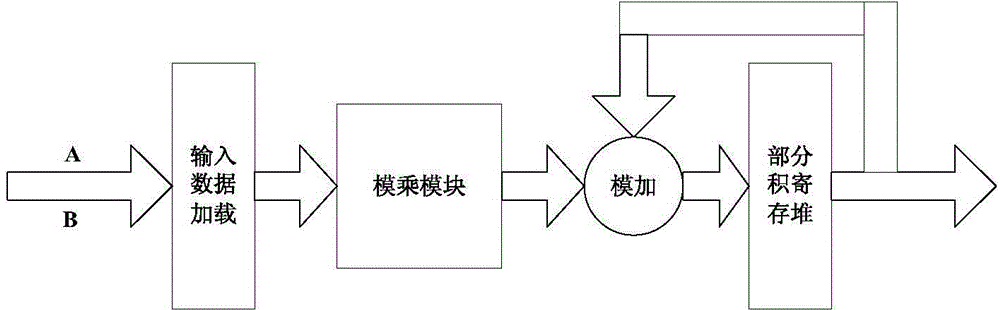
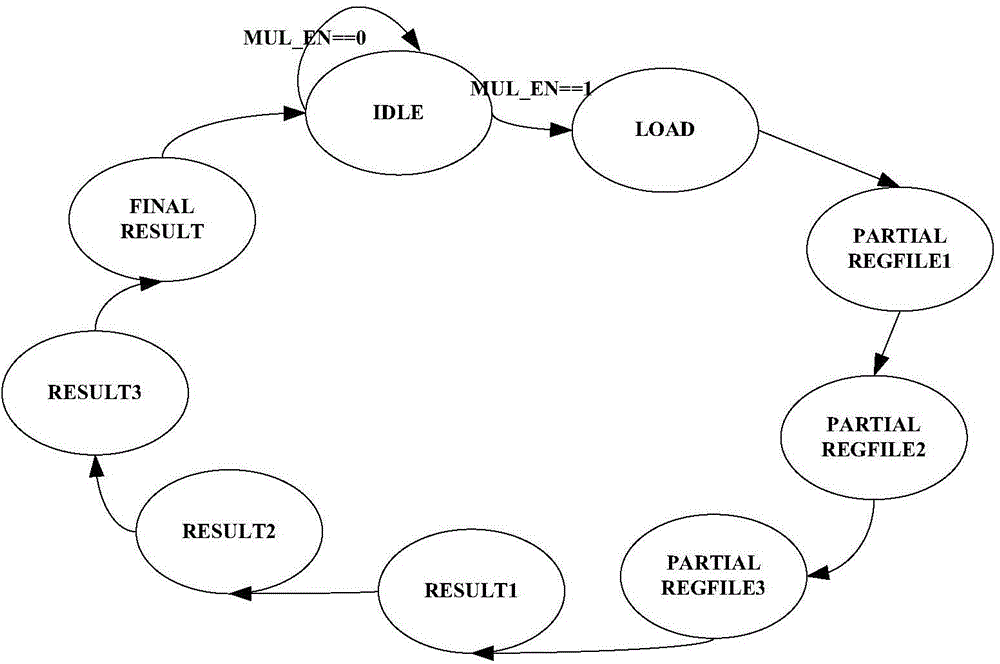
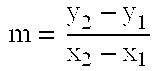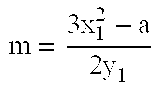Patents
Literature
145 results about "Elliptic curve cryptography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
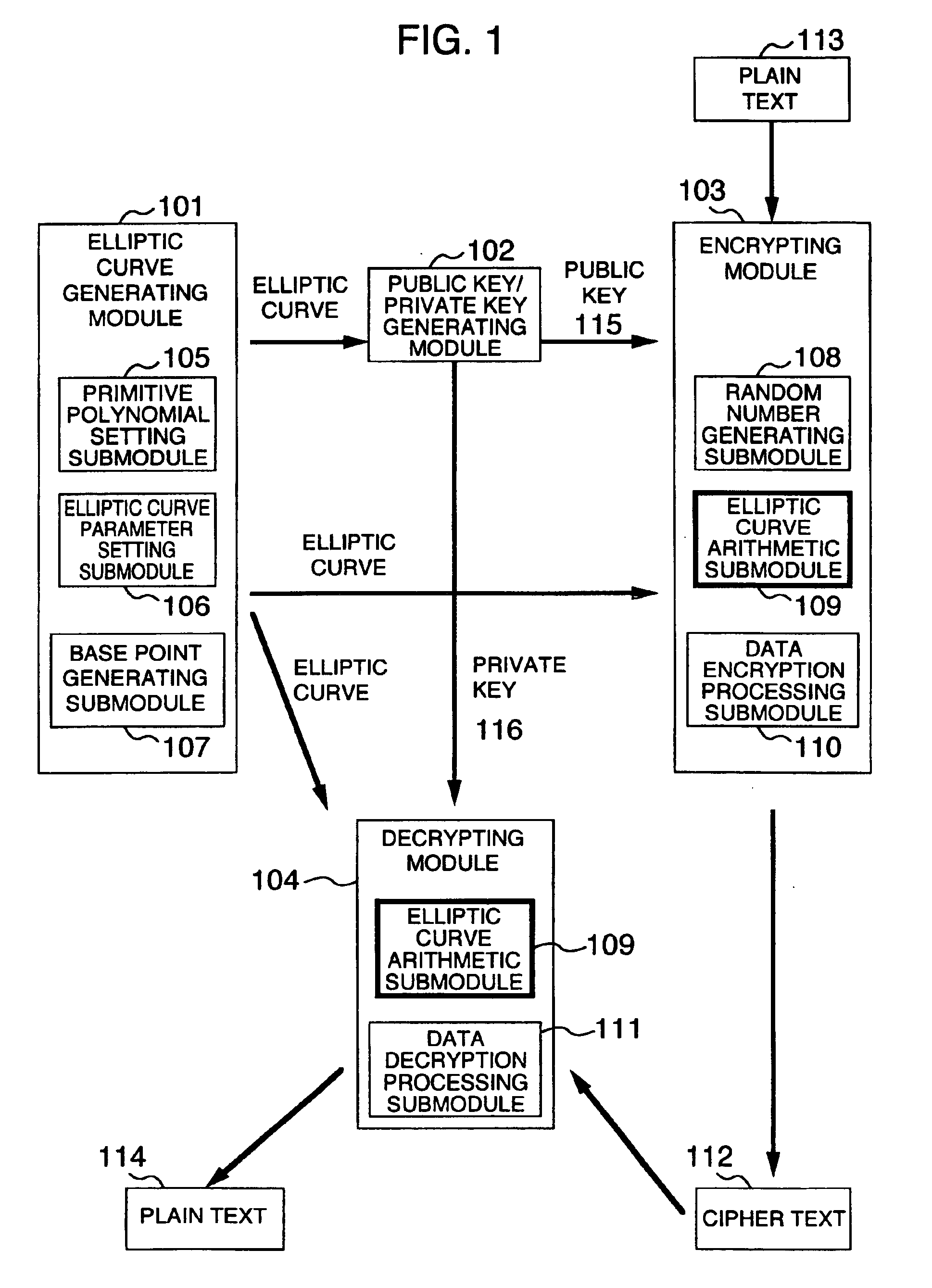
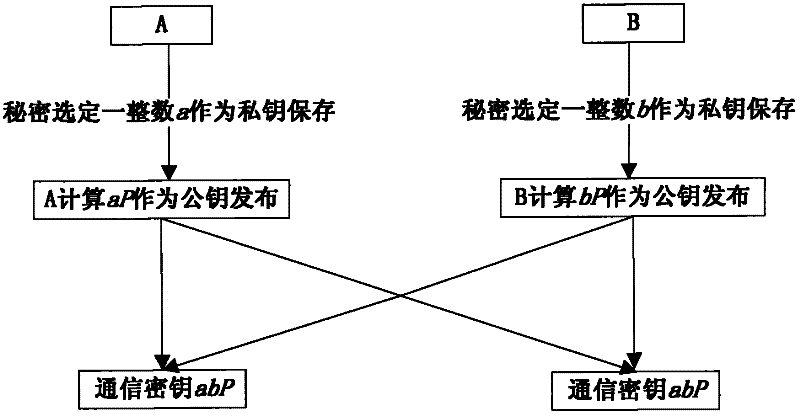
Elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC) is an approach to public-key cryptography based on the algebraic structure of elliptic curves over finite fields. ECC requires smaller keys compared to non-EC cryptography (based on plain Galois fields) to provide equivalent security.
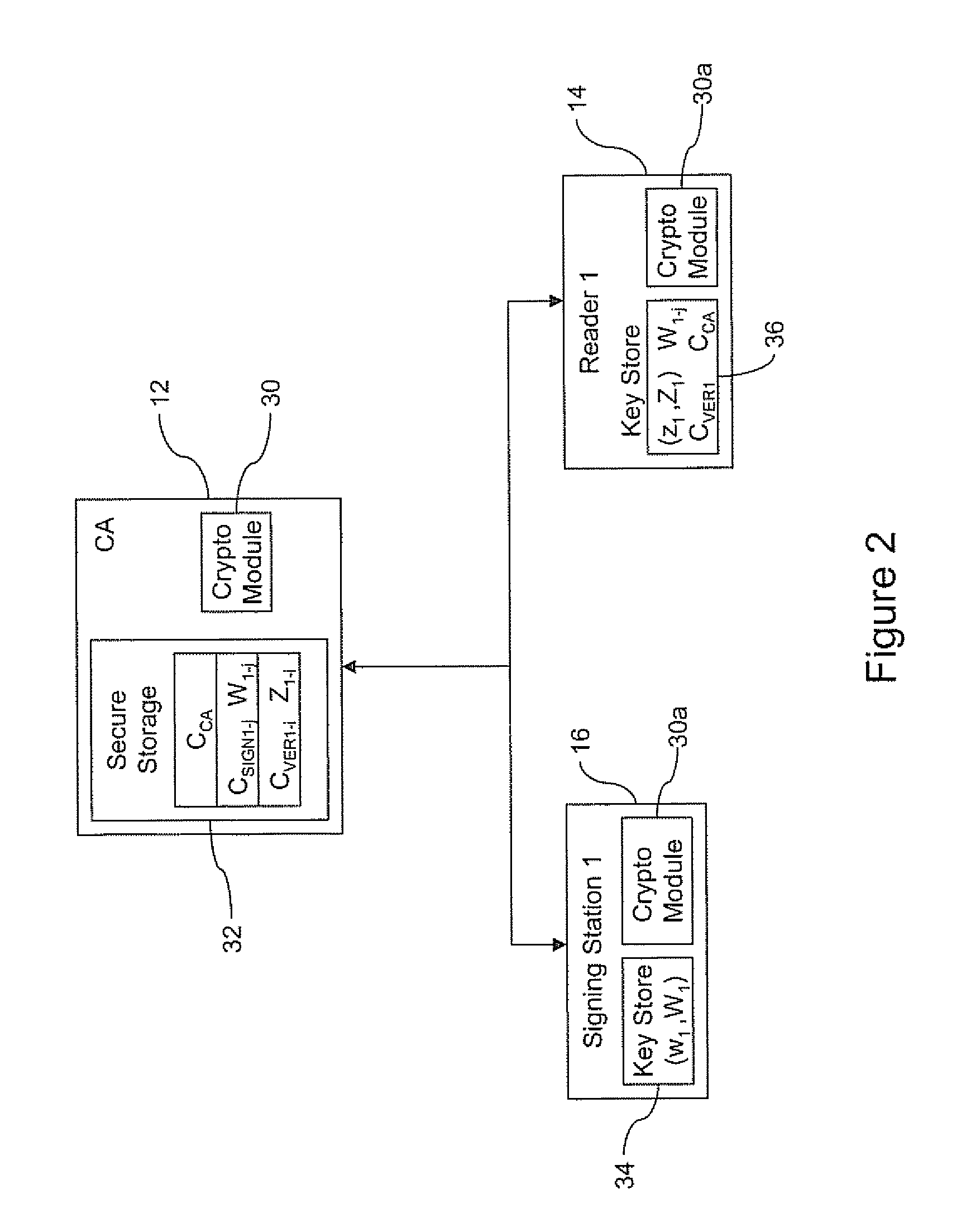
Aggregate signature schemes
ActiveUS20080069347A1Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageAggregate signatureManagement system
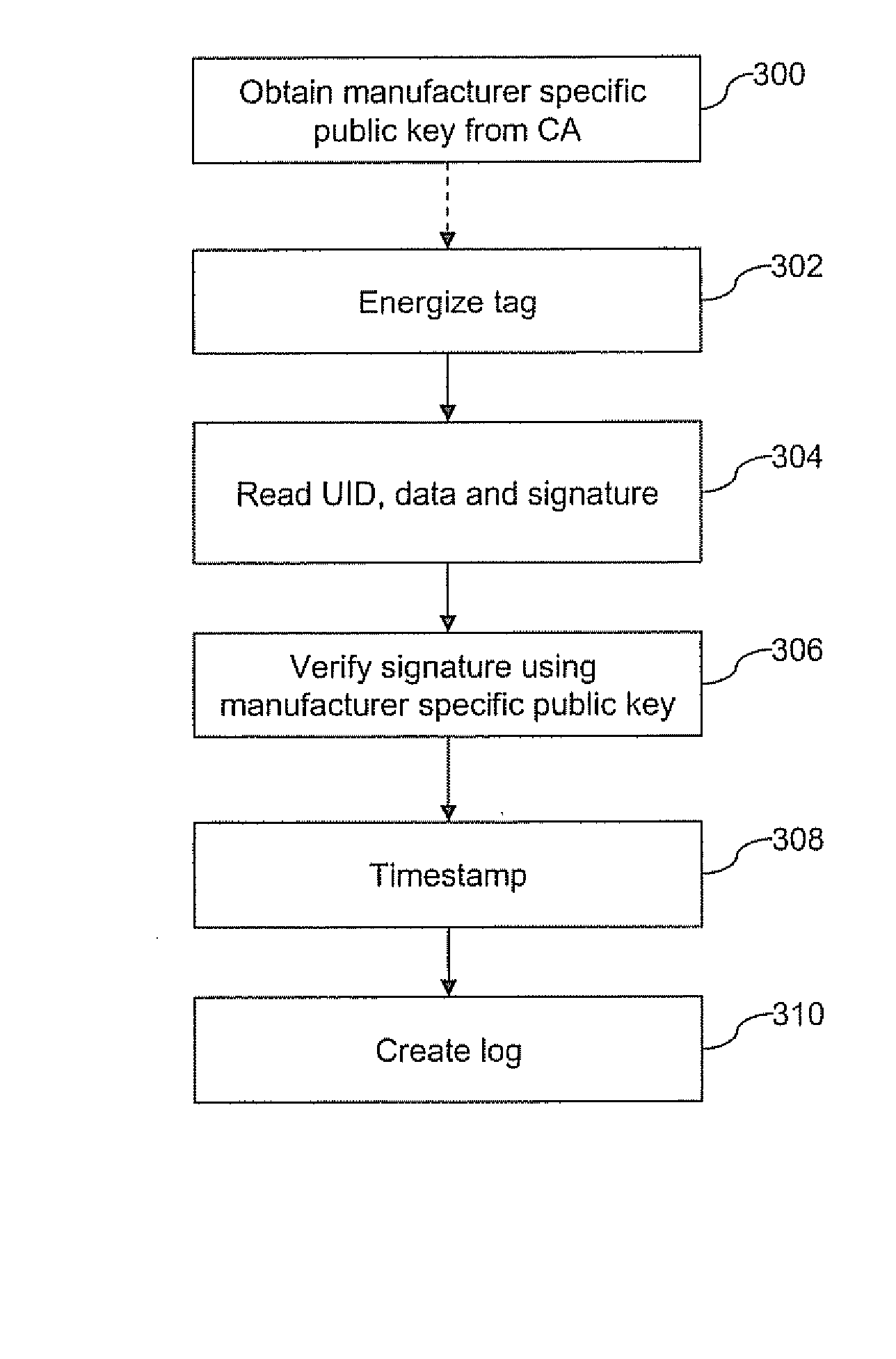
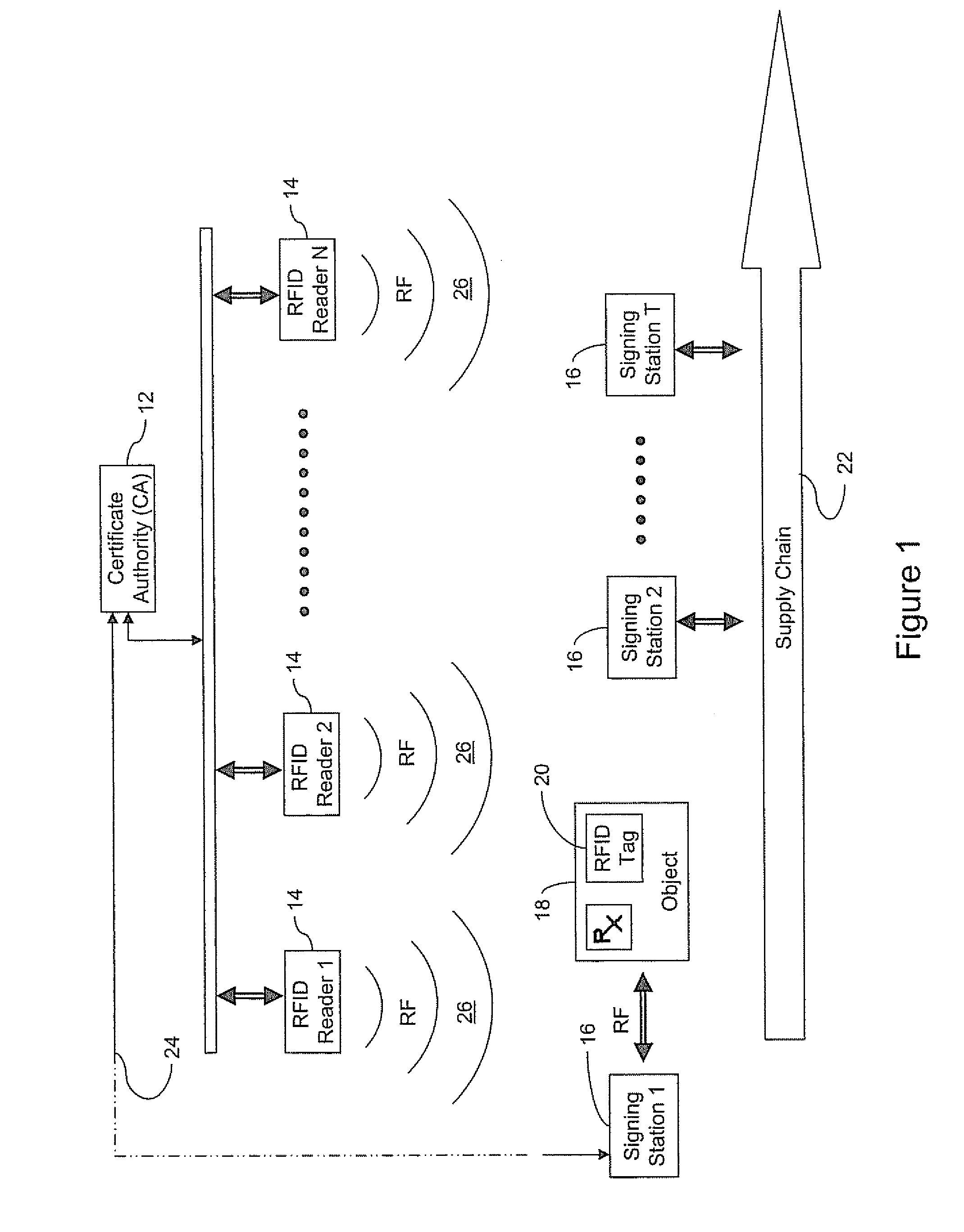
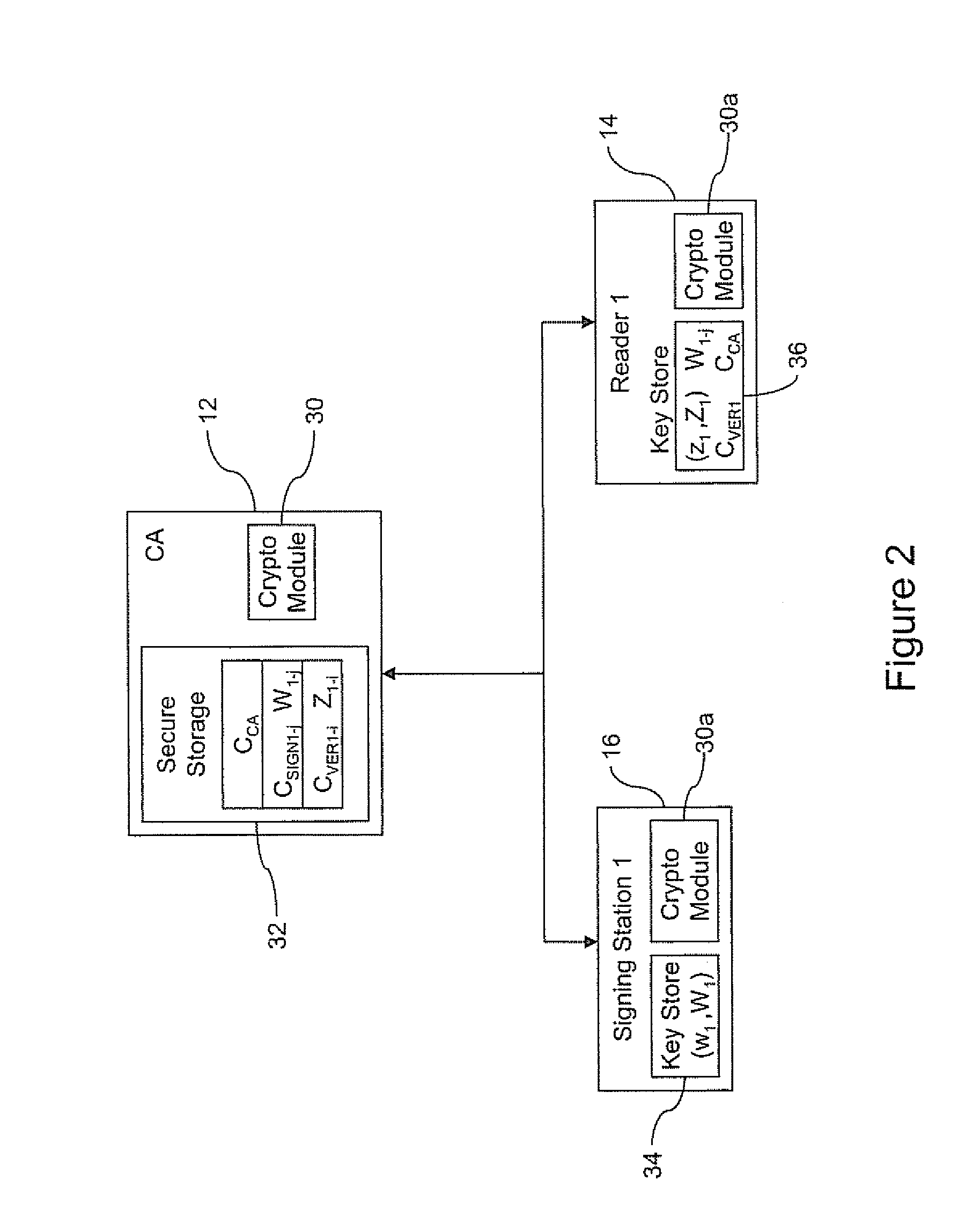
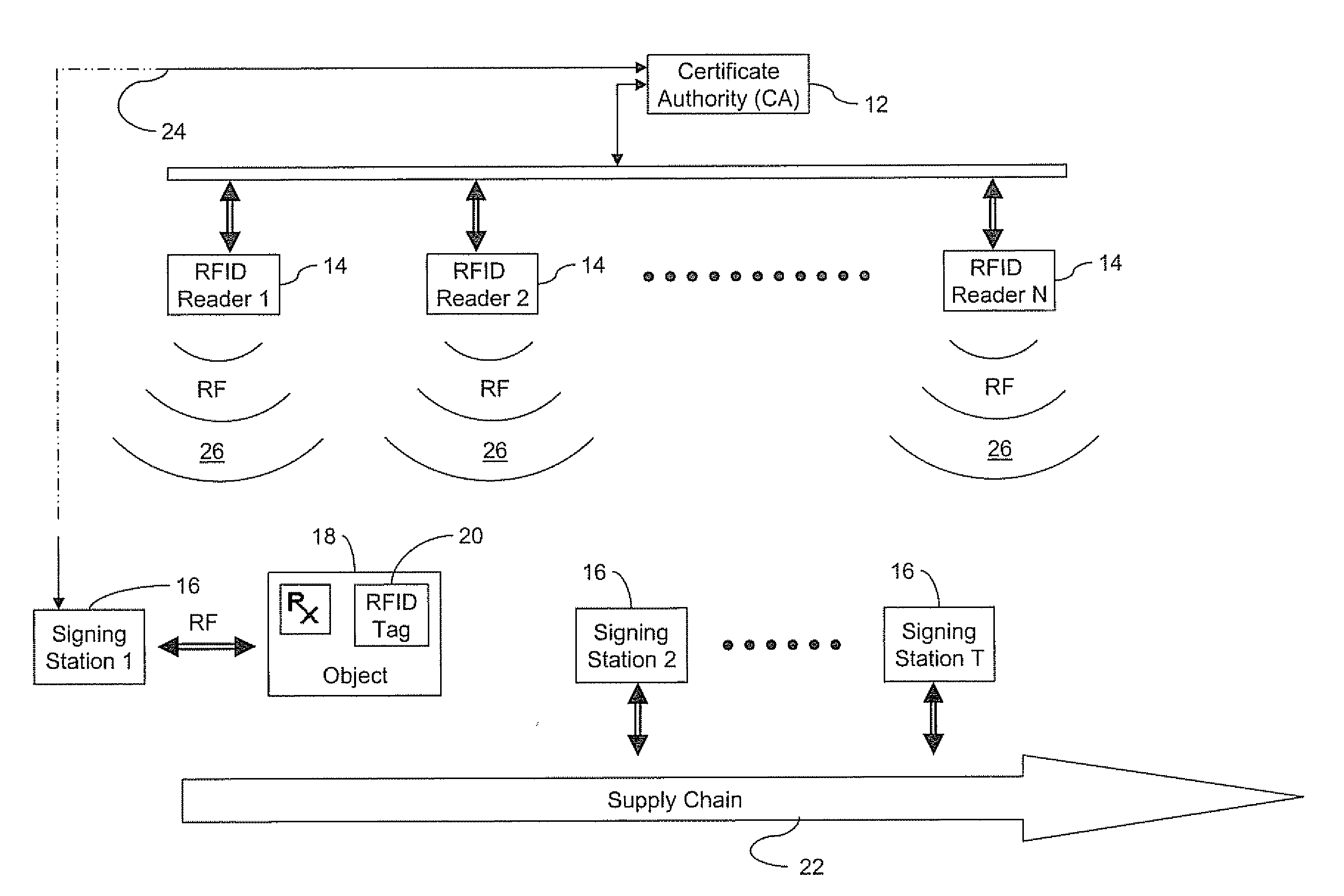
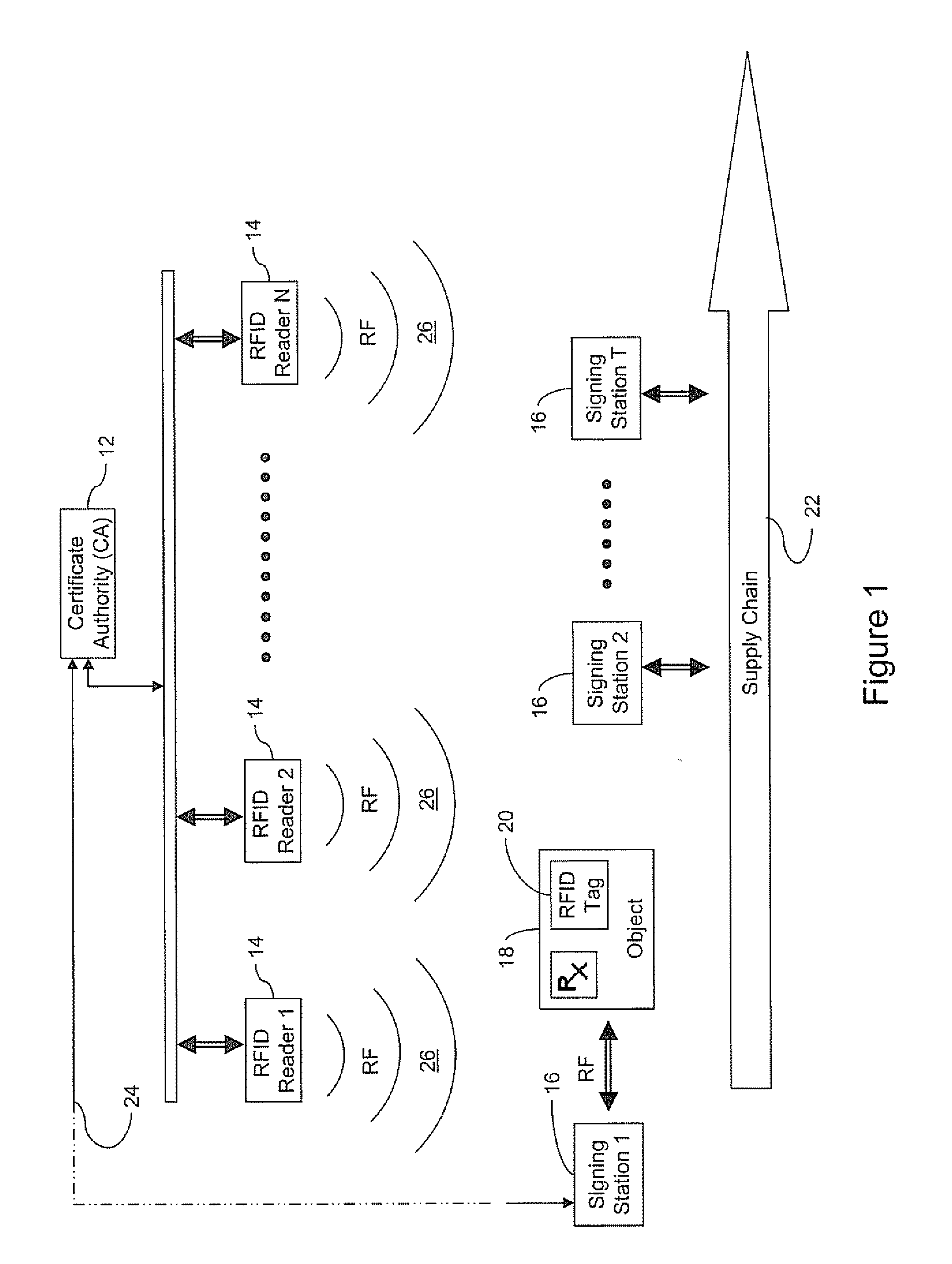
An authenticated RFID system is provided that uses elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) to reduce the signature size and read / write times when compared to traditional public key implementations such as RSA. Either ECDSA or ECPVS can be used to reduce the signature size and ECPVS can be used to hide a portion of the RFID tag that contains sensitive product identifying information. As a result, smaller tags can be used or multiple signatures can be written at different stages in a manufacturing or supply chain. A key management system is used to distribute the verification keys and aggregate signature schemes are also provided for adding multiple signatures to the RFID tags, for example in a supply chain.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus for elliptic curve cryptography and recording medium therefore
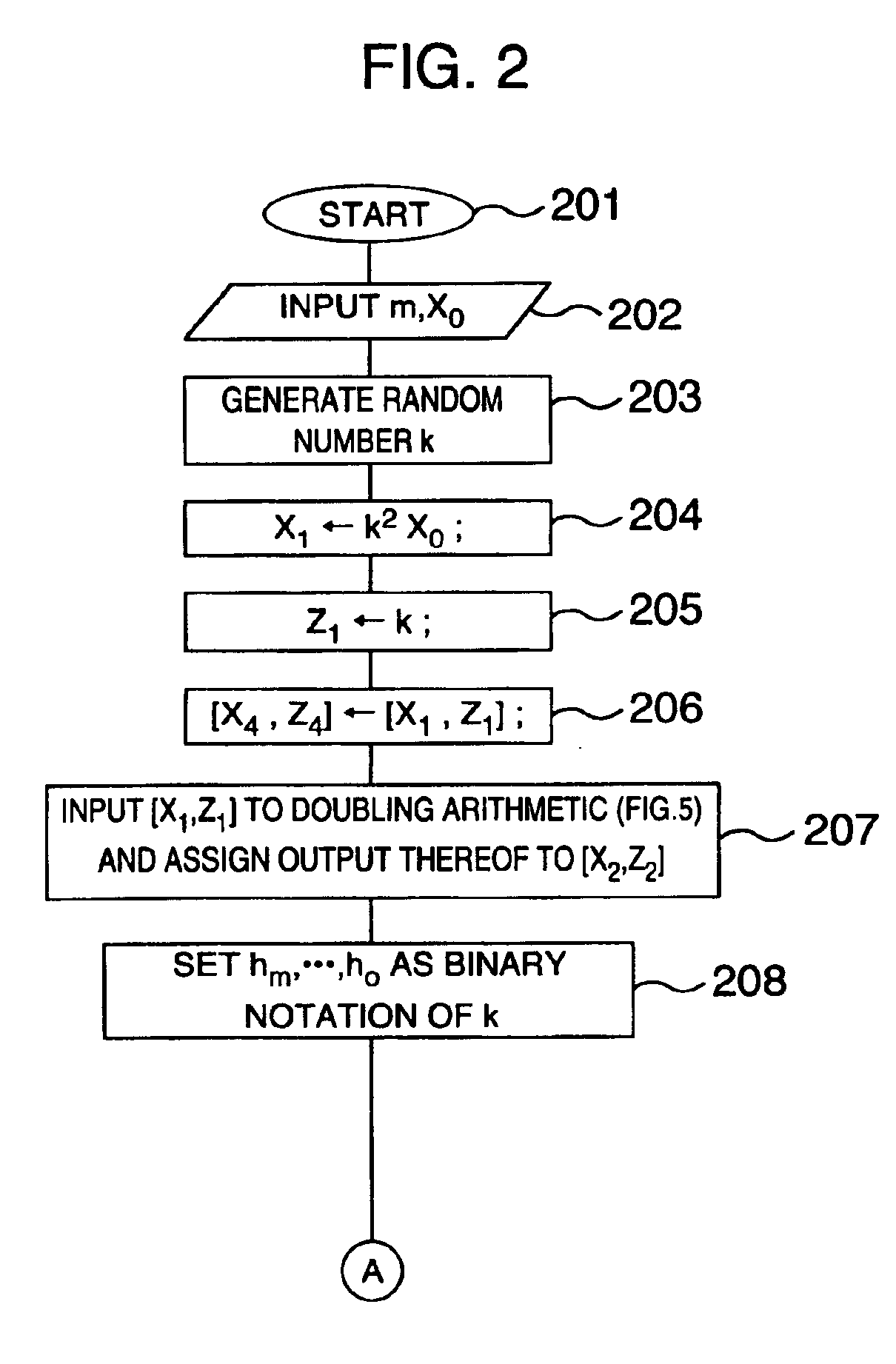
InactiveUS6876745B1Prevent leakageRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
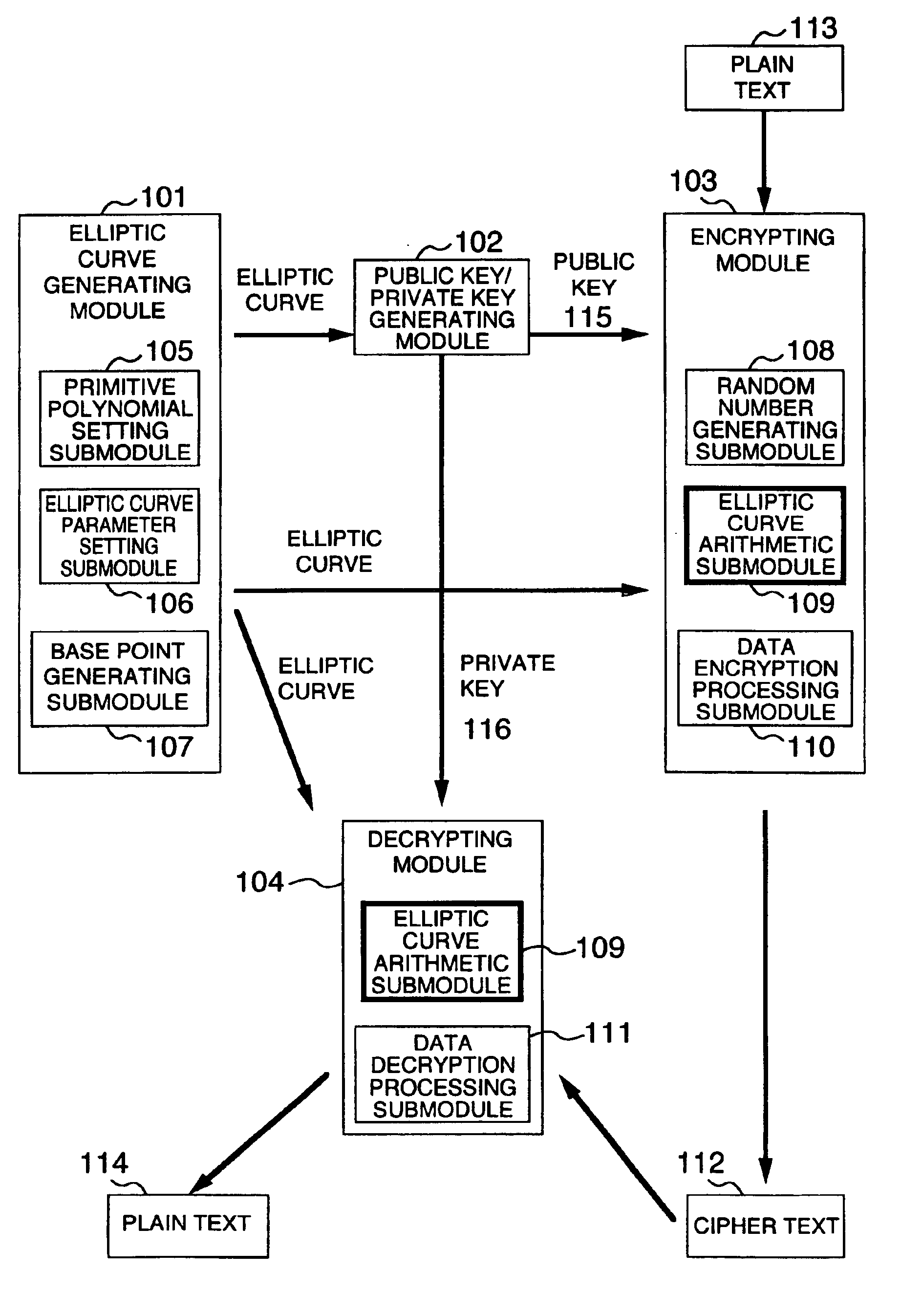
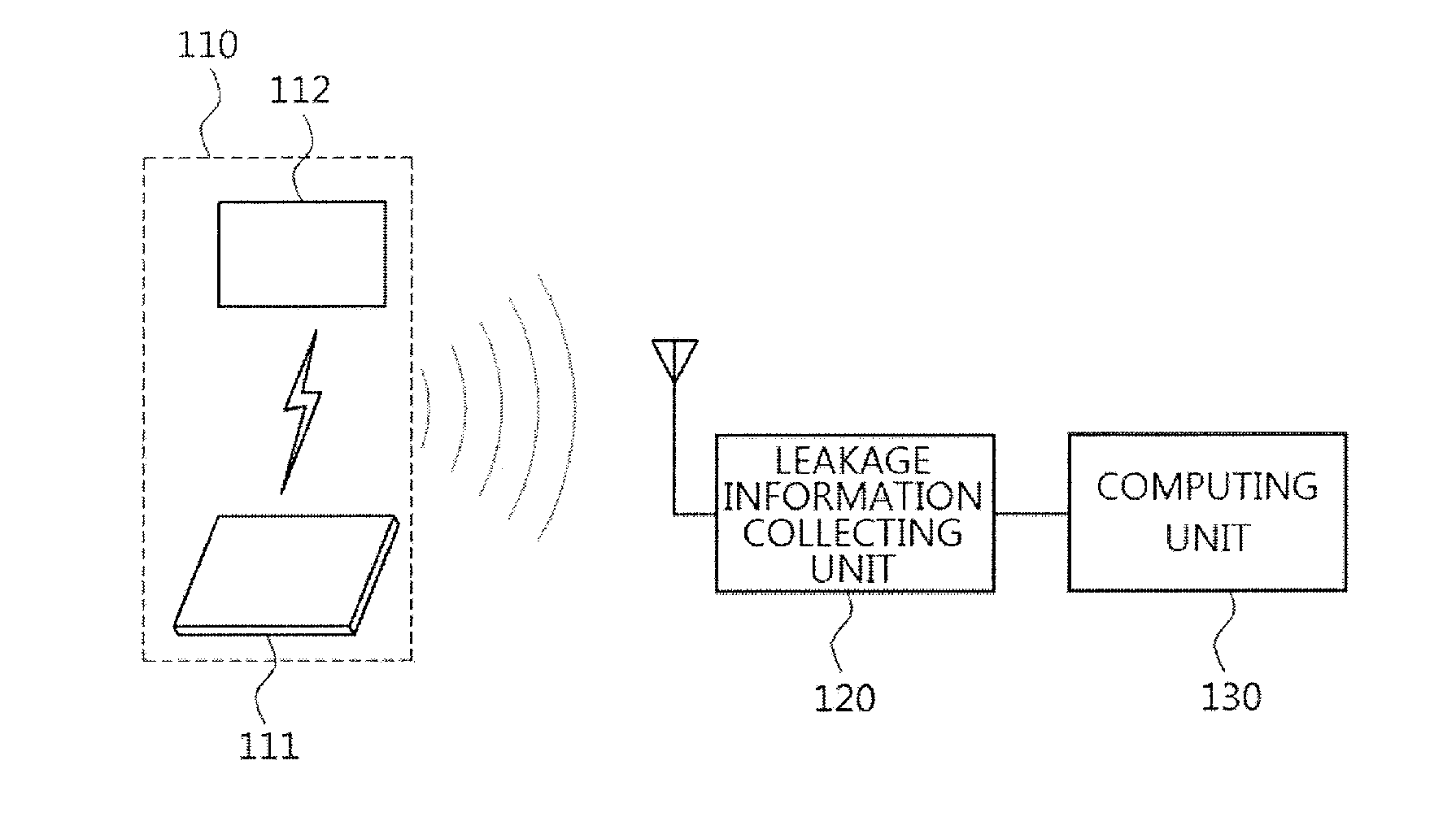
A method and an apparatus capable of realizing at a high speed an elliptic curve cryptography in a finite field of characteristic 2, in which the elliptic curve is given by y2+xy=x3+ax2+b (b≠0) and an elliptic curve cryptography method which can protect private key information against leaking from deviation information of processing time to thereby defend a cipher text against a timing attack and a differential power analysis attack are provided. To this end, an arithmetic process for executing scalar multiplication arithmetic d(x, y) a constant number of times per bit of the private key d is adopted. Further, for the scalar multiplication d(x, y), a random number k is generated upon transformation of the affine coordinates (x, y) to the projective coordinates for thereby effectuating the transformation (x, y)→[kx, ky, k] or alternatively (x, y)→[k2x, k3y, k]. Thus, object for the arithmetic is varied by the random number (k).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
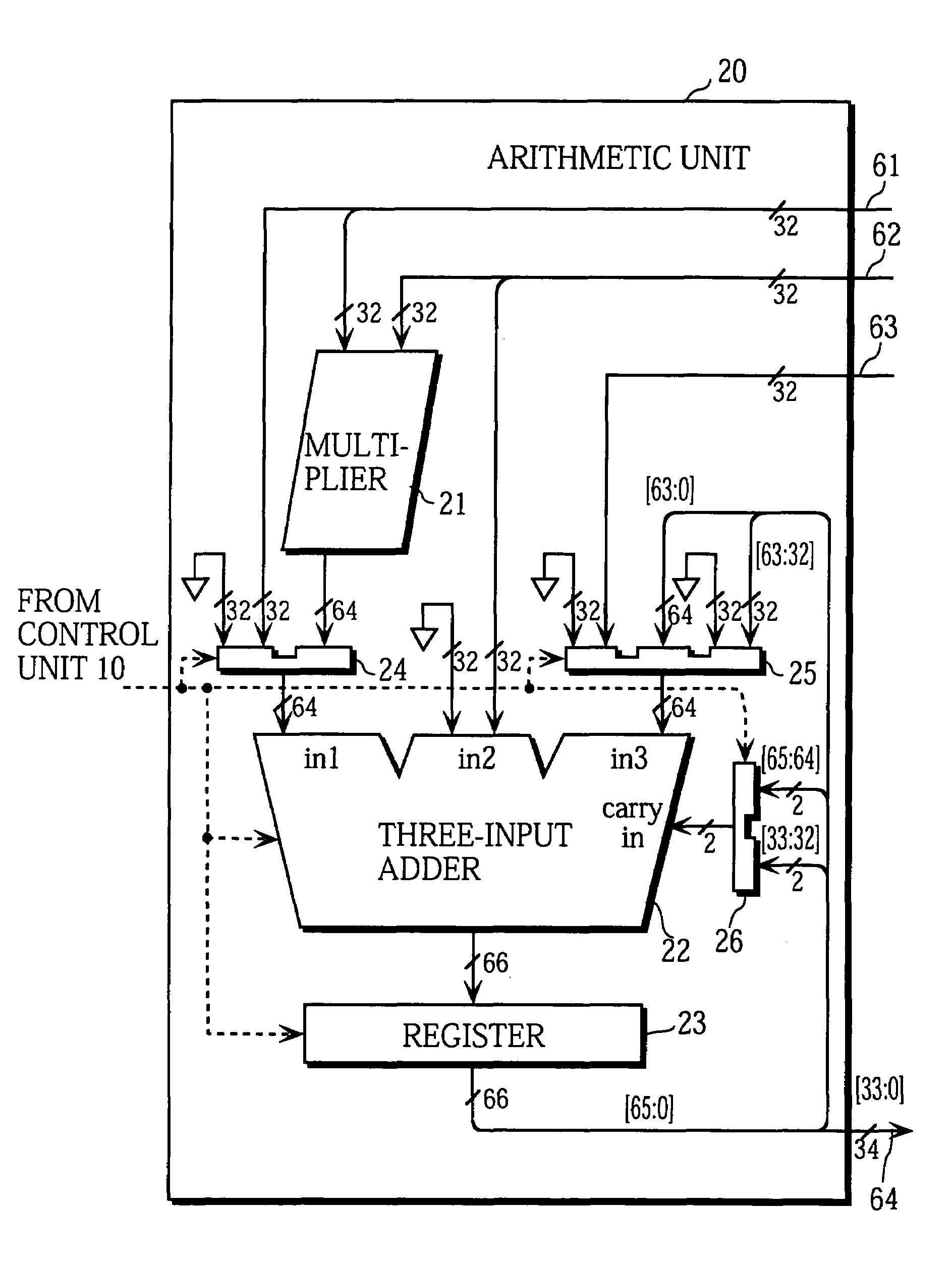
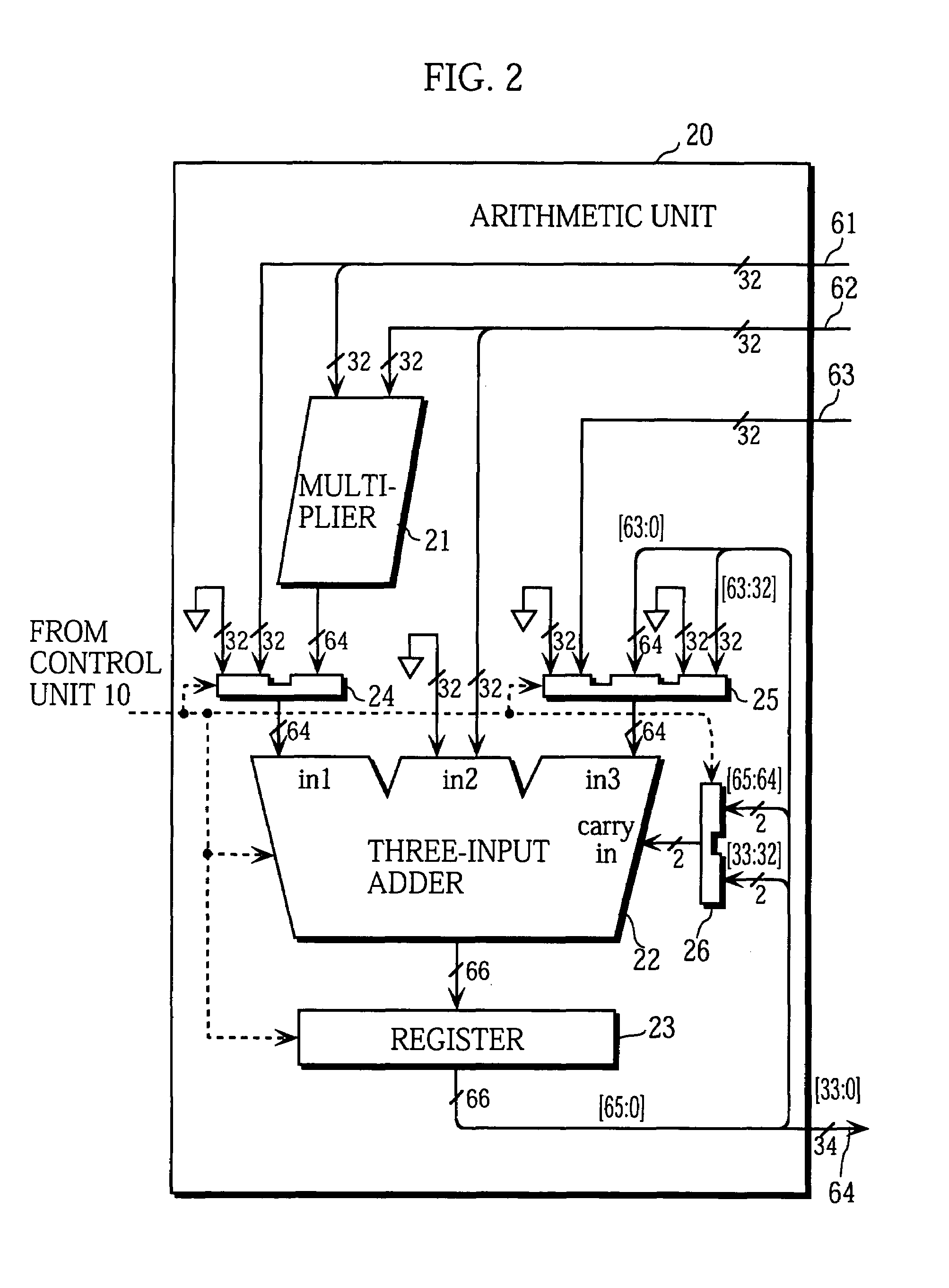
Code calculating device
