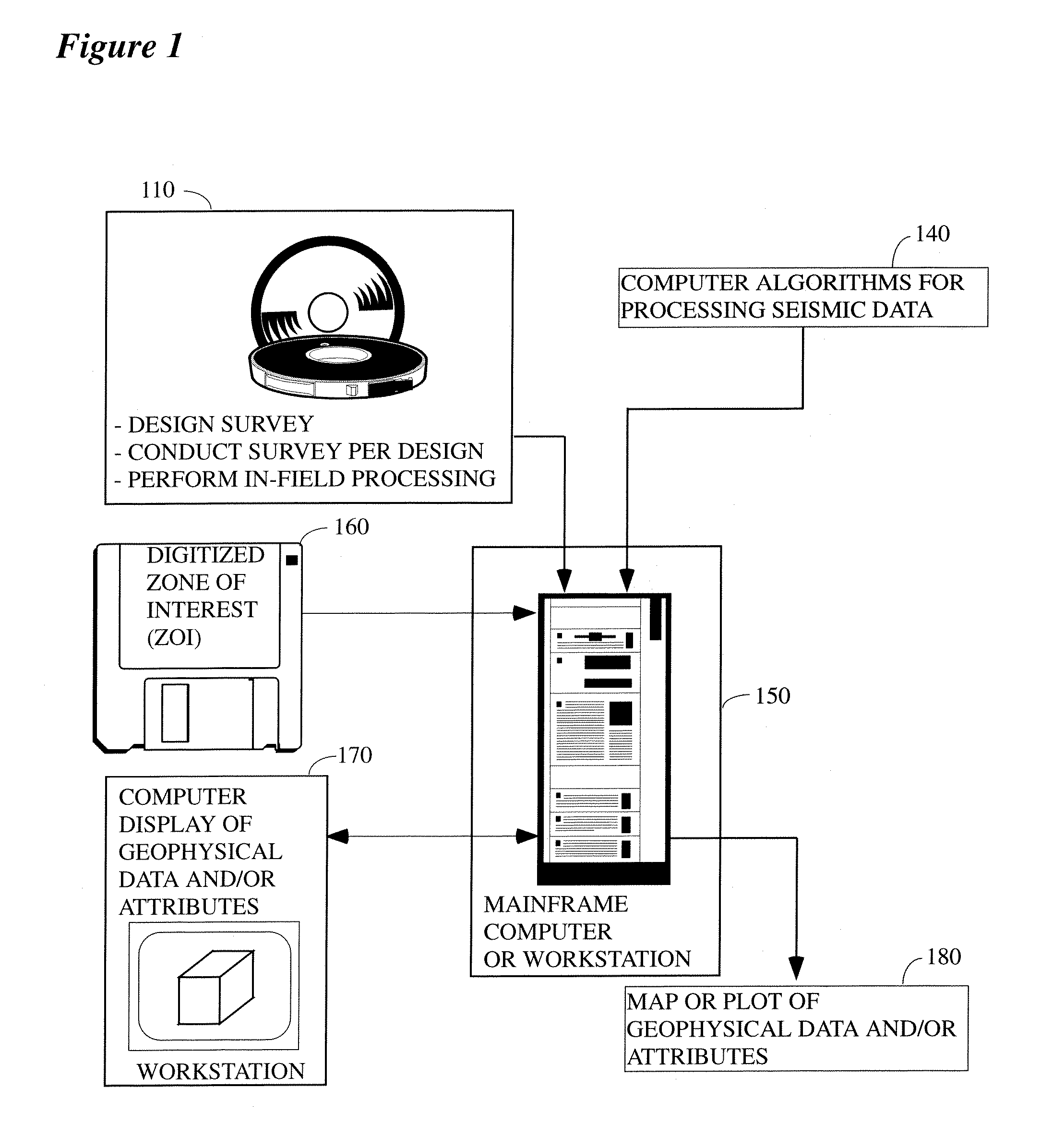
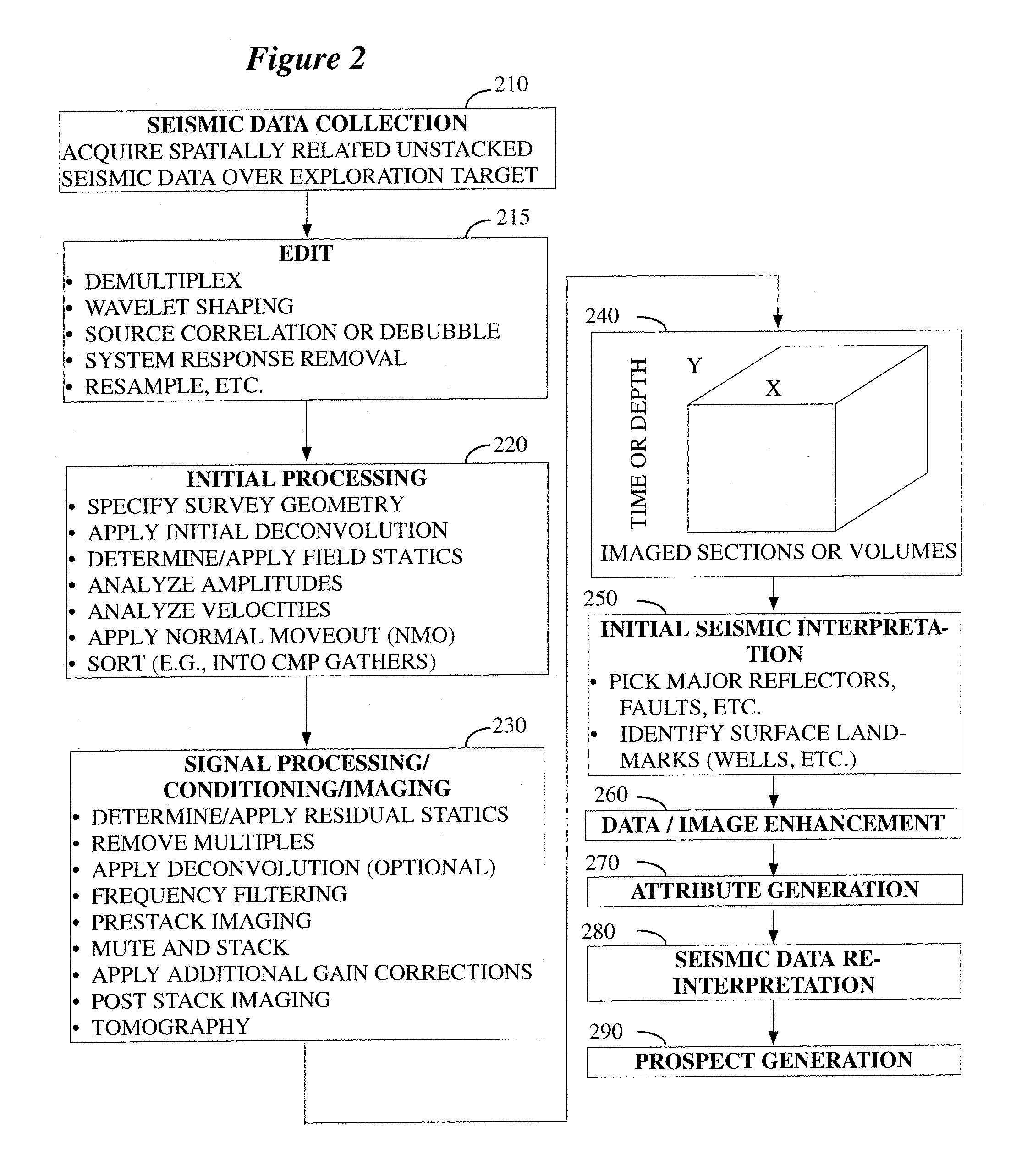
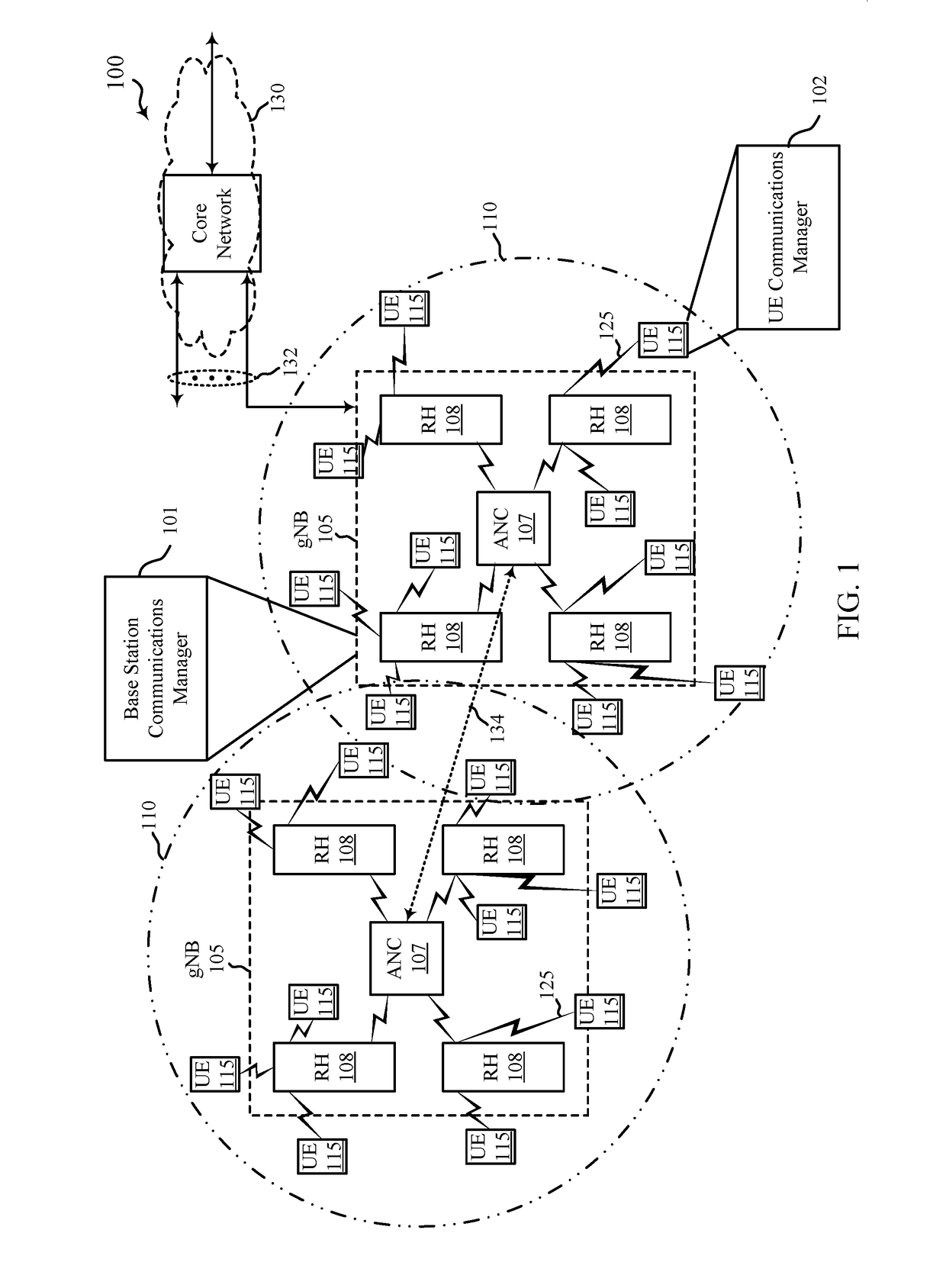
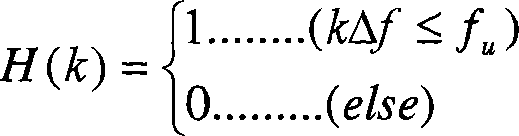Patents
Literature
2012 results about "Discrete Fourier transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced samples of a function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a complex-valued function of frequency. The interval at which the DTFT is sampled is the reciprocal of the duration of the input sequence. An inverse DFT is a Fourier series, using the DTFT samples as coefficients of complex sinusoids at the corresponding DTFT frequencies. It has the same sample-values as the original input sequence. The DFT is therefore said to be a frequency domain representation of the original input sequence. If the original sequence spans all the non-zero values of a function, its DTFT is continuous (and periodic), and the DFT provides discrete samples of one cycle. If the original sequence is one cycle of a periodic function, the DFT provides all the non-zero values of one DTFT cycle.
Separating motion from cardiac signals using second order derivative of the photo-plethysmogram and fast fourier transforms
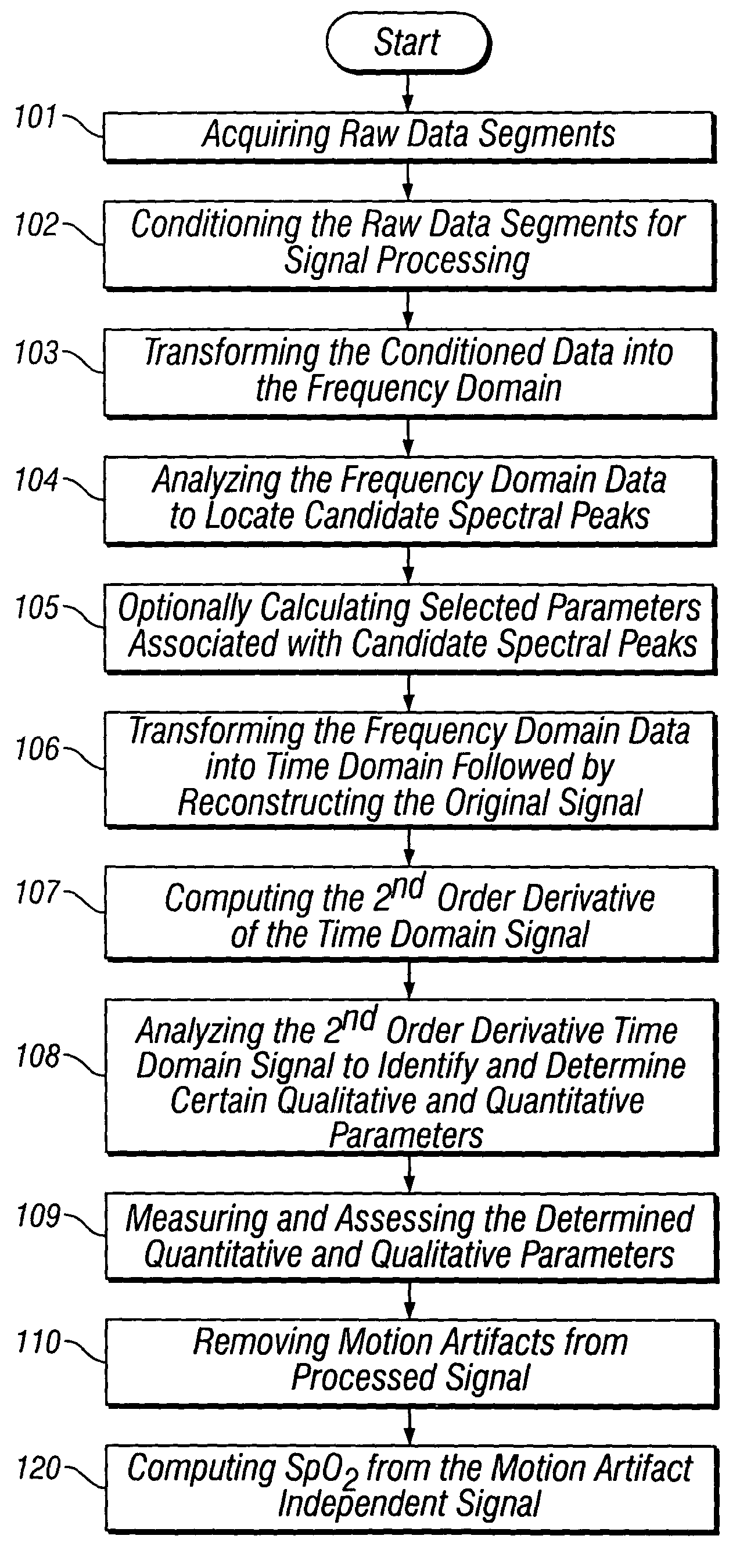
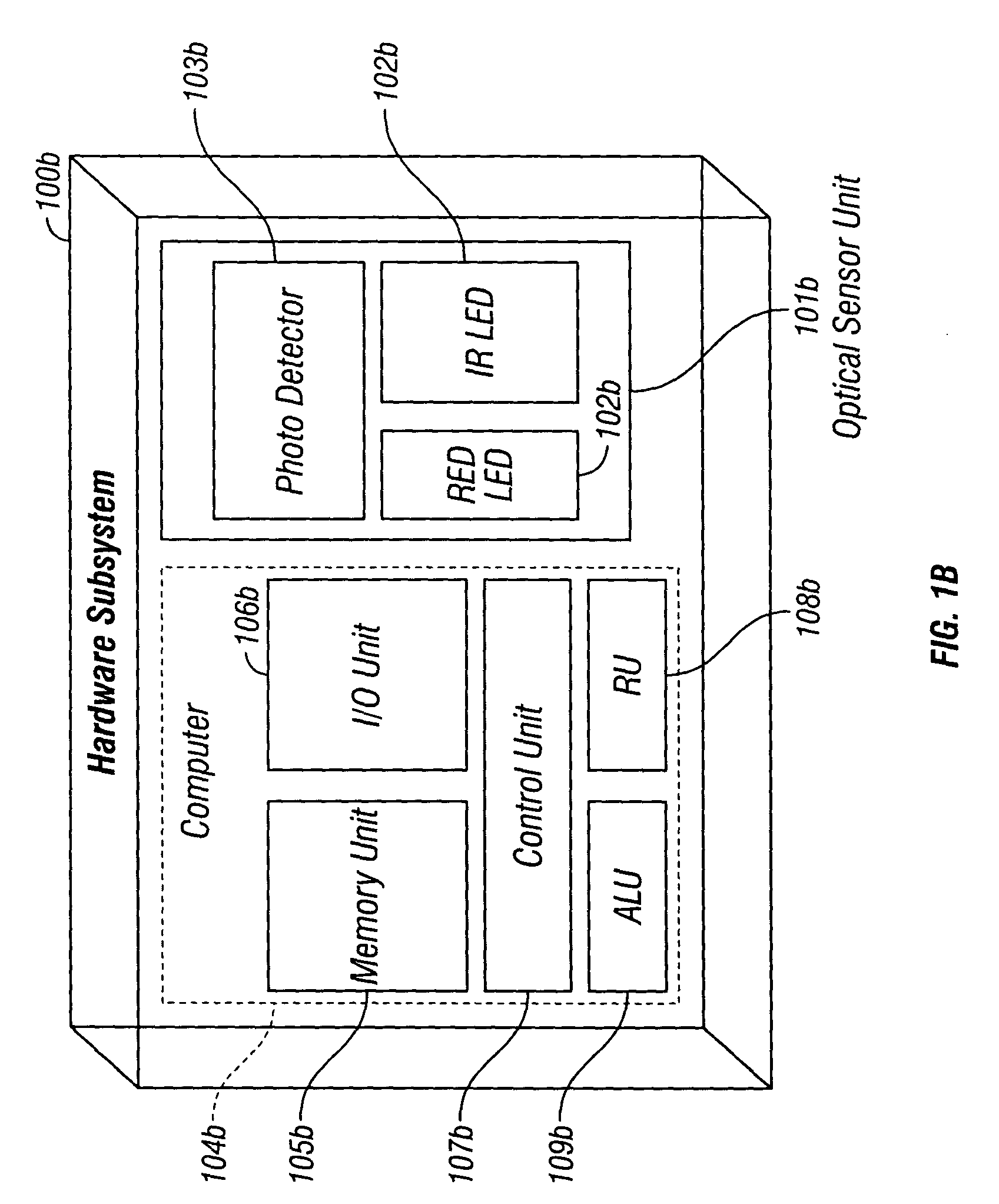
The present invention is directed toward a pulse oximetry system for the determination of a physiological parameter capable of removing motion artifacts from physiological signals comprises a hardware subsystem and a software subsystem. The software subsystem is used in conjunction with the hardware subsystem to perform a method for removing a plurality of motion artifacts from the photo-plethysmographic data and for obtaining a measure of at least one physiological parameter from the data. The method comprises acquiring the raw photo-plethysmographic data, transforming the data into the frequency domain, analyzing the transformed data to locate a series of candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), reconstructing a photo-plethysmographic signal in the time domain with only the candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), computing the second order derivative of the reconstructed photo-plethysmographic signal, analyzing the candidate second order derivative photo-plethysmographic signal to determine the absence or presence of cardiac physiologic signal characteristics, and finally selecting the best physiologic candidate from the series of potential cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics) based upon a second derivative scoring system. This scoring system is preferentially based upon second derivative processing analysis, but can be equally applied using the first, third, fourth or other similar derivative processing analysis.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LLC
Data compression method for use in wellbore and formation characterization
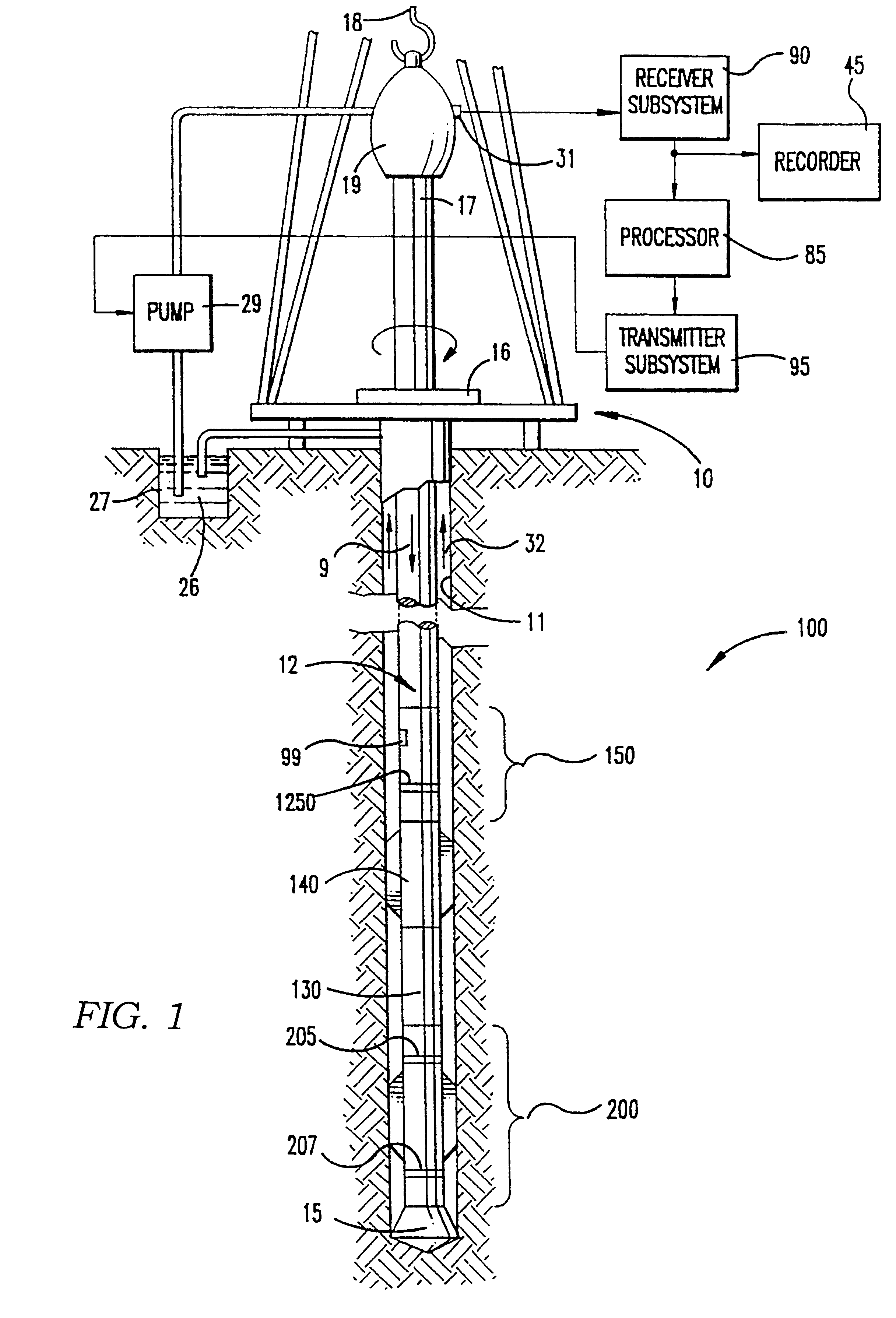
