Patents
Literature
208 results about "Speckle reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
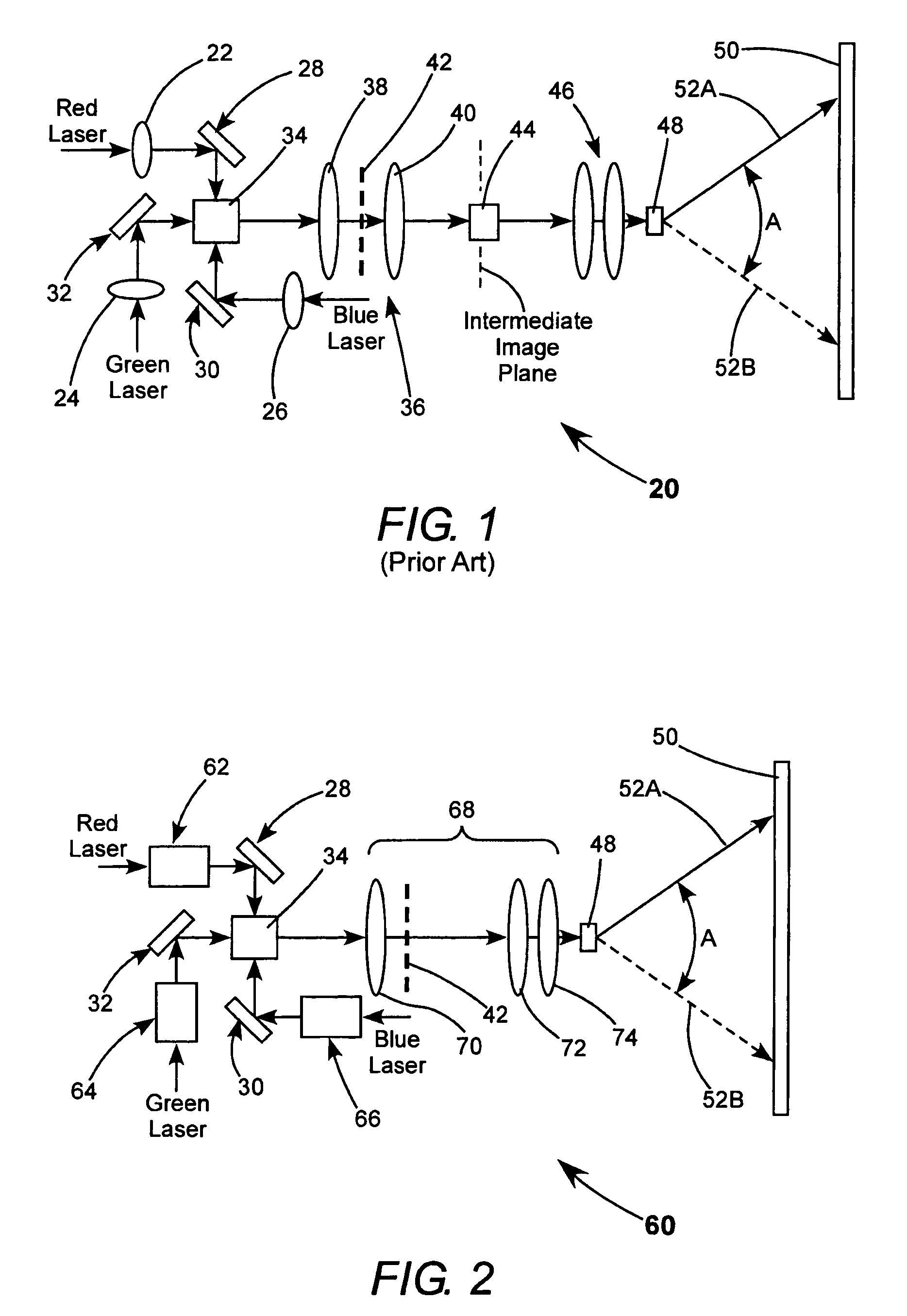
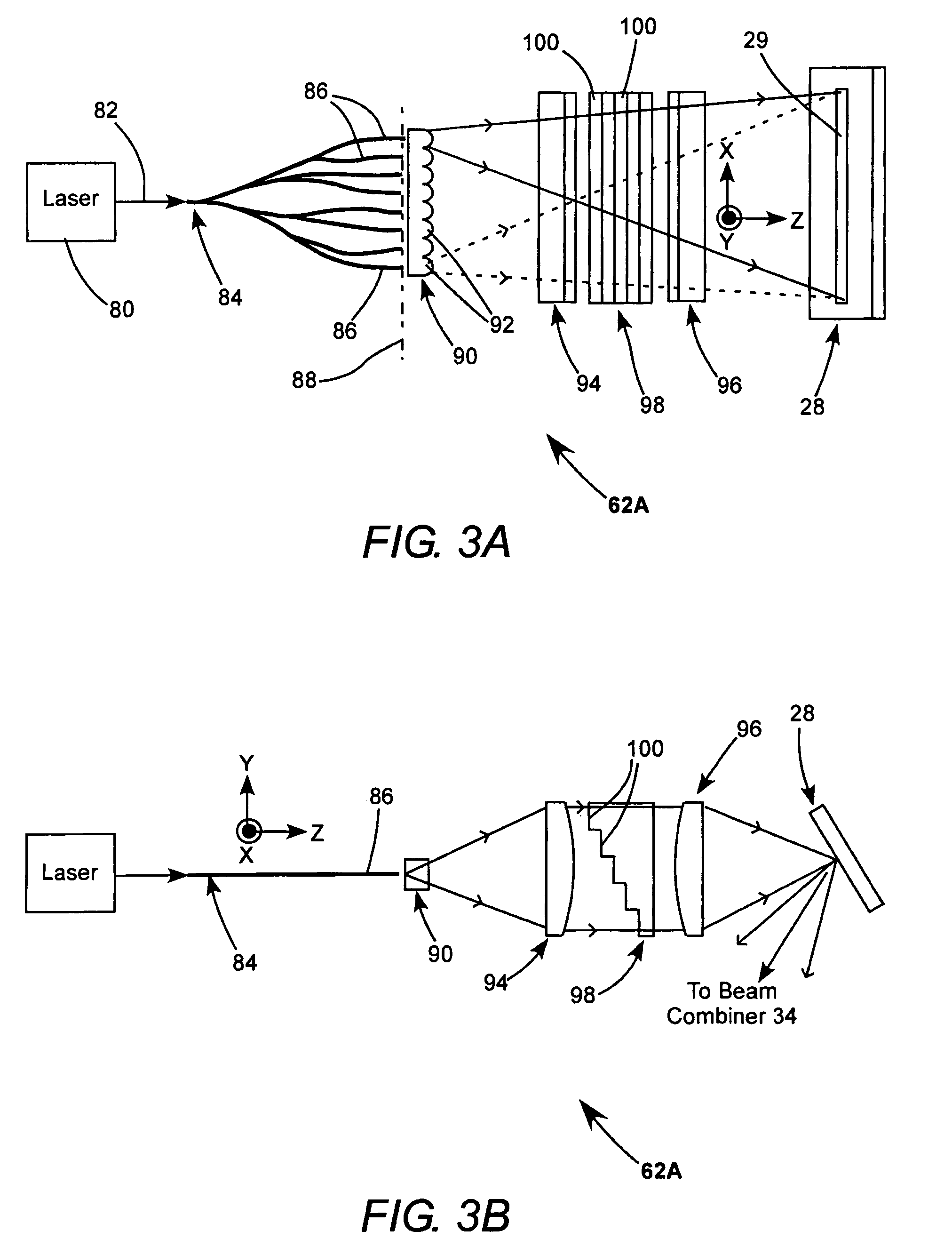
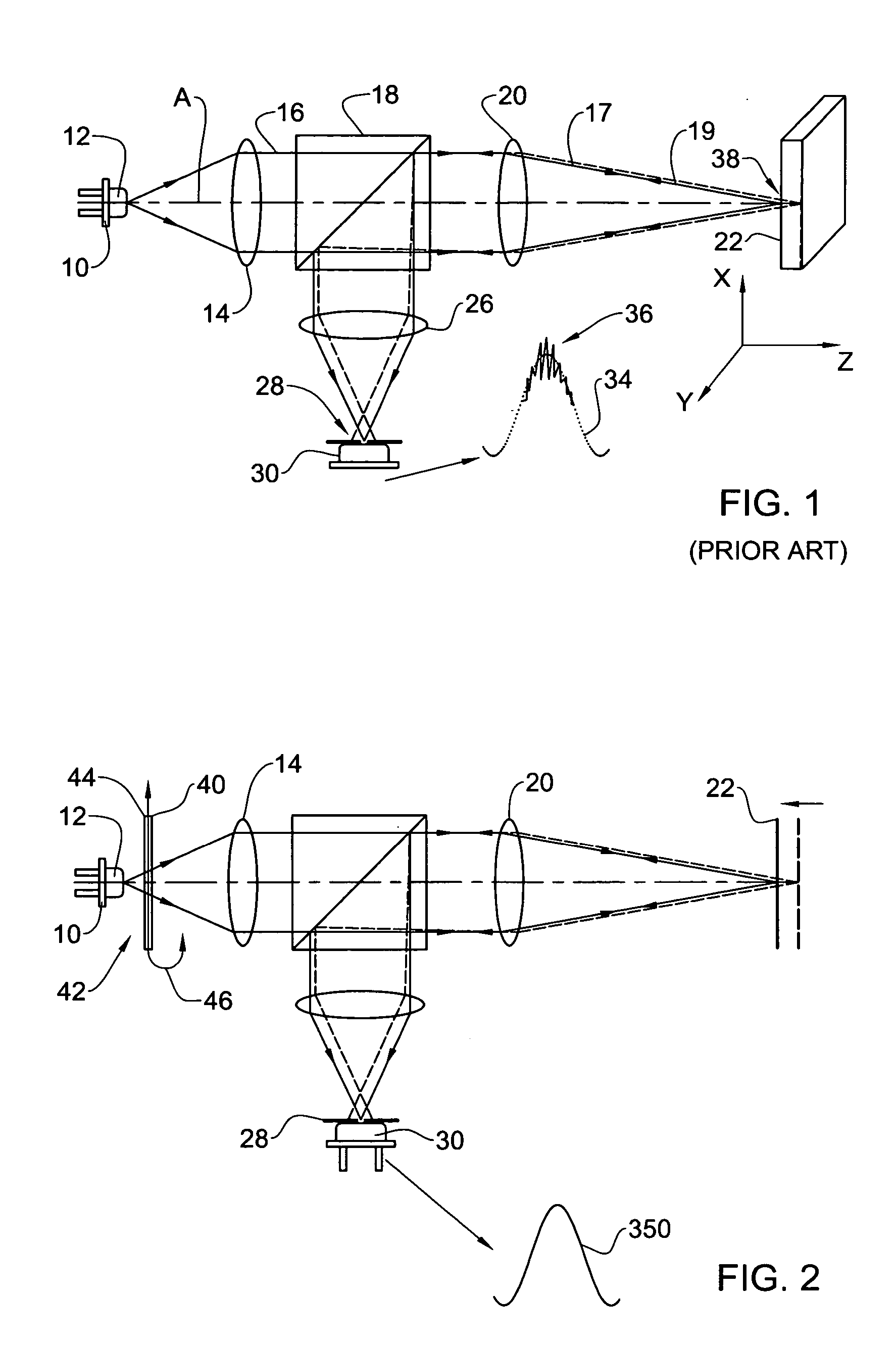
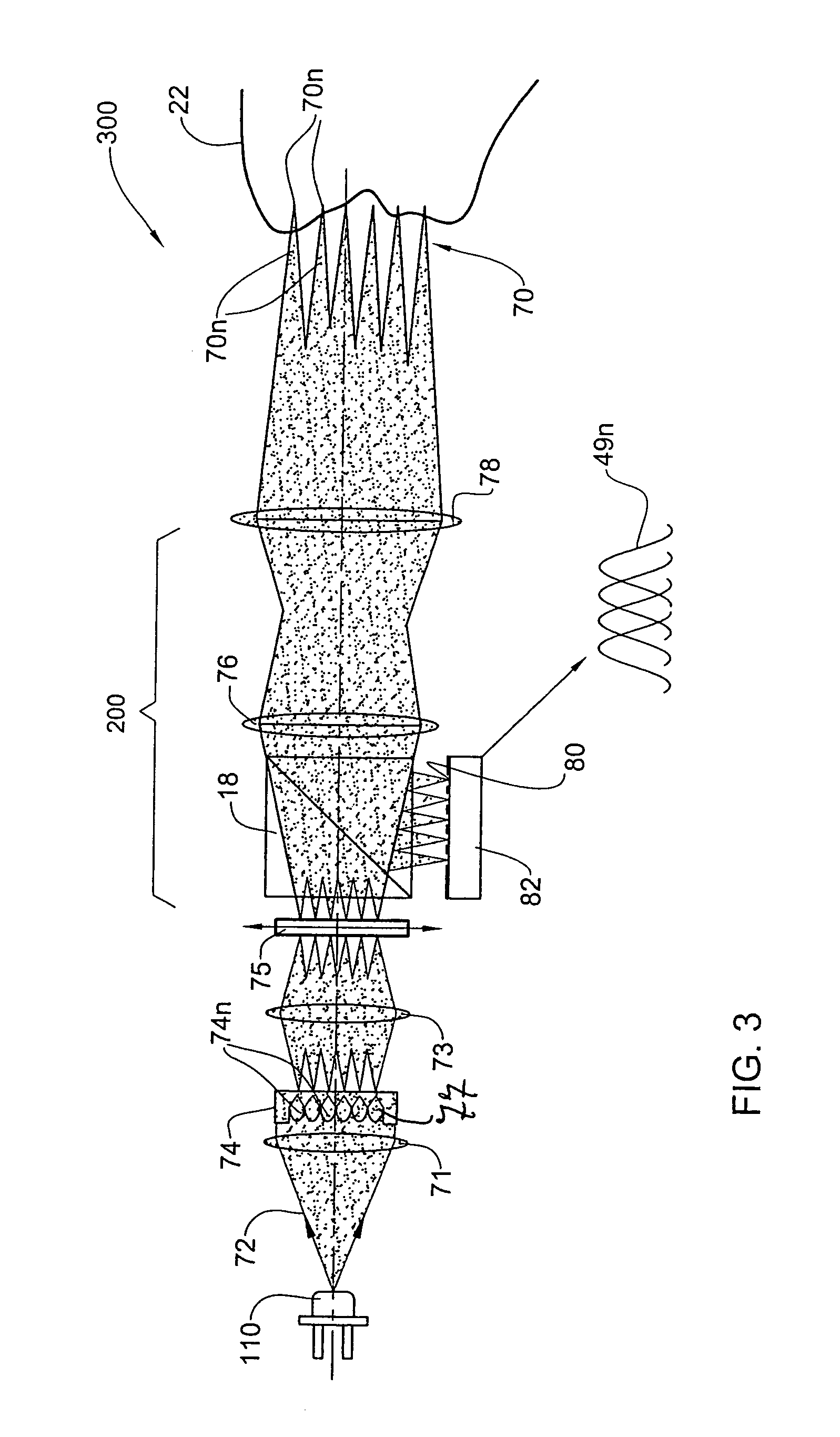
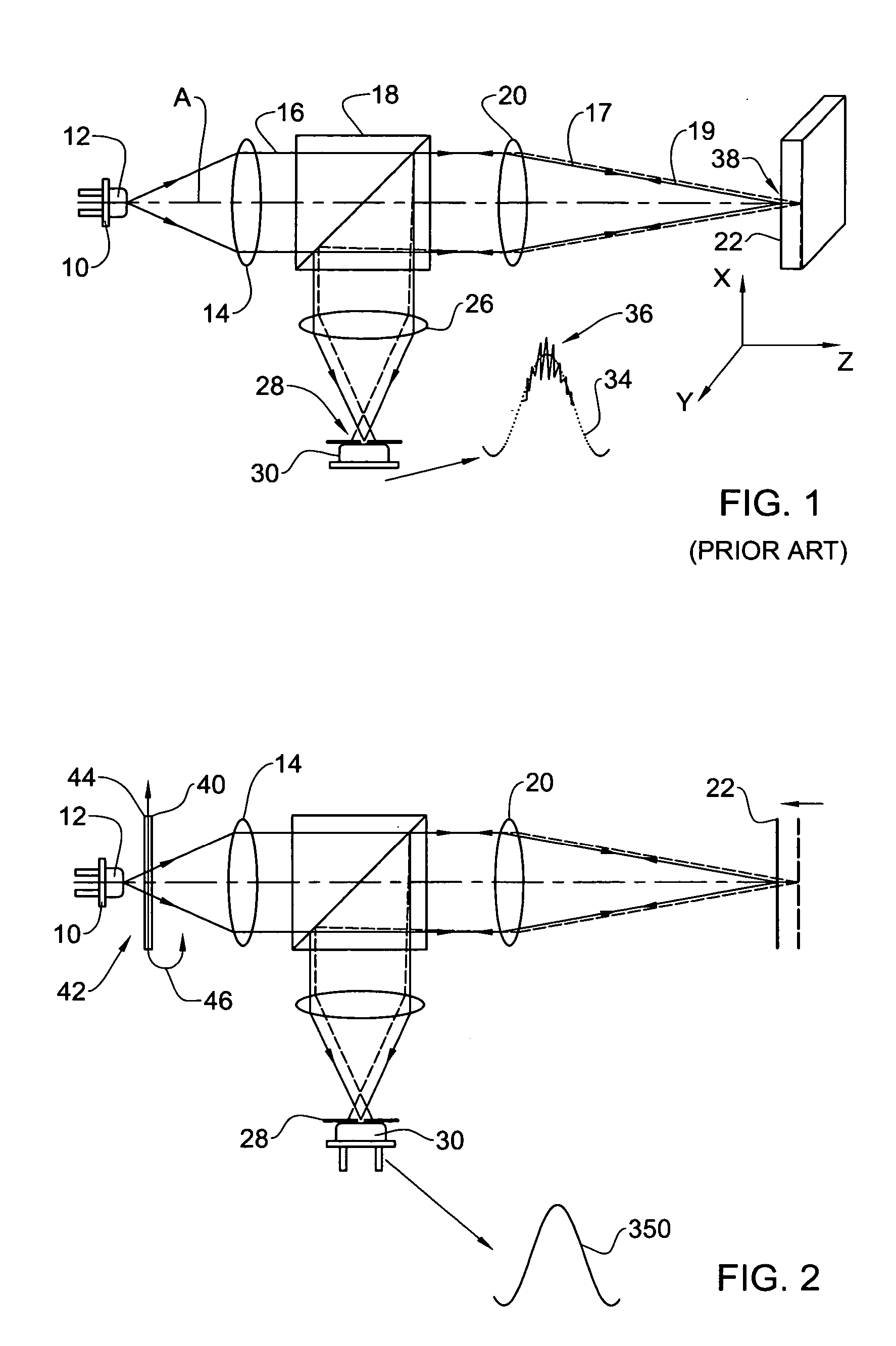
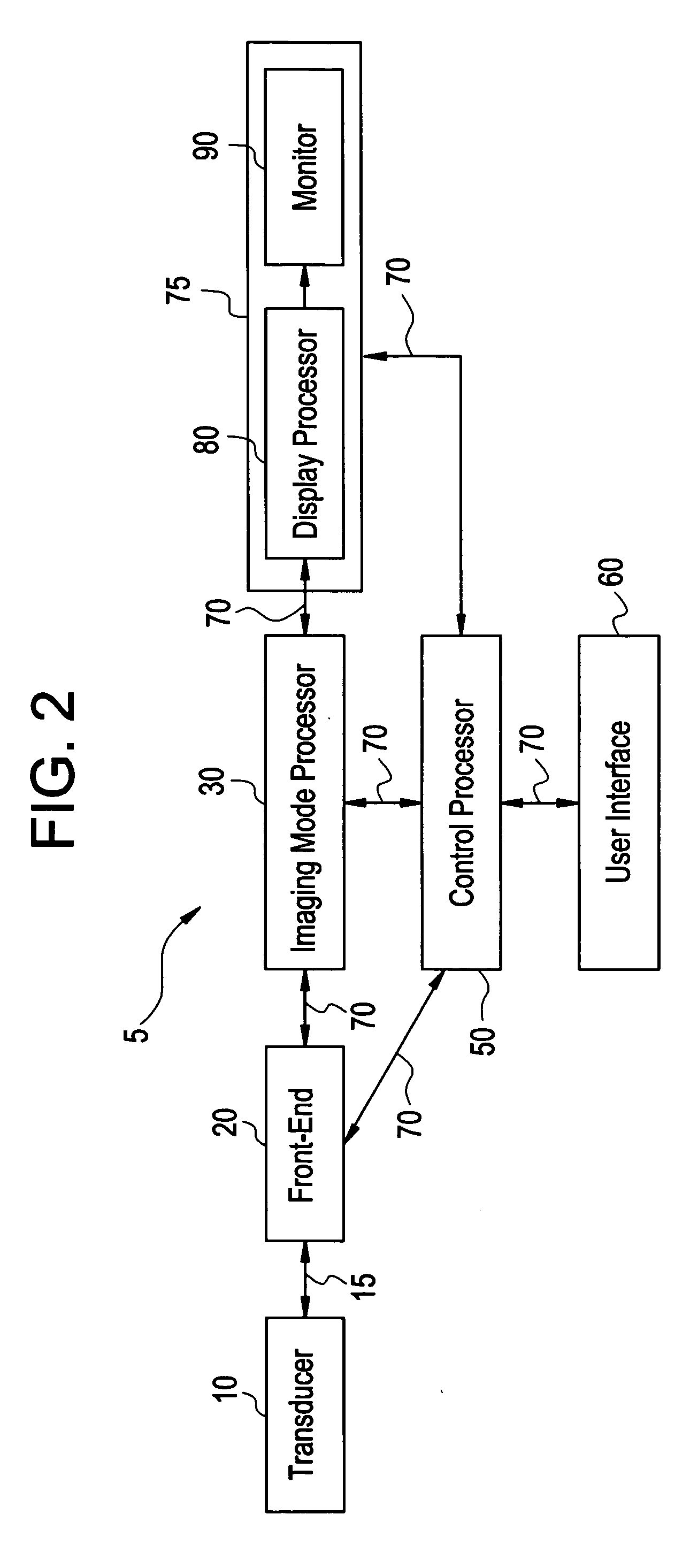
Speckle reduction is based on averaging N independent speckle configurations within the spatial and temporal resolution of the detector. The term independent means that the speckle configurations are (i) uncorrelated, and (ii) non-interfering.
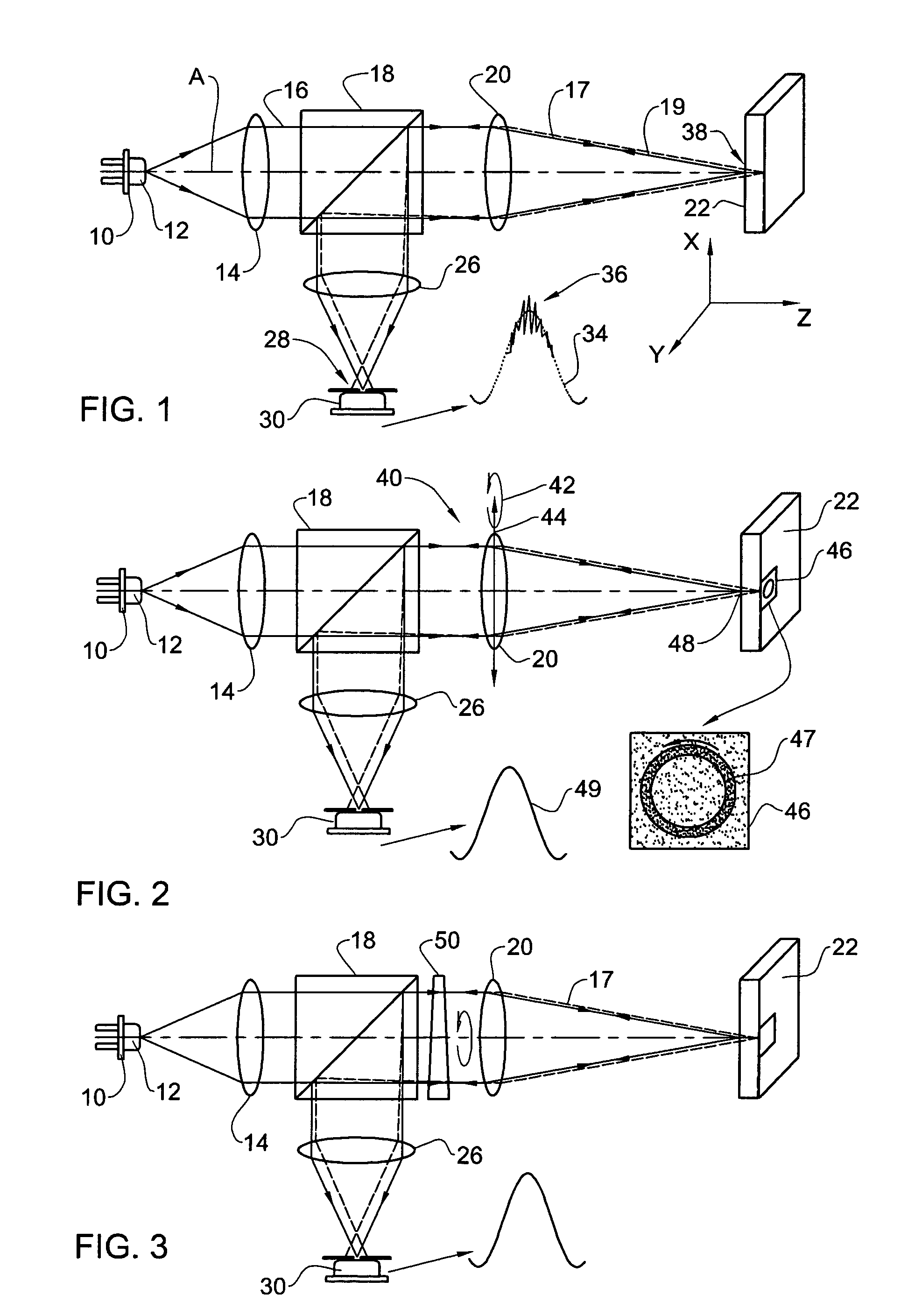
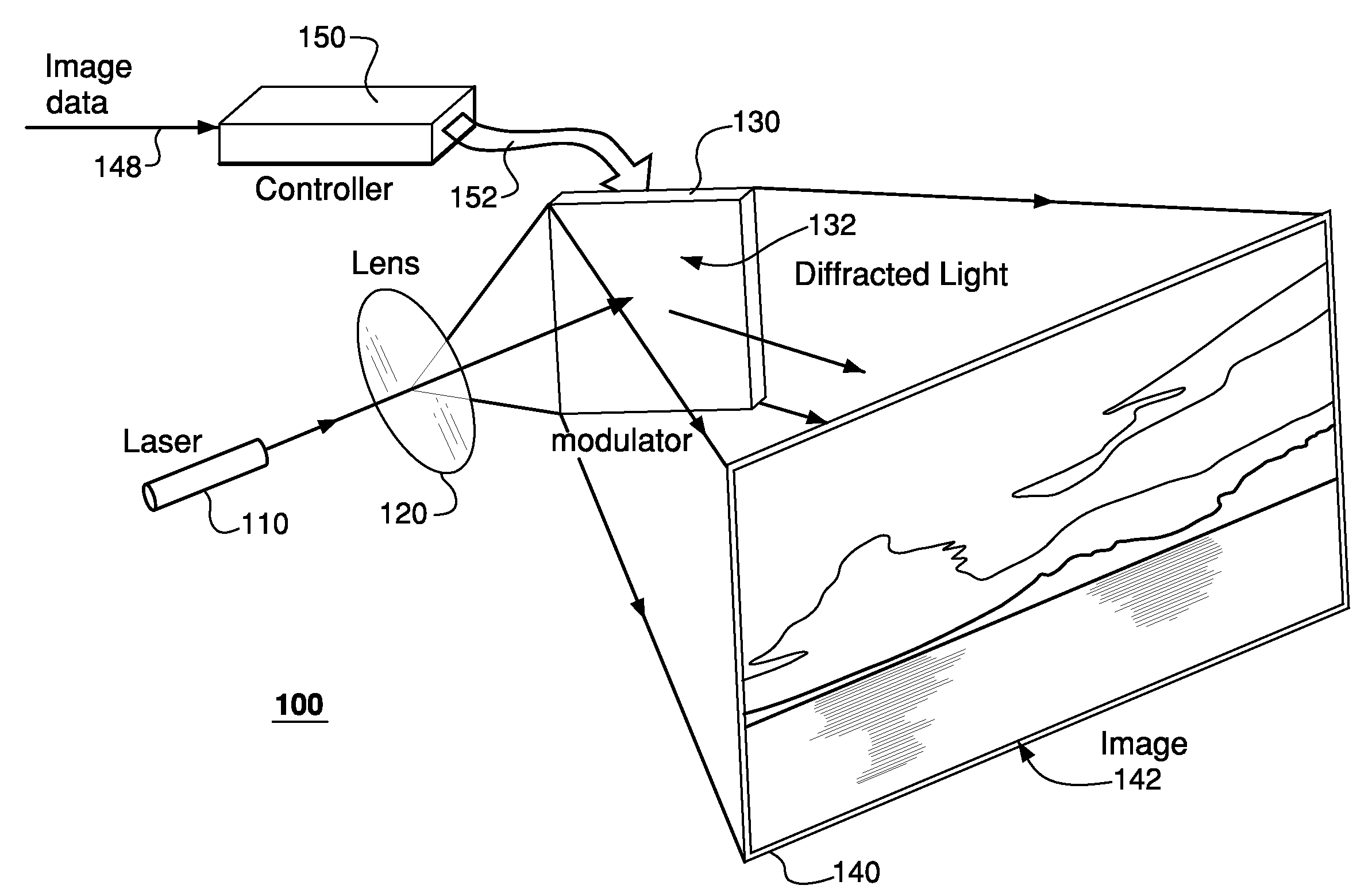
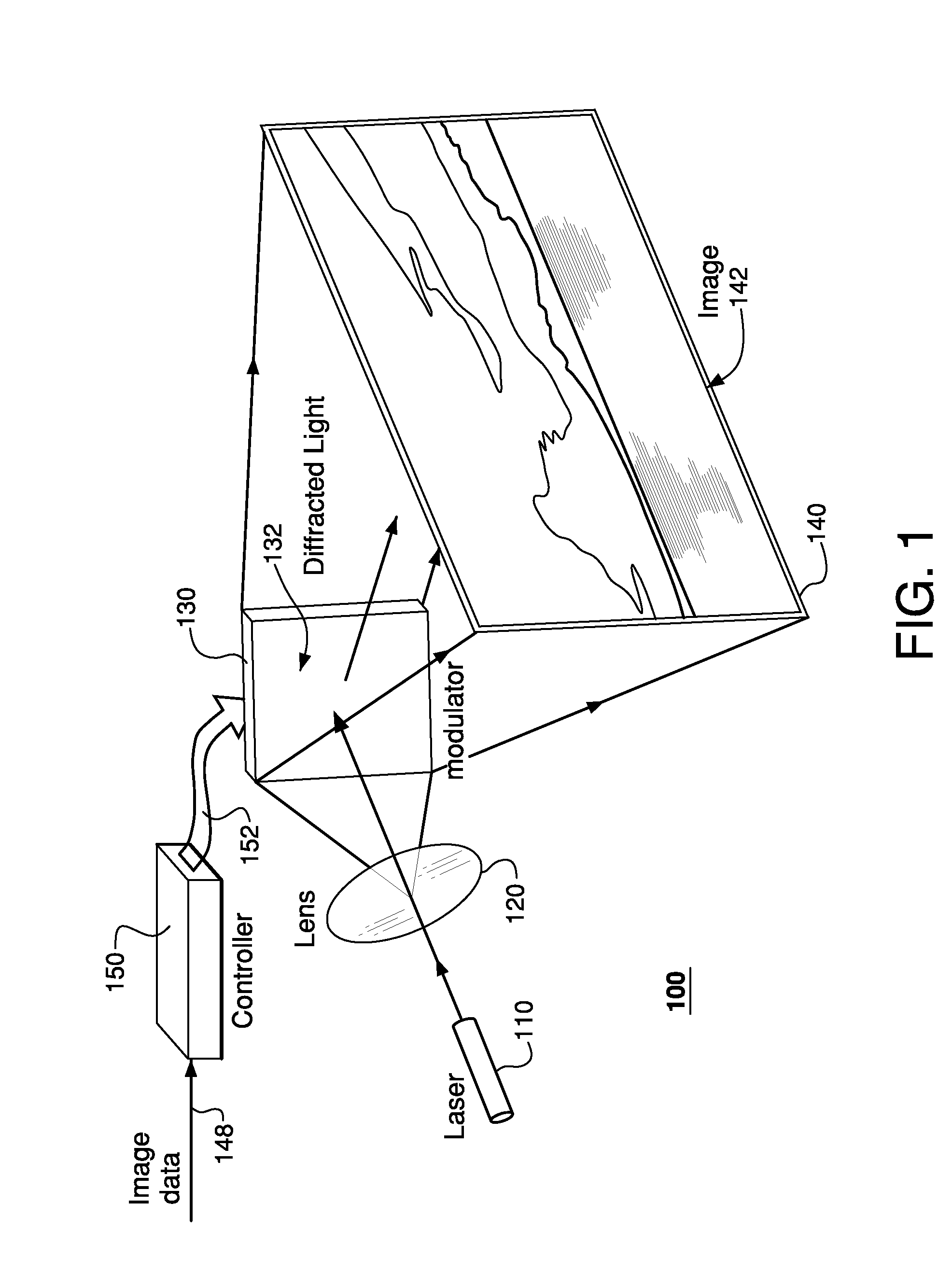
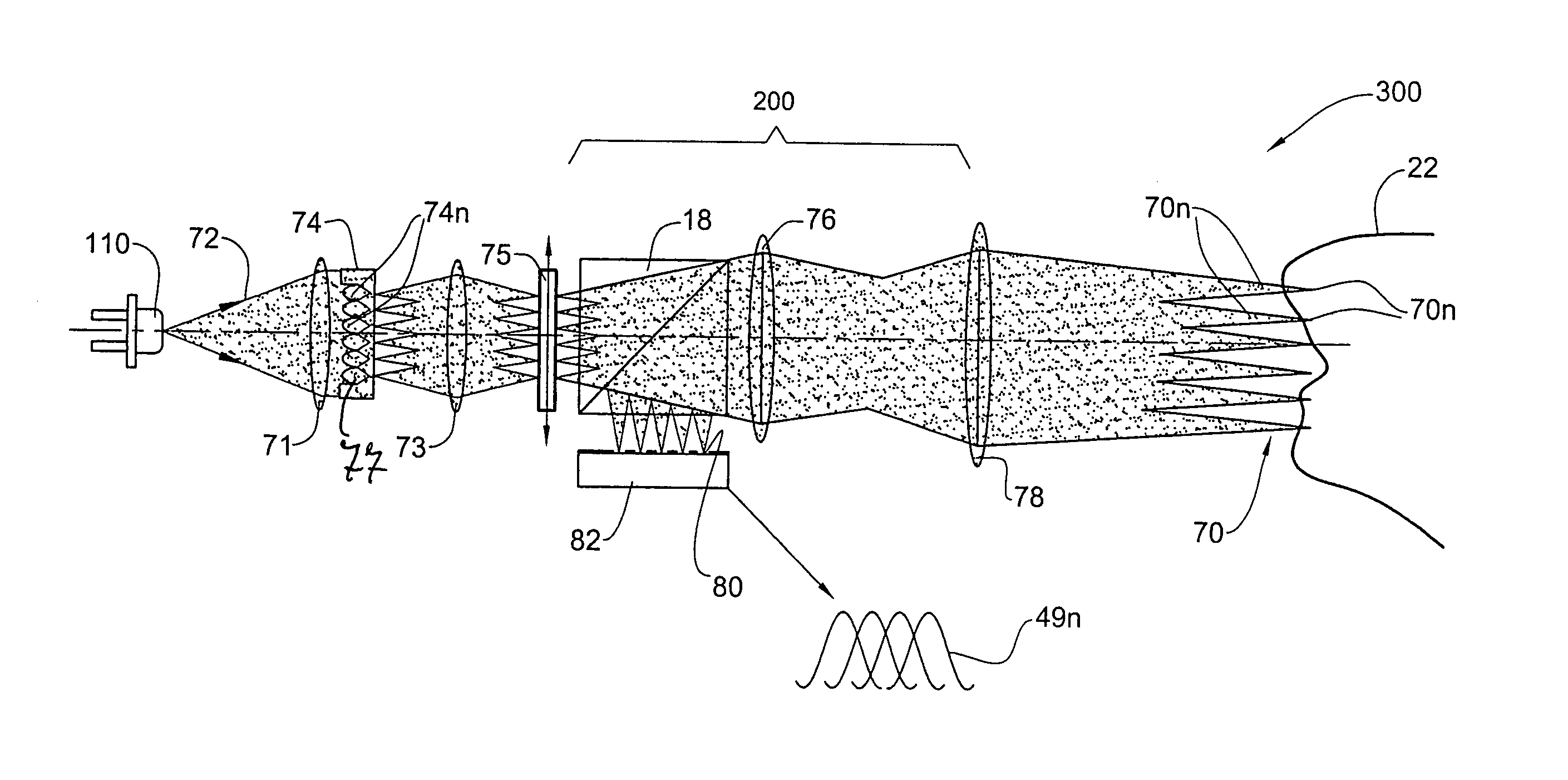
Laser speckle reduction element
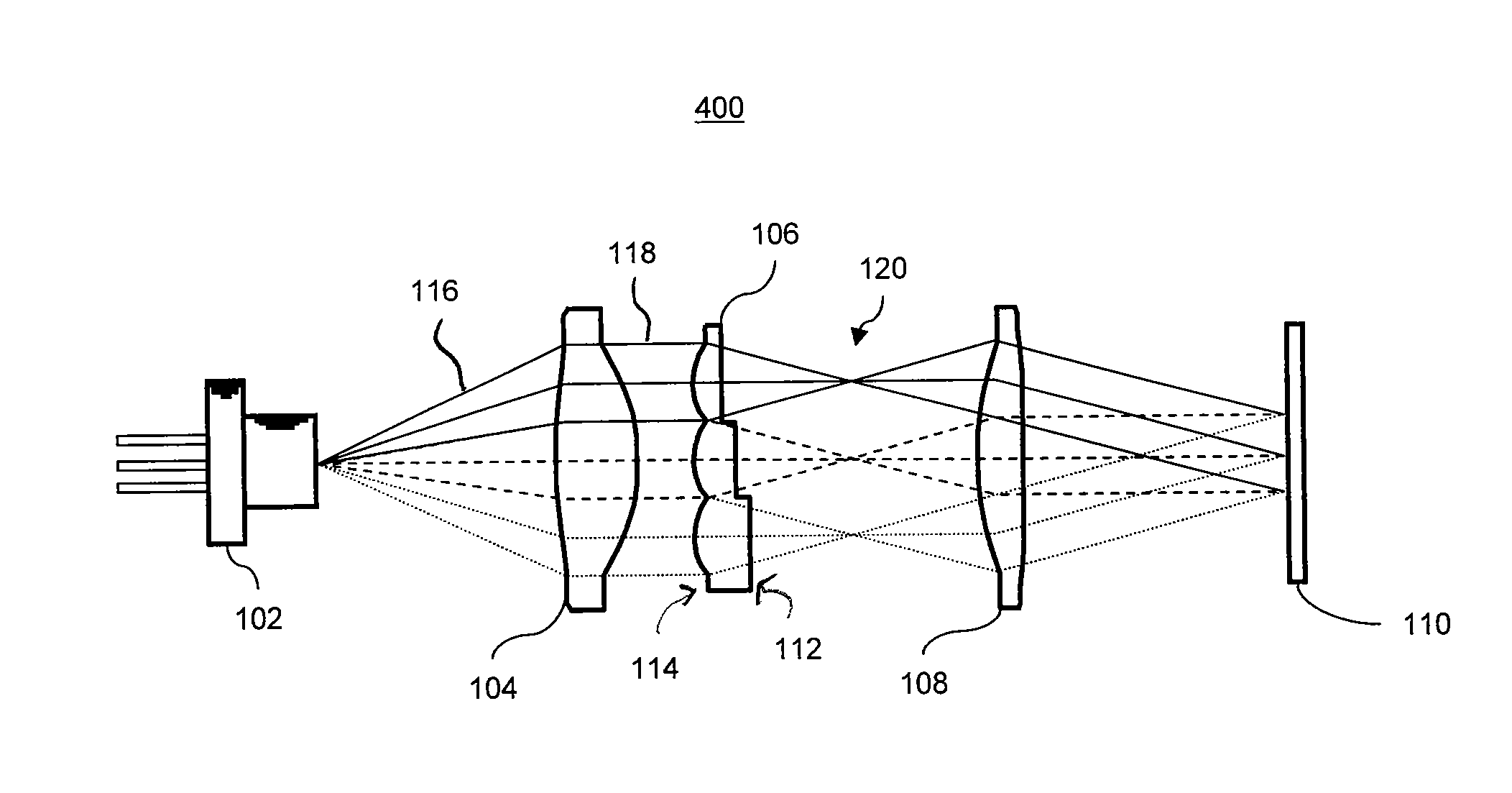
ActiveUS20120081786A1Reduce coherenceBroaden wavelength bandwidthPolarising elementsLight beamOptical pathlength
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
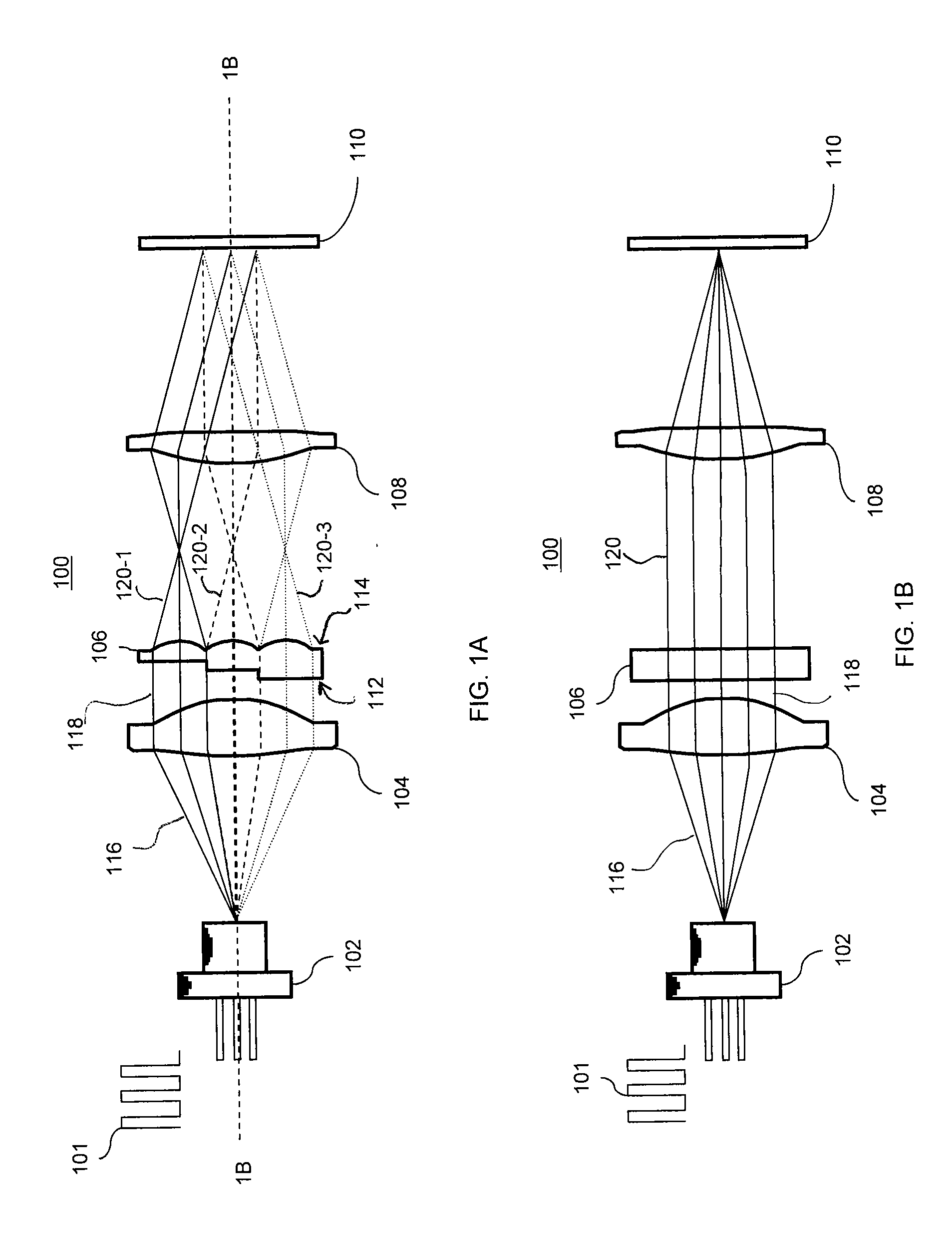
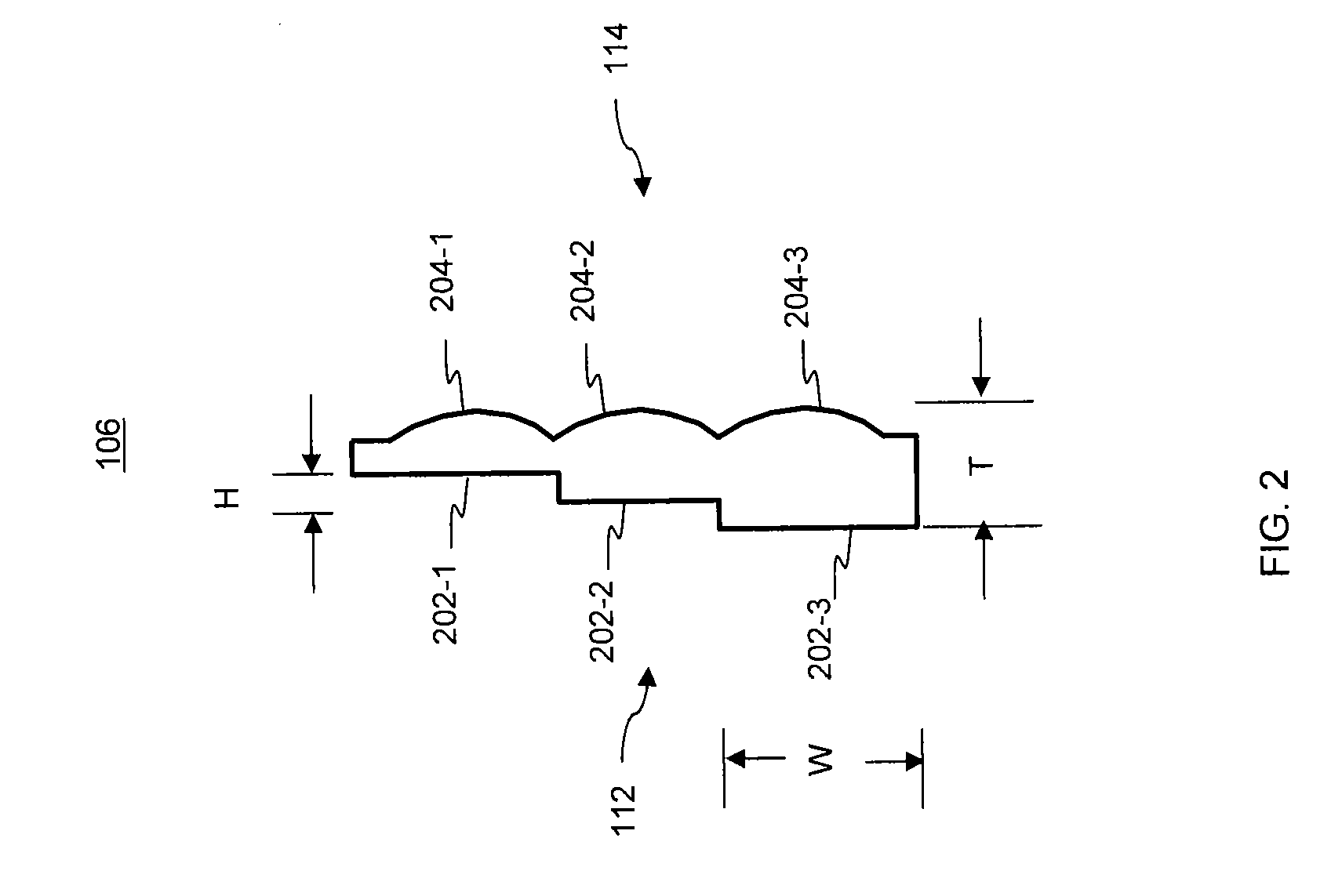
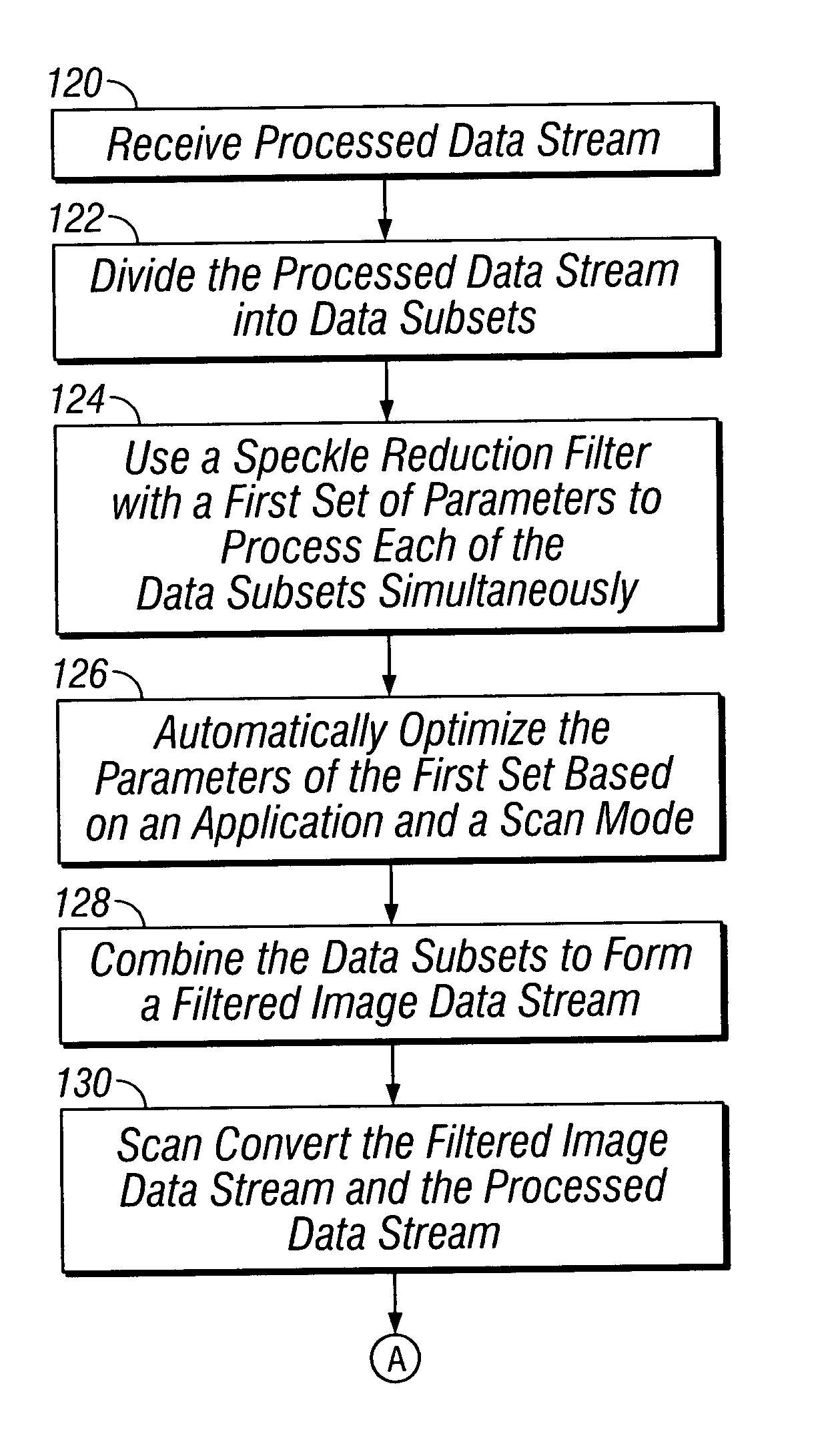
Systems and methods for implementing a speckle reduction filter
InactiveUS20050053305A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementData streamOperating system
A method for implementing a speckle reduction filter are described. The method includes receiving a processed data stream from a processor, dividing the processed data stream into data subsets, simultaneously filtering the data subsets by using a speckle reduction filter to produce filtered data subsets, and producing an image data stream based on the filtered data subsets.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
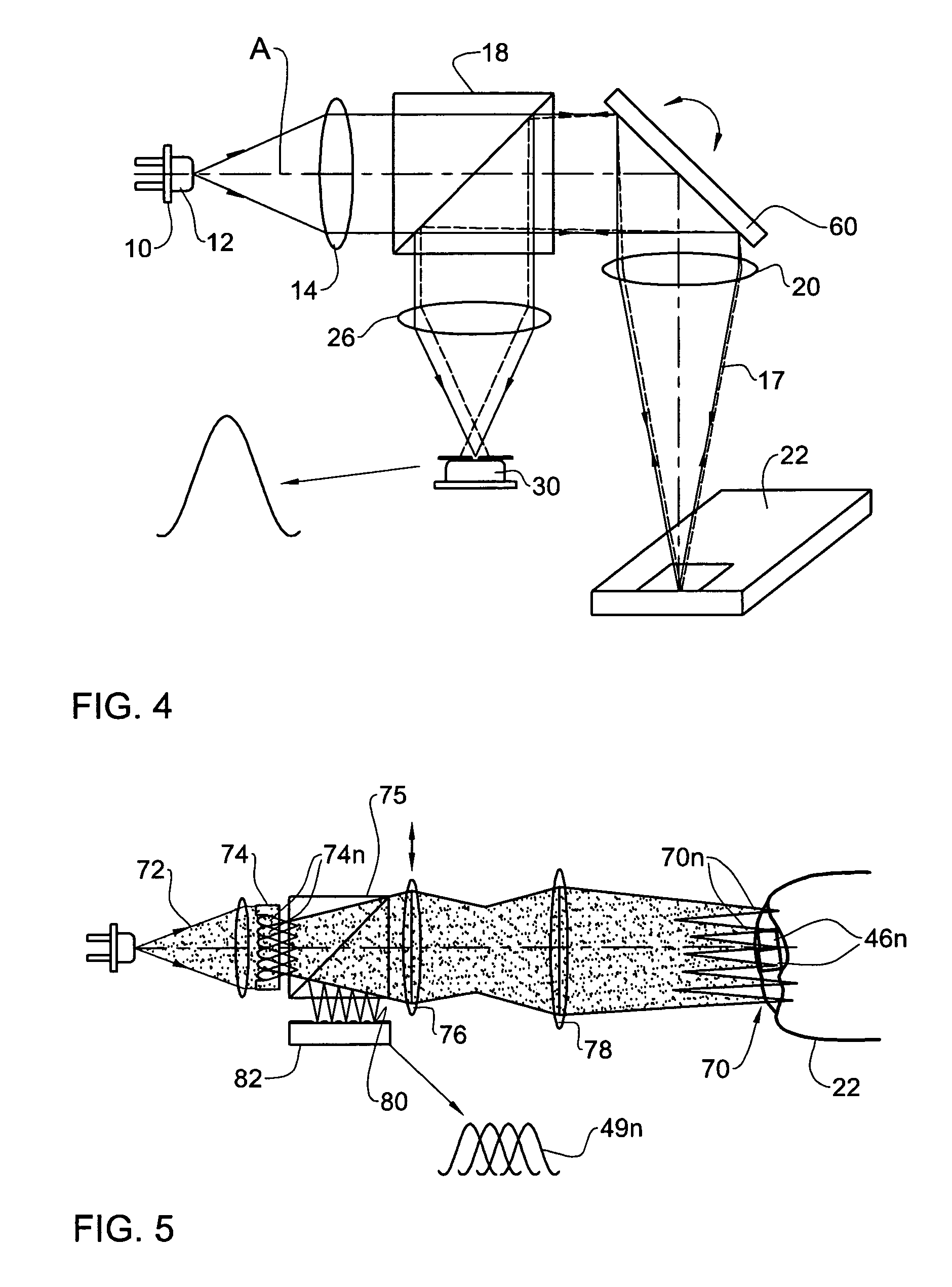
