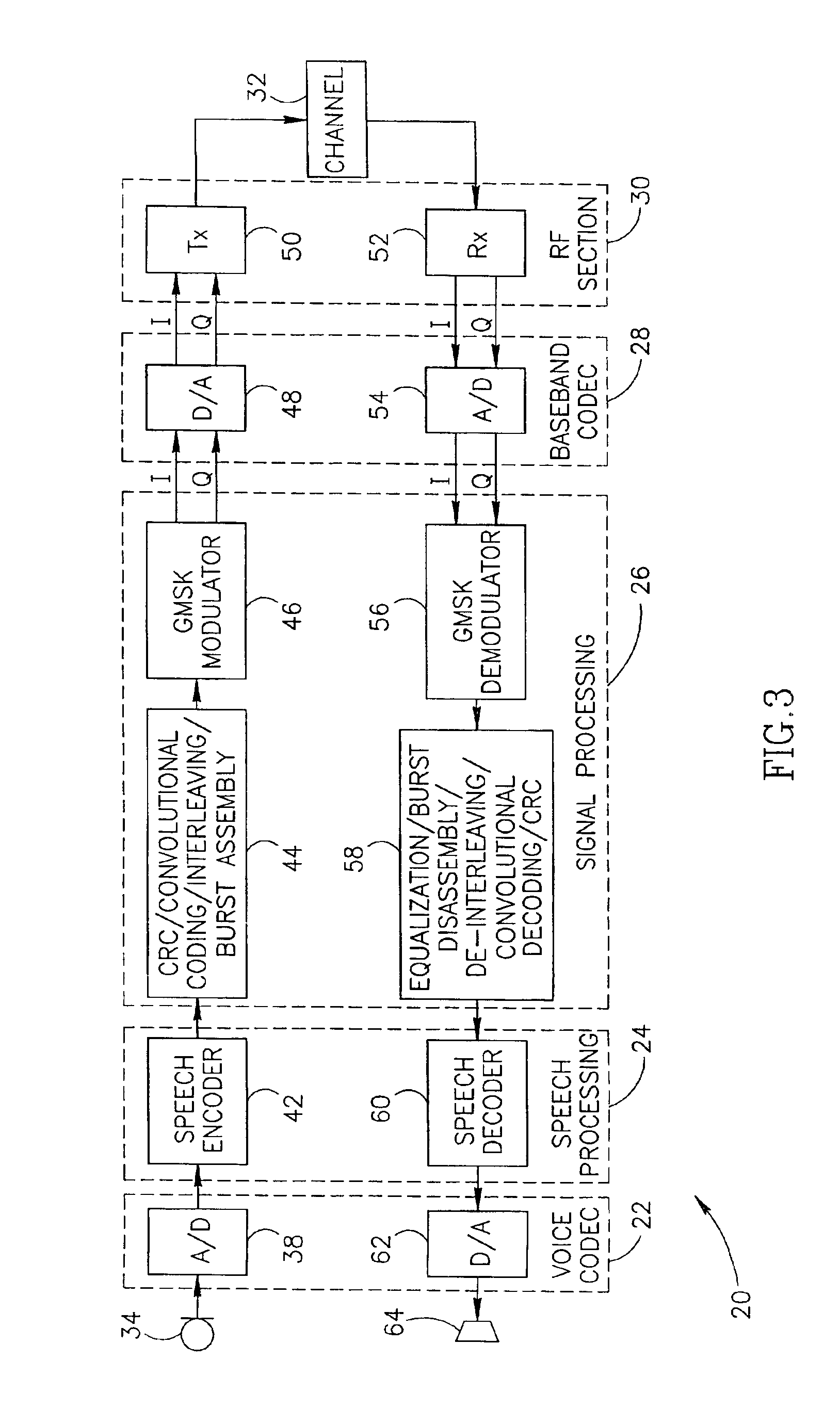
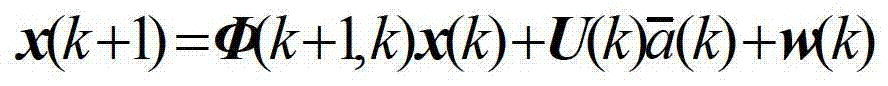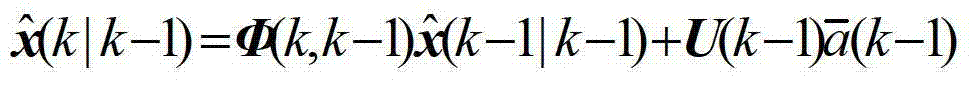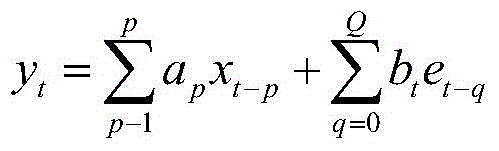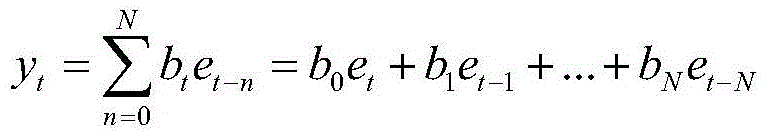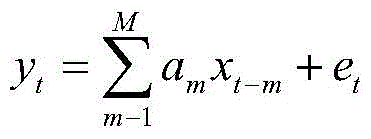Patents
Literature
135 results about "Zero mean" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zero is the integer denoted 0 that, when used as a counting number, means that no objects are present. It is the only integer (and, in fact, the only real number) that is neither negative nor positive . A number which is not zero is said to be nonzero. A root of a function is also sometimes known as "a zero of ."
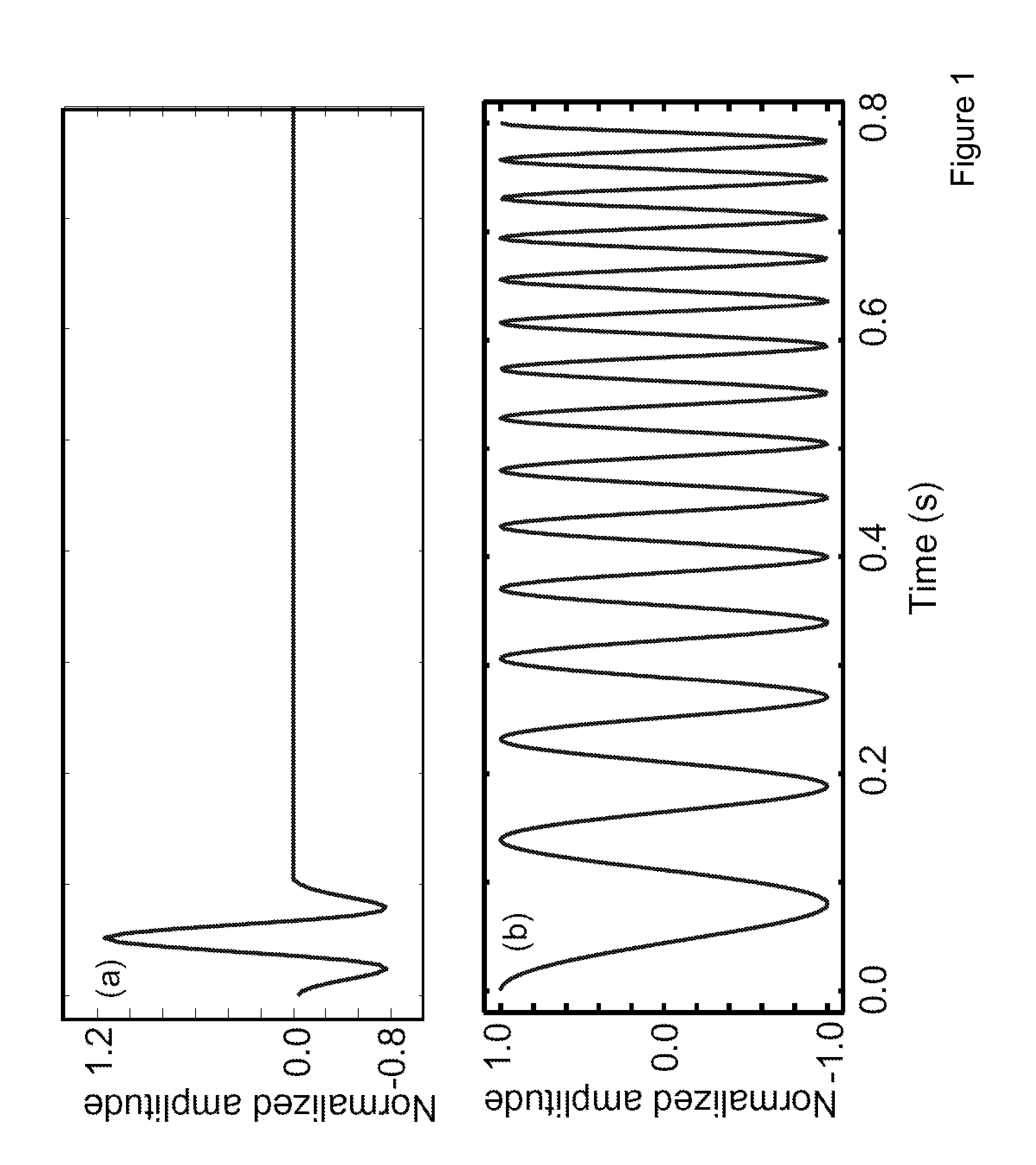
Coding and Decoding: Seismic Data Modeling, Acquisition and Processing
InactiveUS20070274155A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSource encodingData modeling
A method for coding and decoding seismic data acquired, based on the concept of multishooting, is disclosed. In this concept, waves generated simultaneously from several locations at the surface of the earth, near the sea surface, at the sea floor, or inside a borehole propagate in the subsurface before being recorded at sensor locations as mixtures of various signals. The coding and decoding method for seismic data described here works with both instantaneous mixtures and convolutive mixtures. Furthermore, the mixtures can be underdetemined [i.e., the number of mixtures (K) is smaller than the number of seismic sources (I) associated with a multishot] or determined [i.e., the number of mixtures is equal to or greater than the number of sources). When mixtures are determined, we can reorganize our seismic data as zero-mean random variables and use the independent component analysis (ICA) or, alternatively, the principal component analysis (PCA) to decode. We can also alternatively take advantage of the sparsity of seismic data in our decoding process. When mixtures are underdetermined and the number of mixtures is at least two, we utilize higher-order statistics to overcome the underdeterminacy. Alternatively, we can use the constraint that seismic data are sparse to overcome the underdeterminacy. When mixtures are underdetermined and limited to single mixtures, we use a priori knowledge about seismic acquisition to computationally generate additional mixtures from the actual recorded mixtures. Then we organize our data as zero-mean random variables and use ICA or PCA to decode the data. The a priori knowledge includes source encoding, seismic acquisition geometries, and reference data collected for the purpose of aiding the decoding processing.The coding and decoding processes described can be used to acquire and process real seismic data in the field or in laboratories, and to model and process synthetic data.
Owner:IKELLE LUC T
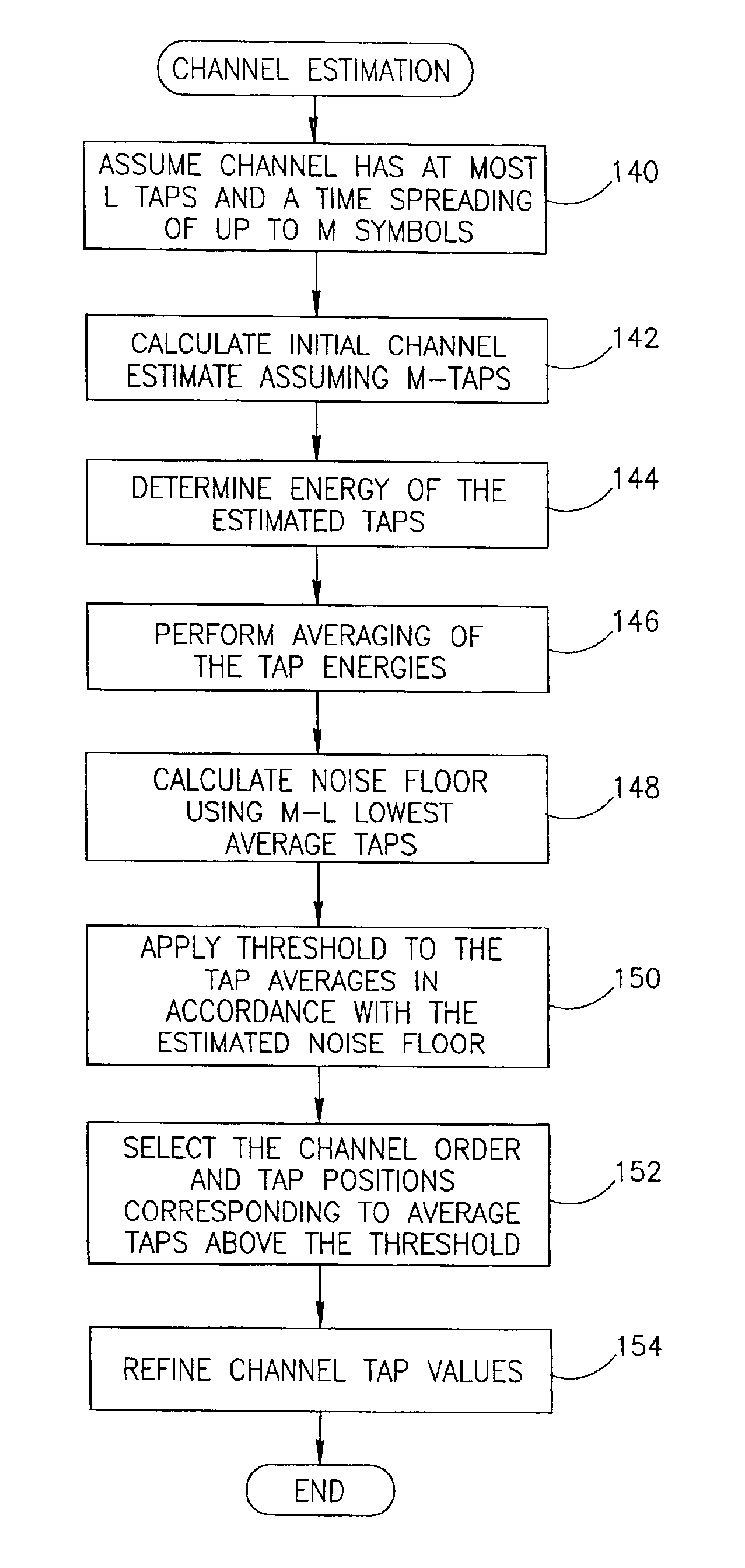
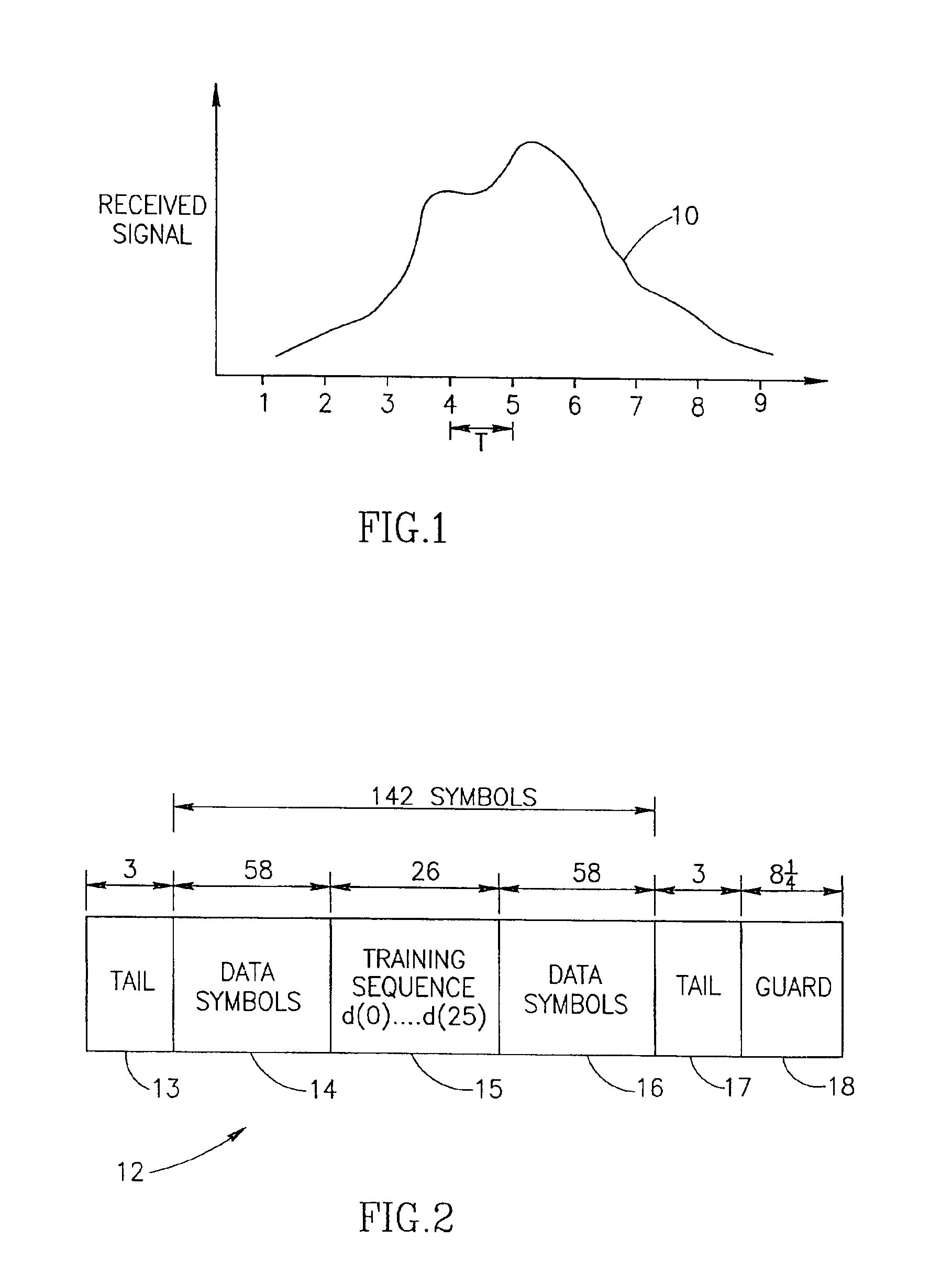
Method of channel order selection and channel estimation in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS6907092B1Choose accuratelyLarge energyError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemImpulse response
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of determining the channel order and channel estimate in a communications system such as a wireless communication system including cellular and cordless. Such channels are typically characterized by rapidly changing impulse response and their taps can be modeled as zero-mean, complex, Gaussian random processes. A sufficiently long, initial channel estimate of length is performed so as to ensure that the actual channel taps will be contained in the estimated taps thus making certain that the equalizer will effectively eliminate intersymbol interference. Channel estimation is performed during each burst using the training sequence transmitted in the middle of the burst. The tap energies are averaged so as to track slow variations in the pattern of resultant channel taps. A noise floor is calculated using the lowest averaged taps and a threshold is computed based thereon and applied to the average taps. The channel order and the tap positions are then selected in accordance those average taps that are above the threshold.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
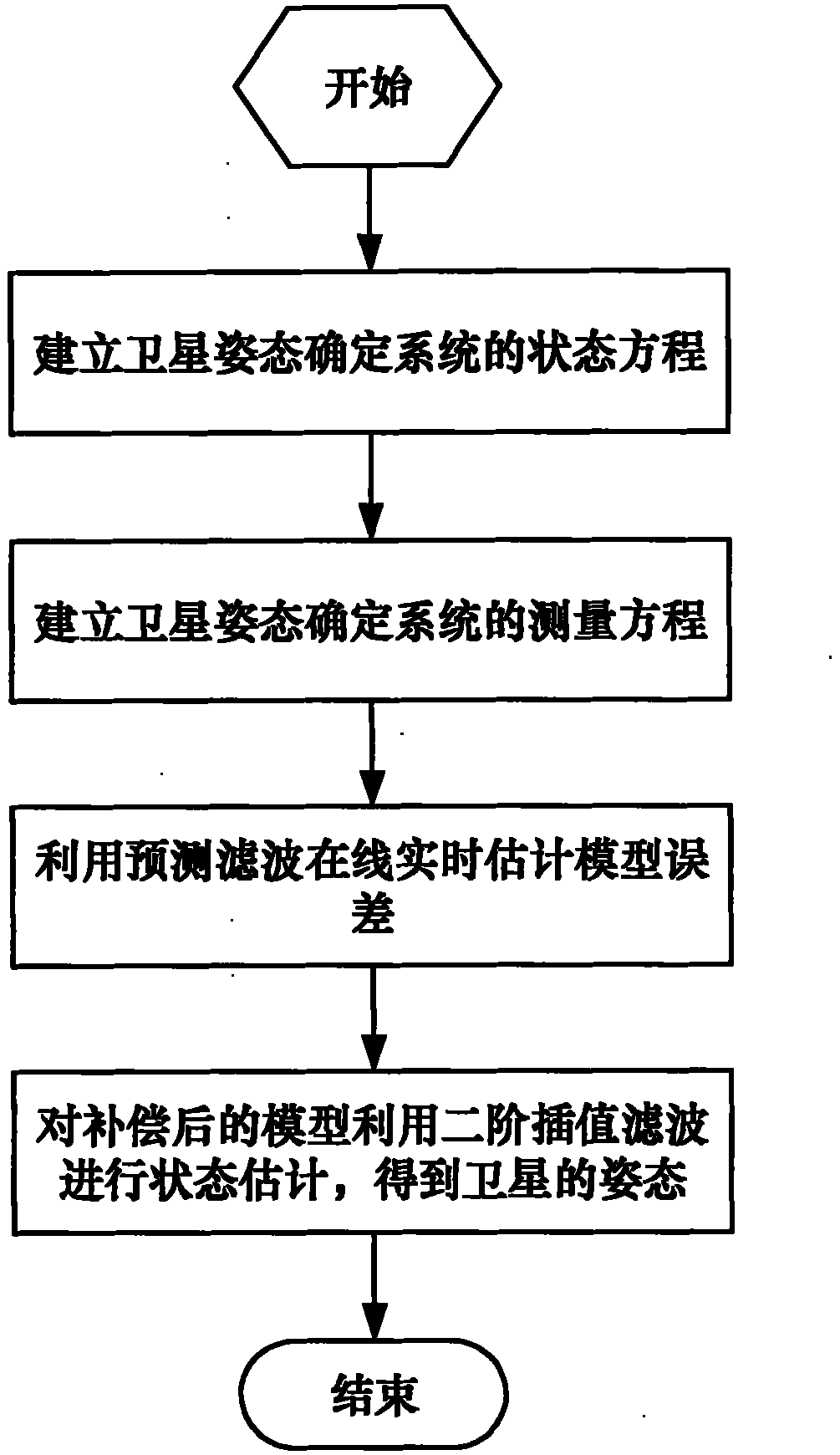
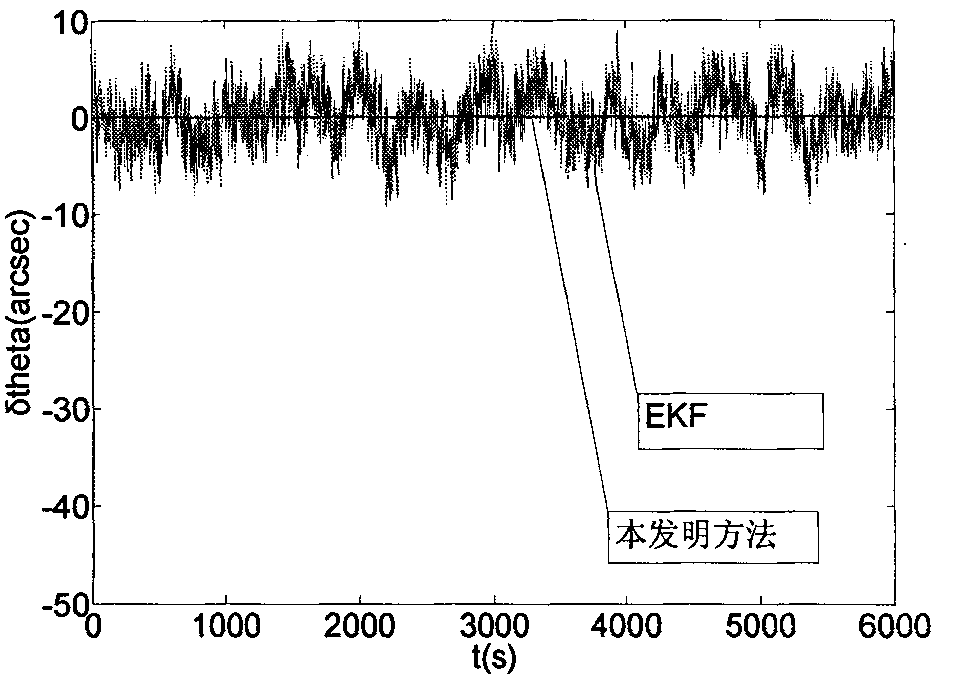
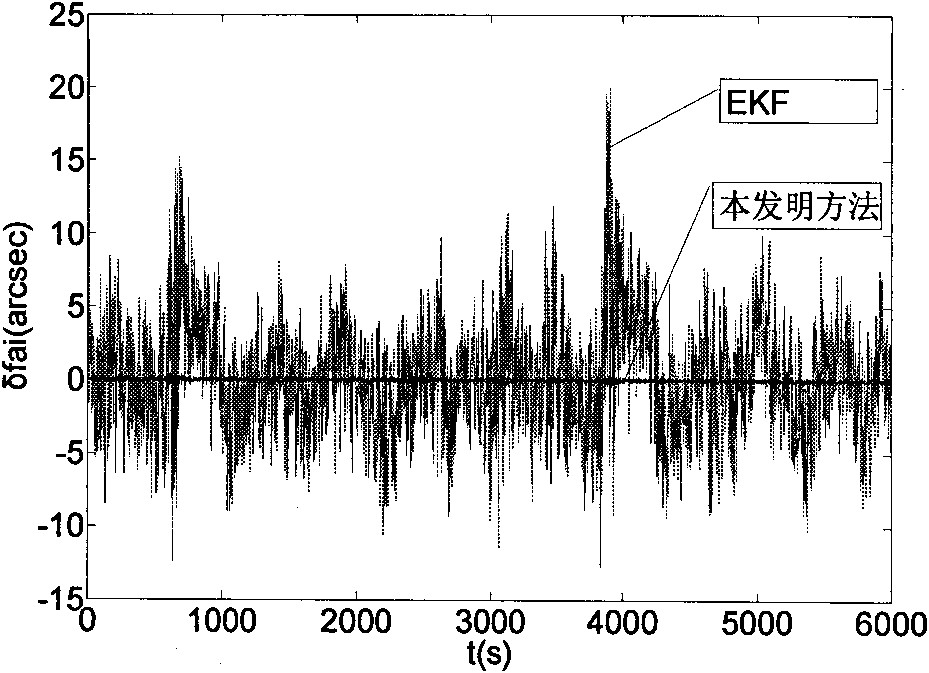
High-precision satellite attitude determination method based on star sensor and gyroscope
InactiveCN101846510AOvercome the disadvantage of error processing as zero-mean white noiseHigh precisionAngle measurementNavigation instrumentsGyroscopeZero mean
