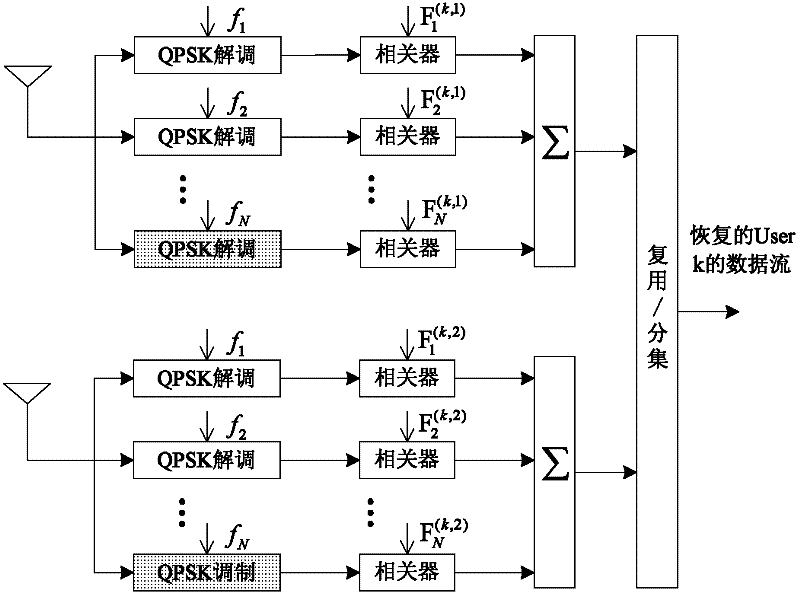
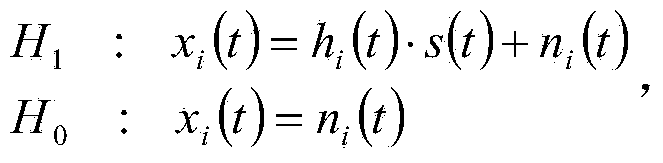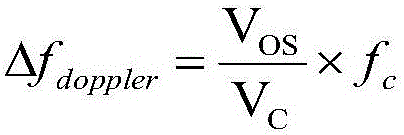Patents
Literature
191 results about "Additive white Gaussian noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) is a basic noise model used in Information theory to mimic the effect of many random processes that occur in nature. Wideband noise comes from many natural noise, such as the thermal vibrations of atoms in conductors (referred to as thermal noise or Johnson–Nyquist noise), shot noise, black-body radiation from the earth and other warm objects, and from celestial sources such as the Sun. The central limit theorem of probability theory indicates that the summation of many random processes will tend to have distribution called Gaussian or Normal.
Communication signal modulation mode identification method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN108234370ASimple feature constructionEasy to identifyModulation type identificationNeural architecturesUp conversionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
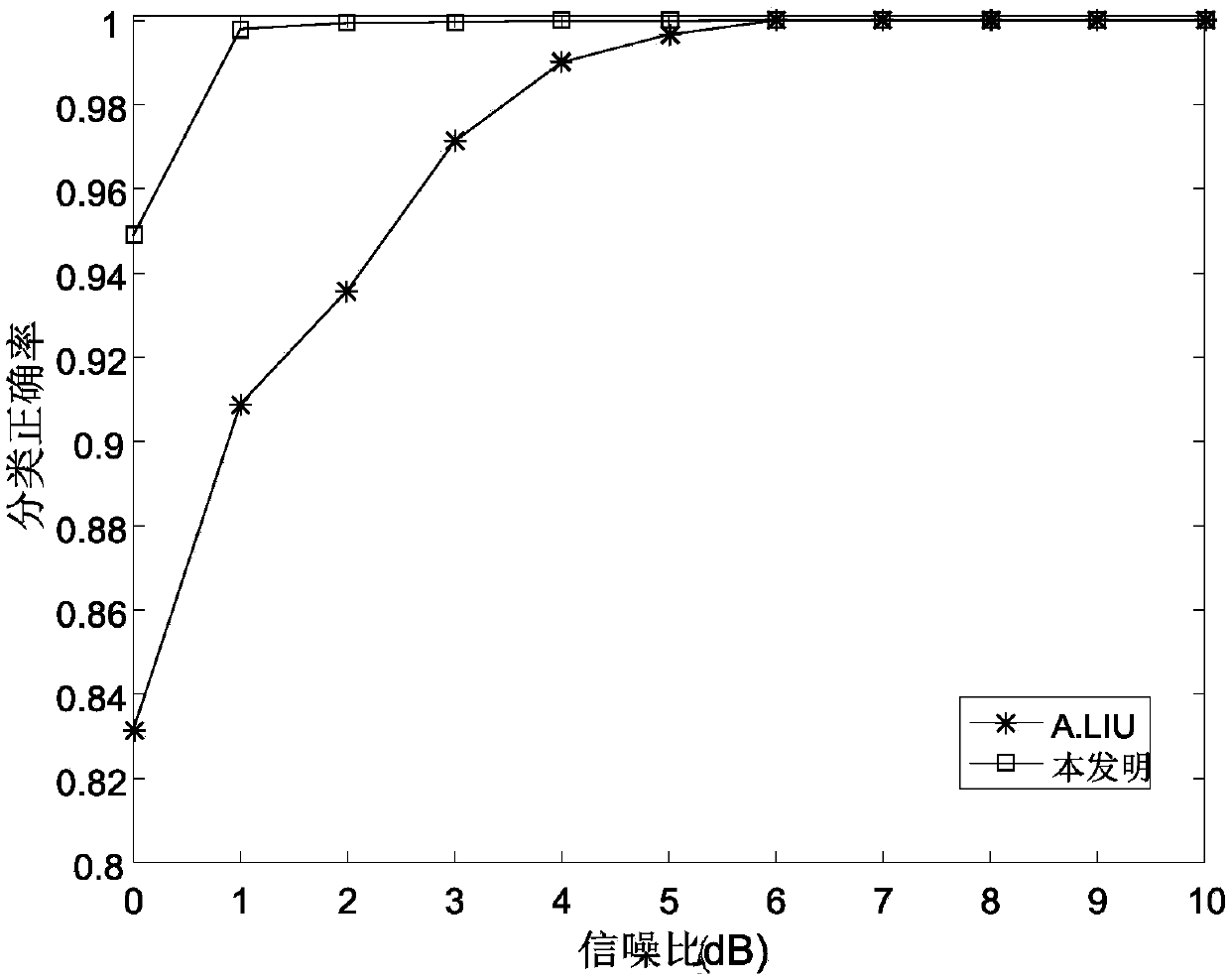
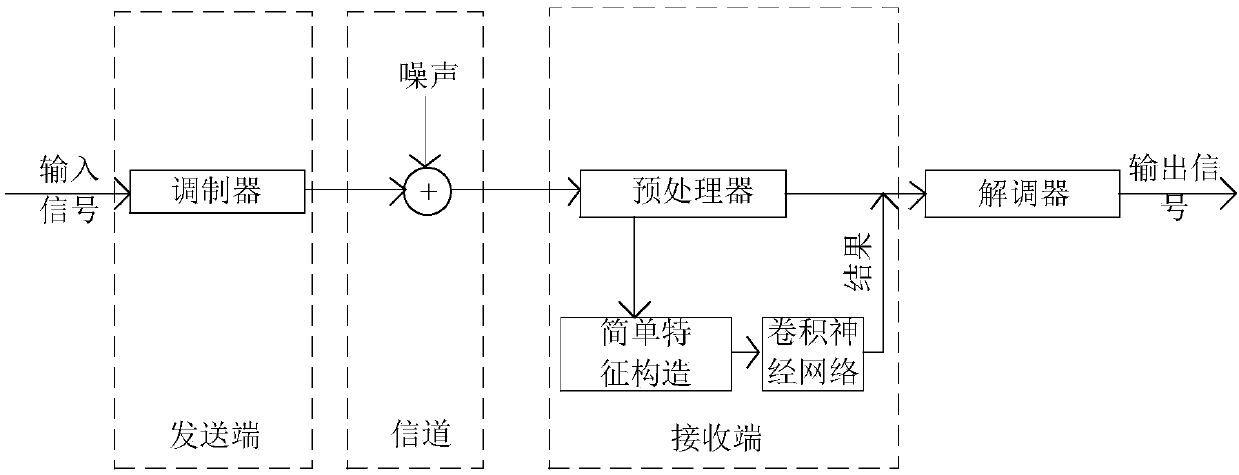
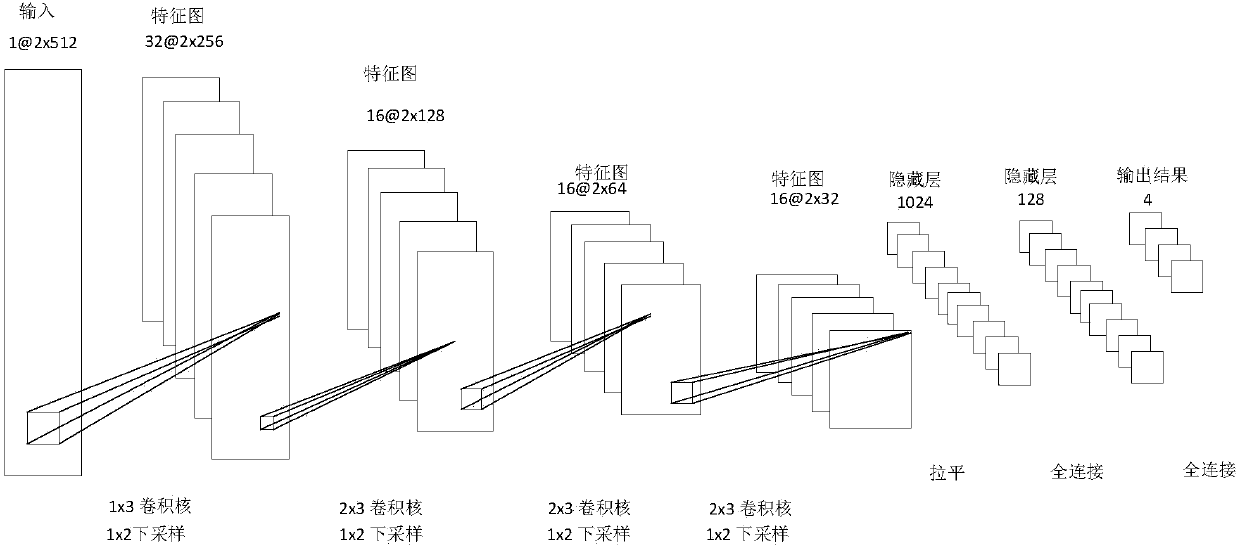
The invention discloses a modulation mode identification system and method based on a convolutional neural network, which solve the problems of complex feature extraction steps and low identificationrate under a low signal-to-noise ratio in the prior art. The simple feature in the identification system is constructed as a simple feature using a co-directional component and a quadrature componentof a baseband signal as signals, and the simple feature is sent to a convolutional neural network module for identification. The identification method comprises the steps of: modulating a transmittedsignal and performing pulse shaping; performing up-conversion on the transmitted signal and then transmitting the transmitted signal through an additive white Gaussian noise channel; performing pre-processing first by a receiving end to obtain the co-directional component r(t) of the analyzed signal; constructing the simple feature, i.e., constructing the co-directional component r(t) and the quadrature component of the analyzed signal into a two-dimensional matrix; performing feature learning and classification by the convolutional neural network; and sending a modulation method to a demodulation end to obtain a demodulated signal. The method is low in feature design complexity, avoids explicit feature extraction, has high classification correctness, and can be applied to communication systems having high recognition performance requirements.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Adaptive channel coding using polarization
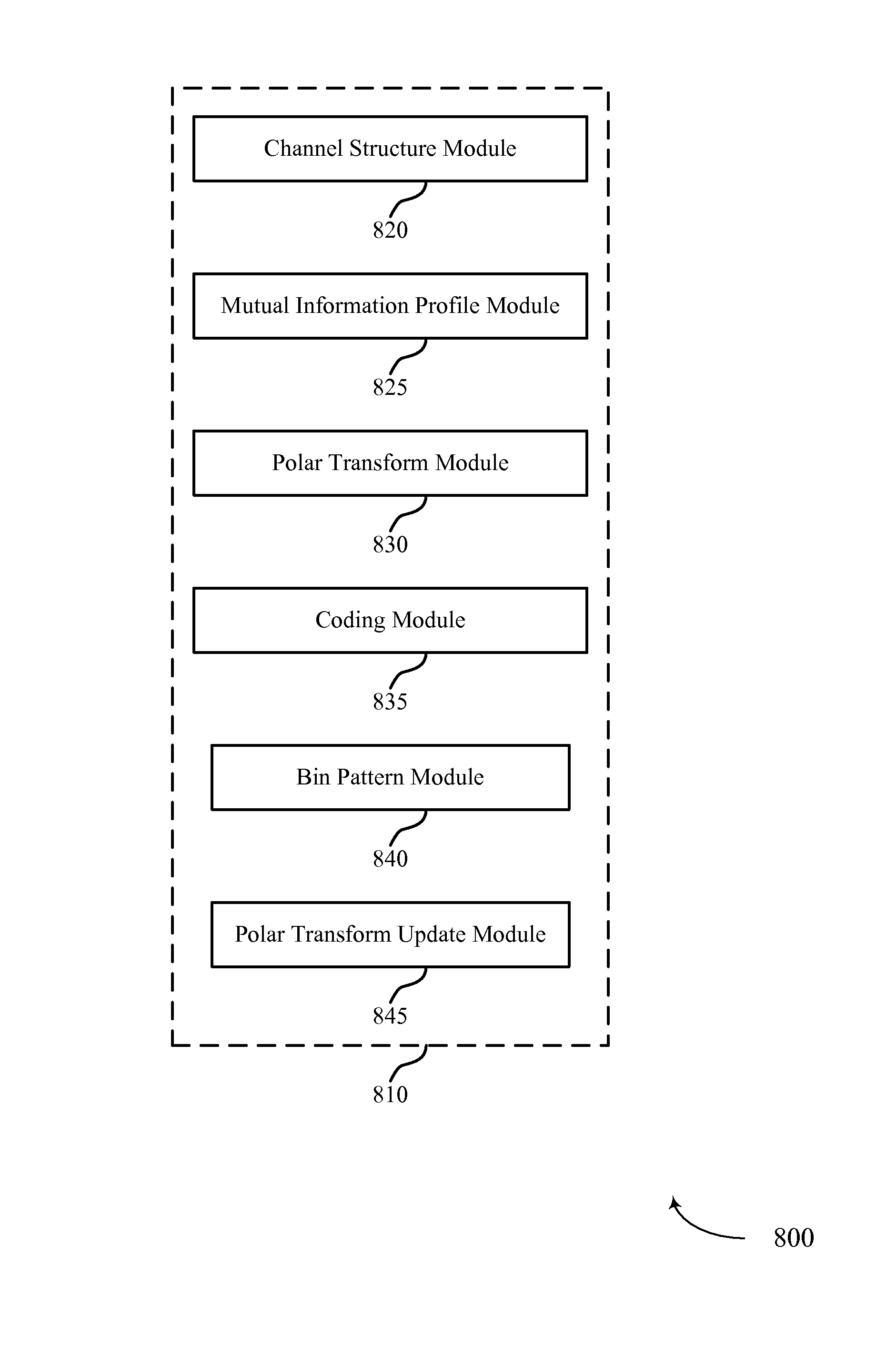
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communications at a wireless device. A wireless device may adaptively select a parity check matrix to increase the reliability of signal transmission by adapting to different channel statistics and channel types (e.g., erasure channels, channels with additive white Gaussian noise, and channels with discrete or continuous alphabets). For example, polarization codes (i.e., codes based on rows of a polarization matrix) may be used to construct parity check matrices “on-the-fly” given an estimation of dynamic channel conditions or diverse channel structures. The channel may be decomposed into polarized sub-channels corresponding to the polarization codes, and mutual information profiles may be determined for each of the polarized sub-channels. The parity check matrix corresponding to the polarization codes may be constructed based on the mutual information profile of all polarized sub-channels. The wireless device may encode or decode data based on the constructed parity check matrix.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Robust transmission system and method for mobile television applications
InactiveUS20070277209A1Consumes less powerFreedom of movementTime-division multiplexAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMobile televisionTransmitter
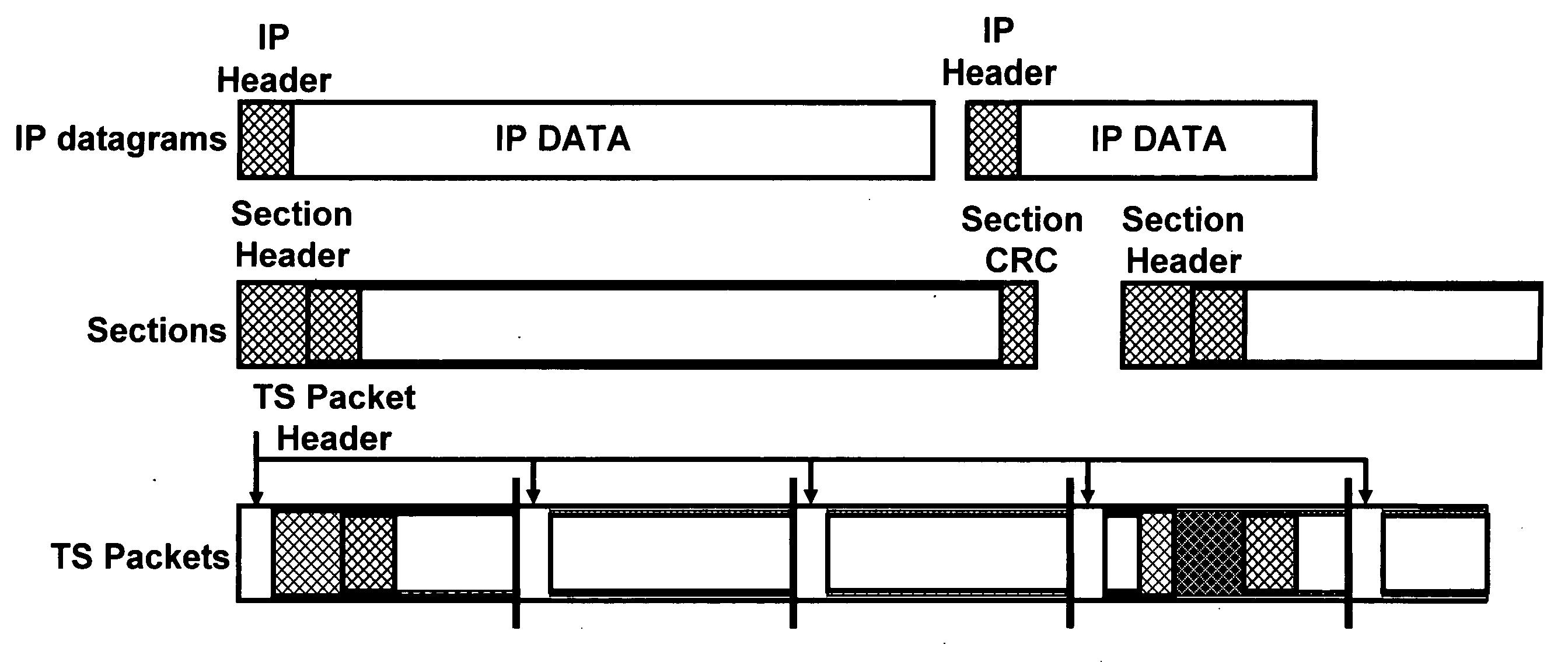
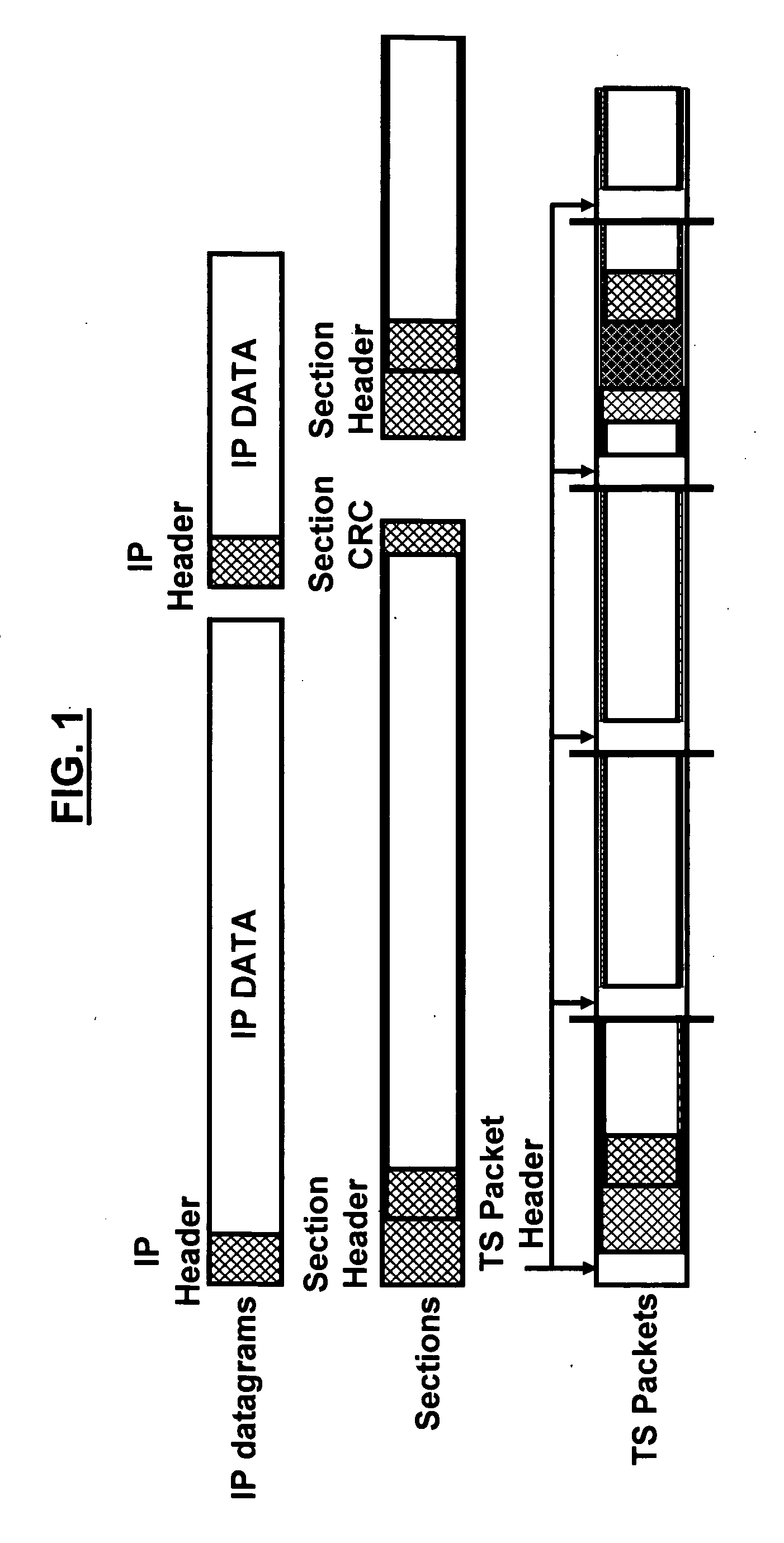
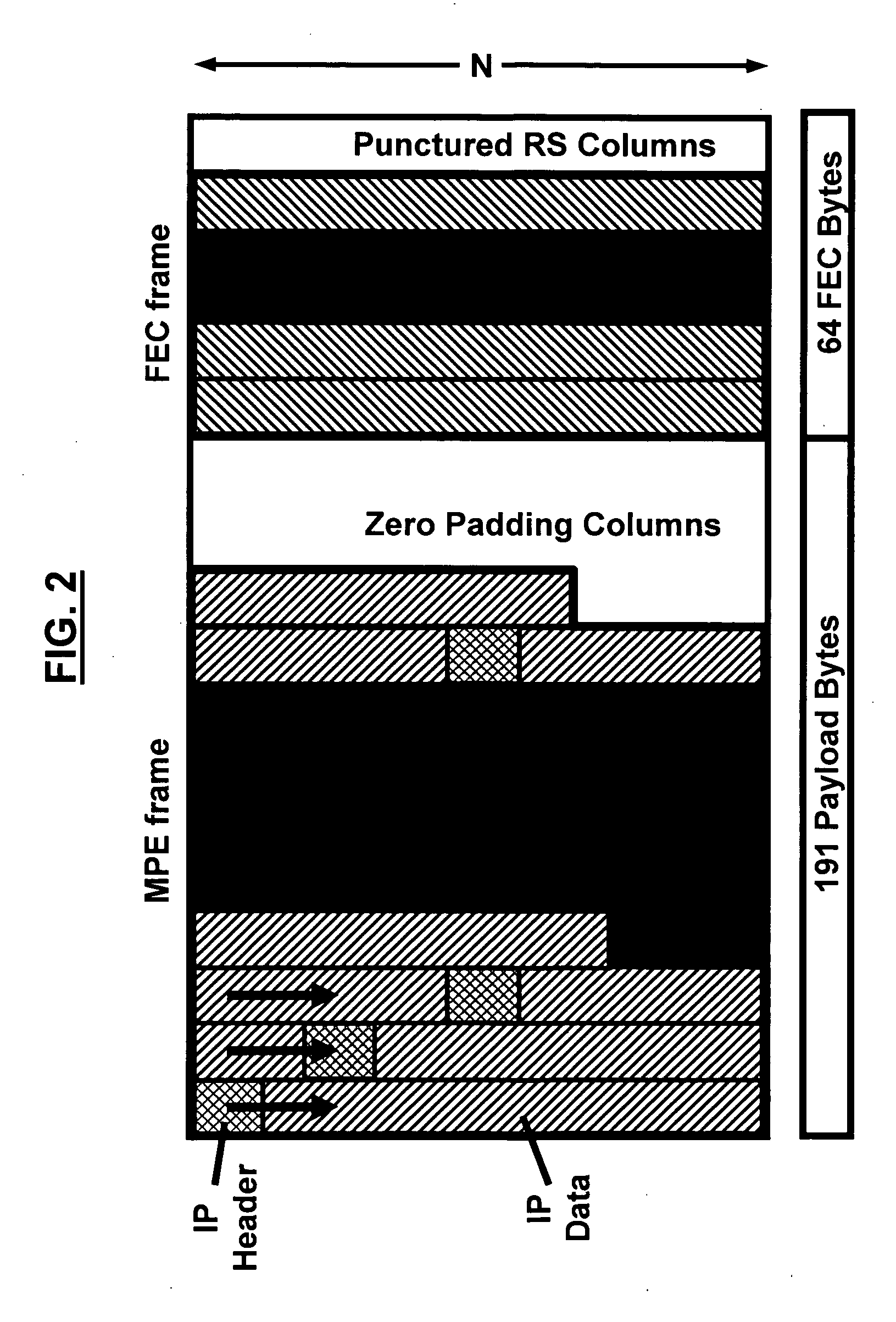
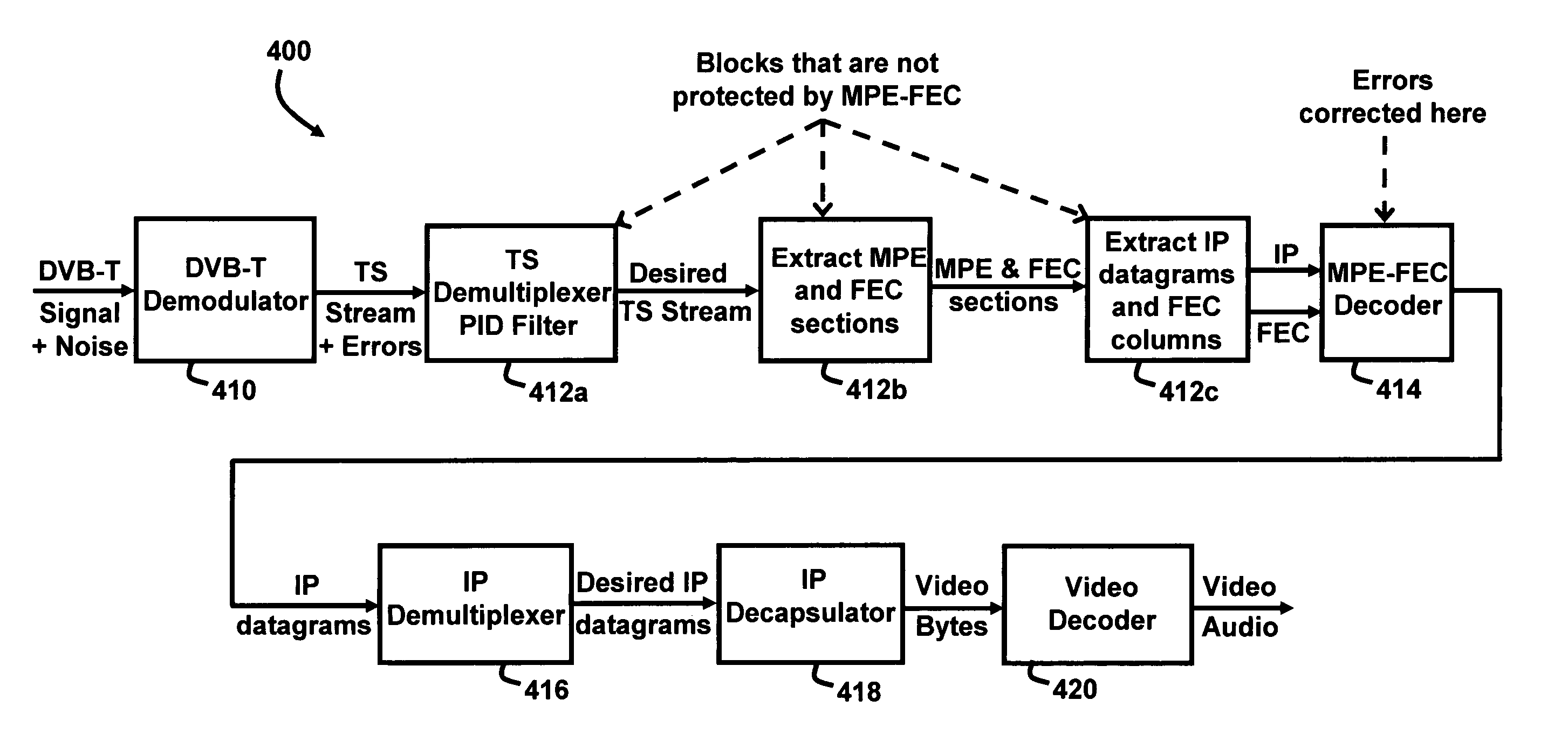
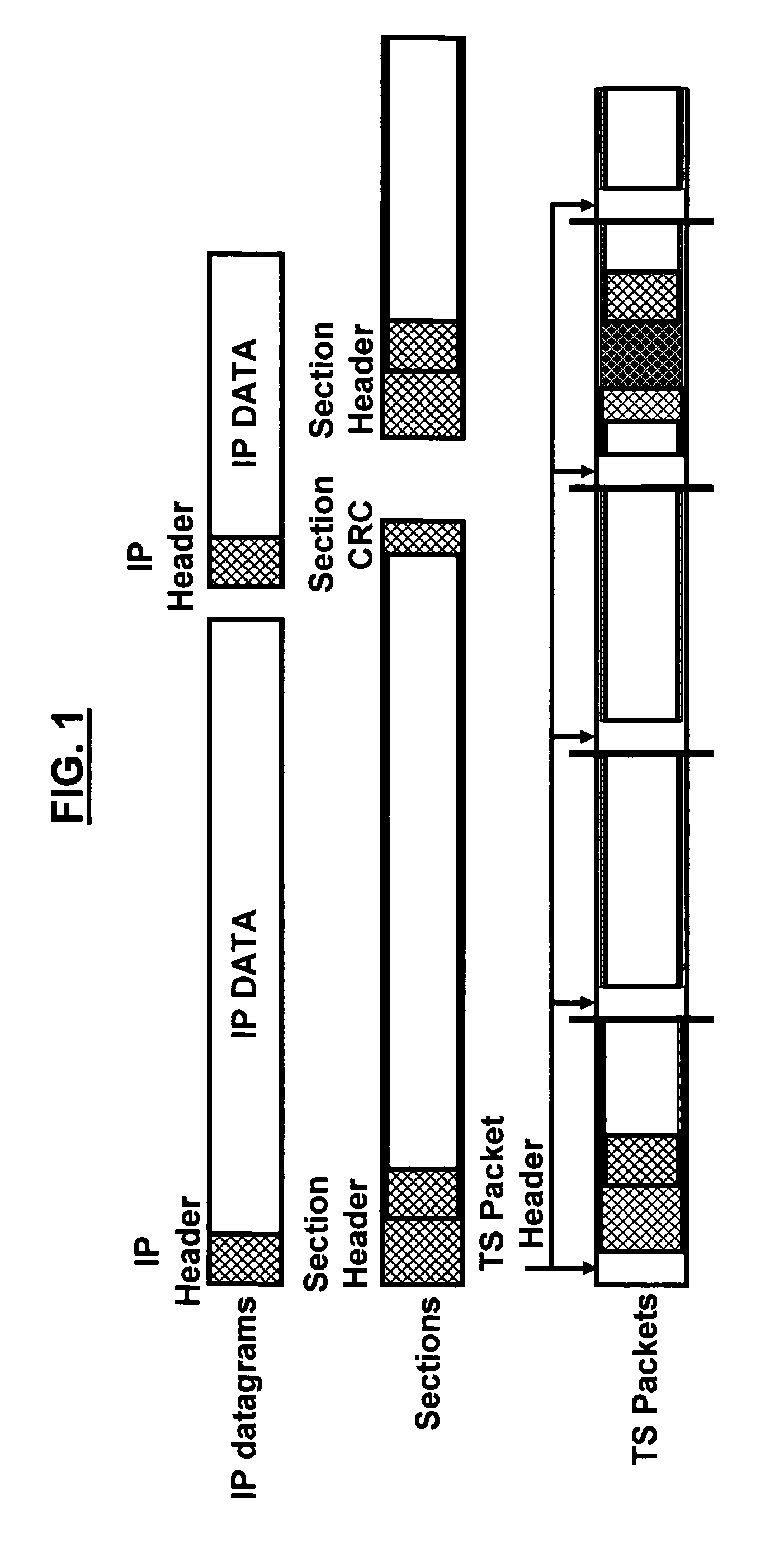
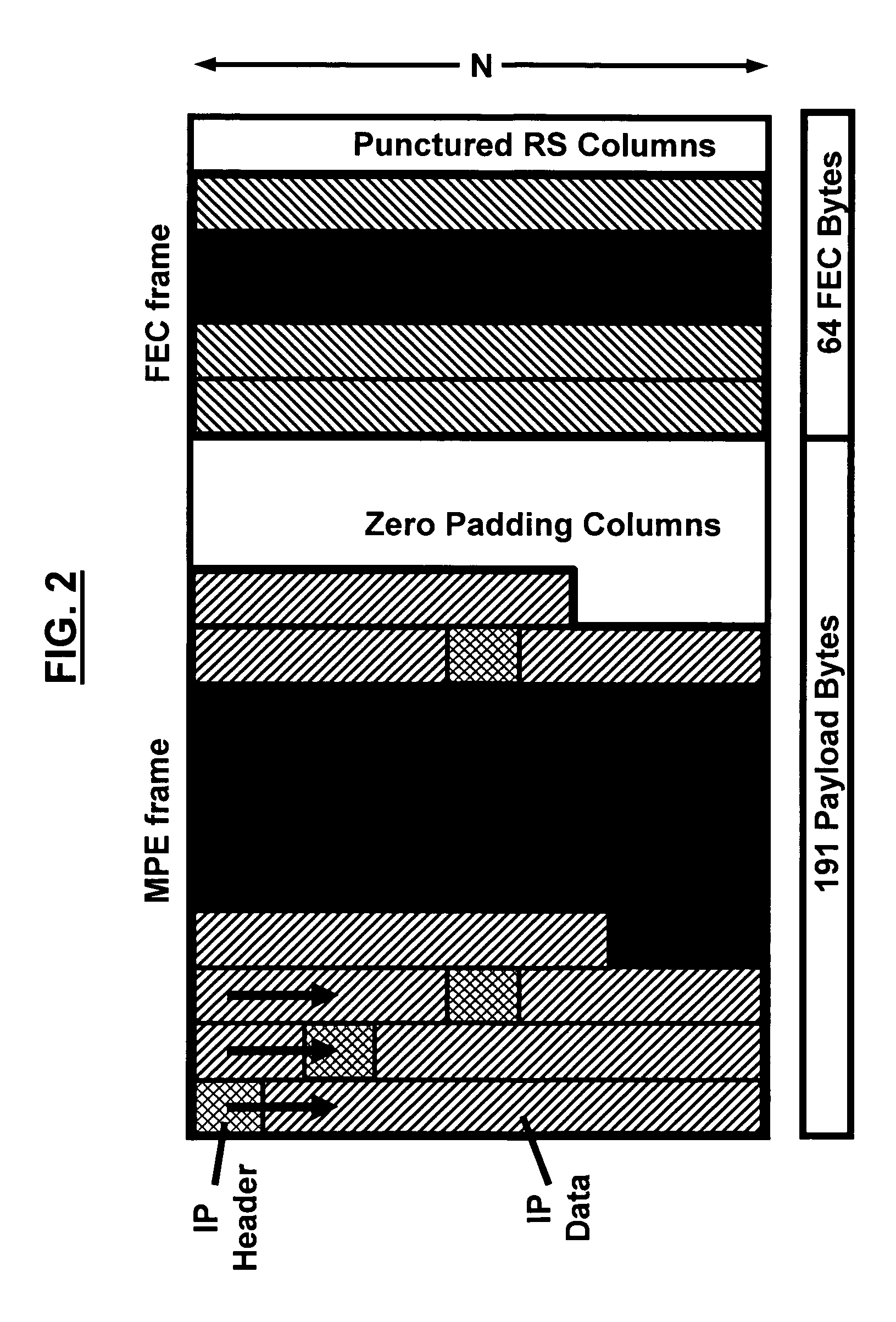
A data transmission system and method for DVB-H signals for enhancing data robustness of a DVB-H receiver in additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channels includes transmitting IP datagrams from a DVB-H transmitter to the DVB-H receiver; applying a MPE section and a FEC section to the transmitted IP datagrams; mapping the transmitted IP datagrams to TS packets; aligning boundaries of the transmitted IP datagrams to a given number of TS packets; fixing a size of the IP datagrams to a known value at the DVB-H receiver; and extracting the IP datagrams from the DVB-H receiver.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Ordered successive interference cancellation receiver processing for multipath channels
InactiveUS20050008092A1Improve performancePolarisation/directional diversitySecret communicationTransmission channelMultipath channels
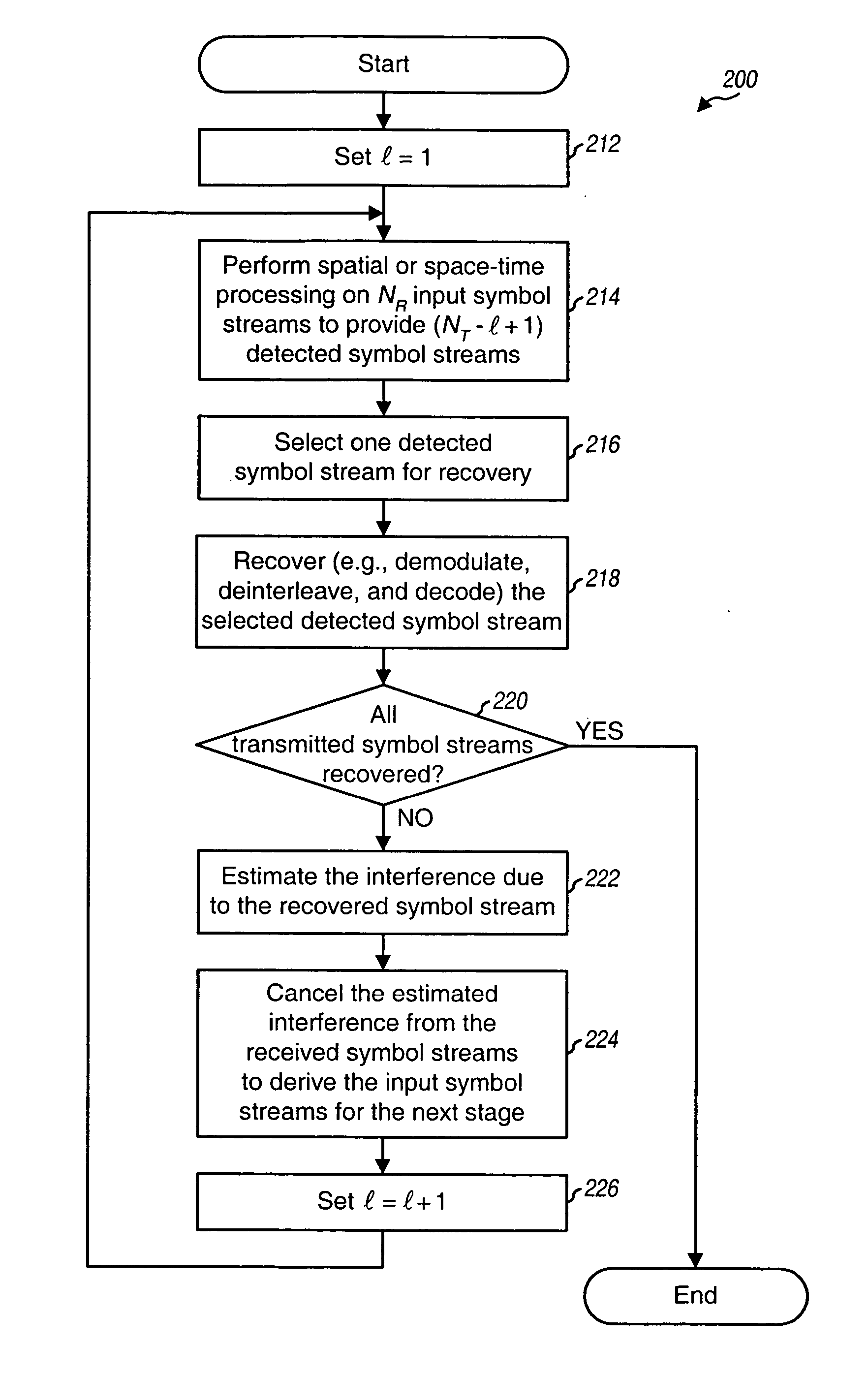
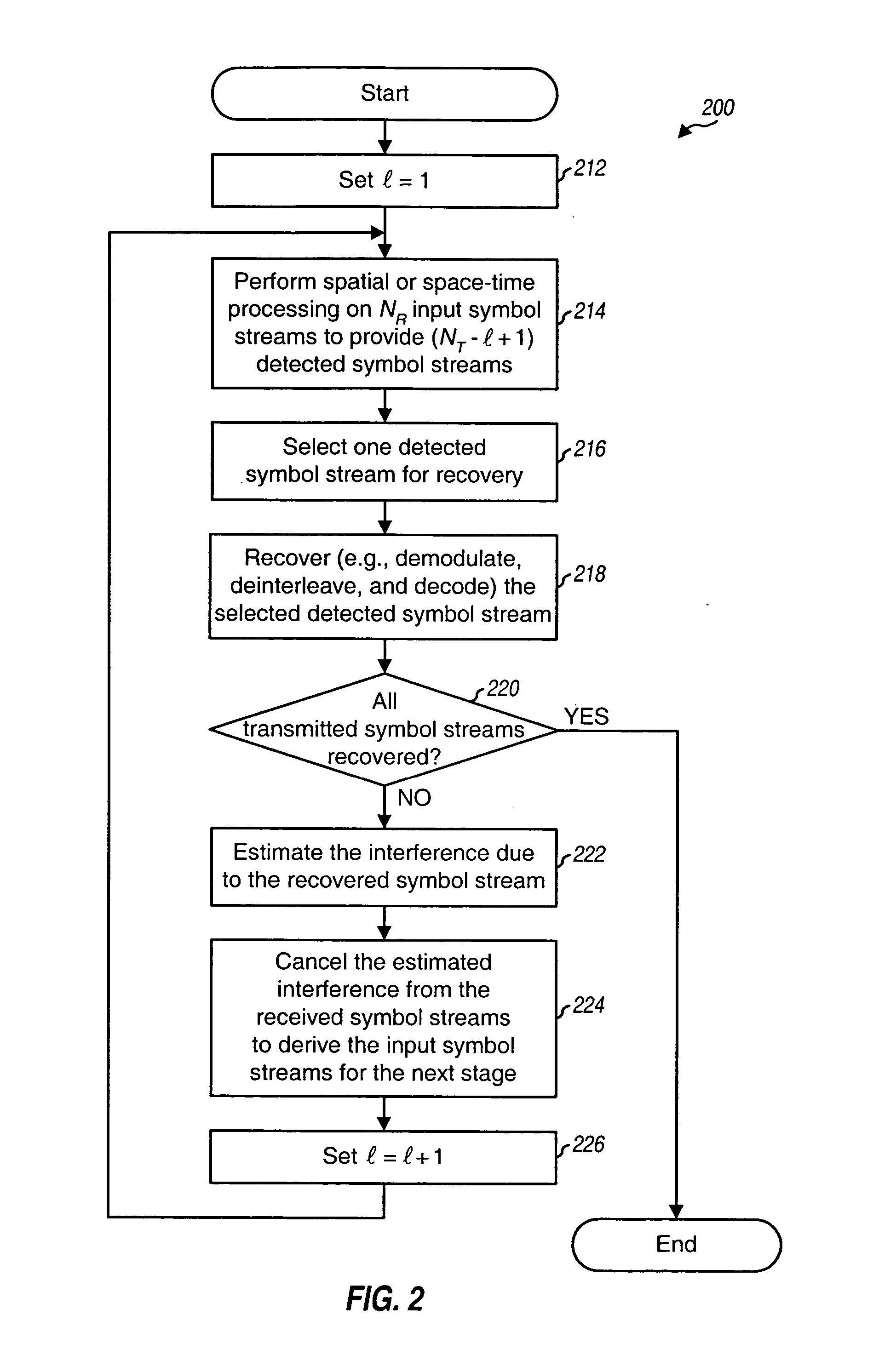
