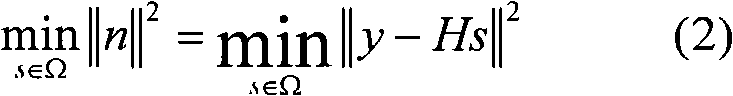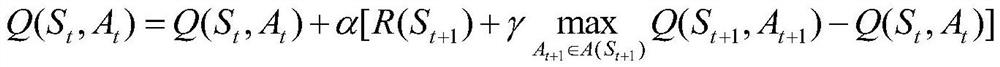Patents
Literature
58 results about "Q-matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, a Q-matrix is a square matrix whose associated linear complementarity problem LCP(M,q) has a solution for every vector q.
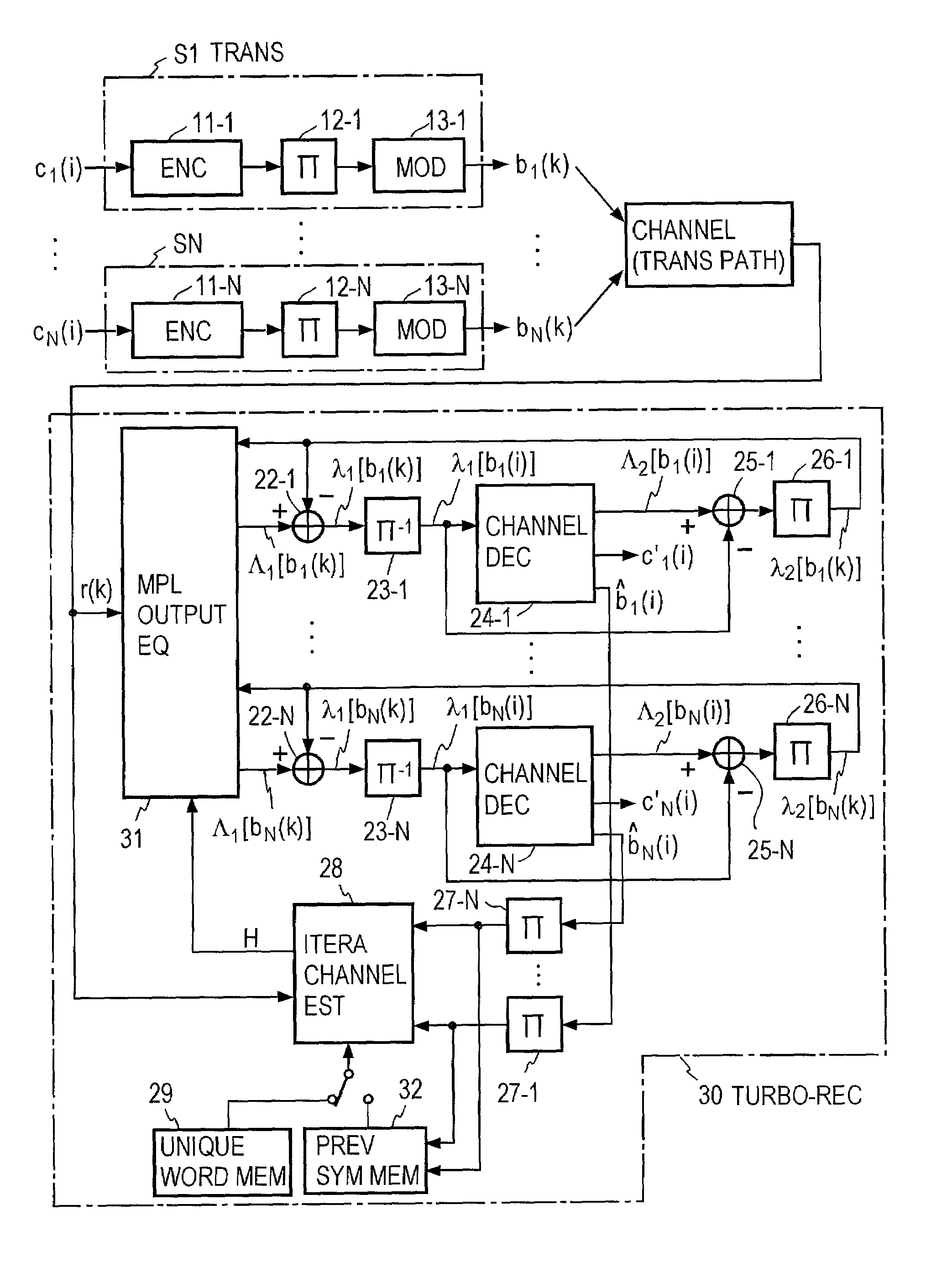
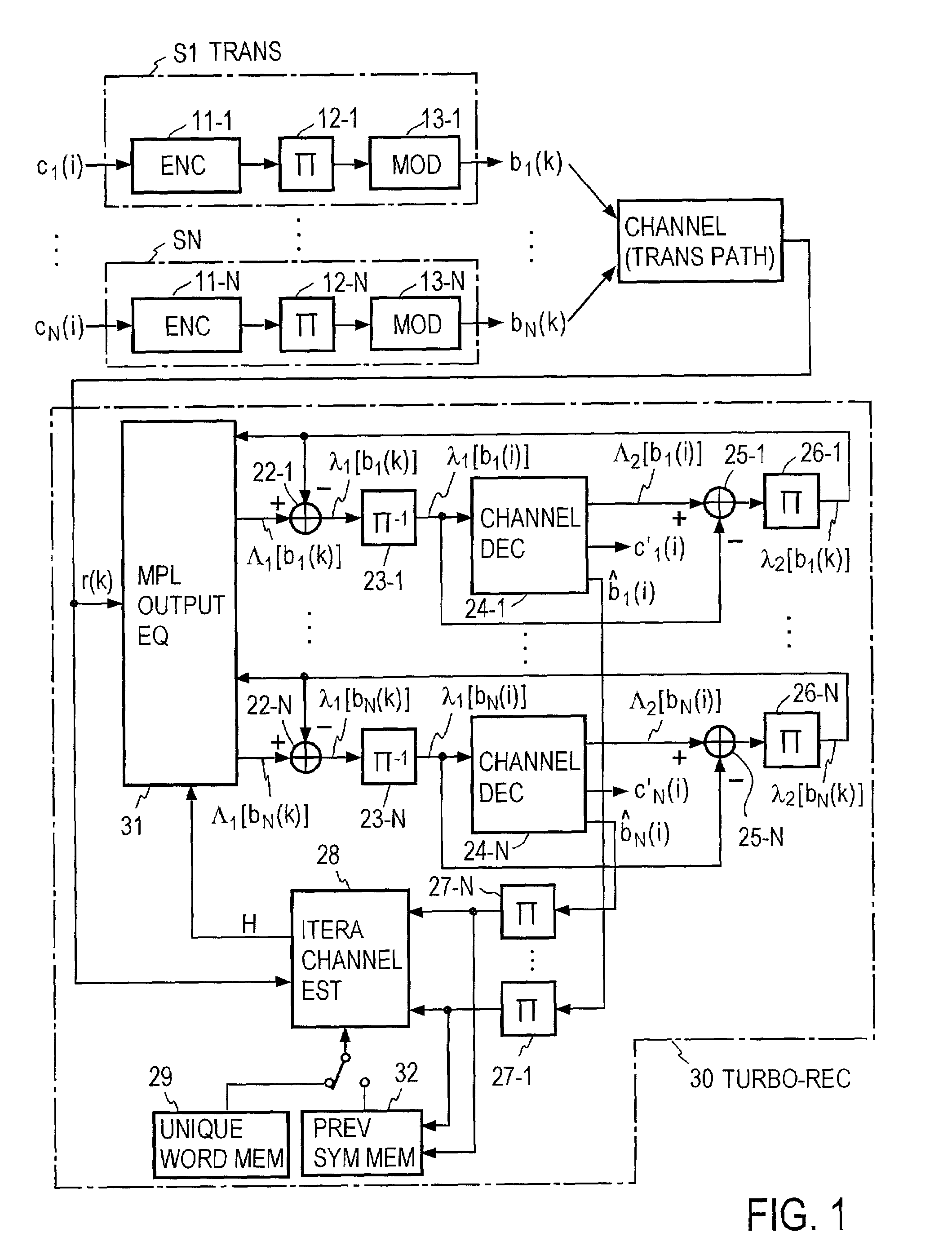
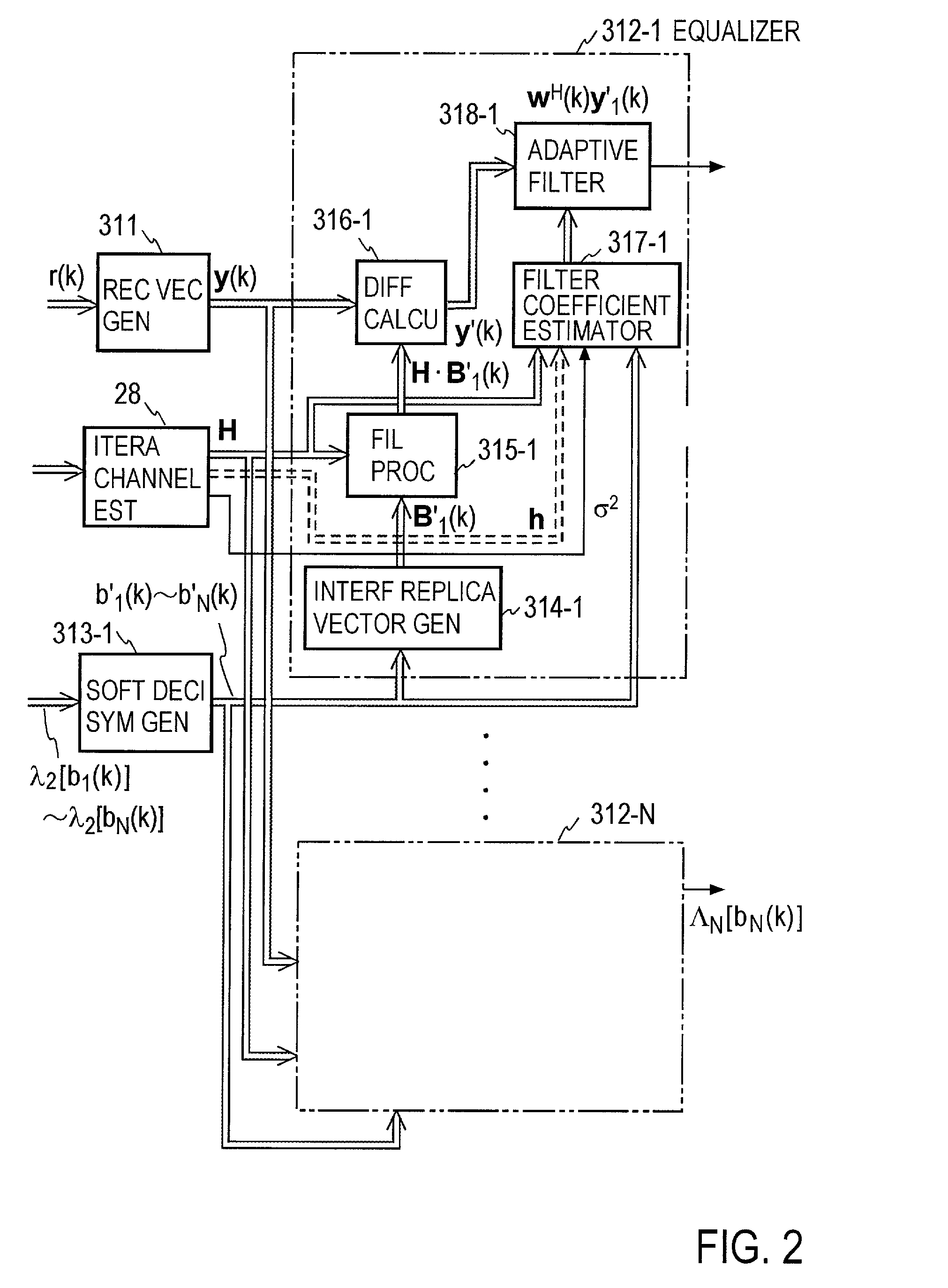
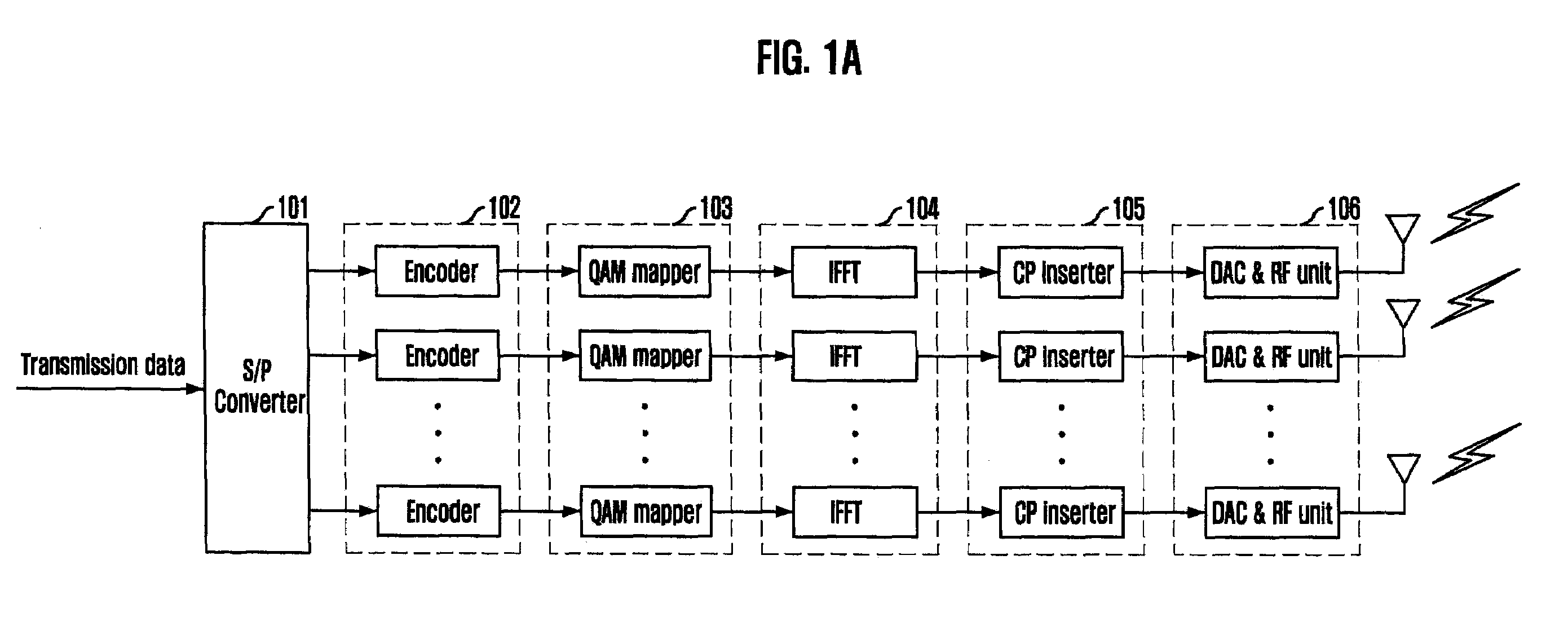
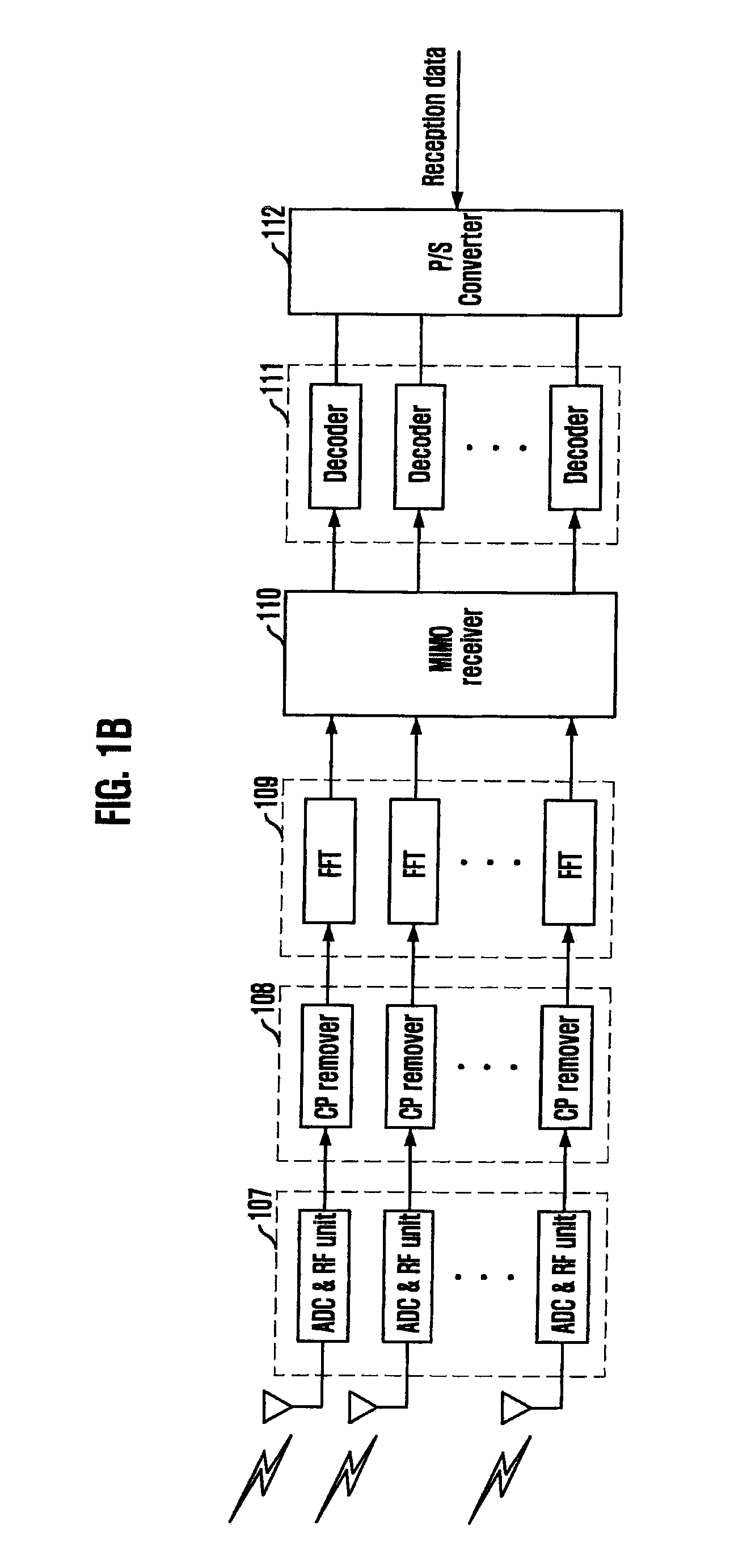
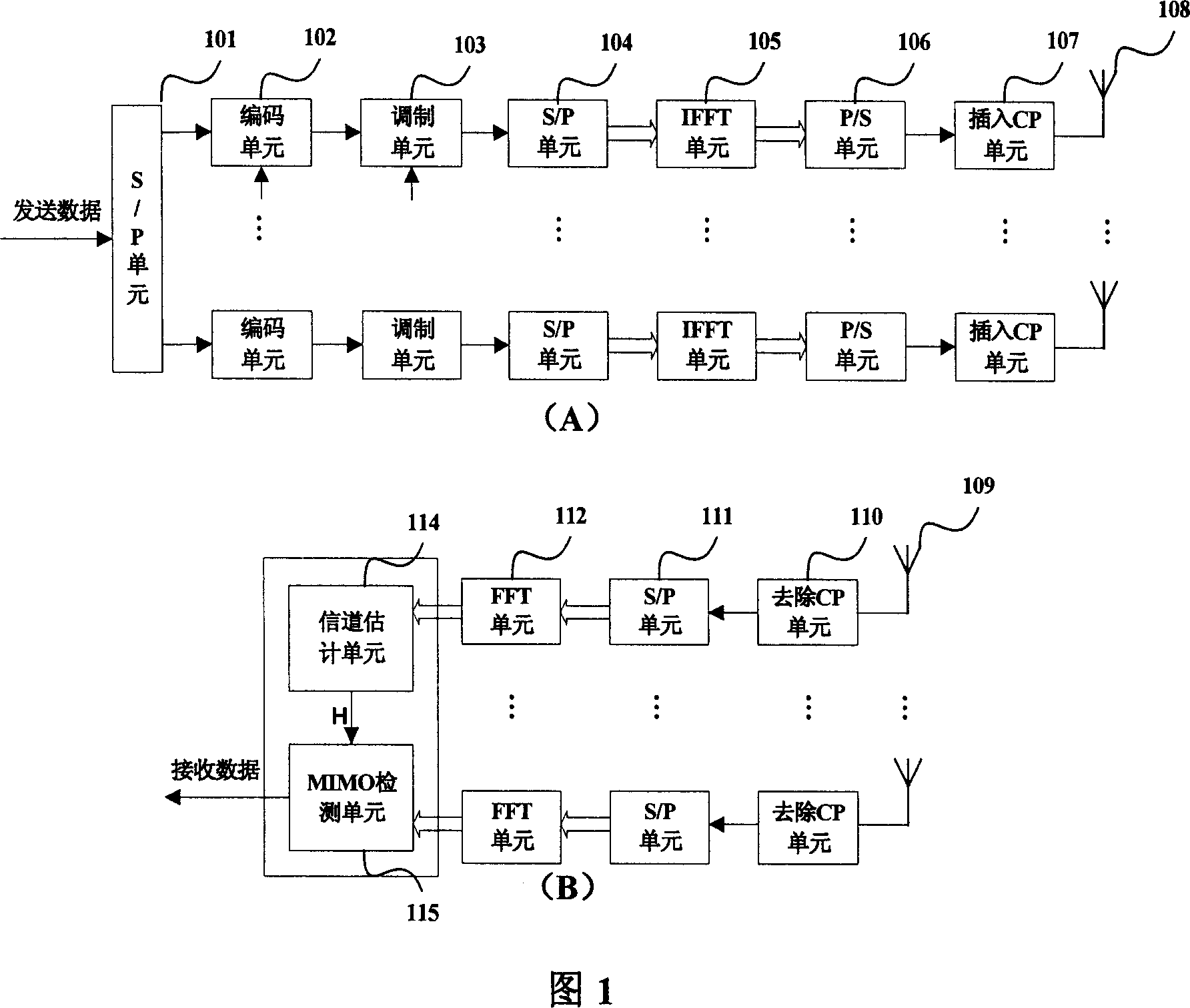
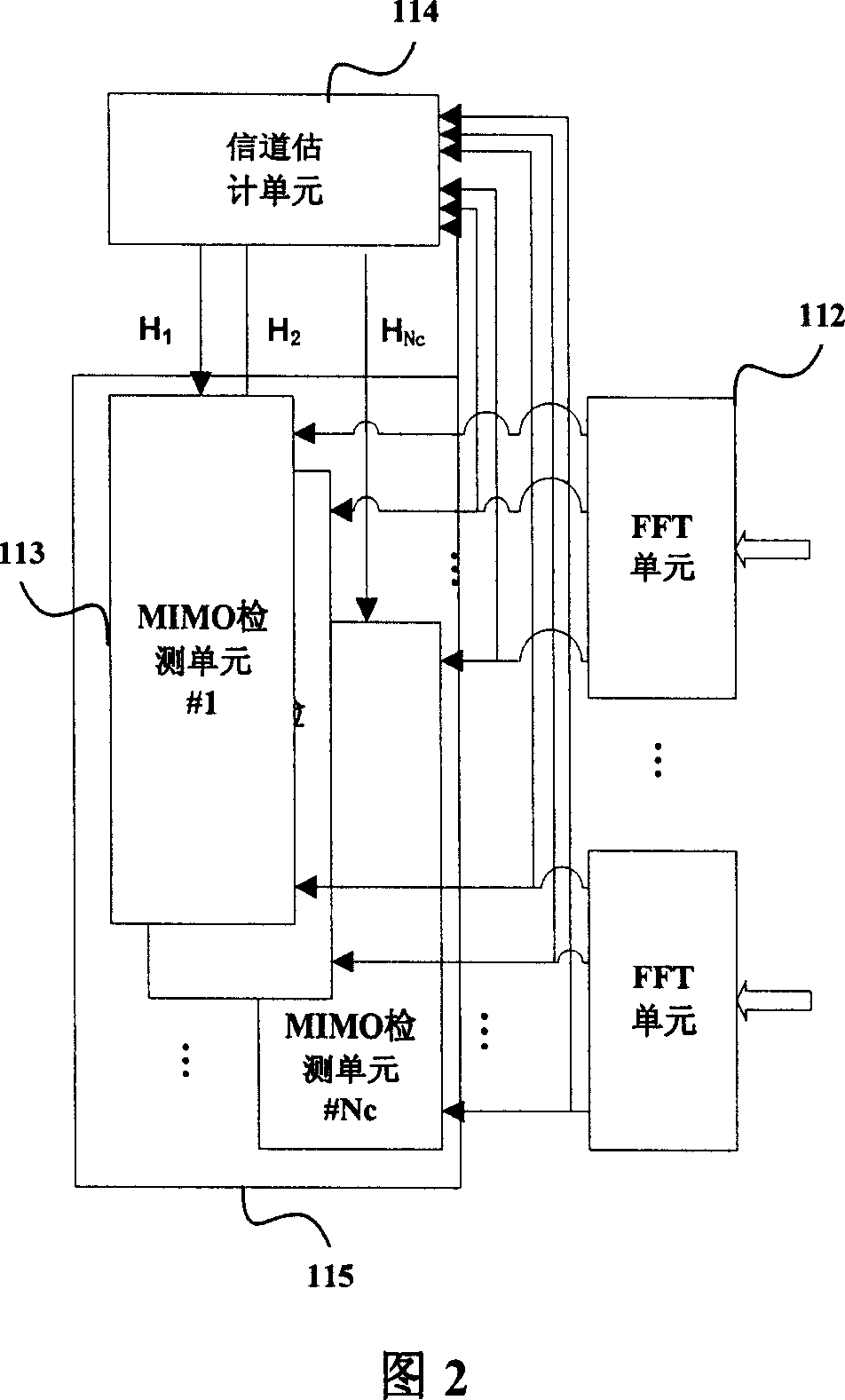
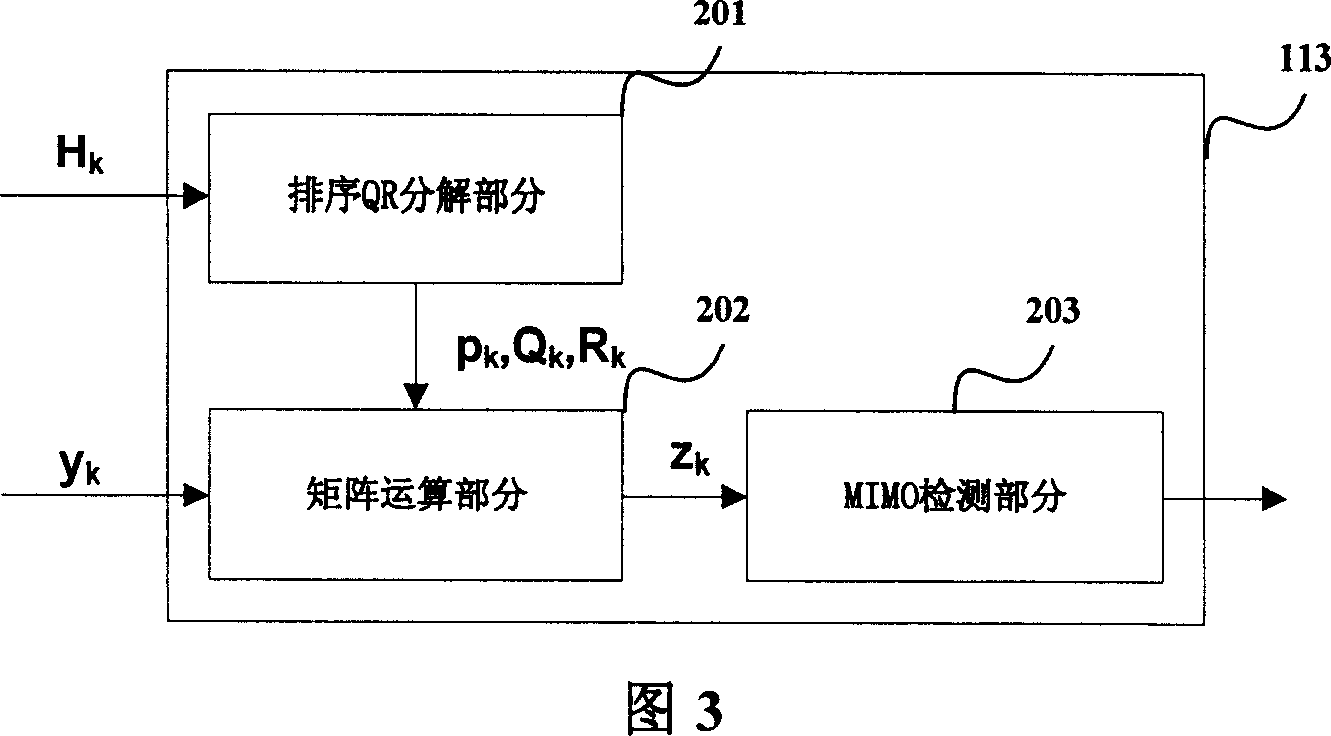
Turbo-reception method and turbo-receiver
InactiveUS7027533B2Improve accuracyData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionQ-matrixResidual interference
An impluse response hmn(q) of each transmission path is estimated from N received signals rm (m=1, . . . , M) and a known signal (for a number of users equal to N, n=1, . . . , N). M×N matrix H (q) having hmn(q) as an element and a Q×Q matrix H having H(q) as an element are determined (where Q represents a number of multipaths of each transmitted wave and q=0, . . . , Q−1). A soft decision value b′n(k) is determined from decoded λ2 [bn(k)], and this is used to generate an interference component matrix B′(k) to generate an interference replica H·B′(k). The interference replica H·B′(k) is subtracted from a received matrix y(k) to determine y′(k). y(k) and H are used to determine an adaptive filter coefficient wn(k) to be applied to an n-th user in order to eliminate residual interference components in y′(k) according to the minimum mean square error criteria. y(k) is passed through wn(k) to provide a log-likelihood ratio as a received signal from the user n from which interferences are eliminated.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
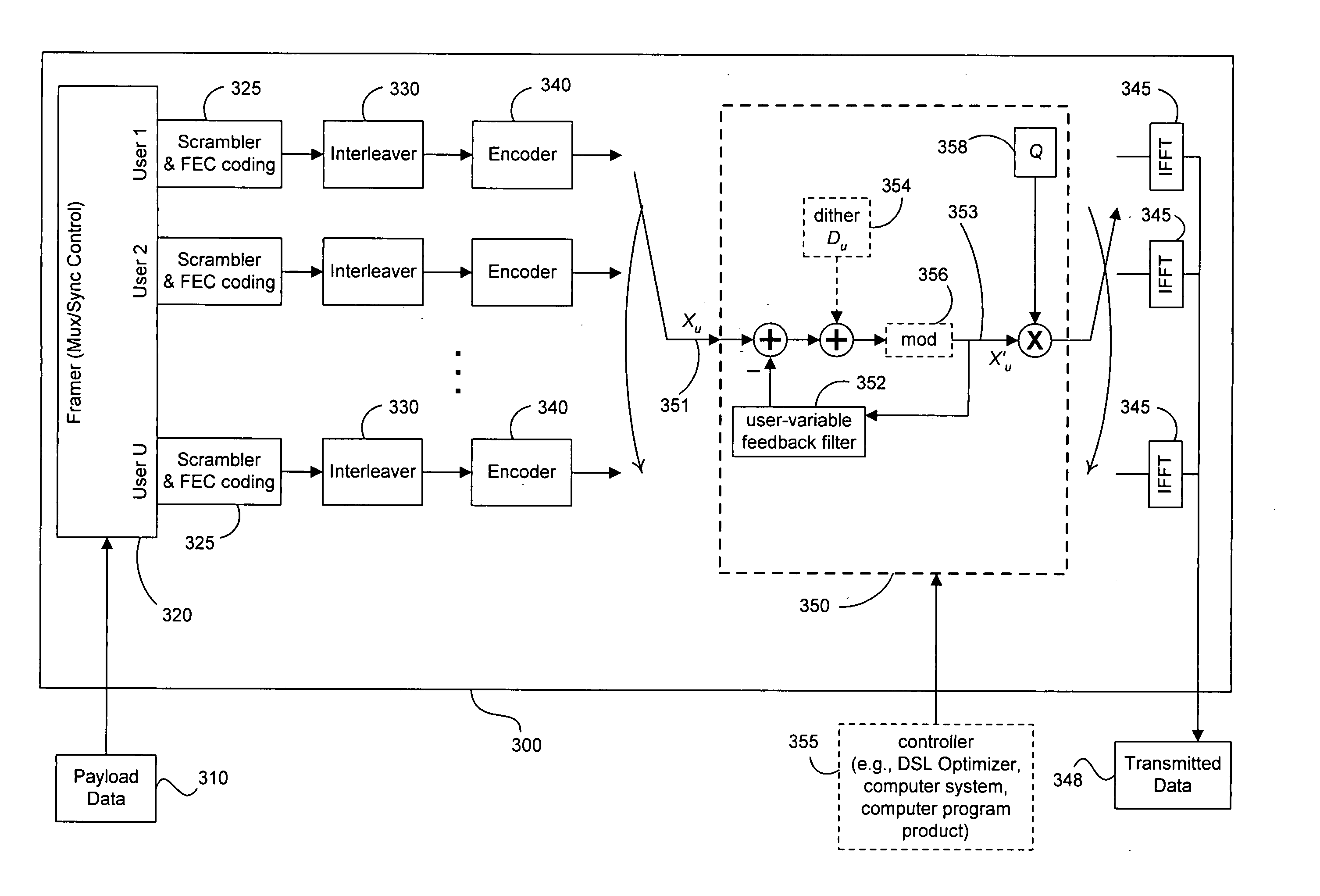
Tonal precoding
ActiveUS20060274825A1Mitigate and remove interference signalReduce removalDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationQ-matrixPrecoding
Precoding mitigates or removes interference signals (especially crosstalk) among multiple users with interconnected transmitters in vectored DSL systems and the like. Efficient implementation is provided of the R matrix in RQ factorization that characterizes multi-user downstream vector channels (such as DMT VDSL one-sided or two-sided transmission channels). A set of precoder coefficients can vary with each tone used by each user and depend upon the encoding order of users selected for each tone. In adaptive operation, the coefficients of the R and Q matrices can be updated when changes occur to the transmission environment. Variable modulo arithmetic mitigates the power-enhancement problem, and the base of modular arithmetic also can vary with each user within a single precoder for a single tone. The user order of preceding need not be the same on each tone, and the modular arithmetic progression may thus also be different on each tone because multi-user situations create an unusual situation for precoding in that the modulo arithmetic used for each user can be different (thus imposing a larger power increase) and because digital duplexed or synchronized DMT systems can separately implement a precoder for each tone. Further, the precoding process terminates each DMT symbol, after processing up to the total number of users. An optional dither signal, known to both transmitter and receiver, can be added at the transmit side and removed at the receiver side to smooth the precoding process and ensure that aberrations in the transmitted constellation size and characteristics are consistent despite any unusual variations in the feedback signal that exits the feedback filter matrix G before being subtracted from the user signal of interest. Some embodiments use a “subtraction only” mode while other embodiments use a dither signal and / or modulo arithmetic, though embodiments of the present invention do not require use of identical constellations by both transmitter and receiver.