The present invention discloses a high-precision satellite attitude determination method based on star sensor and gyroscope, which comprises the following steps: step 1. establishing a status equation of a satellite attitude determination system; step 2. establishing a measurement equation of the satellite attitude determination system; step 3. performing an online real-time model error estimation through predictive filtering; and step 4. performing a status estimation on a compensated model through 2-order interpolation filtering to obtain the attitude of a satellite. By applying predictive filtering to performing an online real-time model error estimation and correcting the system model, the invention overcomes the shortcoming existing in the conventional estimation process that error is processed into zero-mean white noise; and in addition, the invention can process any nonlinear system and noise conditions to obtain an estimation result of higher precision and is applicable to thefield of high-precision attitude determination.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
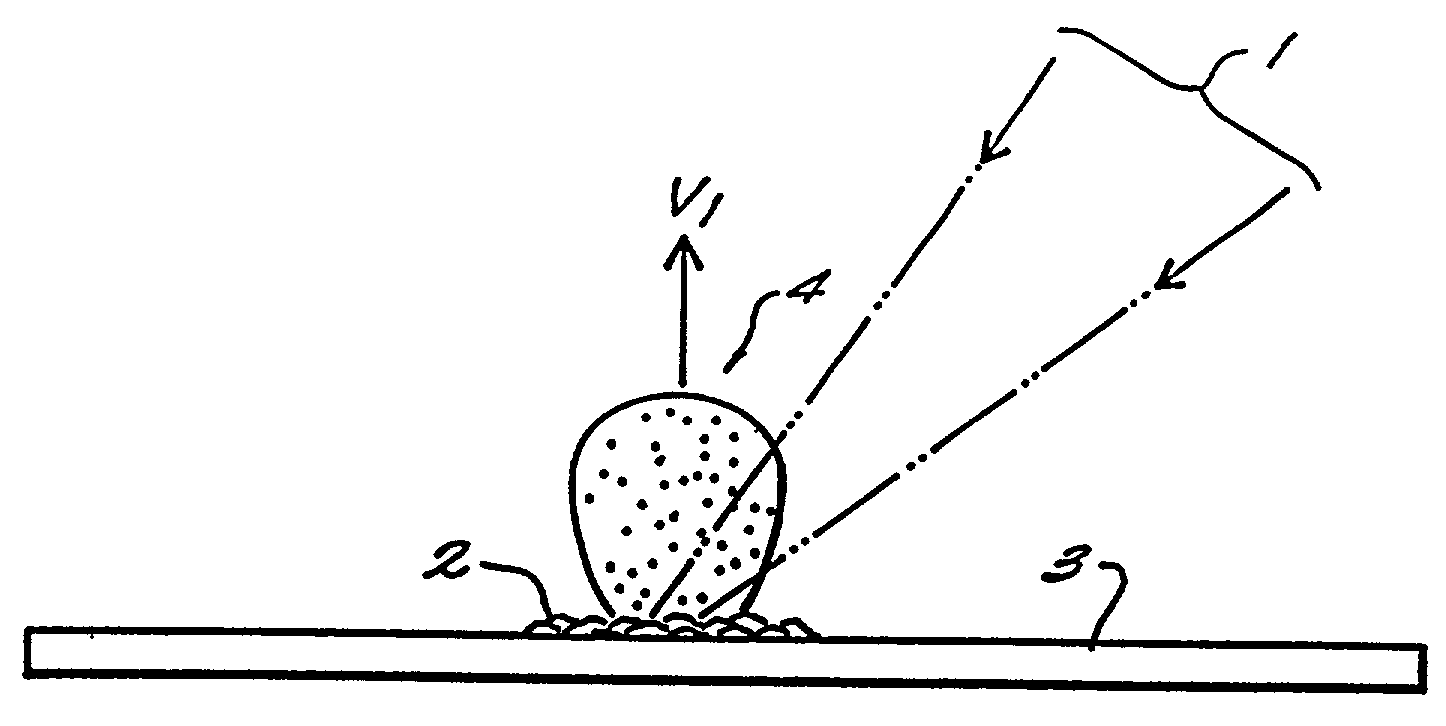
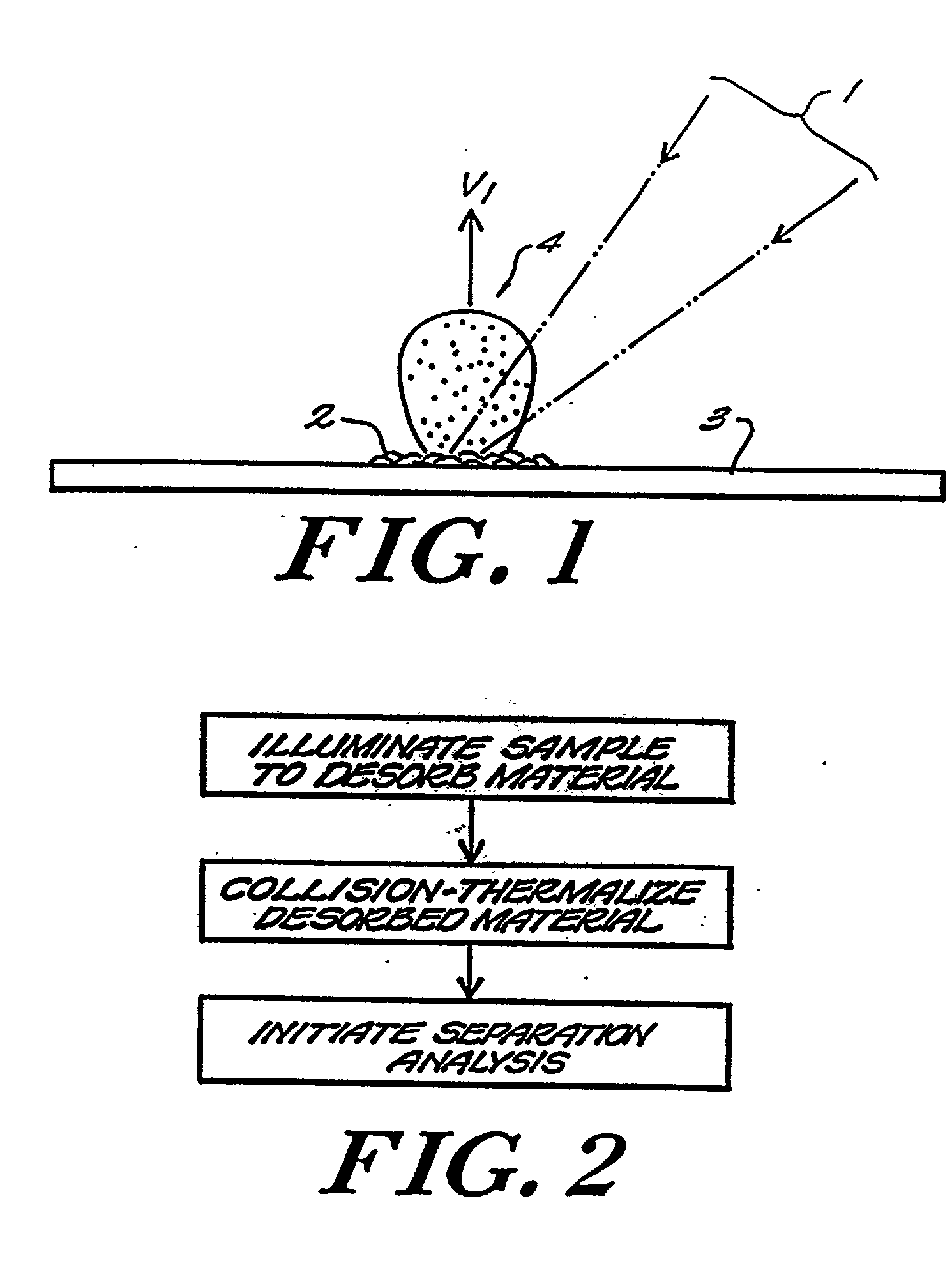
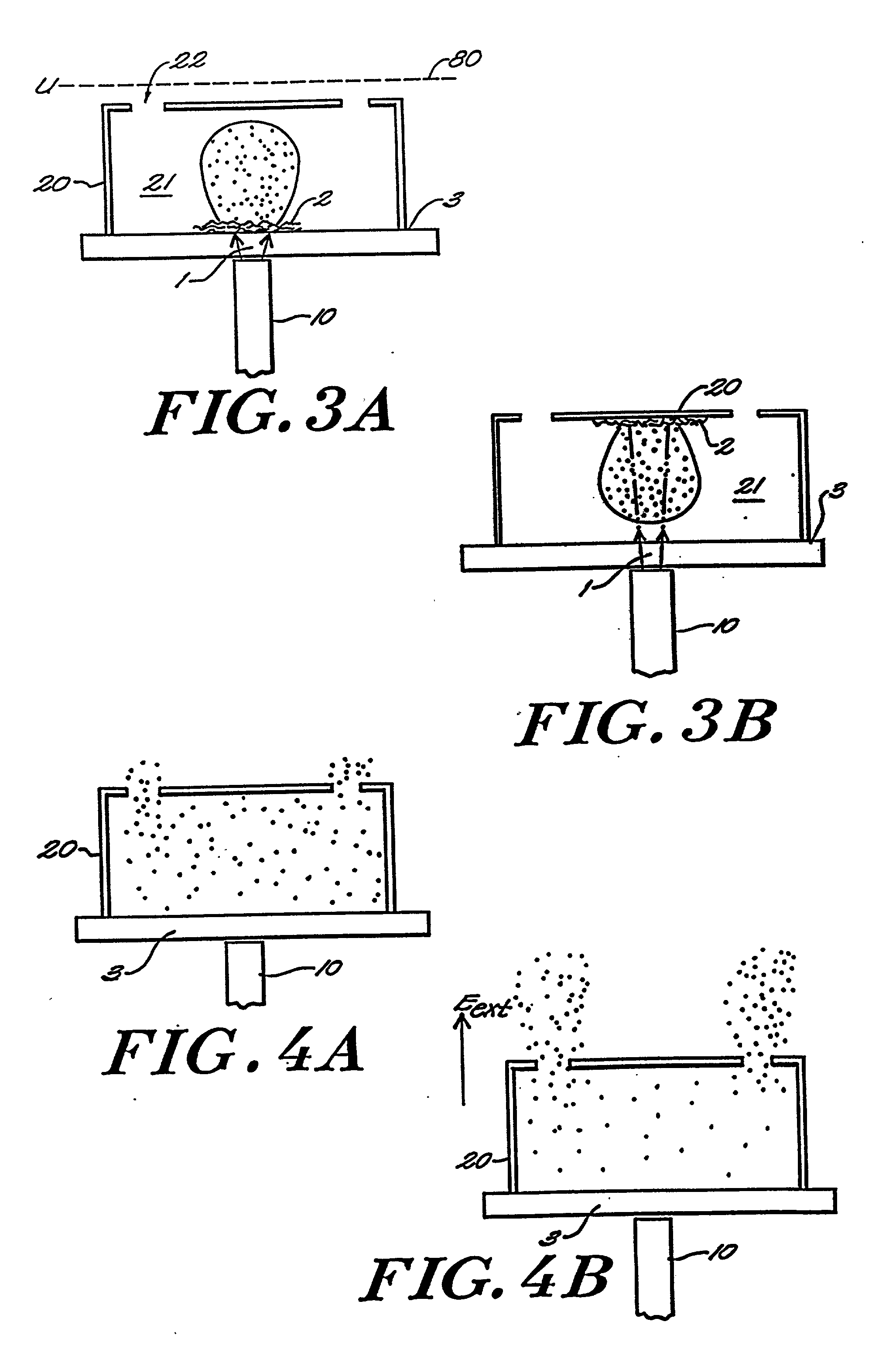
Method and apparatus for maldi analysis
InactiveUS20020005478A1Extended stayBroaden TOF peak widthSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFiberPeak value
Matrix assisted laser desorption / ionization is performed in a manner to thermalize large analyte ions in a plume of desorbed material for spectroscopic analysis. The thermalized ions have a low or zero mean velocity and are presented at a well-defined instant in time, reducing artifacts and sharpening the spectral peaks. In one embodiment the light is delivered to a matrix or sample holder having a cover, baffle or compartment. The baffle or compartment impedes or contains a plume of desorbed material and the analyte undergoes collisions to lower its mean velocity and directionality. Thus "thermalized" the analyte ions are passed to a mass analysis instrument. In a preferred embodiment an optical fiber butts up against a thin transparent plate on which the specimen resides, with the matrix side in a vacuum acceleration chamber. A mechanical stage moves the specimen in both the x- and y- directions to select a point on the specimen which is to receive the radiation. The use of a fiber optic illuminator allows the entire stage assembly to be subsumed essentially within the dimensions of a conventional stage. In other embodiments, a thermalizing compartment is provided in a capillary tube about the end of the illumination fiber and the sample matrix is deposited along the inner cylindrical wall of the tube, so the capillary forms a migration path to the outlet for thermalization of the desorbed analyte. In other embodiments microstructures having the shape of a small lean-to, overhang or perforated cover plate, or providing a high aspect surface texture, provide the necessary containment to promote thermalization of the released analyte. A thin layer or cover of fibrous or permeable material may also be used to thermalize the analyte before mass analysis, and in other embodiment this material may also act as the substrate. An automated instrument may include a fixed array of illumination fibers which are illuminated at different times to eject samples from a corresponding array of points on the specimen.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
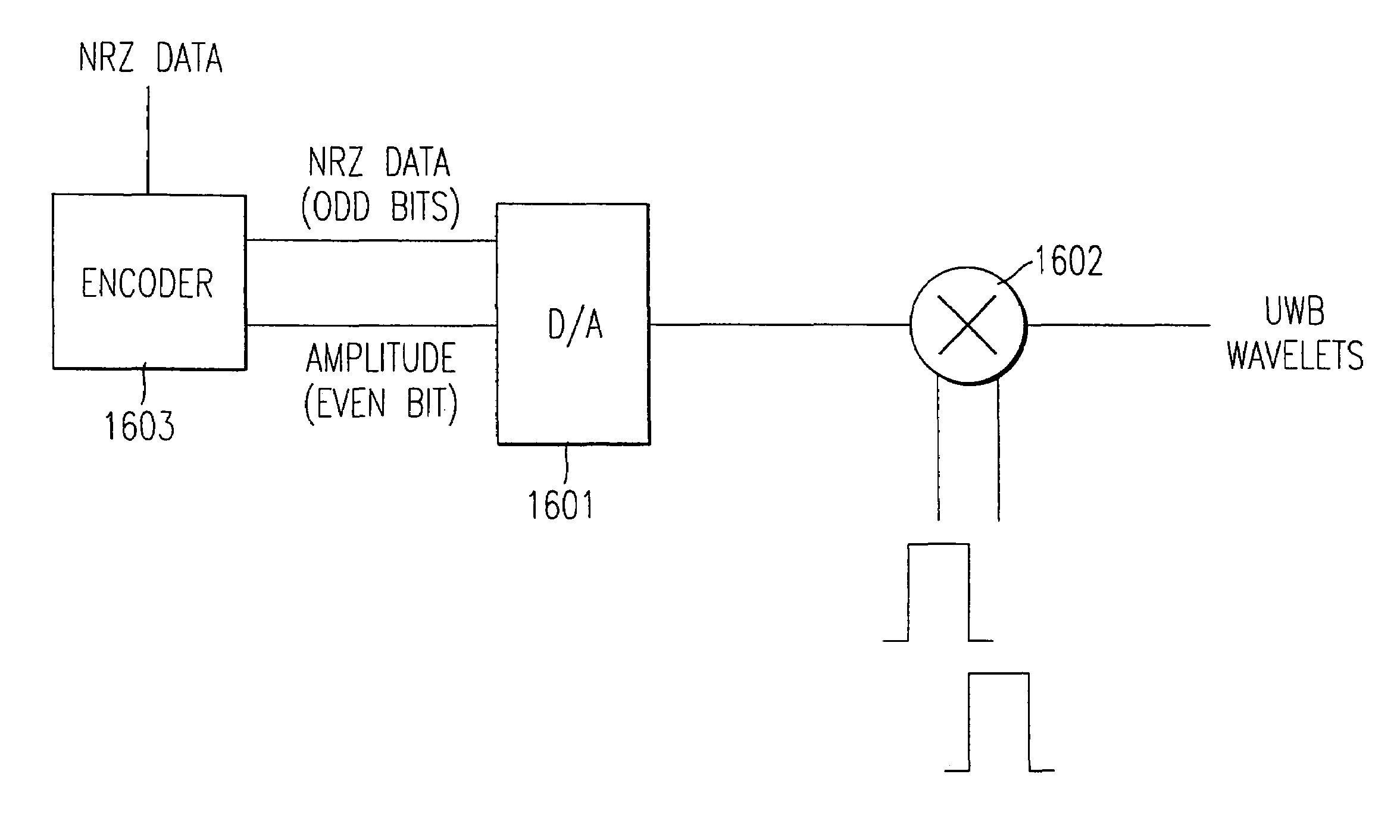
System and method for generating ultra wideband pulses
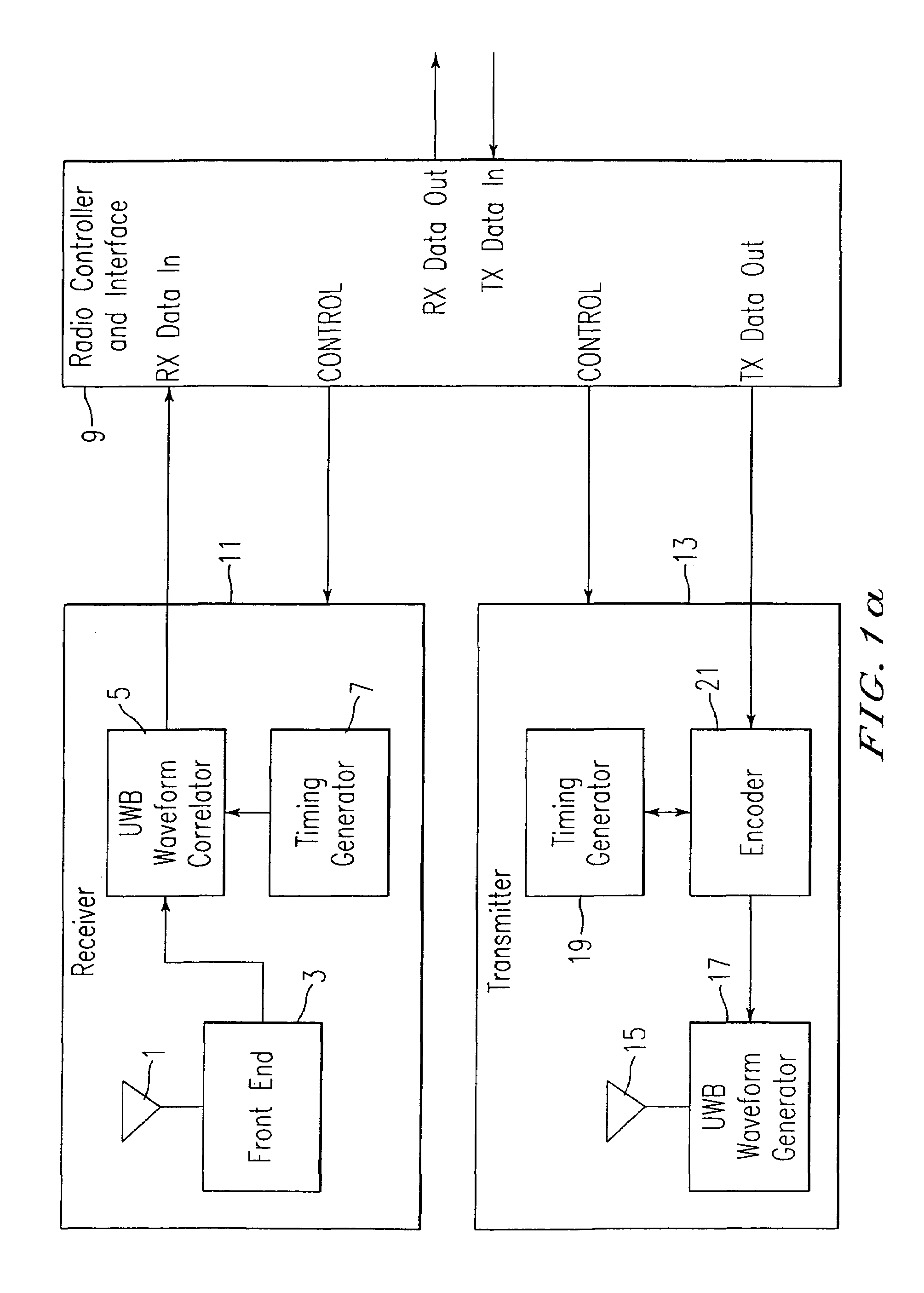
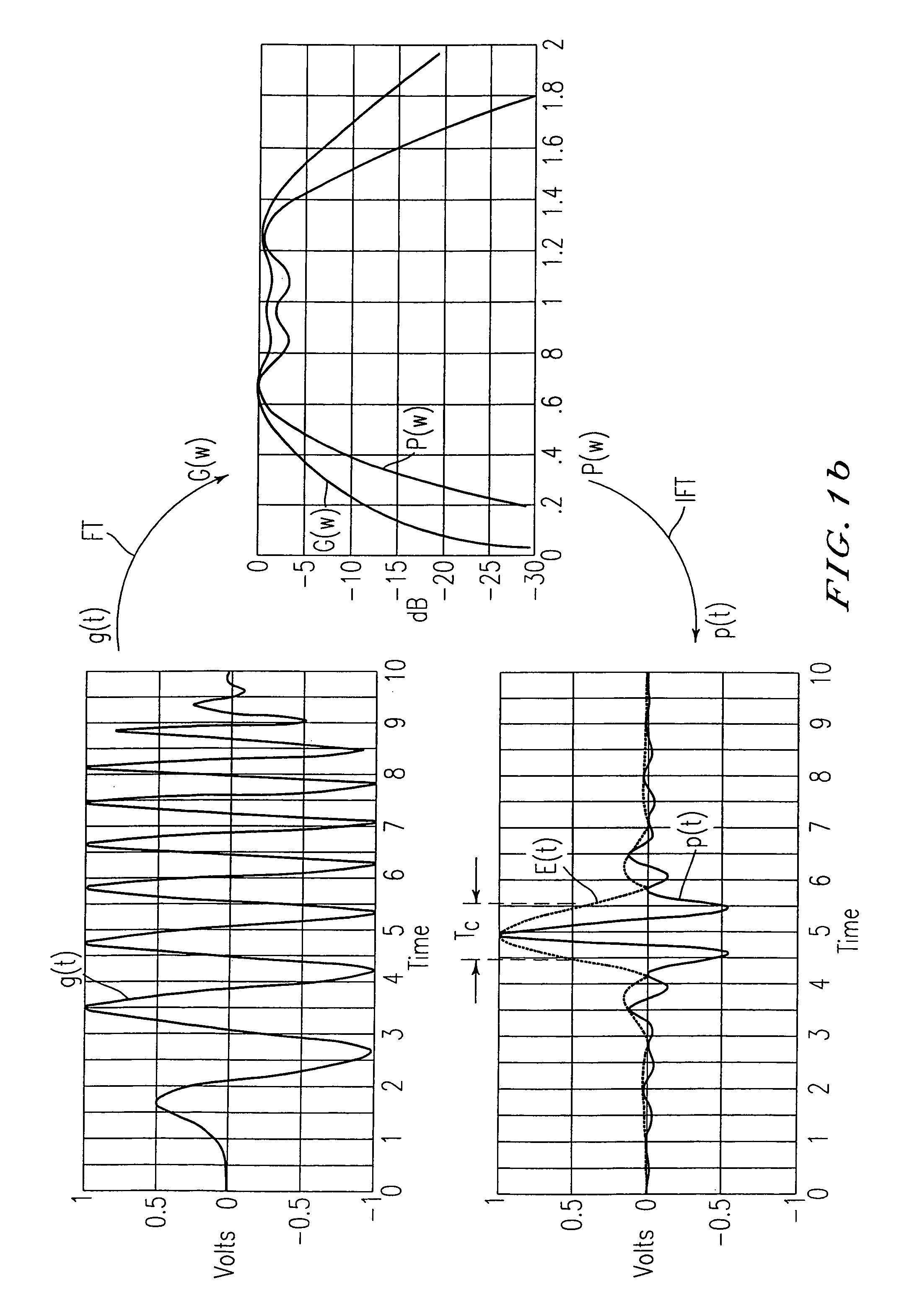
InactiveUS7010056B1Modulated carrier system with waveletsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandPeak value
An ultra-wide band (UWB) waveform generator and encoder for use in a UWB digital communication system. The UWB waveform is made up of a sequence of shaped wavelets. The waveform generator produces multi-amplitude, multi-phase wavelets that are time-constrained, zero mean, and can be orthogonal in phase, yet still have a −10 dB power spectral bandwidth that is larger than the frequency of the peak of the power spectrum In one embodiment, the wavelets are bi-phase wavelets. The encoder multiplies each data bit by an n-bit identifying code, (e.g., a user code), resulting in a group of wavelets corresponding to each data bit. The identifying codeword is passed onto the UWB waveform generator for generation of a UWB waveform that can be transmitted via an antenna.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Systems and methods for orientation independent sensing