Techniques to process a number of “received” symbol streams in a Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) system with multipath channels such that improved performance may be achieved when using successive interference cancellation (SIC) processing. In an aspect, metrics indicative of the quality or “goodness” of a “detected” symbol stream are provided. These metrics consider the frequency selective response of the multipath channels used to transmit the symbol stream. For example, the metrics may relate to (1) an overall channel capacity for all transmission channels used for the symbol stream, or (2) an equivalent signal-to-interference noise ratio (SNR) of an Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channel modeling these transmission channels. In another aspect, techniques are provided to process the received symbol streams, using SIC processing, to recover a number of transmitted symbol streams. The particular order in which the symbol streams are recovered is determined based on the metrics determined for symbol streams detected at each SIC processing stage.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Methodology and method and apparatus for signaling with capacity optimized constellations
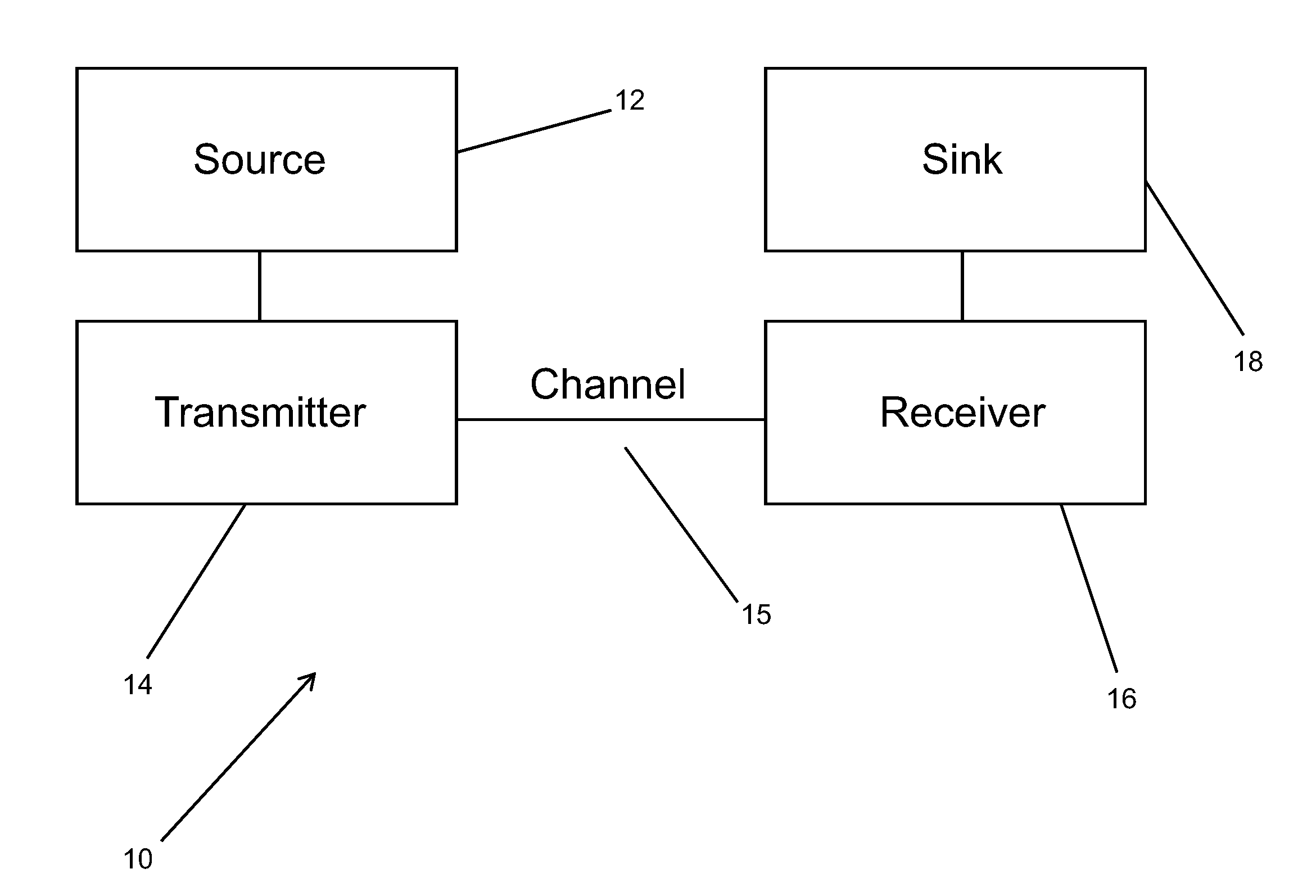
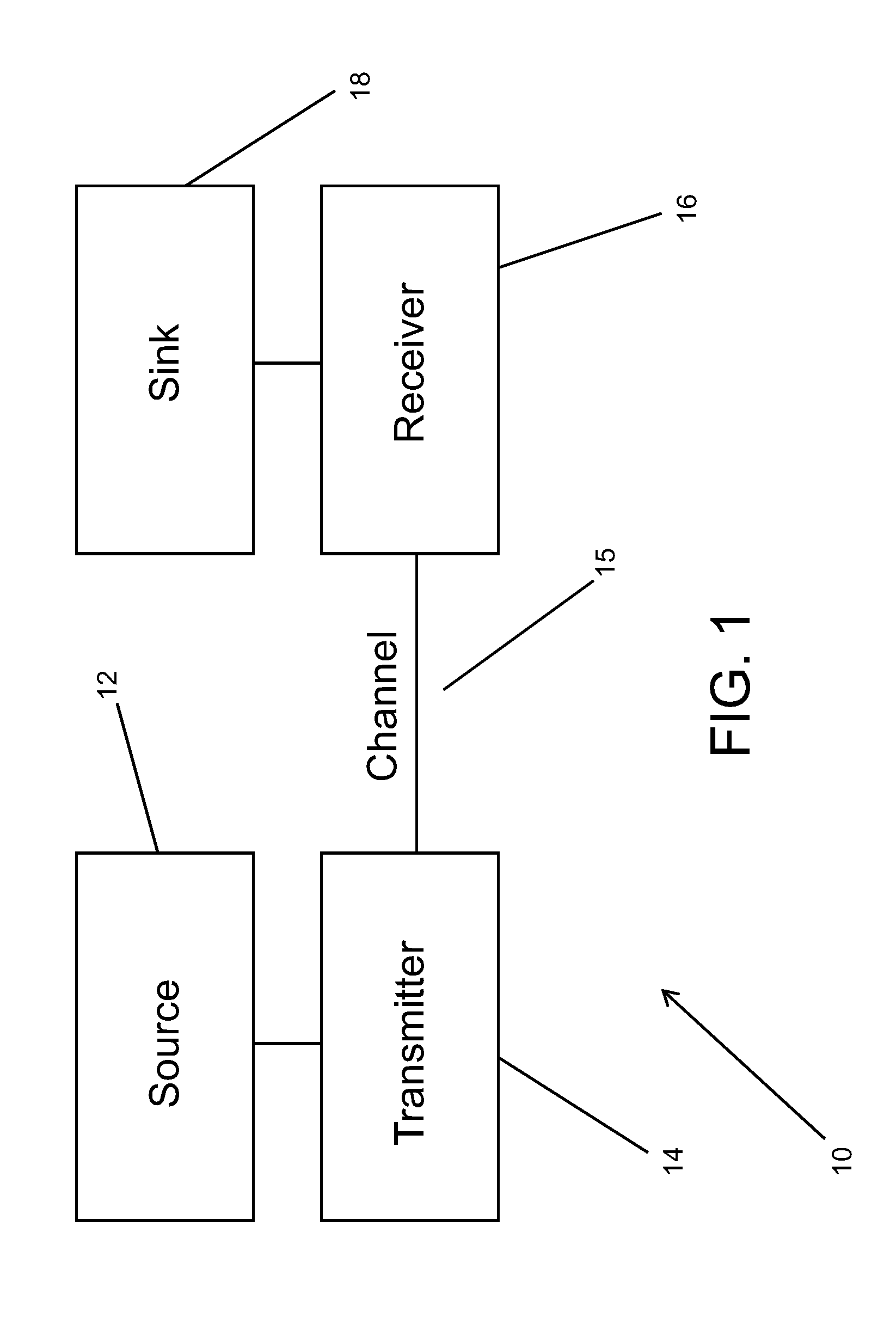
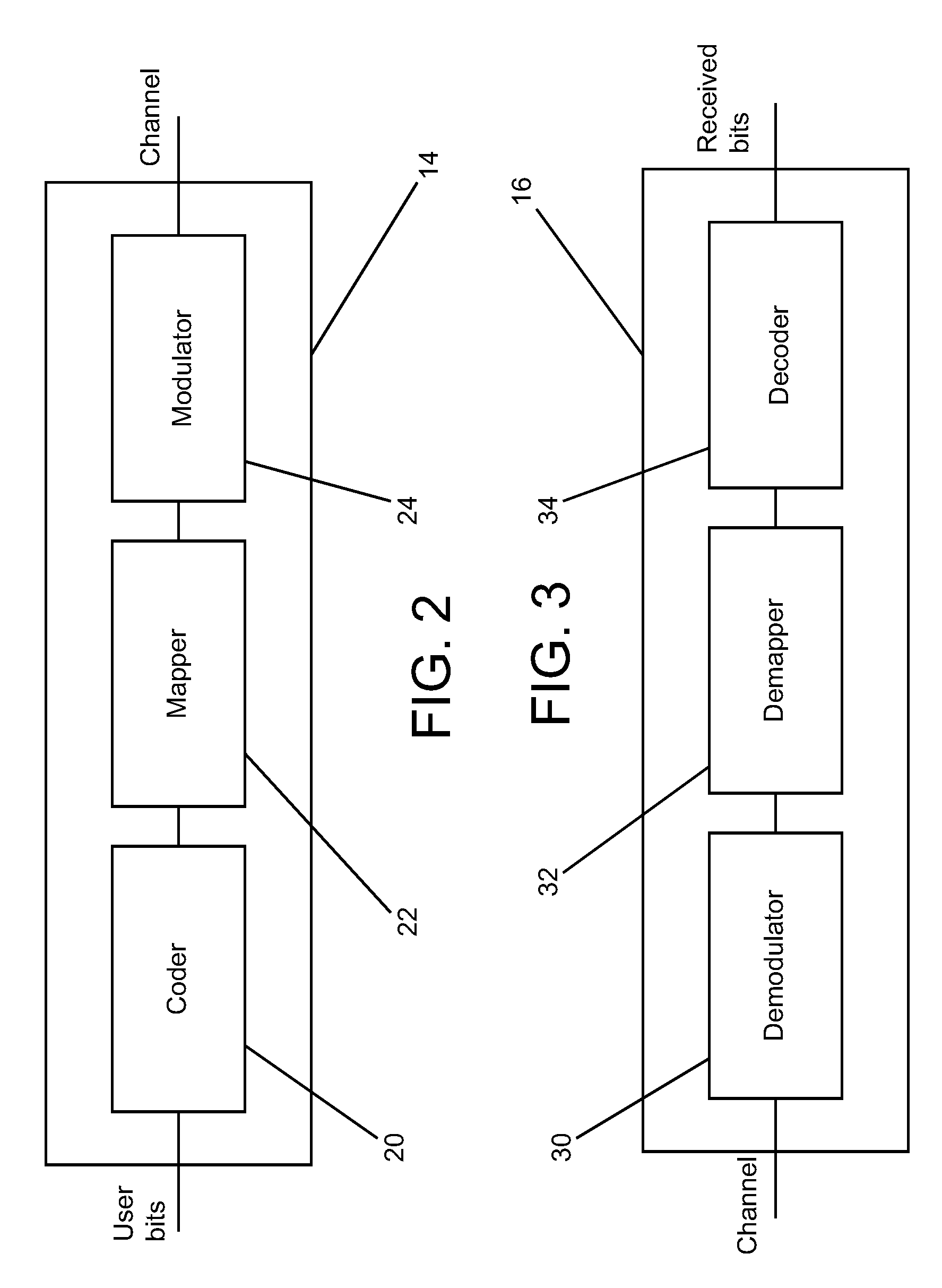
ActiveUS20090097582A1Eliminate gapsMaximize capacityModulated-carrier systemsError correction/detection using LDPC codesEngineeringCapacity optimization
Communication systems are described that use geometrically shaped constellations that have increased capacity compared to conventional constellations operating within a similar SNR band. In several embodiments, the geometrically shaped is optimized based upon a capacity measure such as parallel decoding capacity or joint capacity. In many embodiments, a capacity optimized geometrically shaped constellation can be used to replace a conventional constellation as part of a firmware upgrade to transmitters and receivers within a communication system. In a number of embodiments, the geometrically shaped constellation is optimized for an Additive White Gaussian Noise channel or a fading channel. In numerous embodiments, the communication uses adaptive rate encoding and the location of points within the geometrically shaped constellation changes as the code rate changes. One embodiment of the invention includes a transmitter configured to transmit signals to a receiver via a communication channel, wherein the transmitter, includes a coder configured to receive user bits and output encoded bits at an expanded output encoded bit rate, a mapper configured to map encoded bits to symbols in a symbol constellation, a modulator configured to generate a signal for transmission via the communication channel using symbols generated by the mapper. In addition, the receiver includes a demodulator configured to demodulate the received signal via the communication channel, a demapper configured to estimate likelihoods from the demodulated signal, a decoder that is configured to estimate decoded bits from the likelihoods generated by the demapper. Furthermore, the symbol constellation is a capacity optimized geometrically spaced symbol constellation that provides a given capacity at a reduced signal-to-noise ratio compared to a signal constellation that maximizes dmin.
Owner:CONSTELLATION DESIGNS LLC
Robust transmission system and method for mobile television applications
InactiveUS7525993B2Consumes less powerFreedom of movementTime-division multiplexAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMobile televisionTransmitter
A data transmission system and method for DVB-H signals for enhancing data robustness of a DVB-H receiver in additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channels includes transmitting IP datagrams from a DVB-H transmitter to the DVB-H receiver; applying a MPE section and a FEC section to the transmitted IP datagrams; mapping the transmitted IP datagrams to TS packets; aligning boundaries of the transmitted IP datagrams to a given number of TS packets; fixing a size of the IP datagrams to a known value at the DVB-H receiver; and extracting the IP datagrams from the DVB-H receiver.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
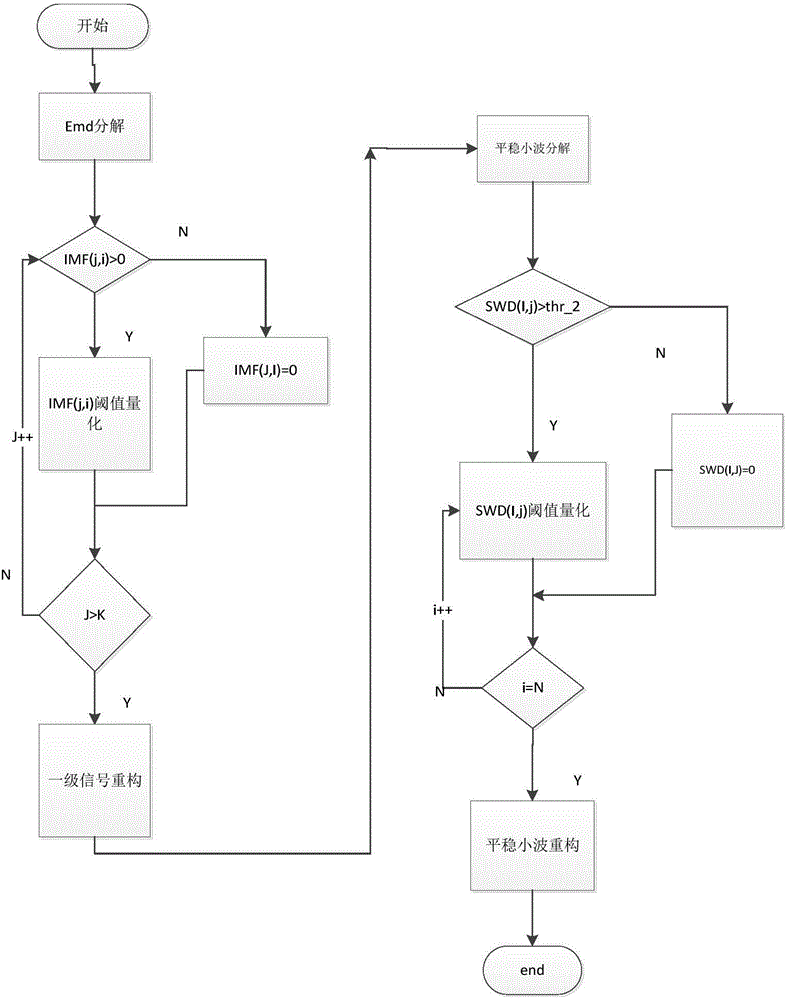
Signal combined denoising method based on empirical mode decomposition (EMD) and wavelet analysis
InactiveCN104636609ASolve the selection problemGood denoising performanceSpecial data processing applicationsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Decomposition
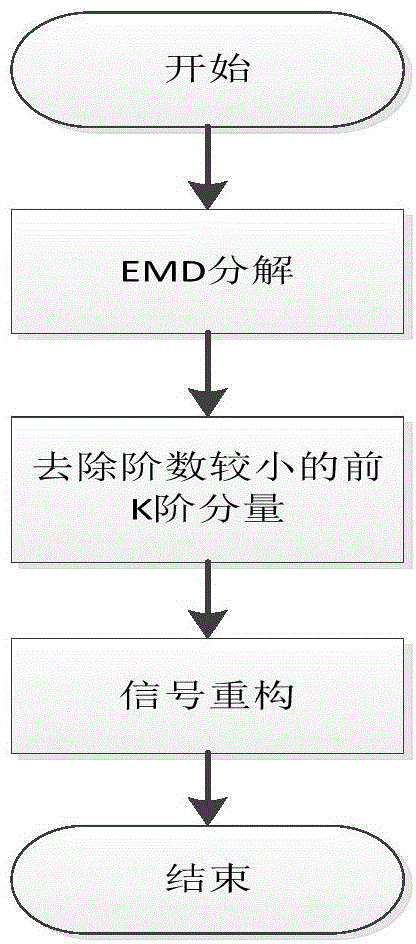
The invention belongs to the field of signal processing technologies, and particularly relates to a denoising method of additive white gaussian noise signals at a low signal to noise rate. The method includes the steps that according to autocorrelation of signals, autocorrelation of the signals is solved, the autocorrelation functions of the signals obtain the maximum values at zero points, the amplitude change along with change of time difference and will not attenuate to a small value quickly; EMD is performed on the signals mixed with the gaussian white noise, due to the nature of EMD, the gaussian white noise is not the real white noise any more, however, the statistical property of the white noise approximately exists, in other words, the autocorrelation functions of all the signals mixed with the gaussian white noise obtain the maximum values at zero points, the amplitudes change along with change of the time difference and will attenuate to the small value quickly. Through the difference, IMF components of which the noise plays a main role are selected, and the influences of the noise on the signals can be effectively reduced. Under the condition of the low signal to noise rate, the denoising performance of the method is superior to that of a traditional method, and signal denoising can be completed under the condition of the low signal to noise rate.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Beaulieu series approach to optimal UMTS RACH preamble detection estimation
