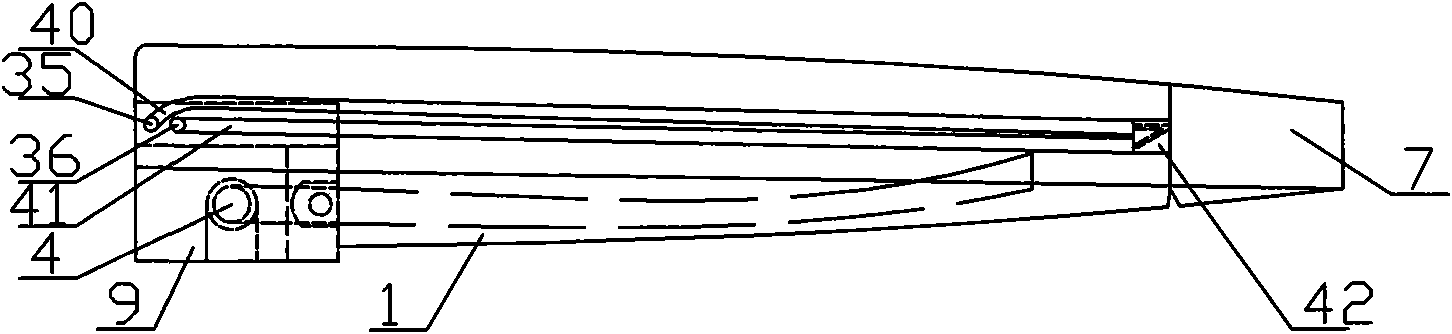Patents
Literature
76 results about "Epiglottis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
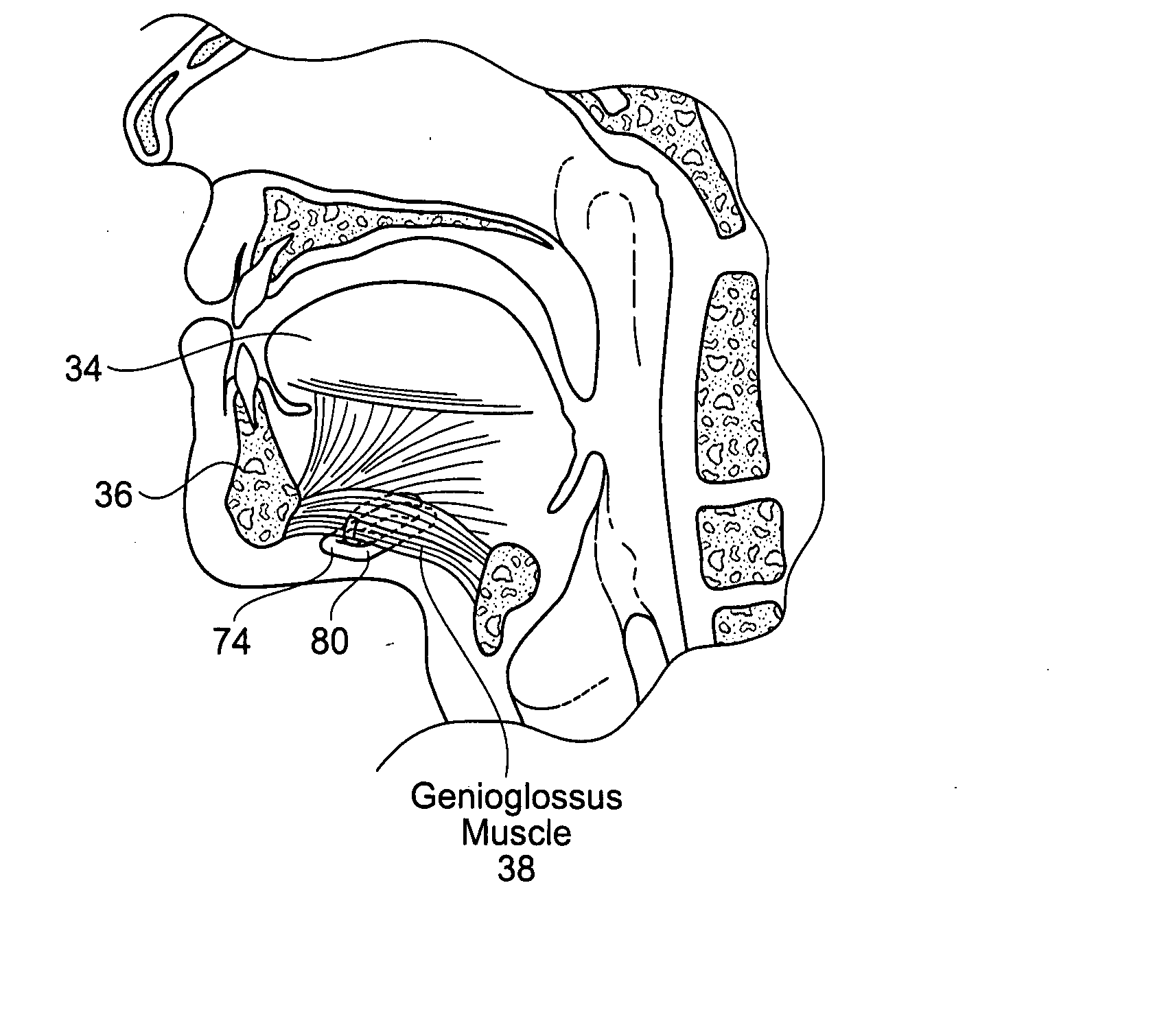
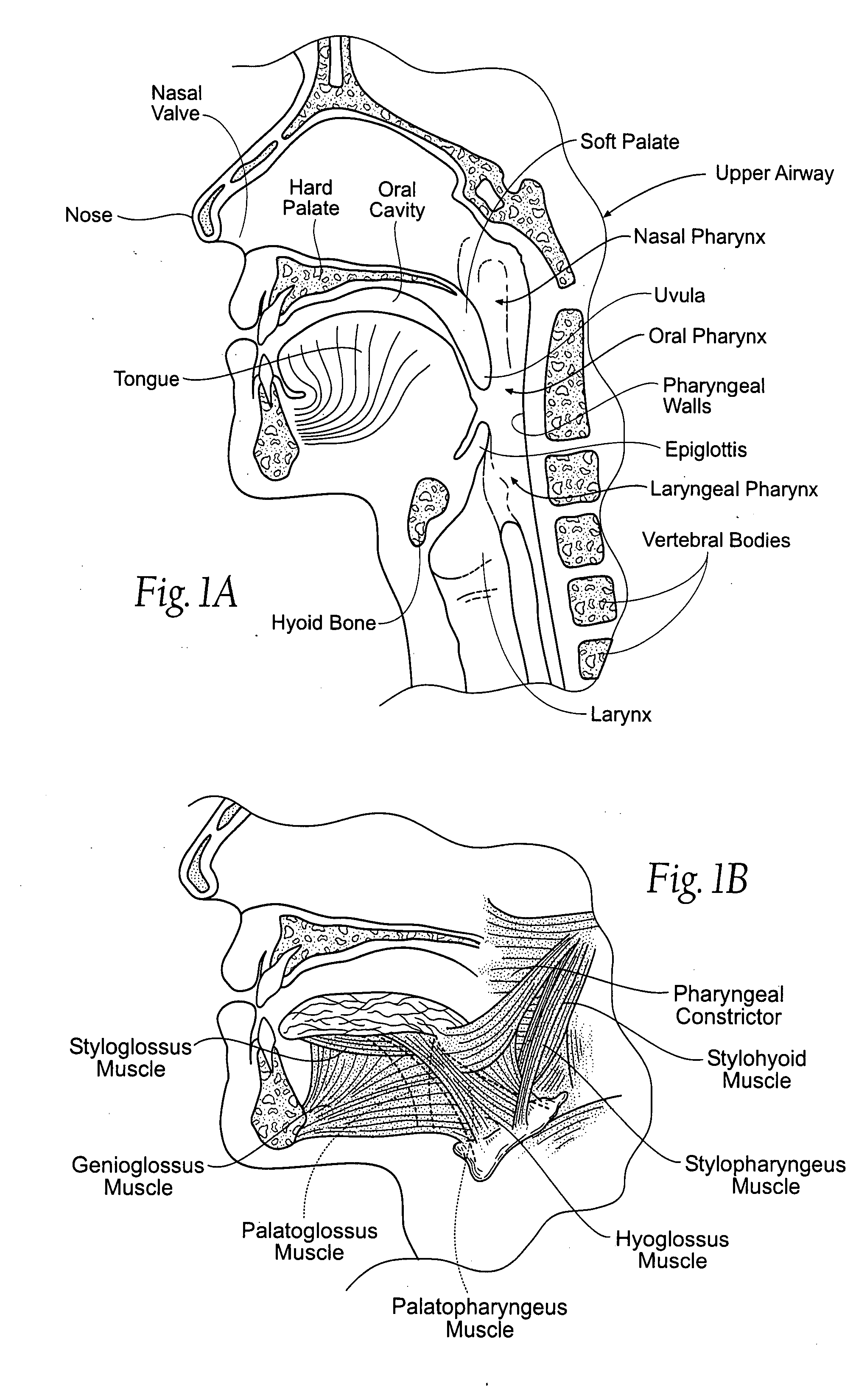
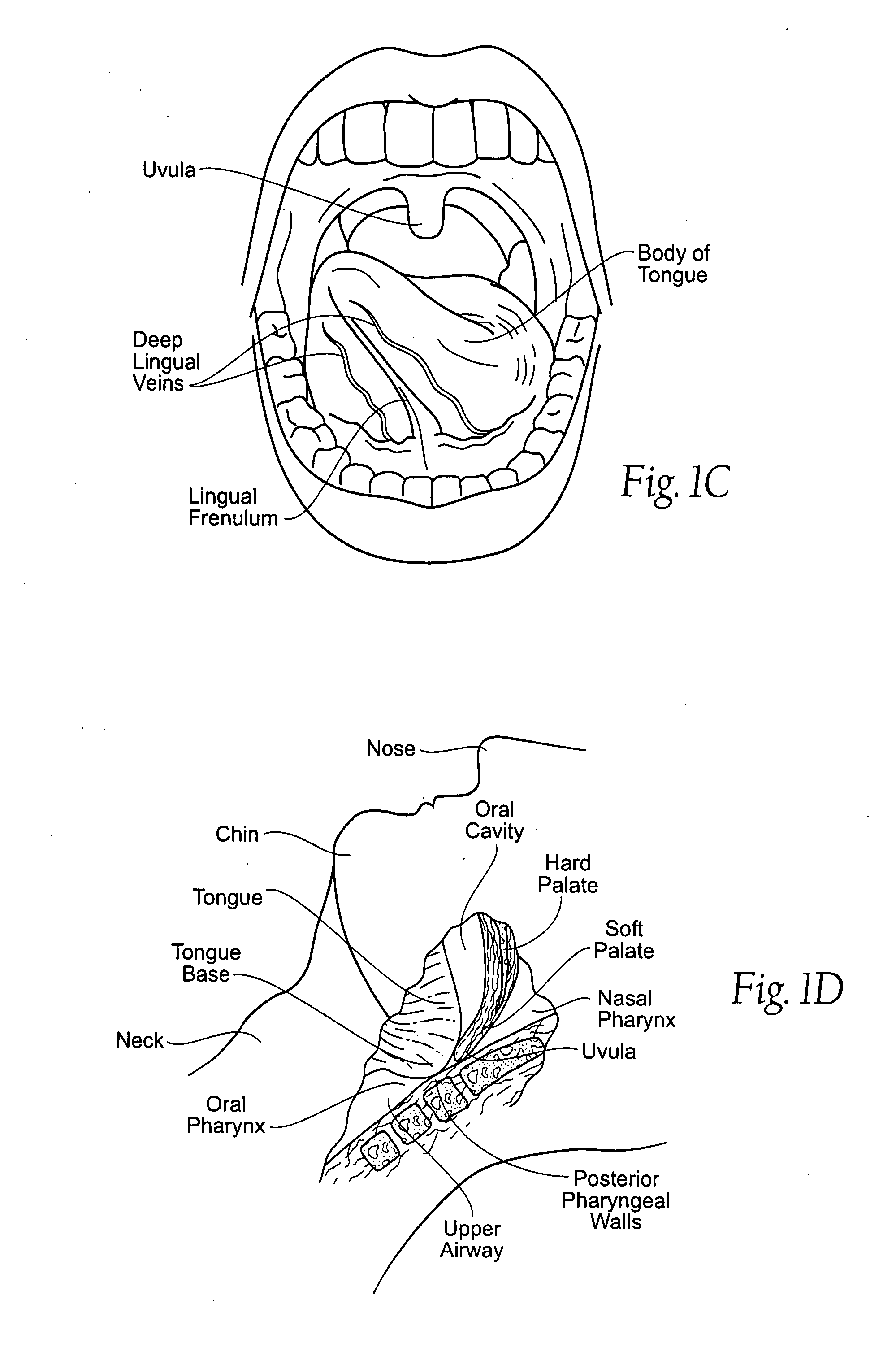
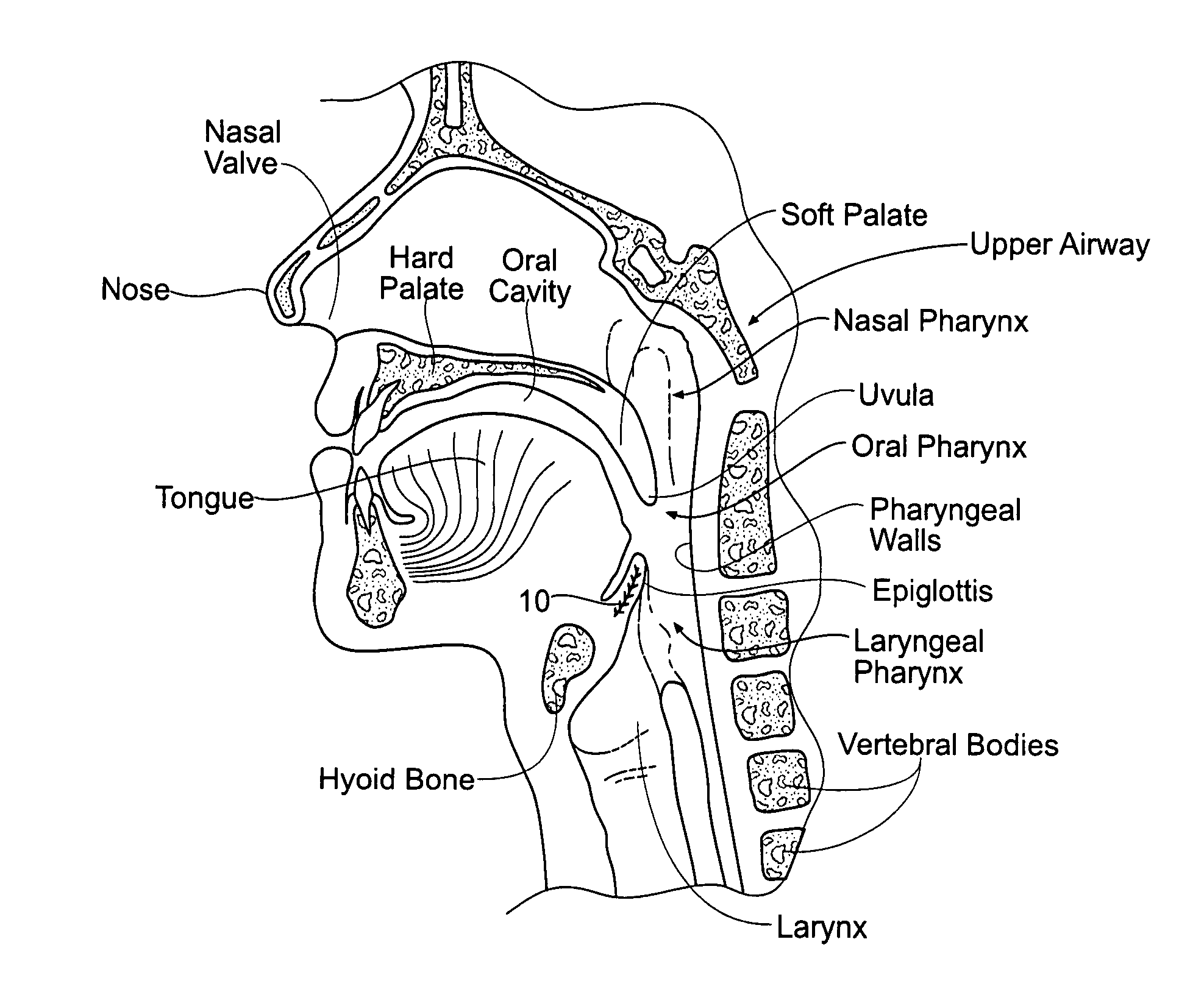
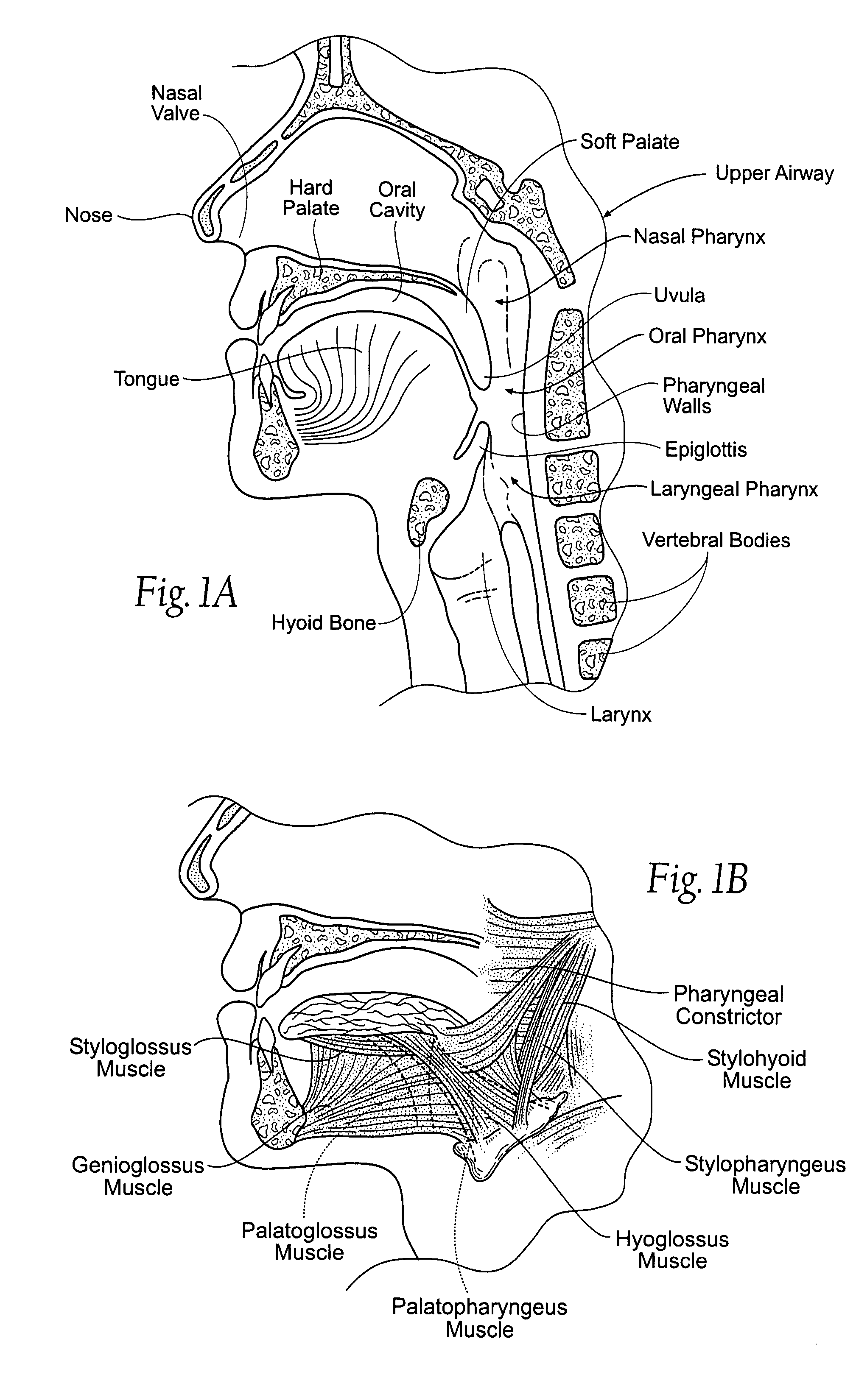
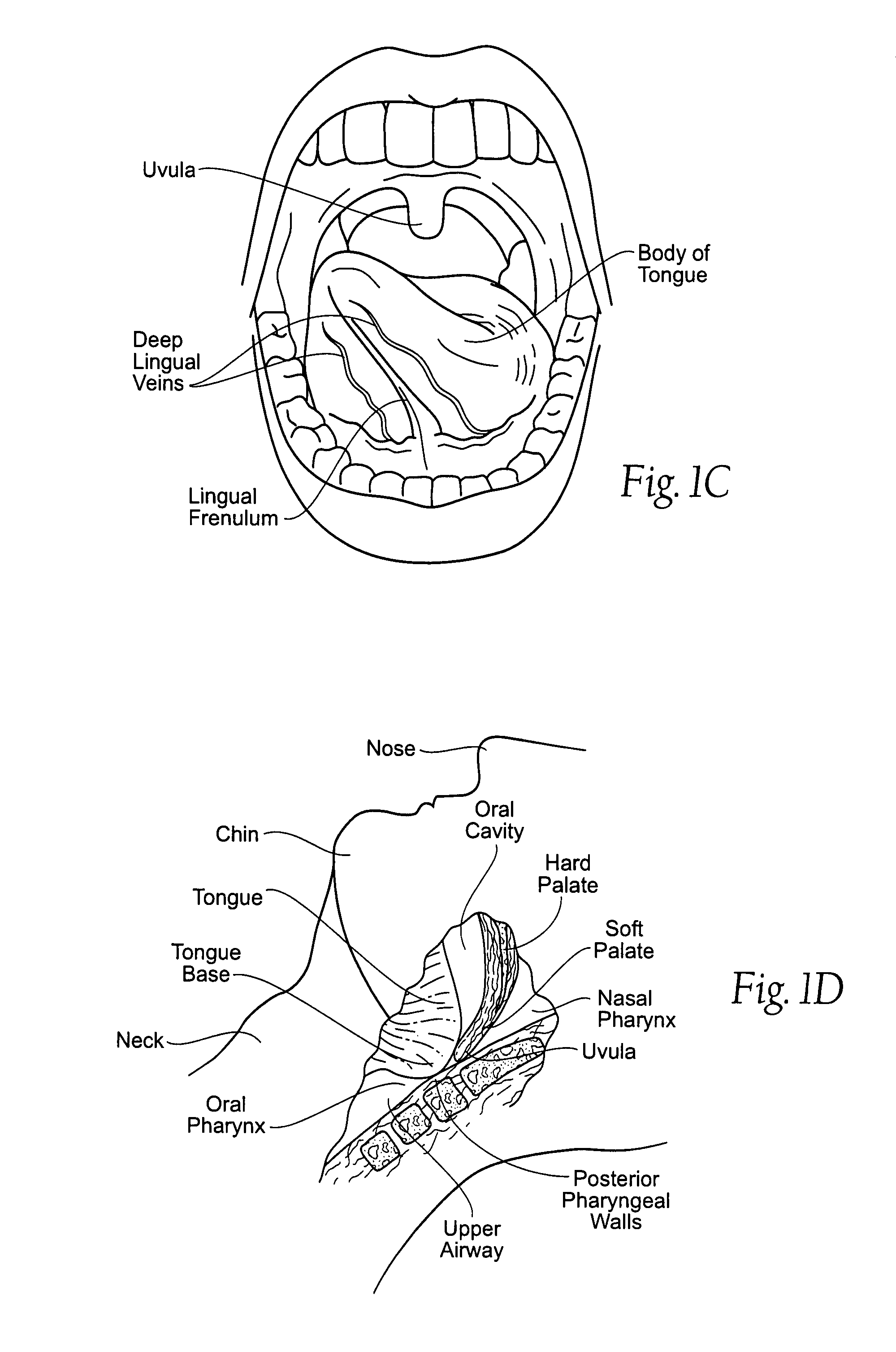
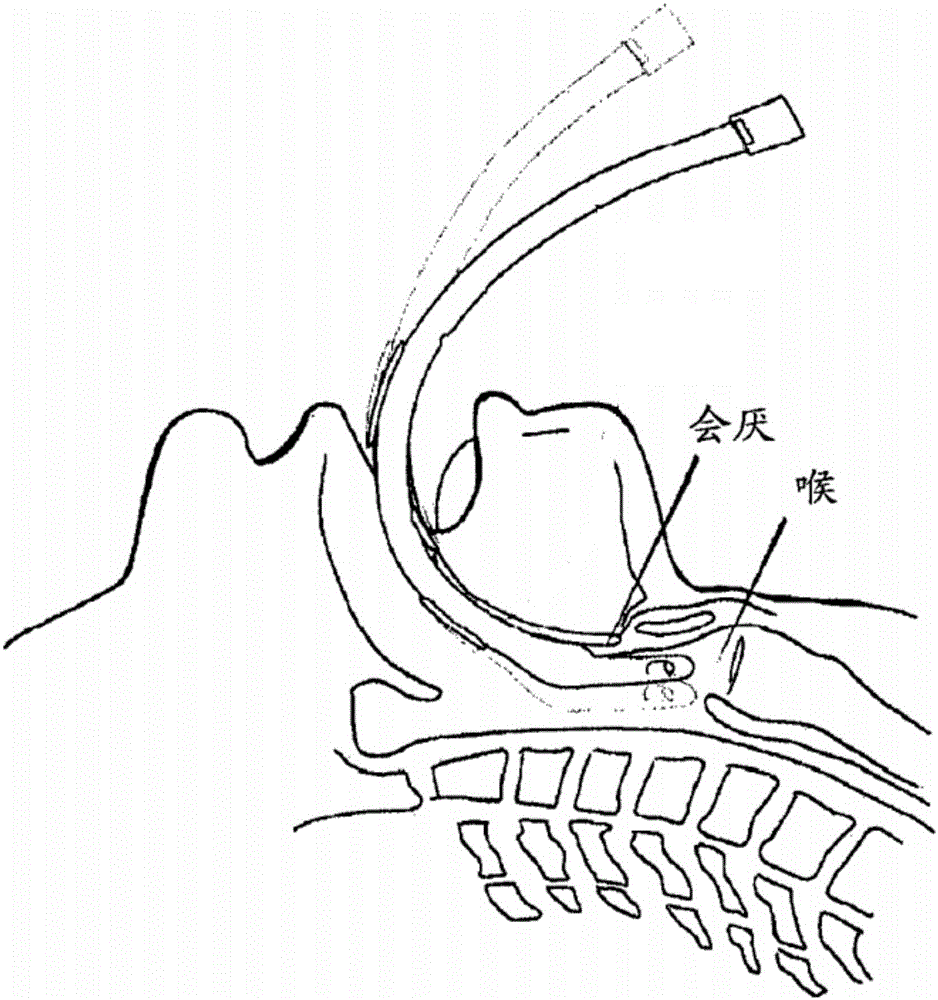
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that keeps food from entering the windpipe and the lungs. The flap is made of elastic cartilage covered with a mucous membrane, attached to the entrance of the larynx. It projects upwards and backwards behind the tongue and the hyoid bone. It stands open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration and forcing the swallowed liquids or food to go along the esophagus instead. It is thus the valve that diverts passage to either the trachea or the esophagus.