A system and method for obtaining an OIS coordinate frame comprising an electronic control unit configured to determine a local 3D electric field loop, create a zero mean version of E(t) over a depolarization interval, compute an Ė value at each of a plurality of time intervals, compute an initial estimate of ŵ from a cross product of E and the Ė value for each of the plurality of time intervals, average the initial estimate of ŵ from each of the plurality of time for a best estimate of ŵ, determine a plurality of â(θ) values and using the corresponding {circumflex over (n)}(θ) values, compute a composite match score, and choose at least one best value for â and a best value for {circumflex over (n)}.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Robust process model identification in model based control techniques
ActiveUS20070244575A1Robust methodAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSimulator controlGeneration processTest input
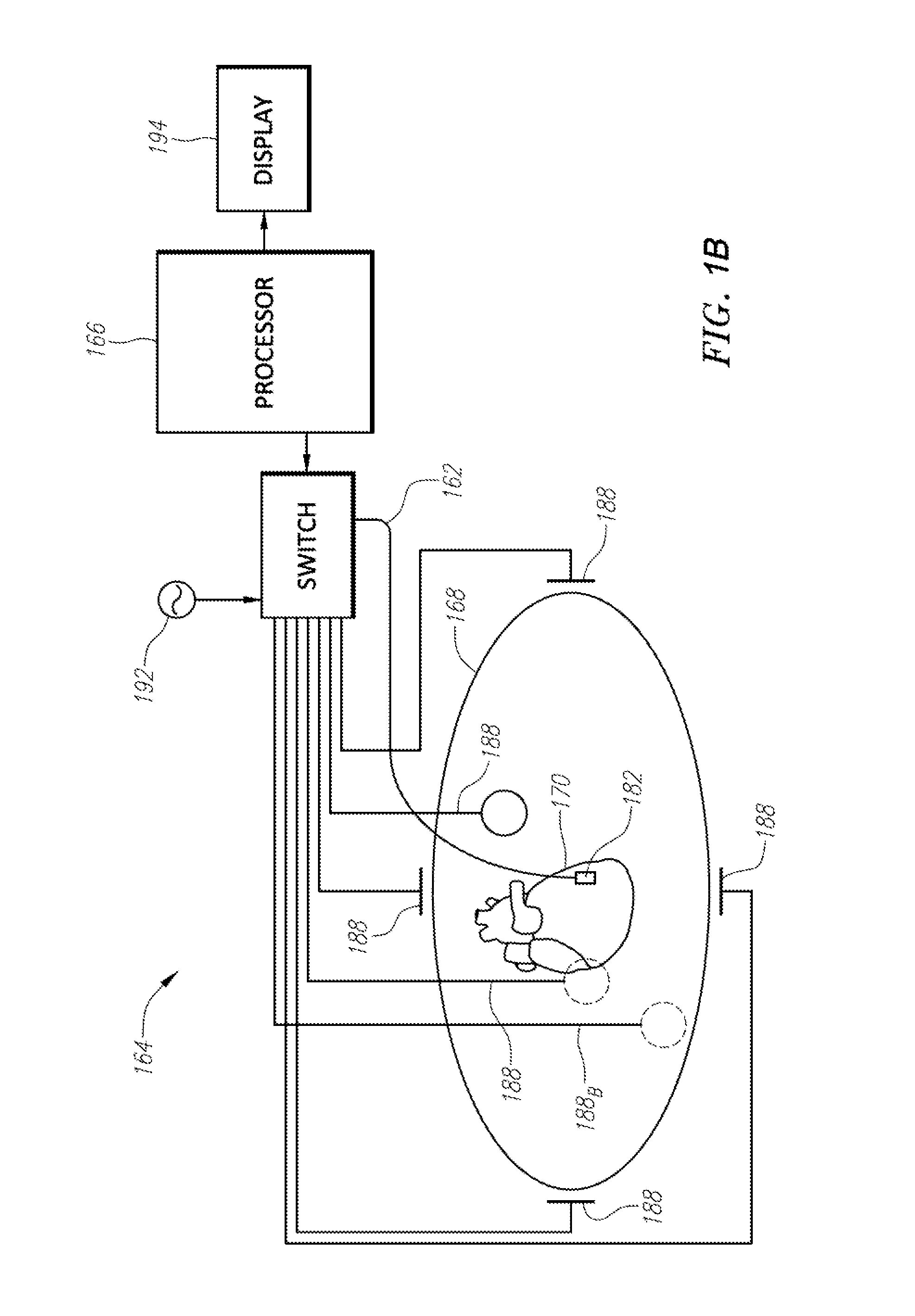
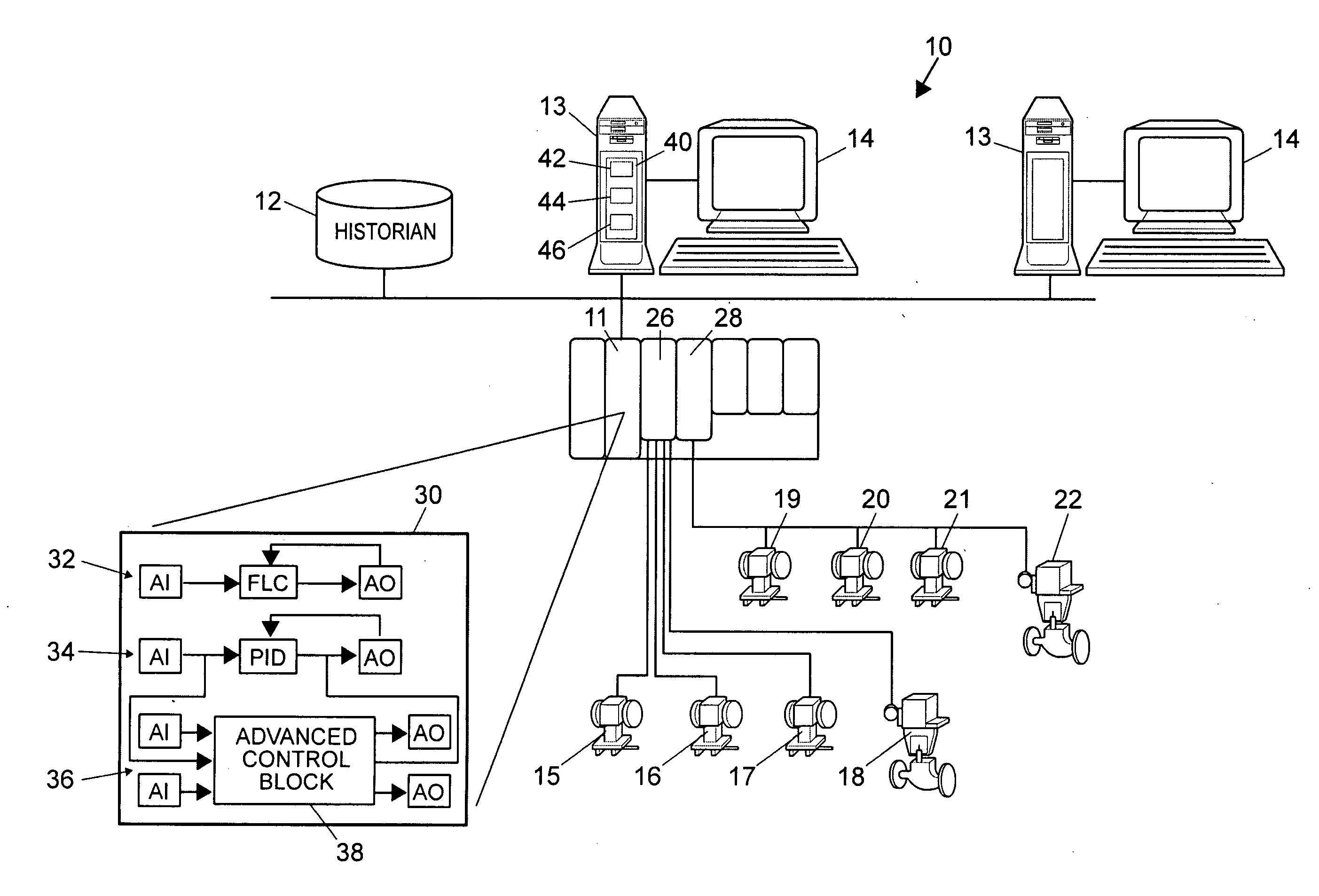
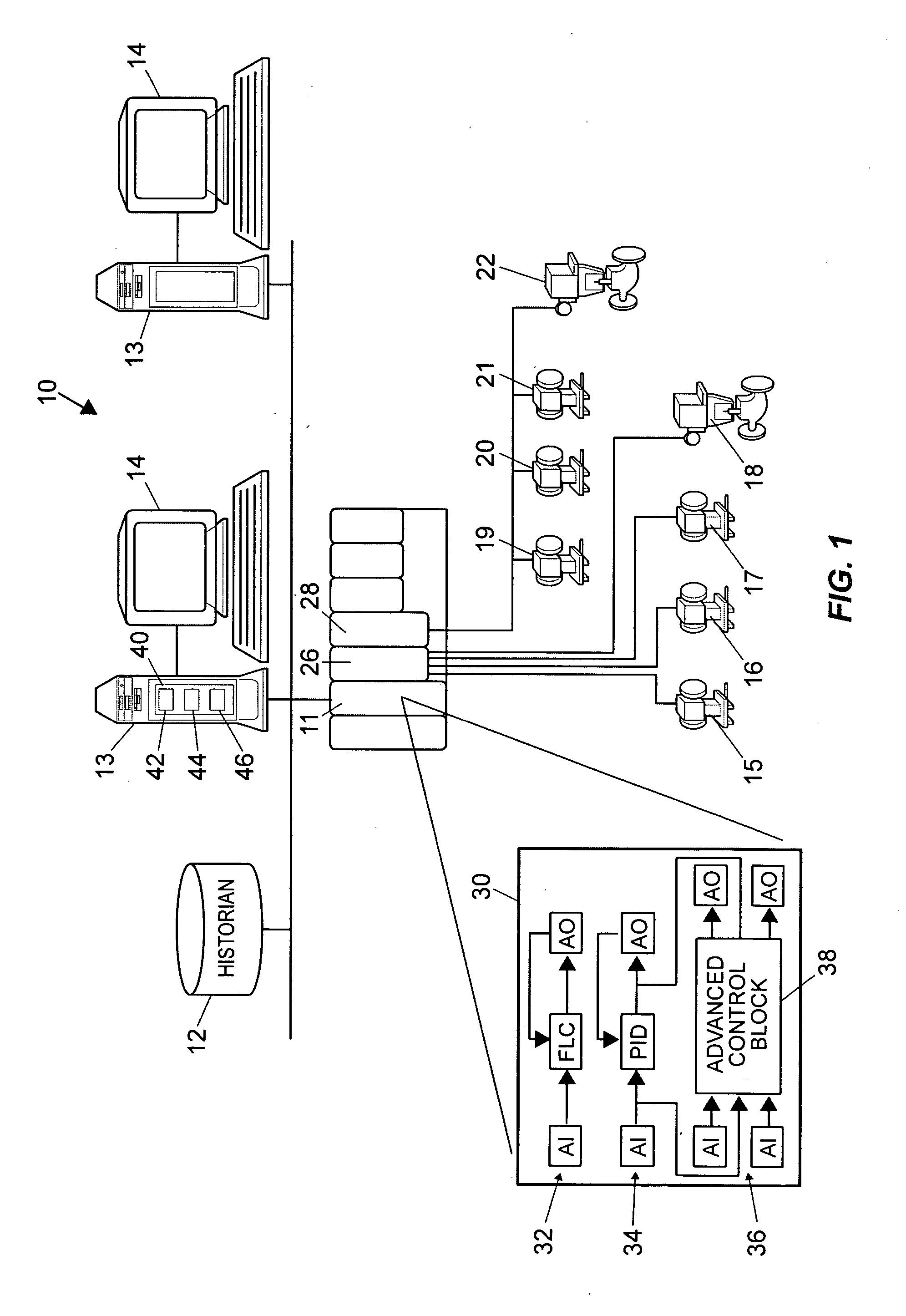
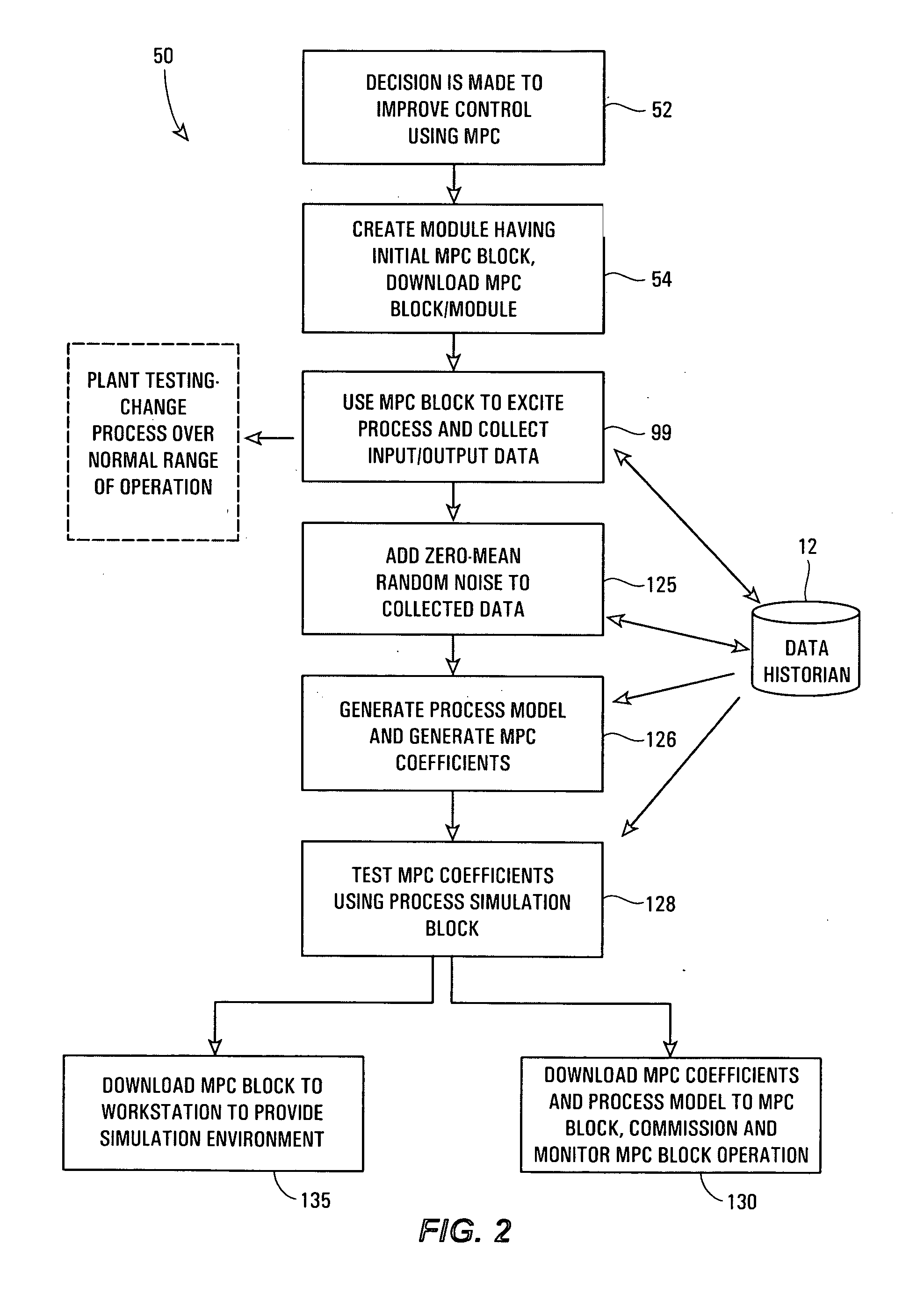
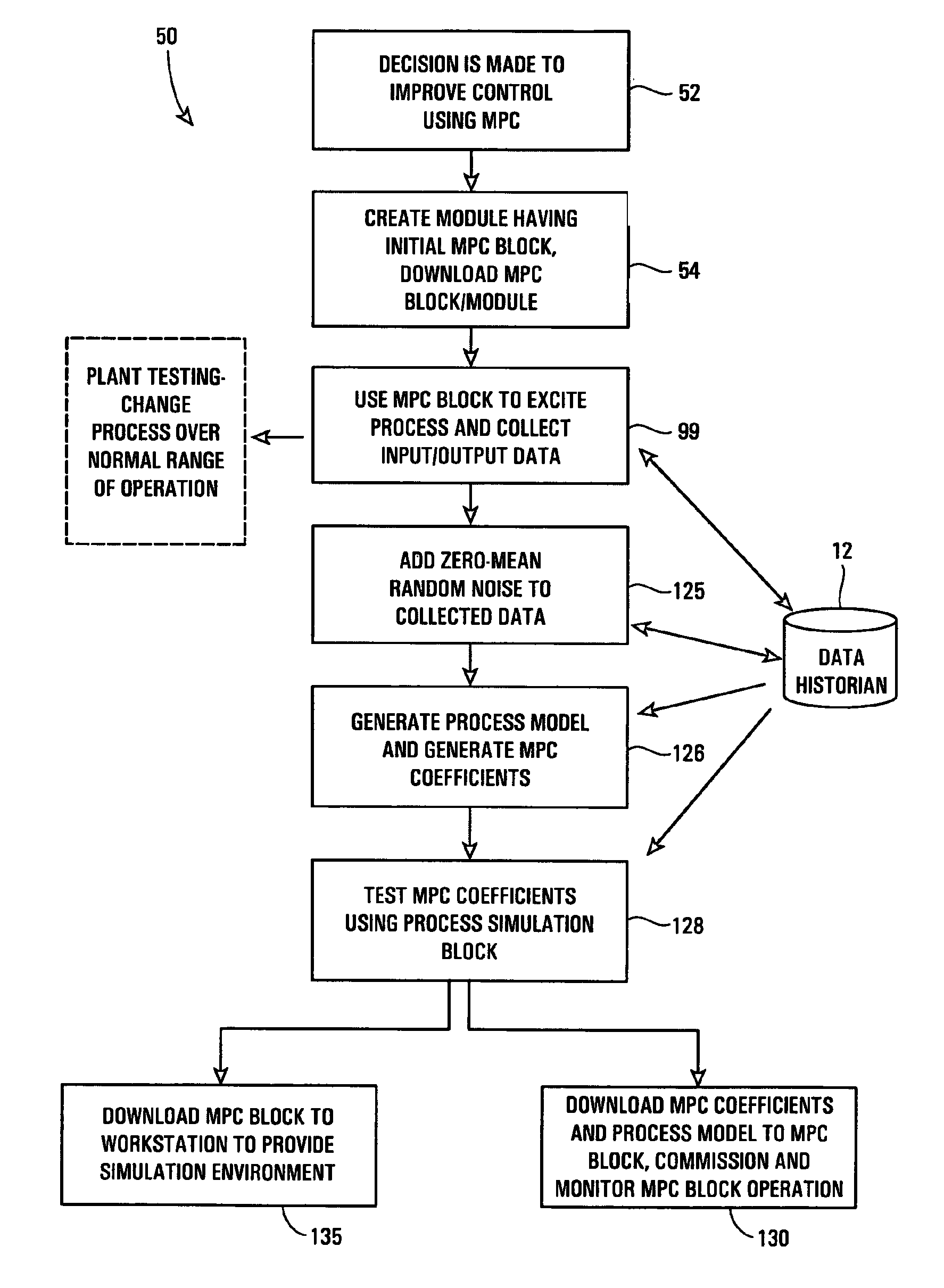
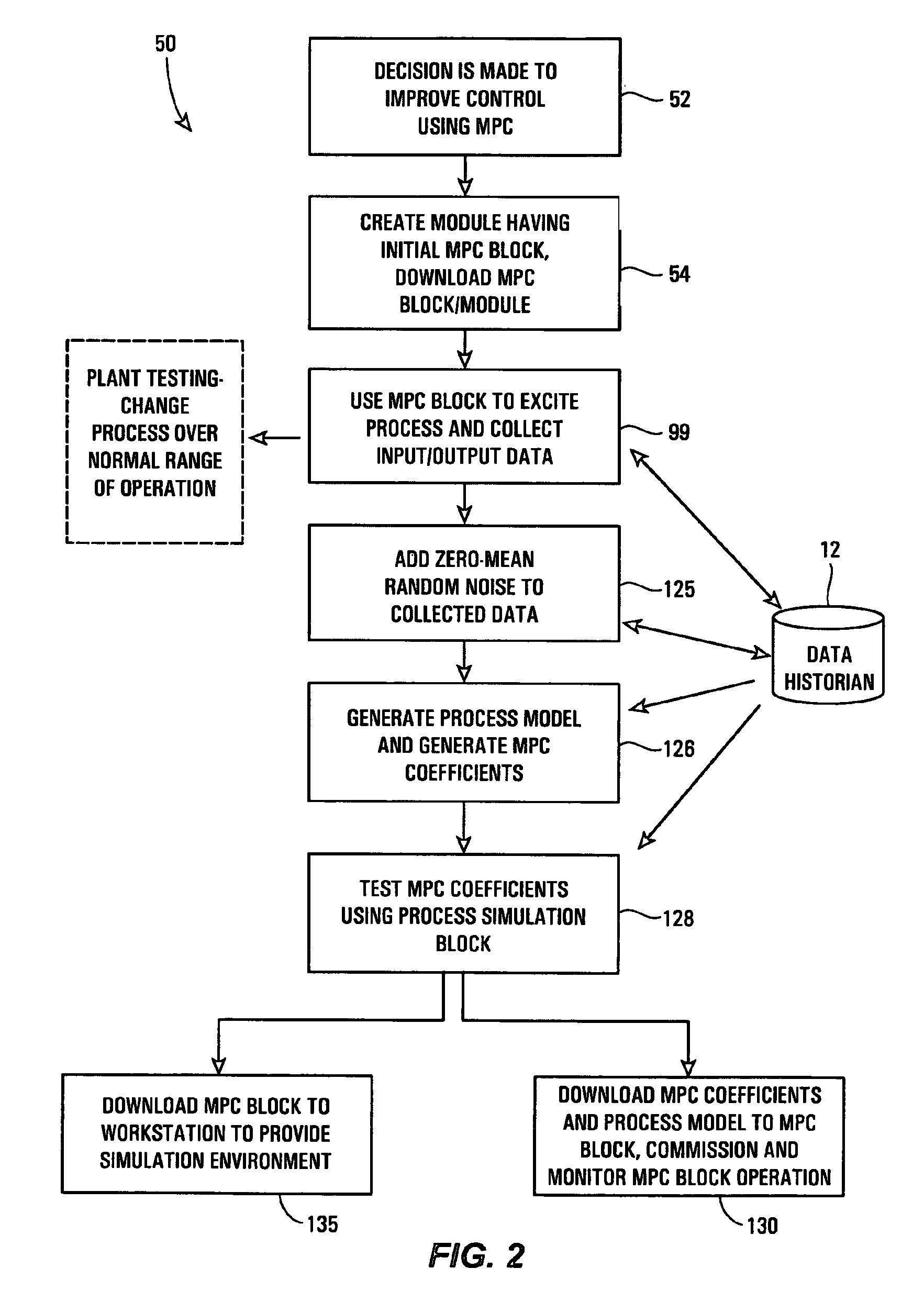
A robust method of creating process models for use in controller generation, such as in MPC controller generation, adds noise to the process data collected and used in the model generation process. In particular, a robust method of creating a parametric process model first collects process outputs based on known test input signals or sequences, adds random noise to the collected process data and then uses a standard or known technique to determine a process model from the collected process data. Unlike existing techniques for noise removal that focus on clean up of non-random noise prior to generating a process model, the addition of random, zero-mean noise to the process data enables, in many cases, the generation of an acceptable parametric process model in situations where no process model parameter convergence was otherwise obtained. Additionally, process models created using this technique generally have wider confidence intervals, therefore providing a model that works adequately in many process situations without needing to manually or graphically change the model.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
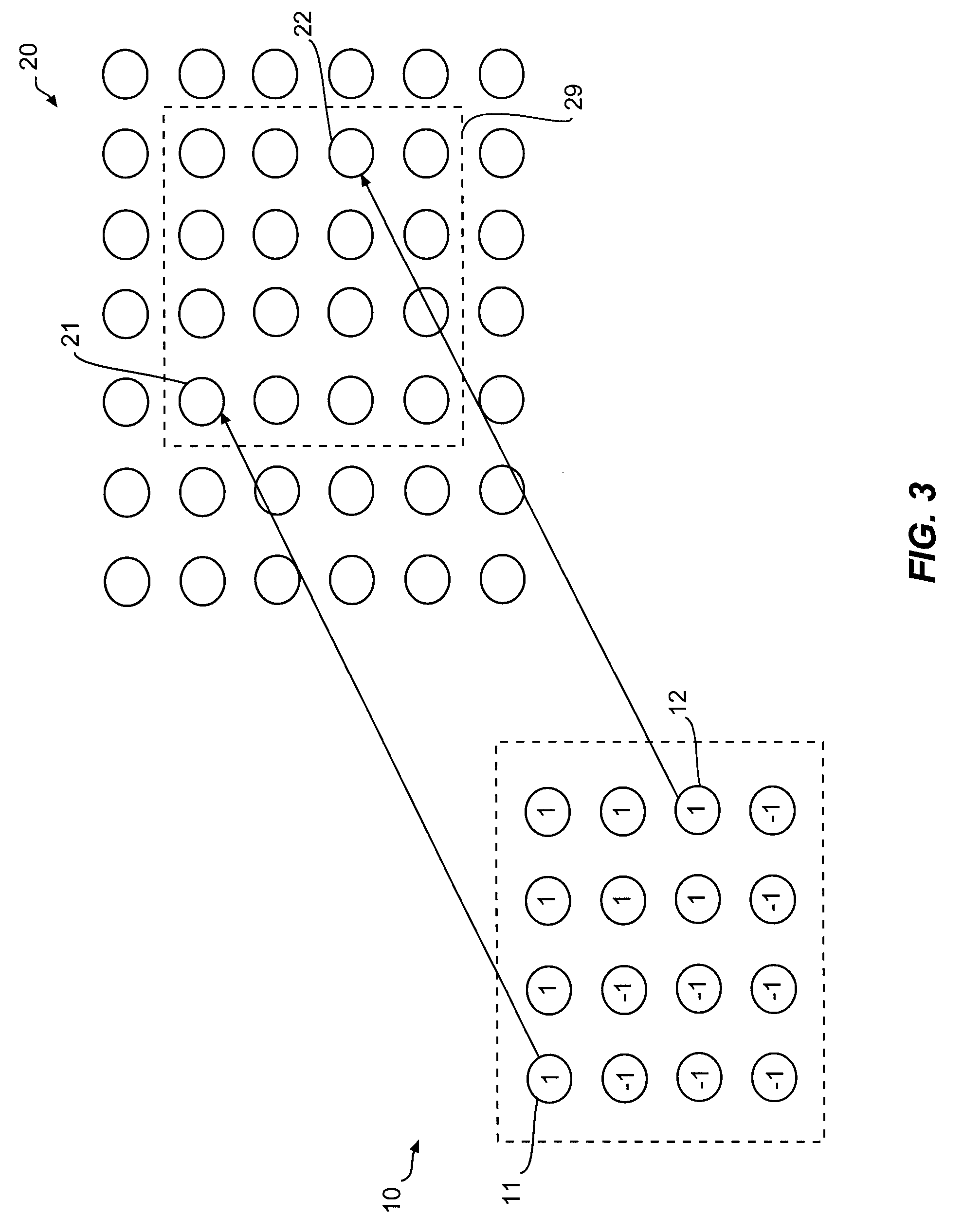
Watermarking with random zero-mean patches for copyright protection
InactiveUS6522766B1Efficient detectionUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionRandom choiceProtection system
A steganographic method embeds hidden information like digital watermarks and digital fingerprints into an image by applying one or more zero-mean patches to a digital signal that conveys the image. Each zero-mean patch comprises elements having an average value substantially equal to zero. A copyright protection system is implemented by selecting one or more zero-mean patches in pseudo-random fashion, modifying the patches by perturbing their elements in pseudo-random fashion, and applying the patches to image pixels at locations that are selected in pseudo-random fashion. The copyright protection system further includes a procedure for checking for the presence of a watermark in a digital signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
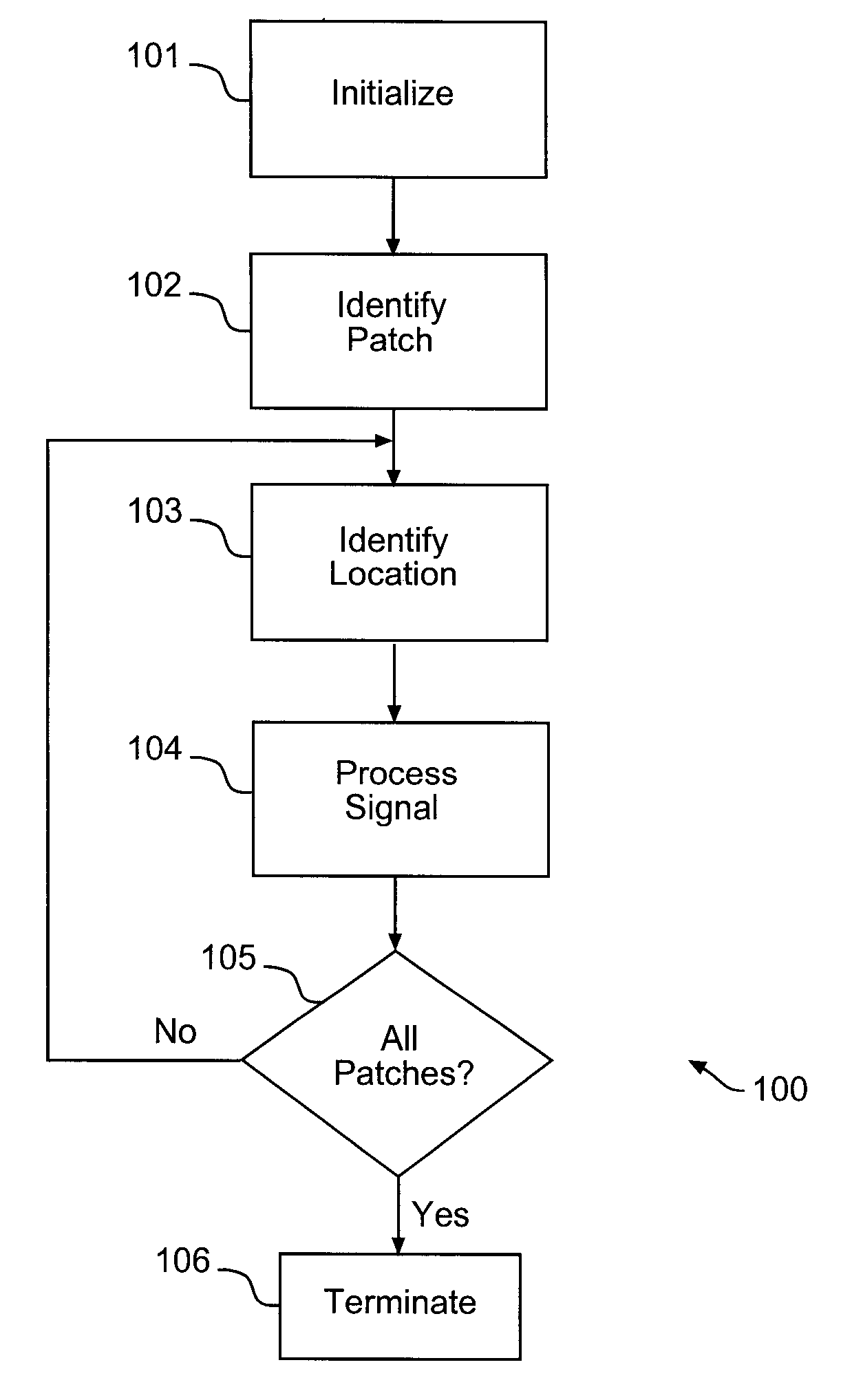
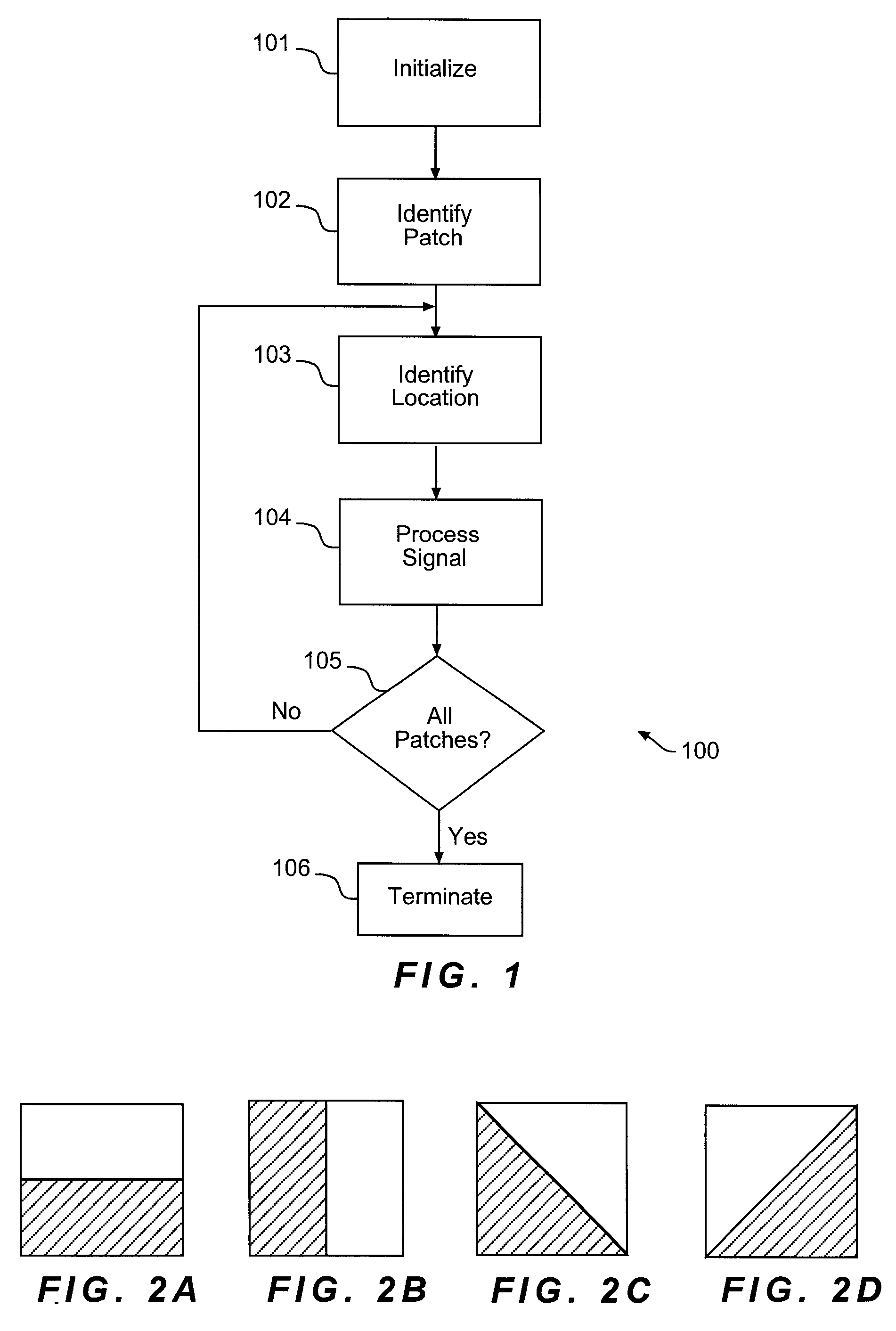
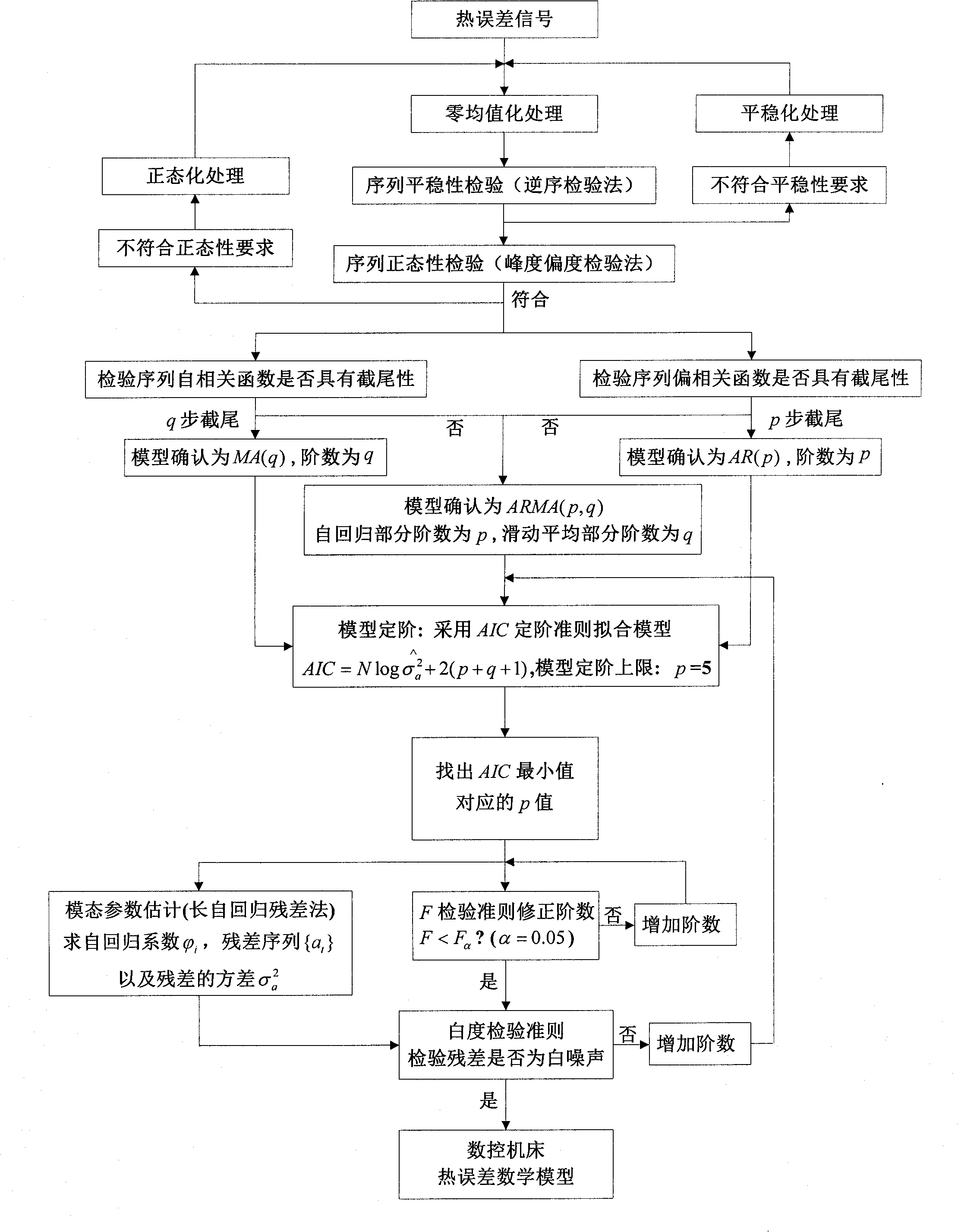
Numerical control machine tool thermal error real-time compensation modeling method based on time series algorithm
InactiveCN102736558AReduce hardware costsReduce complexityProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlMathematical model
The invention relates to a numerical control machine tool thermal error real-time compensation modeling method based on a time series algorithm, which belongs to the technical field of precision machining. The method comprises the steps of (1) carrying out data zero mean pretreatment, namely employing an inverted sequence test method and a kurtosis and skewness test method to judge the stationarity and the normality of the data; (2) using an autocorrelation function, a partial correlation function, and the censored results as judgment criteria to carry out the pattern recognition of a thermal error mathematical model; (3) employing a least square estimation method or a long autoregressive residual calculating method to realize the parameter estimation of the thermal error mathematical model; (4) determining the order of the thermal error mathematical model, namely employing a judgment method that combines an AIC order determination criterion, an F test order determination criterion, and a whiteness test order determination criterion to realize the order determination of the thermal error mathematical model; (5) and carrying out integration processing of synthesizing judgment conditions, namely constructing a complete forecasting mathematical model formula. The modeling method provided by the invention has the advantages that less hardware is required, the applicability is wide, and the established model has high prediction precision and reliability.