A code computing apparatus with an error detection code (CRC) generating function and an elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) function, comprising a matrix element computation part 30 for generating matrix elements from parameter values set in first and second registers 201 and 202, a matrix element register 51 for holding the matrix elements generated by the matrix element computation part, and an inner product calculation part 40 for executing inner product calculation between the matrix elements held by the matrix element register and data set in a third register. The matrix element computation part selectively generates matrix elements for error detection and matrix elements for encryption by changing the parameters to be set in the first and second registers, and the inner product calculation part is shared to error control code generation and data encryption by altering the matrix elements to be held in the matrix element register.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Generic implementations of ellipitic curve cryptography using partial reduction
ActiveUS20030208518A1Digital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticBinary multiplierOperand
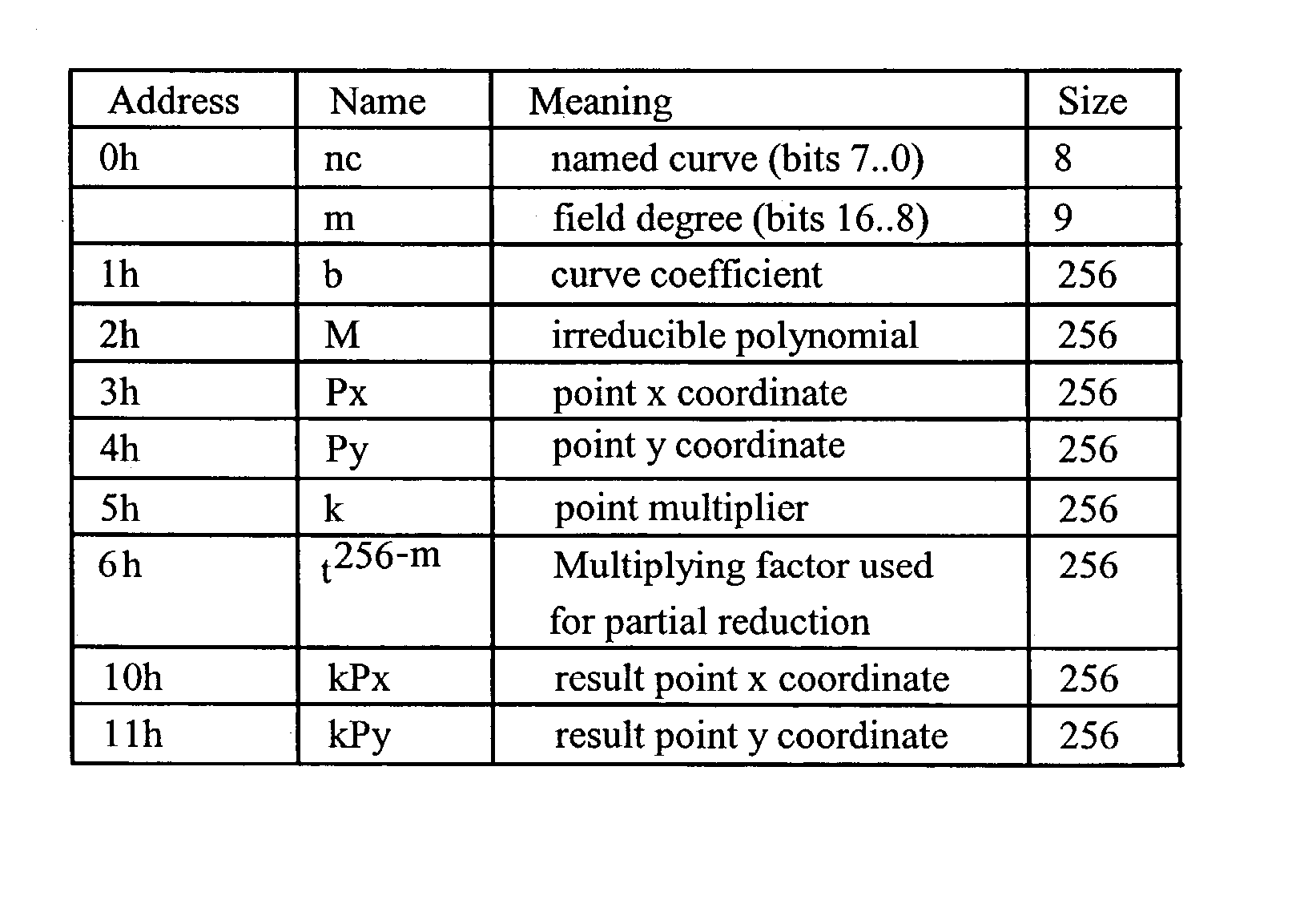
A reduction operation is utilized in an arithmetic operation on two binary polynomials X(t) and Y(t) over GF(2), where an irreducible polynomial Mm(t)=t<m>+am-1t<m-1>+am-2t<m-2>+ . . . +a1t+a0, where the coefficients as are equal to either 1 or 0, and m is a field degree. The reduction operation includes partially reducing a result of the arithmetic operation on the two binary polynomials to produce a congruent polynomial of degree less than a chosen integer n, with m<=n. The partial reduction includes using a polynomial M'=(Mm(t)-t<m>)*t<n-m>, or a polynomial M''=Mm(t)*t<n-m >as part of reducing the result to the degree less than n and greater than or equal to m. The integer n can be the data path width of an arithmetic unit performing the arithmetic operation, a multiple of a digit size of a multiplier performing the arithmetic operation, a word size of a storage location, such as a register, or a maximum operand size of a functional unit in which the arithmetic operation is performed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
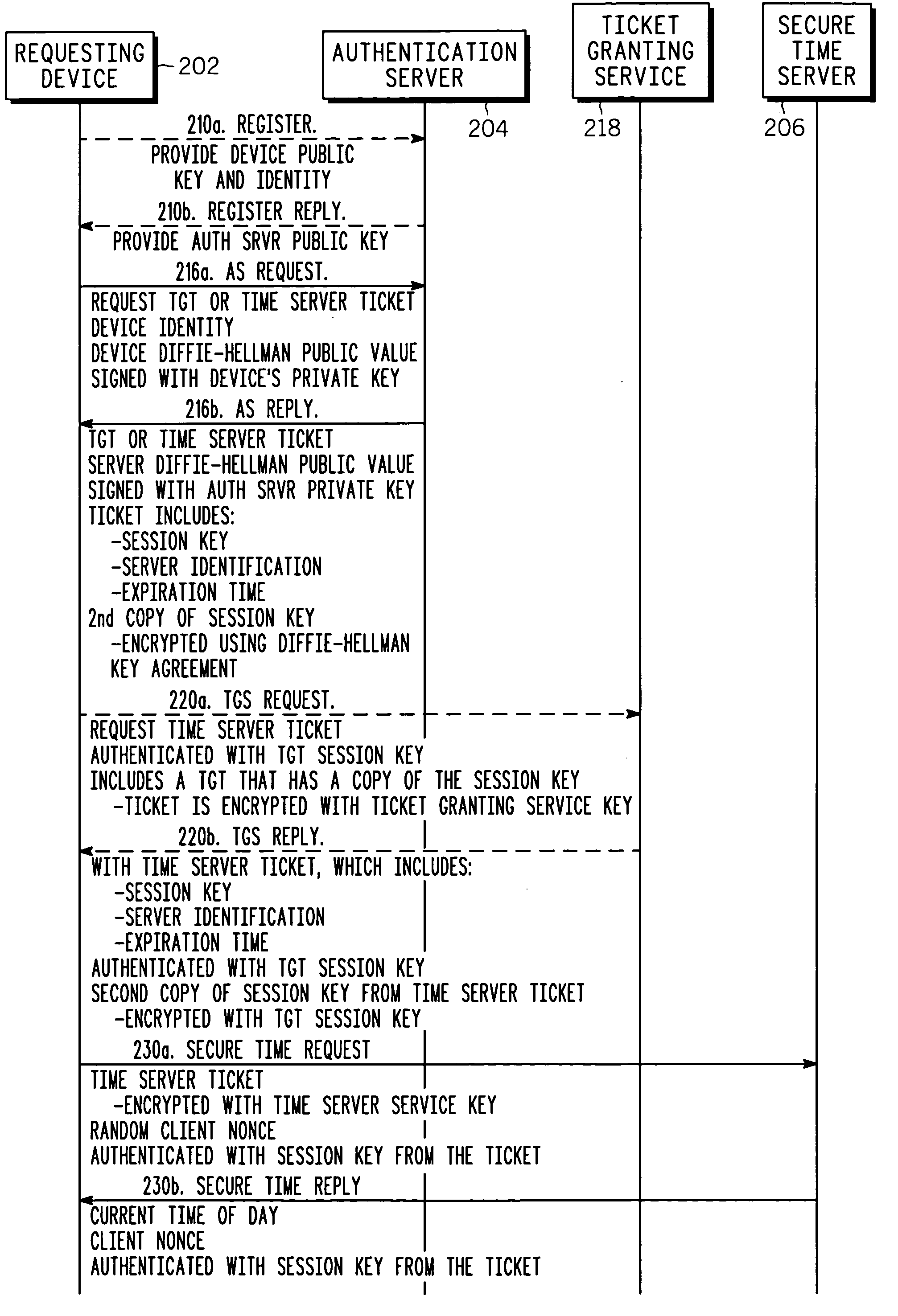
Ticket-based secure time delivery in digital networks
InactiveUS20050005114A1Reduce decryptionReduce digital signature processingKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTime ProtocolClient-side
A ticket-based secure time protocol is used to provide client devices, or users, with secure time signals. In a preferred embodiment, the secure time signals are provided by a secure time server so that multiple clients can be time-synchronized. Ticket-based authentication uses digital certificates and public key cryptography, such as Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) to reduce key administration overhead and decryption processing. Standard authentication architectures and approaches, such as Kerberos, can be used for some aspects of the invention. A preferred embodiment uses Request and Reply messages that provide added security and functionality, such as authentication, sequence-checking and verification of target destination.