Owner:ADAPTIVE SPECTRUM & SIGNAL
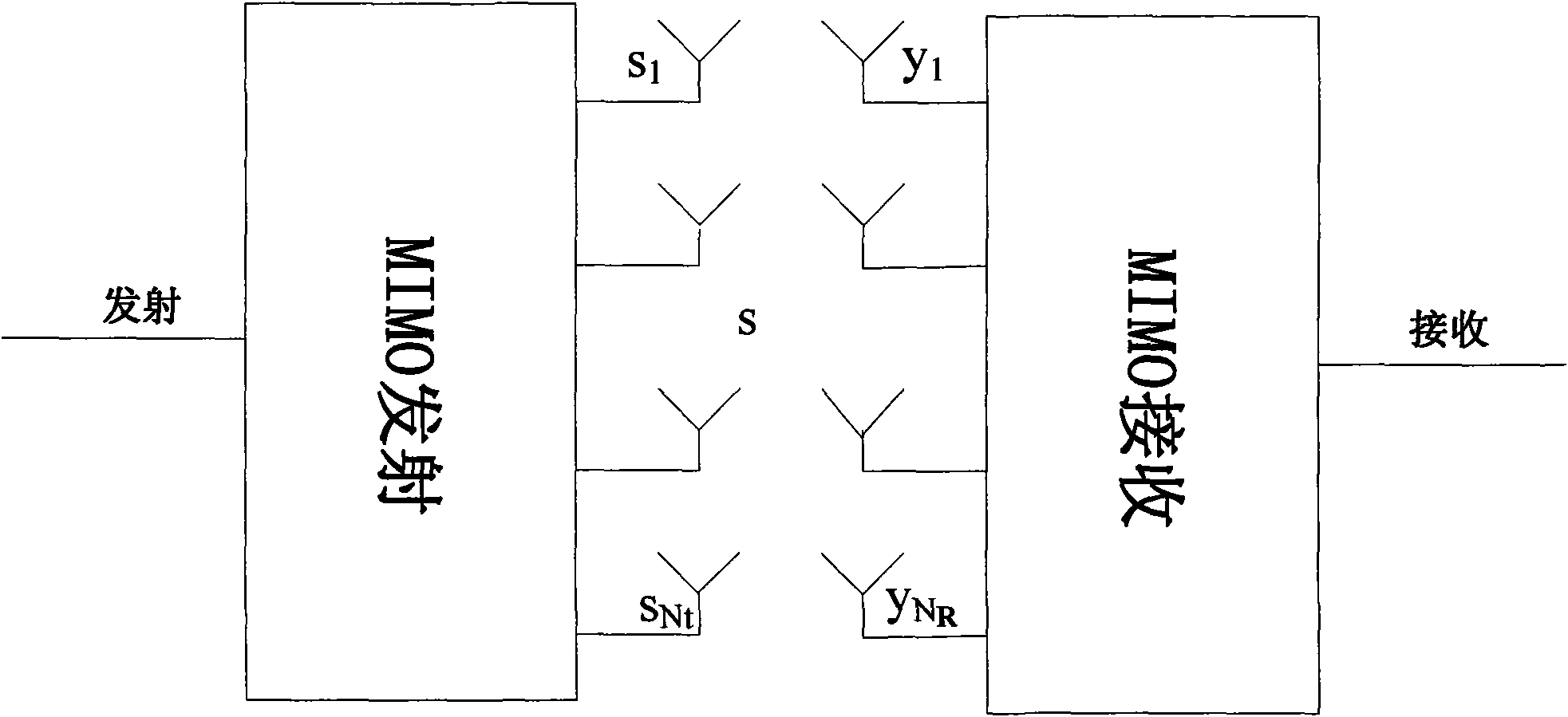
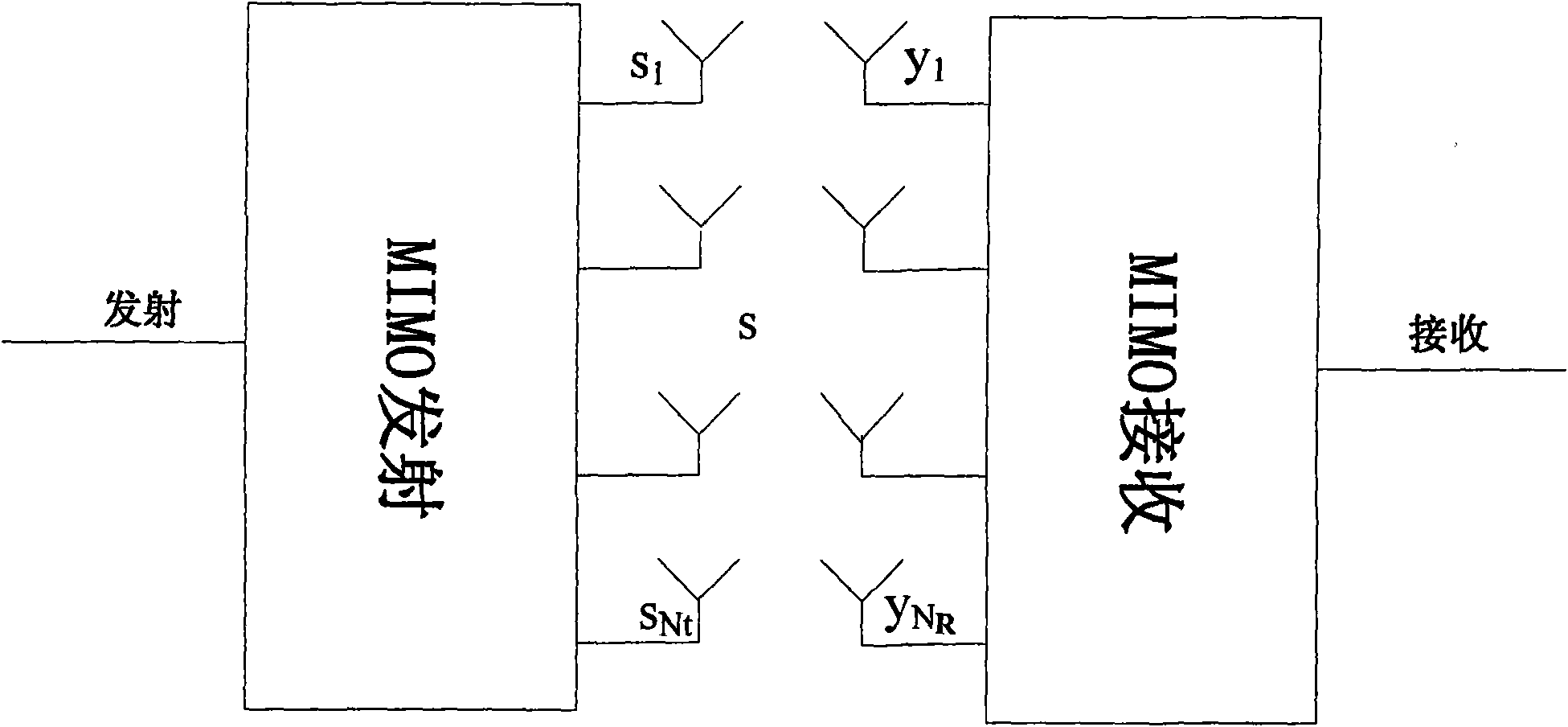
Multi-user MIMO transmission method in wireless communication system, base station and user terminal
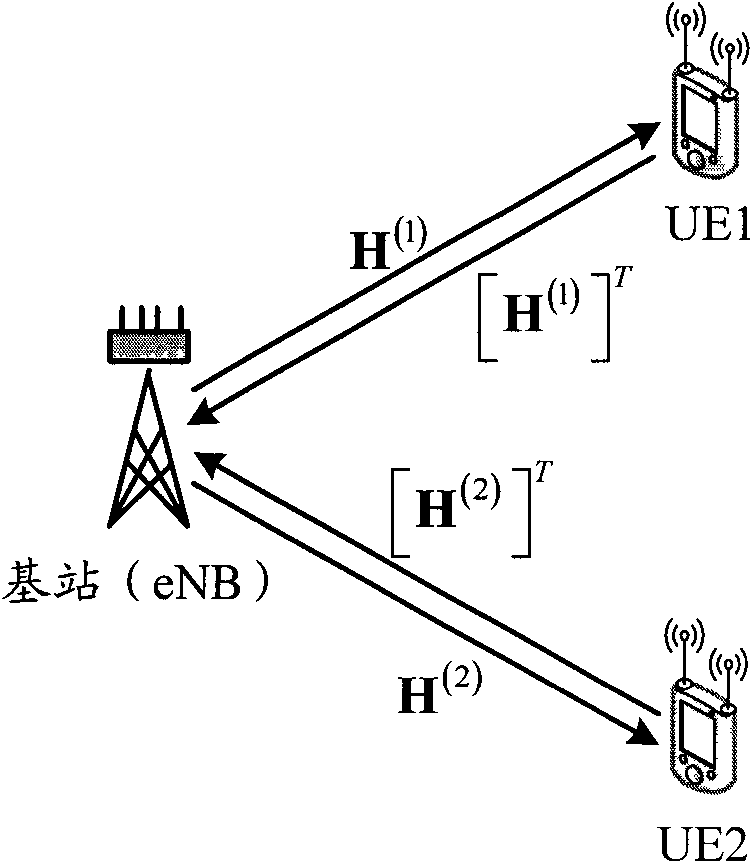
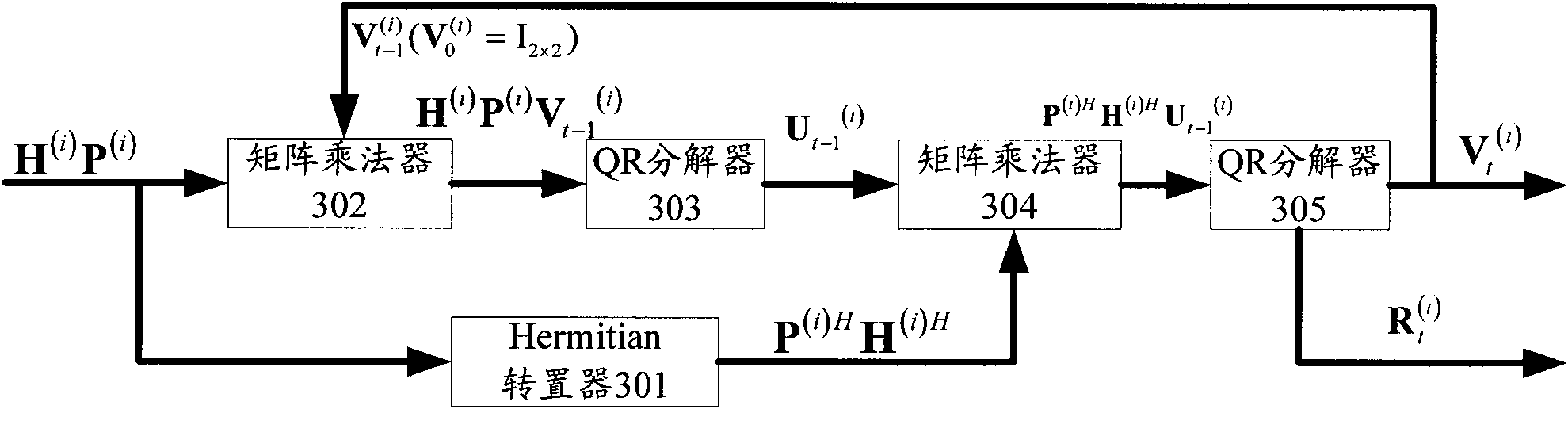
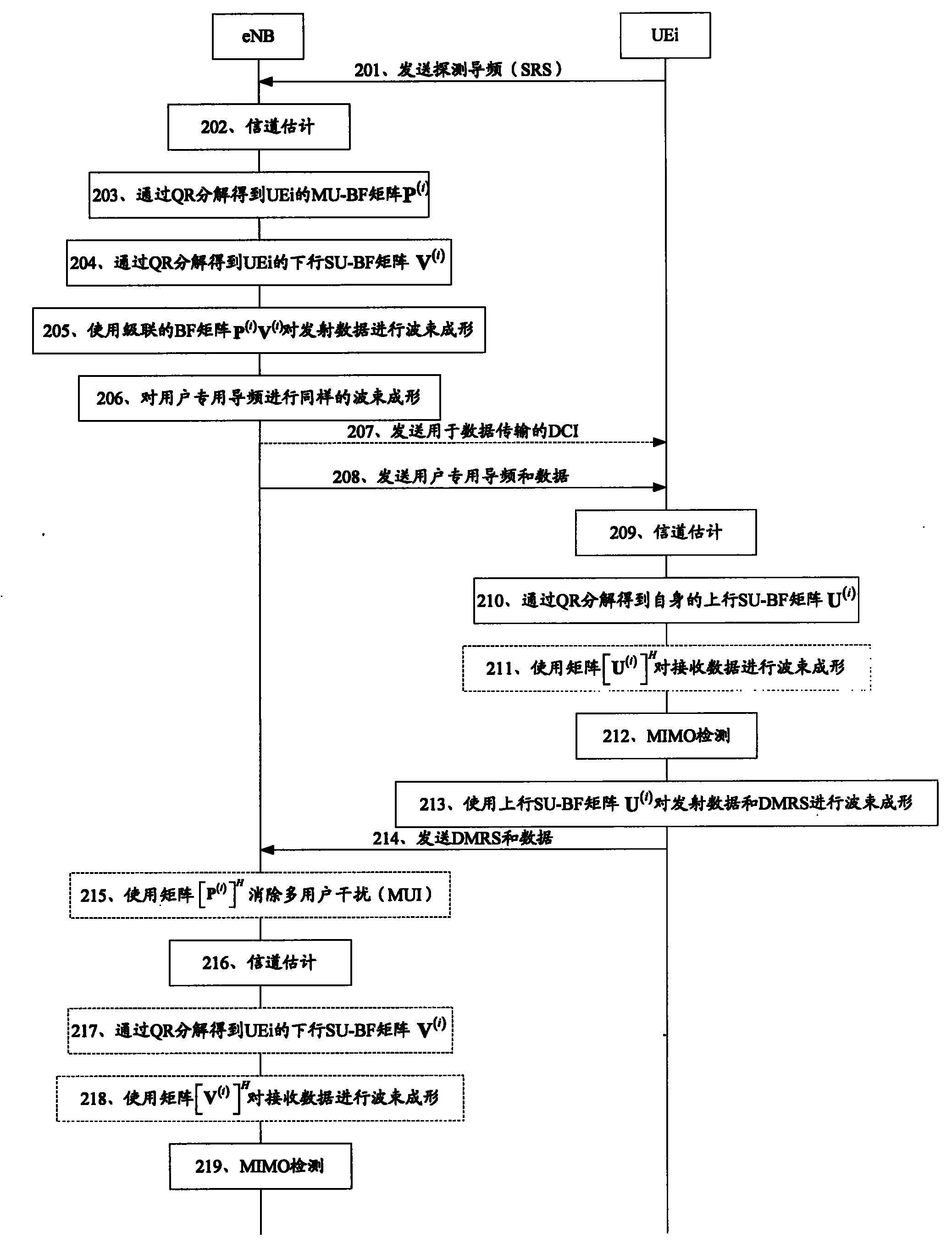
ActiveCN102104404ATake advantage of reciprocityExact matchSpatial transmit diversityRadio transmission for post communicationQ-matrixQR decomposition
The invention discloses a multi-user multiple input multiple output (MU-MIMO) transmission method in a wireless communication system, a base station and a user terminal. The method comprises the following steps that: the base station receives detection pilot frequency SRS of N users to perform channel estimation and acquires downlink channel information according to the channel estimation result and channel reciprocity of the system, wherein N is more than 1; the base station performs quick response (QR) decomposition on the downlink channel information, acquires a multi-user beamforming (MU-BF) matrix P (i) of the ith user from a Q matrix acquired through decomposition, and acquires a downlink single-user beamforming (SU-BF) matrix V (i) of the ith user further, wherein i=1, ...,N; and the base station performs beamforming processing on transmitting data of the ith user according to the MU-BF matrix P (i) and the SU-BF matrix V (i). The method and equipment acquire beamforming matrixes for uplink and downlink MU-MIMO transmission by means of the channel reciprocity of the system and the QR decomposition, and the MU-MIMO transmission performance can be improved.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Tonal rotors
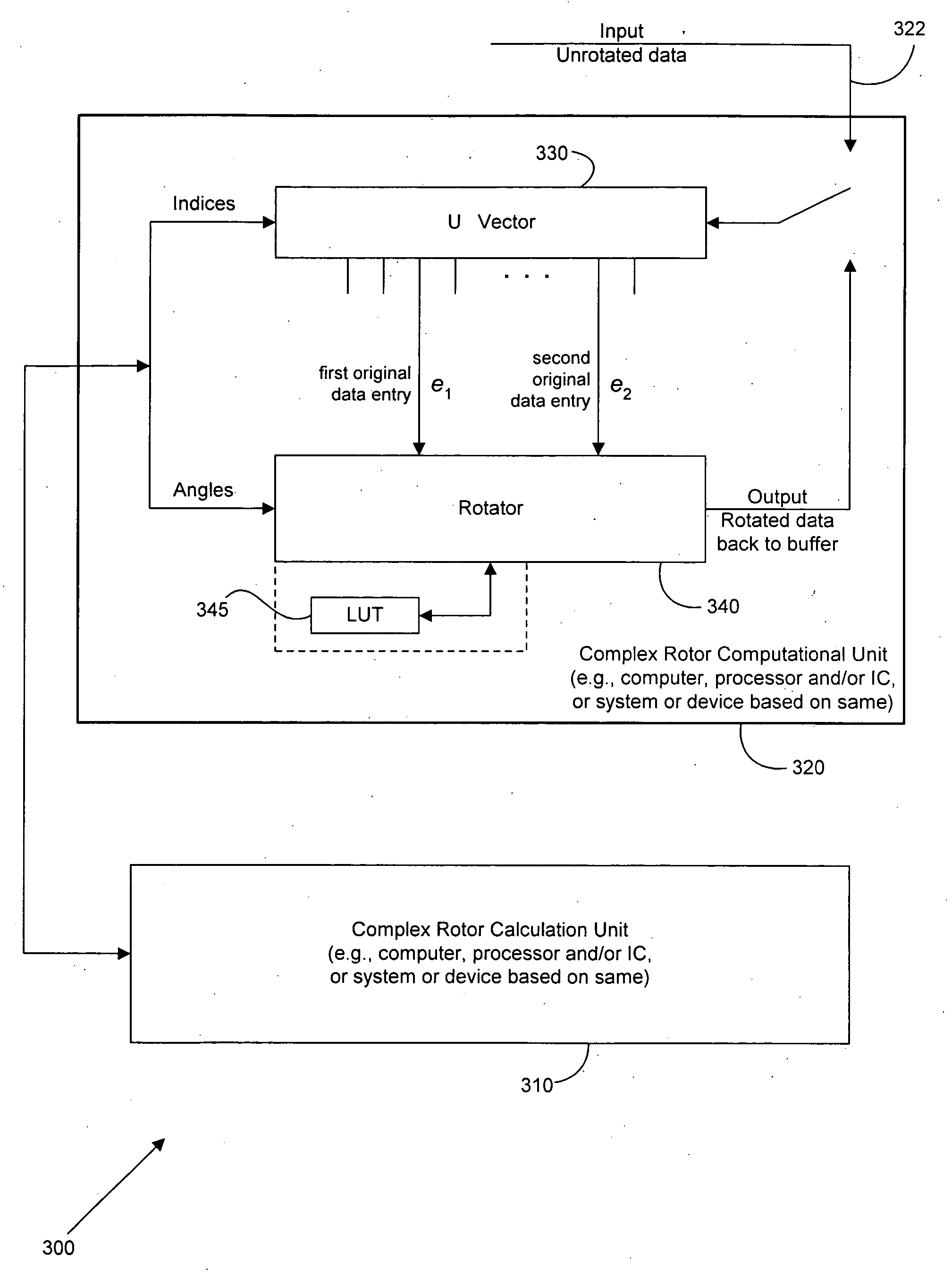
InactiveUS20060259535A1Efficient implementationSave computational complexityError preventionMultiplex communicationMatrix decompositionQ-matrix
A set of complex rotations are used to implement a unitary “Q” matrix that can arise in various transmitters and / or receivers in communication line vectoring. Each complex rotation is a set of real rotations, where the minimum number of real rotations to perform the complex rotation is three, and where the minimum number of angles to characterize the real rotations is two. An order of rotations is also provided. The invention assists in the efficient implementation of any unitary “Q” matrix in a QR or other sophisticated matrix factorization. A complex form of the so-called “Givens” implementation of the Q matrix is characterized in terms of a sequence of complex rotations that can implemented using a complex rotor computational unit that accepts a minimum of two real angles and a pair of integer indices for each of a set of successive complex rotor calculations and then implements the complex rotation as a series of a minimum of three real rotations with one real angle used twice and the other real angle used once, providing two complex outputs (that is, two rotated data entries from a data vector comprising indexed communication data) for two complex inputs (two original data entries from a data vector comprising indexed communication data). The index-angle sets for each successive rotation can be provided by a complex rotor calculation unit, which may be collocated with the complex rotor computational unit, located in a controller such as a DSL optimizer, or located in any other suitable device or apparatus that has performed the QR factorization upon supplied matrix MIMO transfer functions for the vectored channel.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
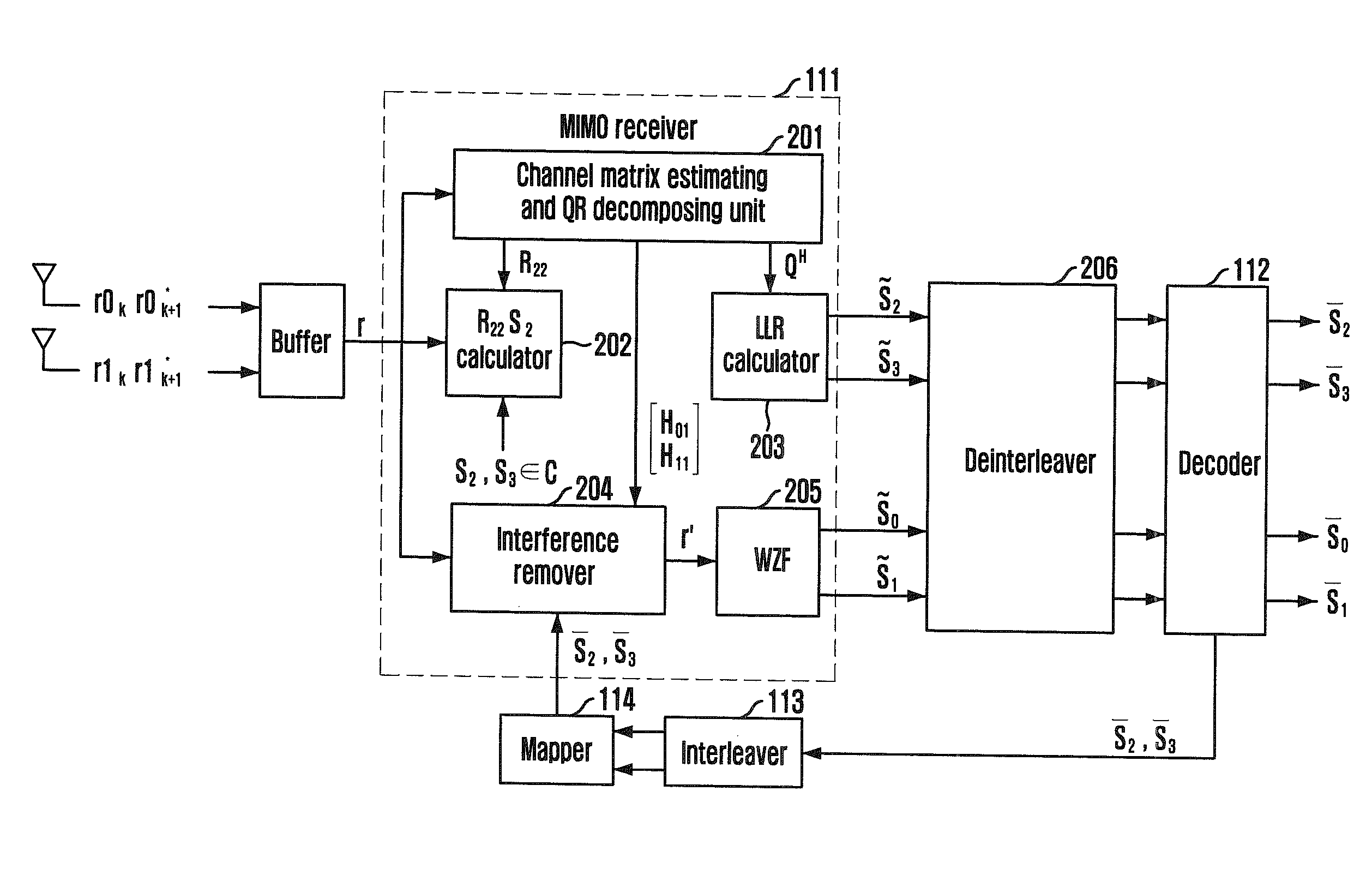
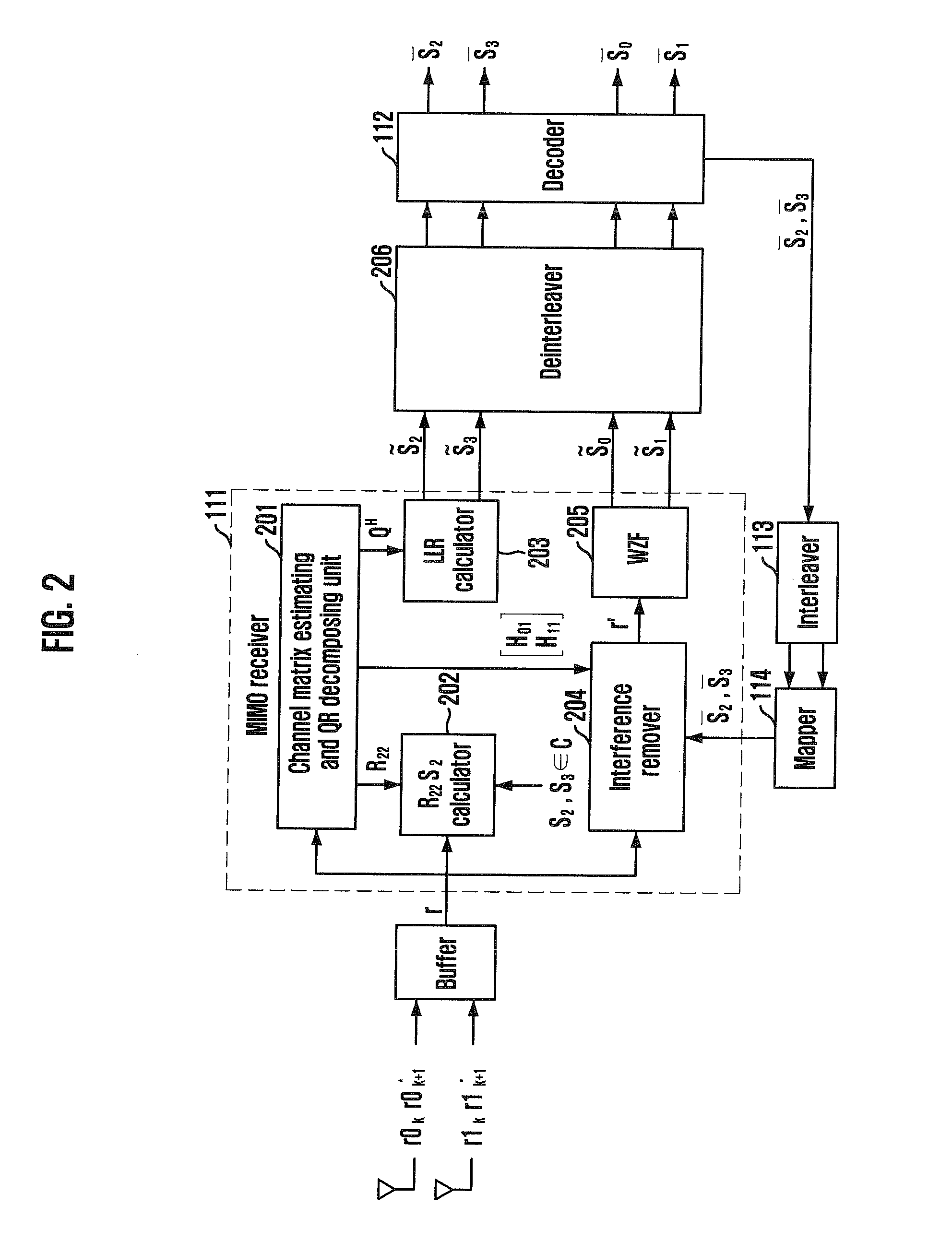
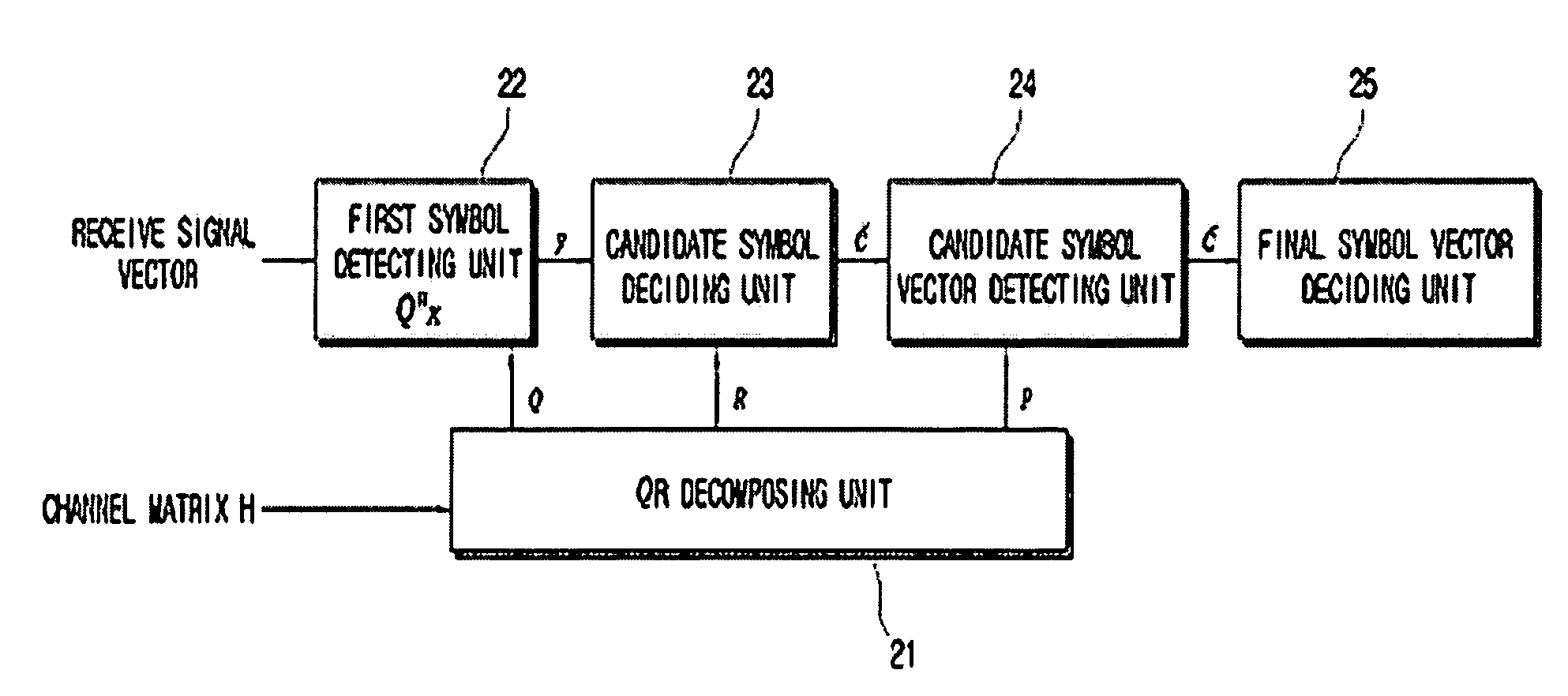
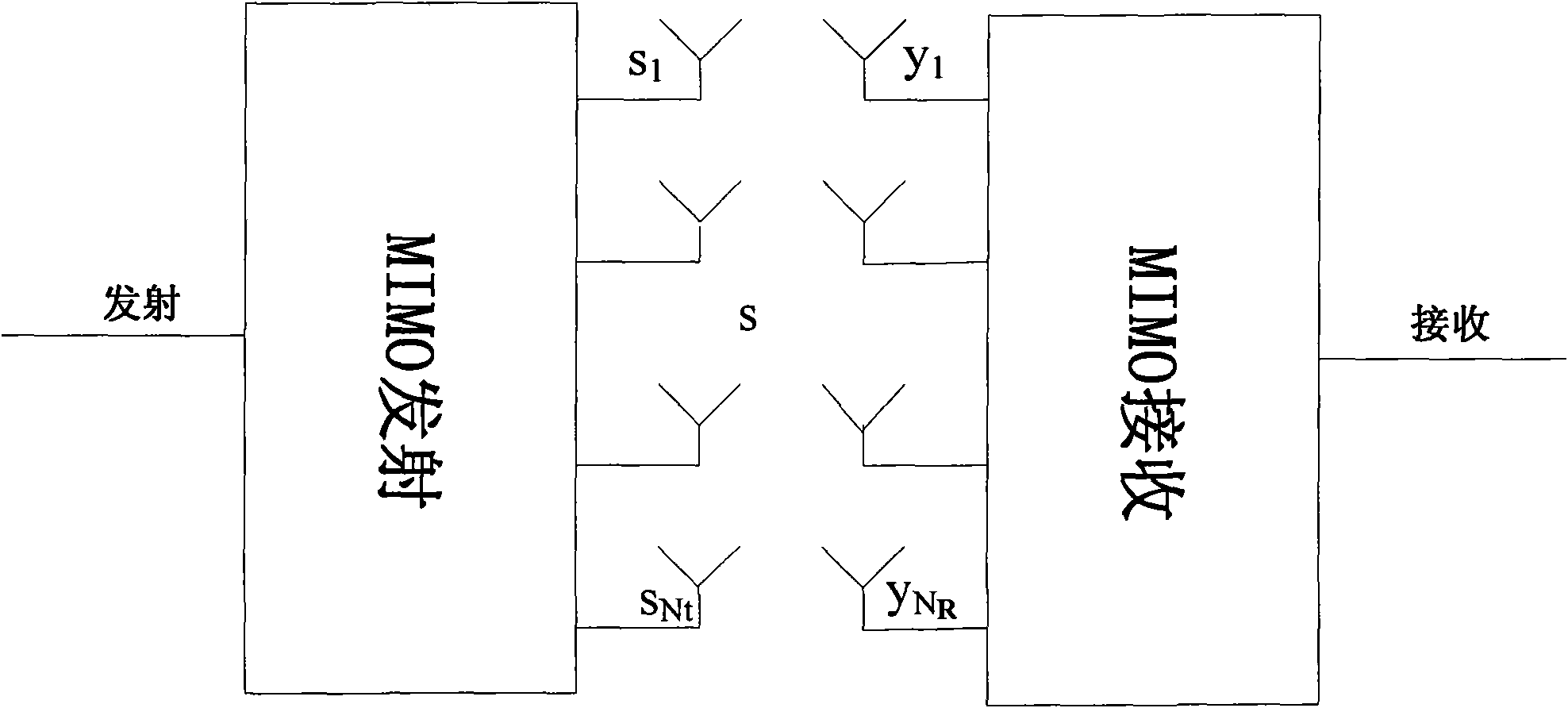
Receiving apparatus and method for MIMO system
InactiveUS20090154608A1Reduce latencyType of reductionSpatial transmit diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsQ-matrixQR decomposition
Provided are a receiving apparatus for a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) system and a method thereof. The receiving apparatus includes a QR decomposing unit for calculating a single (Q) matrix vector and an upper triangle (R) matrix vector for a receiving signal vector; a first symbol estimation unit for estimating predetermined symbols using the calculated Q matrix vector and R matrix vector; a log likelihood ratio (LLR) calculating unit for calculating log likelihood ratios of unit bits for the estimated symbols; an interference removing unit for receiving a decoded signal that is decided using the calculated log likelihood ratios and removing interference from the receiving signal vector; and a second symbol estimation unit for linearly estimating remaining symbols for the interference removed signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
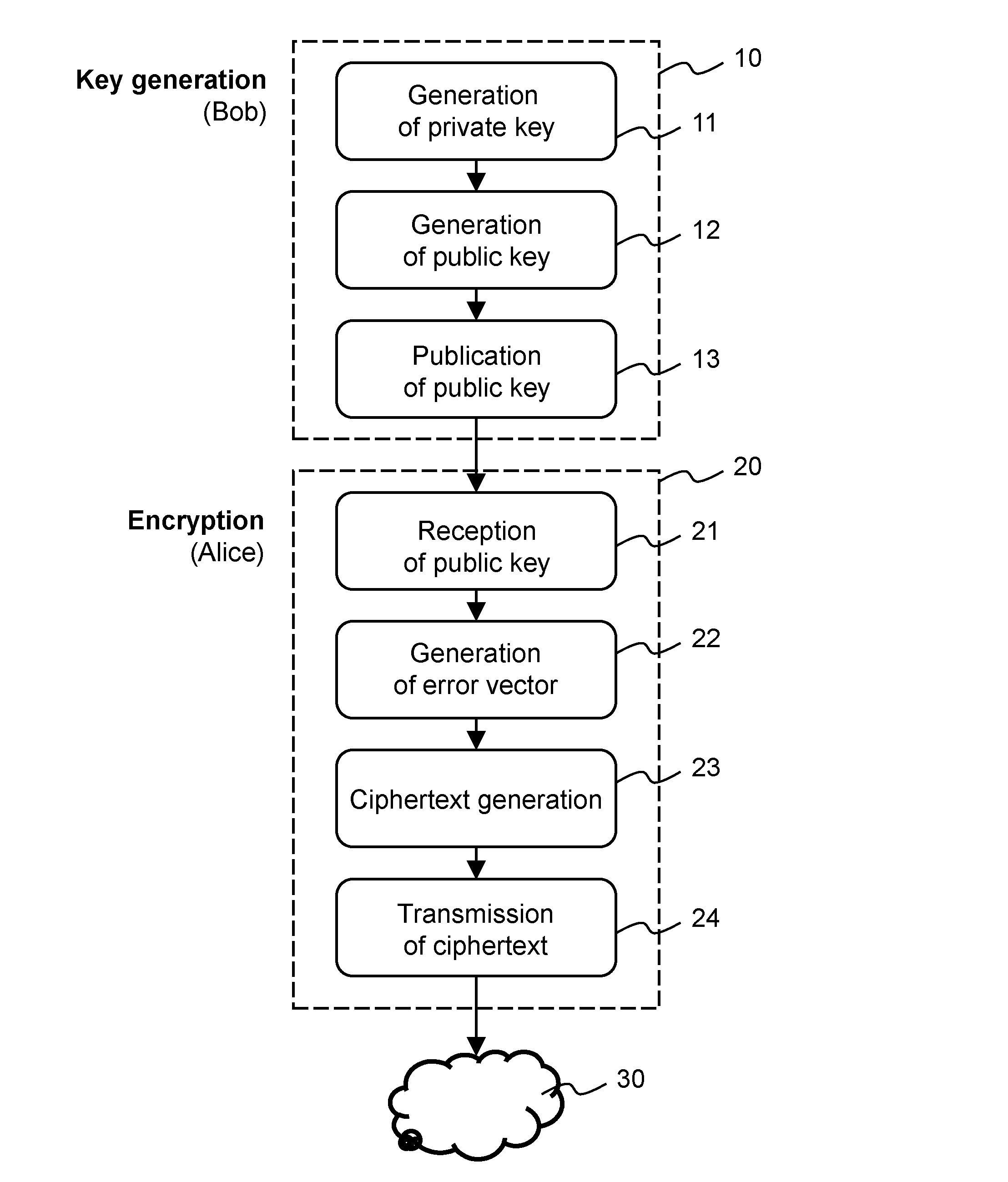
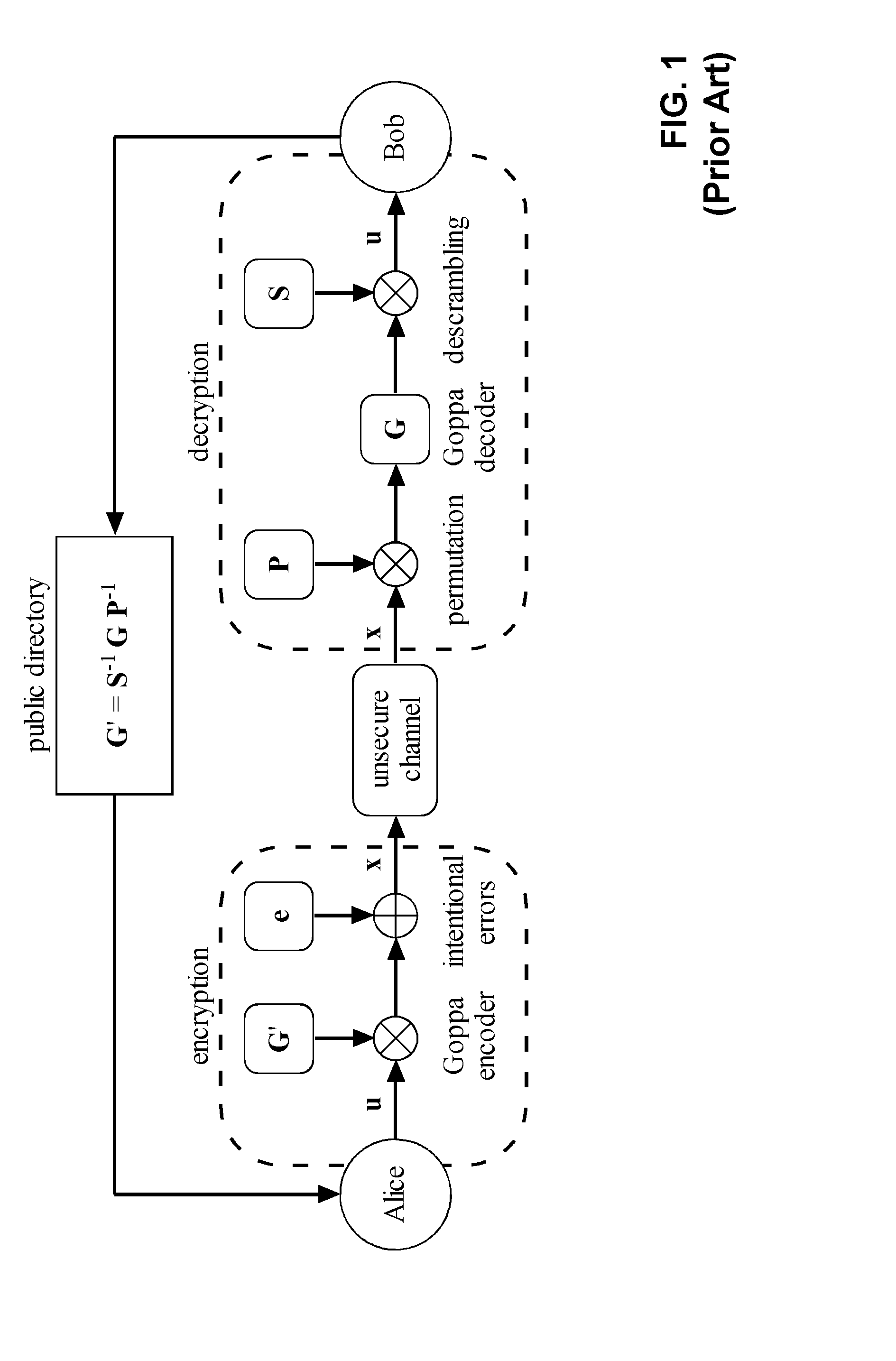
Method and apparatus for public-key cryptography based on error correcting codes
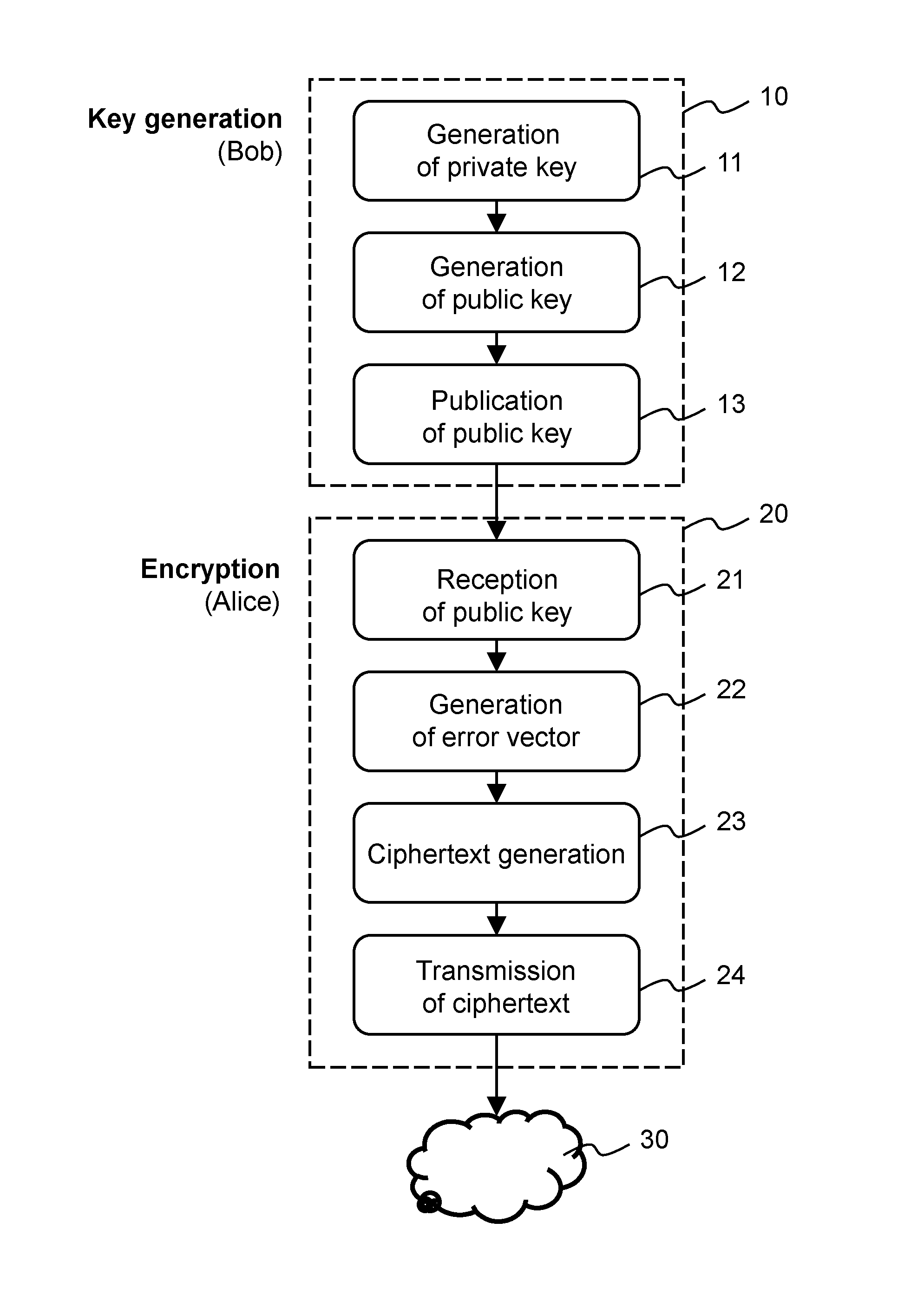
