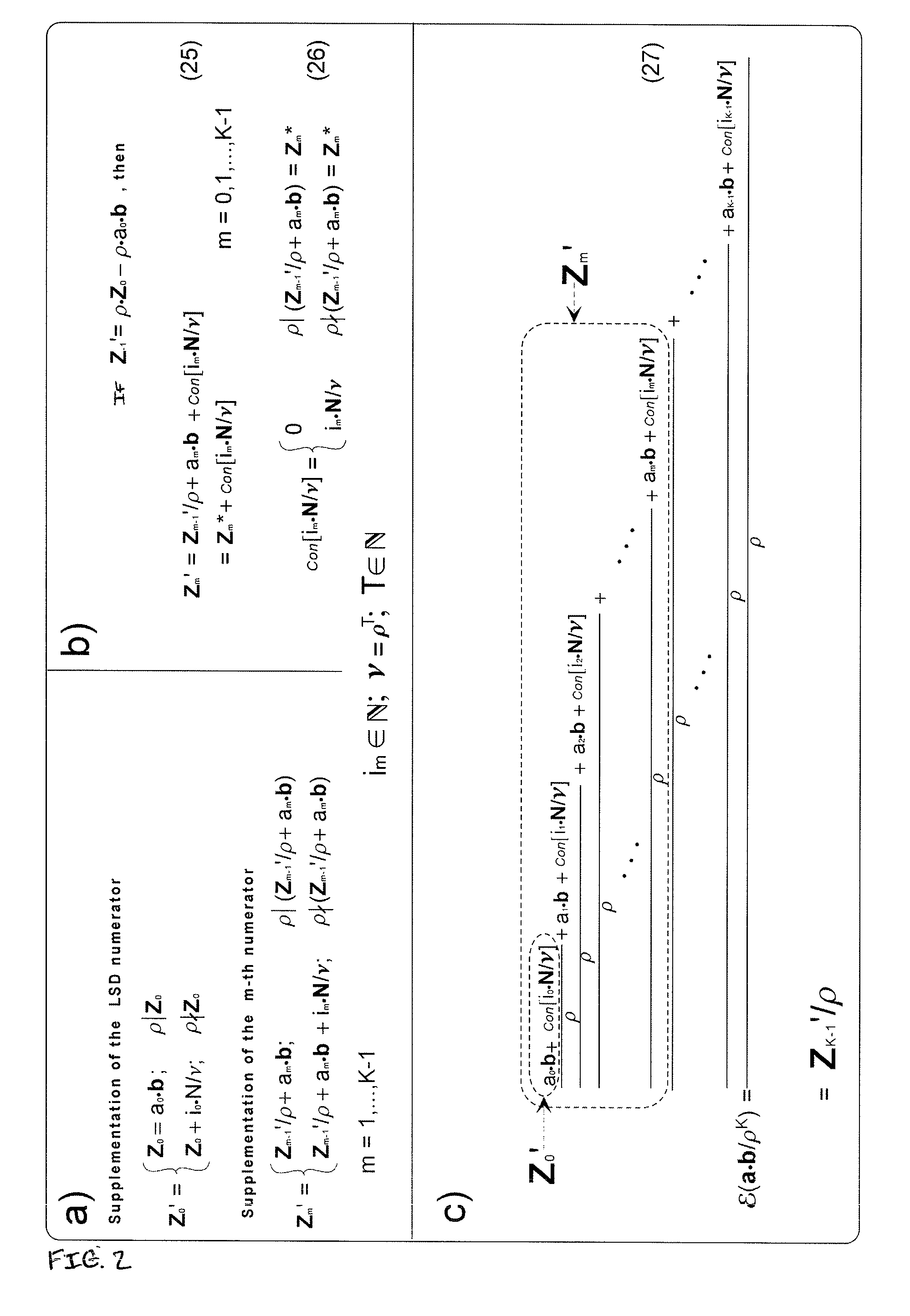
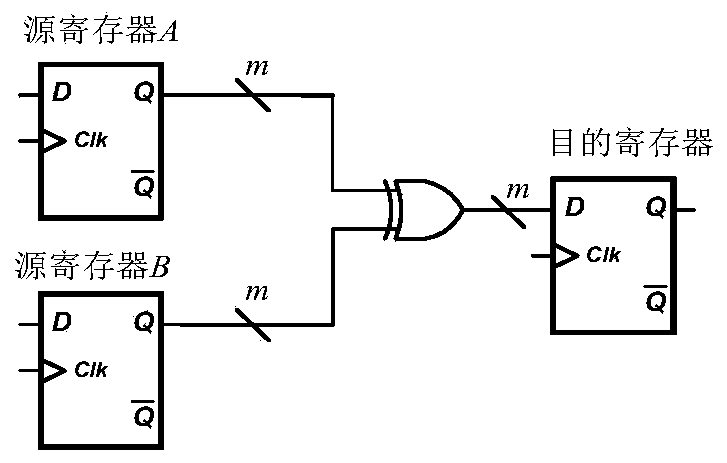
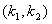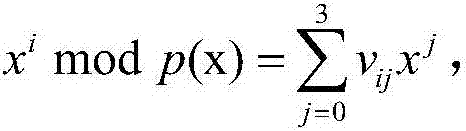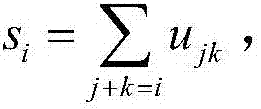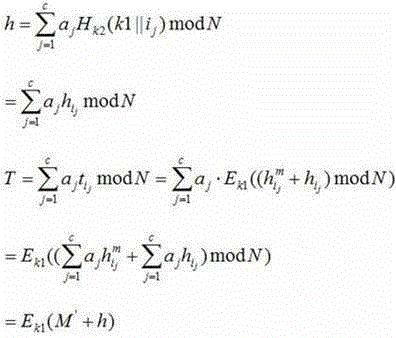Patents
Literature
85 results about "Modular arithmetic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" when reaching a certain value—the modulus (plural moduli). The modern approach to modular arithmetic was developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss in his book Disquisitiones Arithmeticae, published in 1801.
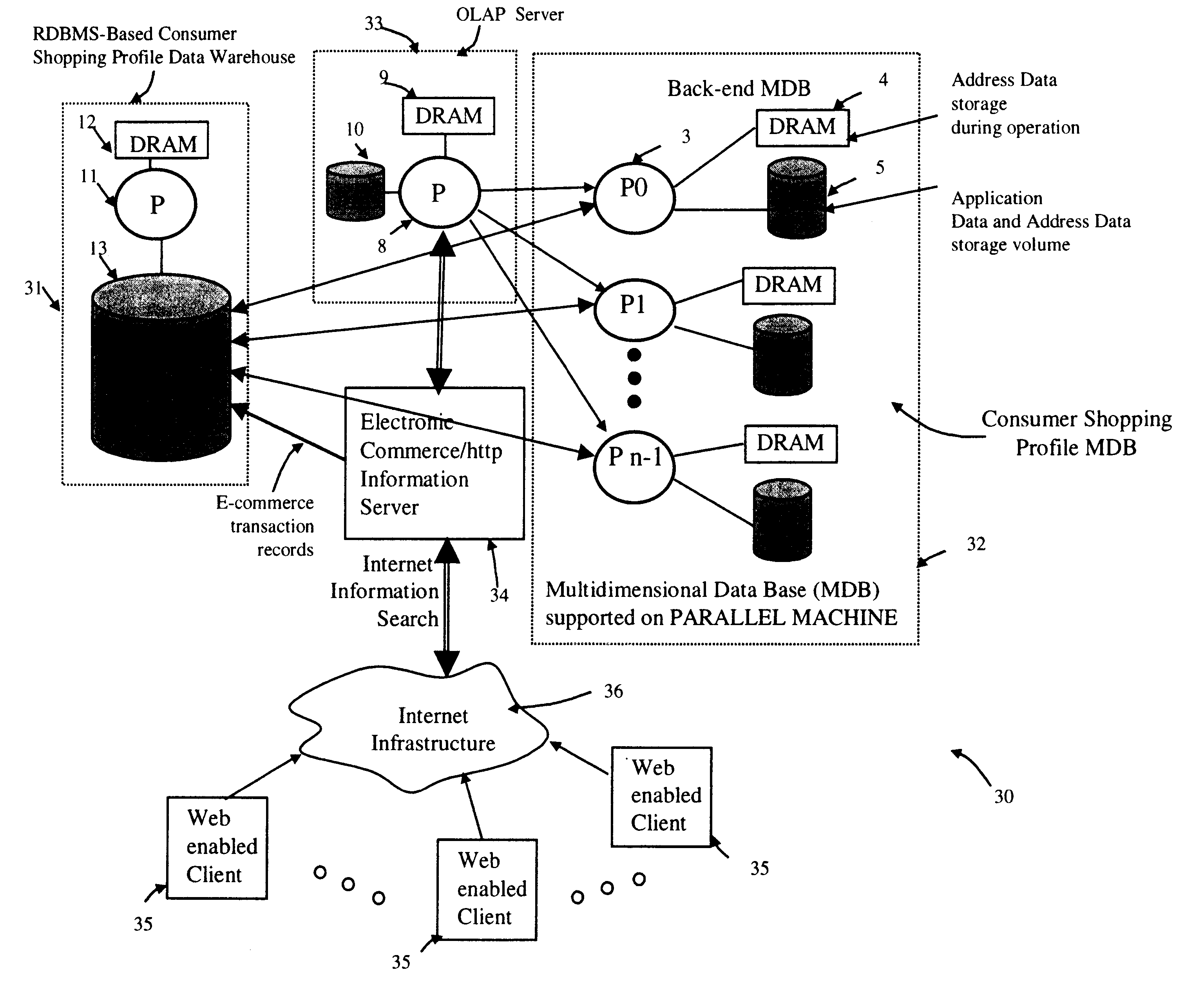
Method of and system for managing multi-dimensional databases using modular-arithmetic based address data mapping processes on integer-encoded business dimensions
InactiveUS6408292B1Improve performanceFast knowledge discoveryData processing applicationsMulti-dimensional databasesData warehouseThe Internet
An improved method of and a system for managing data elements in a multidimensional database (MDB) supported upon a parallel computing platform using modular-arithmetic based address data mapping (i.e. translation) processes on integer-encoded business dimensions. The parallel computing platform has a plurality of processors and one or more storage volumes for physically storing data elements therein at integer-encoded physical addresses in Processor Storage Space (i.e. physical address space in the one or more storage volumes associated with a given processor). The location of each data element in the MDB is specified in MDB Space by integer-encoded business dimensions associated with the data element. A data loading mechanism loads the integer-encoded business dimensions and associated data elements from a data warehouse. The address data mapping mechanism performs a two part address mapping processing. The first step maps the integer-encoded business dimensions associated with each data element to a given processor identifier (which uniquely identifies the processor amongst the plurality of processors of the parallel computing platform). The second step maps the integer-encoded business dimensions associated with each data element into an integer-encoded physical data storage address in Processor Storage Space associated with the processor identified by the processor identifier generated in the first mapping step. The mapping performed in this second step is based upon size of the integer encoded business dimensions. The data management mechanism manages the data elements stored in the storage volumes using the integer-encoded data storage addresses generated during the two-part address data mapping process. The use of modular-arithmetic functions in the two-part address data mapping mechanism ensures that the data elements in the MDB are uniformly distributed among the plurality of processors for balanced loading and processing. The present invention can be used to realize (i) an improved MDB for supporting on-line analytical processing (OLAP) operations, (ii) an improved Internet URL Directory for supporting on-line information searching operations by Web-enabled client machines, as well as (iii) diverse types of MDB-based systems for supporting real-time control of processes in response to complex states of information reflected in the MDB.
Owner:MEC MANAGEMENT LLC +1
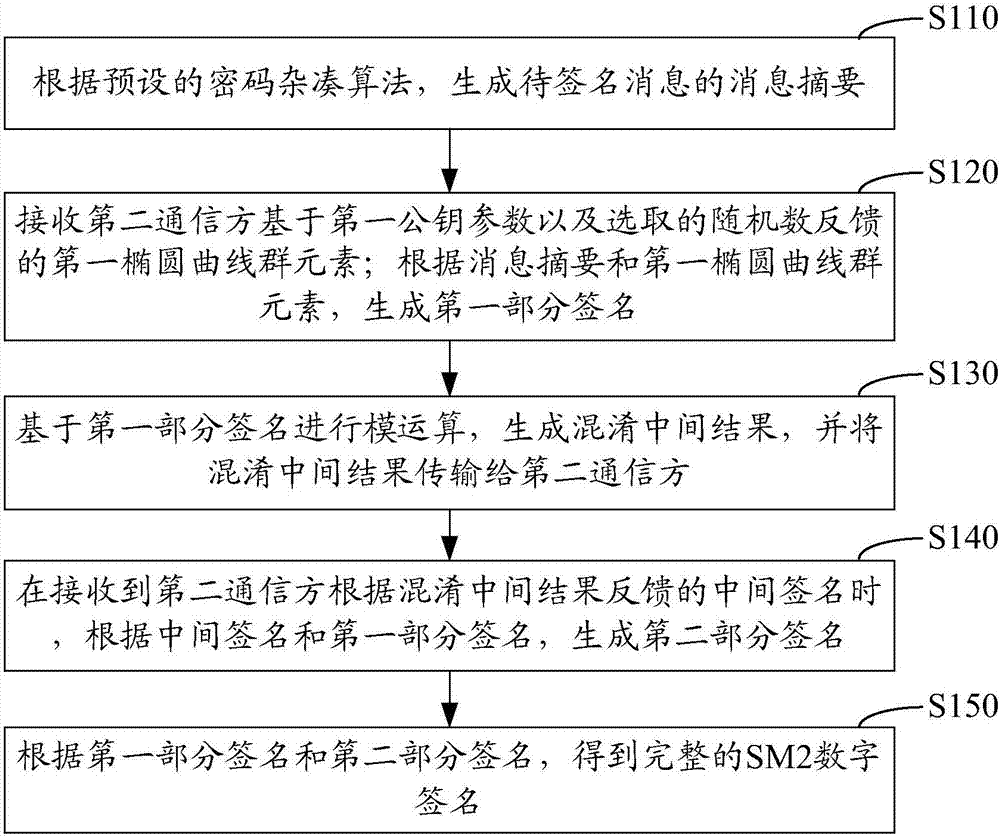
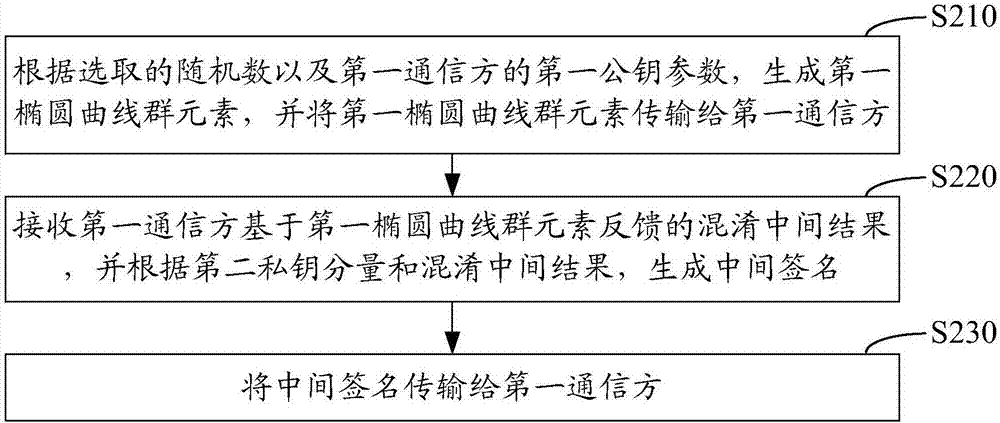
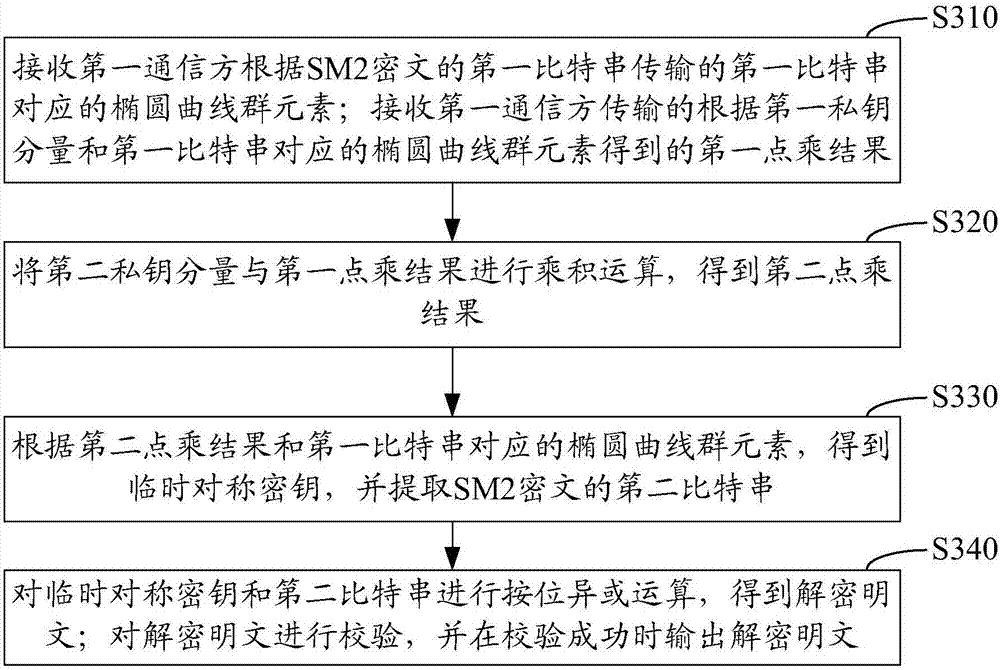
Collaborative signature and decryption method, apparatus and system of SM2 algorithm
ActiveCN107196763APrivacy protectionPrevent forgeryPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPasswordDigital signature
The invention relates to a collaborative signature and decryption method, apparatus and system of an SM2 algorithm. The collaborative signature method of the SM2 algorithm implemented from the angle of a first communication party comprises the following steps: generating a message abstract of a to-be-singed message according to a preset password hash algorithm; receiving a first elliptic curve group element fed back by a second communication party based on a first public key parameter and a selected random number; generating a first part signature according to the message abstract and the first elliptic curve group element; performing modular arithmetic based on the first part signature to generate a confused intermediate result, and transmitting the confused intermediate result to the second communication party; when the intermediate signature fed back by the second communication party according to the confused intermediate result is received, generating a second part signature according to the intermediate signature and the first part signature; and obtaining a complete SM2 digital signature according to the first part signature and the second part signature.