ActiveUS20050254604A1Accurate estimateLimited operating rangeDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsEngineeringDetection threshold
A method for preamble detection in mobile unit to base unit wireless telephony sets a preamble detection threshold based upon a Beaulieu series computation dependent upon preamble correlation data. This preamble detection threshold adjusts for noise by assuming the noise is additive White Gaussian noise (AWGN) with a known variance. The method determines the threshold for achieving a probability of false detection of the preamble from noise input of less than 0.001.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Wireless information and power transfer system maximum safety rate optimization method based on NOMA
ActiveCN108495337AOptimize power distributionMaximum safe transmission ratePower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemSuperposition coding
The invention discloses a wireless information and power transfer system maximum safety rate optimization method based on NOMA; the method comprises the following steps: firstly, a wireless information and power transfer system based on the NOMA is provided, the system is provided with a cell base station BS, M information receivers IRs and K energy receivers ERs, wherein the ER obtains energy from a radio frequency signal transmitted by the BS and eavesdrops on the information sent by the BS to the IR; according to the principle of the NOMA technology, the information transmitted by the BS tothe IR transmits a signal through a superposition coding technology, and the expression is as follows: formula; in the formula, am is the signal transmission power distribution coefficient of the mthIR, P is the signal transmission total power of the BS, xm is the confidential information of the mth IR, and sigma 2 is the additive gaussian white noise; and an optimization parameter AM is adjusted according to the method, certain energy can be provided for the ER, and a certain information rate is provided for the IR; and the purpose of providing the maximum safety information rate is provided for the IR in the case of the ER eavesdropping on information.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
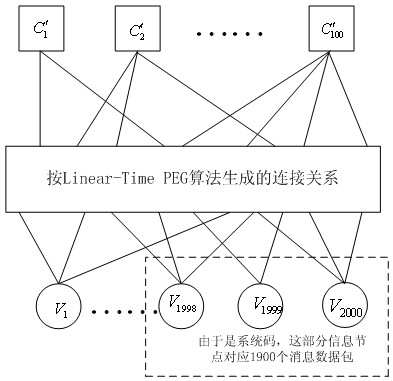
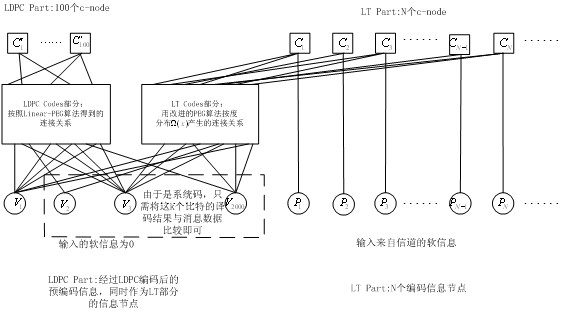
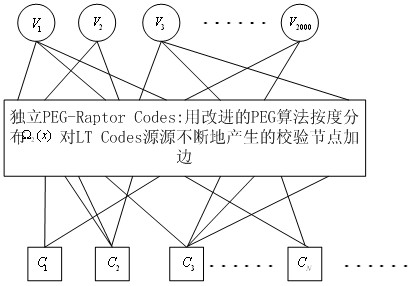
Raptor Codes encoding/decoding method suitable for medium/short code lengths of additive white Gaussian noise channel
InactiveCN102324998AImprove effectivenessReliable deliveryError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTanner graphReliable transmission
The invention discloses a Raptor Codes encoding / decoding method suitable for medium / short code lengths of an additive white Gaussian noise channel. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the degree distribution of the inner codes, i.e. LT (Linear-Time) Codes, of the Raptor Codes which are more suitable for the medium / short code lengths is proposed; and the improved PEG (Progressive Edge-Growth) algorithm is used for encoding the inner codes, i.e. the LT codes, of the Raptor Codes, wherein the encoding manner consists of two PEG encoding manners, i.e. independently carrying out PEG composition on the LT Codes and carrying out the PEG composition on the LT Codes through combining with outer codes, i.e. LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) Codes, thus the problem that excessive shortloops appear in a Tanner graph, caused by randomly selecting information packets in an LT encoding stage, is solved. With the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the effectiveness for the transfer of soft information when the BP (Background Processing) iterative decoding is carried out is therefore enhanced, the performance better than that of a random composition manner is obtained, and the more reliable transmission for the rateless codes with the medium / short code lengths is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Adaptive channel coding using polarization
ActiveCN107113009AError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDynamic channelChannel statistics
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communications at a wireless device. A wireless device may adaptively select a parity check matrix to increase the reliability of signal transmission by adapting to different channel statistics and channel types (e.g., erasure channels, channels with additive white Gaussian noise, and channels with discrete or continuous alphabets). For example, polarization codes (i.e., codes based on rows of a polarization matrix) may be used to construct parity check matrices on-the-fly given an estimation of dynamic channel conditions or diverse channel structures. The channel may be decomposed into polarized sub-channels corresponding to the polarization codes, and mutual information profiles may be determined for each of the polarized sub-channels. The parity check matrix corresponding to the polarization codes may be constructed based on the mutual information profile of all polarized sub-channels. The wireless device may encode or decode data based on the constructed parity check matrix.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for bit interleaving encoding and modulation
