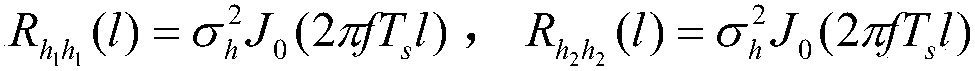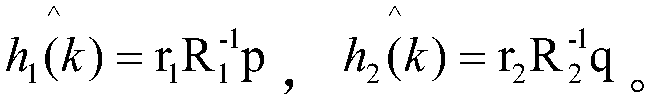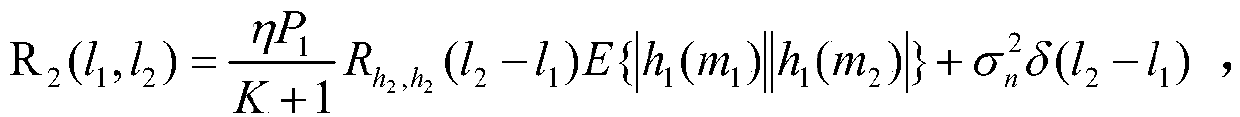Channel estimation method of amplify-and-forward repeater adopting wireless energy collection
A technology of amplification and forwarding and channel estimation, which is applied in channel estimation, radio transmission system, baseband system, etc., and can solve the problems of lack of estimation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0044] Specific implementation manner 1: This implementation manner is a channel estimation method for amplifying and forwarding relay using wireless energy harvesting, which includes the following steps:
[0045] Step 1: Establish a Jakes model of time-varying Rayleigh fading;
[0046] Step 2: Determine the energy collection strategy adopted by the amplifying and forwarding relay, the strategy including a time allocation strategy and a power cutting strategy;
[0047] Step 3: Use the linear minimum mean square error theory at the relay and the destination to calculate the channel gains from the source to the relay link and the relay to the destination link in the two strategies for specific energy harvesting strategies . Specifically:
[0048] a, calculate the channel gain autocorrelation function The calculation formula is:
[0049]
[0050] The J 0 (x) is the zero-order Bessel function of the first kind; the f is the carrier frequency; the T s Is the symbol interval; the fT s Assi...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0055] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further limitation of the first embodiment, and the step b also includes:
[0056] If the amplifying and forwarding relay adopts the energy collection strategy of time distribution, then:
[0057] Calculate the correlation vector r 1 , The r 1 The l-th element of is: The P 1 Is the transmission power of the source, assigned a value of 1;
[0058] Calculate the autocorrelation matrix R 1 , The R 1 The first (l 1 ,l 2 The elements of) are:
[0059]
[0060] The δ(x) is the Dirac pulse function; the Is the variance of the additive white Gaussian noise, Assign a value of 1;
[0061] Calculate the correlation vector r 2 , The r 2 The l-th element of is: The E{|h 1 (m)|}In the time-varying Rayleigh fading model: For any m, Said η is the conversion efficiency of the energy harvester and is assigned a value of 1;
[0062] Calculate the autocorrelation matrix R 2 , The R 2 The first (l 1 ,l 2 The elements of) are:
[0063] The E{|h 1 (m 1...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0065] Specific embodiment 3: This embodiment is a limitation of the second embodiment, and the step b also includes:
[0066] If the amplifying and forwarding relay adopts the energy harvesting strategy of power cutting, then:
[0067] Calculate the correlation vector r 1 , The r 1 The l-th element of is:
[0068] The said ρ is the power cutting factor, which is assigned a value of 0.3 according to the simulation experiment; the P 1 Is the transmission power of the source, assigned a value of 1;
[0069] Calculate the autocorrelation matrix R 1 , The R 1 The first (l 1 ,l 2 The elements of) are:
[0070] The δ(x) is the Dirac pulse function; the Is the additive white Gaussian antenna noise with zero mean n 1a (k) variance; said Is the additive white Gaussian transition noise with zero mean n 1d (k) variance, assignment
[0071] Calculate the correlation vector r 2 , The r 2 The l-th element of is:
[0072] Said Approximately with scale parameters in the time-varying Rayleigh fad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com