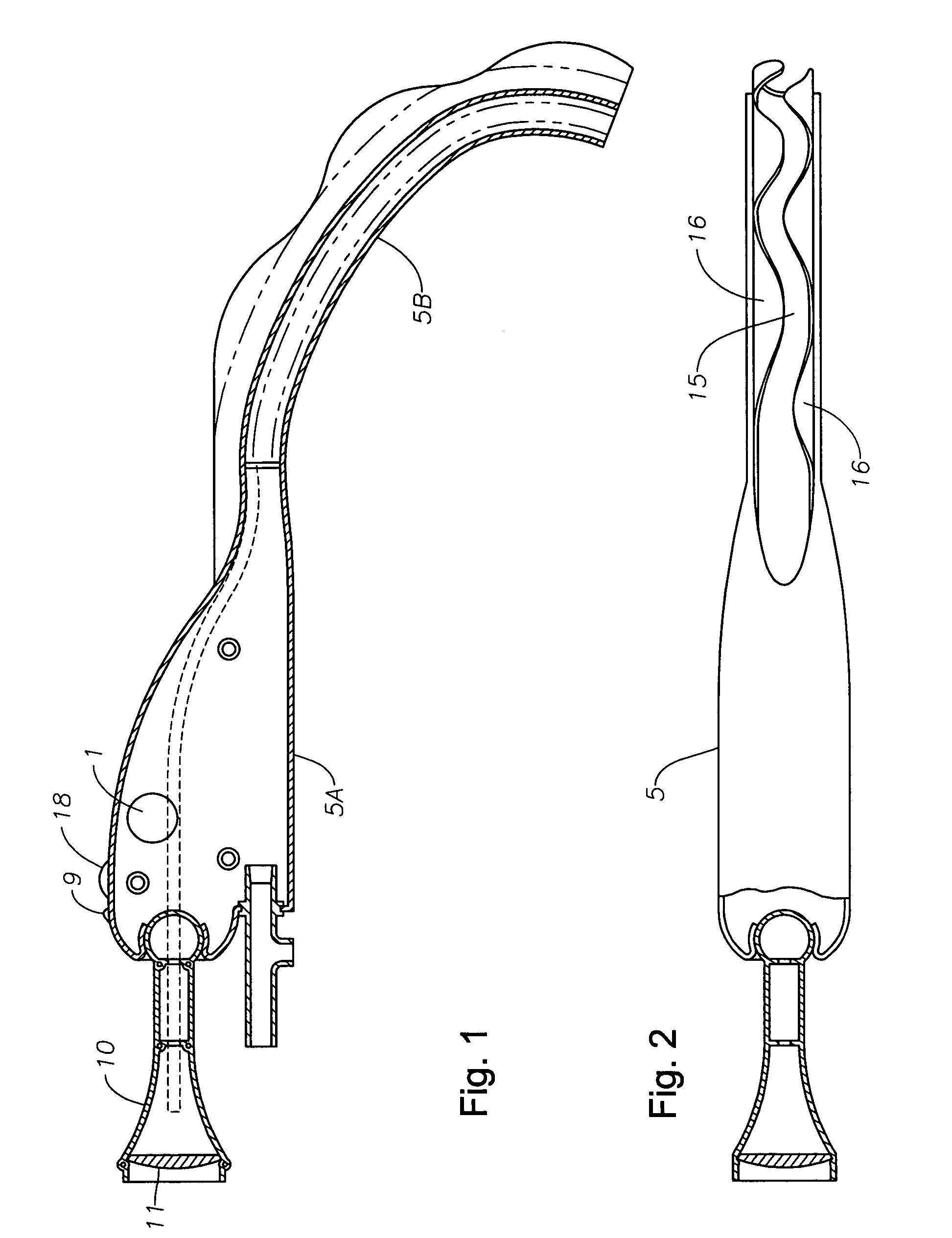
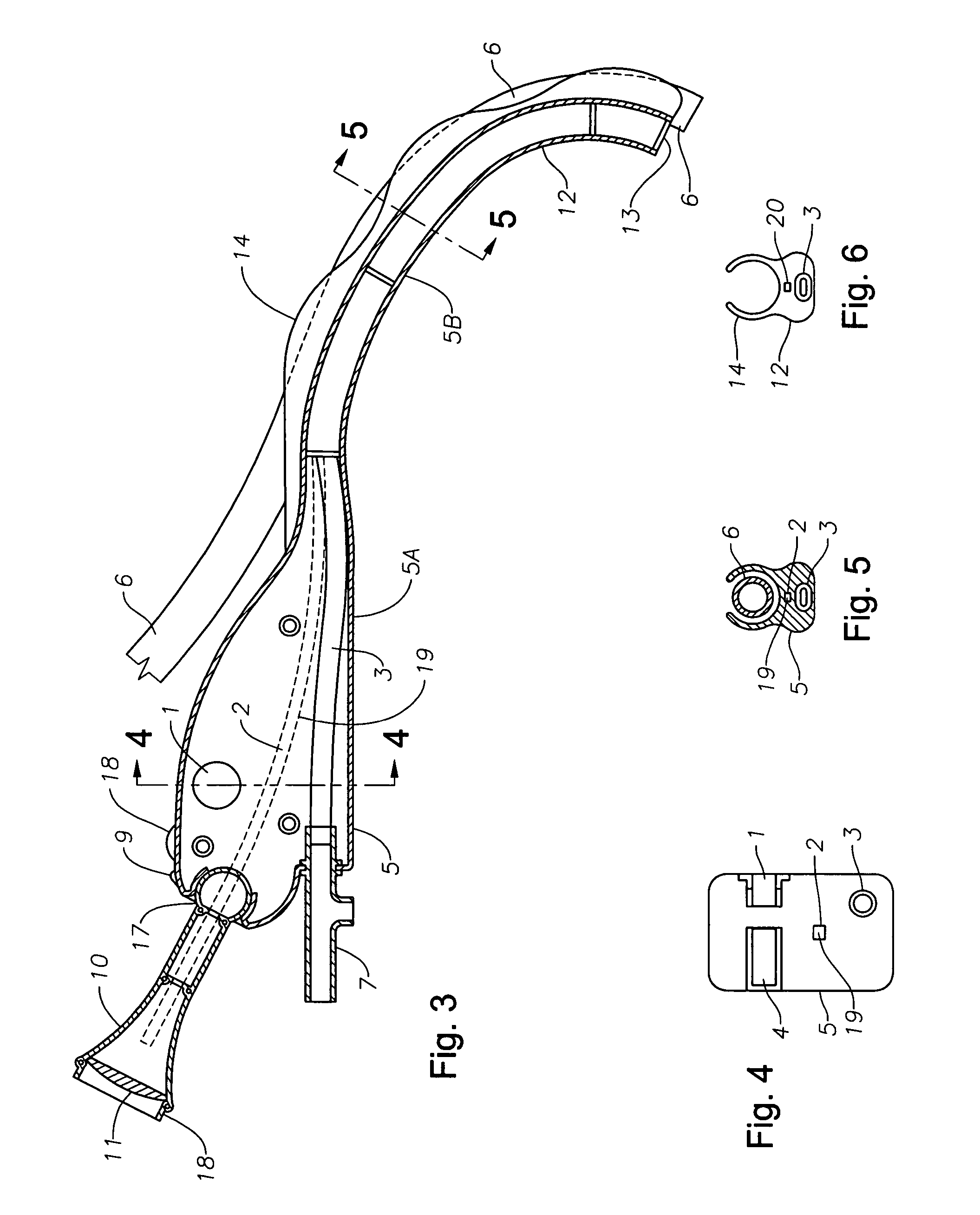
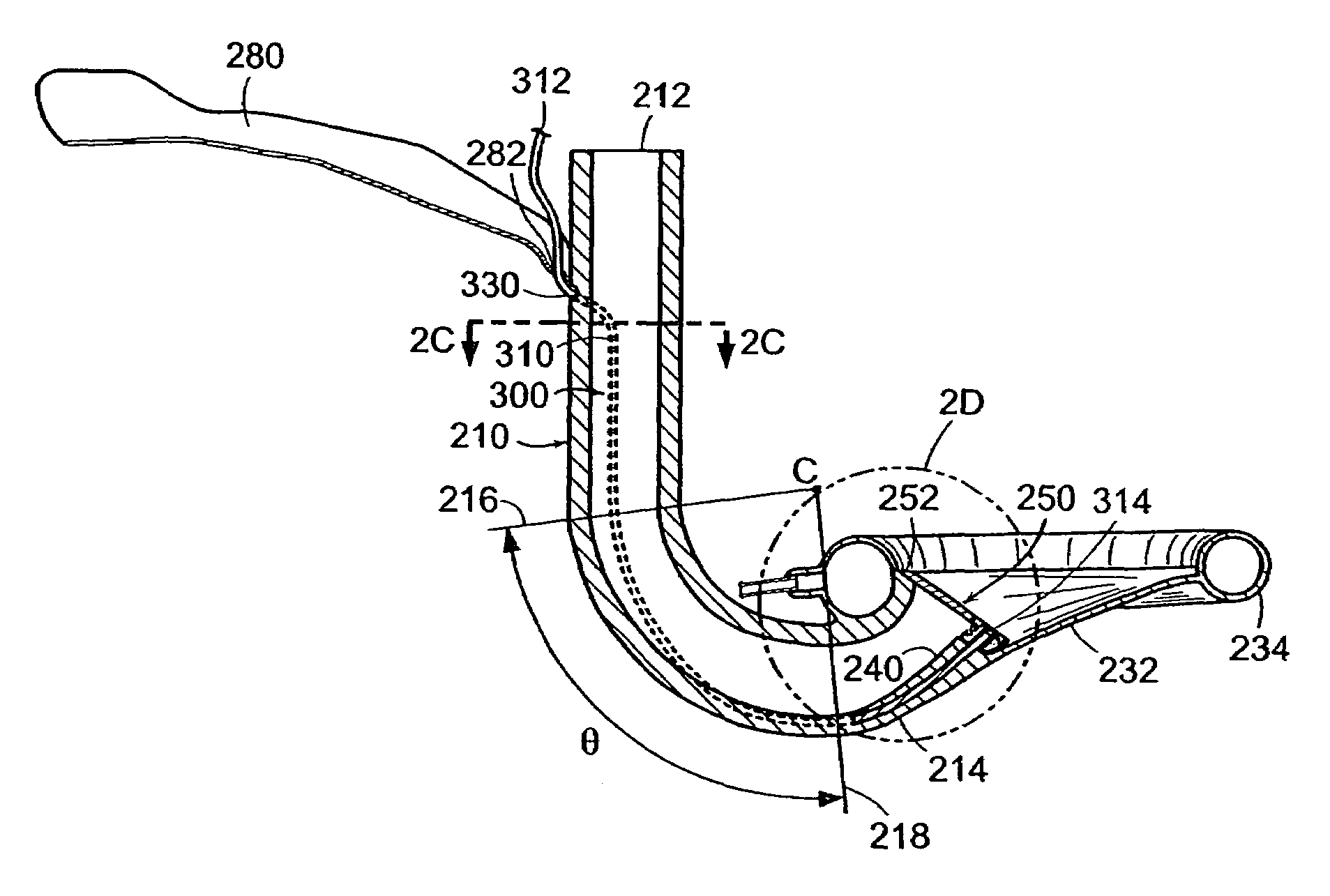
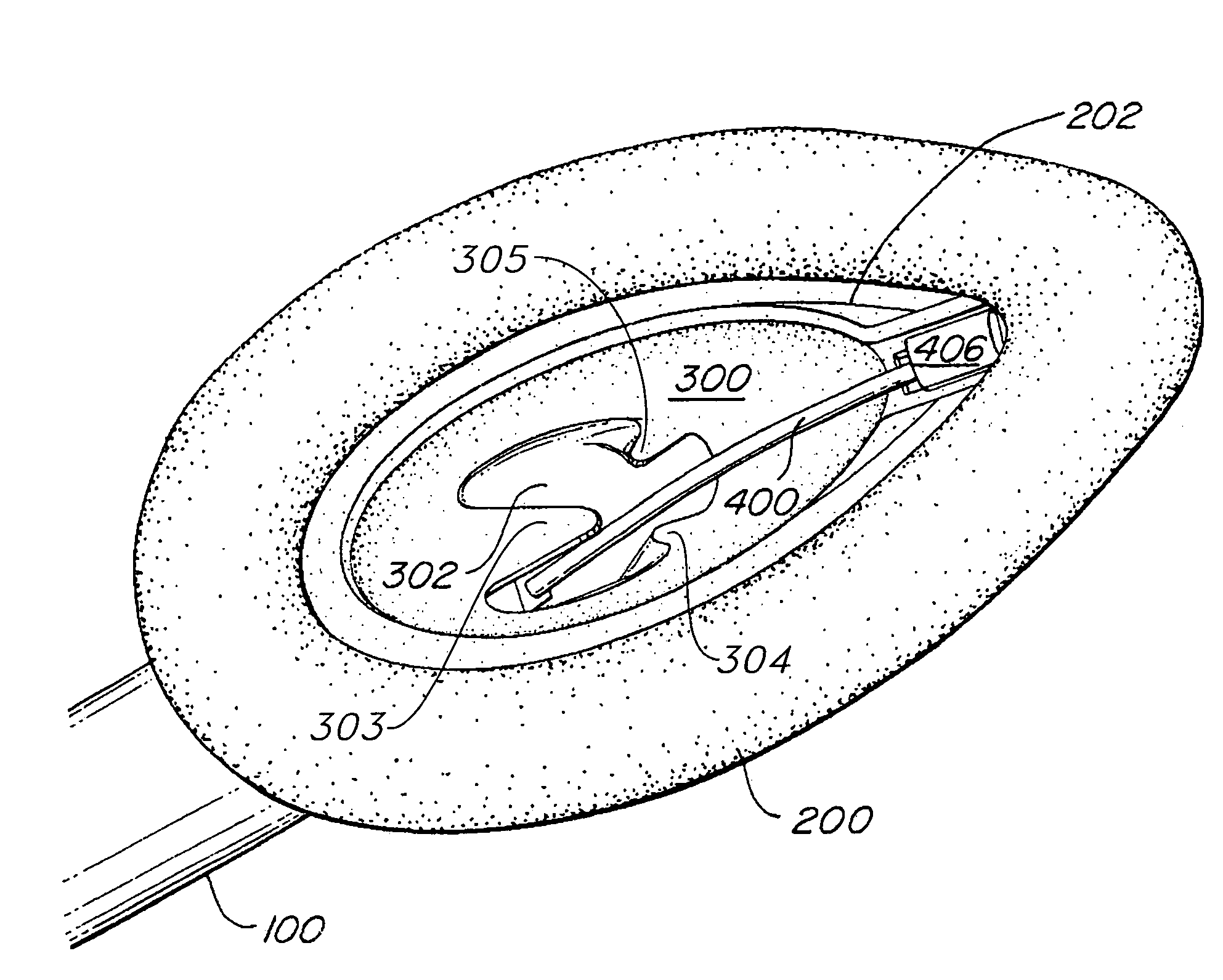
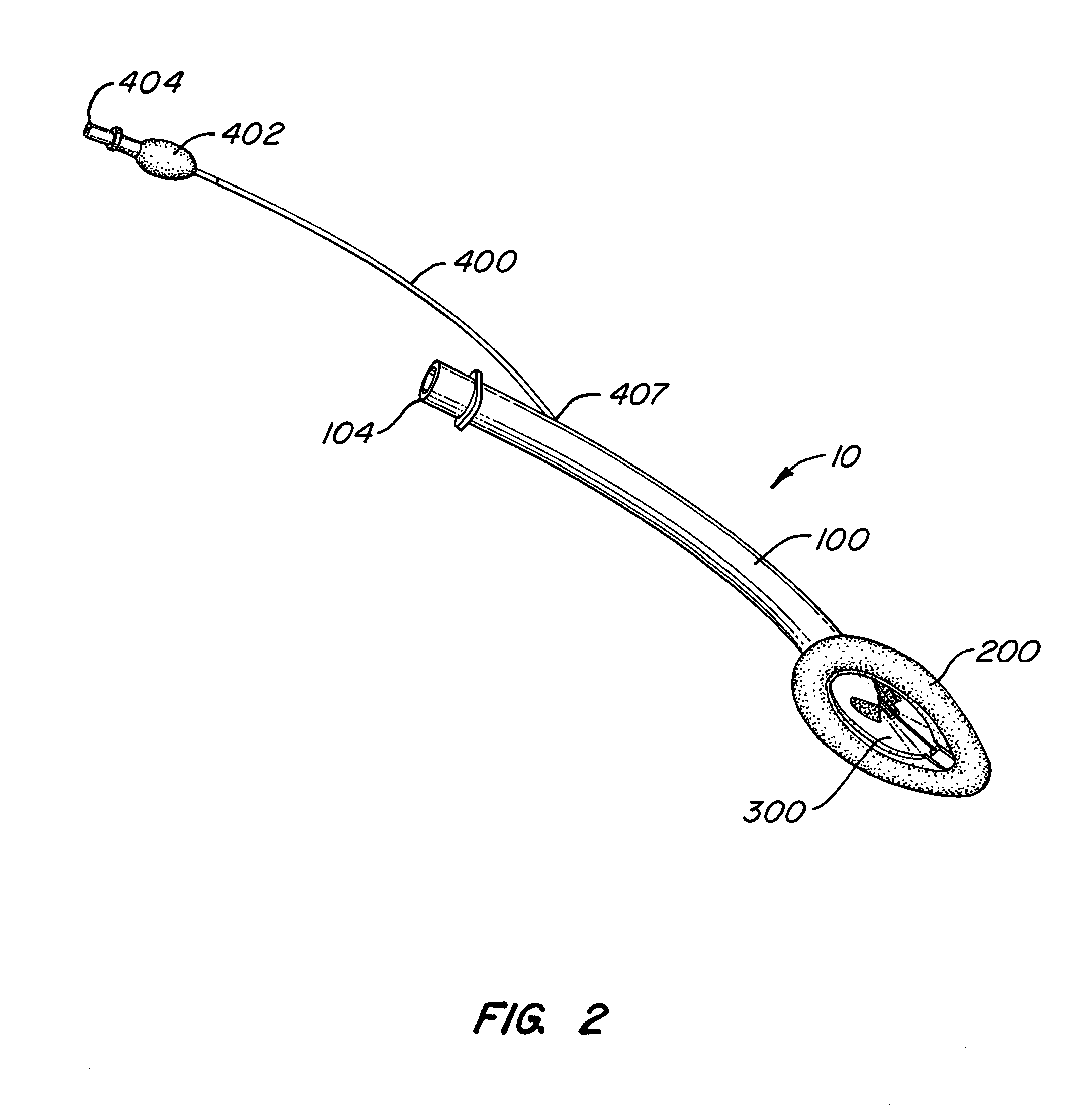
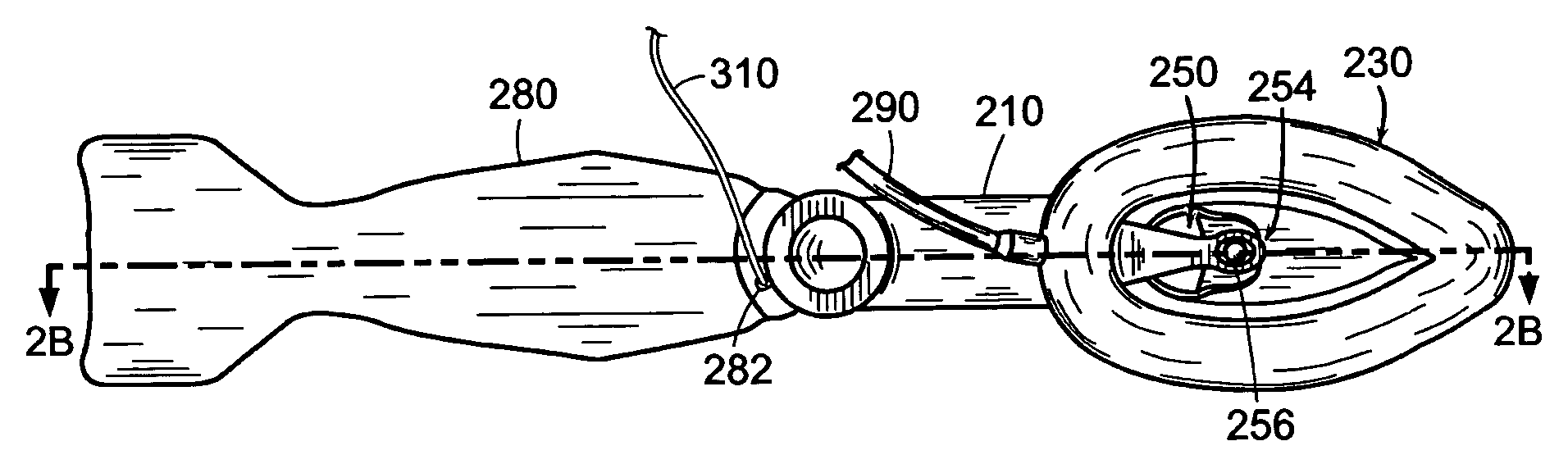
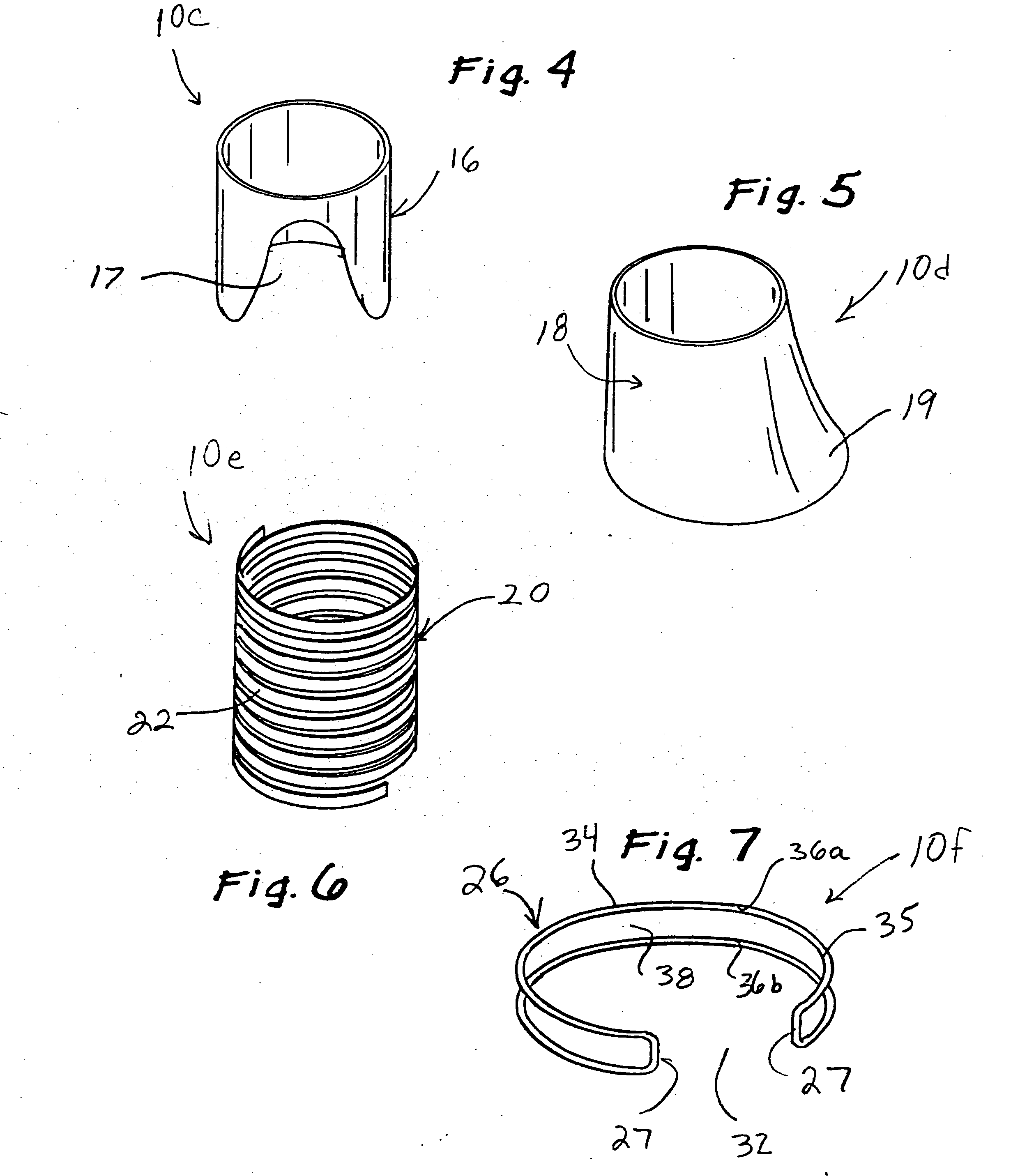
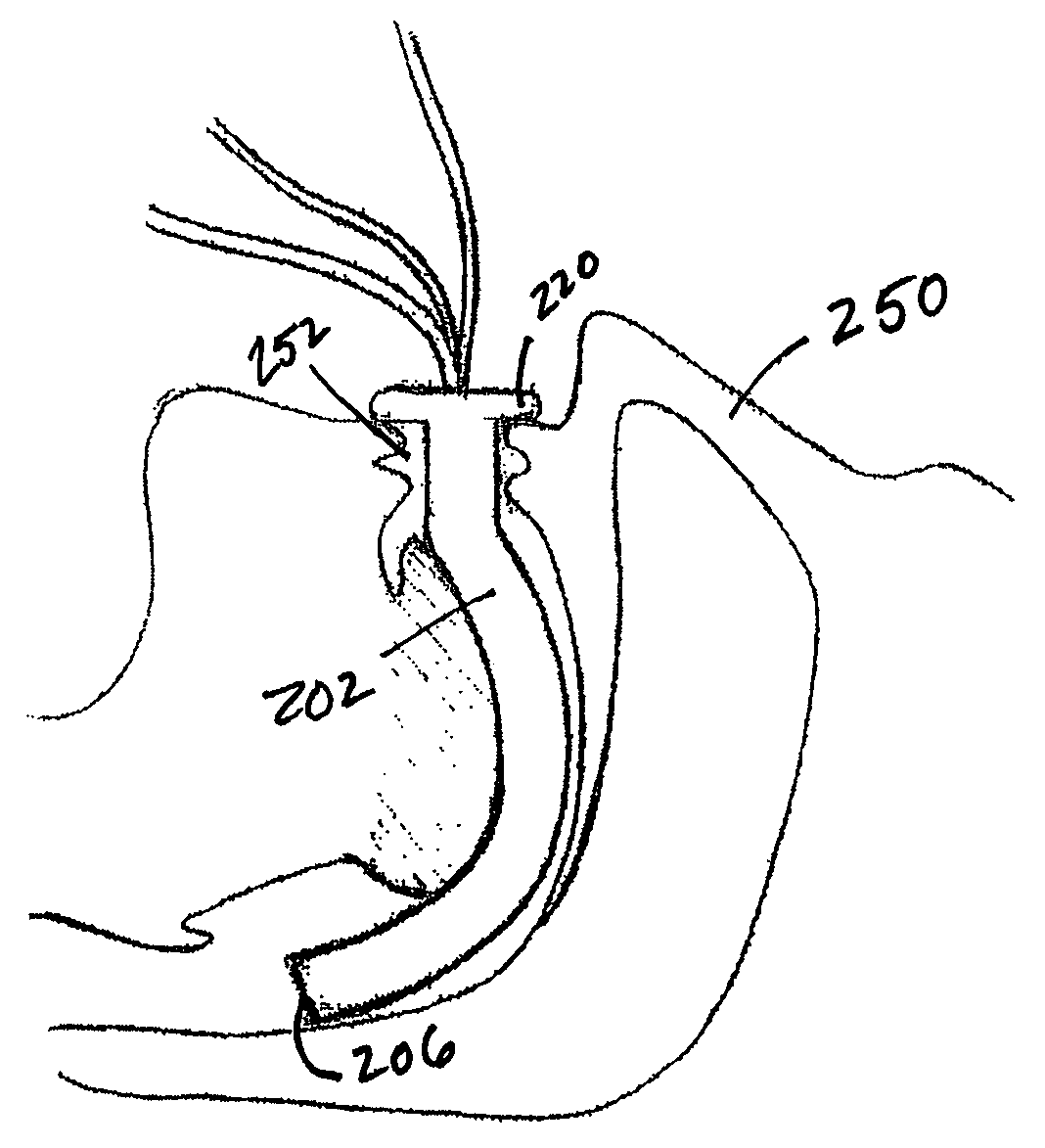
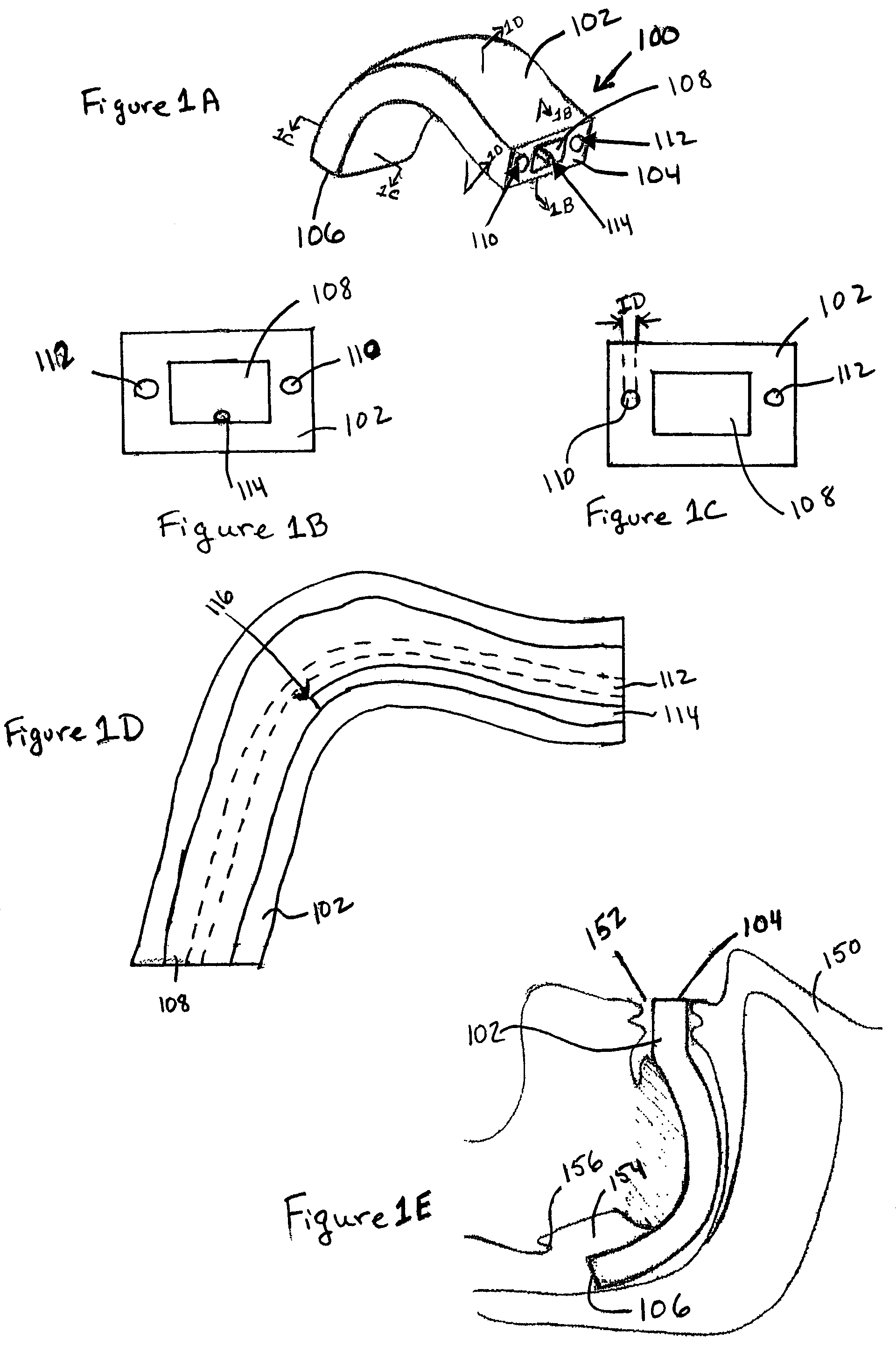
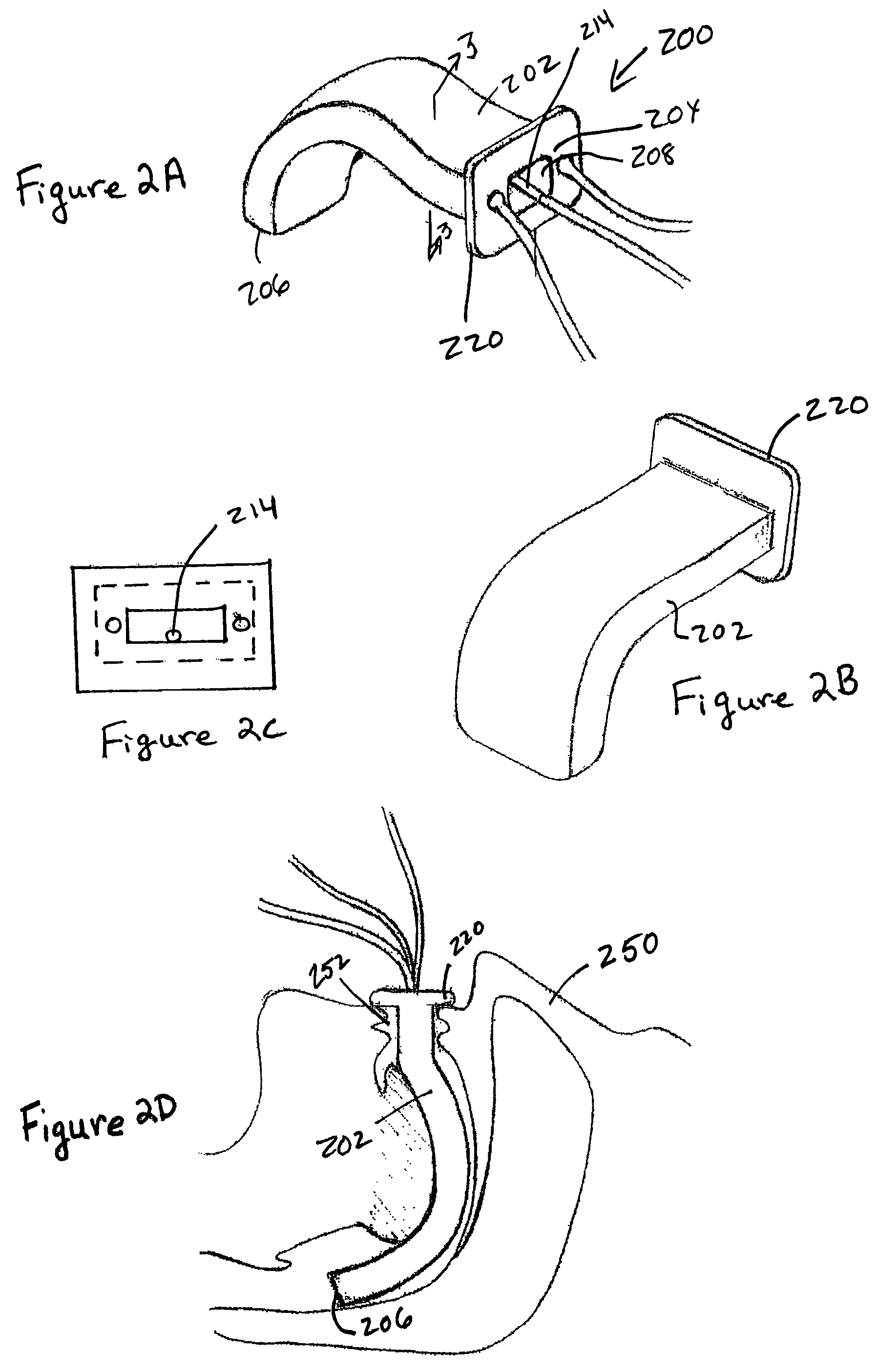
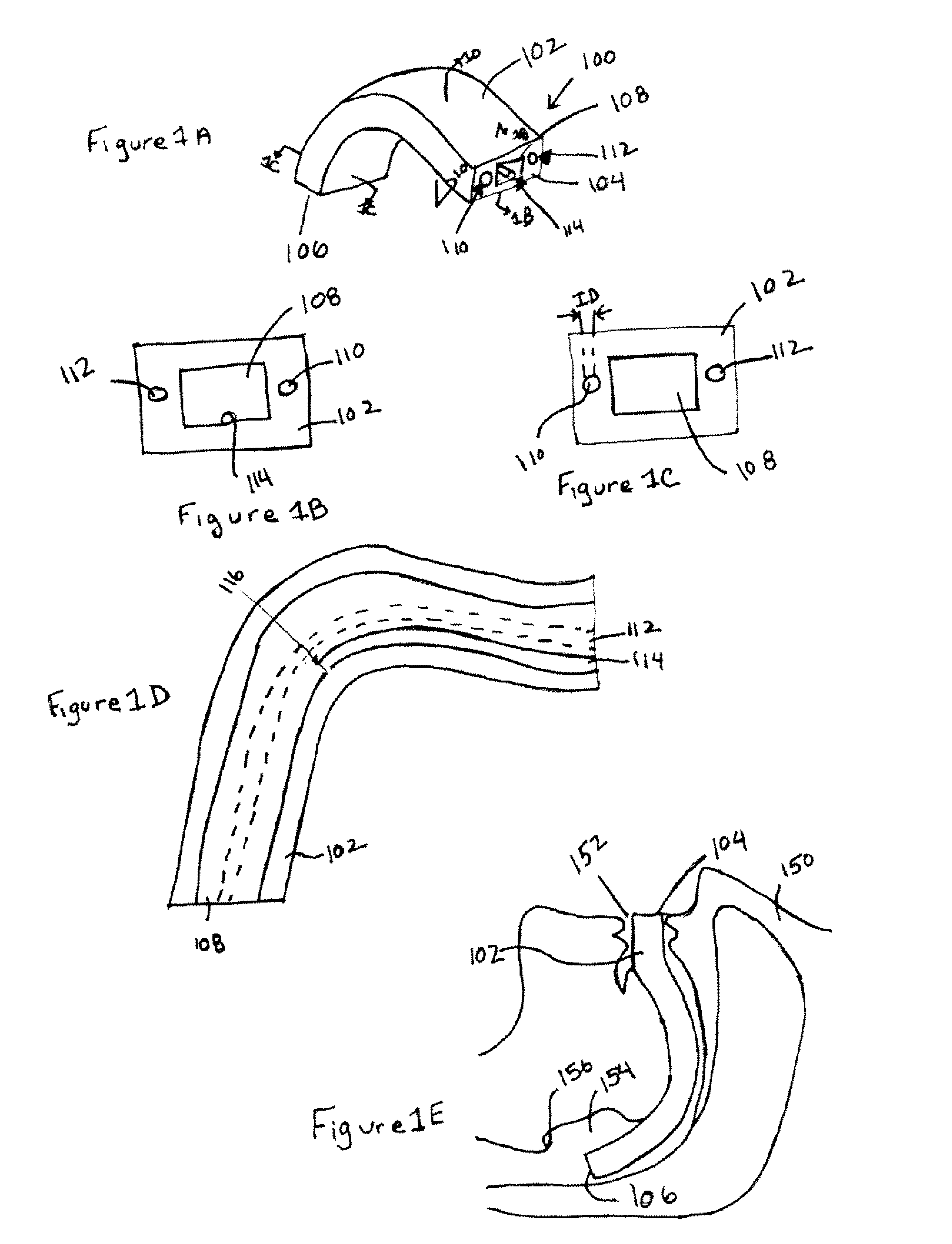
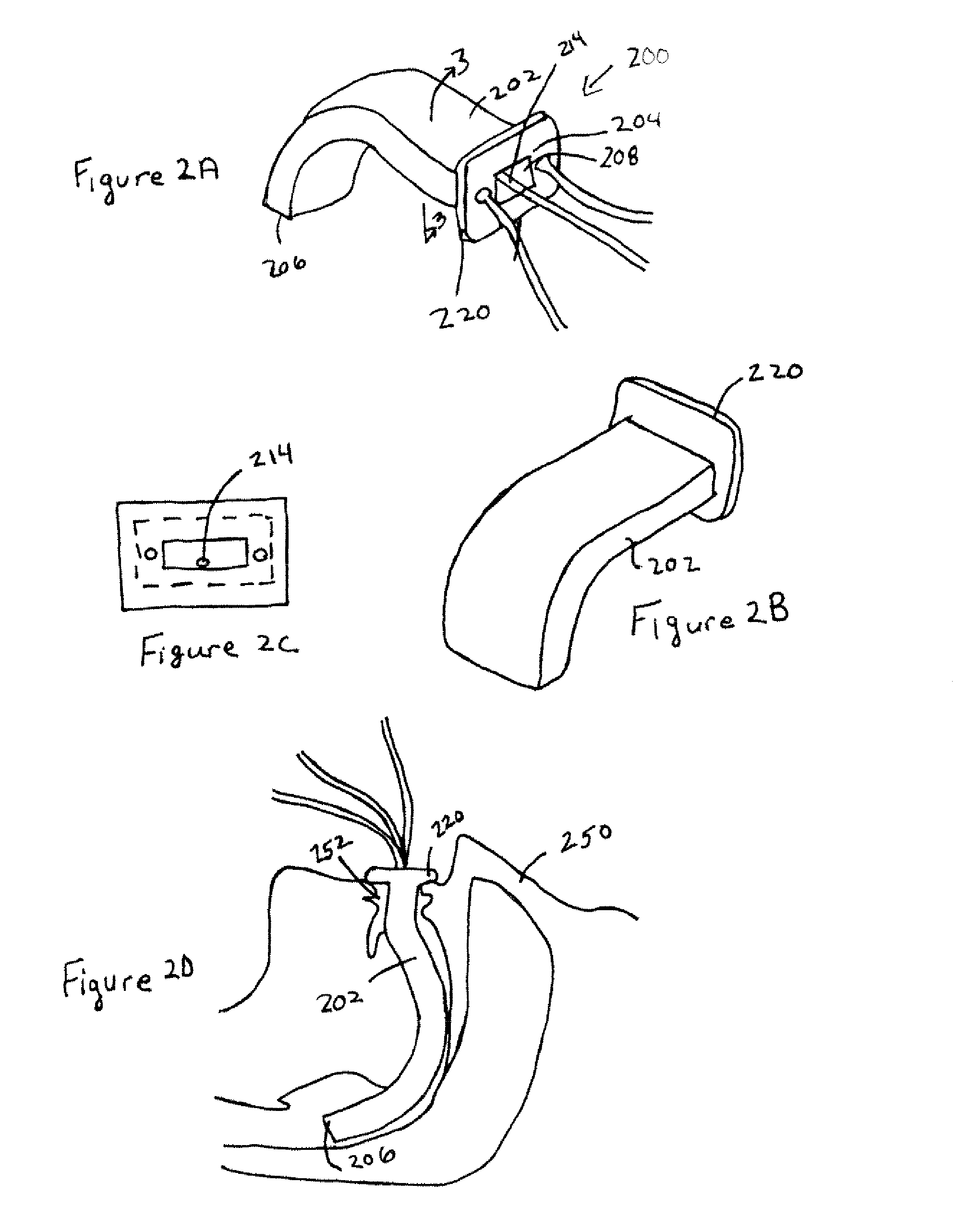
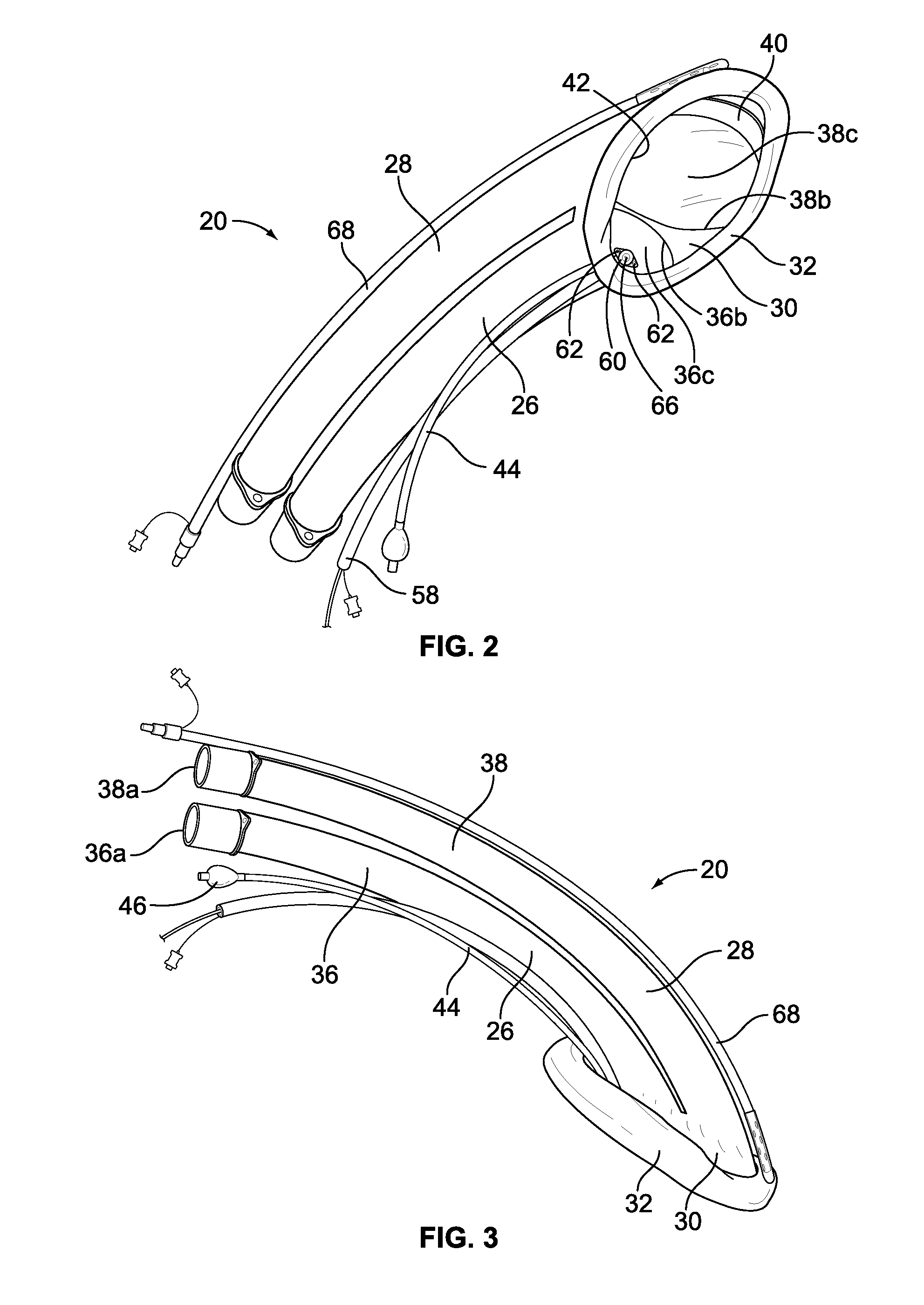
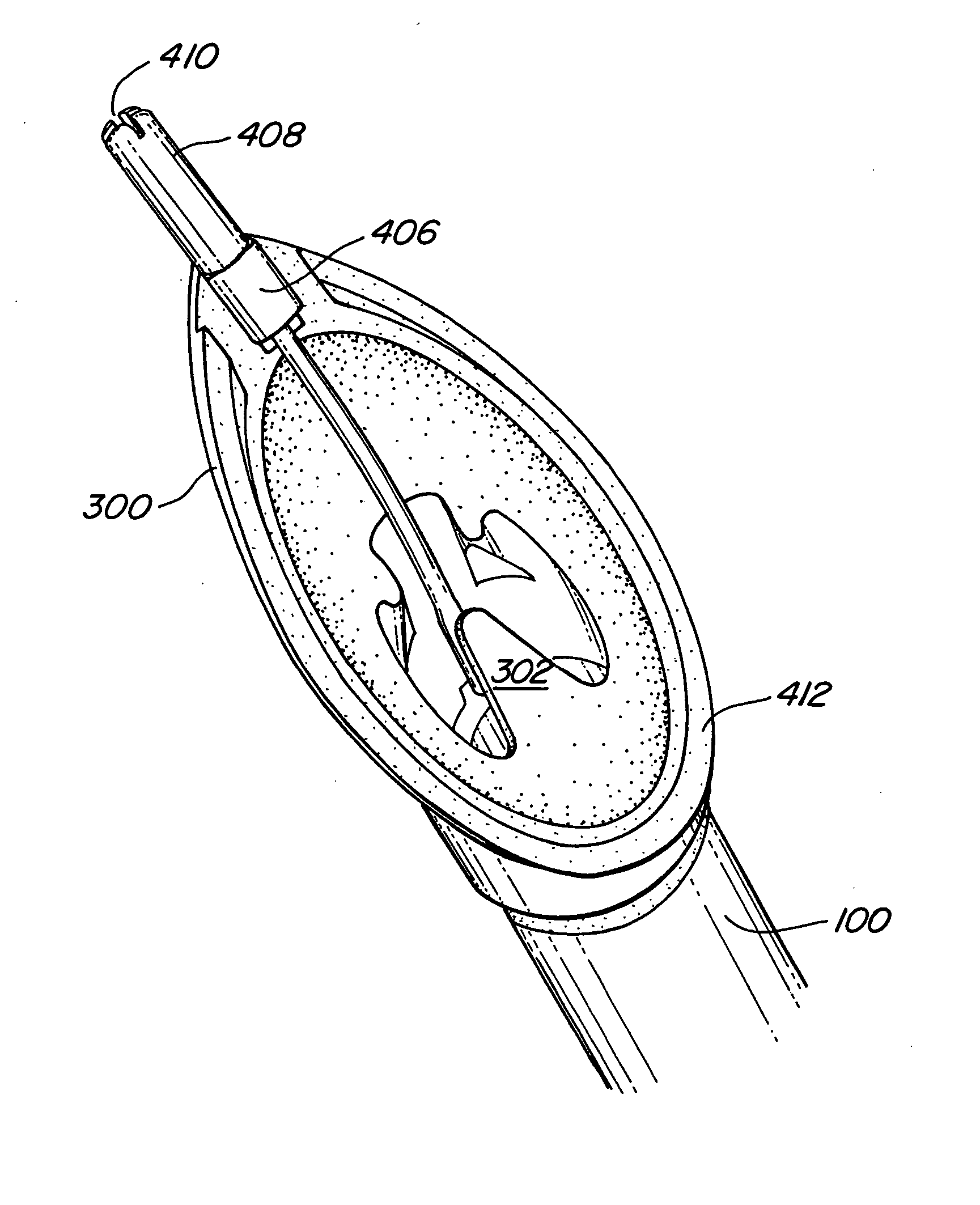
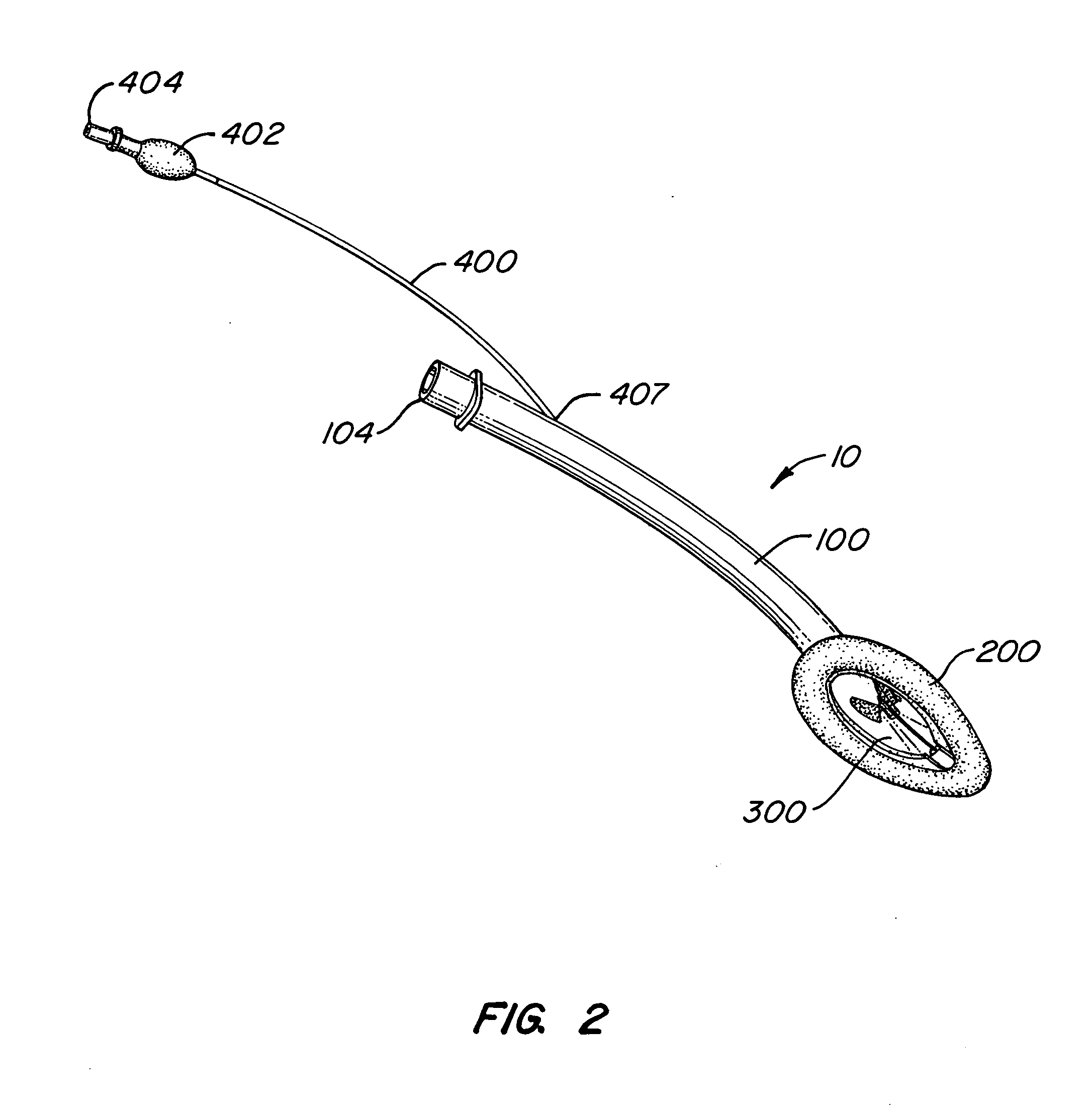
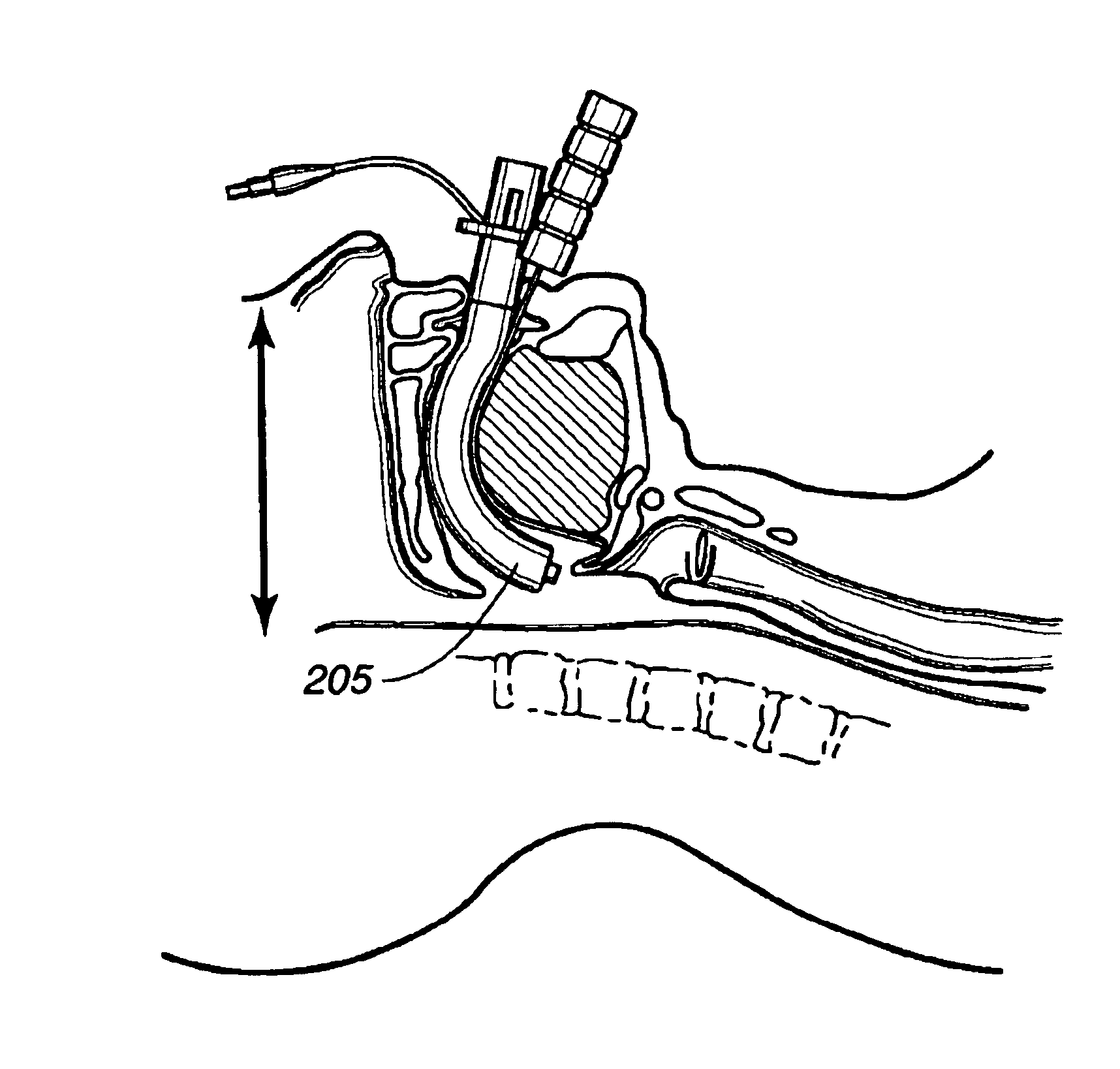
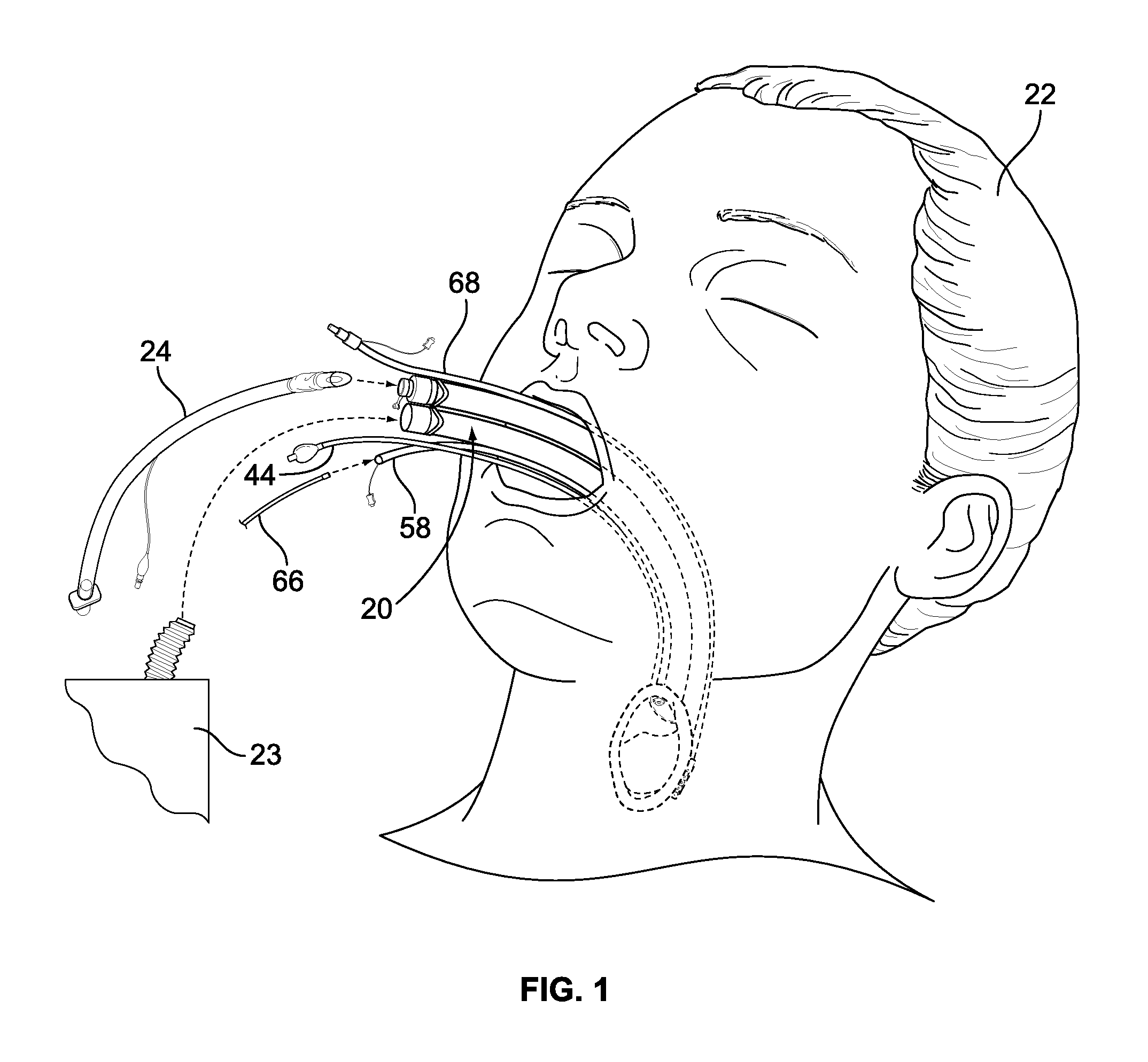
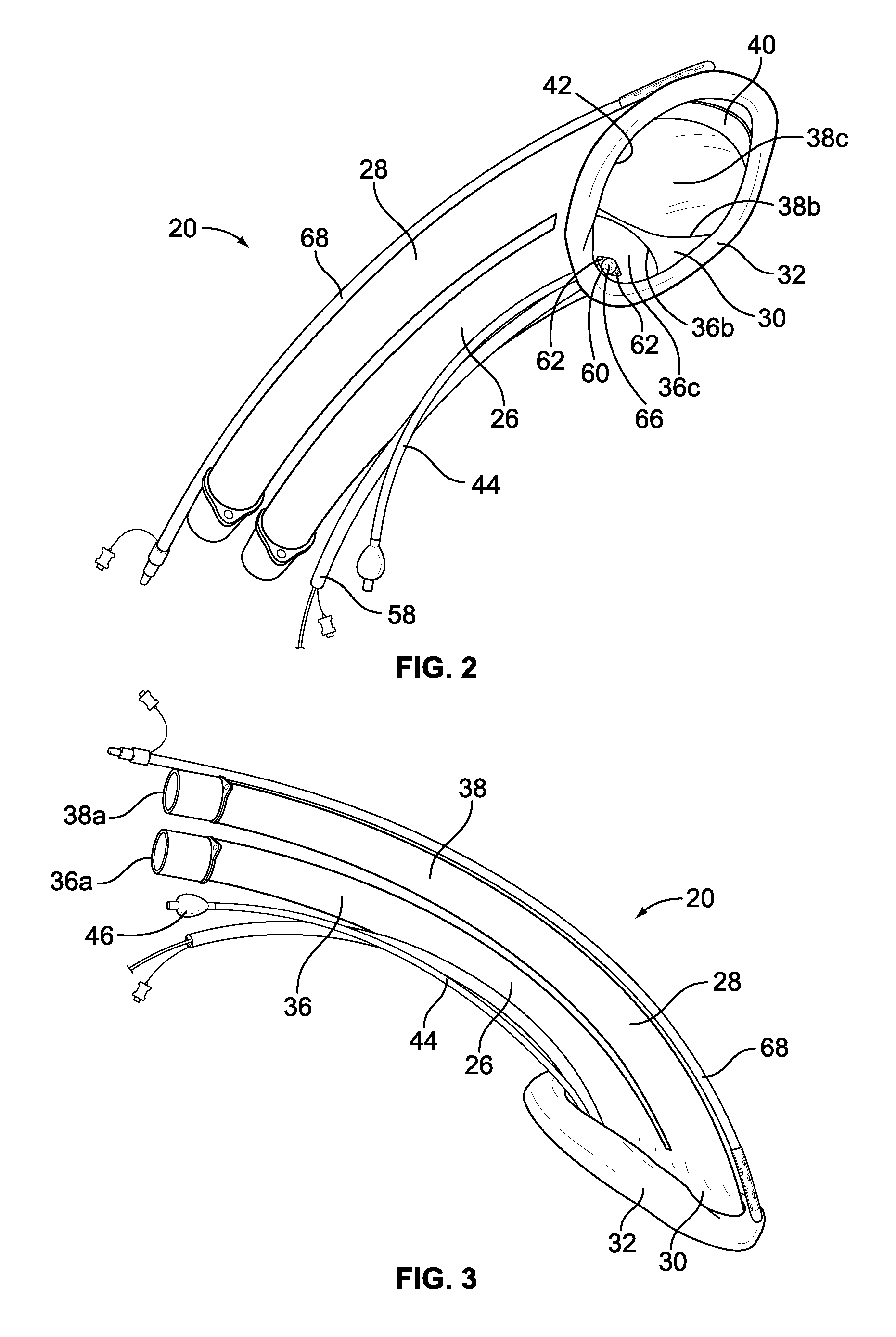
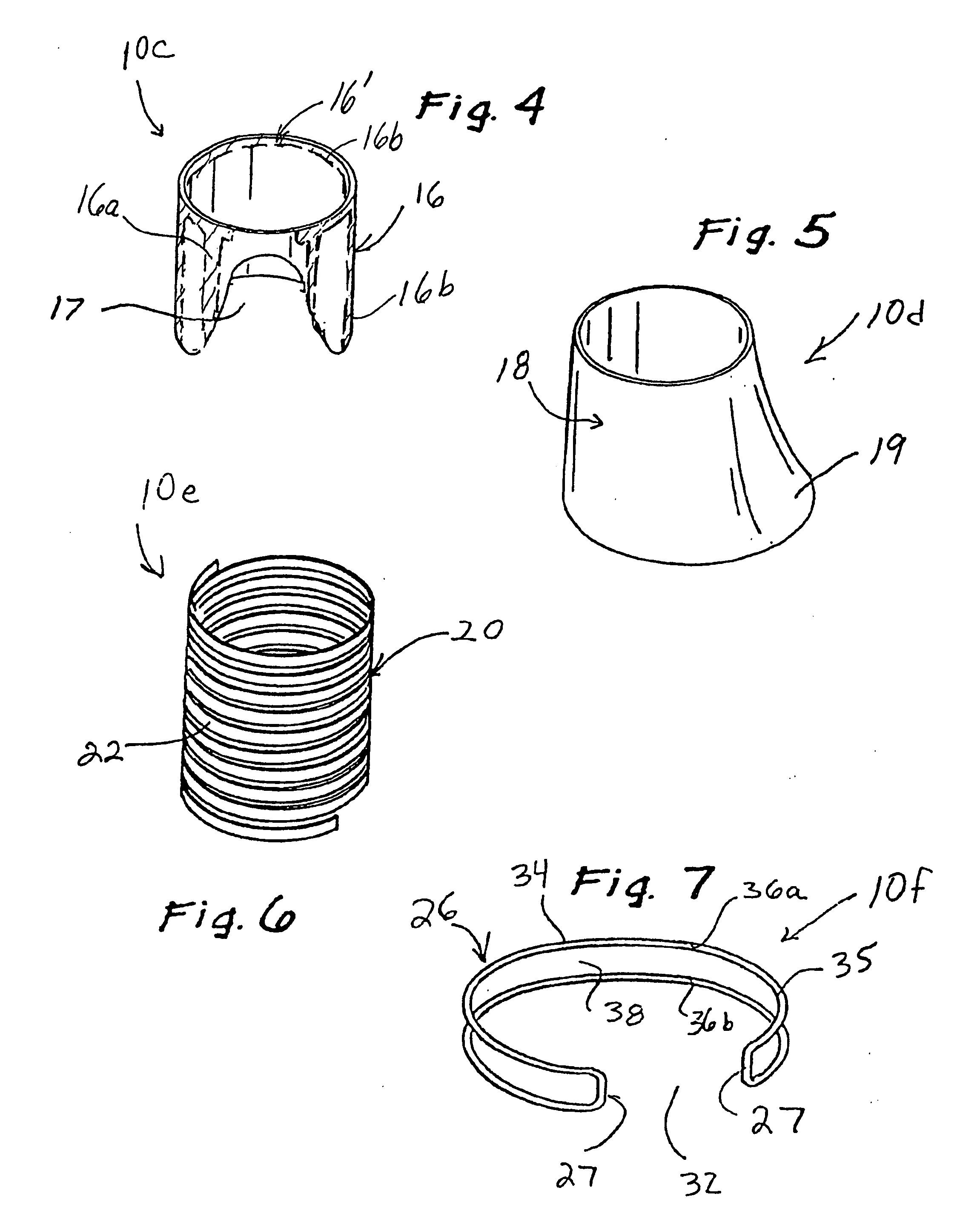
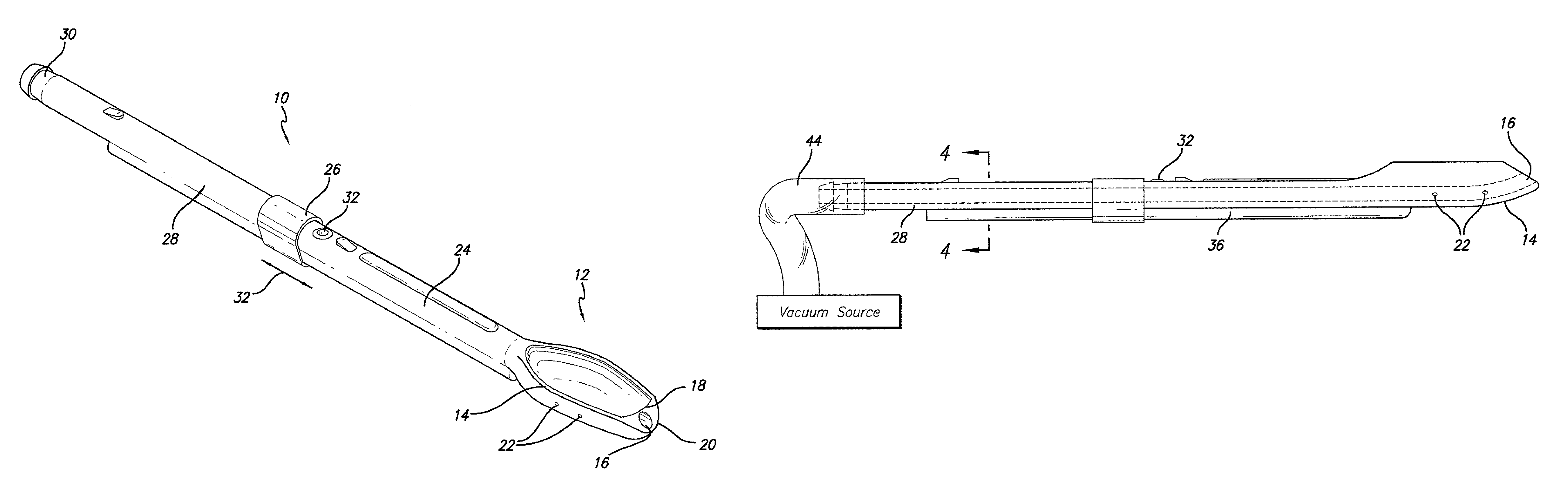
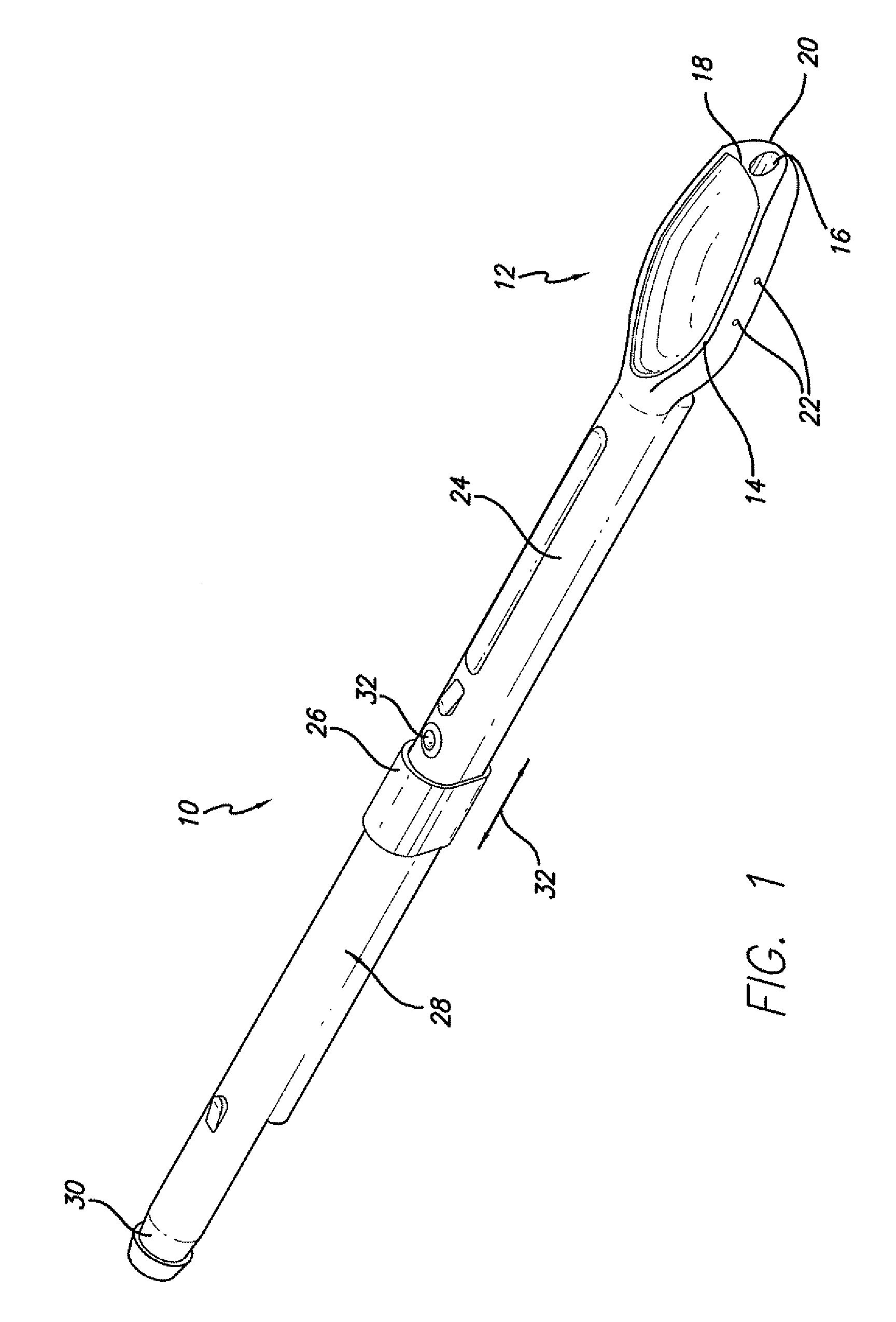
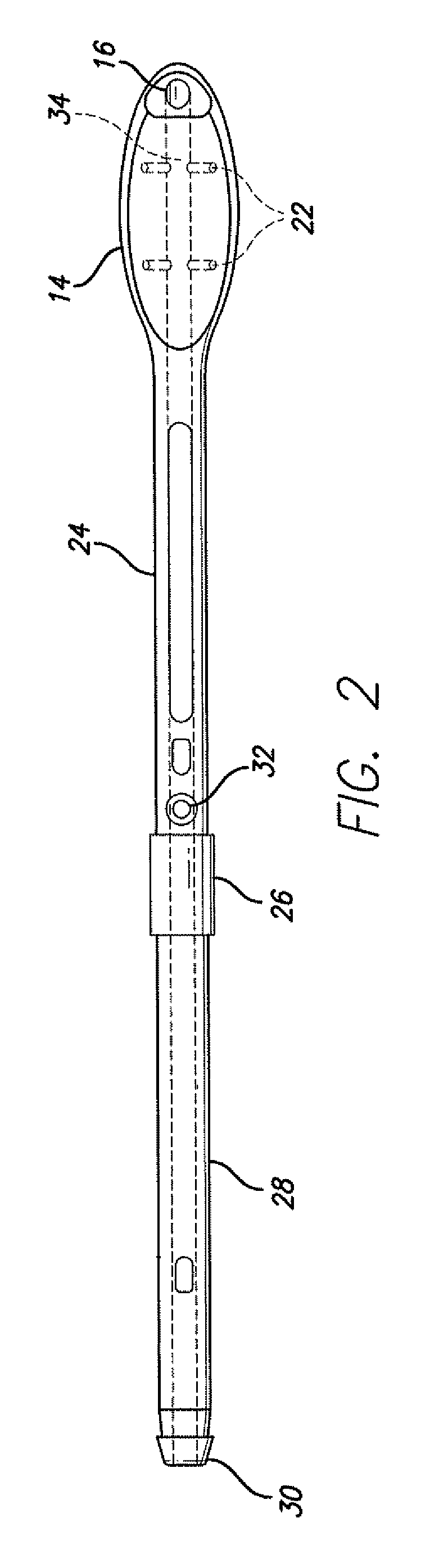
Implantable devices, systems, and methods for maintaining desired orientations in targeted tissue regions
