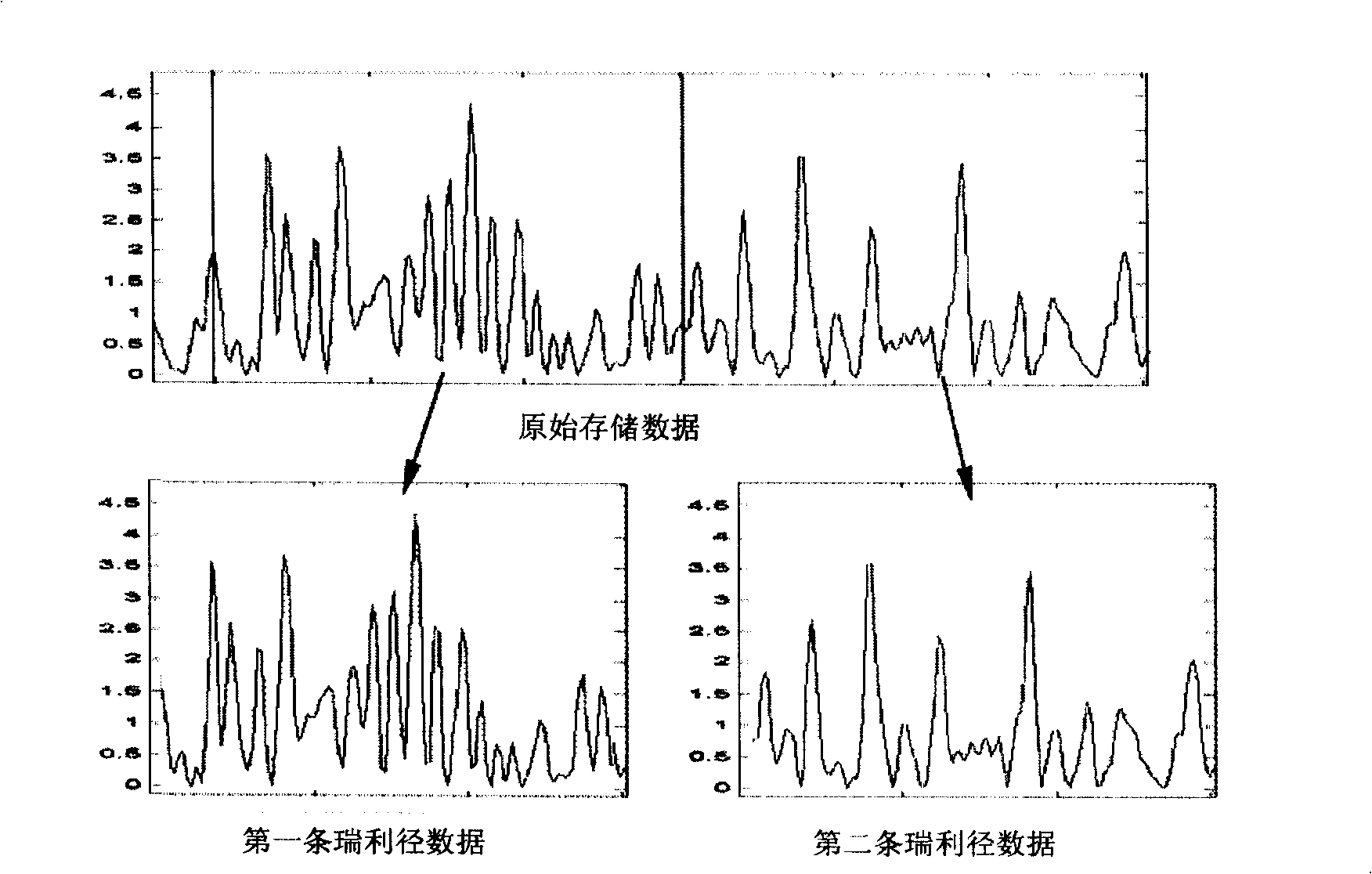
Provided is a method system simulation in a wireless system and a device, comprising: obtaining related parameters of a mobile device in a district, under special condition, obtaining a rayleigh fading length, obtaining all fast fading data in the district in the rayleigh fading length, wherein T-limit is the correlation time threshold, with the value larger than the rayleigh fading correlation time value corresponding to the smallest user speed required to be simulated by the system. In the system simulation system, for each fast fading path of each activation link of each mobile device in the district, corresponding fast fading data are read spacingly in smallest time of rayleigh fading, finally, the whole system simulation is completed, wherein the read time interval is larger than T-limit. According to the invention, under the condition that the hardware of the computer is limited, wireless communicating system simulation of rayleigh fading is computed according to the smallest time grain, thereby greatly advancing simulation time efficiency, shortening development cycle, saving development cost.
Owner:李利军
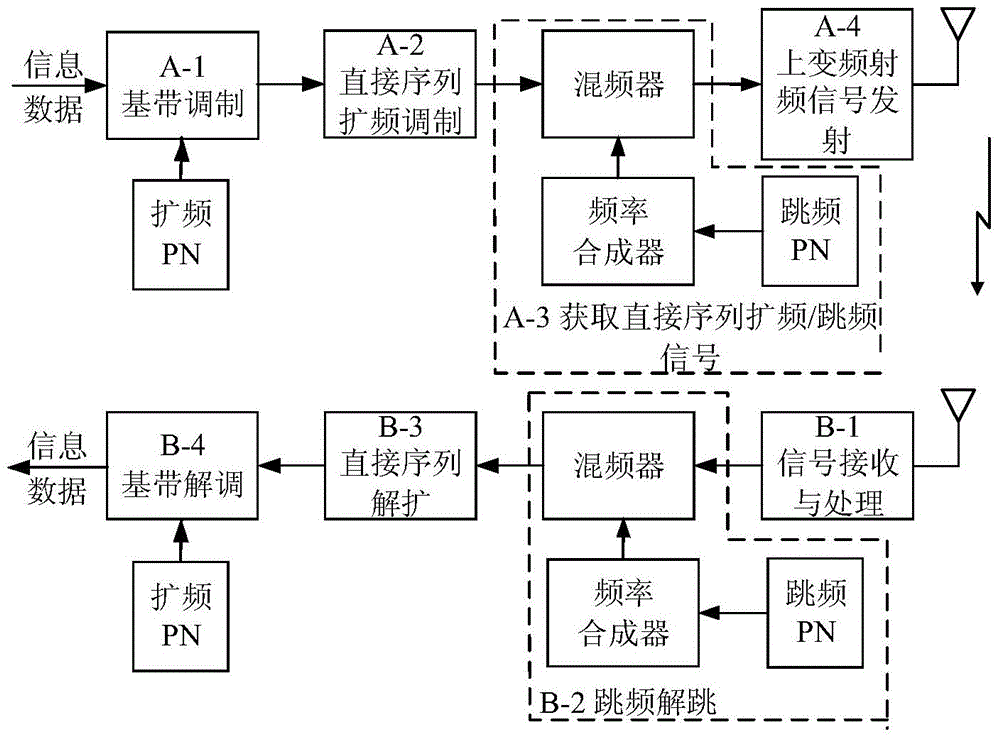
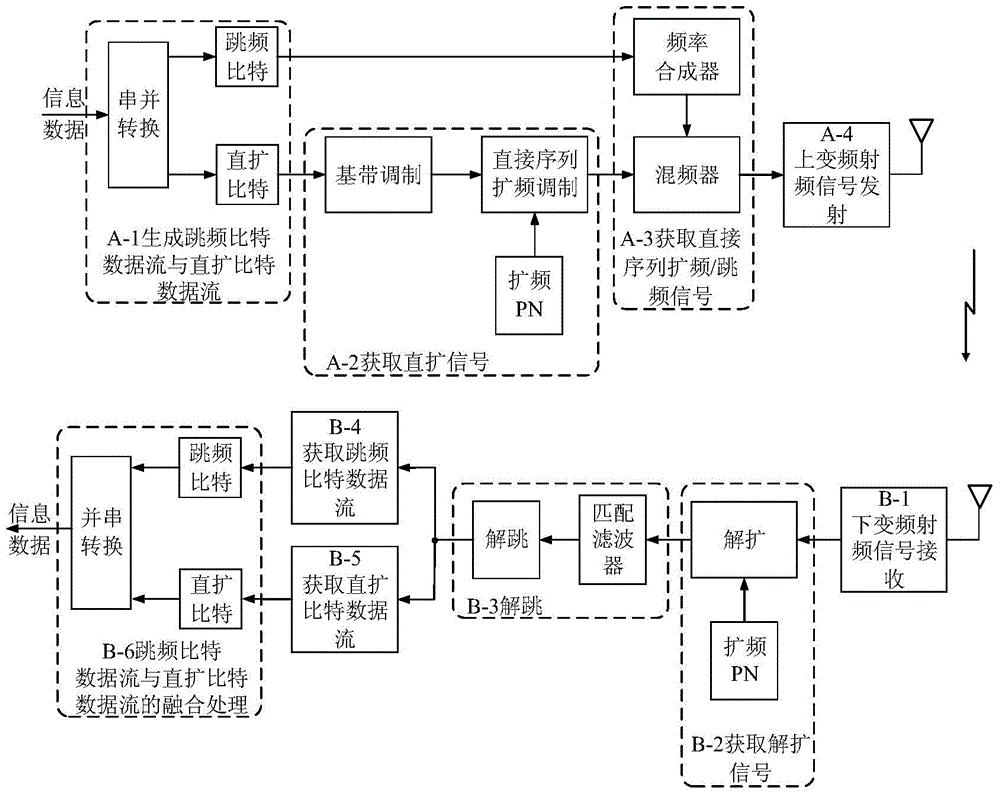
Communication method for driving frequency spreading/frequency hopping of direct sequence by adopting information
InactiveCN104393891AReduce complexityImprove bit error rateTransmissionFrequency spectrumData stream
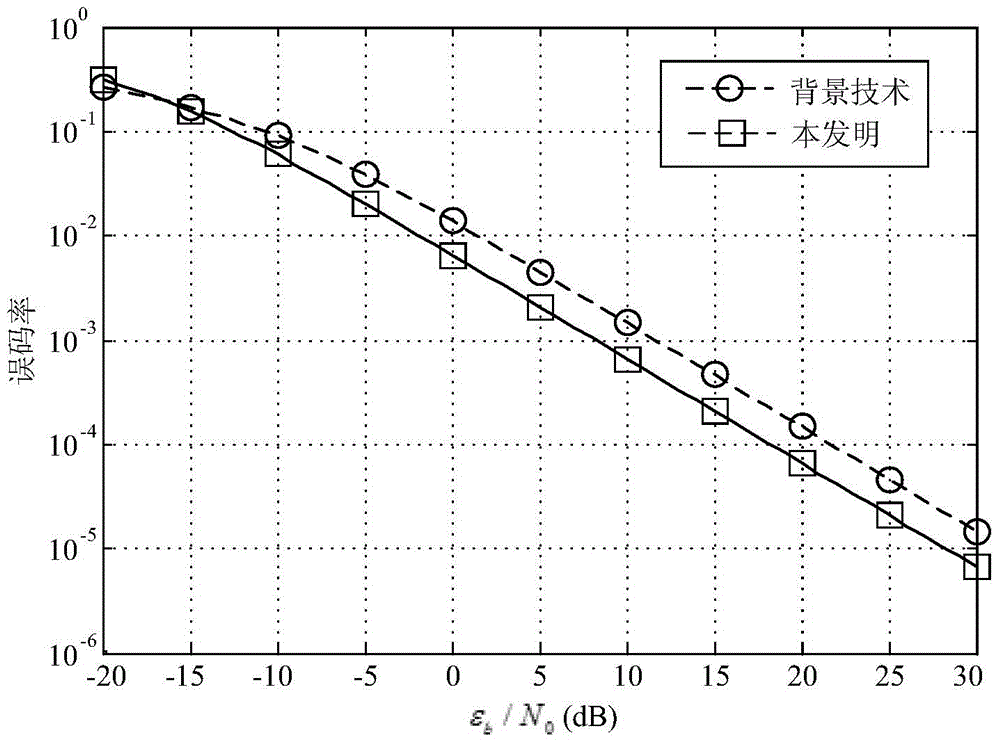
The invention discloses a communication method for driving frequency spreading / frequency hopping of a direct sequence by adopting information. The method comprises the following steps: generation of frequency hopping bit data stream and direct spreading bit data stream at a transmitting end, acquiring a direct sequence frequency spreading signal and a direct sequence frequency spreading / frequency hopping signal, and performing up-conversion treatment and radio-frequency signal transmission; signal receiving and down-conversion radio-frequency treatment at a receiving end, acquiring a despreading, dehopping, and acquiring frequency hopping bit data stream and direct spreading bit data stream and information data input to the transmitting end. Compared with the prior art, in a Rayleigh fading