Patents
Literature
727 results about "Fixation point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical Definition of fixation point. : the point in the visual field that is fixated by the two eyes in normal vision and for each eye is the point that directly stimulates the fovea of the retina.
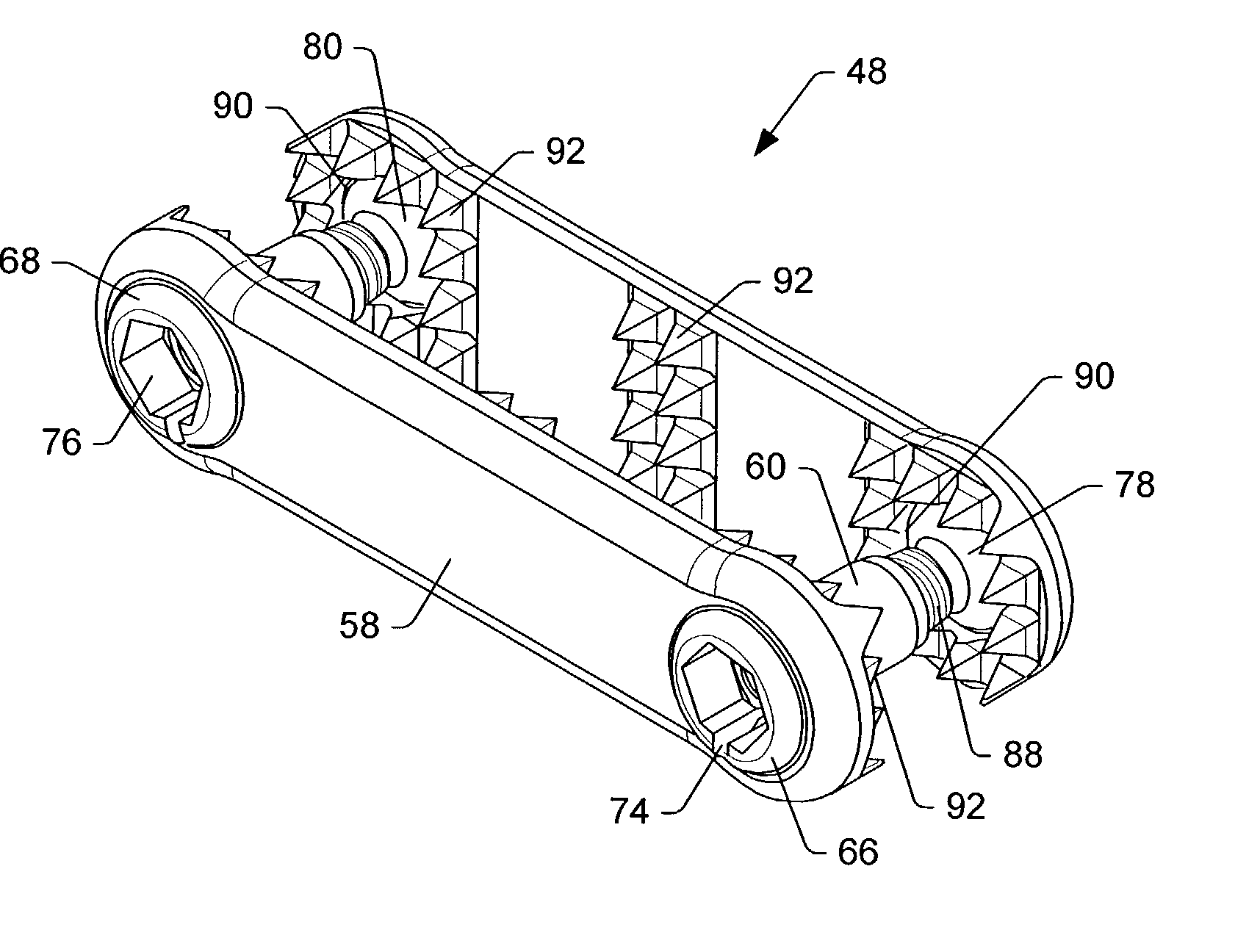
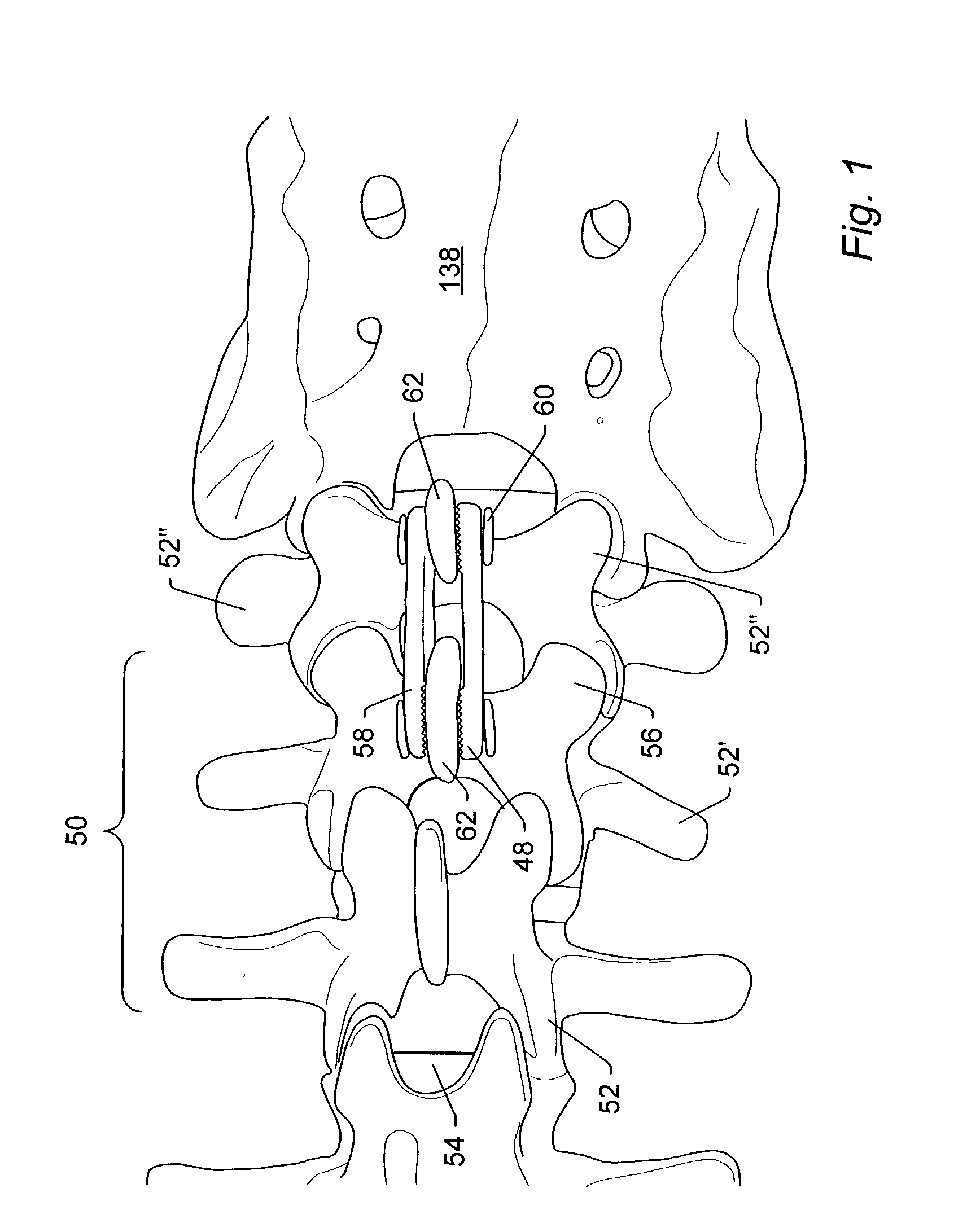
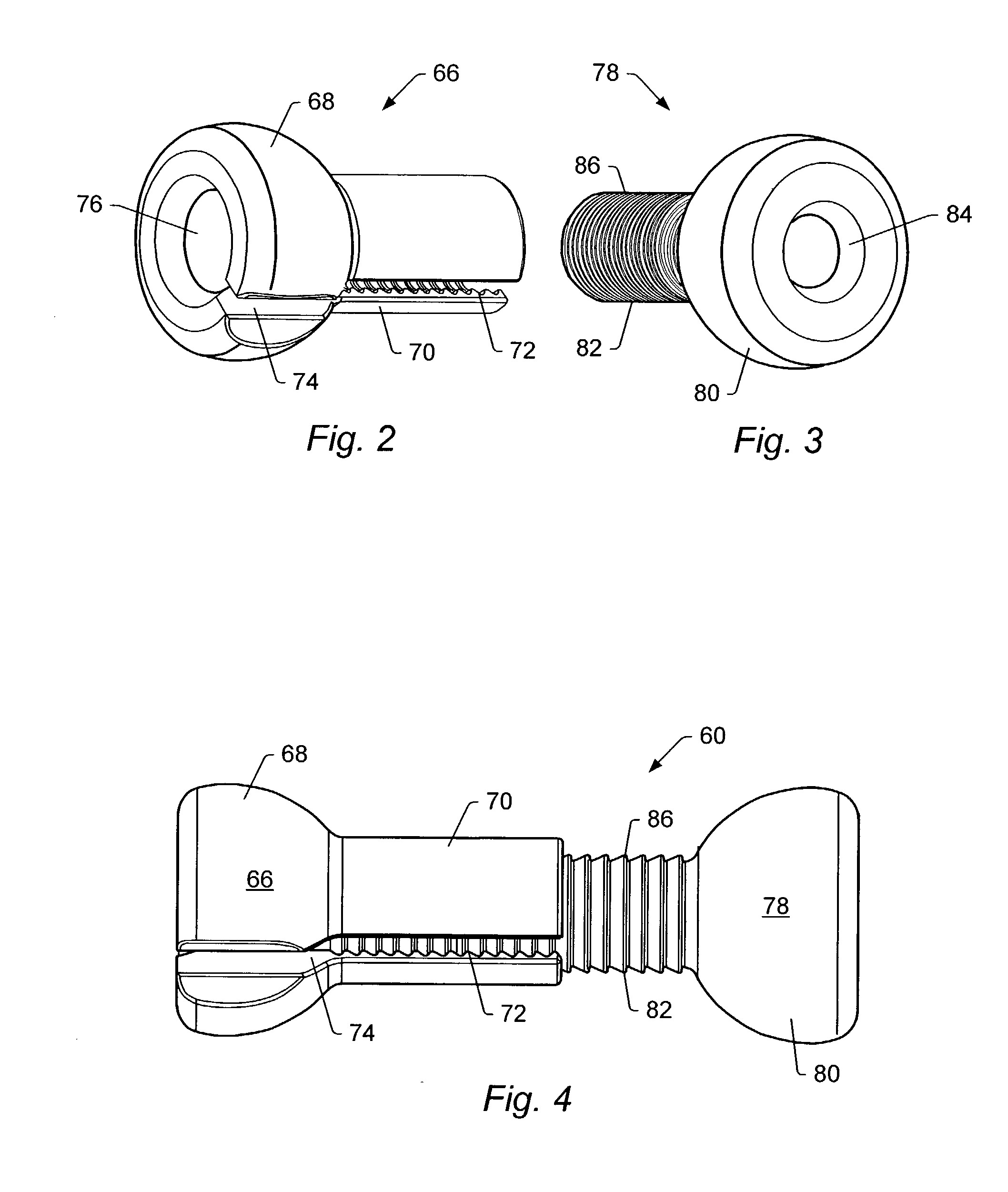
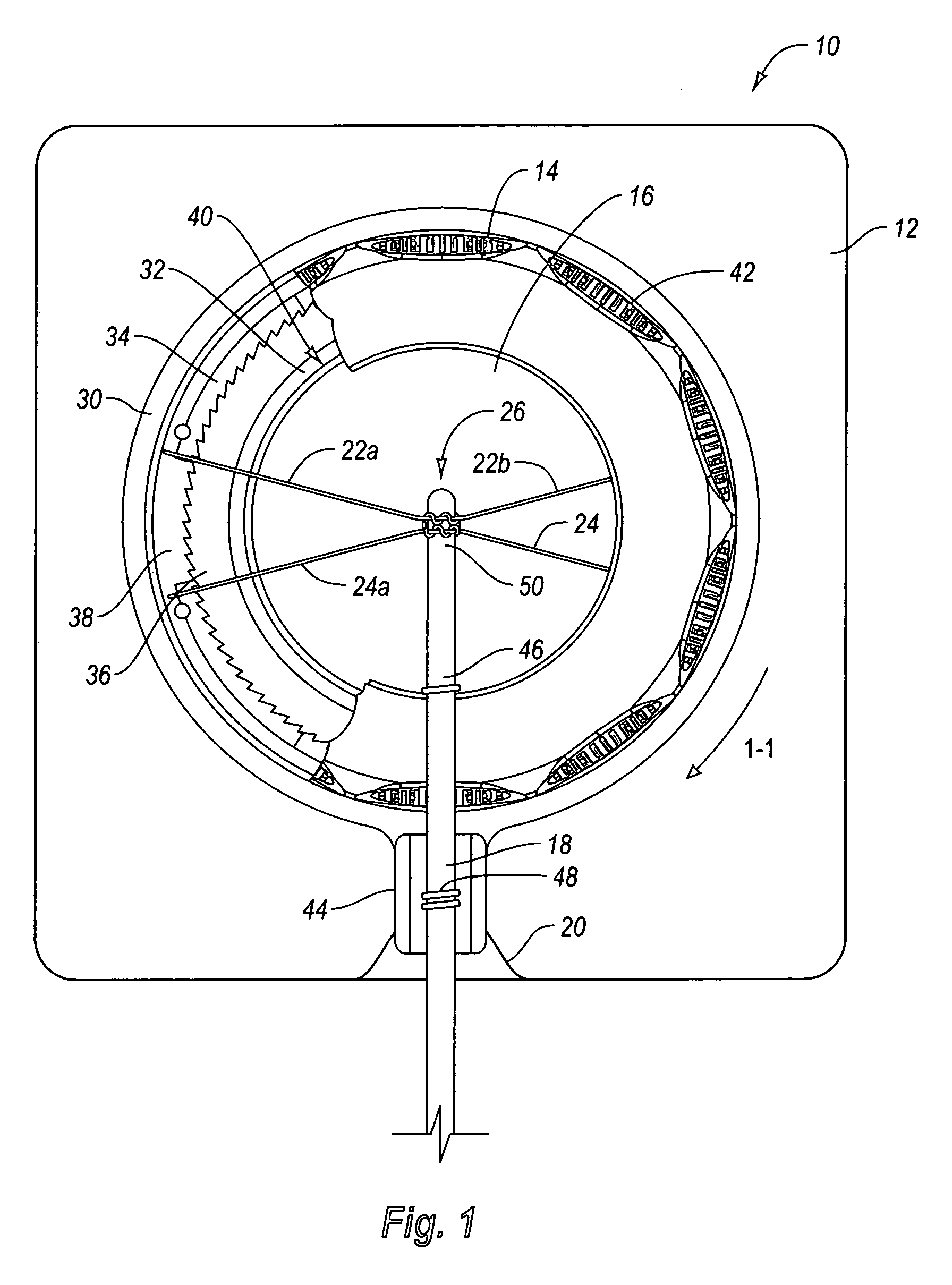
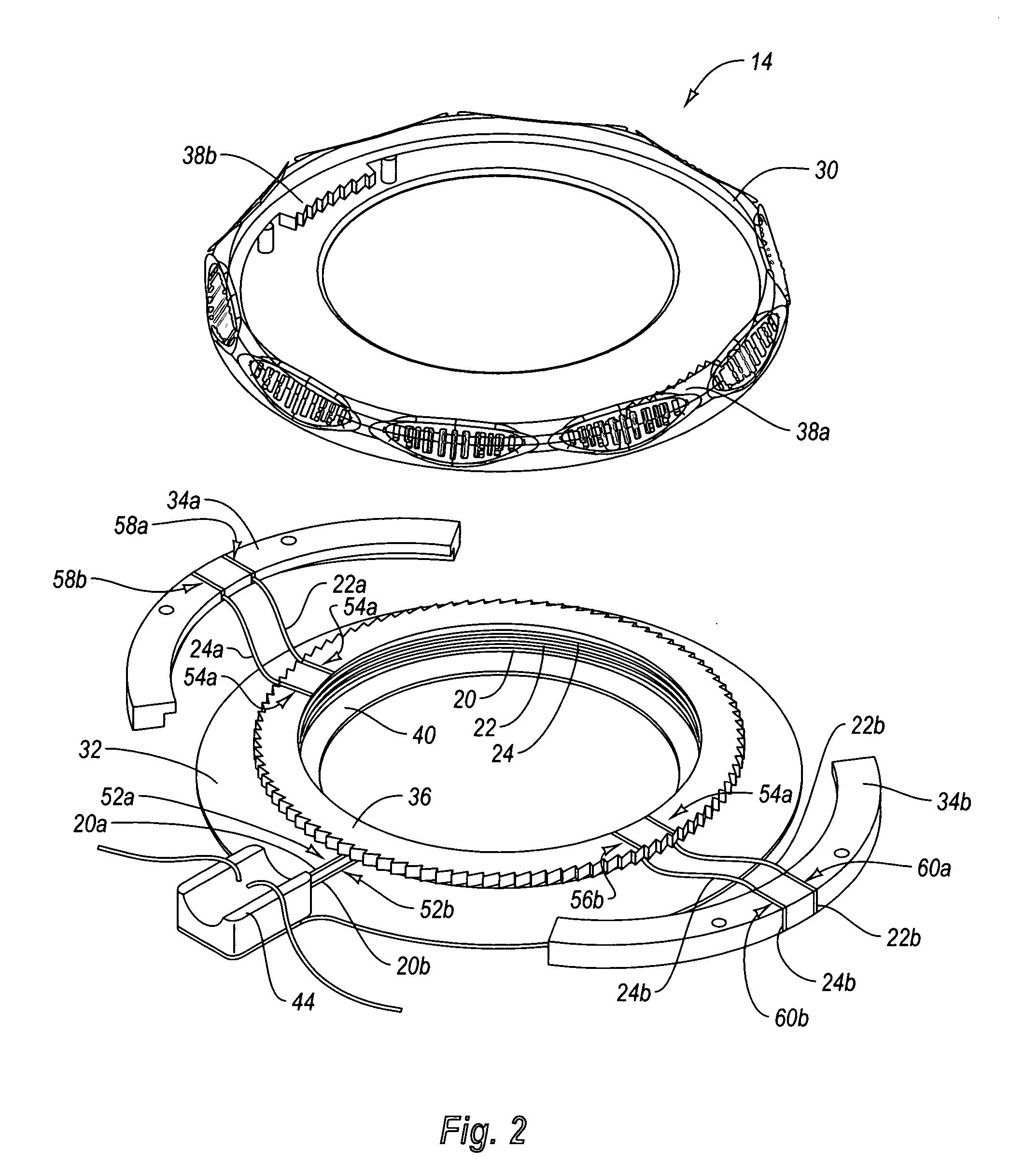
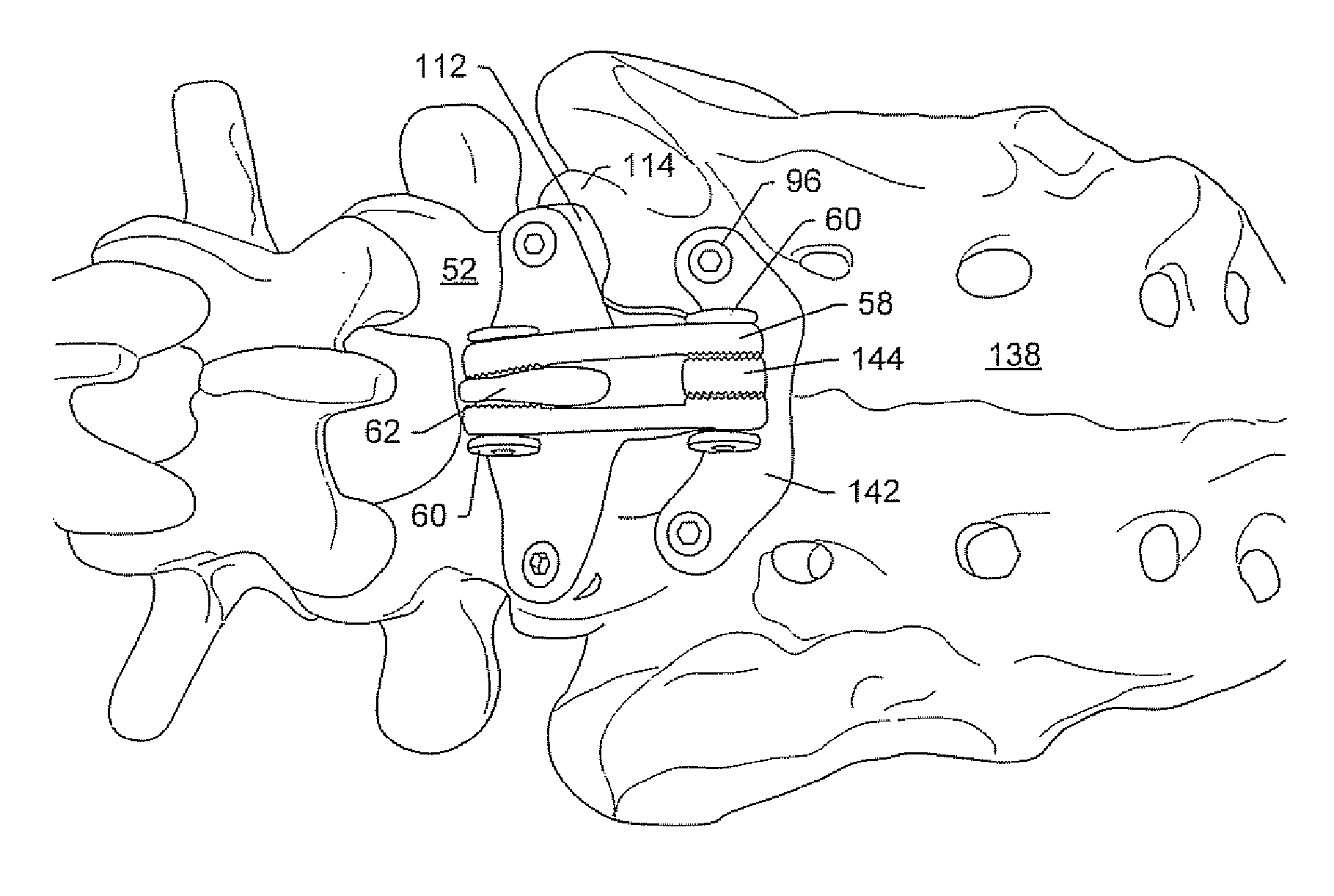
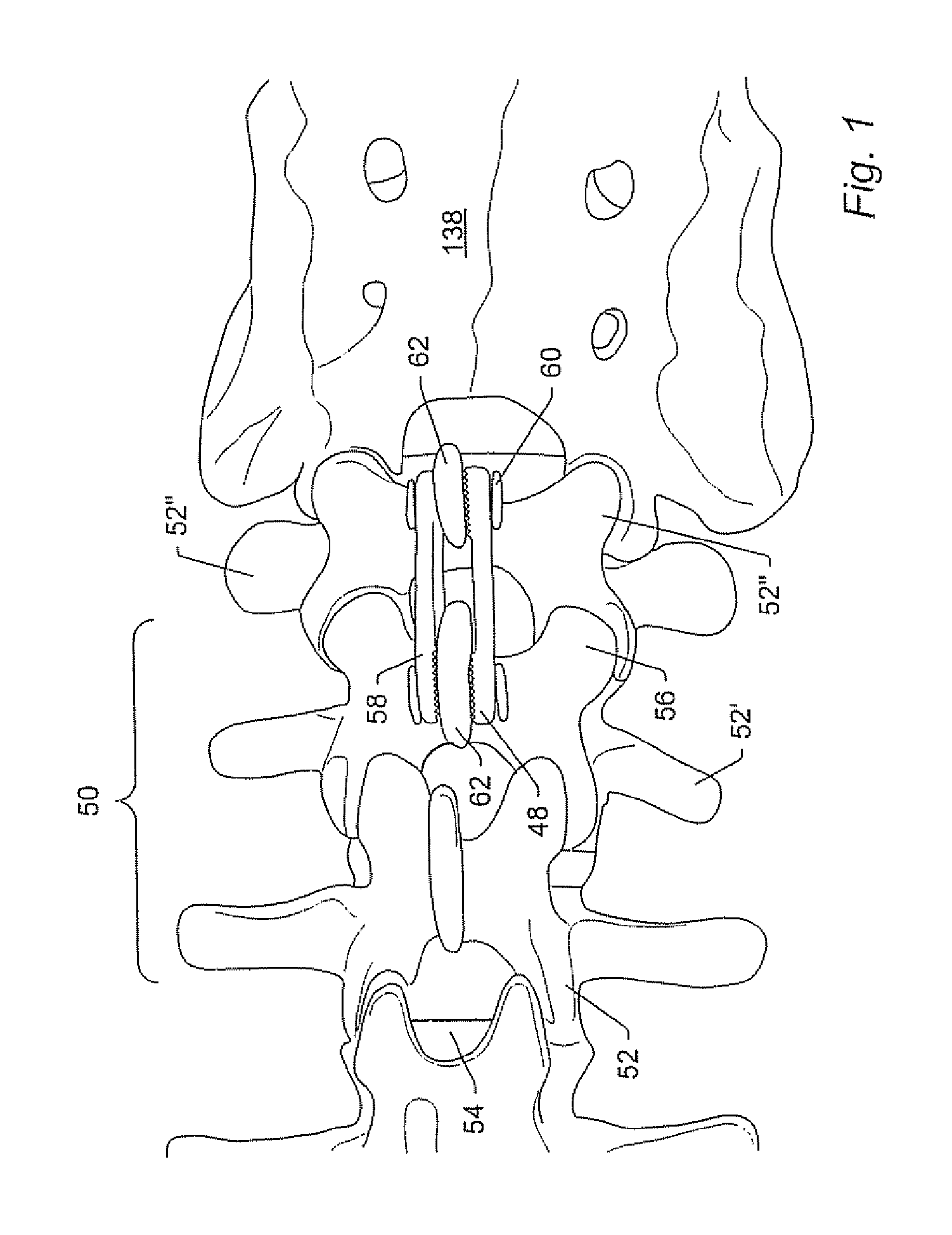
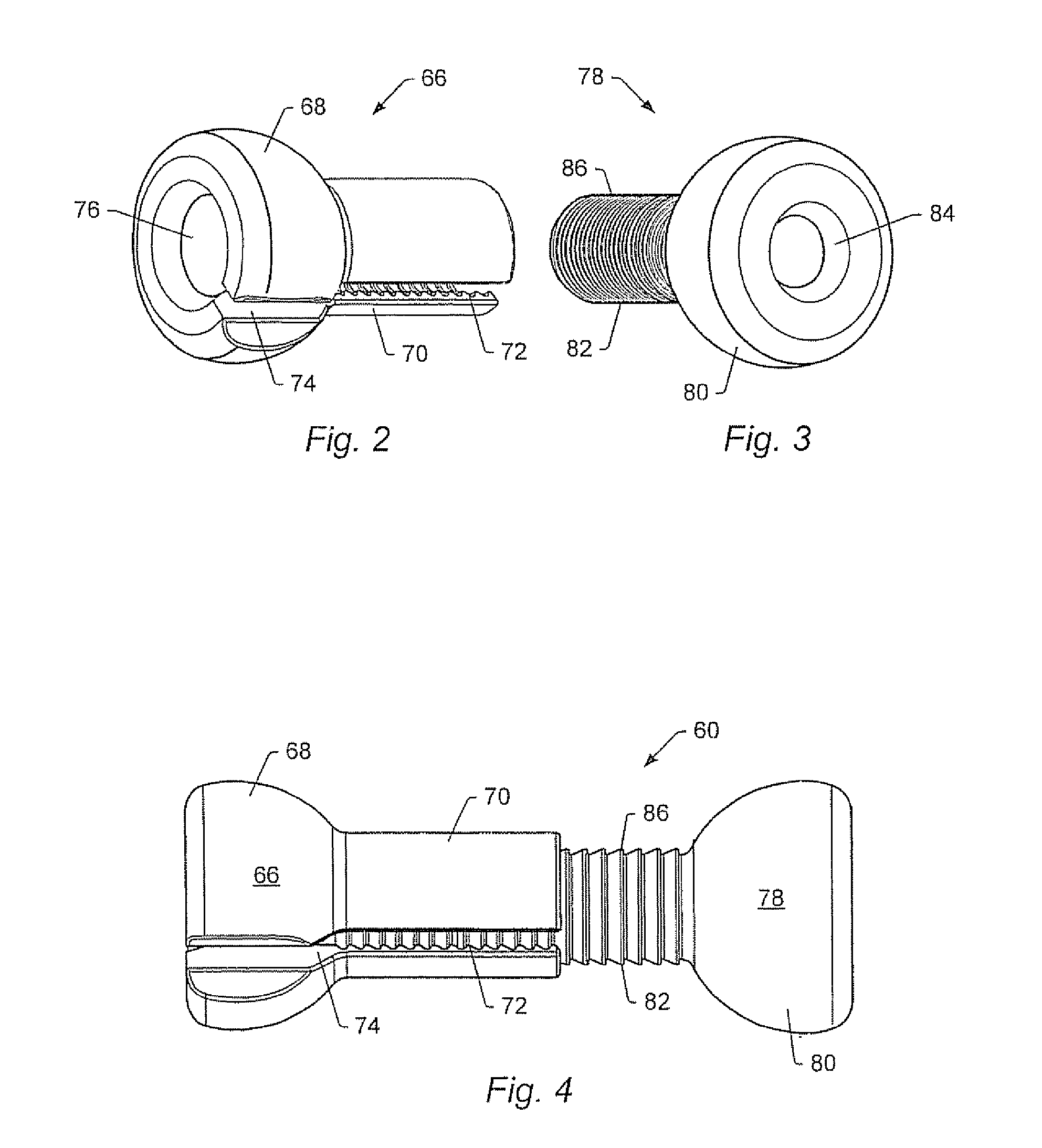
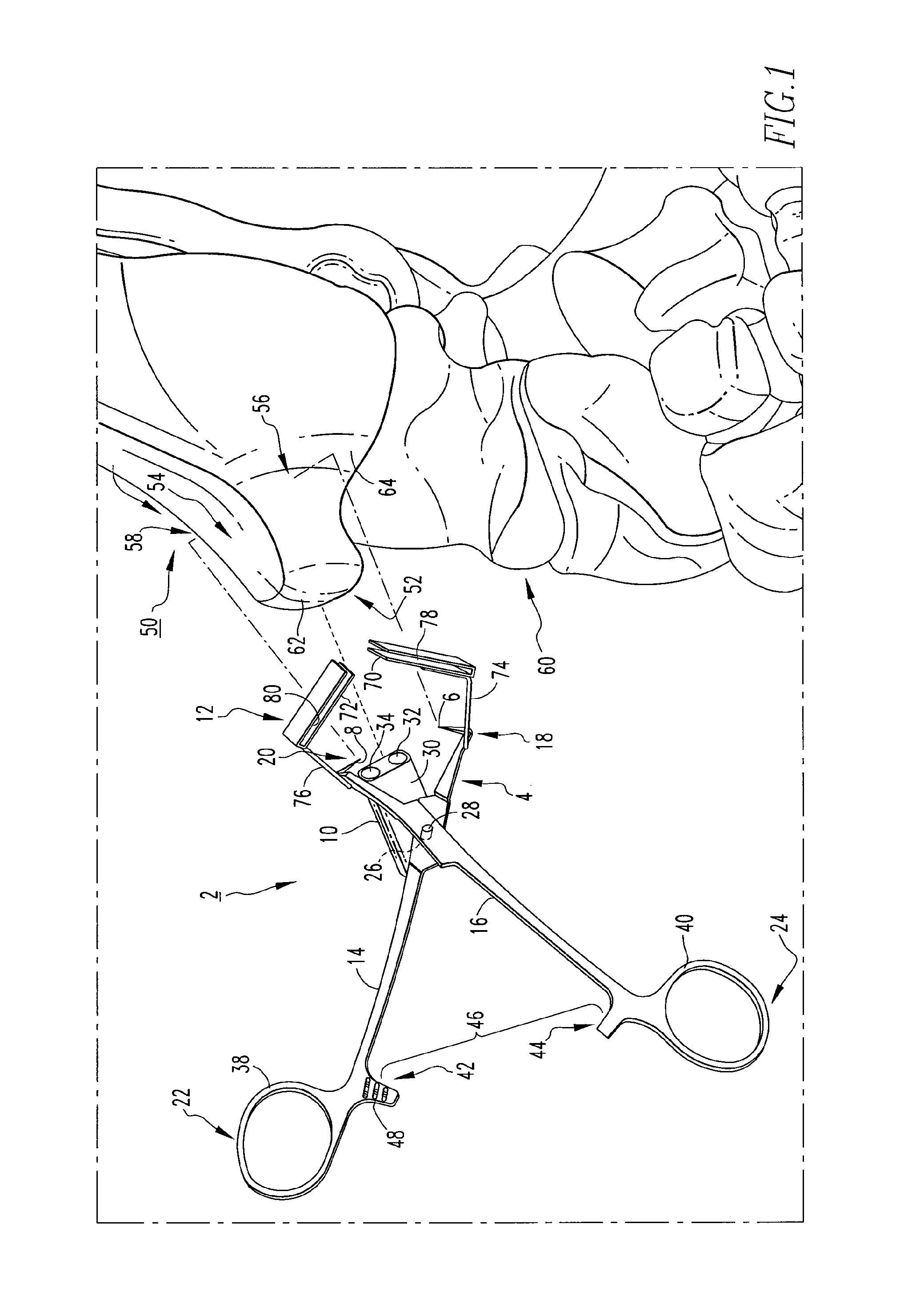
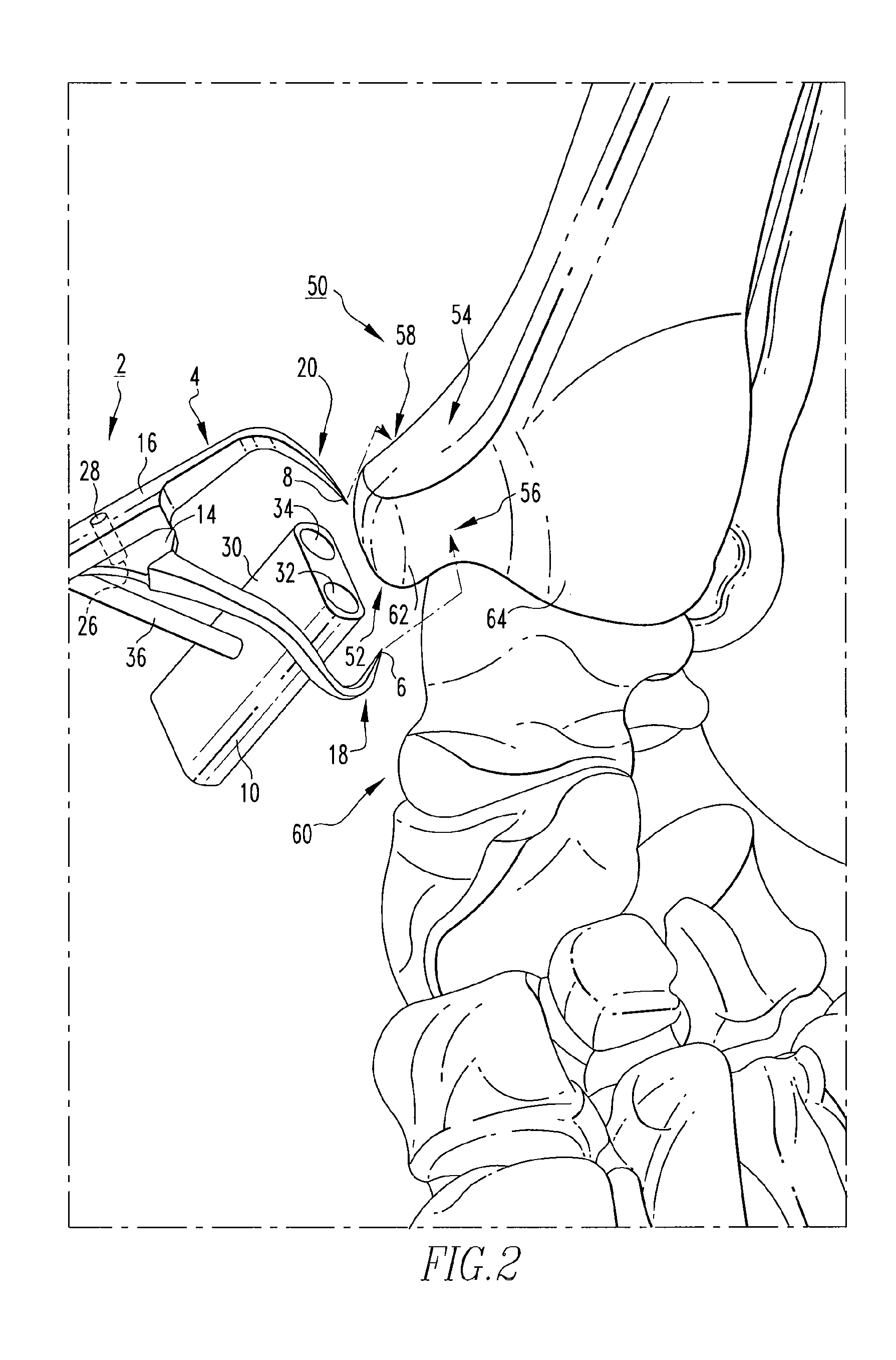
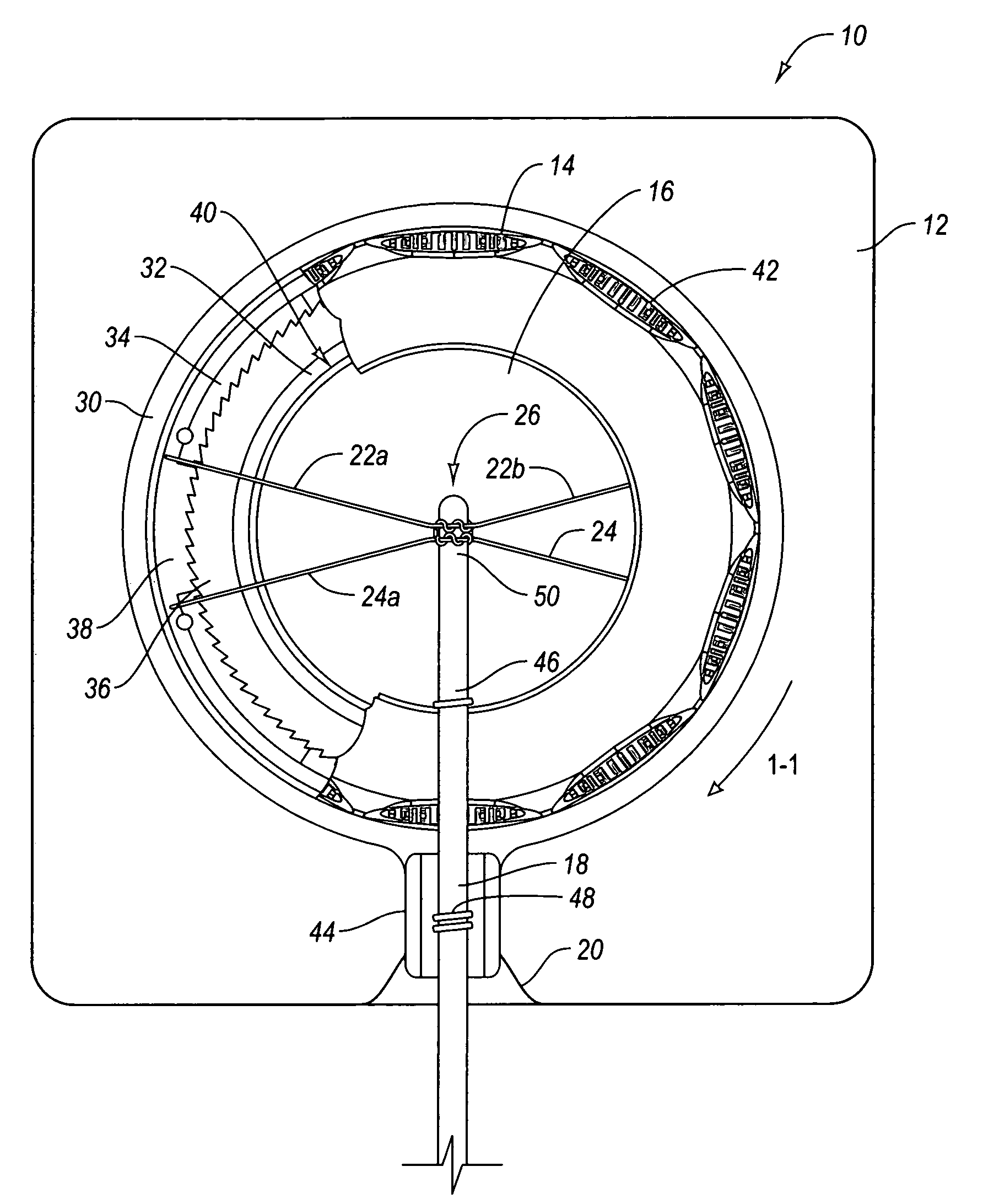
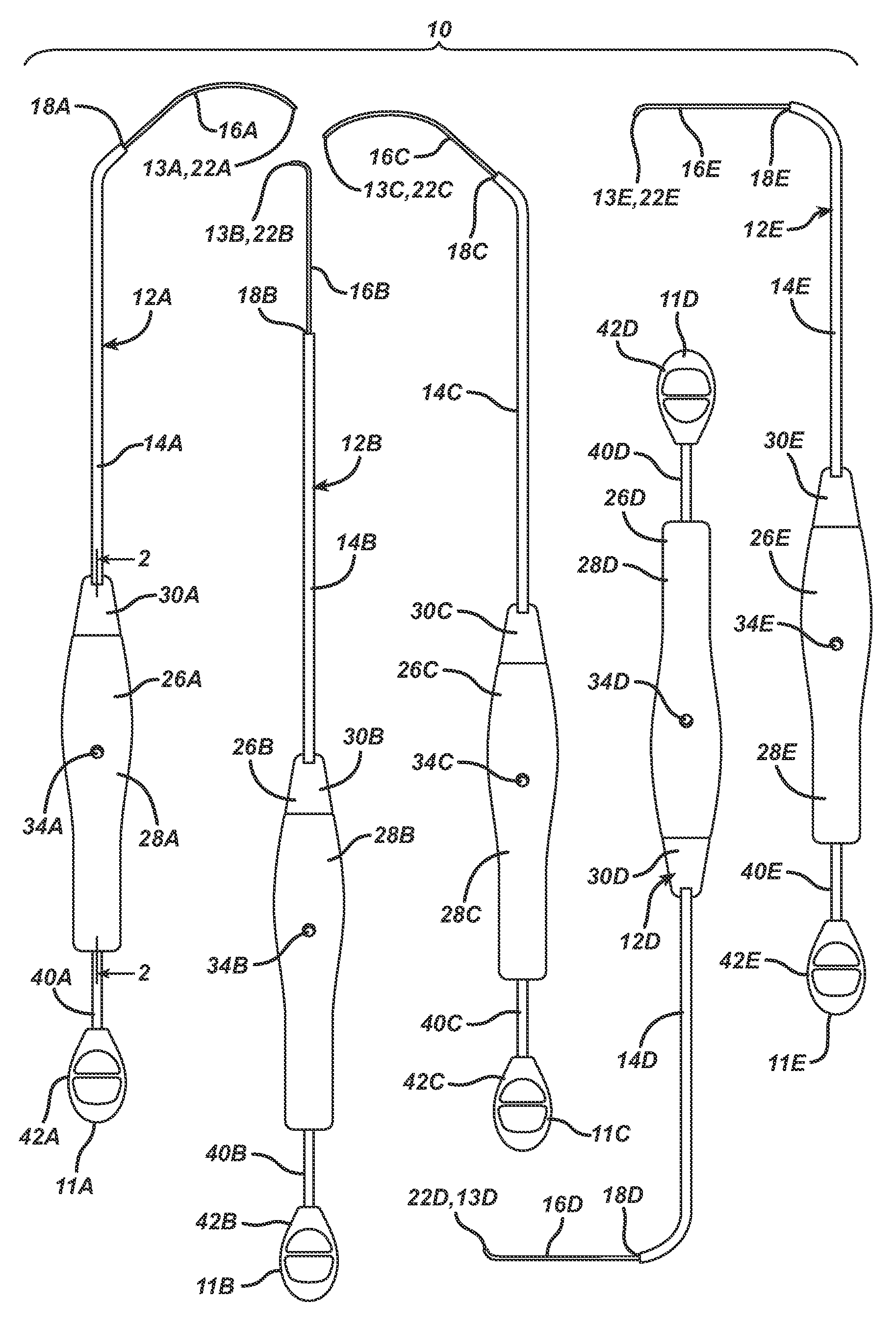
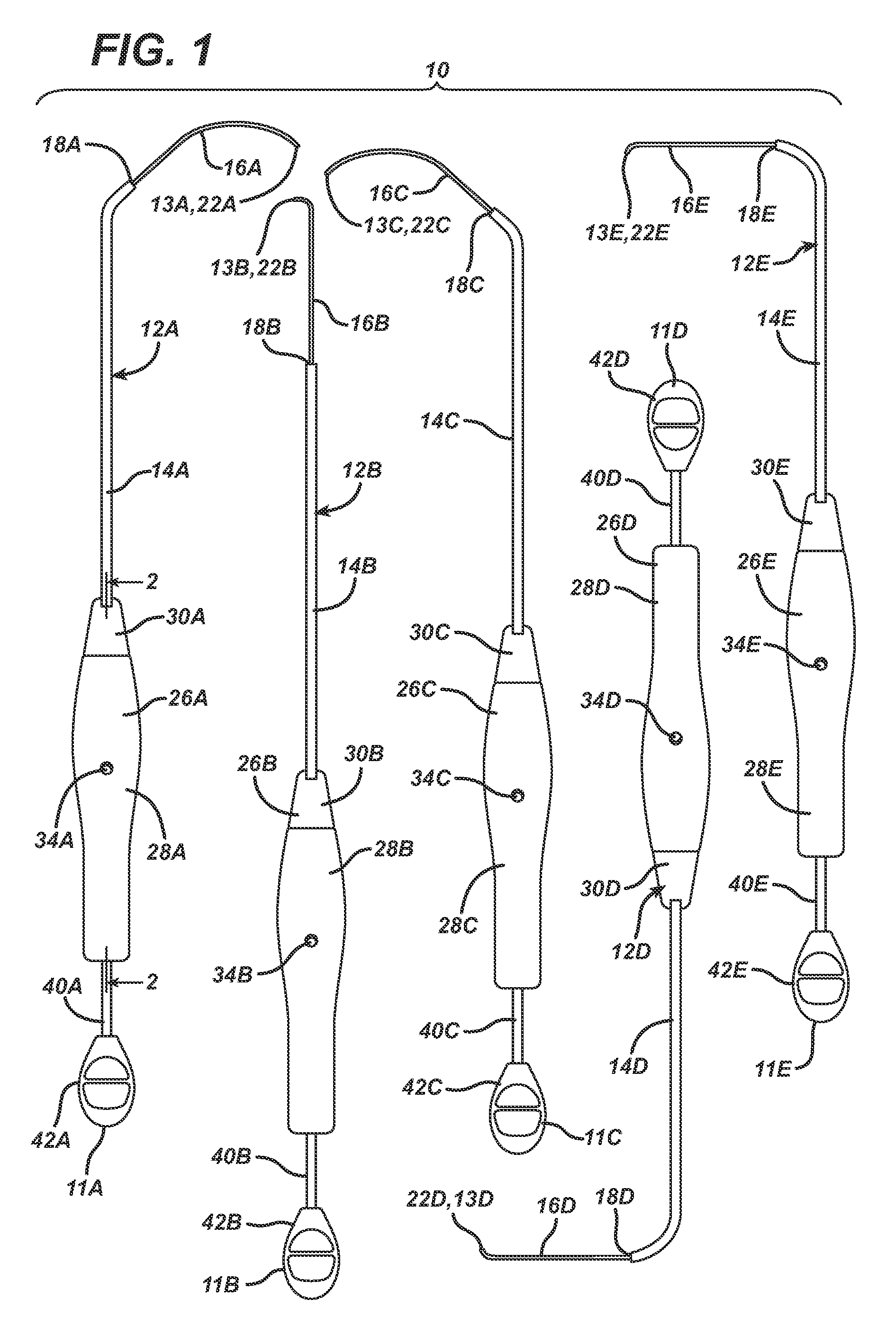
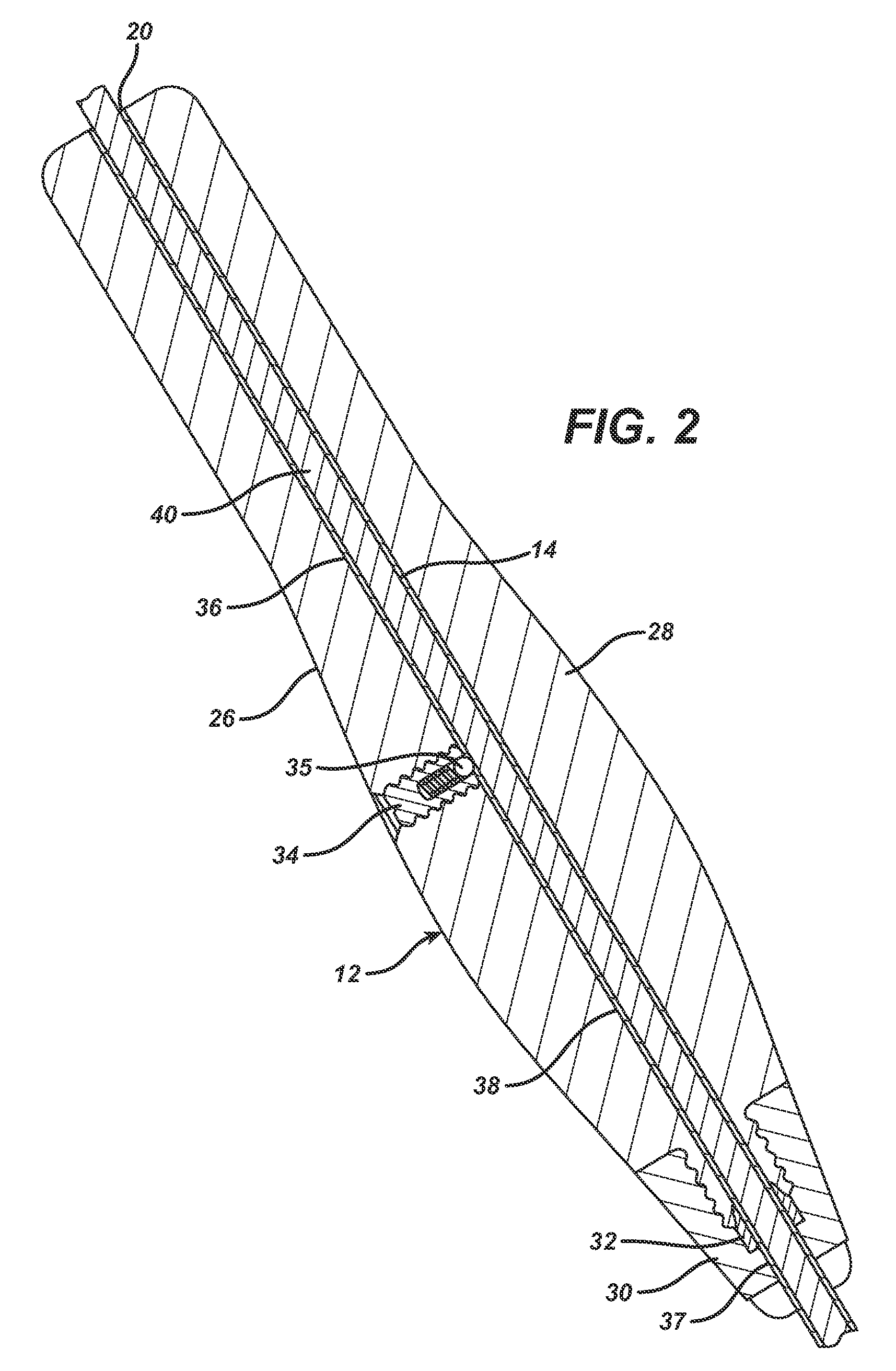
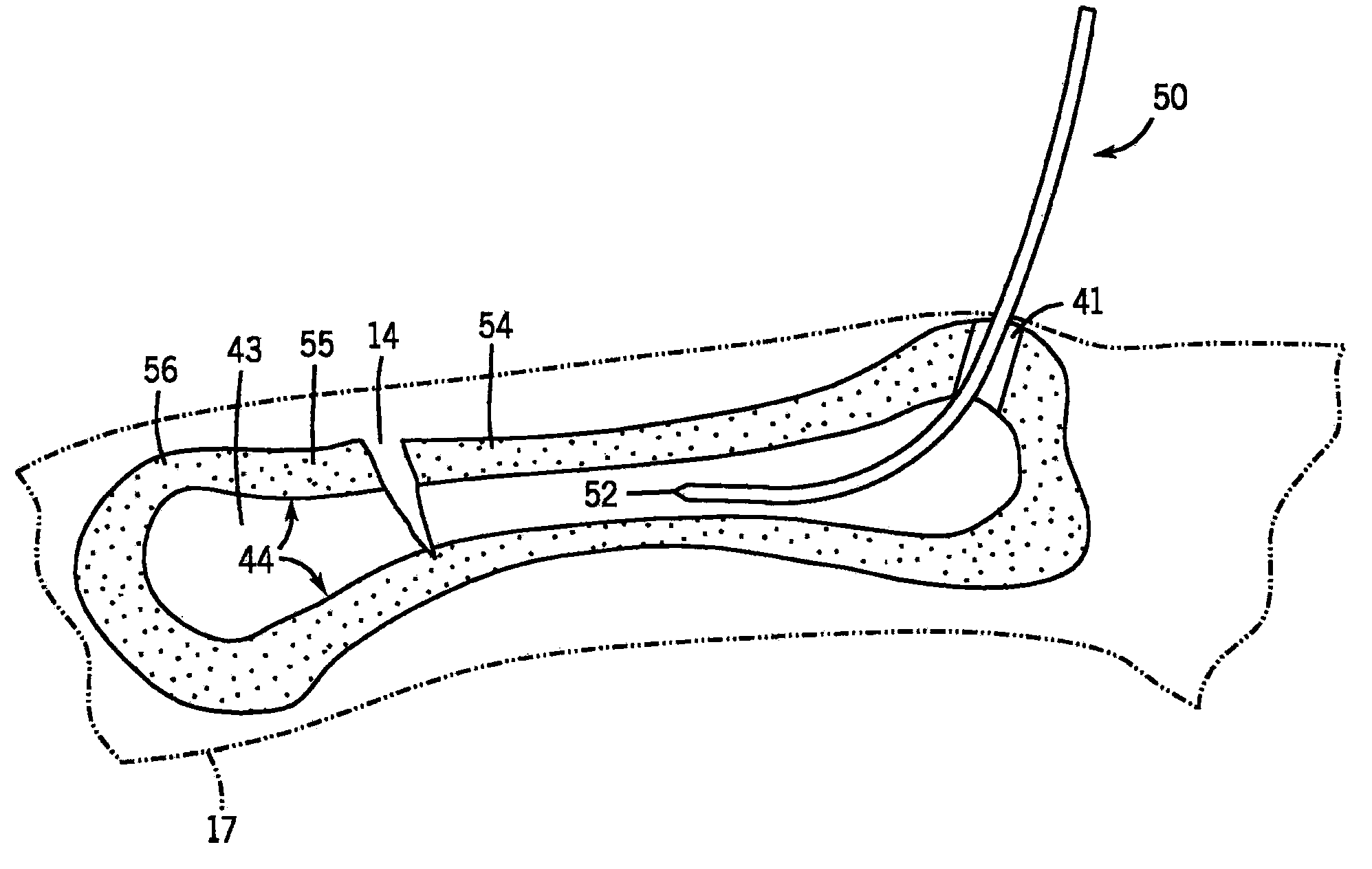
Spinal stabilization system and method
A spinal stabilization system may include a pair of structural members coupled to at least a portion of a human vertebra with connectors. Connectors may couple structural members to spinous processes. Some embodiments of a spinal stabilization system may include fasteners that couple structural members to vertebrae. In some embodiments, a spinal stabilization system provides three points of fixation for a single vertebral level. A fastener may fixate a facet joint between adjacent vertebrae and couple a stabilization structural member to a vertebra. Connectors may couple the structural members to the spinous processes of the vertebrae. Use of a spinal stabilization system may improve the stability of a weakened or damaged portion of a spine. When used in conjunction with an implant or other device, the spinal stabilization system may immobilize vertebrae and allow for fusion of the implant or other device with vertebrae.