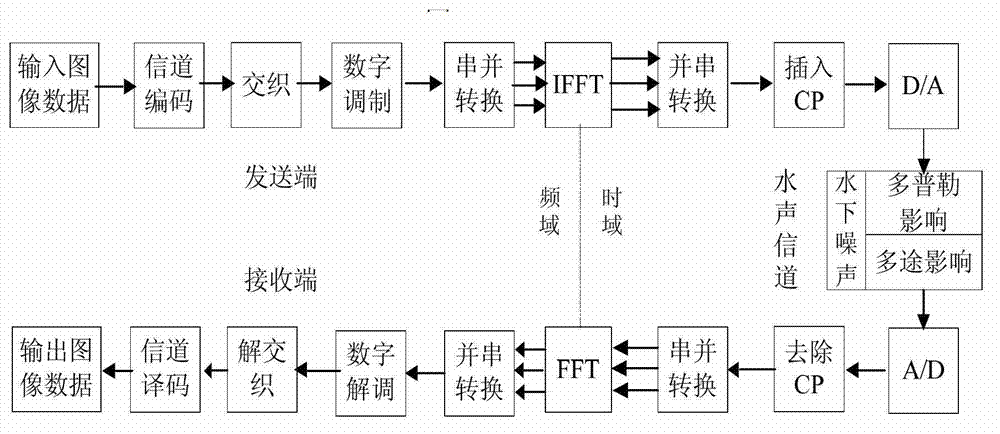
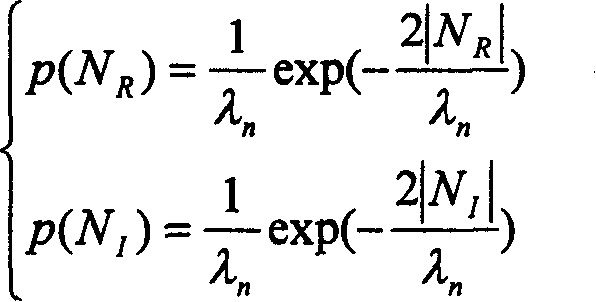Patents
Literature
835 results about "Minimum mean square error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
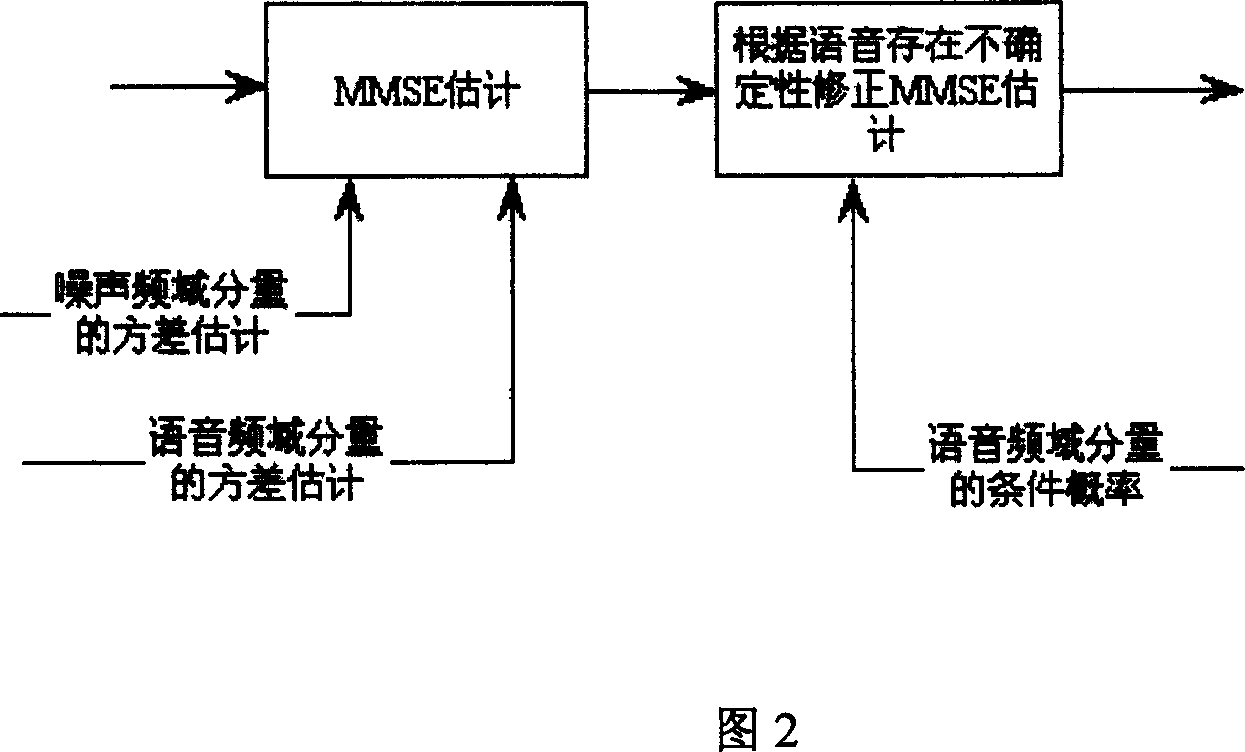
In statistics and signal processing, a minimum mean square error (MMSE) estimator is an estimation method which minimizes the mean square error (MSE), which is a common measure of estimator quality, of the fitted values of a dependent variable. In the Bayesian setting, the term MMSE more specifically refers to estimation with quadratic loss function. In such case, the MMSE estimator is given by the posterior mean of the parameter to be estimated. Since the posterior mean is cumbersome to calculate, the form of the MMSE estimator is usually constrained to be within a certain class of functions. Linear MMSE estimators are a popular choice since they are easy to use, easy to calculate, and very versatile. It has given rise to many popular estimators such as the Wiener–Kolmogorov filter and Kalman filter.
Selective fusion location estimation (SELFLOC) for wireless access technologies
ActiveUS20040203904A1Easy to calculatePosition fixationData switching by path configurationEngineeringMinimum mean square error
In an RF environment serviced by 802.11, Bluetooth (TM), or other network transmitters, or combinations, location-estimation methods and systems can advantageously use redundancy to refine an estimated location of an RF receiver. In one embodiment, a method for finding a receiver's location includes receiving signals from fixed transmitters, calculating preliminary location estimates, and combining the estimates using predetermined reference information on the RF environment. The reference information preferably includes minimum mean-squared error optimizing coefficients.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Apparatus and method for adaptive 3D artifact reducing for encoded image signal
InactiveUS20060050783A1Efficient reductionReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementRandom noiseNoise reduction
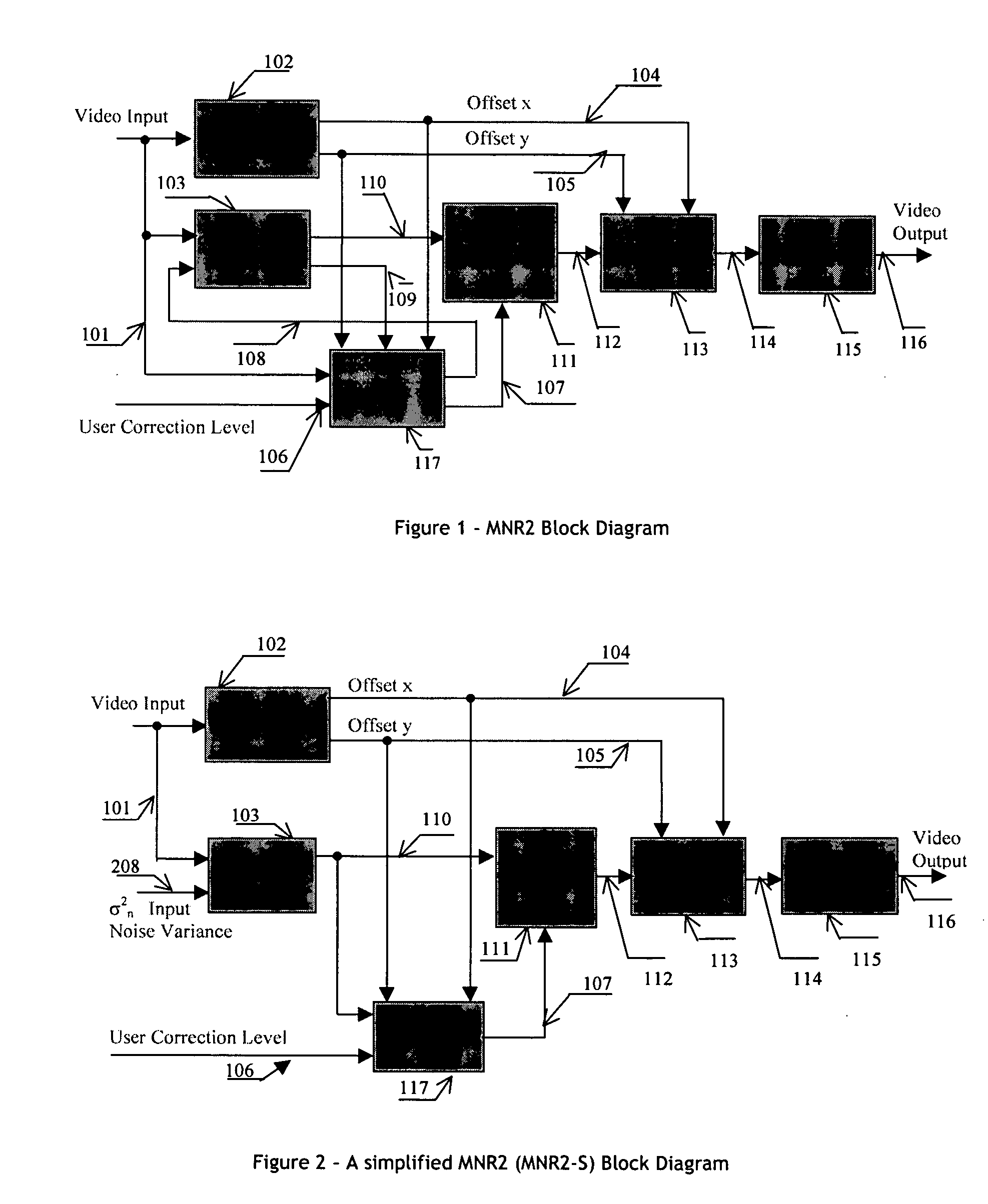
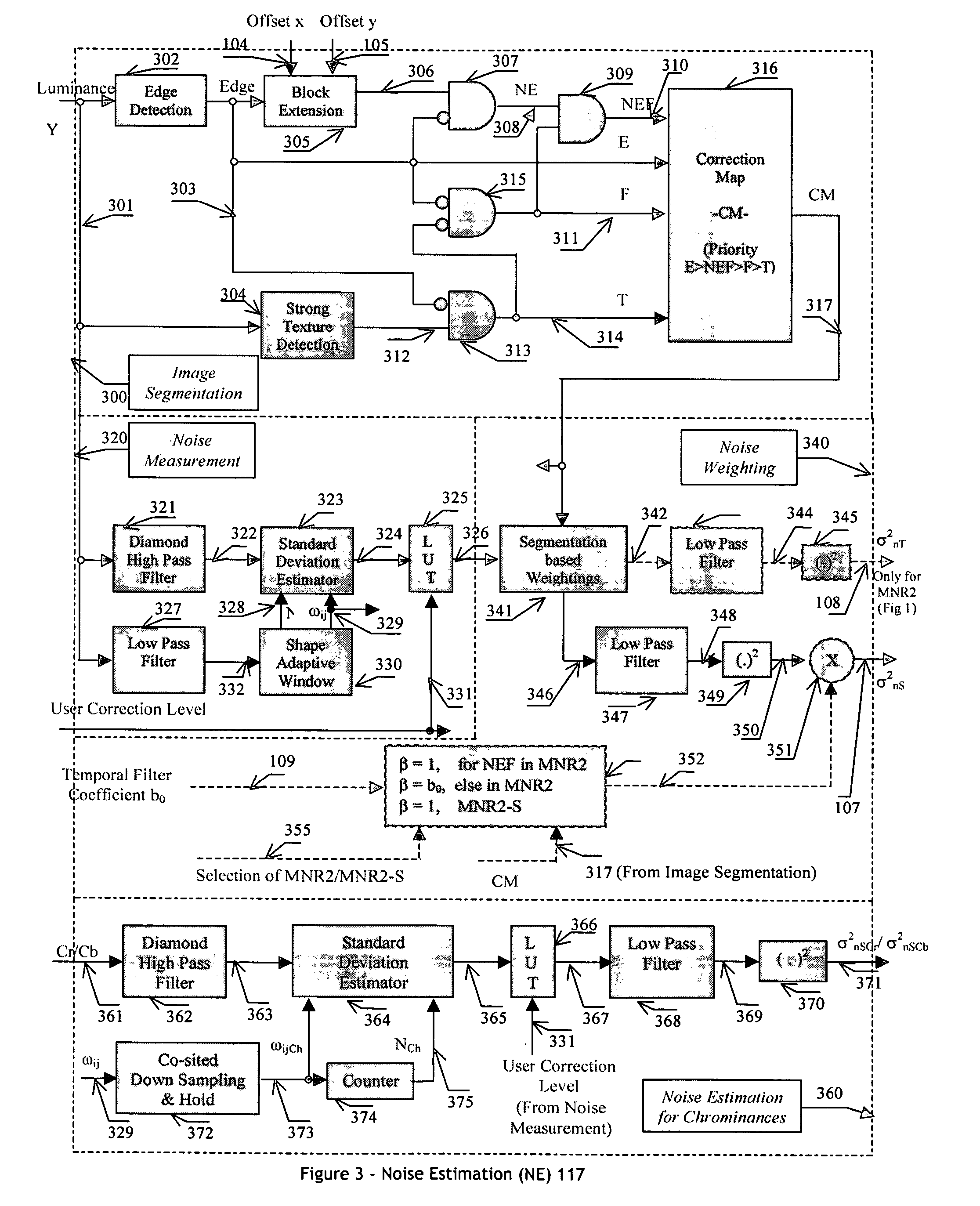
An efficient and non-iterative 3D post processing method and system is proposed for mosquito noise reduction, block localization and correction in DCT block-based decoded images. The 3D post processing is based on a simple classification that segments a picture in multiple regions such as Edge, Near Edge, Flat, Near Flat and Texture regions. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient and shape adaptive local power estimation for equivalent additive noise and provides simple noise power weighting for each above cited region. Temporal filtering configurations using Minimum Noise Variance Criterion are proposed for reducing temporally varying coding artifacts. A Minimum Mean Square Error or Minimum Mean Square Error-like noise reduction with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing is utilized for smoothing mosquito and / or random noise for the whole image, particularly for Edge regions. The proposed technique comprises also signal domain histogram analysis based Block Localization and adaptive edge based Block artifact correction. Finally, is also proposed an optional adaptive detail enhancer which can enhances the luminance signal in eight directions differently.
Owner:SENSIO TECHNOLOGIES
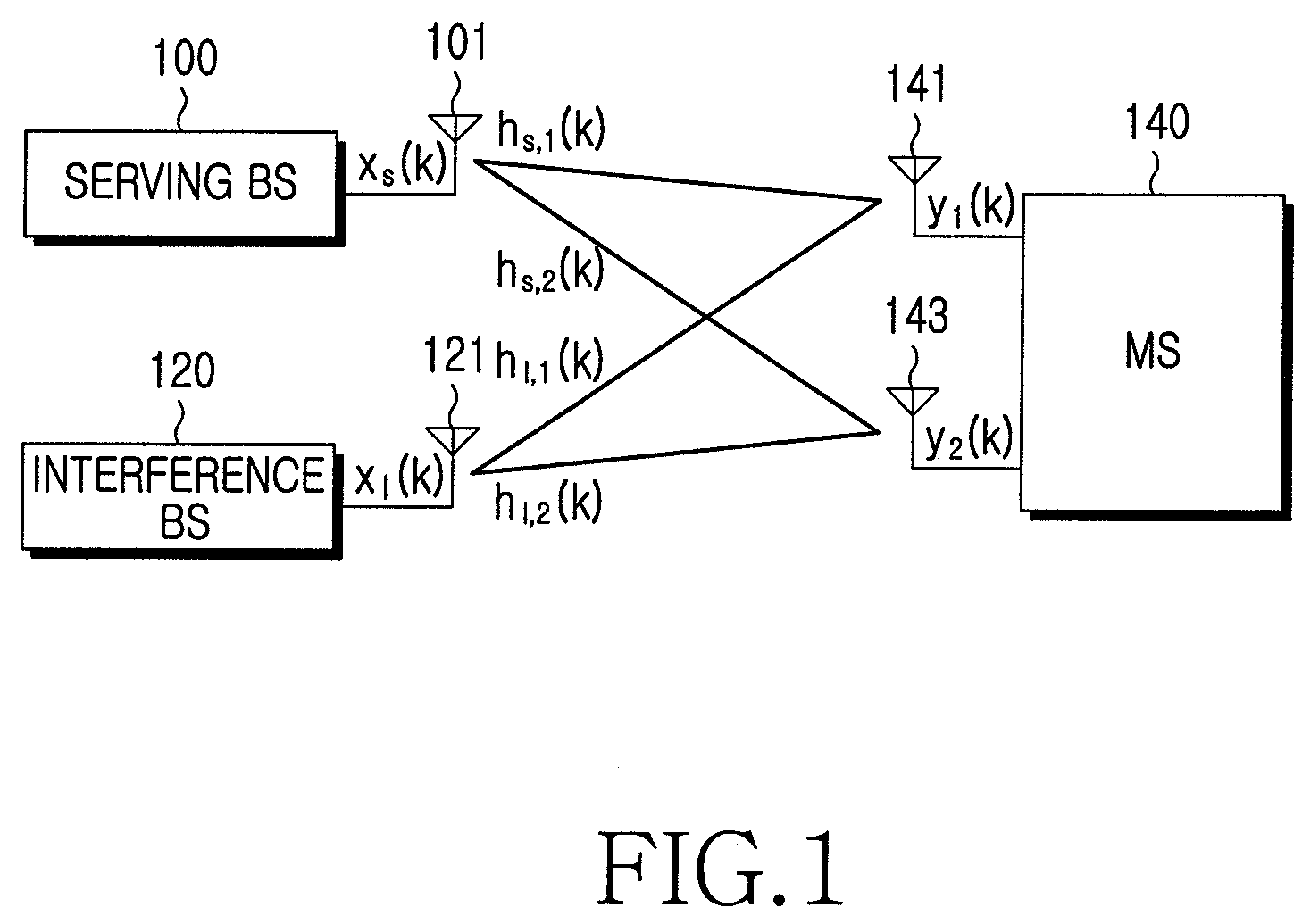
Hybrid time-frequency domain equalization over broadband multi-input multi-output channels
InactiveUS20080304558A1Good flexibilityMore reliabilityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMulti inputData stream
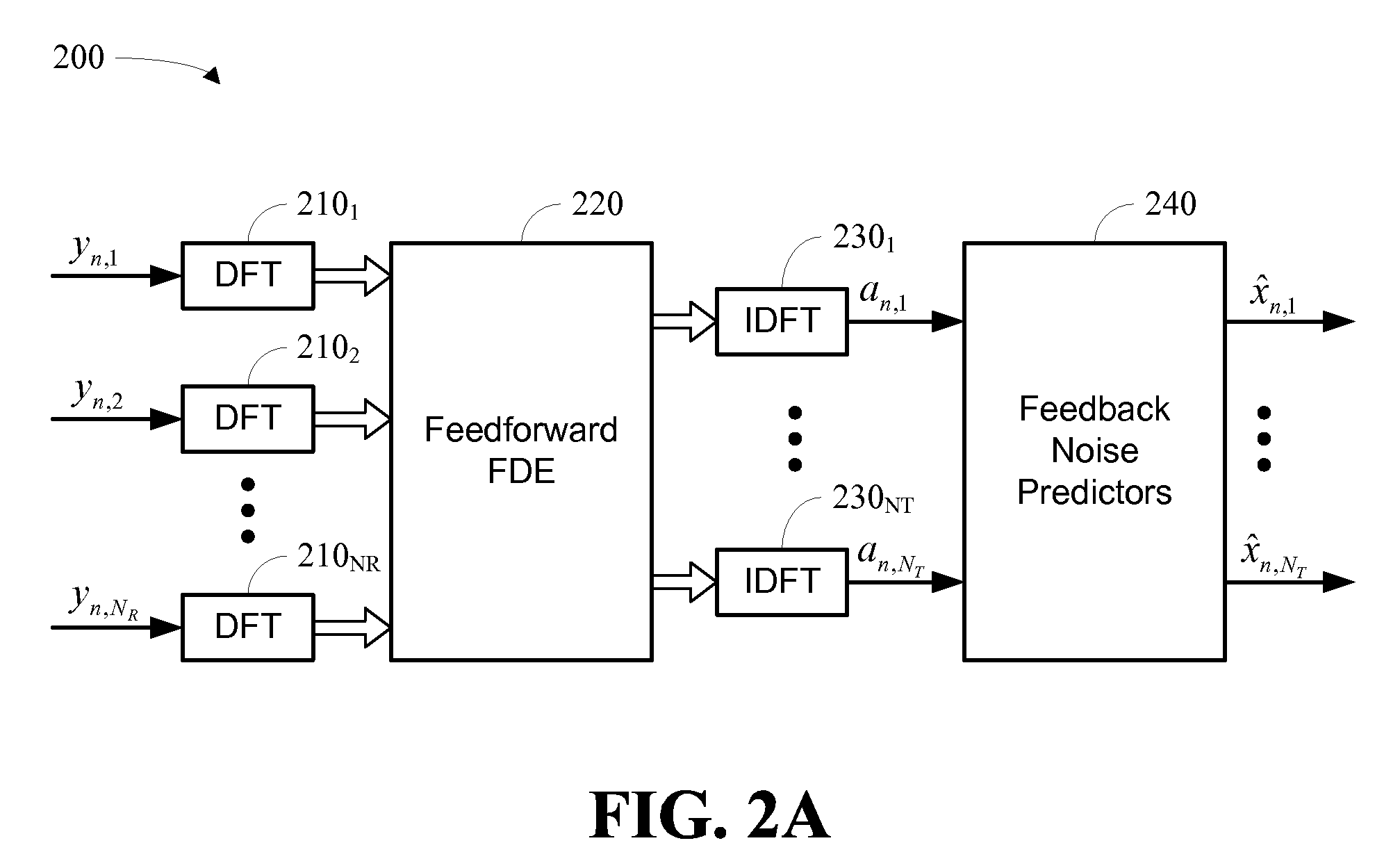
A system and methodology for channel equalization are provided. According to one aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs frequency domain equalization (FDE) with noise prediction (FDE-NP). The FDE-NP structure may include a feedforward linear frequency domain equalizer and a group of time domain noise predictors (NPs), which may operate by predicting a distortion corresponding to a given linearly equalized data stream based on previous distortions of all linearly equalized data streams. According to another aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs FDE-NP with successive interference cancellation (FDE-NP-SIC), which can extend the functionality of FDE-NP by ordering all linearly equalized data streams according to their minimum mean square errors (MMSEs) and detecting those streams which have a low MMSE first, thereby allowing current decisions of lower-indexed streams to be considered along with previous decisions for all data streams for noise prediction. According to a third aspect, a method for analyzing the performance of a MIMO system with equalization is provided. Pursuant to the method, a general expression of MMSE may first be derived. The MMSE expression may then be related to an error bound by applying the modified Chernoff bounding methodology in a general MIMO system. The parameters in the result may then be varied for applicability to single-input single-output (SISO), multiple-input single-output (MISO), and single-input multiple-output (SIMO) systems with receiver equalization technology.