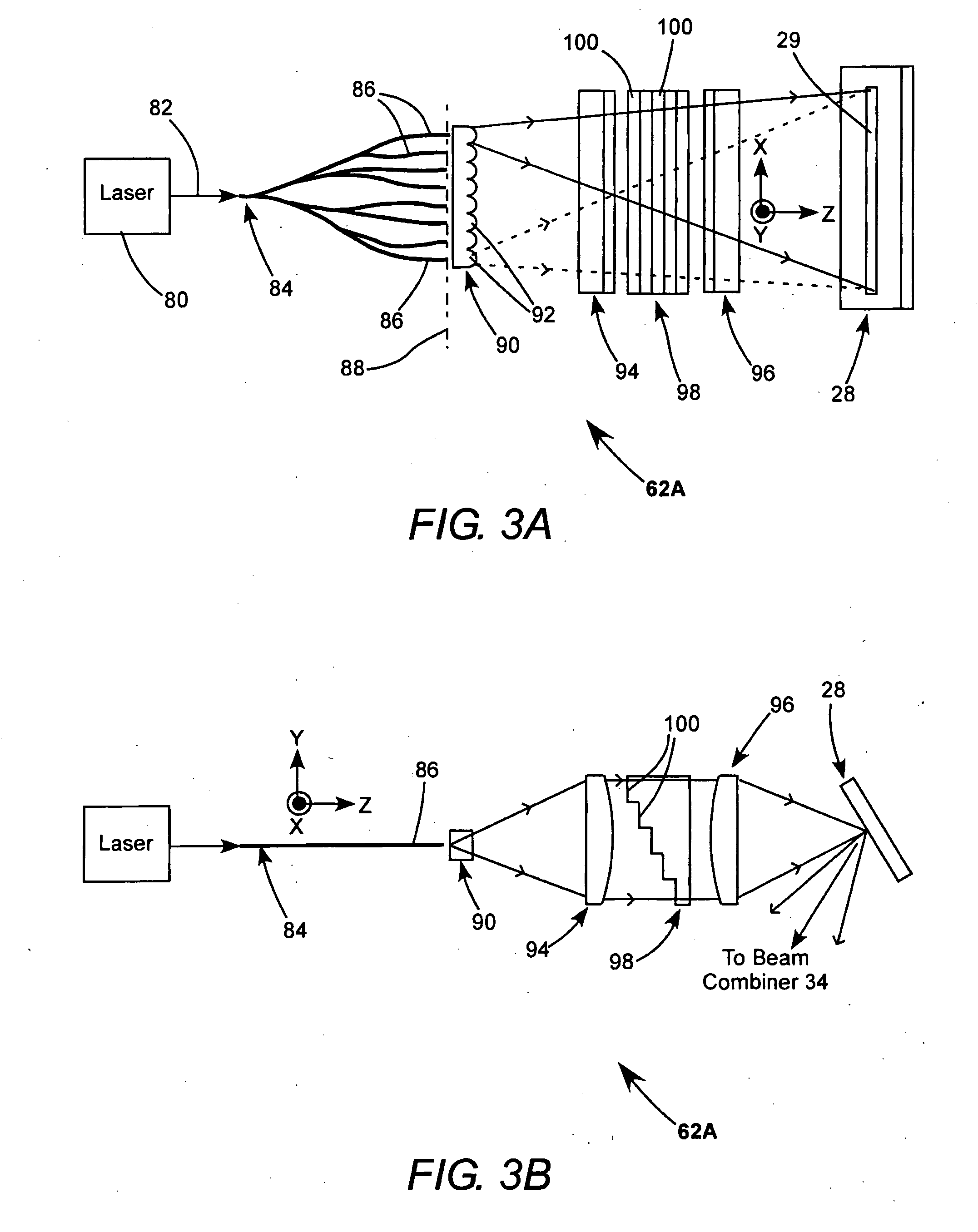
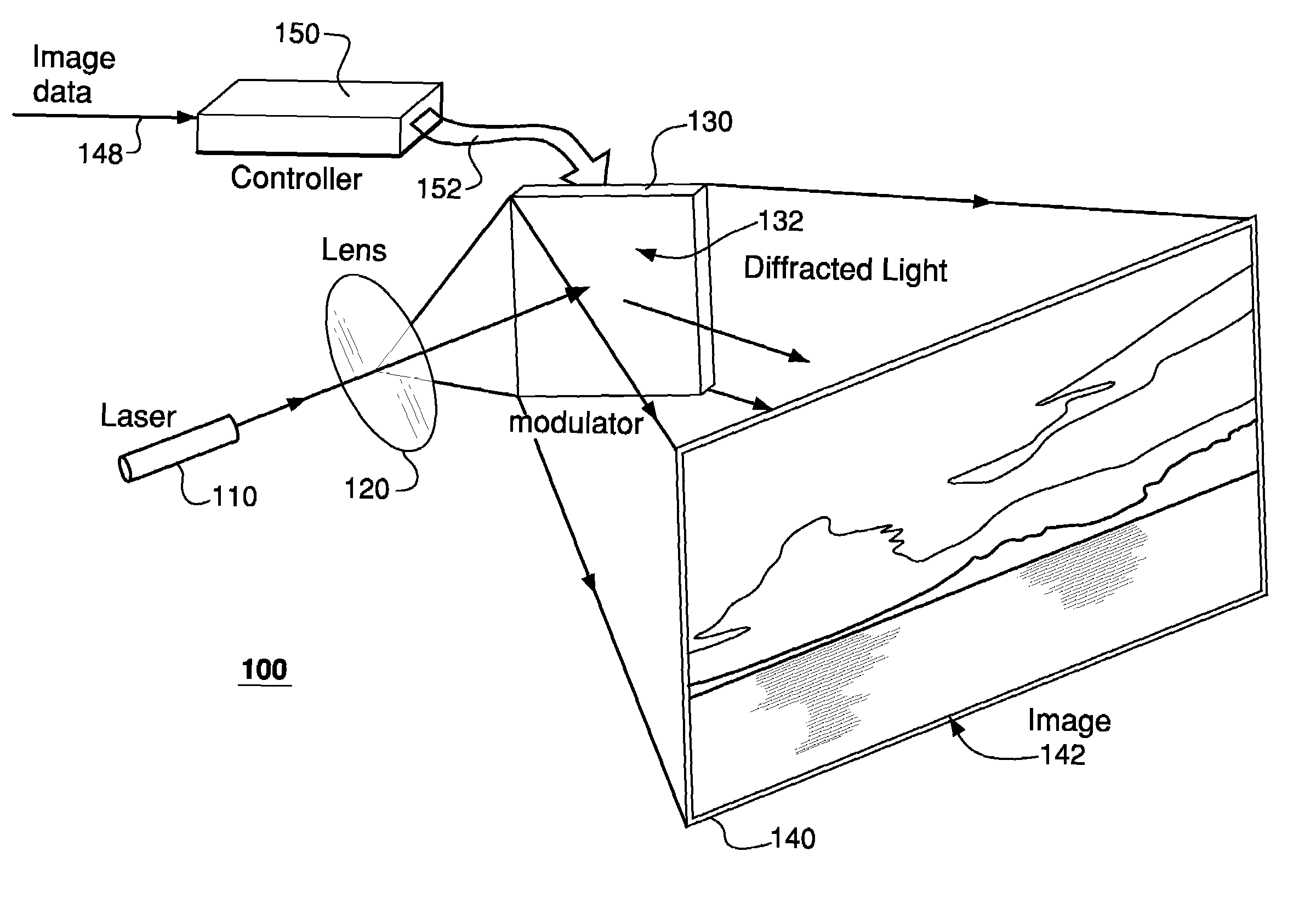
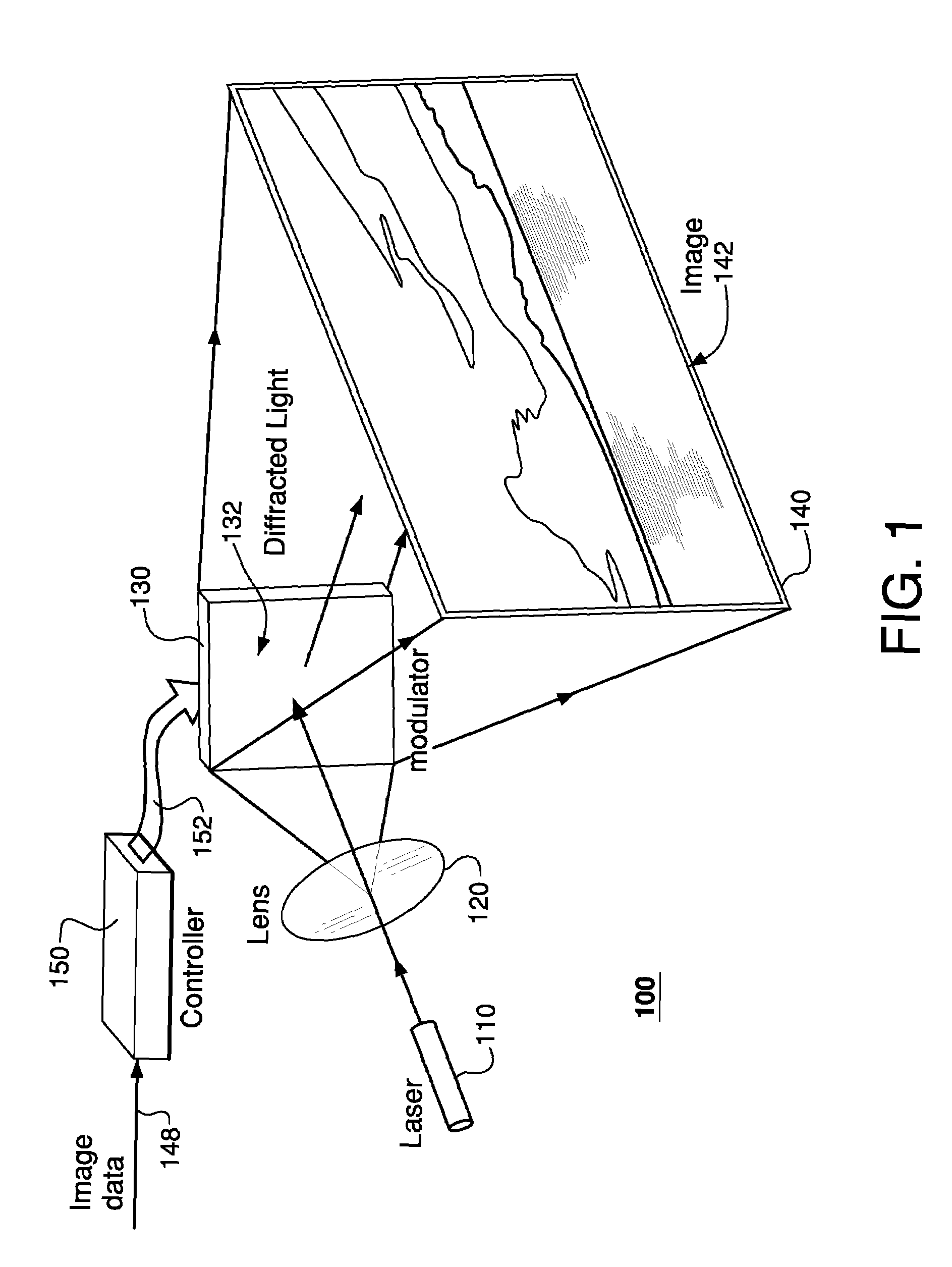
Apparent speckle reduction apparatus and method for MEMS laser projection system
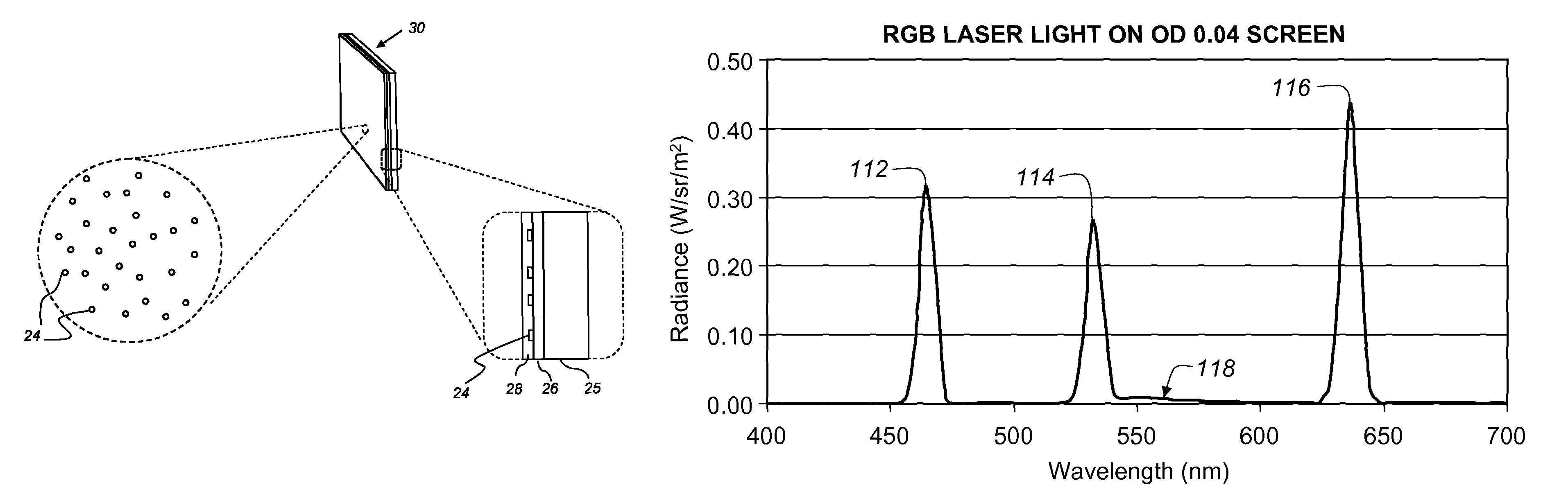
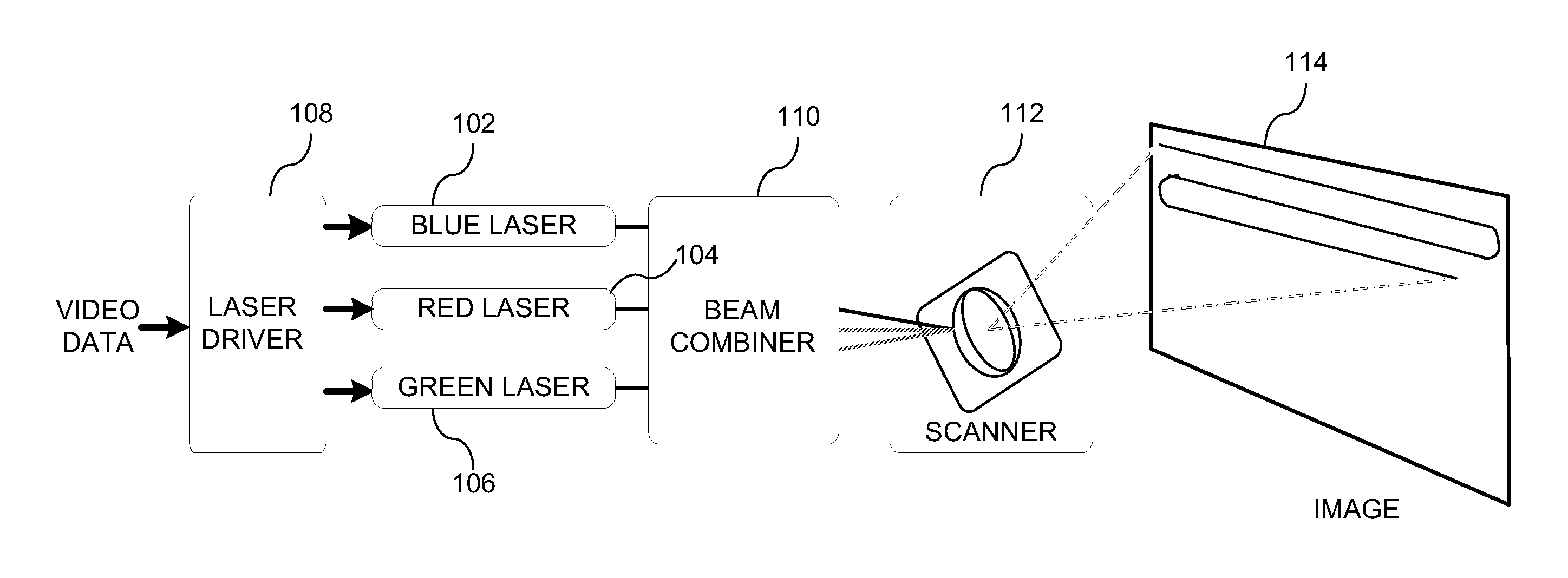
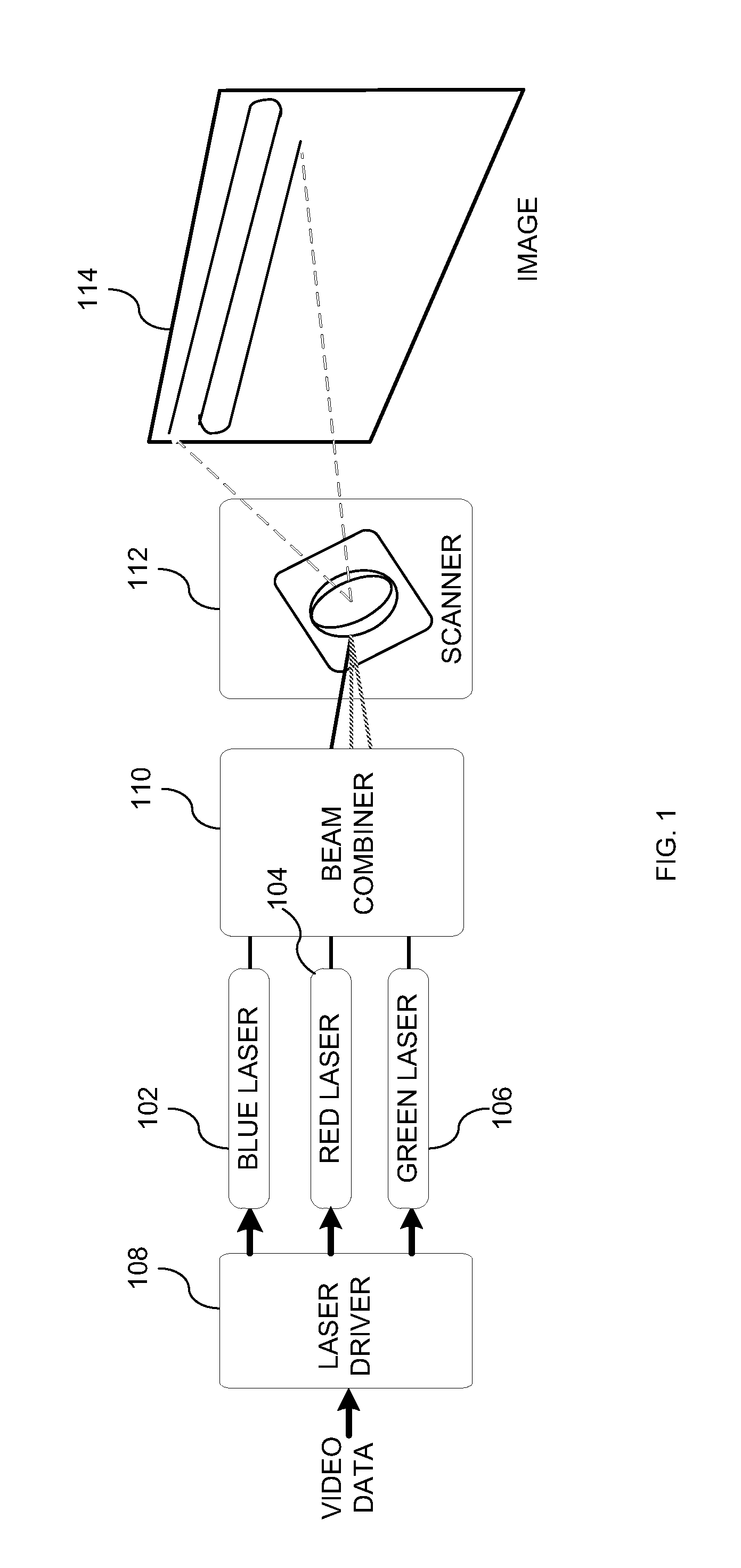
A laser projection system is disclosed having reduced apparent speckle. The system includes a laser emitting a first beam on an optical element. The optical element emits a second beam incident on a scanner that scans the beam onto a projection screen. The optical element may be an exit pupil expander, delay plate, or have a locally electrically modulated index of refraction. In other embodiments, the laser has a tunable wavelength distribution that is changed for each frame displayed by the projection system to reduce apparent speckle. In still other embodiments, the angular content of a beam incident on a scanner is modulated to produce a time varying speckle pattern.
Owner:MICROVISION
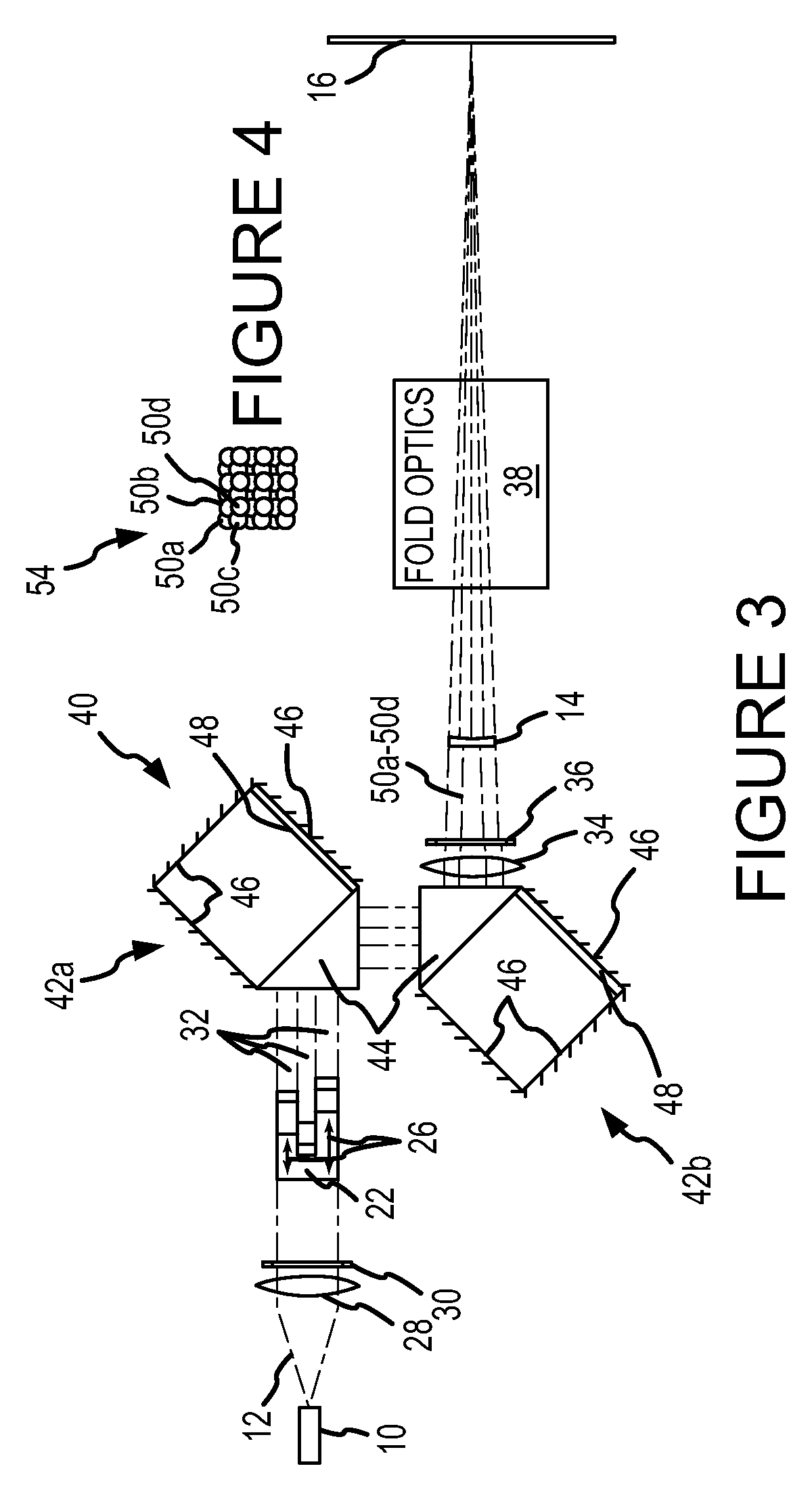
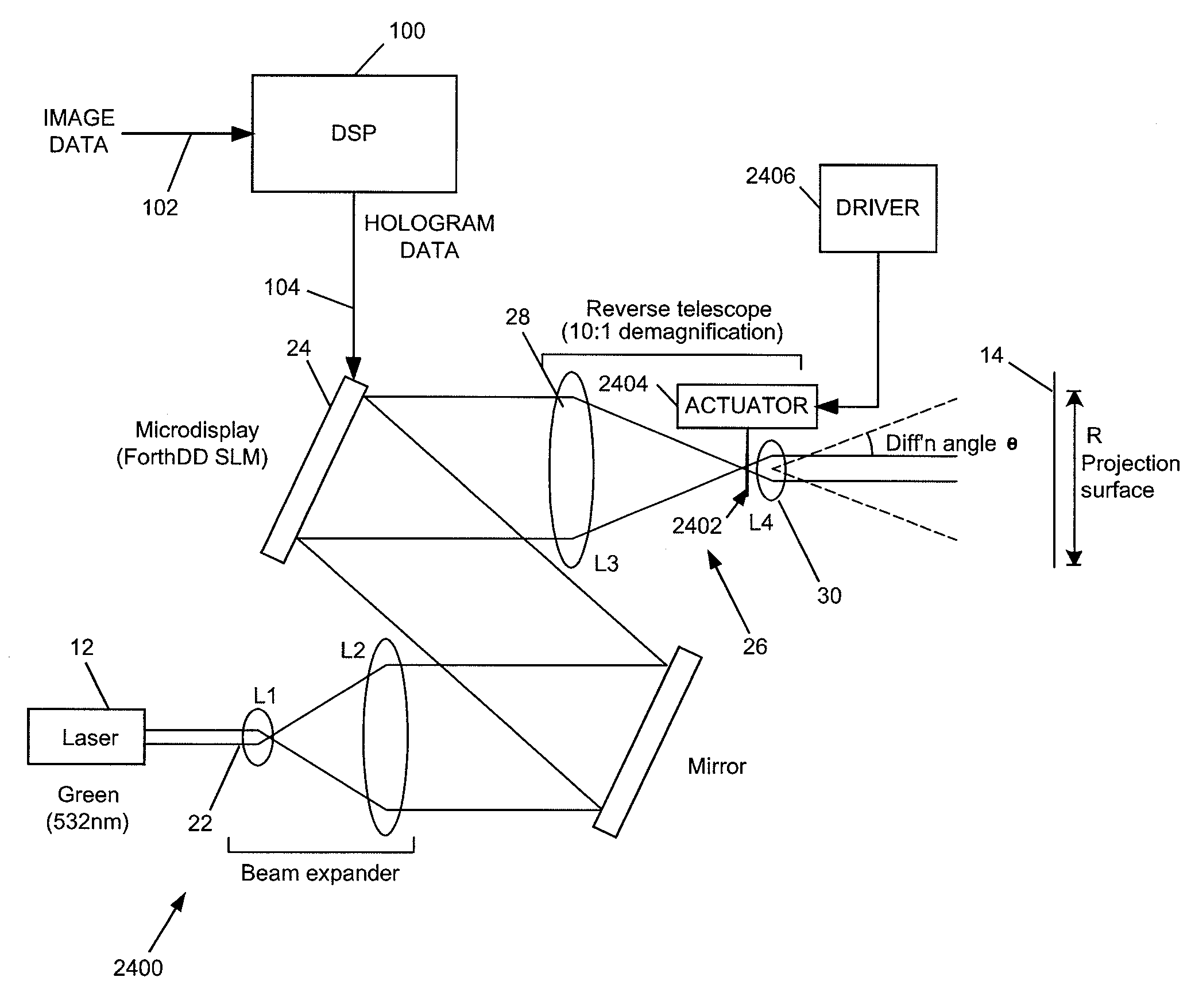
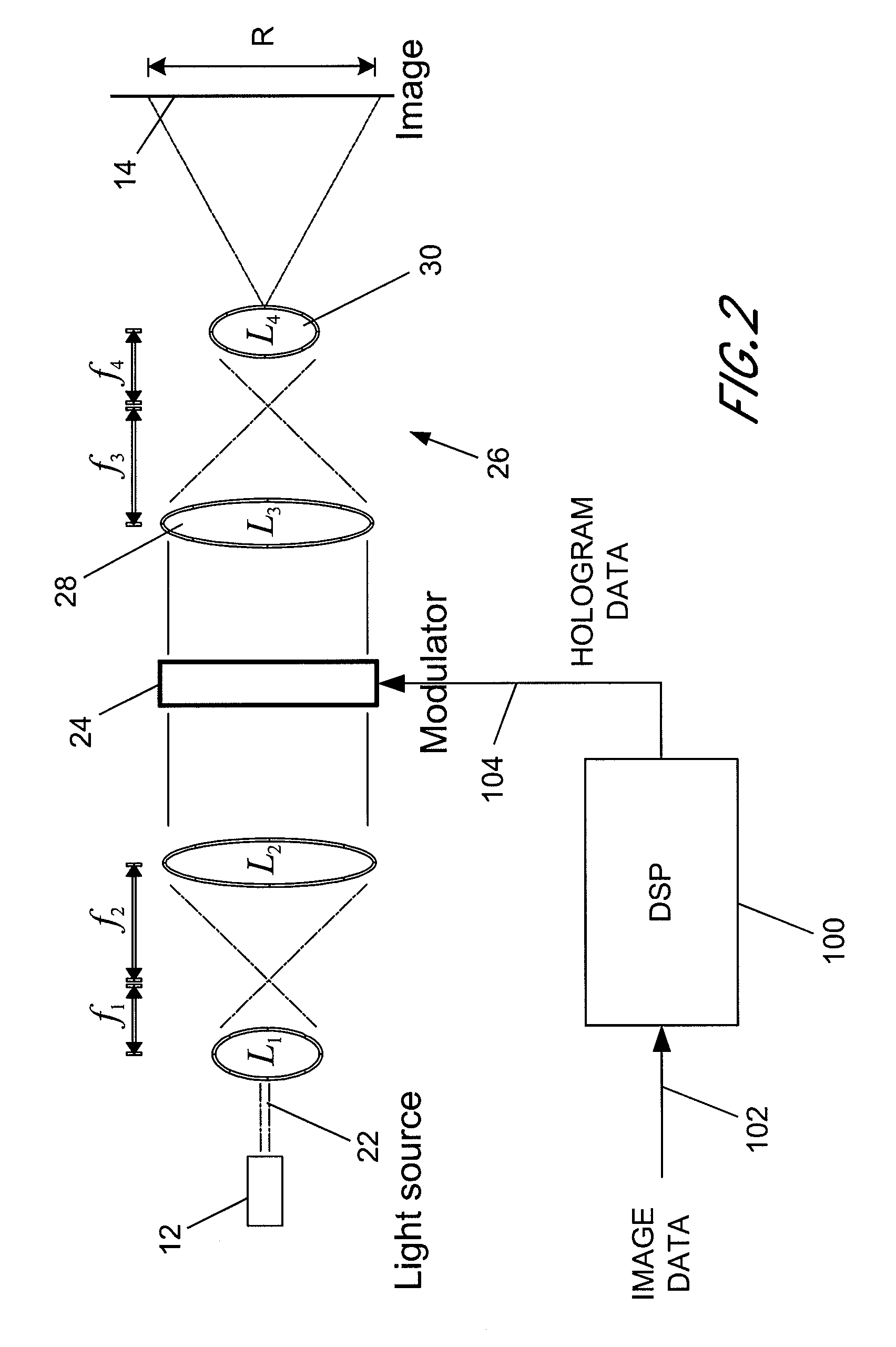
Holographic image display systems
InactiveUS20110002019A1Speckle reductionTelevision system detailsDiffusing elementsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
The invention relates to techniques for speckle reduction in holographic optical systems, in particular holographic image display systems. We describe a holographic image display system for displaying an image holographically on a display surface, the system including: a spatial light modulator (SLM) to display a hologram; a light source to illuminate said displayed hologram; projection optics to project