ActiveCN104426630AGuaranteed transmission reliabilityReduce complexityForward error control useCommunications systemForward error correction
The invention provides a method and a system for bit interleaving encoding and modulation. The method comprises the following steps of performing forward error correction and encoding on original traffic channel data which is inputted into a communication system, and generating an encoding bit flow; performing the bit interleaving on the encoding bit flow, and generating unit characters, wherein the bit interleaving process comprises the steps of writing the encoding bit flow into a bit interleaver according to lines, performing the line permutation on the bit interleaver, reading out the bits of the bit interleaver according to rows, obtaining an output bit flow, and mapping the output bit flow into unit characters; mapping the unit characters into modulation symbols. The method has the advantages that by designing LDPC (low density parity check) code parameters and structures, the working range of the communication system can downwards extend to -3.6dB in an AWGN (additive white gaussian noise) channel; on the basis of the designed LDPC codes, an auxiliary bit interleaving scheme is designed, the traffic data transmission property of the next-generation wireless broadcasting communication system is further improved by 0.05-0.3dB, the complexity of a receiver in the design and implementation processes is decreased, and the transmission reliability of the traffic data is guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and apparatus for link error prediction in a communication system
InactiveUS20050182994A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method is provided to accurately predict the probability of successfully recovering frames of (coded) information received over a wireless link, without having to decode the frame. This method, which consists of three steps, requires only limited information about the received signals and the forward error correction code and retransmission scheme being used. First, the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of each of the received signals is measured, where the average SNR is determined for multiple segments that together constitute the frame. Next, an algorithm is employed that takes these SNR values as inputs and determines the so-called effective SNR. The algorithm translates the measured SNR values using an appropriate convex metric, and subsequently combines the resulting values, thereby factoring in the effects of fading, multi-path, and other signal degradations. In the third stage, the effective SNR is used to determine the frame error rate by using a look-up table of a single reference curve that specifies the frame error rate of the actual error control code over an additive white Gaussian noise channel. This suffices to accurately predict the performance of a wide range of mobile communication channels. This method can be applied to a variety of retransmission strategies, including hybrid automatic-repeat request (ARQ) and incremental redundancy (IR) and combinations of these two strategies.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
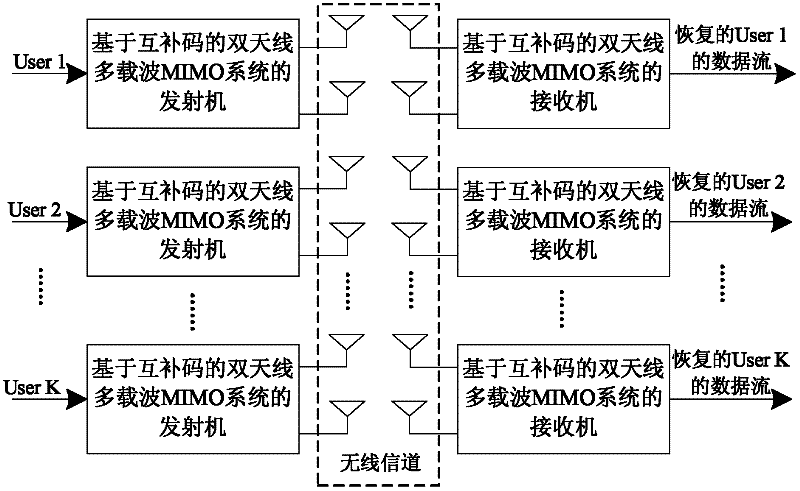
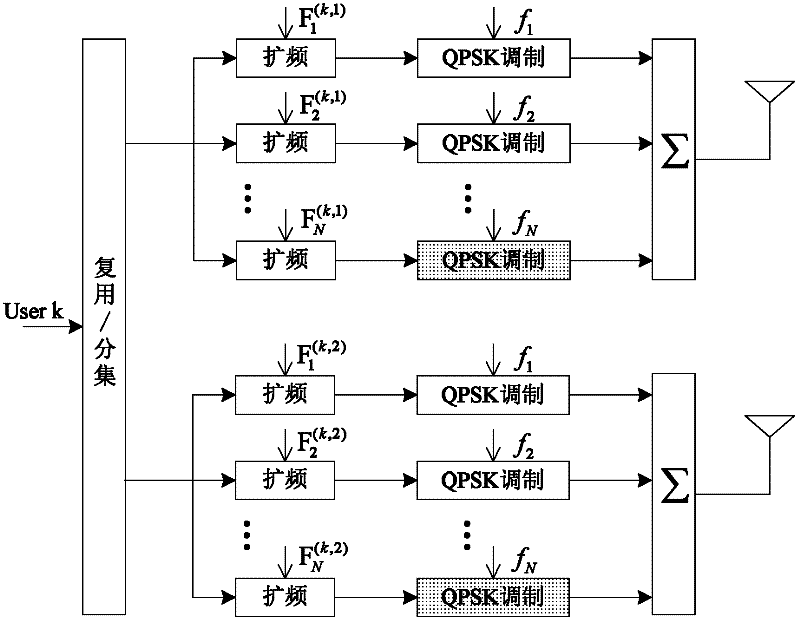
Double-antenna multi-carrier wave MIMO (multi-input and multi-output) system based on mutual complementing codes
InactiveCN102394683AImproved performance against multi-user interferenceAnti-interferenceSpatial transmit diversityMulti user interferenceMulti input
A double-antenna multi-carrier wave MIMO (multi-input and multi-output) communication method based on mutual complementing codes relates to a double-antenna multi-carrier wave communication method based on mutual complementing codes and solves the problems that the existing encoded MIMO system is poor in multi-user interference resisting performance, poor in multi-path interference resisting performance, and poor in Doppler effect capacity. The system adopts the mutual complementing codes to carry out spread spectrum, and adopts a multi-carrier wave system framework in signal emitting process; and the system adopts the mutual complementing codes to carry out demodulation spread in signal receiving process. The system adopts the mutual complementing codes to be used as spread spectrum codes of system carrier waves and adopts the multi-carrier wave system framework, so that the multi-user interference resisting performance of the MIMO system is greatly improved, under an AWGN (additive white Gaussian noise) channel, the complete multi-user interference resisting performance can be realized, under time selective fading brought by Doppler frequency shift, the system can resist multi-user interference with 75 percent rate, and under frequency selective fading caused by multi-path interference, the system can resist the multi-user interference with 50 percent rate.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Polar code construction method and device, electronic equipment and readable memory medium