Owner:YIM TU INVESTMENTS
MMSE equalizers for DMT systems with cross talk
InactiveUS6097763ABetter signal to noise ratioRaise the ratioSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
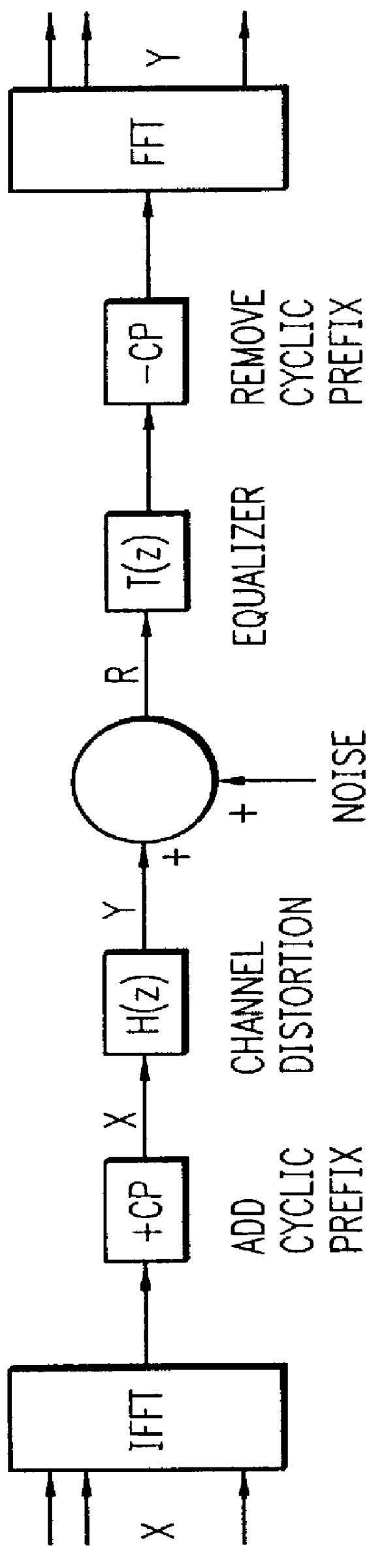
A improved method for optimally equalizing a multicarrier communications system in the presence of both intersymbol interference (ISI) and colored noise. The method provides a frequency-domain training algorithm to obtain a minimum mean square error (MMSE) equalizer that accounts for both intersymbol interference (ISI) and colored noise, maximizes the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of systems using Discrete Multitone (DMT) modulation, and results in significant performance gains over prior equalization methods.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Signal detection by a receiver in a multiple antenna time-dispersive system
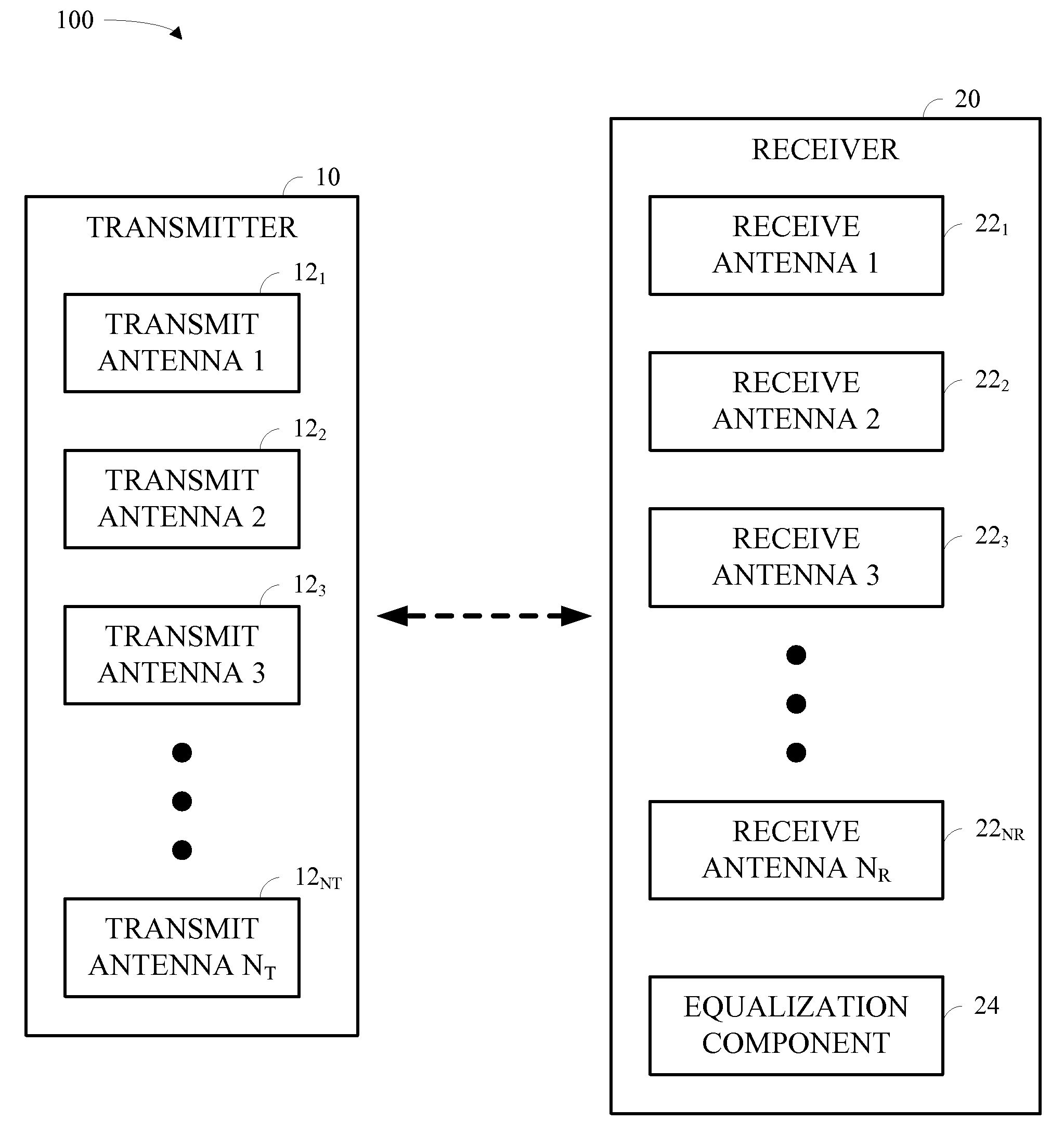
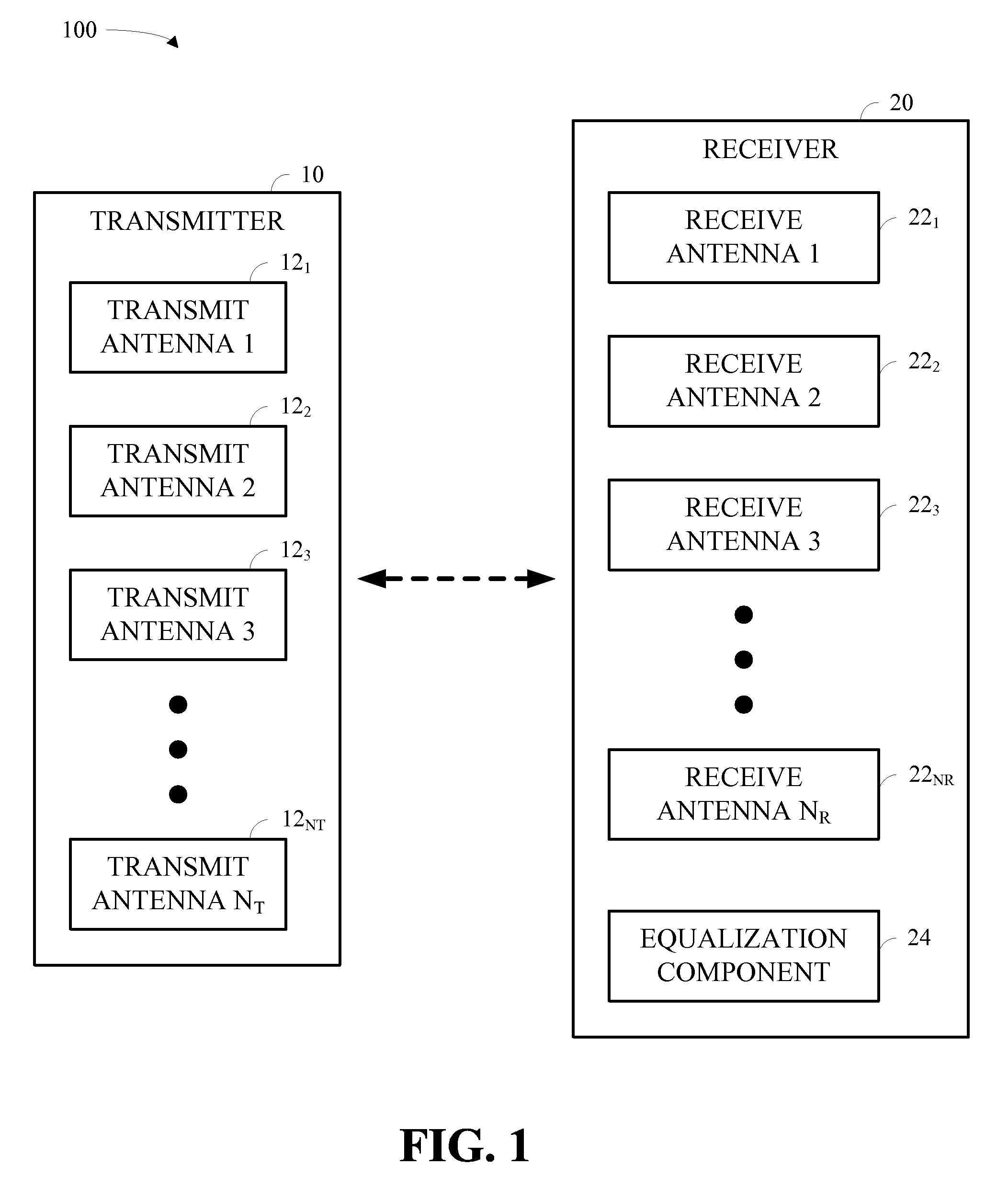
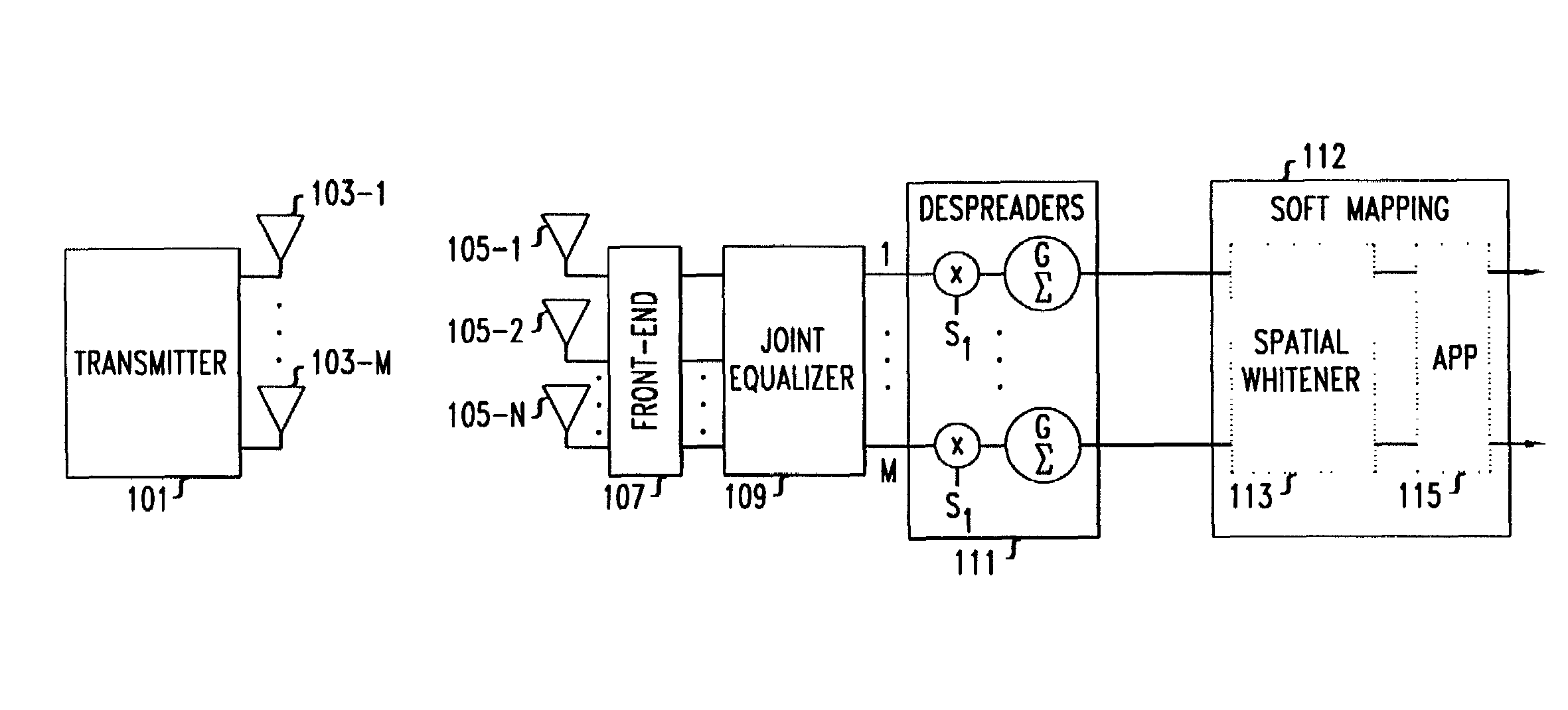
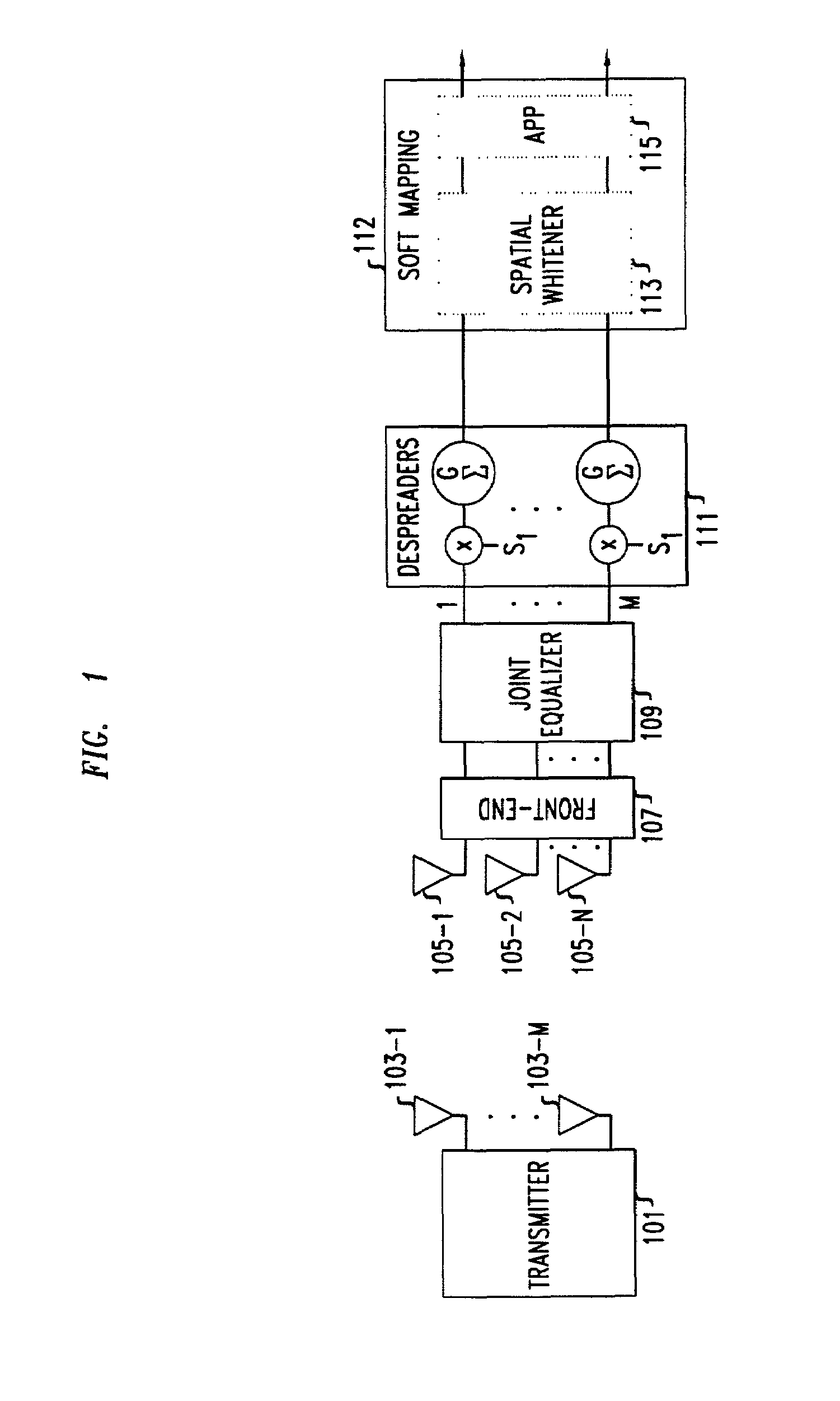
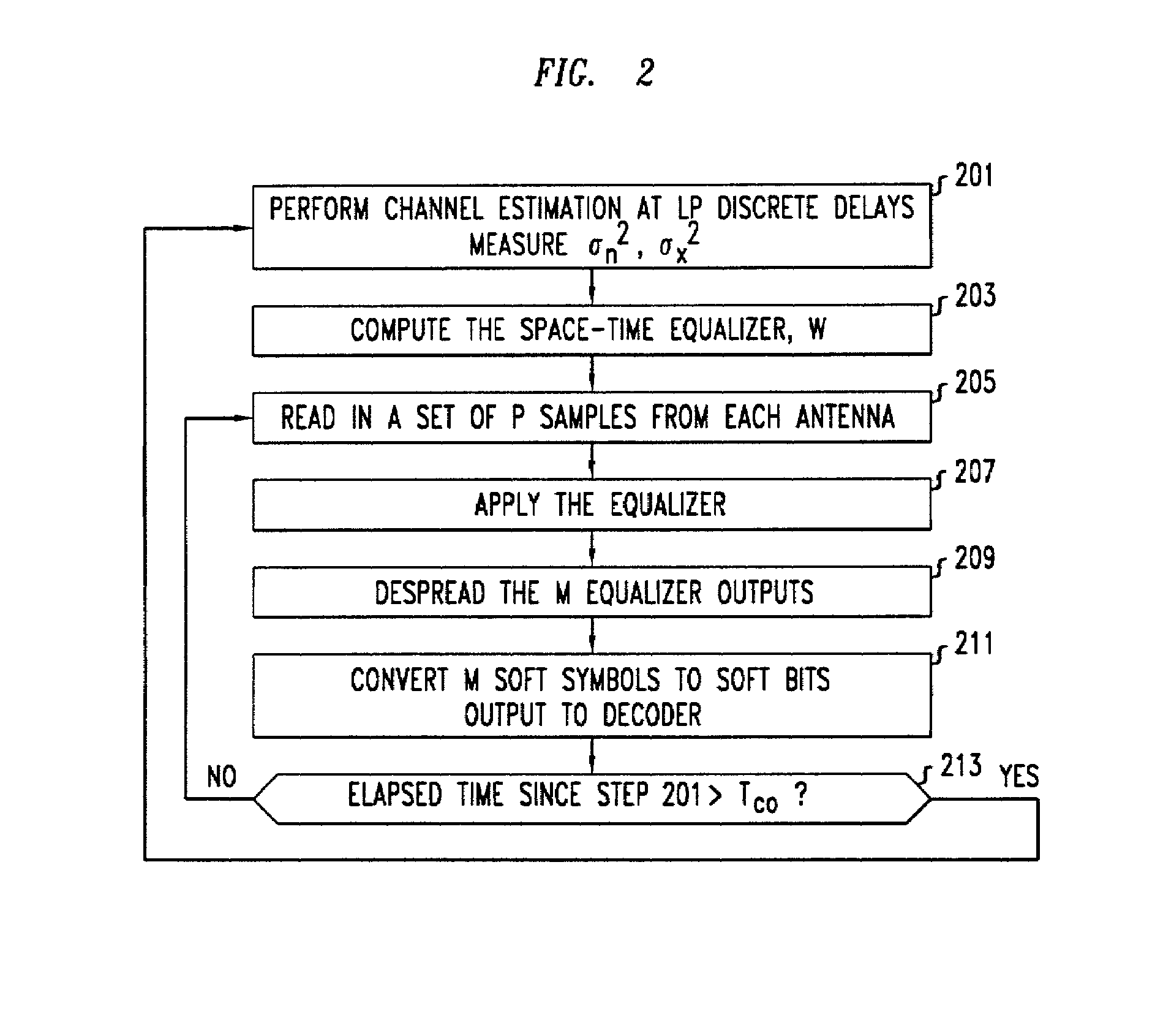
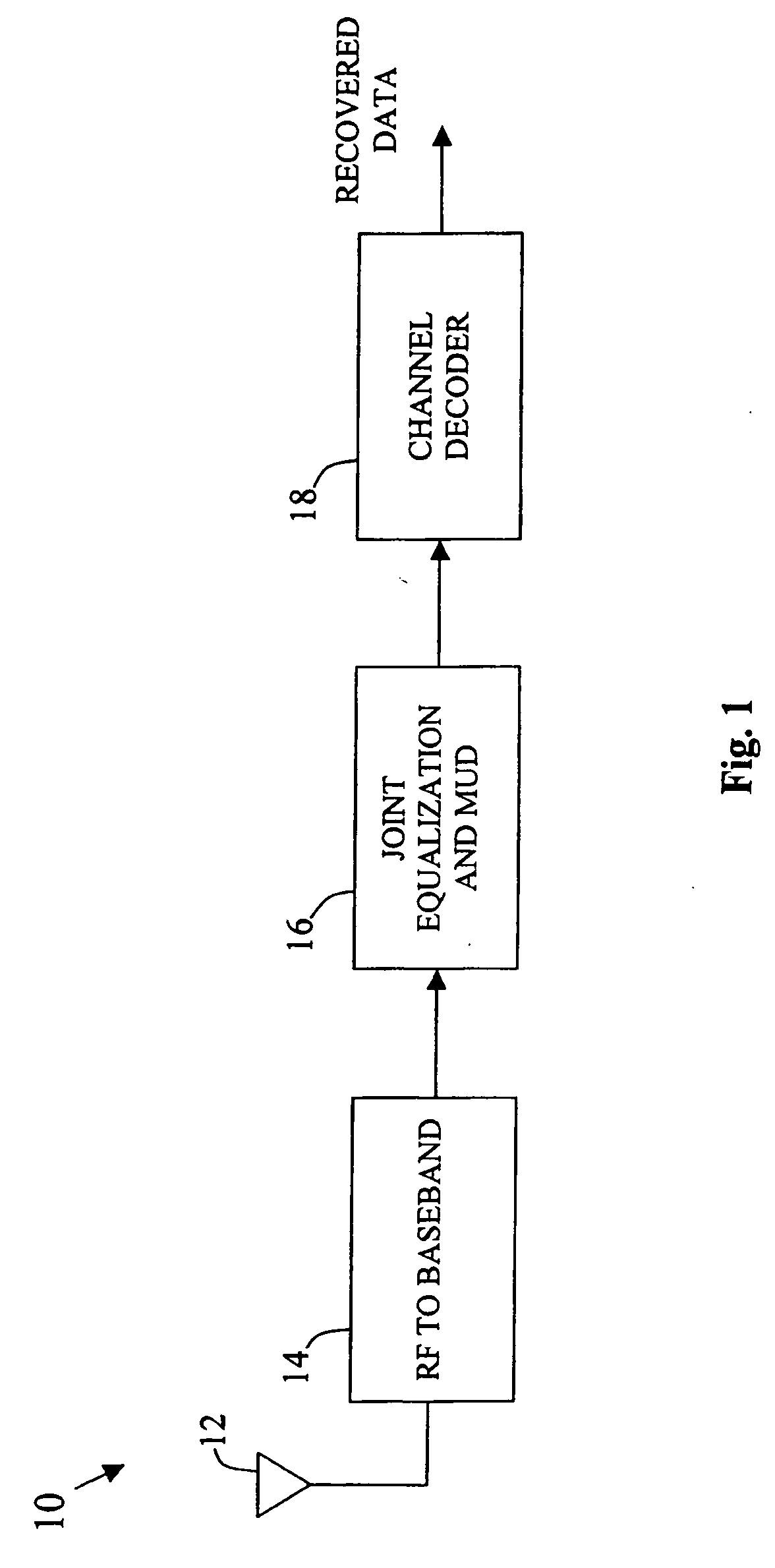
In a MIMO system the bit error rate floor caused by time dispersion is reduced by employing a joint minimum mean square error (MMSE) equalizer for all of the respective transmit antenna—receive antenna pairings that are possible in the MIMO system. The resulting joint equalization compensates not only for the impact of the channel on the transmit antenna—receive antenna pairings but also for the interference of the other transmit antennas on any given receive antenna. The joint equalization outperforms simply replicating the prior art minimum mean square error (MMSE) equalizer for each transmit antenna—receive antenna pairings.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS
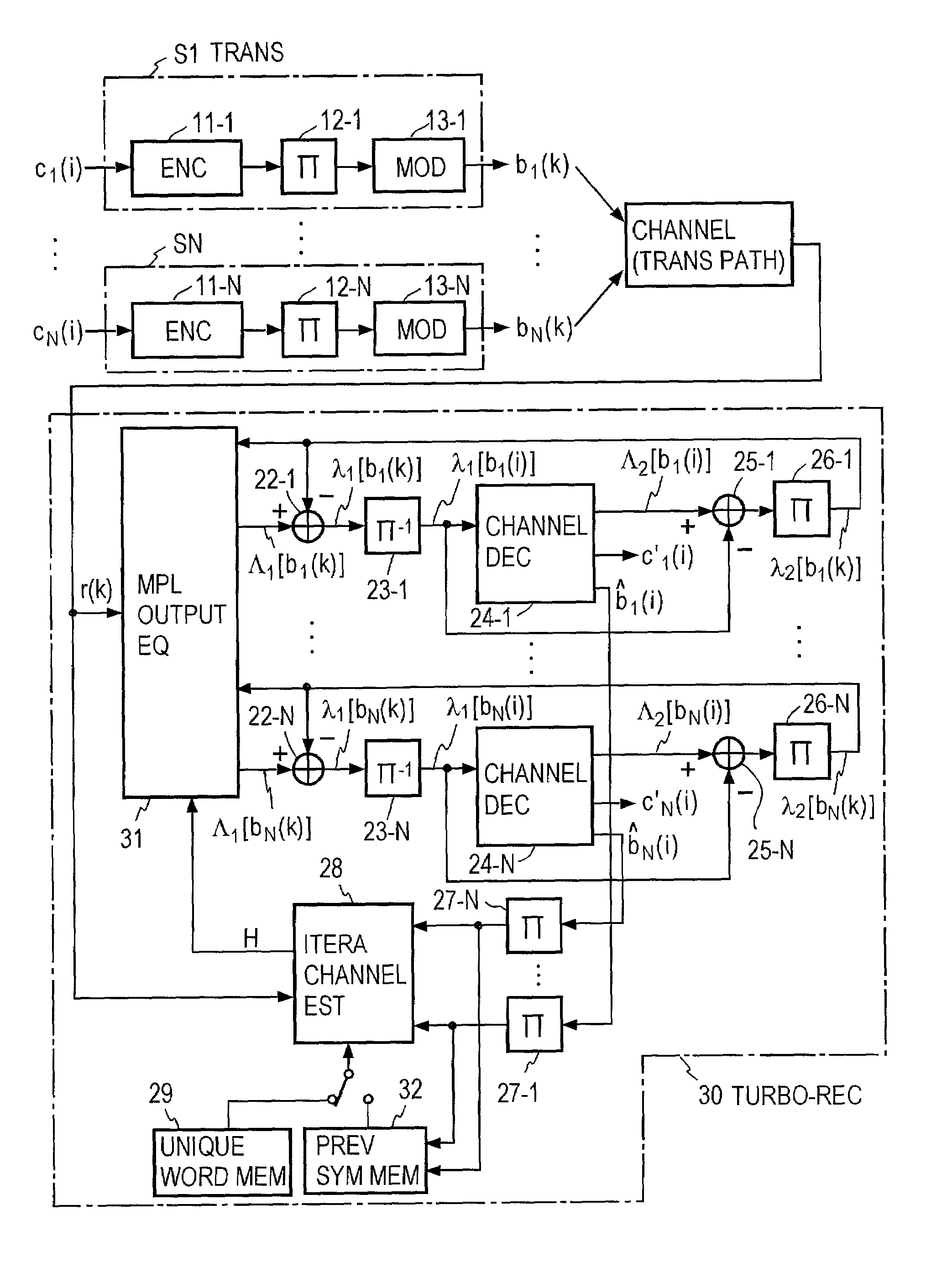
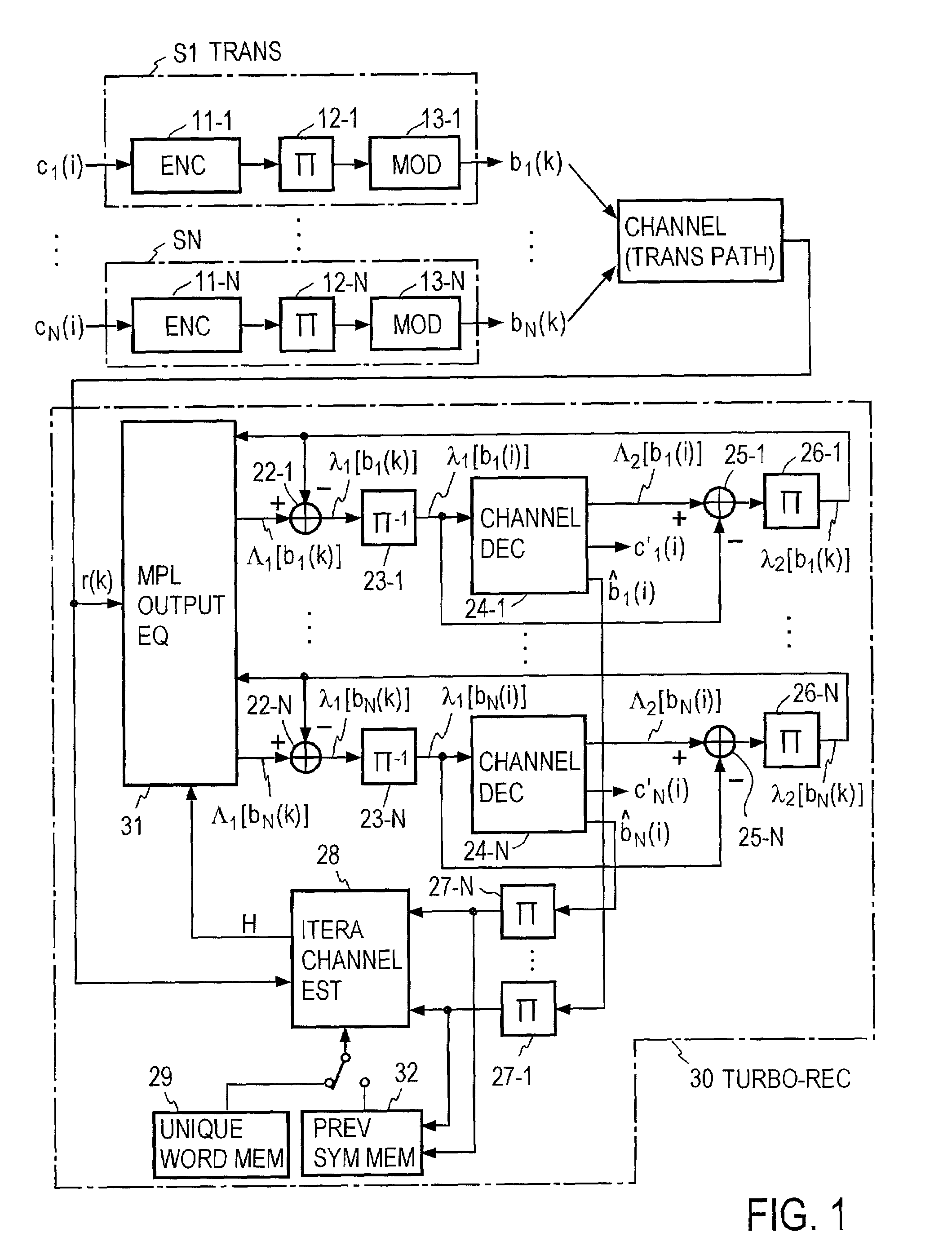
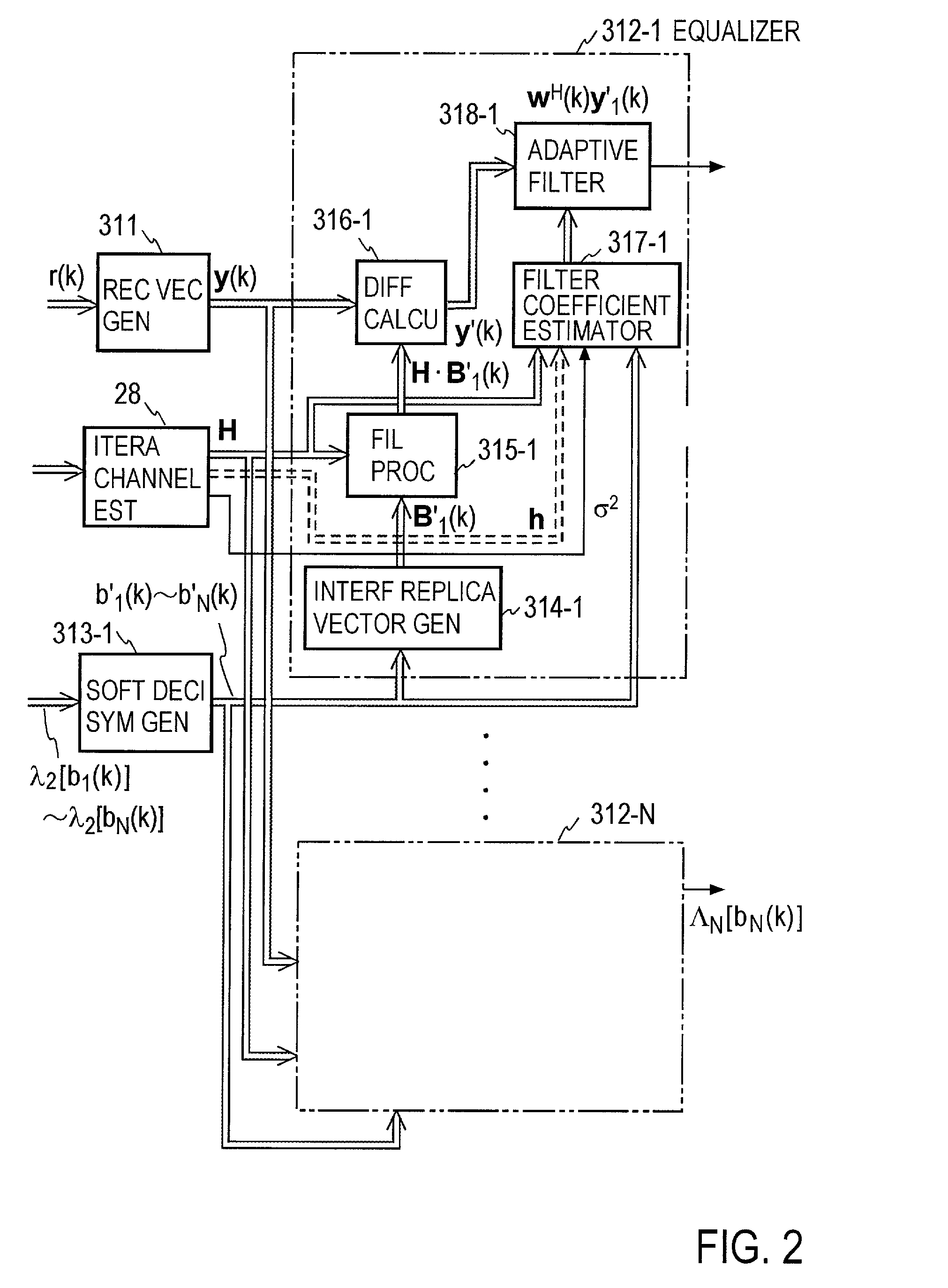
Turbo-reception method and turbo-receiver
InactiveUS7027533B2Improve accuracyData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionQ-matrixResidual interference
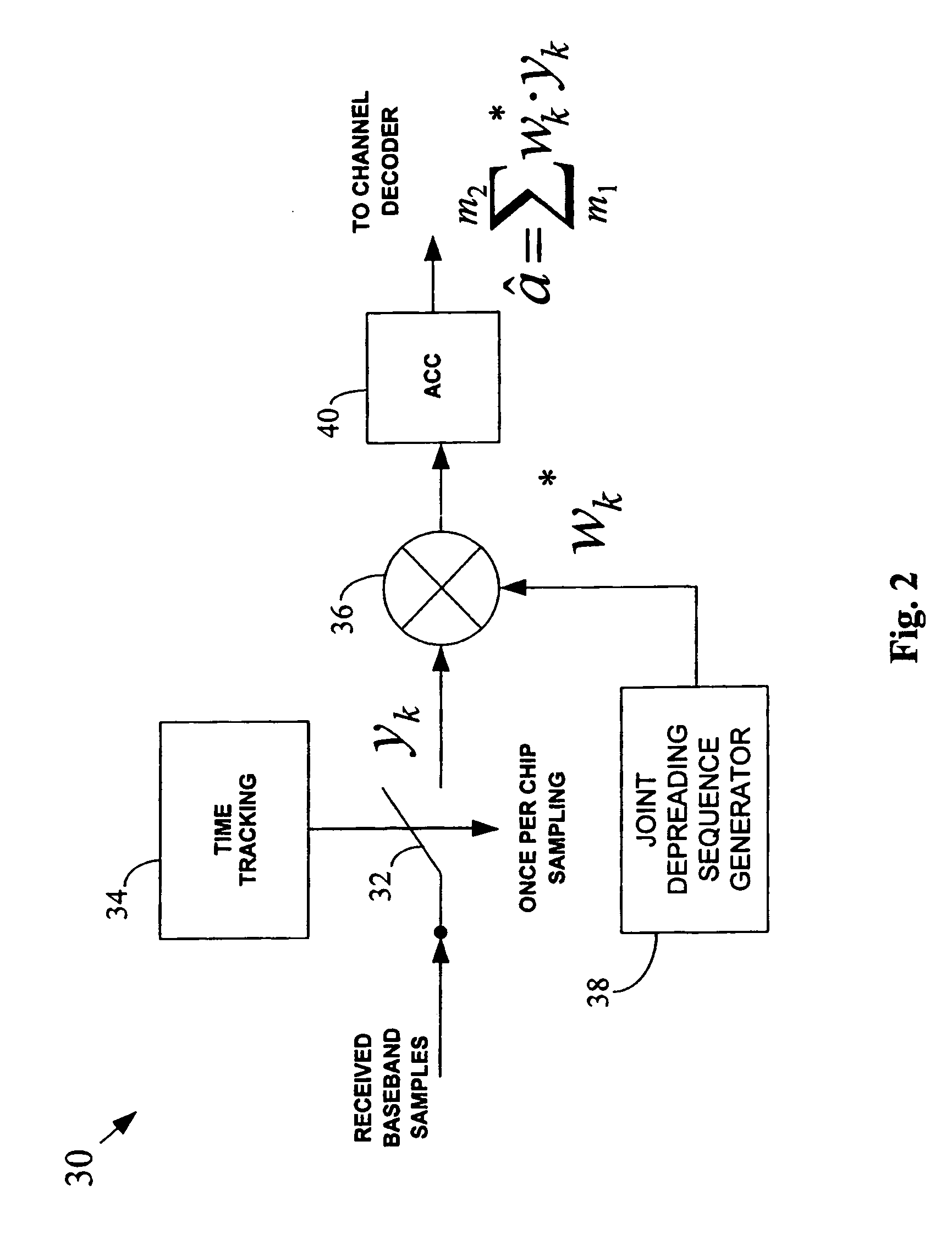
An impluse response hmn(q) of each transmission path is estimated from N received signals rm (m=1, . . . , M) and a known signal (for a number of users equal to N, n=1, . . . , N). M×N matrix H (q) having hmn(q) as an element and a Q×Q matrix H having H(q) as an element are determined (where Q represents a number of multipaths of each transmitted wave and q=0, . . . , Q−1). A soft decision value b′n(k) is determined from decoded λ2 [bn(k)], and this is used to generate an interference component matrix B′(k) to generate an interference replica H·B′(k). The interference replica H·B′(k) is subtracted from a received matrix y(k) to determine y′(k). y(k) and H are used to determine an adaptive filter coefficient wn(k) to be applied to an n-th user in order to eliminate residual interference components in y′(k) according to the minimum mean square error criteria. y(k) is passed through wn(k) to provide a log-likelihood ratio as a received signal from the user n from which interferences are eliminated.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
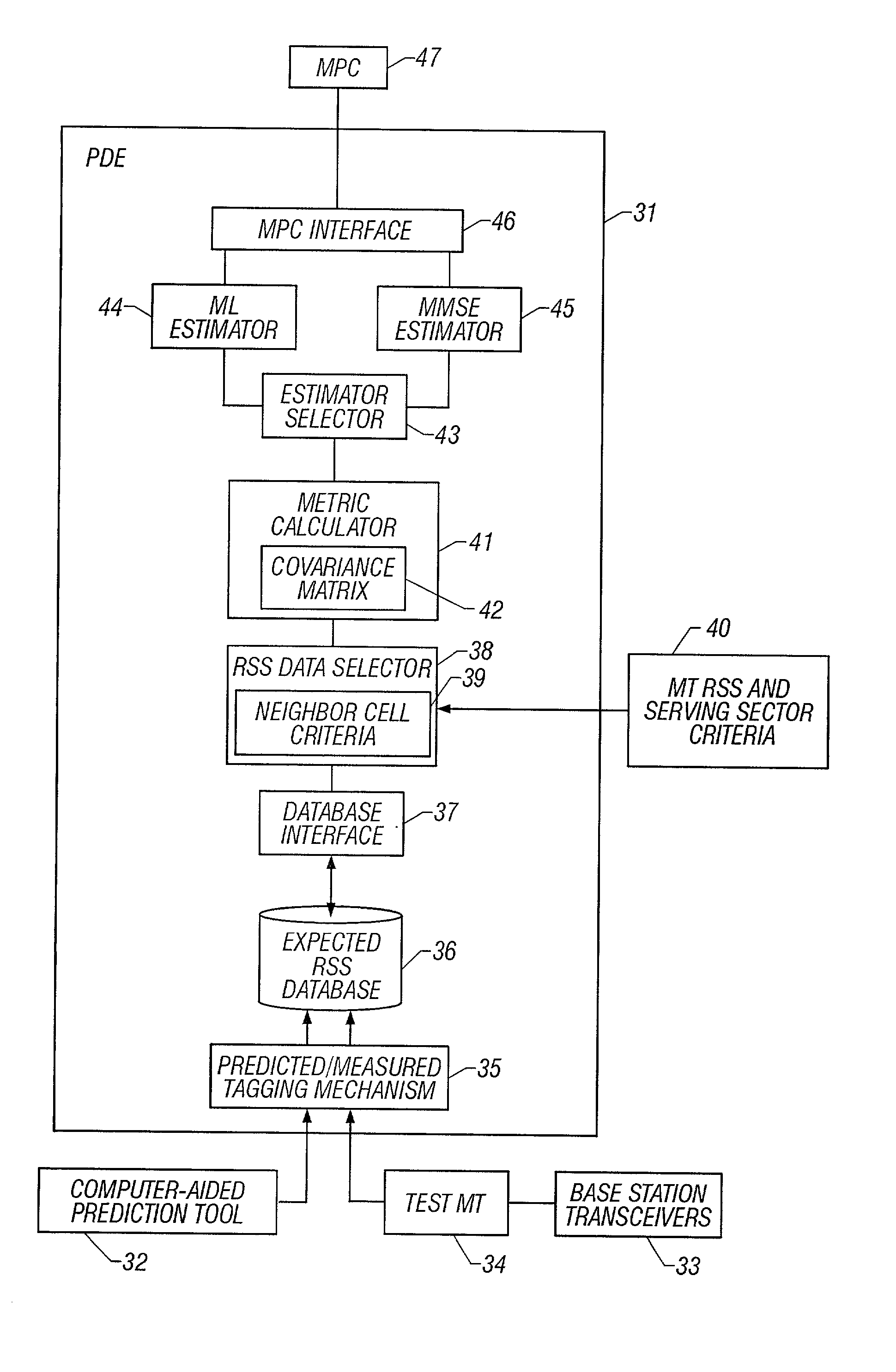
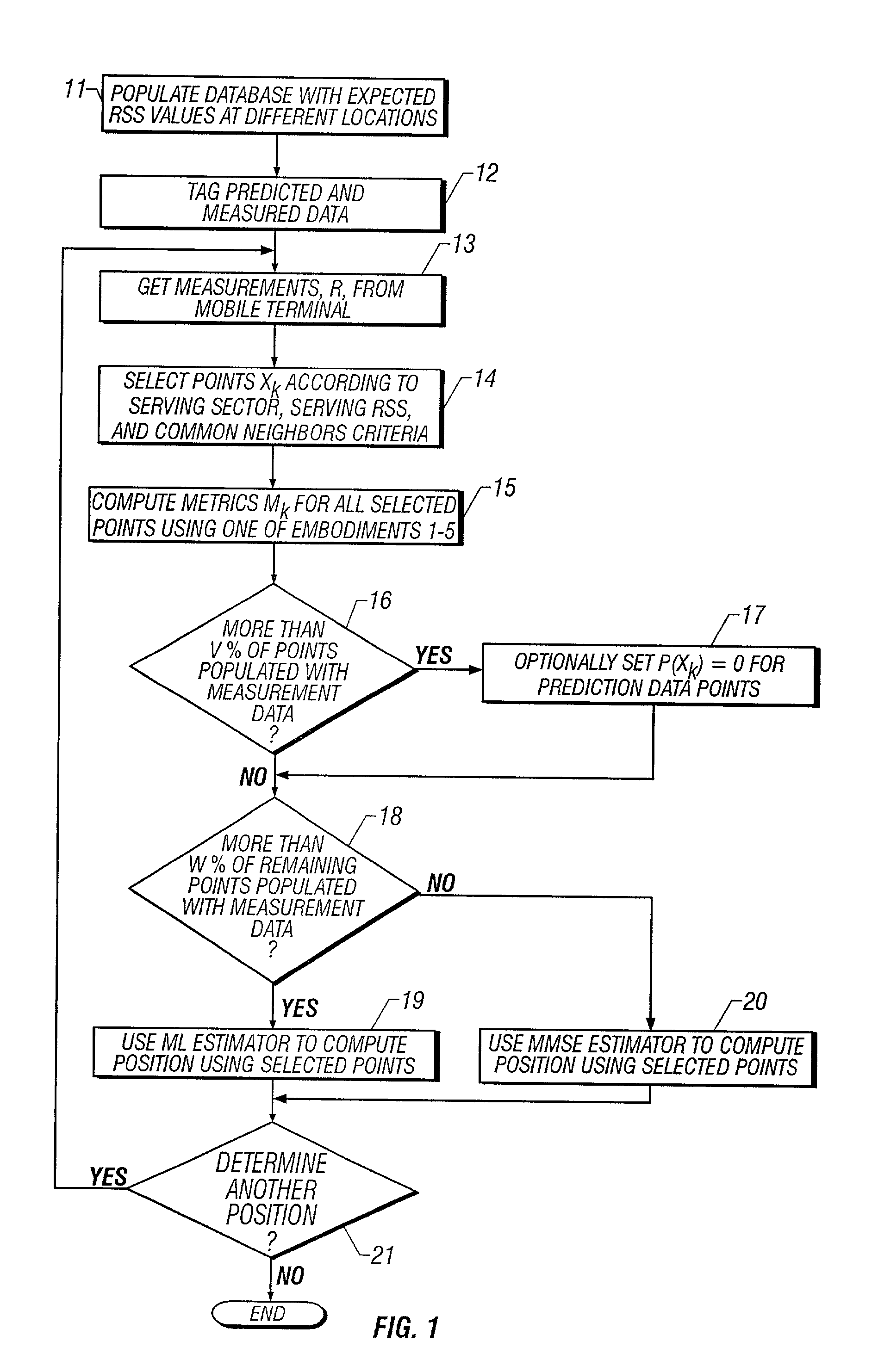
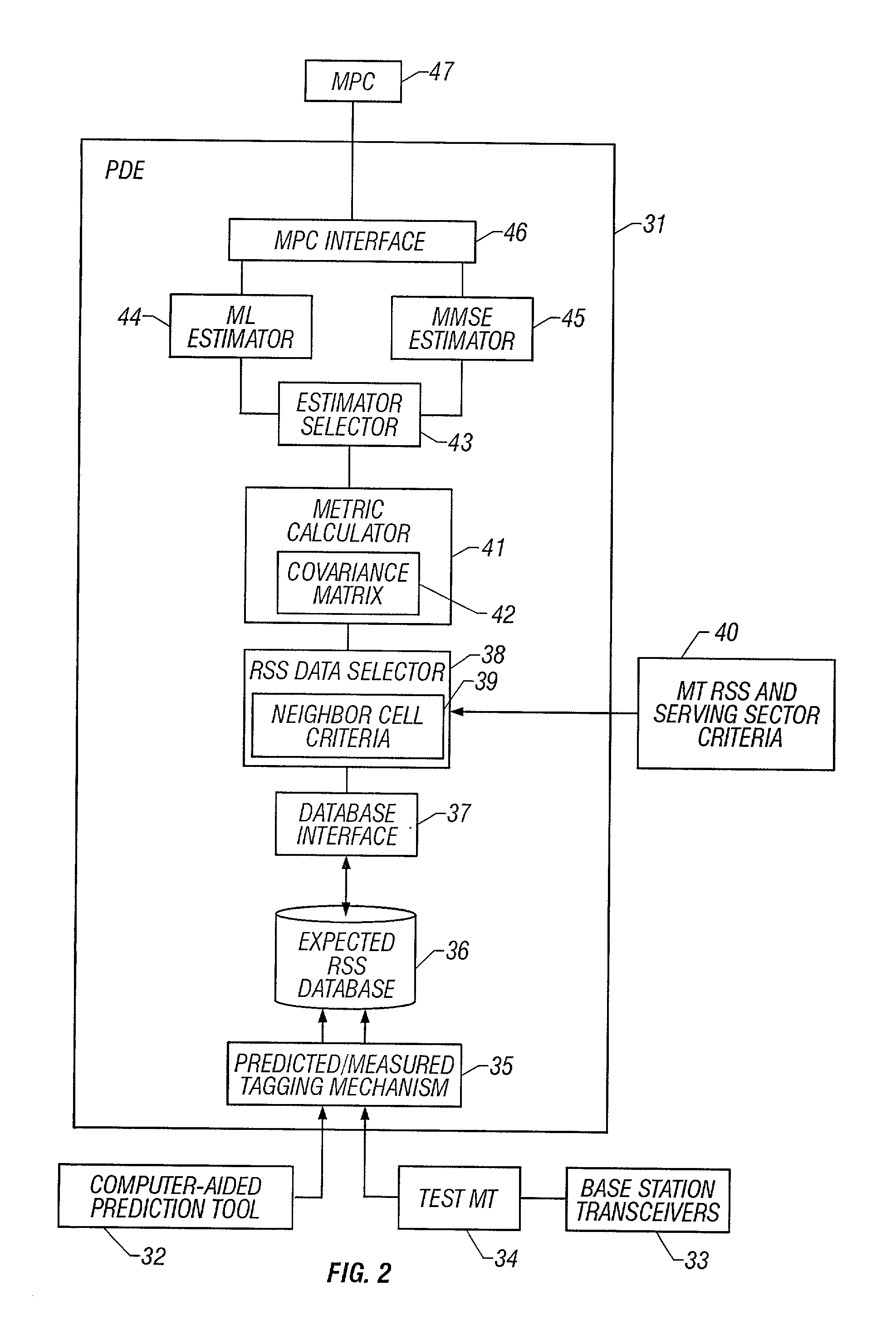
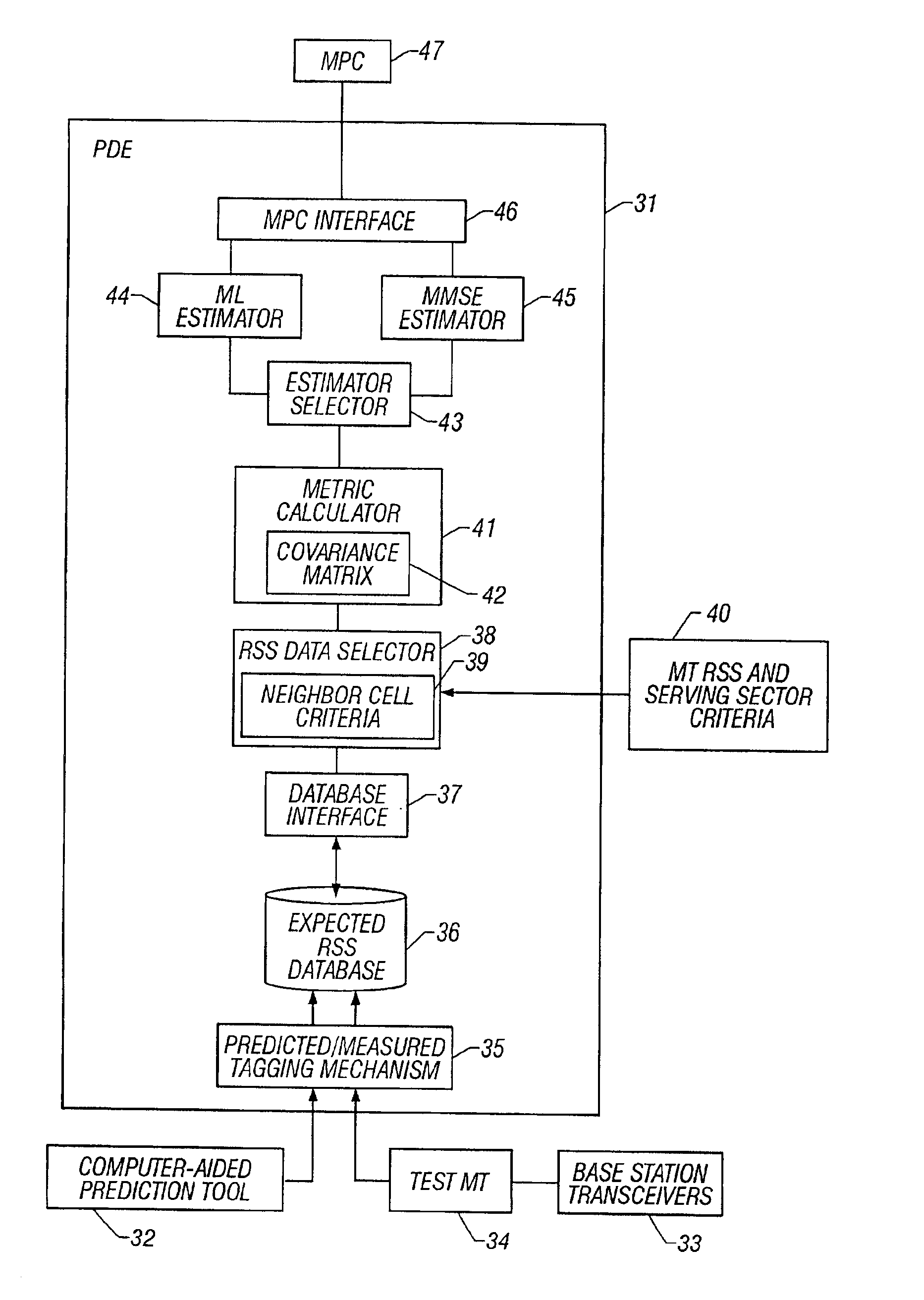
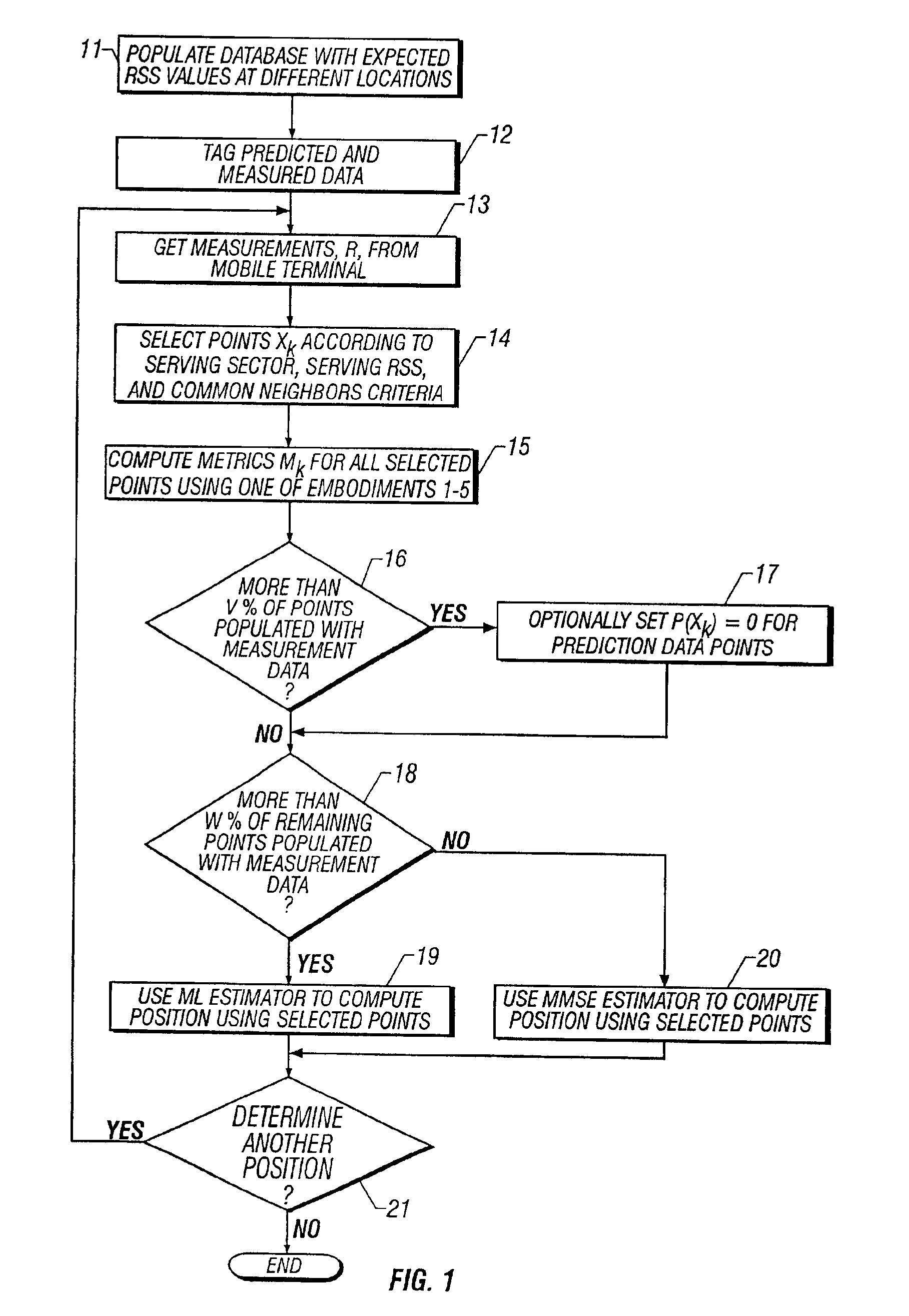
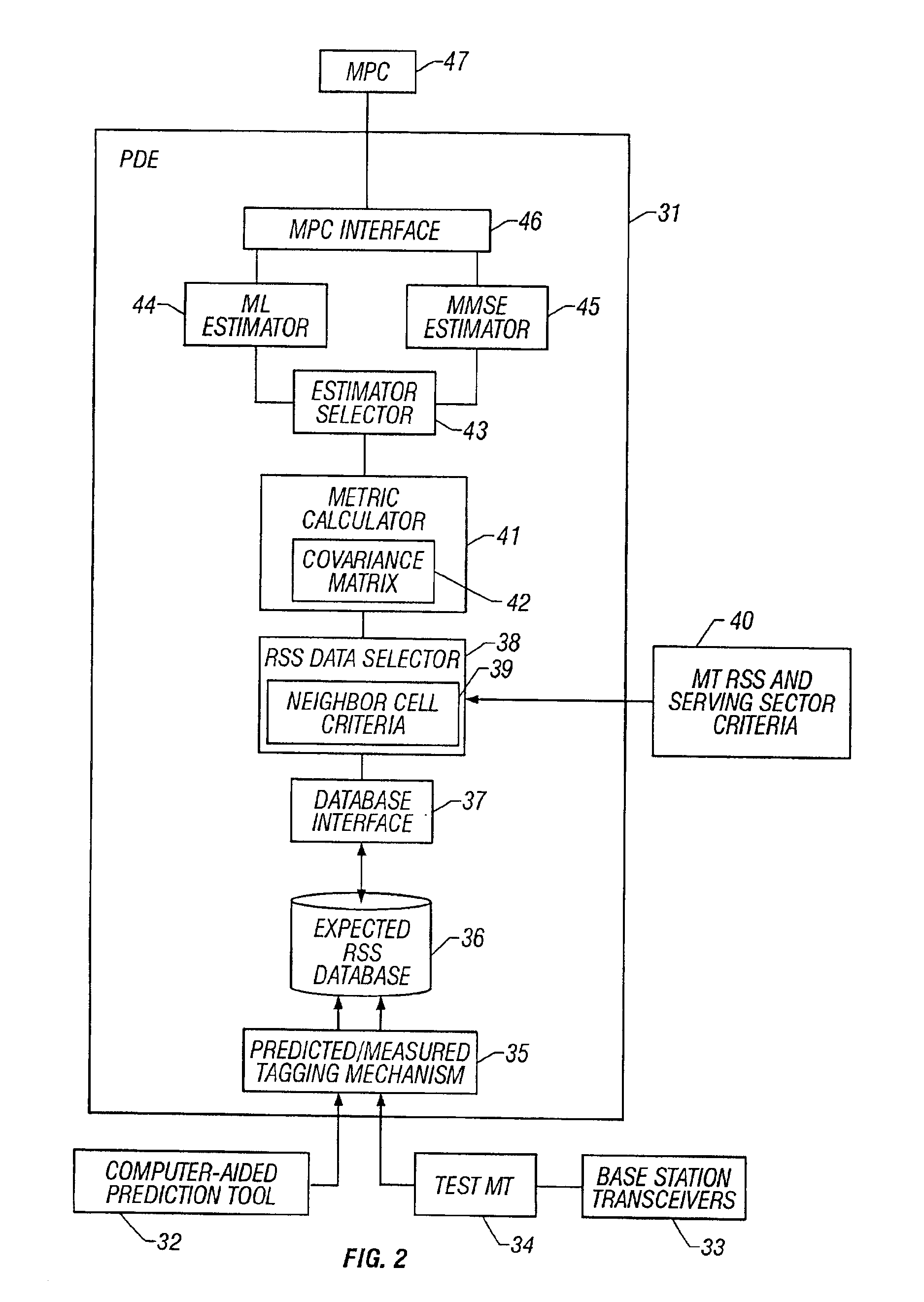
System and method of estimating the position of a mobile terminal in a radio telecommunications network
InactiveUS20030129992A1Direction finders using radio wavesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverTelecommunications network