A method is disclosed for compressing a frame of data representing parameter values, a time at which each parameter value was recorded, and an orientation of a sensor at the time each parameter value was recorded. Generally the method includes performing a two-dimensional transform on the data in the orientation domain and in a domain related to the recording time. In one embodiment, the method includes calculating a logarithm of each parameter value. In one embodiment, the 2-D transform includes generating a Fourier transform of the logarithm of the parameter values in the azimuthal domain, generating a discrete cosine transform of the transform coefficients in the time domain. This embodiment includes quantizing the coefficients of the Fourier transform and the discrete cosine transform. One embodiment of the method is adapted to transmit resistivity measurements made by an LWD instrument in pressure modulation telemetry so that while-drilling images of a wellbore can be generated. The one embodiment includes encoding the quantized coefficients, error encoding the encoded coefficients, and applying the error encoded coefficients to the pressure modulation telemetry.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
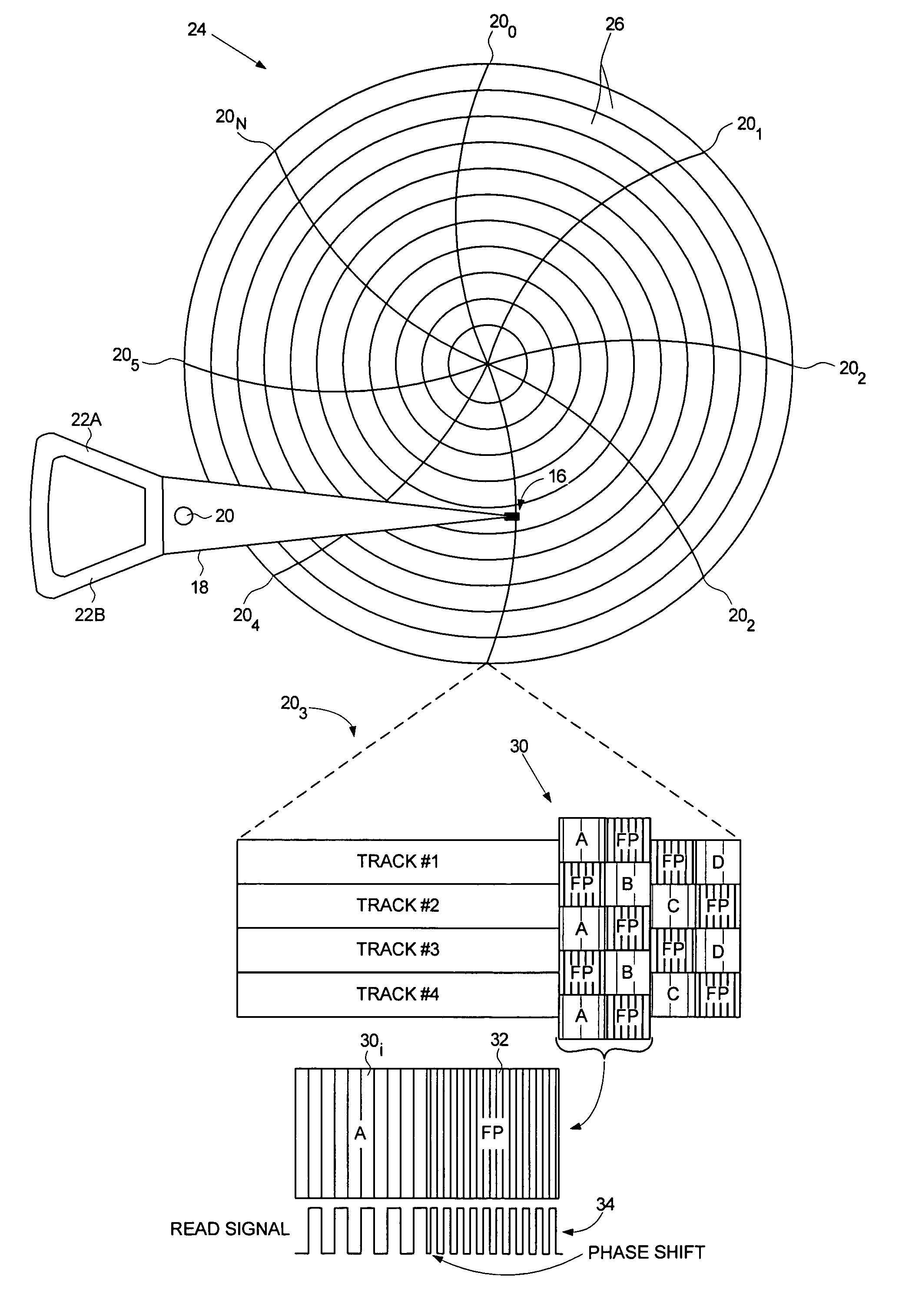
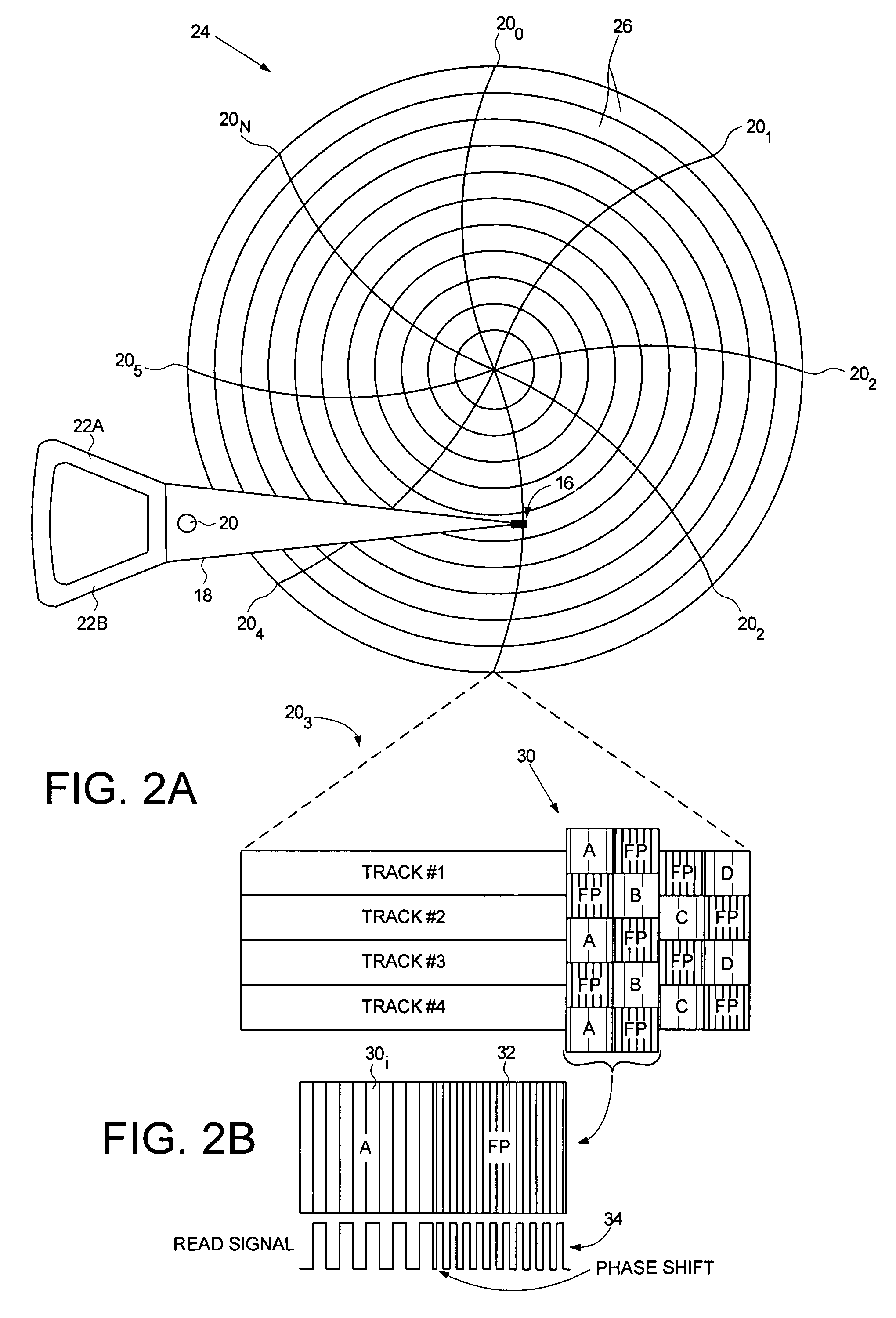
Servo writing a disk drive by overwriting a harmonic frequency fill pattern in the servo burst area
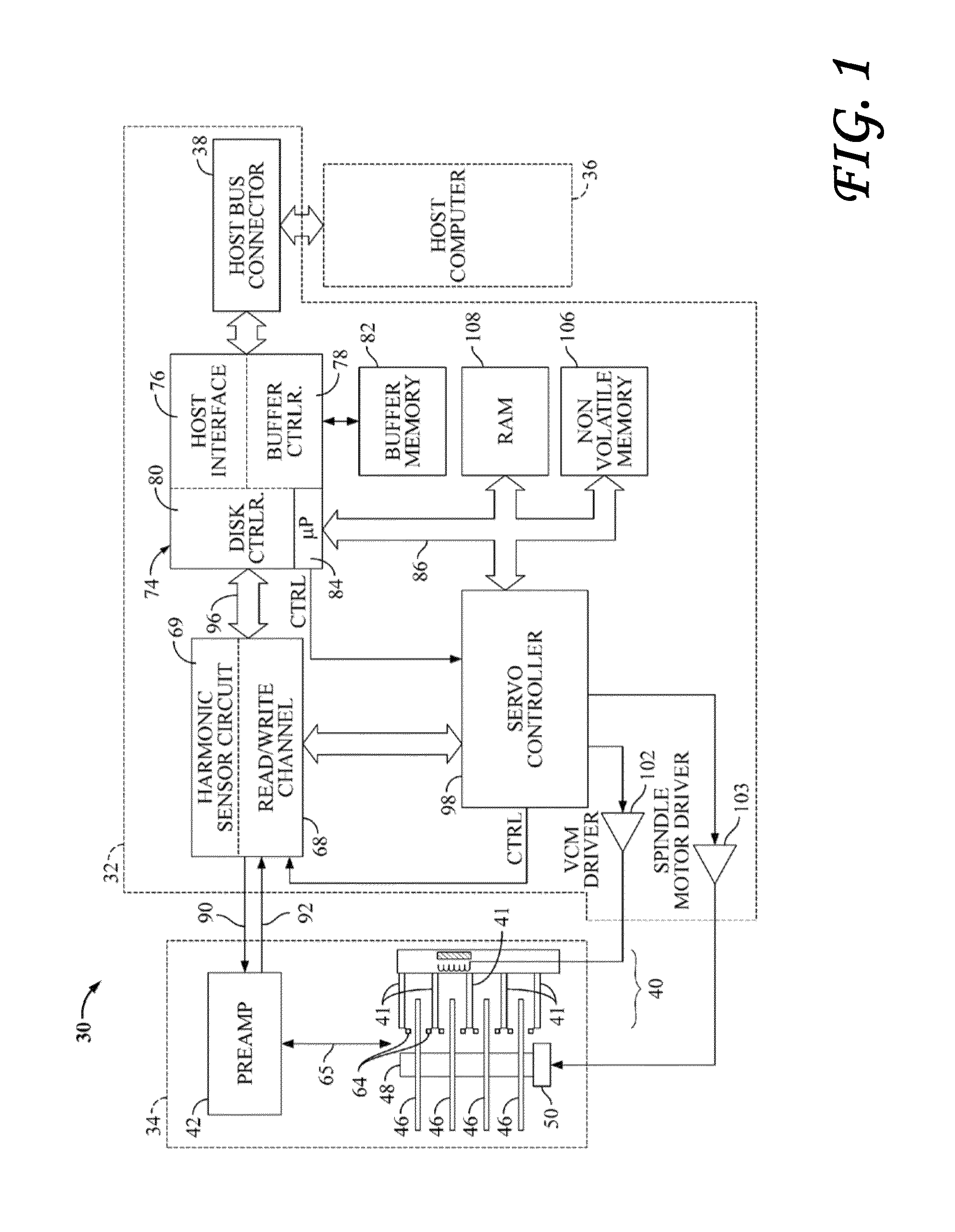
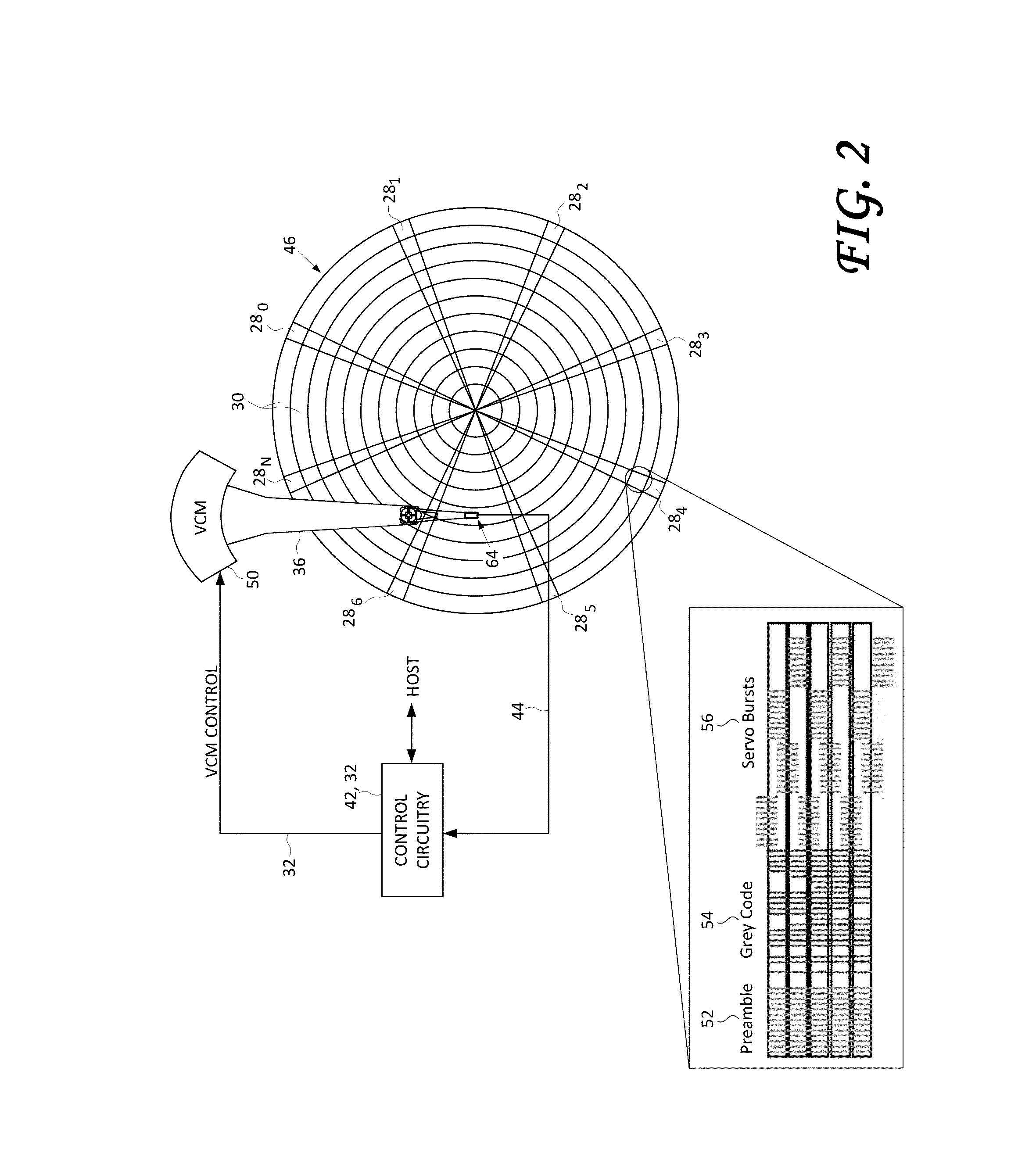
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk having a plurality of servo bursts written using perpendicular magnetic recording, wherein each servo burst is written at a servo burst frequency. A fill pattern is written between the servo bursts using perpendicular magnetic recording at a frequency substantially equal to an even harmonic of the servo burst frequency, and a phase shift occurs at the transition between the servo burst and the fill pattern. A head is actuated over the disk, and a sampling device samples a read signal emanating from the head to generate a sequence of read signal sample values. Control circuitry demodulates the servo bursts from the sequence of read signal sample values by computing a single-point Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) at the servo burst frequency.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
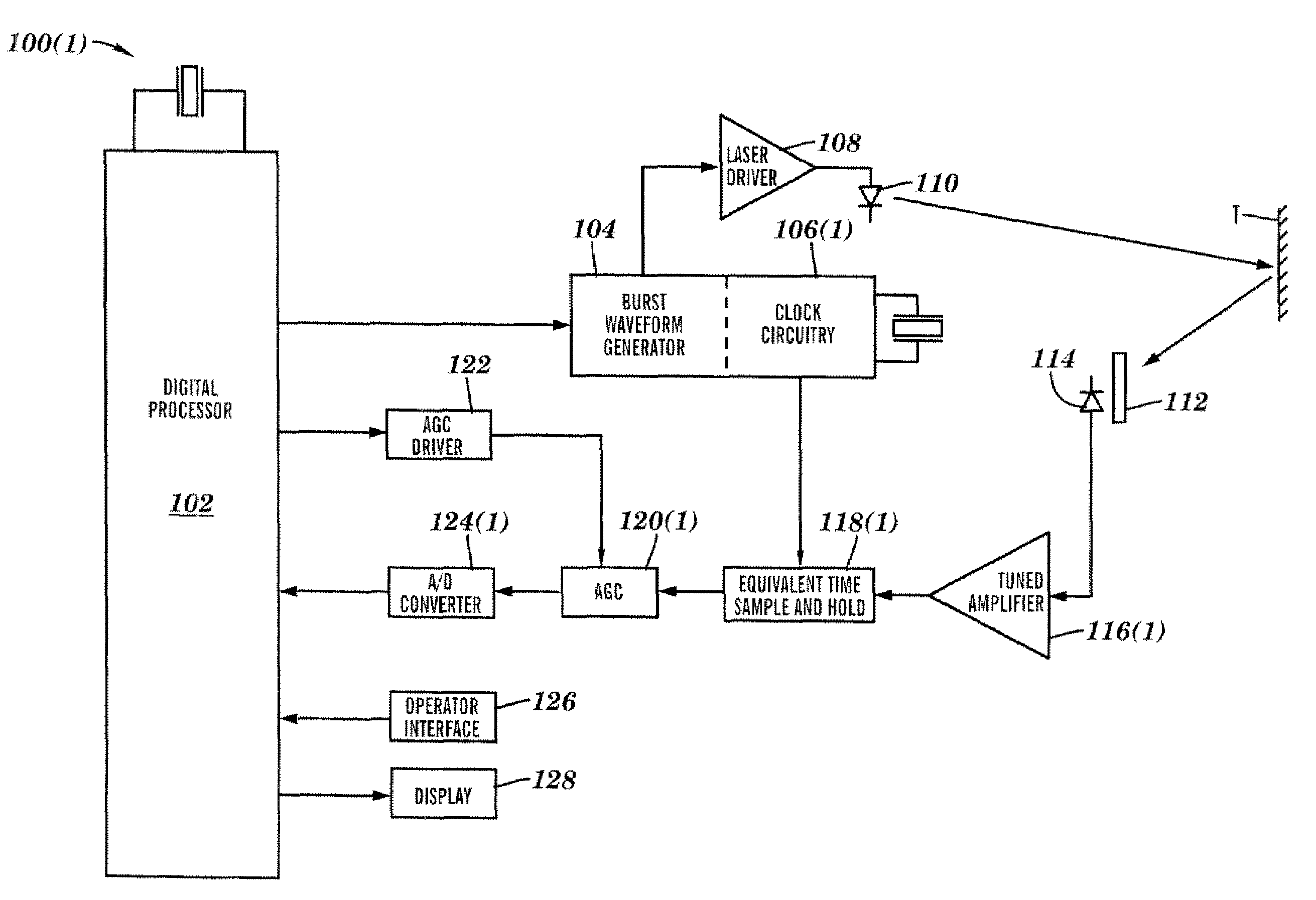
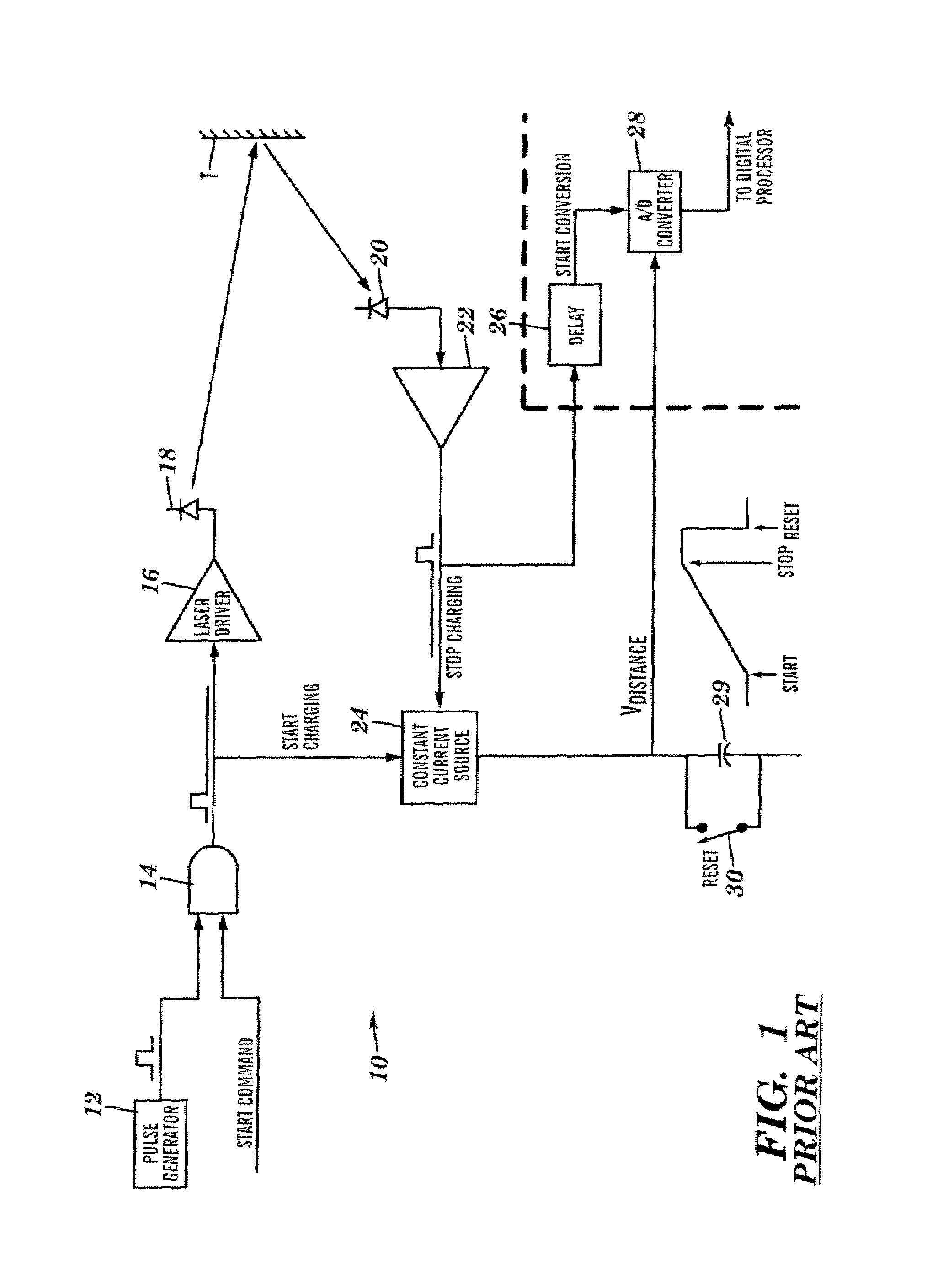
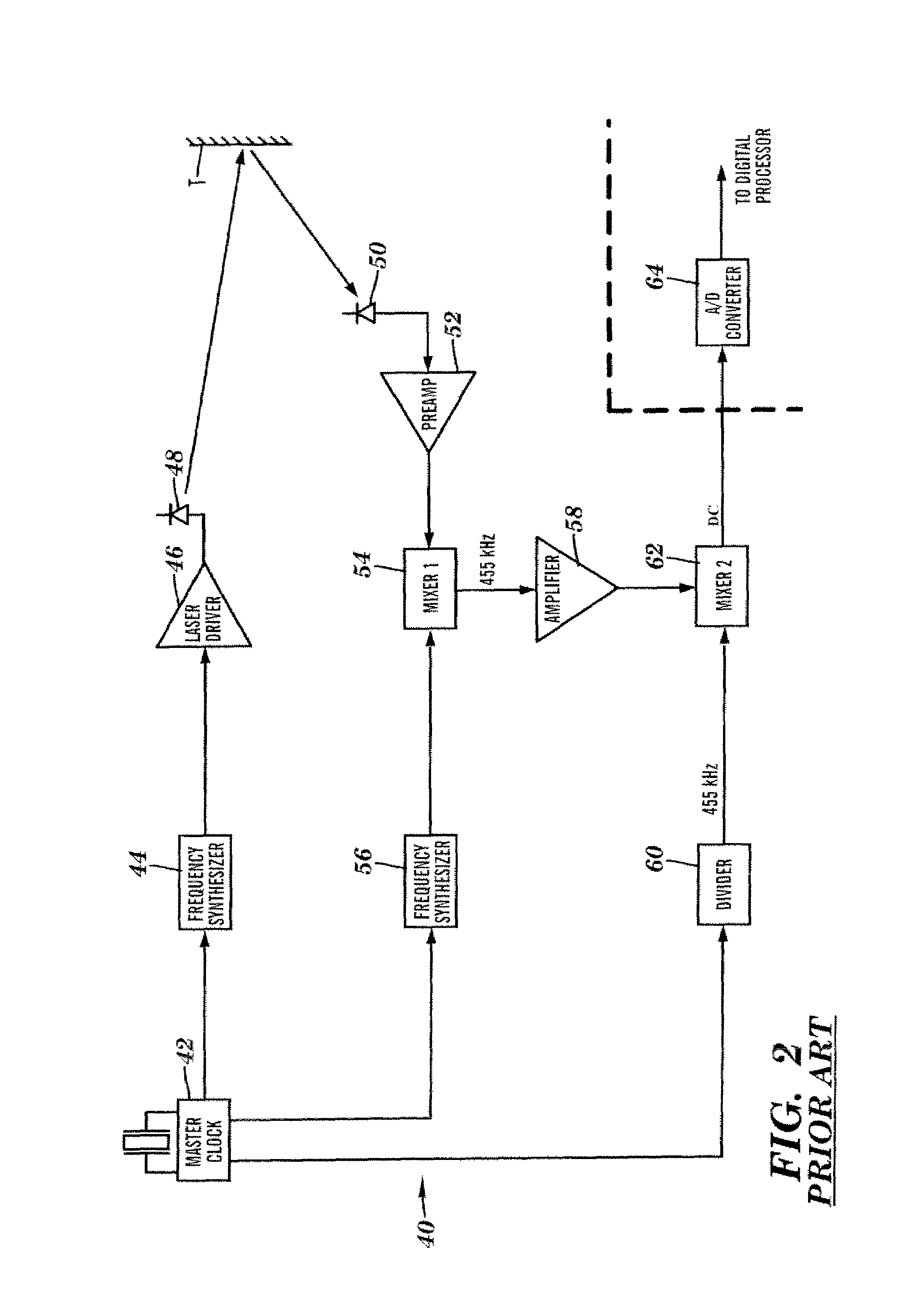
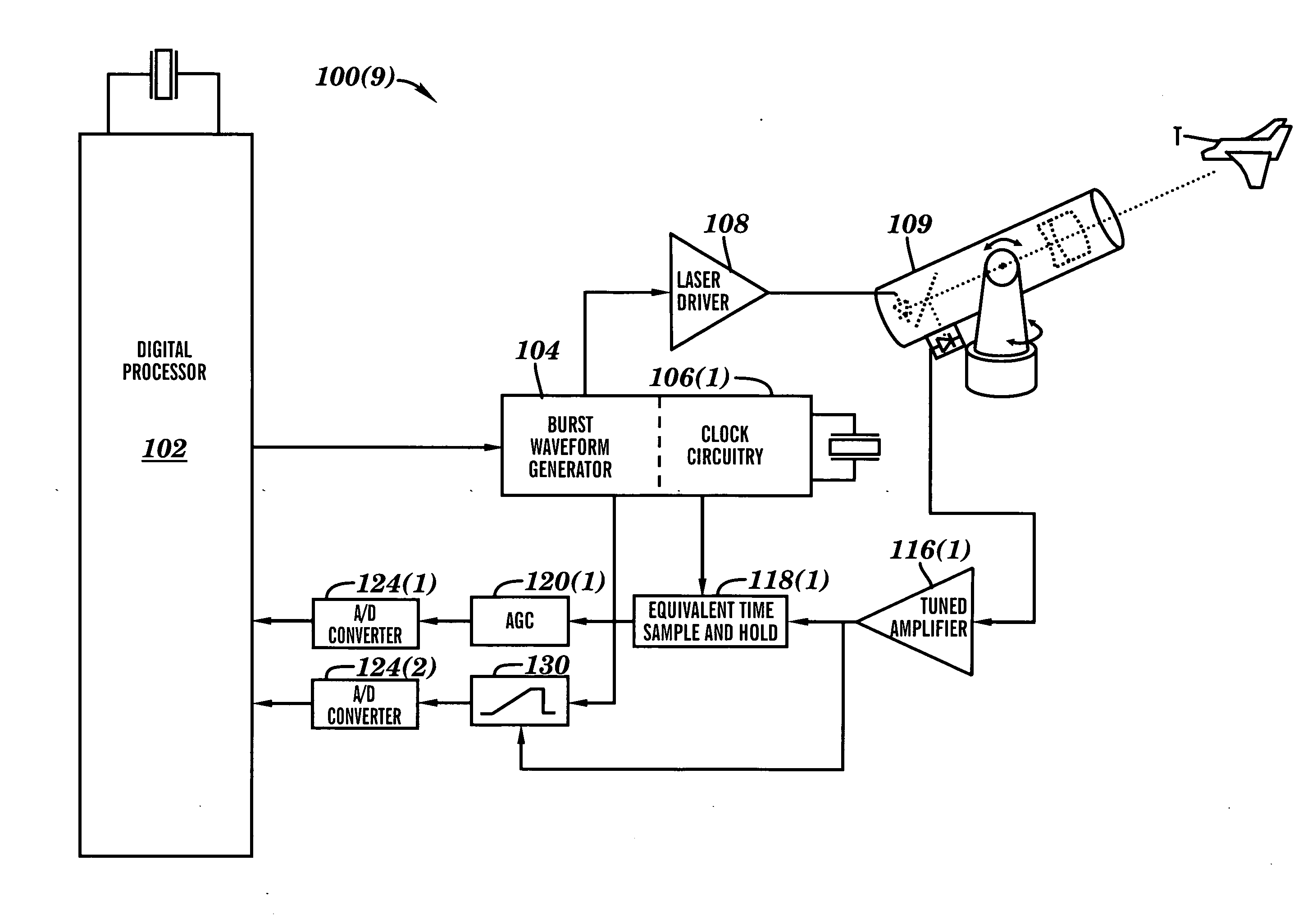
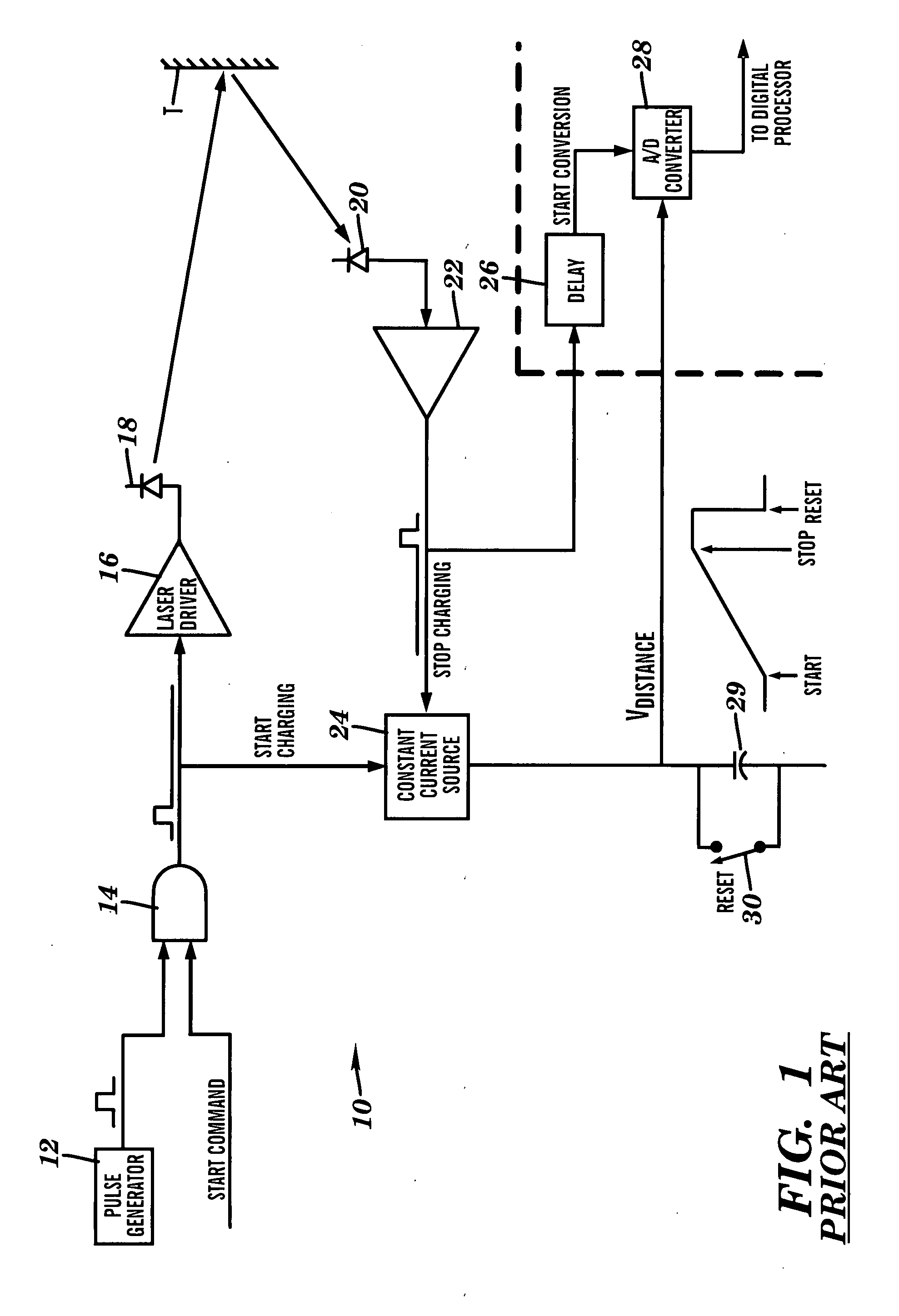
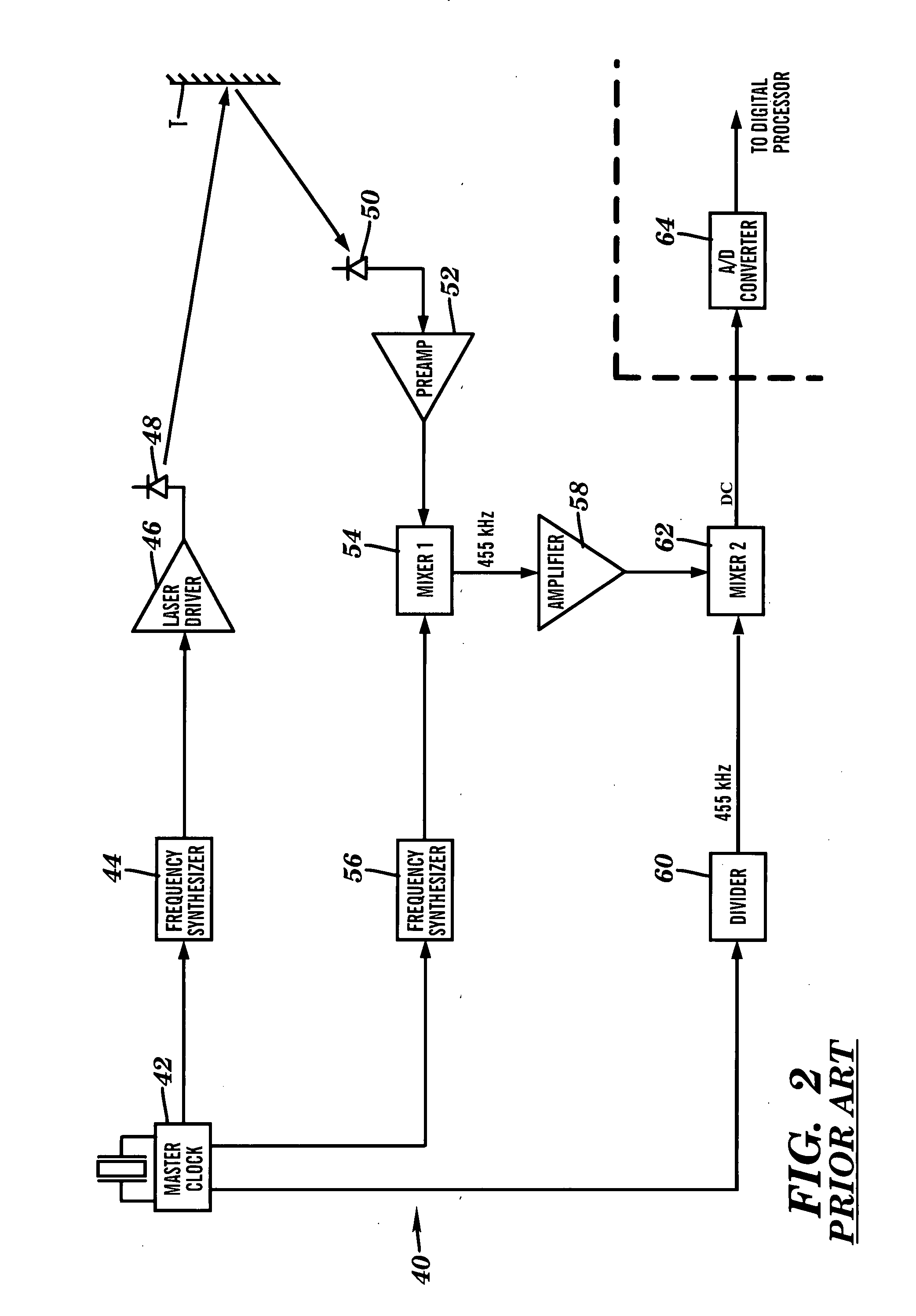
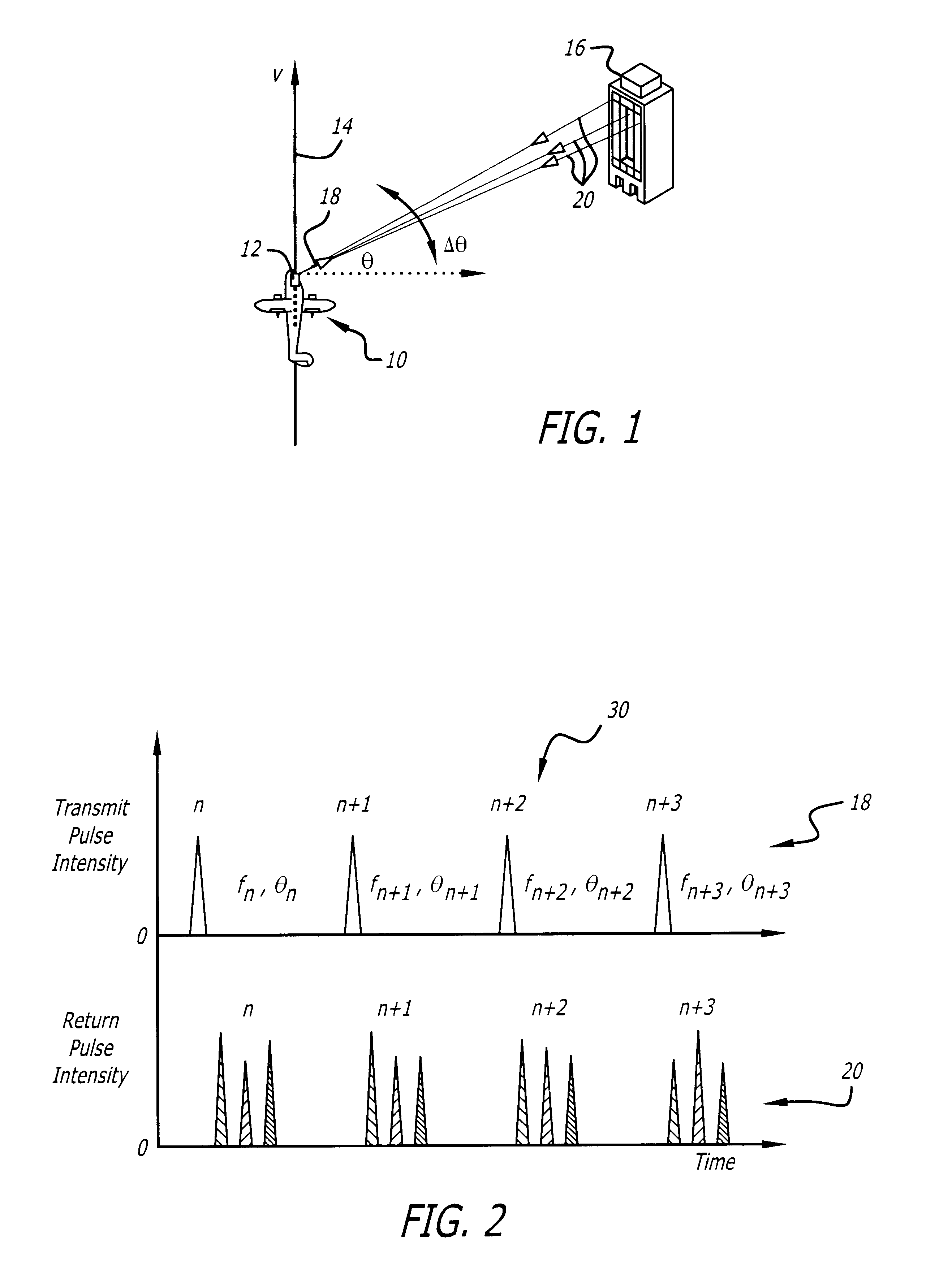
Apparatus for high accuracy distance and velocity measurement and methods thereof
InactiveUS7202941B2Increase costLow costOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationEngineeringDiscrete Fourier transform
A system and method for measuring a parameter of a target in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes transmitting at least one signal towards a target and receiving at least a portion of the transmitted signal back from the target. The measured parameter is one of distance velocity, or reflectivity. The transmitted signal is of the coherent burst waveform, and upon reception is processed with equivalent time sampling, AGC with minimal, if any, error, and a discrete Fourier transform.
