Patents
Literature
572 results about "Noise floor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In signal theory, the noise floor is the measure of the signal created from the sum of all the noise sources and unwanted signals within a measurement system, where noise is defined as any signal other than the one being monitored.
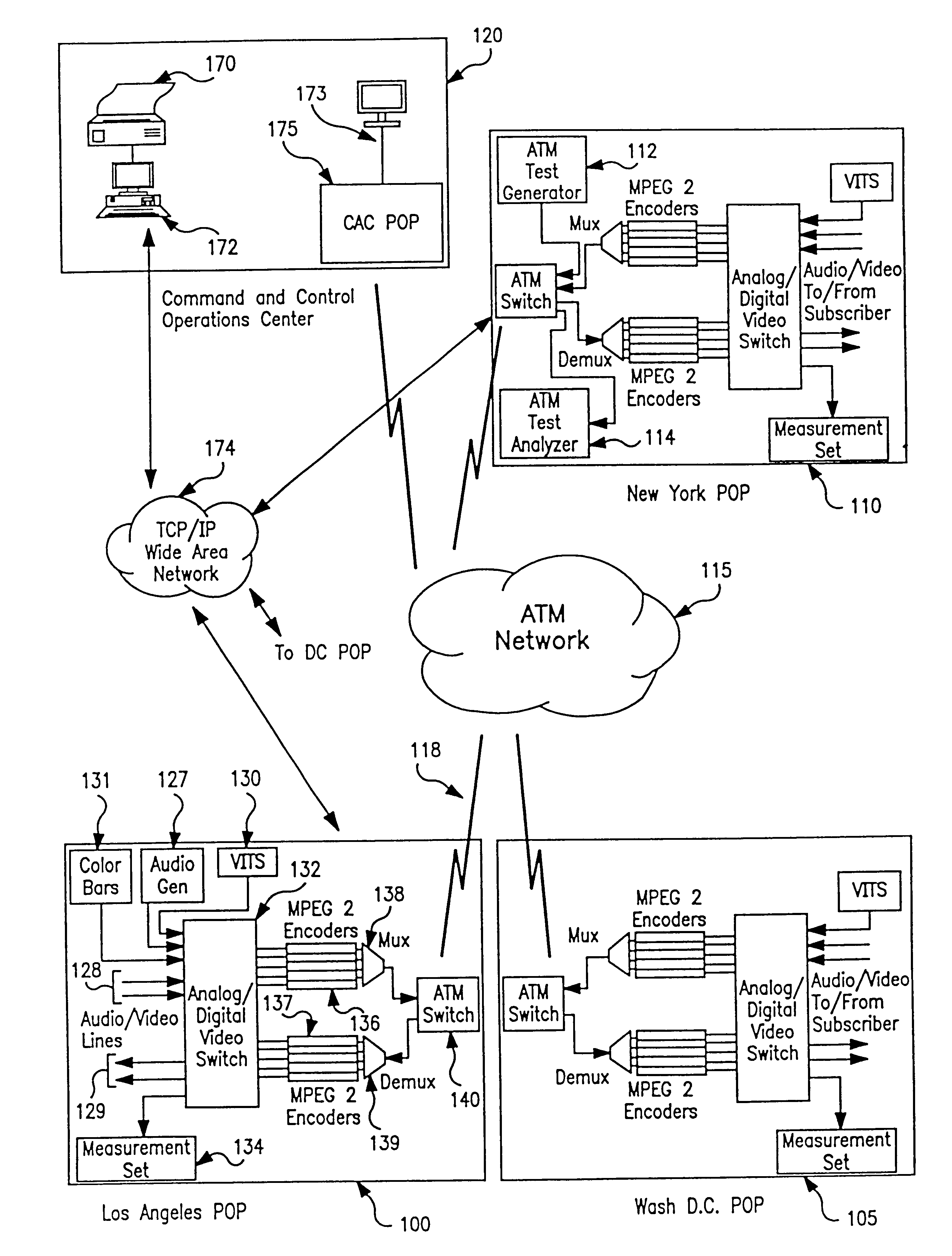
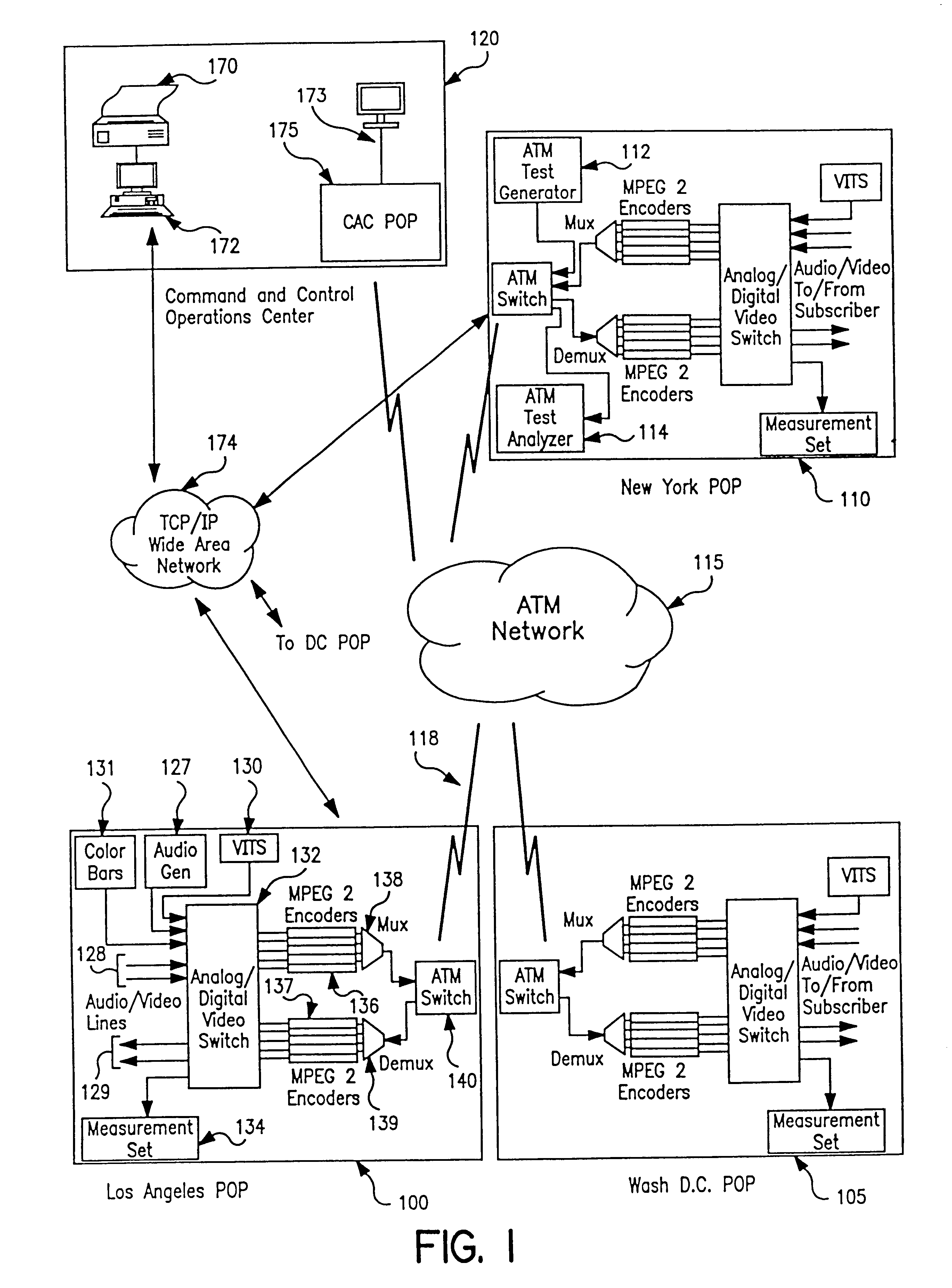
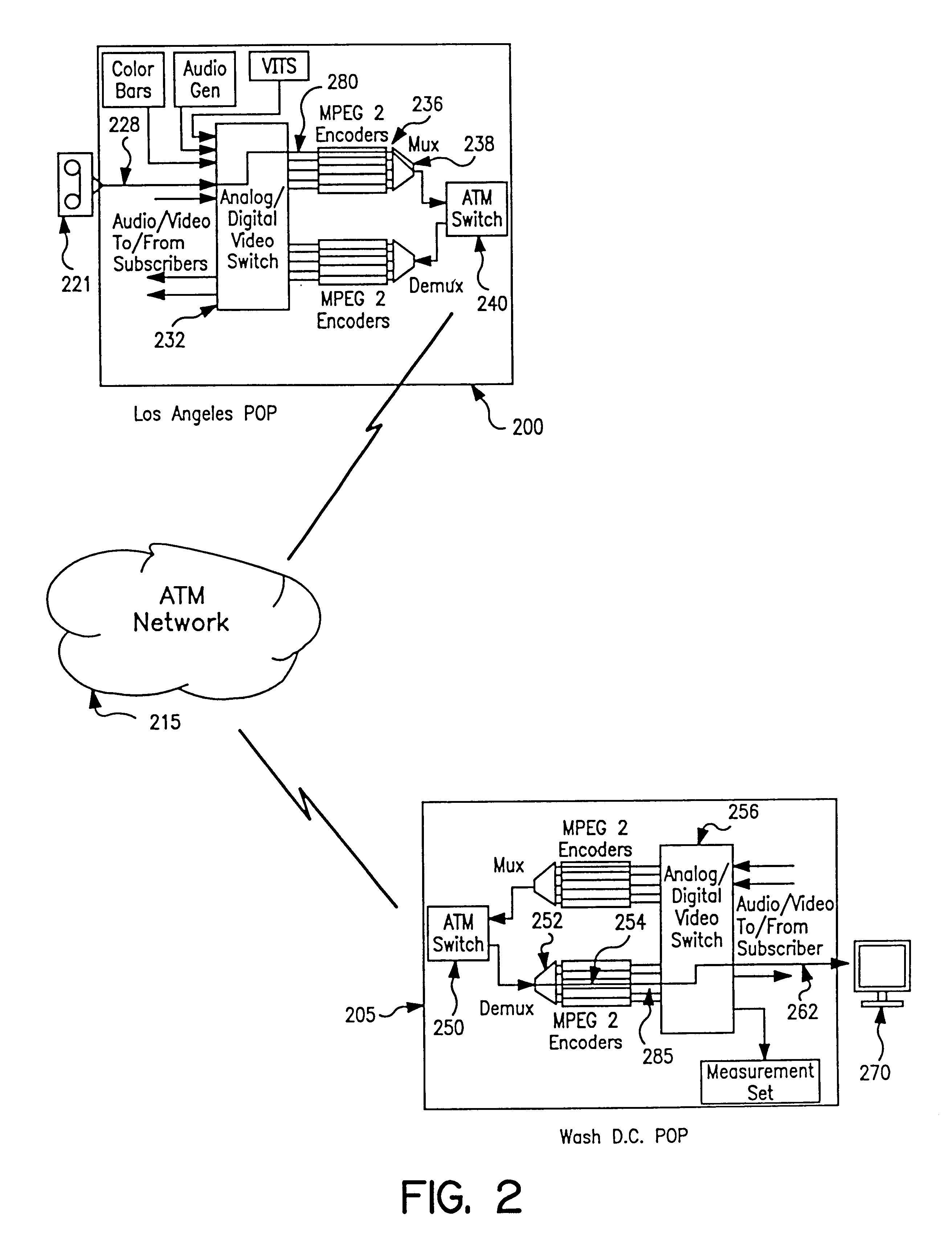
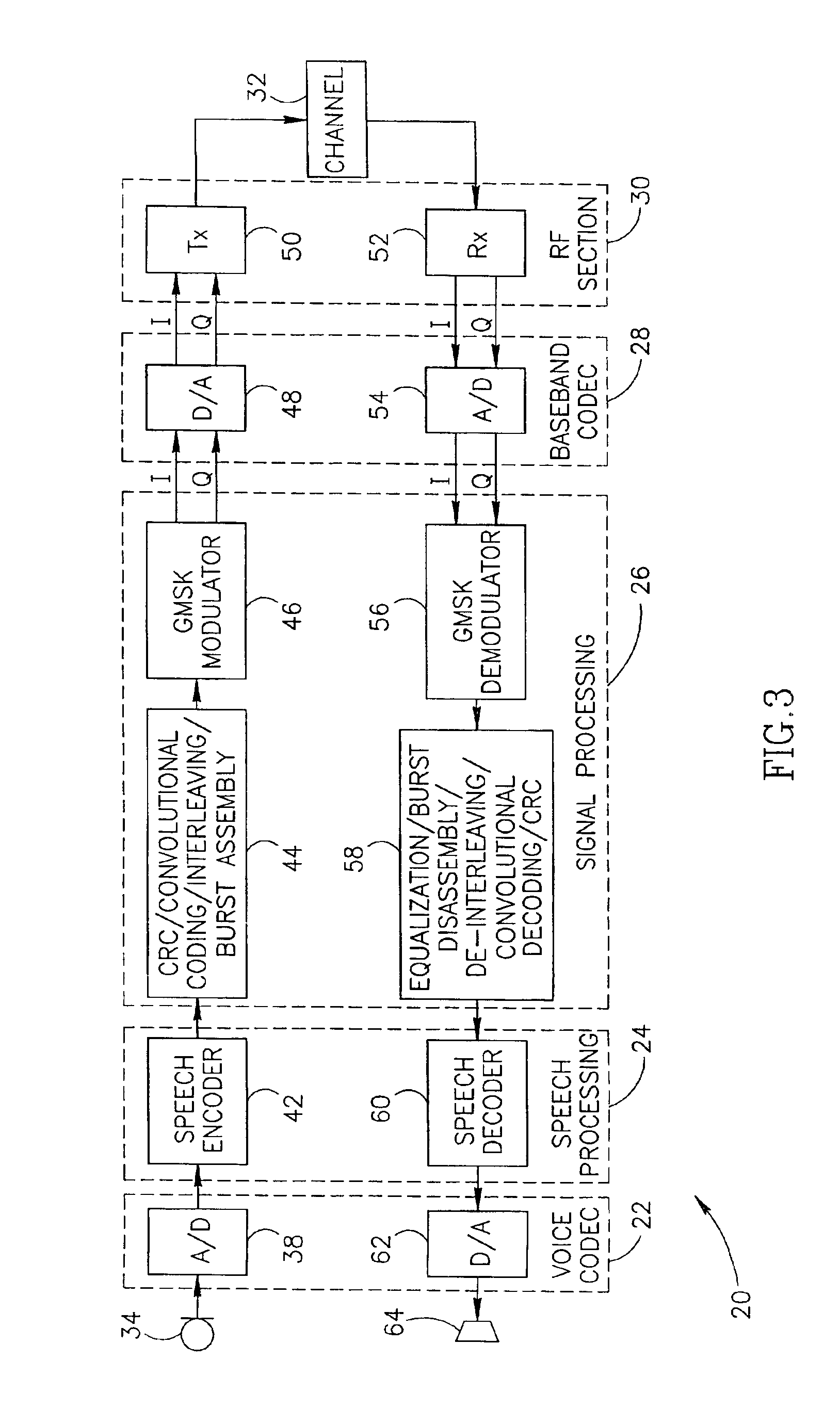
Apparatus and method of in-service audio/video synchronization testing
InactiveUS6414960B1Easy to testTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationVideo-signal generatorNoise level
An apparatus and method provide non-intrusive in-service testing of audio / video synchronization testing without using traditional audio marker tones. The network includes an A / V synchronous test signal generator which injects video and audio markers into the video and audio non-intrusively and routes the two signals into a switch where they are switched into a channel for encoding and transmission via the ATM network. At the distant end the signal is decoded and routed by a switch into the A / V test generator and measurement set where the markers are detected and the A / V skew calculated, after which the audio and video are routed to the subscriber. The A / V test set signal generator includes a Video Blanking Interval (VBI) test signal generator and a white noise generator, the former injecting a marker into the video signal and the later injecting an audio marker into the audio signal. The video marker is injected into the VBI and broadband, background audio noise to measure the delay between the audio and video components of a broadcast. The marking of the audio is accomplished by gradually injecting white noise into the audio channel until the noise level is 6 dB above the noise floor of the audio receiver. As a precursor A / V sync signal, a small spectrum of the white noise is notched or removed. This signature precludes inadvertent recognition of program audio noise as the audio marker.
Owner:IBM CORP
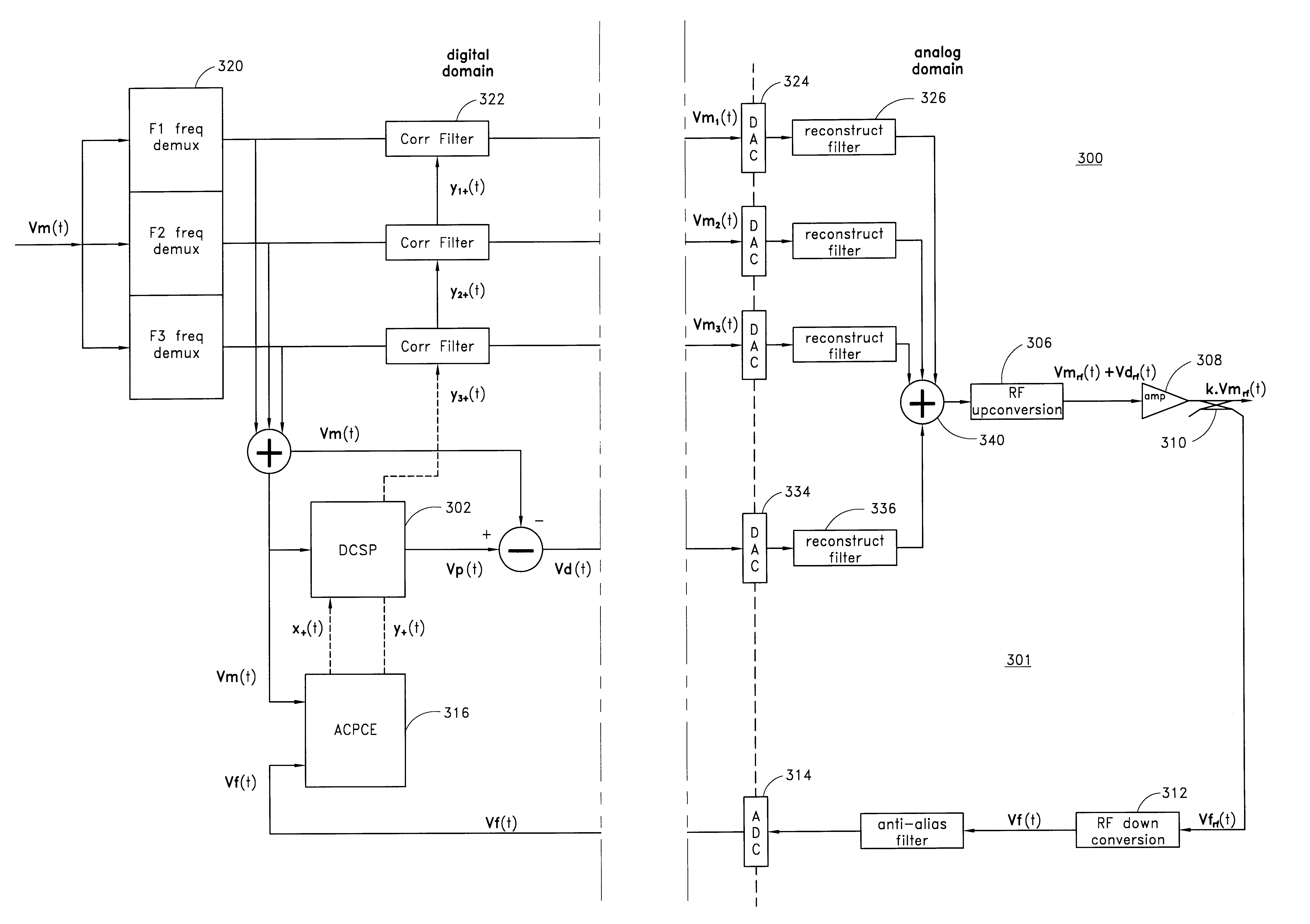
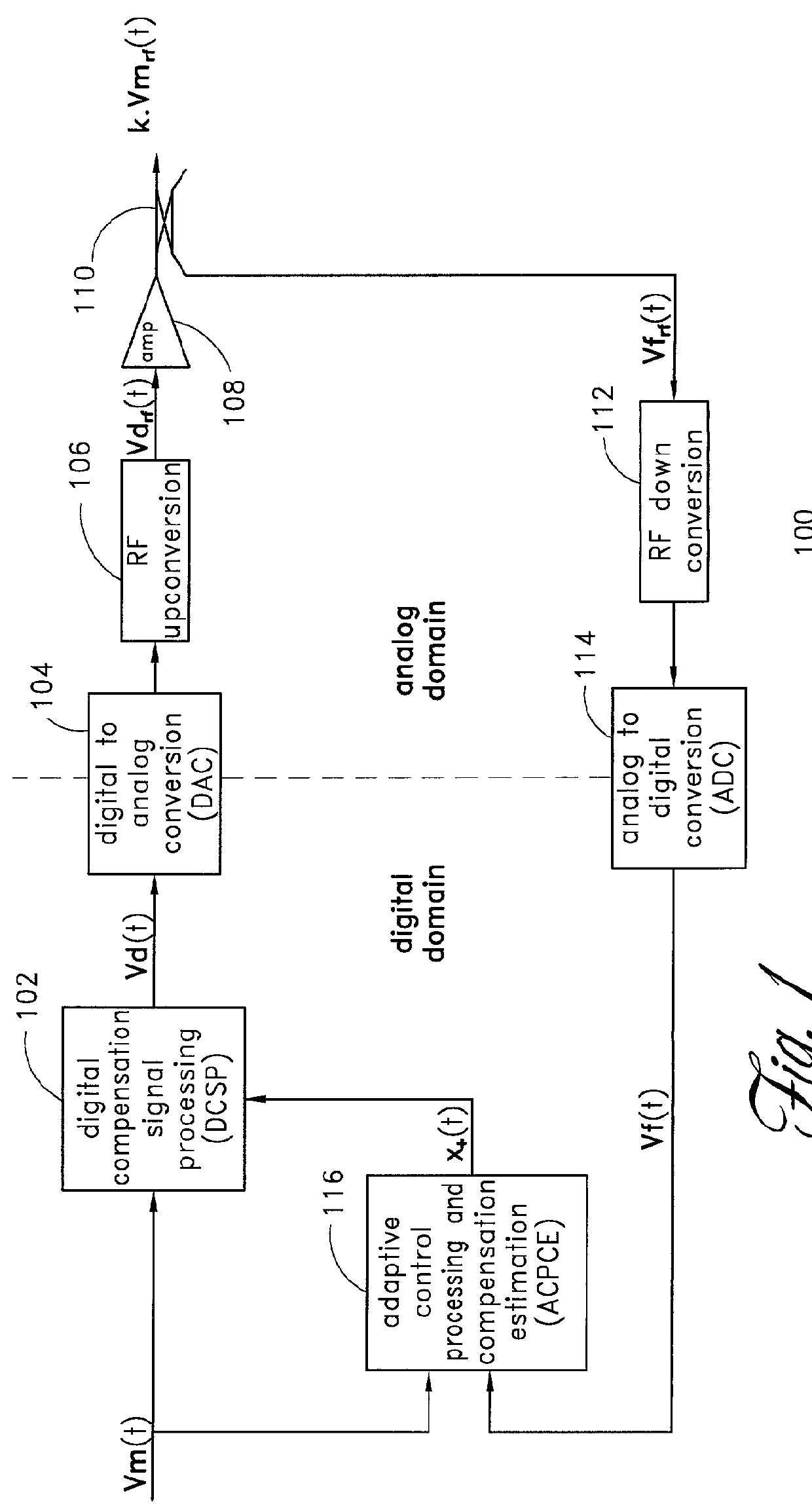
Low noise wideband digital predistortion amplifier
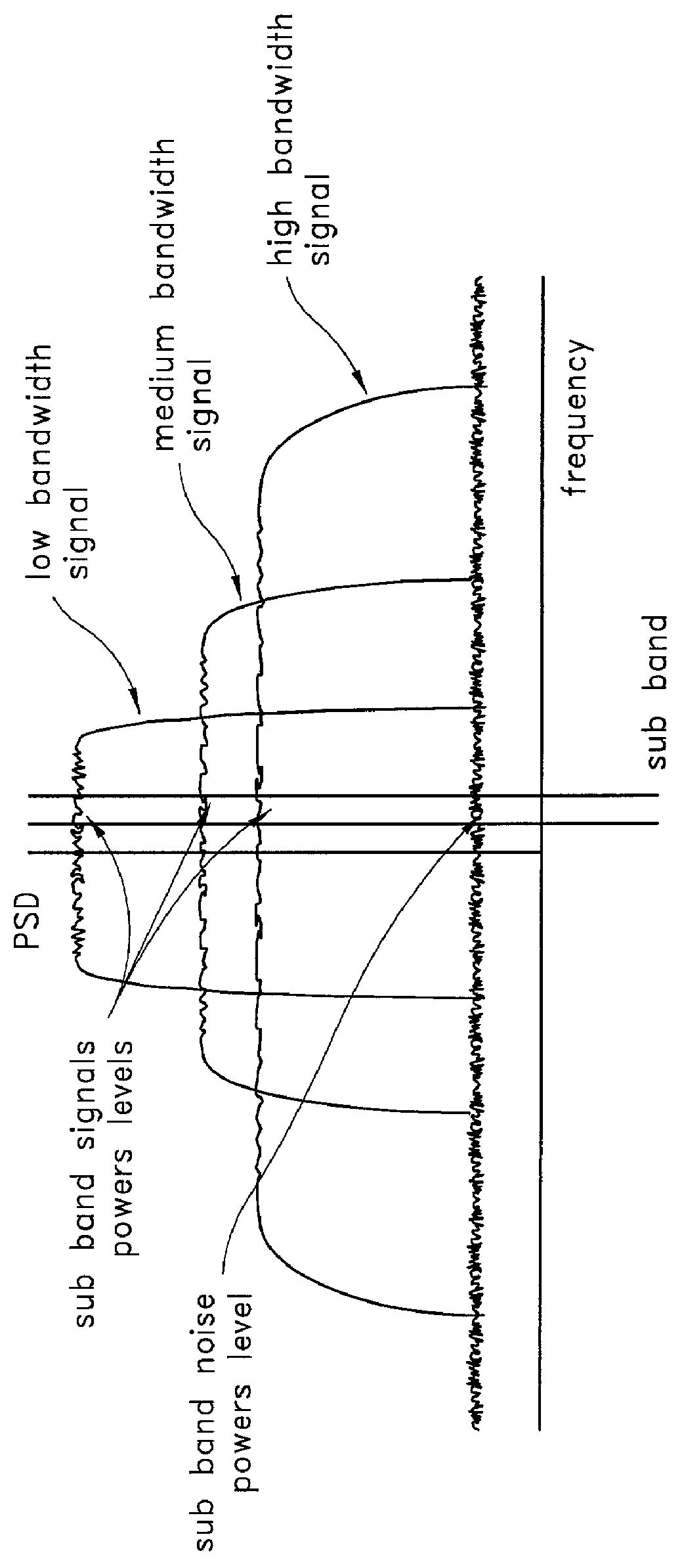
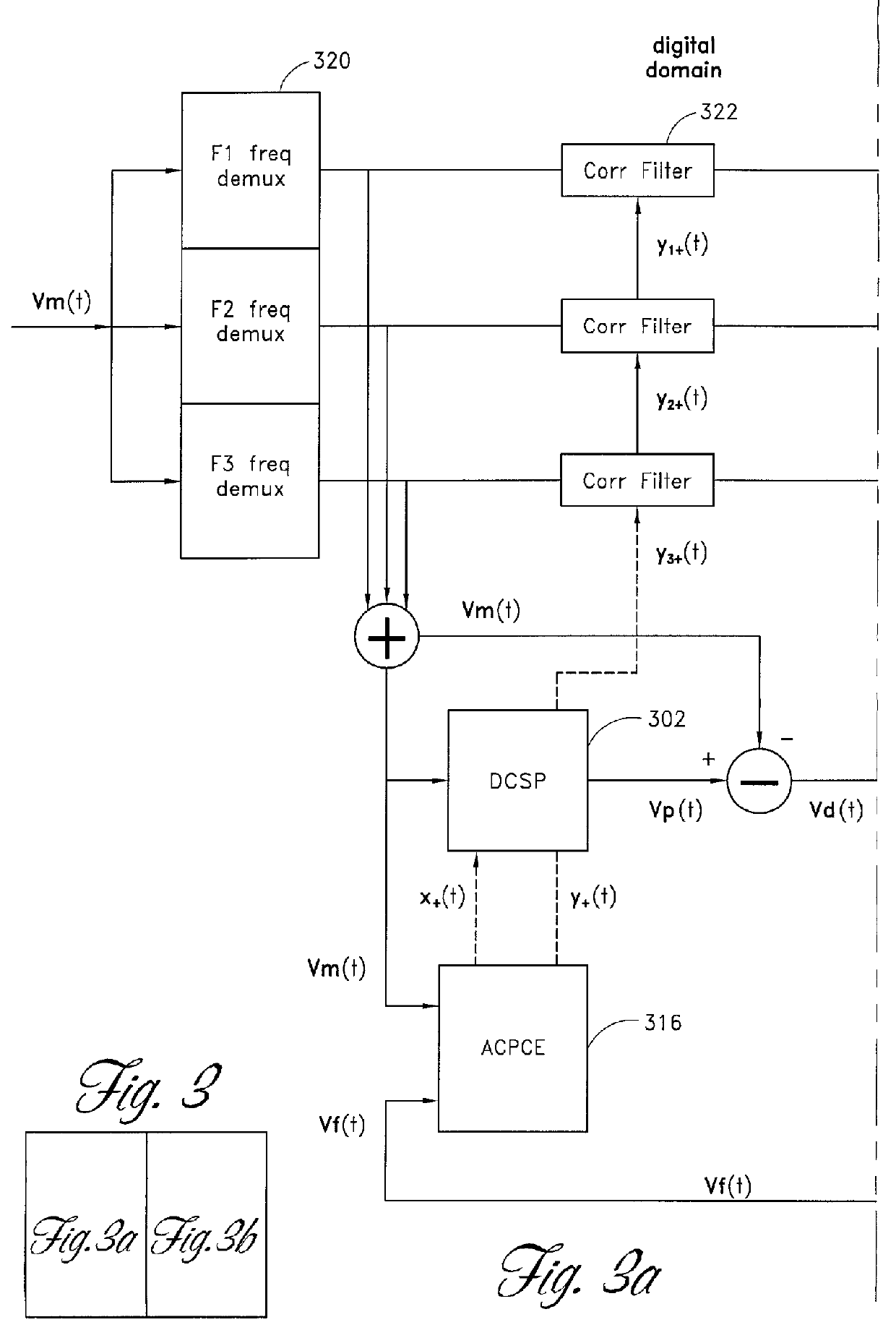
InactiveUS6570444B2Low bandwidthReduce total powerAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsLow noiseSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
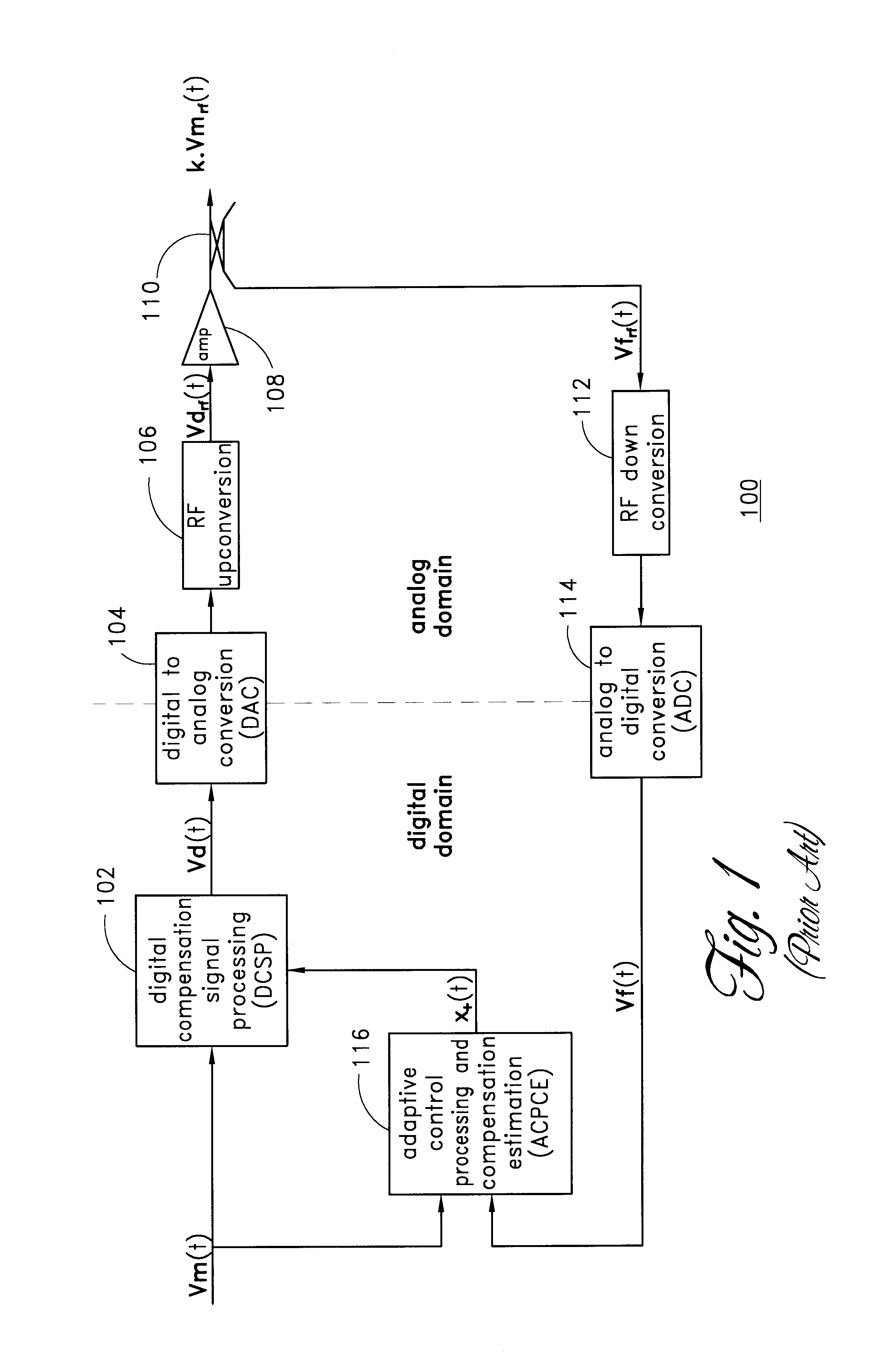
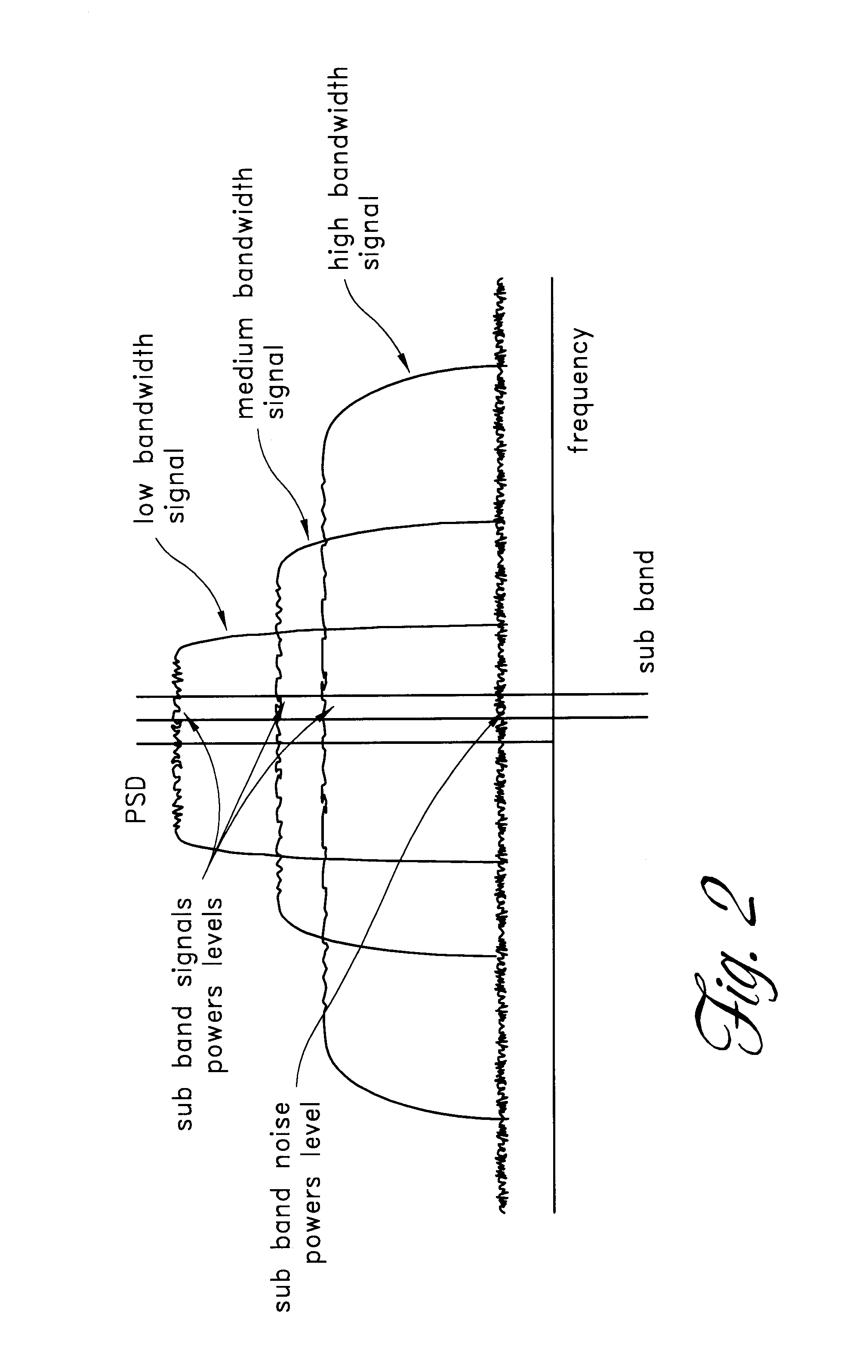