light from said illuminated displayed hologram onto said display surface to form a holographically generated two-dimensional image, said projection optics being configured to form, at an intermediate image surface, an intermediate two-dimensional image corresponding to said holographically generated image; a diffuser located at said intermediate image surface; and an actuator mechanically coupled to said diffuser to, in operation, move said diffuser to randomise phases over pixels of said intermediate image to reduce speckle in an image displayed by the system.
Owner:LIGHT BLUE OPTICS
Apparatus for beam homogenization and speckle reduction
InactiveUS6895149B1Quality improvementWash out unwanted variationMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansPhase variationFiber bundle
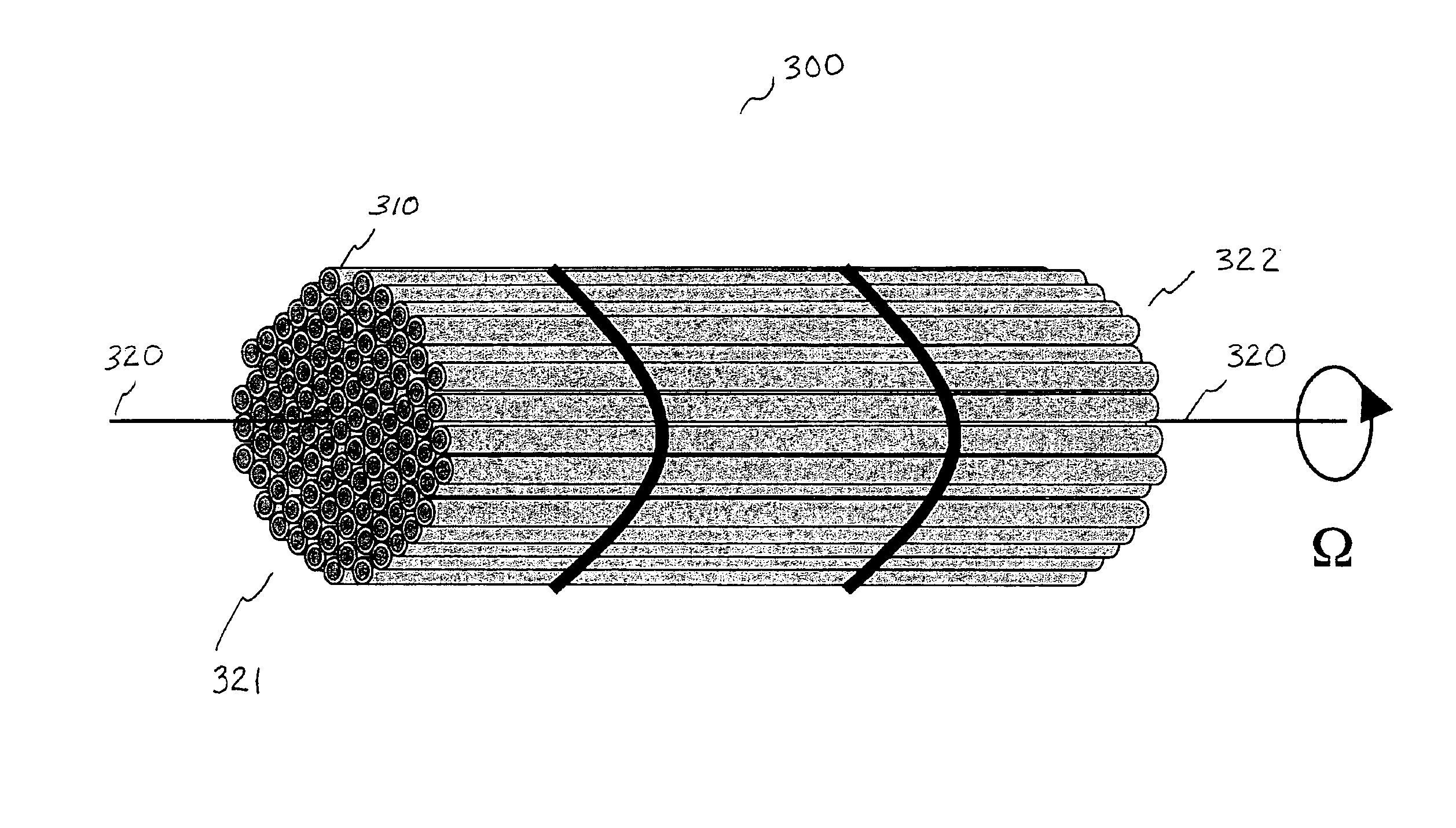
This invention greatly improves the quality of images obtained using optical systems illuminated by coherent light. It does so by removing the undesirable psuedo-random variations in the final image due to interference speckle and inhomogeneities in the spatial intensity distribution of the light source. A bundle of light-guiding fibers is interposed between the illumination source and the imaging system. Non-uniform propagation within the fiber bundle creates a psuedo-random phase variation across the illumination beam, which gives rise to a dynamic interference speckle pattern superimposed upon the desired image acquired by the optical system. Rotating the fiber bundle around the axis of propagation, whilst simultaneously integrating the output of the photosensitive detector over a period of time, substantially removes variations due to source inhomogeneities and coherent interference.
