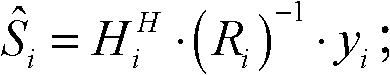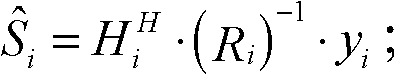Patents
Literature
53 results about "Mixed radix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
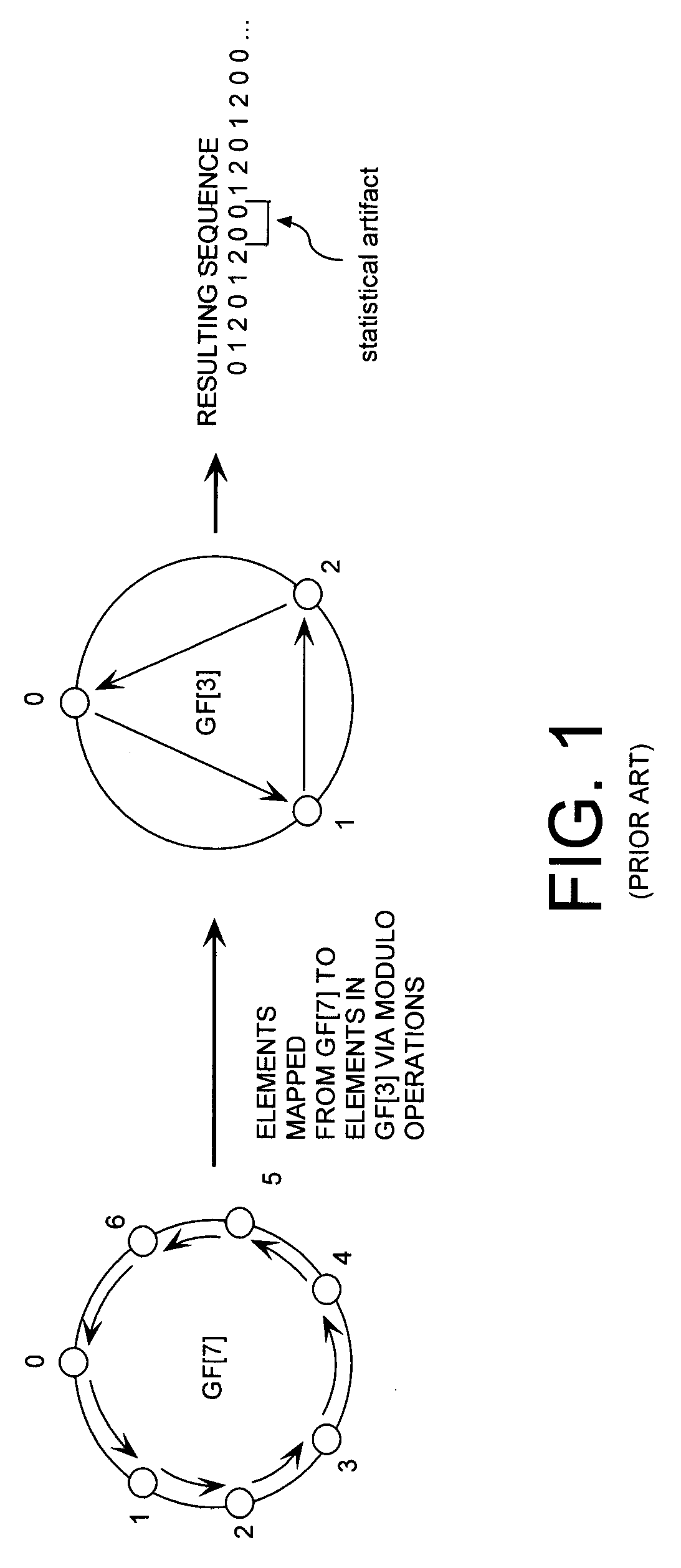
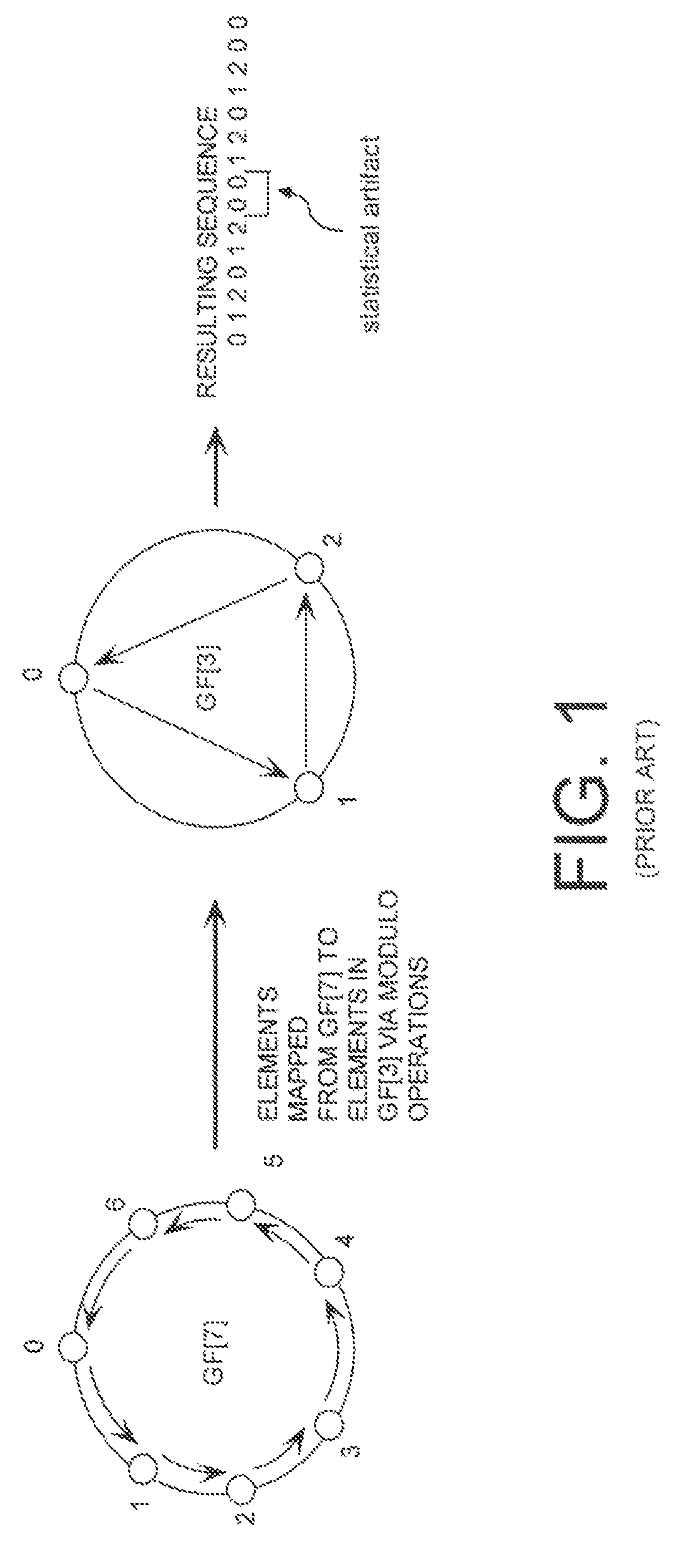
Mixed radix numeral systems are non-standard positional numeral systems in which the numerical base varies from position to position. Such numerical representation applies when a quantity is expressed using a sequence of units that are each a multiple of the next smaller one, but not by the same factor. Such units are common for instance in measuring time; a time of 32 weeks, 5 days, 7 hours, 45 minutes, 15 seconds, and 500 milliseconds might be expressed as a number of minutes in mixed-radix notation as...
Ring arithmetic method, system, and apparatus
ActiveUS20030044004A1Public key for secure communicationData switching by path configurationComputer scienceBit numbering
A data encryption method performed with ring arithmetic operations using a residue number multiplication process wherein a first conversion to a first basis is done using a mixed radix system and a second conversion to a second basis is done using a mixed radix system. In some embodiments, a modulus C is be chosen of the form 2w-L, wherein C is a w-bit number and L is a low Hamming weight odd integer less than 2(w-1) / 2. And in some of those embodiments, the residue mod C is calculated via several steps. P is split into 2 w-bit words H1 and L1. S1 is calculated as equal to L1+(H12x1)+(H12x2)+ . . . +(H12xk)+H1. S1 is split into two w-bit words H2 and L2. S2 is computed as being equal to L2+(H22x1)+(H22x2)+ . . . +(H22xk)+H2. S3 is computed as being equal to S2+(2x1+ . . . +2xk+1). And the residue is determined by comparing S3 to 2w. If S3<2w, then the residue equals S2. If S3>2w, then the residue equals S3-2w.
Owner:NCIPHER LIMITED ACTING BY & THROUGH ITS WHOLLY OWNED SUBSIDIARY NCIPHER +1
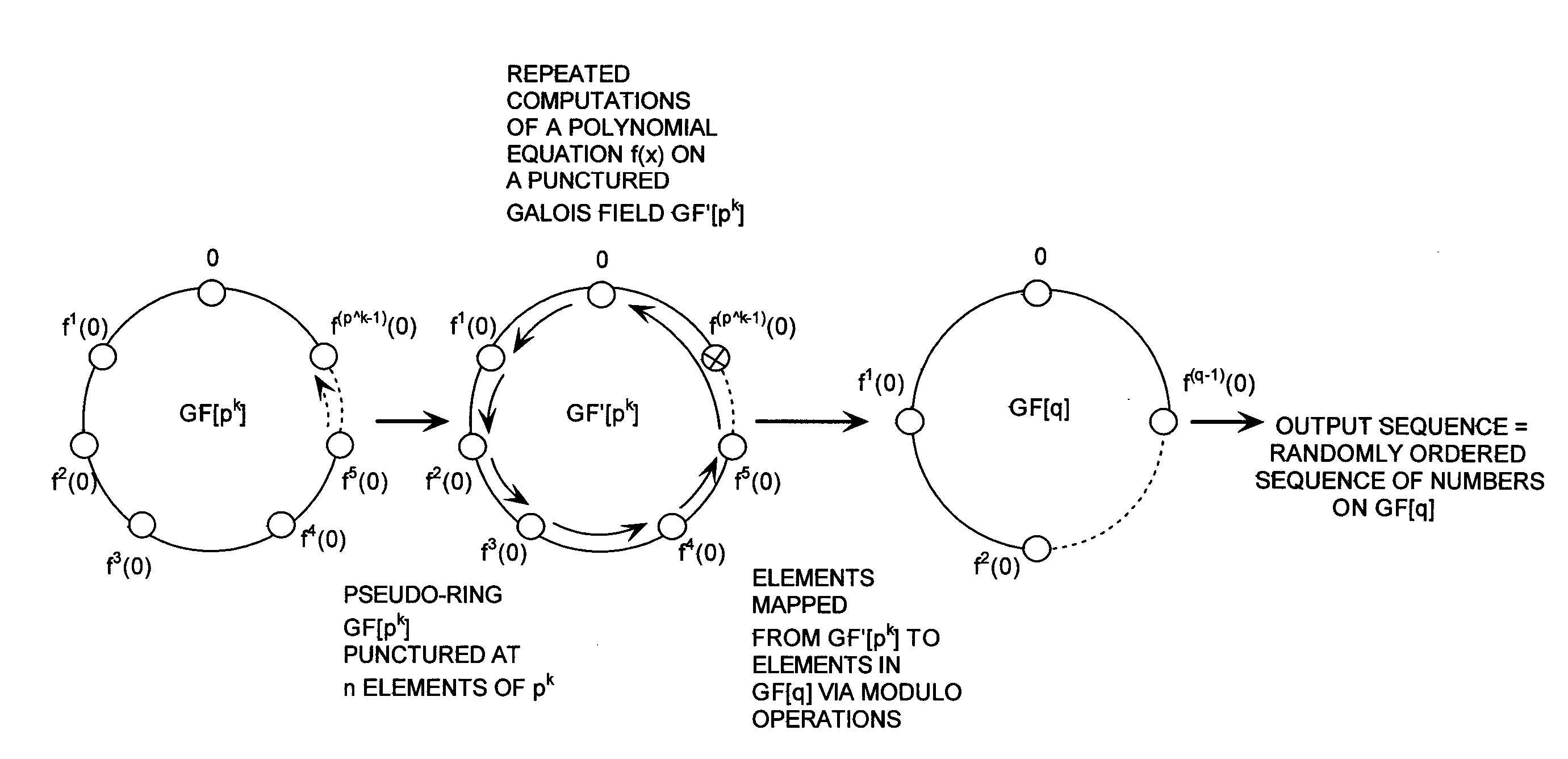
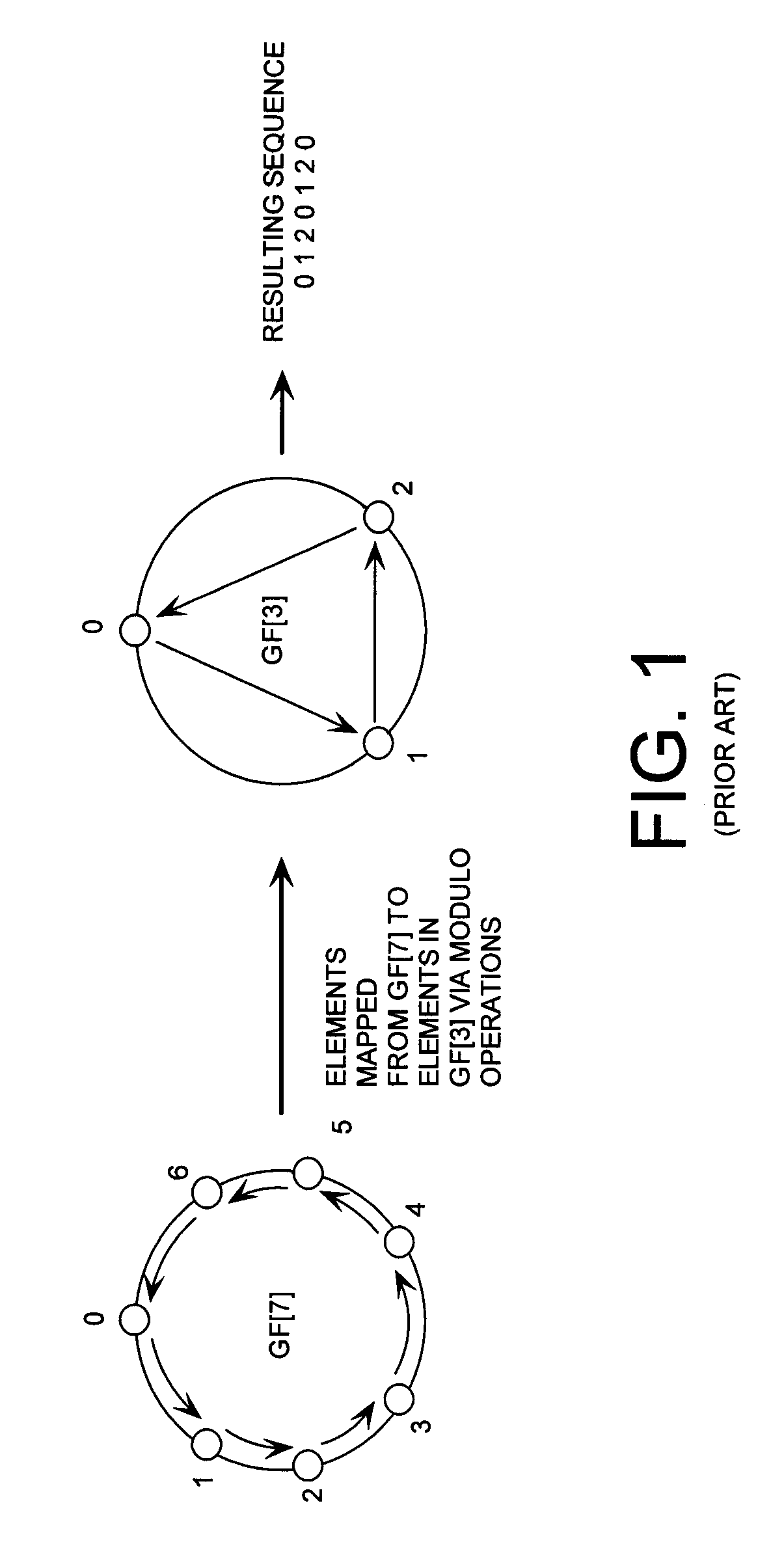
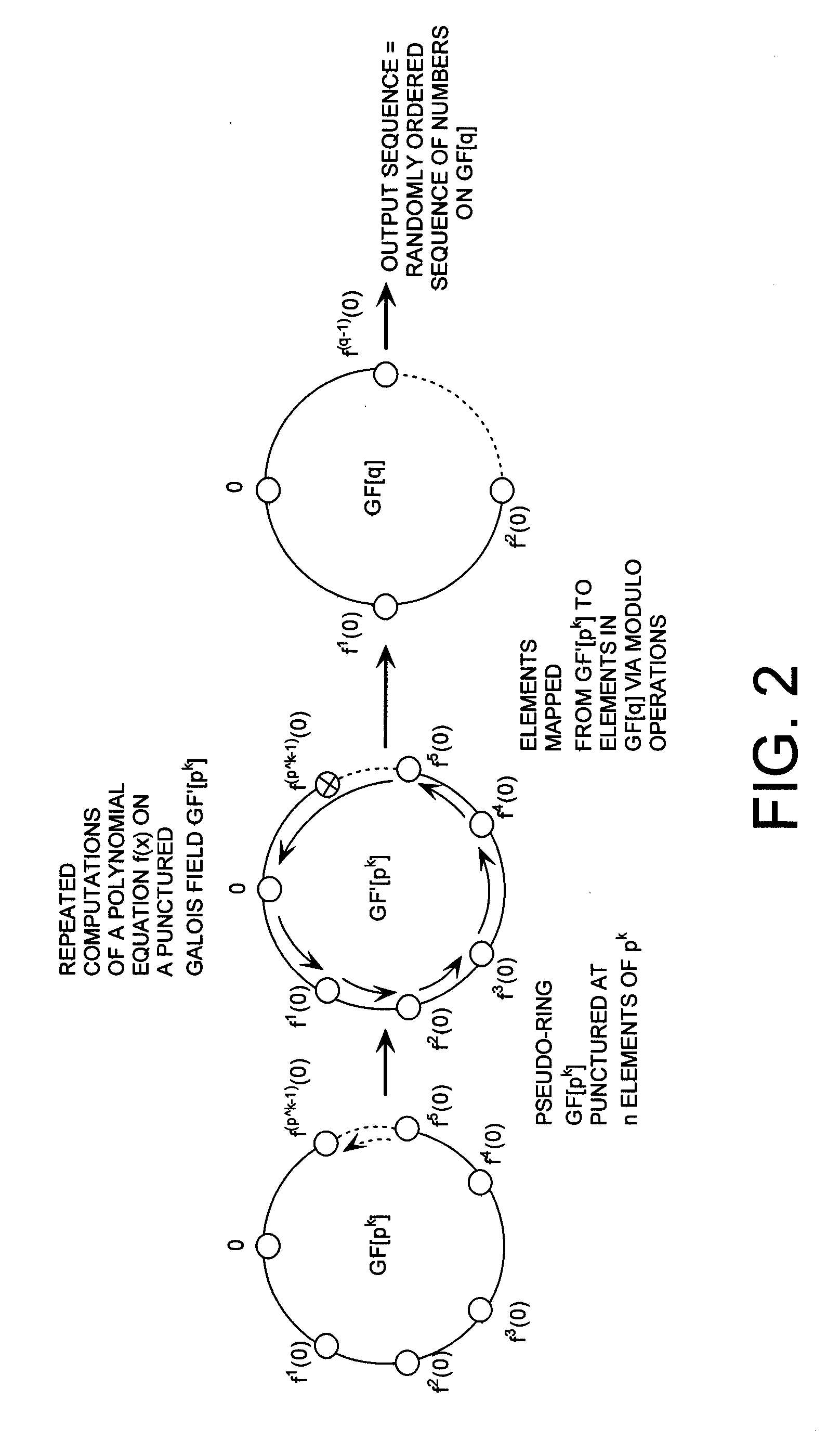
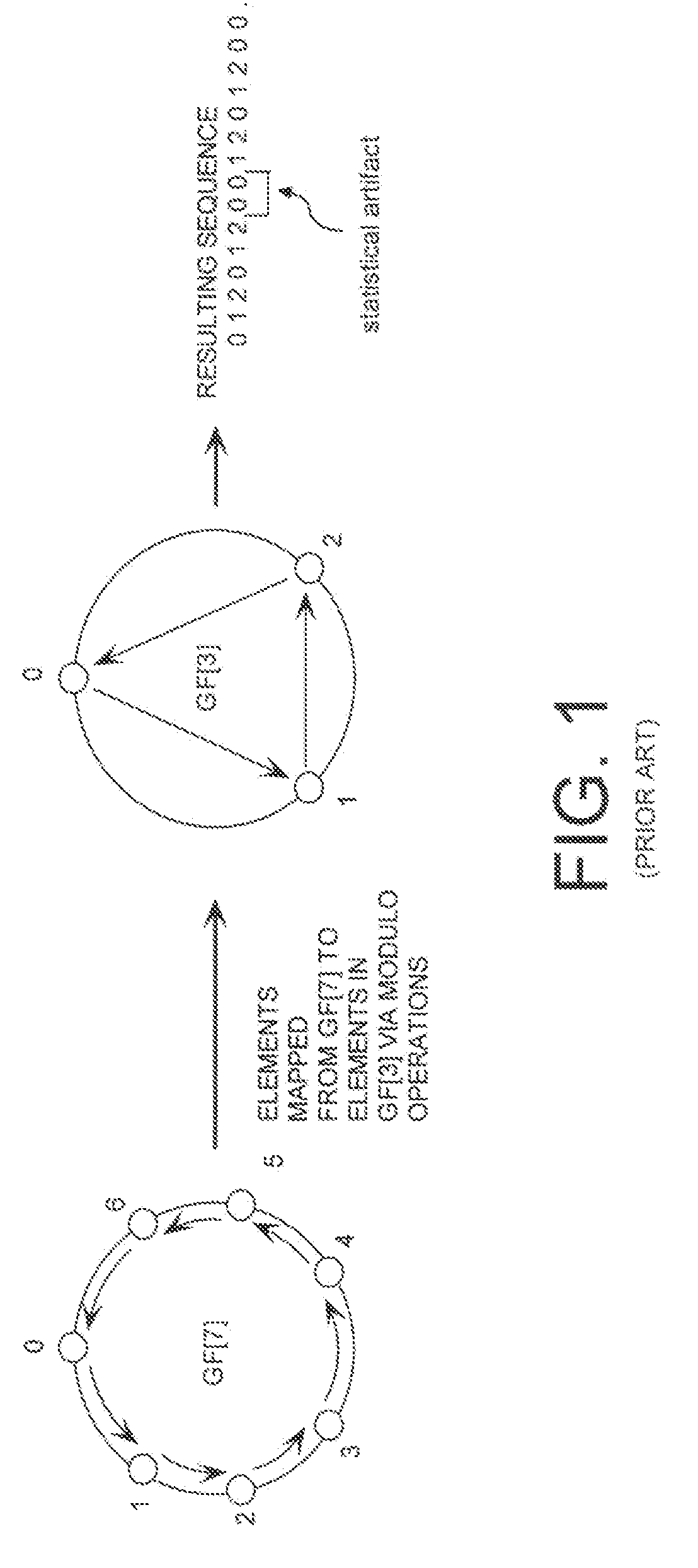
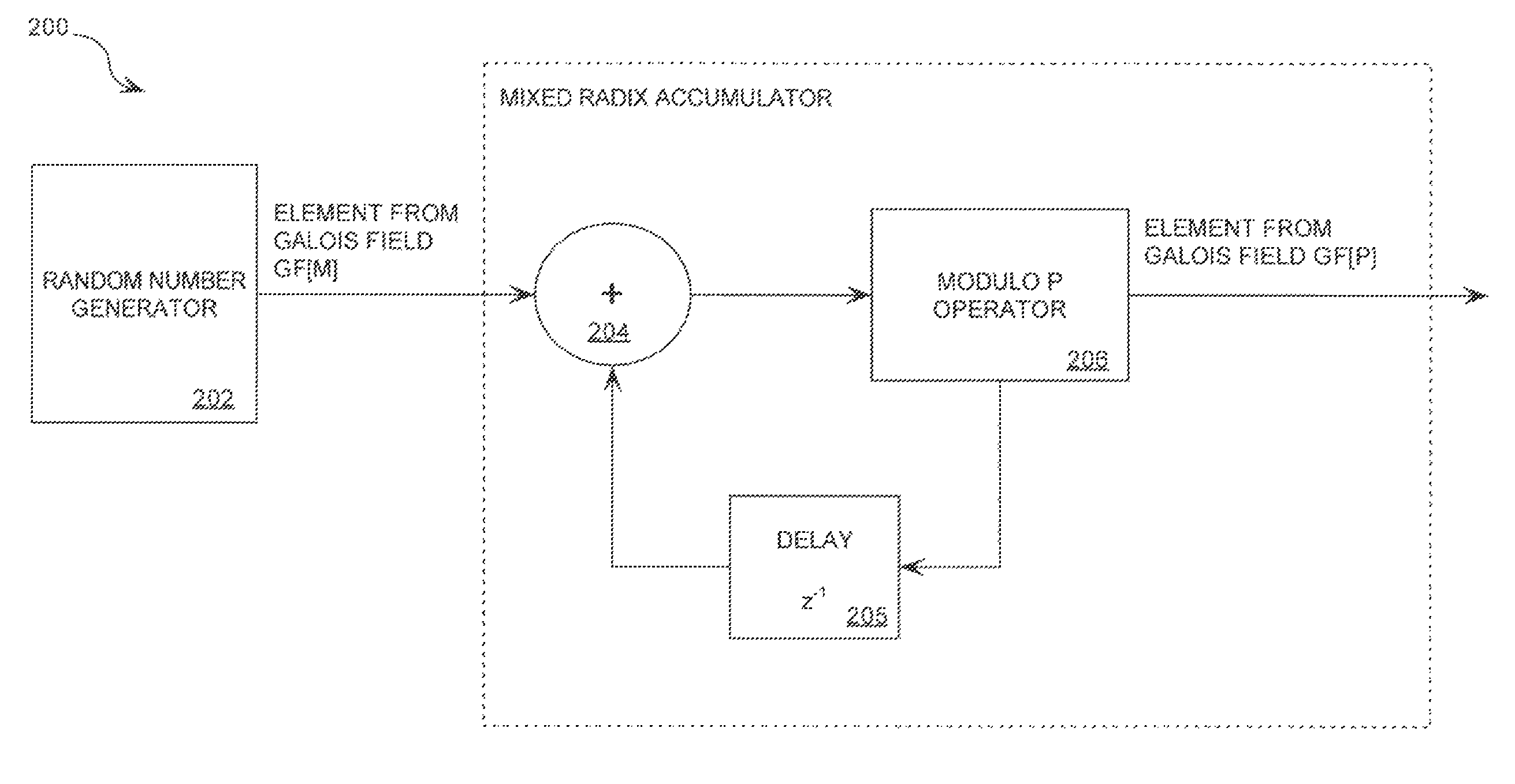
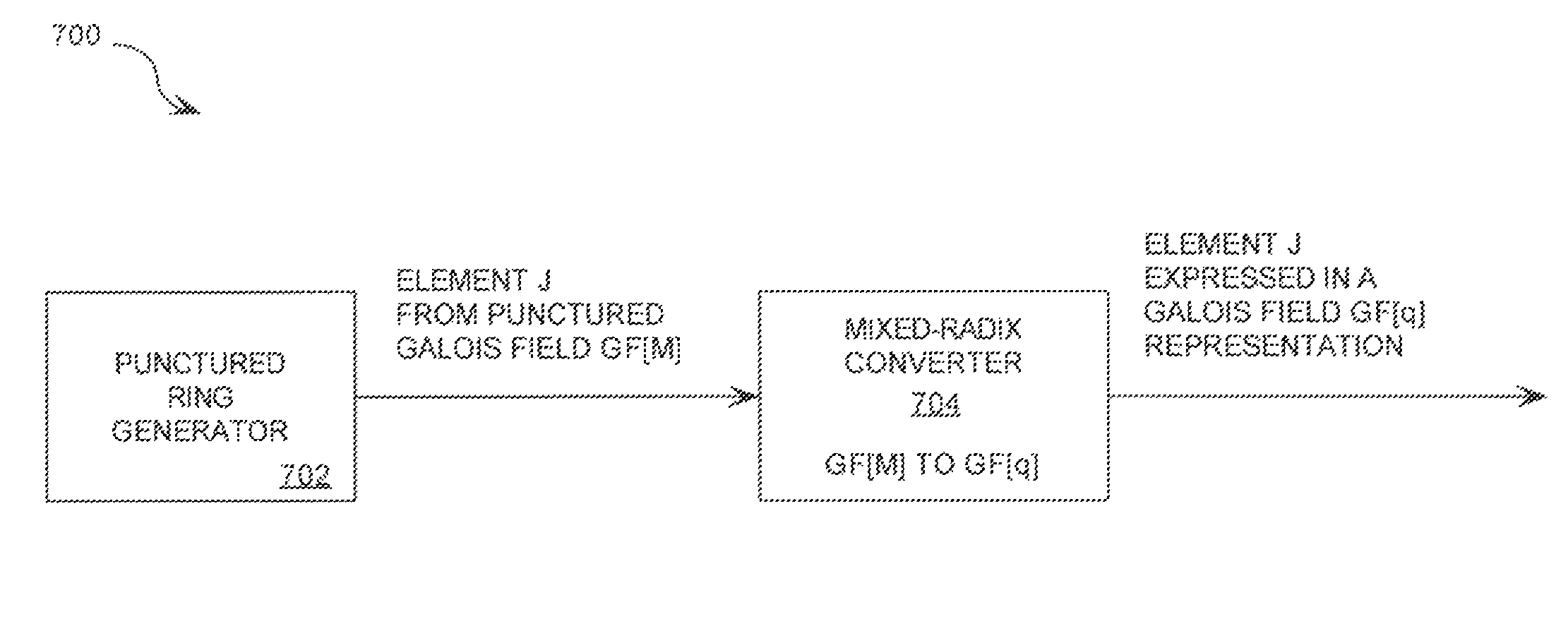
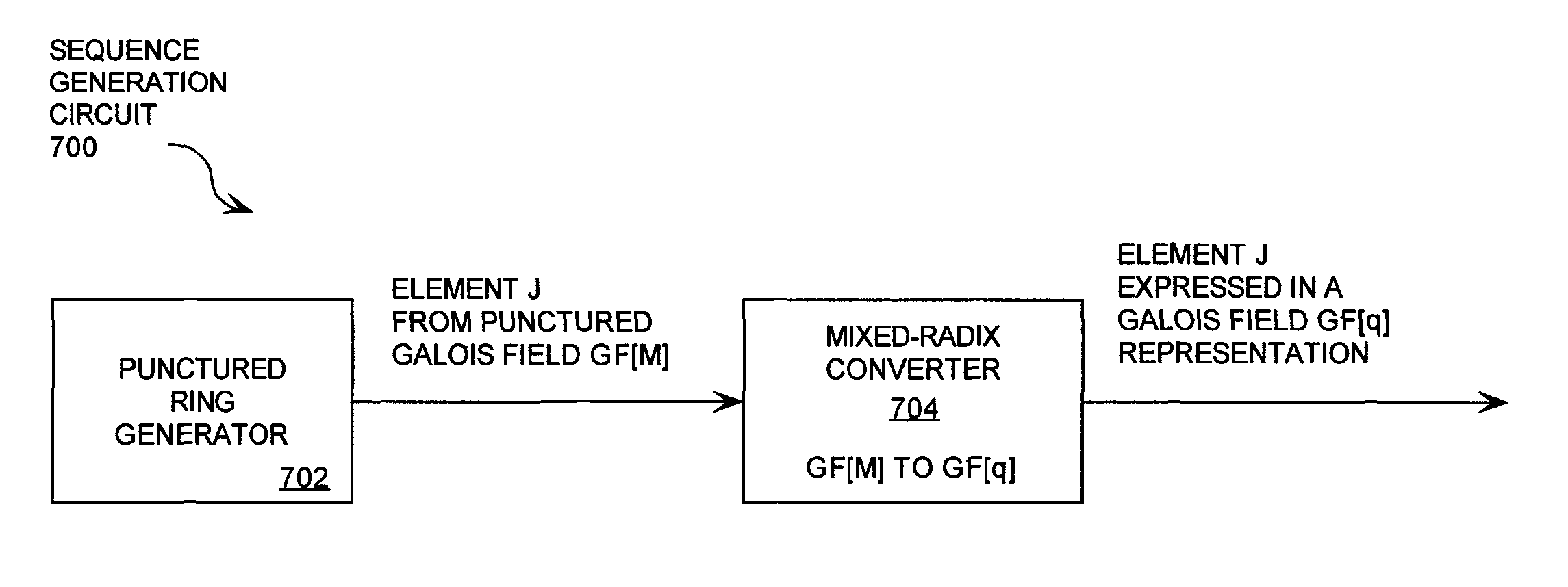