channel, when the bit error rate is 10-3, the background technology needs to be 8.5dB in signal to noise ratio, the communication method disclosed by the invention needs to be 5dB in signal to noise ratio, the signal to ratio gain of the communication method disclosed by the invention is increased by 3.5dB. Therefore, the communication method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being high in spectrum effectiveness, high in data transmission capability, low in complexity of a direct sequence frequency spreading / frequency hopping communication system and synchronization requirements of both transmitting and receiving sides, obviously improved in performance of the bit error rate in comparison with the background technology and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
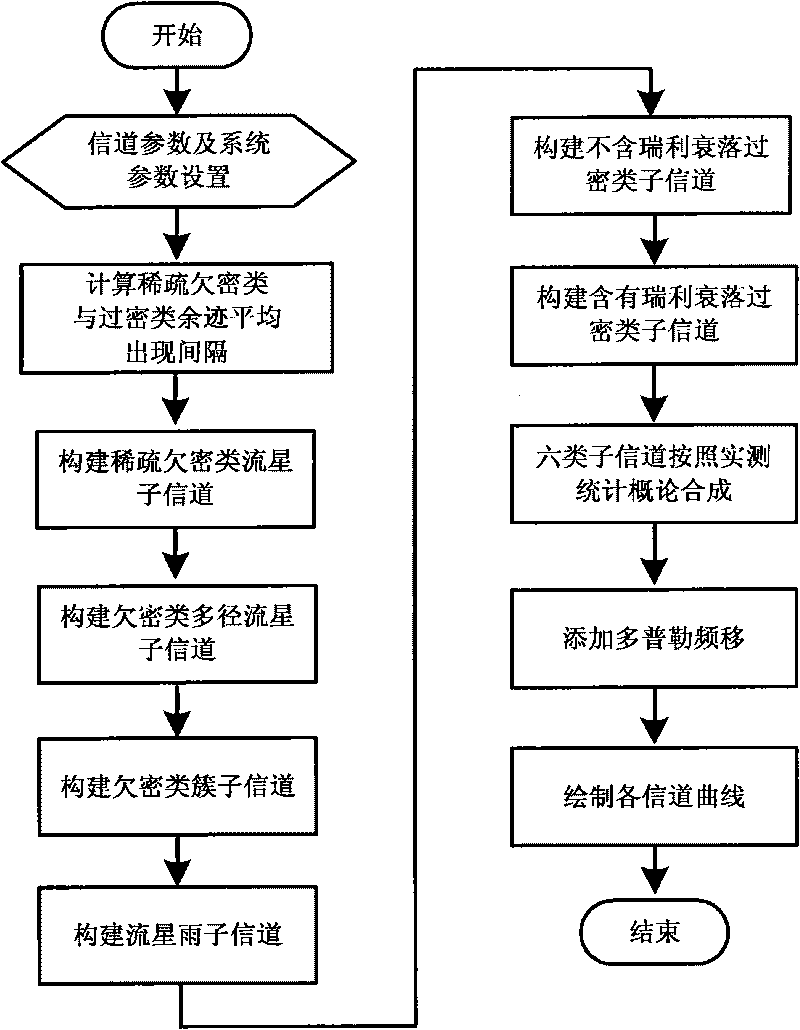
Construction method of meteor trail communication channel
InactiveCN101714902AHigh precision simulationAchieve seamless integrationTransmission monitoringCommunication qualityComputer science
The invention discloses a construction method of a meteor trail communication channel module, mainly solving the problem of seamless compatibility between the traditional channel model with the simulation of the traditional communication transmission mechanism and a key technology. The construction method comprises the following steps of: firstly, dividing a meteor trail communication channel into a sparse underdense subchannel, an underdense multi-path subchannel, an underdense cluster subchannel, a meteor shower subchannel, an over-dense meteor subchannel without Rayleigh fading and an over-dense subchannel containing Rayleigh fading; respectively constructing channel models, wherein the high precision of each subchannel approaches to the physical characteristics of actual representative channel; then combining the six subchannels according to the actually measured statistical probability; and finally, acquiring a channel computer model capable of embodying various physical characteristics of a practical meteor trail channel. The invention has the advantages of simple calculation, easy expansion, easy modification and seamless compatibility link simulation and can improve the communication quality of the meteor trail.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