A digital predistortion amplifier design compensates for non-linear amplification of an input signal using predistortion techniques. The design provides a reduced noise floor by using separate digital to analog converters (DAC) to separately convert the input signal and an error correction signal. Furthermore, the input signal can be separated into two or more subbands of narrower bandwidth. Each of the subbands are converted to analog using a separate DAC. By reducing the power and / or bandwidth to be handled by any one DAC, the available levels of quantization of the DAC are applied to a lower power signal and therefore the signal to noise ratio resulting from the conversion process is improved. In addition, each digital subband is passed through a correction filter, which is driven by an adaptive control processing and compensation estimator to compensate for relative gain, phase, and delay inconsistencies between the different subbands.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
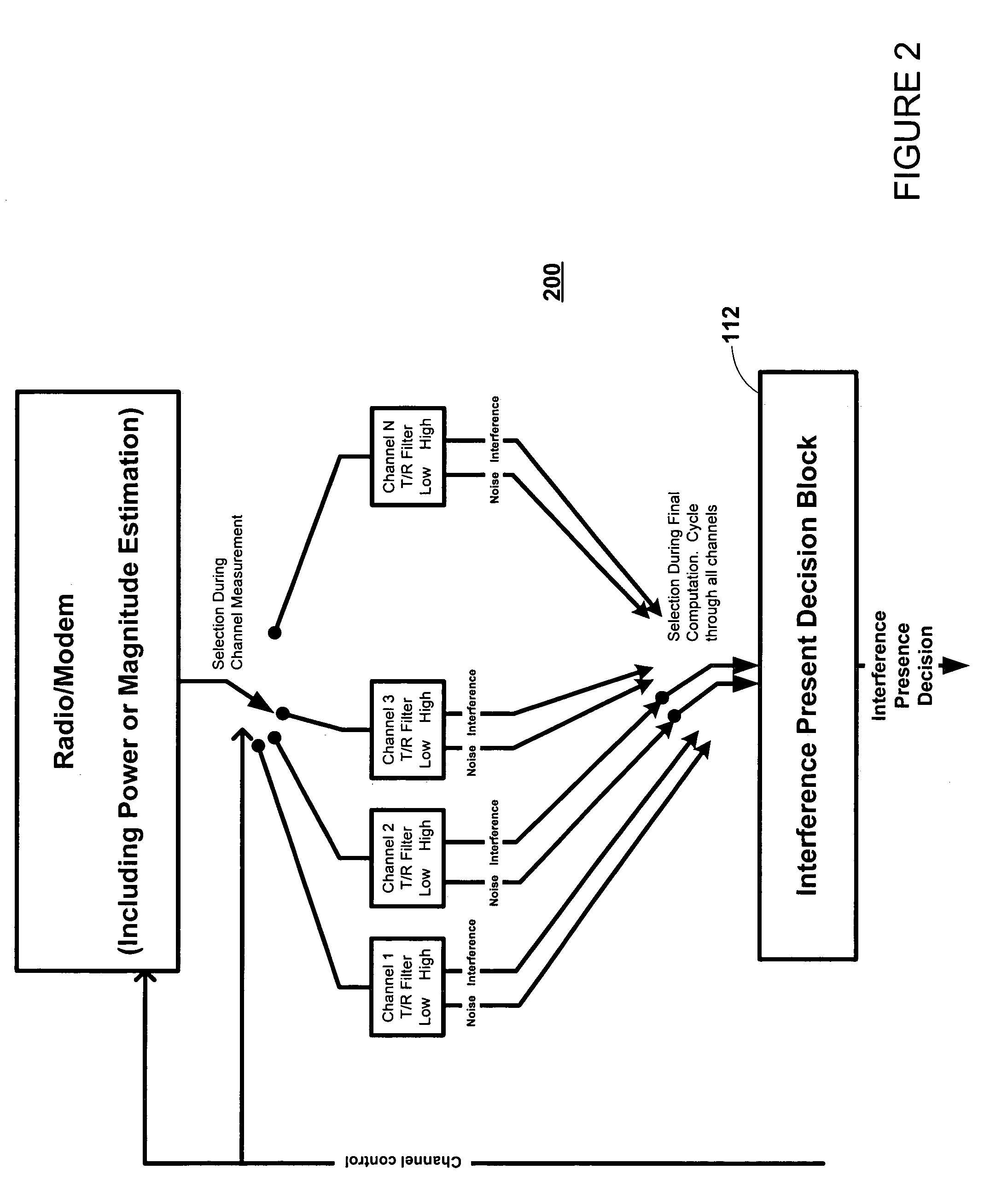
Method and apparatus determining the presence of interference in a wireless communication channel
ActiveUS7103316B1Reduce observationReduce processTransmission monitoringTransmission noise suppressionWireless dataLow input
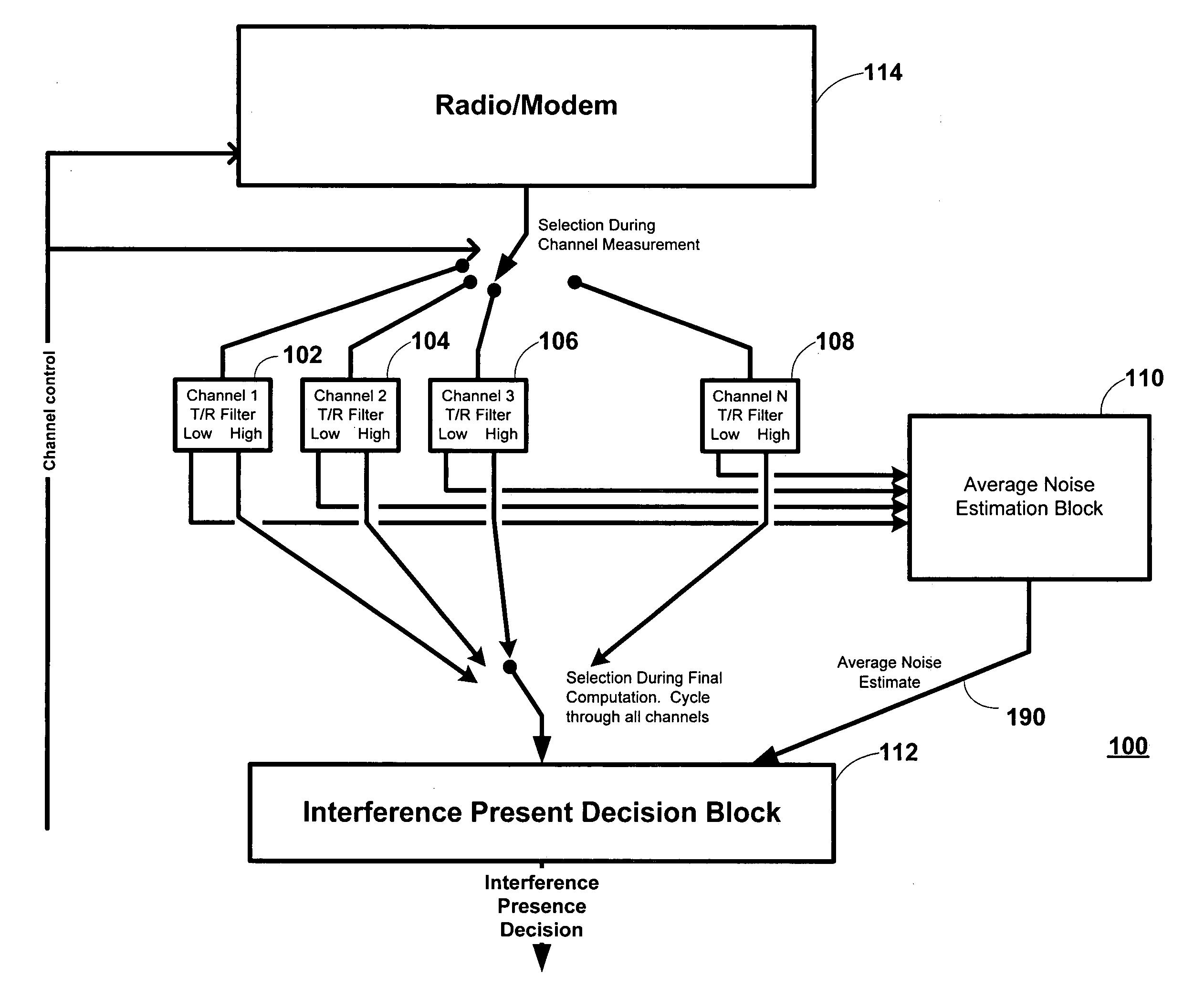
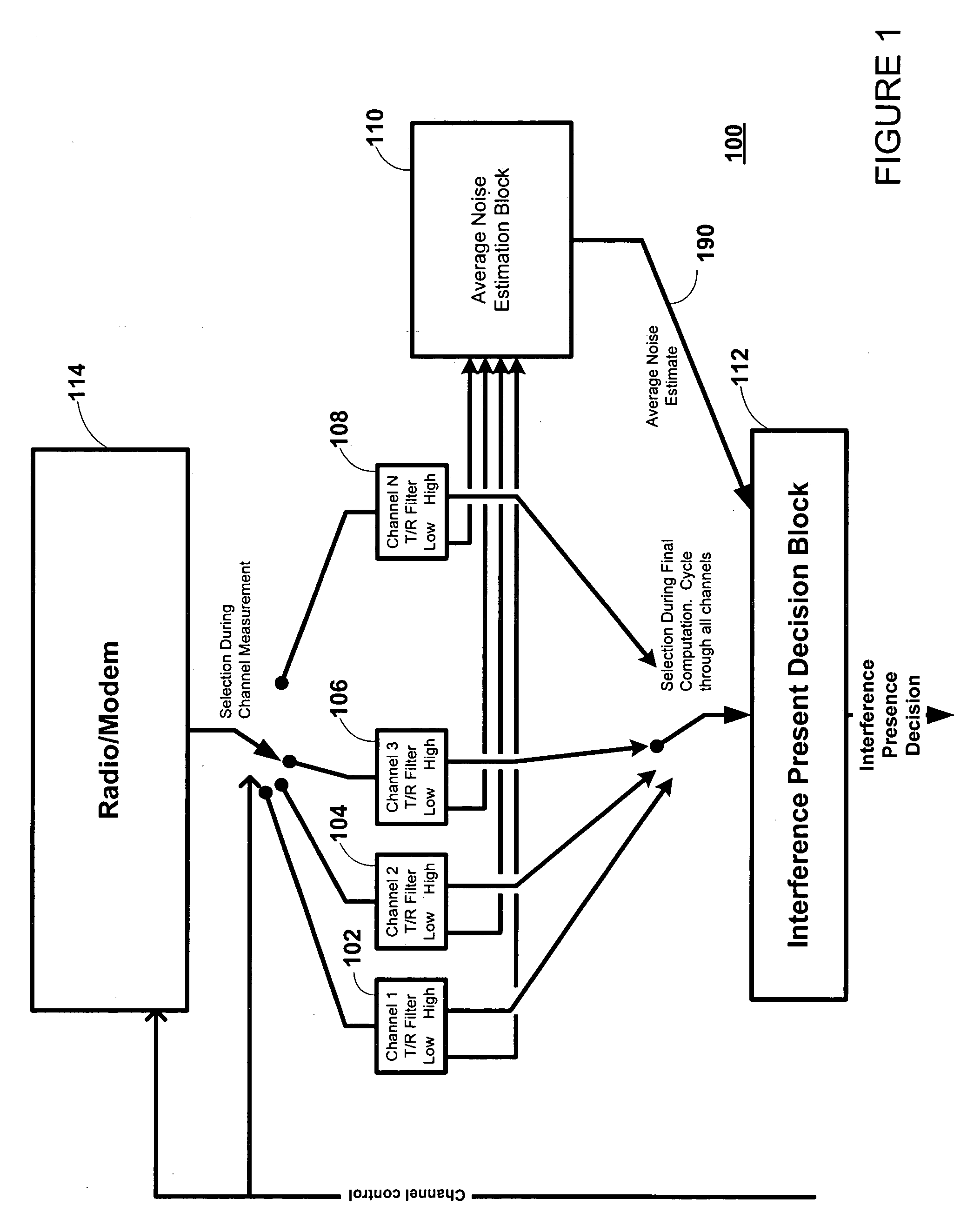
A method and apparatus for estimating the presence of RF interference in a wireless data channel is described. The method and apparatus comprises a set of identical tracking / register (T / R) filter blocks, each T / R filter block associated and corresponding to an RF channel of interest. Each T / R filter block includes a pair of tracking / register (T / R) filters. Power / magnitude estimates from an RSSI calculation are input to the T / R filter blocks. One T / R filter is used to estimate the noise floor (in the absence of interference). The T / R filter latches and filters the lowest input values received from a power / magnitude circuit. The other T / R filter estimates the level of an interferer, if present, by latching and filtering the largest valued outputs of the power / magnitude circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
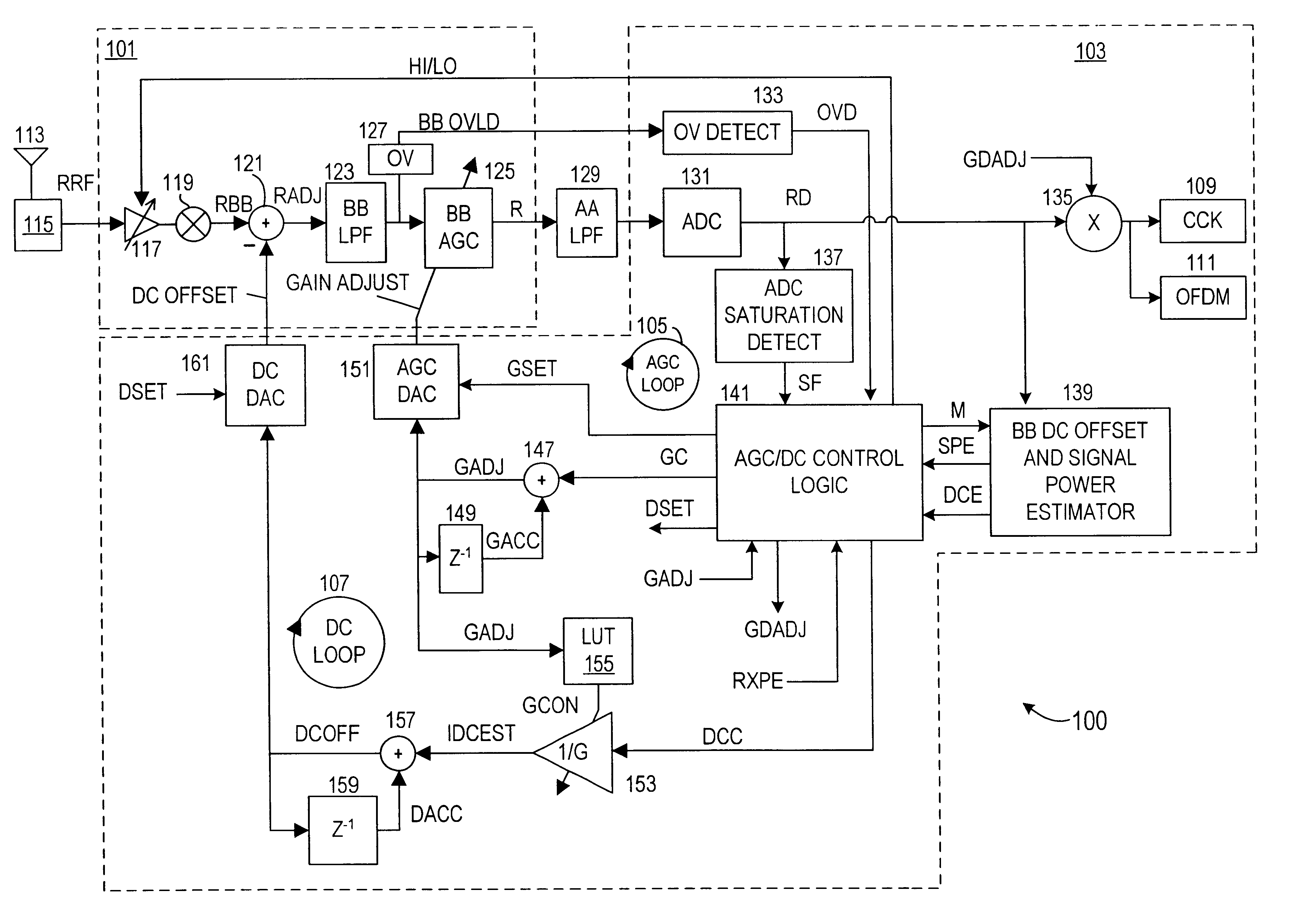
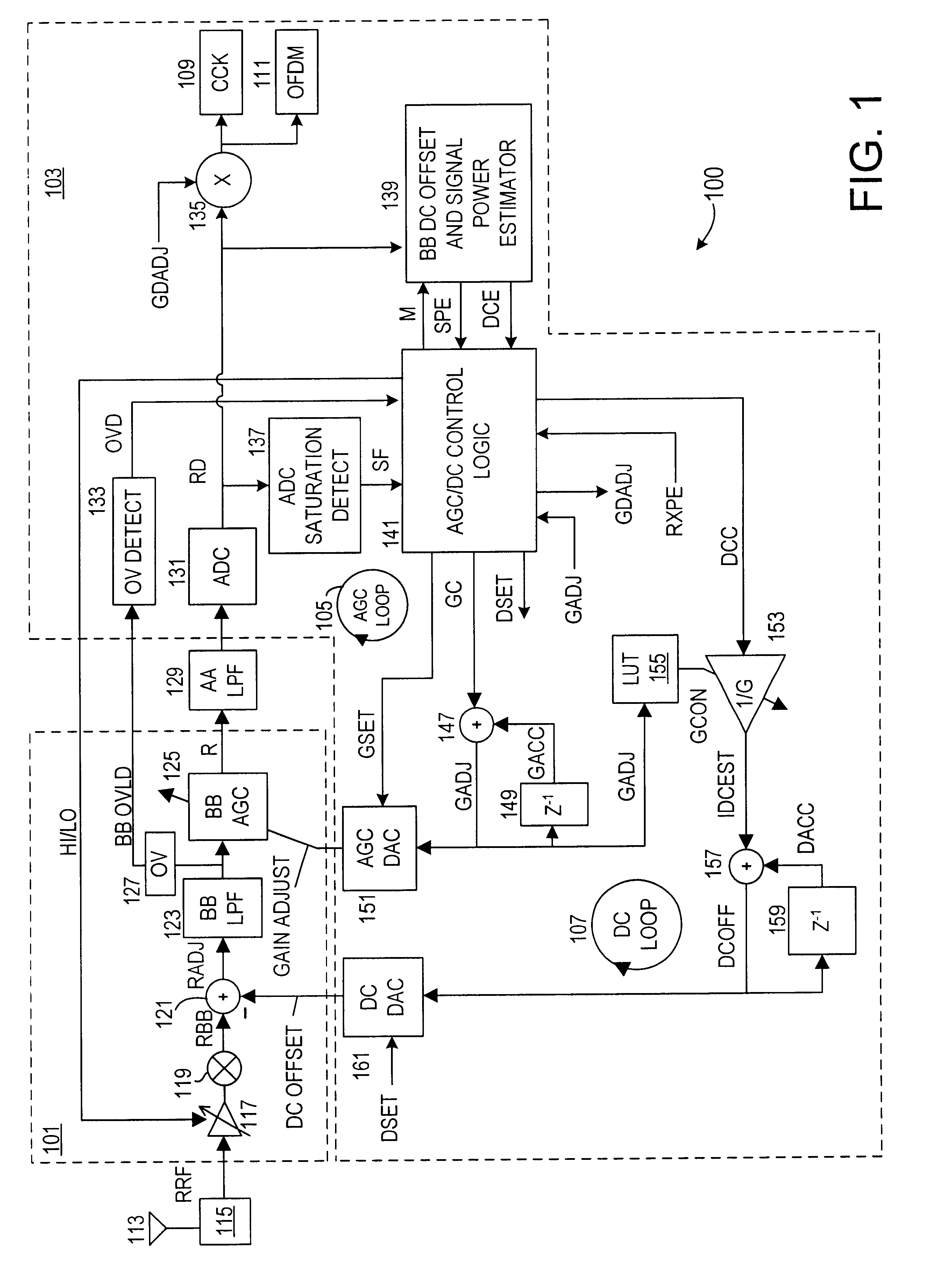
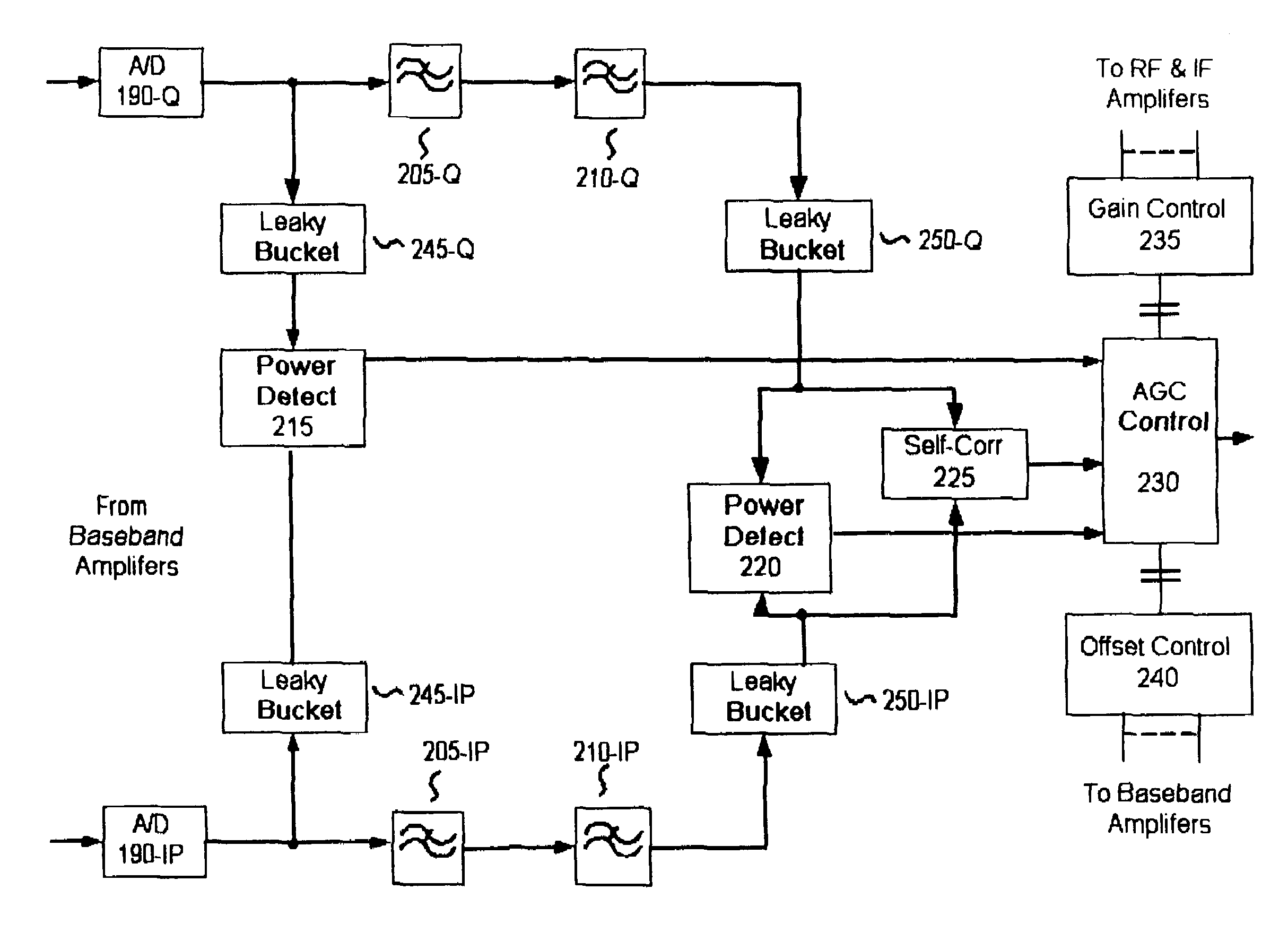
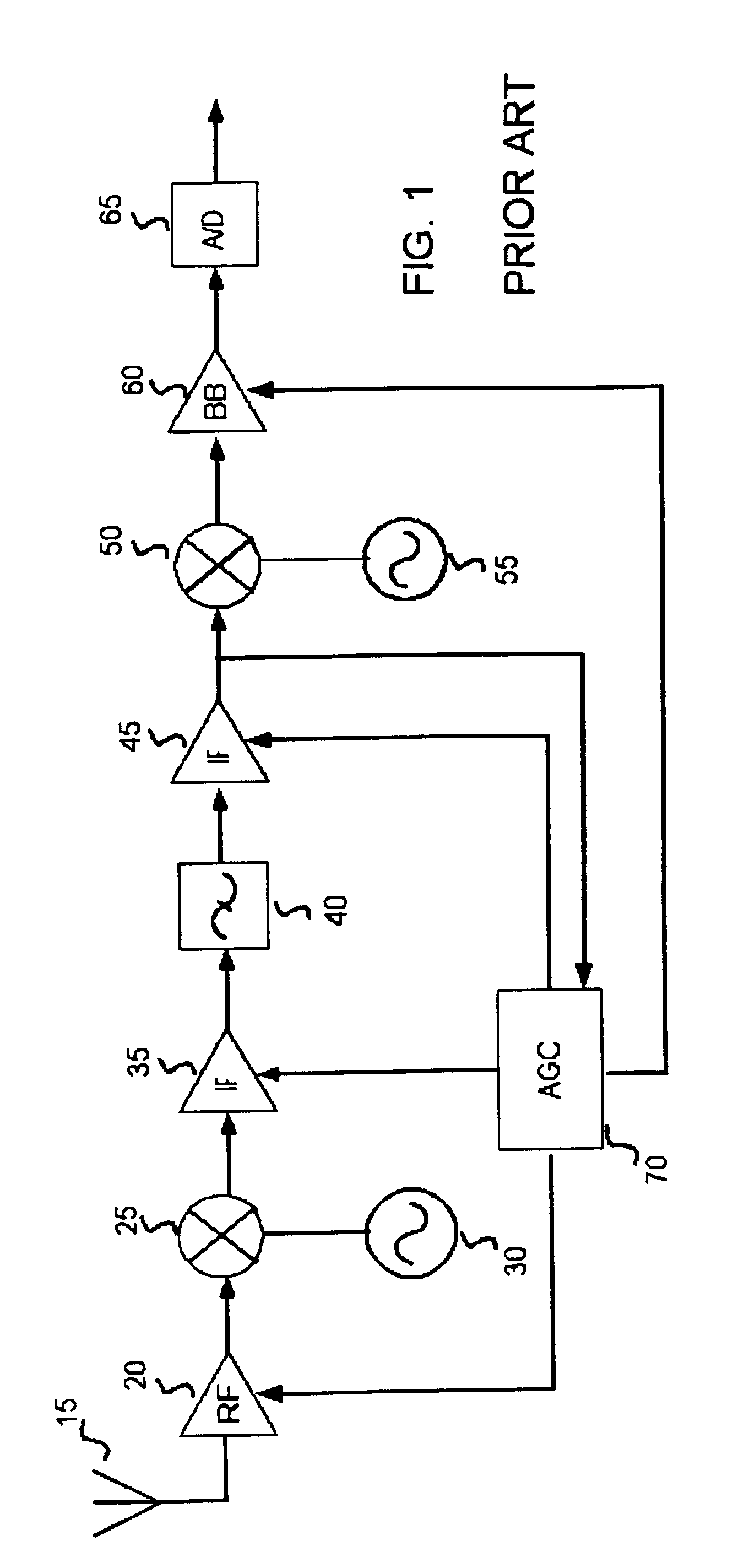
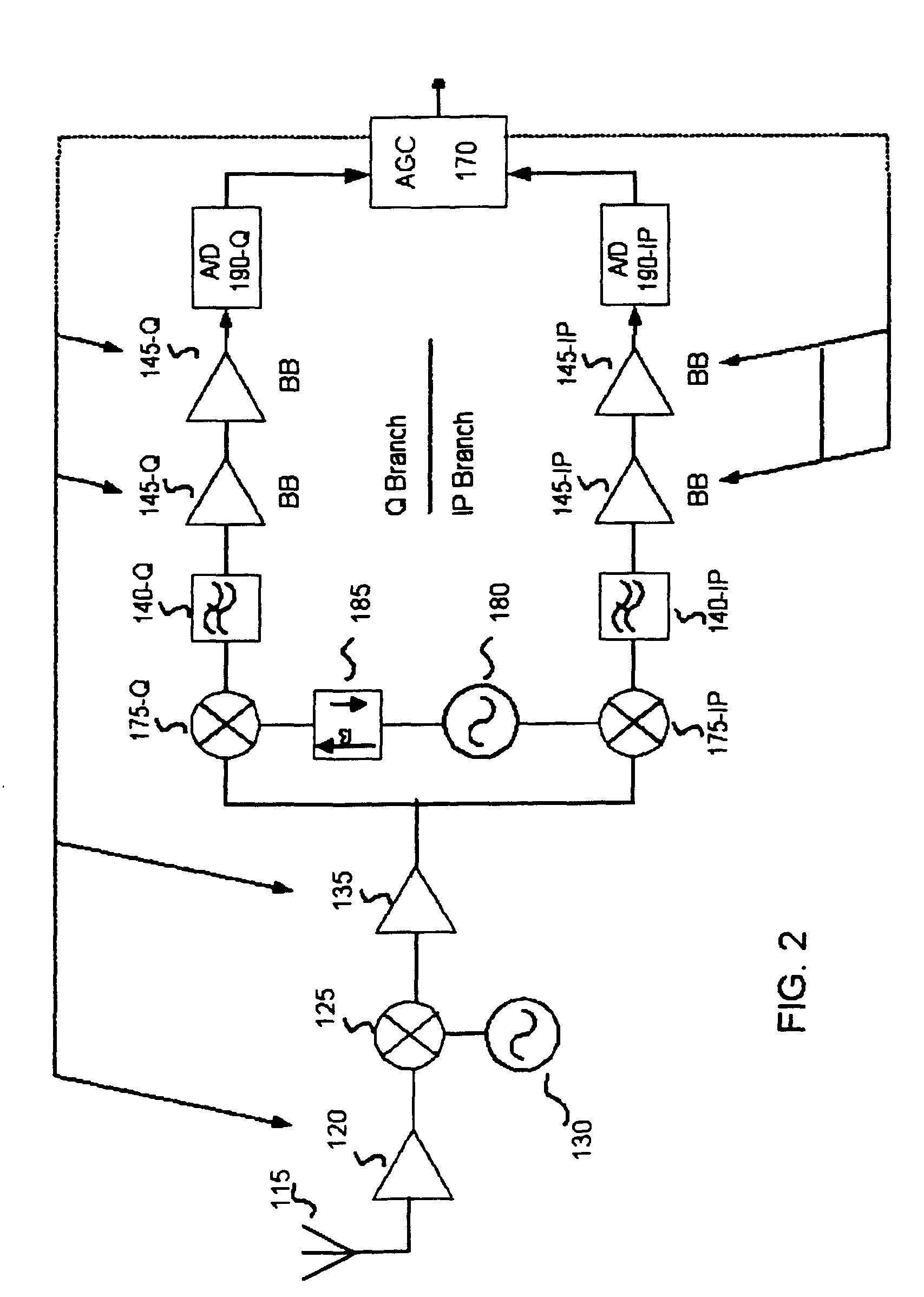
Automatic gain control system and method for a ZIF architecture
A system and method for controlling amplification of a signal received by a ZIF radio having a power level within a full power range relative to a minimum noise floor. The ZIF radio includes a ZIF receiver front end, an overload detector, an ADC, a saturation detector, a DC and power estimator, and control logic. The control logic utilized full visibility of the ADC to limit gain of the baseband amplifier to a maximum gain setting sufficient to view the minimum noise floor and to view a received signal having a power level within any of several segments of the power spectrum. The segmentation of the power spectrum is based on an overload condition of the ZIF receiver front end and a saturation condition of the ADC. The control logic further employs limited gain stepping of the baseband amplifier to avoid exceeding a DC budget of the ADC.