Owner:JACOB JAMES JEFFERY +2
Speckle reduction method and apparatus
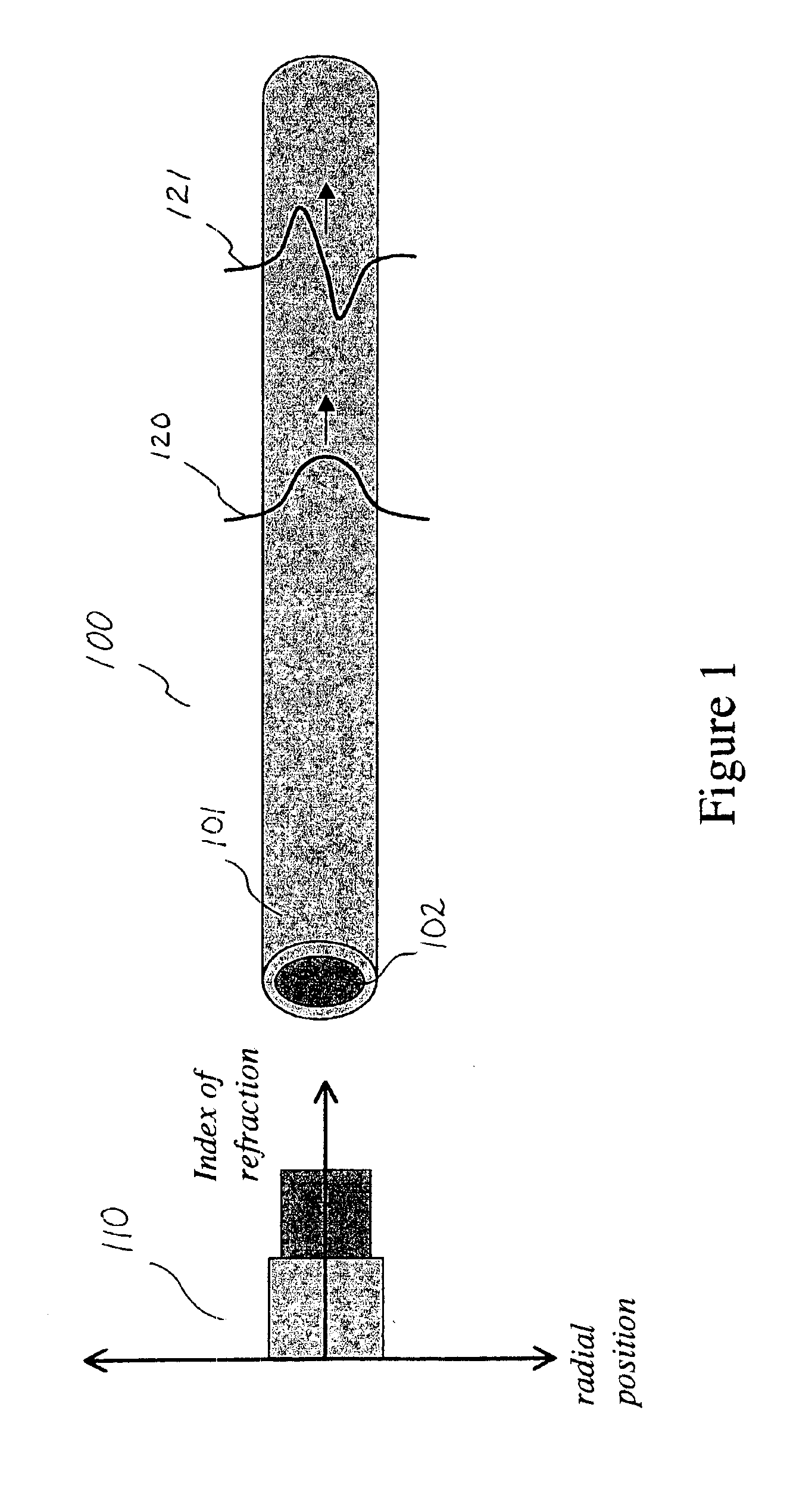
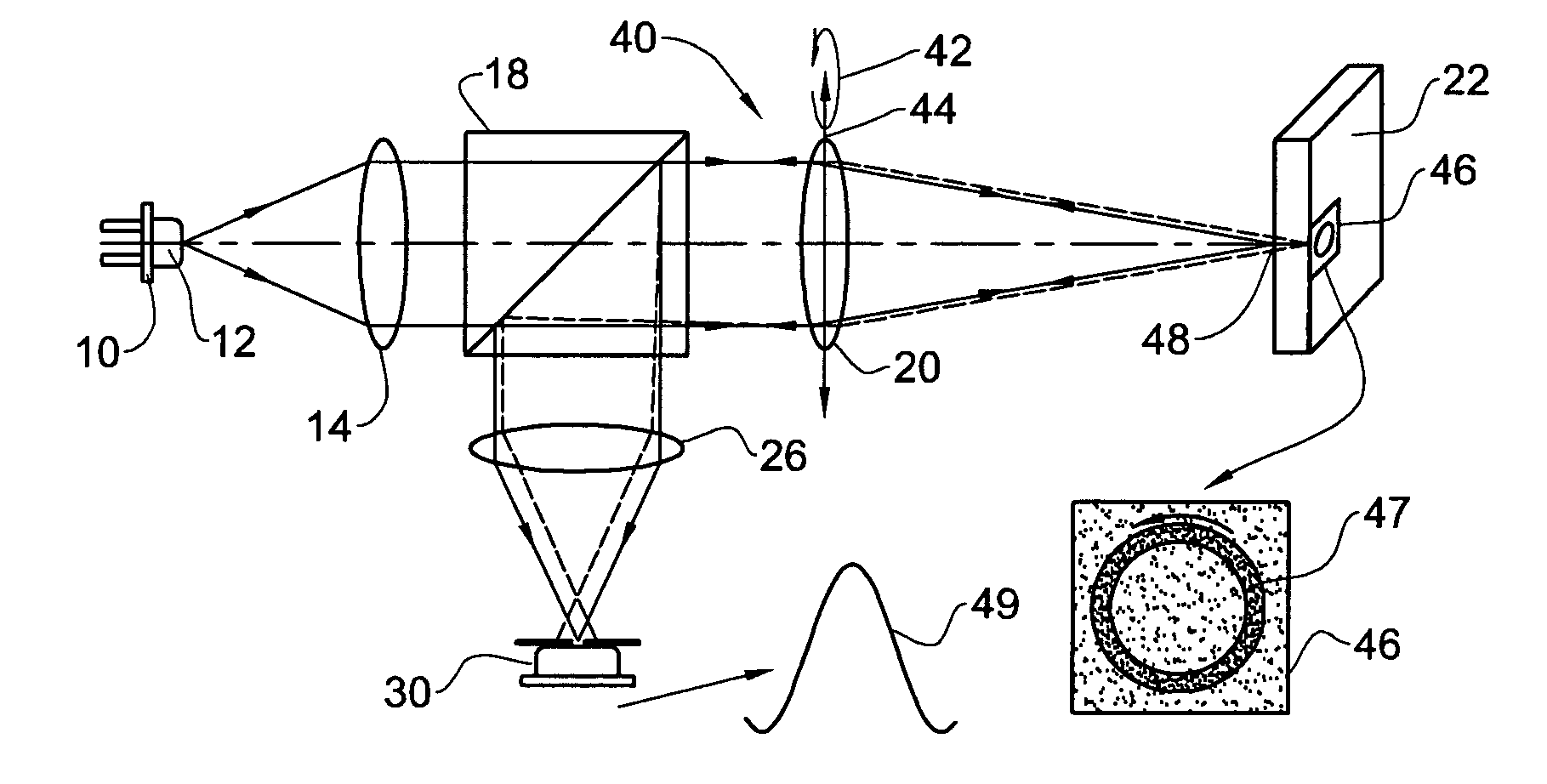
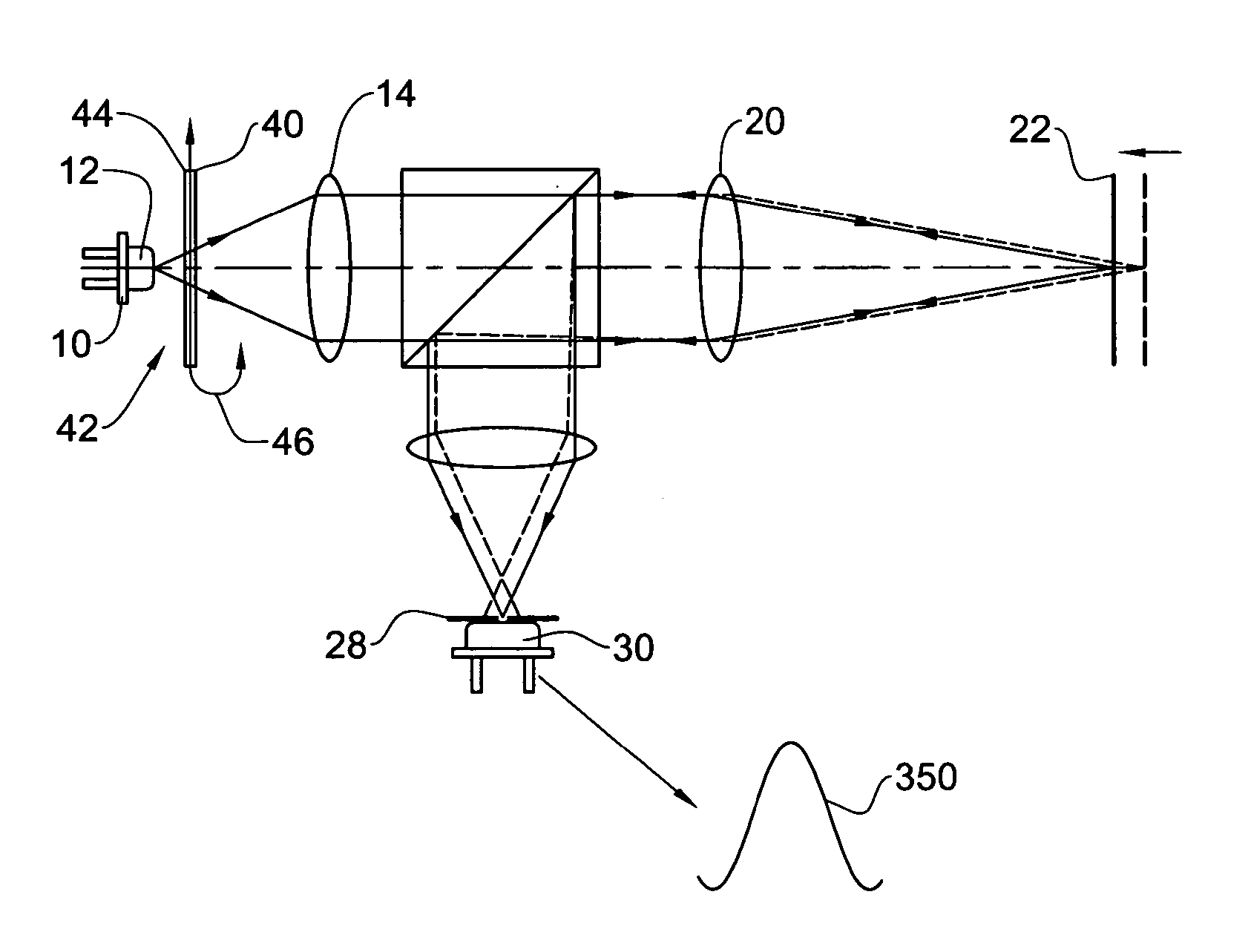
An apparatus adapted for confocal imaging of a non-flat specimen comprising a coherent light source for producing a light beam, imaging optics adapted to focus the light beam into at least one spot on a surface of a specimen, and a detector adapted to receive and detect light reflected from the specimen surface. The imaging optics comprise at least one optical component located so that the light reflected from the specimen surface passes therethrough on its way to the detector. The optical component is movable so as to move the at least one spot, within a range of movement, to a number of distinct locations in a plane perpendicular to the apparatus' optical axis, within the detector's integration time.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
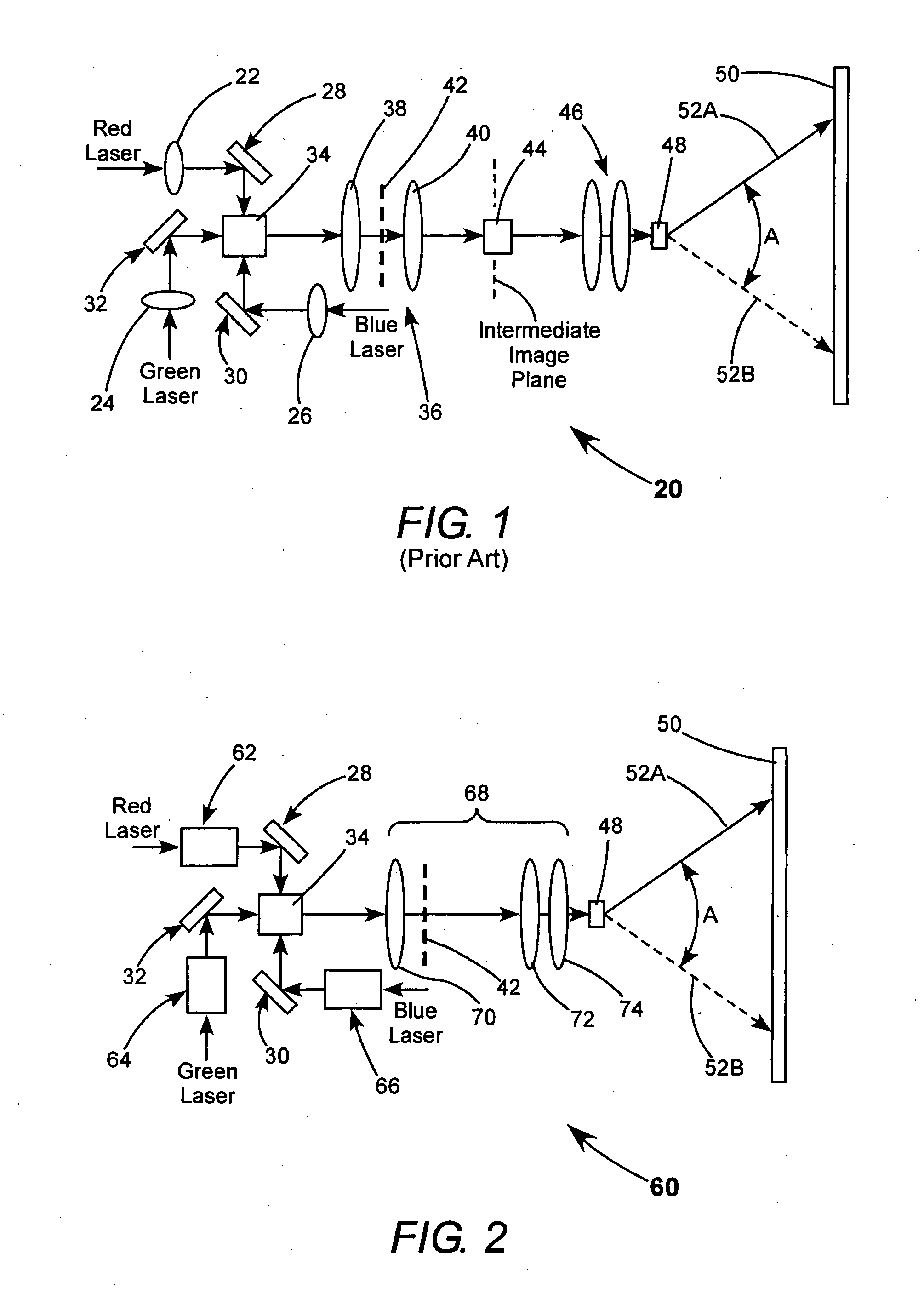
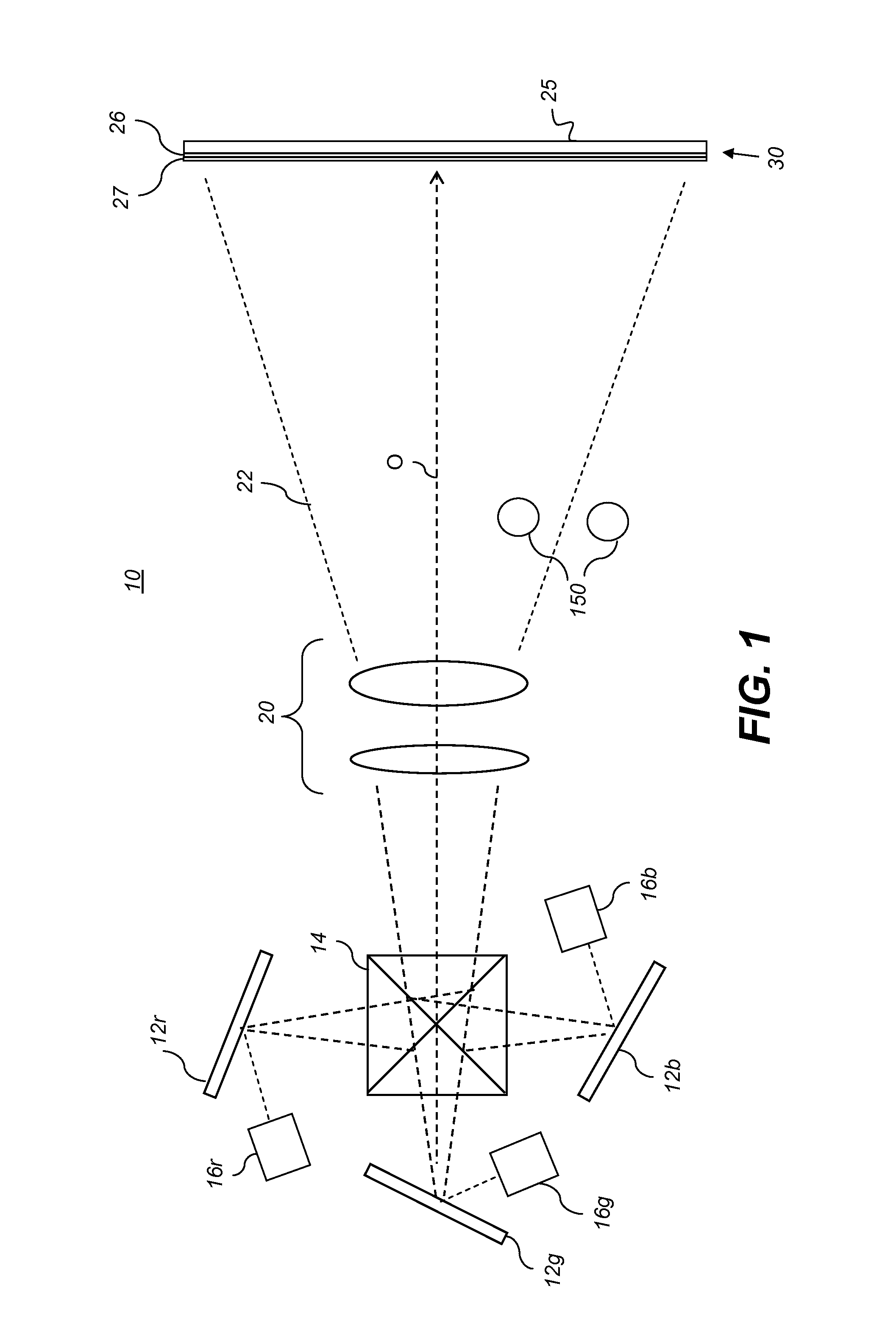
Speckle reduction in laser illuminated projection displays having a one-dimensional spatial light modulator
A projection display including a one-dimensional light modulator includes an optical arrangement for projecting light from a laser onto the modulator in the form of a line of light. Light from the laser is divided to create in effect a two-dimensional array of mutually incoherent light sources. Light from one axis of the array is projected onto the modulator to form the length of the line of light and light from the other axis of the array is projected onto the modulator to form the width of the line of light. Division of the light is accomplished without the use of any moving component.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Speckle reduction in laser-projector images
InactiveUS20080212034A1Reduce appearance problemsSpeckle reductionProjectorsMountingsSpatial light modulatorSpecular reflection
A laser projector having a configurable spatial light modulator (SLM) adapted to display various spatial modulation patterns and redirect illumination from a laser to form an image on the viewing screen. The laser projector drives the SLM to change spatial modulation patterns at a rate that causes the corresponding sequence of projected images to fuse to mitigate appearance of speckle in the resulting fused image. The SLM can be designed to redirect the illumination using either diffraction or specular reflection of light from the displayed spatial modulation pattern. In one embodiment, the SLM is a MEMS device having an array of individually addressable mirrors supported over a substrate and adapted to move (e.g., translate and / or rotate) with respect to the substrate.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Speckle reduction using screen vibration techniques and apparatus
Disclosed herein are systems and related methods for reducing speckle on display screen. More specifically, screen vibration is used to reduce speckle, and in accordance with the disclosed principles, the vibration may be achieved by using wave-based actuation (e.g., acoustic or electromagnetic waves) to vibrate the screen. In an exemplary embodiment, a speckle reducing system may comprise at least one actuating element located proximate to, but not in physical contact with, a display screen. In addition, the at least one actuating element may be configured to generate waves directed towards the display screen. When the waves impact the display screen, the waves impart vibration to the display screen.
Owner:REAID INC
Speckle reduction in laser illuminated projection displays having a one-dimensional spatial light modulator
A projection display including a one-dimensional light modulator includes an optical arrangement for projecting light from a laser onto the modulator in the form of a line of light. Light from the laser is divided to create in effect a two-dimensional array of mutually incoherent light sources. Light from one axis of the array is projected onto the modulator to form the length of the line of light and light from the other axis of the array is projected onto the modulator to form the width of the line of light. Division of the light is accomplished without the use of any moving component.
Owner:COHERENT INC
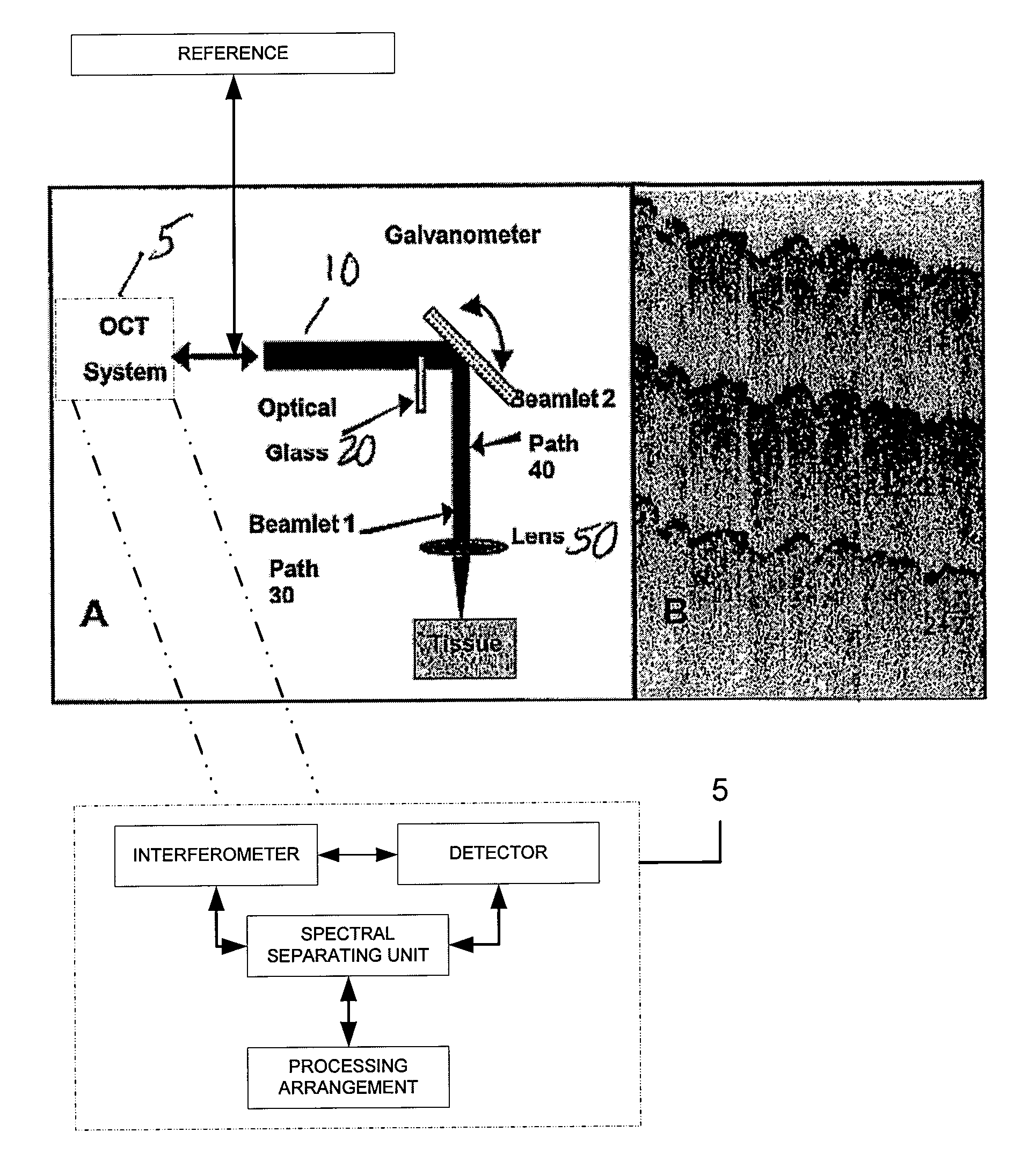
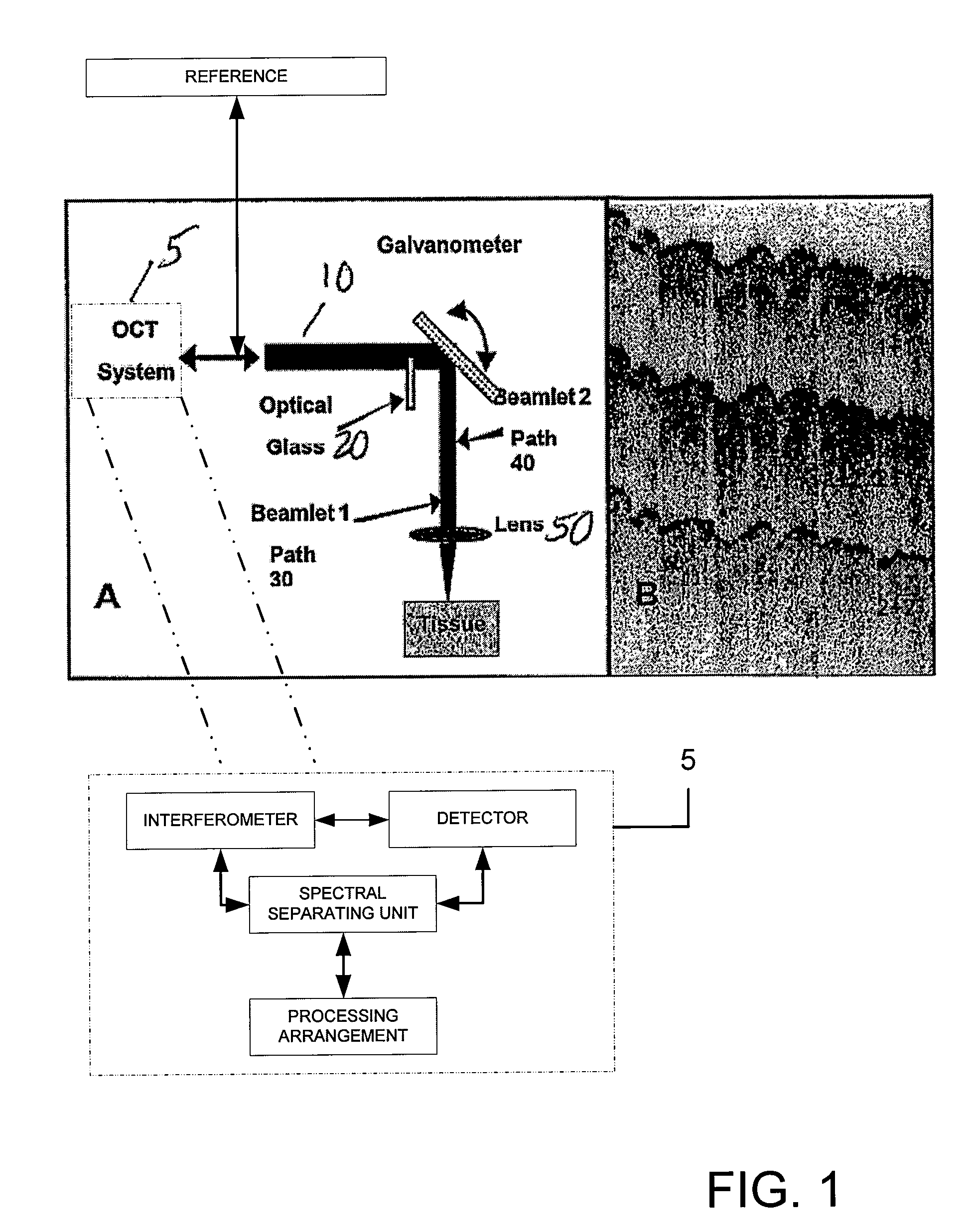
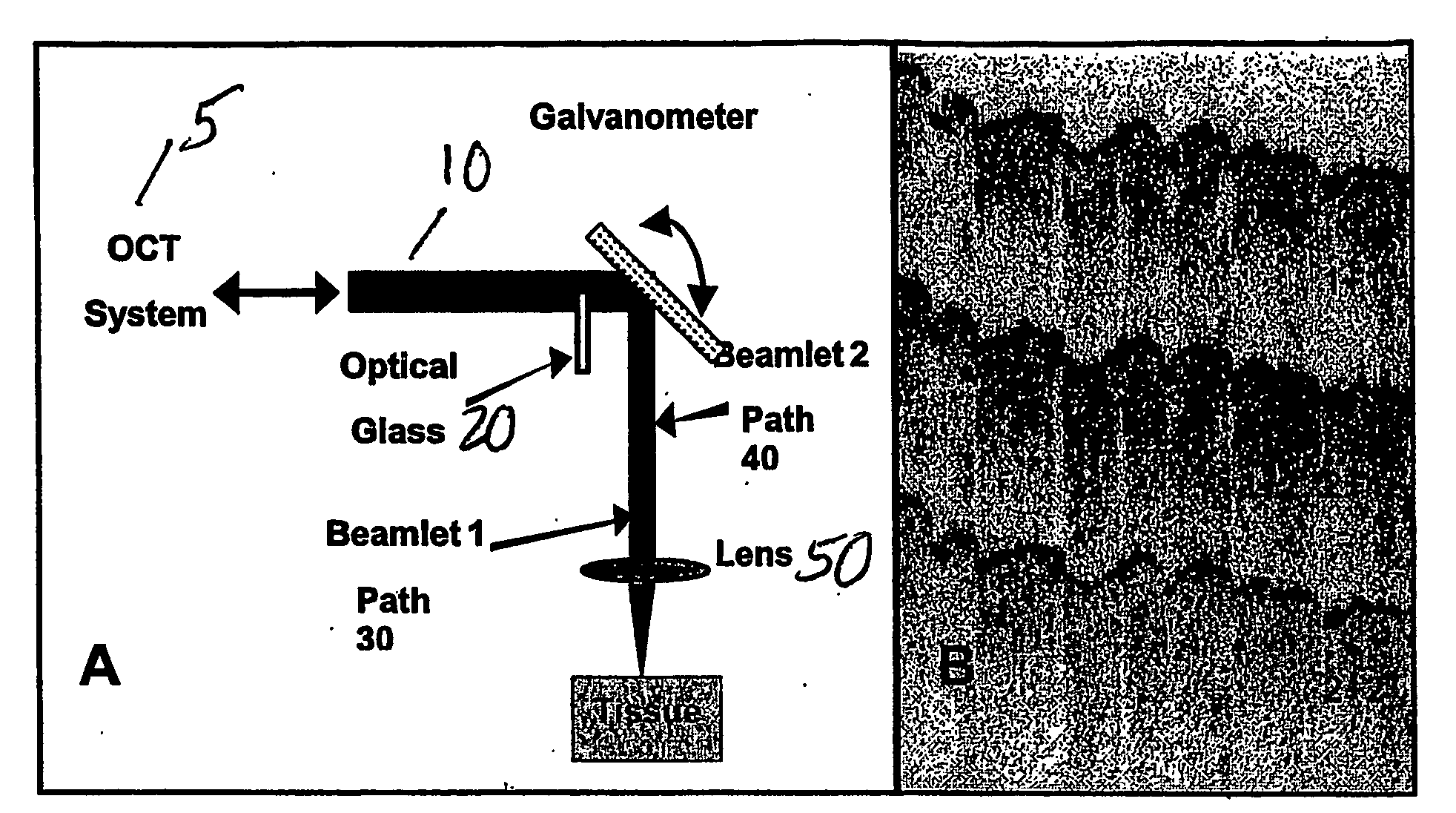
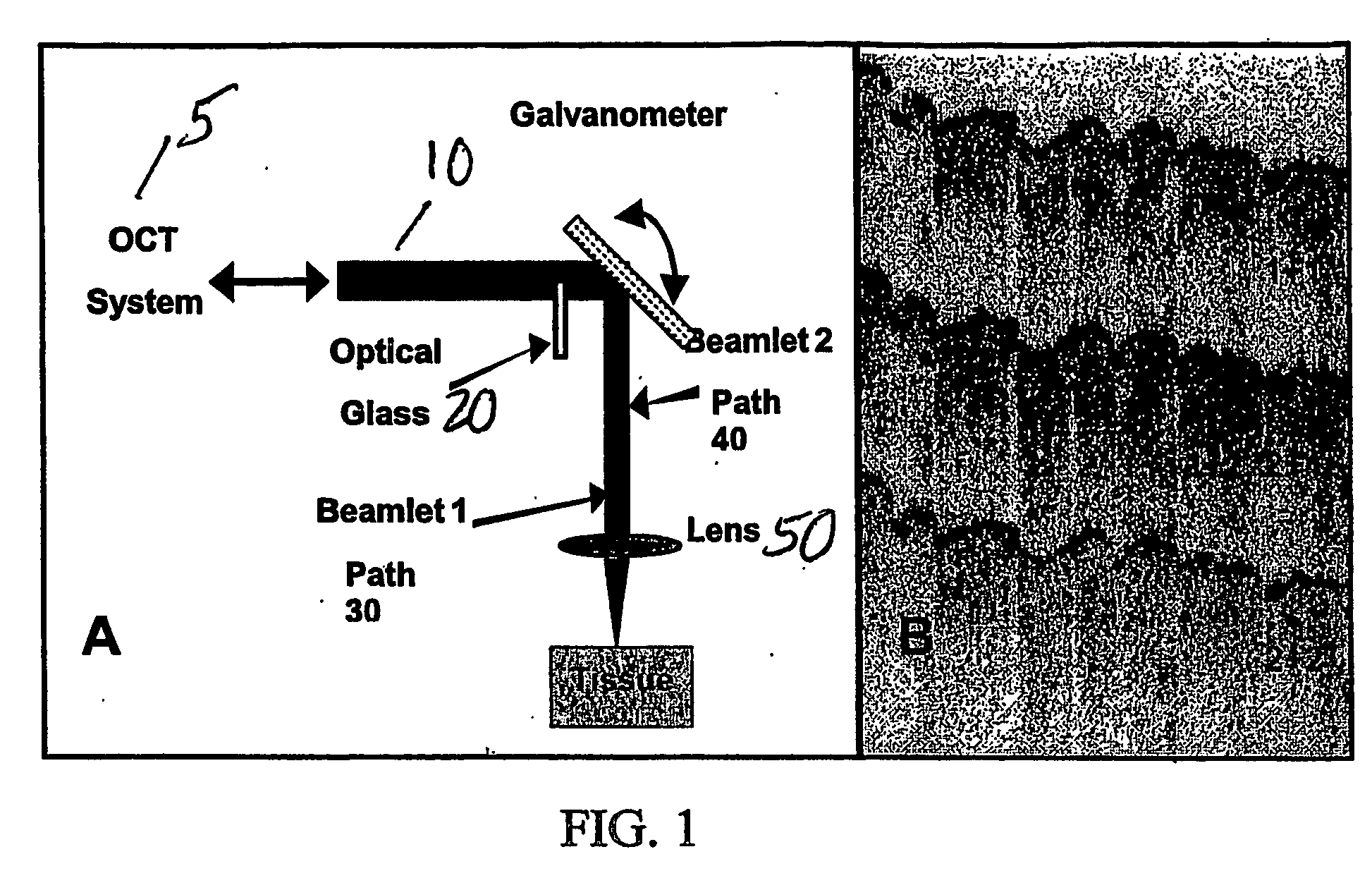
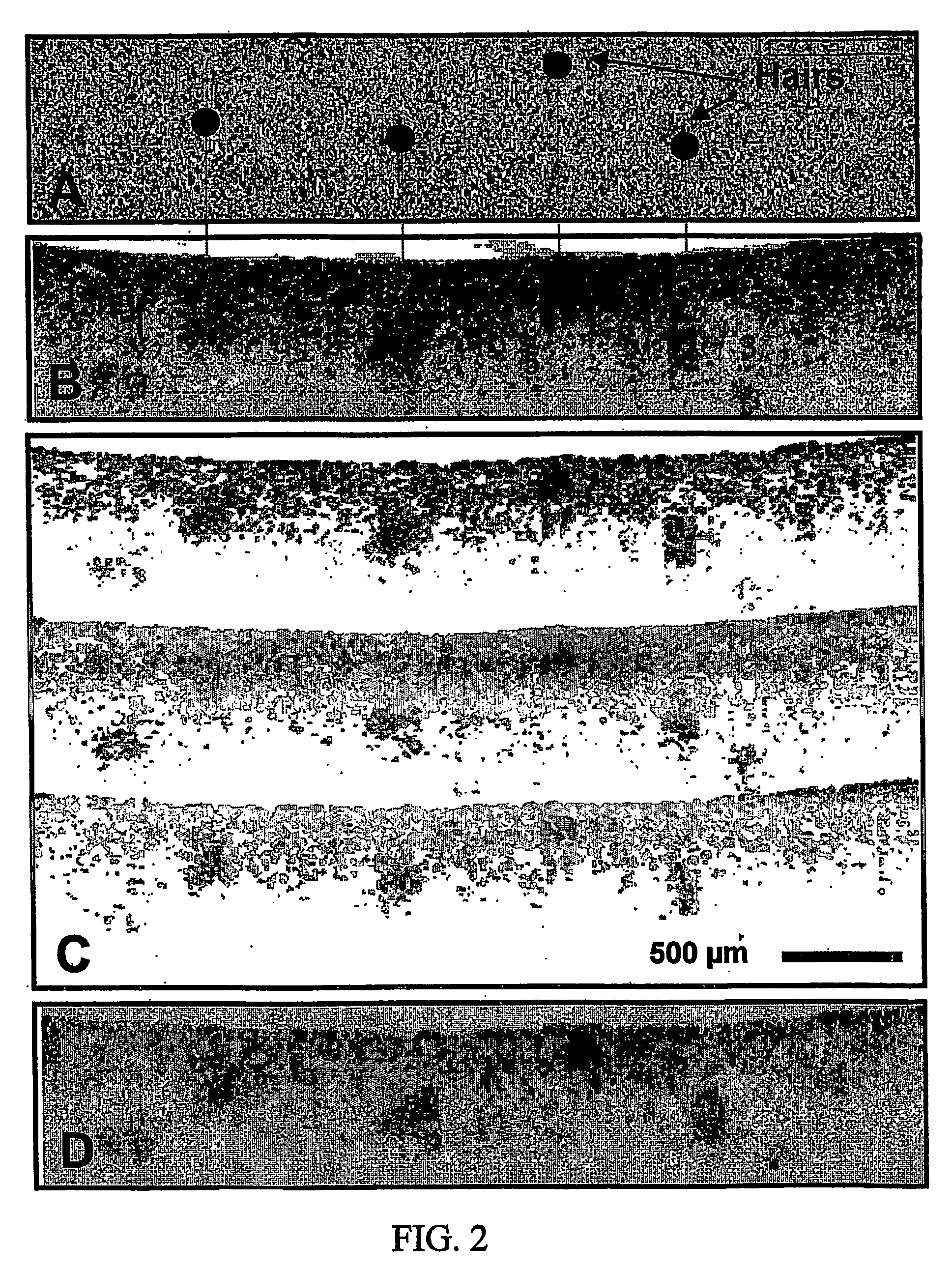
Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by path length encoded angular compounding
ActiveUS7567349B2Speckle reductionMinimal modificationOptical measurementsDiagnostics using lightDiseasePath length
