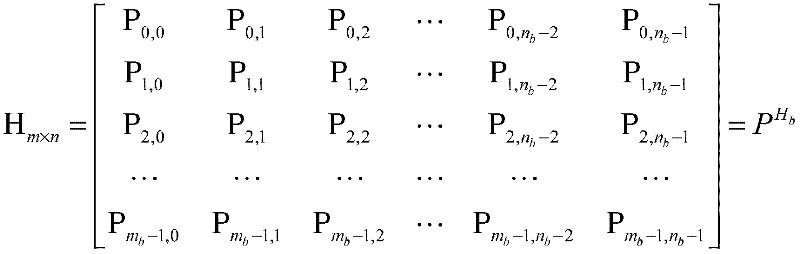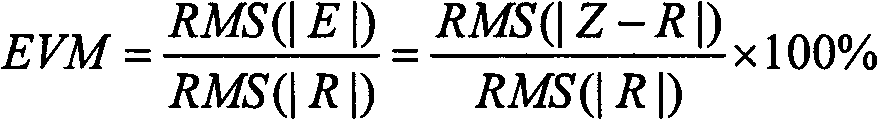Patents
Literature
60 results about "Mobile communication channels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
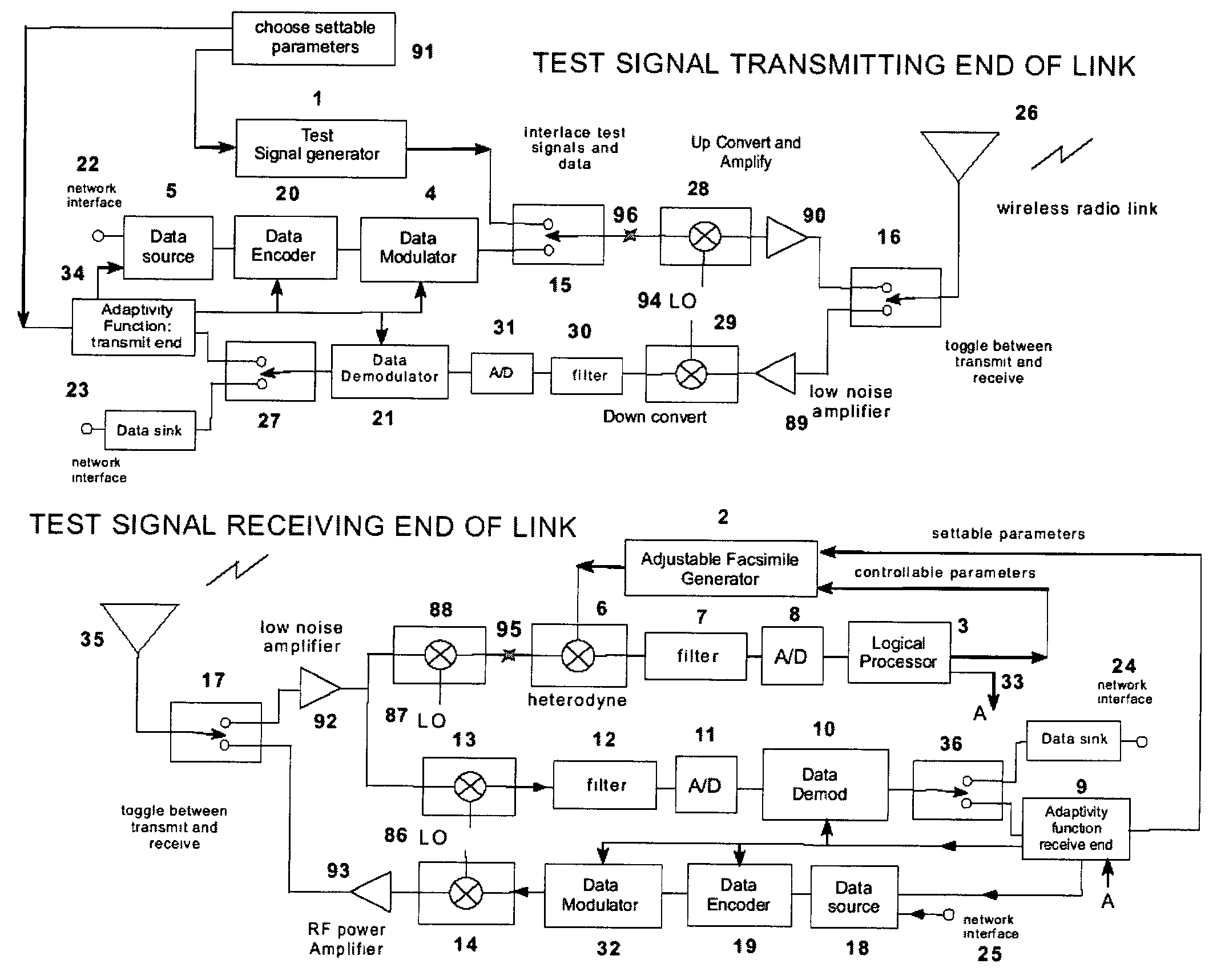
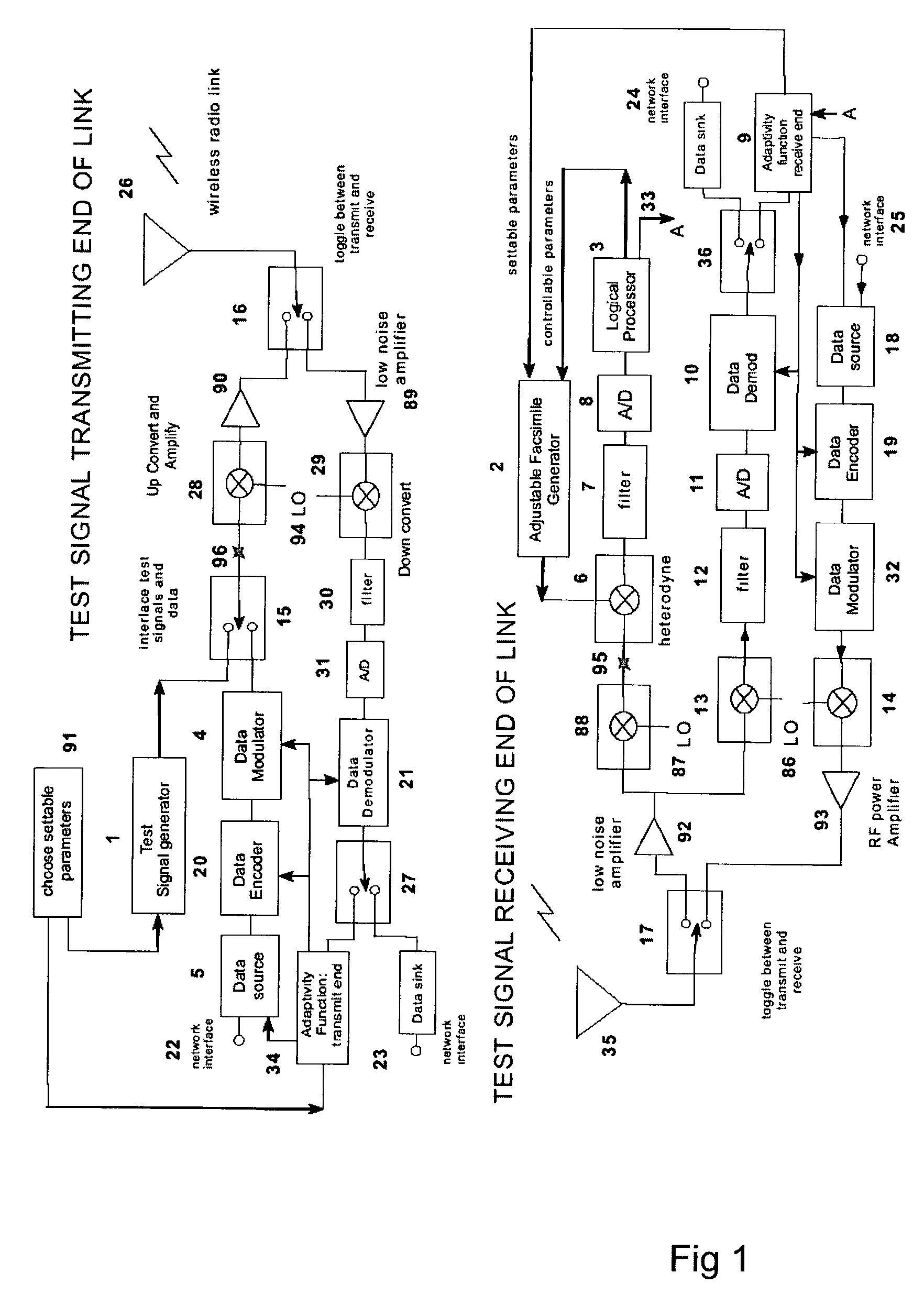
Vector network analyzer applique for adaptive communications in wireless networks
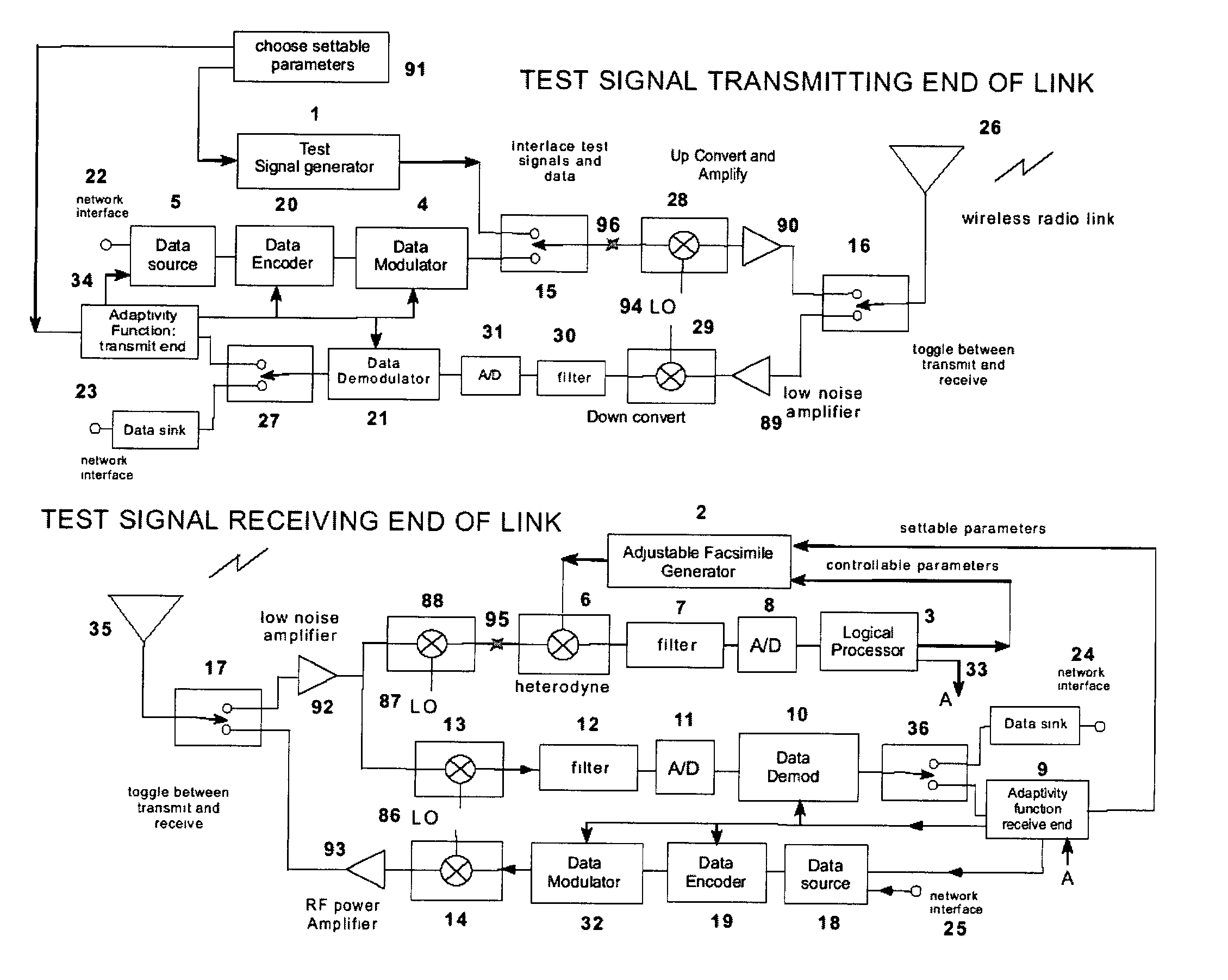
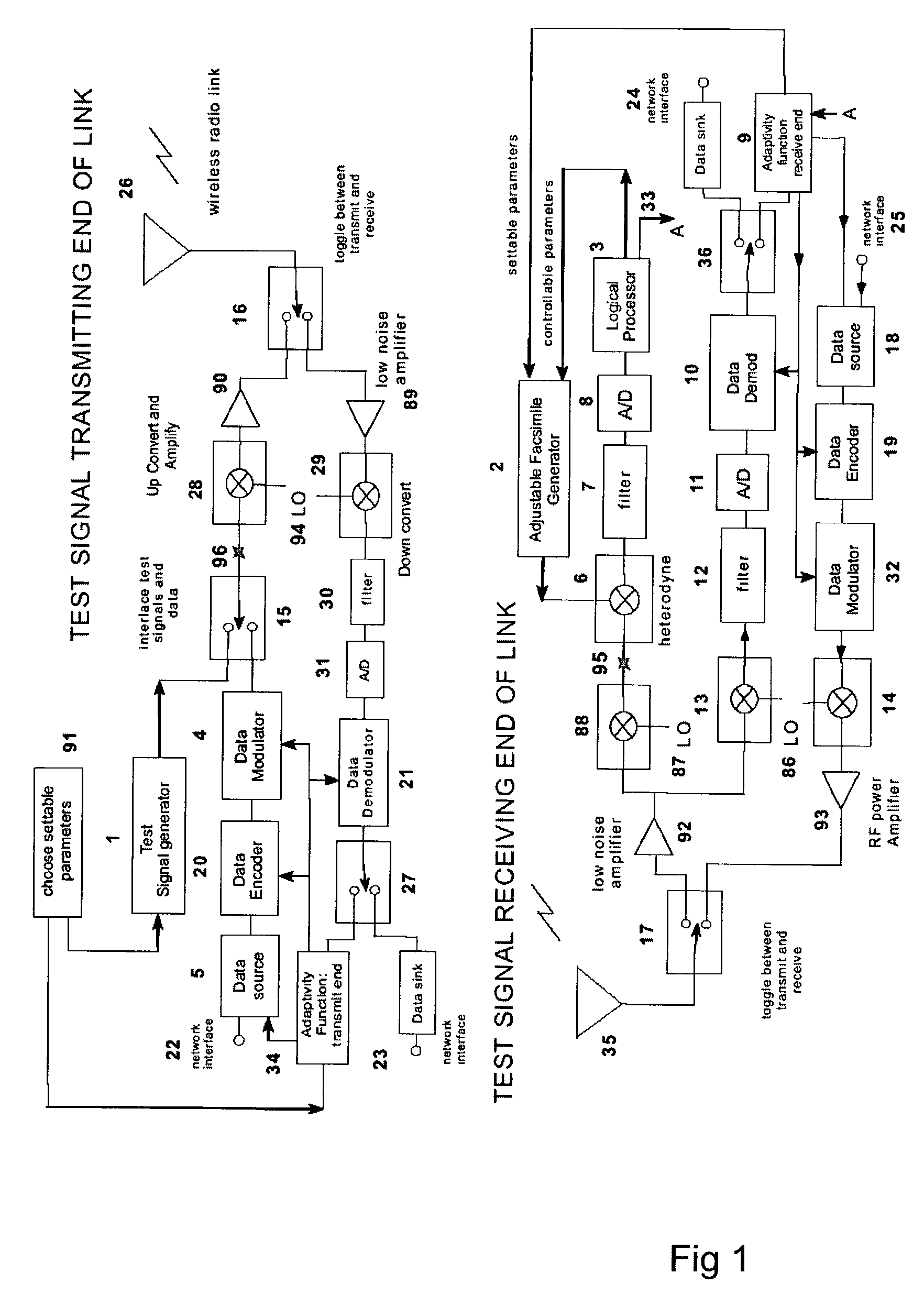
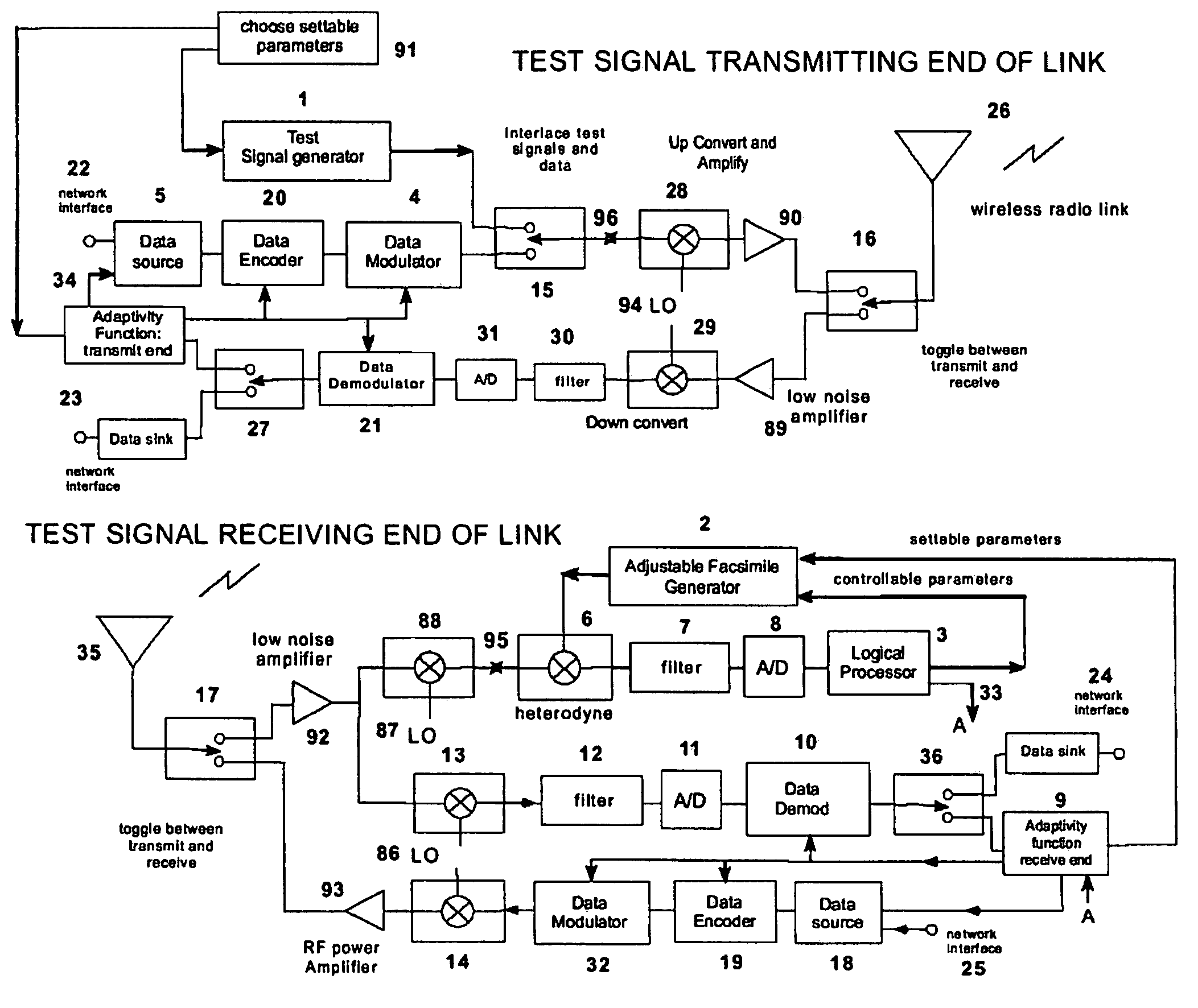
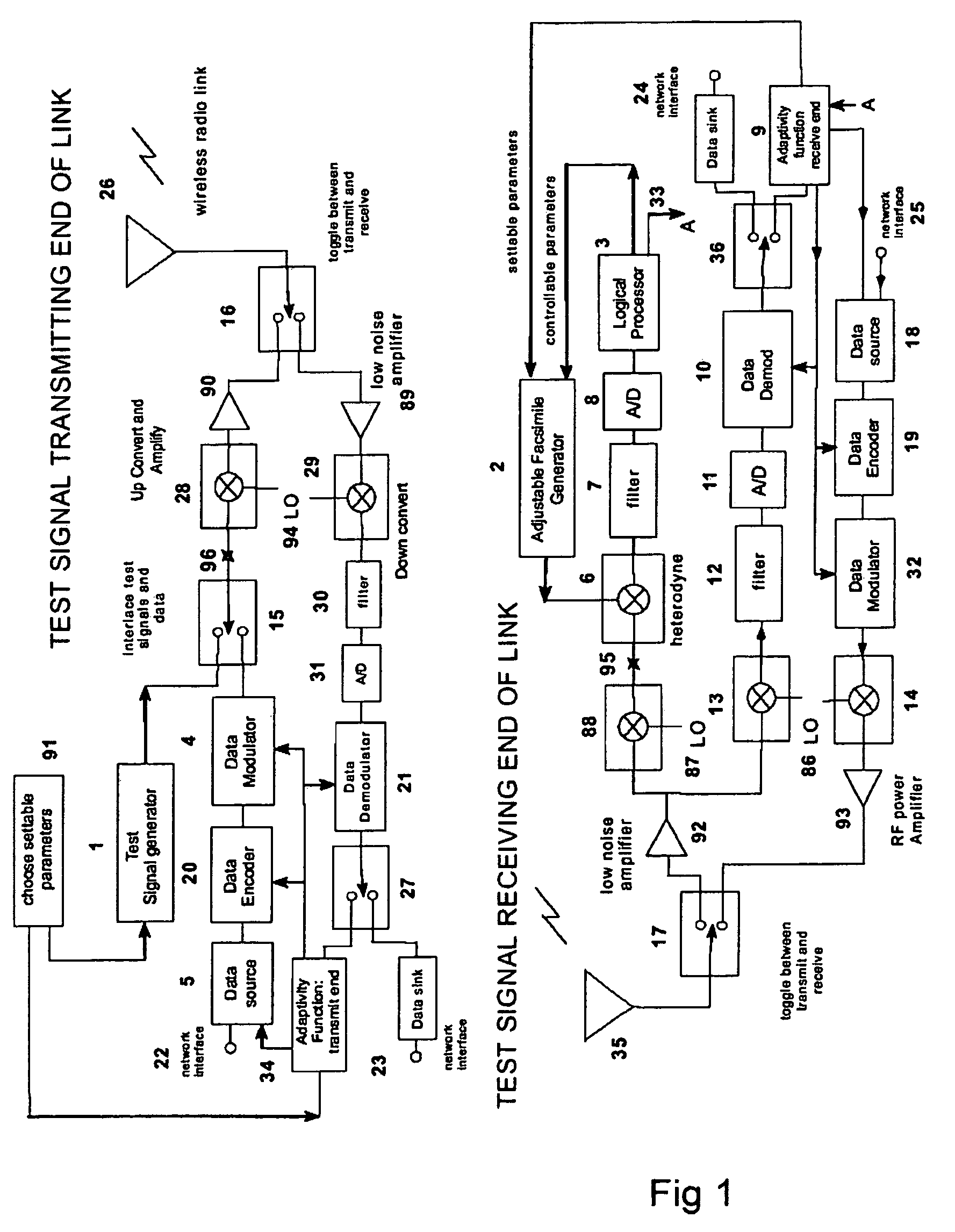
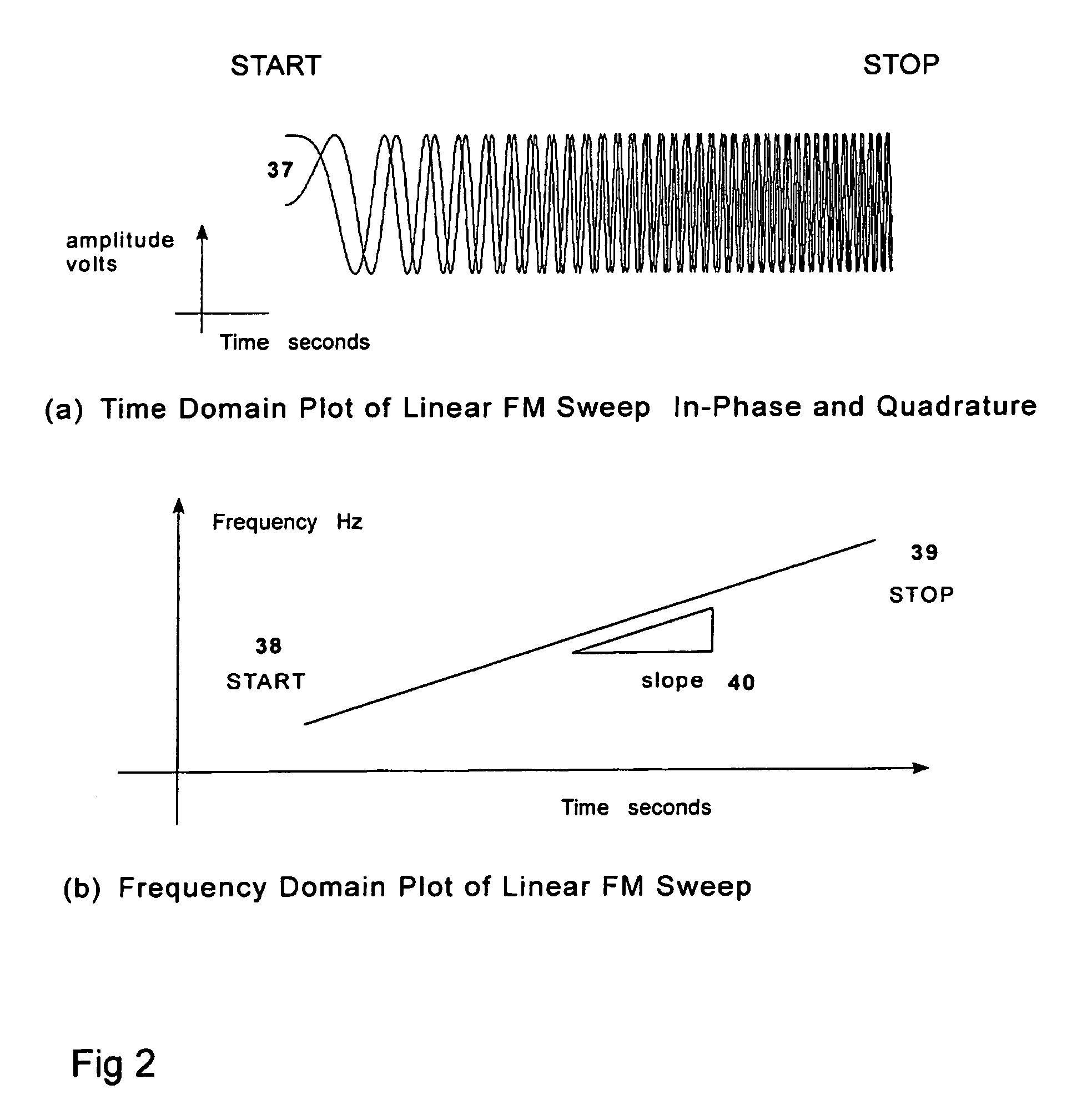
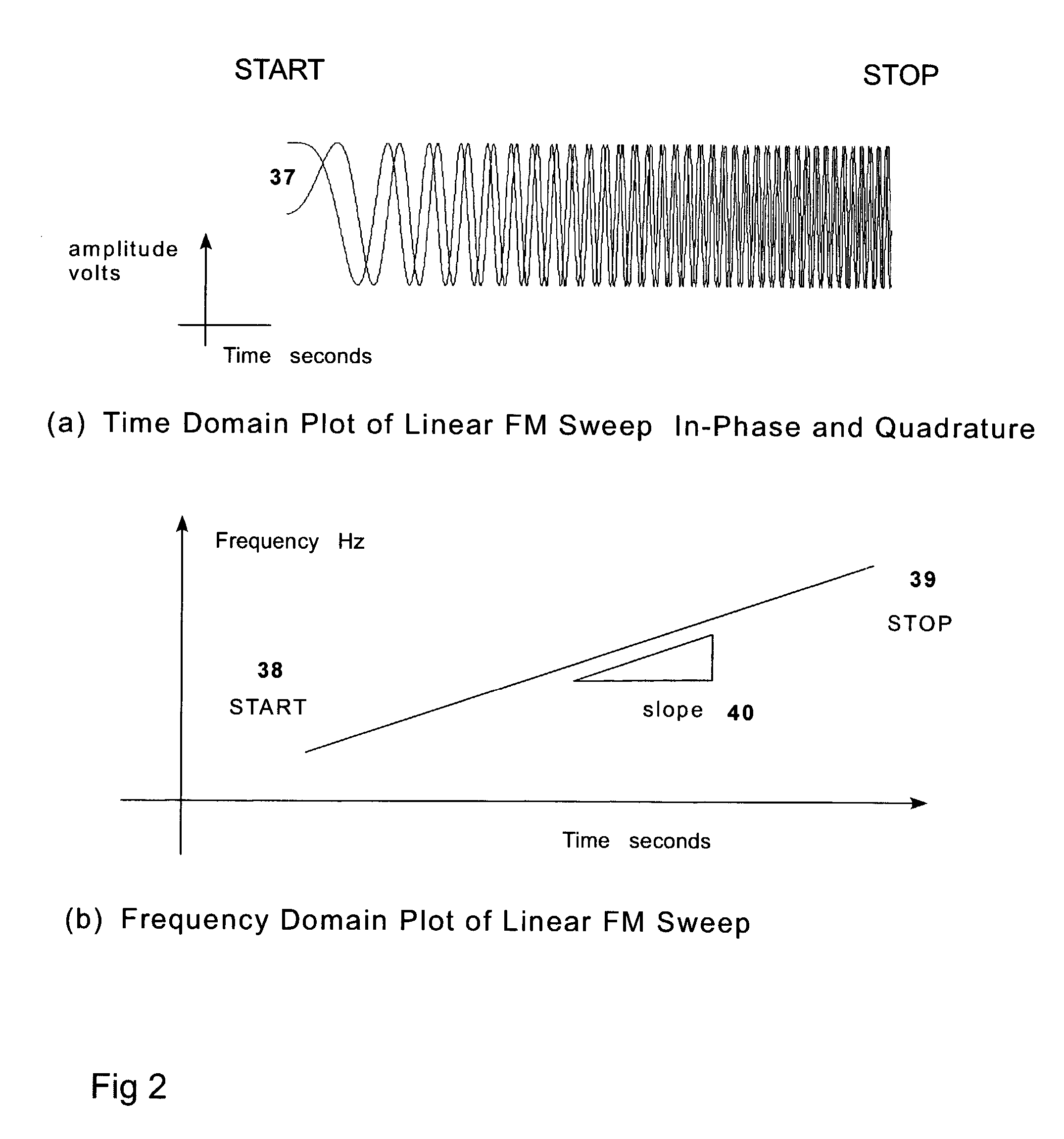
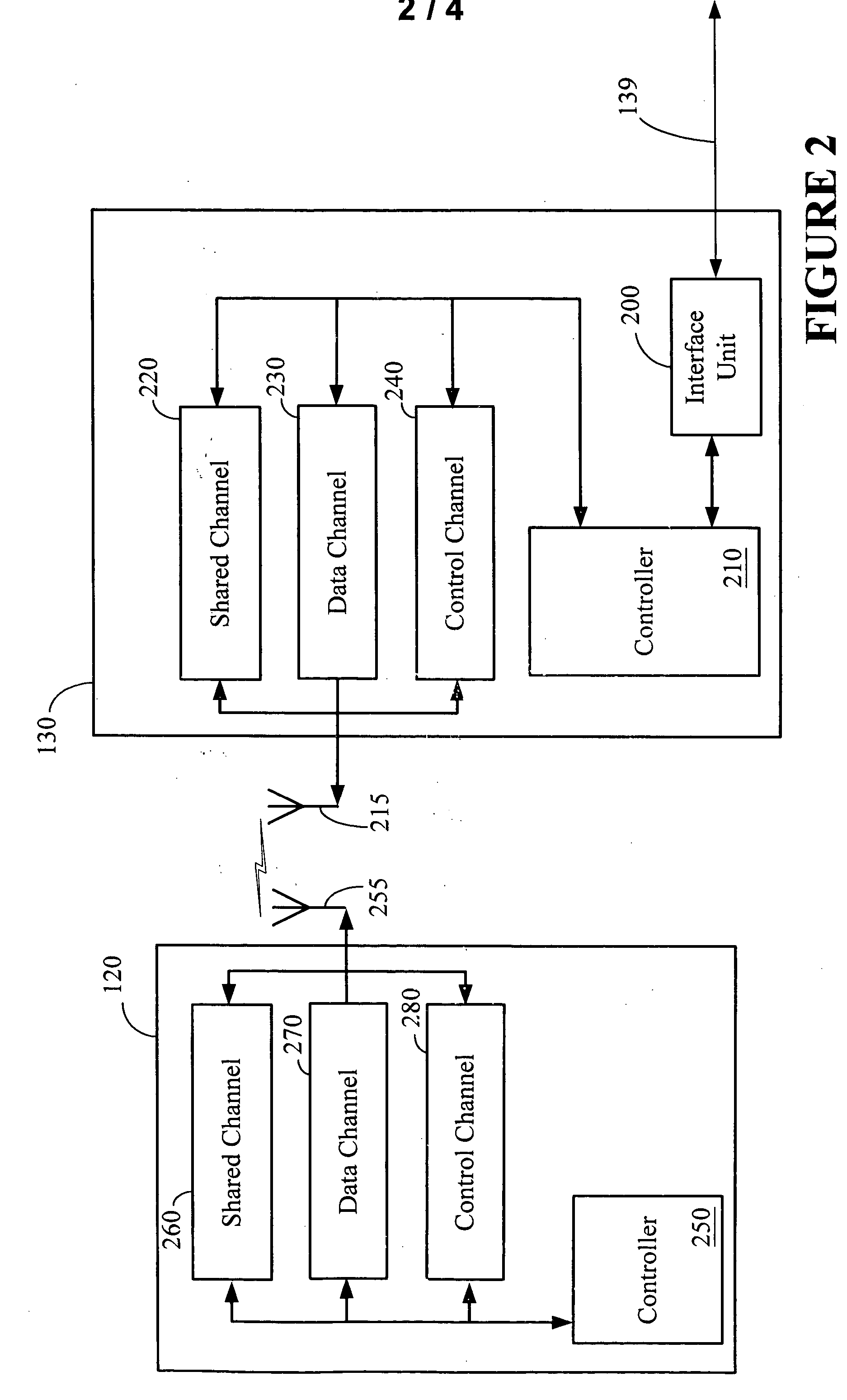
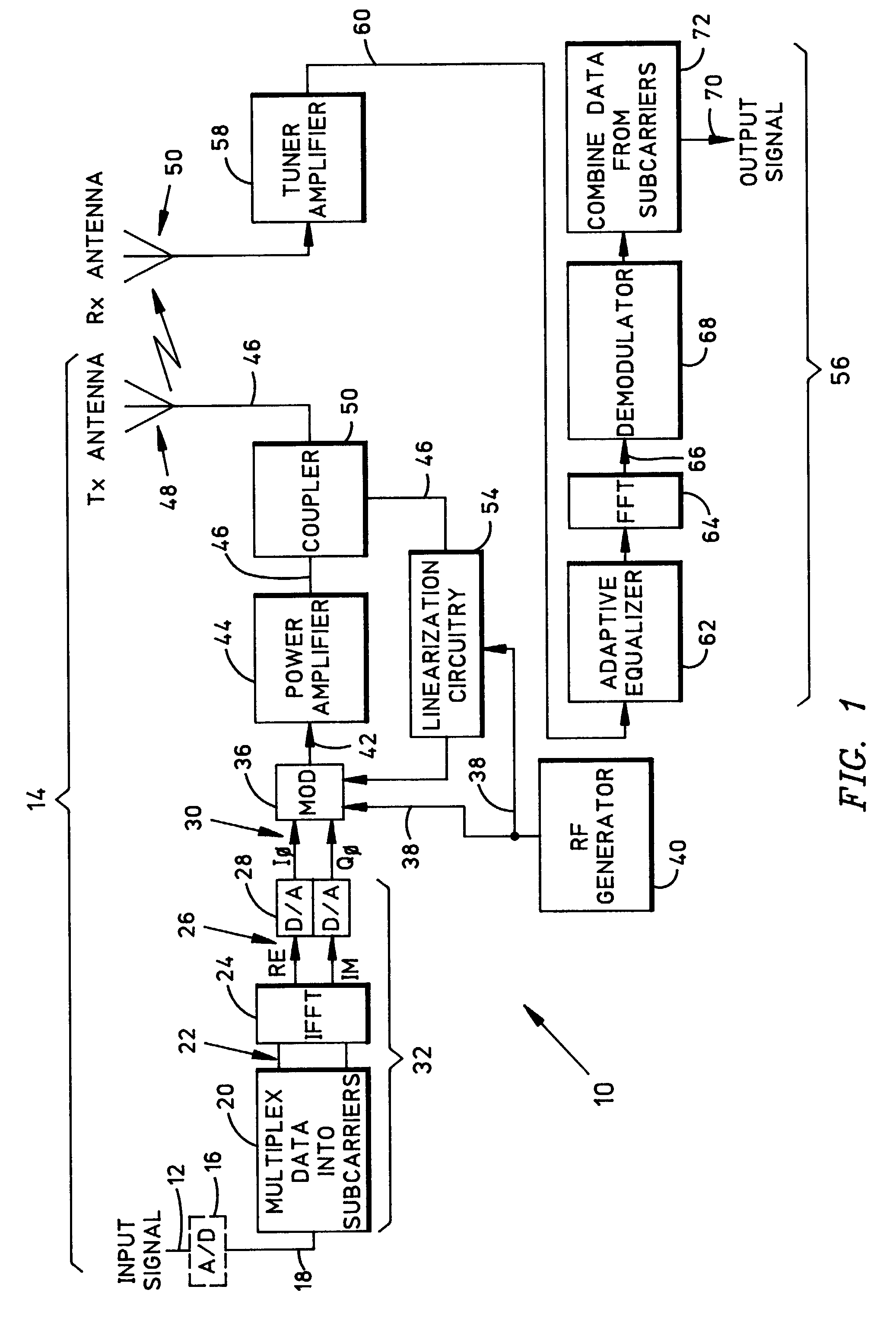
A test signal generator at a transmitter station and a facsimile generator at a receiver station go through an acquisition and tracking process which aligns the two signals so that a logical processor can compute the frequency transfer function of the entire propagation path for use in an adaptive, concurrently sent communication signal. The frequency transfer function is conveyed back to the transmit end via a control channel permitting an adaptivity function at the transmit end to influence subsequent selection of communication parameters, among which are typically transmitted data rate, selection of modulation, selection of forward error correcting coding, and selection of frequency band for transmission. The same measurement is conveyed to an adaptivity function at the receive end for use in the communications receiver to select demodulator variables such as gain control, and equalization of amplitude and phase, versus frequency. The adaptivity function also permits interspersing of reverse-direction communications over the same frequency bands in a time-share mode between forward-direction and reverse-direction communication with the measurement signals having to be transmitted in only one direction. An alternate embodiment invention of this type is described which is additionally useful for mobile communications channels. Another variation embodiment is described for pure propagation measurements only, absent conveyance of end-user information.
Owner:SARABAND WIRELESS
Channel estimation applique for wireless communications
A test signal generator at a transmitter station and a facsimile generator at a receiver station go through an acquisition and tracking process which aligns the two signals, removing errors in the time base of generation, the frequency offset of generation and the time of arrival, so that a logical processor can compute the frequency transfer function of the entire propagation path for use in an adaptive, concurrently sent communication signal. The frequency transfer function is conveyed back to the transmit end via a control channel permitting an adaptivity function at the transmit end to influence subsequent selection of communication parameters, among which are typically transmitted data rate, selection of modulation, selection of forward error correcting coding, and selection of frequency band for transmission. The same measurement is conveyed to an adaptivity function at the receive end for use in the communications receiver to select demodulator variables such as gain control, and equalization of amplitude and phase, versus frequency. The adaptivity function also permits interspersing of reverse-direction communications over the same frequency bands in a time-share mode between forward-direction and reverse-direction communication with the measurement signals having to be transmitted in only one direction. An alternate embodiment invention of this type is described which is additionally useful for mobile communications channels. Another variation embodiment is described for pure propagation measurements only, absent conveyance of end-user information.
