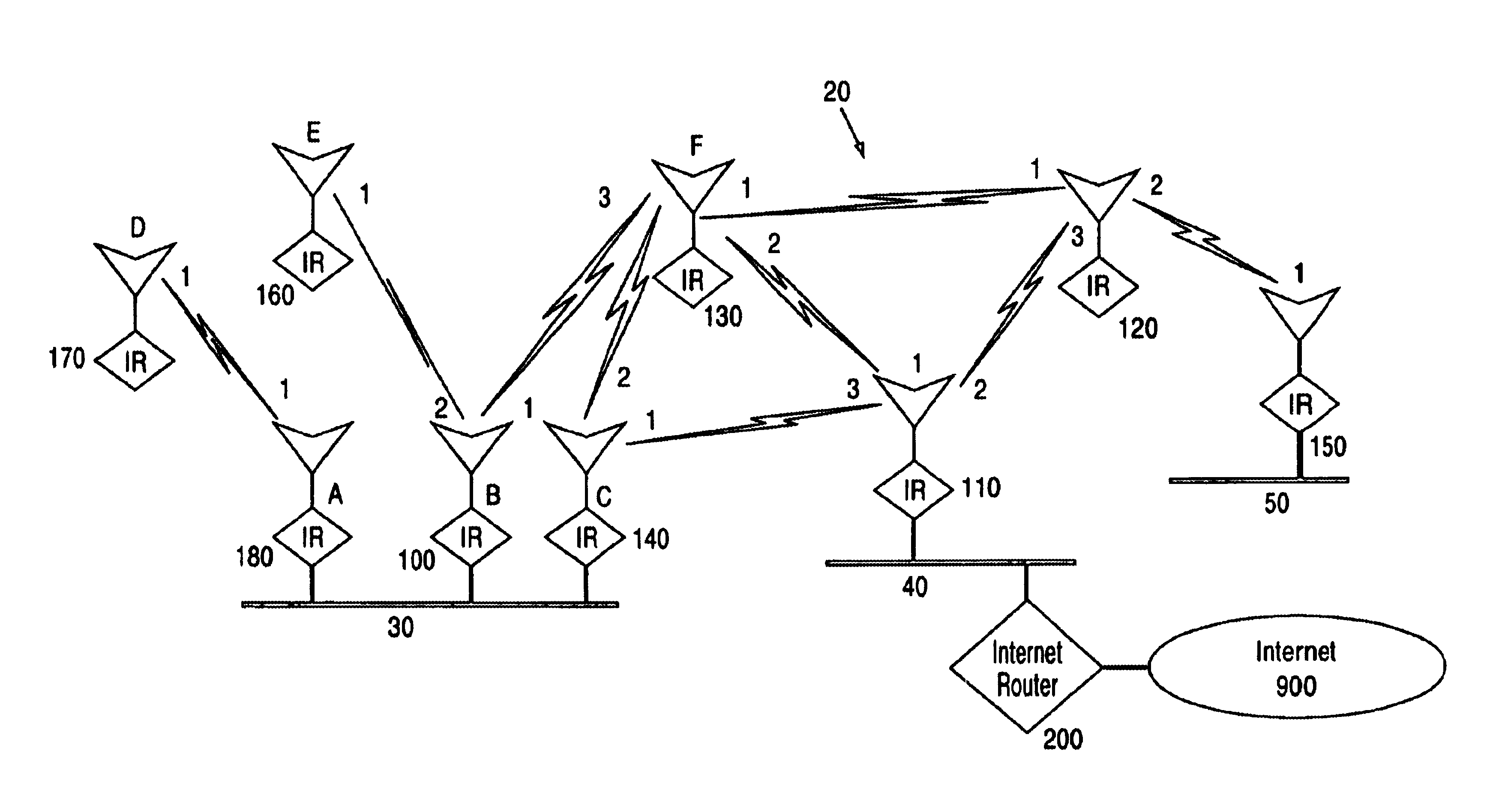
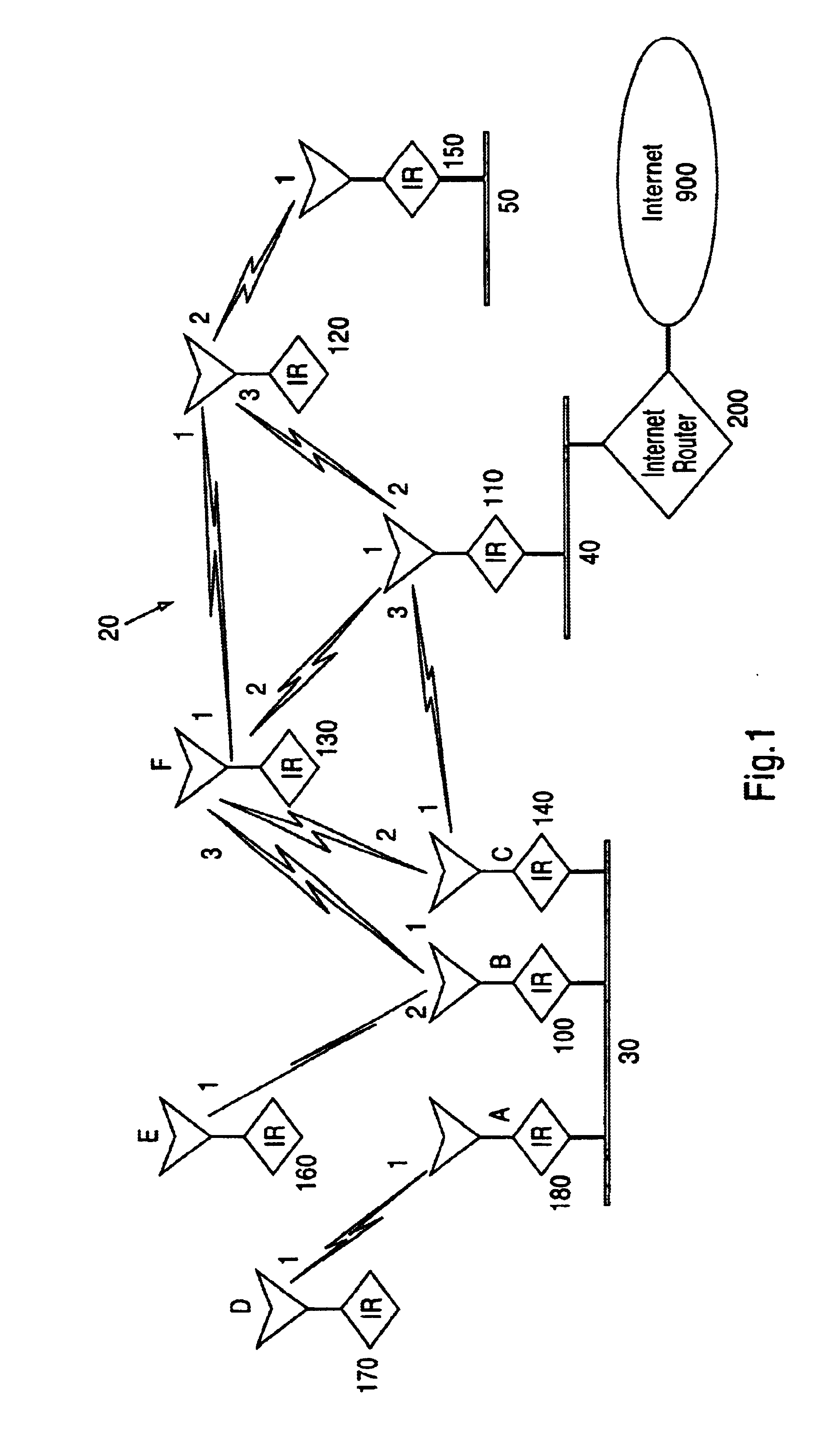
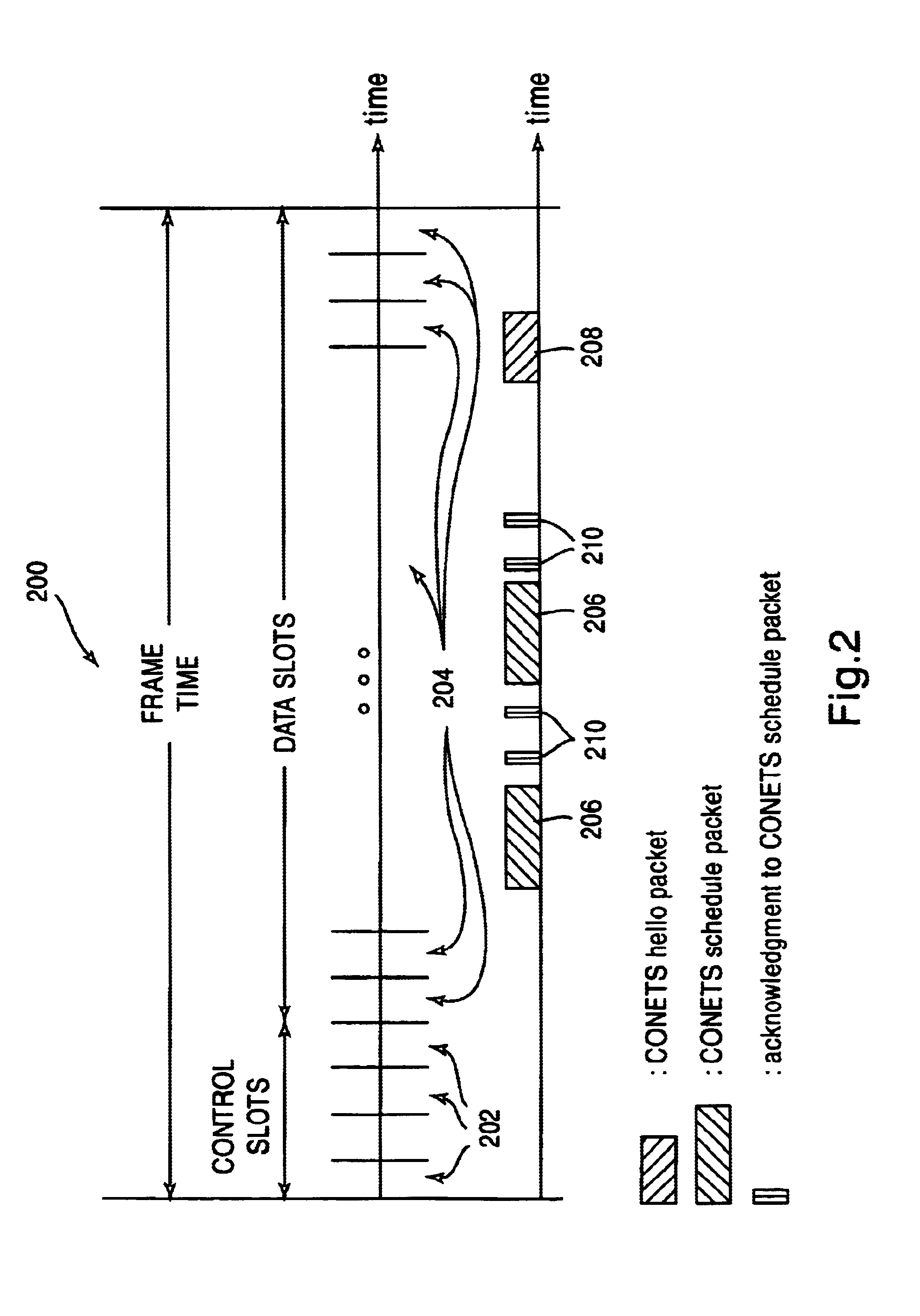
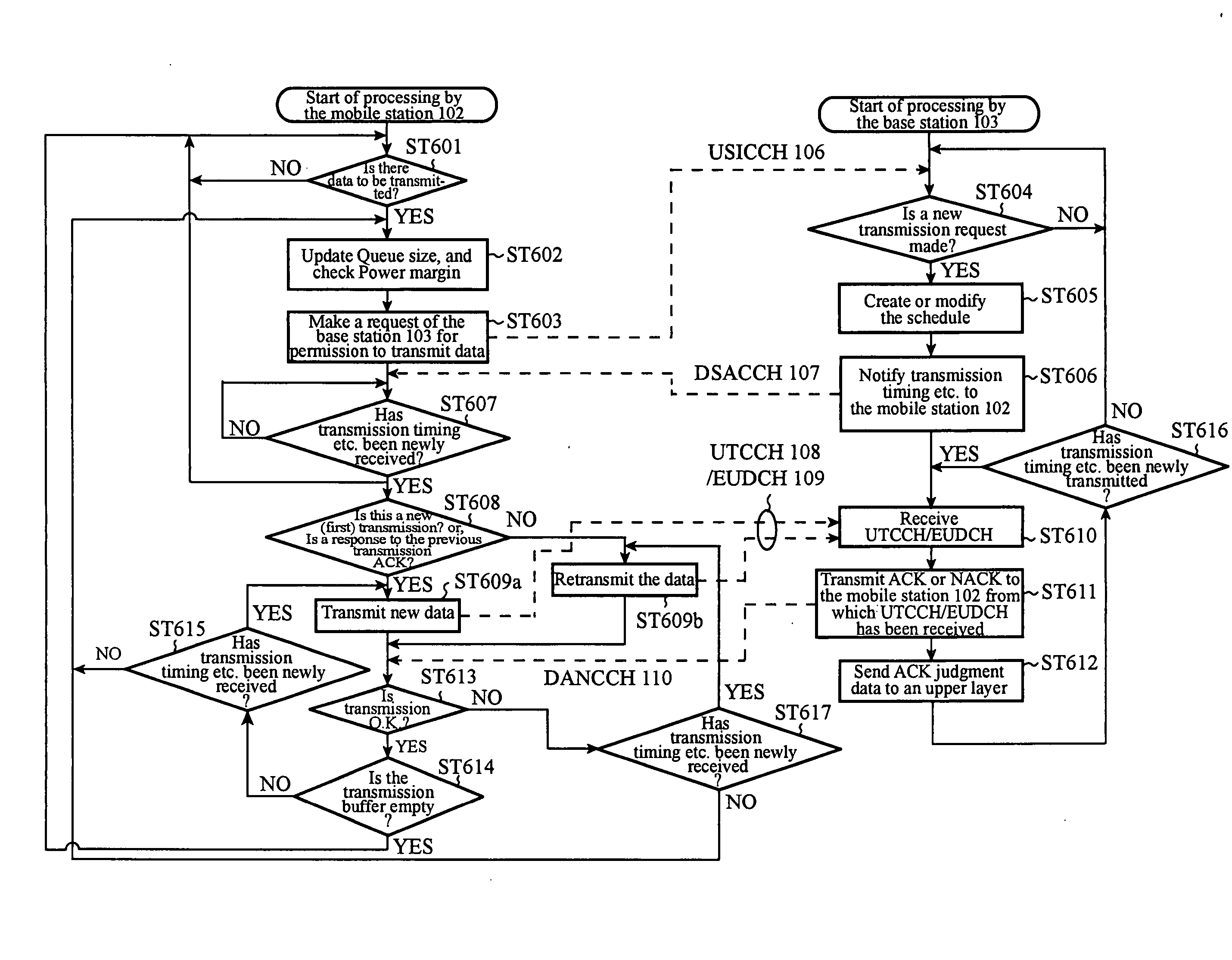
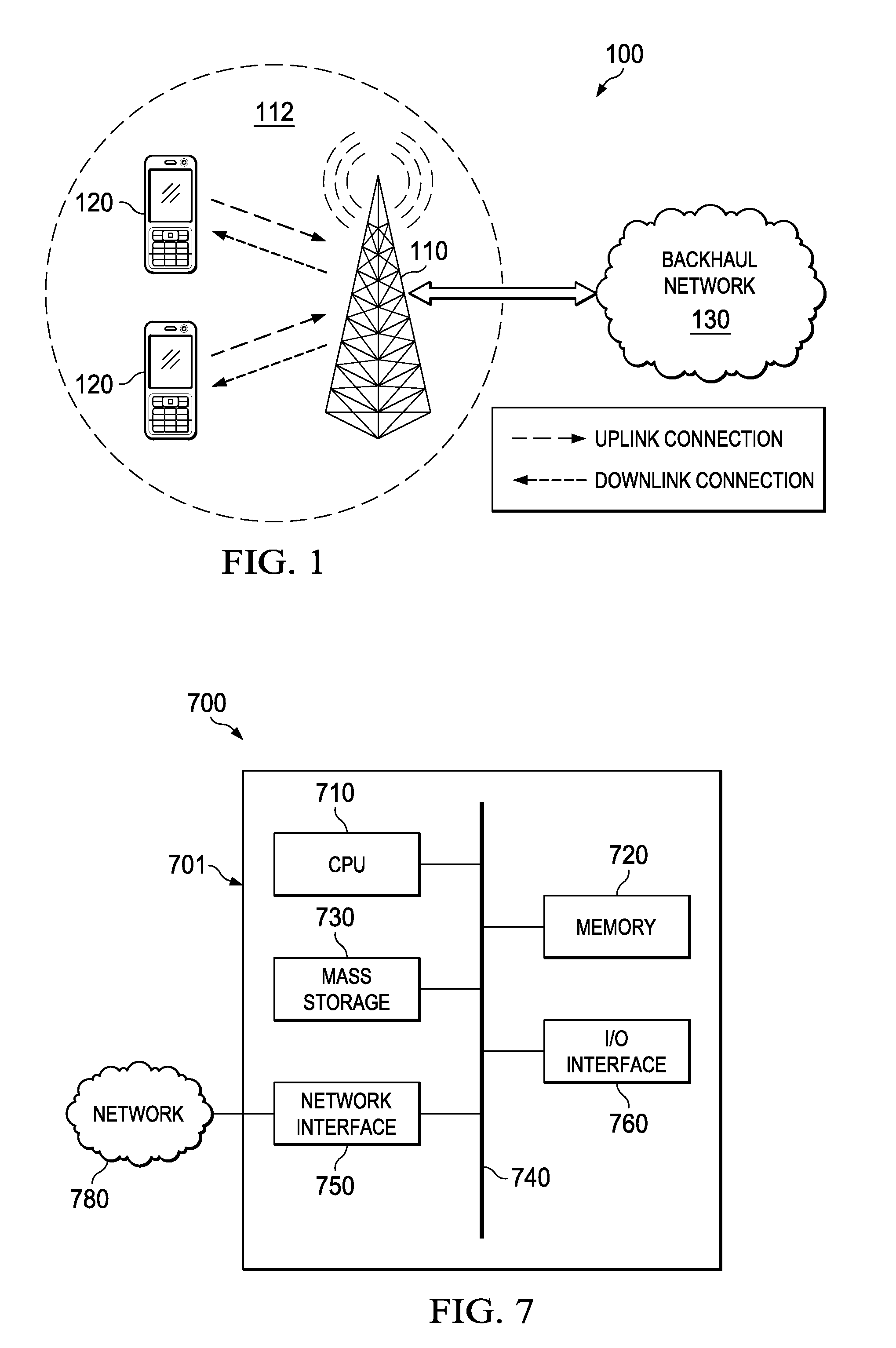
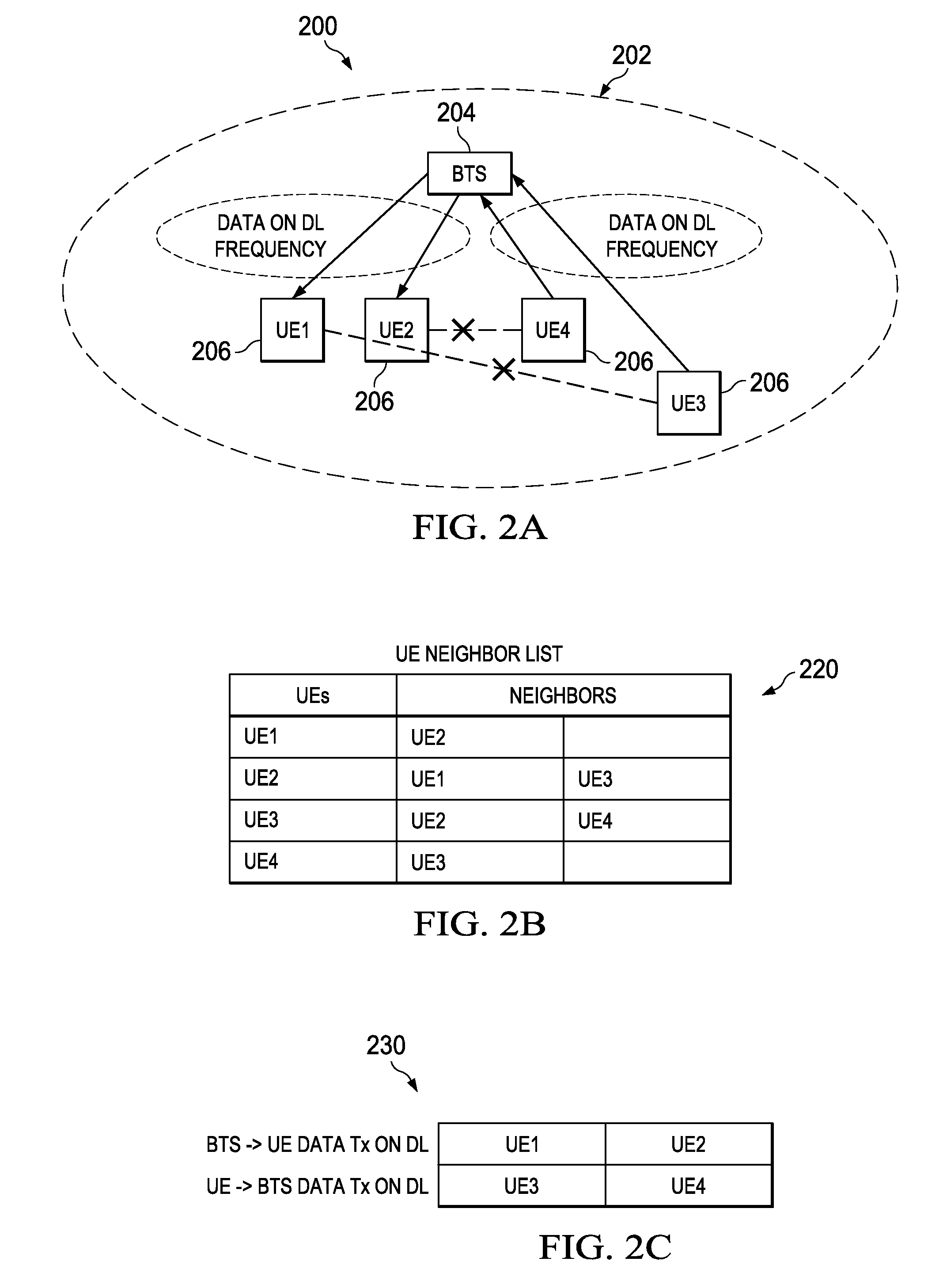
Patents
Literature
271 results about "Transmission schedule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transmission Schedule. Each beacon transmits once on each band once every three minutes, 24 hours a day. A transmission consists of the callsign of the beacon sent at 22 words per minute followed by four one-second dashes.