Speckle, a factor reducing image quality in optical coherence tomography (“OCT”), can limit the ability to identify cellular structures that are important for the diagnosis of a variety of diseases. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention can facilitate an implementation of an angular compounding, angular compounding by path length encoding (“ACPE”) for reducing speckle in OCT images. By averaging images obtained at different incident angles, with each image encoded by path length, ACPE maintains high-speed image acquisition and implements minimal modifications to OCT probe optics. ACPE images obtained from tissue phantoms and human skin in vivo demonstrate a qualitative improvement over traditional OCT and an increased signal-to-noise ratio (“SNR”). Accordingly, exemplary embodiments of an apparatus probe catheter and method can be provided for irradiating a sample. In particular, an interferometer may forward forwarding an electromagnetic radiation. In addition, a sample arm may receive the electromagnetic radiation, and can include an arrangement which facilitates a production of at least two radiations from the electromagnetic radiation so as to irradiate the sample. Such exemplary arrangement can be configured to delay a first radiation of the at least two radiations with respect to a second radiation of the at least two radiations.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
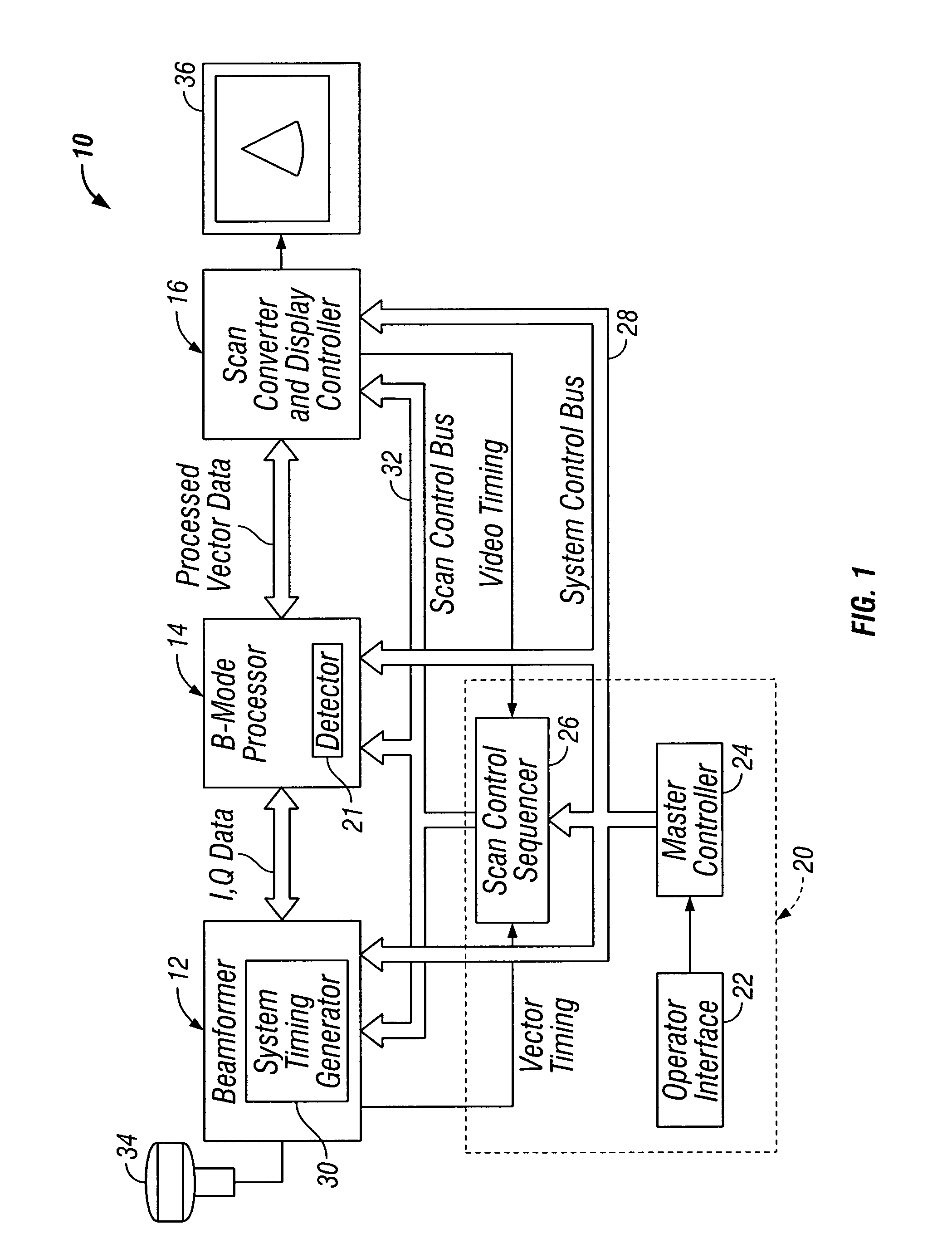
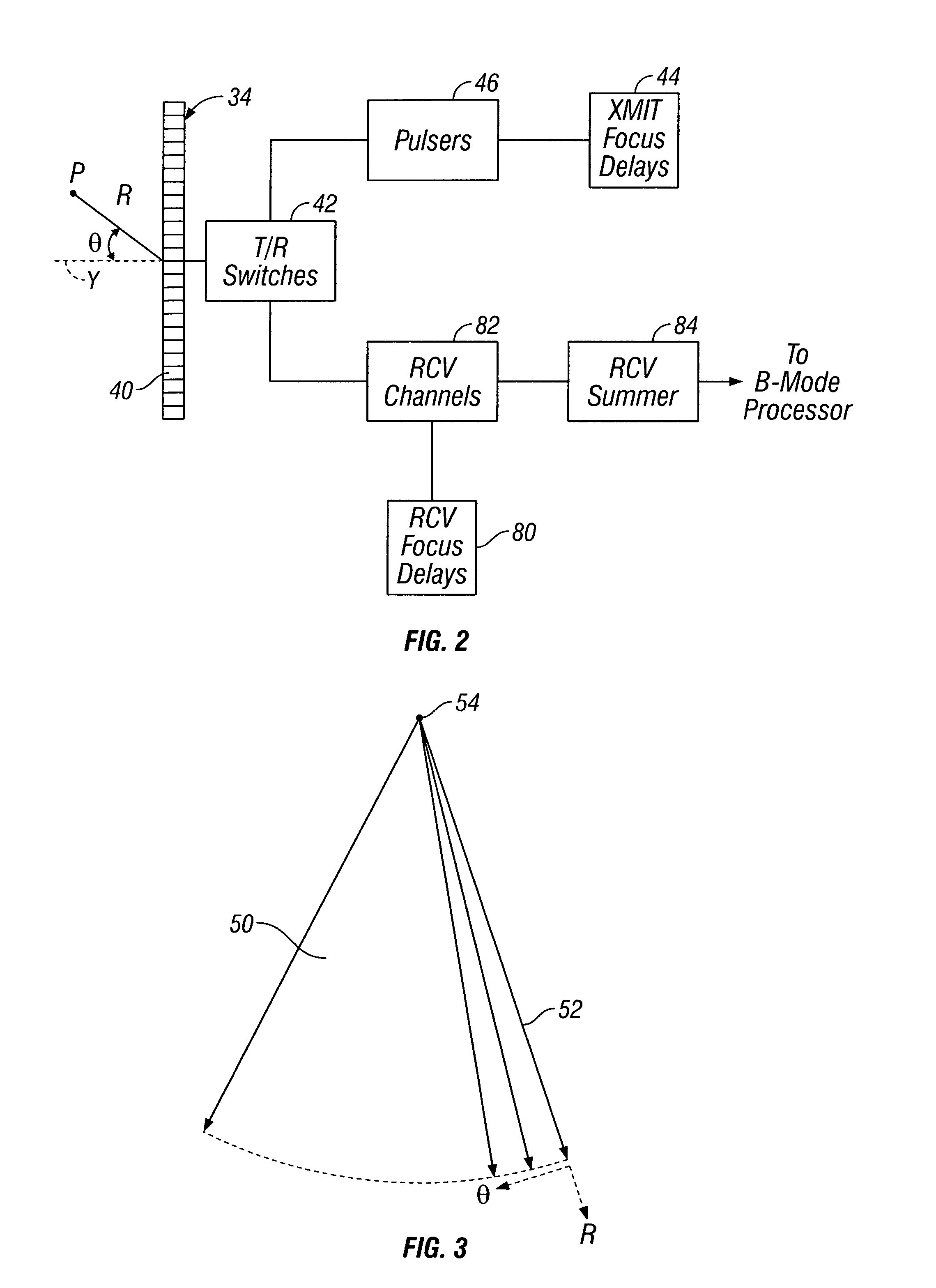
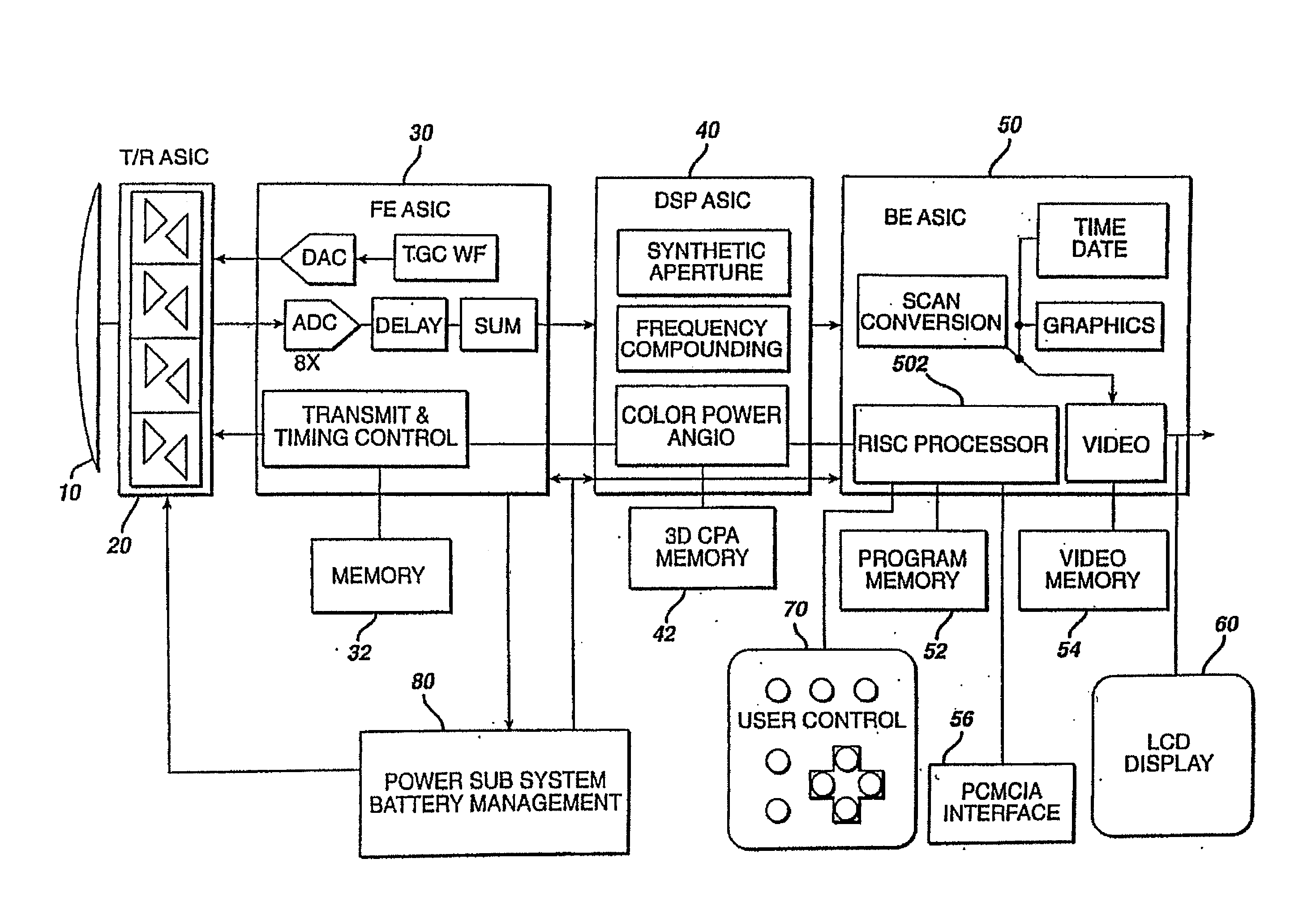
Ultrasonic signal processor for a hand held ultrasonic diagnostic instrument
InactiveUS7604596B2Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsDigital signal processingTransceiver
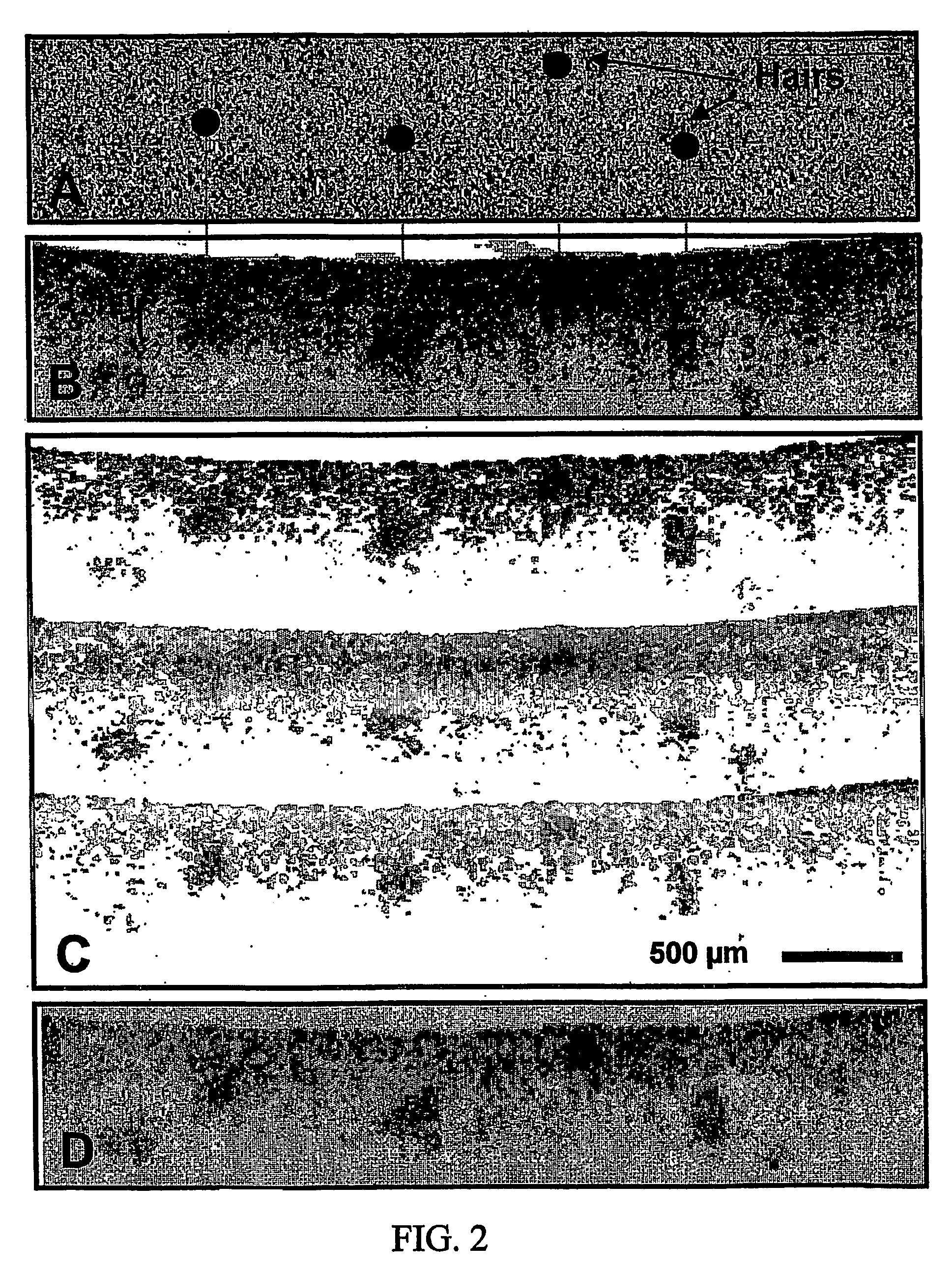
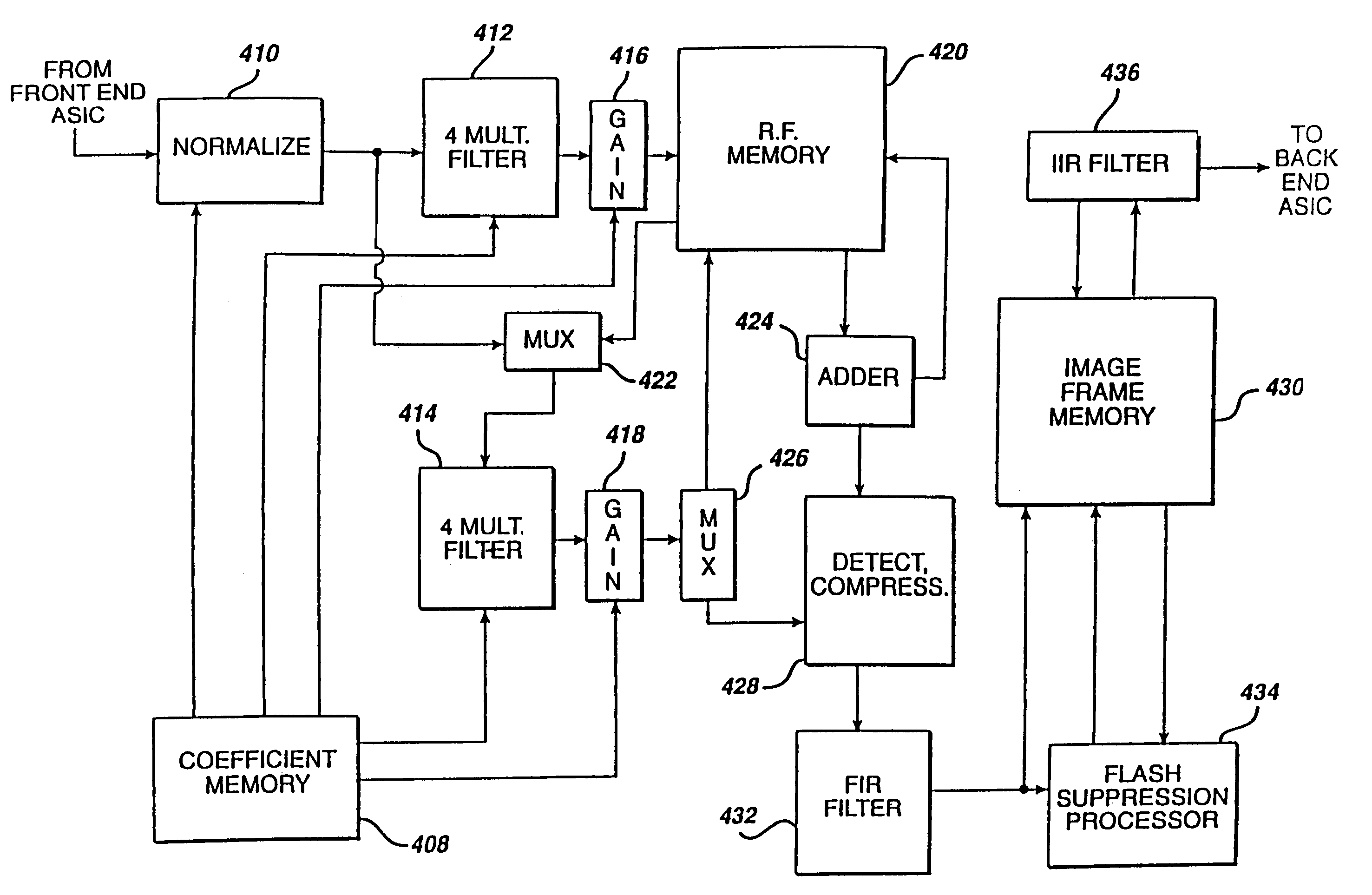
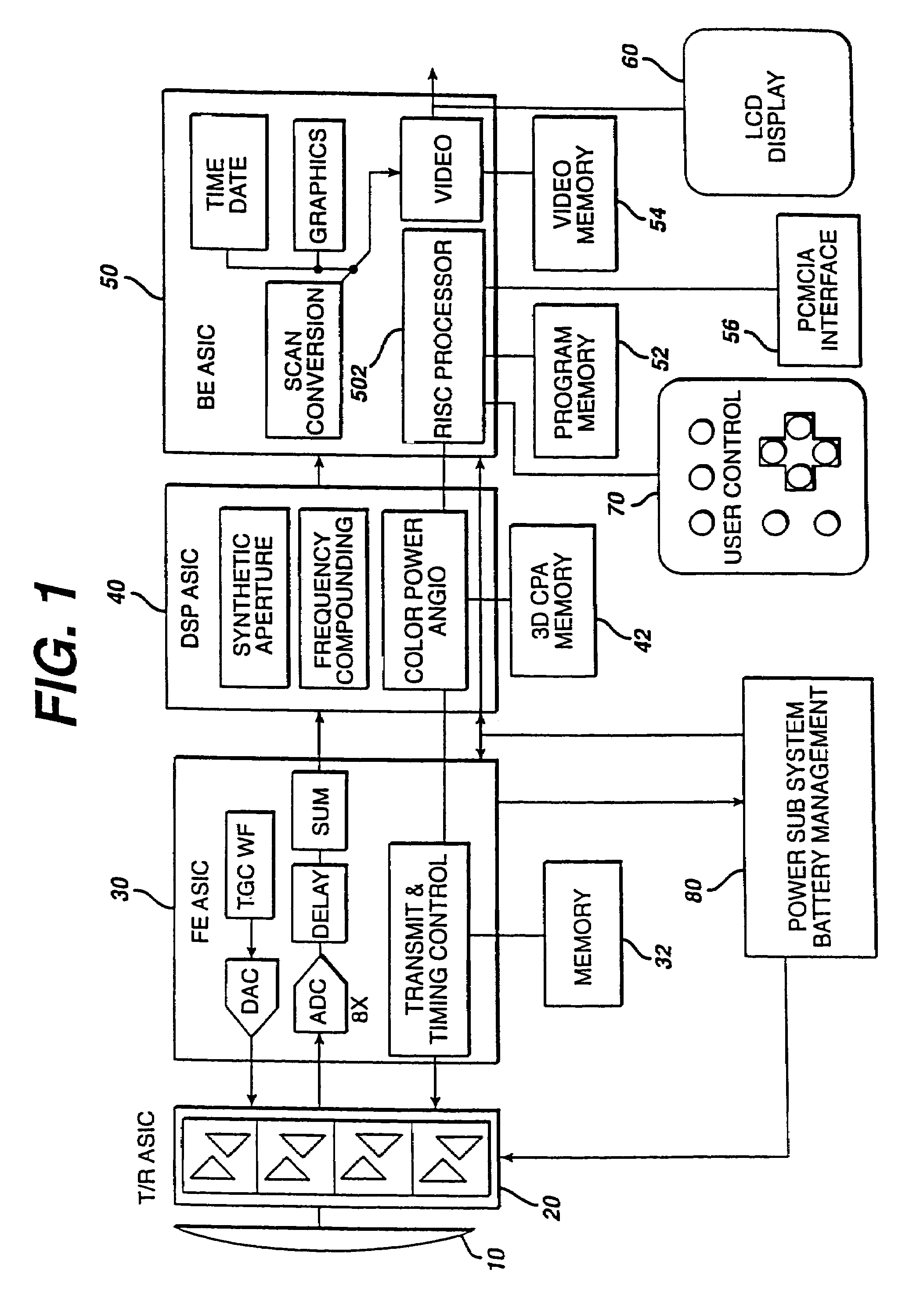
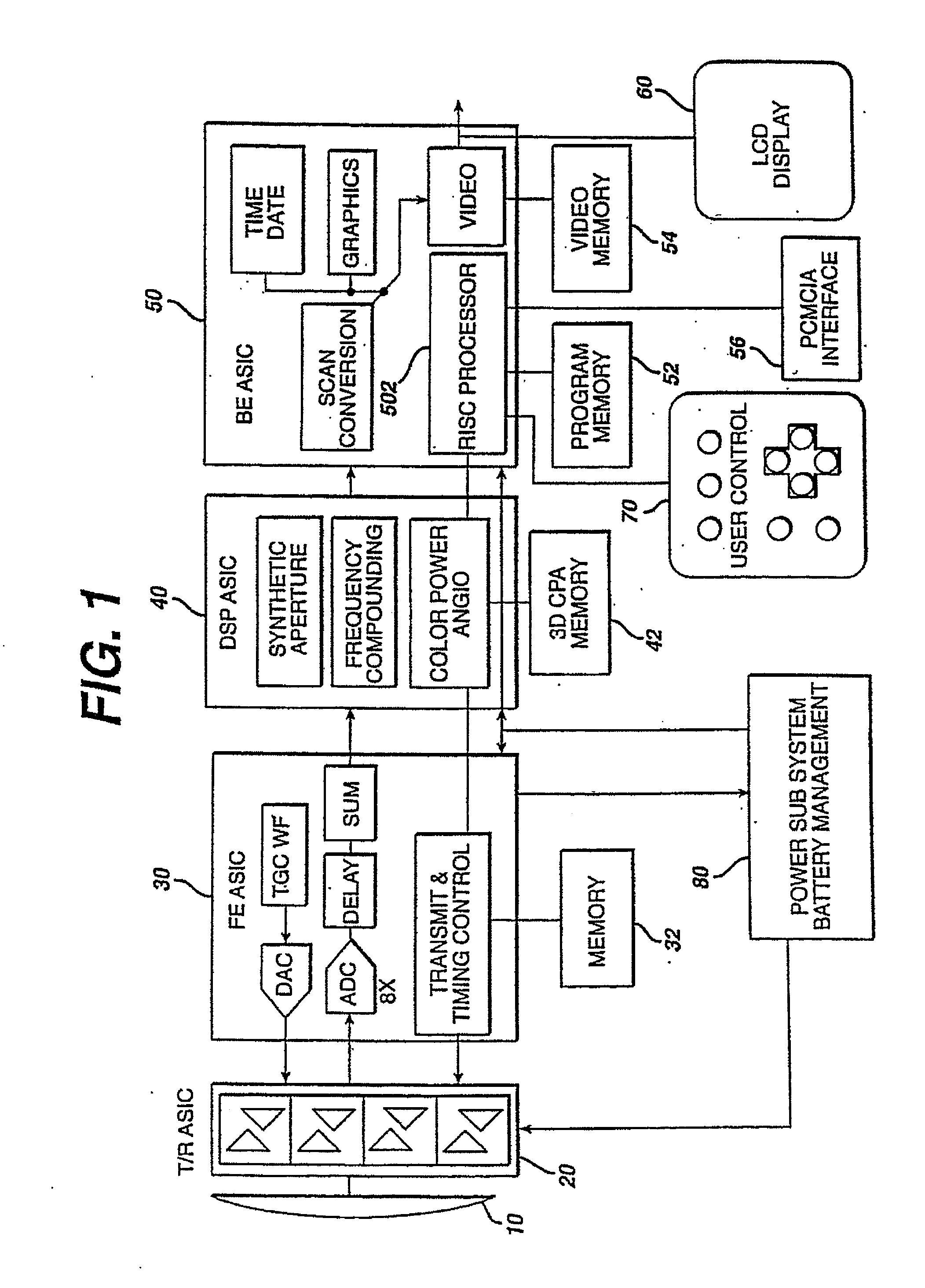
A hand held ultrasonic instrument is provided in a portable unit which performs both B mode and Doppler imaging. The instrument includes a transducer array mounted in a hand-held enclosure, with an integrated circuit transceiver connected to the elements of the array for the reception of echo signals. A digital signal processing circuit performs both B mode and Doppler signal processing such as filtering, detection and Doppler estimation, as well as advanced functions such as assembly of multiple zone focused scanlines, synthetic aperture formation, depth dependent filtering, speckle reduction, flash suppression, and frame averaging.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
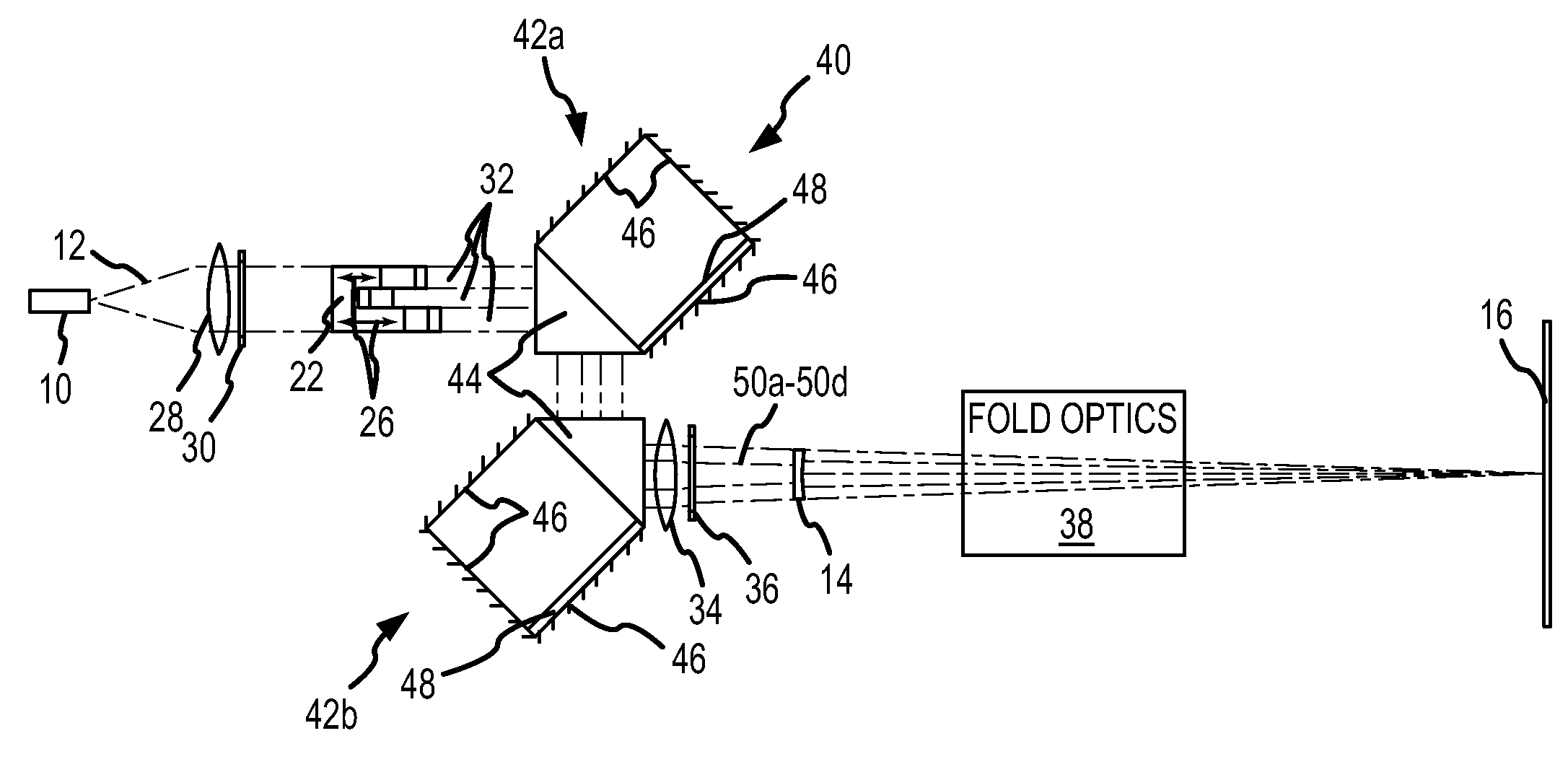
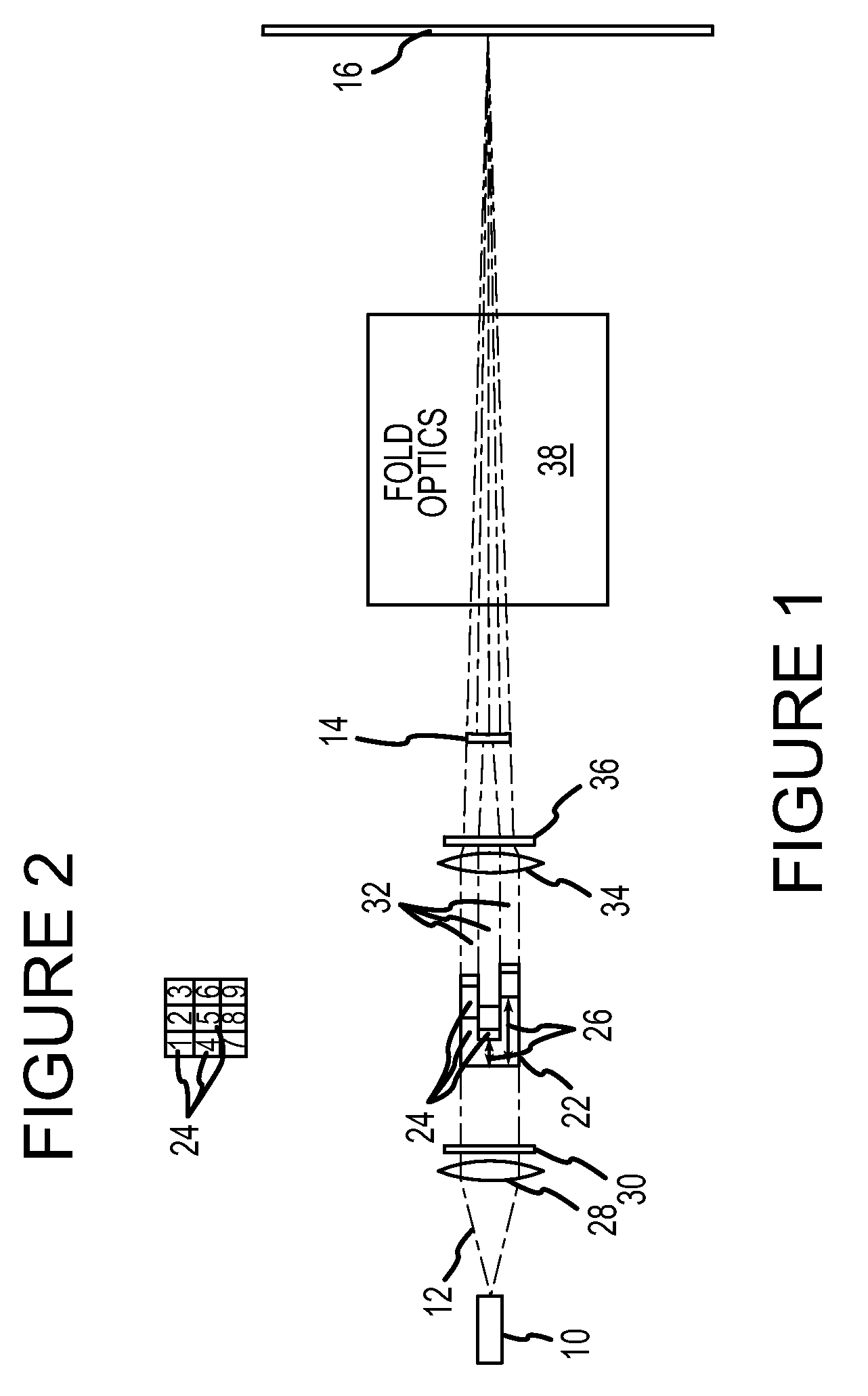
Apparatus and method for providing high intensity non-coherent light and for speckle reduction
ActiveUS7202466B2Non-electric lightingBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamHigh intensity
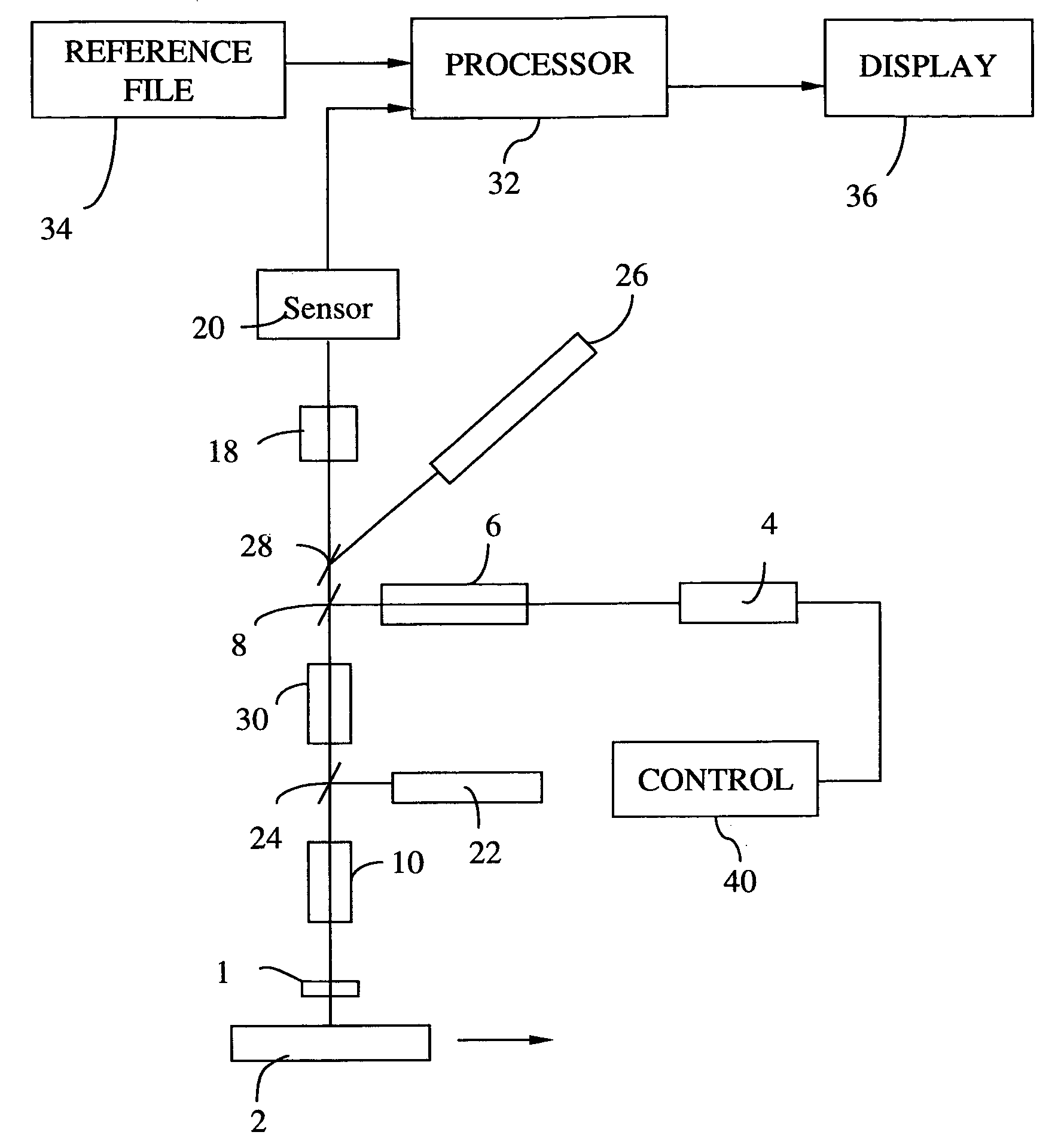
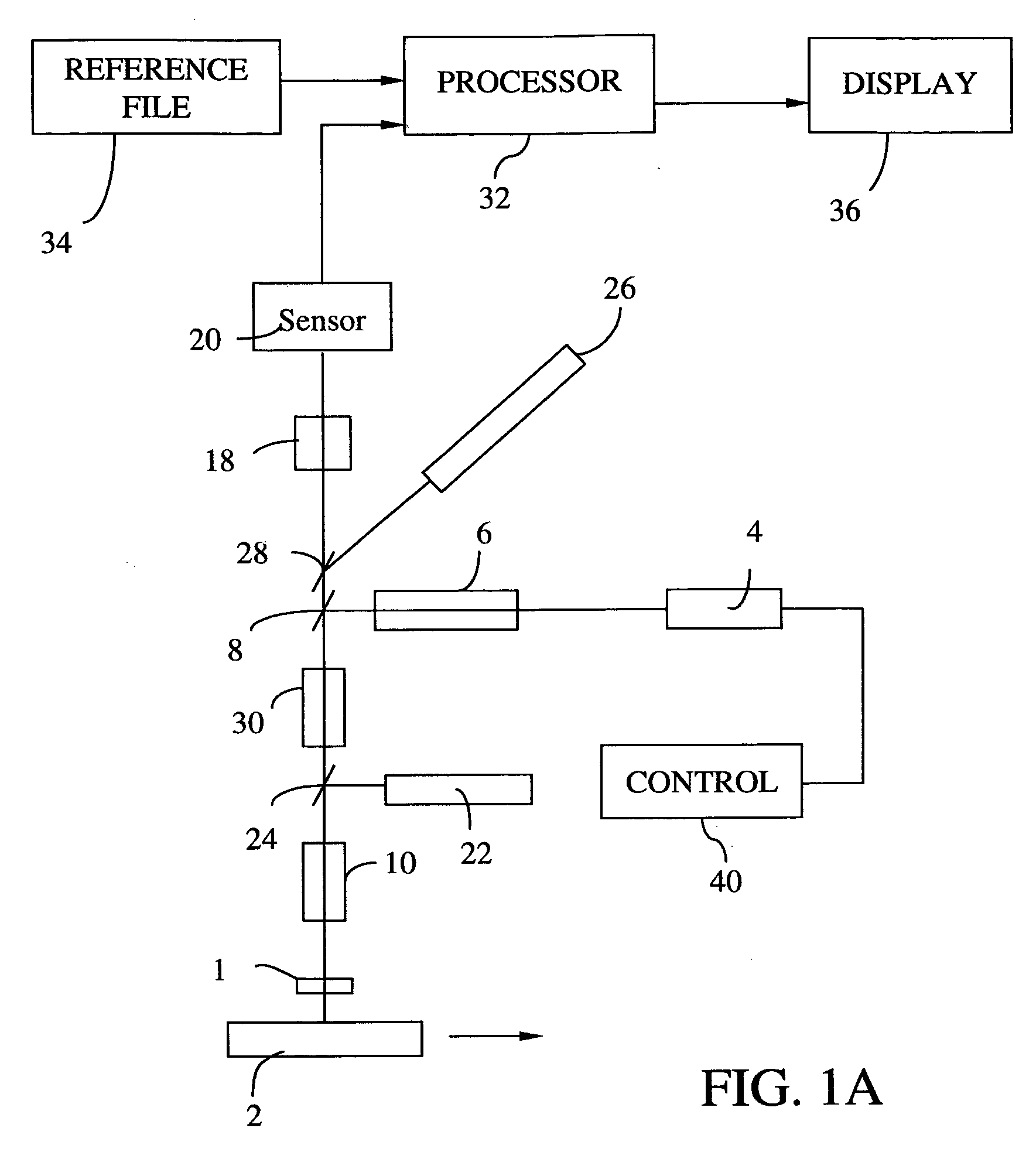
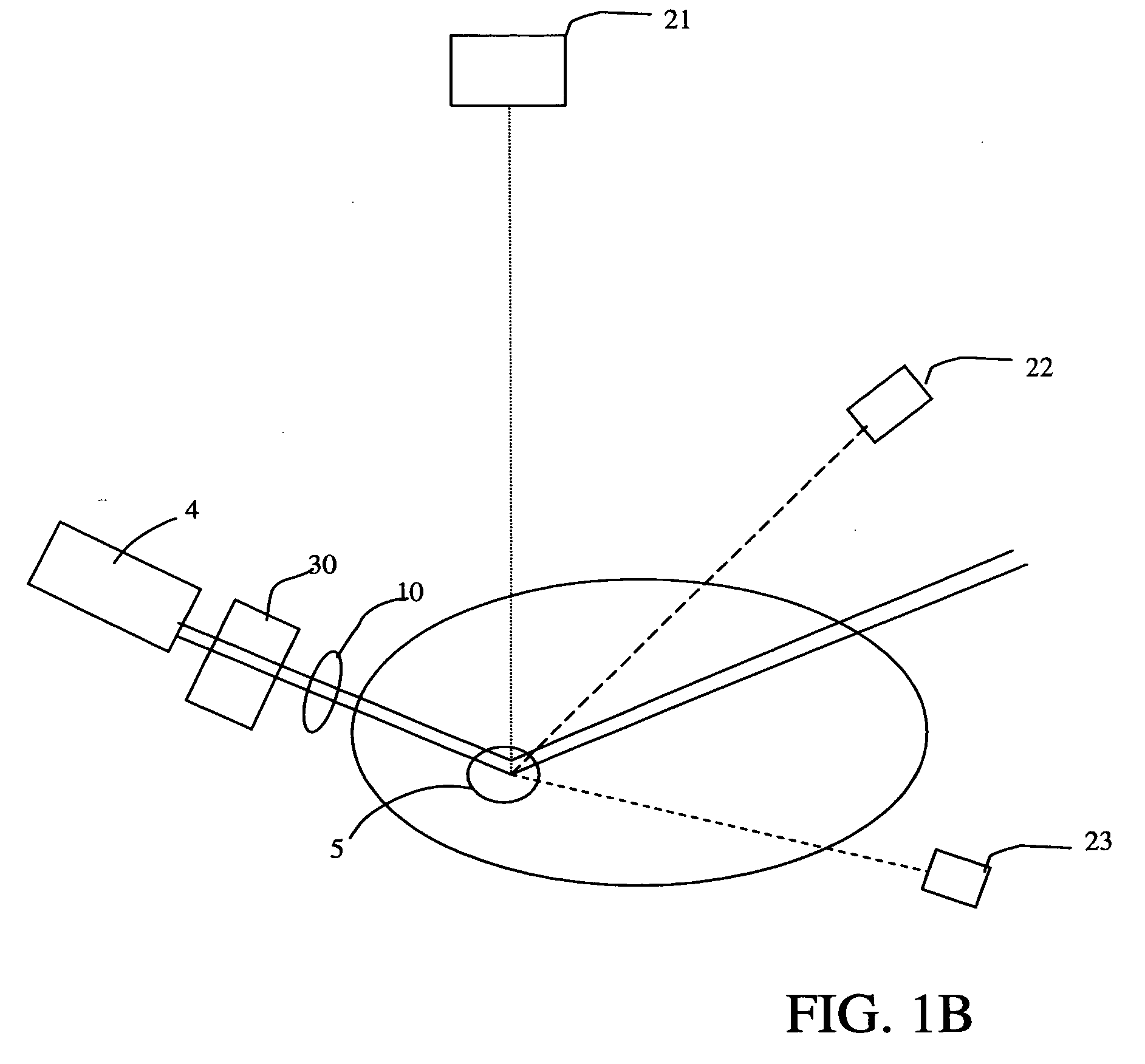
An apparatus adapted for confocal imaging of a non-flat specimen comprising a light source for producing a light beam, imaging optics adapted to focus the light beam into at least one spot on a surface of a specimen, and a detector adapted to receive and detect light reflected from the specimen surface. The light source comprises an optical system for converting a coherent beam into a plurality of beams, each of which is modified by a moving diffuser within a range of movement that is correlated to the detector's integration time.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Ultrasonic Signal Processor for a Hand Held Ultrasonic Diagnostic Instrument
InactiveUS20100121196A1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsDigital signal processingTransceiver
A hand held ultrasonic instrument is provided in a portable unit which performs both B mode and Doppler imaging. The instrument includes a transducer array mounted in a hand-held enclosure, with an integrated circuit transceiver connected to the elements of the array for the reception of echo signals. A digital signal processing circuit performs both B mode and Doppler signal processing such as filtering, detection and Doppler estimation, as well as advanced functions such as assembly of multiple zone focused scanlines, synthetic aperture formation, depth dependent filtering, speckle reduction, flash suppression, and frame averaging.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
Speckle reduction in display systems that employ coherent light sources
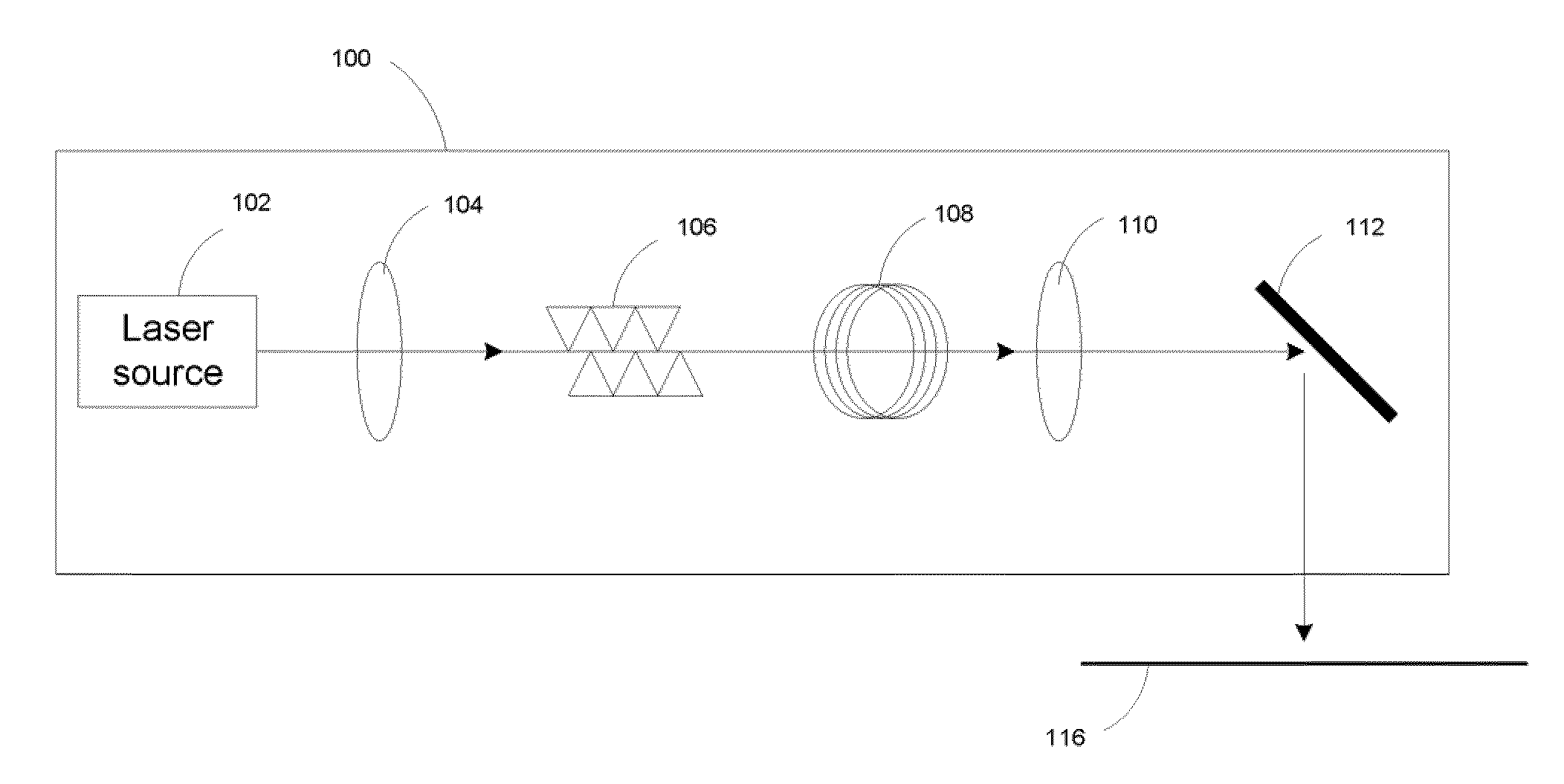
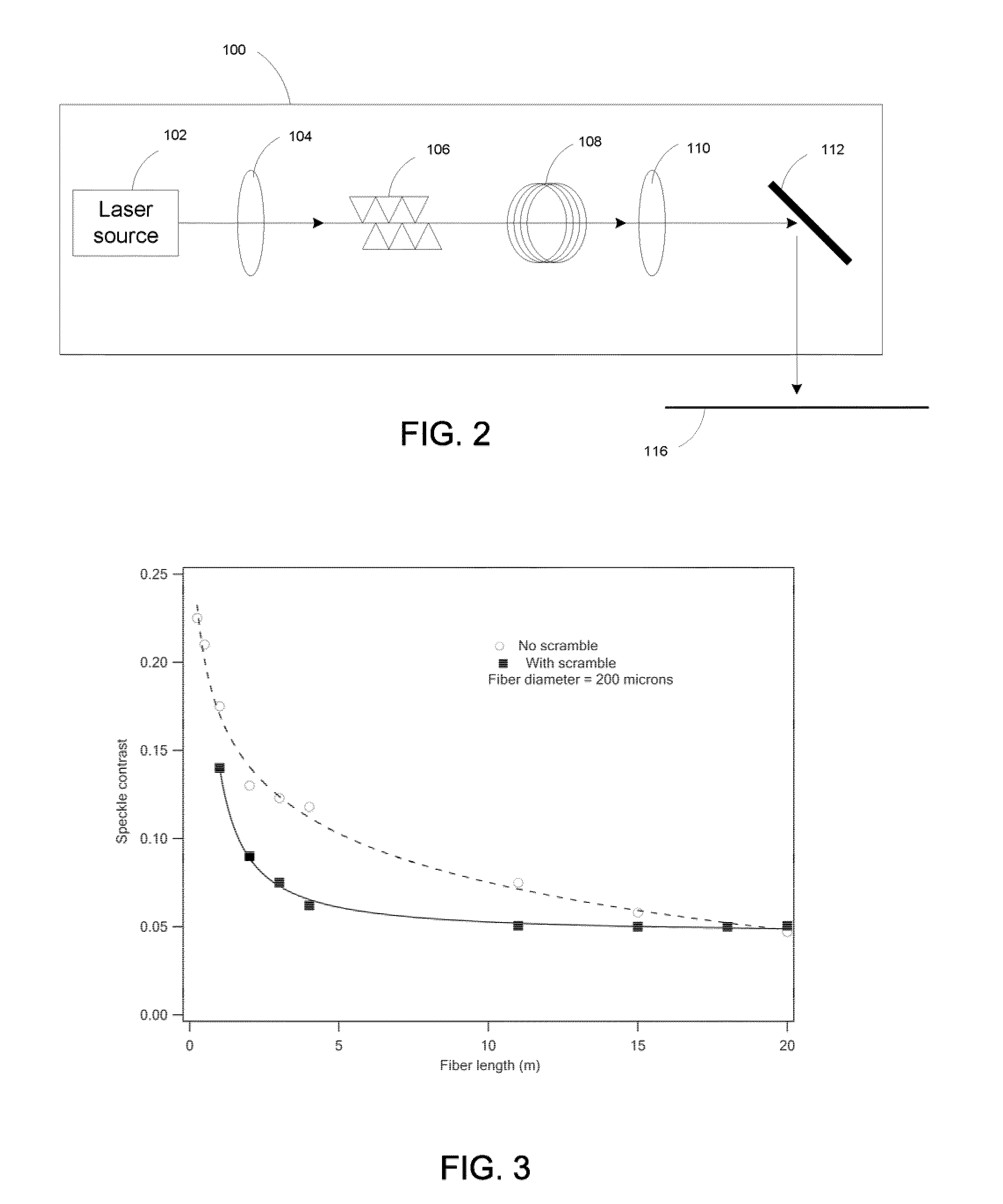
Speckle effect in display system is reduced by utilizing the instability of phase-coherent light and the transmission of the instable phase-coherent light through a multi-mode optical fiber with a suitable length.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Imaging engine employing planar light illumination and linear imaging
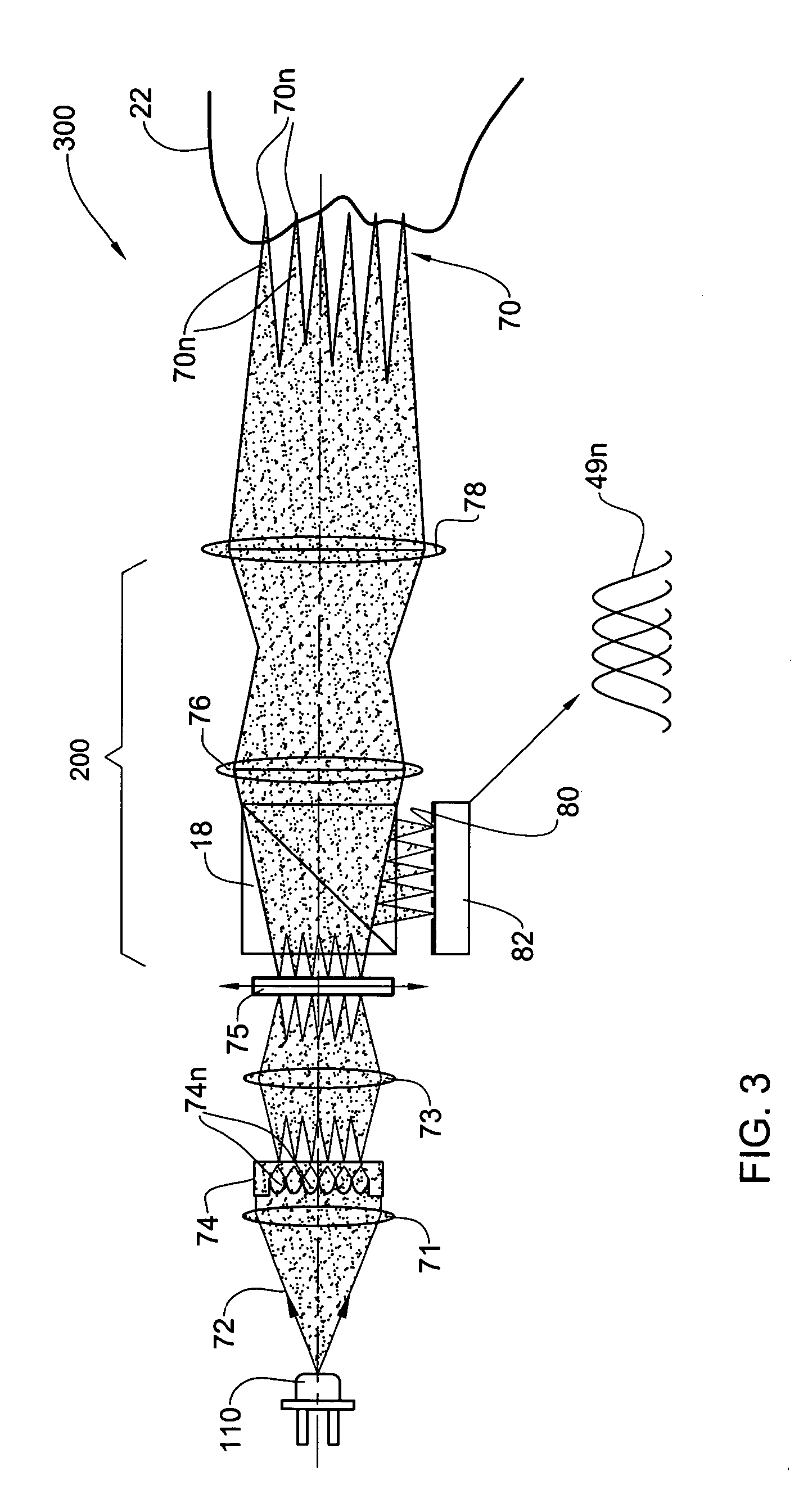
InactiveUS20030091244A1Low costReduce speckle noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesTime signalImage based
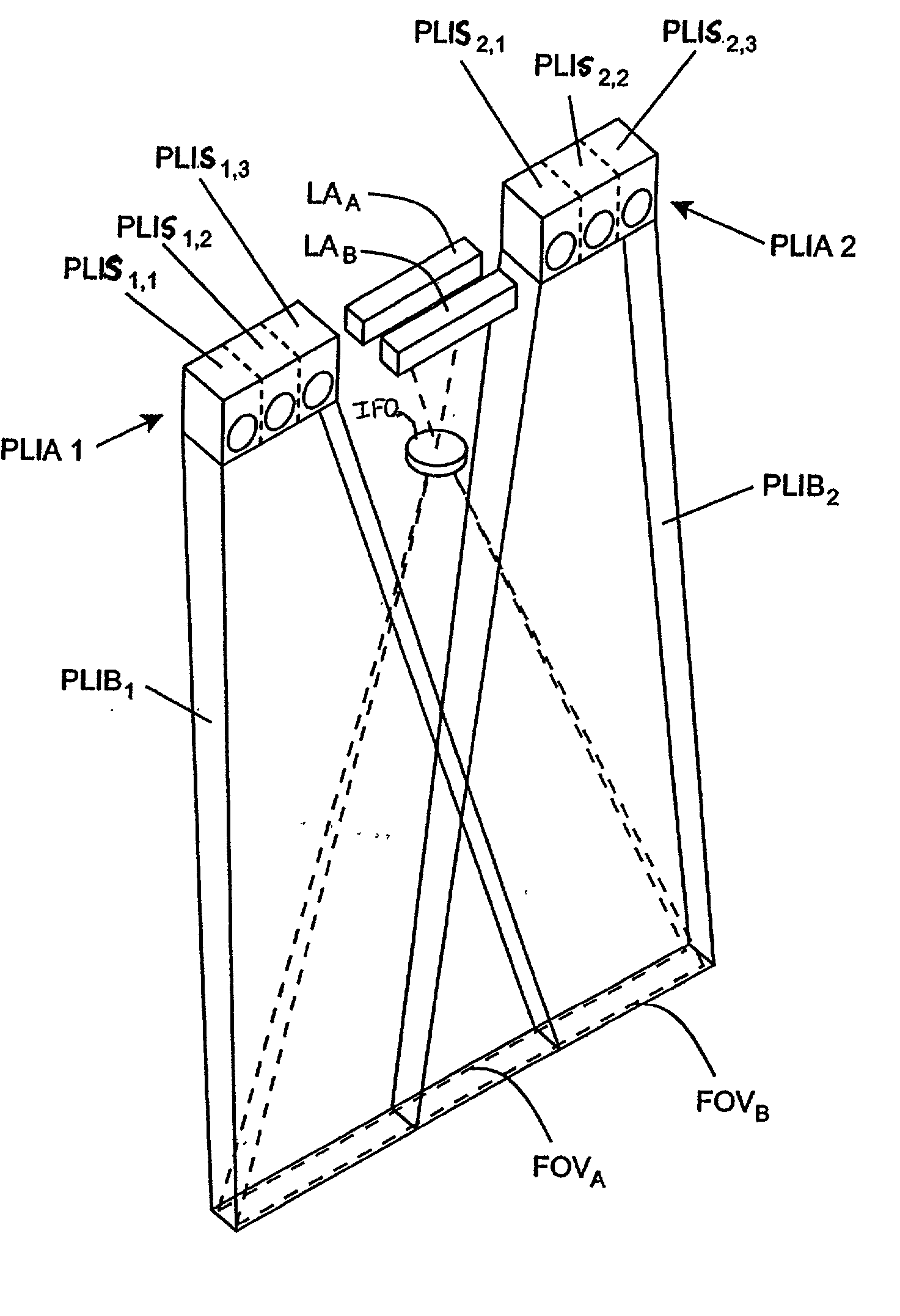
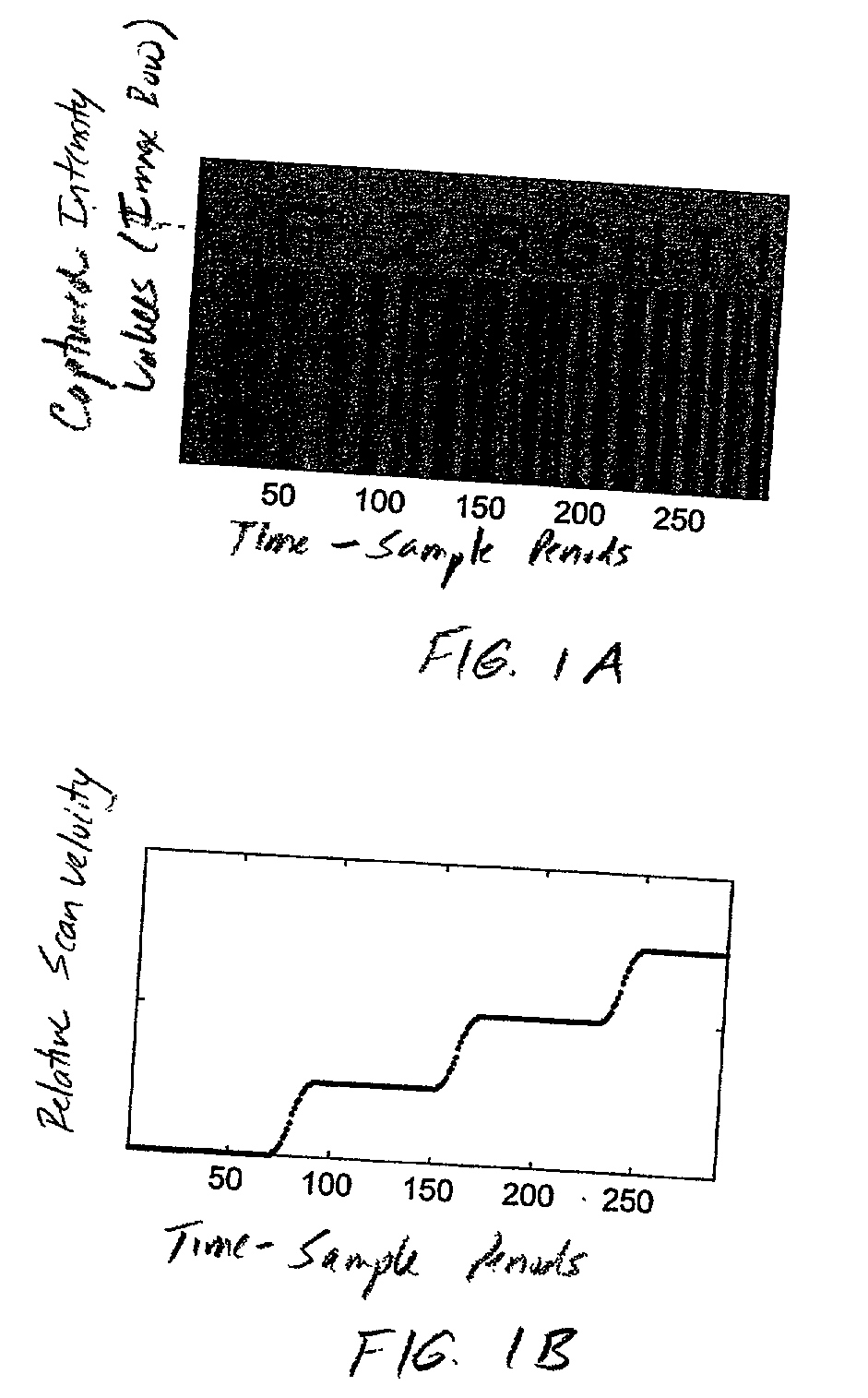
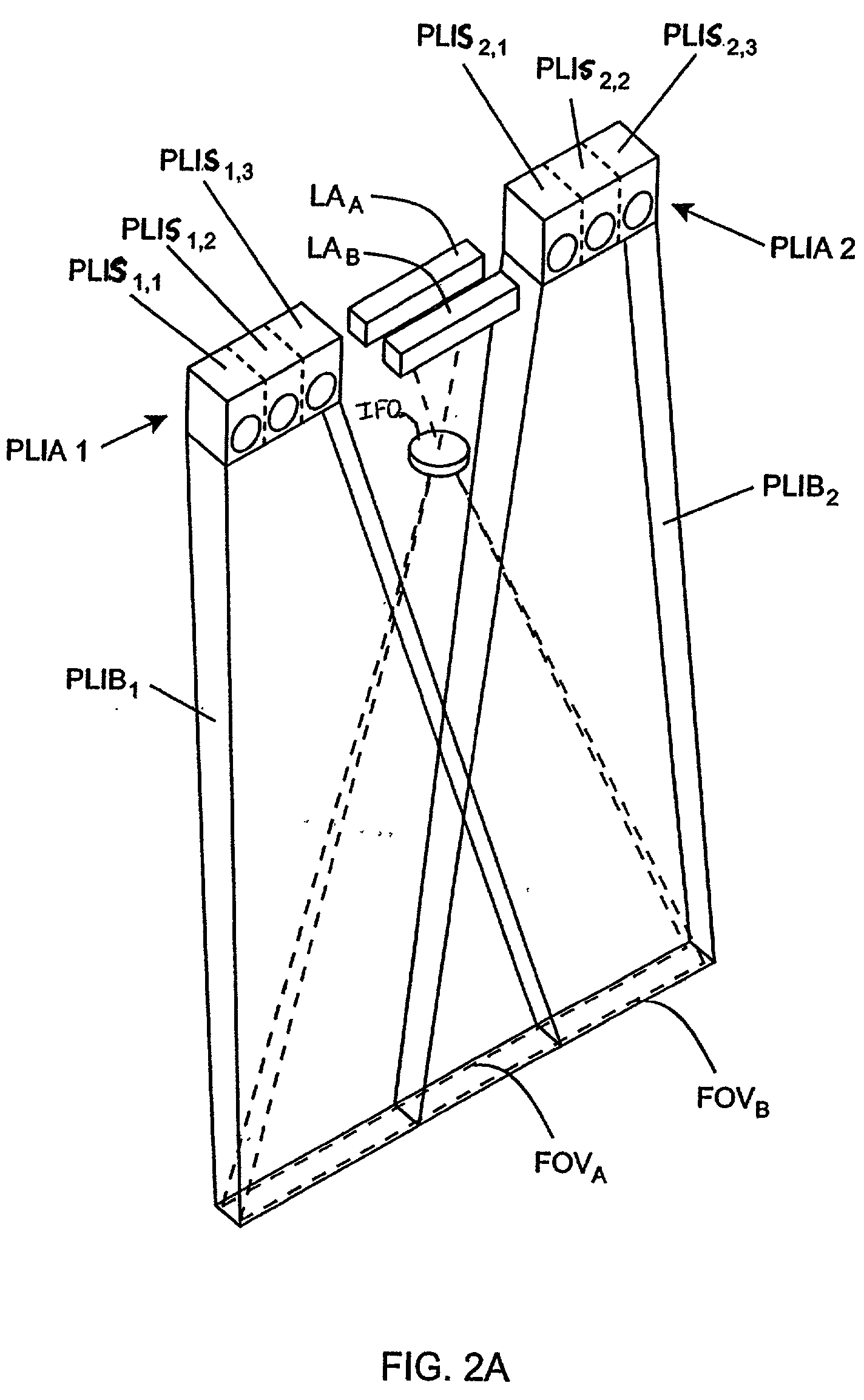