A system and method of estimating the position of a mobile terminal (MT) operating in a radio telecommunications network. Expected Received Signal Strength (RSS) values are predicted by a computer-aided prediction tool, and / or are measured by a test MT from base station transceivers. The predicted and measured RSS values are then tagged to indicate whether each value was predicted or measured. The RSS values are then stored at a plurality of locations in a database. When RSS measurements are received from the MT being located, a covariance matrix is used to compute metrics for the locations in the database. If more than a threshold percentage of the locations were populated with measured values, a Maximum-Likelihood (ML) estimator is used to estimate the position of the MT. If fewer than the threshold percentage of locations were populated with measured values, a Minimum-Mean-Square-Error (MMSE) estimator is used to estimate the position.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Method for effectively recognizing digital modulating signals in non-Gaussian noise
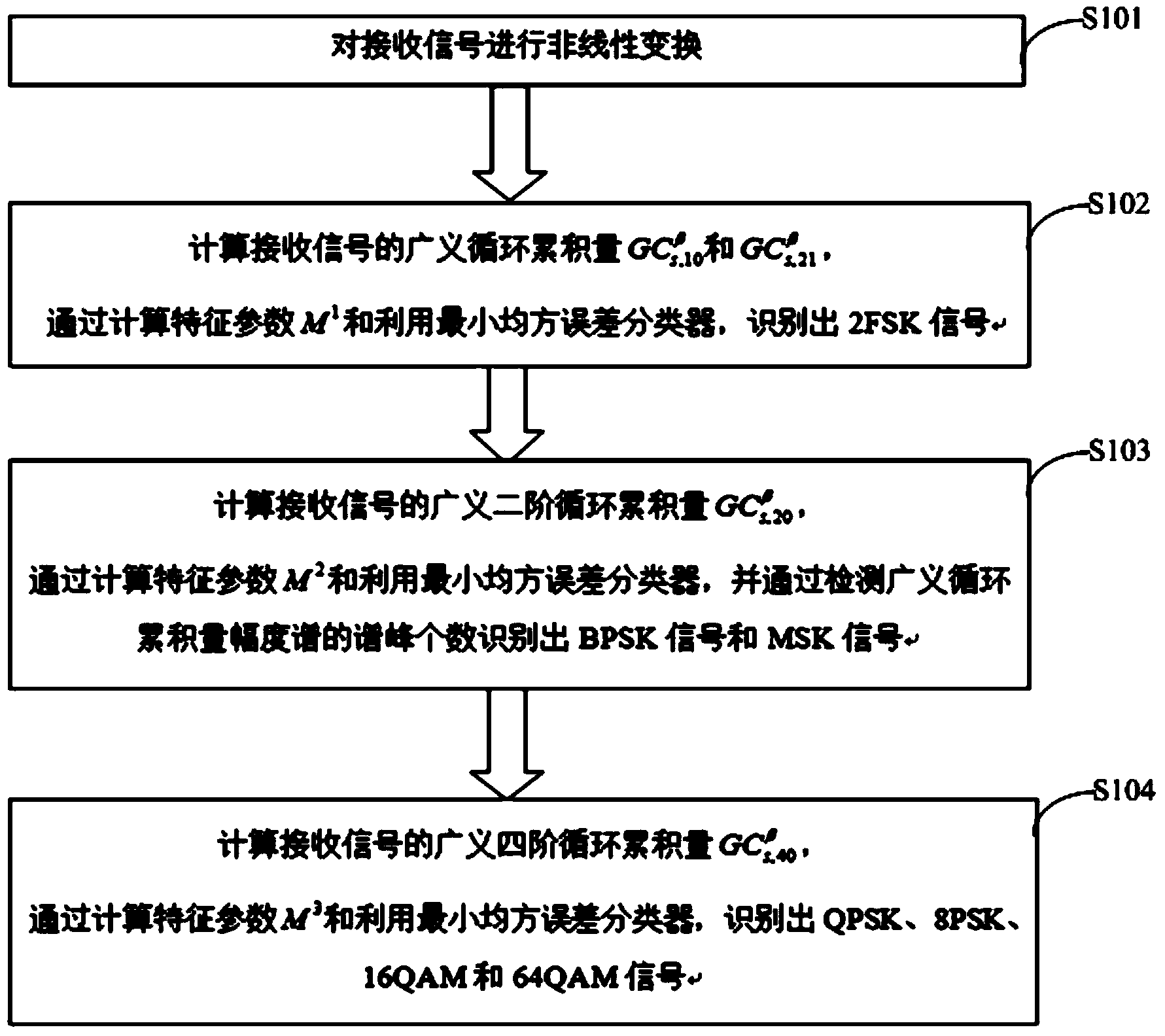
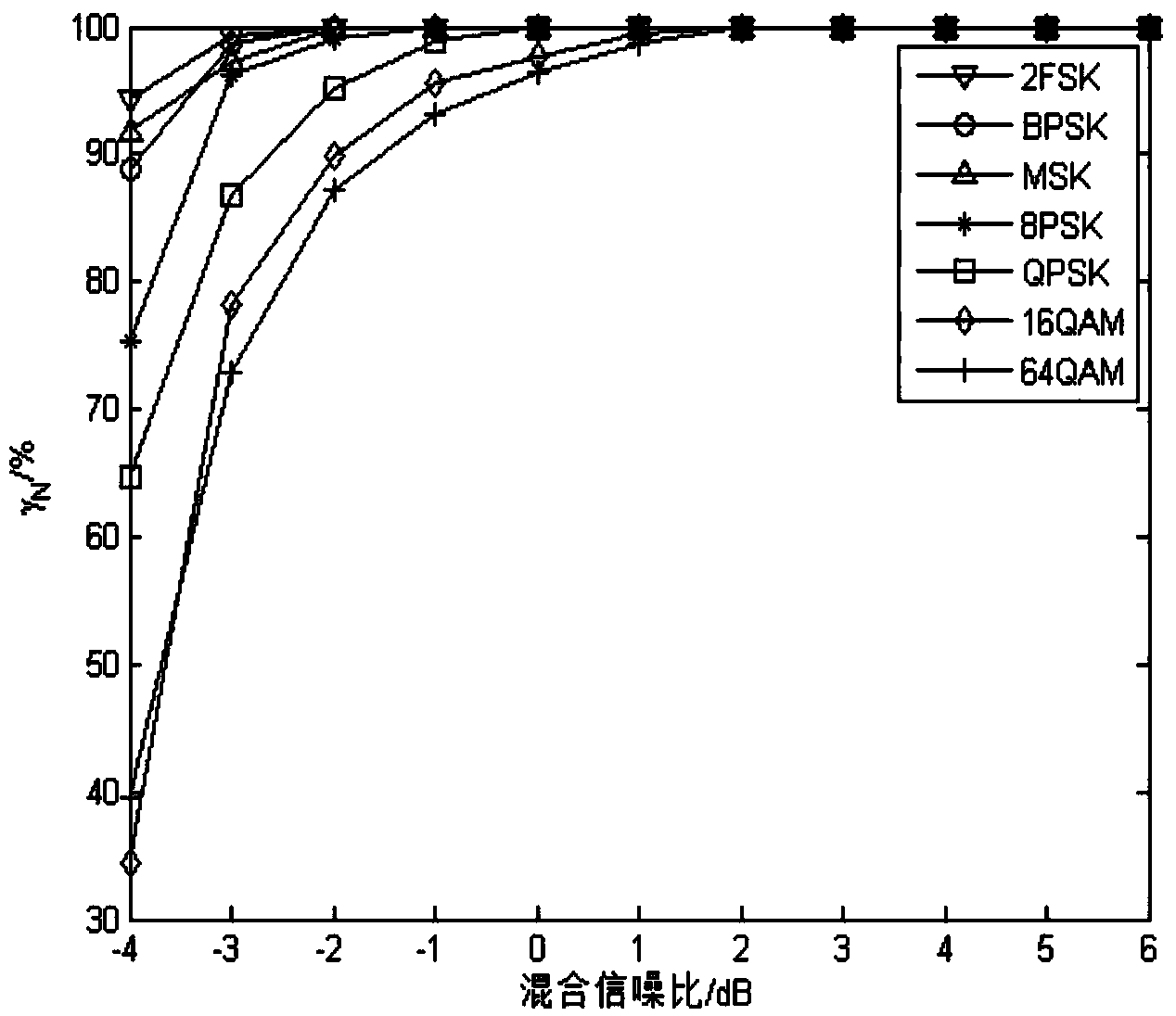
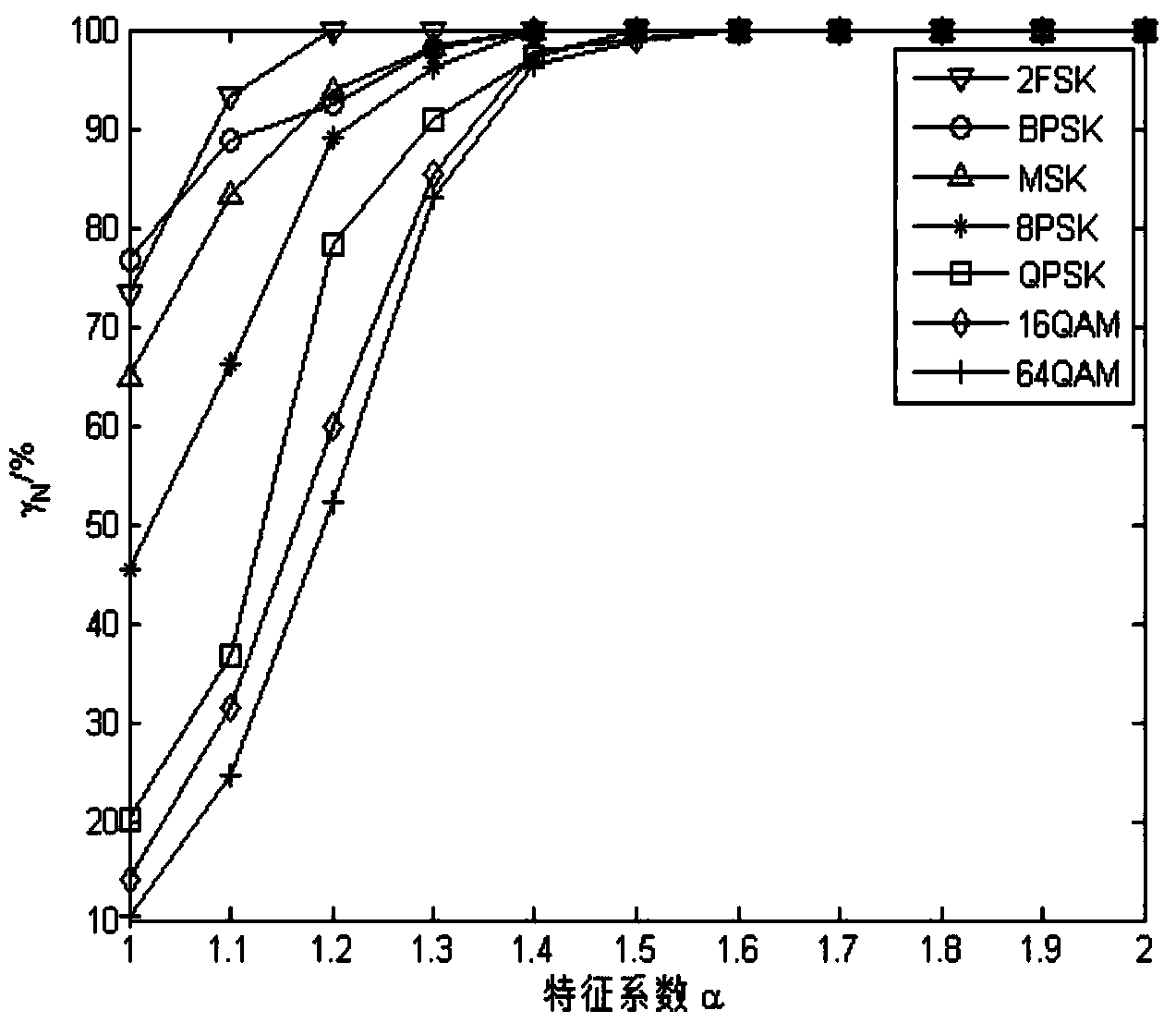
InactiveCN103457890AImprove performancePracticalModulated-carrier systemsHigher-order statisticsMinimum mean square error
The invention discloses a method for effectively recognizing digital modulating signals in non-Gaussian noise. Non-linear transformation is performed on a received signal s(t); the generalized first-order cyclic cumulant and the generalized second-order cyclic cumulant of the received signal s(t) are calculated, and a 2FSK signal is recognized by calculating the characteristic parameters of the received signal s(t) and utilizing a minimum mean square error classifier; the generalized second-order cyclic cumulant of the received signal s(t) is calculated, and by calculating the characteristic parameters of the received signal s(t) and utilizing the minimum mean square error classifier, the number of spectral peaks of a generalized cyclic cumulant magnitude spectrum is detected so that a BPSK signal and an MSK signal can be recognized; the generalized fourth-order cyclic cumulant of the received signal s(t) is calculated, and a QPSK signal, an 8PSK signal and other signals are recognized through the calculated characteristic parameters and the minimum mean square error classifier. The method for effectively recognizing digital modulating signals in non-Gaussian noise solves the problem that signals in Alpha stable distribution noise do not have second or higher order statistics, effectively recognizes the digital modulating signals and can be used for recognizing the modulation mode of the digital modulating signals in the Alpha stable distribution noise.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
System and method of estimating the position of a mobile terminal in a radio telecommunications network
InactiveUS6873852B2Direction finders using radio wavesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunications networkTransceiver
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
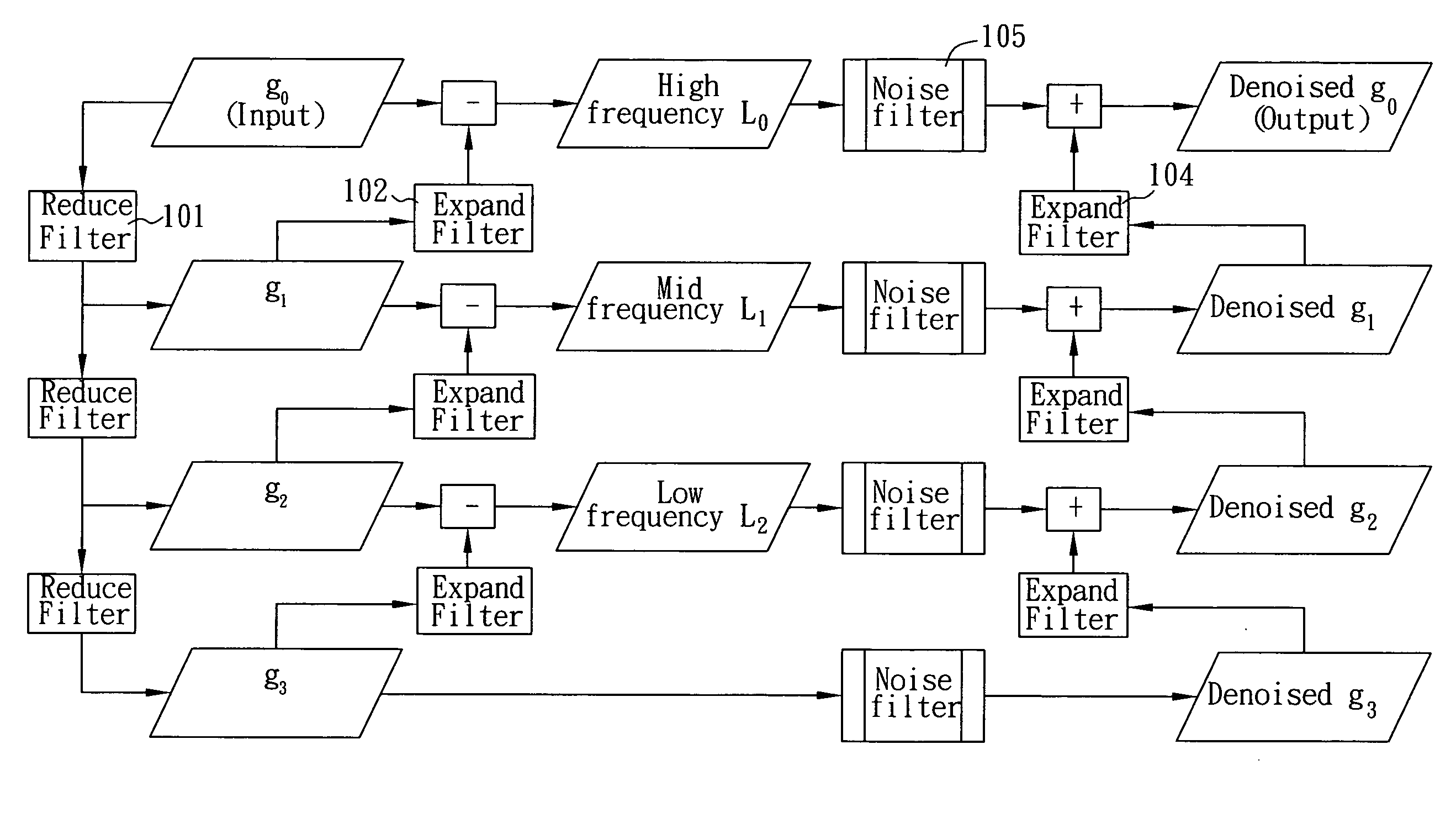
Denoise method on image pyramid
ActiveUS20080253678A1Easy to embedAvoid quality lossImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionNoise level
The present invention is to provide a denoise method on Gaussian / Laplacian image pyramid, which integrates Pyramid analysis / synthesis algorithm, MMSE (minimum mean square error) filter and NL (non local) filter on the image pyramid to reconstruct and output a denoised image of an original input image through a plurality of iterative procedures, and utilizes an auto-adaptive noise estimation algorithm to find parameter of noise level used by the NL filter, so as to be easily embedded in mobile or handheld devices for obtaining better noise removing and anti-shaking results and remove noise much faster than the conventional denoise method, but only with less quality loss.