Owner:MUNRO JAMES F
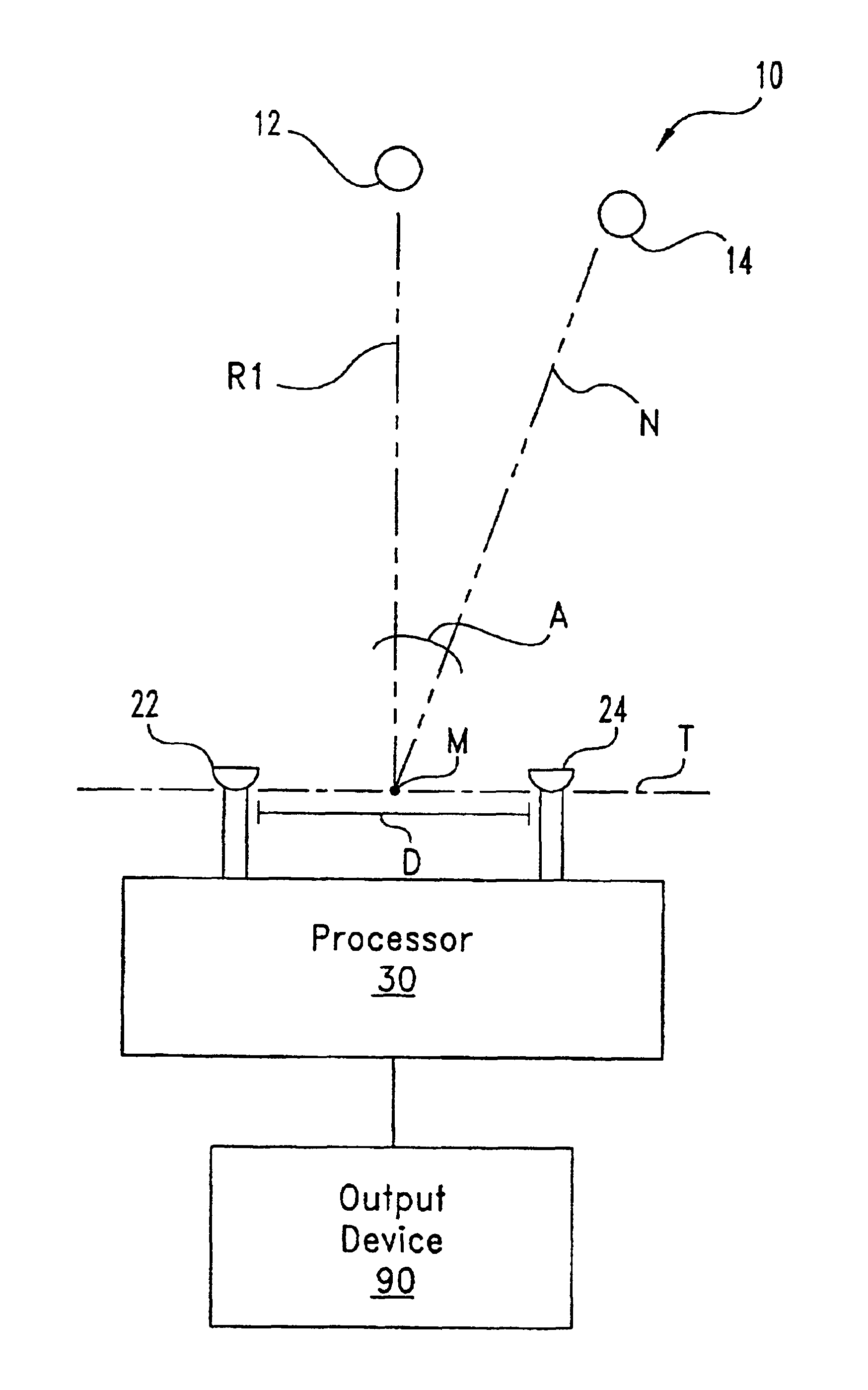
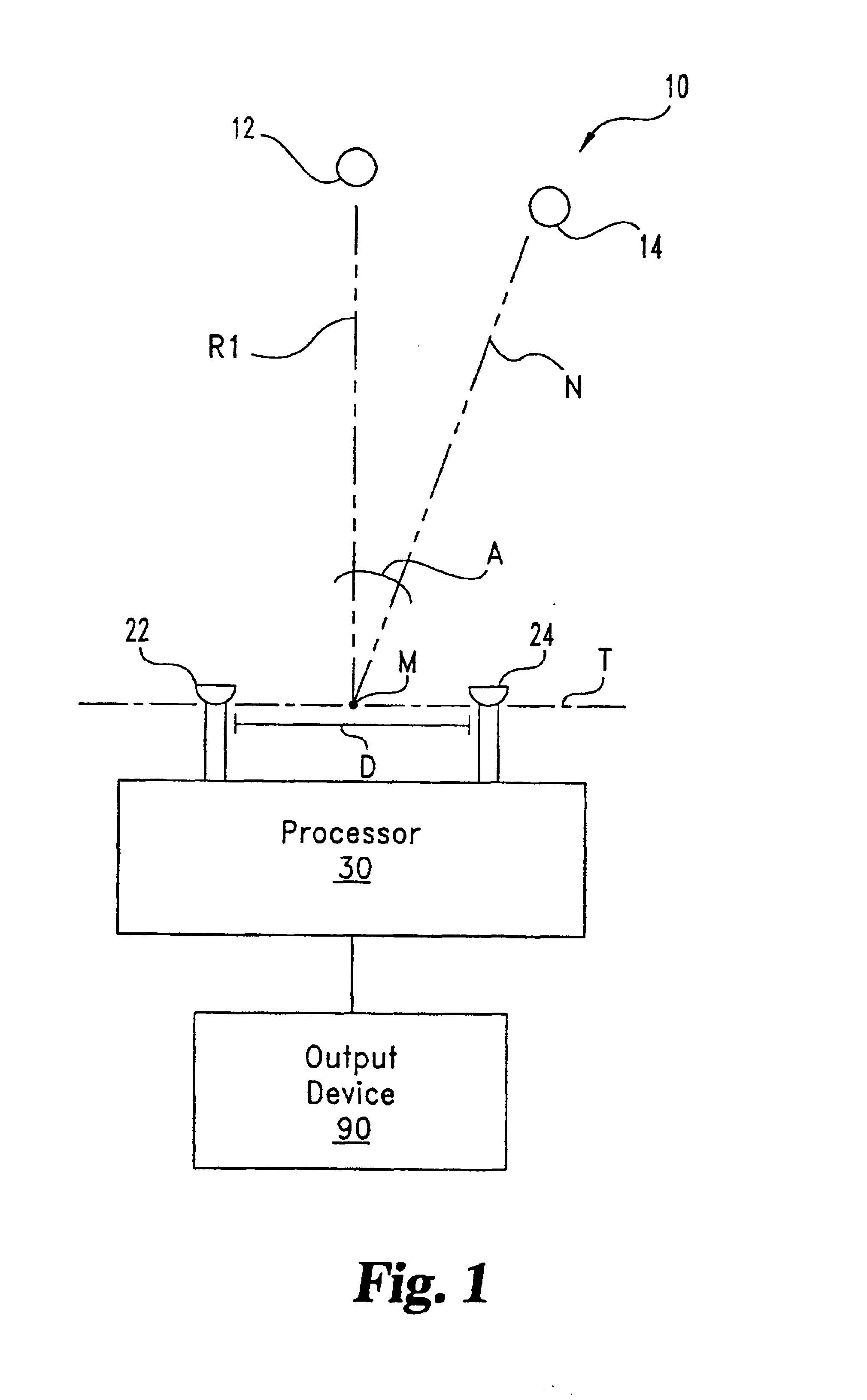
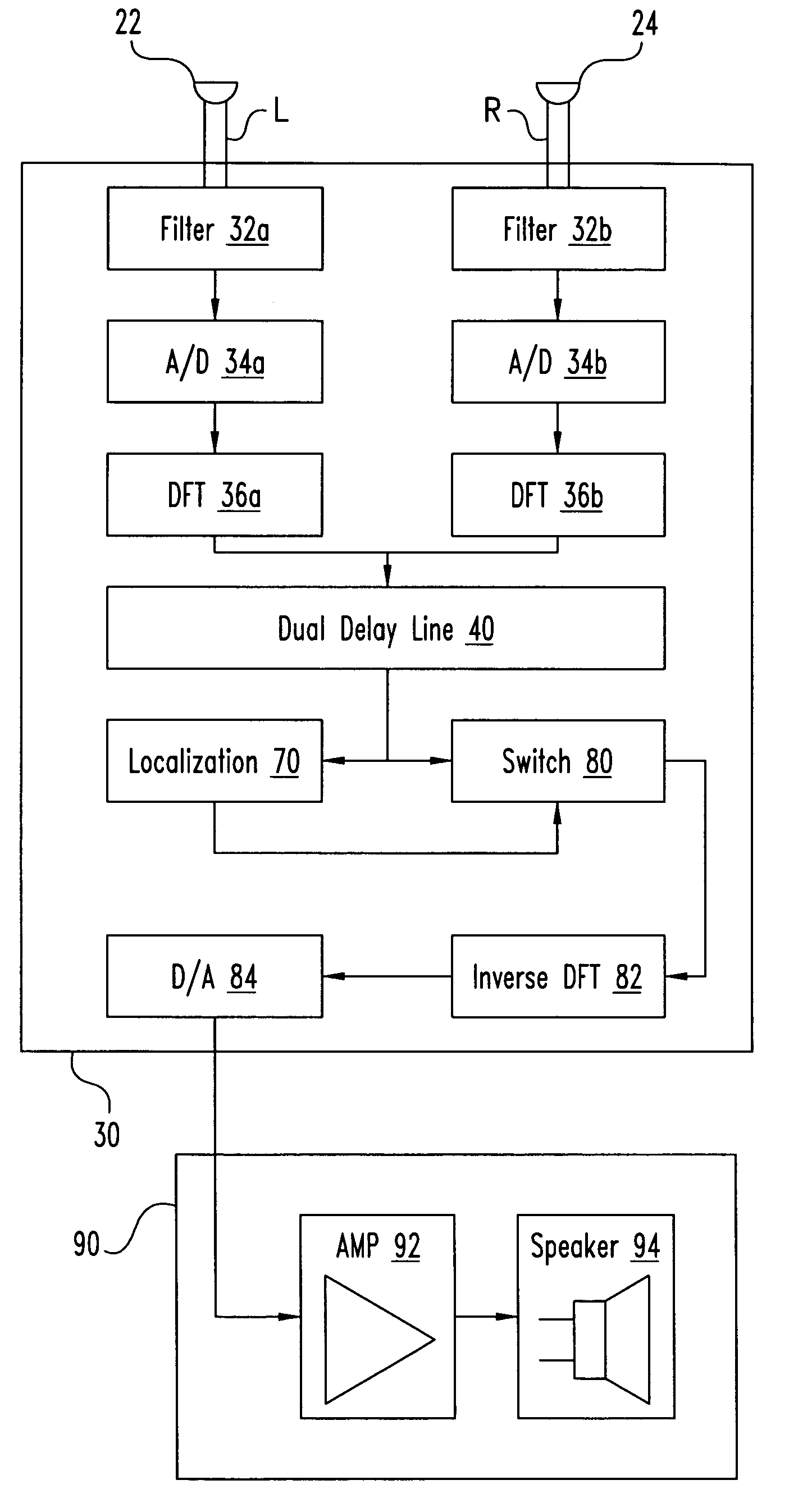
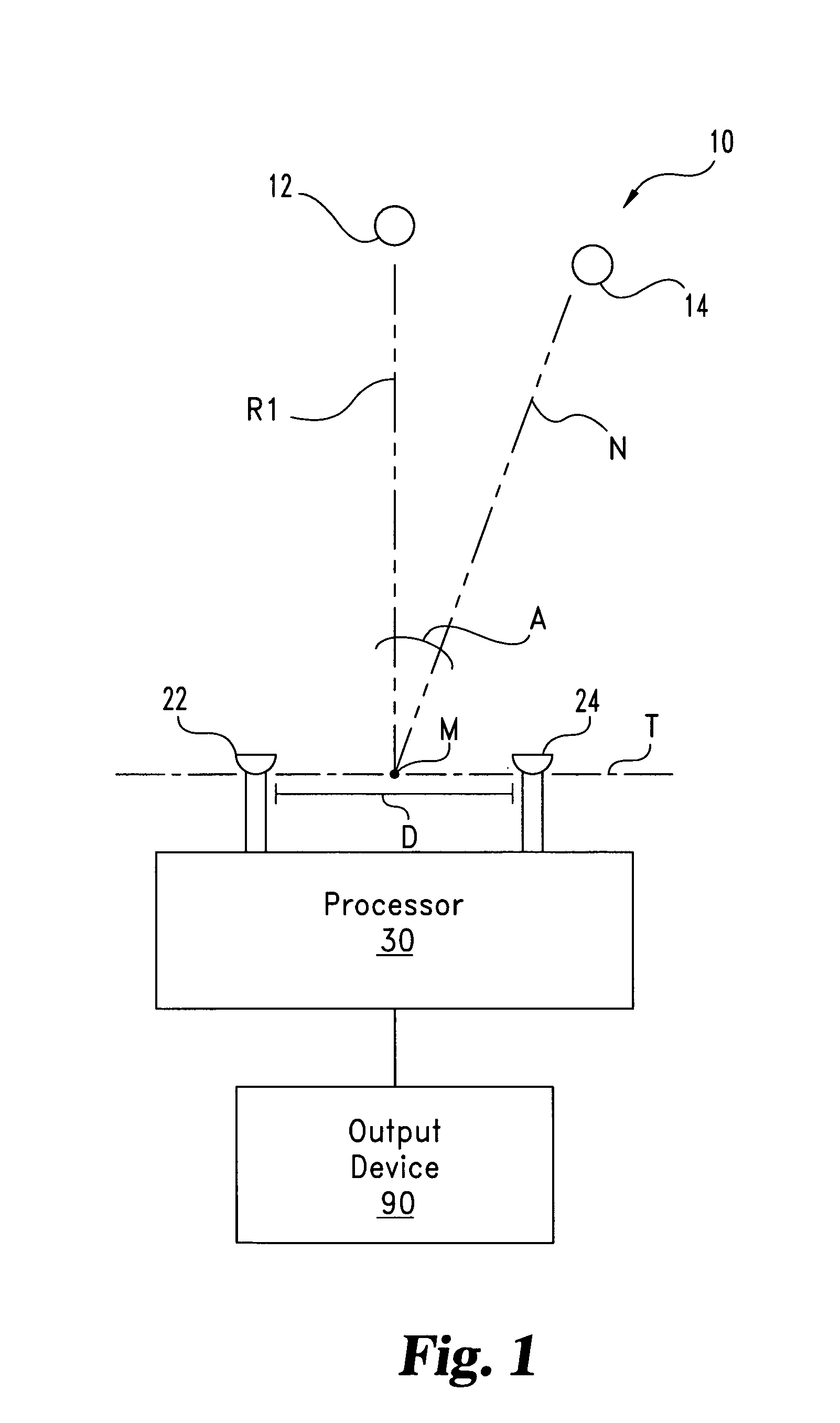
Binaural signal processing using multiple acoustic sensors and digital filtering
InactiveUS6978159B2Easy extractionExtensive computationTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstation equipmentFrequency spectrumSound sources
A desired acoustic signal is extracted from a noisy environment by generating a signal representative of the desired signal with processor (30). Processor (30) receives aural signals from two sensors (22, 24) each at a different location. The two inputs to processor (30) are converted from analog to digital format and then submitted to a discrete Fourier transform process to generate discrete spectral signal representations. The spectral signals are delayed to provide a number of intermediate signals, each corresponding to a different spatial location relative to the two sensors. Locations of the noise source and the desired source, and the spectral content of the desired signal are determined from the intermediate signal corresponding to the noise source locations. Inverse transformation of the selected intermediate signal followed by digital to analog conversion provides an output signal representative of the desired signal with output device (90). Techniques to localize multiple acoustic sources are also disclosed. Further, a technique to enhance noise reduction from multiple sources based on two-sensor reception is described.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
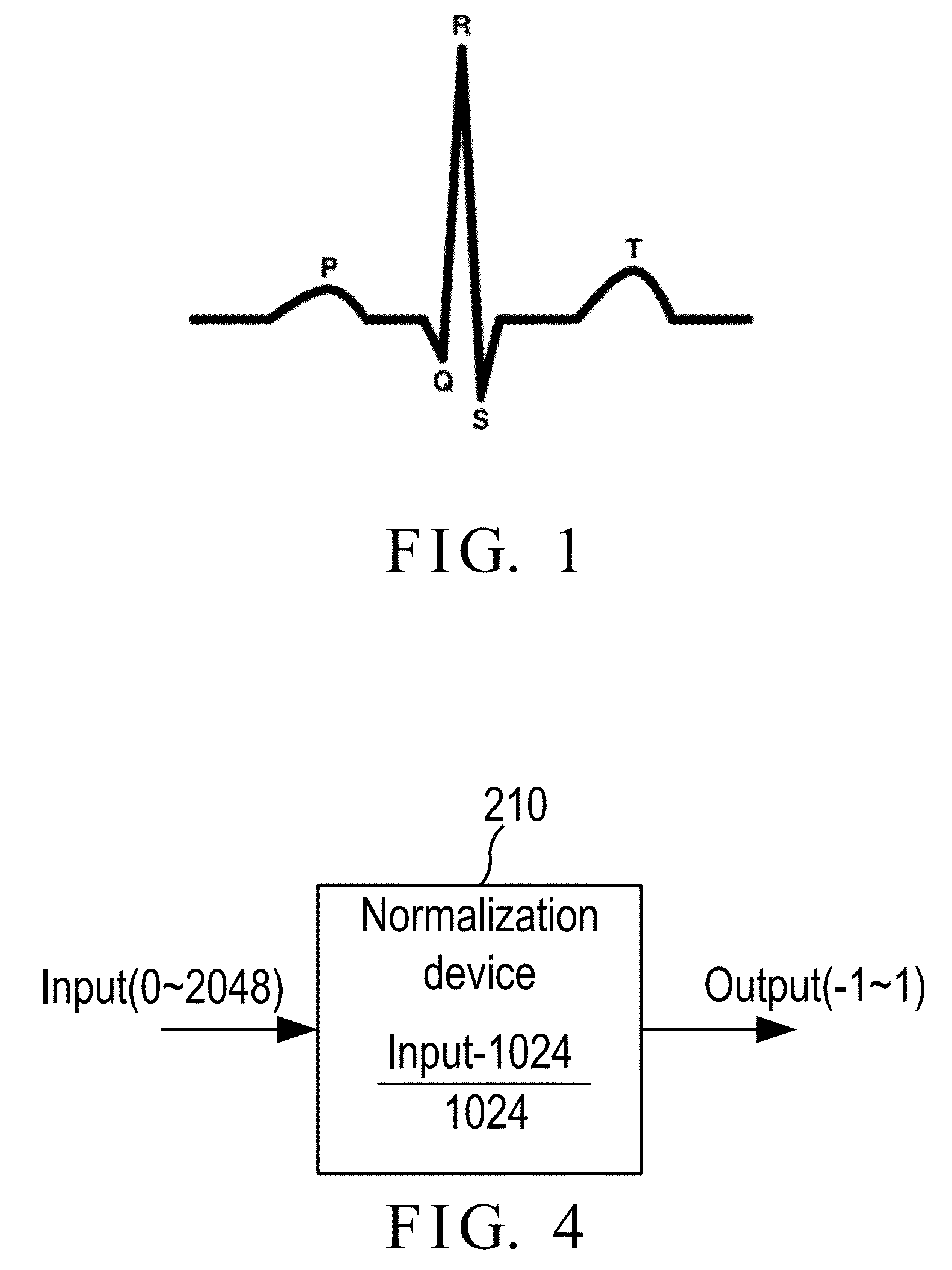
Electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system
InactiveUS20130243105A1Improve quality scoreLow distortion rateCode conversionComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionEcg signalFrequency spectrum
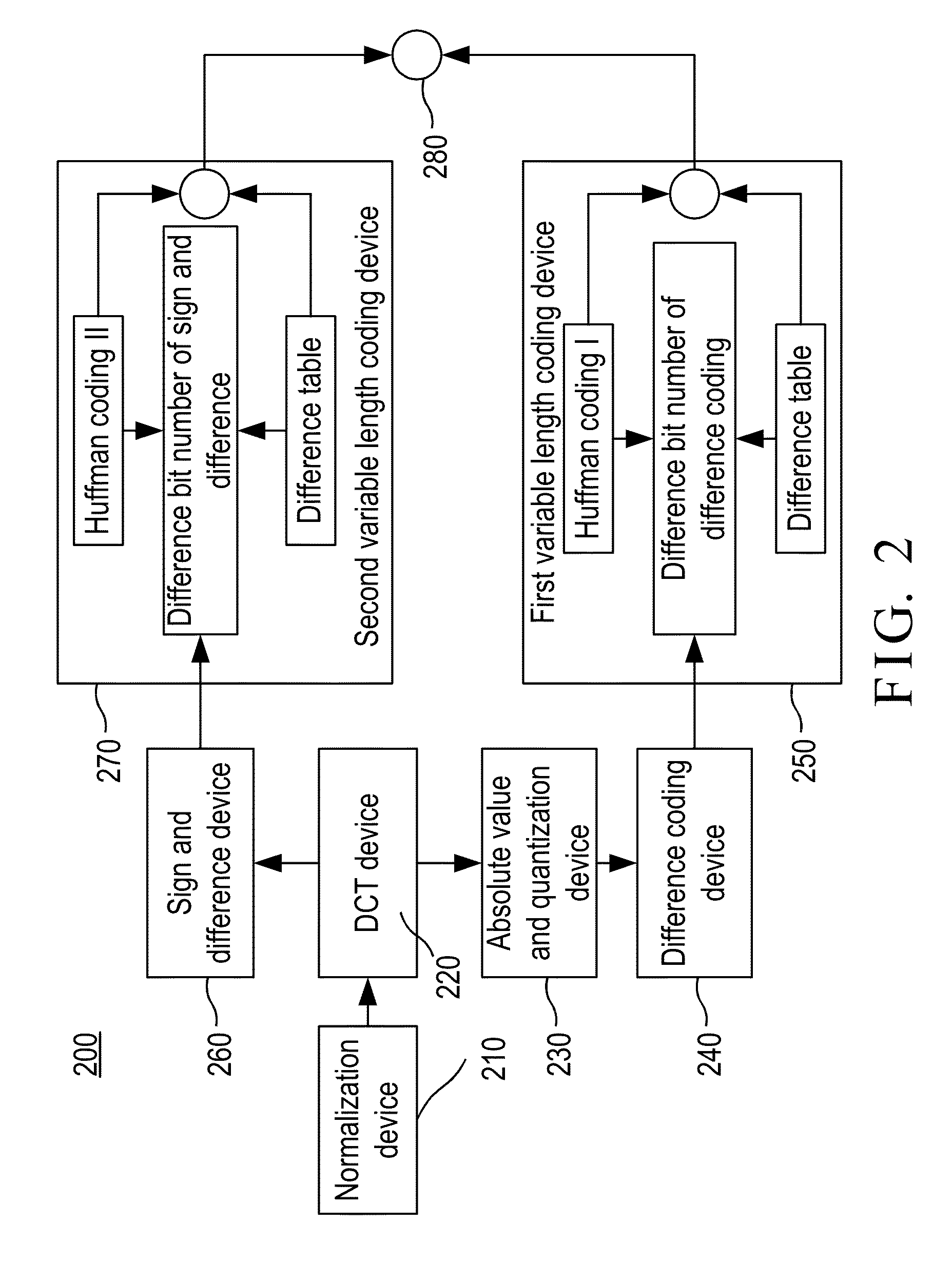
The invention provides an electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system. The invention uses the sign characteristics of the coefficients of the discrete cosine transform type IV and the characteristics of quantization of spectrum to perform the differential pulse code modulation of the spectrum for preserving the high frequency characteristics of the spectrum of the discrete Fourier transform. The invention also uses the Huffman coding to increase the compression ratio. Different from the conventional compression technology, the invention uses the fact that the quantization values of the spectrum in the high frequency are almost the same to increase the compression ratio and preserve the characteristics of high frequency components of the spectrum.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Calculation of head media separation (HMS) from servo preamble in a hard disk drive
InactiveUS8654466B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHard disc driveAudio power amplifier
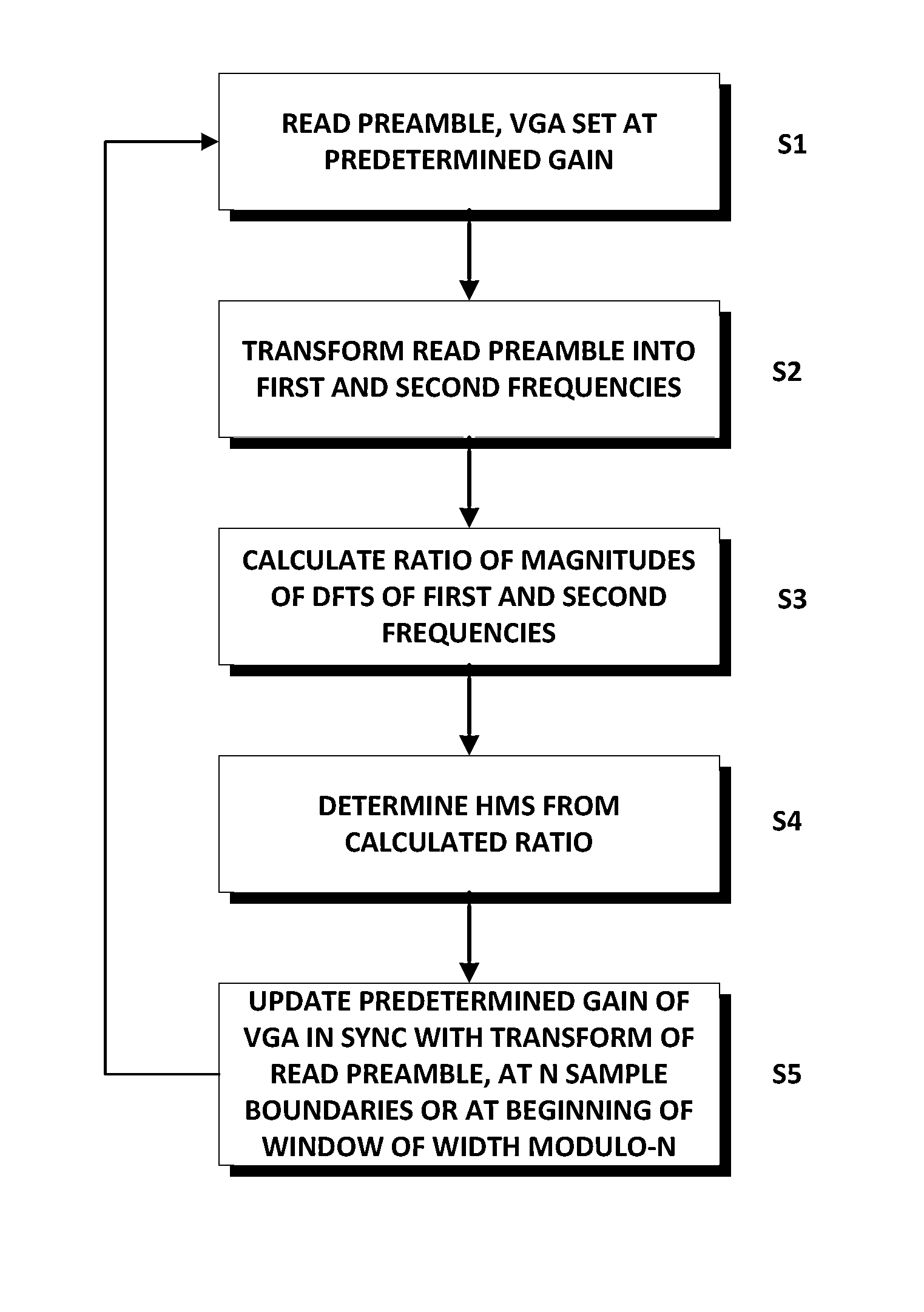
A method of calculating a Head Media Separation (HMS) from a preamble of embedded servo sectors in a disk drive may include steps of reading the preamble, the read preamble being amplified by a variable gain amplifier (VGA) set at a predetermined gain; transforming samples of the read preamble into a first and a second frequency using a discrete time-to-frequency domain transform such as a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT); calculating the ratio of the magnitude of the discrete time-to-frequency domain transform of the first frequency to the magnitude of the discrete time-to-frequency domain transform of the second frequency; determining the HMS from the calculated ratio, and enabling the predetermined gain to be updated in synchronism with the transforming step.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
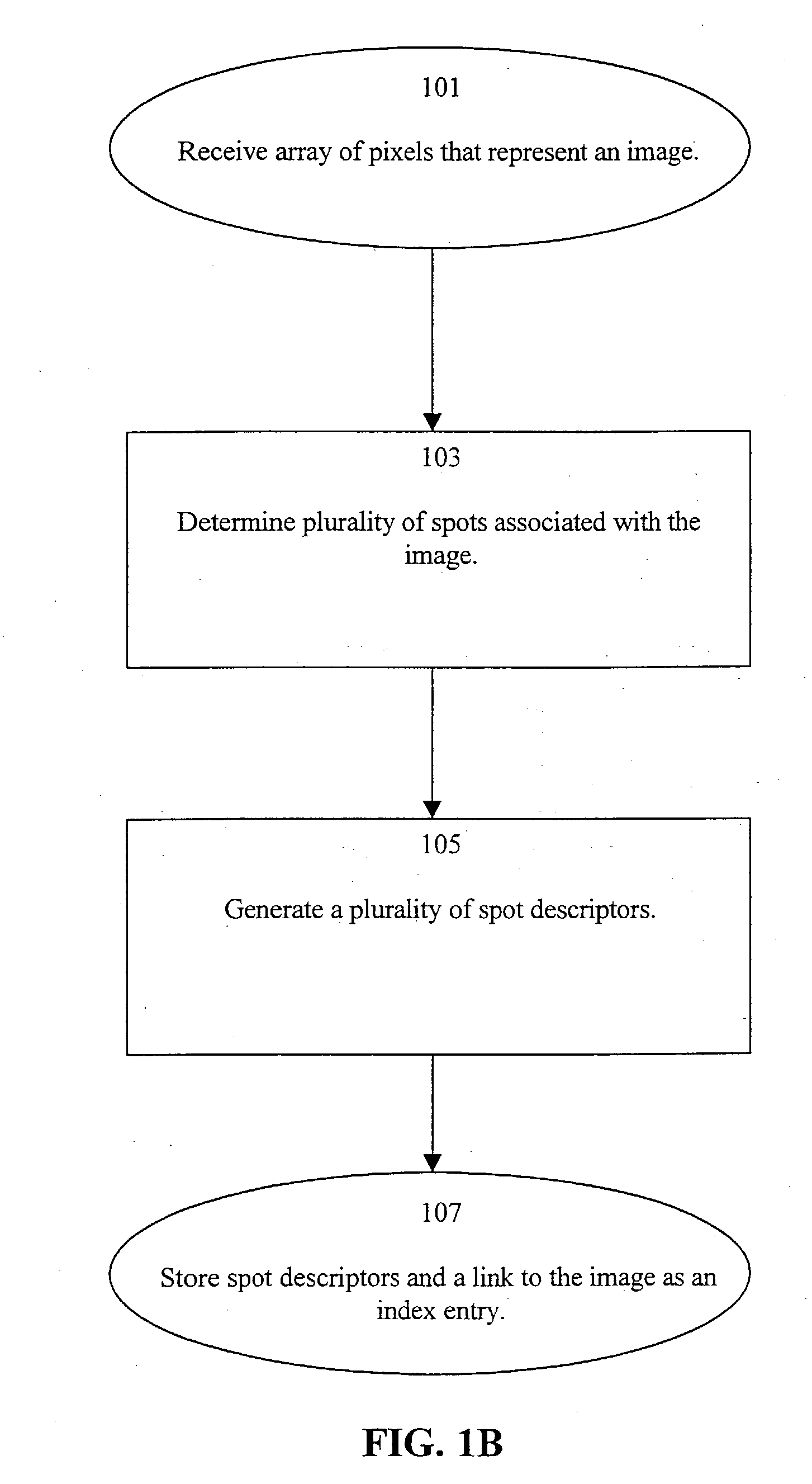
Perceptual similarity image retrieval
InactiveUS7031555B2High degreeNoise insensitiveData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalWeb serviceContinuous tone
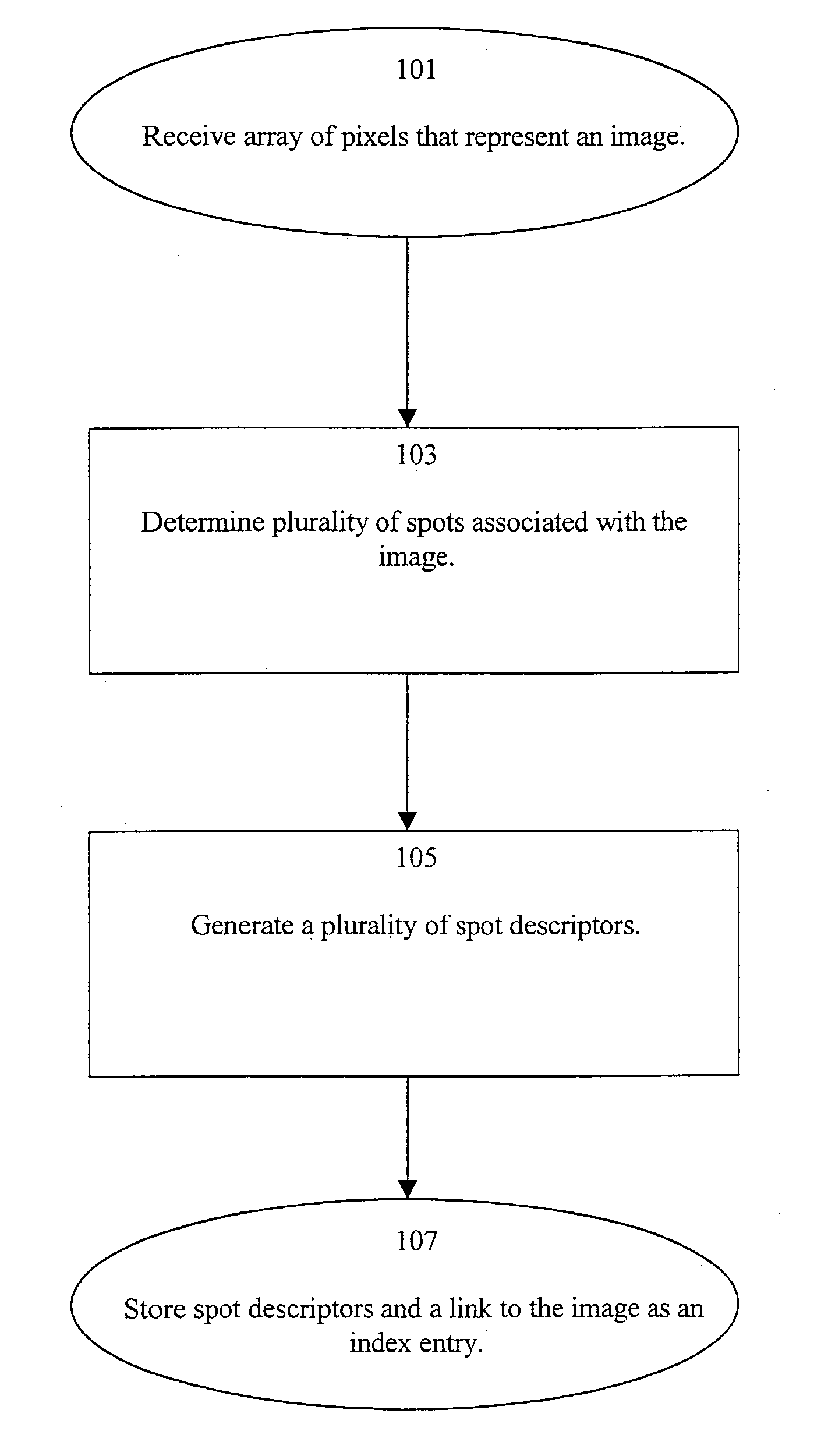
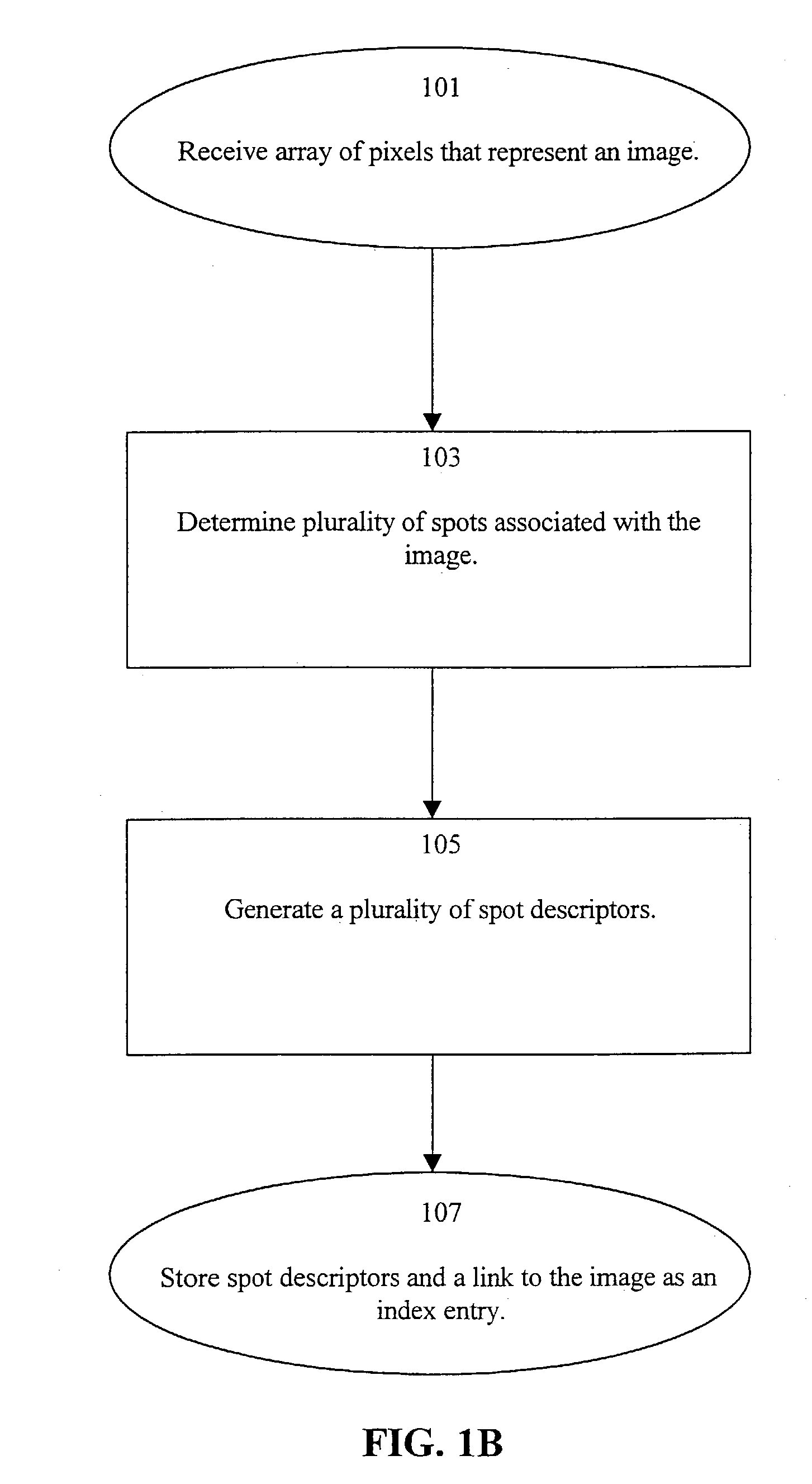
A system and method indexes an image database by partitioning an image thereof into a plurality of cells, combining the cells into intervals and then spots according to perceptual criteria, and generating a set of spot descriptors that characterize the perceptual features of the spots, such as their shape, color and relative position within the image. The shape preferably is a derivative of the coefficients of a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of the perimeter trace of the spot. The set of spot descriptors forms as an index entry for the spot. This process repeated for the various images of the database. To search the index, a key comprising a set of spot descriptors for a query image is generated and compared according to a perceptual similarity metric to the entries of the index. The metric determines the perceptual similarity that the features of the query image match those of the indexed image. The search results are presented as a scored list of the indexed images. A wide variety of image types can be indexed and searched, including: bi-tonal, gray-scale, color, “real scene” originated, and artificially generated images. Continuous-tone “real scene” images such as digitized still pictures and video frames are of primary interest. There are stand alone and networked embodiments. A hybrid embodiment generates keys locally and performs image and index storage and perceptual comparison on a network or web server.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
System and method for 3D frequency domain waveform inversion based on 3D time-domain forward modeling
ActiveUS7725266B2Reduce computing costElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyTime domainData set