Owner:GENERAL INSTR CORP
Method for ensuring security and privacy in a wireless cognitive network
ActiveUS20110138183A1Improve protectionFacilitate sharing of available WRAN channelsUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationConfidentialityNetwork management
In some embodiments, authentication, confidentiality, and privacy are enhanced for a wireless network of cognitive radios by encryption of network management and control messages as well as data traffic, thereby protecting information pertaining to node identification, node location, node-sensed incumbent transmissions, CRN frequency channel selections, and such like. During initial network registration, a temporary ID can be issued to a node, and then replaced once encrypted communication has been established. This prevents association of initial, clear-text messages with later encrypted transmissions. Elliptic curve cryptography can be used for mutual authentication between subscribers and the base station. ECC-based implicit digital certificates can be embedded in co-existence beacons used by CRN nodes to coordinate use of frequency channels, thereby preventing denial of service attacks due to transmitting of falsified beacons. Similar certificates can be embedded within identity beacons used to protect certain incumbents from interference by the CRN.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Key generation method using quadratic-hyperbolic curve group
InactiveUS20100020964A1Increase speedShort timeDigital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationTheoretical computer scienceKey generator
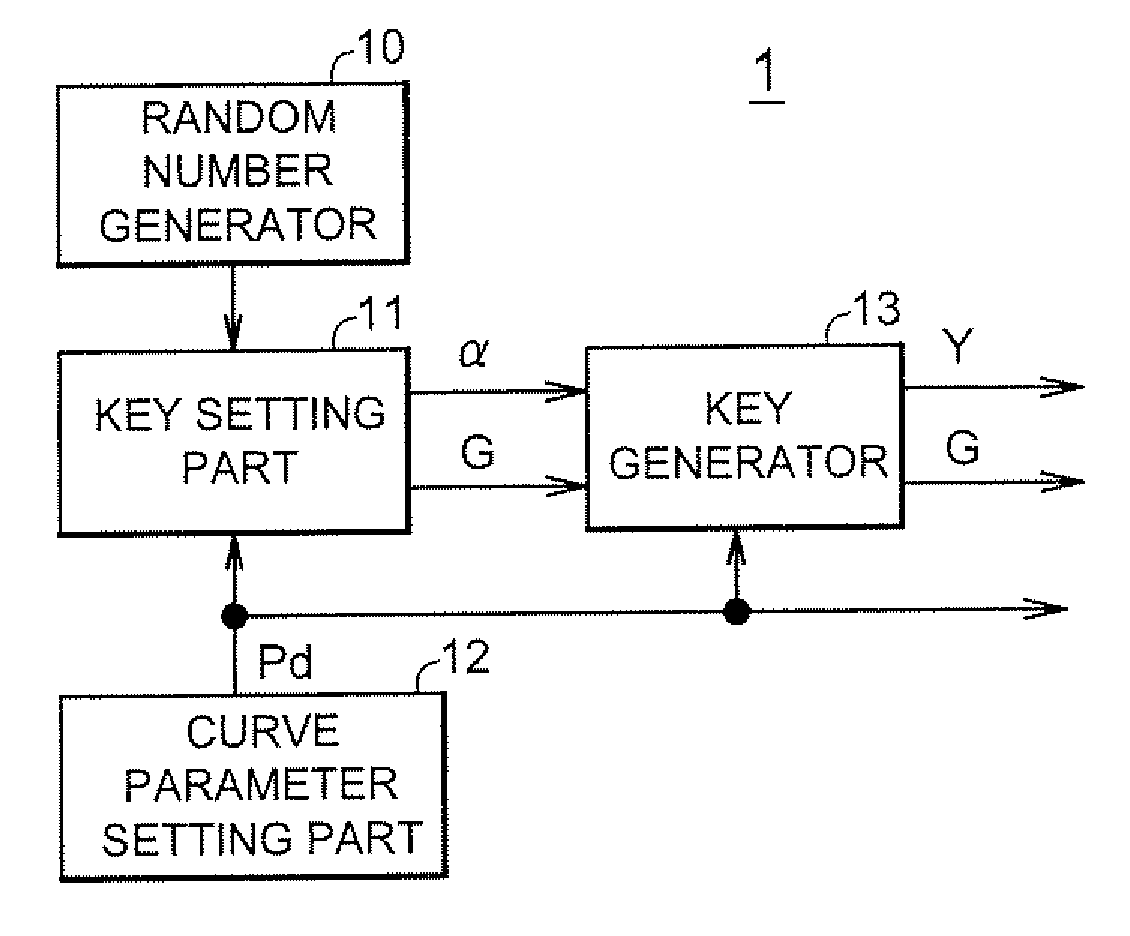
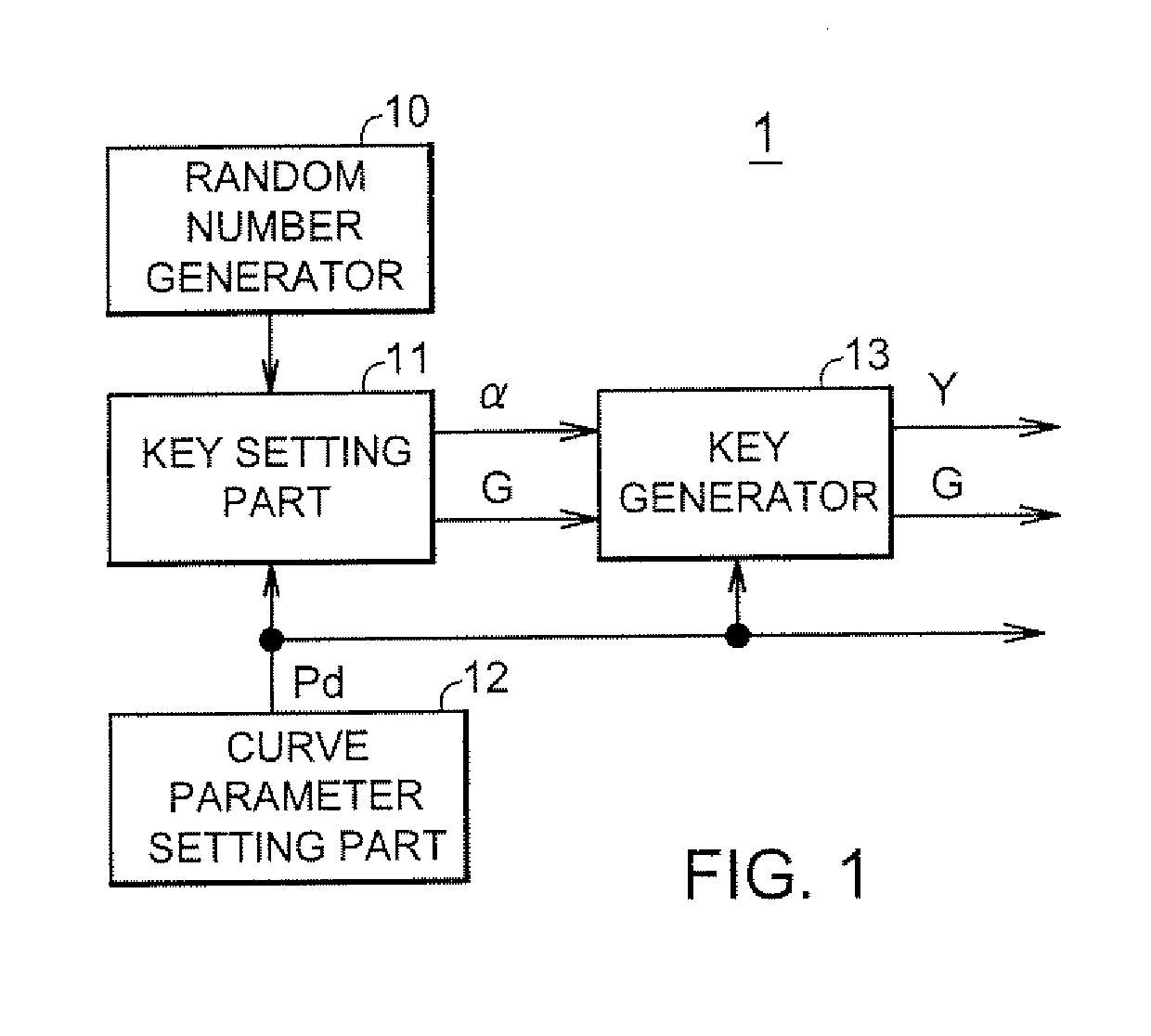
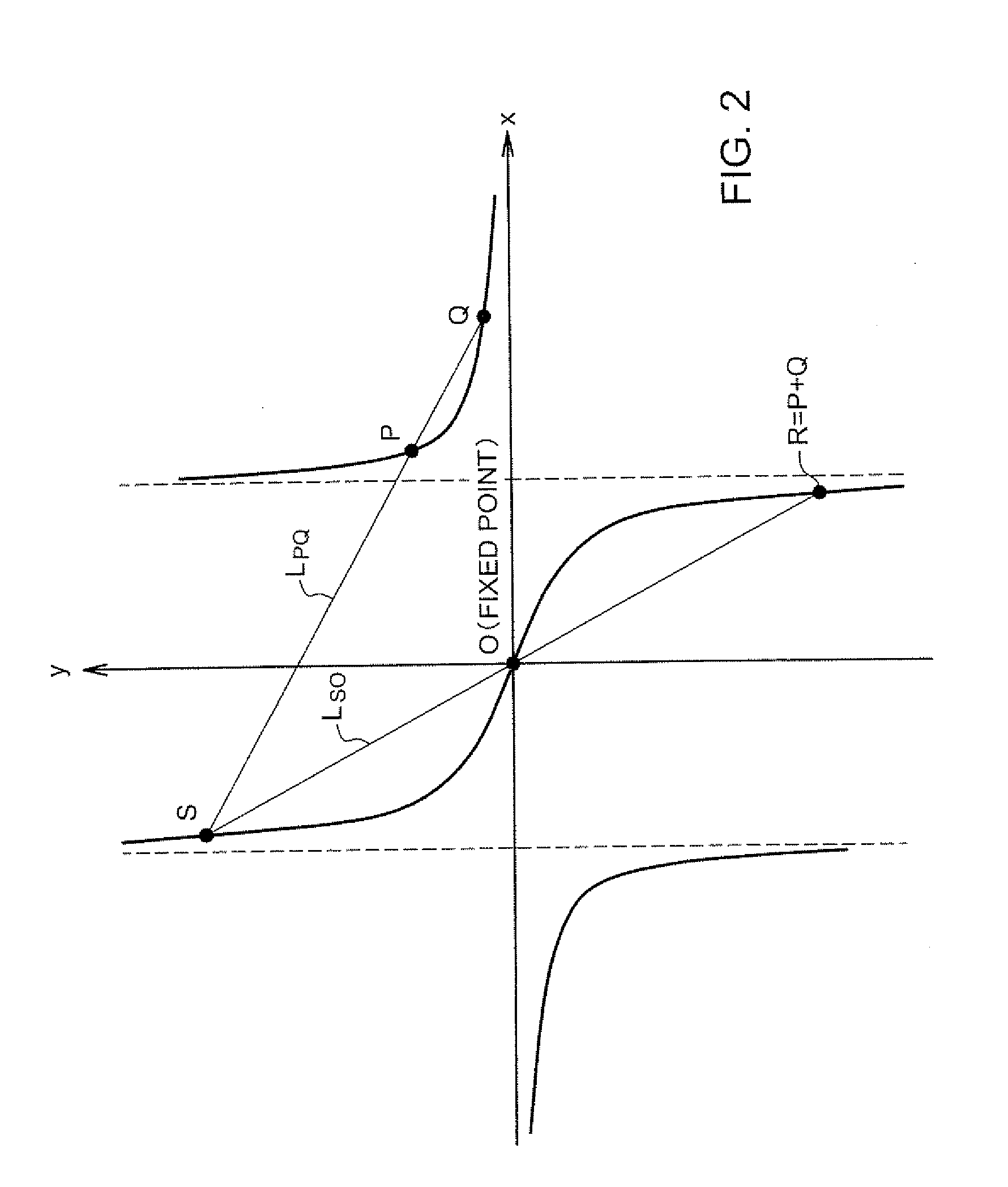
Disclosed is a key generation apparatus which uses a finite commutative group defined by a number-theoretical (or arithmetical) function that can be substituted for the elliptic curve, thereby enabling the computational difficulty equivalent to that of breaking the elliptic curve cryptography. The key generation apparatus comprises a key setting part and a key generator. The key setting part sets a secret key α, and selects an element of the finite commutative group as a public key G. The key generator performs an addition operation defined for the finite commutative group on the public key G, thereby to multiply the public key G by the secret key α representing a scalar coefficient to generate a public key Y. The finite commutative group is a set of pairs (x,y) of a dependent variable y of a quadratic-hyperbolic function defined on a finite ring and an independent variable x of the quadratic-hyperbolic function.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Hardware accelerator for elliptic curve cryptography
ActiveUS20030206629A1Public key for secure communicationDigital computer detailsEllipseElliptic curve cryptography
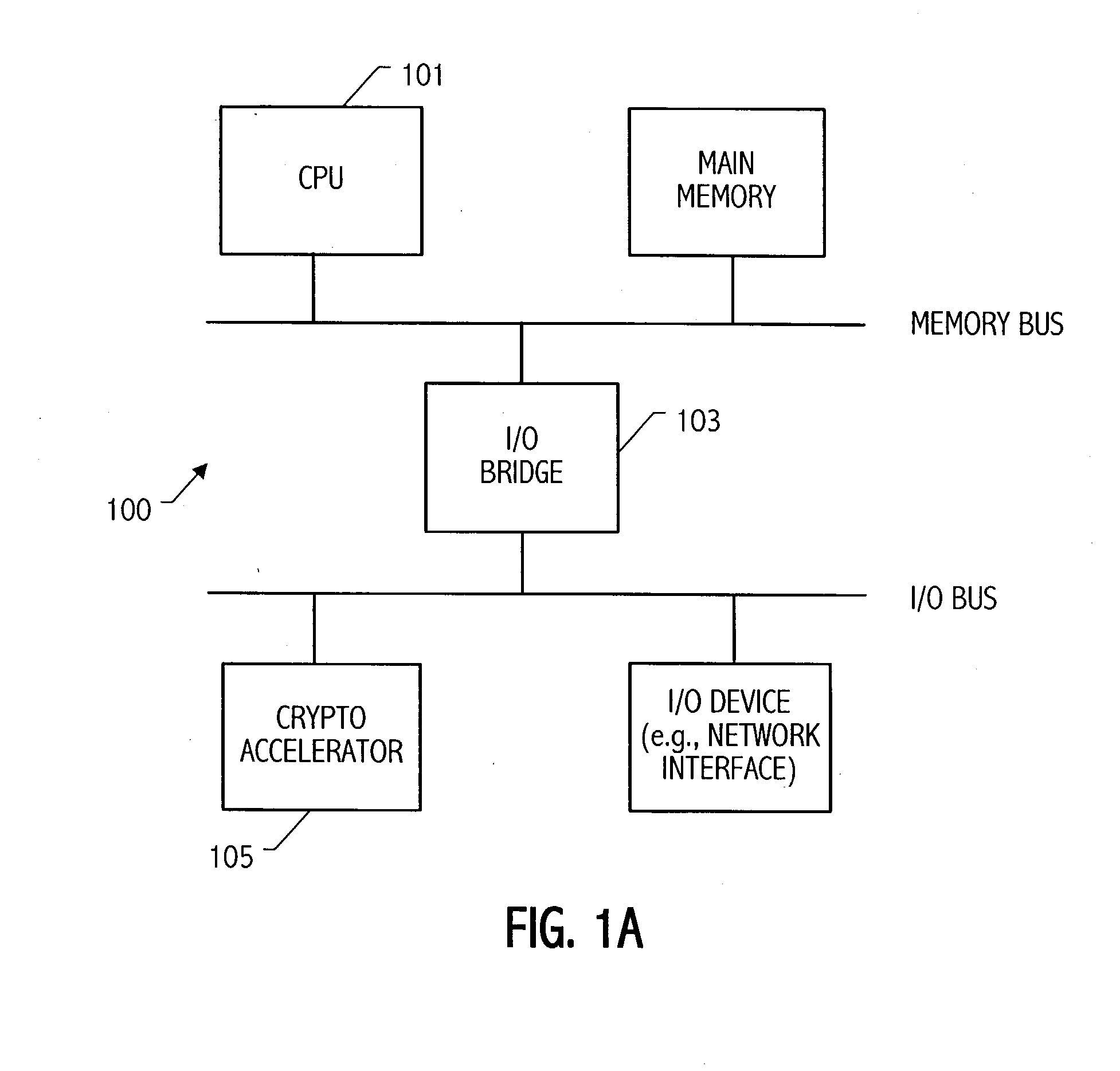
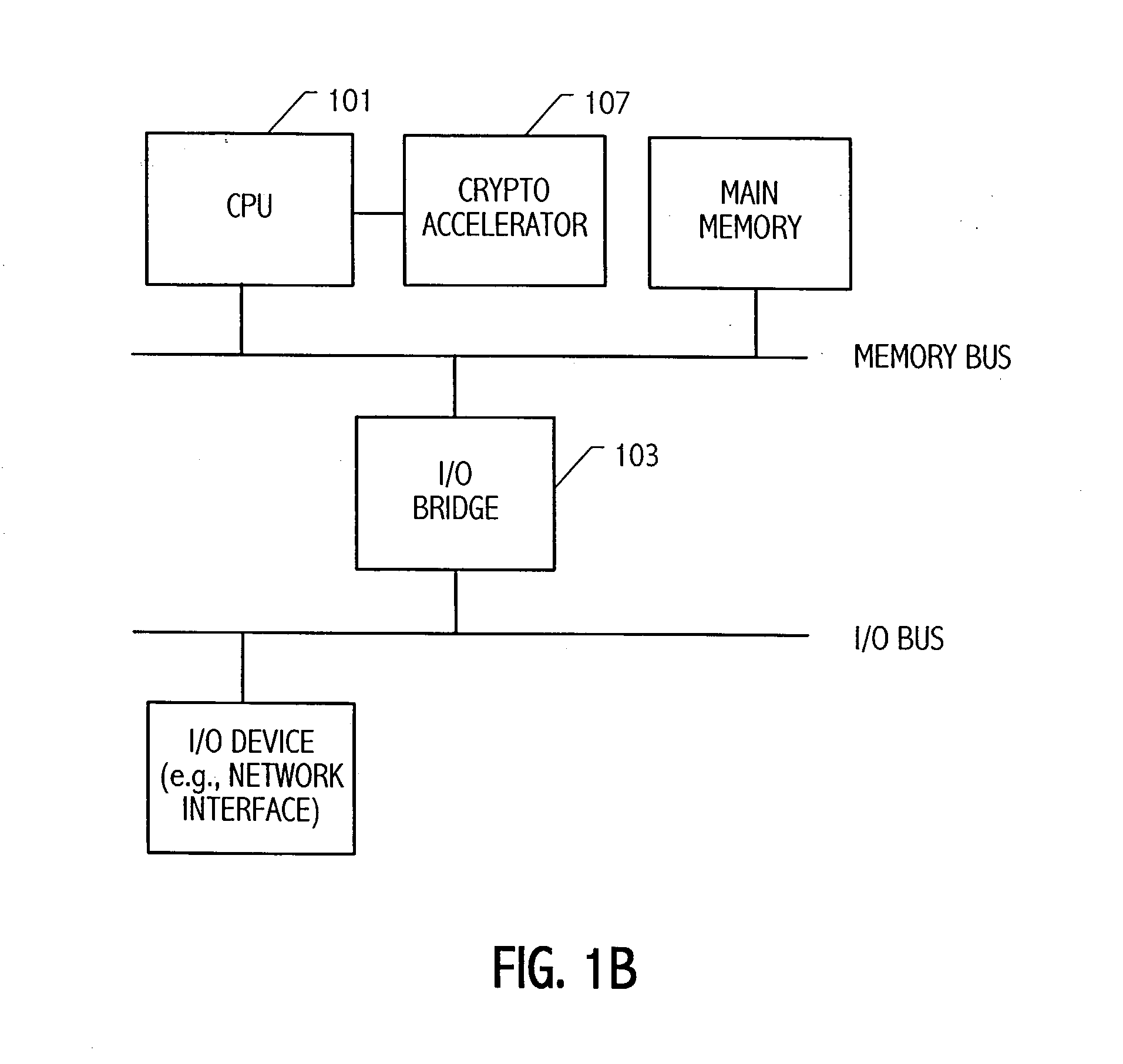
An elliptic curve processing apparatus that performs operations on elliptic curves specified over binary polynomial fields includes a functional unit that has a digit serial multiplier with a digit size of at least two bits. The elliptic curve processing apparatus performs reduction for respective generic curves using arbitrary irreducible polynomials, which correspond to respective ones of the generic curves. The elliptic curve processing apparatus may include hardwired reduction circuits in the functional unit for use with respective named curves. A storage location in the elliptic curve processing apparatus may be used to specify whether an operation is for one of the named curves or for one of the generic curves. The elliptic curve processing apparatus responds to an arithmetic instruction to utilize a respective one of the hardwired reduction circuits for reduction for respective named curves and a multiplier circuit for reduction for a plurality of generic curves, the multiplier coupled to perform reduction for respective generic curves using arbitrary irreducible polynomials, the arbitrary irreducible polynomials corresponding to respective ones of the generic curves. The elliptic curve processing apparatus operable on elliptic curves specified over binary polynomial fields performs a conditional branch according to whether a curve being processed is a generic curve or a named curve.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Cryptographic method capable of protecting elliptic curve code from side channel attacks
ActiveUS20050169462A1Requires minimizationSafe and efficientKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationScalar multiplicationElliptic curve cryptography