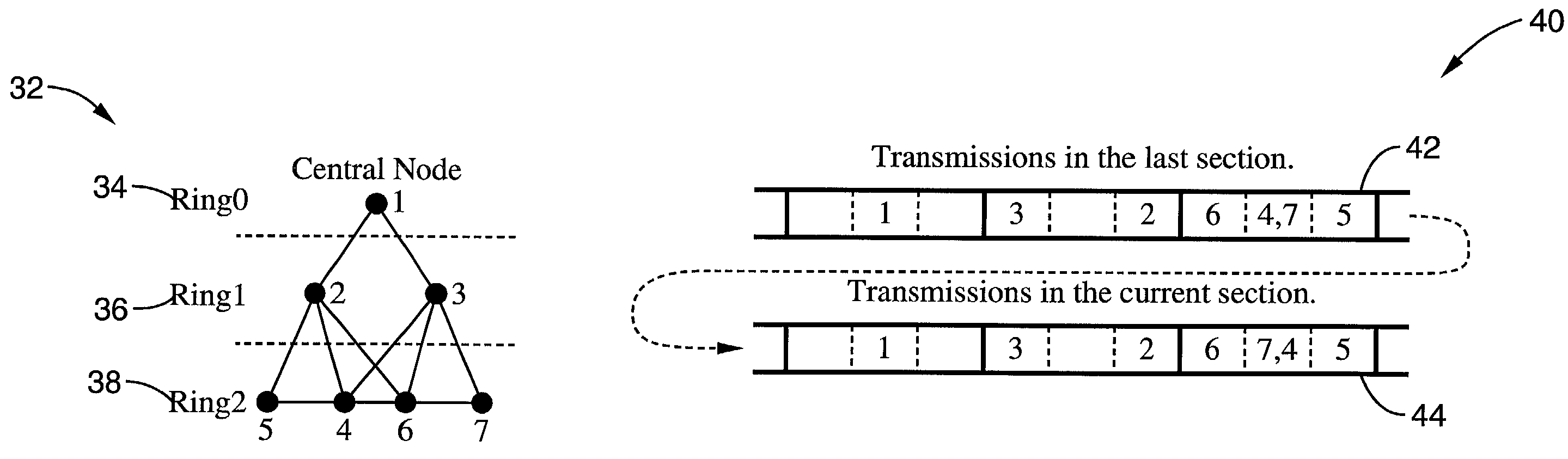
System and method for ad hoc network access employing the distributed election of a shared transmission schedule
InactiveUS20020067736A1Eliminate negotiationMore controlledNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessTransmission schedule
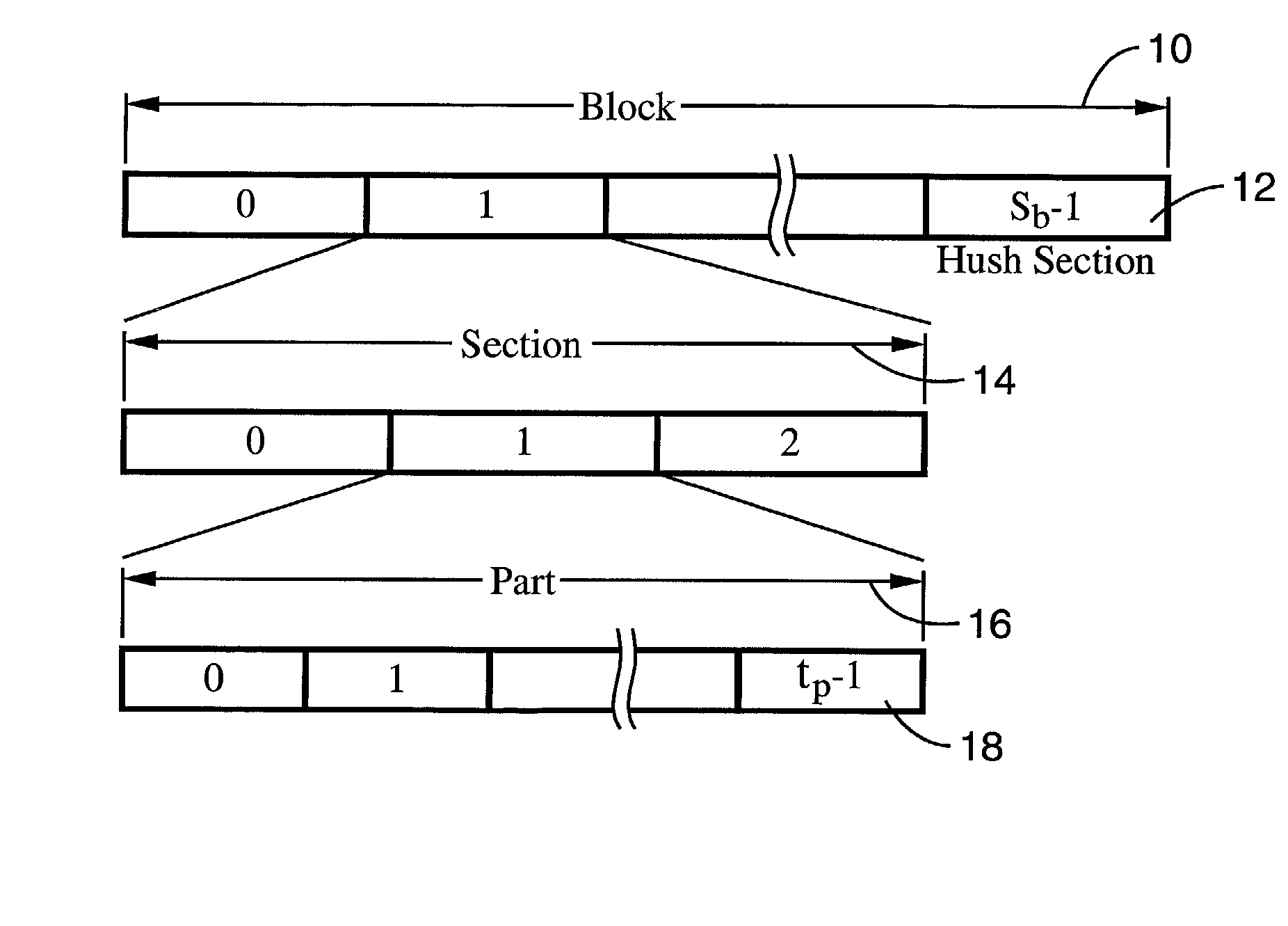
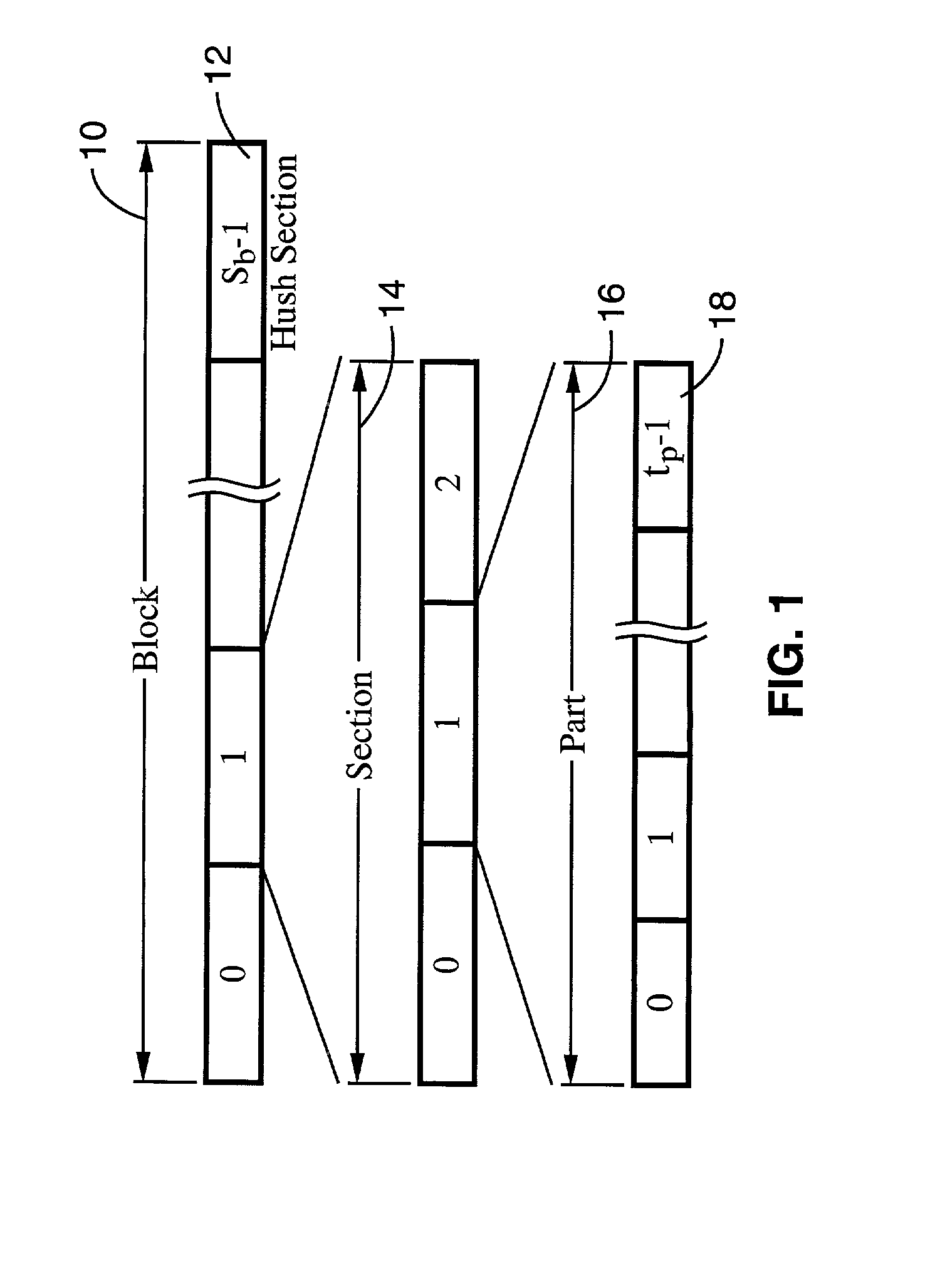
A system and method of providing distributed election of a shared transmission schedule within an ad hoc network. The invention includes a collision-free access protocol which resolves channel access contentions for time division multiple access (TDMA) of a single channel. Time-slots are organized into part numbers, which are included within sections, a sequence of which define a block. Each node is given a ring number according to its location within the network topology and maintains local neighbor information along with its own part number and message digest. Collision-free channel access is automatically scheduled and repetitious contention phases are resolved by a random permutation algorithm operating in message digests. An empty time-slot utilization method is also described and data packets may also be transmitted subject to a non-zero collision probability within a blind section of the block.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
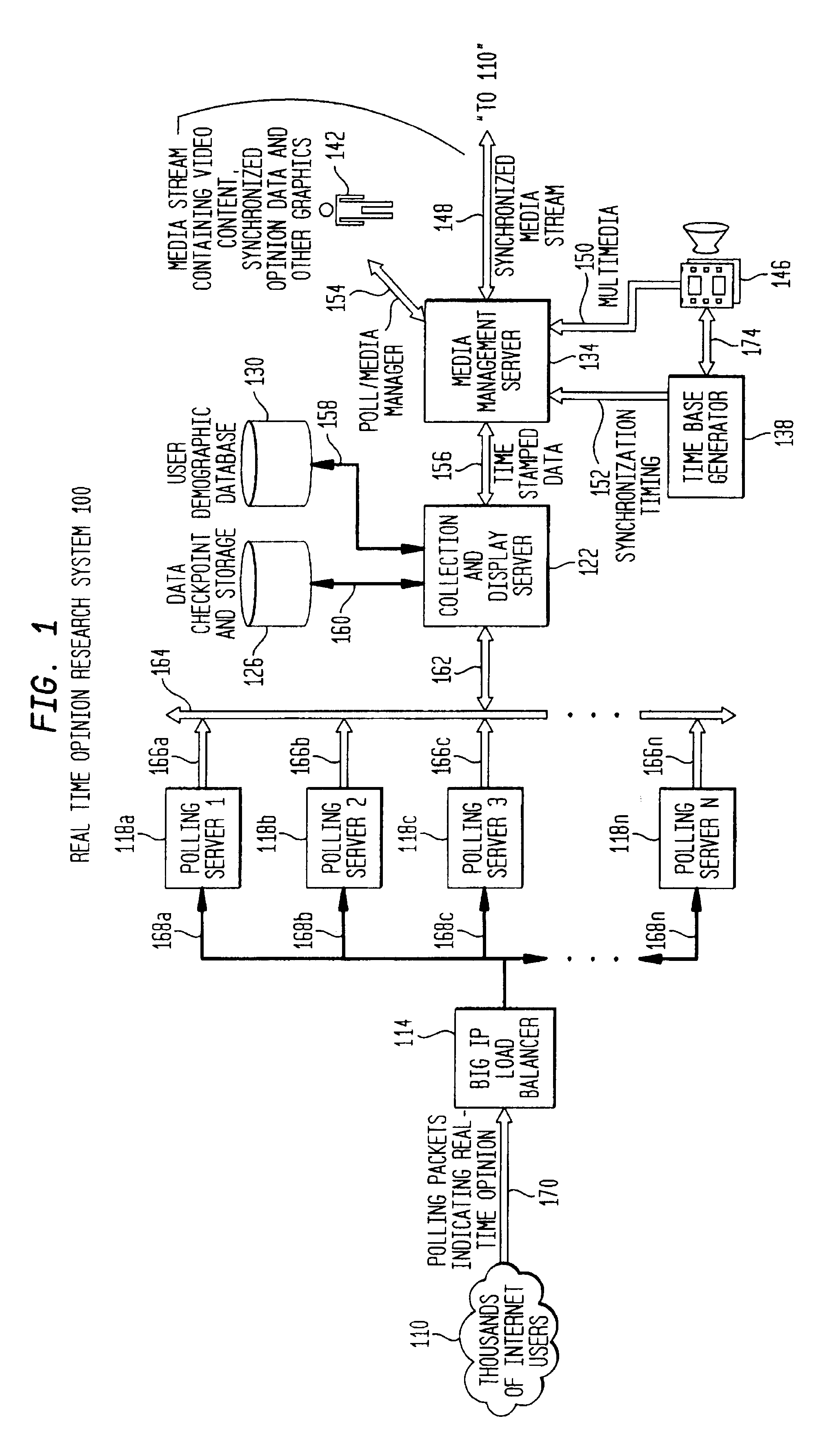
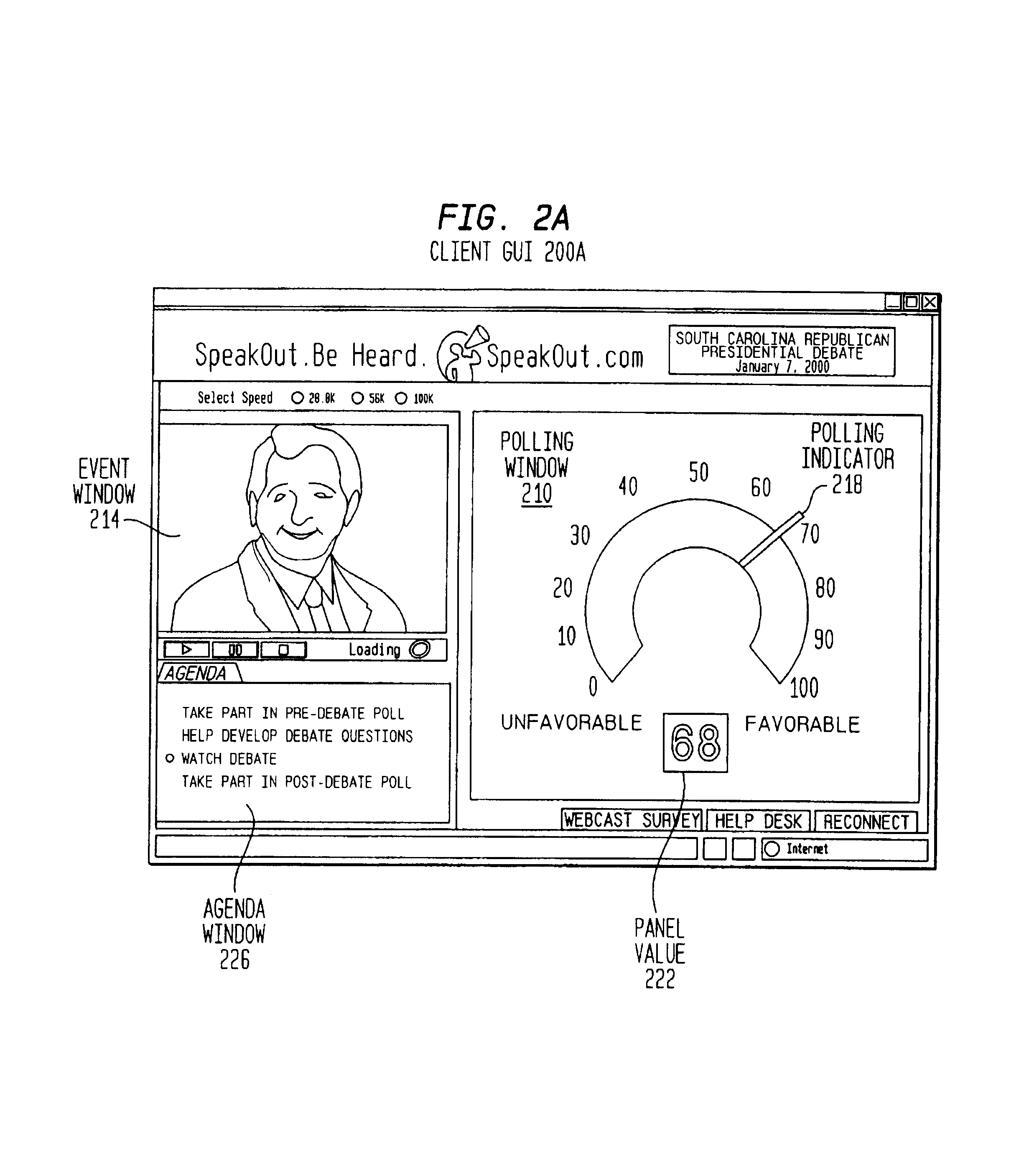
Method of modulating the transmission frequency in a real time opinion research network
ActiveUS7254605B1Increase the number ofVoting apparatusError detection/correctionTTEthernetManagement unit
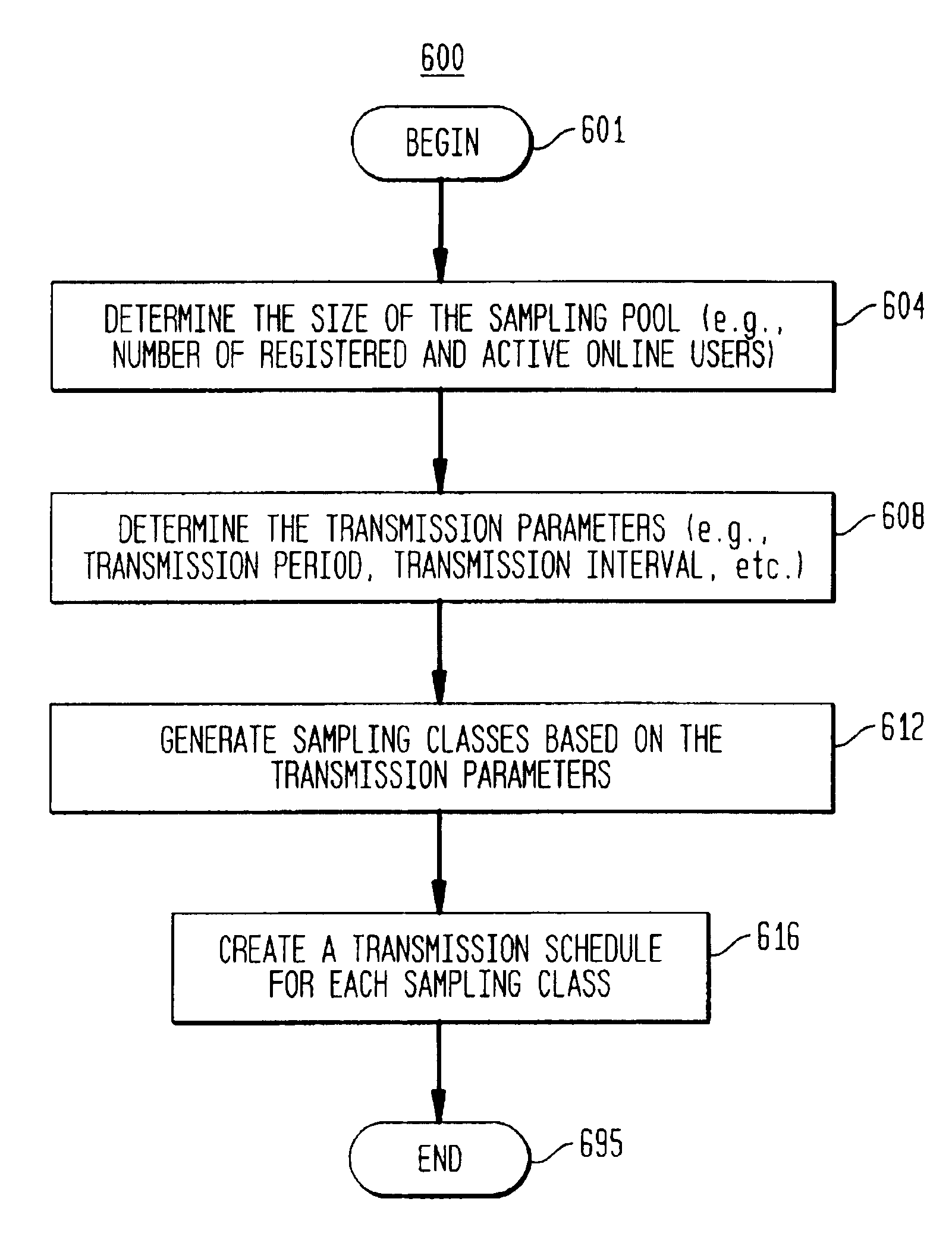
A computer-implemented transmission scheme is provided to control client-server interchanges within a distributed communications network, such as a real time opinion research system. Interchanges include transmitting media streams between one or more clients to a server over a computer network, including the global Internet. A polling management unit sets and manages the transmission mode that includes event-driven and periodic interchanges. Periodic interchanges can be simultaneously or staggeredly transmitted to a sampling pool of active clients. A transmission mode unit implements the transmission scheme set by the polling management unit. A parameter selector establishes the transmission interval and transmission period which are used to trigger each communication interchange. A client assignor creates one or more sampling classes from the sampling pool by applying a sampling quotient that is generated by the parameter selector. A schedule editor produces a transmission schedule for the active clients. If more than one sampling class has been created, each sampling class would receive a separate transmission schedule for providing staggered transmissions at designated transmission intervals. The transmission schedule can include other data preparation and formatting instructions for compression, aggregation and packetization.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Wireless communication
ActiveUS20040162093A1Increase installation costHigh maintenance costSynchronisation arrangementTransmission control/equalisingTelecommunicationsTransmission schedule
The invention is directed to a method of synchronising transmission between two nodes in a wireless network. The method comprises the steps of obtaining an expected interference profile for each node; and agreeing a synchronised transmission schedule between the nodes, where the expected interference profile of the or each node meets predetermined criteria.