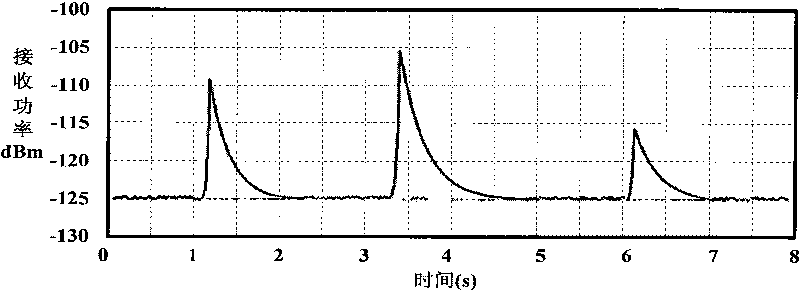
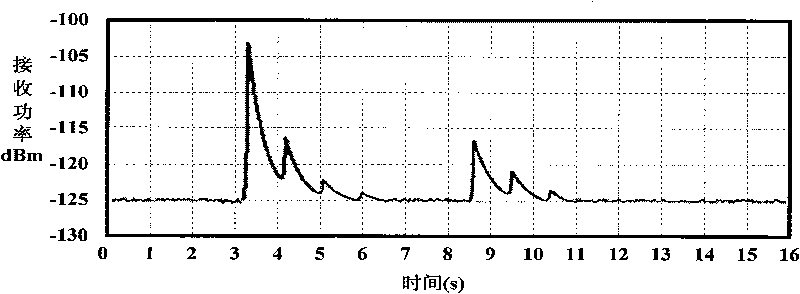
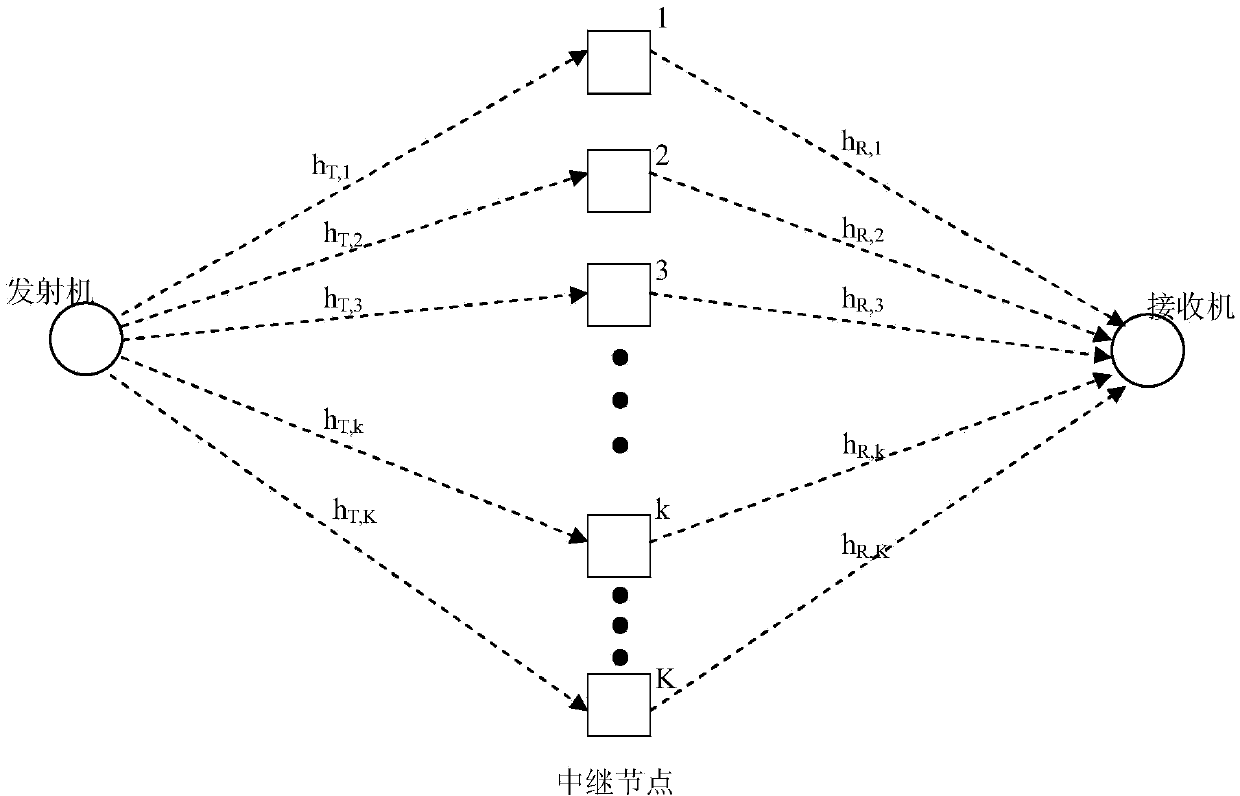
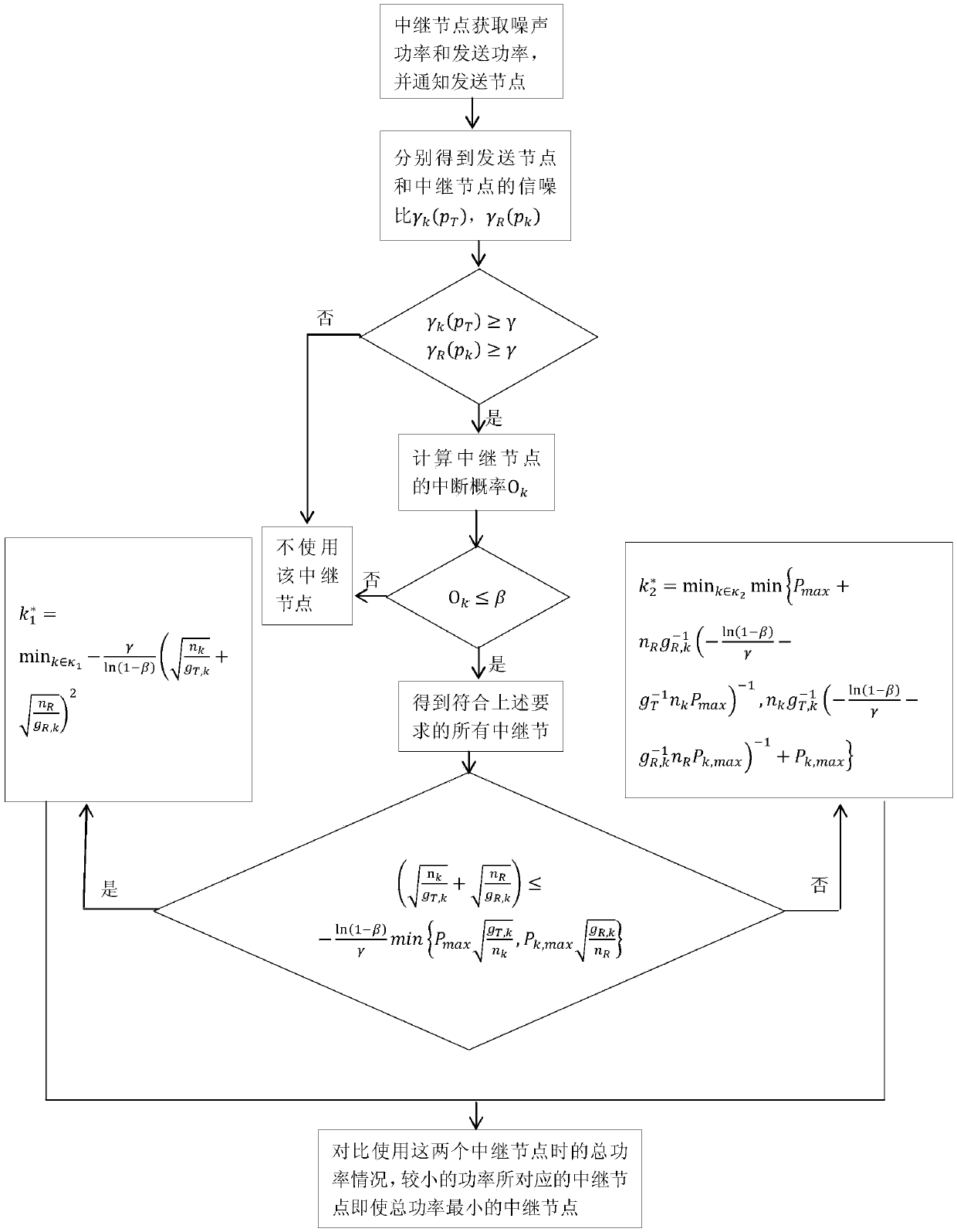
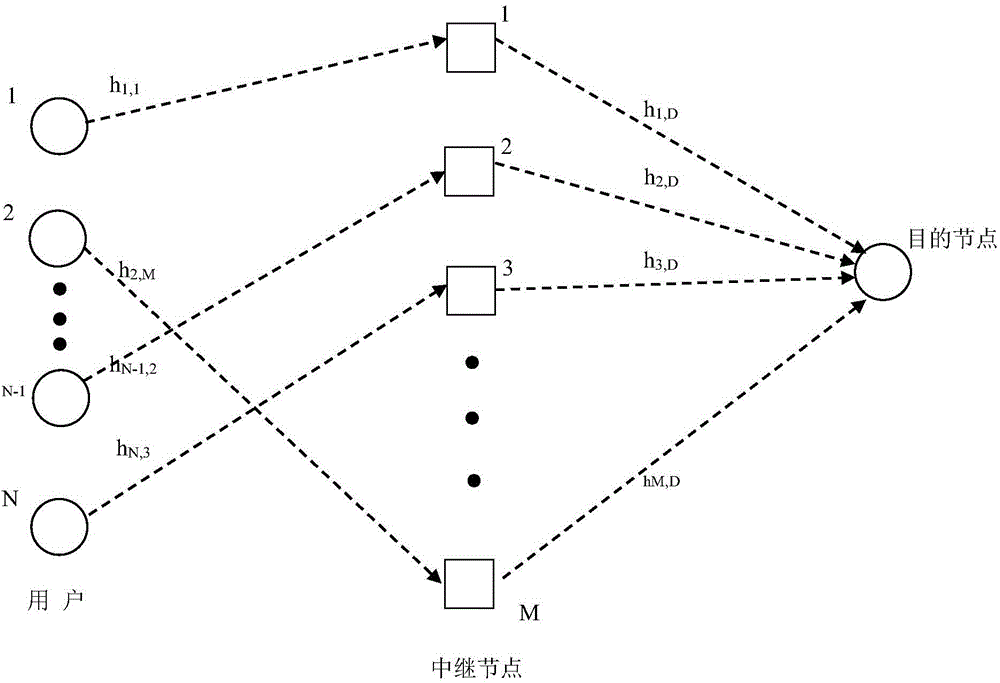
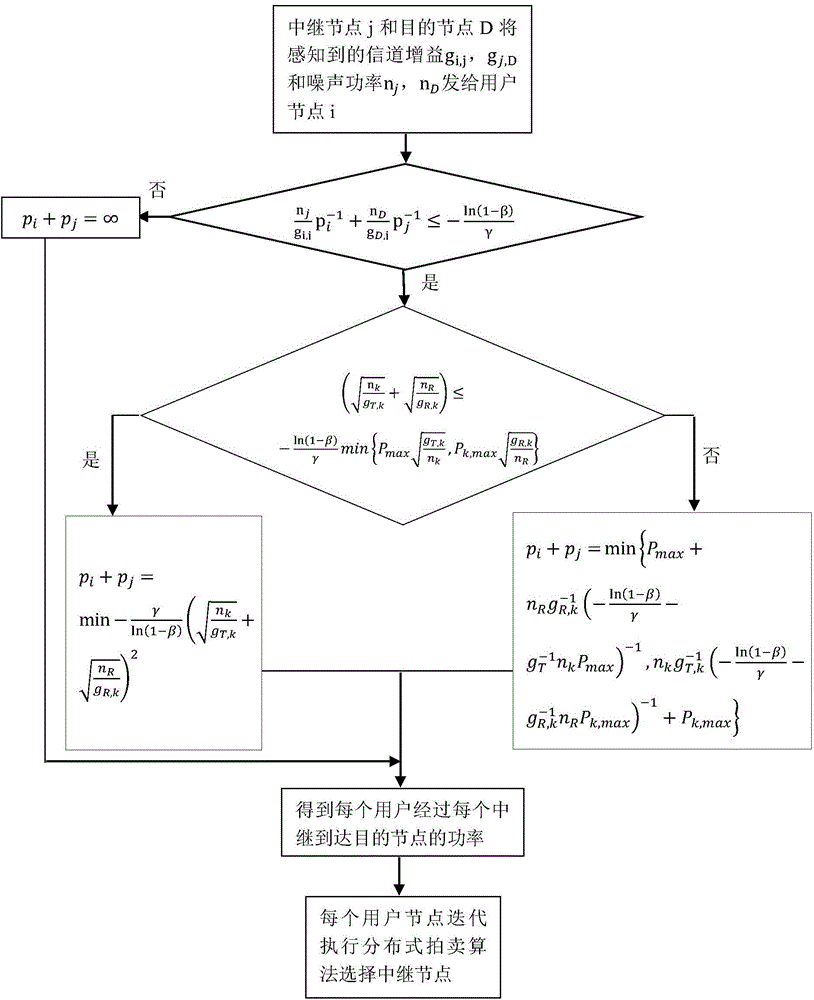
Relay node selection method for minimizing end-to-end sending power in Rayleigh fading channel
InactiveCN104202788AIncrease system efficiencyReduce power consumptionHigh level techniquesWireless communicationComputer networkChannel gain
The invention discloses a relay node selection method for minimizing end-to-end sending power in Rayleigh fading channel. The method comprises the following steps: 1) each relay node perceiving channel gain from a sending node to the relay node and channel gain from the relay node to a receiving node, and then notifying the sending node of the channel gains and the maximum sending power of the relay node; 2) the sending node selecting all satisfactory relay nodes; 3) the sending node dividing all satisfactory relay nodes into two types k1 and k2; 4) respectively selecting optimal relay node in the two types, k*1 and k*2, comparing power conditions while using two relay nodes, and selecting the optimal relay node. The invention provides a relay node selection method that the end-to-end node selects the relay node capable of transmitting in minimum total transmission power in the Rayleigh fading channel.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
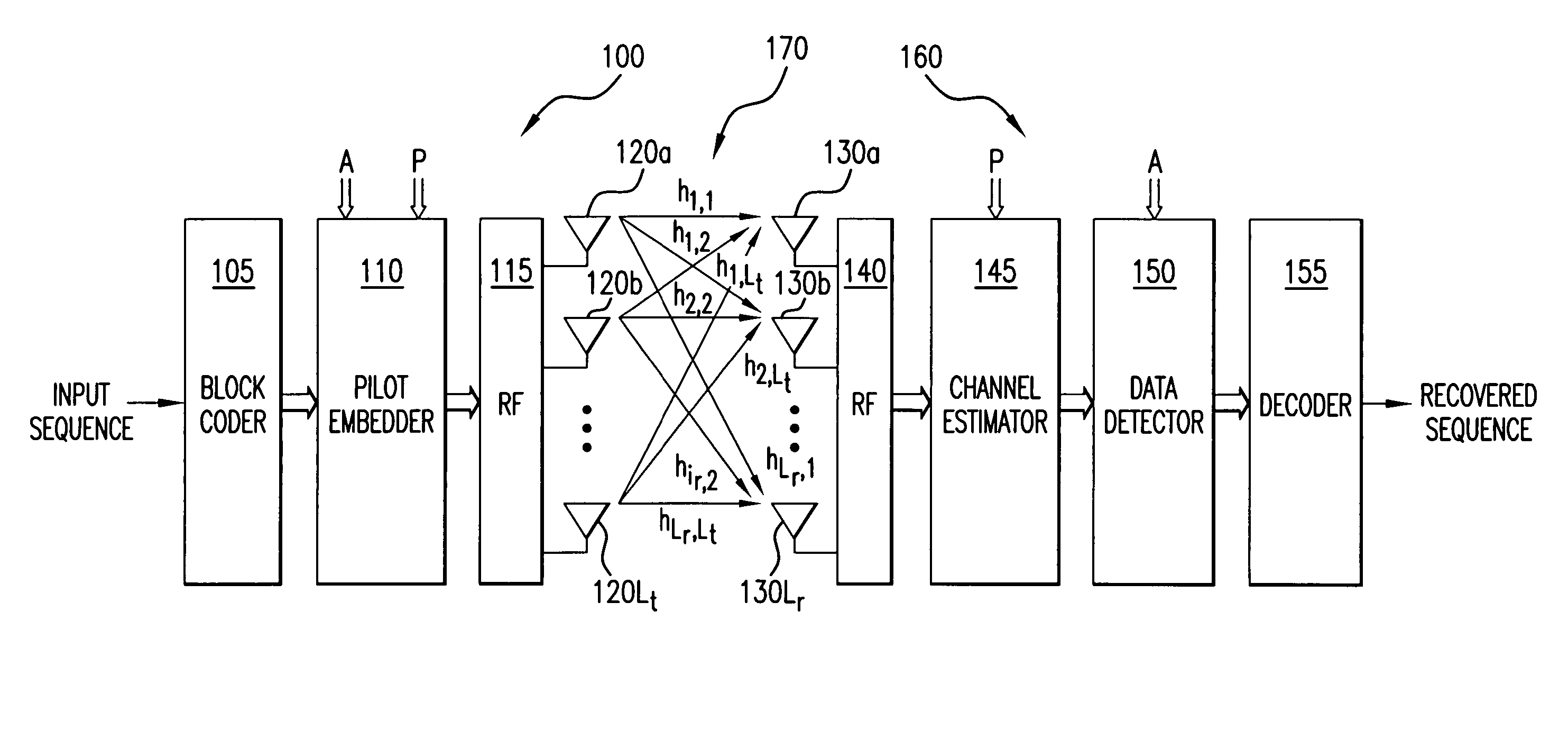
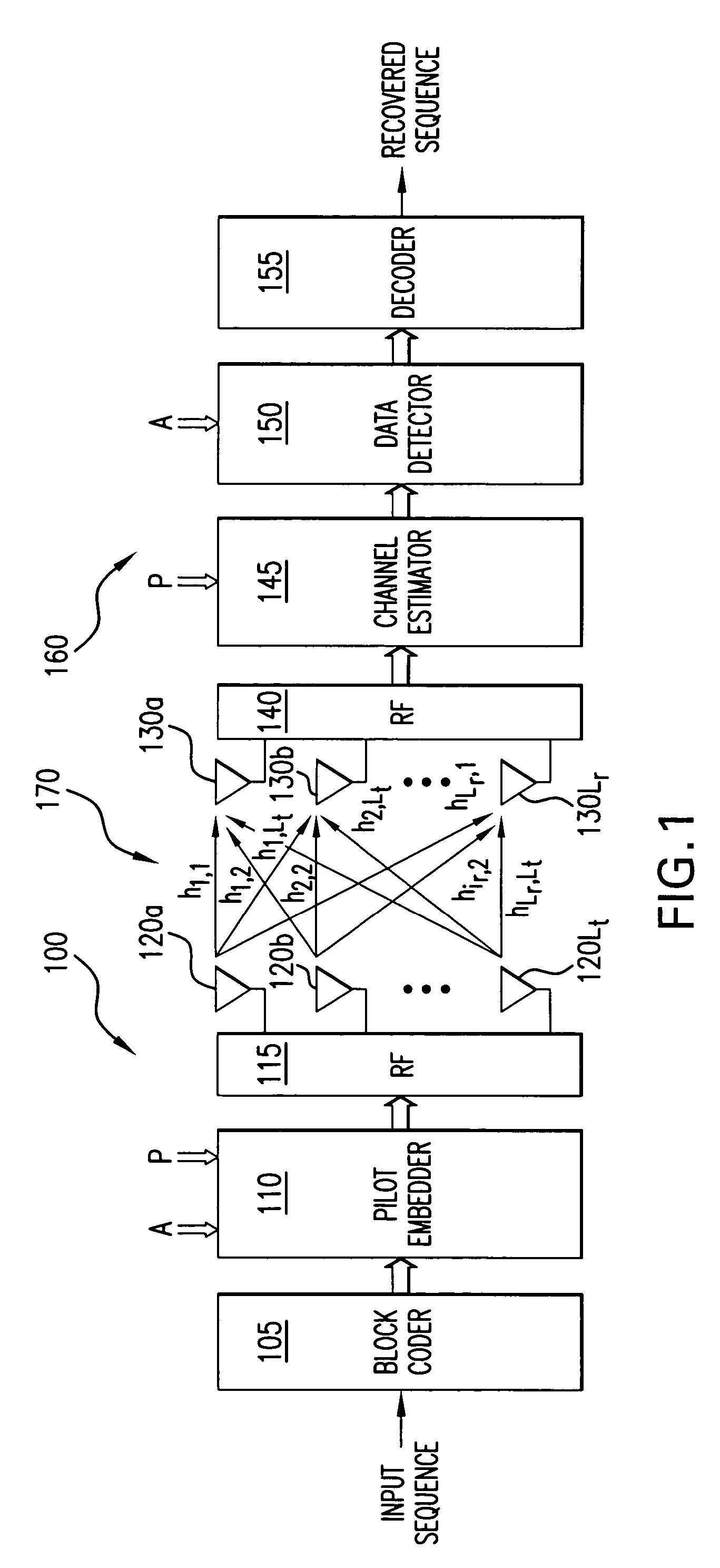
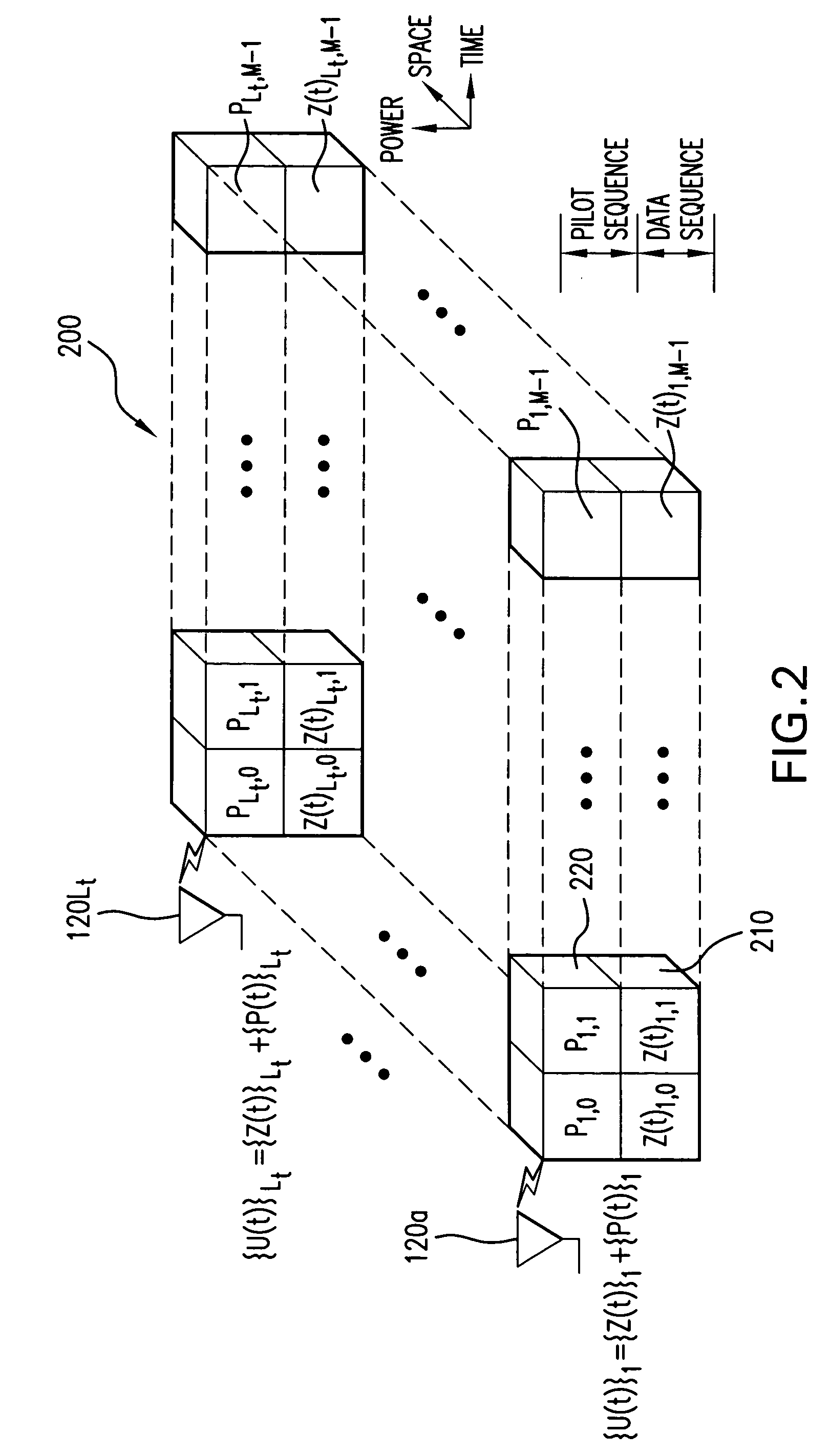
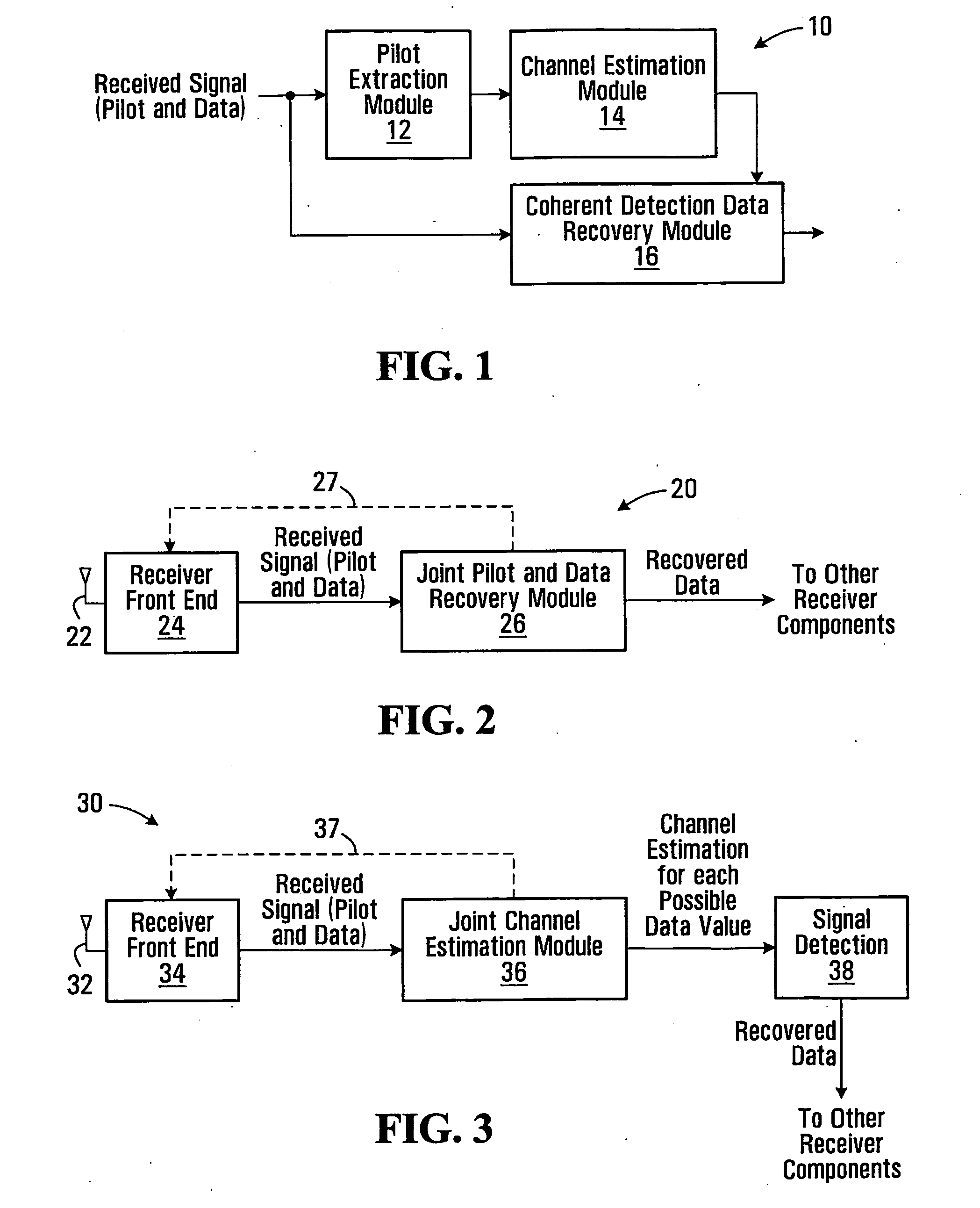
Data communication with embedded pilot information for timely channel estimation
Pilot data and data-bearer data are formed to be mutually orthogonal and in each other's null-space. Data to be transmitted is first modulated with the data-bearer matrix and then pilot data is added thereto. The pilot data may be added to each modulated symbol, thereby increasing significantly the density of pilot information available at the receiver for channel state estimation. When pilot data is added across an entire transmitted block of data, data detection performance is improved for even fast fading Rayleigh fading channels.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