Owner:M RED INC
Interference Classification with Minimal or Incomplete Information
ActiveUS20110188544A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationMonitor modeFrequency spectrum
Interference classification with minimal or incomplete information. Receivers in access points and in other network devices on a wireless digital network may be switched to a spectrum monitor mode in which they provide amplitude-versus-frequency information for a chosen part of the spectrum. This may be performed by performing a FFT or similar transform on the signals from the receiver. Receivers are calibrated with known interference sources in controlled environments to determine peaks, pulse frequency, bandwidth, and other identifying parameters of the interference source in best and worst case conditions. These calibrated values are used for matching interference signatures. Calibration is also performed using partial signatures collected over a short period in the order of microseconds. These partial signals may be used to detect interferers while scanning. Another aspect of the invention is to record the variation of noise floor in the presence of interference sources. Multiple interference sources may be detected. While data collection is performed in one or more APs, classification may be performed in theAP or on other systems associated with the network collecting and processing spectrum information from one or more APs.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method of channel order selection and channel estimation in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS6907092B1Choose accuratelyLarge energyError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemImpulse response
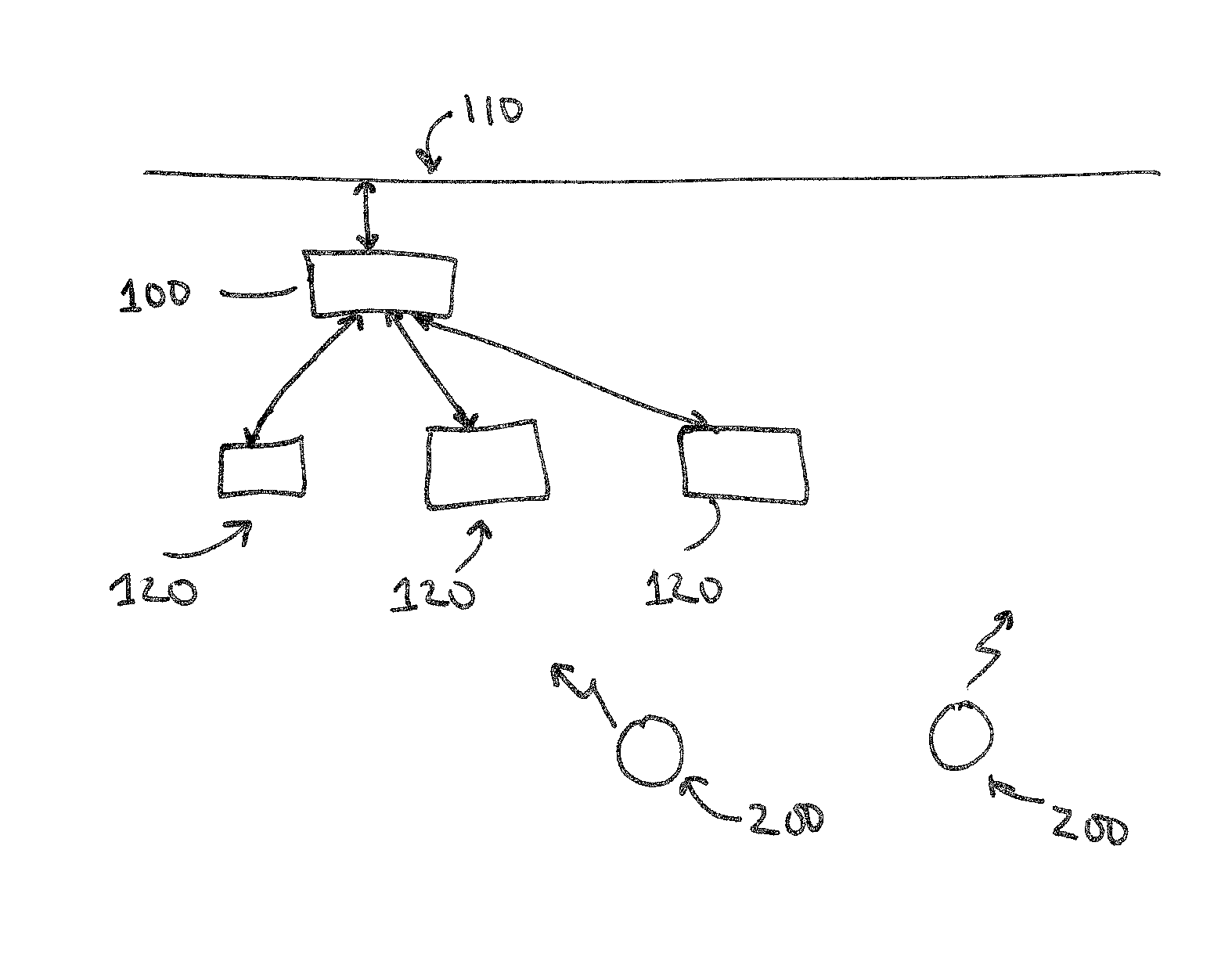
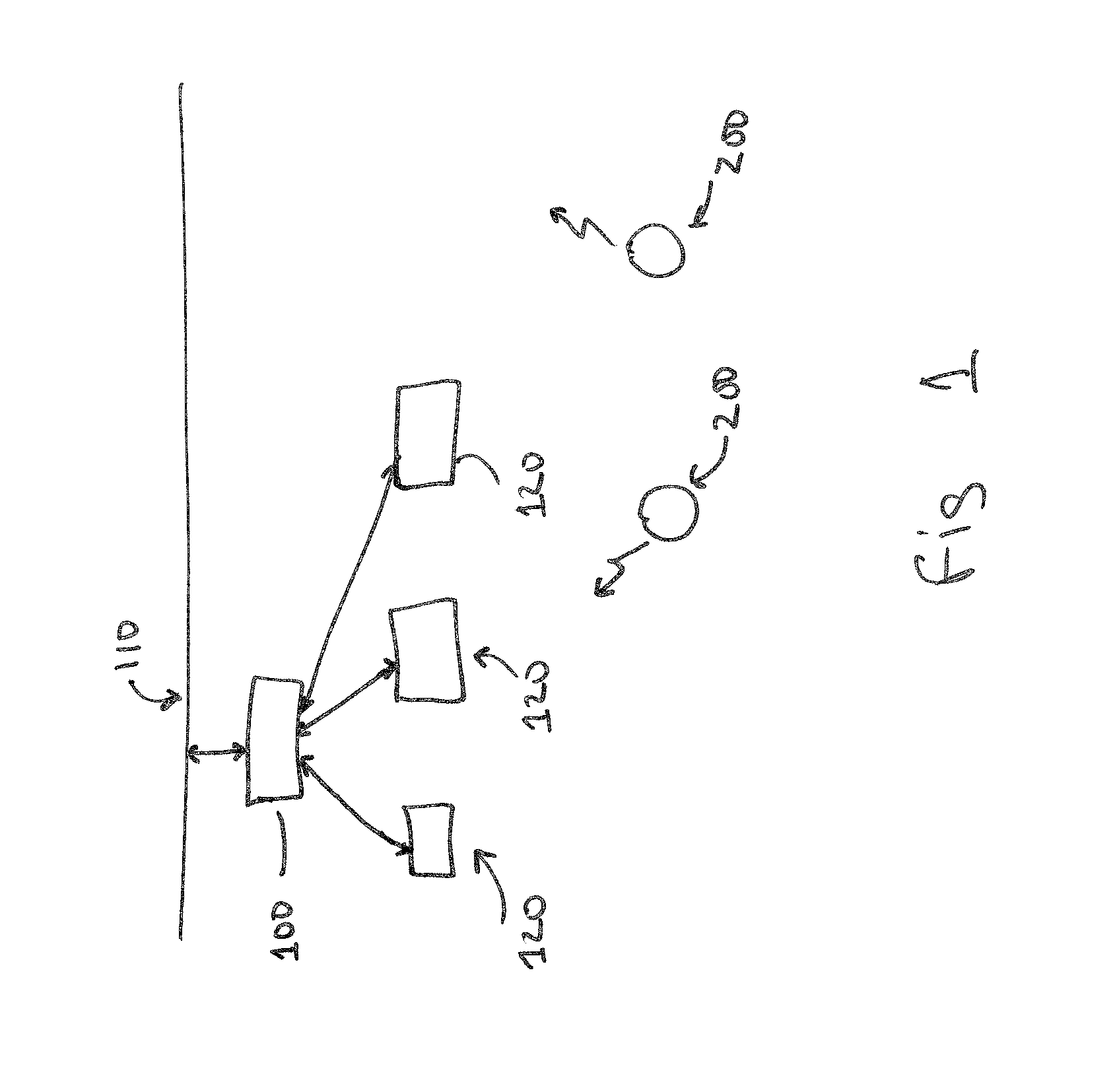
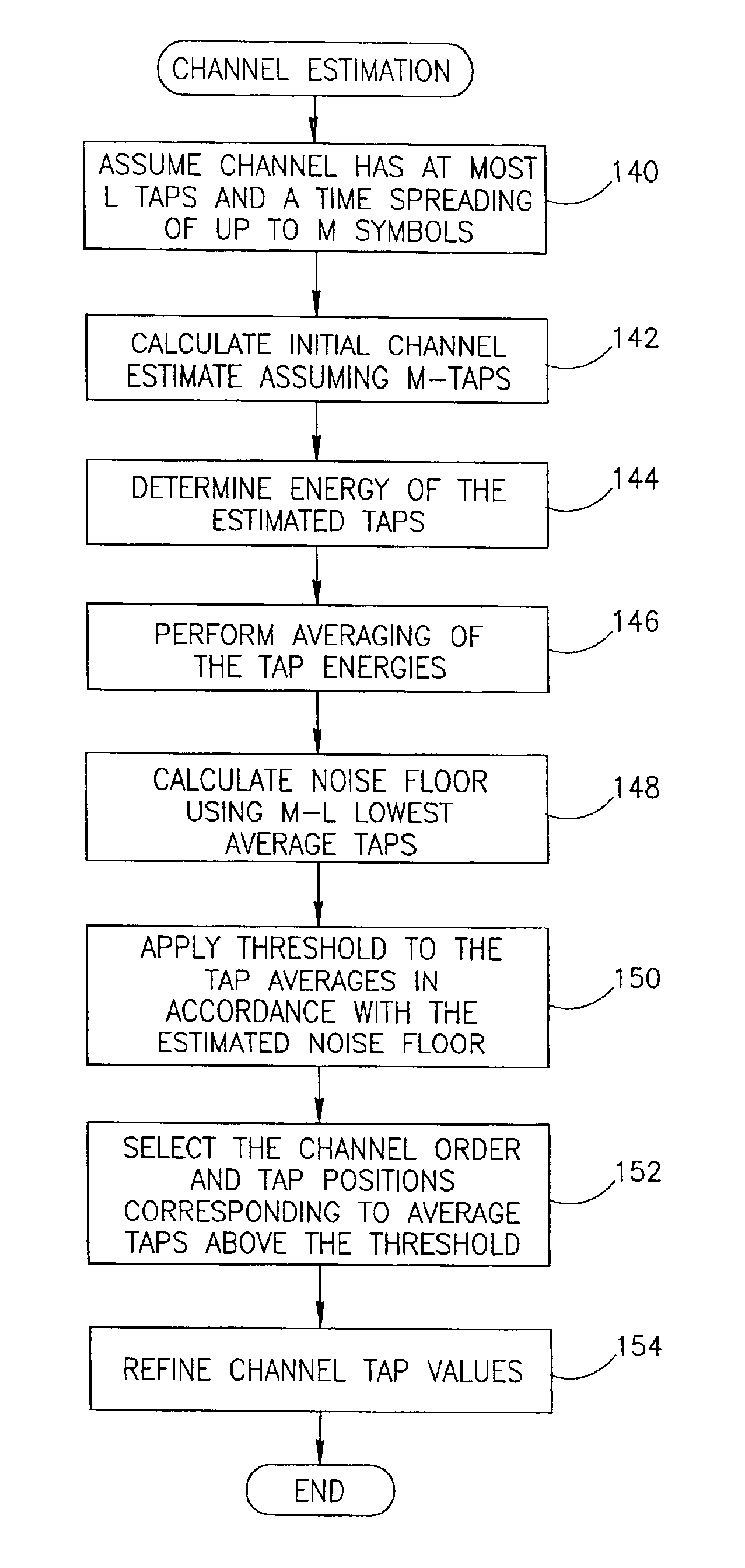
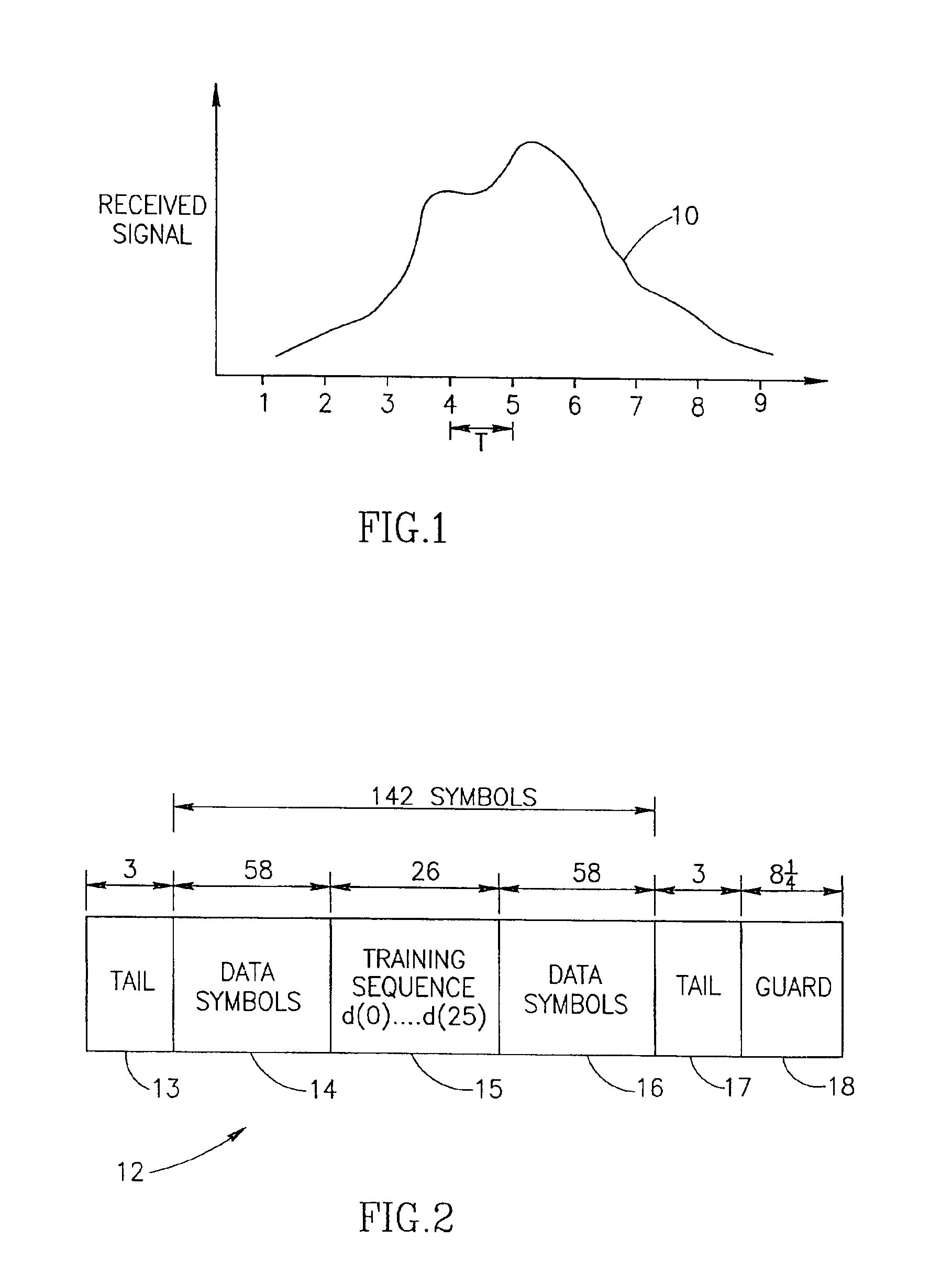
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of determining the channel order and channel estimate in a communications system such as a wireless communication system including cellular and cordless. Such channels are typically characterized by rapidly changing impulse response and their taps can be modeled as zero-mean, complex, Gaussian random processes. A sufficiently long, initial channel estimate of length is performed so as to ensure that the actual channel taps will be contained in the estimated taps thus making certain that the equalizer will effectively eliminate intersymbol interference. Channel estimation is performed during each burst using the