Owner:APPLE INC
Delivery of data via omnidirectional digital transmission
InactiveUS7272227B1EffectiveGHz frequency transmissionAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTime scheduleNetwork connection
Owner:BERAN DAVID
Multiband mobile communication system and transmitter used therein
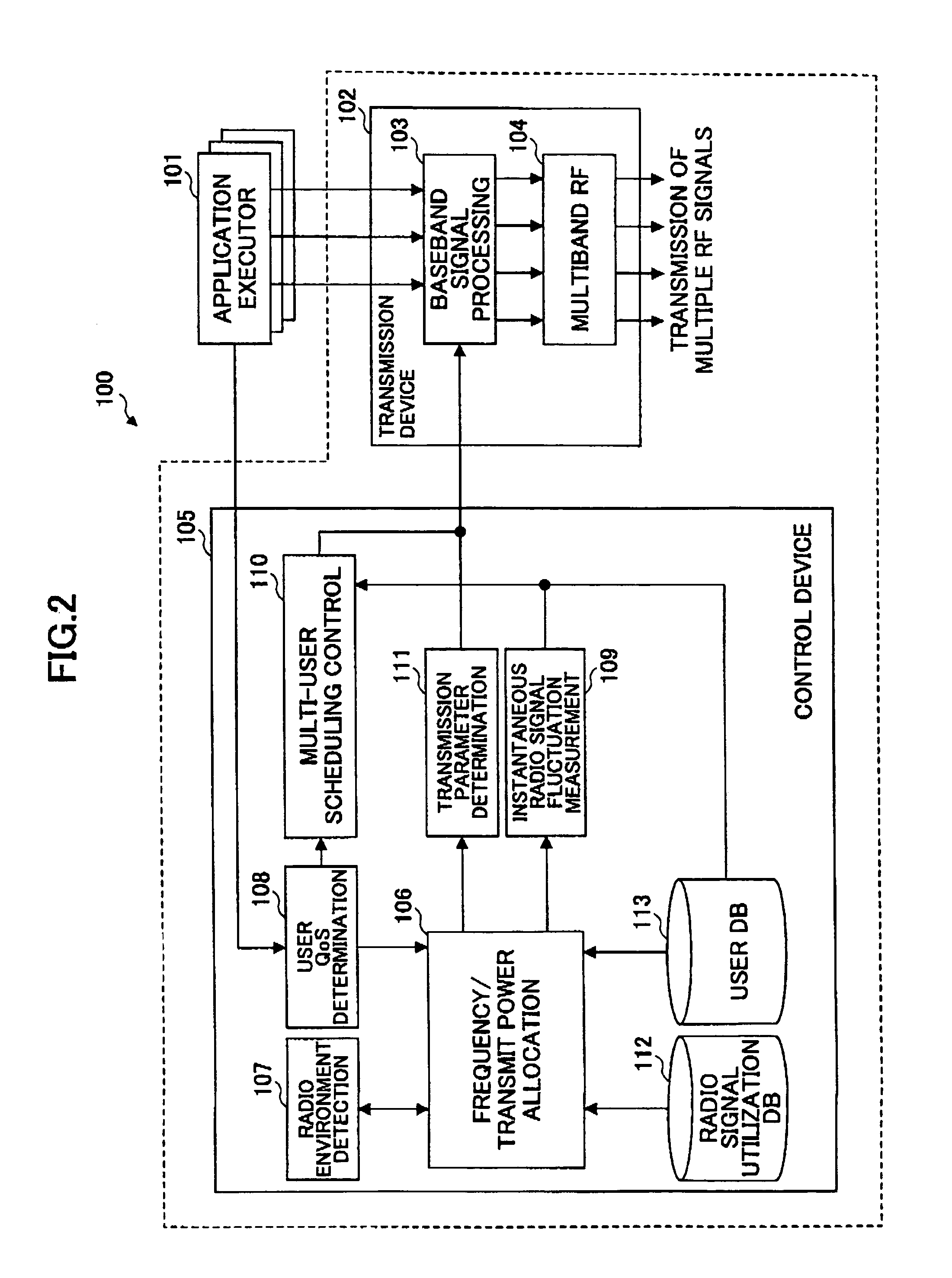
InactiveUS20060063543A1Improve efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplexFrequency bandTransmission schedule
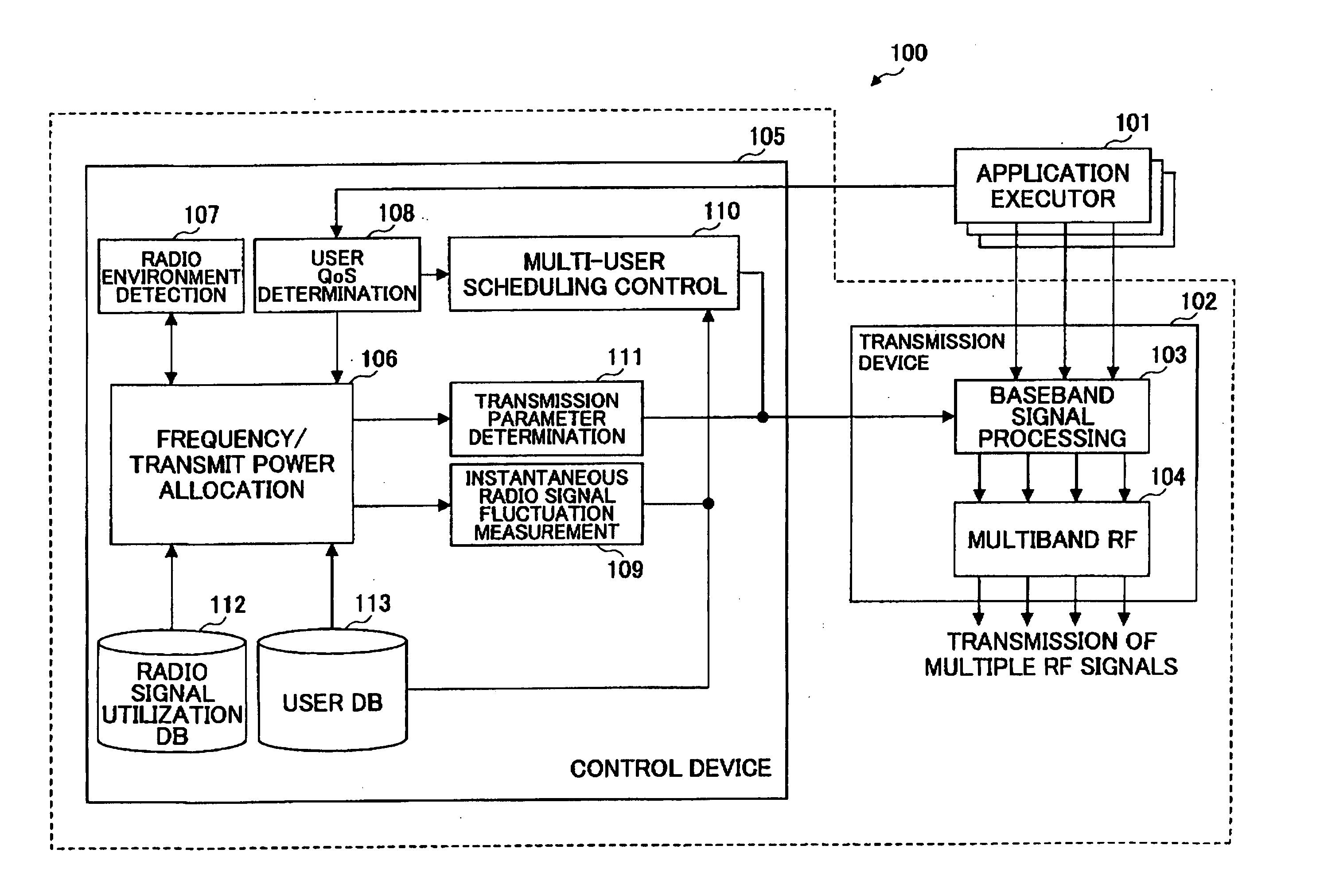
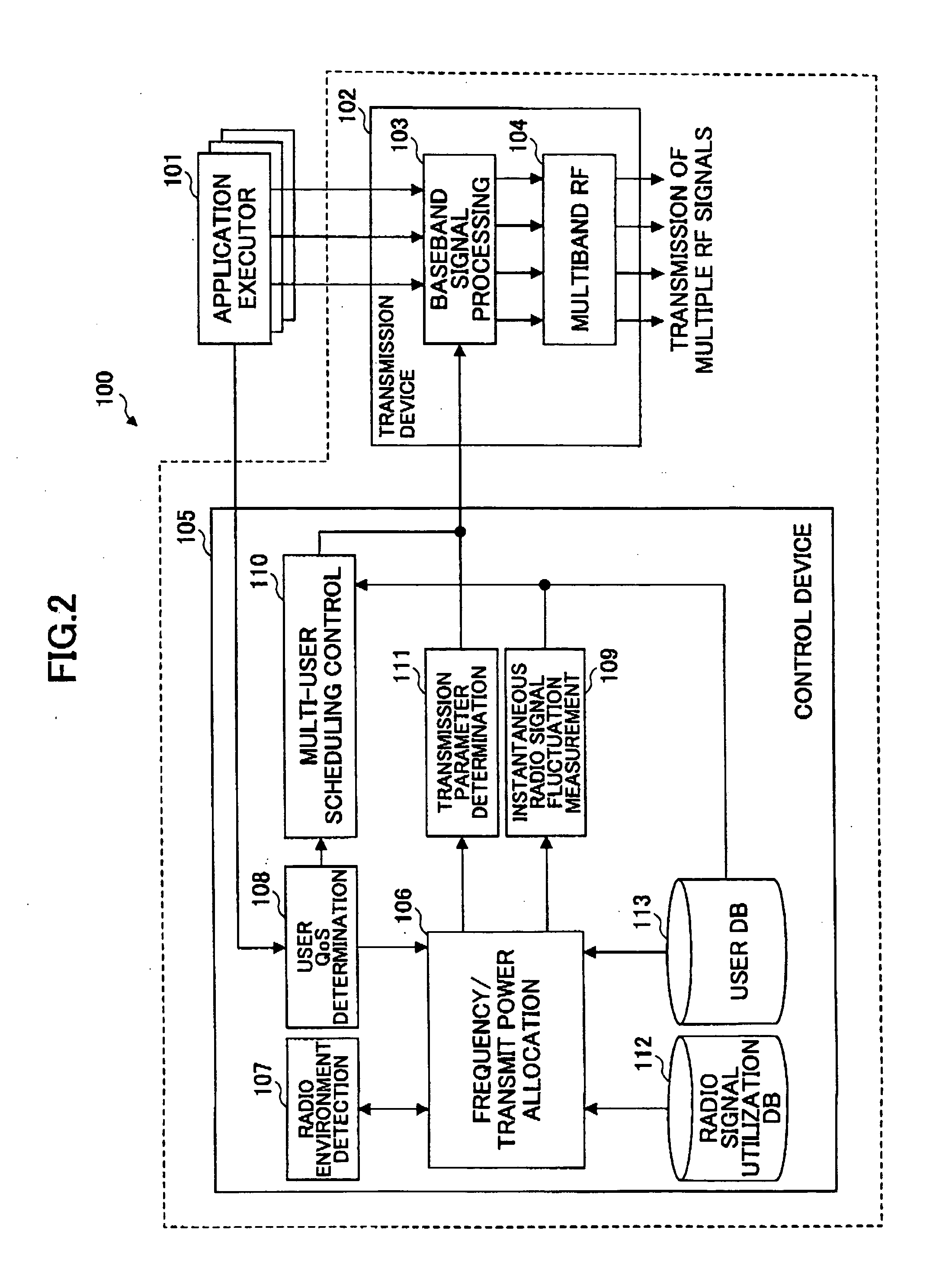
A transmitter used in the multiband environment includes a frequency allocation unit (106) configured to select and allocate a frequency band that satisfies a user QoS from among multiple separate frequency bands currently available for the user, a parameter determination unit (111) configured to determine a transmission parameter required for signal transmission based on the allocated frequency band, and a multi-user scheduling control unit (110) configured to determine a transmission schedule for multiple users taking into account the frequency bands allocated to the multiple users.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Schedule-Based Coordination of Audio Sources
ActiveUS20180165055A1Reduce acoustic cross-talkSynchronisation arrangementPublic address systemsComputer hardwareTime schedule
An audio / video (A / V) hub that coordinates playback of audio content is described. In particular, the A / V hub may calculate current time offsets between clocks in electronic devices and a clock in the A / V hub based on differences between receive times when frames are received from electronic devices and expected transmit times of the frames. For example, the expected transmit times may be based on coordination of clocks in the electronic devices and a clock in the A / V hub at a previous time and a predefined transmit schedule of the frames. Then, the A / V hub may transmit, to the electronic devices, one or more frames that include audio content and playback timing information, which may specify playback times when the electronic devices are to playback the audio content based on the current time offsets.
Owner:B & W GRP LTD
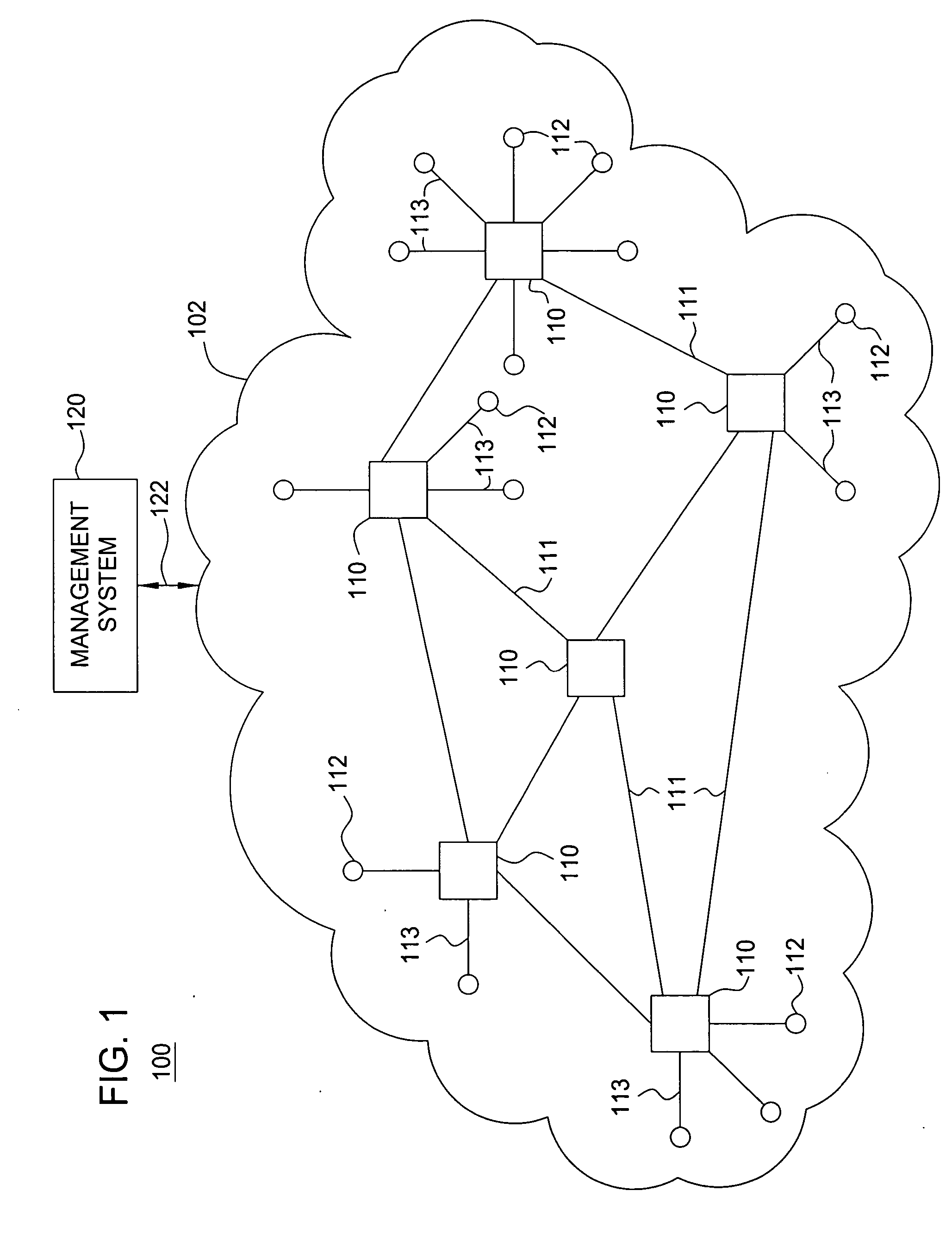
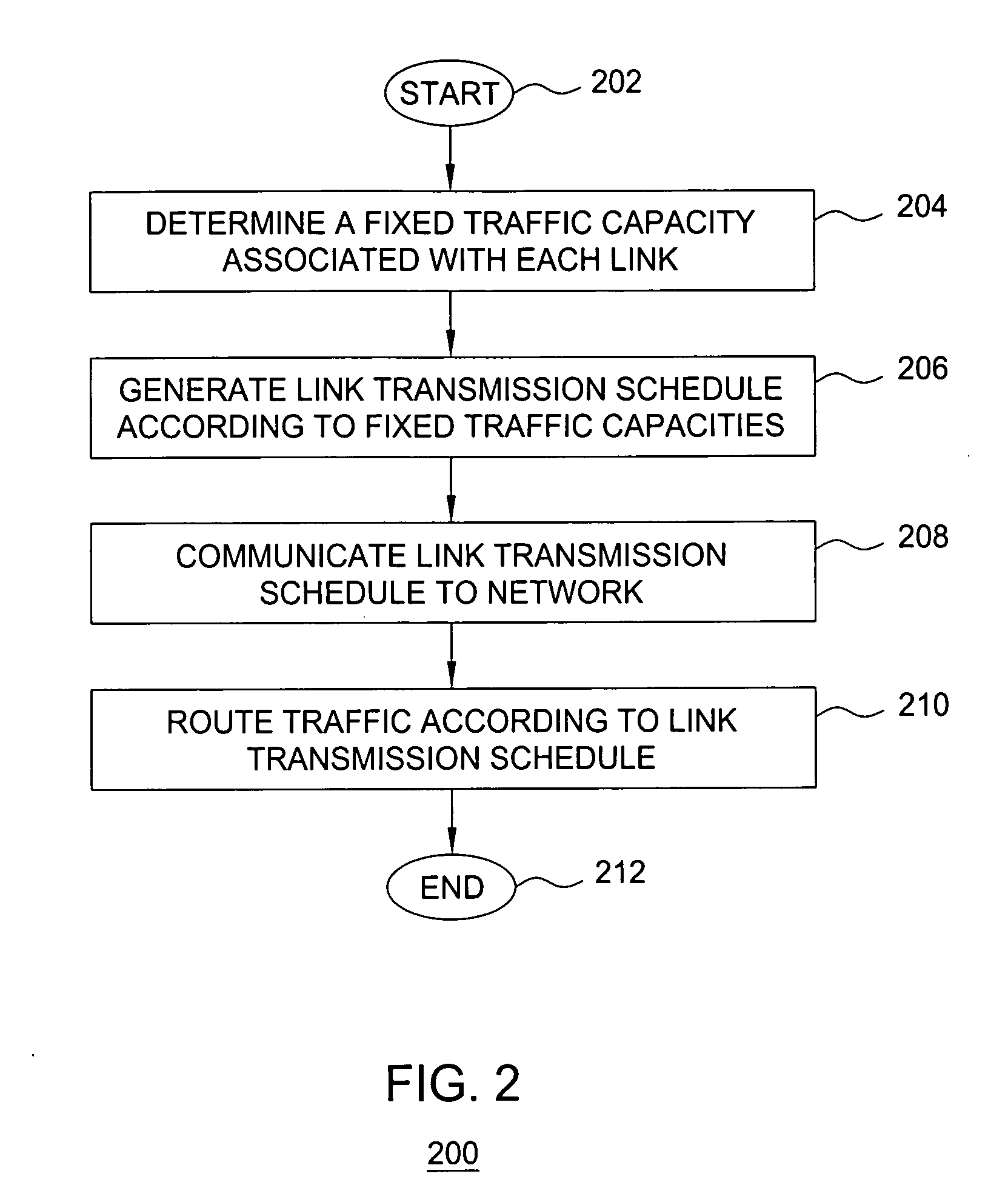
Method and apparatus for link transmission scheduling for handling traffic variation in wireless mesh networks
ActiveUS20070237081A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementTraffic capacityWireless mesh network
The invention includes a method and apparatus for generating a link transmission schedule for handling traffic variation in wireless networks without dynamic scheduling or routing. The method includes determining fixed traffic capacities associated with respective wireless links of a wireless network according to a routing algorithm, and generating, using the routing algorithm and the fixed traffic capacities, a link transmission schedule including at least one condition by which traffic is transmitted using each of the network links. The link transmission schedule is adapted to remain substantially fixed during dynamic traffic changes. The routing algorithm may be a two-phase routing algorithm in which traffic is distributed by each node in the wireless network to every node in the wireless network using traffic split ratios. For two-phase routing, fixed traffic capacities may be determined using ingress and egress traffic capacities and traffic split ratios associated with respective nodes in the wireless network.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
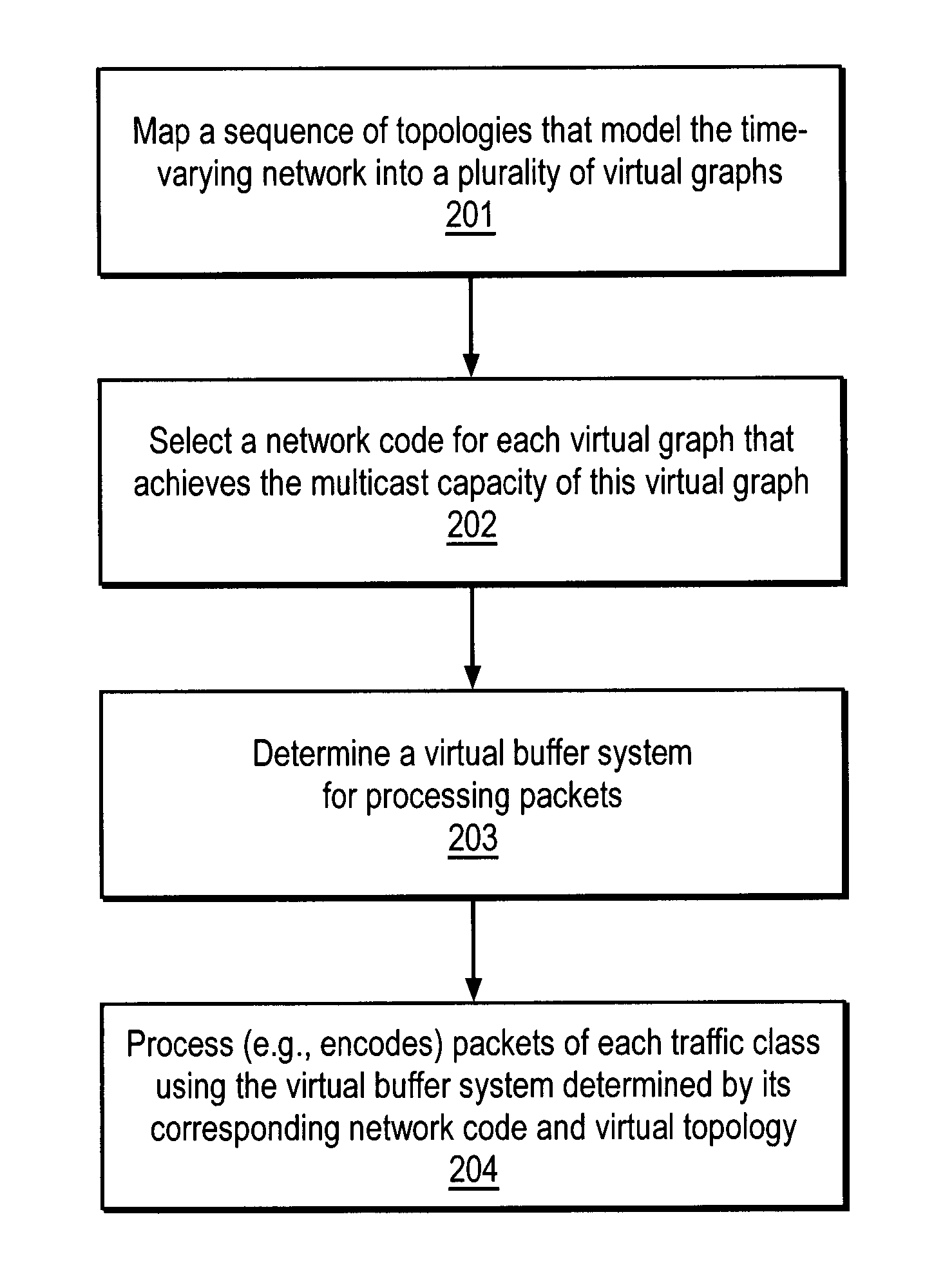
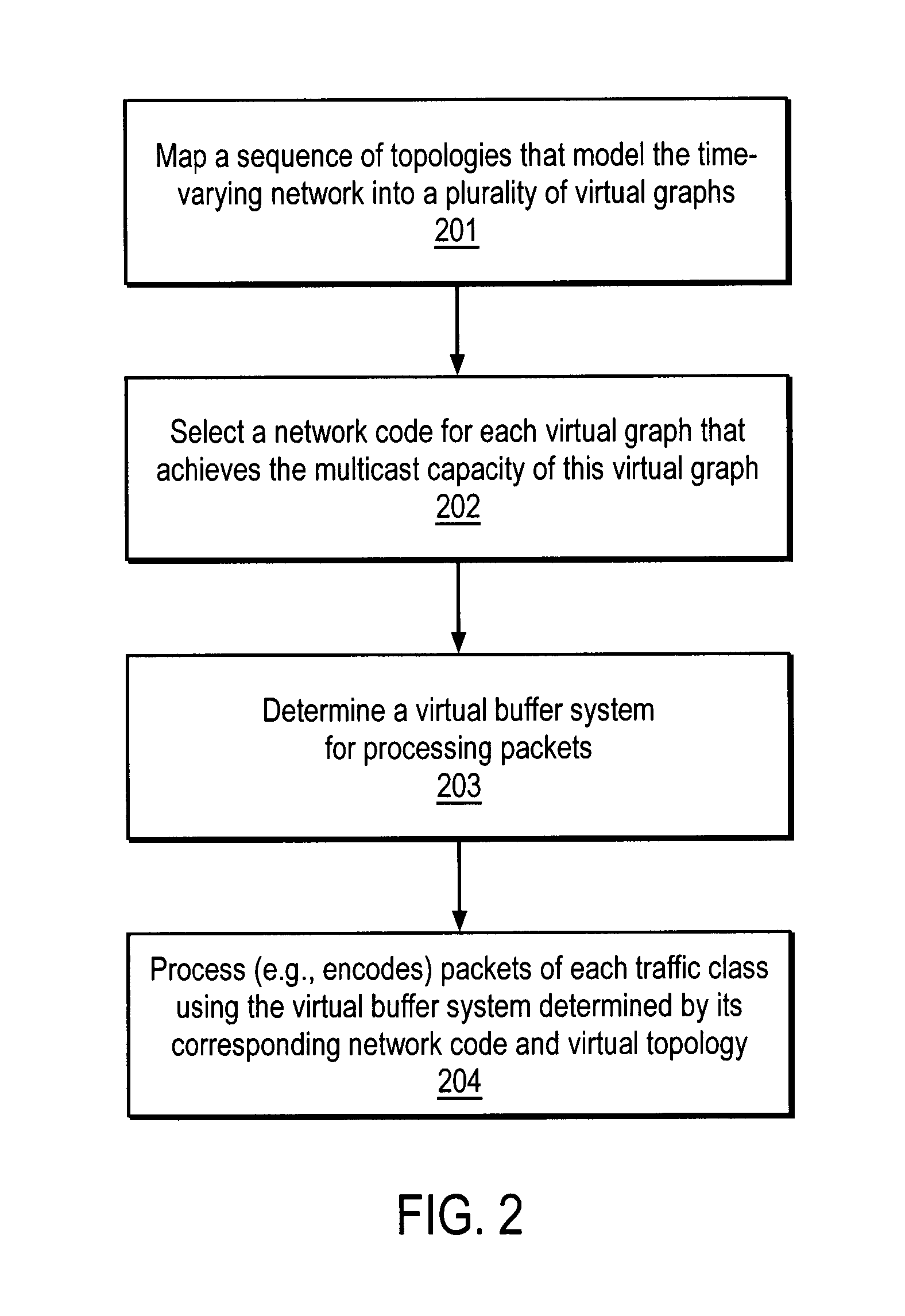
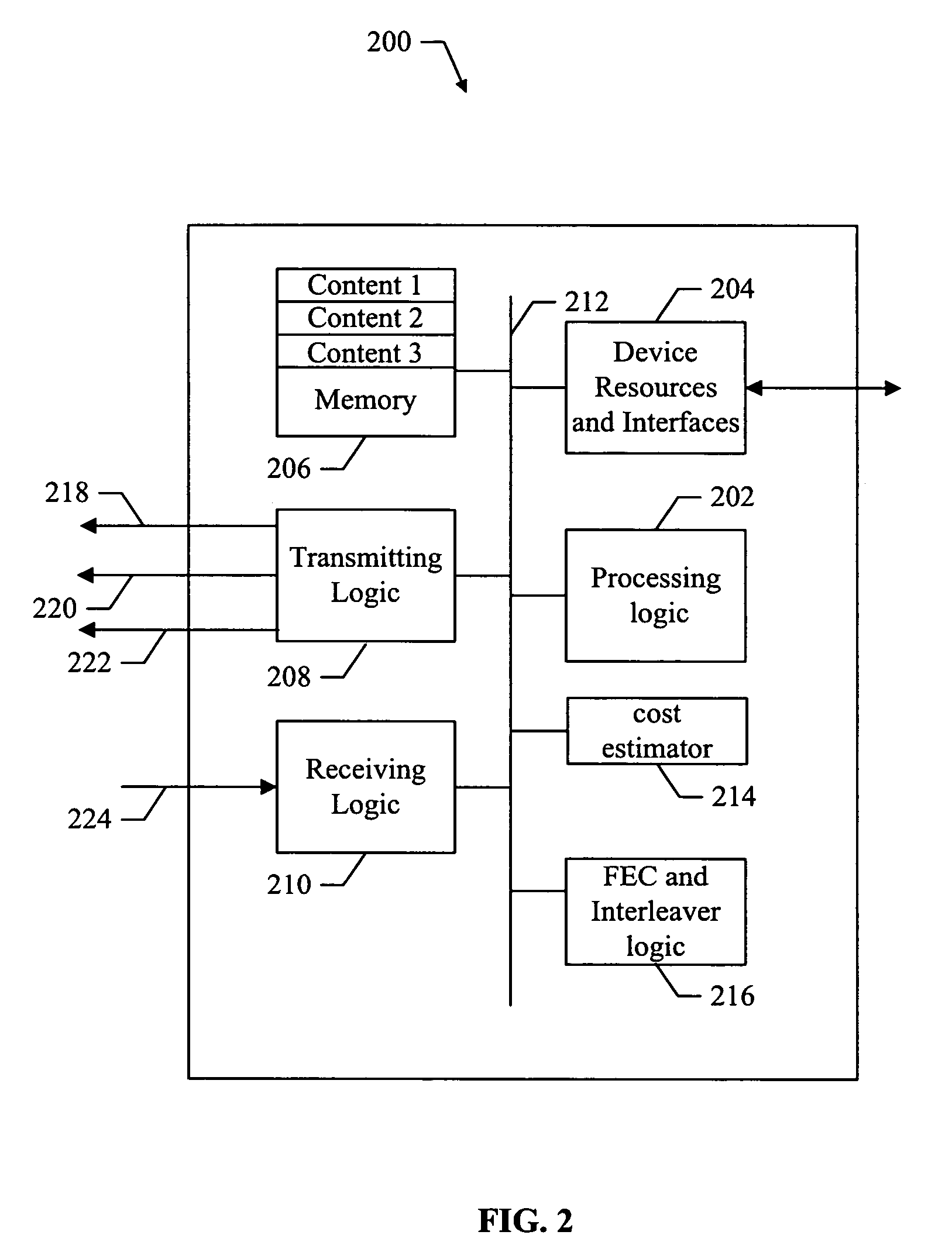
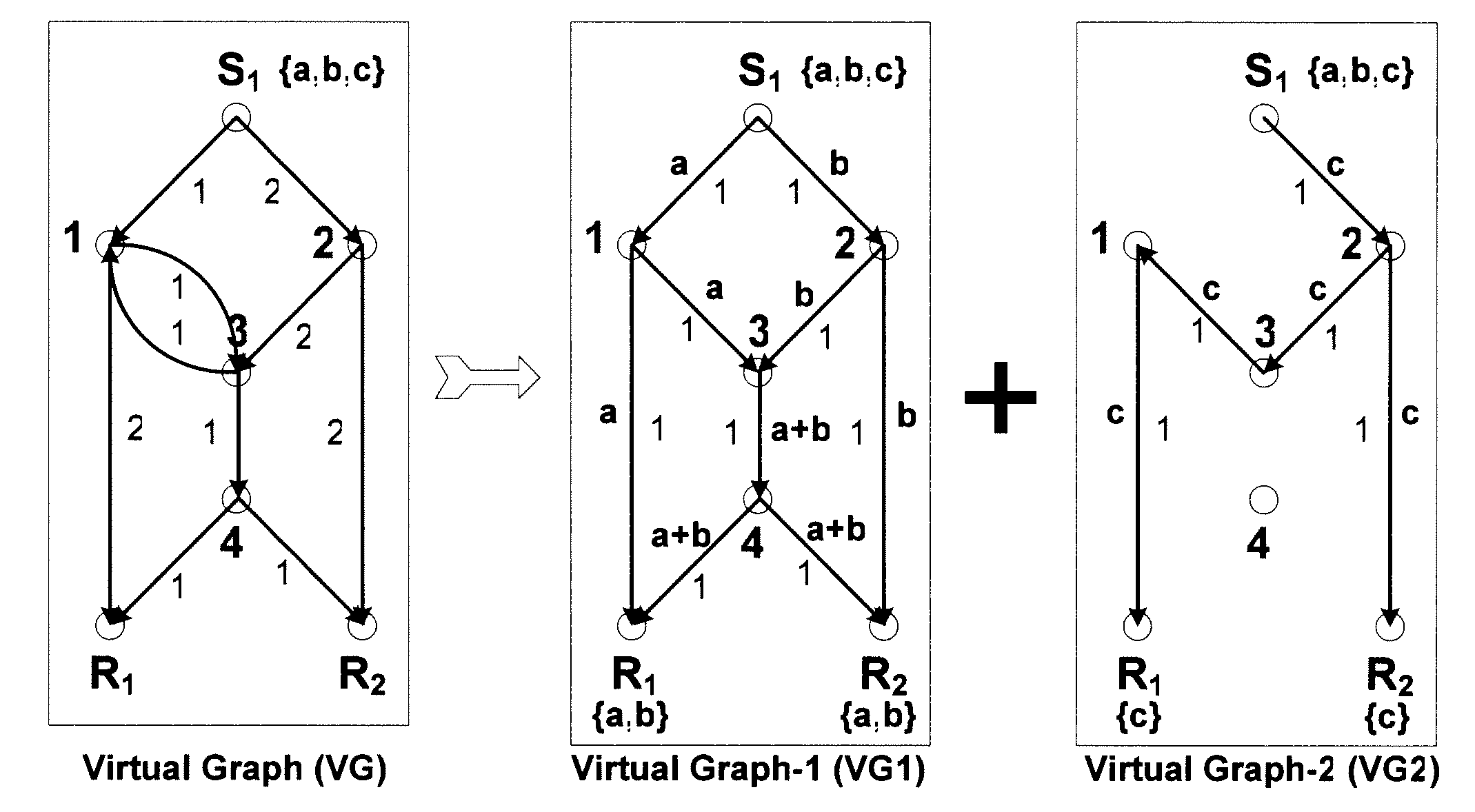
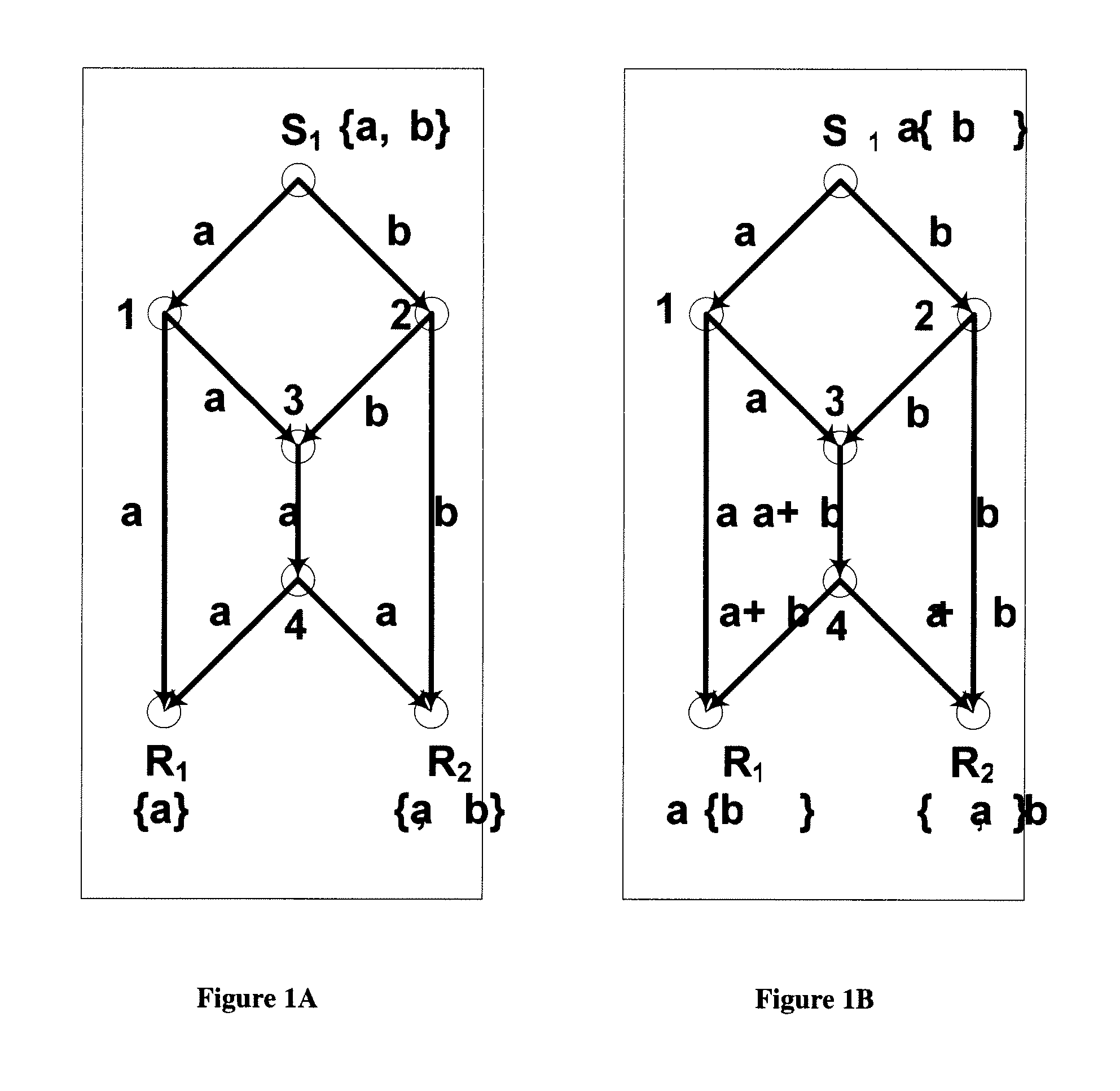
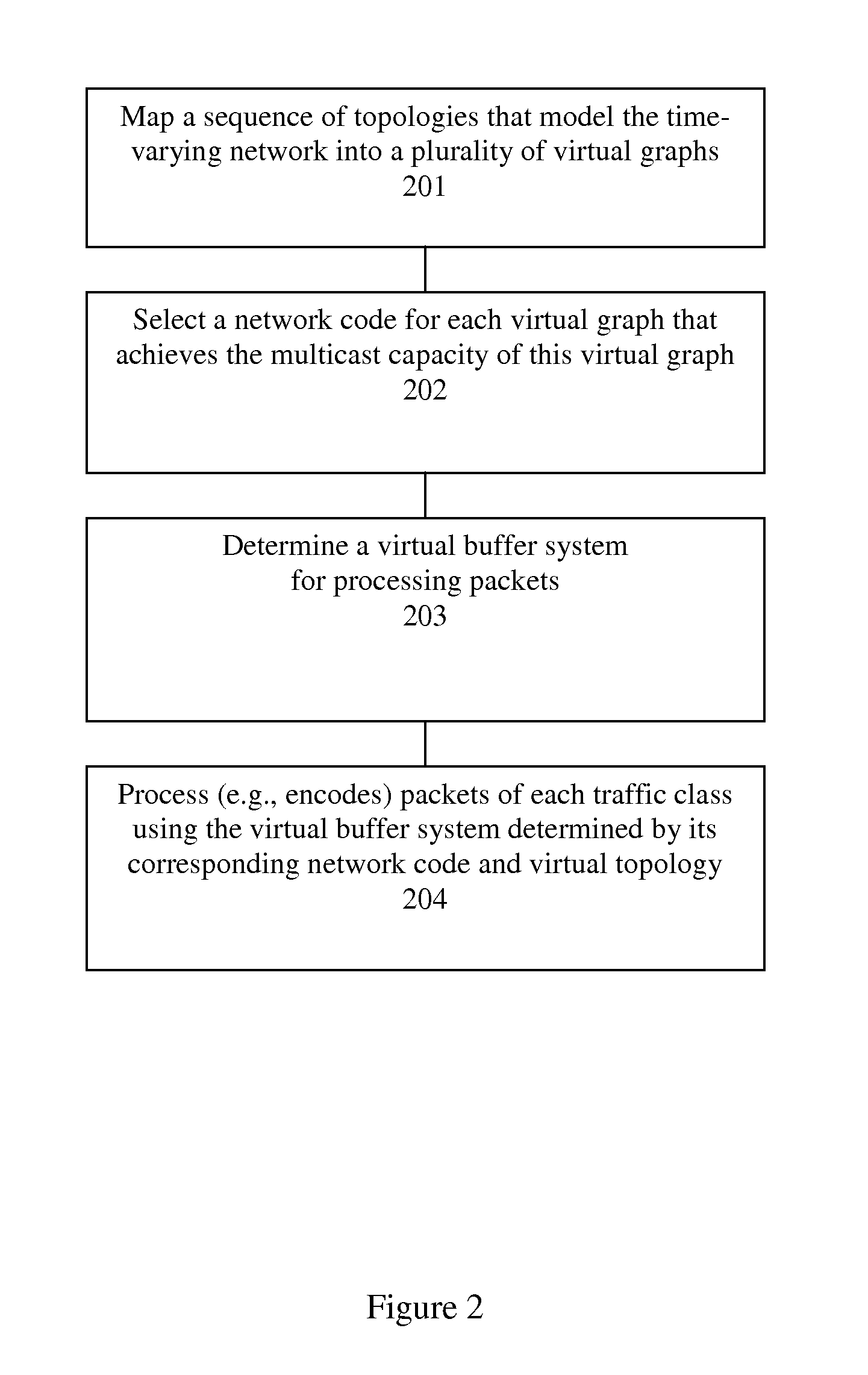
Method and apparatus for prioritized information delivery with network coding over time-varying network topologies
ActiveUS8861356B2Special service provision for substationError preventionTraffic capacityTopological graph
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
System and method for ad hoc network access employing the distributed election of a shared transmission schedule
InactiveUS7046639B2Eliminate CollisionsControl moreNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessTransmission schedule