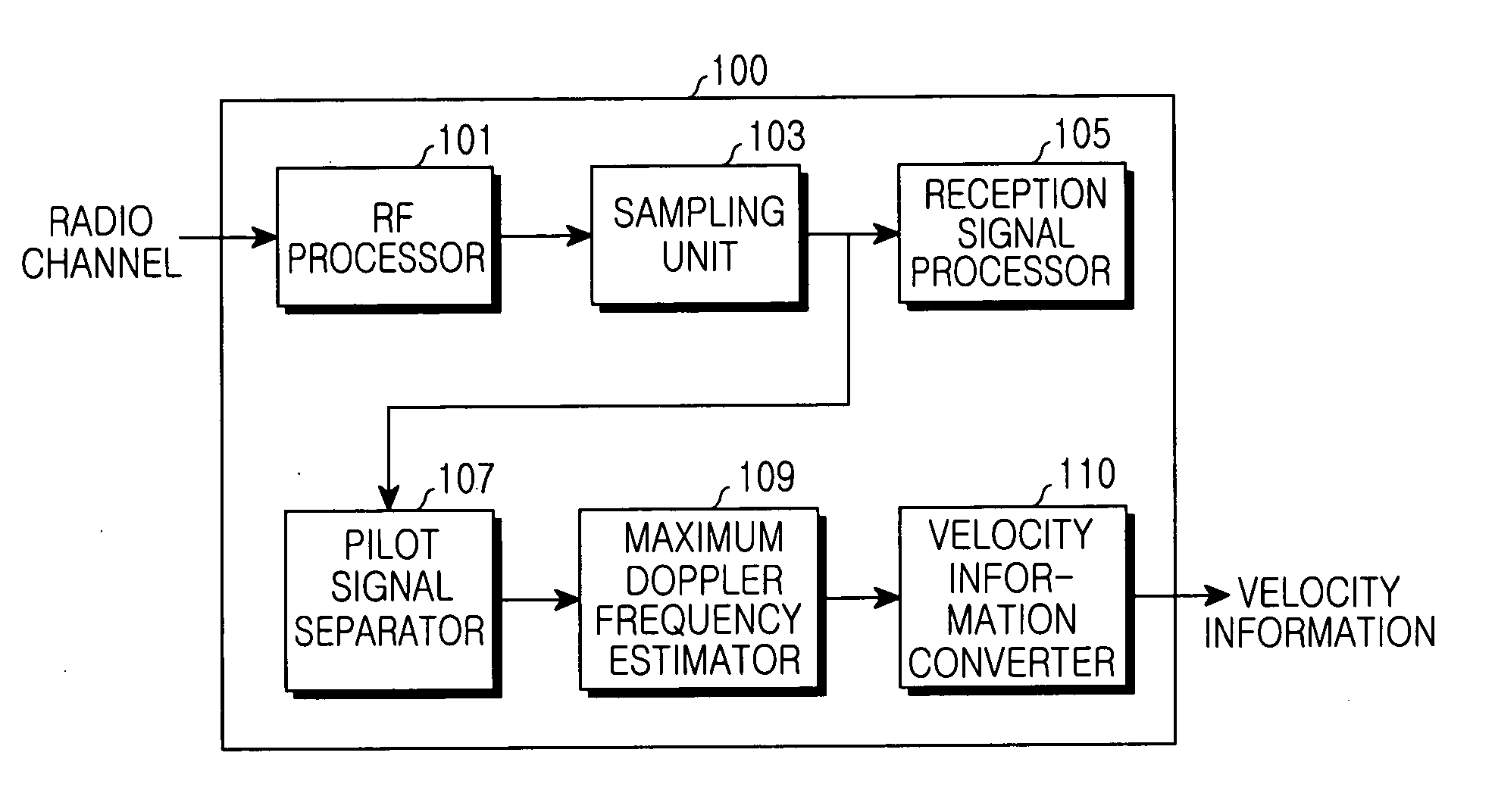
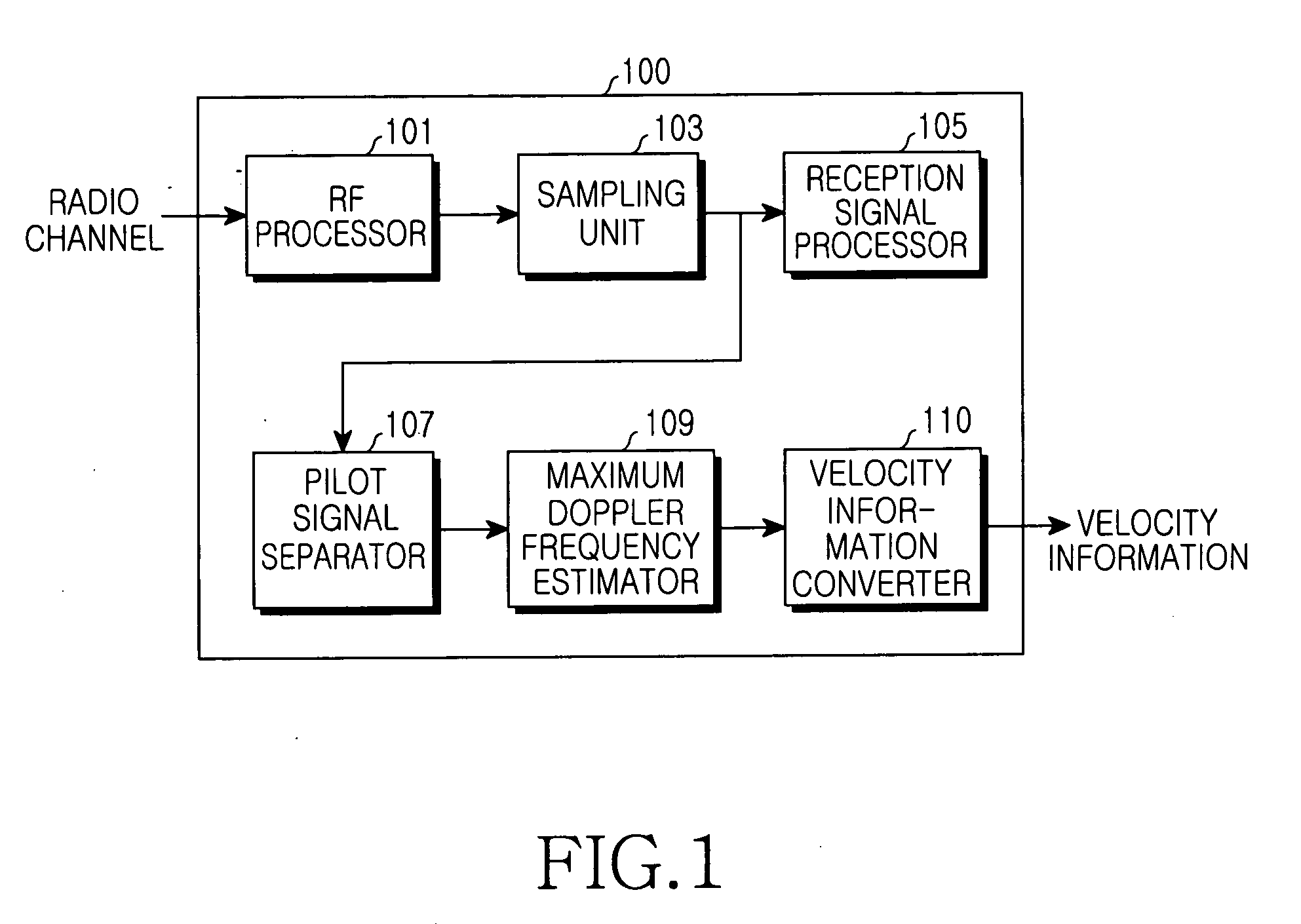
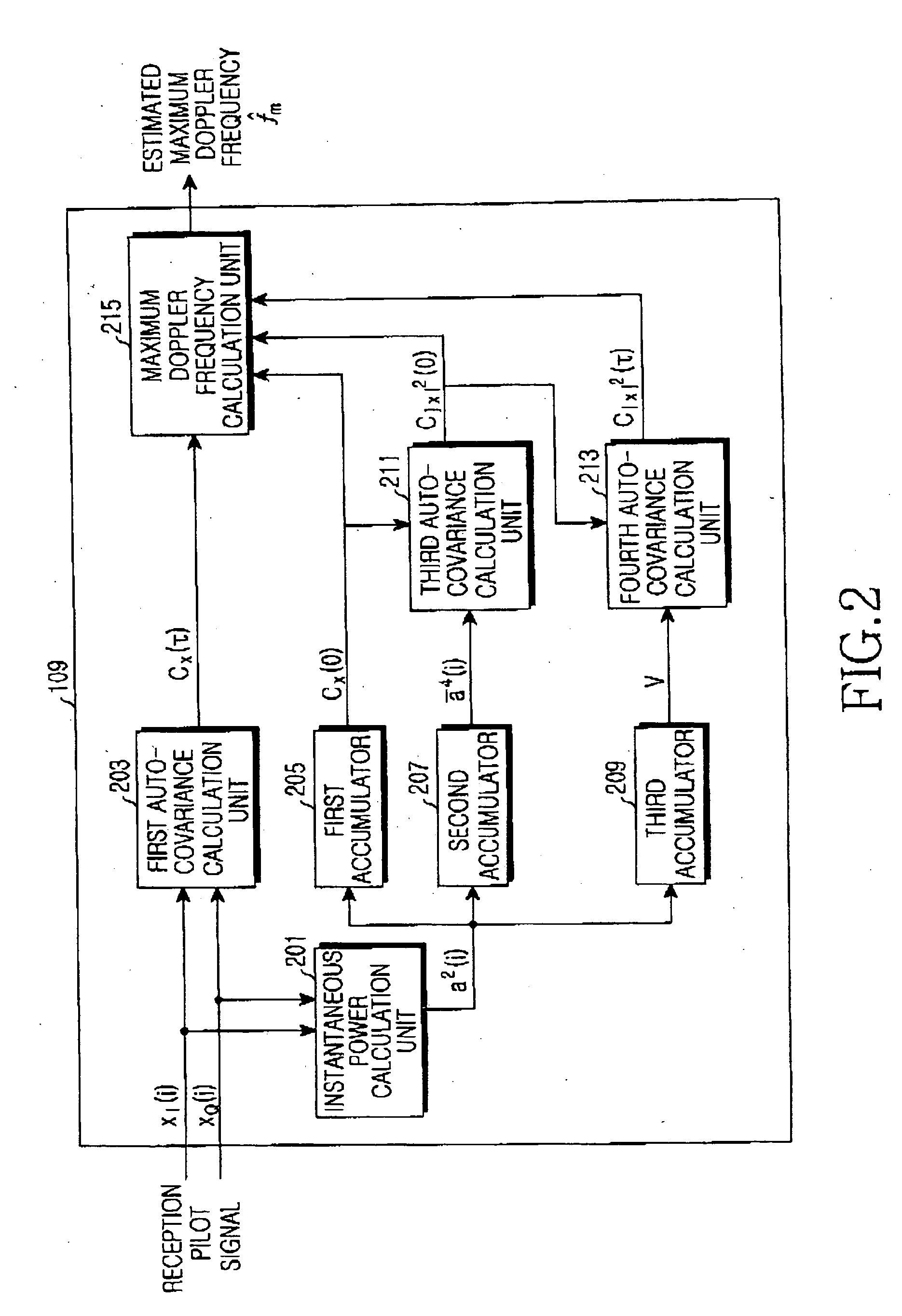
Velocity estimation apparatus in mobile communication environments
ActiveUS20050282499A1Speed efficientUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsRician fadingEngineering
Disclosed is a method for estimating the velocity of a mobile station in Rician fading environments in which a direct wave exists. Cellular mobile communication environments include two environments, Rician fading environments in which a direct wave exists and Rayleigh fading environments in which a direct wave does not exist. Generally, many methods for estimating the velocity of a mobile station have been known in Rayleigh fading environments. However, in Rician fading environments in which a direct wave exists, many errors occurs in estimating the velocity of a mobile station due to difficulty in estimation of a Rician coefficient K and an incident angle θ0. According to the invention, a method is provided wherein error is mostly eliminated in estimating the velocity of a mobile station by obtaining a maximum Doppler frequency of the mobile station, even without directly obtaining a Rician coefficient K and an incident angle θ0.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Channel estimation method of amplify-and-forward repeater adopting wireless energy collection
InactiveCN108900444AAccurately getGet quicklyRadio transmissionChannel estimationEstimation methodsEngineering
The invention discloses a channel estimation method of an amplify-and-forward repeater adopting wireless energy collection. The channel estimation method comprises the following steps: establishing atime-selective Rayleigh fading model; calculating channel gains from two strategy lower information sources to a repeater chain and from the repeater to a destination chain on a repeater and a destination by adopting a linear minimum mean square error theory. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the technical problems in the prior art that the channel estimation method of the amplify-and-forward repeater adopting the wireless energy collection is lacked are solved; a channel estimation value can be rapidly and accurately obtained, and the calculation is accurate and effective.
Owner:国网新疆电力有限公司信息通信公司