An imaging engine includes a plurality of linear imaging arrays, image formation optics, at least one illumination module and supporting circuitry that are embodied within a modular engine housing. The plurality of linear imaging arrays and image formation optics are mounted on an optical bench (which is integral to the engine housing) and provide field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear image arrays. The at least one illumination module produces planar light illumination that substantially overlaps the field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear imaging arrays. The supporting circuitry includes: timing signal generation circuitry that supplies timing signals to the linear imaging arrays in order to read out the row image data produced by such arrays (such row image data may be read out at a constant line rate or at a variable line rate); illumination control circuitry that supplies current to the illumination sources in the at least one illumination module; analog-to-digital conversion circuitry, which optionally filters row data image signal supplied thereto (to remove unwanted noise components) and converts the row image data supplied thereto into digital form; and data buffering circuitry, for storing the digital row image data generated by the analog-to-digital conversion circuitry and communicating the row image data stored therein over a data communication bus. One linear image array (e.g., linear imaging array C) may have a variable line rate that is controlled by the timing signals supplied thereto such that the image capture operations performed by the one linear imaging array (e.g. linear imaging array C) maintain a substantially constant aspect ratio, to thereby compensate for aspect ratio distortions that result from variations in velocity of engine with respect to target object(s). The variable line rate is based upon velocity estimates derived from processing of the pixel data values of other linear imaging arrays disposed therein. The supporting circuitry may optionally include a line rate adjustment module, preferably realized as part of a programmed controller, that is operably coupled to timing signal generation circuitry and adjusts the variable line rate of the one linear image device (e.g., linear imaging array C); output illumination control module, preferably realized as part of the programmed controller, that is operably coupled to the illumination control circuitry and adjusts the optical power level and / or illumination time period for the illumination that overlaps one or more of the FOVs of the linear imaging arrays of the engine for speckle reduction / constant white levels; and / or imaging processing circuitry, operably coupled to the data buffering circuitry over the data communication bus, that realizes portions of image-based mechanisms / techniques for image velocity estimation, aspect ratio compensation, jitter estimation and compensation, bar code detection, OCR, and image lift.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Apparatus and method for providing high intensity non-coherent light and for speckle reduction
ActiveUS20050207160A1Speckle reductionNon-electric lightingBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamHigh intensity
An apparatus adapted for confocal imaging of a non-flat specimen comprising a light source for producing a light beam, imaging optics adapted to focus the light beam into at least one spot on a surface of a specimen, and a detector adapted to receive and detect light reflected from the specimen surface. The light source comprises an optical system for converting a coherent beam into a plurality of beams, each of which is modified by a moving diffuser within a range of movement that is correlated to the detector's integration time.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Method and apparatus for ultrasound compound imaging with combined fundamental and harmonic signals
ActiveUS20050101865A1Improved compounding imagingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSteering angleSonification
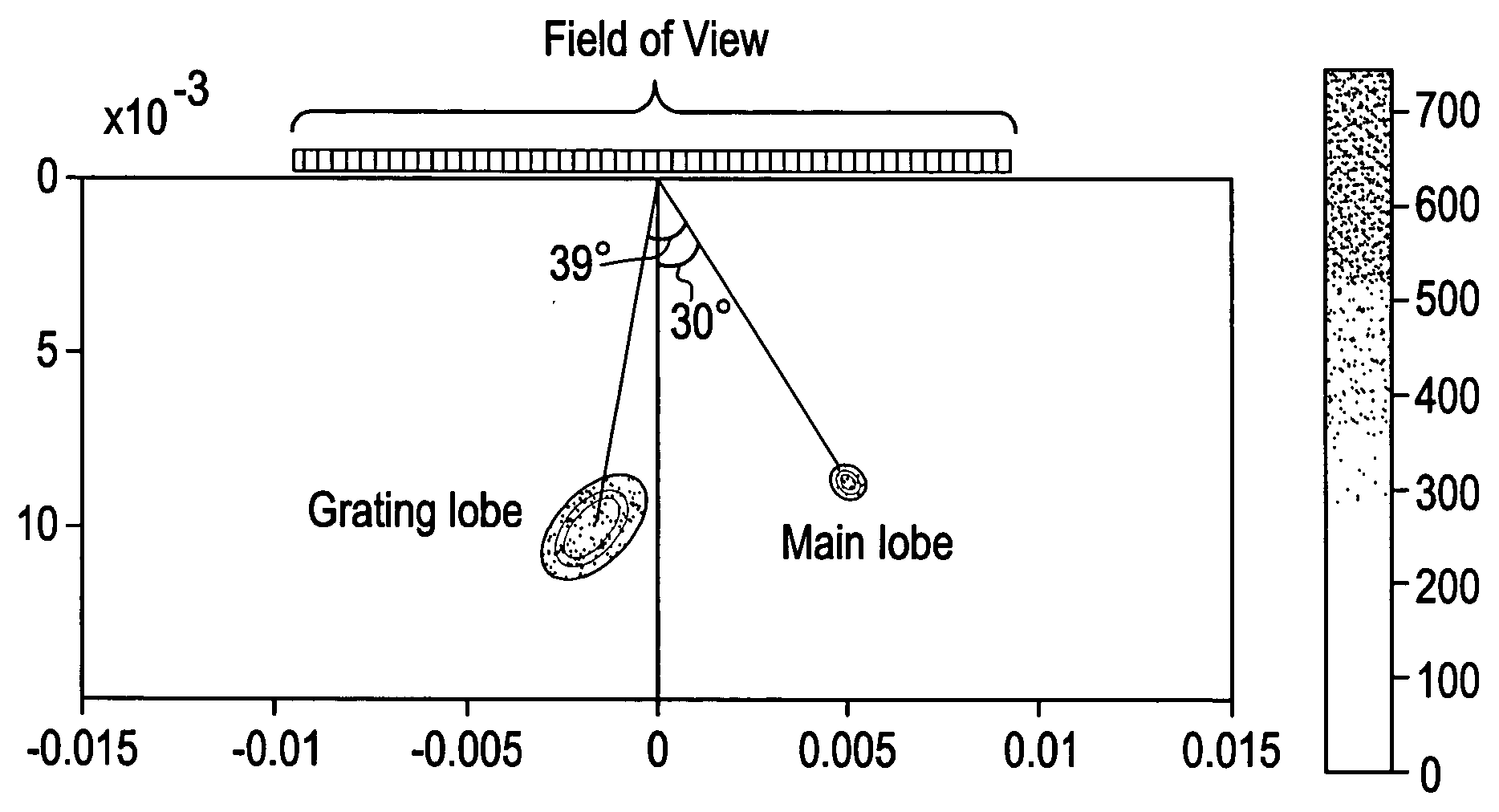
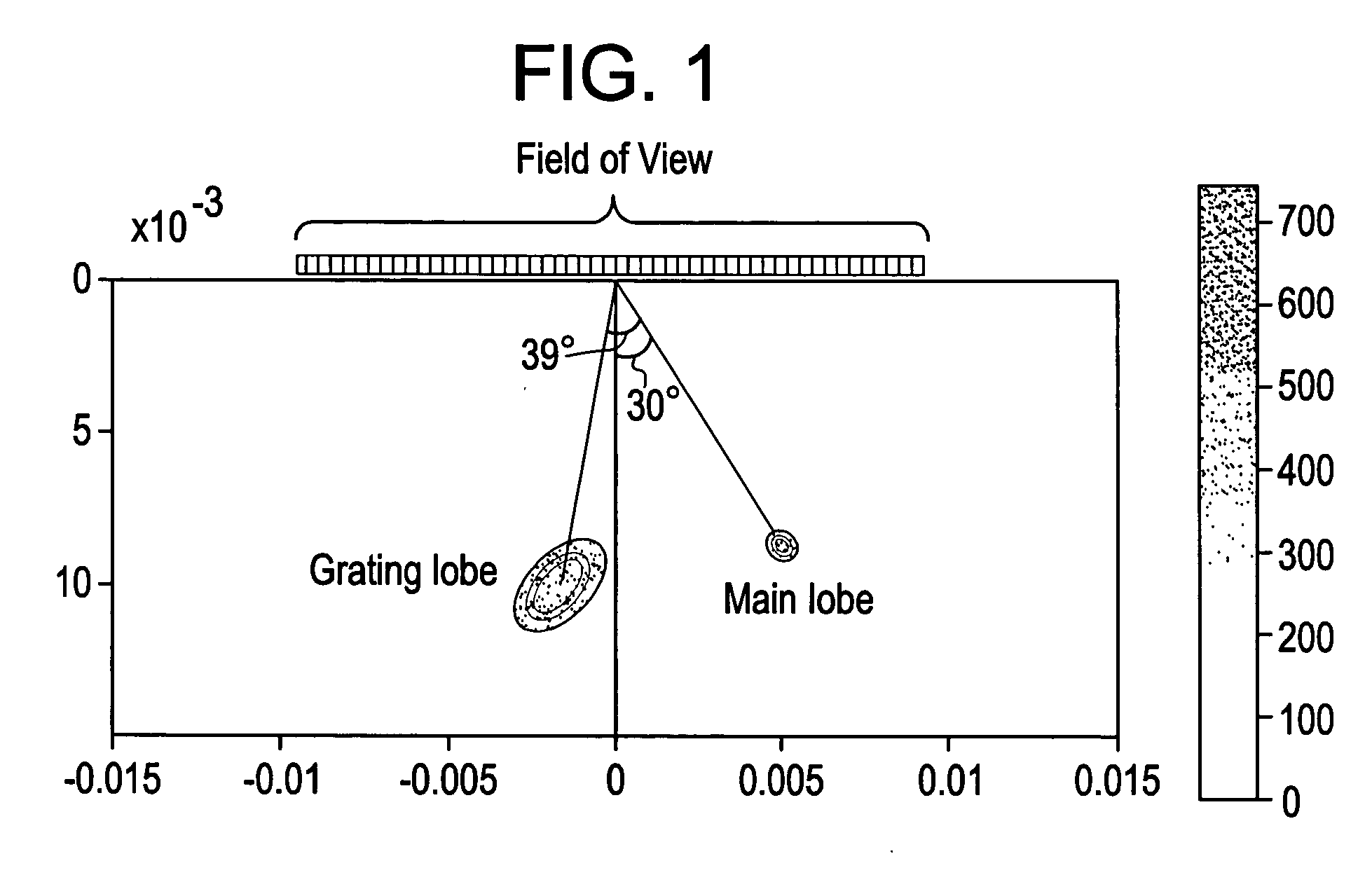
Certain embodiments include a system and method for improved compound imaging using a plurality of imaging modes. In an embodiment, a plurality of echo signals are received in response to a plurality of beams formed based on different imaging modes corresponding to different steering angles, such as steered or non-steered angles. The plurality of echo signals is compounded to form a compound image. In an embodiment, the imaging mode includes at least one of harmonic, fundamental, coded harmonic, and variable frequency imaging. Parameters may be generated for the plurality of beams formed based on different imaging modes corresponding to different steering angles. Additionally, the parameters may be stored. The echo signals may be filtered. Imaging mode may be controlled based on steering angle. Employing different imaging modes based on steering angles for spatial compound imaging helps reduce grating lobe artifacts while improving speckle reduction effect.
Owner:G E MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL
Speckle reduction in laser-projector images
InactiveUS7502160B2Reduce appearance problemsSpeckle reductionProjectorsMountingsSpatial light modulatorProjection image
A laser projector having a configurable spatial light modulator (SLM) adapted to display various spatial modulation patterns and redirect illumination from a laser to form an image on the viewing screen. The laser projector drives the SLM to change spatial modulation patterns at a rate that causes the corresponding sequence of projected images to fuse to mitigate appearance of speckle in the resulting fused image. The SLM can be designed to redirect the illumination using either diffraction or specular reflection of light from the displayed spatial modulation pattern. In one embodiment, the SLM is a MEMS device having an array of individually addressable mirrors supported over a substrate and adapted to move (e.g., translate and / or rotate) with respect to the substrate.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Projection display surface providing speckle reduction