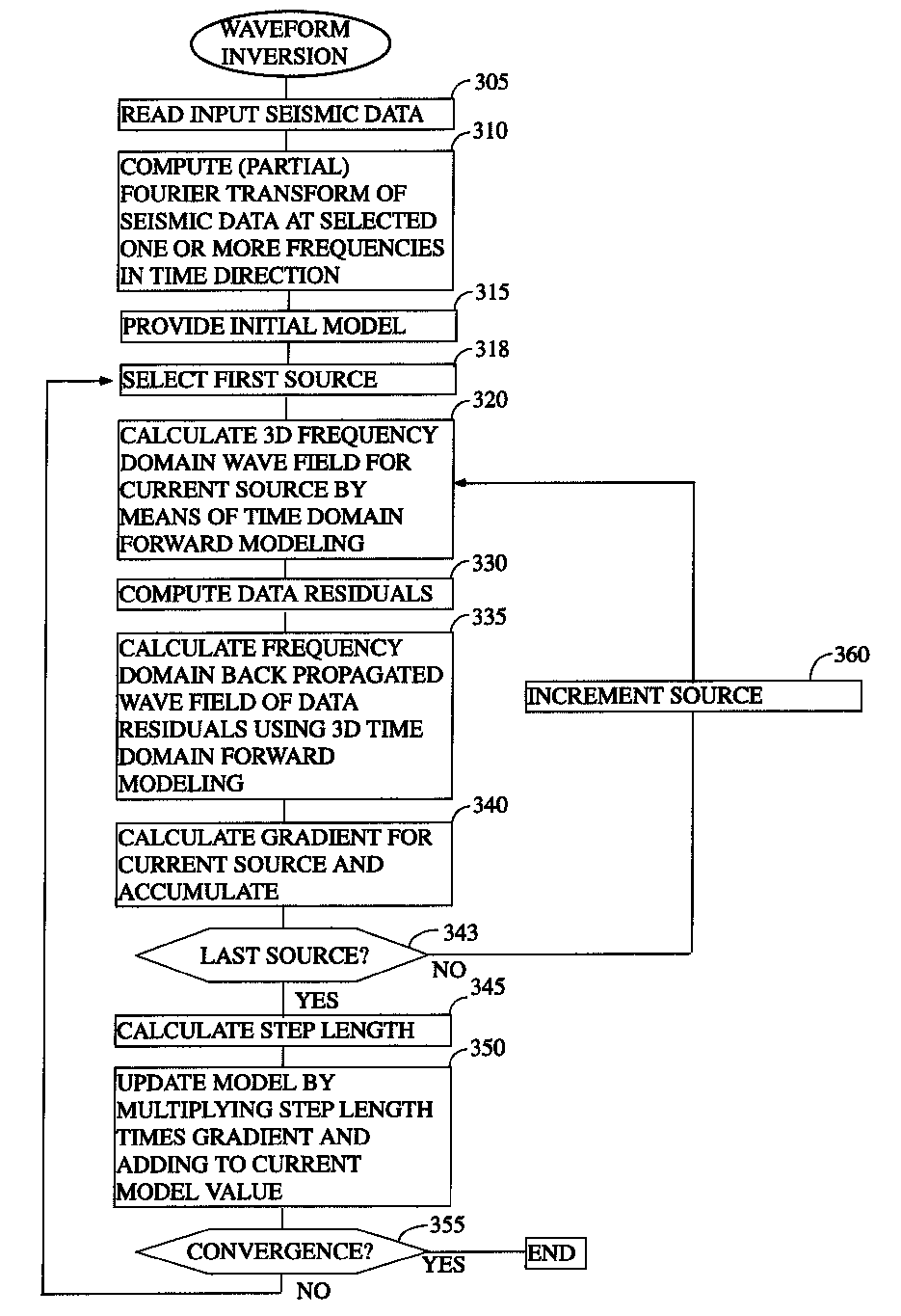
According to a first preferred aspect of the instant invention, there is provided an efficient method of computing a 3D frequency domain waveform inversion based on 3D time domain modeling. In the preferred arrangement, 3D frequency domain wavefields are computed using 3D time-domain modeling and a discrete Fourier transformation that is preferably computed “on the fly” instead of solving the large systems of linear equations that have traditionally been required by direct frequency domain modeling. The instant invention makes use of the theory of gradient-based waveform inversion that estimates model parameters (for example velocities) by matching modeled data to field data sets. Preferably the modeled data are calculated using a forward modeling algorithm.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
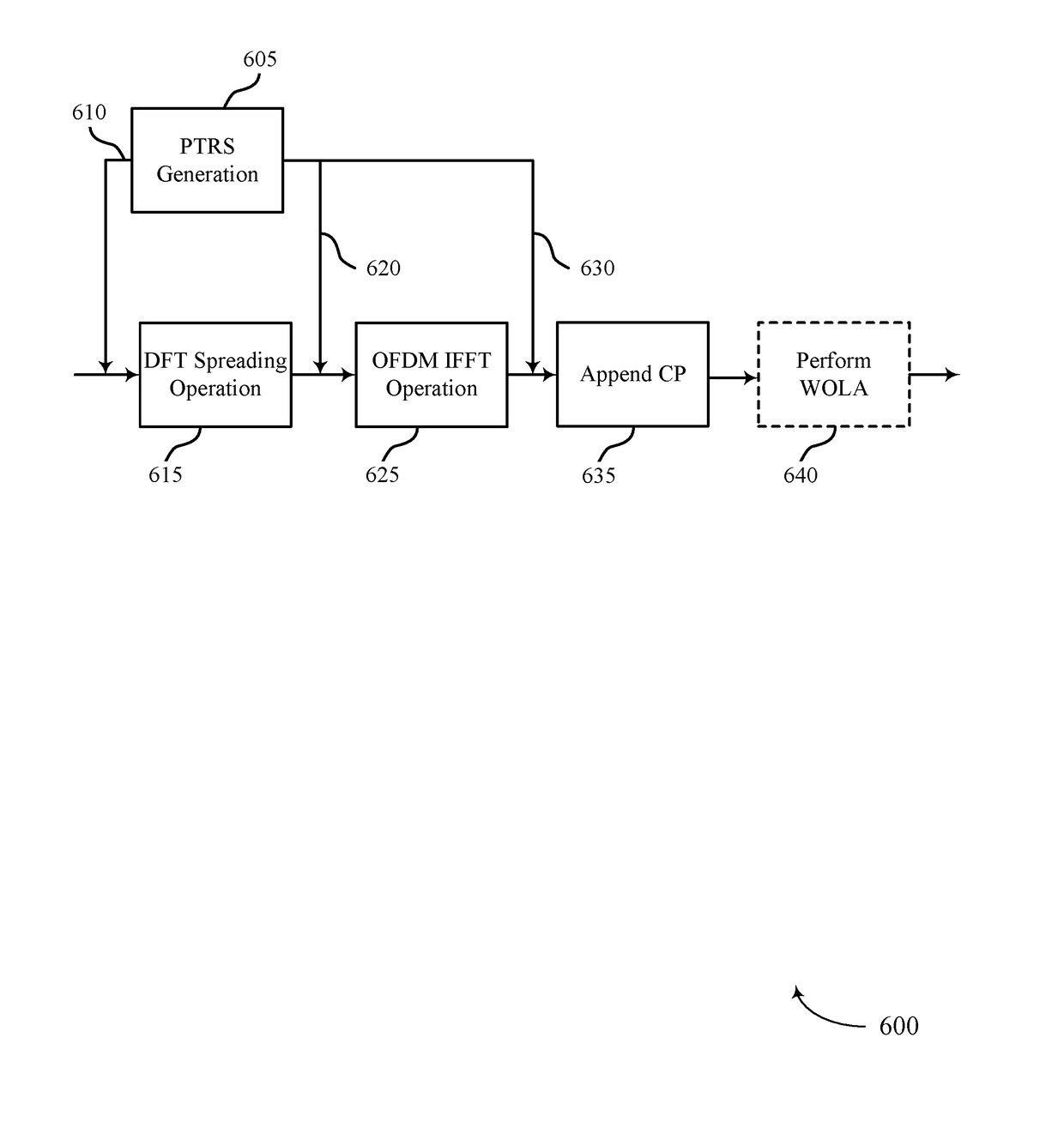
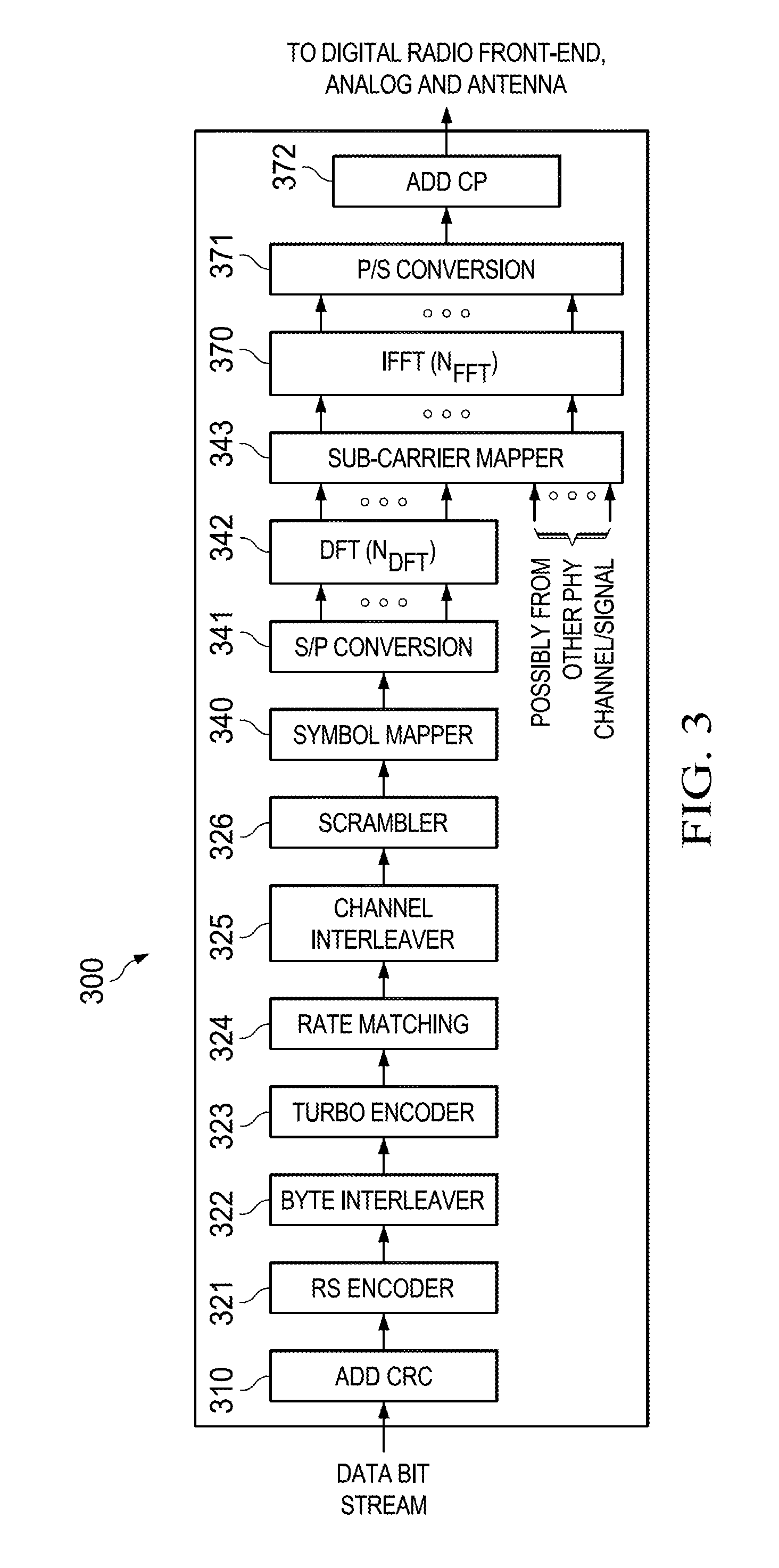
Enhancements to phase-noise compensation reference signal design and scrambling
ActiveUS20180091350A1Efficient receptionIncrease flexibilityNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionTime domainPhase noise
Methods, systems, and devices for wireless communication are described. In one example, phase-noise compensation tracking signals (PTRS) may be transmitted using sets of resource blocks (RBs), where a frequency for each PTRS within the sets RBs is different from a frequency corresponding to a direct current (DC) tone. In another example, a time-domain-based PTRS may be used, where a discrete Fourier transform (DFT)-spread-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (DFT-s-OFDM) symbol may include a cyclic prefix and a PTRS inserted in the DFT-s-OFDM symbol. Additionally or alternatively, a guard-interval-based DFT-s-OFDM symbol may include a PTRS that replaces part or all of a guard interval. In some examples, subsets of tones used for PTRS across a system bandwidth may be transmitted using a scrambled modulation symbol, where at least one antenna port may be used for the transmission of PTRS.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for hybrid CDM OFDMA wireless transmission
ActiveUS7729433B2Transmission control/equlisationFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless transmissionData stream
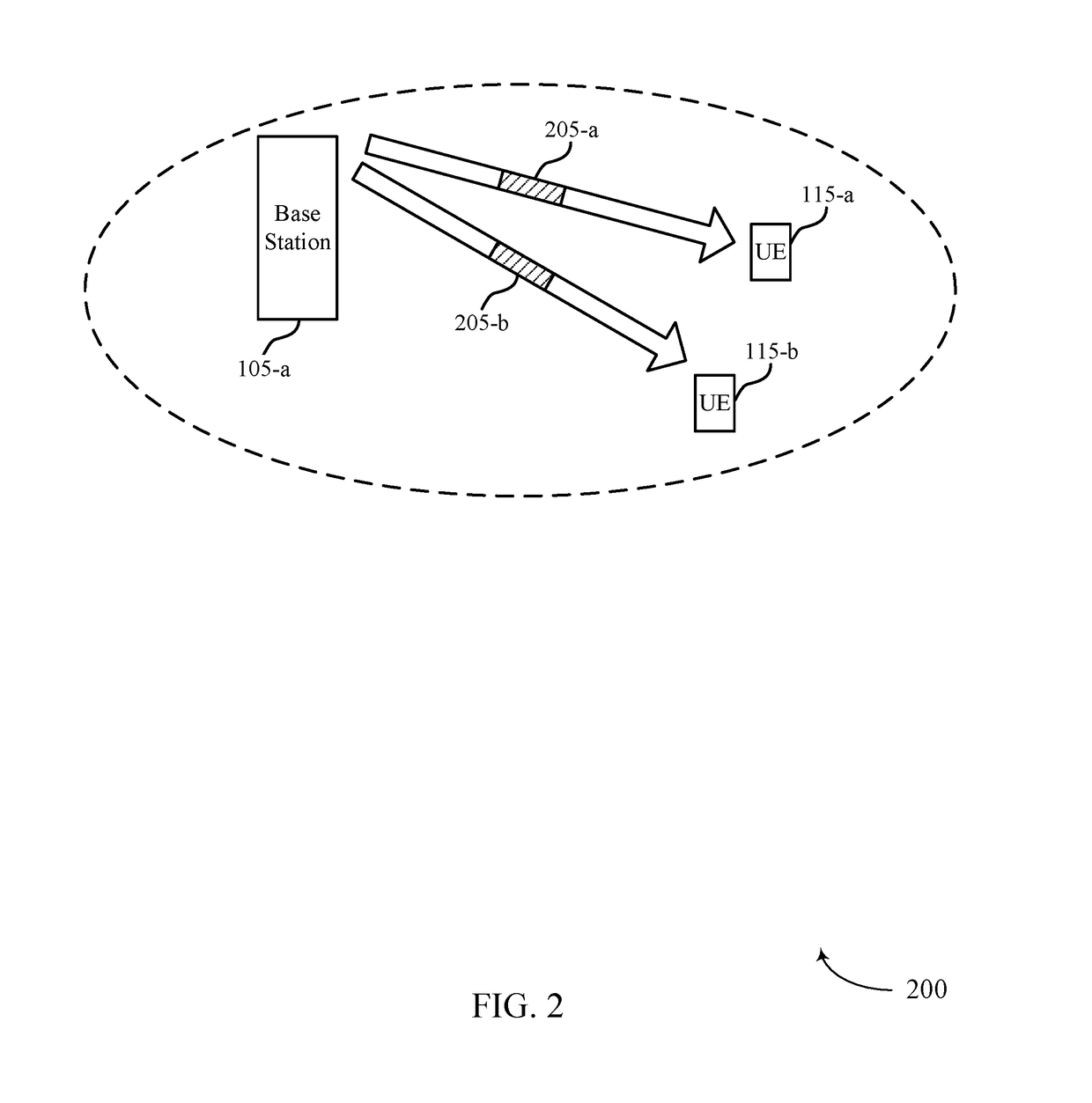
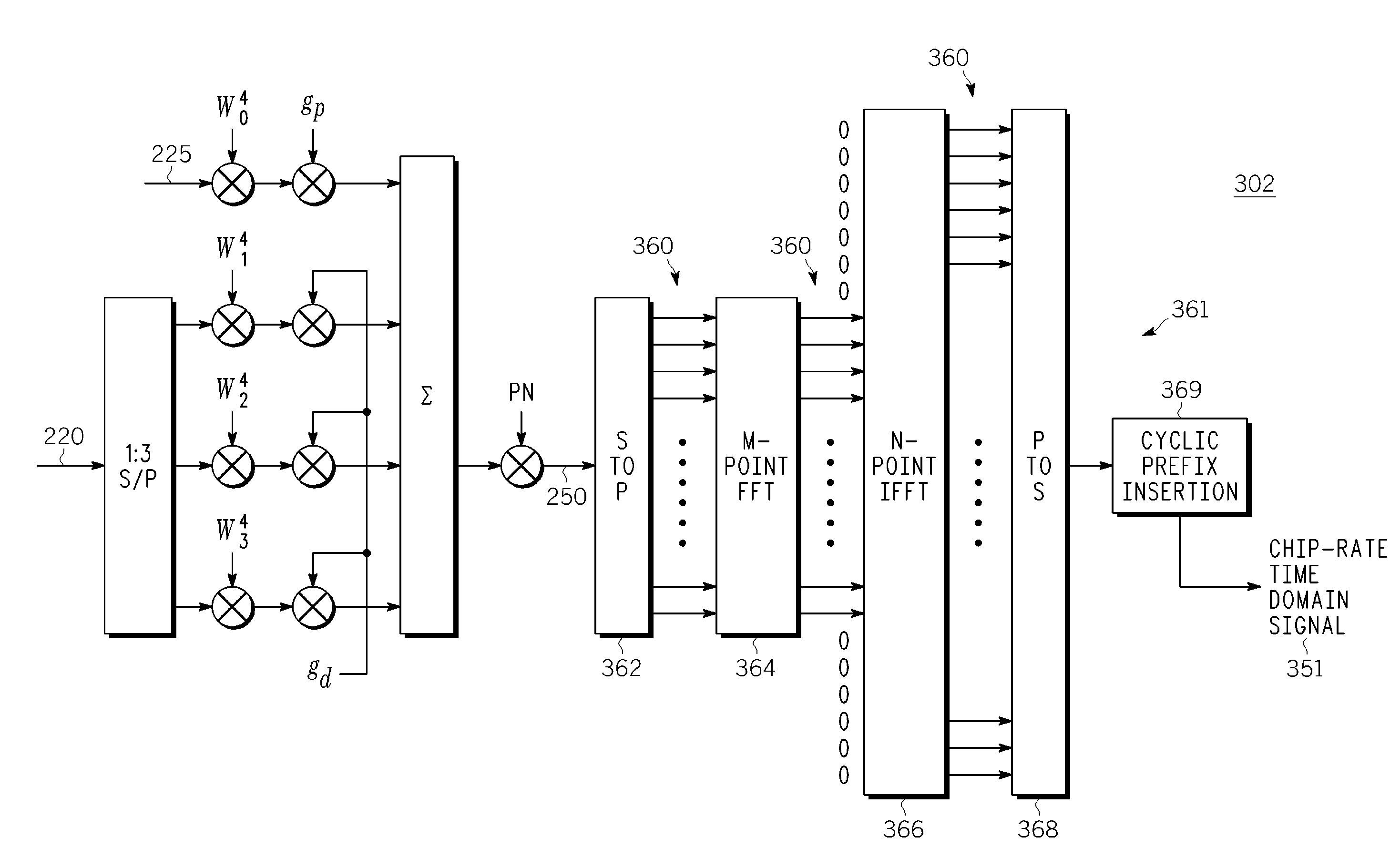
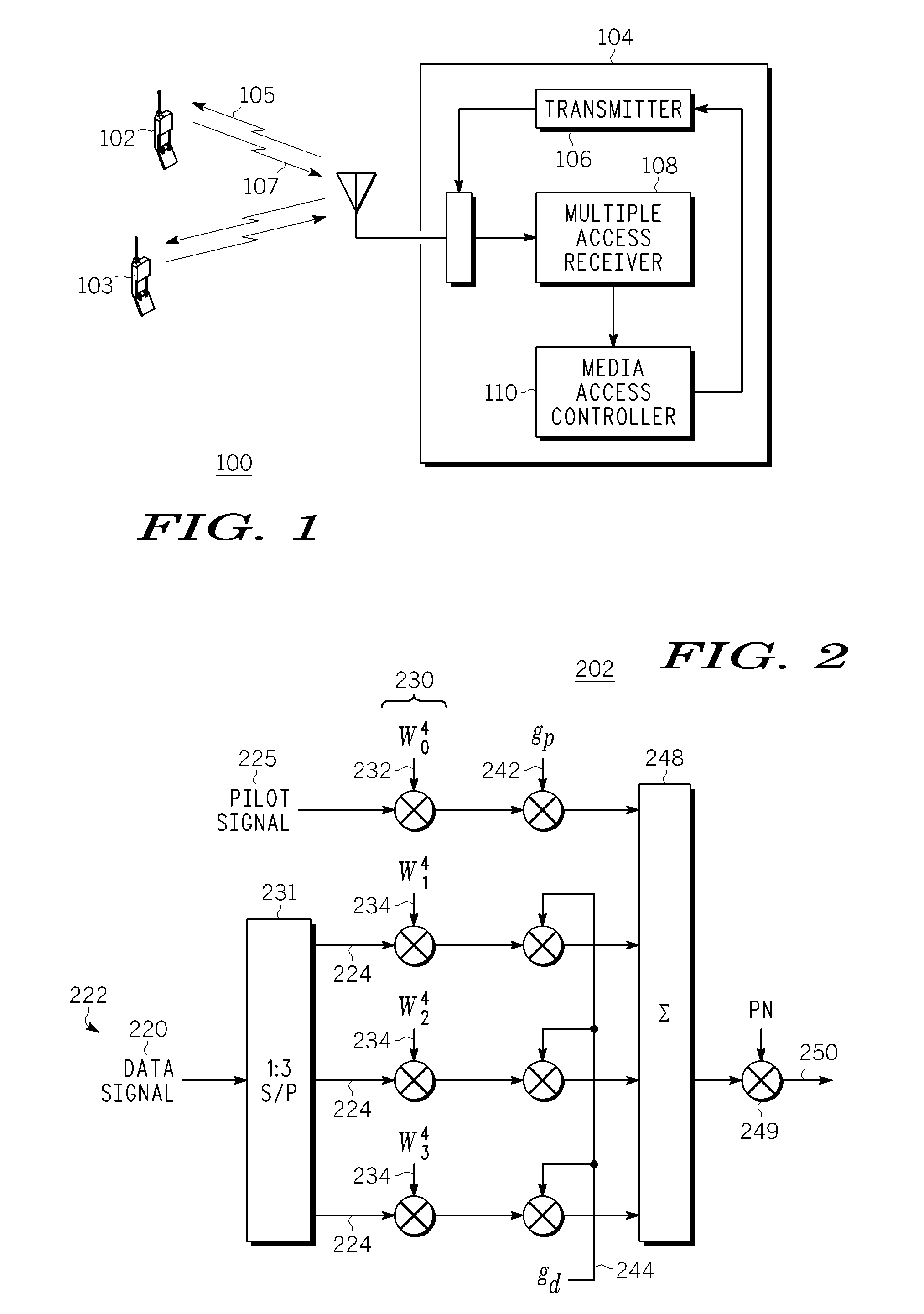
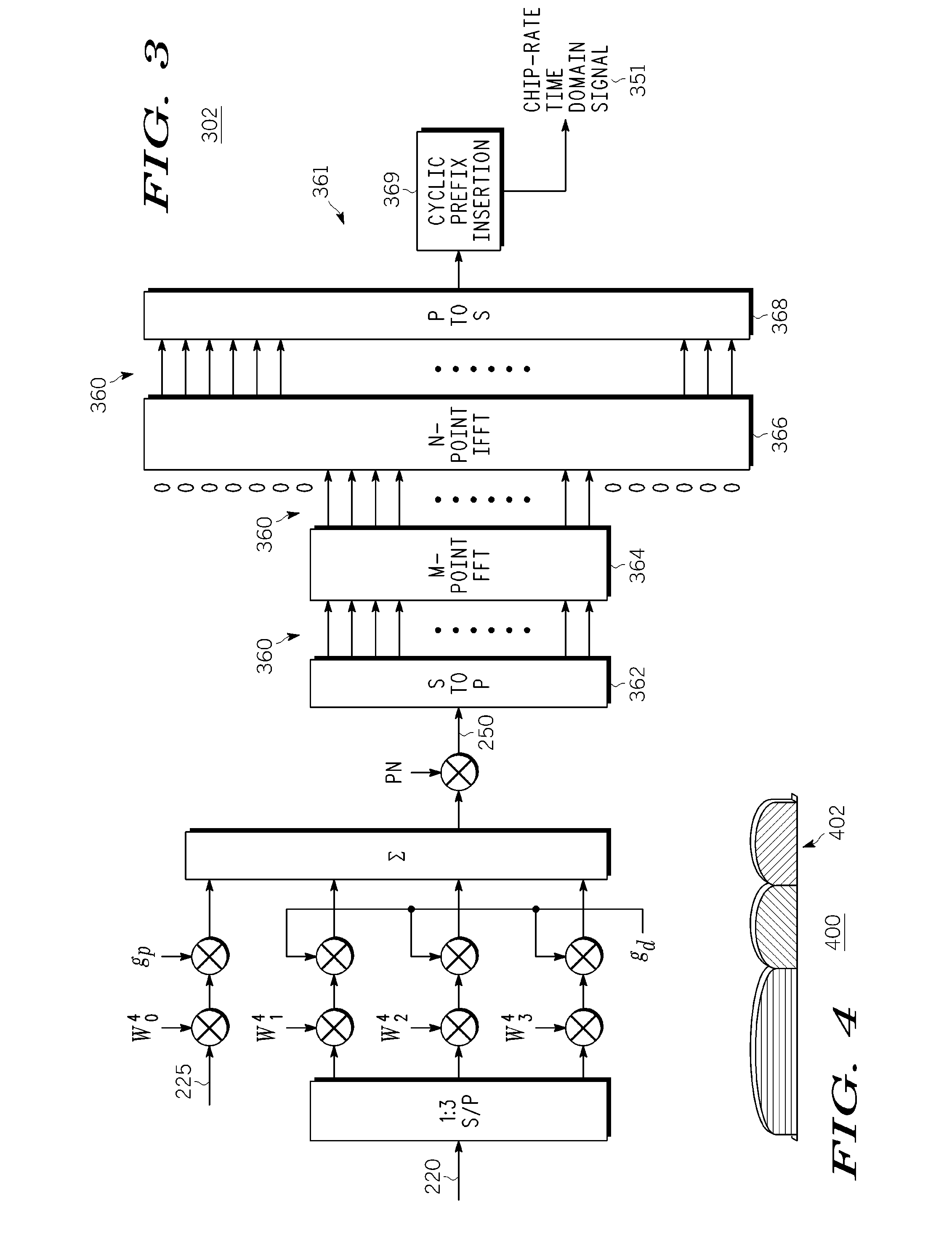
A method and apparatus for wireless transmission from a mobile unit to a base station includes multiplexing a pilot signal and a data signal, wherein the data signal operates at a data rate by splitting the data signal into a plurality of data streams; applying a pilot gain to the pilot channel, wherein the data gain and the pilot gain are a function of the data rate; and combining the plurality of data streams and the pilot signal into a subset of sub-carriers. The subset of sub-carriers are transmitted using Discrete Fourier Transform Spread OFDMA.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Apparatus for high accuracy distance and velocity measurement and methods thereof
InactiveUS20080100822A1Accurate distanceVelocity accuratelyOptical rangefindersScattering properties measurementsEngineeringDiscrete Fourier transform
Owner:MUNRO JAMES F
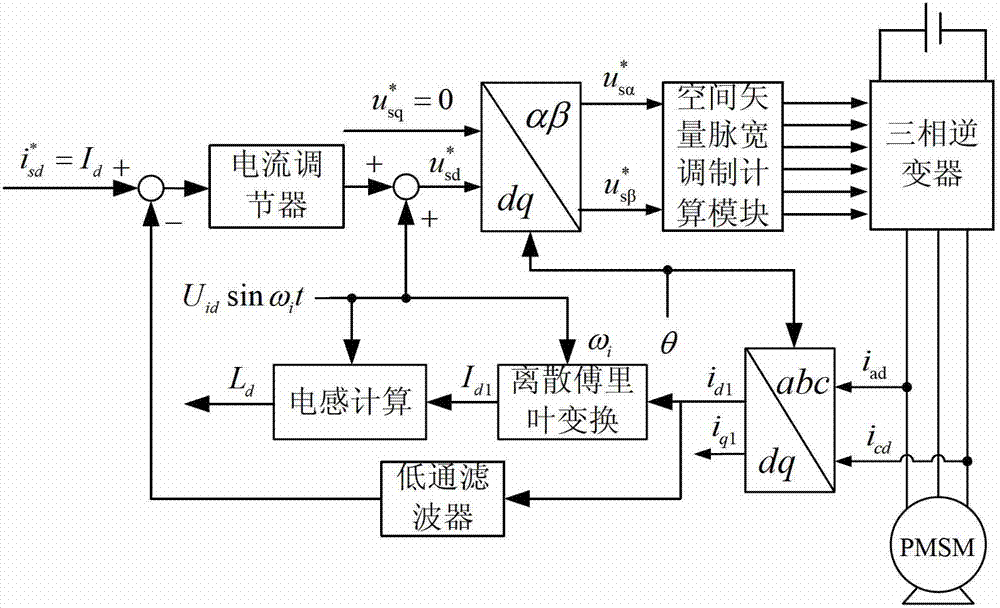
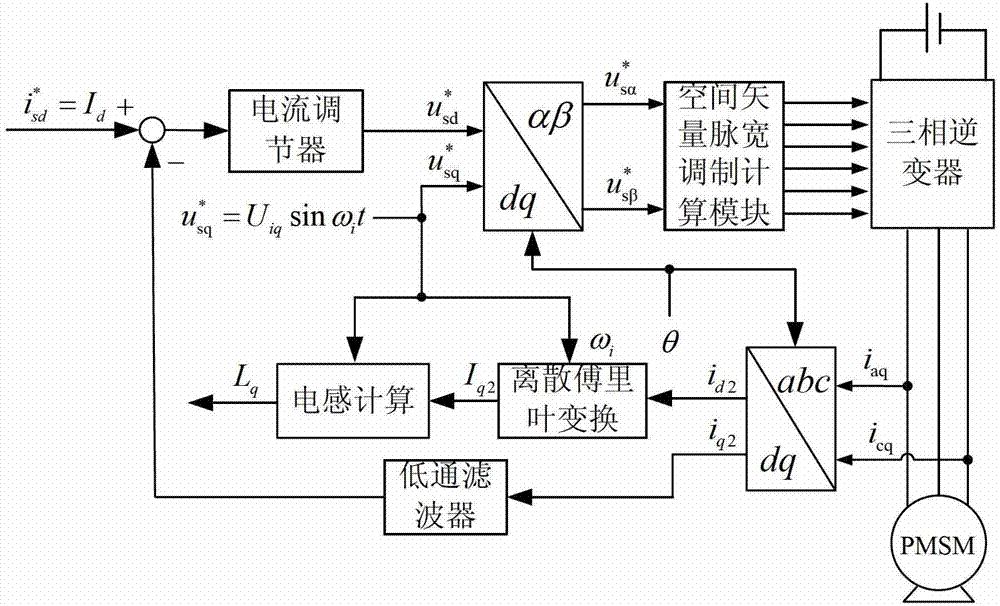
Parameter offline identification method for permanent magnet synchronous motor under condition of rest
InactiveCN103178769AImprove consistencyEliminate the effects ofElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention discloses a parameter offline identification method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor under the condition of rest, belonging to the field of motor control and solving the problems of rotor external locking, overlong identification time, poor result consistency, poor practicability and the like of the existing parameter offline identification method for the permanent magnet synchronous motor under the condition of rest. The parameter offline identification method comprises the steps of: always keeping a rotor in a rest state, injecting a high-frequency voltage signal in a straight axis of a rotor winding, detecting a three-phase stator current and transforming into two-phase rotational coordinates, carrying out discrete Fourier transform on the current to obtain a straight axis high-frequency current amplitude so as to obtain a straight-axis inductance value through calculation; then injecting a high-frequency voltage signal in a quadrature axis of the stator winding, obtaining a quadrature axis inductance value by using the same method; and then introducing a linearly increasing current into the straight axis of the stator winding so as to obtain a voltage generating a corresponding current through reconstruction of a voltage of an inverter, calculating and fitting a straight slope by using a least square method by using a straight axis voltage value as a longitudinal coordinate and a straight axis current value as a transverse coordinate, and finally obtaining a slope value, wherein the slope value is a stator resistance value.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
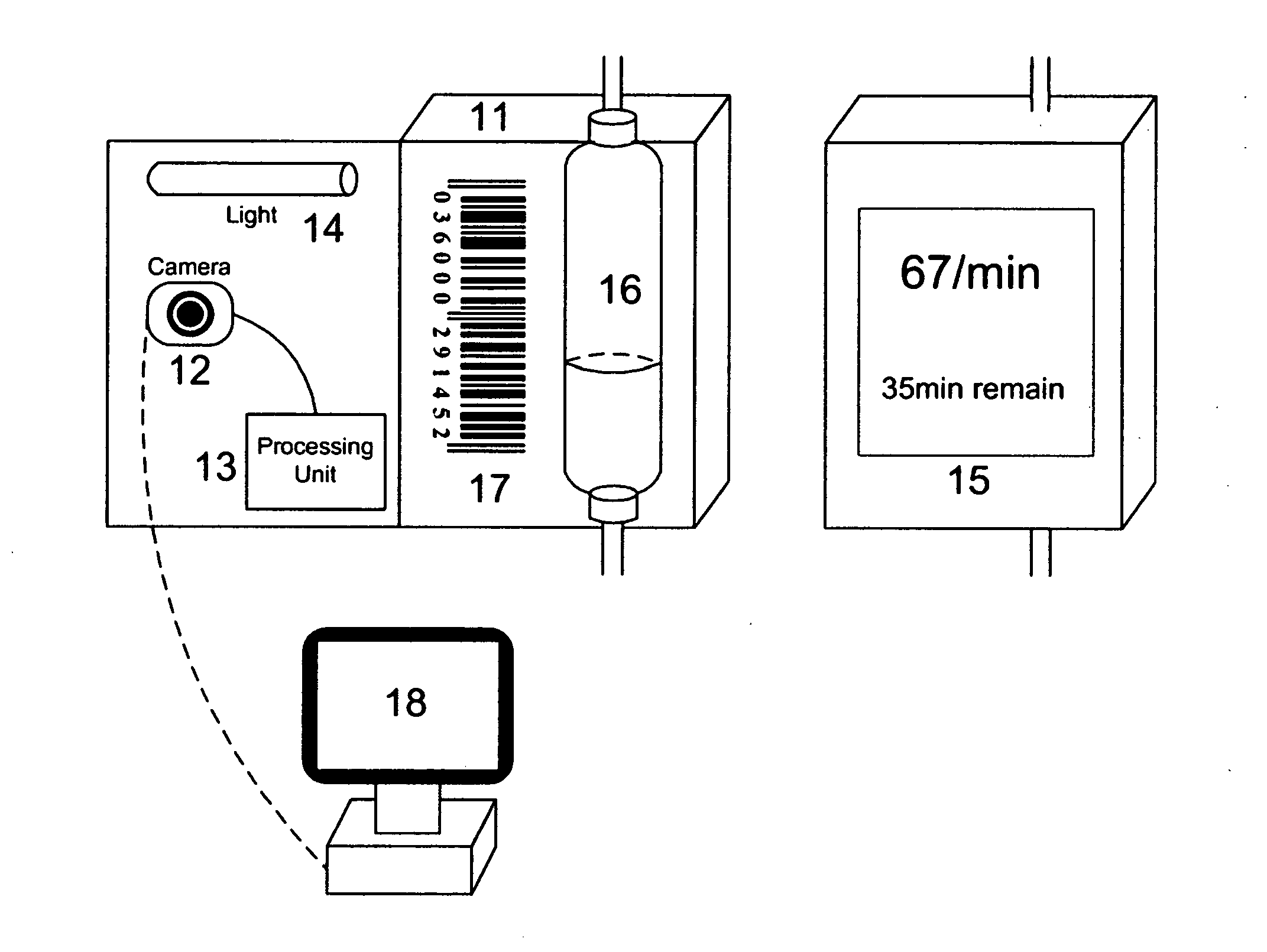
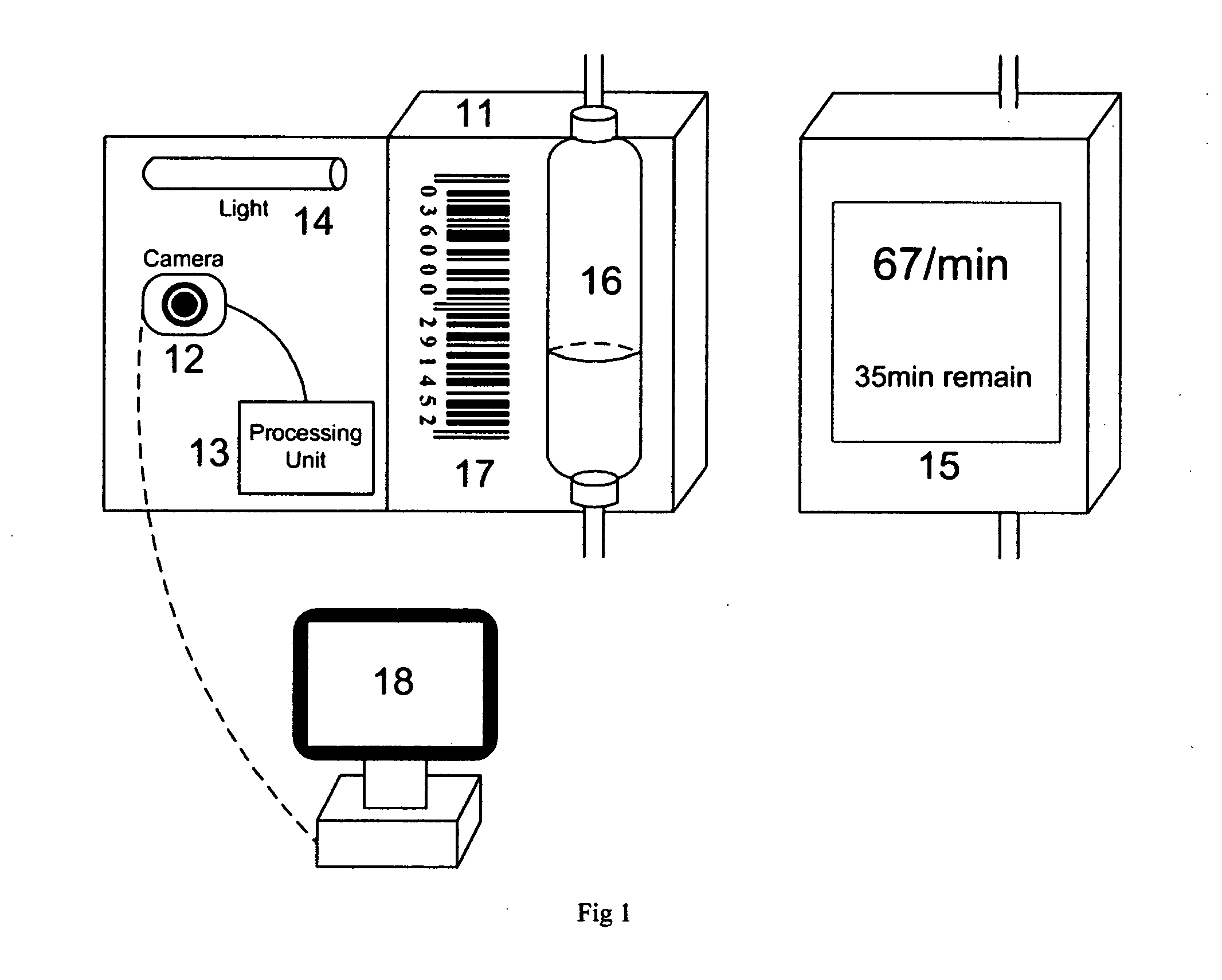
IV monitoring by video and image processing
InactiveUS20120013735A1Eliminate the effects ofSave countless timeTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