Owner:ARCSOFT
Time/frequency recovery of a communication signal in a multi-beam configuration using a kinematic-based kalman filter and providing a pseudo-ranging feature
InactiveUS20070218931A1Inability to efficientlyEffectively obviatedSynchronisation arrangementRadio transmissionErrors measurementKalman filter
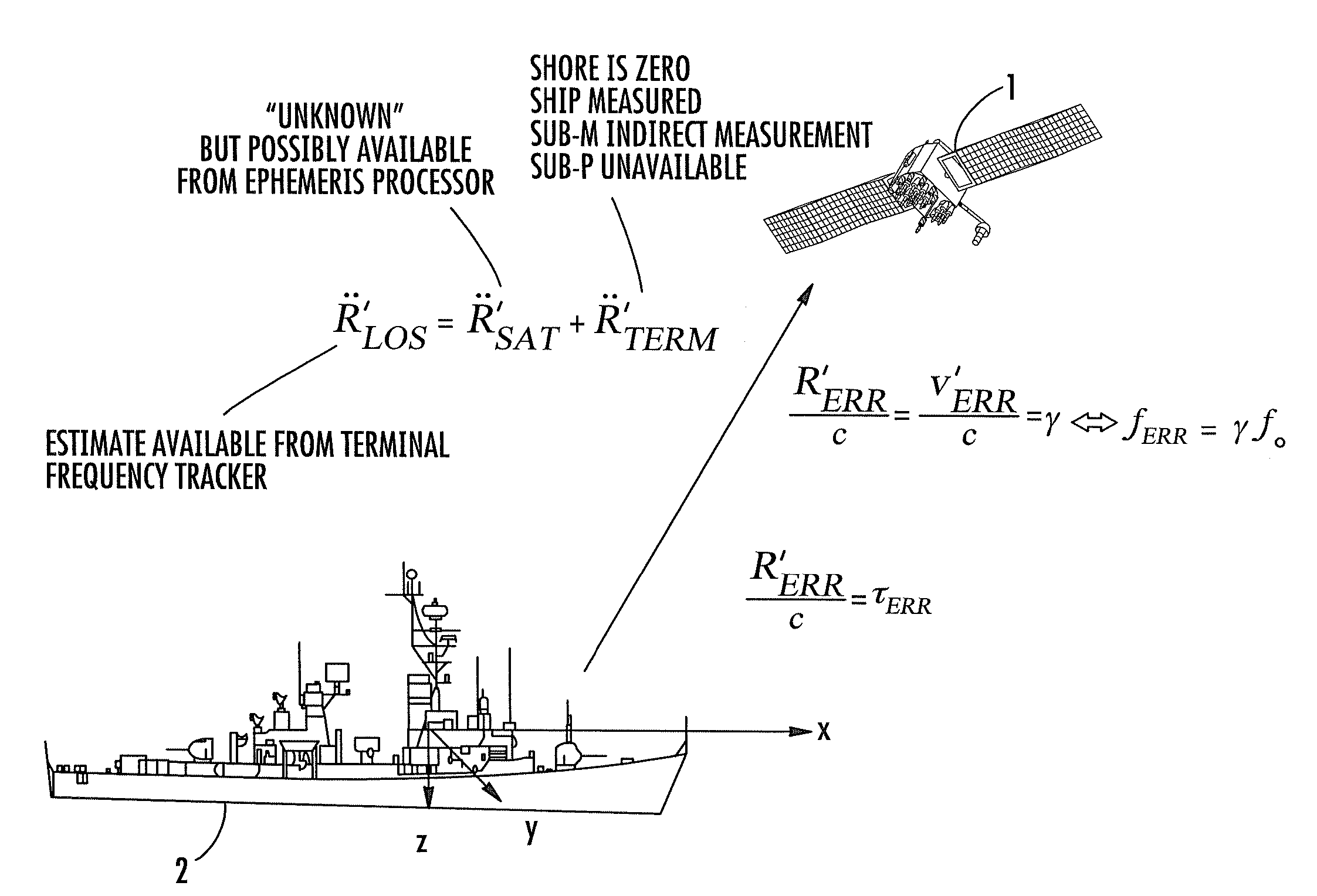
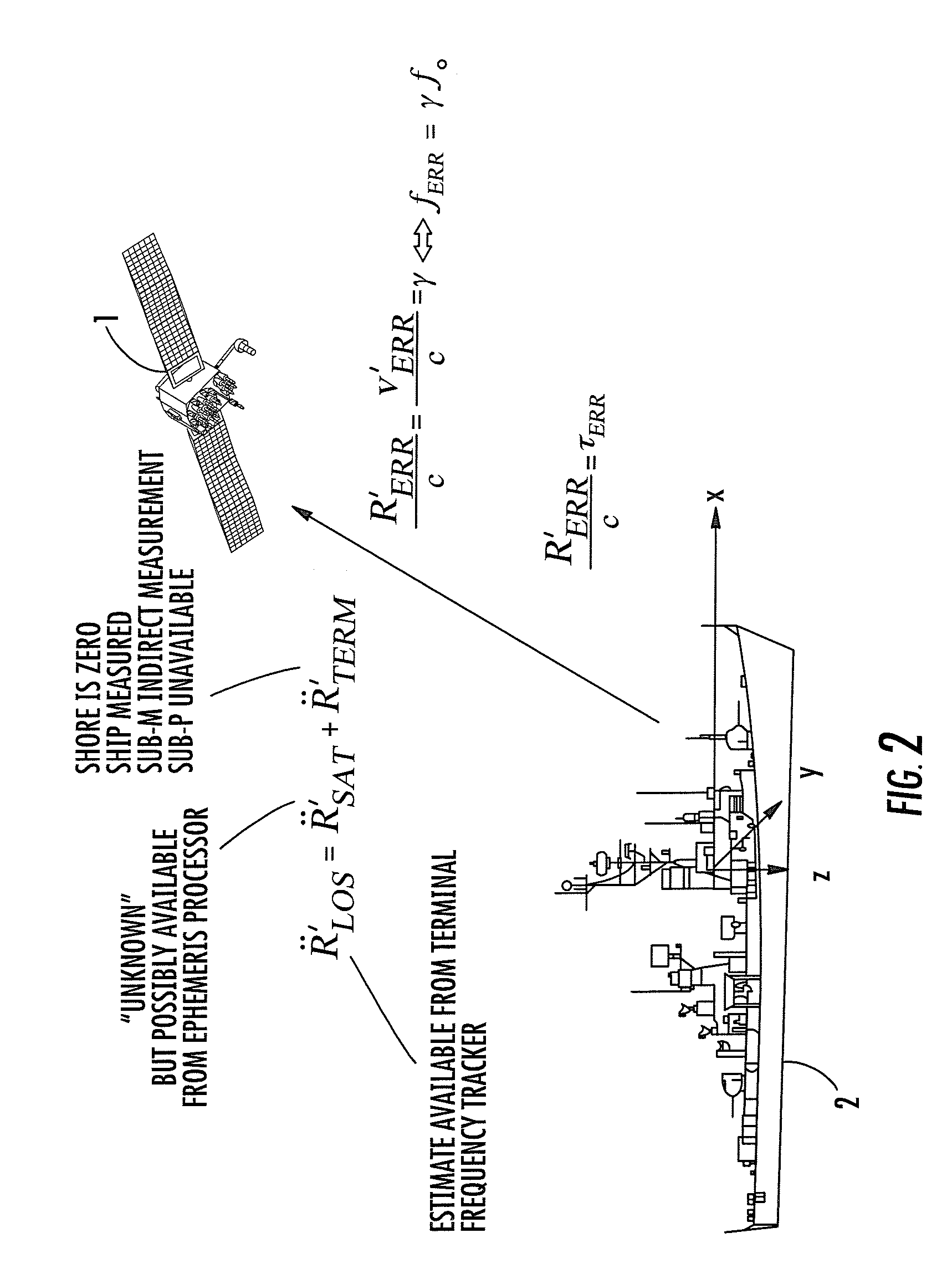
A downlink time / frequency tracker for a receiver terminal, which may be mounted to a static platform on the earth, or to a dynamic platform, such as a ship. The tracker is operative to acquire and track time and frequency variations in time- and frequency-hopped synchronization signals from different data rate sources in a dynamic platform, such as a satellite. Characteristics of the Kalman filter are updated in accordance with data representative of timing error and frequency error measurements carried out on the synchronization signals, as well as data representative of local kinematic domain measurements carried out with respect to the receiver terminal. The Kalman filter outputs minimum mean square error estimates of timing and frequency errors in the receiver terminal's demodulator clock. These error estimates are used to synchronize the demodulator's clock with the clock embedded in the downlink signal, so as to enable demodulation and recovery of data.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Method and apparatus providing low complexity equalization and interference suppression for SAIC GSM/EDGE receiver
InactiveUS20050036575A1Improve performanceReduce complexityError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringCo-channel interference
Disclosed is a RF receiver that includes baseband circuitry for performing Minimum Mean-Square Error (MMSE) optimization for substantially simultaneously suppressing inter-symbol interference (ISI) and co-channel interference (CCI) on a signal stream that comprises real and imaginary signal components. In a preferred embodiment the receiver includes a single receive antenna, and operates as a single / multi antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) receiver. The baseband circuitry operates to determine a set of In-Phase and Quadrature Phase (I-Q) MMSE vector weights that are used to perform the ISI suppression and the CCI suppression. A method for operating the receiver is also disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and apparatus for multipath delay estimation in direct sequence spread spectrum communication systems
InactiveUS6839378B1Solve the real problemRadio transmission for post communicationMean squareSide information
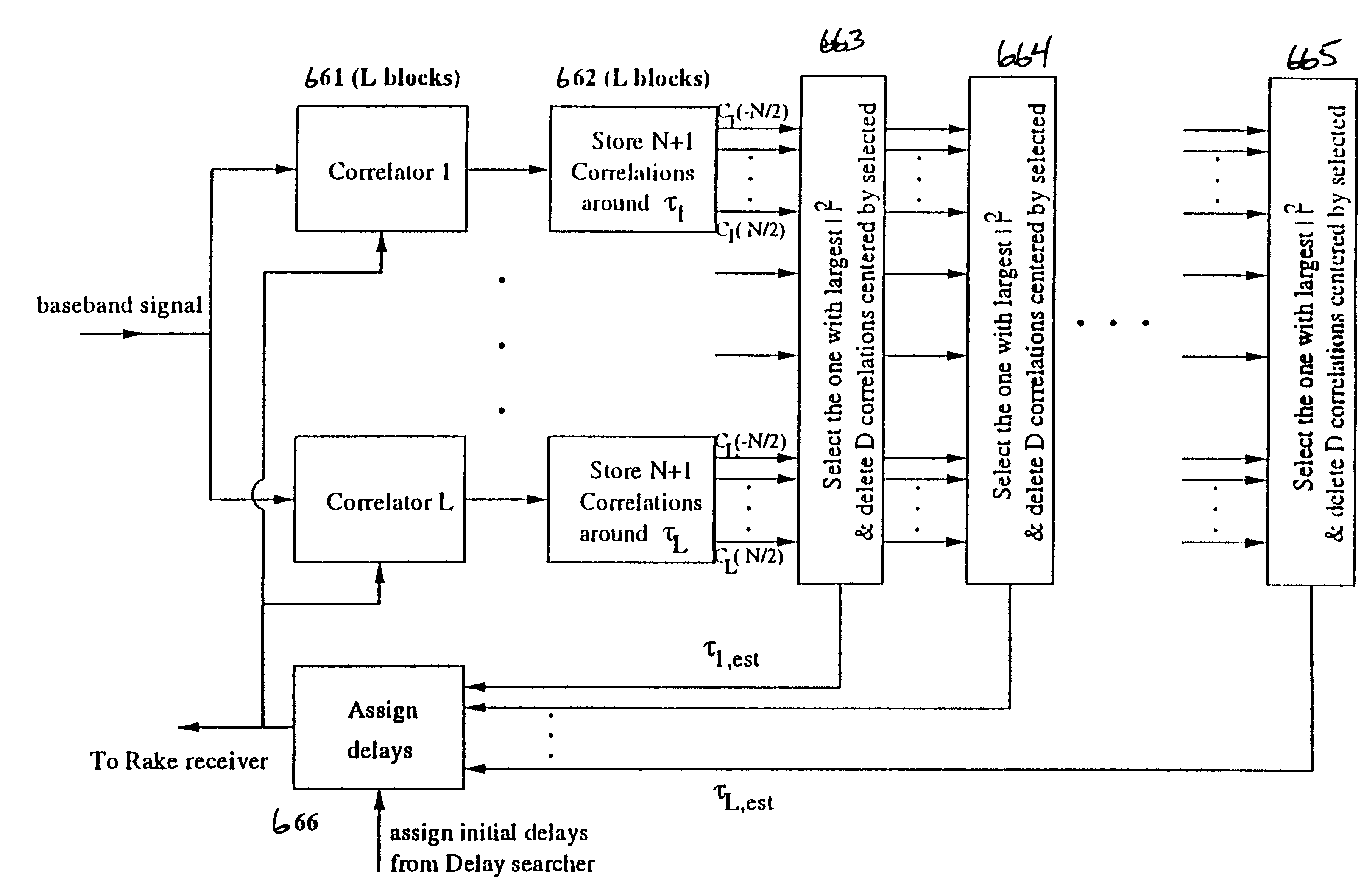
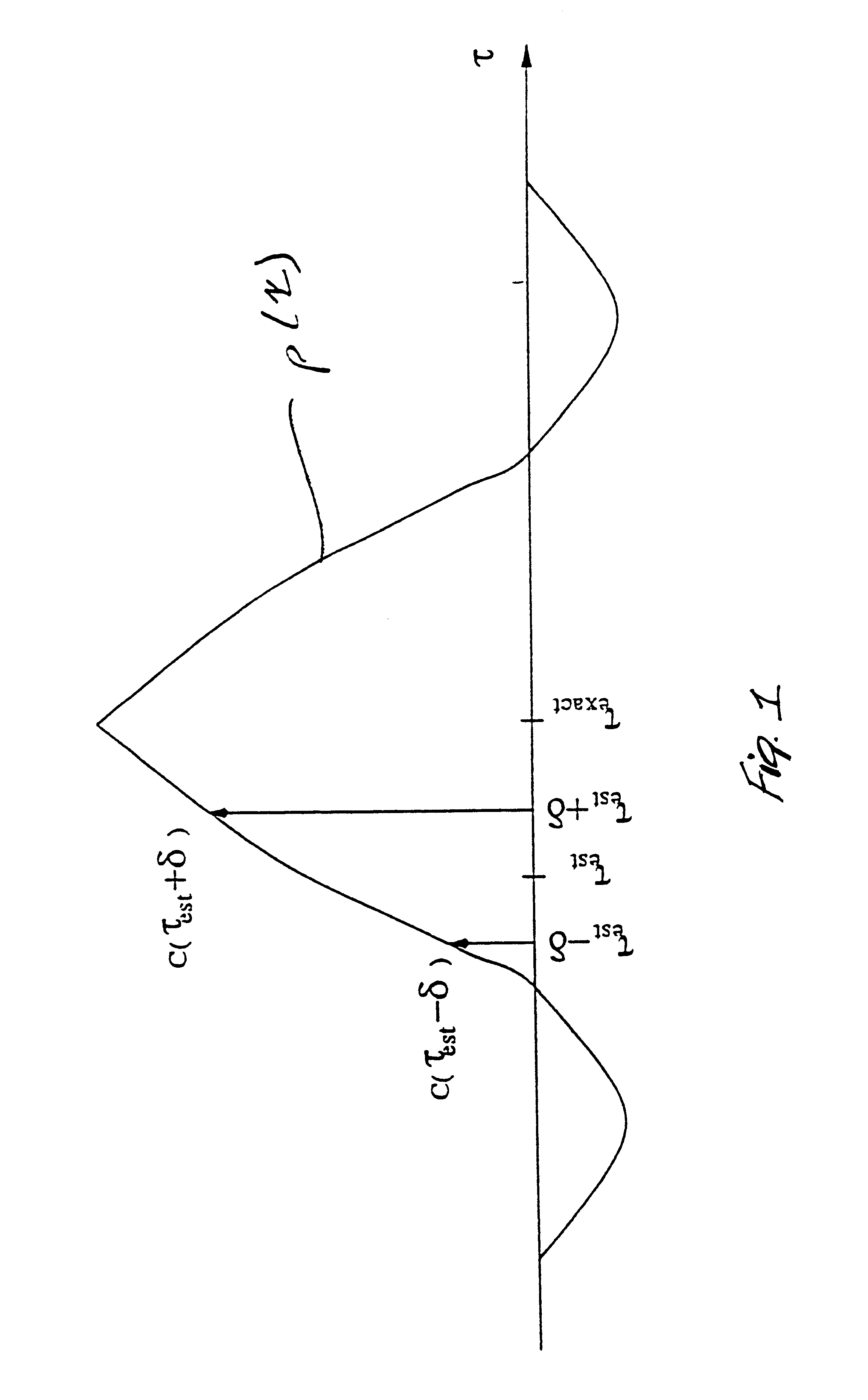
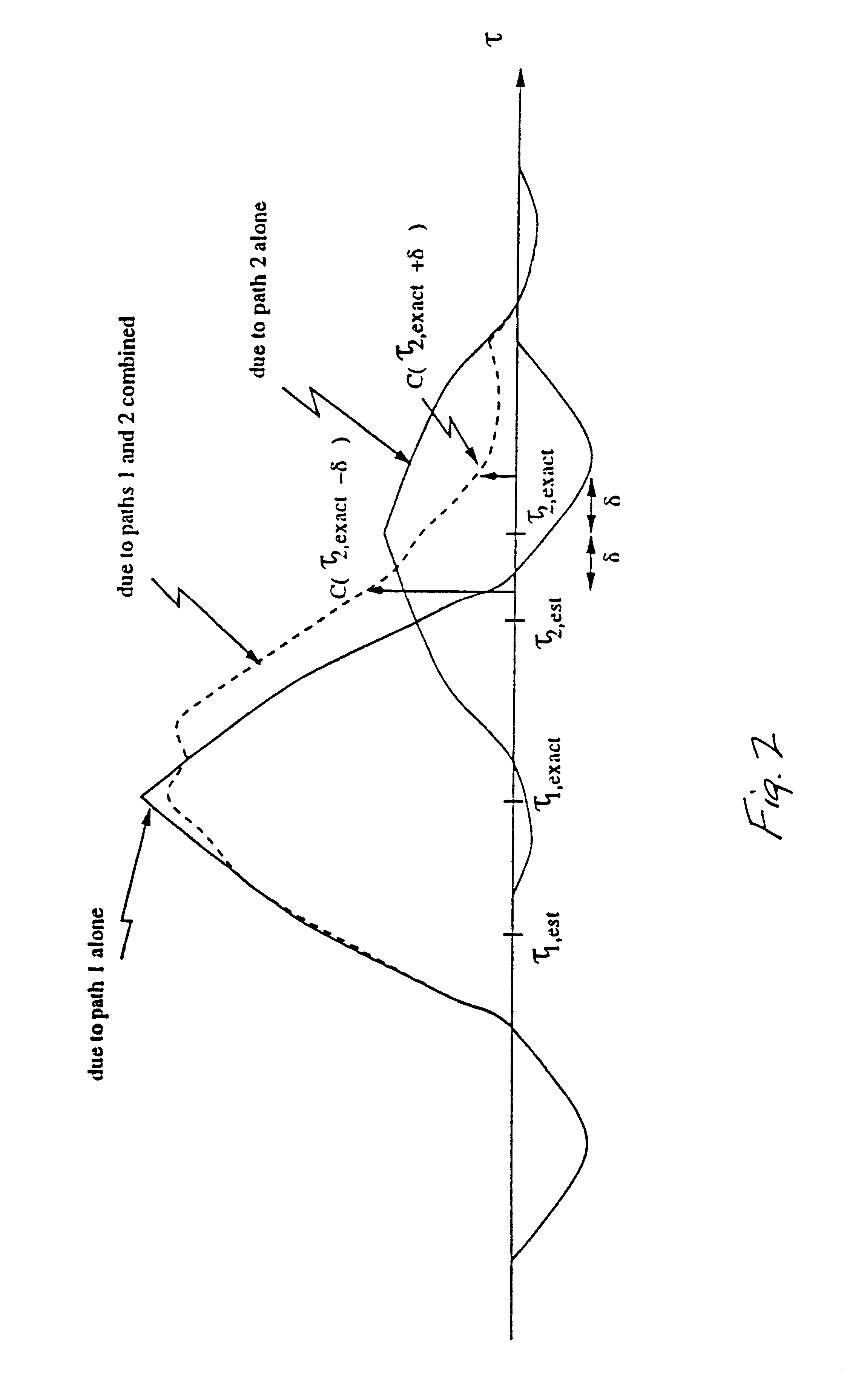
Multipath delay estimation of a direct sequence spread spectrum (DS-SS) signal transmitted in a multipath fading channel is accomplished by measuring the envelope of the signal to determine a new delay estimate. Delay estimates are also obtained in ray strength order, by subtracting out the influence of the stronger rays on the weaker ones. This subtraction approach can be performed iteratively, allowing further refinement of the delay estimates. Delay estimates can also be determined by minimizing the mean square error (MSE) between a measured correlation function and a modeled correlation function. The minimum mean square error (MMSE) approach can performed iteratively, to further refine the delay estimates. Maximum likelihood (ML) delay estimates can also be obtained by exploiting side information regarding the transmit and receive pulse shapes.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
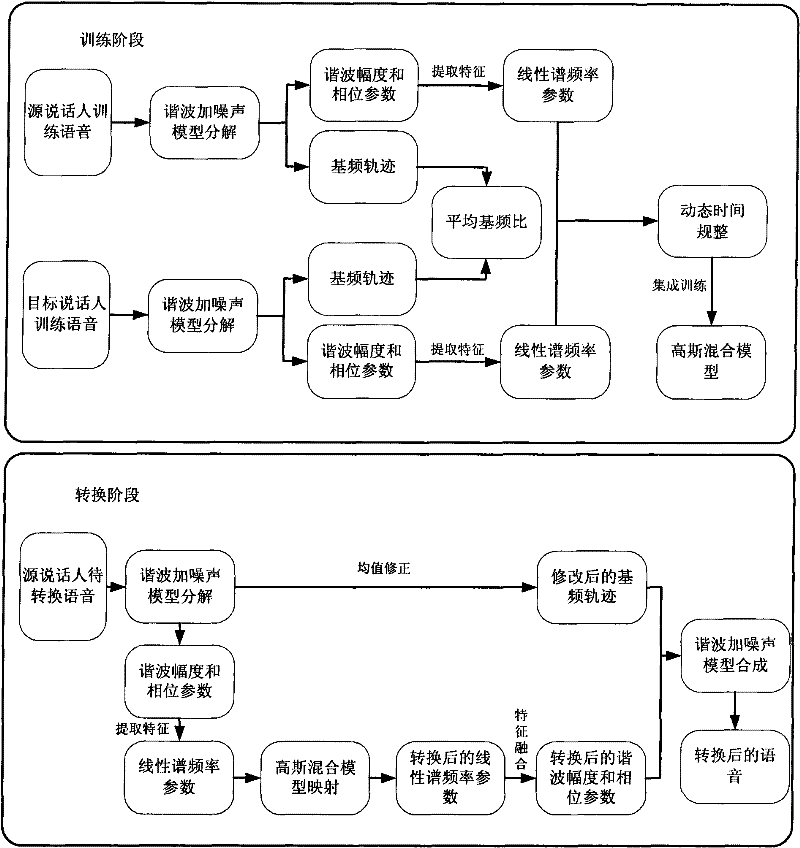
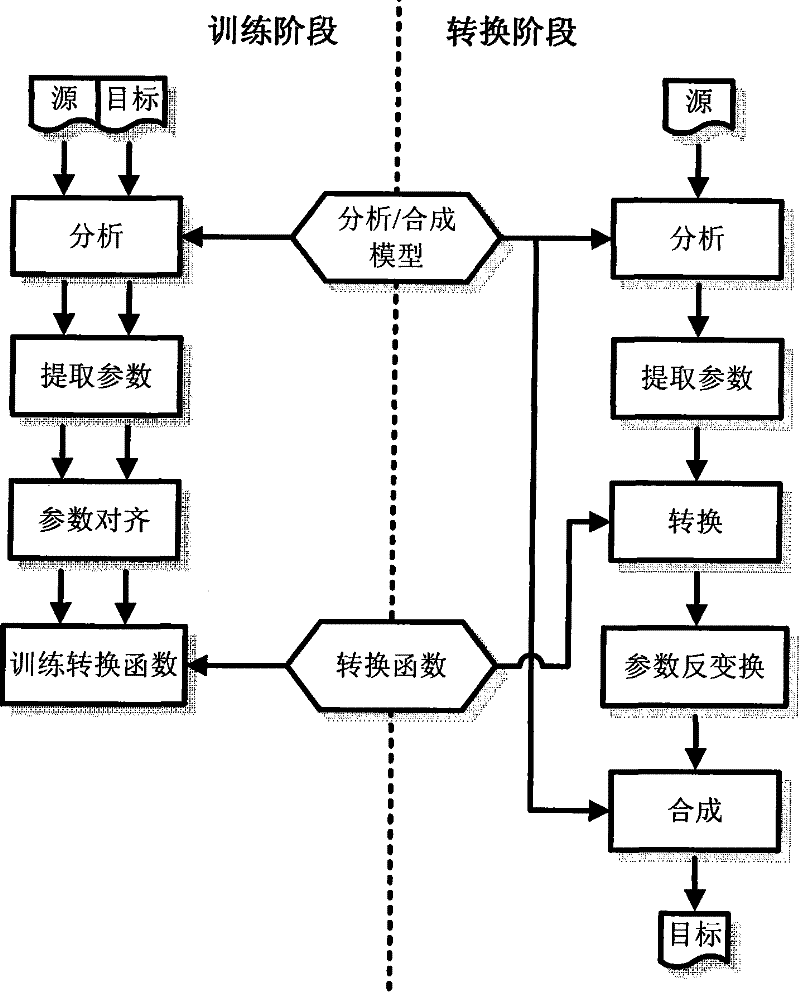
Real-time voice conversion method under conditions of minimal amount of training data
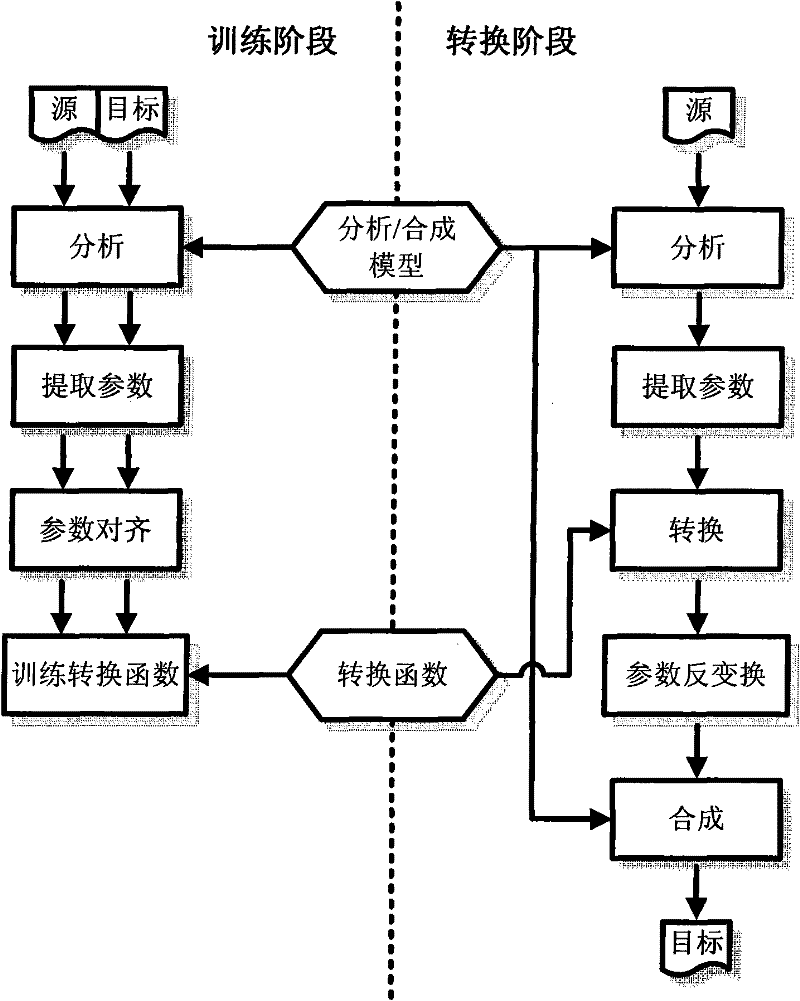
InactiveCN101751921AImprove distributionPrevent overfittingSpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisAlgorithmMinimum mean square error
The invention provides a real-time voice conversion method under conditions of minimal amount of training data. The method utilizes an ensemble learning theory to carry out modeling of a Gaussian mixture model to the collected data and design a mapping function under the rule of minimum mean square error. The method solves the problem that a standard GMM easily leads to over-fitting in the case of very minimal amount of data, and increases the robustness of a voice conversion algorithm for amount of data issues. At the same time, the GMM with more standard computational complexity is low in the process of estimating GMM parameters by the method, so the method is suitable for real-time voice conversion.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