training sequence transmitted in the middle of the burst. The tap energies are averaged so as to track slow variations in the pattern of resultant channel taps. A noise floor is calculated using the lowest averaged taps and a threshold is computed based thereon and applied to the average taps. The channel order and the tap positions are then selected in accordance those average taps that are above the threshold.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
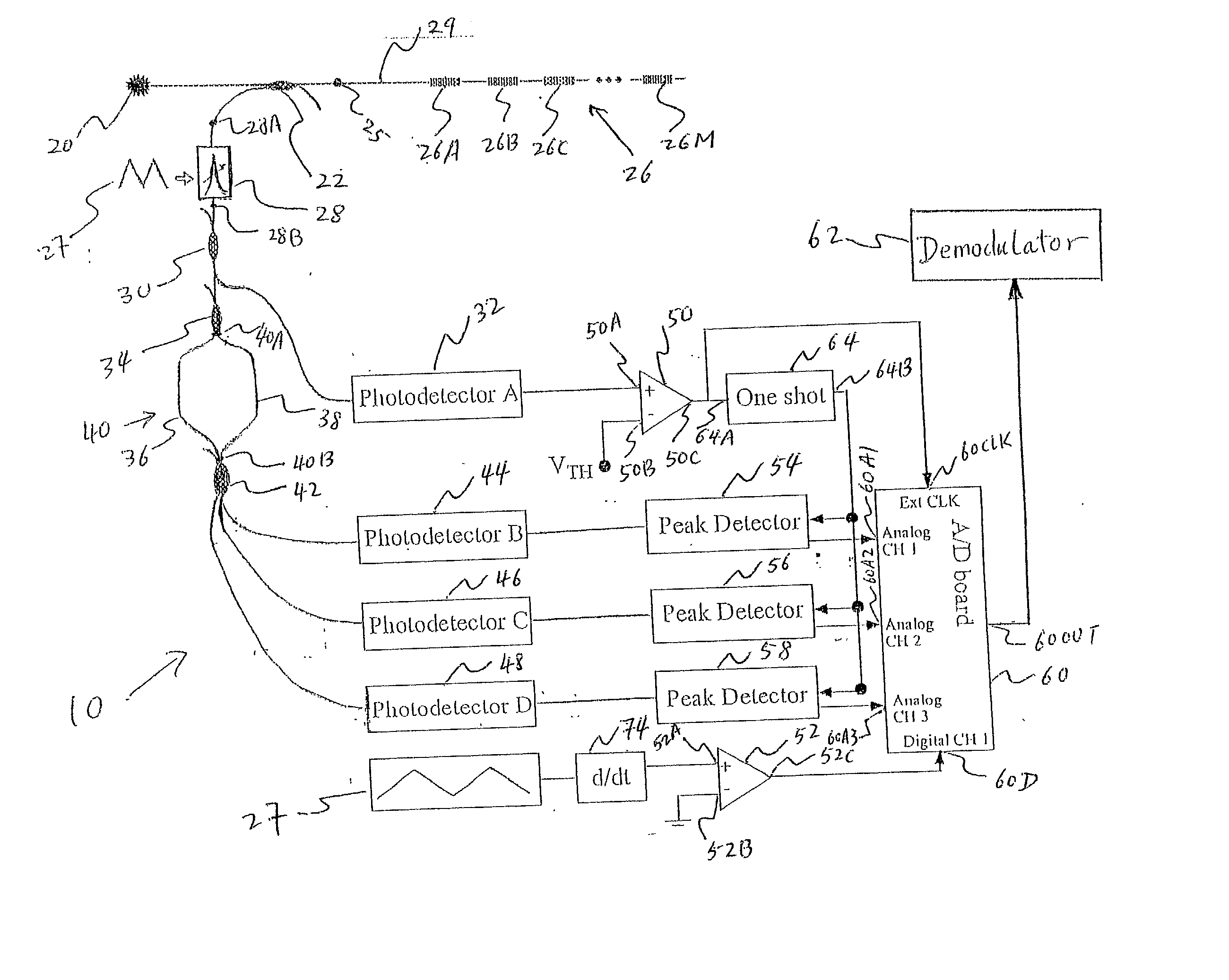
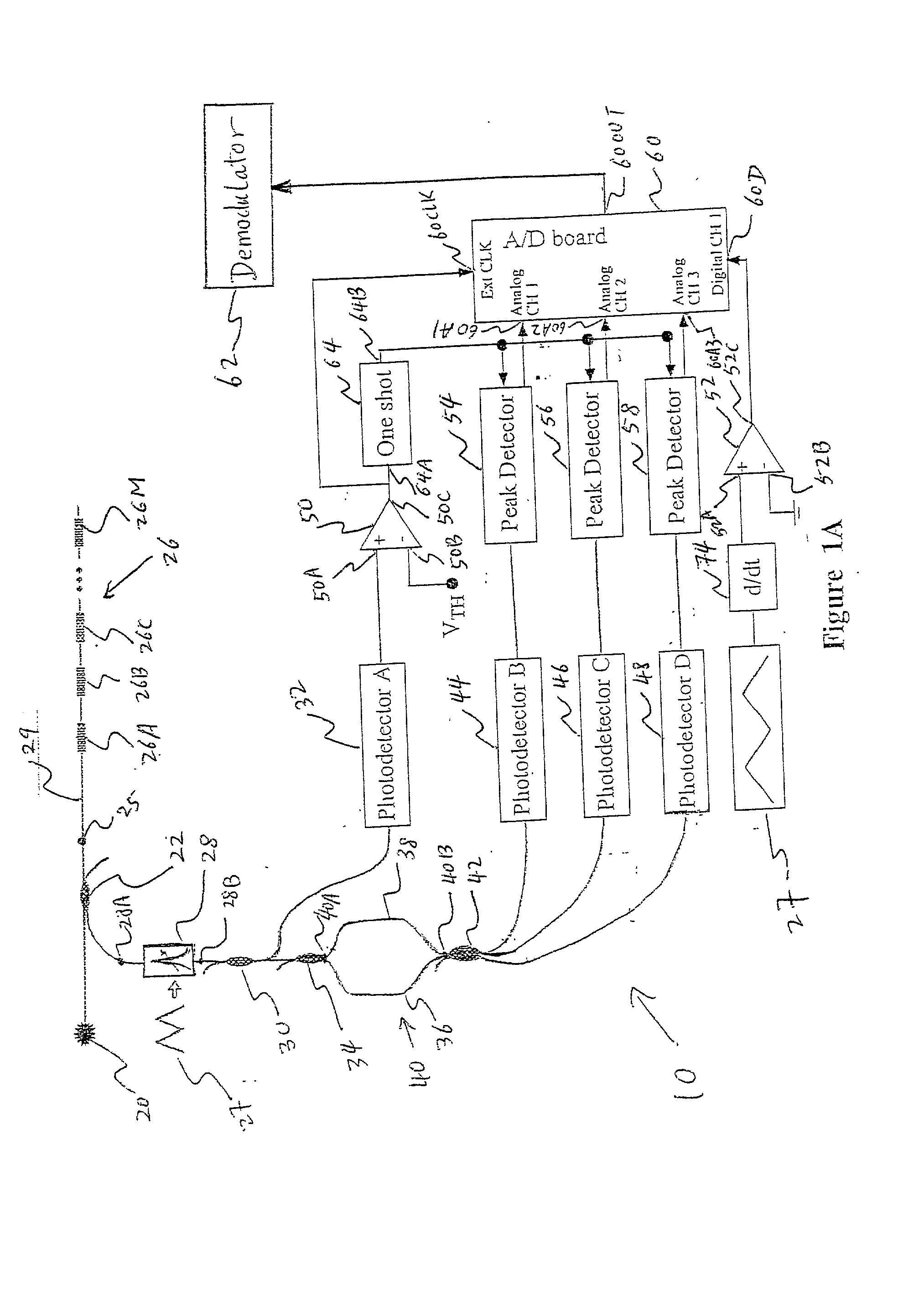
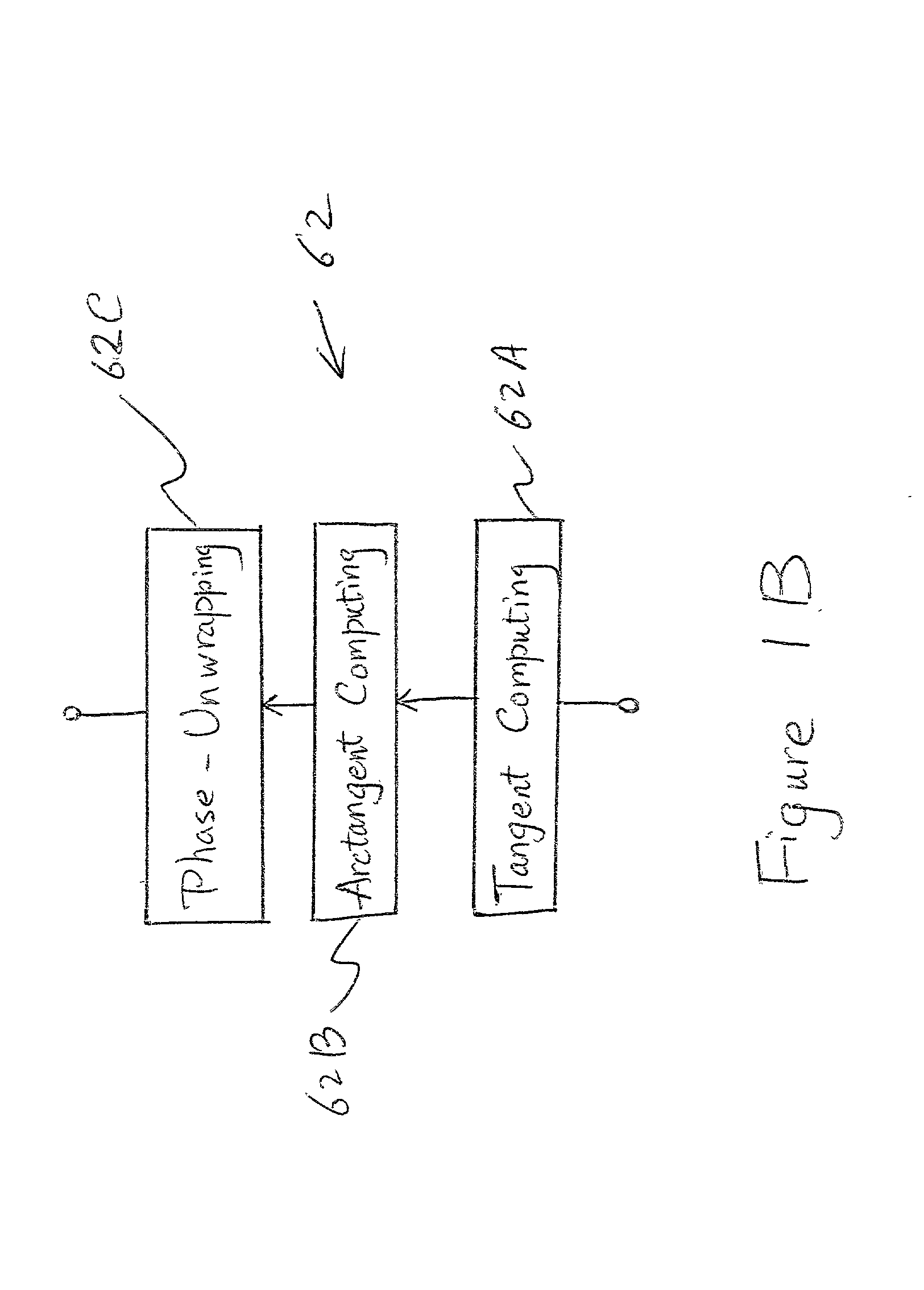
Optical sensing device containing fiber bragg gratings
InactiveUS20020041722A1Limit bandwidthLimit dynamic rangeForce measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesBandpass filteringMultiplexing
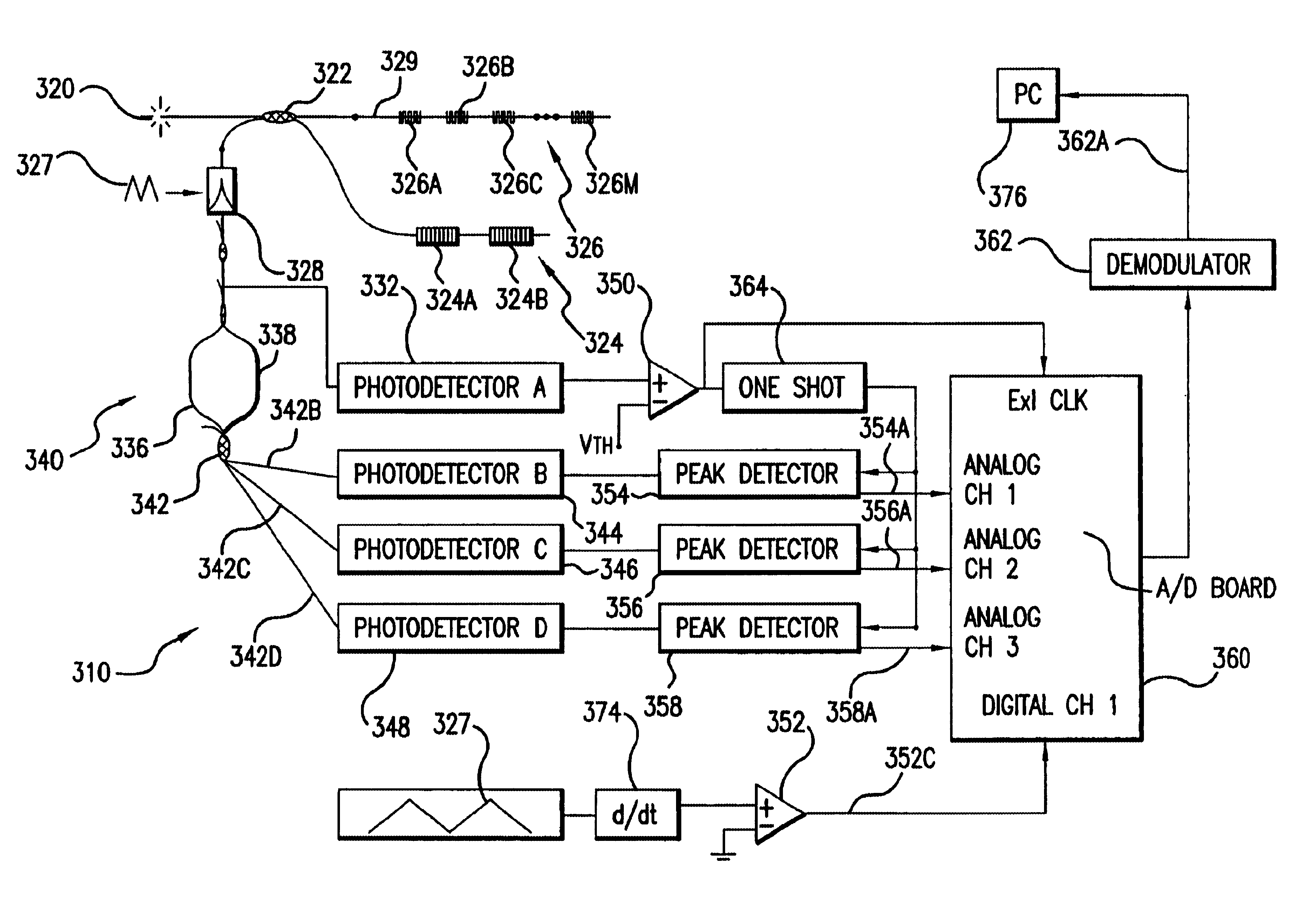
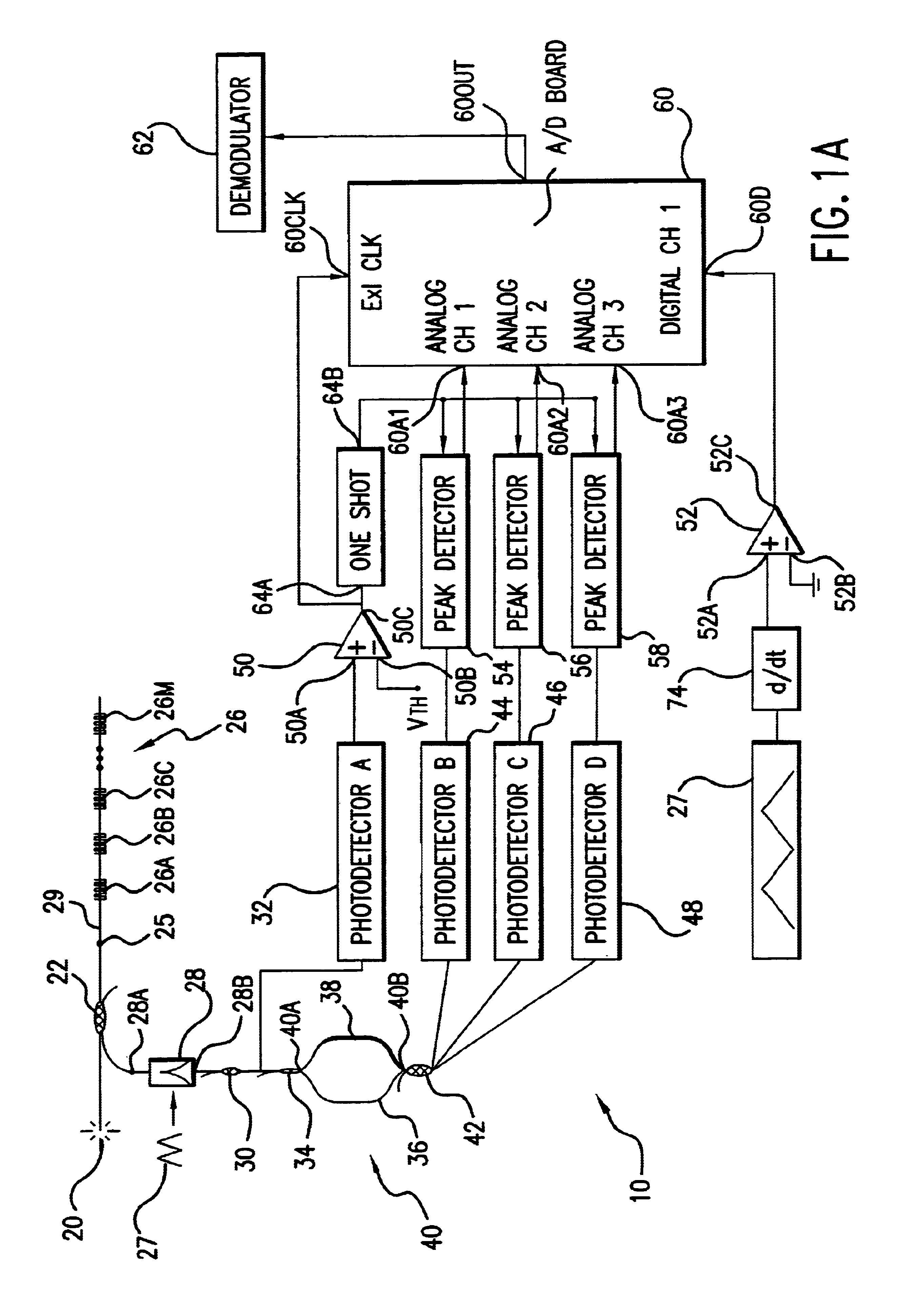
A new optical sensing device containing fiber Bragg gratings, a scanning bandpass filter, an interferometer and multiple photodetectors is disclosed. The present invention also describes a new system and method for fibre Bragg grating (FBG) sensor interrogation and multiplexing. The new system combines a scanning Fabry-Perot (SFP) bandpass filter used to wavelength-multiplex multiple gratings in a single fiber, and an unbalanced Mach-Zehnder fibre interferometer made with a 3x3 coupler to detect strain-induced wavelength shifts. A passive technique for interferometer drift compensation using non-sensing FBGs is included in the system. A complete prototype system interrogates four gratings in a single fiber at a Nyquist sampling rate up to 10 kHz, with a noise floor measured near 4 nepsi Hz-½ above 0.1 Hz. The inclusion of the interferometer drift compensation technique is shown to make quasi-static measurements feasible.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Low noise wideband digital predistortion amplifier
InactiveUS20010054974A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsLow noiseSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A digital predistortion amplifier design compensates for non-linear amplification of an input signal using predistortion techniques. The design provides a reduced noise floor by using separate digital to analog converters (DAC) to separately convert the input signal and an error correction signal. Furthermore, the input signal can be separated into two or more subbands of narrower bandwidth. Each of the subbands are converted to analog using a separate DAC. By reducing the power and / or bandwidth to