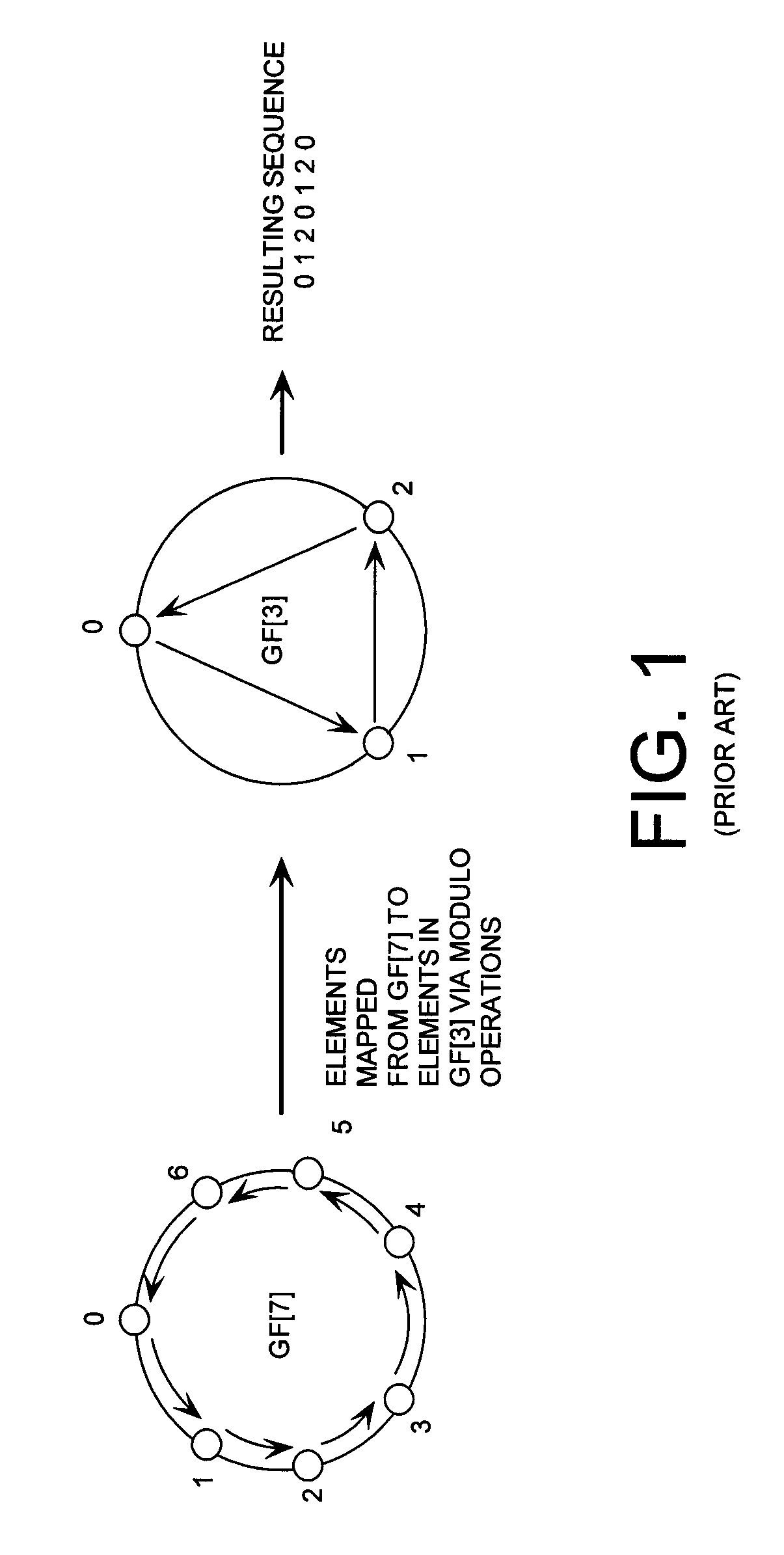
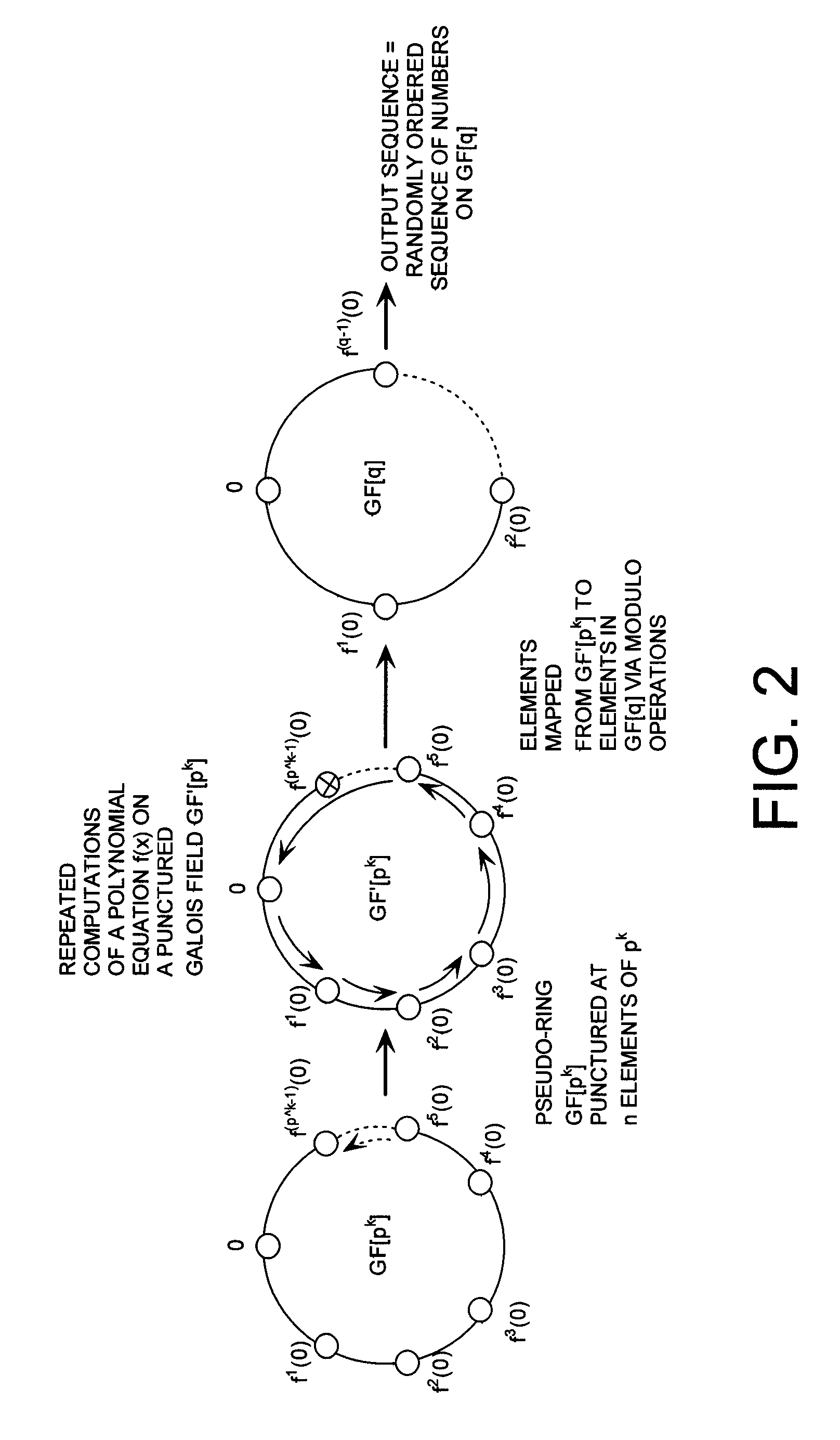
Cryptographic system configured to perform a mixed radix conversion with a priori defined statistical artifacts
ActiveUS20090202067A1Eliminate artifactsRandom number generatorsDigital computer detailsData streamComputer science
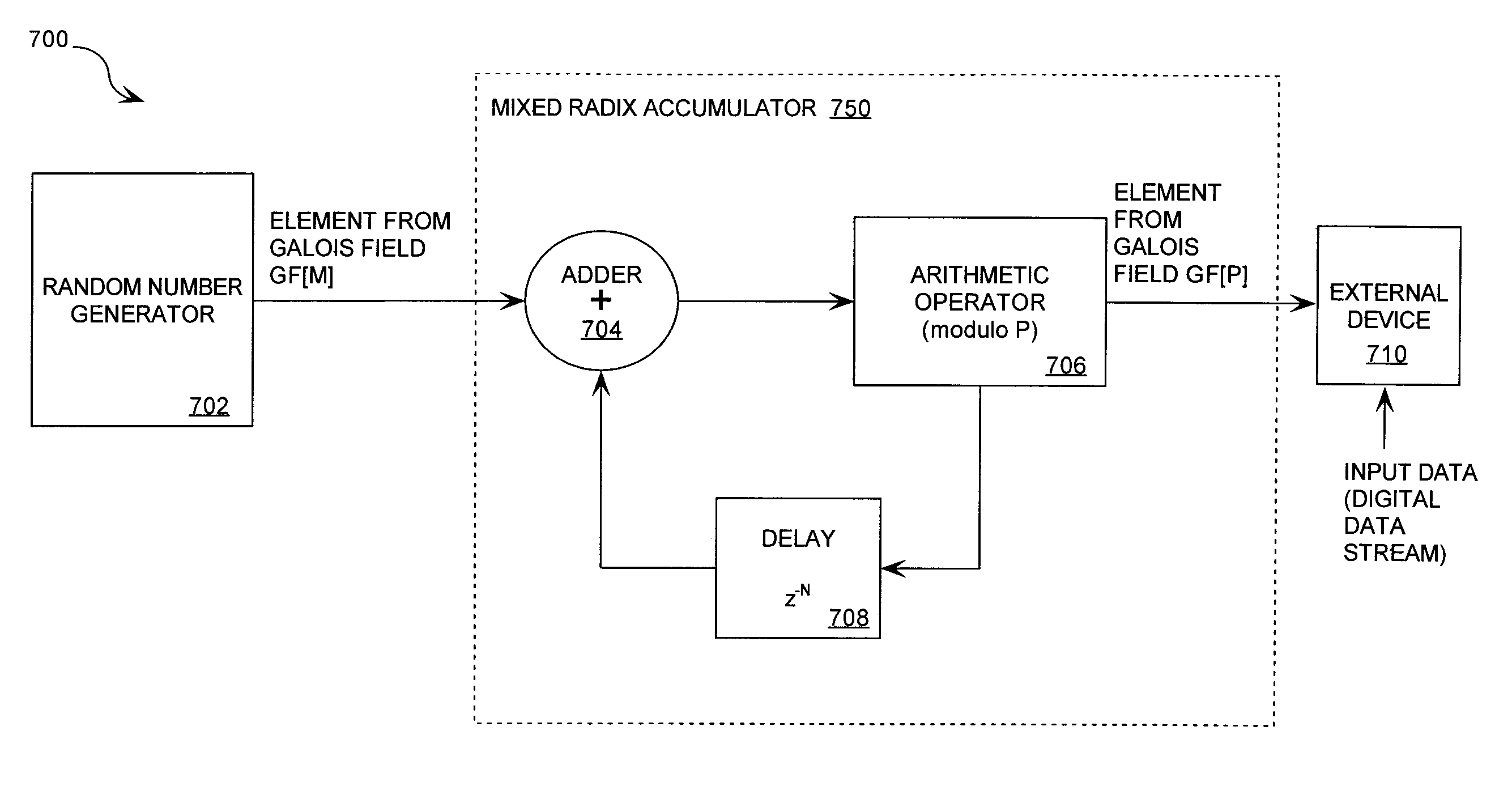
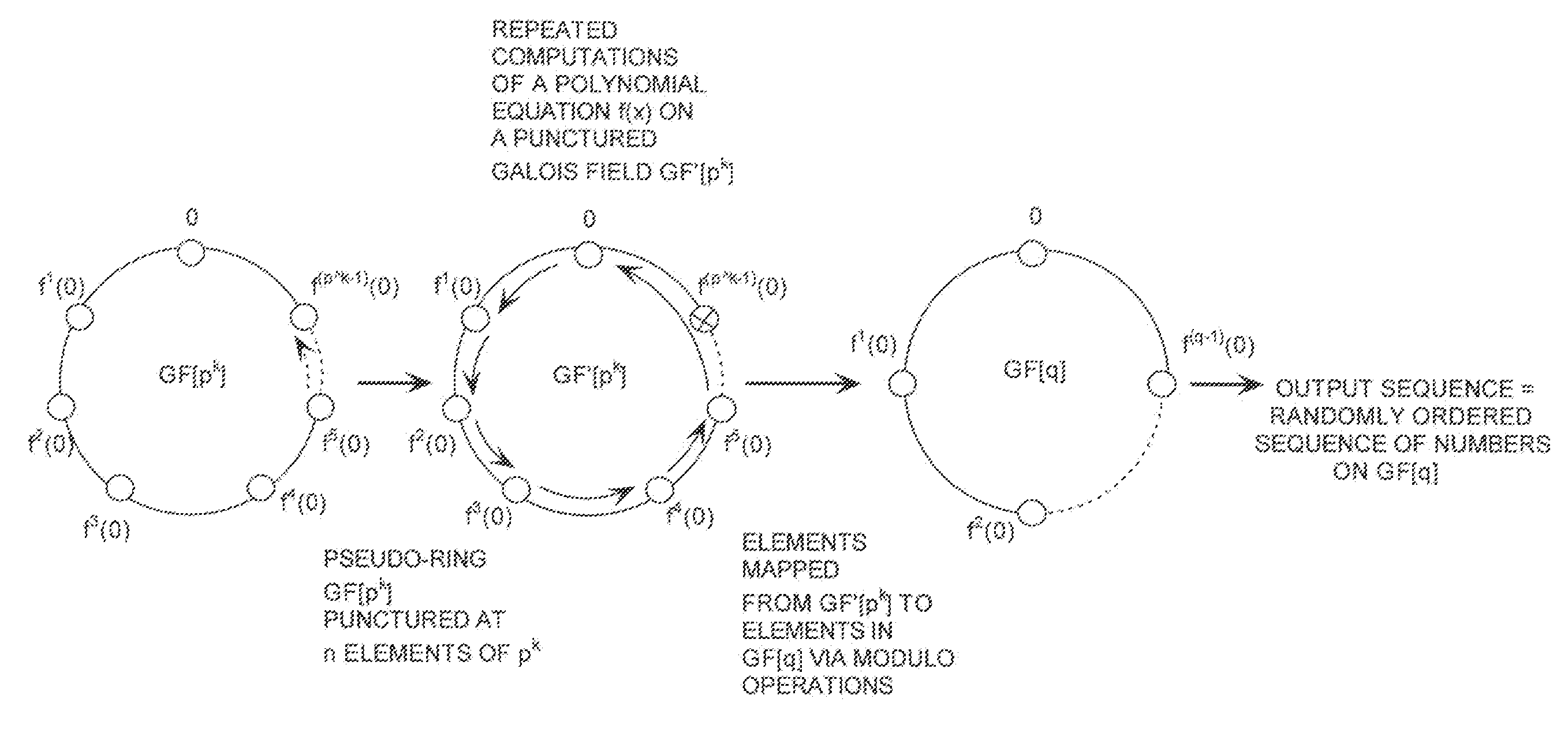
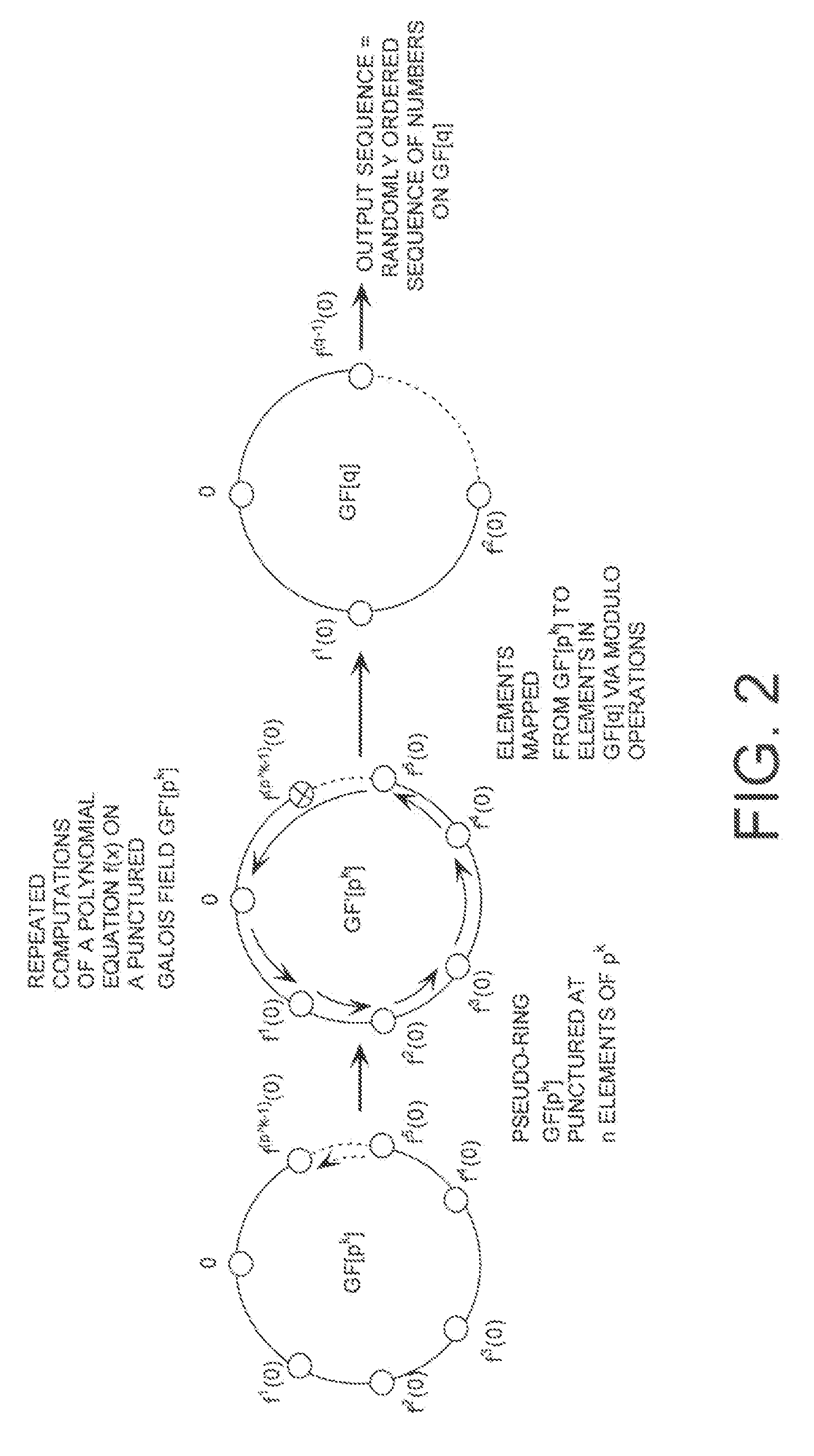
A cryptographic system (CS) is provided. The CS (800) comprises a data stream receiving means (DSRM), a generator (702), a mixed radix converter (MRC) and an encryptor (908). The DSRM (902) is configured to receive a data stream (DS). The generator is configured to selectively generate a random number sequence (RNS) utilizing a punctured ring structure. The MRC (704) is coupled to the generator and configured to perform a mixed radix conversion to convert the RNS from a first number base to a second number base. The encryptor is coupled to the DSRM and MRC. The encryptor is configured to generate an altered data stream by combining the RNS in the second number base with the DS. The punctured ring structure and the MRC are configured in combination to produce an RNS in the second number base which contains a priori defined statistical artifacts after the mixed radix conversion.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
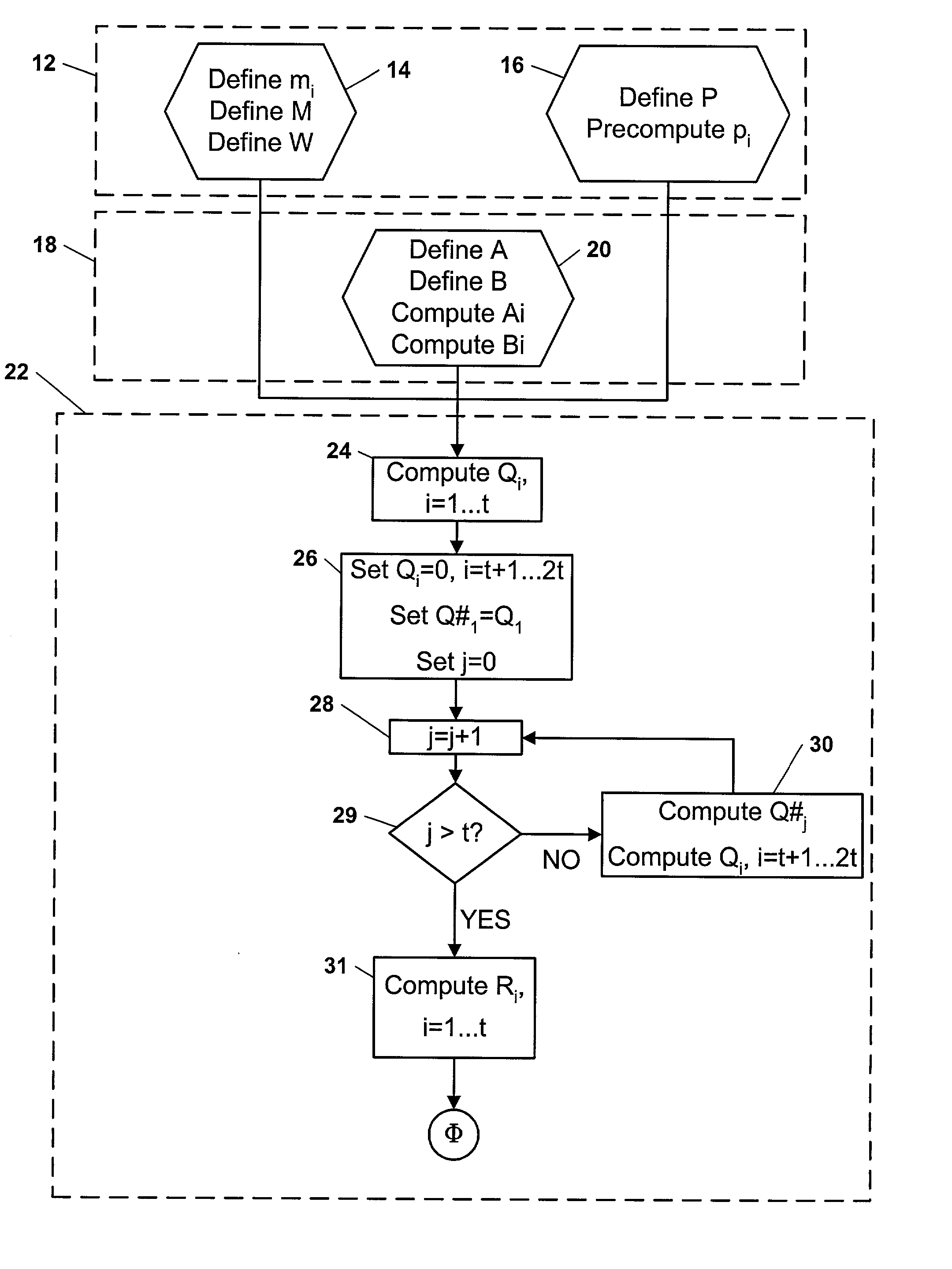
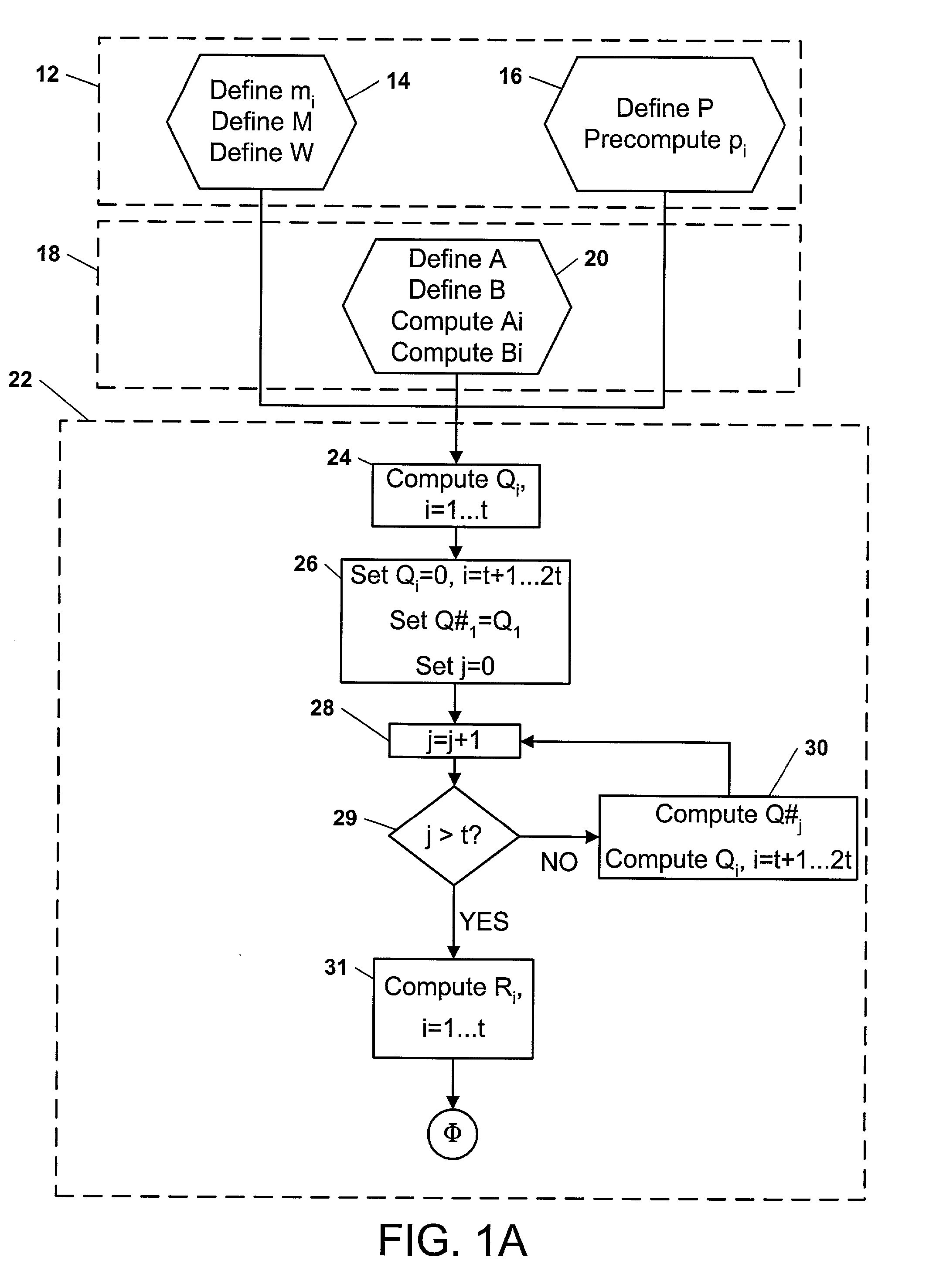
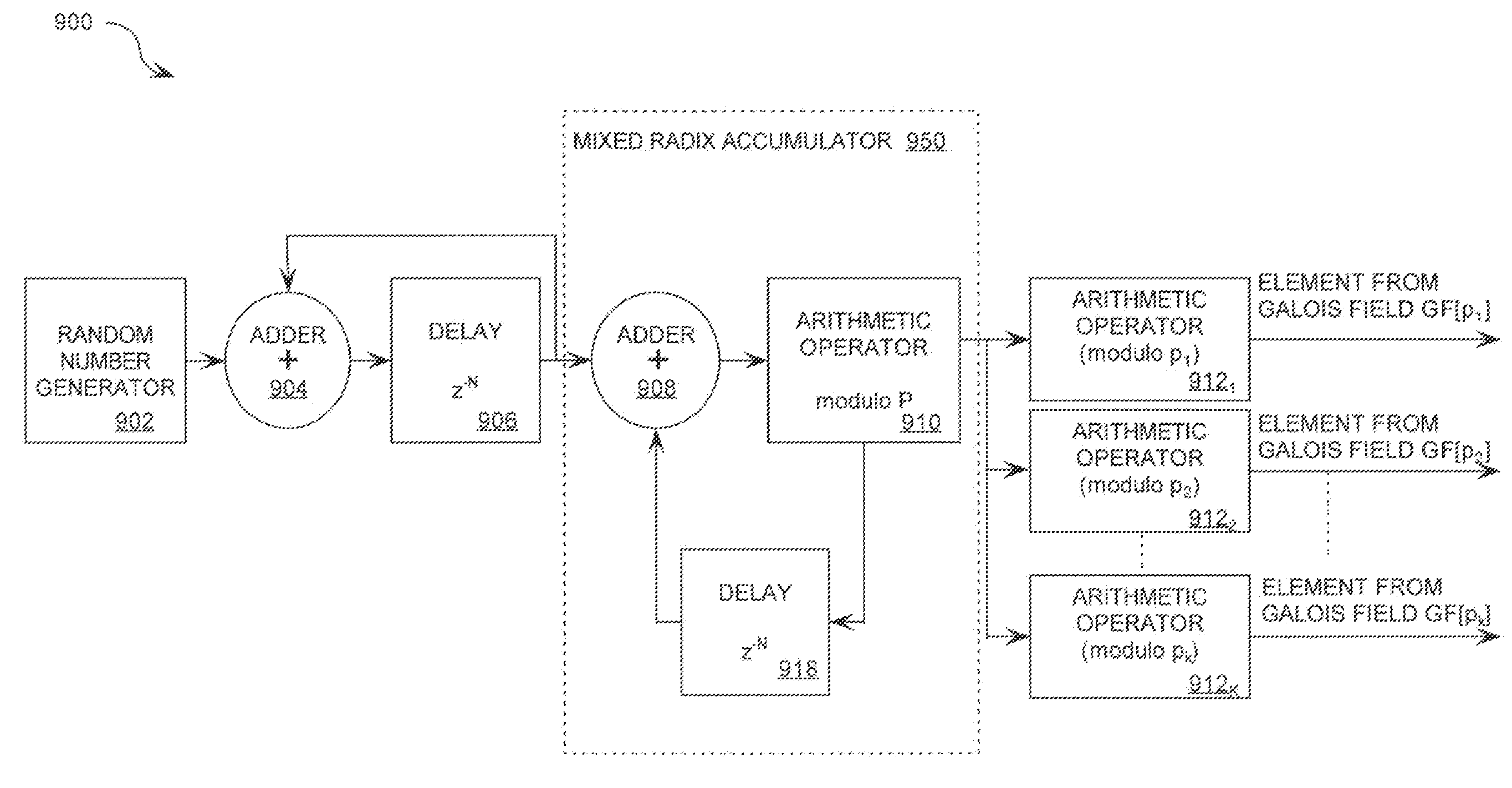
Mixed Radix Number Generator with Chosen Statistical Artifacts
Owner:HARRIS CORP
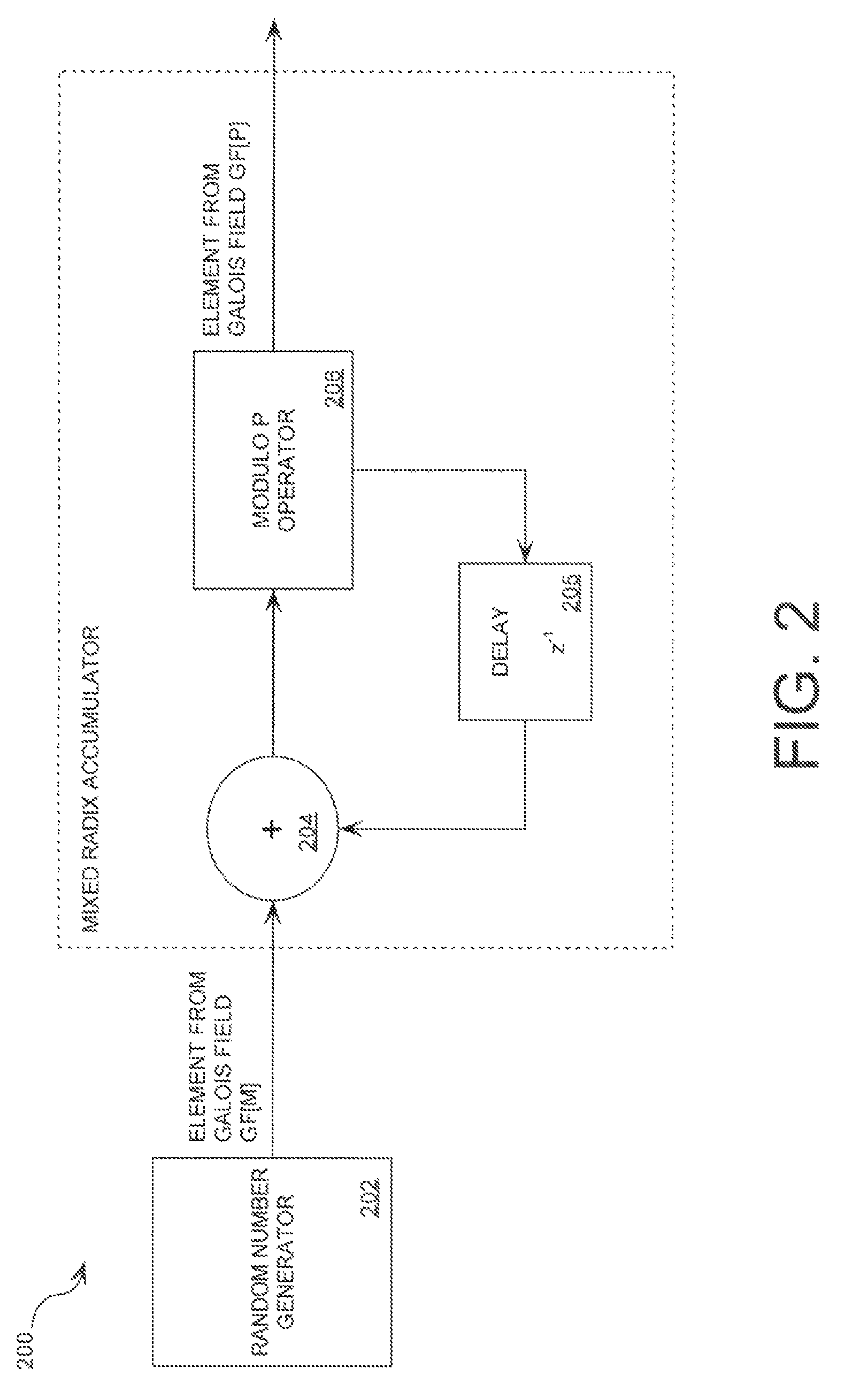
Cryptographic system including a mixed radix number generator with chosen statistical artifacts
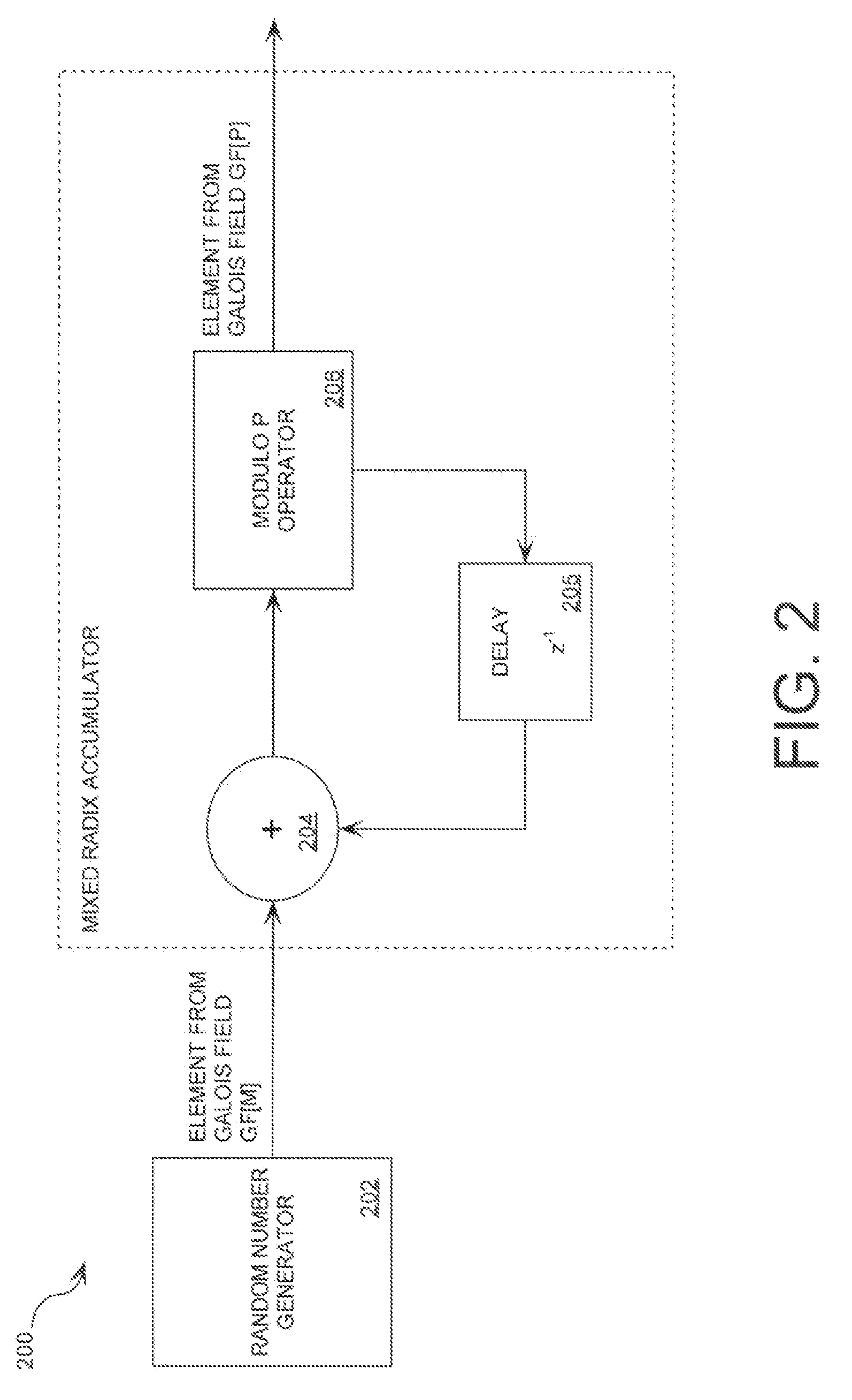
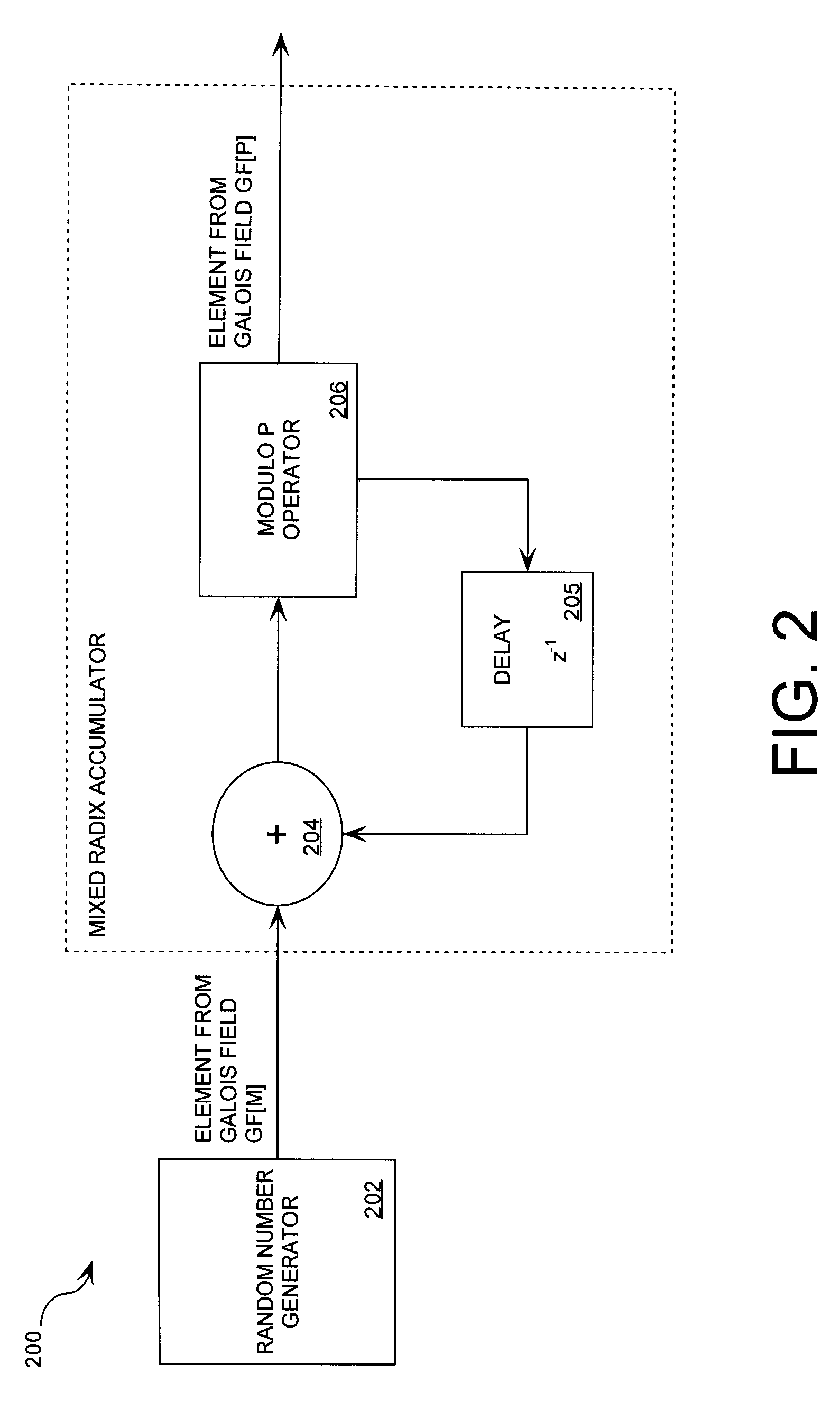
A cryptographic system (1000) is provided. The cryptographic system includes a data stream receiving means (DSRM), a number generator (NG), a mixed radix accumulator (MRA) and an encryptor. The DSRM (1002) receives a data stream (DS). The NG (702) generates a first number sequence (FNS) contained within a Galois Field GF[M]. The MRA (750) is configured to perform a first modification to a first number (FN) in FNS. The first modification involves summing