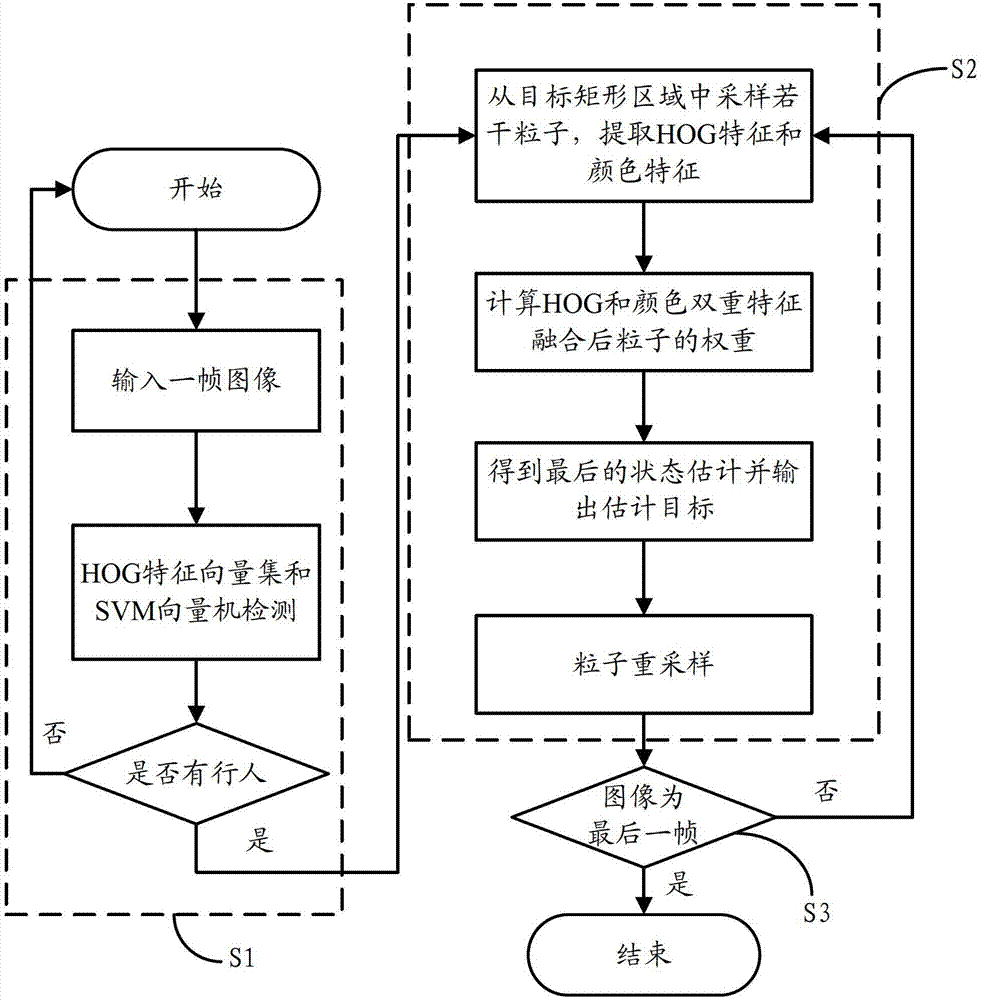
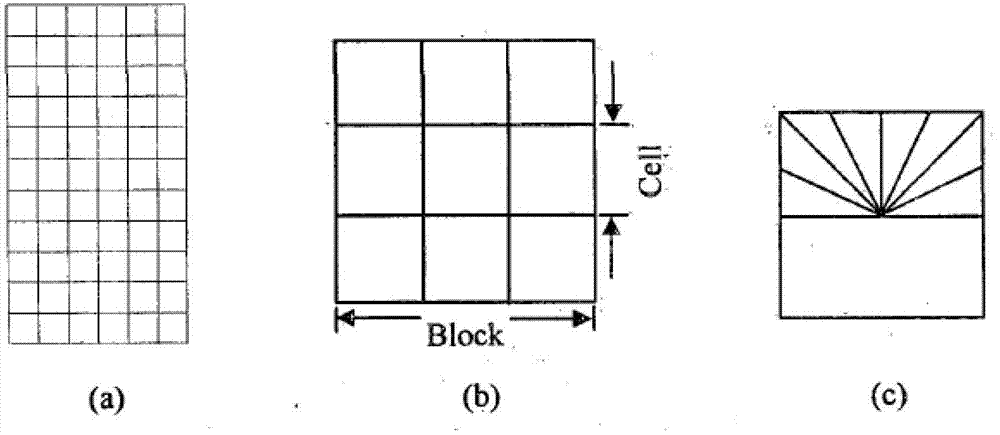
Method and system for automatically tracking moving pedestrian video based on particle filtering
InactiveCN102831409AImprove robustnessReduce instabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorHistogram of oriented gradients
The invention discloses a method and a system for automatically tracking a moving pedestrian video based on particle filtering. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting one frame of images, and carrying out detection through an HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradient) feature vector set and an SVM (Support Vector Machine) vector machine; in order to realize particle filtering tracking based on double HOG and color features, firstly obtaining an initial rectangular area of target pedestrian, sampling a plurality of particles from a target rectangular area, extracting an HOG feature and a color feature, computing the weight of the particles after the double HOG and color features are fused, obtaining the final state estimation through a minimum mean square error estimator, outputting an estimation target and then resampling; and closely locking the tracked target pedestrian. The method extracts the double HOG and color features to increase the robustness of a particle filtering likelihood model and eliminate the unstable situation in the tracking process, the method combines the HOG feature to build the better likelihood model through a fusion strategy of weighted mean, the robustness of the tracking algorithm is greatly increased, and the stable tracking is completed.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
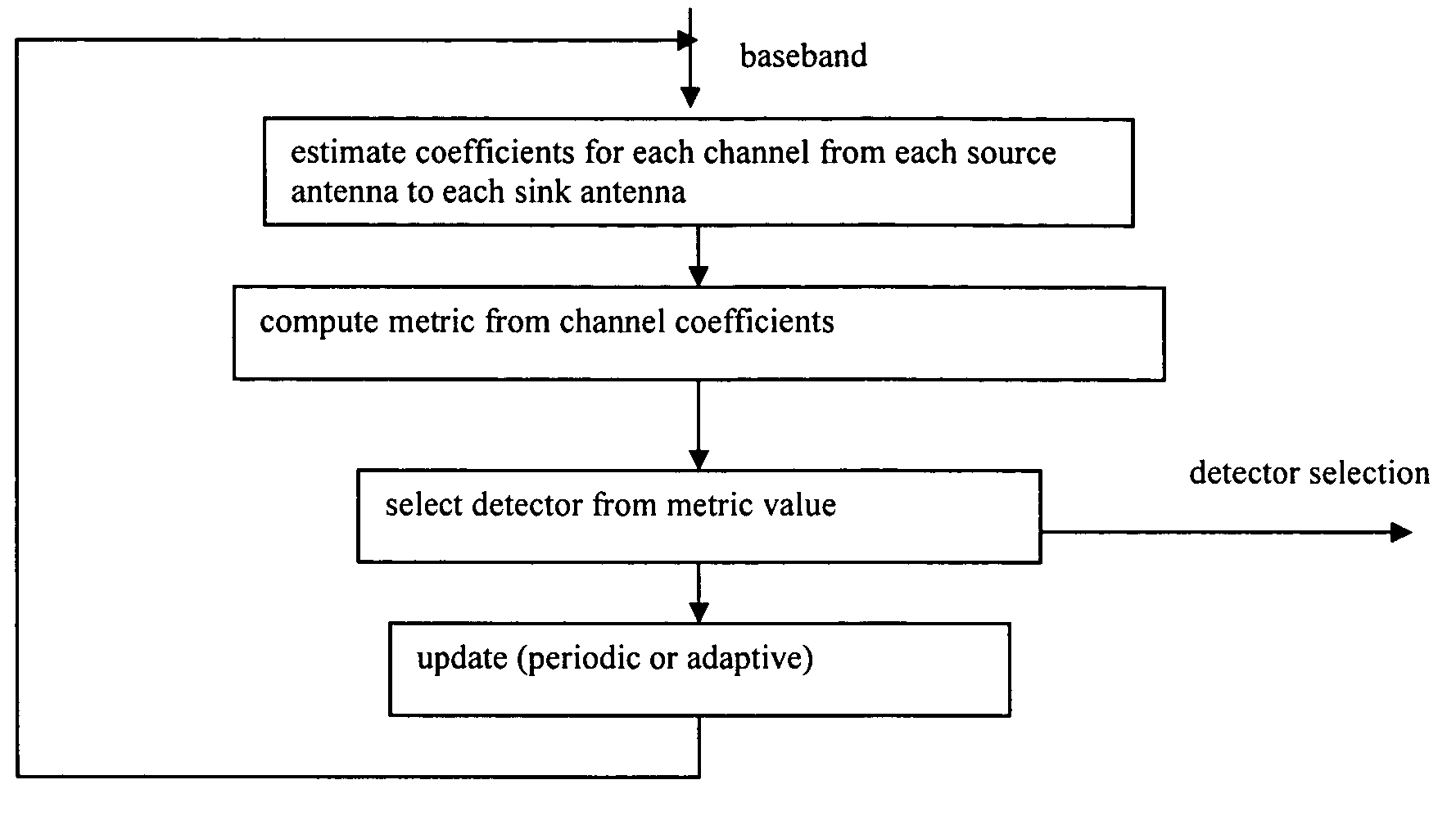
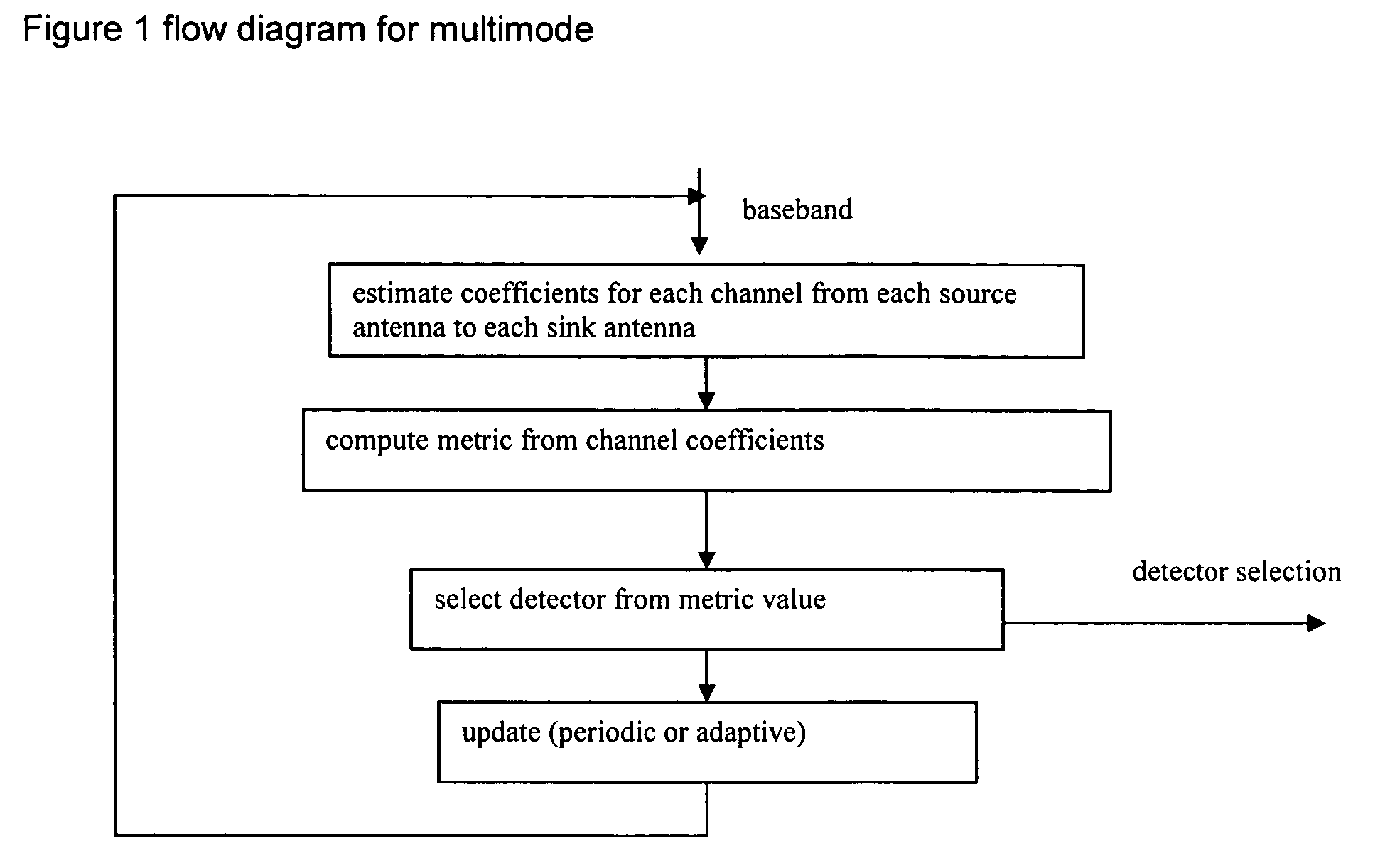
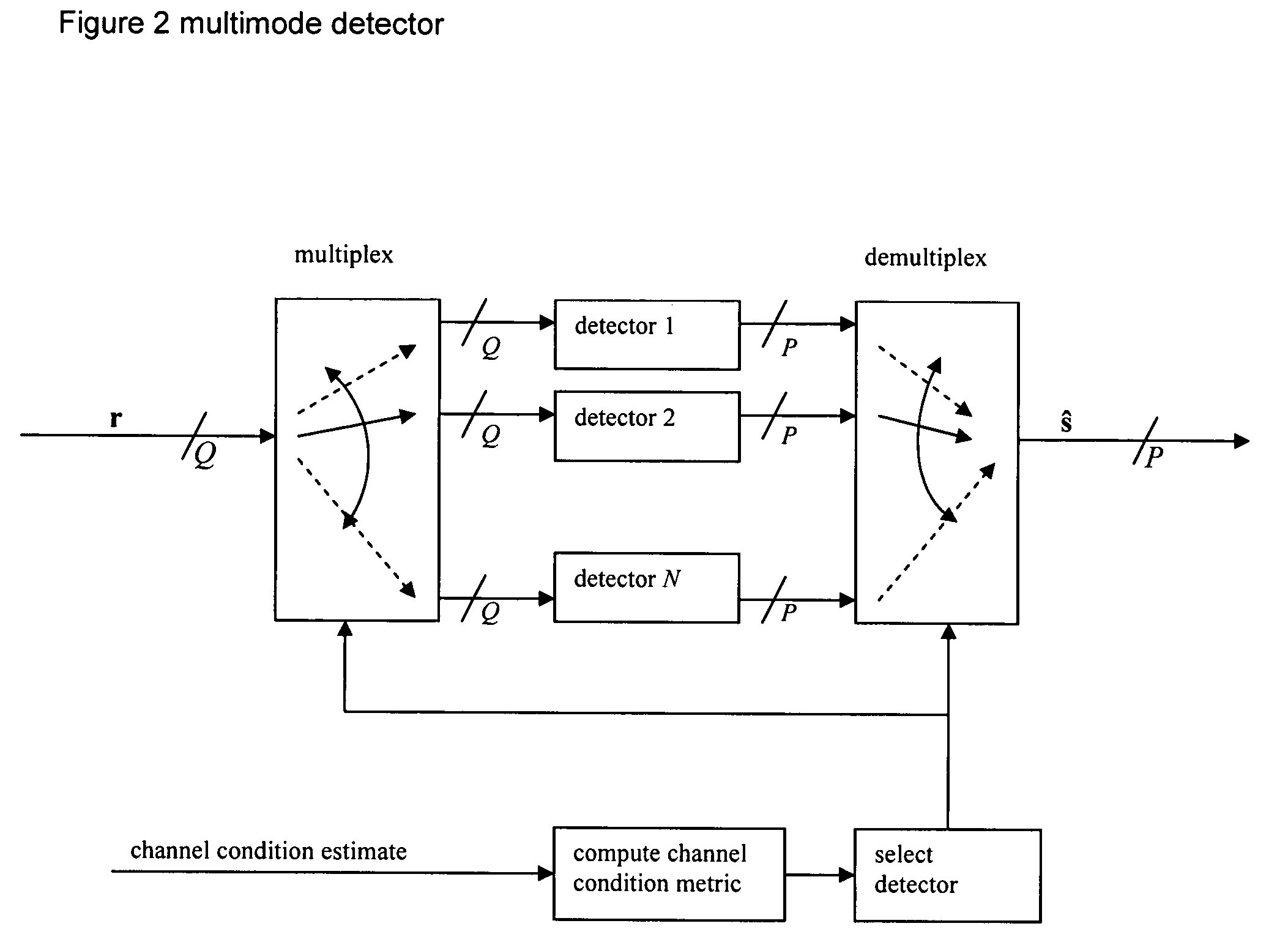
Multimode detection
InactiveUS20060018410A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionMinimum mean square errorWireless systems
In a wireless MIMO system, a multimode detector selects detection mode by channel estimation: ill-conditioned channels trigger use of high performance detection, whereas well-behaved channels lead to low complexity detection. Detection modes typically include maximum likelihood, minimum mean squared error, zero forcing, and so forth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
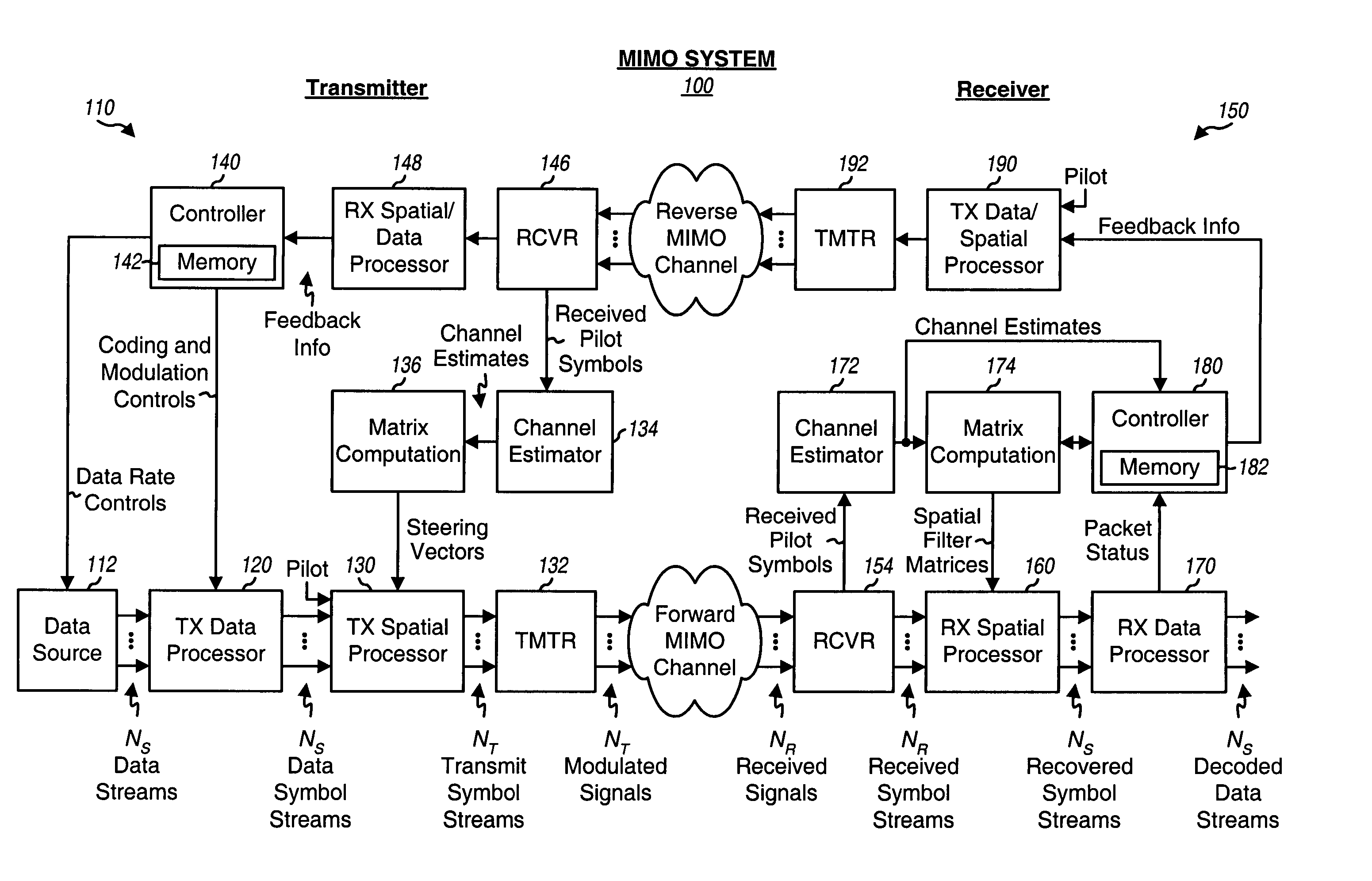
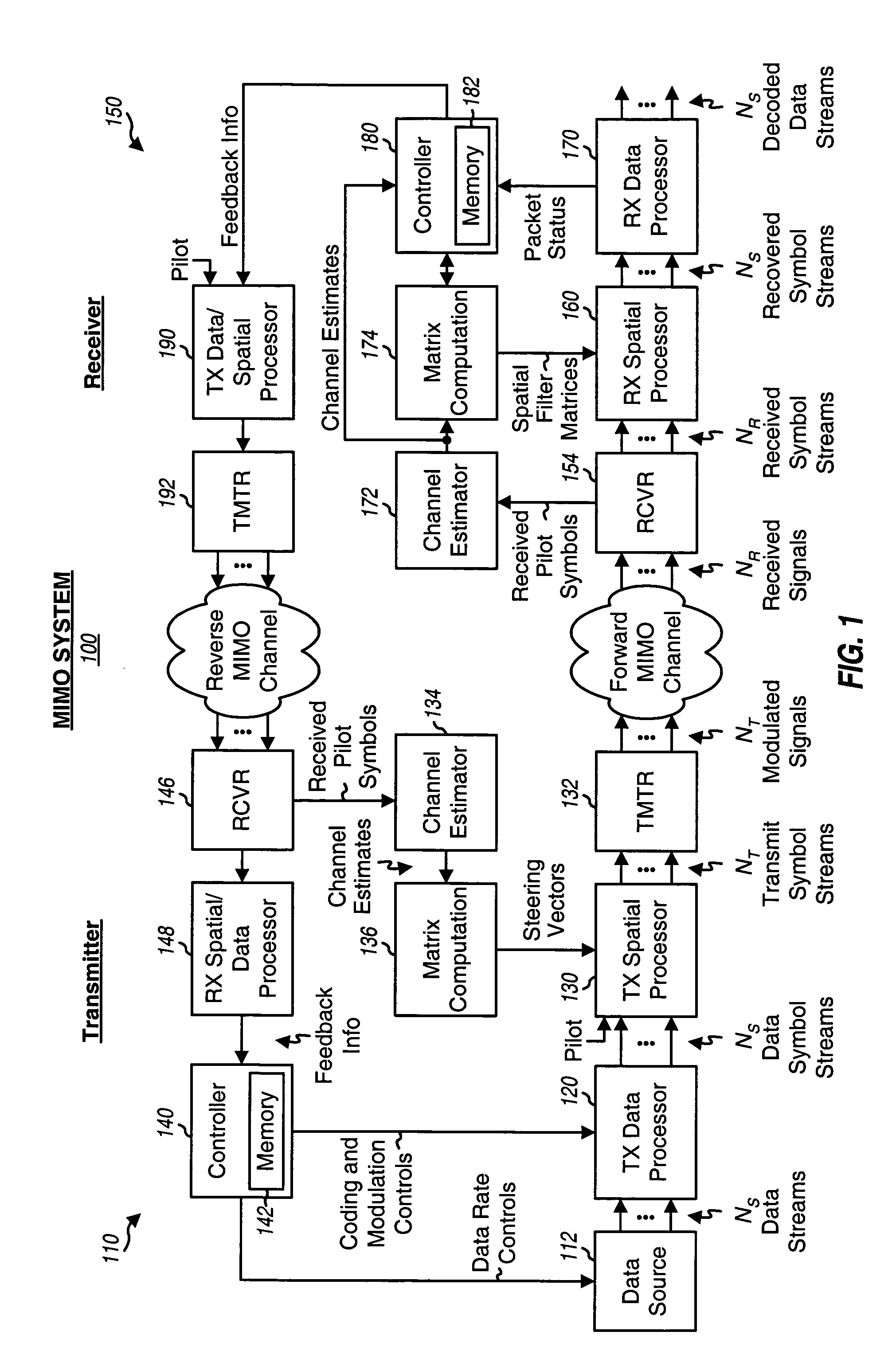
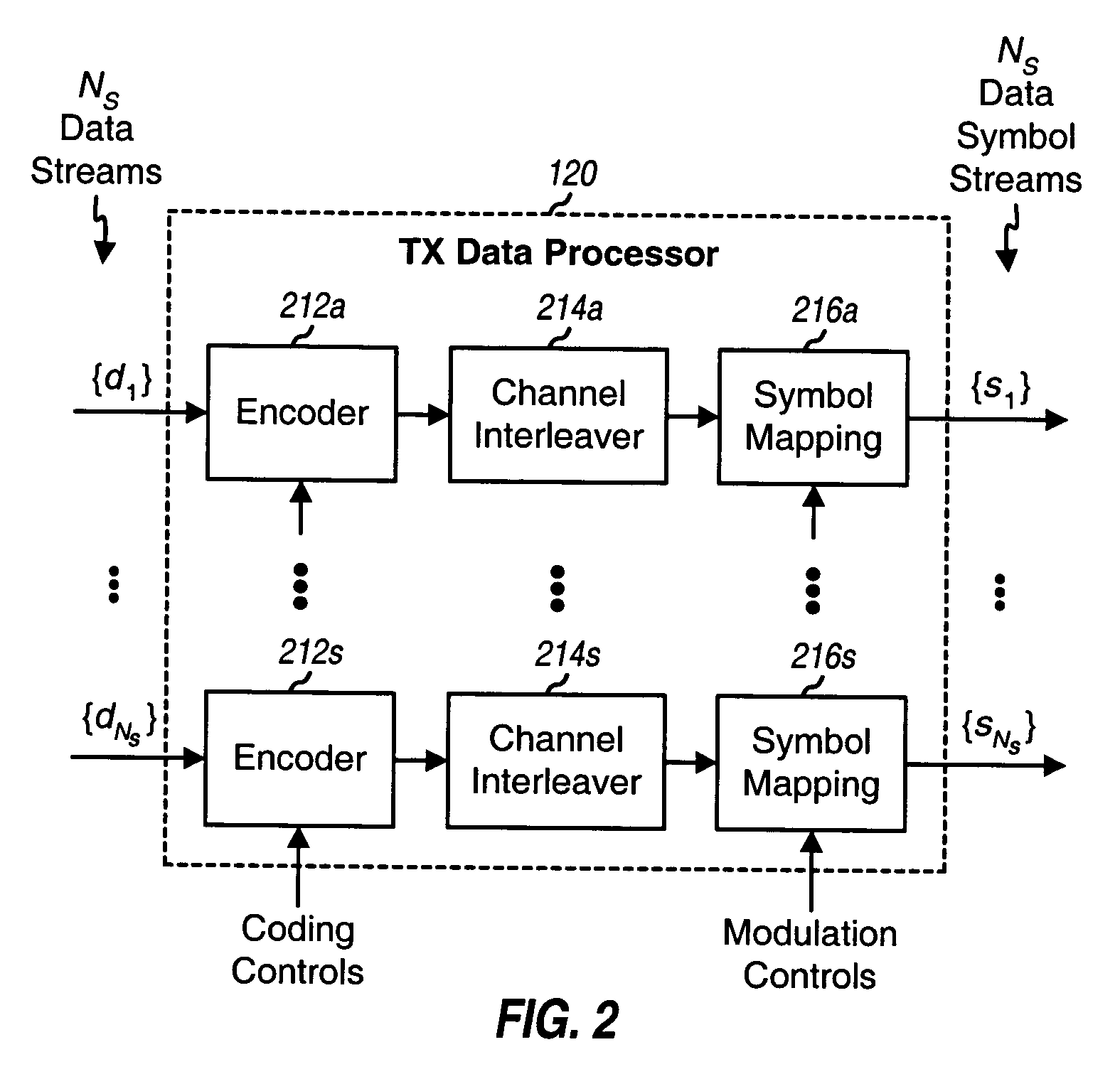
Receiver spatial processing for eigenmode transmission in a MIMO system
ActiveUS20050078762A1Reduce crosstalkImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityFir systemData stream
For eigenmode transmission with minimum mean square error (MMSE) receiver spatial processing, a transmitter performs spatial processing on NS data symbol streams with steering vectors to transmit the streams on NS spatial channels of a MIMO channel. The steering vectors are estimates of transmitter steering vectors required to orthogonalize the spatial channels. A receiver derives a spatial filter based on an MMSE criterion and with an estimate of the MIMO channel response and the steering vectors. The receiver (1) obtains NR received symbol streams from NR receive antennas, (2) performs spatial processing on the received symbol streams with the spatial filter to obtain NS filtered symbol streams, (3) performs signal scaling on the filtered symbol streams with a scaling matrix to obtain NS recovered symbol streams, and (4) processes the NS recovered symbol streams to obtain NS decoded data streams for the NS data streams sent by the transmitter.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
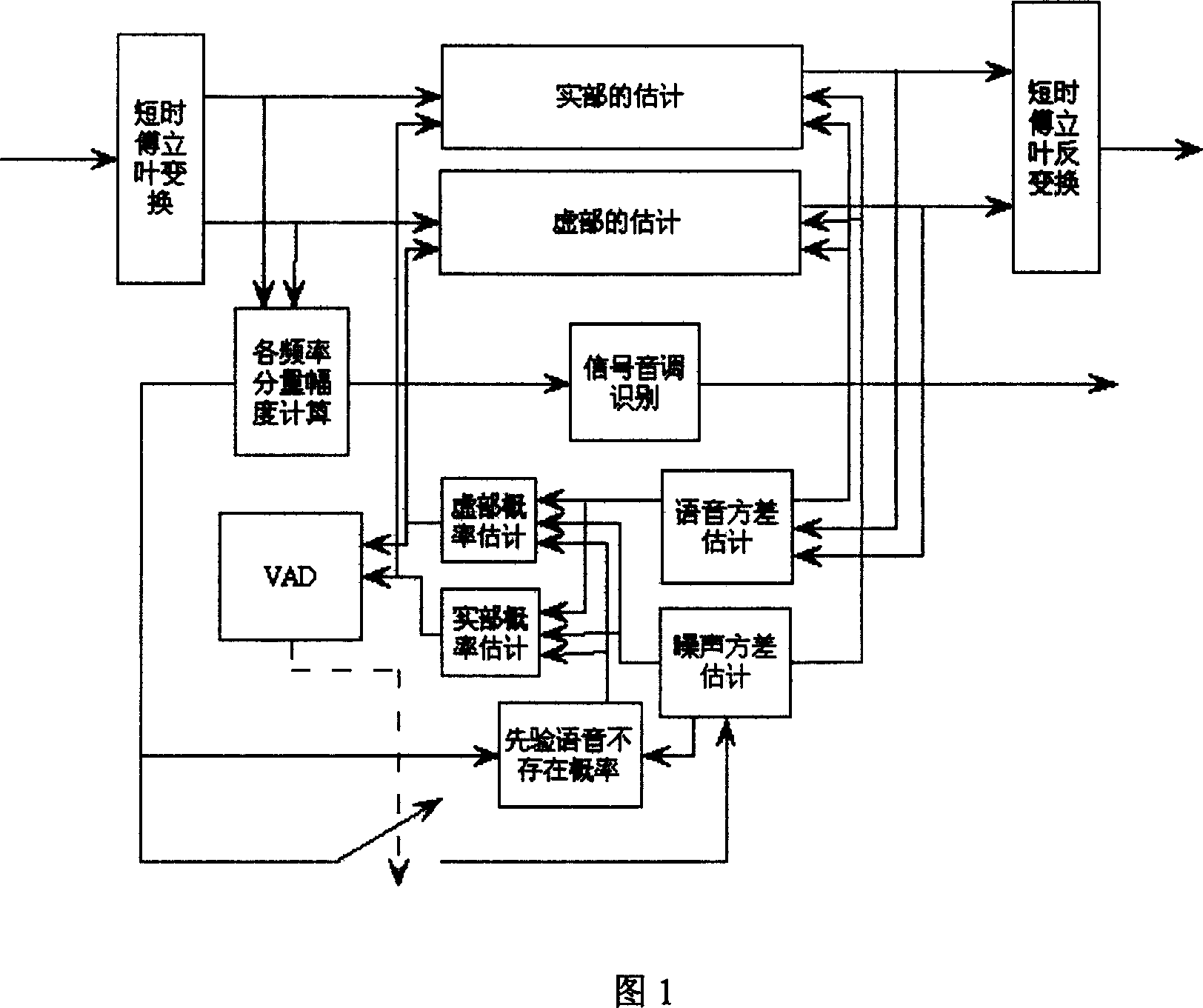
Method for realizing background noise suppressing based on multiple statistics model and minimum mean square error
InactiveCN101079266AExact true distributionReduce adverse effectsSpeech recognitionComputation complexityMean square