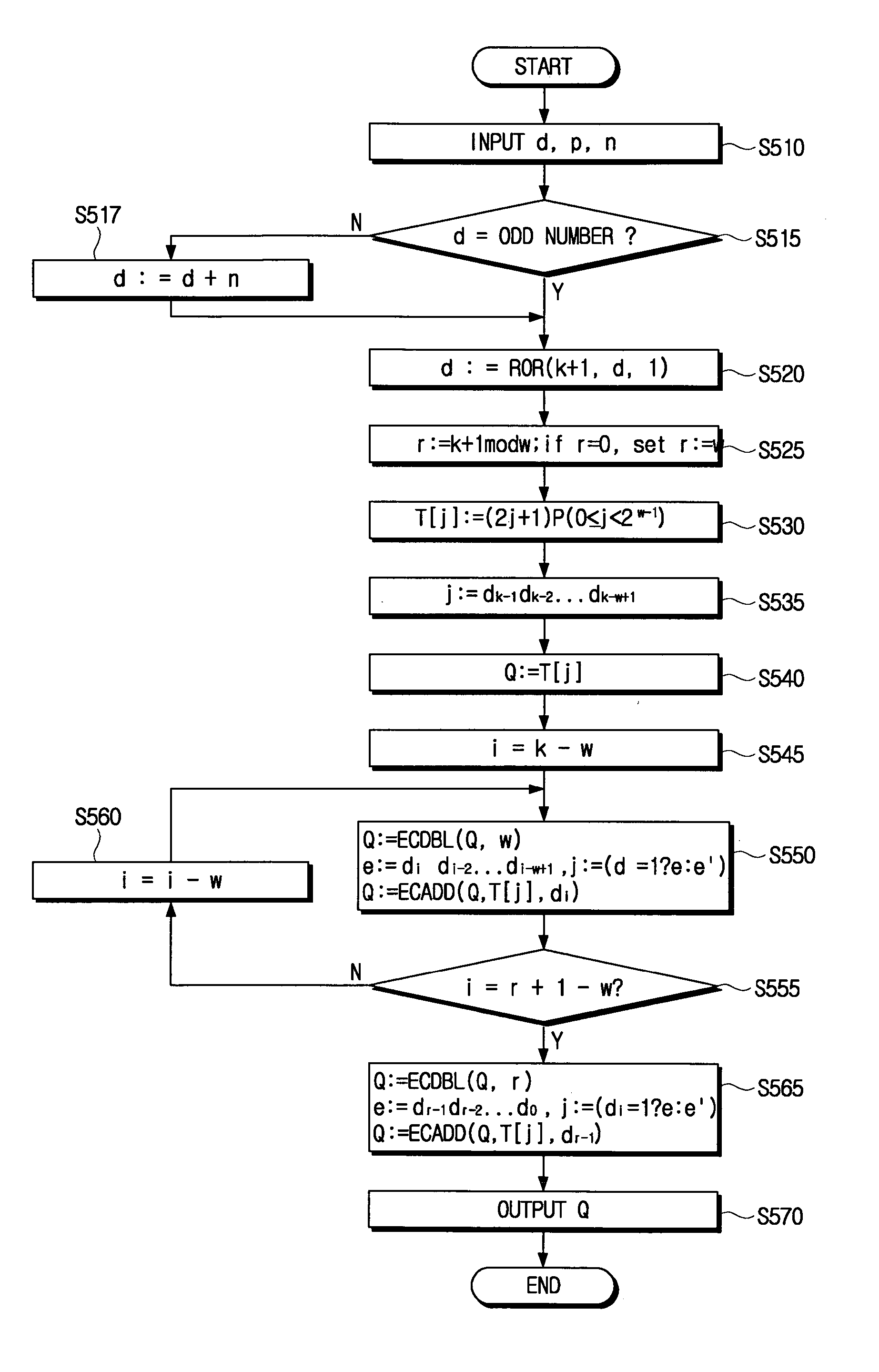
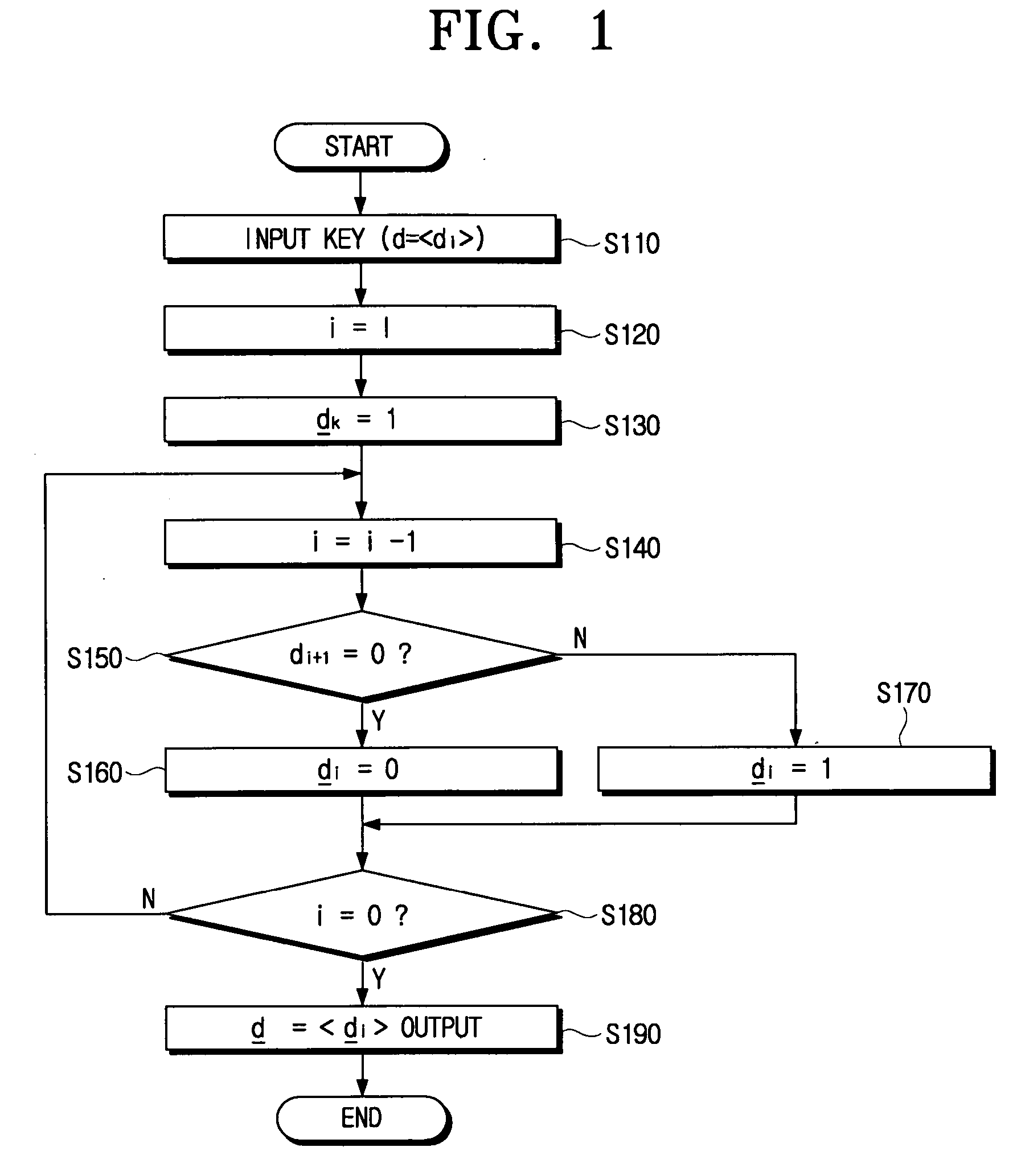
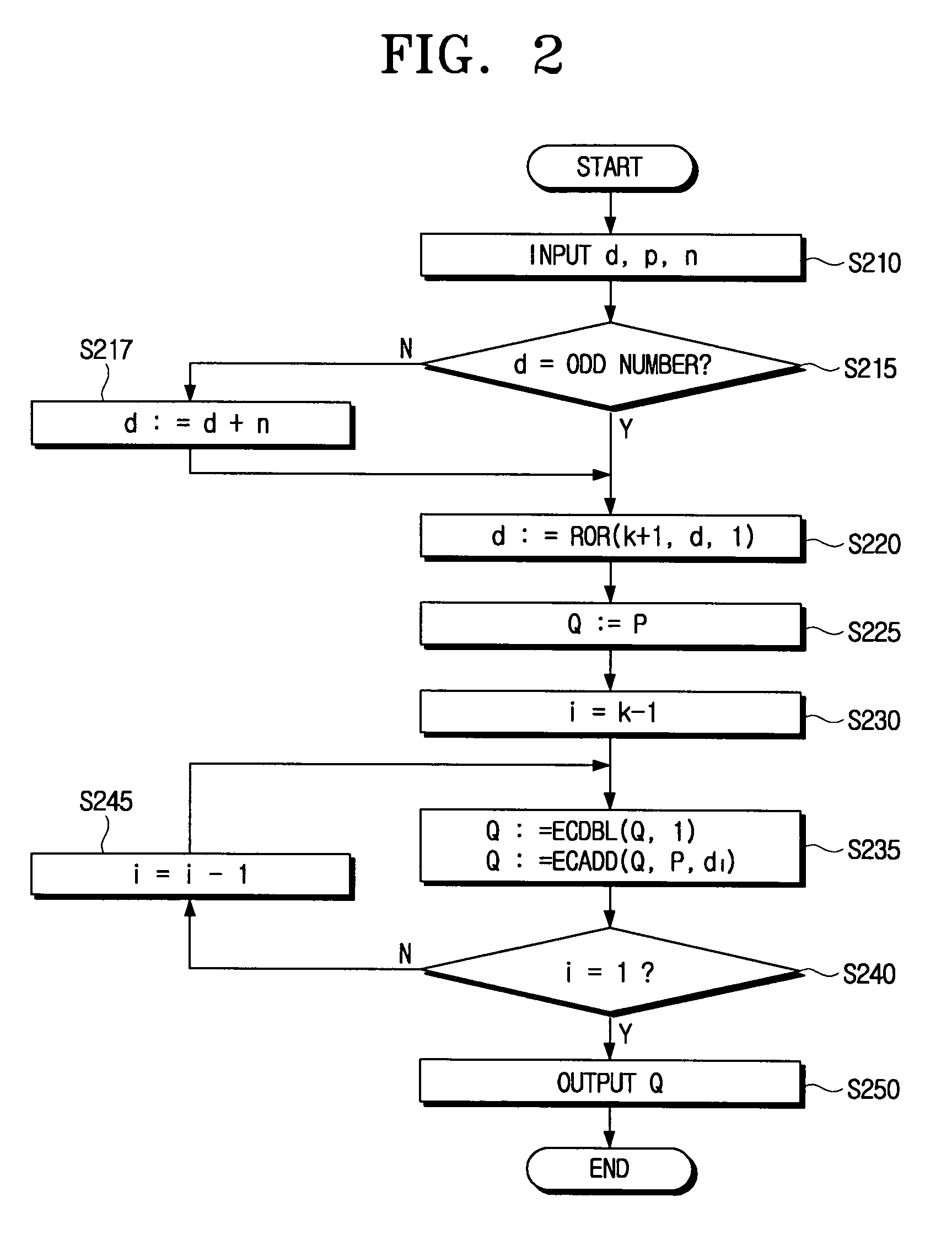
An elliptic curve cryptography method which generates a public key for use in a communication encryption using an elliptic curve, including: changing a number of a secret key (d) of (k) bits to an odd number; encoding the secret key to yield an encoded secret key (d) in which a most significant bit (MSB) is (1) and a rest positional number is (1) or (−1); and computing the public key (Q=Dp) by multiplying the encoded secret key (d) by a predetermined point (P) on the elliptic curve by a scalar multiplication.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hash functions using elliptic curve cryptography
InactiveUS20100166174A1Finite divisionUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareHash function
The hash functions using elliptic curve cryptography are hash functions that are produced using both an elliptic curve and a twist of the elliptic curve. Hash points are assigned values that either correspond to points on the elliptic curve or to points on the twist, depending upon whether the scalar value of the corresponding message block produces a quadratic residue or a quadratic non-residue when substituted as the x-value into the elliptic curve equation. The corresponding hash point x-coordinates are concatenated to form the hash bit string. The hash points may be doubled, and the hash functions may be applied to multimedia data by applying a media compression method to the message data before computing the hash points.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Multi-word arithmetic device for faster computation of cryptosystem calculations
InactiveUS6963644B1Good flexibilityHigh-speed executionPublic key for secure communicationDigital computer detailsCryptosystemMontgomery reduction
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
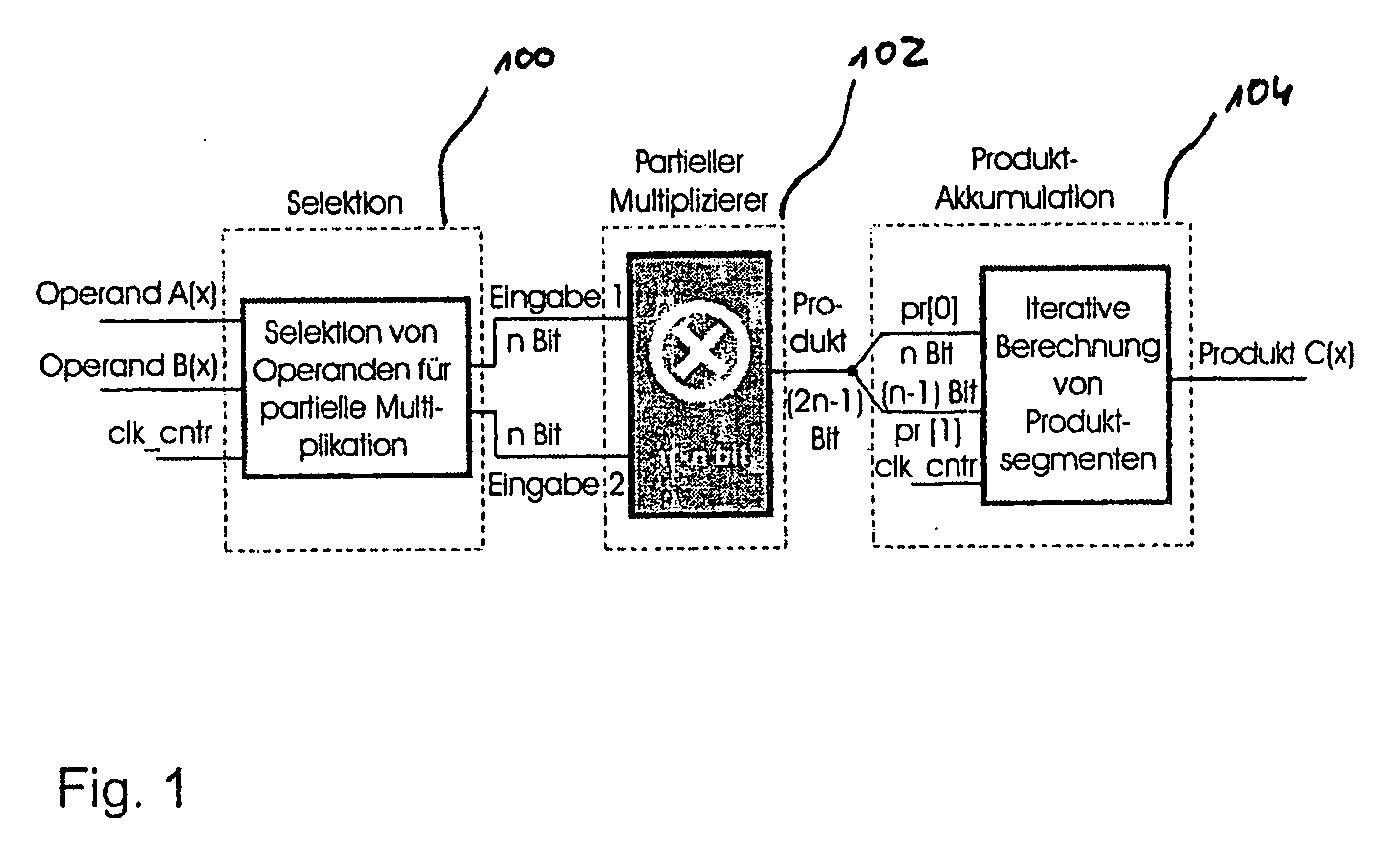
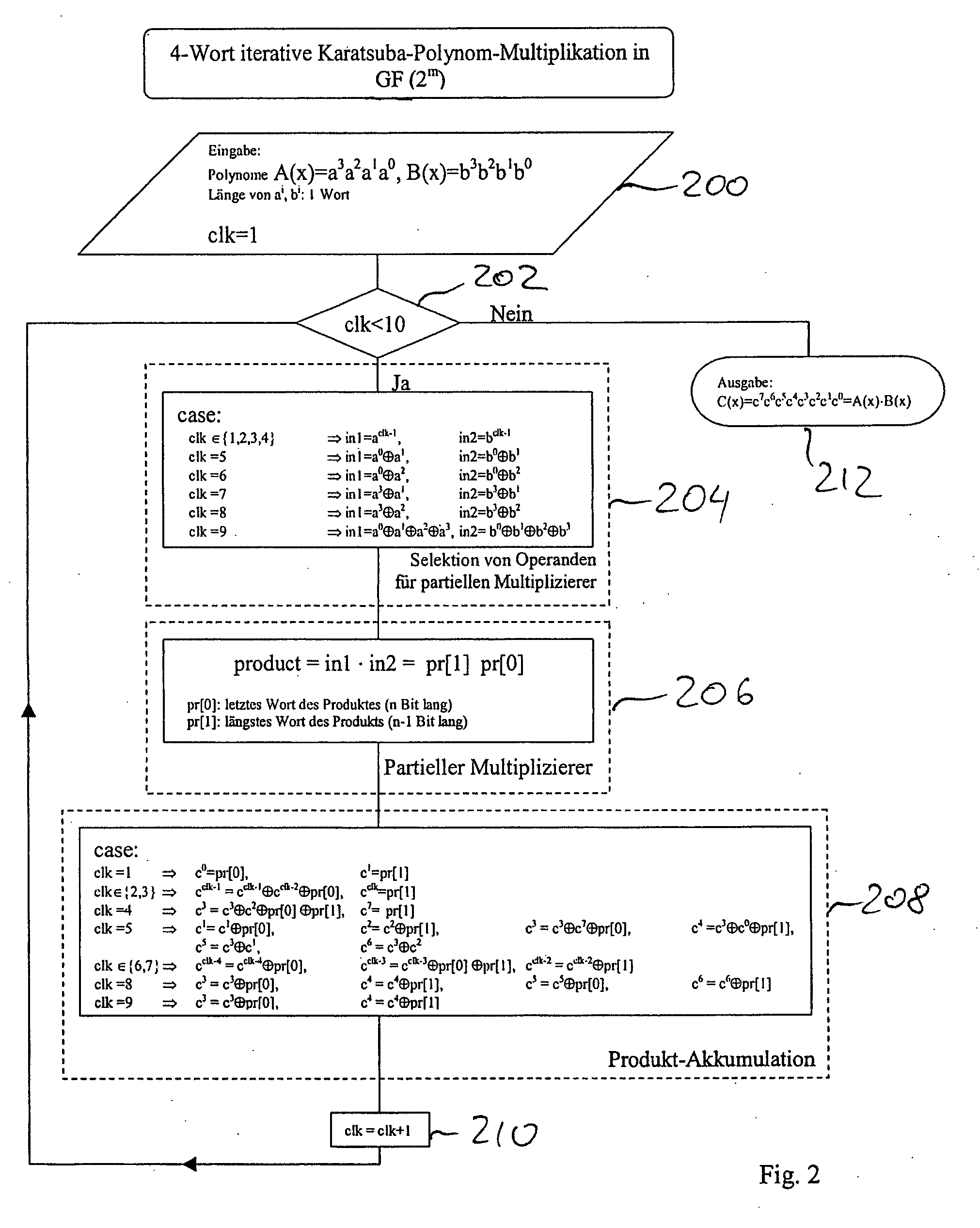
Method and Apparatus for Calculating a Polynomial Multiplication, In Particular for Elliptic Curve Cryptography
ActiveUS20090136022A1Easy to operateEnergy efficient ICTPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePosynomial
Safeguarding communication channels is required in particular in wireless networks. The use of encryption mechanisms in the form of software is limited by the required calculation and energy capacities of mobile terminals. Costs are of significance when using hardware solutions for cryptographic operations. The present invention provides an approach which simultaneously tackles all those points. It concerns a hardware accelerator for polynomial multiplication in extended Galois fields (GF), wherein the per se known Karatsuba method is iteratively applied in accordance with the invention. When using the invention the area requirement can be reduced for example from 6.2 mm2 to 2.1 mm2. The solution according to the invention also reduces the energy consumption in comparison with solutions in accordance with the state of the art by 30%.
Owner:IHP GMBH - INNOVATIONS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE MICROELECTRONICS INST FOR INNOVATIVE MIKROLEKEKTRONIK
Key derivation method and device applicable to digital currency
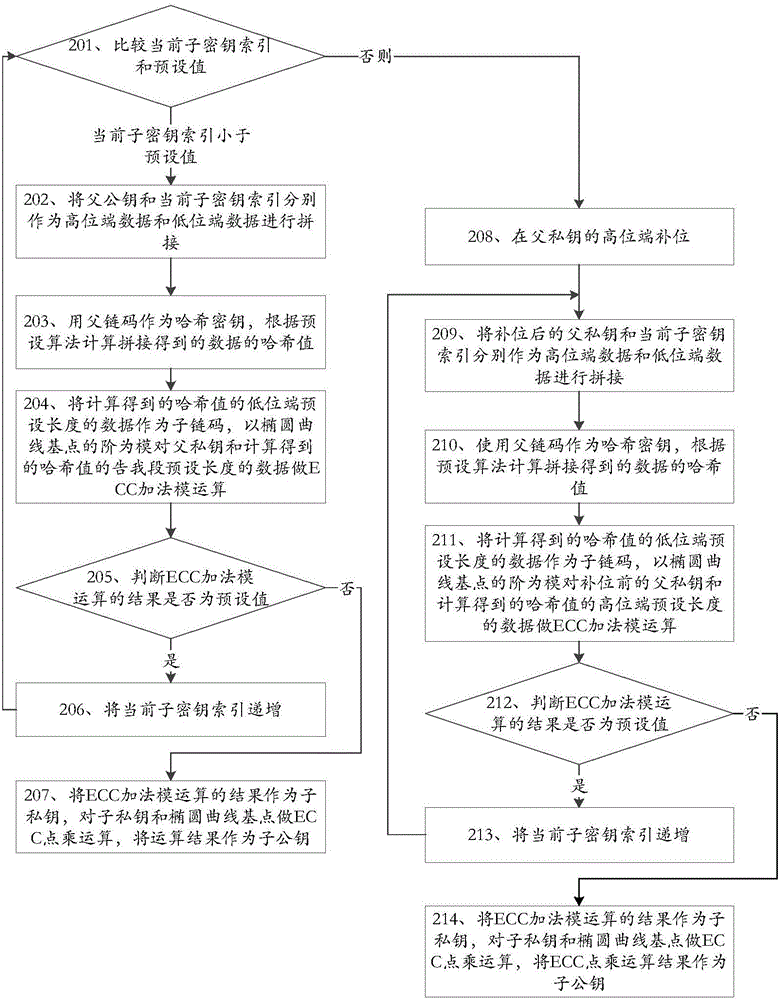
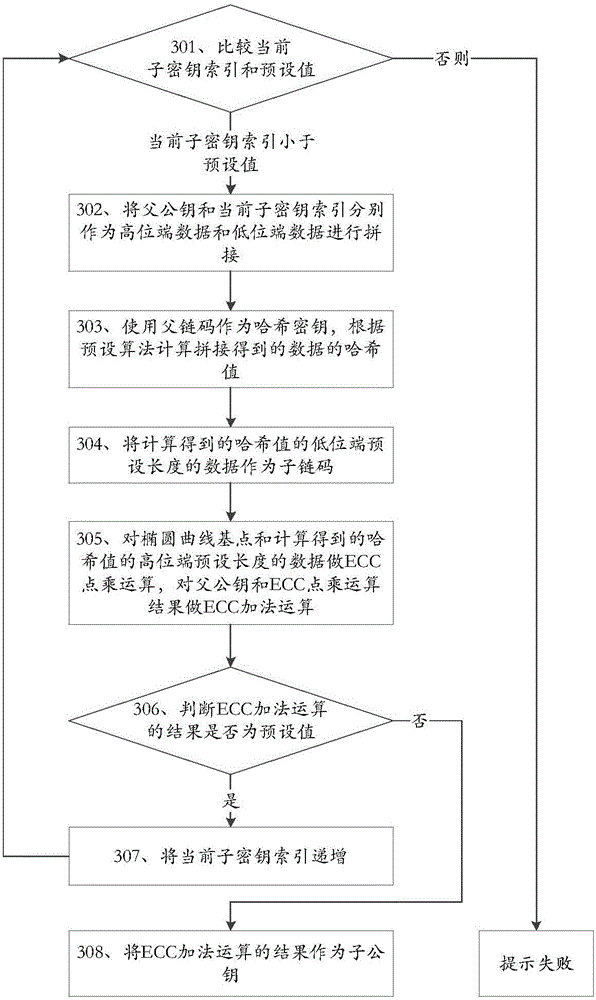
ActiveCN106411506AImprove securityAvoid lostKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital currencyRelationship - Father
The invention discloses a key derivation method and device applicable to digital currency and belongs to the field of information security. The key derivation method applicable to digital currency comprises the steps of splicing indexes of father public keys and sub-key indexes according to a sequence; using father chain codes as Hash keys, and calculating Hash values of spliced data based on a preset algorithm; obtaining sub-chain codes based on the Hash values; performing ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) addition modular operation on captured residual data; if the operation results are not preset values, regarding the operation results as sub-private keys; and performing ECC point multiplication operation on the sub-private keys to obtain sub-public keys. The key derivation method and device applicable to digital currency have the beneficial effects that backup of key seeds rather than all the keys is required as all the keys can be derived based on the key seeds, the backup volume is small, and loss caused by key damage also can be avoided.