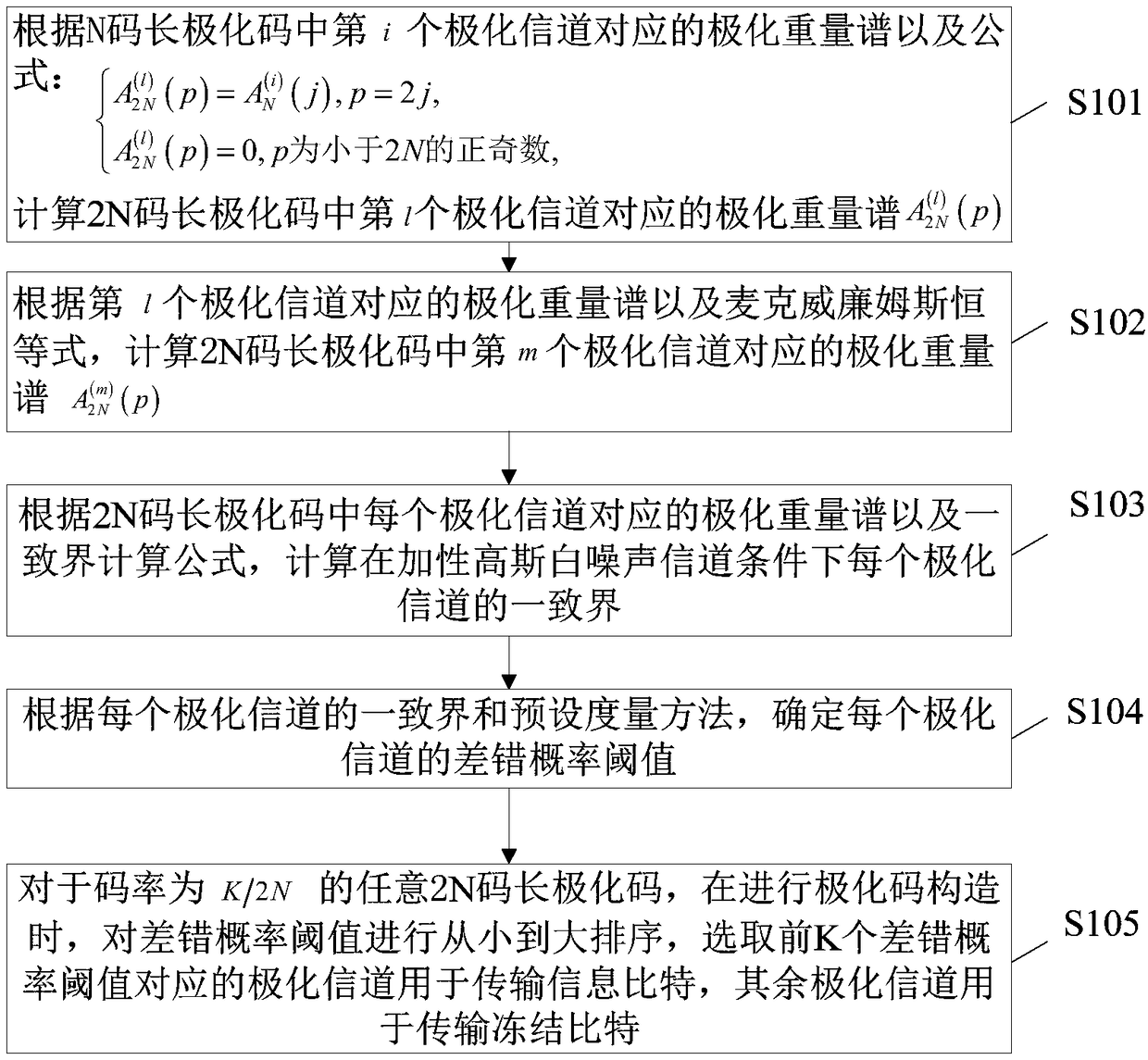
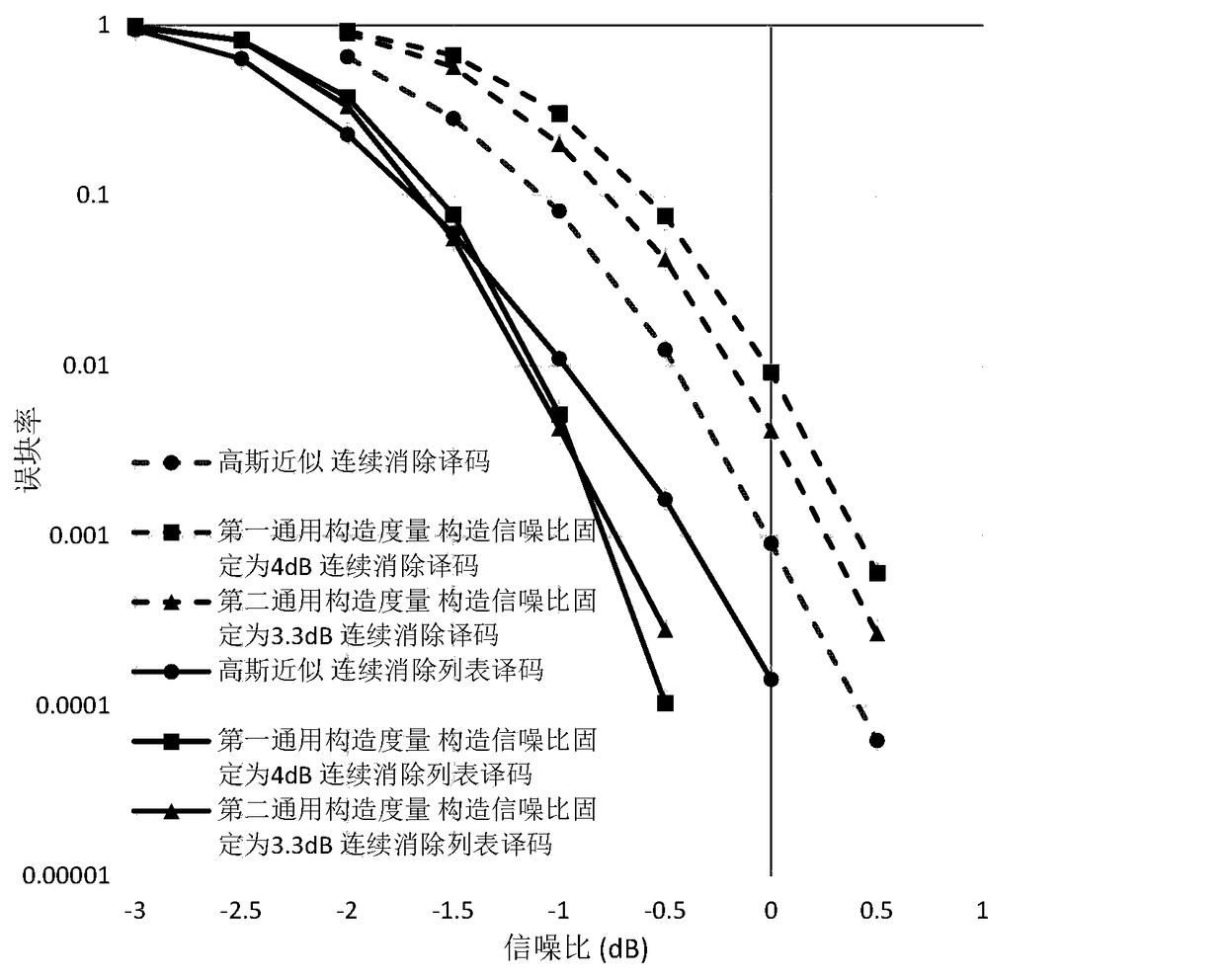
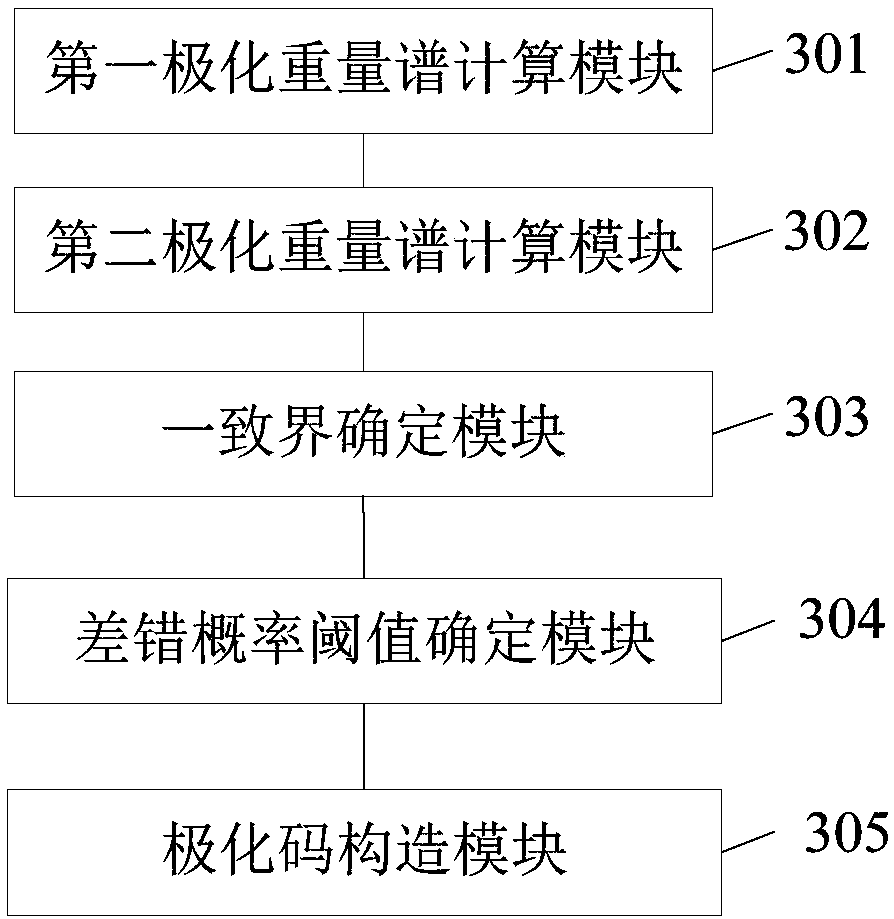
ActiveCN109361495AReduce complexityError preventionChecking code calculationsWilliam's medium EBit rate
The embodiment of the invention provides a polar code construction method and device, electronic equipment and a readable memory medium and applies to the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises the steps of computing weight hierarchies corresponding to polar channels in a 2N-code-length polar code according to the weight hierarchies corresponding to the polar channels in an N-code-length polar code, and a McWilliams identical equation; computing a uniform bound of each polar channel under an additive white Gaussian noise channel condition according to the weight hierarchies corresponding to the polar channels in the 2N-code-length polar code, and a uniform bound computing formula; determining an error probability threshold of each polar channel according to the uniform bounds and a preset measurement method; and for any 2N-code-length polar code with a bit rate of K / 2N, when polar code construction is carried out, sorting the error probability thresholds in anascending mode, selecting the polar channels corresponding to the first K error probability thresholds for transmission of information bits, wherein the other polar channels are used for transmittingfreeze bits. According to the method, the device, the electronic equipment and the readable memory medium, polar code construction complexity can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Incomplete CSI (Channel State Information)-based distributed antenna system adaptive modulation method
InactiveCN104702557AMeet target BER requirementsIncrease effective transmission efficiencySpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsFrequency spectrumQam modulation
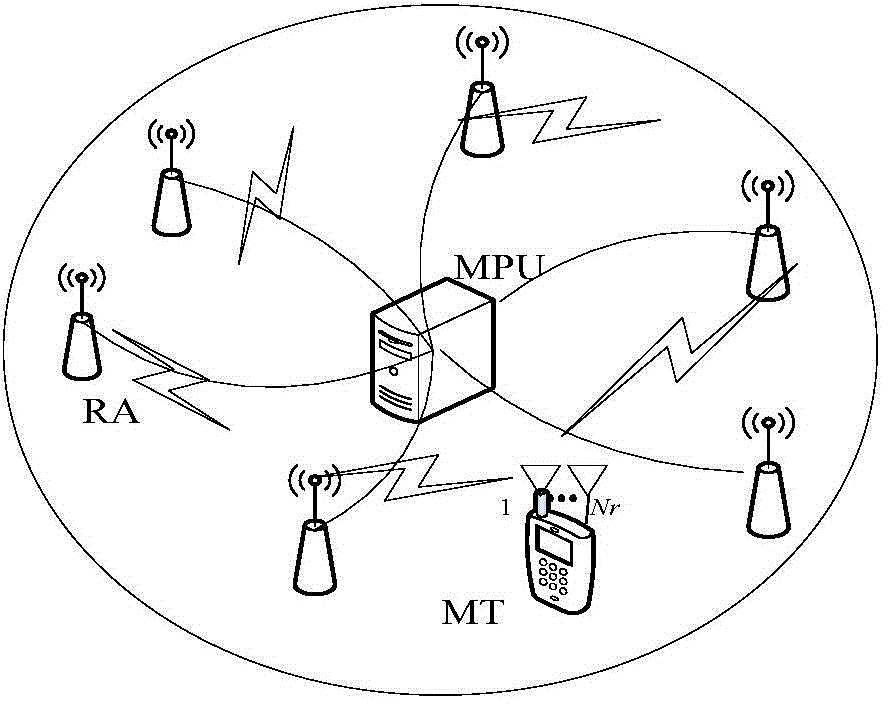
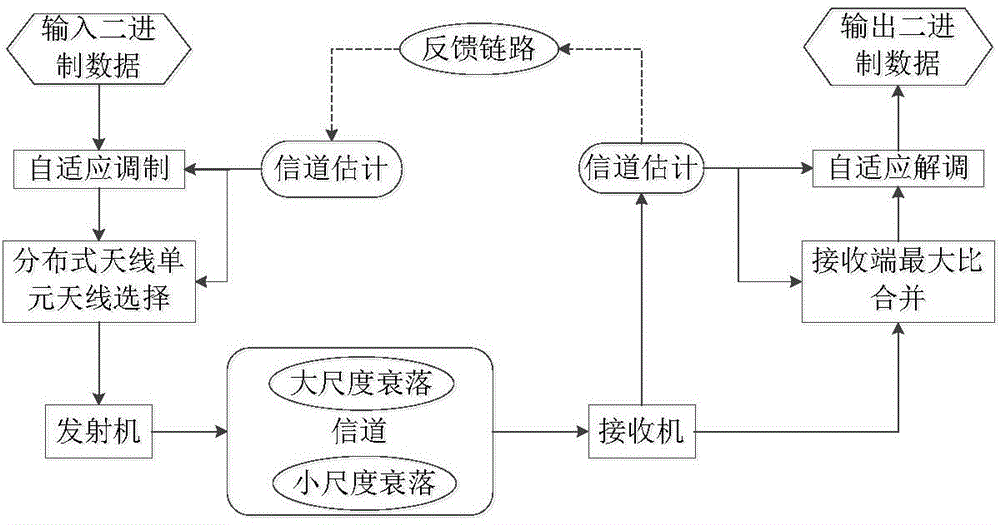
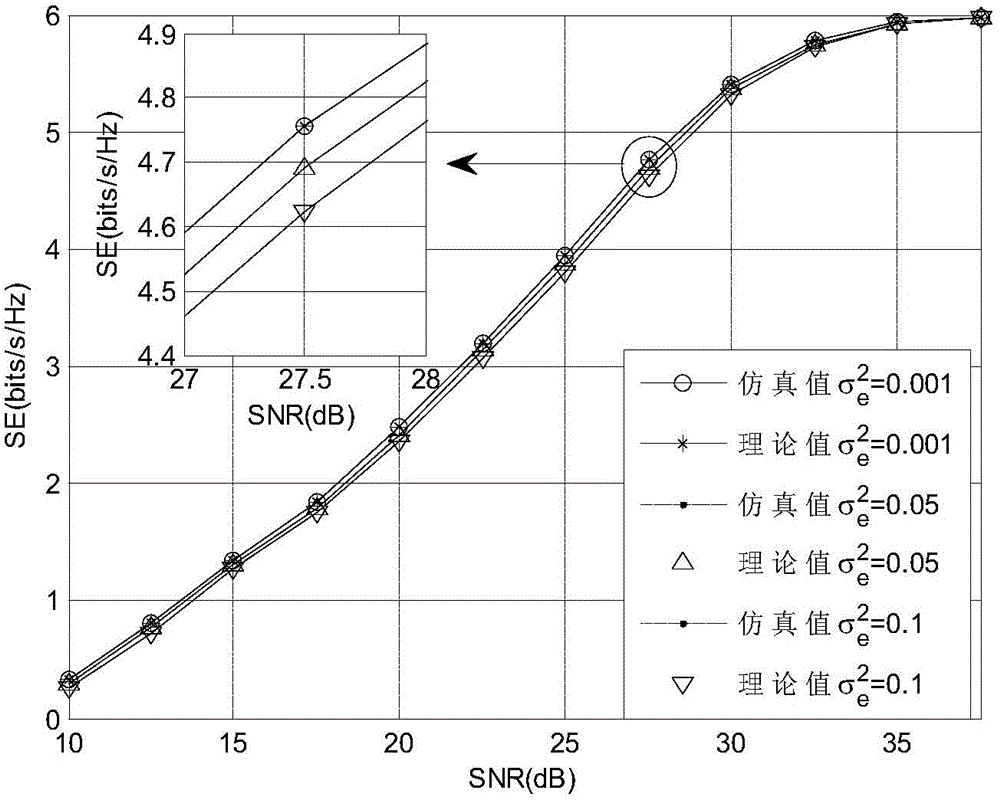
The invention discloses an incomplete CSI (Channel State Information)-based distributed antenna system adaptive modulation method. A distributed antenna system model is constructed by using multiple remote transmitting antennas, a Rayleigh fading channel model is constructed, channel estimation is performed on small-size fading of the Rayleigh fading channel model to obtain an estimated signal-noise ratio between the remote antennas and an MT (Mobile Terminal); by using an antenna selection technology, the remote transmitting antenna with the maximum estimated signal-noise ratio is selected to perform signal transmission; an adaptive modulation method and adaptive switching threshold setting are designed according to maximum average spectral efficiency; adaptive modulation switching threshold is calculated by using a BER (Bit Error Rate) formula of a precise M-QAM (Mulriple Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) modulation mode under an additive white Gaussian noise channel; average effective transmission efficiency SE and average bit error rate BER are calculated by using an integral transformation formula and a numerical analysis method. The adaptive modulation method and the adaptive switching threshold guarantee that the SE of the system is improved by meeting the requirement of a target BER.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
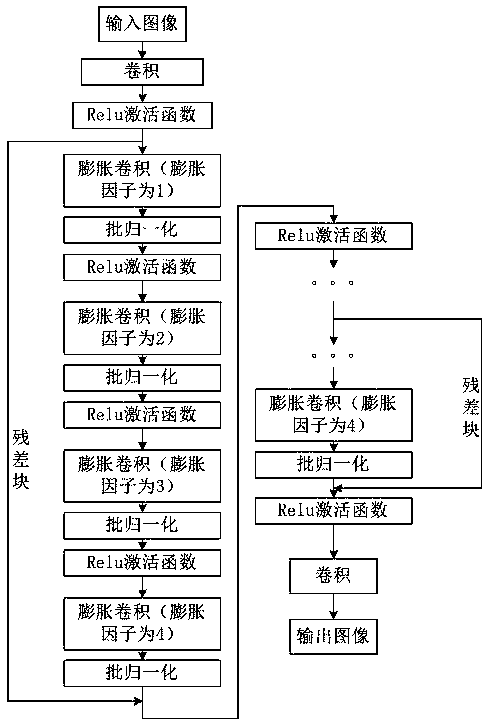
Image denoising method based on expansion convolution
ActiveCN108830809APleasant visual effectsShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingPattern recognition
The invention relates to an image denoising method based on expansion convolution. The method specifically comprises the following steps of 1, preparing training data; 2, building a model; 3, compiling an image acquired in the step 2 to acquire a compiled model; 4, adding additive white Gaussian noise on the block image in the step 1 to acquire batch pictures with noise; 5, training the batch pictures with noise acquired in the step 4, thus acquiring a trained model; 6, preparing test data; and 7, importing the acquired test image into a prediction function of the model acquired in the step 5to acquire the denoised image. According to the denoising method provided by the invention, the sharp edge and fine details can be recovered, and the enjoyable visual effect can also be generated in the smooth area; furthermore, the network structure in the method is composed of 14 layers, the needed time can be reduced, and the efficiency can be improved.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
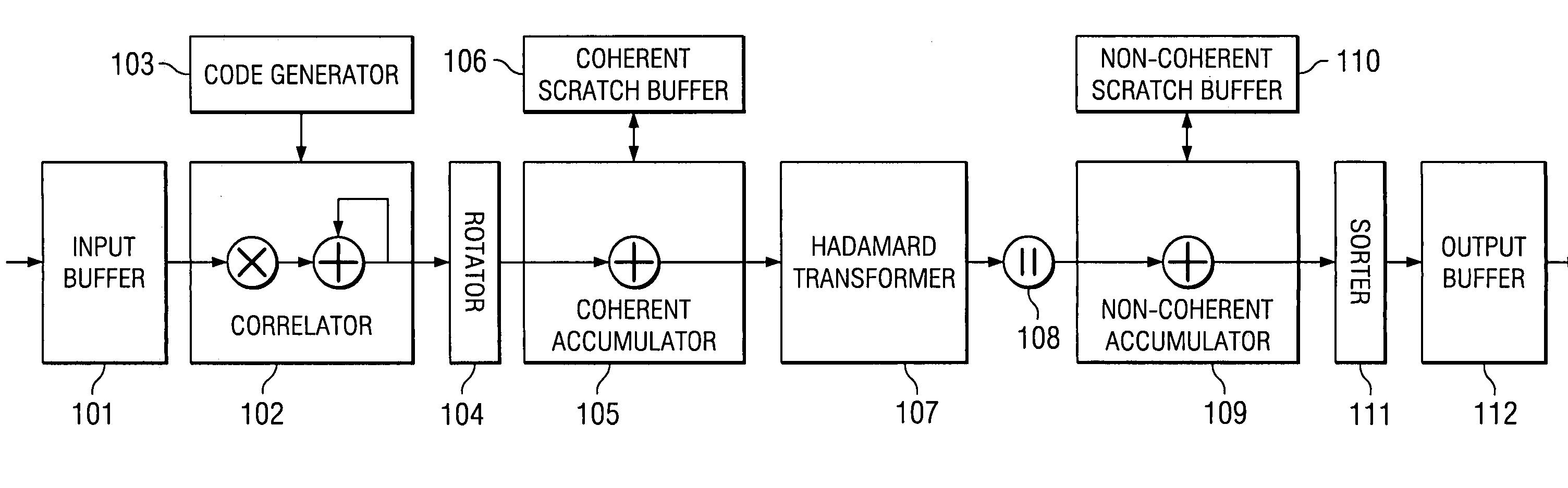
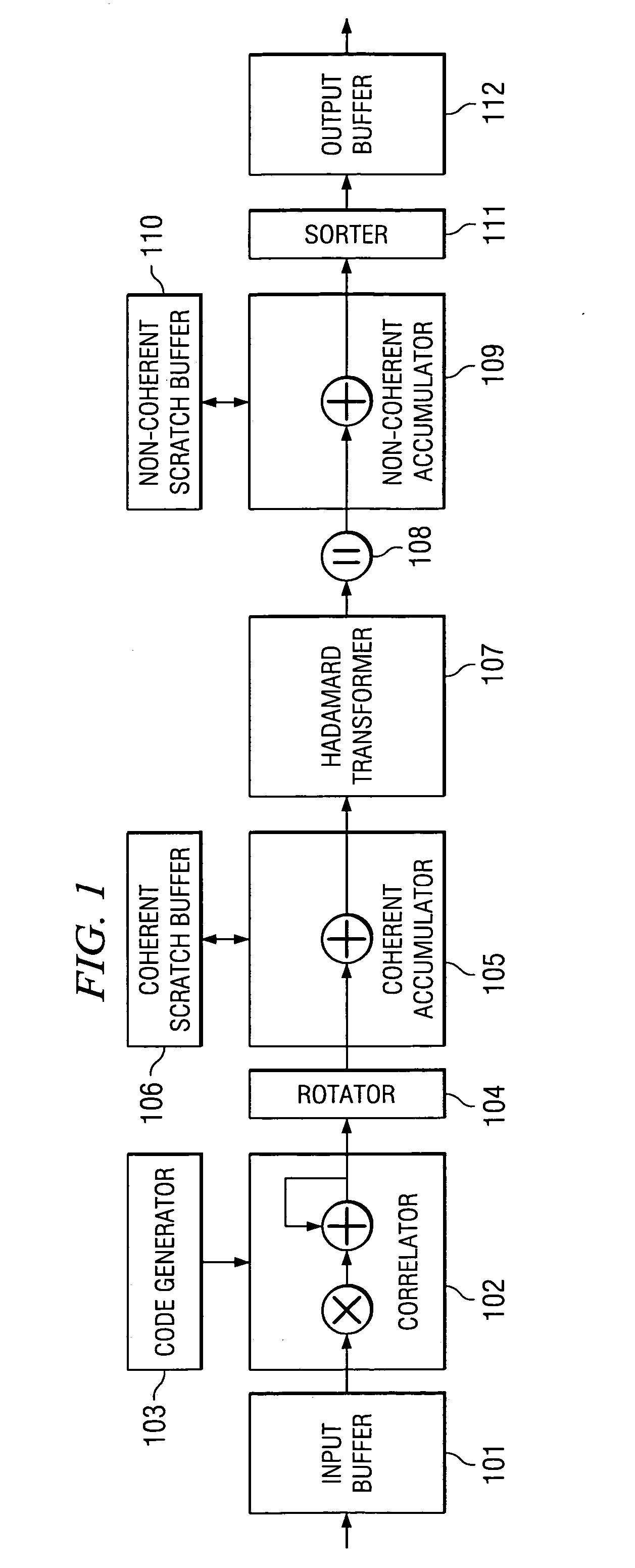
Sparse superposition encoder and decoder for communications system
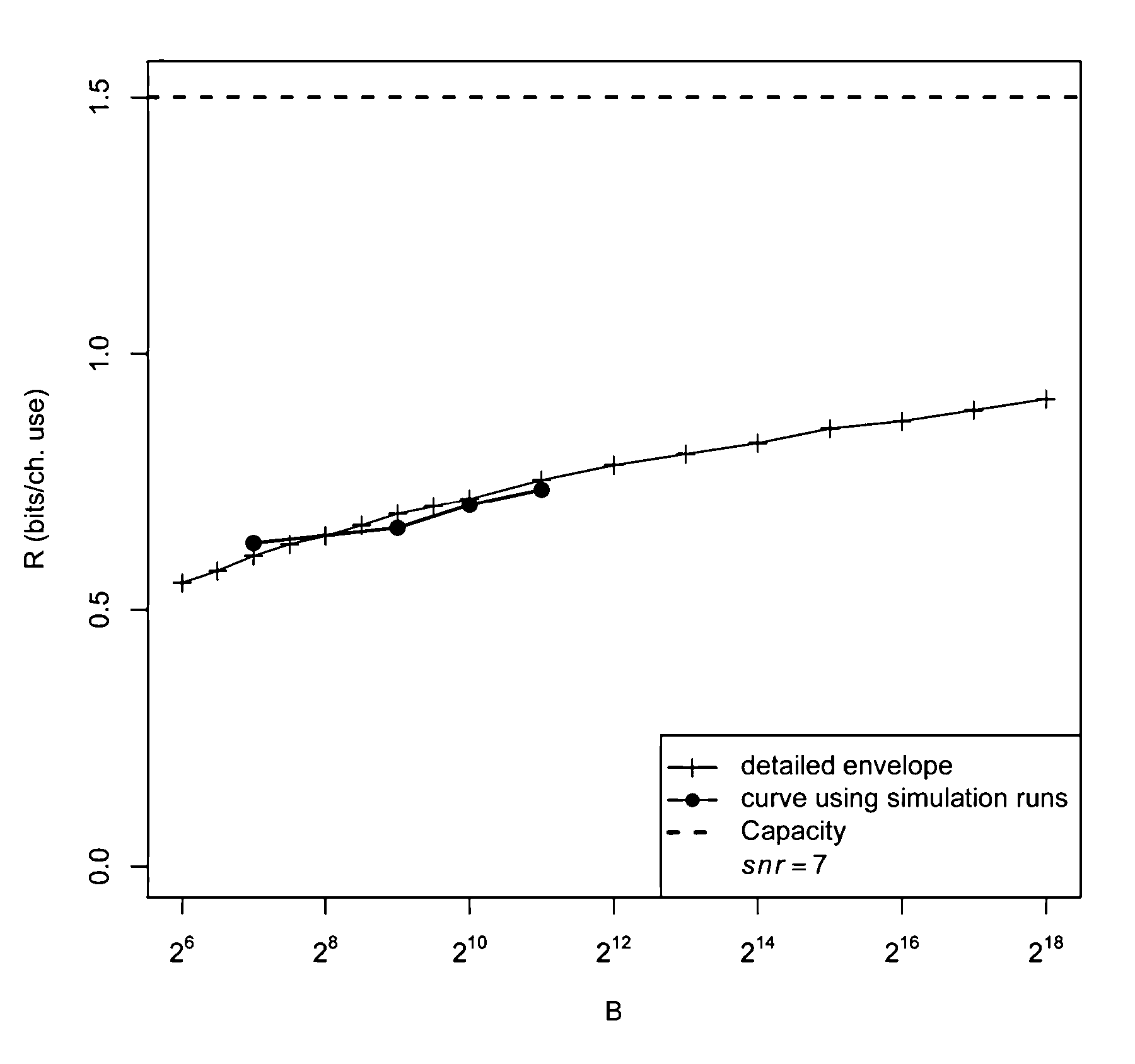
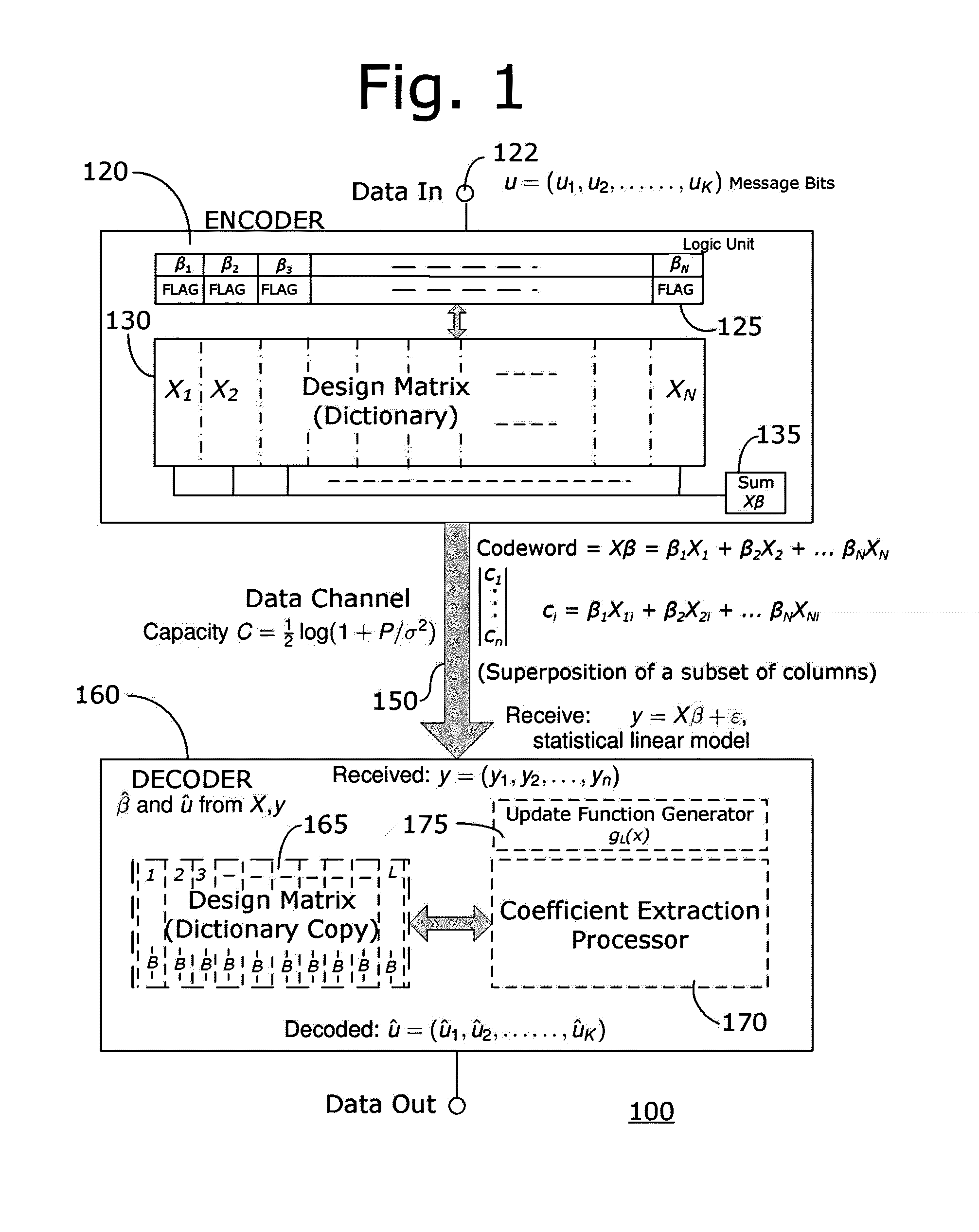
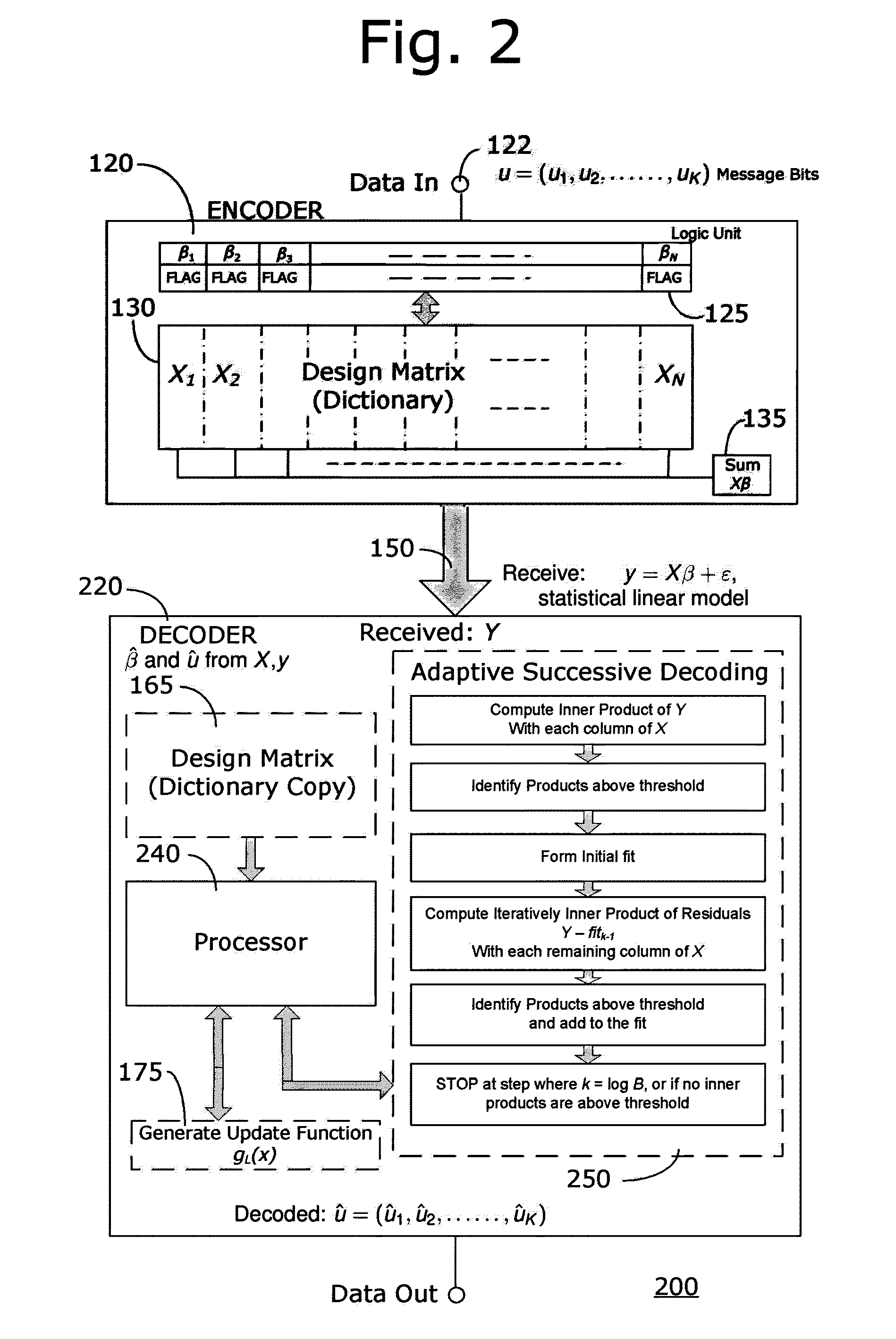
A computationally feasible encoding and decoding arrangement and method for transmission of data over an additive white Gaussian noise channel with average codeword power constraint employs sparse superposition codes. The code words are linear combinations of subsets of vectors from a given dictionary, with the possible messages indexed by the choice of subset. An adaptive successive decoder is shown to be reliable with error probability exponentially small for all rates below the Shannon capacity.