Owner:SARABAND WIRELESS
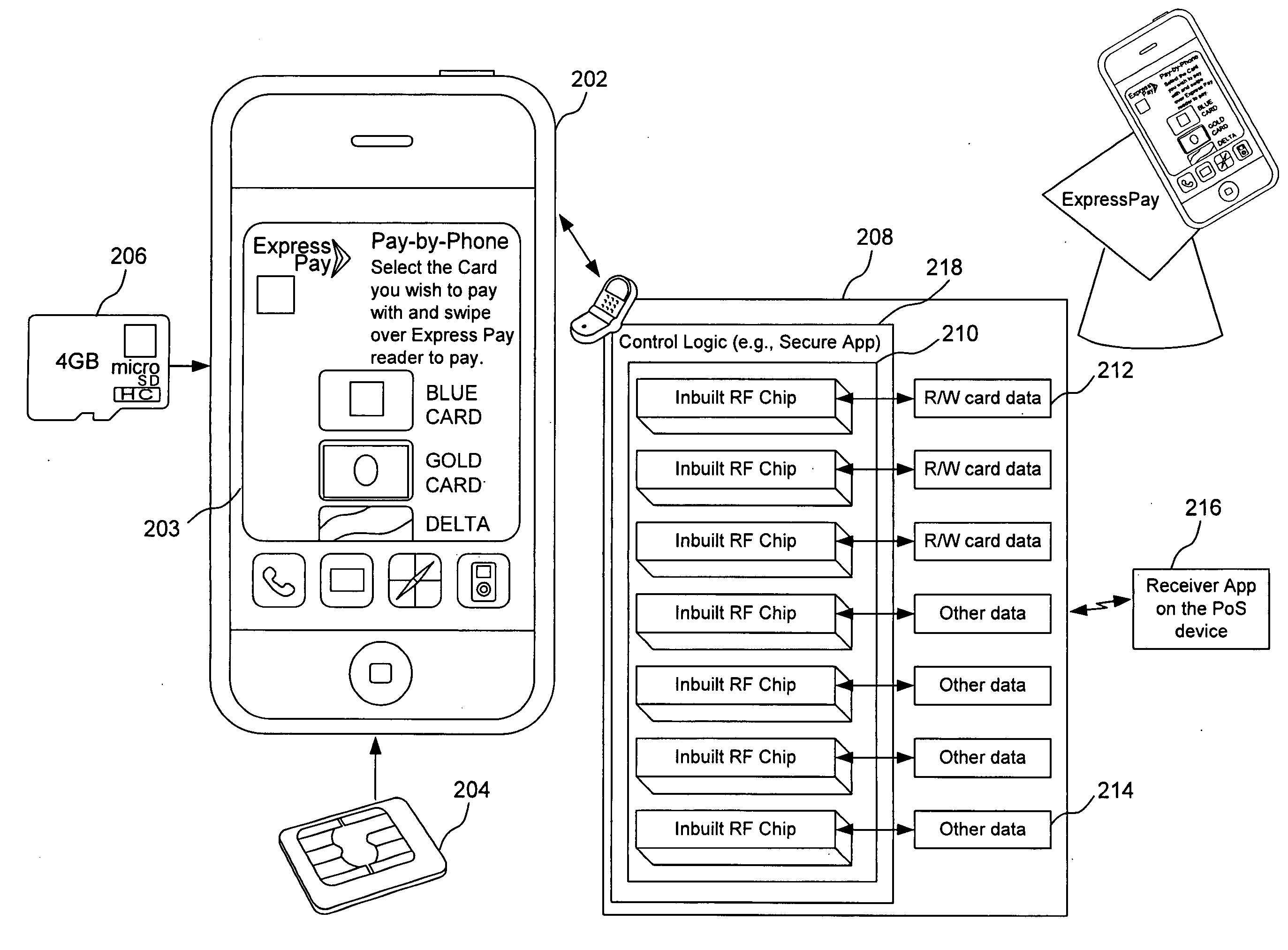
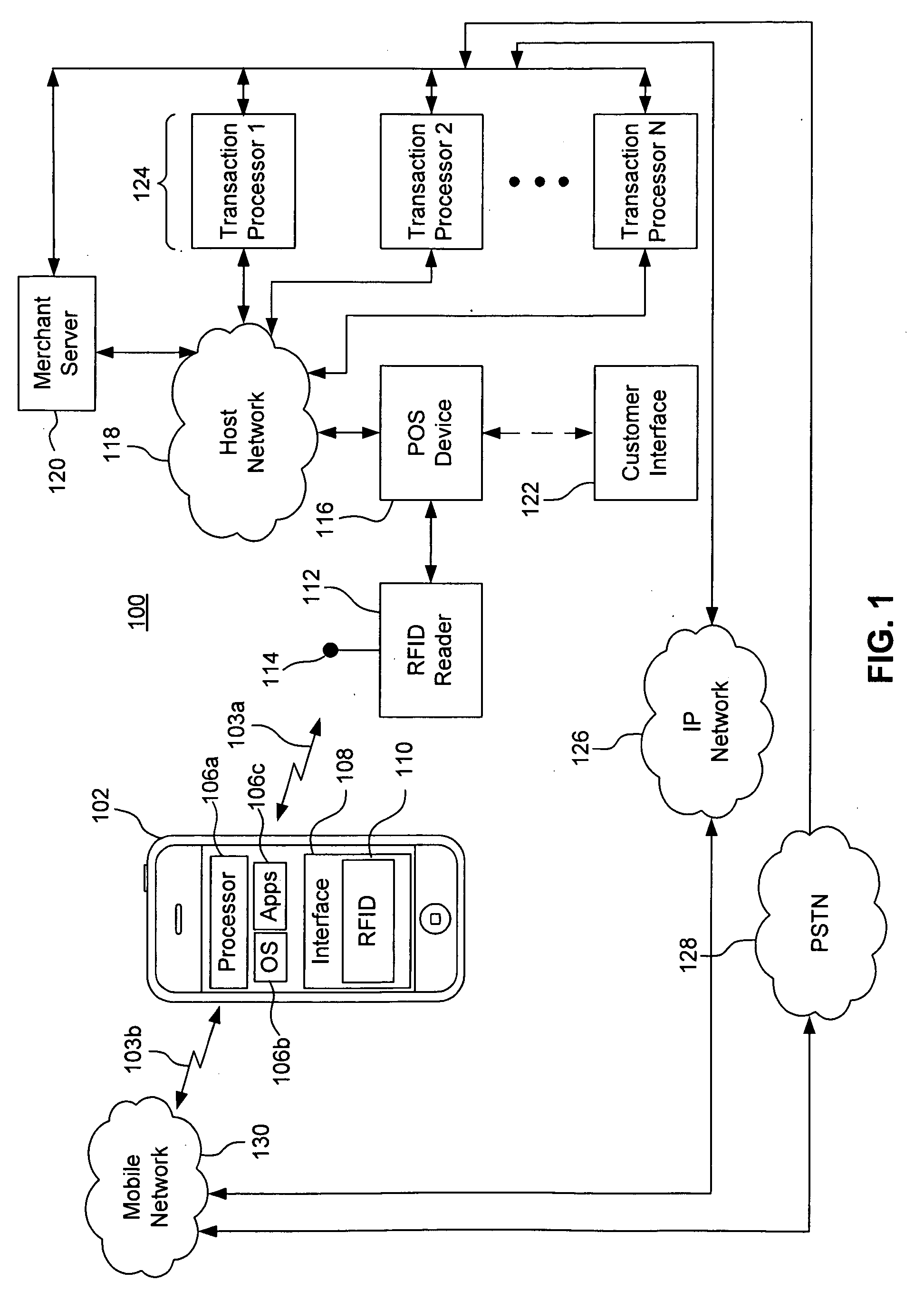
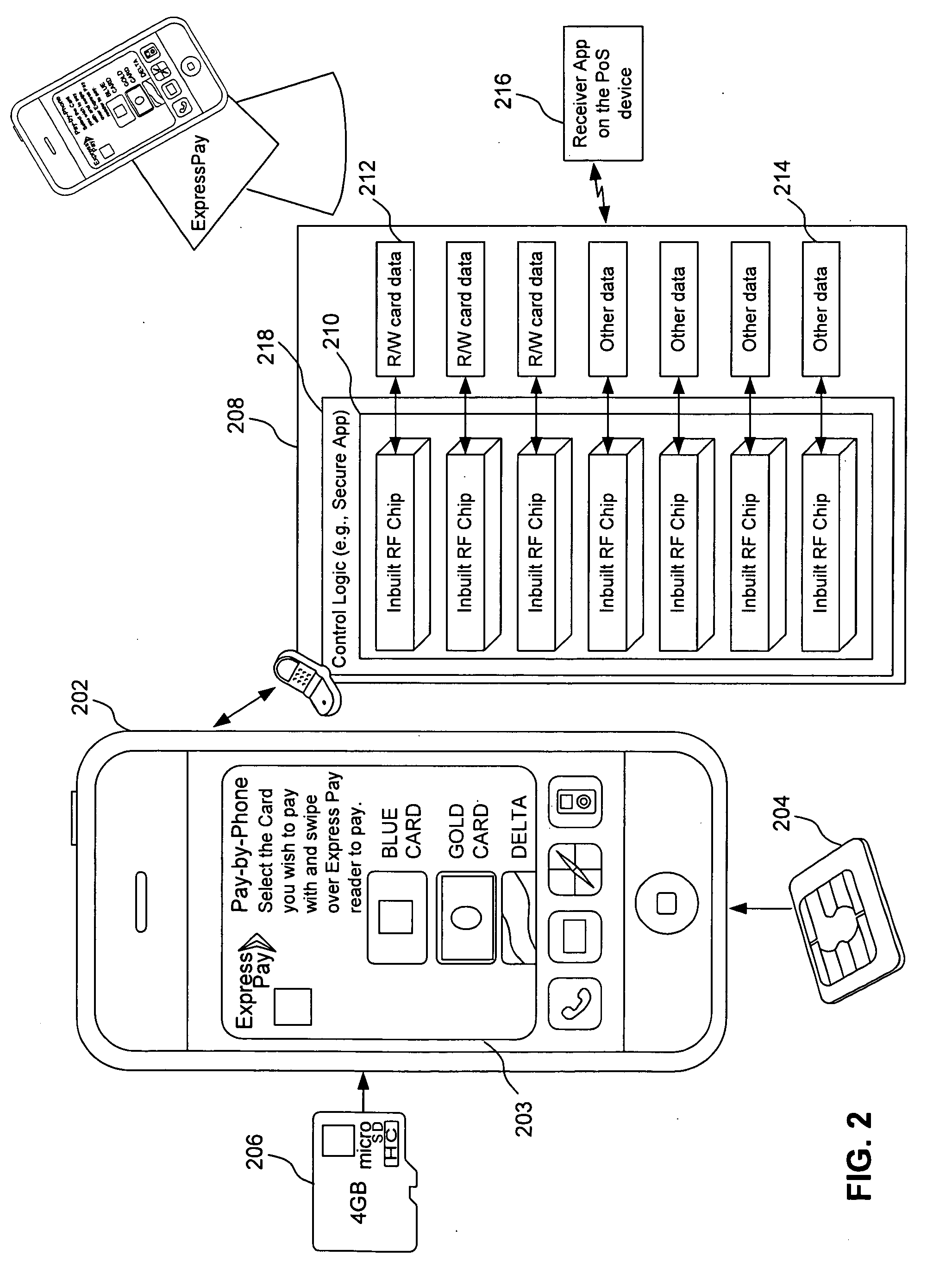
System, method, apparatus and computer program product for interfacing a multi-card radio frequency (RF) device with a mobile communications device
InactiveUS20100153269A1FinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsComputer hardwareMobile communication channels
An interface for a mobile communication device is provided, including at least one memory unit configured to store read / write data associated with transaction accounts, at least one user interface software application, and at least one contactless communication protocol application. A radio frequency identifier unit having an antenna communicates with a radio frequency identifier reader through a contactless transaction account communications channel distinct from a mobile communications channel of the mobile communication device. An input / output interface unit communicates with a corresponding input / output interface unit of the mobile communication device and provide access to and control of the at least one memory unit and the radio frequency identifier unit by a processor of the mobile communication device.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Vector network analyzer applique for adaptive communications in wireless networks
A test signal generator at a transmitter station and a facsimile generator at a receiver station go through an acquisition and tracking process which aligns the two signals so that a logical processor can compute the frequency transfer function of the entire propagation path for use in an adaptive, concurrently sent communication signal. The frequency transfer function is conveyed back to the transmit end via a control channel permitting an adaptivity function at the transmit end to influence subsequent selection of communication parameters, among which are typically transmitted data rate, selection of modulation, selection of forward error correcting coding, and selection of frequency band for transmission. The same measurement is conveyed to an adaptivity function at the receive end for use in the communications receiver to select demodulator variables such as gain control, and equalization of amplitude and phase, versus frequency. The adaptivity function also permits interspersing of reverse-direction communications over the same frequency bands in a time-share mode between forward-direction and reverse-direction communication with the measurement signals having to be transmitted in only one direction. An alternate embodiment invention of this type is described which is additionally useful for mobile communications channels. Another variation embodiment is described for pure propagation measurements only, absent conveyance of end-user information.