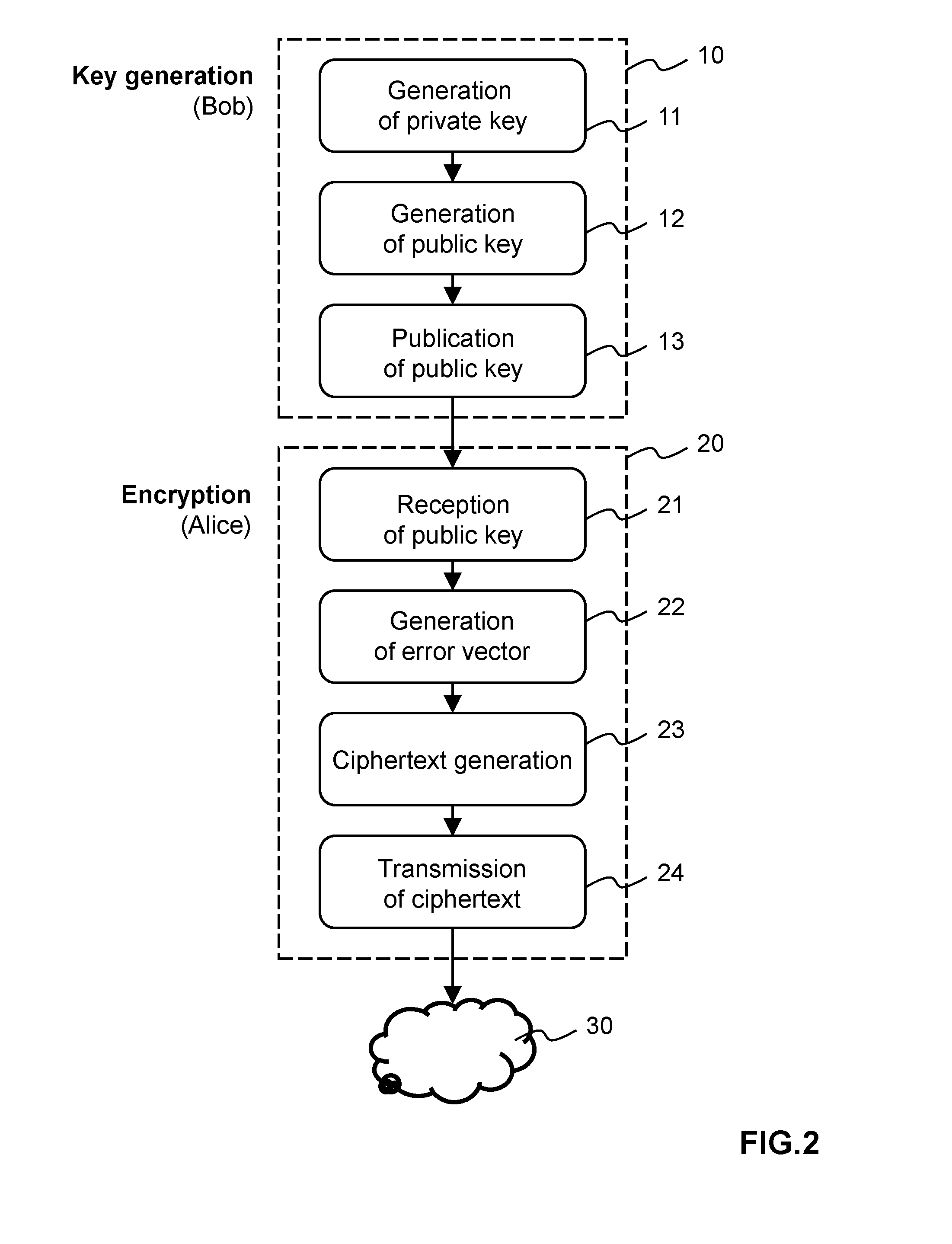
ActiveUS20140105403A1Improve security levelShort processKey distribution for secure communicationQ-matrixComputer hardware
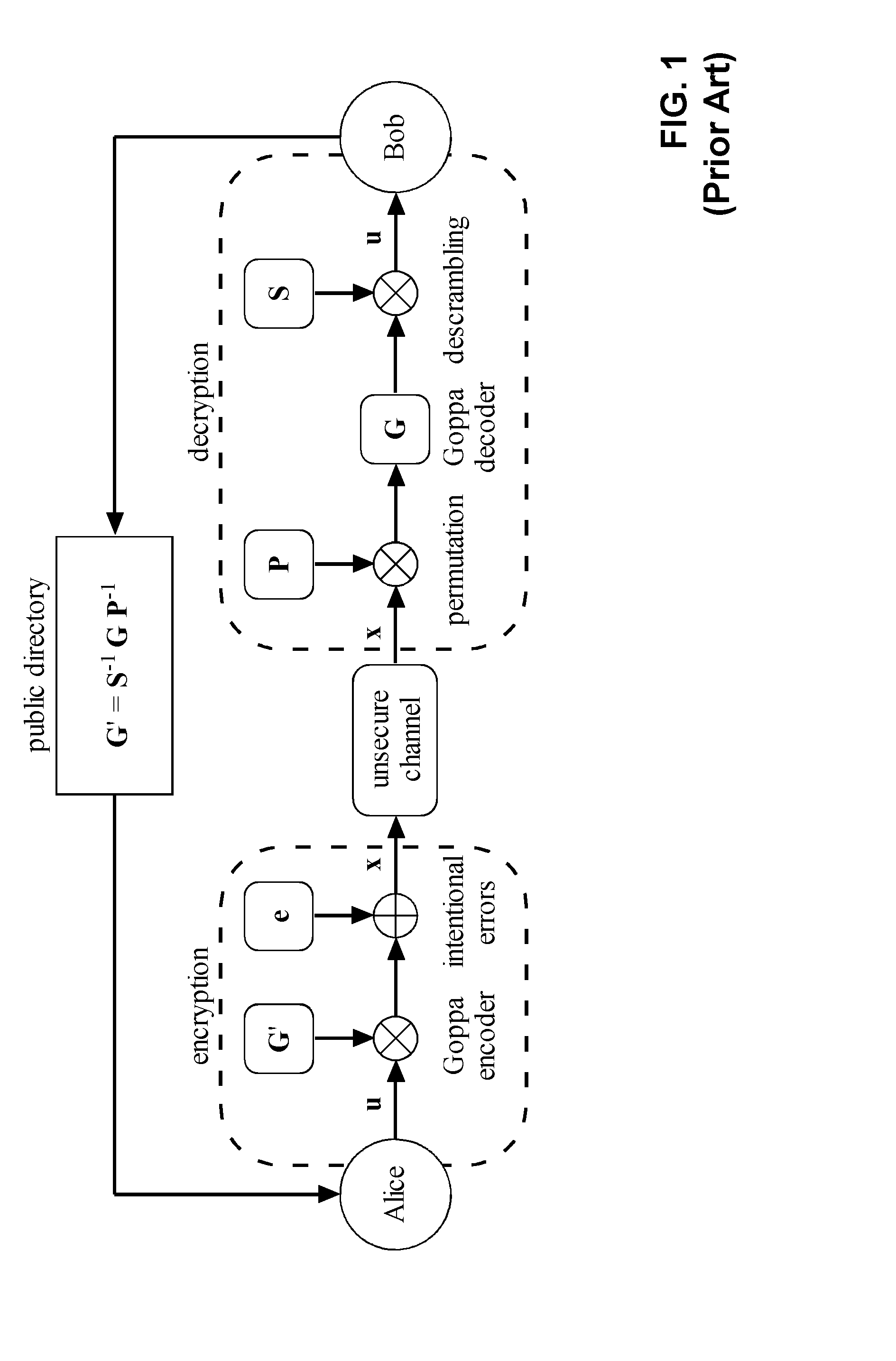
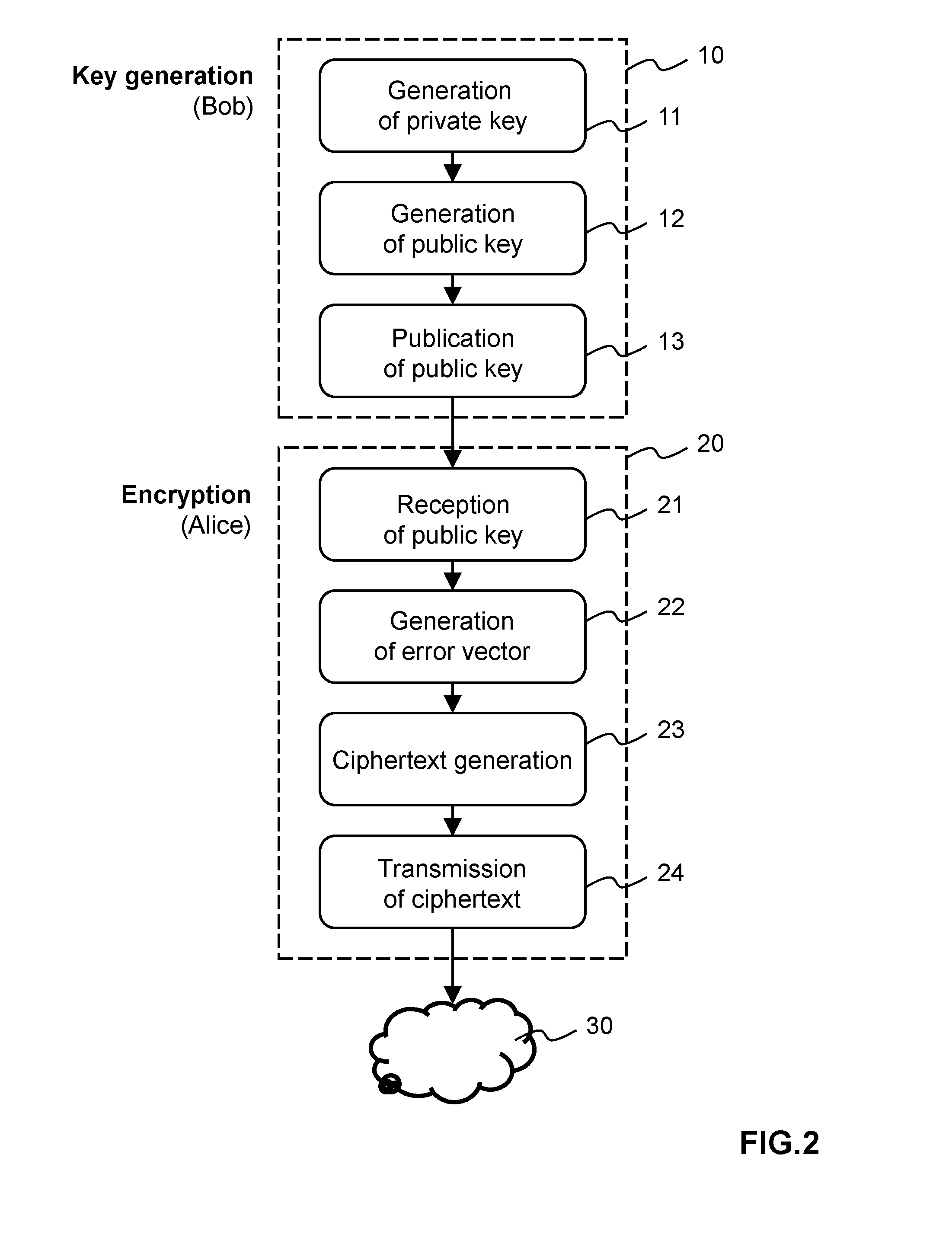
Methods and apparatus for generating a private-public key pair, for encrypting a message for transmission through an unsecure communication medium (30), and for decrypting the message are disclosed. The methods are based on the well-known McEliece cryptosystem or on its Niederreiter variant. More general transformation matrices Q are used in place of permutation matrices, possibly together with an appropriate selection of the intentional error vectors. The transformation matrices Q are non-singular n×n matrices having the form Q=R+T, where the matrix R is a rank-z matrix and the matrix T is some other matrix rendering Q non-singular. The new Q matrices, though at least potentially being dense, have a limited propagation effect on the intentional error vectors for the authorized receiver. The use of this kind of matrices allows to better disguise the private key into the public one, without yielding any further error propagation effect. Based on this family of Q matrices, the presently proposed cryptosystem enables the use of different families of codes than Goppa codes, such as RS codes, by ensuring increased public key security.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
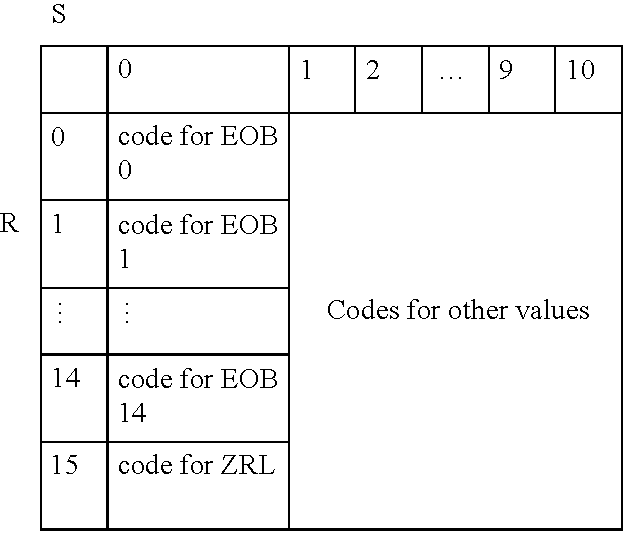
Signaling adaptive-quantization matrices in JPEG using end-of-block codes
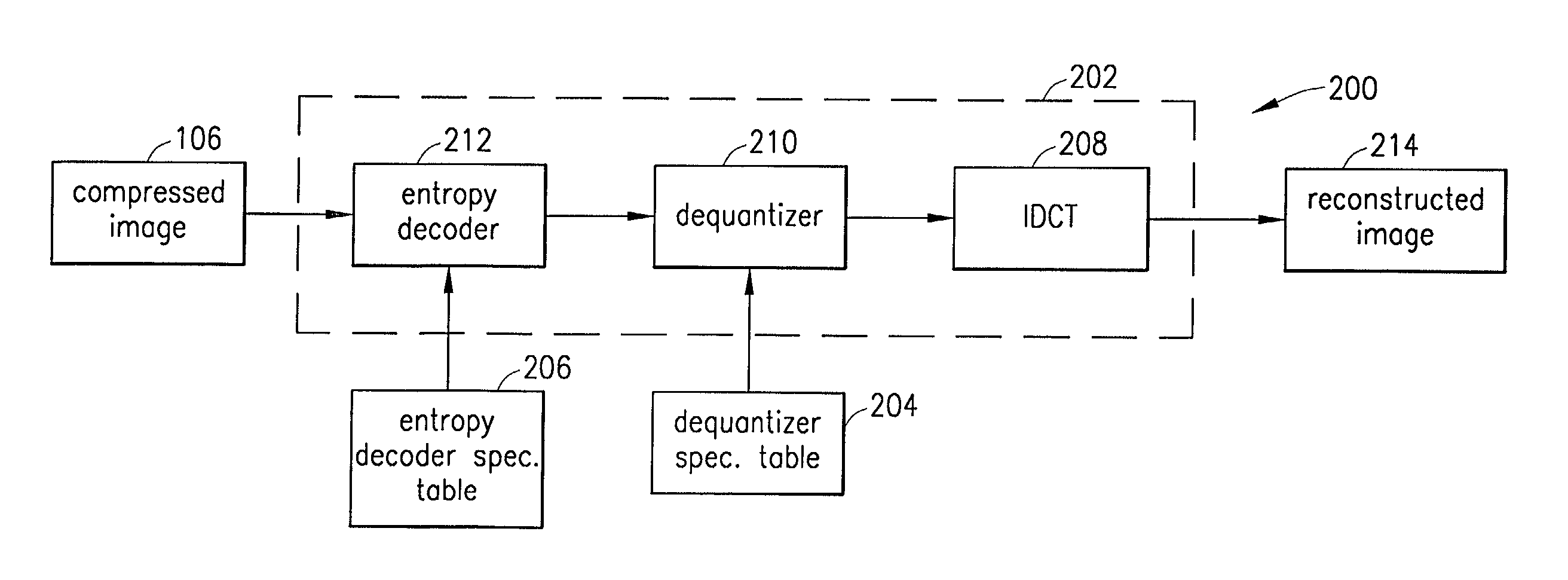
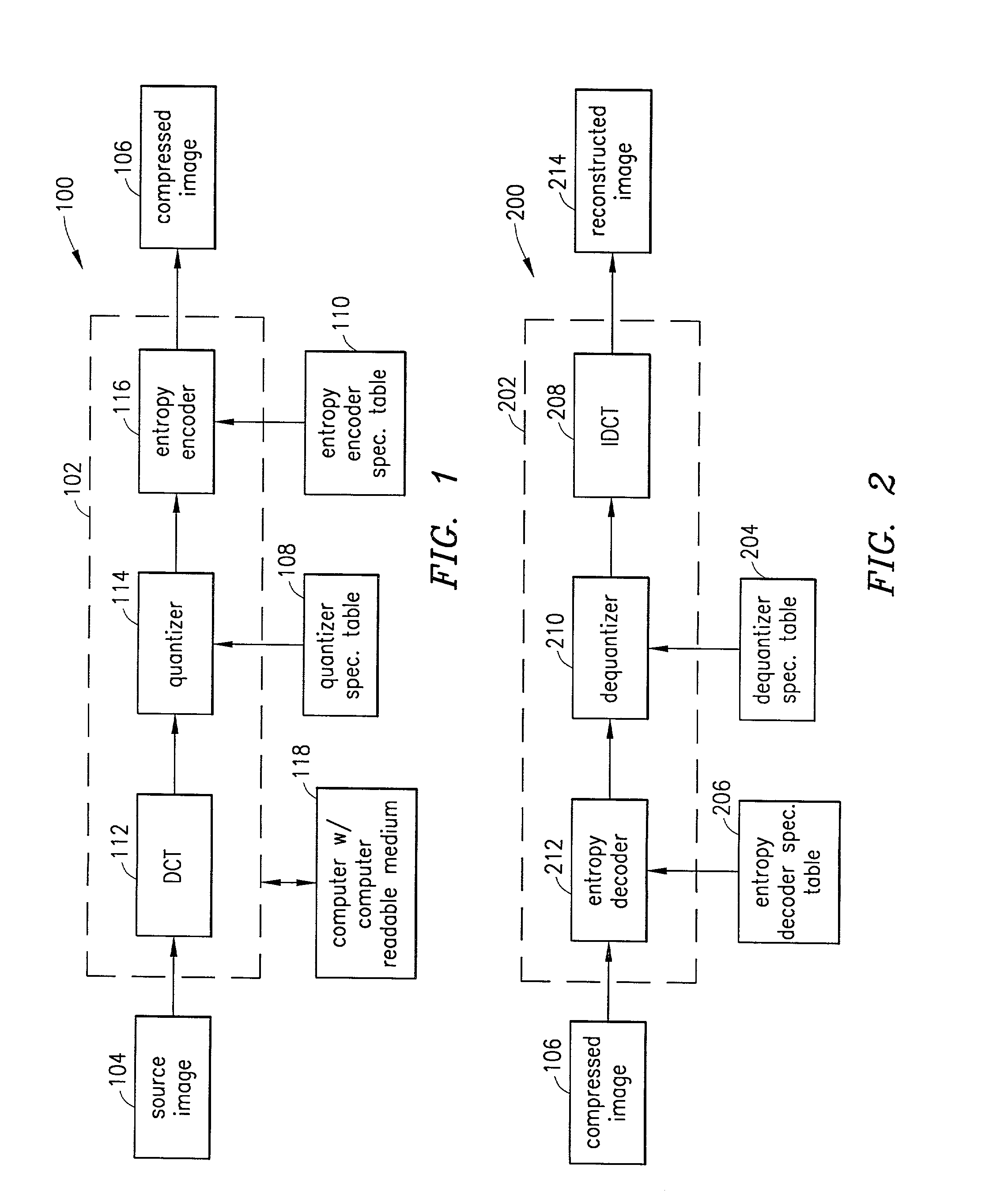
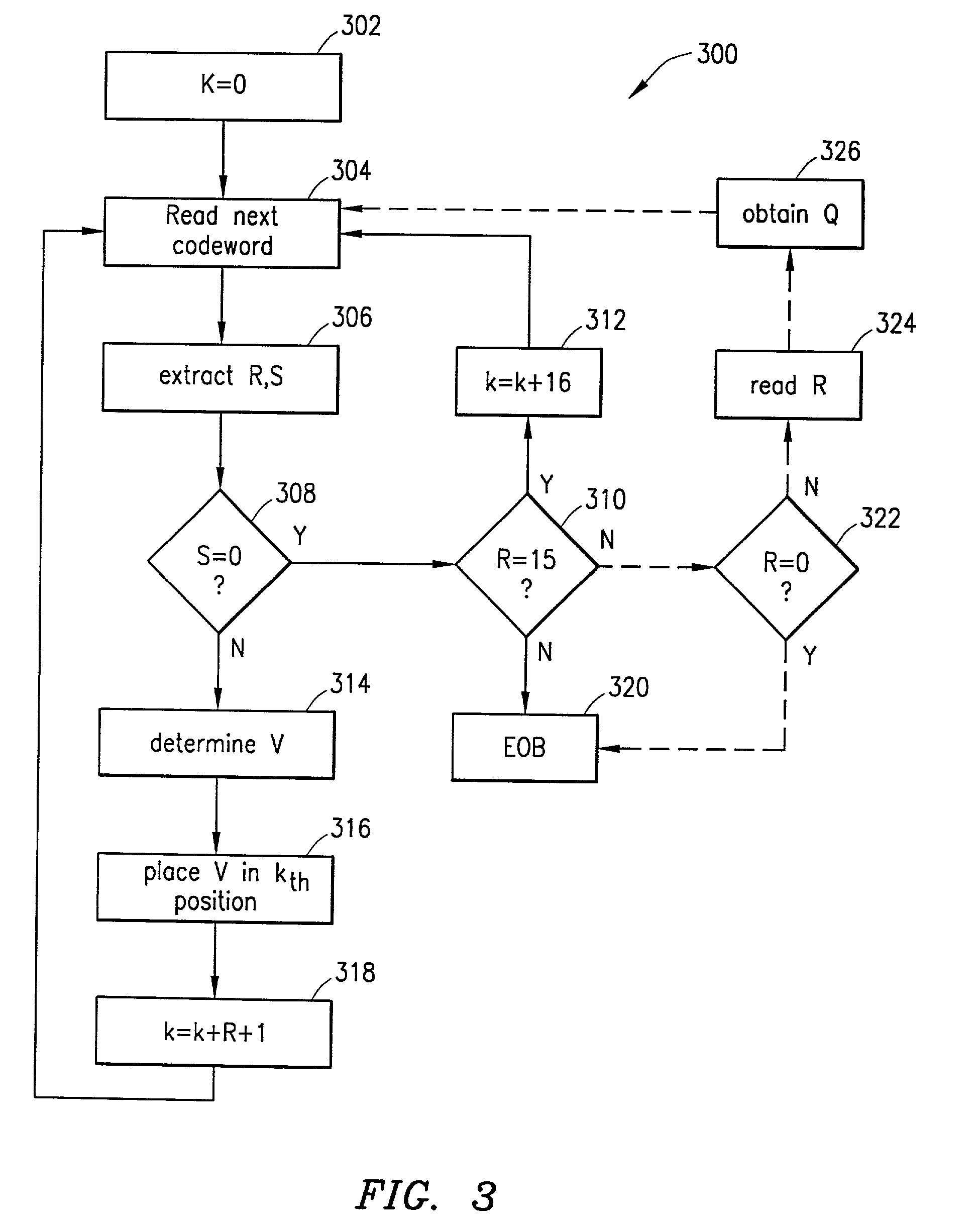
Previously-unused slots in a Huffman code table associated with a Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) image file are associated with various quantization matrices (Q matrices) that are used to quantize data blocks of the JPEG image file. Huffman codes associated with the various Q matrices permit the particular Q matrix used to quantize a given data block to be signaled by a decoder as an end-of-block (EOB) code. The EOB codes and the Huffman code table are sent with the JPEG image file. Upon decoding of the image file, a standard JPEG decoder reads each of the EOB codes as a standard JPEG EOB code and does not vary the Q matrix. A modified decoder reads from each of the EOB codes which Q matrix was used to encode each particular data block of the image and uses that Q matrix to dequantize the data block.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
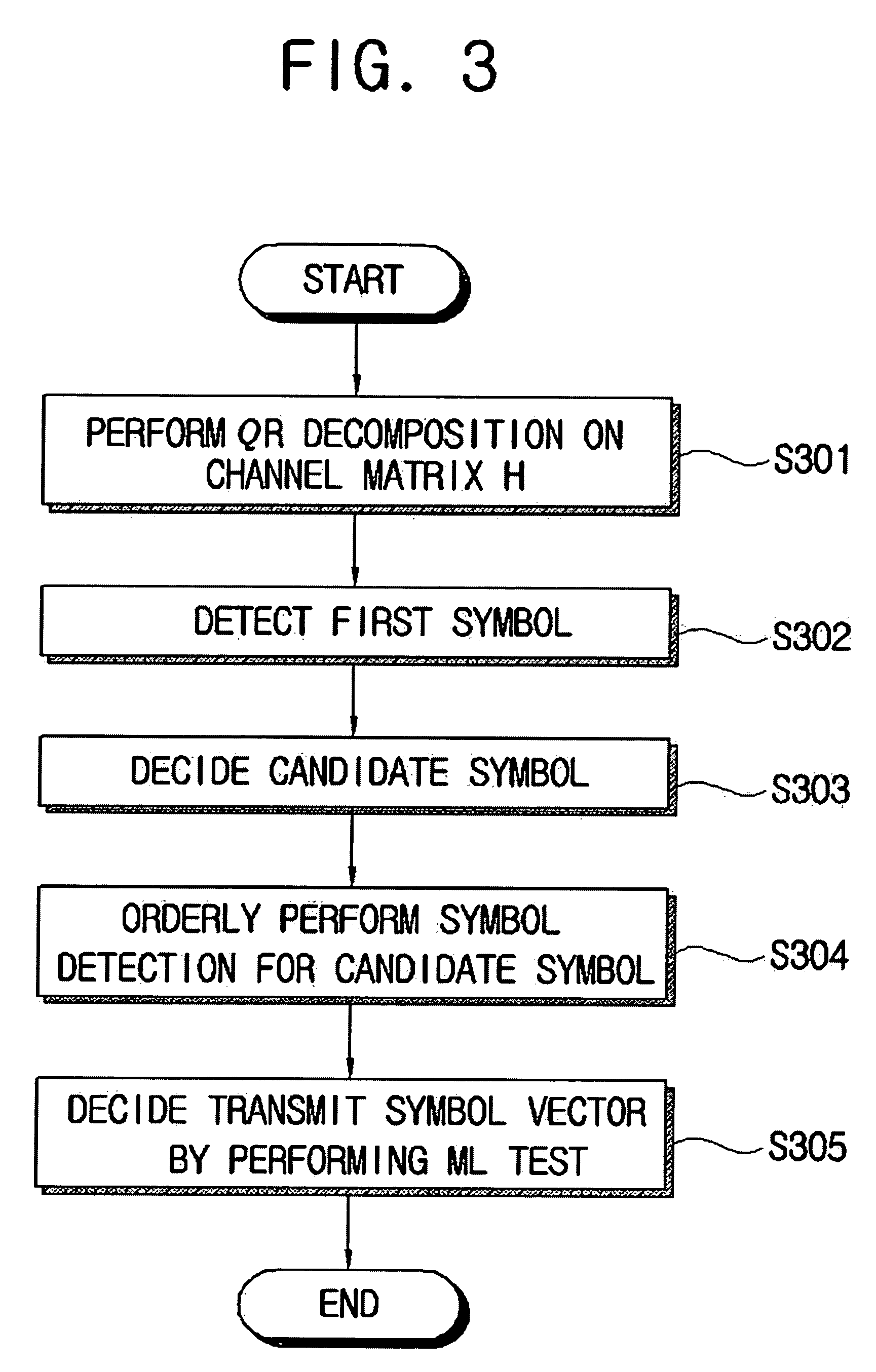
Apparatus for detecting symbol in SDM system and method thereof
InactiveUS20060251061A1Improve system performanceLowering an error probability of a first detected symbolCyclesMultiplex system selection arrangementsQR decompositionQ-matrix
An apparatus for detecting a symbol in a space division multiplexing system and a method thereof are disclosed. The apparatus includes: a QR decomposing unit for performing a QR decomposition on a channel matrix H to decompose the channel matrix H to a Q matrix and a R matrix; a first symbol detecting unit for detecting a first symbol from a receive signal vector by using the result of the QR decomposition; a candidate symbol deciding unit for deciding the detected first symbol and Nc−1 symbols adjacent to the detected first symbol on a constellation as candidate symbols, wherein the Nc is an positive integer number; a candidate vector detecting unit for detecting Nc candidate transmit symbol vectors from the detected Nc candidate symbols; and a transmit symbol vector deciding unit for deciding an optimized transmit symbol vector among the detected Nc candidate transmit symbol vectors.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY
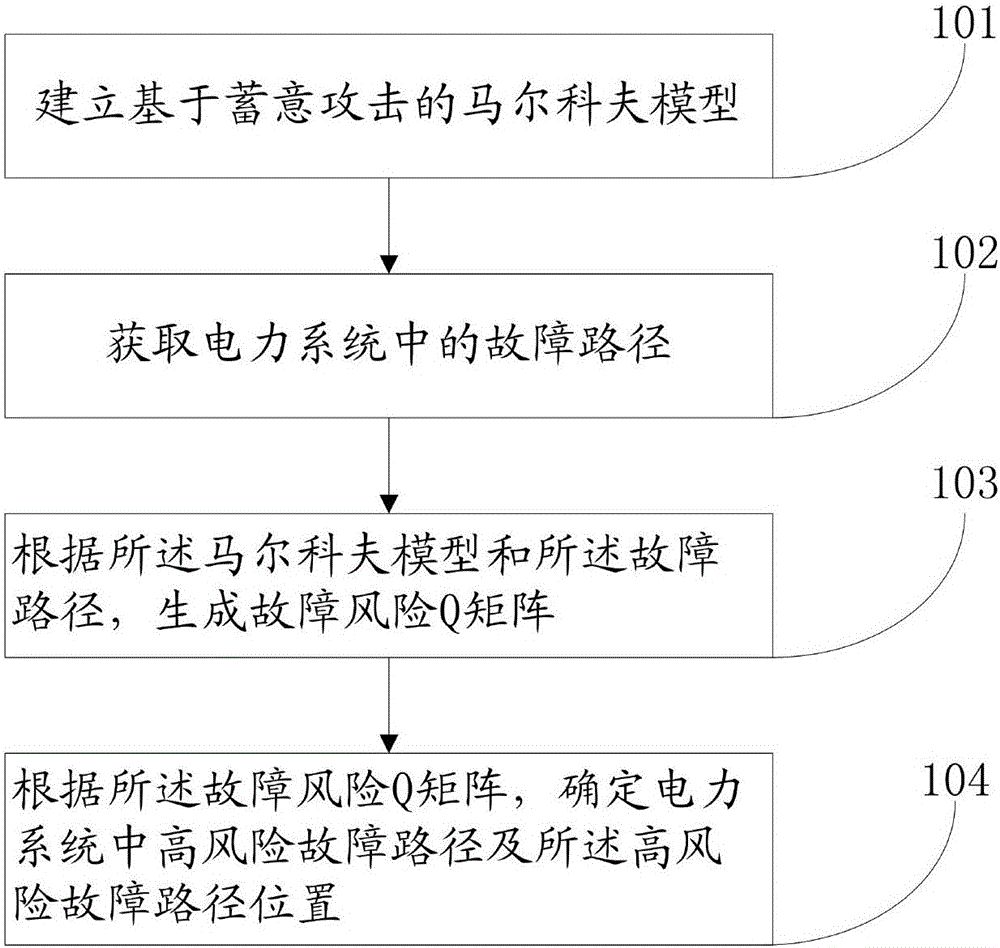
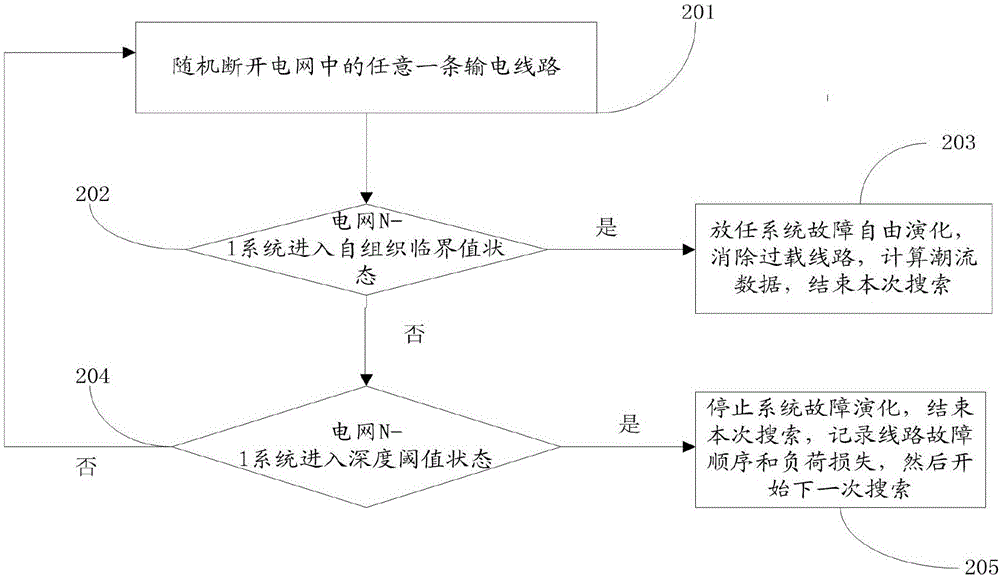
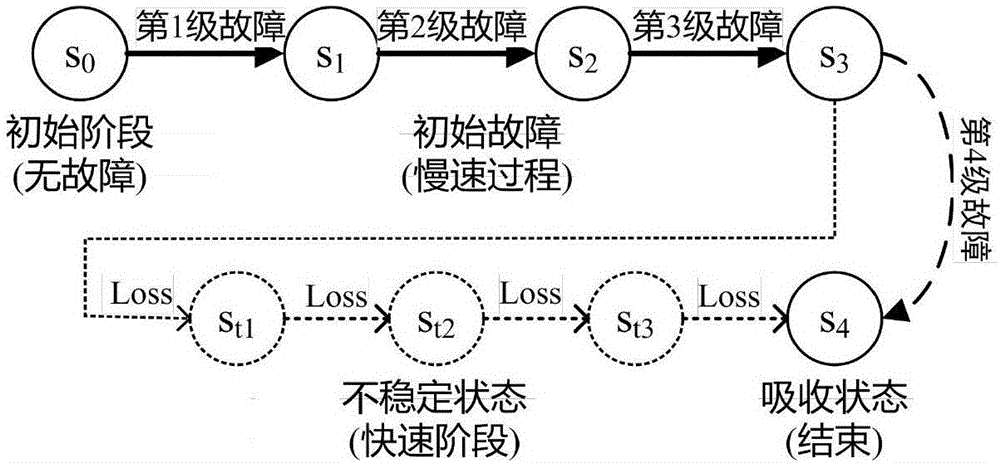
Identification method and system for cascading failure critical line of power system
The invention provides an identification method and system for a cascading failure critical line of a power system. The method comprises the steps of establishing a Markov model based on an intentional attack; obtaining a failure path in the power system; generating a failure risk Q matrix according to the Markov model and the failure path; and determining a high risk failure path in the power system and a position of the high risk failure path according to the failure risk Q matrix. According to the method and the system, the line combinations in the power system are taken into full consideration; and the accuracy of identifying the high risk failure path is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
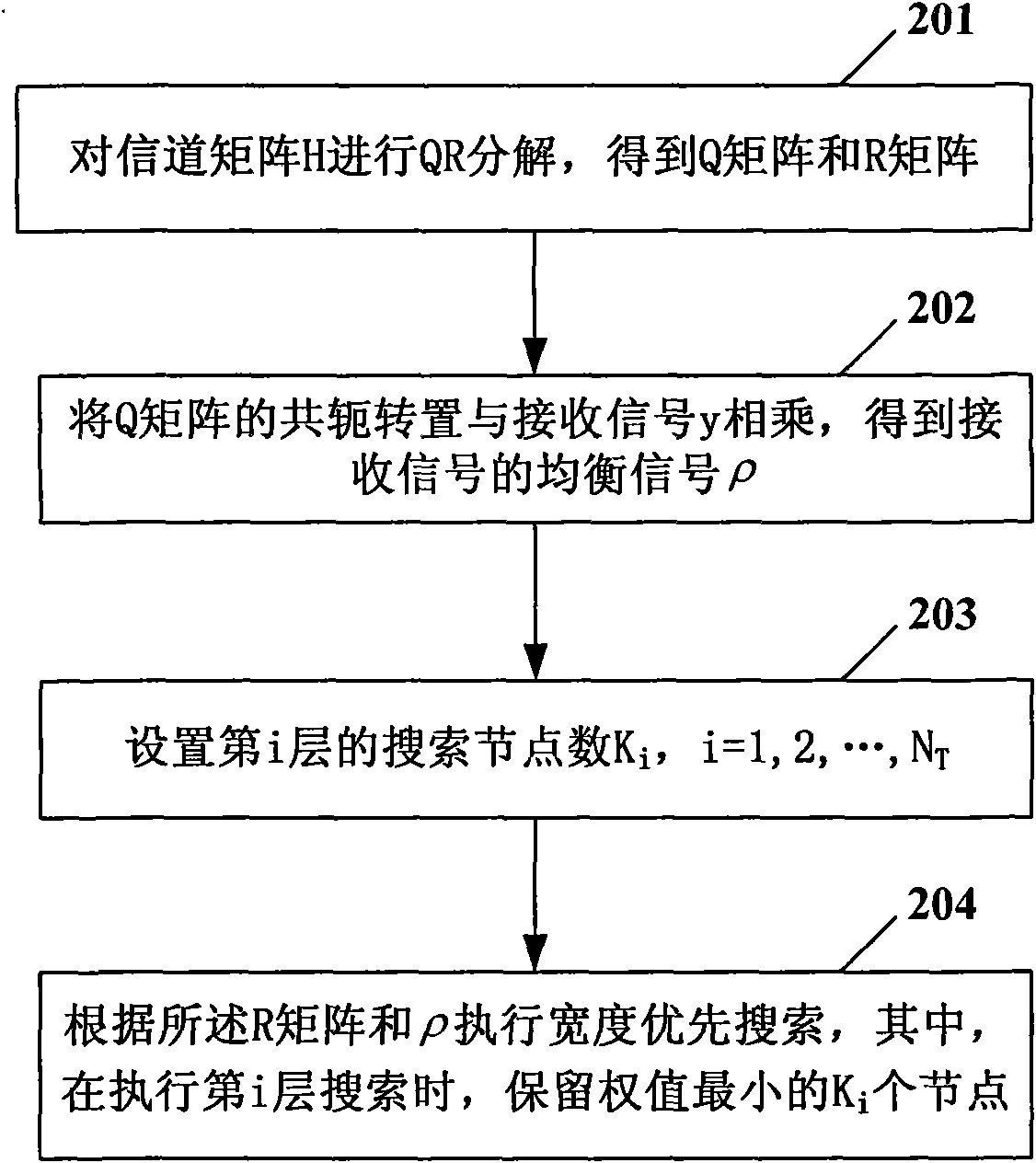
Method for detecting spherical decode based on depth-first search
InactiveCN101562464AReduce operational complexityEasy to implementError prevention/detection by diversity receptionQ-matrixQR decomposition
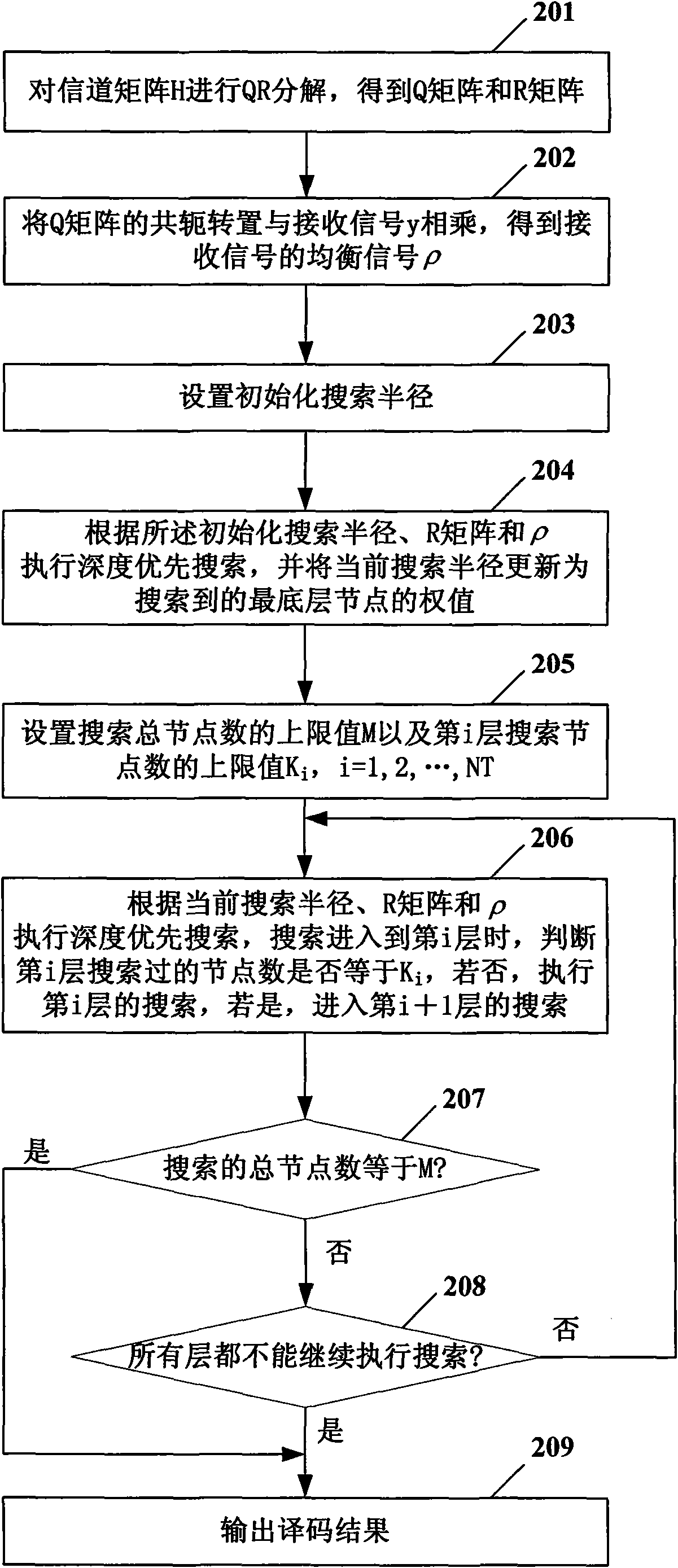