the FN with a result of a modulo P operation performed on a second number in FNS that proceeds FN. The MRA is also configured to perform a second modification to FN utilizing a modulo P operation. The MRA is further configured to repeat the first and second modification for numbers in FNS to generate a second number sequence (SNS). The encryptor (1004) is configured to generate a modified data stream by combining SNS and DS.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Mixed Radix Conversion with a Priori Defined Statistical Artifacts
A method is presided for masking a process used in generating a random number sequence. The method includes generating a random number sequence. This step involves selectively generating the random number sequence utilizing a ring structure which has been punctured. The method also includes performing a mixed radix conversion to convert the random number sequence from a first number base to a second number base. The method further includes puncturing the ring structure by removing at least one element therefrom to eliminate a statistical artifact in the random number sequence expressed in the second number base. The first number base and second number base are selected so that they are respectively defined by a first Galois field characteristic and a second Galois field characteristic.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
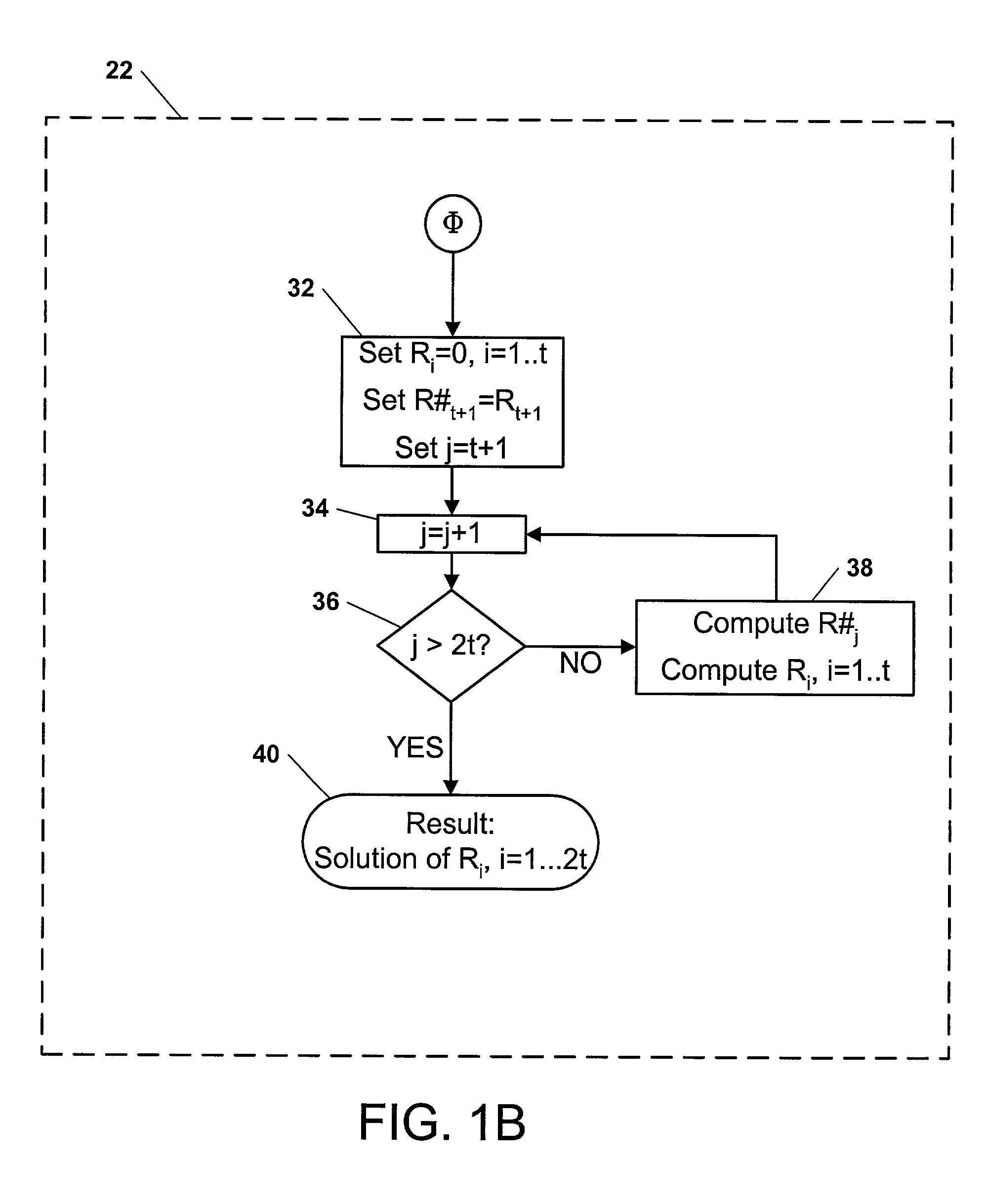
Residue number arithmetic logic unit
ActiveUS20130311532A1Improve performanceConservingProgram controlComputation using denominational number representationArithmetic logic unitNumbering system
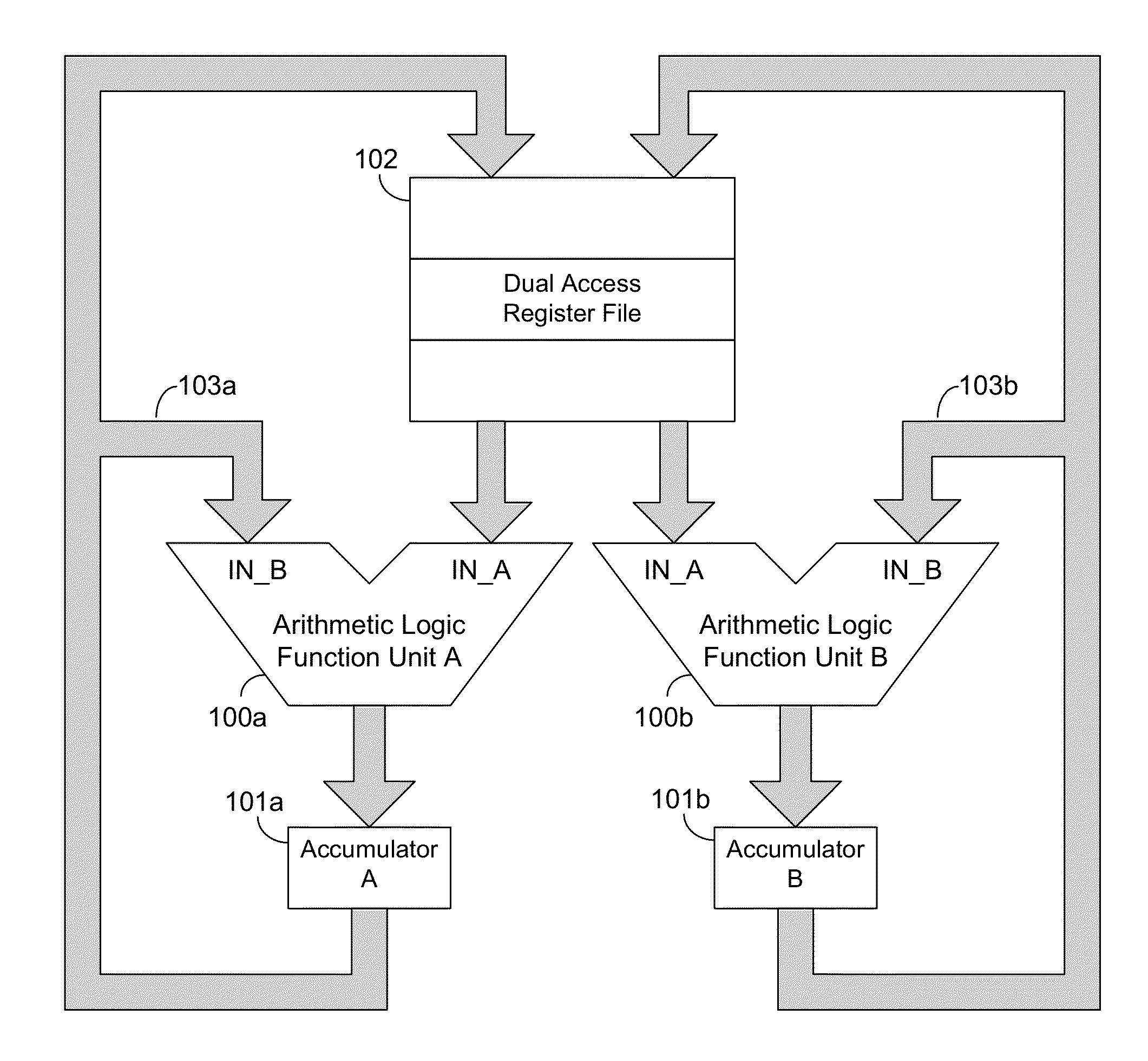
Methods and systems for residue number system based ALUs, processors, and other hardware provide the full range of arithmetic operations while taking advantage of the benefits of the residue numbers in certain operations. In one or more embodiments, an RNS ALU or processor comprises a plurality of digit slices configured to perform modular arithmetic functions. Operation of the digit slices may be controlled by a controller. Residue numbers may be converted to and from fixed or mixed radix number systems for internal use and for use in various computing systems.