Owner:SARABAND WIRELESS
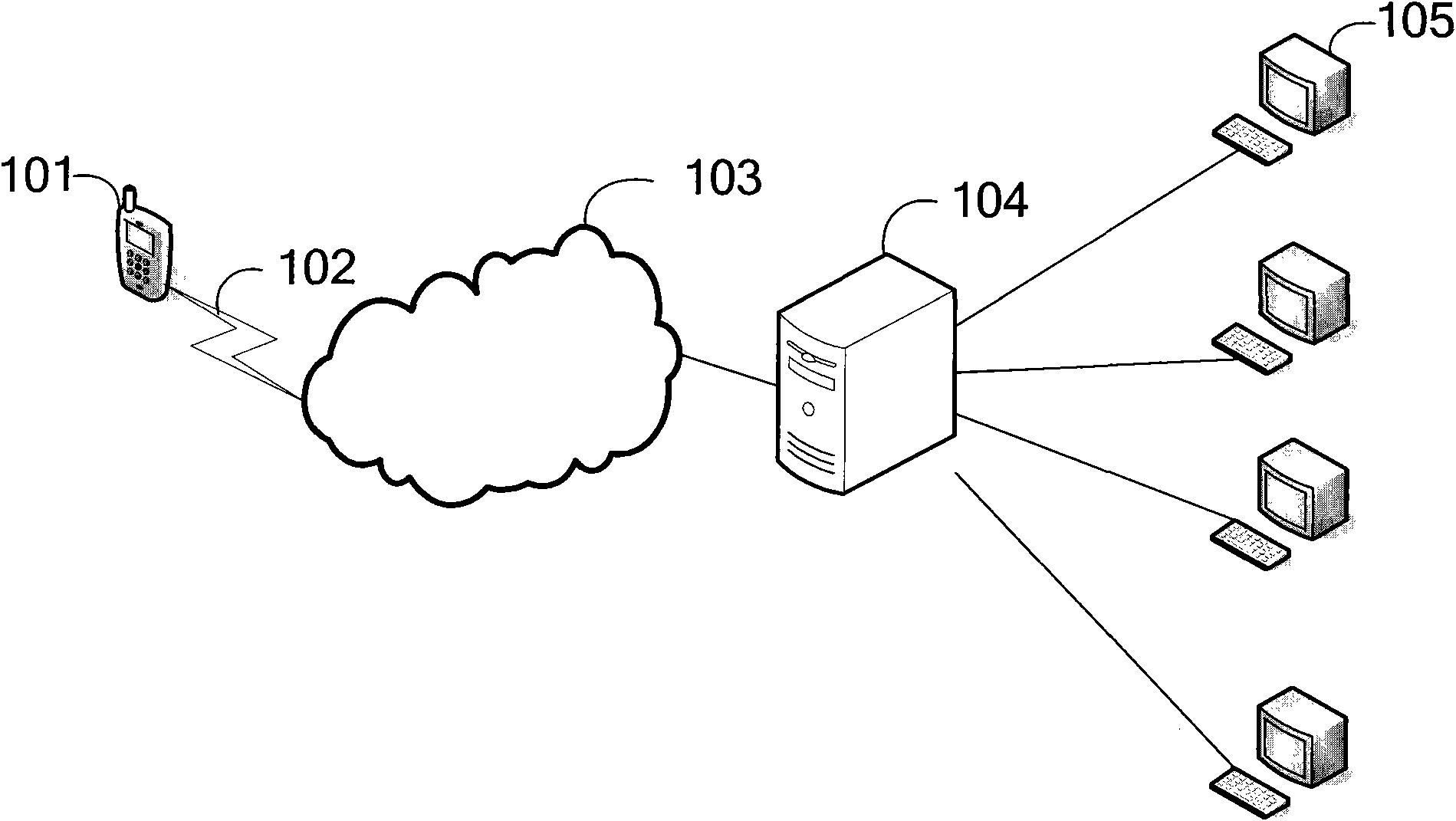
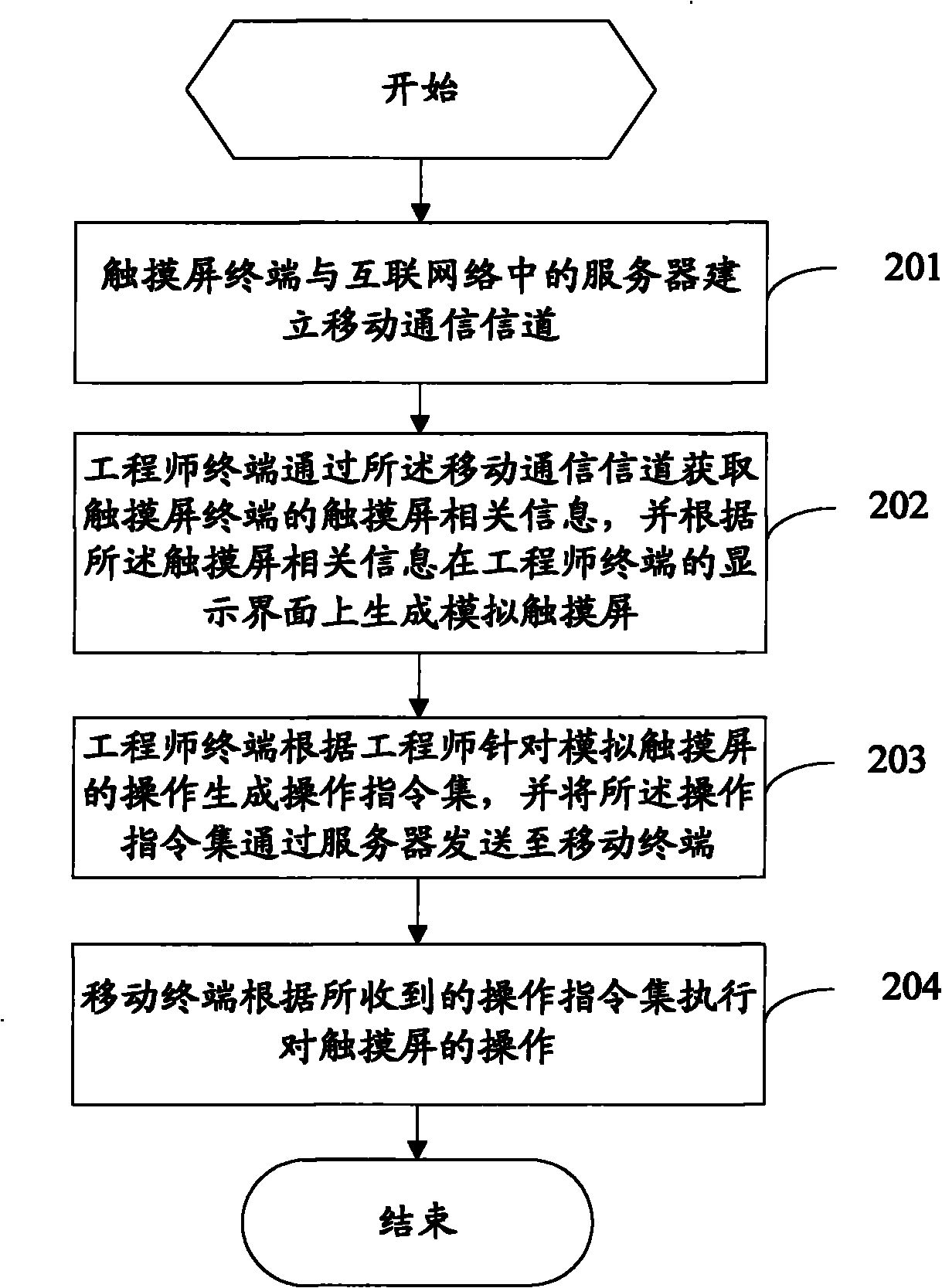
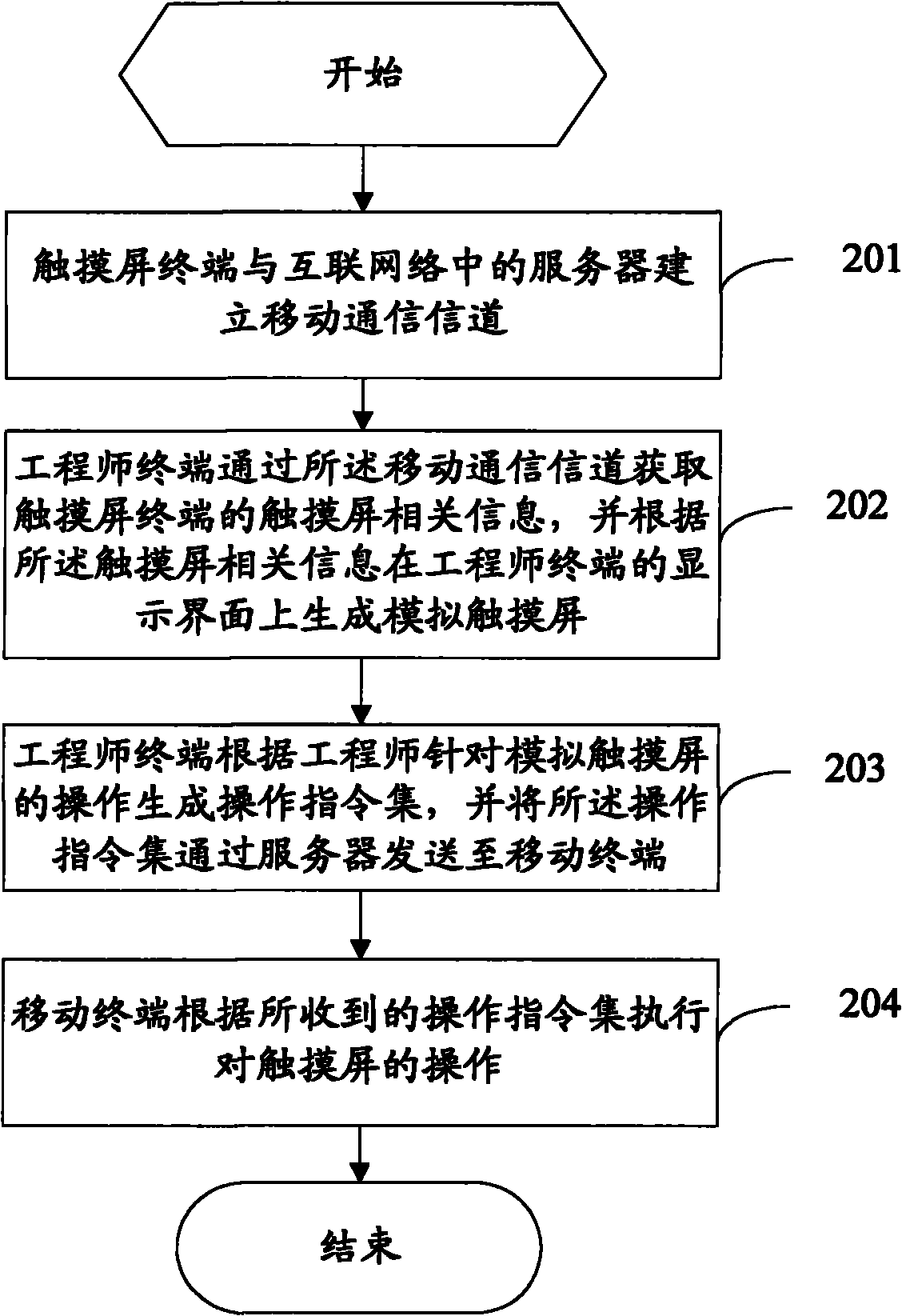
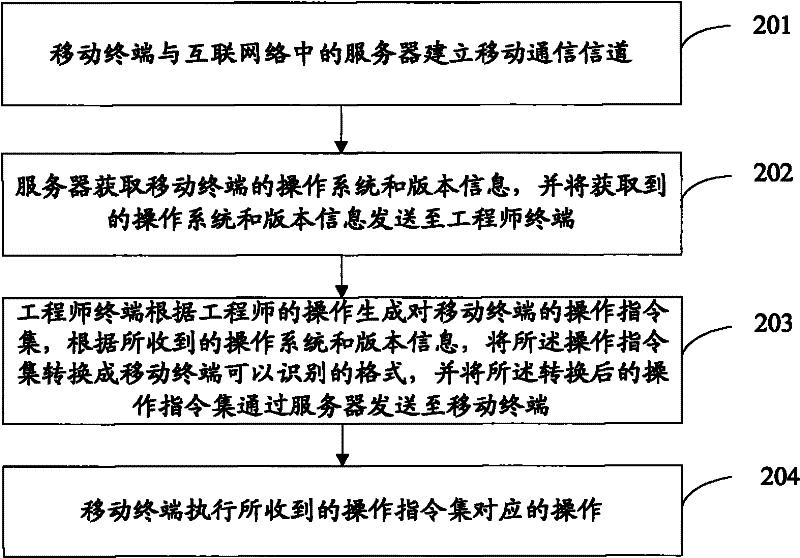
Method and system for providing remote services for touch screen terminal
ActiveCN102143235ATransmissionInput/output processes for data processingThe InternetComputer terminal
The invention provides a method for providing remote services for a touch screen terminal, comprising the following steps: establishing mobile communication channels between the touch screen terminal and a server in internet; acquiring information related to a touch screen of the touch screen terminal by the server, and sending the acquired information related to the touch screen to an engineer terminal; generating a simulated touch screen on a display interface by the engineer terminal in accordance with the information related to the touch screen; generating an operational instruction set by the engineer terminal in accordance with operations of an engineer aiming at the simulated touch screen, and sending the operational instruction set to a mobile terminal by the server; and executing operations on the touch screen by the mobile terminal in accordance with the received operational instruction set.
Owner:张林 +1
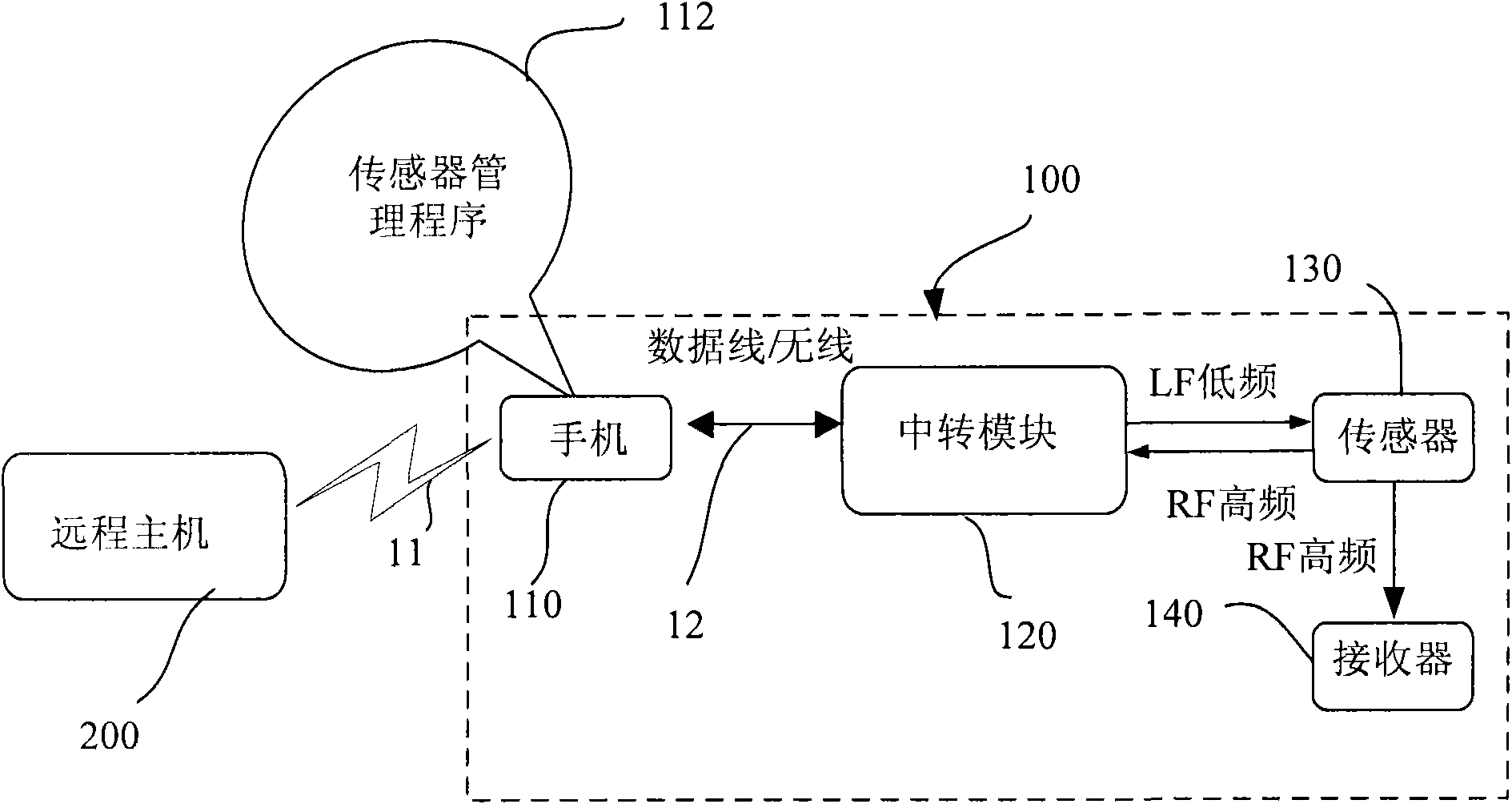
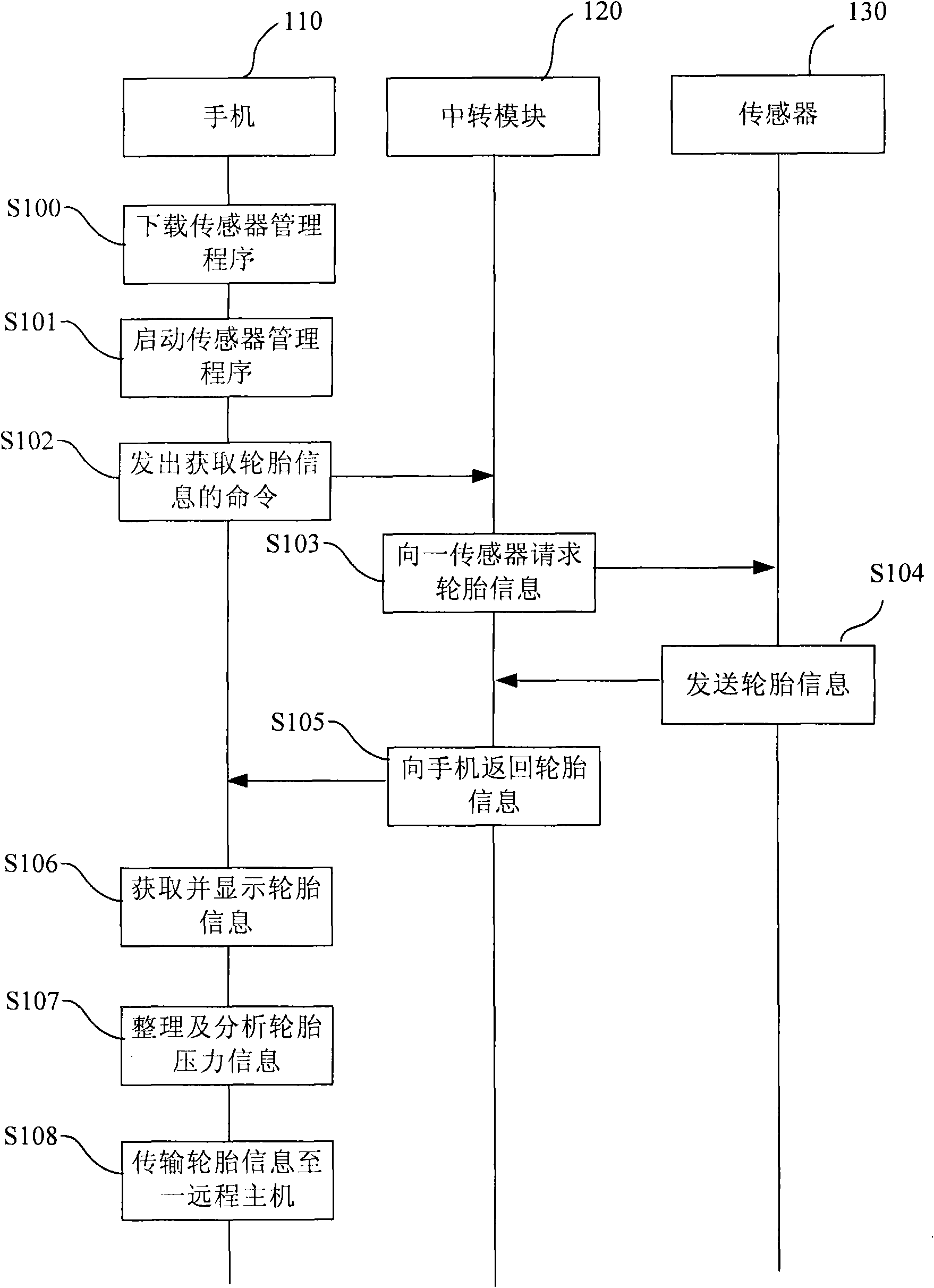
Tire pressure monitoring system and sensor management method
ActiveCN102118486AReduce volumeFlexible accessSubstation equipmentTyre measurementsComputer moduleMobile communication channels
The invention relates to a tire pressure monitoring system and a sensor management method. The tire pressure monitoring system comprises a sensor and a receiver. In the sensor management method, a portable tool is used, for instance, a mobile phone serves as a platform, and a sensor management program is loaded in and operated to monitor the sensor and update programs of the sensor. In a tire information monitoring flow, a command for obtaining tire information is sent to a transition module through a wired or wireless channel of the mobile phone; and the transition module returns the tire information back to the mobile phone through the wired or wireless channel after obtaining the tire information from the sensor. In a sensor program updating flow, a new sensor program is received through a mobile communication channel of the mobile phone and is transmitted to the sensor through the transition module, so that the sensor program is updated in at least one sensor. Compared with the former way utilizing a special sensor detecting tool, the management method is more flexible in operation and facilitates the observation, the classification and the analysis of tire pressure data.