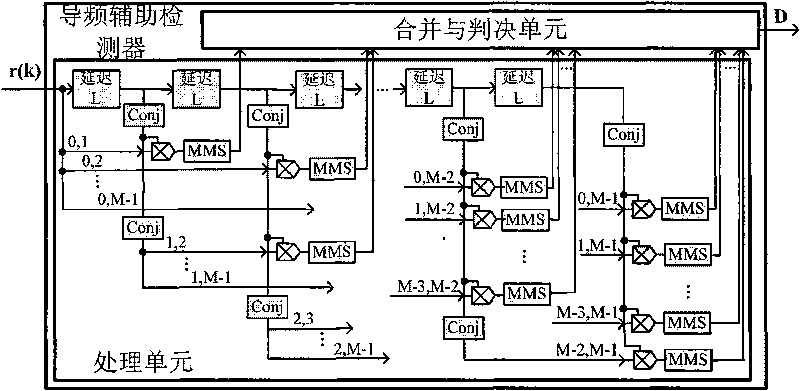
Implementation method of pilot-assisted detector for DVB-T signals in cognitive radio network
InactiveCN101741487AEnhanced Periodic Persistent Pilot ComponentIncrease weightTransmission monitoringSpectrum availabilityFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to an implementation method of a pilot-assisted detector for DVB-T signals in a cognitive radio network. Most countries in the world use DVB-T as the signal standard for ground digital televisions, the nodes in a cognitive radio network acquire spectra-available information on the wave band of the digital television signals mainly by means of spectra perception, and therefore, the research into spectra perception methods for DVB-T signals has significant value. The invention provides a pilot-assisted detector for DVB-T signals. Firstly, a processing unit in the detector strengthens the periodic pilot components in a DVB-T signal received by a secondary user through the sum of product movements but inhibits other components; and secondly, a combination and judgment unit in the detector combines the outputs of the processing unit and judges whether a master user signal exists. The theoretical analysis and the simulation result indicate that the detector is free from the effects of multidiameter Rayleigh fading, can differentiate the master user signal from interference under the conditions of no synchronizing information and low signal-to-noise ratio, and enhances the detection performance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Pilot symbol assisted modulation signal processing systems and methods
InactiveUS20090034659A1Maximize functionalityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsChannel estimationPhase shiftedRician fading
Pilot symbol assisted modulation (PSAM) techniques for Rayleigh and Rician fading channels are derived. Previous techniques implement PSAM signal detectors as an ad-hoc design, using pilot symbols to first estimate channel gain, and then using channel gain estimates in a conventional coherent detector to make data decisions. Although this structure may be effective for binary phase shift keying in Rayleigh fading, it is suboptimal for Rician fading and for 16-ary quadrature amplitude modulation in Rayleigh fading. According