A system and method of providing distributed election of a shared transmission schedule within an ad hoc network. The invention includes a collision-free access protocol which resolves channel access contentions for time division multiple access (TDMA) of a single channel. Time-slots are organized into part numbers, which are included within sections, a sequence of which define a block. Each node is given a ring number according to its location within the network topology and maintains local neighbor information along with its own part number and message digest. Collision-free channel access is automatically scheduled and repetitious contention phases are resolved by a random permutation algorithm operating in message digests. An empty time-slot utilization method is also described and data packets may also be transmitted subject to a non-zero collision probability within a blind section of the block.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Antenna-aware method for transmitting packets in a wireless communication network
ActiveUS20100046439A1Assess restrictionBroadcast service distributionBroadcast transmissionTransmission schedule
A method for transmitting packets in a wireless communication network includes taking into consideration an antenna mode prior to transmission. The method includes determining a transmit antenna mode for a transmission between the node and at least one other node; when the transmit antenna mode is omni-directional, broadcasting a transmission schedule for the transmission omni-directionally; and when the transmit antenna is beamforming directional, broadcasting a transmission schedule for the transmission directionally on one or more transmitter beams. The method optionally can also take into consideration an antenna mode of a receive antenna between the node.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
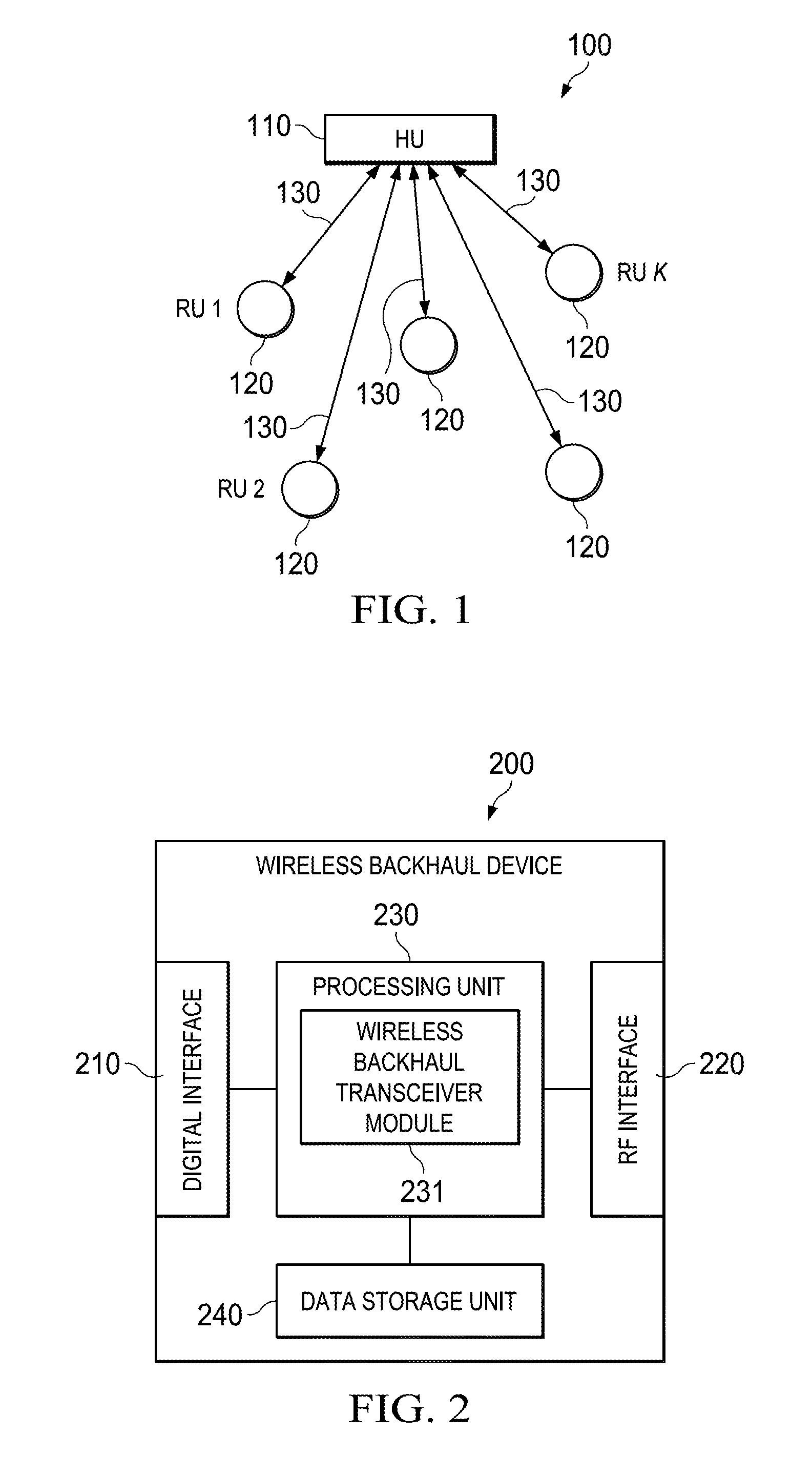
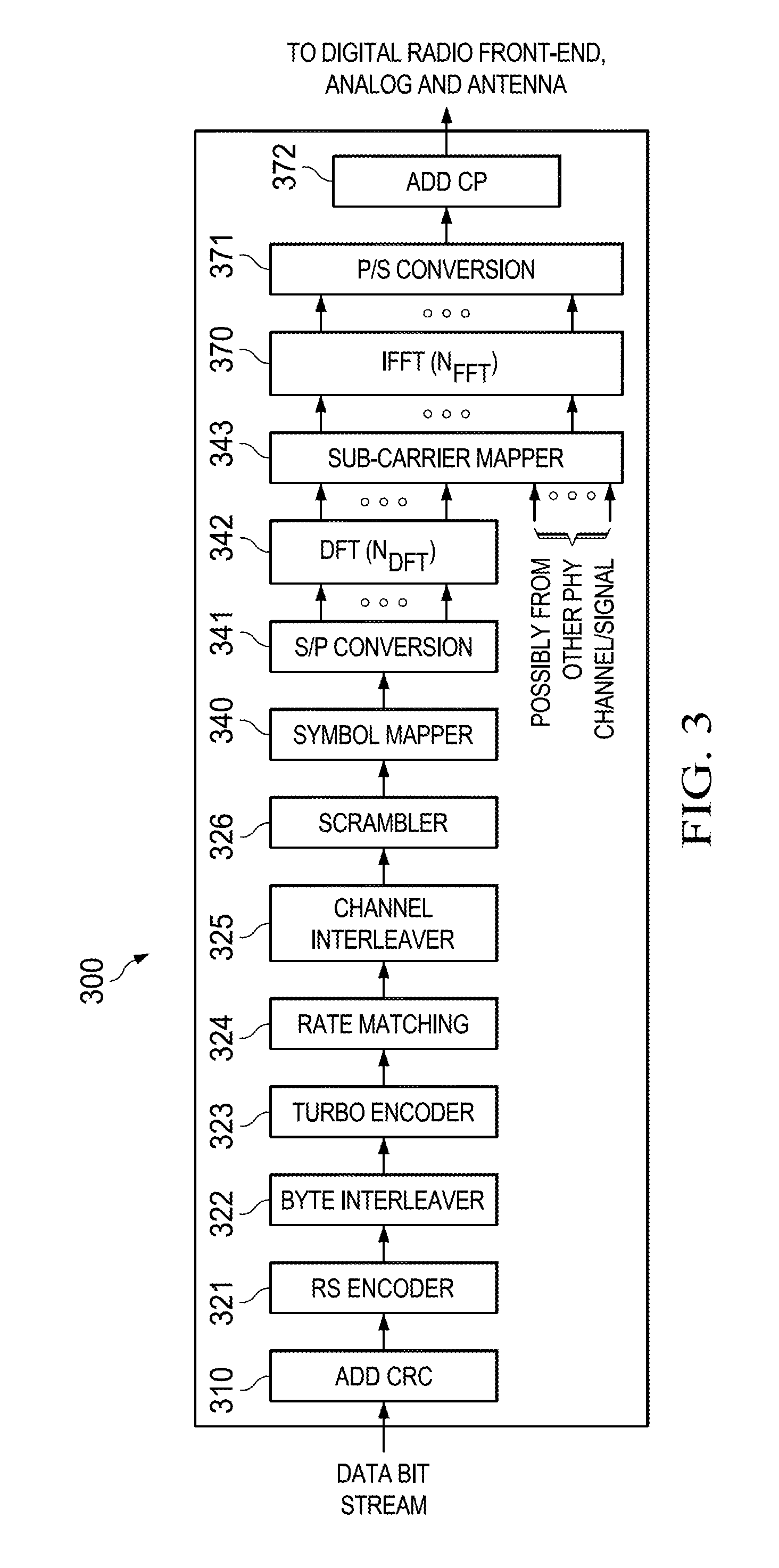
Nlos wireless backhaul downlink communication
ActiveUS20140362701A1Transmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementBroadcast channelsFourier transform on finite groups
A method for communicating over a wireless backhaul channel comprising generating a radio frame comprising a plurality of time slots, wherein each time slot comprises a plurality of symbols in time and a plurality of sub-carriers in a system bandwidth, broadcasting a broadcast channel signal comprising a transmission schedule to a plurality of remote units in a number of consecutive sub-carriers centered about a direct current (DC) sub-carrier in at least one of the time slots in the radio frame regardless of the system bandwidth, and transmitting a downlink (DL) control channel signal and a DL data channel signal to a first of the remote units, wherein the DL data channel signal is transmitted by employing a single carrier block transmission scheme comprising a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) spreading for frequency diversity.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multiband mobile communication system and transmitter used therein
InactiveUS7502341B2Improve efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplexTransmission scheduleMobile communication systems
A transmitter used in the multiband environment includes a frequency allocation unit (106) configured to select and allocate a frequency band that satisfies a user QoS from among multiple separate frequency bands currently available for the user, a parameter determination unit (111) configured to determine a transmission parameter required for signal transmission based on the allocated frequency band, and a multi-user scheduling control unit (110) configured to determine a transmission schedule for multiple users taking into account the frequency bands allocated to the multiple users.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
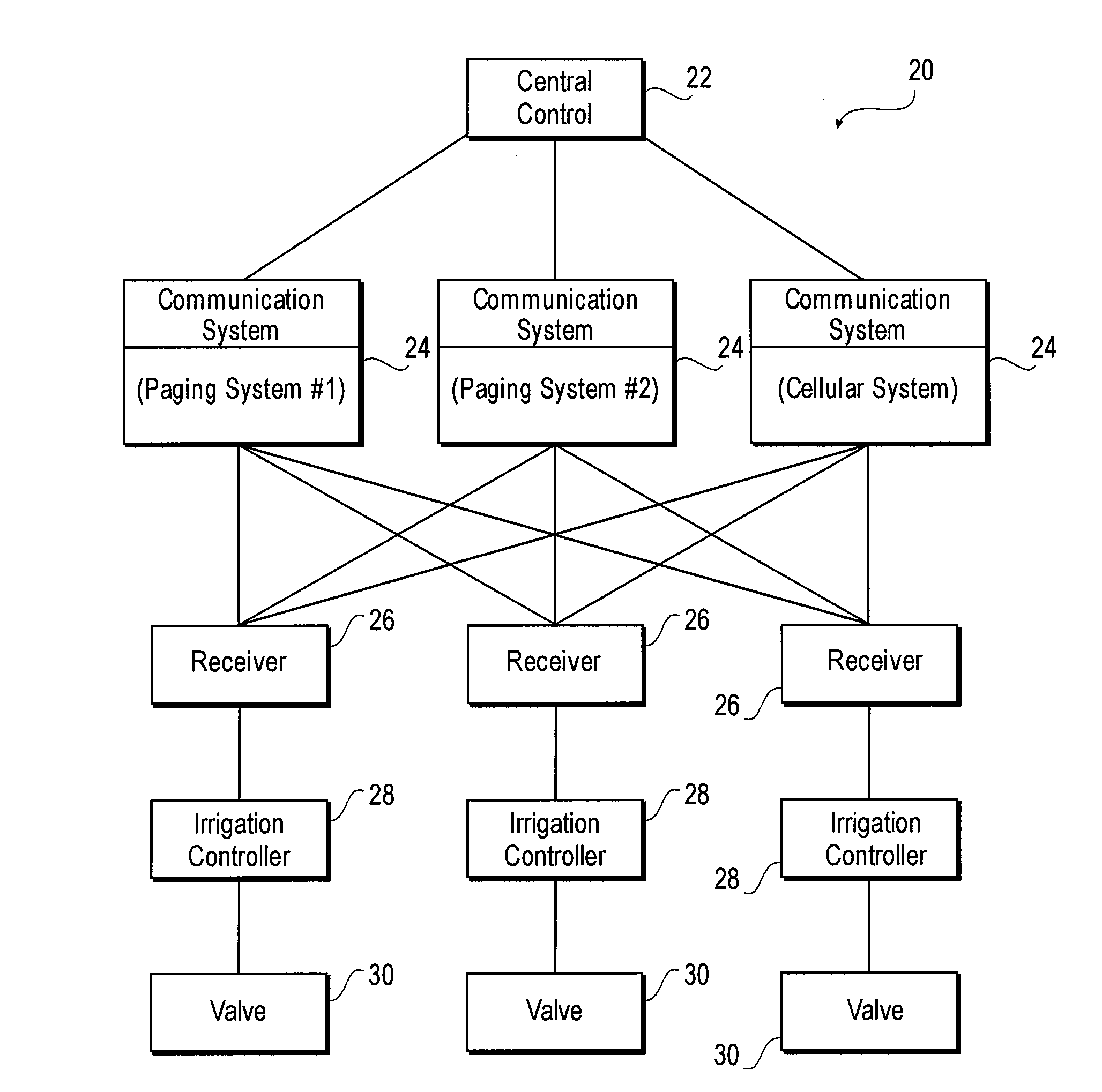
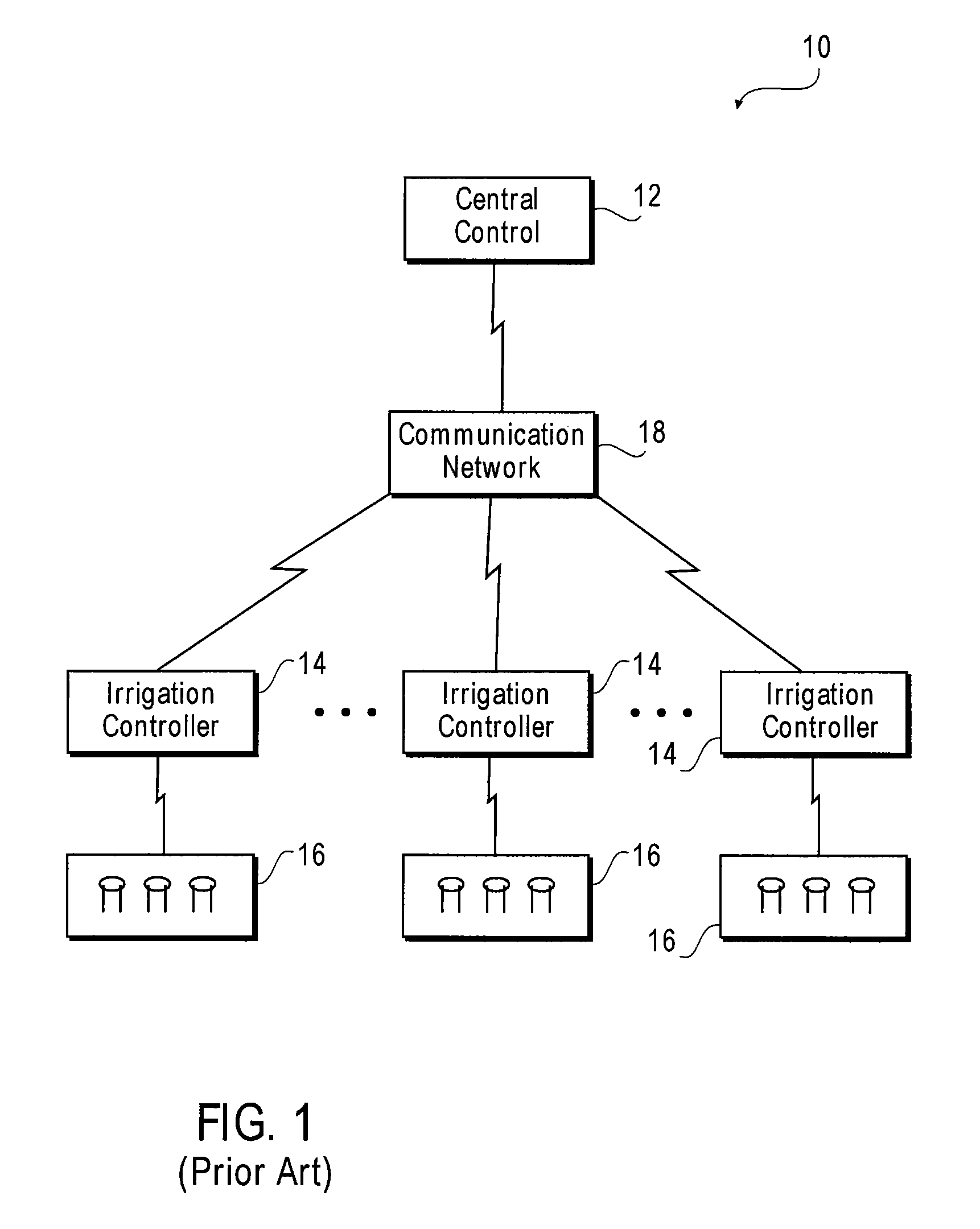
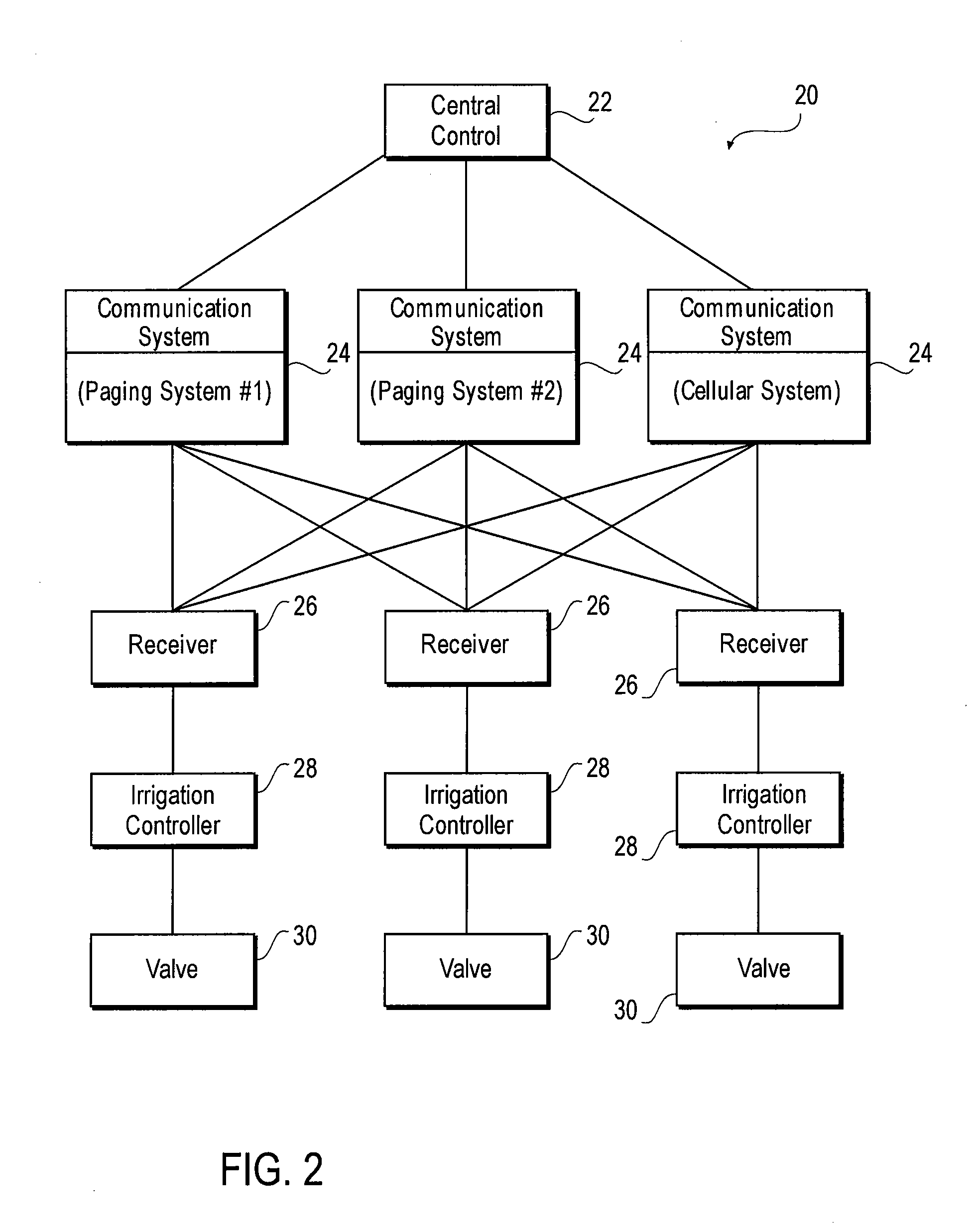
System and method for facilitating control of irrigation systems
InactiveUS7182272B1Reliable communicationSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesCommunications systemTransmission channel
A system for providing reliable communications between components of an irrigation system is provided. The system includes a central control, a number of communication systems each representing a transmission channel, an irrigation controller having a receiver that is configured to receive signals from the communication systems, and one or more valves controlled by the irrigation controller to provide irrigation. According to one aspect of the system, in order to direct the irrigation controller to take certain actions, the central control first generates a message. The message is then delivered to the communication systems. In one instance, the message is transmitted by the communication systems in a rotating manner, i.e., the communication systems take turn in transmitting the message in a predetermined cycle. To ensure proper reception of the message, the irrigation controller conforms to the rotational transmission schedule of the communication systems and monitors the incoming signals accordingly. The received message is then used by the irrigation controller to act on the valves, alter an irrigation schedule or otherwise control irrigation.