Owner:GUANGDONG CERTIFICATE AUTHORITY +1
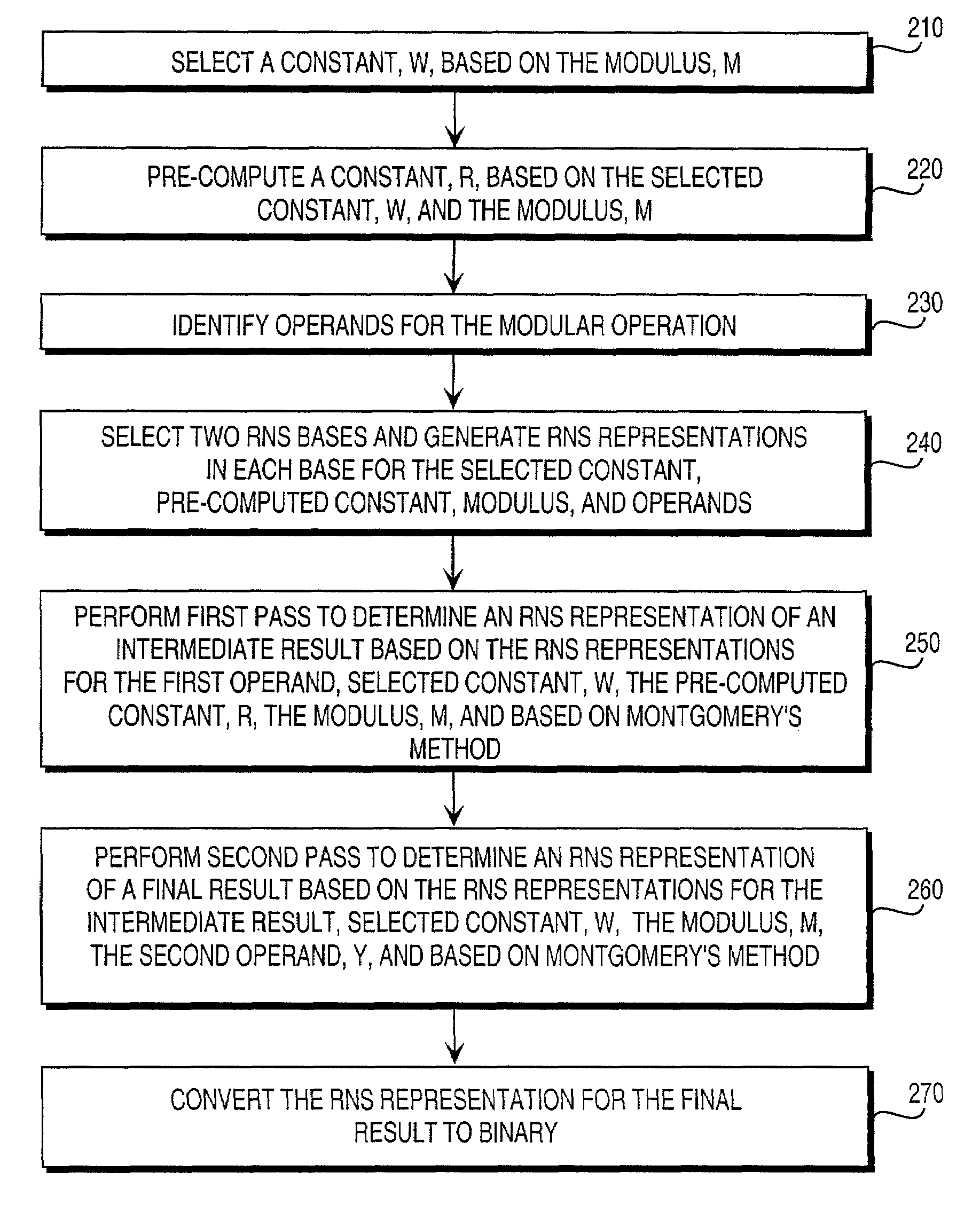
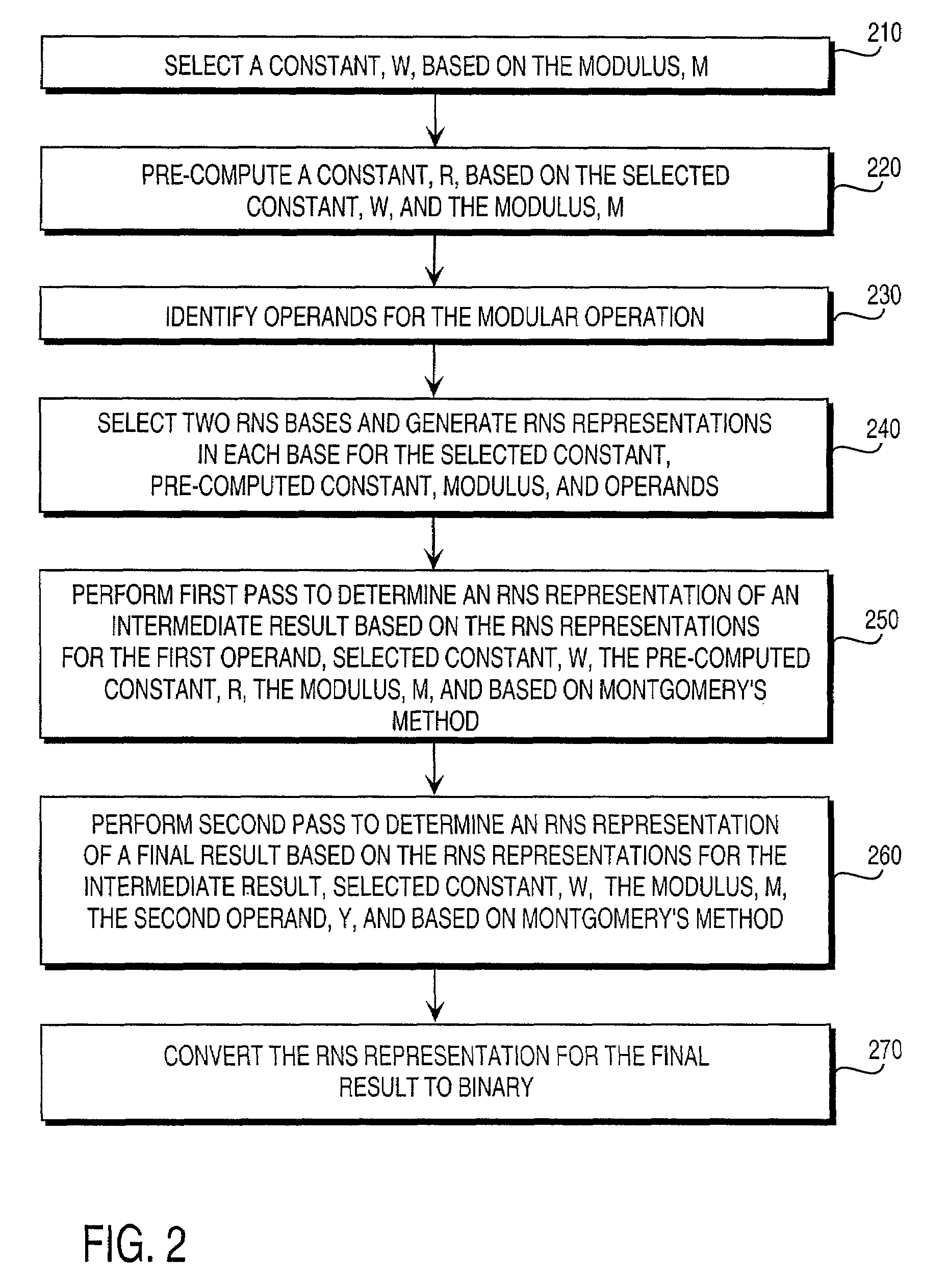
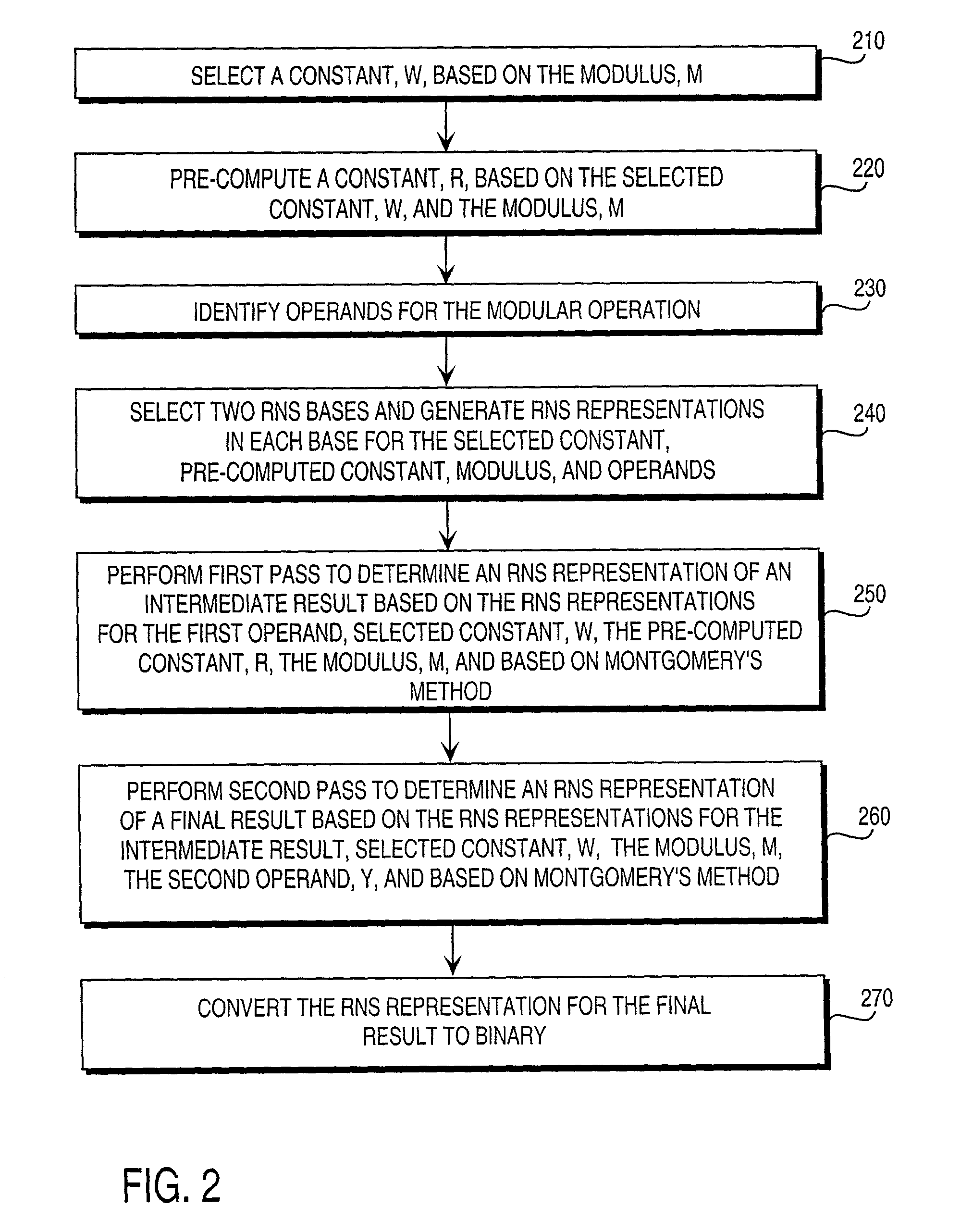
Residue number system based pre-computation and dual-pass arithmetic modular operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits
InactiveUS7027598B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerModularity
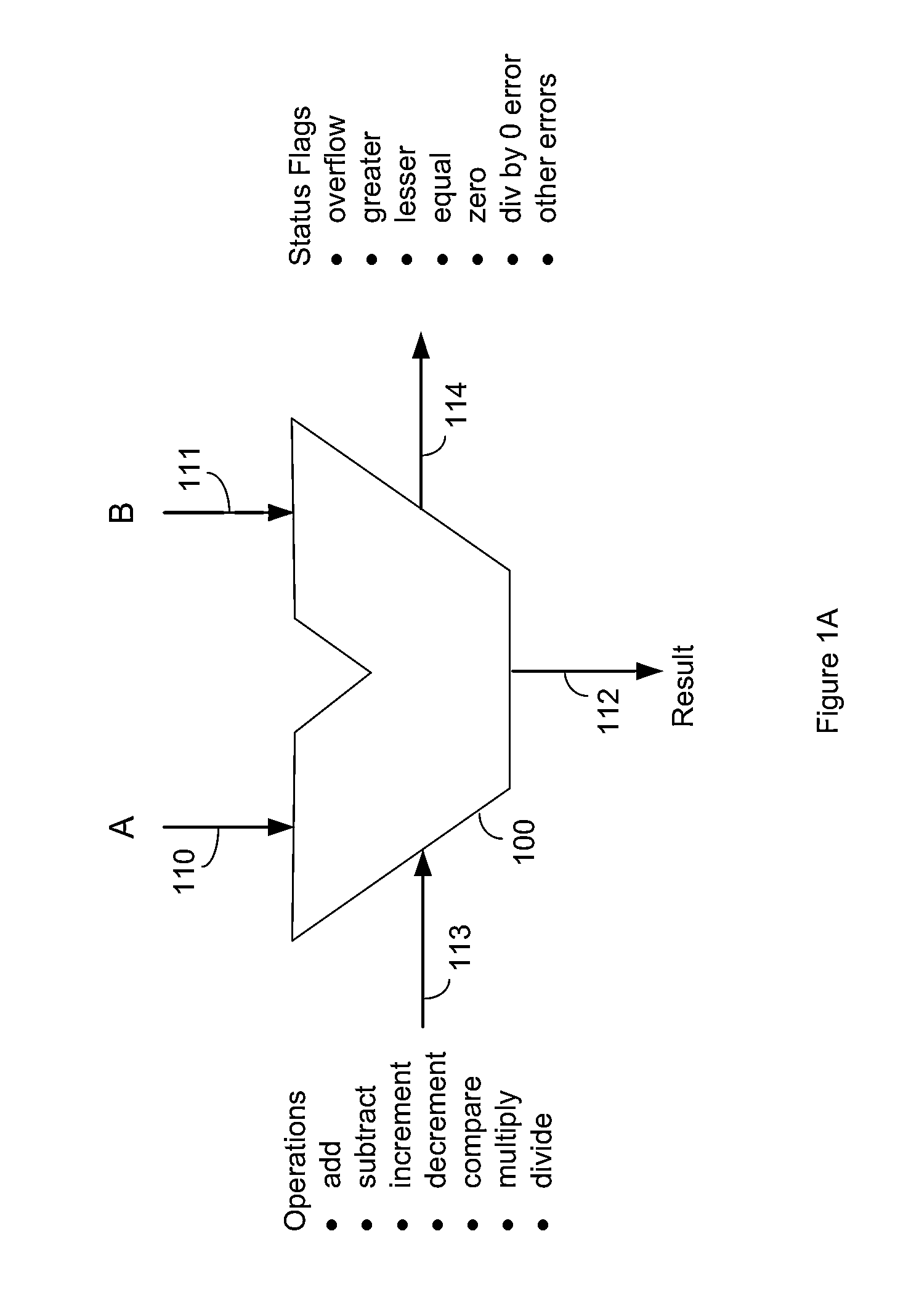
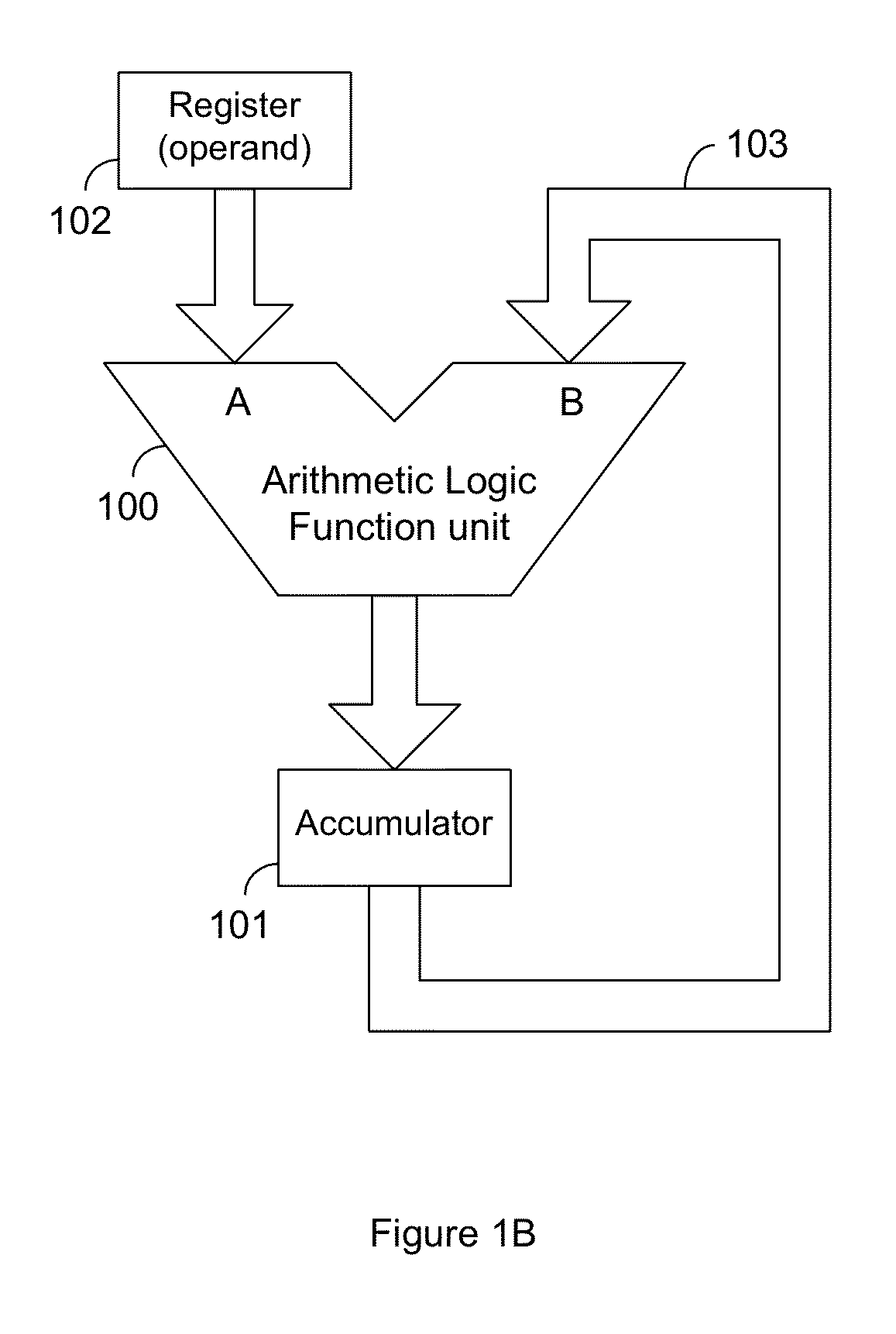
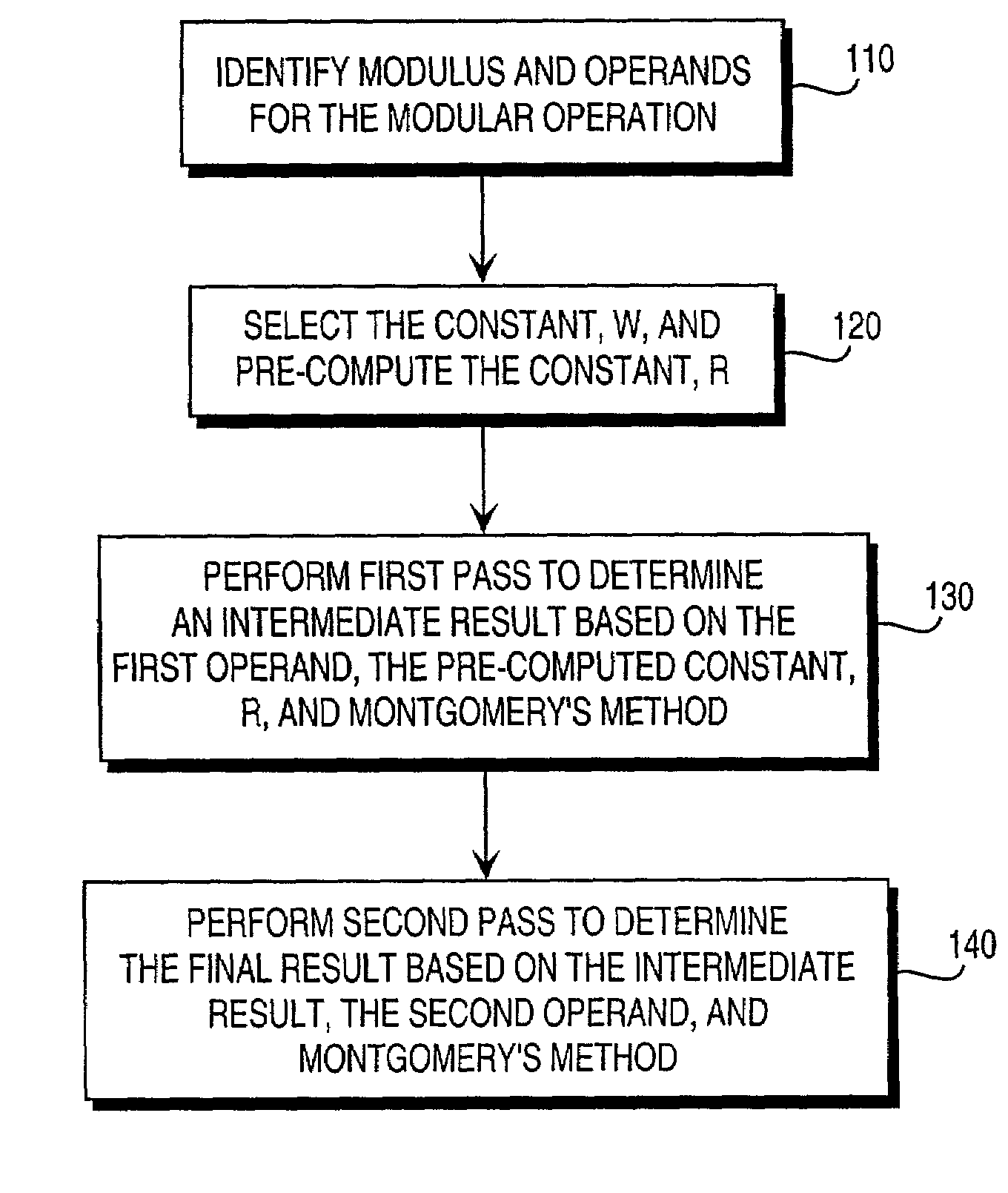
A pre-computation and dual-pass modular operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits is disclosed. An encrypted electronic message is received and another electronic message generated based on the encryption protocol. Two passes of Montgomery's method are used for a modular operation that is associated with the encryption protocol along with pre-computation of a constant based on a modulus. The modular operation may be a modular multiplication or a modular exponentiation. Modular arithmetic may be performed using the residue number system (RNS) and two RNS bases with conversions between the two RNS bases. A minimal number of register files are used for the computations along with an array of multiplier circuits and an array of modular reduction circuits. The approach described allows for high throughput for large encryption keys with a relatively small number of logical gates.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Systems and methods for raster-to-block converter
ActiveUS8355570B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationExtensibilityGrating
A raster to block converter and equivalently a block to raster converter can be implemented using enough memory to contain a single image band, that is a band of pixels of height equal to a single block but spanning the entire width of an image. The raster to block converter can operate at full rate so that as soon as a pixel is read out from the memory a new pixel can be stored in its place. The location of a pixel can be tracked using a mapping involving basic modular arithmetic. This raster to block converter is scalable so that it can work with any size image and block size.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
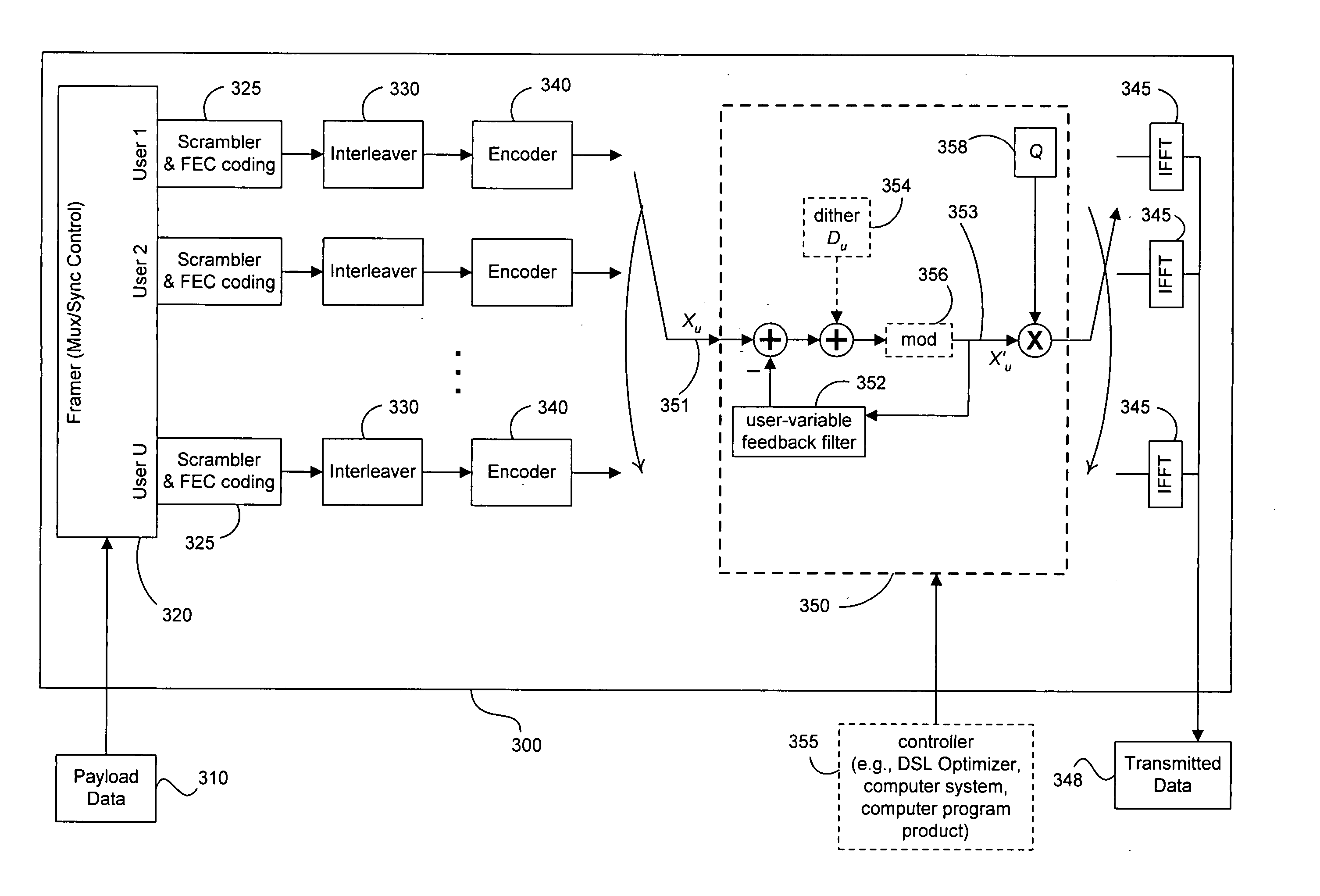
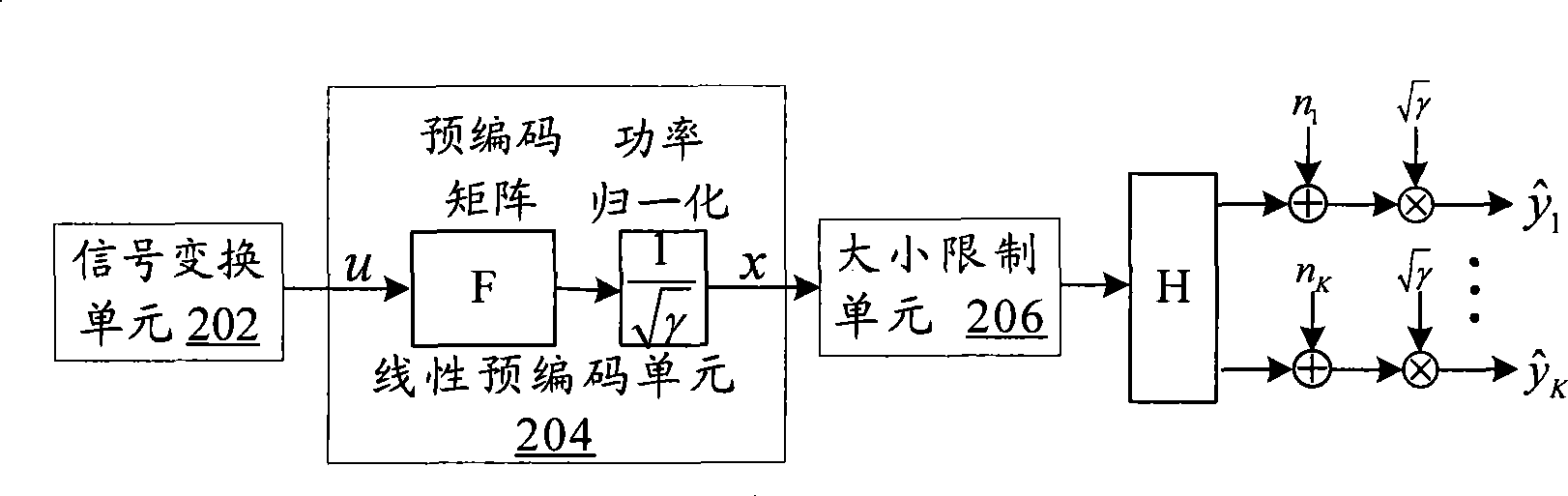
Tonal precoding
ActiveUS20060274825A1Mitigate and remove interference signalReduce removalDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationQ-matrixPrecoding
Precoding mitigates or removes interference signals (especially crosstalk) among multiple users with interconnected transmitters in vectored DSL systems and the like. Efficient implementation is provided of the R matrix in RQ factorization that characterizes multi-user downstream vector channels (such as DMT VDSL one-sided or two-sided transmission channels). A set of precoder coefficients can vary with each tone used by each user and depend upon the encoding order of users selected for each tone. In adaptive operation, the coefficients of the R and Q matrices can be updated when changes occur to the transmission environment. Variable modulo arithmetic mitigates the power-enhancement problem, and the base of modular arithmetic also can vary with each user within a single precoder for a single tone. The user order of preceding need not be the same on each tone, and the modular arithmetic progression may thus also be different on each tone because multi-user situations create an unusual situation for precoding in that the modulo arithmetic used for each user can be different (thus imposing a larger power increase) and because digital duplexed or synchronized DMT systems can separately implement a precoder for each tone. Further, the precoding process terminates each DMT symbol, after processing up to the total number of users. An optional dither signal, known to both transmitter and receiver, can be added at the transmit side and removed at the receiver side to smooth the precoding process and ensure that aberrations in the transmitted constellation size and characteristics are consistent despite any unusual variations in the feedback signal that exits the feedback filter matrix G before being subtracted from the user signal of interest. Some embodiments use a “subtraction only” mode while other embodiments use a dither signal and / or modulo arithmetic, though embodiments of the present invention do not require use of identical constellations by both transmitter and receiver.
Owner:ADAPTIVE SPECTRUM & SIGNAL
Residue number arithmetic logic unit
ActiveUS20130311532A1Improve performanceConservingProgram controlComputation using denominational number representationArithmetic logic unitNumbering system
Methods and systems for residue number system based ALUs, processors, and other hardware provide the full range of arithmetic operations while taking advantage of the benefits of the residue numbers in certain operations. In one or more embodiments, an RNS ALU or processor comprises a plurality of digit slices configured to perform modular arithmetic functions. Operation of the digit slices may be controlled by a controller. Residue numbers may be converted to and from fixed or mixed radix number systems for internal use and for use in various computing systems.