The invention provides a method for detecting spherical decode based on depth-first search, which comprises the following steps: A, performing QR deposition on a channel matrix; B, multiplying a conjugate transpose and a received signal of a Q matrix to obtain an equalizing signal rho; C, setting an initial search radius; D, executing the depth-first search according to the initial search radius, an R matrix and the rho, and updating the search radius; E, setting an upper limit value M of the search total node number and an upper limit value Ki of the ith layer search node number; F, executing the depth-first search according to the current search radius, the R matrix and the rho, and when the search gets to the ith layer, judging whether the searched node number on the ith layer is equal to Ki or not, otherwise, executing the search on the ith layer, and if so, getting to search the i+1th layer; and G, repeating the step F until the searched total node number is equal to M or all the layers cannot be searched any more, and outputting a decoding result. The method can effectively reduce the operation complexity of the sphere decoding, and is easy to achieve through hardware.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
Fault diagnosis method and device based on device working condition
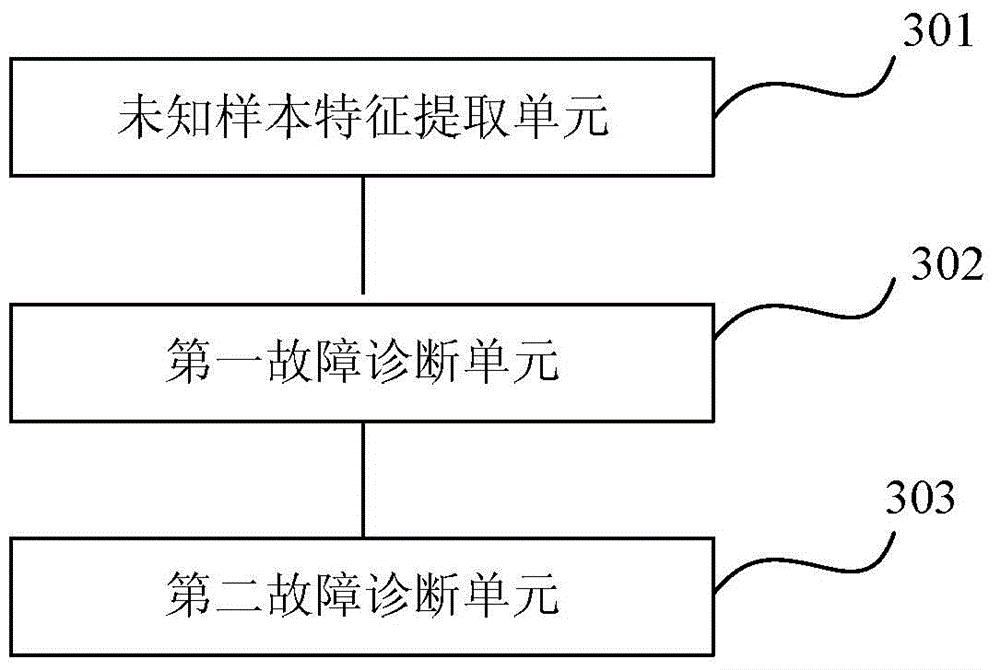
ActiveCN104156627AImprove the accuracy of fault diagnosisSpecial data processing applicationsDiagnostic dataQ-matrix
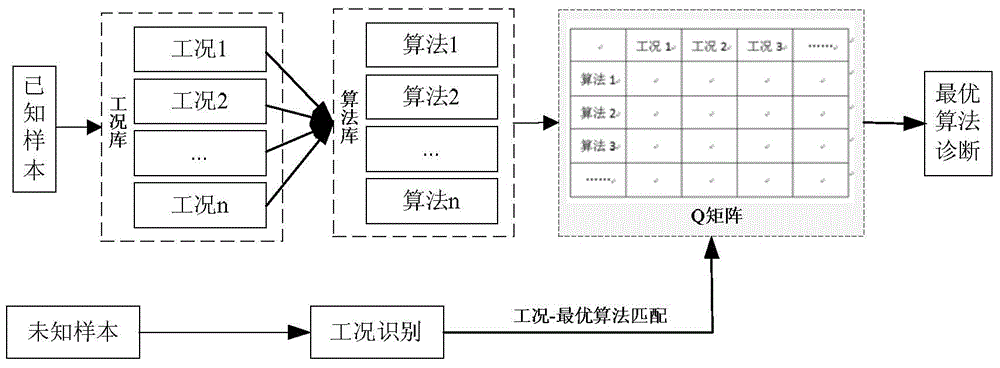
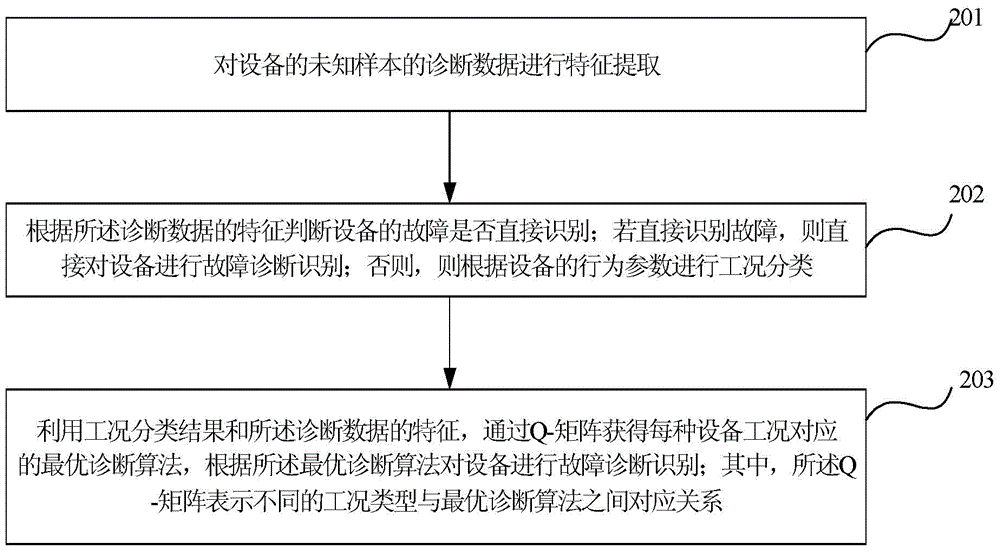
The invention relates to a fault diagnosis method and device based on device working condition. The method comprises the steps that feature extraction is conducted on diagnosis data of unknown samples of a device; whether the fault of the device can be recognized directly or not is judged according to features of the diagnosis data; if the fault is recognized directly, fault diagnosis recognition is conducted on the device directly; if not, working condition recognition and classification are conducted according to behavior parameters of the device; optical diagnosis algorithms corresponding to all the working conditions of the device are obtained through a Q-matrix by the adoption of the working condition classification result and the features of the diagnosis data, wherein the Q-matrix represents the corresponding relation between different working condition types and the optical diagnosis algorithms.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Signaling adaptive-quantization matrices in JPEG using end-of-block codes
Previously-unused slots in a Huffman code table associated with a Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) image file are associated with various quantization matrices (Q matrices) that are used to quantize data blocks of the JPEG image file. Huffman codes associated with the various Q matrices permit the particular Q matrix used to quantize a given data block to be signaled by a decoder as an end-of-block (EOB) code. The EOB codes and the Huffman code table are sent with the JPEG image file. Upon decoding of the image file, a standard JPEG decoder reads each of the EOB codes as a standard JPEG EOB code and does not vary the Q matrix. A modified decoder reads from each of the EOB codes which Q matrix was used to encode each particular data block of the image and uses that Q matrix to dequantize the data block.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Galois field multiplying unit realizing device
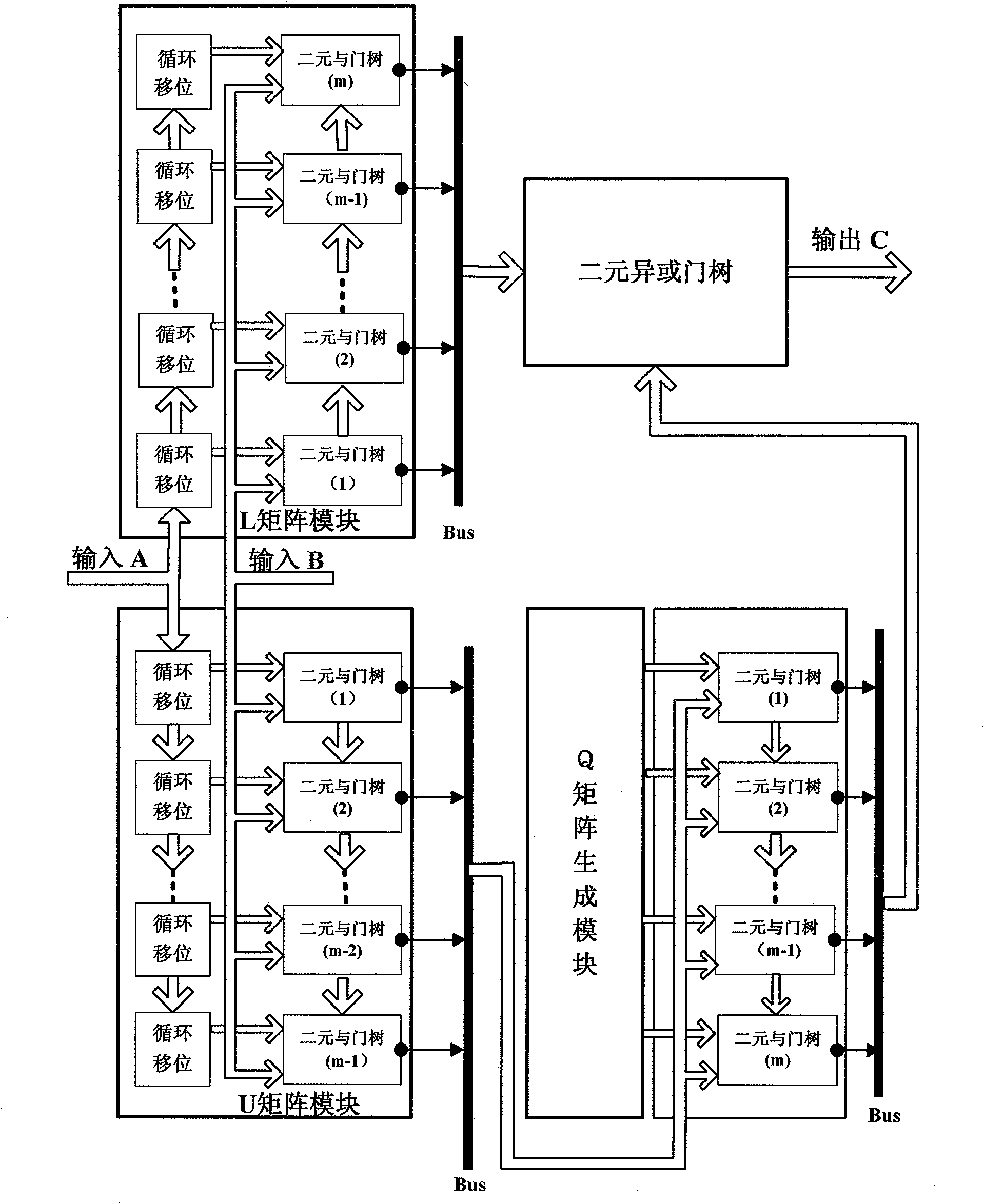
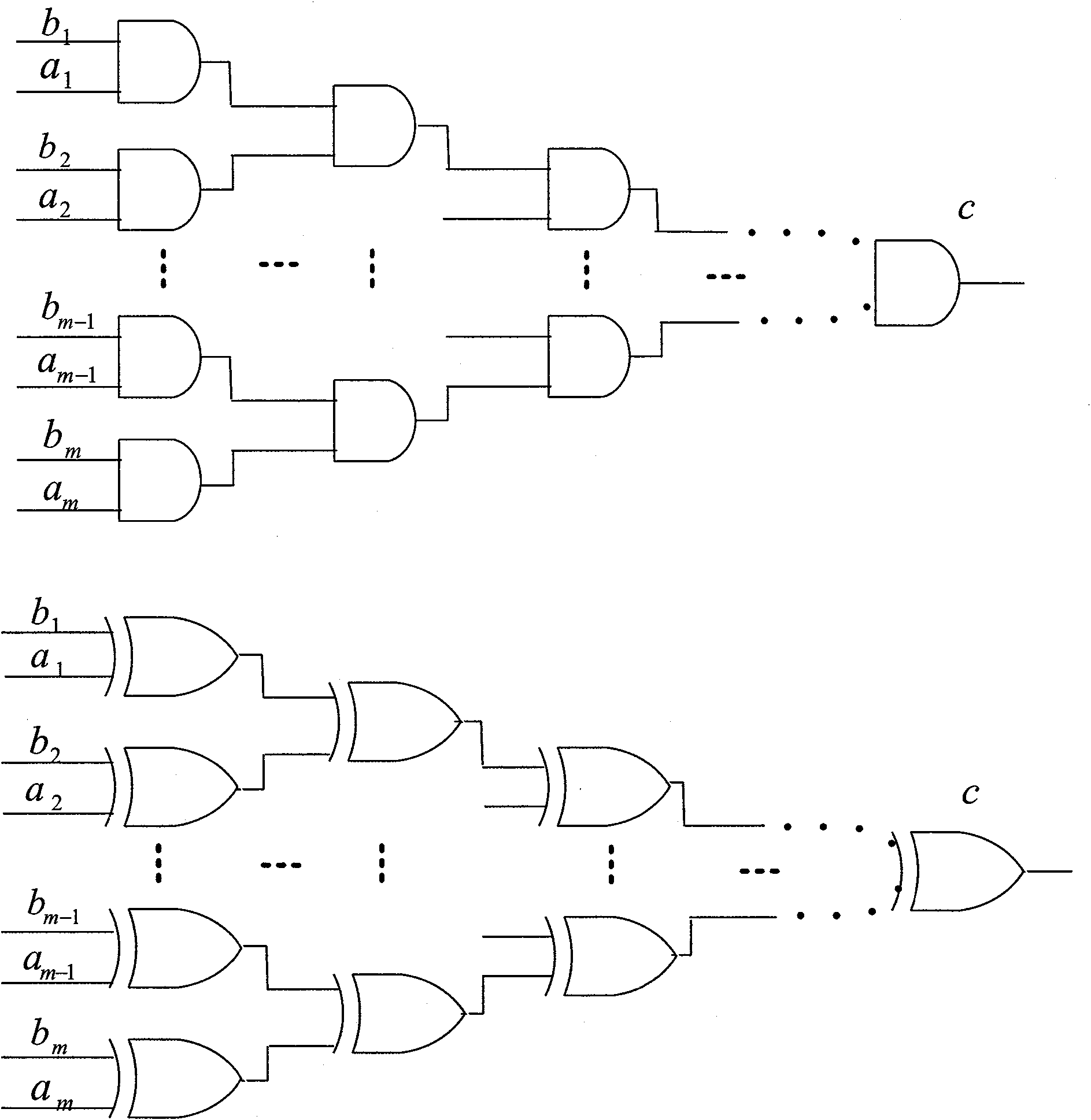
The invention discloses a Galois field multiplying unit realizing device which converts the calculation of Galois field multiplication into the multiplication of matrix modules. The Galois field multiplying unit realizing device comprises an L matrix module, a U matrix module, an m-bit data input / output interface, a Q matrix generating module and the like. The structure of the Galois field multiplying unit realizing device relates to a 3m-1 group of binary and gate trees and one group of exclusive or gate trees. The embodiment of the invention provides an example for realizing a Galois field GF (2<128>) multiplying unit on a basis of an FPGA when m=128. The multiplying unit can be used for the hardware realization of a G-hash function and can achieve a calculation speed of over 10Gbps.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
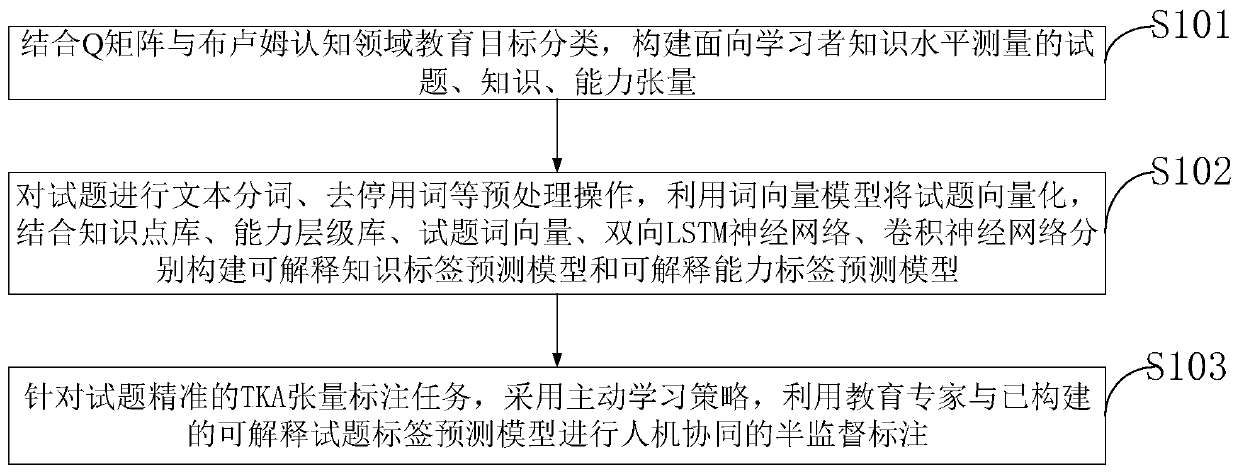
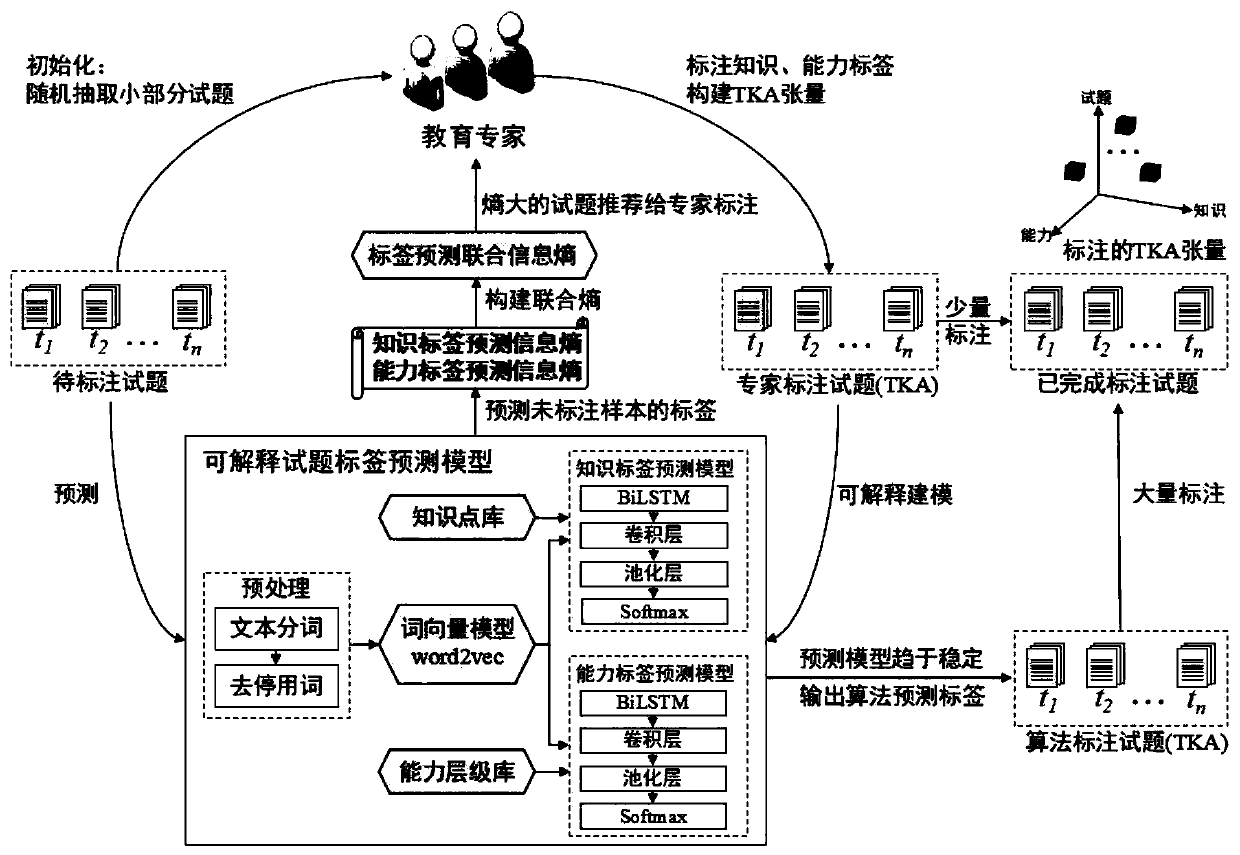
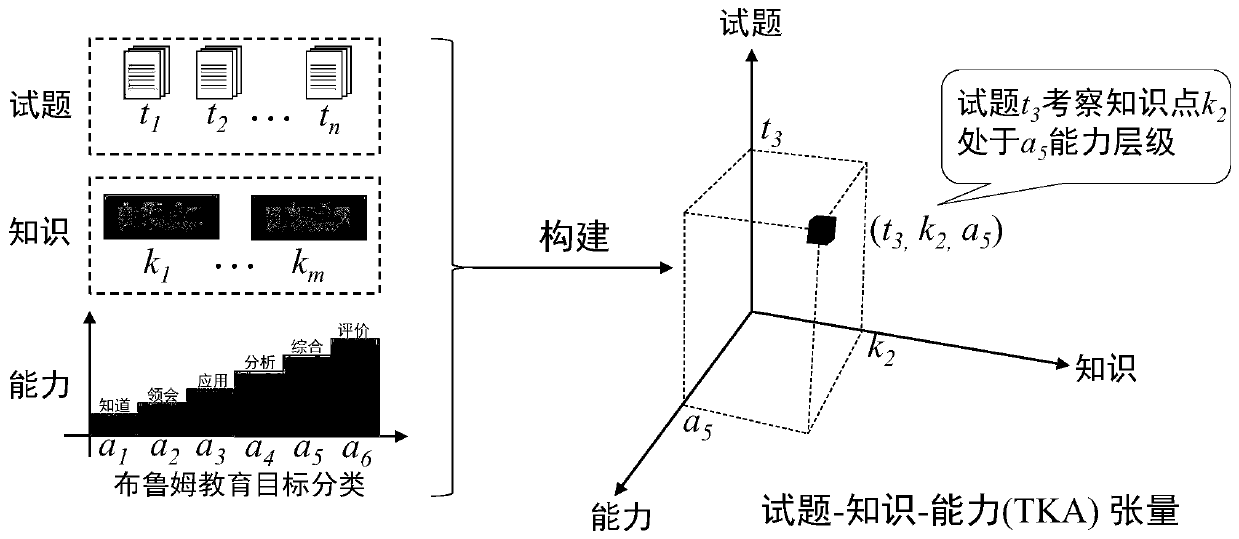
Knowledge measurement-oriented test question, knowledge and ability tensor construction and labeling method
ActiveCN111241243AExplanatoryTo achieve collaborative annotationCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesQ-matrixTest question