Owner:HYDROPOINT DATA SYST
Method and apparatus for delivering multimedia content based on network connections
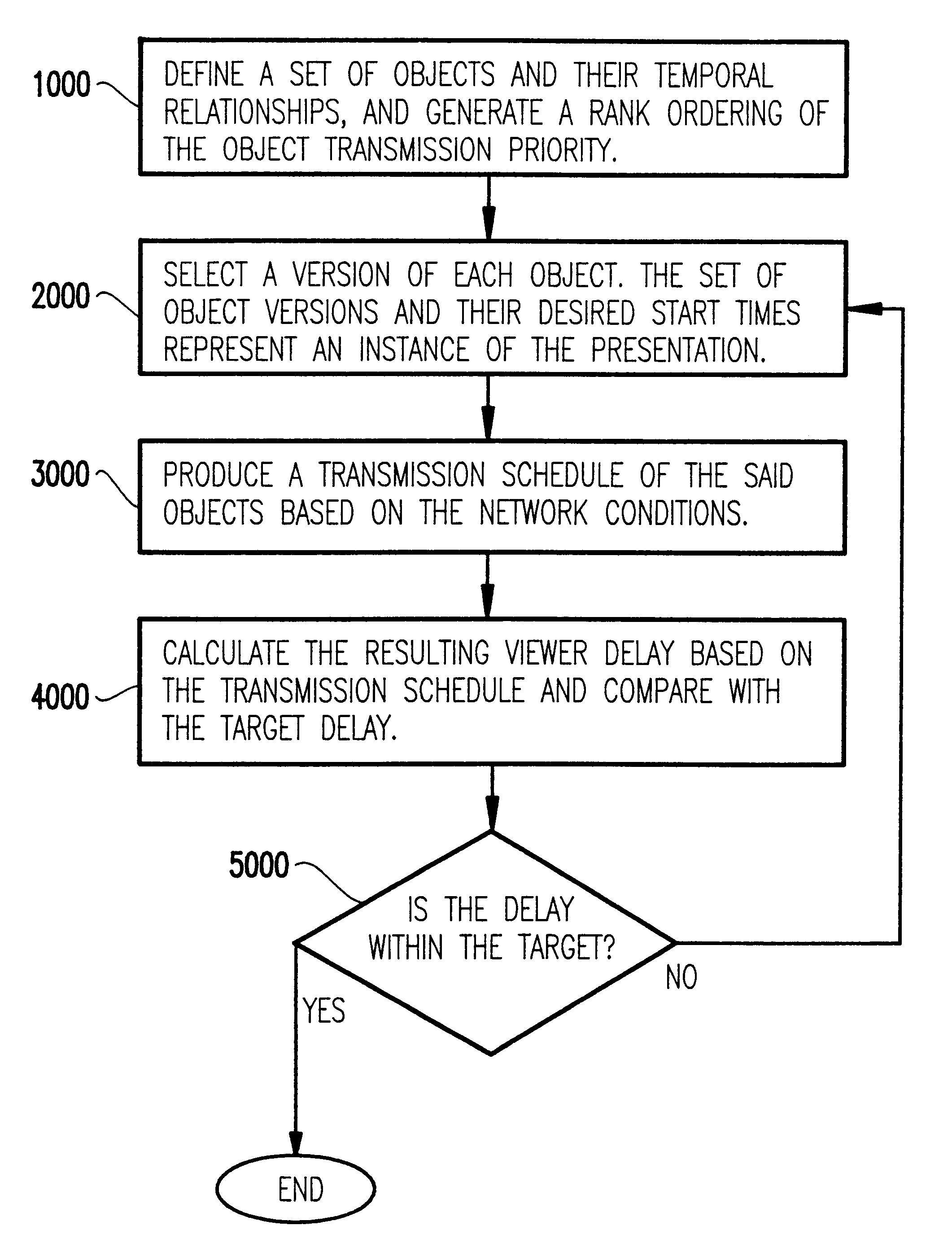
InactiveUS6219704B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksNetwork conditionsTransmission schedule
A method and an apparatus adaptively and dynamically deliver multimedia content based on continuously monitored network conditions. Given the temporal relationships among the multimedia items in the multimedia data stream and also the current network condition, the method and apparatus compute a transmission schedule such that the transmission delay and the burstyness of the network bandwidth utilization are minimized, while maintaining the integrity of the multimedia presentation.
Owner:IBM CORP
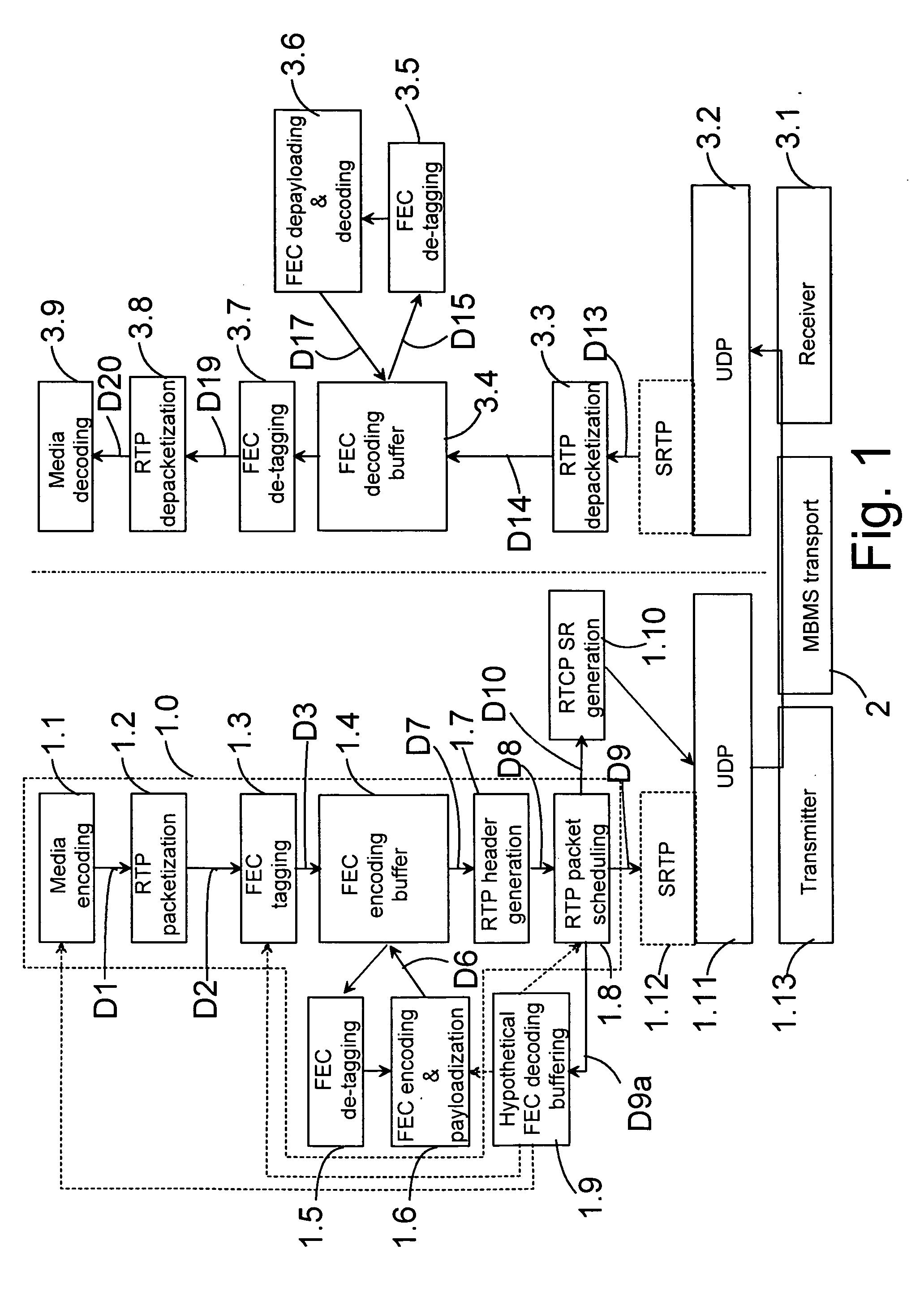
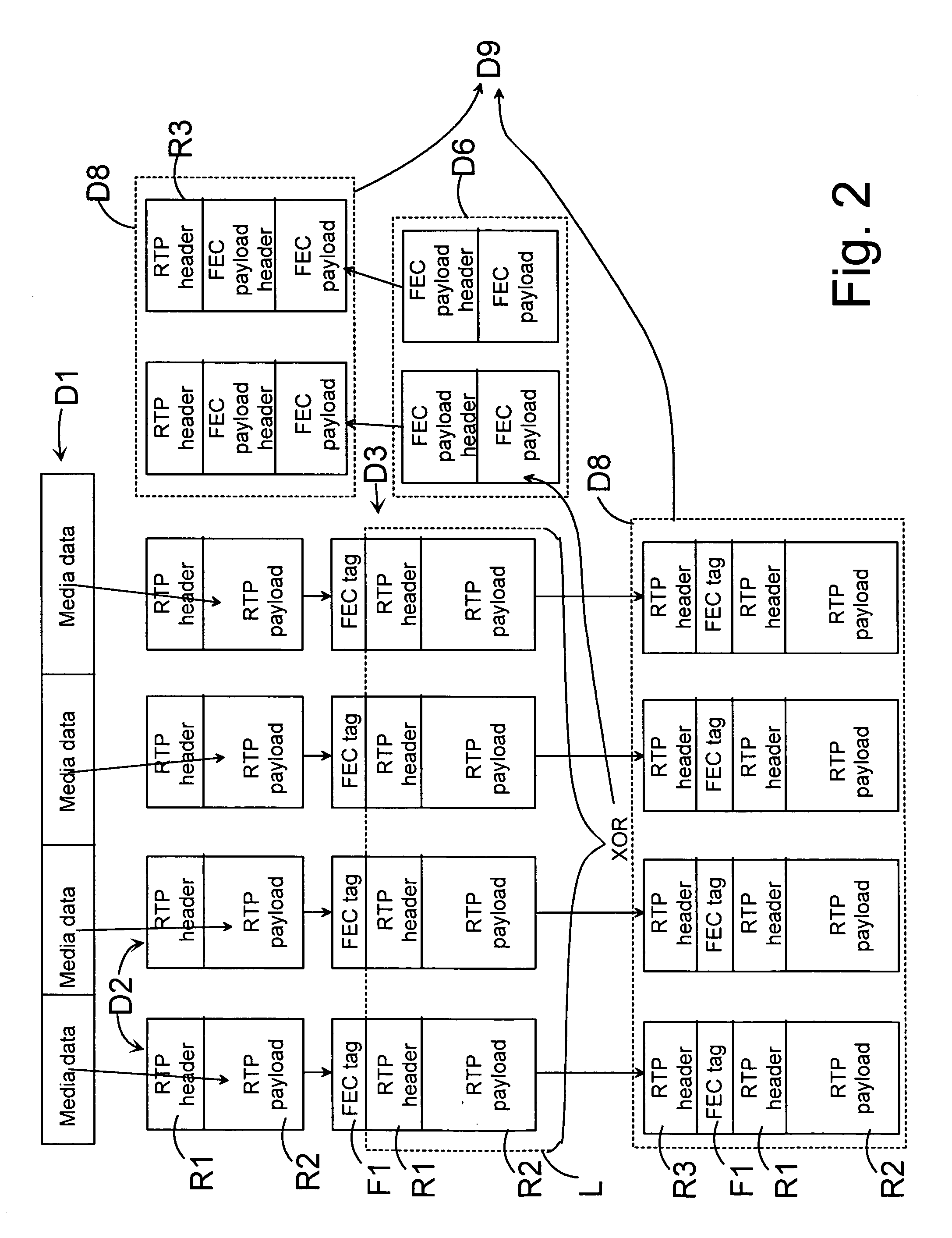
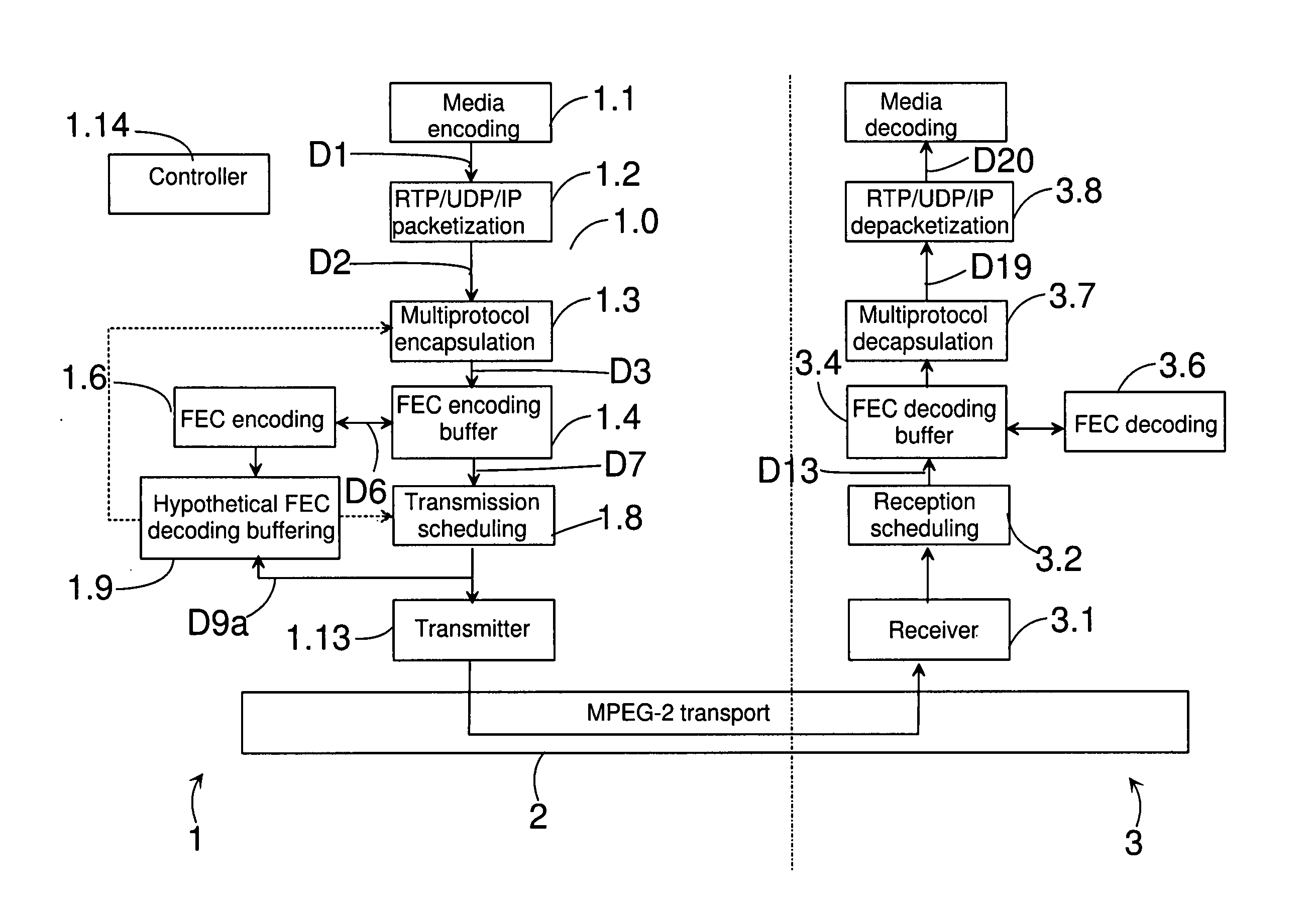
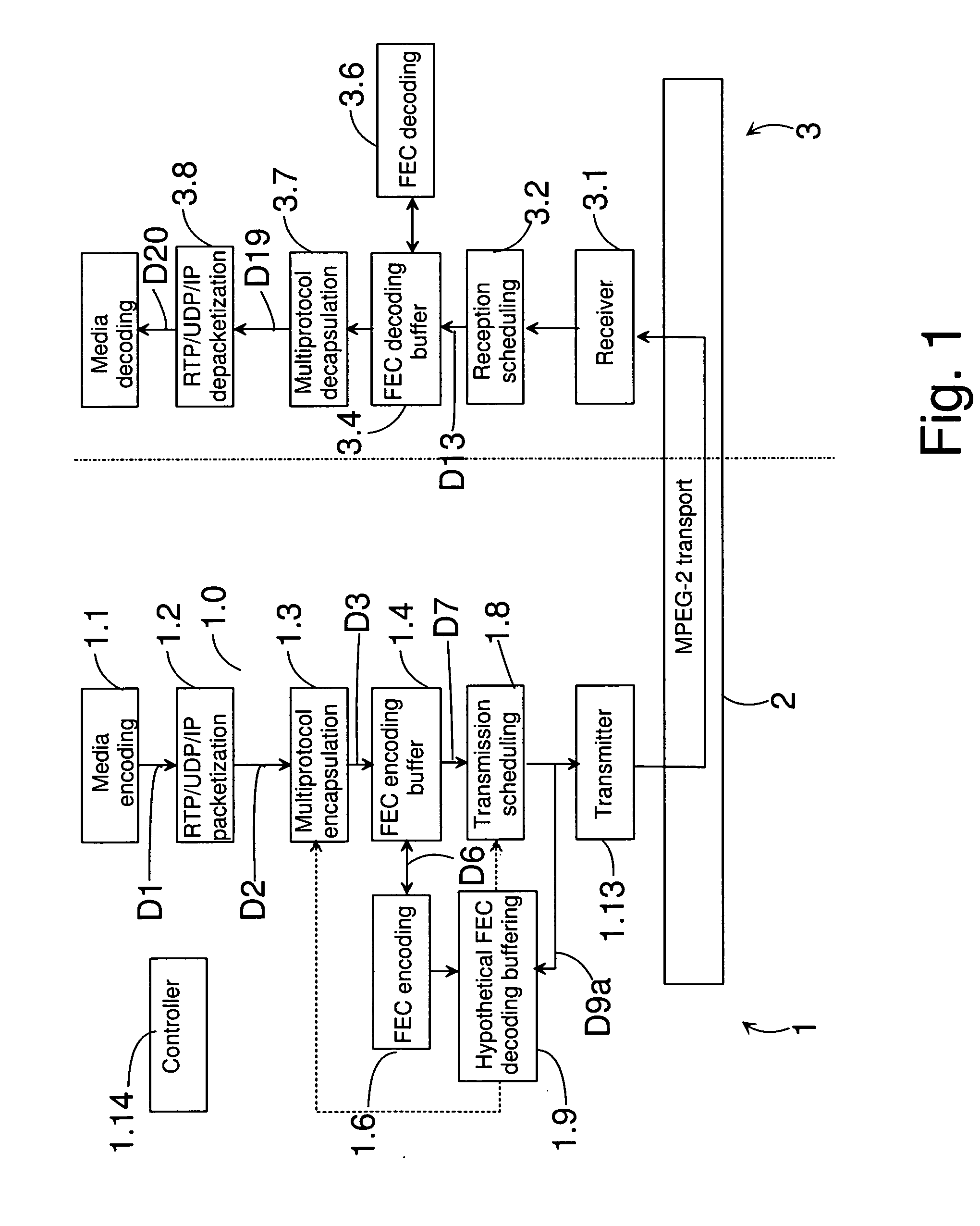
Buffering packets of a media stream
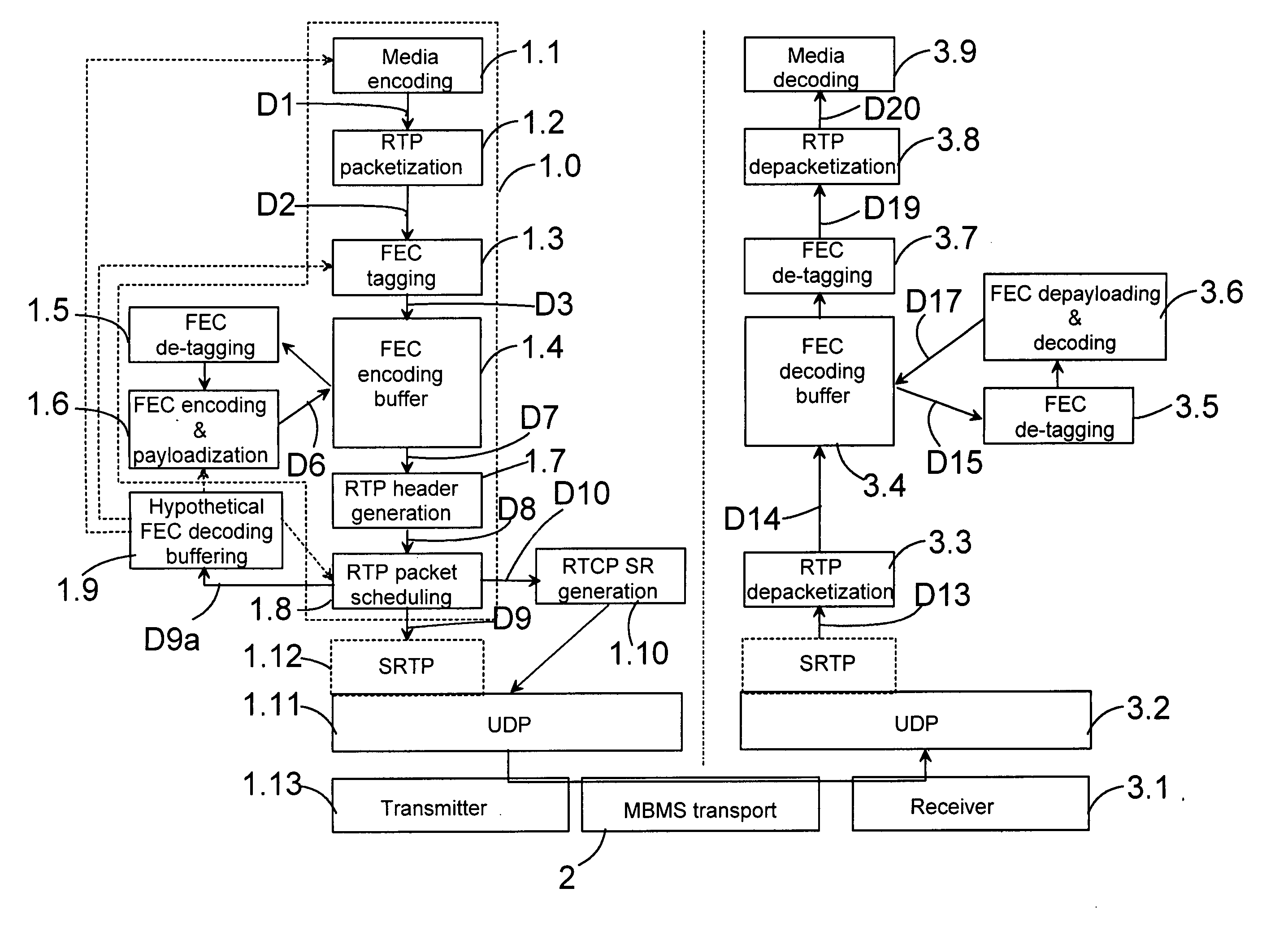
Buffering packets of a media stream for transmission from a transmitting device to a receiving device. Media packets are formed from at least one kind of media information in a stream generator; forward error correction data is formed on the basis of the media packets; one or more repair packets are formed on the basis of the forward error correction data; and a transmission schedule is generated for packets to be transmitted. In addition, hypothetical decoding is also performed according to the transmission schedule. The hypothetical decoding comprises buffering the packets to be transmitted according to the transmission schedule to a hypothetical decoding buffer; and controlling the buffer occupancy level of the hypothetical decoding buffer by controlling the operation of the stream generator.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
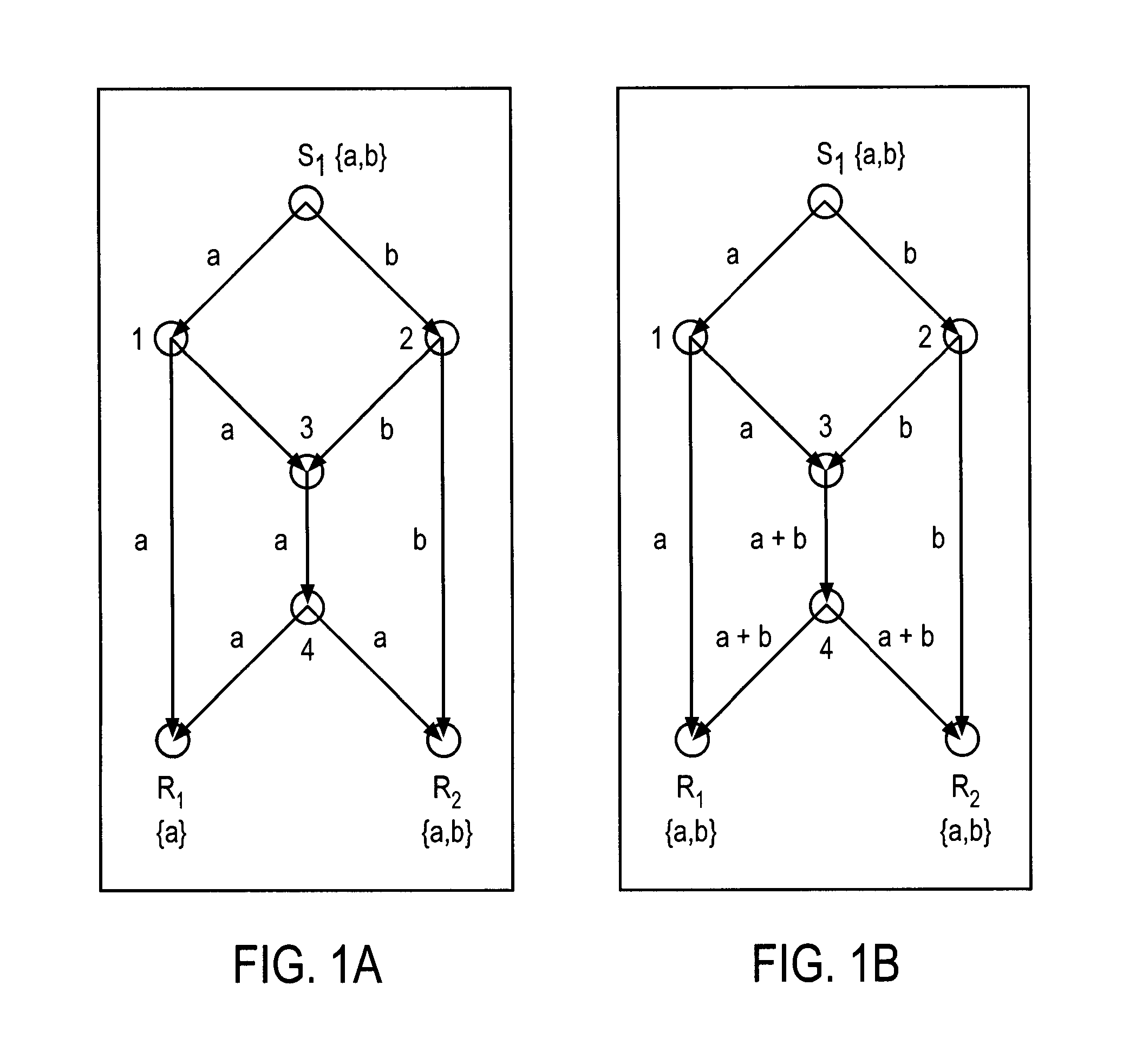
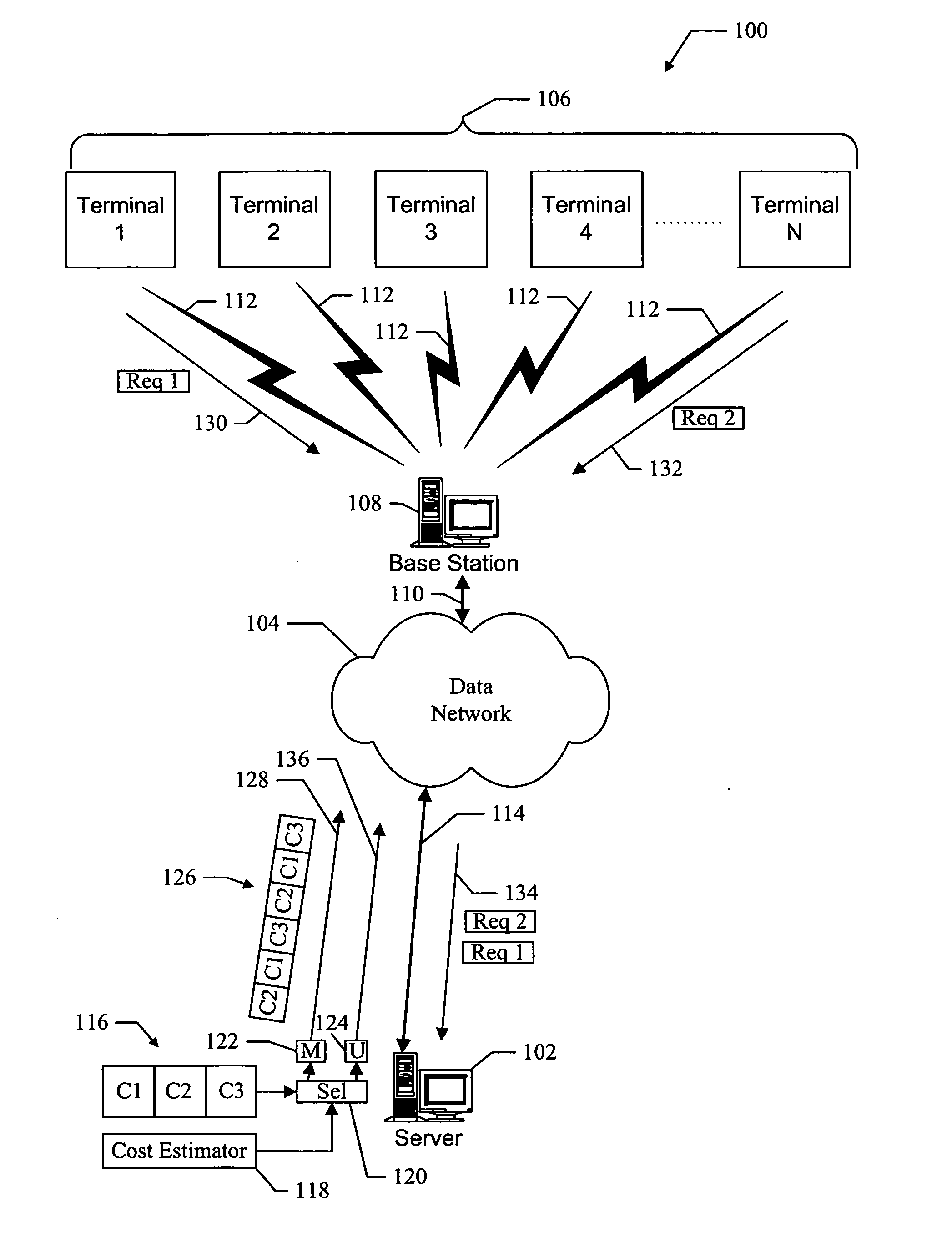
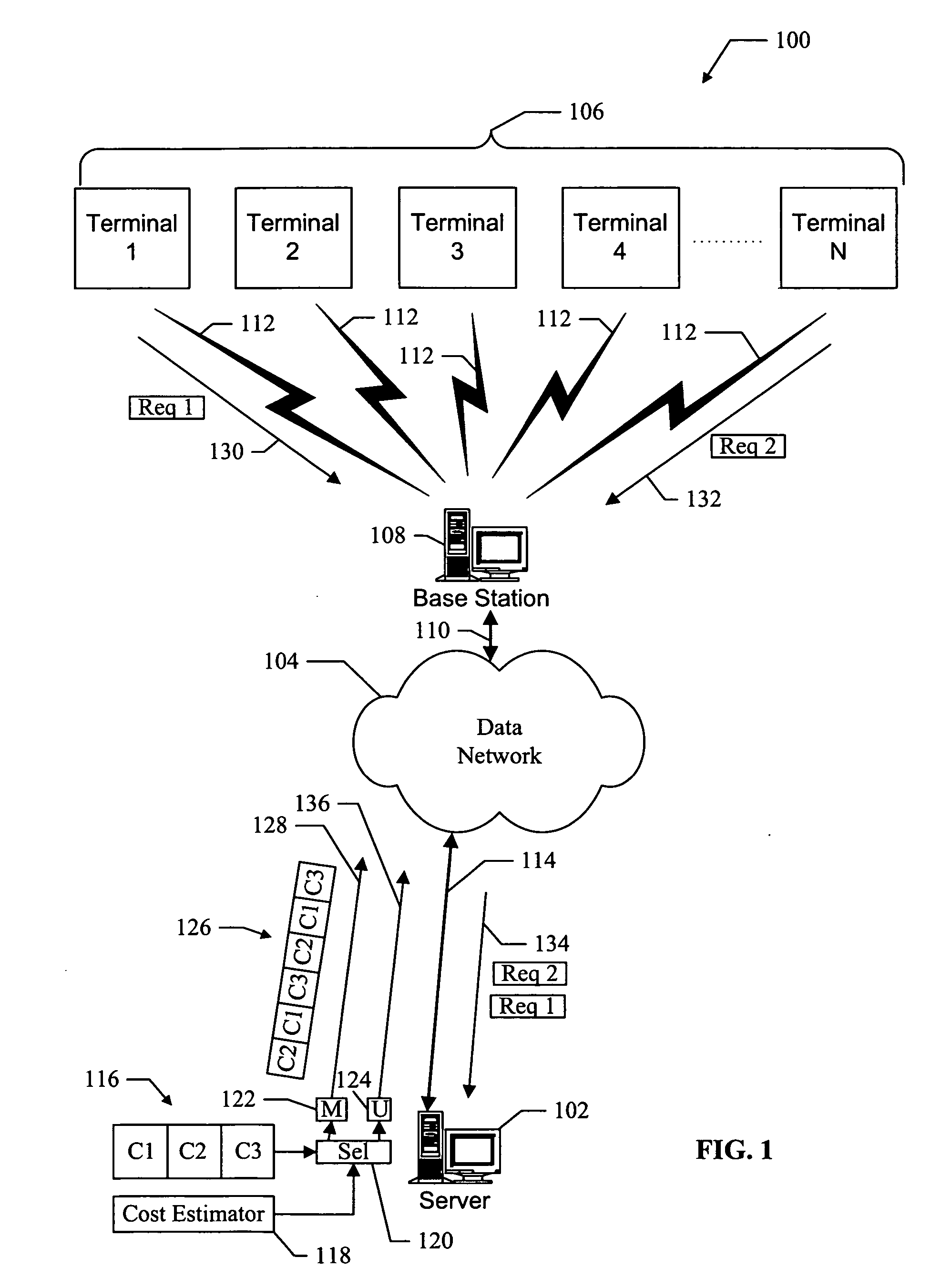
Methods and apparatus for hybrid multicast and unicast transmissions in a data network
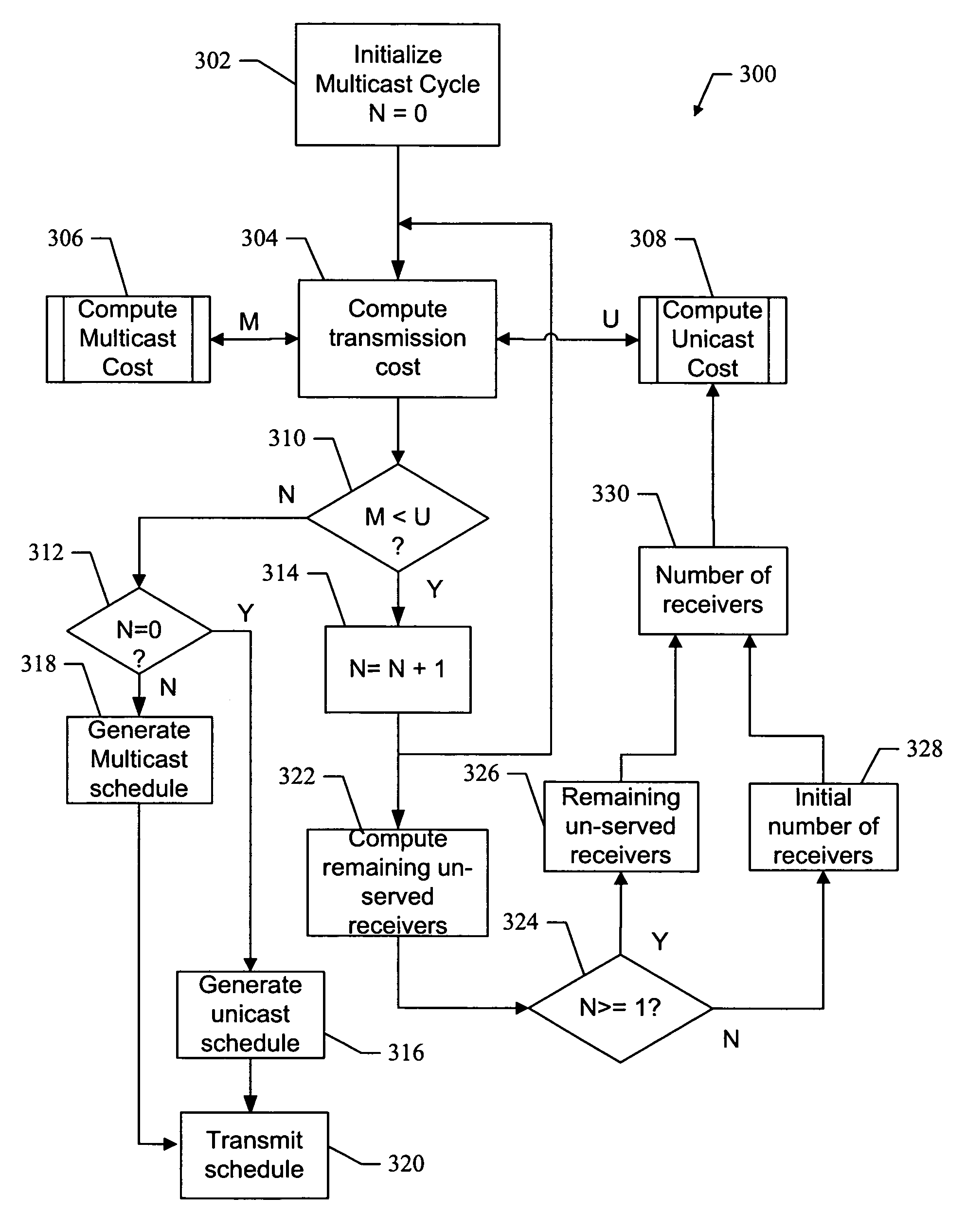
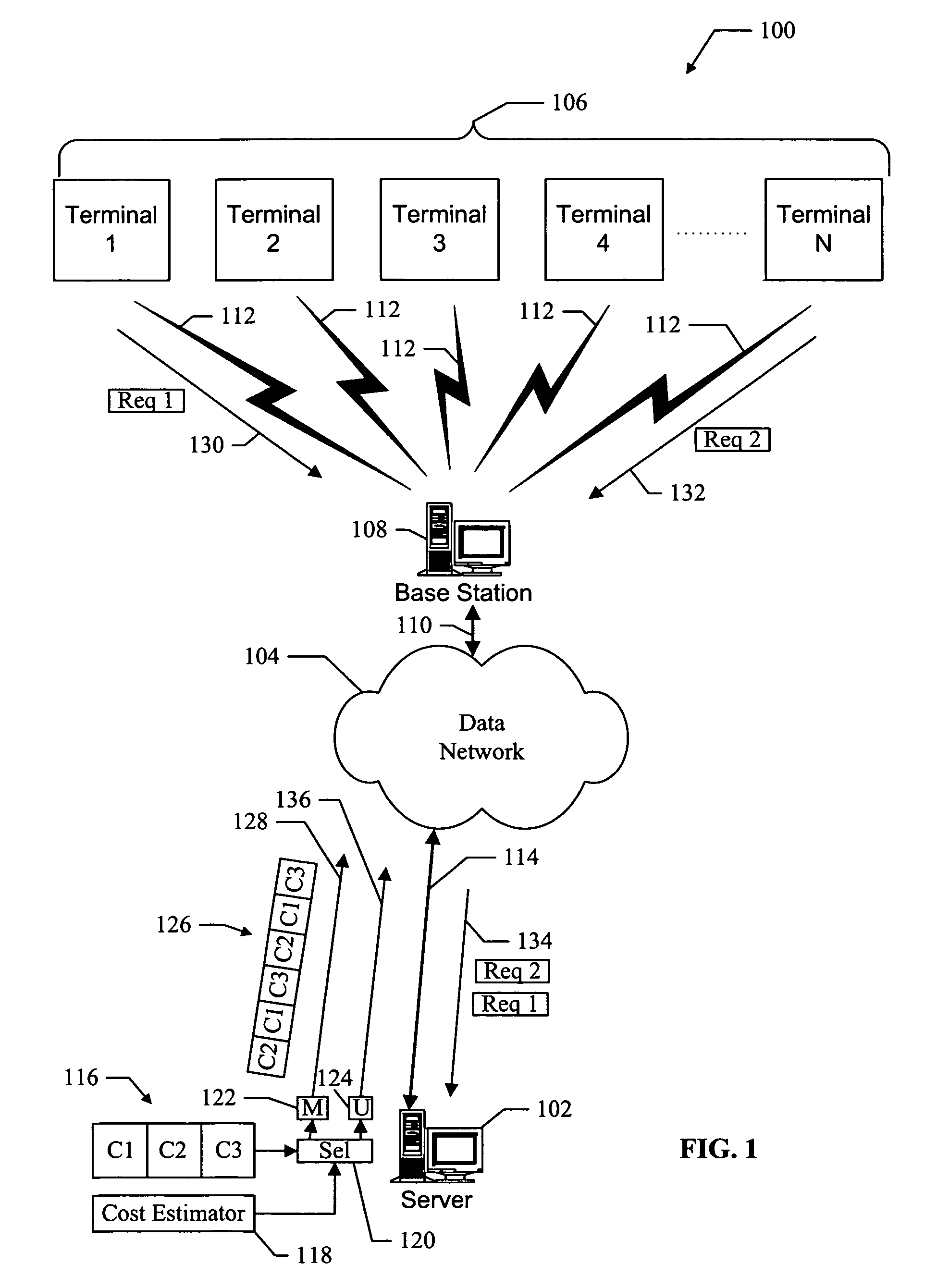
InactiveUS20050259584A1Avoids costly re-broadcastsEfficient use ofSpecial service provision for substationError preventionTransmission scheduleNetwork method
Methods and apparatus for hybrid multicast and unicast transmissions in a data network. A method is provided for operating a server on a data network. The method includes computing a multicast cost indicator and a unicast cost indicator that are associated with multicast and unicast transmission of data. The method also includes determining that the multicast cost indicator is less than the unicast cost indicator, and generating a transmission schedule that describes when the data will be multicasted on the data network. The method also includes transmitting the transmission schedule, and multicasting the data according to the transmission schedule
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Systems and Methods for Interference Alignment in Wi-Fi
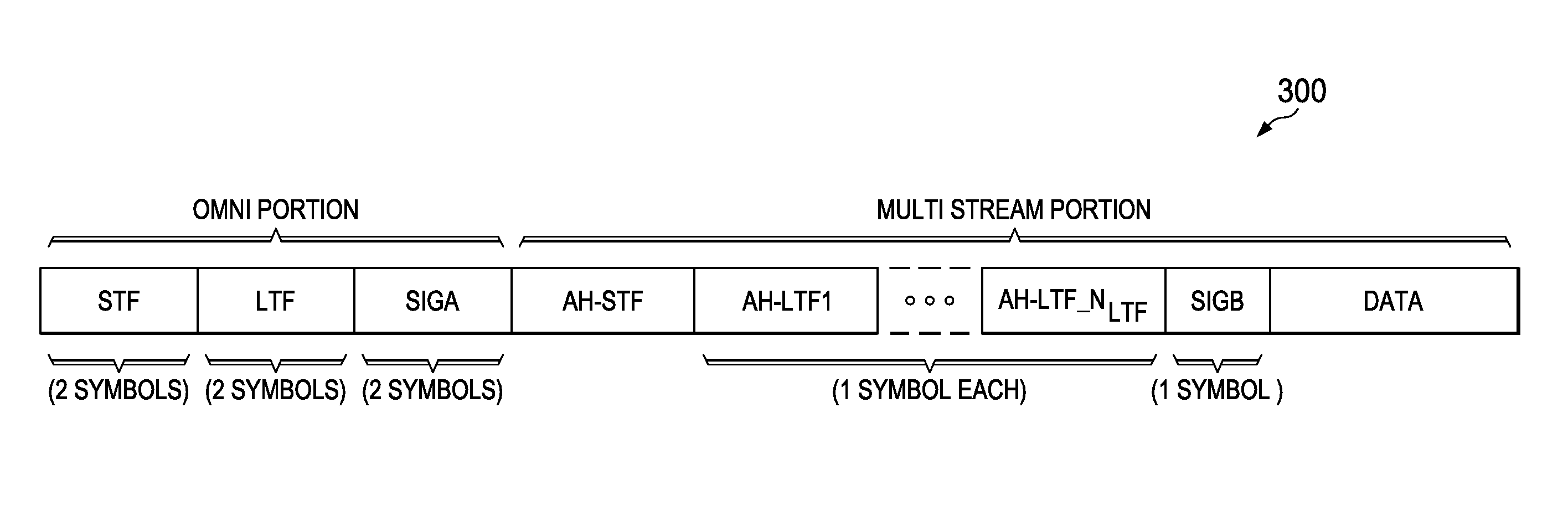
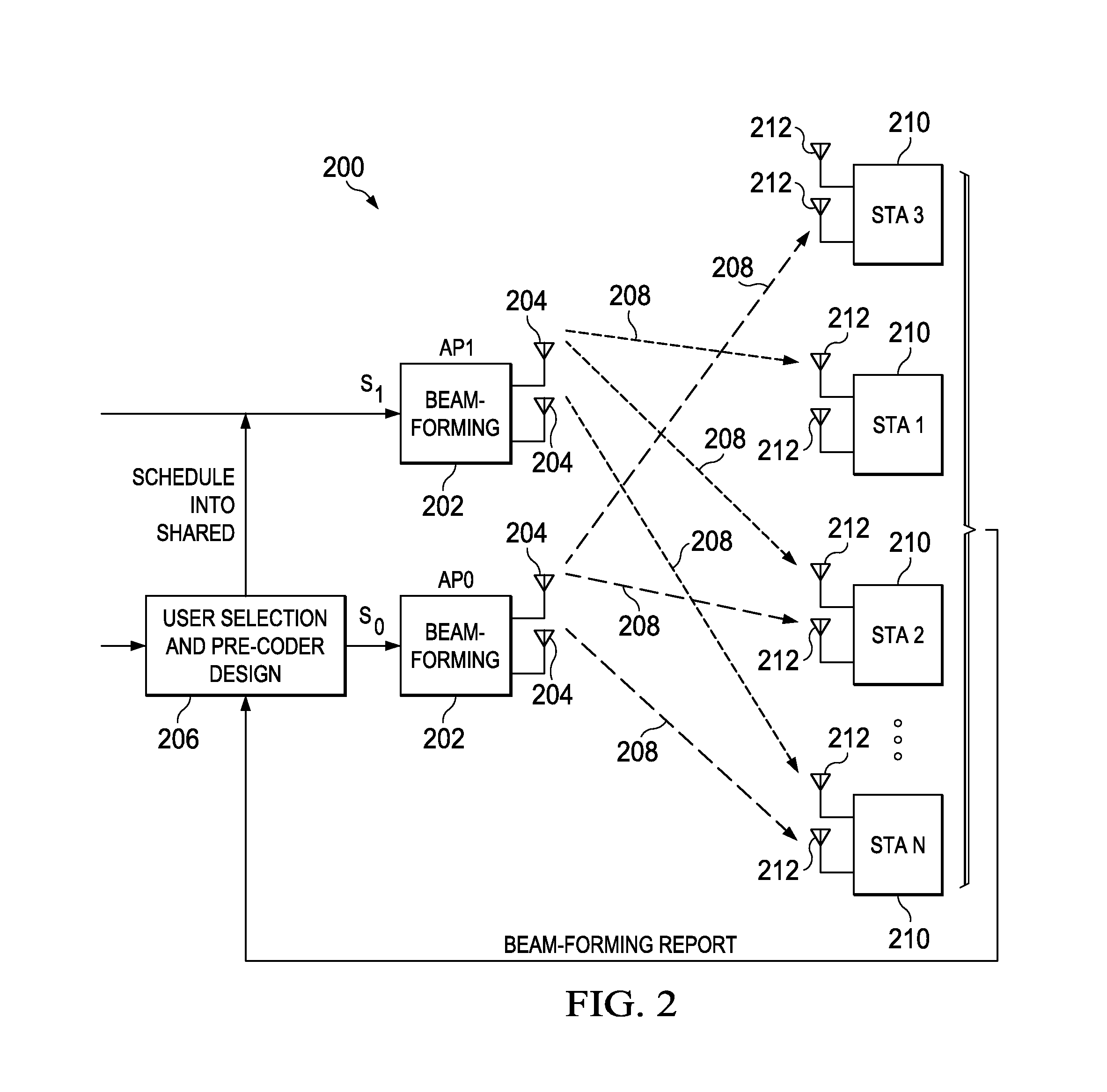