Owner:YALE UNIV
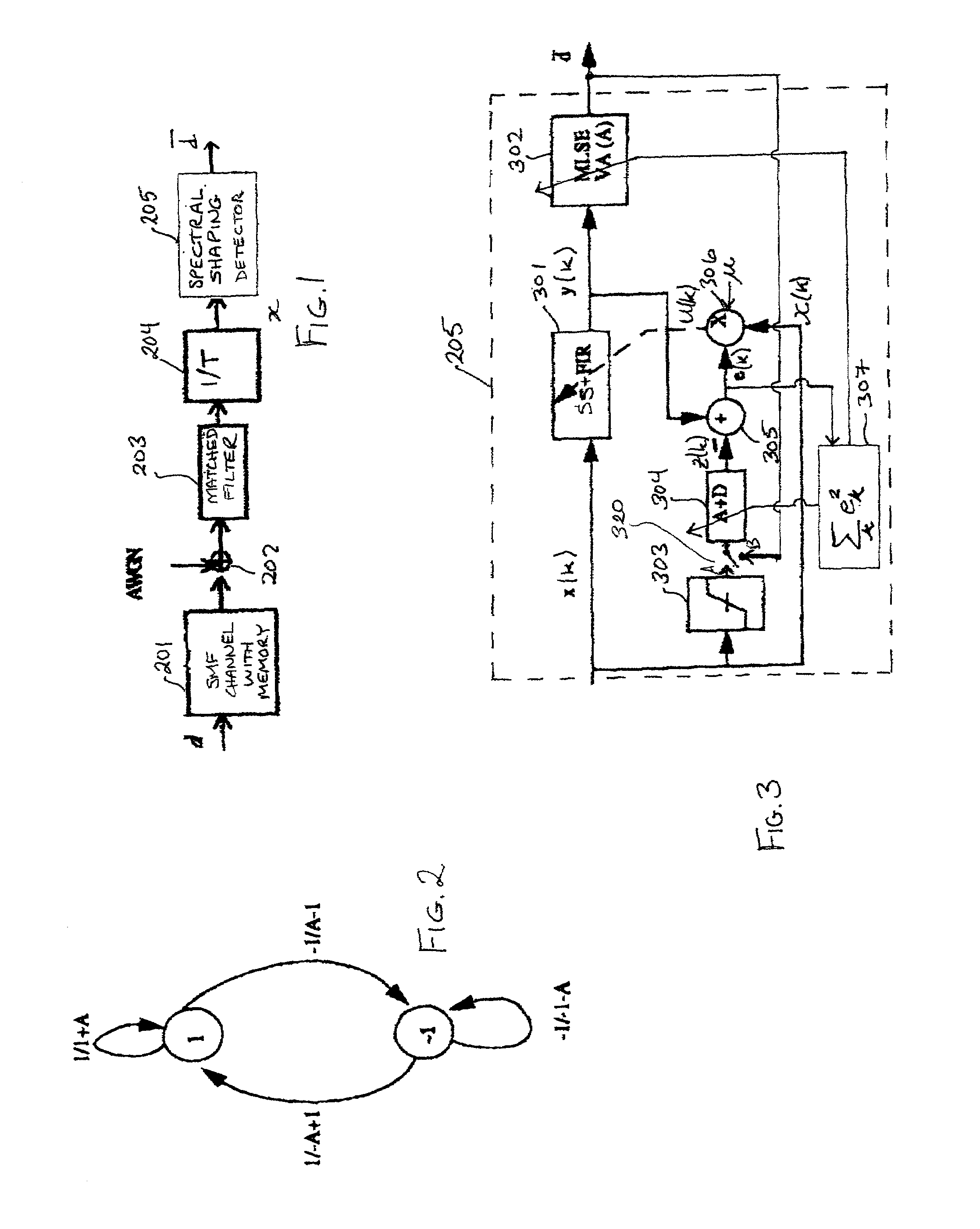
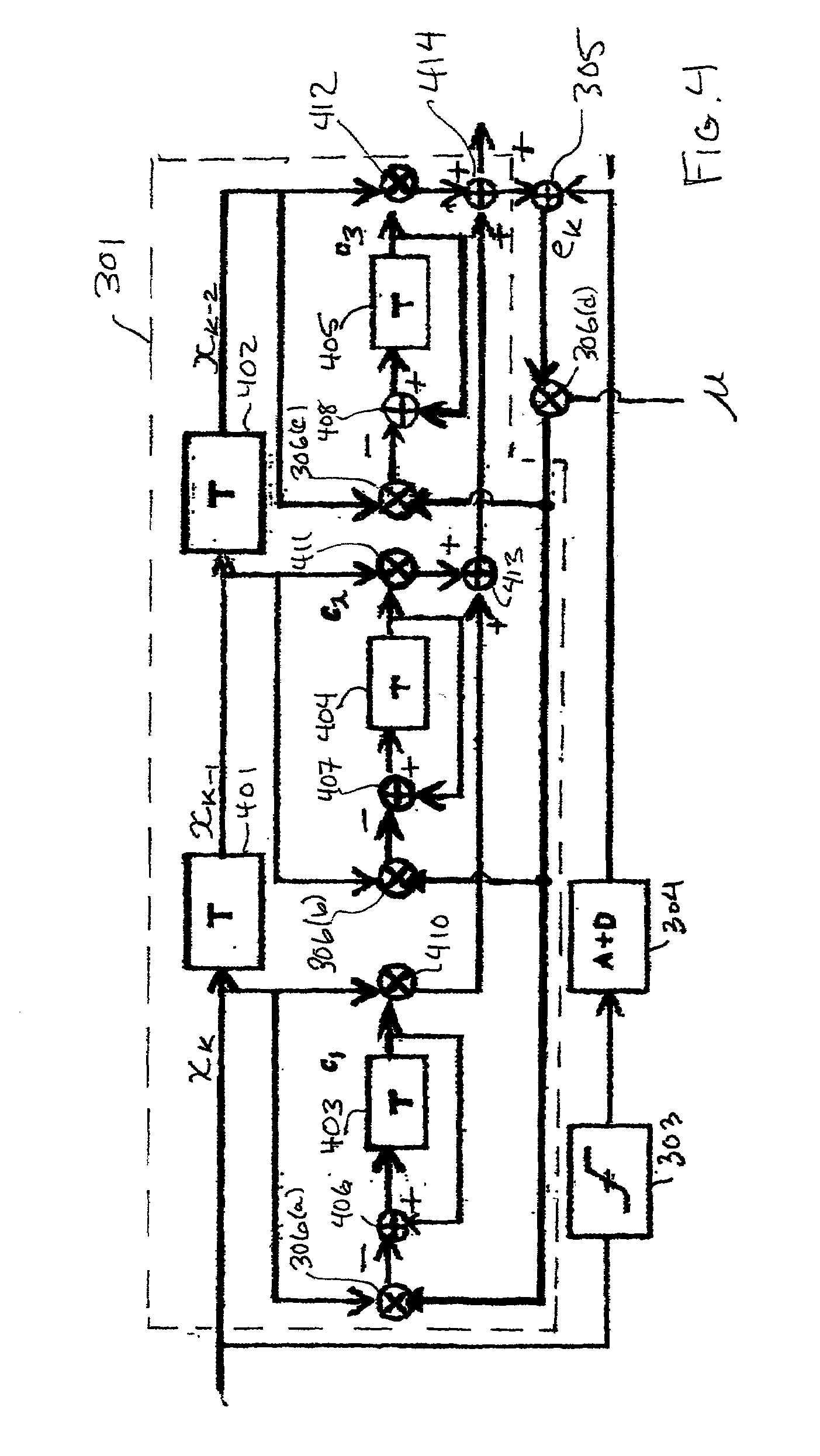
Compensation of polarization mode dispersion in single mode fiber for maximum-likelihood sequence estimation
InactiveUS7110683B2Distortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic receiversTarget ResponsePolarization mode dispersion
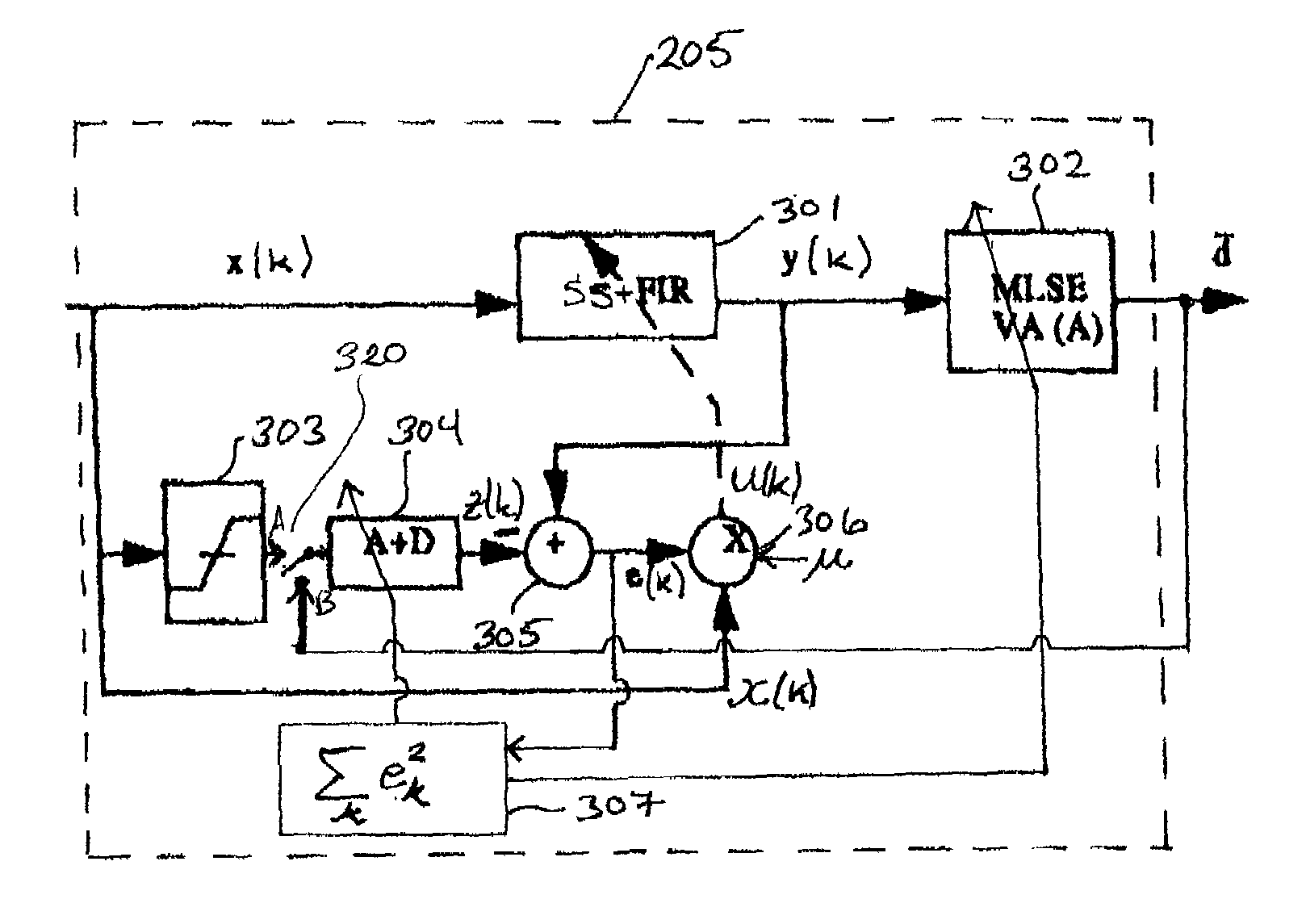
An output signal of a single mode fiber (SMF) is spectrally shaped to achieve characteristics of a predefined channel “target” response. The target response is that of a partial-response, maximum-likelihood channel with additive white Gaussian noise. A receiver employs a maximum-likelihood sequence estimation (MLSE) detector having its detection algorithm, such as a Viterbi algorithm (VA), matched to the target response. Thus, state, branch, and path metric calculations for a Viterbi trellis may be optimized for a channel having this target response.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
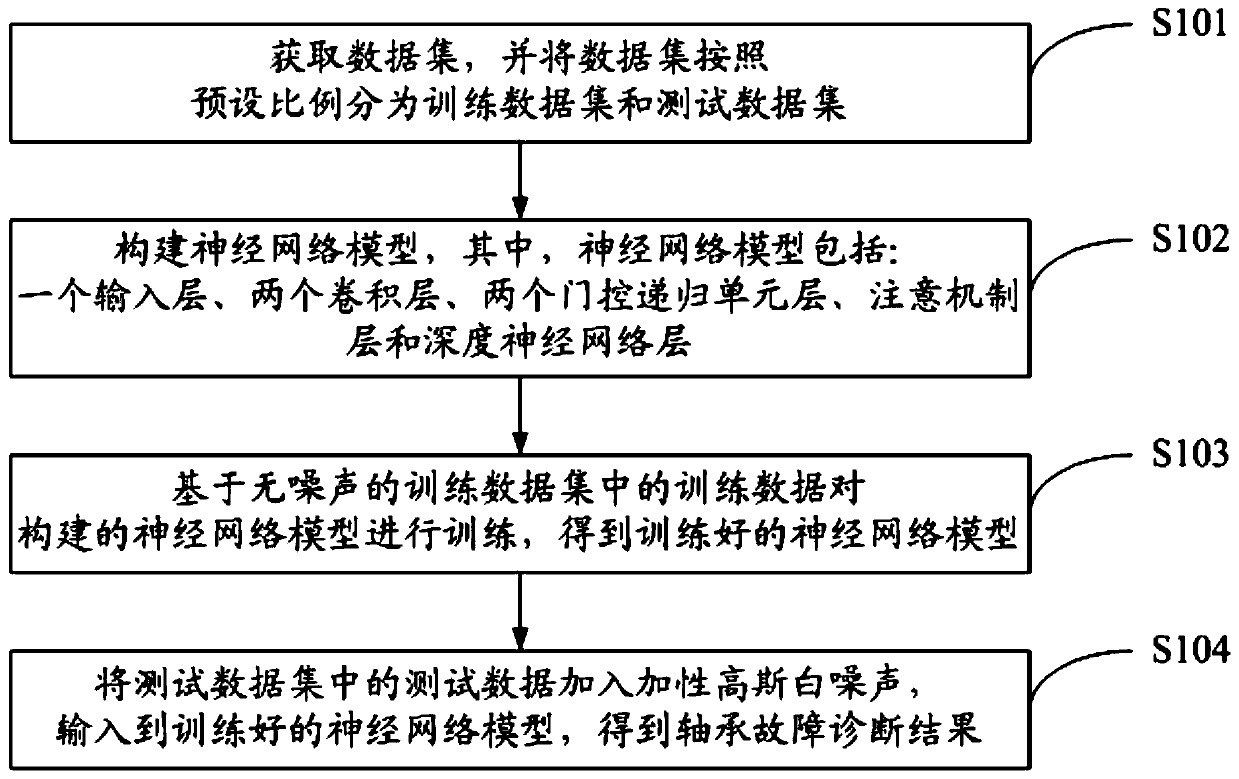
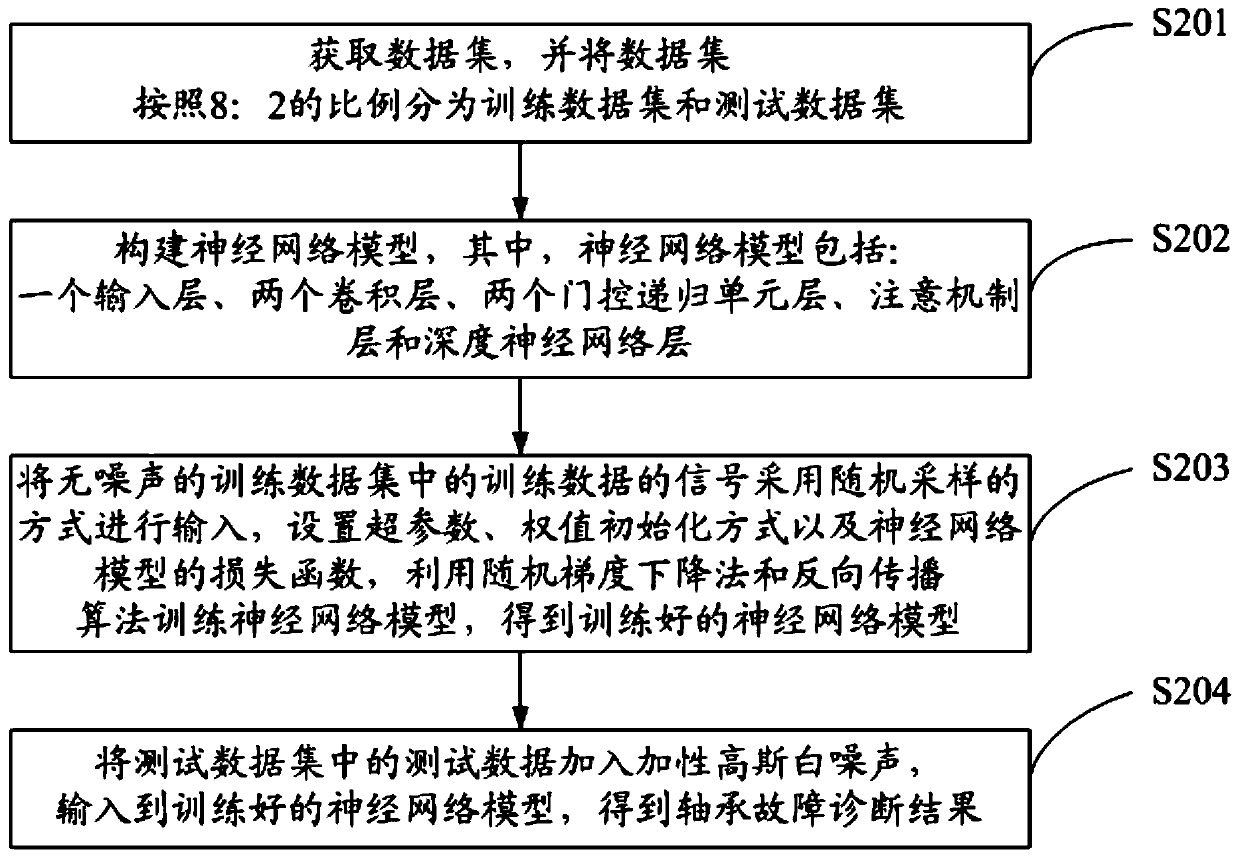
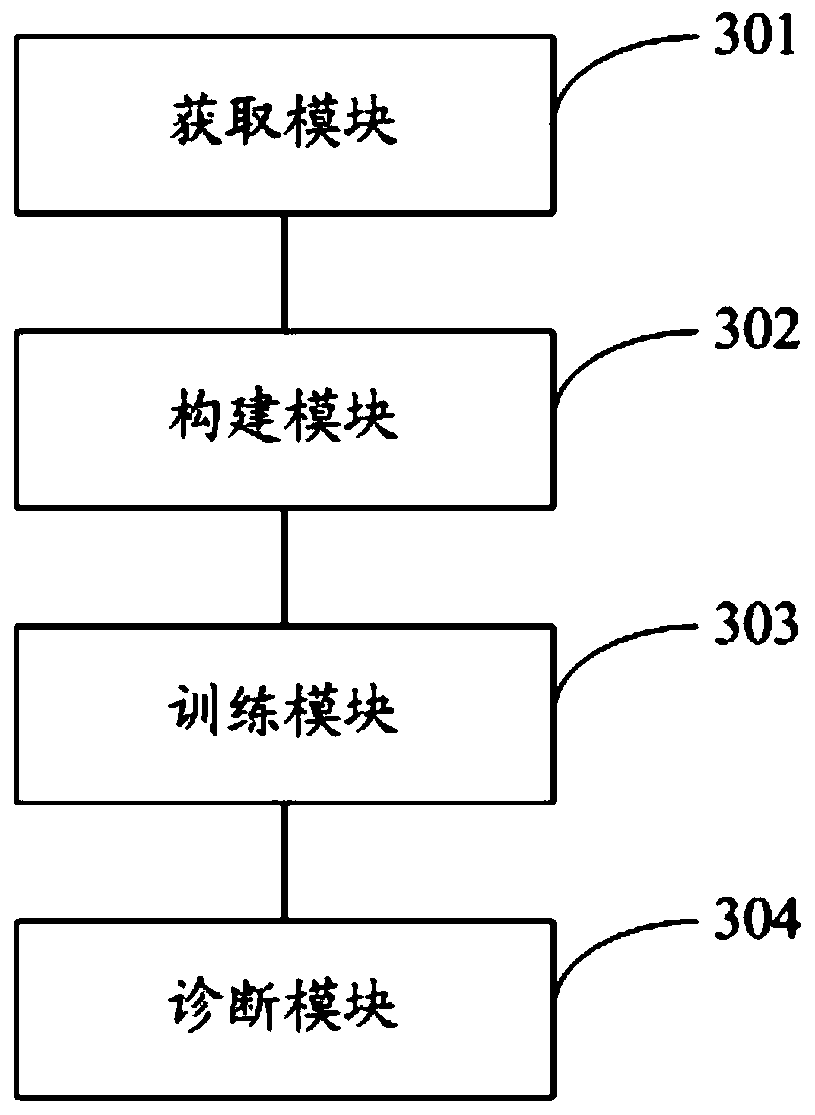
Bearing fault diagnosis method and system based on adaptive anti-noise neural network
The invention discloses a bearing fault diagnosis method and system based on an adaptive anti-noise neural network, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a data set, and dividing the data setinto a training data set and a testing data set according to a preset proportion; a neural network model is constructed, wherein the neural network model comprises an input layer, two convolution layers, two gating recursion unit layers, an attention mechanism layer and a deep neural network layer; training the constructed neural network model based on training data in a noiseless training data set to obtain a trained neural network model; and adding the additive white Gaussian noise into the test data in the test data set, and inputting the additive white Gaussian noise into the trained neural network model to obtain a bearing fault diagnosis result. Features can be automatically extracted from original signals, manual feature selection and denoising are not needed, different fault typesand fault severity degrees can be distinguished, and the method can adapt to different noise environments.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
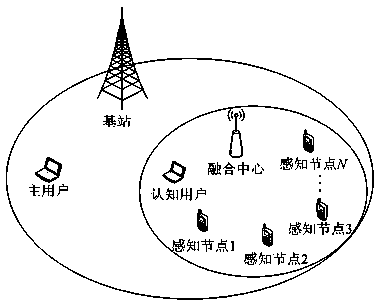
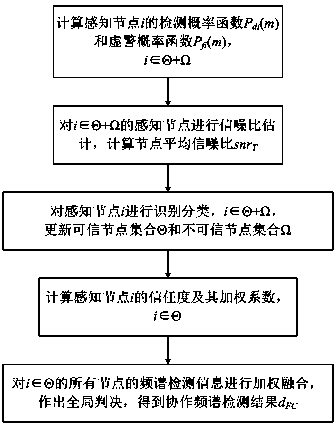
Method for cooperative spectrum detection based on node recognition
ActiveCN104065430AEliminate the effects ofEasy to detectTransmission monitoringWireless communicationFusion centerFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a method for cooperative spectrum detection based on node recognition. In a cognition wireless network comprising at least one master user, N cognition users and at least one fusion center, the master users generate master user signals s(t) of authorized spectrums, and the N cognition users form N sensor nodes. The method is characterized in that signals xi(t) received in the ith sensor node spectrum detection process are divided into signals H1 of the busy authorized spectrums in the network and signals H0 of the idle spectrums, the gain of a channel of an ith node is hi(t), additive white Gaussian noise of the channel is ni(t), wherein i = 1...N, node spectrum detection can be modeled into a binary hypothesis testing problem which can be seen in the specification, hypothesis testing is conducted on the received signals xi(t) through the ith sensor node, a local detection result '1' or '0' is acquired, '1' means that the hypothesis H 1 is valid, and '0' means that the hypothesis H0 is valid. The method is used for spectrum detection, the bad influences of faults or malicious nodes on collaboration spectrum detection are eliminated, and cost of a cognition network system is reduced.