Owner:FEITIAN TECHNOLOGIES
Secure mutual authentication and key agreement protocol under Internet of Things environment
InactiveCN107483195AFix the leakFix security issuesKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationMutual authenticationElliptic curve cryptography
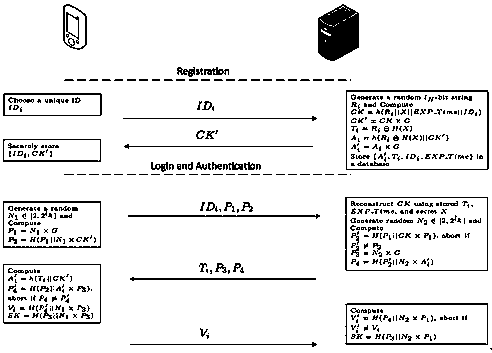
The invention discloses a secure mutual authentication and key agreement protocol under the Internet of Things environment. The secure mutual authentication and key agreement protocol comprises the following steps: step A, a registration phase: submitting own ID information to a server S by a user Ui, and registering to become a legal user; and step B, a login and authentication phase: performing two-way identity authentication and key agreement by the registered user Ui and the server S, and establishing a session key for the communication. The secure mutual authentication and key agreement protocol under the Internet of Things environment provided by the invention solves the unsafe problems of information leakage and stealing of the two communication parties in the Internet of Things communication, and has higher performance and efficiency in the similar security protocols. The invention adopts an elliptic curve cryptography algorithm, and realizes key negotiation and establishment with low consumption and high security on devices such as embedded devices and so on with limited computing power and storage resources.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
IBE (Internet Booking Engine) data encryption system based on medium digital certificate
InactiveCN102255729ASolve technical difficultiesPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationThe InternetXML Encryption
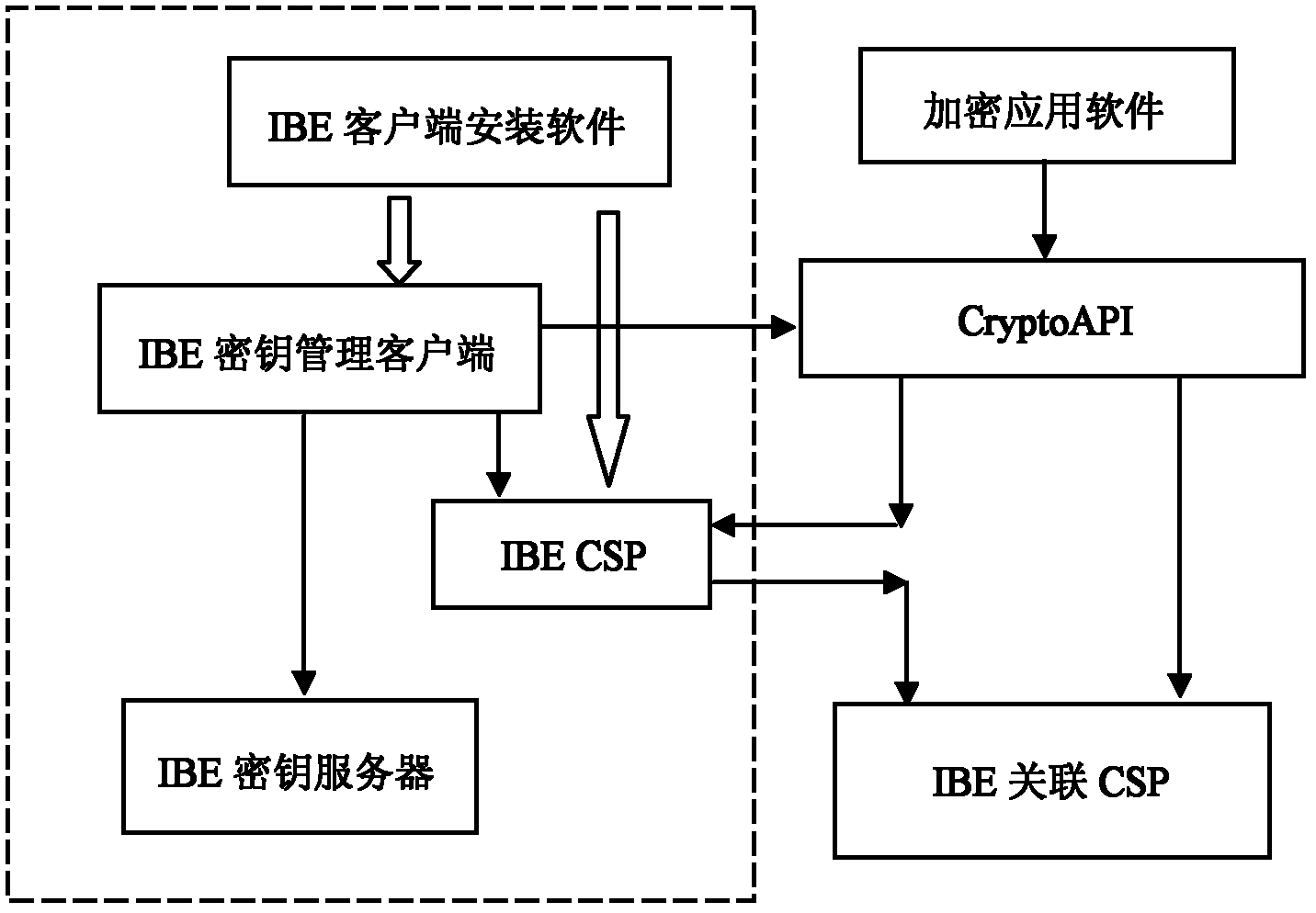
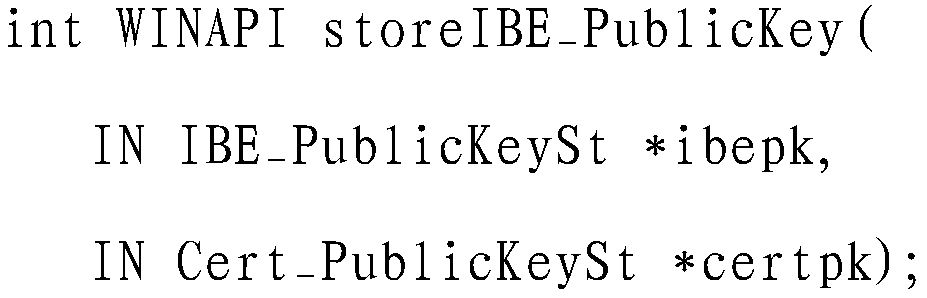
The invention relates to an IBE (Internet Booking Engine) data encryption system based on a medium digital certificate, and comprises four components: an IBE CSP (Cryptographic Service Provider), an IBE key management client, an IBE key server and an IBE client installing software, wherein the IBE CSP is the core and key of the IBE data encryption system. The IBE data encryption system is used for enabling the system and the application which do not support an IBE encryption process to utilize the IBE process to encrypt and decrypt. In the IBE data encryption system, the medium digital certificate is taken as a bridge, an asymmetric key algorithm which is supported by RSA (Rivest Shamir Adleman), ECC (Elliptic Curves Cryptography) or other X509 certificate is provided by a register, but actually a Windows CSP of the IBE algorithm is realized, the data encryption and decryption operations based on the RSA, ECC or other asymmetric key algorithms are automatically converted into the corresponding data encryption and decryption operations based on the IBE algorithm.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH +1
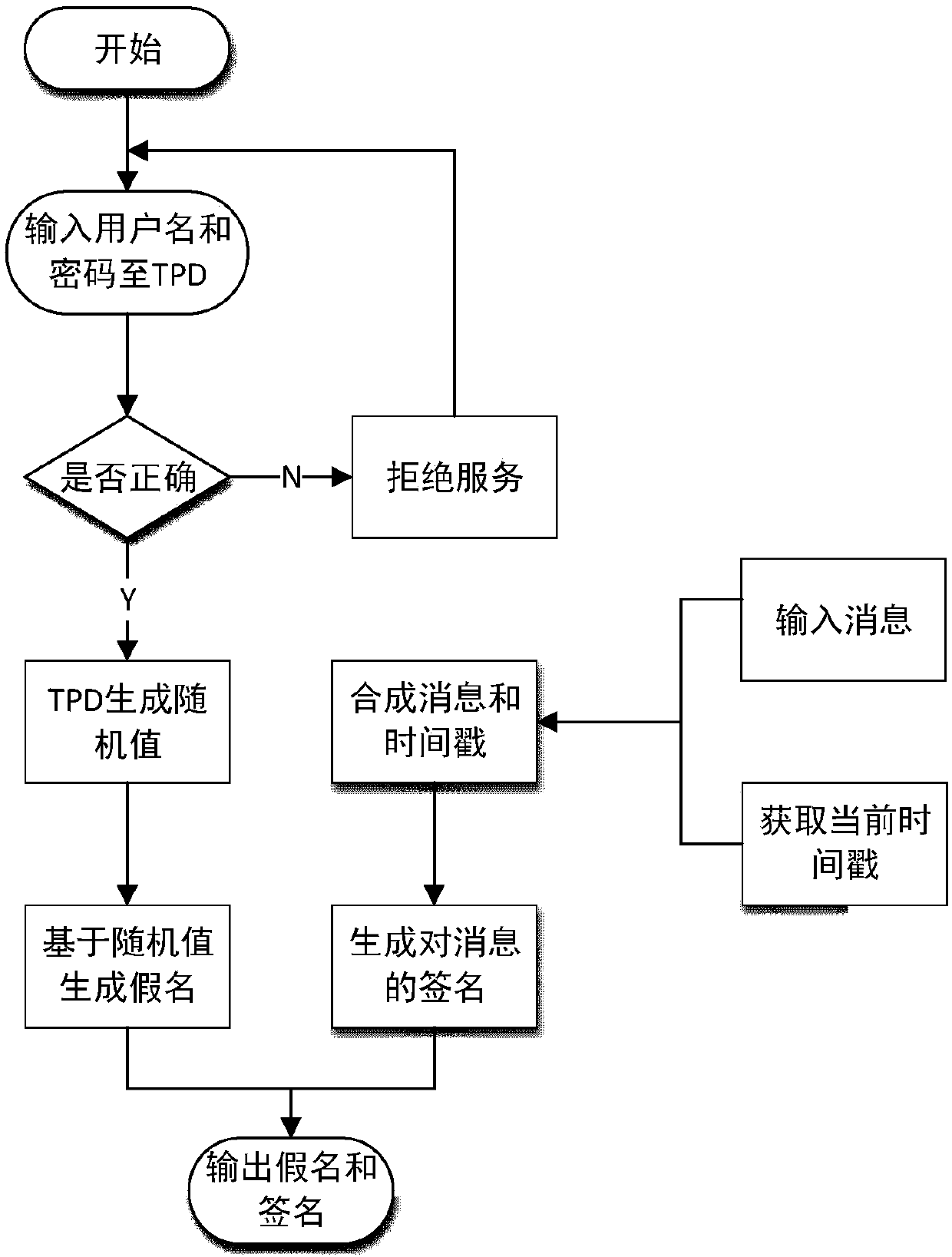
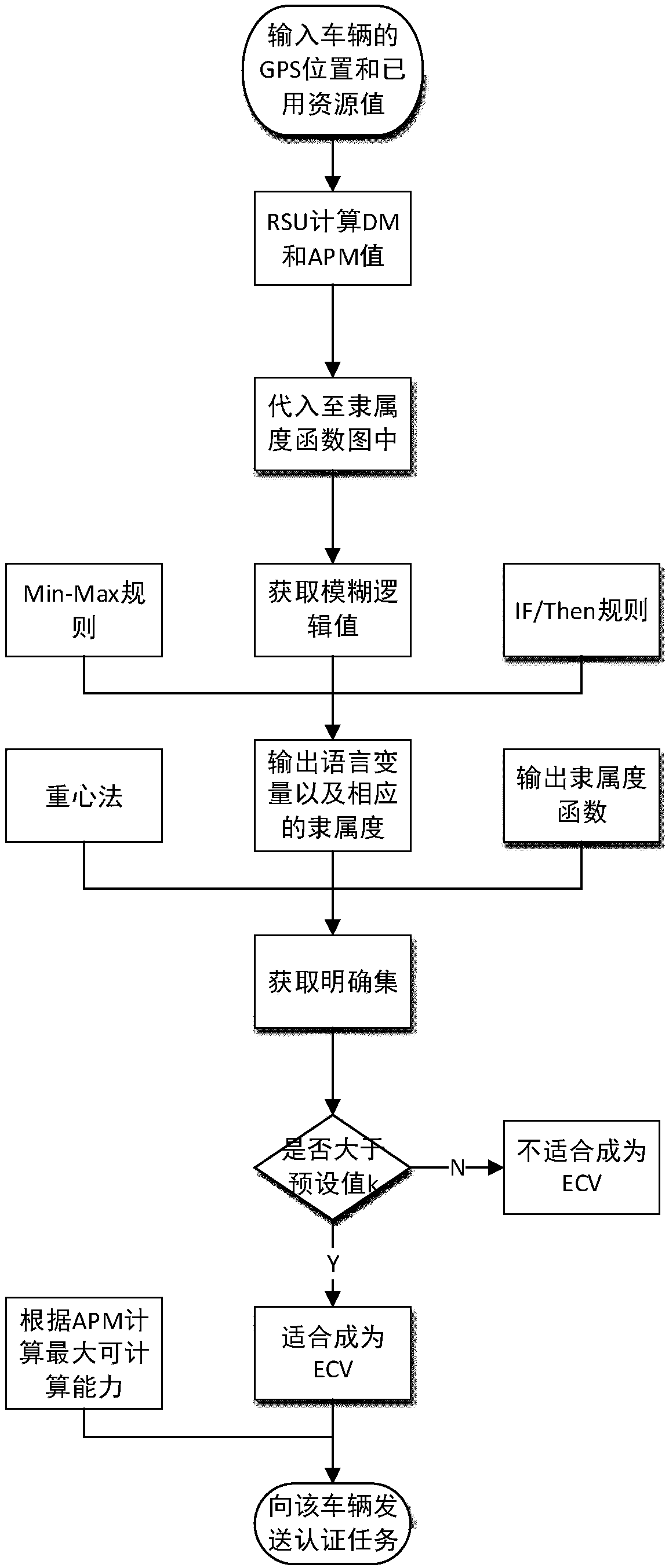
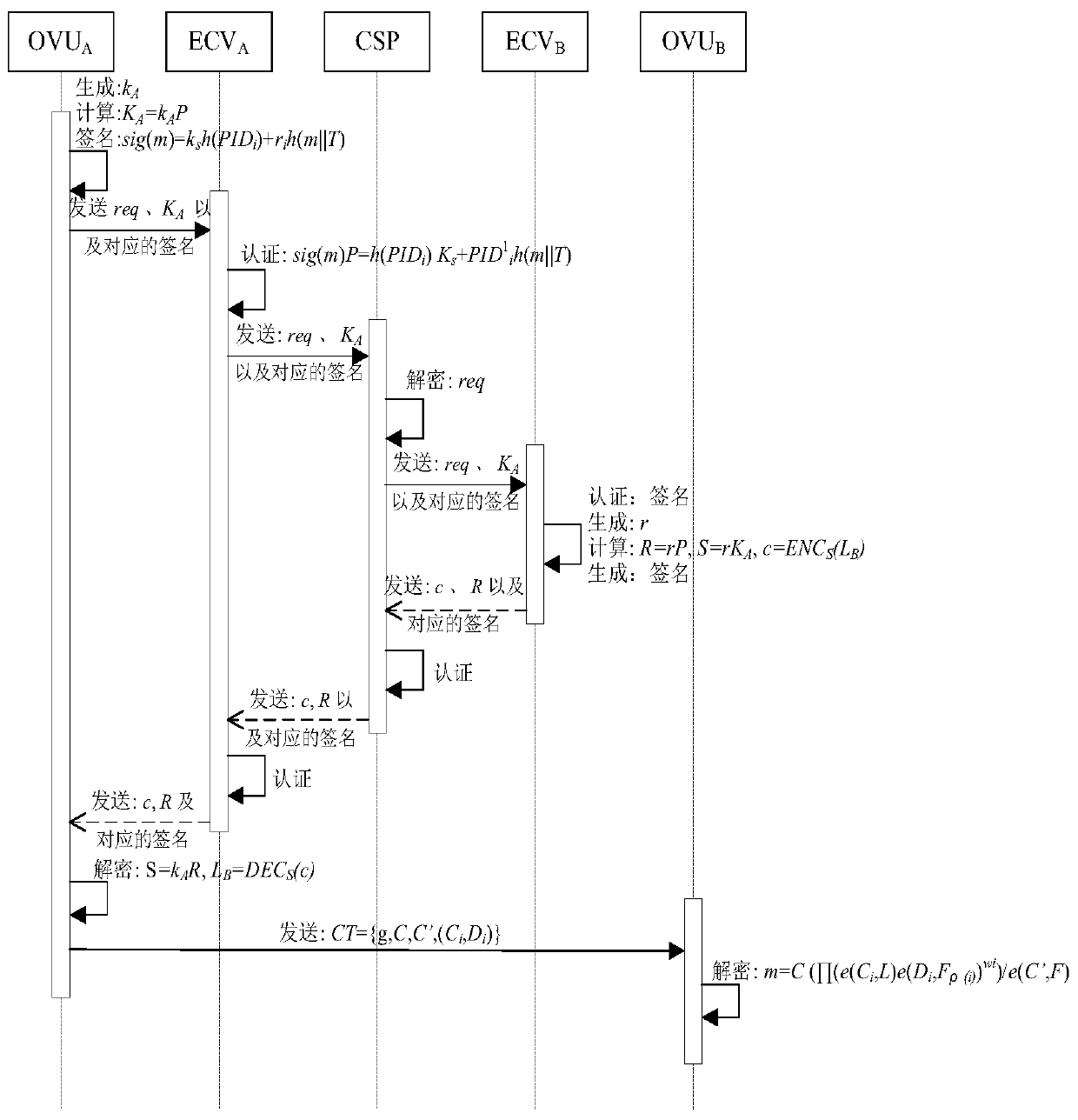
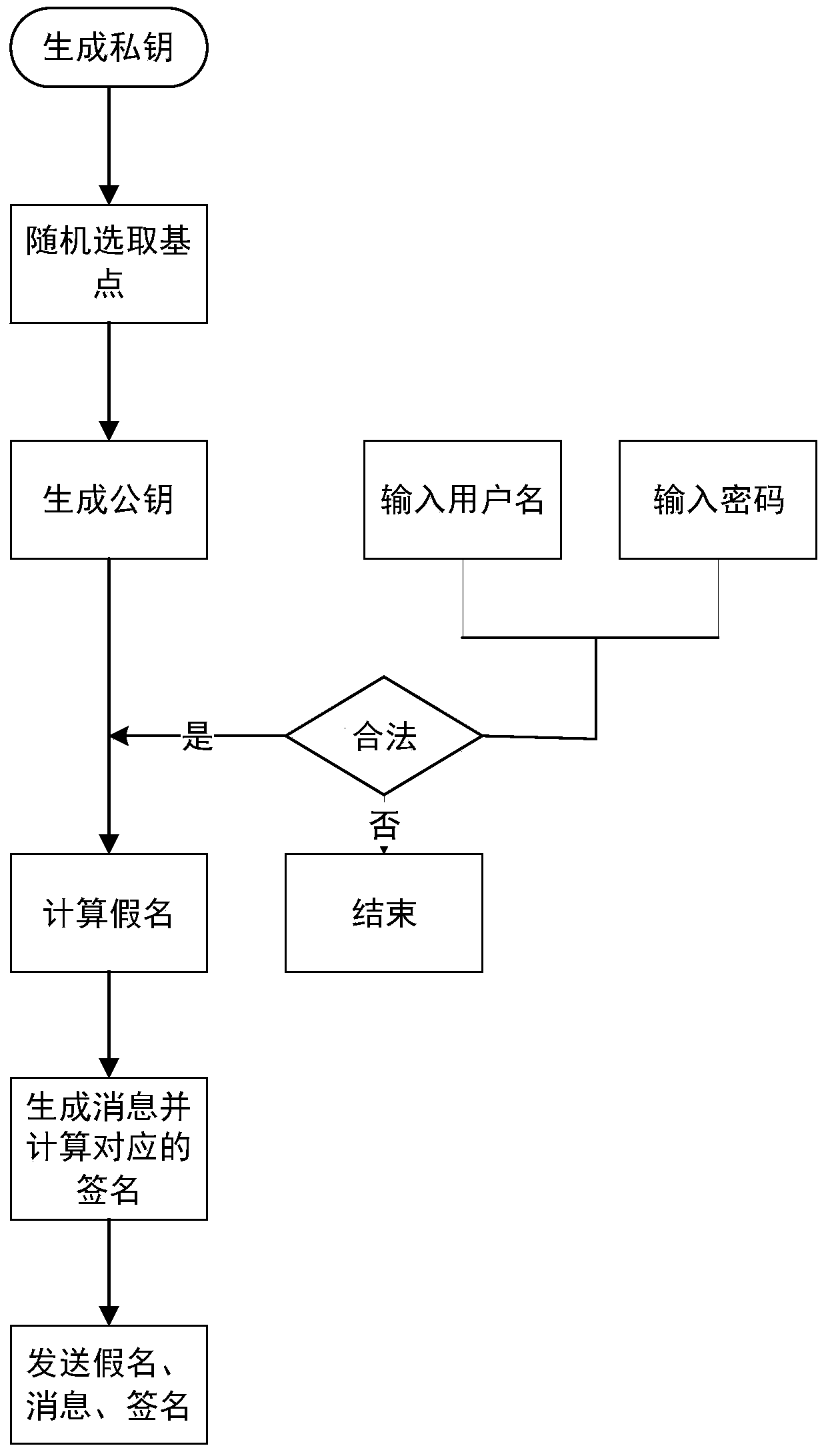
Efficient message authentication method for vehicular ad hoc network based on edge computing
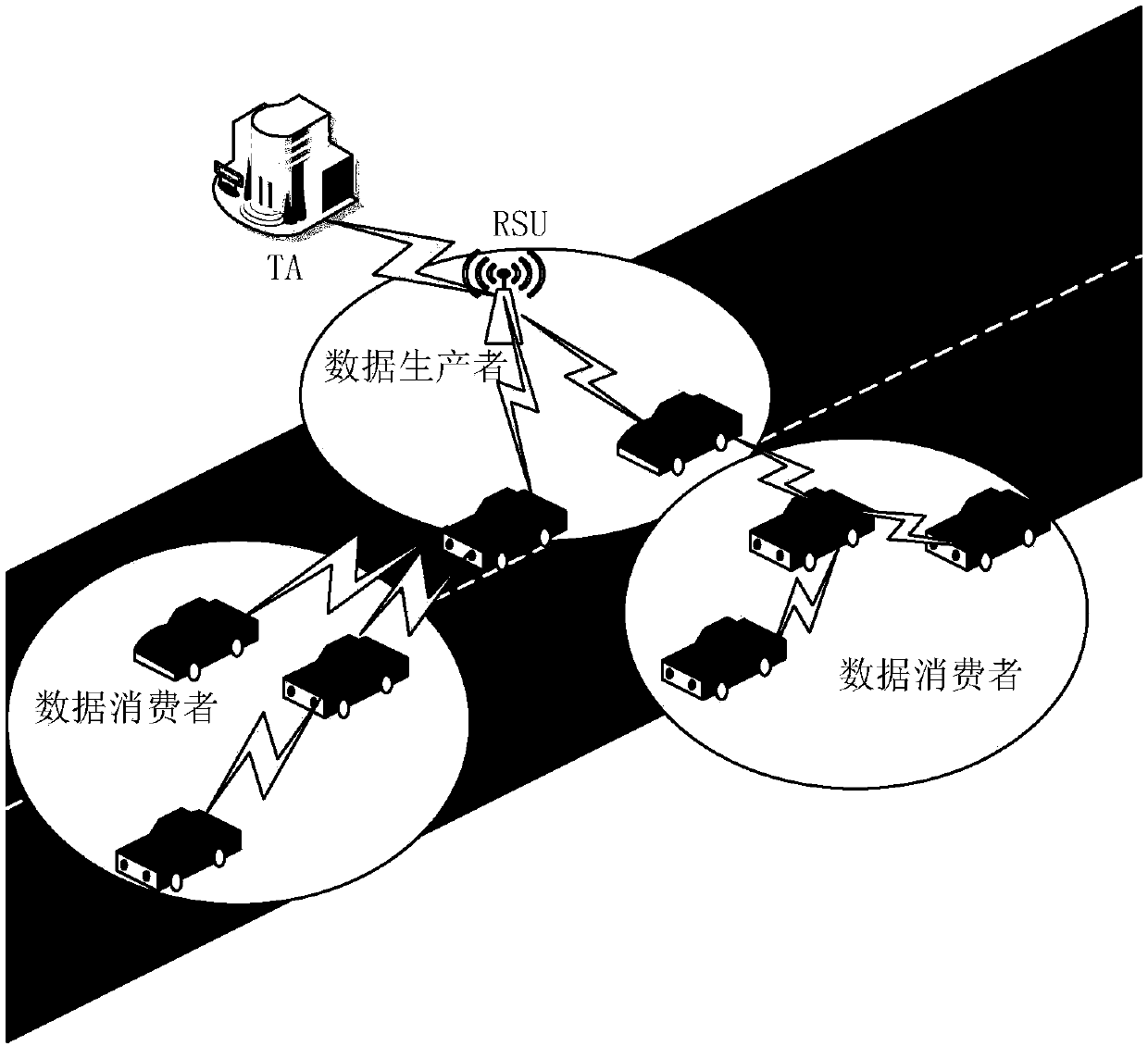
ActiveCN107634837AReduce overheadLow message authentication redundancyKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationLocal optimumEdge computing
The invention discloses an efficient message authentication method for a vehicular ad hoc network based on edge computing, which comprises the steps of system initialization of participating entitiesof the Internet of vehicles, wherein the step comprises two processes such as parameter generation and vehicle pseudonym and signature generation; and (2) message authentication of an RSU (Roadside Unit) and a vehicle, wherein the step comprises four processes such that the RSU elects an edge computing vehicle (ECV), the ECV executes a task, the RSU checks an authentication result of the ECV and vehicle message authentication is performed. The signing portion of the invention adopts an elliptic curve cryptography based operation, thereby enabling the computation and transmission overhead to below; further the ECV is elected according to a fuzzy logic control theory to achieve local optimal election; the ECV is set to help the RSU to achieve quick and accurate message signature authentication; and the RSU reduces the redundant authentication of the whole system to the maximum extent through broadcasting the authentication result, and the operating efficiency of the whole vehicular ad hoc network is improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Authenticated radio frequency identification
ActiveUS20080150702A1Subscribers indirect connectionSecuring communicationAggregate signatureElliptic curve cryptography
An authenticated RFID system is provided that uses elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) to reduce the signature size and read / write times when compared to traditional public key implementations such as RSA. Either ECDSA or ECPVS can be used to reduce the signature size and ECPVS can be used to hide a portion of the RFID tag that contains sensitive product identifying information. As a result, smaller tags can be used or multiple signatures can be written at different stages in a manufacturing or supply chain. A key management system is used to distribute the verification keys and aggregate signature schemes are also provided for adding multiple signatures to the RFID tags, for example in a supply chain.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and device for managing secret keys in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN102186170AImprove securityProtection securityNetwork topologiesSecurity arrangementSecure communicationWireless sensor networking
The invention discloses a method for managing secret keys in a wireless sensor network. The method comprises the following steps: 1. clustering the nodes of a sensor by adopting DECA (distributed energy-core algorithm) based on the spatial position information of the nodes, wherein a base station only communicates with cluster heads; the cluster heads communicate with the common nodes in the cluster; the cluster heads can not directly communicate with each other; and shared nodes do not exist among the clusters; and 2. during distributing the communication secret keys, adopting elliptic curve cryptography algorithm to encrypt and decrypt the wireless sensor network and carrying out communications among the nodes by utilizing a symmetric encryption method after establishing safe communication links. Dot multiplication of the elliptic curve cryptography algorithm is optimized by adopting a window sliding method to reduce the number of the continuous nonzero integers. By adopting the method, the safety of the wireless sensor network system can be remarkably improved. The invention also discloses a device for managing secret keys in the wireless sensor network. The device comprises a clustering module, a secret key management module and an elliptic curve cryptography algorithm optimization module.