Owner:BAOLONG HUF SHANGHAI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
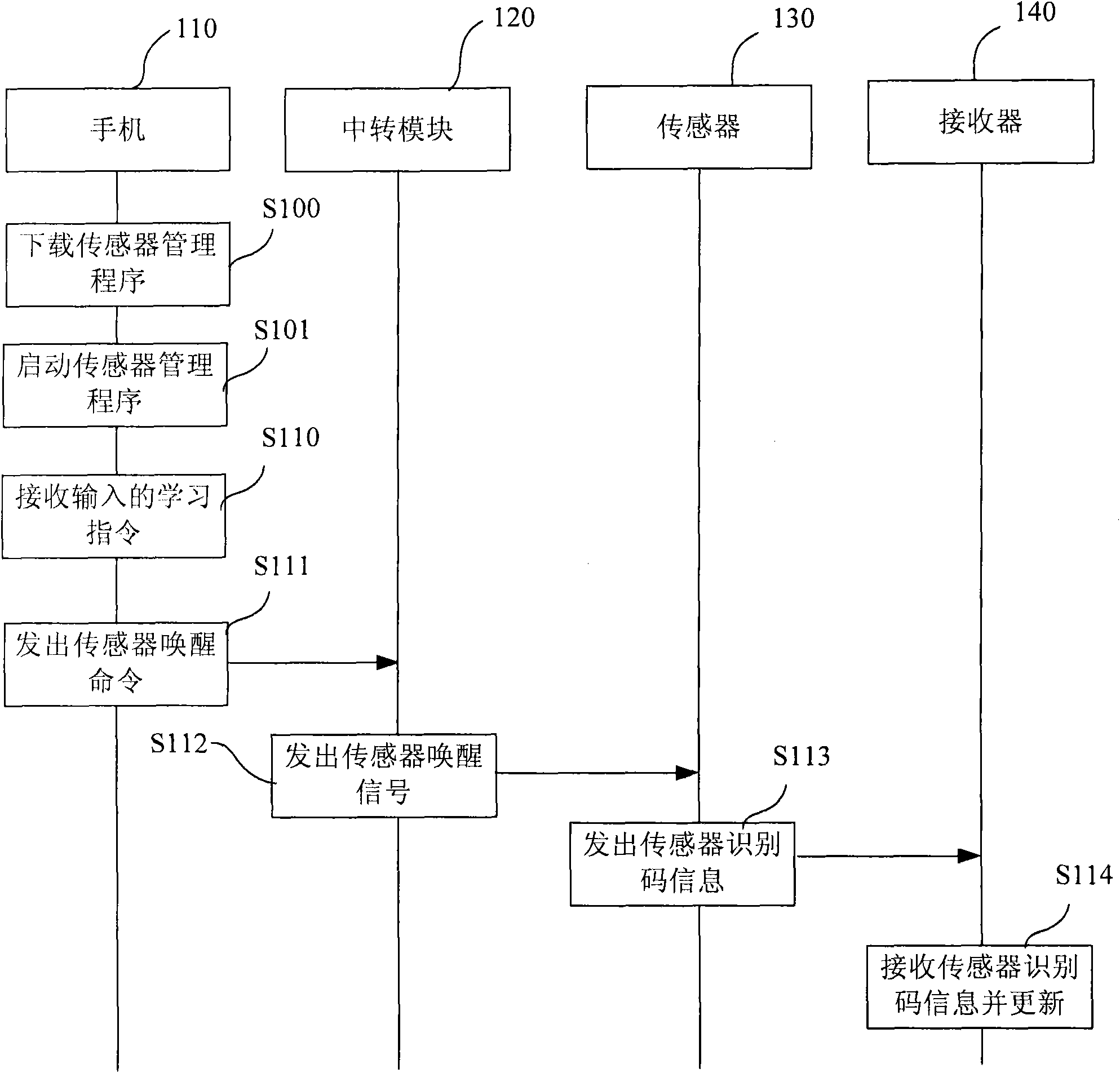
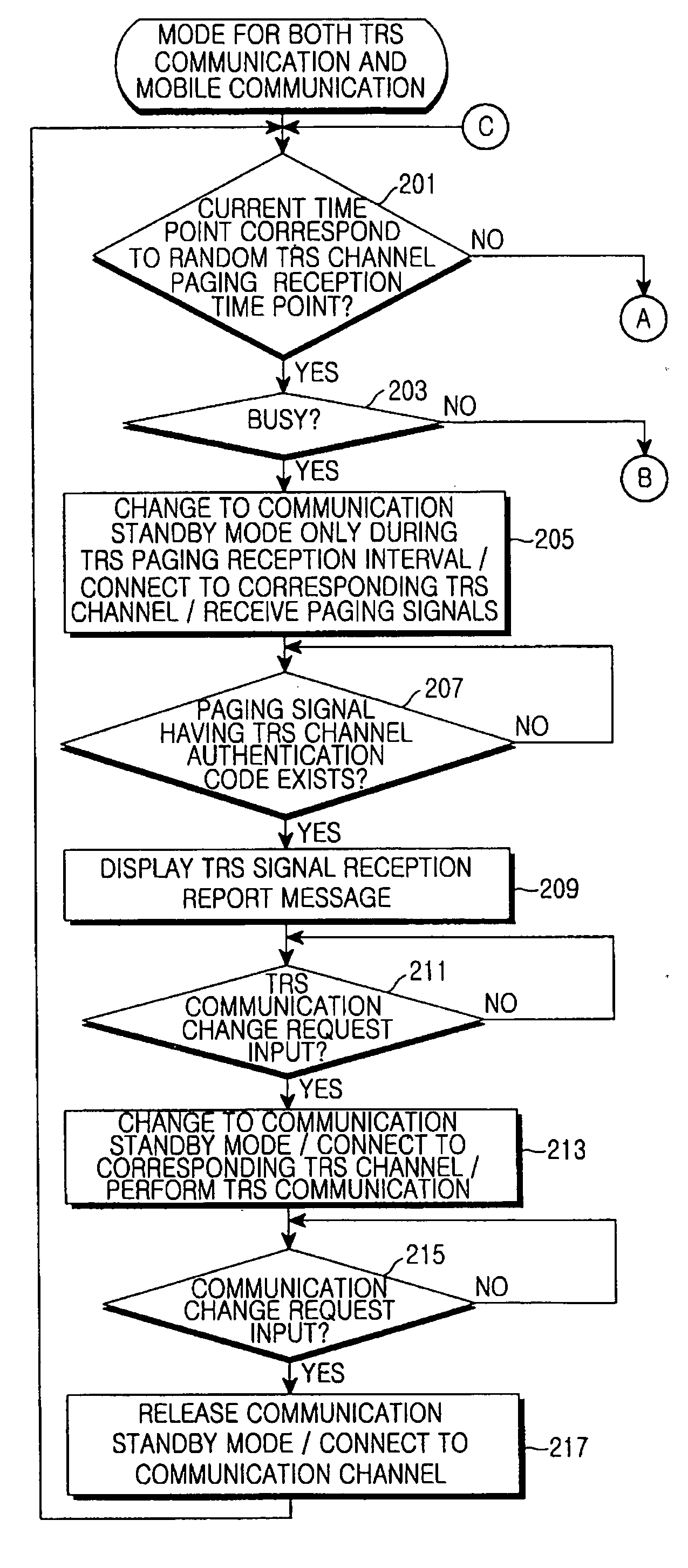
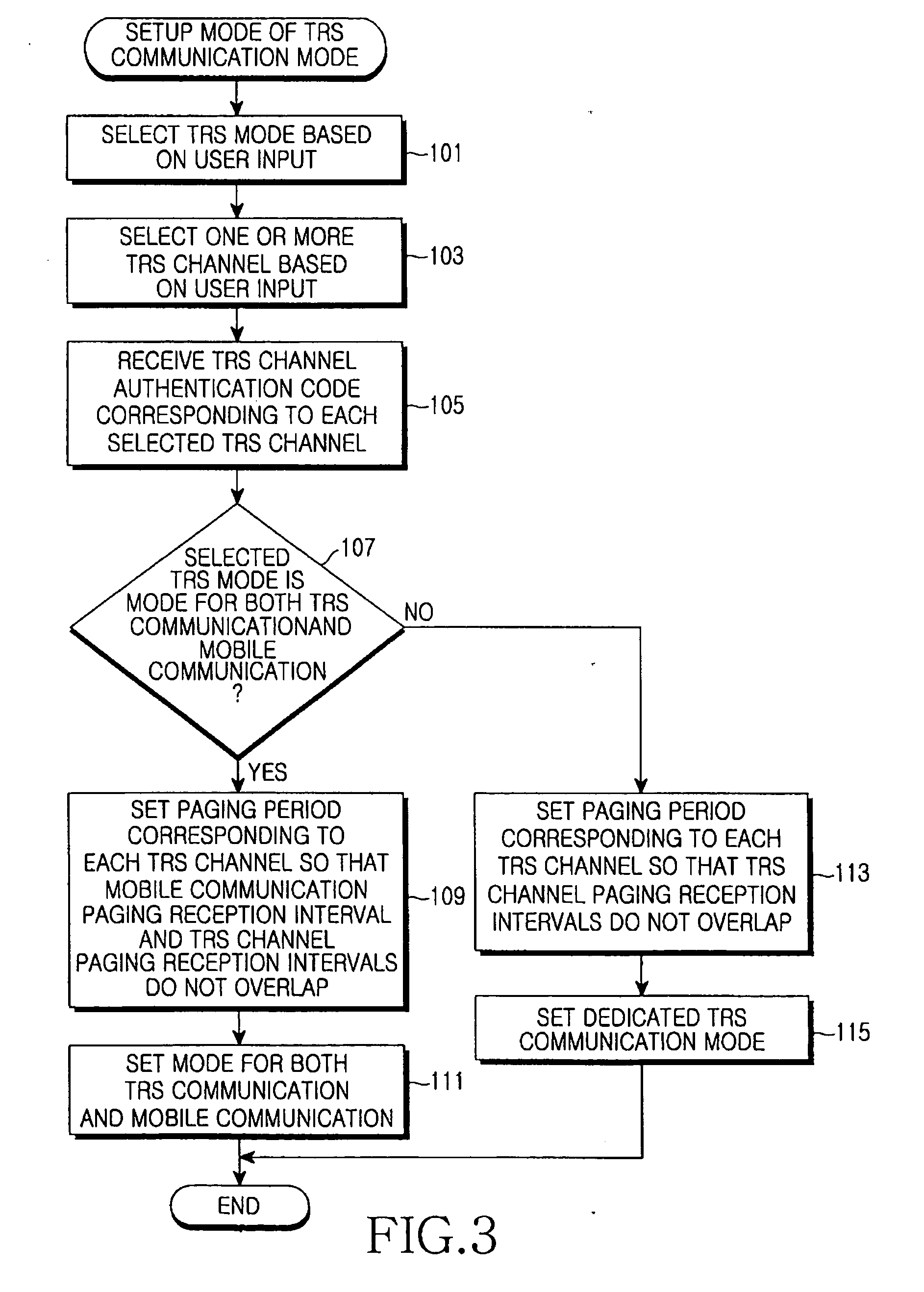
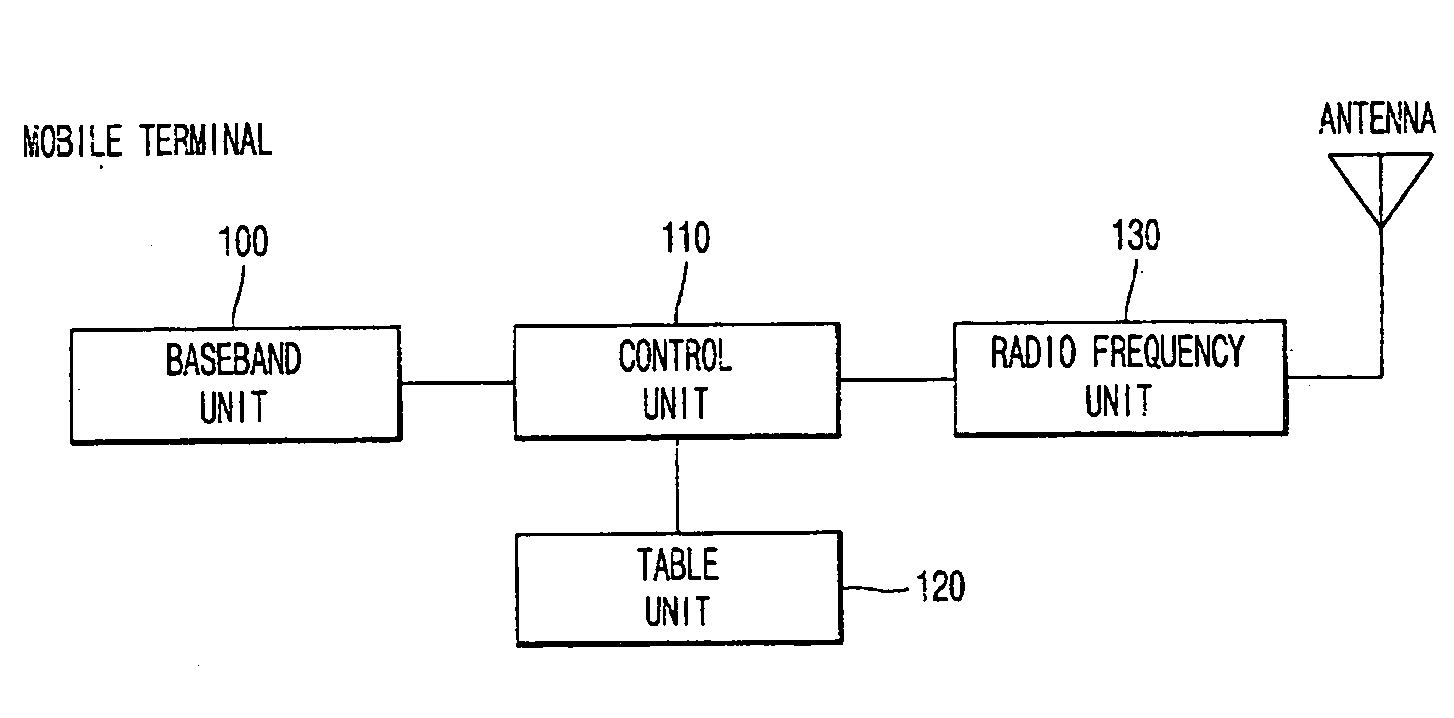
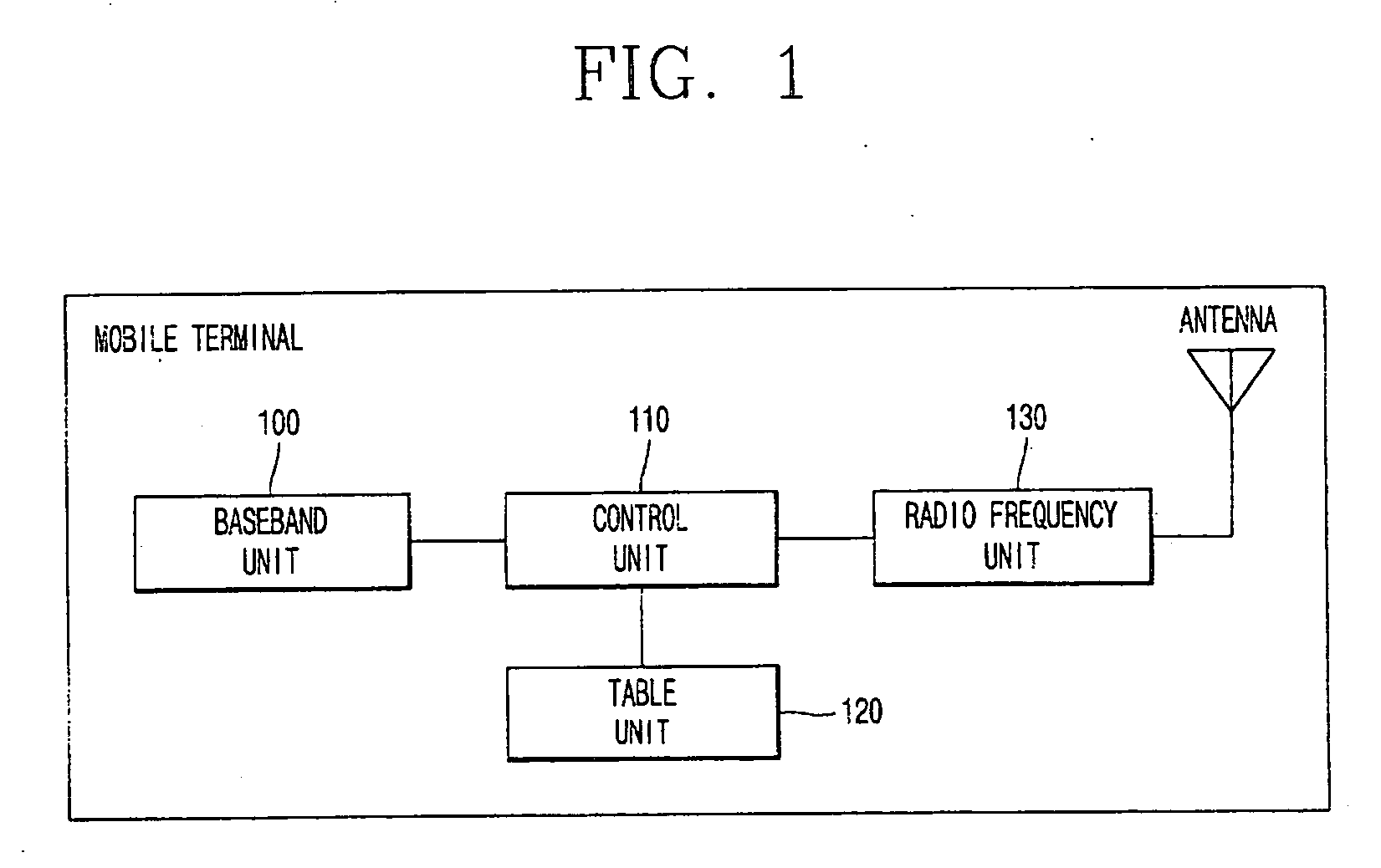
Method for performing TRS communication in a mobile communication terminal
InactiveUS20060234748A1Efficient searchReduce power consumptionNetwork topologiesConnection managementTelecommunicationsMobile communication channels
A method for performing communication in a mobile communication terminal capable of TRS communication. In the method, the mobile communication terminal periodically searches for another TRS channel or a mobile communication paging channel even though the mobile communication terminal is in communication or is in TRS communication, and informs a user of reception of TRS paging signals having a TRS channel authentication code or call termination, thereby either performing another TRS communication or mobile communication through connection to a communication channel according to user's selection. Accordingly, it is possible to efficiently manage a plurality of TRS channels or mobile communication channels, and receive and process only TRS signals including a specific TRS channel authentication code from among TRS signals of unspecified persons. Further, it is possible to curtail power consumption of the mobile communication terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus for scanning a mobile communication channel and method therefor
InactiveUS20050143082A1Improve communication efficiencyAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesMobile communication systemsMobile communication channels
The present invention provides for scanning a channel of a mobile communication system for determining availability to transmit or receive a signal. The scanning of channels is based on priority. The priority for occupying is determined by availability of a frequency group (with a frequency band) and / or an occupation number of a channel (corresponding to availability to utilize the channel).
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
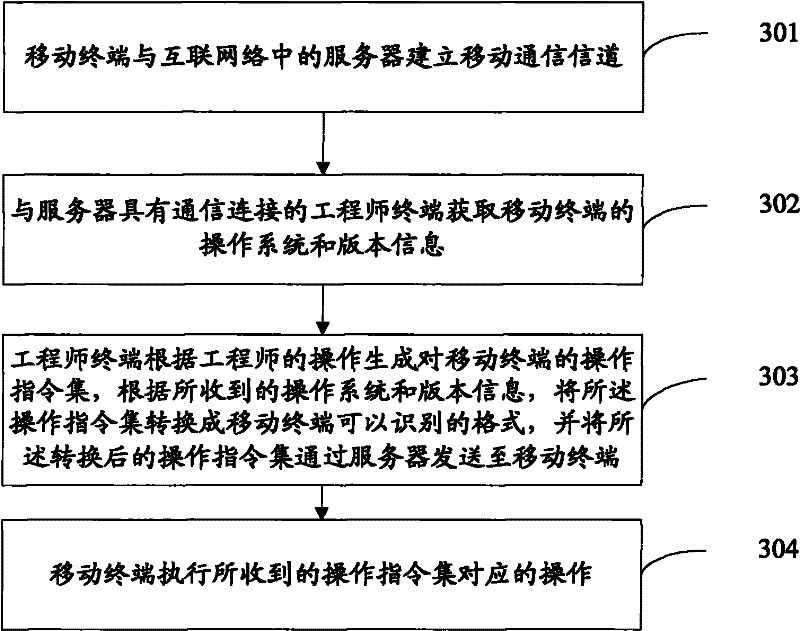
A method and system for providing remote services to mobile terminals
InactiveCN102291249AFunction activationData switching networksNetwork data managementOperating instructionOperational system
The invention provides a method for providing remote services to a mobile terminal. The mobile terminal establishes a mobile communication channel with a server in the Internet; the server obtains the operating system and version information of the mobile terminal, and sends the obtained operating system and version information to to the engineer’s terminal; the engineer’s terminal generates an operation instruction set for the mobile terminal according to the engineer’s operation, converts the operation instruction set into a format recognizable by the mobile terminal according to the received operating system and version information, and converts the converted The following operation instruction set is sent to the mobile terminal through the server; the mobile terminal executes the operation corresponding to the received operation instruction set. The invention also provides a system for providing remote service to the mobile terminal.
Owner:张林 +1
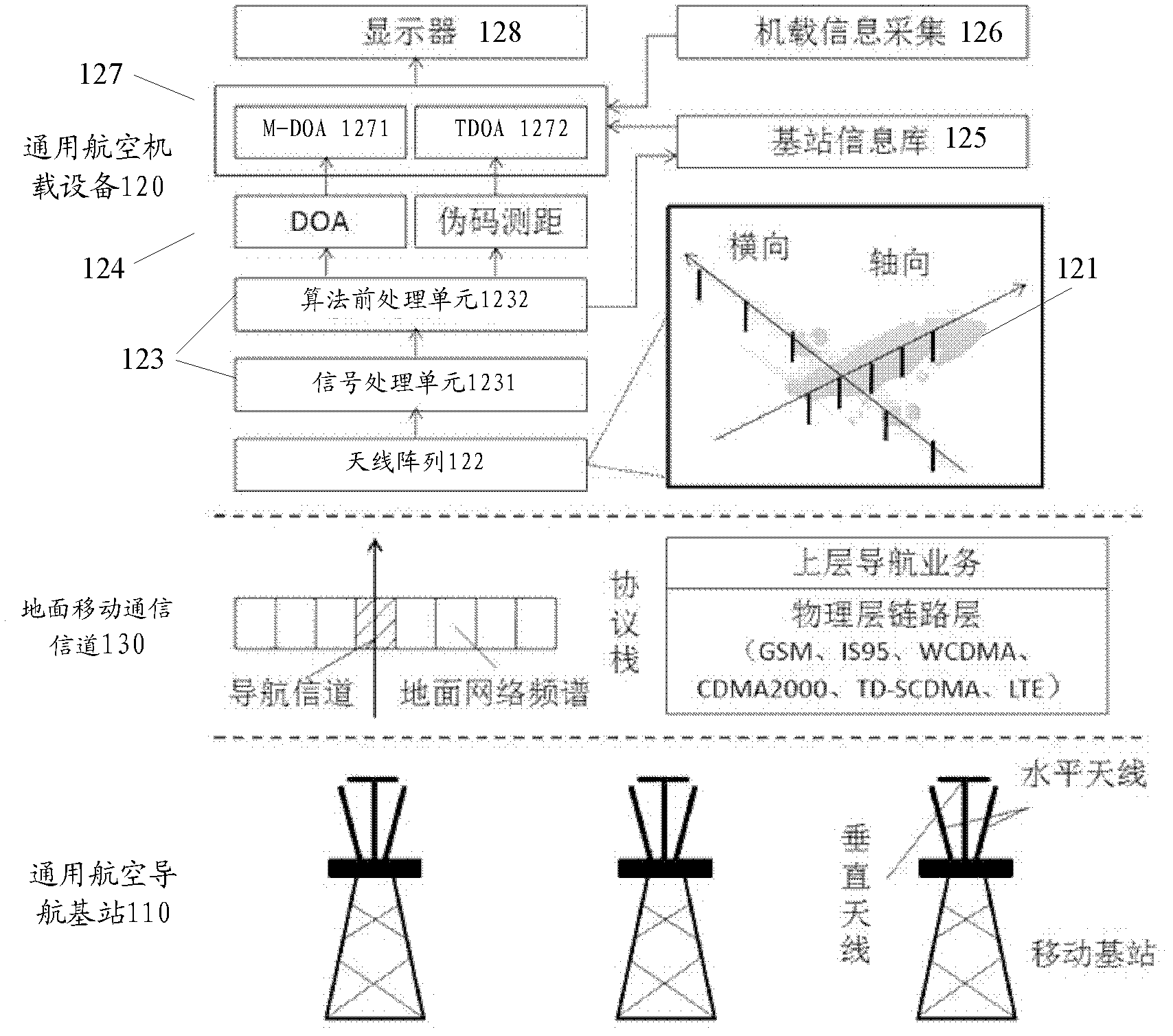
General airborne navigation system based on ground mobile communication network
InactiveCN102435194AMake up for low-altitude coverage blind spotsAvoid interferenceInstruments for comonautical navigationGeneral aviationMobile communication channels
The invention provides a general airborne navigation system based on a ground mobile communication network, which comprises a general airborne navigation base station used for transmitting a navigation signal to a preset airspace range of 0-3000m by a ground mobile communication channel, a general aircraft, and general airborne equipment which is arranged on the general aircraft and is used for calculating by utilizing the navigation signal, three-dimensional coordinate information of the general airborne navigation base station and altitude data and height information of the general aircraftto obtain position information of the general aircraft, wherein the communication channel employed for navigation is a unidirectional transmission mode, which transmits the navigation signal in a form of broadcast. According to the embodiment of the invention, the navigation system has short construction cycle and low construction cost and can meet high-efficiency general airborne navigation positioning demand. In addition, because the special ground mobile communication channel and antenna design are employed in the general airborne navigation system, the navigation system cannot generate aninterference with not only a civil aircraft navigation system but ground mobile communication user and system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
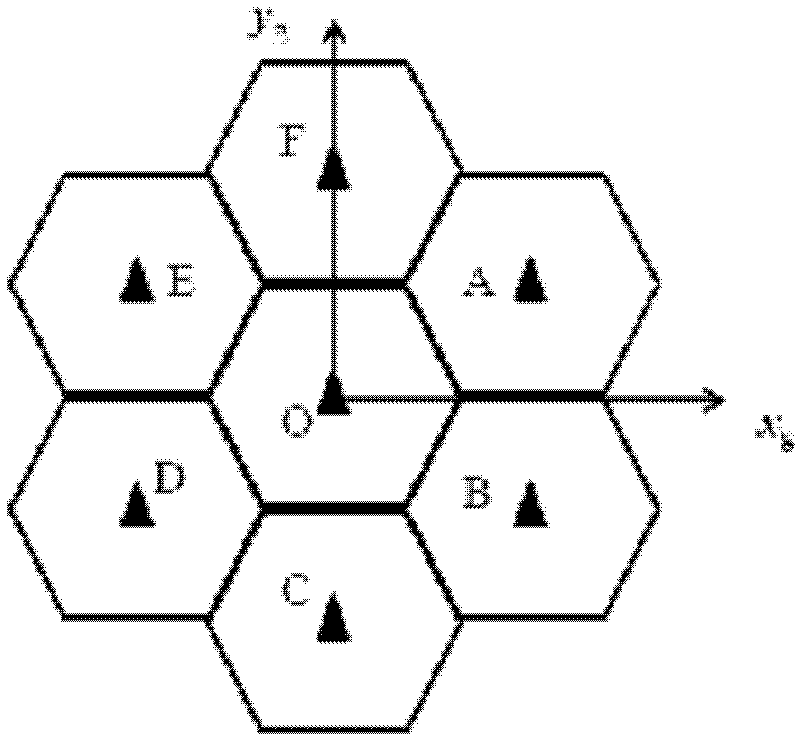
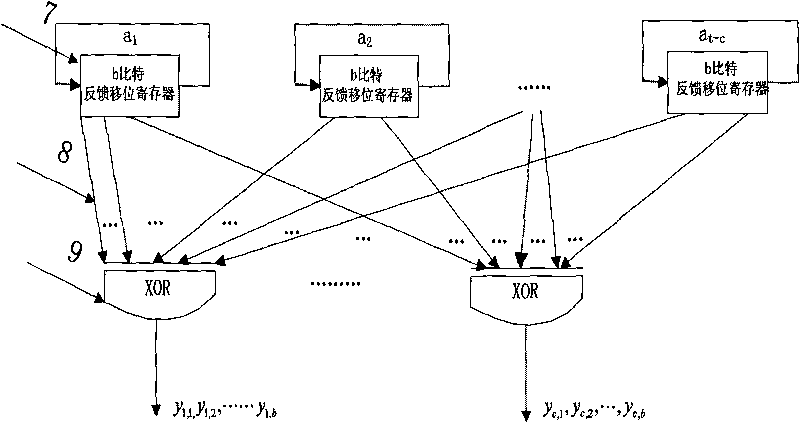
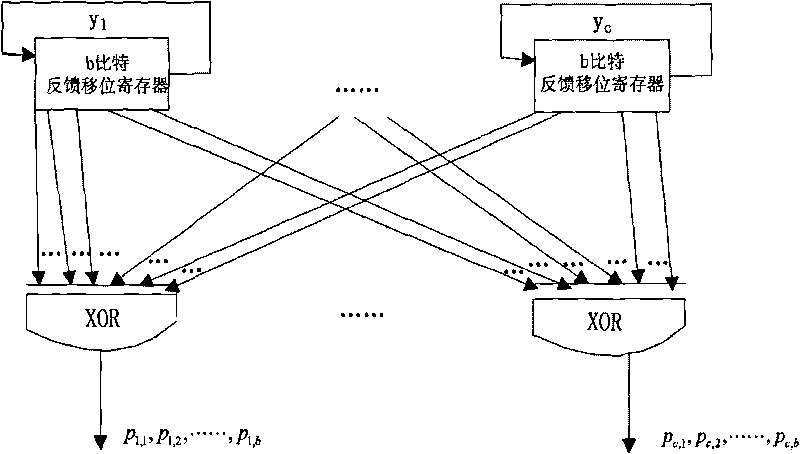
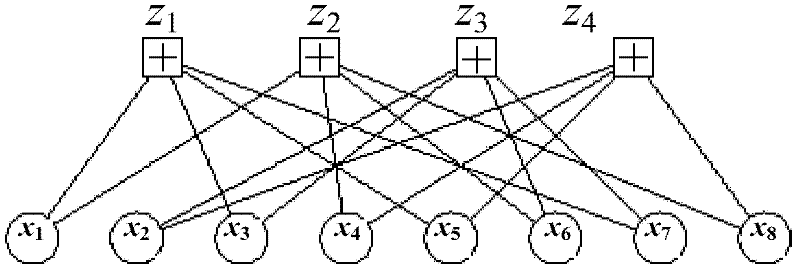
High-speed LDPC code coder and coding method thereof
InactiveCN101699770AFast encodingImprove coding efficiencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsShift registerComputer architecture
The invention relates to a high-speed LDPC code coder and a coding method thereof, belonging to the technical field of mobile communication channel coding. The coder comprises a primary and a secondary coding circuits, a temporary storage module and a control module. The primary and the secondary coding circuits each include a feedback shift register and an exclusive or gate. The primary coding circuit may obtain an intermediate vector based on a check matrix and an information bit. The temporary storage module is a register bank. The coder is characterized in that the output ends of two branches of primary circuits are connected with the register input ends of two branches of temporary storage modules; the output end of the register in the temporary storage module after passing through the control module is connected with the input end of the feedback shift register of the secondary coding circuit; and the secondary coding circuit obtains a check bit based on the intermediate vector and the check matrix. The method realizes coding by directly using the information of the check matrix, wherein the intermediate vector is obtained firstly and then the check bit is obtained based on the intermediate vector and the information in the check matrix. The method has high coding efficiency and can be widely applied to the technical field of the mobile communication channel coding.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
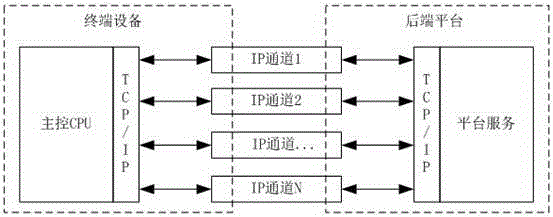
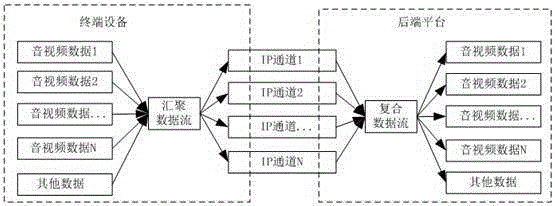
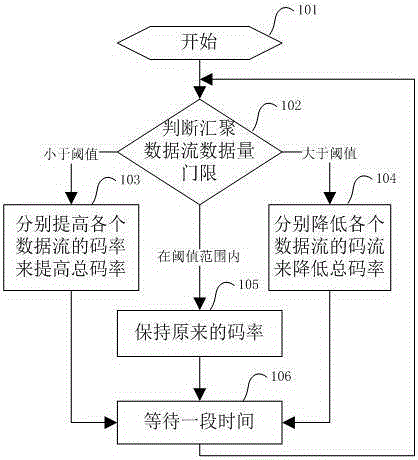
Multichannel real-time data transmission method of self-adaptive bandwidth
InactiveCN105245321AHigh bandwidthMeet transfer requirementsNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path multiple useData streamCode rate
The invention provides a multichannel real-time data transmission method of a self-adaptive bandwidth. The method comprises the following steps: compounding a plurality of data streams existent on a terminal device into a converged data stream; self-adaptively adjusting code rate of each data stream according to the total data volume of the converged data stream; dividing the converged data stream into a plurality of data packets suitable for transmission volume of an IP network, and selecting an IP channel for each data packet; transmitting each data packet to a back-end platform through the IP channel selected for the data packet. Through the adoption of the method provided by the invention, a plurality of mobile channels are compounded into a communication channel, the total bandwidth of the mobile communication channel is increased, and a transmission requirement of a higher data bandwidth is satisfied; the sending rate can be self-adaptively adjusted, so that the channel bandwidth can be utilized in maximum efficiency, and the data delay can be controlled in a reasonable range, the demand of real-time video transmission is satisfied.