to techniques disclosed herein, a PSAM signal detector jointly processes pilot symbols and data symbols. The performance of signal detectors according to embodiments of the invention is analyzed and compared with that of conventional detectors. Numerical results are presented to show that the performance gain of a proposed new PSAM signal detector over conventional PSAM detectors can be as much as 2 or 3 dB for Rician fading in some cases.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Adaptive iterative receiver in low-density parity check code and continuous phase modulation system
ActiveCN102710367AAvoid enteringReduce the number of iterationsError preventionIterative methodLow complexity
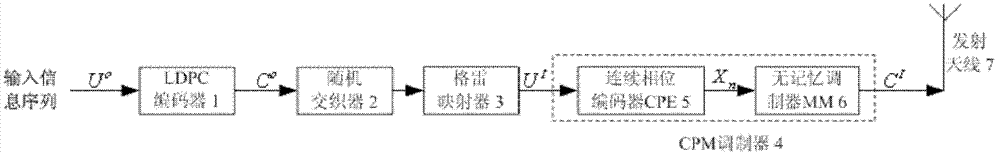
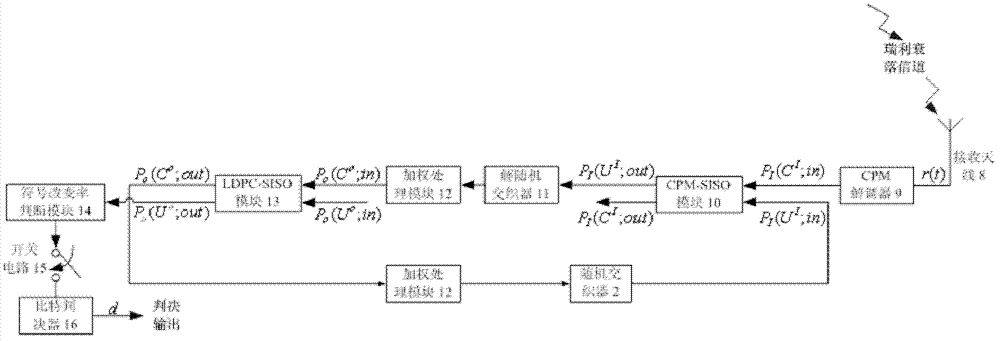
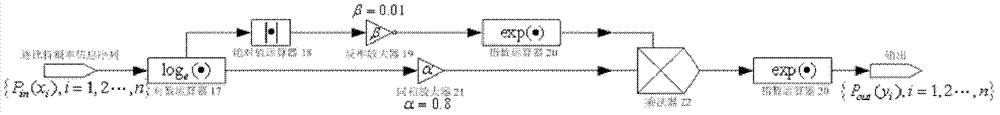
The invention provides an adaptive iterative receiver in a low-density parity check code and continuous phase modulation system. The adaptive iterative receiver comprises a receiving antenna (8), a CPM (continuous phase modulation) demodulator (9), a CPM soft-input and soft-output module (10), a random deinterleaver (11), a weighted processing module (12), an LDPC (low density parity check) code soft-input and soft-output module (13), a random interleaver (2), a sign change rate judging module (14), a switching circuit (15) and a bit decision device (16). The weighted processing module (12) and the sign change rate judging module (14) are introduced and used together. Iterative times are adaptively set by the receiver according to change conditions of a Rayleigh fading channel, an iterative process is prevented from entering a positive feedback state, iterative detection is automatically stopped at a position with a small bit error rate, average iterative times are reduced, iterative detection time is saved, and convergence, reliability and instantaneity of a system are improved. In addition, the adaptive iterative receiver has the advantages of reliable performance, low complexity, easiness in maintenance and the like, and has popularization and application values in satellite communication, deep space communication and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
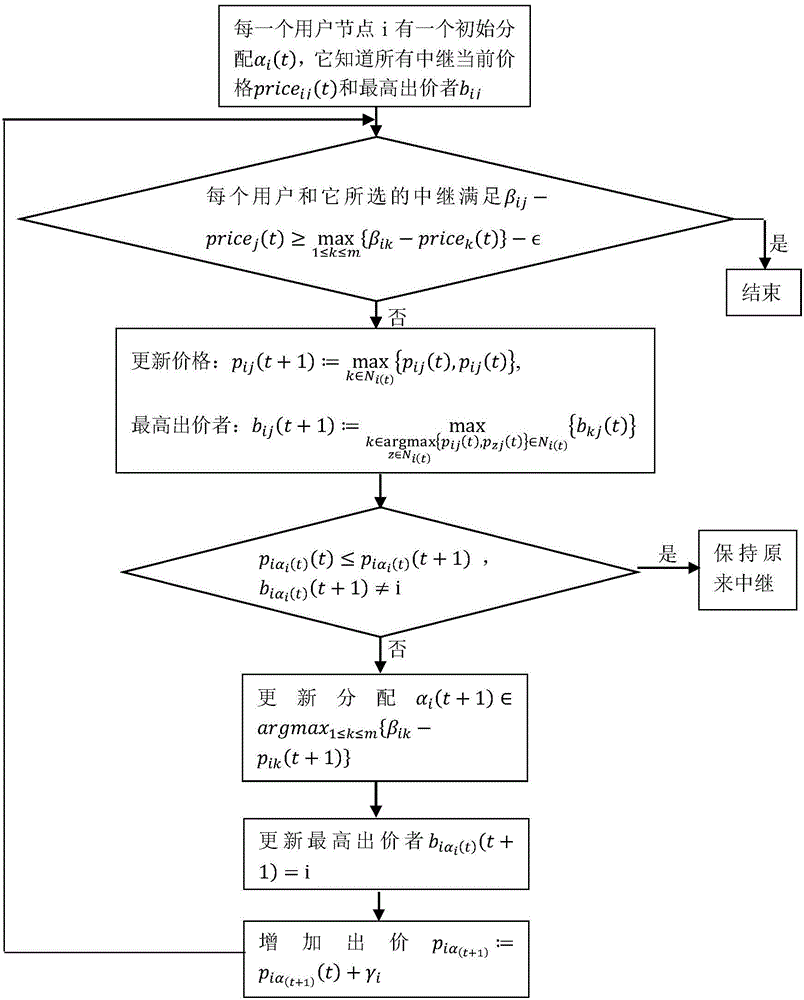