Owner:上海睿涛信息科技有限公司
Robust process model identification in model based control techniques
ActiveUS7840287B2Robust methodAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSimulator controlGeneration processTest input
A robust method of creating process models for use in controller generation, such as in MPC controller generation, adds noise to the process data collected and used in the model generation process. In particular, a robust method of creating a parametric process model first collects process outputs based on known test input signals or sequences, adds random noise to the collected process data and then uses a standard or known technique to determine a process model from the collected process data. Unlike existing techniques for noise removal that focus on clean up of non-random noise prior to generating a process model, the addition of random, zero-mean noise to the process data enables, in many cases, the generation of an acceptable parametric process model in situations where no process model parameter convergence was otherwise obtained. Additionally, process models created using this technique generally have wider confidence intervals, therefore providing a model that works adequately in many process situations without needing to manually or graphically change the model.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
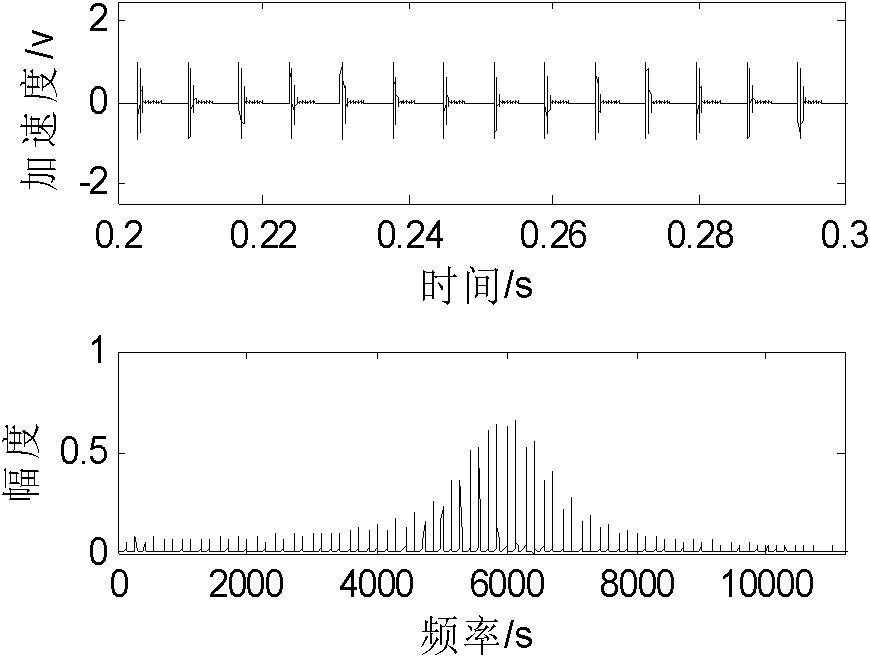
Self-adaptive failure diagnosis method of rotary mechanical component based on continuous wavelet transformation
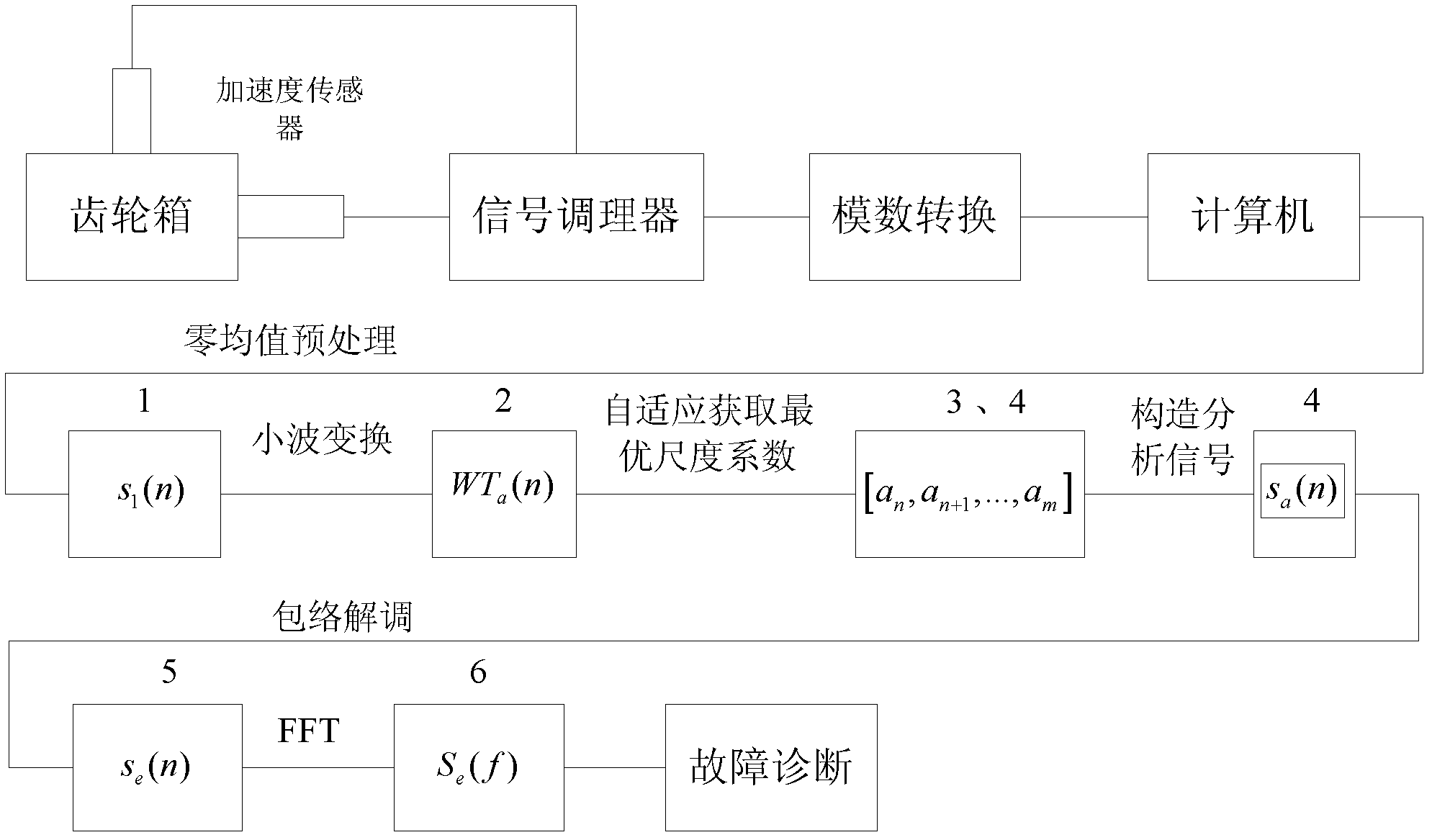
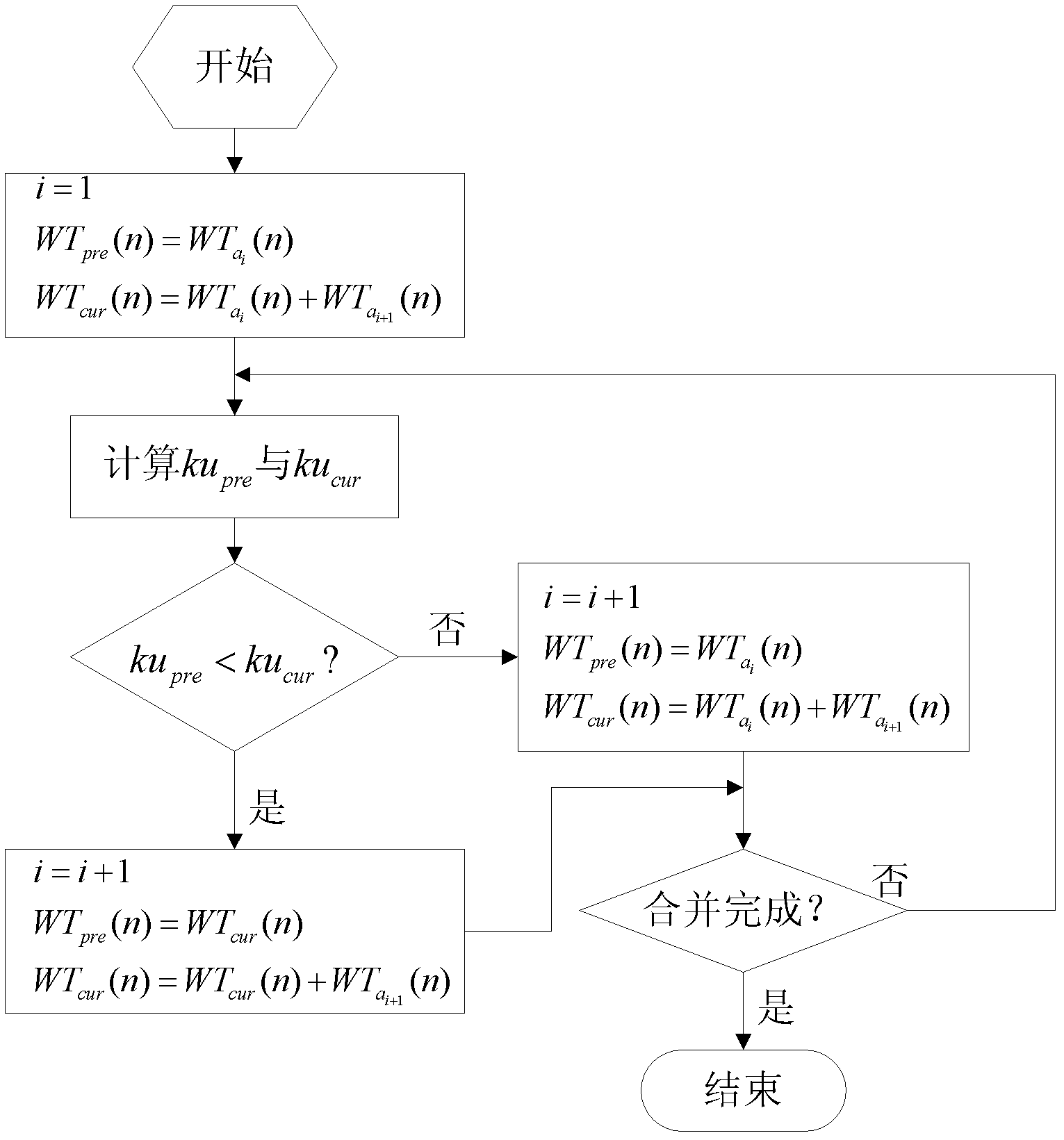
InactiveCN102539150AAvoid influenceImprove accuracyMachine gearing/transmission testingMachine bearings testingMechanical componentsZero mean
The invention relates to a self-adaptive failure diagnosis method of a rotary mechanical component based on continuous wavelet transformation. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, performing zero-mean preprocessing on an acquired discrete initial vibration signal to obtain a preprocessed signal from which a direct-current component is eliminated; 2, performing continuous wavelet transformation on the preprocessed signal obtained in the step 1 to obtain a wavelet coefficient which corresponds to each scale parameter; 3, calculating the kurtosis of the wavelet coefficient which corresponds to each scale parameter in the step 2 respectively; 4, searching for a wavelet scale parameter which corresponds to large kurtosis in the wavelet scale parameter obtained in the step 3 with a self-adaptive algorithm to configure an optimal analysis signal; and 5, performing envelope demodulation on the optimal analysis signal obtained in the step 4 to obtain an envelope signal. The method has the beneficial effects that: the accuracy of failure diagnosis is increased, and the method is particularly suitable for failure diagnosis of mechanical parts with impact damages.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for calculating guy cable vibrating base frequency
InactiveCN101586997AAccurate calculationRaise the level of automaticTension measurementVibration accelerationVibratory signal
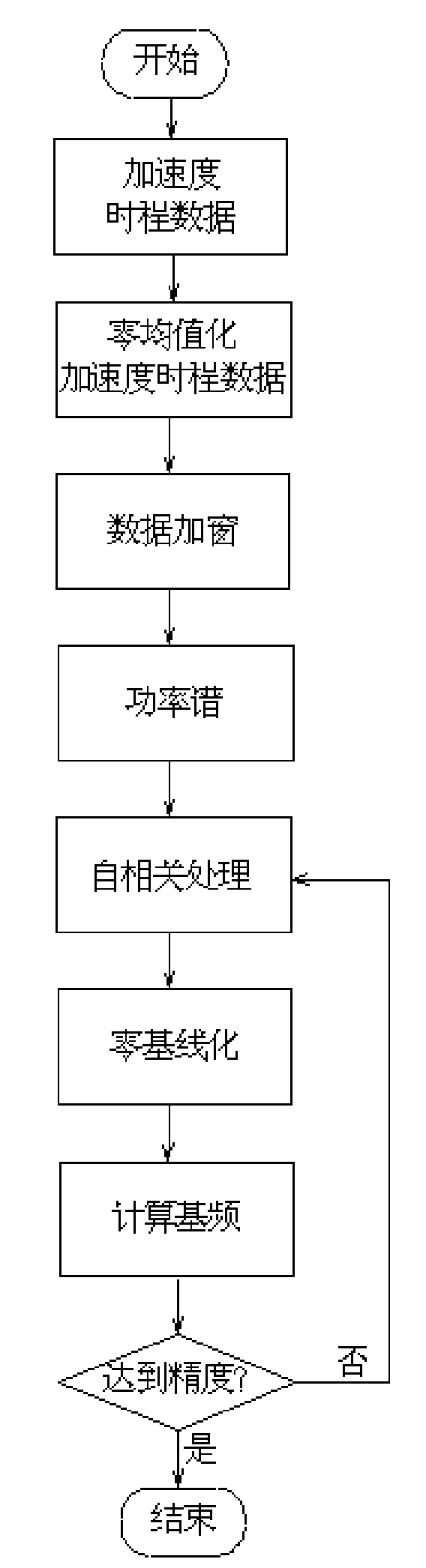
The present invention discloses a method for calculating the guy cable vibrating base frequency, including collecting the vibration acceleration data of the guy cable to implement a zero mean and window adding operation to calculate a power spectrum of the vibration acceleration; based on the power spectrum of the vibration acceleration, extracting near periodic spectrum peaks from the power spectrum of the vibration acceleration by autocorrelation calculation, and processing the autocorrelation calculated result by a zero base line operation; then calculating the base frequency and implementing a plurality of iteration operations until the error of the base frequency calculated results is less than 0.01Hz, the final base frequency value is the base frequency of the guy cable. The invention is capable of calculating the vibrating base frequency of the inclined guy cable accurately to meet the precision requirement for measuring a cable force, improving the base frequency recognition precision effectively, and calculating the vibrating base frequency of the guy cable accurately when the guy cable vibrating signal contains an environment vibration noise signal, thus the invention has good robustness and accuracy.