Owner:OLSEN IP RESERVE
Modulation apparatus using mixed-radix fast fourier transform
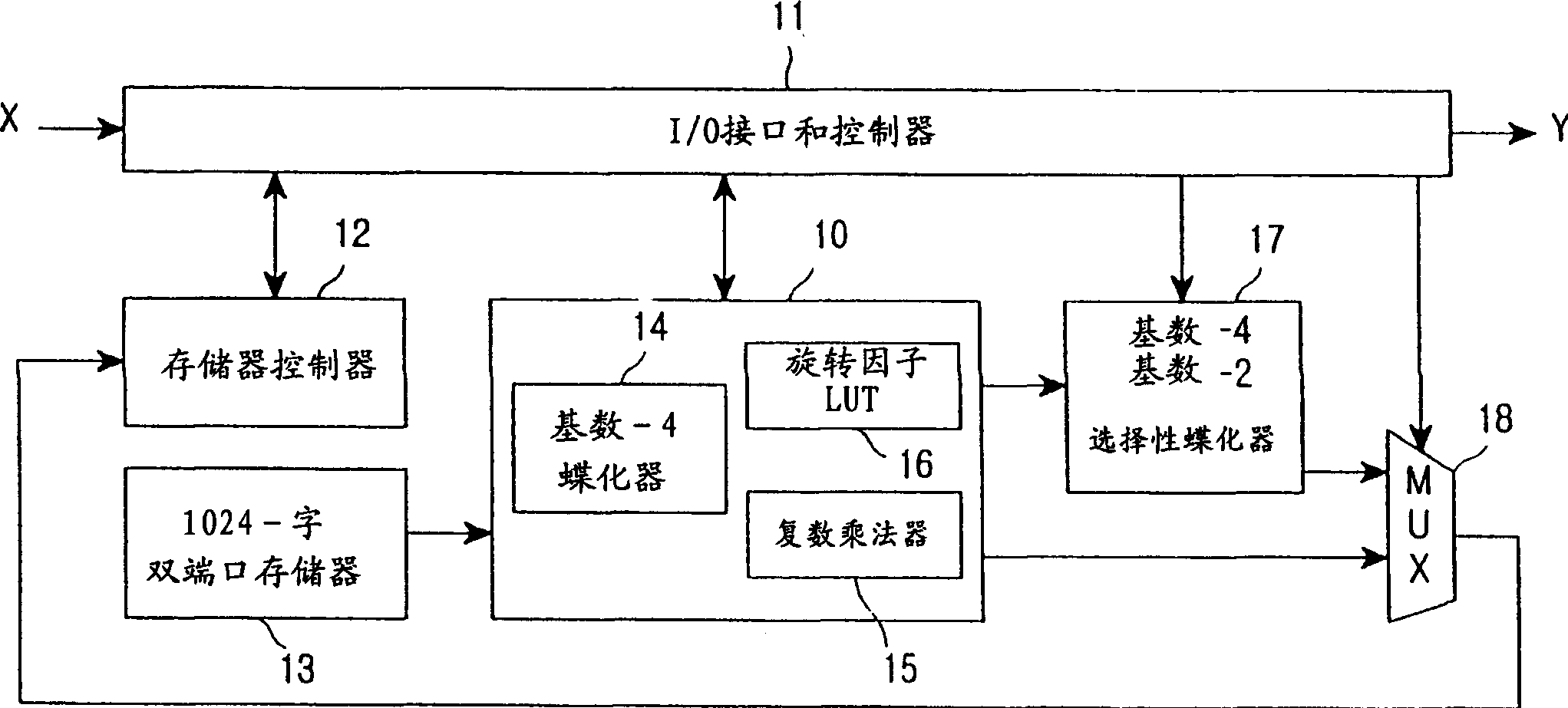
ActiveUS7164723B2Minimized in sizeMinimize complexityCode conversionDigital computer detailsModem deviceParallel computing
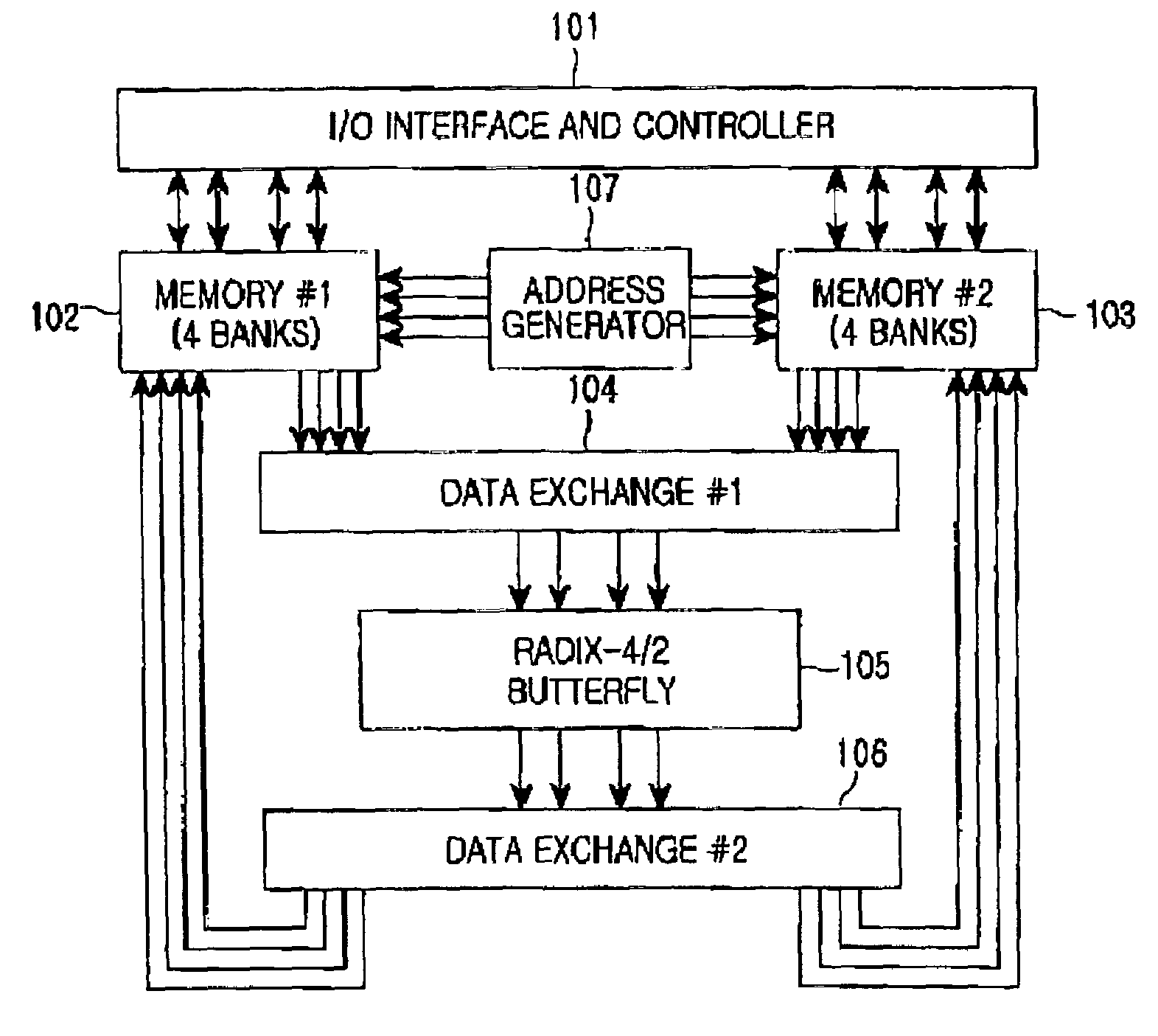
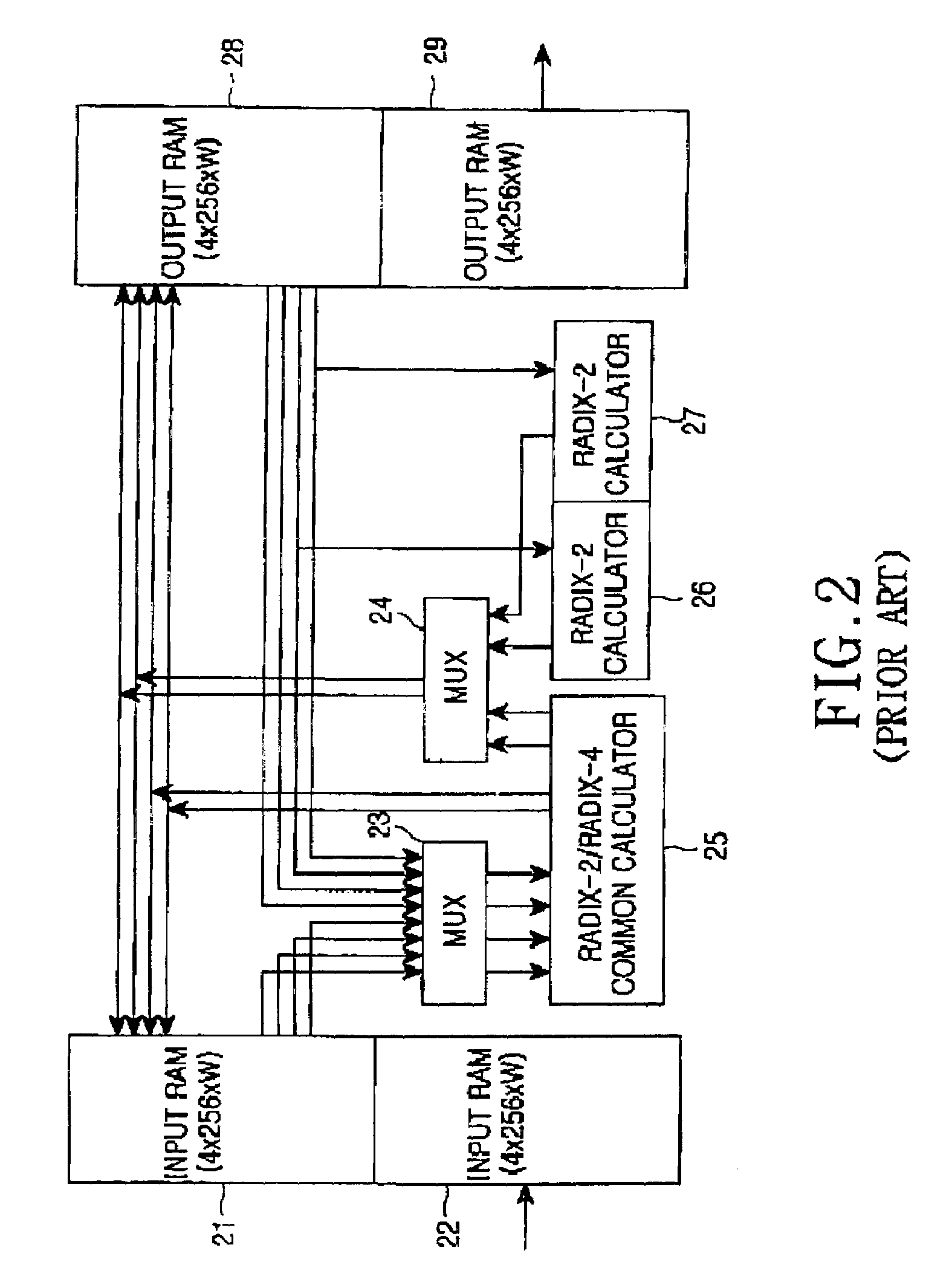
An FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) processor is disclosed which is a core block of an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) or DMT (Discrete Multi-tone) MODEM. The FFT processor simultaneously performs sequential input and output by applying an in-place algorithm for a mixed-radix multi-bank memory, thereby realizing continuous processing with only a 2N-word memory having 4 banks. The FFT processor minimizes its complexity while satisfying a high-speed calculation requirement.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
Vdsl2 Transmitter/Receiver Architecture
ActiveUS20090063604A1Minimal hardware costIncrease hardware costModulated-carrier systemsDigital computer detailsTime domainLow speed
The invention suggests a novel pipeline FFT / IFFT architecture that not only produces time-domain samples (after IFFT) but also pushes time-domain samples into FFT in a time-based sequential order. This reduces external memory requirement for buffering the time-domain samples. Also the design is based on a mixed radix-2 and radix-22 algorithm aiming at reducing number of multipliers and adders. Compared with other FFT / IFFT design methodologies such as radix-4, it achieves the minimum multiplier use, the minimum adder use and the minimum operating memory use. On the other hand, the design architecture not only can support different FFT / IFFT size required by different VDSL2 profiles but also utilizing a novel pipeline control mechanism to reduce logic switching at low-speed profiles. This effectively further reduces the power consumption at lower profiles and enables our VDSL2 digital chipsets to compete with ADSL2+ systems in terms of power consumption.
Owner:TRIDUCTOR TECH SUZHOU
Mixed radix number generator with chosen statistical artifacts
Owner:HARRIS CORP
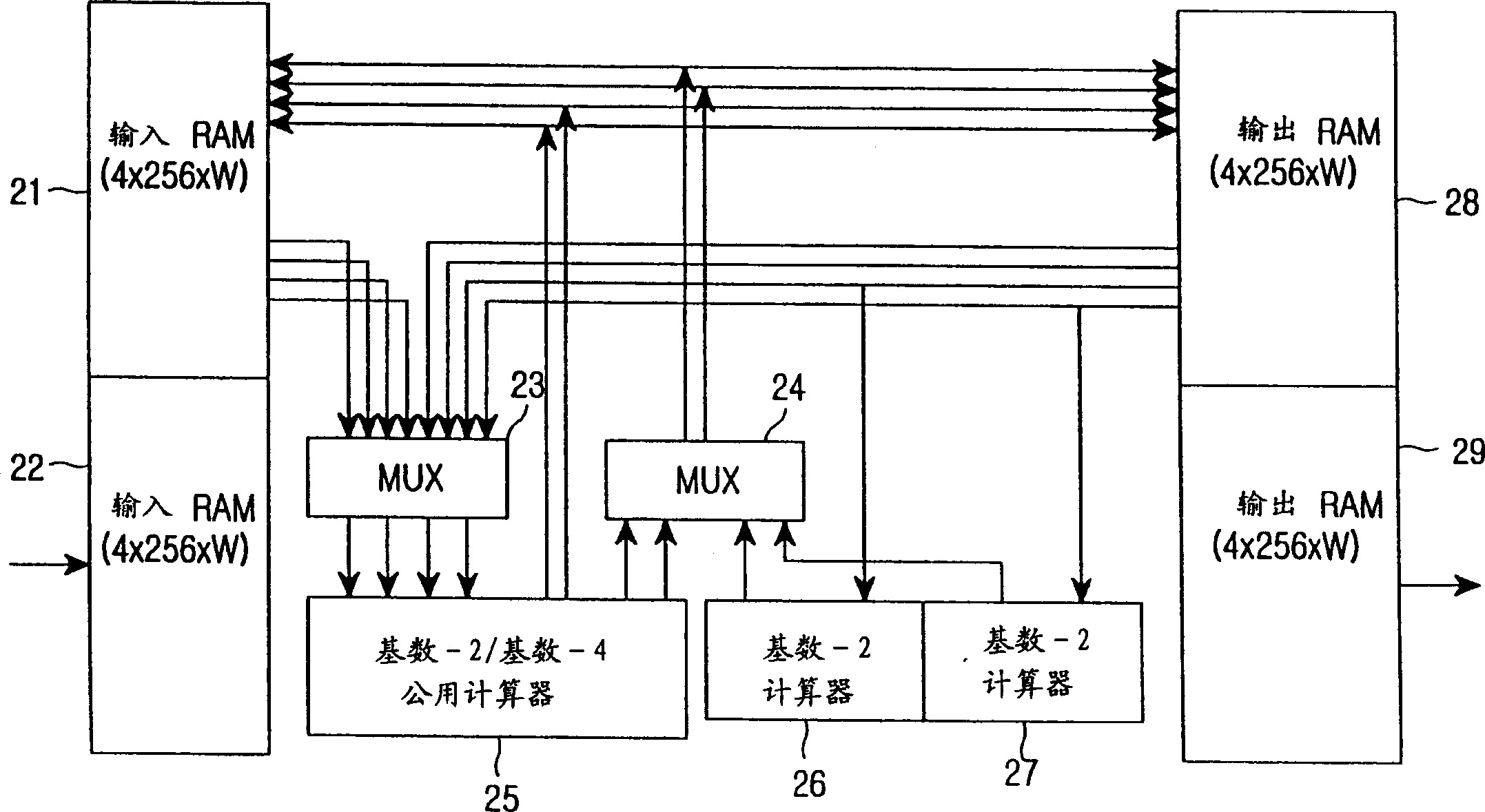
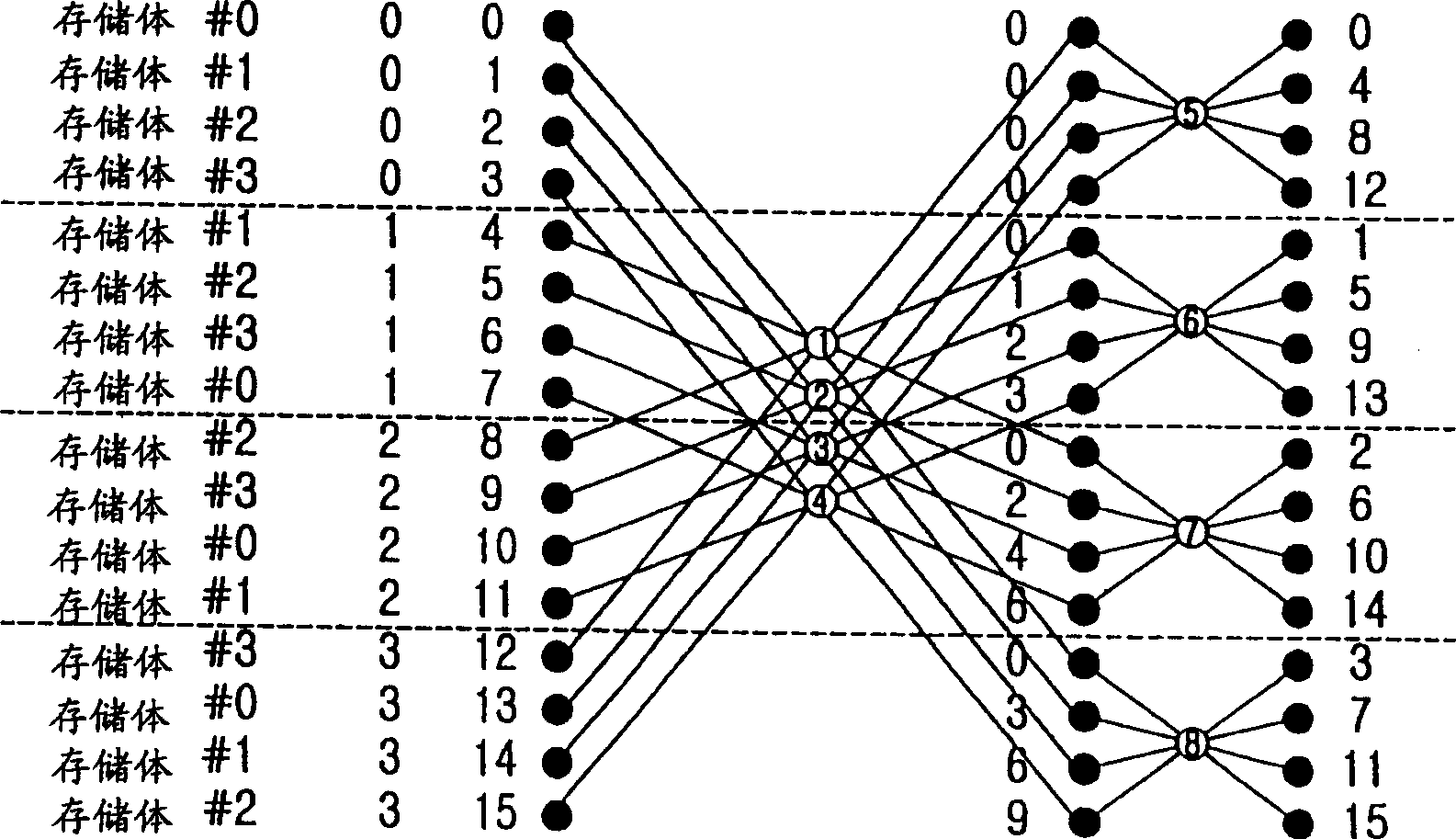
In-Place Fast Fourier Transform Processor
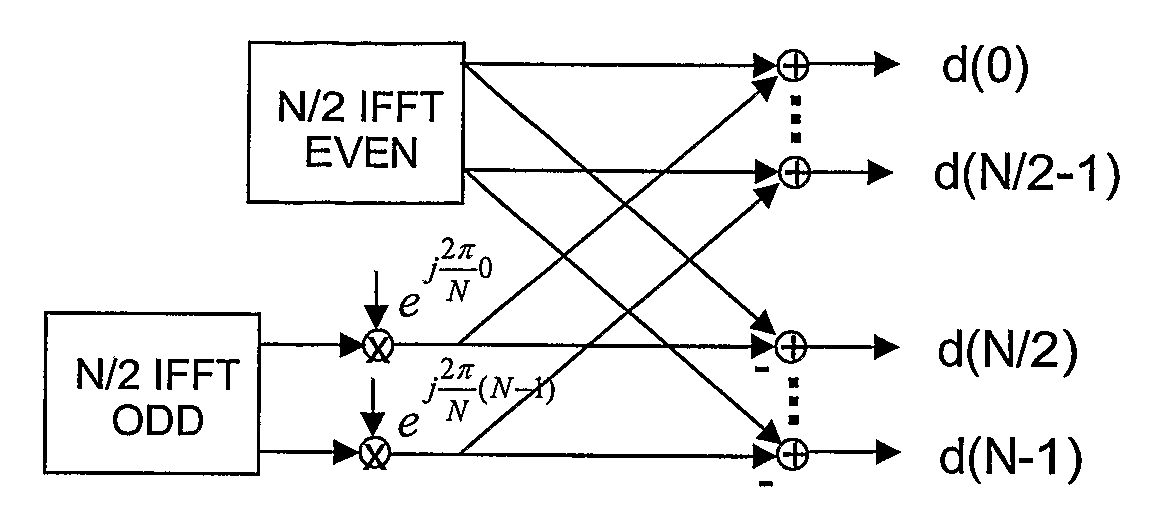
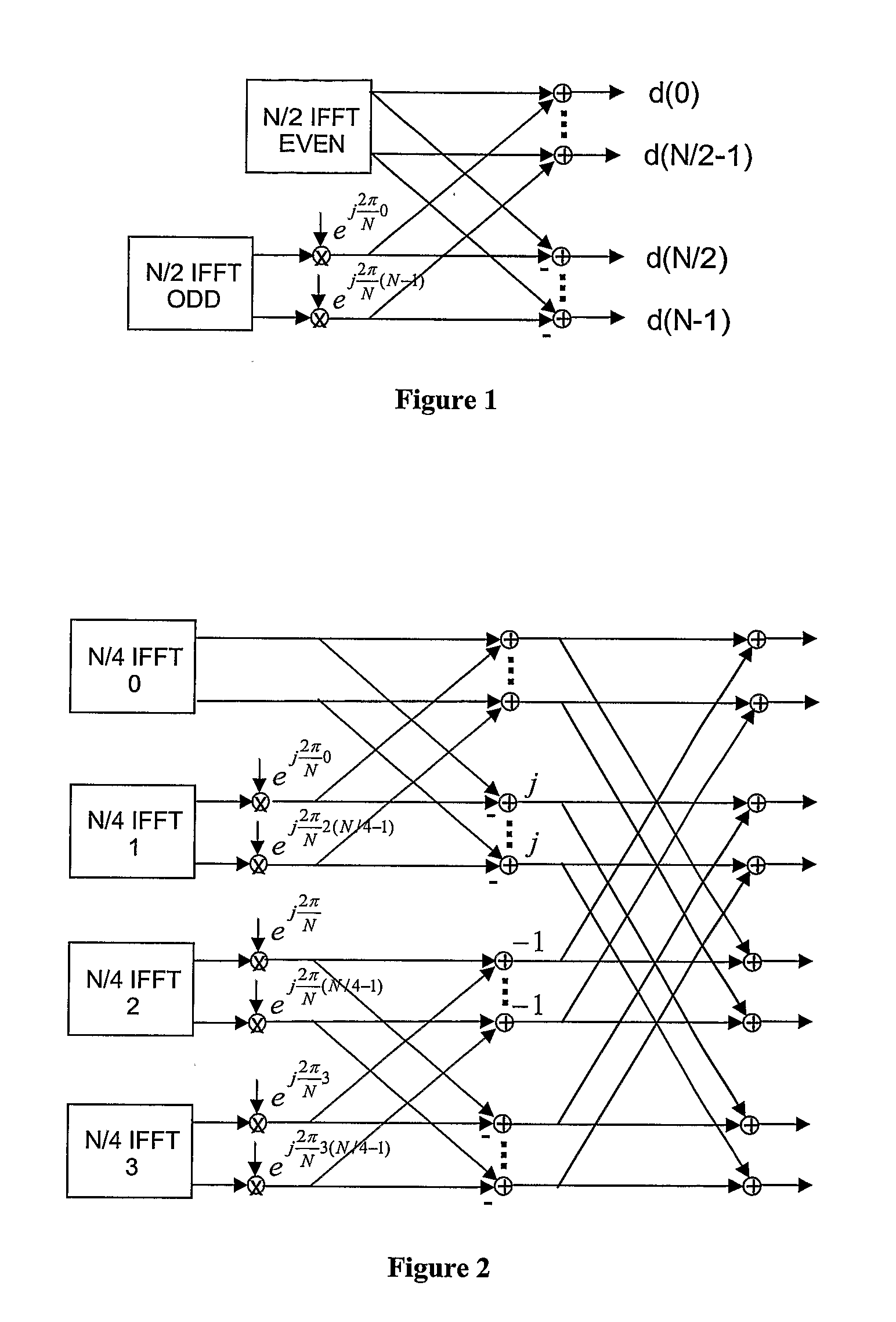
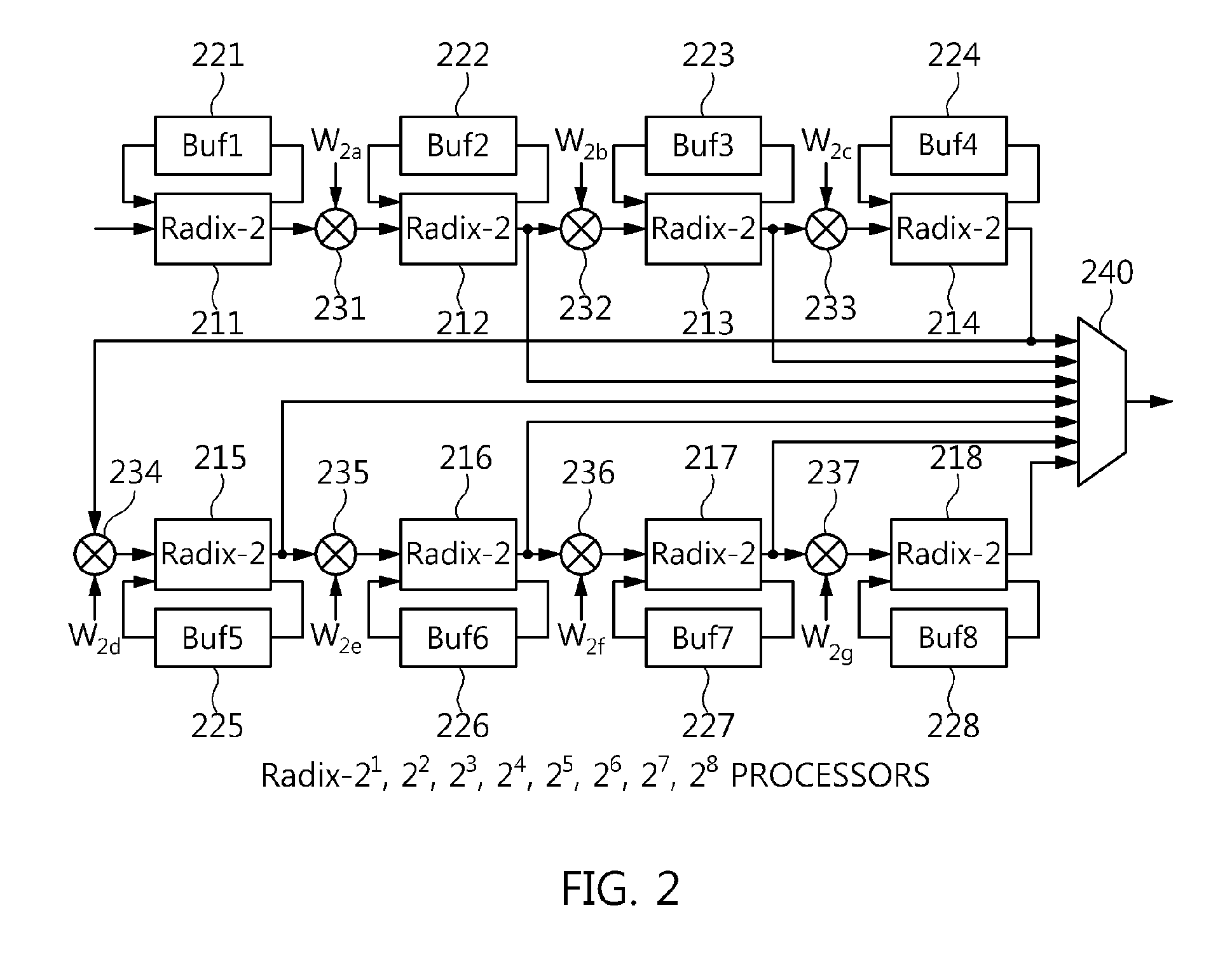
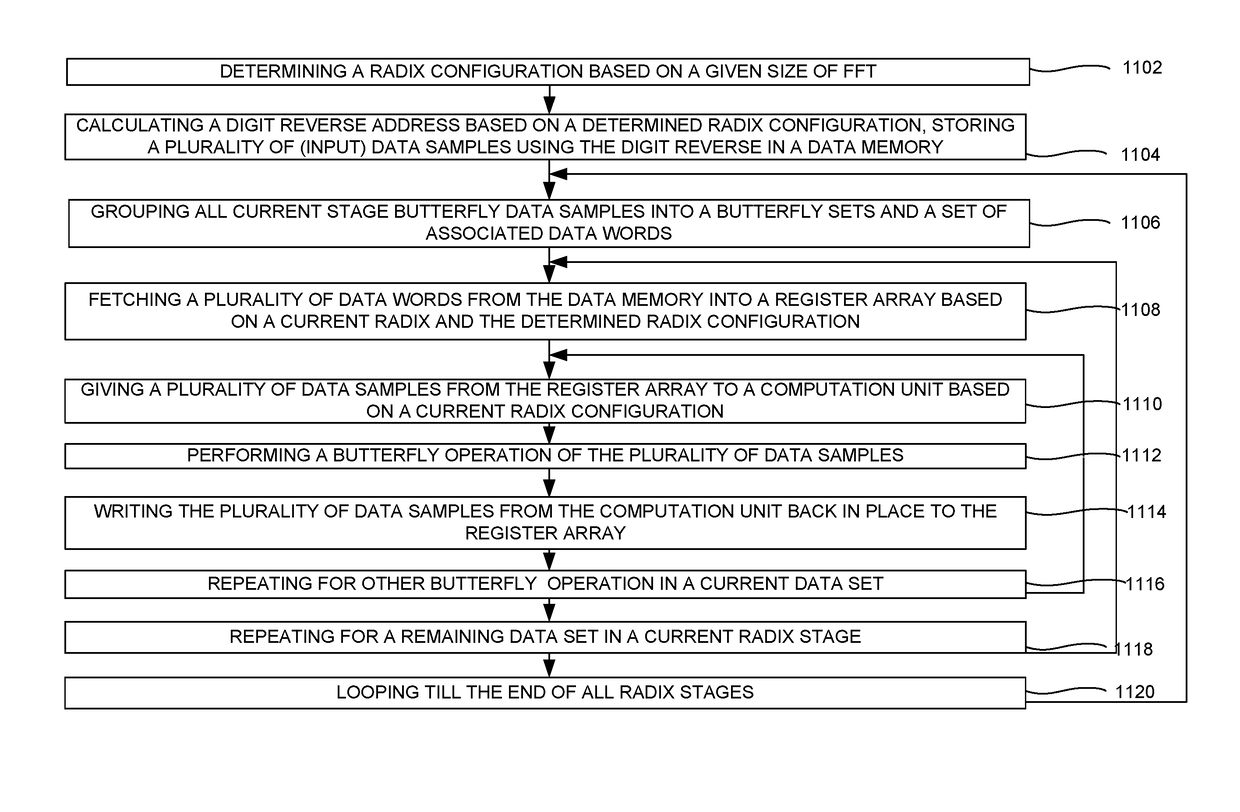
An N-point Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) using mixed radix stages with in-place data sample storage may be performed by decomposing N into a product of R sequential mixed radix stages of radix-r(i). N data samples are partitioned into at least B memory banks, where B is equal to a largest radix of the R radix stages. Each input data sample to each radix-r(i) butterfly comes from r(i) different memory banks and the output data samples are written to the same memory locations in the r(i) memory banks. Determining from which memory bank the input data samples and output data samples of the butterflies are stored is done based on the radix size and sequential position of the radix stage. Determining the address of the input data samples and the output data samples within each memory bank is based on the radix size and sequential position of the radix stage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Pipeline-based reconfigurable mixed-radix FFT processor
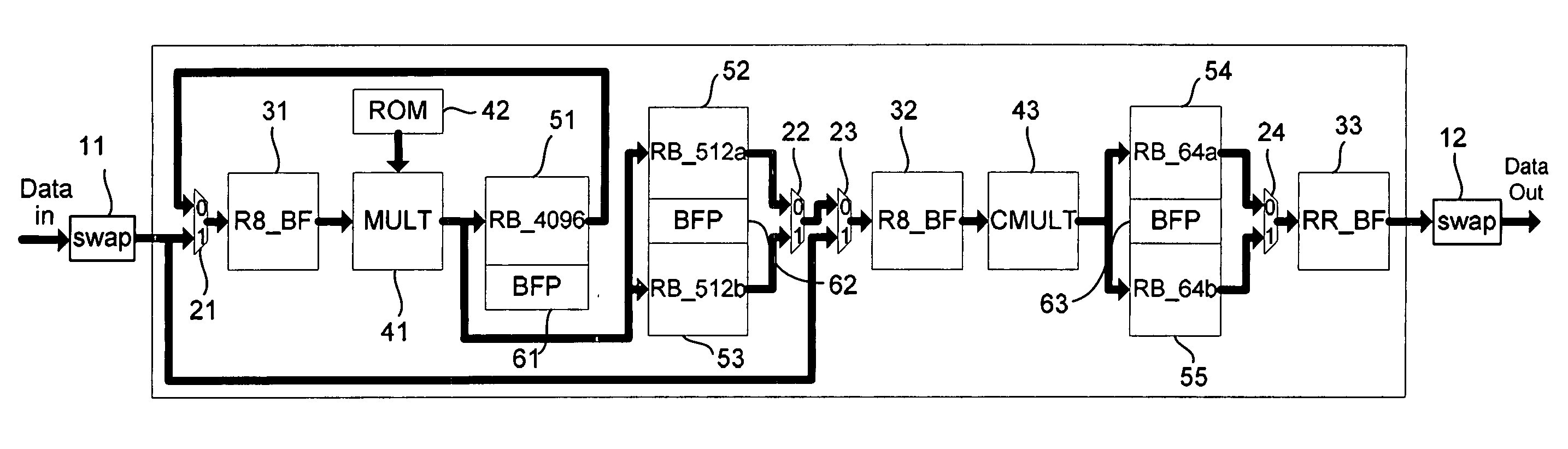
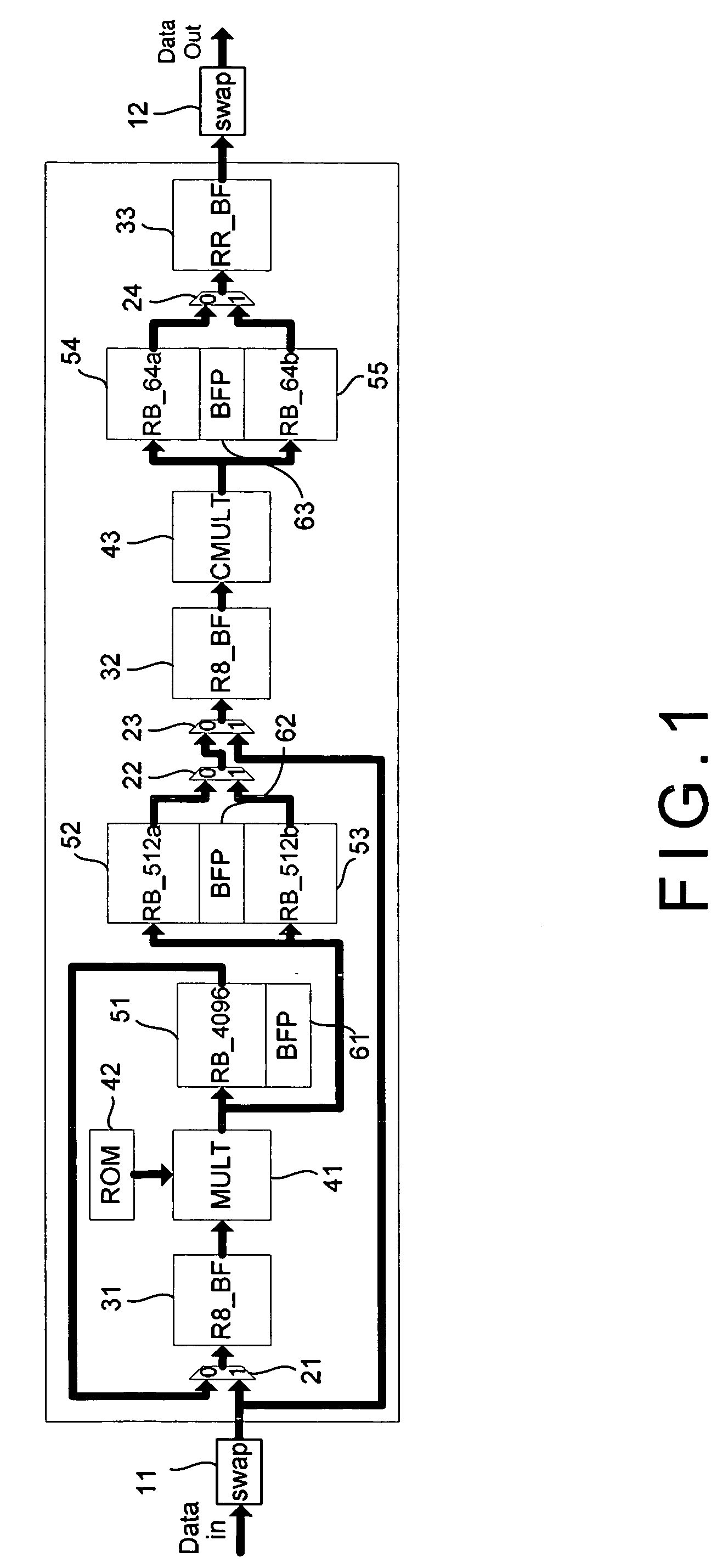
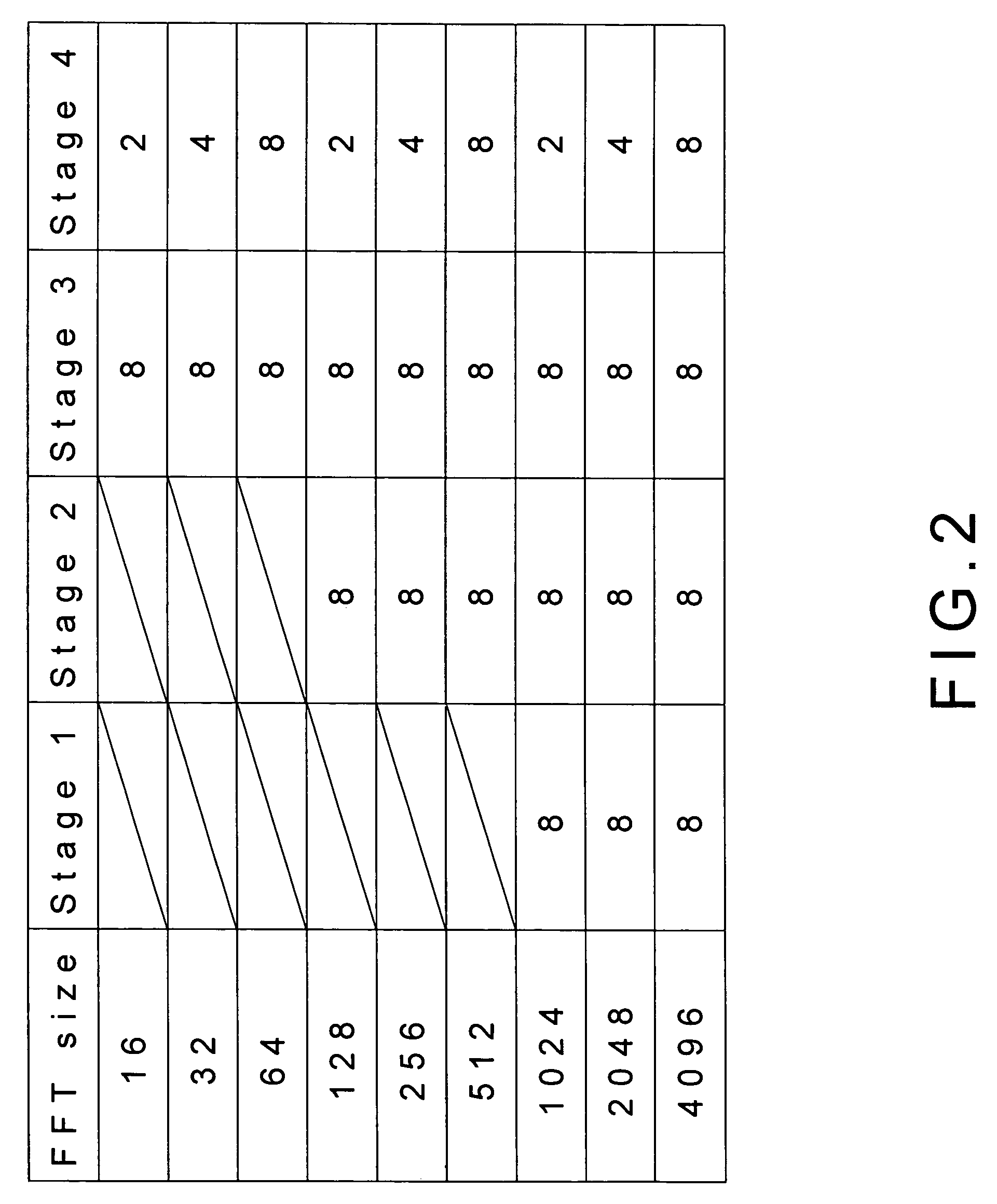
ActiveUS20080155003A1Reduce computing time costsReduce hardware costsDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Block floating-point
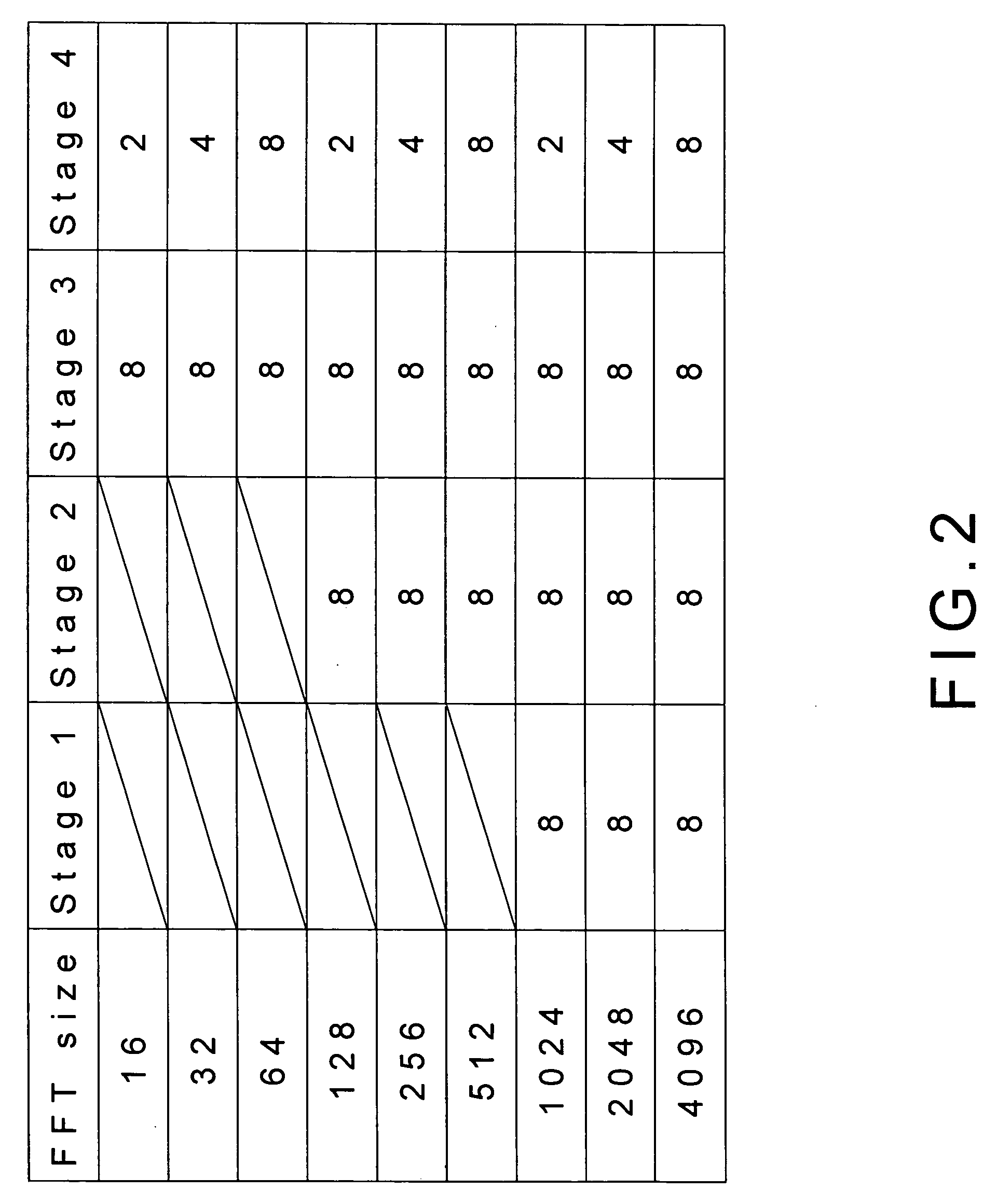
The present invention discloses a fast Fourier transform (FFT) processor based on multiple-path delay commutator architecture. A pipelined architecture is used and is divided into 4 stages with 8 parallel data path. Yet, only three physical computation stages are implemented. The process or uses the block floating point method to maintain the signal-to-noise ratio. Internal storage elements are required in the method to hold and switch intermediate data. With good circuit partition, the storage elements can adjust their capacity for different modes, from 16-point to 4096-point FFTs, by turning on or turning off the storage elements.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Conversion apparatus for a residue number arithmetic logic unit