Owner:OLSEN IP RESERVE
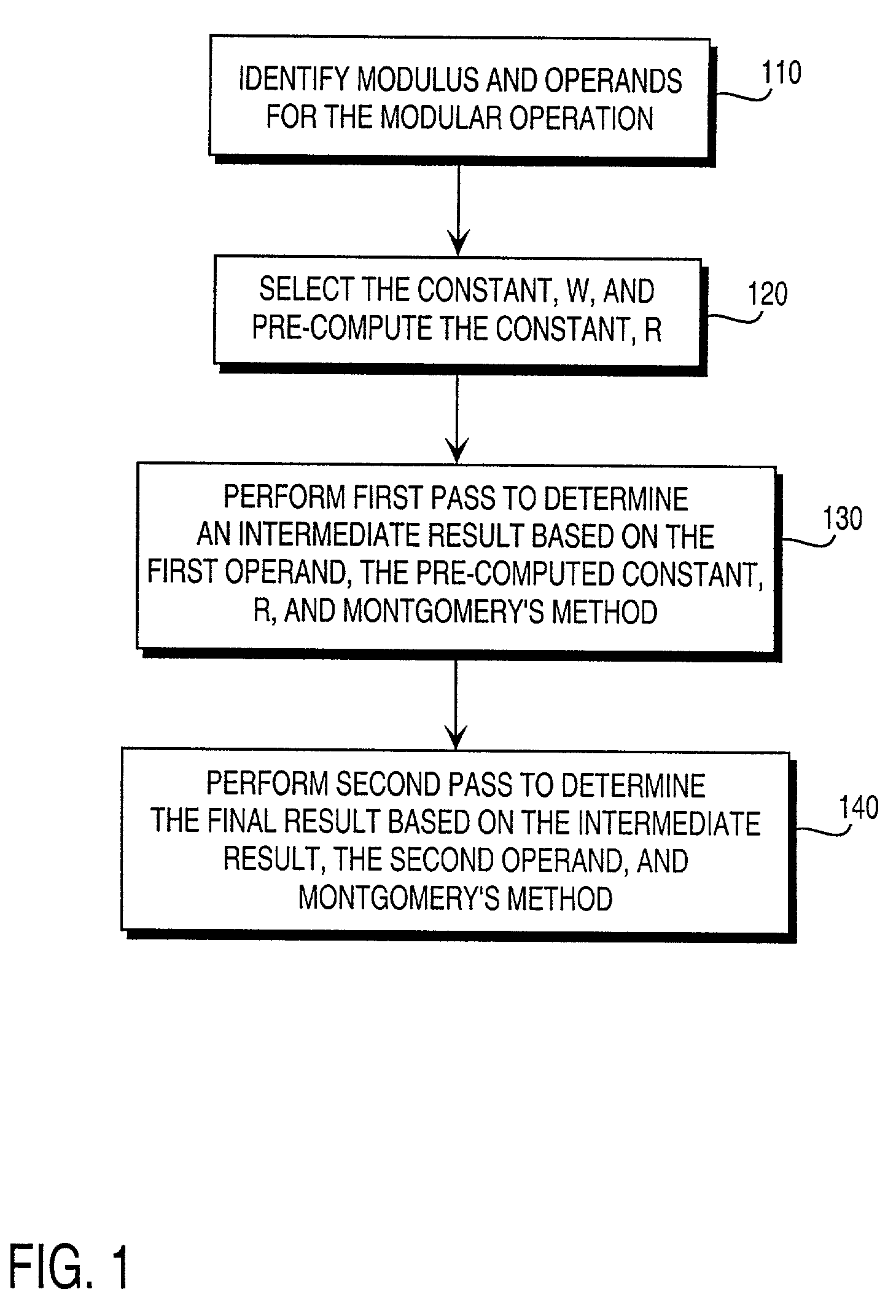
Pre-computation and dual-pass modular arithmetic operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits
InactiveUS7027597B1Effective encryptionEfficient implementationComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerModularity
A pre-computation and dual-pass modular operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits is disclosed. An encrypted electronic message is received and another electronic message generated based on the encryption protocol. Two passes of Montgomery's method are used for a modular operation that is associated with the encryption protocol along with pre-computation of a constant based on a modulus. The modular operation may be a modular multiplication or a modular exponentiation. Modular arithmetic may be performed using the residue number system (RNS) and two RNS bases with conversions between the two RNS bases. A minimal number of register files are used for the computations along with an array of multiplier circuits and an array of modular reduction circuits. The approach described allows for high throughput for large encryption keys with a relatively small number of logical gates.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
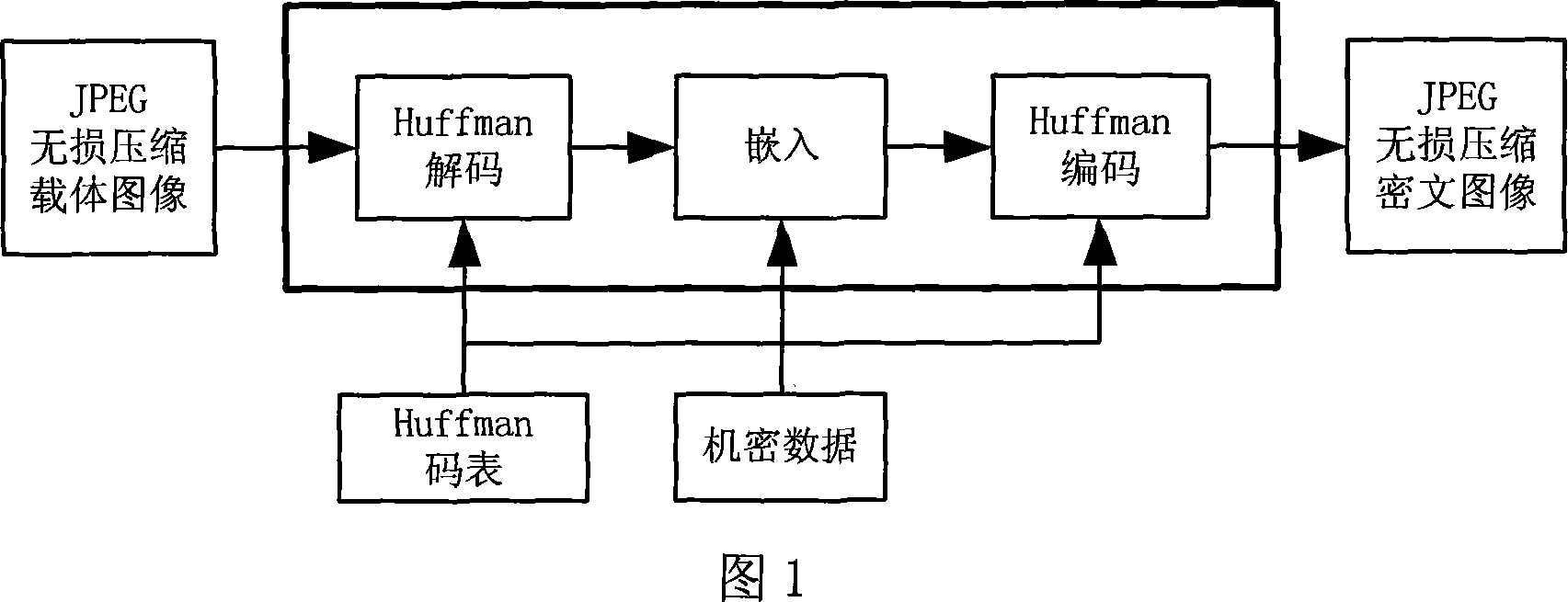
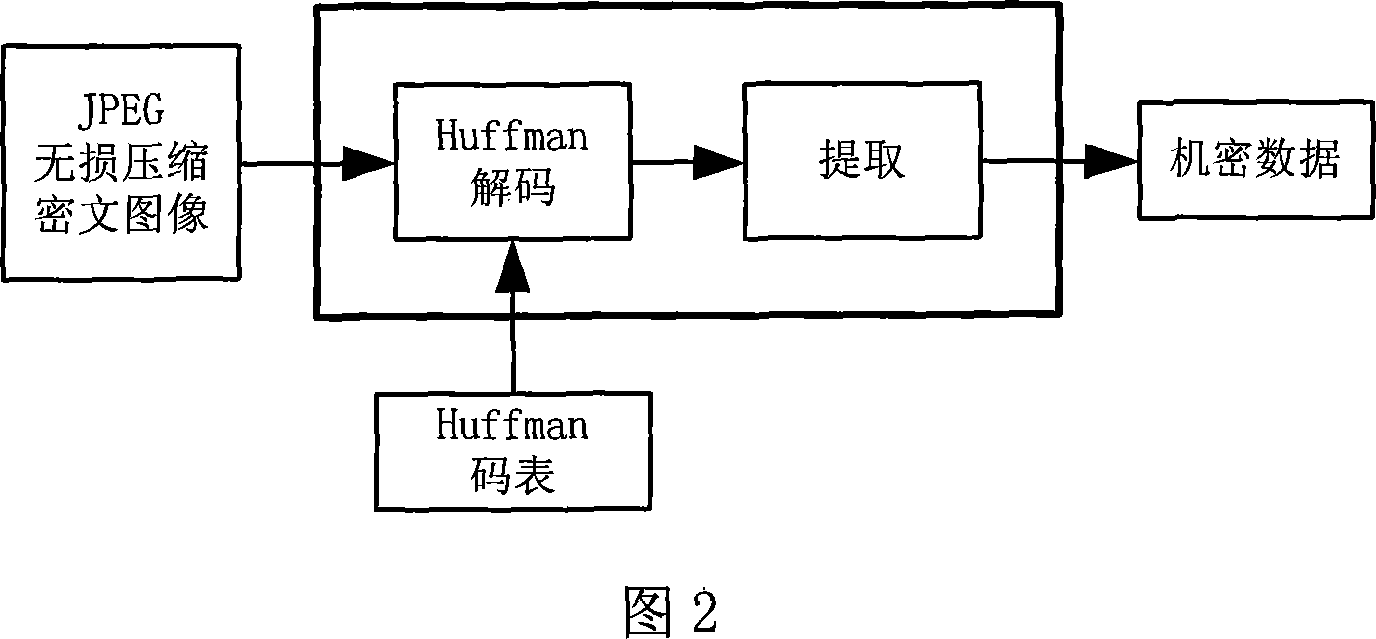
A JPEG lossless compression image hide writing method based on predictive coding
InactiveCN101080013AAvoid damageImprove securityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationLossless codingCiphertext
This invention discloses a hidden-writing method for JPEG lossless compressed images based on forecast coding, when inserting data in a JPFG lossless compressed image, it first of all carries Huffman decoding to get a forecast error, then inserts secret data in the forecast error and finally carries out Huffman coding to the modified forecast error to generate cryptograph image of the JPEG lossless coding, which utilizes modular arithmetic when inserting, which not only reduces alteration of data insertion to carrier images to keep a rather high image quality but also stores the inserted data either in the lossless compressed JPRG code streams or in the compressed cryptograph images.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Fingerprint detail information hiding and restoring method based on orthogonal matrix and modular arithmetic
InactiveCN103279697ARealize the modulo addition operationImprove securityDigital data authenticationPasswordModular arithmetic
The invention discloses a fingerprint detail information hiding and restoring method based on orthogonal matrix and modular arithmetic. According to the method, fingerprint detail characteristic information is divided into fingerprint detail point position coordinate information and fingerprint detail point direction information, and through the utilization of a random transformed orthogonal matrix of a sub-secret-key of a password secret key, matrix transformation arithmetic of the password secret key and position information is achieved to protect the fingerprint detail point position coordinate information. Through the utilization of the other sub-secret-key of the password secret key, modular arithmetic of the password secret key and direction information is achieved to protect the fingerprint detail point direction information. The fingerprint detail information hiding and restoring method based on the orthogonal matrix and modular arithmetic overcomes the defects that a fingerprint template easily receives attacks inside a system or attacks outside the system, and the fact that fingerprint characteristics become invalid is caused. By the further utilization of the combination of the dual authentication of the password secret key and the fingerprint characteristics, safety of a protected system and privacy of fingerprint characteristic data are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Signal processing method and system for multi-user MIMO
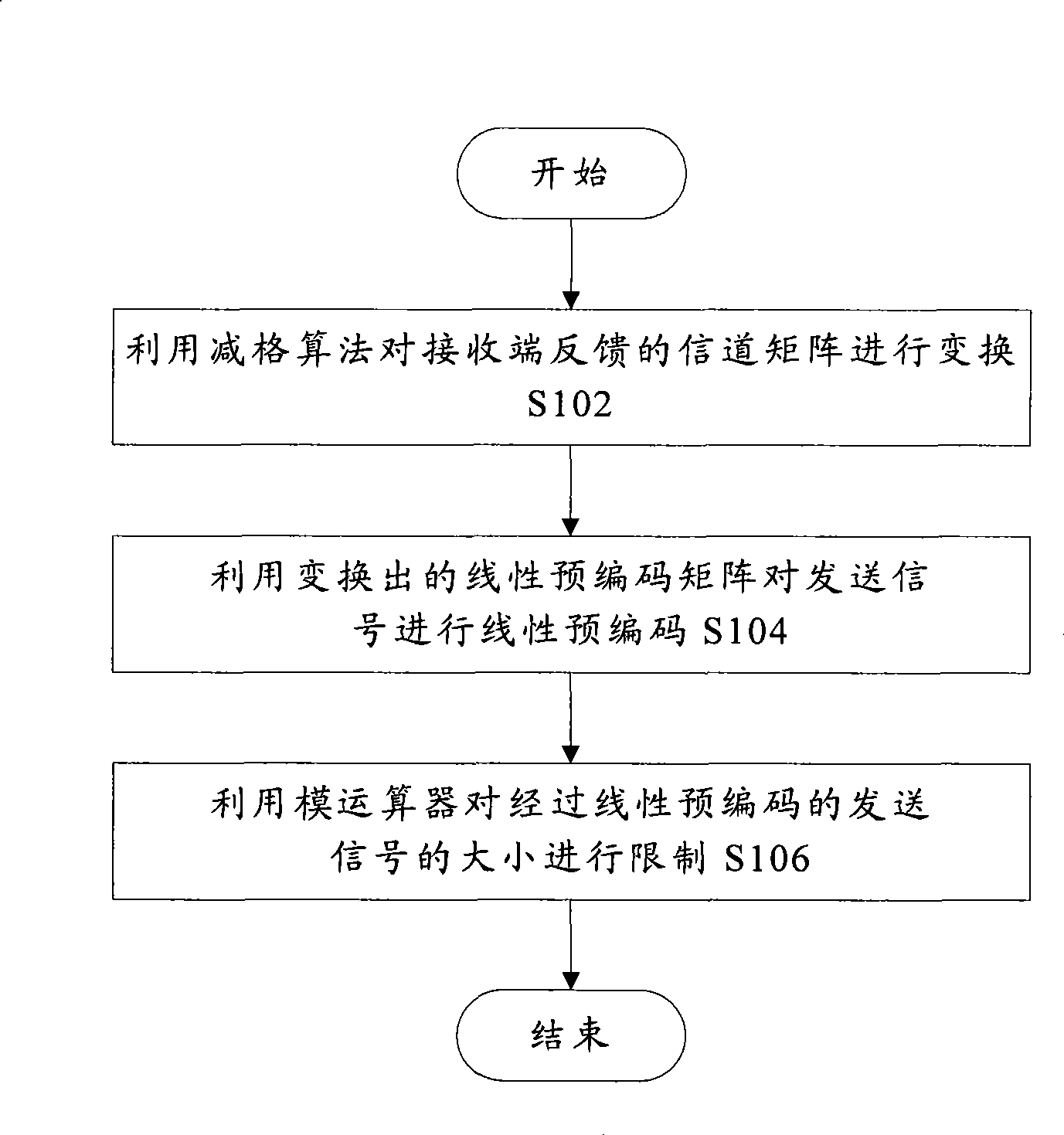
InactiveCN101459488AImprove bit error rate performanceTransmit signal power reductionError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsMulti inputSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a signal processing method for a multi-user multi-input multi-output downlink and a system thereof, wherein the system comprises the following steps: an S102 step that transforming a channel matrix fed back by a receiving end through the lattice-reduction algorithm, an S104 step that conducting the linear precode for a sending signal through a transformed linear precode matrix, and an S106 step that restricting the size of the sending signal passing through the linear precode through a modular arithmetic unit. The invention effectively reduces the emitting power of thelinear precode algorithm, inhibits the noise enhancement, increases the receiving signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and improves the error code percentage performance of the system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Circuits for modular arithmetic based on the complementation of continued fractions
InactiveUS20120057695A1Increase demandReduce computing timeDigital data processing detailsSecret communicationModular arithmeticComputer science
Owner:MICRONAS
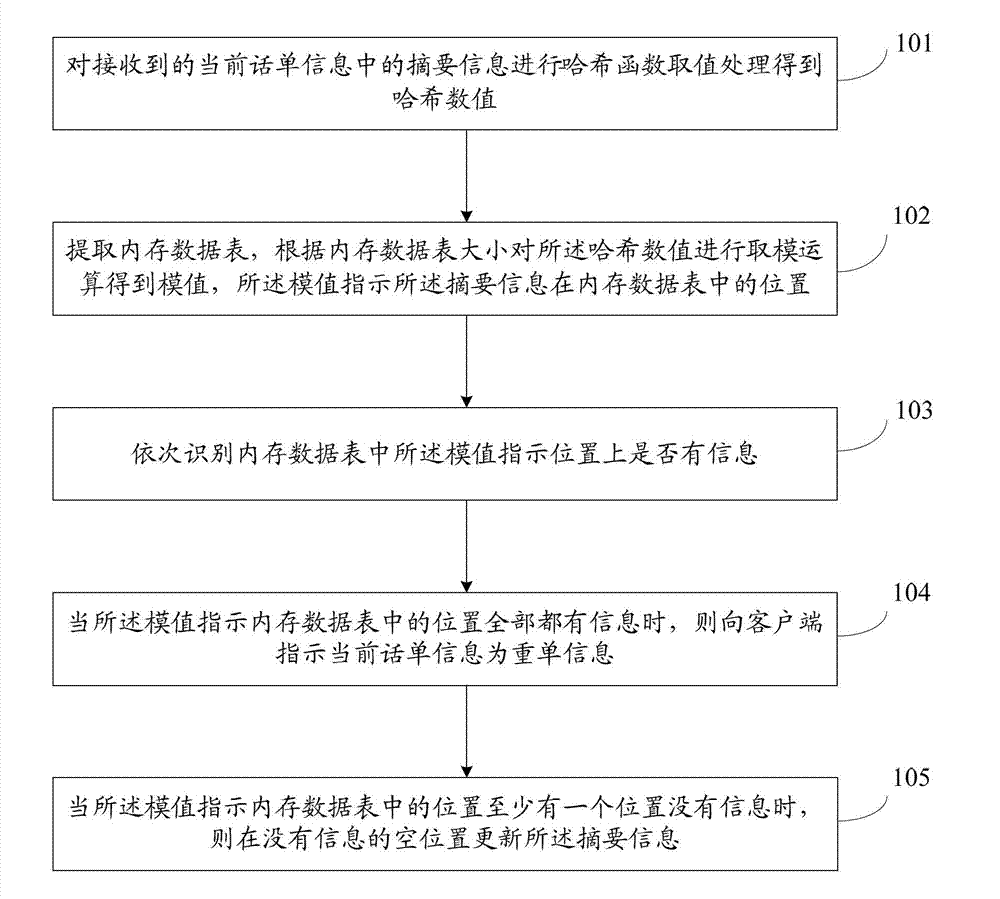
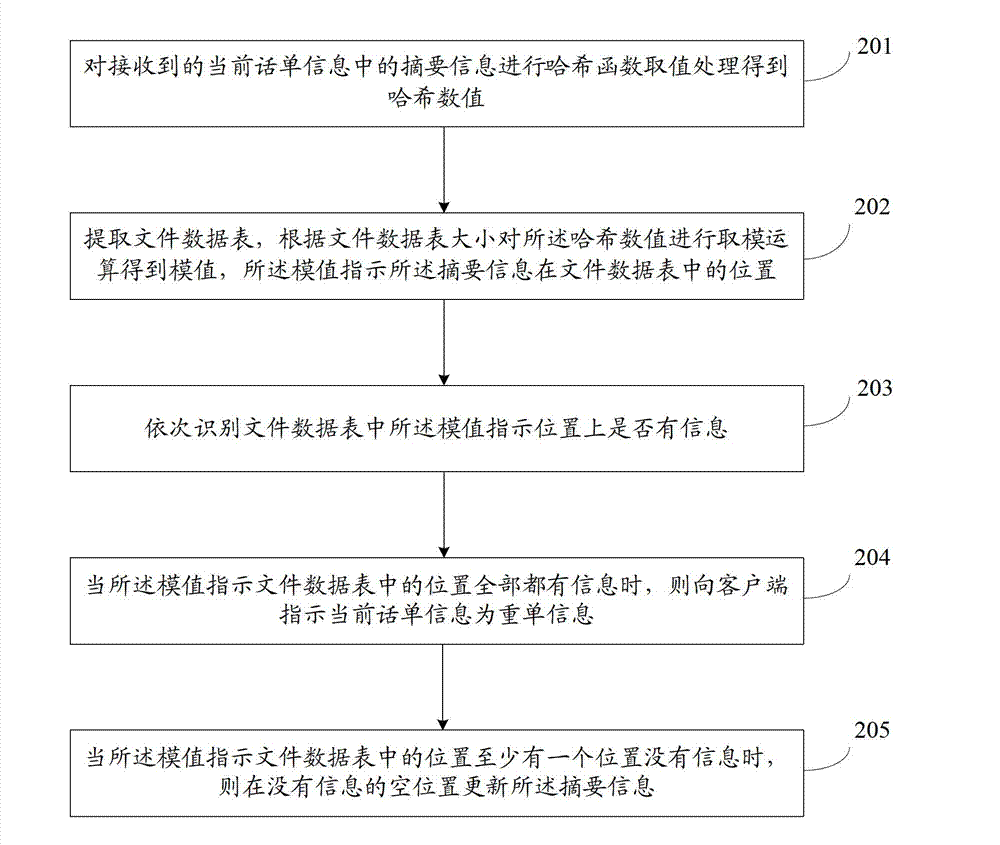
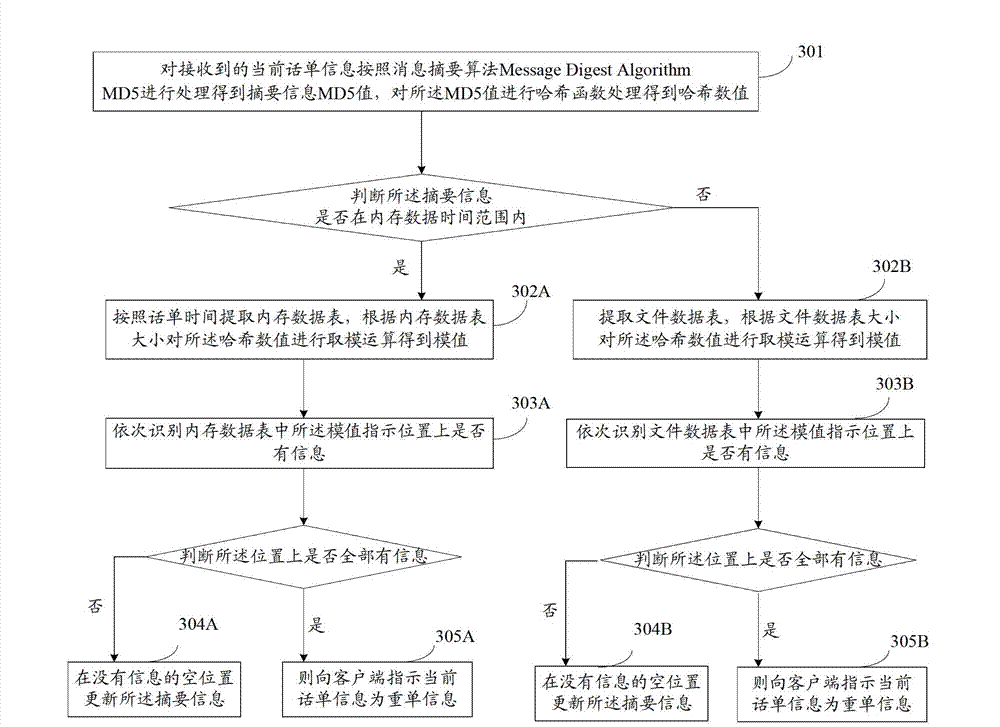
Call bill repetition removing method and call bill repetition removing device
ActiveCN103037344ASolve the problem that cannot continue to deduplicateFast deduplicationAccounting/billing servicesSpecial data processing applicationsInternal memoryHash function
The invention discloses a call bill repetition removing method and a call bill repetition removing device. The method comprises the steps of carrying out hash function evaluation processing to summary information in received current call bill information to obtain hash values; extracting a stored data sheet and carrying out modular arithmetic to the hash values according to the size of the stored data sheet to obtain module values, wherein the module values indicate the positions of the summary information in the stored data sheet; judging whether information are on the positions, in the stored data sheet, indicated by the module values in sequence; indicating to a client-side that the current call bill information is repetition bill information when the information are on all the positions in the stored data sheet, indicated by the module values; and updating the summary information on empty positions without information when at least one position, in the stored data sheet, indicated by the module values is without information. According to the call bill repetition removing method and the call bill repetition removing device, internal memory demanding of a call bill is reduced and repetition removing efficiency is improved.