The invention belongs to the technical field of education data mining, and discloses a knowledge measurement-oriented test question, knowledge and ability tensor construction and labeling method. In combination of a Q matrix and Bloom cognitive field education target classification, knowledge point mastering is divided into six cognitive ability levels: knowing, understanding, application, analysis, integration, evaluation and test question, knowledge and ability tensor construction. An interpretable test question label prediction model is constructed by adopting an active learning strategy, interpretable label prediction information entropies are obtained, unlabeled samples are input into the prediction model by utilizing the trained interpretable test question label prediction model, andthe label prediction information entropies with relatively high interpretability are fed back, so that man-machine coordination is carried out. According to the method, the influence of subjectivityof manual labeling on the TKA tensor is reduced, the labeling accuracy and efficiency are high, and the expert labor cost is greatly reduced. The method is high in mobility, can be applied to examination and annotation of test question knowledge points of all subjects, and is better in applicability.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
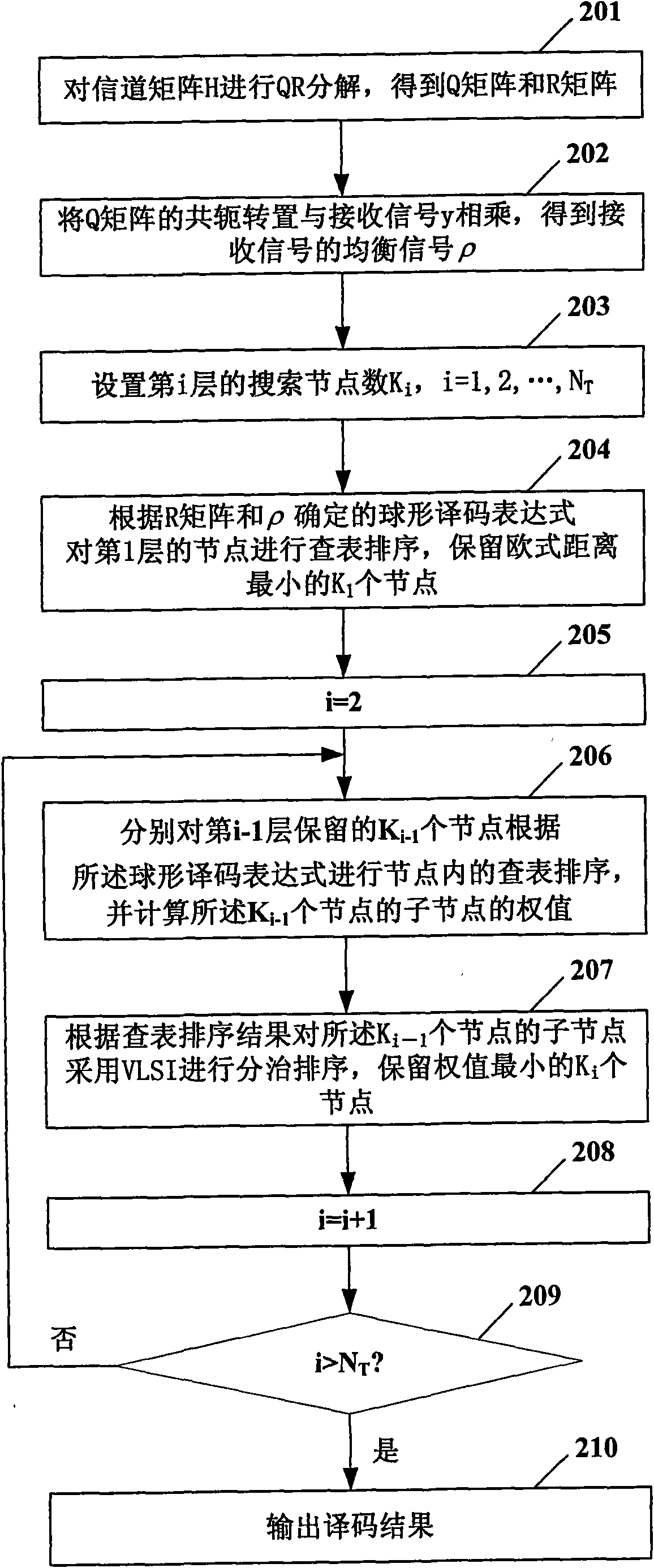
Sphere decoding detection method based on ultra large scale integrated circuit
InactiveCN101557269AReduce operational complexityImprove resource utilizationCode conversionCode division multiplexQR decompositionQ-matrix
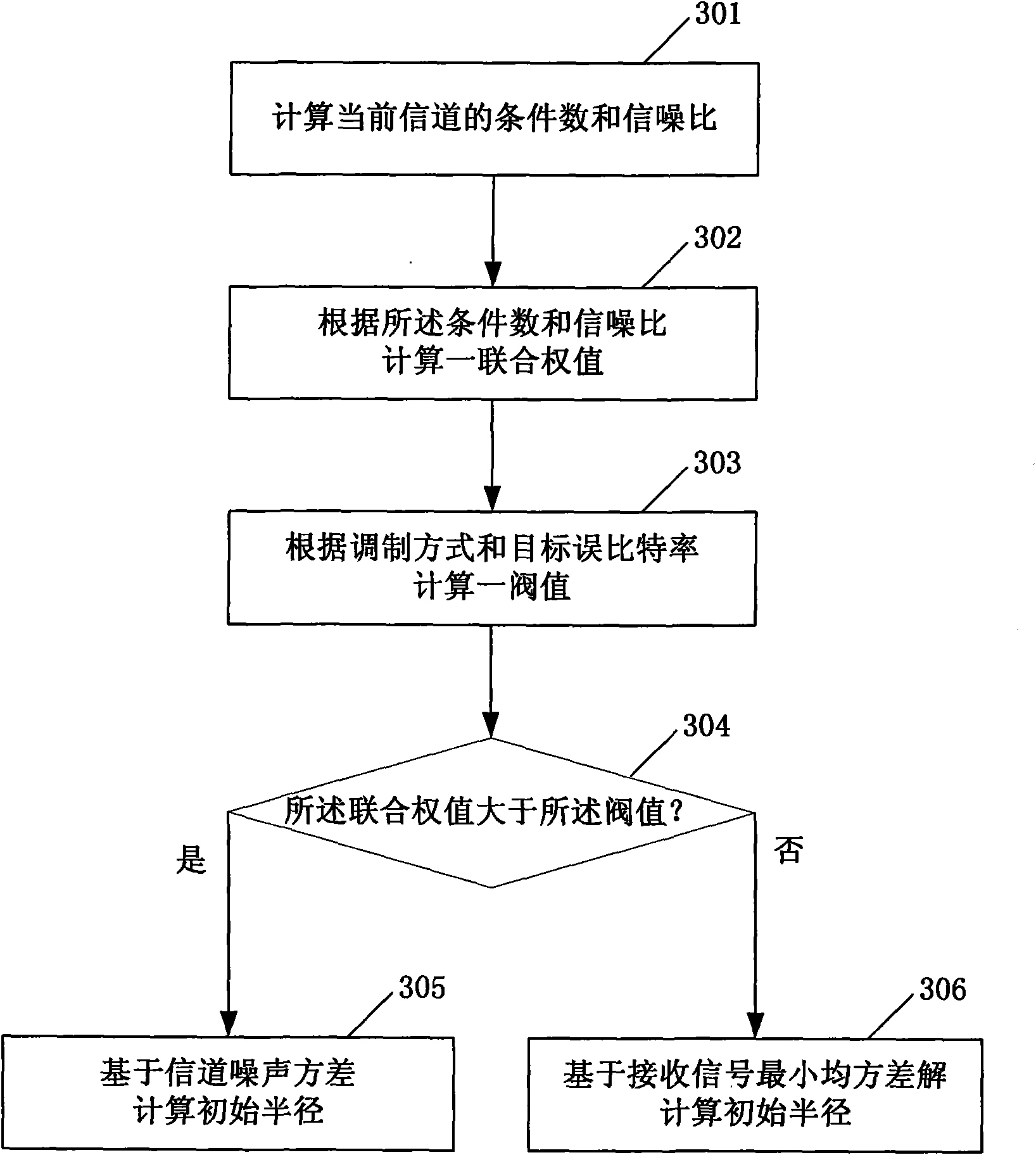
The invention provides a sphere decoding detection method based on an ultra large scale integrated circuit, comprising the following steps of: A. carrying out QR decomposition to a channel matrix; B. multiplying conjugate transpose of a Q matrix and received signals to obtain an equalizing signal Rho; C. setting the searching node number Ki of an ith layer; D. determining sphere decoding expression according to an R matrix and Rho, carrying out table-looking-up sequencing to the nodes of the 1st layer and reserving K1 of nodes with minimum Euclidean distances; E. respectively executing searching of the ith layer, carrying out table-looking-up sequencing in nodes according to the sphere decoding expression to the Ki-1 of nodes reserved by the ith-1st layer, calculating weights of subnodes of the Ki-1 of nodes, then carrying out divide-and-conquer sequencing to subnodes of the Ki-1 of nodes by adopting VLSI according to the result of table-looking-up sequencing and reserving Ki of nodes with minimum weights; and F. outputting decoding result when searching the last layer. The sphere decoding detection method can effectively reduce the operation complexity of sphere decoding.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
QR decomposition in an integrated circuit device
InactiveUS8539016B1Promote decompositionReduce hardware costsData mergingComplex mathematical operationsQ-matrixQR decomposition
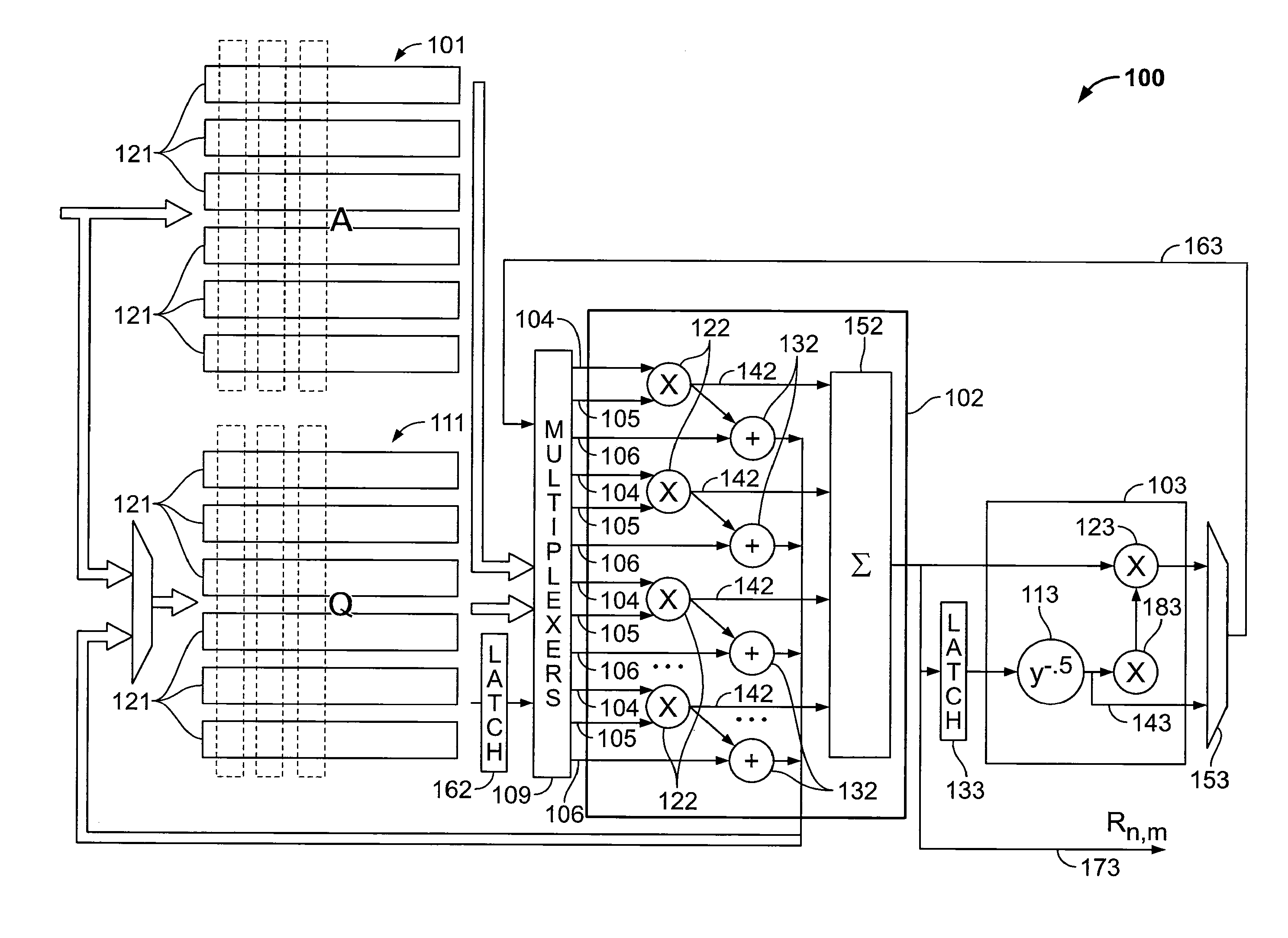
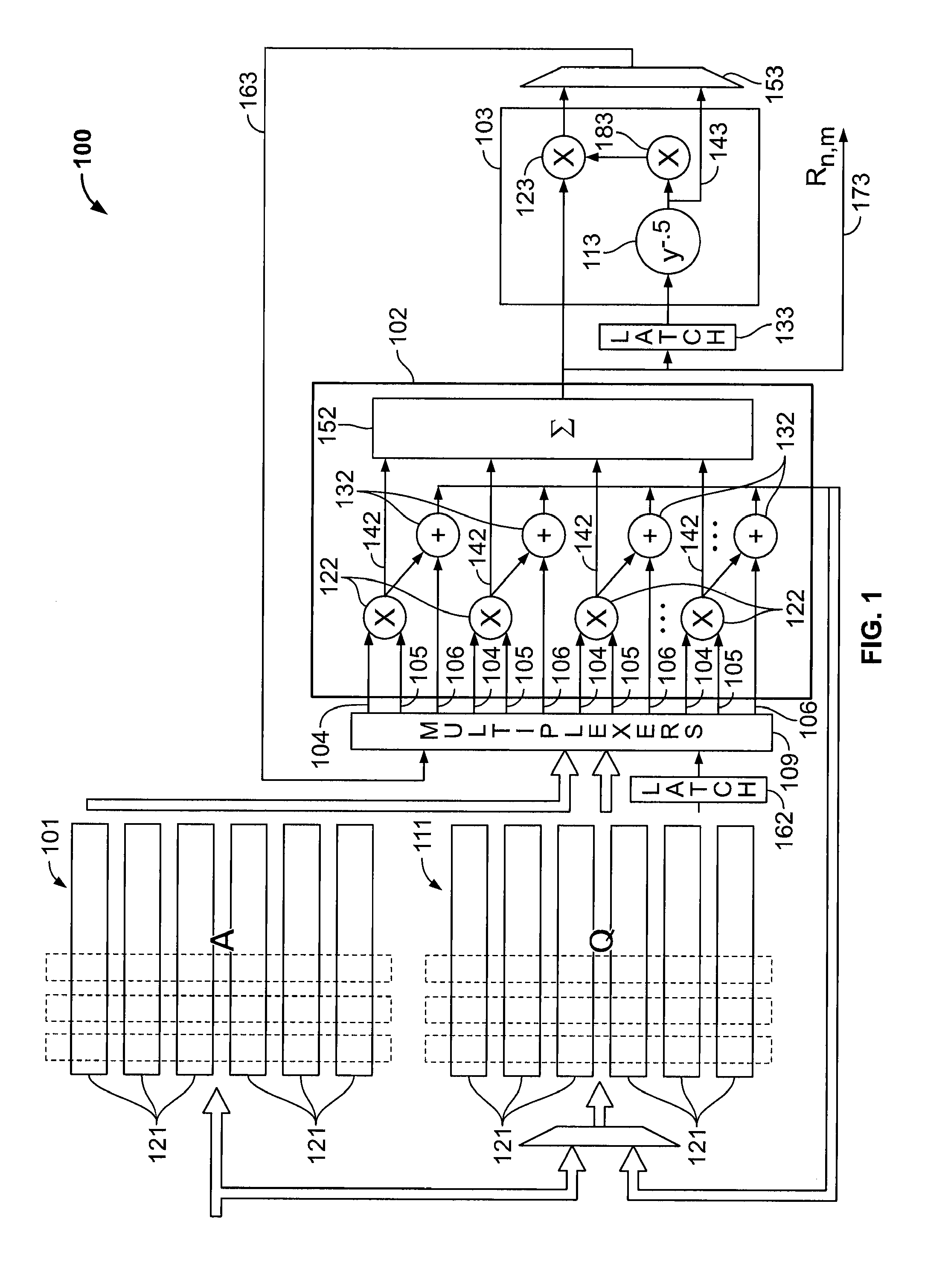
Circuitry speeds up the QR decomposition of a matrix. The circuitry can be provided in a fixed logic device, or can be configured into a programmable integrated circuit device such as a programmable logic device. This implementation performs Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization with no dependencies between iterations. QR decomposition of a matrix can be performed by processing entire columns at once as a vector operation. Data dependencies within and between matrix columns are removed, as later functions dependent on an earlier result may be generated from partial results somewhere in the datapath, rather than from an earlier completed result. Different passes through the matrix are timed so that different computations requiring the same functional units arrive at different time slots. After the Q matrix has been calculated, the R matrix may be calculated from the Q matrix by taking its transpose and multiplying the transpose by the original input matrix.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
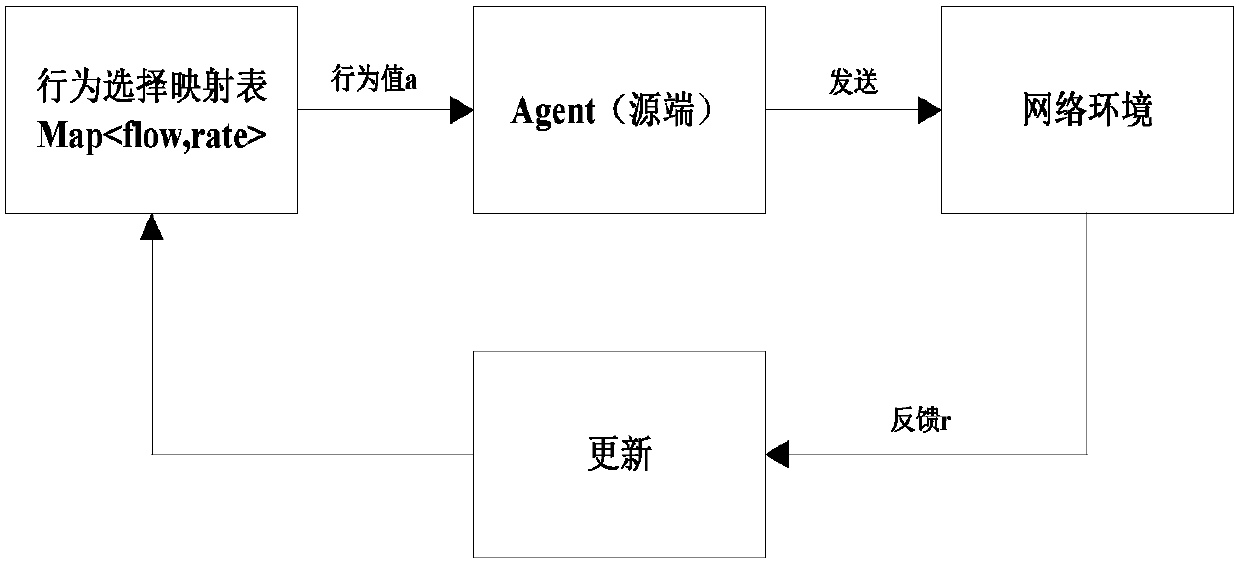
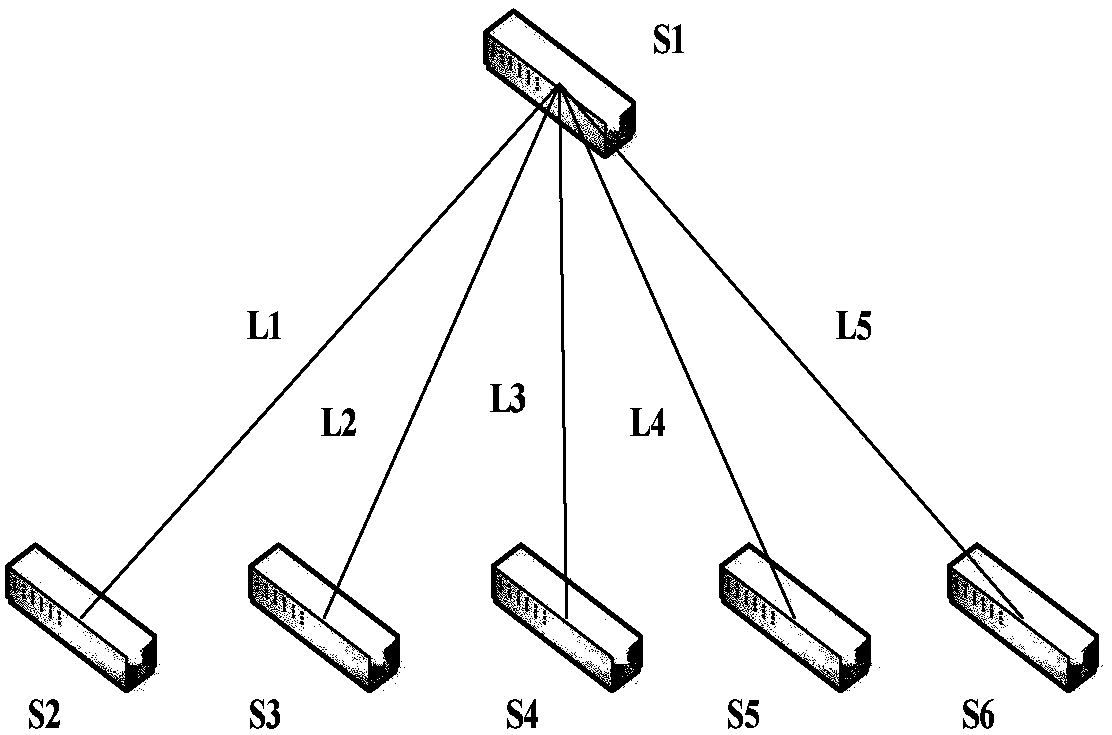
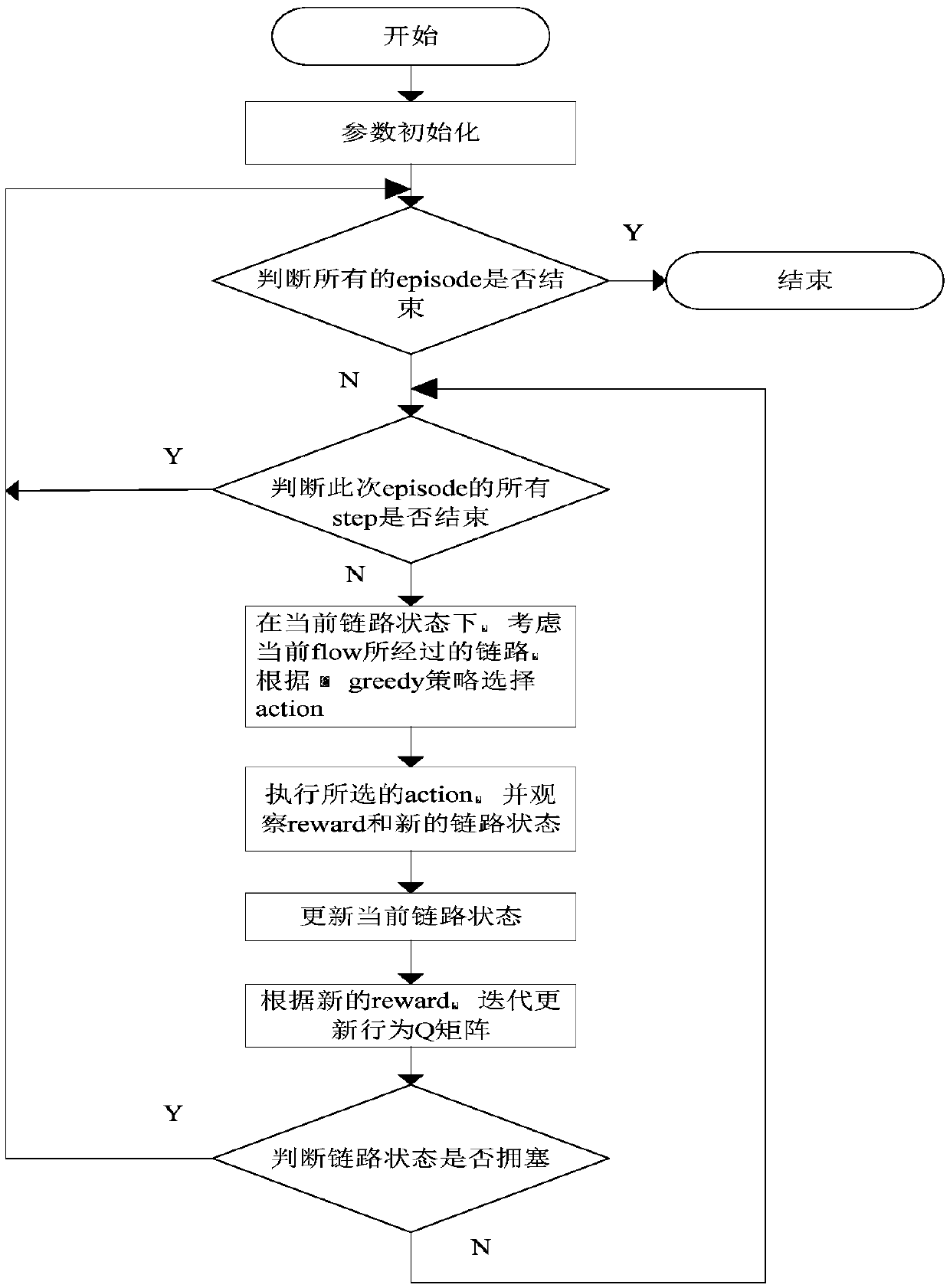
SDN data center congestion control method based on Sarsa
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Qr decomposition apparatus and method for MIMO system
InactiveUS20090154579A1Simple processReduce in quantitySpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityQ-matrixQR decomposition
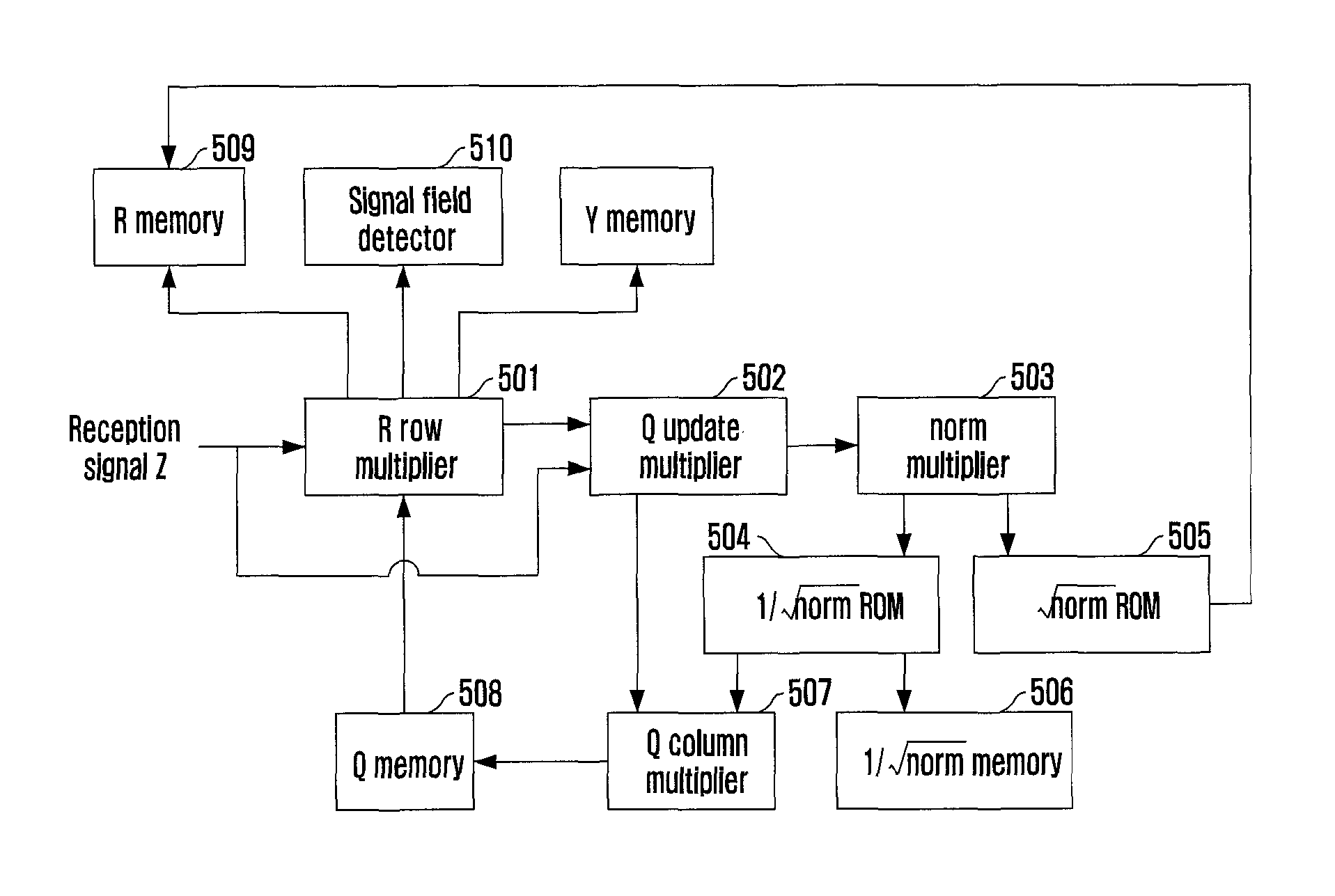
Provided is a QR decomposition apparatus and method that can reduce the number of computers by sharing hardware in an MIMO system employing OFDM technology to simplify a structure of hardware. The QR decomposition apparatus includes a norm multiplier for calculating a norm; a Q column multiplier for calculating a column value of a unitary Q matrix to thereby produce a Q matrix vector; a first storage for storing the Q matrix vector calculated in the Q column multiplier; an R row multiplier for calculating a value of an upper triangular R matrix by multiplying the Q matrix vector by a reception signal vector; and a Q update multiplier for receiving the reception signal vector and an output of the R row multiplier, calculating an Q update value through an accumulation operation, and providing the Q update value to the Q column multiplier to calculate a next Q matrix vector.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Sphere decoding detection method based on breadth-first search