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
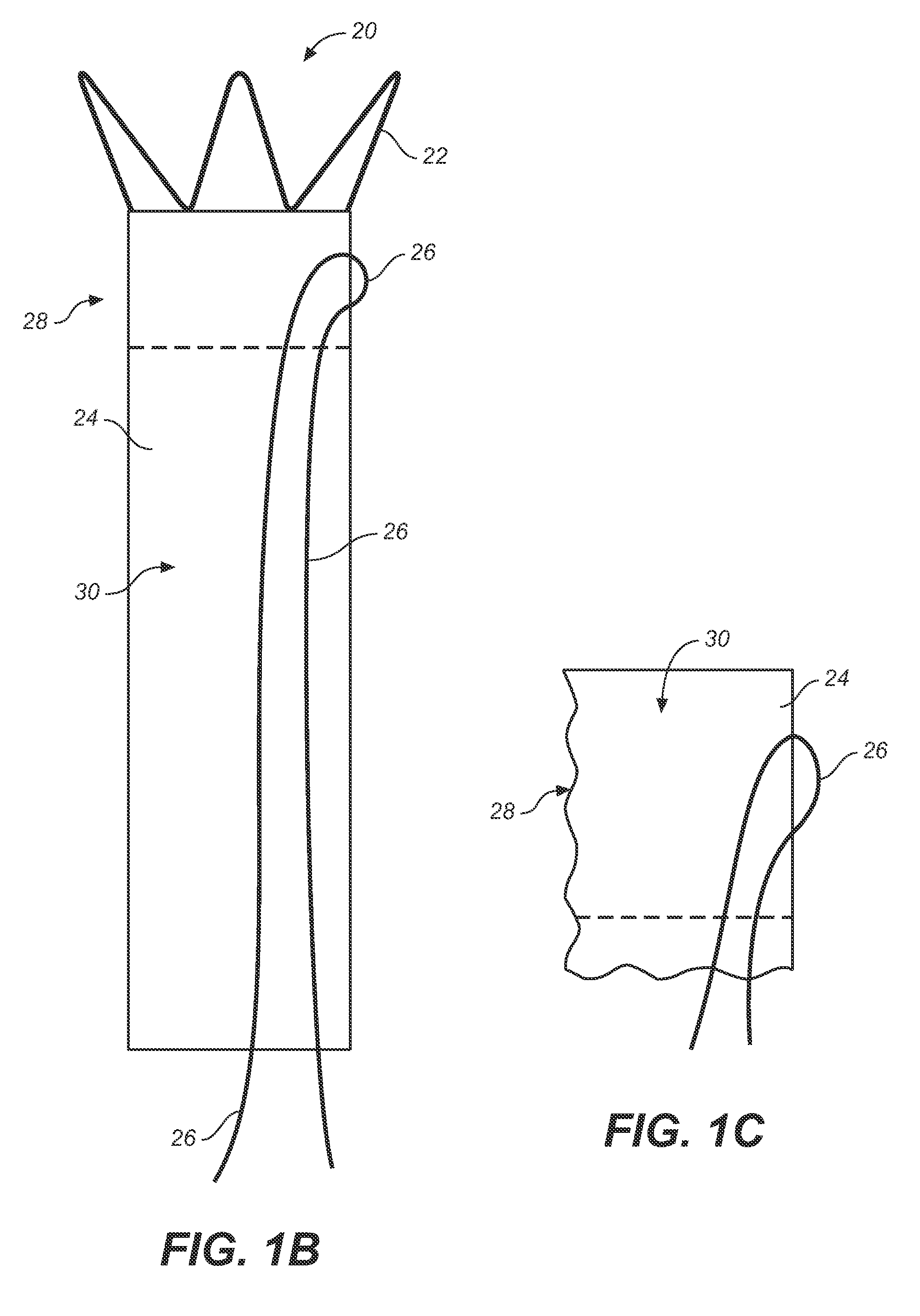
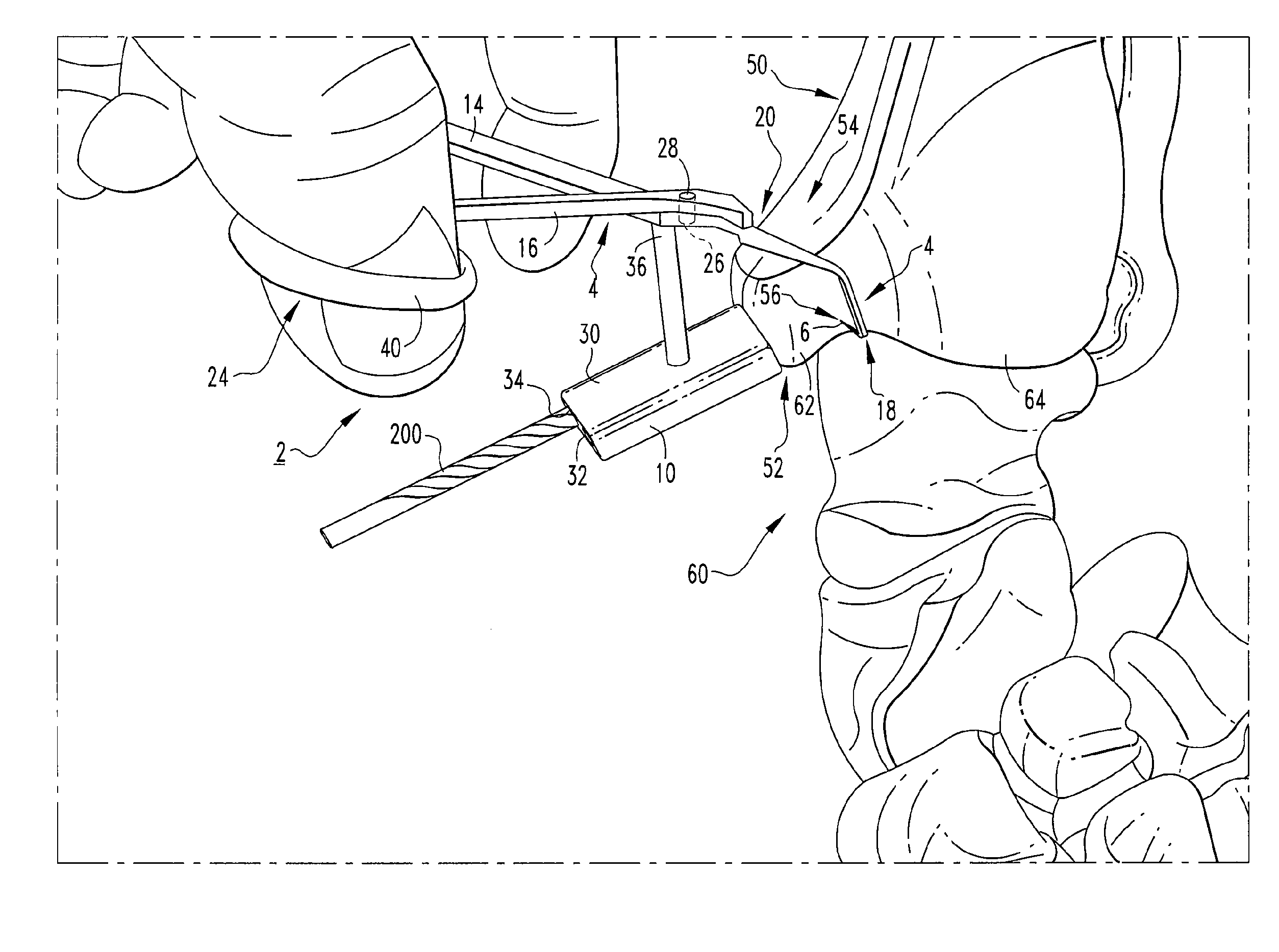
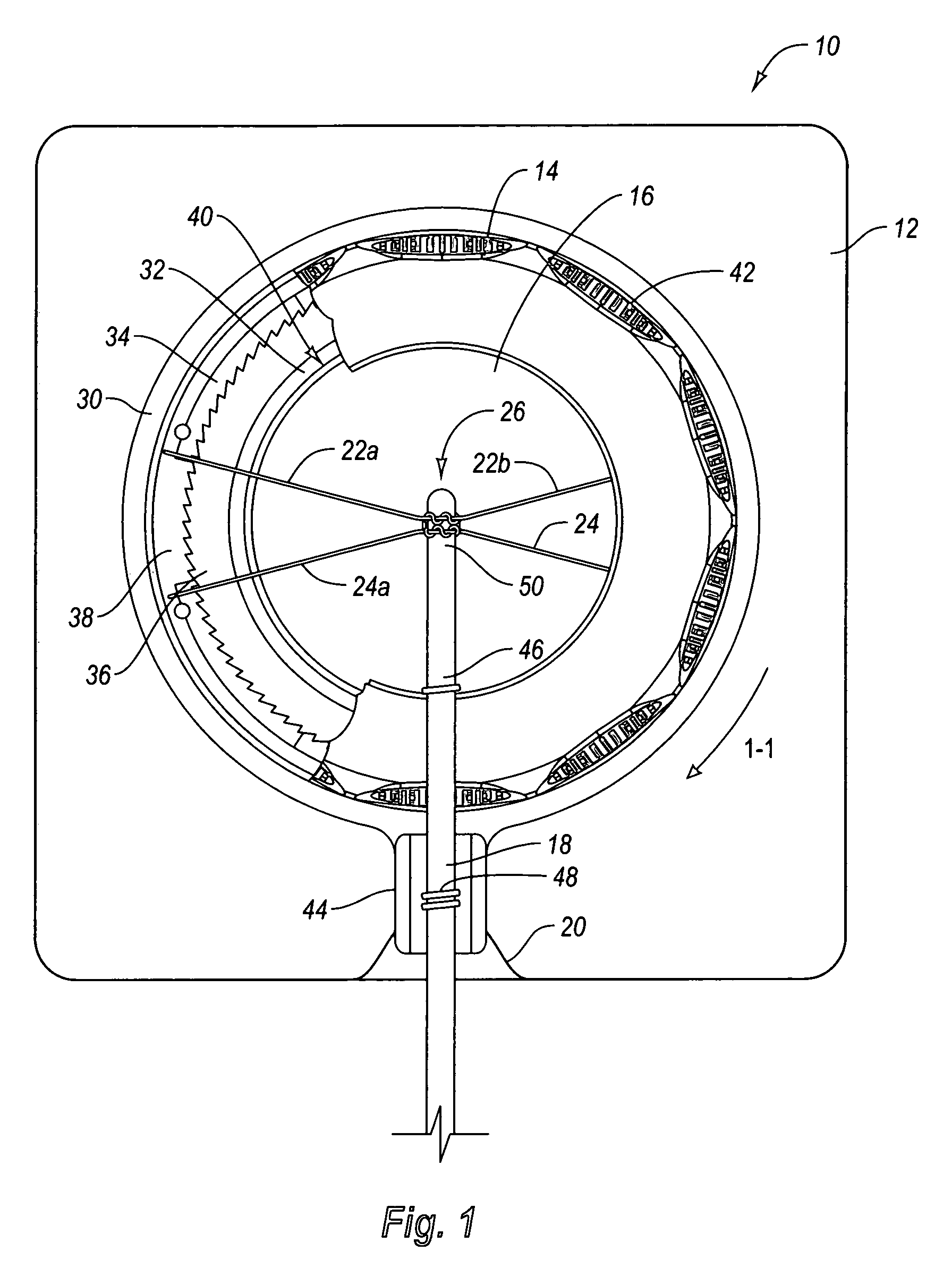
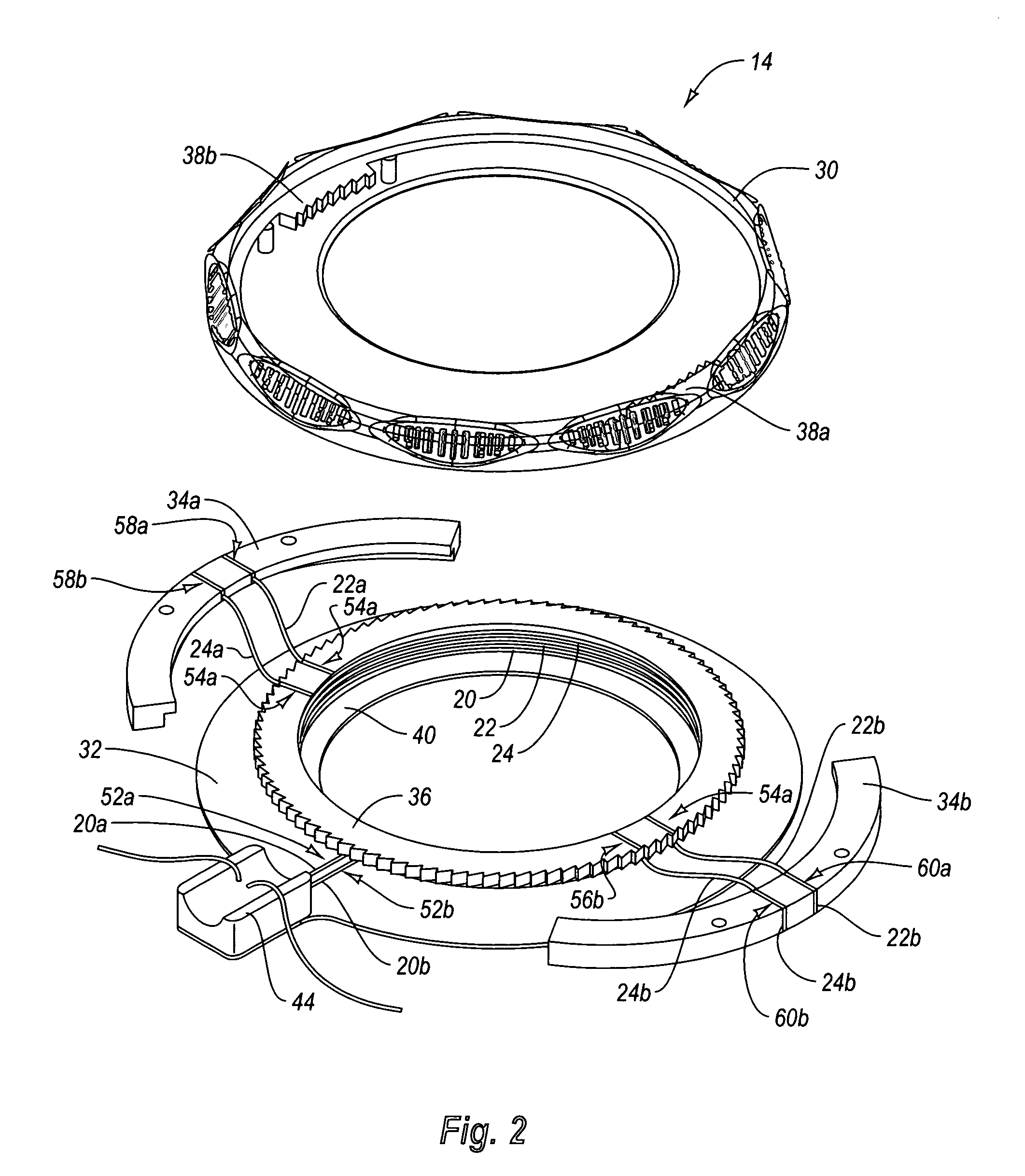
Self-suturing anchor device for a catheter
ActiveUS20060095009A1Reduce tensionPrevent movementSuture equipmentsCatheterFixation pointSuture anchors
A self-suturing anchor device includes rotatable ring adapted to automatically deploy sutures to secure a catheter. The rotatable ring is utilized in connection with a ratchet mechanism which allows movement of the rotatable ring in a first direction while preventing movement of the rotatable ring in the opposite direction. The rotatable ring is also utilized in connection with a bearing member to facilitate smooth and efficient rotation of the rotatable ring. An extension saddle is utilized to provide a desired amount of displacement between suture securement points to minimize pivotal movement of the catheter. The rotatable ring is wider than its height to minimize kinking of the catheter tube and to relieve pressure when pressed between the patient and a support surface. In another embodiment, a plurality of scallops or other gripping members are utilized to facilitate easy gripping and rotation of the rotatable ring.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
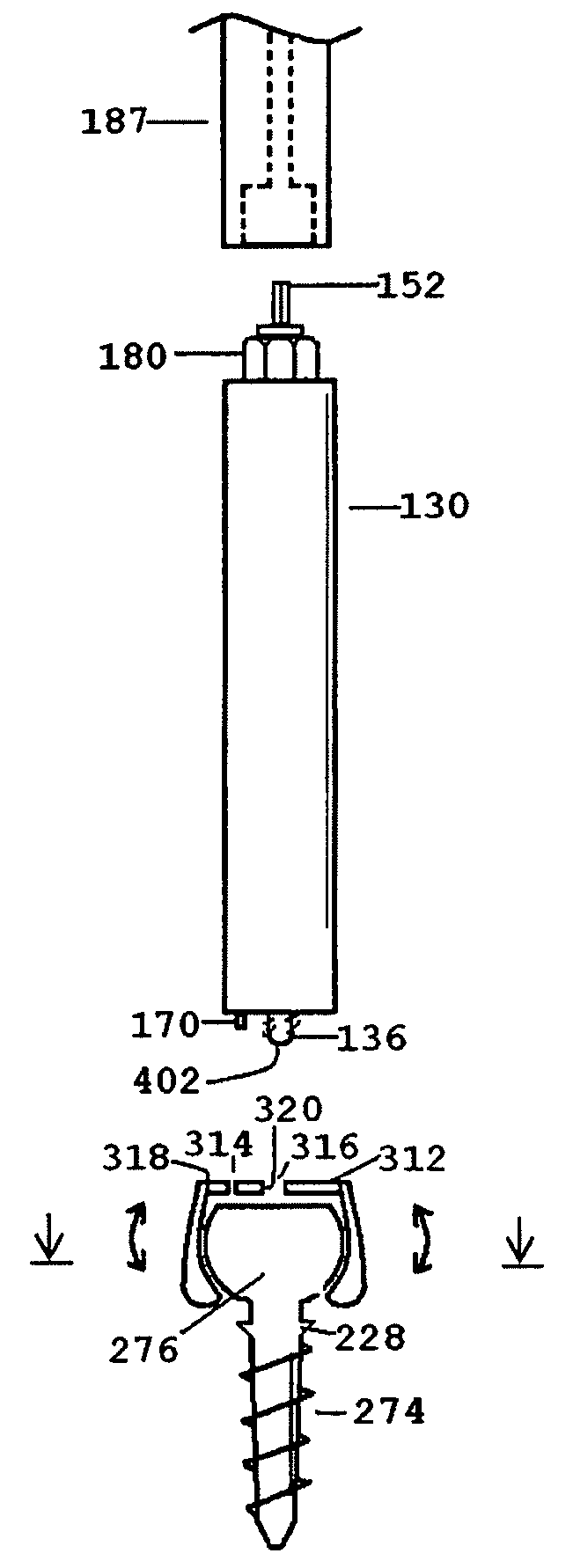
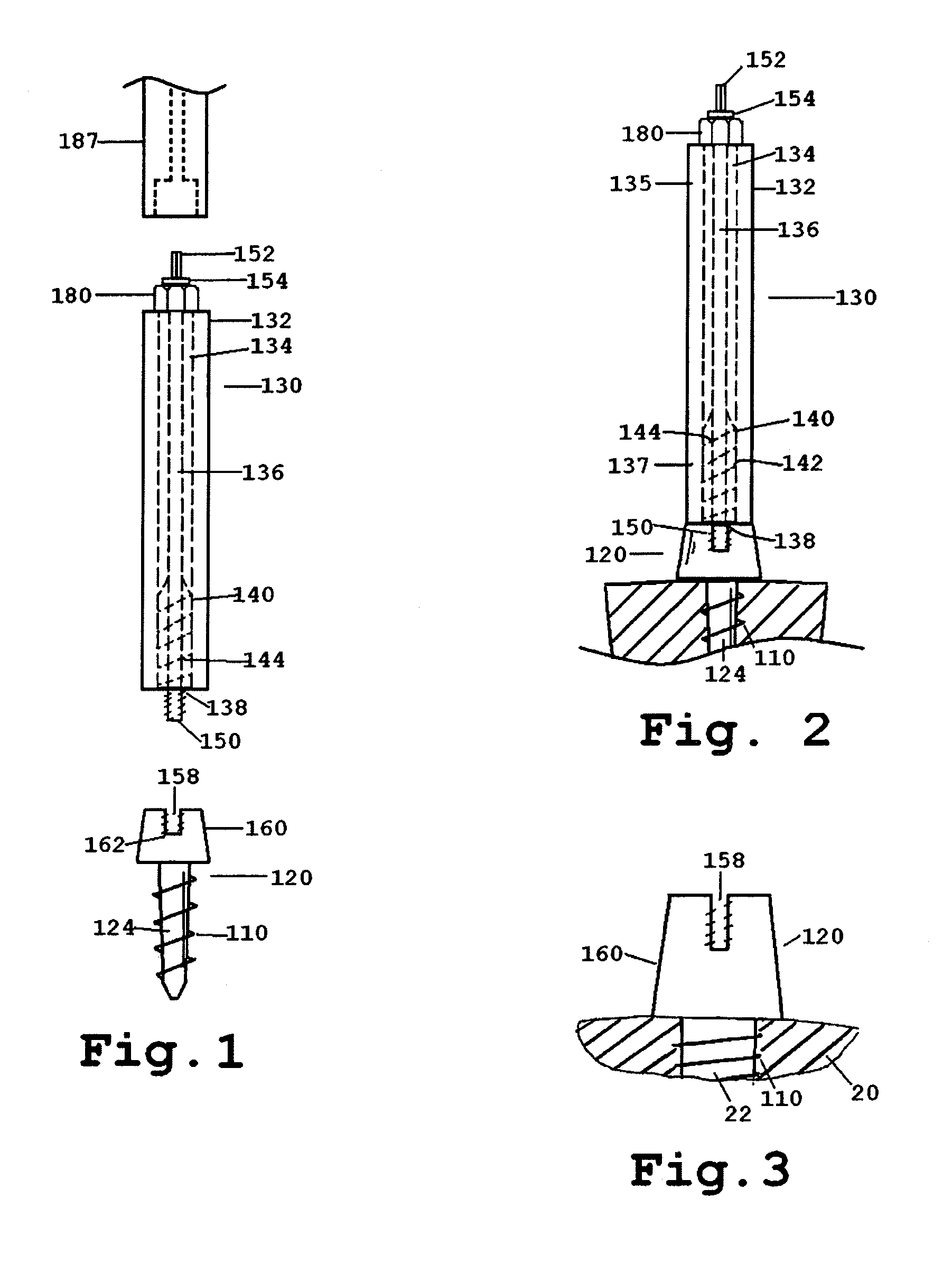
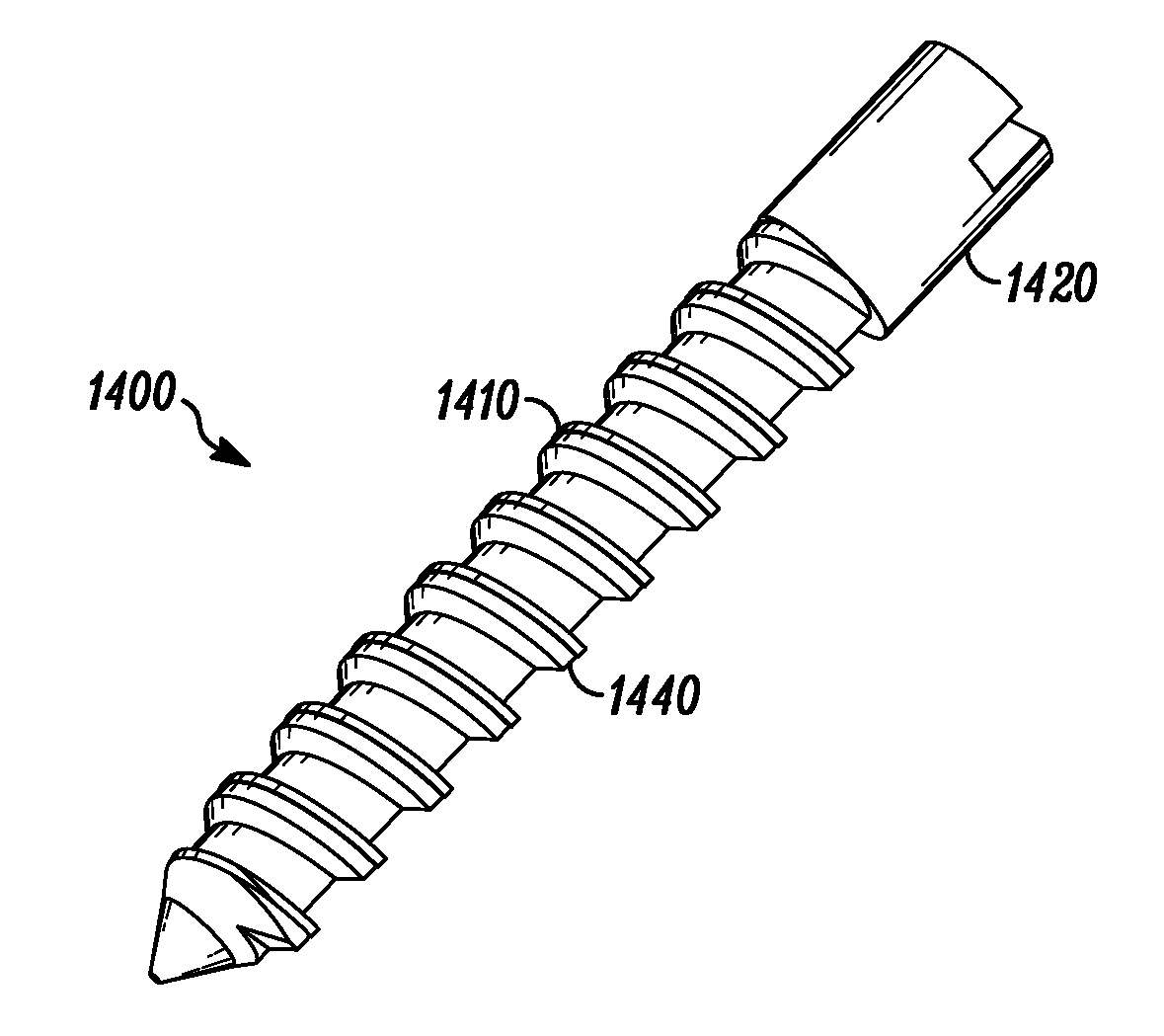
Distraction screw for skeletal surgery and method of use
ActiveUS7476228B2Improve functionalityAccurate placementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisDistractionFixation point
An improved distraction bone screw and a method for its use are described. The distraction screw is comprised of an implantable distal segment and a detachably secured proximal segment. The distal segment includes a head portion and a threaded shank portion. The proximal segment is represented as an elongated body having an internal bore that extends through its length. A deployable member is disposed within the bore, which is extendible outside the internal bore to securely couple to the distal segment. As an assembly, the distraction screw is used to affix and realign bone during surgical reconstruction. Upon completion of the surgical work, the proximal segment is removed and the distal segment is left attached to the reconstructed bone. Securely affixed, the distal segment provides an additional point of fixation for the skeletal plates that are used to preserve the bony alignment while bone healing occurs. The affixed distal segment will also provide a ready mechanism for distraction screw replacement at the time of surgical revision without obligatory plate removal. Different embodiments of the proximal segment, distal segment and the rotational locking mechanisms which inhibit the rotation of one segment relative to the other during deployment were also described. In addition, in cases where the distraction screw must be placed into the bone at an inclined angle, poly-axial heads were provided so that proper skeletal plate placement can still be accomplished.