Owner:GUIZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving data processing precision of star sensors
InactiveCN101696885ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsObservational errorIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a method for improving data processing precision of star sensors. Star-sensor measurement errors are divided into three categories: A, low-frequency errors caused by star-sensor internal deformation, star-sensor installation position changes and other factors; B, intermediate-frequency errors caused by satellite-orbit parameter changes, star map transformation, jitter and vibration of satellites in orbit movement and other factors; C, high-frequency errors of star sensors, namely random errors obeying zero-mean Gaussian white noise distribution. After the star-sensor measurement errors are solved, the deviation of attitude estimation is basically eliminated, and attitude determination accuracy is increased by over 15 percent.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
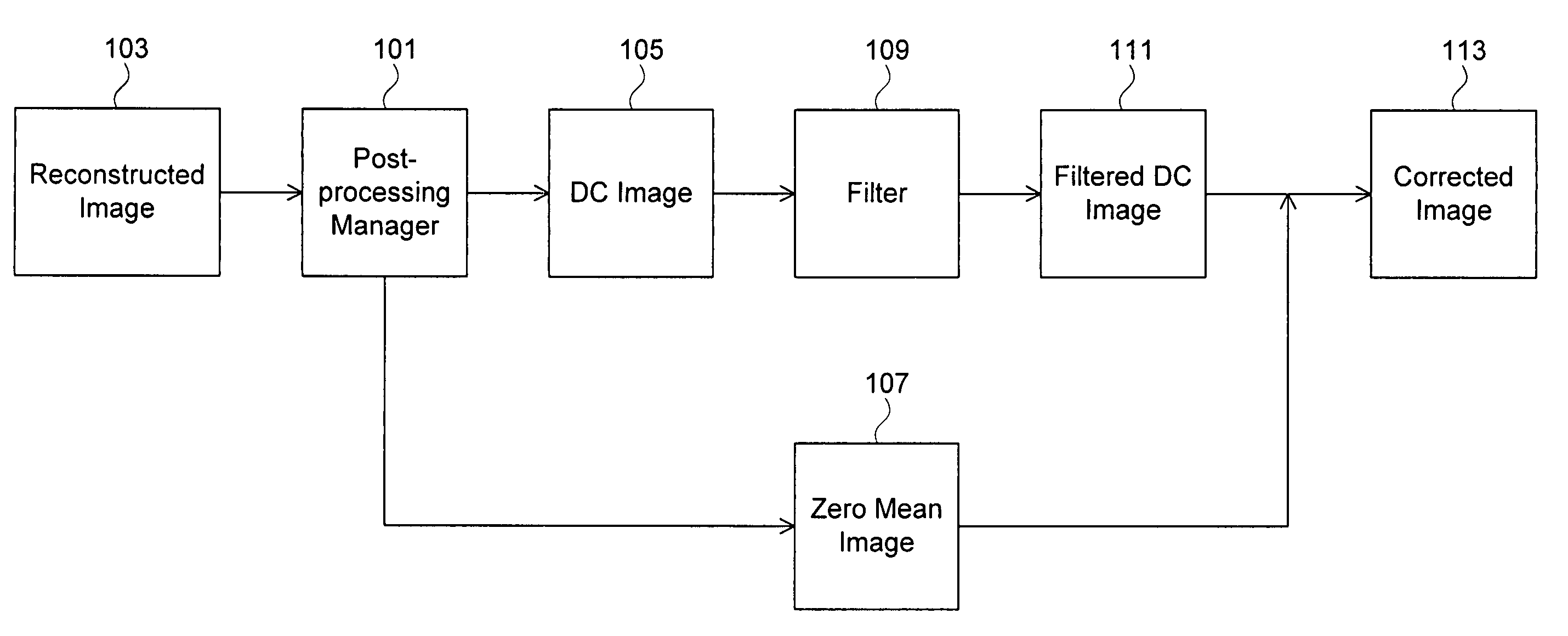
Reducing undesirable block based image processing artifacts by DC image filtering
InactiveUS7616829B1Reduce blockinessSmooth luminanceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage Processing Artifact
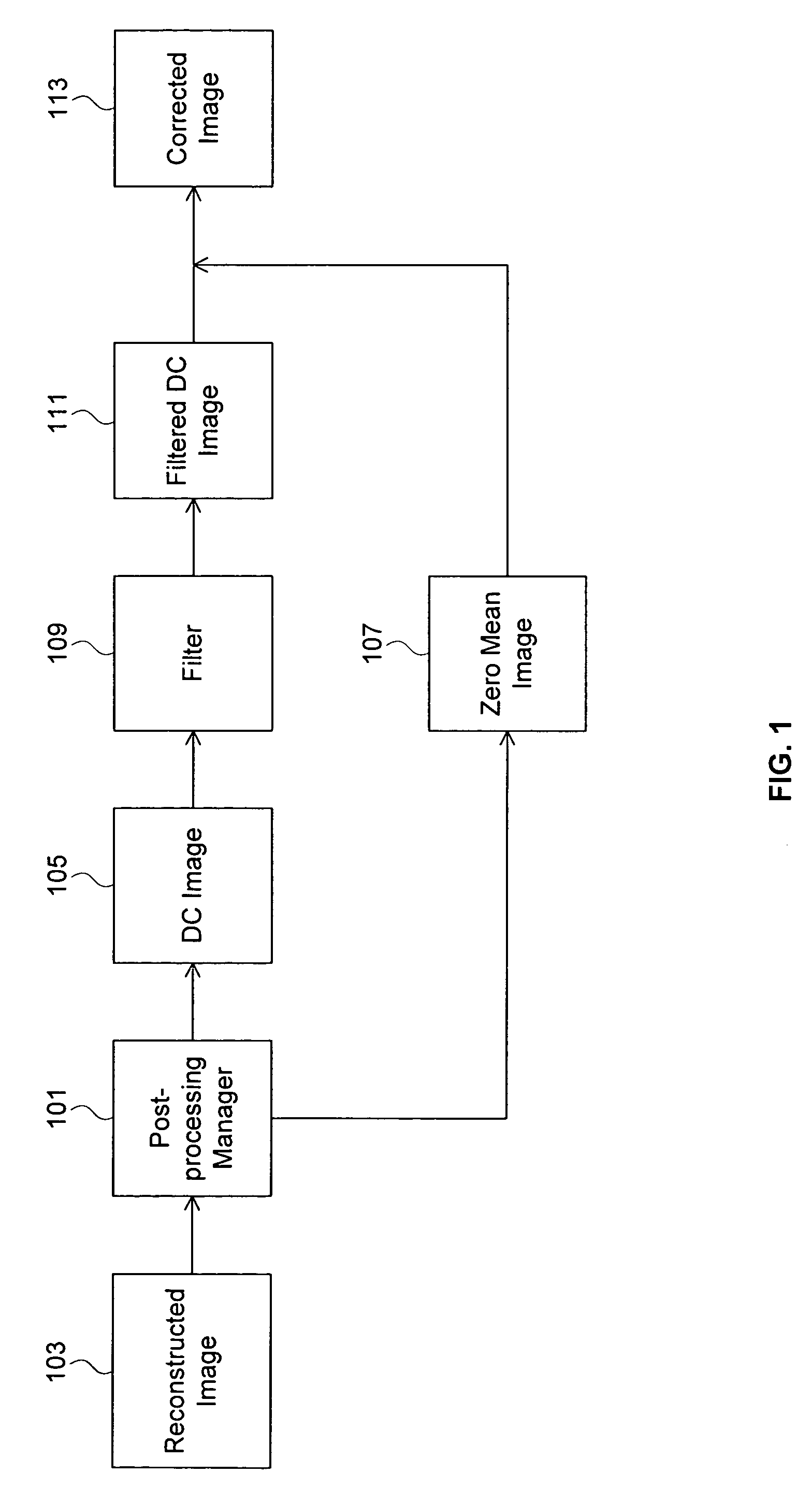
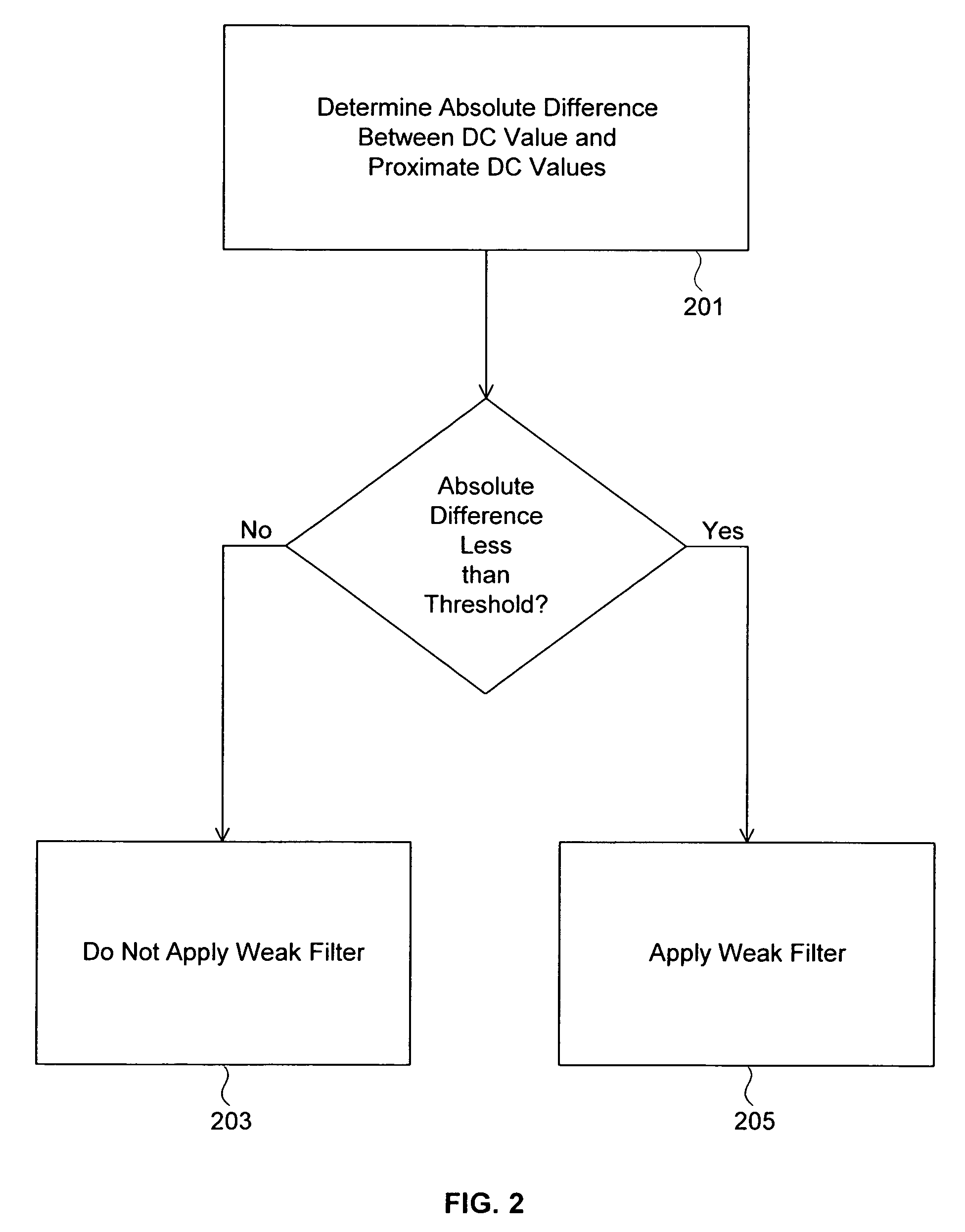
A post-processing manager provides reconstructed block based picture post-processing that is uncoupled from picture decoding by dividing a reconstructed image that was encoded using block based processing into non-overlapping blocks, creating a DC image by computing the DC value of each block, creating a zero mean image by subtracting the DC value of each block from the corresponding pixels of that block, filtering the DC image and adding the filtered DC image to the zero mean image. A weak filtering operation can be applied to reduce blocking artifacts, and a strong filtering operation can be applied to smooth luminance transitions.
Owner:APPLE INC
SAR image speckle suppression method based on dictionary learning in wavelet domain
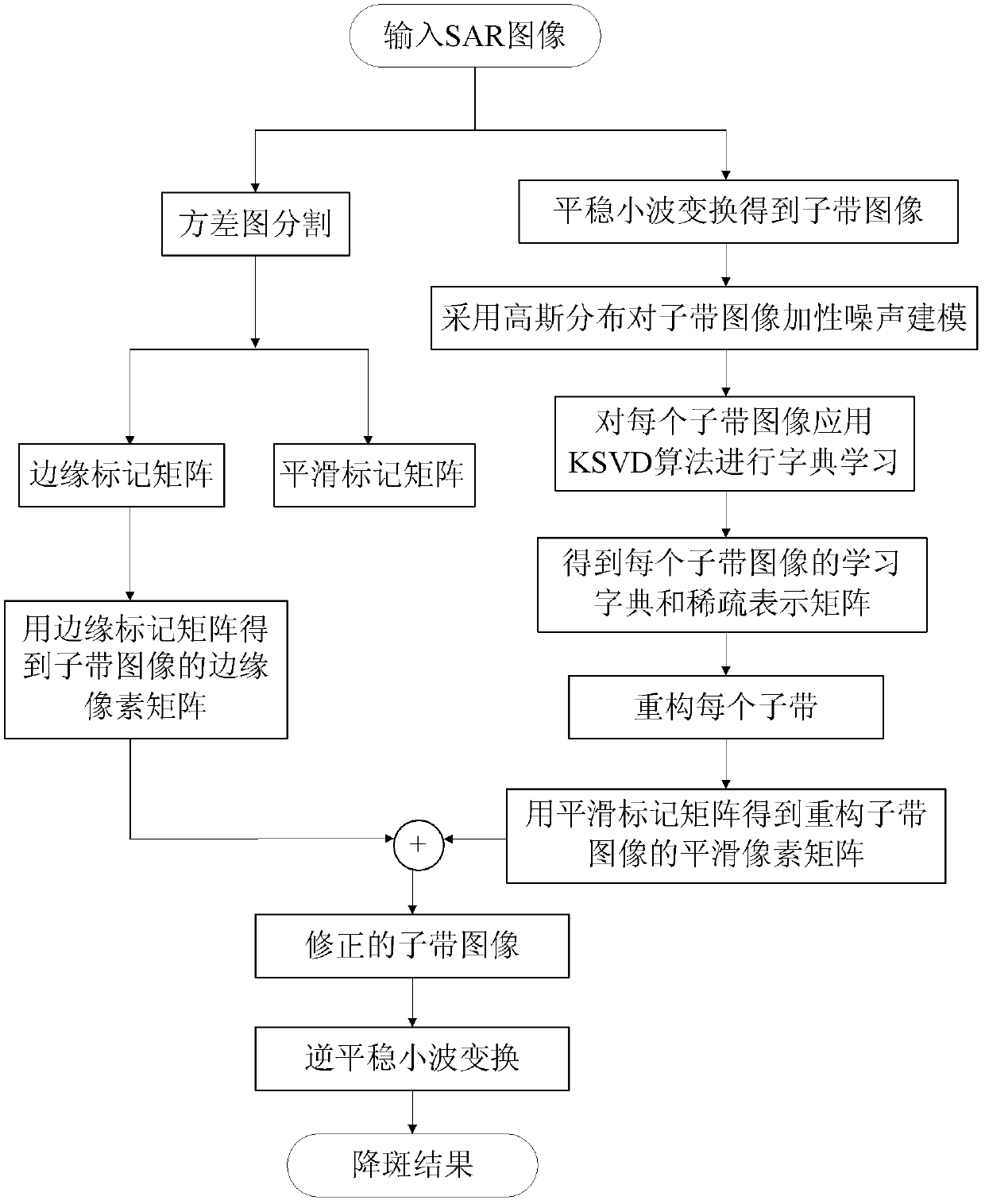
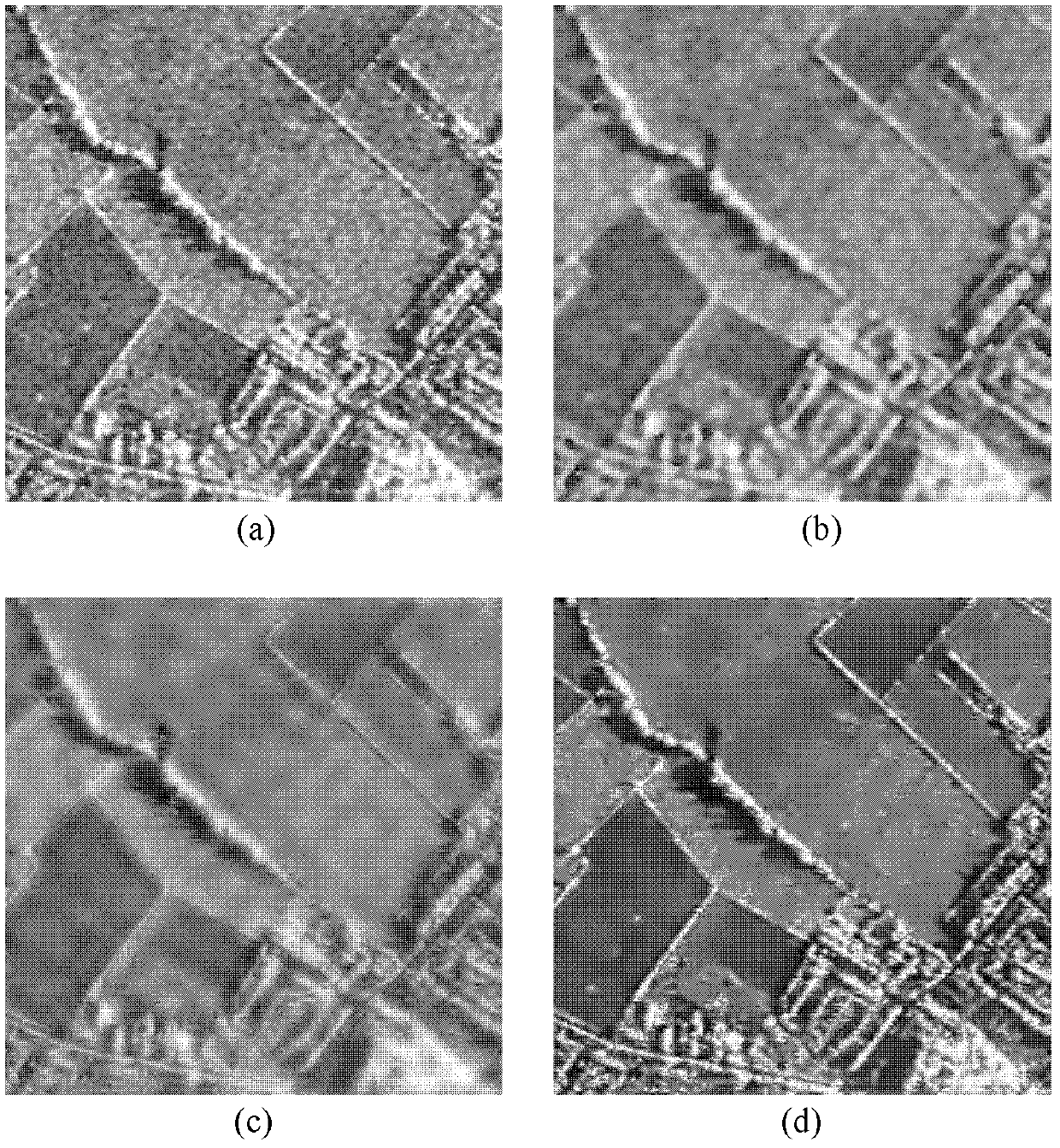
ActiveCN102496153AEasy to keepSuppress speckle noiseImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionDictionary learning
The invention discloses a SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image speckle suppression method based on dictionary learning in wavelet domain, which mainly solves the problems that the edge is not clear enough and the homogenous region is not smooth enough in the existing speckle reduction technology. The implementation process of the method comprises the following steps of: firstly, segmenting an original SAR image Y by a variogram method to obtain a smooth mark matrix SY and an edge mark matrix EY; performing N-level stationary wavelet transformation on the original SAR image Y to obtain sub-band images WY(s); modeling for a non-logarithmic additive noise in the WY(s) by zero-mean-value Guassian distribution; using an approximation KSVD (Singular Value Decomposition) algorithm to obtain a learner's dictionary D's and a sparse representative matrix Lambda's of each sub-band image WY(s), obtaining a reconstructed sub-band image according to the D's and the Lambda's, and obtaining an edge region of the sub-band images WY(s) by the edge mark matrix EY, and substituting the edge region in the reconstructed sub-band image to obtain modified sub-band images W'Y(s); performing inverse stationary wavelet transformation on the W'Y(s) to obtain the speckle- reduced image. The method has the advantages that the edge information after speckle reduction is complete and the homogenous region issmooth, and can be used for the pretreatment process of SAR image understanding.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High-precision tracking method applied to non-engine maneuvering target
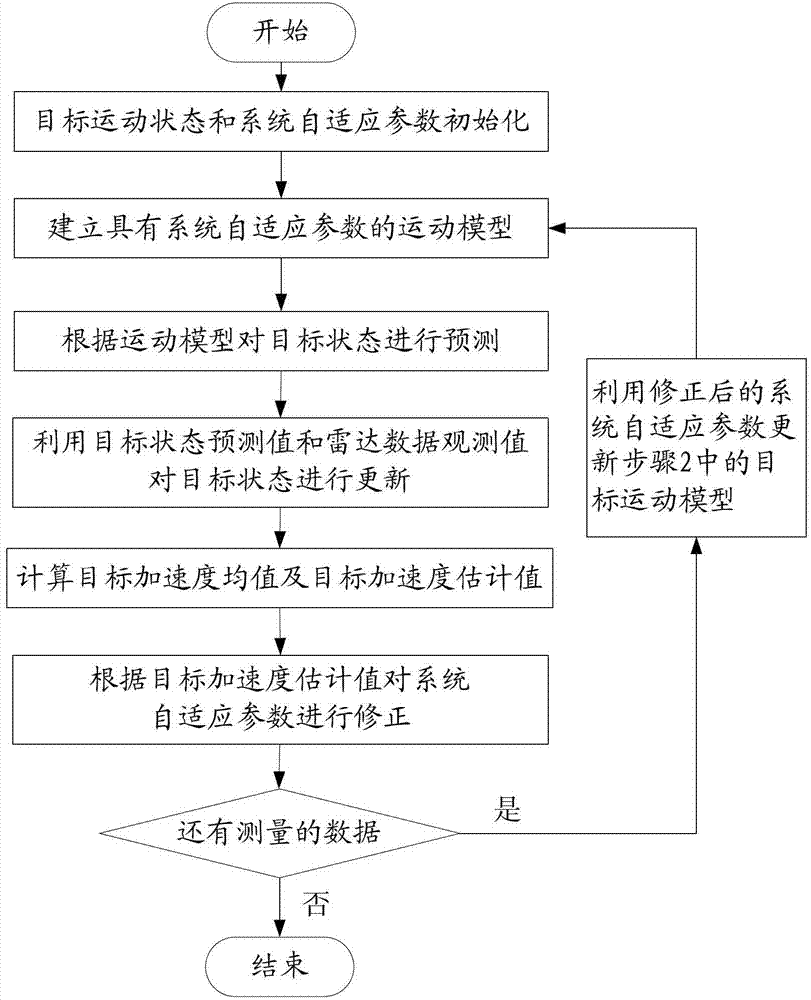
ActiveCN103308896AGuaranteed real-time accuracyRealize high-precision trackingWave based measurement systemsRadar observationsSelf adaptive
The invention relates to a high-precision tracking method applied to a non-engine maneuvering target. According to the method, firstly, a target motion model containing system adaptive parameters is built according to the non-zero mean time relevant random process characteristic met by the accelerated speed in the actual target motion; secondly, the target motion characteristic is predicated according to the built target motion model; then, the current state estimation value of the target is calculated through utilizing the target state predicating value and the radar observation data value; and finally, the system adaptive parameters are corrected according to the accelerated speed estimation value of the target, the corrected system adaptive parameters are utilized for updating the target motion model, and the updated target motion model is utilized for carrying out next predication and estimation. The method has the advantages that the target with the non-engine maneuvering random character realizes the online estimation, the accuracy of a maneuvering target model for describing the actual motion characteristics is improved, and the tracking precision of the non-engine maneuvering target is improved.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
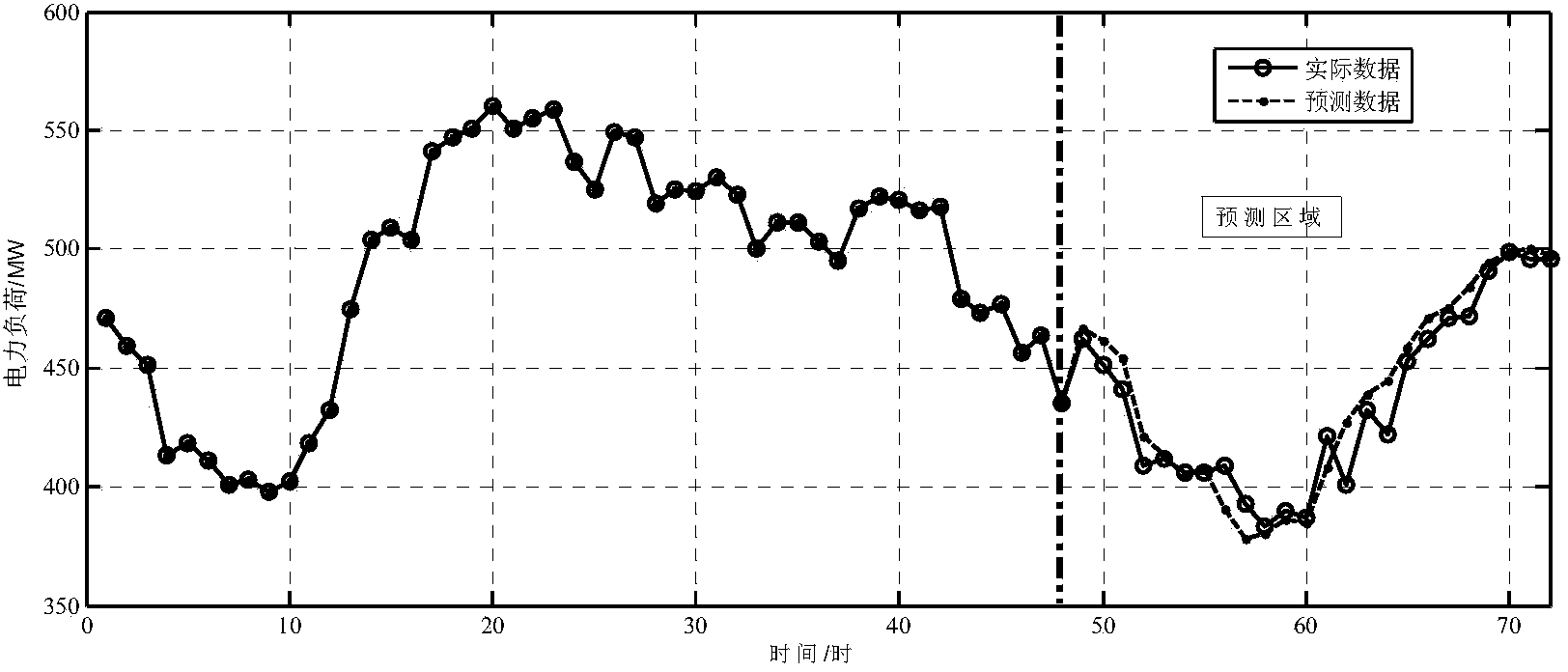
Short-term load prediction method based on time sequence
InactiveCN105701559AImprove management levelHighly innovativeForecastingPredictive methodsInterference factor
The invention discloses a short-term load forecasting method based on time series, which belongs to the technical field of power supply. It conducts statistical analysis on the historical load of the existing regional power grid, and preprocesses the collected daily power consumption data to obtain a stable, normal, zero-mean time series; establishes a mathematical model based on the historical data of daily power load , use this mathematical model to describe the statistical regularity of the random variable change process of electric load; on the basis of this mathematical model, establish the mathematical expression of daily electric load forecasting, and predict the future load. In this technical solution, the power load to be measured is used as the dependent variable, and the past value of the power load is used as the independent variable. The obtained mathematical model successfully reflects the relationship between the dependent variable and the independent variable as well as the interference factors hidden in it. , especially suitable for short-term daily electricity load forecasting. It can be widely used in the fields of load forecasting and load management in power systems.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO
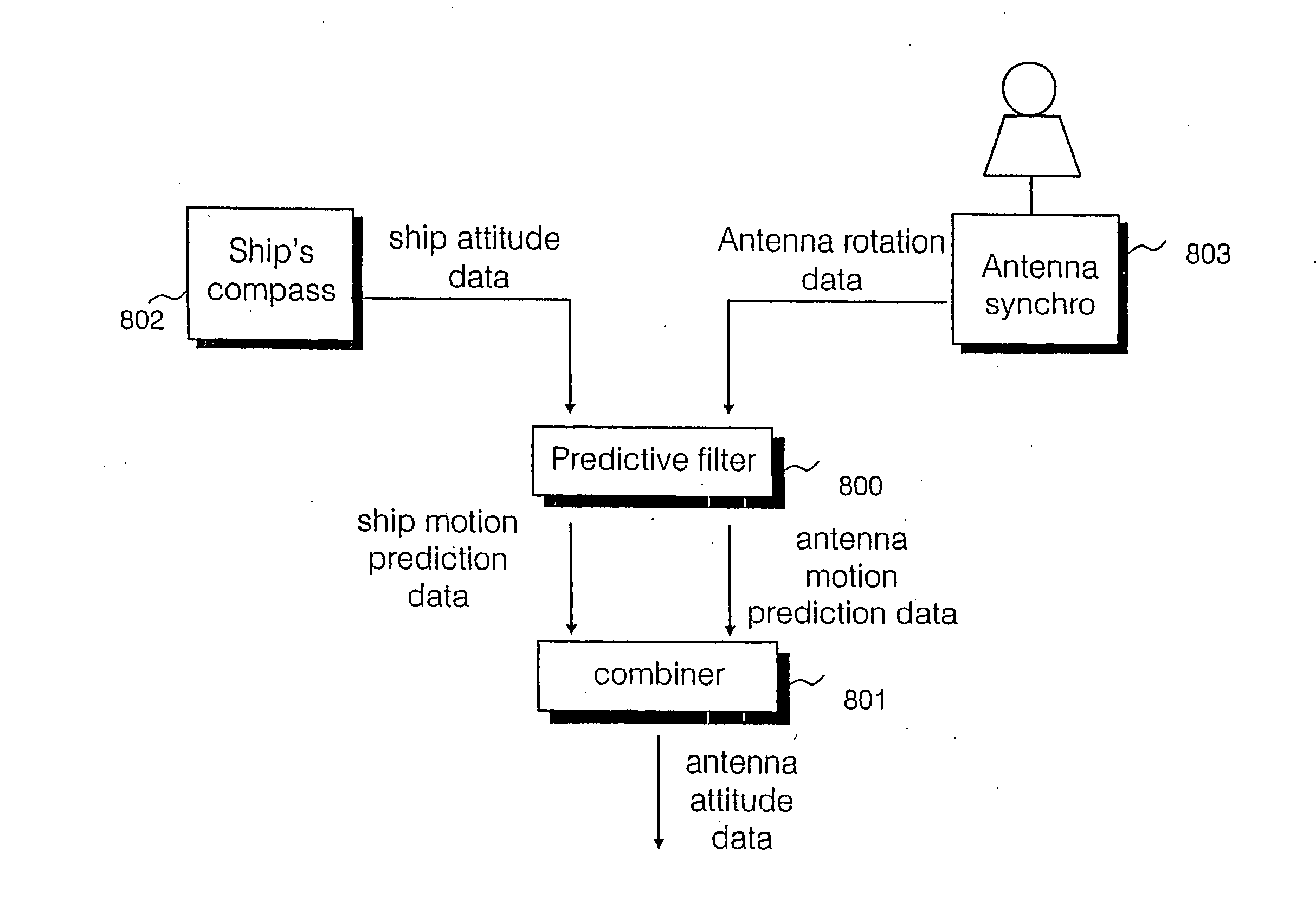
Ship motion predictor
There is disclosed a predictive filter for predicting the future position of a look direction of a rotating directional antenna mounted on a vessel. Prediction of a look direction of the antenna at any instant is made from input of ship's compass data including roll data, pitch data and heading data, as well as data describing a rotational position of the antenna, output from an antenna synchro device. Smoothing of the digital roll, pitch and heading data and antenna position data is followed by application of a moving time window, filter which removes any offset from the data within of the moving time window to produce data having a zero mean. The zero mean data is input into an auto-regression algorithm, the output of which is combined with mean roll, pitch, heading, position and antenna velocity data to obtain predicted positions of the antenna relative to the vessel, and a predicted motion of the vessel. The combined vessel motion prediction and antenna position and velocity prediction can be used to establish a predictive future look direction of the antenna for a period of between 0.1 and 5 seconds into the future.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
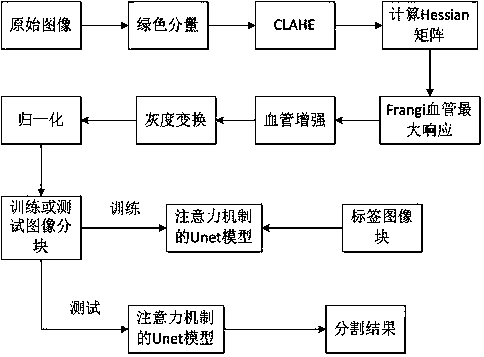
Fundus image blood vessel segmentation method based on Frangi enhancement and attention mechanism UNet
ActiveCN110473188AThe segmentation result is accurateIncrease contrastImage enhancementImage analysisImage extractionThree vessels