System and method embodiments are provided for interference alignment in a wireless local area network (LAN) with an overlapping basic service set (OBSS). In an embodiment, a method includes instructing a first access point (AP) in the wireless LAN to broadcast a null data packet (NDP) sounding packet to a plurality of stations when no other AP is broadcasting, wherein the NDP sounding packet comprises a plurality of long training field (LTFs), and wherein a total number of LTFs is equal to a total number of transmission streams, receiving channel beamforming (BF) information and a signal plus interference to noise ratio (SINR) from each of the stations, wherein each of the stations computes the channel BF information and the SINR from sounding packets received from each of the APs in the wireless LAN, and determining a transmission schedule according to the SINRs and the channel BF information.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transmission-scheduling coordination among collocated internet radios
InactiveUS6928061B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork topologiesBroadcast packetComputer network
A method for collocated nodes communicating over a first interface to agree on a conflict-free transmission schedule among themselves, which they can then use to collaborate with neighbors accessed through a second interface, for example through wireless links in order to obtain collision-free transfers of unicast, multicast and broadcast packets over wireless channels, and channel access delay guarantees. The collocated nodes behave as a single virtual node for the purpose of establishing a consistent transmission schedule throughout the nodes of a multihop wireless network.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
Mobile station, base station, communication system, and communication method
InactiveUS20070165575A1Reduce latencyGuaranteed normal transmissionData switching by path configurationCode division multiplexCommunications systemDelayed time
In a communications system, a mobile station sends a transmission request for permission to transmit packet data to a base station and transmits the packet data to the base station according to transmission schedule information about a transmission schedule which the base station determines in response to the transmission request, and the base station transmits a result of judgment of reception of packet data which it has received to the mobile station. The mobile station transmits transmission request information about new packet data which it will transmit to the base station next before completing reception of a result of judgment of reception of packet data which the mobile station has transmitted to the base station from the base station. As a result, since the mobile station can notify a transmission request for permission to transmit next packet data to the base station efficiently, a delay time which occurs due to retransmission of packet data can be shortened.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
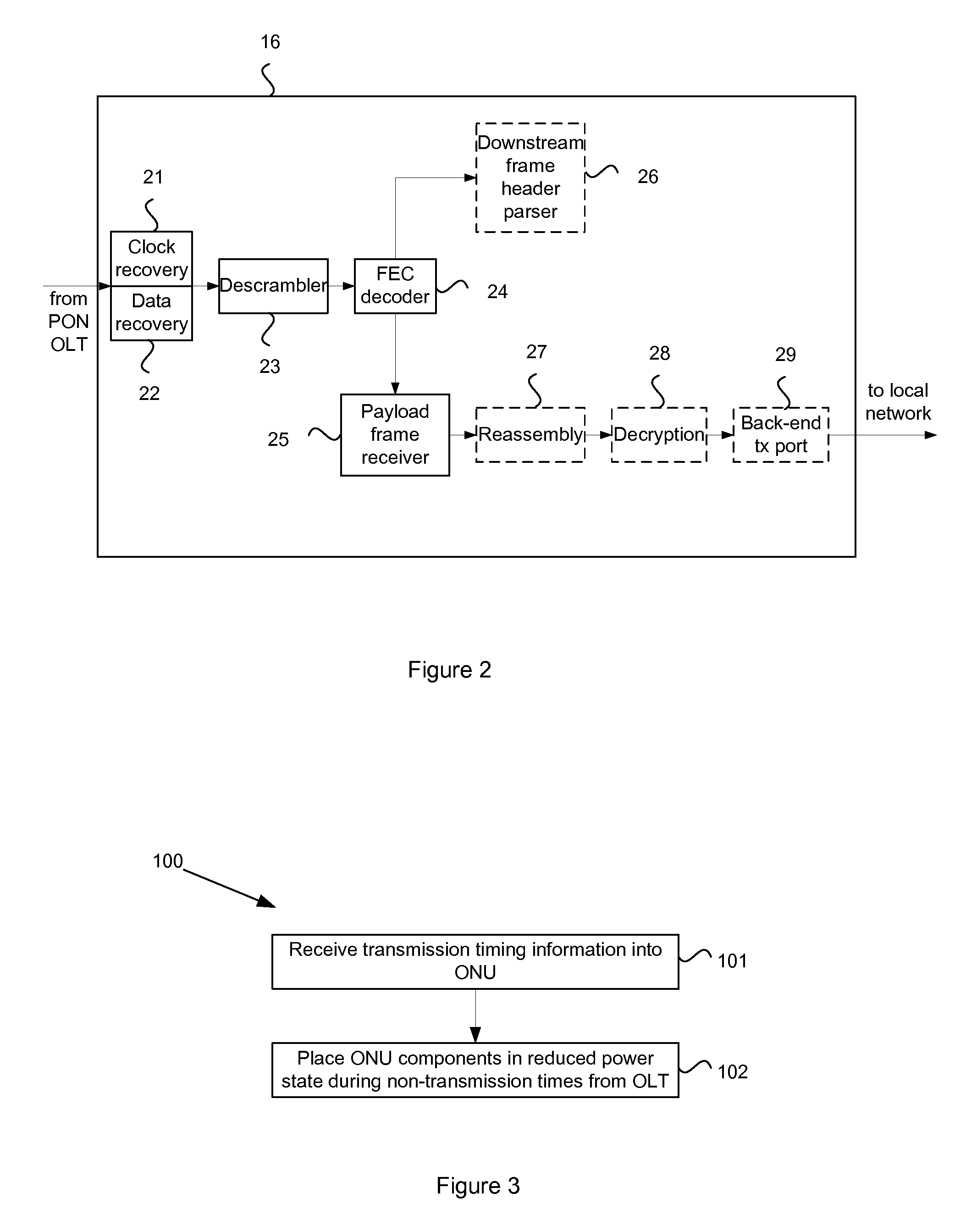
System and method for energy-efficient operation of optical network units based on scheduled payload reception
InactiveUS20100316387A1Low power stateTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexTransmission scheduleEngineering