InactiveUS20080066767A1Reducing and preventing snoringReducing and preventing and sleep disordered breathing eventSnoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesEpiglottisRadiology
At least one elongated body is sized and configured for implantation in a desired orientation in an epiglottis and / or in a muscle along an upper respiratory tract. An array of projections extends from the elongated body, which is sized and configured to engage tissue and resist a reorientation of the elongated body within the tissue region out of the desired orientation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
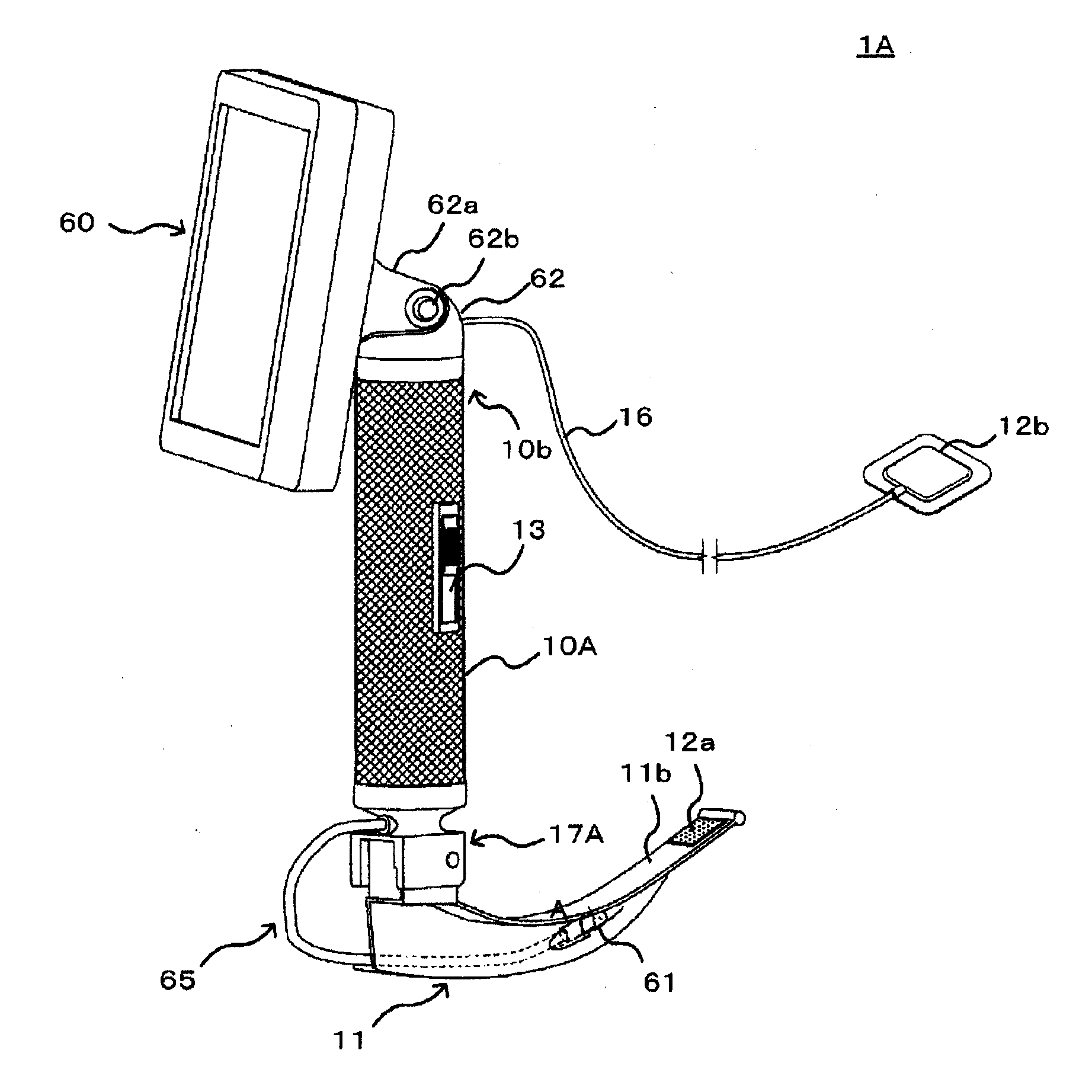
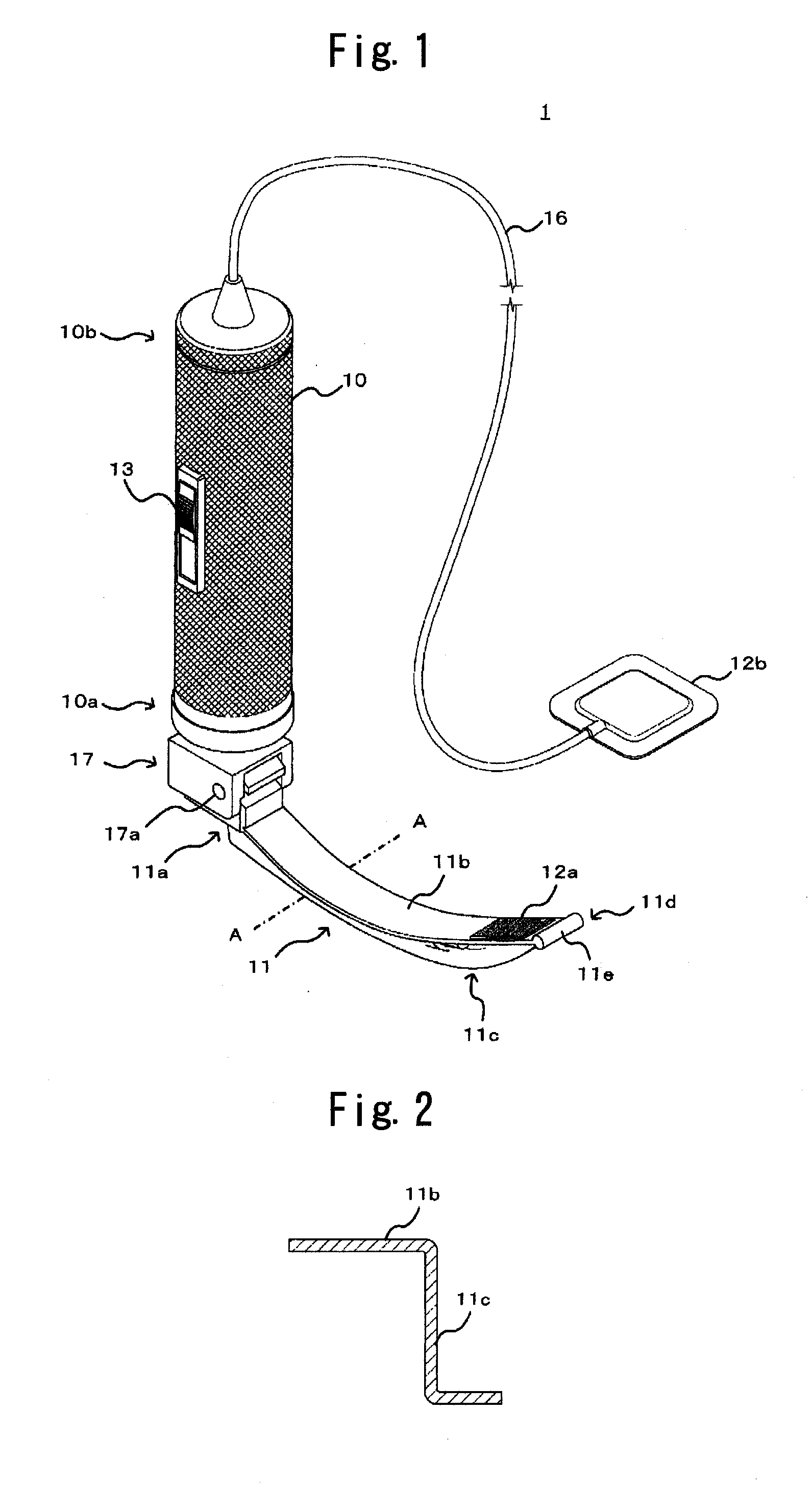
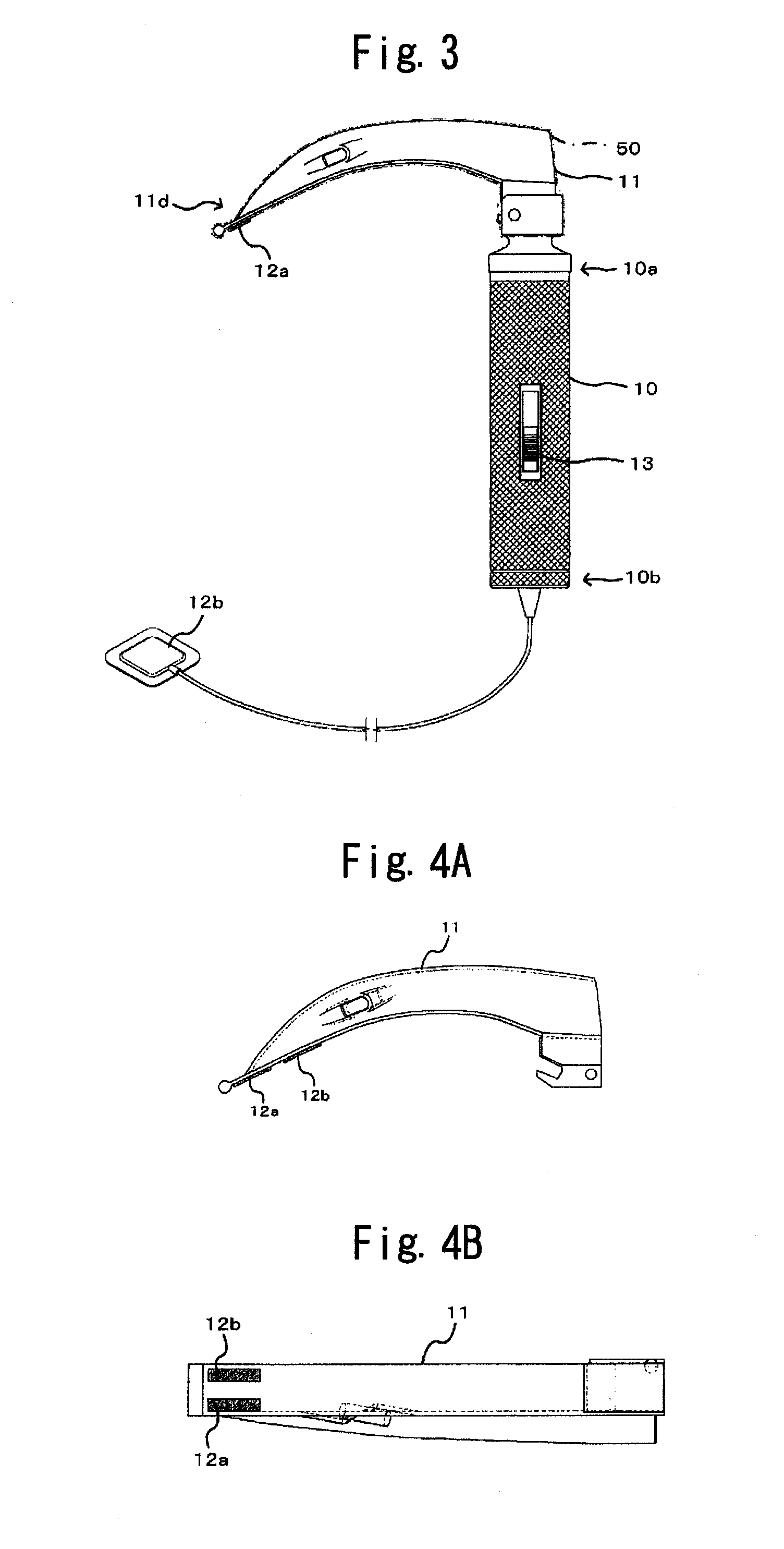
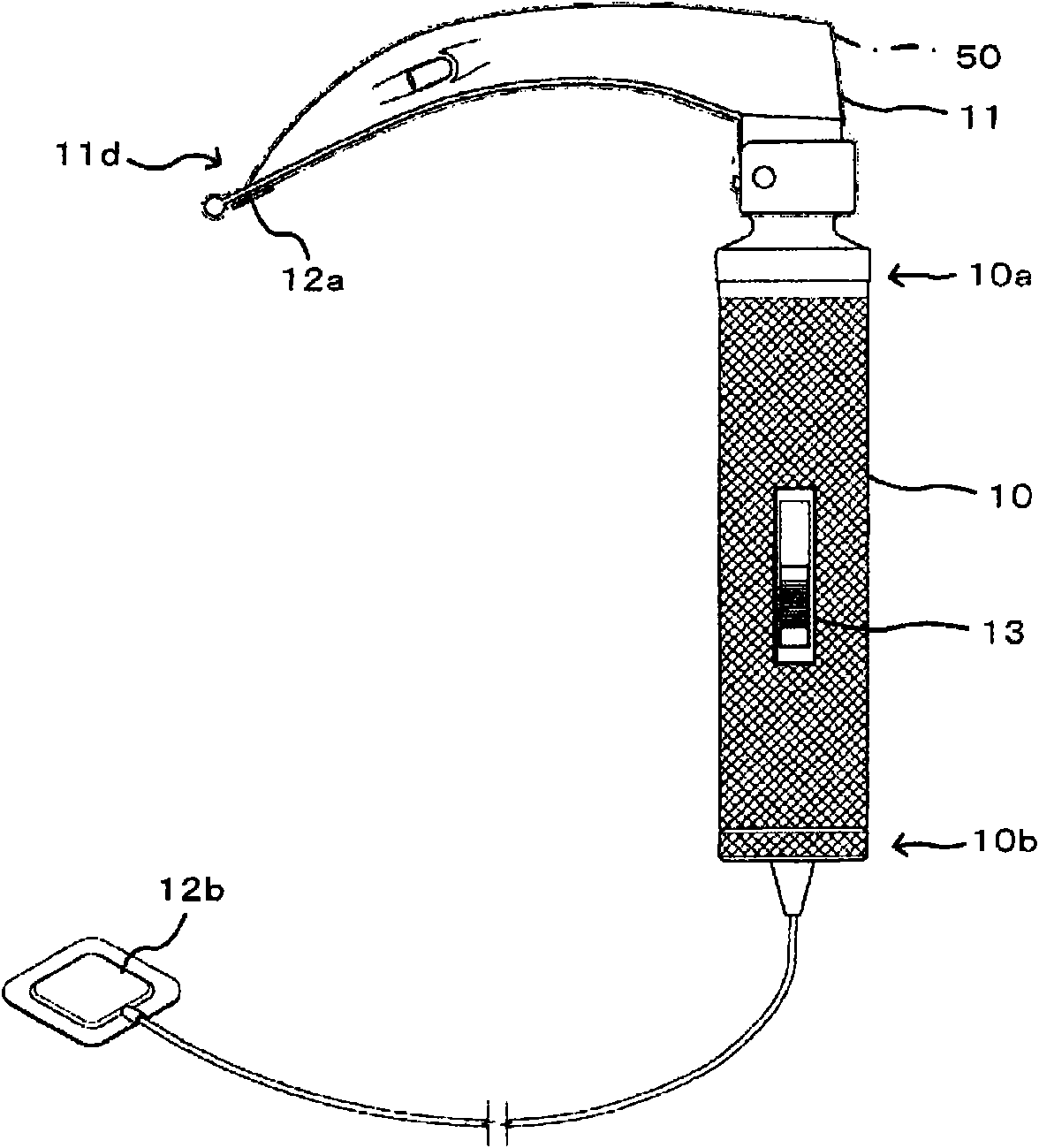
Res-Q-Scope
A multiple function laryngoscope to be used for the safe intubation of a patient's trachea during a respiratory emergency or as an elective procedure. A two section instrument. Proximally, a reusable handle that houses a rechargeable battery, electronic circuits that feed a distal digital image to variable position LCD screen or viewing port, switches and low battery indicator light. Distally, the handle electrically couples with a disposable curved scabbard. The scabbard features a dorsal endotracheal tube channel with a wavy opening which allows preloading and gentle extraction of different size endotracheal tubes once the patient's trachea has been intubated. The scabbard's distal end strategically houses a distal sweeper that engages the epiglottis and exposes the glottis, an opening for the exit of a preloaded endotracheal tube, a LED light, a suction / oxygenation port, and a lens coupled with a digital imaging system (CMOS) to digitize and transport a distant wide field of view. Safe LCD view of one or serial rapid intubations are possible by rapidly replacing for a clean disposable scabbard in case of multiple emergencies.