Relay selection method based on multi-source multi-relay wireless network power minimization
ActiveCN104320839AIncrease system efficiencyExtend your lifePower managementComputer networkWireless network
A relay selection method based on multi-source multi-relay wireless network power minimization comprises the following steps that 1 each relay node senses channel gain from a sending node to the relay node and channel gain from the relay node to a destination node then informs the channel gain and the maximum sending power of the relay node to the sending node; 2 each source node calculates minimum sending powers of a next source node and the relay node under the condition that the outage probability requirement is met; 3 each user needs to select one relay node to enable the total transmission power of a whole system to be minimum for a wireless communication network; 4 the maximum sending power of the source node i and the relay node j is calculated according to the outage probability of a channel from a user i to the destination node D under the condition that channel interruption does not occur; 5 the user i selects the relay node enabling benefit to be maximum so as to facilitate information transfer. According to the relay selection method, the relay node minimizing total transmission power of the system serves as the source node in a Rayleigh fading channel.
Owner:青岛华师智慧科技有限公司
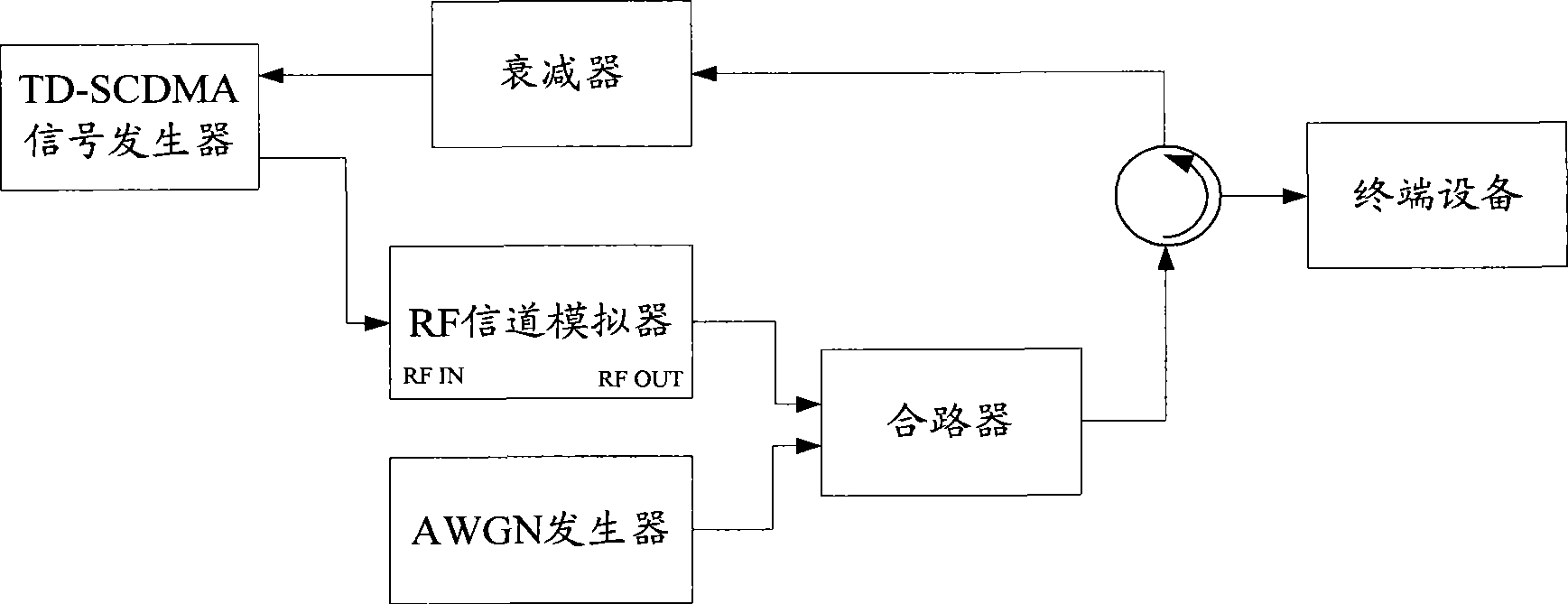
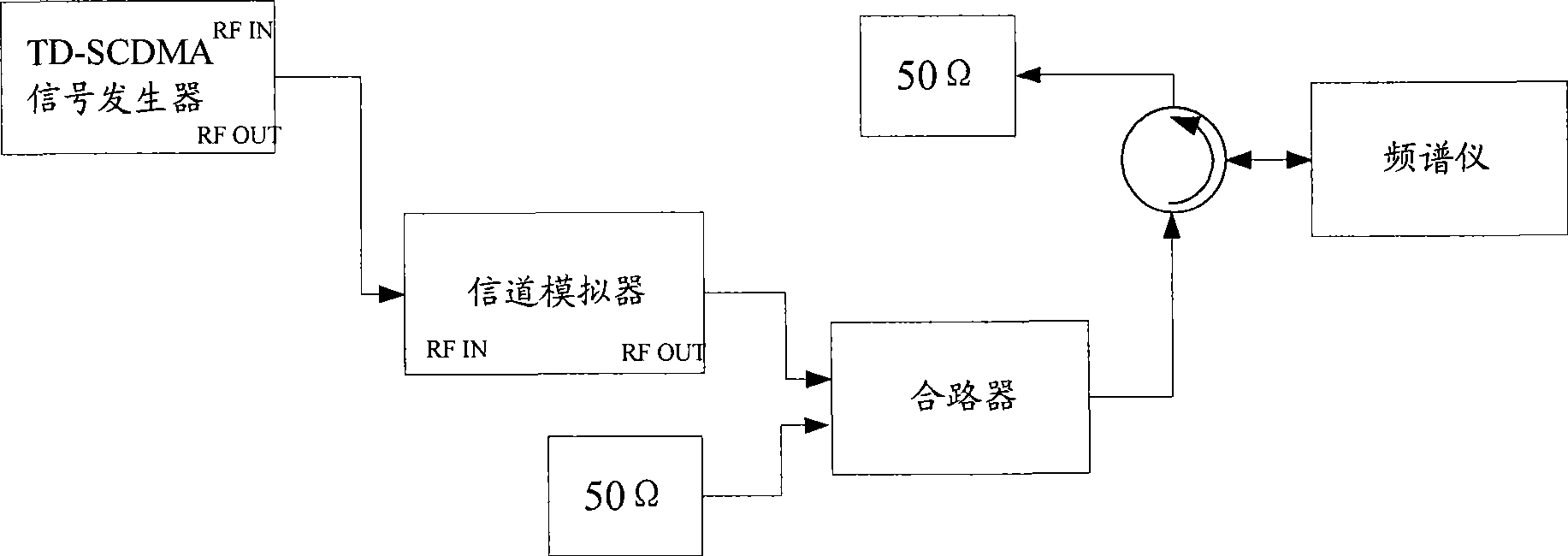
Link calibration method and device
ActiveCN101425854AImprove calibration efficiencyImprove calibration accuracyTransmission monitoringWireless communicationUltrasound attenuationTD-SCDMA
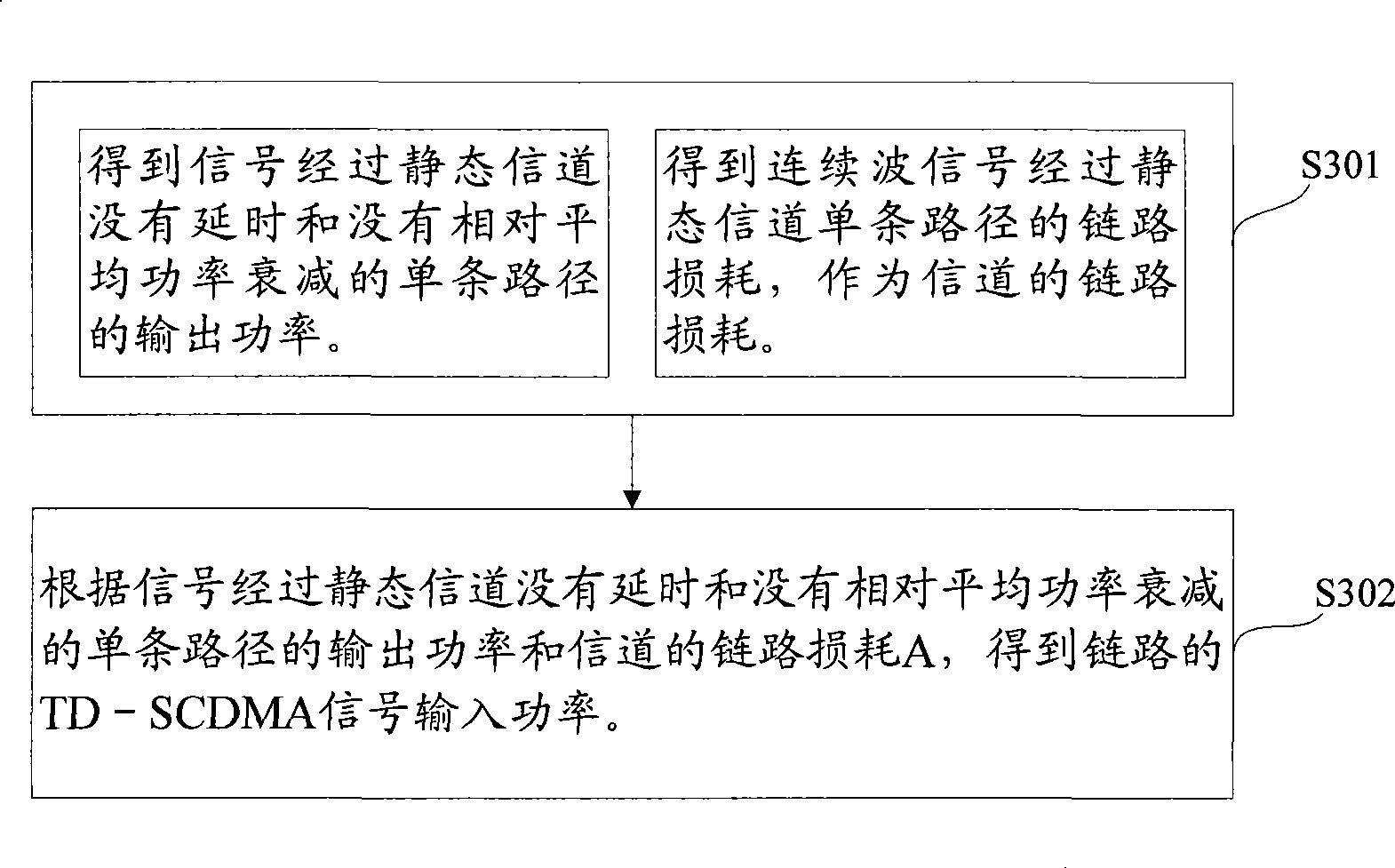
The invention discloses a method for the correction of link and a device thereof, the technique comprises: the relationship between the output powers of TD-SCDMA signals through a Rayleigh fading channel and the output powers of the signal through a static channel is obtained according to the requirement of performance test to the characteristic of a channel simulator, the single-path output powers of the signals through the static channel without delay or relatively average power attenuation are obtained by utilizing the relationship; the single-path link loss of the continuous wave signals through the static channel is obtained, the