Owner:BEIJING TOPSEC TECH
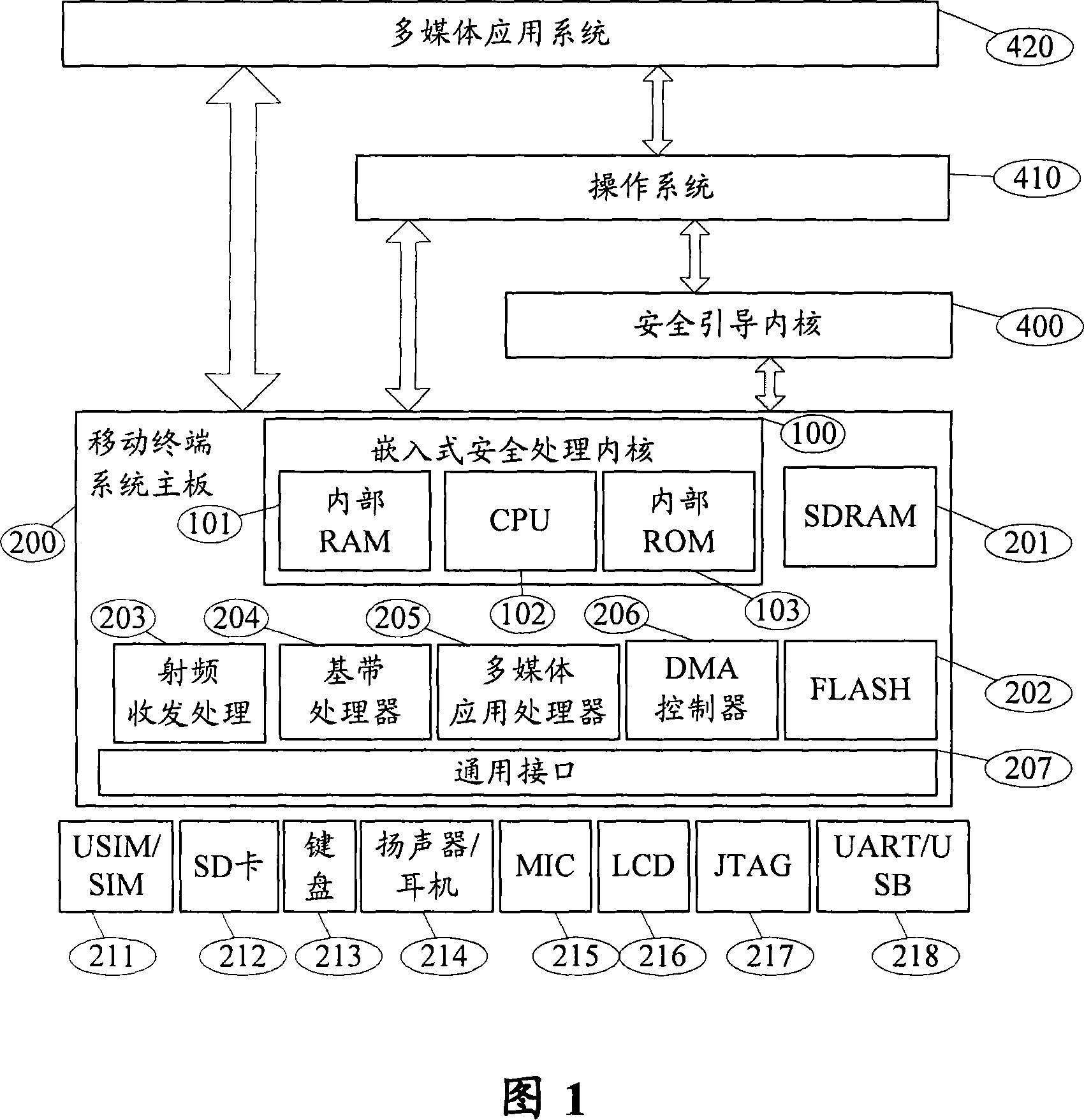
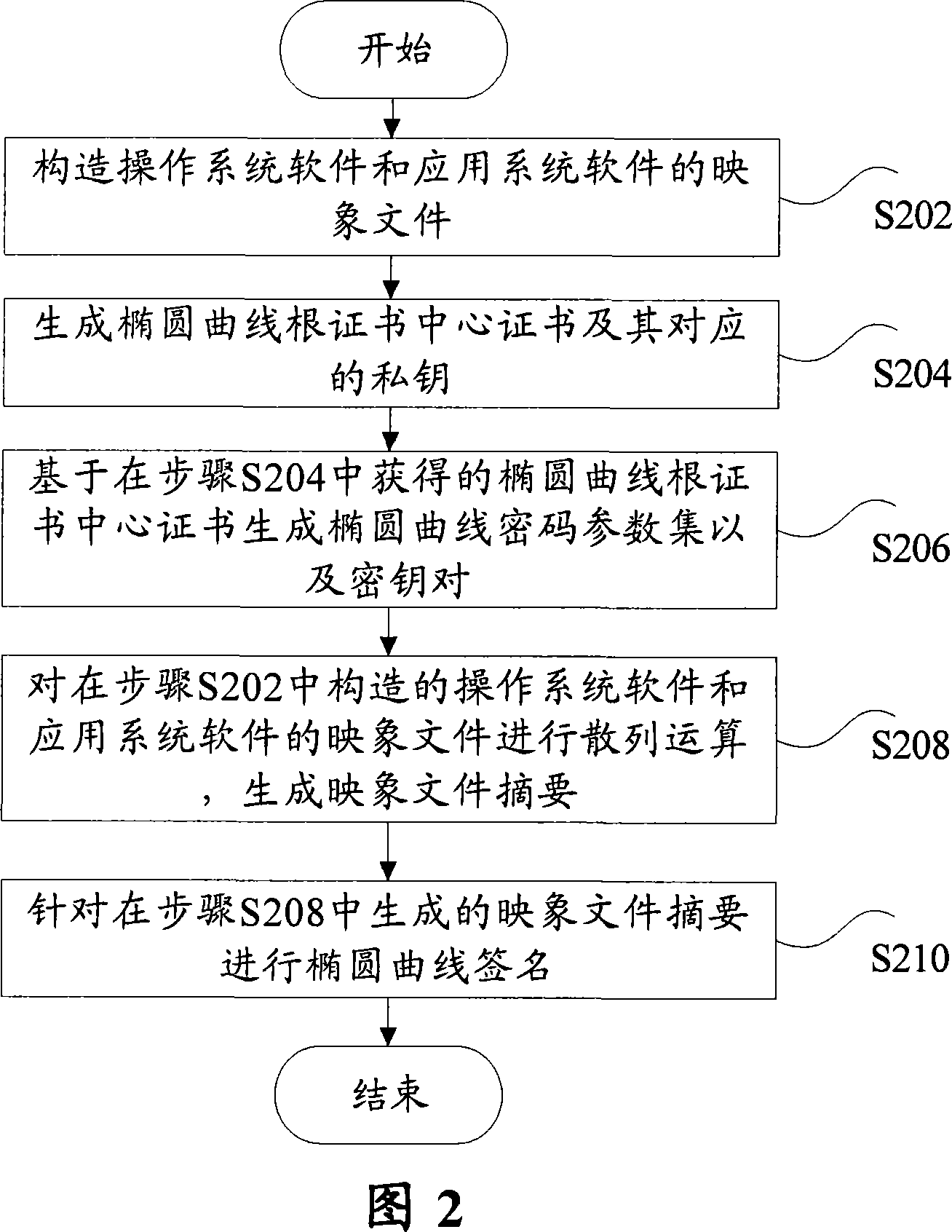
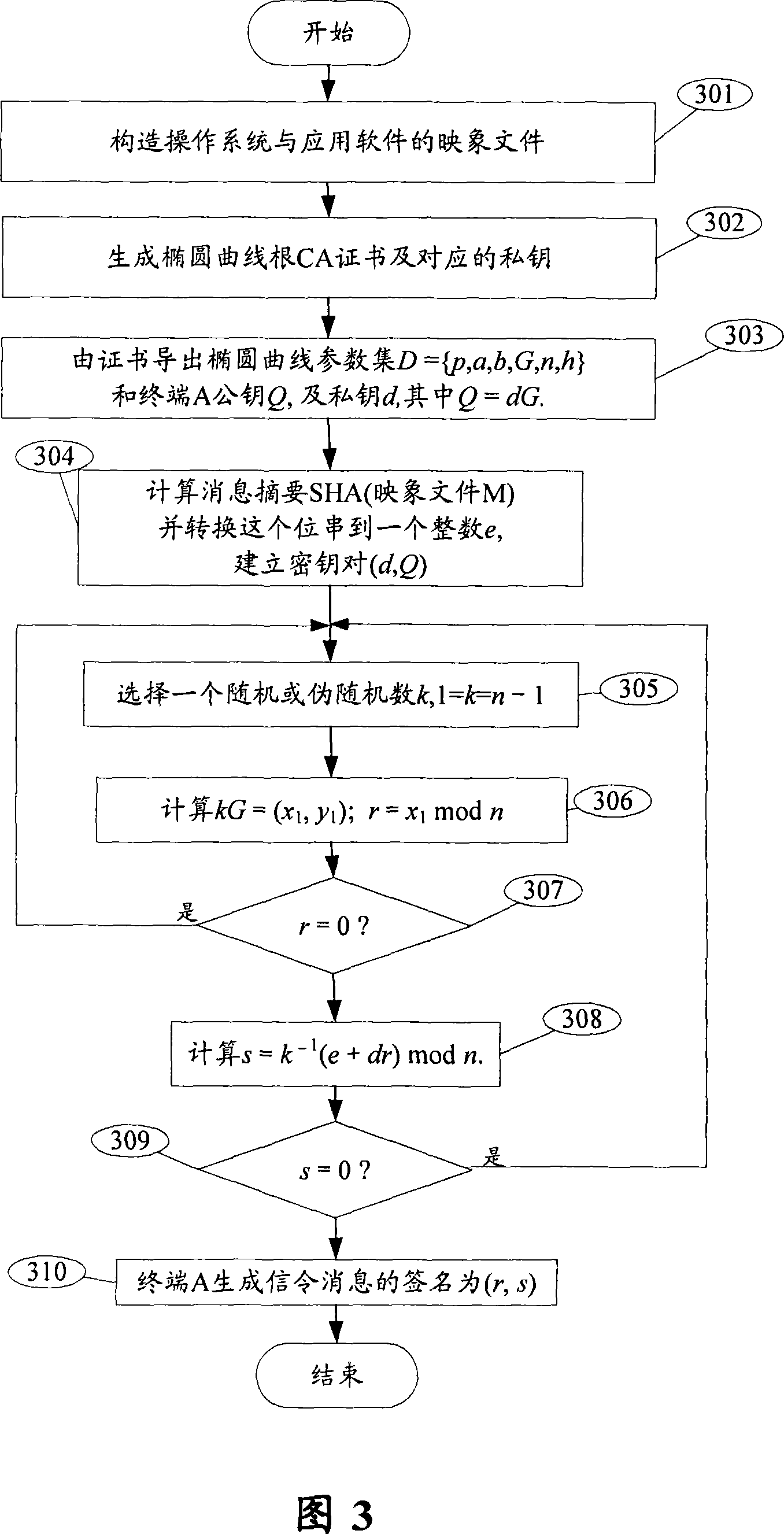
Secure guiding system, method, code signature construction method and authentication method
ActiveCN101034991AEnsure safetyAvoid churnPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationOperational systemCode signing
The invention is a mobile terminal safe booting method, comprising the steps of: 1. safe booting program builds an interrupt vector list in the internal RAM of a safe processing kernel; 2. initializing the internal RAM; 3. the safe processing kernel boots program to build access to the internal RAM and makes hardware initialization, where the hardware comprises flash memory out of safe processing kernel chip; 4. loading and processing configuration data in the flash memory; 5. loading operating system software mapping file and completing authentication on the operating system software mapping file based on ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography); 6. loading application system software mapping file and completing authentication on the application system software mapping file based on ECC; and 7. after the application system software mapping file passes the authentication, transmitting the control to the application system. And the invention also discloses a mobile terminal safe booting system, and a code signing constructing method and a code signing authentication method.
Owner:BEIJING SHENZHOU ANFU TECH CO LTD
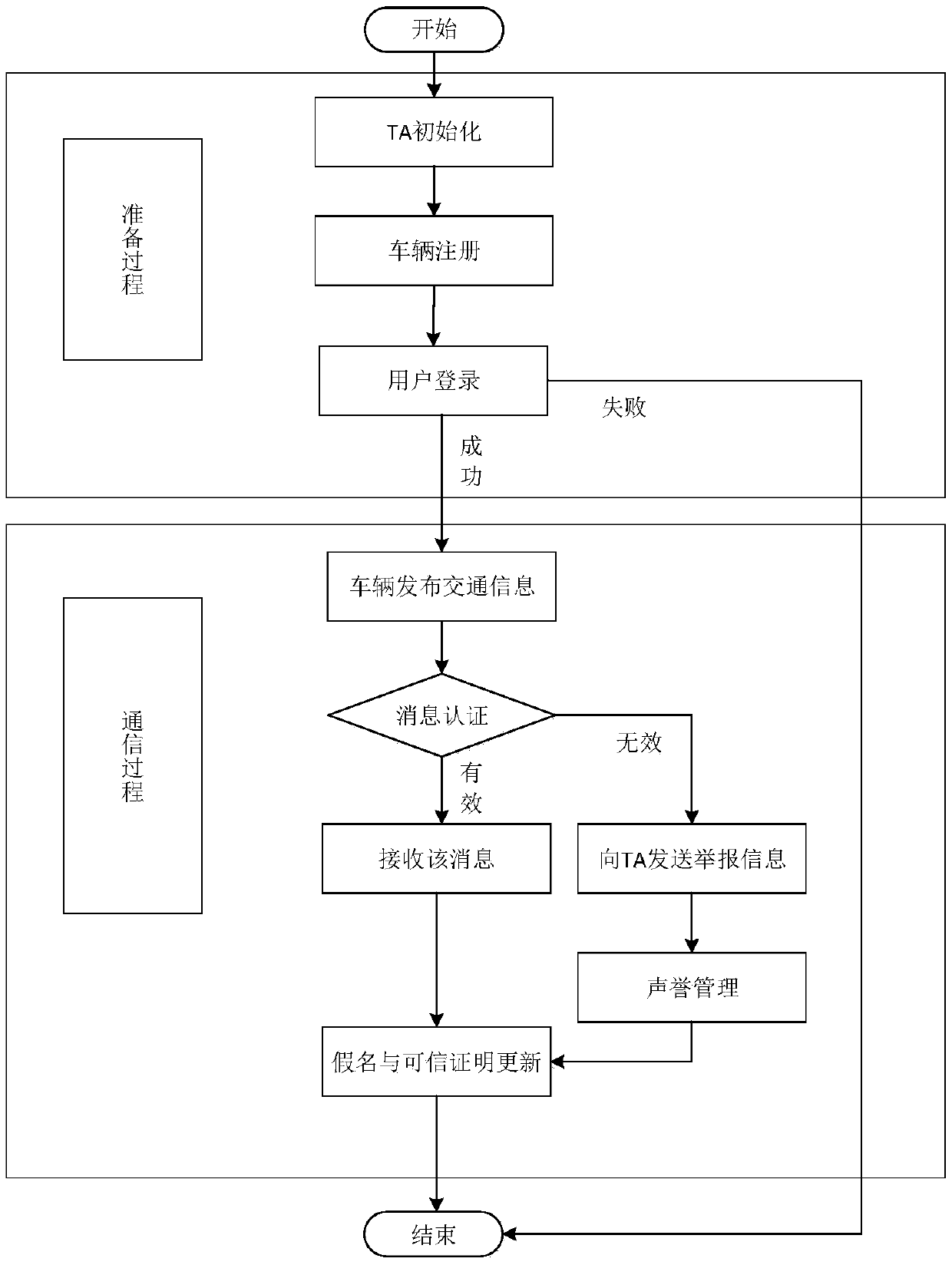
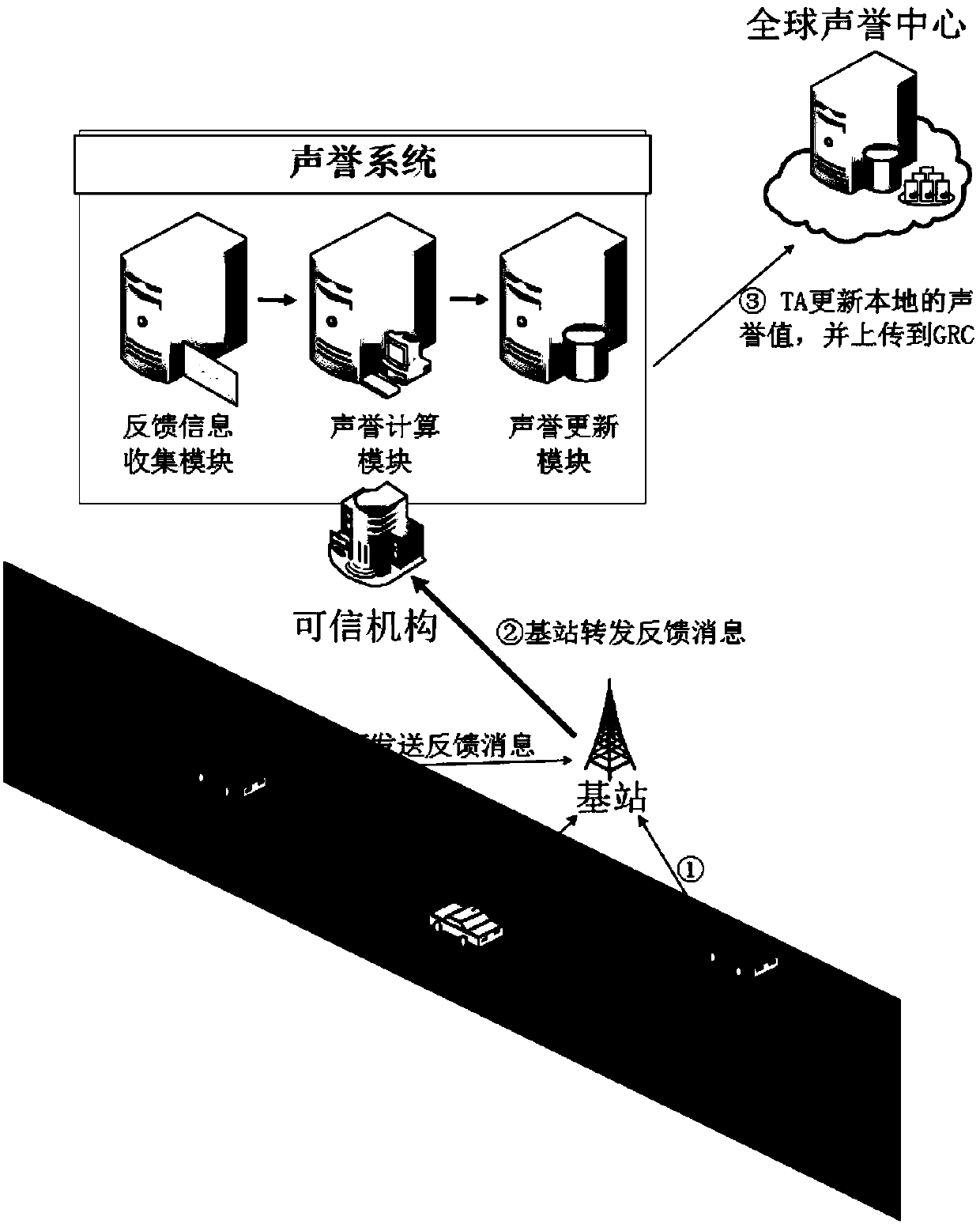
A fast message authentication method for 5G vehicle networking based on reputation system
ActiveCN109005542AImprove reliabilityImprove message authentication efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesMessage authentication codeElliptic curve cryptography
The invention discloses a 5G vehicle networking fast message authentication method based on a reputation system, which comprises the steps of TA initialization, vehicle registration, user login, vehicle publishing traffic information, message authentication, reputation management, updating of pseudonym and trustworthiness certification and the like. The invention uses a reputation system to improve the reliability of messages, because vehicles with reputations below the threshold cannot obtain from the TA the trustworthy proof required to participate in the communication, the 5G vehicle networking communication model in the invention is no longer limited to the mandatory assumption that the roadside base station is completely trusted or has been fully deployed, only the 5G base station isneeded to assist in transmitting the message in the vehicle networking, in addition, the signature part in the invention adopts the operation based on the elliptic curve cryptography and supports thebatch authentication of the message, so the calculation is low in transmission cost and the overall message authentication efficiency is higher.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
End-to-end safety control method for wireless sensor network and internet intercommunication
InactiveCN102546650AReduce energy consumptionEnhanced Access ControlKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEnd to end securityWireless mesh network
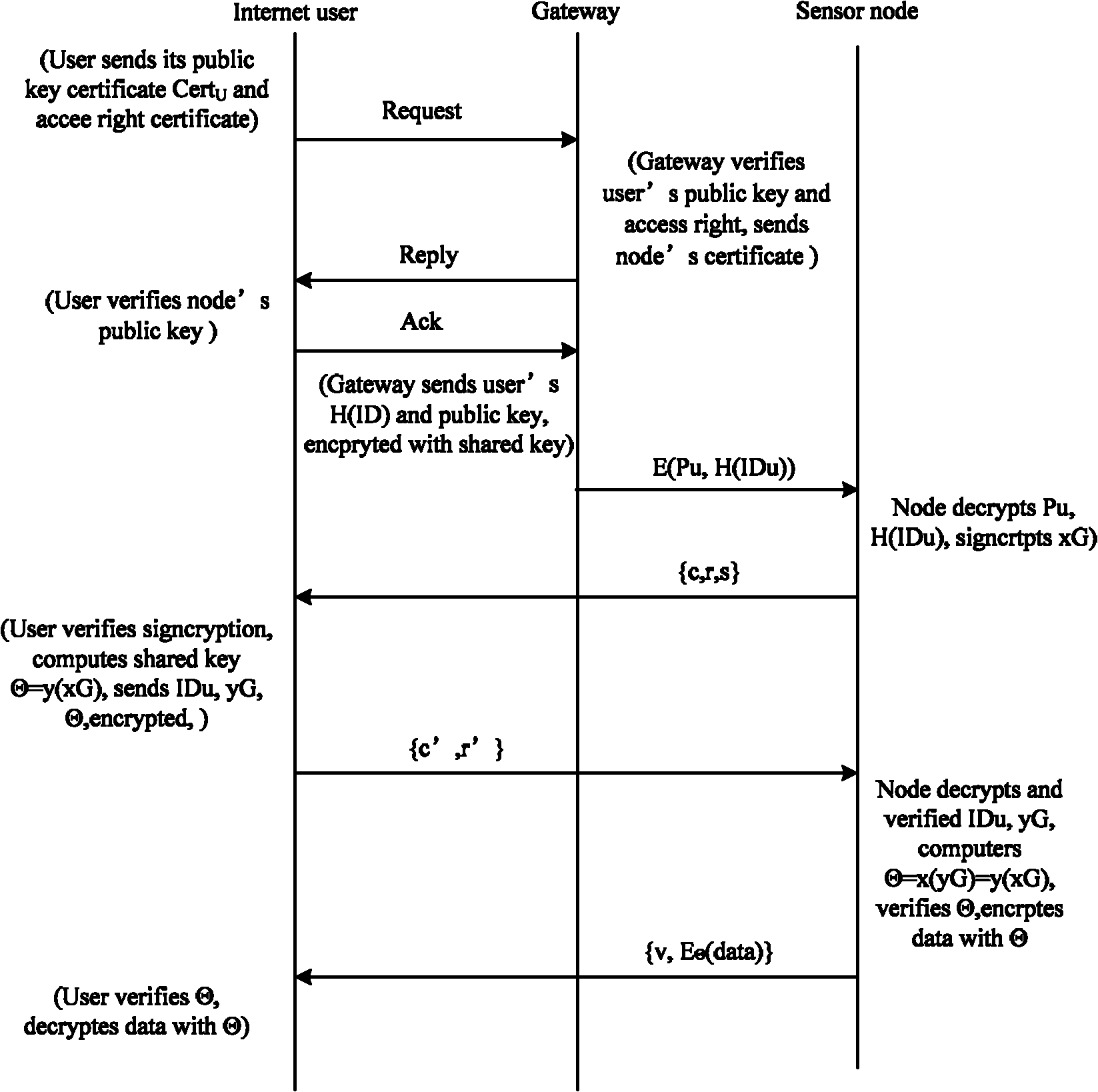
The invention provides an end-to-end safety control method for wireless sensor network and internet intercommunication. Part of the certification and access control work is transferred to the gateway of the wireless sensor network, an asymmetric key negotiation mode based on elliptic-curve signcryption technology is adopted to place unsigncryption operation with large computing amount in an Internent remote terminal, and the symmetric key decryption operation is placed in the sensor nodes. Compared with the improved ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)-based SSL (Security Socket Layer) protocol and the improved TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol based on elliptic-curve identity, the energy consumption of the sensor nodes is effectively reduced, access control and privacy protection are enhanced and Dos (Disk Operating System) attack can be resisted.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Song ci poetry text message hiding technology based on hybrid encryption
InactiveCN106254074AAchieve covert communicationSafety managementEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPublic key for secure communicationCiphertextXML Encryption
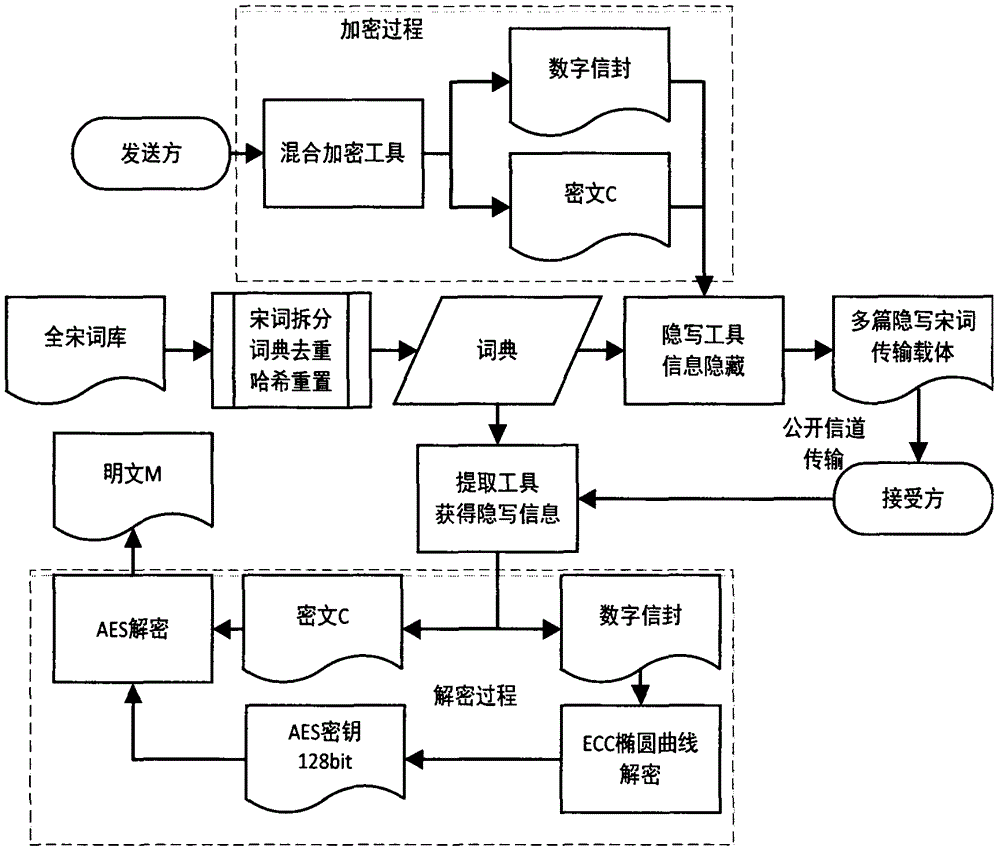
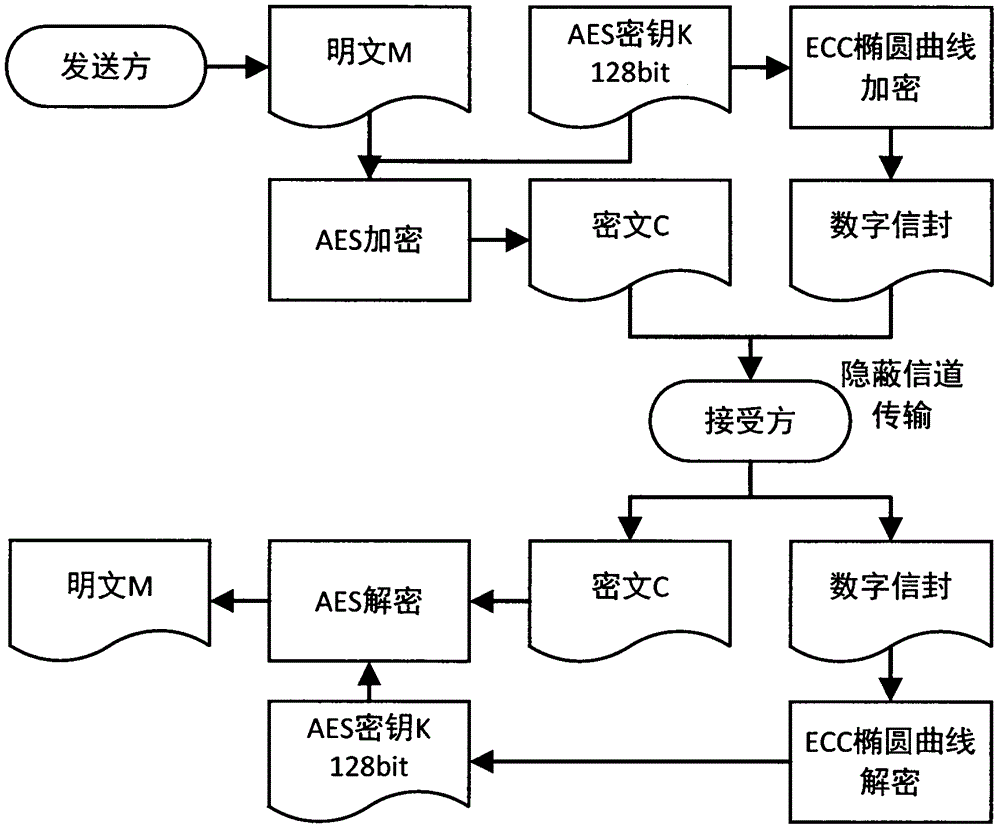
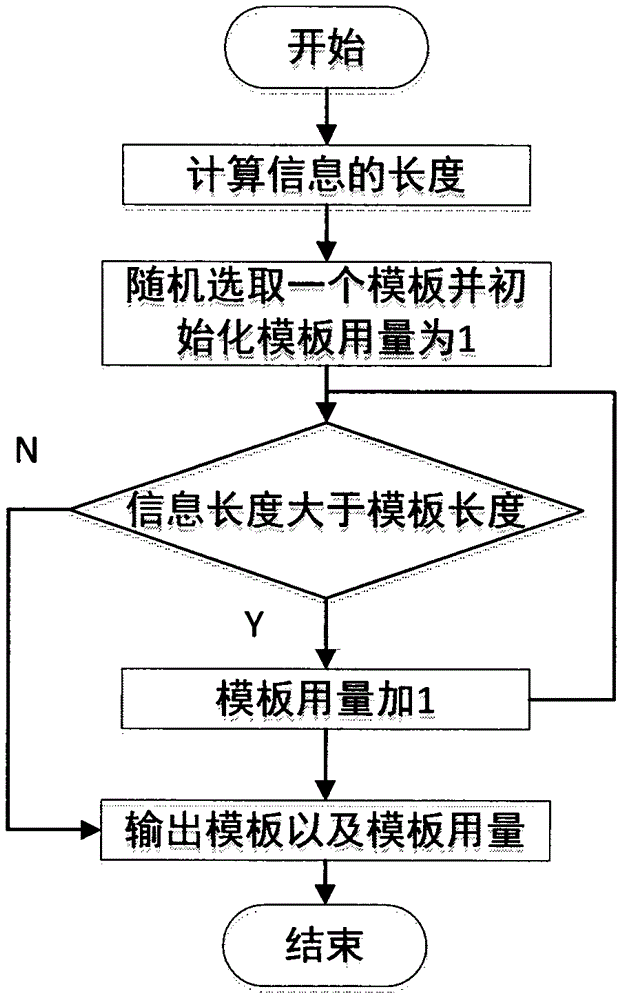