Owner:亚信时代科技集团有限公司
Method for imaging actual aperture foresight on basis of subspace projection
InactiveCN102608598ANo corner flicker phenomenonImprove detection accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingDecomposition
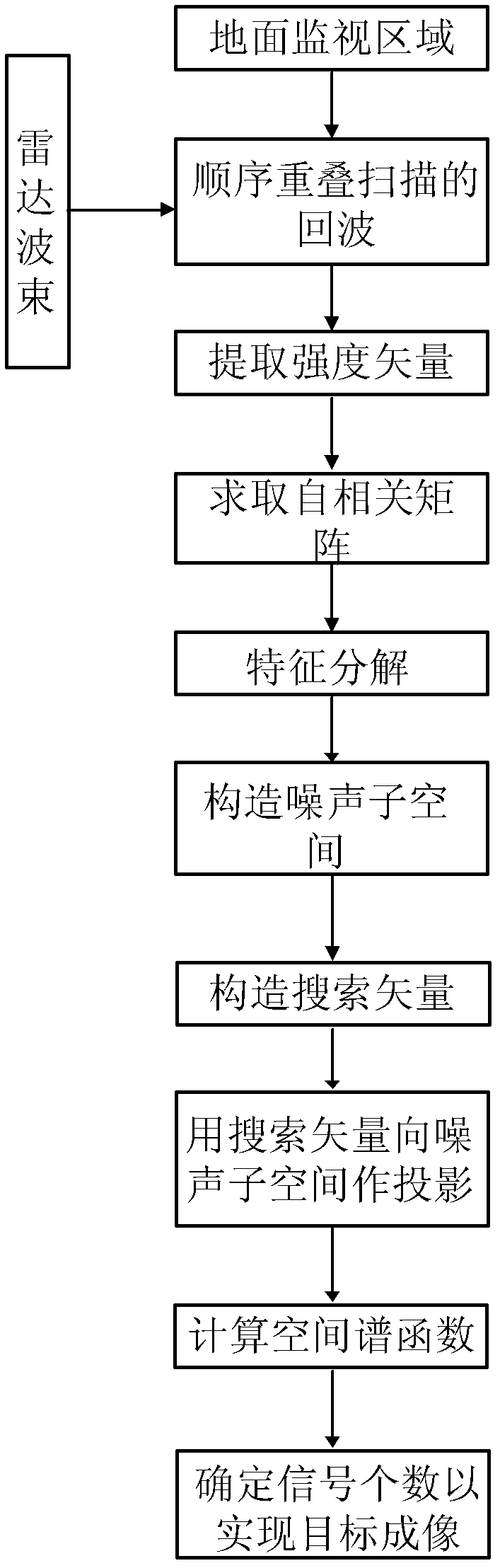
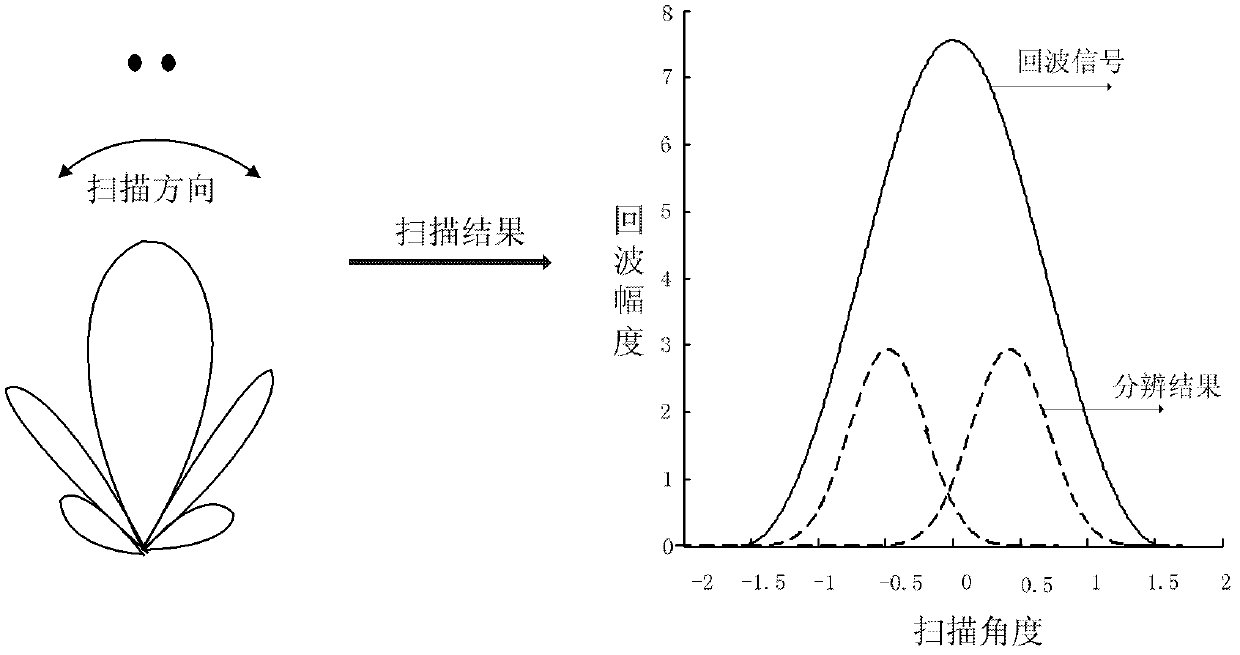
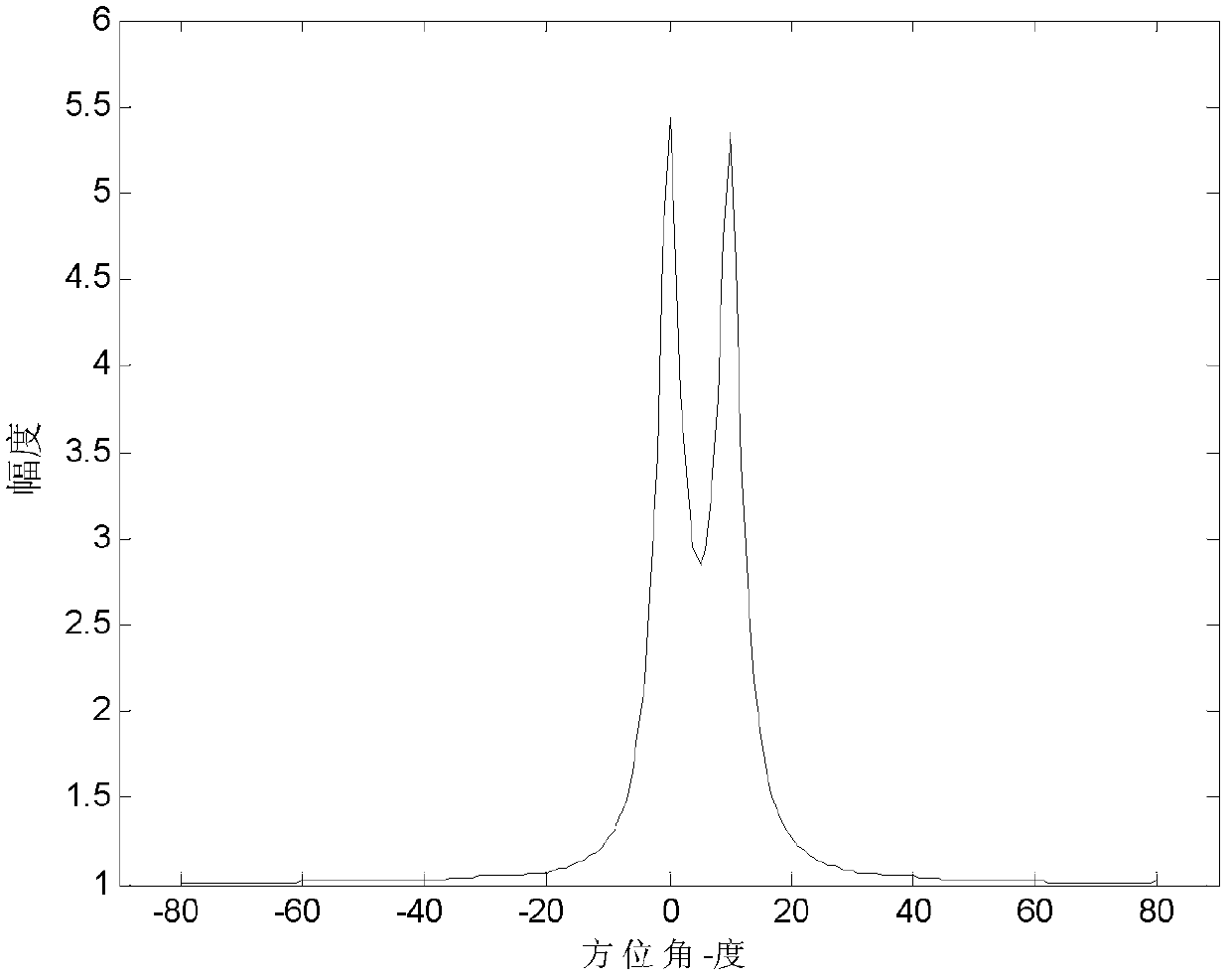
The invention discloses a method for imaging an actual aperture foresight on basis of subspace projection, which mainly solves the high resolution imaging problem of a right ahead object of a flightpath. The method has the detection processes that: 1) radar beams are sent out at equal intervals for carrying out sequence overlap scanning on a ground monitoring area to obtain the radar return data; 2) a modular arithmetic is utilized to extract the intensity vector of the return data; 3) the autocorrelation matrix of the intensity vector of the return data is gained; 4) eigen decomposition is carried out on the autocorrelation matrix; 5) the corresponding eigenvector of a small eigenvalue is used for forming a noise subspace; 6) a pattern search vector is defined; 7) the pattern search vector is projected into the noise subspace; 8) the peak values of a spatial spectrum function are calculated; and 9) the number of the signal is determined according to the number of the peak values of the spatial spectrum function for realizing foresight imaging. The method has the advantage of improving the resolution precision of an adjacent target in a main lobe, and can be used for an airborne radar monitoring system in the imaging field for realizing the detection and the recognition for a target on a track line.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
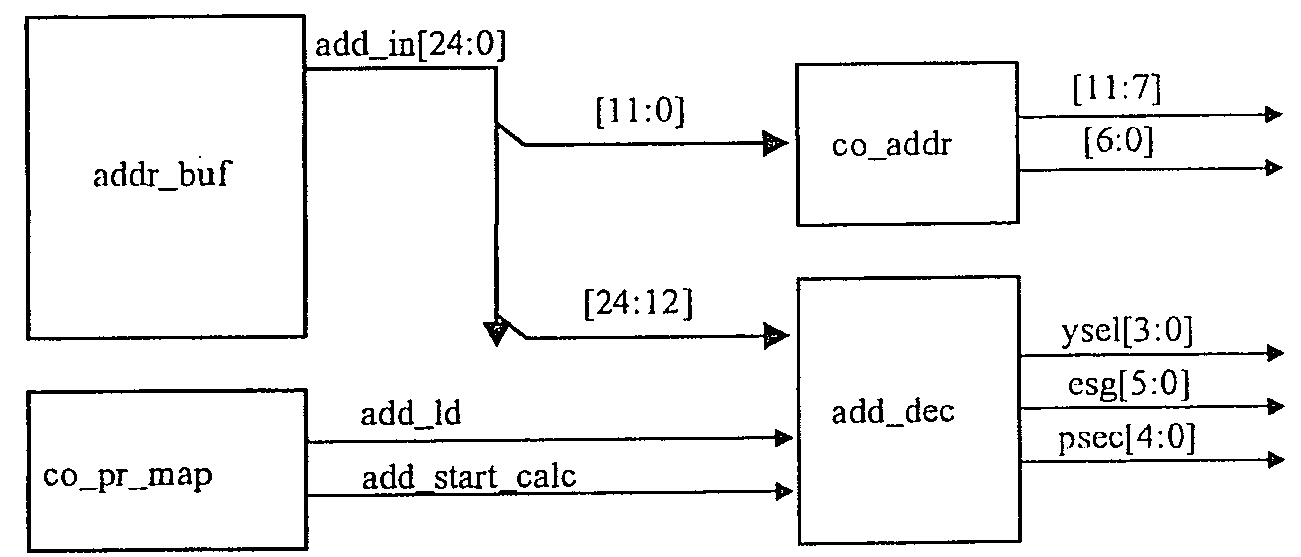
Non binary flash array architecture and method of operation
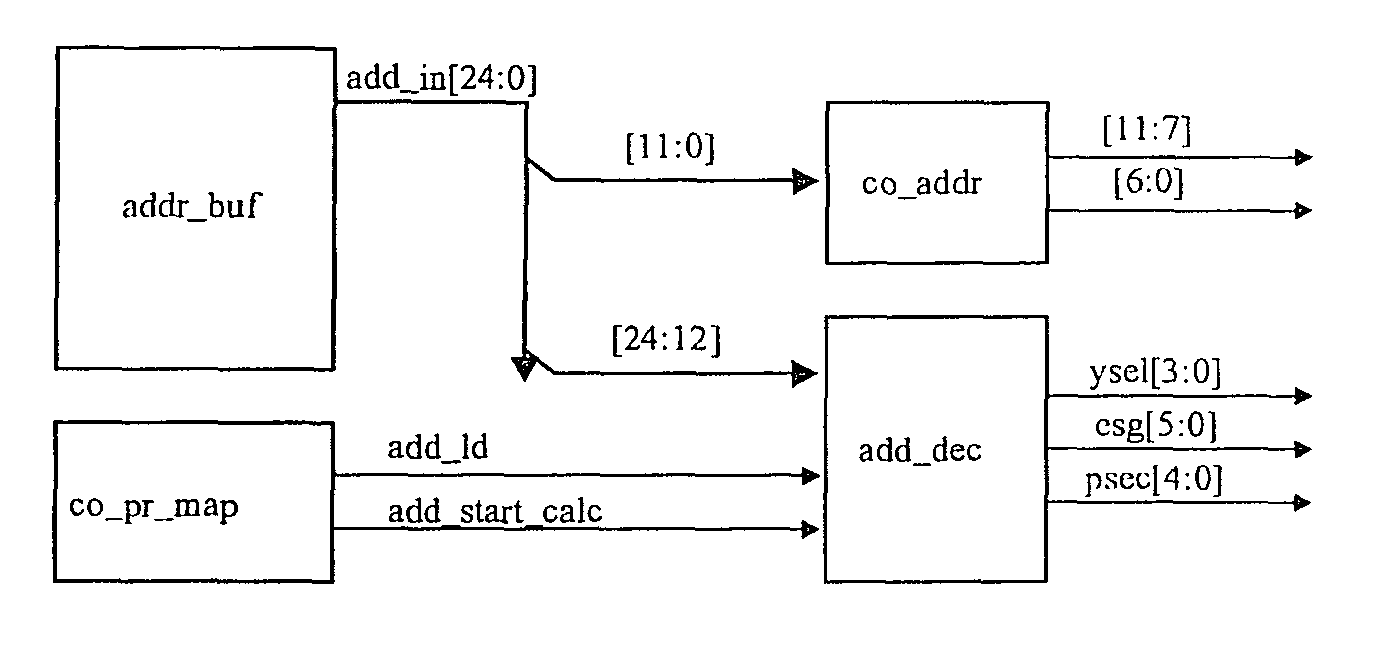
ActiveUS20090204747A1Improve layout efficiencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPhysical addressModular arithmetic
A Flash memory array comprises a plurality of Erase Sectors (Esecs) arranged in a plurality of Erase Sector Groups (ESGs), Physical Pages (slices), and Physical Sectors (PSecs), and there is a non-binary number of at least one of the Erase Sector Groups (ESGs), Physical Pages (slices), and Physical Sectors (PSecs). A user address is translated into a physical address using modular arithmetic to determine pointers (ysel, esg, psec) for specifying a given Erase Sector (ESec) within a given Erase Sector Group (ESG); a given Erase Sector Group (ESG) within a given Physical Sector (Psec); and a given Physical Sector (PSec) within the array.
Owner:SPANSION ISRAEL
Elliptic curve encryption coprocessor suitable for RFID security communication
ActiveCN103903047AEasy transferReduce usageComputations using residue arithmeticRecord carriers used with machinesArithmetic logic unitCoprocessor
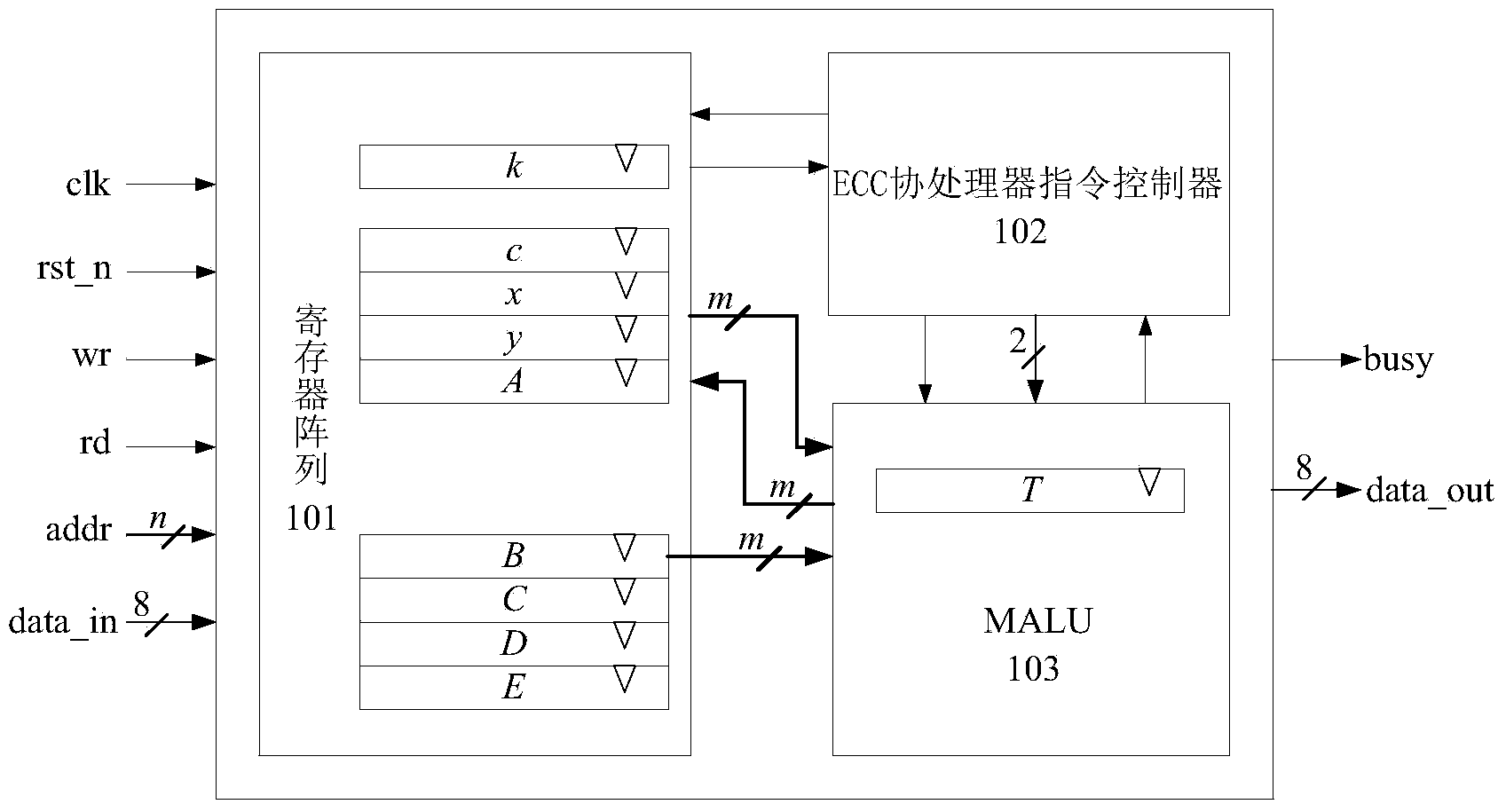
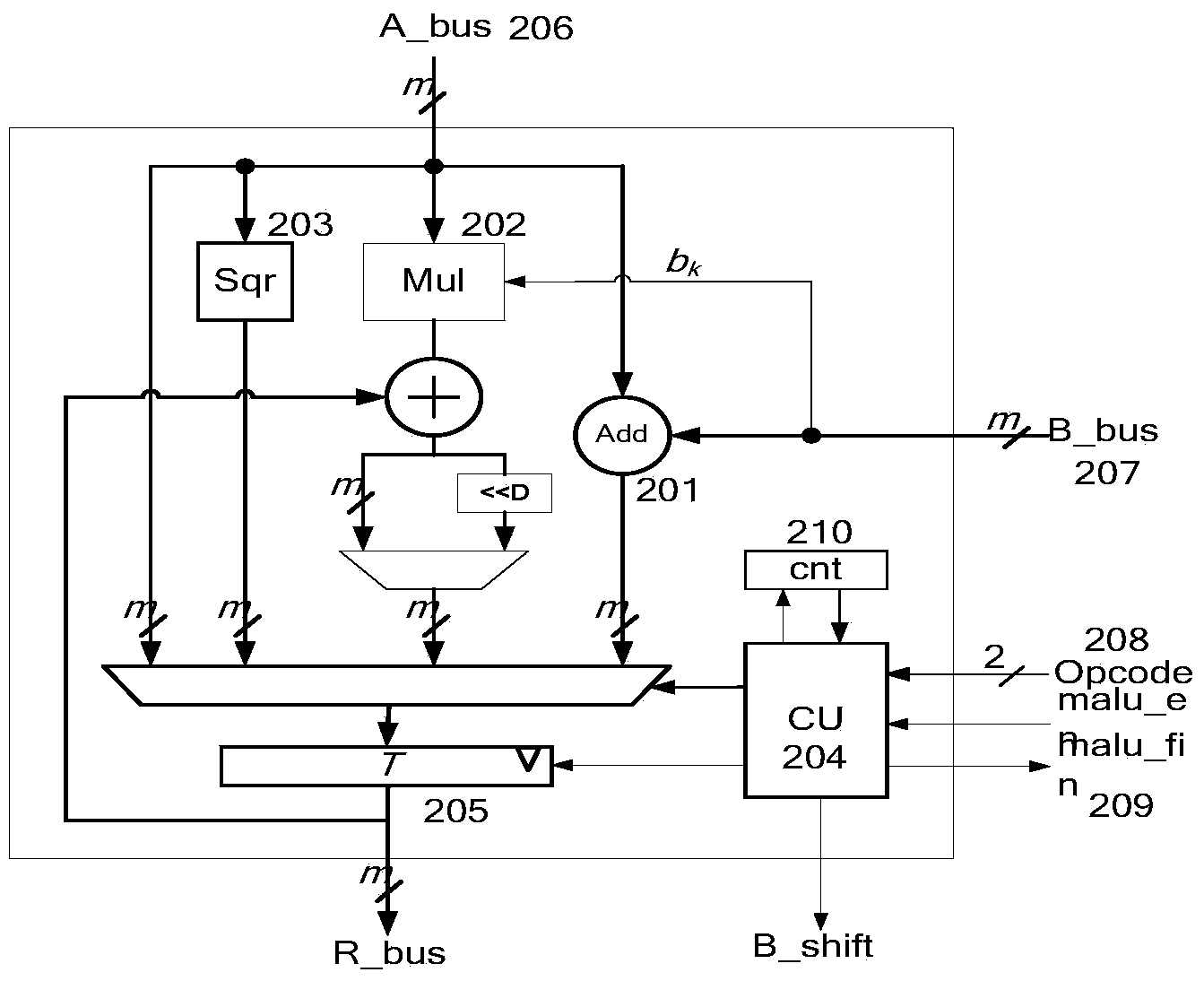
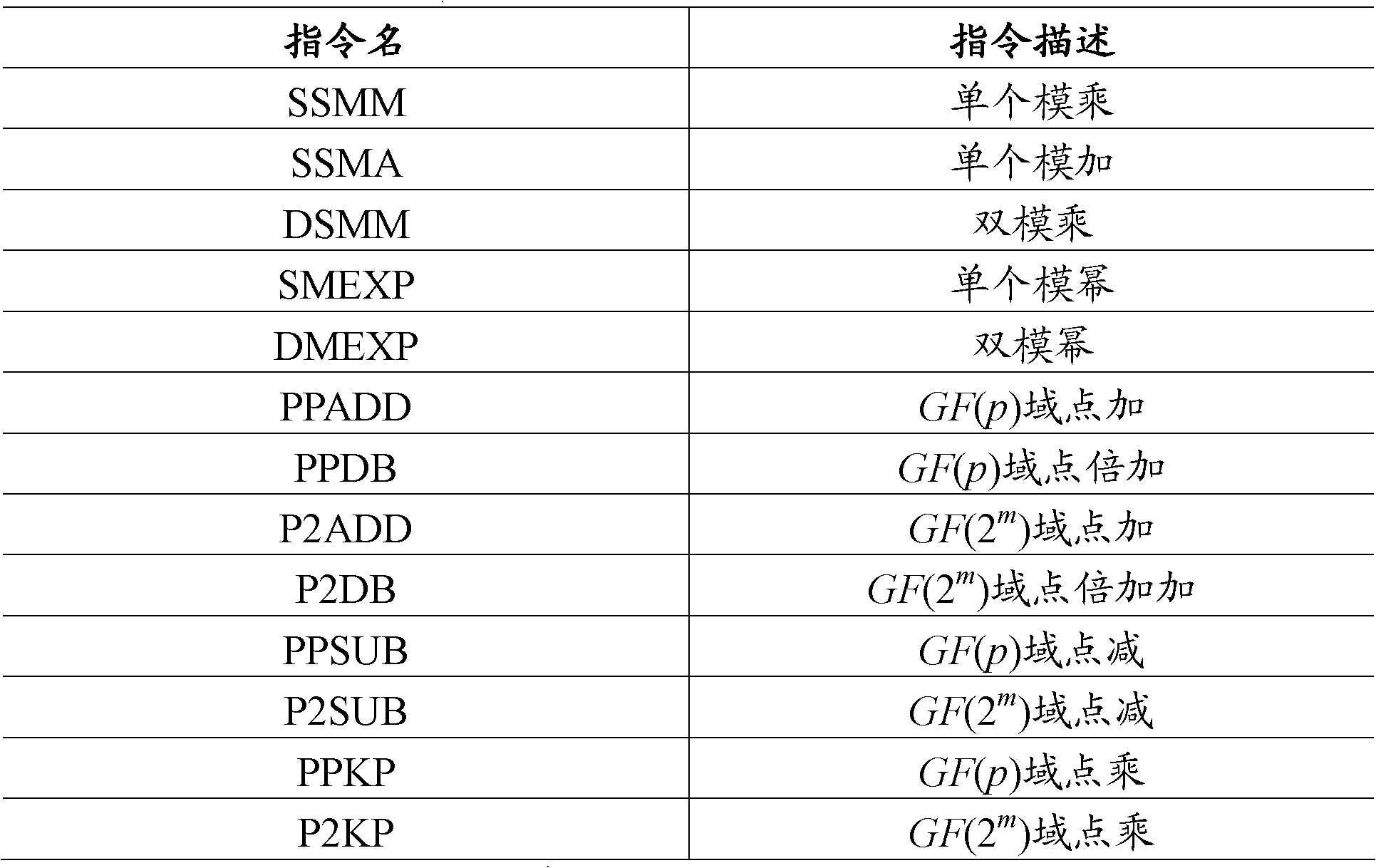
The invention discloses an elliptic curve encryption coprocessor suitable for RFID security communication. The elliptic curve encryption coprocessor comprises a register array, a modular arithmetic logic unit and an ECC coprocessor instruction controller. The register array is used for storing elliptic curve parameters, the private key, calculation process data and the calculation result in the elliptic curve encryption calculation process. The modular arithmetic logic unit comprises a summing circuit, a multiplying circuit, a squaring circuit, a control unit and a register T and is used for completing add operation, multiplication and squaring operation. The ECC coprocessor instruction controller is used for sending an add operation instruction, a multiplication instruction, a squaring operation instruction and a moving instruction to the modular arithmetic logic unit, receiving the calculation result obtained through the modular arithmetic logic unit, and conducting dot doubling and dot calculation according to the result so as to complete elliptic curve point multiplication calculation. The elliptic curve encryption coprocessor has the advantages of being small in area, low in power consumption and high in security, and is suitable for an RFID tag chip.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Window width and window level adjusting method for pixel set with large data volume
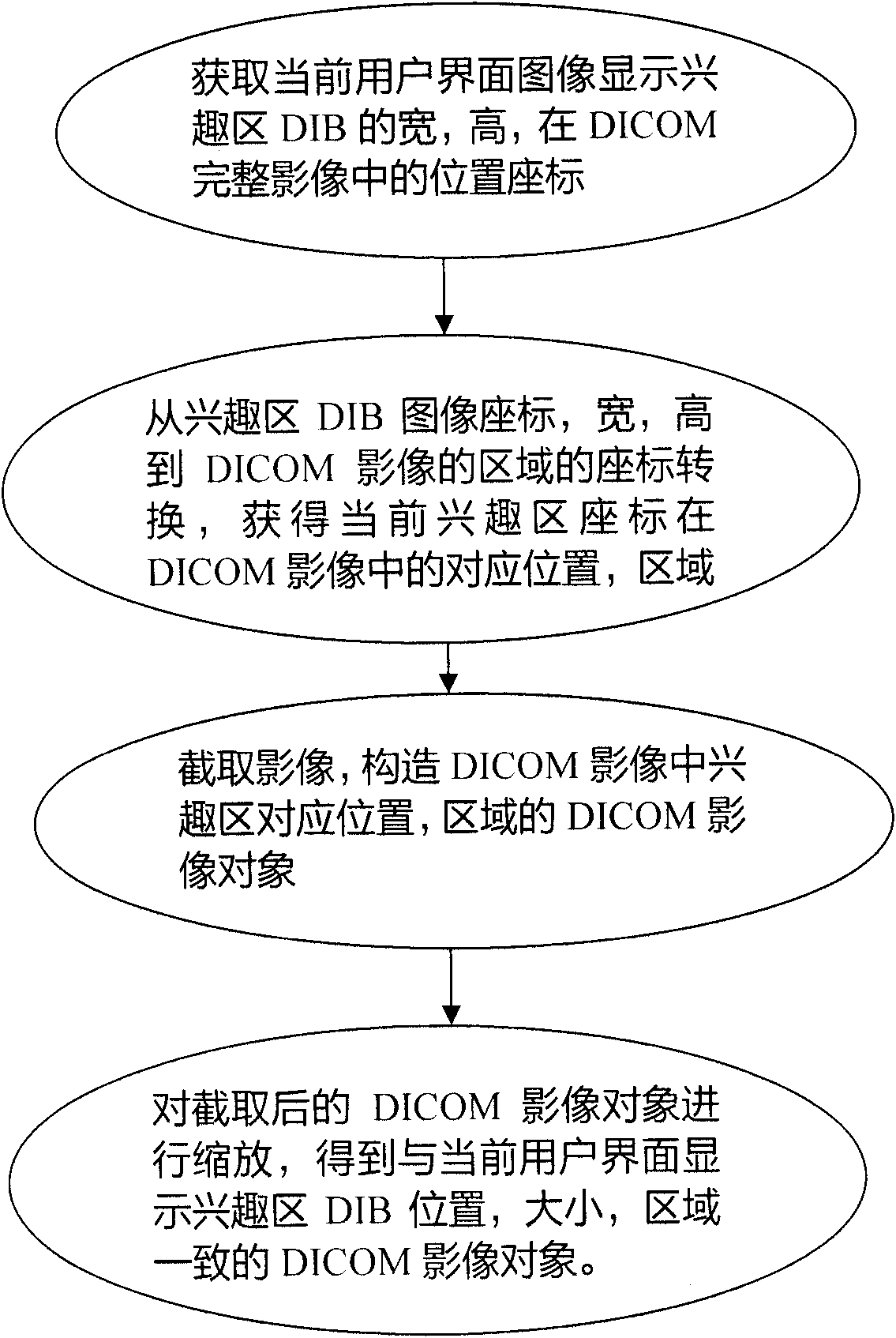