Owner:ABDOU M SAMY
Depth based foveated rendering for display systems
Methods and systems for depth-based foveated rendering in the display system are disclosed. The display system may be an augmented reality display system configured to provide virtual content on a plurality of depth planes using different wavefront divergence. Some embodiments include monitoring eye orientations of a user of a display system based on detected sensor information. A fixation point is determined based on the eye orientations, the fixation point representing a three-dimensional location with respect to a field of view. Location information of virtual objects to present is obtained, with the location information indicating three-dimensional positions of the virtual objects. Resolutions of at least one virtual object is adjusted based on a proximity of the at least one virtual object to the fixation point. The virtual objects are presented to a user by display system with the at least one virtual object being rendered according to the adjusted resolution.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Precision Approach Control
ActiveUS20080071431A1Great and easy controlSimple and inexpensive solutionVessels for aircraftDigital data processing detailsFixation pointControl system
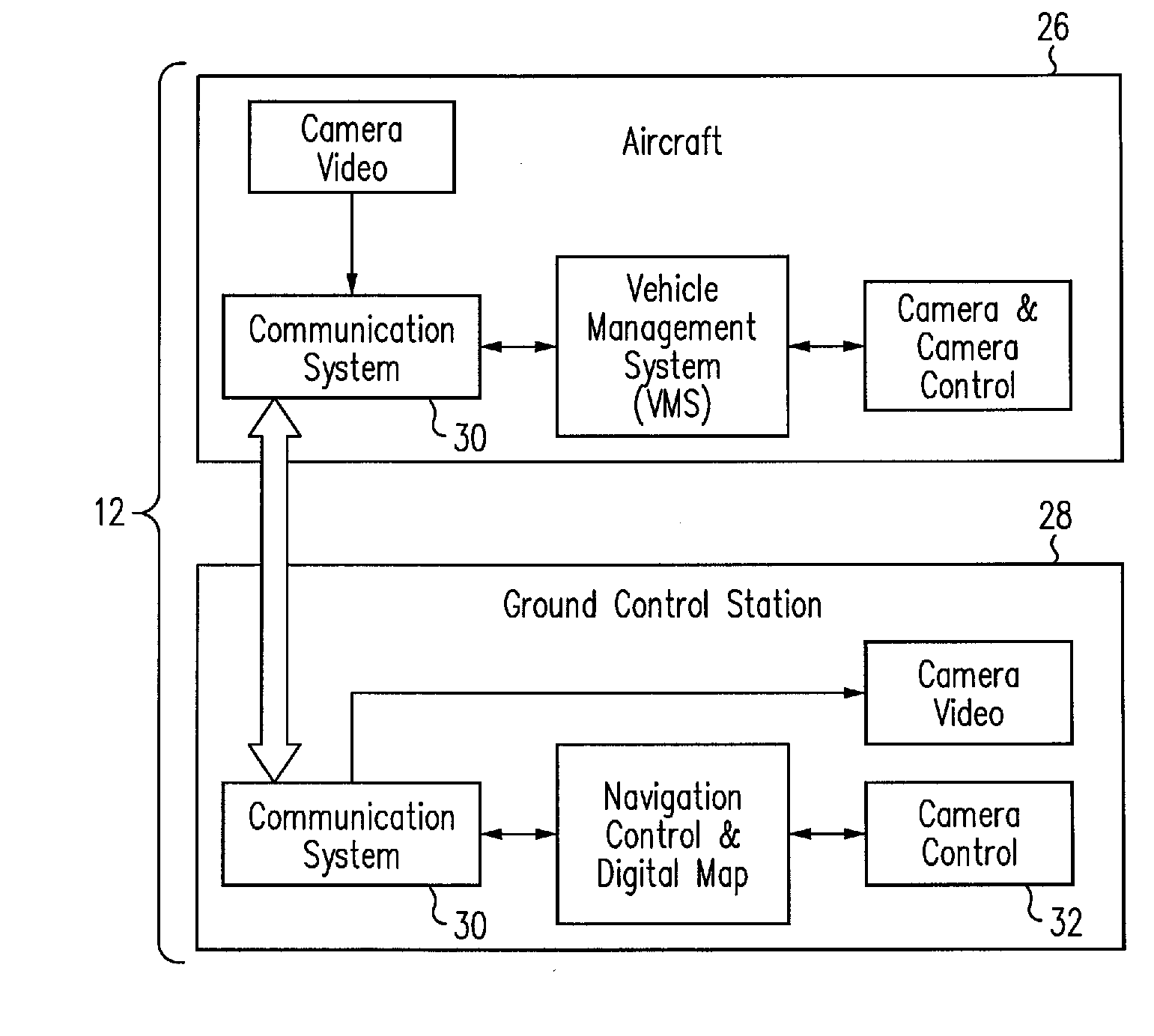
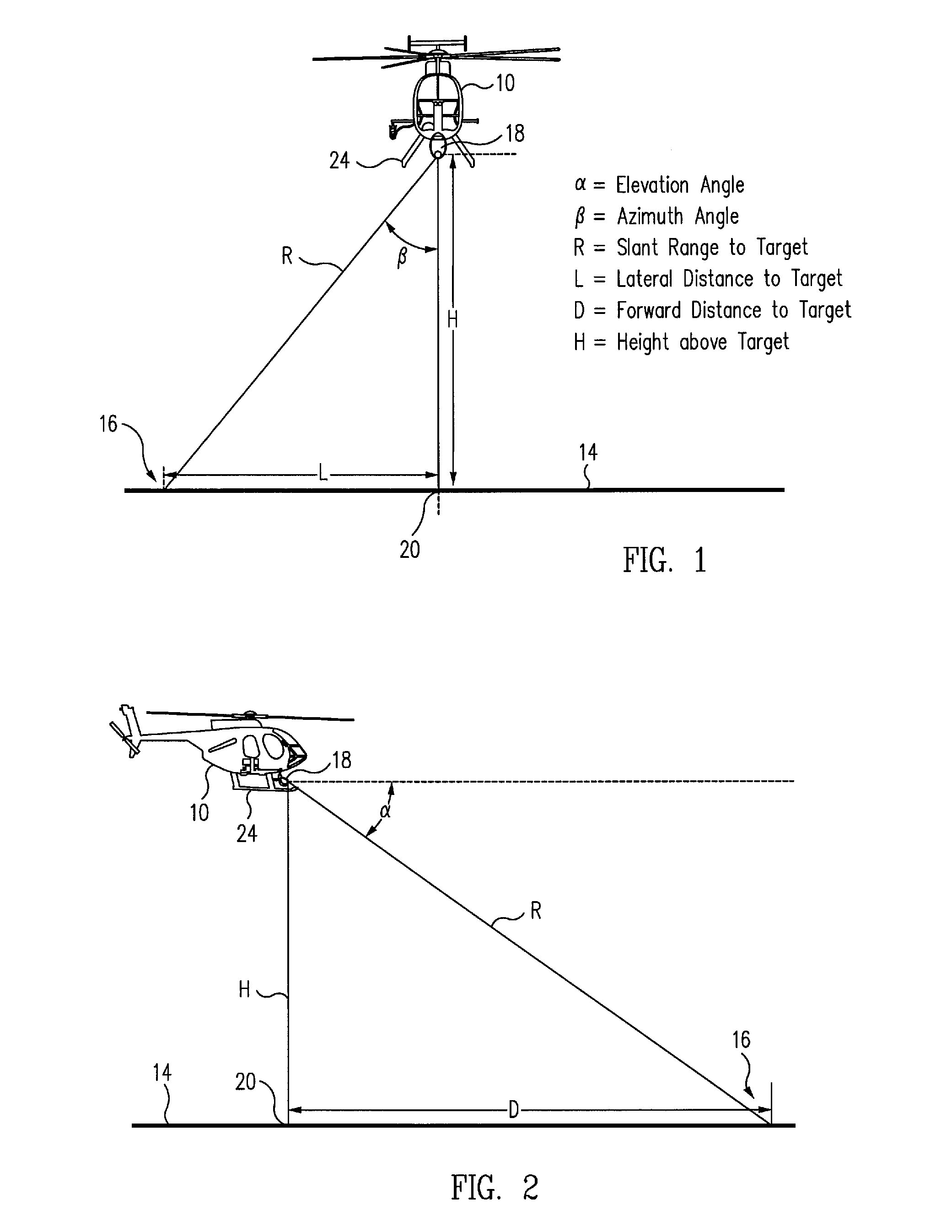
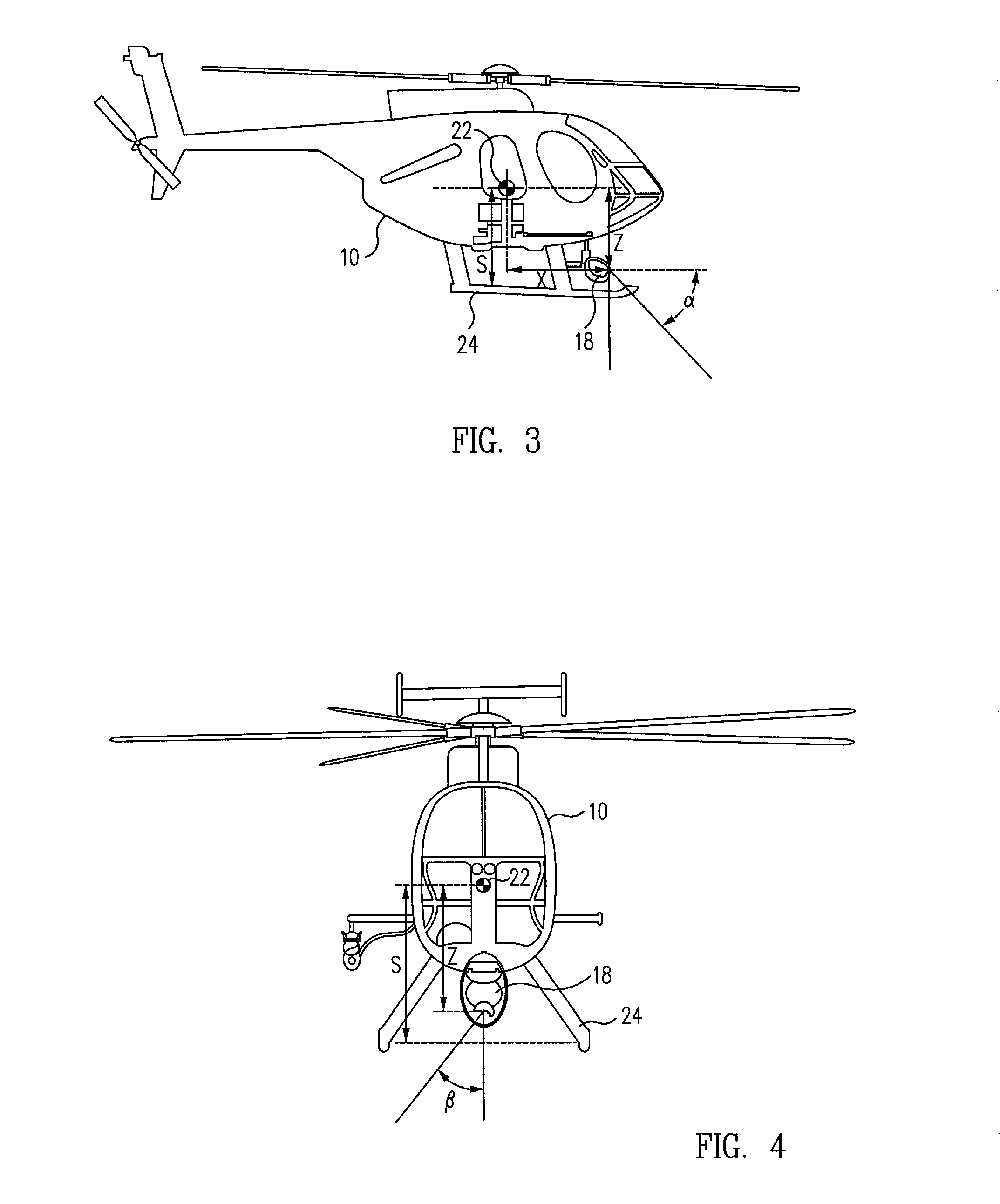
An aircraft control system for operations close to the ground includes a camera having a rangefinder for measuring the azimuth, elevation and slant range from a fixed point on the aircraft relative to a selected target point on a surface below the aircraft, a navigation system for measuring the latitude and longitude of the aircraft on the surface, a computer for computing the position of the fixed point on the aircraft relative to the target point from the respective measurements of the camera and the navigation system, and a controller for controlling the movement of the aircraft such that the fixed point is positioned at a selected position above the selected target point on the surface. The controller may also include an automatic tracking mechanism for maintaining the position of the fixed point on the aircraft at the selected position above a moving object.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Spinal stabilization system and method
ActiveUS20080140125A1Improve stabilityProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnFixation point
A spinal stabilization system may include a pair of structural members coupled to at least a portion of a human vertebra with connectors. Connectors may couple structural members to spinous processes. Some embodiments of a spinal stabilization system may include fasteners that couple structural members to vertebrae. In some embodiments, a spinal stabilization system provides three points of fixation for a single vertebral level. A fastener may fixate a facet joint between adjacent vertebrae and couple a stabilization structural member to a vertebra. Connectors may couple the structural members to the spinous processes of the vertebrae. Use of a spinal stabilization system may improve the stability of a weakened or damaged portion of a spine. When used in conjunction with an implant or other device, the spinal stabilization system may immobilize vertebrae and allow for fusion of the implant or other device with vertebrae.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
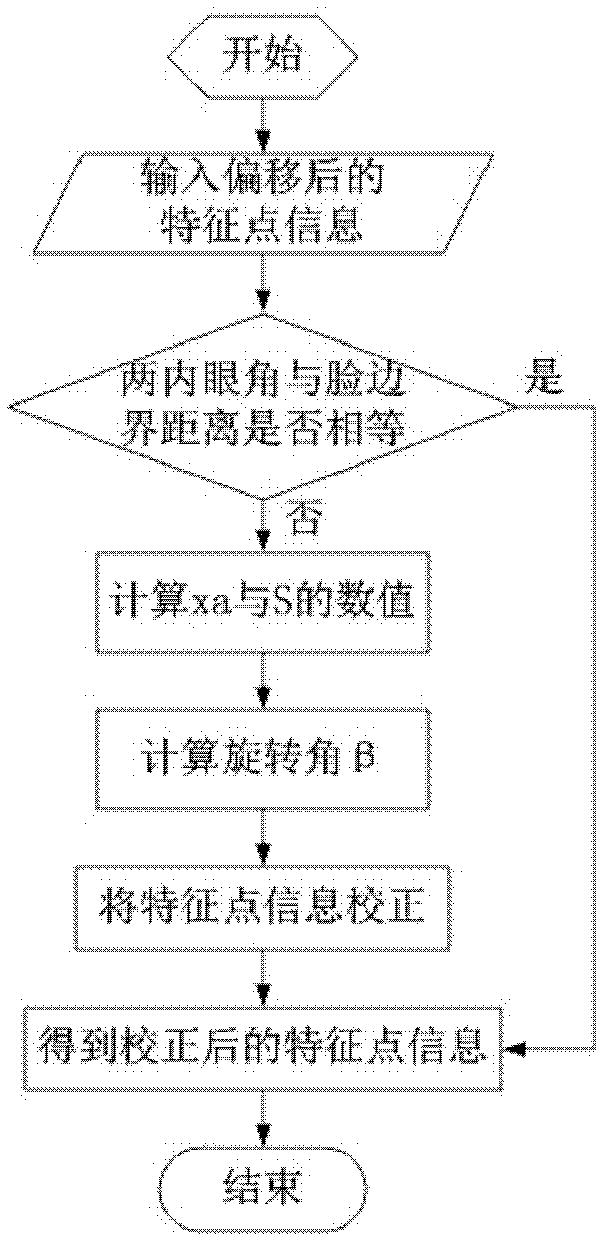
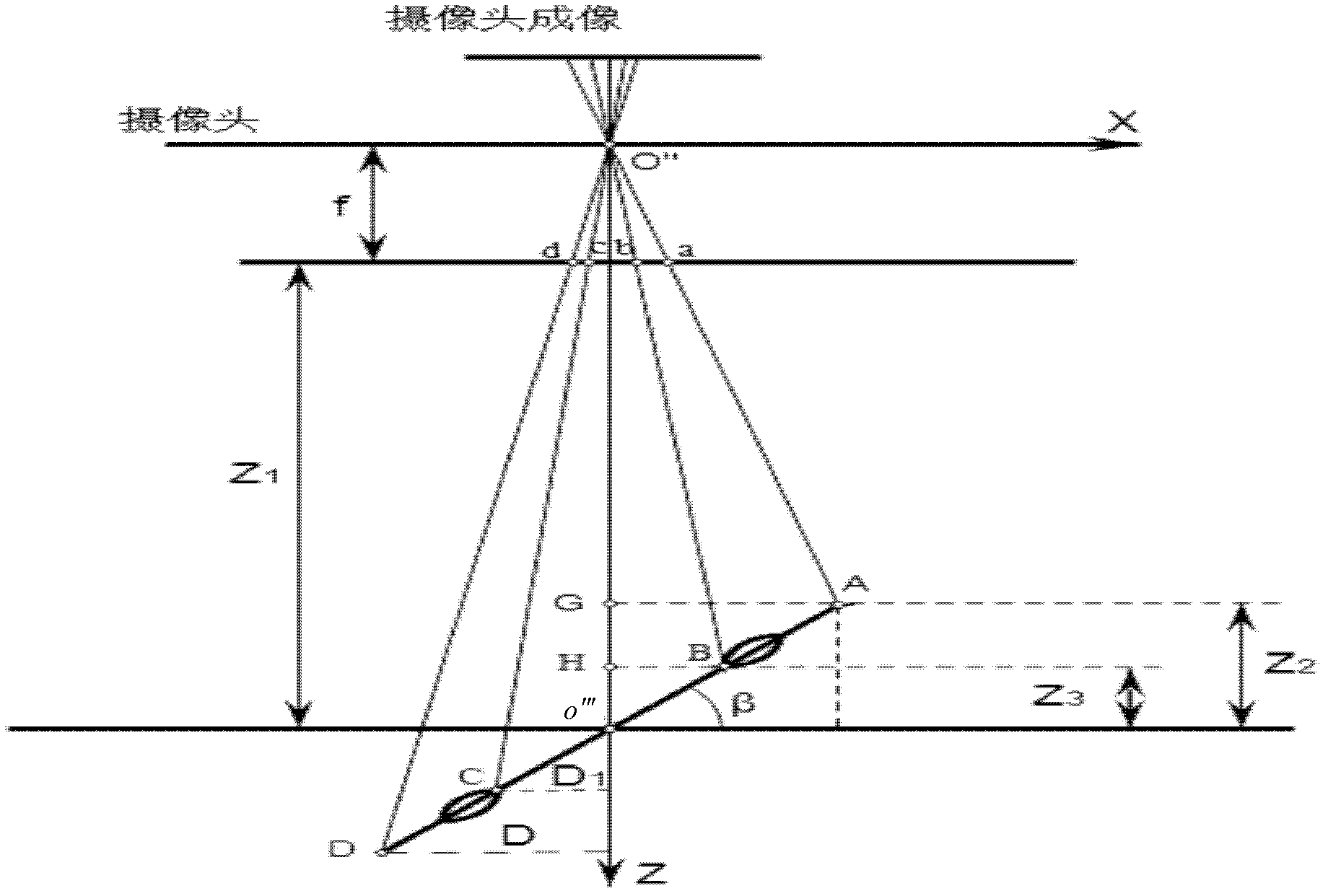
Gaze estimation method
ActiveCN102662476AImprove adaptabilityImprove estimation accuracyInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionHead movementsFixation point
The invention discloses a gaze estimation method. The gaze estimation method comprises the following steps: finding out calibration error by aligning; then estimating the distance between a face plane and a screen and establishing a three-dimensional model to obtain optical axis information of eyeballs by offset correction of the head and rotary correction of the head; and finally, obtaining the position of a fixation point. According to the gaze estimation method, only a camera is used and no auxiliary equipment is needed; the aim of furthering increasing the estimation precision is achieved by using a correction link by a user; in addition, due to the utilization of estimation of the distance between the face plane and the screen and the offset and rotation correction of the head, limiting conditions are reduced as much as possible, a comfortable use environment for a user is provided and the gaze estimation method has better precision and adaptability of the head motion; and on the basis of an eyeball of a human eye, the gaze estimation method based on a three-dimensional model is established so as to achieve the aim of increasing the estimation precision. According to the gaze estimation method, extra auxiliary equipment is reduced, the adaptability to the head motion is improved, and the better precision for sight light estimation is obtained.
Owner:BINHAI IND RES INST OF TIANJIN UNIV CO LTD
Medical device delivery system and method
A tendon repair implant delivery system and methods incorporating a guide member having a temporary fixation member on or adjacent to the distal end. The point of fixation defines a target site for placement of the tendon repair implant which is subsequently affixed to the tendon.
Owner:ROTATION MEDICAL
Rapid computation of local eye vectors in a fixed point lighting unit
InactiveUS6014144ADigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingFixation pointSpecular reflection
A rapid method for calculating a local eye vector in a fixed point lighting unit. For a given triangle primitive which is to be projected into a given viewport in screen space coordinates, the local eye vector corresponds to a given eye position and a first vertex of the given triangle primitive. (A different local eye vector is calculated for each vertex of the given triangle primitive). The method first comprises generating a view vector matrix which corresponds to the given eye position and corner coordinates of the given viewport, where the corner coordinates are expressed in screen space coordinates. The view vector matrix is usable to map screen space coordinates to an eye vector space which corresponds to the given viewport. The method next includes receiving a first set of coordinates (in screen space) which correspond to the first vertex. The first set of coordinates are then scaled to a numeric range which is representable by the fixed point lighting unit. Next, the first set of coordinates are transformed using the view vector matrix, which produces a non-normalized local eye vector within the eye vector space for the given viewport. The non-normalized local eye vector is normalized to form a normalized local eye vector. The normalized local eye vector is then usable to perform subsequent lighting computations such as computation of specular reflection values for infinite light sources, producing more realistic lighting effects than if an infinite eye vector were used. These more realistic lighting effects do not come at decreased performance, however, as the local eye vector may be calculated rapidly using this method.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Stent graft fixation system and method
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Mechanically Competent Scaffold for Rotator Cuff and Tendon Augmentation
A device has been developed to augment the rotator cuff tendon tissue as it proceeds in healing. The device has two purposes: to provide initial stability to the rotator cuff repair site to allow early mobilization of the upper extremity of the patient, and to allow for reinforcement of rotator cuff tendon repairs to increase the likelihood of successful rotator cuff tendon repairs. The device consists of an inter-connected, open pore structure that enables even and random distribution and in-growth of tendon cells. The braided structure allows for distribution of mechanical forces over a larger area of tissue at the fixation point(s).