be handled by any one DAC, the available levels of quantization of the DAC are applied to a lower power signal and therefore the signal to noise ratio resulting from the conversion process is improved. In addition, each digital subband is passed through a correction filter, which is driven by an adaptive control processing and compensation estimator to compensate for relative gain, phase, and delay inconsistencies between the different subbands.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
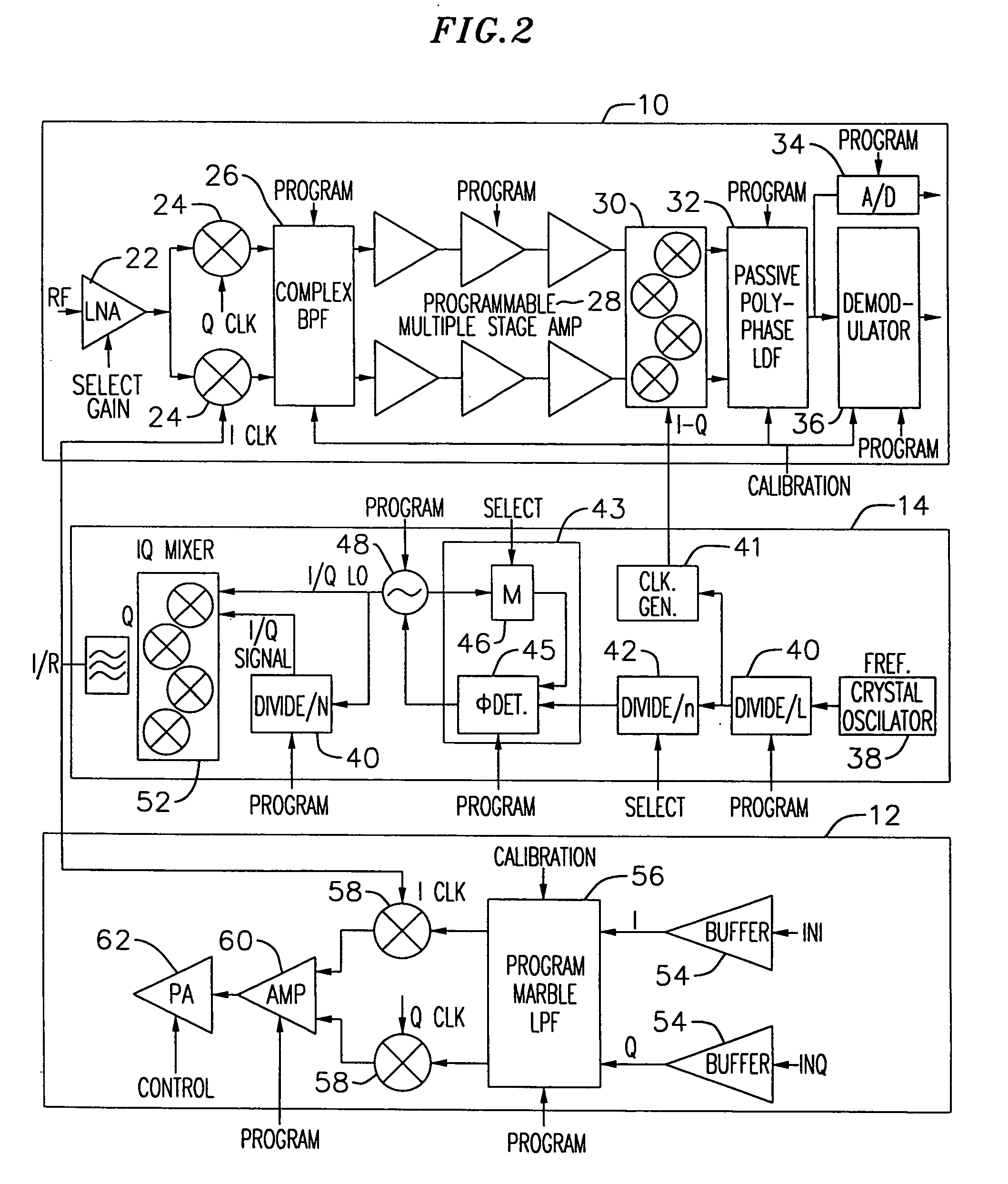
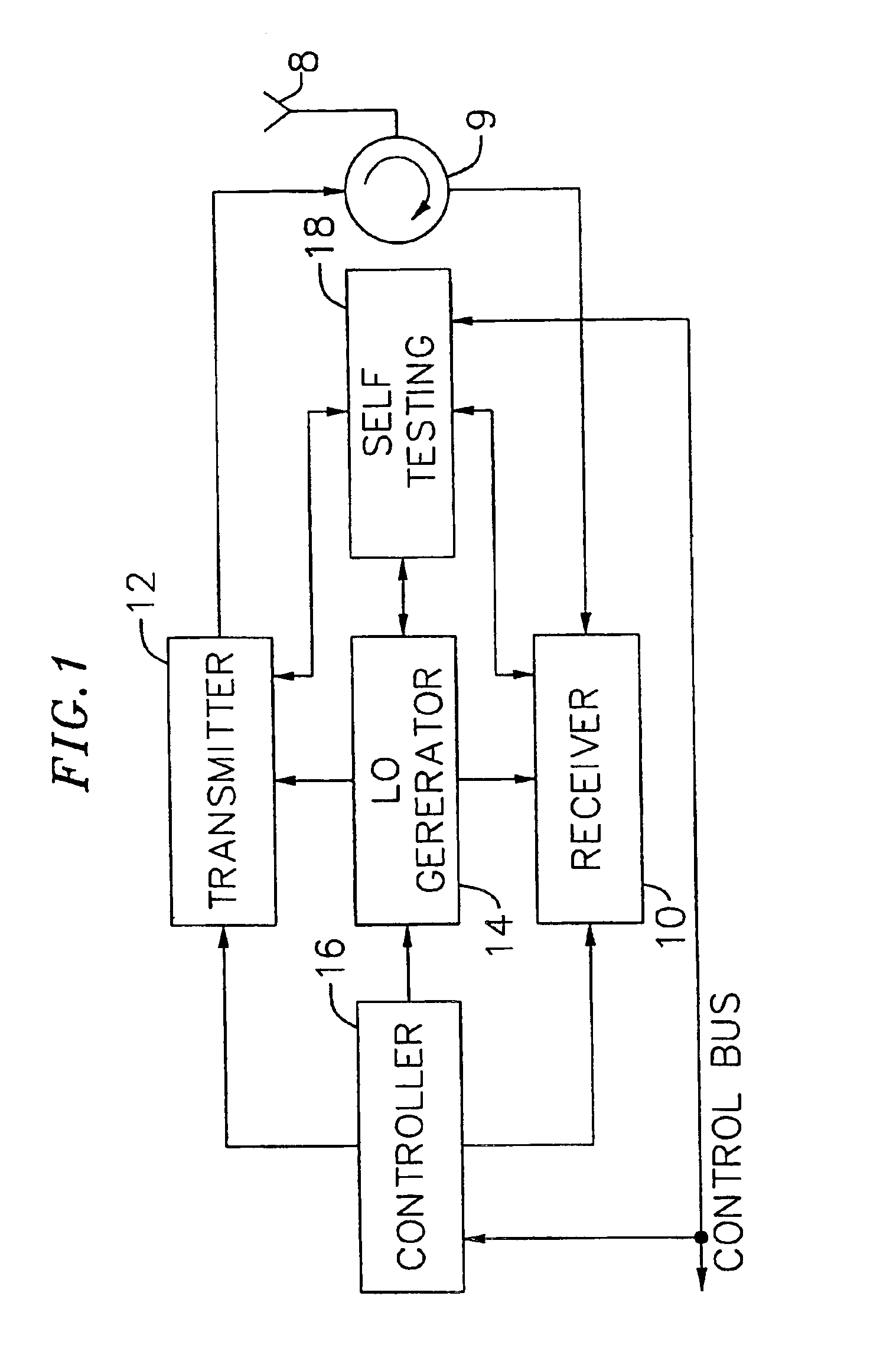
Adaptive radio transceiver with floating MOSFET capacitors
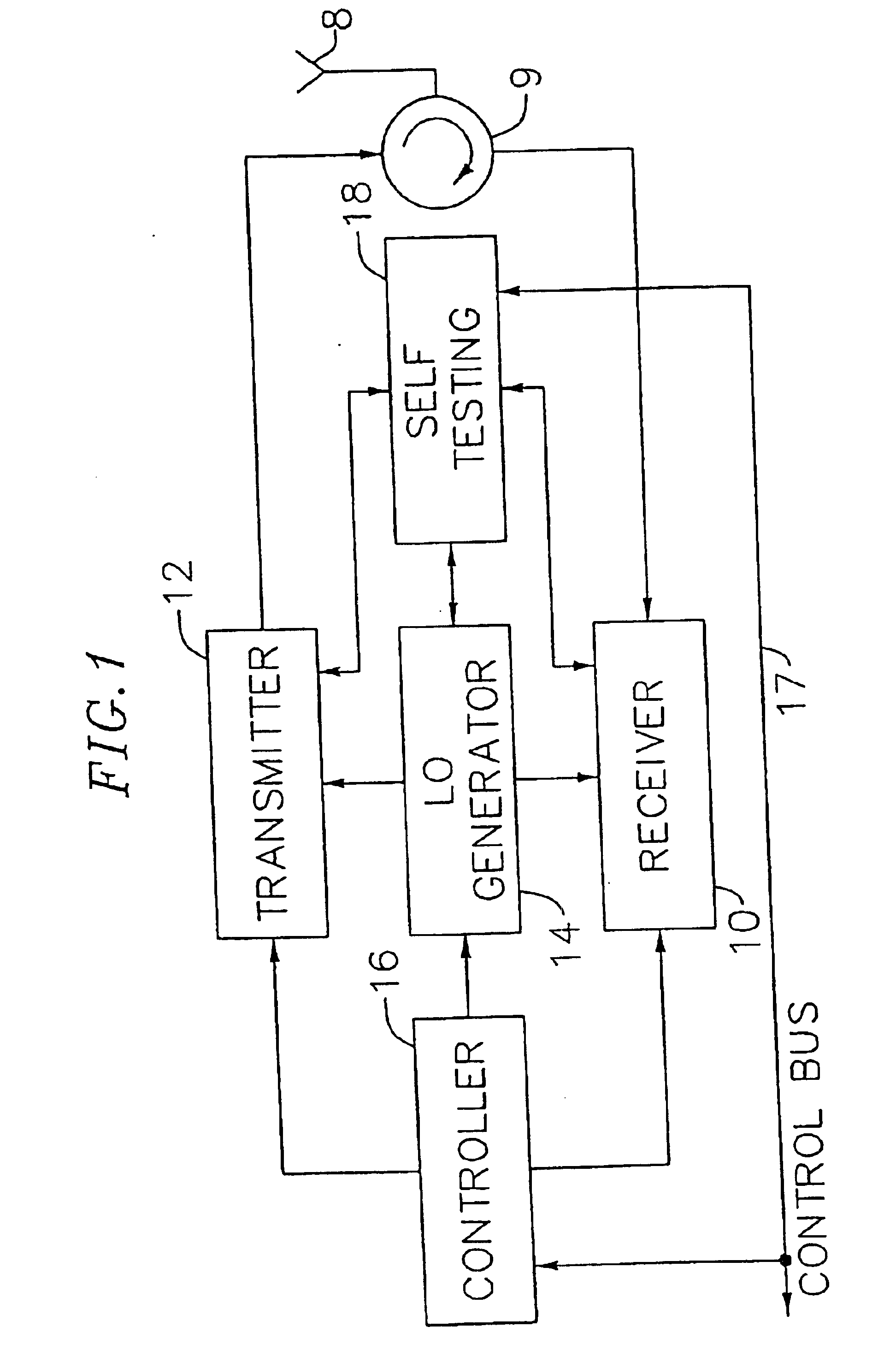
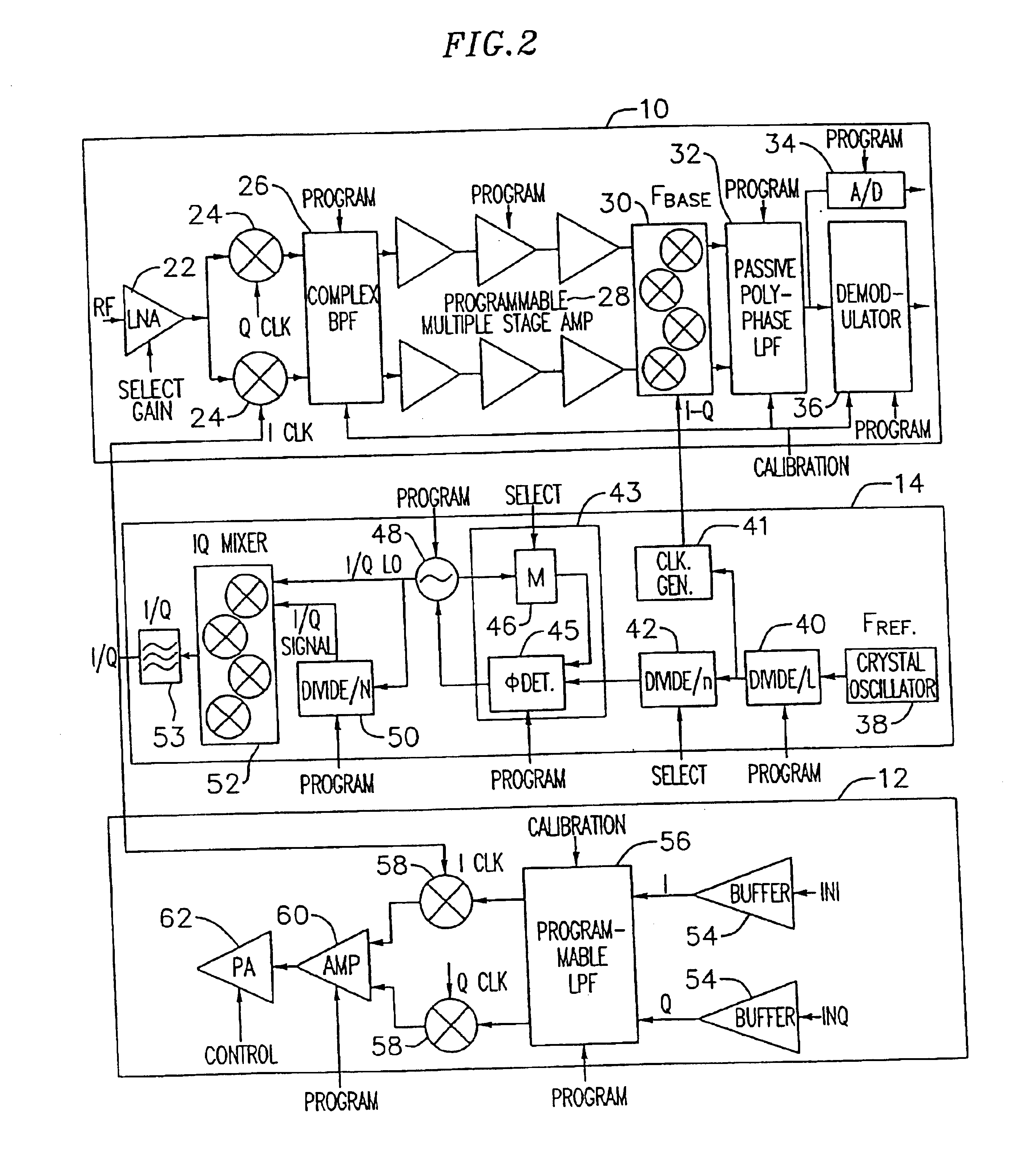
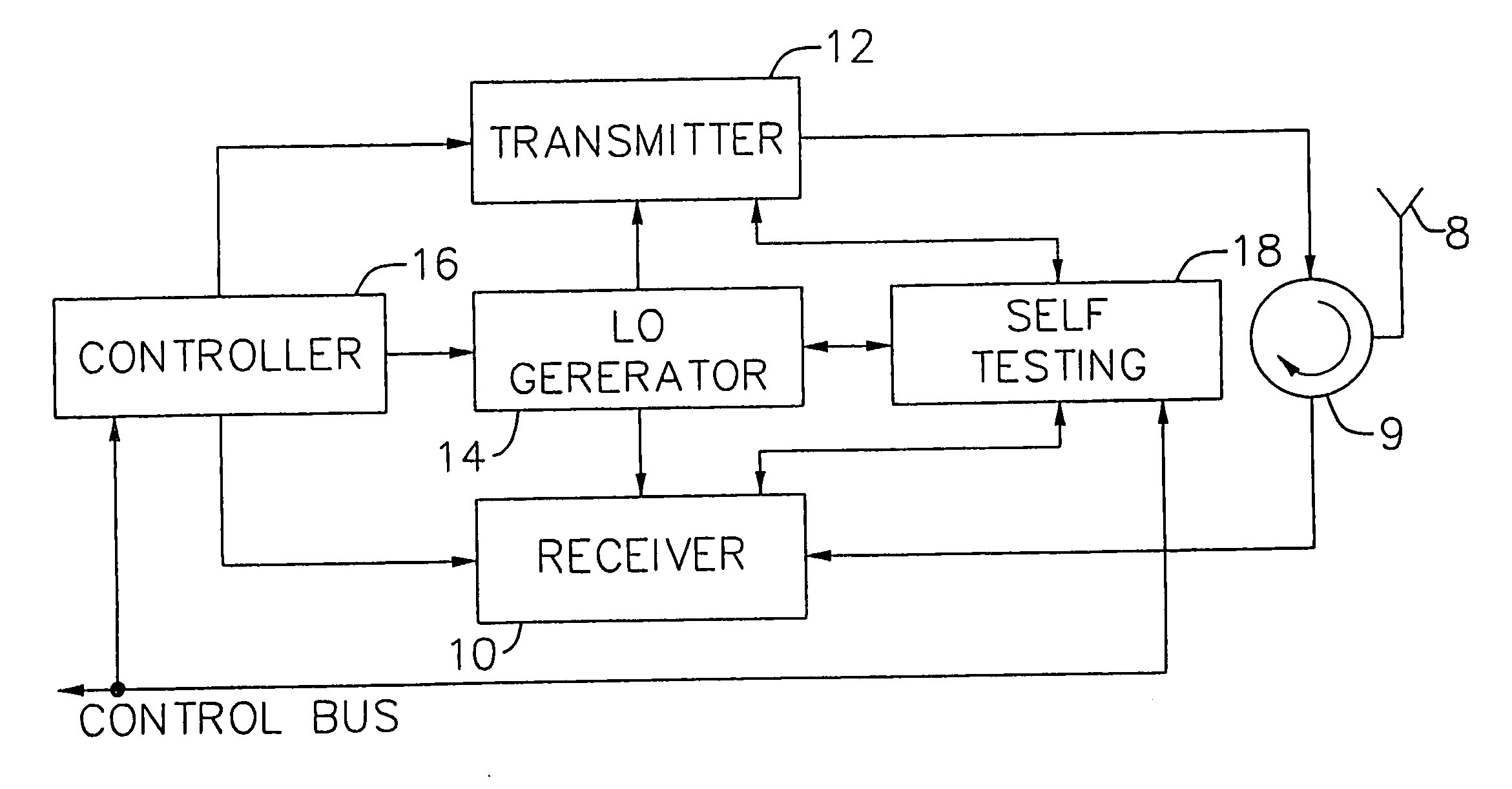
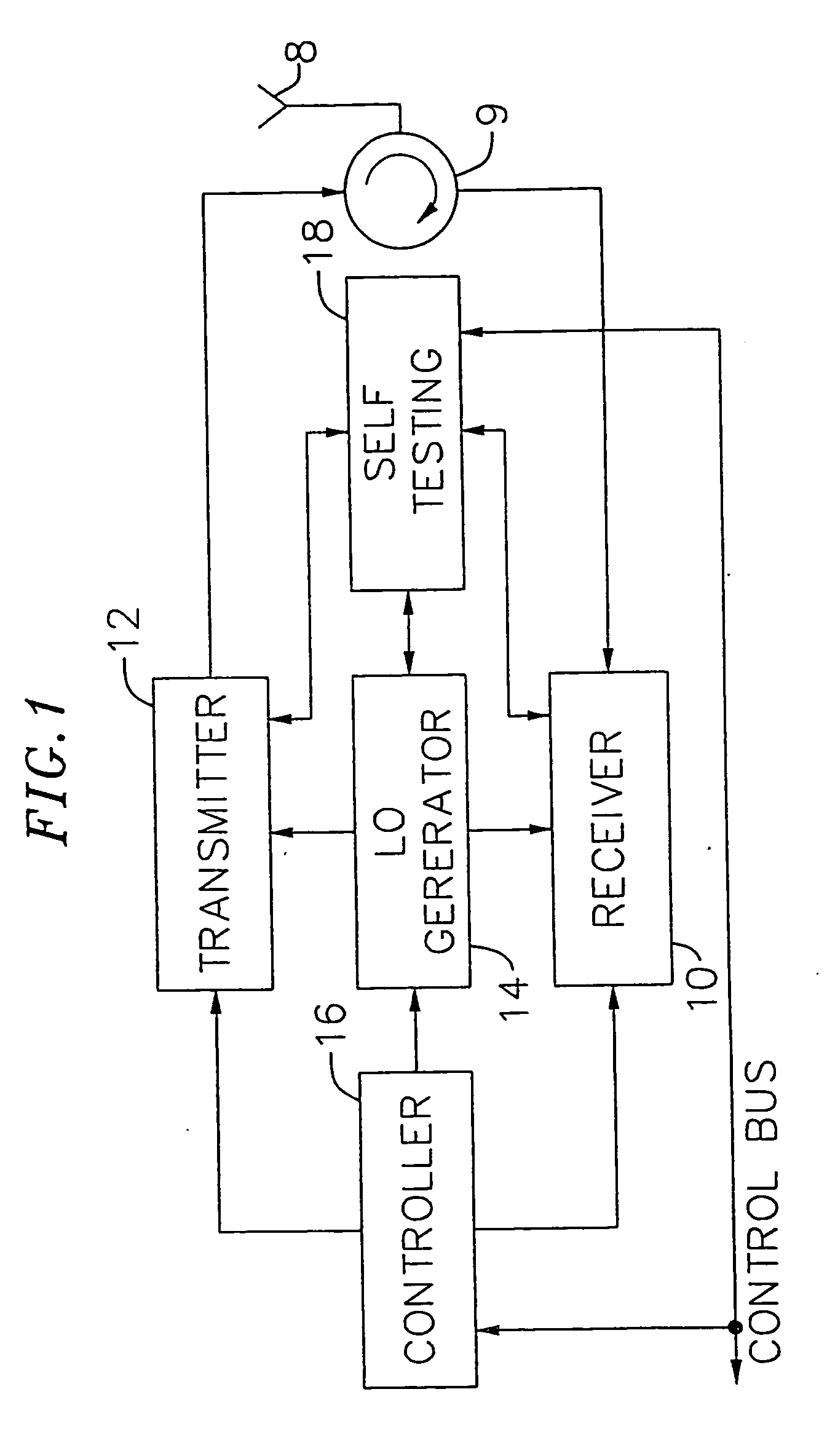
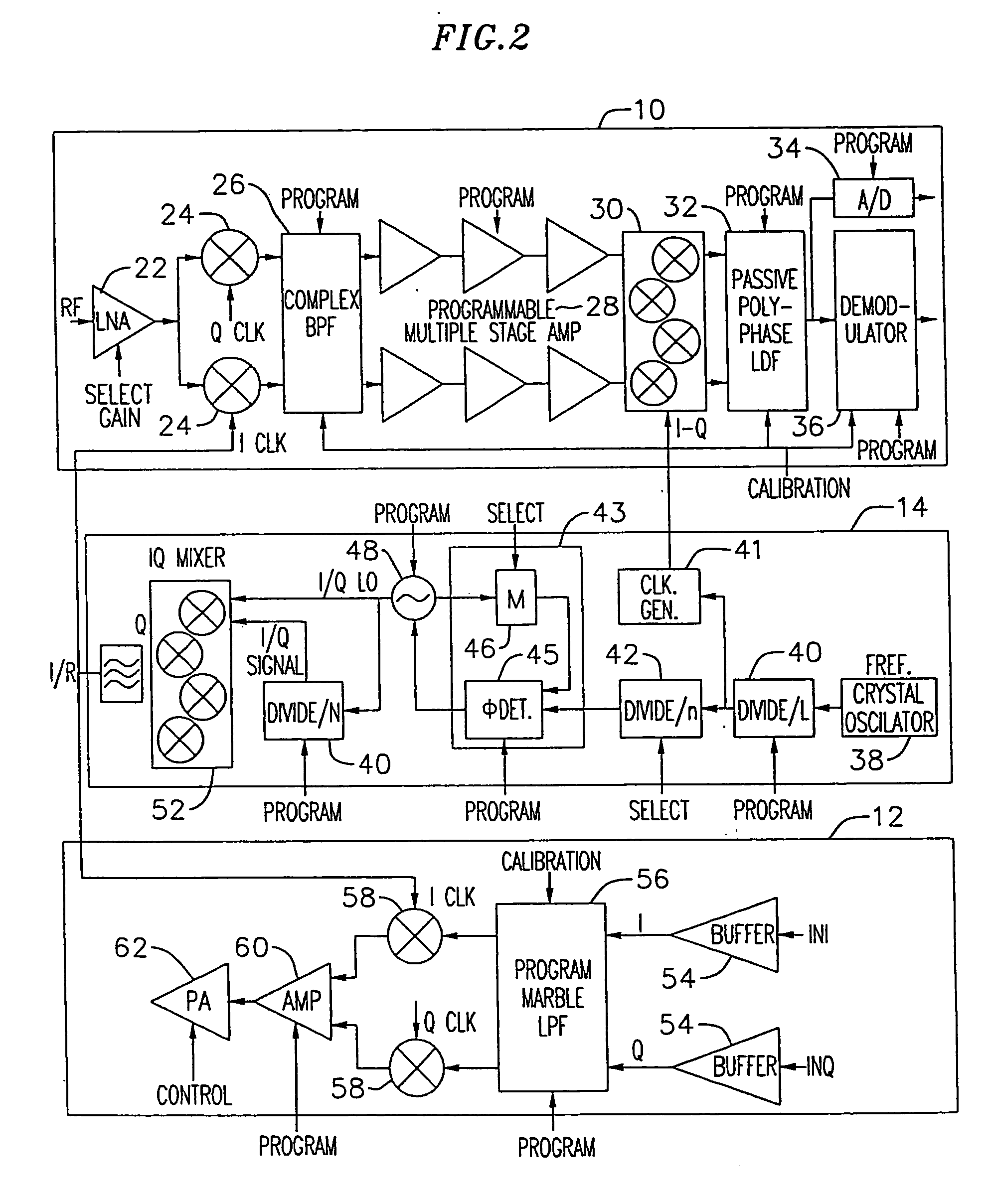
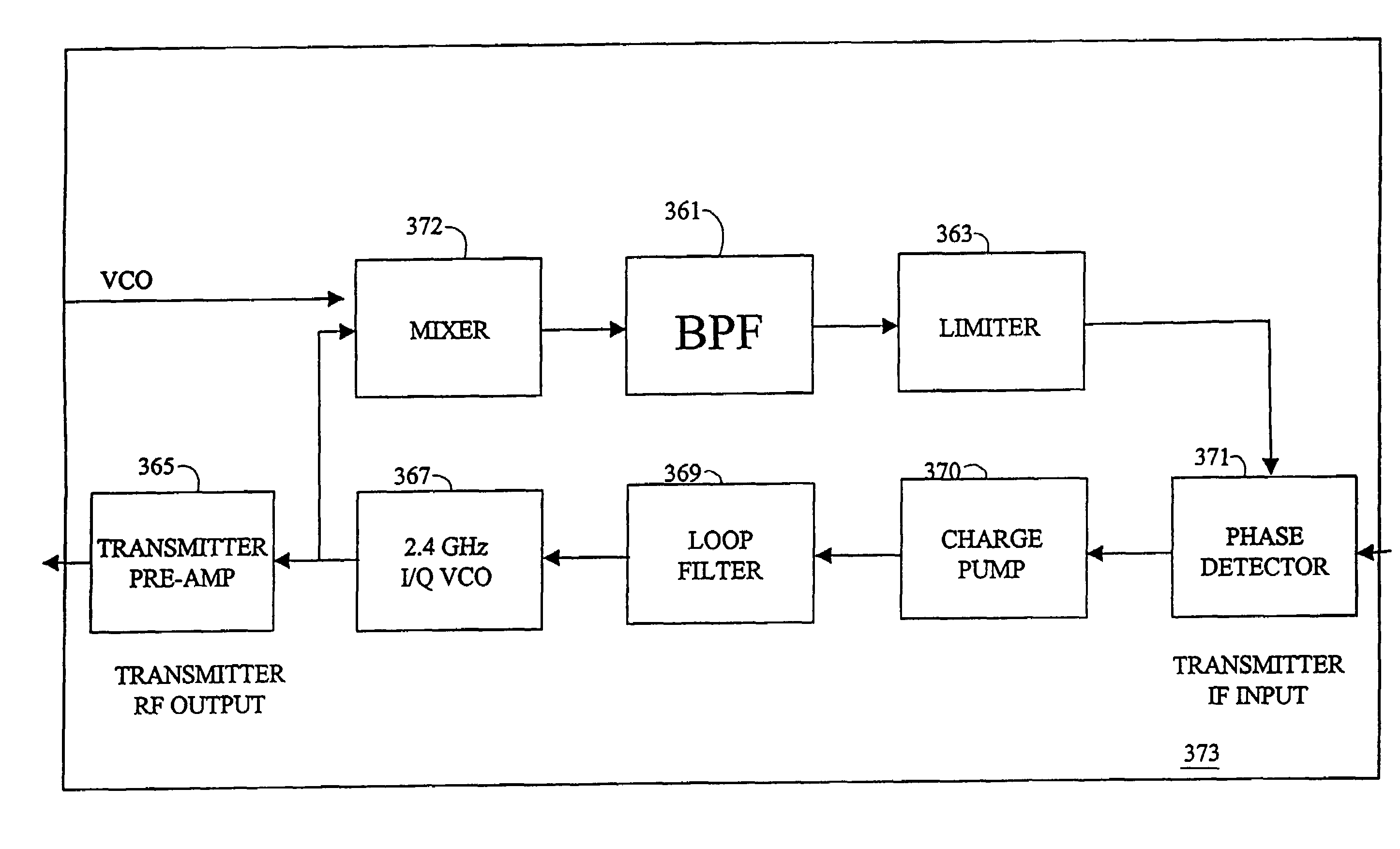
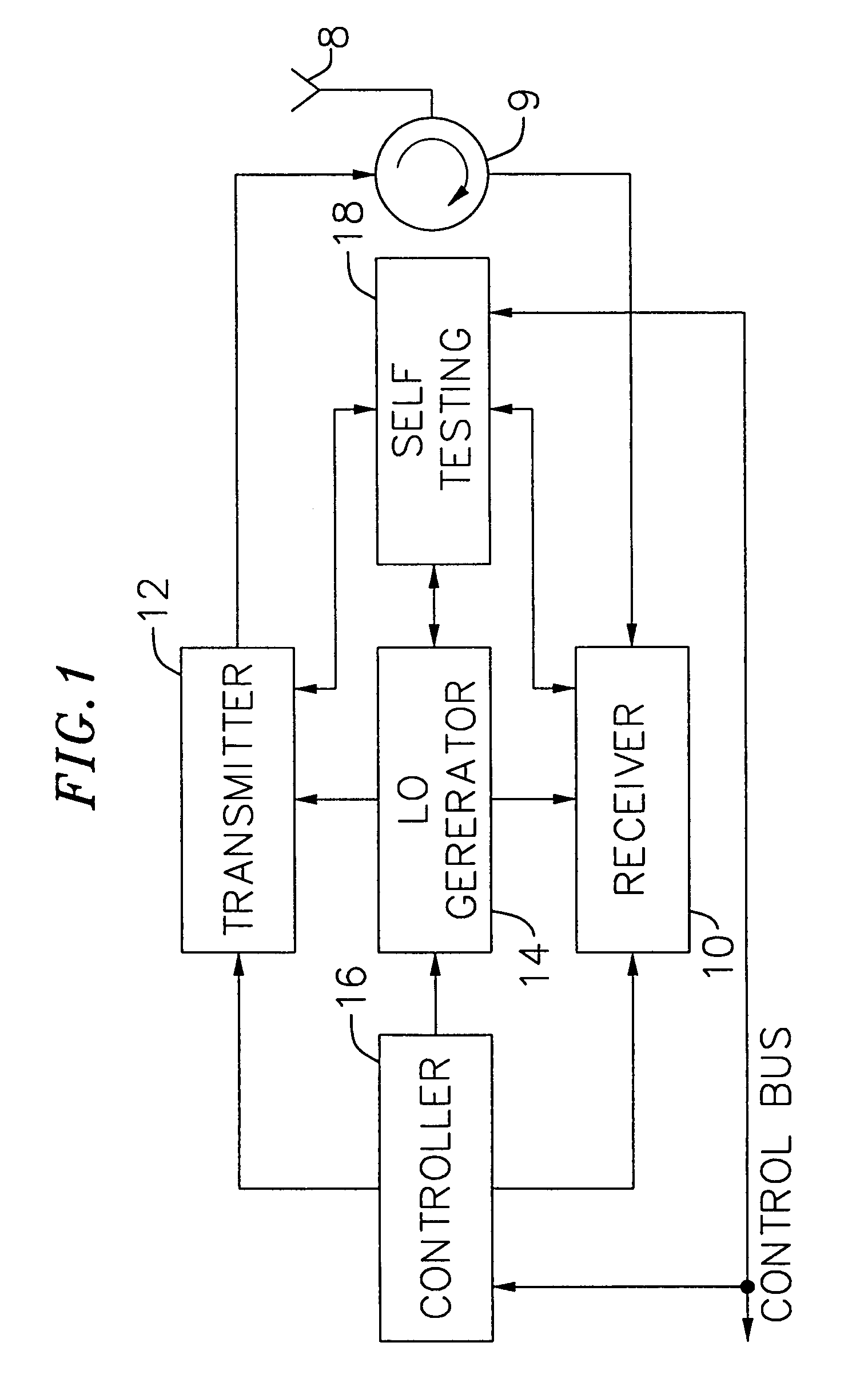
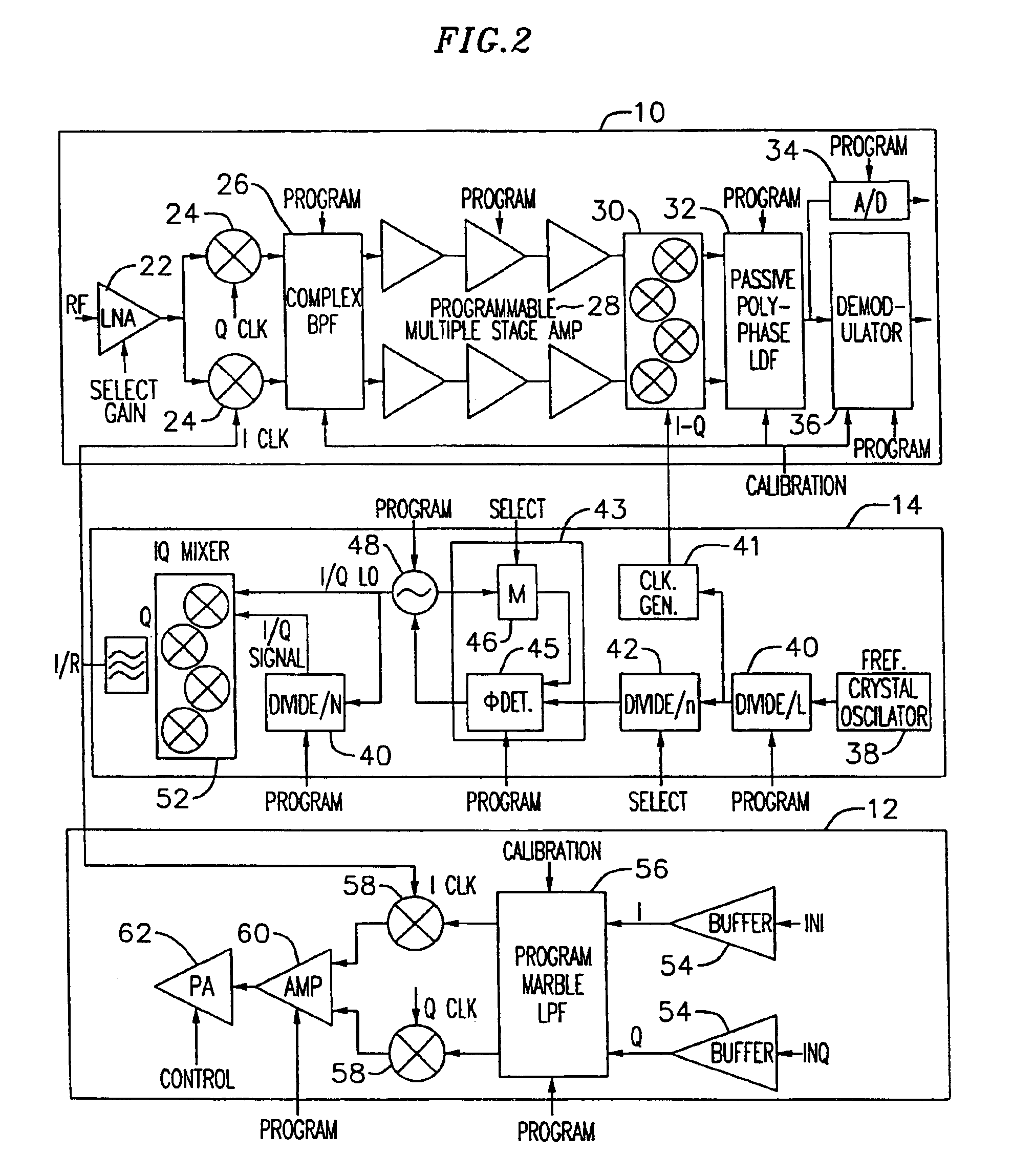
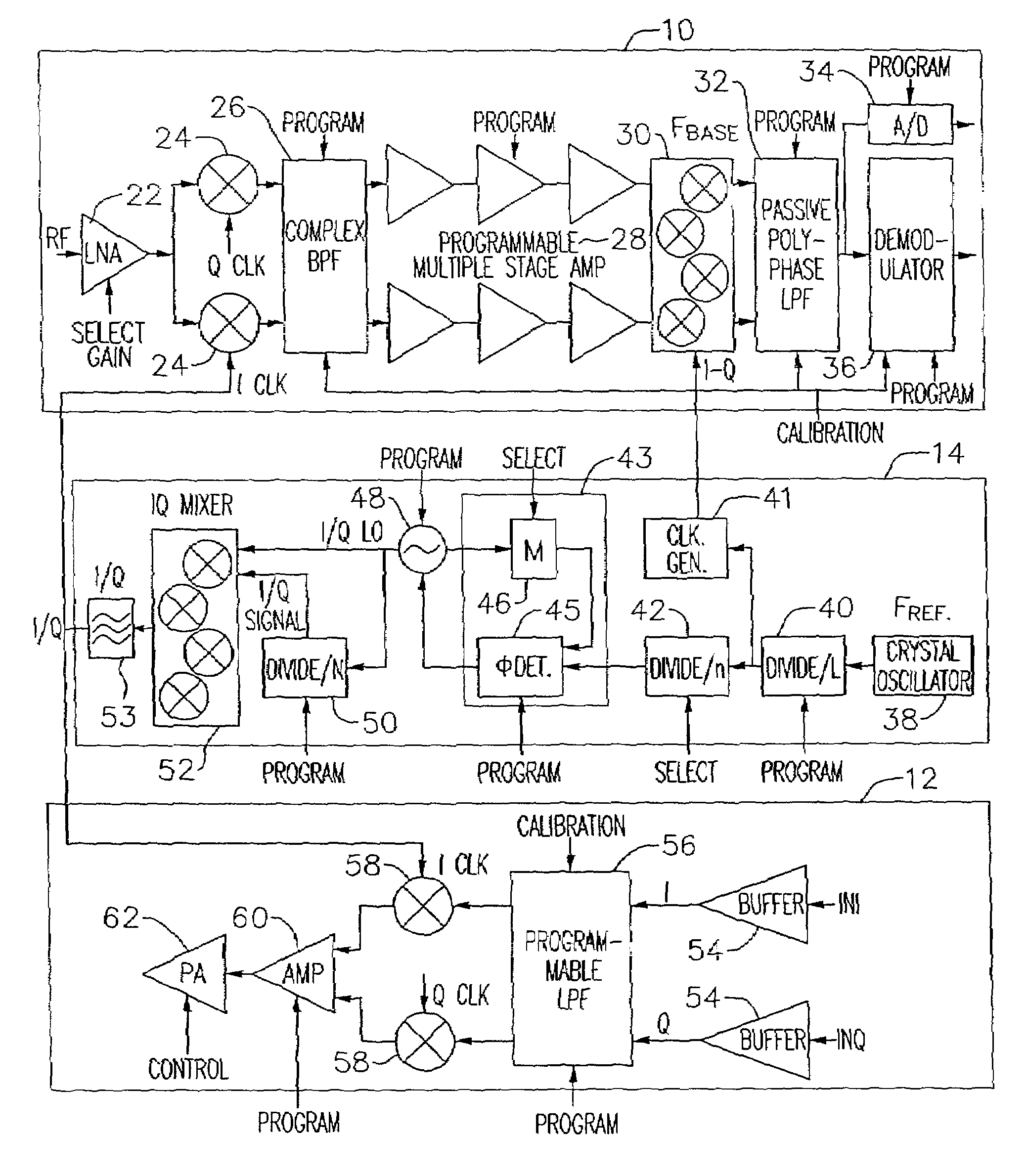
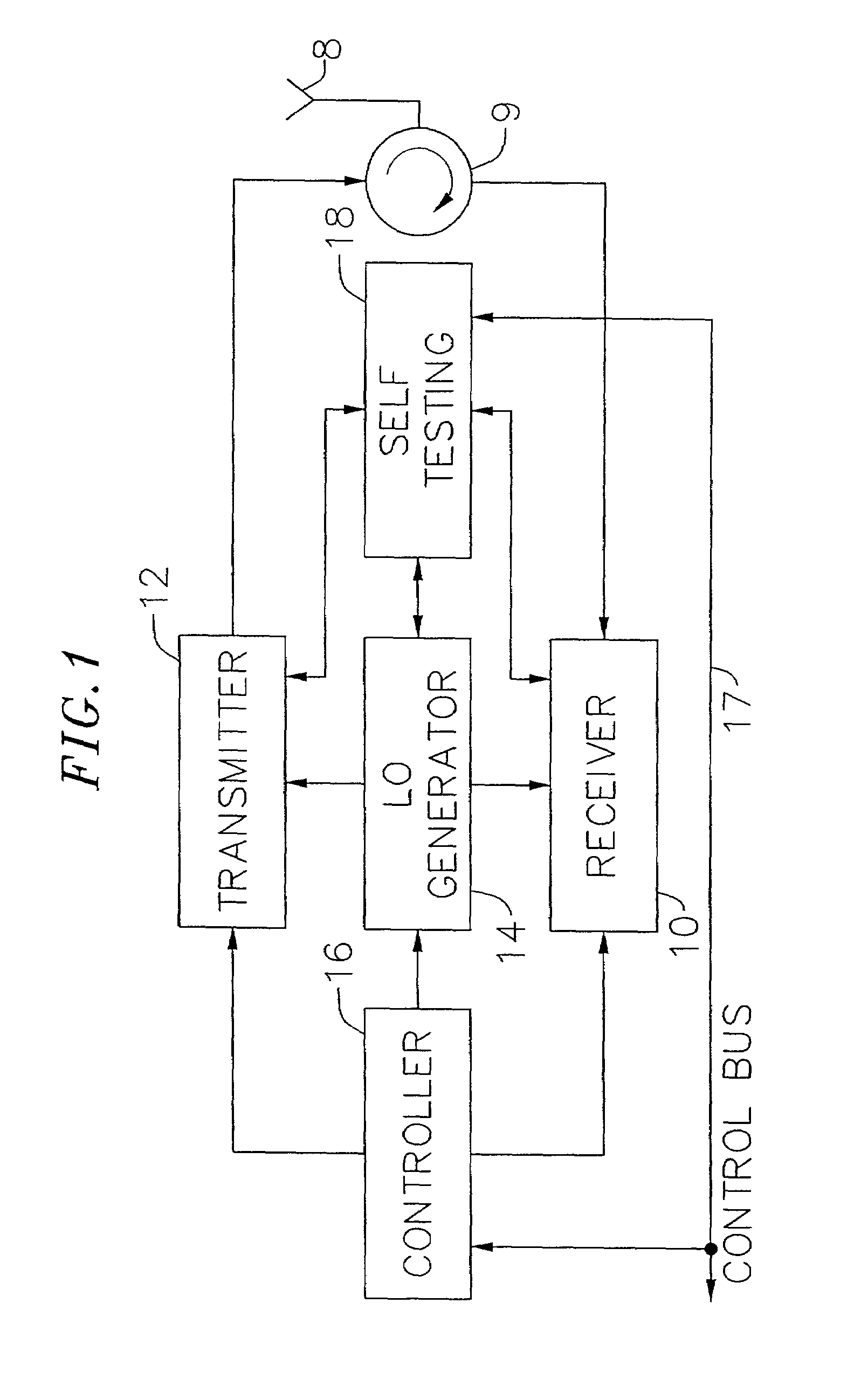
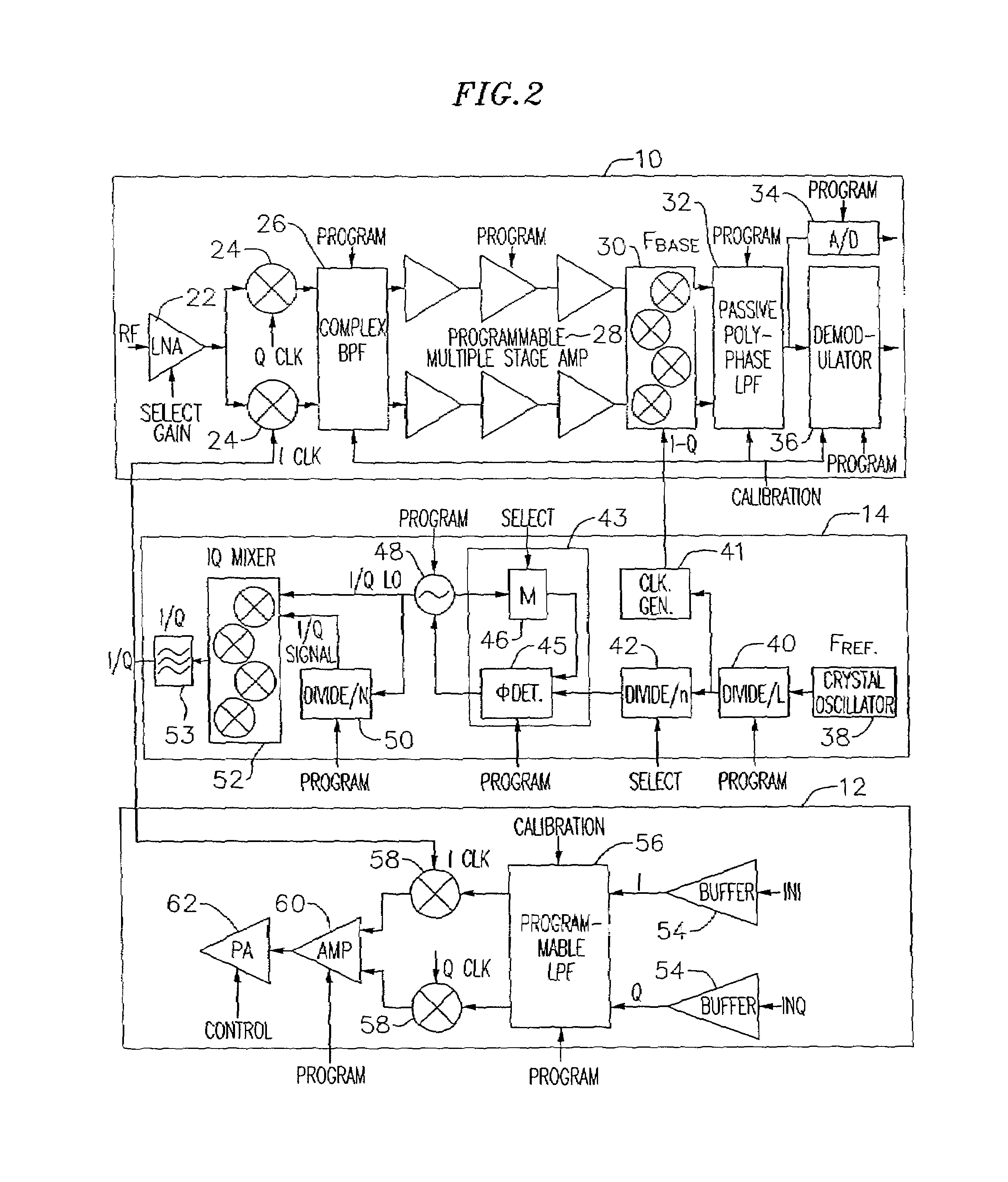
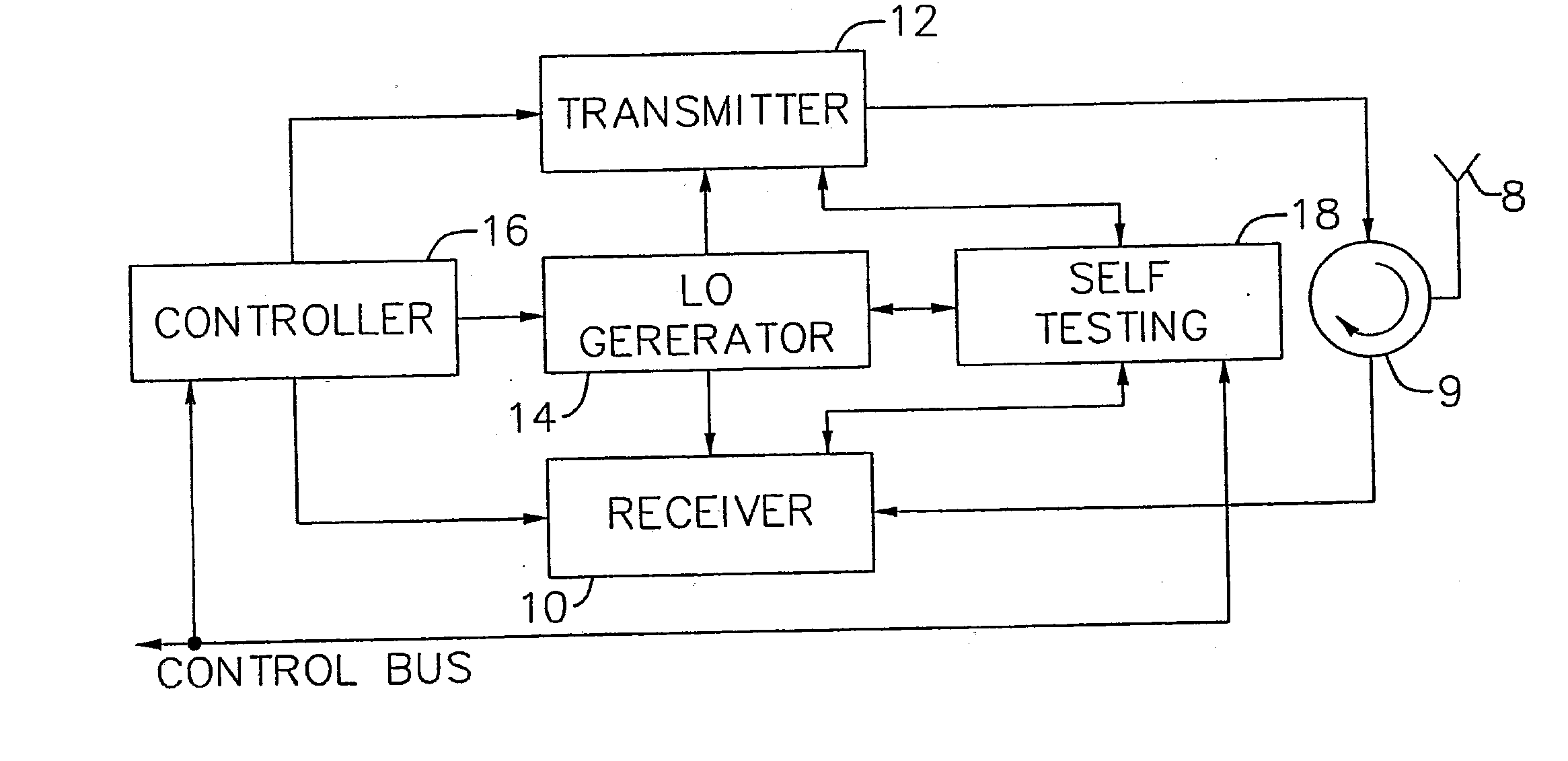
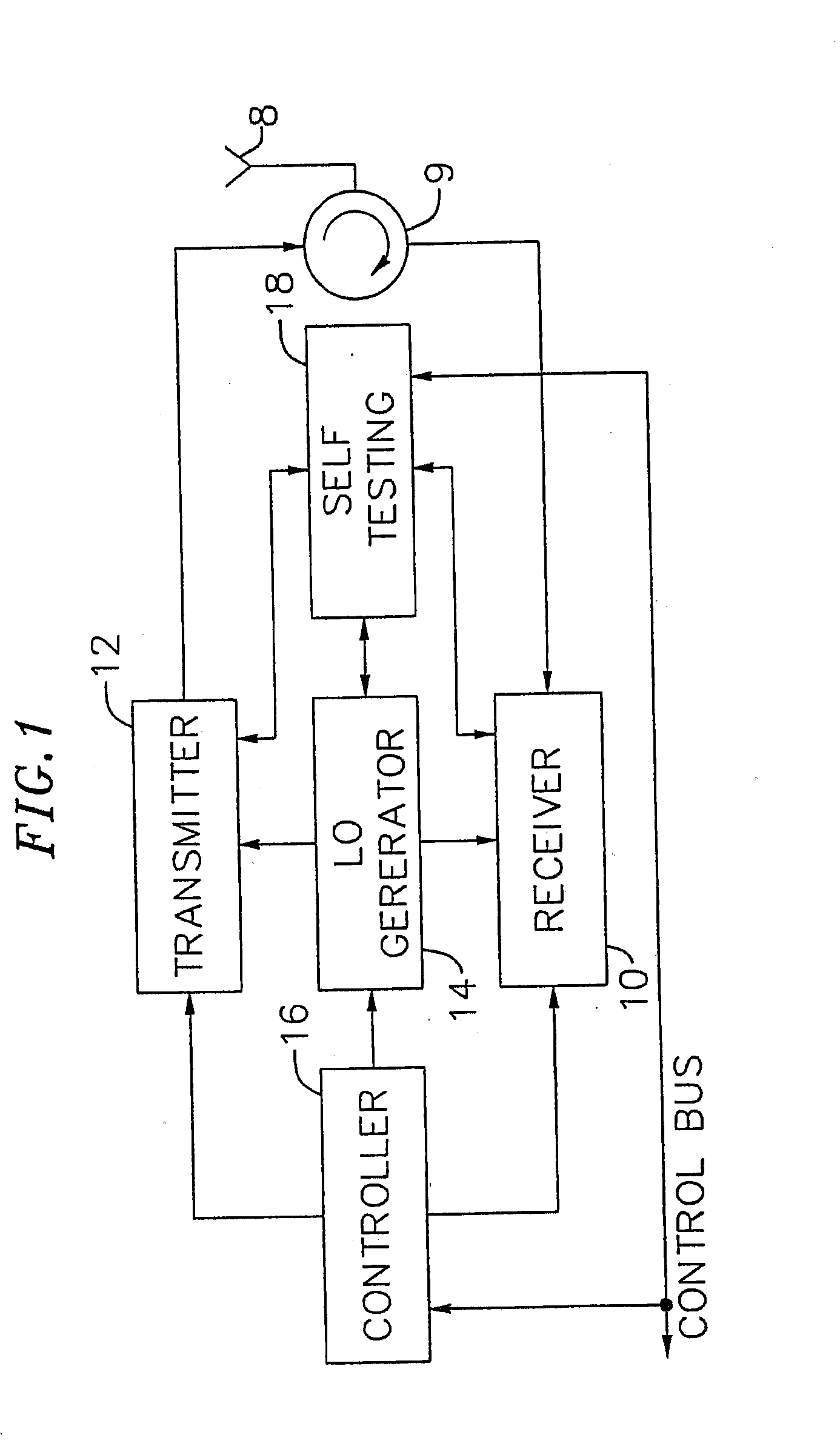
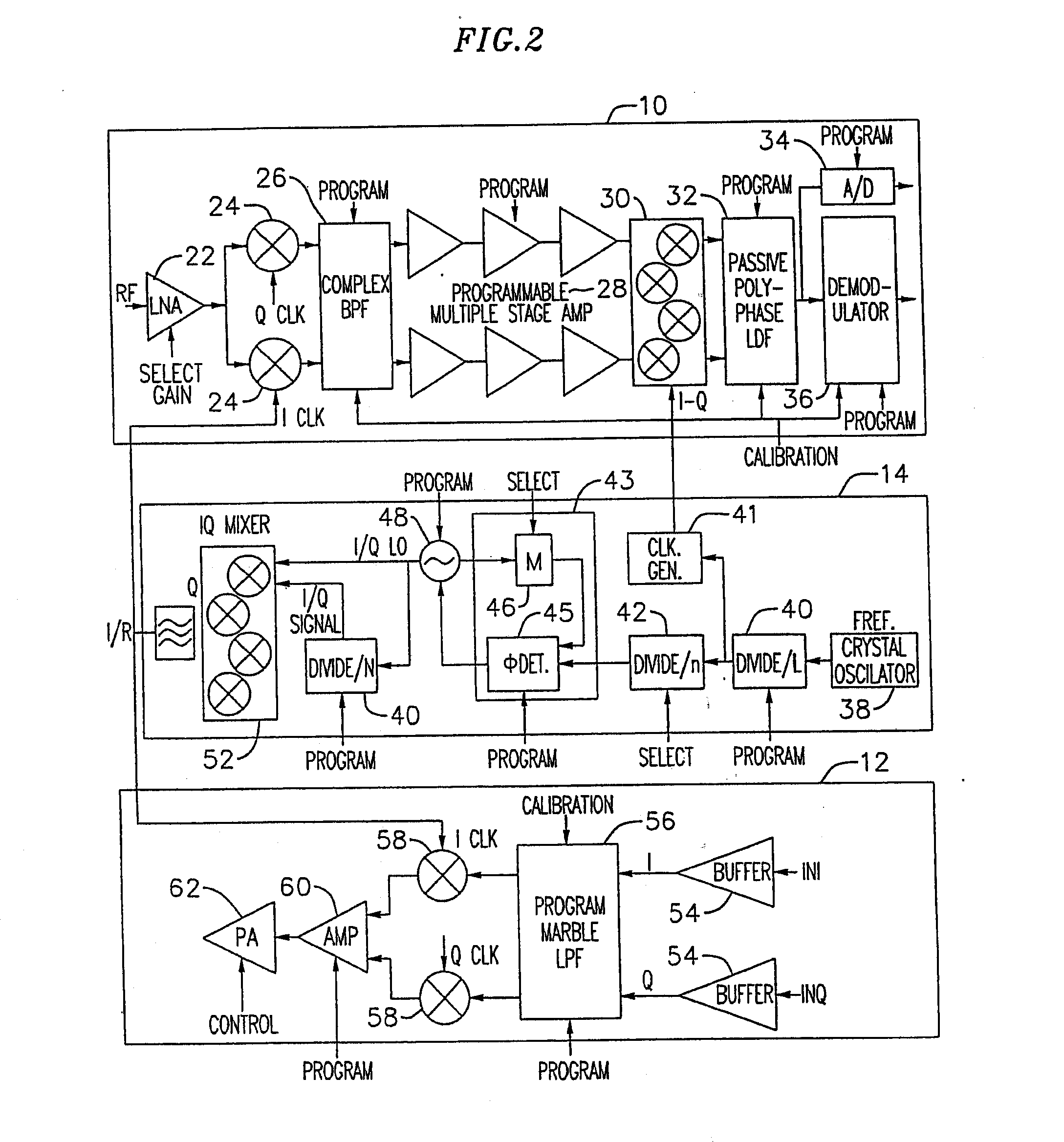
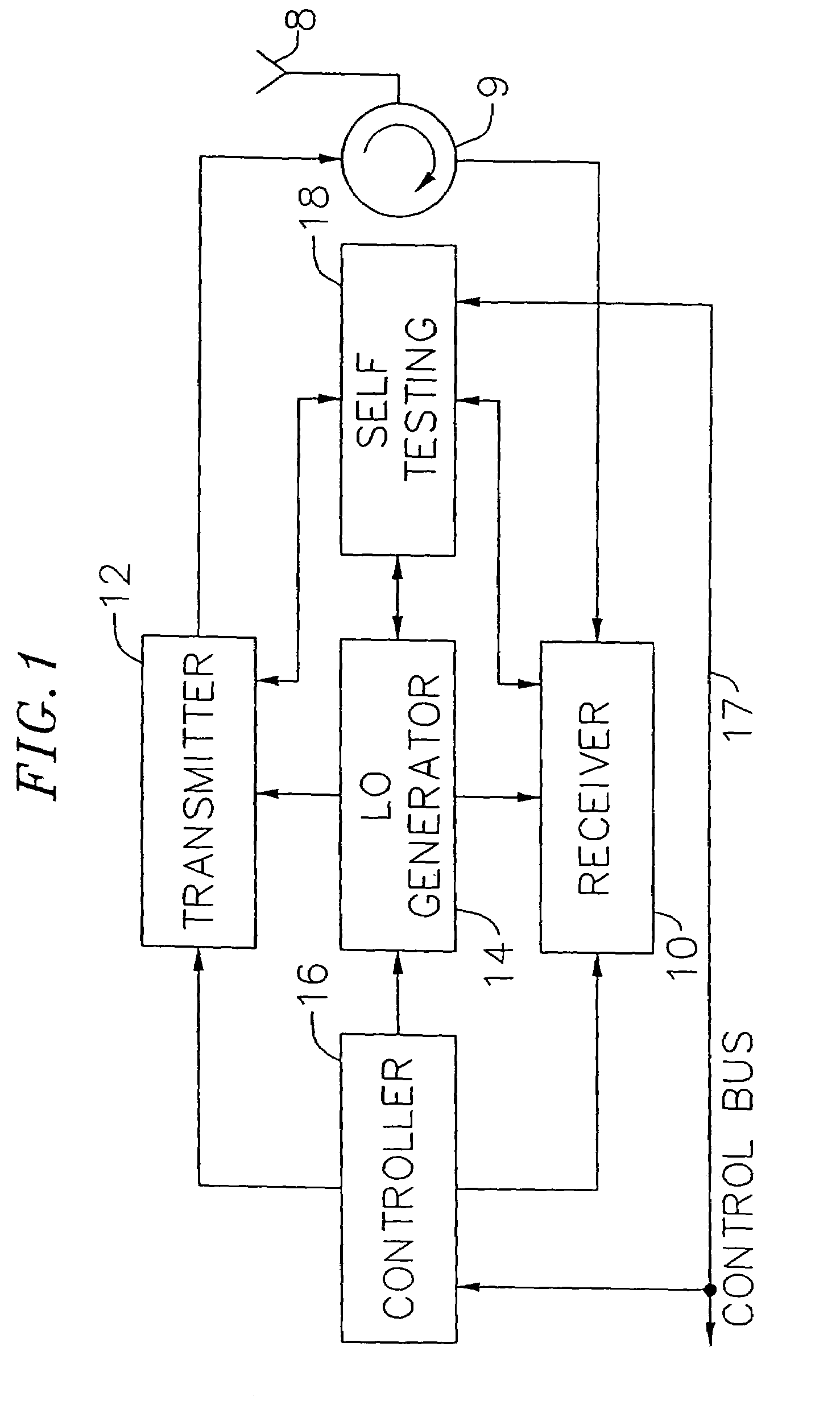
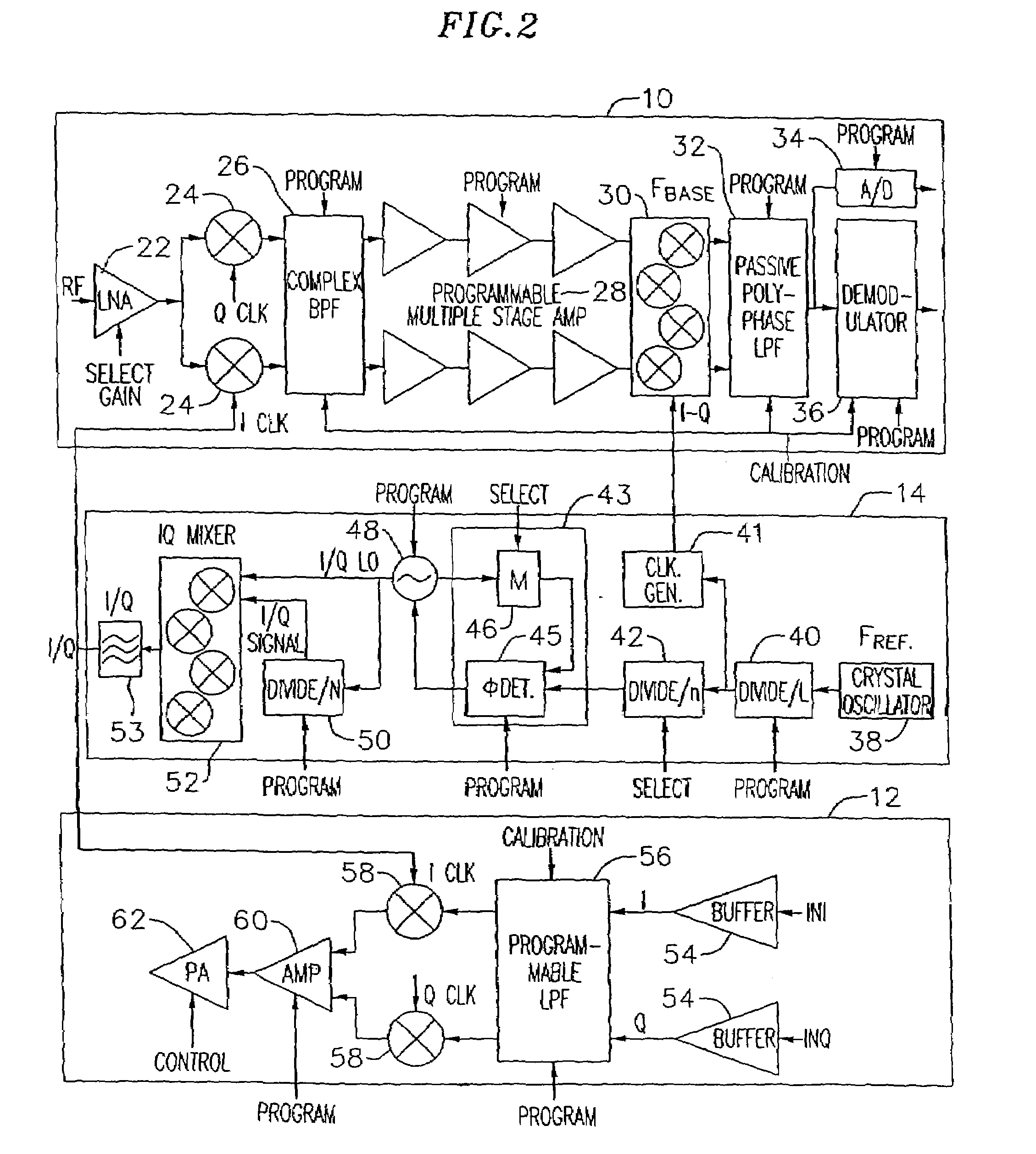
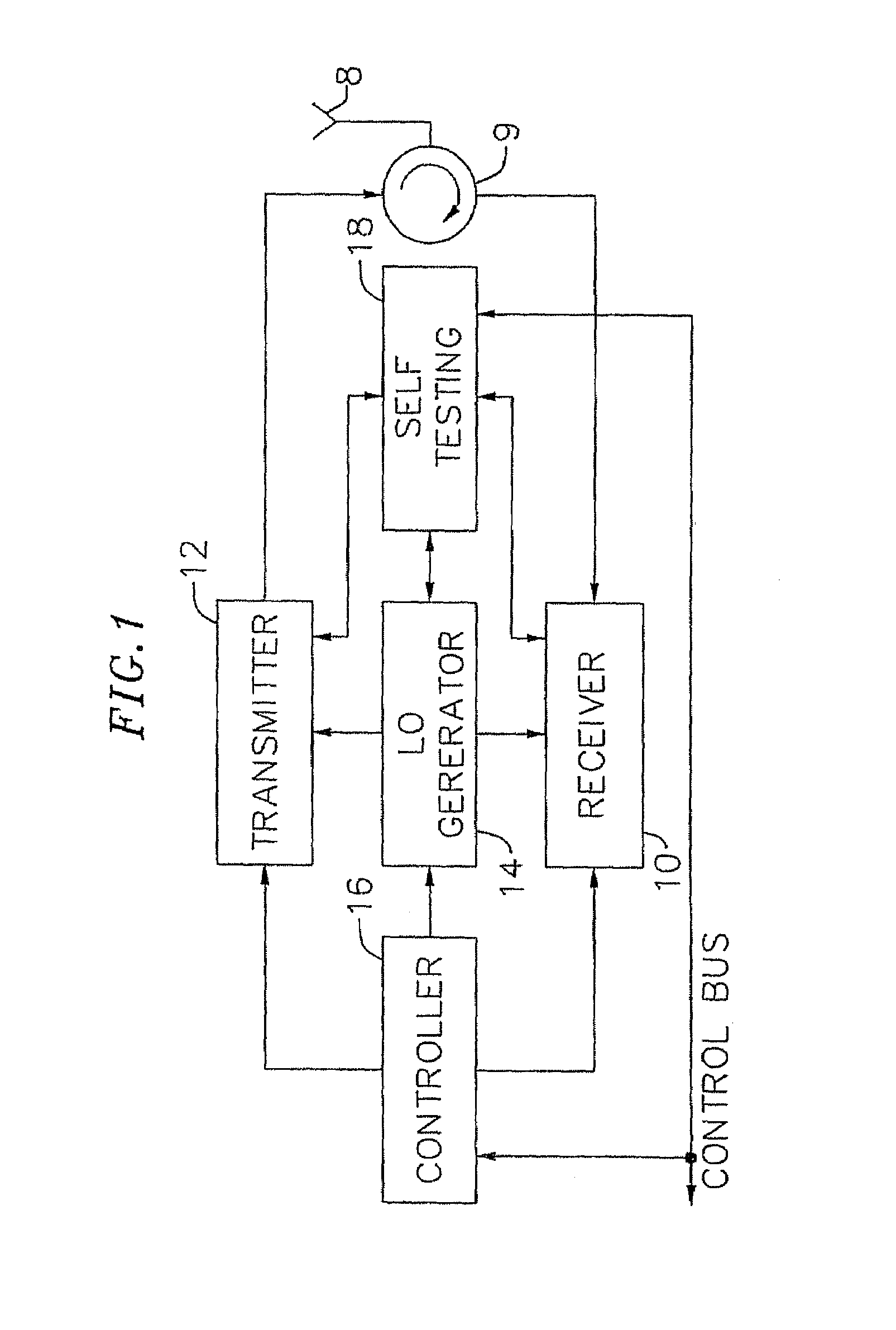
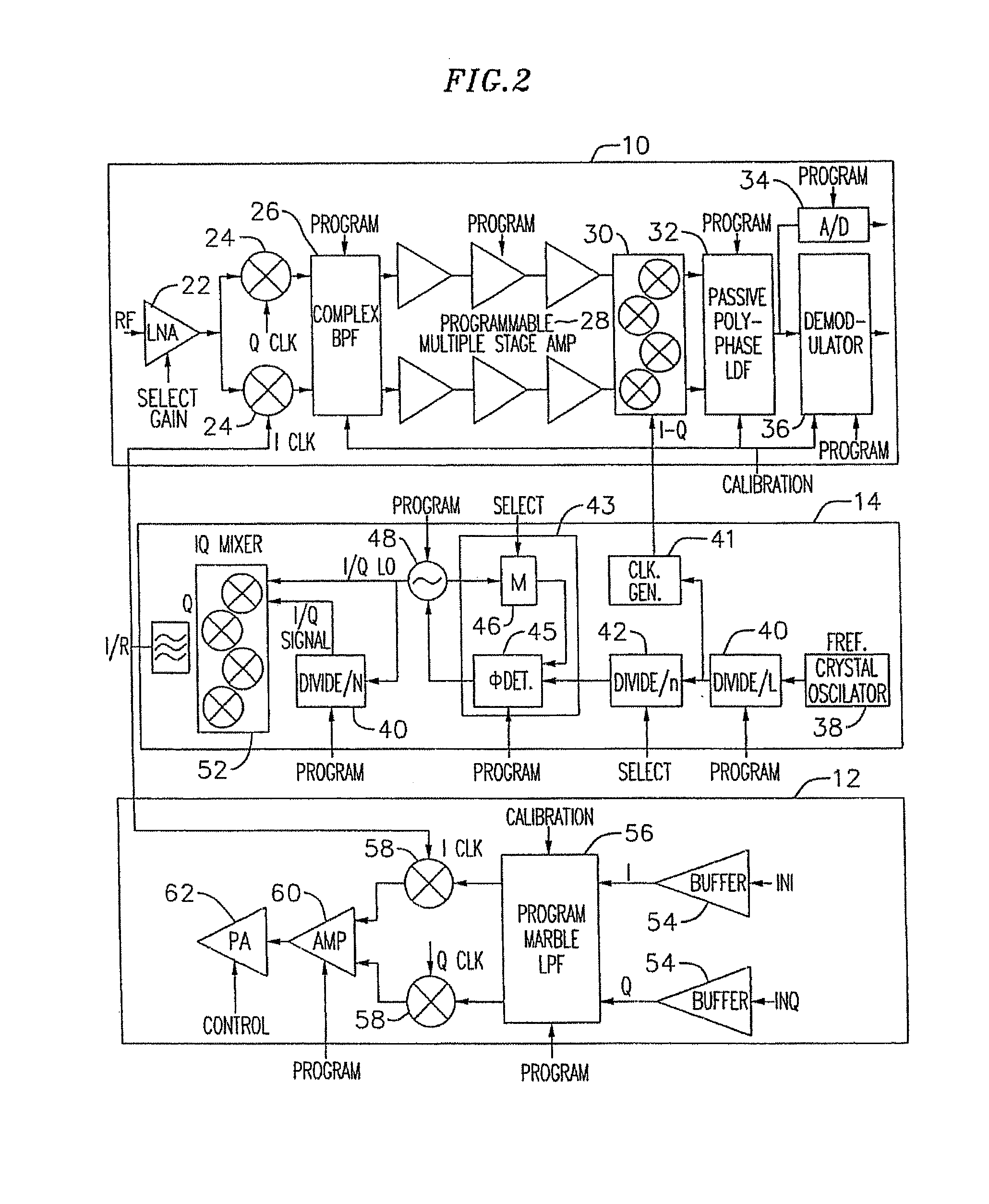
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Geo-fencing GPS-enabling assets
InactiveUS7498985B1Used in placePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingUltrasound attenuationSide information
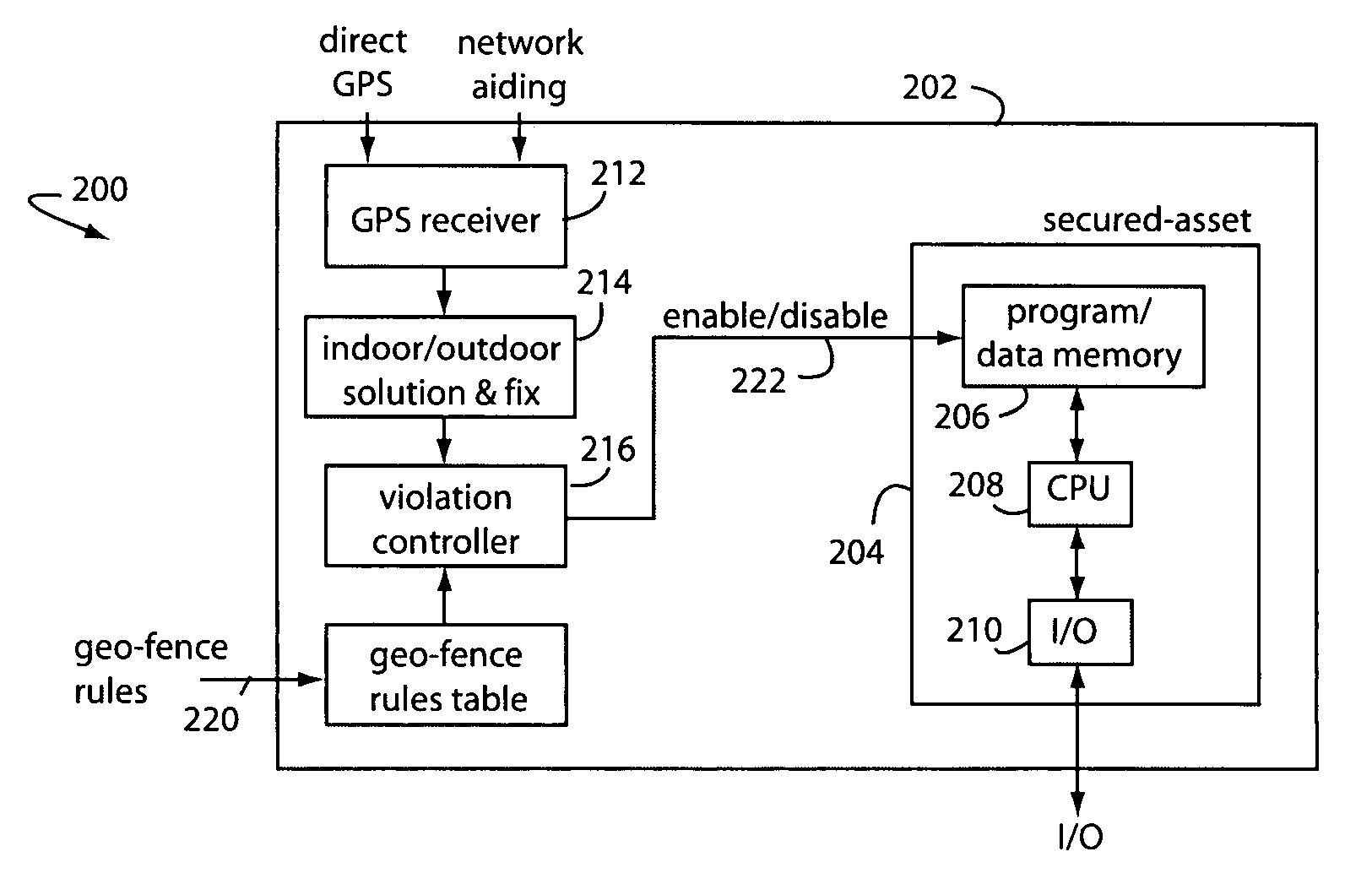
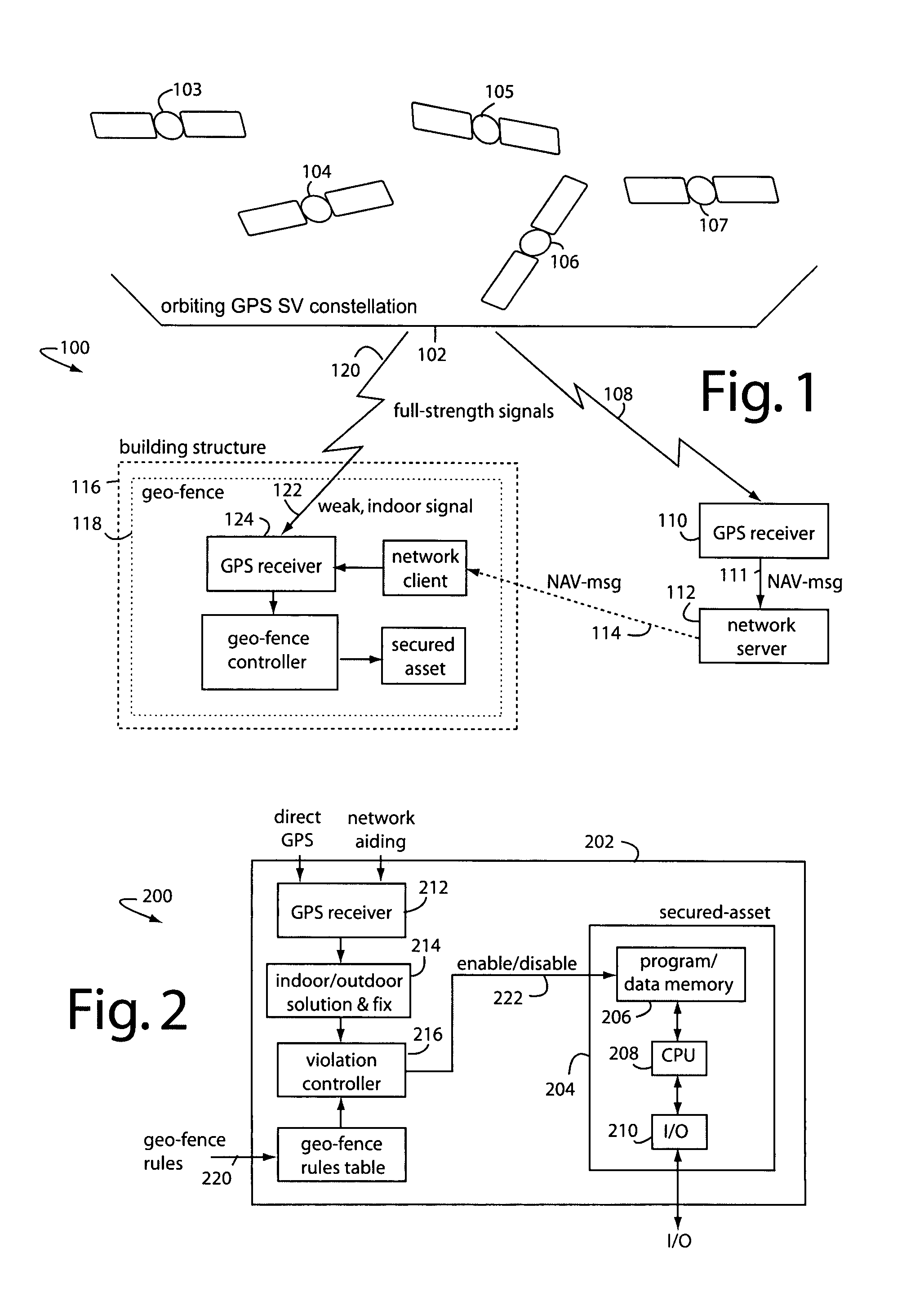
A security system comprises a secured asset associated with a high-sensitivity GPS receiver that can receive network aiding information. Indoors, the pseudo-ranges from orbiting GPS satellites can be computed by using digital correlators to pull directly received satellite signal transmissions from the noise floor, but the NAV-data transmissions cannot be demodulated well enough due to the attenuation caused by the building structure. So a wireless network is relied upon to provide aiding information that supplies the almanac and ephemeredes. The fact that the NAV-data transmissions cannot be demodulated well enough is taken as indicia that the system is being operated indoors, and such can be used in a geo-fence control to decide if indoor or outdoor use is not permitted. The secured asset can be temporarily or permanently disabled according to such geo-fence controls.