ActiveUS20140129601A1Increase in sizeEasy to processDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsArithmetic logic unitComputer science
Methods and systems for conversion of binary data to residue data, and for conversion of residue data to binary data, allow fully extensible operation with related methods and systems for residue number based ALUs, processors and other hardware. In one or more embodiments, a residue to binary data converter apparatus comprises a mixed radix to fixed radix conversion apparatus. In one or more embodiments, a mixed radix converter apparatus assists internal processing of a related residue number based ALU, processor or other hardware.
Owner:OLSEN IP RESERVE
Mixed radix conversion with a priori defined statistical artifacts
A method is presided for masking a process used in generating a random number sequence. The method includes generating a random number sequence. This step involves selectively generating the random number sequence utilizing a ring structure which has been punctured. The method also includes performing a mixed radix conversion to convert the random number sequence from a first number base to a second number base. The method further includes puncturing the ring structure by removing at least one element therefrom to eliminate a statistical artifact in the random number sequence expressed in the second number base. The first number base and second number base are selected so that they are respectively defined by a first Galois field characteristic and a second Galois field characteristic.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
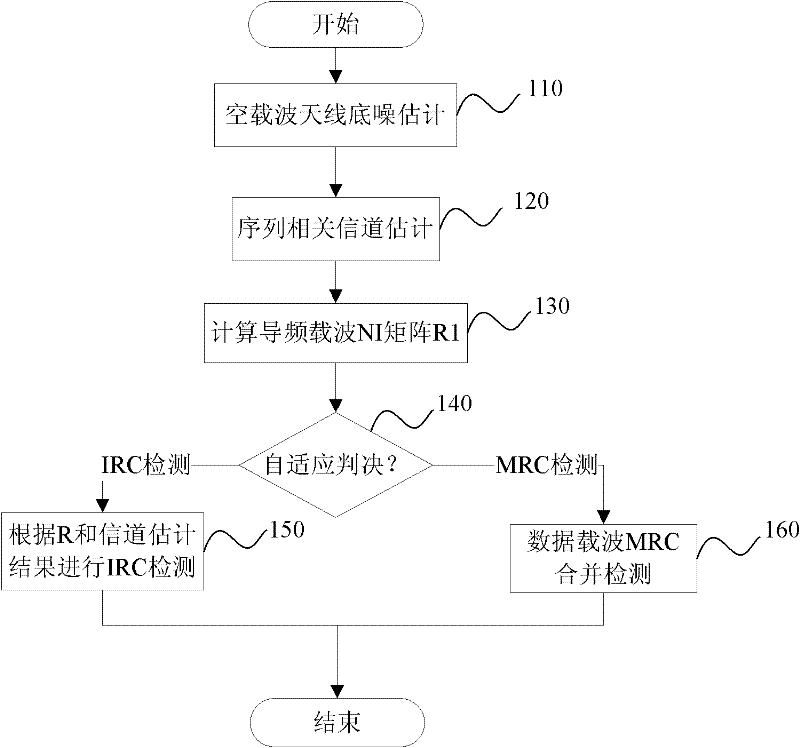
Self-adaptive method and device for eliminating interference of multiple antennae through diversity and mergence
InactiveCN102480314AImprove performanceSuppress interferenceSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringCarrier signalMerge algorithm
The invention discloses a self-adaptive method and device for eliminating interference of multiple antennae through diversity and mergence. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring noise power of each receiving antenna; judging whether the ratio of the sum of diagonal elements of an NI (Noise Index) matrix of a data carrier to be detected to an average value of the noise power of all receiving antennae is larger than a preset threshold value; if so, carrying out interference suppression and mergence detection on the data carrier to be detected; and if not, carrying out noninterference suppression and mergence detection on the data carrier to be detected. Starting from an NI estimation matrix as the most fundamental factor influencing an IRC (Interference Rejection Combining) merging algorithm, whether the currently obtained NI matrix contains more interference components is judged through the specific numerical value characteristic of the NI matrix, and then, an IRC algorithm or MRC (Mixed Radix Conversion) algorithm is selected, so that the system obtains the optimal performance.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Realization method for fast computation of discrete Fourier transform with non-second power points
InactiveCN103020015AMaintain propertiesNo increase in sampling pointsComplex mathematical operationsFinite fourier transformDecomposition
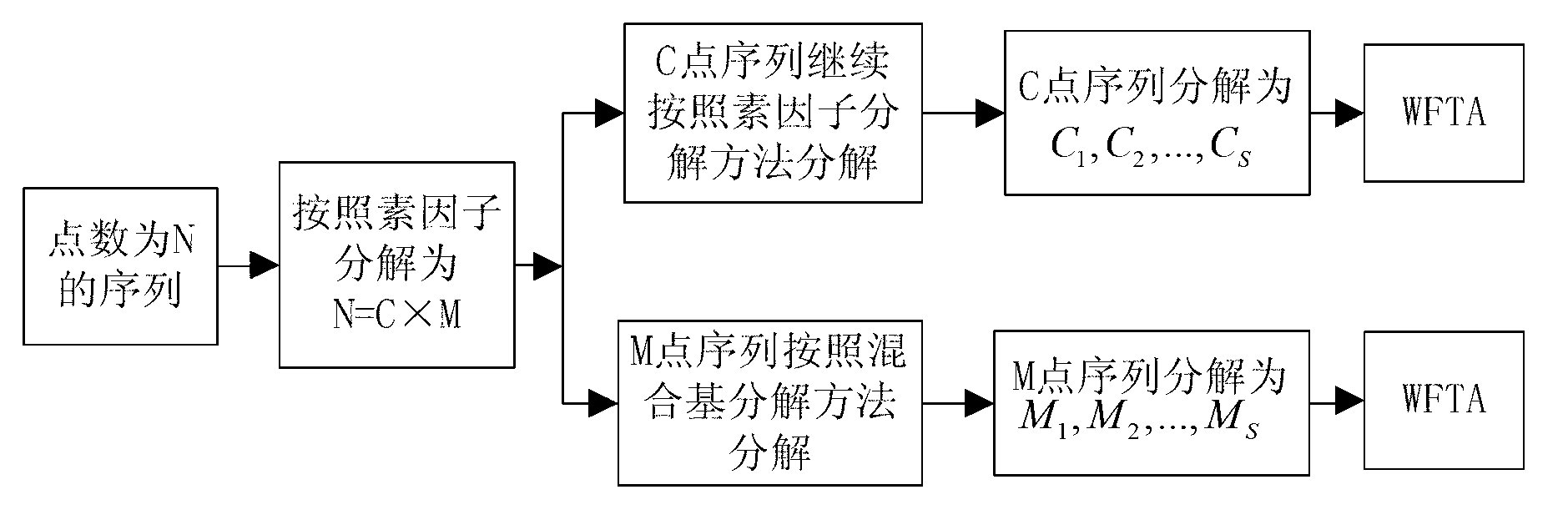
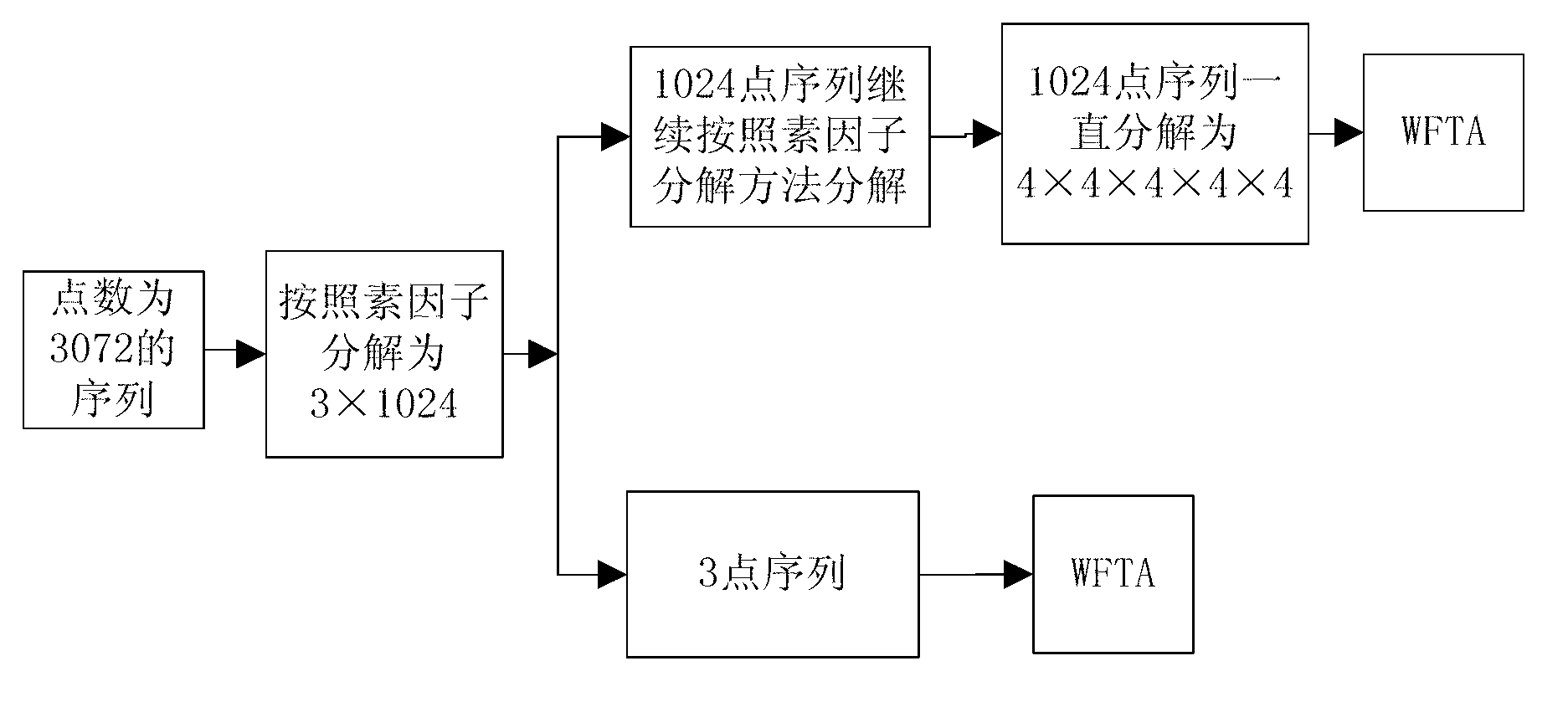
The invention discloses a realization method for fast computation of discrete Fourier transform with non-second power points. The realization method is an improvement obtained by comprehensively using a prime factor decomposition algorithm, a mixed-radix FFT (fast Fourier transform) algorithm and a WFTA (Winograd Fourier transform algorithm) decomposition method, and the sequence of non-second power points is decomposed layer by layer through common factor decomposition and prime factor decomposition. The realization method for fast computation of discrete Fourier transform with non-second power points has the characteristics of less computation, high computation efficiency and small overhead for realization.