Owner:CUBB ANTHONY
Implantable devices, systems, and methods for maintaining desired orientations in targeted tissue regions
InactiveUS7845356B2Reducing and preventing snoringSnoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesEpiglottisImplanted device
At least one elongated body is sized and configured for implantation in a desired orientation in an epiglottis and / or in a muscle along an upper respiratory tract. An array of projections extends from the elongated body, which is sized and configured to engage tissue and resist a reorientation of the elongated body within the tissue region out of the desired orientation.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Intubating laryngeal mask airway device with fiber optic assembly
InactiveUS7128071B2Improved intubating laryngeal mask airwayPrecise alignmentTracheal tubesRespiratory apparatusFiberLaryngeal airway
The disclosed laryngeal mask airway device includes a rigid airway tube, a mask portion, and one or more optical fibers. The airway tube extends from a proximal end to a distal end. The airway tube defines an internal passage and a first notch. The first notch extends along a length of the tube from a location on the tube towards the distal end of the tube. The mask portion is coupled to the distal end of the airway tube. The mask portion includes an inflatable cuff. The cuff defines a central opening at least when inflated. The mask portion is insertable through a mouth of a patient to an inserted location within the patient. The cuff surrounds a glottic opening of the patient when inflated and when the mask portion is at the inserted location. A sealed airway passage extends from the proximal end of the tube through the internal passage to the glottic opening when the cuff is inflated and when the mask portion is at the inserted location. The mask portion includes an epiglottis elevator bar that extends from a proximal end to a distal end. The distal end of the bar defines an aperture. The bar is positionable in a resting position and an open position. The optical fibers extend from a proximal end to a distal end. A lens is connected to the distal end of the fibers. The fibers extend through the first notch. The lens is disposed near the aperture defined by the bar when the bar is in the resting position. The fibers and lens provide a view of a region that extends from the lens through the aperture defined by the bar.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI PTE LTD
Laryngeal airway device
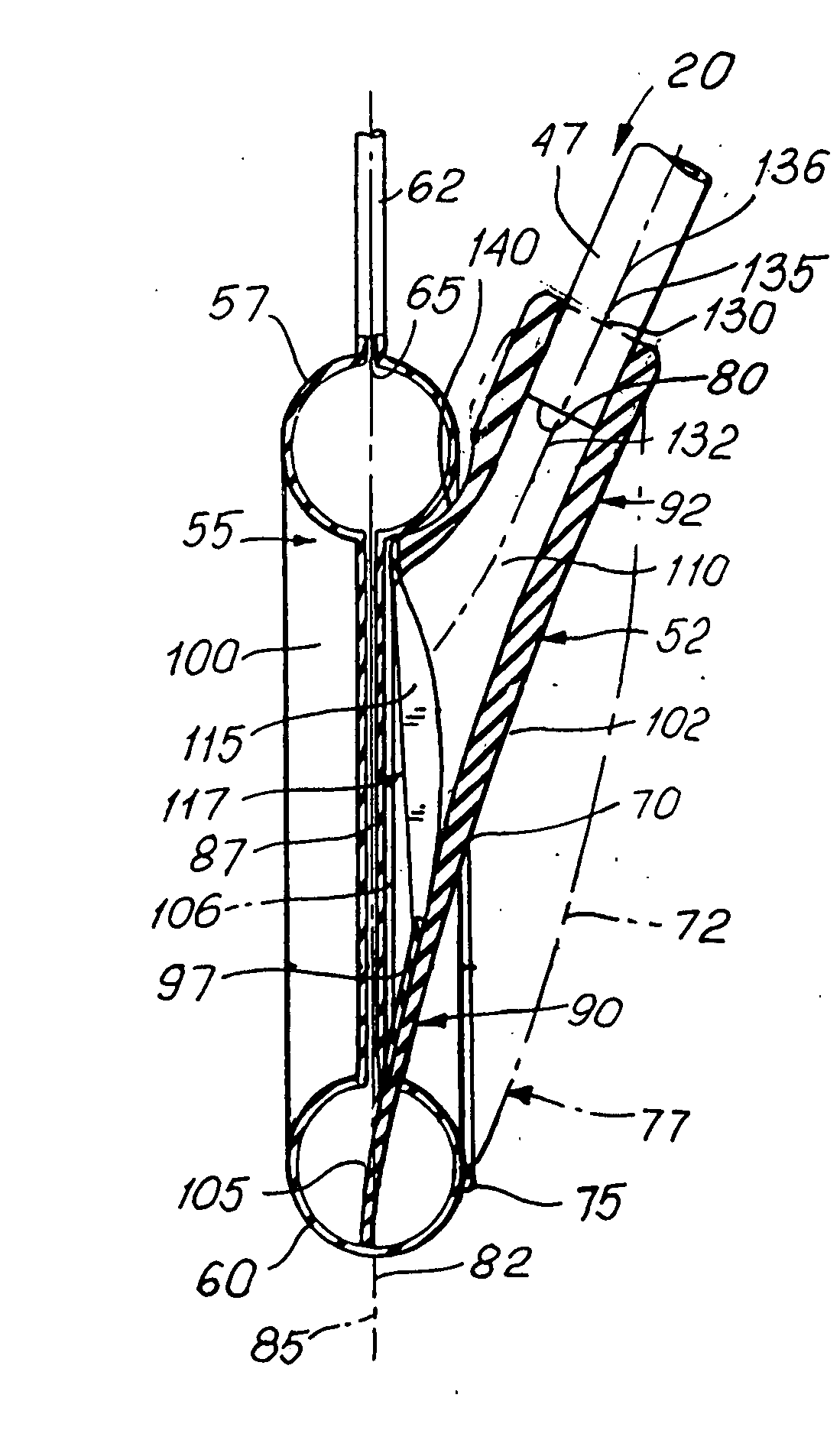
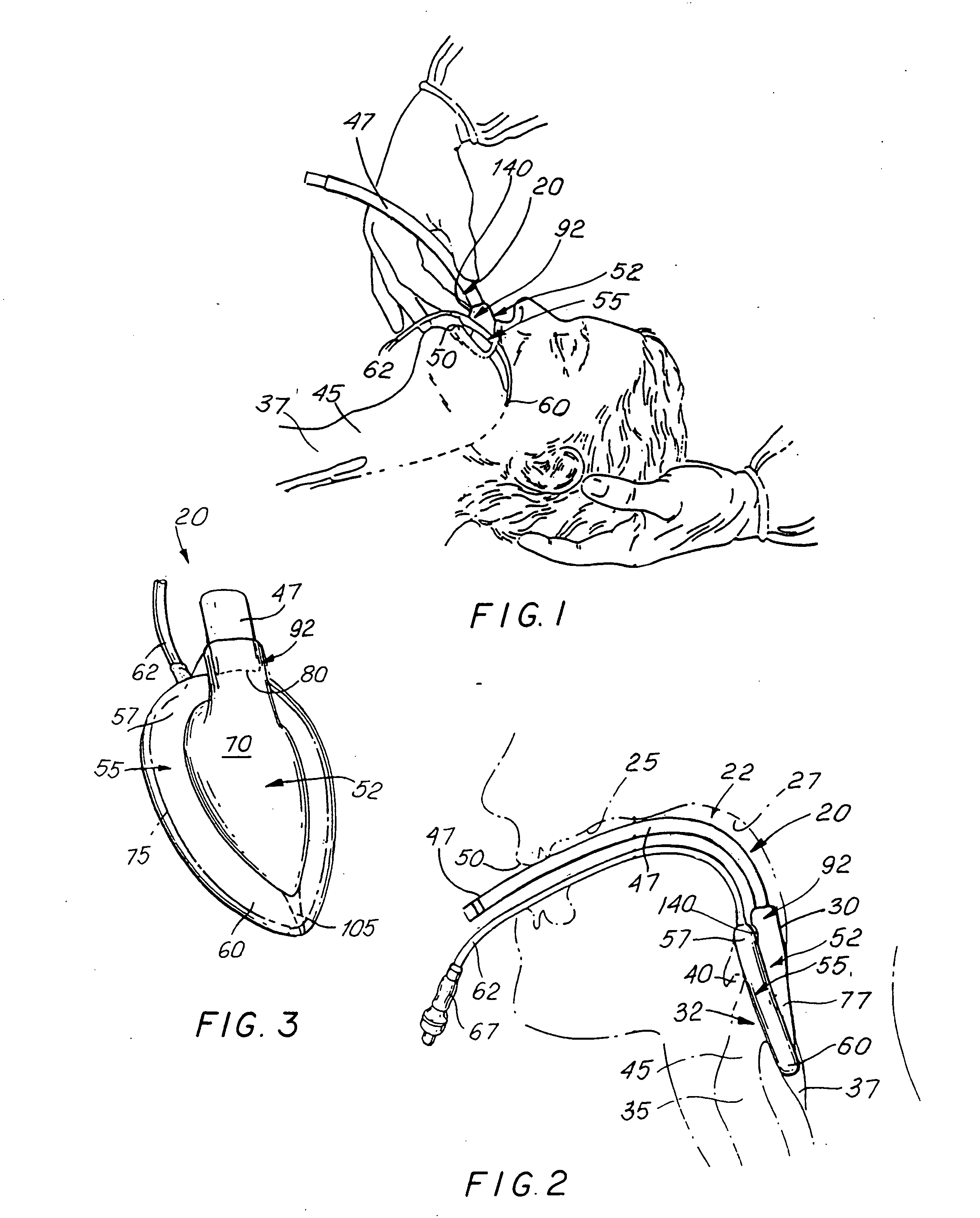
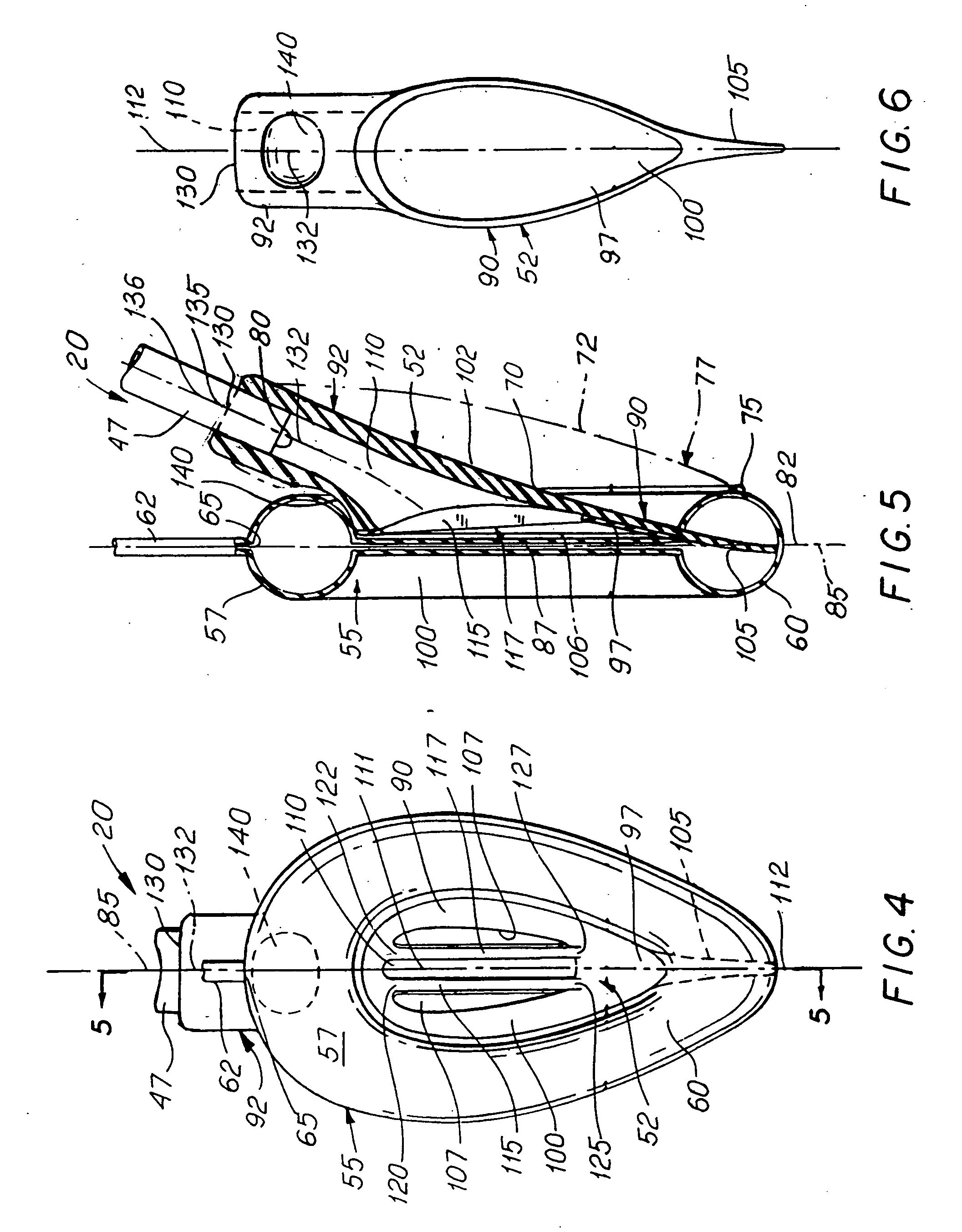
A laryngeal airway device, having an airway tube which has an internal passage in the airway tube wall for receiving a cuff inflation line, and a dome having an inlet and an outlet, where the dome is connected at its inlet with the distal end of the airway tube. The device also includes an annular spoon-shaped inflatable cuff connected with the periphery of the outlet of the dome; a cuff inflation line configured to be in fluid communication with the internal space of the cuff; and a multi-lobed aperture formed in the dome. The aperture is configured to be in fluid communication with the proximal end of the airway tube. The dome has protrusions forming the multi-lobed aperture, such that a flap is configured to prevent the obstruction of the aperture by a patient's epiglottis when the device is inserted into the patient.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Intubating laryngeal mask airway device with fiber optic assembly
ActiveUS20050051175A1Precise alignmentInexpensive materialsTracheal tubesRespiratory apparatusLaryngeal airwayFiber
The disclosed laryngeal mask airway device includes a rigid airway tube, a mask portion, and one or more optical fibers. The airway tube extends from a proximal end to a distal end. The airway tube defines an internal passage and a first notch. The first notch extends along a length of the tube from a location on the tube towards the distal end of the tube. The mask portion is coupled to the distal end of the airway tube. The mask portion includes an inflatable cuff. The cuff defines a central opening at least when inflated. The mask portion is insertable through a mouth of a patient to an inserted location within the patient. The cuff surrounds a glottic opening of the patient when inflated and when the mask portion is at the inserted location. A sealed airway passage extends from the proximal end of the tube through the internal passage to the glottic opening when the cuff is inflated and when the mask portion is at the inserted location. The mask portion includes an epiglottis elevator bar that extends from a proximal end to a distal end. The distal end of the bar defines an aperture. The bar is positionable in a resting position and an open position. The optical fibers extend from a proximal end to a distal end. A lens is connected to the distal end of the fibers. The fibers extend through the first notch. The lens is disposed near the aperture defined by the bar when the bar is in the resting position. The fibers and lens provide a view of a region that extends from the lens through the aperture defined by the bar.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI PTE LTD
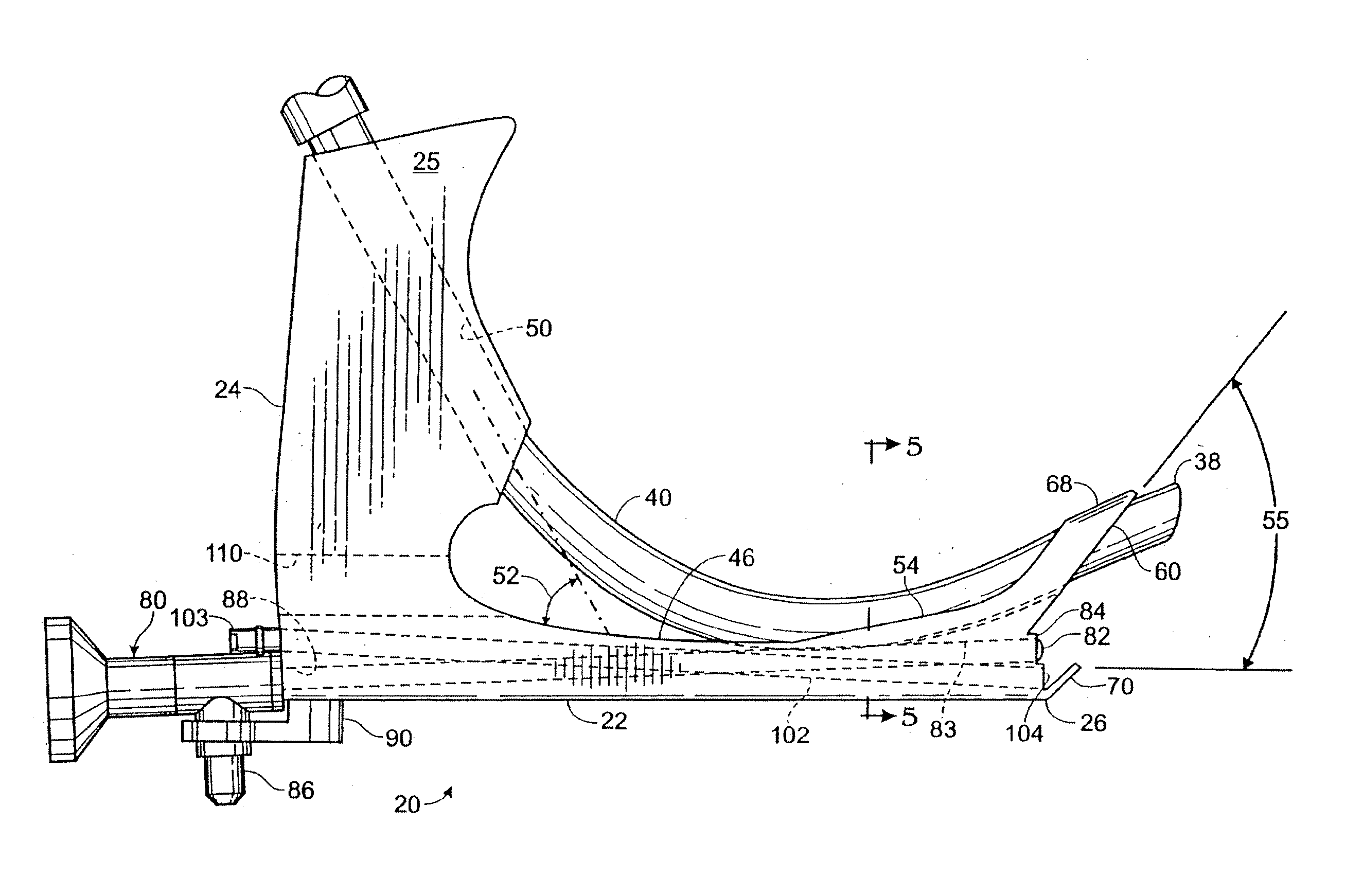
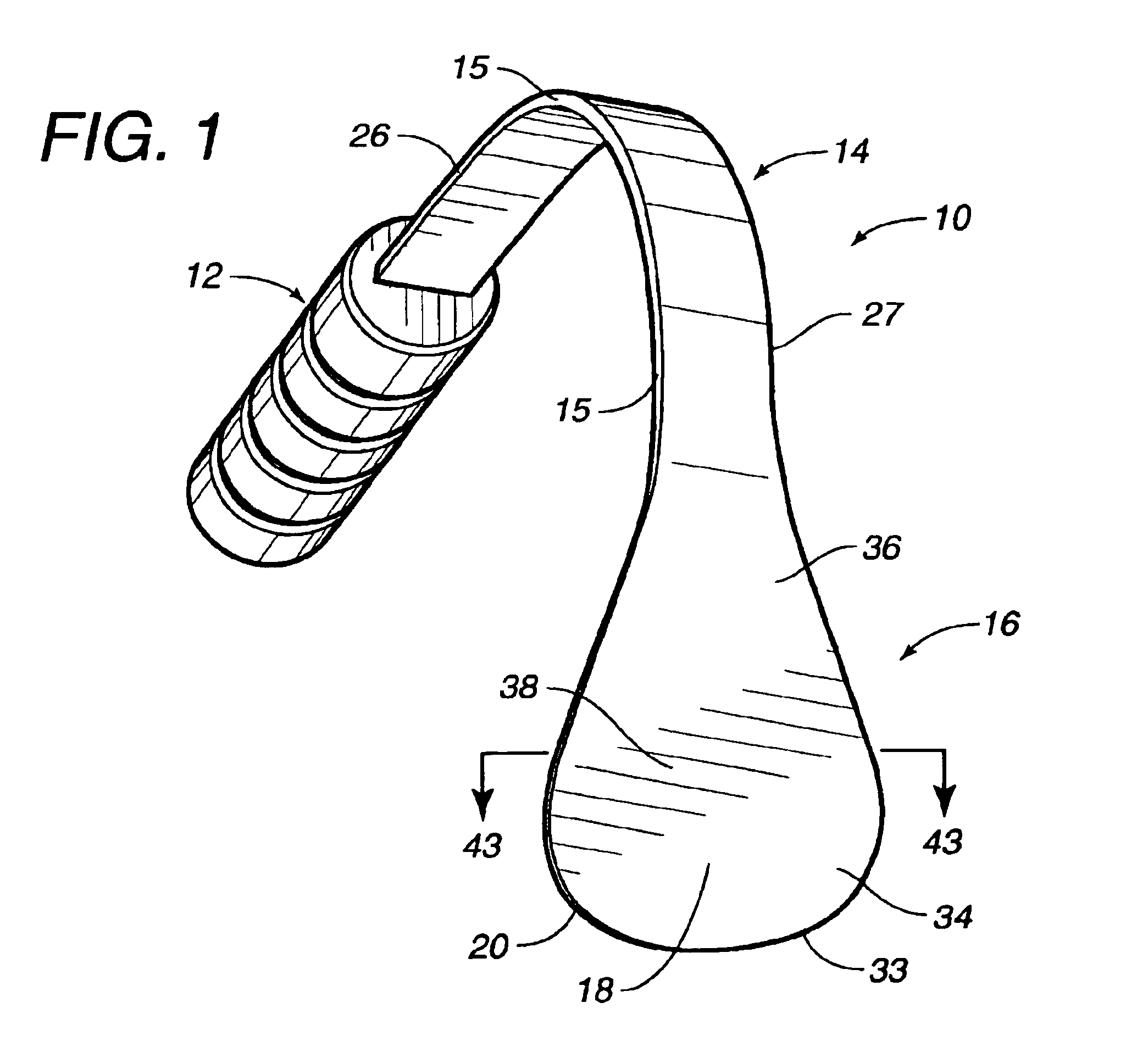
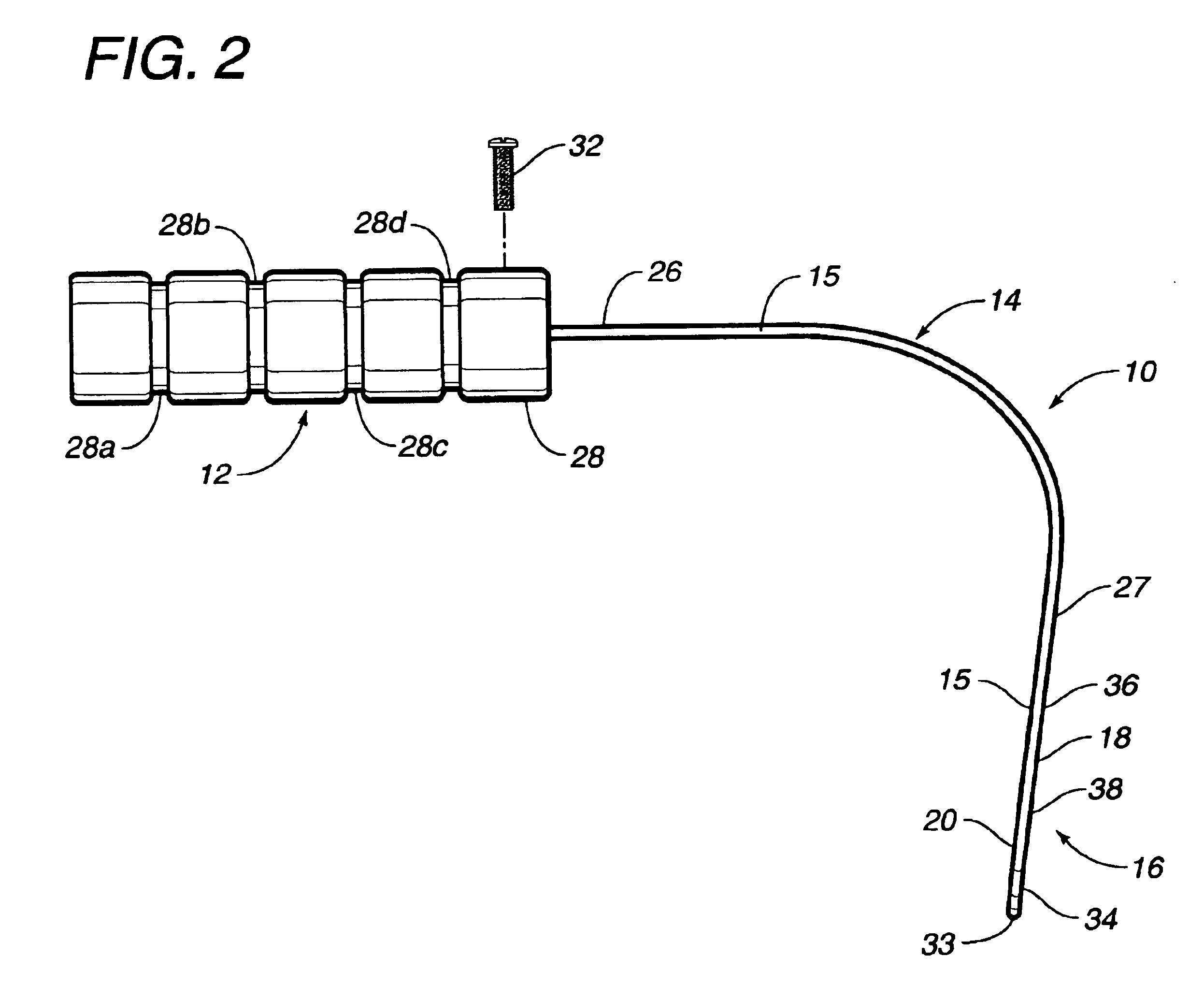
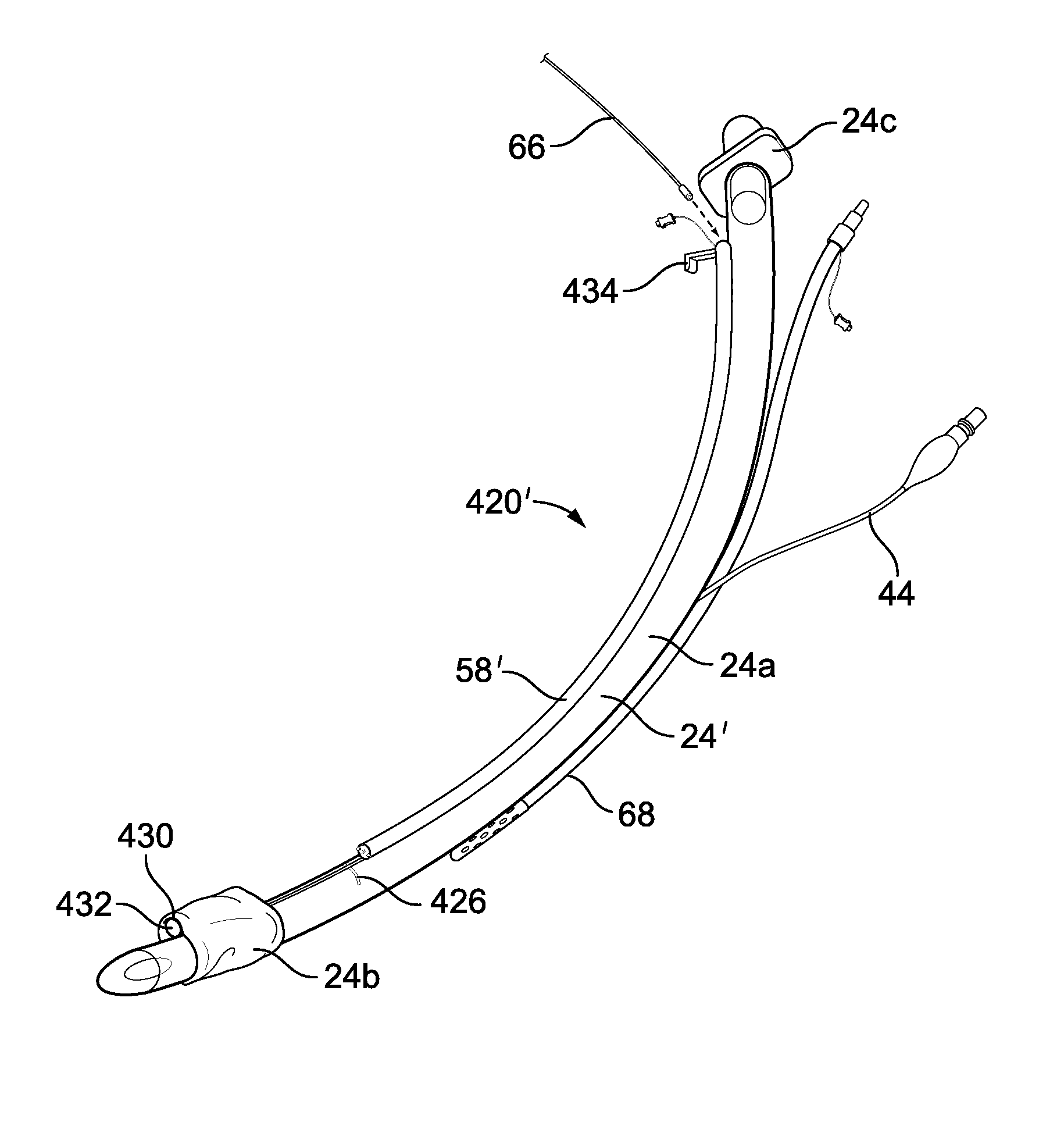
Apparatus and methods for treating sleep apnea
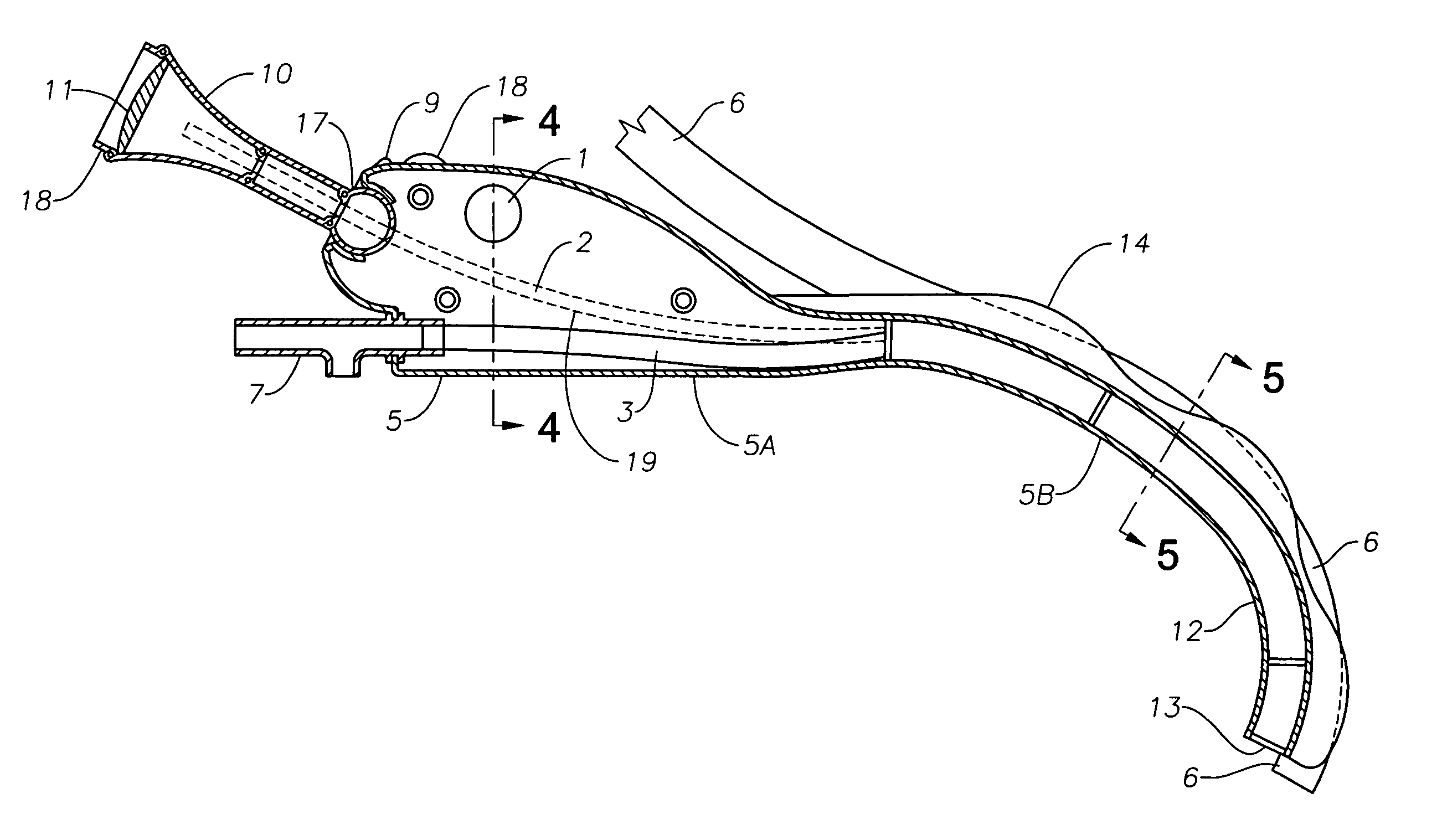
An apparatus and method for treating sleep apnea and / or snoring is provided. The apparatus includes an appliance sized and structured to be placed in the pharyngeal region of a human or animal and being effective in treating sleep apnea and / or snoring, for example in maintaining openness of an oropharyngeal region of a human or animal during natural sleep, advantageously while not interfering with normal functioning of the epiglottis. Preferably, the appliance is non-circumferential in form and includes rounded, spaced apart end portions.
Owner:QUIESCENCE MEDICAL
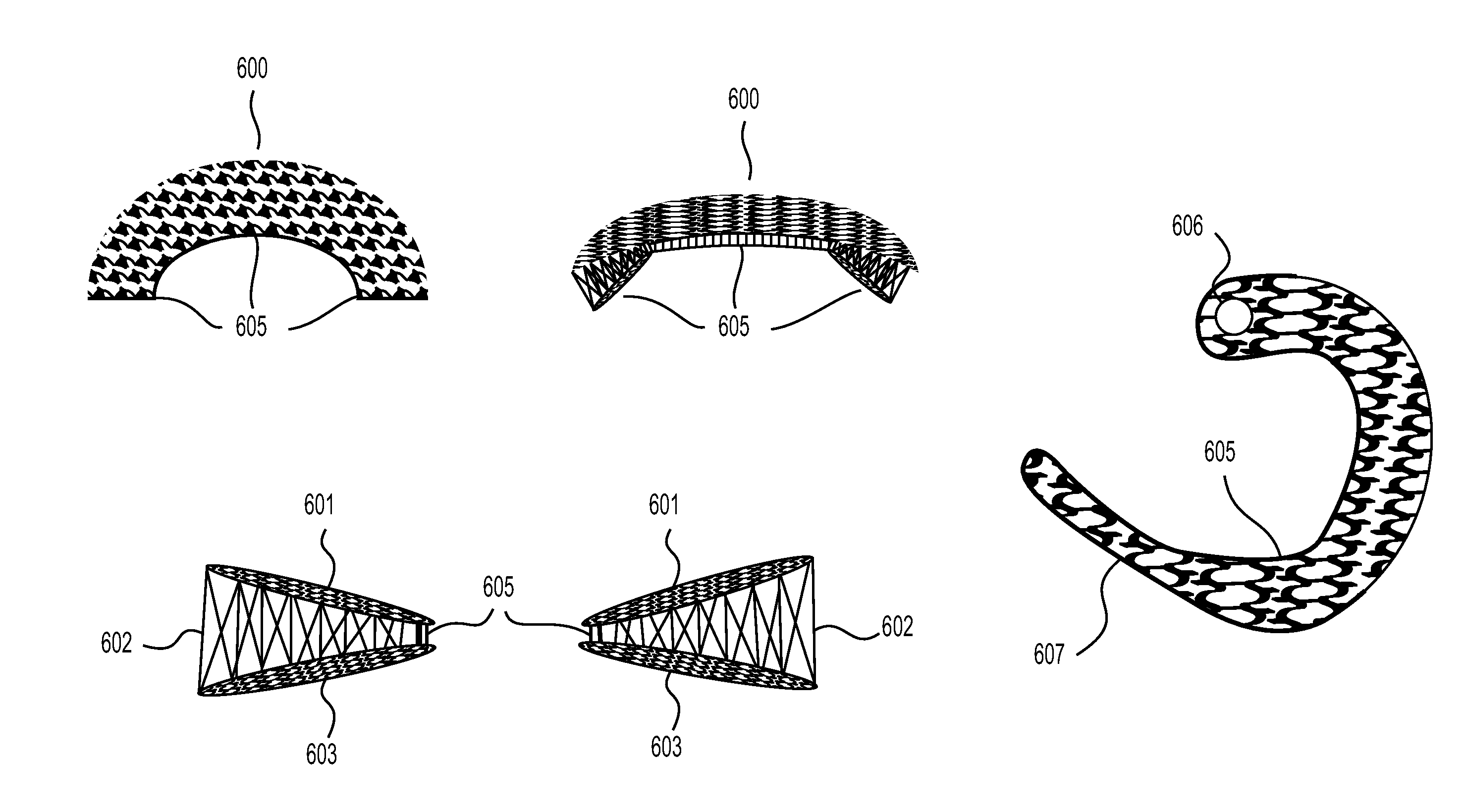
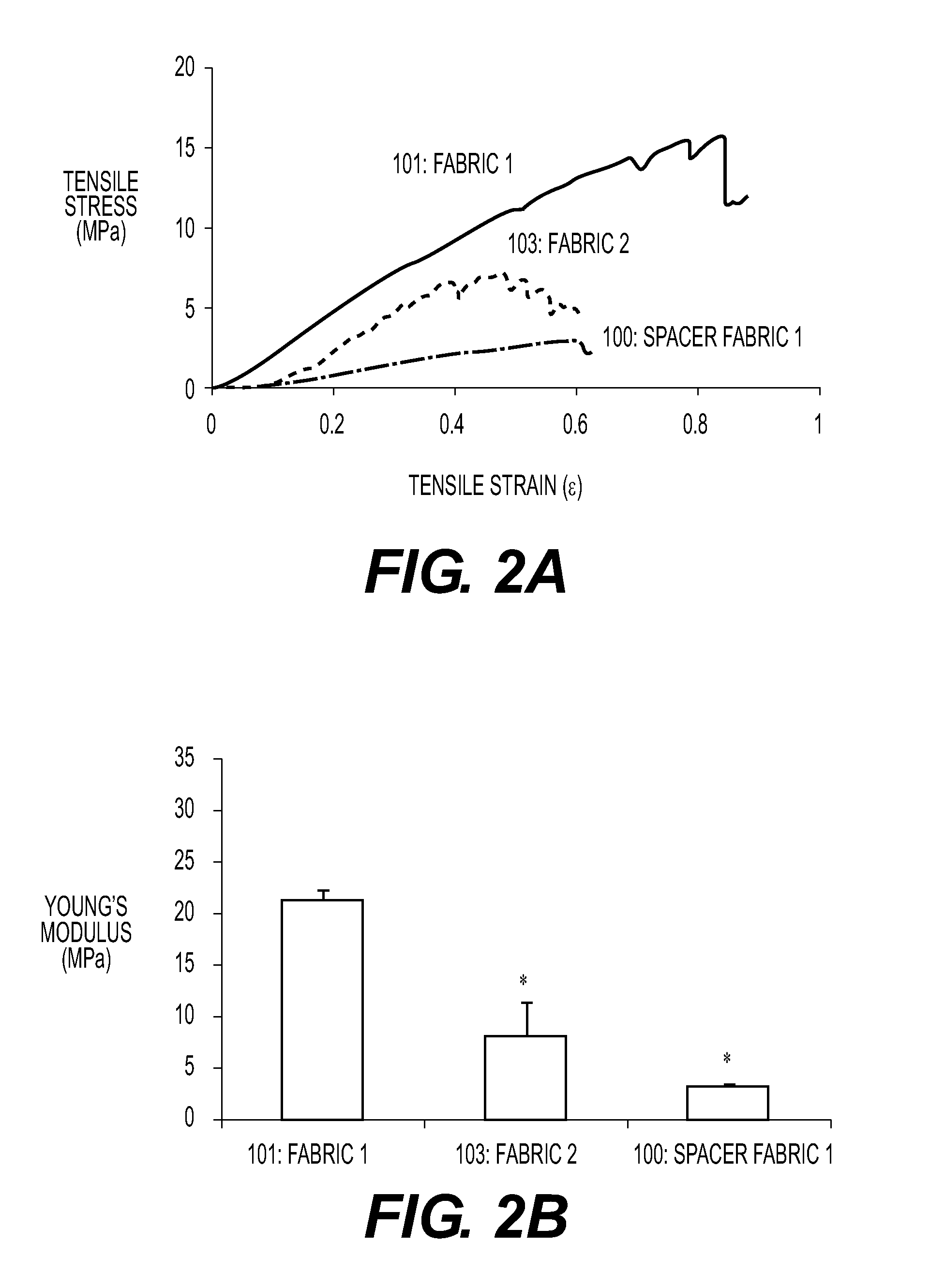
Implantable Devices for Musculoskeletal Repair and Regeneration
This application describes an implantable device for tissue repair comprising at least two fabrics with interconnecting spacer elements transversing, connecting, and separating the fabrics, forming the device. Some embodiments have fixation points which can be an extension of at least one of the fabrics. The implantable device allows modification of the two fabrics having varying constructions, chemistries, and physical properties. The spacer elements create a space between the two fabrics, which can be used for the loading of biological materials (peptides, proteins, cells, tissues), offer compression resistance (i.e. stiffness), and compression recovery (i.e., return to original dimensions) following deformation and removal of deforming load. The inclusive fixation points of the fabrics are designed to allow for fine adjustment of the sizing and tension of the device to promote integration with the surrounding tissues as well as maximize the compressive resistance. The fixation points can include either the first fabric, the second fabric, or the combination of both fabrics. This device is suitable for soft and hard tissue regeneration or replacement with a preference for musculoskeletal tissues including but not limited to cartilage (including hyaline (referred to as articular, e.g. cartilage on the ends of long bones), fibrous (e.g. meniscus or intervertebral discs), elastic (e.g. ear, epiglottis)), bone, muscle, tendon, ligament, and fat.