Owner:嘉兴市燕知网络科技有限公司
Silence detection method based on minimum energy wavelet frame
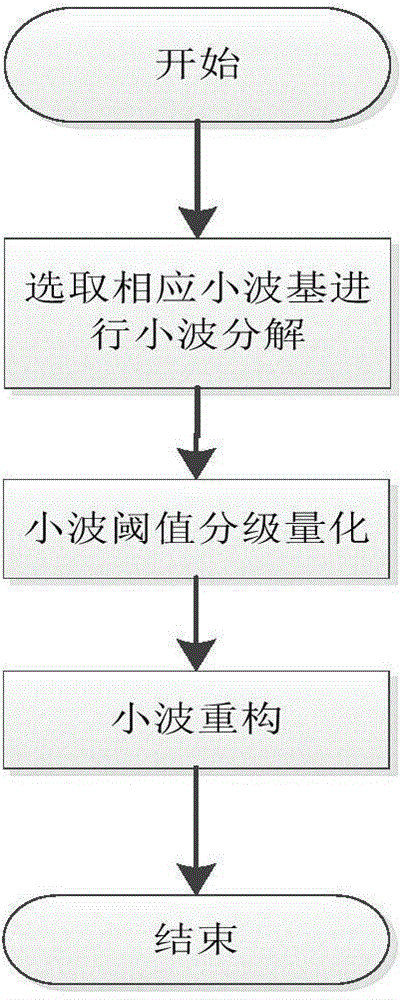
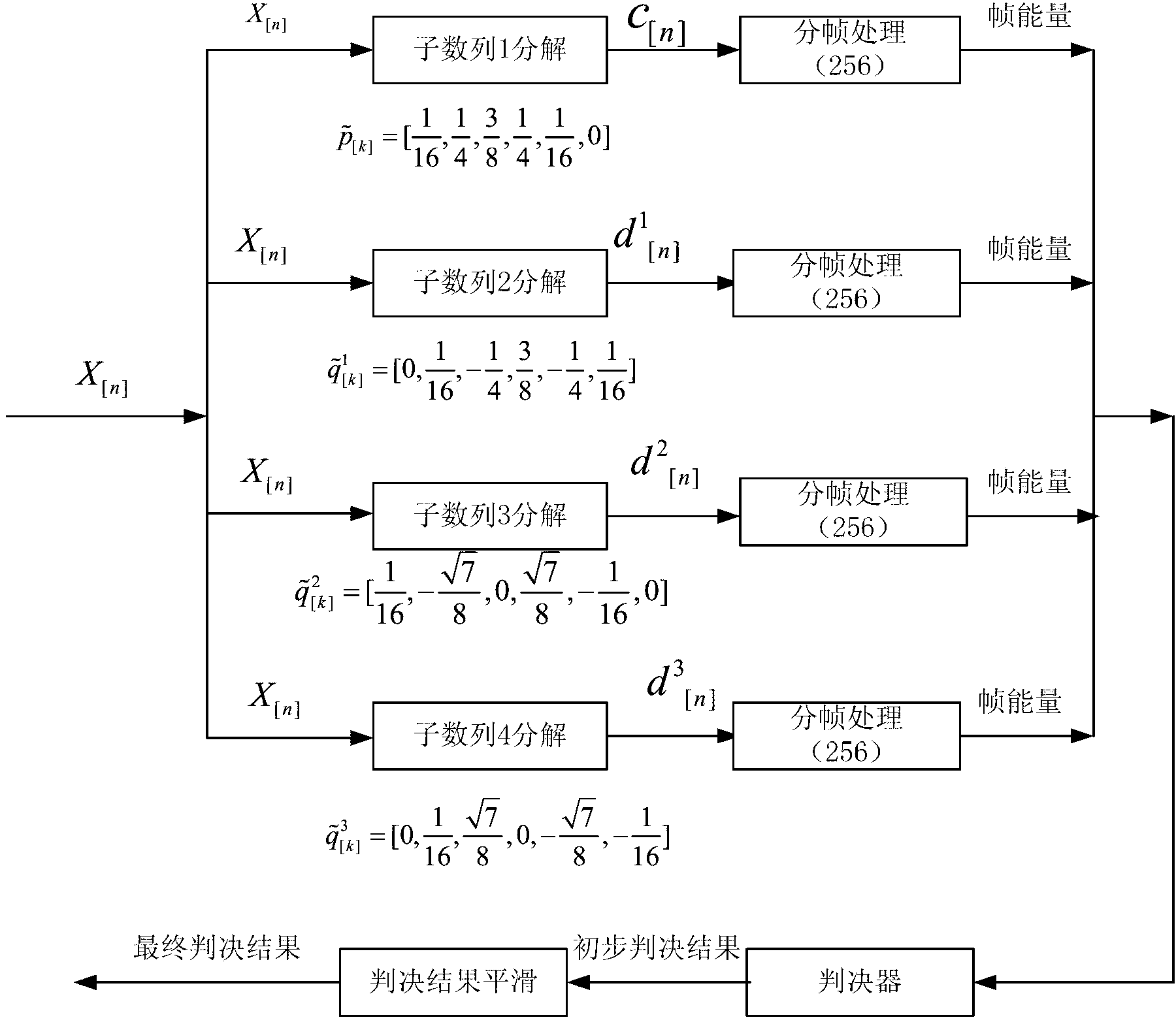
ActiveCN103325388AReduce computational complexityAdaptableSpeech analysisComputation complexityThree stage
The invention discloses a silence detection method based on a minimum energy wavelet frame. The silence detection method comprises the following steps that (1) analog voice signals which are polluted by additive white gaussian noise are sampled to obtain digital voice sampling signals; (2) in a discrete signal space, the minimum energy wavelet frame is used for decomposing the digital voice sampling signals into a plurality of sub signals; (3) framing processing is conducted on all sub signals decomposed in the step (2) simultaneously, the amounts of the frame energy in the same time shafts of all the sub signals are calculated respectively, then the amounts are added, and then the specific values of VAD judgment variables are calculated; (4) a judging device is used for judging the specific values of the VAD judgment variables, the primary judgment result of a three-stage judgment threshold is obtained, a judgment result smoothing algorithm is used, a final VAD judgment result is obtained, and therefore a voice signal silent area and a voice signal acting area in the signals are judged. The silence detection method based on the minimum energy wavelet frame has the advantages of being low in calculating complexity, strong in self-adaptivity, high in VAD effect accuracy and low in hardware cost.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HAIGE COMM GRP INC
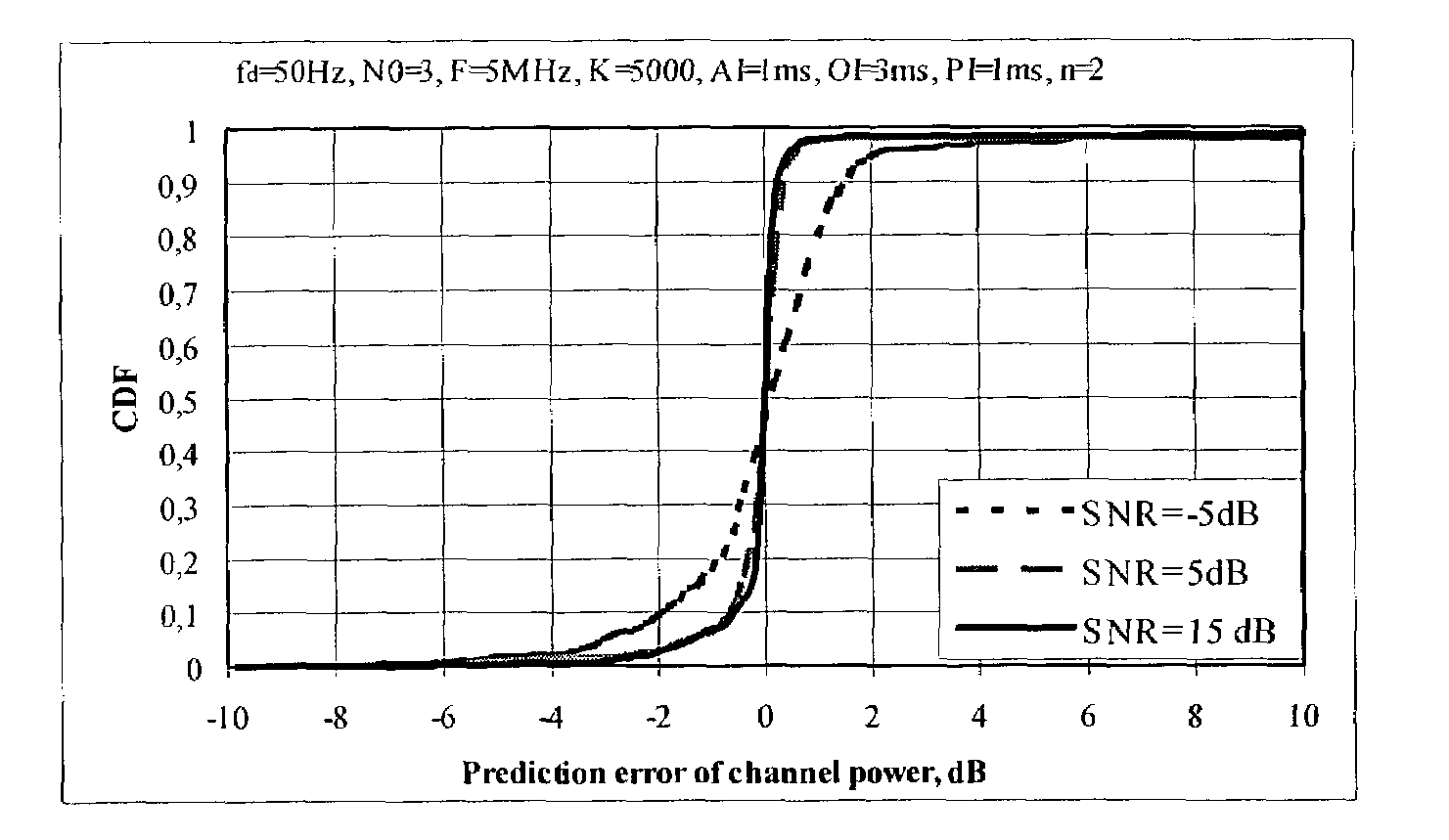
Method of predicting wireless signal power
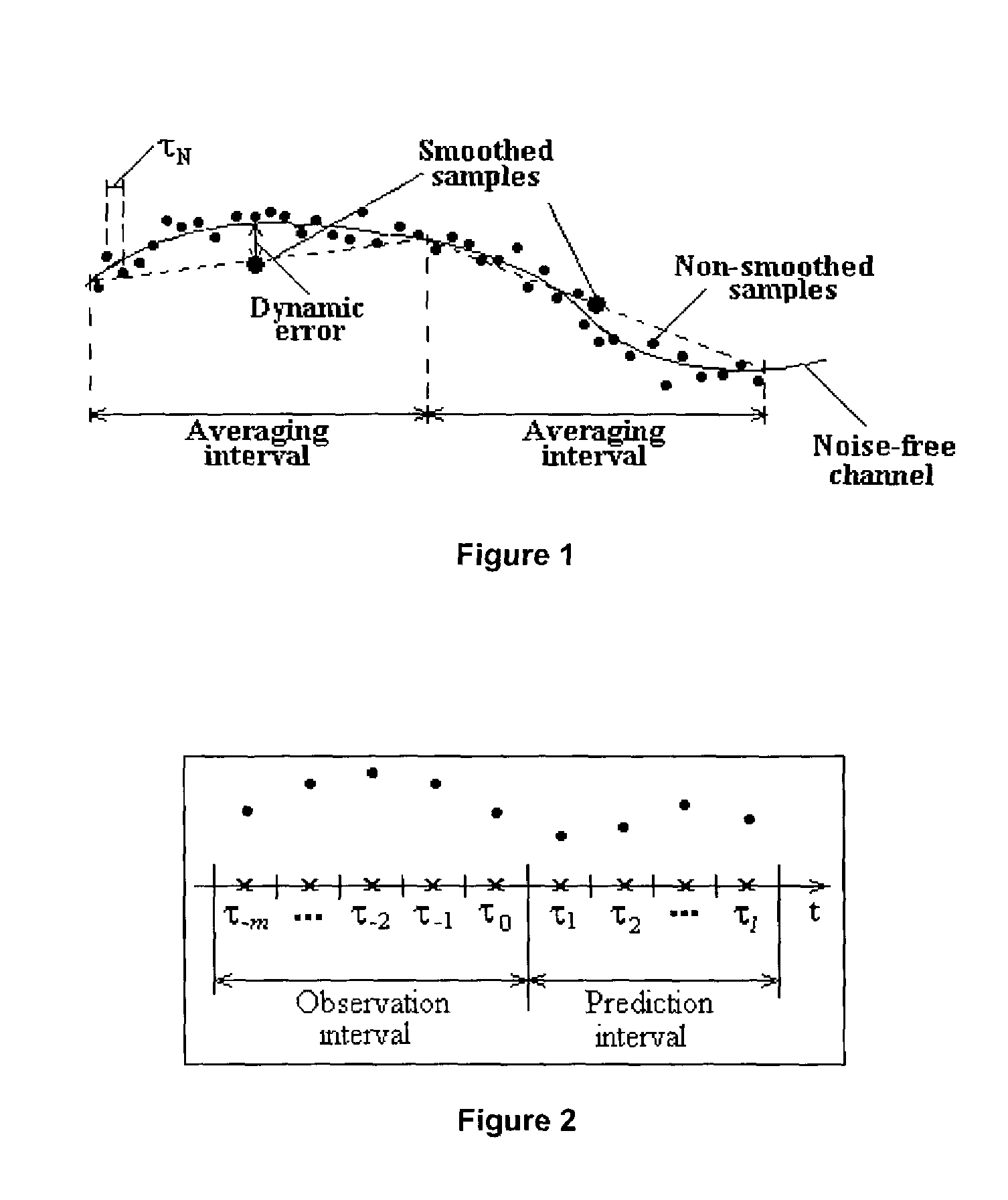
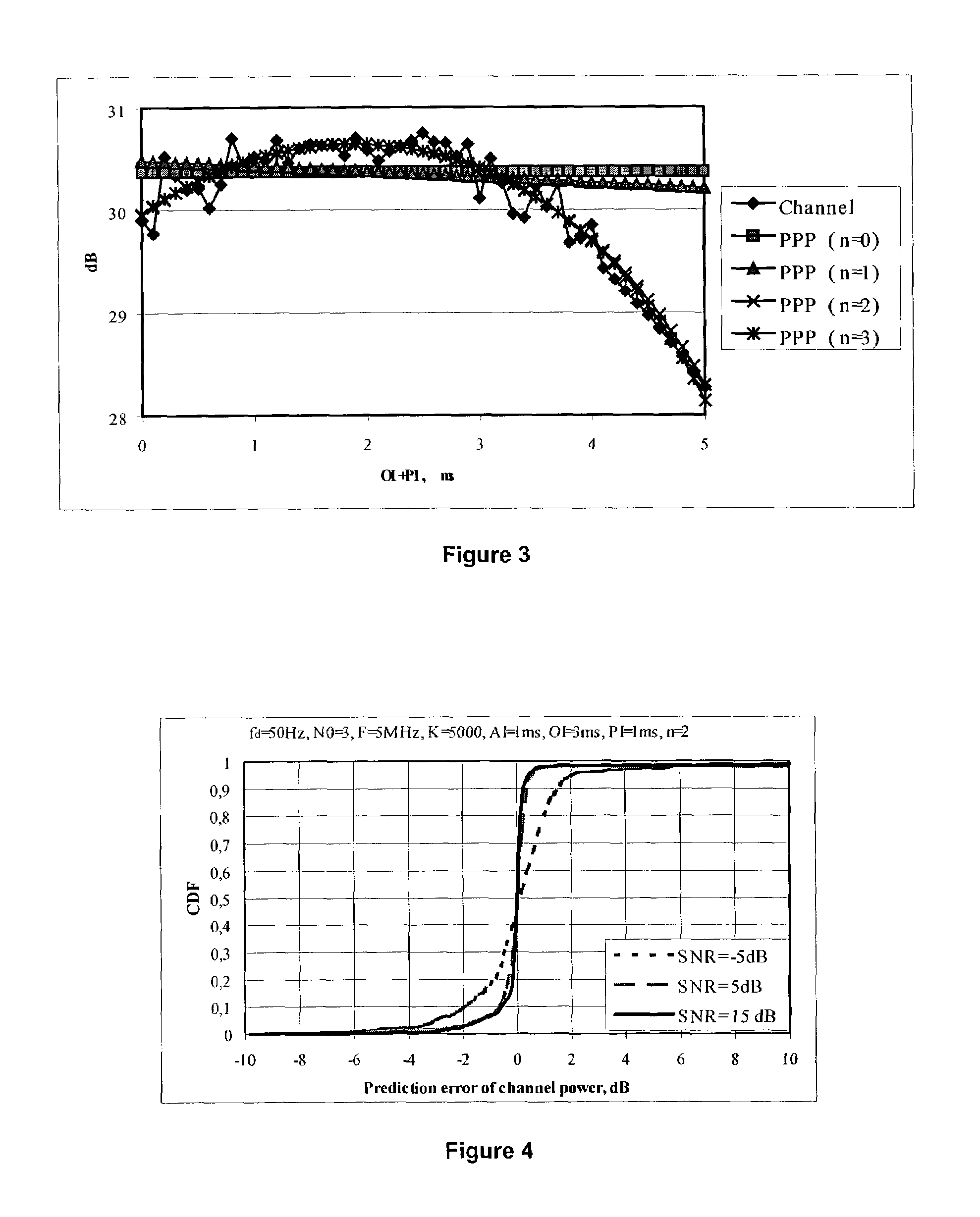
The invention provides a method of predicting the power of a received wireless signal (e.g. as received by a mobile device), the method having the steps of: sampling the power of the received wireless signal over an observation interval to obtain a series of values representative of the power of the received wireless signal over the observation interval; and extrapolating the series of values beyond the observation interval to predict the future power of the received wireless signal. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the method has the steps of: sampling the power of the received wireless signal over an observation interval to obtain a first series of values representative of the power of the received wireless signal over the observation interval; performing an additive white gaussian noise smoothing operation on the first series of values to give a series of smoothed samples over the observation interval, and removing the bias due to the influence of the additive white gaussian noise; performing least mean squares curve fitting on the smoothed samples; fitting a second order polynomial curve to the smoothed samples; and extrapolating the fitted curve beyond the observation interval to predict the future power of the received wireless signal. Also provided are a wireless device (e.g. a mobile phone) having signal processing apparatus operable to perform such a method, and a wireless communications network including a plurality of such wireless devices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
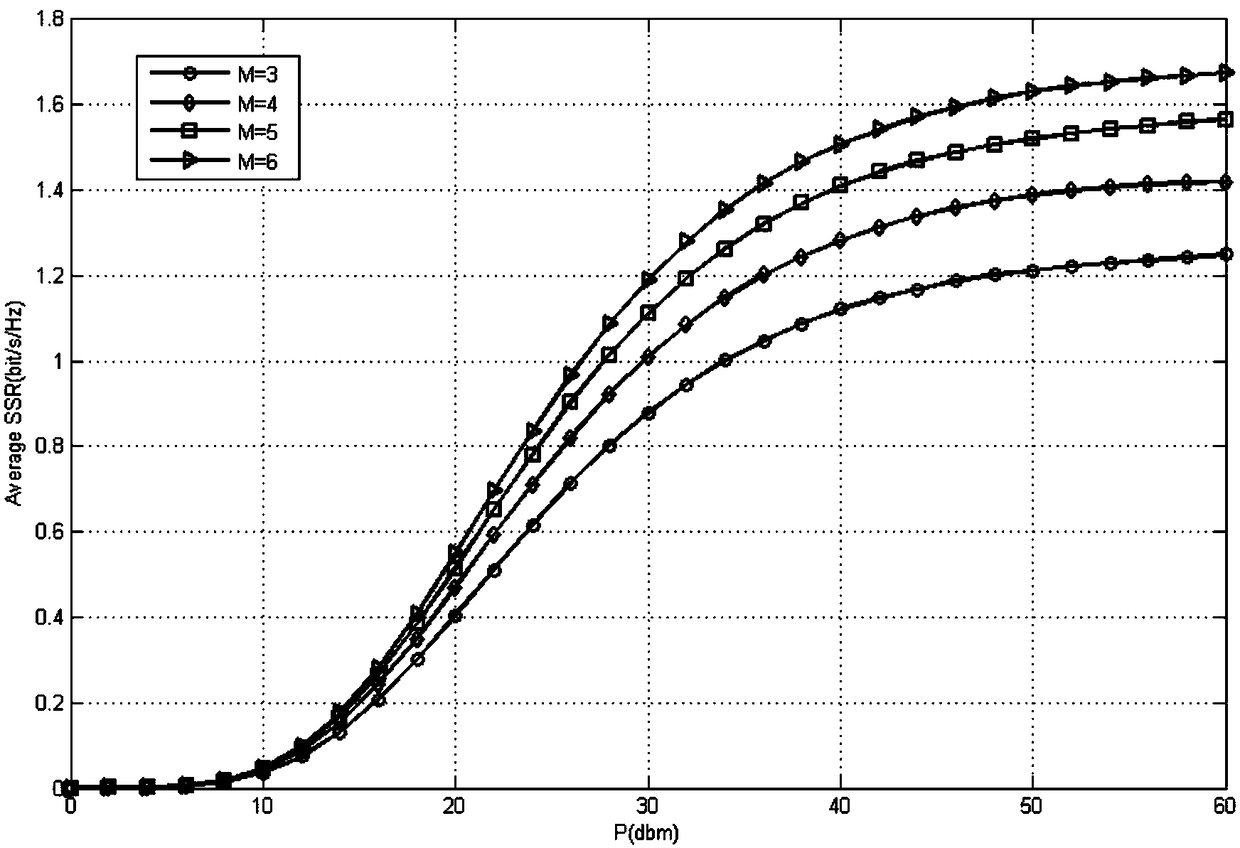
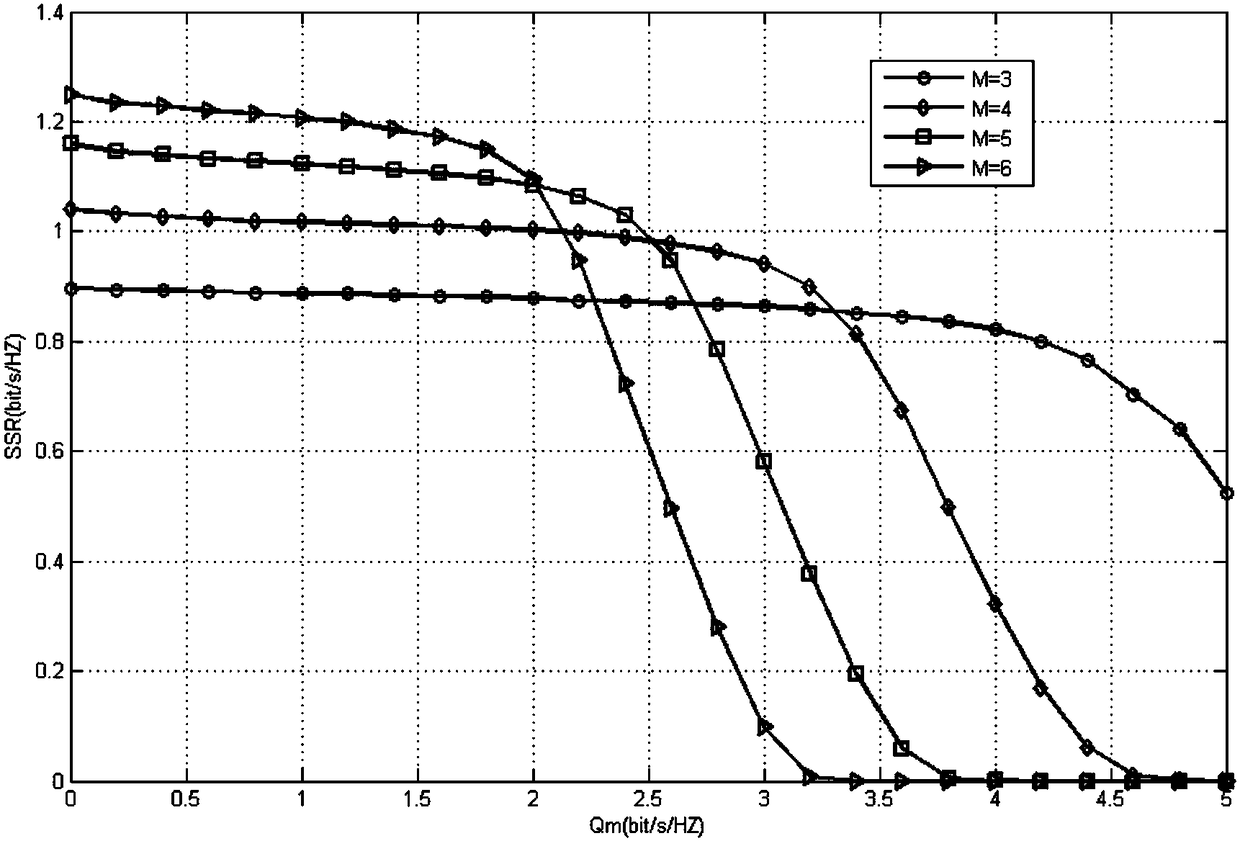
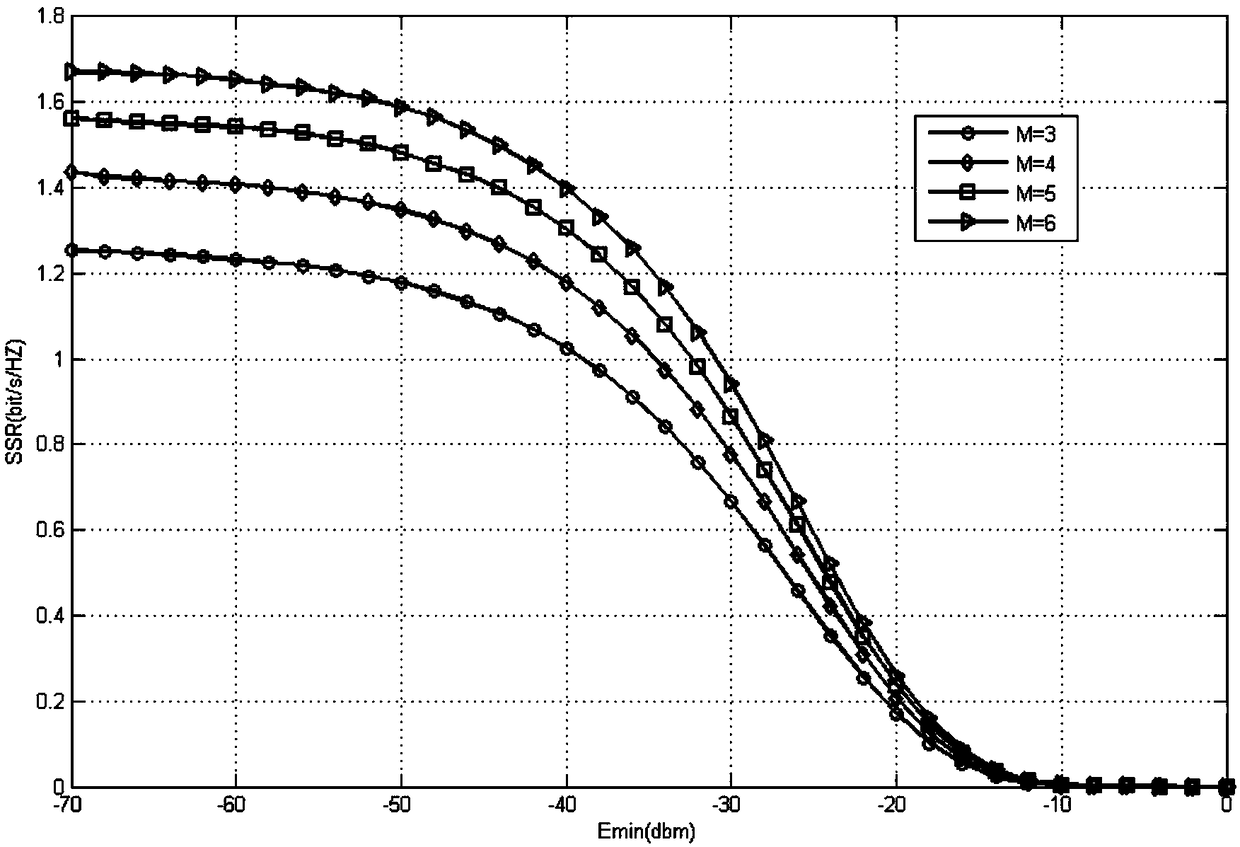
Power control method applicable to Raptor Codes under additive white Gaussian noise channel
ActiveCN102244922AImprove performanceReduce transmit powerPower managementError preventionCurrent channelTransmitted power
The invention discloses a power control method applicable to Raptor Codes under an additive white Gaussian noise channel. In the power control method, by utilizing the self-adaptive link fitting characteristic of the Raptor Codes, on the premise of constant total transmitting energy, if a transmitting end reduces the transmitting power and increases the code length, the difference value between the capacity C and code rate R of the channel can be increased, so that the performance of the Raptor Codes is obviously improved. By utilizing the characteristic of the Raptor Codes, the transmitting power can be controlled by the transmitting end so as to meet the requirement of the current channel. For channels with higher requirements for the transmission time, the transmitting power can be increased as high as possible on the premise of meeting the total transmitting energy so as to reduce the transmission time; and for channels with higher requirements for the transmission energy consumption, the transmitting power can be reduced as low as possible on the premise of meeting the maximum transmission time so as to reduce the total transmission energy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for detecting underwater acoustic leading signal based on energy concentration under sparse channel
ActiveCN106936514AImprove robustnessEasy to detectPropogation channels monitoringMatched filterDetection rate
The invention provides a method for detecting an underwater acoustic leading signal based on energy concentration (EC) under a sparse channel. The method is applied to an underwater acoustic communication system under the sparse channel. According to the method, the false drop rate of the leading signal is reduced, the detection rate is improved, the detection performance of the system is improved and the system communication efficiency is improved. Through sparse signal reconstruction and an OMP algorithm, the method estimates the energy concentration of several important elements (components) to judge whether a sparse signal is reconstructed successfully and can be applied to underwater acoustic communication, underwater acoustic location and tracking, military science, ocean navigation, radar and sonar. Compared with the existing technology, the method has the following advantages that 1.the method has strong robustness under the additive white Gaussian noise and different types of disturbances; 2.compared with a detection technology based on a matching filter, the method has better detection performance under multipath channels; and 3.compared with other existing technologies, the method has more ideal detection performance in the complicated and changeable actual underwater environment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
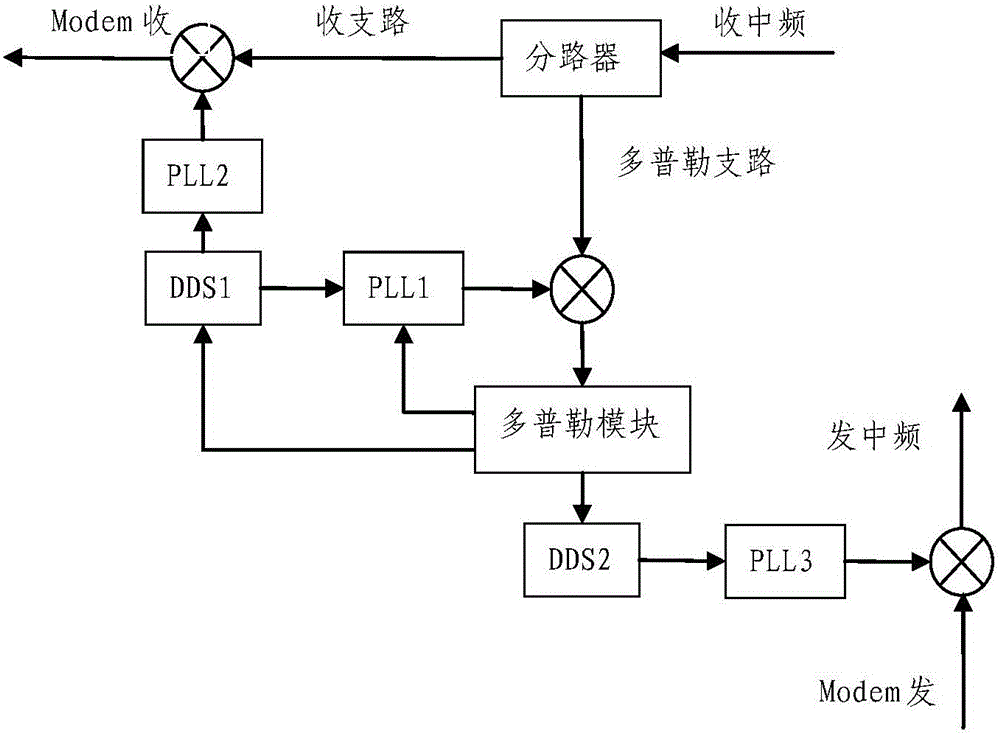
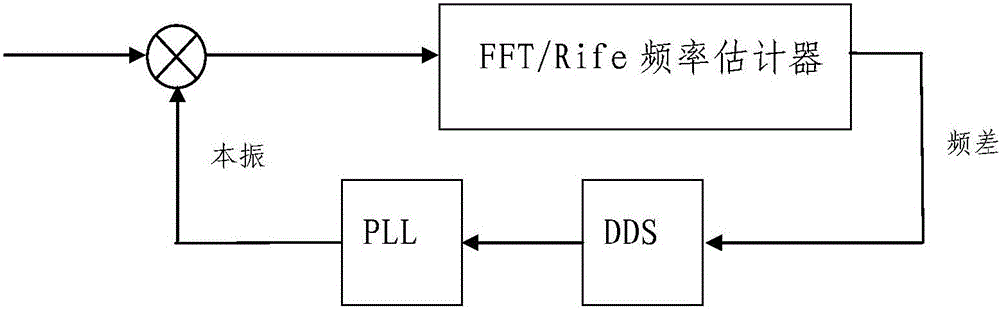
High-precision detection and compensation method for Doppler frequency shift in airborne satellite communication
ActiveCN105847203AImprove performanceAccurate Frequency Estimation ResultsCarrier regulationCorrection algorithmSample sequence