Owner:BIOREZ INC
Osteotomy Guide and Method of Cutting the Medial Distal Tibia Employing the Same
InactiveUS20100069910A1Easy to replaceDiagnosticsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAnkle joint replacementDistal tibia
An osteotomy guide is provided for cutting a bone, such as the medial distal tibia, to facilitate an ankle replacement. The osteotomy guide includes a positioning device having a number of fixation points, a first guide member structured to align with a first portion of the bone, in order to perform a first procedure, thereon, and a second guide member structured to align with a second portion of the bone, in order to perform a second procedure thereon. The fixation points engage the bone and maintain alignment of the first guide member with respect to the first portion during the first procedure, and maintain alignment of the second guide member with respect to the second portion during the second procedure, in order that the first procedure and the second procedure are substantially reproducible.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
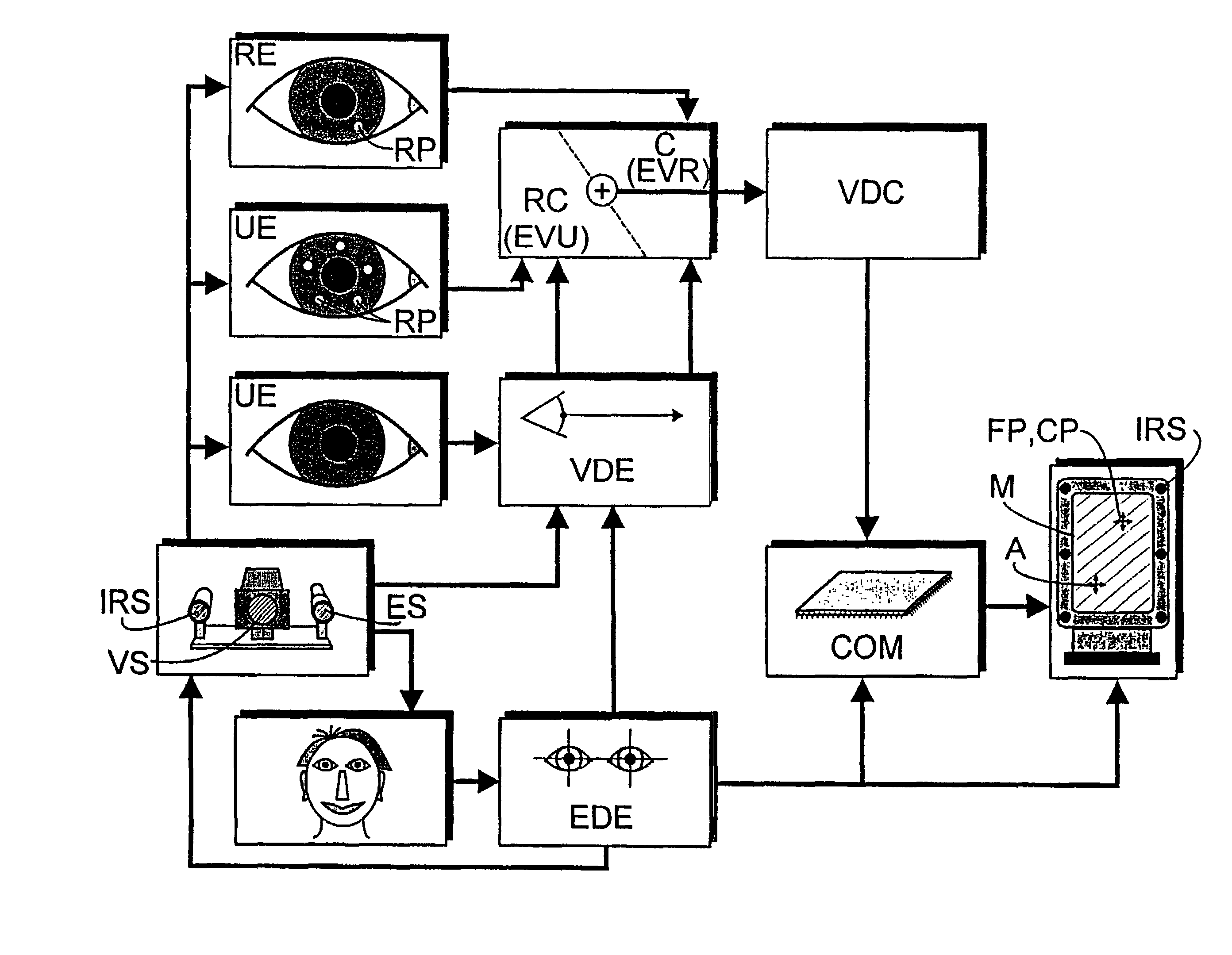
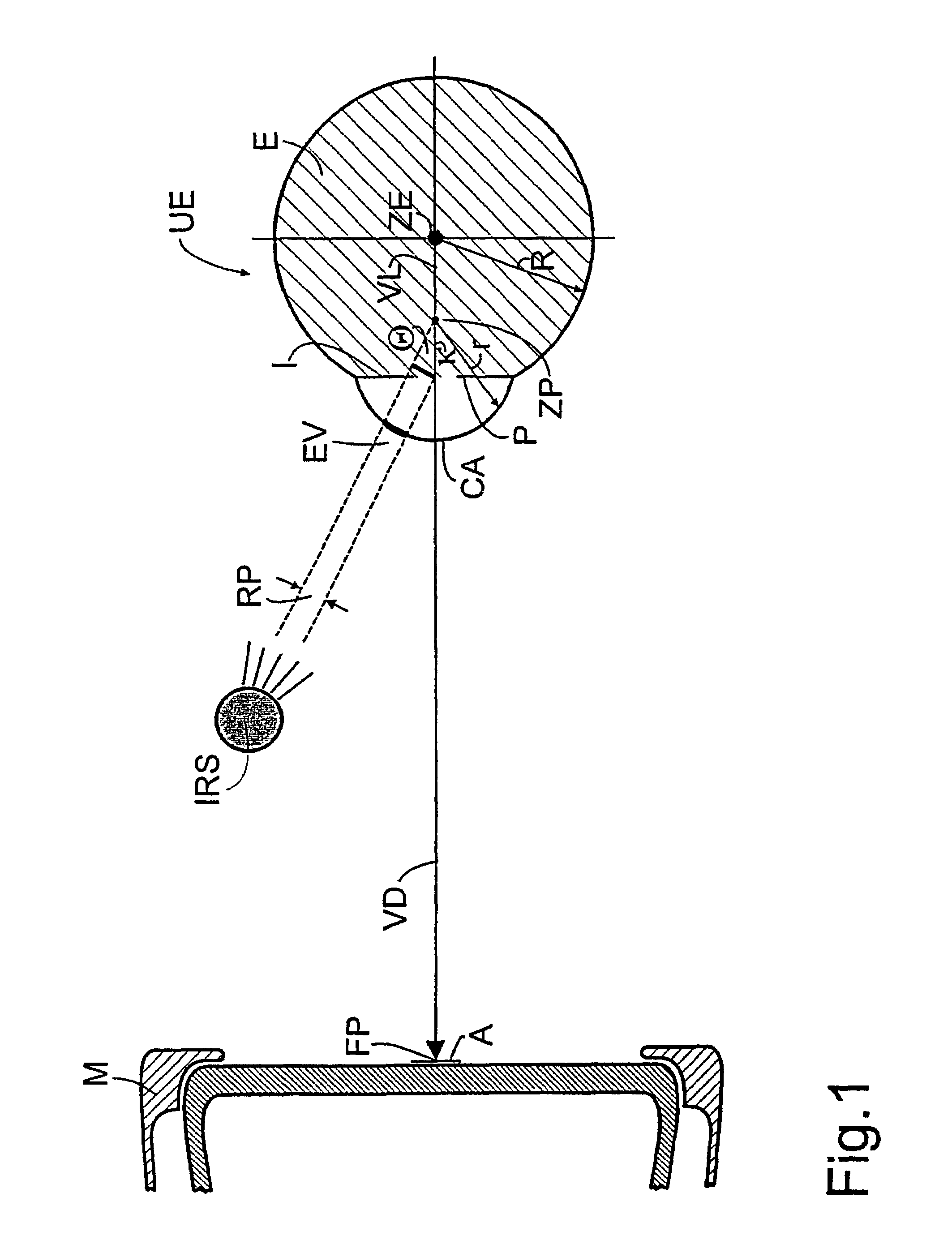
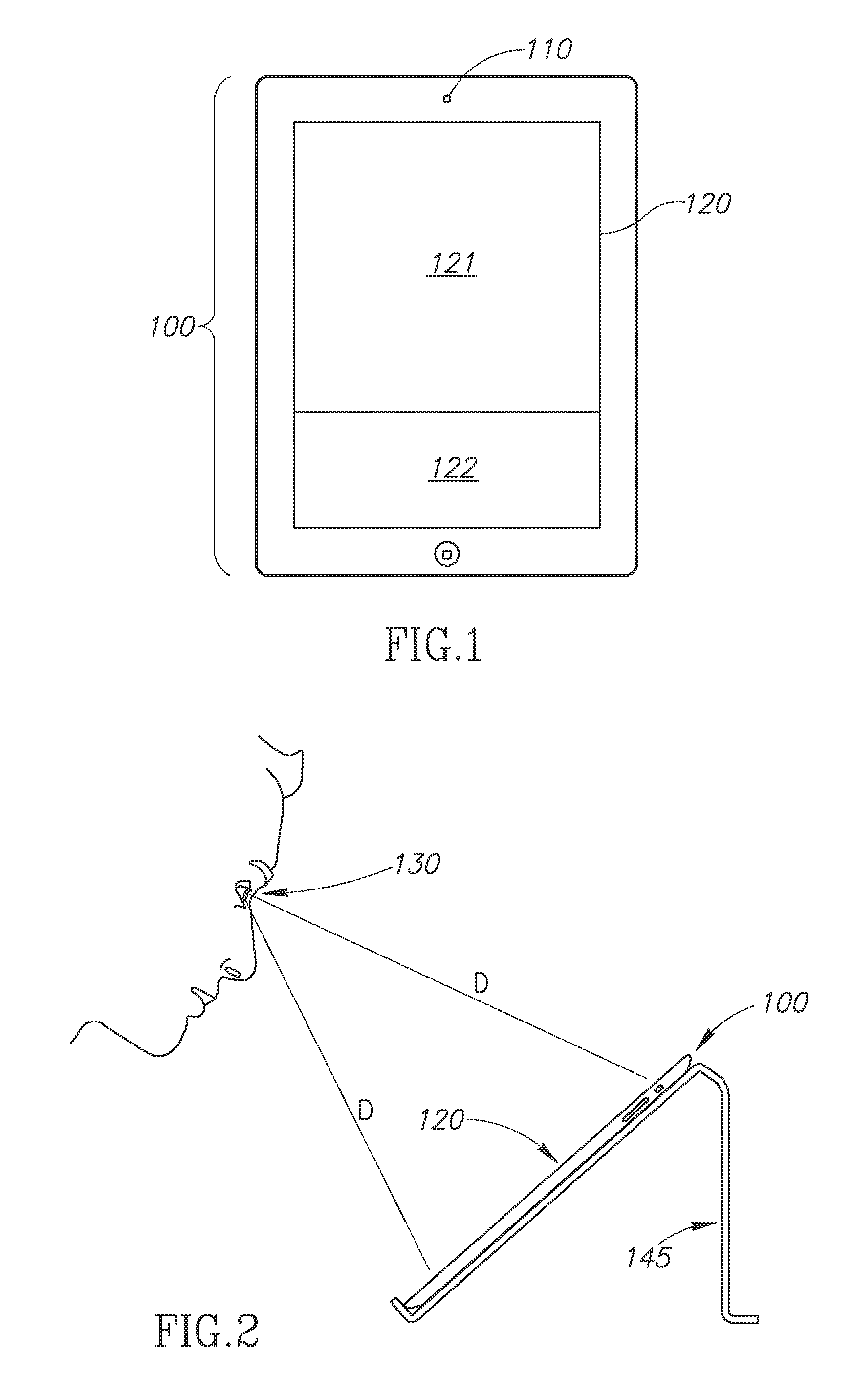
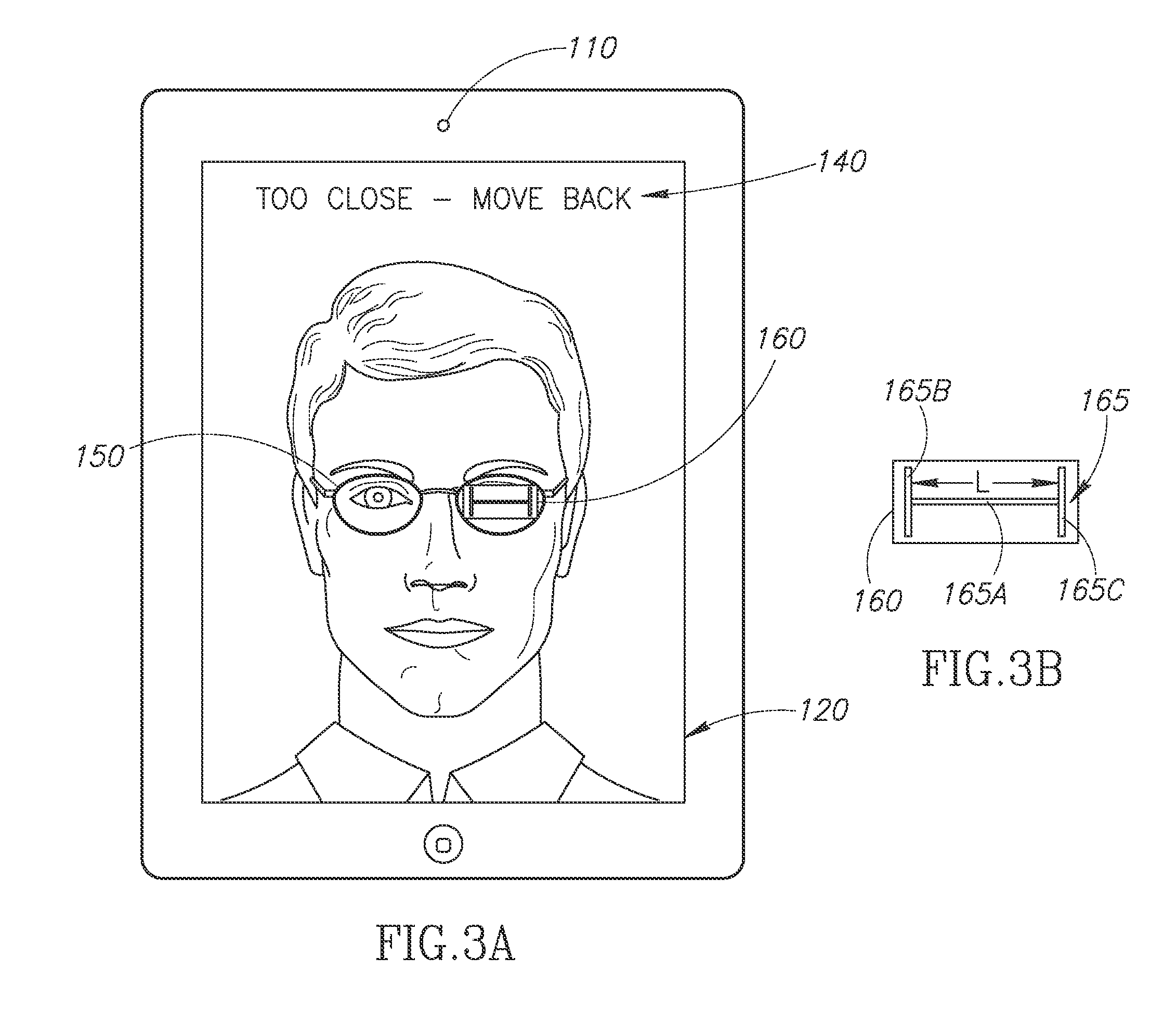
Method and apparatus for computer-aided determination of viewer's gaze direction
InactiveUS7538744B1Maximum precisionMinimal discomfortInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsFixation pointCorneal reflex
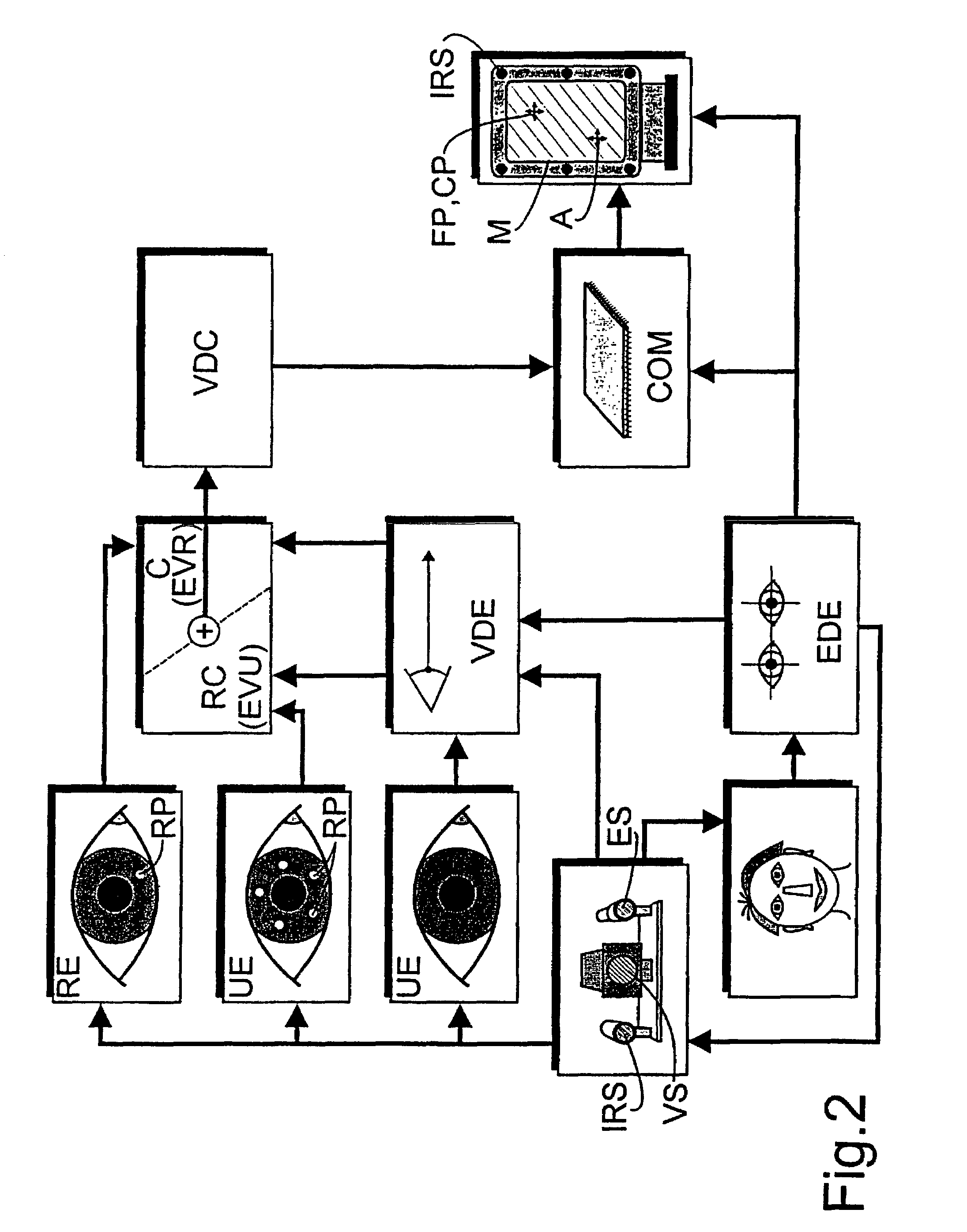
The corneal reflex method is used to detect the current direction of view (VD) of a user (UE) to perform specifically selected functions on a computer. Eye vectors (EV) can be detected between the pupil center (ZP) and reflection points (RP) on the cornea (CA) that can be associated with a fixation point (FP) on a computer screen using infrared light (IRS). The association is produced as a function of the direction of view (VDF), so the relationship is detected during an initial calibration (C) by a referenced user (RE) to develop a set of reference eye vectors (EVR). A shorter self-balancing recalibration (RC) is then carried out for each subsequent user (UE). A mapping function (MF) is detected during the recalibration (RC) so that the individual eye vectors (EVU) can be converted to the reference eye vectors (EVR) by the mapping function. The recalibration (RC) can take place without the user (UE) realizing it. The method is useful in medical diagnostics, psycho-optical examinations and eye-controlled interaction with multimedia computers.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
A method and system for local image recognition based on AR intelligent glasses
ActiveCN109086726AImprove experienceImage recognition is accurateInput/output for user-computer interactionImage data processingFixation pointMotion vector
The invention belongs to the application technical field of AR intelligent glasses, and discloses a local image recognition method and a system based on the AR intelligent glasses. The method comprises steps calibrating the consistency of an intelligent glasses imaging screen, a front camera picture of the intelligent glasses and a visual field picture of a real environment around the intelligentglasses; recognizing the human eye image and calculating the eye motion vector to obtain the eye motion coordinates; identifying whether the focal point of the extended line of human binocular visionis an imaging screen or a real three-dimensional space; obtaining the mapping relationship of human eyes in the real world around them; according to the embedded mapping algorithm, the coordinates ofthe human eye fixation point on the glasses imaging screen and the front camera image being obtained respectively. The invention obtains the eye image information of the human eye through the eye movement instrument, synchronously calibrates the eye image and the scene camera, obtains the fixation point area of the human eye in the real scene, and performs image recognition only on the fixation point area during processing, thereby greatly reducing the image processing pressure of the GPU and improving the image processing efficiency.
Owner:幻蝎科技(武汉)有限公司
Self-suturing anchor device for a catheter
ActiveUS7470256B2Reduce tensionPrevent movementSuture equipmentsCatheterFixation pointSuture anchors
A self-suturing anchor device includes rotatable ring adapted to automatically deploy sutures to secure a catheter. The rotatable ring is utilized in connection with a ratchet mechanism which allows movement of the rotatable ring in a first direction while preventing movement of the rotatable ring in the opposite direction. The rotatable ring is also utilized in connection with a bearing member to facilitate smooth and efficient rotation of the rotatable ring. An extension saddle is utilized to provide a desired amount of displacement between suture securement points to minimize pivotal movement of the catheter. The rotatable ring is wider than its height to minimize kinking of the catheter tube and to relieve pressure when pressed between the patient and a support surface. In another embodiment, a plurality of scallops or other gripping members are utilized to facilitate easy gripping and rotation of the rotatable ring.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
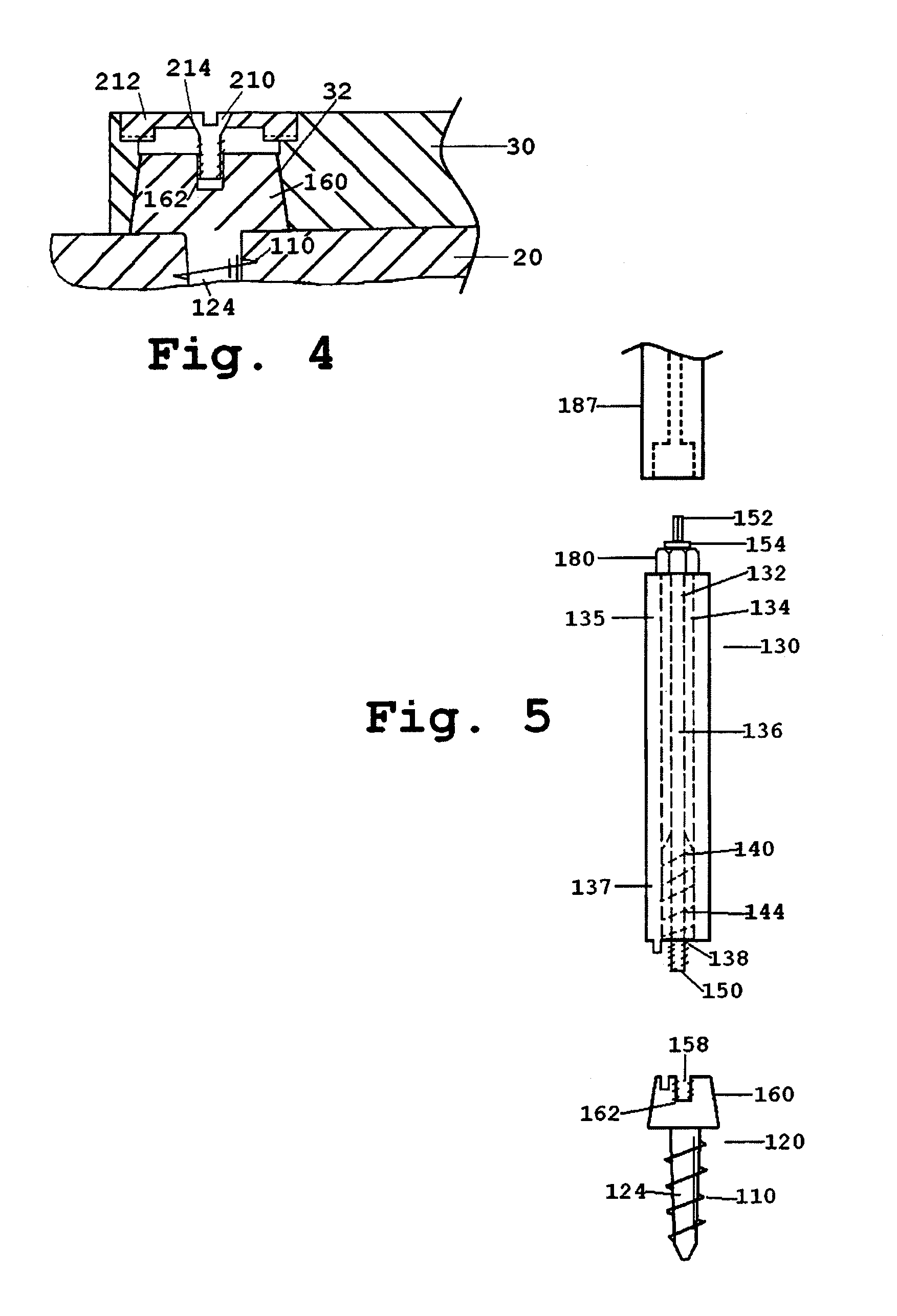
Porous Bone Fixation Device
A porous bone fixation device has a body including non-porous areas that provide superior long term fixation and osteointegration performance. The porous areas provide an in-growth surface in strategic sections such as the threaded section of the fixation device that allow substantially more contact area between in-growth surface and bone. The in-growth material is a network of interconnected porosity in a matrix of bio compatible, preferably titanium. Examples of bone fixation devices include bone screws, bone anchors, dental implants, and similar devices used to provide a fixation point in bone.