Owner:MCCULLEN SETH
Oropharyngeal airway
An oropharyngeal device for insertion into the mouth of a patient. The device includes a body having a distal end and a proximal end with a flange formed at the proximal end. The distal end is inserted into the mouth until the flange is disposed outside and adjacent to the patient's mouth. The flange keeps the proximal device from entering the mouth. The body is sized such that the distal end of the body is disposed within the pharynx above the epiglottis. The device includes a channel that forms an airway between the ends. The device also includes at least three separate conduits integrated into the body for administering oxygen, suctioning, and for assessing ventilation thorough end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring. The conduits for oxygenation and suctioning extend through the body between its proximal and distal ends. The conduit for end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring terminates within the channel.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Intubation instrument
InactiveUS20080146879A1Facilitate rapidEasy to place safelyTracheal tubesBronchoscopesCMOSEpiglottis
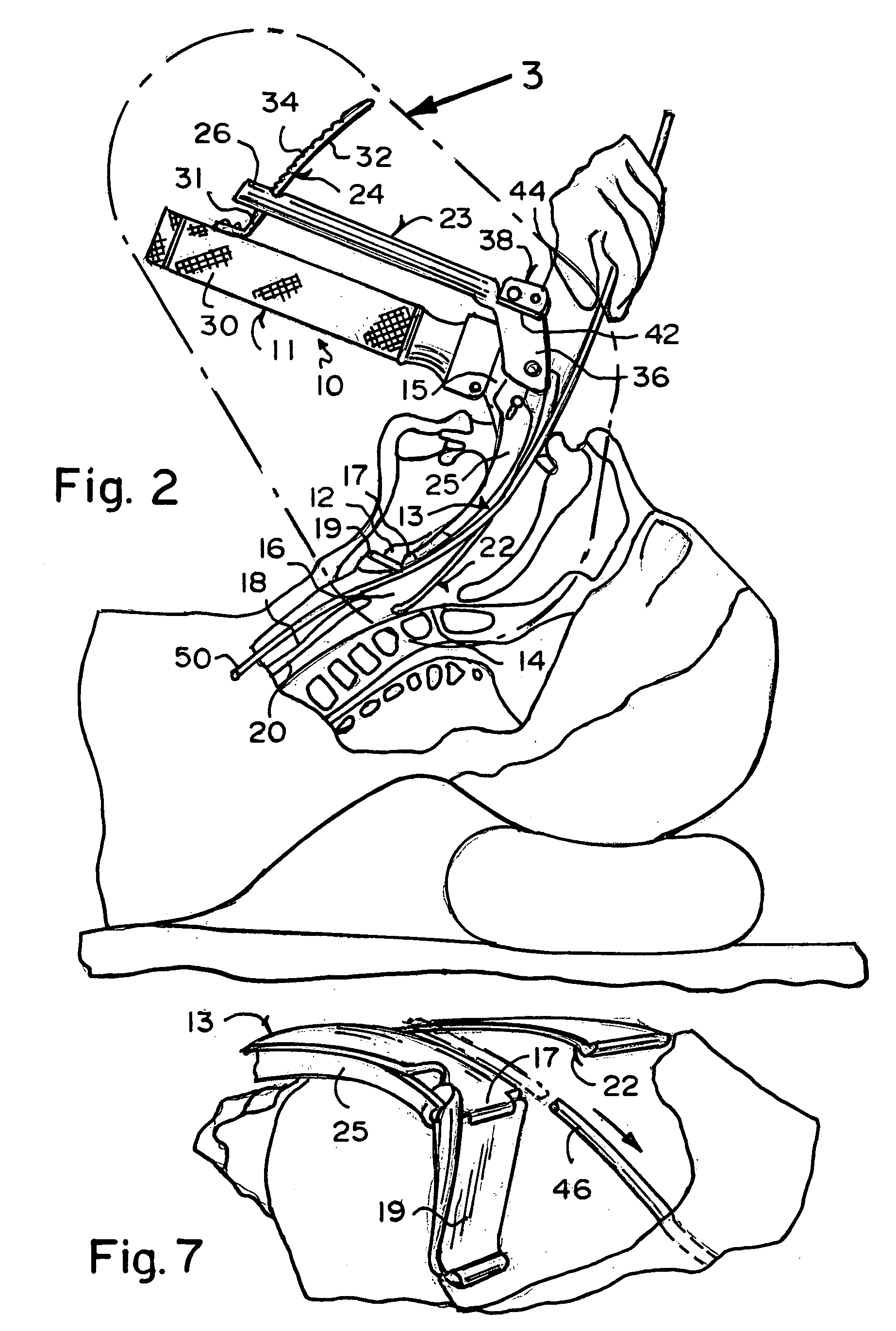
The configuration and arrangement of the instrument greatly facilitate safe placement of the instrument and an associated endotracheal tube. The instrument includes a handle with an arm extending therefrom. The arm includes a base portion and a distal lifter portion preferably having an angle between 5° and 85°, inclusive, and the lifter is sized and shaped to engage or lift the patient's epiglottis, thereby to expose the glottis. In a preferred embodiment, the base portion and lifter portion are substantially the same length, and a viewing device, which is preferably a CCD or CMOS camera positioned near the transition portion between the base and lifter portions, is aligned to provide a perspective view toward the distal end of the lifter. Lights, which are preferably LED units, are positioned toward the distal end of the lifter to facilitate viewing. A transparent protective sheathing may be positioned over the assembly to facilitate cleaning and provide sterile multiple use of the device, and the lifter may be pivotally secured to the base portion to facilitate on-site adjustment by the practitioner.
Owner:VERATHON
Laryngoscope for simultaneously facilitating the illuminating of a throat pathway and inserting an intubation tube
ActiveUS7153260B1Avoid disadvantagesEasy to useBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesEpiglottisMechanical engineering
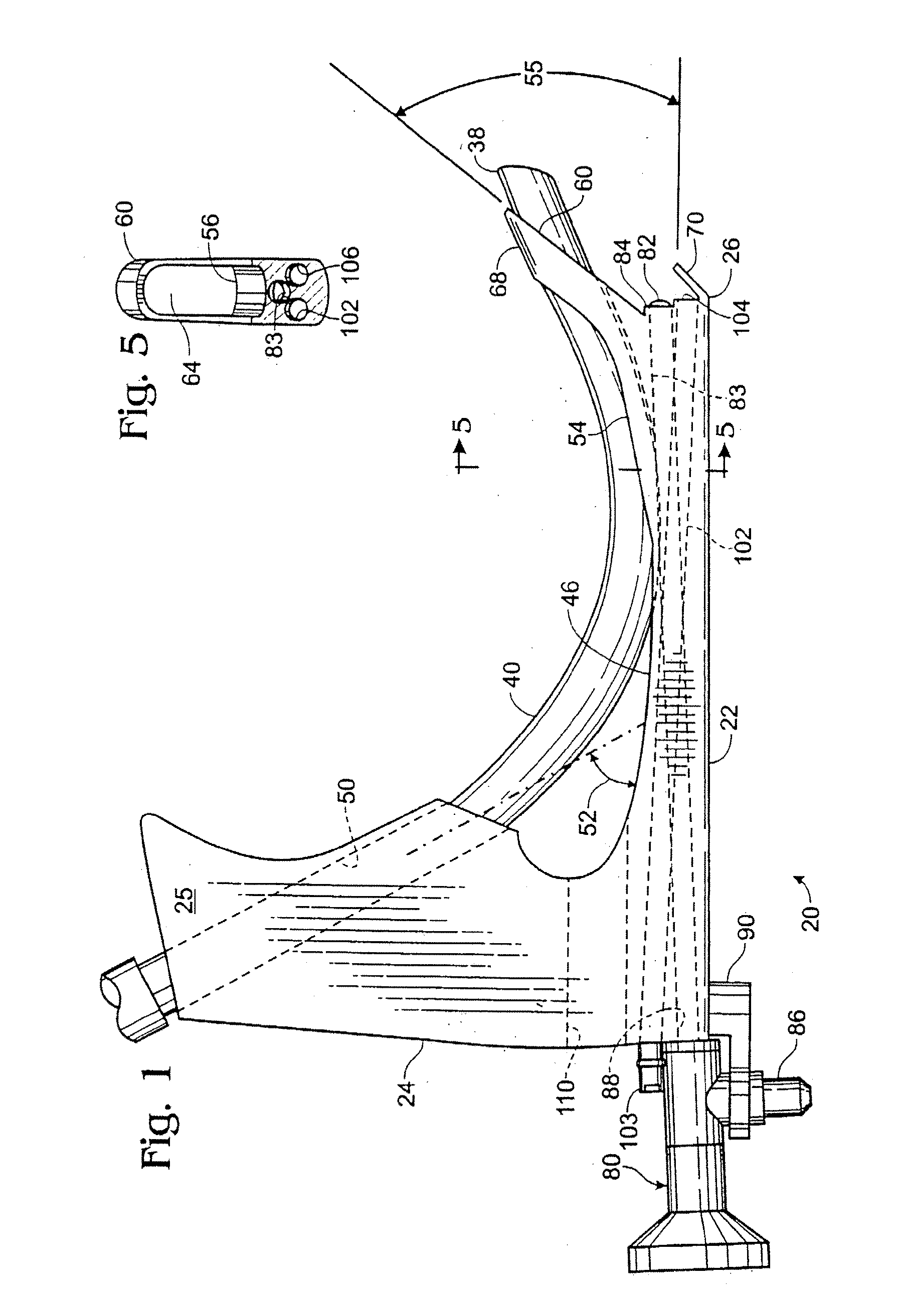
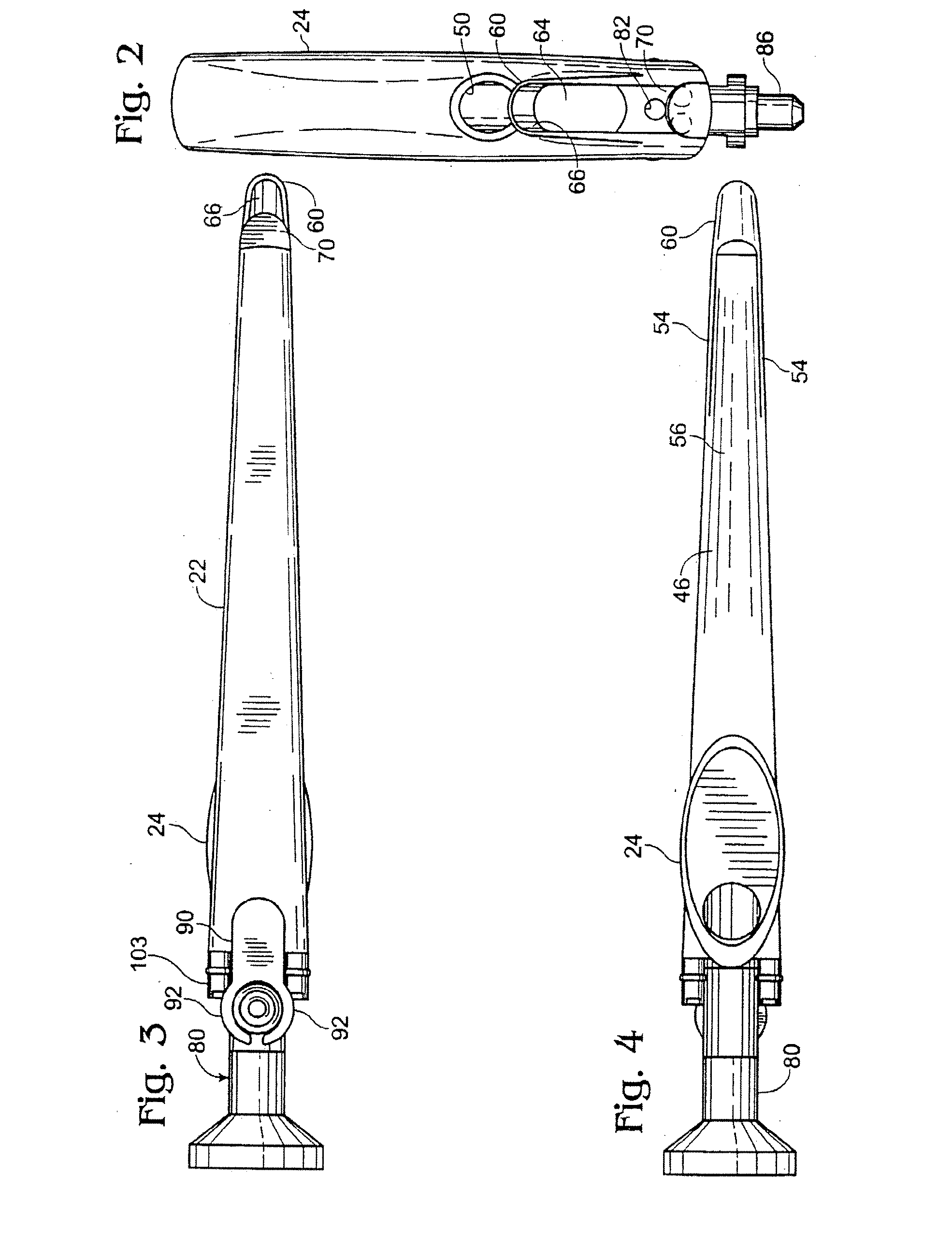
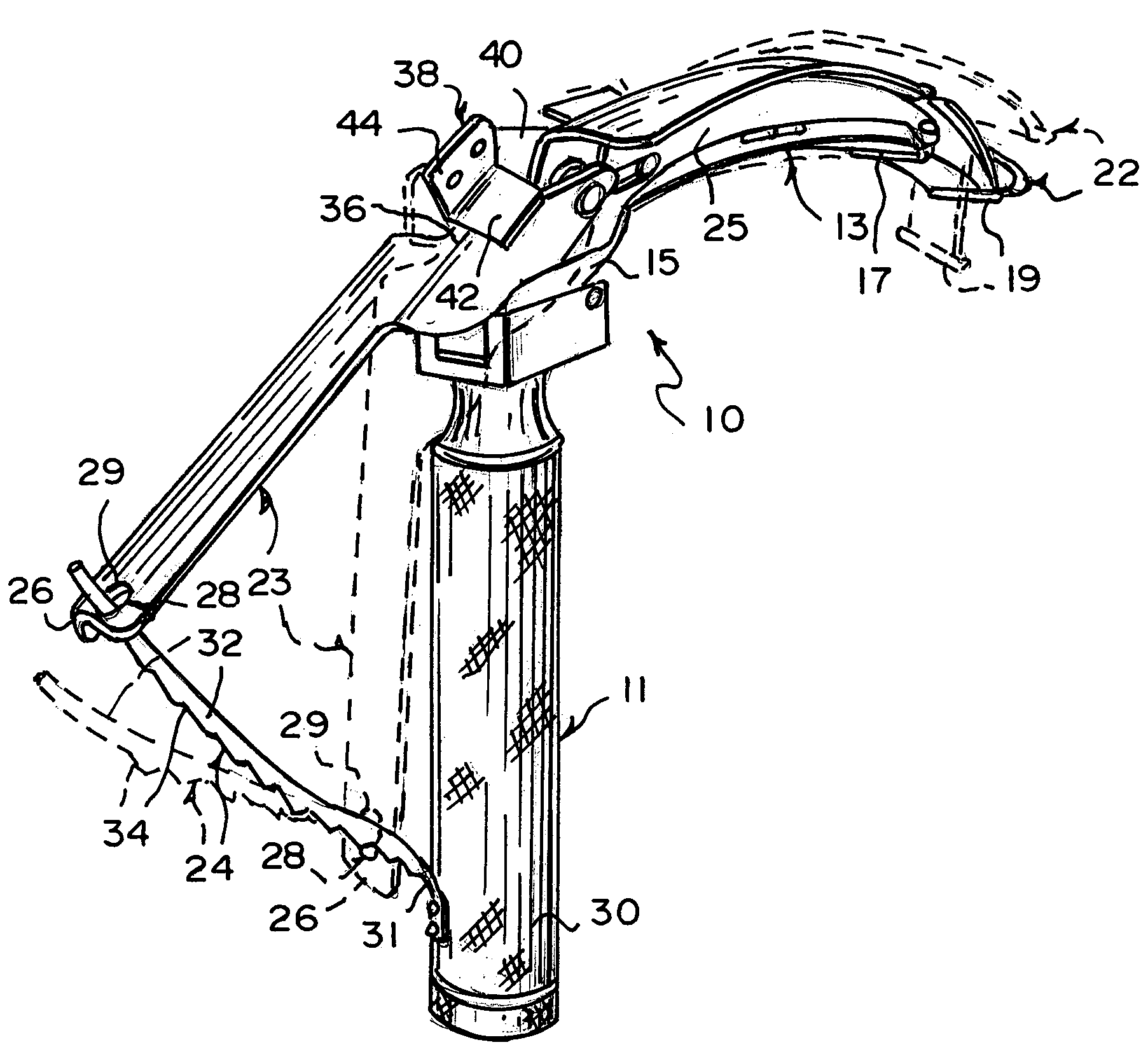
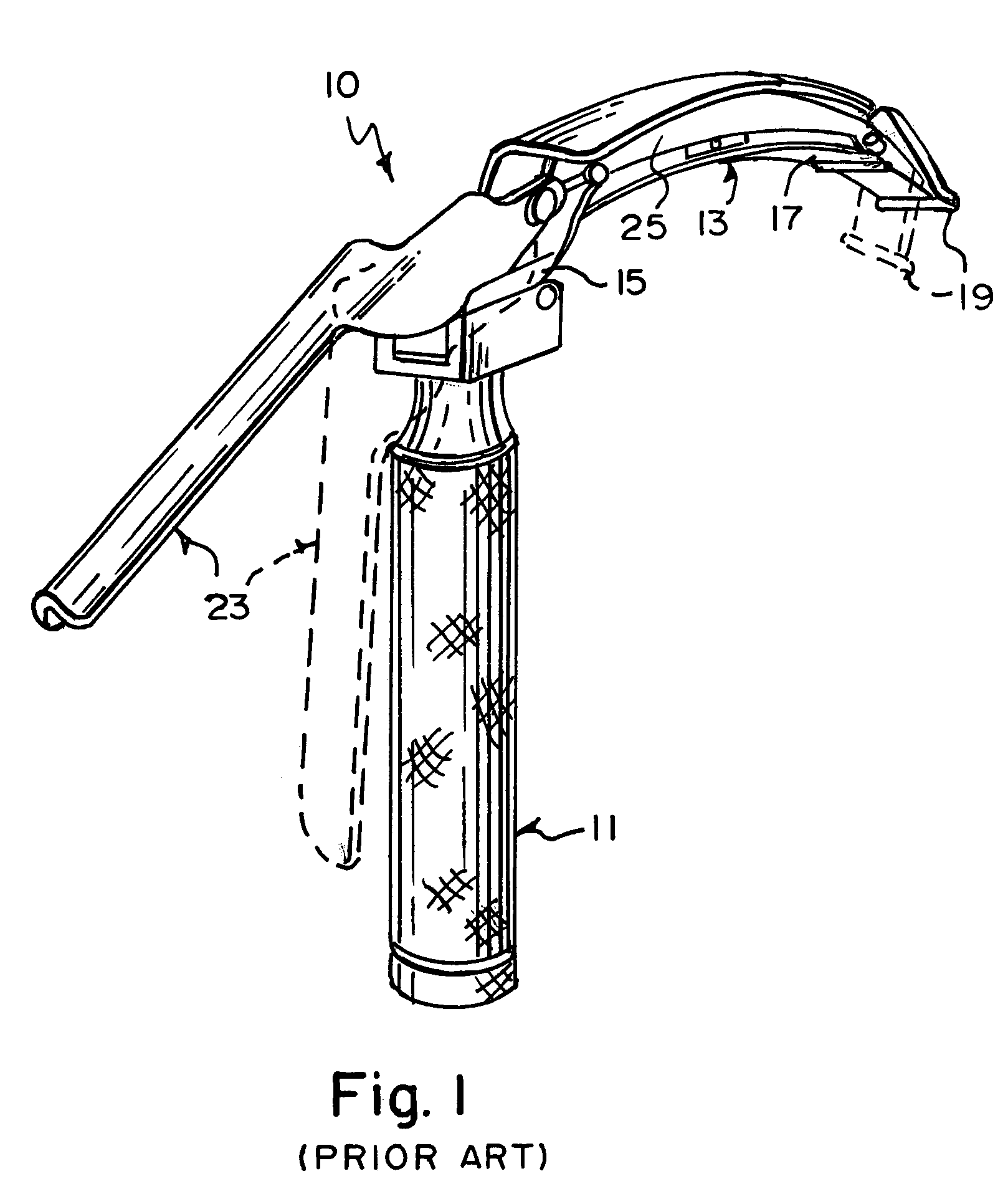
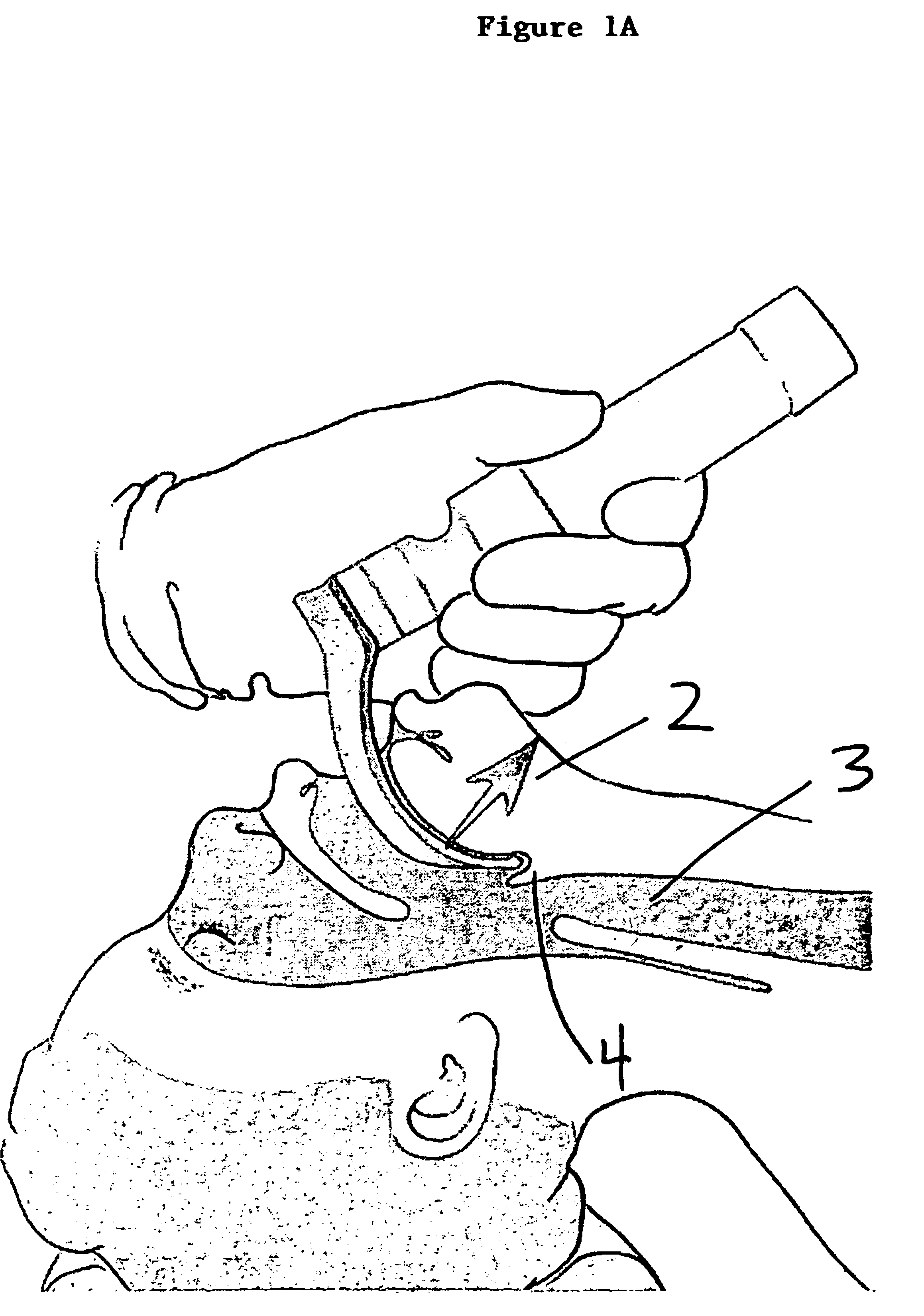
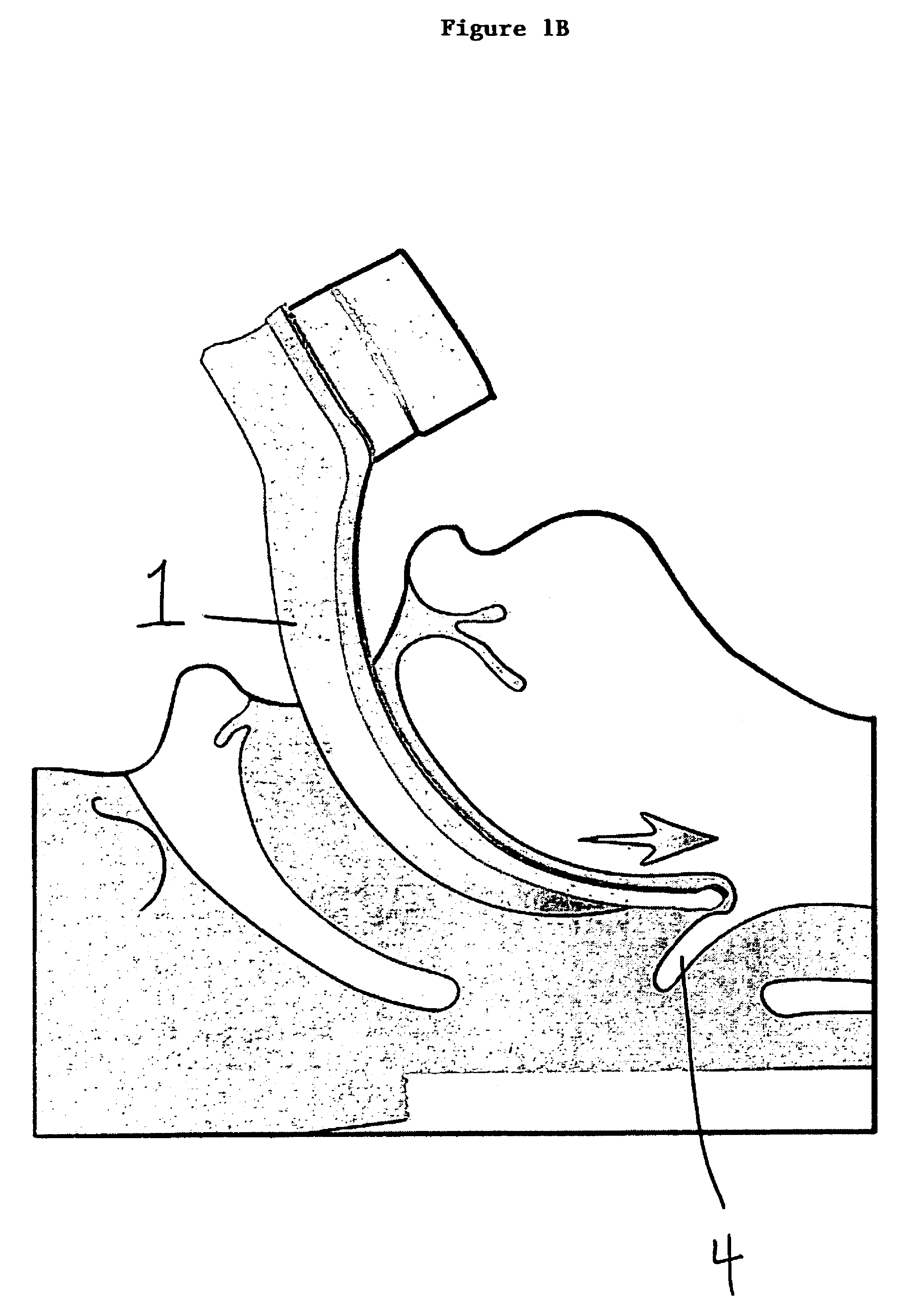
An improved laryngoscope of the type having a stationary handle, a stationary blade affixed to the stationary handle, a tip pivotally attached to the stationary blade, a movable handle pivotally attached to the stationary blade, and an arm pivoting the tip downwardly when the movable handle is moved towards the stationary handle depressing the epiglottis. The improvement includes a movable blade pivotally attached to the stationary blade and affixed to the movable handle so as to allow the movable blade to pivot away from the stationary blade when the movable handle is moved towards the stationary handle and spread the posterior tissue defining the superior opening of the larynx away from the epiglottis simultaneously as the tip depresses the epiglottis and both thereby opening up the trachea exposing the larynx, and a lock locking the movable blade in a desired positioned by locking the movable handle affixed thereto.