InactiveCN101582750AReduce operational complexityEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionQ-matrixQR decomposition
The invention provides a sphere decoding detection method based on breadth-first search, comprising the following steps: step A, carrying out QR decomposition on channel matrix H to obtain Q matrix and R matrix; step B, multiplying conjugate transpose of Q matrix with received signal y to obtain equalizing signal rho of the received signal; step C, setting search nodes of Ki, i=1, 2, ..., N, and N is the number of sending antennae; and step D, carrying out breadth-first search on R matrix and rho, wherein preserving Ki nodes with the lowest weight when carrying out the i layer search. The method of the invention can effectively reduce operating complexity of the sphere decoding and is easy to realize by hardware.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
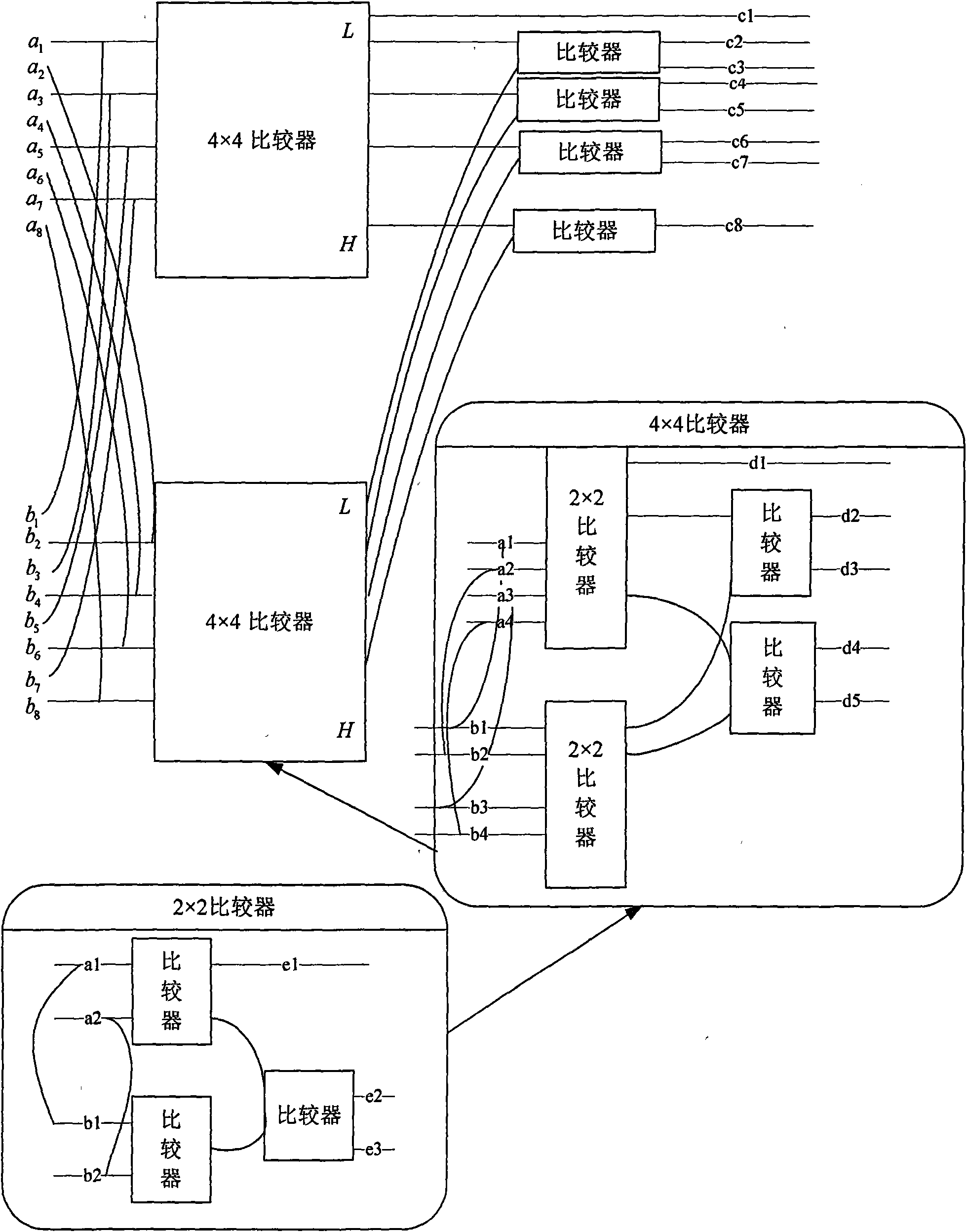
Sorted QR decomposition method and MIMO detection method
InactiveCN1968238AReduce implementation complexityImprove sorting effectMultiplex communicationRadio transmissionQ-matrixQR decomposition
The invention relates to a sequence QR decompose method and MIMO checking method, wherein it comprises that: a, selecting one frequency unit form several frequency units, processing QR decompose on the channel characteristic matrix, to obtain relative Q matrix, R matrix and sequence, while said sequence is used as initial sequence of present frequency unit near the frequency unit; b, based on the diagonal amplitude of present R matrix, judging if present position and next position exchanged initial sequence can reduce code error transmission; c, if it can reduce the error code transmission, exchanging present position and next position, to obtain the sequence result; d, via said result, processing QR decompose on the channel characteristic matrix, to obtain Q and R matrixes. The invention has low complexity and better sequence property.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
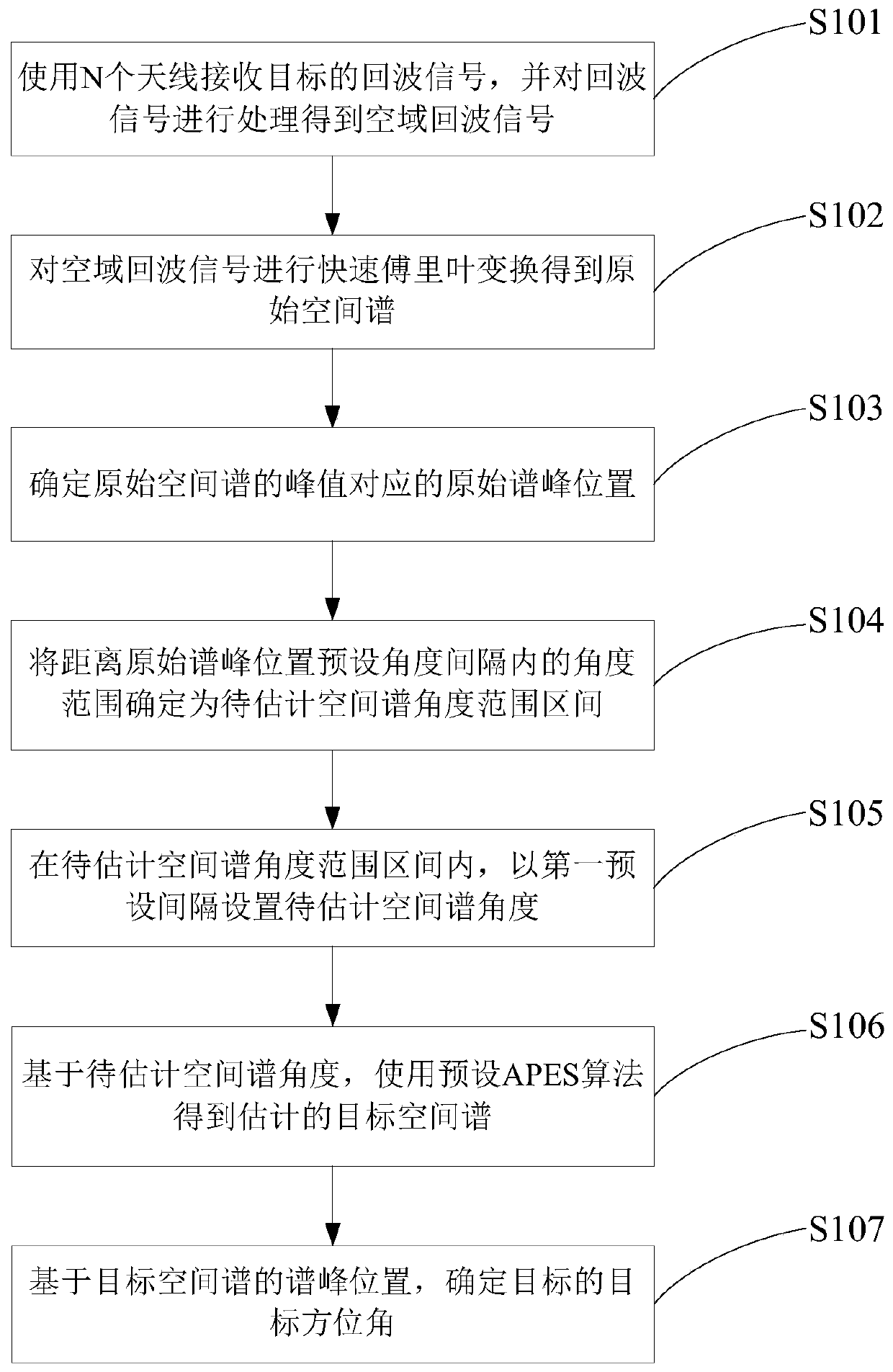
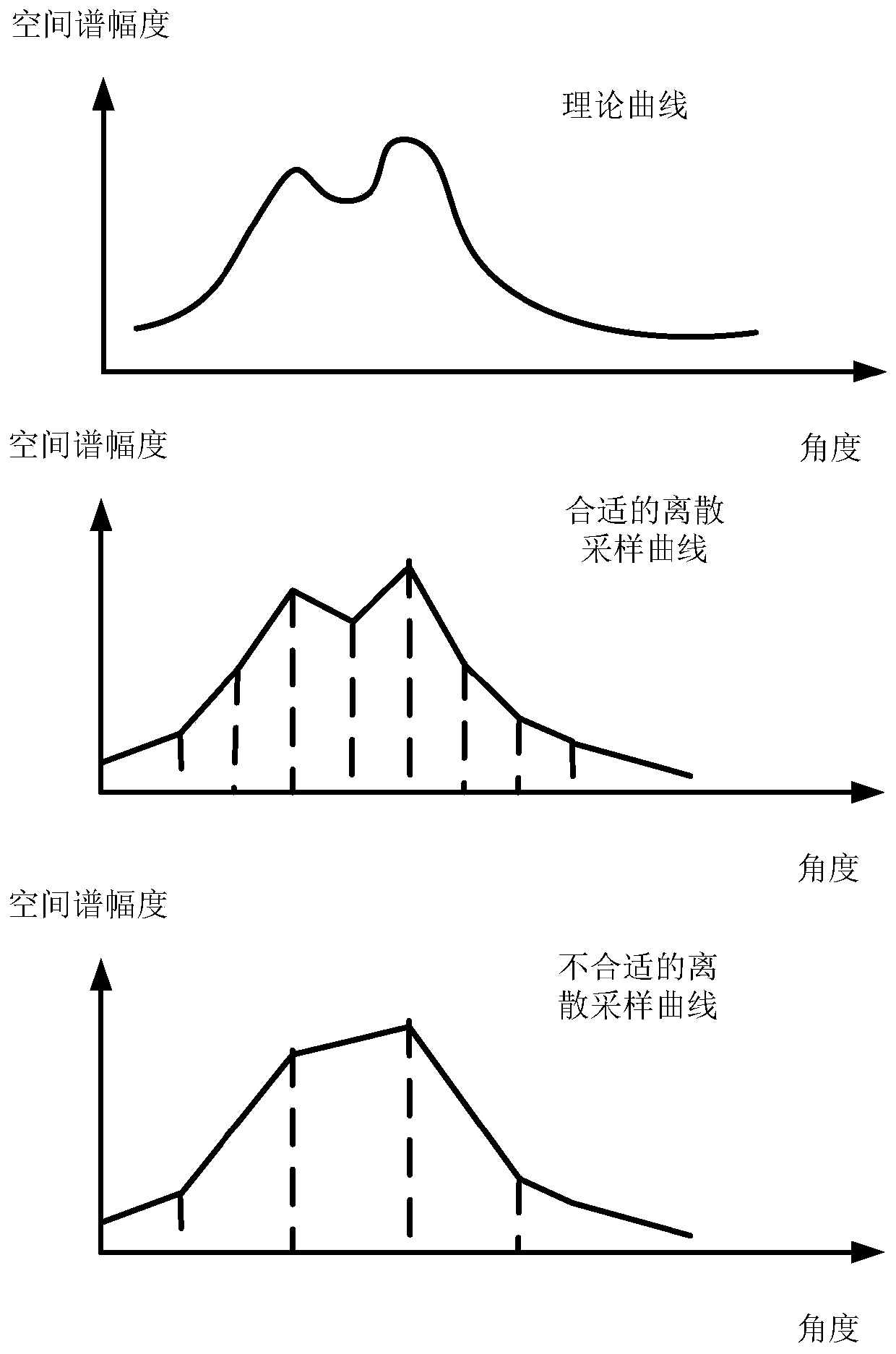
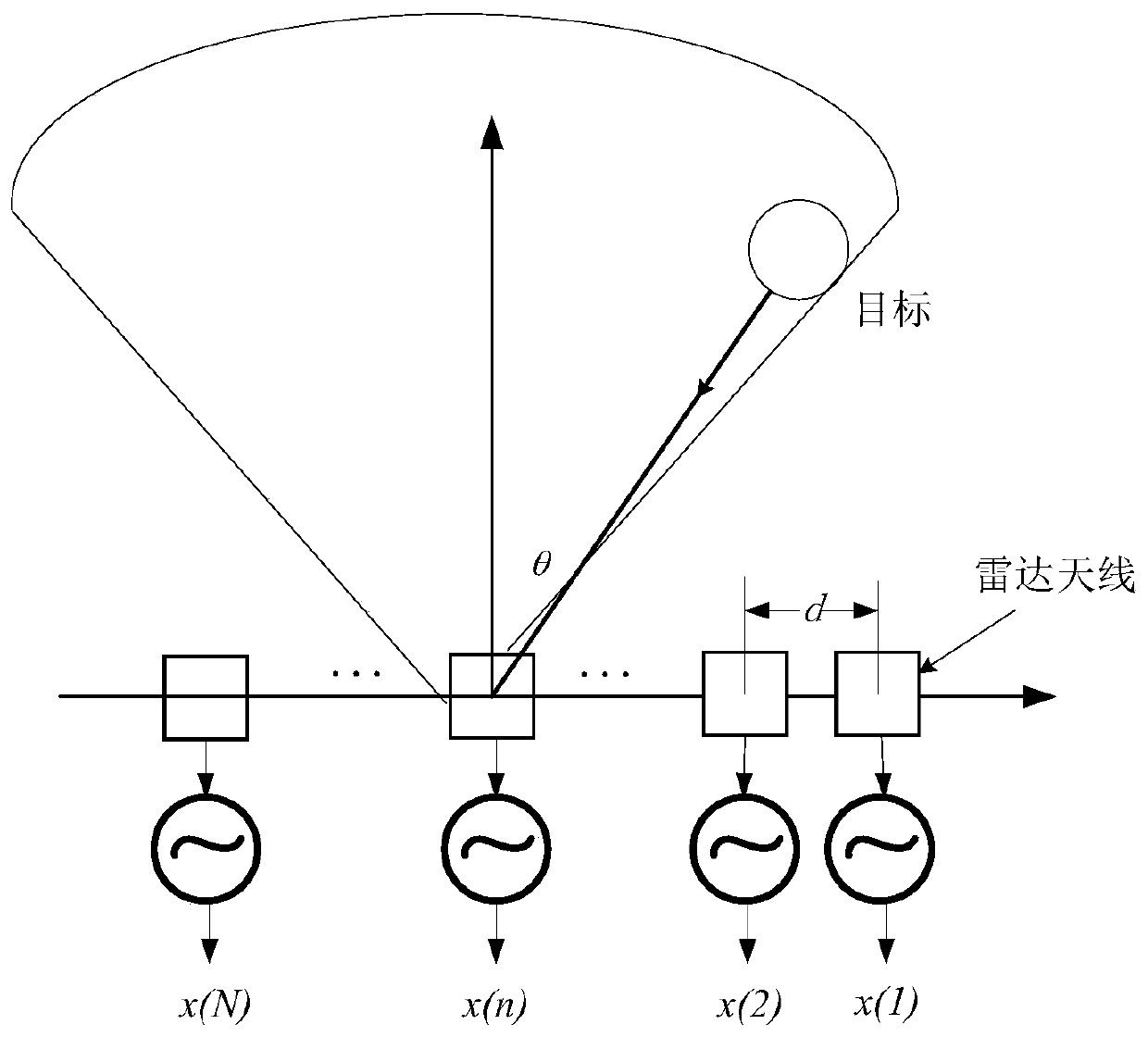
Method for measuring target azimuth angle by using vehicle-mounted radar and vehicle-mounted radar
ActiveCN110501682ANarrow down the range of valuesReduce computationWave based measurement systemsQ-matrixPeak value
The invention discloses a method for measuring a target azimuth angle by using a vehicle-mounted radar and a vehicle-mounted radar. According to the method and the vehicle-mounted radar, spatial domain echo signals are obtained according to the received echo signals of a target; an original spectral peak position corresponding to the peak value of an original spatial spectrum obtained according tothe spatial domain echo signals is determined; a to-be-estimated spatial spectrum angle range interval is determined based on the original spectral peak position; a to-be-estimated spatial spectrum angle is set; a preset APES algorithm is adopted for the angle so as to obtain the estimation result of a target spatial spectrum; and the target azimuth angle of the target is estimated based on the estimated spectral peak position of the target spatial spectrum. According to the method, the to-be-estimated spatial spectrum angle range interval is obtained through fast Fourier transform, so that the value range of the original to-be-estimated spatial spectrum angle can be narrowed; a Q matrix in the preset APES algorithm is obtained only according to a sample correlation matrix, so that the Qmatrix does not transform along with the to-be-estimated spatial spectrum angle; and inversion operation needs to be performed on the Q matrix once, and therefore, the calculation of super-resolutionangle measurement can be realized in a short time.
Owner:BEIJING JINGWEI HIRAIN TECH CO INC
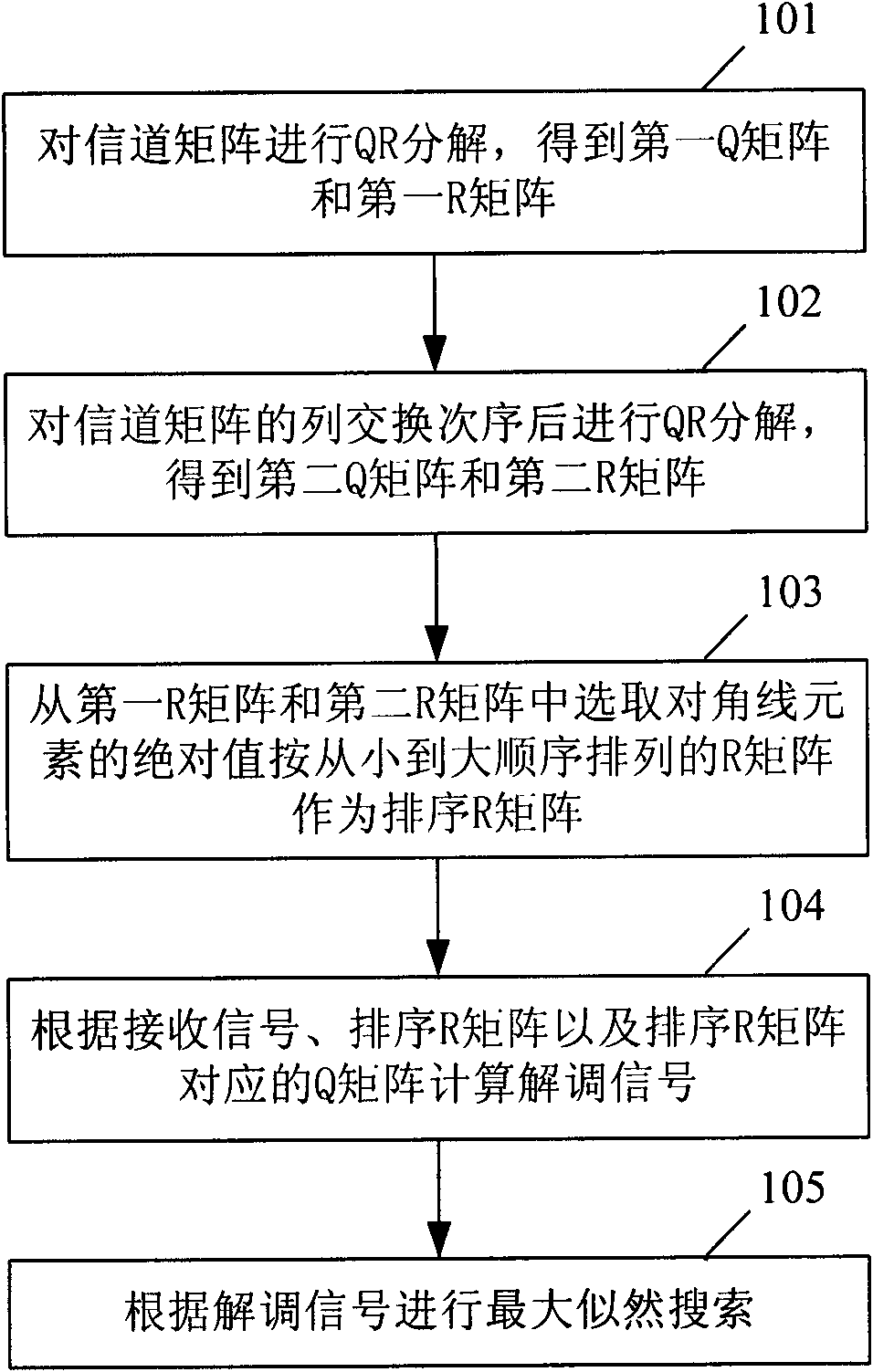
Maximum likelihood detection method and device in multi-input multi-output system
InactiveCN101615980AReduce complexityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionQR decompositionMulti input
The invention provides a maximum likelihood detection method and a device in a multi-input multi-output system. The method comprises the following steps: A. carrying out QR decomposition on a channel matrix to obtain a first Q matrix and a first R matrix; B. carrying out QR decomposition on rows of the channel matrix after exchanging the sequence so as to obtain a second Q matrix and a second R matrix; C. selecting the R matrix with the absolute valves of diagonal elements of being arranged according to the sequence from small to large from the first R matrix and the second R matrix as a quenching R matrix; D. by receiving signals, exchanging R matrix and sequencing the Q matrix corresponding to the R matrix, calculating demodulated signals; and E. carrying out maximum likelihood searching according to the demodulated signals. The invention can effectively reduce the algorithm complexity of MIMO detection when the number of the receiving antennas is 2.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