The invention provides a Song ci poetry text message hiding technology based on hybrid encryption, which belongs to the information hiding and data security directions in the field of computers. The Song ci poetry text message hiding technology comprises the steps of encrypting secret information to be hidden by using an advanced encryption standard (AES) in a hybrid manner, encrypting an AES secret key by using an elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) algorithm, passing all information after encryption processing through a 140 tune name template library of the complete collection of Song ci poetry, and hiding the information by means of the system which is composed of templates, a dictionary, a steganographic device and an extractor, wherein the system can generate steganographic Song ci poetry through a random selection or template designation method according to the length of a cryptograph, and the sentence length, grammatical style and intonation sentence pattern of the steganographic Song ci poetry conform to the original Song ci poetry completely, thereby achieving the purposes of obfuscating attackers and ensuring secure transmission of the hidden information. The Song ci poetry text message hiding technology disclosed by the invention can solve the security problem of data transmission in channels, can provide double security measures of information hiding and data encryption, and has high practical application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
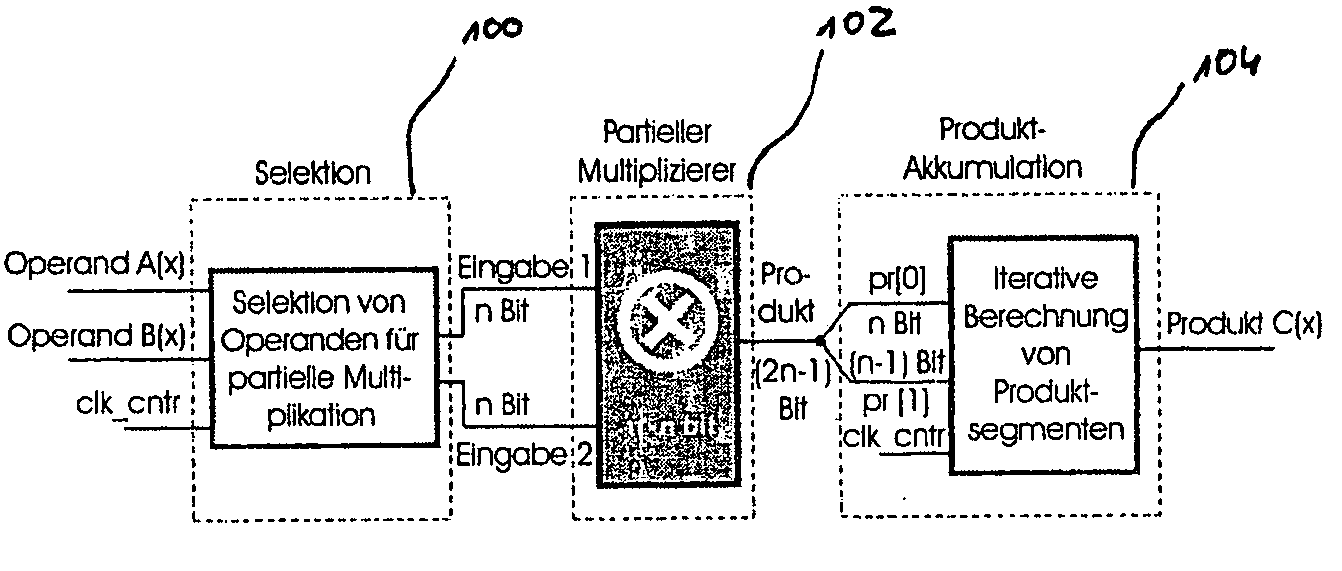
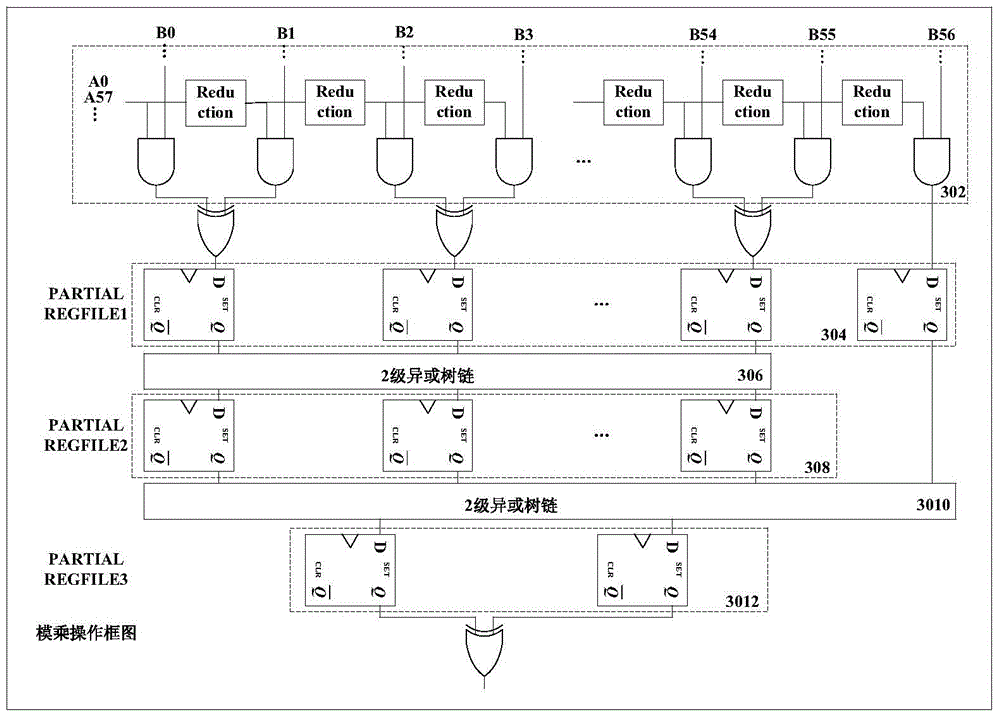
Multiplying unit on finite field GF (2 227) and modular multiplication algorithm
InactiveCN104679474ASave resourcesSimple designDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierProcessor register
The invention discloses a multiplying unit on a finite field GF (2 227) and a modular multiplication algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of the encryption and decryption of data information. The multiplying unit comprises a partial product overlapping module, a first register, a first accumulation module, a second register, a second accumulation module, a third register, a modular addition module and a fourth register. A multiply operation unit 227*57 is reused by the modular multiplication algorithm, a modular multiplication module of which m is equal to 227 applied to an ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) system of which the bit width m is equal to 226 is provided; when m is equal to 226, an AOP (All One Polynomial) type reduction polynomial is generated, and the redundant of an operand is represented by a formula that m is equal to 227, therefore the reduction polynomial can be simplified, and the modular multiplication performance can be improved; furthermore, the registers are inserted into the partial product overlapping part, and a path for modular multiplication can be cut off, therefore the length of a critical path can be reduced, the modular multiplication can be executed in a streamline way, the clock frequency can be improved, the processing speed and data throughout can be improved, and resource saving can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
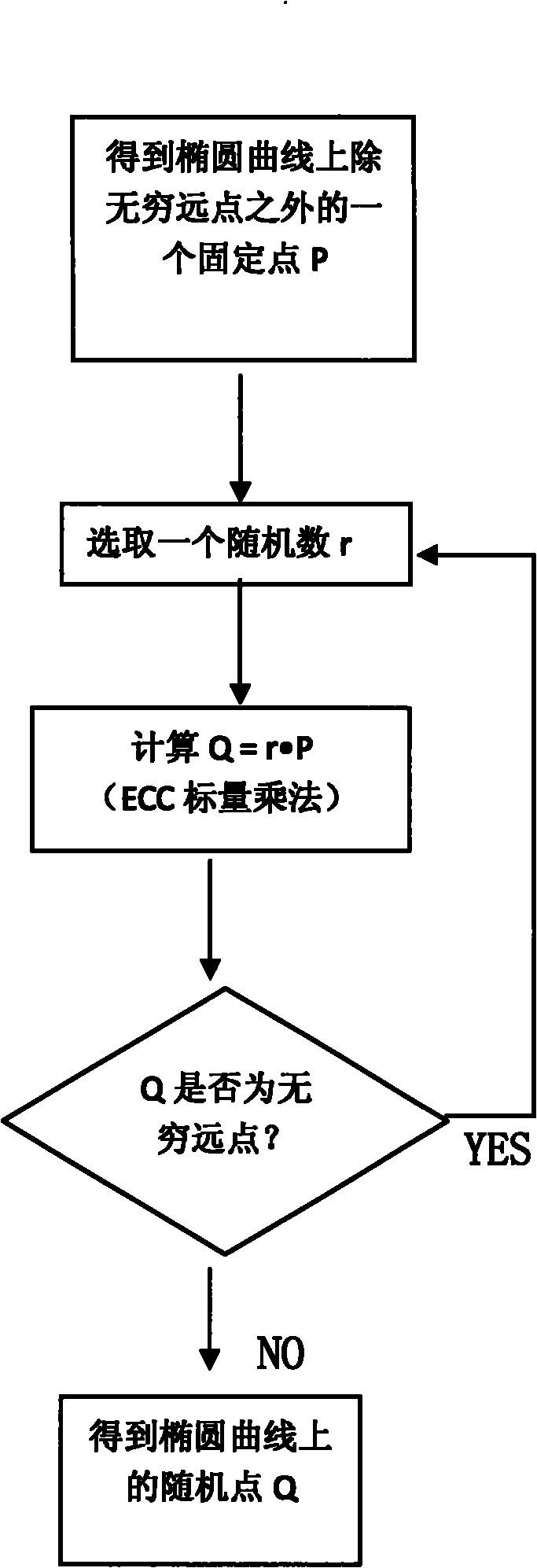
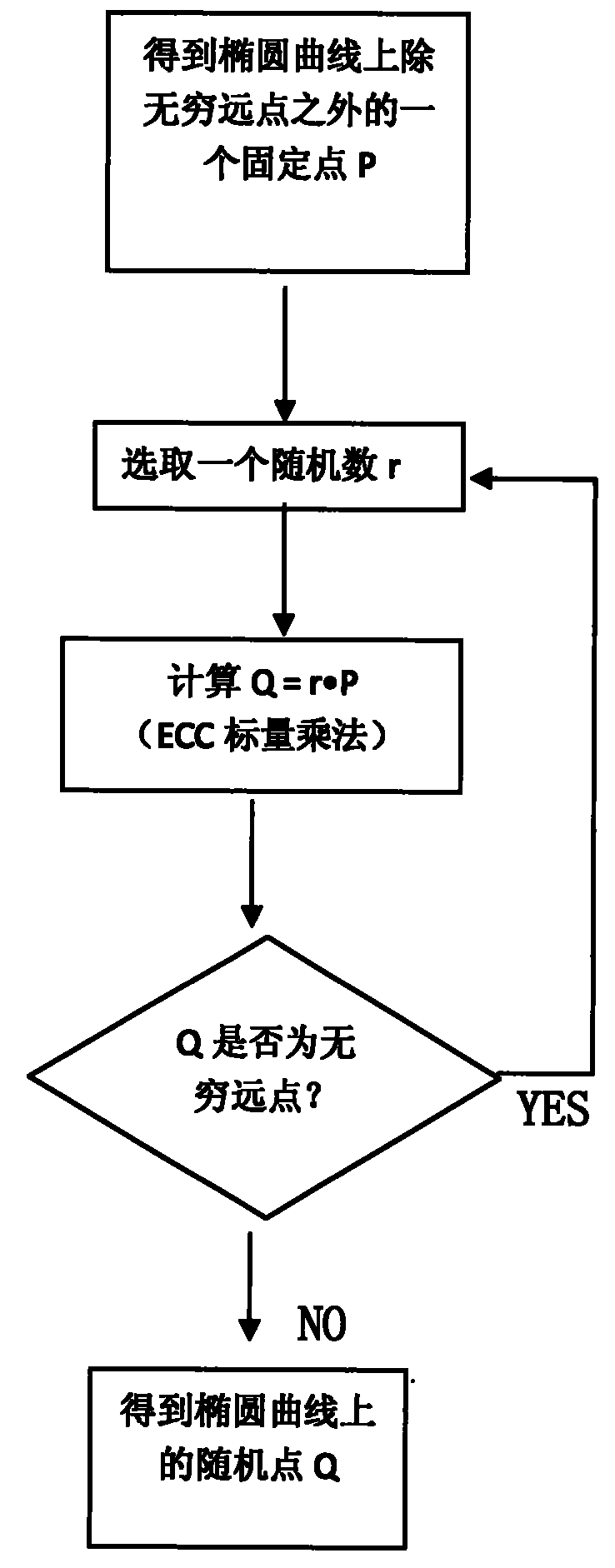
Random point generation method suitable for elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) safety protection
The invention discloses a random point generation method suitable for elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) safety protection. The method comprises the following steps: (1) finding a fixed point P on a certain elliptic curve except an infinite point; (2) selecting a random number r; (3) calculating scalar multiplication of r and P to obtain a calculation result Q; (4) determining whether Q is the infinite point, if yes, returning to the step (2), and otherwise, executing the step (5); and (5) obtaining the random point Q on the certain elliptic curve. The method can obviate the large amount of modular multiplication by obviating the evolution of large numbers or the operation for solving a quadratic equation with one unknown. Therefore, the method provided by the invention can greatly improve the operation speed and reduce the time for generating the random point on the elliptic curve.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Homogeneous Atomic Pattern for Double, Add, and Subtract Operations for Digital Authentication Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography
ActiveUS20160087802A1Efficiently authenticatingReduced side-channel detectabilityUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionCountermeasureElliptic curve cryptography
A method of performing finite field addition and doubling operations in an elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) authentication scheme as a countermeasure to side-channel attack. The addition and doubling operations are executed using atomic patterns that involve the same sequence and number of operation types, so that the noise consumption and electromagnetic emanation profile of circuitry performing the operations is identical regardless of operation. A subtraction operation using such an atomic pattern is also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of performing xz-elliptic curve cryptography for use with network securtiy protocols
InactiveUS20140064491A1Avoid problemsEasy to upgradeKey distribution for secure communicationEllipseLogit