Owner:ERIDE +1
Optical sensing device containing fiber Bragg gratings
InactiveUS6674928B2Limit bandwidthLimit rangeForce measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesBandpass filteringMultiplexing
A new optical sensing device containing fiber Bragg gratings, a scanning bandpass filter, an interferometer and multiple photodetectors is disclosed. The present invention also describes a new system and method for fibre Bragg grating (FBG) sensor interrogation and multiplexing. The new system combines a scanning Fabry-Perot (SFP) bandpass filter used to wavelength-multiplex multiple gratings in a single fiber, and an unbalanced Mach-Zehnder fibre interferometer made with a 3x3 coupler to detect strain-induced wavelength shifts. A passive technique for interferometer drift compensation using non-sensing FBGs is included in the system. A complete prototype system interrogates four gratings in a single fiber at a Nyquist sampling rate up to 10 kHz, with a noise floor measured near 4 nepsilon Hz<-1 / 2 >above 0.1 Hz. The inclusion of the interferometer drift compensation technique is shown to make quasi-static measurements feasible.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
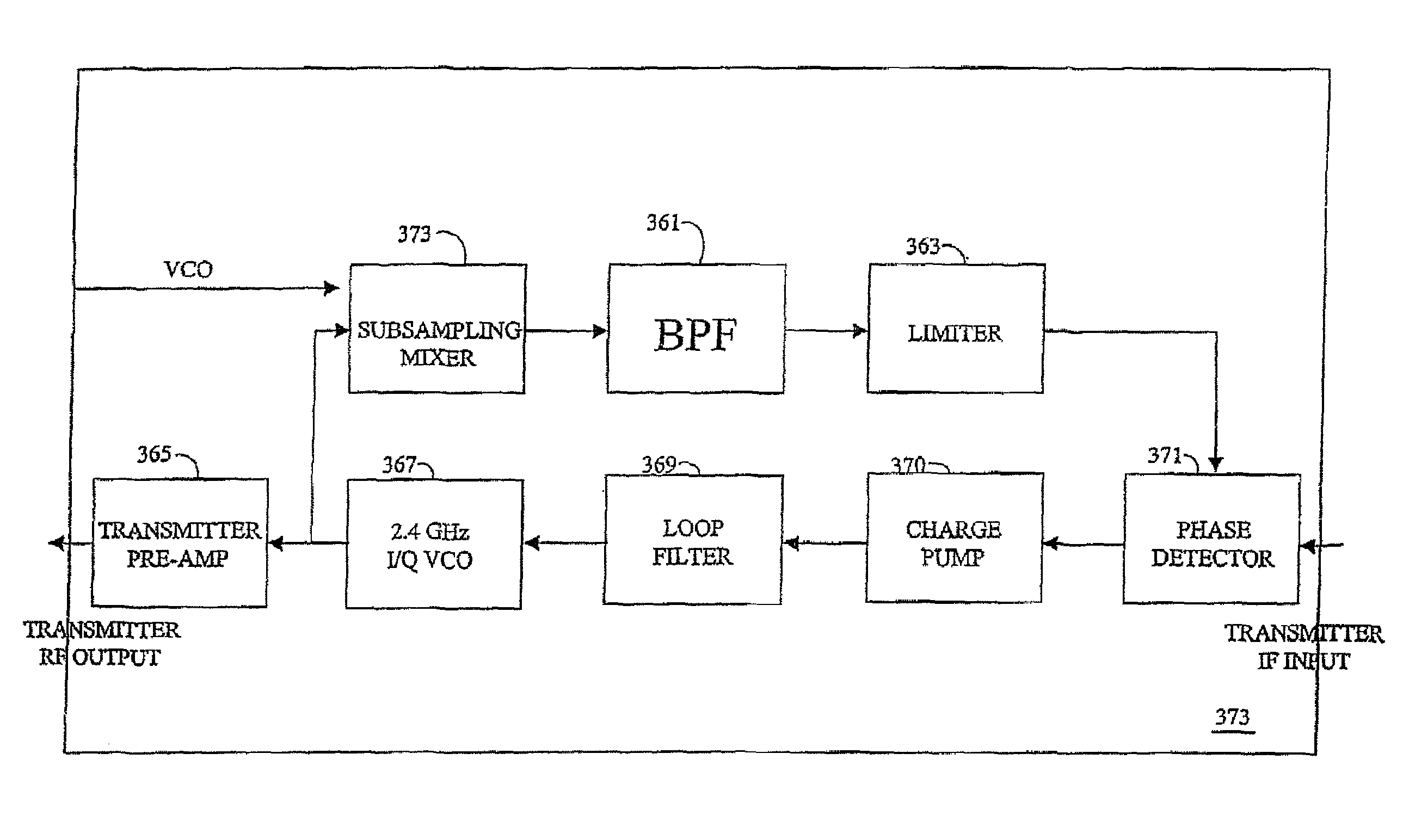
Adaptive radio transceiver with offset PLL with subsampling mixers
InactiveUS20050186930A1Minimize adverse effectsReduce power consumptionTransmitters monitoringResonant long antennasTransceiverAdaptive programming
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Adaptive radio transceiver with CMOS offset PLL
InactiveUS7082293B1Minimize adverse effectsReduce power consumptionTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringCMOSAdaptive programming
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
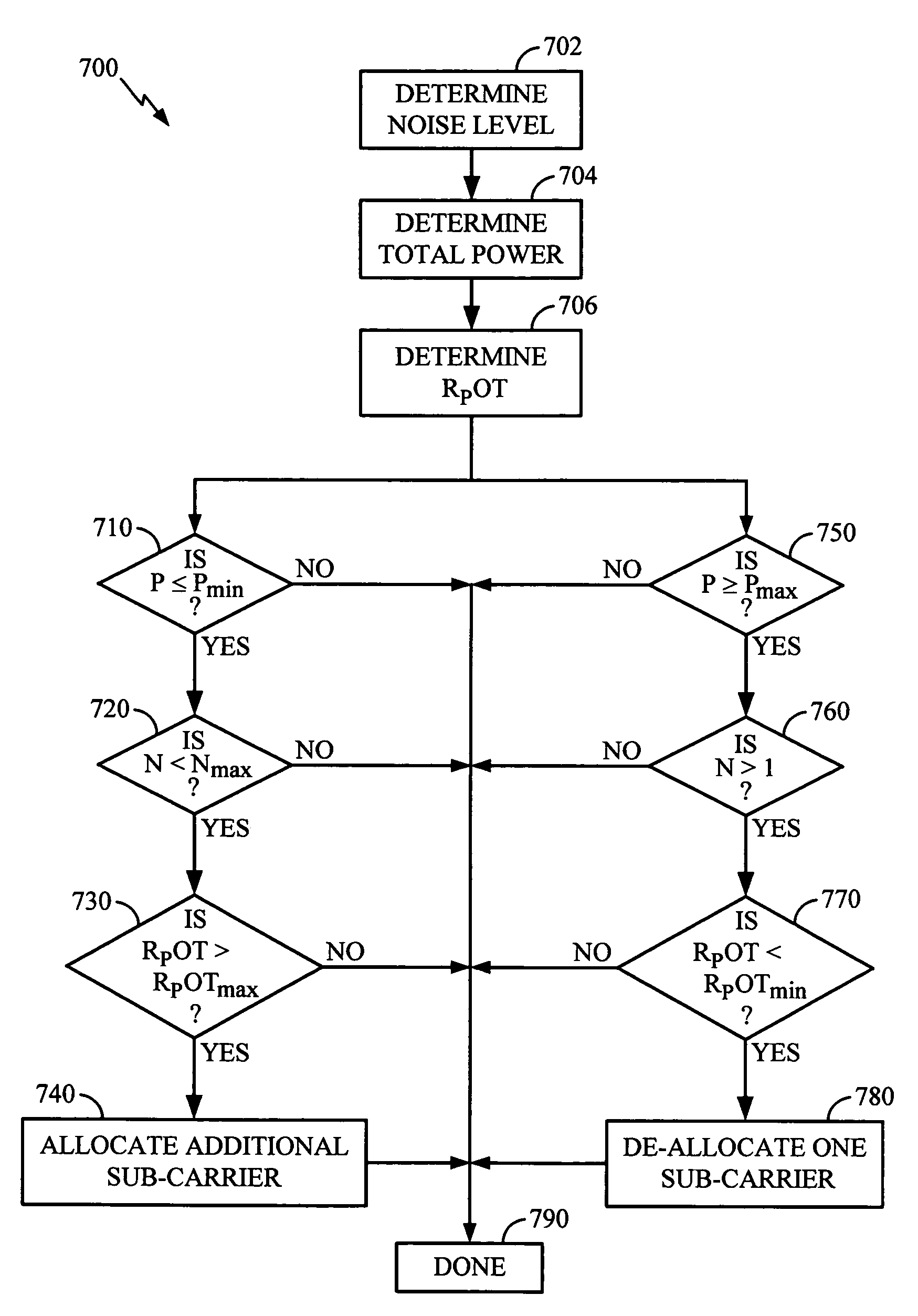
Power control and scheduling in an OFDM system
A system and method for power control and scheduling of sub-carriers in an OFDM communication system. The receiver dynamic range can be minimized by a power control loop that attempts to maintain received power over a noise floor in a predetermined range. If the received power relative to a noise floor in allocated sub-carriers exceeds the predetermined range and the total received power is at the minimum, the scheduling system allocates an additional sub-carrier to the communication link. Additionally, if the received power relative to the noise floor is less than the predetermined range minimum, and the total received power is at a maximum, the scheduling system de-allocates a sub-carrier from the communication link. The scheduling system may also adjust an encoding rate to maintain a relatively constant symbol rate in each sub-carrier.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
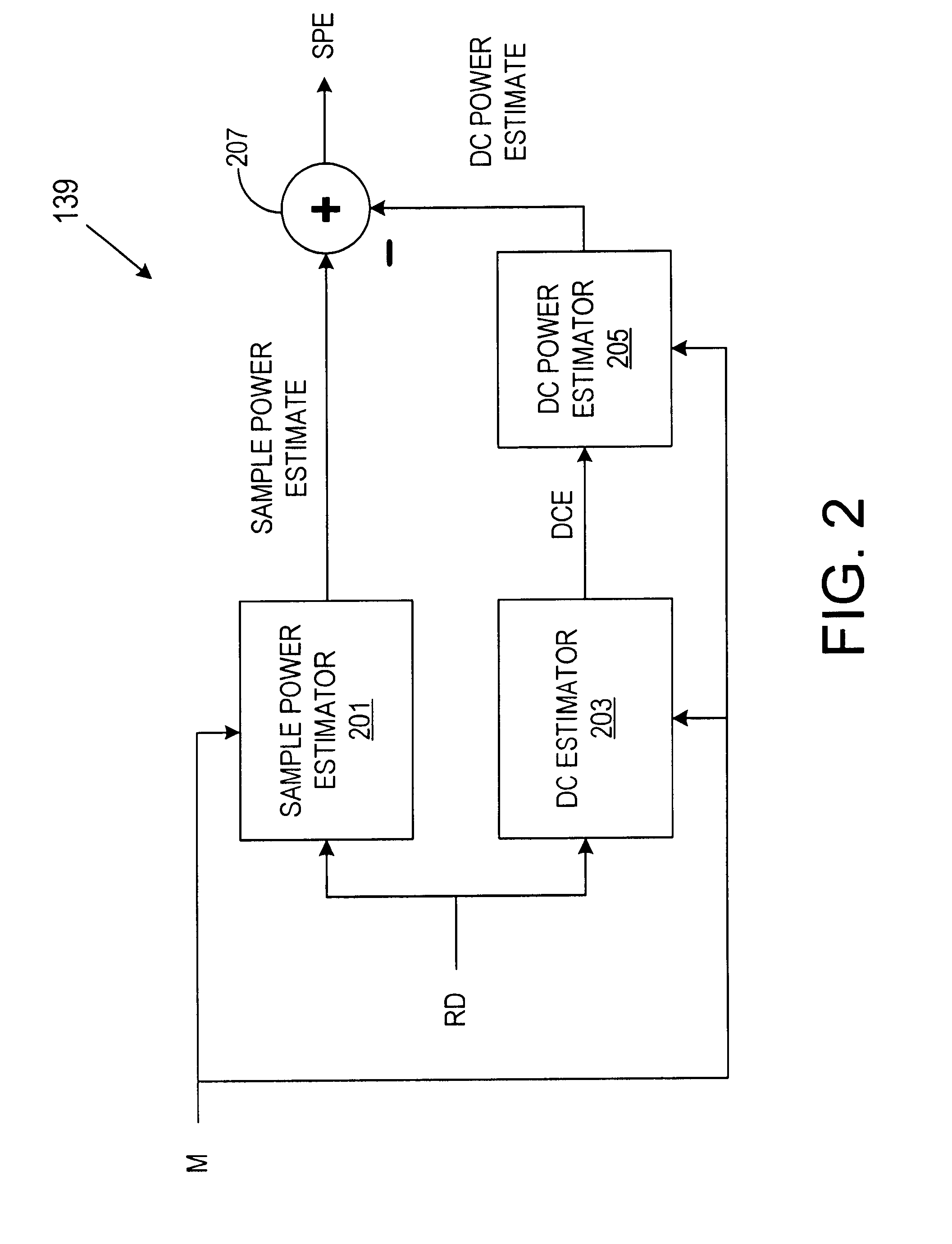
Method and system for noise floor calibration and receive signal strength detection
A system for detecting the level of the noise floor due to circuit noise as seen at the ADC for a wireless receiver. The system measures power after digitizing and filtering, and subtracts off any variable gain used in the analog front end to determine differentially the size of the signal at the antenna. The system further differentially detects the signal size of any incoming signal at the antenna in a similar fashion, and determines its size relative to the measured noise floor. If the level of the circuit noise of the receiver is known absolutely, the absolute signal size of the incoming signal can likewise be determined with this inventive method and system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
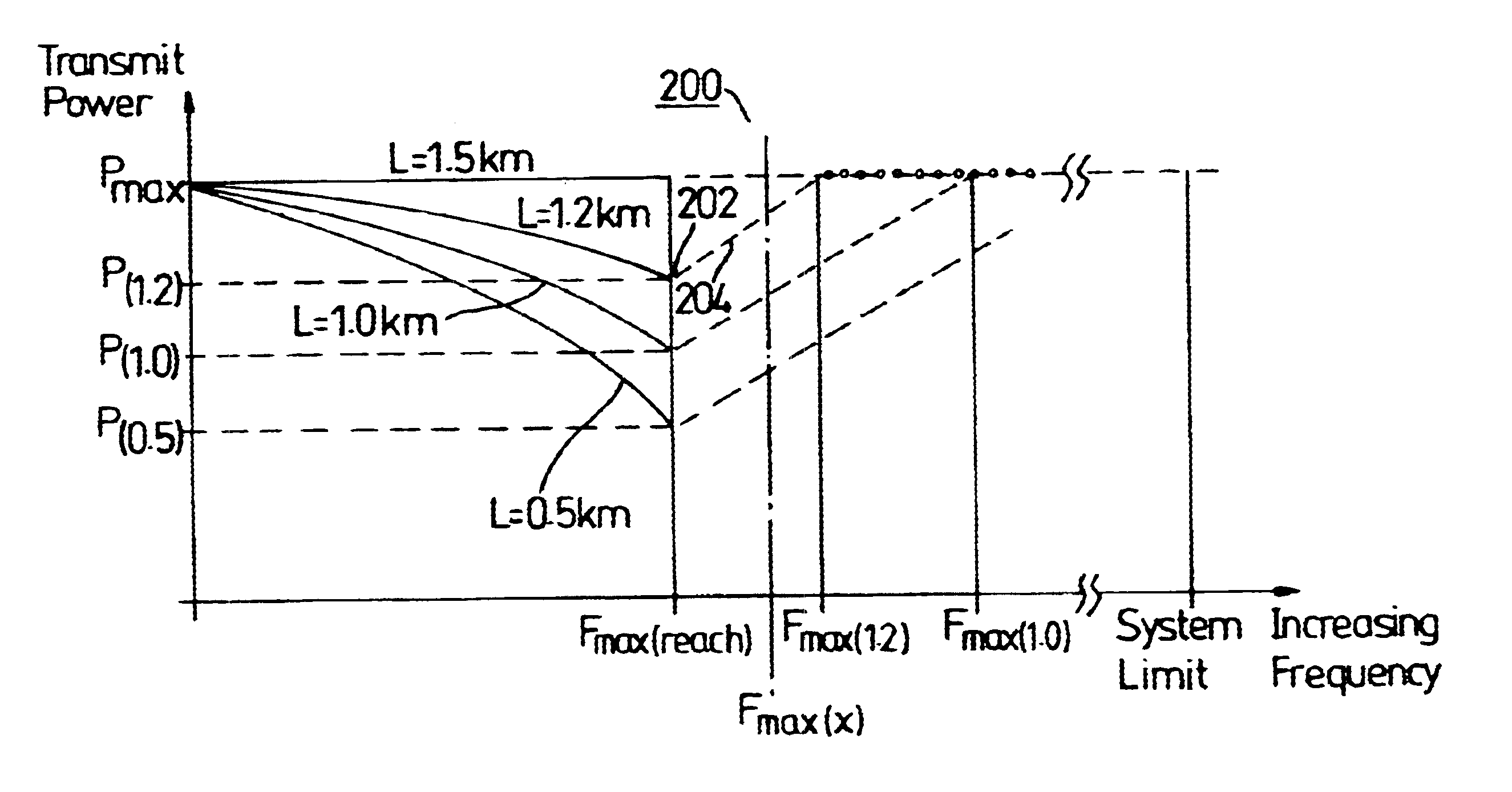
Wireline communication system and method of frequency allocation therein
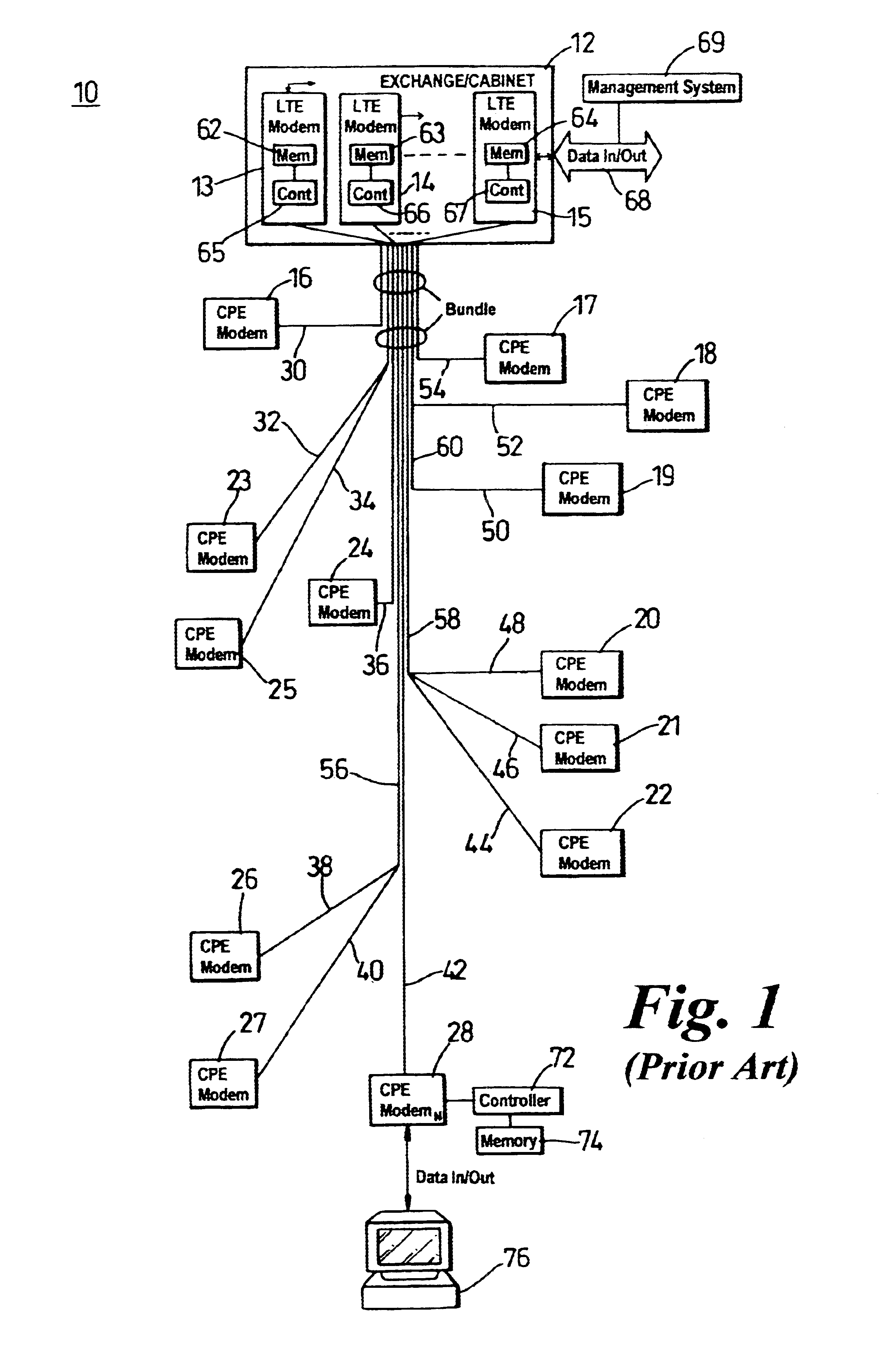
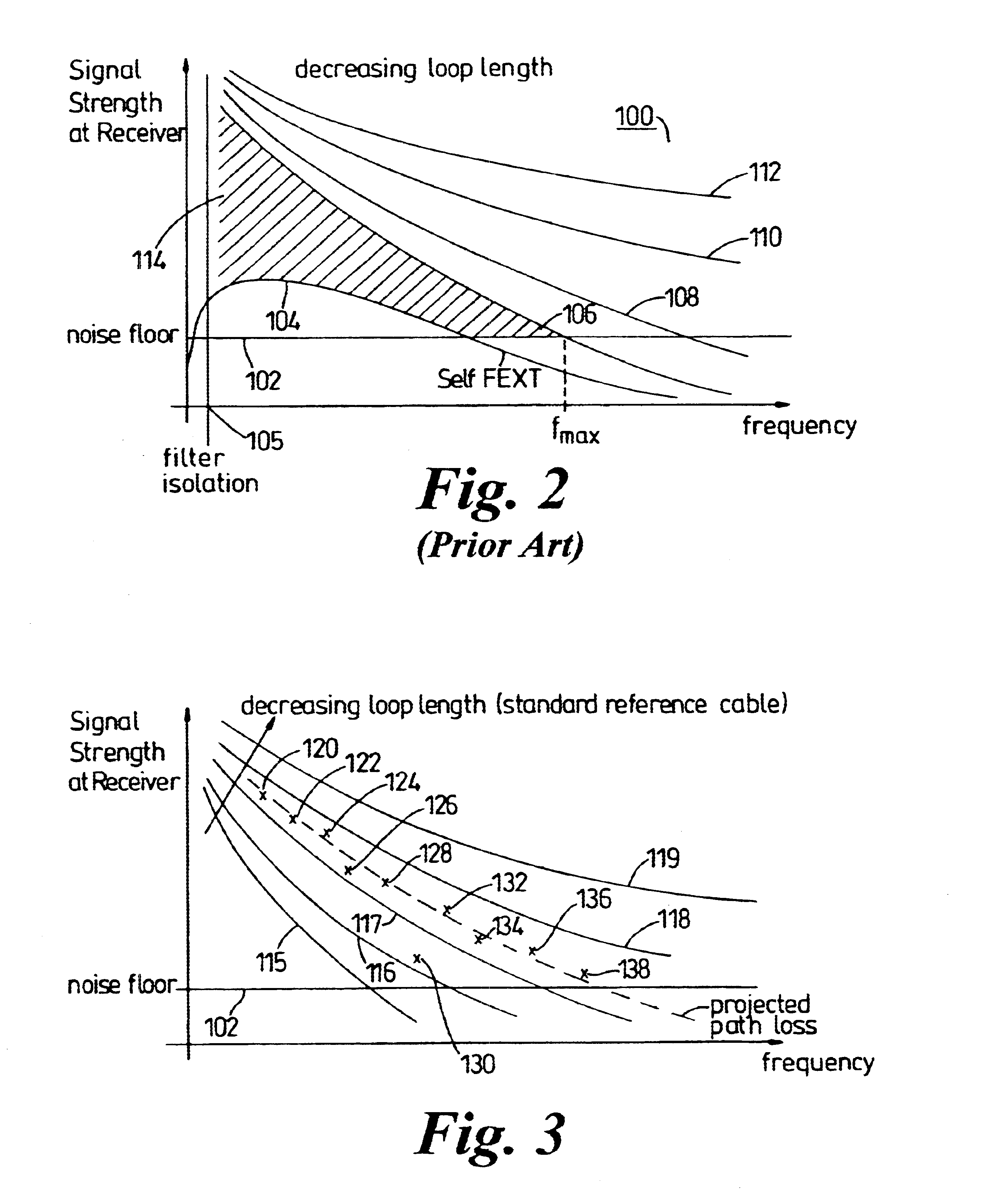
InactiveUS6650697B1Reduce impactImprove performanceTelephonic communicationLink quality based transmission modificationModem deviceFrequency spectrum
To alleviate the requirement to back-off all up-link performance, such as by limiting power spectral density, to overcome far-end cross-talk problems otherwise associated with relatively short loop-length wireline links, the present invention partitions the frequency spectrum based on an estimate of the loop length of a subscriber unit (CPE) modem from an exchange (LTE) modem. Up to a threshold frequency (fmax) at which received transmissions from a subscriber having a longest loop length (115) become indistinguishable by the LTE modem from a noise floor (102), up-link performance on all loop lengths is limited to correspond to that of the longest loop. At frequencies above the threshold frequency (fmax), subsets of subscribers (152-154) having relatively short loop lengths (116-119) use high frequency carriers that have signal to noise ratios sufficient to support information transmission in these elevated frequency bands.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Adaptive radio transceiver with offset PLL with subsampling mixers
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
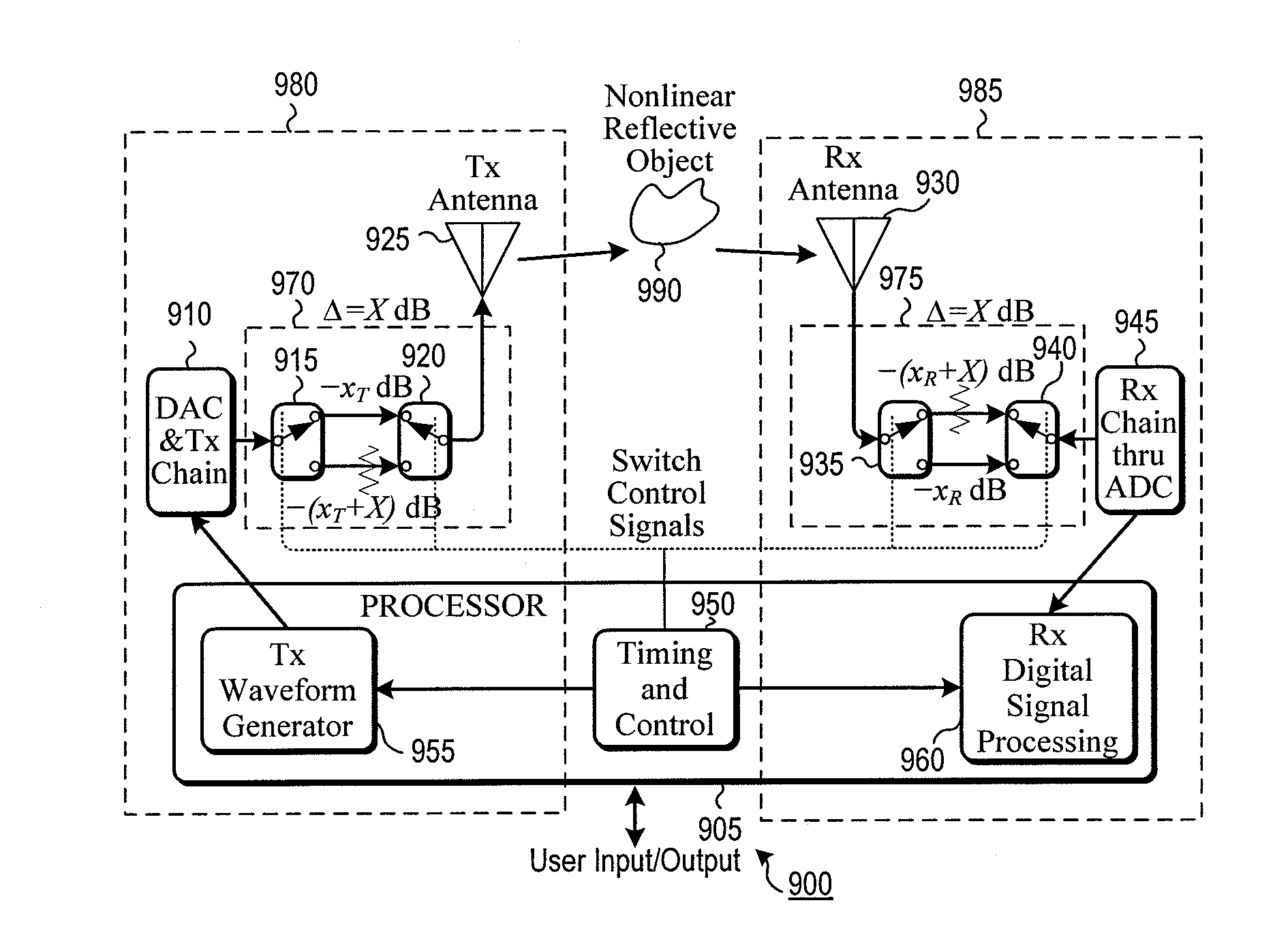
System and method for nonlinear radar
A non-linear radar is disclosed that is able to detect non-linear target responses that are below the harmonic-noise floor of the radar. To accomplish this below-the-noise-floor sensitivity feature the proposal specifically addresses all of the problems commonly faced by non-linear radar such as linearity of the transmitter path, receiver path, and size, weight, and power, and cost (SWaP-C). The radar operates in both standard and nonlinear modes with signal processing that allows display of nonlinear alone, linear alone, or both types of backscatter. Different combinations of six methodologies allow customization to fit different application needs, from low-cost modest performance, to higher cost and extremely high performance.