Owner:ANHUI TSINGLINK INFORMATION TECH
Fast multivariate LDPC code decoding method with low decoding complexity
ActiveCN107863972ASave storage spaceGood effectError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionFast Fourier transformRound complexity
The invention discloses a fast multivariate LDPC code decoding method with a low decoding complexity, belonging to the technical field of mobile communication channel coding. According to the multivariate LDPC code decoding method, when storing decoding messages, only the decoding messages corresponding to the location of a non-zero element in a check matrix H are stored, and due to the sparsity of the check matrix H, the decoding method can greatly reduce the storage space occupied by the decoding messages when being implemented by using software or hardware. During decoding, the addressing speed of the decoding messages can be accelerated by using pre-calculated information of the non-zero element in the check matrix H, wherein the information includes the row number, the column number and an element value of the non-zero element; and meanwhile, in a decoding iteration process, fast Fourier transform is introduced to reduce the complexity of a decoding operation when processing a check node message, and thus the decoding speed can be accelerated. The decoding method disclosed by the invention has a relatively low decoding complexity, requires a small storage space, and can also increase the decoding speed to a great extent.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for link error prediction in a communication system
InactiveUS20050182994A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method is provided to accurately predict the probability of successfully recovering frames of (coded) information received over a wireless link, without having to decode the frame. This method, which consists of three steps, requires only limited information about the received signals and the forward error correction code and retransmission scheme being used. First, the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of each of the received signals is measured, where the average SNR is determined for multiple segments that together constitute the frame. Next, an algorithm is employed that takes these SNR values as inputs and determines the so-called effective SNR. The algorithm translates the measured SNR values using an appropriate convex metric, and subsequently combines the resulting values, thereby factoring in the effects of fading, multi-path, and other signal degradations. In the third stage, the effective SNR is used to determine the frame error rate by using a look-up table of a single reference curve that specifies the frame error rate of the actual error control code over an additive white Gaussian noise channel. This suffices to accurately predict the performance of a wide range of mobile communication channels. This method can be applied to a variety of retransmission strategies, including hybrid automatic-repeat request (ARQ) and incremental redundancy (IR) and combinations of these two strategies.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
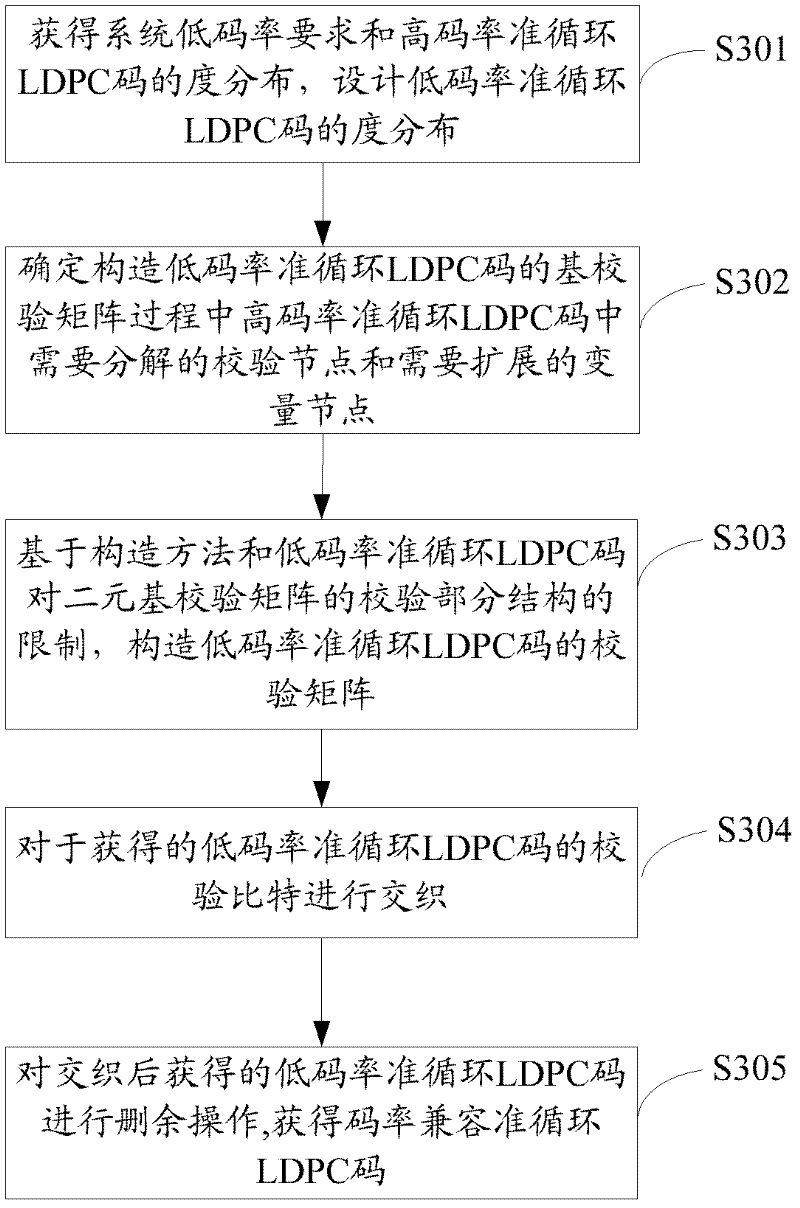
Method and device for generating code rate compatible with low density parity check (LDPC) codes and hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) schemes
InactiveCN102651652ALow degreeReduce control overheadError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceLow-density parity-check code
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile communication channel coding, in particular to a method and a device for generating code rate compatible with quasi-cyclic low density parity check (LDPC) codes. The method comprises the following steps that: the degree distribution of high-code-rate quasi-cyclic LDPC codes and the low-code-rate requirement of a system are obtained, and the degree distribution of low-code-rate quasi-cyclic LDPC codes is designed; variable nodes to be expanded and check nodes to be resolved in the high-code-rate quasi-cyclic LDPC codes in the low-code-rate quasi-cyclic LDPC code constructing process are determined; check matrixes of the low-code-rate quasi-cyclic LDPC codes are constructed on the basis of a constructing method and the limitation of the low-code-rate quasi-cyclic LDPC codes on the check matrix check part structure; and the check bits of the obtained quasi-cyclic LDPC codes are interwoven, and then, code rate compatible codes are obtained through residue deletion. The embodiment of the invention also provides the device for implementing the method and provides hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) schemes based on the code rate compatible quasi-cyclic LDPC codes.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
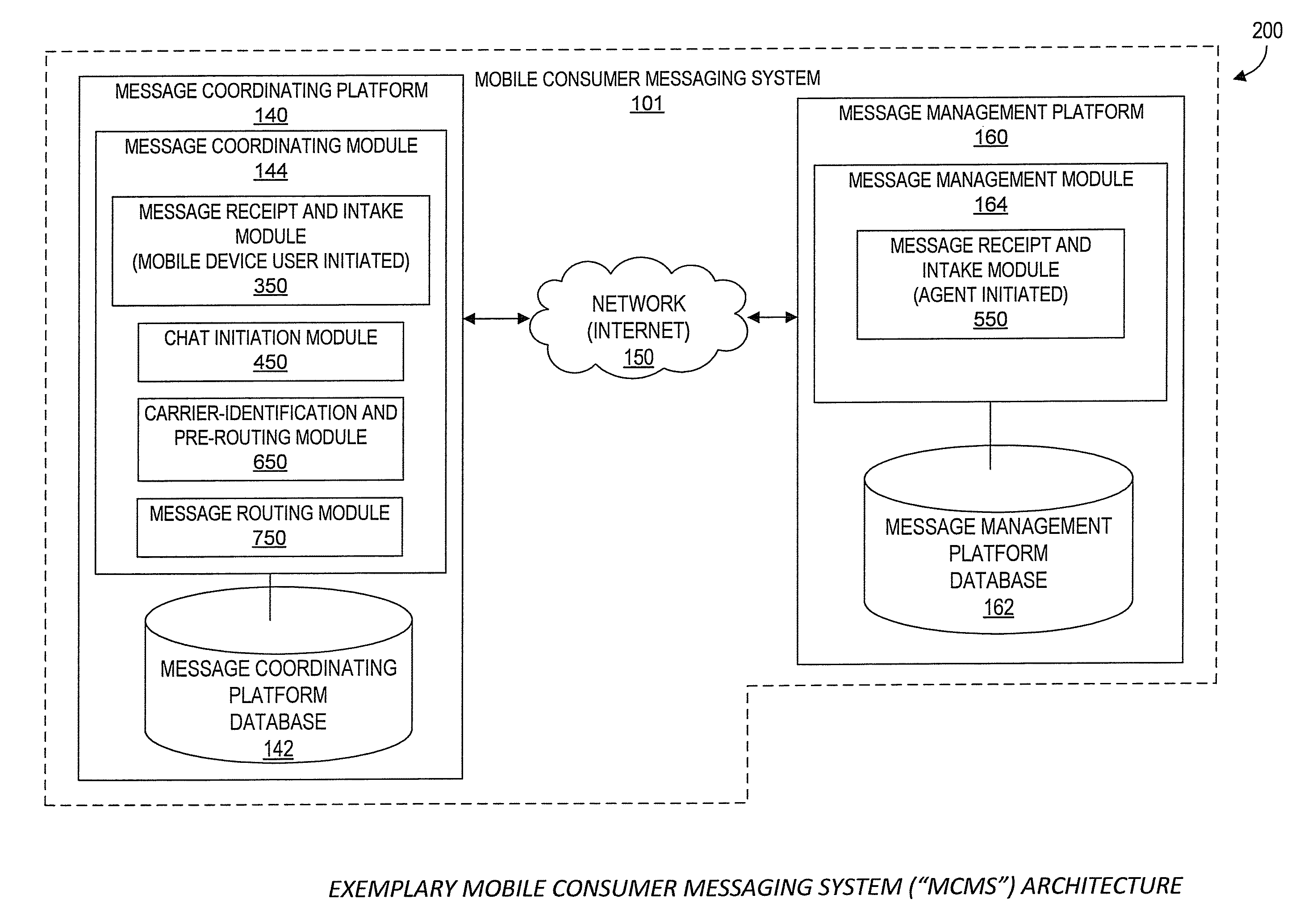
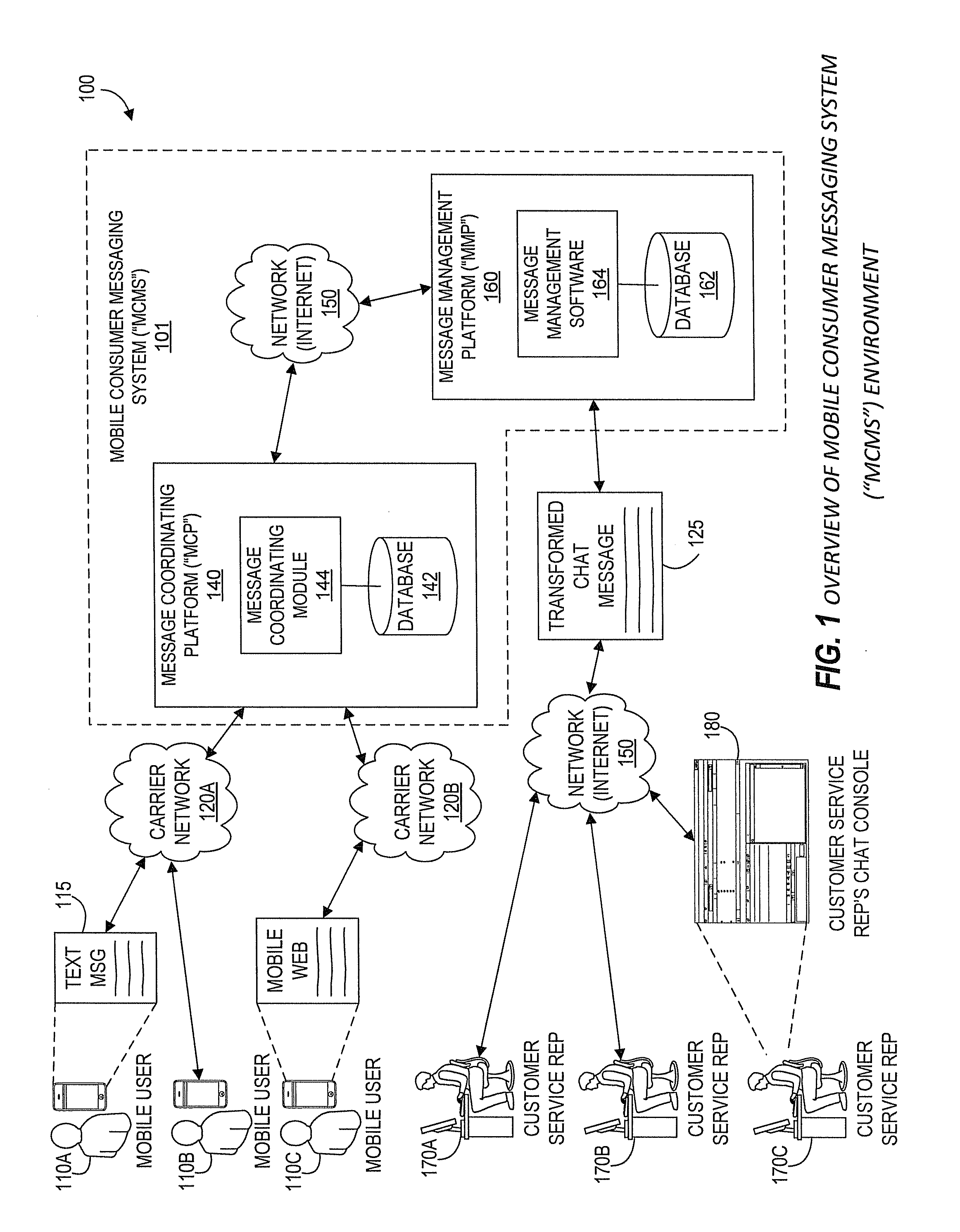
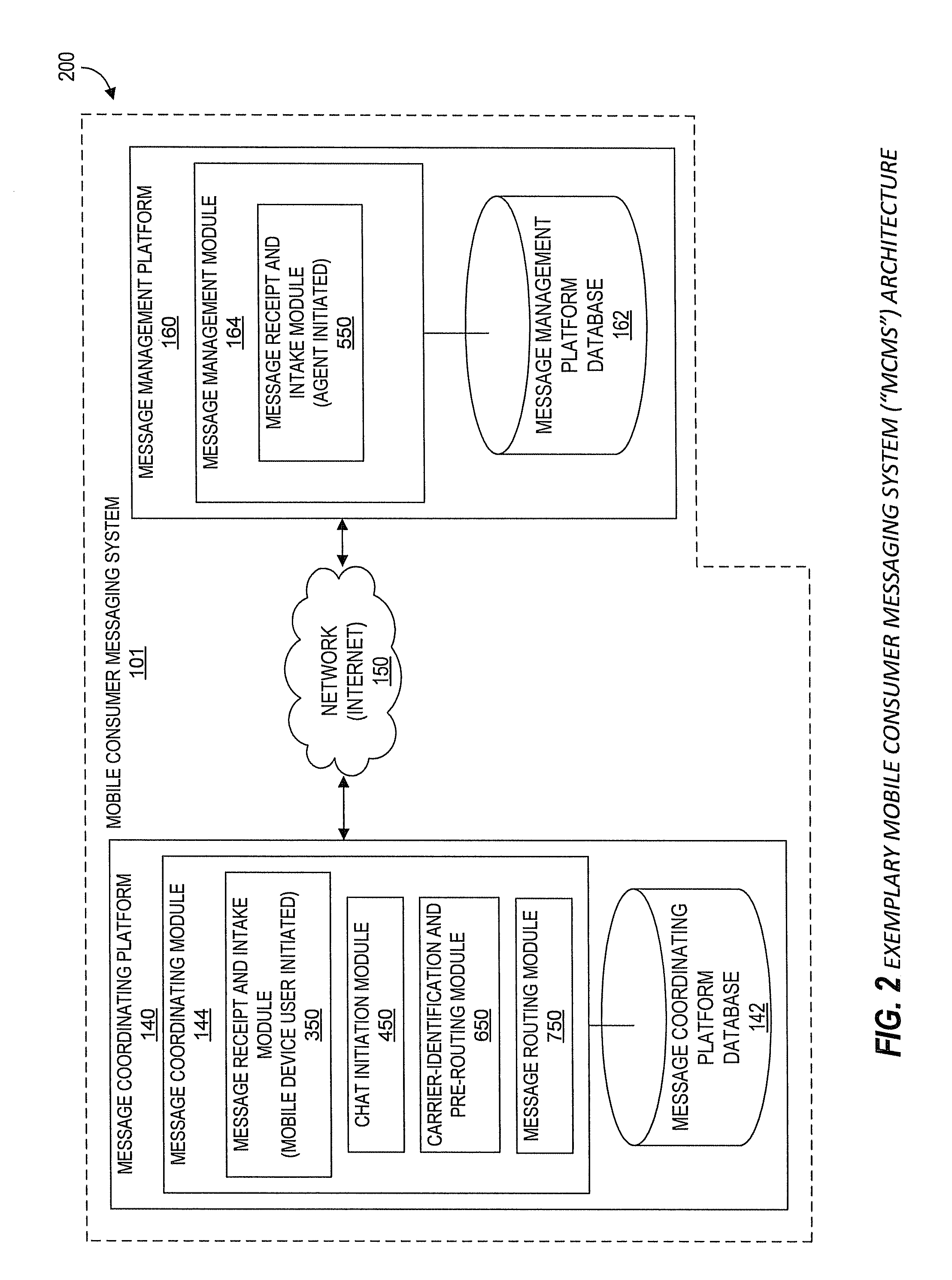
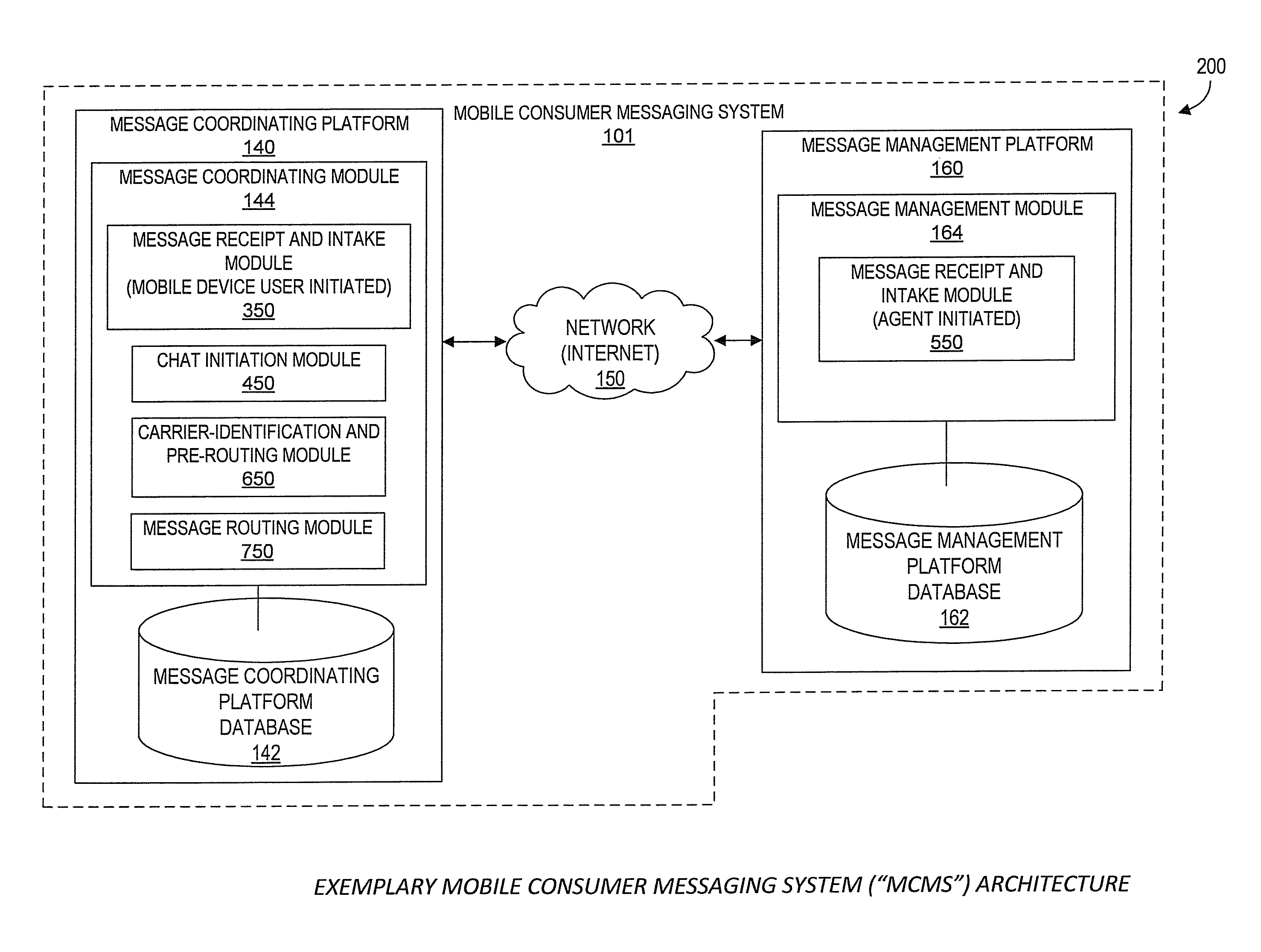
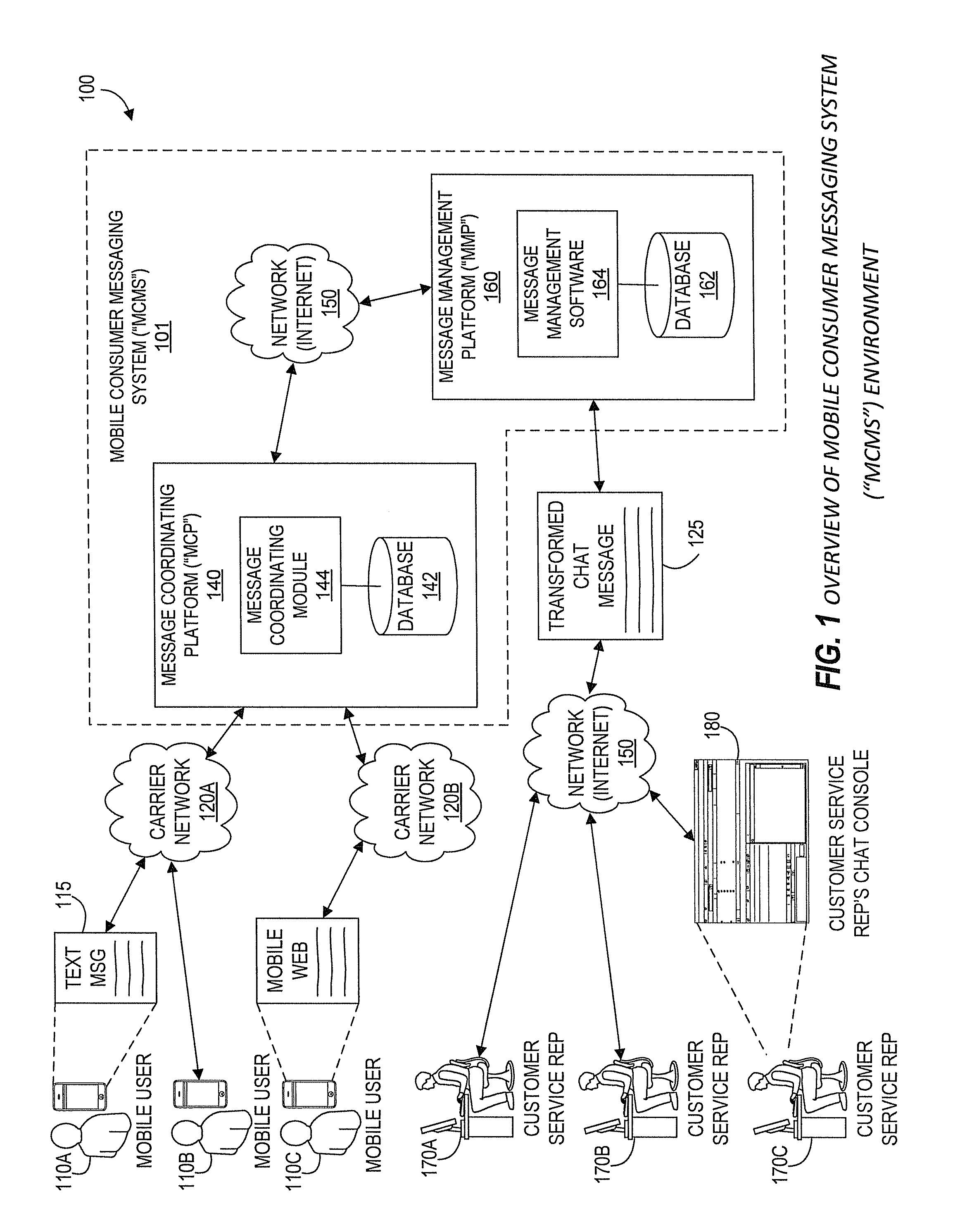
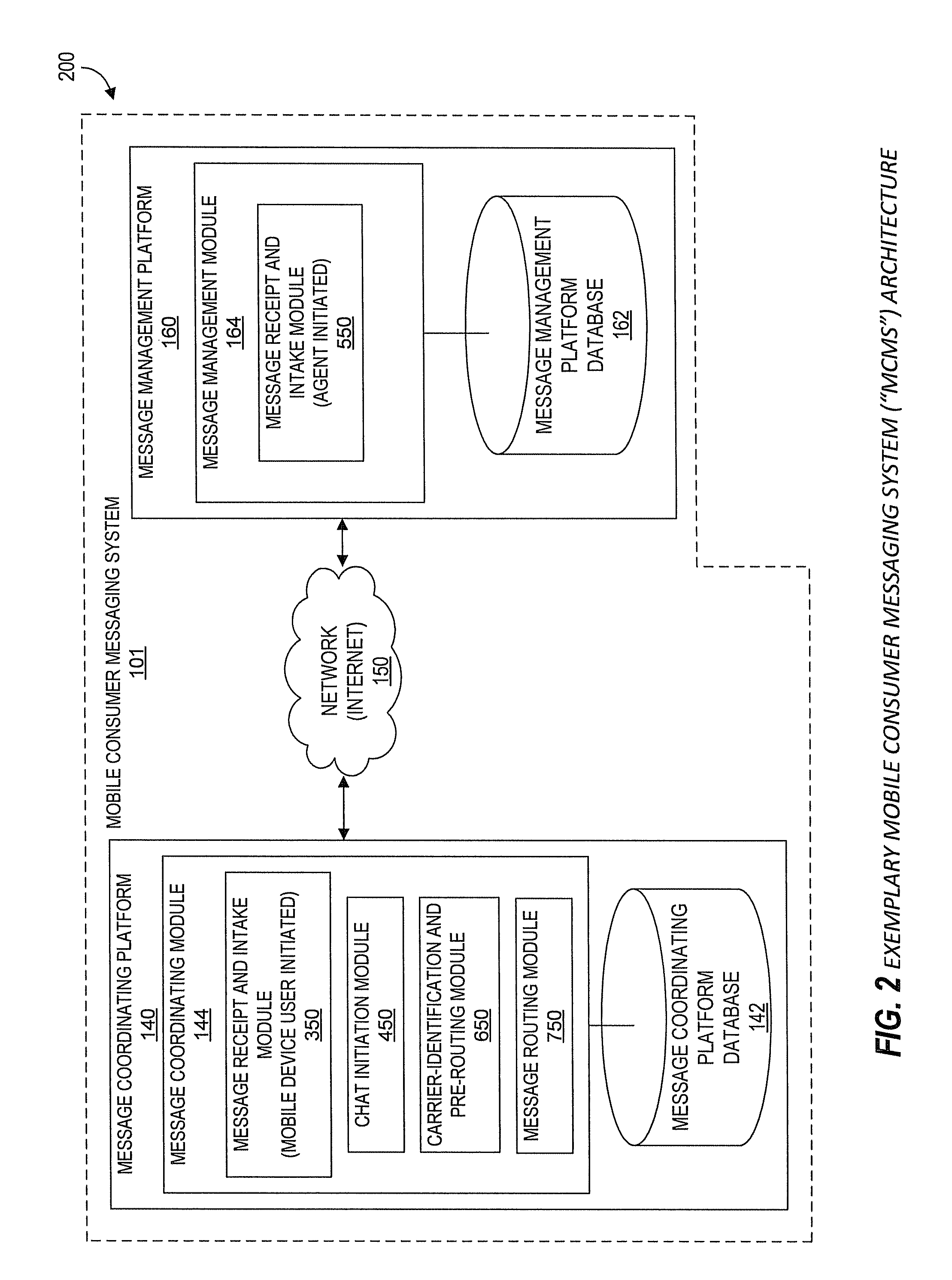
Systems and Methods for Performing Live Chat Functionality Via a Mobile Device
ActiveUS20130060871A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksMobile communication channelsMobile device
Aspects of the present disclosure generally relate to systems and methods for extending chat capabilities of traditional computer-to-computer chat systems to mobile devices. As will be generally understood, chat sessions typically allow users and chat agents to type and send / receive messages through a chat system. According to one aspect, such a mobile consumer messaging system (MCMS) utilizes existing mobile communication channels to interface with existing traditional chat systems. Specifically, in various embodiments of the MCMS, chat agents using existing, traditional chat systems are able to participate in chat sessions with end users through the users' mobile devices without specific modifications to the existing chat system. Further, according to one embodiment, chat agents utilize a single chat platform to participate in chat sessions with end users through the end users' mobile devices as well as with various other users utilizing a traditional chat system on a computer.