InactiveCN102104784AReduce window response frequencyReduce the response frequencyColor signal processing circuitsDICOMDigital imaging
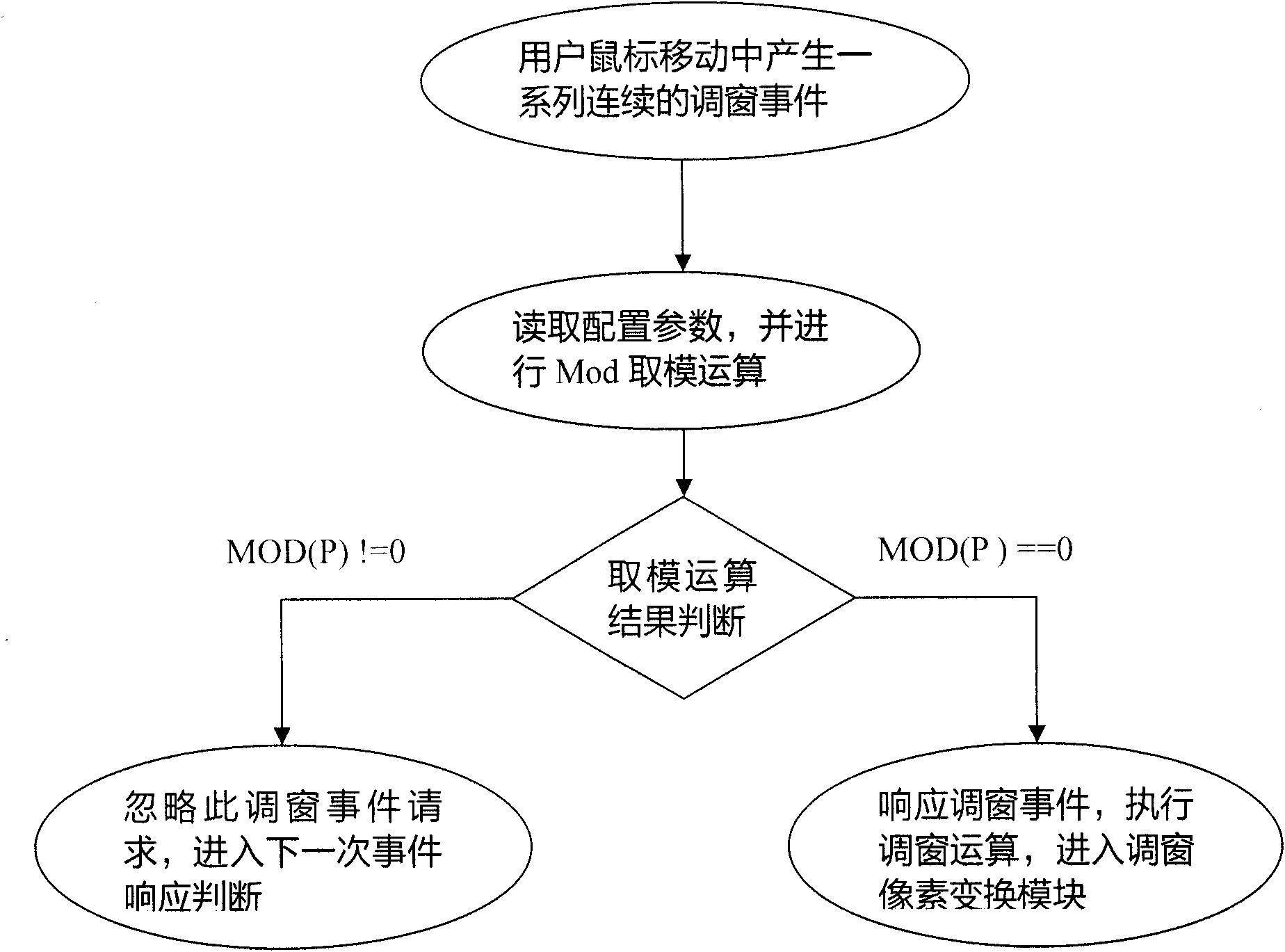
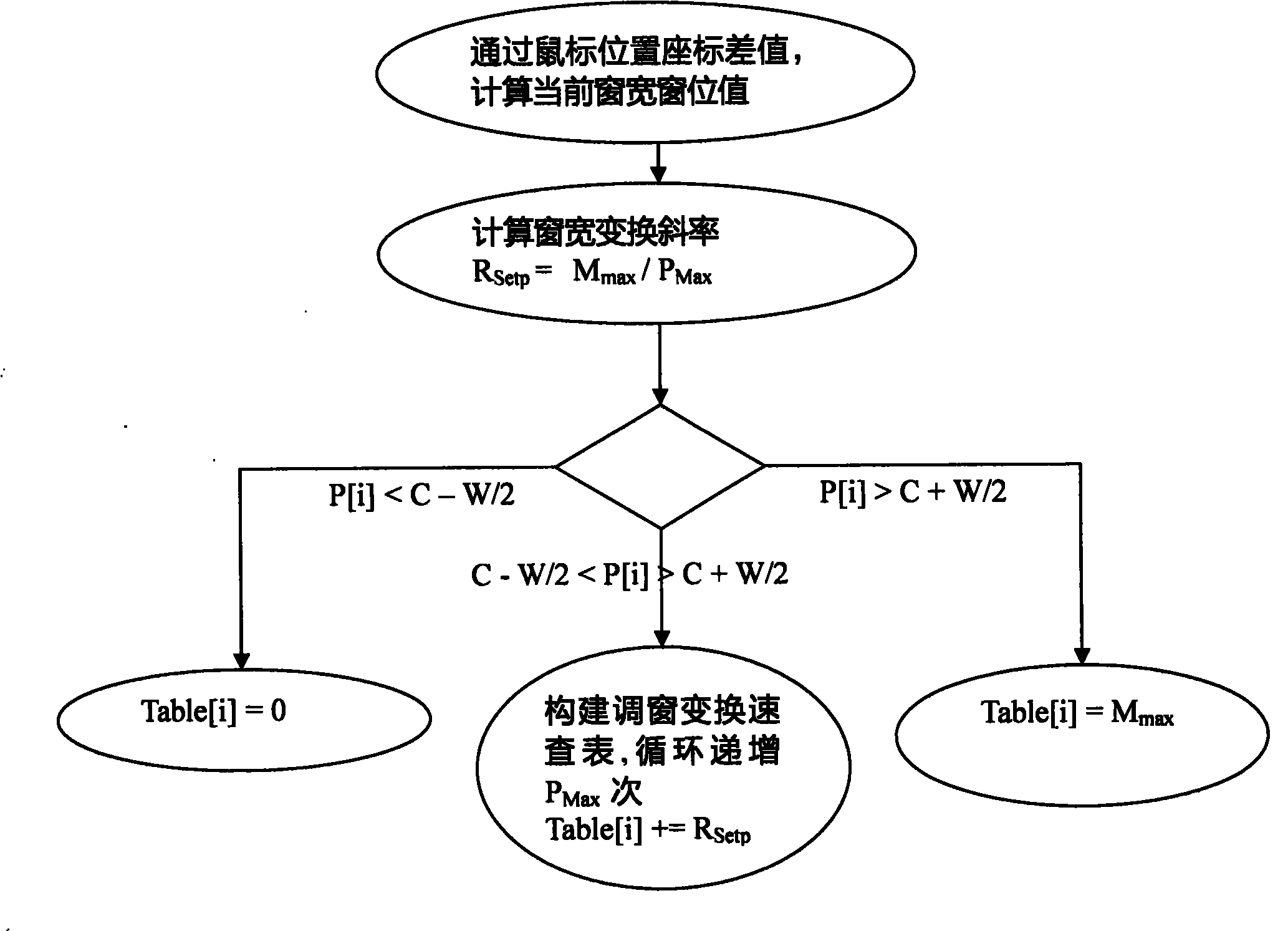
The invention relates to a window width and window level adjusting method for a pixel set with large data volume, which comprises the following steps of: displaying a gray level image on an ordinary RGB (Red, Green and Blue) display in a window-adding manner through setting a DIB (Device Independent Bitmap) color contrast table aiming at a digital medical image of DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) format; during the process of adjusting the window width and the widow level of the image in real time, filtering a response frequency through modular arithmetic; intercepting and zooming an interest region of the image; establishing a window adjusting transformation rapid access table, and searching a pixel set in the traversal interest region of the window adjusting transformation rapid access table to obtain a method of displaying a gray level value and the like so as to reduce the amount of calculation during the window adjusting process of the pixel set, so that the window width and the window level can be adjusted continuously and smoothly in real time even for an image file with very large data volume.
Owner:梁威
Finite field multiplier based on irreducible trinomial
InactiveCN107015782AObvious speed advantageDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierExclusive or
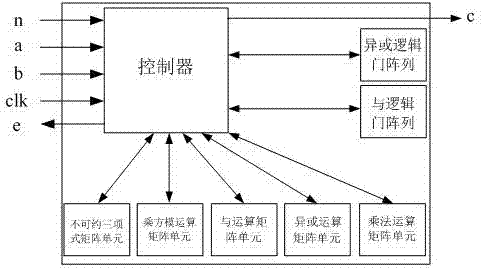
The invention provides a finite field multiplier based on an irreducible trinomial. The multiplier comprises a controller, an input port, an output port, an exclusive or logic gate array, an and logic gate array, an irreducible trinomial matrix, a power modular arithmetic matrix, an and operation matrix, an exclusive or operation matrix and a multiplication operation matrix; the input port comprises a port for inputting a multiplication operand a(x), a port for inputting a b(x), a port for inputting the size of GF(2n) where the multiplication is located, and a port for inputting a clock signal; the output port comprises a port for outputting a multiplication result c(x), and a port for outputting feedback information about whether operation is within the multiplier operation range or not; the controller comprises a processor and an analyzer which are connected and is connected with the other components; the irreducible trinomial matrix stores the irreducible trinomial on different GF(2n); the and operation matrix stores the and operation results among bits of the a(x) and bits of the b(x). Compared with an existing multiplier, the finite field multiplier has the obvious speed advantage on multiplication on GF(2n) calculation.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
High-performance extensible public key password coprocessor structure
InactiveCN102043916AEasy to integrateImprove performanceDigital data protectionInternal memoryComputer architecture
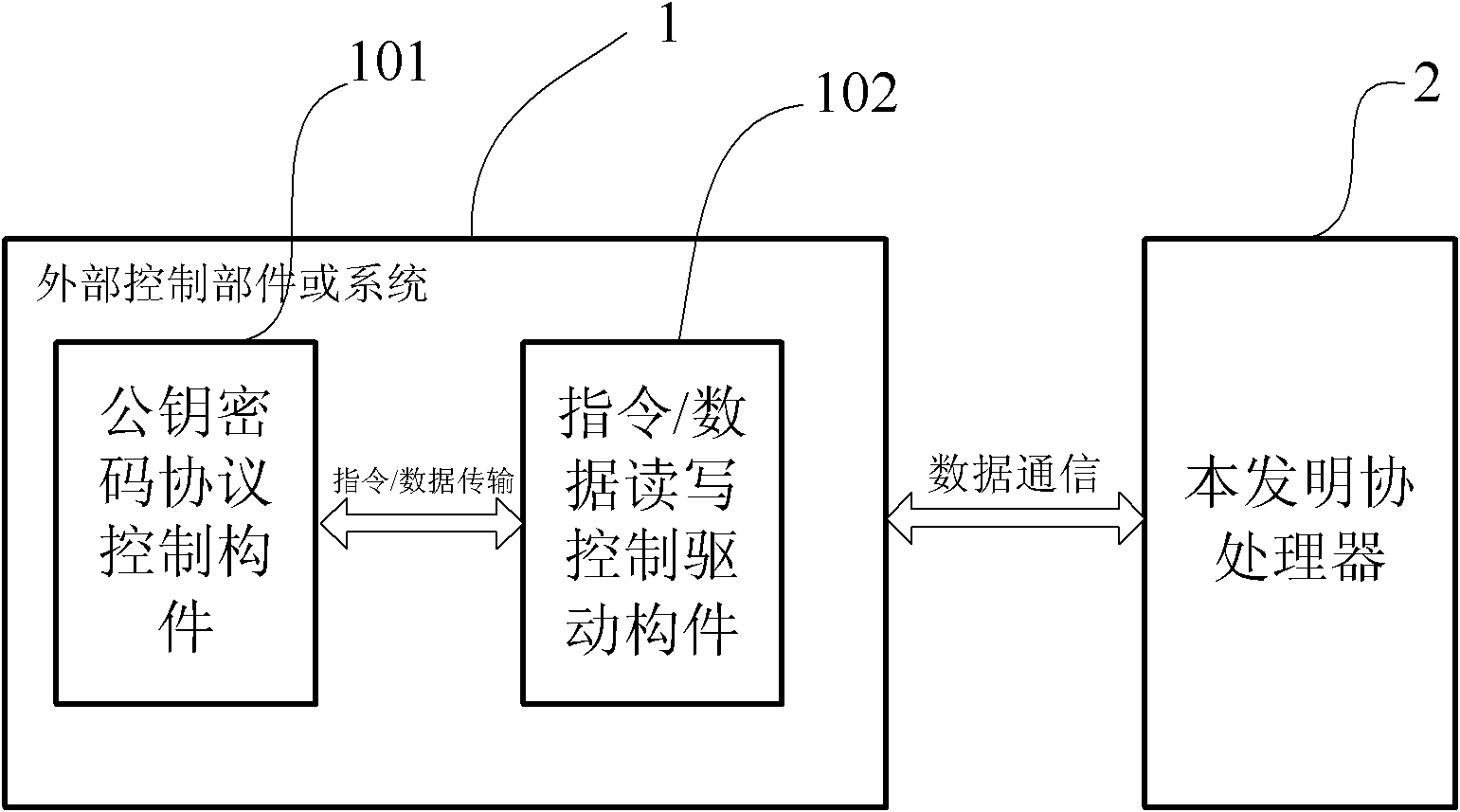
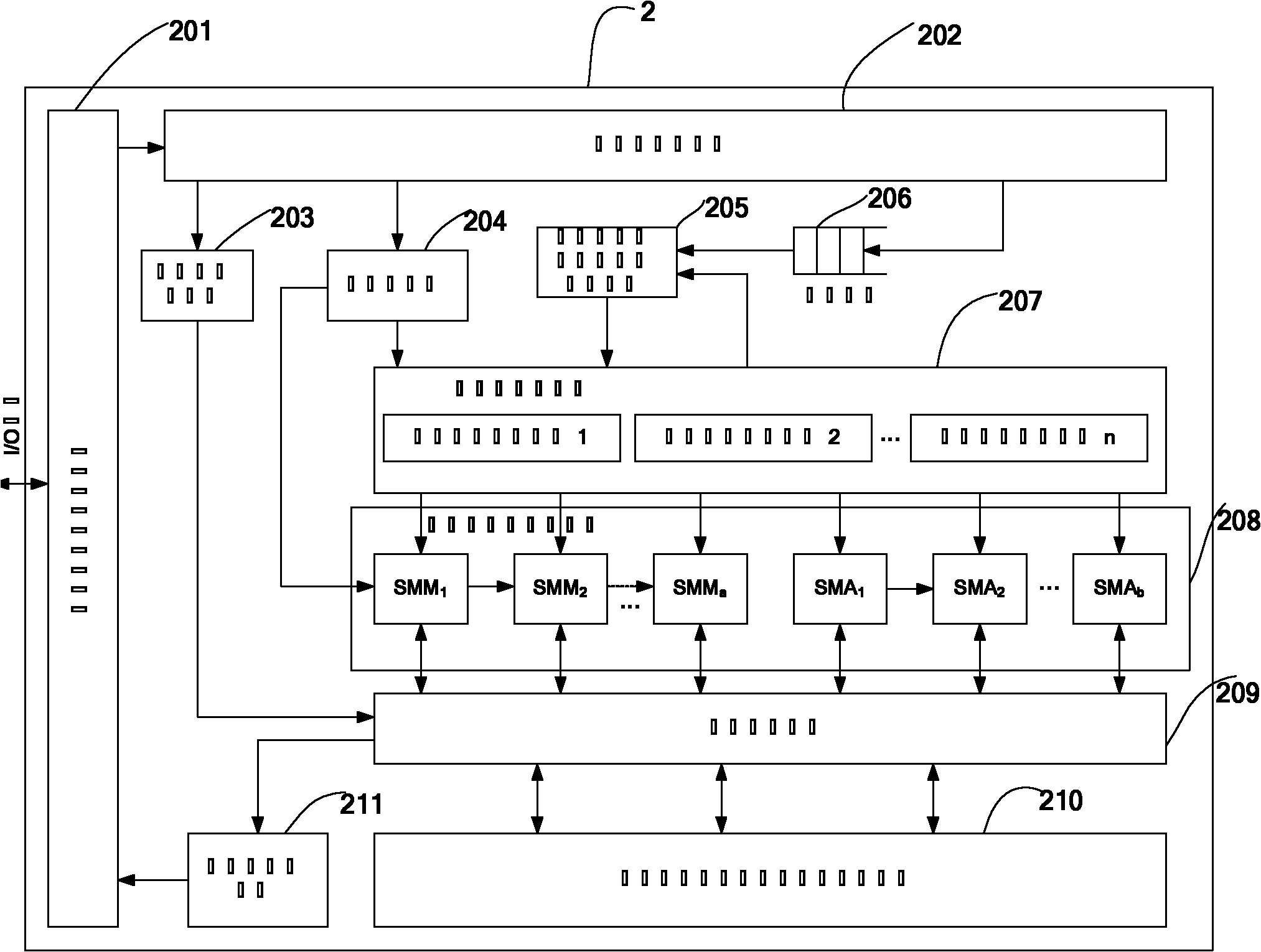
The invention relates to a high-performance extensible public key password coprocessor structure, comprising a basic instruction set. In the structure, a memory mapping interface circuit is respectively connected with an external control component or system, an input buffer circuit and an output buffer circuit; the input buffer circuit is respectively connected with a data controller circuit, a configuration register and an instruction queue; the data controller circuit is connected with a memory controller; the configuration register is respectively connected with an instruction execution controller and a modular arithmetic operation cell array; an instruction decoding unit based on a wired state machine is respectively connected with the instruction queue and the instruction execution controller; the instruction execution controller is connected with the modular arithmetic operation cell array; the modular arithmetic operation cell array is connected with the memory controller, and the memory controller is respectively connected with an internal memory cell for a register file and the like and an output buffer circuit. The structure in the invention is configured according to the actual requirement, so as to meet specific application requirement with low power consumption and high cost performance.