Owner:PRAXIS POWDER TECH
Minimally invasive spine restoration systems, devices, methods and kits
ActiveUS20080015585A1Restore qualityRestore stateInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsArticular surfacesFixation point
The invention discloses methods, devices, systems and kits for repairing, replacing and / or augmenting natural facet joint surfaces and / or facet capsules. An implantable facet joint device of one embodiment comprises a cephalad facet joint element and a caudal facet joint element. The cephalad facet joint element includes a member adapted to engage a first vertebra, and an artificial cephalad bearing member. The caudal facet joint element includes a connector adapted for fixation to a second vertebra at a fixation point and an artificial caudal bearing member adapted to engage the cephalad bearing member. The artificial caudal bearing member is adapted for a location lateral to the fixation point. In another embodiment, an implantable facet joint device comprises a cephalad crossbar adapted to extend mediolaterally relative to a spine of a patient, the crossbar having opposite first and second ends, a connector element adapted to connect the crossbar to a first vertebra, a first artificial cephalad bearing member adapted for connection to the first end of the crossbar and adapted to engage a first caudal facet joint element connected to a second vertebra, and a second artificial cephalad bearing member adapted for connection to the second end of the crossbar and adapted to engage a second caudal facet joint element connected to the second vertebra. In yet another embodiment, an implantable facet joint device comprises a caudal cross-member adapted to extend mediolaterally relative to a spine of a patient and adapted to connect to a first vertebra, a first artificial caudal bearing member adapted for connection to the caudal cross-member, and adapted to engage a first cephalad facet joint element connected to a second vertebra, and a second artificial caudal bearing member adapted for connection to the caudal cross-member at a predetermined spacing from the first bearing member, the second bearing member being adapted to engage a second caudal facet joint element connected to the second vertebra.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
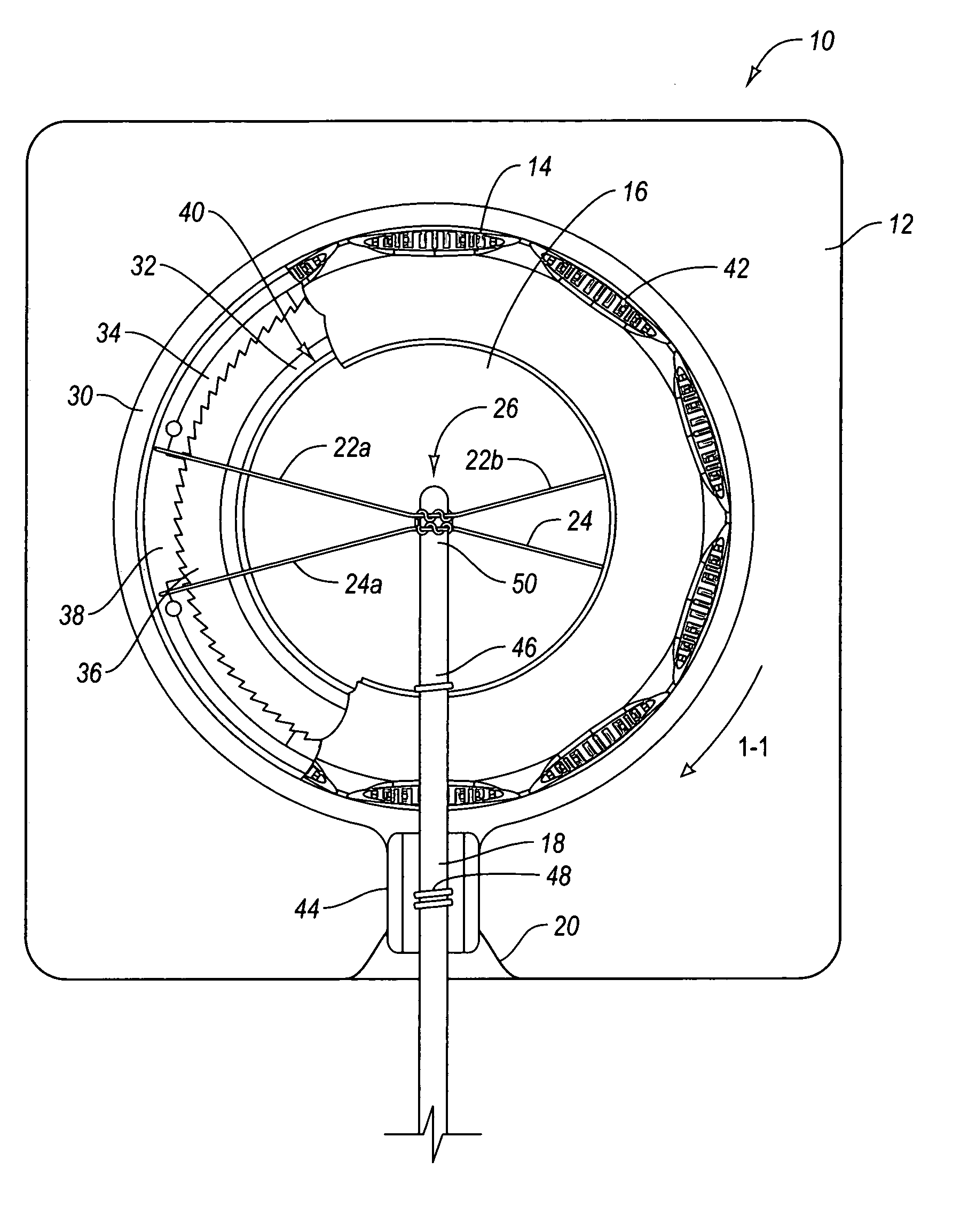
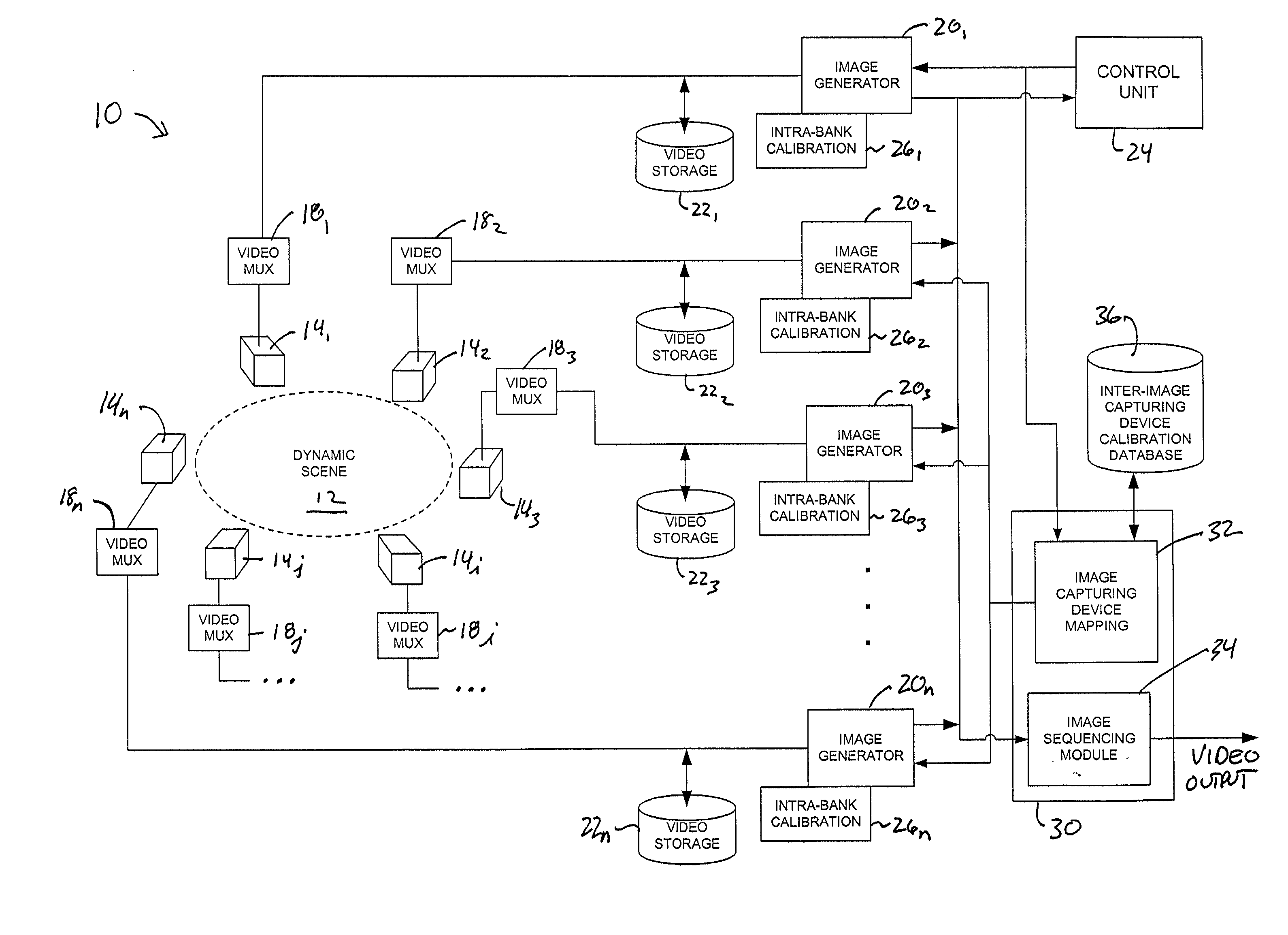
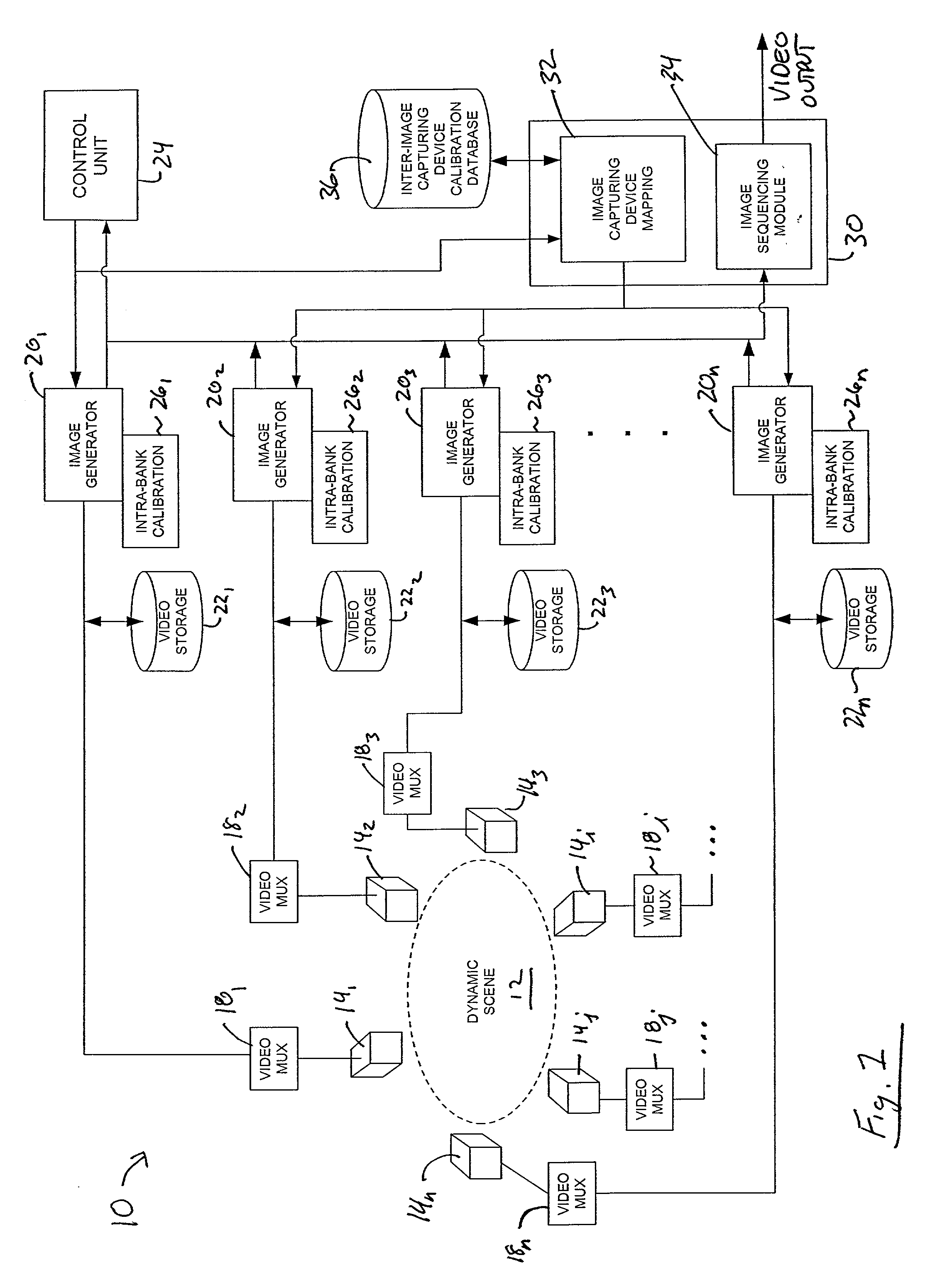
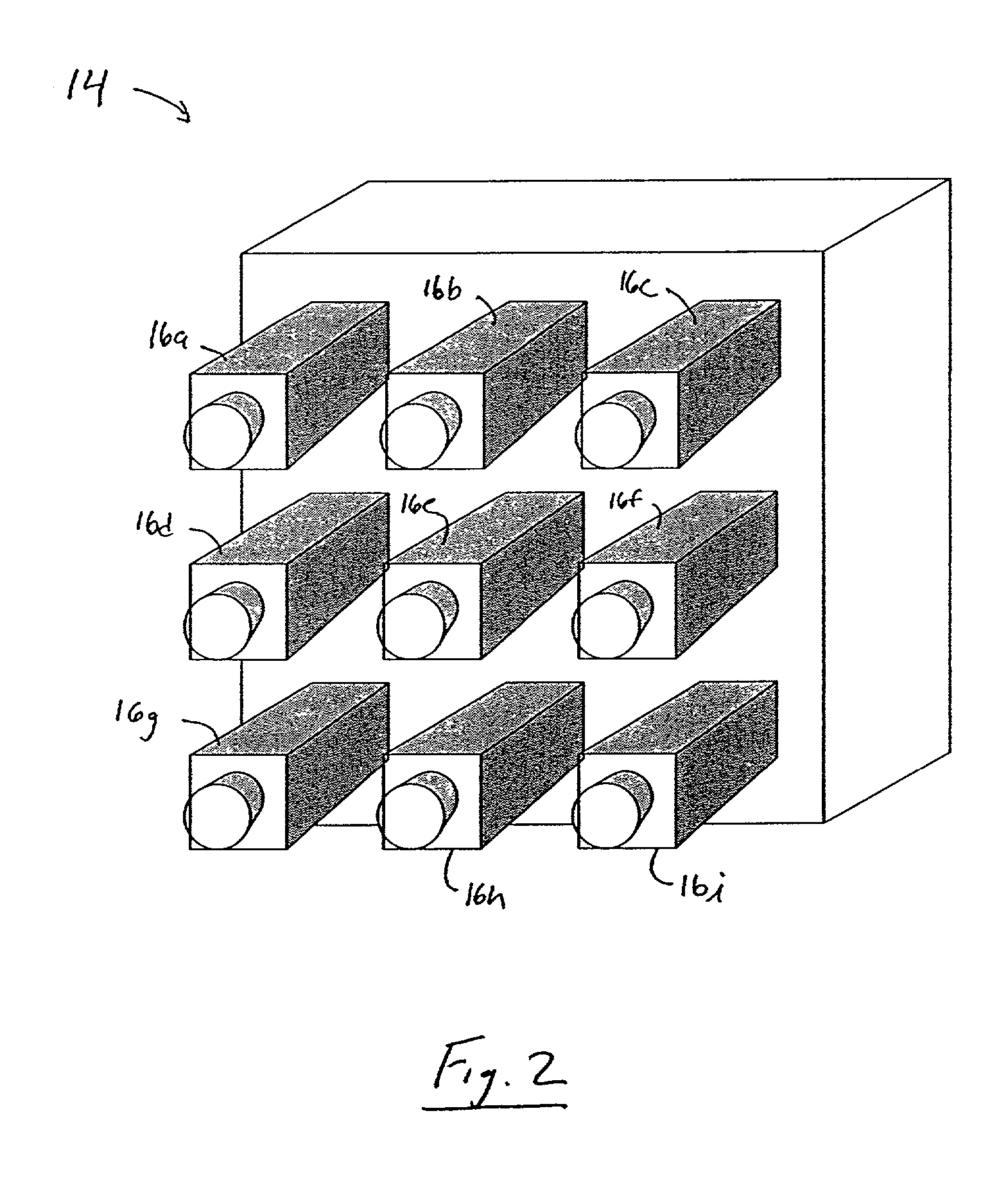
System and method for obtaining video of multiple moving fixation points within a dynamic scene
InactiveUS20030076413A1Television system detailsColor television detailsFixation pointVideo sequence
A system and method for obtaining video of a moving fixation point within a scene. According to one embodiment, the system includes a control unit and a plurality of non-moving image capturing devices positioned around the scene, wherein the scene is within a field of view of each image capturing device. The system also includes a plurality of image generators, wherein each image generator is in communication with one of the image capturing devices, and wherein a first of the image generators is responsive to a command from the control unit. The system also includes a surround-view image sequence generator in communication with each of the image generators and responsive to the command from the control unit for generating a surround-view video sequence of the fixation point within the scene based on output from certain of the image generators.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Ophthalmology oct system and ophthalmology imaging method
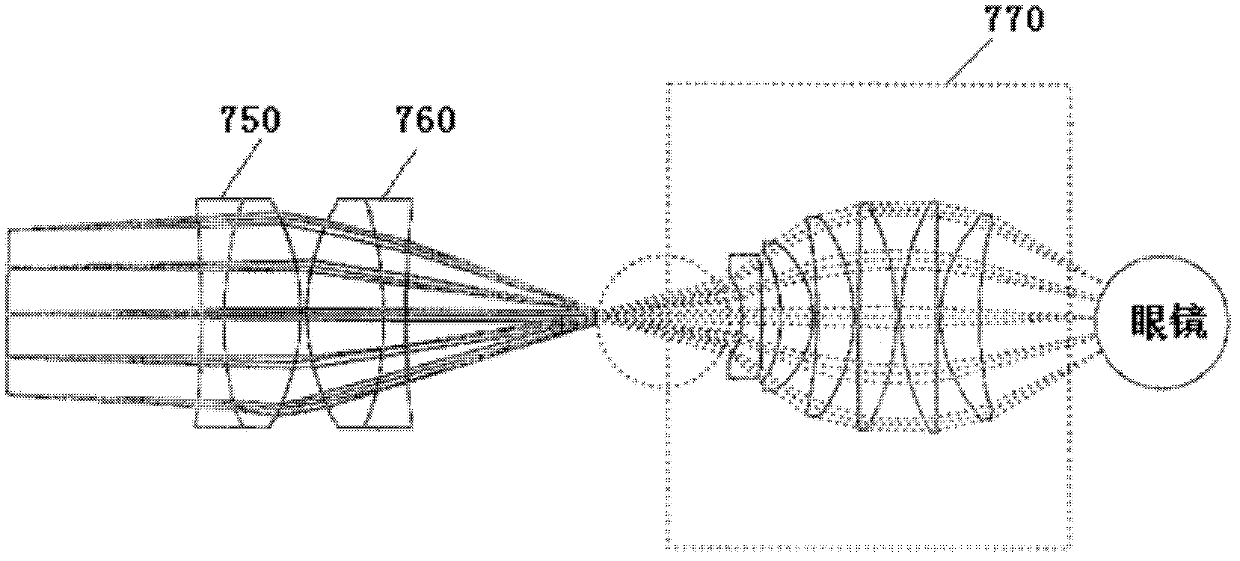
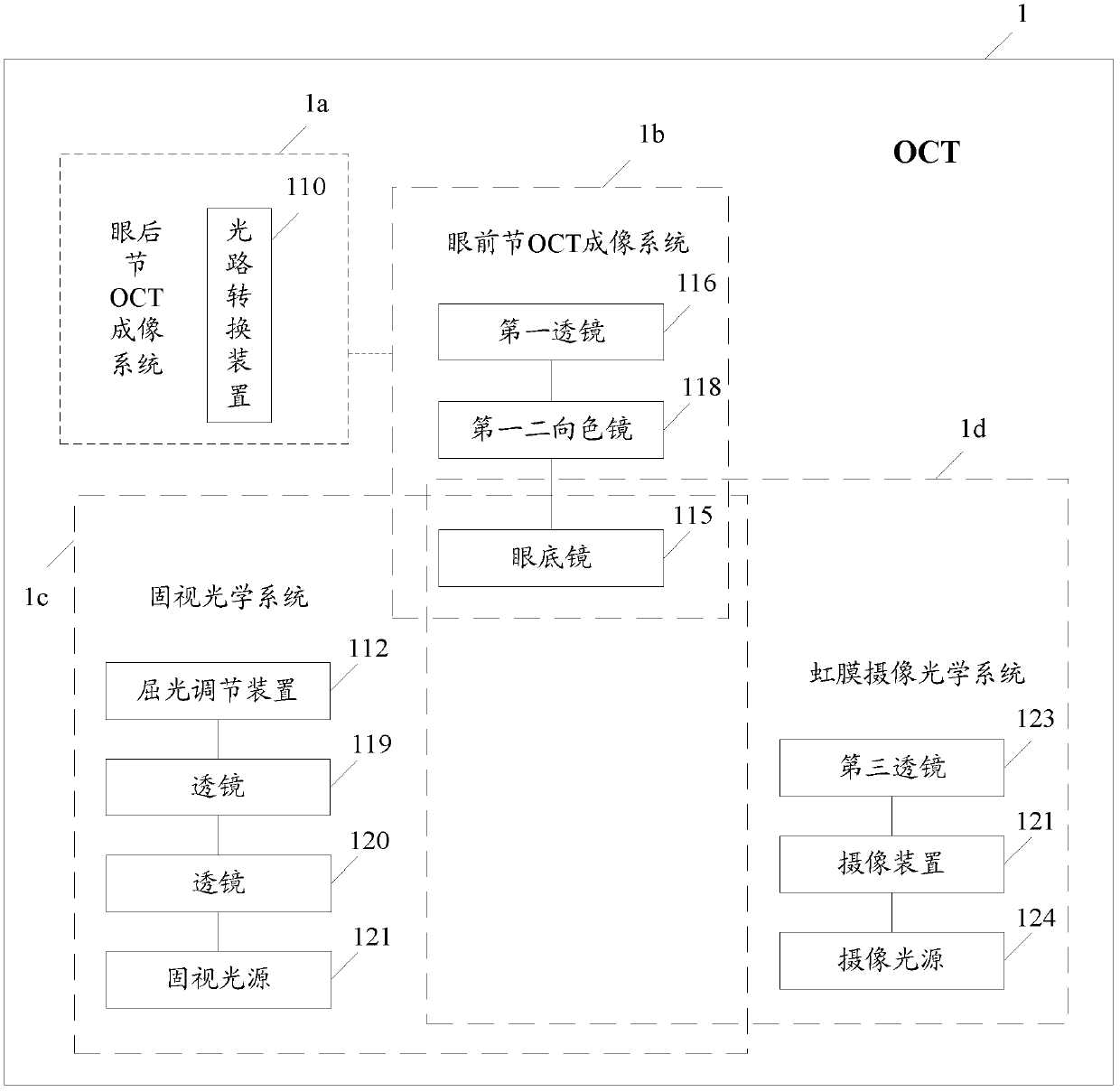
ActiveCN102438505ASimple structureEasy to operateMaterial analysis by optical meansEye diagnosticsFixation pointImaging quality
The embodiment of the invention discloses an ophthalmology OCT system, comprising a posterior segment intraocular OCT imaging system and an anterior eye segment OCT imaging system. The posterior segment intraocular OCT imaging system comprises a light path conversion device, the anterior eye segment OCT imaging system comprises an anterior eye segment probe imaging device comprising an ophthalmoscope, a first dichroscope and a first lens; wherein, when the ophthalmology OCT system carries out an anterior eye segment scanning imaging, and after the light path conversion device receives a light path conversion instruction, signal light passing through a collimating mirror and a scanning device respectively are converted to the anterior eye segment probe imaging device; the anterior eye segment probe imaging device drives the first dichroscope to reflect the signal light to the ophthalmoscope to carry out the anterior eye segment scanning imaging. Correspondingly, the invention also discloses an ophthalmology OCT imaging method. By employing the invention, when the anterior eye segment imaging is carried out on human eye, fixation points can always be kept clear via refractive compensation, and the anterior eye segment probe imaging quality is not affected.
Owner:SHENZHEN CERTAINN TECH CO LTD +1
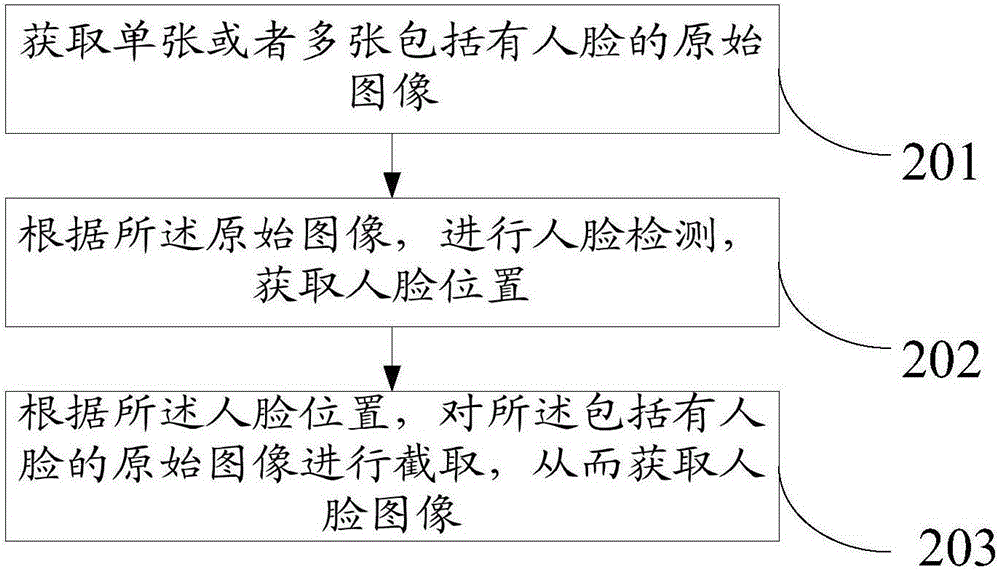
Living body human face recognition method and device
ActiveCN105184277AImprove anti-counterfeiting performanceImprove securityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFixation point
The invention relates to the technical field of identity verification, and particularly relates to a living body human face recognition method, a device and a system. The method comprises steps: multiple human face images are acquired instantly; according to the human face images, a fixation point of at least one eye in each human face image or a motion track of the fixation point is acquired; according to the fixation point of the eye or the motion track of the fixation point, whether the eye moves according to a hint is judged; if yes, living body verification is passed. According to the method, when a user carries out facial feature verification, the eye moves according to the hint; as facial features and eye moving data are extracted from the same picture or one group of pictures or video, an illegal logon person can not cheat the verification device by using a face image or video prepared in advance, and thus, the method can judge that the user agrees to the face features, and the face information is from the living body in reality.