The method of performing XZ-elliptic curve cryptography for use with network security protocols provides a computerized method that allows for the encryption of messages through elliptic polynomial cryptography and, particularly, with the embedding of either a symmetric secret key or a public key in the message bit string. The method of performing XZ-elliptic polynomial cryptography is based on the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem. It is well known that an elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem is a computationally “difficult” or “hard” problem.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
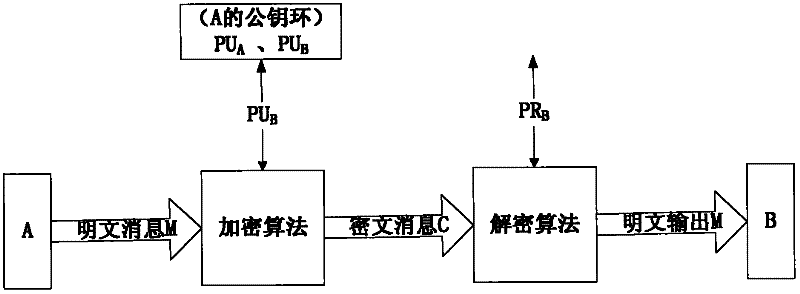
Information transfer system, encryption device, and decryption device using elliptic curve cryptography
InactiveCN1890916AShorten data lengthPublic key for secure communicationCiphertextInformation transfer
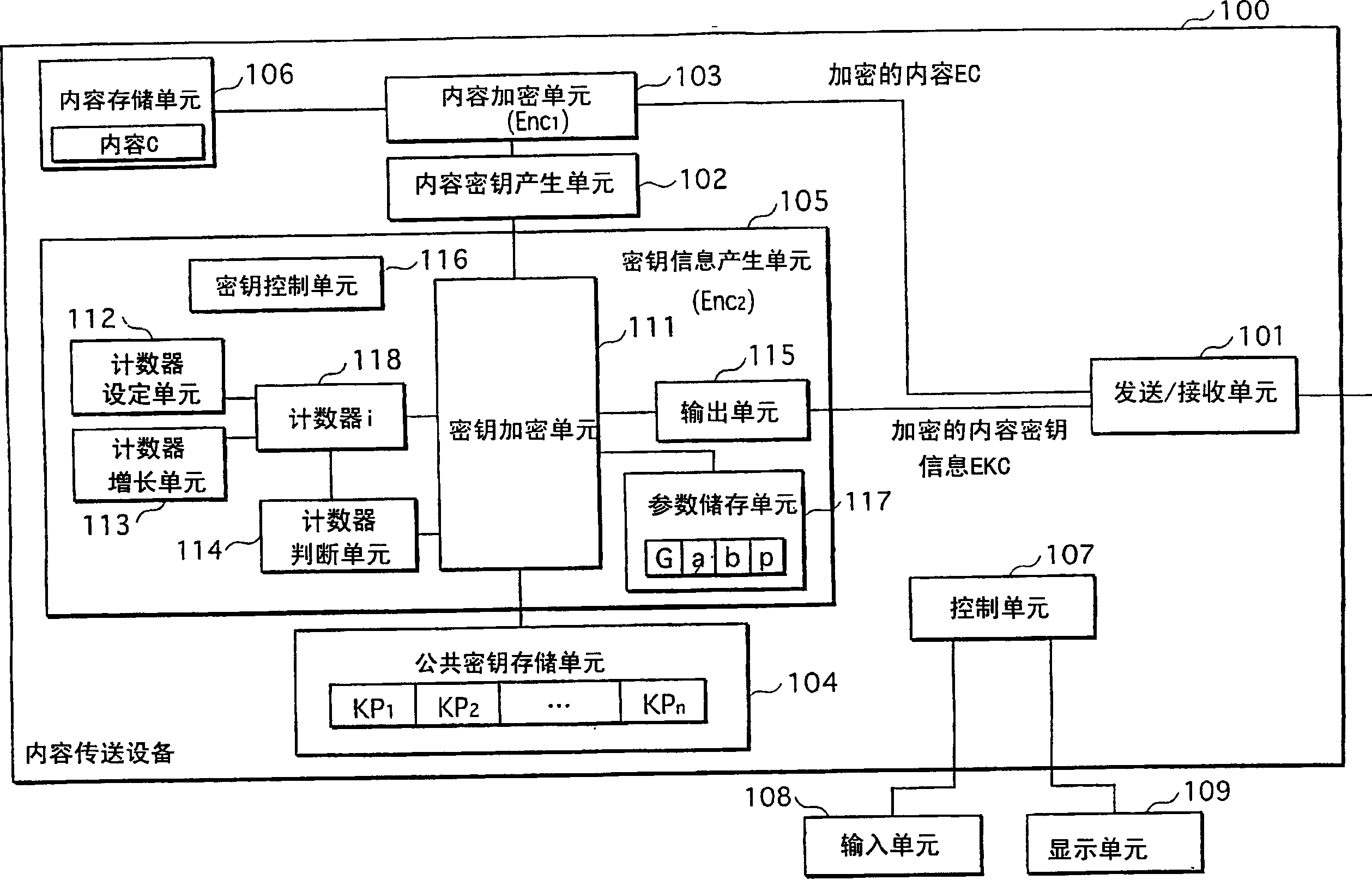
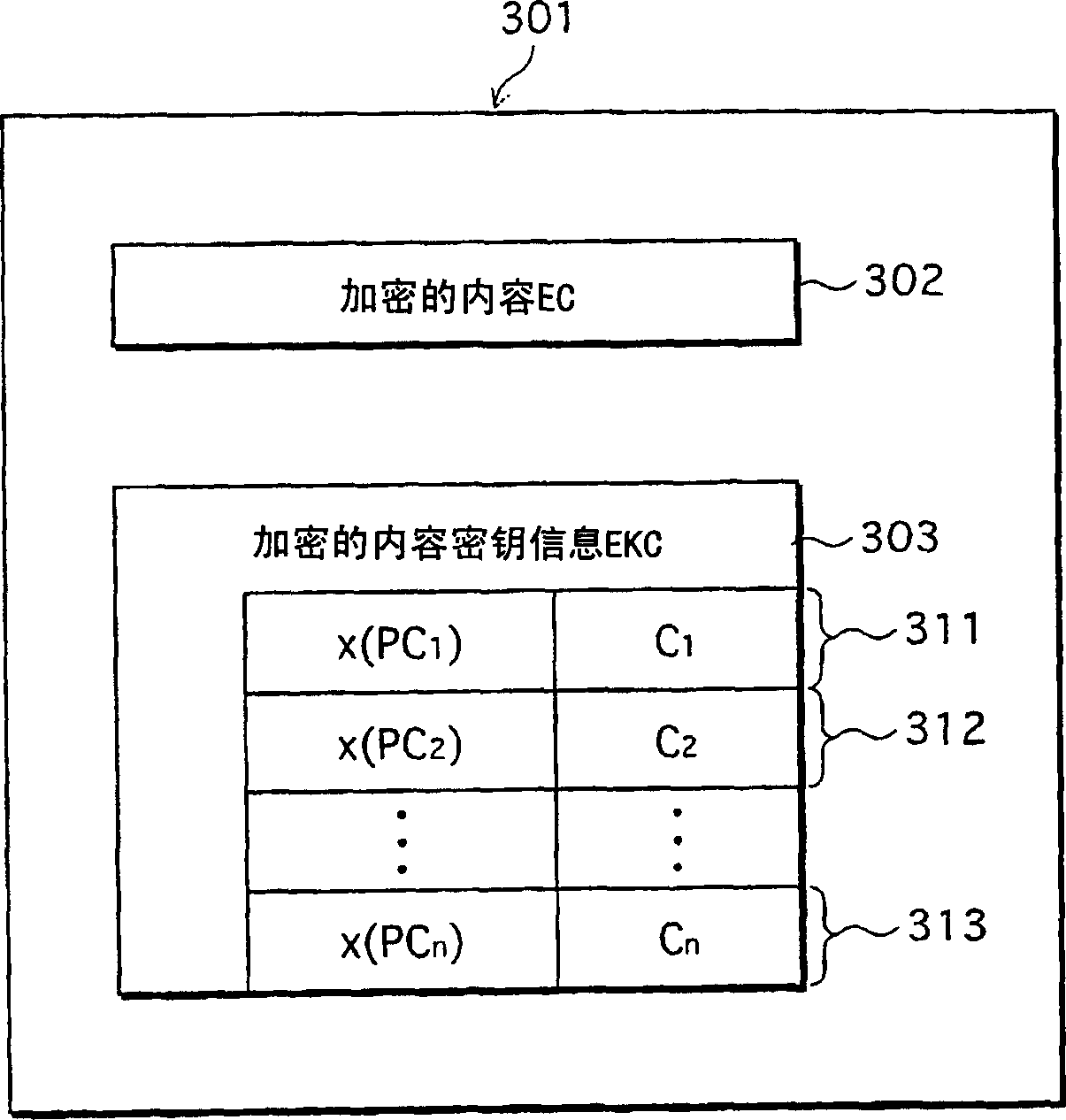
To provide a content delivery system which enables a ciphertext to be reduced in size when using the ElGamal cipher. A content delivery device performs elliptic curve encryption on a content key, generates an encrypted content key that includes an x coordinate of an elliptic curve point obtained by the elliptic curve encryption, and outputs the encrypted content key. A content reception device receives the encrypted content key, and calculates a y coordinate of the elliptic curve point using the x coordinate included in the encrypted content key. The content reception device then performs elliptic curve decryption using the elliptic curve point and other information included in the encrypted content key, to generate a decrypted content key.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
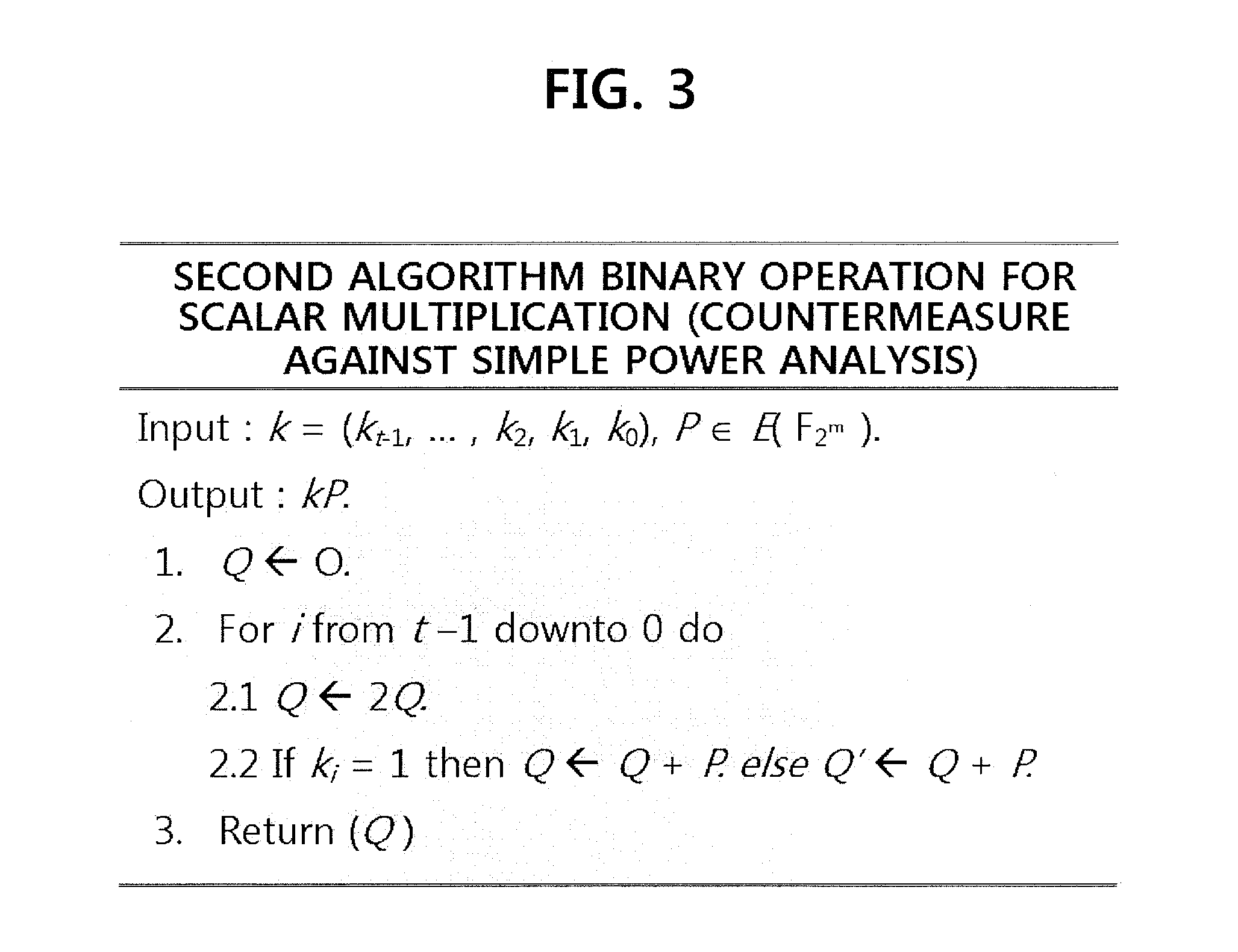
Method for elliptic curve cryptography with countermeasures against simple power analysis and fault injection analysis and system thereof
InactiveUS20140098951A1Easy to analyzeSecret communicationCryptographic attack countermeasuresPower analysisCountermeasure
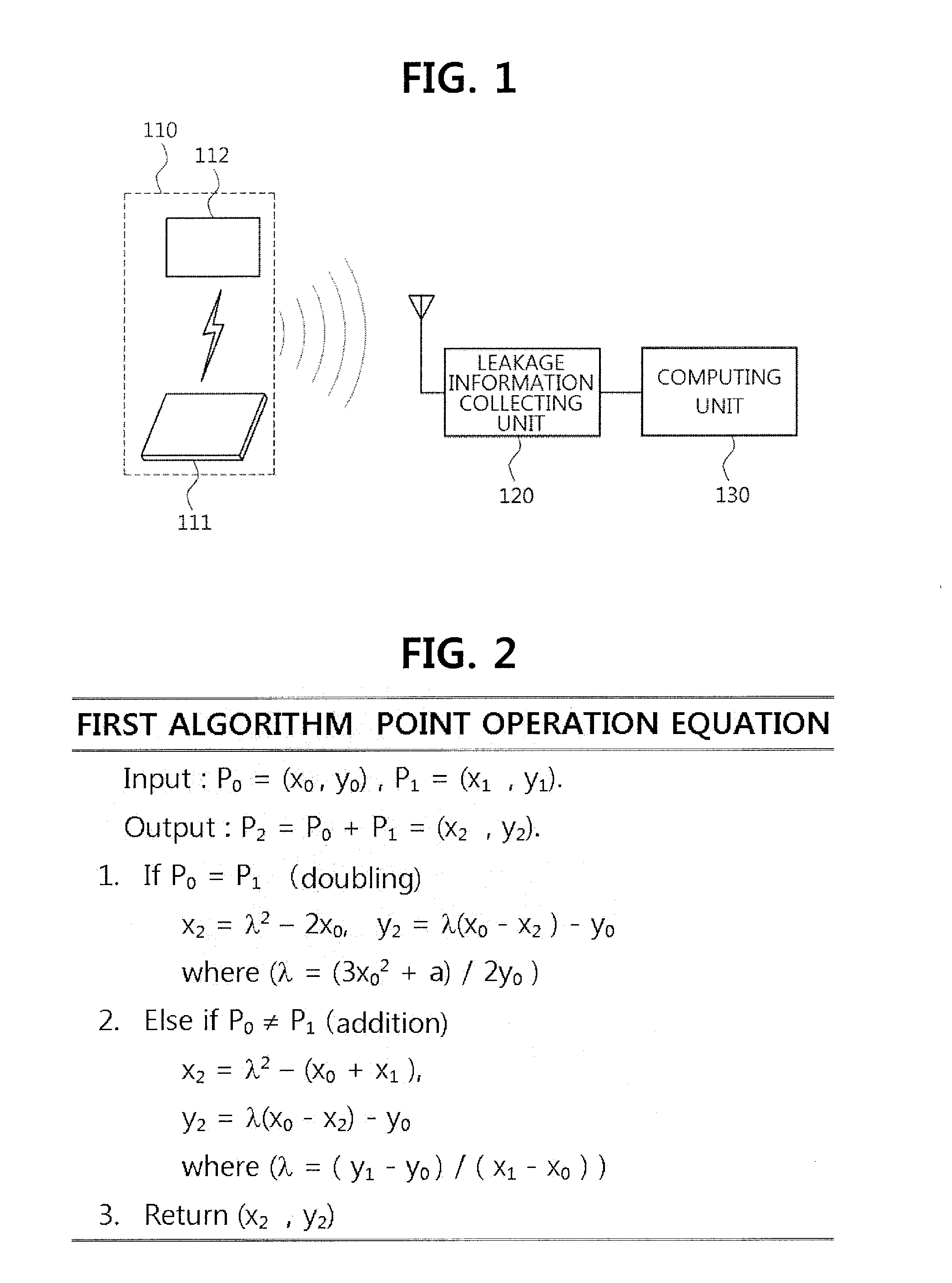
There are provided a method for elliptic curve cryptography with countermeasures against simple power analysis and fault injection analysis, and a system thereof. According to an aspect, there is provided a method for elliptic curve cryptography, in which an elliptic curve point operation is performed to generate an elliptic curve code, including: receiving a first point and a second point on the elliptic curve, wherein the first point is P0=(x0, y0) and the second point is P1=(x1, y1); and performing doubling if the first point is the same as the second point, and performing addition if the first point is different from the second point, to thereby obtain a third point, wherein the third point is P2=P0+P1=(x2, y2). Accordingly, it is possible to provide countermeasures against a side channel analysis attack.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
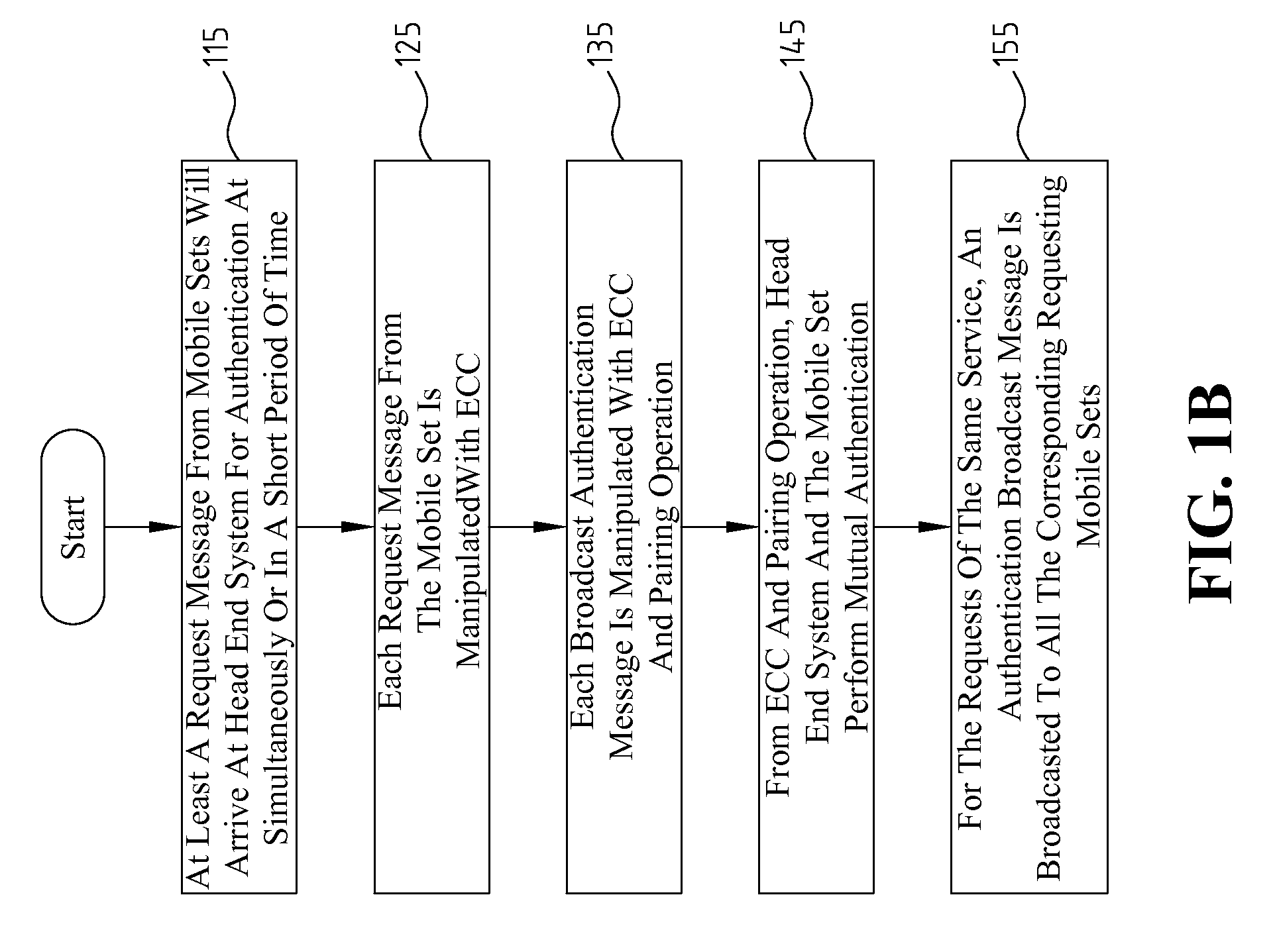
Authentication Method Employing Elliptic Curve Cryptography
ActiveUS20090180612A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareEnd system
Disclosed is an authentication method employing elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), applicable to a mobile broadcast TV system having one or more head end systems, at least a transmitter, and at least a mobile set. The authentication method comprises at least one request message from mobile sets simultaneously or in a short period of time arriving at a head end system for authentication; manipulating each broadcast authentication message by ECC; manipulating each service request message by ECC and pairing operation; performing a mutual authentication between the head end system and mobile sets by ECC and pairing operation; and broadcasting one group of authentication messages to all the mobile sets of many requests arrived at the head end system simultaneously or in a short period of time for the same service.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
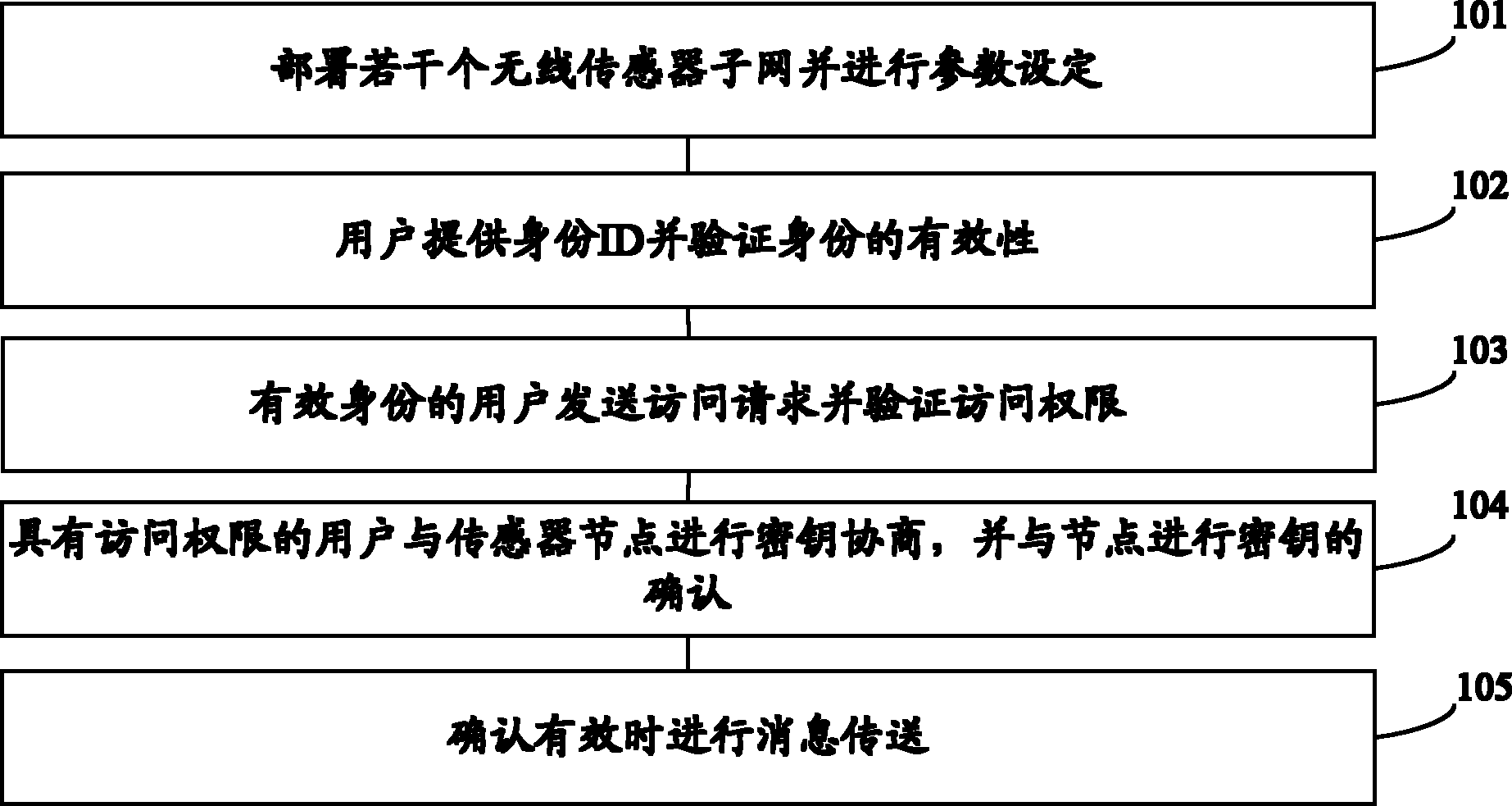
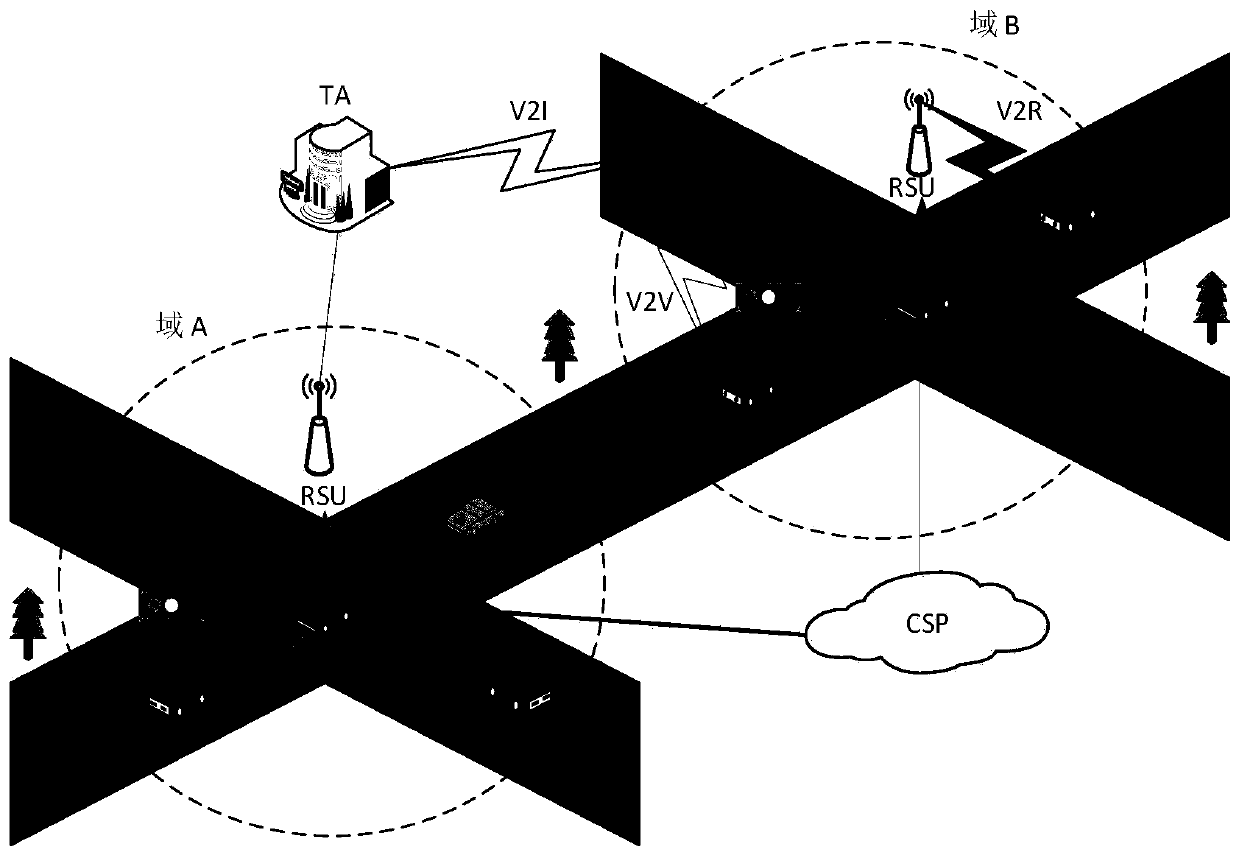
Internet of Vehicles security data sharing method based on edge computing
InactiveCN110099367ALow costSupport access controlPublic key for secure communicationParticular environment based servicesTrusted authorityCiphertext
The invention discloses an Internet of Vehicles safety data sharing method based on edge computing, which comprises the following steps: (1) initializing all entities of the Internet of Vehicles, including generating system parameters by a trusted authority (TA), and issuing necessary parameter information to each vehicle; and (2) safe sharing of data between vehicles, wherein the step comprises four processes of enabling a vehicle to release request information, enabling ECV to process and forward the request information, enabling a data release vehicle to encrypt the data and enabling a datarequest vehicle to decrypt the data. According to the attribute strategy encryption and decryption part, operation based on elliptic curve cryptography is used, so that the calculation and transmission expenditure is relatively low; through an attribute encryption algorithm based on a ciphertext strategy, the data sender can control the accessibility of the data by defining an attribute access strategy, thereby facilitating the sharing of the data among vehicles in different domains.
Owner:河南工学院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com