Owner:MGAGE
Radio safety transmission method for signal data of locomotive
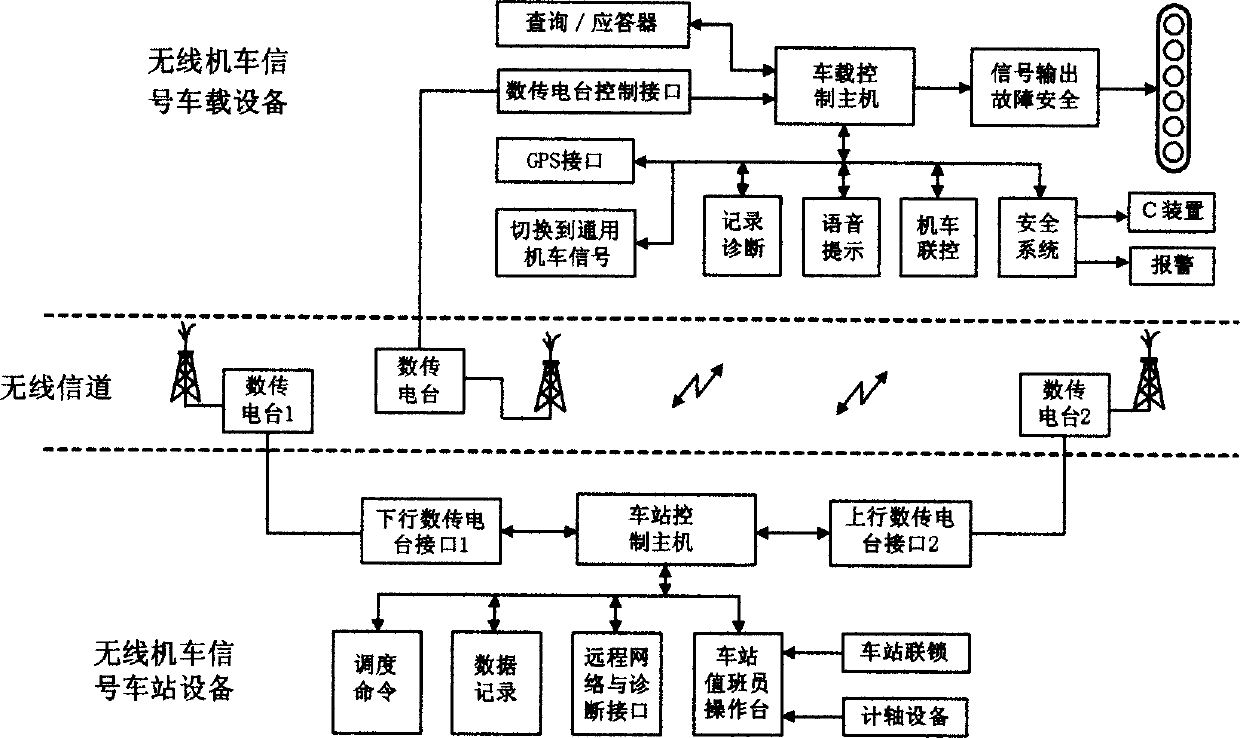
InactiveCN1794689AIncrease the level of automationFast data transferElectric signal transmission systemsStar/tree networksTransmission protocolSignal response
This invention discloses a method for safely transmitting sigal data of wireless locomotives including a wireless transmission channel structure and a safety transmission protocol, in which, the transmitting channels can be two modes of digital transmission broadcast stations and GSM-R: 1, since the data channel structure of the digital transmission broadcast stations is composed of a dynamic networking, a star structure, a mode of frequency alternation between stations and address selection, a transmission way and a communication protocol, it solves the problem of interference of same frequencies, conflict of transmission frames, locking the broadcast stations, signal covering, hand off and communication protocols, 2, based on the structure of the data transmission channel of the GSM-R digital mobile communication channel, the access way of loading and the ground devices and device interfaces, 3, related transmission protocol, 3-D control and signal response confirmation can secure the reliable and safe transmission.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Error vector magnitude measurement device and method for satellite mobile communication terminal
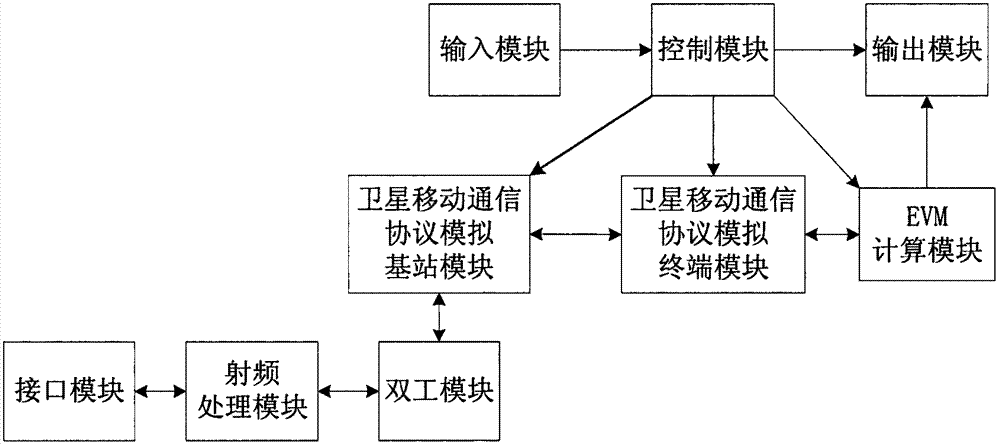
ActiveCN102739328AImprove measurement accuracyReduce calculation errorsRadio transmissionRelay systems monitoringMeasurement deviceProcess module
The invention discloses an error vector magnitude measurement device and a method for a satellite mobile communication terminal. The device comprises an input module, an output module, a control module, an EVM (Error Vector Magnitude) calculation module, a satellite mobile communication protocol simulation terminal module, a satellite mobile communication protocol simulation base station module, a duplexing module, a radio frequency processing module and an interface module. Through the simulation of a mobile communication channel and the calculation of error vector magnitude simulator to the actual communication process, the requirement on the testing of a satellite mobile communication system is met, and further, the vector magnitude device and the method are applicable to a GMR (Giant Magneto Resistance) system and very significant for actual engineering application.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transferring multiple symbol streams at low bit-error rates in a narrowband channel
InactiveUS7116726B2Accurate identificationImprove discriminationSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsLow speedTransceiver
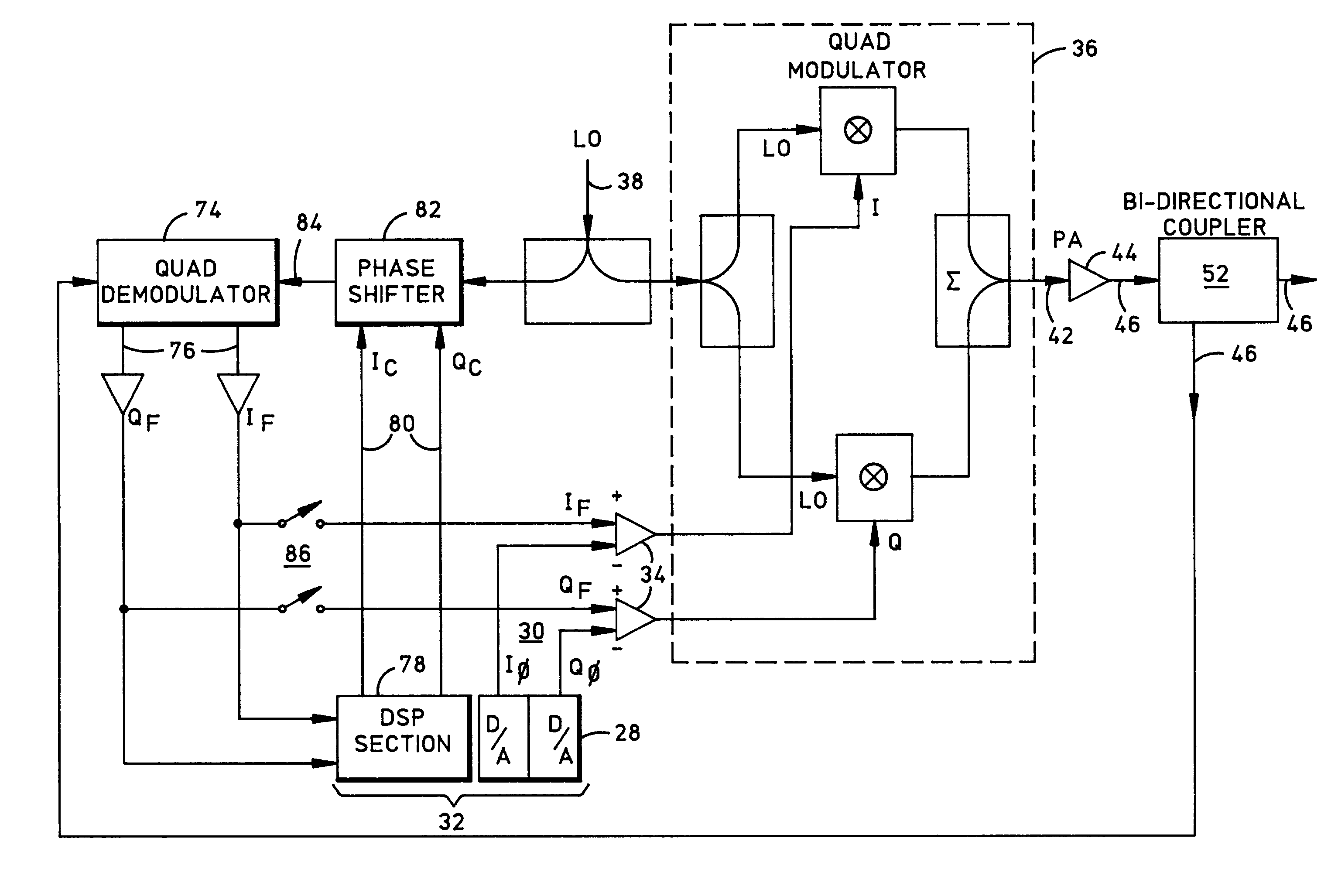
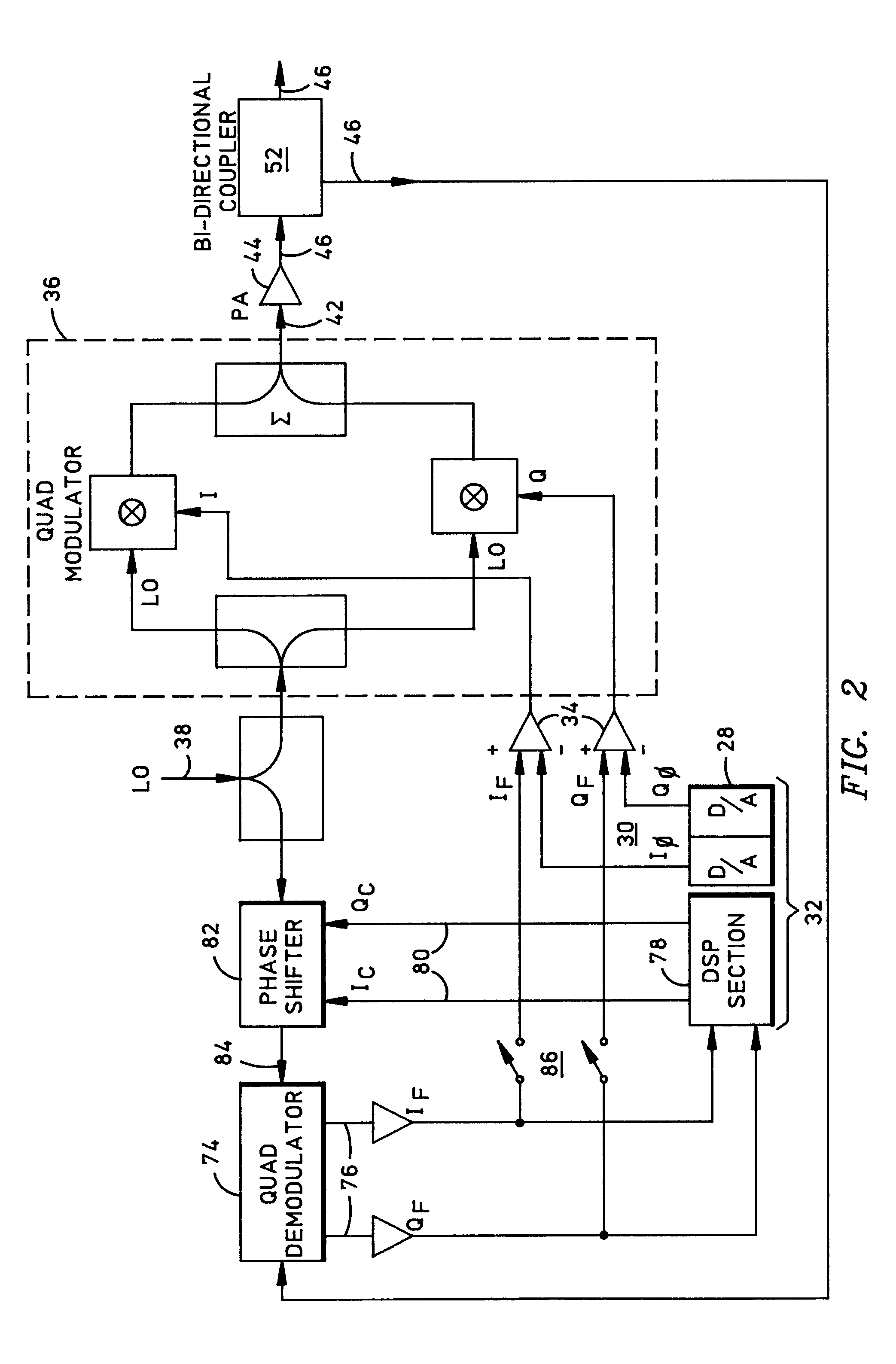
A transceiver system employing vector feedback to linearize the transmitter over a narrowband channel to support concurrent low-rate subchannels, each providing a low bit error rate (BER). Symbols in each subchannel are transmitted at a rate sufficiently slow to avoid multipath errors, thereby spreading each signal component across the entire channel bandwidth to eliminate any remaining discrete non-linearity. The system provides for generating constellations of signal states that can be optimized for both phase and amplitude to represent symbols within existing narrowband mobile communications channels. Symbols are transmitted at a rate sufficiently slow in each subchannel to decorrelate multipath interference at the receiver, thereby better discriminating adjacent symbol states. This transceiver is particularly useful for mobile environments, although it applies equally well to stationary environments. Data sequences may be transferred at up to 110 kbits / sec within a standard 25 kHz RF channel for slow scan video applications.
Owner:CUBIC CORP
Information processing method and mobile terminal
InactiveCN104601827AAchieve communicationImprove communication efficiencySubstation equipmentWireless commuication servicesInformation processingTelecommunications
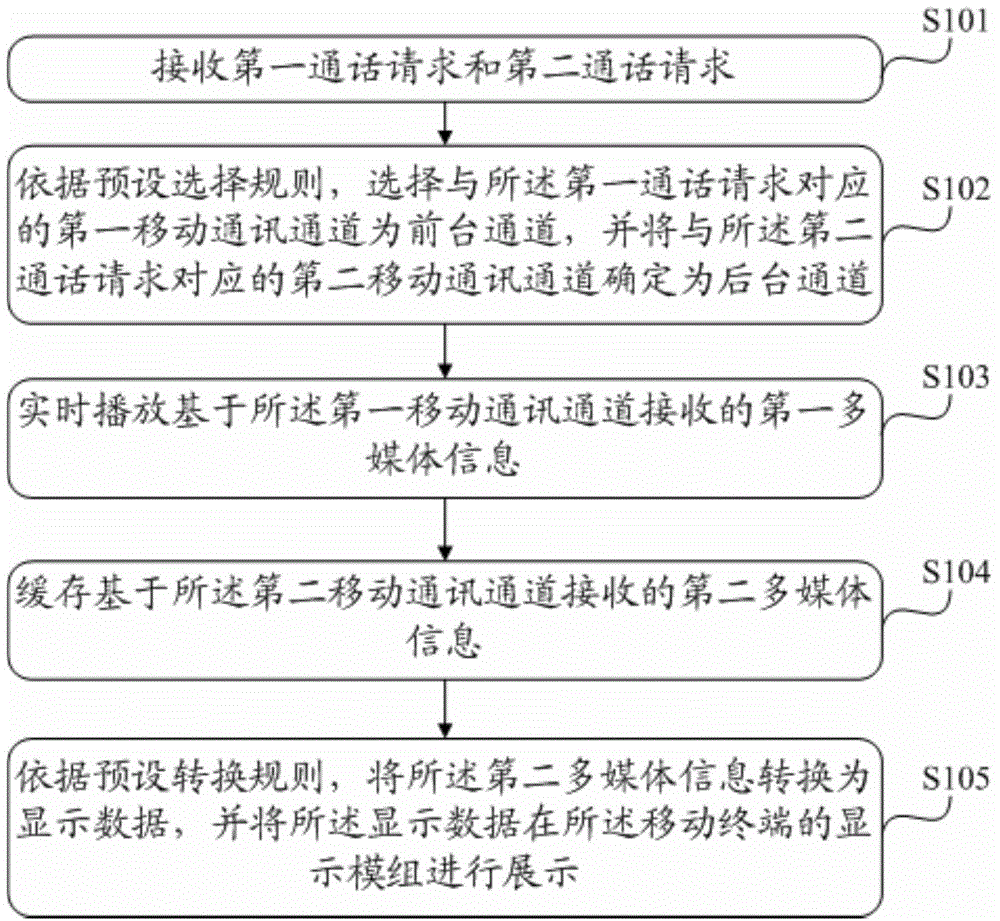
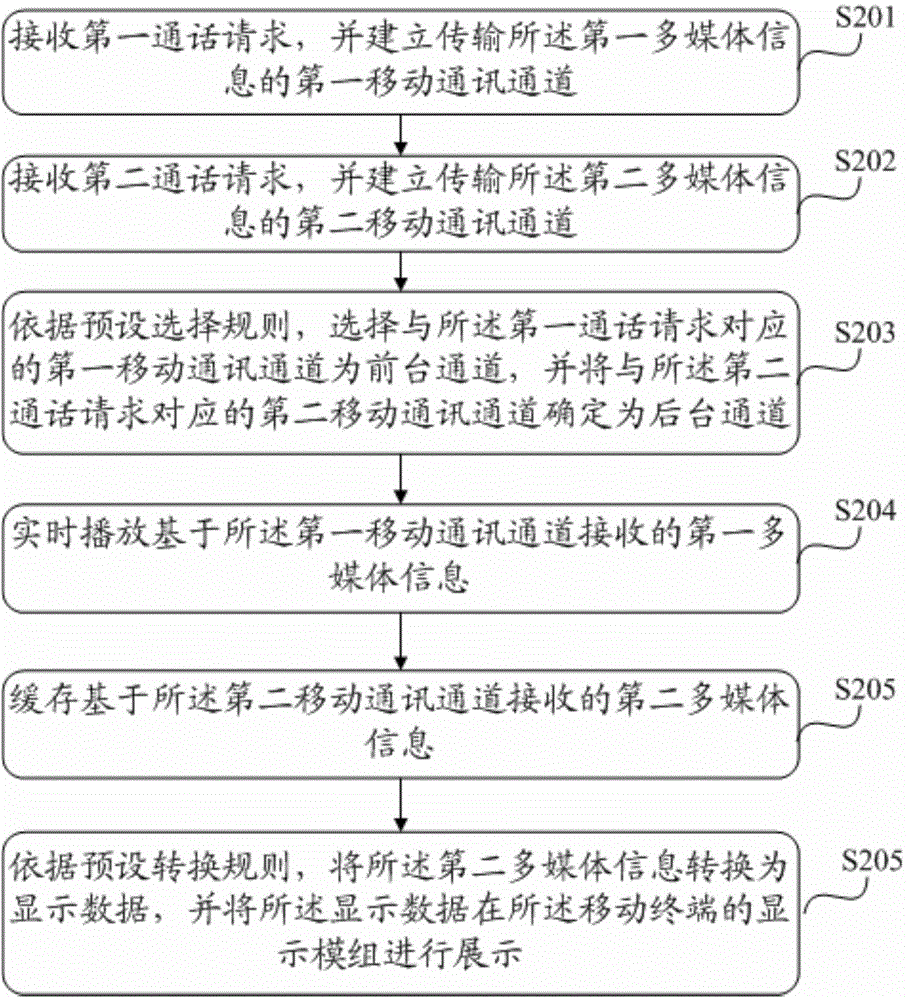
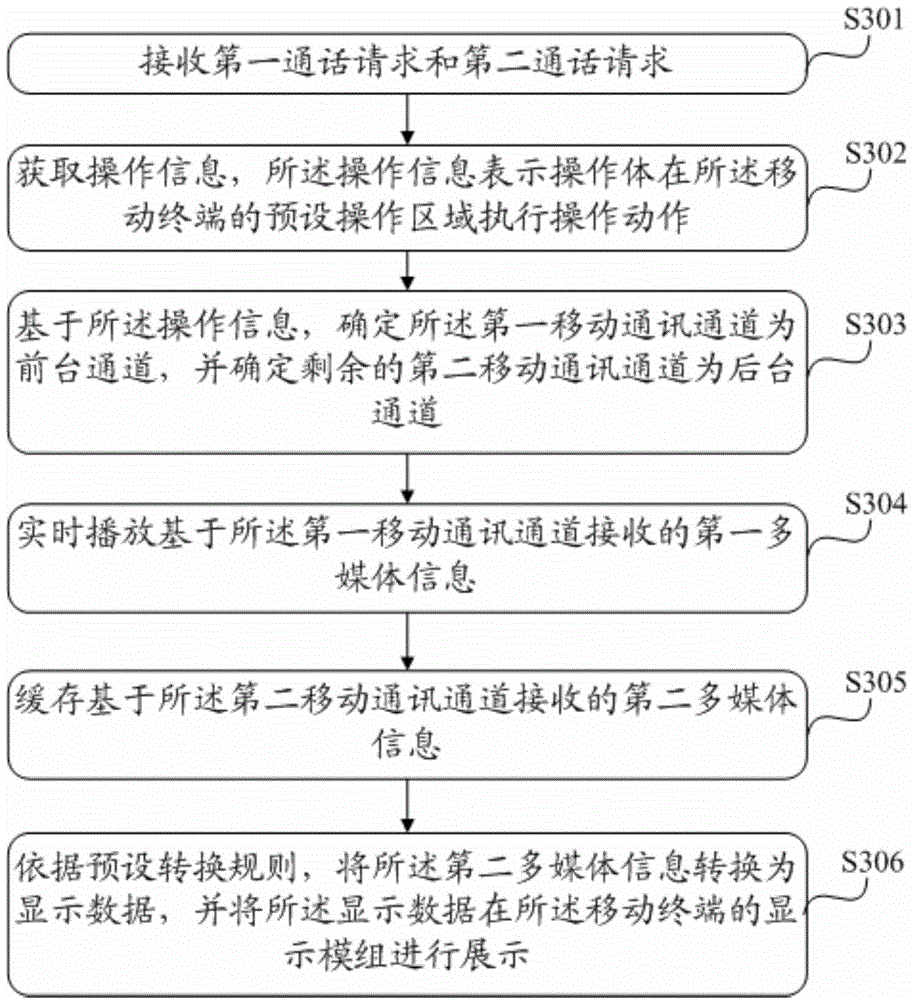
The invention provides an information processing method applied to a mobile terminal. The mobile terminal is provided with at least two mobile communication processing units and is capable of performing multimedia communication through at least two mobile communication channels; the method includes receiving the multimedia information through the first mobile communication channel and the second mobile communication channel, after selecting the first mobile communication channel corresponding to a first communication request as a front stage channel, playing the first multimedia information transmitted by the first mobile communication channel, performing real-time communication, determining the second mobile communication channel corresponding to a second communication request as the backstage channel, performing cache transformation of the second multimedia information of the second mobile communication channel, acquiring the display data, and displaying the display data through a display module of the mobile terminal to allow users to acquire the content of the second multimedia information directly by viewing the display module. The communication between the mobile terminal and the users is implemented, and the communicating efficiency is improved.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