Owner:GUILIN KSW COMM TECH
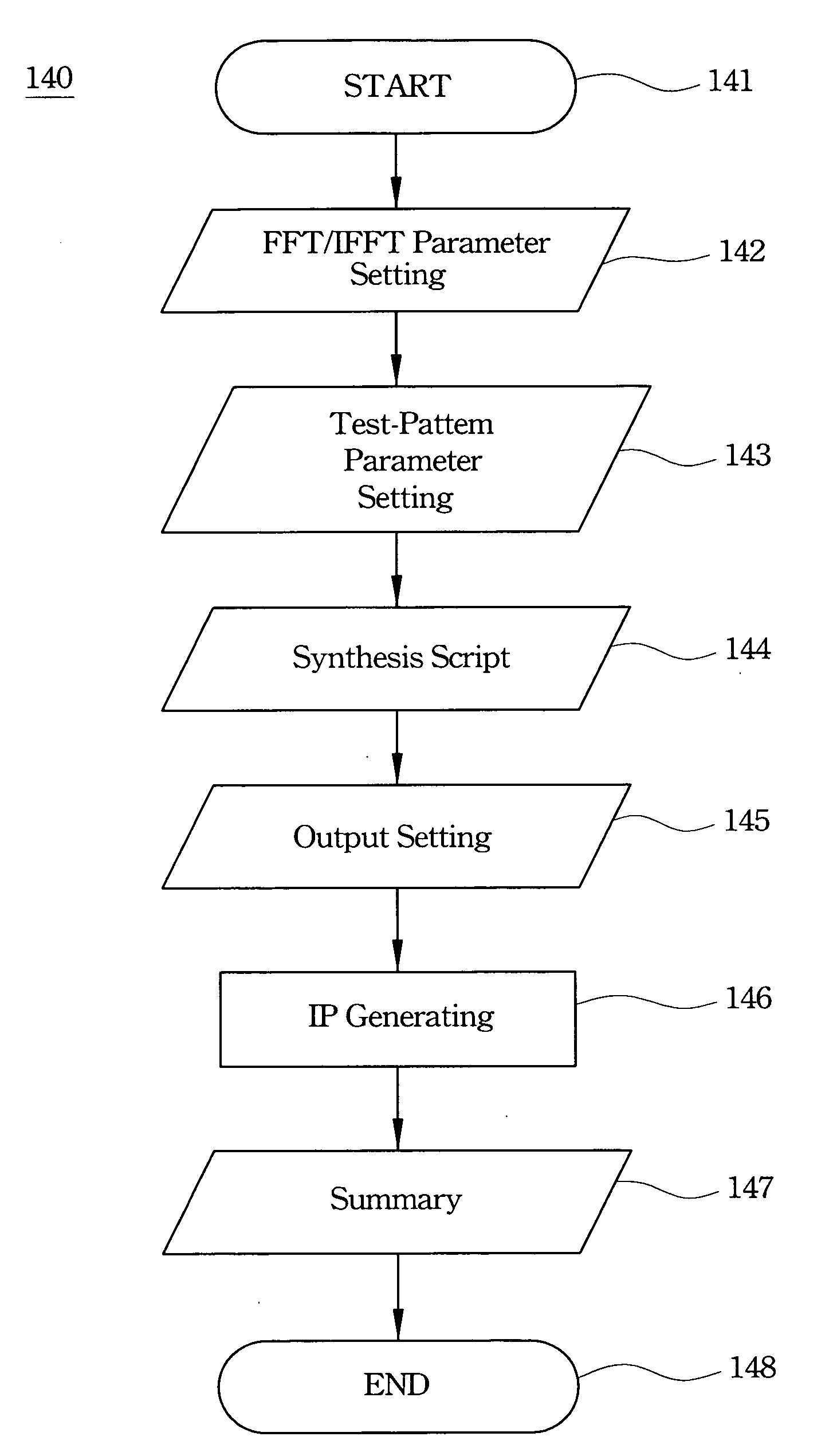
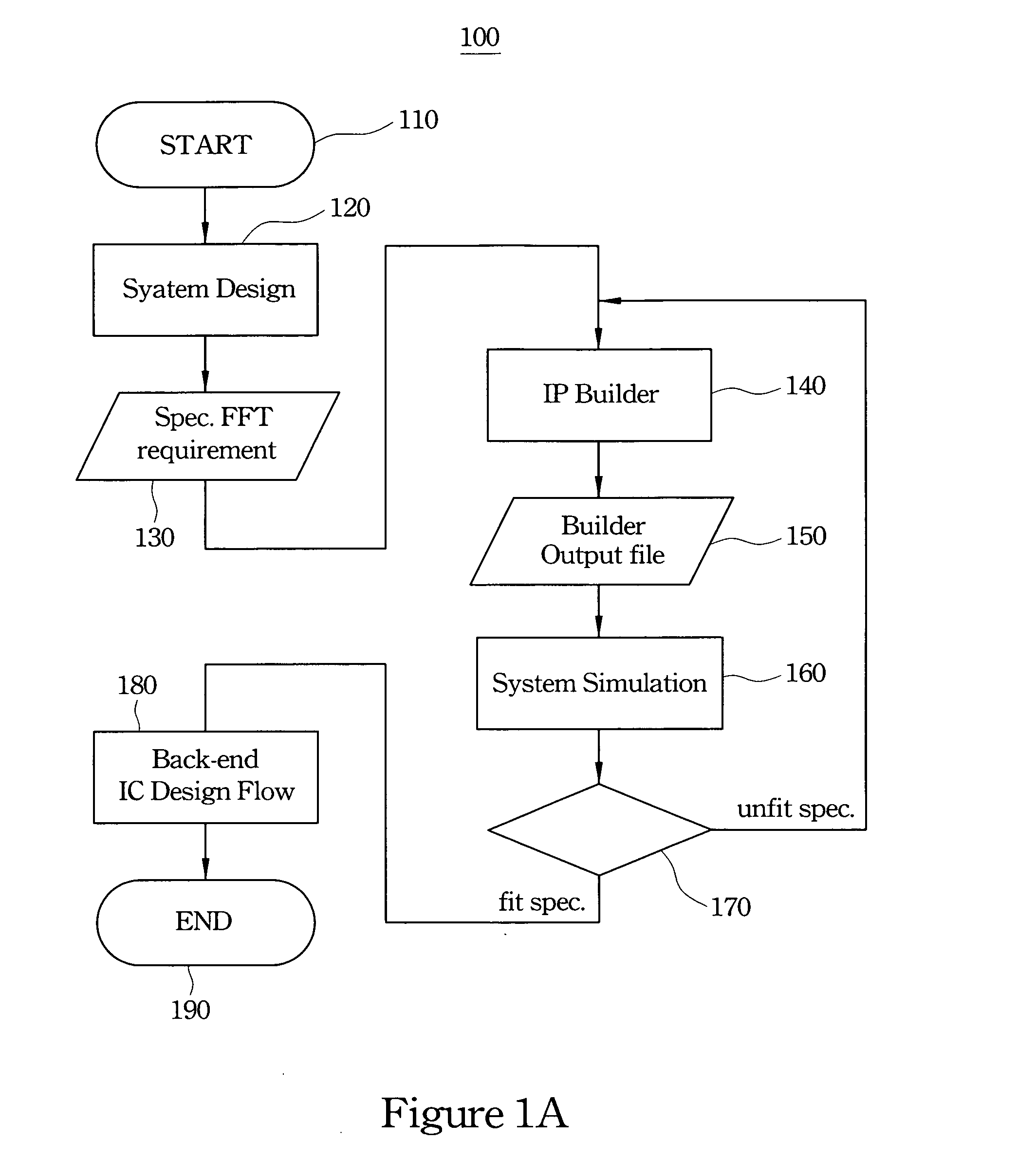
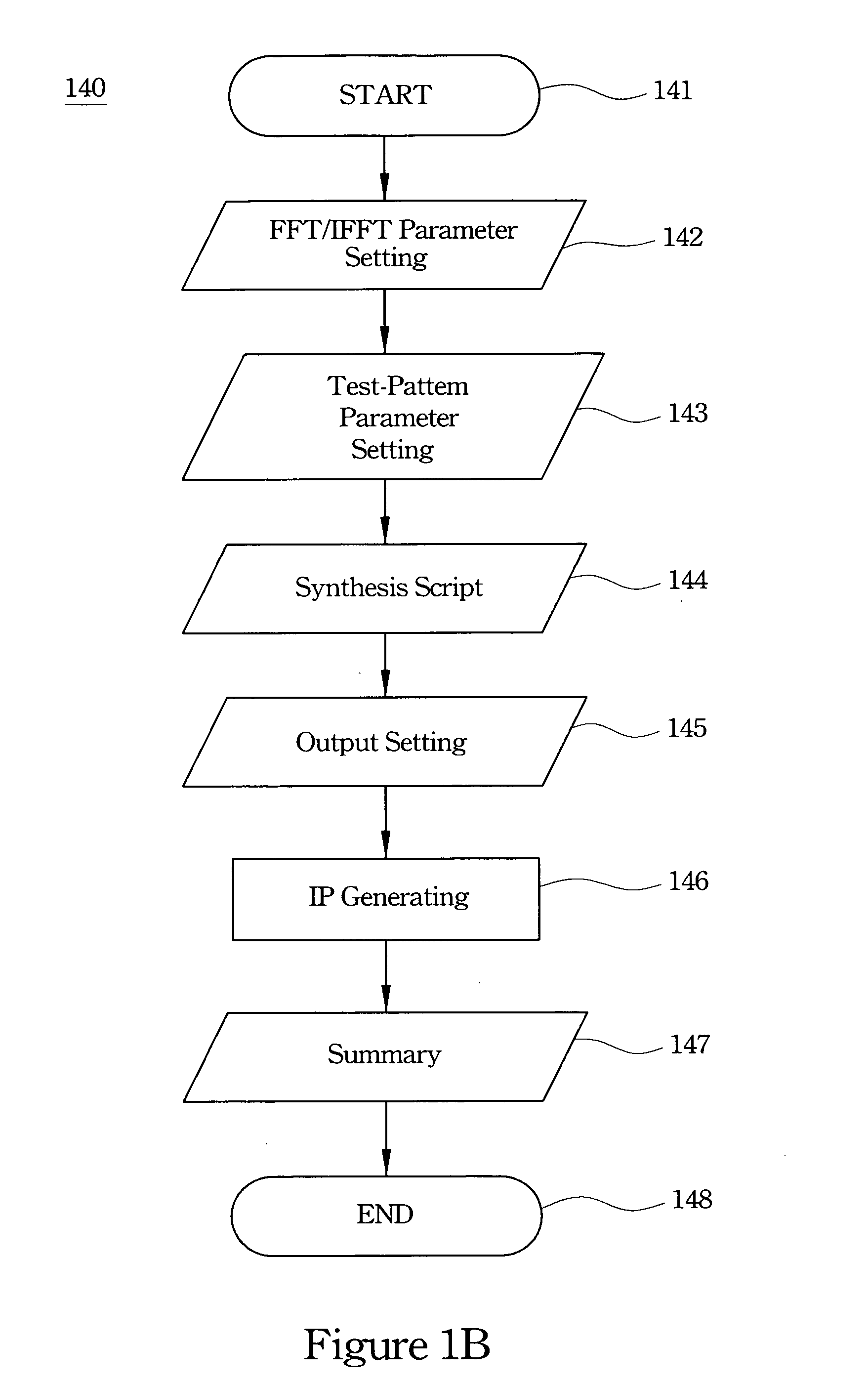
FFT/IFFT processor and intellectual property builder
InactiveUS20080126026A1Digital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationGraphicsComputational science
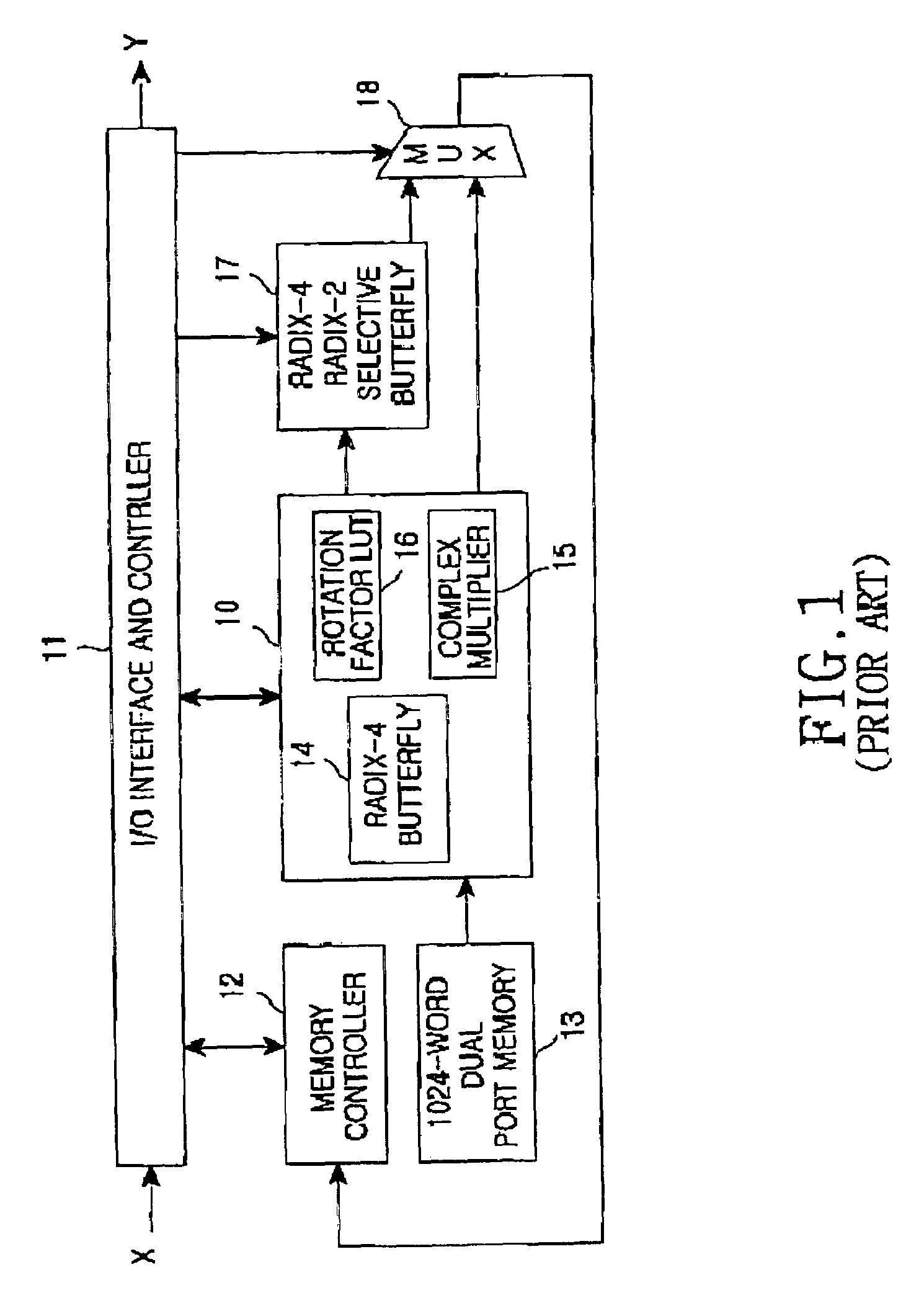
A FFT / IFFT processor and an intellectual property (IP) builder are disclosed. Which include a circuit applying the mixed-radix algorithm and a parametric graphic user interface (GUI). The circuit is for a parametric IP builder. The parametric GUI is for user to complete hardware design and functional test of FFT / IFFT processor by software. The IP builder could accelerate the progress of processor design and SOC integration.
Owner:LEE SHUENN YUH
Modulation apparatus using mixed-radix fast fourier transform
InactiveCN1663208ASmall sizeReduce complexityCode conversionMulti-frequency code systemsMultiplexingModem device
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
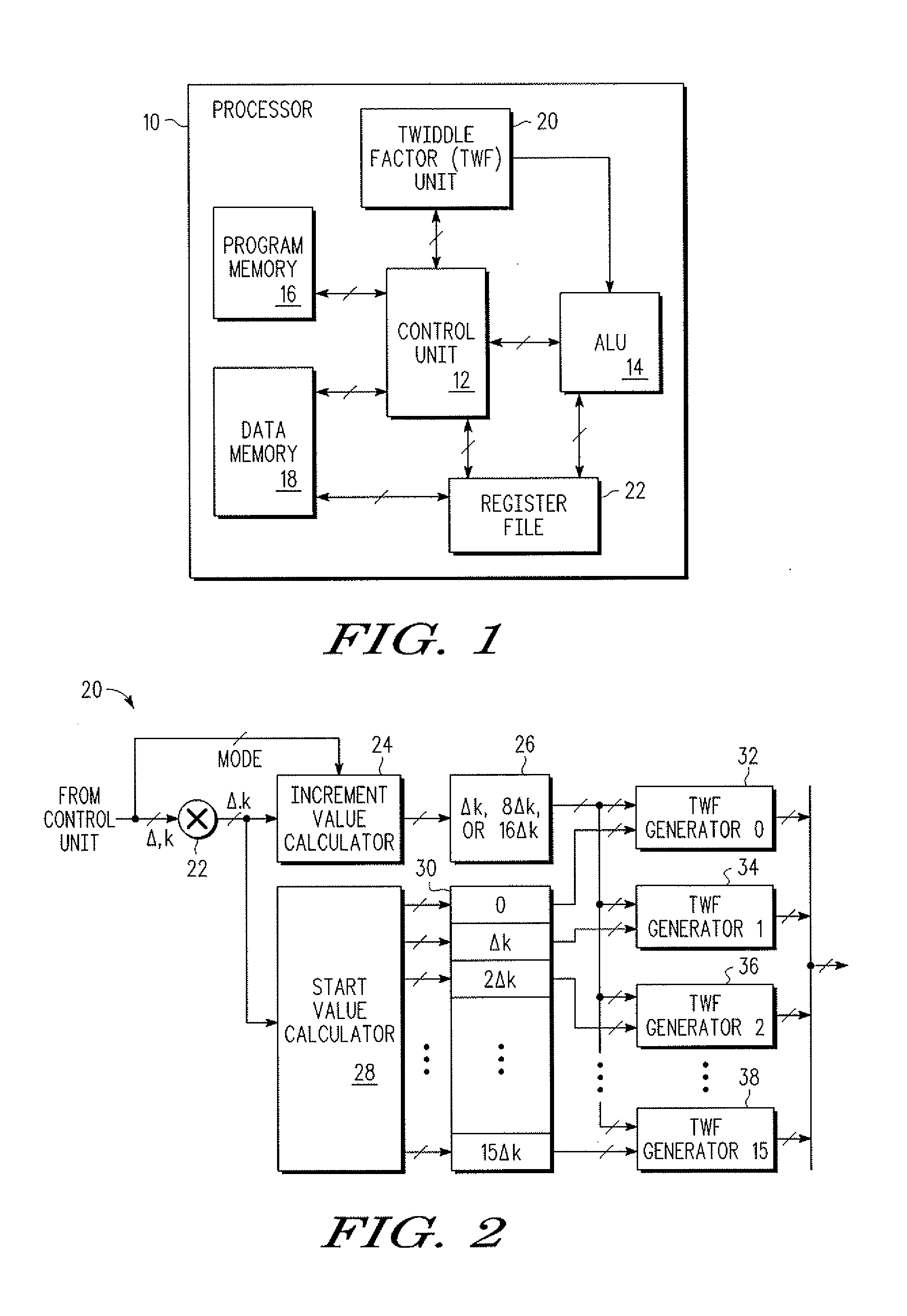
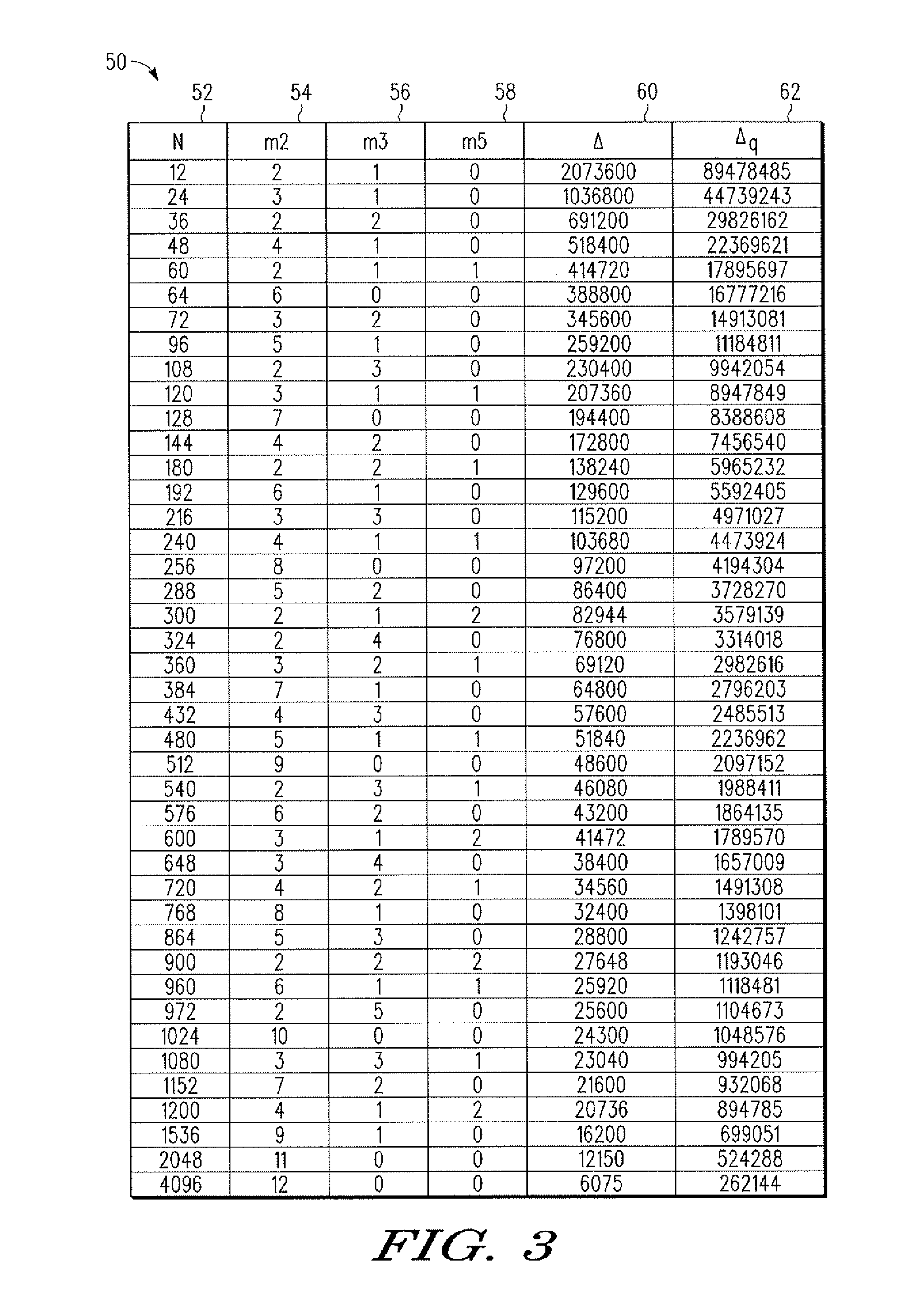
Fourier transform processing and twiddle factor generation
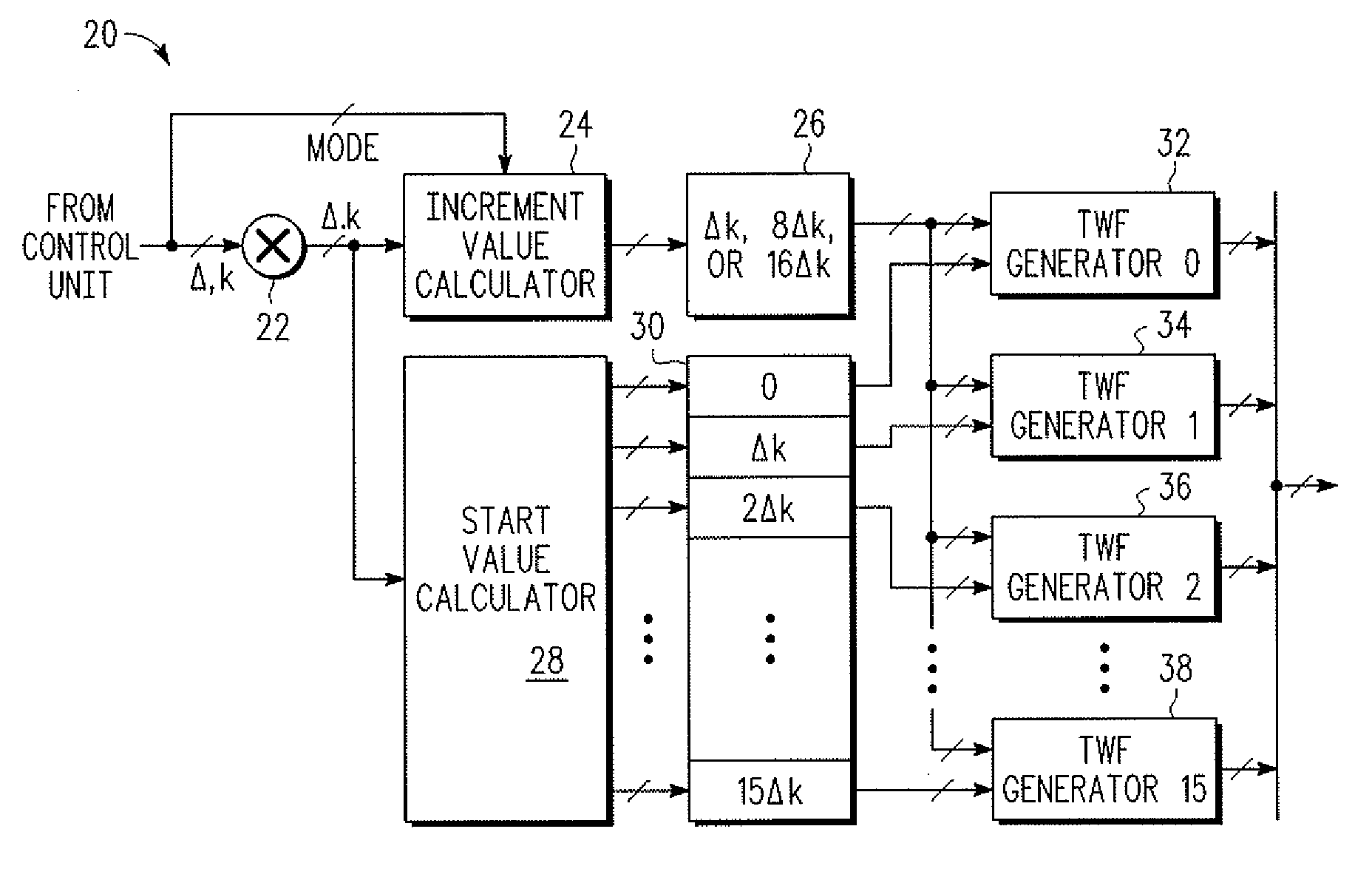
ActiveUS20100070551A1Digital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsData processing systemParallel computing
In a data processing system, having a twiddle factor unit, a method for performing a mixed-radix discrete Fourier transform (DFT) having a block size, N, and a maximum block size, Nmax, wherein the maximum block size includes a radix that is not a power of 2 is provided. The method includes receiving a delta value at an input of the twiddle factor unit, the delta value representing a ratio of a modified maximum bock size to the block size, wherein the modified maximum block size is a power of 2. The method further includes using the delta value to obtain a step size for generating indices of a look-up table stored within the twiddle factor unit, wherein the look-up table stores real and imaginary components of twiddle factors corresponding to a set of block sizes of the DFT.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Nucleotide sequence and method for identifying radix cyathulae genunie medicinal materials
ActiveCN101445827AEasy to distinguishQuick distinctionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMedicinal herbsMedicine
The invention discloses a nucleotide sequence for identifying radix cyathulae genunie medicinal materials; the sequence is rDNA ITS sequence from genuine radix cyathulae (white bidentata) used for identifying radix cyathulae genunie medicinal materials; analyzing the hereditary feature of radix cyathulae germ plasm resource on DNA level supplies effective molecular marker for differentiating the genuine radix cyathulae, mixed radix cyathulae and radix achyranthis bidentatae and so on, and is good for truth identification of kinds and quality identification of the radix cyathulae genunie medicinal materials and filtering the better kinds. Furthermore, the invention provides a method of identifying radix cyathulae genunie medicinal materials using the nucleotide sequence; the method has simple and accessible operation and can make a purpose of conveniently, rapidly, objectively and exactly differentiating the radix cyathulae genunie medicinal materials with other achyranthes materials.
Owner:雅安三九中药材科技产业化有限公司
Pipeline-based reconfigurable mixed-radix FFT processor
ActiveUS7849123B2Low costShorten the timeDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Block floating-point
The present invention discloses a fast Fourier transform (FFT) processor based on multiple-path delay commutator architecture. A pipelined architecture is used and is divided into 4 stages with 8 parallel data path. Yet, only three physical computation stages are implemented. The process or uses the block floating point method to maintain the signal-to-noise ratio. Internal storage elements are required in the method to hold and switch intermediate data. With good circuit partition, the storage elements can adjust their capacity for different modes, from 16-point to 4096-point FFTs, by turning on or turning off the storage elements.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
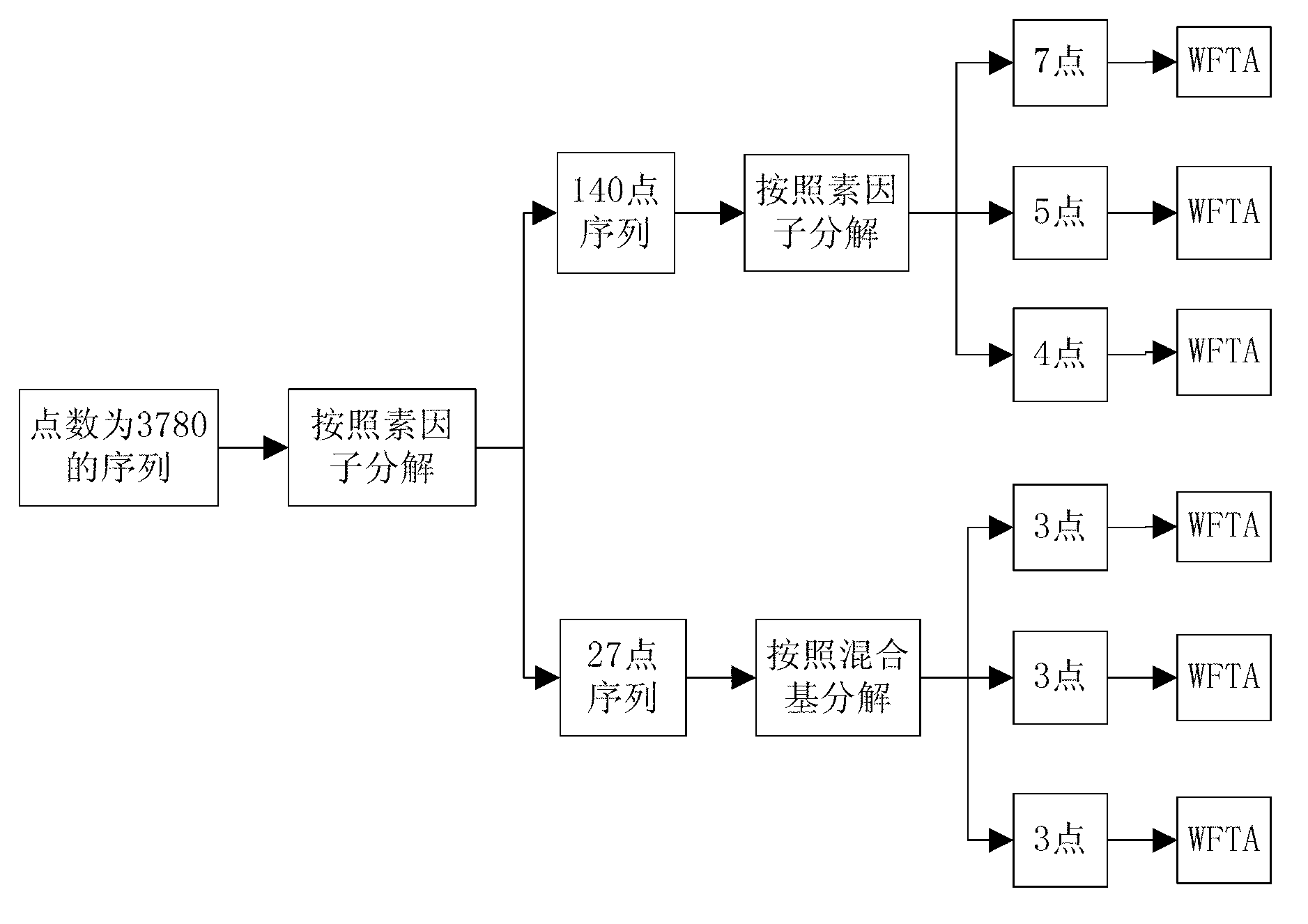
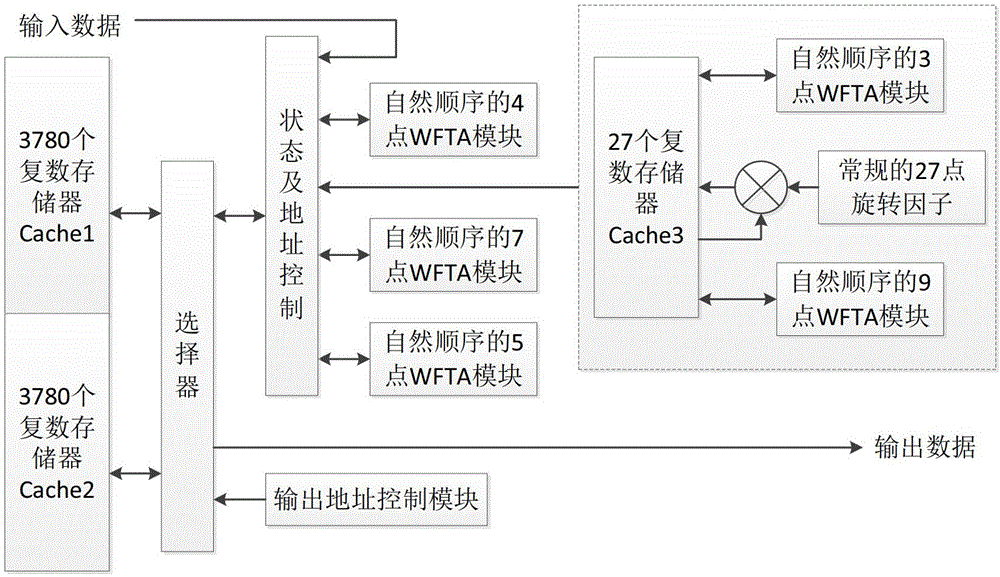
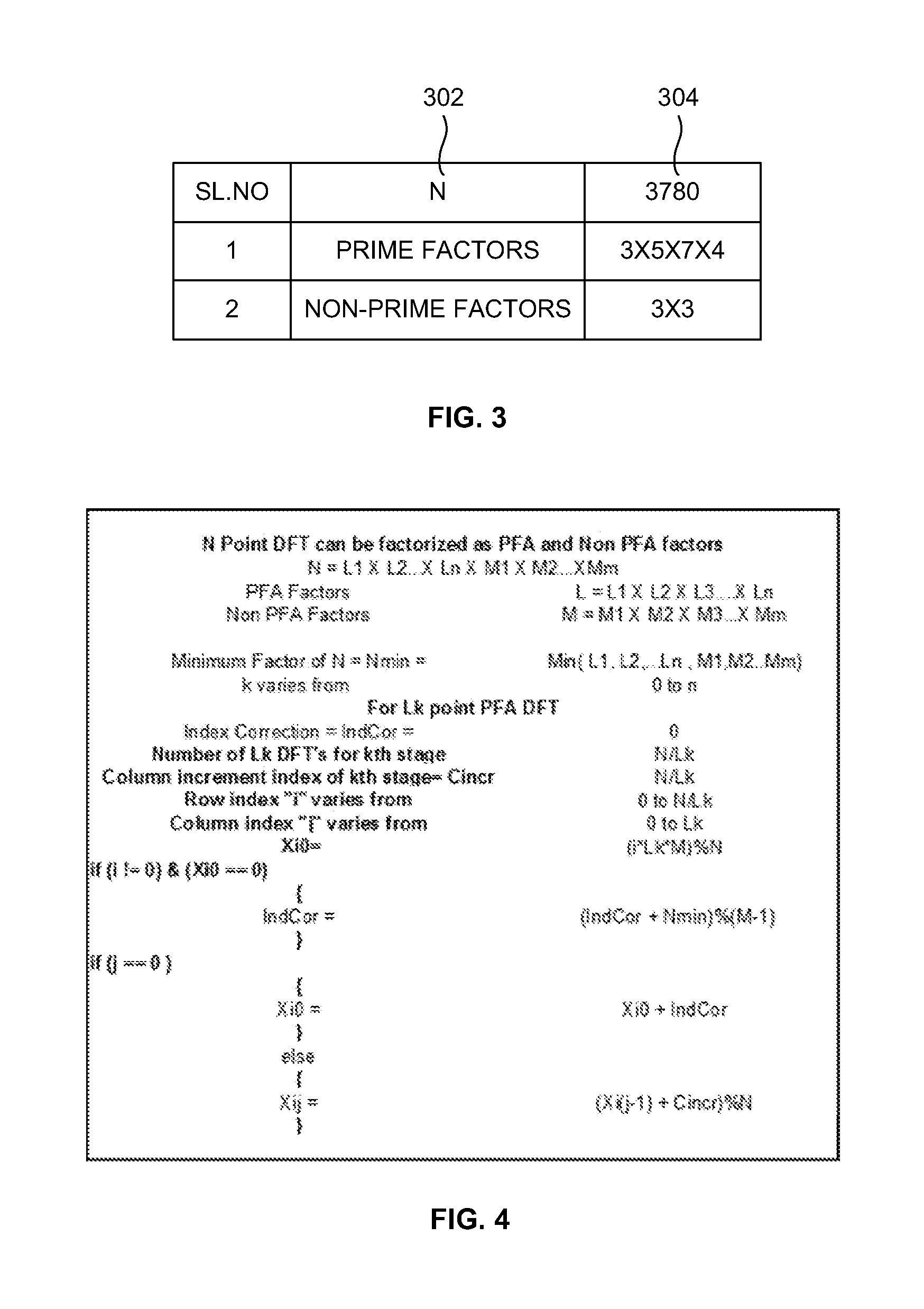
High-precision processing device and high-precision processing method for 3780-point FFT (fast Fourier transform) by sequential output
The invention provides a high-precision processing device for 3780-point FFT (fast Fourier transform) by sequential output. The high-precision processing device for 3780-point FFT by sequential output is characterized in that the device decomposes 3780-point FFT to 4X5X7X27 by prime factors according to a prime factor algorithm, achieves high-precision FFT operation according to the small point operation sequence of 4 points, 3 points, 9 points, 7 points and 5 points and achieves conventional FFT operation of 4 points, 5 points, 7 points and 27 points by comprehensively using a WFTA (winograd Fourier transform algorithm) algorithm and a mixed-radix algorithm; and extra sequencing operation is not needed for an intermediate processing process and a final output process of the device by the aid of a memory of a 'ping-pong' structure and an address control module of a modulus accumulator structure, and accordingly time for processing required storage resources is greatly saved.