Owner:戴葵
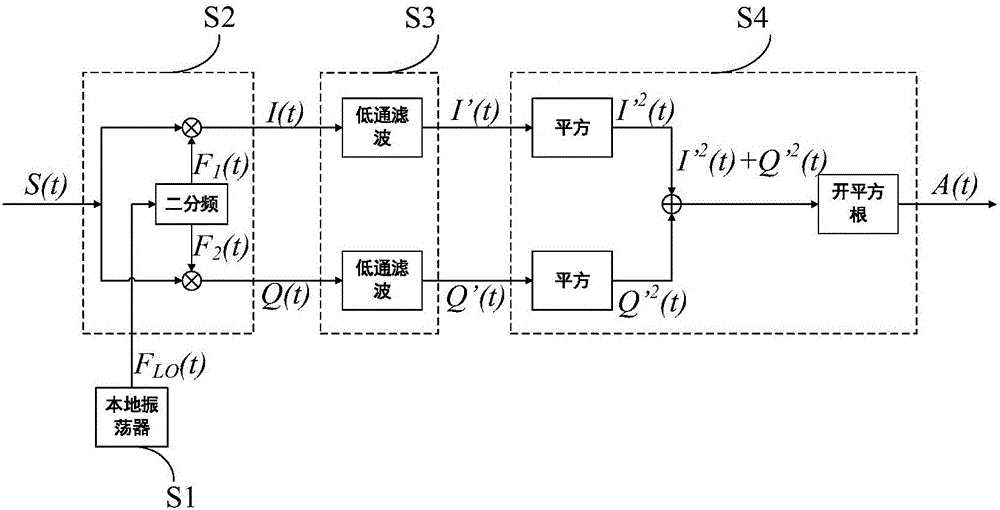
Method and circuit for forming pulse flow in ultrasonic signal sparse sampling
ActiveCN105738885AAccurate extractionReduce Design ComplexityWave based measurement systemsLow speedSonification
The invention discloses a method and a circuit for forming a pulse flow in the ultrasonic signal sparse sampling. The method includes the steps that: S1, a local oscillator generates an oscillating signal having the oscillating frequency two times of the center frequency of an ultrasonic signal S(t); S2, two divided-frequency is carried out on the oscillating signal, so that two paths of square signals are generated, and the two paths of square signals and the S(t) are independently modulated and mixed; S3, the two paths of modulated and mixing signals pass a low pass filter, and two paths of output signals are generated; S4, the square operation is respectively carried out on the two paths of output signals of the S3, square values are added, and then a square root value of an addition value is obtained, and a final output signal A(t) which is the pulse flow obtained by detecting the ultrasonic signal S(t) is obtained. A circuit function module comprises a local oscillation module, an orthogonal frequency mixing module, a low pass filtering module and a modular arithmetic module. The method and the circuit for forming the pulse flow in the ultrasonic signal sparse sampling are especially suitable for realizing the sparse sampling at a low speed in the ultrasonic signal sparse sampling system based on a limited rate of innovation. The speed of the sparse sampling is greatly lower than a conventional Nyquist sampling speed. On the basis of maintenance of original signal information, the problem of a large data amount of a conventional sampling method is solved, and the ultrasonic pulse flow can be formed in real time.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
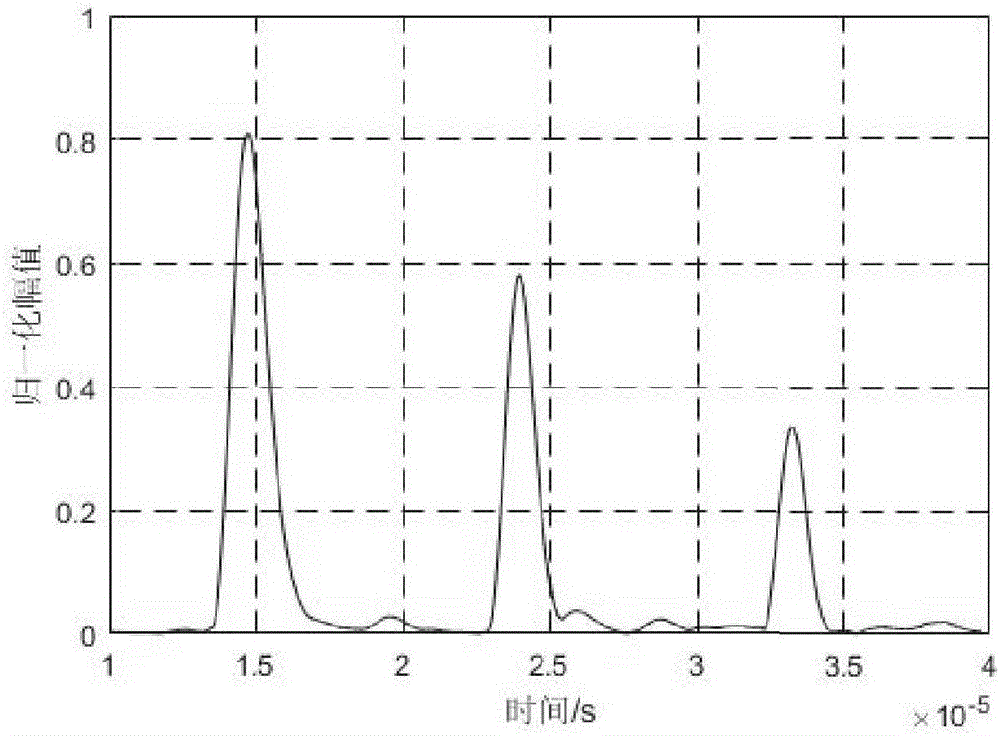
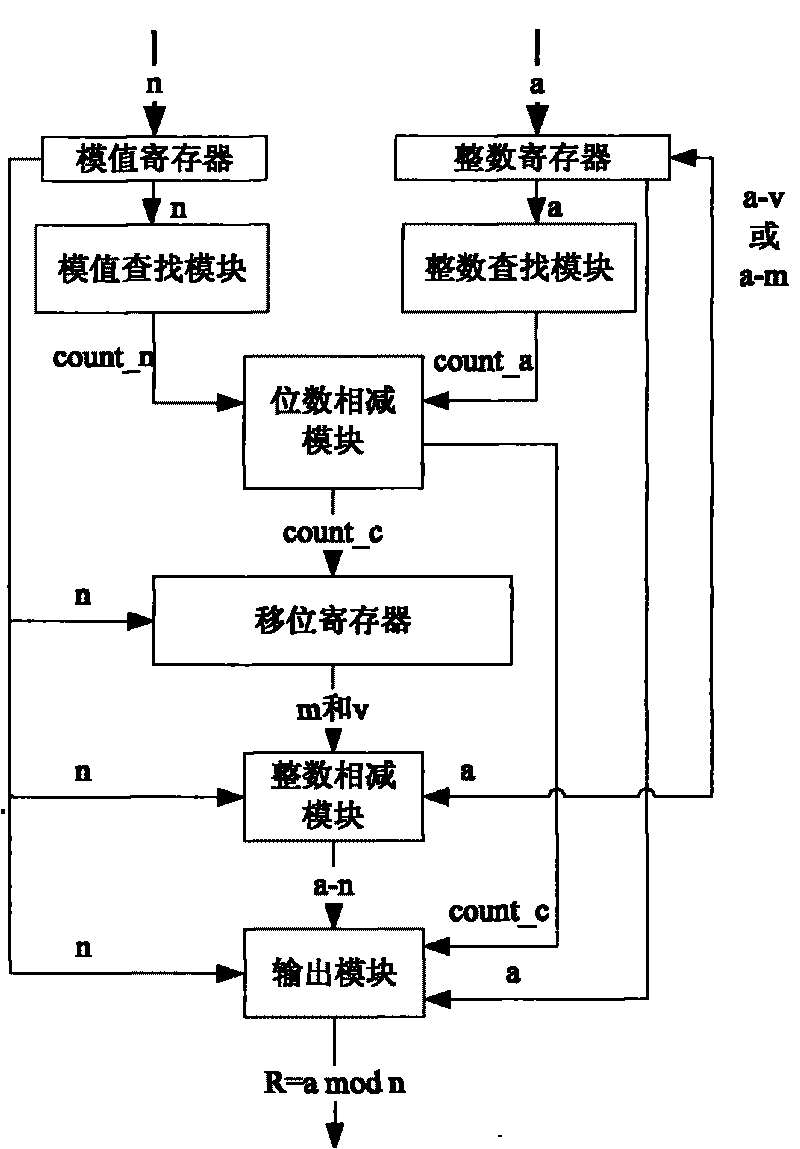
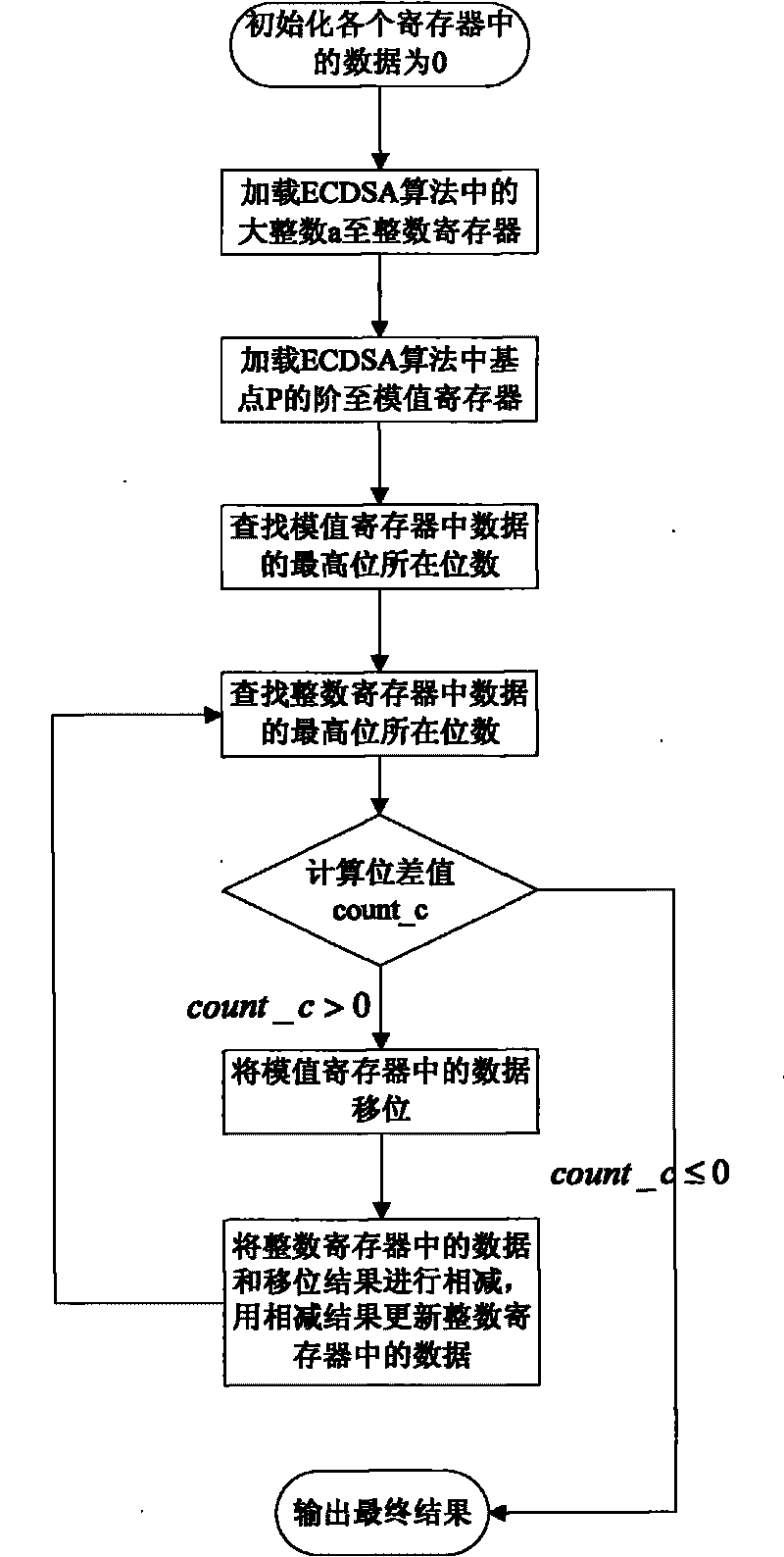
Large integer modular arithmetic device for realizing signature algorithm in ECC cryptosystem and modular method therefor
InactiveCN101763241ASimple theoryEasy to implementUser identity/authority verificationComputations using residue arithmeticShift registerProcessor register
The invention discloses a large integer modular arithmetic device for realizing signature algorithm in an ECC cryptosystem; the device comprises an integer register, a module value register, an integer searching module, a module value searching module, a digit number subtraction module, a shift register, a data subtraction module and an output module, wherein the integer register stores the value of integer a to be modularized; the module value register stores the value of module n; the module value searching module searches the digit number of the most significant digit of the module n; the integer searching module searches the bit number of most significant digit of the data a in the integer register; the digit number subtraction module calculates the digit difference between the most significant digit of the integer a and the most significant digit of the module n; when the digit difference is more than 0, the shift register shifts data n to the left twice, and then the data subtraction module subtract the integer a from shifted result to obtain value a', and then the data subtraction module updates the data a in the integer register module into the value a'; when the digit difference is less than or equal to 0, the output module finally outputs the final modular result. Compared with the prior art, the invention has lower cost, strong generality, and high efficiency.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Methods of factoring and modular arithmetic
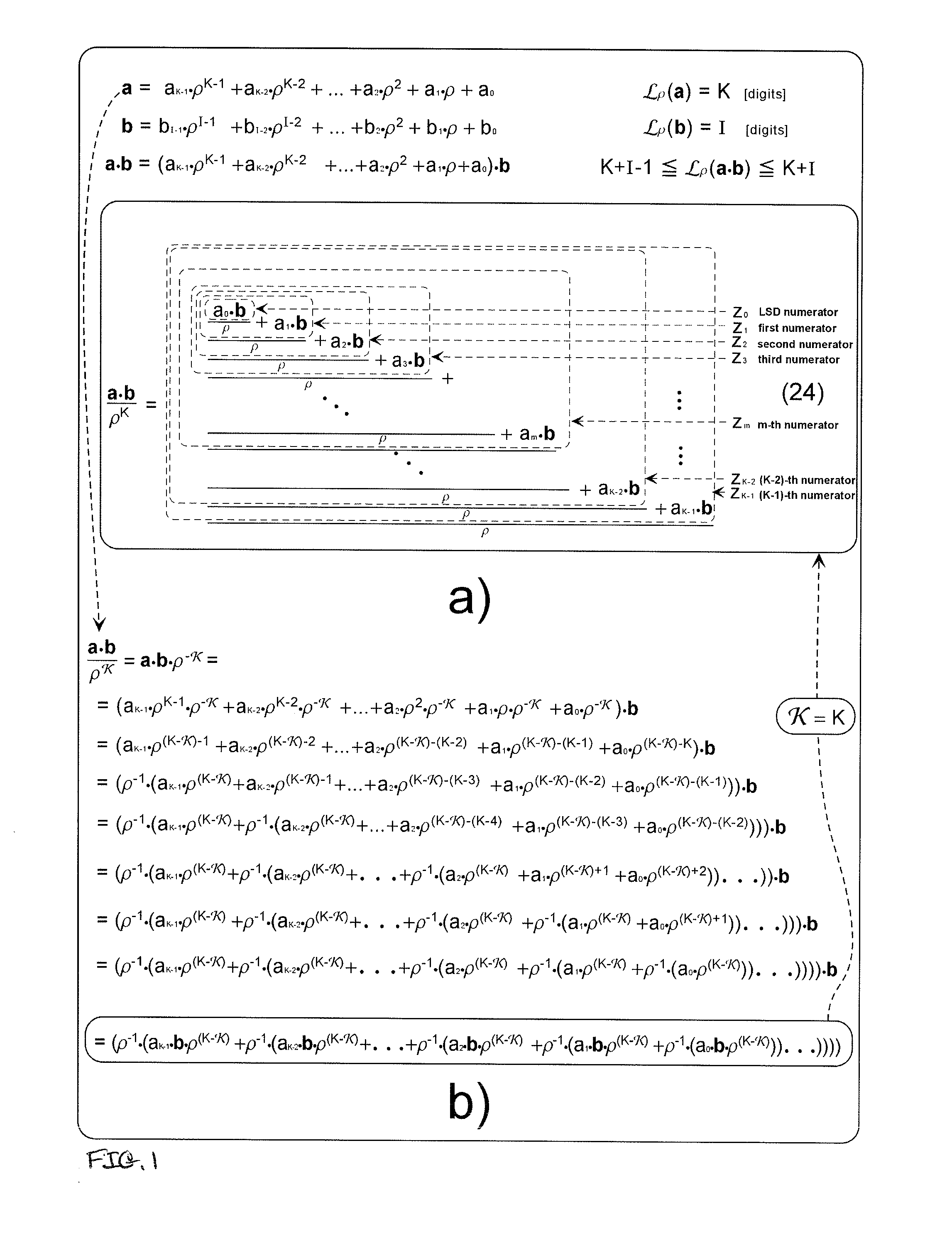
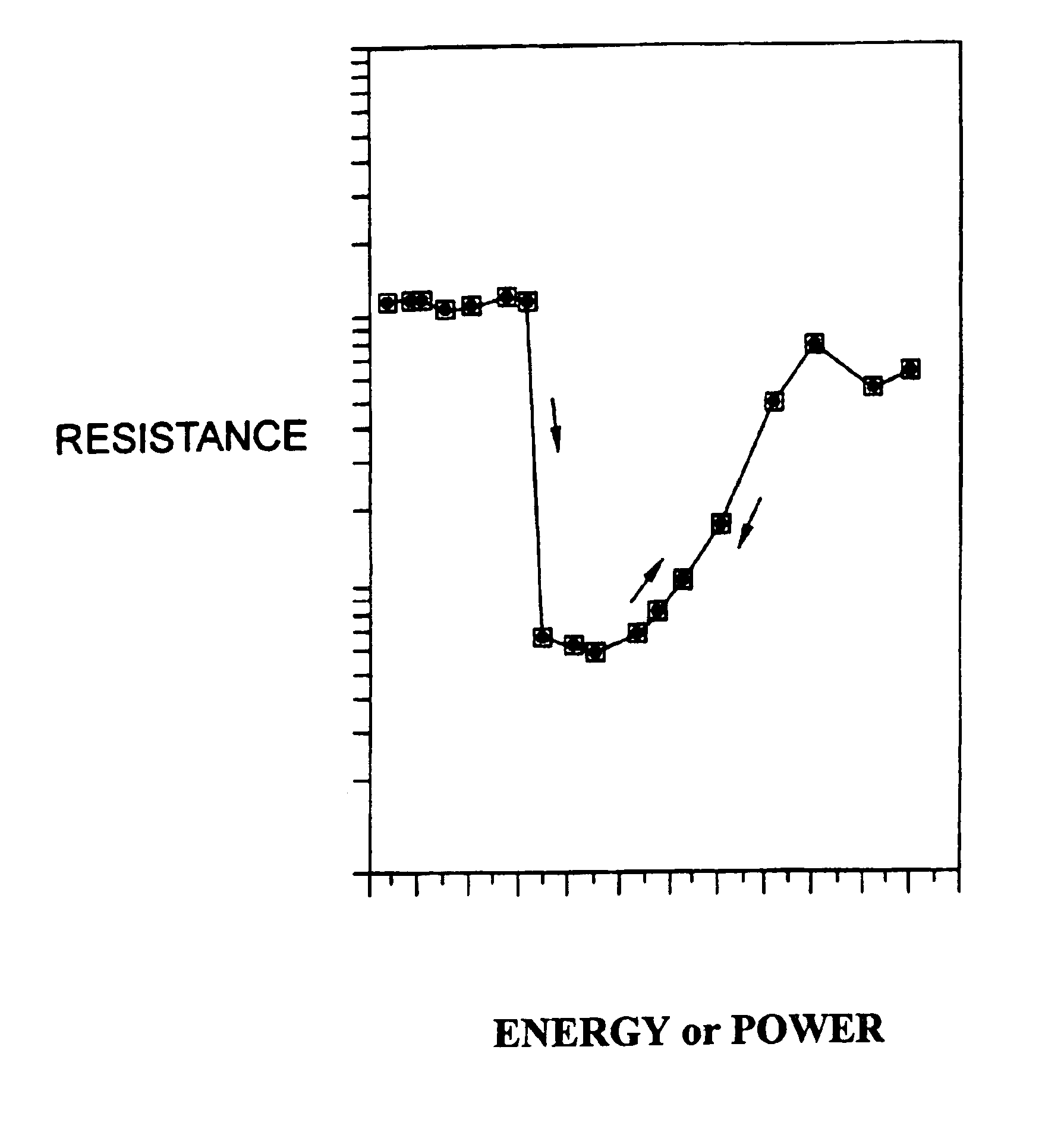
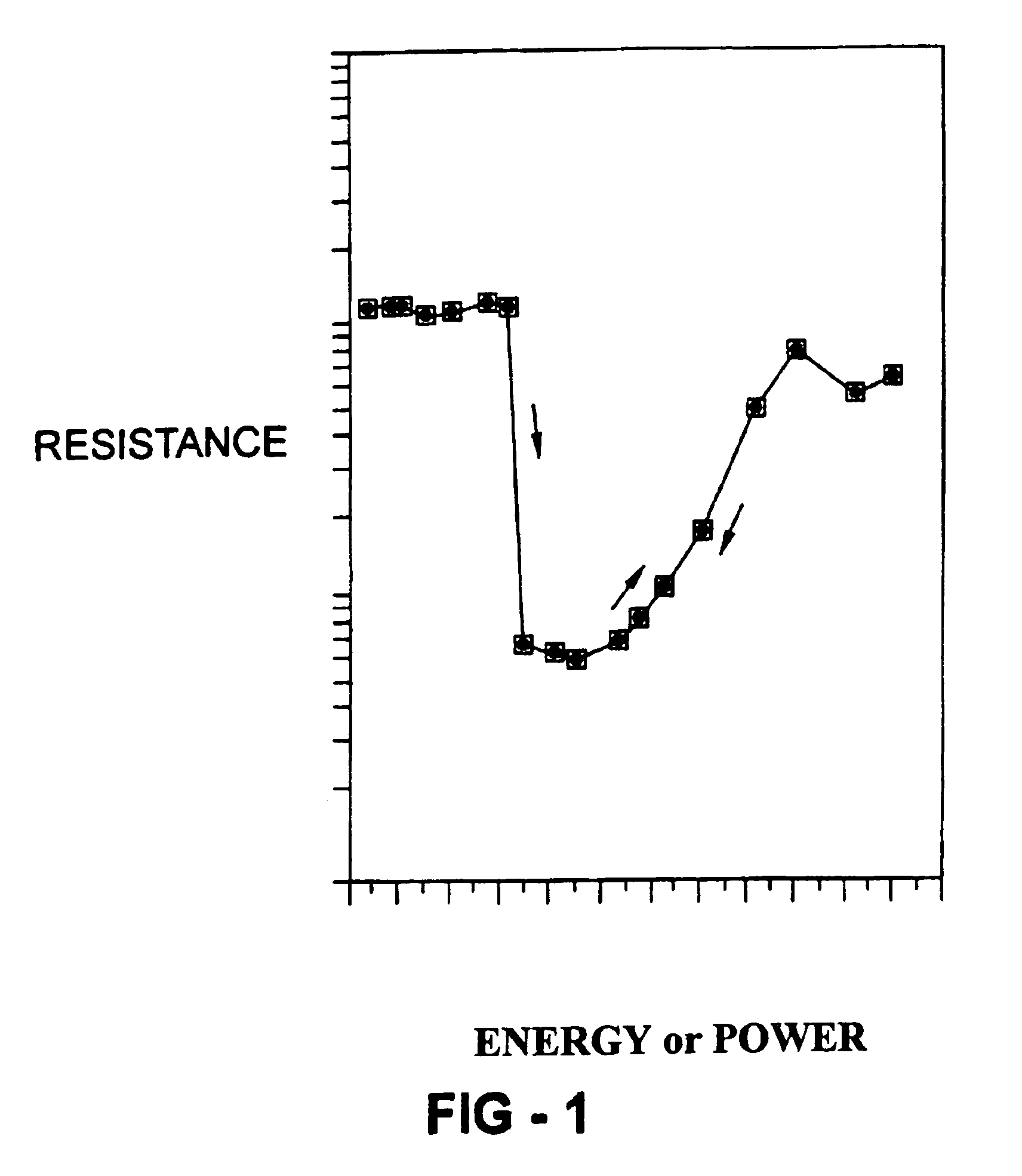
InactiveUS6963893B2Efficient factoringComputation using non-contact making devicesSolid-state devicesE factorModular arithmetic
A method of factoring numbers in a non-binary computation scheme and more particularly, a method of factoring numbers utilizing a digital multistate phase change material. The method includes providing energy in an amount characteristic of the number to be factored to a phase change material programmed according to a potential factor of the number. The programming strategy provides for the setting of the phase change material once for each time a multiple of a potential factor is present in the number to be factored. By counting the number of multiples and assessing the state of the phase change material upon execution of the method, a determination of whether a potential factor is indeed a factor may be made. A given volume of phase change material may be reprogrammed for different factors or separate volumes of phase change material may be employed for different factors. Parallel factorization over several potential factors may be achieved by combining separate volumes of phase change material programmed according to different potential factors. Methods of addition and computing congruences in a modular arithmetic system are also included.