Conditional Establishment of a Communications Connection with a Mobile Terminal in Response to a Query From the Mobile Terminal
A mobile implementation channel supports the processing of a request for requested information for a customer of a business. The request may be generated through a wireless terminal and include a customer identification of the customer. Profile information about the customer may then be accessed and the user identification mapped to a device type of the customer. When the profile information indicates that the customer should be invited to interact with a representative the business, an invitation message is directed through the corresponding mobile communication channel type to the customer's device of the customer. The invitation message may include contact information and the requested information. The contact information may then be utilized to establish a communications connection between the customer and the representative of the business. Otherwise, only the requested information is directed through the mobile communication channel type to the customer's device.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
Telematics control system and method
ActiveUS20160173157A1Reduce vehicle battery power consumptionReduce battery power consumptionPower managementWireless commuication servicesModem deviceControl system
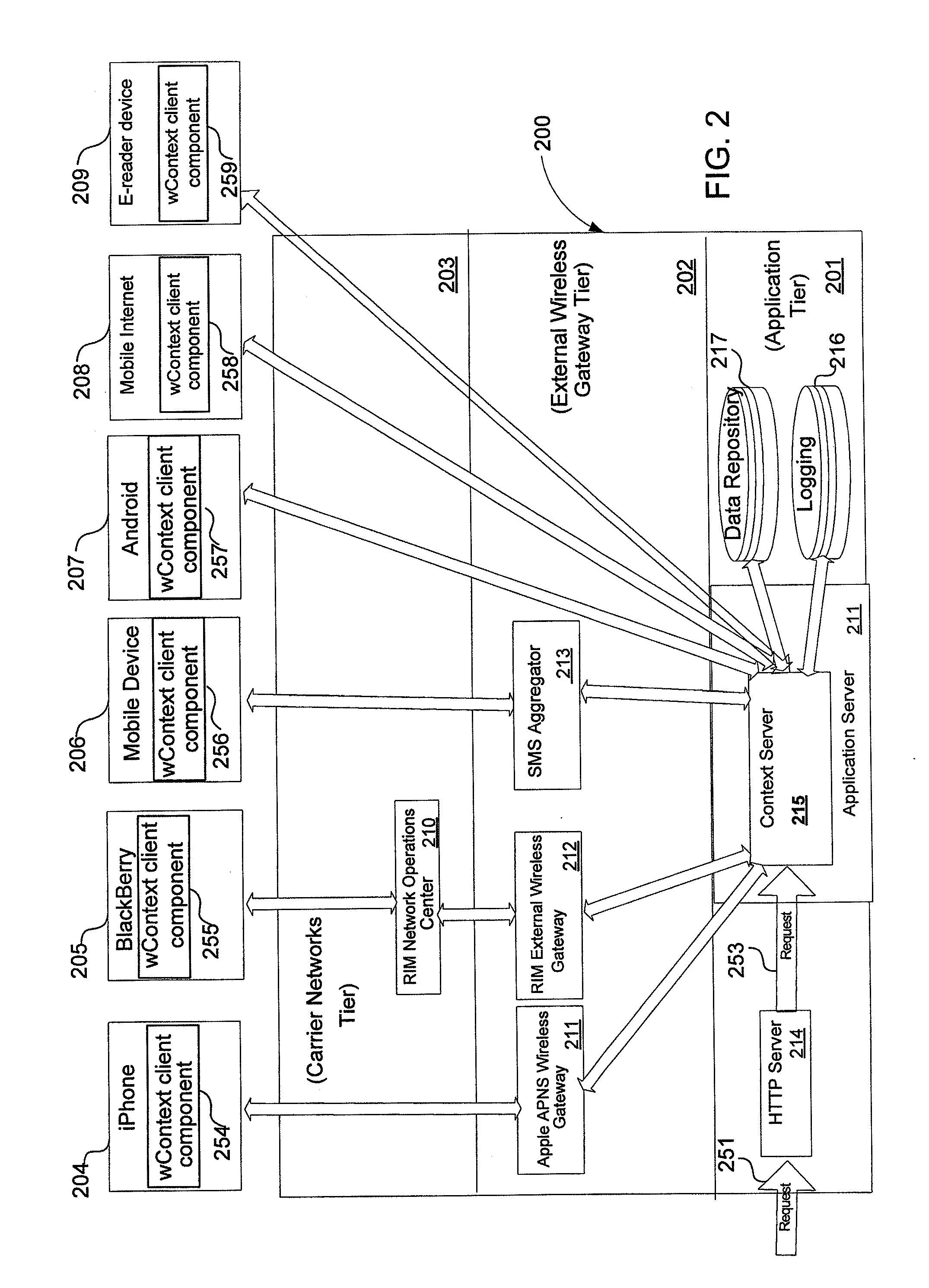
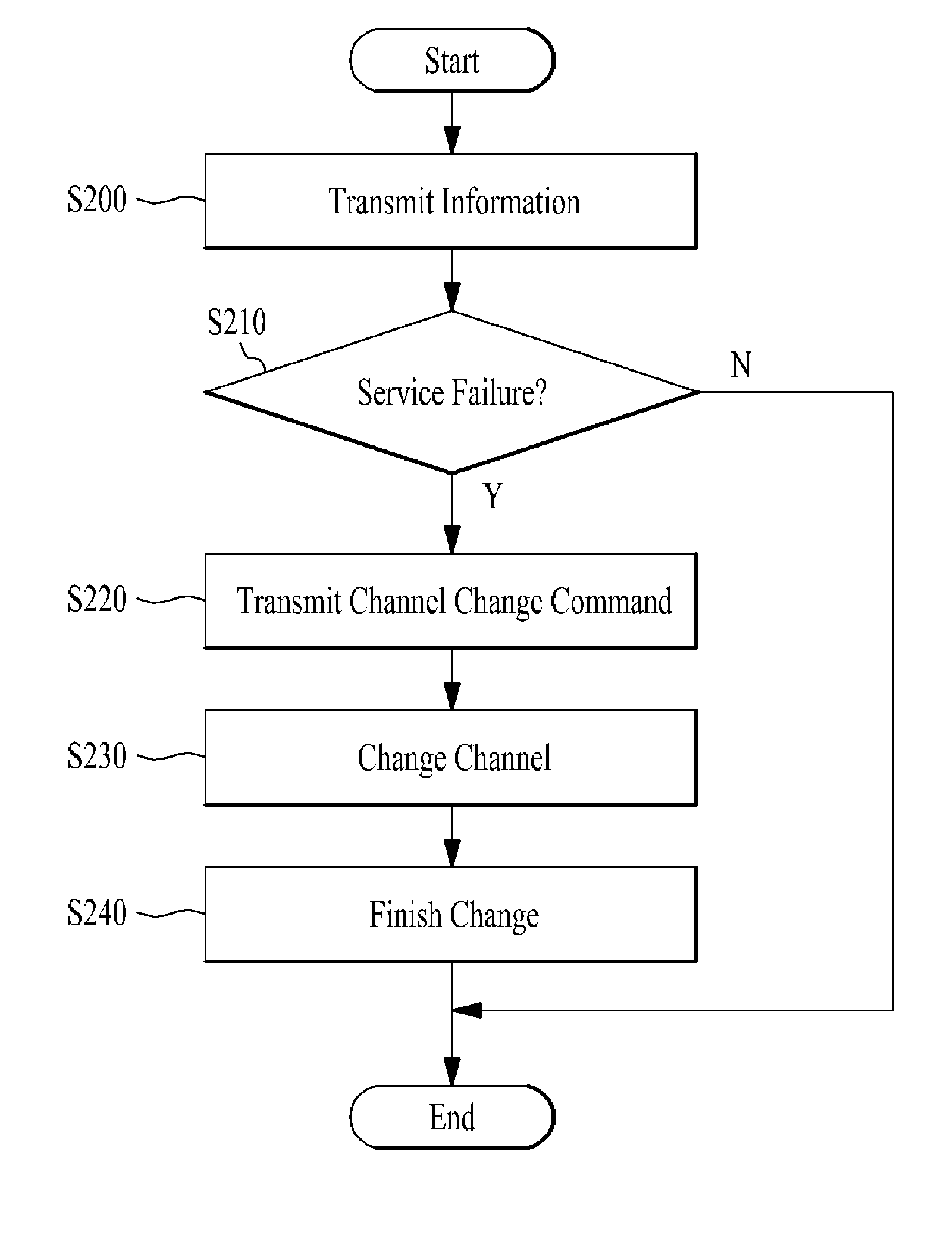
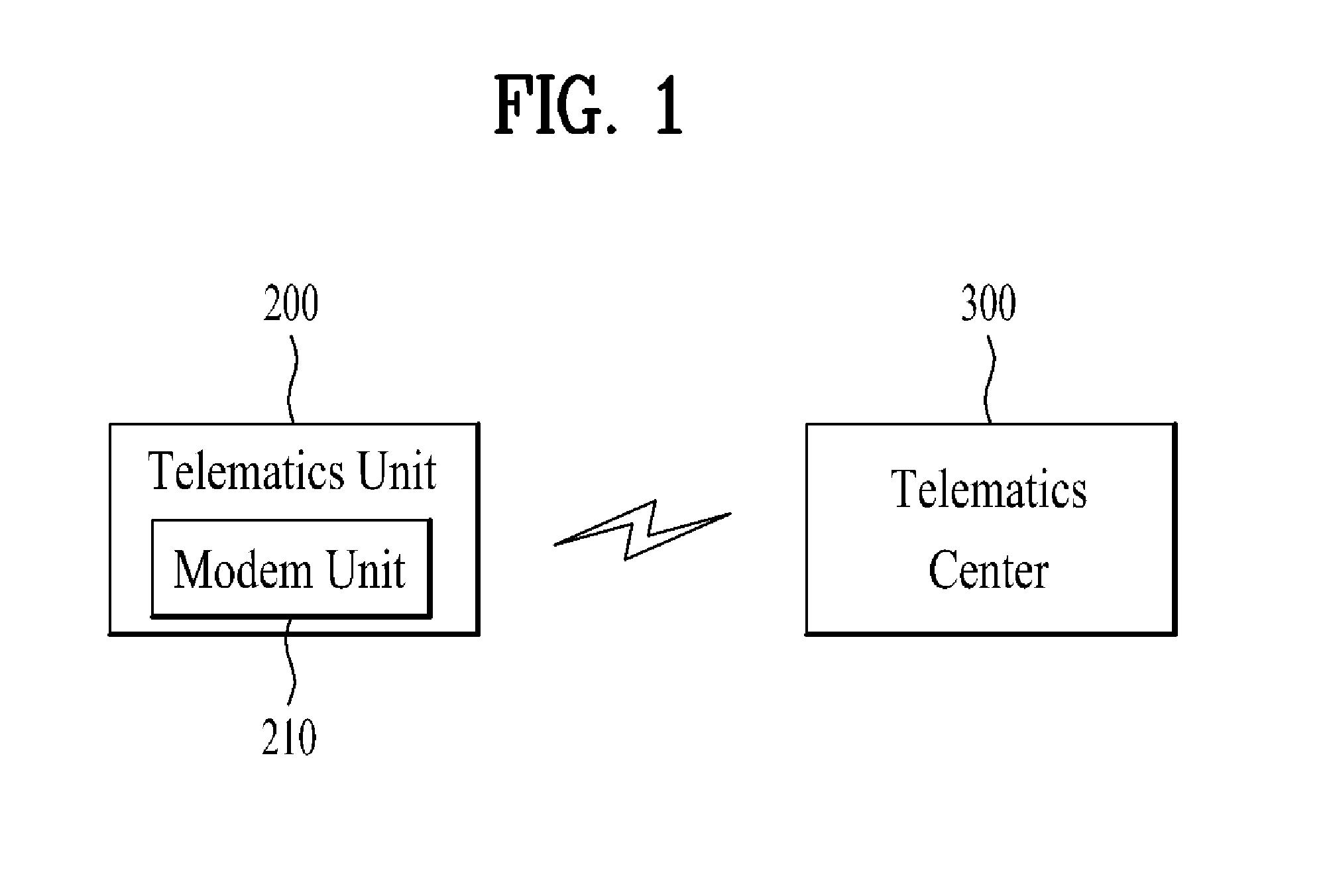
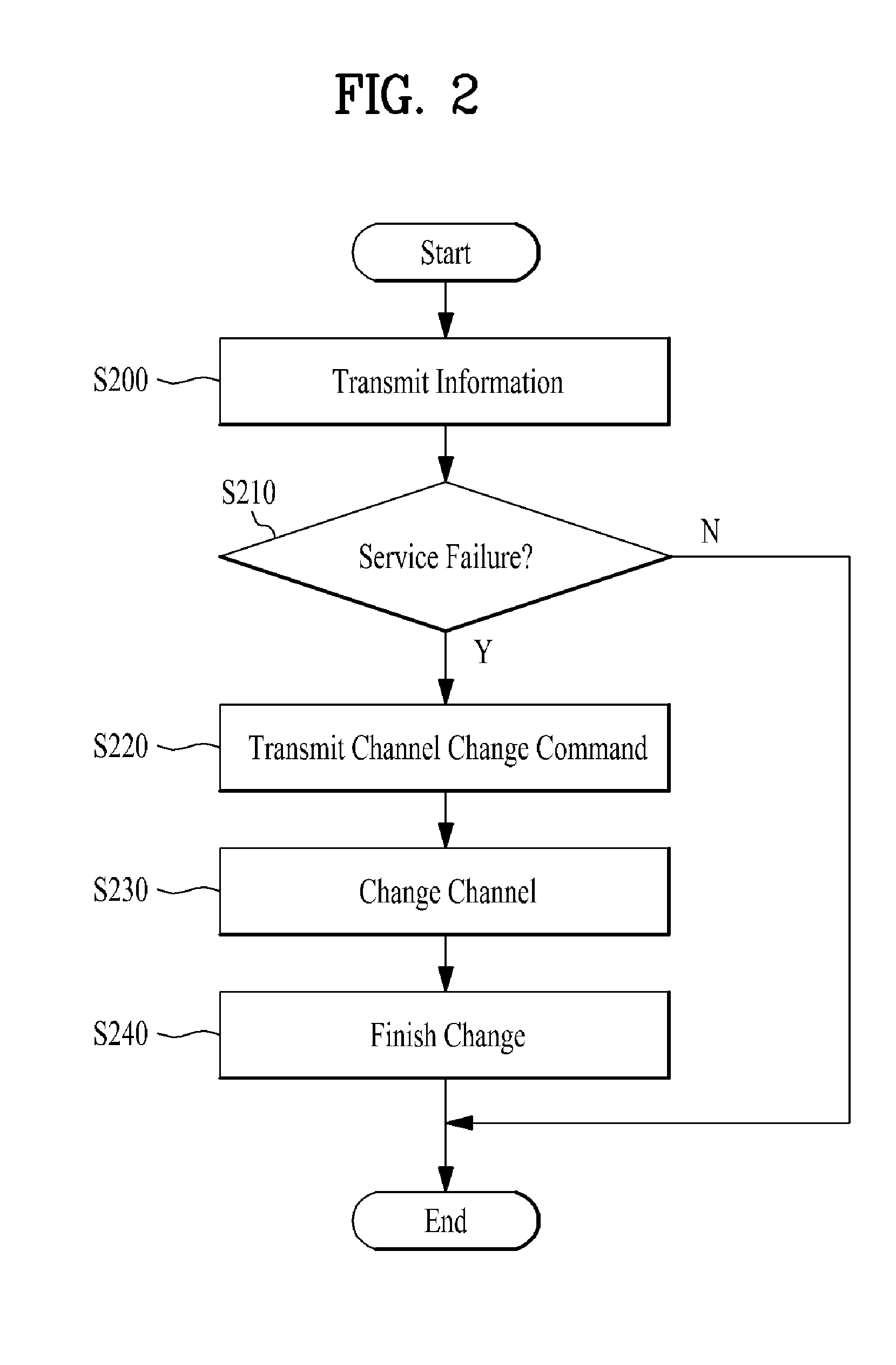
A telematics control system includes: a telematics unit in a vehicle including a modem unit that transmits vehicle information via an external mobile communication channel; and a telematics center transmitting and receiving channel change information of the modem unit based on a message indicating a channel state of a paging mode or a quick paging mode of a channel selected according to communication environment information acquired from the telematics unit.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Retransmitting method of broadcasted data in network of single frequency
ActiveCN101286826ASolve wasteSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency spectrumControl signal
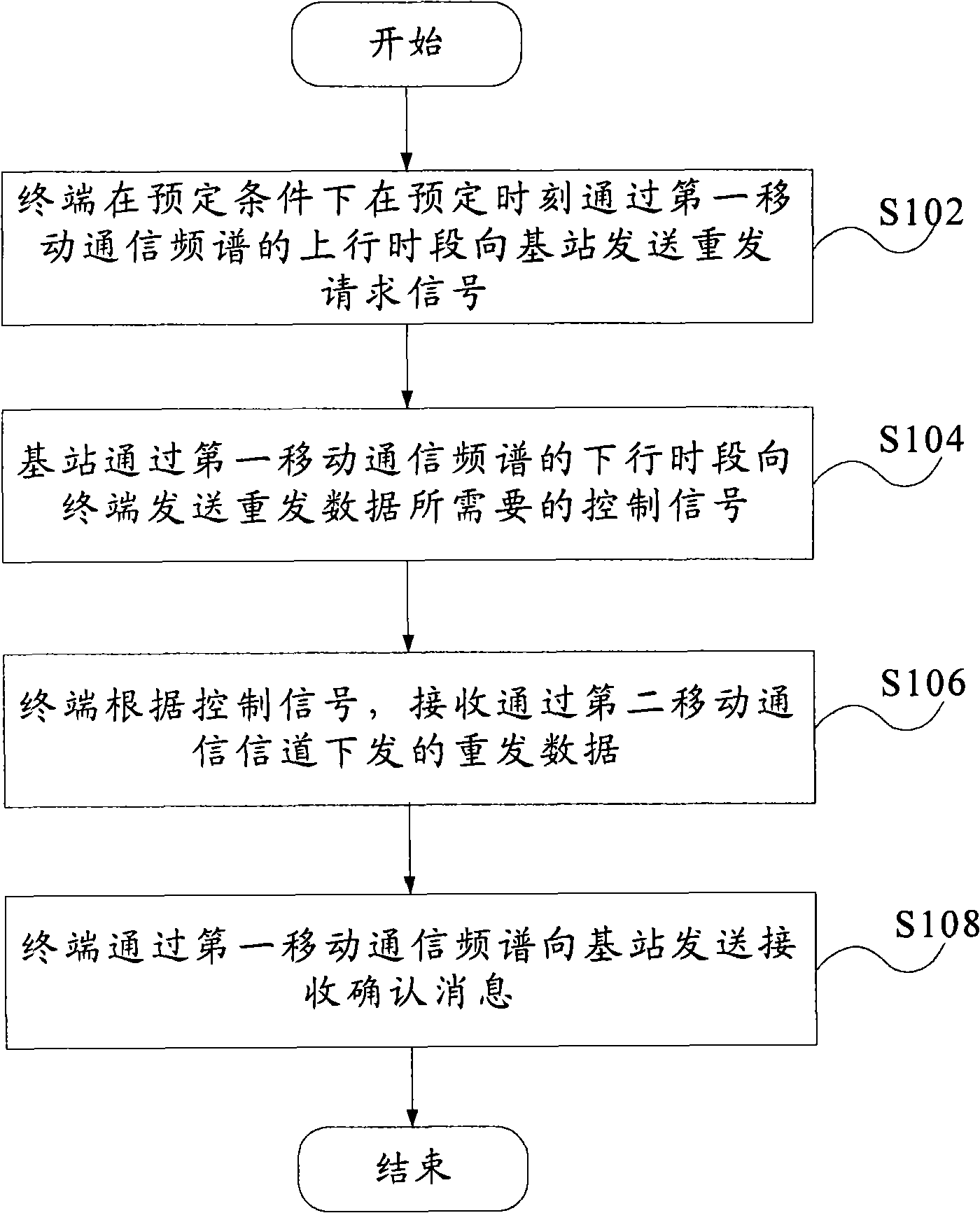
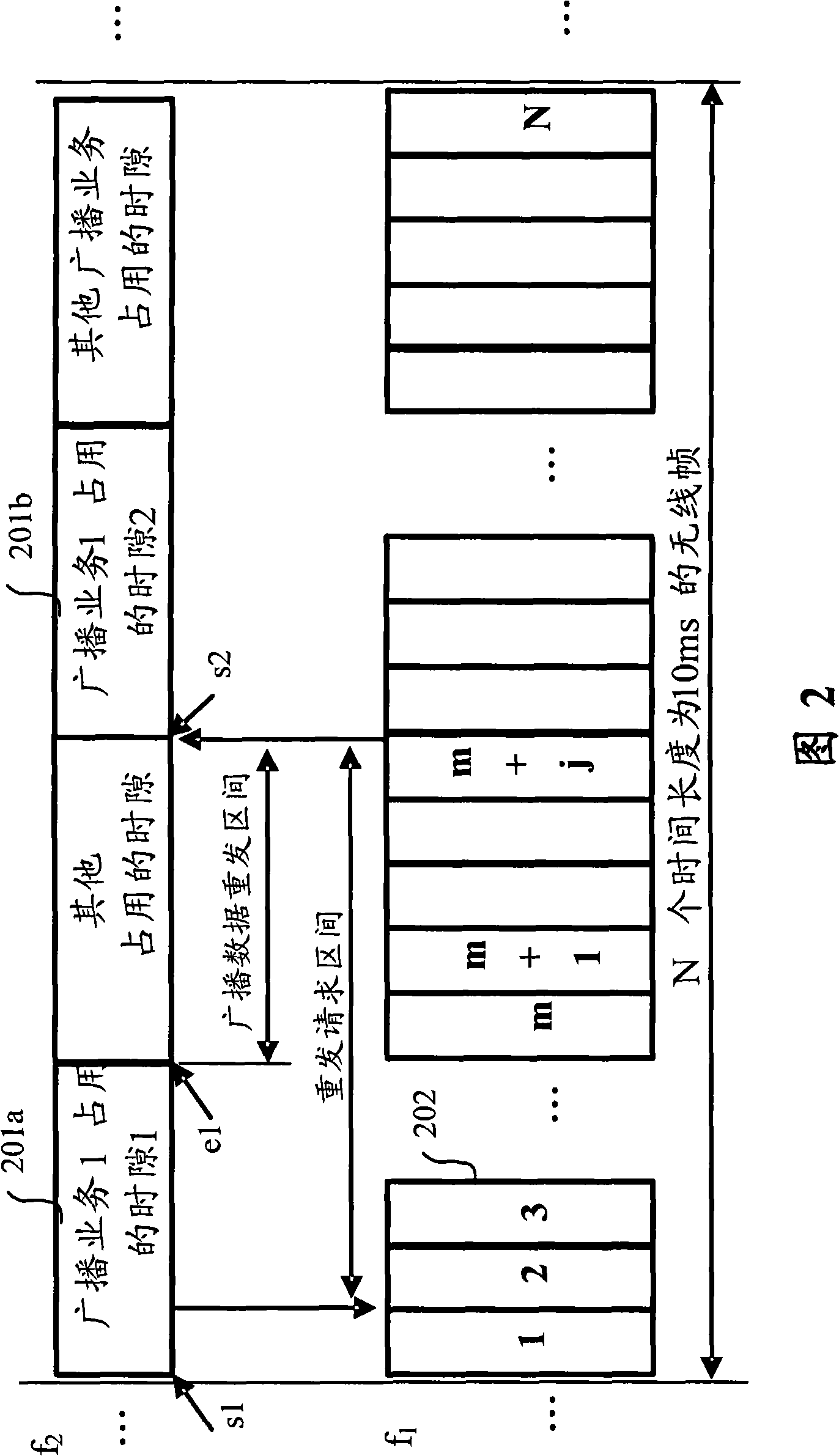
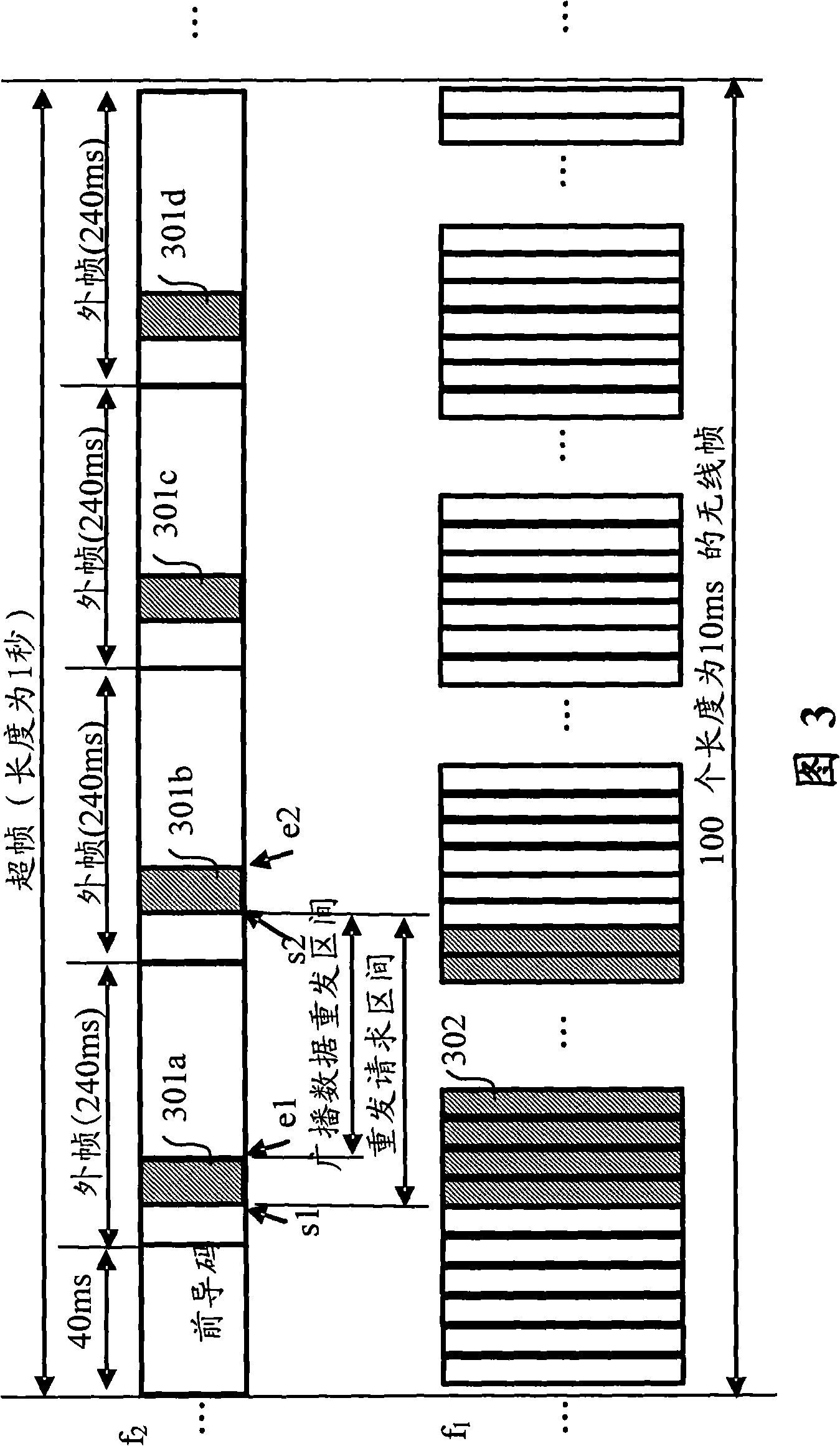
The invention provides a method for retransmitting broadcasting data of a single frequency network, which comprises the steps that: step S102, a terminal retransmits request signals towards a base station under a preset condition at a preset time by the upstream period of a first mobile communication spectrum; step S104, the base station sends control signals required by data retransmission to the terminal by the downstream period of the first mobile communication spectrum; step S106, the terminal receives retransmission data sent by a second mobile communication channel according to the control signals. Therefore, the invention solves the problems of spectrum resource waste existing in the data retransmission in the present MBMS SFN network and can retransmit broadcasting data on the SEN network to the terminal which requires retransmission by using the two-way link of the mobile communication base station without stopping the present MBMS SFN service broadcasting.
Owner:福建省永阳国有资本投资集团有限公司
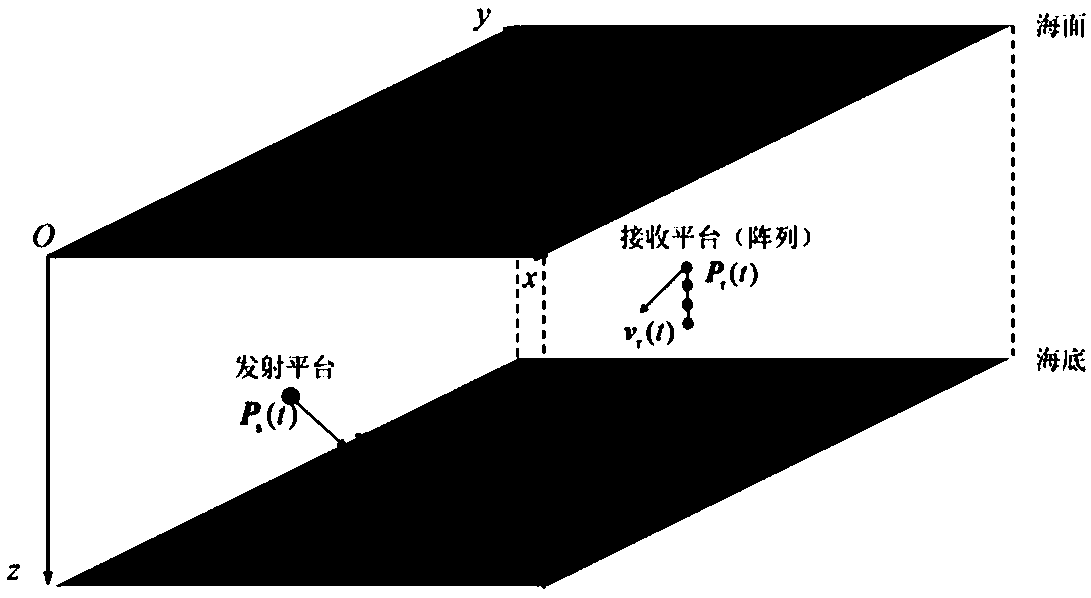
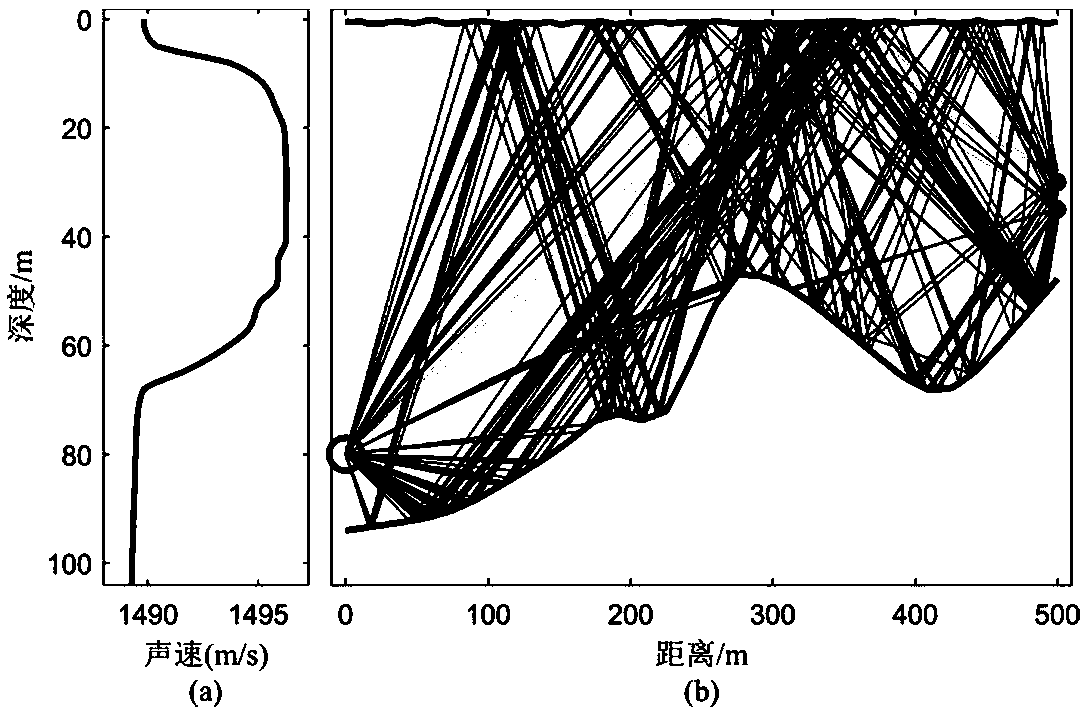
An underwater mobile channel simulation method
ActiveCN109039506AReasonable selection of parametersAvoid wastingTransmission monitoringTime domainChannel impulse response
The invention discloses an underwater mobile channel simulation method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) setting environmental parameters and signal parameters of a three-dimensional underwater space communication scene, establishing a motion model of an acoustic source emission platform and a receiving platform and a sea surface height model; 2) real-timely sampling the state of the channel by calling the ray track model for many times to obtain a series of channel snapshots at different time, and calculating a time-varying channel impulse response according to the obtained snapshots; 3) dynamically filtering the transmit signal of the acoustic source transmitting platform in the time domain by using the time-varying channel impulse response to obtain the received signal. Themethod of the invention ensures the accuracy and the precision of the underwater mobile communication channel simulation to a certain extent, and at the same time, the complexity of the simulation realization can be effectively reduced, the memory requirement can be reduced, and the computer operation efficiency can be improved.