Owner:APPLIED SIGNALS INTELLIGENCE
Adaptive radio transceiver with a local oscillator
InactiveUS7031668B2Increase data rateIncrease costTransmitters monitoringResonant circuit tuningTransceiverAdaptive programming
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Clock generation system
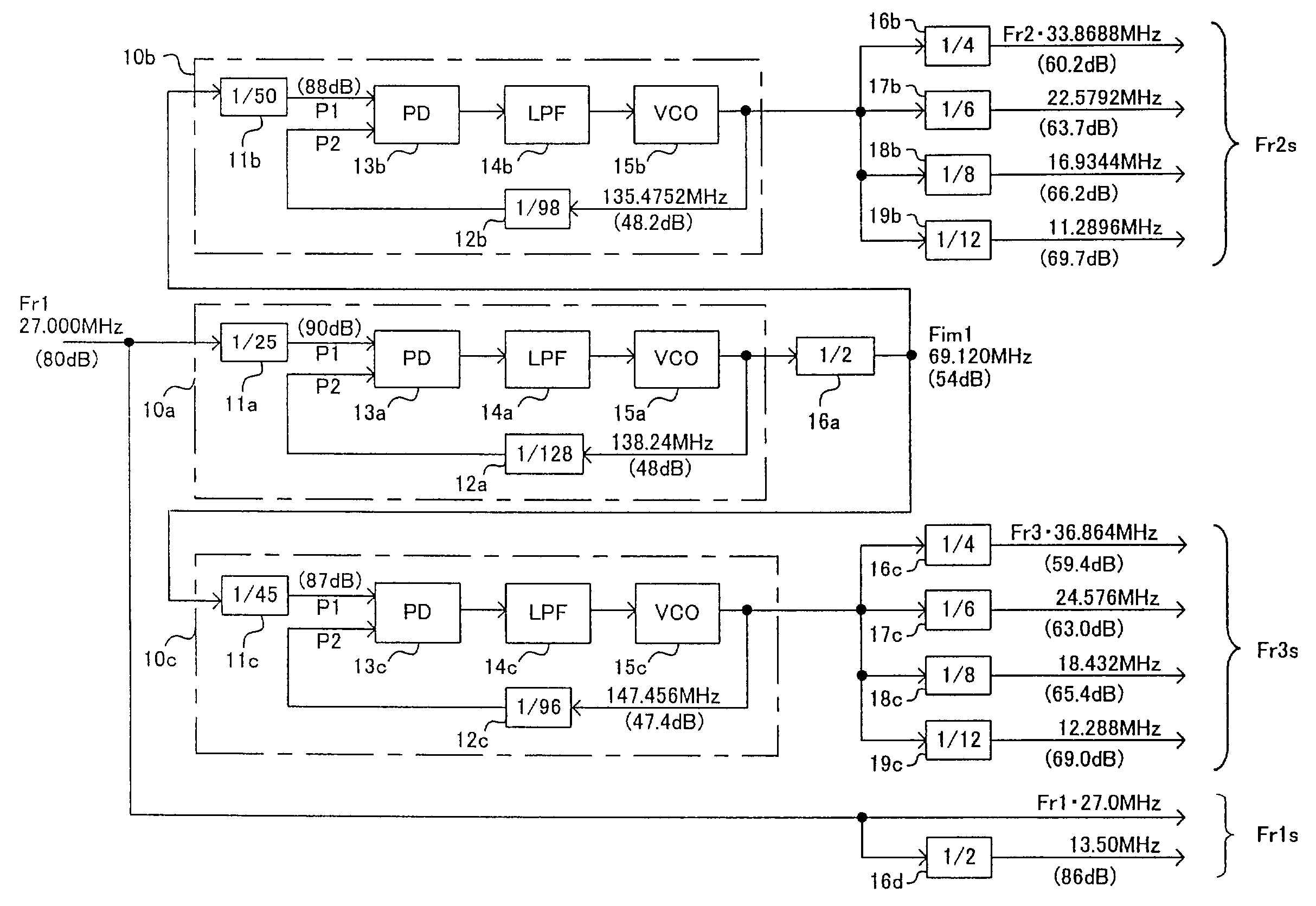
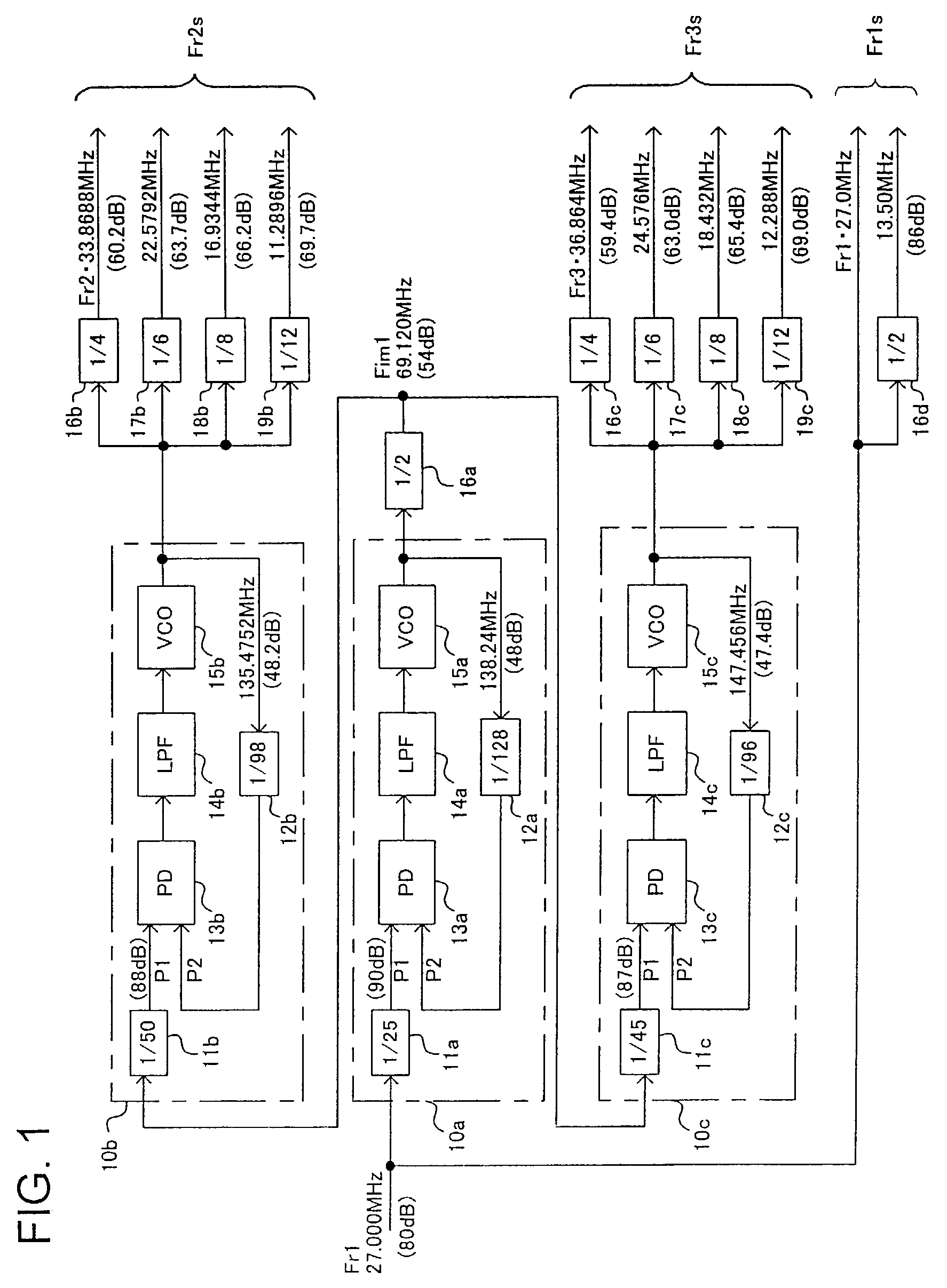
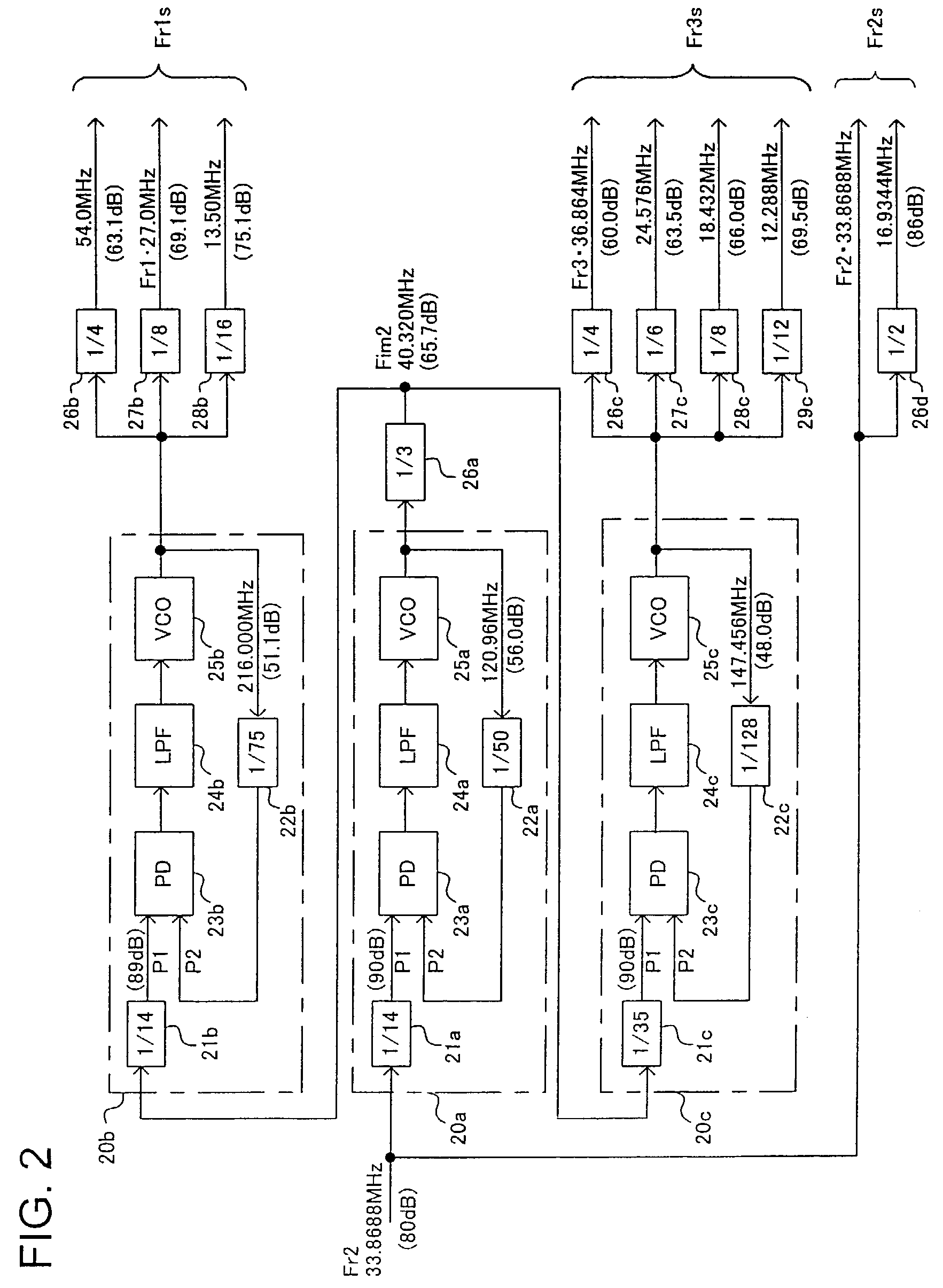
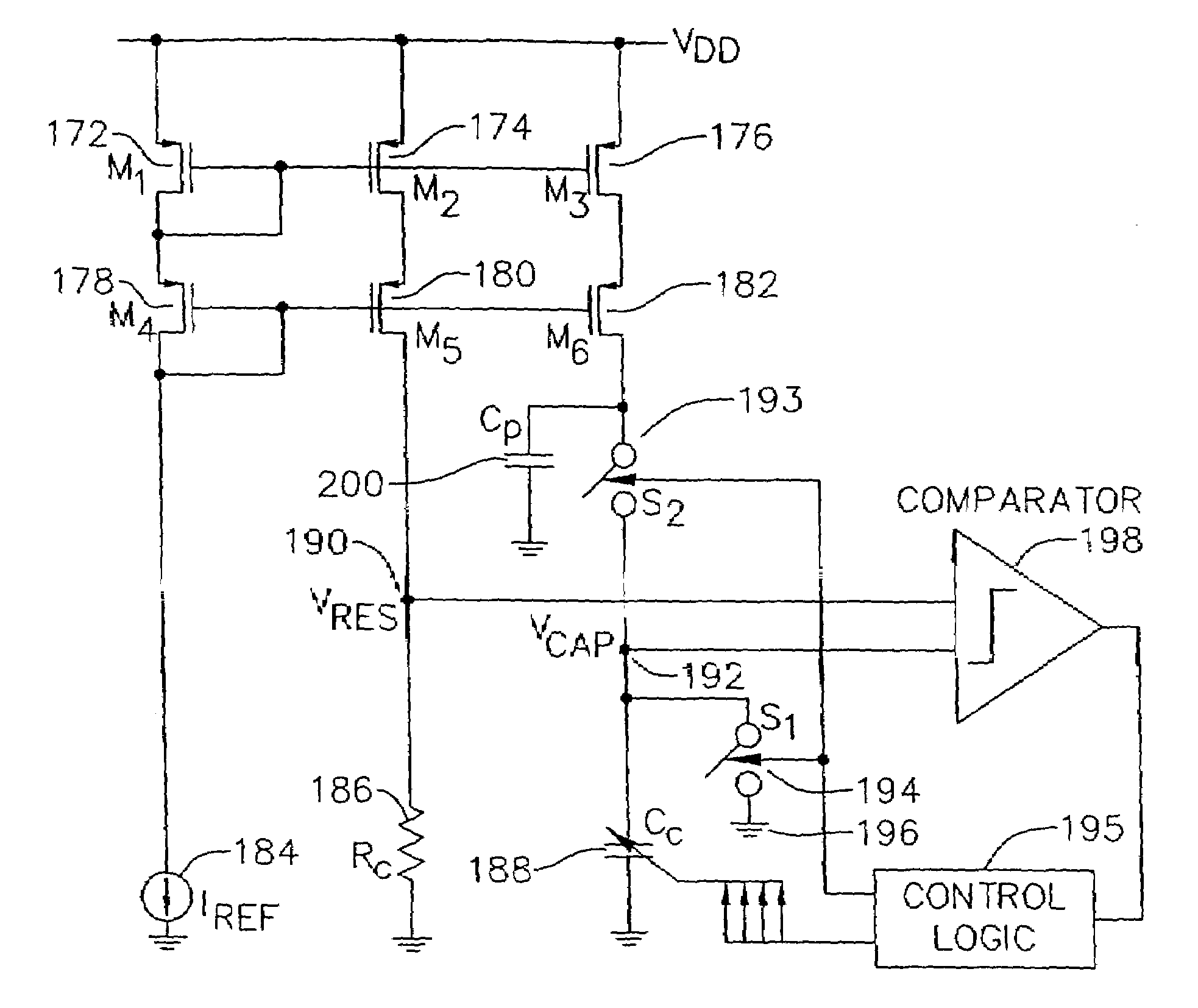
ActiveUS7216249B2Elimination of the limitation,Weaken influencePulse automatic controlError detection/correctionIntermediate frequencyNoise floor
A clock generation system for generating a first-, a second-, and a third-reference frequency clocks having respective frequencies having predetermined ratios to the reference frequency of a reference clock, using PL circuits in such a way that the clocks have sufficient S / N ratios in spite of the S / N ratio limitation by the noise floor. A first reference frequency clock is supplied to a first PLL circuit to generate an intermediate-frequency clock having an intermediate frequency having a predetermined ratio to the reference clock. The intermediate-frequency clock is supplied to a second and a third PLL circuits to generate a second and a third reference frequency clocks having frequencies respectively having a second and a third ratios to the intermediate frequency, respectively.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Adaptive radio transceiver
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Adaptive radio transceiver with calibration
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
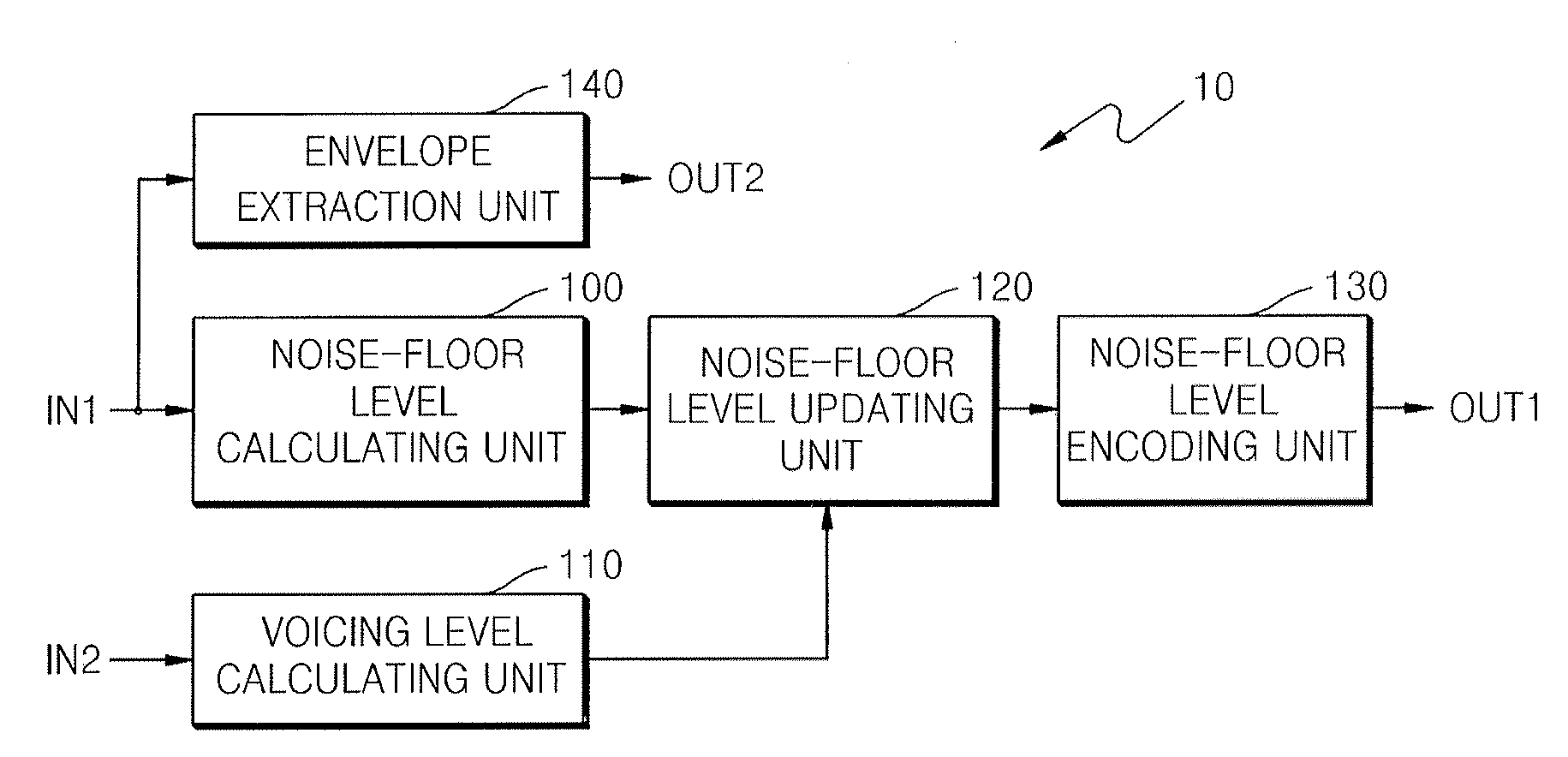
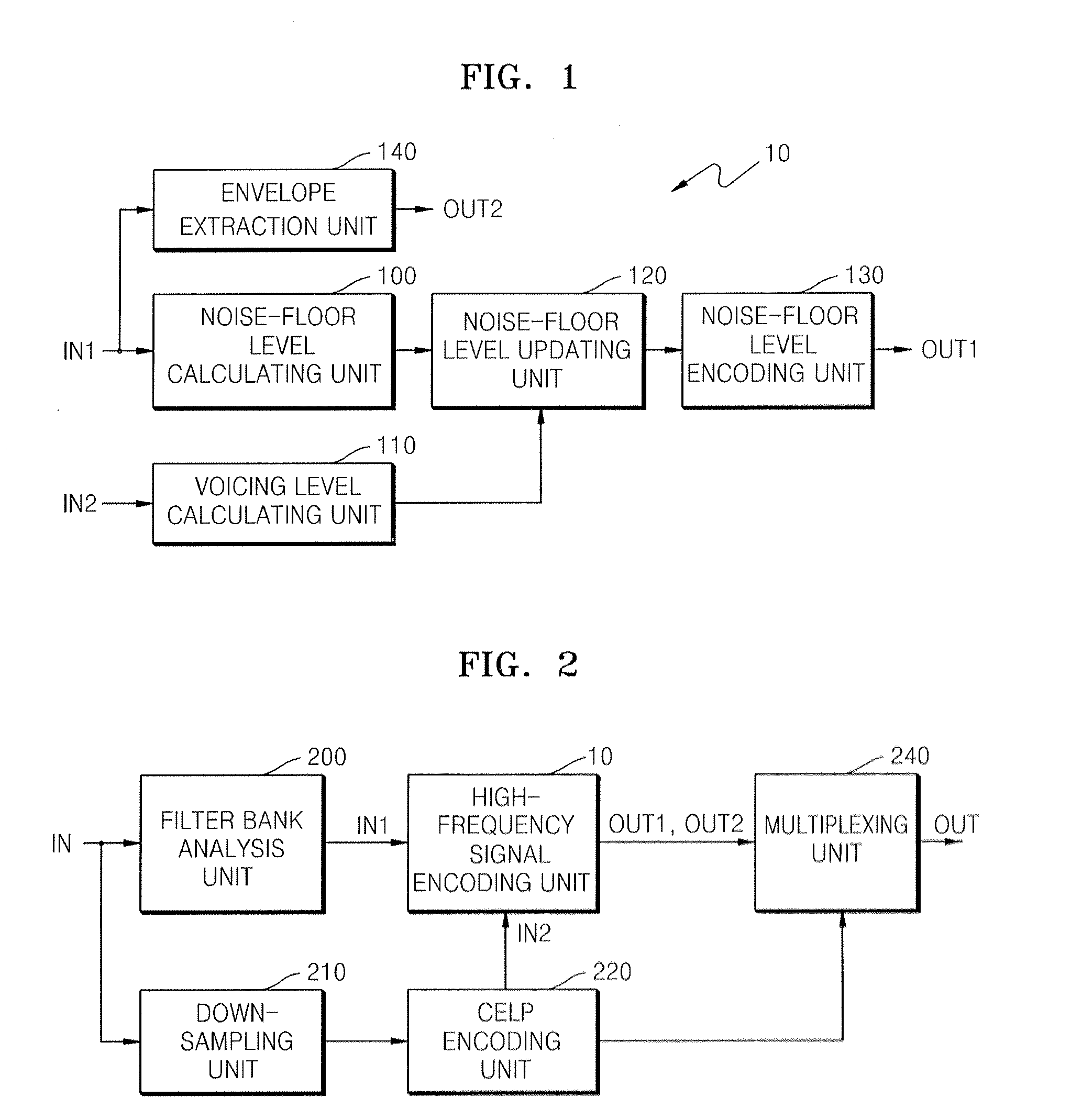
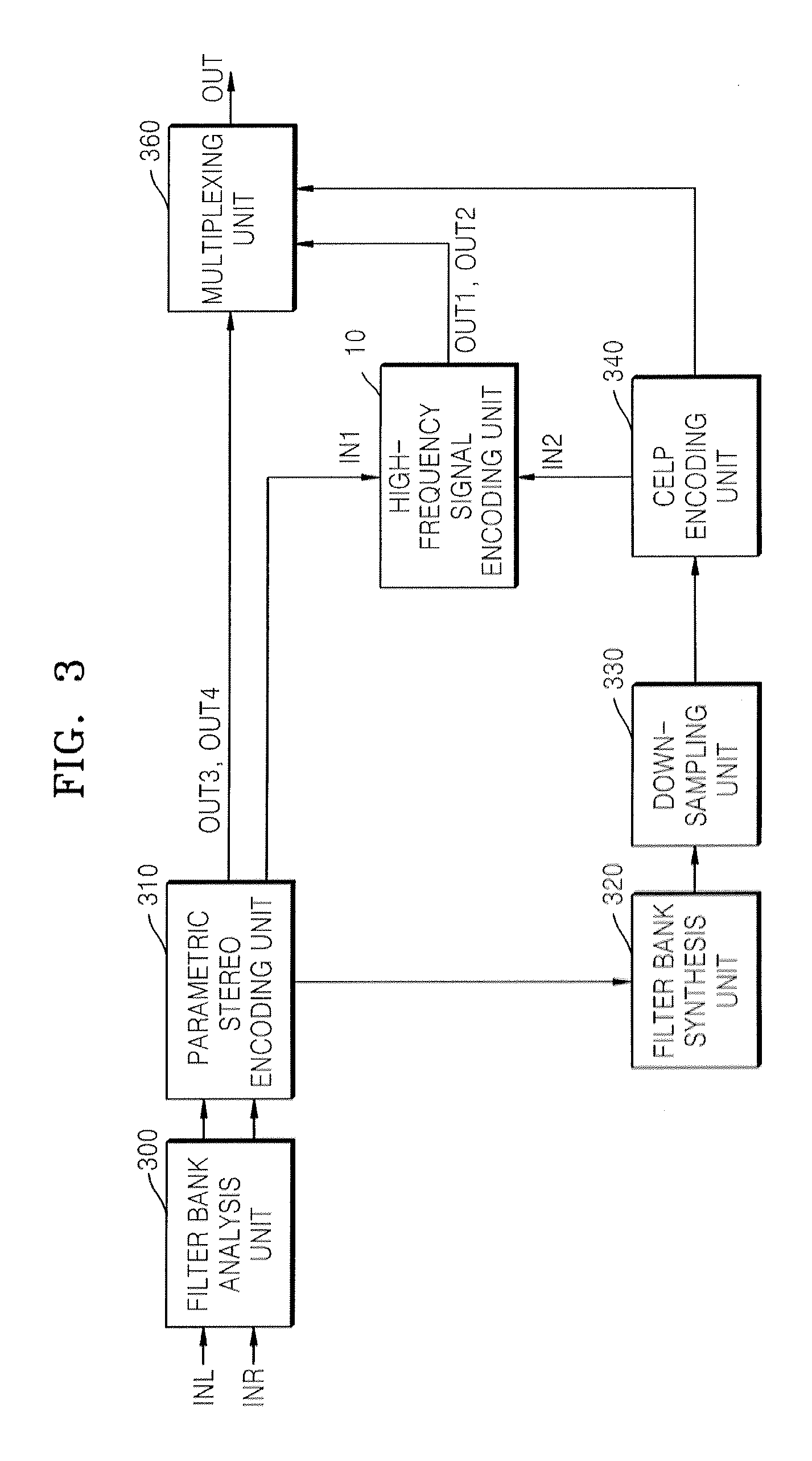
Apparatus, medium and method to encode and decode high frequency signal
A method and apparatus to encoding or decoding an audio signal is provided. In the method and apparatus, a noise-floor level to use in encoding or decoding a high frequency signal is updated according to the degree of a voiced or unvoiced sound included in the signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
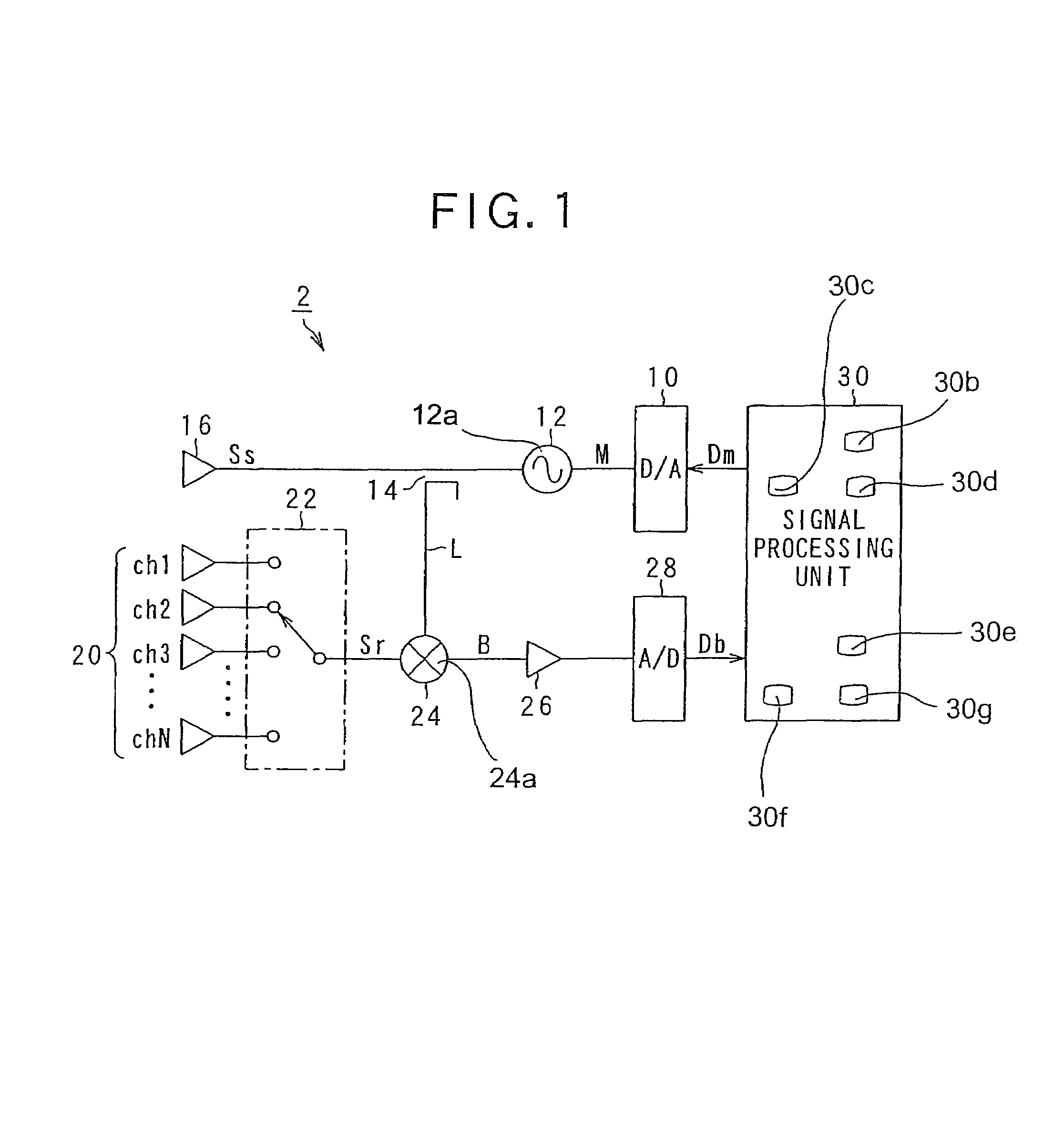
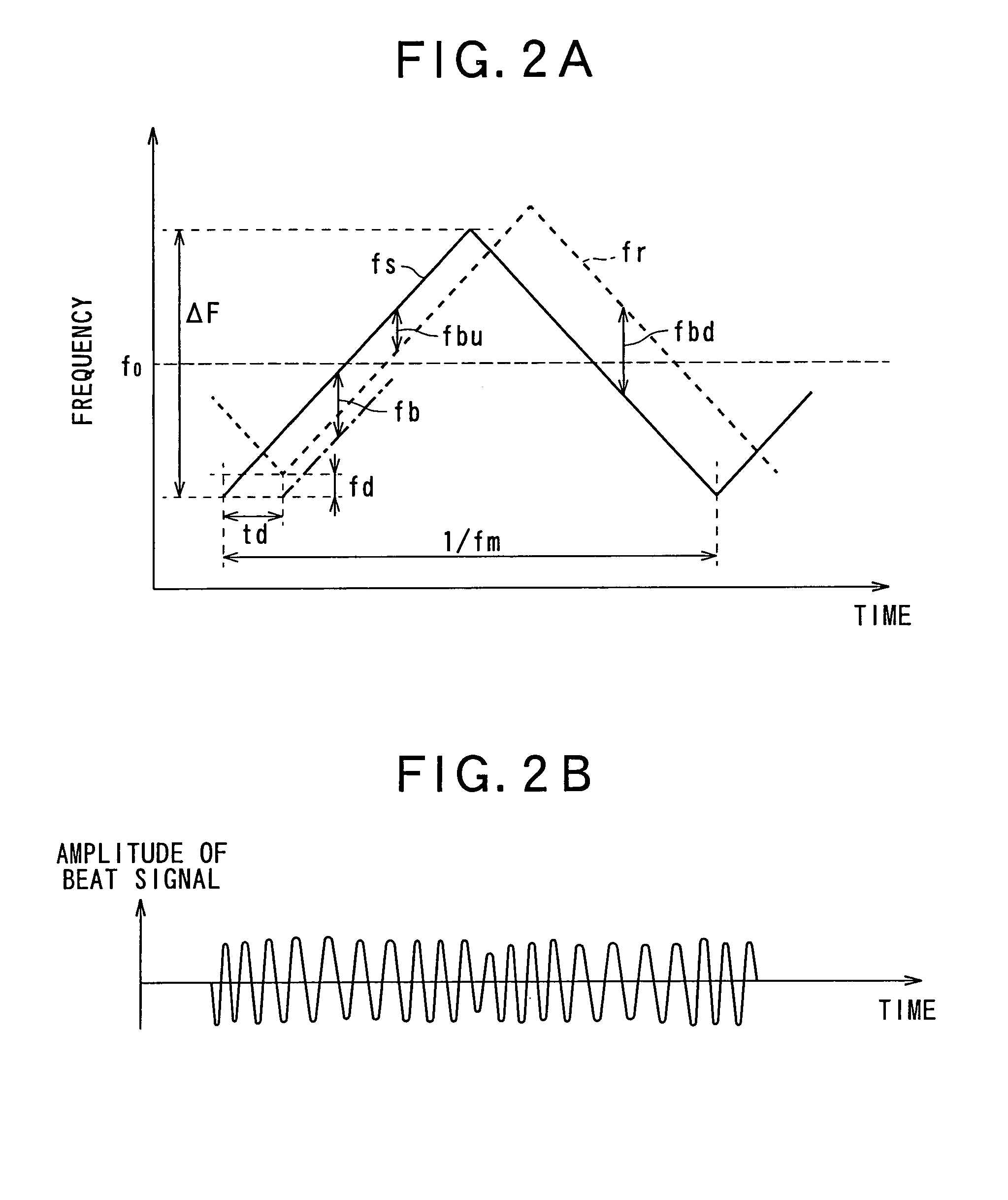
Method for determining noise floor level and radar using the same
ActiveUS7567204B2Accurate noiseNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarElectric signal
A method for a radar for detecting a noise floor level of an electric signal corresponding to an incident radio wave received by the radar, the incident radio wave including a return of a radar wave that is transmitted from the radar toward a measuring range of the radar to detect target object characteristic including presence of a target object within the measuring range of the radar, a distance between the target object and the radar, and a relative speed of the target object to the radar is provided. The method includes steps of: calculating a histogram of intensities of frequency components, the frequency components exceeding a predetermined value relating to the measuring range, and extracting an intensity having the maximum height in the histogram as the noise floor level of the electric signal.