The invention discloses an inhibiting method of background noise based on multiple statistical models and minimum mean square deviation, which comprises the following steps: proceeding short-time Fuliye transmission for voice signal corresponding to present input frame; utilizing the frame to retain the pure voice amplitude variance estimation and noise amplitude variance estimation on each frequency; calculating the estimation of real part and imaginary part corresponding to each frequent component of voice signal in the present frame; counting the probability of non-existed prior voice of each component frequency of the input frame; modifying the estimation result of real part and imaginary part of each frequency component; obtaining the true distribution of voice and noise in the real applying precisely; improving the inhibiting effect with stable estimating course; reducing the calculating complexity; fitting for kinds of voice communicating systems.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Signal transmission/reception apparatus and method to minimize inter-cell interference in a communication system
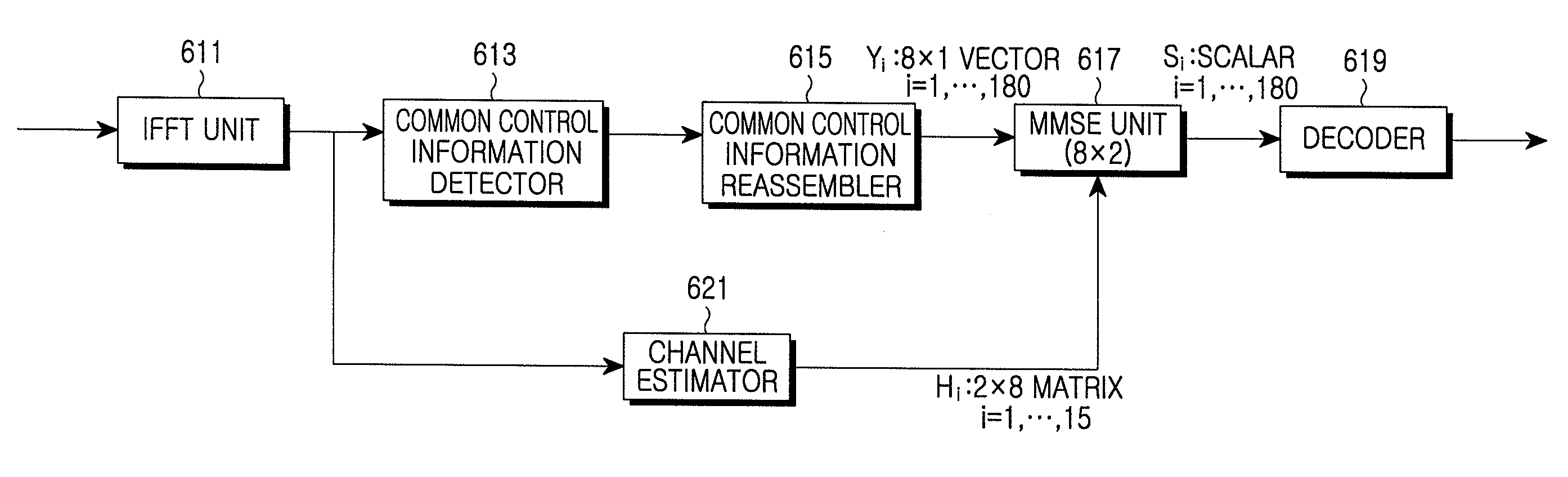
InactiveUS20080075185A1Minimize ICITransmission path divisionTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemCarrier signal
An apparatus and method to transmit / receive a signal in a communication system are provided. A base station (BS) generates repetitive information by repeating information a number of times, allocates a subcarrier for transmitting the repetitive information using a subcarrier allocation scheme that all BSs included in the communication system use in a same way, and transmits the repetitive information using the allocated subcarrier. When the communication system includes a serving BS and one interference BS, a mobile station (MS) detects R-times repeated information from a corresponding subcarrier of a signal received via K reception antennas, estimates a channel using the received signal, reassembles the detected information, and performs R×2×k Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE) processing on the reassembled information using the channel-estimated value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
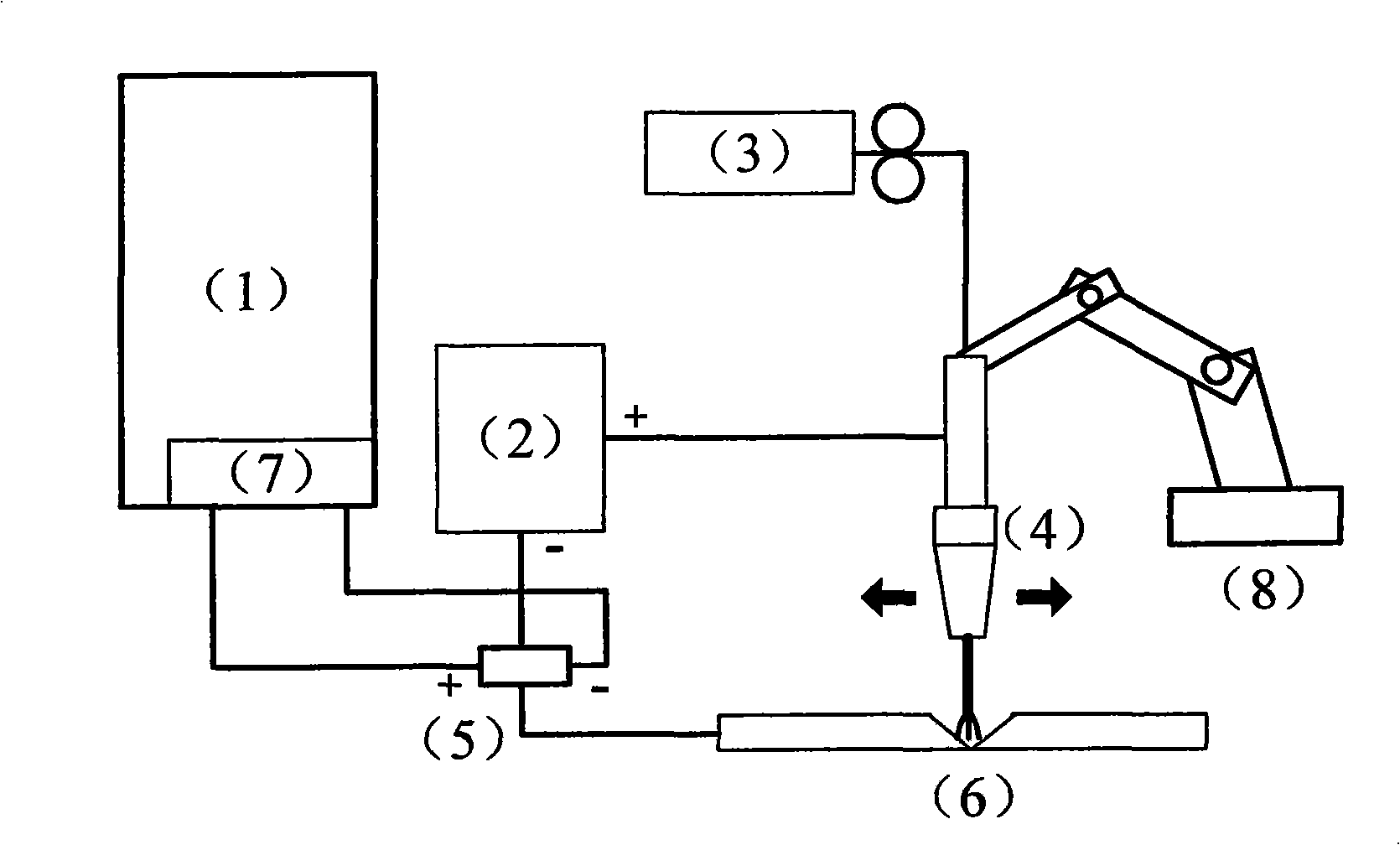
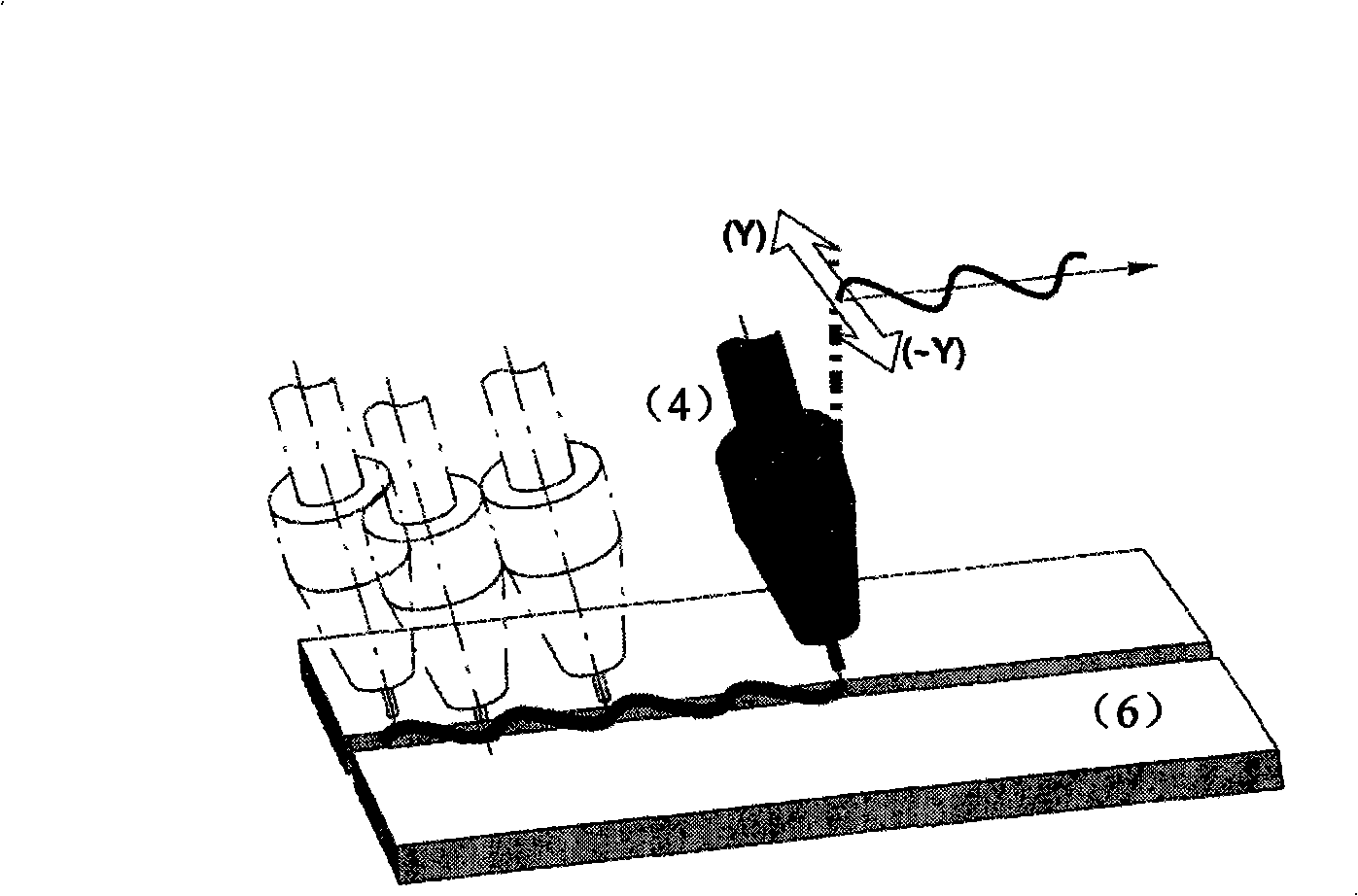
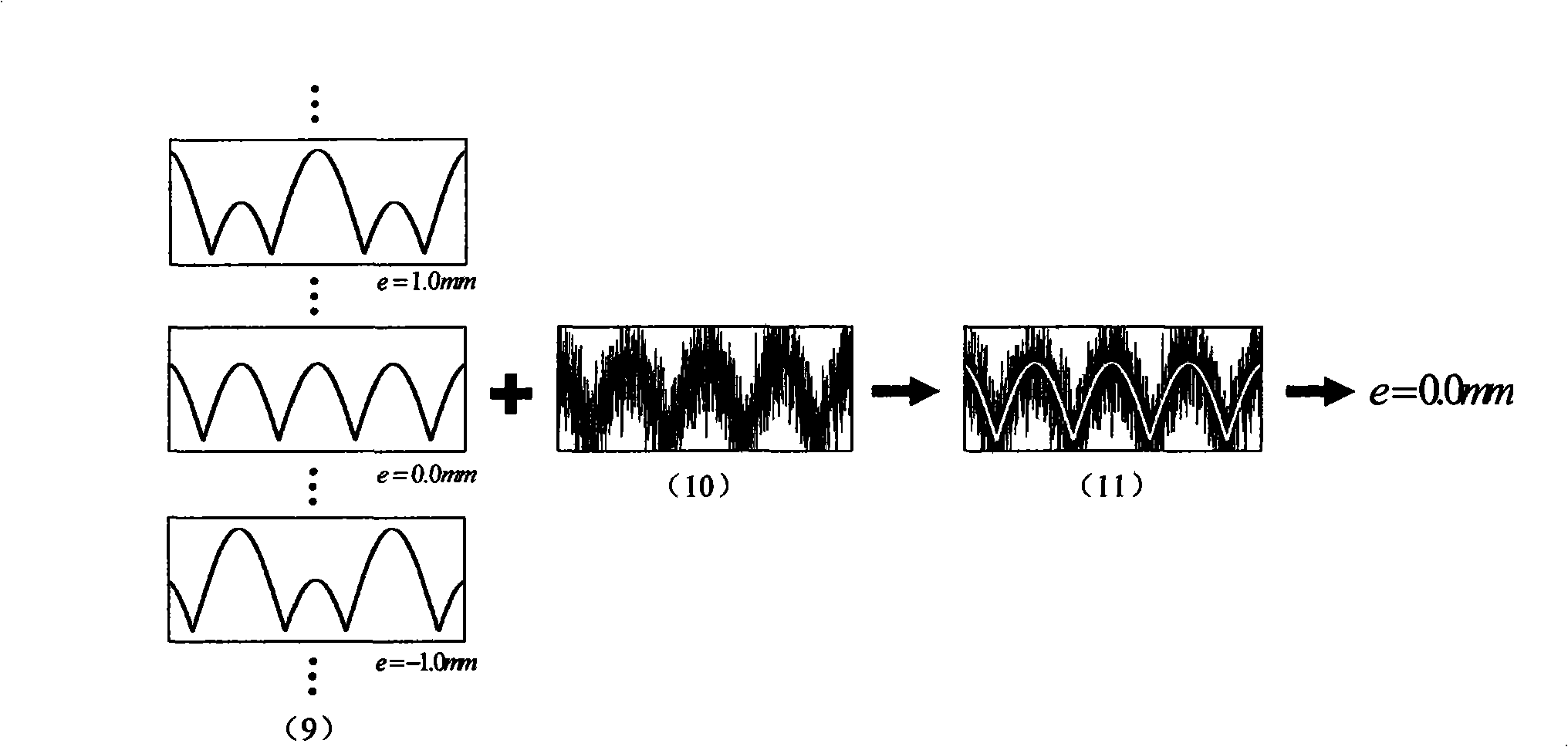
Method for extracting arc sensor welding gun position deviation information
InactiveCN101514886AImprove anti-interference abilityReliable extraction resultsArc welding apparatusUsing electrical meansEngineeringMinimum mean square error
The invention introduces a method for extracting arc sensor welding gun position deviation information. The basic idea of the method is combining a sampling result of a welding current signal with approximation of function to calculate the deviation information of the welding gun position. In the method, the relation of the welding current signal and the welding gun position deviation information under the condition of not considering the interference is derived firstly; then a welding current waveform which is most similar to an actual welding current sampling signal is calculated in minimum mean-square error sense; and the deviation value corresponding with the waveform is the deviation information of the welding gun position to be extracted. The method introduced by the invention can improve the precision of the arc sensor and also considers the integral characteristic of the welding current sampling signal completely to ensure that the deviation extraction result is more reliable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Adaptive transmitter/receiver
InactiveUS7031368B1Reduce distractionsSuppress interferenceSpatial transmit diversityAntennasTransceiverMinimum mean square error
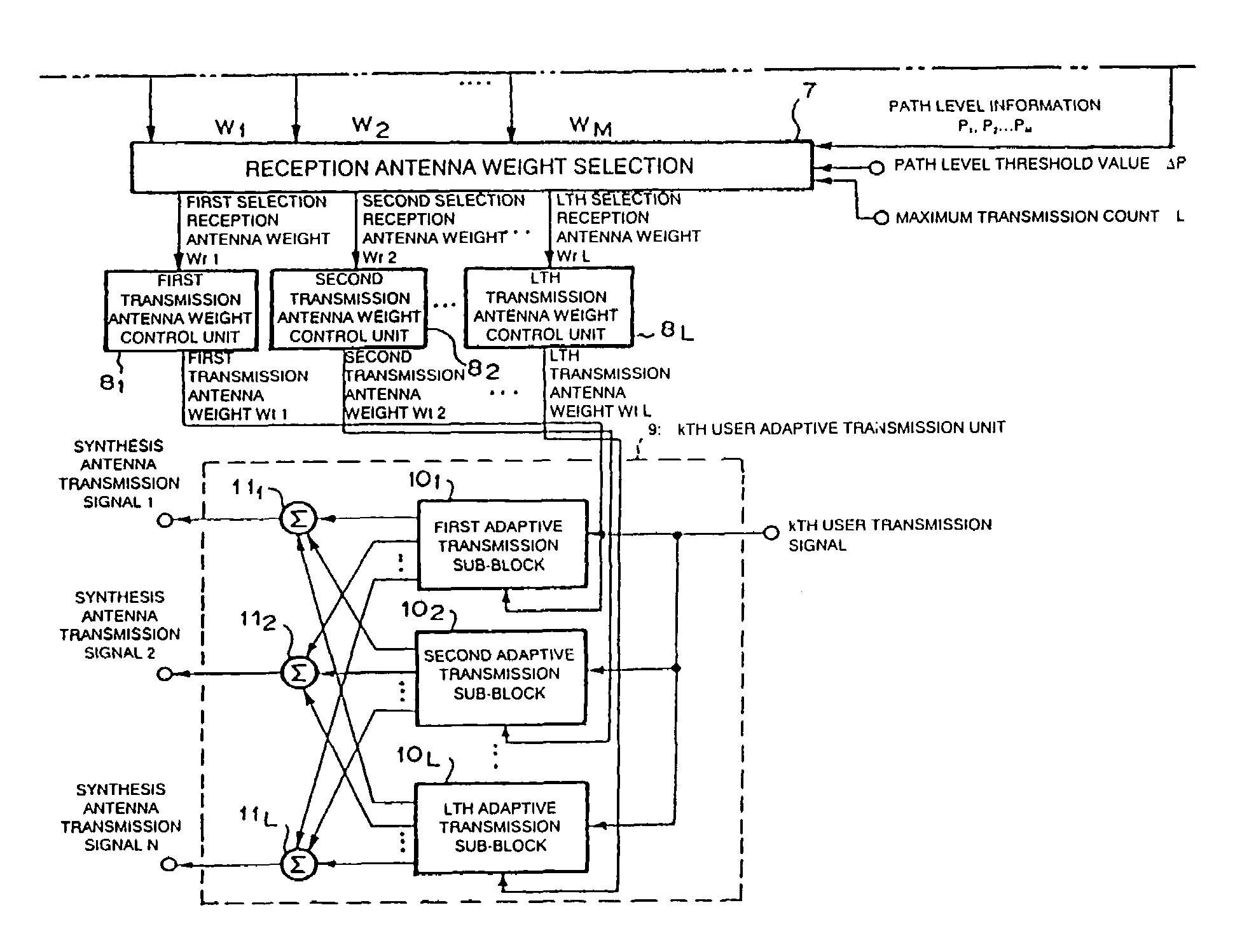
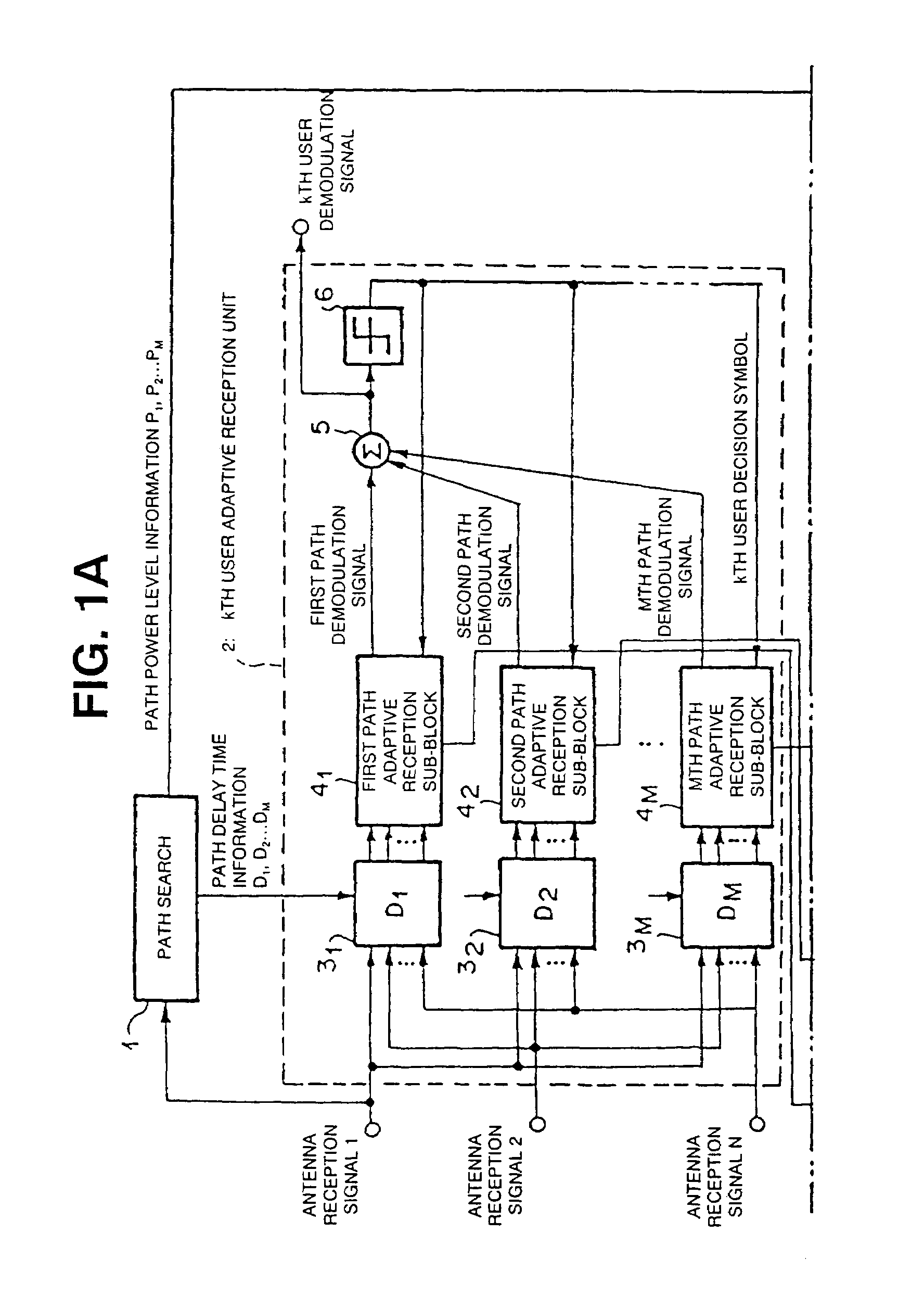
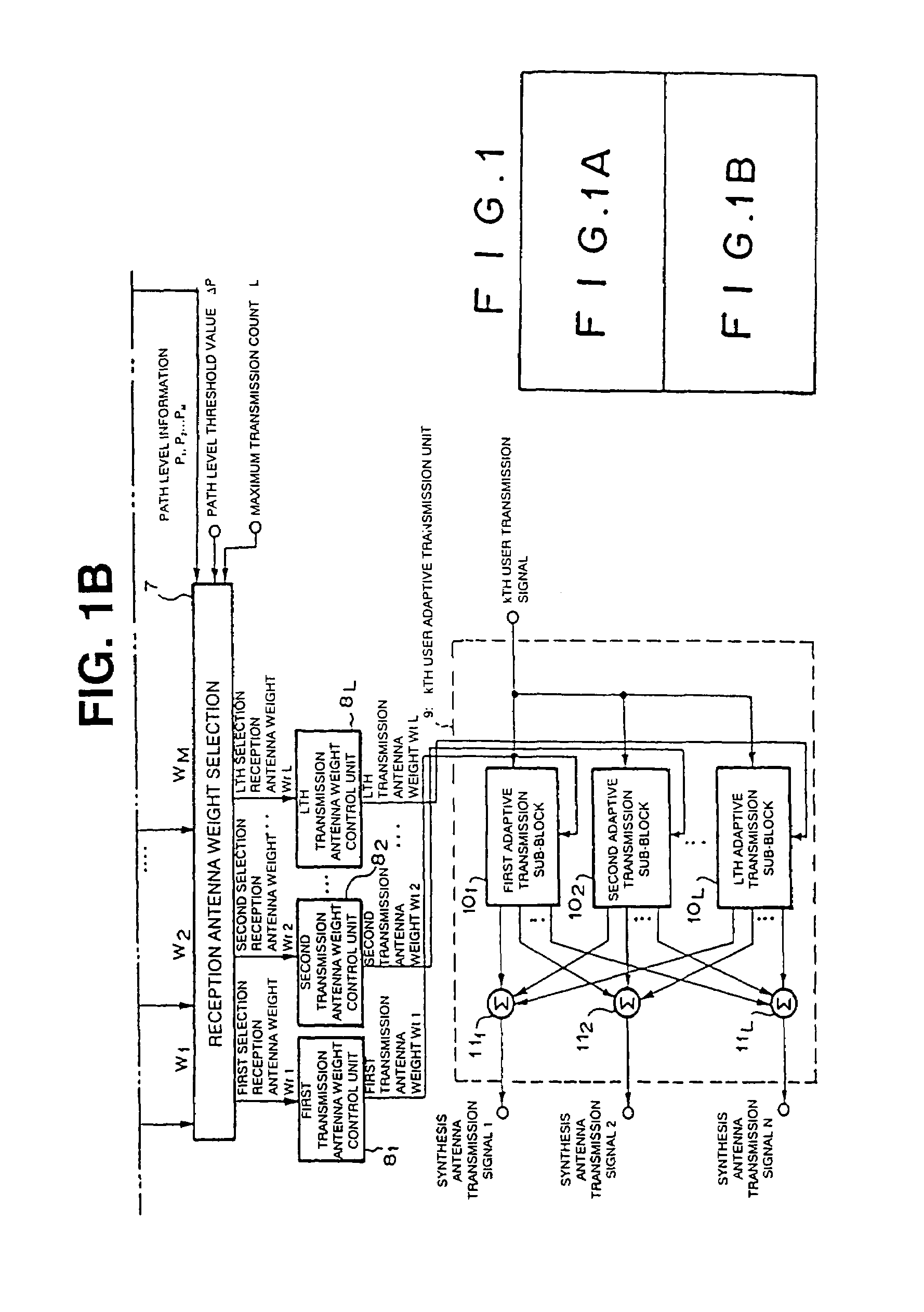
There is provided an adaptive transceiver device which estimates a path arrival direction of a desired wave signal by using a reception antenna weight of a k-th user adaptive reception unit using a control method based on the minimum mean square error (MMSE) standards and which generates a transmission antenna weight on the basis of the path arrival direction. The adaptive transceiver device is characterized in that in reception, a directivity pattern for suppressing interference caused by another user or a multi-path is formed, an arrival direction of a path is estimated from the reception antenna weight, and a transmission direction is predicted from the estimated arrival direction to generate a transmission antenna weight, and in transmission, a directivity pattern for decreasing interference to another user is formed and transmitted.