We describe a method and apparatus for monitoring the dripping speed in IV process, as well as detecting the its end. The apparatus includes a camera and a processing unit to analyze the information from the acquired video. Features from the image sequence are extracted and the dripping speed is computed accordingly by discrete Fourier transform. The apparatus is also capable of detecting the end of the dripping process by finding the location of liquid surface in the drip chamber. We also describe the use of barcode to provide information to the monitoring device and program.
Owner:TAO KAI
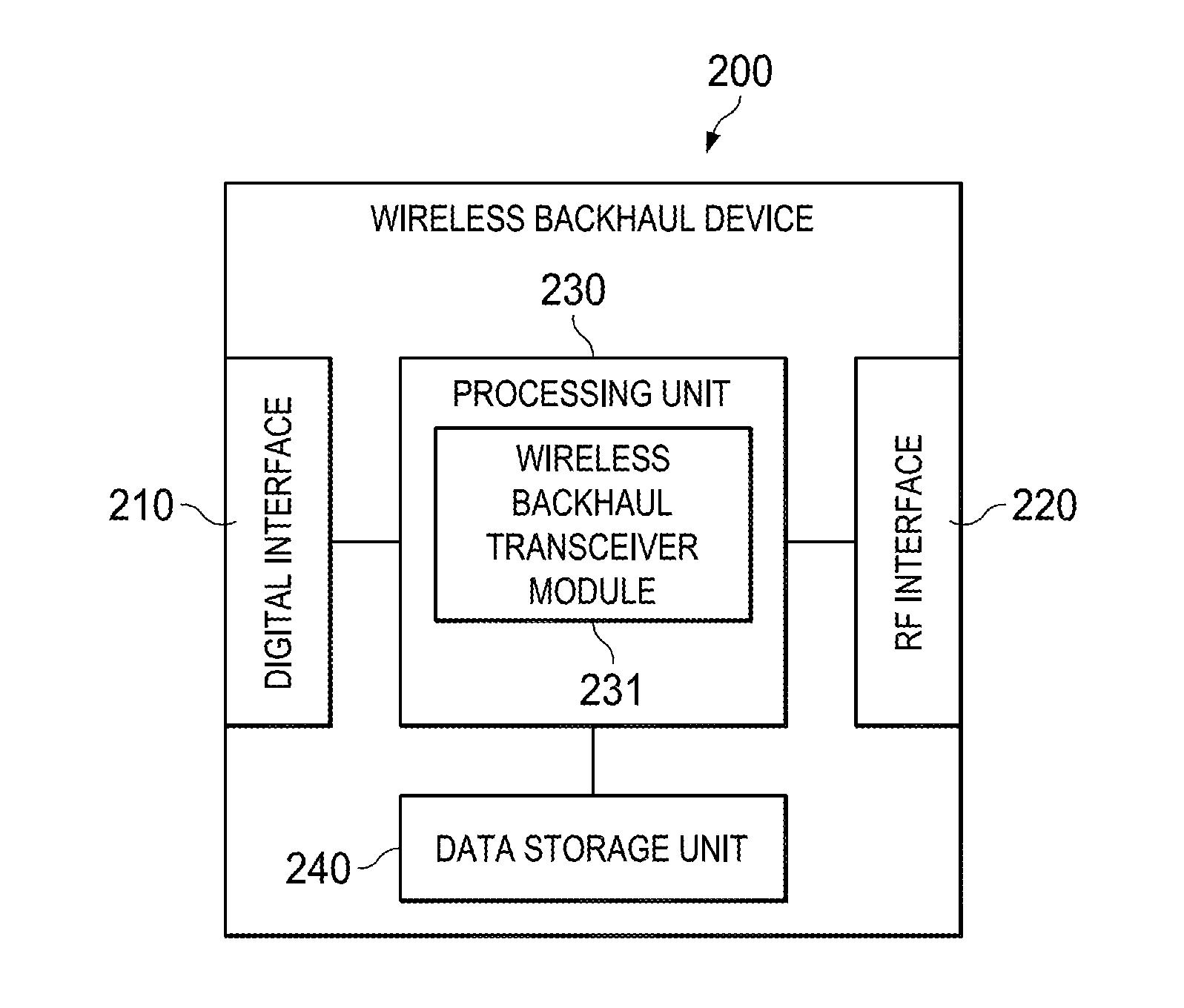
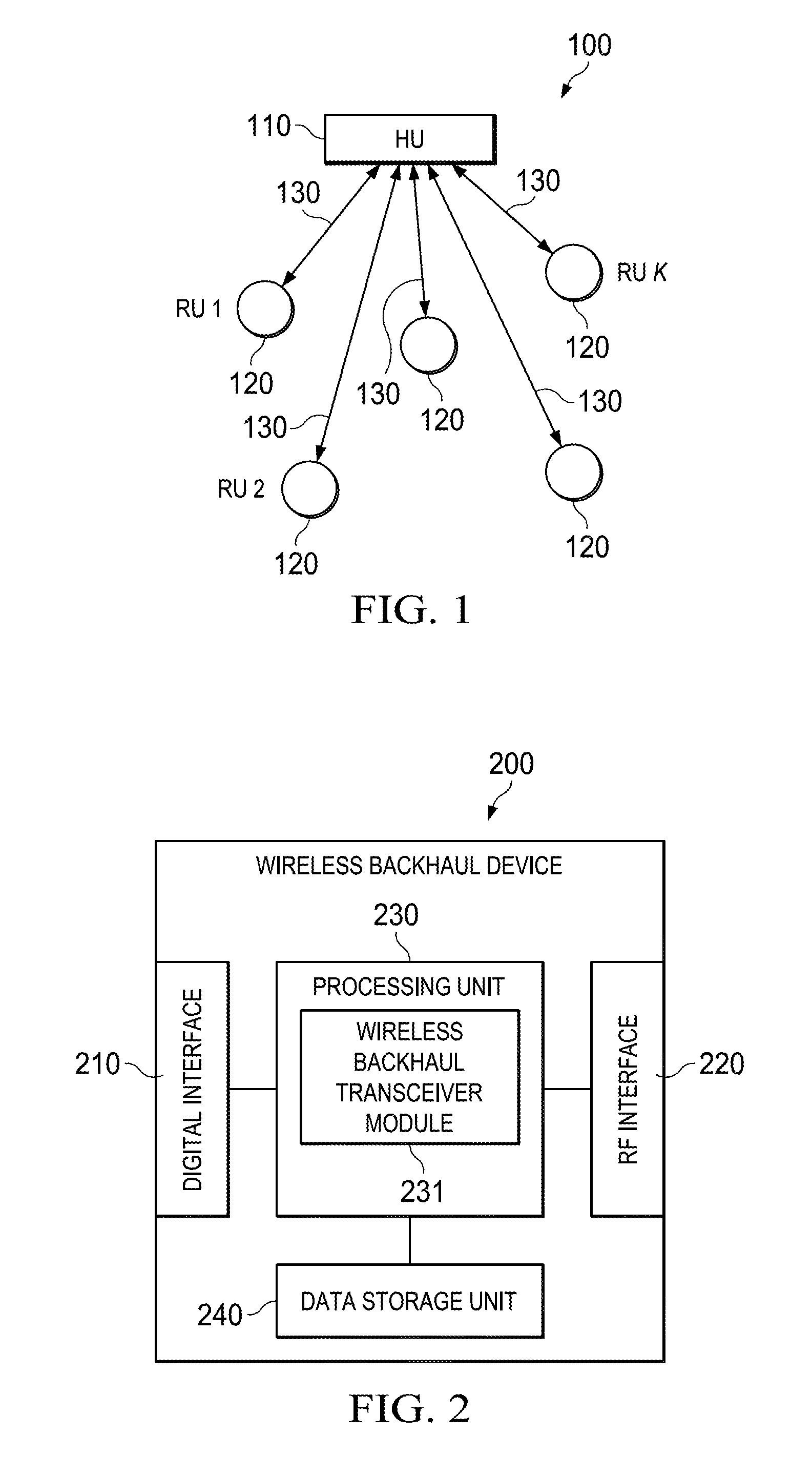
Nlos wireless backhaul downlink communication
ActiveUS20140362701A1Transmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementBroadcast channelsFourier transform on finite groups
A method for communicating over a wireless backhaul channel comprising generating a radio frame comprising a plurality of time slots, wherein each time slot comprises a plurality of symbols in time and a plurality of sub-carriers in a system bandwidth, broadcasting a broadcast channel signal comprising a transmission schedule to a plurality of remote units in a number of consecutive sub-carriers centered about a direct current (DC) sub-carrier in at least one of the time slots in the radio frame regardless of the system bandwidth, and transmitting a downlink (DL) control channel signal and a DL data channel signal to a first of the remote units, wherein the DL data channel signal is transmitted by employing a single carrier block transmission scheme comprising a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) spreading for frequency diversity.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Perceptual similarity image retrieval
InactiveUS20030231806A1High degree of successInsensitive to irrelevant detailData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalWeb serviceContinuous tone
A system and method indexes an image database by partitioning an image thereof into a plurality of cells, combining the cells into intervals and then spots according to perceptual criteria, and generating a set of spot descriptors that characterize the perceptual features of the spots, such as their shape, color and relative position within the image. The shape preferably is a derivative of the coefficients of a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of the perimeter trace of the spot. The set of spot descriptors forms as an index entry for the spot. This process repeated for the various images of the database. To search the index, a key comprising a set of spot descriptors for a query image is generated and compared according to a perceptual similarity metric to the entries of the index. The metric determines the perceptual similarity that the features of the query image match those of the indexed image. The search results are presented as a scored list of the indexed images. A wide variety of image types can be indexed and searched, including: bi-tonal, gray-scale, color, "real scene" originated, and artificially generated images. Continuous-tone "real scene" images such as digitized still pictures and video frames are of primary interest. There are stand alone and networked embodiments. A hybrid embodiment generates keys locally and performs image and index storage and perceptual comparison on a network or web server.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
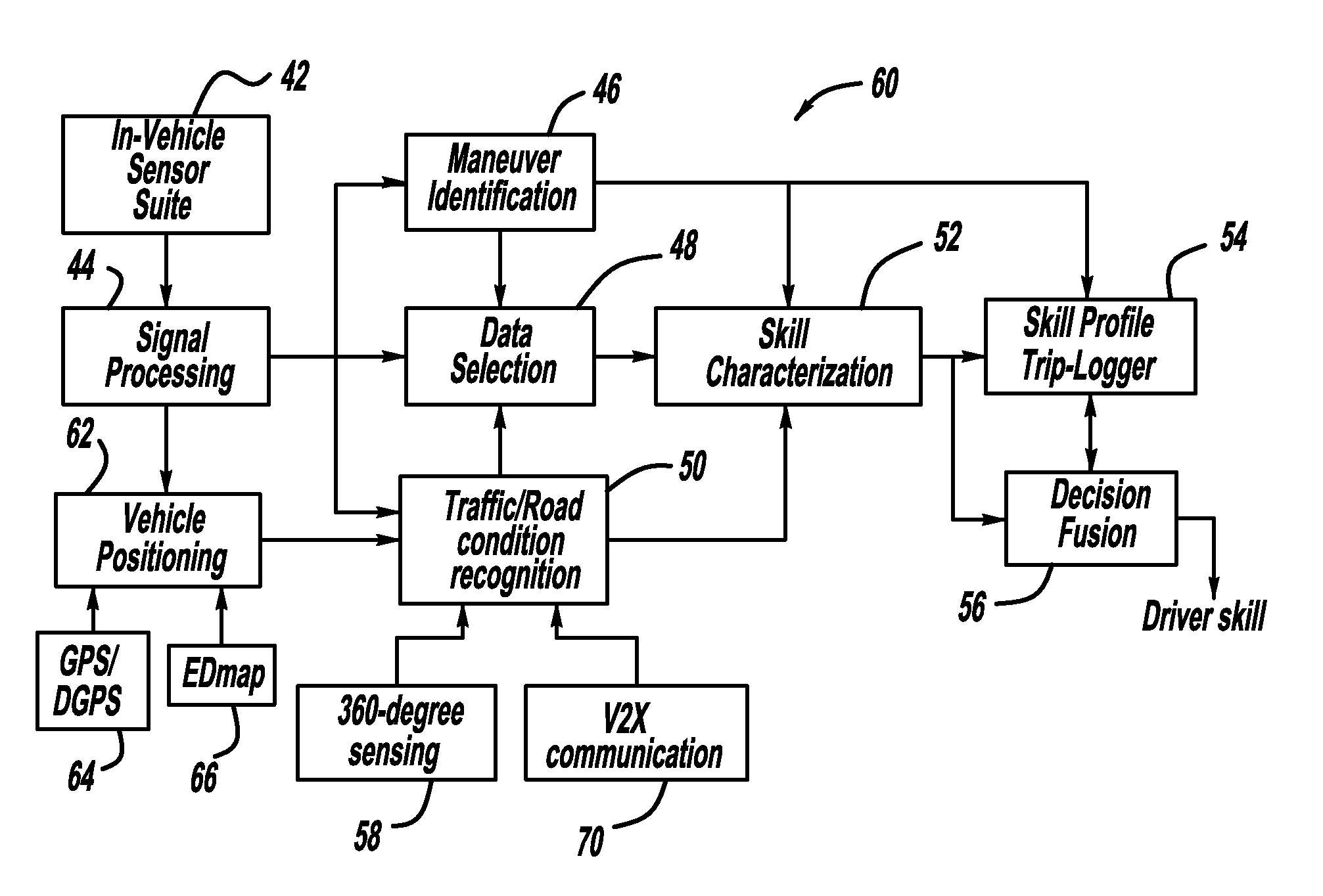
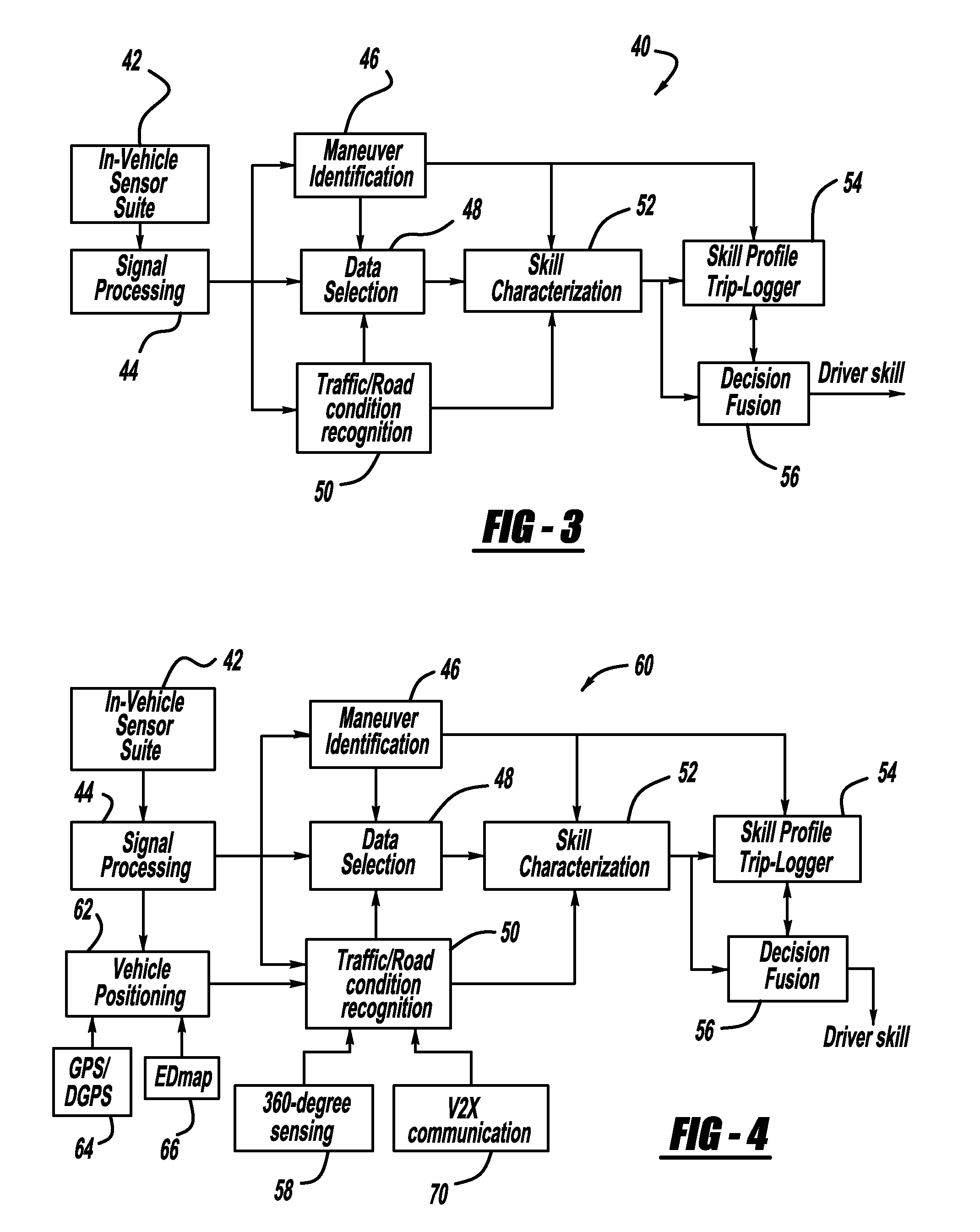
Driving skill recognition based on stop-and-go driving behavior
InactiveUS20100209891A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsDriver/operatorFourier transform on finite groups
A skill characterization processor classifies driver skill based stop and go maneuvers. A maneuver identification processor determines whether the vehicle is in a braking maneuver, and the system determines the vehicle longitudinal deceleration, the brake pedal position and the brake pedal rate from the brake pedal position. The skill characterization processor then classifies the driver's driving skill based on the brake pedal rate, the brake pedal position and the vehicle longitudinal deceleration generally under normal driving conditions. In one embodiment, the processor classifies driver skill by performing frequency analysis on the brake pedal rate using a discrete Fourier transform to find a frequency component of the brake pedal rate to obtain a power spectrum density.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
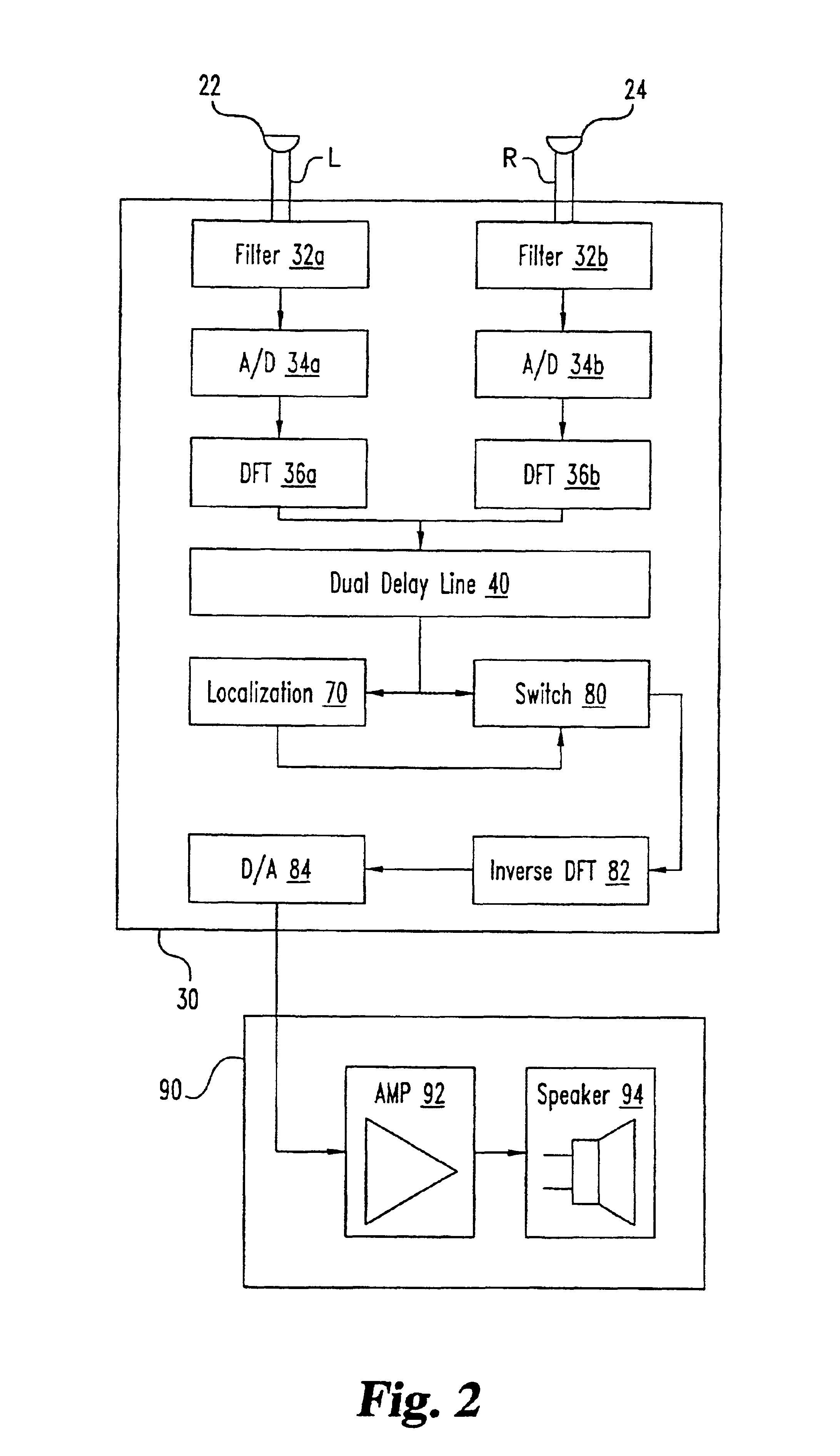
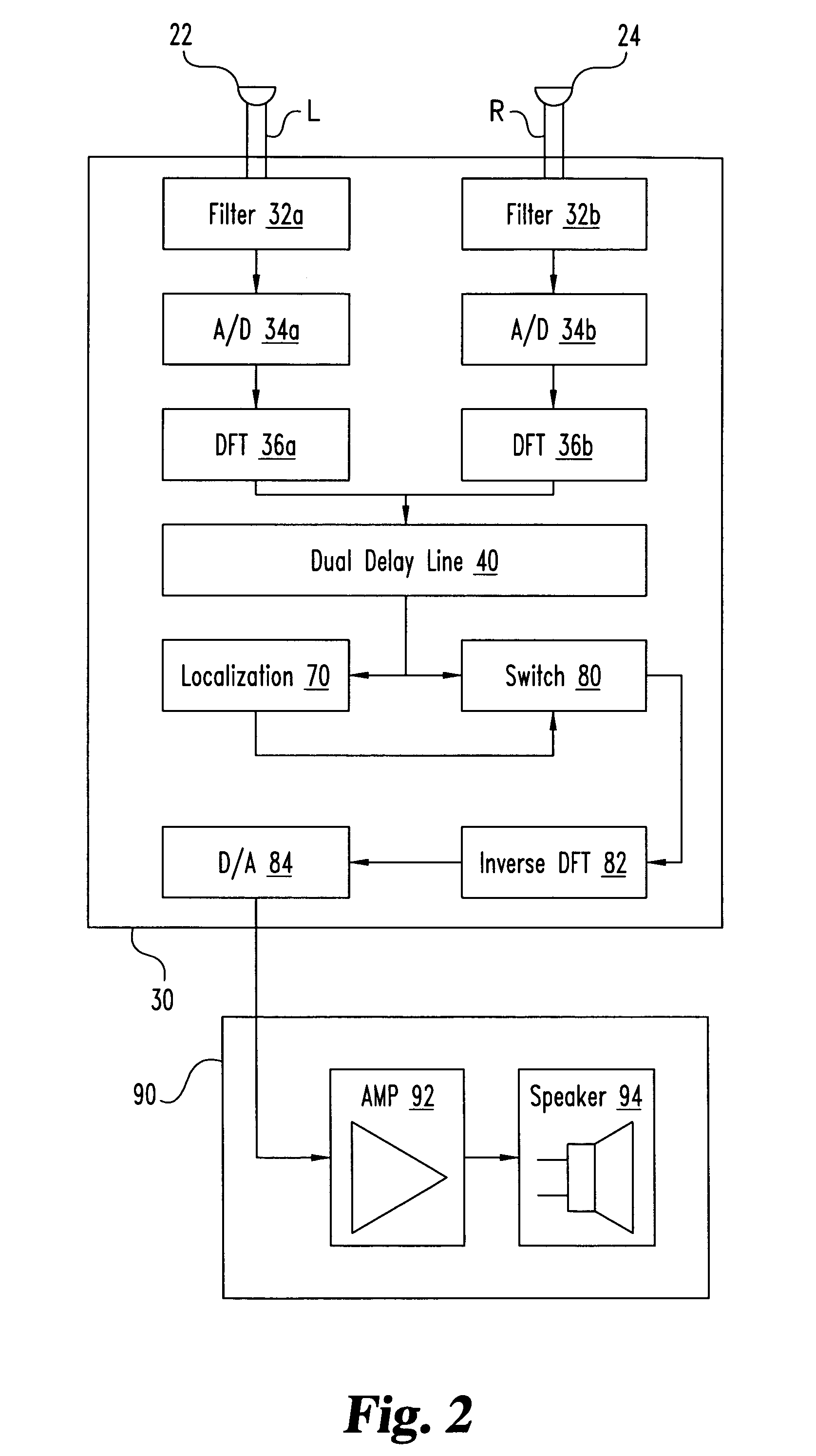
Binaural signal processing techniques
InactiveUS6987856B1Easy to zeroImprove localizationDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesTransmission noise suppressionFrequency spectrumSound sources
A desired acoustic signal is extracted from a noisy environment by generating a signal representative of the desired signal with a processor. The processor receives aural signals from two sensors each at a different location. The two inputs to the processor are converted from analog to digital format and then submitted to a discrete Fourier transform process to generate discrete spectral signal representations. The spectral signals are delayed by a number of time intervals in a dual delay line to provide a number of intermediate signals, each corresponding to a different spatial location relative to the two sensors. Locations of the noise source and the desired source are determined and the spectral content of the desired signal is determined from the intermediate signal corresponding to the noise source locations. Inverse transformation of the selected intermediate signal followed by digital to analog conversion provides an output signal representative of the desired signal. Techniques to localize multiple acoustic sources are also disclosed. Further, a technique to enhance noise reduction from multiple sources based on two-sensor reception is described.