ActiveUS8085467B1Speckle reductionImpact image qualityProjectorsColor photographyOptical fluorescenceReflective layer
A projection display surface for reducing speckle artifacts from a projector having at least one narrow band light source having an incident visible wavelength band, wherein the incident visible wavelength band has an incident peak wavelength and an incident bandwidth, comprising: a substrate having a reflective layer that reflects incident light over at least the incident visible wavelength band; and a fluorescent agent distributed over the reflective layer, wherein the fluorescent agent absorbs a fraction of the light in the incident visible wavelength band and emits light in an emissive visible wavelength band having an emissive peak wavelength and an emissive bandwidth; wherein return light from the projection display surface produced when incident light in the incident visible wavelength band is incident on the projection display surface contains light in both the incident visible wavelength band and emissive visible wavelength band, thereby reducing speckle artifacts.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
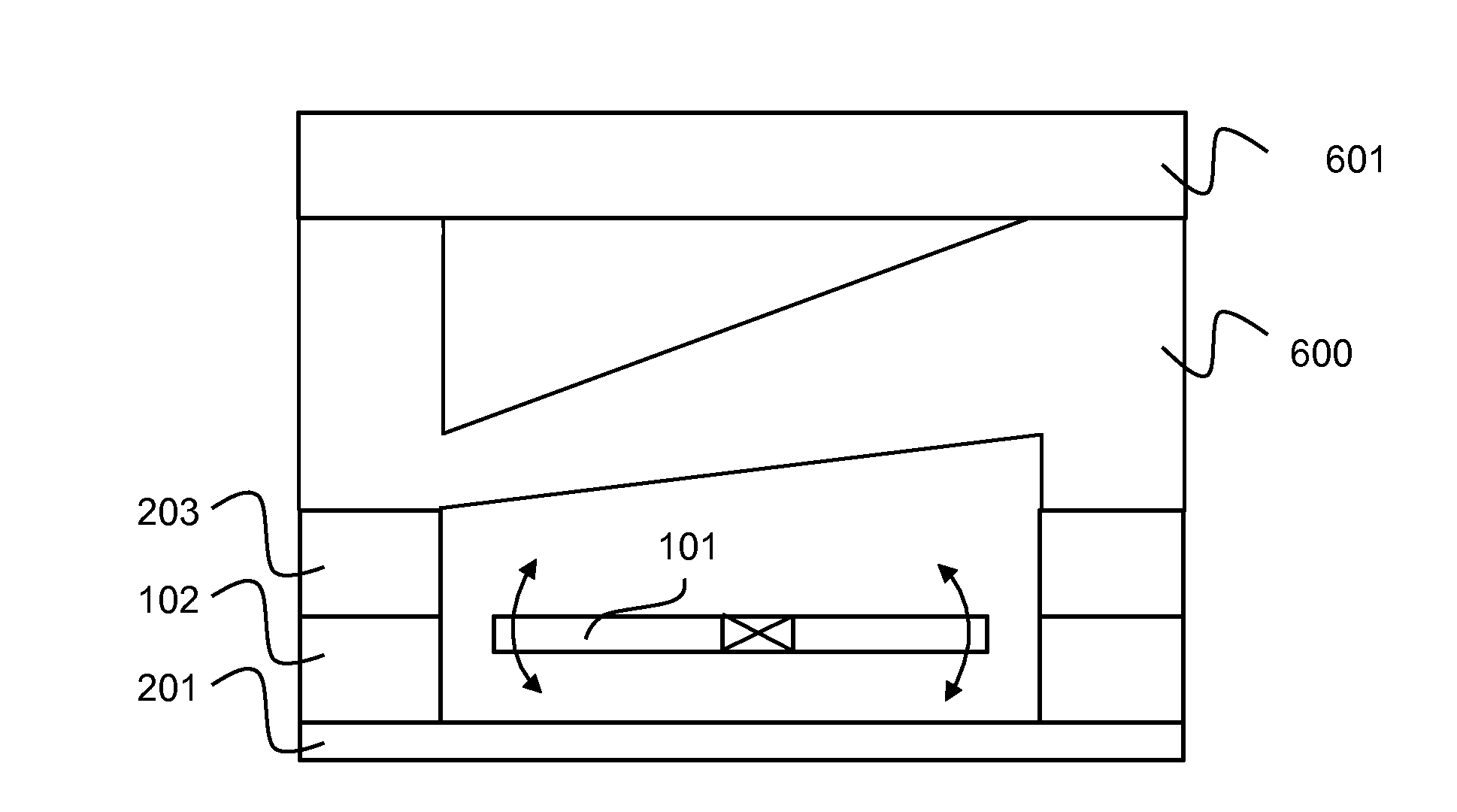
Optical MEMS scanning micro-mirror with speckle reduction
ActiveUS20130242275A1Reducing and suppressing speckleAvoid parasitic reflectionsProjectorsOptical elementsNeutral planePrism
Optical MEMS scanning micro-mirror comprising:—a movable scanning micro-mirror (101) pivotally connected to a MEMS body (102) substantially surrounding the lateral sides of the micro-mirror;—an transparent prism (500, 600) substantially covering the reflection side of the micro-mirror;—wherein said prism has its outer face non-parallel to the micro-mirror neutral plane N-N, thereby providing a dual anti-speckle and anti-reflection effect, namely against parasitic light. The invention also provides the corresponding micro-projection system and method for reducing speckle.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Speckle reduction laser and laser display apparatus having the same
ActiveUS7489714B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionResonanceLaser light
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
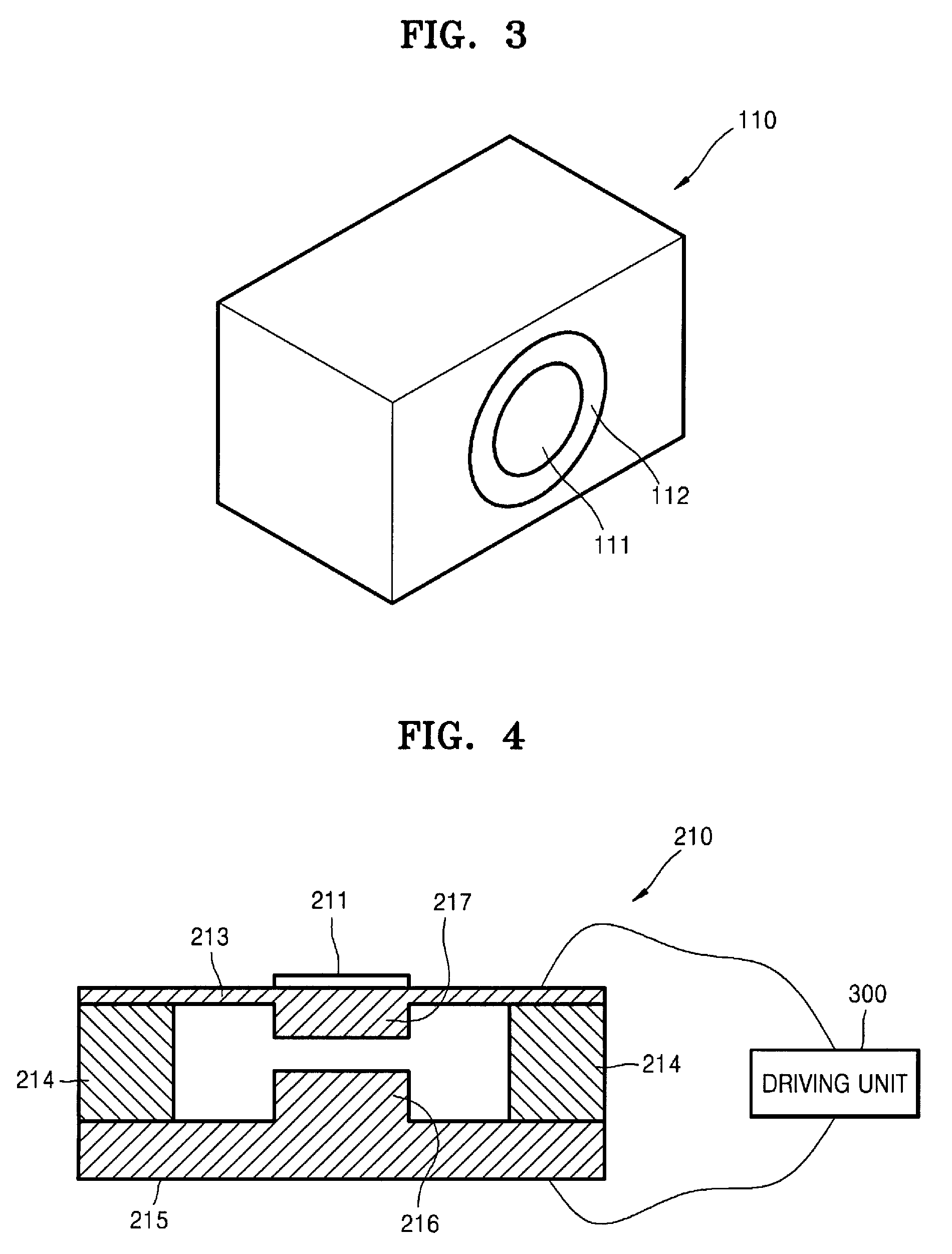
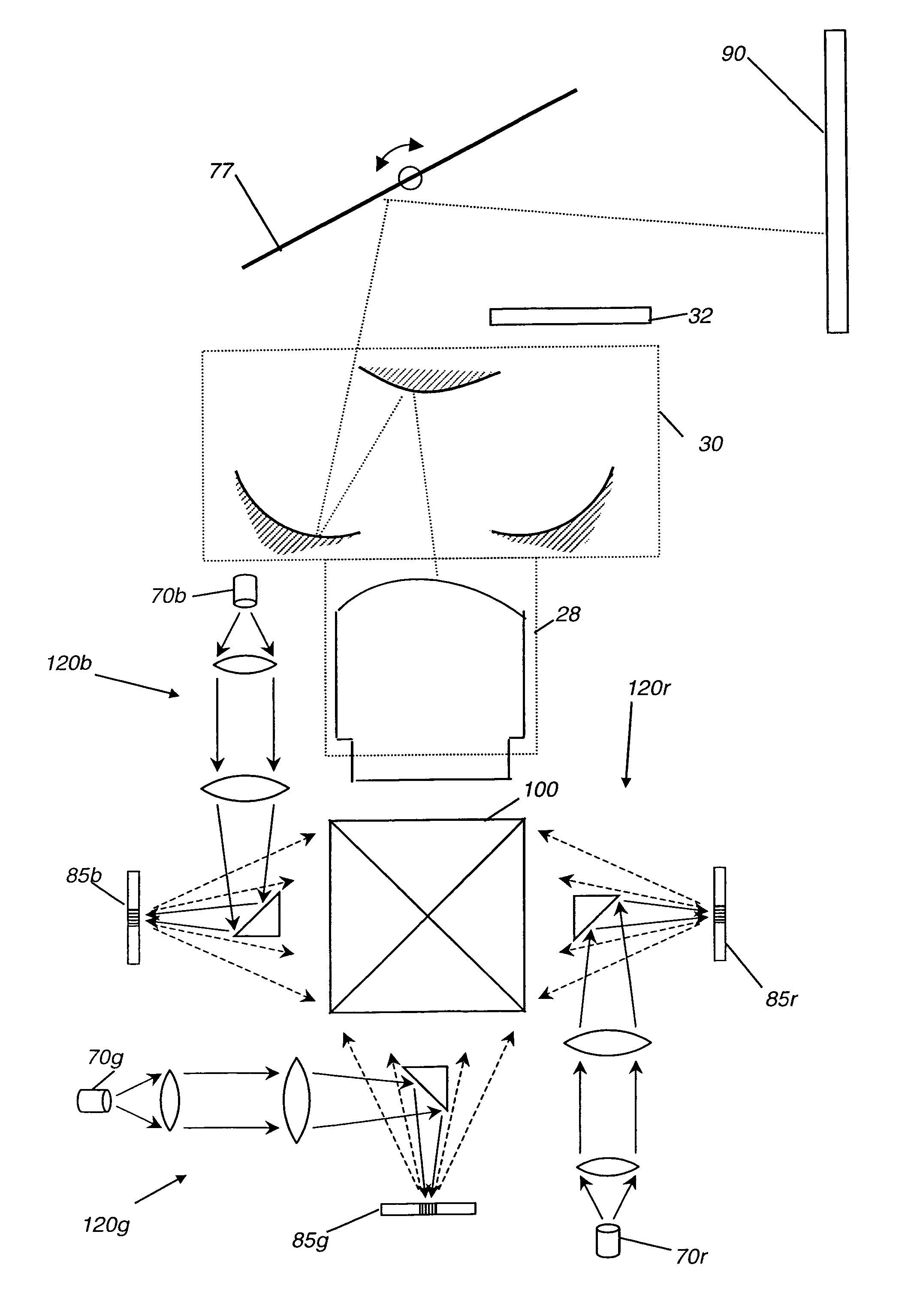
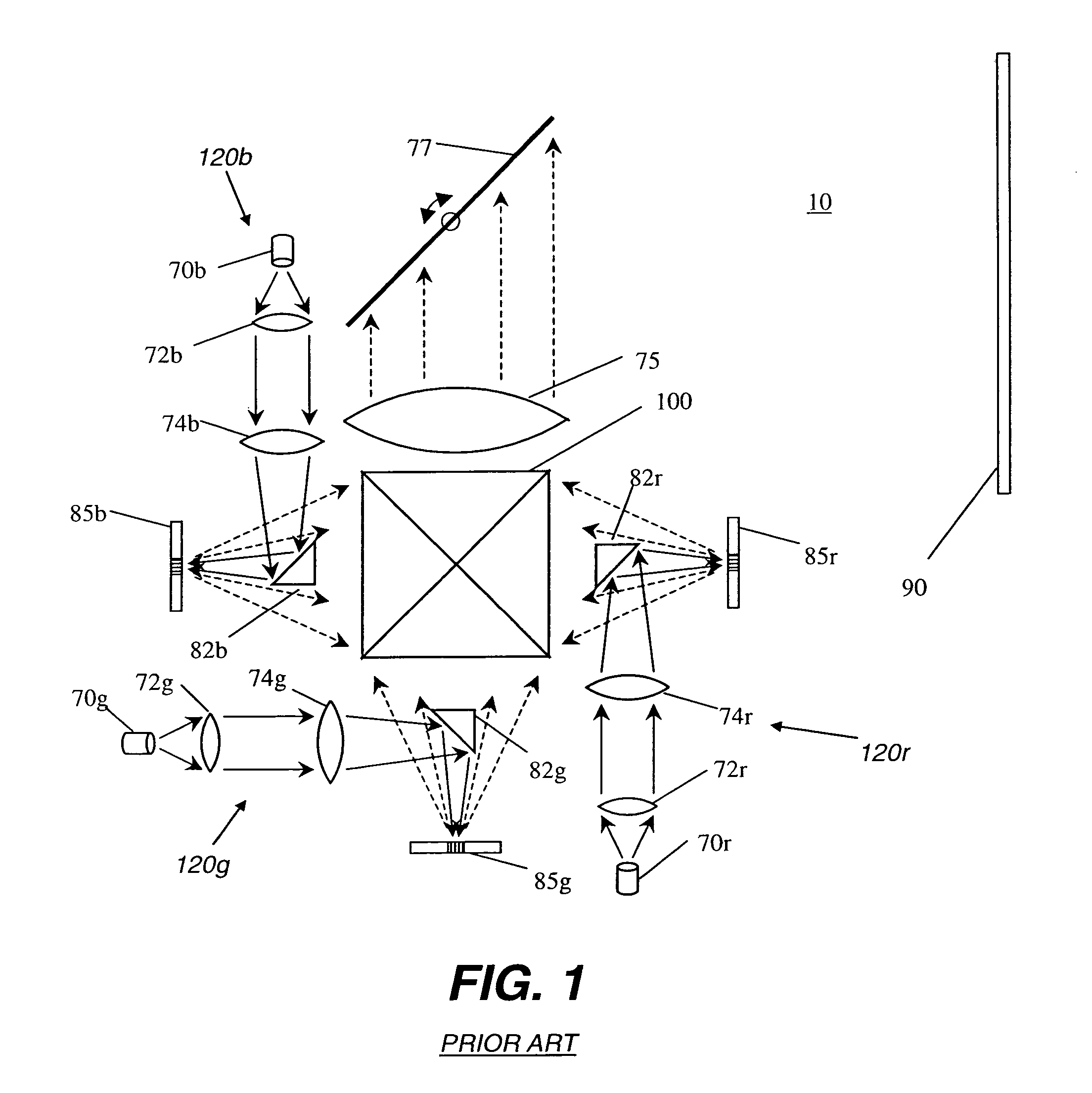
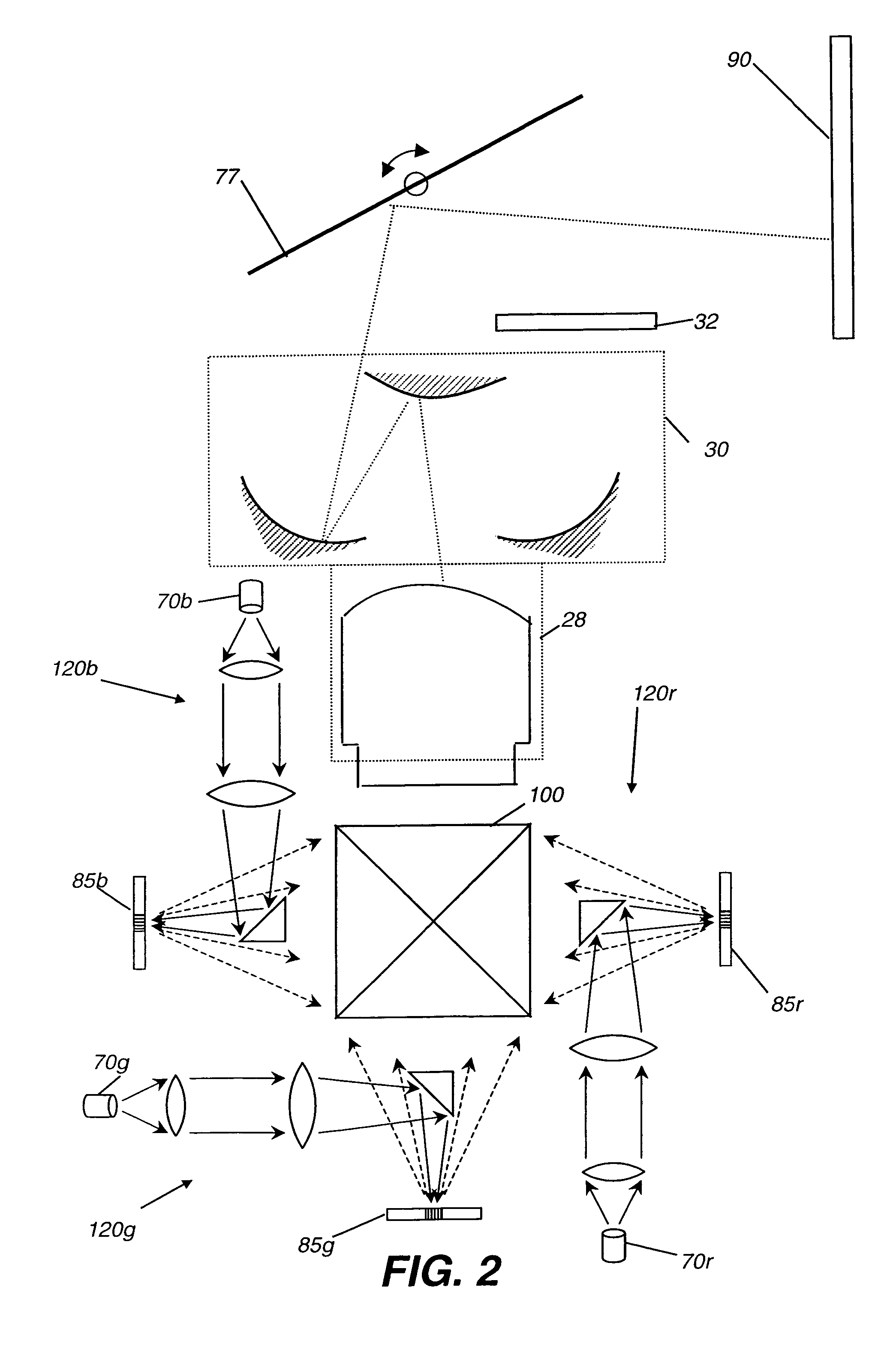
Speckle reduction for display system with electromechanical grating
InactiveUS7119936B2Lower Level RequirementsReduce in quantityTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesGratingLight beam
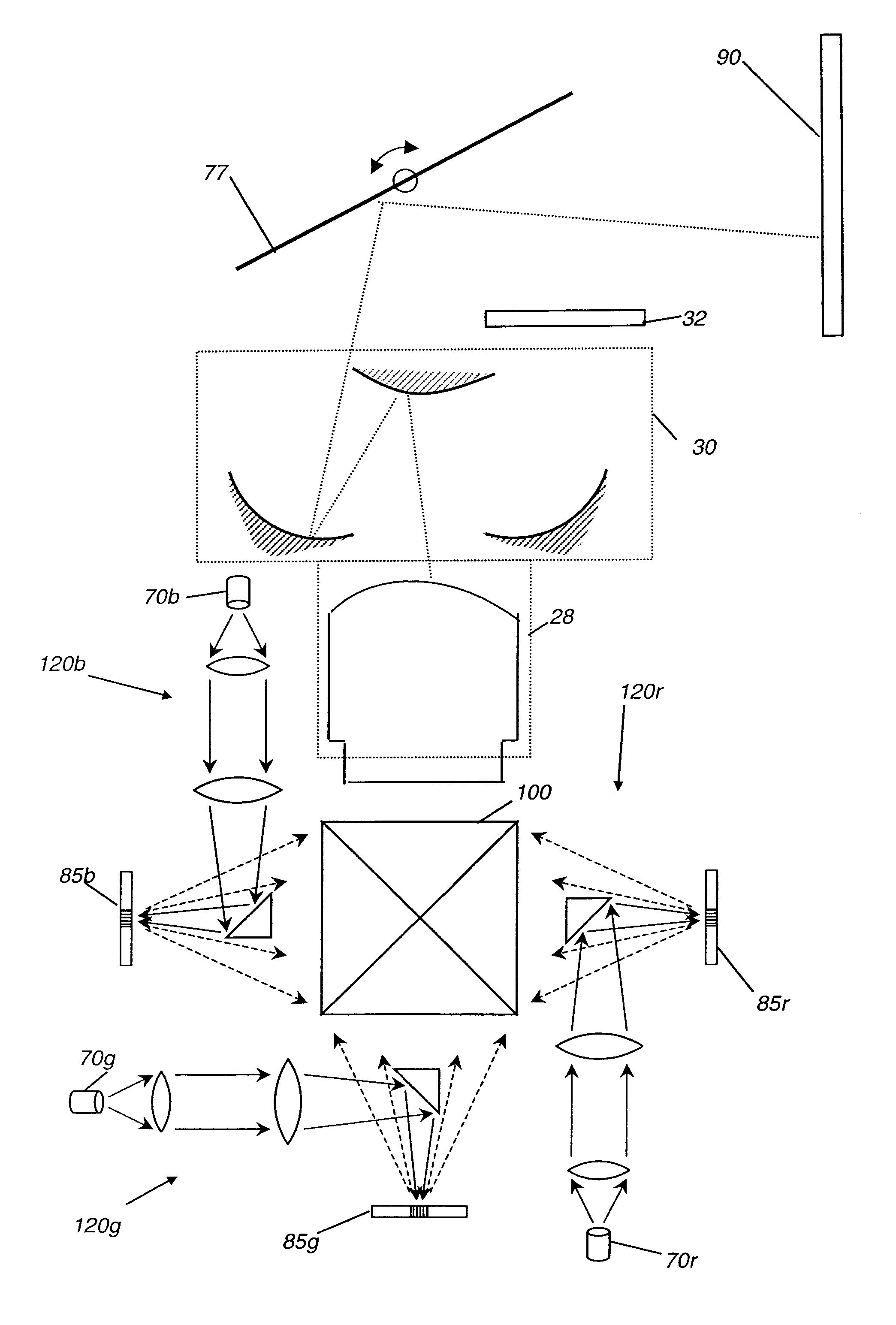
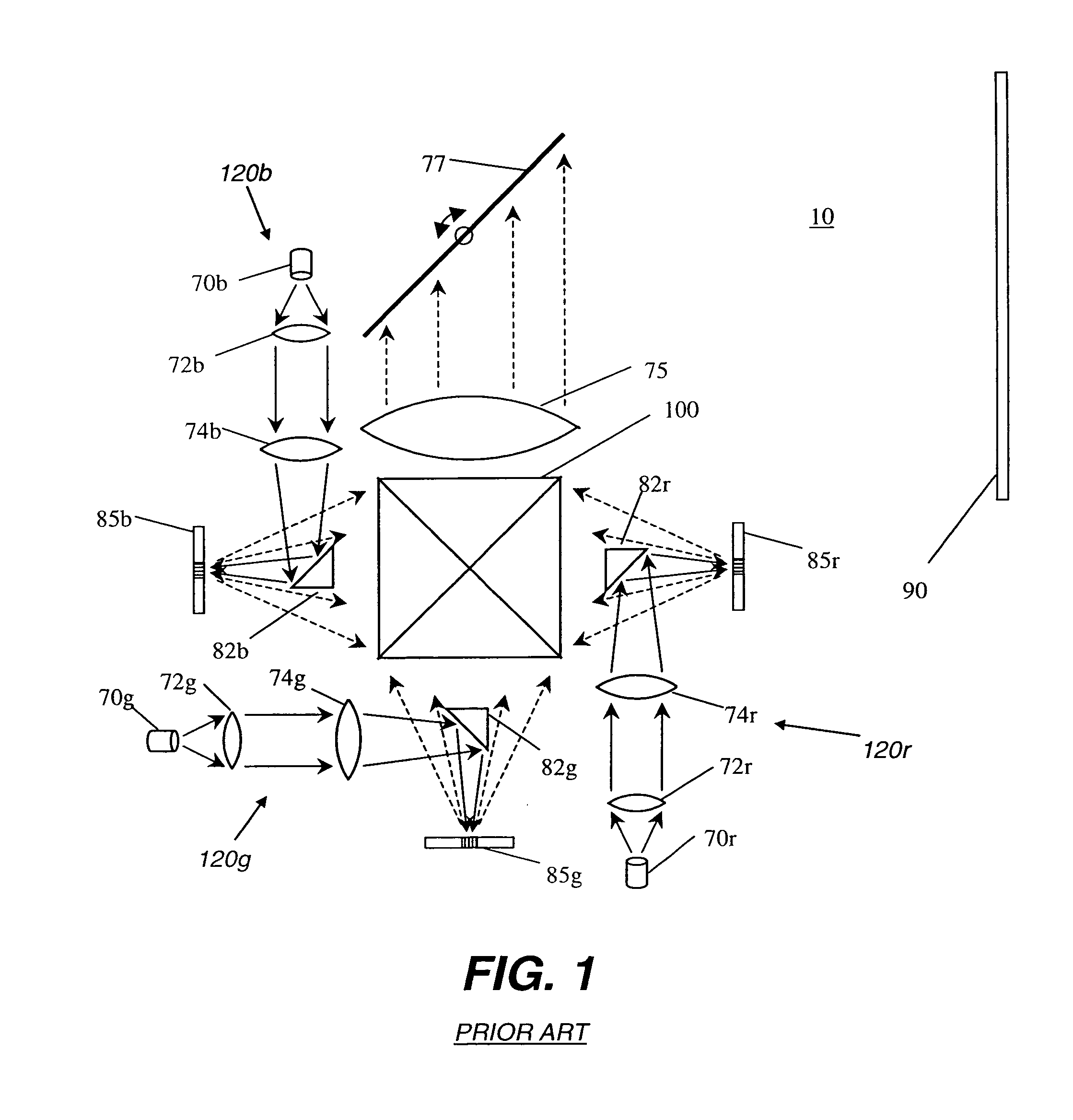
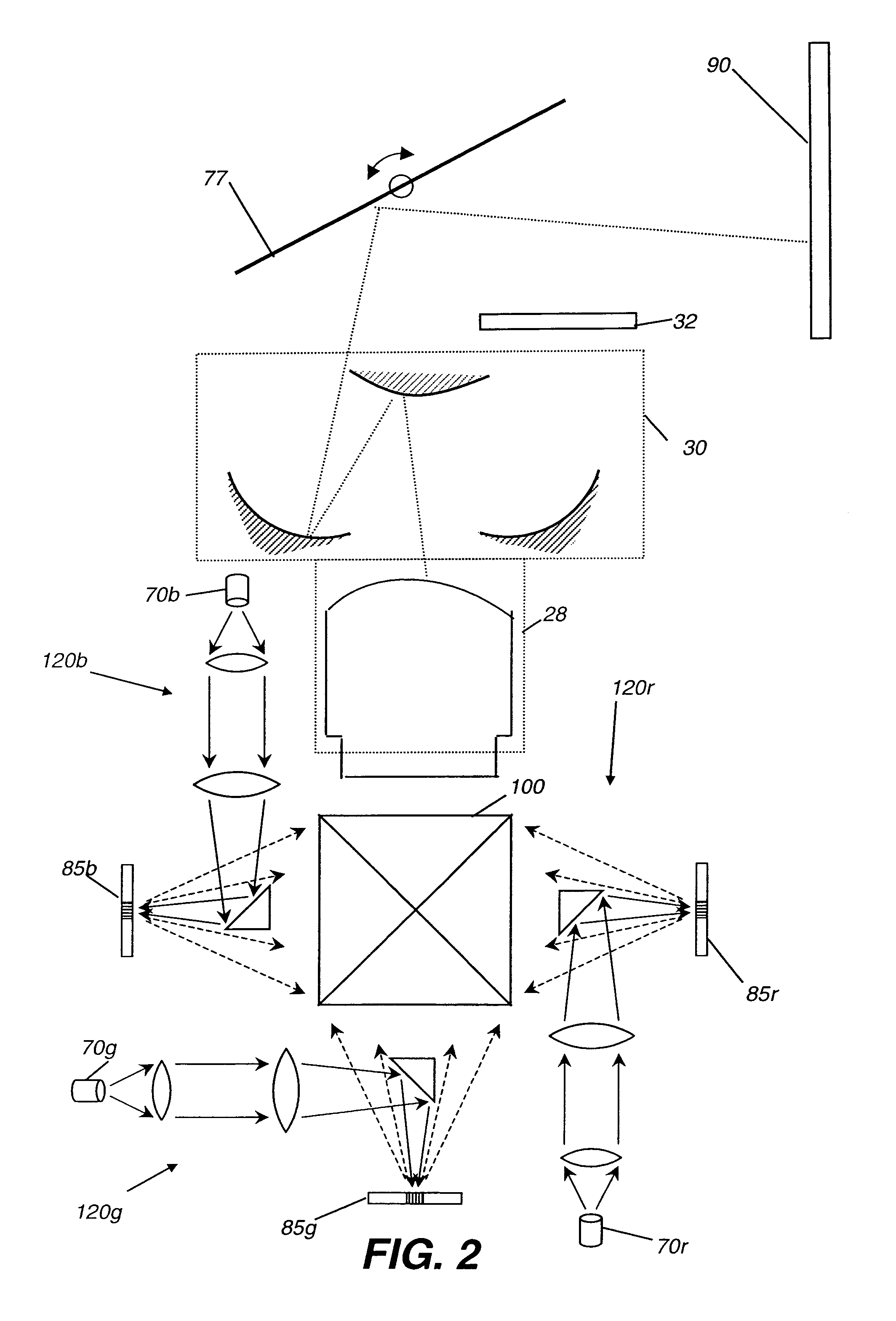
A display system (10) with reduced speckle has a light source (70) providing an illumination beam and a linear light modulator (85) having at least one linear array of light modulating devices for forming a modulated beam. The modulated beam has a plurality of orders of diffracted light. An obstructing element (82r,82g,82b) blocks a zeroeth order reflected light from the modulated beam. An angle-transforming optical assembly (30) anamorphically conditions the modulated beam. A scanning element (77) scans the modulated beam toward a display surface (90) for forming a two-dimensional image thereon.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method and apparatus for article inspection including speckle reduction
InactiveUS20050128473A1Small and simpleConvenient in introducing large optical path length variationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsGratingOptical pathlength
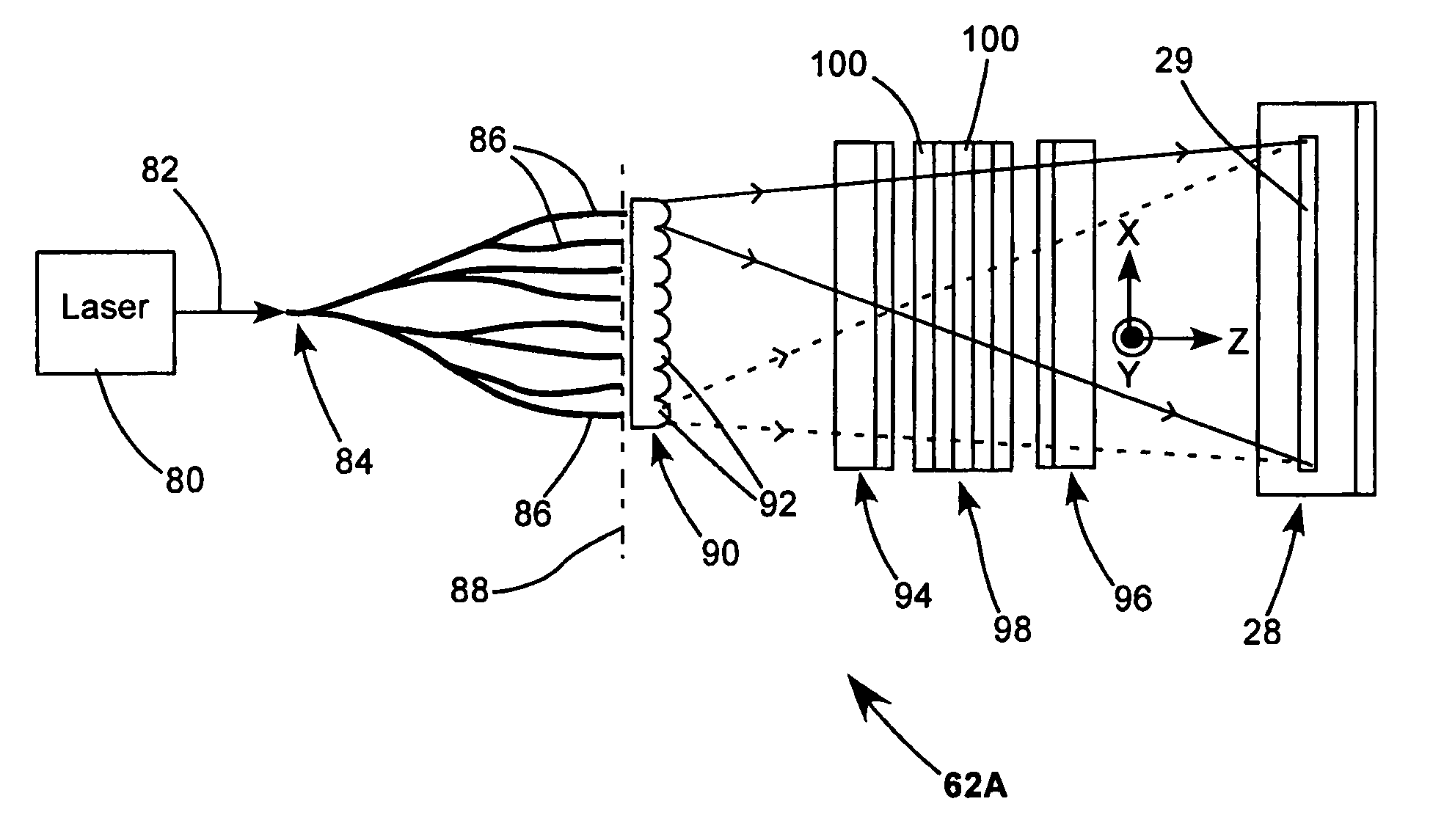
A method and apparatus for reducing speckle during inspection of articles used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, including wafers, masks, photomasks, and reticles. The coherence of a light beam output by a coherent light source, such as a pulsed laser, is reduced by disposing elements in a light path. Examples of such elements include optical fiber bundles; optical light guides; optical gratings; an integrating sphere; and an acousto-optic modulator. These various elements may be combined as desired, such that light beams output by the element combinations have optical path length differences that are greater than a coherence length of the light beam output by the coherent light source.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
SAR image speckle suppression method based on dictionary learning in wavelet domain
ActiveCN102496153AEasy to keepSuppress speckle noiseImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionDictionary learning
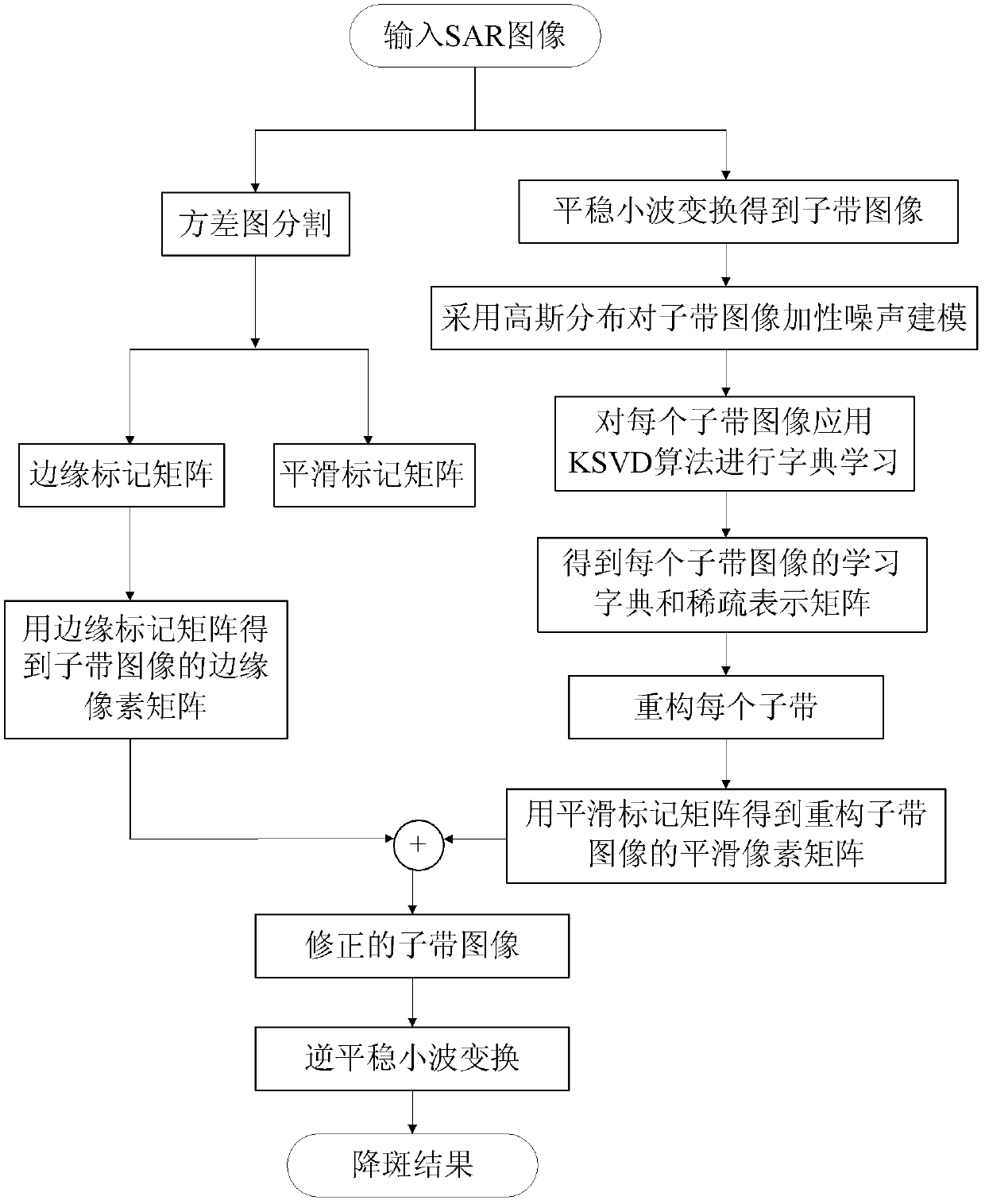