The invention relates to a fundus image blood vessel segmentation method based on Frangi enhancement and an attention mechanism UNet, and the method comprises the steps: firstly extracting a green component from an input image, and carrying out the contrast adjustment on the basis of the extracted green component through a contrast-limited histogram equalization method; calculating a Hessian matrix of each pixel point in the image after the contrast ratio is adjusted; constructing a Frangi vascular similarity function by utilizing the characteristic value of the Hessian matrix under the condition of a scale factor, and obtaining the maximum response; respectively subtracting the product of the maximum response value and the enhancement factor factor factor from the pixel values of the RGBthree same channels of each pixel point of the input image; then, carrying out gray scale transformation on the image after frangi enhancement, and carrying out zero mean normalization operation on each pixel value to be between [0, 1]; and finally, inputting the obtained training image blocks and label image blocks into an attention mechanism UNet network for training; and obtaining a segmentation result through testing. According to the invention, the generalization ability of the model is improved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
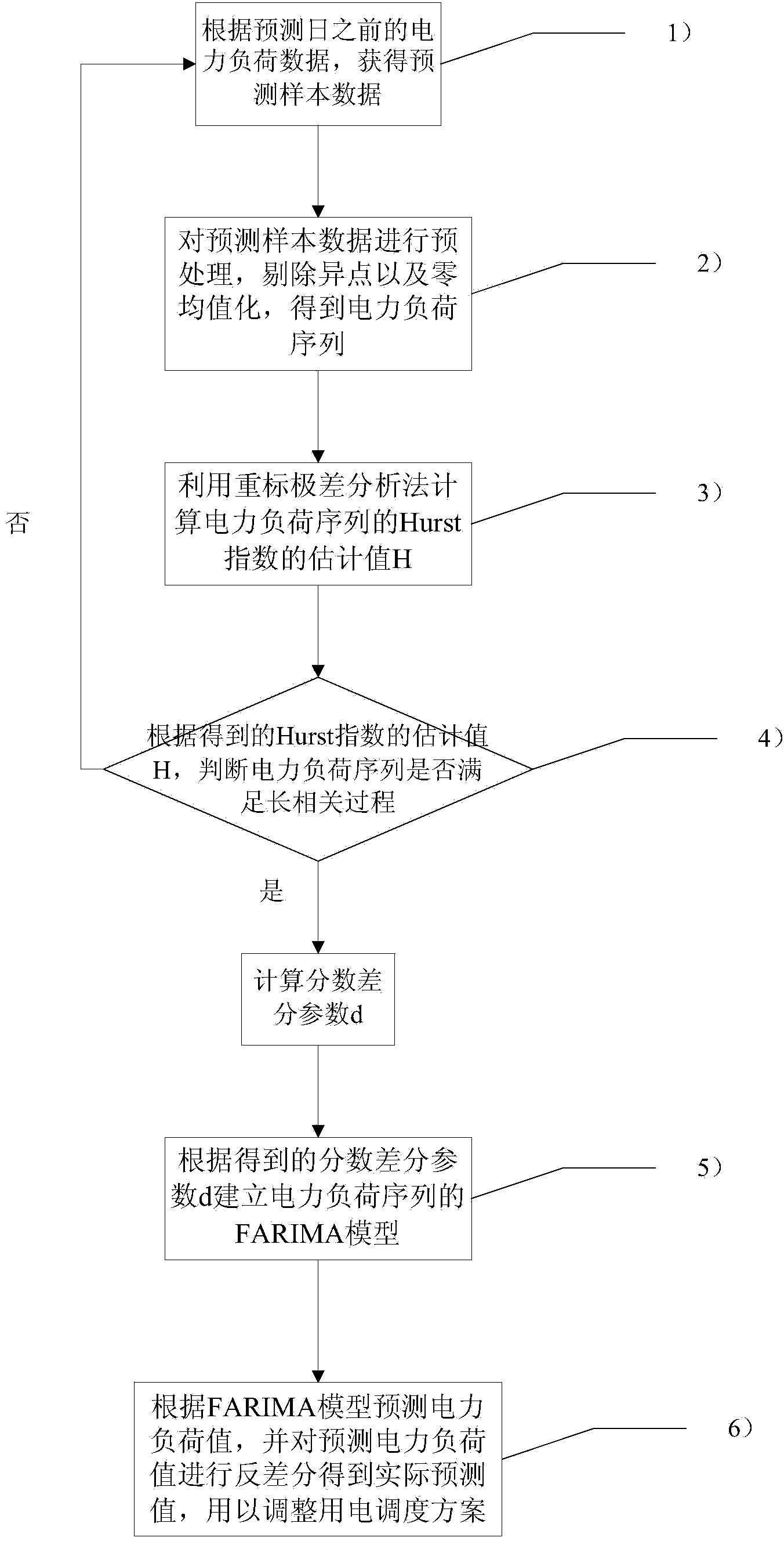
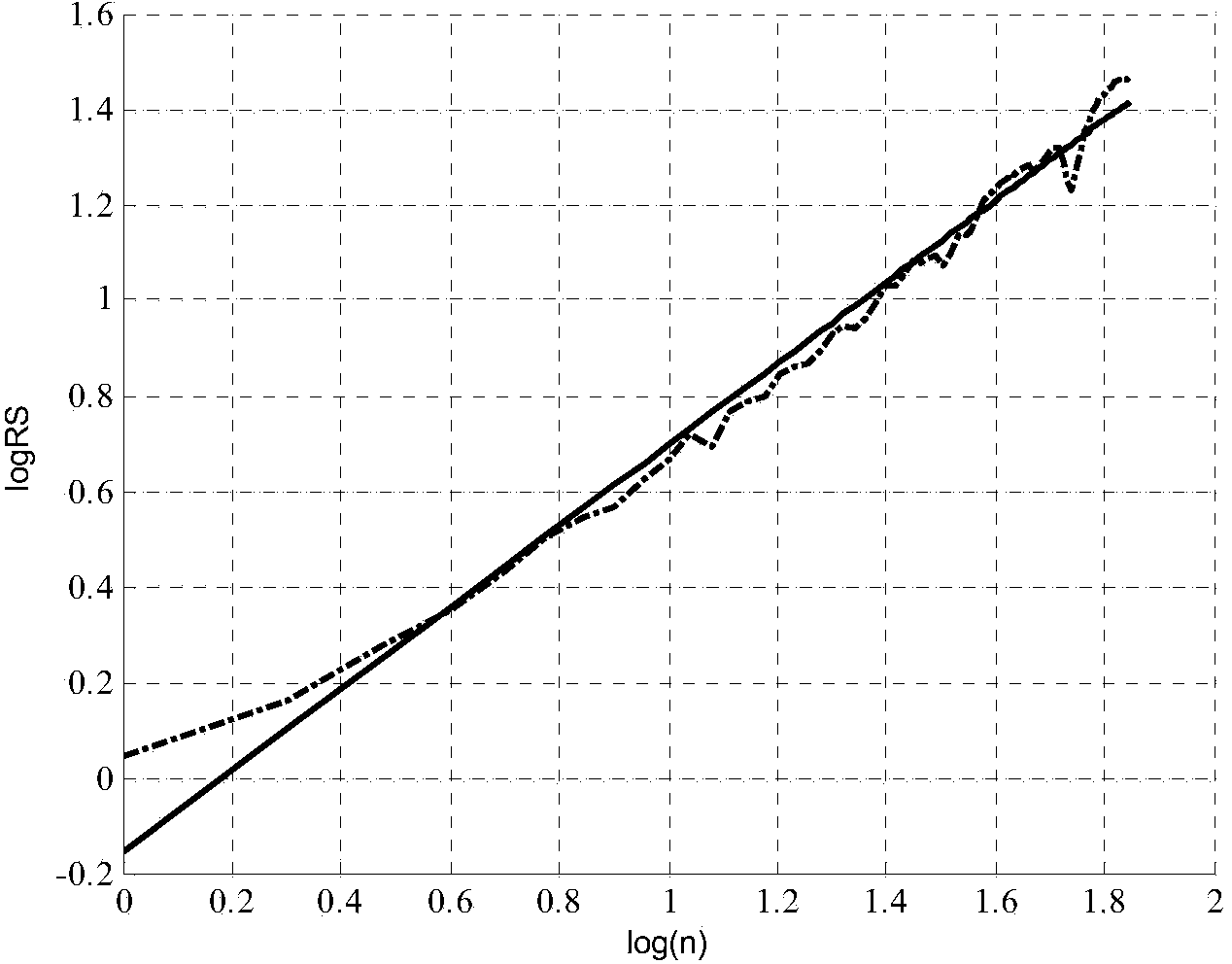
Short-time power load forecasting method based on long-range dependence FARIMA model
ActiveCN104318334AReduce scheduling workloadThe result is accurateForecastingLoad forecastingBusiness forecasting
The invention relates to a short-time power load forecasting method based on a long-range dependence FARIMA model. The method includes the following steps that (1) forecasting sample data are obtained according to power load data before a forecasting day; (2) the forecasting sample data are preprocessed, singular points and zero-mean-value are eliminated to obtain a power load sequence {Xt}; (3) an estimated value H of a Hurst index of the power load sequence {Xt} is calculated by means of a rescaled range analysis method; (4) whether the power load sequence meets the requirement of a long-range dependence process is judged according to the obtained estimated value H of the Hurst index, if the answer is positive, a fractional difference parameter d is calculated, and if the answer is negative, the step (1) is repeated; (5) according to the obtained fractional difference parameter d, the FARIMA model of the power load sequence {Xt} is built; (6) according to the FARIMA model, a power load value is forecasted, and an actual forecast value is obtained by carrying out inverse difference on the forecasted power load value to adjust a power scheduling scheme. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of being accurate in result, high in practicality and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
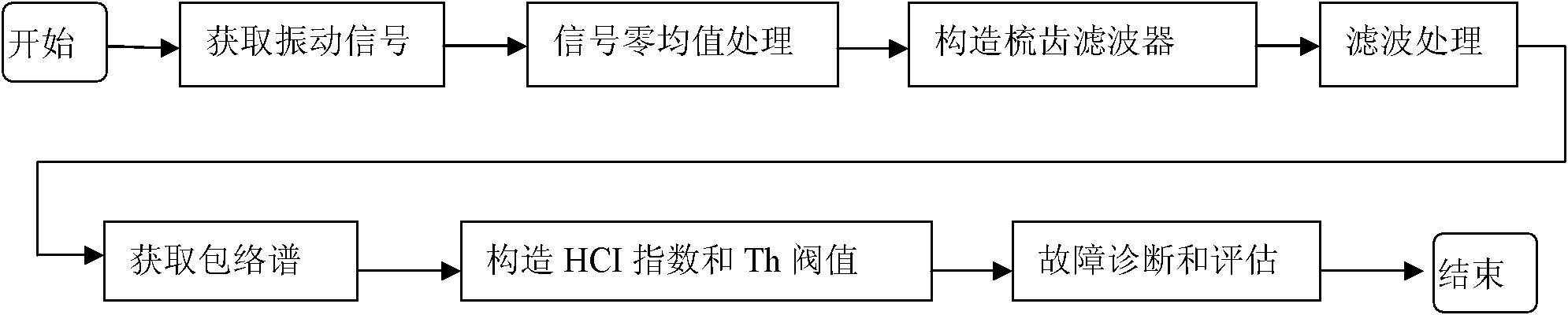
Method for evaluating degradation of state of fan bearing
The invention relates to a method for evaluating degradation of a state of a fan bearing. The method is especially suitable for fault diagnosis of a radiating fan bearing. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring an initial vibration signal; 2) performing zero-mean treatment on the initial vibration signal obtained in the step 1, thereby obtaining a pretreated vibration signal; 3) constructing a comb filter according to a fault characteristic frequency of a bearing element; 4) utilizing the comb filter to filter the pretreated vibration signal obtained in the step 2, thereby obtaining a filtered vibration signal; 5) performing Hilbert demodulation on the filtered vibration signal s2(t) obtained in the step 4, thereby obtaining an enveloped signal s3(t), and then performing Fourier transform, thereby obtaining an enveloped frequency spectrum S3(f); 6) utilizing the enveloped frequency spectrum S3(f) obtained in the step 5 to construct a health condition index (HCI) and an alarm threshold value (Th); and 7) realizing the fault diagnosis and state evaluation for the radiating fan bearing. The method has the beneficial effects that the fault state of a bearing can be efficiently monitored and an alarm can be given out.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Support vector machine based classification method of base-band time-domain voice-frequency signal
InactiveCN102760444ARealize authenticationImplement classificationSpeech recognitionSingular value decompositionFrequency spectrum
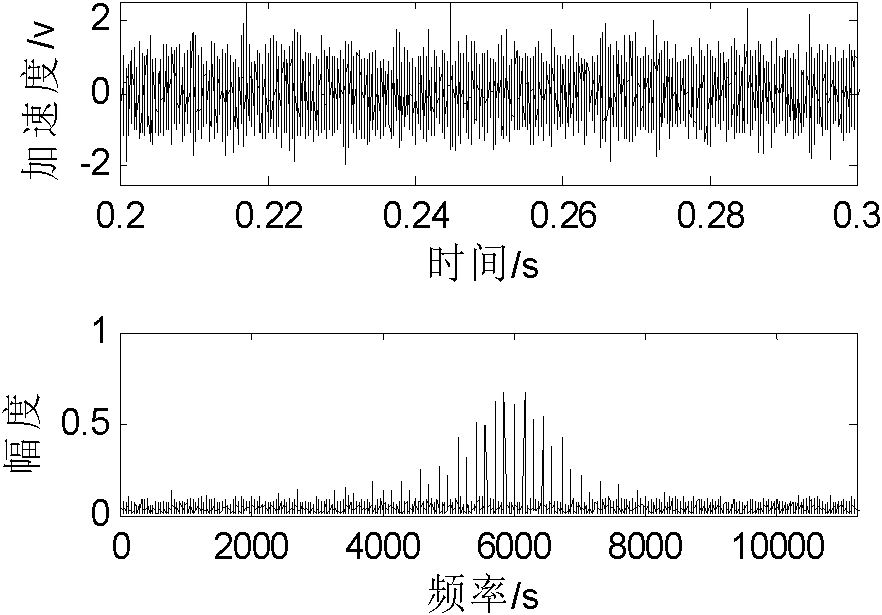
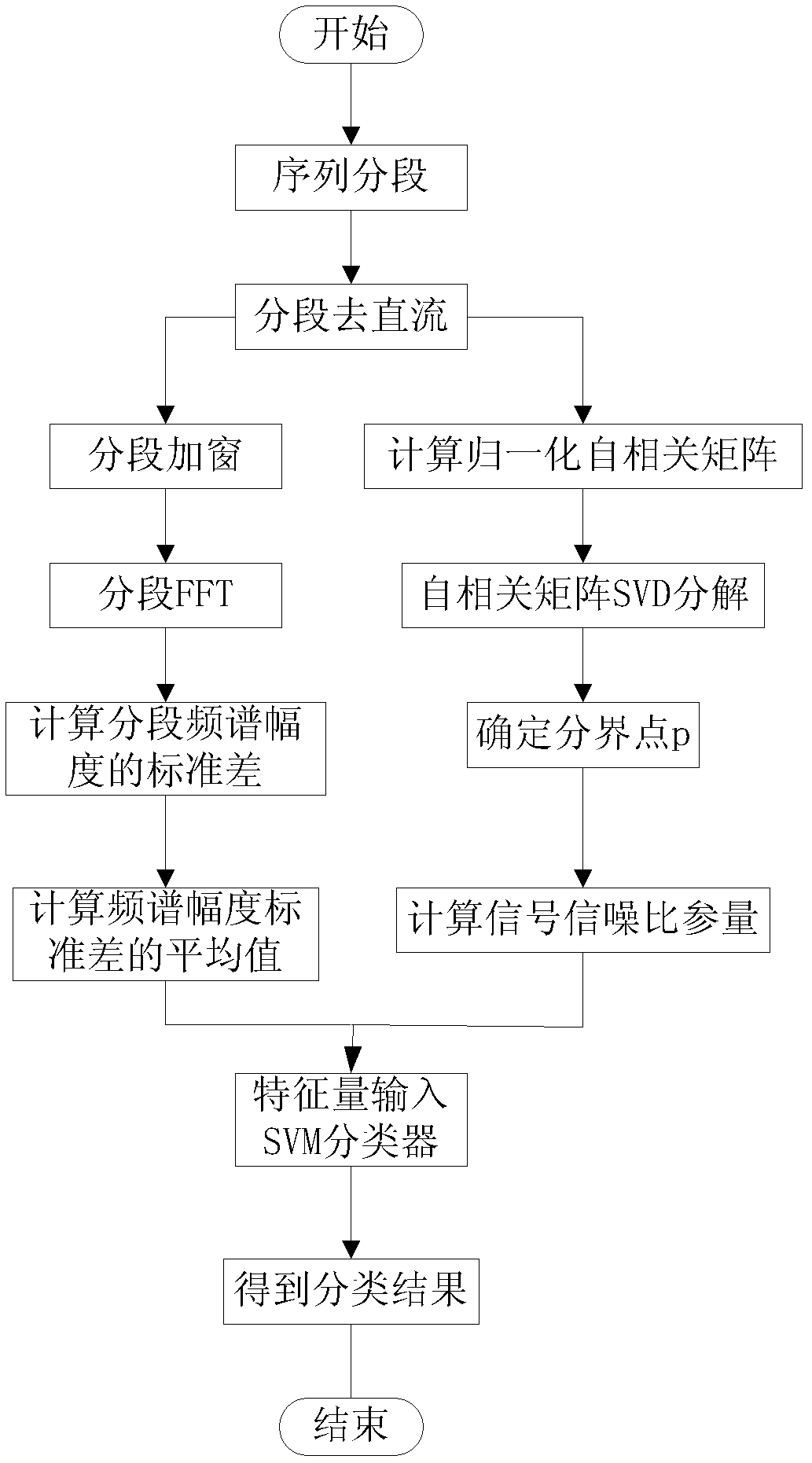
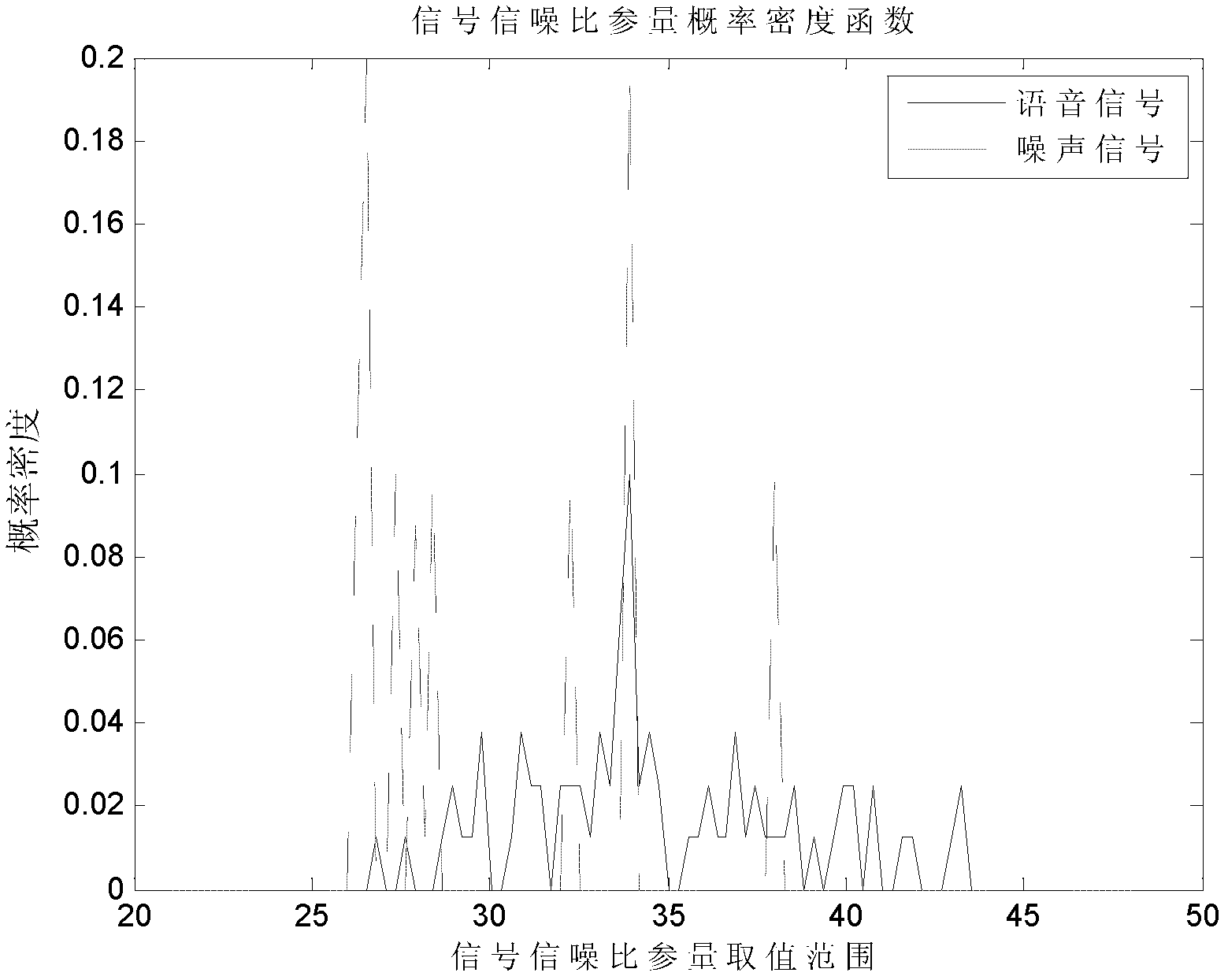
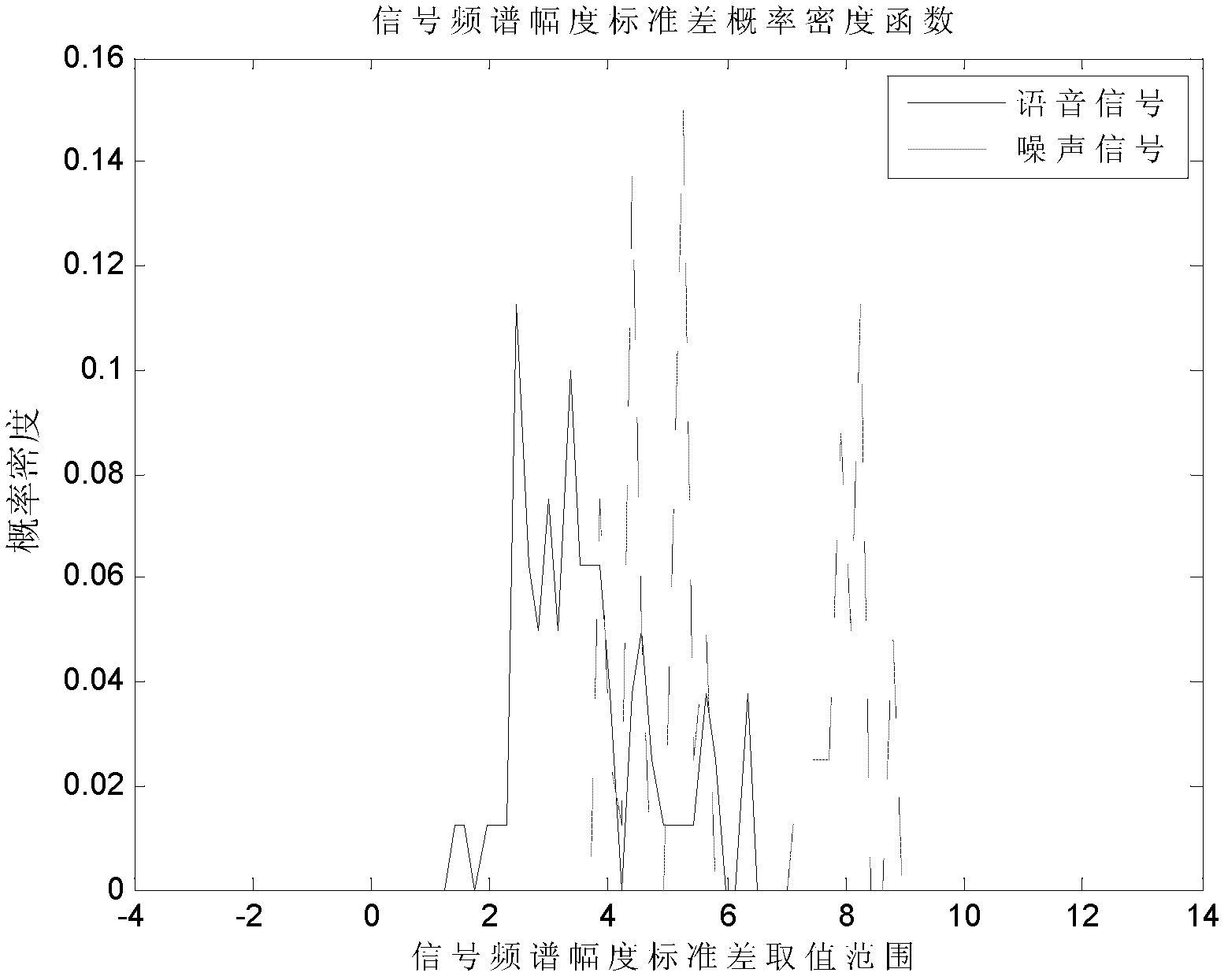
The invention relates to a support vector machine based classification method of base-band time-domain voice-frequency signals, comprising the following steps of: firstly segmenting a base-band time-domain voice-frequency signal sequence to obtain initial segmented subsequences; then respectively subtracting respective mean value from each initial segmented subsequence to obtain zero-mean-value segmented subsequences; then carrying out windowing treatment on each zero-mean-value segmented subsequence, respectively carrying out Fourier transformation treatment on results to obtain the spectrum amplitudes of the zero-mean-value segmented subsequences, and respectively solving the standard difference of each spectrum amplitude to obtain a characteristic quantity; sequentially combining the zero-mean-value segmented subsequences into a long subsequence according to an order; then calculating a normalized autocorrelation matrix of the long subsequence, and carrying out singular value decomposition on the normalized autocorrelation matrix to obtain a demarcation point of a subspace; then calculating the signal to noise ratio parameter of an other characteristic quantity; and finally sending an input vector composed of the two characteristic quantities into a trained SVM (Support Vector Machine) classifier to identify the classification of base-band time-domain voice-frequency signals and distinguish a voice signal and a noise signal.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
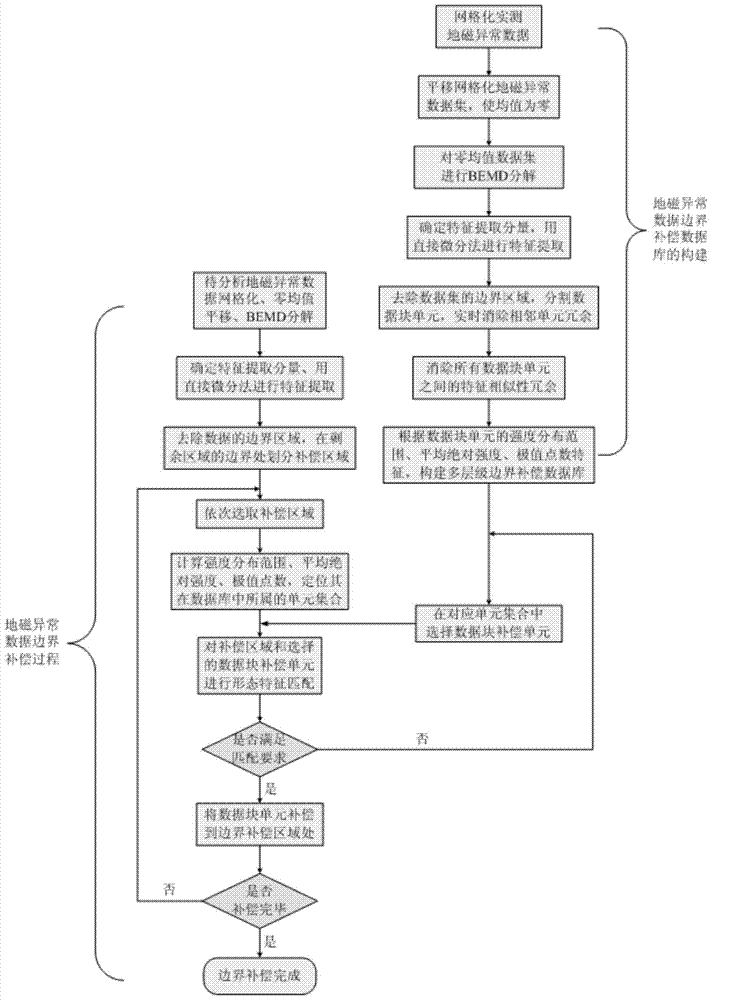
Method for boundary compensation based on morphological characteristics of geomagnetic anomaly data
ActiveCN103577607AImprove boundary effectImprove scalabilityNavigation by terrestrial meansSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionRegular grid
The invention belongs to the field of geomagnetic navigation, and particularly relates to a method for boundary compensation based on morphological characteristics of geomagnetic anomaly data. The method for boundary compensation based on the morphological characteristics of the geomagnetic anomaly data comprises the steps that regular meshing processing is conducted on the actually-measured geomagnetic anomaly data; a geomagnetic anomaly mesh data set is translated, so that a mean value is zero; two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition is conducted on the translated mesh data set with the zero mean value; the morphological characteristics of a two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition result are extracted; a data block unit is segmented and characteristic similarity redundancy of adjacent units is eliminated in real time; characteristic similarity redundancy of all the data block units is eliminated; a multilayer geomagnetic anomaly data boundary compensation database is established; boundary compensation is conducted on the geomagnetic anomaly data to be analyzed. According to the method for boundary compensation based on the morphological characteristics of the geomagnetic anomaly data, the problem of the boundary effect in local geomagnetic anomaly data analysis can be effectively solved, and compared with other methods, the method is better in applicability and better in use convenience.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Multi-microphone method for estimation of target and noise spectral variances
InactiveCN104902418AImprove intelligibilitySpeech analysisMicrophones signal combinationTarget signalTime–frequency representation
The application relates to an audio processing system and a method of processing a noisy (e.g. reverberant) signal comprising first (v) and optionally second (w) noise signal components and a target signal component (x), the method comprising a) Providing or receiving a time-frequency representation Y i (k,m) of a noisy audio signal y i at an i th input unit, i=1, 2, ..., M, where M‰¥2; b) Providing (e.g. predefined spatial) characteristics of said target signal component and said noise signal component(s); and c) Estimating spectral variances or scaled versions thereof » v, »x of said first noise signal component v (representing reverberation) and said target signal component x, respectively, said estimates of »v and »x being jointly optimal in maximum likelihood sense, based on the statistical assumptions that a) the time-frequency representations Y i (k,m), X i (k,m), and V i (k,m) (and W i (k,m) ) of respective signals y i (n), and signal components x i , and v i (and w i ) are zero-mean, complex-valued Gaussian distributed, b) that each of them are statistically independent across time m and frequency k, and c) that X i (k,m) and V i (k,m) (and W i (k,m)) are uncorrelated. An advantage of the invention is that it provides the basis for an improved intelligibility of an input speech signal. The invention may e.g. be used for hearing assistance devices, e.g. hearing aids.