Owner:ILLINOIS UNIV OF BOARD OF TRUSTEES THE
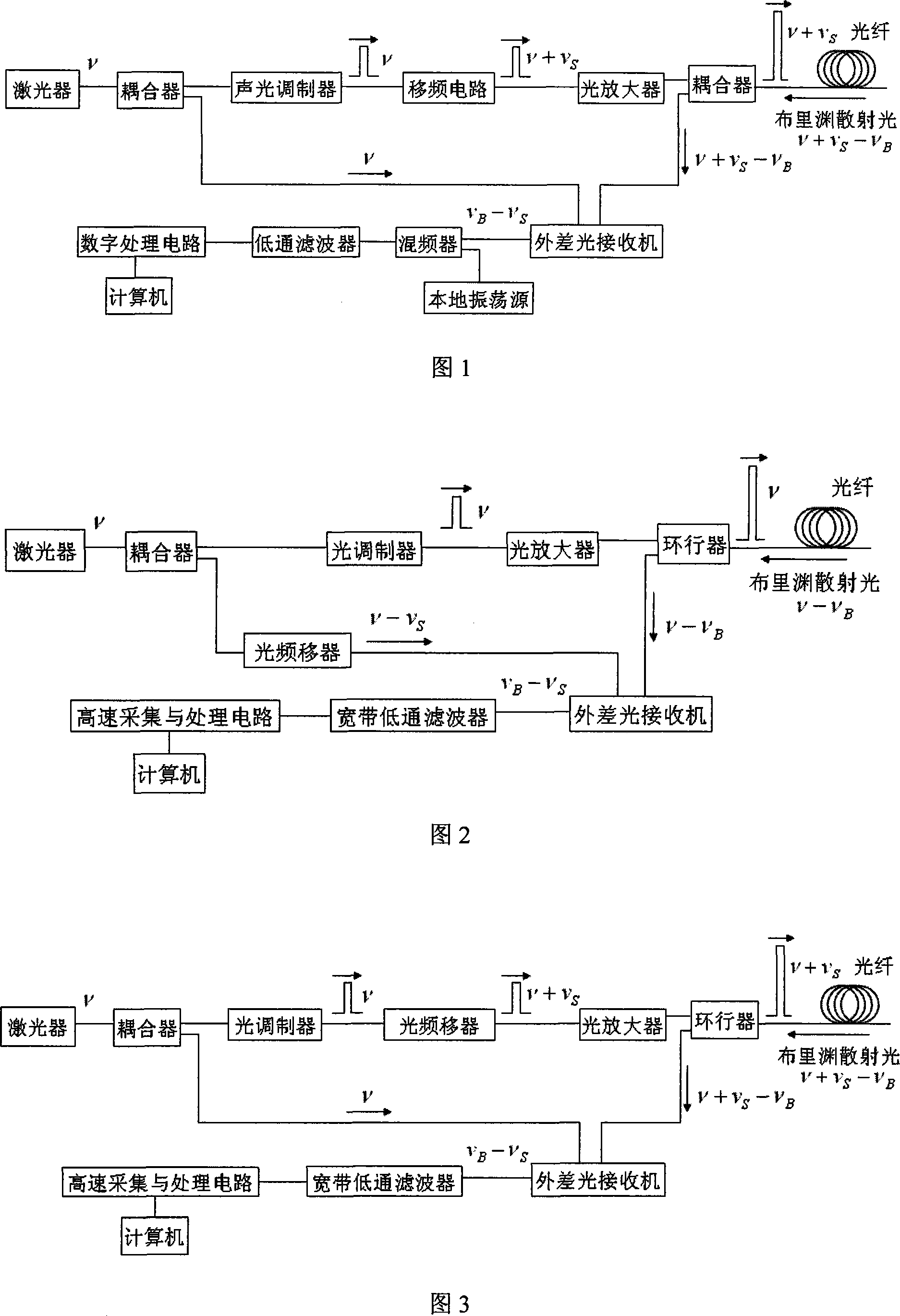
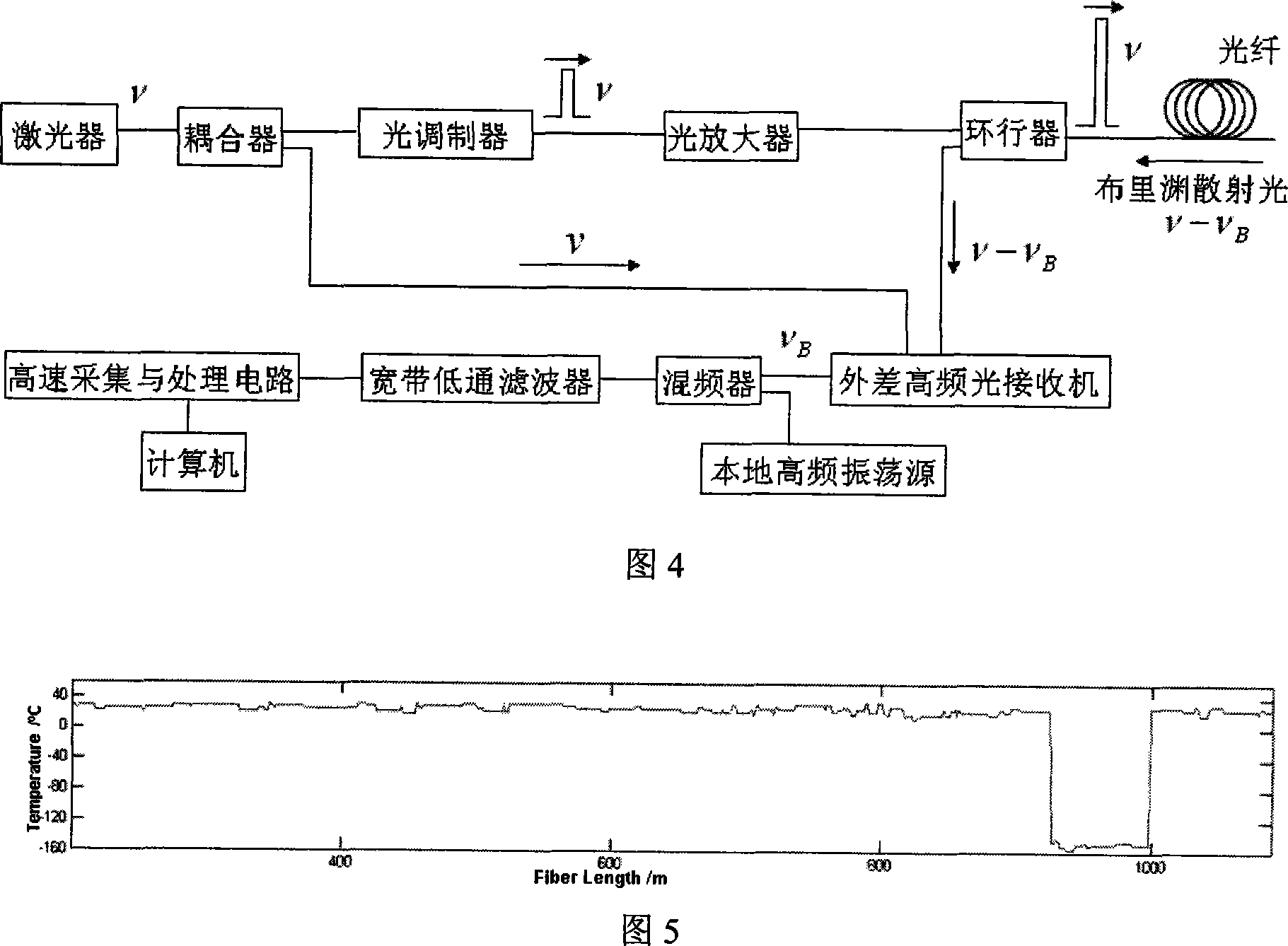
Brillouin optical time domain reflection measuring method based on quick fourier transform
InactiveCN101144729AFast measurementHigh measurement accuracyThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention interferes local reference light with Brillouin diffused light transferred back by a sensing optical fiber, a Brillouin diffused spectrum electrical signal generated completely passes through a broadband low pass wave filter, the sampling is performed by the high speed acquisition and the processing circuit, a quick speed Fourier transformation is performed, a Brillouin diffused spectrum is obtained; then a Lorentz fitting is performed, and a Brillouin frequency shift of each unit on the whole optical fiber is obtained finally; the relation of the Brillouin diffused spectrum, and the strain or the temperature is utilized to realize a full-distribution type measurement of the strain or the temperature. The whole Brillouin diffused spectrum on the whole sensing optical fiber can be obtained in an impulse detecting circle by a processing method of the high speed acquisition, and the processing circuit and the quick speed Fourier transformation adopted by the invention, the measuring speed is improved to an order of magnitude compared with the prior technology on the premise of not decreasing the resolution of a measuring space and the measuring accuracy, thereby improving a speech to noise ratio to more than a plurality of times, the measuring accuracy is improved to a great extent, and the structure of the invention device is simple.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
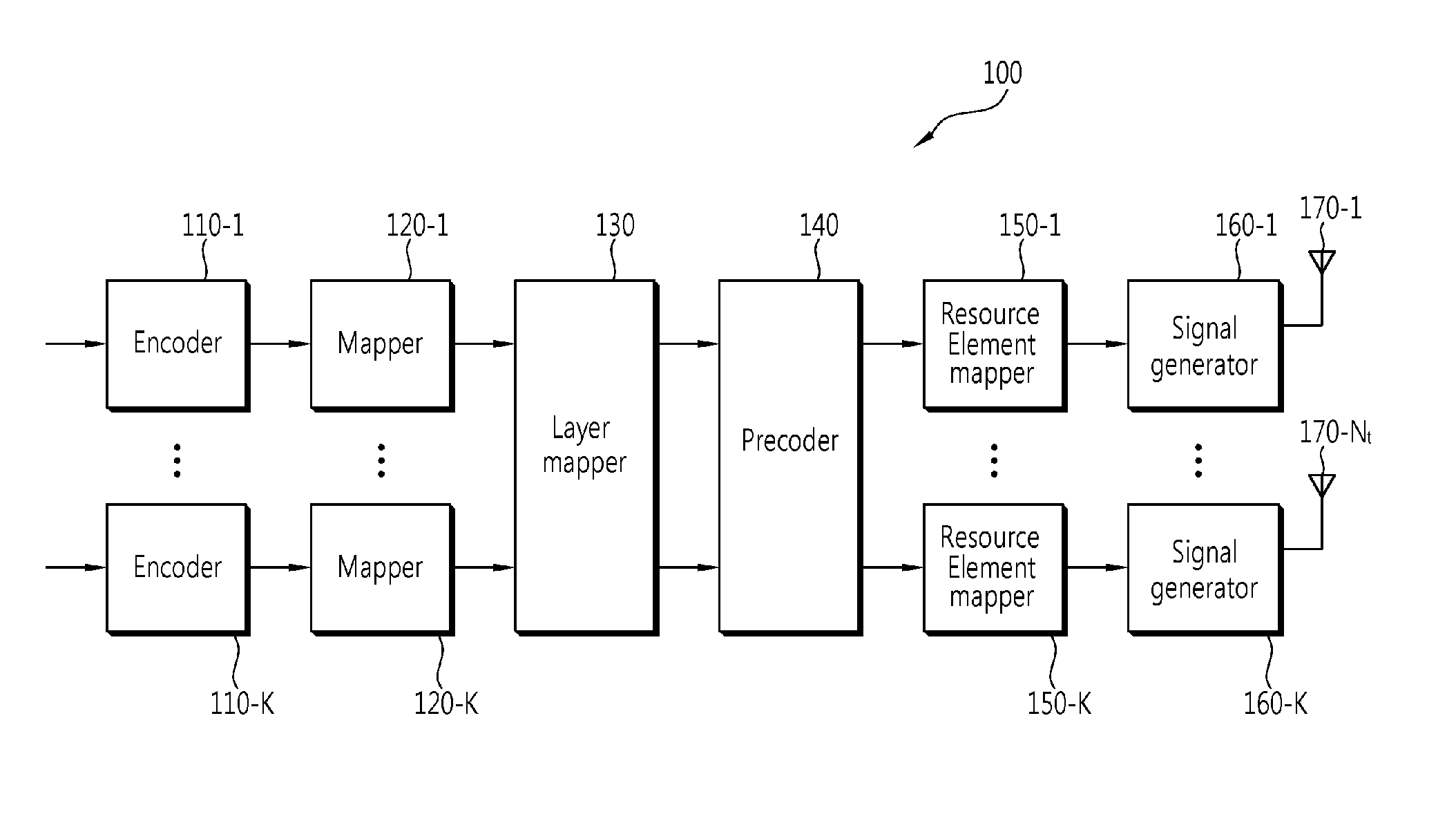
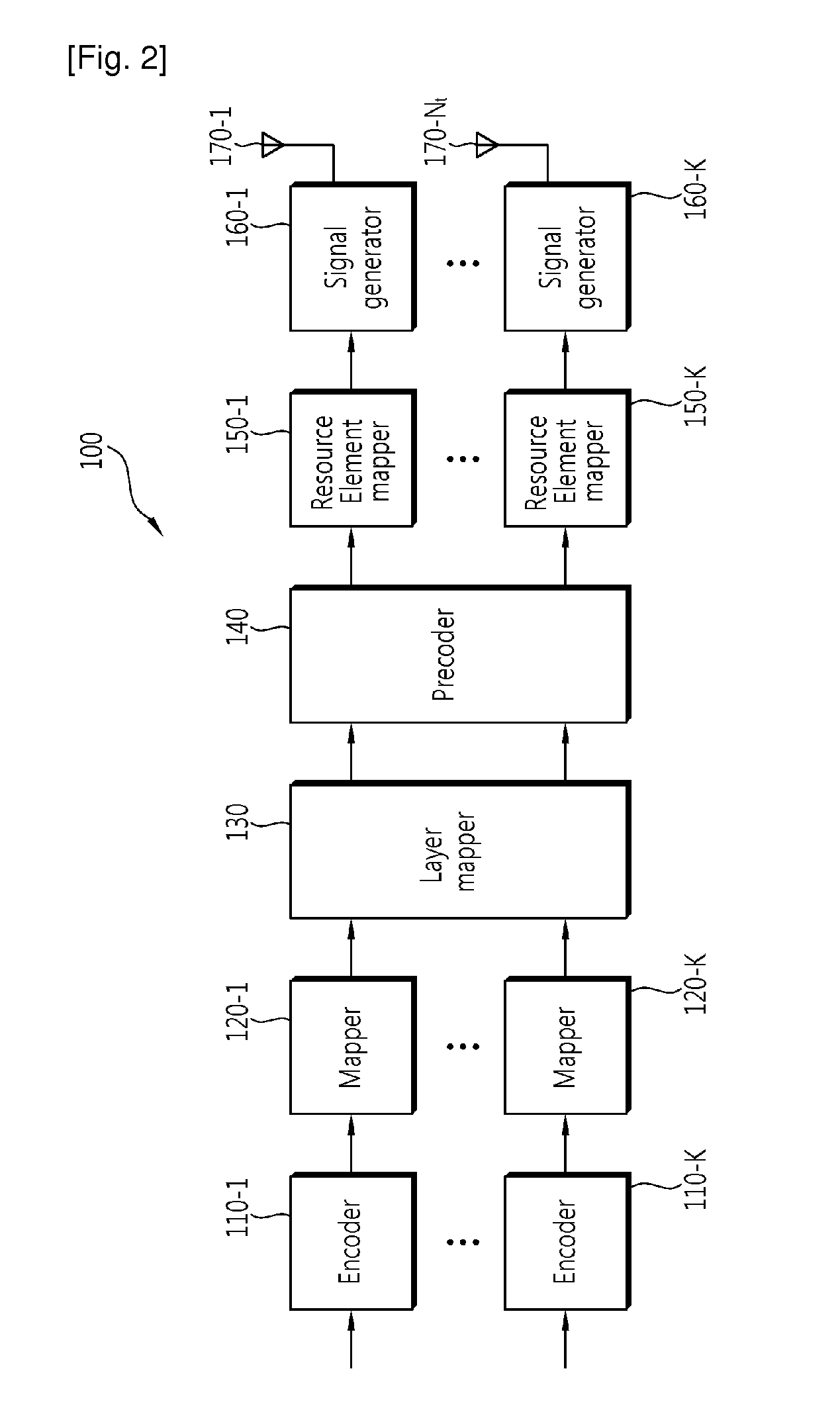
Method of transmitting data using spatial multiplexing
InactiveUS20110134902A1Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsPrecodingFast Fourier transform
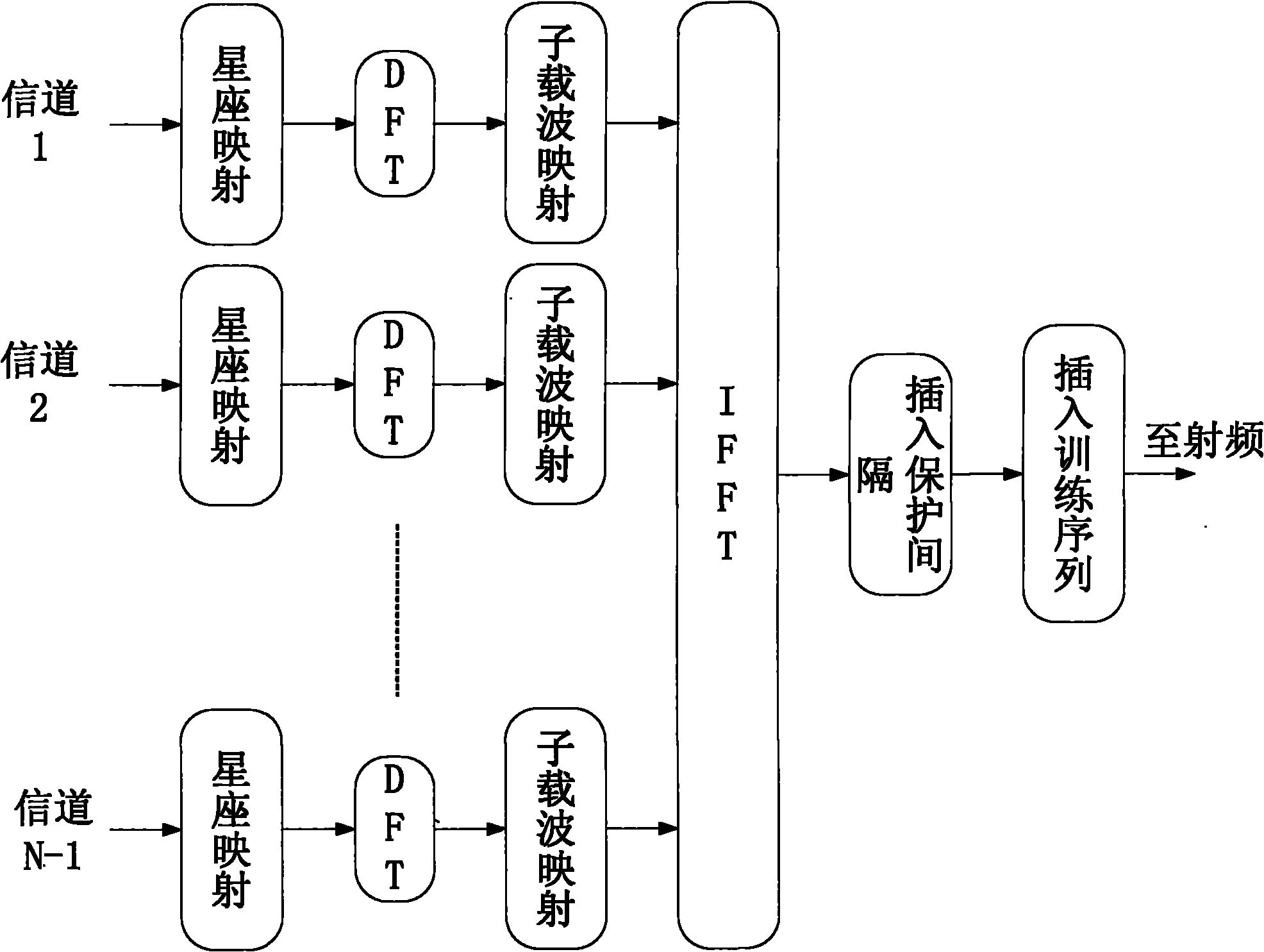
A data transmission method using spatial multiplexing is disclosed. The data transmission method using spatial multiplexing includes modulating at least one codeword to generate at least one modulation symbol, mapping the at least one modulation symbol to a layer whose number is determined according to its rank to generate a layer-mapped symbol stream, performing discrete Fourier transform (DFT) on the layer-mapped symbol stream to generate a frequency domain symbol stream, performing precoding on the frequency domain symbol stream, mapping the precoded frequency domain symbol stream to subcarriers, and then performing inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) on the precoded frequency domain symbol stream-mapped subcarriers to generate SC-FDMA symbols; and transmitting the SC-FDMA symbols by using a plurality of transmission antennas. Spatial multiplexing having a low PAPR can be possibly performed in an SC-FDMA system.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
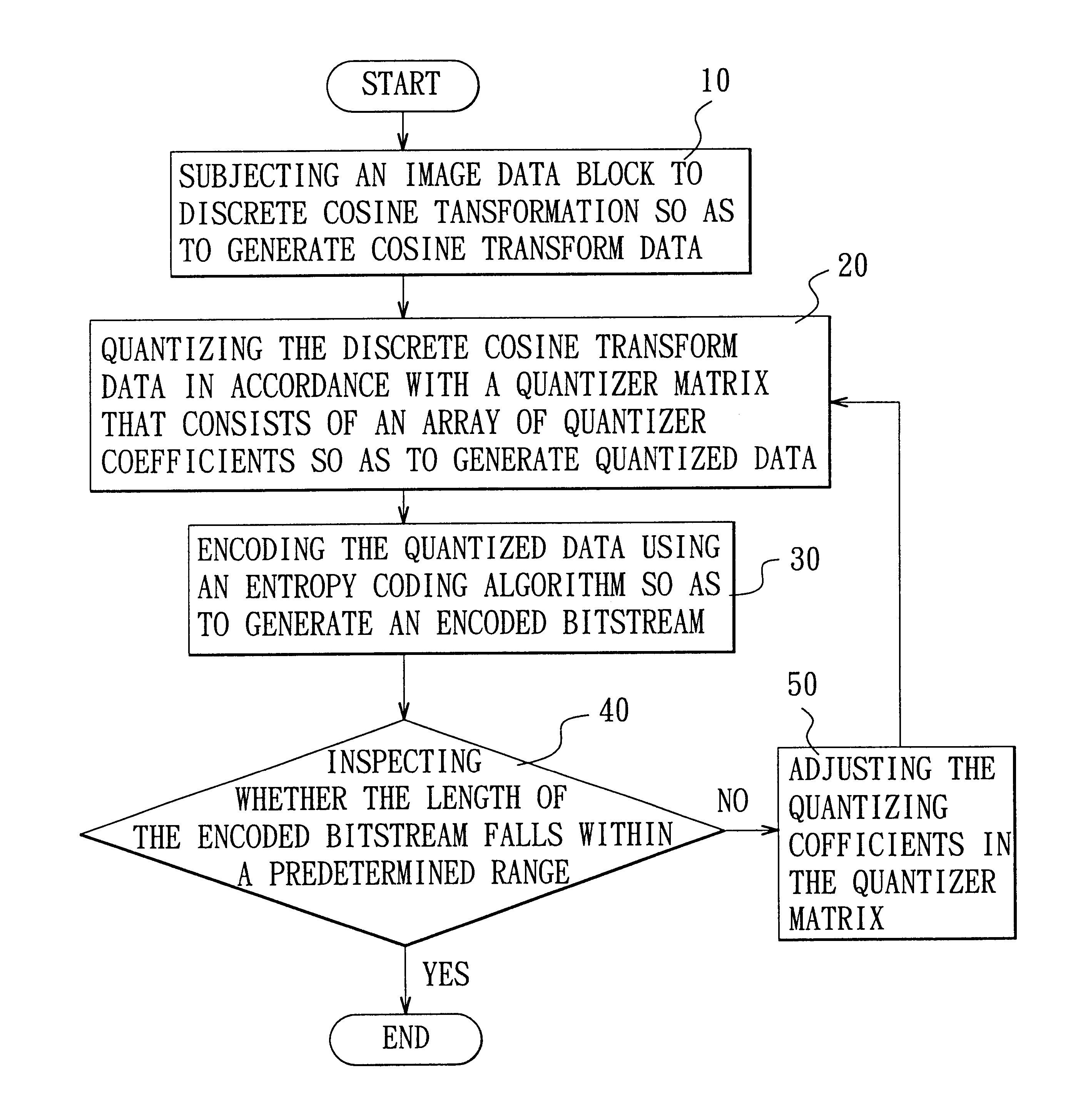
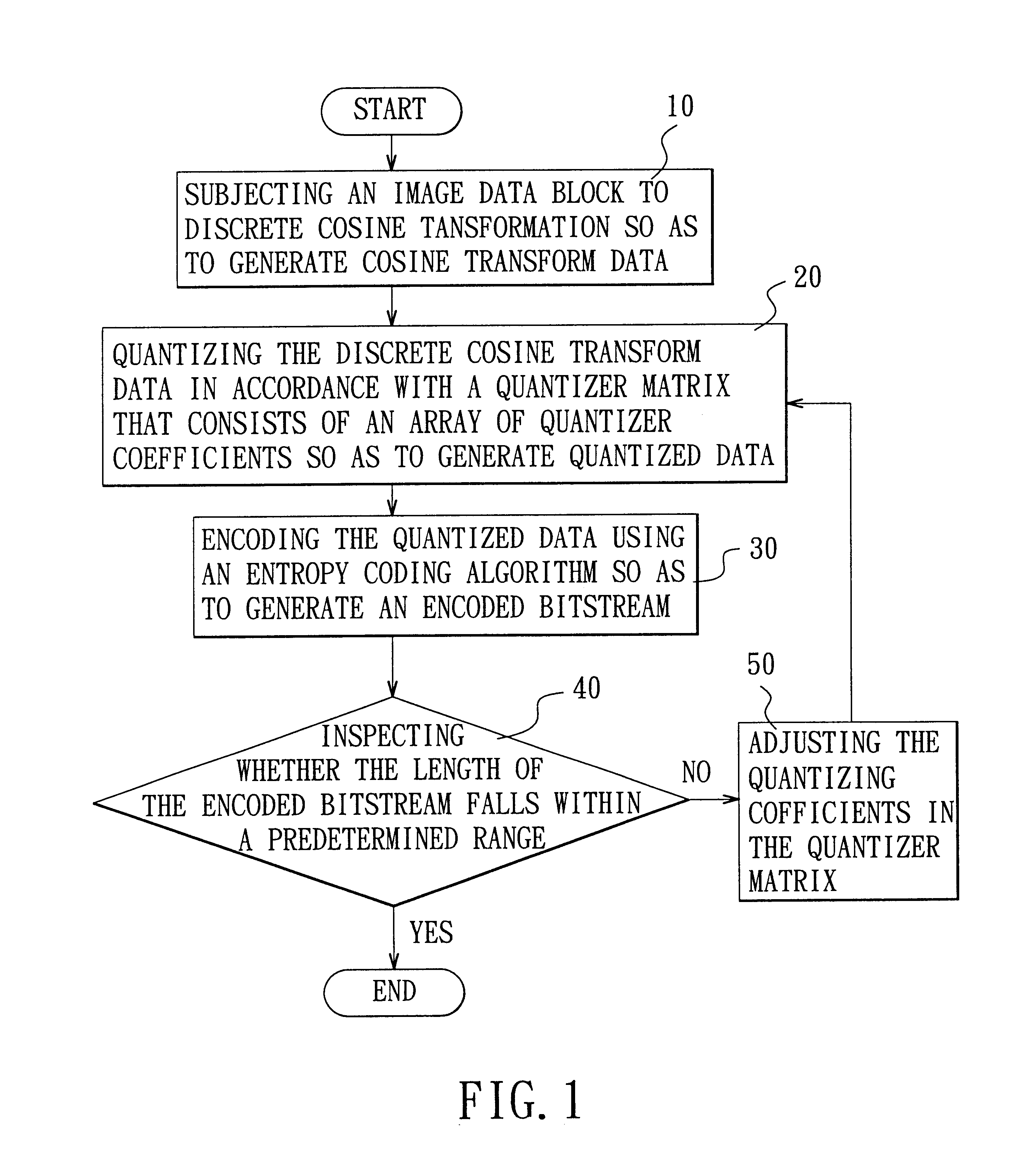
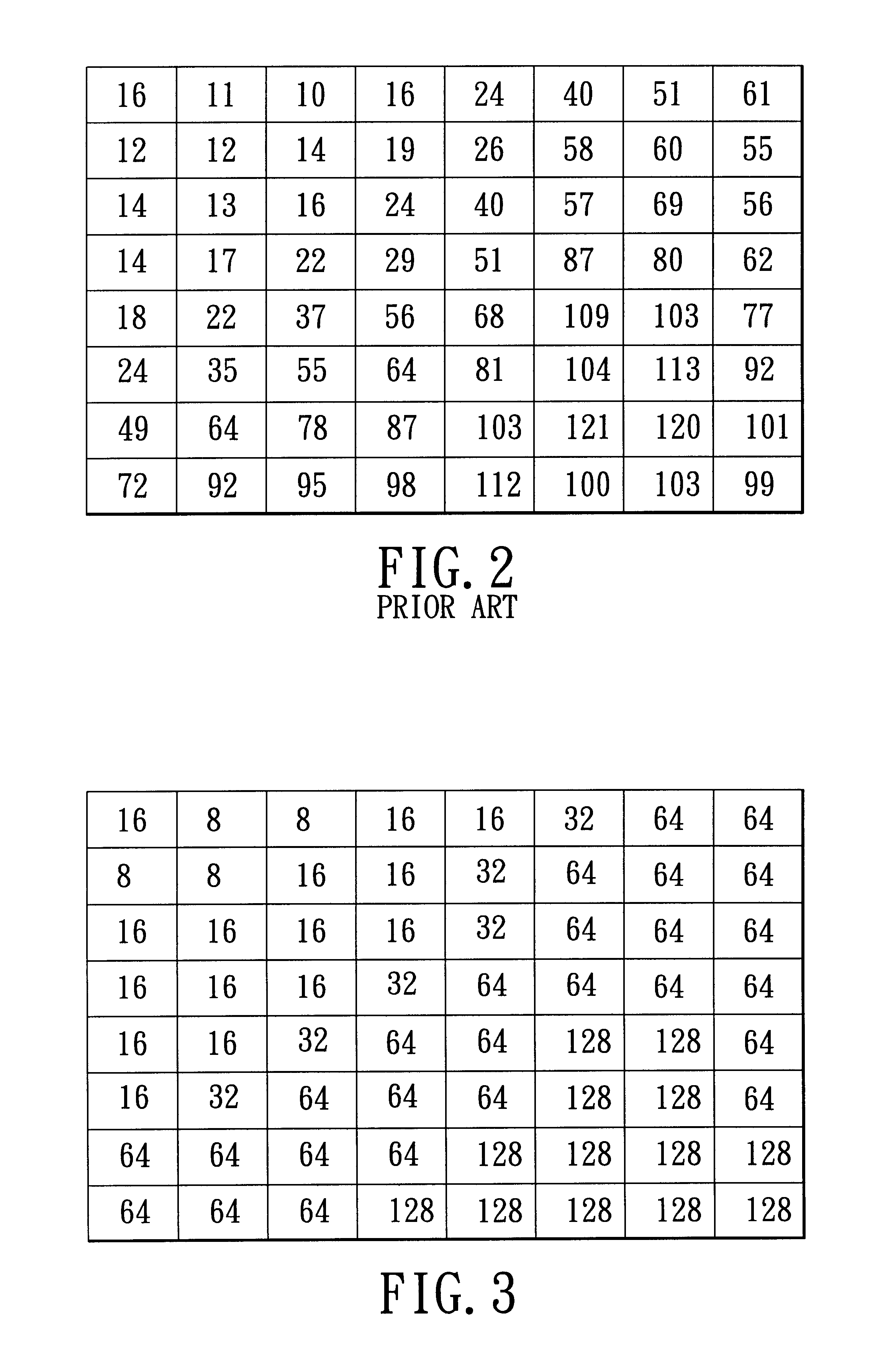
Adaptive quantization using code length in image compression
InactiveUS6882753B2Low memory and bus bandwidth requirementImprove processing efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionLandau quantization
A method is adapted for compressing an image data block, and includes the steps of:(a) subjecting the image data block to discrete cosine transformation so as to generate discrete cosine transform data;(b) quantizing the discrete cosine transform data in accordance with a quantizer matrix that consists of an array of quantizing coefficients so as to generate quantized data;(c) encoding the quantized data using an entropy coding algorithm so as to generate an encoded bitstream; and(d) when the length of the encoded bitstream does not fall within a predetermined range, adjusting the quantizing coefficients in the quantizer matrix and repeating steps (b) and (c) until the length of the encoded bitstream falls within the predetermined range.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
Virtual oscillating table detection signal processing method and equipment thereof
InactiveCN101113936AReduce testing costsGuaranteed test accuracyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesVibration testingElectricitySignal conditioning
The invention relates to a vibration table detection instrument field. In order to overcome the defects of the prior art, a signal processing approach is designed to allow a virtue instrument to be applied to the measurement field and an instrument suitable for measurement is designed accordingly on the basis of the signal processing approach. More particularly, the invention relates to a virtual vibration table detecting signal processing method and the instrument. The method comprises the processes: (1) the acceleration value of the vibration table is collected and converted into electric signals; (2) the signal is conditioned by a signal conditioning instrument; (3) the conditioned signal is collected by a data collecting card and transmitted to a computer; (4) the signal is preprocessed by the computer; (5) the preprocessed signal is discrete Fourier transformed and digital signal frequency domain filtered; (6) in the end, a speed component is output after the signal is integrated for one time; a displacement component is output after the signal is integrated for two times. The detection instrument comprises an acceleration sensor, a signal conditioning instrument, a data collecting card and a computer.