Owner:GIRGIS MAGDY S
Laryngeal mask airway device
InactiveUS20050274383A1Easy to deflateReduce the possibilityTracheal tubesMedical devicesLaryngeal airwayEpiglottis
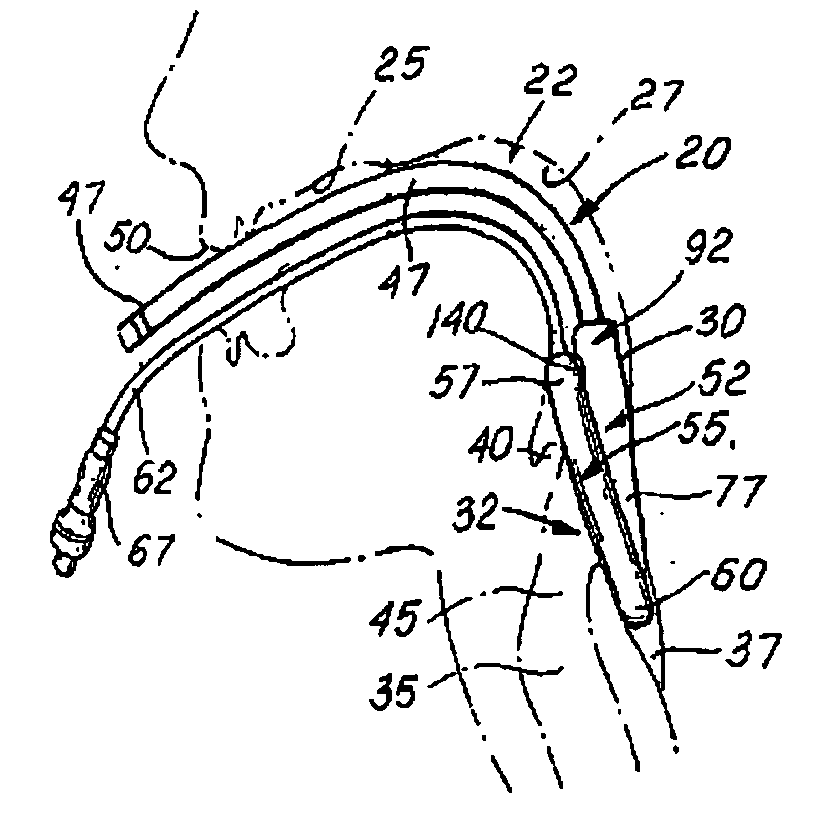
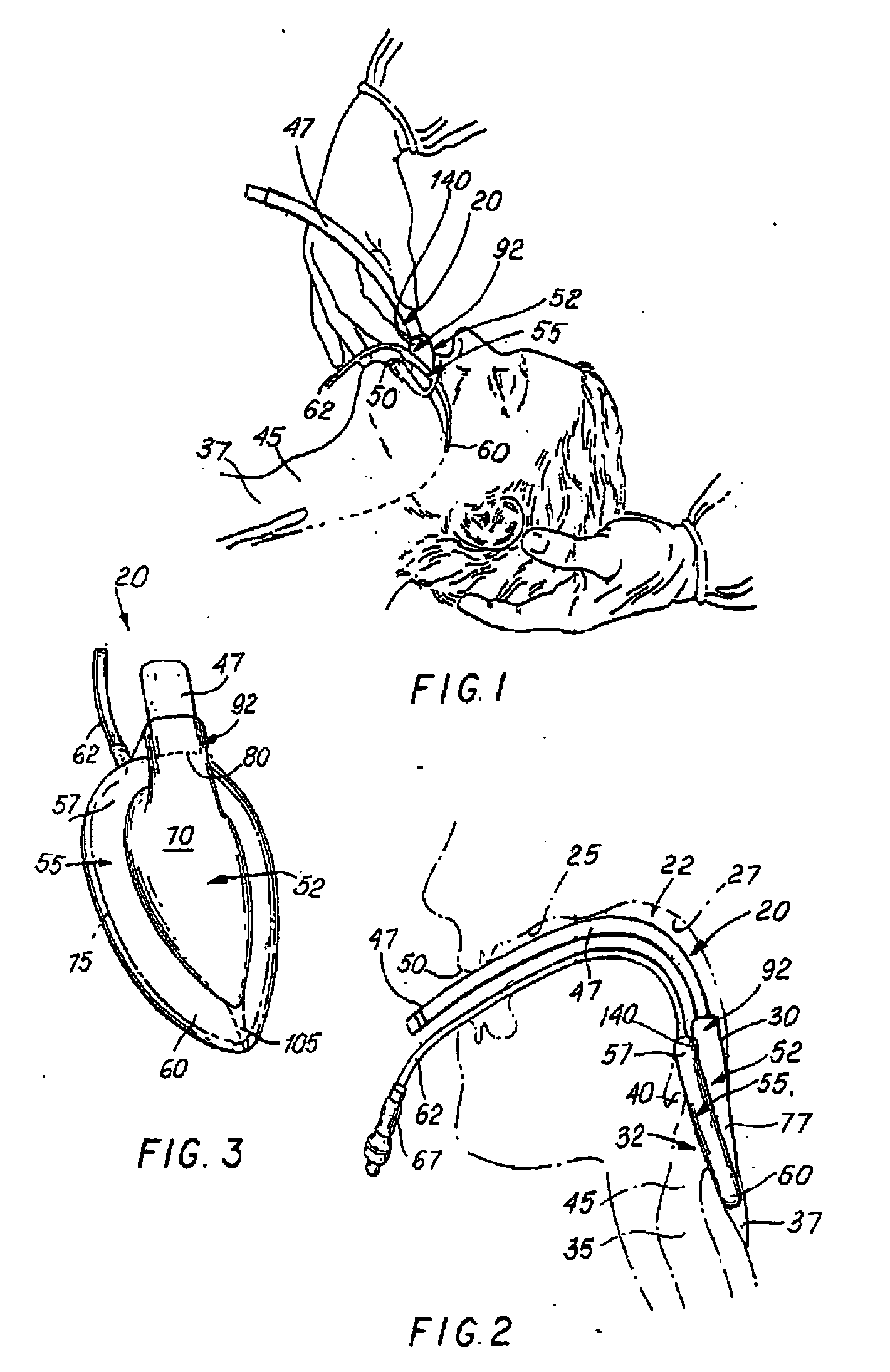
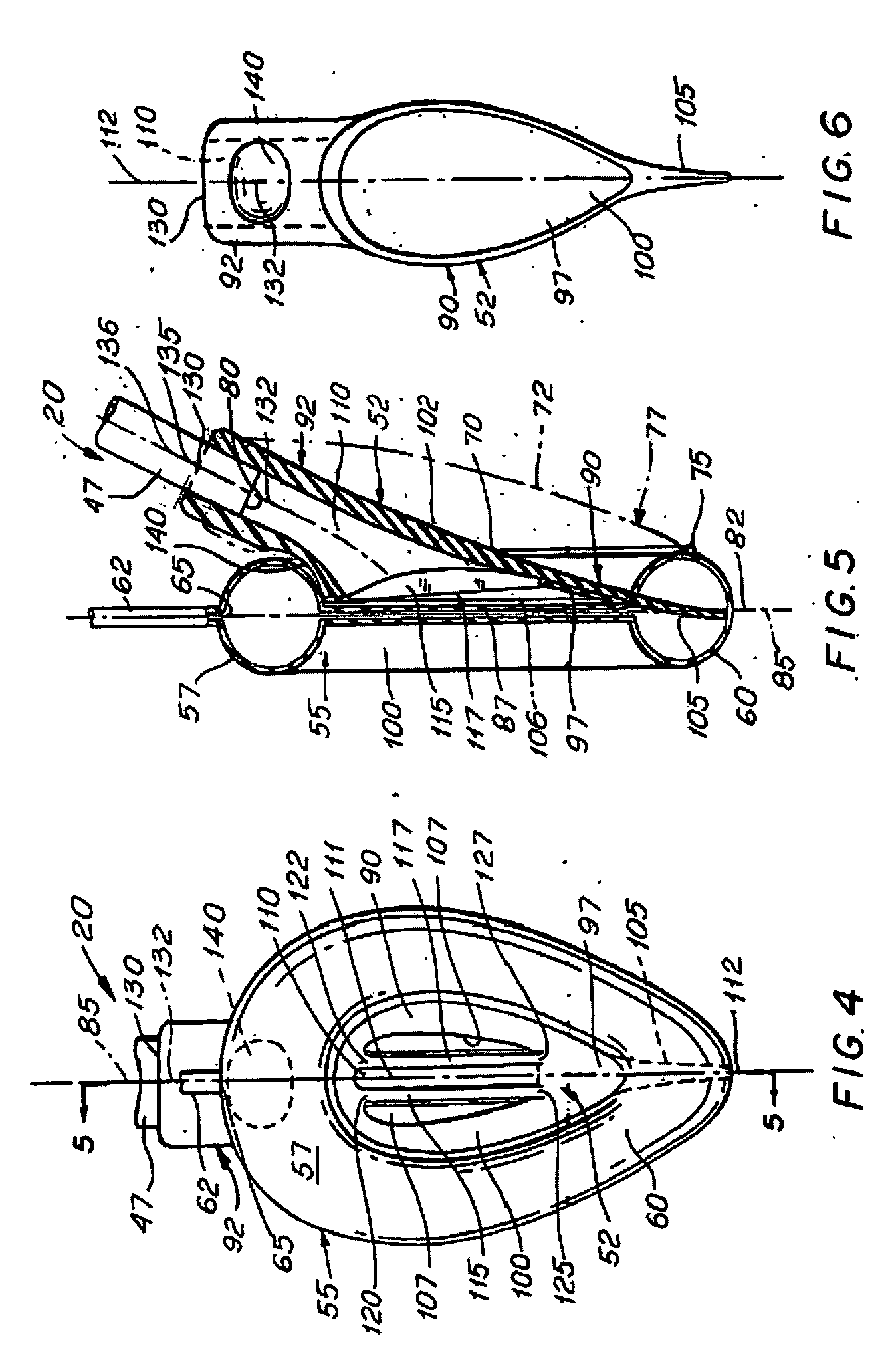
A modified laryngeal mask airway device (LMA-device) is provided with means to improve ease of insertion, reliability of function and higher seal pressure (i.e., cuff pressure ratio). The LMA-device includes an indented section of the airway tube to offer locating means and purchase for the inserting finger, and extended mask aperture bars to increase the effective ventilating area of the mask and reduce the possibility of epiglottis displacement occasioned by mask insertion. The LMA-device further includes a modification of the airway tube angle of attachment to the mask, and provision of a posterior or back-cushion covering the entire posterior surface of the mask.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI PTE LTD
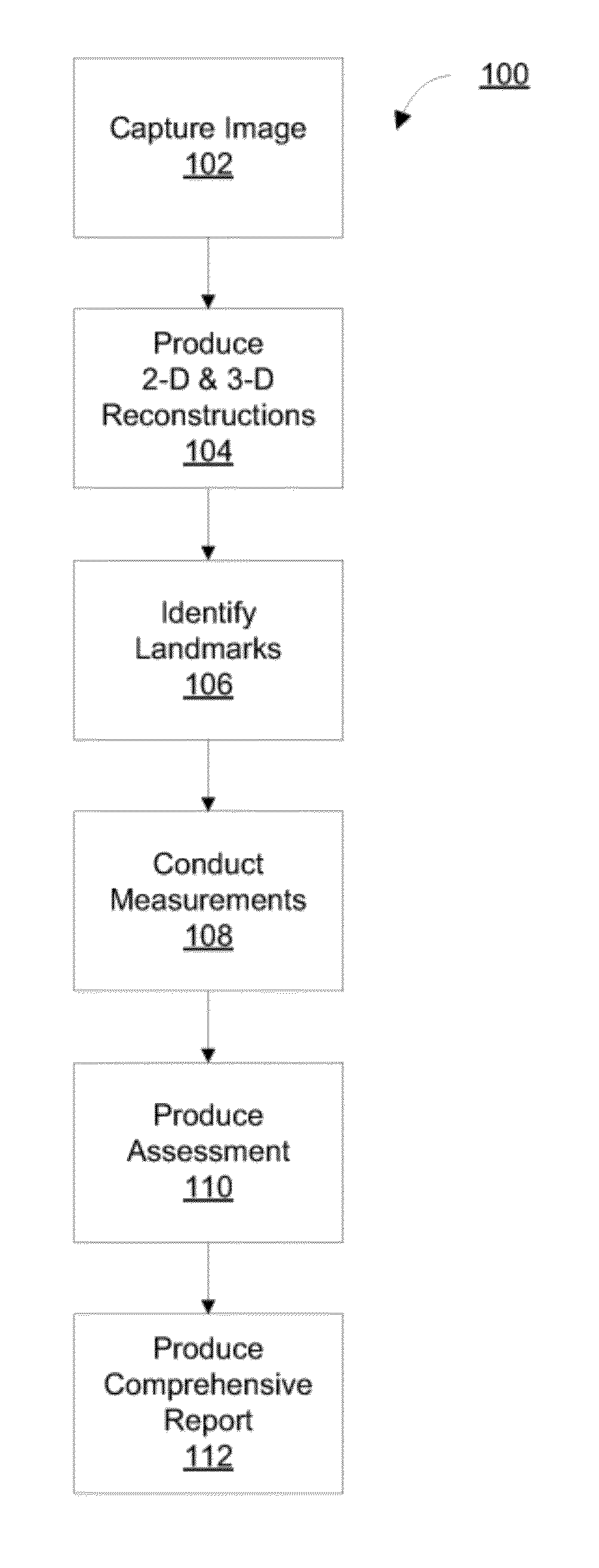
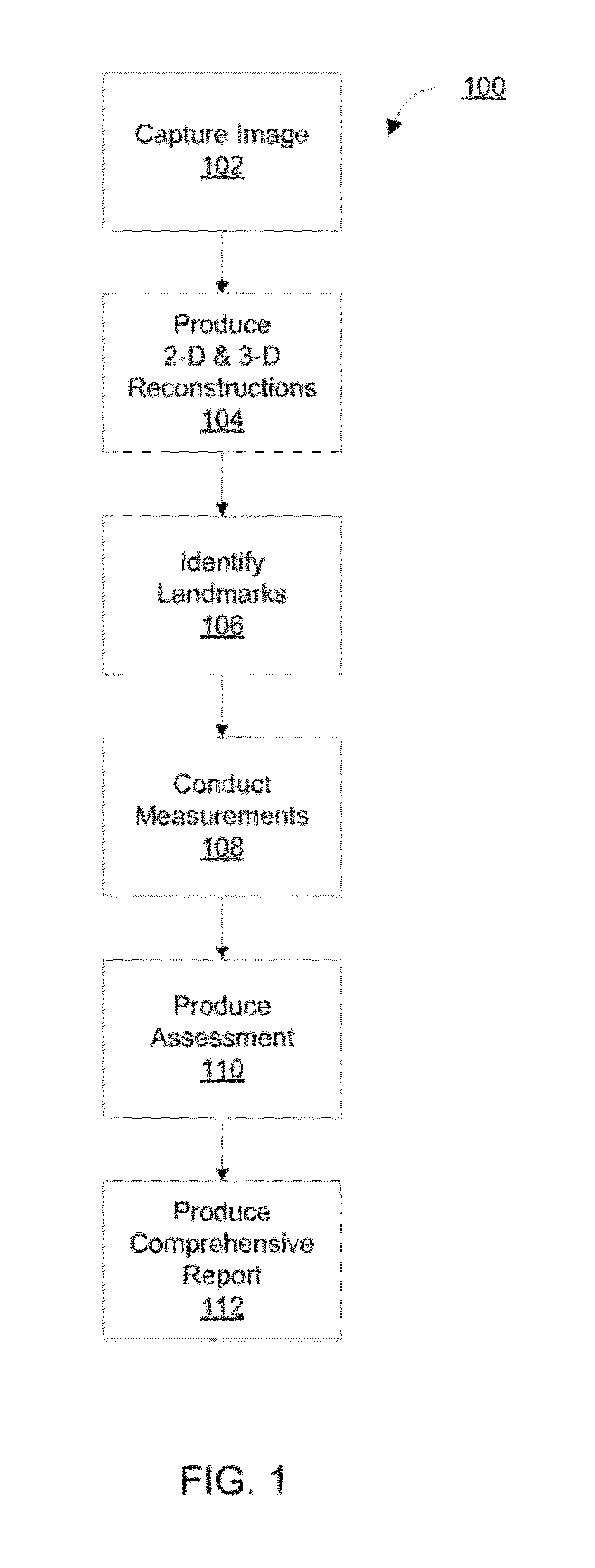
Diagnosing Airway Obstructions
InactiveUS20120022365A1Well representedReliable diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComputerised tomographsPartial obstructionEpiglottis
Methods, devices, and computer program products facilitate characterization of a patient's upper airway including nose, palate, oral cavity, epiglottis, pharynx and larynx. Identification of full or partial obstructions in the upper airway enables the production of a full assessment the patient's airway. A report is produced that details the various contributing factors to the patient's airway obstructions. The comprehensive assessments can be utilized to effectively carry out various surgical and non-surgical procedures for treating sleep apnea.
Owner:MANSFIELD ENTERPRISES
Oropharyngeal Airway
An oropharyngeal device for insertion into the mouth of a patient. The device includes a body having a distal end and a proximal end with a flange formed at the proximal end. The distal end of the body is inserted into the mouth of the patient until the flange at the proximal end is disposed outside and adjacent to the patient's mouth. The flange keeps the proximal device from entering the mouth. The body is sized such that the distal end of the body is disposed within the pharynx above the epiglottis. The device includes a channel through the body that forms an airway between its proximal and distal ends. The device also includes at least three separate conduits integrated into the body for administering oxygen, suctioning, and for assessing ventilation through end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring. The conduits for oxygenation and suctioning extend through the body between its proximal and distal ends. The conduit for end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring extends along and is attached to a side wall of the channel and terminates within the channel.
Owner:GANESH ARJUNAN +2
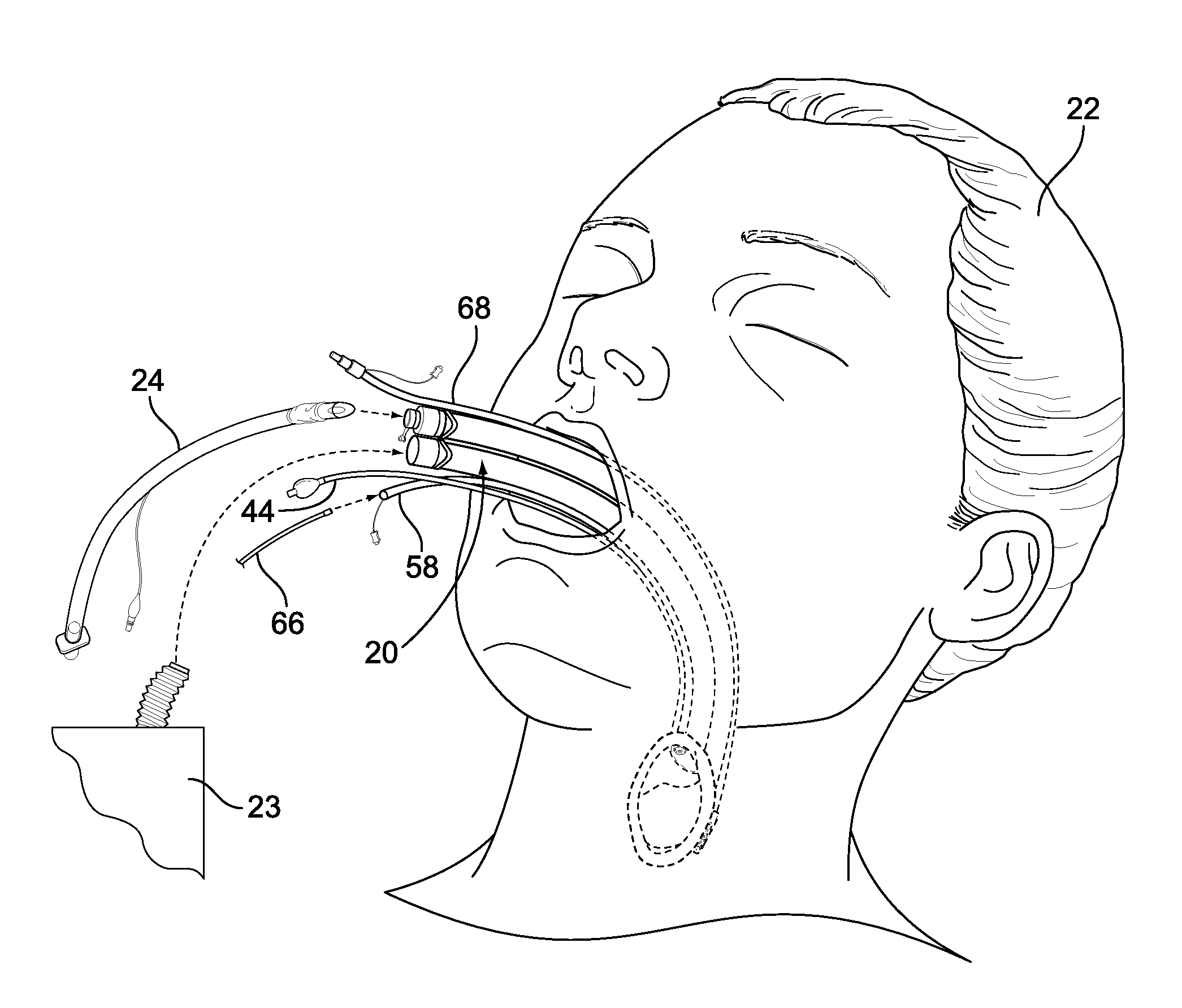
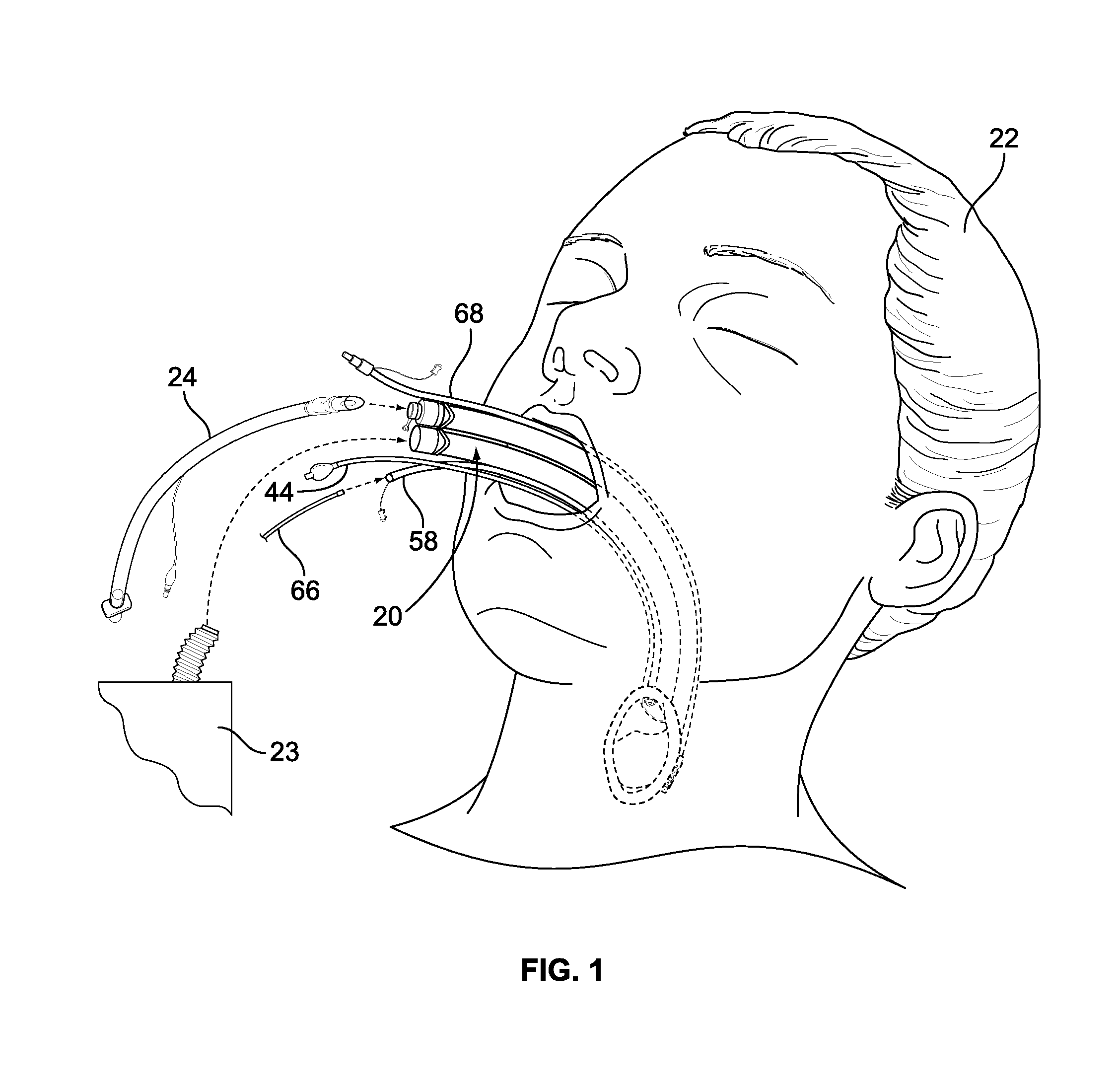
Medical device, and the methods of using same
A medical device is provided for insertion into a cavity of a patient to visual the internal membranes of the patient. The medical device can be an endotracheal tube, a suction tube, a bronchoscope, a tube changer, an esophageal tube, an intubating tube, an esophageal tube in combination with a separate intubating tube, a device for manipulating the position of the epiglottis of the patient, a stylet, or a tube insertable into the vagina of the patient. The medical device has a camera lumen having a sealed window at one end thereof attached thereto, and a separate camera which is insertable into the camera lumen and is removable from the camera lumen. The camera is used to monitor the internal membranes of the patient during the medical procedure.
Owner:WM & DG
Laryngeal airway device
A laryngeal airway device, having an airway tube which has an internal passage in the airway tube wall for receiving a cuff inflation line, and a dome having an inlet and an outlet, where the dome is connected at its inlet with the distal end of the airway tube. The device also includes an annular spoon-shaped inflatable cuff connected with the periphery of the outlet of the dome; a cuff inflation line configured to be in fluid communication with the internal space of the cuff; and a multi-lobed aperture formed in the dome. The aperture is configured to be in fluid communication with the proximal end of the airway tube. The dome has protrusions forming the multi-lobed aperture, such that a flap is configured to prevent the obstruction of the aperture by a patient's epiglottis when the device is inserted into the patient.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Superglottic and peri-laryngeal apparatus for supraglottic airway insertion
InactiveUS6901928B2Minimizing tissue traumaMinimizing complicationTracheal tubesBronchoscopesSupraglottic airwayEpiglottis
A superglottic and peri-laryngeal apparatus for supraglottic airway device insertion that contemporaneously clears a patient's upper airway of the tongue and other pharyngeal tissues, and raises the epiglottis without use of the medical practitioner's fingers in the upper airway. The insertion apparatus comprises an offset member with a compressor-lever shield at a distal insertion end and a handle at the proximal end thereof. The offset member, medially disposed between the handle and the compressor-lever shield, should preferably be configured to be substantially flat, consistent in thickness throughout and having a tight, arcuate shape. The compressor-lever shield member preferably widens from its junction with the offset member into a broad tip at its leading distal edge.
Owner:LOUBSER PAUL G
Medical device, and the methods of using same
A medical device is provided for insertion into a cavity of a patient to visual the internal membranes of the patient. The medical device can be an endotracheal tube, a suction tube, a bronchoscope, a tube changer, an esophageal tube, an intubating tube, an esophageal tube in combination with a separate intubating tube, a device for manipulating the position of the epiglottis of the patient, a stylet, or a tube insertable into the vagina of the patient. The medical device has a camera lumen having a sealed window at one end thereof attached thereto, and a separate camera which is insertable into the camera lumen and is removable from the camera lumen. The camera is used to monitor the internal membranes of the patient during the medical procedure.
Owner:WM & DG
Apparatus and methods for treating sleep apnea
An apparatus and method for treating sleep apnea and / or snoring is provided. The apparatus includes an appliance sized and structured to be placed in the pharyngeal region of a human or animal and being effective in treating sleep apnea and / or snoring, for example in maintaining openness of an oropharyngeal region of a human or animal during natural sleep, advantageously while not interfering with normal functioning of the epiglottis. The appliance may be made of a super elastic material, for example, Nitinol, and may be submucossally implanted in the pharyngeal walls.