Owner:OVONYX
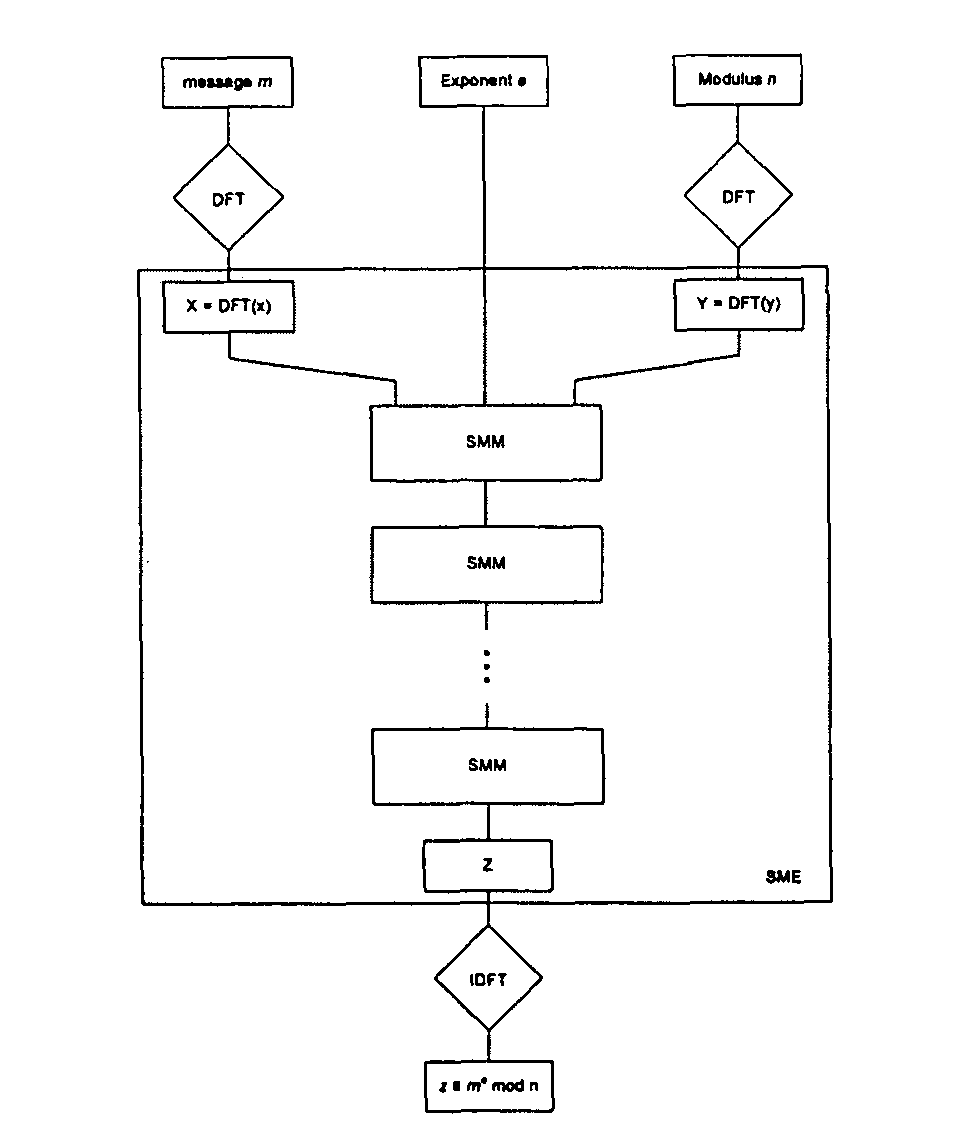
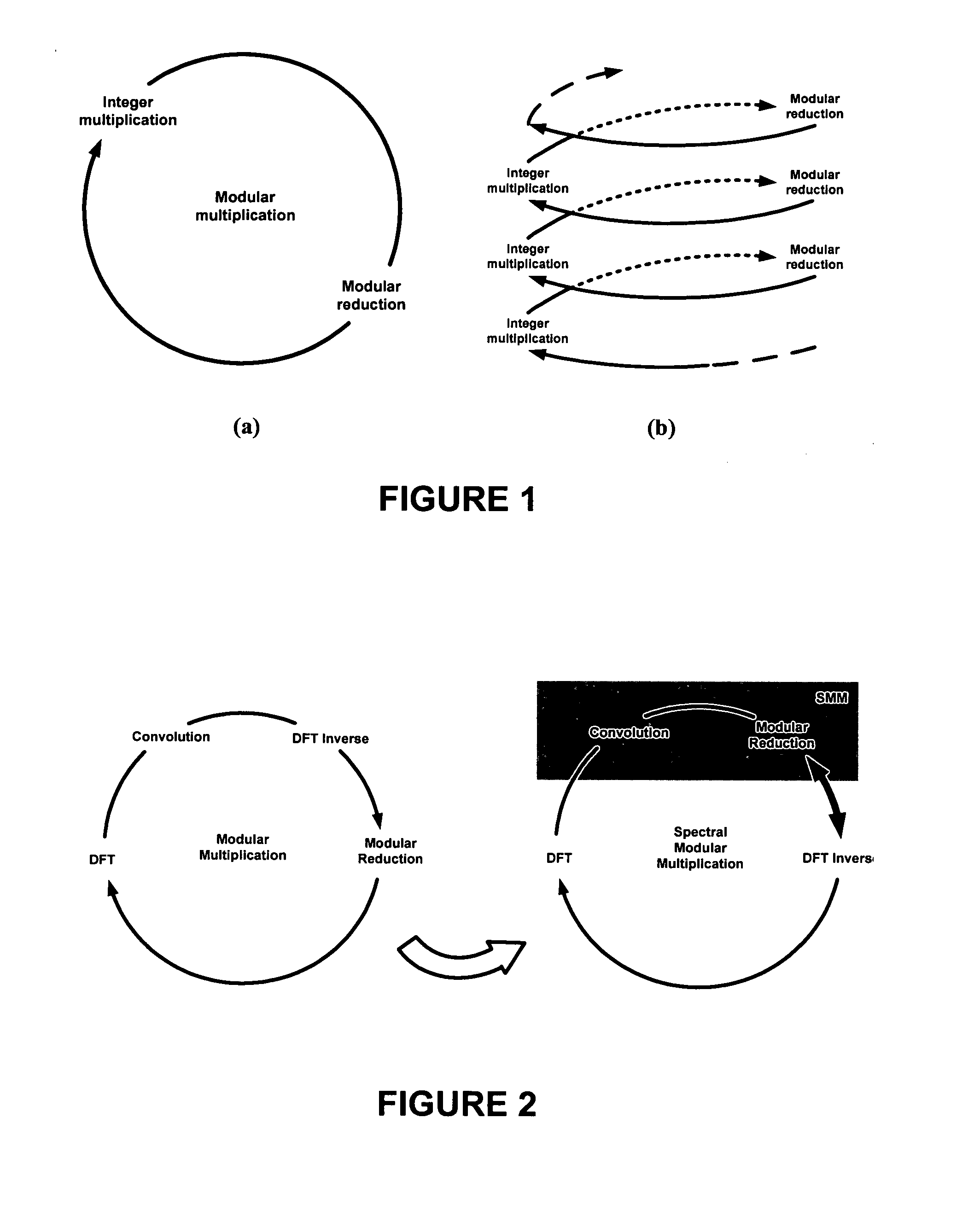
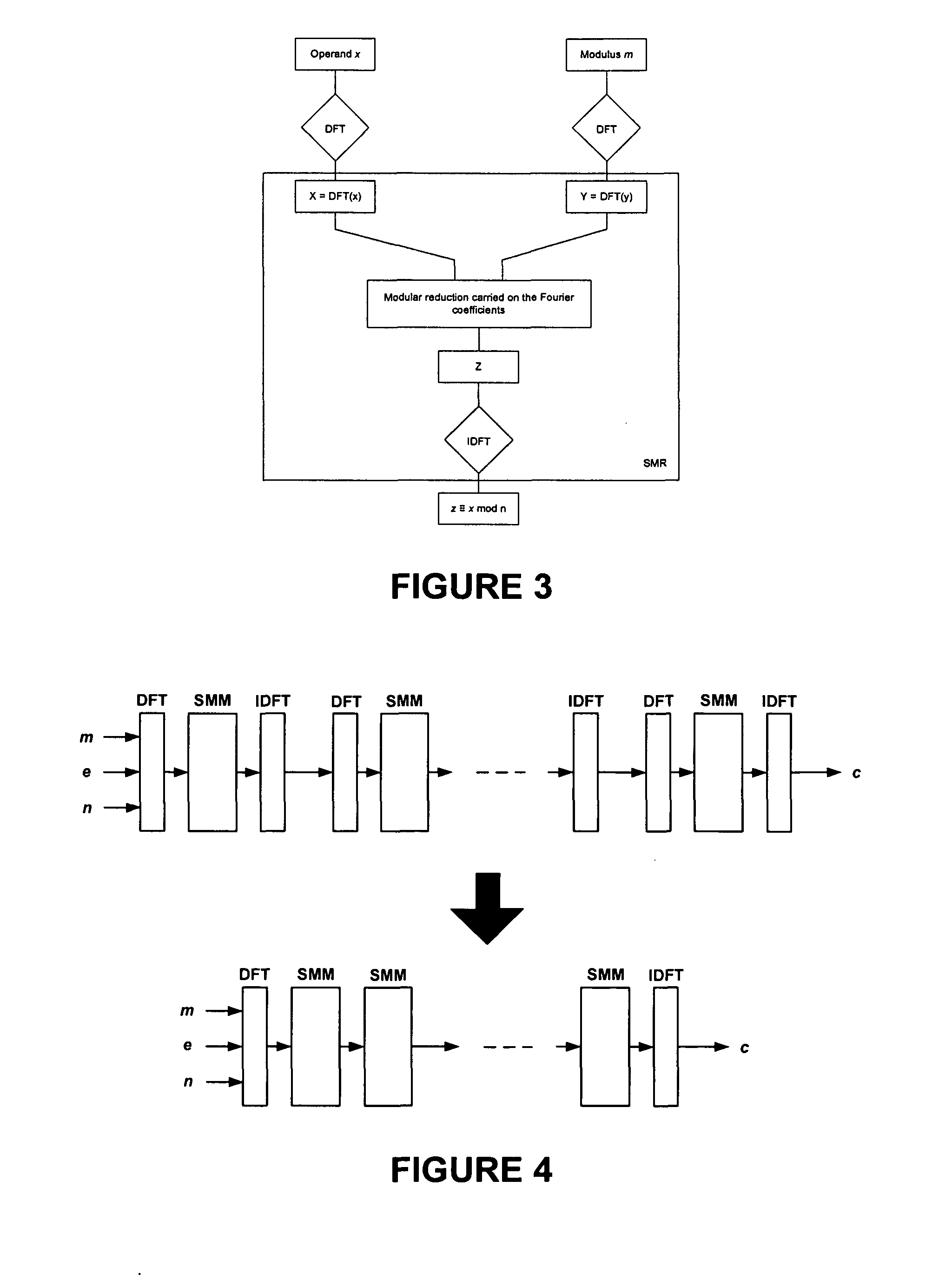
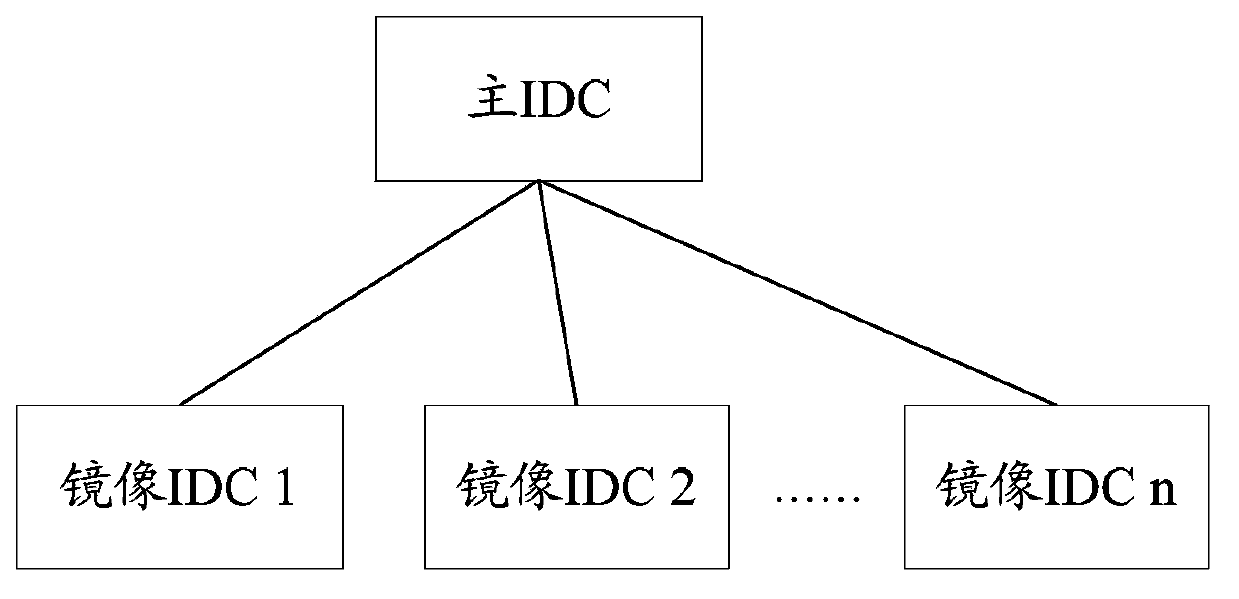
Spectral modular arithmetic method and apparatus
InactiveUS8719324B1Efficient and highly parallelEfficient and highly parallel architectureComputation using denominational number representationHardware architectureModularity
A new hardware architecture is disclosed that performs the modular exponentiation operation, i.e., the computation of c=me mod n where c, m, e, n are large integers. The modular exponentiation operation is the most common operation in public-key cryptography. The new method, named the Spectral Modular Exponentiation method, uses the Discrete Fourier Transform over a finite ring, and relies on new techniques to perform the modular multiplication and reduction operations. The method yields an efficient and highly parallel architecture for hardware implementations of public-key cryptosystems which use the modular exponentiation operation as the basic step, such as the RSA and Diffie-Hellman algorithms. The method is extended to perform the multiplication operation in extension fields which is necessary to perform exponentiation or various other operations over these extension fields.
Owner:KOC CETIN K +1
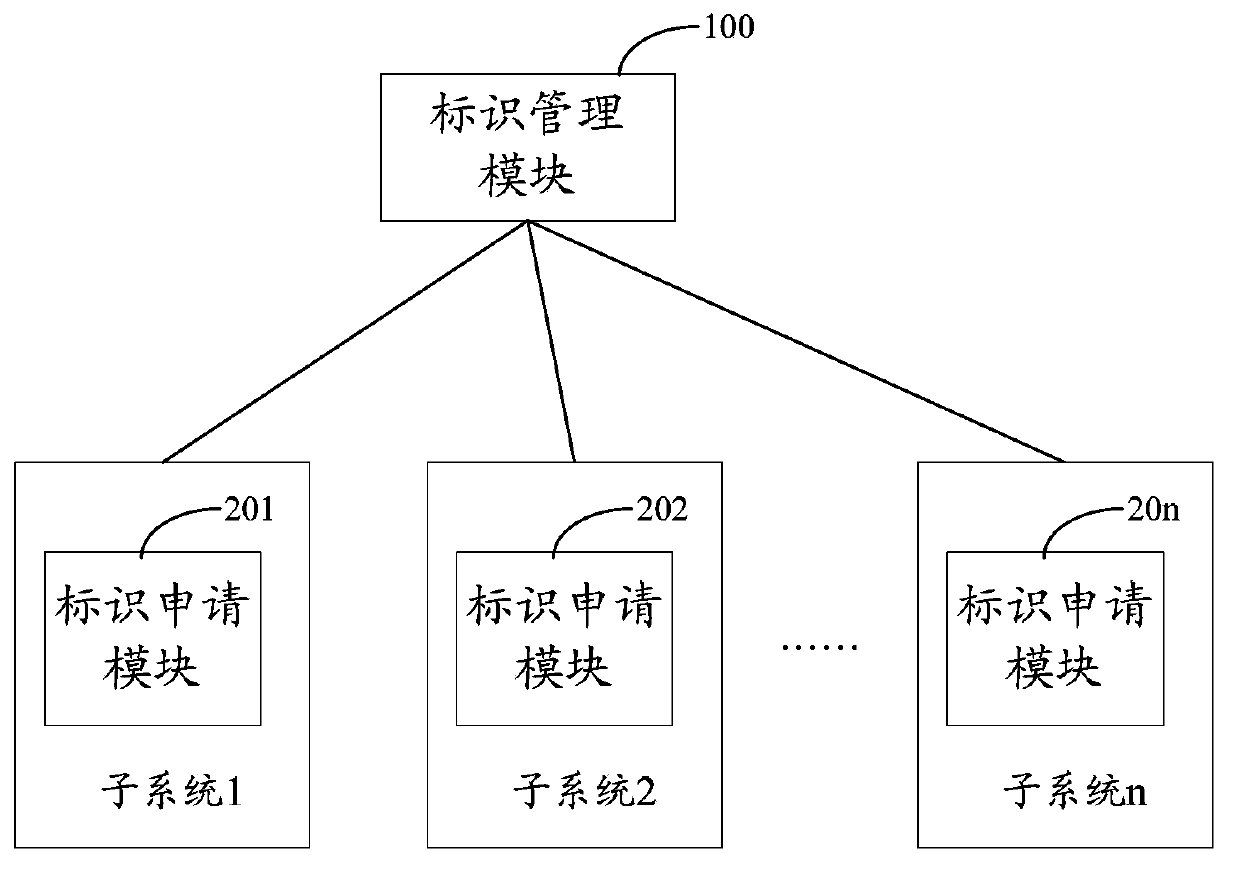
Identity resource allocation method and system thereof
ActiveCN103873389AGuaranteed continuityMeet Information ManagementData switching networksModular arithmeticIdentity management
The invention discloses an identity resource allocation method and a system thereof. The identity resource allocation method comprises the following steps: an identity management module segments an identity resource space based on fixed segment size in advance and numbers each segment consecutively, and each segment is classified to N fragments according to modular arithmetic result of serial number, wherein N is modulus; a currently-available segment with the minimum serial number in all N fragments is polled when some subsystem needs to apply identity resources; and the identity management module allocates the segment with the minimum serial number in the N segments to the subsystem. With the application of the scheme, continuity of identity serial number allocation can be guaranteed from a macroscopic view. Thus, various requirements such as information management and practical application can be better met.
Owner:SHANGHAI YOUYANG XINMEI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
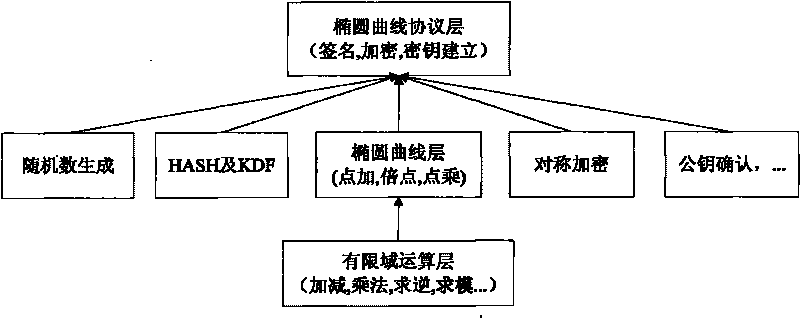
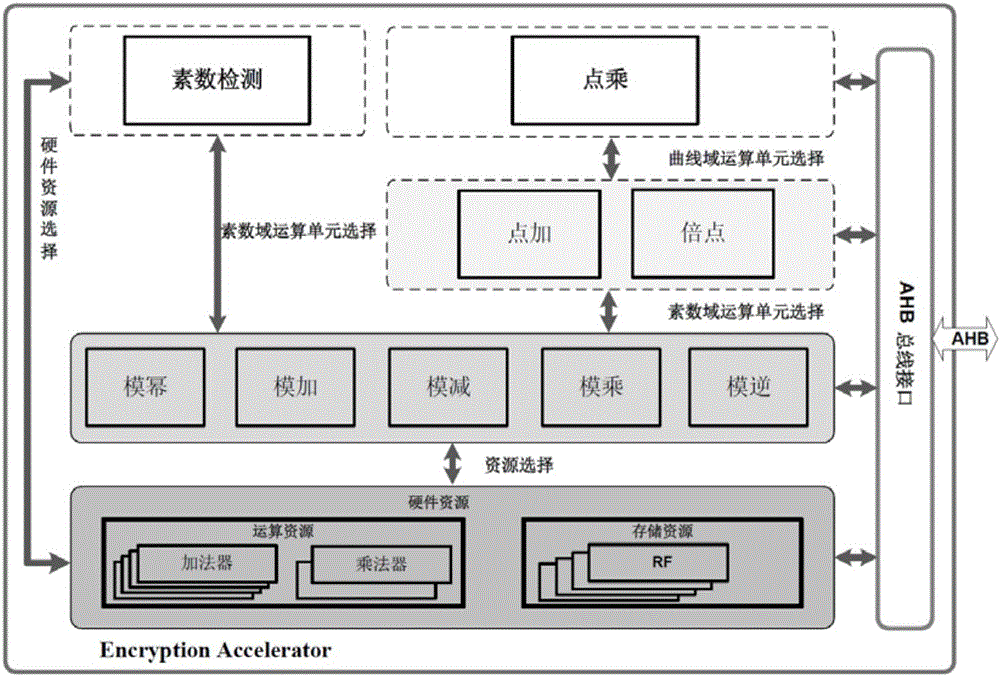
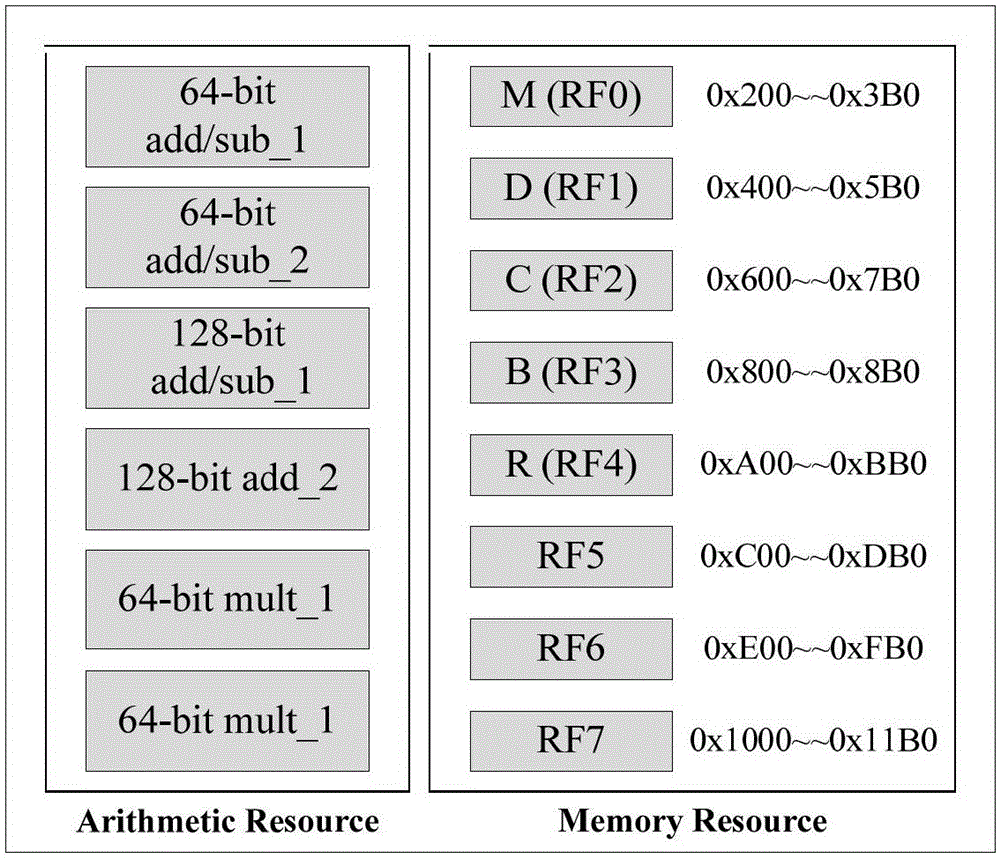
Prime number field elliptic curve cryptography system of VLSI realization accelerator
InactiveCN105790939AImprove portabilityStrong unit reusabilityPublic key for secure communicationVlsi implementationsProcessor register
The invention provides a prime number field elliptic curve cryptography system of a VLSI realization accelerator. The elliptic curve cryptography system comprises a modular arithmetic layer, a point arithmetic layer, an encryption master operation layer, an encryption mechanism layer, an external interface layer and a hardware resource layer. The accelerator is mounted on a bus as a slave device. A processor enables the accelerator to start working through configuring corresponding registers in the accelerator. According to the system, through rationally dividing hardware and software, an excellent performance to area ratio is obtained; and through adoption of hardware customization, prime number judgment, point addition and point multiplication operation efficiencies of a bottom layer are greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING SMARTCHIP MICROELECTRONICS TECH COMPANY +3
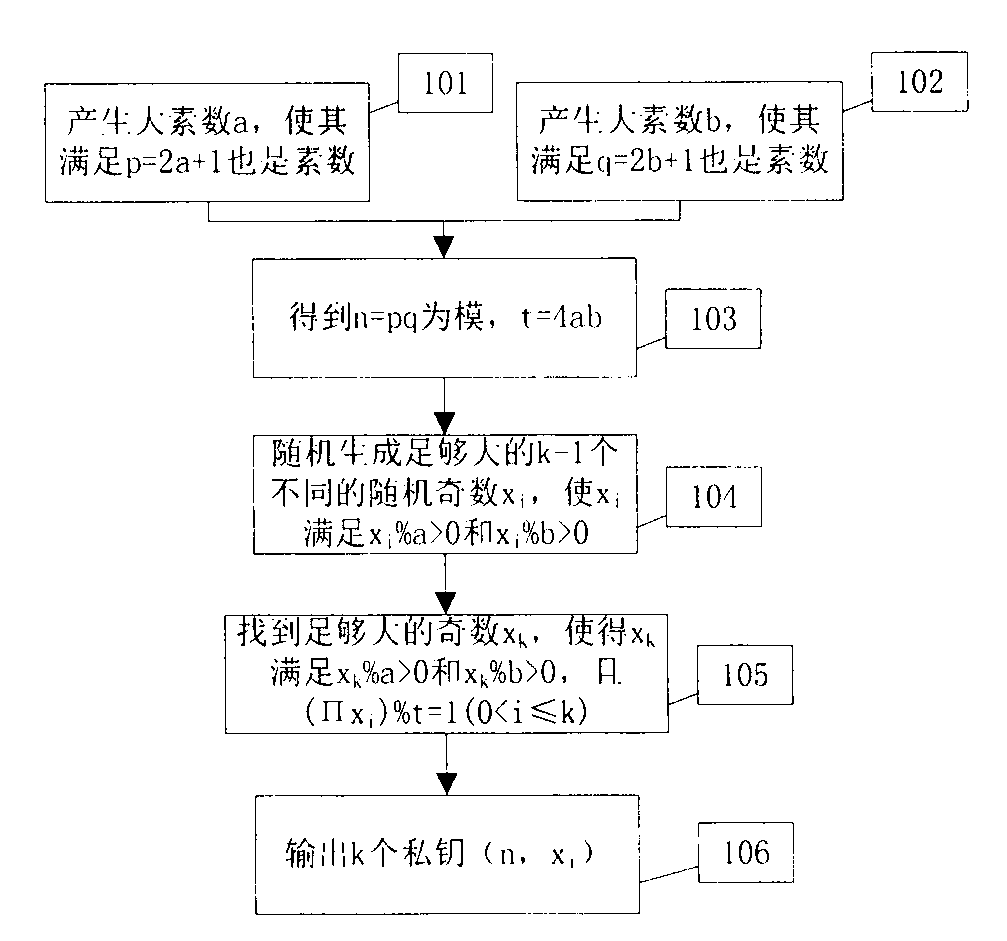
Method for multi-way encryption and signing and zero knowledge certification
InactiveCN103107890AEasy to controlGuaranteed reliabilityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationPlaintextCiphertext
The invention discloses a method for multi-way encryption, signing and zero knowledge certification. Large prime number a, b, p and q are chosen, p=2a+1 and q=2b+1, n=pq, and t=4ab; k large odd numbers xk are found, the requirements that (pi xi) %t=1 (0<i<=k) and xi, a and b are relatively prime respectively; each participant i possesses (xi, n) which serves as a private key, namely, a multi-way encryption system is formed; when I sends a plaintext M to J, after I conducts power modular arithmetic encryption on the plaintext M through a private key of I, a result is sent to other participants in the system so that the private key of the participant is used as the only one iteration encryption until J encodes the plaintext through a private key of J. When signing is conducted in a group, each participant adds self signing to the plaintext behind the signing of other participant for checking. In the condition of zero knowledge certification, a decoded ciphertext is compared with the plaintext so that verification is conducted without leakage of information. The method has the advantage that each participant participates in a iteration encryption process for only once.