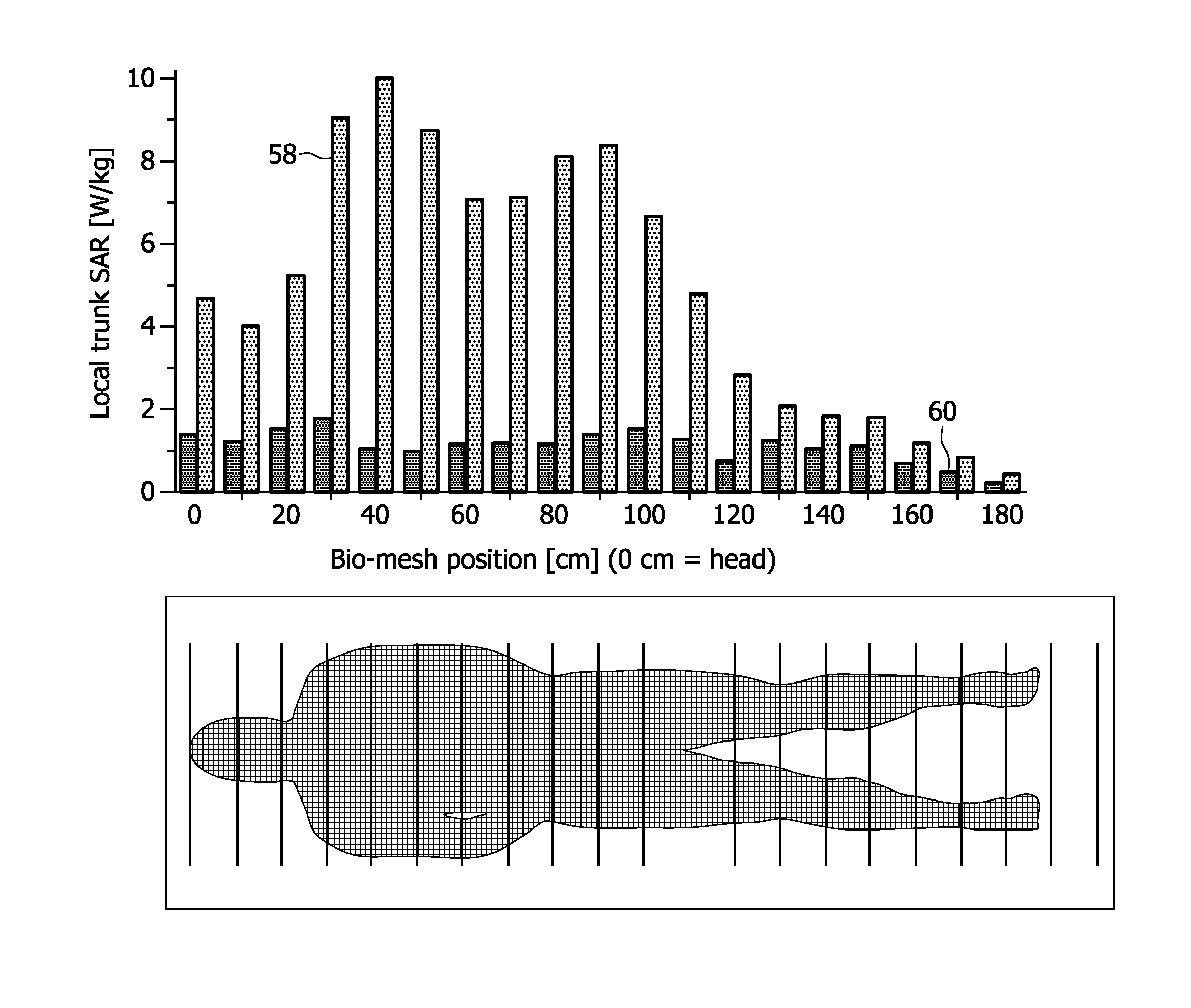
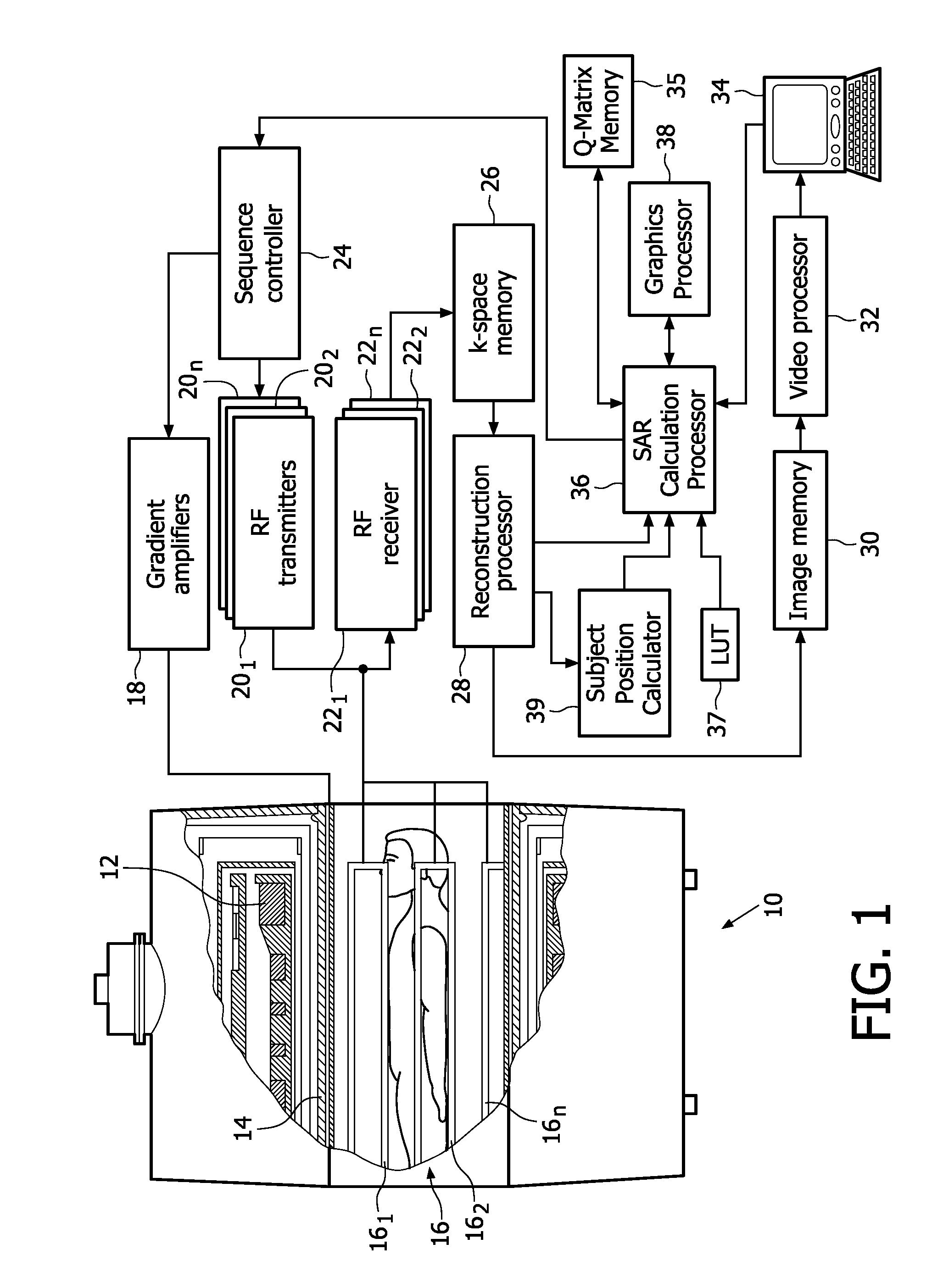
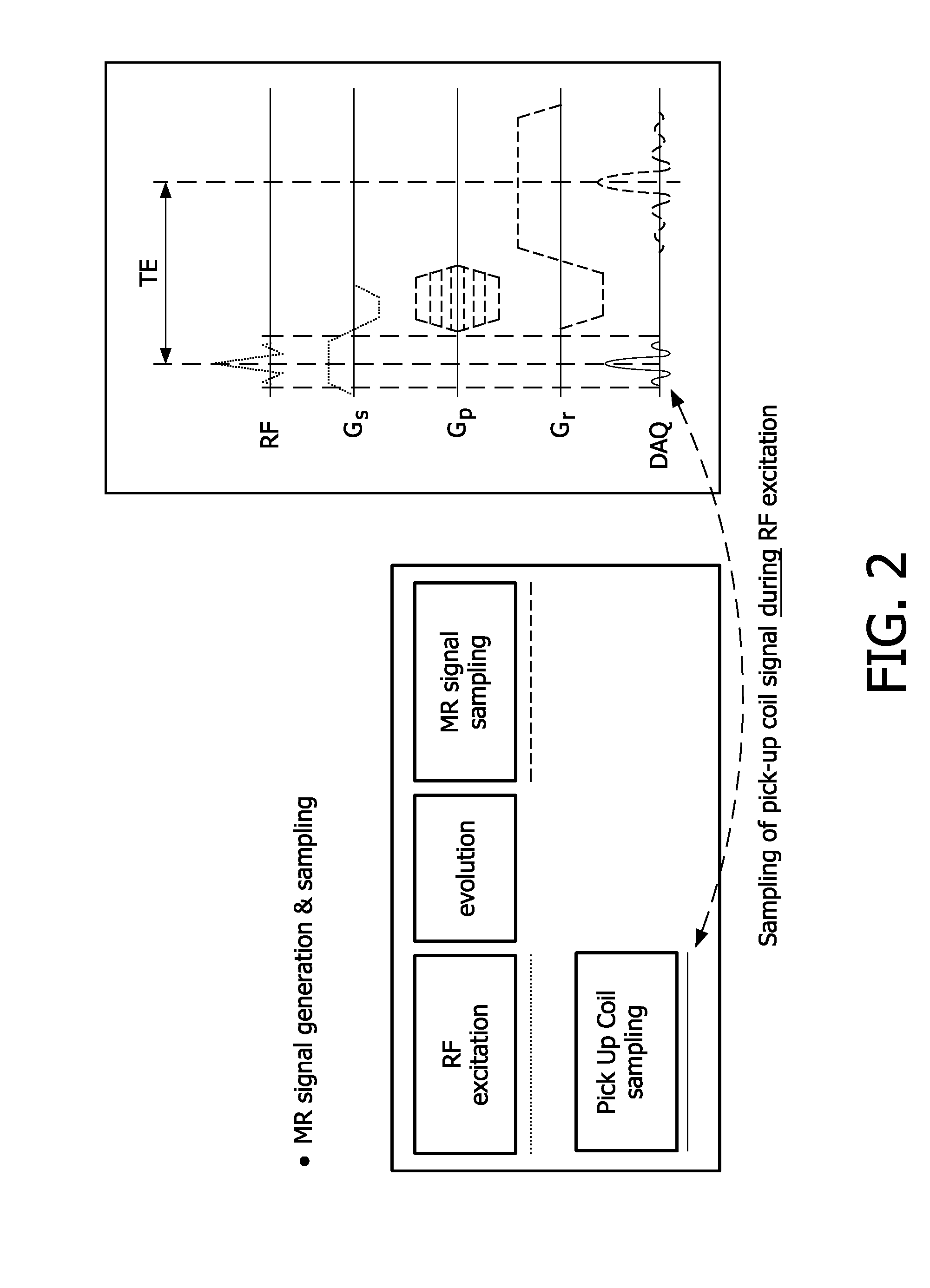
Real-time local and global SAR estimation for patient safety and improved scanning performance
ActiveUS8941380B2Efficient verificationIncreased calculationElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRQ-matrixEnergy absorption
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for public-key cryptography based on error correcting codes
ActiveUS9191199B2Improve securitySmall sizeKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationQ-matrixComputer hardware
Methods and apparatus for generating a private-public key pair, for encrypting a message for transmission through an unsecure communication medium (30), and for decrypting the message are disclosed. The methods are based on the well-known McEliece cryptosystem or on its Niederreiter variant. More general transformation matrices Q are used in place of permutation matrices, possibly together with an appropriate selection of the intentional error vectors. The transformation matrices Q are non-singular n×n matrices having the form Q=R+T, where the matrix R is a rank-z matrix and the matrix T is some other matrix rendering Q non-singular. The new Q matrices, though at least potentially being dense, have a limited propagation effect on the intentional error vectors for the authorized receiver. The use of this kind of matrices allows to better disguise the private key into the public one, without yielding any further error propagation effect. Based on this family of Q matrices, the presently proposed cryptosystem enables the use of different families of codes than Goppa codes, such as RS codes, by ensuring increased public key security.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
QR decomposition apparatus and method for MIMO system
InactiveUS8068560B2Simple hardware structureReduce in quantitySpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityQ-matrixQR decomposition
Provided is a QR decomposition apparatus and method that can reduce the number of computers by sharing hardware in an MIMO system employing OFDM technology to simplify a structure of hardware. The QR decomposition apparatus includes a norm multiplier for calculating a norm; a Q column multiplier for calculating a column value of a unitary Q matrix to thereby produce a Q matrix vector; a first storage for storing the Q matrix vector calculated in the Q column multiplier; an R row multiplier for calculating a value of an upper triangular R matrix by multiplying the Q matrix vector by a reception signal vector; and a Q update multiplier for receiving the reception signal vector and an output of the R row multiplier, calculating an Q update value through an accumulation operation, and providing the Q update value to the Q column multiplier to calculate a next Q matrix vector.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
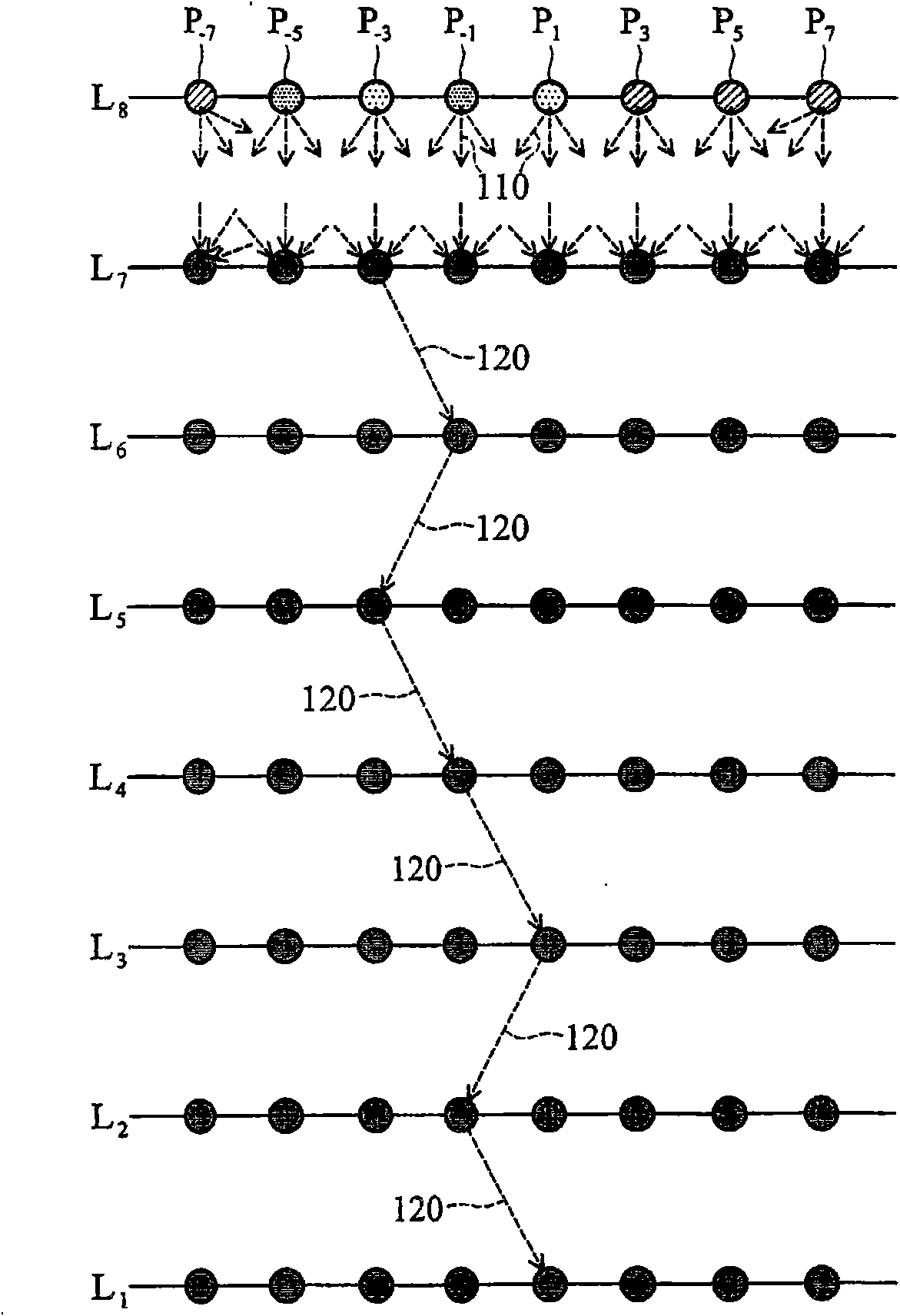
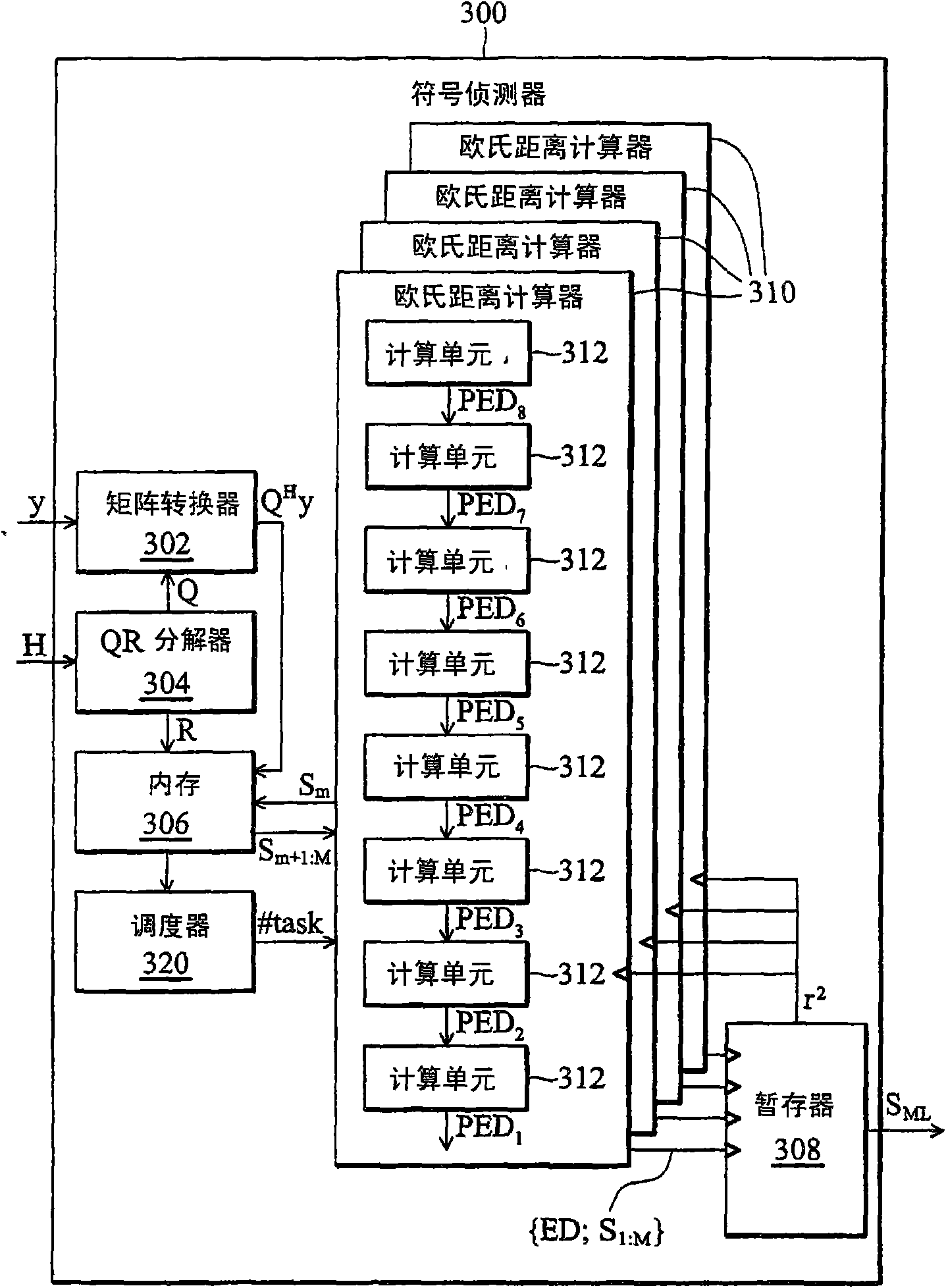
Symbol detector and sphere decoding method
ActiveCN101645758ASpatial transmit diversityMultiple carrier systemsMatrix convertersDecoding methods
The invention provides a symbol detector and a sphere decoding method. The symbol detector can receive a wireless signal and search a maximum similarity solution. In the symbol detector, a QR decomposer can perform a QR decomposing operation on a passage response matrix to generate a Q matrix and an R matrix. A matrix converter generates an inner product matrix according to the Q matrix and the wireless signal. A scheduler plans a searching task into a plurality of independent sub-searching tasks. A plurality of Euclidean distance calculators operate in parallel under the control of the scheduler. A plurality of calculating units in the Euclidean distance calculators read the R matrix and the inner product matrix through a pipelined construction to search the maximum similarity solution.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
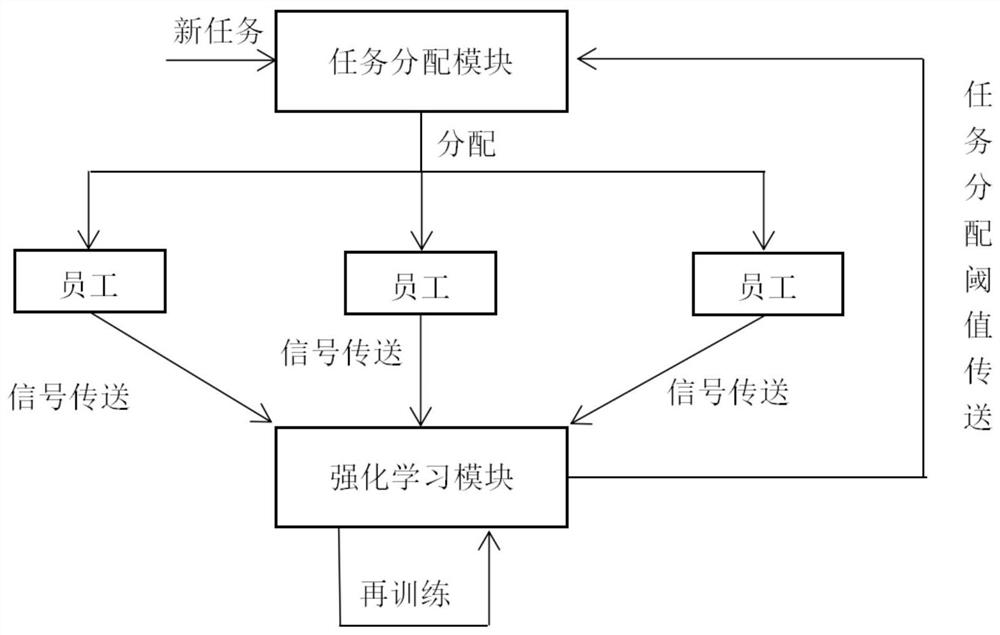
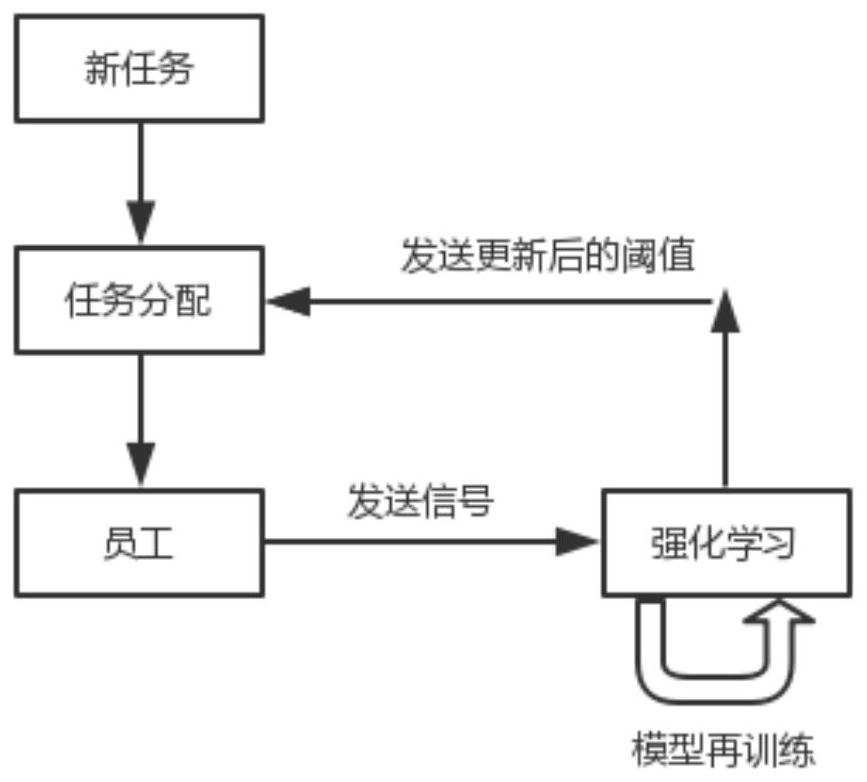
Task allocation method based on reinforcement learning
The invention belongs to the technical field of reinforcement learning, and discloses a task allocation method based on reinforcement learning, which comprises the steps of collecting and obtaining employee information and task information; establishing a reinforcement learning model according to the employee information and the task information, initializing a Q matrix, a state vector S, an action vector A and a reward matrix R, setting hyper-parameters, and performing iterative computation of the Q matrix; updating a current task allocation threshold of the employee by utilizing the reinforcement learning model; obtaining weight information of each employee according to the current task allocation threshold of each employee and the number of currently allocated tasks; and allocating thenew task according to the weight information of all employees of the to-be-allocated task. According to the invention, the problem that the task allocation method based on the labor cost in the priorart cannot efficiently and reasonably perform task allocation is solved, the task allocation can be automatically performed online through a reinforcement learning method, and the defects of manual task allocation are overcome.