Owner:QUIESCENCE MEDICAL
Laryngeal mask airway device
InactiveUS20060254596A1Eliminate disadvantagesRisk minimizationTracheal tubesBreathing masksLaryngeal airwayEpiglottis
A modified laryngeal mask airway device (LMA-device) is provided with means to improve ease of insertion, reliability of function and higher seal pressure (i.e., cuff pressure ratio). The LMA-device includes an indented section of the airway tube to offer locating means and purchase for the inserting finger, and extended mask aperture bars to increase the effective ventilating area of the mask and reduce the possibility of epiglottis displacement occasioned by mask insertion. The LMA-device further includes a modification of the airway tube angle of attachment to the mask, and provision of a posterior or back-cushion covering the entire posterior surface of the mask.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI PTE LTD
Endotracheal intubation assist instrument
InactiveUS20100224186A1Easy to adjustEasy to findBronchoscopesTracheal tubesNasal cavityBronchial tube
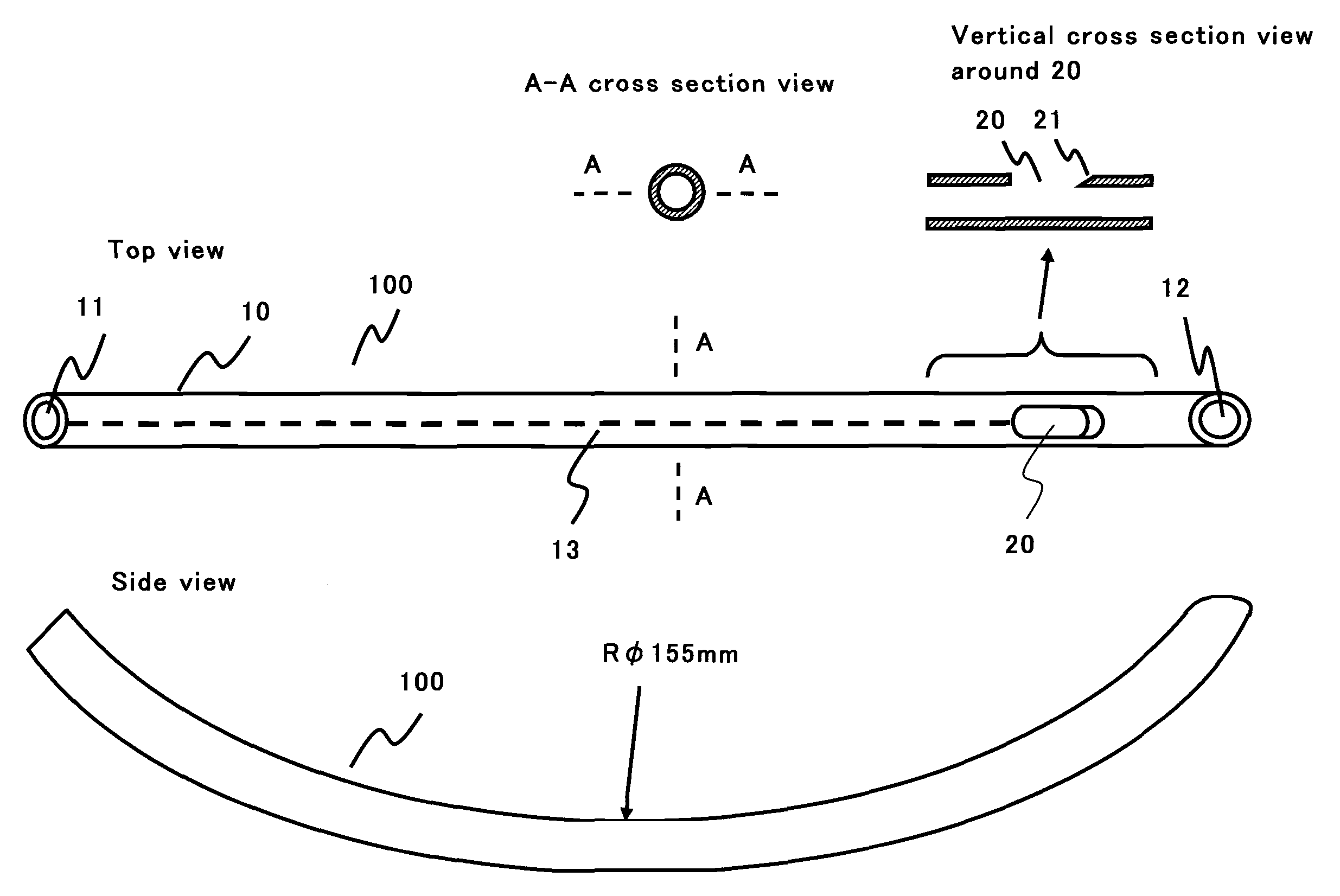
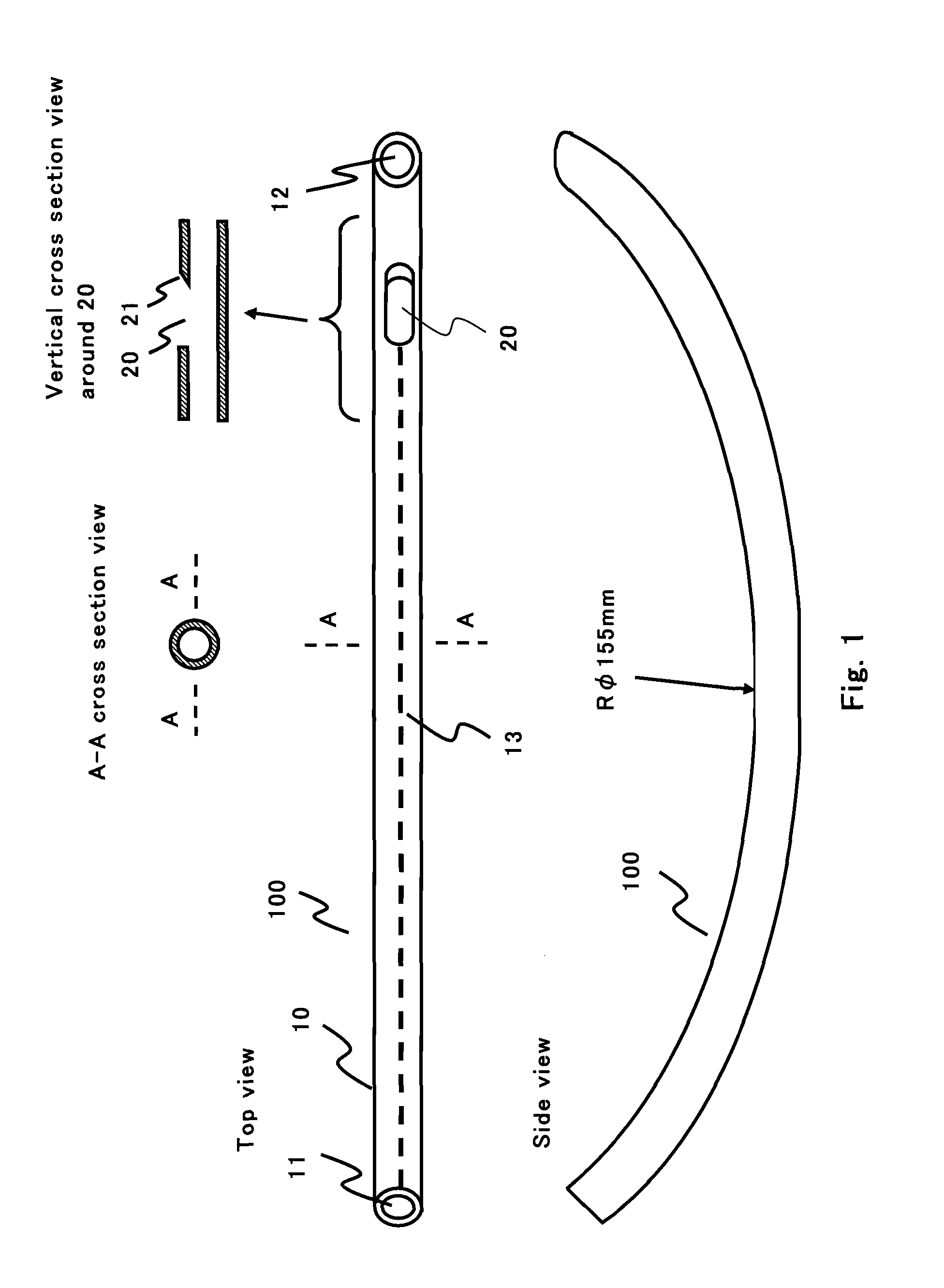
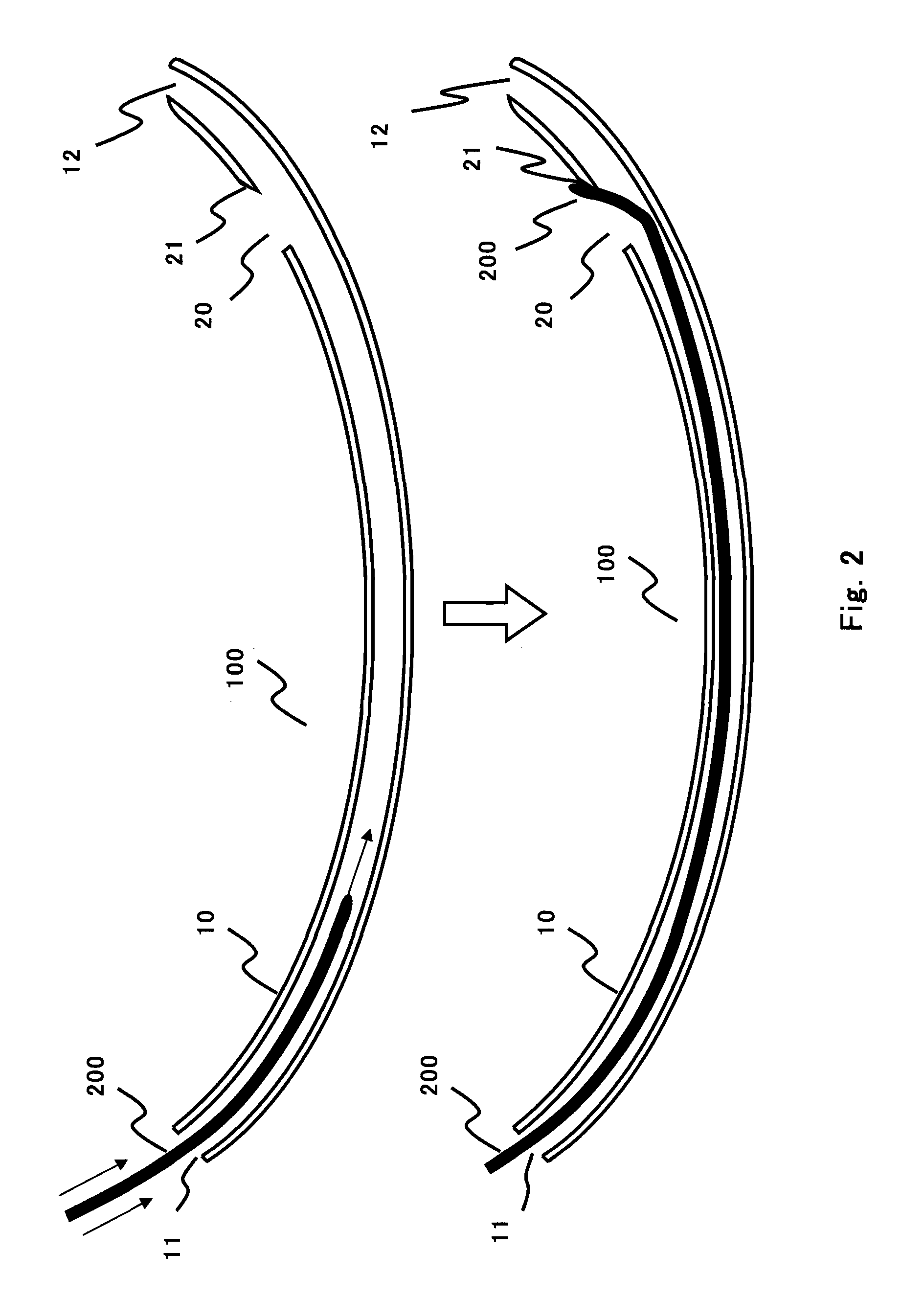
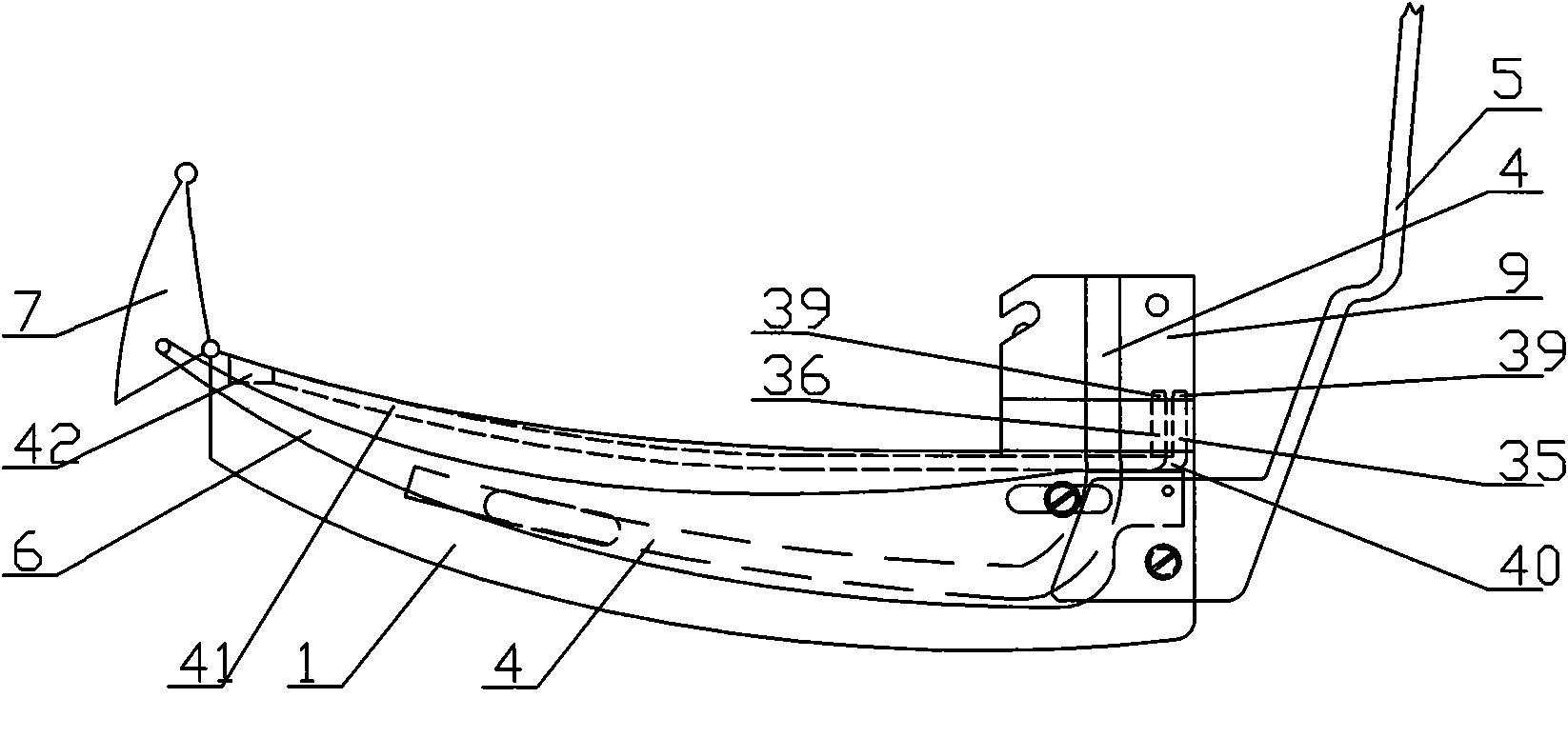
The present invention provides an endotracheal intubation assist instrument for inserting the bronchofiberscope from the oral or nasal cavity to the trachea easily and then inserting the endotracheal tube into the trachea easily. The side hole 20 is installed near the front edge of the guide tube 10. The guide tube 10 advances naturally from the oral cavity, and the front edge of the guide tube 10 reaches the entrance of the esophagus. The view field is obtained by putting the front edge of the bronchofiberscope 200 onto the base 21. The glottis can be found by the view field of the bronchofiberscope 200 while pulling back the guide tube 10 slowly. The path for the bronchofiberscope 200 from the oral cavity to the esophagus can be secured by the guide tube 10 without influence of the obstacles such as a tongue and an epiglottis, and the operatability can be enhanced. Only the guide tube 10 is removed and the bronchofiberscope 200 remains as the guide line for the endotracheal tube insertion. The endotracheal tube is inserted to the trachea by utilizing the bronchofiberscope 200 as the guide line.
Owner:SENKO MED INSTR MFG CO LTD
Hook laryngoscope for difficult injection intubatton
ActiveCN101647691APrecision injectionEfficient injectionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesTongue rootEpiglottis
The invention discloses a hook laryngoscope for difficult injection intubatton, comprising a hook laryngoscope lens, a battery tube, a battery tube base, a handle and a medical liquid tube. A disconnecting switch is fixedly arranged on one side wall of the handle; and the hook laryngoscope lens is provided with an oxygen supply duct, a medical liquid duct and a spraying head. The hook laryngoscope in use can flexibly and conveniently lift up the hypertrophic epiglottis, can immediately spray and anaesthetize the glottis, the larynx and the tongue root to loosen the glottis when the larynx is cramped so as to smoothly finish intubatton while injecting, ventilating and supply oxygen in vivo. The hook laryngoscope for difficult injection intubatton prolongs the safety time of trachea intubatton operation, lowers the danger of trachea intubatton and improves the success ratio of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). The hook laryngoscope for difficult injection intubatton can supply oxygen for administration by manual injection and can also be connected with an injection ventilator for compatible use.
Owner:SHANDONG YIHE MEDICAL TECH
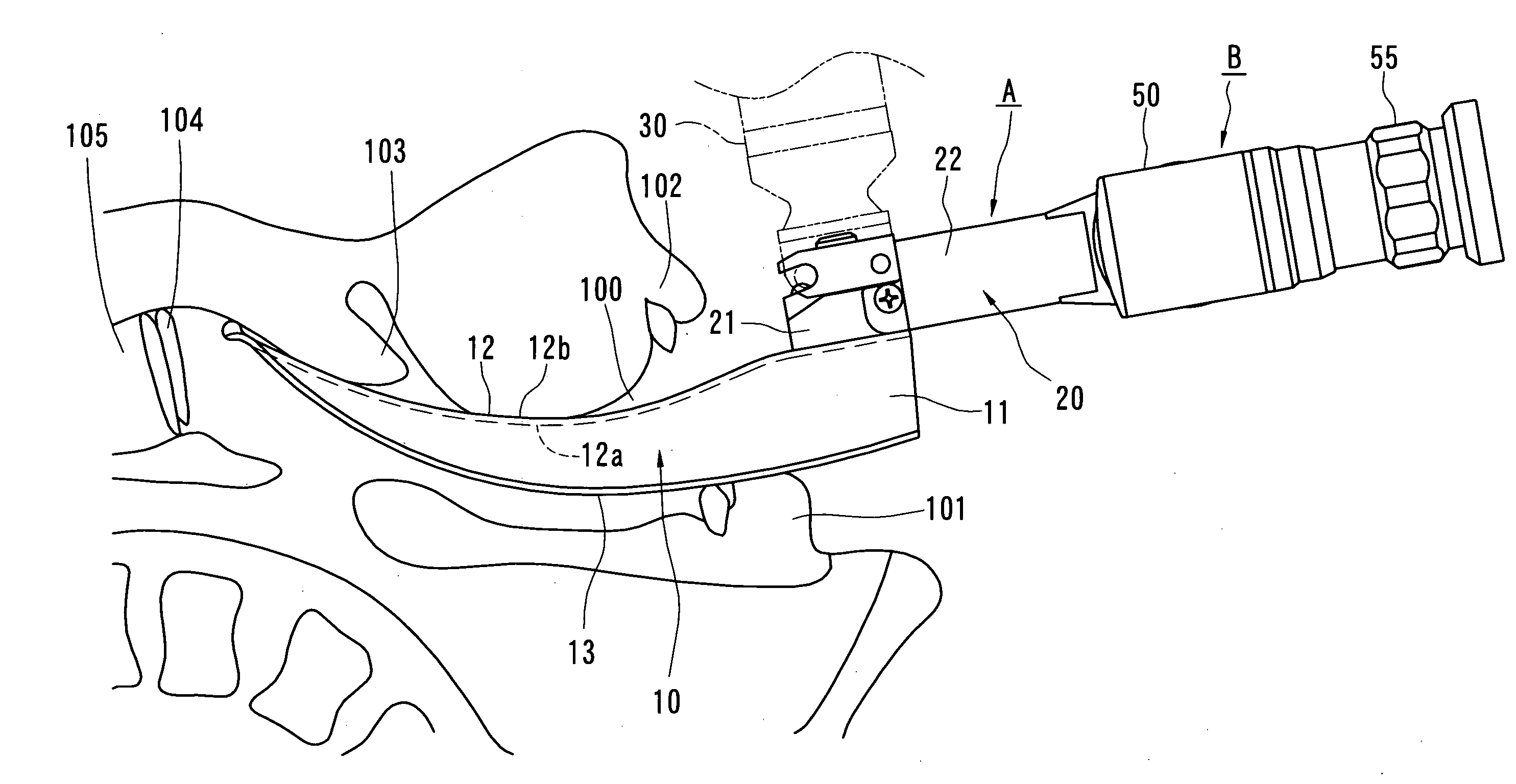
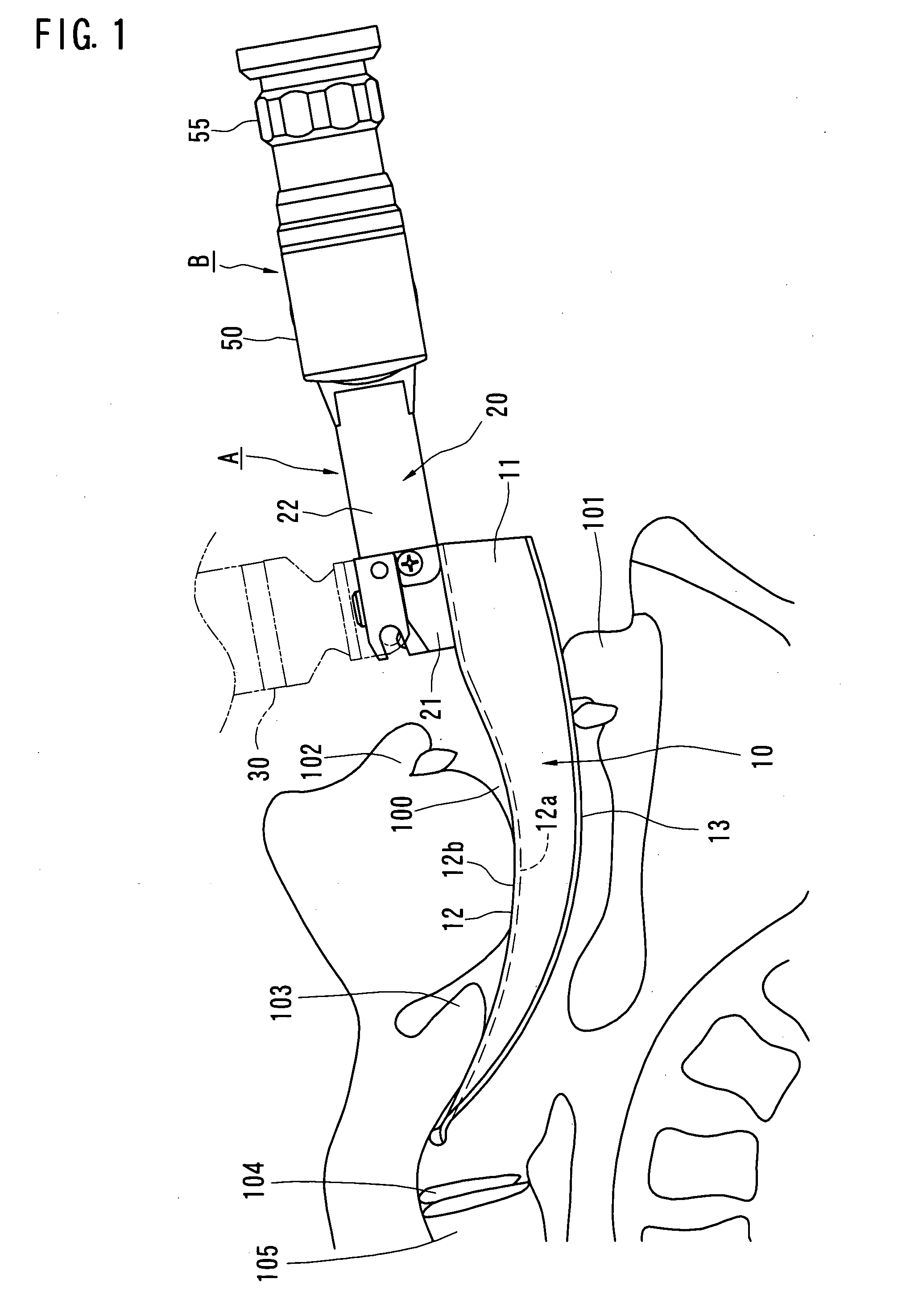
Airway tube guiding apparatus
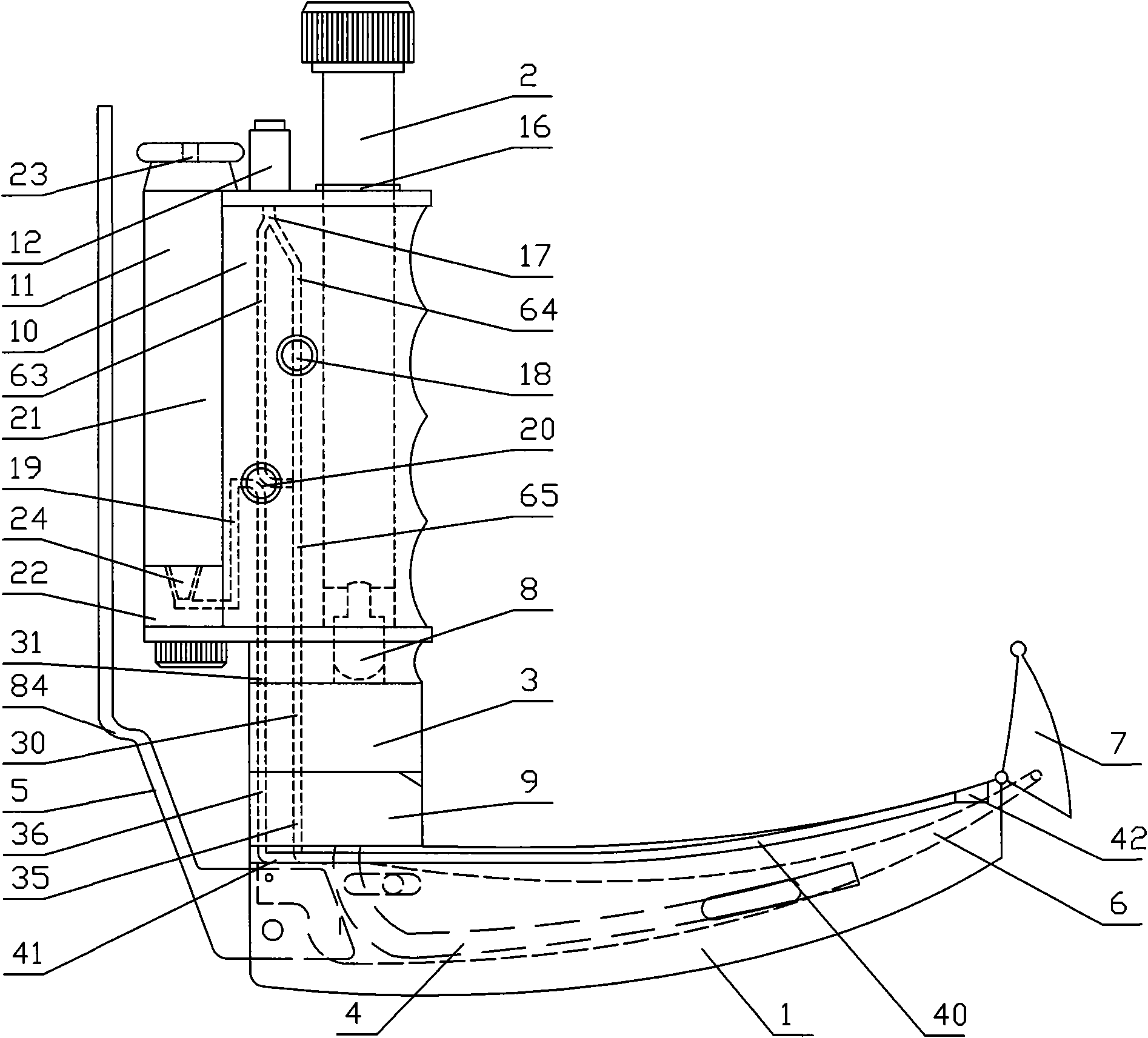
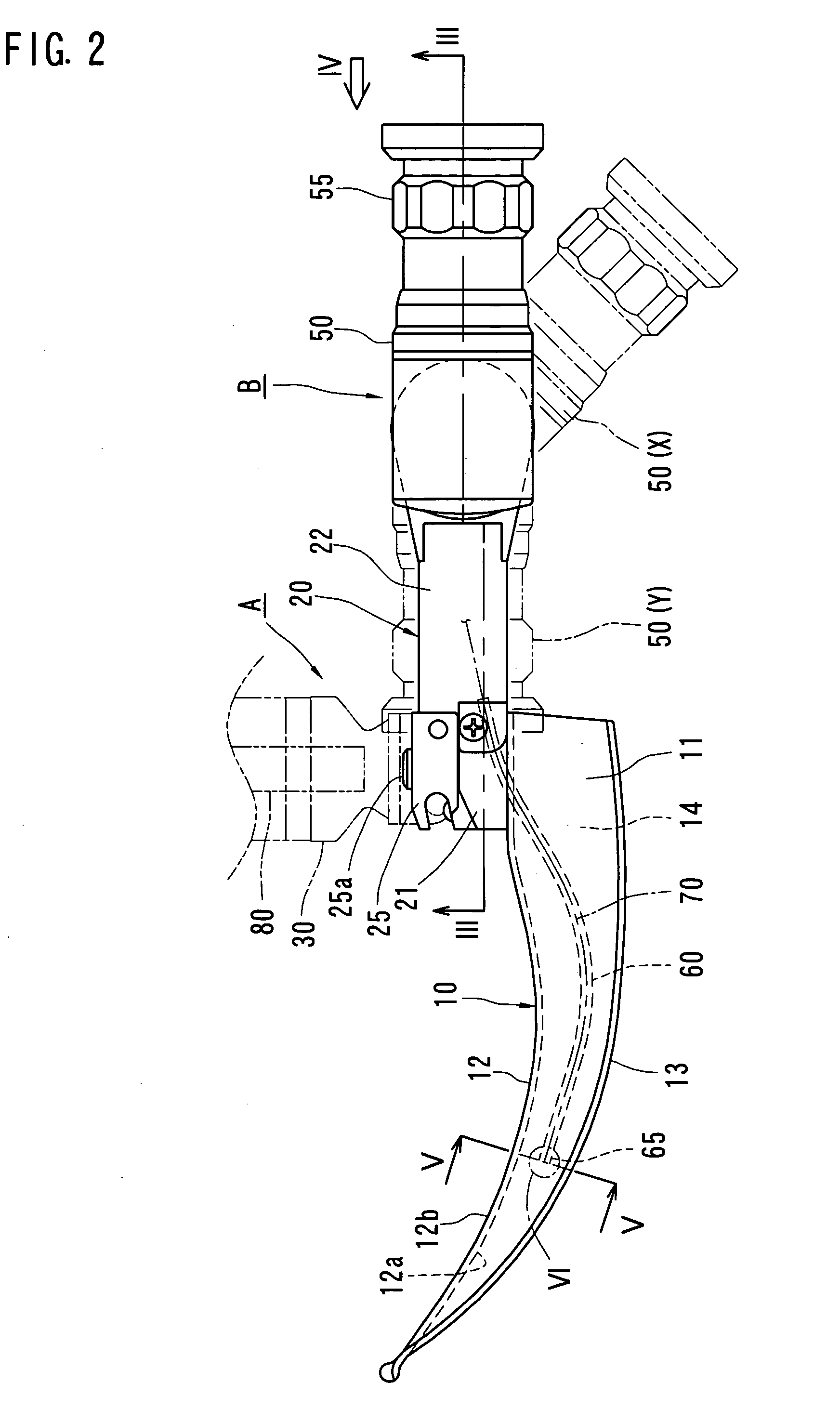
A guiding apparatus to be used when inserting an airway tube from a mouth of a patient includes a body (A) and an endoscope (B) disposed through the body (A). The body (A) includes a blade (10). The blade (10) is inserted from the mouth of the patient to depress the epiglottis with a distal end portion thereof, exposing the glottis. The endoscope (B) includes an objective end portion (65), an ocular end portion (55) and an image guide (70) optically connecting the objective end portion (65) and the ocular end portion (55). The objective end portion (65) is disposed on the blade (10). The ocular end portion (55) is positioned out of alignment with the blade (10) either to the right or the left behind a rear end of the blade (10).
Owner:MACHIDA ENDOSCOPE
Novel laryngeal mask
InactiveCN104841047AIncrease heightAvoid cloggingTracheal tubesSuction devicesOesophageal tubeMain channel
The invention discloses a novel laryngeal mask. The novel laryngeal mask comprises an air bag, a breathing tube, a double-channel joint, an inflating tube, an indication air bag and a one-way valve, wherein an air inlet end of the breathing tube comprises a trachea channel and an esophagus drainage channel which are independent from each other; the trachea channel is divided into a trachea main channel and a trachea branch channel which are connected with each other; an epiglottis lifting table is arranged in front of the trachea main channel; and a wedge-shaped groove is formed in front of the epiglottis lifting table. The novel laryngeal mask is reasonable in design, meets clinical requirements and can be smoothly pressed in the throat of a patient; contents in the esophagus and the stomach of a patient can be drained; breathing of the patient in a surgery is guaranteed; using safety is improved; and tracheal intubation can be carried out through the laryngeal mask.
Owner:田鸣
Laryngoscope
A laryngoscope is provided with which an operator can directly observe the trachea inlet portion of a patient easily by safely and surely lifting the epiglottis of the patient with a proximal end portion of a laryngoscope blade which is inserted in the mouth of the patient. The blade is connected to a distal end portion of a grippable handle, a first electrode is mounted on a distal end portion of the blade, and a second electrode is configured to adhere to a skin surface of the patient in the vicinity of the epiglottis, and a low frequency current is supplied to flow between the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA
Visual laryngoscope
InactiveCN106419811AConforms to the curvatureEasy to insertBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesThroatHuman body
The invention discloses a visual laryngoscope used for lifting up patient tissues nearby the epiglottis and collecting patient throat images; the visual laryngoscope comprises a body and a disposable blade; the body comprises a display and a handle; the disposable blade comprises a sealed camera cavity and a tube guide member; the side portion of the camera cavity is provided with a cover plate; a camera assembly is arranged in the camera cavity, and comprises a camera head assembly, a data line and a flexible circuit board; the end portion of the camera cavity is provided with a shooting window having a camera head support; the camera head assembly is fixed on the camera head support; the tail of the camera cavity is provided with a circuit board mount slot; the flexible circuit board penetrates the circuit board mount slot and is folded and fixed. The visual laryngoscope complies with human body throat characteristic curvature, a trachea conduit can be conveniently inserted, and the camera assembly blade can be assembled with high efficiency; in addition, the body and blade fixing mode can be improved, thus enhancing connecting portion tightness and electric signal connection stabilization and convenience characteristics.
Owner:HANGZHOU CHUANGHUI MEDICAL ELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
Laryngoscope
InactiveCN102481429AMore helpReliable endotracheal tubeTracheal tubesBronchoscopesEpiglottisMedicine
Disclosed is a laryngoscope which is capable of safely and reliably lifting the epiglottis to easily view the entrance to the trachea directly. Specifically disclosed is a laryngoscope in which the base end section of a blade for being inserted from patient's mouth to lift the epiglottis in order to visually identify the entrance to the trachea is consecutively installed at the end of a handle which can be gripped, and which is configured in such a manner that a first electrode is provided to the base end section of the blade and a second electrode can be adhered to the skin surface adjacent to the epiglottis, and that a low-frequency current is energized between the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA
Apparatus for orotracheal intubation
This invention provides a laryngoscope blade, wherein the blade comprises a tube having an opening along one side. This invention further provides a laryngoscope blade comprising at its front portion a first surface for lifting the epiglottis of a patient and a second surface for fixing the portion of the posterior part of the vocal cords of the patient.
Owner:SHAPIRO LEON
Airway suction spoon
Owner:REHMAN JEFF
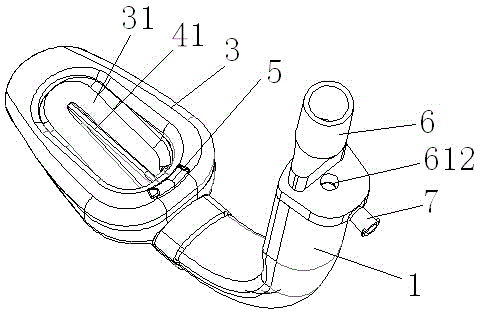
Non-pneumatic laryngeal mask with imbibition function
The invention relates to a non-pneumatic laryngeal mask with an imbibition function. The existing laryngeal mask cannot discharge mucous secretion on the laryngeal part of pharynx in time, and a vent hole of the laryngeal mask is likely to block by epiglottis. The non-pneumatic laryngeal mask with the imbibition function is characterized by also comprising a connector and a flexible rubber capsule, wherein an inflating cavity is formed between the flexible rubber capsule and a mask body, the mask body is provided with a plurality of suction holes, a ventilation pipe is internally provided with a ventilation passage, a feed drain passage and a suction passage, the ventilation passage is communicated with the inflating cavity, the feed drain passage penetrates through the ventilation pipe and the cover body to be connected with a feed hole on the front end of the mask body, the suction hole is communicated with the suction passage, the connector is provided with an inflating opening, a feed opening and a suction opening, the inflating opening is communicated with the ventilation passage, the feed opening is communicated with the feed drain passage, and the suction opening is communicated with the suction passage. The non-pneumatic laryngeal mask is simple in structure, reasonable in design and good in sealing performance; the mucus and coagula on the laryngeal part of pharynx can be discharged in time, the vent hole is unlikely to block, and the injury on a patient is little.
Owner:海盐康源医疗器械有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com