Owner:苏州威士达信息科技有限公司
Mixed-radix pipelined fft processor and fft processing method using the same
InactiveUS20140365547A1Easy to handleImprove throughputDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsIndex mappingParallel computing
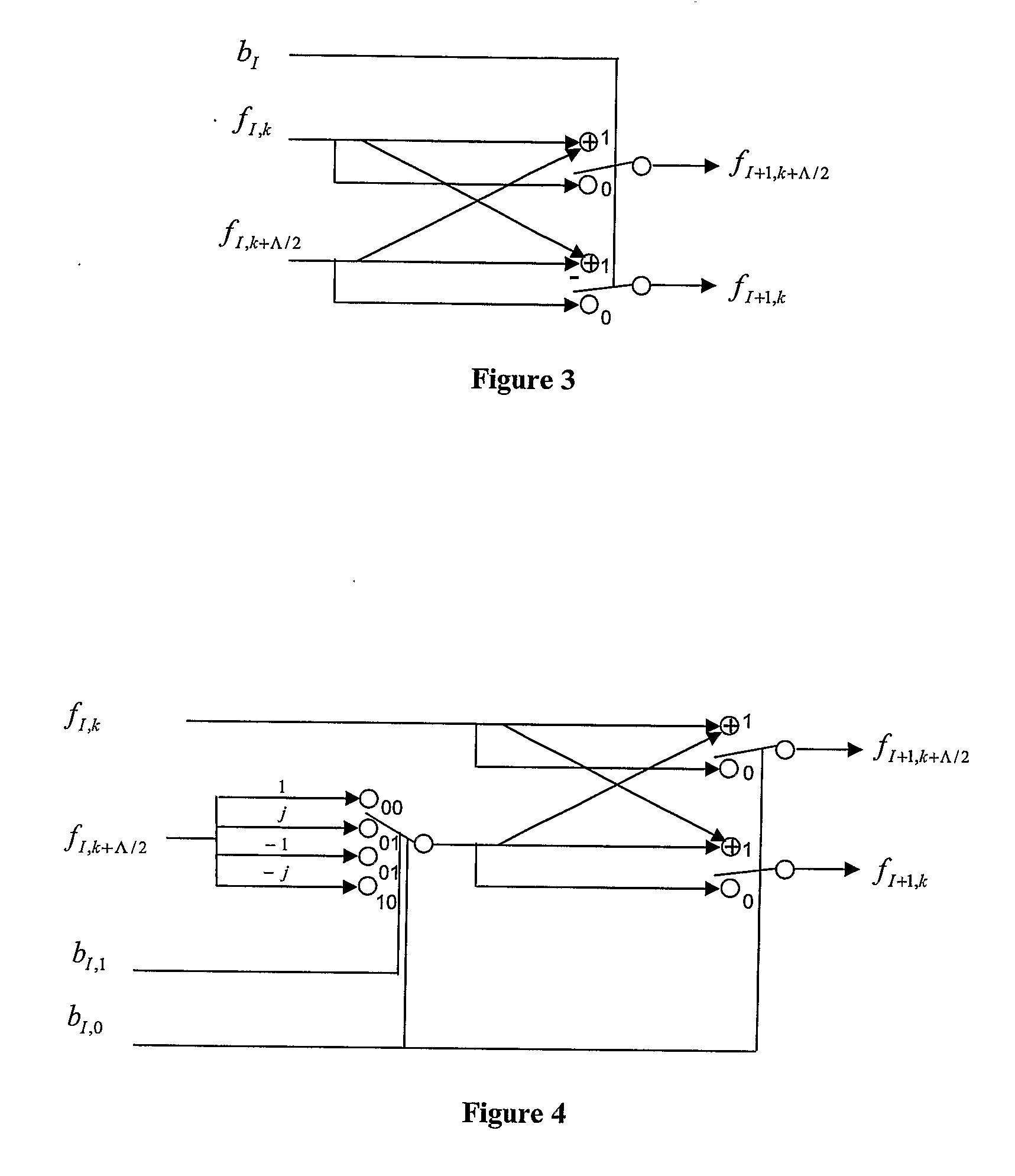
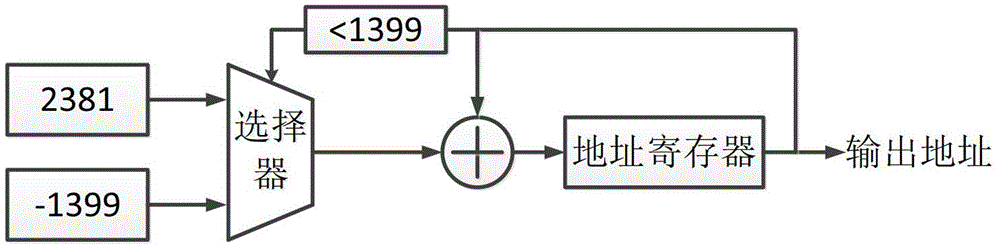
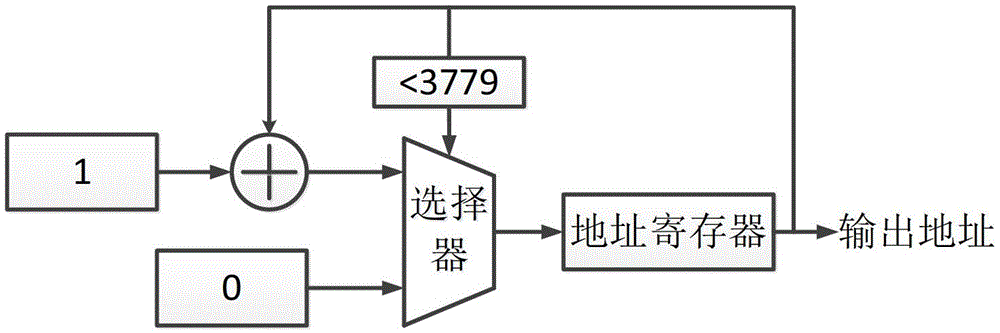
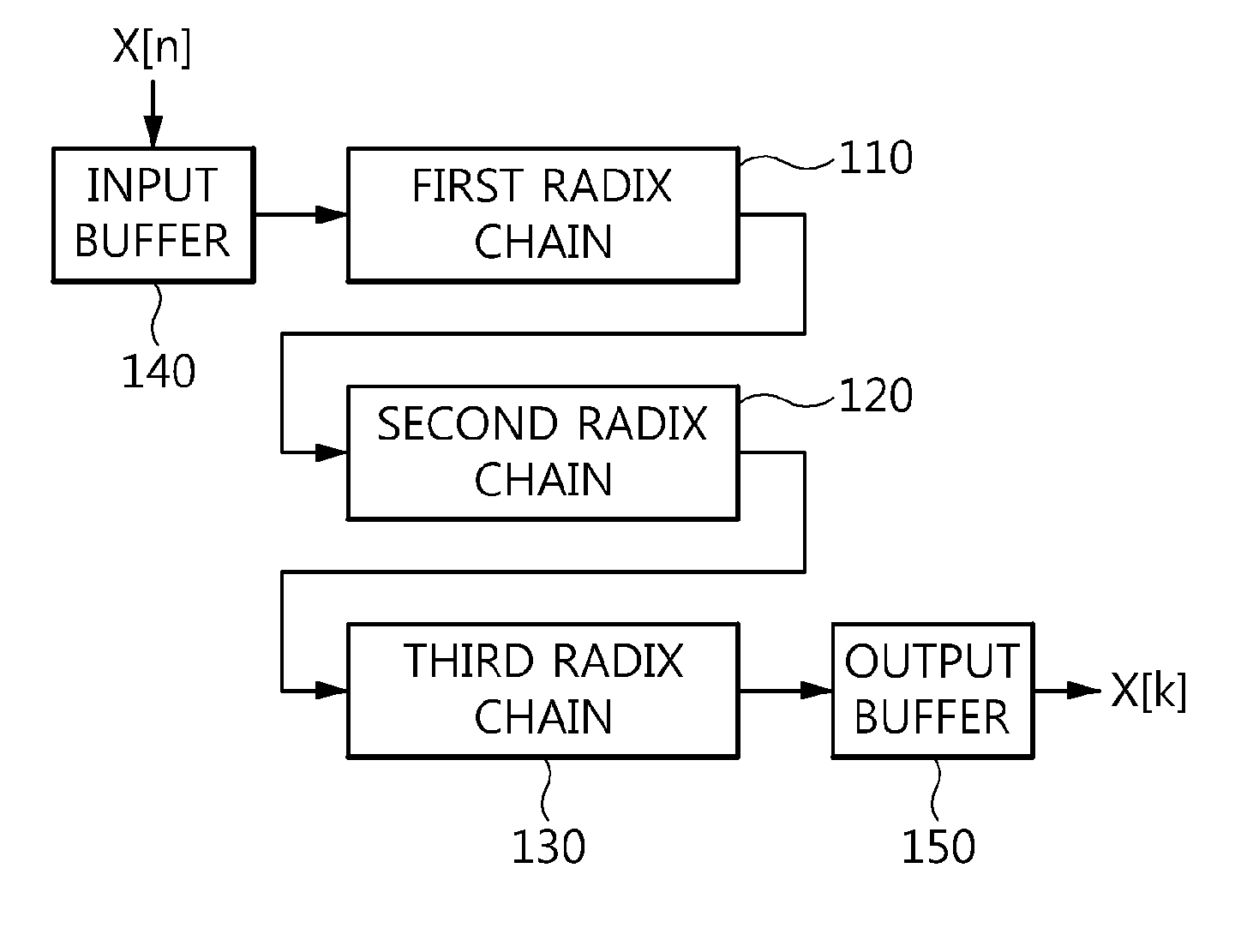
Disclosed herein are a mixed-radix pipelined Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) processor and an FFT processing method using the same. The mixed-radix pipelined Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) processor includes a first radix chain, a second radix chain, an input buffer, and an output buffer. The first radix chain includes first radix processors that are connected in series to each other. The second radix chain includes second radix processors that are connected in series to each other, and is connected in series to the first radix chain. The input buffer performs index mapping on a sequence input to the first radix chain. The output buffer generates a final FFT output by performing index mapping on a sequence generated using outputs of one or more of the first and second radix chains.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Techniques for Improving the Efficiency of Mixed Radix Fast Fourier Transform
ActiveUS20140089366A1Efficient implementation100% utilization of the vector engineModulated-carrier systemsDigital computer detailsFactor baseMemory address
Techniques for implementing mixed-radix FFT on SIMD vector processors efficiently for the latest standard in wireless communication technology by dynamically reordering stages are provided. In one aspect, a mixed-radix FFT implementation method for vector processors is provided which includes the following steps. Input data is decomposed into segments of factors based on a size of the input data, wherein the decomposing is performed in one or more stages, and wherein at each of the stages the input data is processed in blocks using one or more FFT butterfly computations for each of the blocks. The stages in which the decomposing is performed are reordered to insure complete utilization of the vector processors. The butterfly computations for one or more of the blocks are reordered to insure that the input data have memory addresses which are next to each other and contiguous.
Owner:IBM CORP
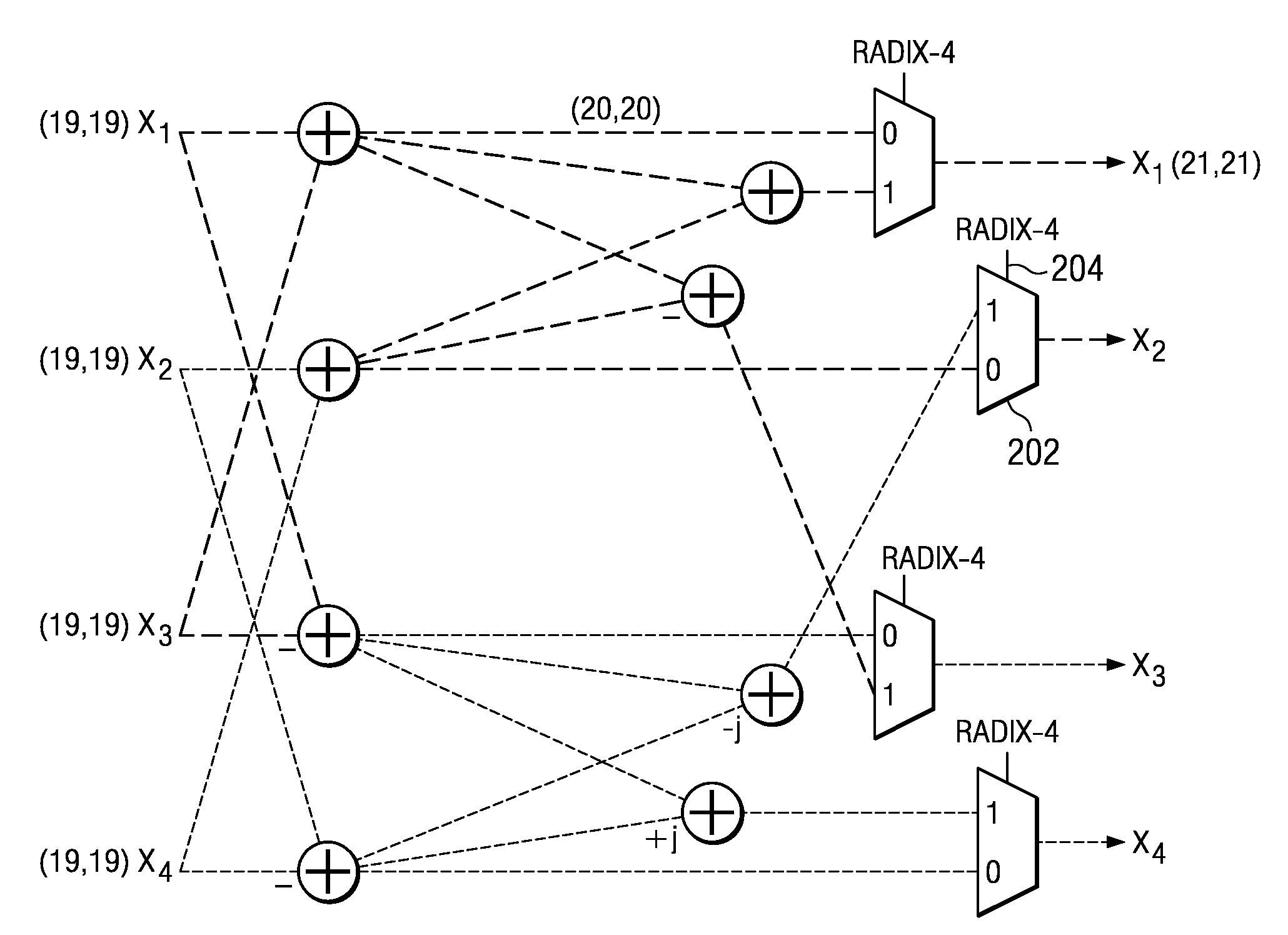
System and method for optimizing mixed radix fast fourier transform and inverse fast fourier transform
ActiveUS20170103042A1Maximize Bandwidth UtilizationComplex mathematical operationsProcessor registerAddress generator
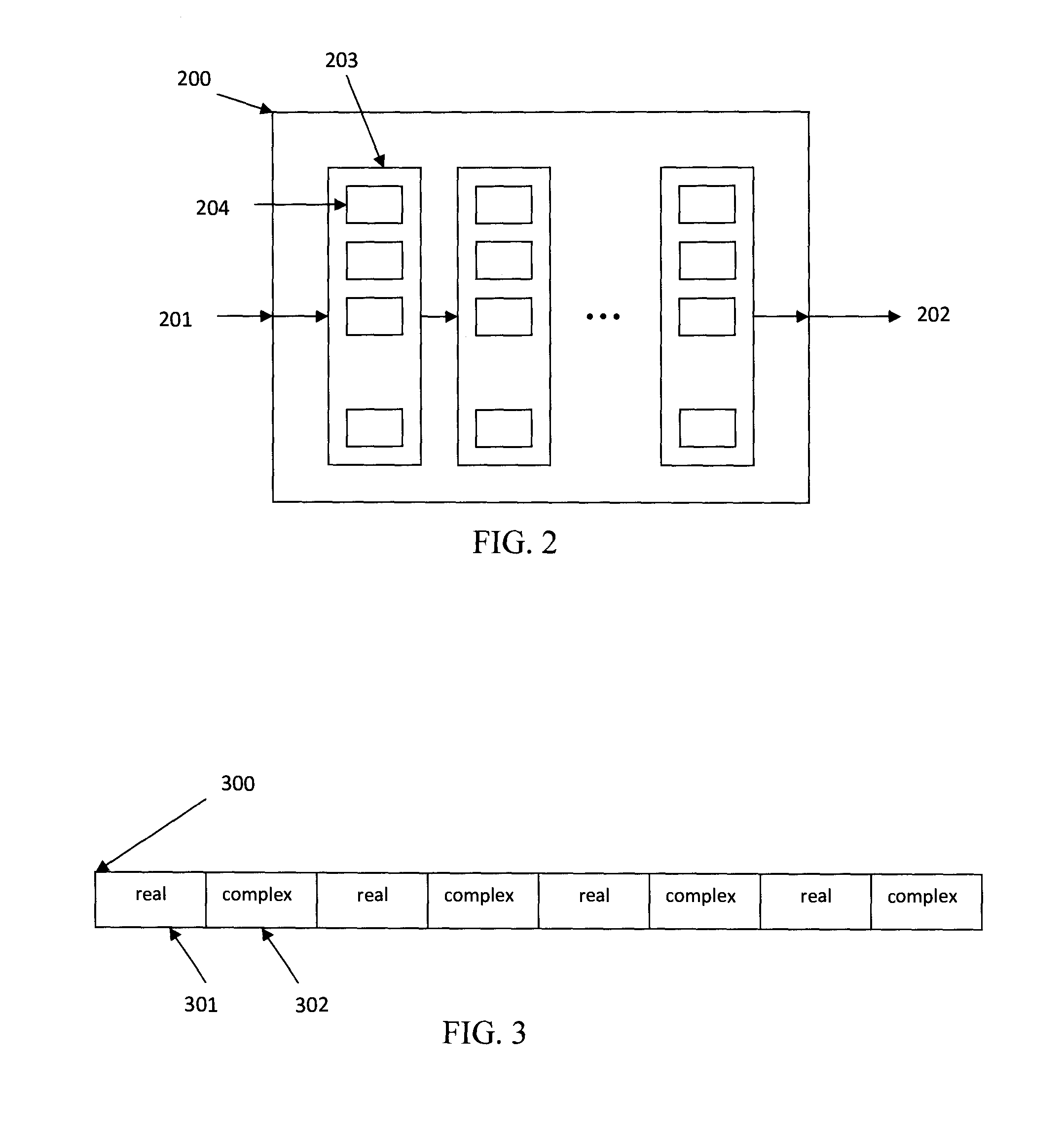
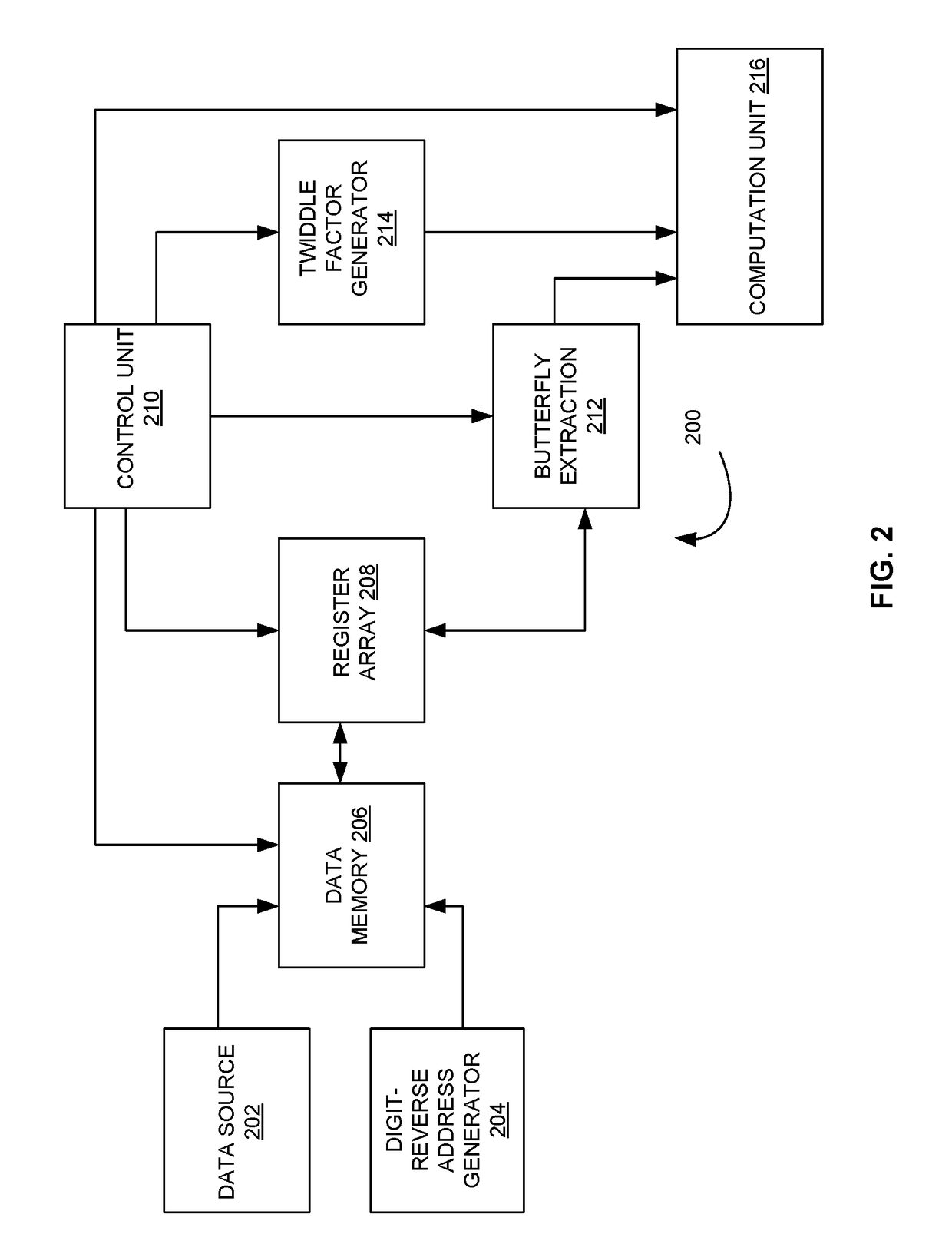
A system for implementing a mixed radix fast fourier transformation is disclosed. The system includes a data source 202, a digit-reverse address generator 204, a data memory 206, a register array 208, a control unit 210, a butterfly extraction unit 212, a twiddle factor generator 214, and a computation unit 216. The data source 202 provides input data. The digit reverse address generator 204 processes the input data (i) to generate a digit reverse index and performs a digits reverse address calculation. The data memory 206 stores the input data. The register array 208 includes one or more registers that are configured to cache multiple data words. The control unit 210 includes of identifying butterfly operations and generate addresses for fetching / storing data. The butterfly extraction unit 212 extracts data samples. The twiddle factor generator 214 generates and outputs a twiddle factors based on the current radix and radix configuration. The computation unit 216 performs twiddle factor multiplications and the butterfly operations for current radix.
Owner:SIGNALCHIP INNOVATIONS
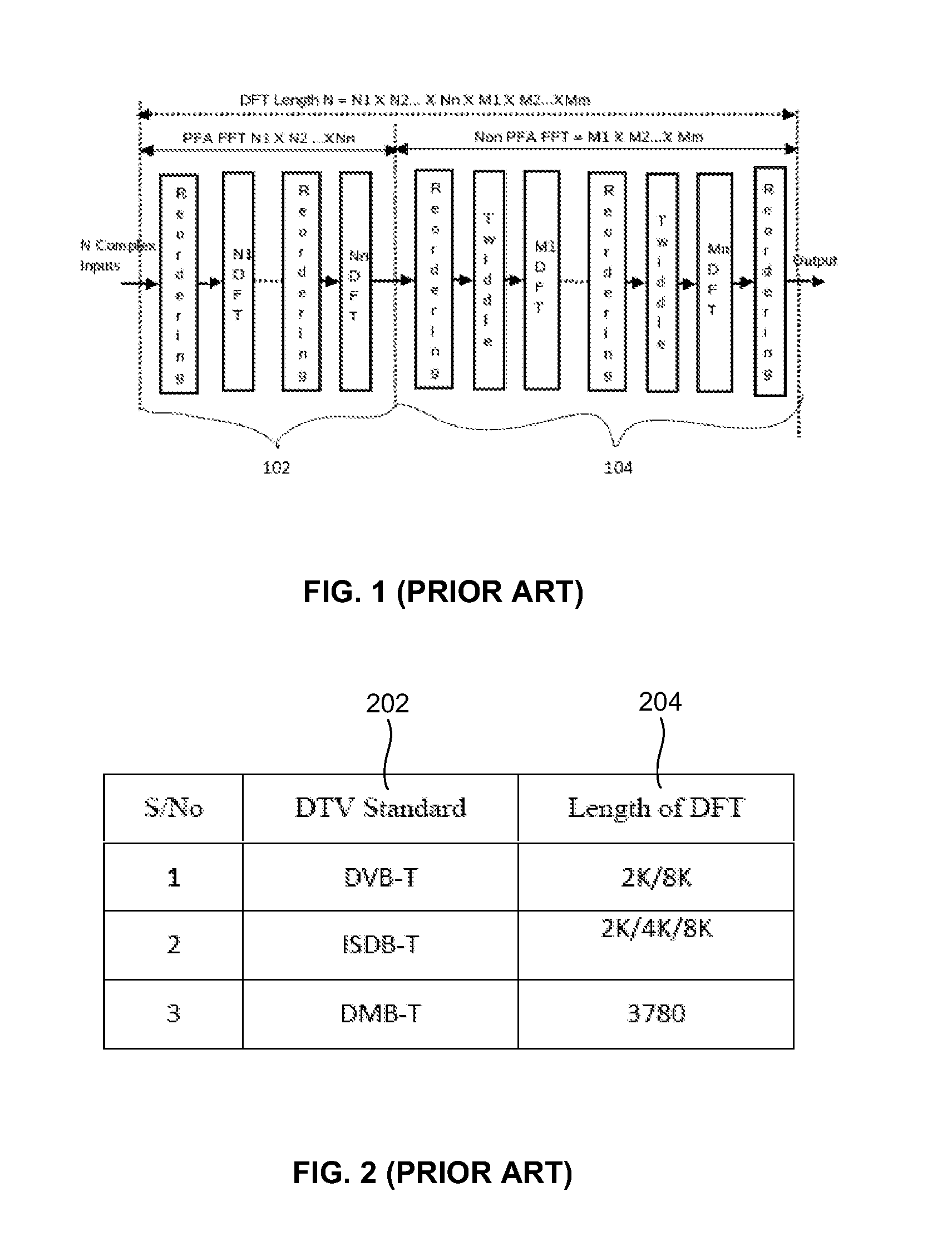
Index Generation Scheme for Prime Factor Algorithm Based Mixed Radix Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
ActiveUS20120254274A1Reduce memory requirementsDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsFourier transform on finite groupsDiscrete Fourier transform
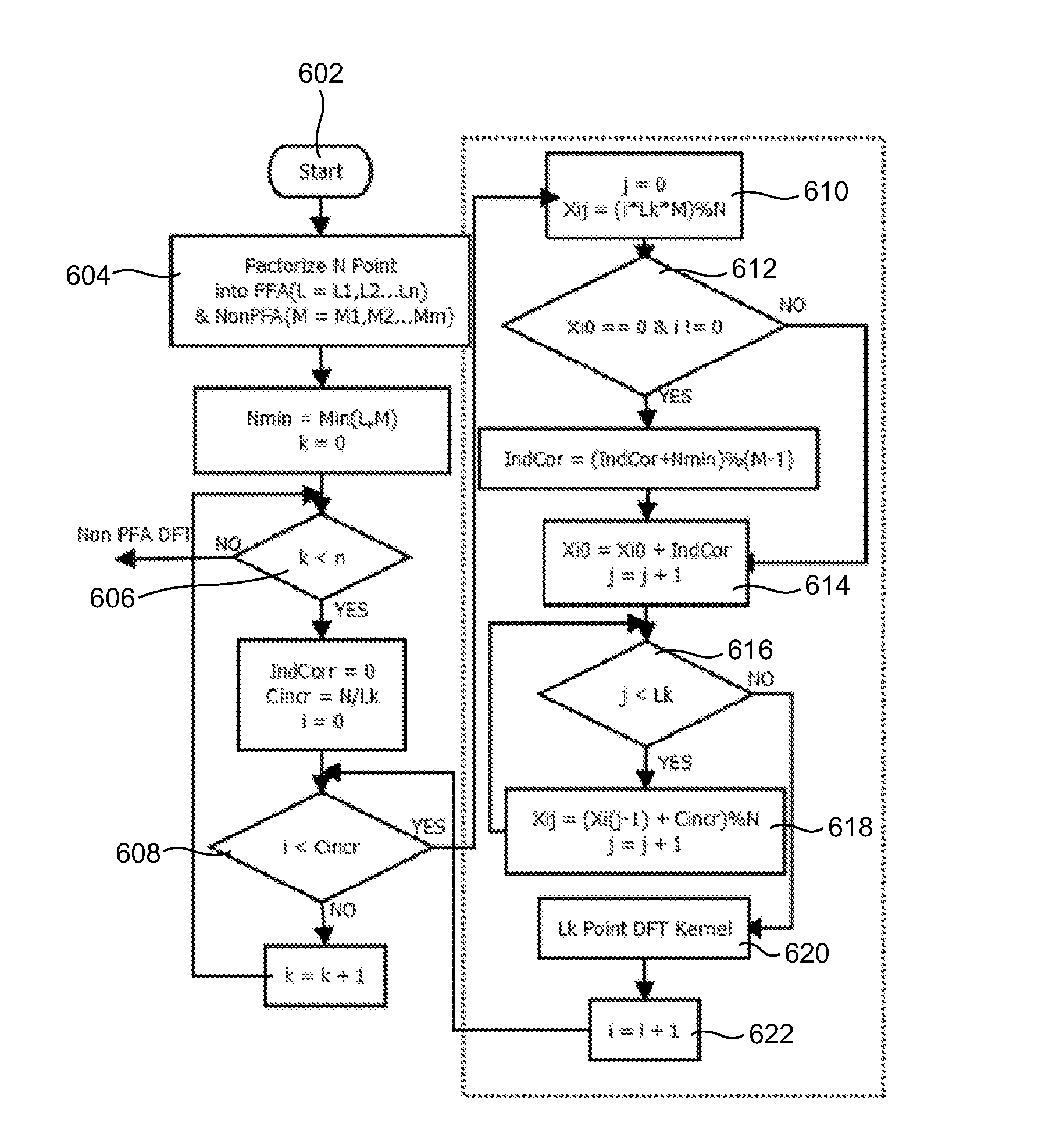
In one embodiment, a processor performs a method of generating pipelined data read indexes and data write indexes for a Prime Factor Algorithm (PFA) Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) without look-up tables. The processor is adapted to factorize an ‘N’ point PFA DFT into one or more mutually prime factors and zero or more non-prime factors, calculate a 0th column index for an ith row (Xi0), calculate an IndCor when the value of Xi0 equals zero and when a row number (i) does not equal zero, calculate Xij, generate the data read indexes, perform a DFT kernel computation on Lk point for the mutually prime factors and the non-prime factors, and generate the data write indexes for the mutually prime factors and the non-prime factors. Xij represents ith row and jth column of 2D input Buffer and enables a selection of a linear index from the 2D input buffer.