Owner:DENSO CORP
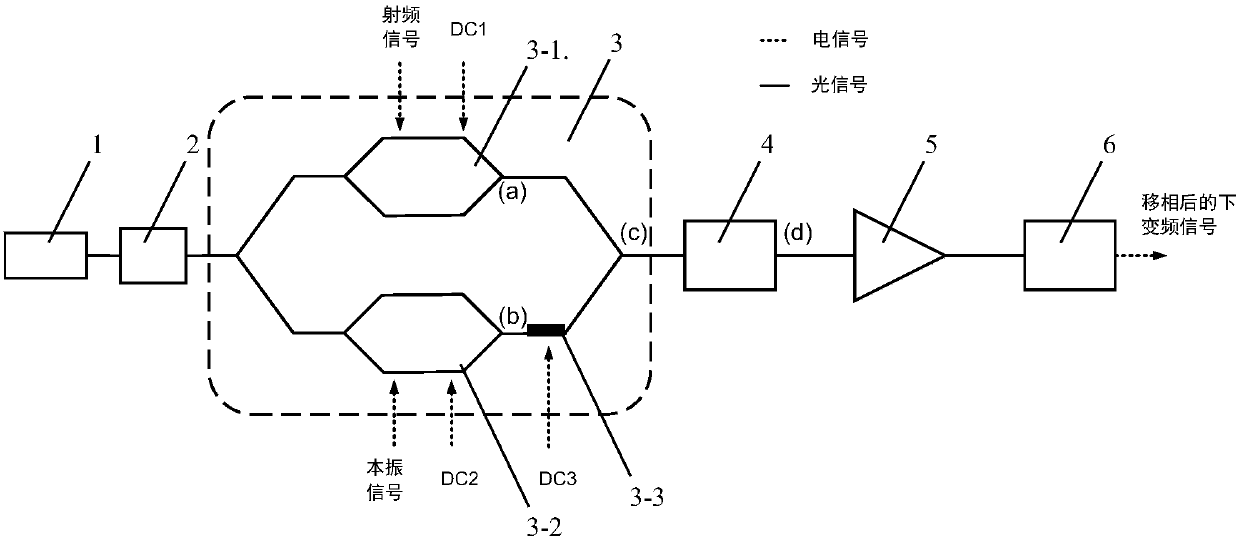
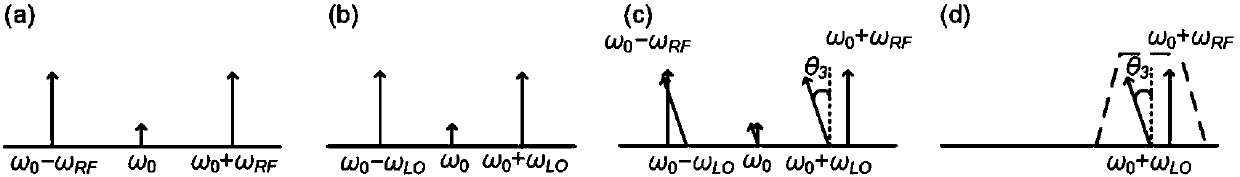
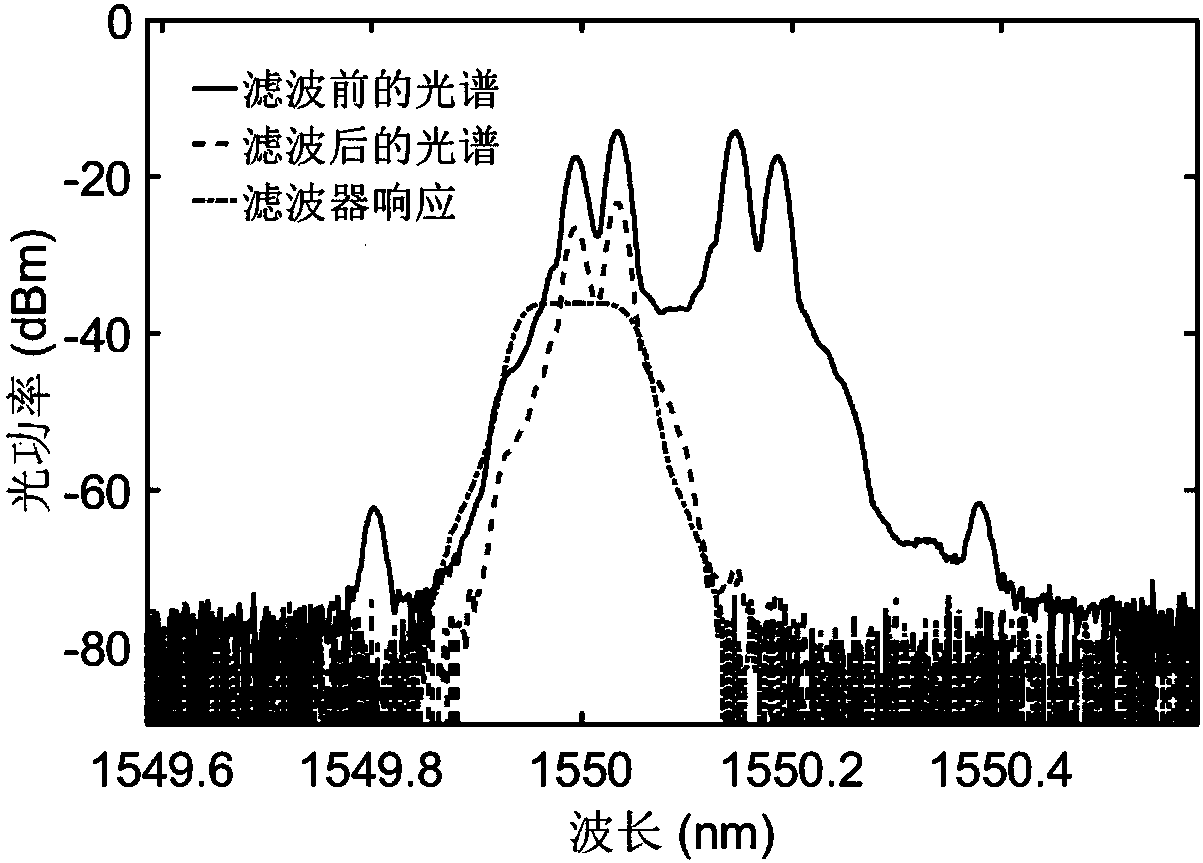
Photon method and system for realizing microwave down-conversion and phase shift by using integrated devices
ActiveCN107846254AImprove performanceRealize functionPhotonic quantum communicationElectromagnetic transmittersBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a photon method and system for realizing microwave down-conversion and phase shift by using integrated devices, and belongs to the field of microwave photonics. Firstly, opticalcarriers generated by a laser are input to a double-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator after passing through a polarization controller, a radio frequency signal is modulated by an upper arm sub-modulator, and carrier suppression double-sideband modulation is realized by DC bias; a local oscillator signal is modulated by a lower arm sub-modulator, and the carrier suppression double-sideband modulation is realized by the DC bias; the DC bias of a main intensity modulator is used for changing the phase difference between the radio frequency optical signal and the local oscillator optical signal. A-1 order optical sideband is filtered from an output carrier suppression double-sideband modulation optical signal by an optical bandpass filter, a +1 order optical sideband is retained, and the useless optical sideband is suppressed below the noise floor. Then, power amplification is performed on the optical signal to compensate the insertion loss of modulator and the filter. At last, a down-conversion signal subjected to phase shift is obtained by performing beat frequency by using a photodetector. A very pure frequency spectrum signal is output, and the performance of an integrated functionlink of down-conversion and phase shift is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +1
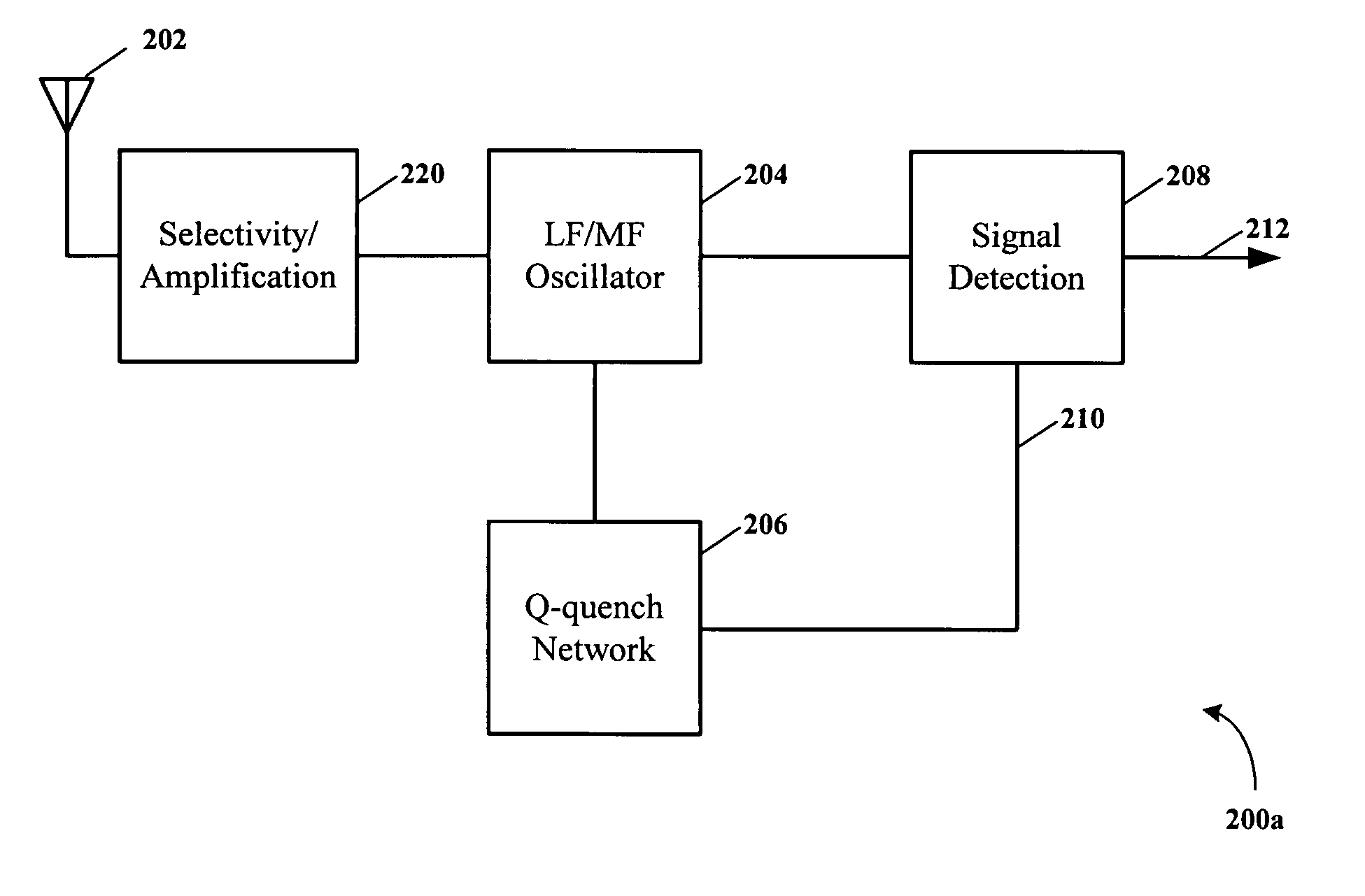
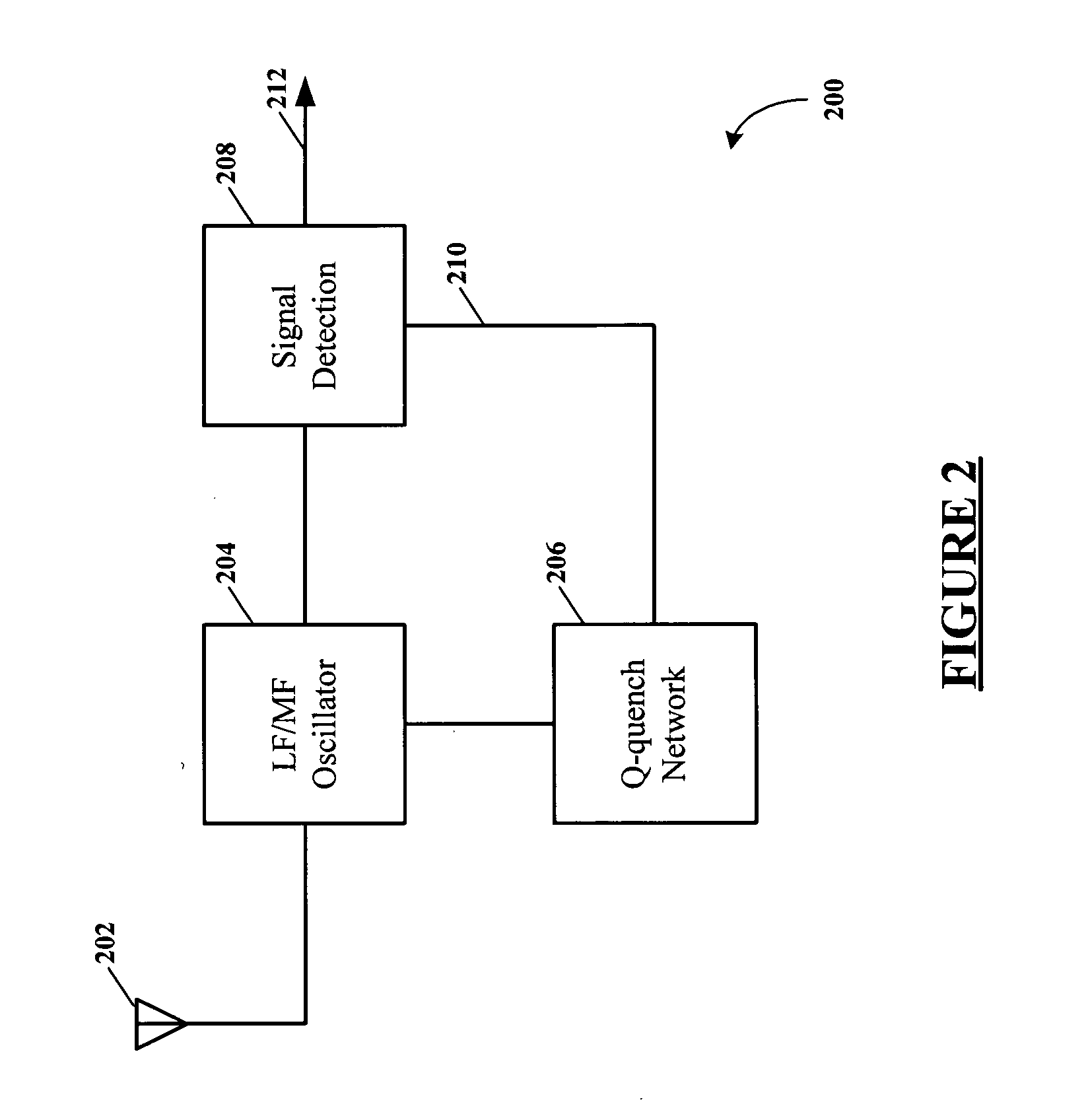
Q-quenching super-regenerative receiver
ActiveUS20050069051A1Reduce radiated noiseLow costAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDemodulator for amplitude-modulated oscillationsEngineeringQuenching
A super-regenerative receiver uses controlled Q-quenching and may limit the resonant tank circuit amplitude by loading the tank circuit as soon as regenerative oscillation is detected. An amplitude detector is coupled to the regenerative amplifier and controls a Q loading circuit coupled to the tank circuit of the regenerative amplifier. The amplitude detector turns on the Q loading circuit which then stops the regenerative amplifier from oscillating, and the Q-loading remains on for a brief time to insure that the regenerative amplifier has stopped oscillating. After the brief time, the Q loading circuit is turned off and the regenerative amplifier goes into oscillation again. This cycle repeats controllably over and over, resulting in a lower self-induced noise floor and improved received signal sensitivity. The super-regenerative receiver may be used in the very low frequency (VLF), low frequency (LF), medium frequency (MF), high frequency (HF), very high frequency (VHF) and super high frequency (SHF) ranges to receive continuous wave (CW), amplitude modulated (AM) and frequency modulated (FM) radio signals.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Adaptive radio transceiver with subsampling mixers
InactiveUS7558556B1Minimize adverse effectsReduce power consumptionResonant long antennasResonant circuit tuningAdaptive programmingTransceiver
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
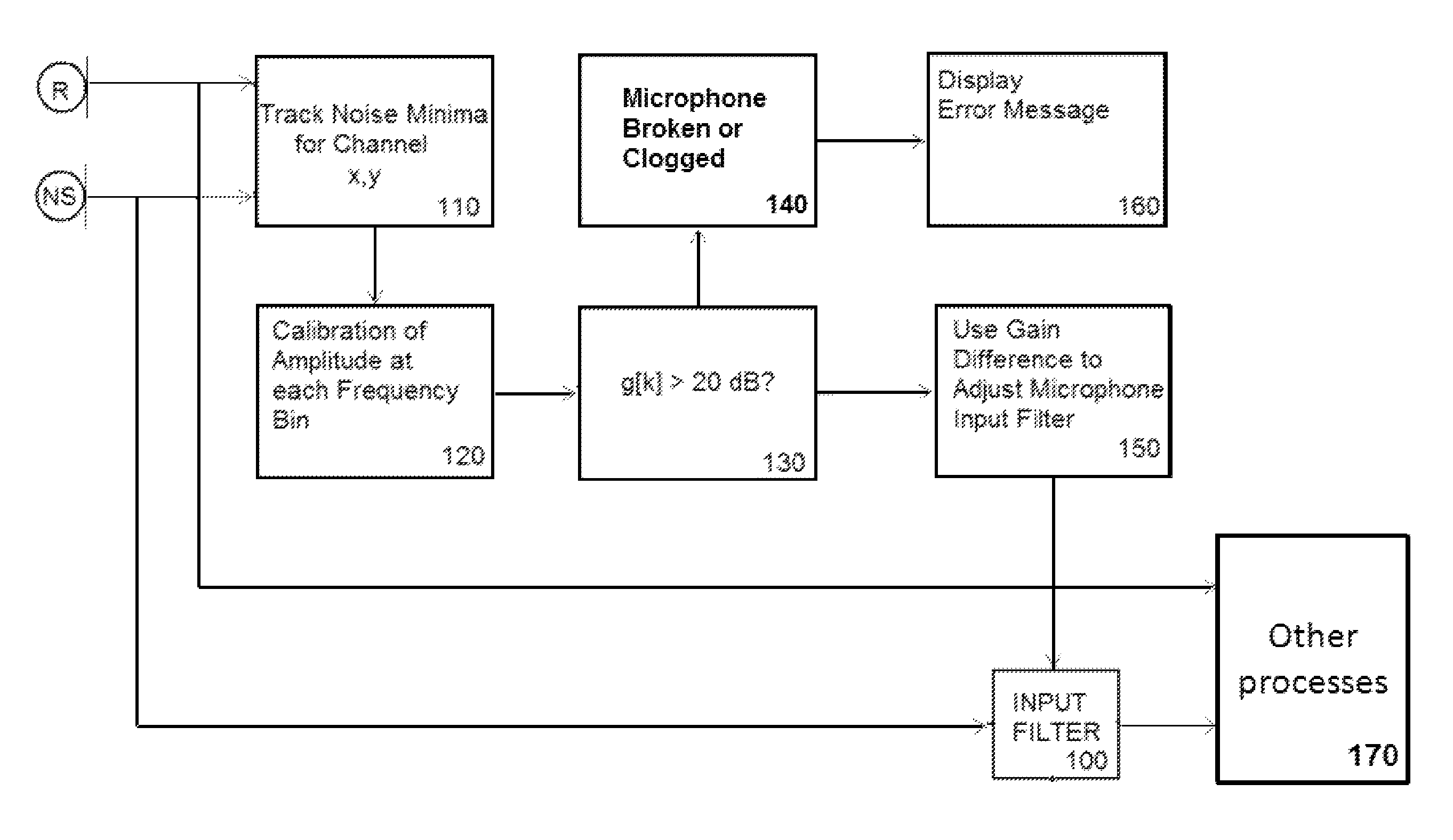
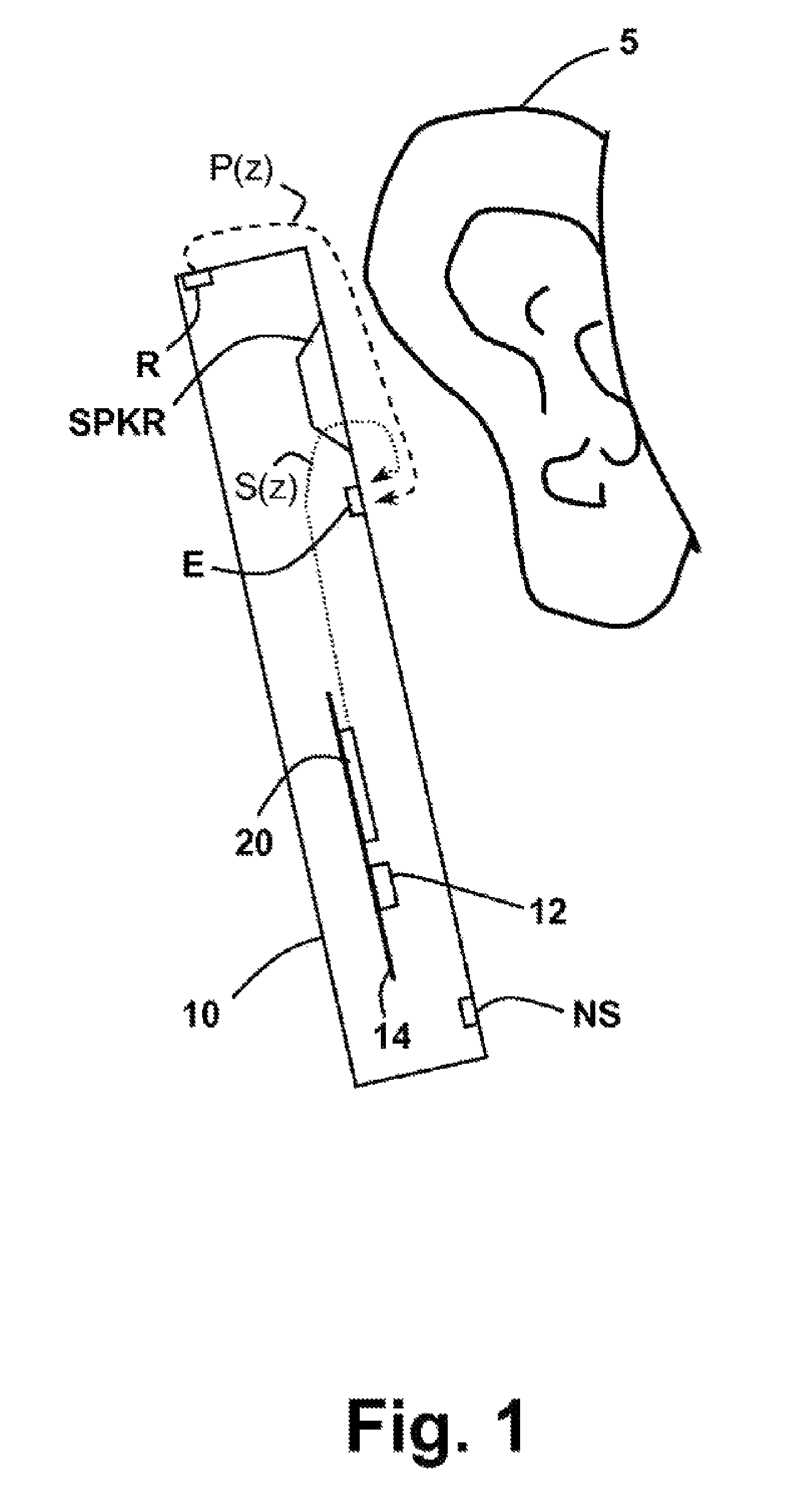
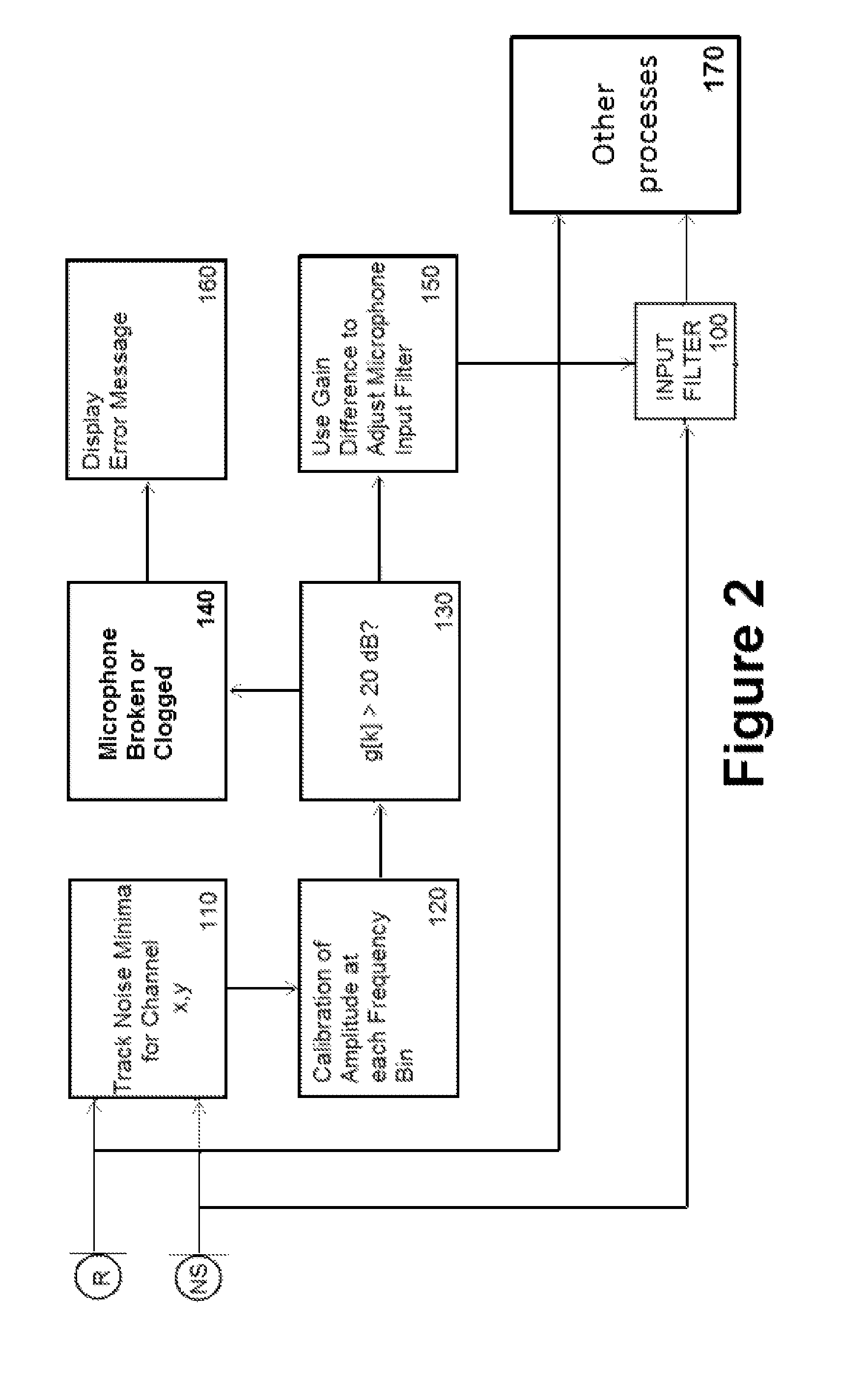
Dual-microphone frequency amplitude response self-calibration
ActiveUS9532139B1MicrophonesHearing device active noise cancellationAmplitude responseCellular telephone
A frequency domain method and system for online self-calibrating microphone frequency amplitude response based on noise floor (minima) tracking are disclosed. A cellular telephone or other system with dual microphones may self-calibrate itself on-the-fly. The system selects one of the microphones as a reference and calibrates the frequency response of the two microphones using the first microphone as a reference, so that they have a matched frequency amplitude response. To achieve this on-the-fly calibration, the system uses background noise for calibration purposes. The signal power spectra of the noise minima at the two microphones is used to calibrate the respective microphone frequency response. The system may then adapt the frequency amplitude responses of the two microphones so that the power spectral density from each microphone matches the other, and the system is then calibrated. This calibration could occur any time the device is receiving a noise minima and could be done continuously as the device is being used.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
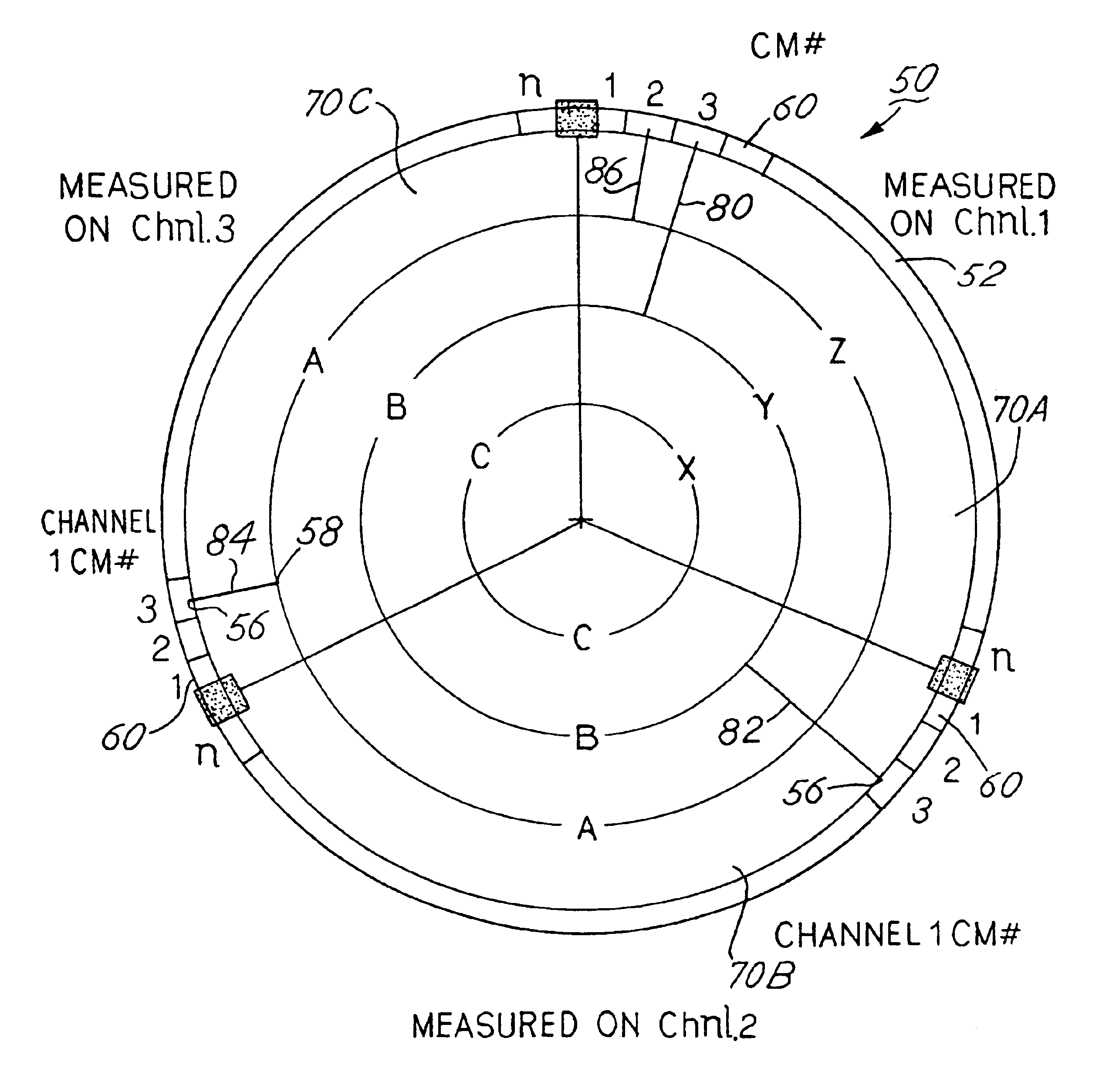
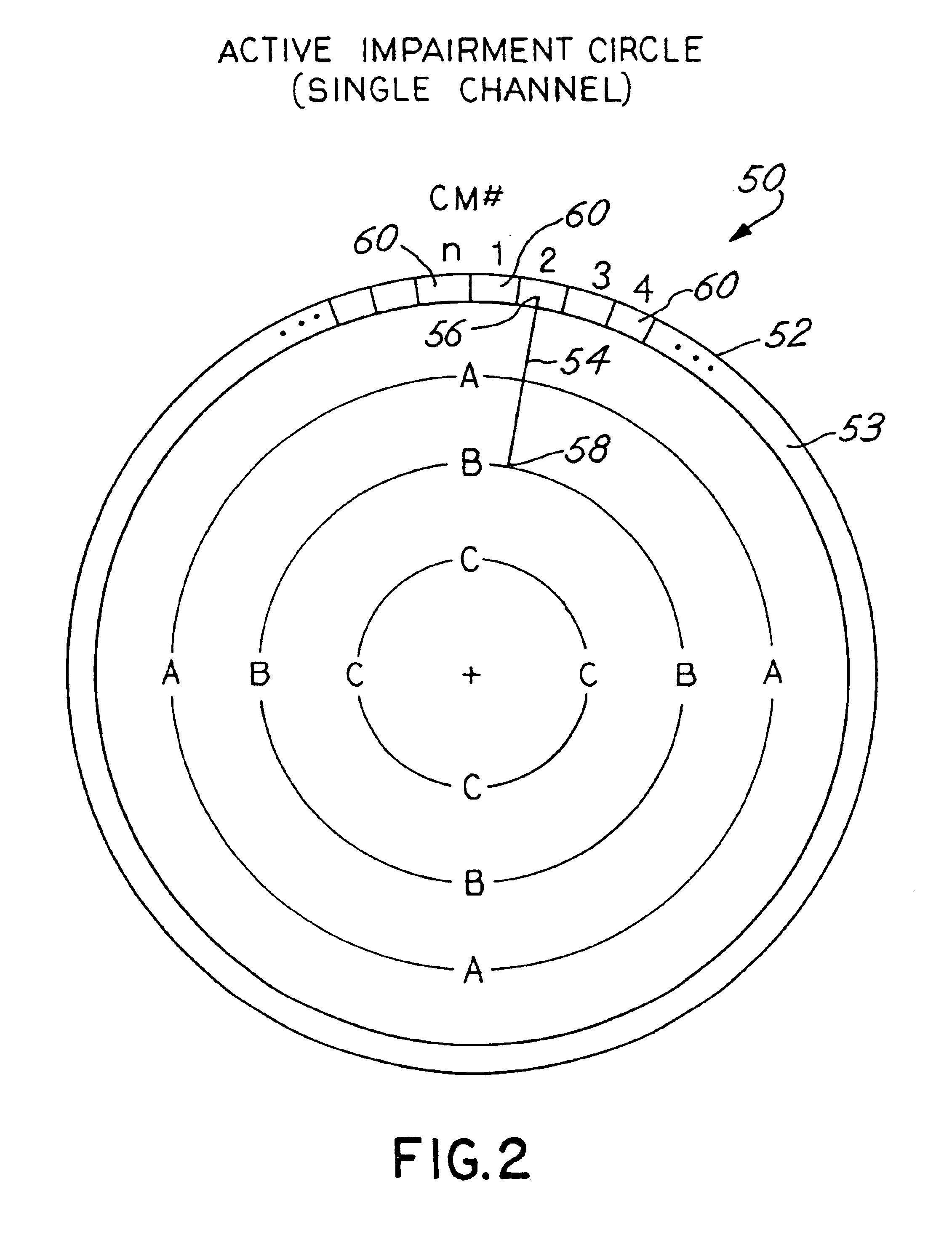
Graphical representation of impairment or other conditions in a data-over-cable system
InactiveUS6757908B1Two-way working systemsData switching networksGraphicsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Impairment or other conditions (e.g., signal to noise ratio or noise floor) in a data-over-cable system are represented graphically in an easy to use and comprehensible manner, enabling quick identification and isolation of the source of the impairment. The graphical representation of the condition, referred to herein as an "impairment circle", is in the form of a circular template with a line segment superimposed thereon representing the impairment. One end of the line segment is placed on the perimeter of the circle at a location associated with a particular cable modem or channel. The other end of the line segment either terminates in the interior of the circle or terminates on another portion of the perimeter. The perimeter of the circle can be divided into multiple sections, each section representing a channel in a transmission path. The sections can be further divided into multiple divisions, each division corresponding to a particular cable modem in the path or number of occurrences. In one type of the impairment circle, the location in which the line segment terminates within the interior of the circle indicates the magnitude of the impairment or other measurement. A single impairment circle can be used to represent impairments or other measurements of multiple channels and multiple cable modems. In another type of impairment circle, the line segment goes from one division of one section to another division of another section, indicating a condition of impairment of other channels when a particular cable modem in one channel is active. Different colors for the line segments and different widths of the line segments can convey additional information, such as the number of occurrences of the condition, or the magnitude of the impairment.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
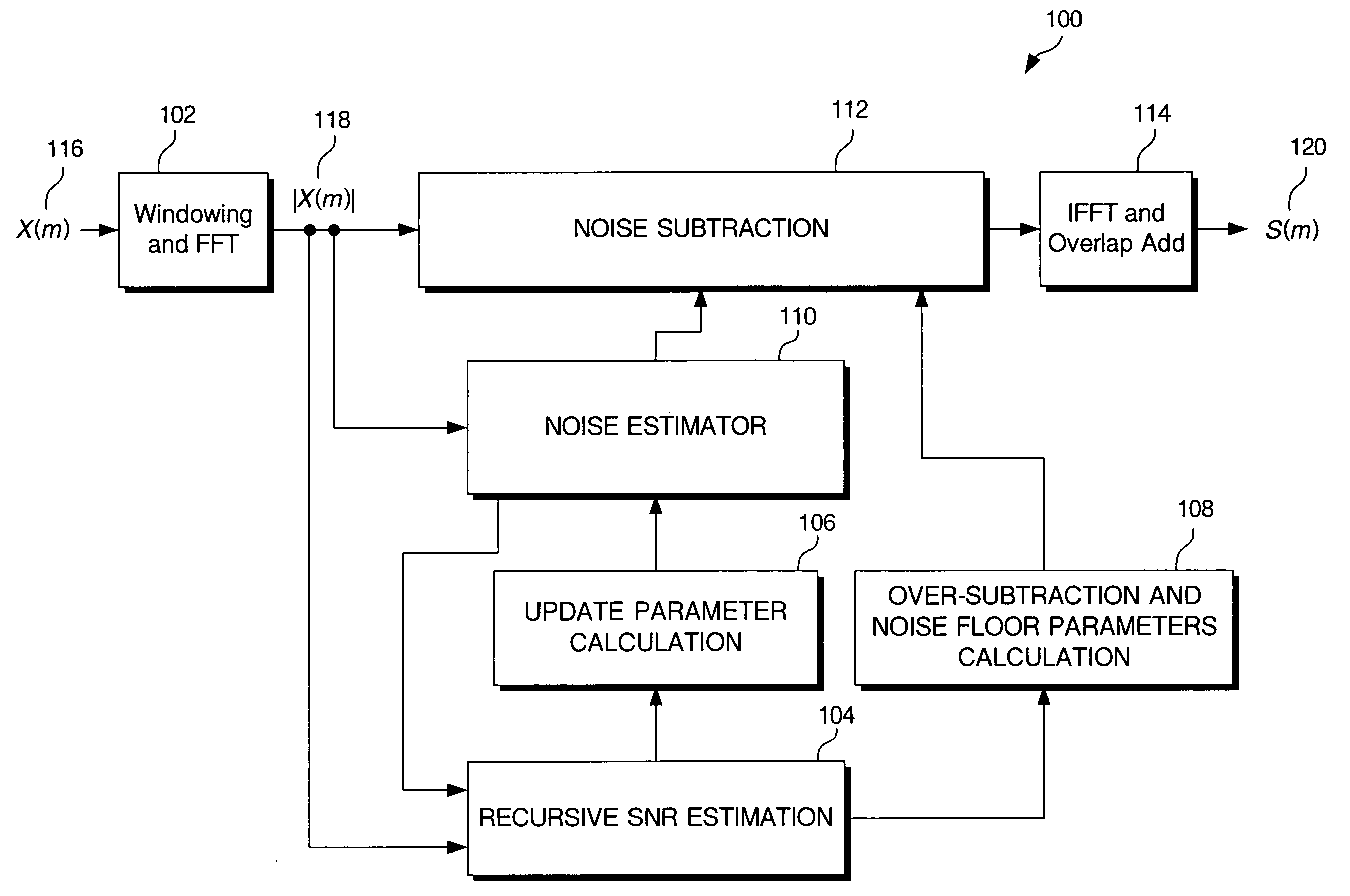
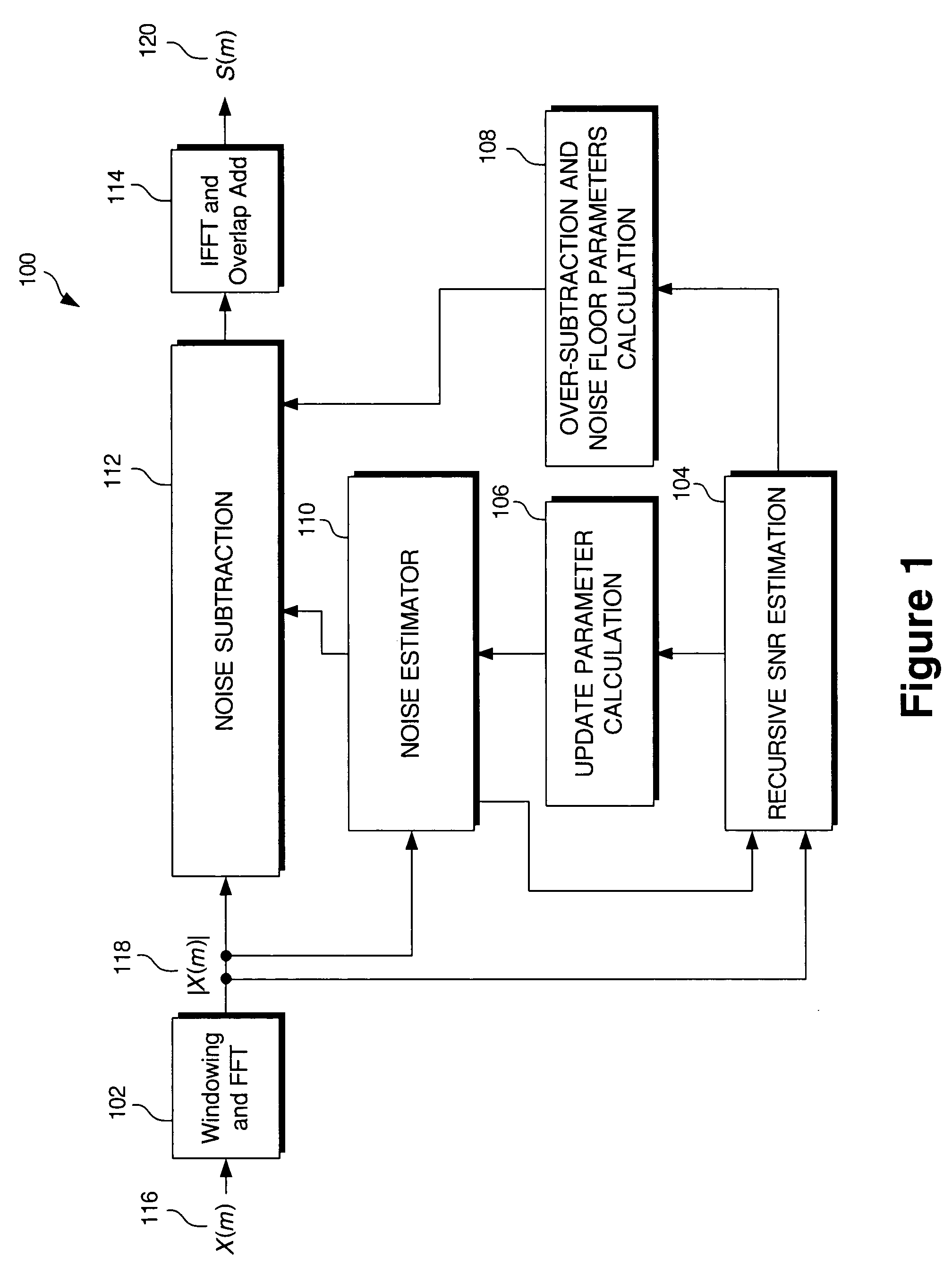
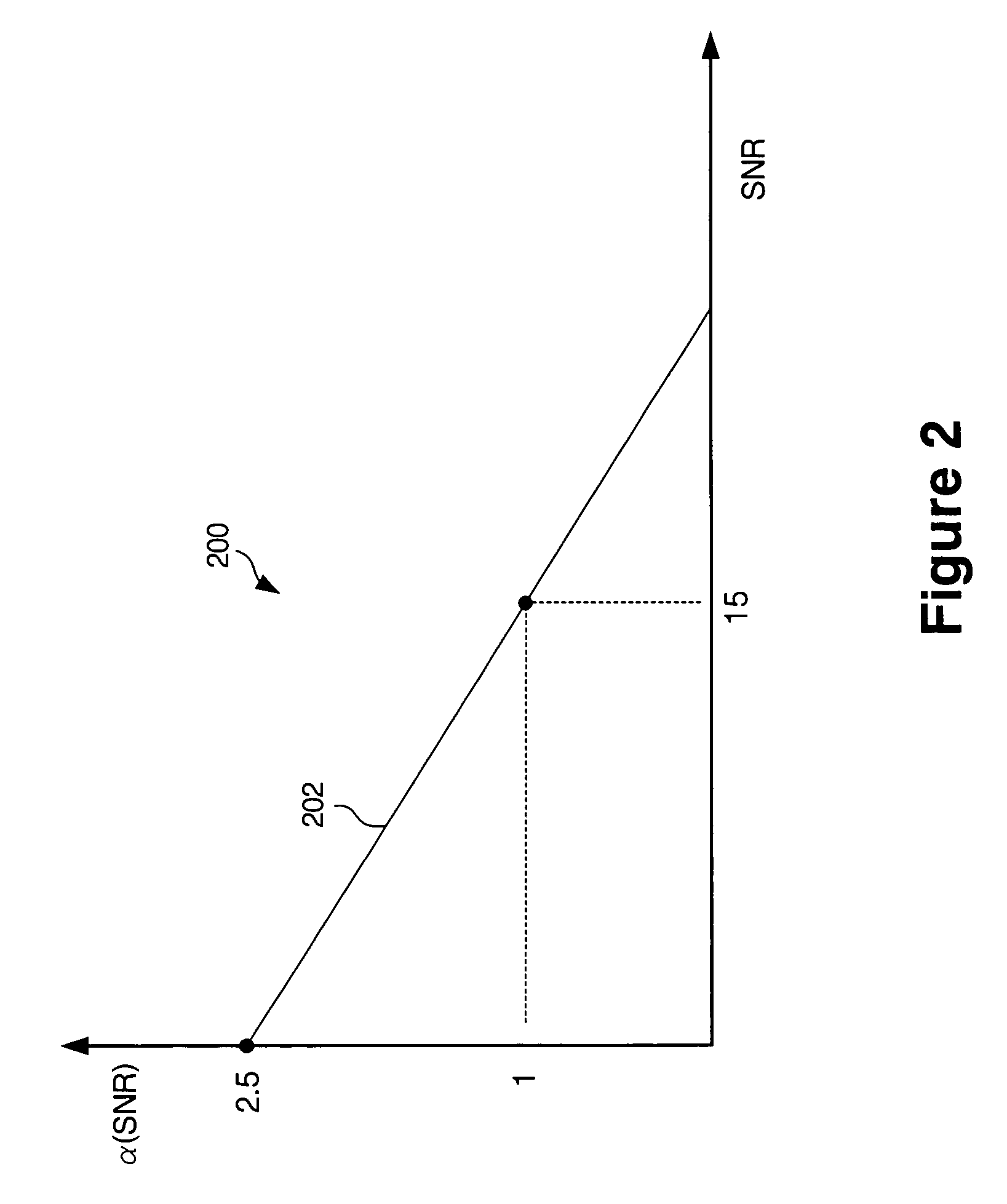
Computationally efficient background noise suppressor for speech coding and speech recognition
ActiveUS7133825B2Efficient and accurate noiseSuppress noiseSpeech recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Suppressor
A noise suppressor for suppressing noise in a source speech signal, where a method utilized by the noise suppressor comprises calculating a signal-to-noise ratio in the source speech signal, calculating a background noise estimate for a current frame of the source speech signal based on said current frame and at least one previous frame and in accordance with the signal-to-noise ratio, wherein the calculating the signal-to-noise ratio is carried out independent from the background noise estimate for the current frame, and subtracting the background noise estimate from the source speech signal to produce a noise-reduced speech signal. The method may also comprise calculating an over-subtraction parameter based on the signal-to-noise ratio, calculating a noise-floor parameter based on the signal-to-noise ratio, wherein the subtracting uses the over-subtraction parameter and the noise-floor parameter to produce the noise-reduced speech signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com