In a passive optical network, power consumption of the ONU can be reduced by communicating a transmission schedule from the OLT to the ONU that indicates time slots in which the ONU is scheduled to receive payload transmissions from the OLT. Components of the ONU that would normally operate continuously, including processing payloads addressed to other ONUs, are placed in a reduced power state outside of the ONU's allocated time slots.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Buffering in streaming delivery
InactiveUS20060253600A1Unsuitable for usePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionTransmission scheduleReal-time computing
Buffering packets of a media stream for transmission from a transmitting device to a receiving device. Media packets are formed from at least one kind of media information in a stream generator; at least one transmission frame is generated on the basis of media packets to be transmitted; packets to be transmitted are formed from the at least one transmission frame; and a transmission schedule is generated for packets to be transmitted. In addition, a first step and a second step of hypothetical decoding are also performed. The first step of hypothetical decoding is performed according to the transmission schedule and comprises buffering the packets to be transmitted according to the transmission schedule to a first hypothetical decoding buffer; and outputting packets from the first hypothetical decoding buffer on a transmission frame basis. The second step of hypothetical decoding comprises controlling the buffer occupancy level of the first hypothetical decoding buffer and the second hypothetical decoding buffer by controlling at least one of the following: the operation of the stream generator; the generation of at least one transmission frame; the transmission schedule.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
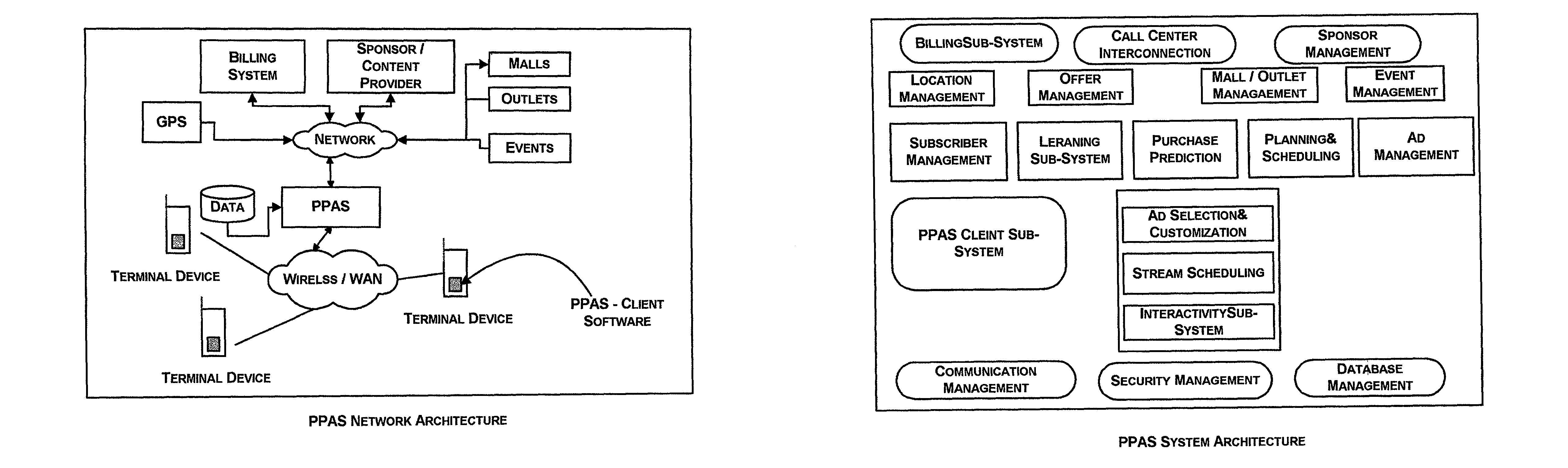
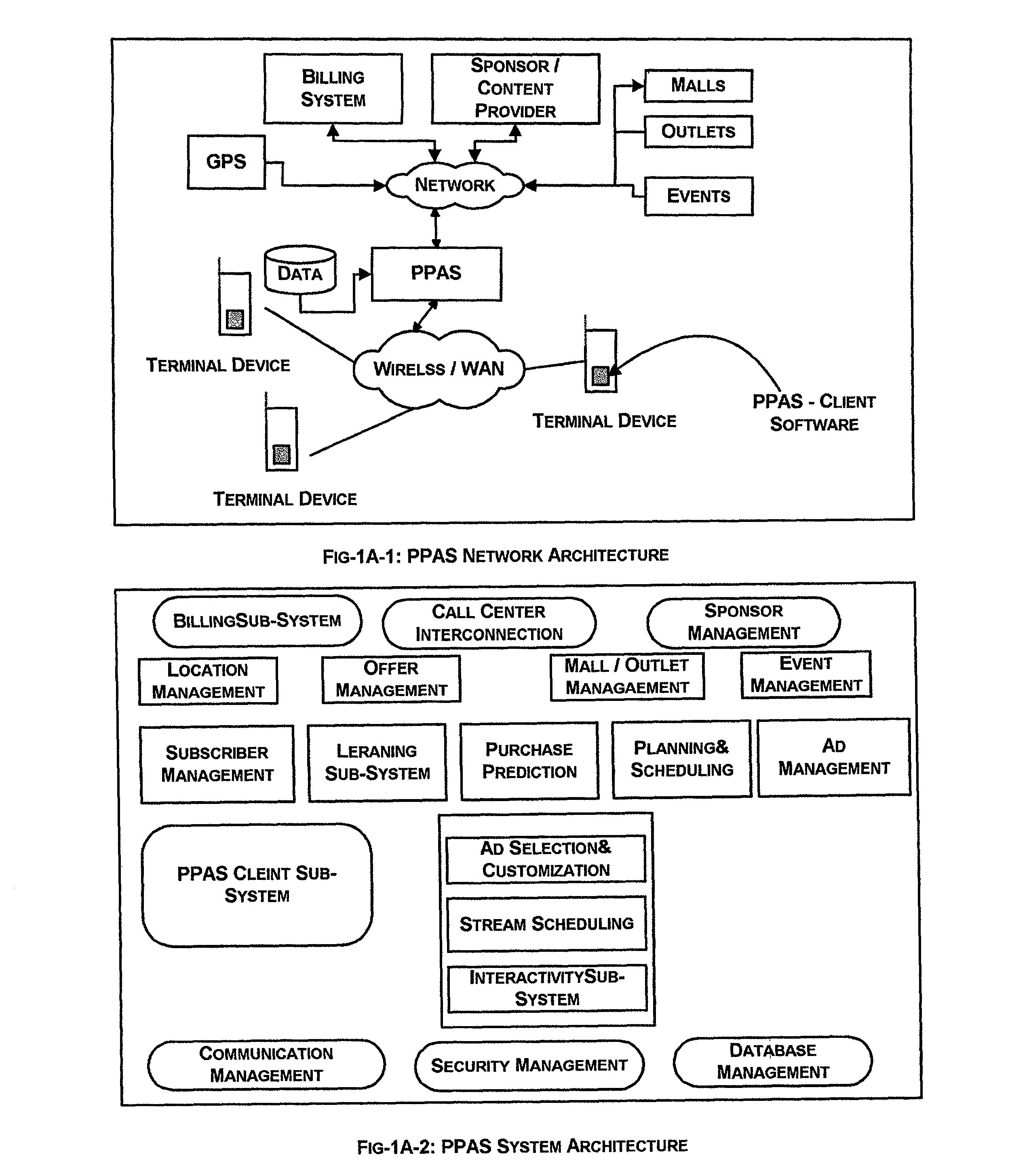
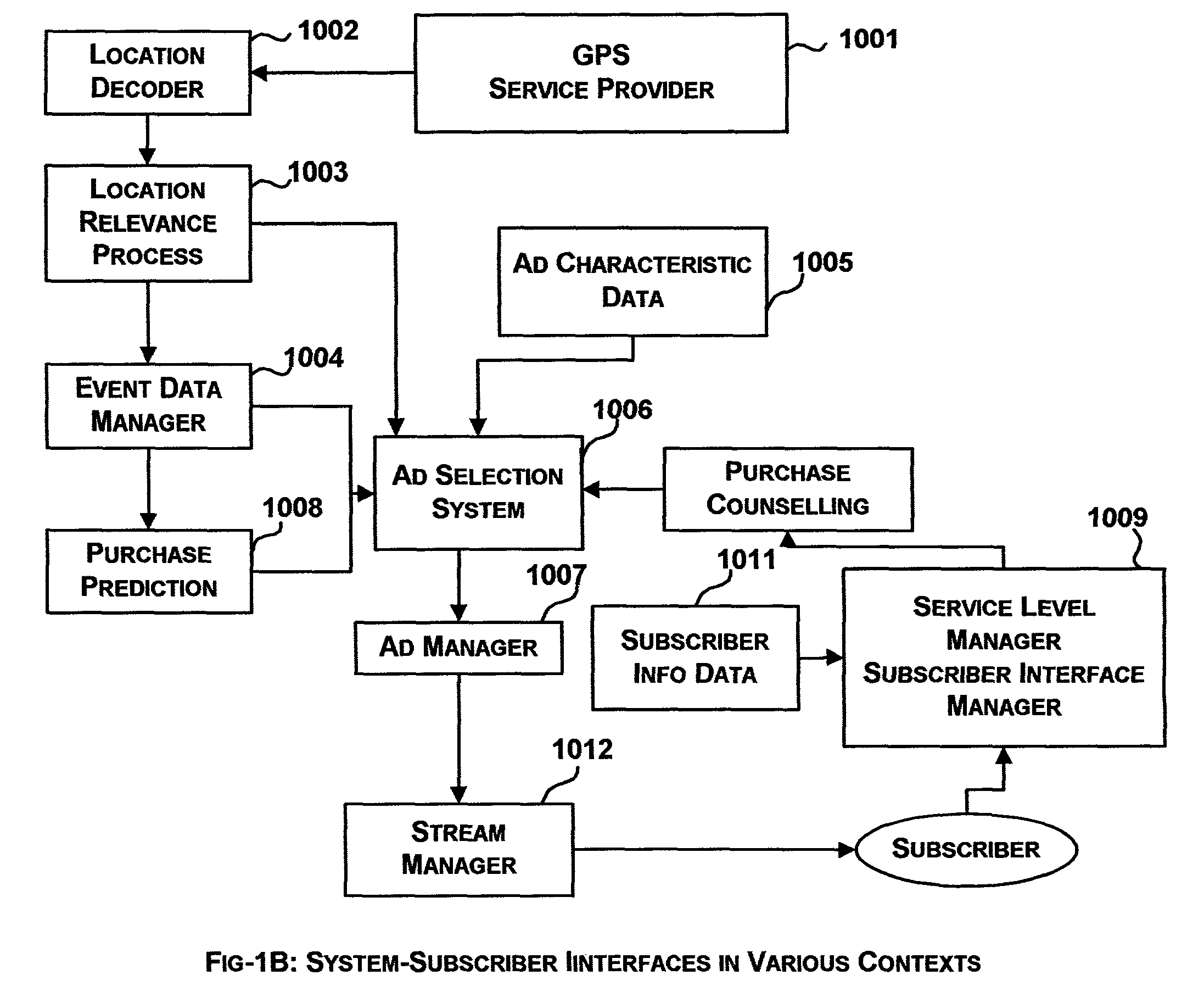
System and method for selective transmission of multimedia based on subscriber behavioral model
InactiveUS8099325B2Facilitate fastFacilitate accurate retrievalAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsSequence analysisTransmission schedule
An advertisement system that provides subscribers with the most relevant advertisements based on their individual purchase prediction of the various products and contextual information such as location, ongoing public events, festivals and personal events. The system customizes the advertisements to suit the audiovisual, language, and textual caption preferences of the subscribers. System provides for tracking of various promotional offers made to the subscribers from the time the offer is made to the time it is redeemed by the subscriber. System consists of methods to learn (a) purchase predictions (b) preferred streaming schedule and (c) the subscriber's preferences in terms of audiovisual aspects of the advertisements. Purchase prediction for individual subscriber is derived from historical purchase data by time series analysis and the influence of events such as co-purchases of other products and organized events such as sales exhibitions and festivals is derived based on Bayesian network models.