Owner:SAANKHYA LABS PVT
Cryptographic system configured to perform a mixed radix conversion with a priori defined statistical artifacts
A cryptographic system (CS) is provided. The CS (800) comprises a data stream receiving means (DSRM), a generator (702), a mixed radix converter (MRC) and an encryptor (908). The DSRM (902) is configured to receive a data stream (DS). The generator is configured to selectively generate a random number sequence (RNS) utilizing a punctured ring structure. The MRC (704) is coupled to the generator and configured to perform a mixed radix conversion to convert the RNS from a first number base to a second number base. The encryptor is coupled to the DSRM and MRC. The encryptor is configured to generate an altered data stream by combining the RNS in the second number base with the DS. The punctured ring structure and the MRC are configured in combination to produce an RNS in the second number base which contains a priori defined statistical artifacts after the mixed radix conversion.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
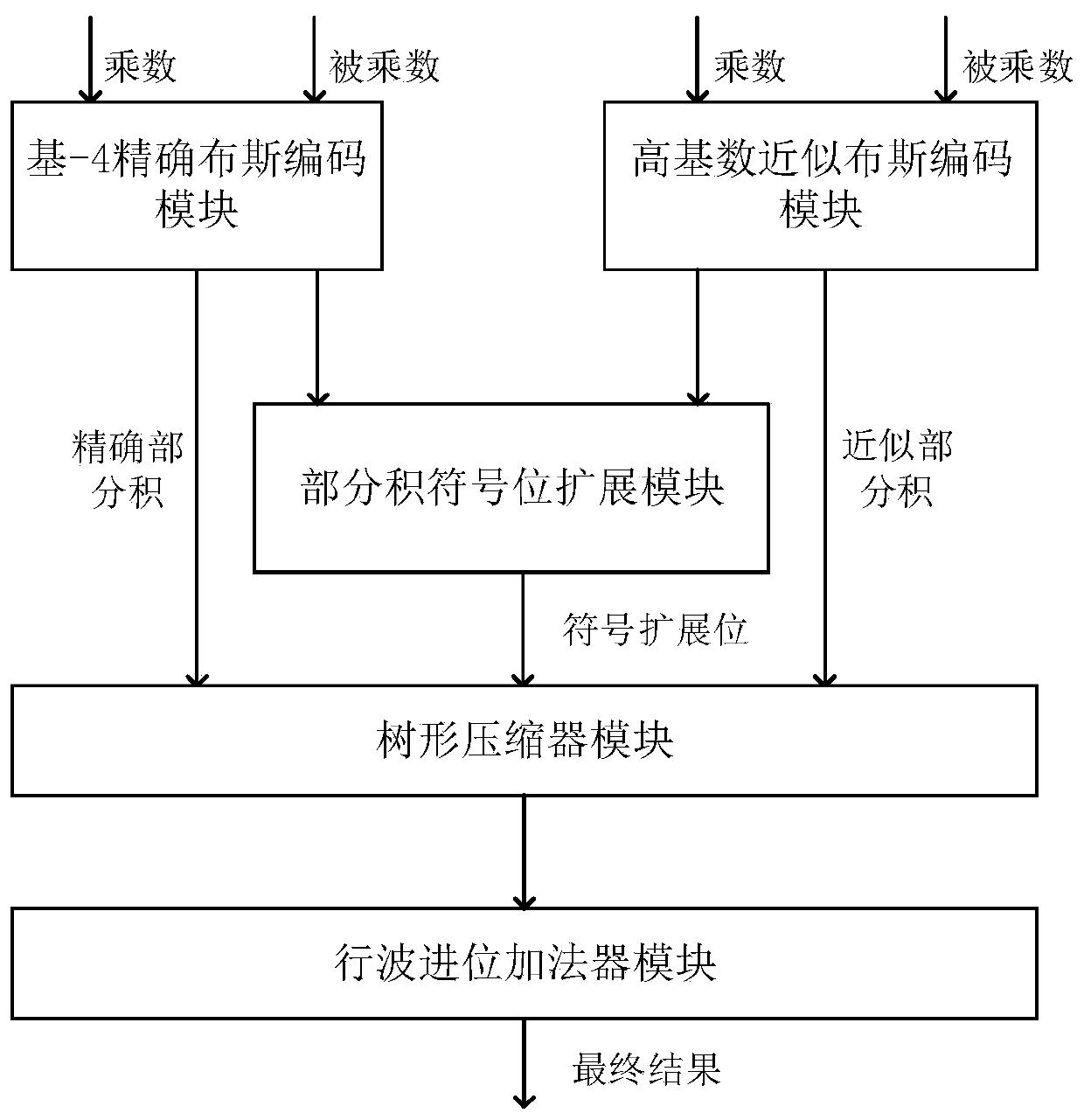
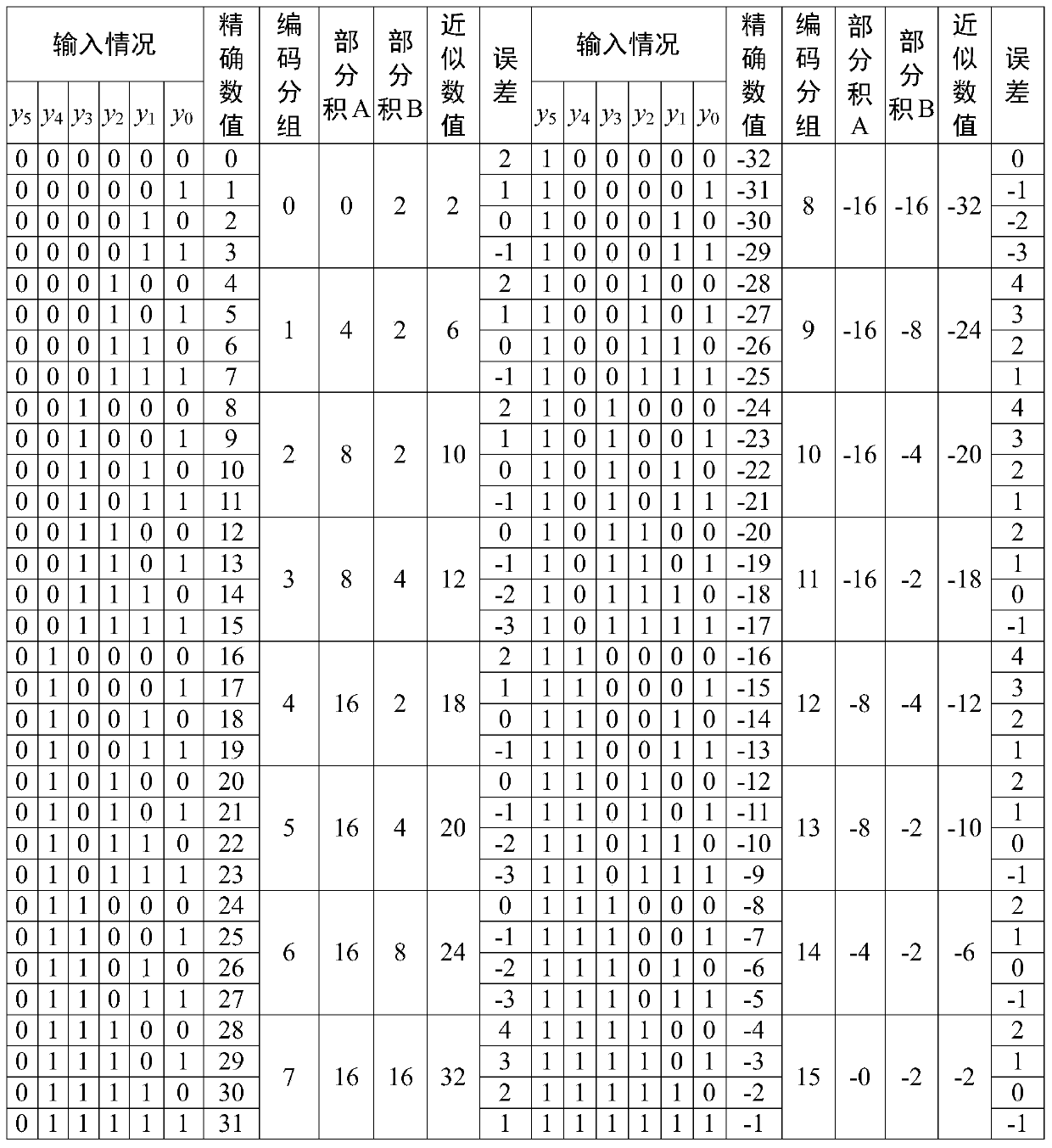
High-cardinal-number approximate Booth encoding method and mixed-cardinal-number Booth encoding approximate multiplier
ActiveCN111488133AReduce hardware complexityReduce structural complexityDigital data processing detailsEnergy efficient computingCode moduleBooth encoding
The invention discloses a high-cardinal-number approximate Booth encoding method and a mixed-cardinal-number Booth encoding approximate multiplier, and belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits. According to the high-cardinal-number approximate Booth encoding method, m bits with lower weights in n-bit multiplicand are encoded, two incomplete partial products A and B are obtained in combination with the n-bit multiplicand, and an approximate encoding result is obtained after addition. The mixed-radix Booth coding approximate multiplier is combined with a precise Booth coding moduleand a high-radix approximate Booth coding module to respectively obtain a precise partial product and an approximate partial product; a partial product array is formed by combining sign extension bitsgenerated by a sign bit extension algorithm provided by the invention, the final calculation result of the approximate multiplier is obtained by compressing and adding the partial product array, andin addition, an error model of the approximate multiplier is deduced to obtain a precision index. The structural complexity of the multiplier is reduced while high calculation precision is guaranteedthrough high-cardinal-number approximate Booth encoding, and hardware design is simplified due to the fact that symbol extension bits avoid accumulation of a large number of identical numbers.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus and method for block interleaving using mixed radix system in MB-OFDM
InactiveUS7511642B1Simple logicReduce complexityCode conversionSecret communicationMulti bandCommunications system
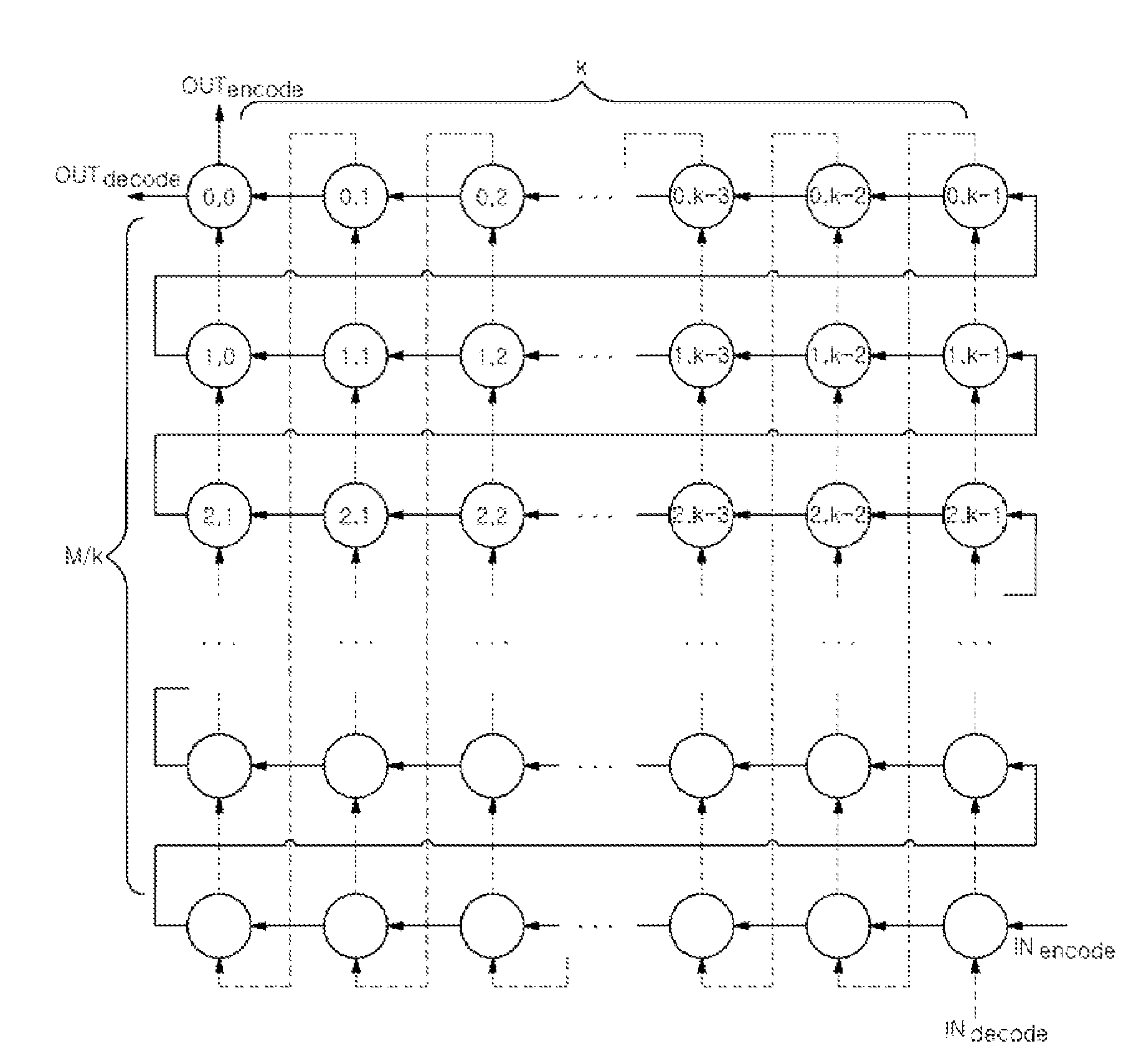
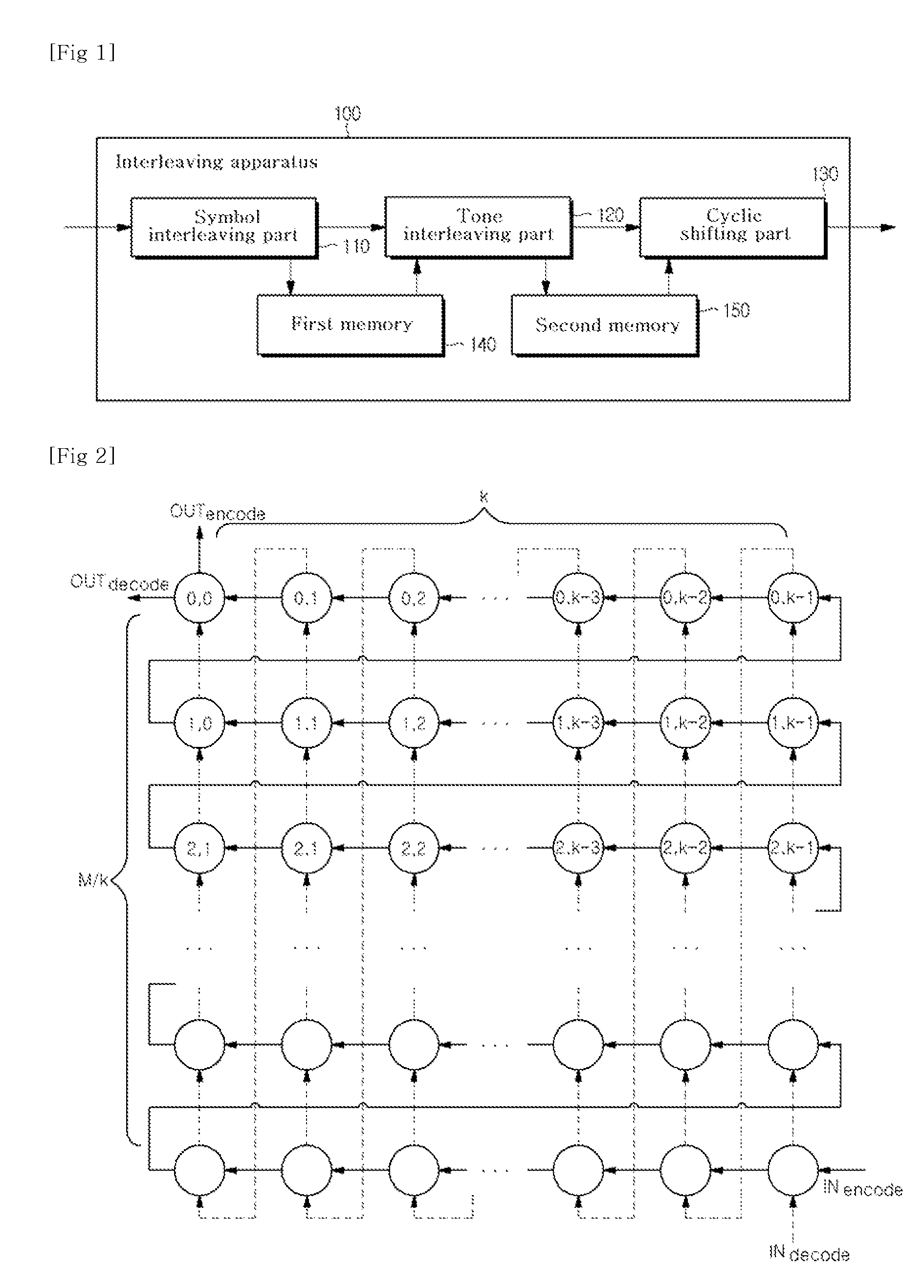
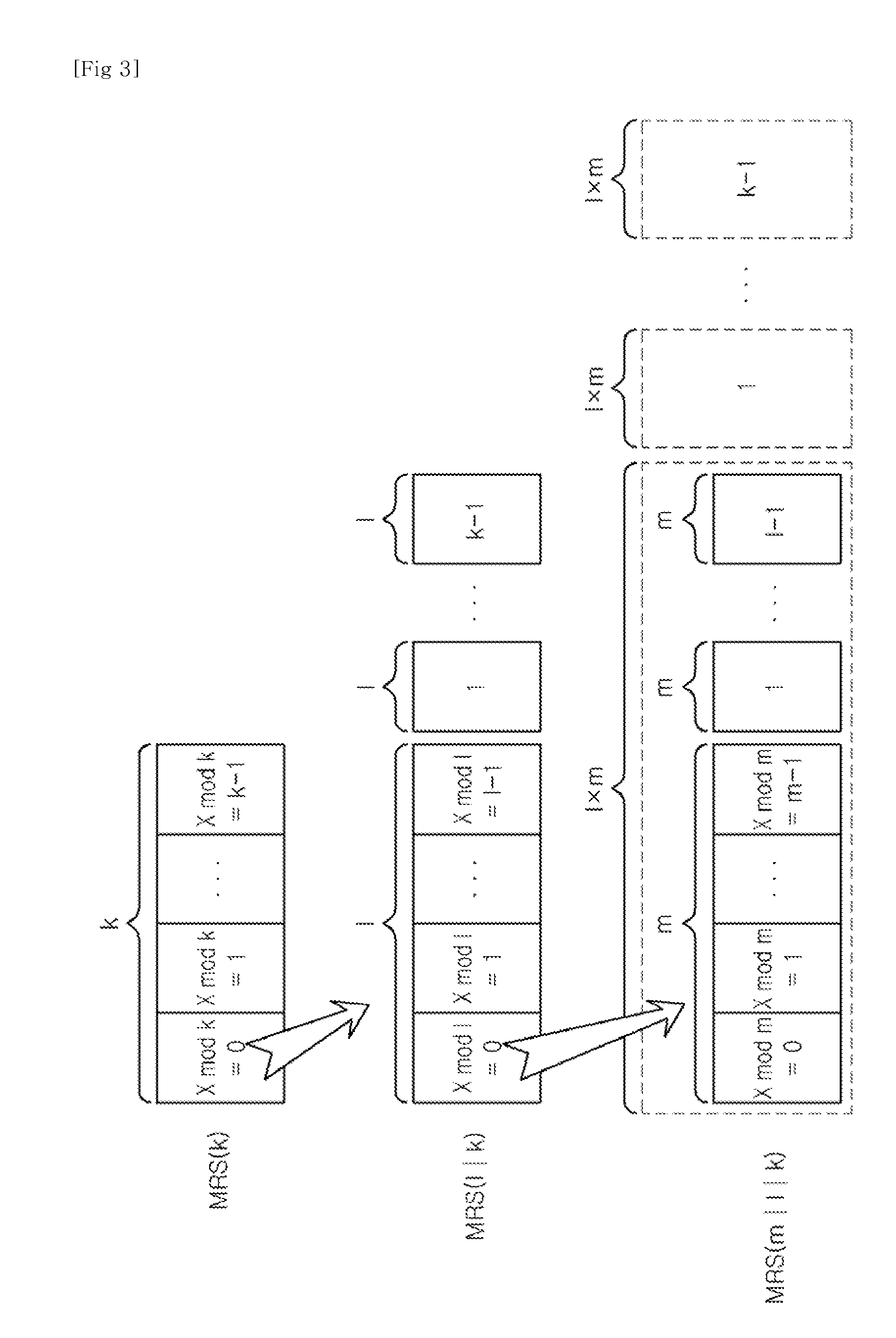
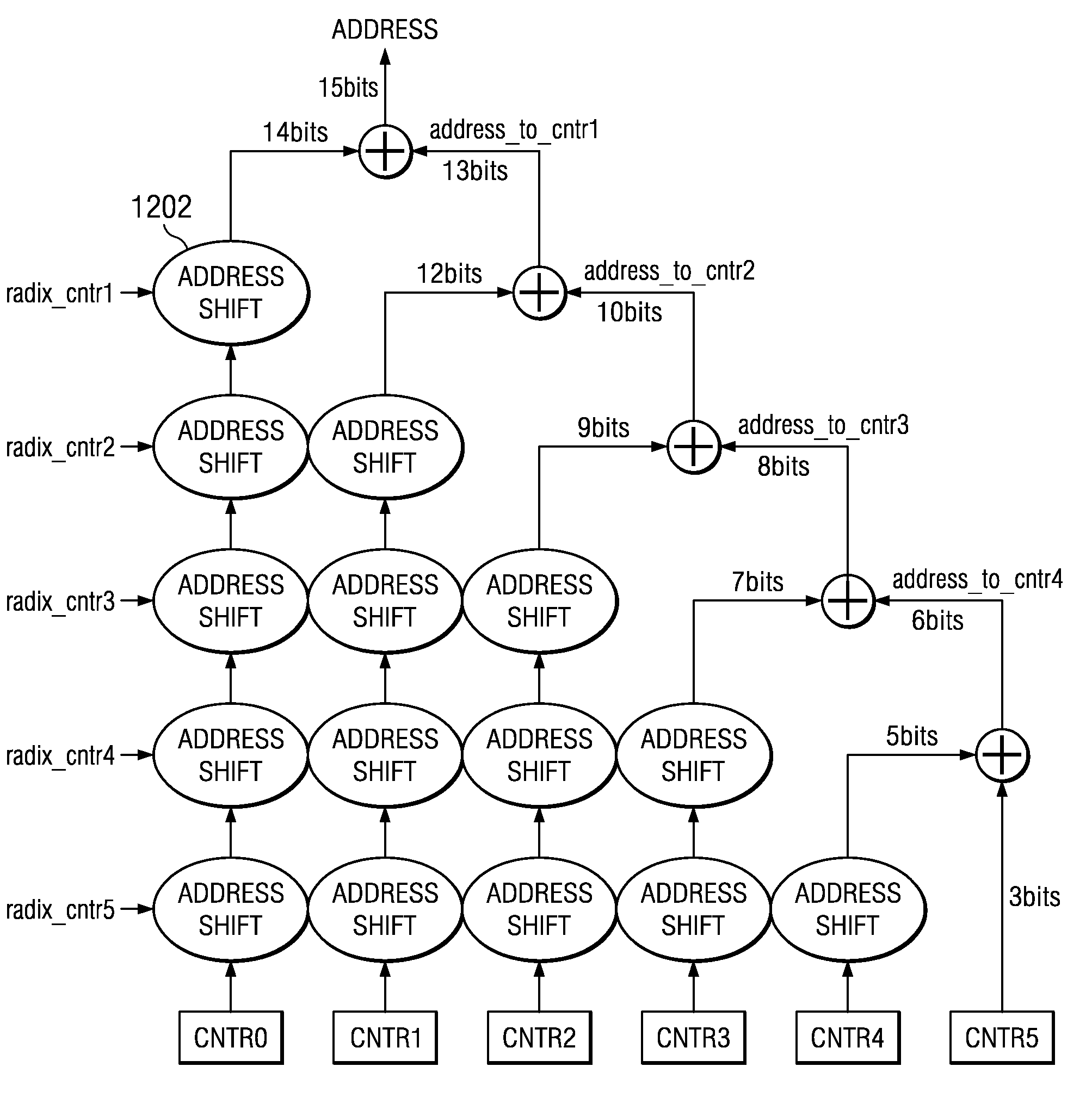
A block interleaving apparatus for block interleaving M-bit input streams to be transferred with a modulus k using a mixed radix system in a multi-band orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system, including an array processor having an array including M cells in which the number of columns is k and the number of rows is M / k. The array processor inputs the input streams from the bottom-right cell up to the top-left last cell in the horizontal direction, and, after the first bit of the input streams reaches the last cell, generates interleaved output streams by changing the output of the array processor from horizontal direction to vertical direction.
Owner:MEWTEL TECH
In-place fast fourier transform processor
An N-point Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) using mixed radix stages with in-place data sample storage may be performed by decomposing N into a product of R sequential mixed radix stages of radix-r(i). N data samples are partitioned into at least B memory banks, where B is equal to a largest radix of the R radix stages. Each input data sample to each radix-r(i) butterfly comes from r(i) different memory banks and the output data samples are written to the same memory locations in the r(i) memory banks. Determining from which memory bank the input data samples and output data samples of the butterflies are stored is done based on the radix size and sequential position of the radix stage. Determining the address of the input data samples and the output data samples within each memory bank is based on the radix size and sequential position of the radix stage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) radix-2-4-8 mixed-radix butterfly operator and application thereof
ActiveCN104657334AReduce resource overheadFlexible useComplex mathematical operationsProduction lineProcessor register
The invention relates to an FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) radix-2-4-8 mixed-radix butterfly operator which comprises a radix-2 unit, a radix-4 unit and a radix-8 unit. The radix-8 unit comprises a prefix operation unit, which is mainly formed by connecting a first complex number adding device with a real operation unit, and the radix-4 unit; the prefix operation unit is connected with the radix-4 unit by a first register; the radix-8 unit, the radix-4 unit and the radix-2 unit are connected in parallel to form a production line architecture. The FFT radix-2-4-8 mixed-radix butterfly operator has the beneficial effects that relative to a complete radix-8 butterfly operator, the FFT radix-2-4-8 mixed-radix butterfly operator is low in resource cost, is more flexible to use and meanwhile, has excellent parallelism for meeting the requirements of a high throughput system; the radix-2-4-8 mixed-radix structure enables the butterfly operator to support the sequence length of a point of an integer power of 2.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com