The invention discloses a high-precision detection and compensation method for Doppler frequency shift in airborne satellite communication. The method is characterized in that a Rife interpolation correction algorithm based on FFT is used for amending a frequency difference, namely a pilot carrier frequency estimation algorithm is used for detecting the Doppler frequency shift in satellite communication; as the FFT computation has a picket fence effect, when the frequency of an input signal is not located at an FFT quantized frequency point, the frequency of a sinusoidal input signal is estimated by directly using the maximal spectral line location, and thus a quantization error is generated; and within the time of 0 to T, single-frequency sinusoidal signals in an additive white Gaussian noise background are sampled, and thus a sample sequence is obtained. According to the method, the Doppler frequency shift in satellite communication is detected by the Rife pilot carrier frequency estimation algorithm based on frequency different amendment, and thus the Doppler frequency shift compensation on downlink signals is achieved.
Owner:PANDA ELECTRONICS GROUP +1
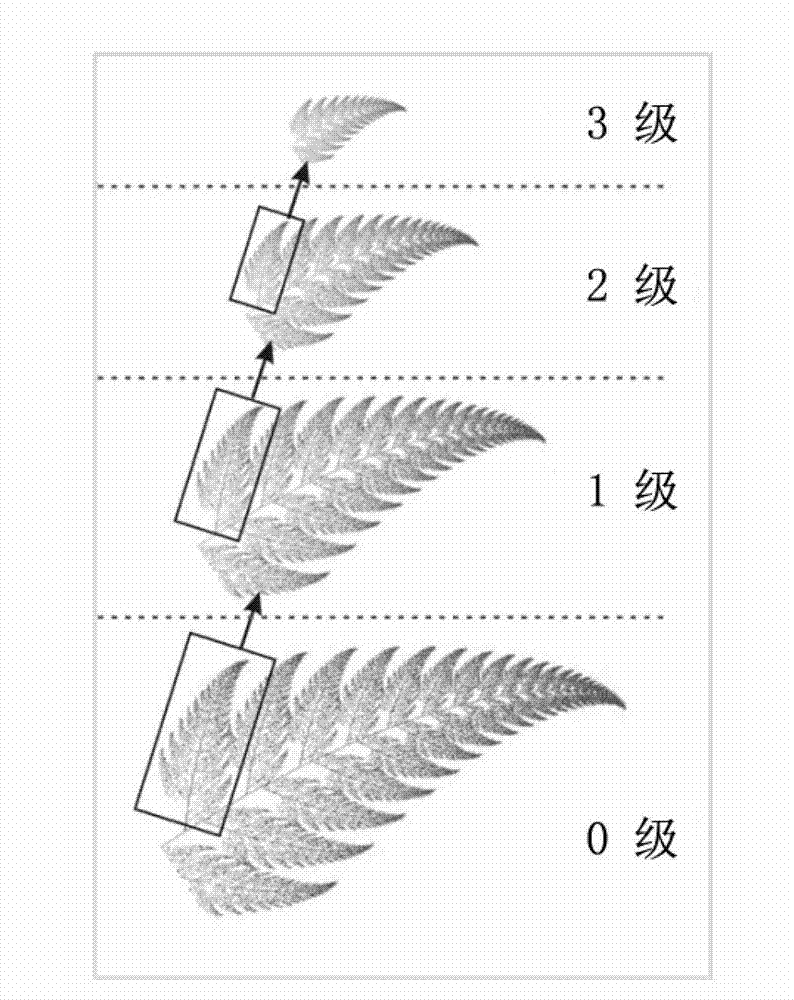
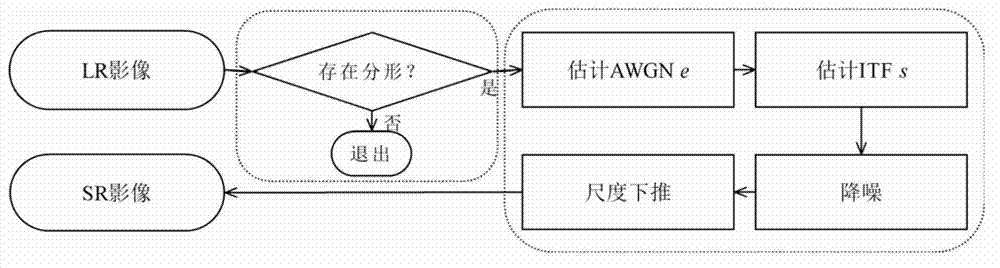
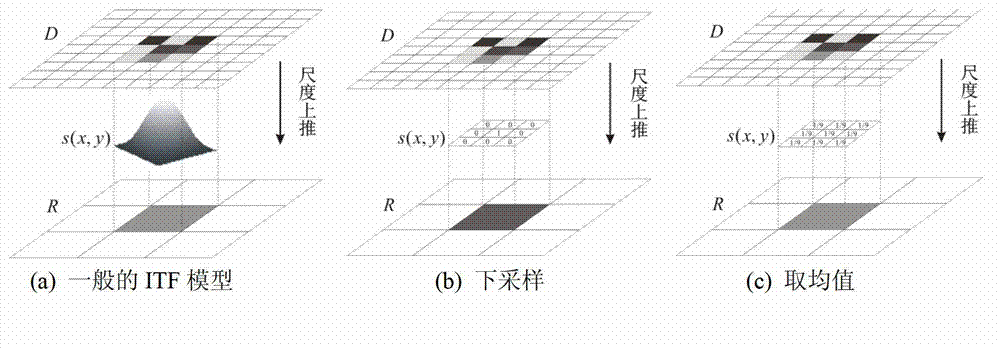
Rebuilding algorithm for super-resolution remote sensing image based on fractal theory
The invention relates to a rebuilding method for a super-resolution remote sensing image based on a fractal theory. The rebuilding method provided by the invention is as follows: connecting fractal similarity or affinity between areas under different scales in an image through fractal coding and transmitting the established connection to a spacial scale with higher resolution through the transmissibility of fractal feature on the scale. According to the invention, an image containing additive white gaussian noise is separated in a quantified way, so that a noise-free high-resolution image can be rebuilt from a noise-containing low-resolution image. The rebuilding for super resolution of a digital elevation image, the effectiveness of the rebuilding method provided by the invention is improved. A fractal-based super-resolution rebuilding model capable of removing noises provided by the invention has theoretical significance and practical value in global environment change study, disaster and environment monitoring.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
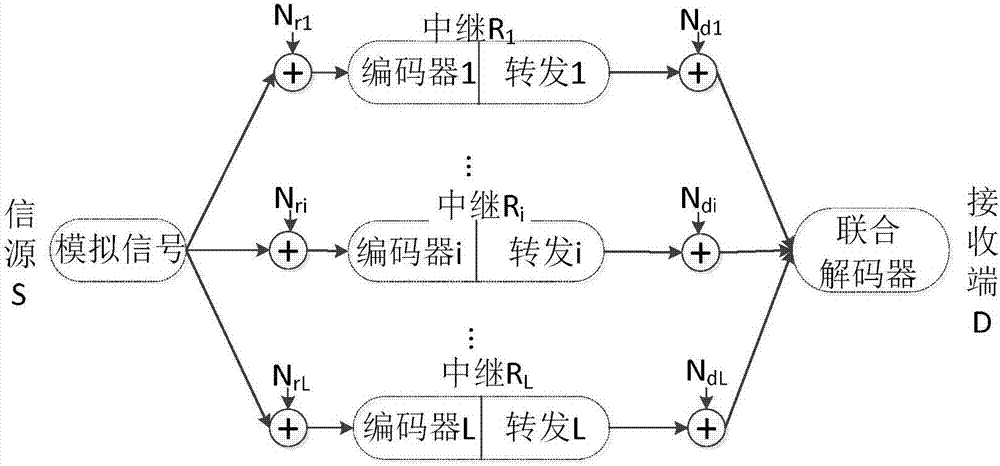
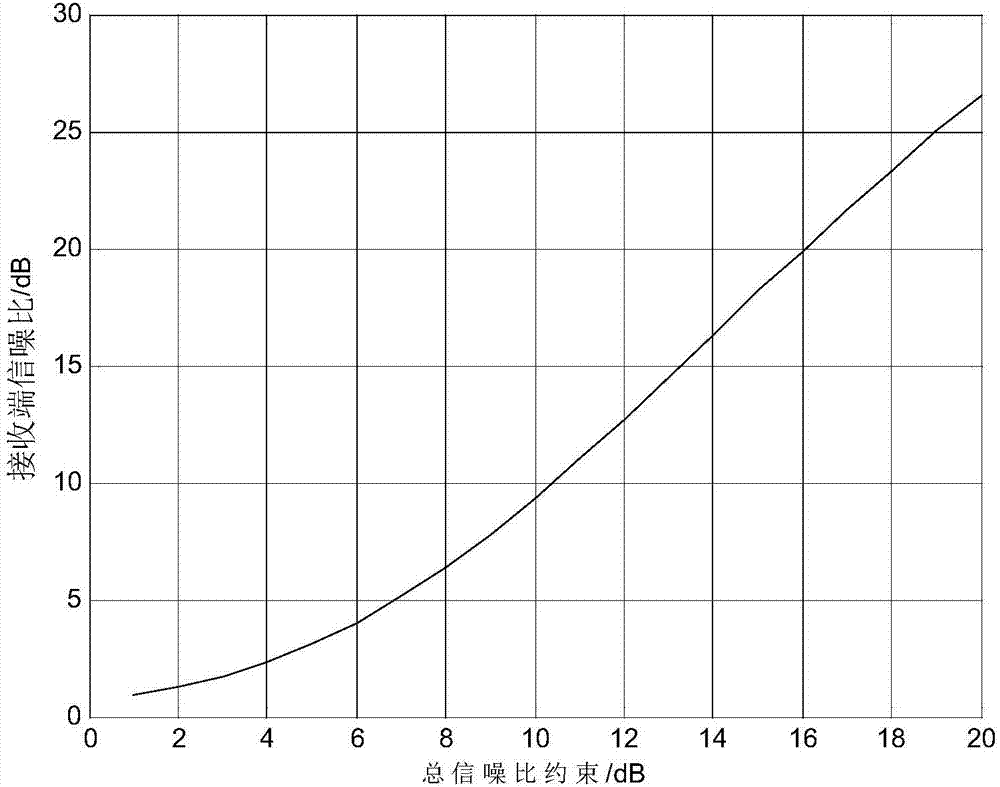
Distributed compressed forwarding system of Gaussian source and optimization method of system
ActiveCN106936542AImproved signal-to-noise ratio performanceImprove transmission performanceSource coding adaptationSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioDistortion function
The invention discloses a distributed compressed forwarding system of a Gaussian source and an optimization method of the system. In the system, the source sends analog Gaussian signals, distributed compressed coding is carried out in relays, and digital transmission is carried out. A theoretical analysis frame of the system is provided by considering that reception signal to noise ratios of different relays satisfy certain proportional relation and a reception end has different receiving signal to noise ratios for different relay signals in an additive white Gaussian noise channel. For a multi-relay distributed source coding problem, a CEO theory is used to establish a rate distortion function of a multi-relay network, transmission rates of the multiple relays are obtained, a Shannon channel capacity theory is combined, the compressed transmission rates of the relay are linked to the capacity of the channel from the relays to the channel, an optimized design equation of the system is provided, and an optimal solving algorithm is provided. Under the condition that the total power is limited, power distribution is carried out between the source and the relay network based on the signal to noise ratios, and the signal to noise ratio performance of the reception end of the system is maximized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Wireless body area network communication system interruption probability analyzing method based on k-mu shadow fading channel
InactiveCN106535243AReduce overheadSpeed up simulation analysisTransmission monitoringWireless communicationNormal densityBody area network
The invention provides a wireless body area network communication system interruption probability analyzing method based on a k-mu shadow fading channel. The method includes the steps of firstly establishing a system model, sequentially calculating the conditional probability density function, the unconditional probability density function and the generalized nonholonomic moment generating function of the signal-interference ratio of a receiver end, and finally calculating the interruption probability of the wireless body area network communication system under the co-channel interference condition. The method effectively solves the technical problem of lack of means for accurately analyzing the interruption probability properties of a wireless body area network communication system, and takes the influence of co-channel interference and additive white Gaussian noise on the system performance into consideration. An enclosed interruption probability expression is obtained by analyzing the statistical characteristics of the signal-interference noise ratio (SINR) of the receiving end, thereby providing theoretical foundation and basis for evaluating the influence of channel fading characteristics and co-channel interference on the wireless body area network communication system.
Owner:SHANDONG COMP SCI CENTNAT SUPERCOMP CENT IN JINAN
Code multiplexing DCSK (Differential Chaotic Shift Keying) modulator-demodulator based on PFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) technology
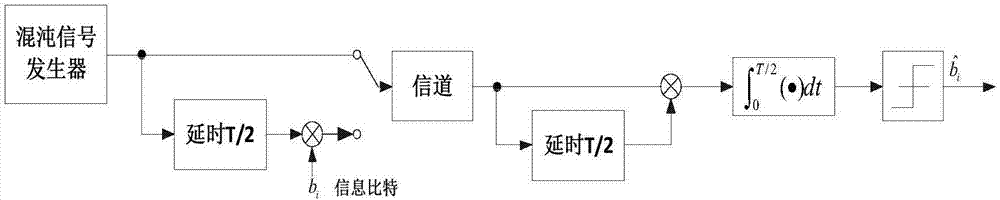
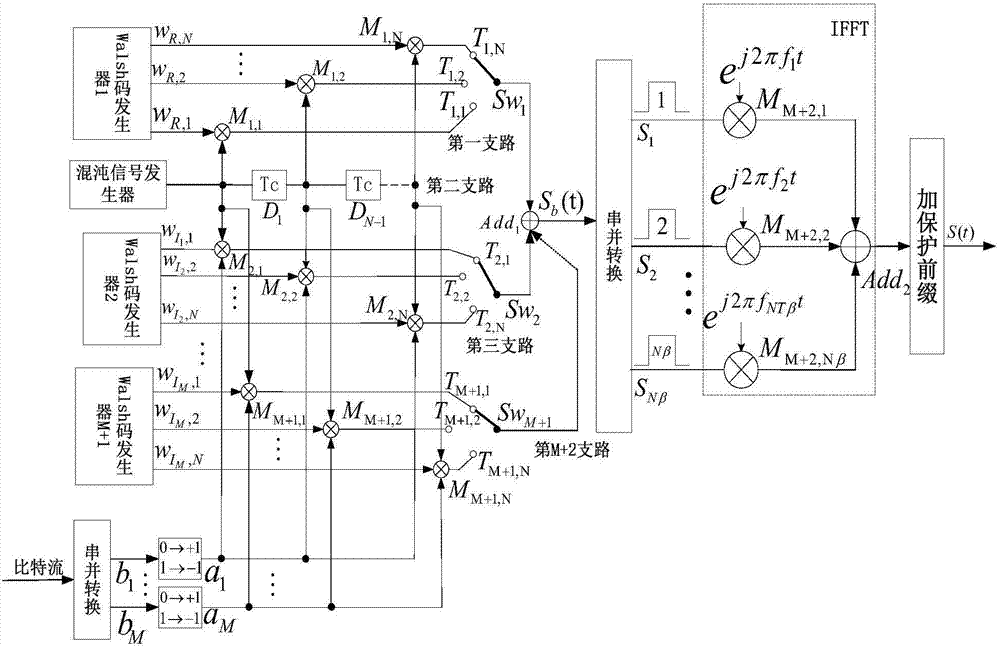
ActiveCN107426124ARespond to different problemsReduce the impactMulti-frequency code systemsModem deviceSignal on
The invention relates to a code multiplexing DCSK (Differential Chaotic Shift Keying) modulator-demodulator based on a PFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) technology, and relates to DCSK modulation and demodulation. By utilizing orthogonality of a Walsh code, orthogonality of a reference signal and an information carrying signal on a code domain and overlapping of the reference signal and the information carrying signal on a time domain are implemented, and the problems of different channel responses and poor transmission performance of the reference signal and the information carrying signal, which are caused by channel time selection, are solved; and by utilizing the OFDM technology, each code chip of one frame of signal is propagated on different sub carriers, so that the problem of intersymbol interference caused by channel frequency selection is avoided. Simulation under an Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channel and a multi-path time-varying channel shows that compared to conventional DCSK, the code multiplexing DCSK system based on the PFDM technology has good transmission performance under the AWGN channel and the multi-path time-varying channel and has resistance to time selection and resistance to frequency selection fading.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com