Owner:武汉实为信息技术股份有限公司
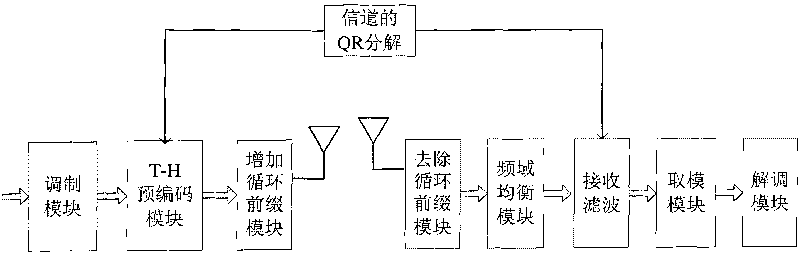
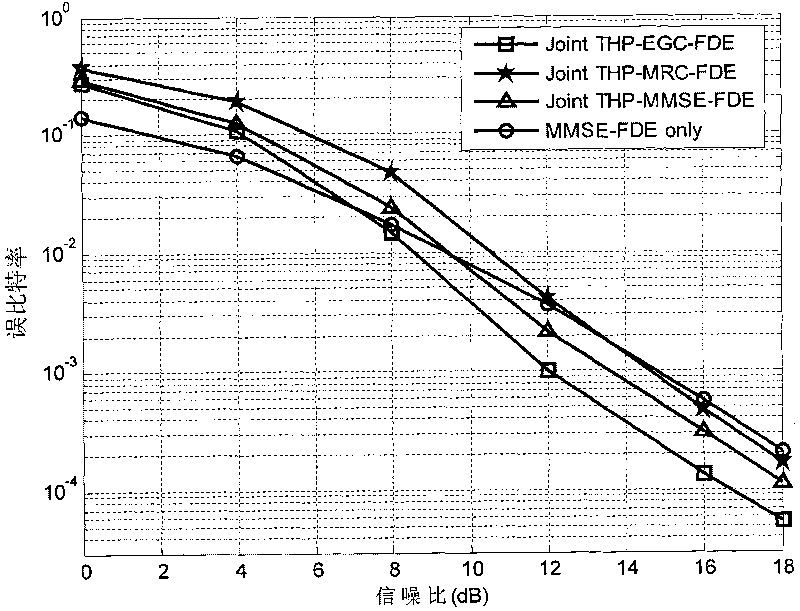
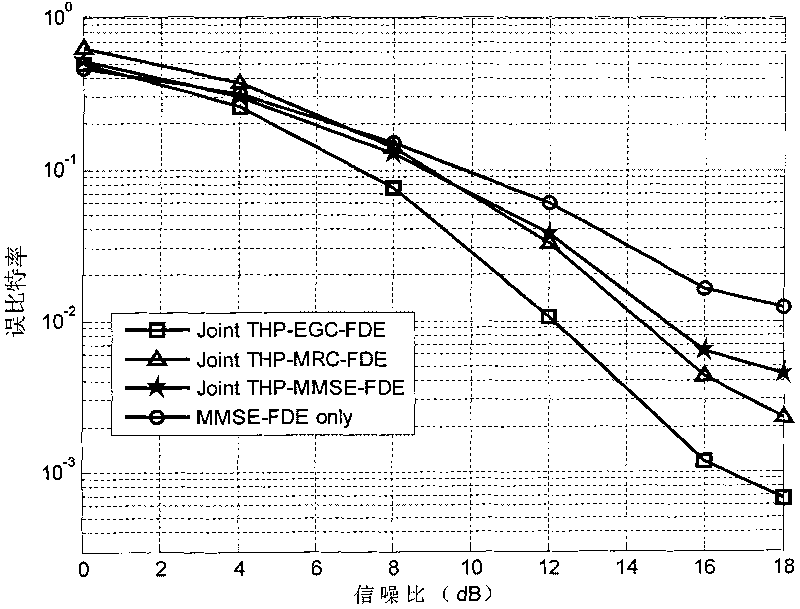
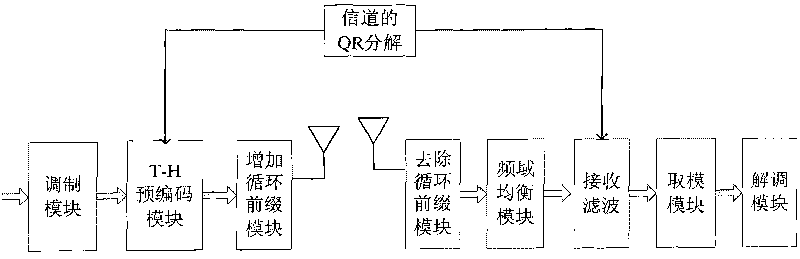
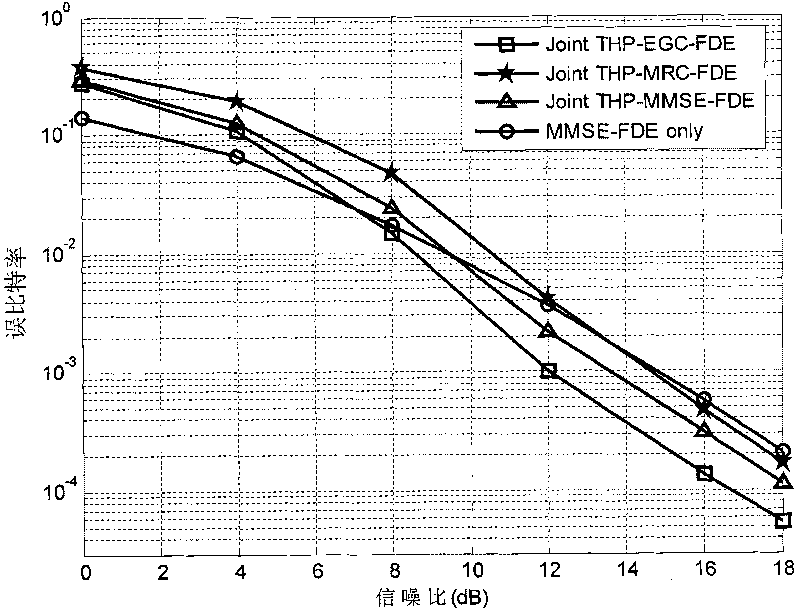
Channel equalization method and communication system thereof based on precoding
InactiveCN101764772AEliminate Error FlatsImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksQ-matrixCommunications system
The invention provides a channel equalization method based on precoding. The method comprises that geometric mean decomposition is carried out on the extended channel matrix H of an original channel matrix H, R matrix, P matrix and Q matrix are obtained and then equalization is carried out, at a sending end, T-H precoding processing is carried out on modulated data according to the R matrix and the data after the T-H precoding is sent and filtered according to the P matrix and at a receiving end, the data after frequency domain signal processing is received and filtered according to the Q matrix. The invention further provides a communication system based on the precoding, which comprises a geometric mean decomposition module based on H, a receiving filtering module and a sending filtering module added to the sending end. The invention can eliminate error floor under high SNR and improve the system performance under low SNR and is compatible with a single or multiple carrier waves communication system. The invention also provides flexible gang scheme so that the system can obtain excellent performance under low complexity.
Owner:GCI SCI & TECH
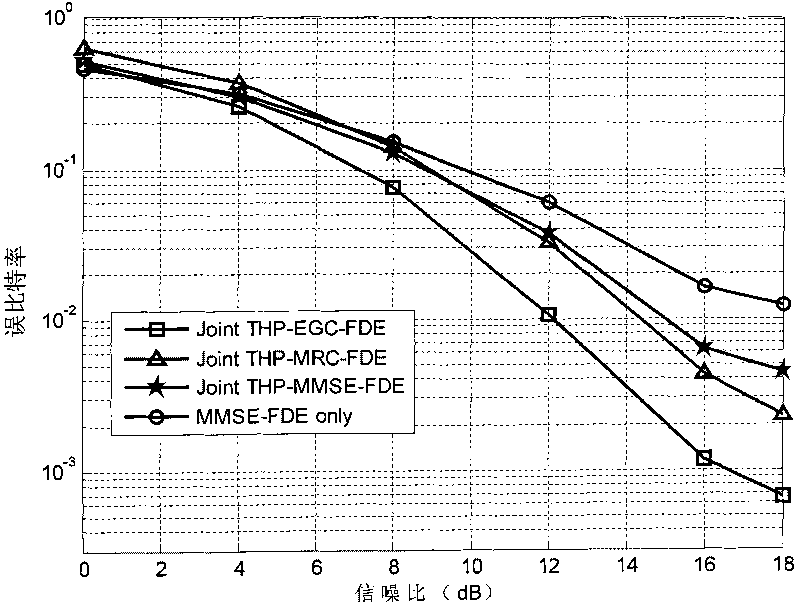
Channel equalization method and communication system thereof based on precoding
InactiveCN101764770AEliminate Error FlatsImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksQ-matrixCarrier signal
The invention provides a channel equalization method based on precoding. The method comprises that geometric mean decomposition is carried out to obtain R matrix, P matrix and Q matrix and then equalization is carried out according to the three matrixes, at a sending end, T-H precoding processing is carried out on modulated data according to the R matrix at first and then the data after the T-H precoding is sent and filtered according to the P matrix and at a receiving end, the data is received and filtered according to the Q matrix. The invention further respectively provides a communicationsystem with a single carrying wave realization way, which is based on the precoding and a communication system with a multiple-carrying wave realization way, which is based on the precoding. The invention eliminates error floor which is generated under high SNR when QR decomposition is used for the prior art and improves the system error code performance and is compatible with a single or multiple carrier waves communication system at the same time. The invention also provides a flexible geometric mean decomposition scheme so that the system can obtain excellent performance under low complexity.
Owner:GCI SCI & TECH
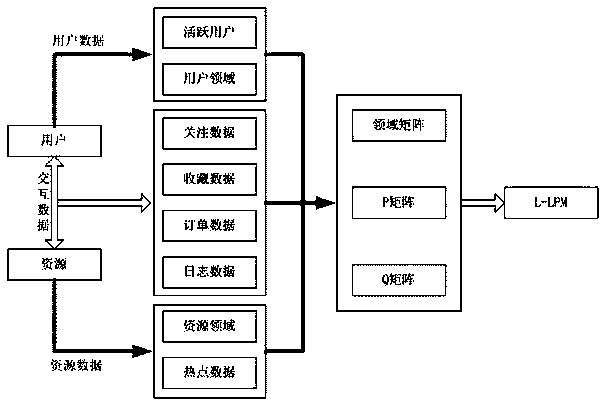
Method for recommending scientific and technological resources based on domain feature and latent semantic analysis
InactiveCN105512323ASolve the cold start problemImprove interpretabilitySemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsQ-matrixData set
The invention provides a method for recommending scientific and technological resources based on a domain feature and latent semantic analysis. According to the method, a user domain and a resource domain are introduced, a classification which is suitable for describing a user and resources is found to help a latent semantic analysis arithmetic to form a meaningful subject classification, the phenomenon that the classification significance cannot be explained by the latent semantic analysis arithmetic is improved, an efficient and quick slope-one arithmetic is utilized first to calculate three large data sets to form a P, L, and Q matrix, the problem that the time complexity of the latent semantic analysis arithmetic is high is solved, the method is applied to the recommendation of the scientific and technological resources with wide cross fields, huge data volume and relatively fixed user groups, and the problem of cold star existing in the latent semantic analysis arithmetic is solved effectively.
Owner:GUANGDONG SCI & TECH INFRASTRUCTURE CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com