obtained link loss is used as the link loss of the channel; and the input powers of the TD-SCDMA signals of the link are obtained by the sum of the single-path output powers of the signals through the static channel without delay or relatively average power attenuation and the link loss of the channel. With the technical proposal provided by the invention, the channel simulator has fast correction time, high efficiency, simple correction platform, high precision as well as simple and feasible implementing in the complicated environment.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
Code multiplexing differential chaotic modulator-demodulator for integrated code subscript modulation
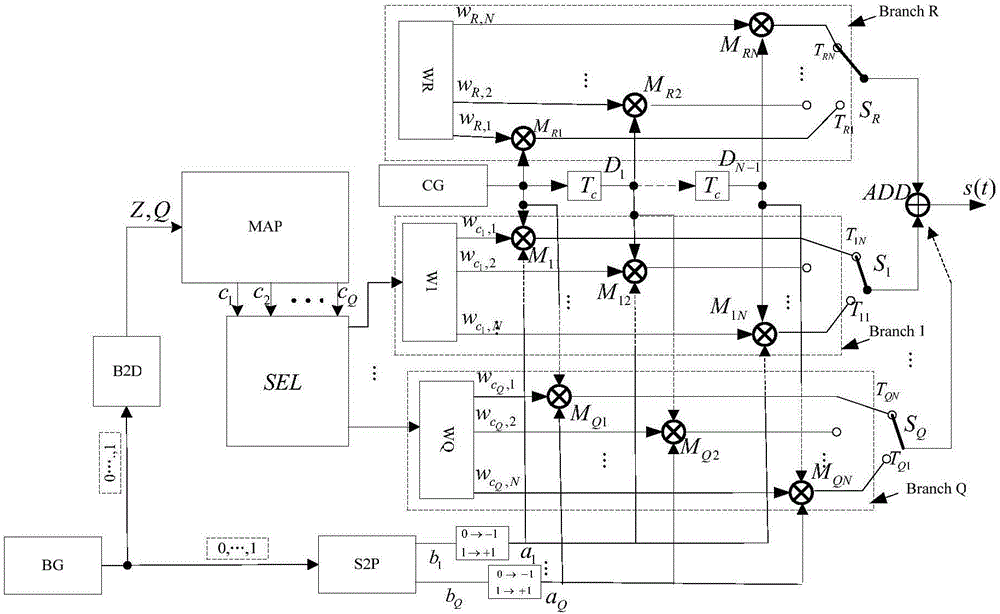
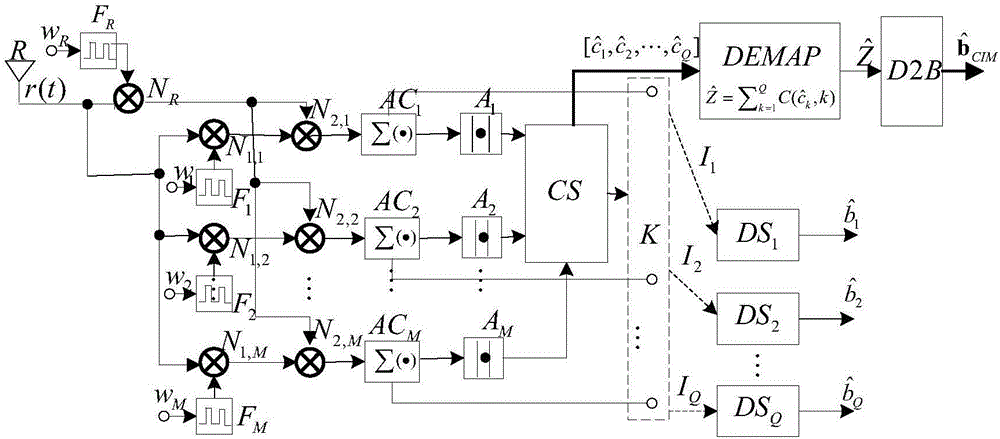
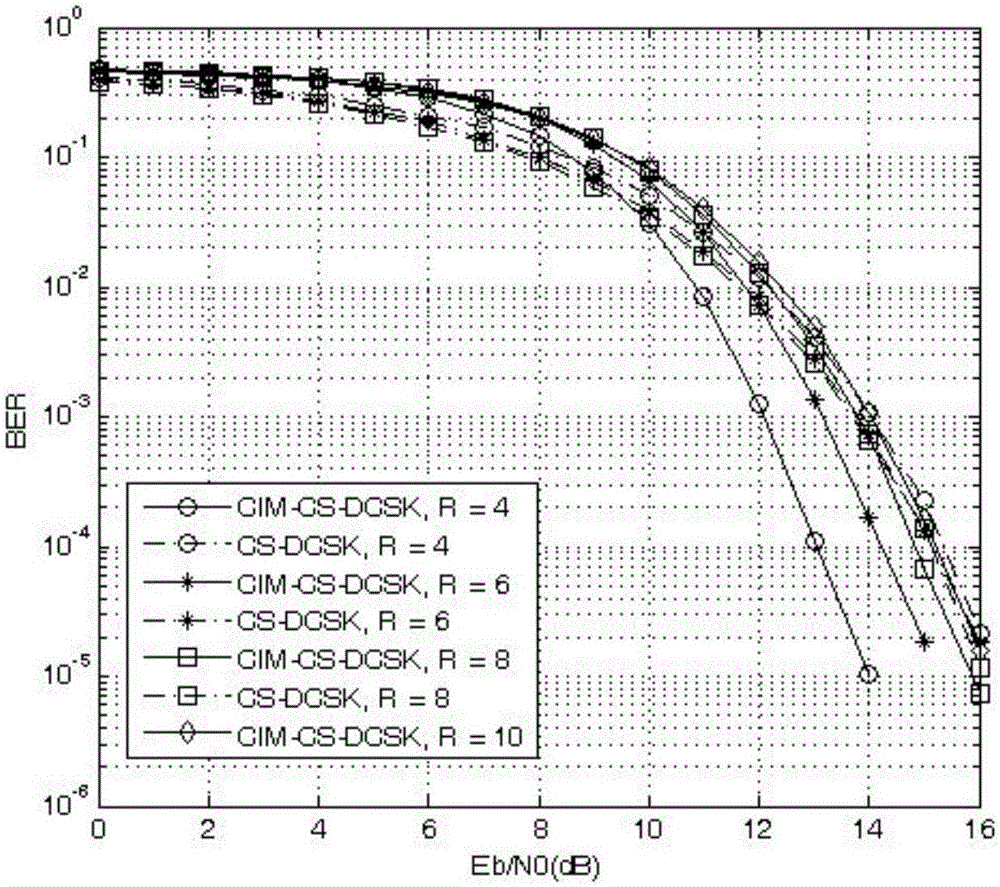
InactiveCN106549894AHigh bandwidthReduce energy consumptionModulated-carrier systemsModem deviceShortest distance
The invention discloses a code multiplexing differential chaotic modulator-demodulator for integrated code subscript modulation and relates to modulation and demodulation in a communication system. The code multiplexing differential chaos modulator-demodulator comprises a modulator and a demodulator. The modulator comprises a binary / decimal converter, a serial / parallel converter, a natural number / combinatorial number mapper, a Walsh code selection controller, a chaotic signal generator, Q+1 Walsh code generators, a multiplier, a time delay unit, a shift switch and an adder. The combinatorial comprises a receiver, a multiplier, a square wave generator, an accumulator, an absolute value resolver, a comparison and selection controller, the shift switch, a decision device, the natural number / combinatorial number mapper and the binary / decimal converter. Transmitted information bits are mapped on selection of a Walsh code, a transmission data rate is improved, the bandwidth is increased, the energy efficiency is improved, and the bit error rate performance under an AWGN channel and a multi-path Rayleigh fading channel is equal to or better than that under conventional DCSK (Differential Chaotic Shift Keying). The modulator-demodulator is competitive in a short-distance communication application.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com