Owner:杨晴虹 +2
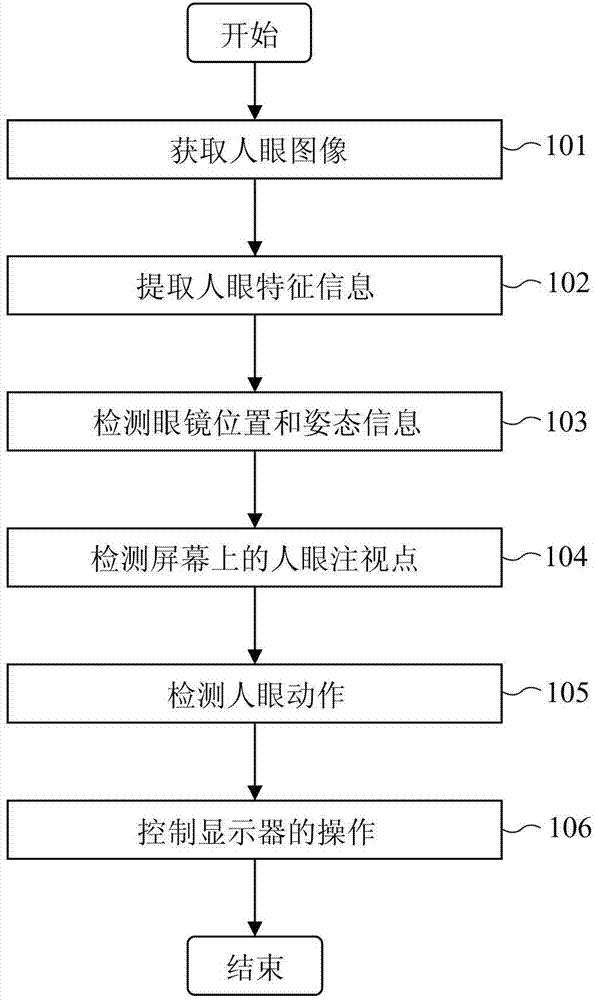
Method and equipment for controlling displayer
ActiveCN103500061ASelective content distributionInput/output processes for data processingFixation pointOphthalmology
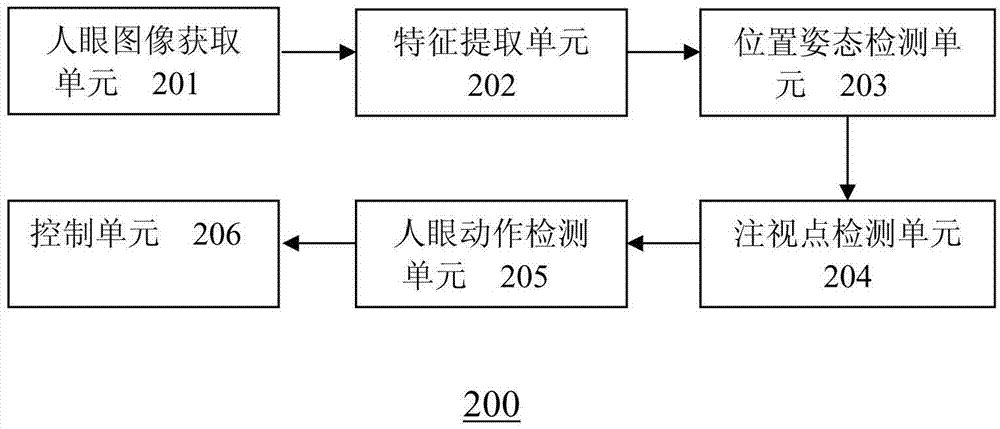
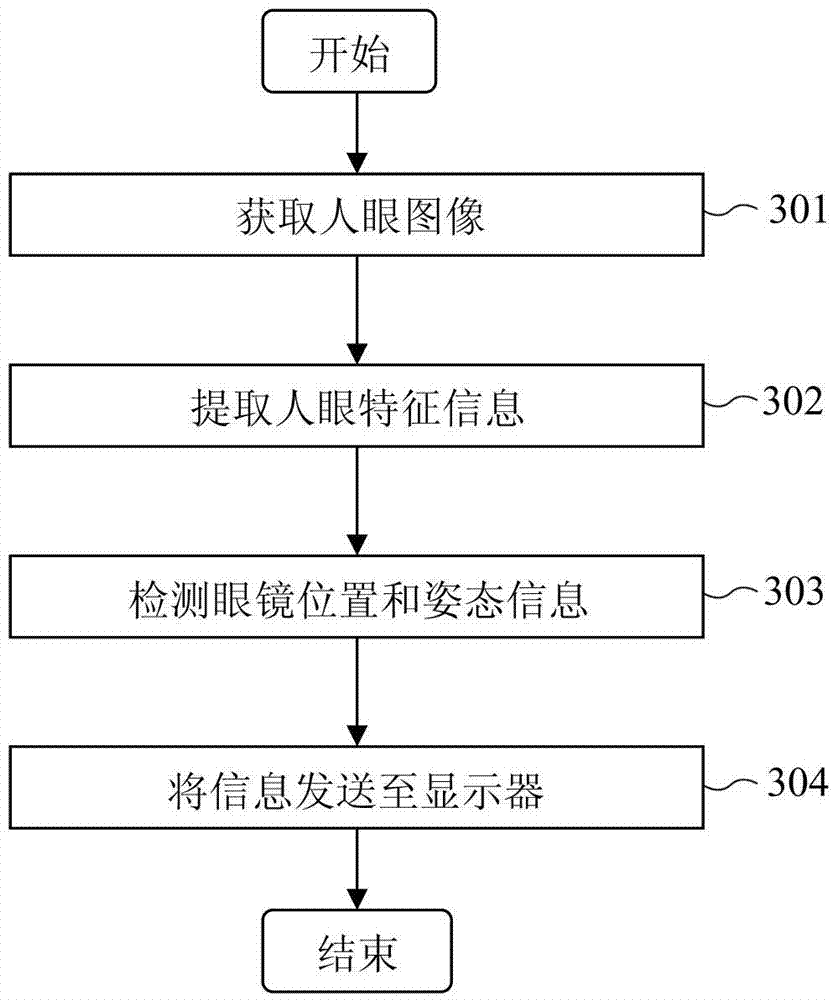
Provided is a method and equipment for controlling a displayer. The method comprises the steps that a human eye image is obtained by shooting a human eye through electronic glasses; human eye feature information is extracted from the human eye image; the glasses position and the gesture information of the electronic glasses are detected; according to the human eye feature information, the glasses position and the gesture information, a human eye fixation point on a screen is detected; according to the human eye feature information and / or the changing situation of the human eye fixation point on the screen, human eye action is detected; displayer operation is controlled according to human eye action and the human eye fixation point on the screen. According to the method and equipment, the displayer can be controlled according to the human eye image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CHINA R&D CENT +1
Implantable Devices for Musculoskeletal Repair and Regeneration
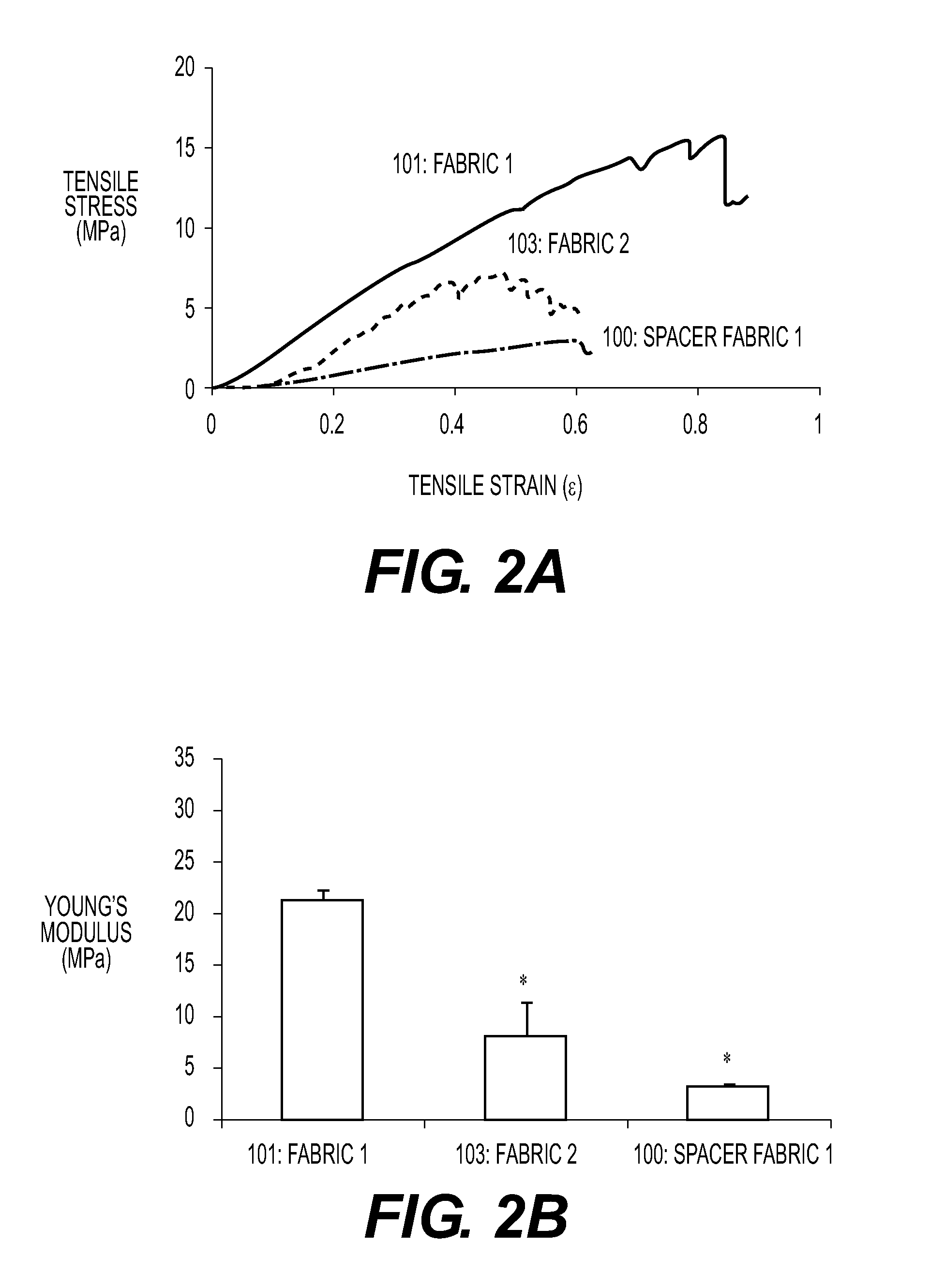
This application describes an implantable device for tissue repair comprising at least two fabrics with interconnecting spacer elements transversing, connecting, and separating the fabrics, forming the device. Some embodiments have fixation points which can be an extension of at least one of the fabrics. The implantable device allows modification of the two fabrics having varying constructions, chemistries, and physical properties. The spacer elements create a space between the two fabrics, which can be used for the loading of biological materials (peptides, proteins, cells, tissues), offer compression resistance (i.e. stiffness), and compression recovery (i.e., return to original dimensions) following deformation and removal of deforming load. The inclusive fixation points of the fabrics are designed to allow for fine adjustment of the sizing and tension of the device to promote integration with the surrounding tissues as well as maximize the compressive resistance. The fixation points can include either the first fabric, the second fabric, or the combination of both fabrics. This device is suitable for soft and hard tissue regeneration or replacement with a preference for musculoskeletal tissues including but not limited to cartilage (including hyaline (referred to as articular, e.g. cartilage on the ends of long bones), fibrous (e.g. meniscus or intervertebral discs), elastic (e.g. ear, epiglottis)), bone, muscle, tendon, ligament, and fat.
Owner:MCCULLEN SETH
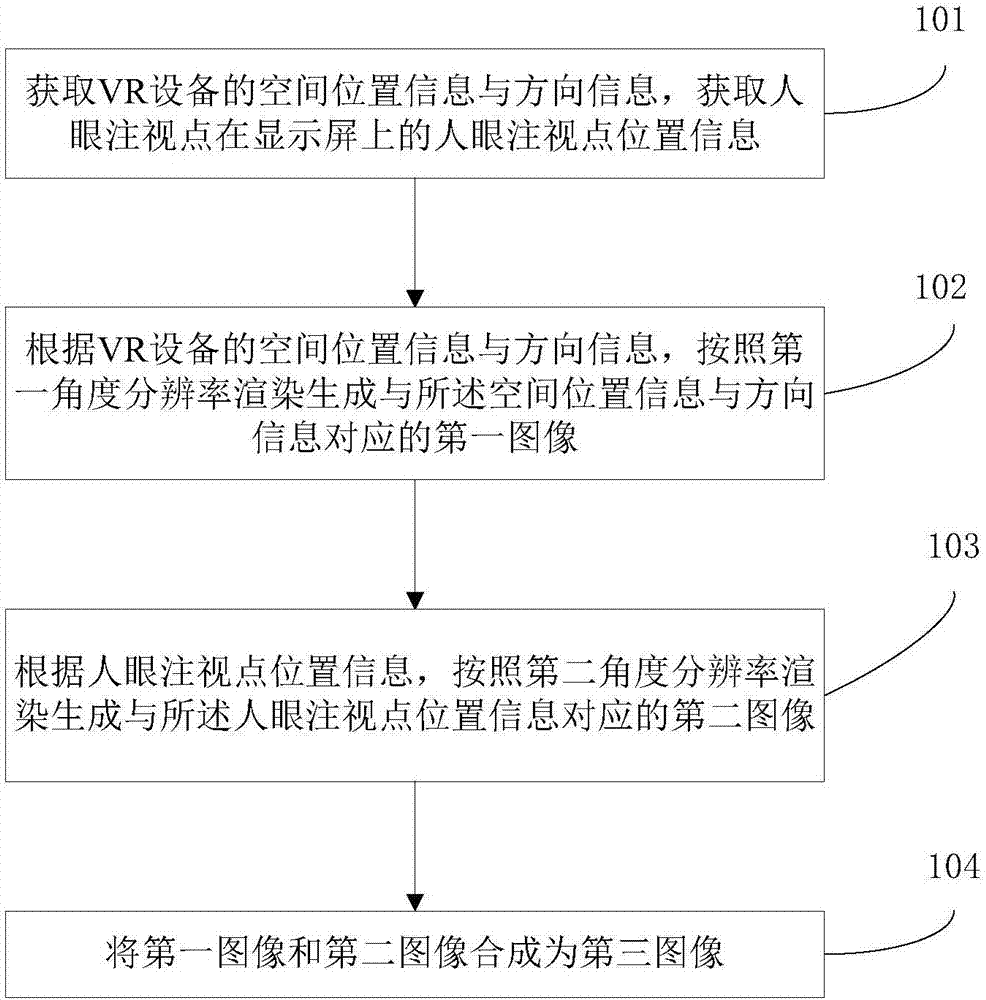
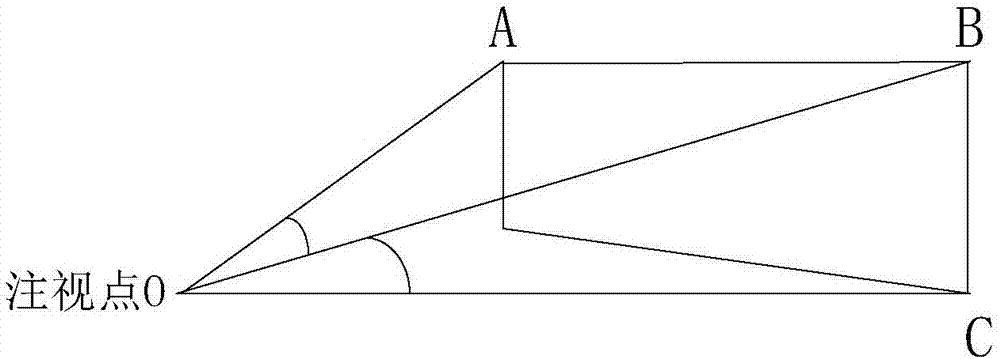
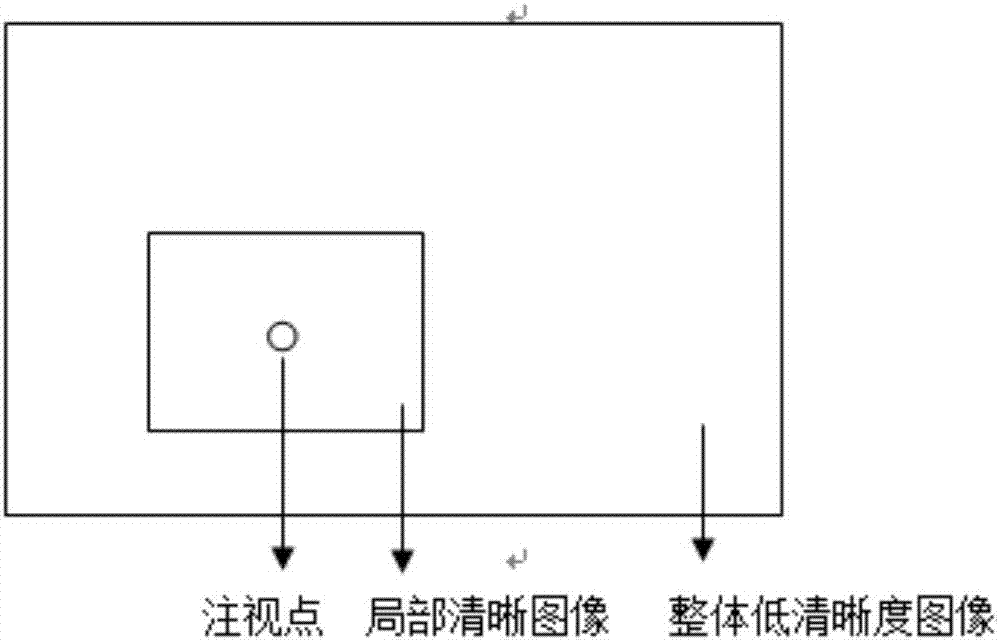
Graphic rendering method and device for virtual reality
InactiveCN107516335ASmall amount of calculationImprove image rendering efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementGraphicsFixation point
The invention discloses a graphic rendering method and device for virtual reality. According to the invention, a first image corresponding to spatial position information and directional information is generated through rendering according to a first angle resolution based on the acquired spatial position information and the directional information of a head-mounted virtual reality device. According to acquired position information of a human eye fixation point on a display screen, a second image corresponding to the human eye fixation point is generated through rendering according to a second angle resolution. A third image is generated through combination of the first image and the second image. According to the invention, when rendering is performed on the virtual reality image, the adopted first angle resolution and the adopted second angle resolution are comparatively low angle resolutions, so that the calculation amount of a GPU can be reduced effectively and image rendering efficiency is improved.
Owner:GOERTEK OPTICAL TECH CO LTD
Depth based foveated rendering for display systems
ActiveUS20190287495A1Change in amountInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementFixation pointWavefront
Methods and systems for depth-based foveated rendering in the display system are disclosed. The display system may be an augmented reality display system configured to provide virtual content on a plurality of depth planes using different wavefront divergence. Some embodiments include determining a fixation point of a user's eyes. Location information associated with a first virtual object to be presented to the user via a display device is obtained. A resolution-modifying parameter of the first virtual object is obtained. A particular resolution at which to render the first virtual object is identified based on the location information and the resolution-modifying parameter of the first virtual object. The particular resolution is based on a resolution distribution specifying resolutions for corresponding distances from the fixation point. The first virtual object rendered at the identified resolution is presented to the user via the display system.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Video game to monitor retinal diseases
Systems and methods for providing a video game to map macular visual acuity comprising a multiple choice test where the fixation point is ensured by brief simultaneous presentation of both a central and pericentral targets. The game may be implemented on a hardware platform including a video display, a user input device, and a video camera. The camera is used to monitor ambient light level and the distance between the device and the eyes of the test subject. The game serves as a macular acuity perimeter that produces a map of the acuity of an eye that may be compared with normative data. The type of acuity tested is preferably Vernier acuity, but resolution acuity can also be tested. The test results are transmitted to a health care professional by telecommunications means to facilitate the diagnosis or monitoring of age-related macular degeneration or other relevant eye diseases.
Owner:GOBIQUITY INC +1
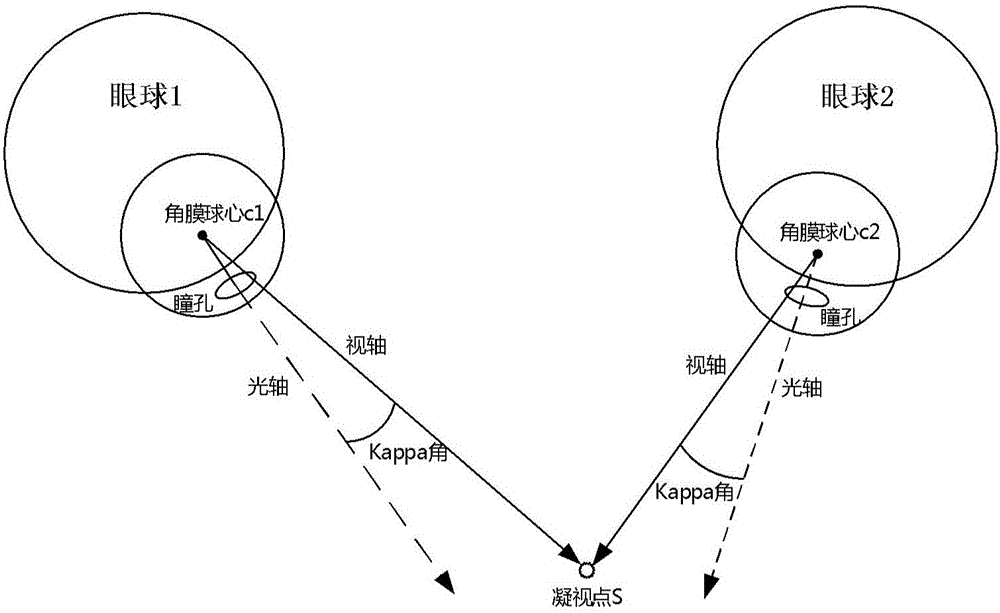
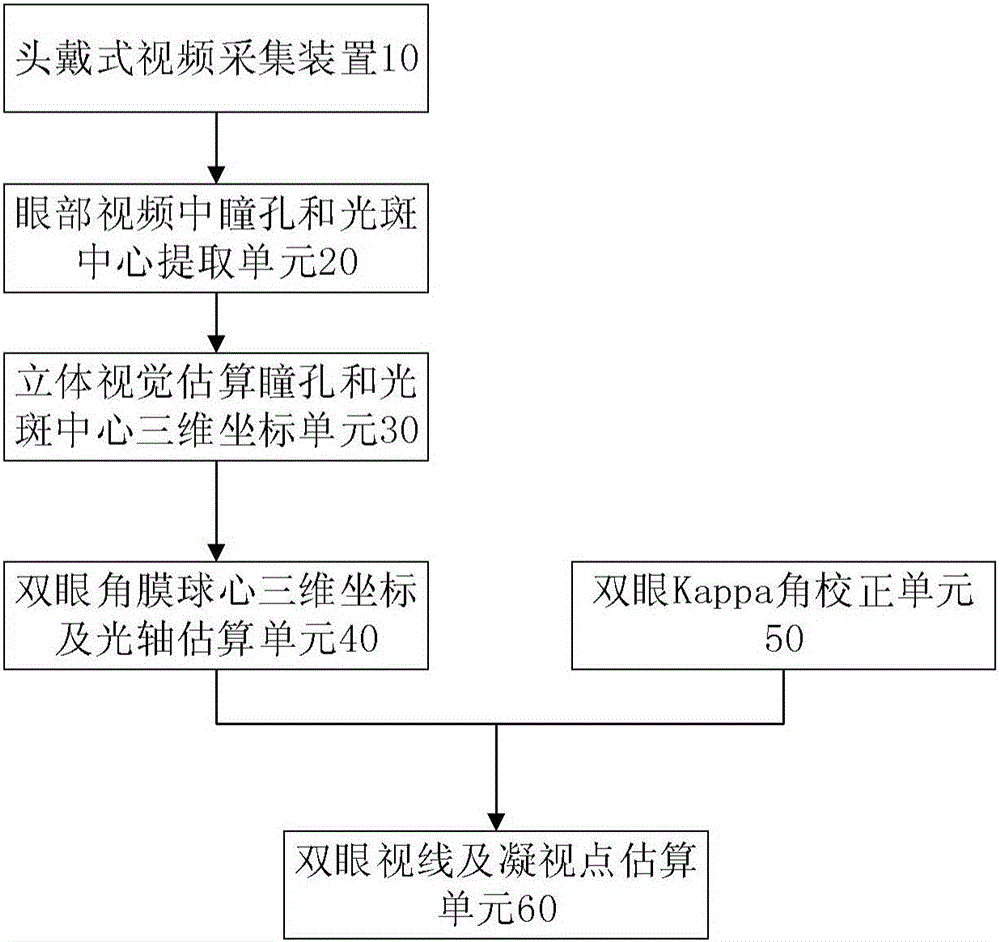
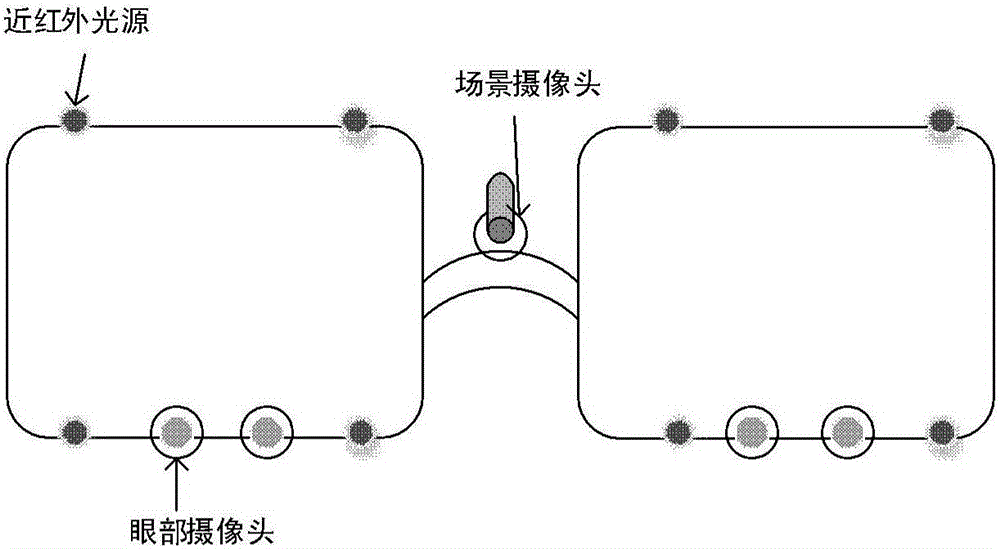
Free-space head-wearing eye-tracking system