Owner:NEC CORP
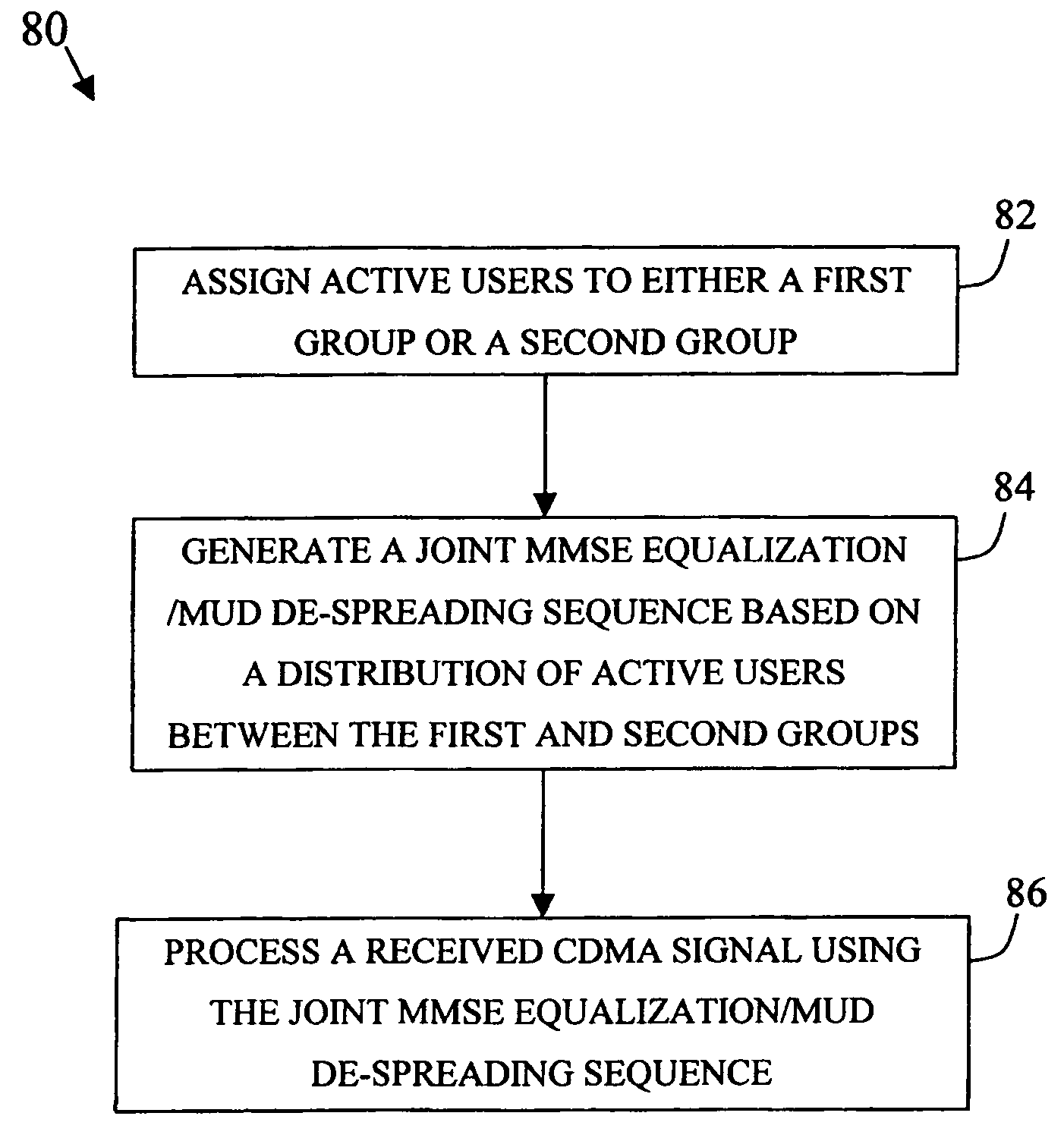
Unified MMSE equalization and multi-user detection approach for use in a CDMA system
ActiveUS20050094713A1Radio transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFir systemMulti user detection
A unified minimum mean square error (MMSE) equalization / multi-user detection (MUD) approach for demodulating direct sequence CDMA (DS-CDMA) signals is described. In at least one embodiment, the unified approach is capable of generating a variety of cost-effective receiver demodulation techniques that may range from, for example, a low cost linear MMSE equalization technique to a relatively high complexity MMSE MUD.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
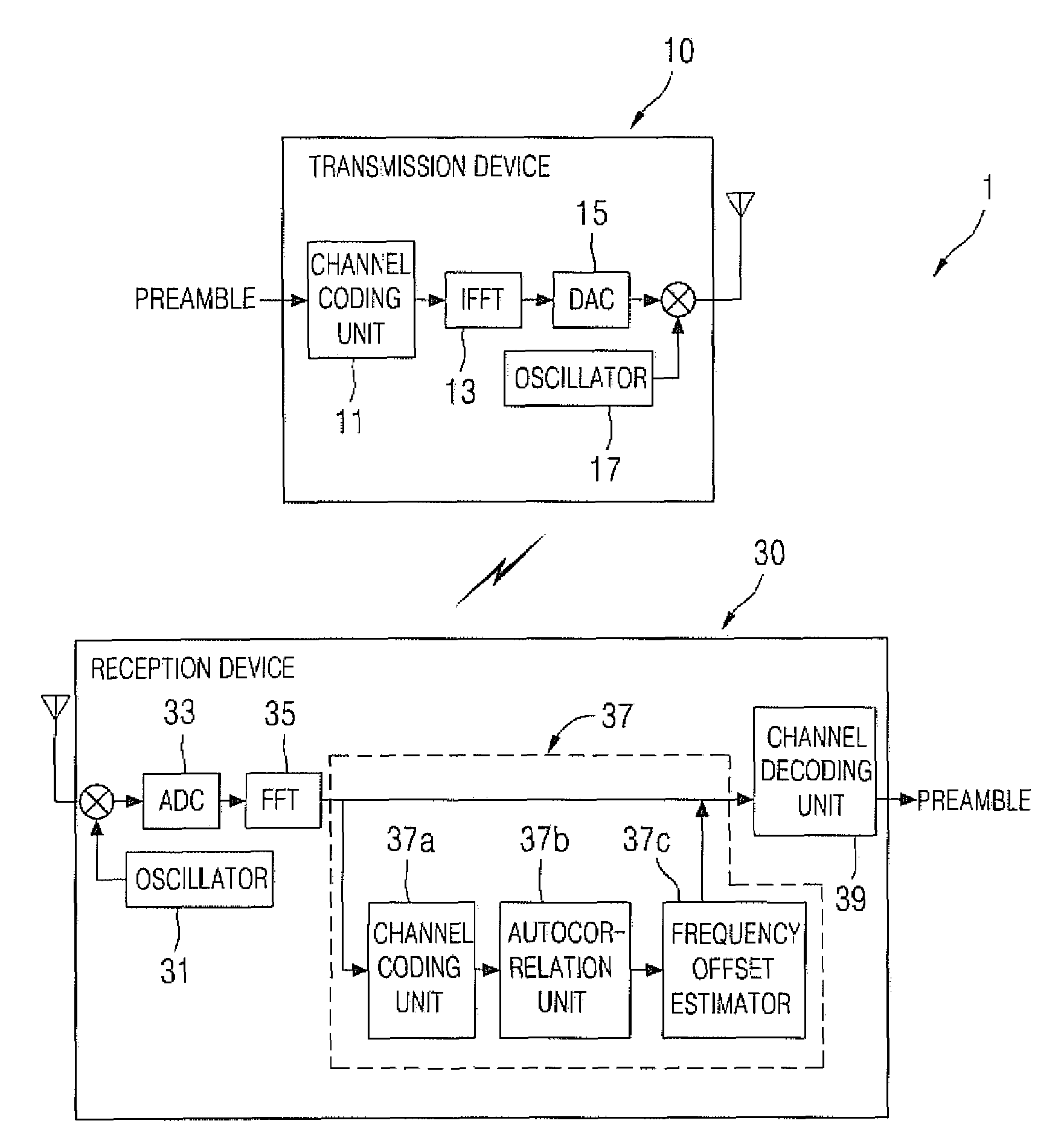
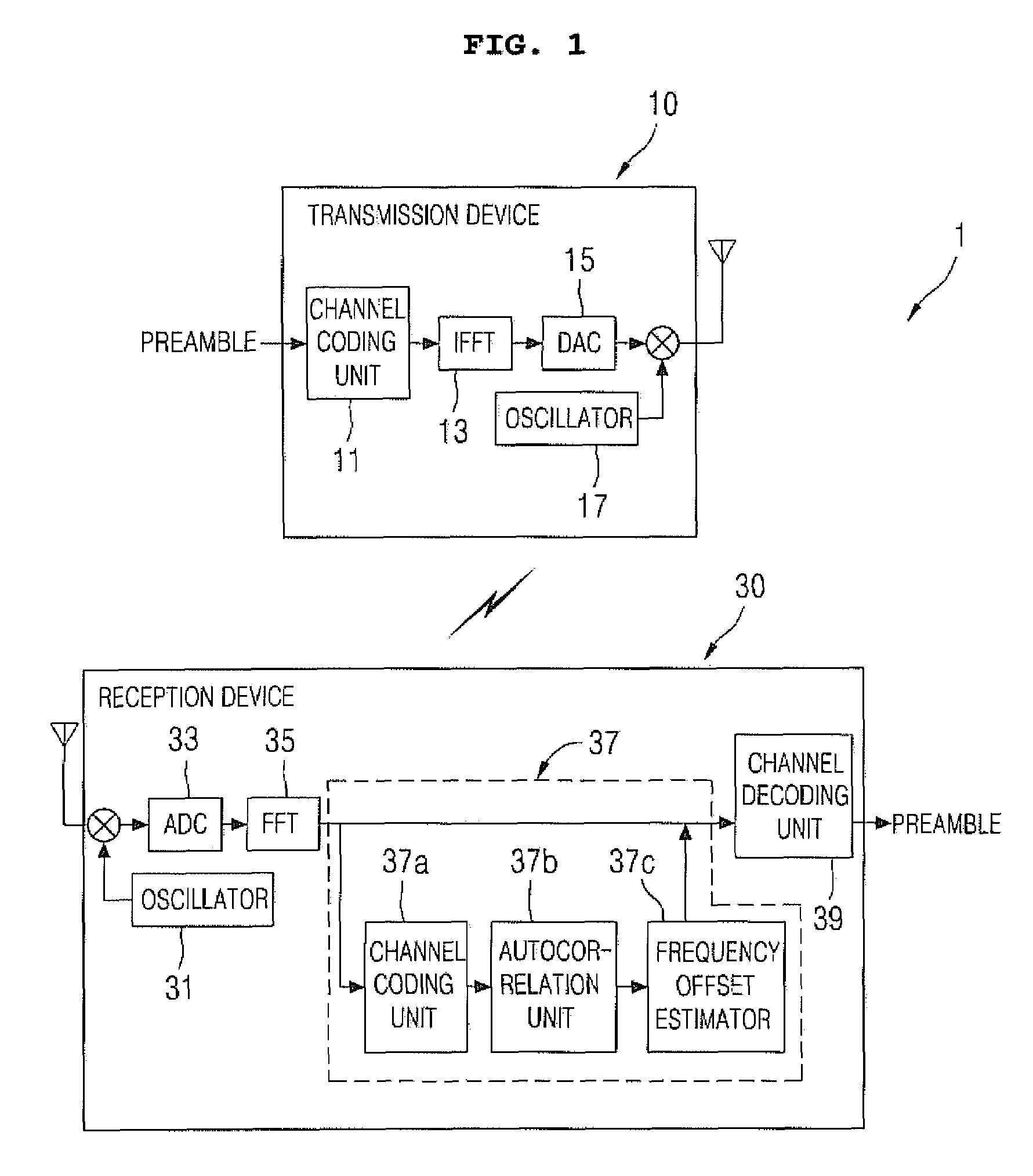
Joint estimation apparatus of channel and frequency offset based on multiband-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing and thereof
InactiveUS20090154625A1Reduce complexityPolarisation/directional diversityTransmission path divisionMulti bandMean square
The present invention relates, in general, to a joint channel and frequency offset estimation apparatus and method based on a multi-band-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system, and, more particularly, to a joint channel and frequency offset estimation apparatus and method based on an MB-OFDM system, which uses low-rank LMMSE channel estimation, in which a low-rank is applied to the MB-OFDM system, thus decreasing complexity, and adds a simple structure using the autocorrelation characteristics of an estimated channel, thus joining channel estimation to frequency offset estimation at low complexity.The apparatus includes a channel estimator for receiving a Fourier-transformed OFDM signal, and calculating results of channel estimation using a Linear Minimum Mean Square Error (LMMSE) channel estimation, which minimizes a Mean Square Error (MSE) between an actual channel value and an estimated channel value. An autocorrelation unit calculates an autocorrelation value using the results, which are calculated through the channel estimator, in which a frequency offset is considered. A frequency offset estimator calculates a frequency offset, having a maximum value calculated by the autocorrelation unit, and estimating an actual frequency offset.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
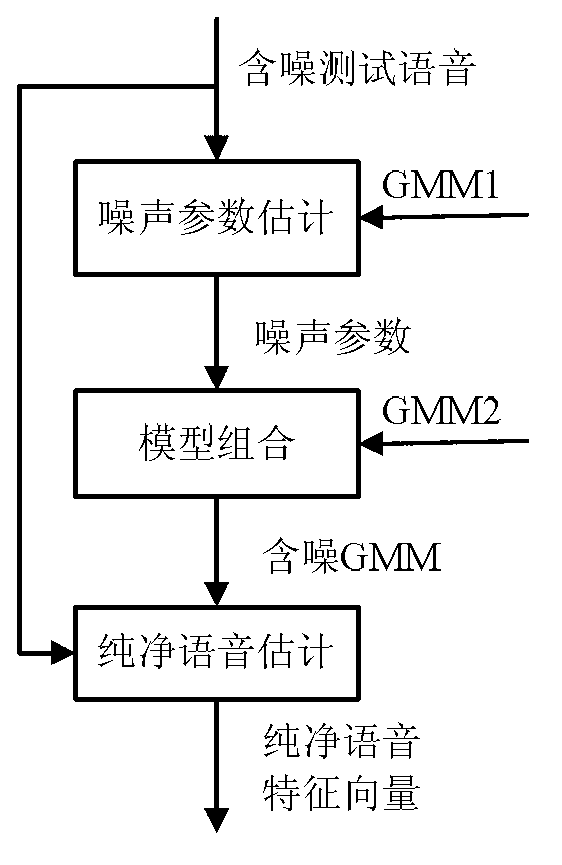
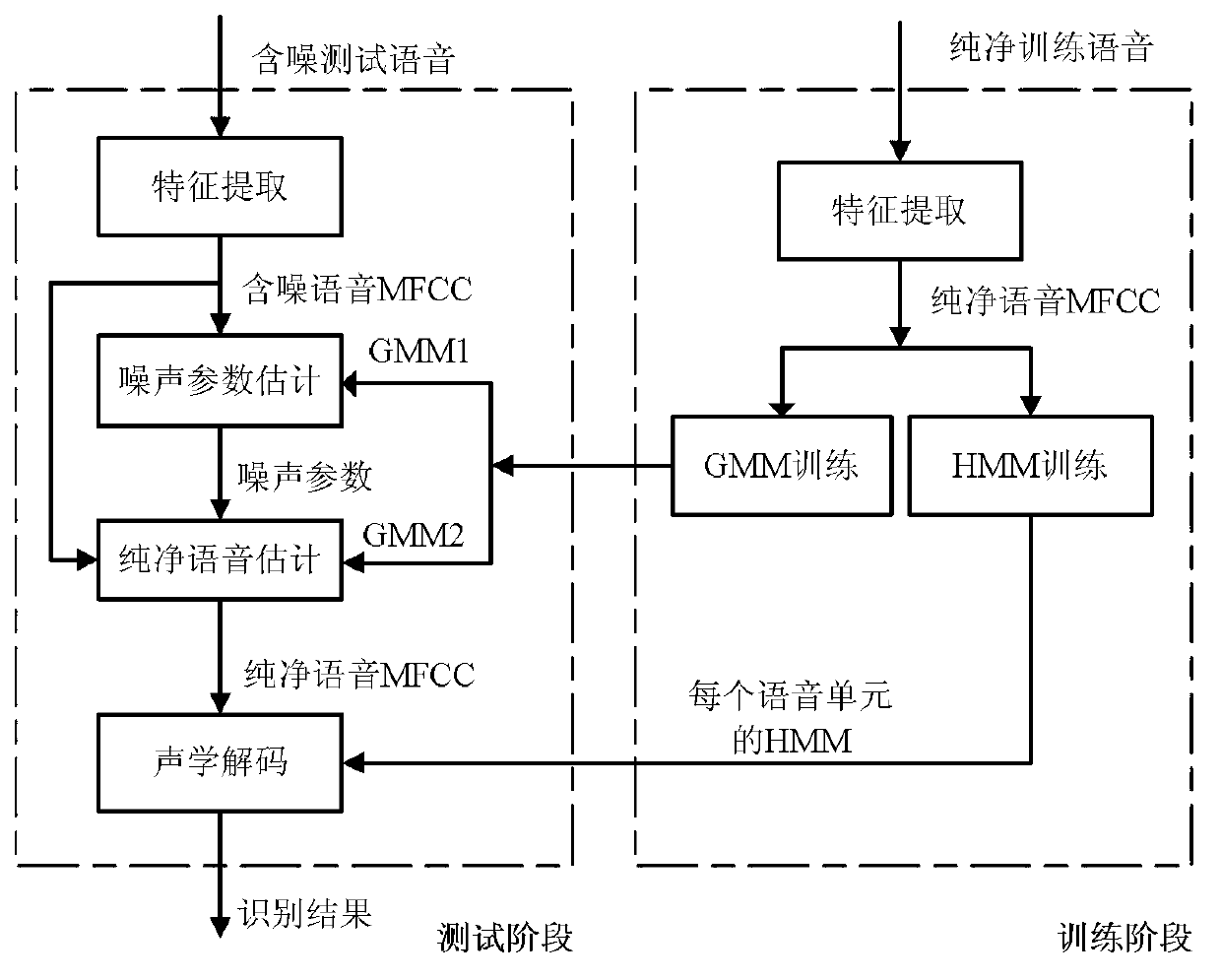
Feature compensation method based on rapid noise estimation in speech recognition system
InactiveCN103000174AGuaranteed accuracySmall amount of calculationSpeech recognitionFeature vectorSpeech identification
The invention discloses a feature compensation method based on rapid noise estimation in a speech recognition system. The method is characterized in that noise parameter estimation in the feature compensation is separated from pure speech estimation, and noise estimation and pure speech estimation are achieved through different Gaussian mixture models (GMMs). A GMM containing less Gaussian units is used for extracting noise parameters from a noisy tested speech; another GMM containing more Gaussian units is used for being combined with an estimated single Gaussian noise model to obtain a noisy GMM matched with the current test environment; and finally the noisy GMM is used for calculating the posterior probability of the noisy tested speech and the pure speech feature vector is estimated from the noisy tested speech through the minimum mean square error method. According to the method, estimation accuracy of the pure speech can be guaranteed while the calculated amount is reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
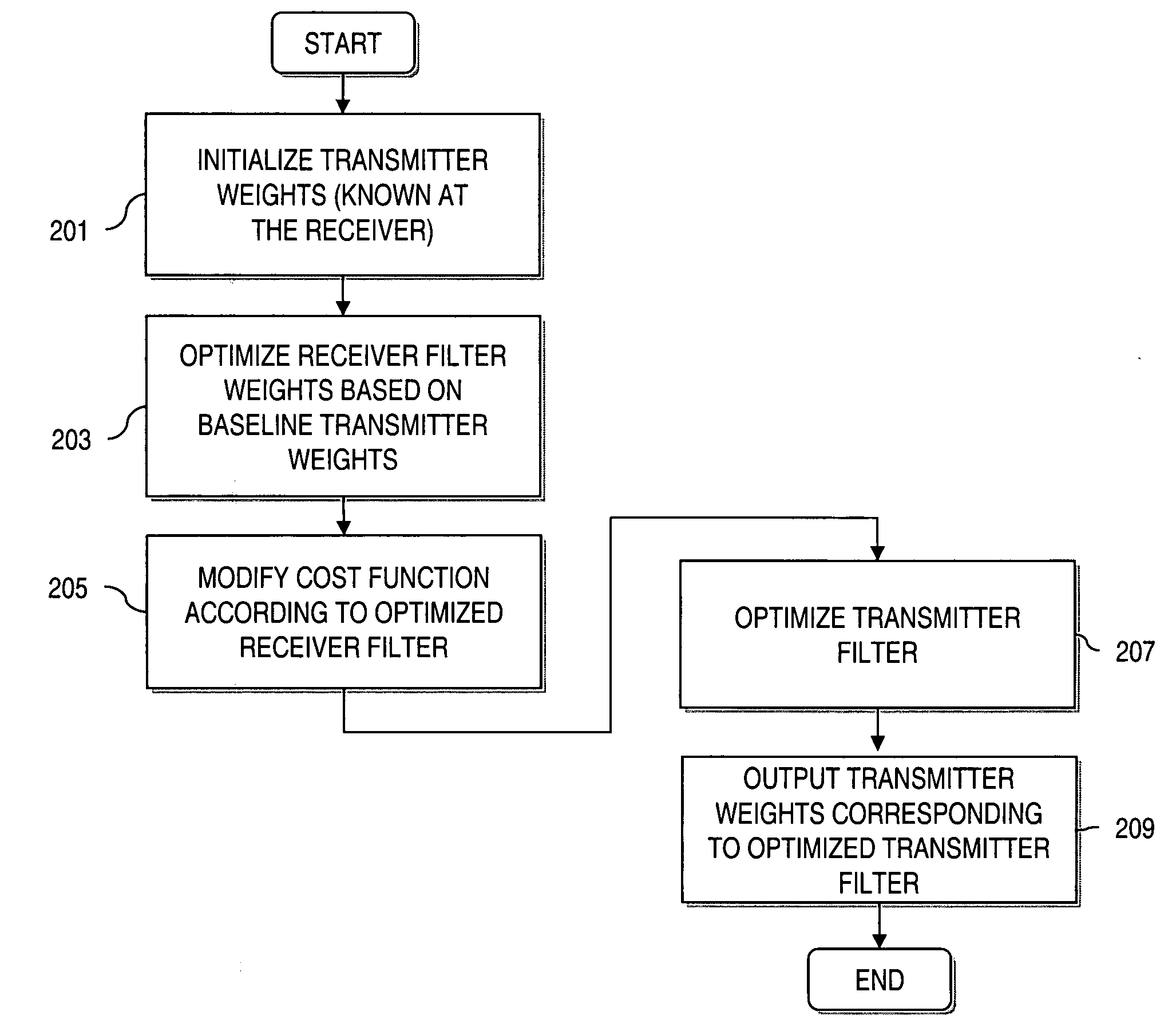
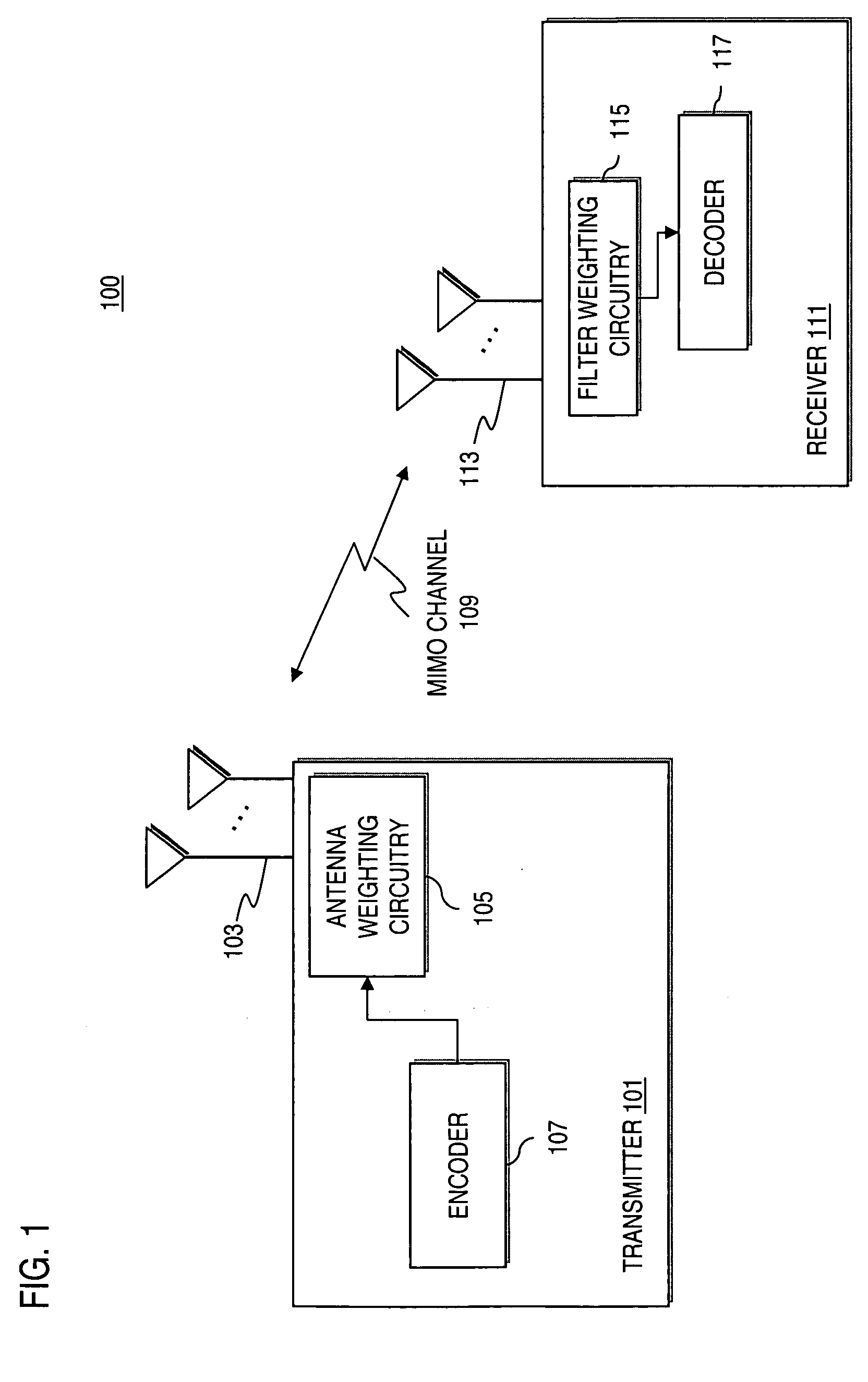
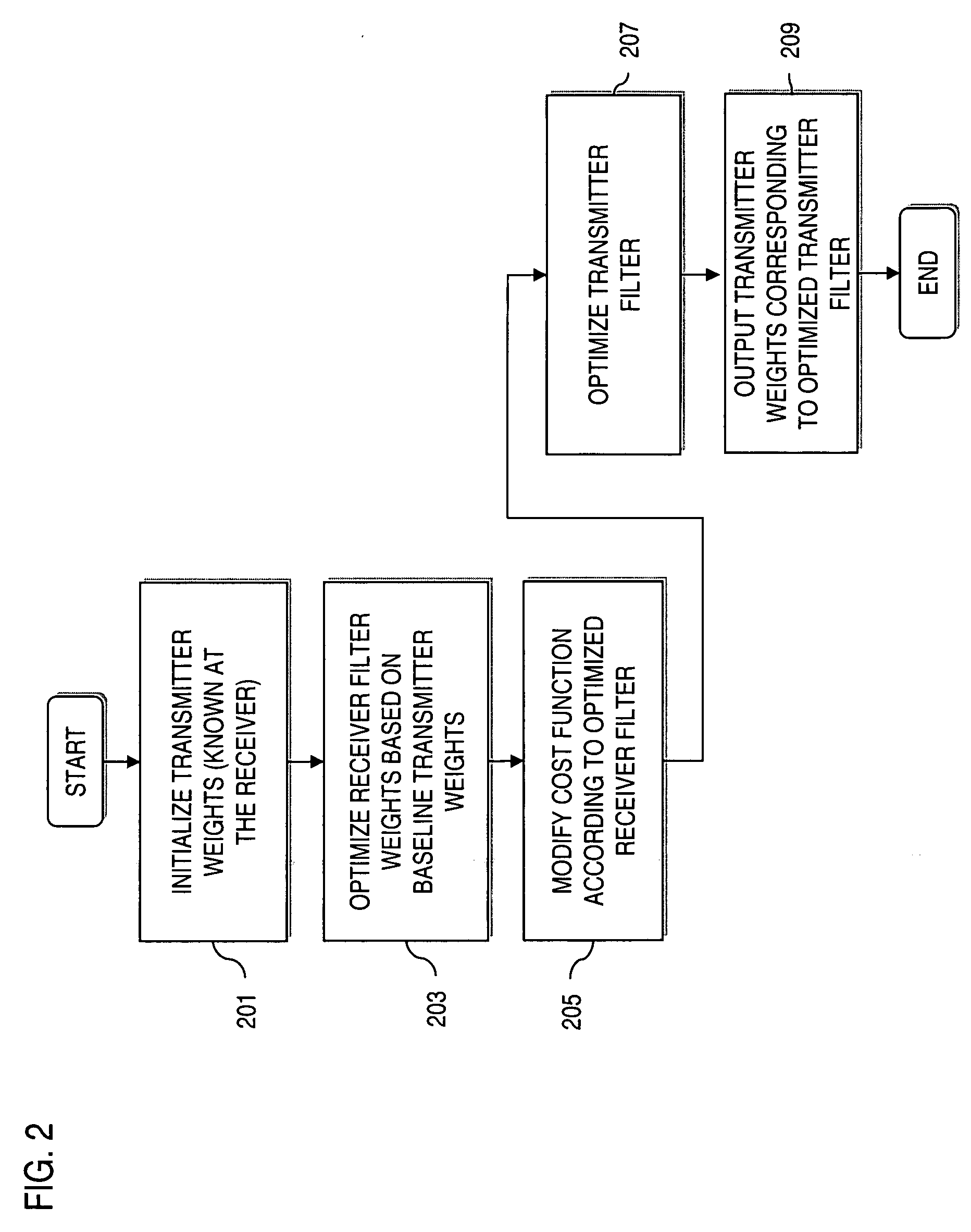
Method and apparatus for estimating transmit weights for multiple antennas
InactiveUS20060146953A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionCommunications systemEngineering
An approach for determining antenna weights in a multiple antenna communication system is provided. The approach jointly optimizes the transmitter weights and the receiver filter. A filter of a receiver (e.g., Linear Minimum Mean Square Error (LMMSE)) is optimized using initial weight values of the transmit antennas. The cost function, which is a mean-squared of a difference between a transmitted signal and an estimated signal, is then modified according to the optimized receiver filter. A transmit filter is then optimized according to the modified cost function. The above approach advantageously can obtain antenna weights when the condition of separability of paths does not exist.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
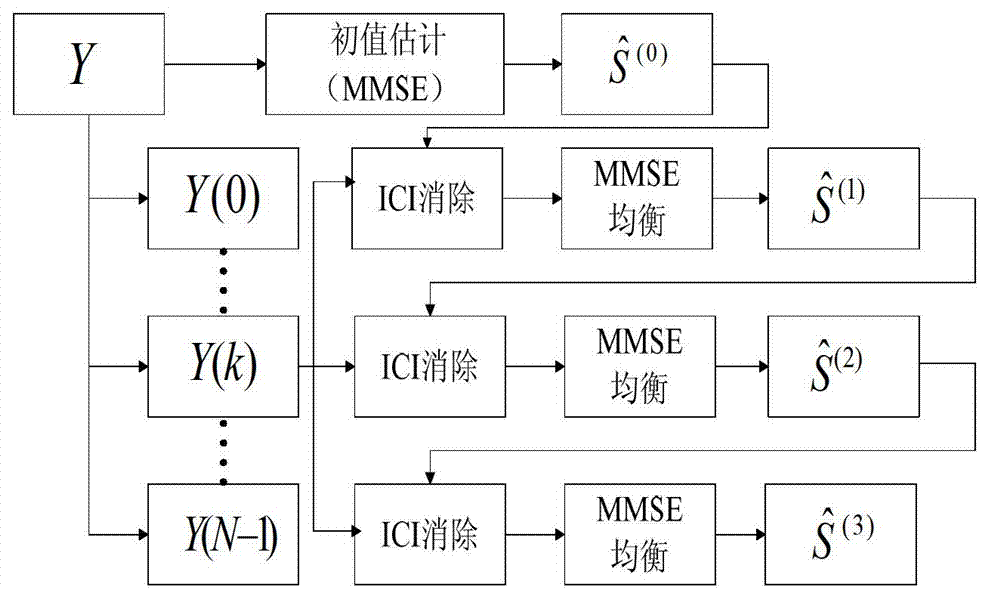
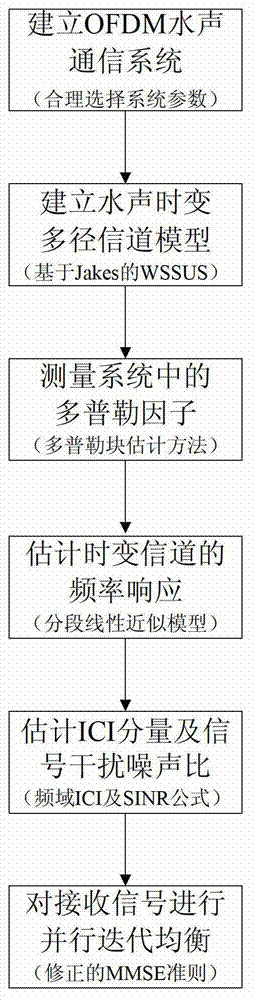
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) underwater acoustic communication parallel iterative inter-carrier interference (ICI) elimination method
InactiveCN103095639ARobust response to time-varying speed changesPrevent inversionMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCarrier signalEngineering
The invention aims at providing an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) underwater acoustic communication parallel iterative inter-carrier interference (ICI) elimination method. The method includes the steps of building an OFDM underwater acoustic communication system, building an acoustic time varying multipath channel model, measuring Doppler factors in the system, estimating frequency response of a time varying channel, estimating an ICI component and a signal interference noise ratio (SINR), and carrying out parallel iterative minimum mean square error (MMSE) equilibrium to received signals. Through combination of a linear approximation method and the MMSE method, and through iteration to improve performance, the parallel iterative ICI elimination method is inducted into the OFDM underwater acoustic communication system, and the method can effectively resist the ICI generated under the underwater acoustic time varying channel, and the OFDM underwater acoustic communication system is steady in response to the change of channel time varying speed. Therefore, inverse operation of a high order matrix is avoided, complexity of the method is reduced, and arithmetic speed is improved.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Method and apparatus for robust two-stage OFDM channel estimation