Owner:广州市计量检测技术研究院
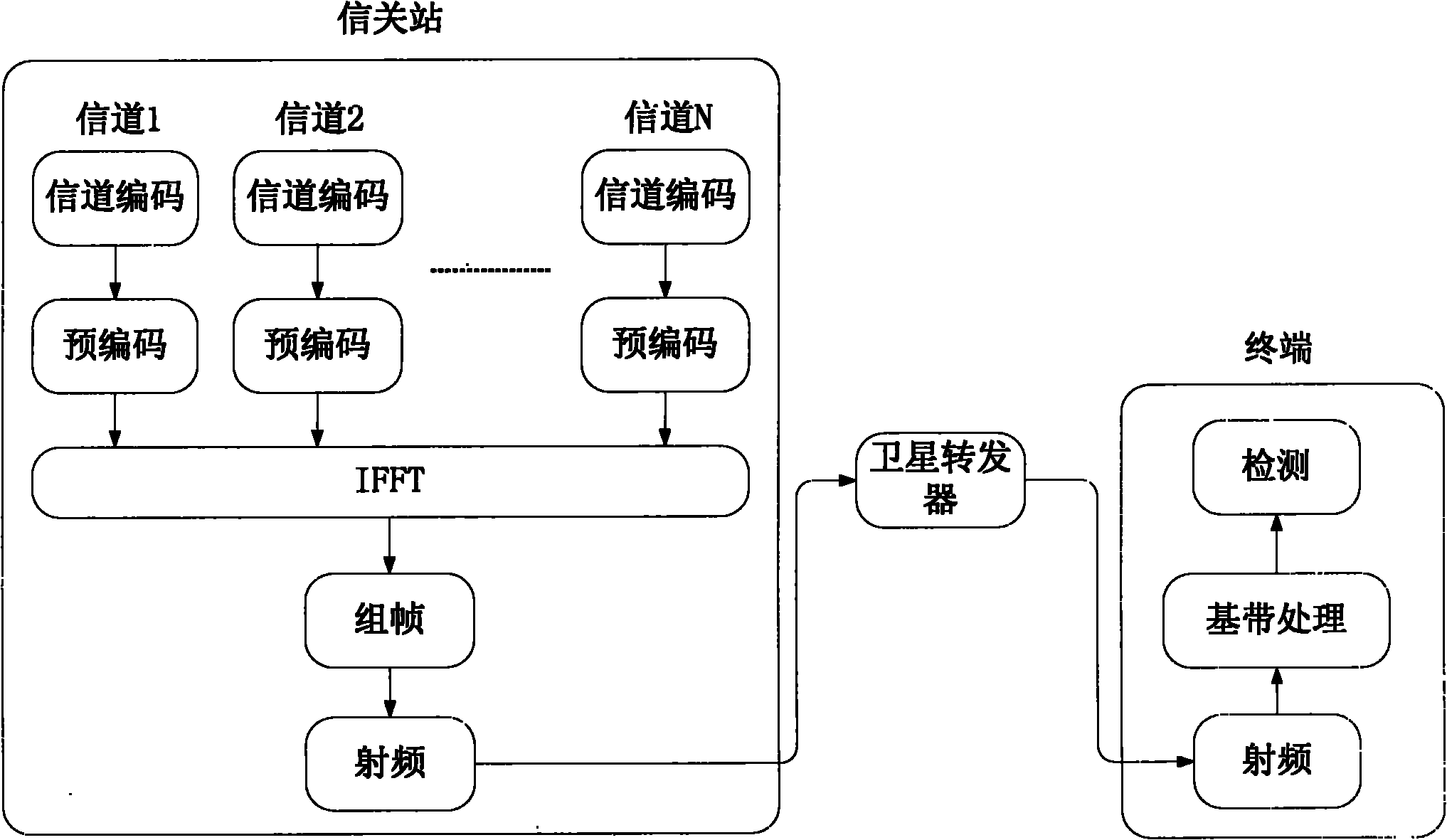
SC-OFDMA-based satellite mobile communication system for forward link
ActiveCN101795152AGuaranteed transmission qualitySolve the problem of high load peak-to-average power ratioRadio transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumResource utilization
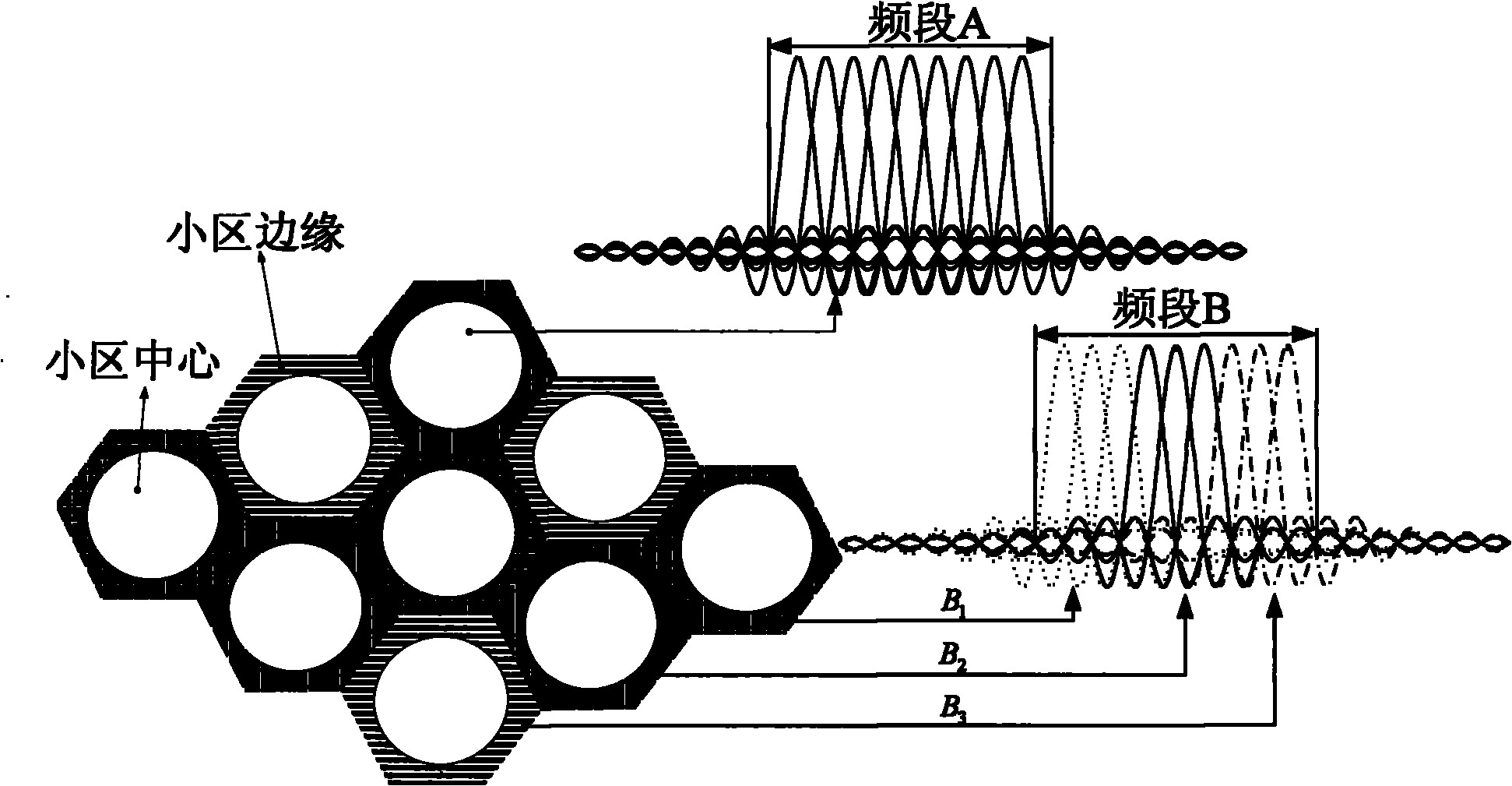
The invention discloses an SC-OFDMA-based satellite mobile communication system for a forward link, which belongs to the field of satellite mobile communication. The SC-OFDMA-based system for the forward link is characterized in that single carrier signals of a user are mapped to different sub-carriers through DFT (discrete Fourier transform) or FFT (fast Fourier transform) and then subjected to IFFT (inverse fast Fourier transform) to realize orthogonal transmission of each user signal so as to improve the utilization rate of high frequency spectrum resources and reduce the peak-to-average power ratio of the satellite forward link; and in the multi-beam-based satellite mobile communication system, different sub-carrier groups are distributed to the users in a beam overlapped area according to the beams belonging to the users so as to reduce the co-channel interference between the low beams and fulfill the aim of improving the capacity of the system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
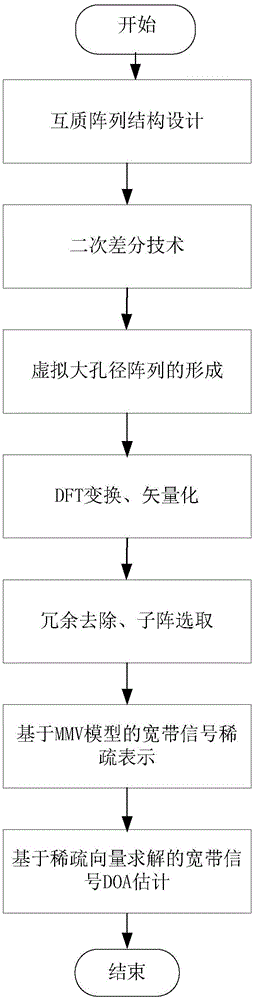
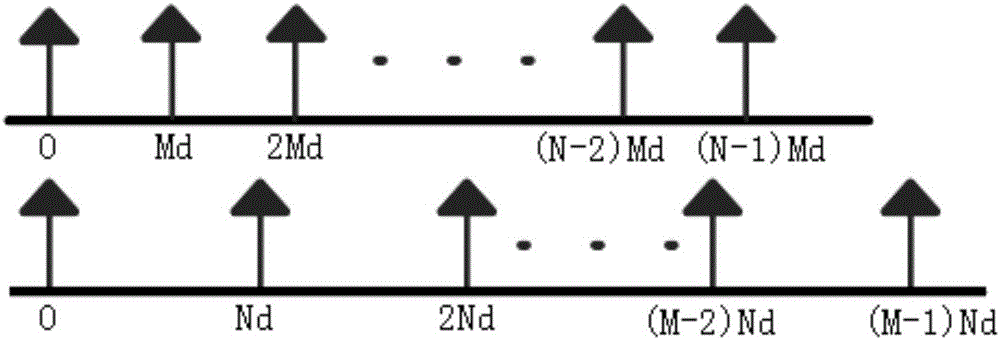
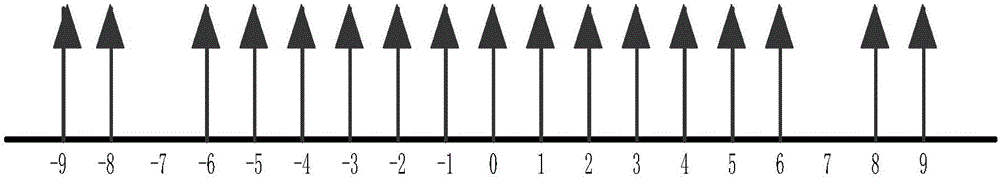
Broadband signal DOA estimation method based on co-prime array
ActiveCN106324558AHigh-resolutionEasy to detectDirection findersSparse constraintSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a broadband signal DOA estimation method based on a co-prime array, and the method comprises the steps: S1, designing a co-prime array structure through an antenna; S2, carrying out the sampling and discrete Fourier transform of a broadband signal received by an antenna in the co-prime array, and obtaining a frequency domain signal output model; S3, calculating an autocorrelation matrix of the frequency domain signal output model, carrying out the vectorization of the frequency domain signal output model, and obtaining a new signal model; S4, carrying out the processing of the new signal model, and obtaining a spatial smooth covariance matrix of the broadband signal; Sa5, dividing a space domain grid, constructing a dictionary, carrying out the sparse representation of the spatial smooth covariance matrix through employing the dictionaries of a plurality of frequency points of the broadband signal, and forming a multi-measurement-vector sparse representation model of a plurality of dictionaries of the broadband signal; S6, achieving the arrival direction estimation of the broadband signal in a mode of solving a sparse inverse problem through the joint sparse constraint of the sparse representation coefficients of the plurality of dictionaries. The method can improve the estimation precision of the direction angle of the broadband signal under the condition of low signal to noise ratio, and reduces the direction finding error.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
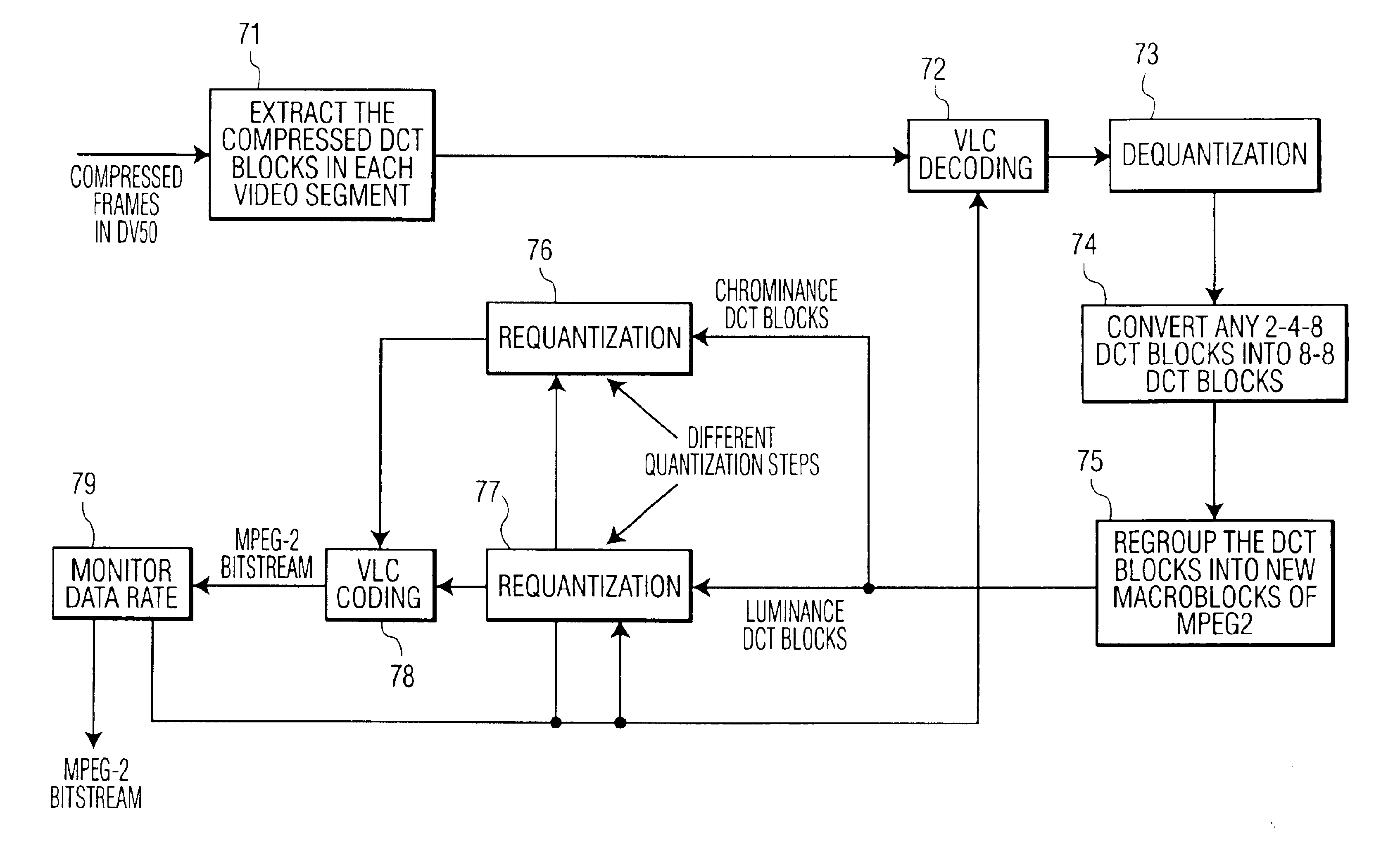
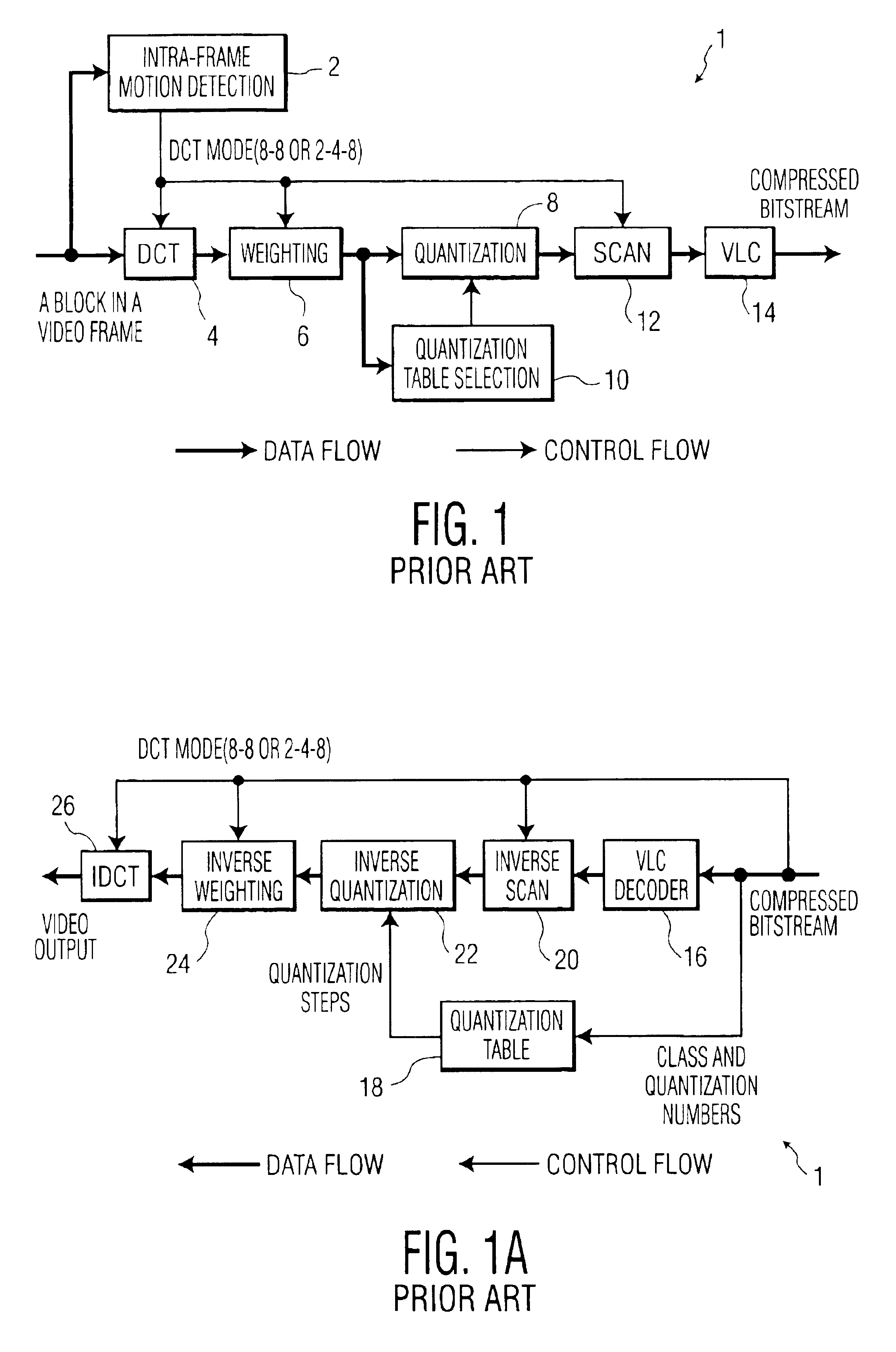
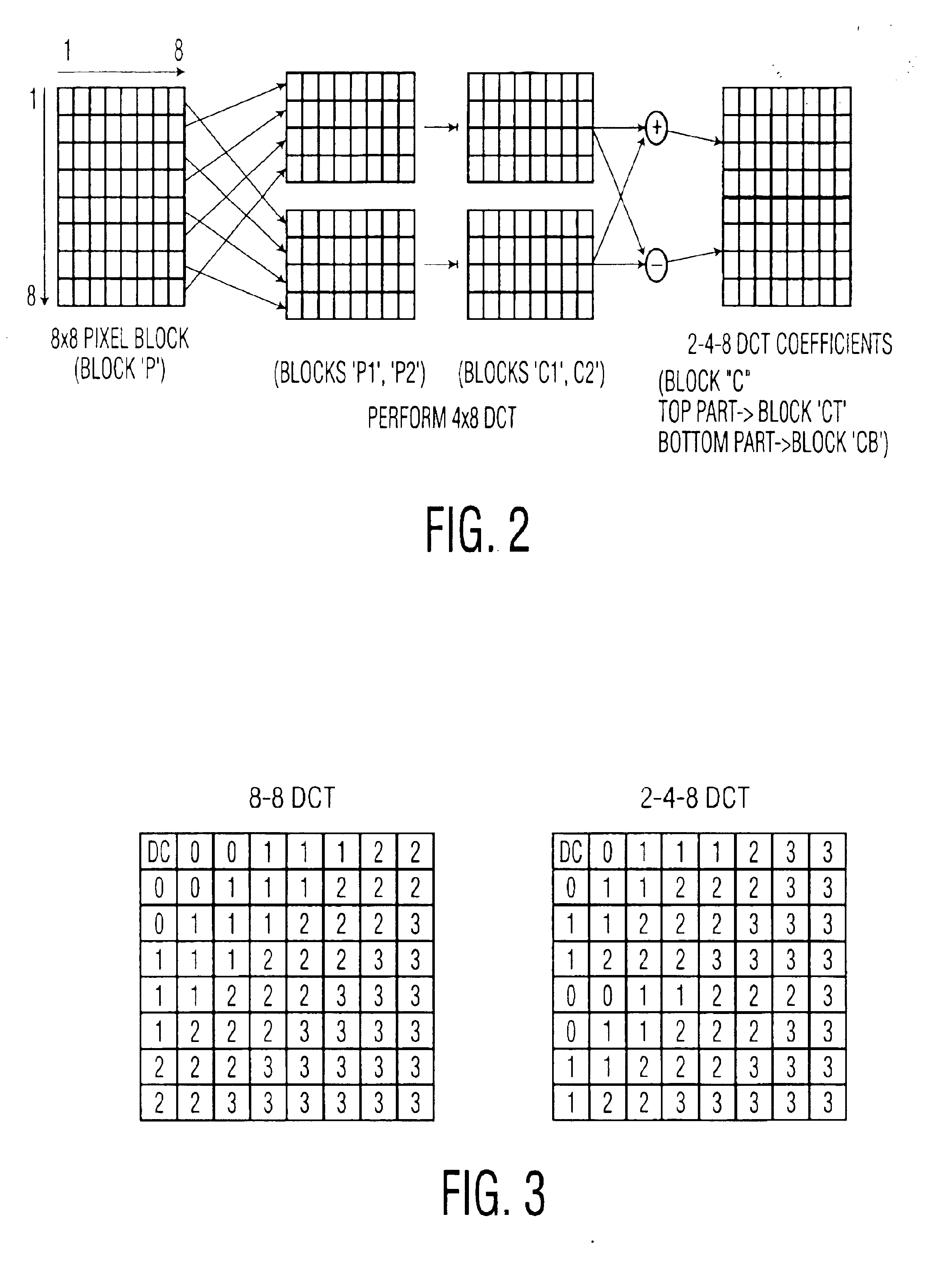
System and associated method for transcoding discrete cosine transform coded signals
InactiveUS6944226B1Low data rateTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMpeg standardsVariable length
A method is provided for transcoding between video signals in two standards, DV and MPEG-2, each standard including discrete cosine transform (DCT) compressed signals. The each of the signals have macroblocks containing a plurality of DCT blocks. The DCT blocks are quantized according to respective quantization methods defined by the standards. The coefficients in each block are zigzag scanned, run-length coded and variable-length coded. The process variable-length decodes the coefficients and translates the quantized coefficients in the DV standard into quantized coefficients in the MPEG standard without fully dequantizing at least some of the DV coefficients and without performing an inverse DCT operation on any of the DCT coefficients. DV blocks that are encoded in a 248 format are translated into an 88 format before they are converted to MPEG-2 blocks. A method for transcoding from MPEG-2 to DV is also described. The MPEG-2 signals are intra-frame encoded, have a 4:2:2 chrominance format and an 88 frame-encoded block format. According to this method, converted 88 DV blocks that represent significant intra-field motion are converted from the 88 format to a 248 format. The method also controls which overflow coefficients in the DV signal are transcoded into corresponding coefficients in the MPEG-2 signal to control the data rate of the MPEG-2 signal.
Owner:PANASONIC OF NORTH AMERICA
System and method for contactless touch screen
ActiveUS8274495B2Improve positioning reliabilityIncrease inputUsing optical meansInput/output processes for data processingSensor arrayDigital signal processing
A touch screen that employs a lens-less linear IR sensor array and an IR light source from a single location at the periphery of the screen to illuminate one or more objects proximate to the screen surface and detect light reflected from such objects. The sensor array is paired with a proximal grid-like barrier / reflector to create Moiré patterns on the sensor array. Digital signal processing converts such patterns into discrete Fourier transforms. The peaks of the lower order discrete Fourier spectrum as well as the complex phases of the lower order peaks can be used to determine the locations of the objects proximal to the screen accurately. A small number of pressure or surface acoustic sensors at the periphery of the screen are utilized to improve positioning reliability by providing redundant positioning information and registering physical contacts with the screen.