Owner:浙江望海潮科技有限公司
Personal finance credit evaluation method based on big data
InactiveCN104599174ALow costImprove reliabilityFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsSpace activityMobile communication channels
The invention relates to a personal finance credit evaluation method based on big data. The personal finance credit evaluation method based on the big data comprises the following steps of (a) verifying a personal mobile communication tool of an evaluation object; (b) acquiring mobile communication data of the evaluation object and social contact and economic activity data in a mobile communication channel in a specific time bucket and removing privacy data; (c) calculating space activity features and economic activity features of the evaluation object in the specific time bucket in batches by using Hadoop big data and performing structuralization and visualization treatment on the data; and (d) combining structuralized data and a credit evaluation system and calculating personal credit integrals of the object. The personal finance credit evaluation method based on the big data has the advantages that the reliability of personal finance credit evaluation is improved; and the cost of finance credit evaluation is reduced, and micro-credit finance services can be provided for individuals.
Owner:上海百筹金融信息服务有限公司
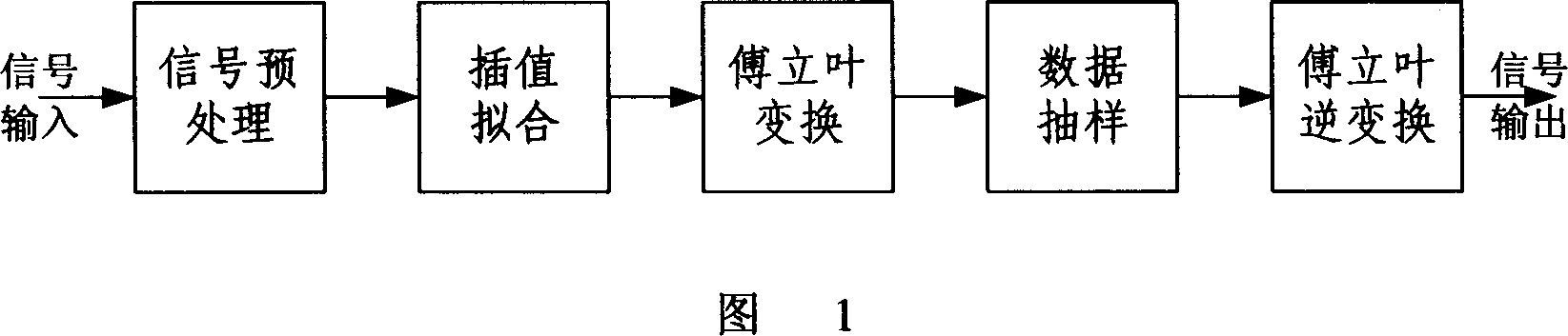
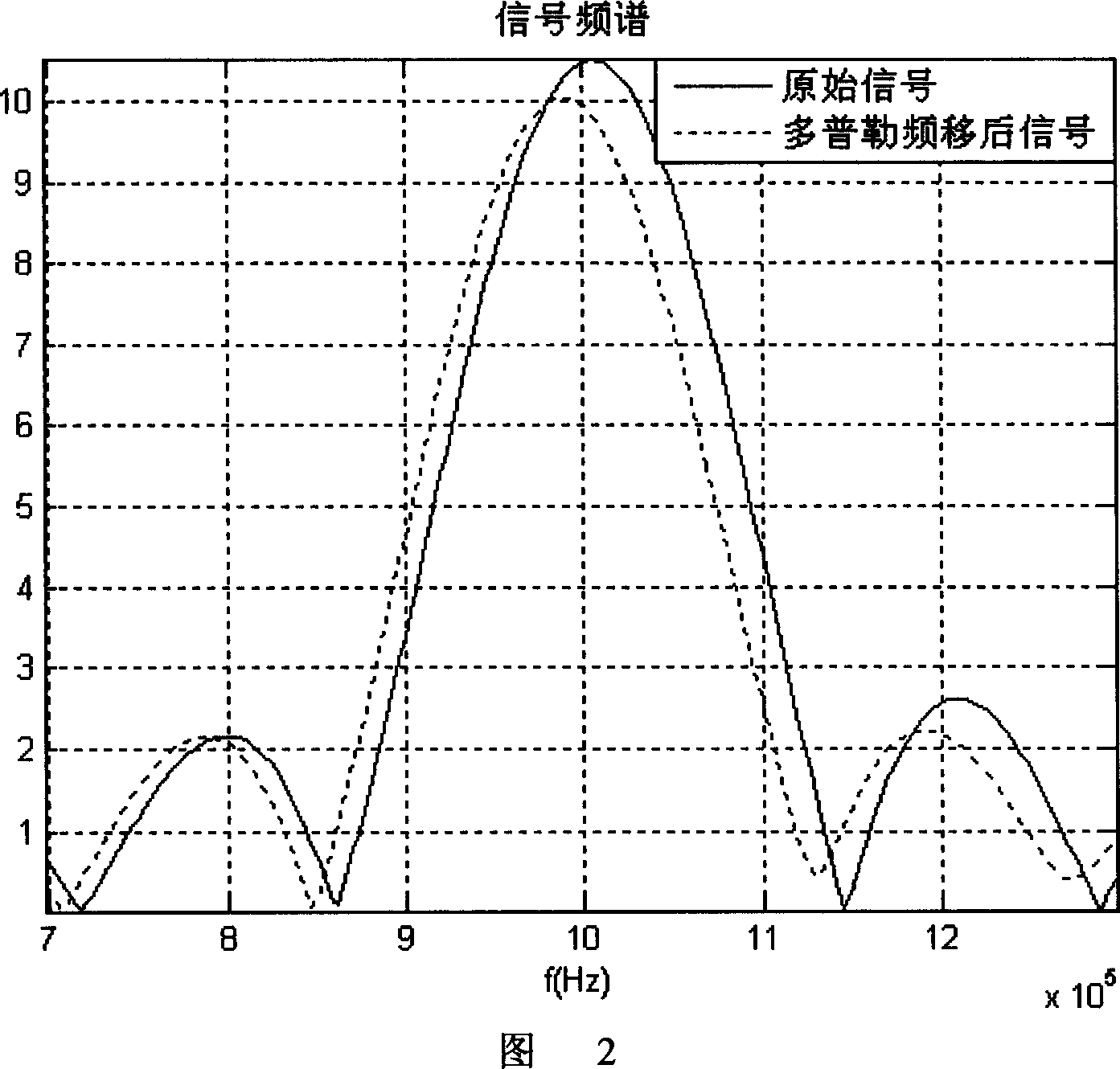
Doppler carrier shift emulator for high-dynamic mobile telecommunication channel
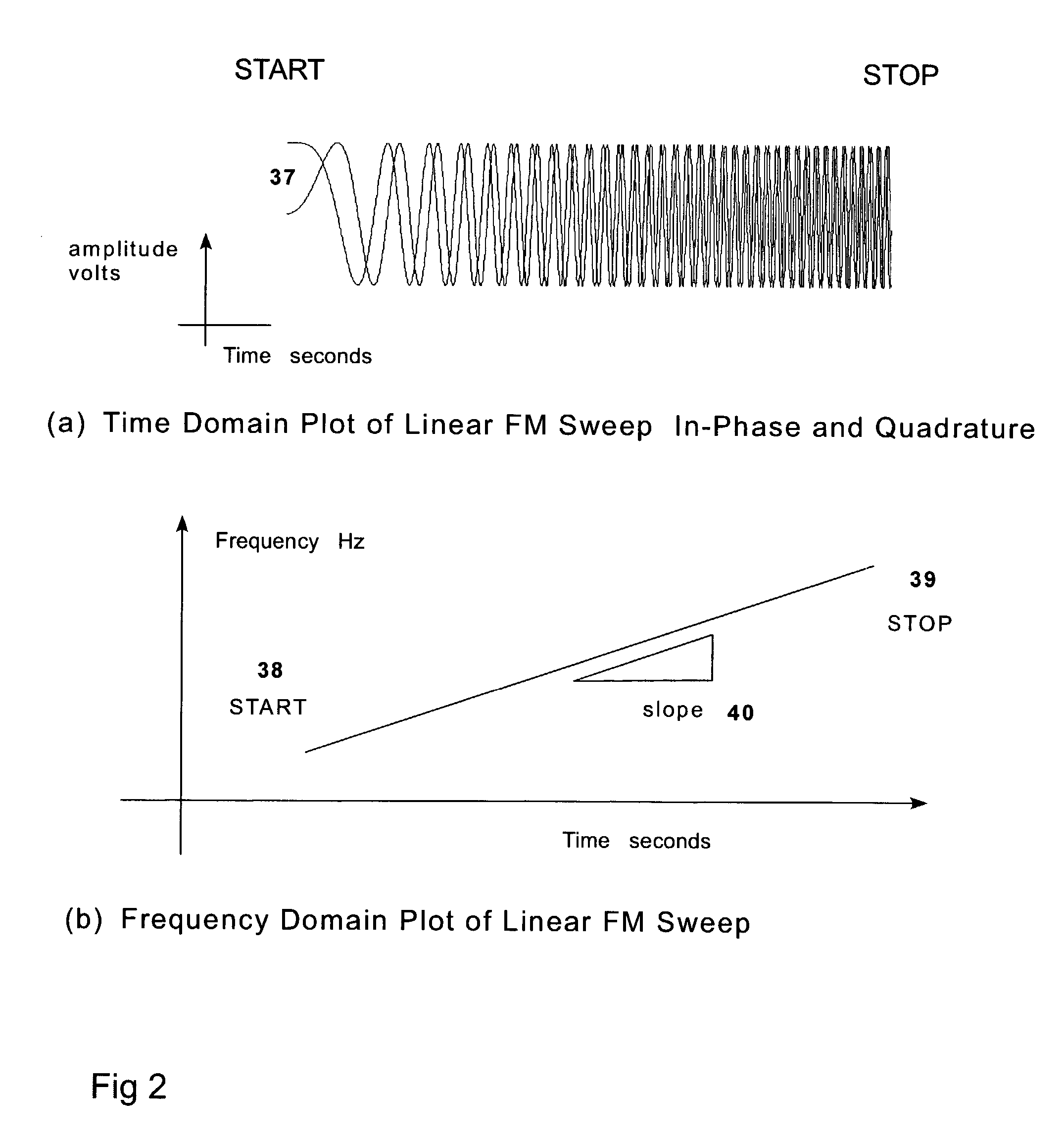
The invention is concerned with the achieving project of the high dynamic mobile communication channel Doppler frequency-shift simulator, the project solves the Doppler frequency-shift simulating problem of the signal transmission at the high dynamic environment by the signal processing technology such as the time frequency domain transform, the interpolation fitting, the sampling.
Owner:中国人民解放军总参谋部第五十四研究所
Improved estimation and compensation method for orthogonal multi-carrier underwater acoustic mobile communication channel
ActiveCN109412997AHigh resolutionGood compensationChannel estimationMulti-frequency code systemsCompensation effectCarrier signal
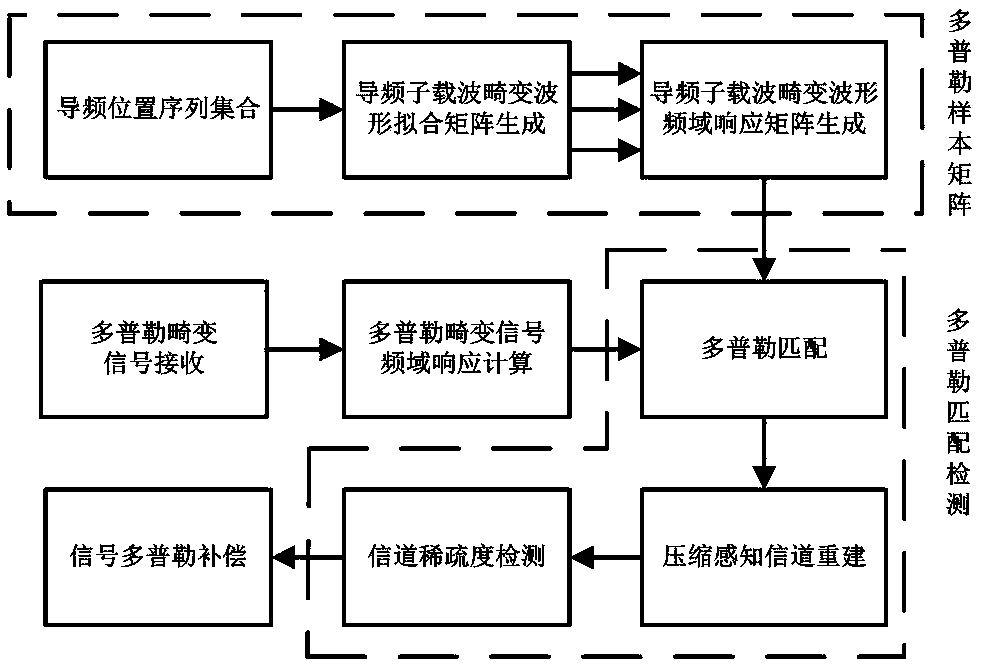
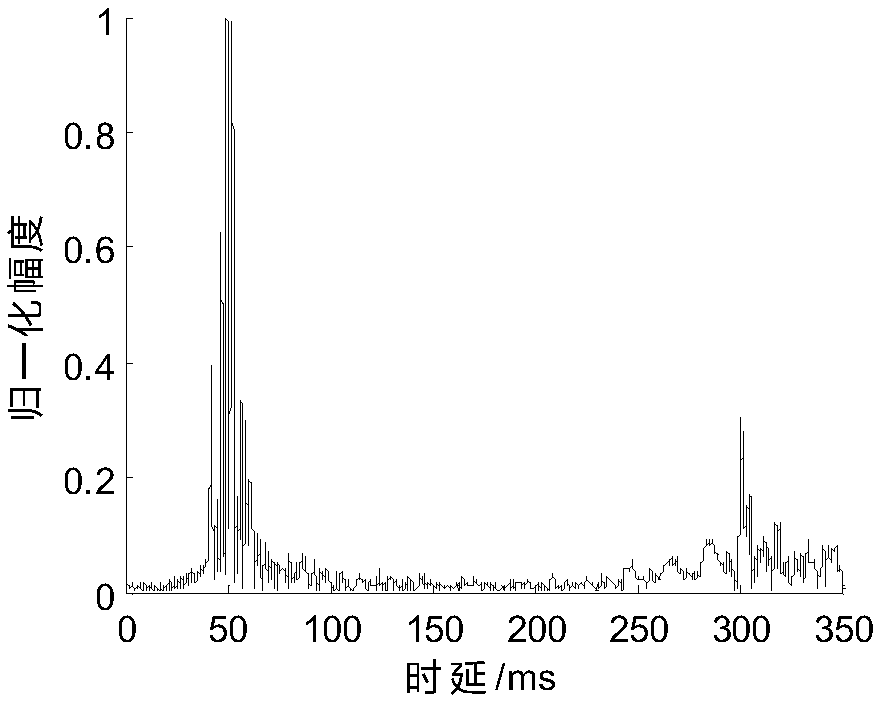
The invention discloses a Doppler estimation and compensation method for sparseness detection of an orthogonal multi-carrier underwater acoustic mobile communication channel. Aiming at the problem caused by limited frequency domain response resolution in a complex multipath time-varying channel environment, the method utilizes the principle that the Doppler distortion signal subcarrier orthogonality is not changed, extracts a pilot subcarrier frequency domain response by local subcarrier Discreet Fourier Transform (DFT), calculates channel impulse responses and sparseness thereof of the signalunder different Doppler compensation conditions, and selects a decompression signal of the compression factor estimation result with the largest channel sparseness, thereby realizing the mobile underwater acoustic communication in the complex multipath time-varying channel environment. The method improves the Doppler estimation accuracy, which is mainly due to the frequency domain resolution accuracy. The carrier demodulation matrix of the method is generated by calcualting a Doppler compression factor, and the Doppler is used to demodulate the carrier matrix of each subcarrier with a relatively higher resolution, so that the Doppler compensation effect is better.
Owner:SUZHOU SOUNDTECH OCEANIC INSTR
Movable transformer base
InactiveCN107025979AEasy to moveImprove shock absorptionTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionHand carts with multiple axesTransformerEngineering
The invention discloses a movable transformer base, which includes a base body, a storage slot is arranged inside the upper end of the base body, a moving rod is arranged inside the storage slot, and a fixed ring is arranged outside the moving rod. The fixed ring is located in the storage slot, one end of the fixed ring is provided with an opening, the opposite side of the opening is provided with a connecting block, and the upper end of the base body is provided with an operation slot communicated with the moving rod. The connecting blocks all go through the operation slot, and there are locking bolts between the two connecting blocks, the locking bolts are screwed to the two connecting blocks, one end of the moving rod goes through the storage slot and is connected with a rotating rod in rotation , the end of the rotating rod away from the moving rod is rotatably connected with a push handle. The movable transformer base can be applied to uneven ground, has high utilization efficiency, and the push handle can be placed in the storage slot, thereby saving floor space.
Owner:盐城市奇翔铜业有限公司
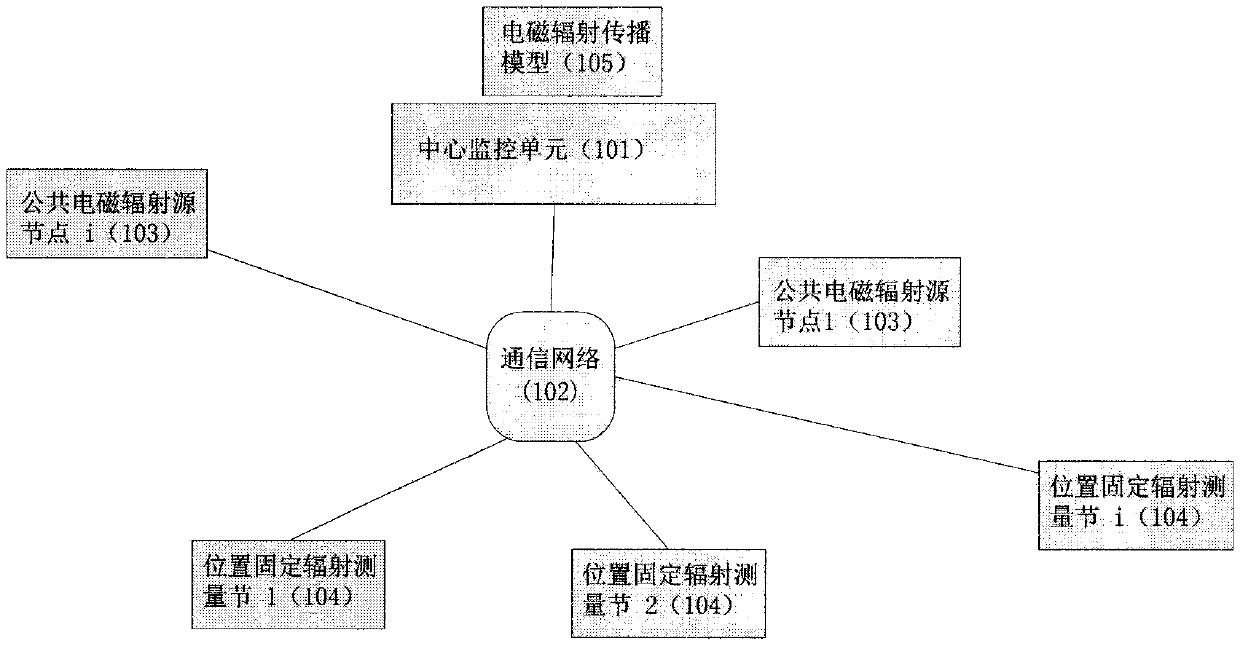
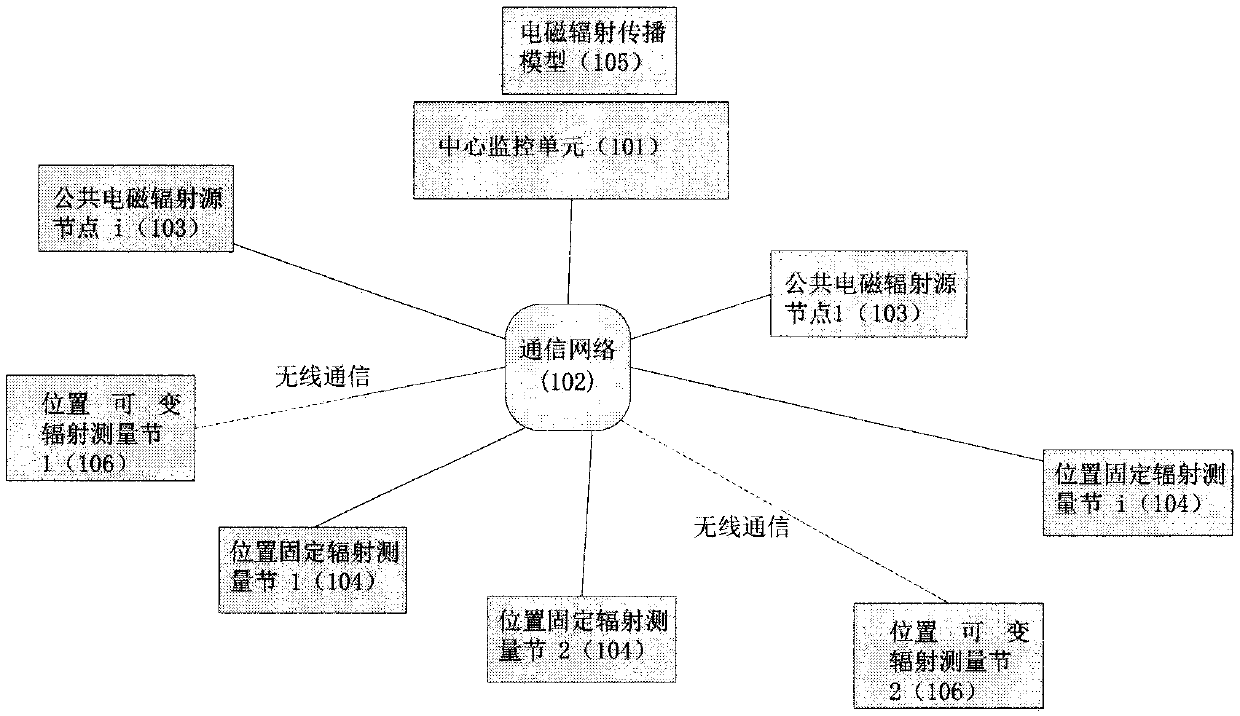
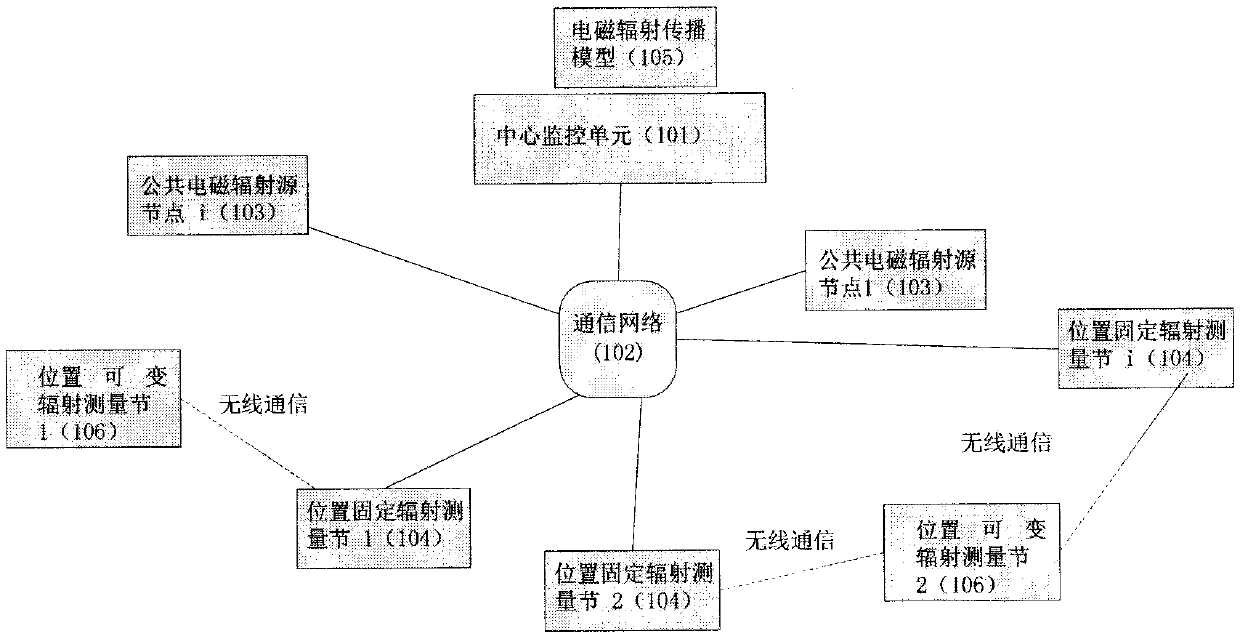
Electromagnetic radiation measuring network and radiation map drawing method
Electromagnetic radiation is an important issue affecting the public. For a long time, there is a lack of relevant technical means to measure the spatial and temporal distribution of electromagnetic radiation in real time. The invention provides an electromagnetic radiation measuring network which is different from the prior art. The electromagnetic radiation measuring network can be combined withthe Internet-of-things technology. With the electromagnetic radiation measuring network, a radio-frequency radiation map can be drawn by using an electromagnetic radiation propagation model and employing the Internet-of-things technology and the big data processing technology according to the data of public electromagnetic radiation sources and the radio-frequency radiation data measured by radiation measurement nodes. On one hand, the generation of a radiation map relies on open public electromagnetic radiation source node information and all kinds of mobile communication channel models obtained from long-time research, and also requires a large number of radiation measurement points to provide measurement data in real time. Finally, the generation of a radiation map relies on the big data processing capacity of a center monitoring unit and related algorithms. The advantages of the network can be reflected very well. The radiation map generated by the electromagnetic radiation measuring network can be offered to the public as a basic resource.
Owner:桂林
Systems and methods for performing live chat functionality via a mobile device
ActiveUS8713117B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksMobile communication channelsMobile device
Aspects of the present disclosure generally relate to systems and methods for extending chat capabilities of traditional computer-to-computer chat systems to mobile devices. As will be generally understood, chat sessions typically allow users and chat agents to type and send / receive messages through a chat system. According to one aspect, such a mobile consumer messaging system (MCMS) utilizes existing mobile communication channels to interface with existing traditional chat systems. Specifically, in various embodiments of the MCMS, chat agents using existing, traditional chat systems are able to participate in chat sessions with end users through the users' mobile devices without specific modifications to the existing chat system. Further, according to one embodiment, chat agents utilize a single chat platform to participate in chat sessions with end users through the end users' mobile devices as well as with various other users utilizing a traditional chat system on a computer.
Owner:MGAGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com