ActiveCN106168853AImprove experienceAccurate CalibrationInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingFixation pointPupil
The invention discloses a free-space head-wearing eye-tracking system. The free-space head-wearing eye-tracking system comprises a head-wearing video collection device, a unit for evaluating the binocular optic axis through stereoscopic vision and a binocular vision and fixation point evaluation unit; the head-wearing video collection device collects four ways of near-infrared eye video and one way of scene video simultaneously, and the four ways of the near-infrared eye video comprise two ways of the near-infrared eye video of the left eye of a wearer who wears the head-wearing video collection device and two ways of the near-infrared eye video of the right eye of the wearer who wears the head-wearing video collection device; coordinates of pupils of both eyes and cornea center are evaluated directly through a stereoscopic vision method, and a binocular optic axis straight line equation is calculated; a binocular visual axis straight line equation is evaluated according to an eyeball Kappa angle and the binocular optic axis straight line equation, a fixation point coordinate is calculated, the position of a fixation point in the scene video is mapped and marked, and the Kappa angle is a fixed included angle between the optic axis and the visual axis of each eyeball.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Coordinate instrument set
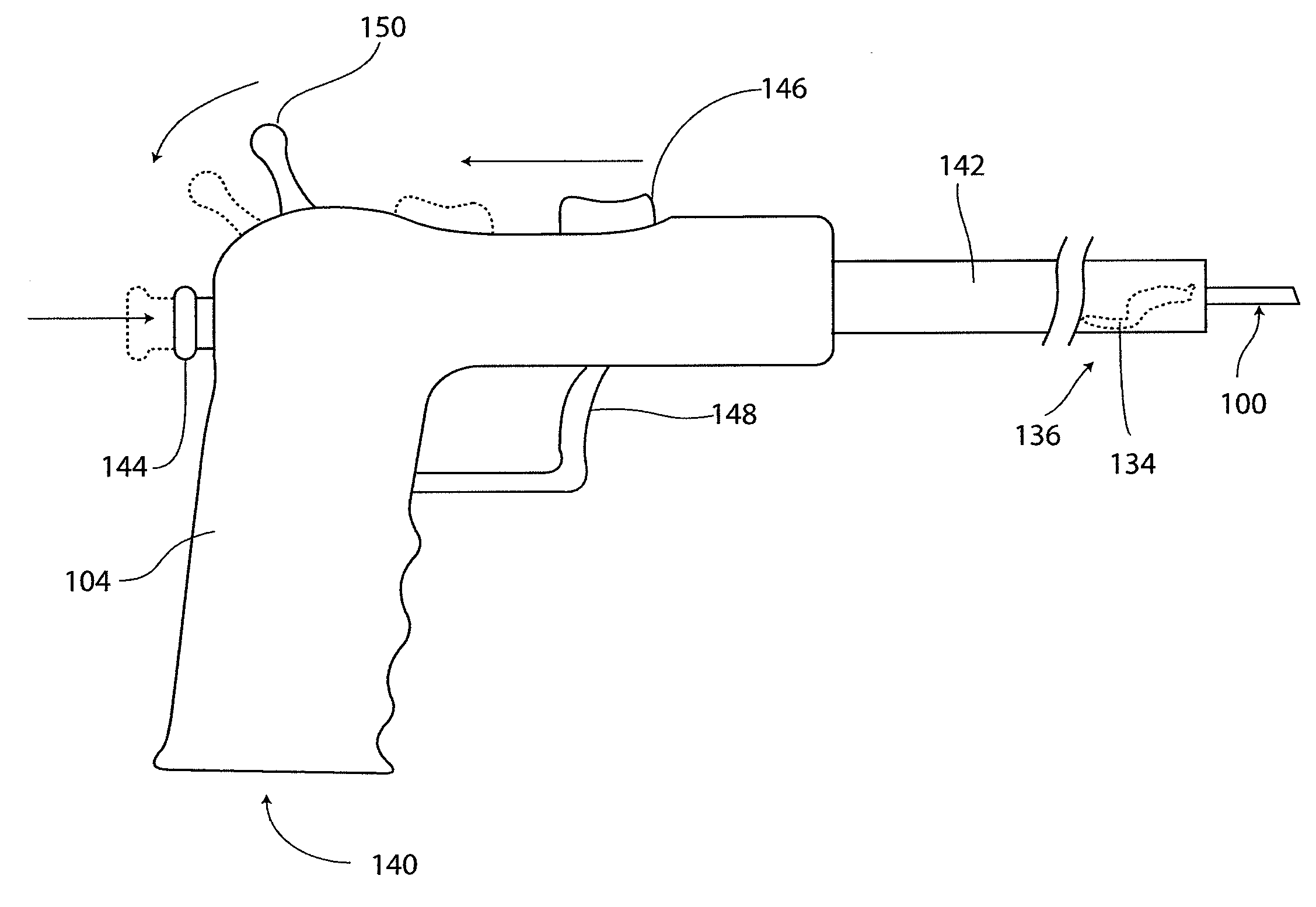
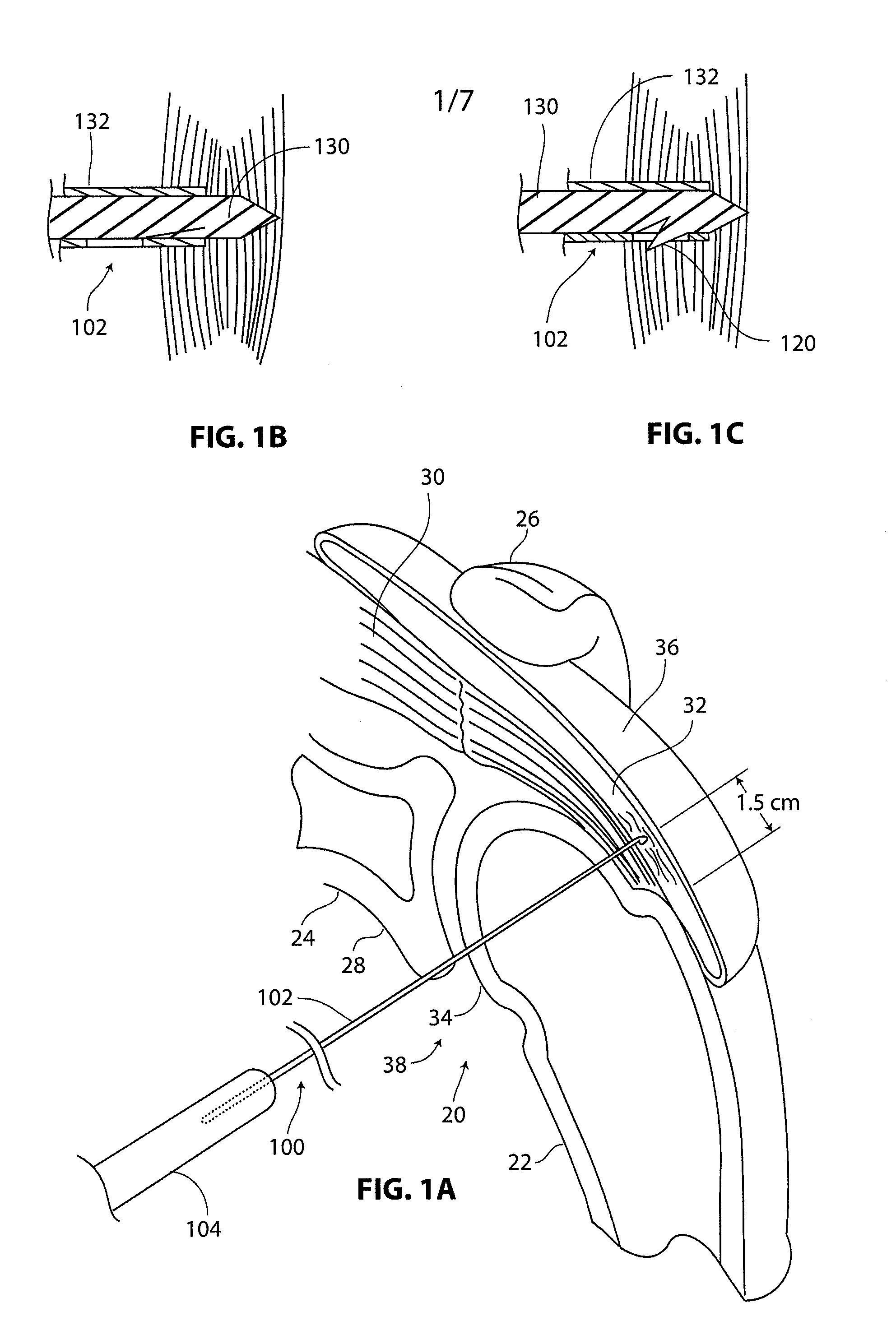
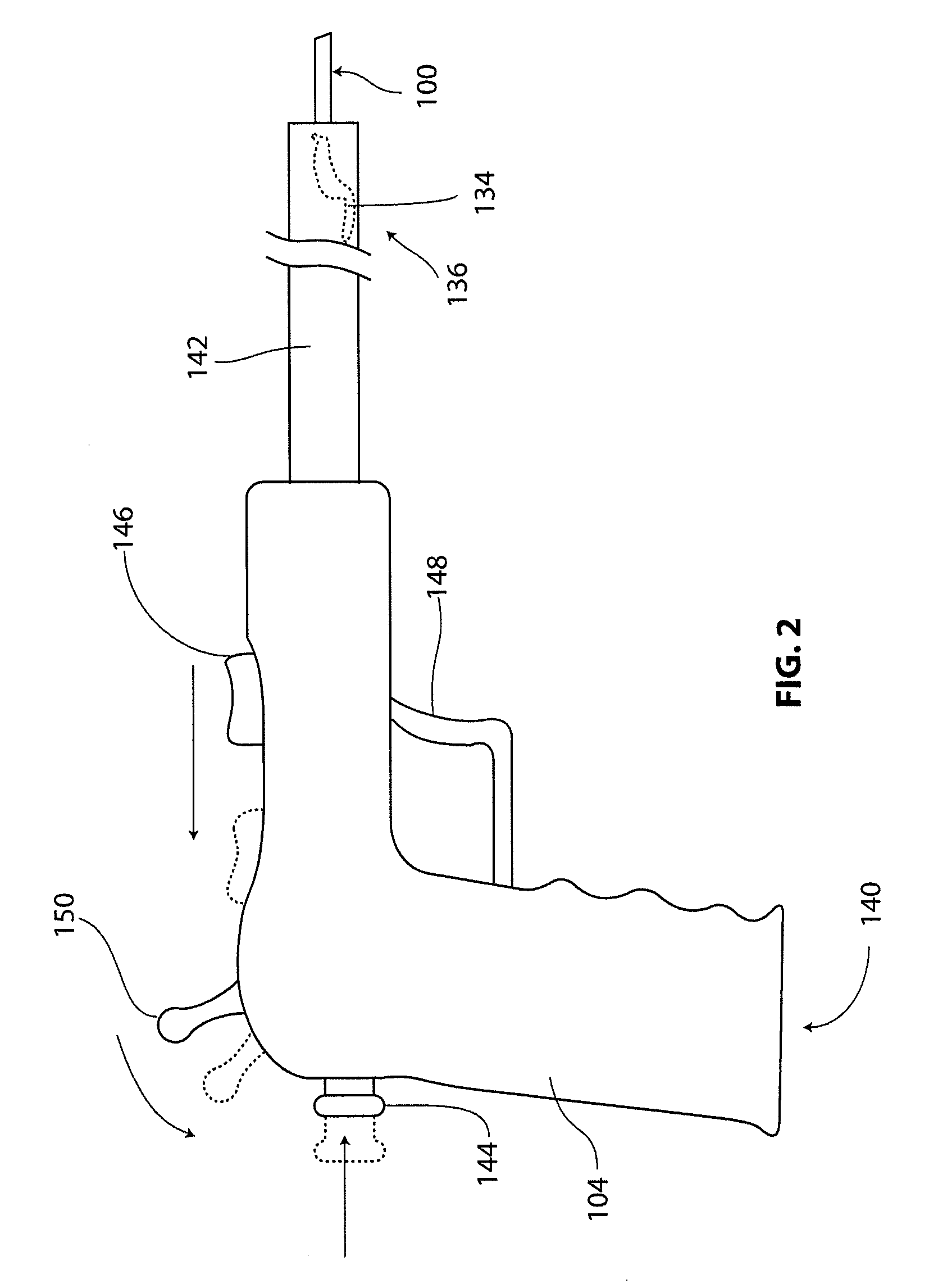
Surgical instruments for use in mapping tissue defects include telescoping rulers and tubes. One of the instruments has a pointed anchoring tip for piercing tissue near the site of the defect. Another instrument has a hook for catching an anatomical landmark. Measuring portions of the rulers of both instruments include distance indicia so that a coordinate system can be established for mapping the location of the defect or of an implant at the defect site. The coordinate system can be re-established at a later time using the same fixation point for the anchoring tip and the same landmark for the hook to evaluate the clinical effects of the treatment selected. The method of using the instrument set is also described.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Intramedullary Fixation Device for Small Bone Fractures
InactiveUS20090275946A1Aggressive curveAdd flexiblyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFixation pointCurve shape
A fracture fixation system particularly useful for bones of the hand and foot is disclosed. The system uses curved shape-memory alloy (e.g., Nitinol) wires that have a predetermined radius of curvature to accommodate different sized bones. These shape-memory alloy wire forms can be inserted into phalanx, metacarpal or metatarsal bones via a percutaneous technique. The technique uses small skin incisions; a specialized drill guide that has holding K-wires to maintain fixation of the drill guide to the bone so that it does not lose the insertion point; a specialized drill as well as a specialized wire cutter and advancement tool to make sure that the level of the wire is below the level of the outer cortical bone. Shape-memory alloy (e.g., Nitinol) based wires with a pre-bent curve have an advantage over the typical standard K-wire in that they can spring back to their predetermined memory shape when inserted into the intramedullary canal of the bone and heated, i.e., a more aggressive curve. By increasing their bending or flexion to increase the arc of curvature, this allows fixation points for the wire, essentially locking it to bone.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
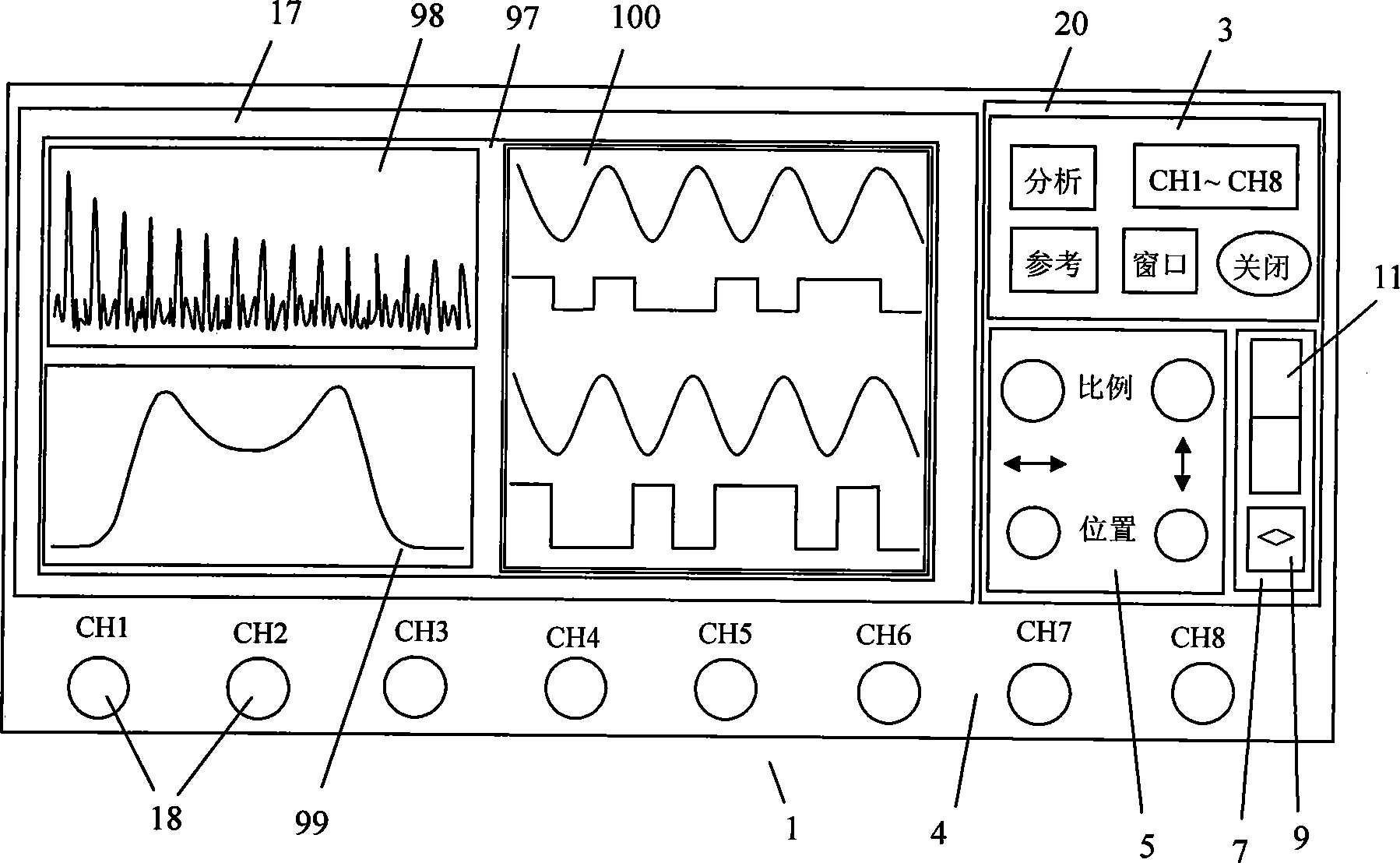
Digital oscilloscope and method for controlling display waveform
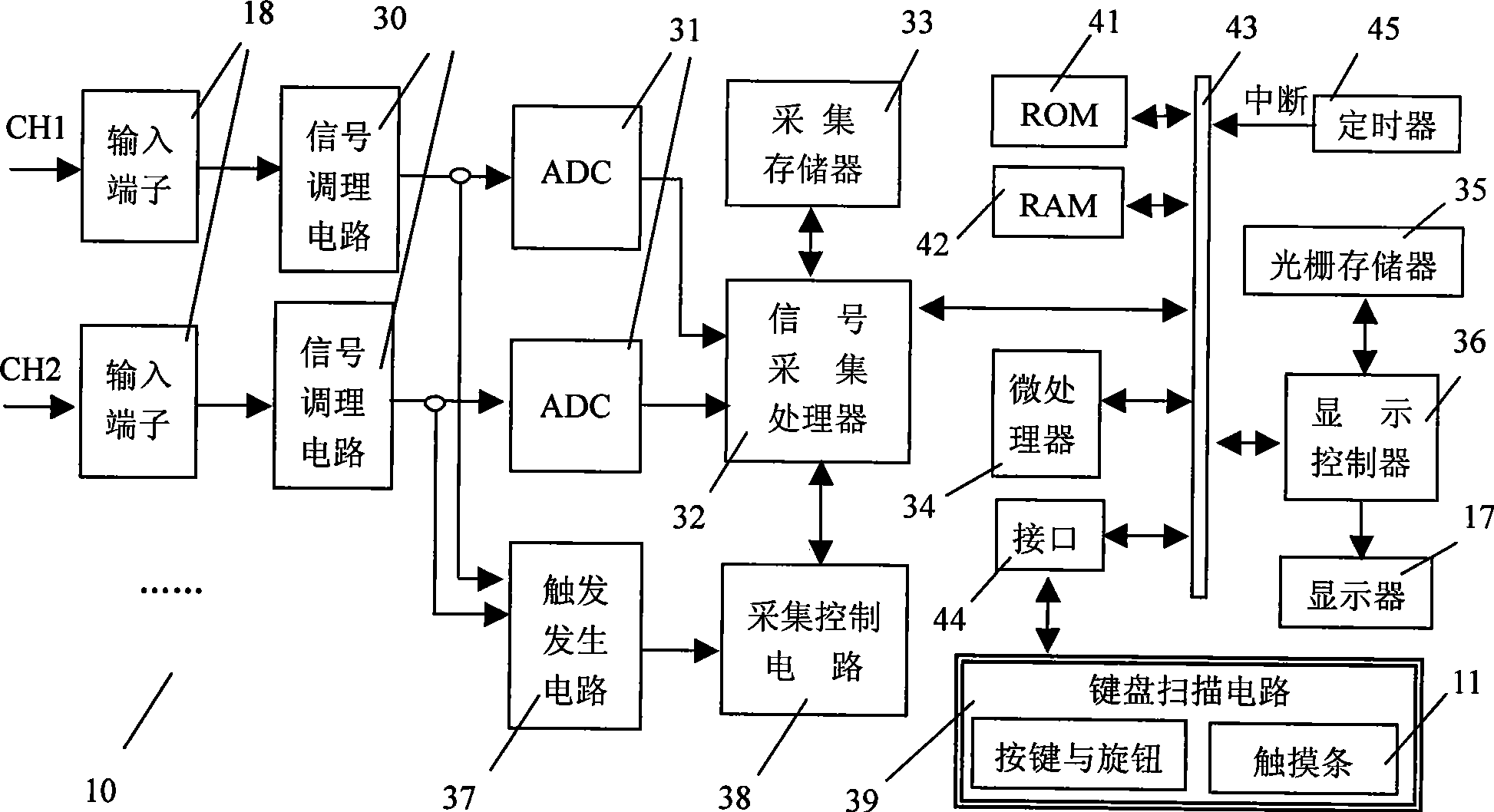
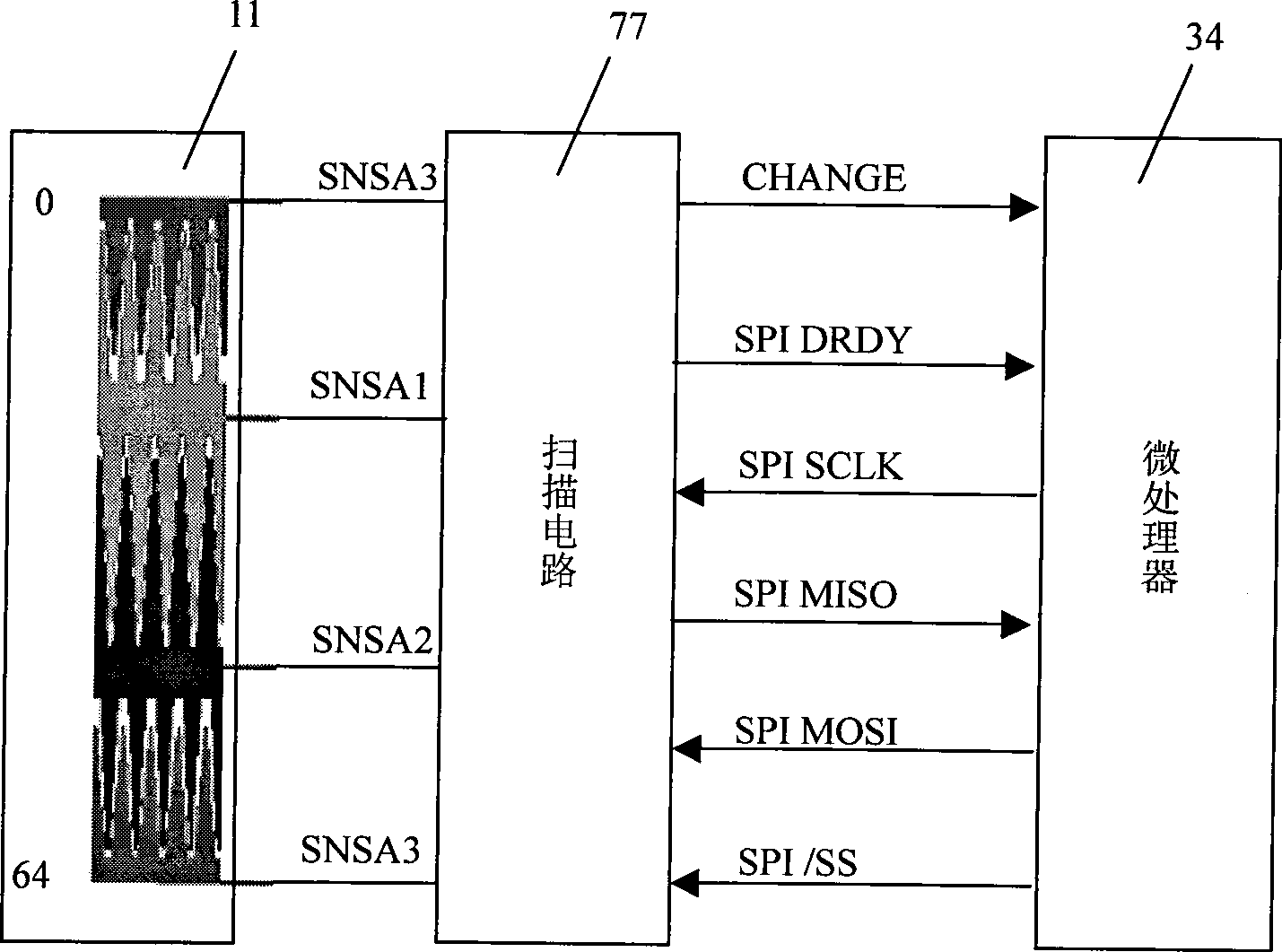
InactiveCN101413968ASmall footprintFlexible placementDigital variable displayFixation pointComputer science
The invention relates to a microprocessor or computer-based digital oscilloscope and a method for manipulating and displaying waveforms in the digital oscilloscope, the digital oscilloscope and the method are characterized in that the digital oscilloscope is provided with a bar-shaped touch device (11) for waveform selection, the coordinates of two key points on the top and the bottom part of each displayed waveform on a display screen are taken as fixation points, a touch point in the bar-shaped touch device (11) is mapped in the display screen by the linear corresponding relation to obtain a mapping position along the vertical direction, and the waveform represented by the fixation points which are most close to the mapping position is selected as the current waveform. When in waveform section, the digital oscilloscope has the advantages of faster, more intuitive and more difficult in making mistakes; the method does not need the precise positioning, the waveform selection device occupies smaller space, thereby being capable of reducing the operation range and reducing the hand fatigue; the placement of the waveform selection device is more flexible, and the waveform selection device can be moved relative to the waveform display screen.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
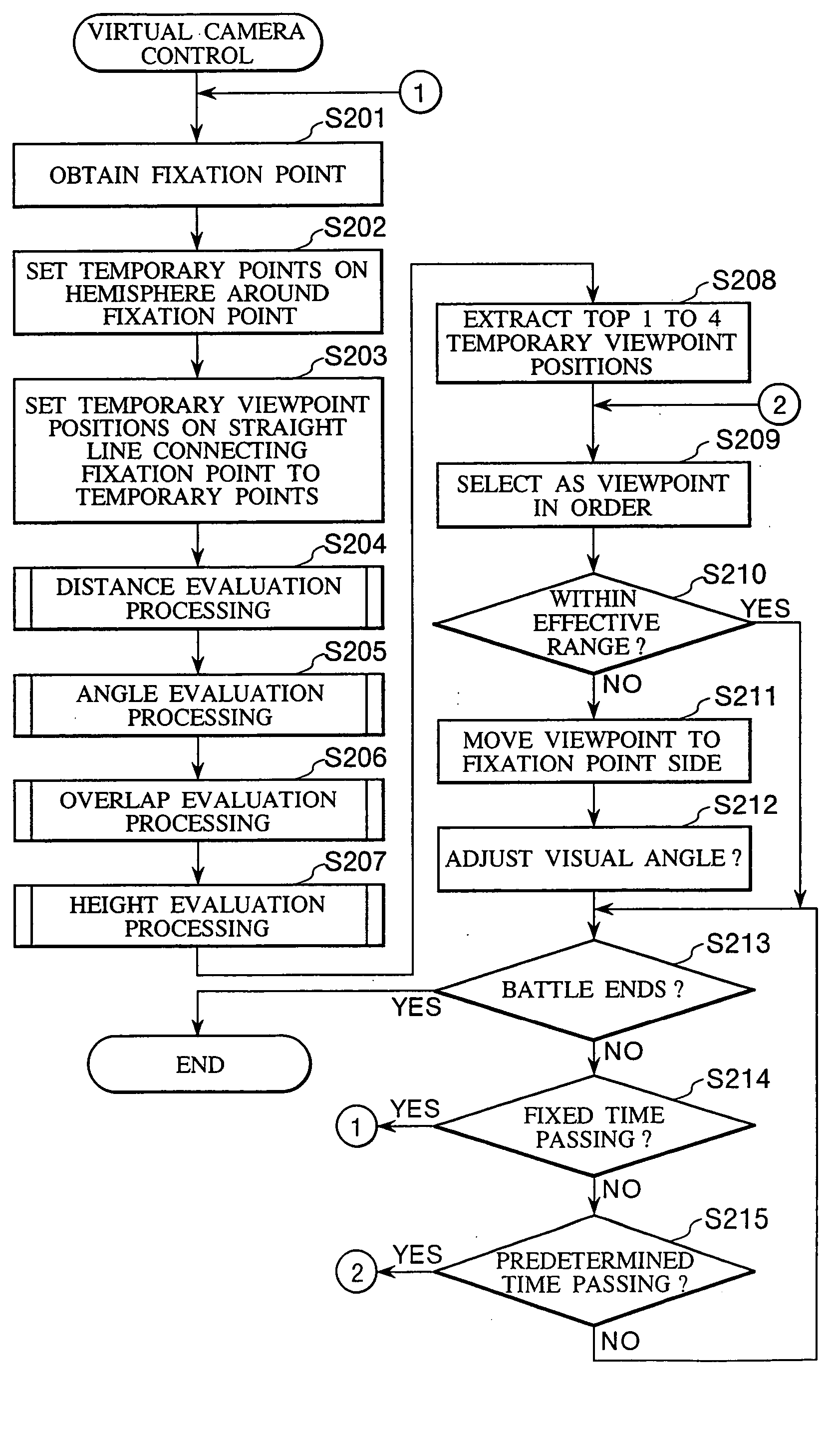
Virtual camera control method in three-dimensional video game
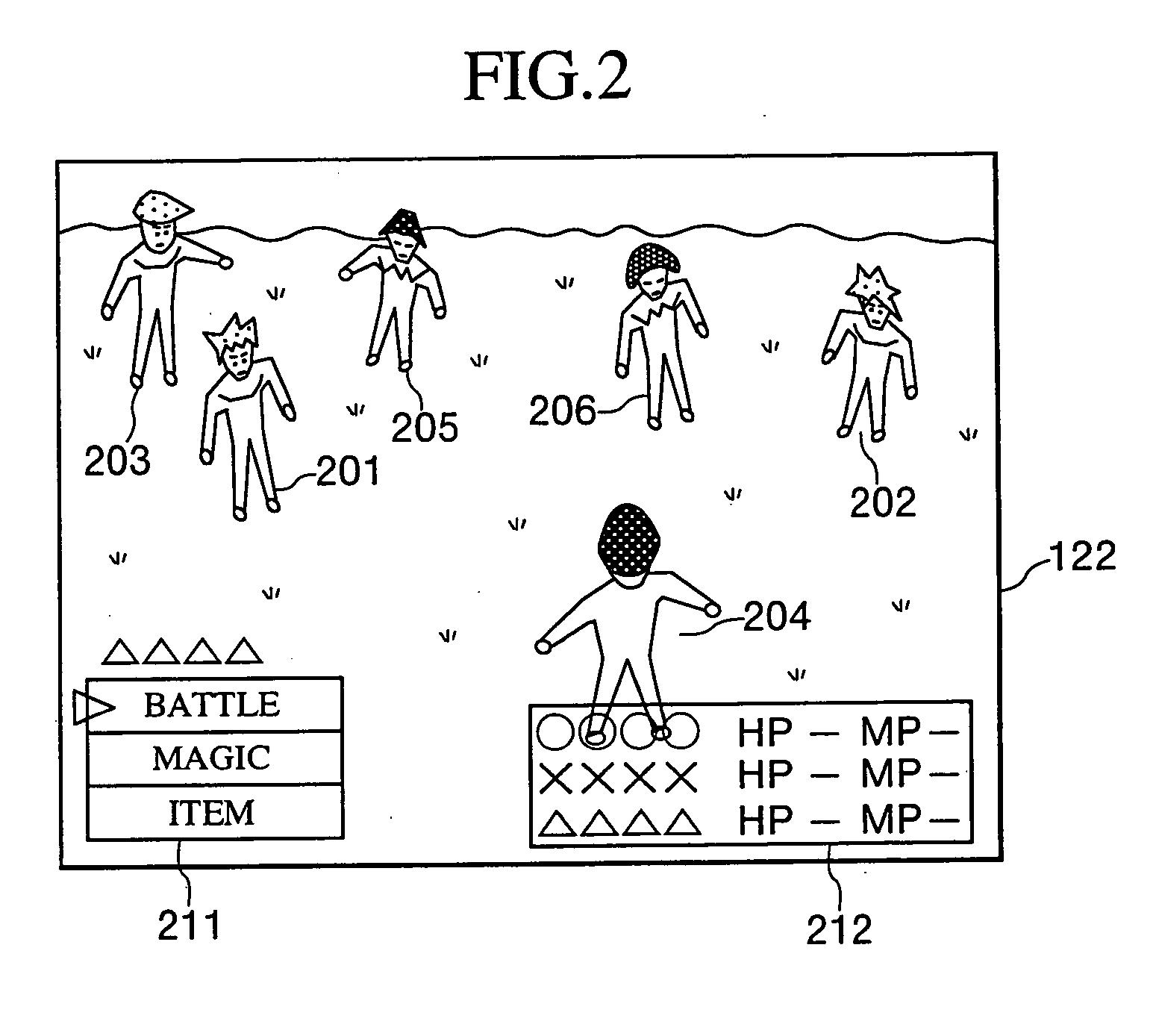
ActiveUS20040176164A1Reduce exerciseEasy to viewVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsViewpointsFixation point
A central position of each character participating in a battle is obtained as a fixation point, and multiple temporary points are set on a hemisphere around the fixation point. Each temporary viewpoint position is set on a straight line connecting the fixation point to each temporary point. Each temporary viewpoint position is a position from which all characters can be projected on a virtual screen when perspective transformation is executed at a predetermined visual angle and a distance to the fixation point is shortest. Points are given to each temporary viewpoint position based on the result of a distance evaluation, an angle evaluation, an overlap evaluation, and a height difference evaluation. The top scoring temporary viewpoint positions are selected as positions where the viewpoint of a virtual camera should be moved.
Owner:SQUARE ENIX HLDG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com