Owner:GENERAL DISPLAY
Large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on deep learning
ActiveCN108390706AHigh speedImprove rebuild qualitySpatial transmit diversityFourier transform on finite groupsModel parameters
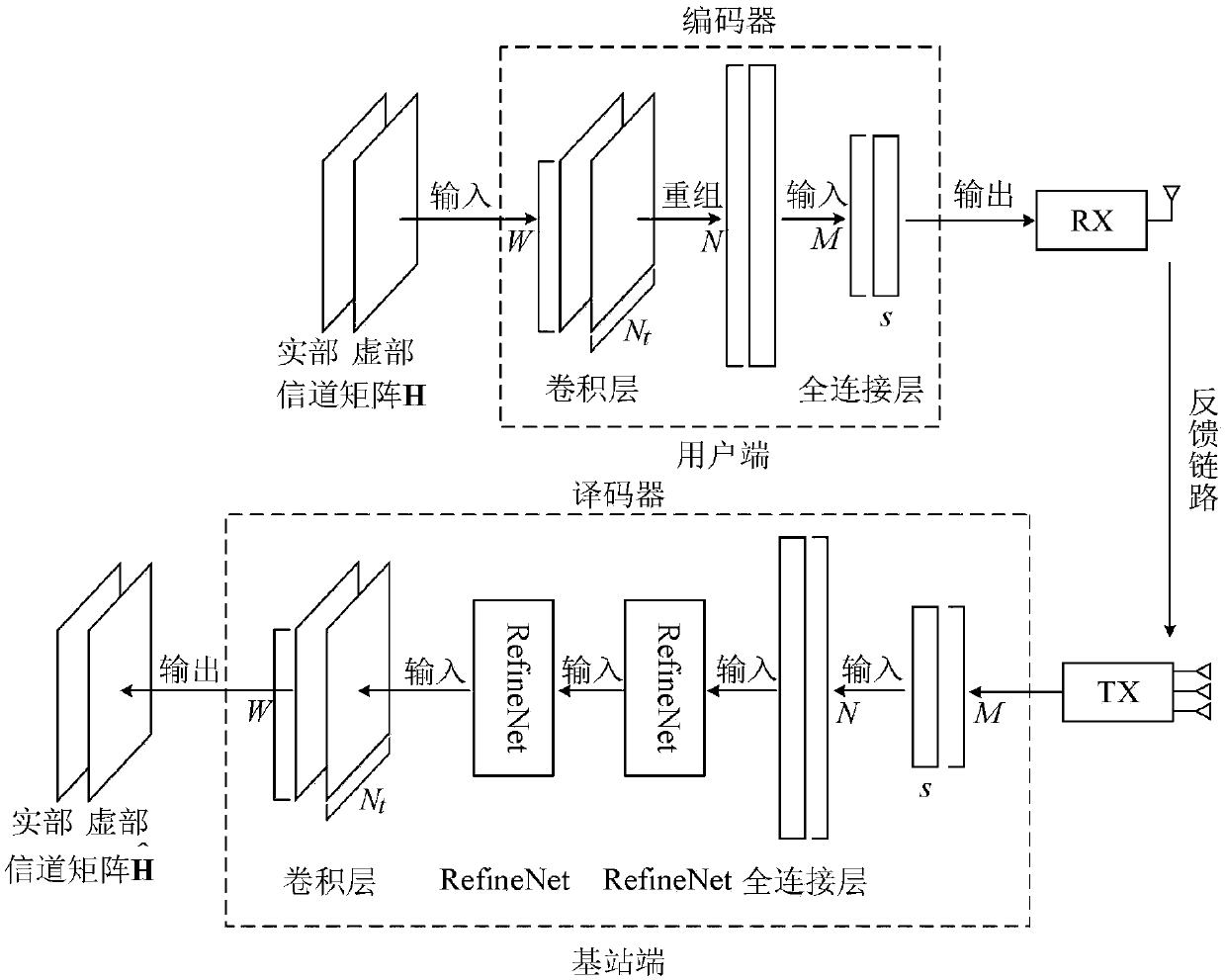
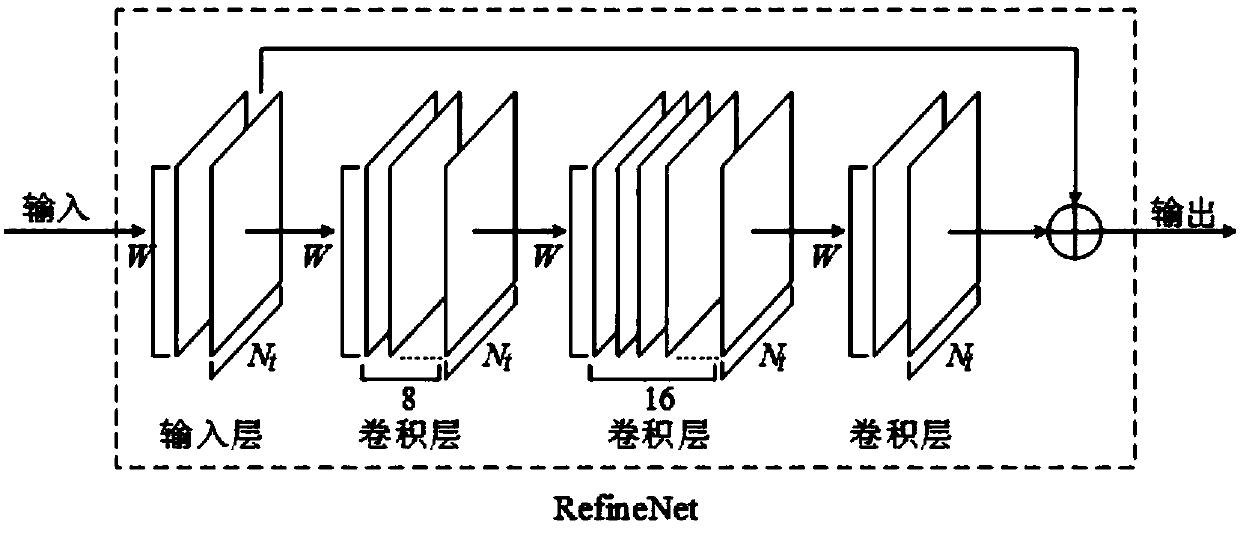
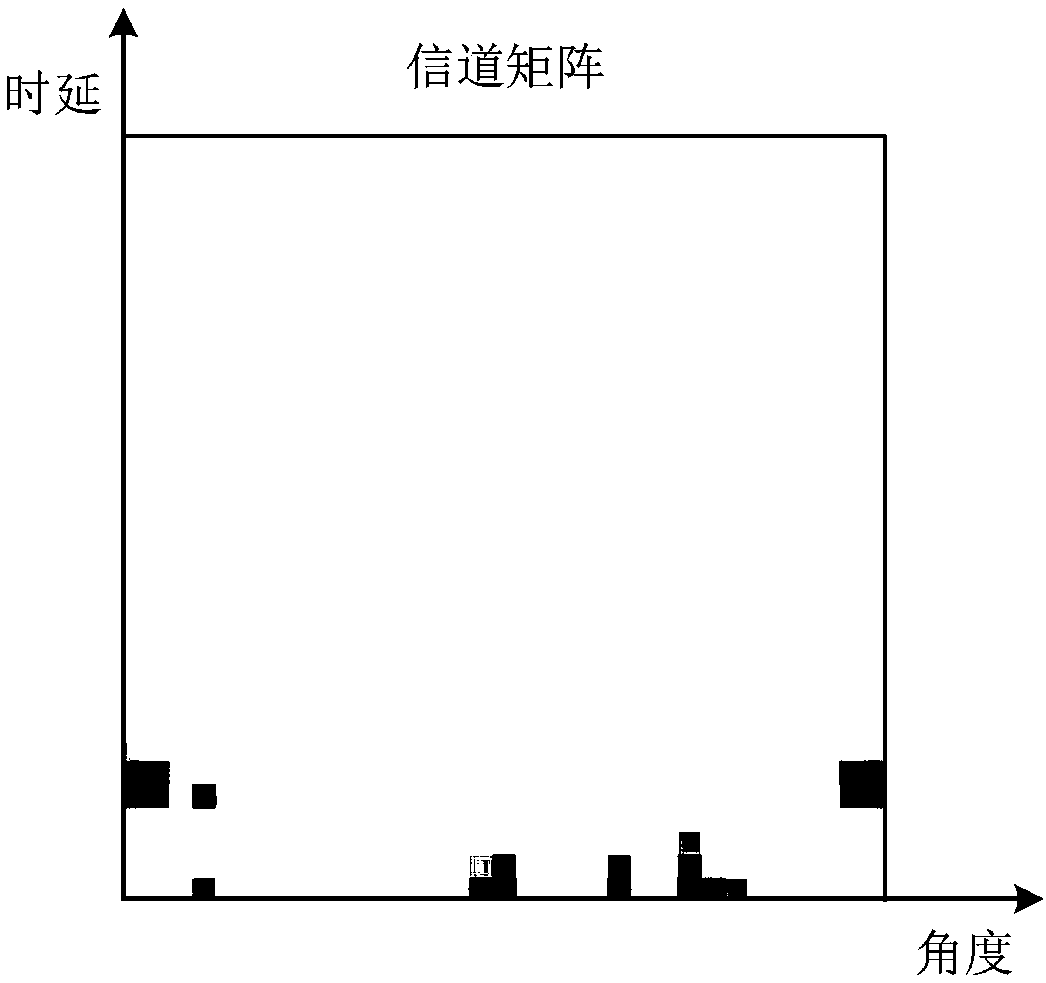
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out two-dimensional discrete Fourier transform (DFT) on a channel matrix H-wave of MIMO channel state information in a spatial frequency domain on a user side, so that a channel matrix H which is sparse in an angle delay domain isobtained; secondly, constructing a model CsiNet comprising a coder and a decoder, wherein the coder belongs to the user side and is used for coding the channel matrix H into codons with a lower dimension, and the decoder belongs to a base station side and is used for reconstructing an original channel matrix estimation value H-arrow from the codons; thirdly, training the model CsiNet to obtain model parameters; fourthly, carrying out two-dimensional inverse DFT on a reconstructed channel matrix H-arrow which is output by the CsiNet, so that a reconstructed value of the original channel matrixH-wave in the spatial frequency domain is recovered; and finally, using the trained model CsiNet for compressed sensing and reconstruction of channel information. The method provided by the inventionhas the advantages that large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback expenditures can be reduced, and an extremely high channel reconstruction quality and an extremely high channel reconstruction speed can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and system for on-line blind source separation
InactiveUS6898612B1Efficient separationAdaptive networkSpeech analysisNO storageFinite impulse response
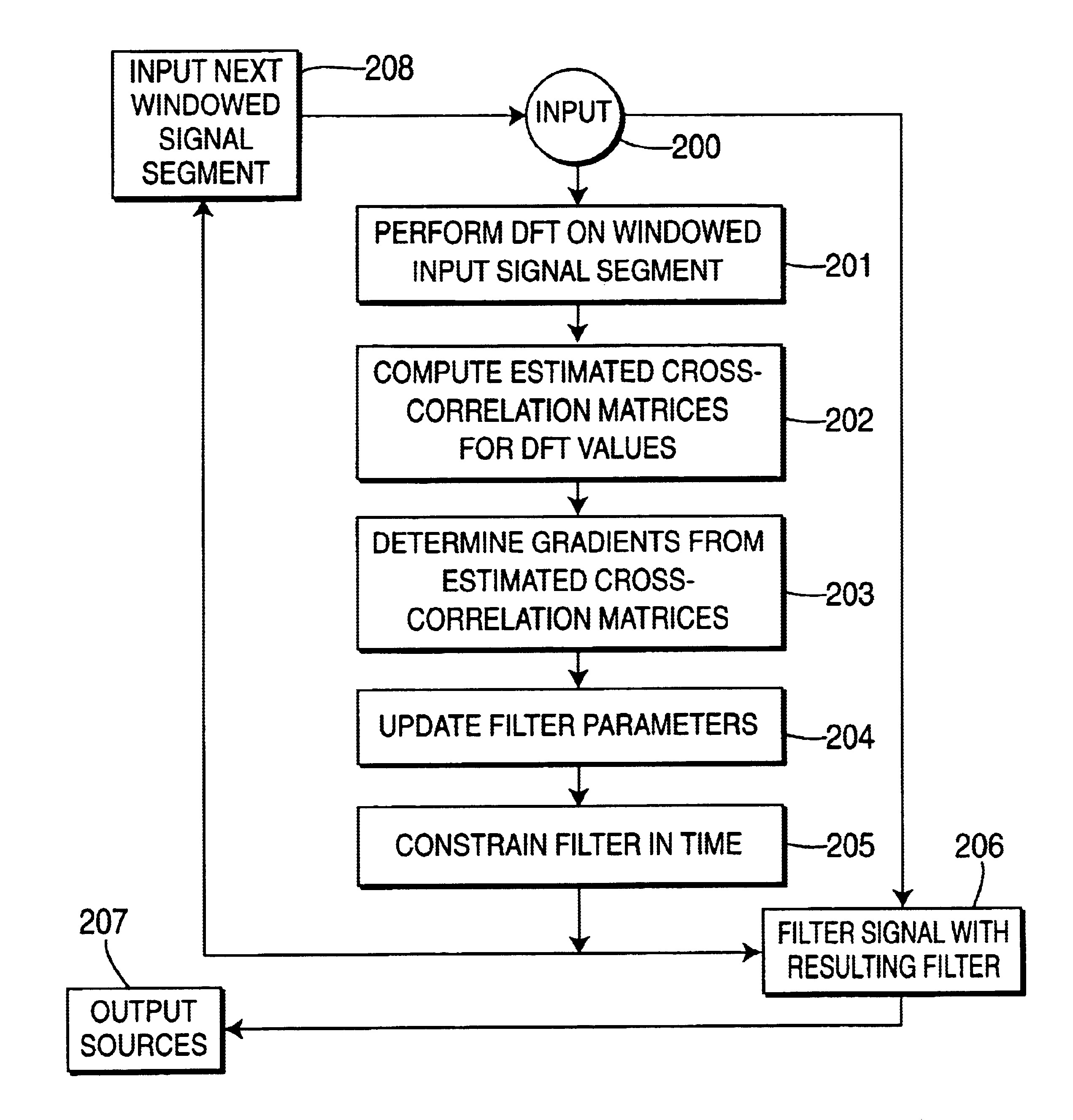
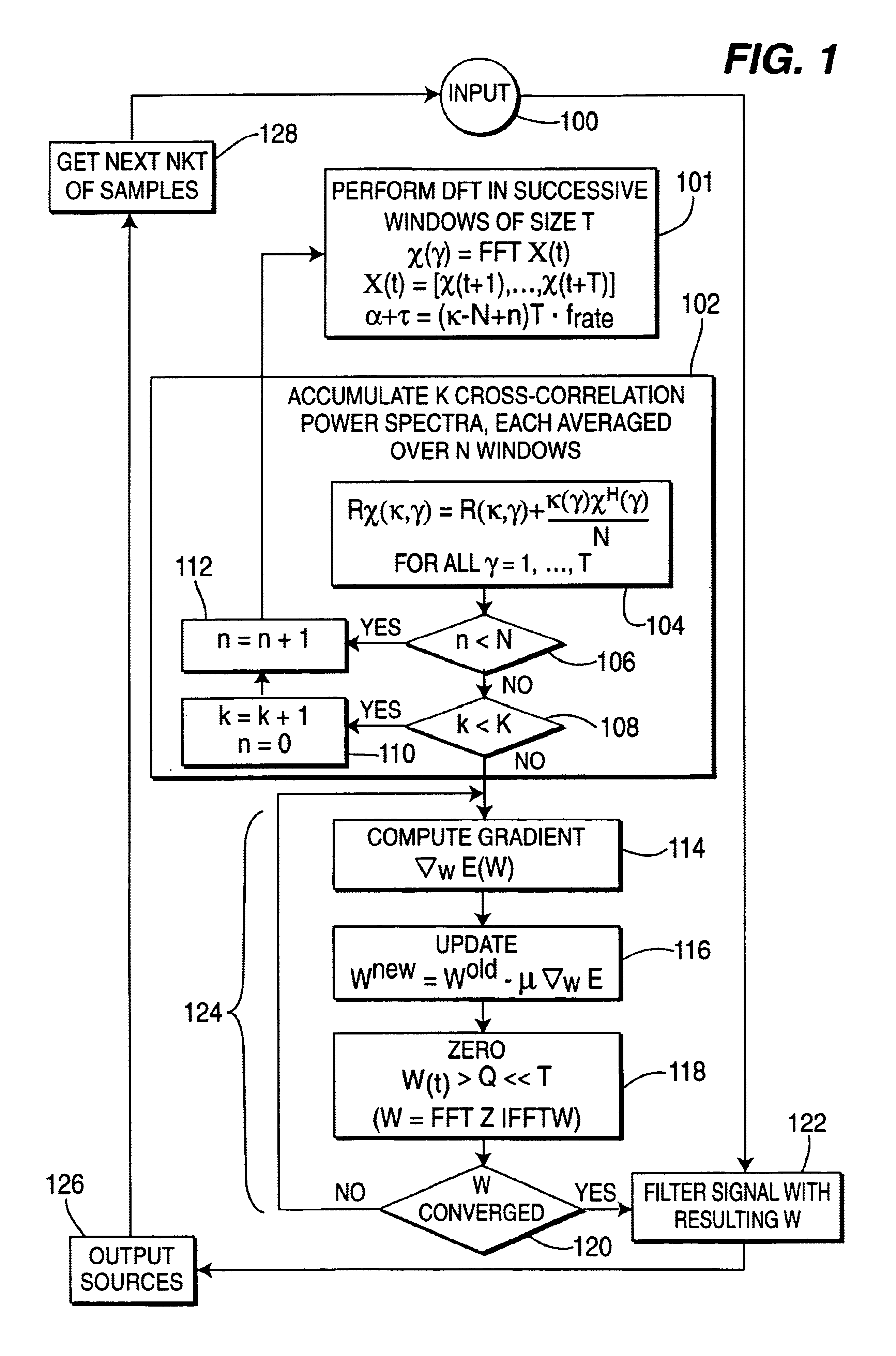
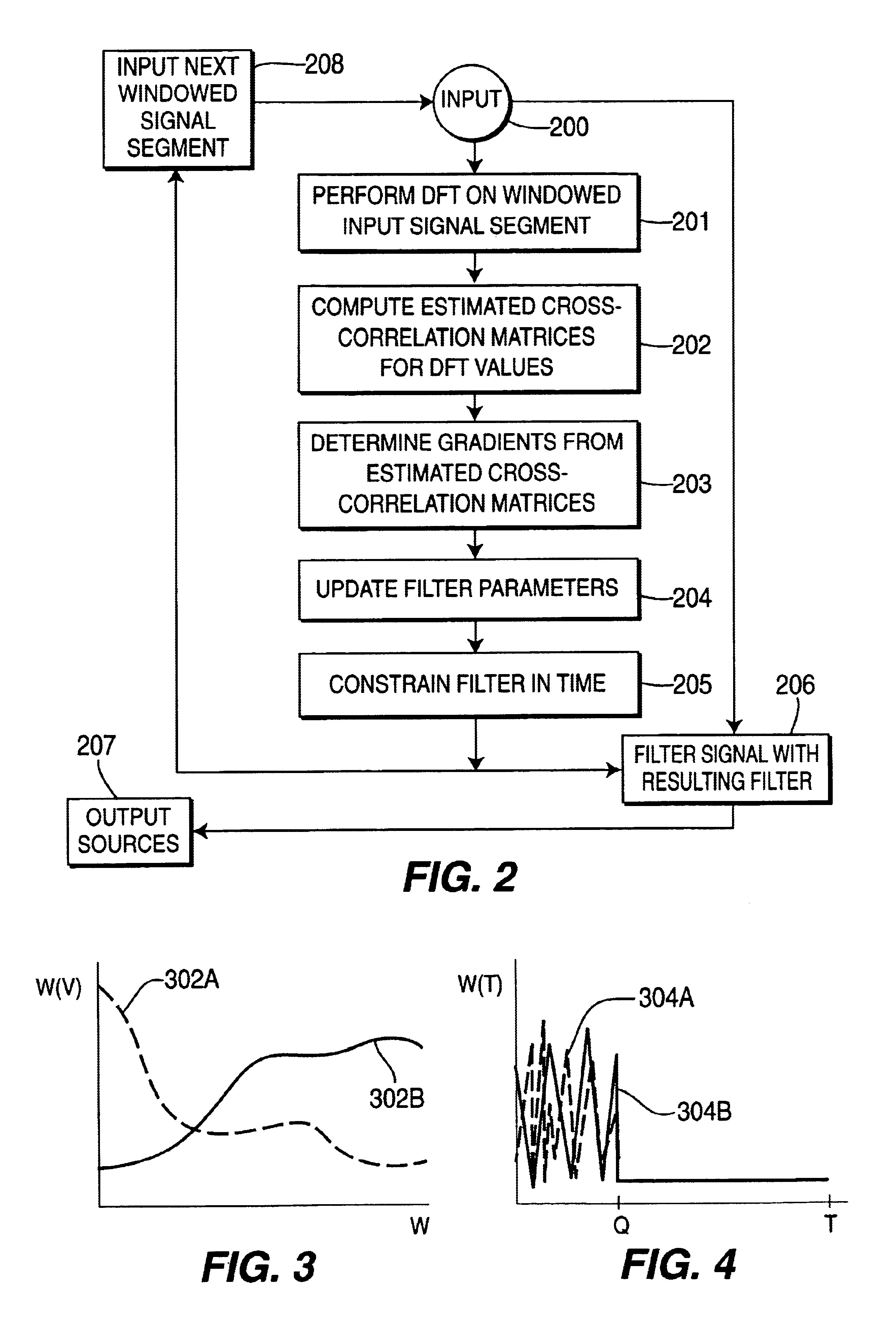
A method and apparatus is disclosed for performing blind source separation using convolutive signal decorrelation. For a first embodiment, the method accumulates a length of input signal (mixed signal) that includes a plurality of independent signals from independent signal sources. The invention then divides the length of input signal into a plurality of T-length periods (windows) and performs a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) on the, signal within each T-length period. Thereafter, estimated cross-correlation values are computed using a plurality of the averaged DFT values. A total number of K cross-correlation values are computed, where each of the K values is averaged over N of the T-length periods. Using the cross-correlation values, a gradient descent process computes the coefficients of a finite impulse response (FIR) filter that will effectively separate the source signals within the input signal. A second embodiment of the invention is directed to on-line processing of the input signal—i.e., processing the signal as soon as it arrives with no storage of the signal data. In particular, an on-line gradient algorithm is provided for application to non-stationary signals and having an adaptive step size in the frequency domain based on second derivatives of the cost function. The on-line separation methodology of this embodiment is characterized as multiple adaptive decorrelation.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
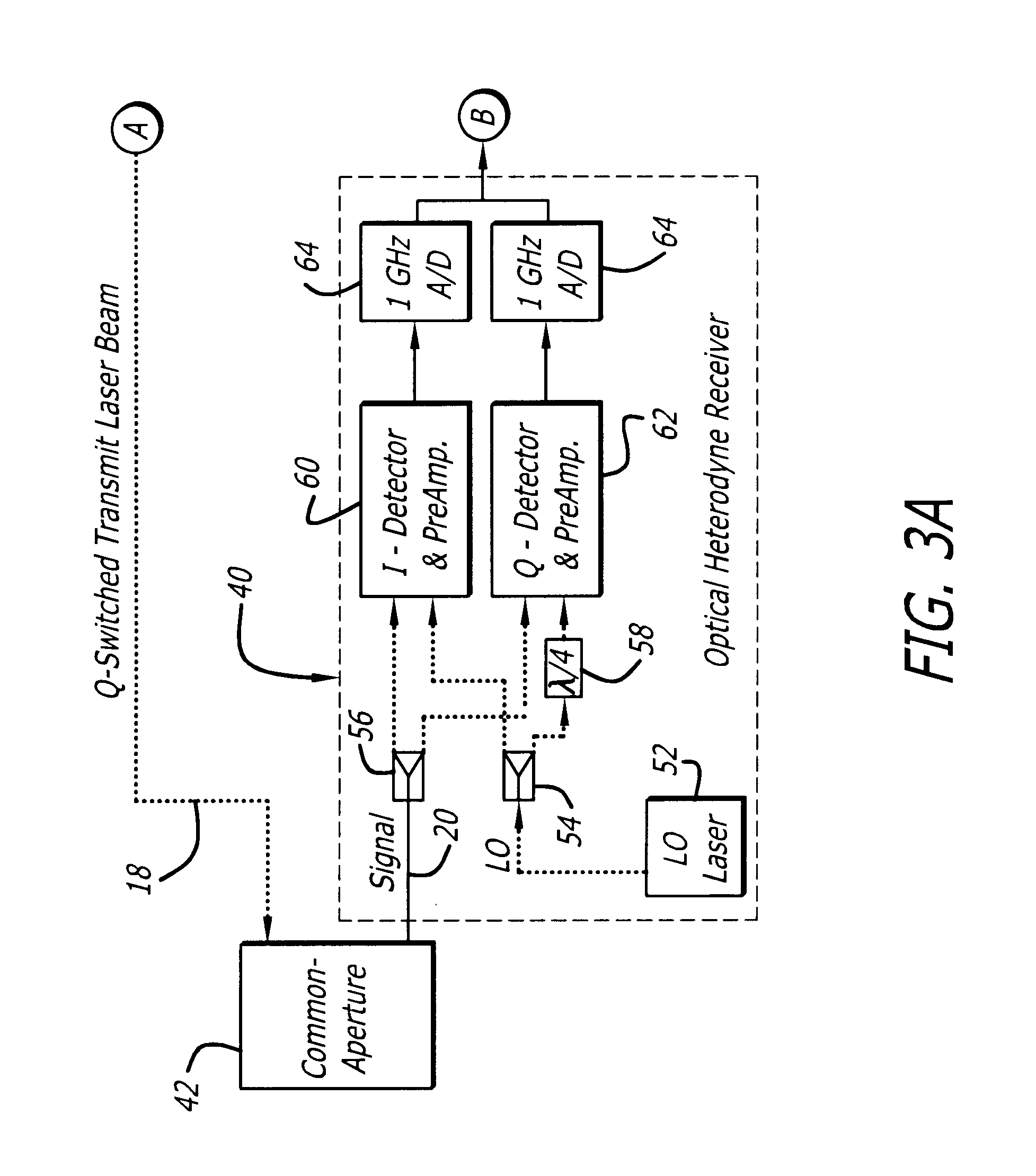
Synthetic aperture ladar system using incoherent laser pulses
InactiveUS6559932B1Optical rangefindersDevices using optical meansRadar systemsSynthetic aperture radar
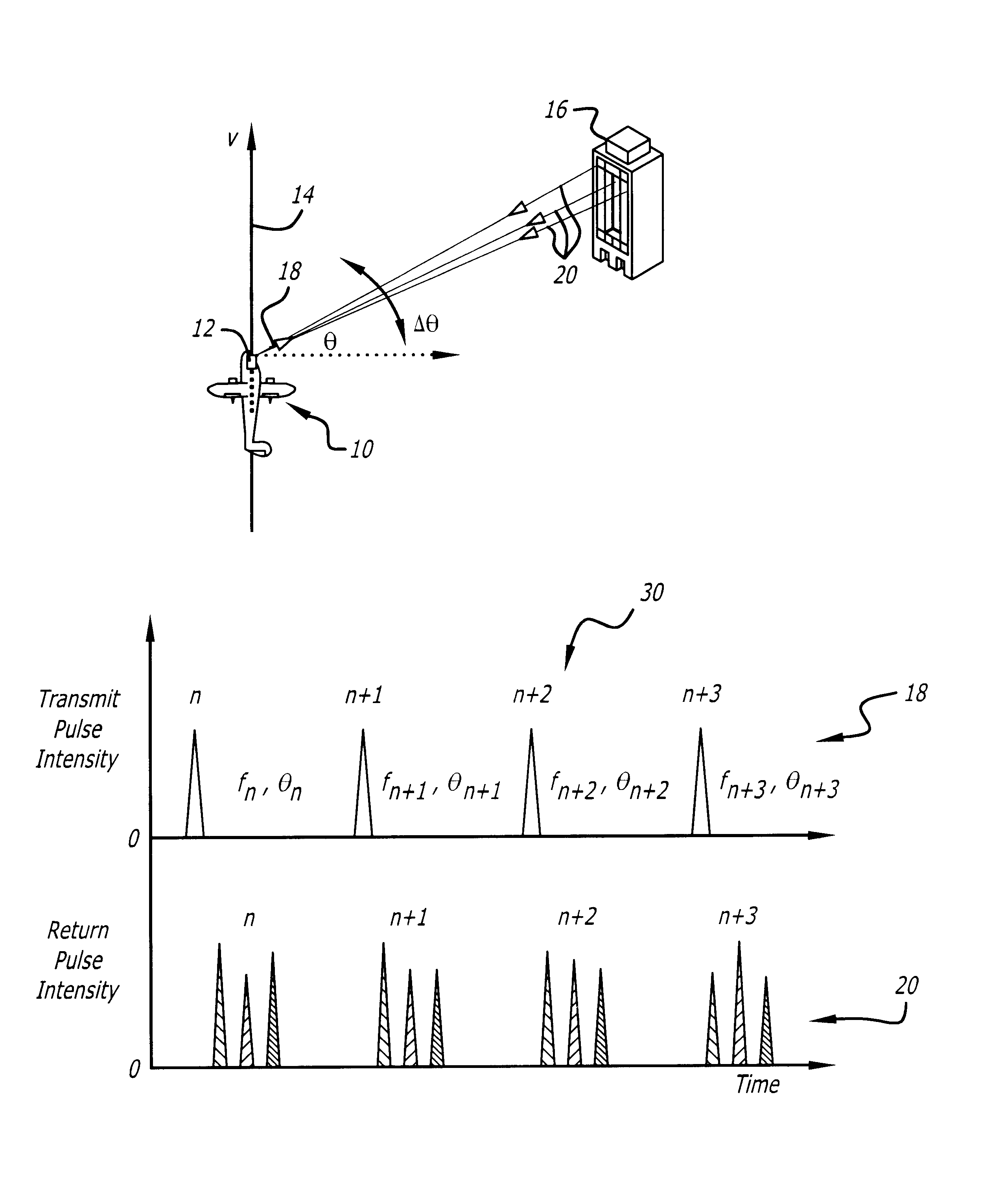
An incoherent ladar transmitter (12) adapted for use with synthetic aperture processing. The system (12) includes a first mechanism (44, 48, 50) for generating a laser beam (18). A second mechanism (44, 68) records phase information pertaining to the laser beam (18) and subsequently transmits the laser beam (18) from the system in response thereto. A third mechanism (40) receives a reflected version (20) of the laser beam and provides a received signal in response thereto. A fourth mechanism (72) corrects the received signal based on the phase information recorded by the second mechanism (44, 68). In a more specific embodiment, the ladar system (12) includes a synthetic aperture processor (46) for correcting the received signal based on the phase information and providing a corrected laser signal in response thereto. The synthetic aperture processor (46) includes a mechanism (76) for applying, a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) to the corrected laser signal to obtain high frequency resolution and cross-range resolution. A fifth mechanism (48) constructs a range-Doppler image based on the corrected laser signal and the movement of the ladar system (12).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
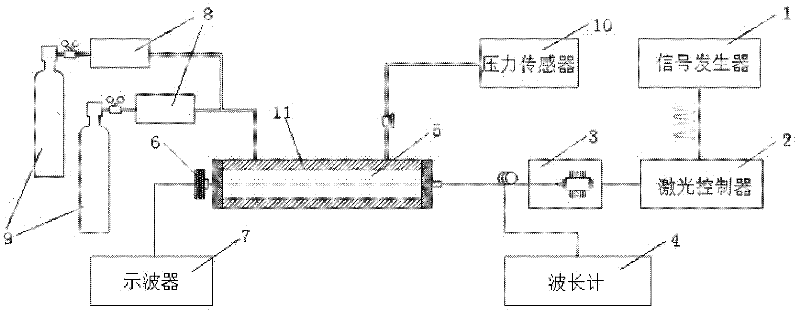
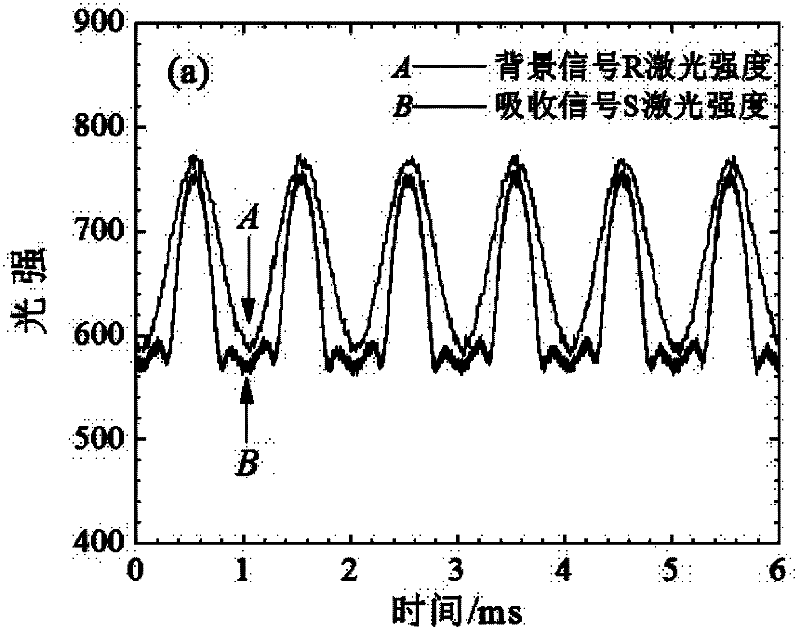
Gas concentration on-line measurement method based on laser absorption spectrum
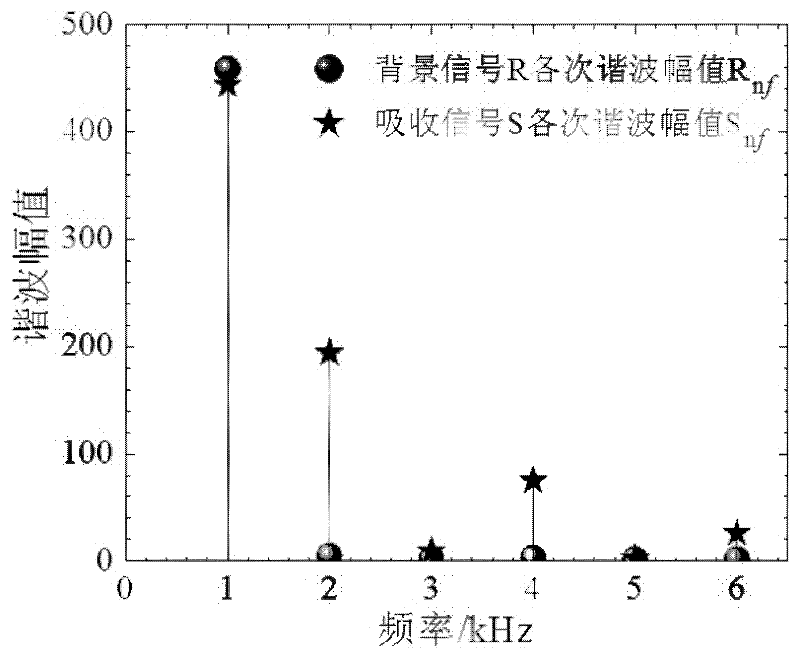
ActiveCN102590138AHigh measurement accuracySuppress background noiseColor/spectral properties measurementsHarmonicHigh frequency modulation
The invention relates to a gas concentration on-line measurement method based on laser absorption spectrum, belonging to the technical field of the tunable laser diode absorption spectrum. The Beer-Lambert principle is subjected to second-order Taylor approximation, the gas concentration is determined based on the ratio of absorption signal second harmonic to background signal first harmonic without calibration experiment. During the measurement process, a laser is subjected to high-frequency modulation on the spectrum line center frequency, and the acquired signal is subjected to discrete Fourier transform (DFT) to obtain each harmonic signal. The gas measurement precision is increased, the wavelength modulation technology is applied at the strong absorption condition, and the application range of the tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) is expanded. In the experiment, a calibration and application phase-lock technique applied on the laser is omitted, the measurement process and the measurement system are simplified and the wide application of the TDLAS technique is facilitated.
Owner:北京新叶科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com