The invention discloses a SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image speckle suppression method based on dictionary learning in wavelet domain, which mainly solves the problems that the edge is not clear enough and the homogenous region is not smooth enough in the existing speckle reduction technology. The implementation process of the method comprises the following steps of: firstly, segmenting an original SAR image Y by a variogram method to obtain a smooth mark matrix SY and an edge mark matrix EY; performing N-level stationary wavelet transformation on the original SAR image Y to obtain sub-band images WY(s); modeling for a non-logarithmic additive noise in the WY(s) by zero-mean-value Guassian distribution; using an approximation KSVD (Singular Value Decomposition) algorithm to obtain a learner's dictionary D's and a sparse representative matrix Lambda's of each sub-band image WY(s), obtaining a reconstructed sub-band image according to the D's and the Lambda's, and obtaining an edge region of the sub-band images WY(s) by the edge mark matrix EY, and substituting the edge region in the reconstructed sub-band image to obtain modified sub-band images W'Y(s); performing inverse stationary wavelet transformation on the W'Y(s) to obtain the speckle- reduced image. The method has the advantages that the edge information after speckle reduction is complete and the homogenous region issmooth, and can be used for the pretreatment process of SAR image understanding.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Speckle reduction for display system with electromechanical grating
InactiveUS7046446B1Lower Level RequirementsReduce in quantityColor television detailsNon-linear opticsGratingLight beam
A method for displaying an image including: forming at least three light beams by diffraction at a single linear light modulator, wherein the at least three light beams have substantially equal intensity and are substantially the same color; projecting the at least three light beams toward a display surface to form an image line; and, scanning the image line across the display surface to form an image thereby.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Speckle reduction for laser projection displays
ActiveUS20120140784A1Reduce speckle noiseLaser detailsColor television detailsDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by path length encoded angular compounding
ActiveUS20060227333A1Easy to produceSpeckle reductionOptical measurementsDiagnostics using lightDiseasePath length
Speckle, a factor reducing image quality in optical coherence tomography (“OCT”), can limit the ability to identify cellular structures that are important for the diagnosis of a variety of diseases. The present invention allows for an implementation of an angular compounding, angular compounding by path length encoding (“ACPE”) for reducing speckle in OCT images. By averaging images obtained at different incident angles, with each image encoded by path length, ACPE maintains high-speed image acquisition and implements minimal modifications to OCT probe optics. ACPE images obtained from tissue phantoms and human skin in vivo demonstrate a qualitative improvement over traditional OCT and an increased signal-to-noise ratio (“SNR”). Accordingly, apparatus probe catheter, and method are provided for irradiating a sample. In particular, an interferometer may forward forwarding an electromagnetic radiation. In addition, a sample arm may receive the electromagnetic radiation, and can include an arrangement which facilitates a production of at least two radiations from the electromagnetic radiation so as to irradiate the sample. Such arrangement can be configured to delay a first radiation of the at least two radiations with respect to a second radiation of the at least two radiations.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
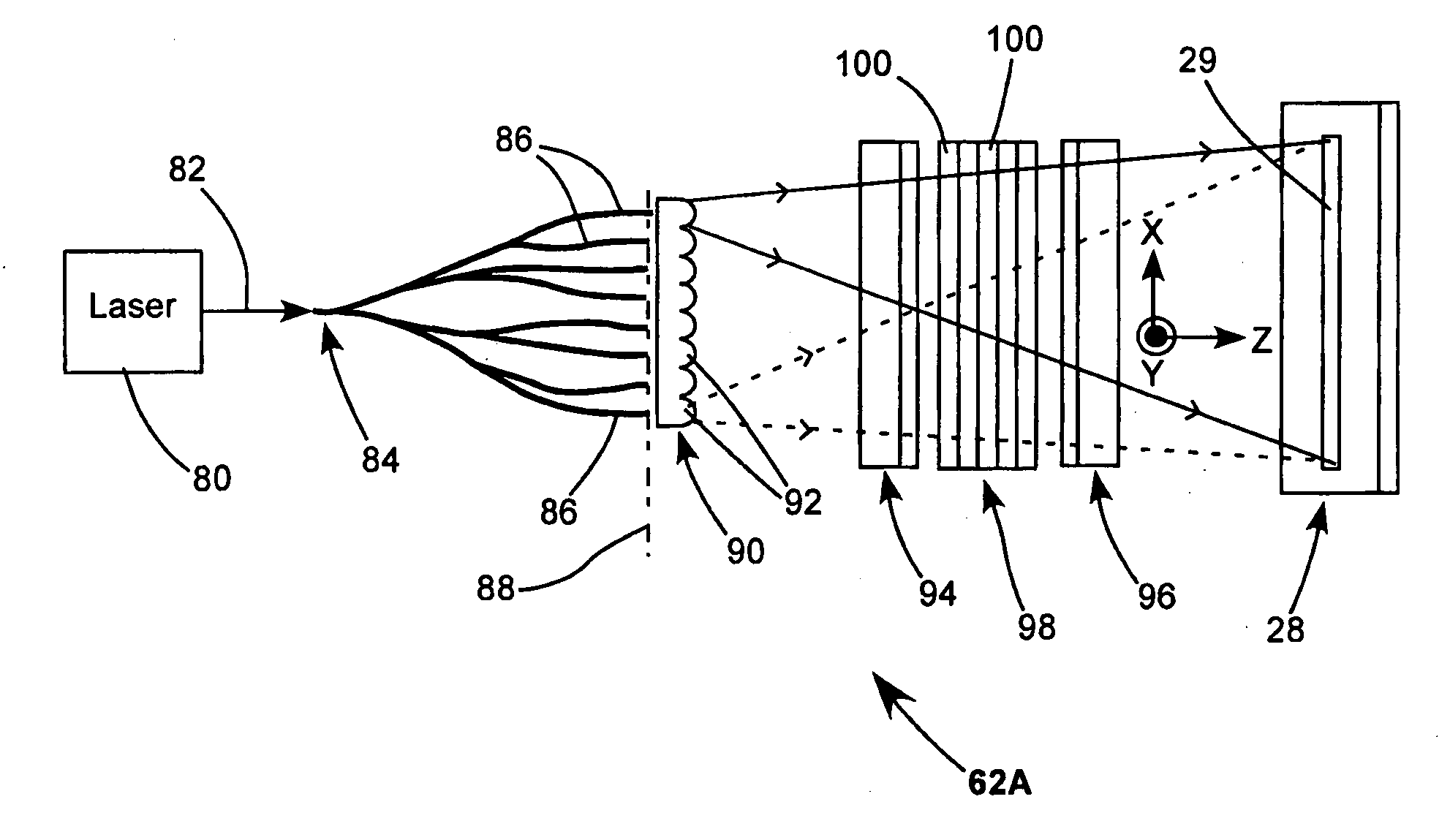
Low-speckle light source device
InactiveUS20090232438A1Cheap to achieveReduce coherenceCoupling light guidesOptical devices for laserLaser lightIntensity modulation
A laser light source device which can inexpensively achieve a visually recognizable level of speckle reduction is disclosed. The laser light source device includes: a laser module including a light source and a first optical waveguide, wherein light emitted from the light source is outputted from an output end of the first optical waveguide; a second optical waveguide connected to the first optical waveguide, wherein the light outputted from the output end of the first optical waveguide is inputted to an input end of the second optical waveguide and guided through the second optical waveguide; and an intensity modulation unit disposed in the vicinity of the second optical waveguide, the intensity modulation unit applying intensity modulation to the second optical waveguide, wherein a core diameter at the input end of the second optical waveguide is larger than a core diameter at the output end of the first optical waveguide.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Speckle reduction using a tunable liquid lens
ActiveUS20090096999A1Speckle reductionProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementSpatial light modulatorProjection system
A representative embodiment of the invention provides a projection system having a laser source that incorporates a tunable liquid lens and a spatial light modulator adapted to modulate light generated by the laser source to project an image on a viewing screen. The tunable liquid lens is adapted to vary focal length, alignment or position with respect to an optical element that is external to the lens, ability to diffuse light, and / or polarization rotation angle.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com