ActiveUS20150229493A1Improve accuracyLess complexError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
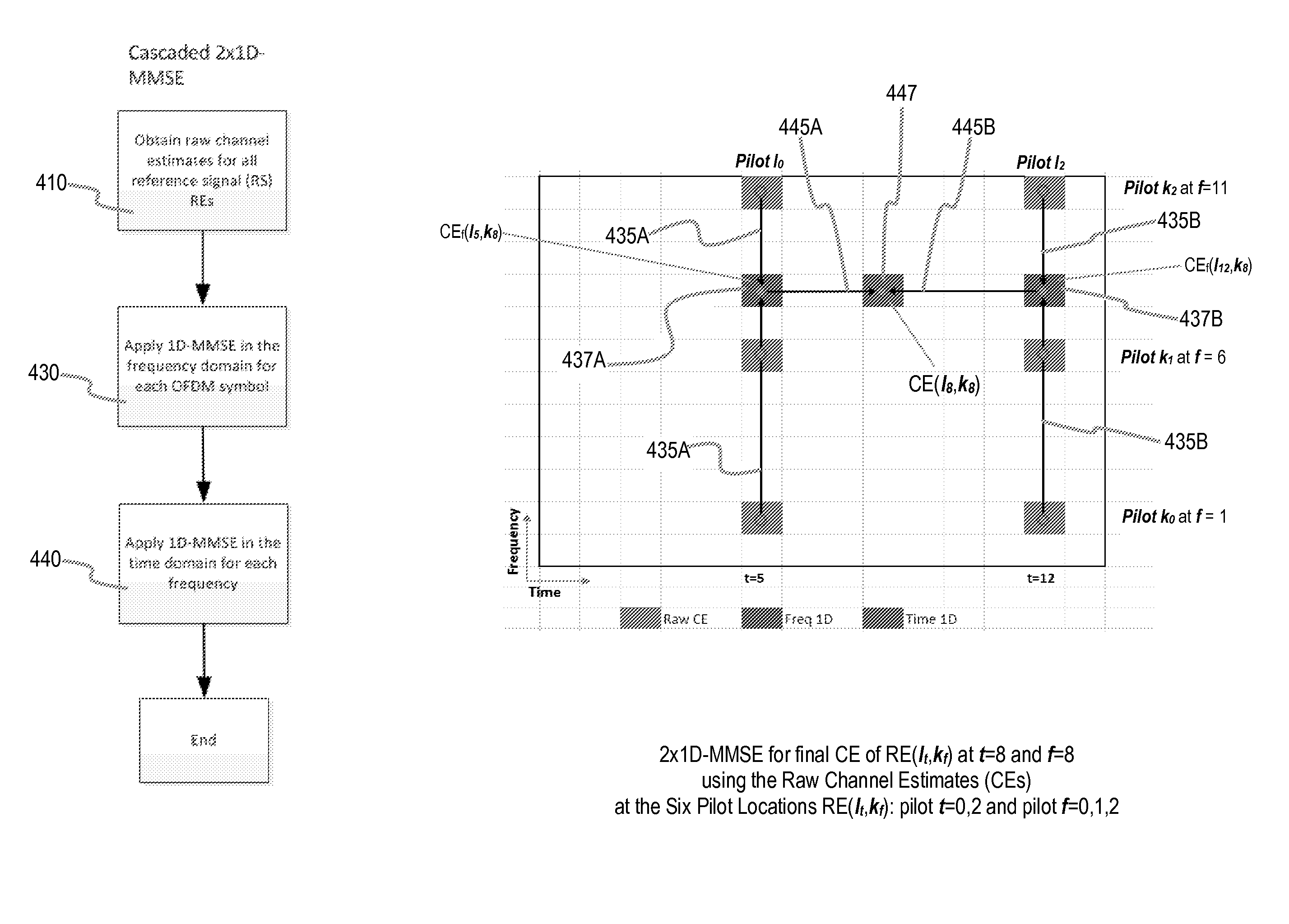
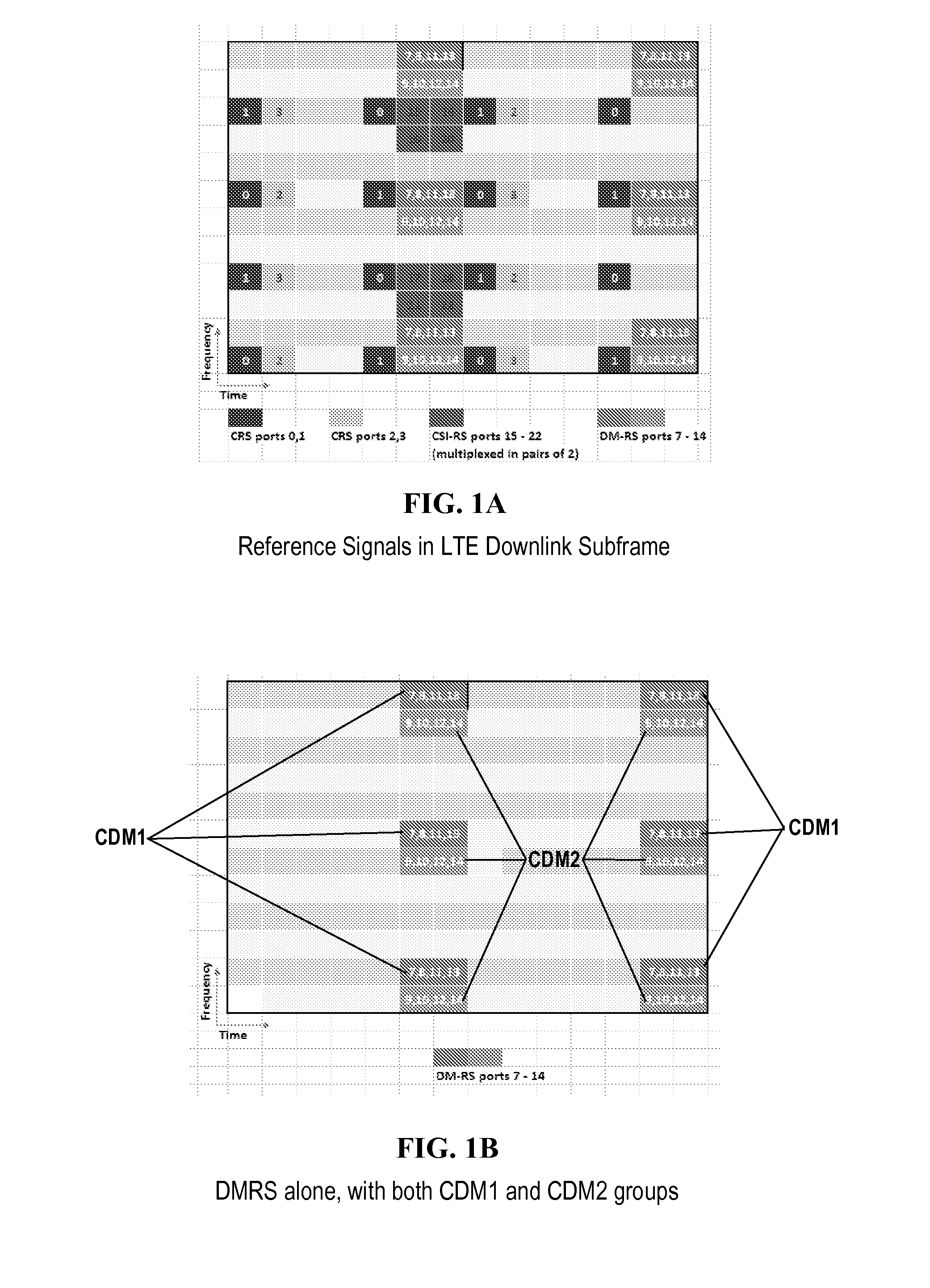
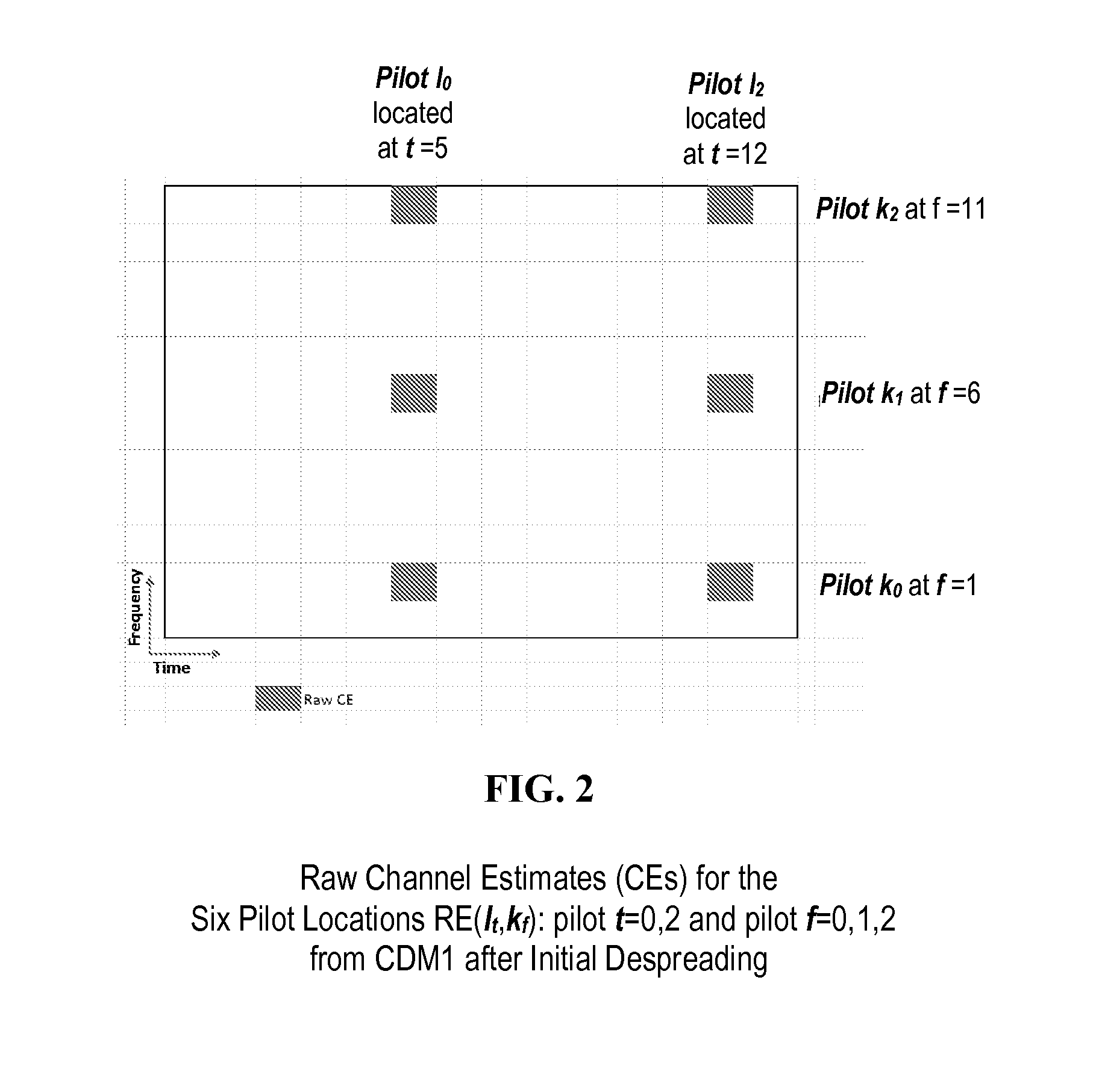
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for improved channel estimation in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system are discussed. In one example discussed herein, joint two-dimensional Minimum Mean-Square Error (2D-MMSE) channel estimation is performed on any Resource Element (REs) containing a reference signal in a Resource Block (RB), one-dimensional Minimum Mean-Square Error (1D-MMSE) channel estimation is performed in the frequency domain on each OFDM symbol in the RB, and then channel estimation is performed in the time domain on each frequency sub-carrier in the RB. In another example discussed herein, Power Delay Profiles (PDPs) and / or frequency correlations are calculated using minimax optimization and then stored in a Look-Up Table (LUT) indexed by estimated Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) and the estimated maximum delay spread. A portable device could use such an LUT in MMSE calculations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
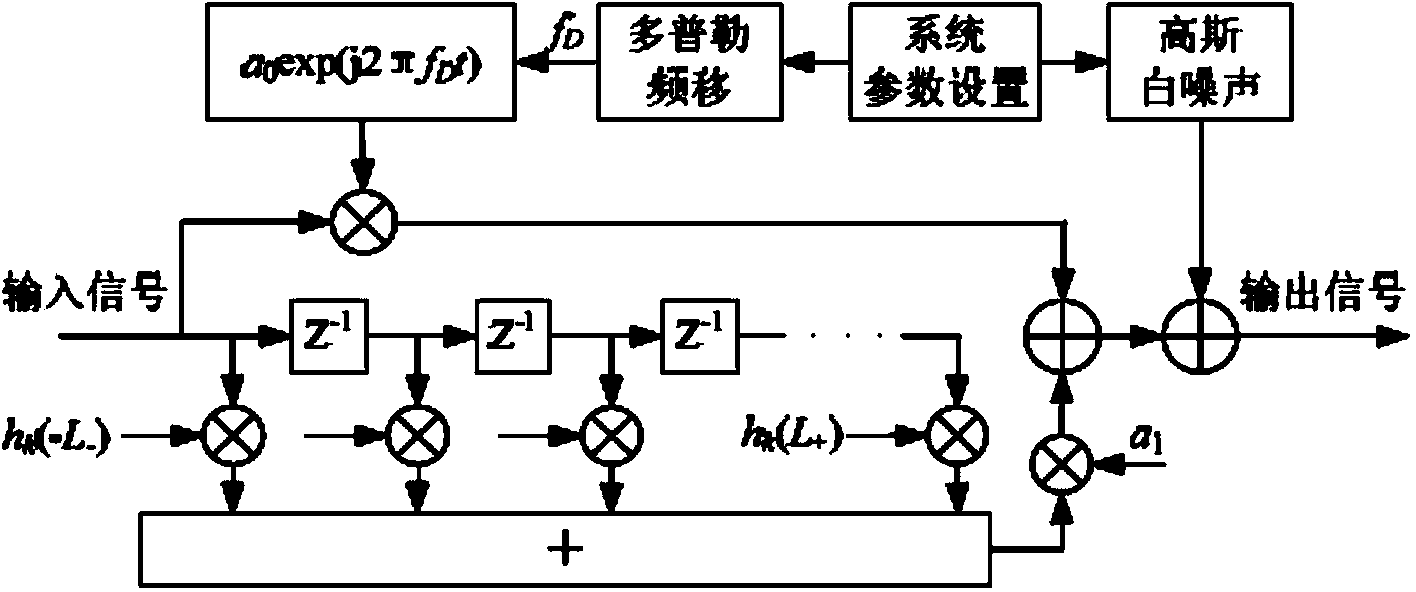
Doppler-compensated radar pulse compression processing system and method
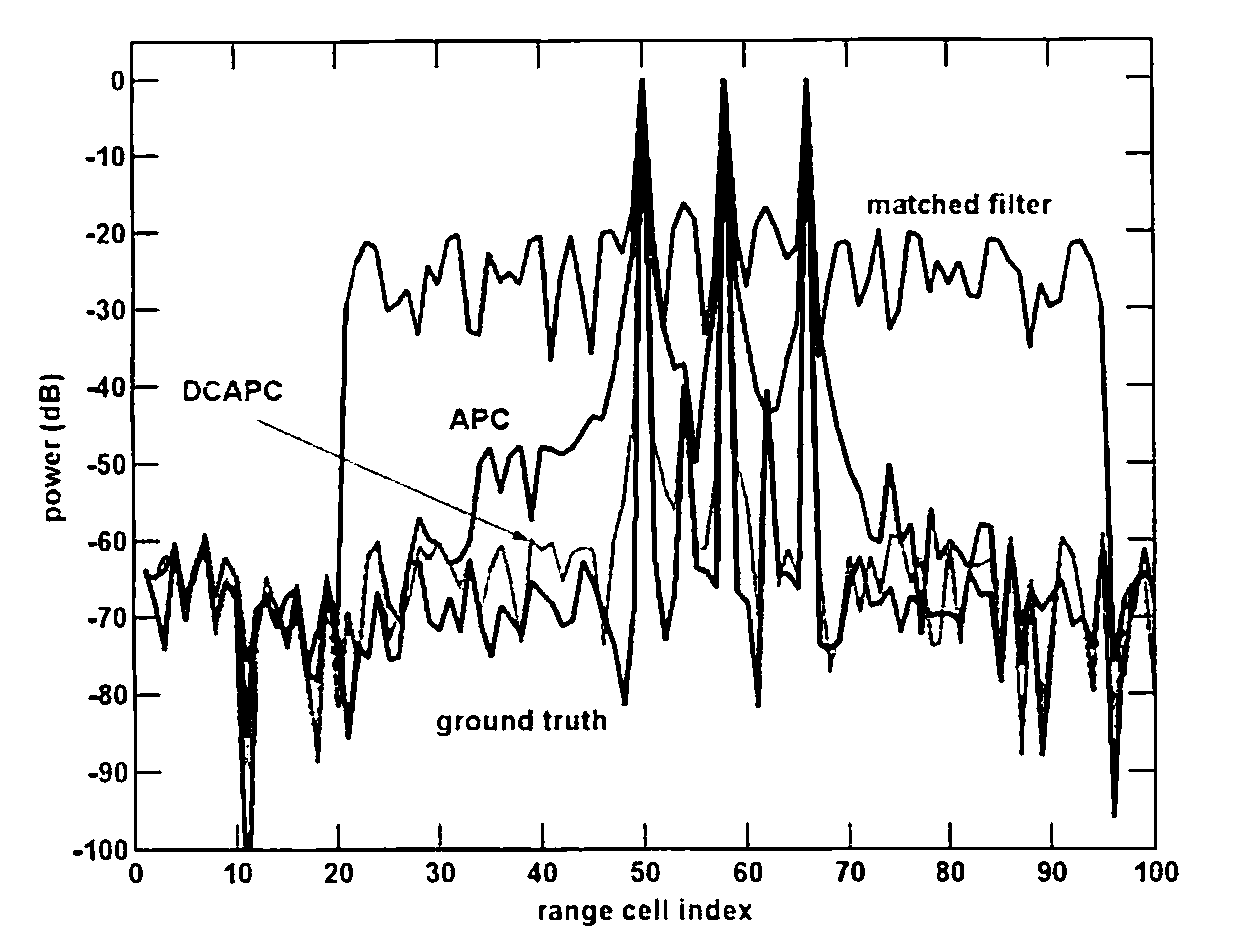
A radar receiver system includes a receiver, a processor including a Doppler Compensated Adaptive Pulse Compressor (DCAPC) algorithm, possible other intermediate processing and a target detector. The DCAPC algorithm processes samples of a radar return signal, applies Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE), or alternatively matched filtering, to the radar return signal to obtain initial radar impulse response estimates, computes power estimates, estimates a range cell Doppler shift for each range cell, computes range-dependent filters, applies the MMSE filters, and then repeats the cycle for subsequent reiterative stages until a desired length−L range window is reached, thereby resolving the scatterer from noise and other scatterers.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Broadband cognitive radio frequency spectrum detection method based on parallelly compressed sensing
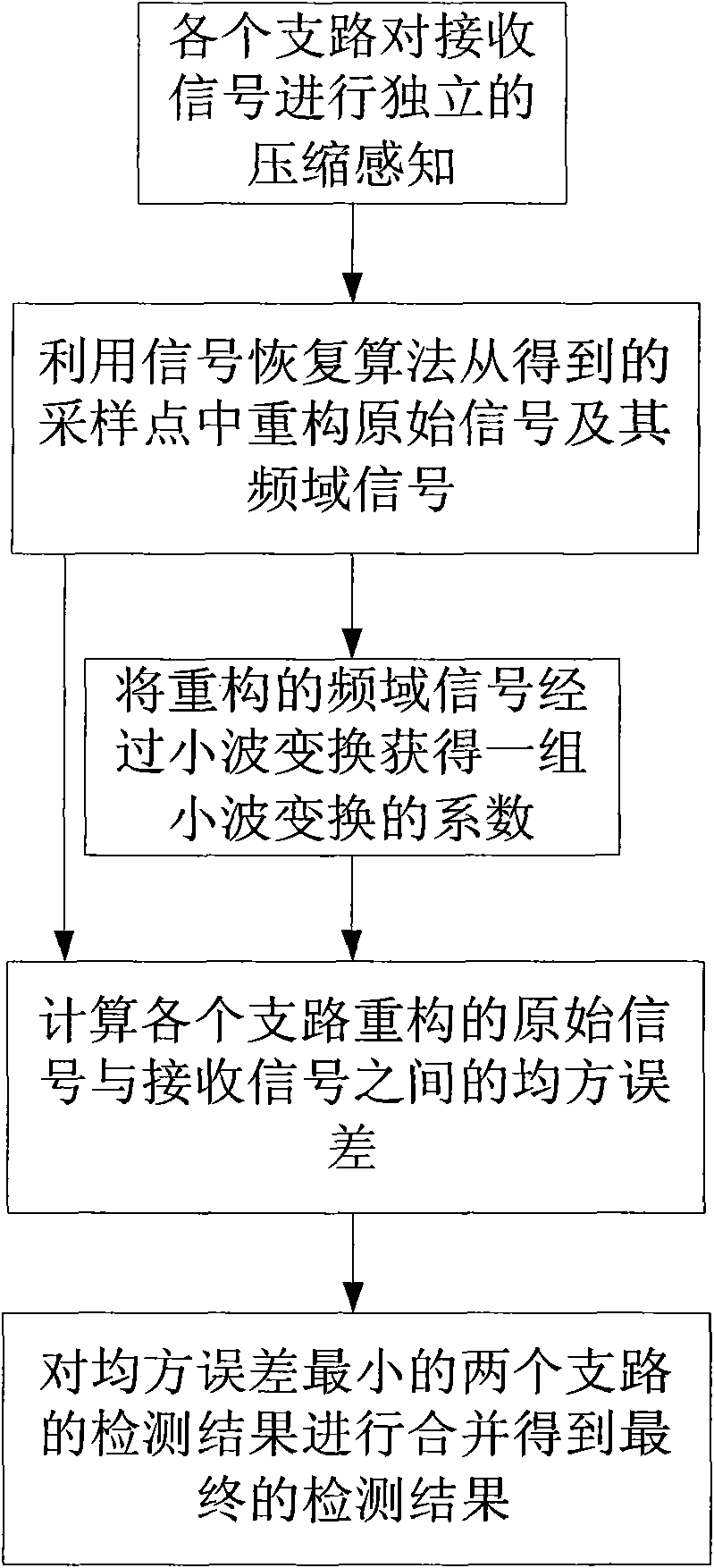
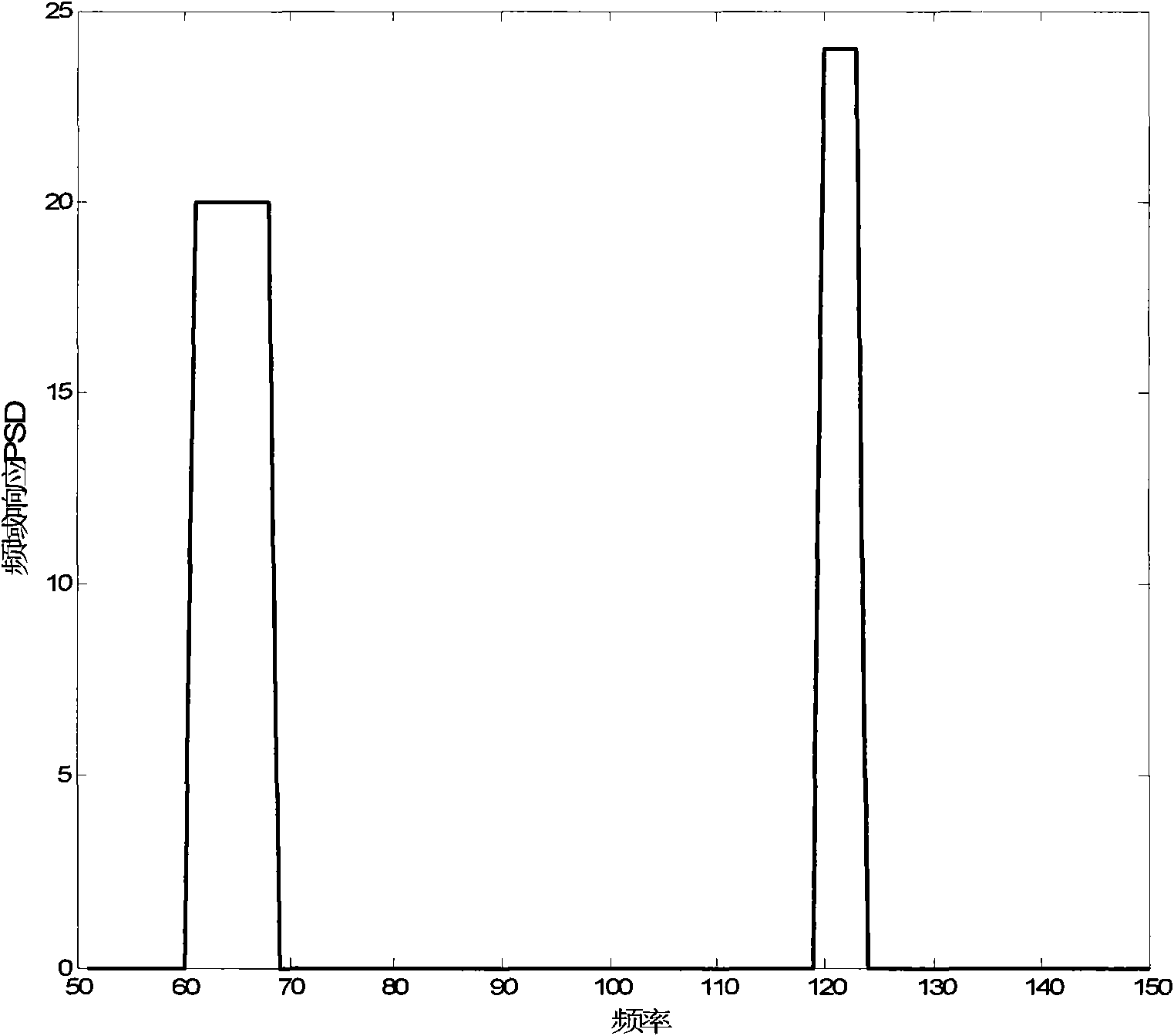
InactiveCN101630982ALower requirementDownsamplingTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumMean square
The invention discloses a broadband cognitive radio frequency spectrum detection method based on parallelly compressed sensing. The realization process is as follows: using each parallel subcircuit of a frequency spectrum detector to carry out independent compressed sensing on received signals to obtain a group of random sampling points of each subcircuit; using single restoration algorithm to reconstruct original signals and frequency domain signals thereof in the obtained sampling points; carrying out wavelet transformation on the reconstructed frequency domain signals to obtain a group of wavelet transformation coefficients; calculating the mean square error between the reconstructed original signals of each subcircuit and the received signals; multiplying the wavelet transformation coefficients of two subcircuits with the minimum mean square error and taking the maximum value to obtain the position of each sub-band, and taking the reconstructed frequency domain signal of the subcircuit with the minimum mean square error as the reconstructed frequency domain signal for final output to finish the detection of the cognitive radio frequency spectrum. The invention can reduce noiseand the influence of randomness of the sampling points, thus improving the probability of correct detection.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Satellite communication timing synchronization error detection method based on full-digital receiving
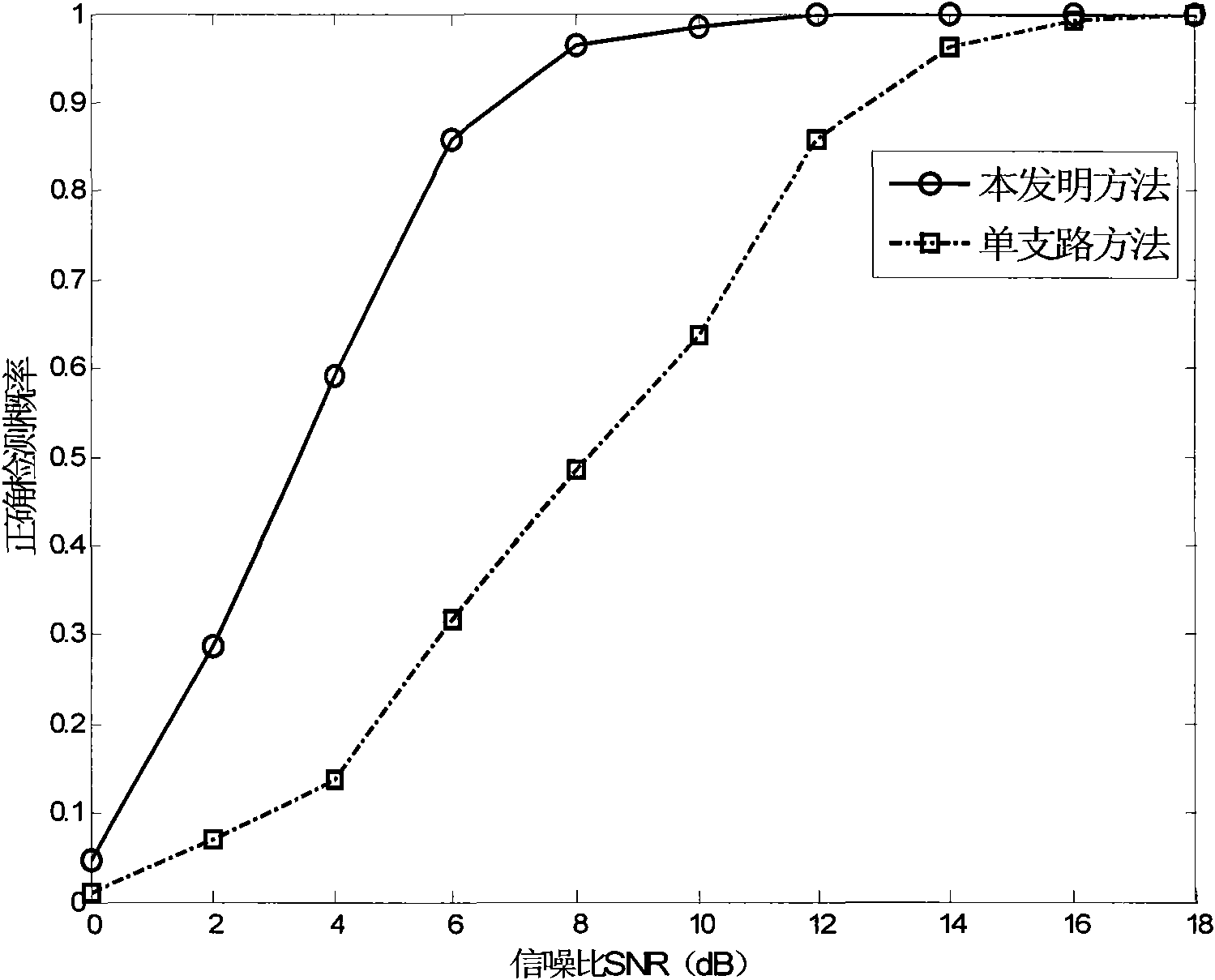
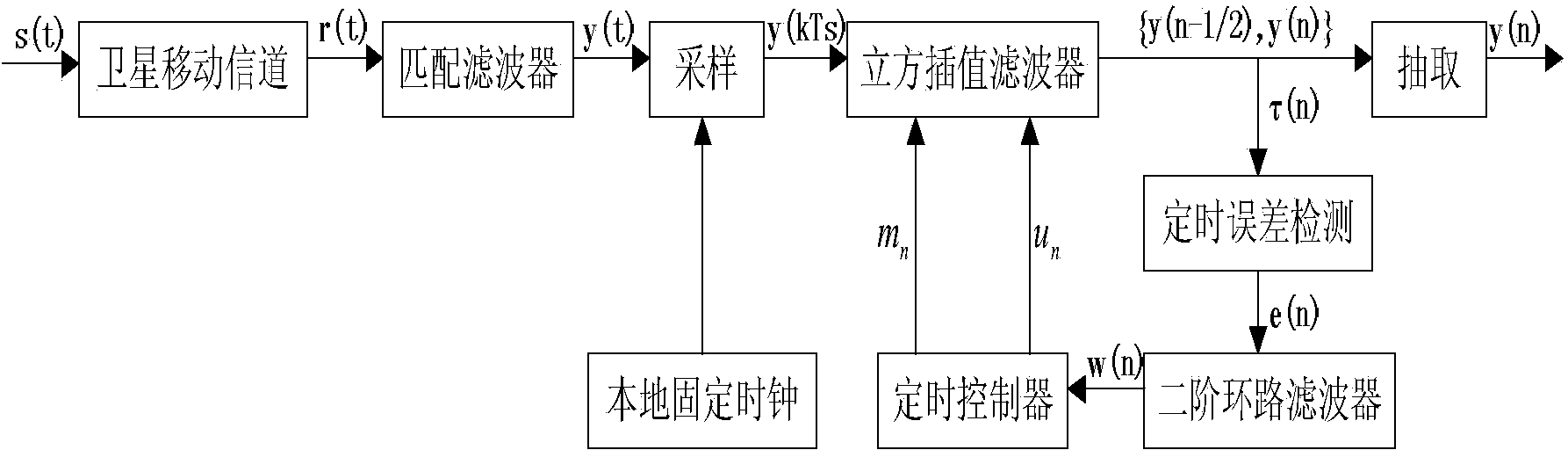
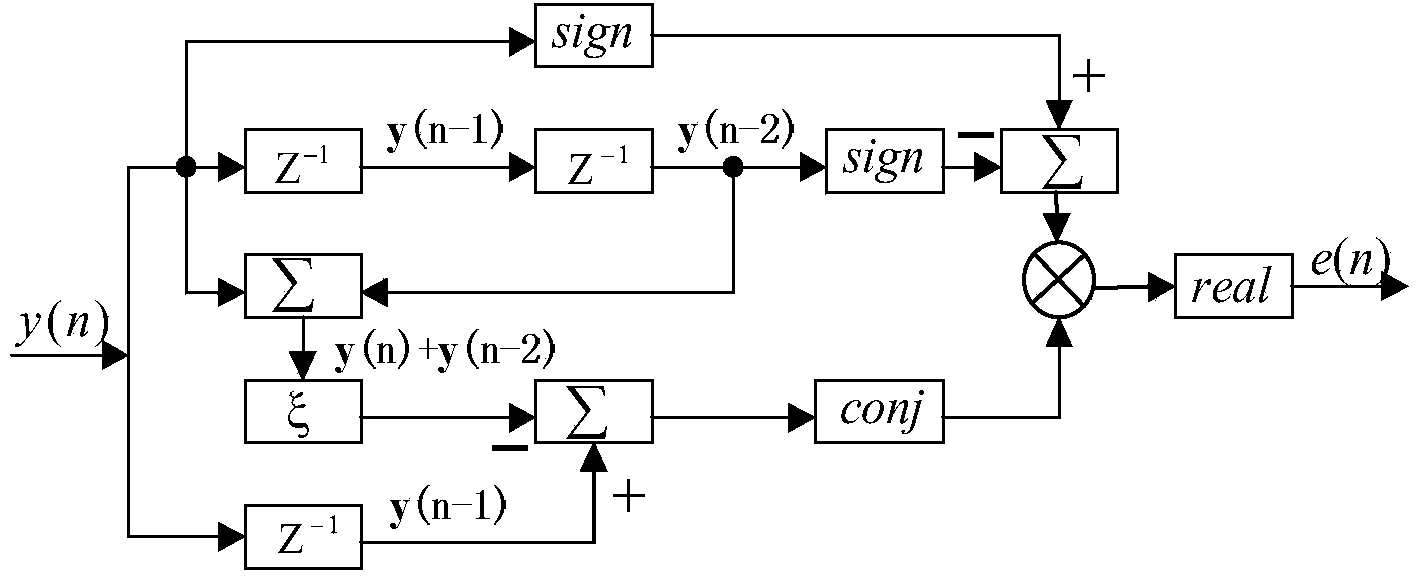
ActiveCN103457680AEliminate timing error skewEasy to lockReceivers monitoringSynchronising arrangementTime informationCoded element
Disclosed is a satellite communication timing synchronization error detection method based on full-digital receiving. In view of wide application of a Gardner algorithm in a timing synchronization loop and the limitation of the Gardner algorithm to band-limited signals, when polarity jump happens to two adjacent symbols, after two adjacent code elements are utilized for cosine roll-off forming filtering, the relation between samples of two best sampling points and the sample of a middle point of the two best sampling points is utilized, the effect of different adjacent symbols to the middle value is firstly taken into consideration and the effect value is calculated according to the minimum mean-square error criterion, and is then eliminated; when polarity jump does not happen to the adjacent symbols, how to reduce self noise generated by the situation that timing information can not be acquired is taken into consideration. A sign function sign (.) in an E-Gardner algorithm is utilized to solve the problem. Under the satellite channel environment, the enhancing algorithm is simple in structure, under the condition of a small roll-off coefficient, the performance of QPSK modulating signal clock capturing and error detection is improved, and the satellite communication timing synchronization error detection method based on full-digital receiving can effectively eliminate self-noise and reduce system resource consumption.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com