Owner:OTICON
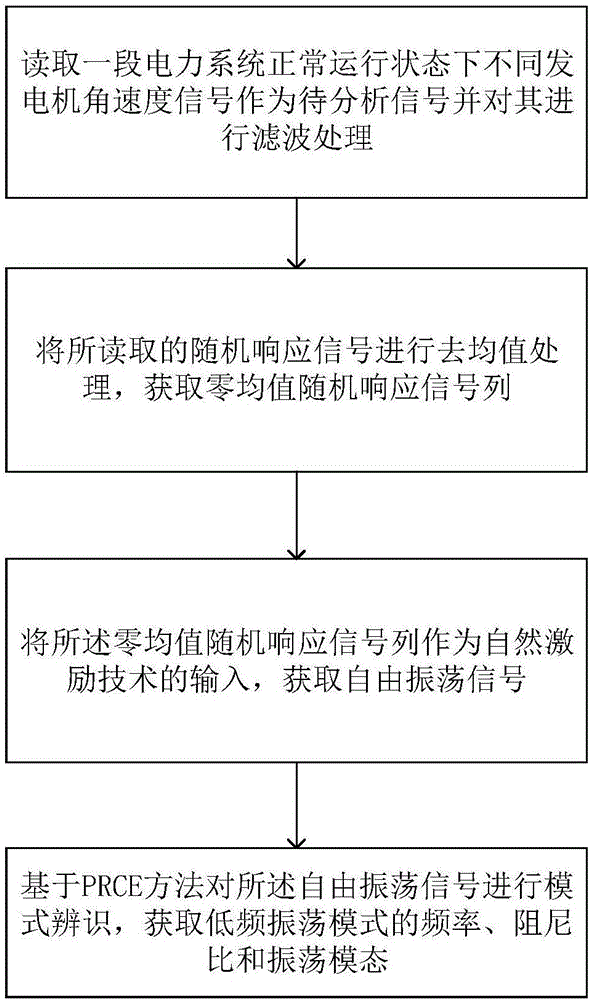
Method for online identification of low-frequency oscillation mode of electric power system based on random response signals
ActiveCN106353623AAccurate identificationThe identification result is accurateElectrical testingZero meanTime range
The invention discloses a method for online identification of a low-frequency oscillation mode of an electric power system based on random response signals. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, reading a section of angular speed signals of different power generators when the electric power system runs normally; then performing mean removal processing on the read signals to obtain zero-mean random response signals; processing the zero-mean random response signals by using a natural excitation technology to obtain free oscillation signals; and finally, performing mode identification on the obtained free oscillation signals by adopting a PRCE method to obtain a frequency, a damping ratio and an oscillation mode state of the low-frequency oscillation mode. The method disclosed by the invention can identify the low-frequency oscillation mode of the electric power system in a wider time range, is better in identification precision, speed and noise immunity, and is more capable of identifying an oscillation mode state, thereby providing a brand-new way and method for low-frequency oscillation analysis of the electric power system.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
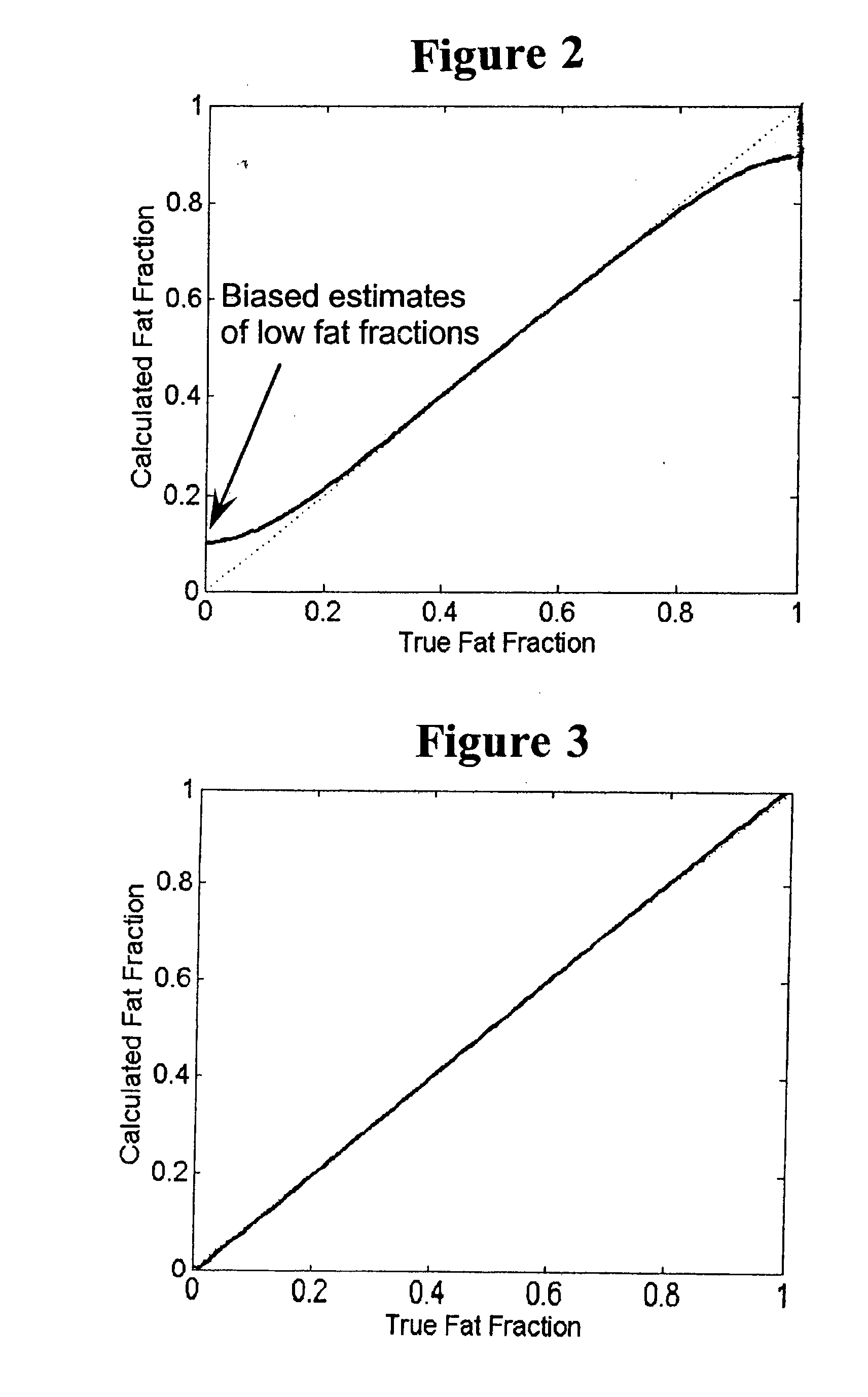
Methods for fat quantification with correction for noise bias
ActiveUS20090112081A1Accurate calculationImprove image signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setVoxel
Methods are disclosed for calculating a fat fraction corrected for noise bias of one or more voxels of interest using a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. A plurality of image data sets are obtained each corresponding to NMR k-space data acquired using a pulse sequence with an individual associated echo time tn. A system of linear equations is formed relating image signal values to a desired decomposed calculated data vector having a component such as a water and fat combination having zero mean noise, or having a real fat component and a real water component. A fat fraction is calculated from at least one component of the decomposed calculated data vector. In another embodiment, the system of linear equations is normalized and can directly estimate a fat fraction or a water fraction having reduced noise bias.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
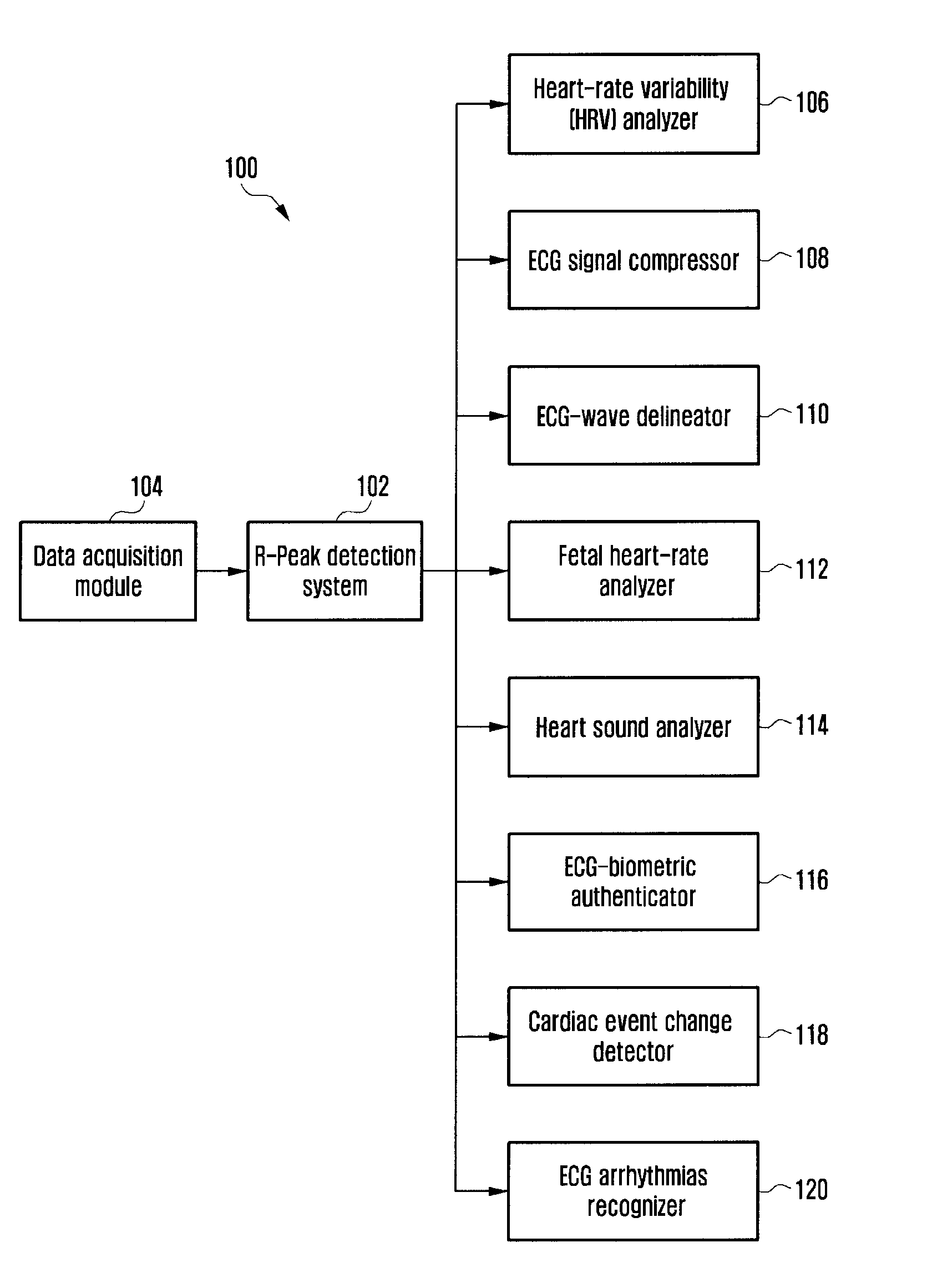
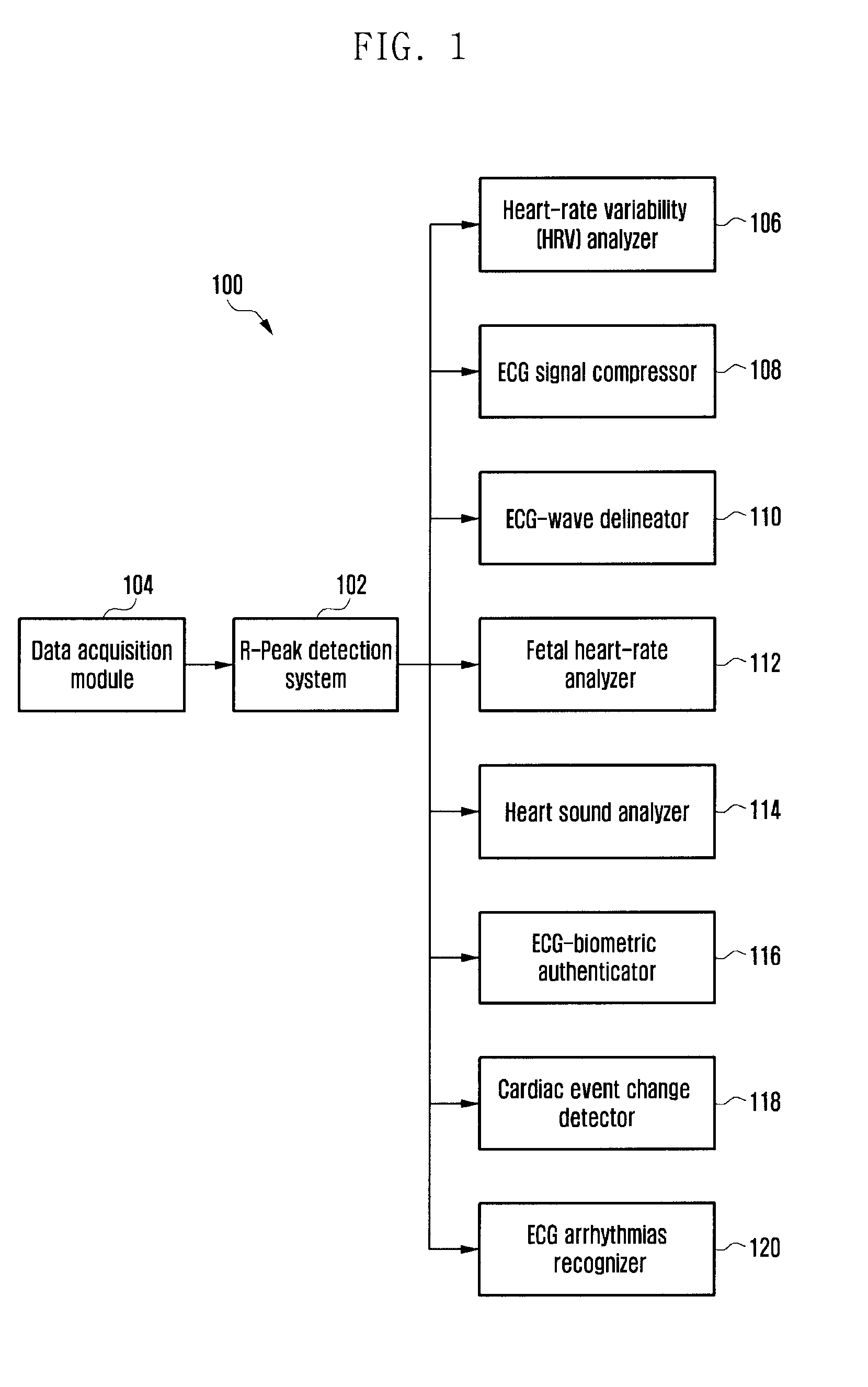
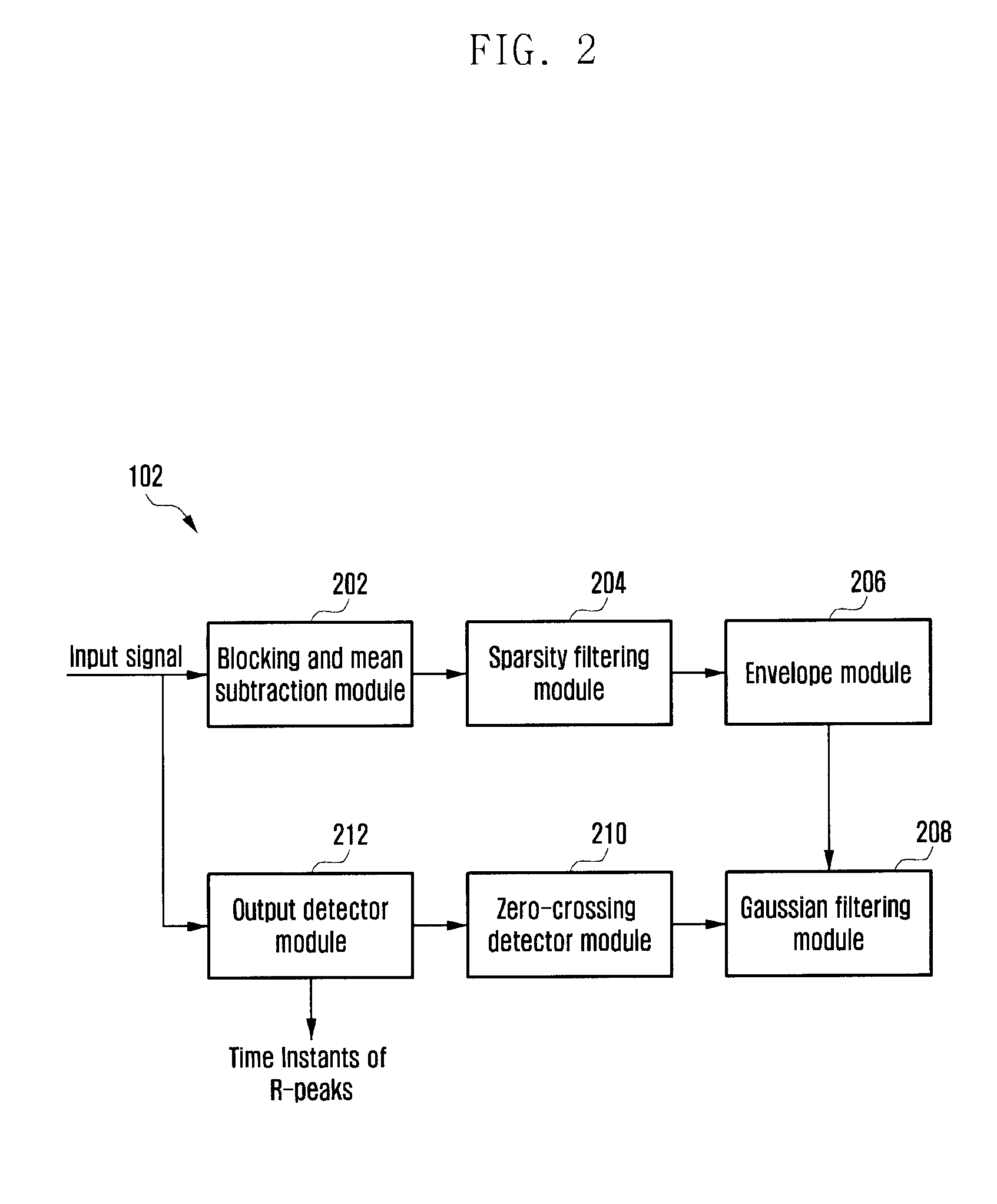
Method and system for determining qrs complexes in electrocardiogram signals
ActiveUS20140088450A1Enhances QRS complexAccurately time instantElectrocardiographySensorsAlgorithmZero mean
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Finger vein recognition method and system
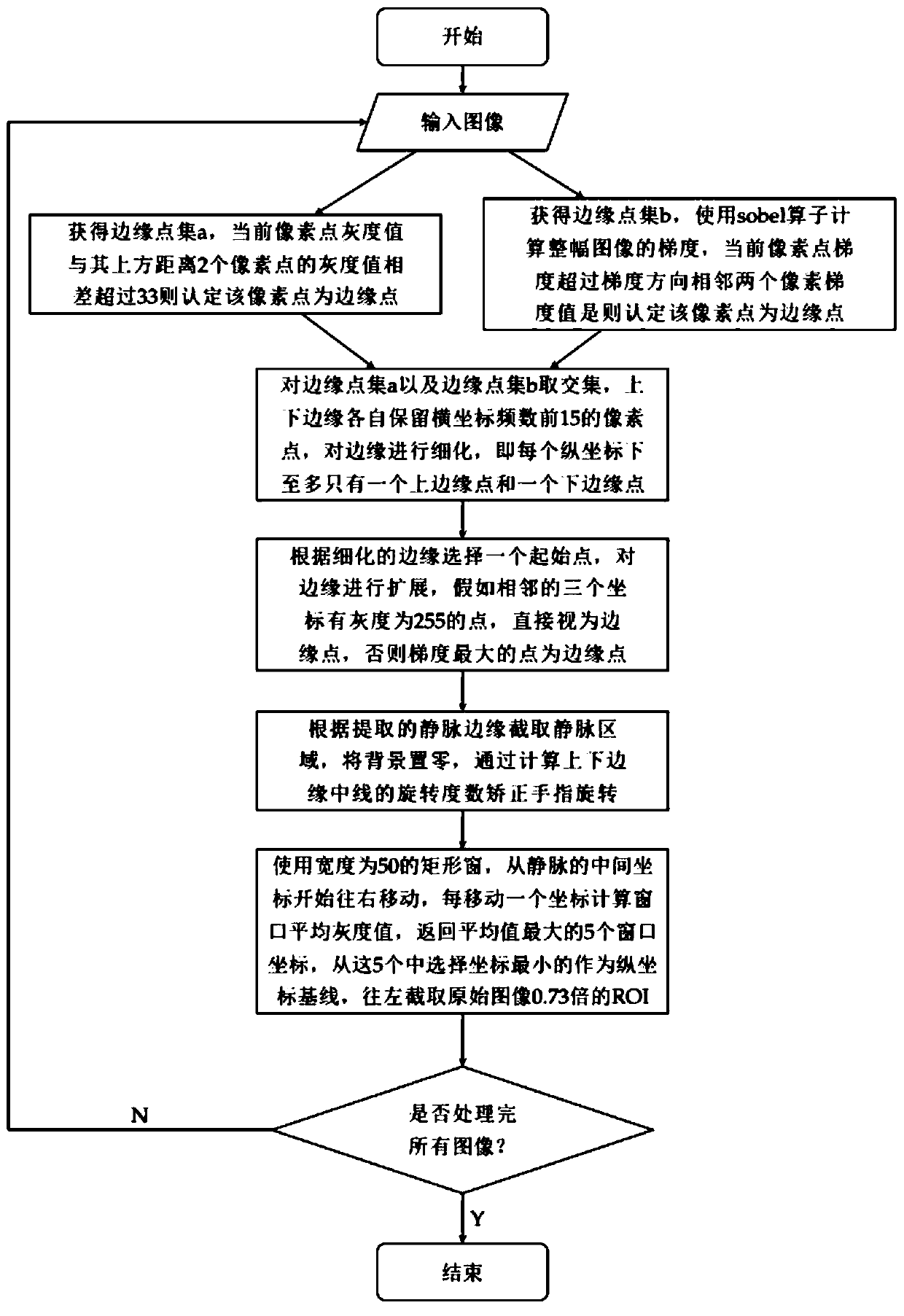
InactiveCN110163119AEnhance texture featuresAccurate extractionAcquiring/reconising fingerprints/palmprintsVeinFinger vein recognition
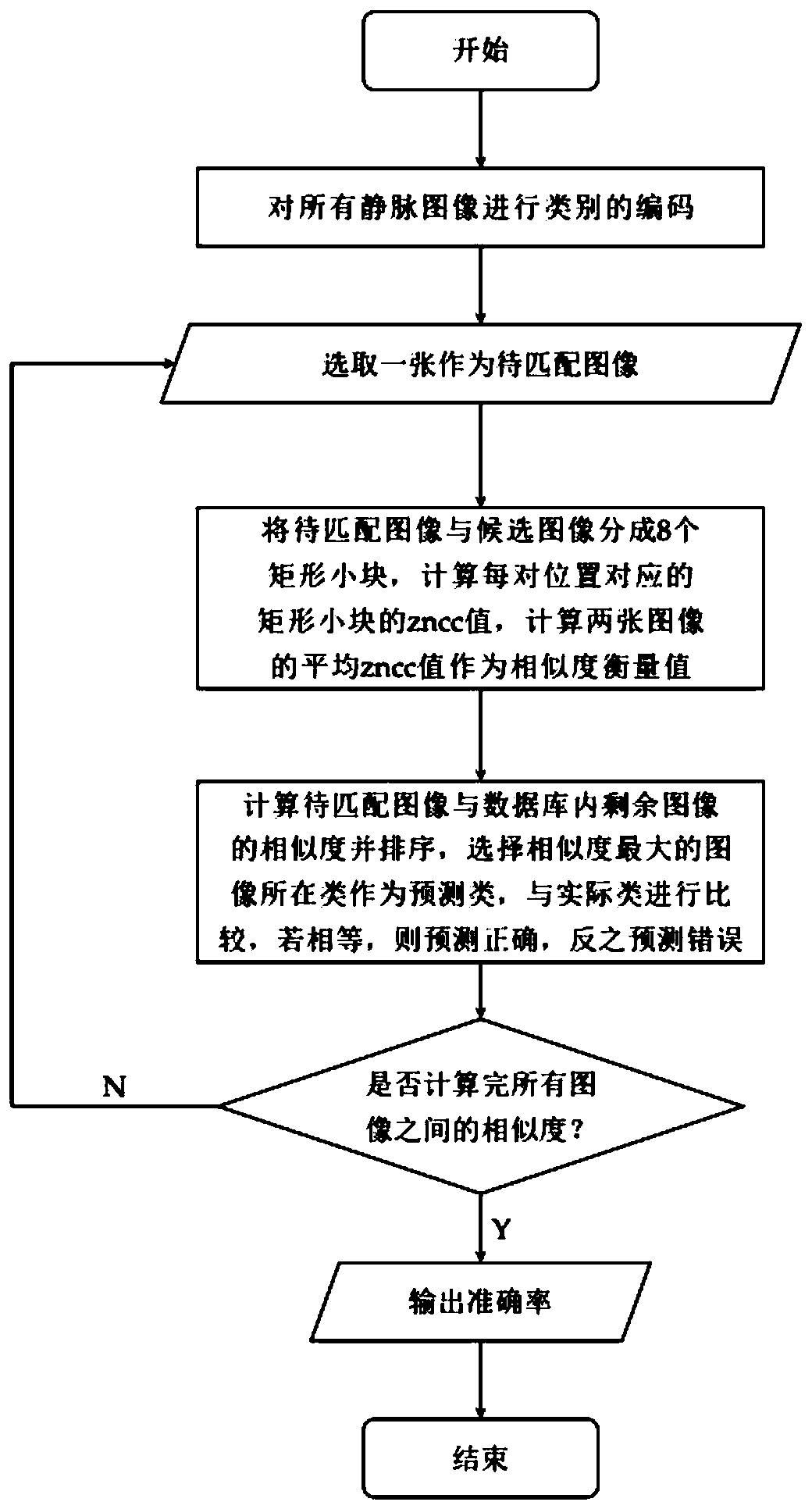
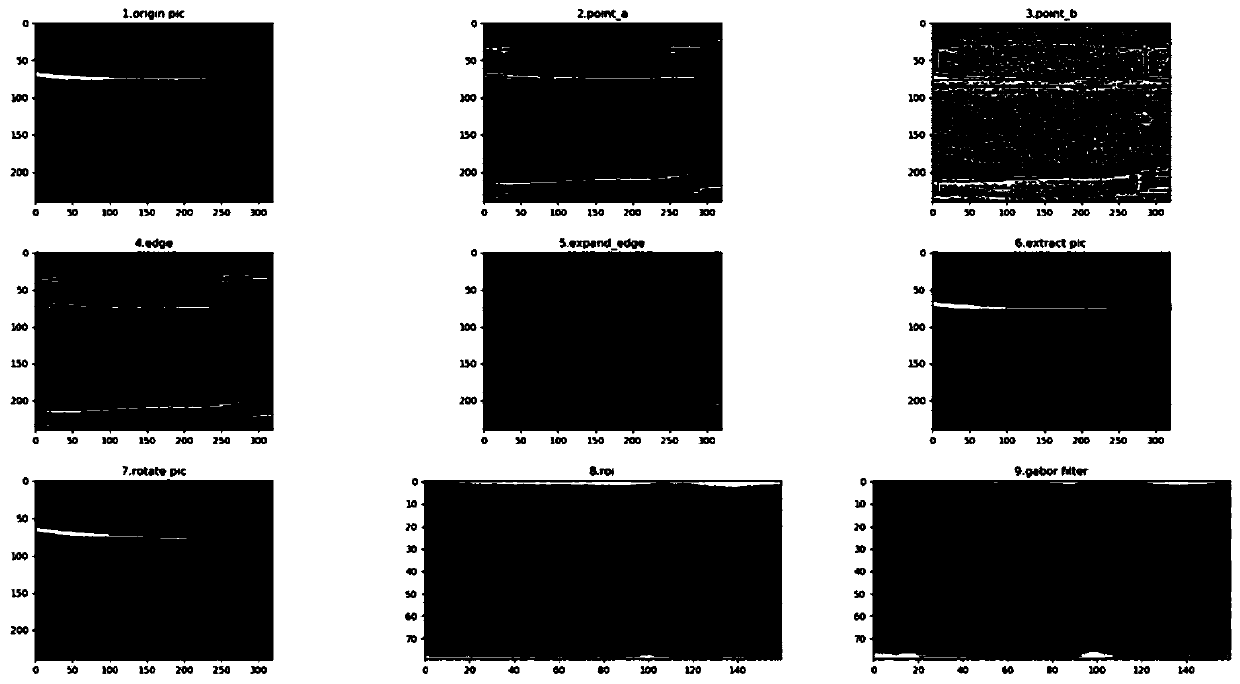
The invention discloses a finger vein recognition method and system, and the method comprises the steps: determining an upper edge point set and a lower edge point set of a finger region, and refiningthe edge to a pixel width; selecting appropriate points from the refined edge point set for edge expansion to obtain a real edge point set; correcting the rotation of the finger according to the obtained pixel coordinates, and setting the background gray value to be 0; obtaining the ROI, wherein the width is selected to be 0.73 time that of the original image, the lowest edge coordinate is selected when the upper edge is intercepted, and the uppermost edge coordinate is selected for height interception when the lower edge is intercepted; performing histogram equalization and Gabor filtering on the ROI; extracting an ROI from 3816 pieces of 636 types of vein images, and storing the ROI; during matching, using a one vs n method, and calculating the similarity scores of the two ROI images in the zero-mean normalization direction, the range is 0-1, the closer the numerical value is to 1, the higher the similarity degree is, and the main body to which the image with the highest similaritydegree with the to-be-matched image belongs is judged as the main body of the to-be-matched image.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Self adaption threshold-based image tampering detecting and positioning method