Owner:彭艳兵
Memory device having a systematic arrangement of logical data locations and having plural data portals
InactiveUS20020062420A1Efficient accessStored dataInput/output to record carriersAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsData portalModular arithmetic
A method and an apparatus for storing data provide data memory in a systematic, cyclical arrangement, provide plural data portals in an arrangement defined by modular arithmetic, and provide sequential, relative movement between the data memory and the data portals. When one or more of the plural portals is selected, data can be input or output in a manner which is predictable, straight-forward, free of scheduling constraints, and very efficient, without contention between the separate portals. Also disclosed are a method and apparatus which provide data memory in a systematic, cyclical arrangement, provide a systematic arrangement of plural data outputs, and provide sequential, relative movement between the data memory and the data outputs. The memory devices of the present invention can be designed so that the memory device circulates data either through or past fixed portals. Alternatively, the data can be stored in fixed locations and the portals moved from location to location. Preferred embodiments of the invention utilize semiconductor memory technology in order to implement the memory devices. Another set of embodiments utilizes memory storage media capable of confining propagating waves in order to implement the memory devices.
Owner:LOT 20 ACQUISITION FOUND LLC +1
Non binary flash array architecture and method of operation
ActiveUS8339865B2Improve layout efficiencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesPhysical addressModular arithmetic
A Flash memory array comprises a plurality of Erase Sectors (Esecs) arranged in a plurality of Erase Sector Groups (ESGs), Physical Pages (slices), and Physical Sectors (PSecs), and there is a non-binary number of at least one of the Erase Sector Groups (ESGs), Physical Pages (slices), and Physical Sectors (PSecs). A user address is translated into a physical address using modular arithmetic to determine pointers (ysel, esg, psec) for specifying a given Erase Sector (ESec) within a given Erase Sector Group (ESG); a given Erase Sector Group (ESG) within a given Physical Sector (Psec); and a given Physical Sector (PSec) within the array.
Owner:SPANSION ISRAEL
Predistortion Apparatus, System, And Method
InactiveUS20090309657A1The degree of freedom becomes largerGood flexibilityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceModular arithmeticLookup table
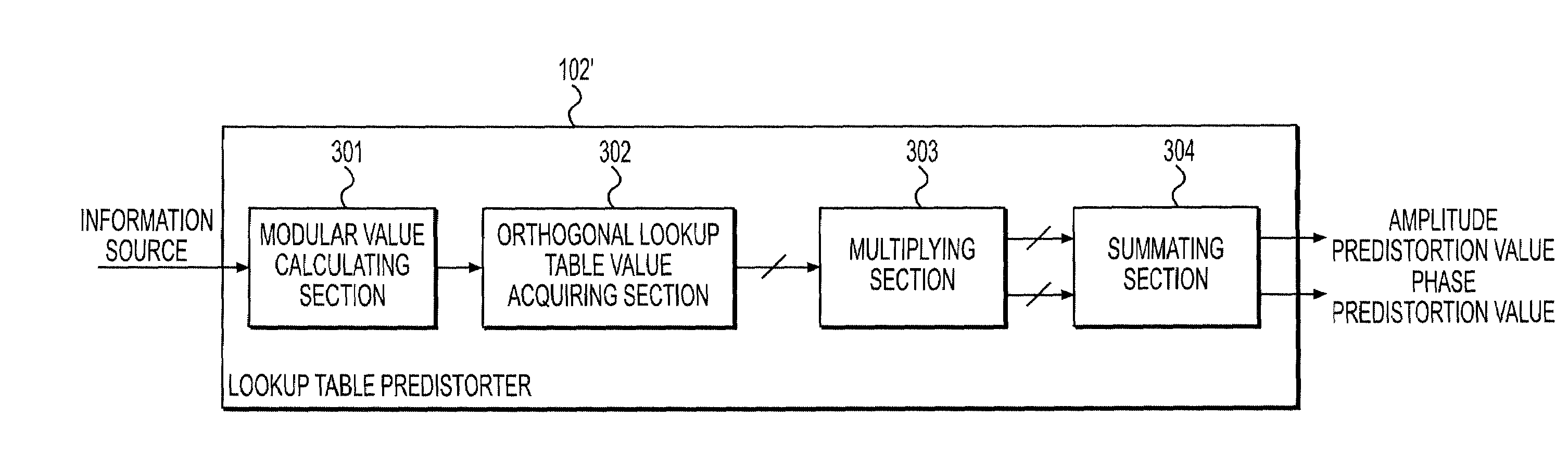
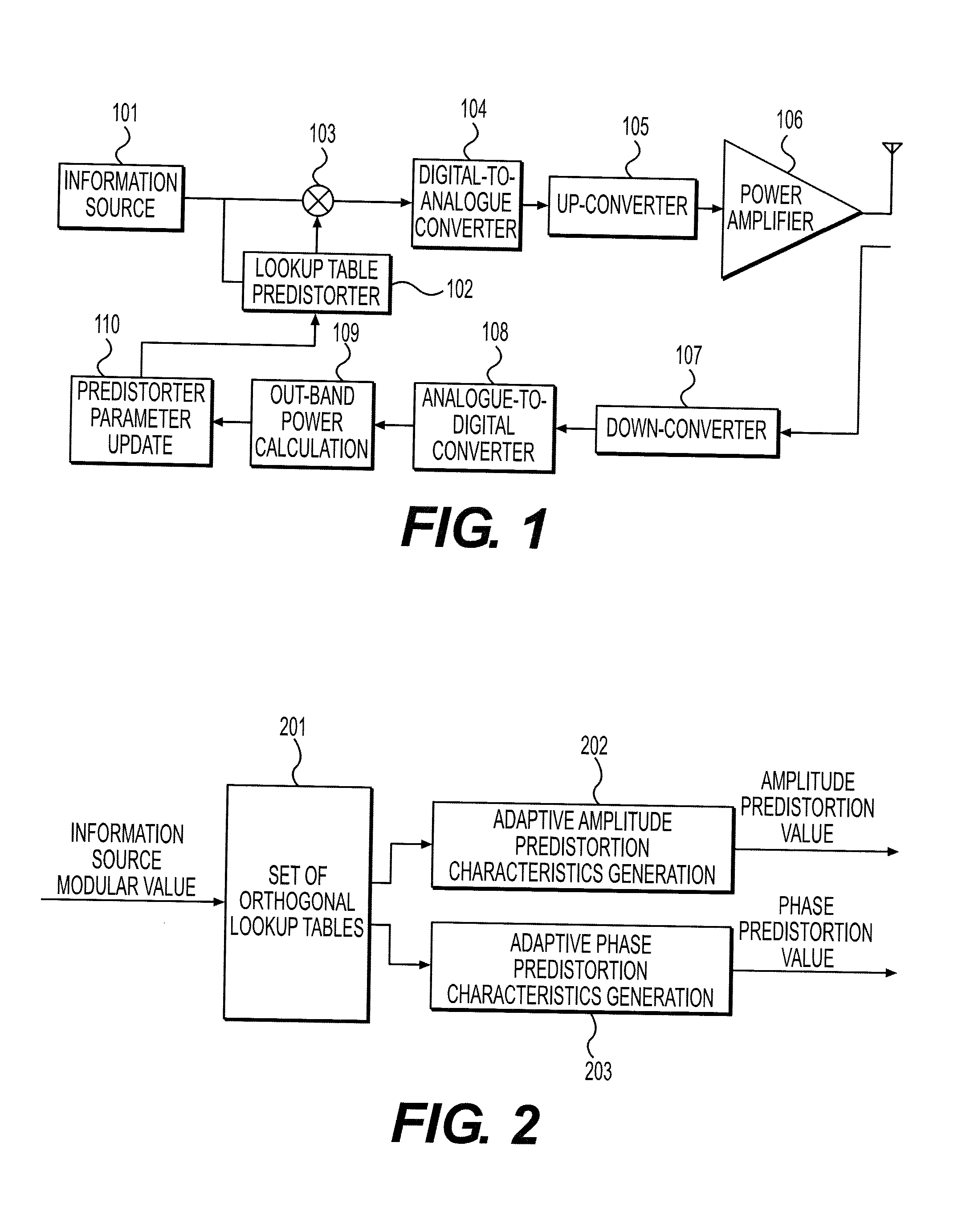
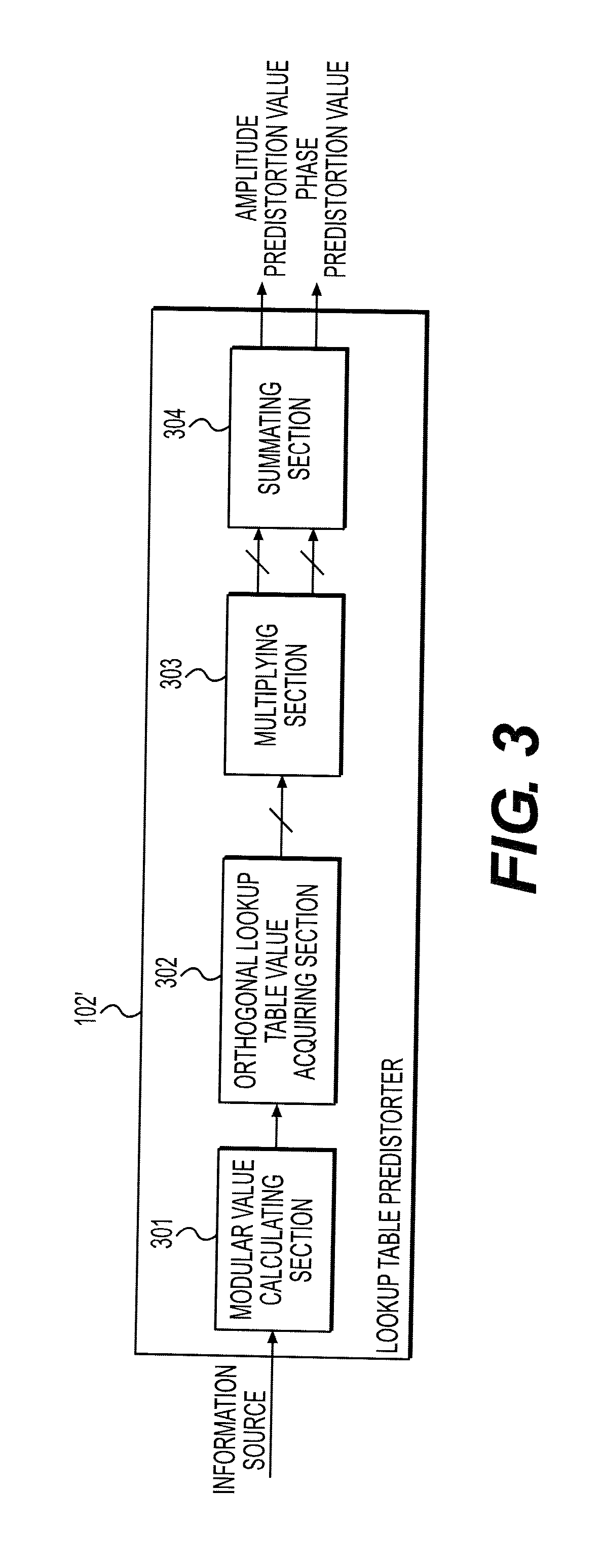
The present invention discloses a predistortion apparatus, a predistortion system and a predistortion method. The predistorter comprises a modular value calculating section, for performing modular arithmetic on an information source input signal inputted from an information source; an orthogonal lookup table value acquiring section, for searching N stored lookup tables orthogonal to one another, finding out corresponding output of each lookup table in accordance with the modular value of the information source input signal, and acquiring N lookup table values, wherein N is an integer greater than 1; a multiplying section, for multiplying the N lookup table values acquired by the orthogonal lookup table value acquiring section with N amplitude adjustment factors to obtain N amplitude adjustment values, and multiplying the N lookup table values with N phase adjustment factors to obtain N phase adjustment values; and a summating section, for summating the N amplitude adjustment values to obtain an amplitude predistortion value, and summating the N phase adjustment values to obtain a phase predistortion value.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Data possession proof scheme
ActiveCN105227549AImprove execution speedImprove securityTransmissionThird partyCloud storage security
The invention discloses a data possessionproof scheme, belonging to the field of information security and being suitable for a cloud storage security management technology. In the scheme, a key generation module, a label generation module, a challenge module, a proof generation module and a verification module are included. The scheme only needs addition, subtraction, multiplication and modular arithmetic and supports modification and additional operations of data blocks, data possession proof of multiple duplicates and third-party verifiable data possessionproof. The scheme disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high security, low computational expense and low requirements for storage space and traffic, and provides a new research orientation for developing the data possession proof scheme.
Owner:SHANGHAI GUAN AN INFORMATION TECH
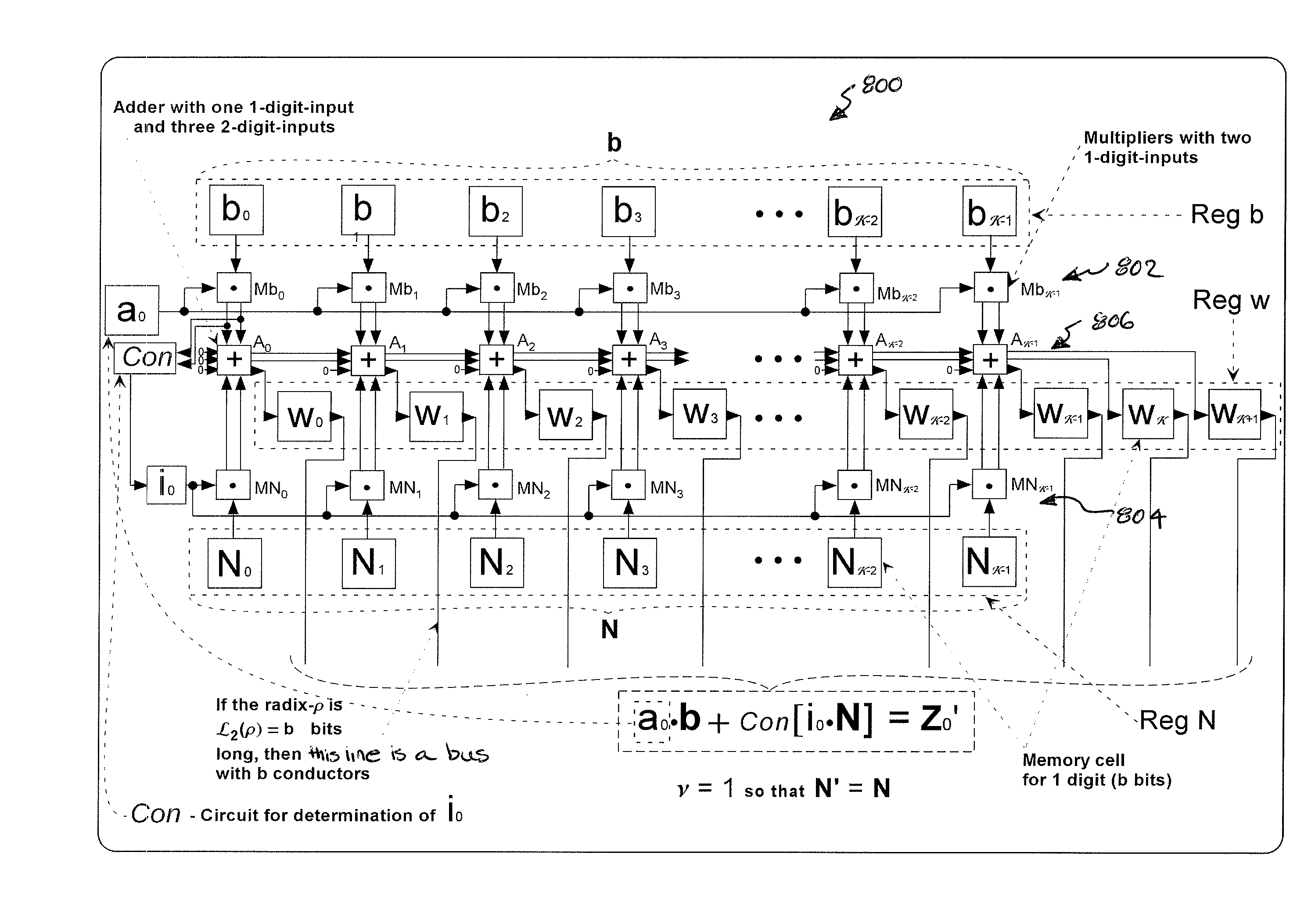
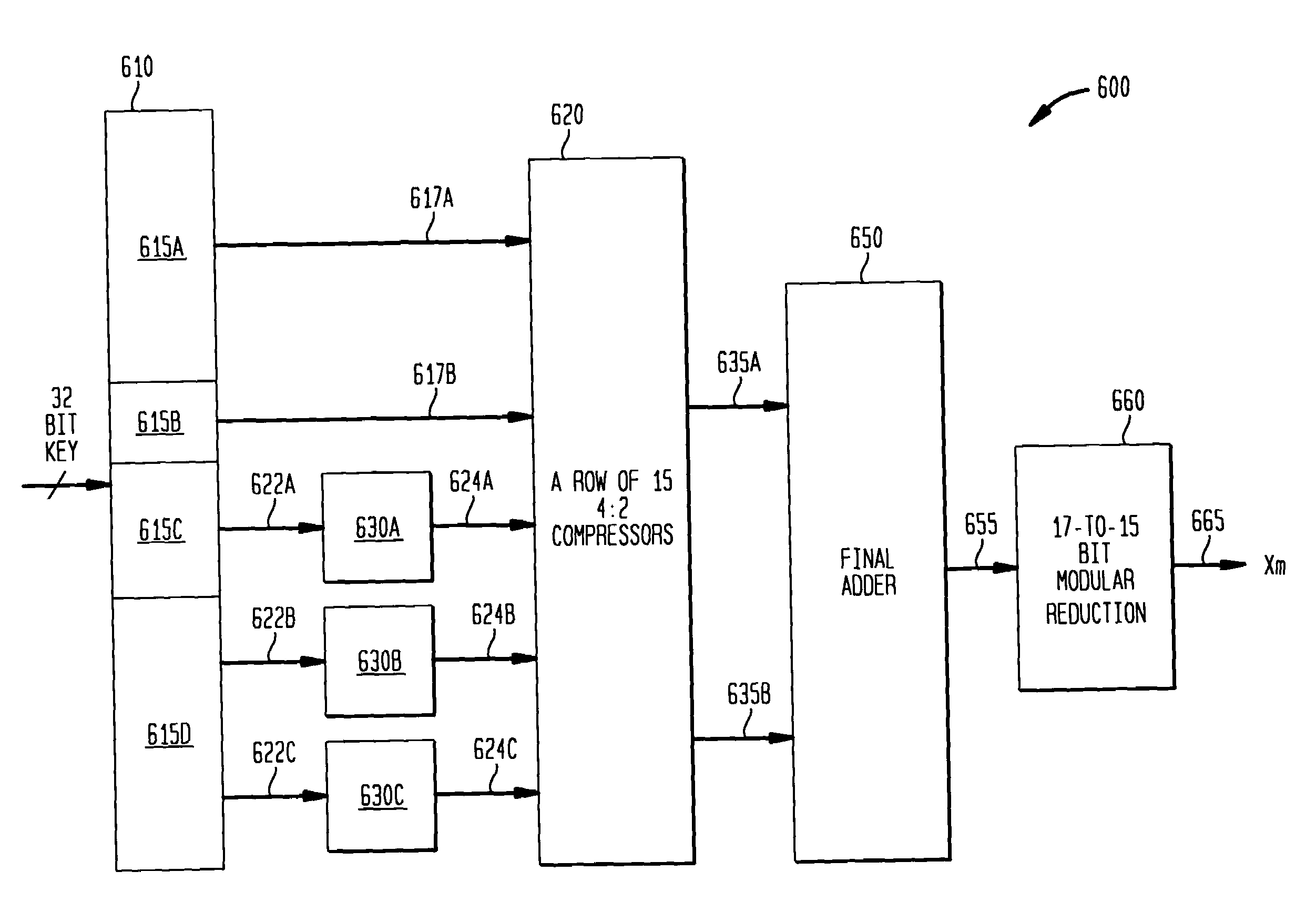
Methods and apparatus for modular reduction circuits
Techniques are provided for performing modular arithmetic on a key composed of many bits. One circuit implementation includes a distributor, one or more lookup tables and a plurality of adders. The distributor segments the key into a plurality of partitions. Each partition is based on a polynomial expression corresponding to a fixed size key. Each of the bits contained within the partitions are routed on a partition basis to one or more lookup tables, the routed bits acting as indices into the one or more tables. The lookup tables store precomputed values based upon the polynomial expression. The outputted precomputed values from one or more lookup tables are outputted to the plurality of adders. The plurality of adders add the bits from a portion of the routed partitions and the outputted precomputed values from the one or more lookup tables to form the binary residue.
Owner:CHASM BRIDGE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com