ActiveCN106097379AEliminate negative effectsImprove detection efficiencyImage analysisReference patternsZero mean
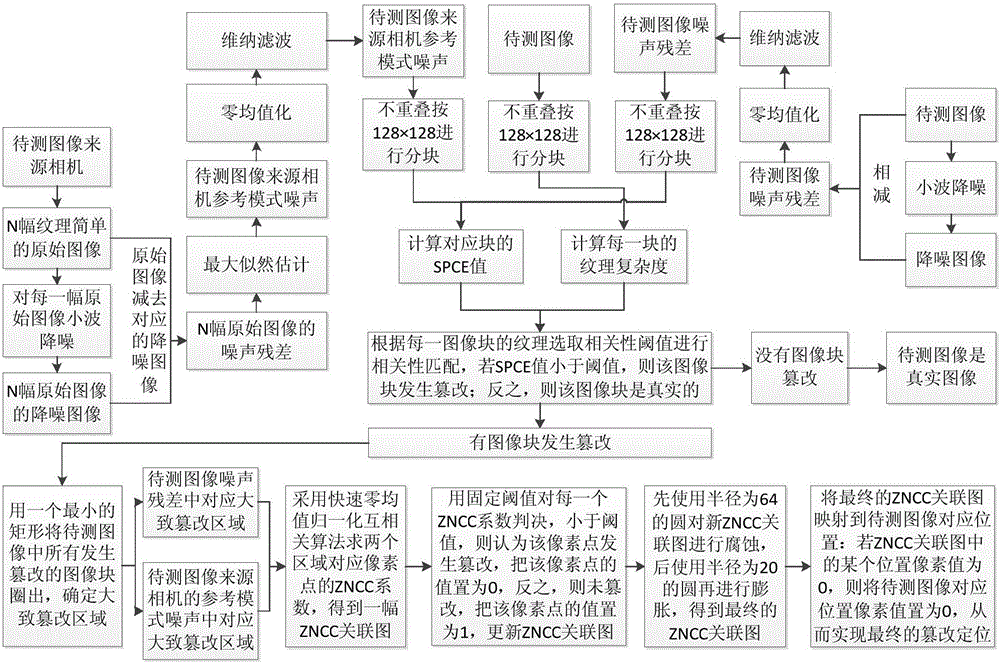
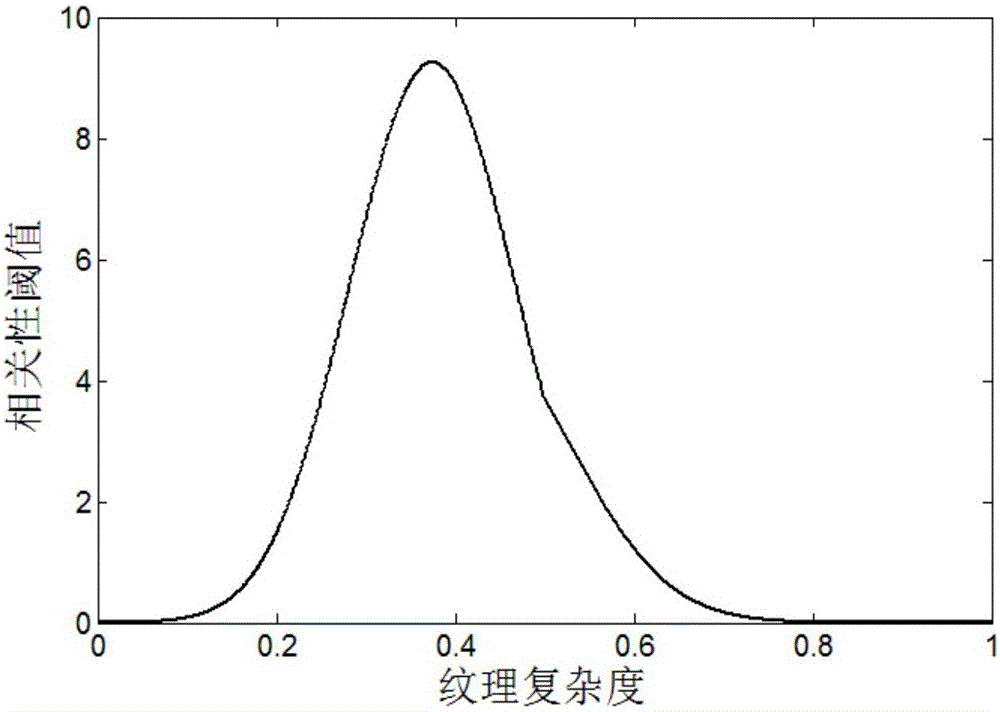
The invention discloses a self adaption threshold-based image tampering detecting and positioning method which is based on mode noise and takes image content into account. The method comprises the following steps: noise residual errors of an image to be detected are extracted; the image to be detected, the noise residual errors of the image to be detected, and a reference mode noise of a source camera of the image to be detected are subjected to non-overlapping partitioning operation; correlation between the noise residual errors of the image to be detected and the reference mode noise of the source camera of the image to be detected is calculated in a partition by partition manner, determination is made according to a texture complexity selection threshold value of the corresponding image to be detected, and negative influence exerted on a detection result by texture complexity can be removed; based on a method of roughly determining a tampering position via the non-overlapping partitioning operation, correlation matching operation is performed via a rapid zero-mean value normalization cross correlation algorithm, tampering detecting and positioning efficiency of the method disclosed in the invention can be greatly improved, and an aim of accurately positioning the tampering can be attained.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Bistable optimal stochastic resonance single-frequency weak signal detection method based on frequency conversion
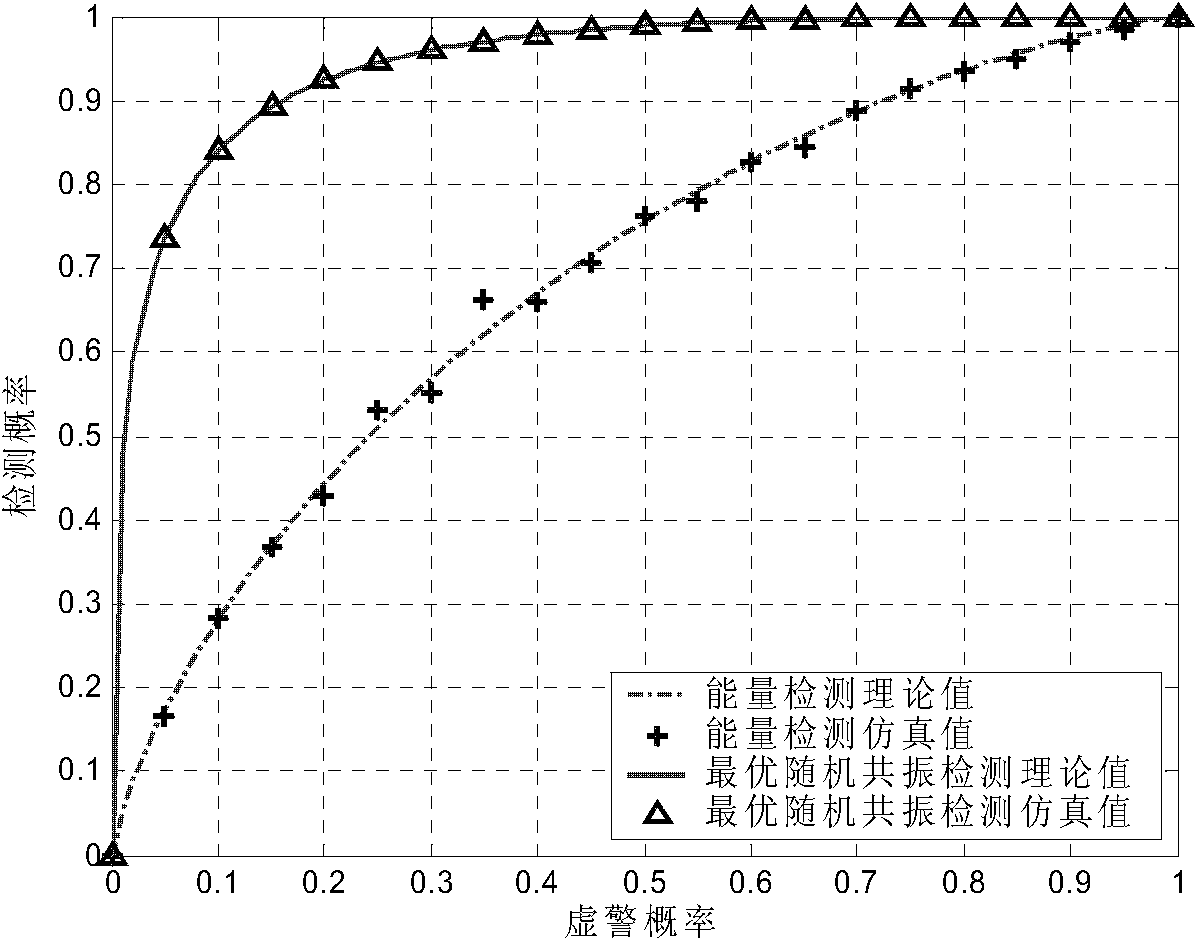
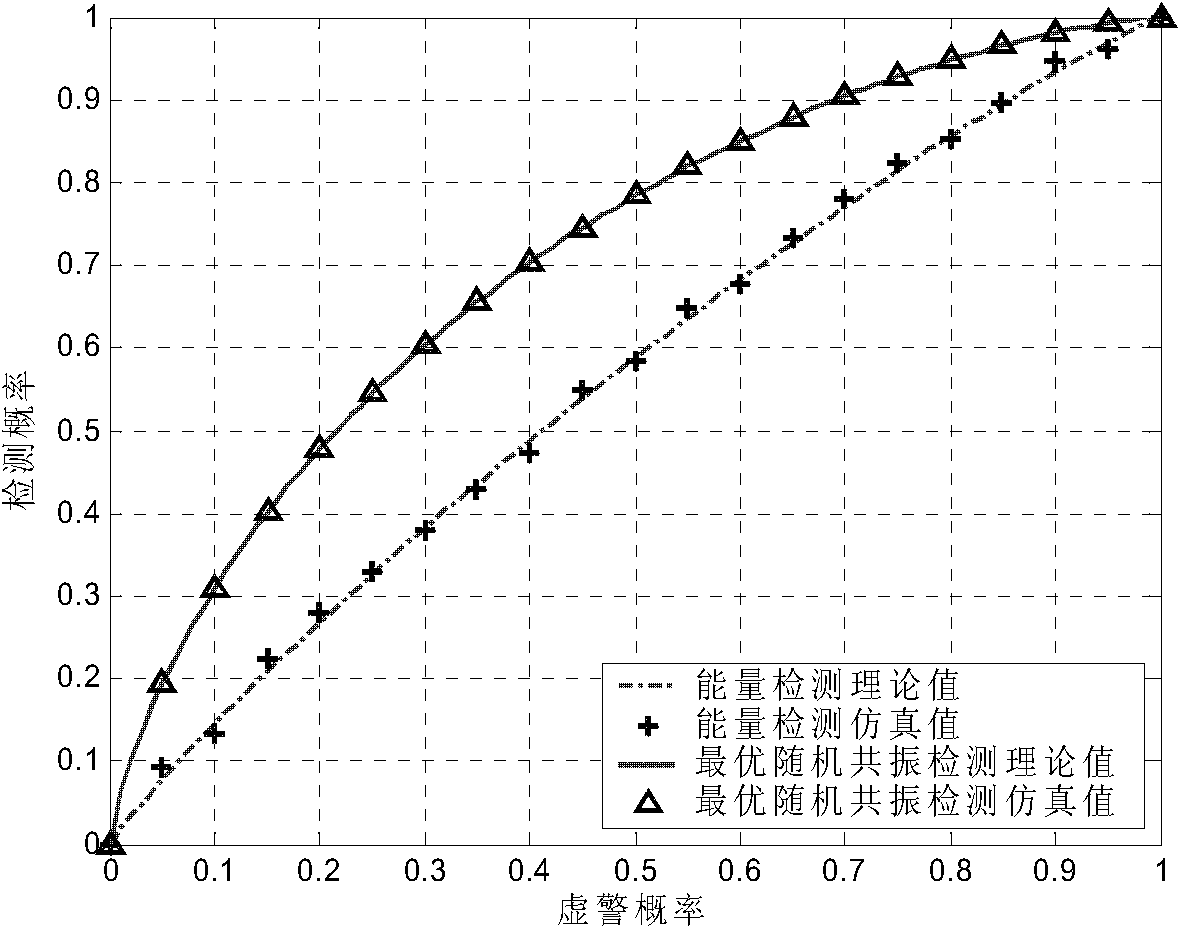
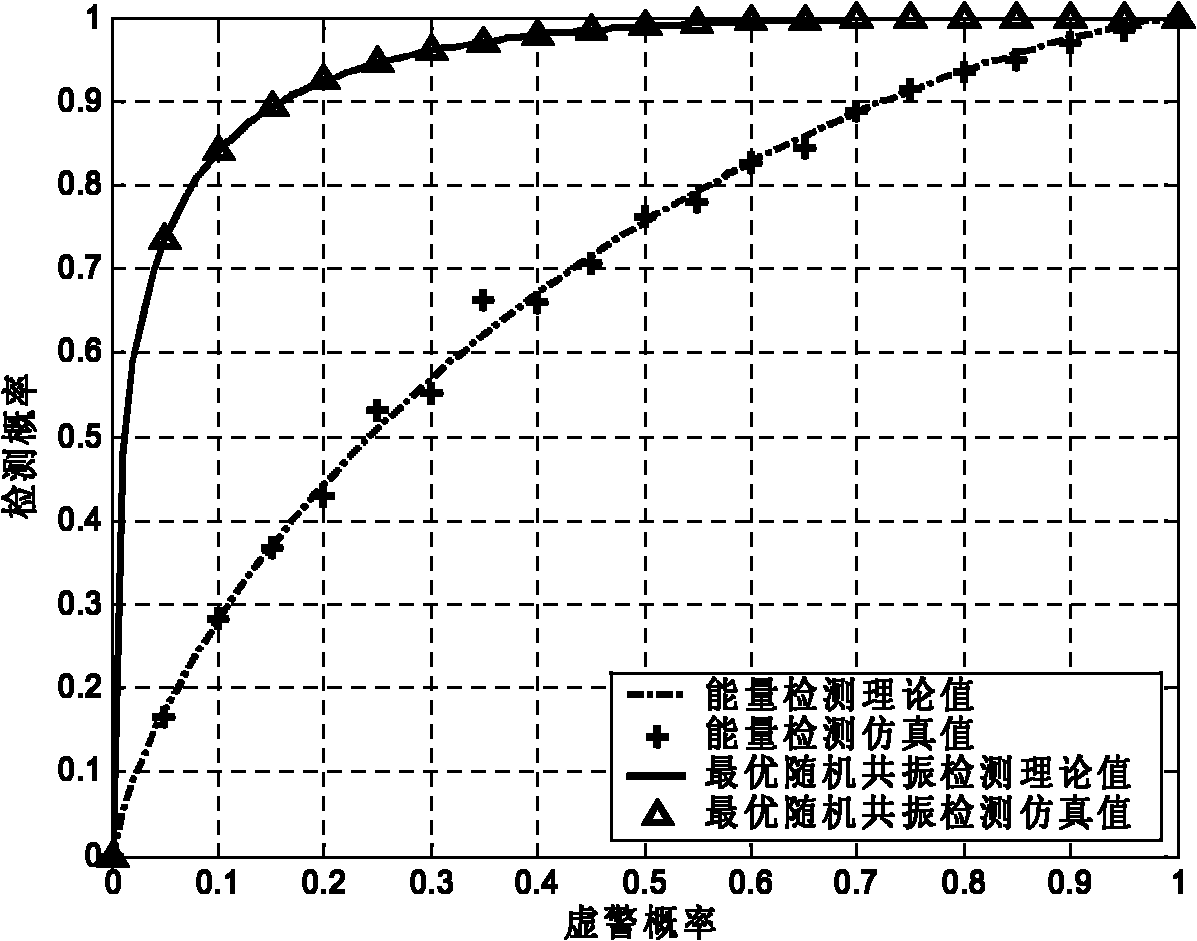
InactiveCN101848177ANot easy to influenceReduce operational complexityPhase-modulated carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksWeight coefficientSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention relates to a bistable optimal stochastic resonance single-frequency weak signal detection method based on variable frequency in the technical field of signal processing. The method comprises the following steps of: multiplying a single-frequency received signal r(t) and a local signal cos([omega]st+2[pi][delta]f*t) to perform frequency conversion; performing weighted summation of the received signal r(t) cos([omega]st+2[pi][delta]f*t) after frequency conversion and a locally generated zero-mean unit power resonance white Gaussian noise nSR(t); inputting the weighted sum signal [k1r(t)cos([omega]st+2[pi][delta]f*t)+k2nSR(t)] into a bistable stochastic resonance system to obtain an output signal-to-noise ratio SNRo of the bistable stochastic resonance system at a frequency [delta]f; performing maximum likelihood optimization on a weighting coefficient to obtain an optimal weighting coefficient; bringing the optimal weighting coefficient into the bistable stochastic resonance system to obtain a state variable output sequence of the system, and inputting the output sequence into an energy detector to obtain the energy of an output signal; and judging that a signal to be detected exists when the energy of the output signal is greater than the set energy threshold,. The invention has advantages of low calculation complexity, good robustness, high detection accuracy and strong feasibility and practicability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com