Owner:SATYAM COMP SERVICES
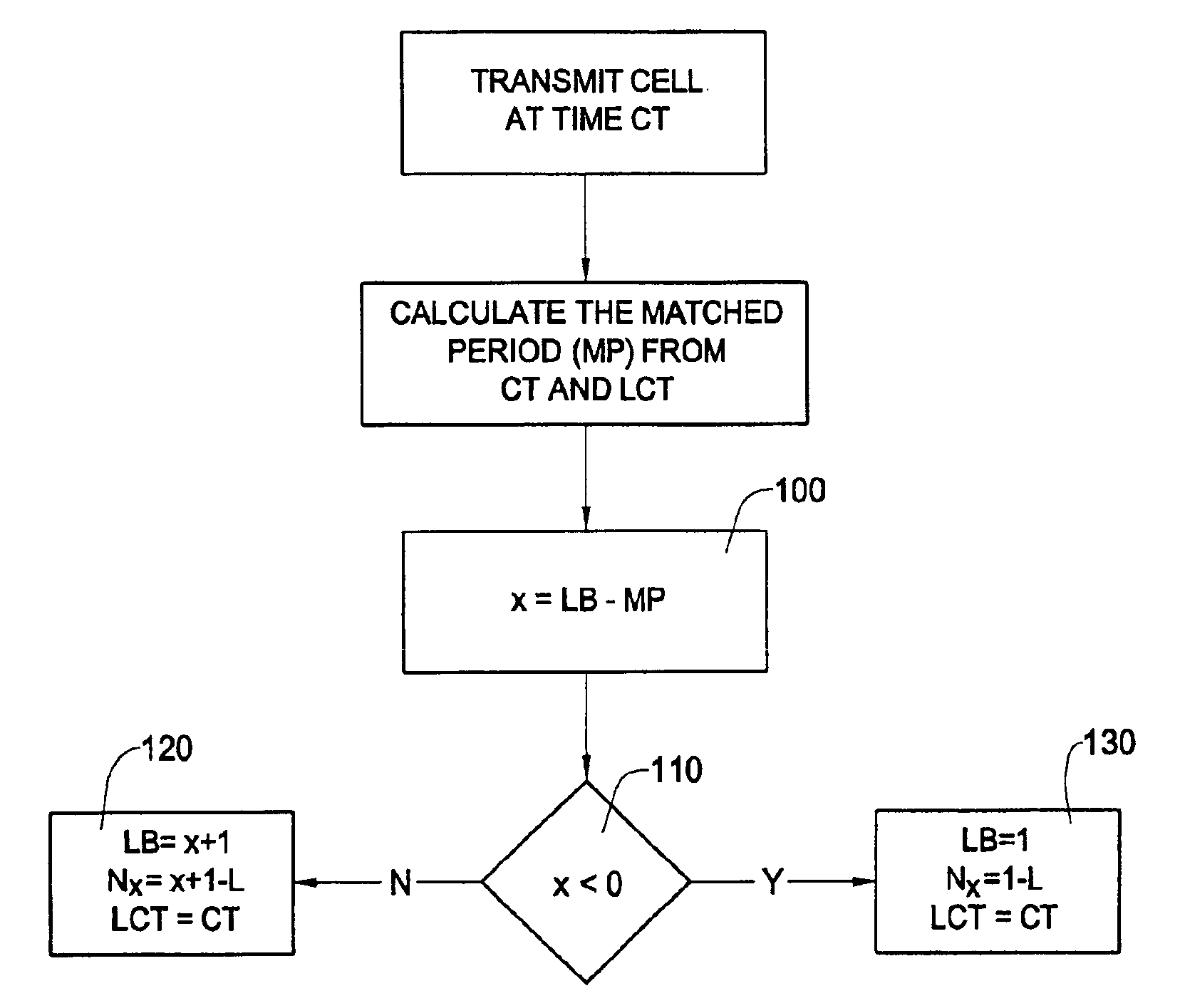
Systems and Methods for Interference Avoidance, Channel Sounding, and Other Signaling for Multi-User Full Duplex Transmission
InactiveUS20140169234A1Radio transmissionSignalling characterisationTransmission scheduleChannel sounding
System and method embodiments are provided for transmission and reception scheduling for wireless devices in a multi-user full duplex transmission environment. The embodiments enable interference avoidance between neighboring wireless devices. The system and method also enable channel sounding. In an embodiment, a method for scheduling transmissions in a multi-user wireless system includes determining, by a transmission point, neighboring wireless devices for each of a plurality of wireless devices located within a coverage area of the transmission point and determining, by the transmission point, a transmission schedules for respective ones of the plurality of wireless devices according to the neighboring information of the devices such that each respective wireless device is scheduled to transmit data over different time-frequency resources than those in which neighboring wireless devices of the respective wireless device are scheduled to receive data.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
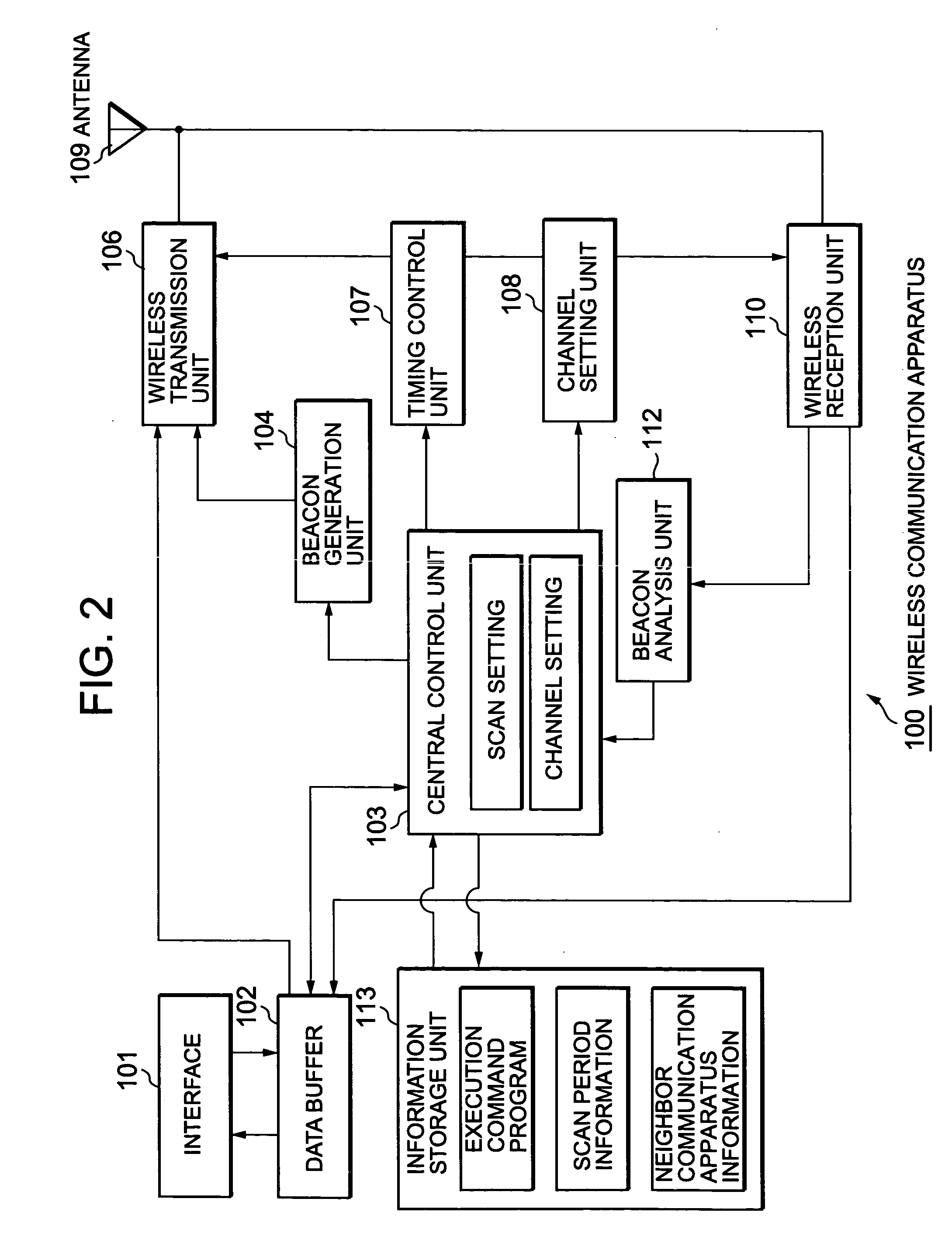
Wireless communication system, wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method and computer program
InactiveUS20050089001A1Accurate configurationPower managementSynchronisation arrangementCommunications systemTransmission channel
A communication station forms a multi-channel self-organized distribution type wireless network effectively without providing an unnecessary transmission pause period. The communication station refers to neighbor apparatus information described in a beacon received from a neighbor station to judge whether or not a beacon transmission channel of a corresponding next neighbor station matches a transmission scheduled channel of its own. In a case where these channels match, a transmission pause period for the next neighbor station is provided and the transmission is postponed. Accordingly, blocking against the beacon reception from the next neighbor station by the neighbor station can be avoided and provision of an unnecessary transmission pause period is not required so that the throughput is improved.
Owner:SONY CORP
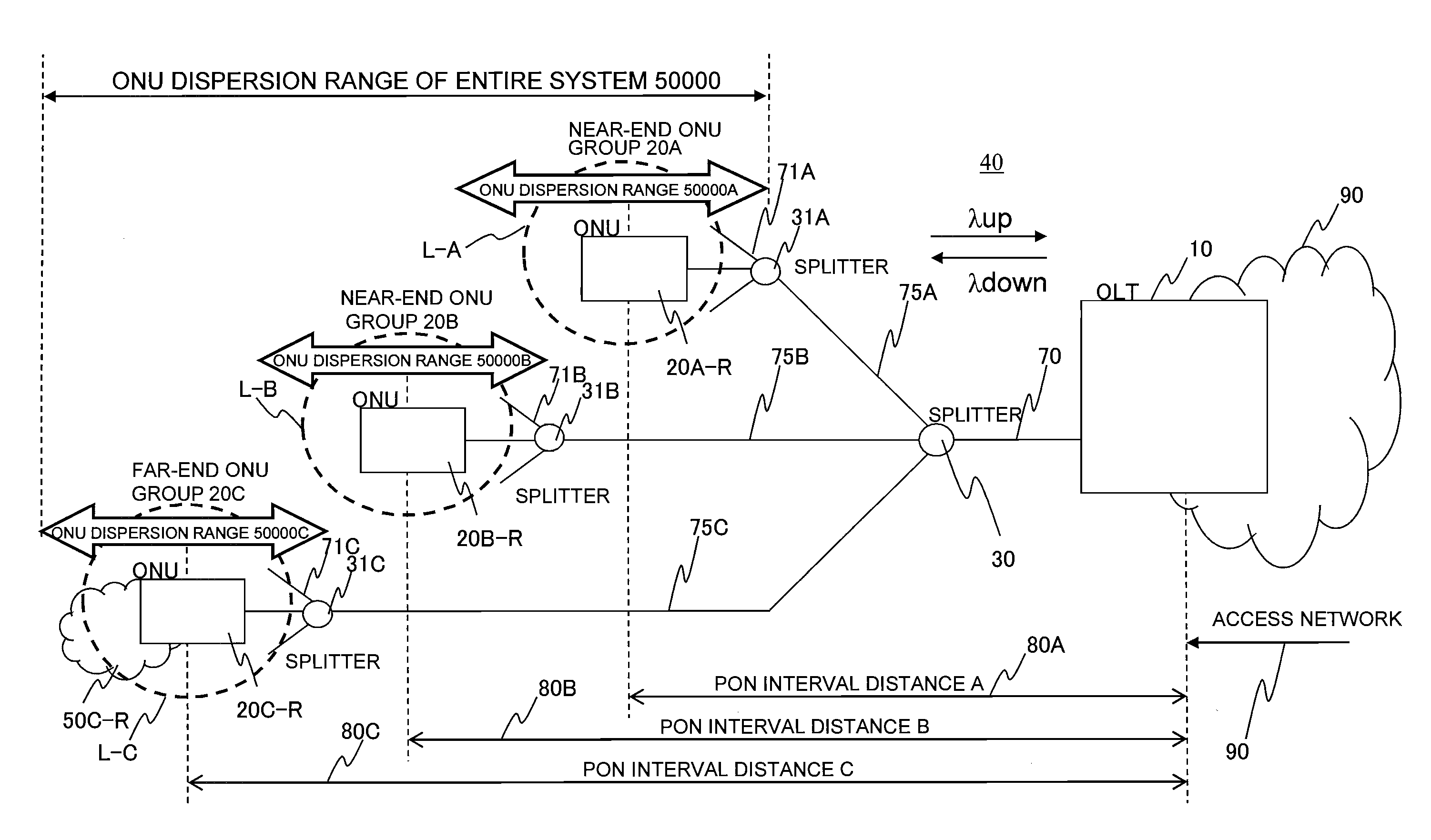
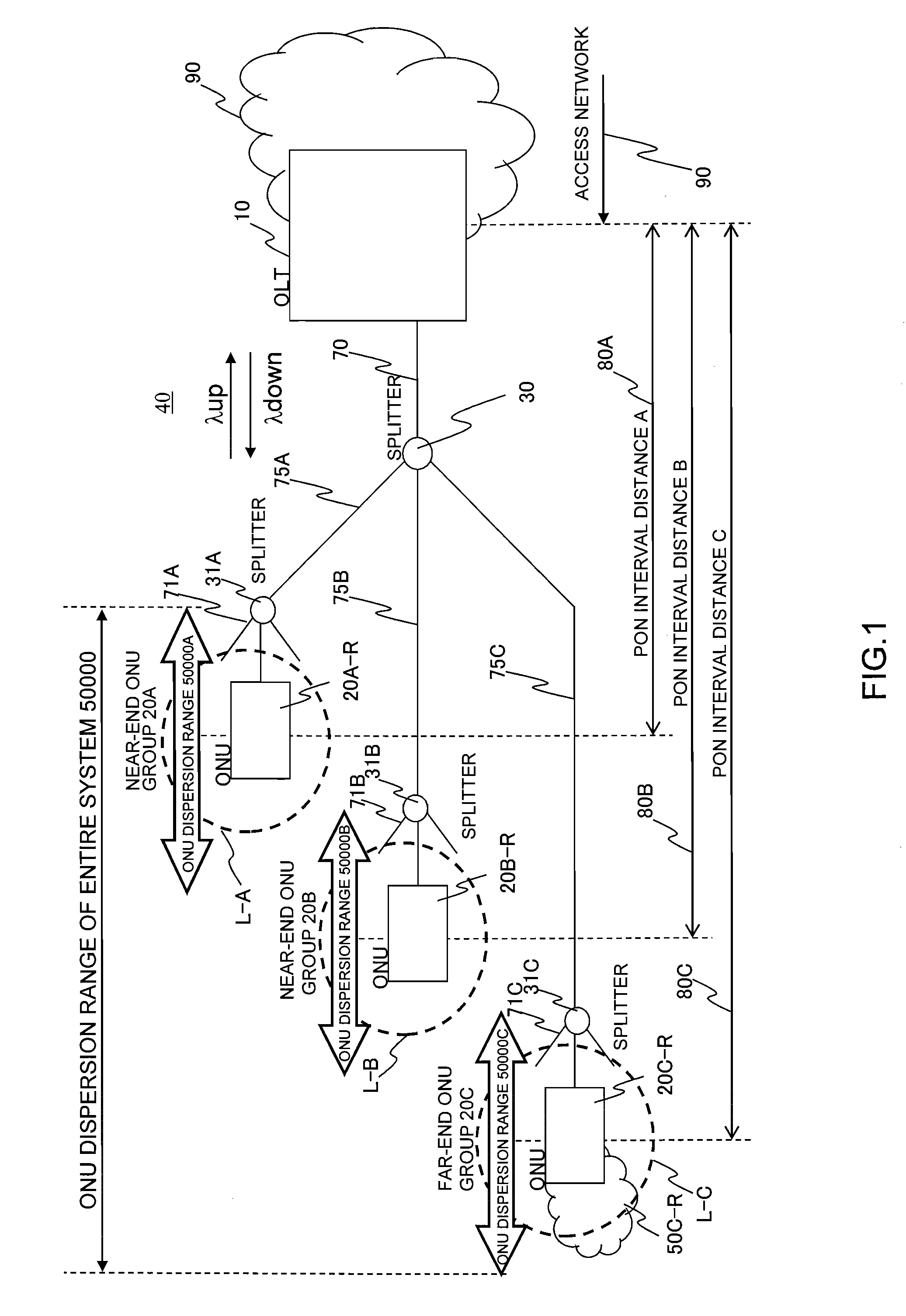
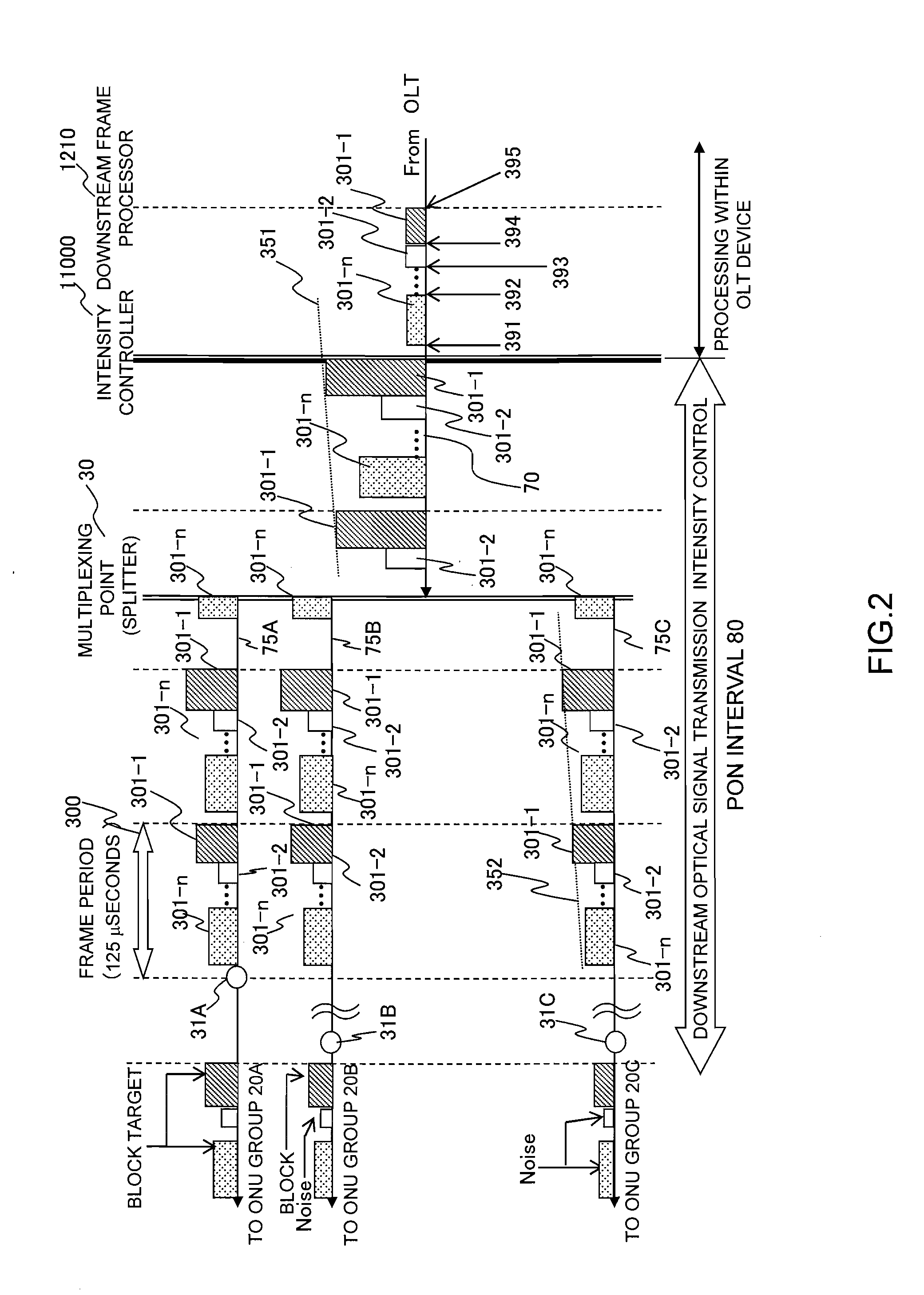
Passive optical network system
InactiveUS20120063774A1Communication distanceImprove communication distanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransceiverTransmission schedule
When an ONU accommodating range is enlarged, and ONUs shorter and ONUs longer in a communication path to an OLT are accommodated in a PON at the same time, there is a need to change a light intensity at the time of transmitting a downstream signal in order that both of the ONUs receive a downstream signal from the OLT. When a near-end ONU receives a signal having a light intensity necessary to communicate between the OLT and a far-end ONU, there arises such a problem that the light intensity is as high as an ONU receiver fails. In order to eliminate the ONU failure of the above problem, prior to transmission of the downstream signal, a downstream signal transmission schedule (downstream light intensity map) is notified to all of the ONUs. An optical transceiver of the OLT has a function of adjusting an output light intensity, and adjusts the light intensity to values receivable by the individual ONUs when the signal arrives at the respective ONUs according to route distances to the respective ONUs.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and system for traffic control
InactiveUS6947996B2Strengthen the systemImprove accuracyMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTraffic capacityAudio power amplifier
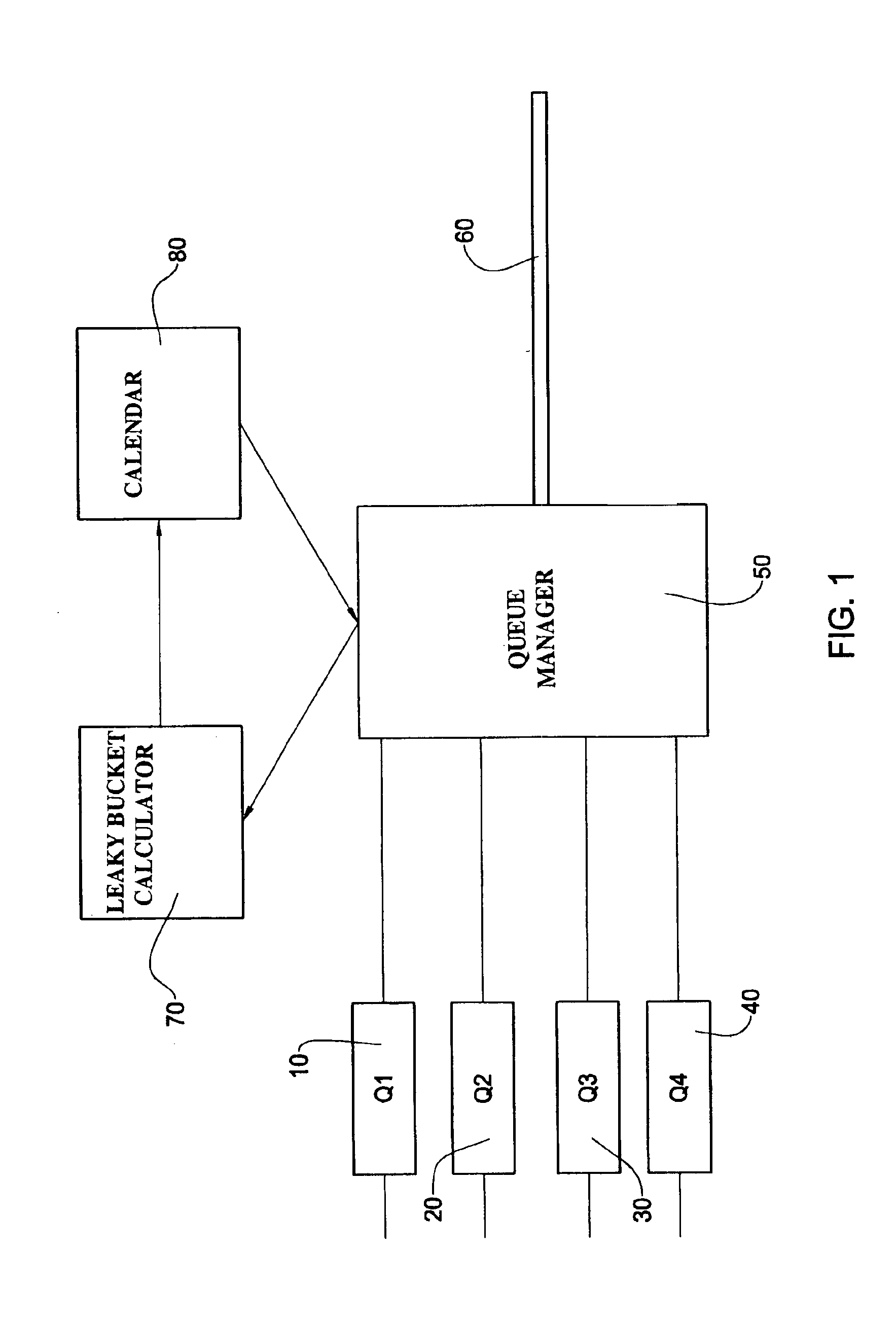
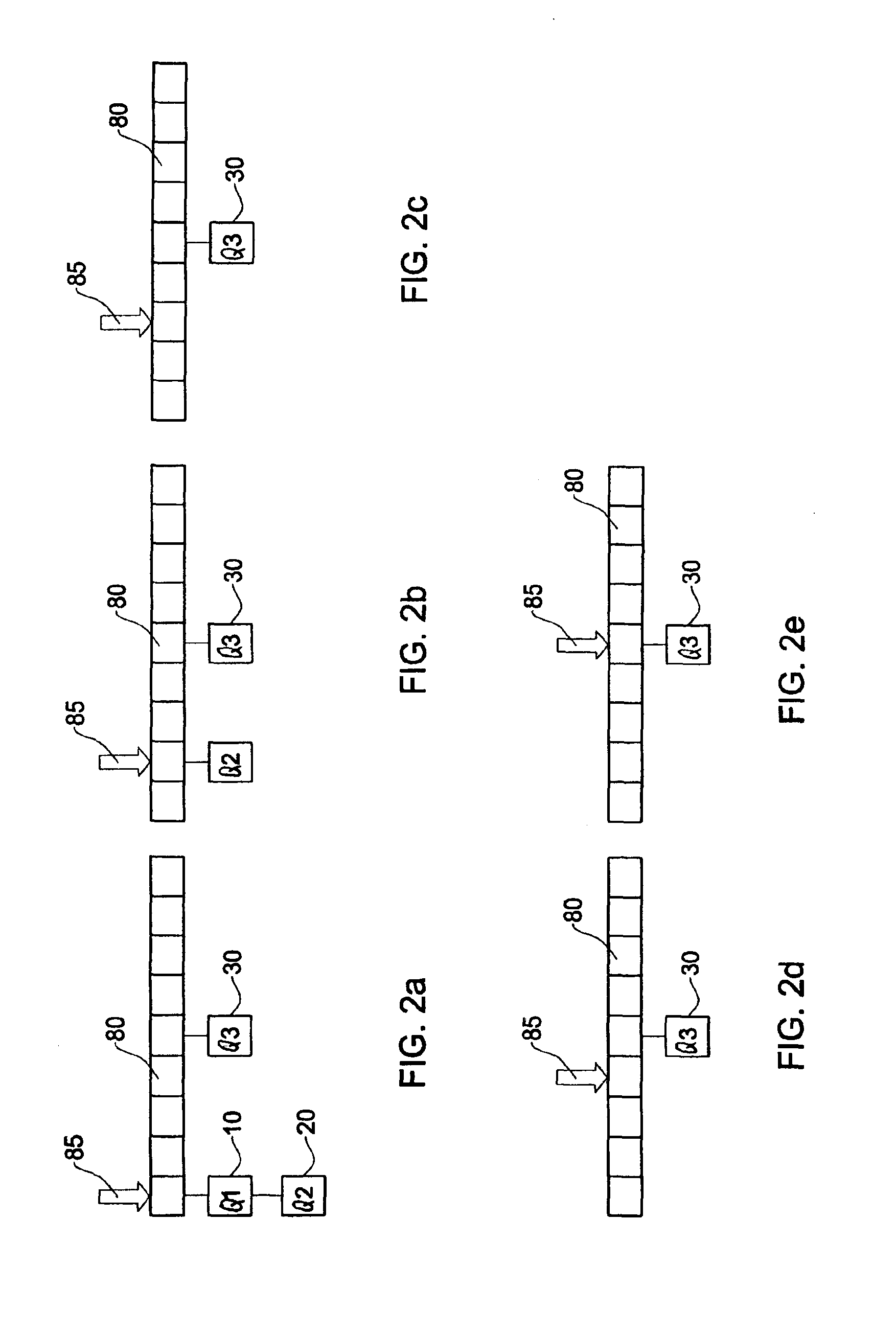
A traffic control method and system are disclosed for scheduling fixed size traffic elements from a number of queues for transmission on a link. Each queue has associated traffic parameters. The system comprises a scheduler and a calendar in a memory for storing a transmission schedule of the queues. The scheduler shapes the transmission schedule by updating the schedule in the calendar in dependence on inputted traffic parameters of each queue. The system also includes an amplifier to amplify the traffic parameters by a factor K prior to input to the scheduler, the scheduler and calendar being adapted to operate using the amplified parameters.
Owner:SEABRIDGE
Navigational aid and carrier sense technique
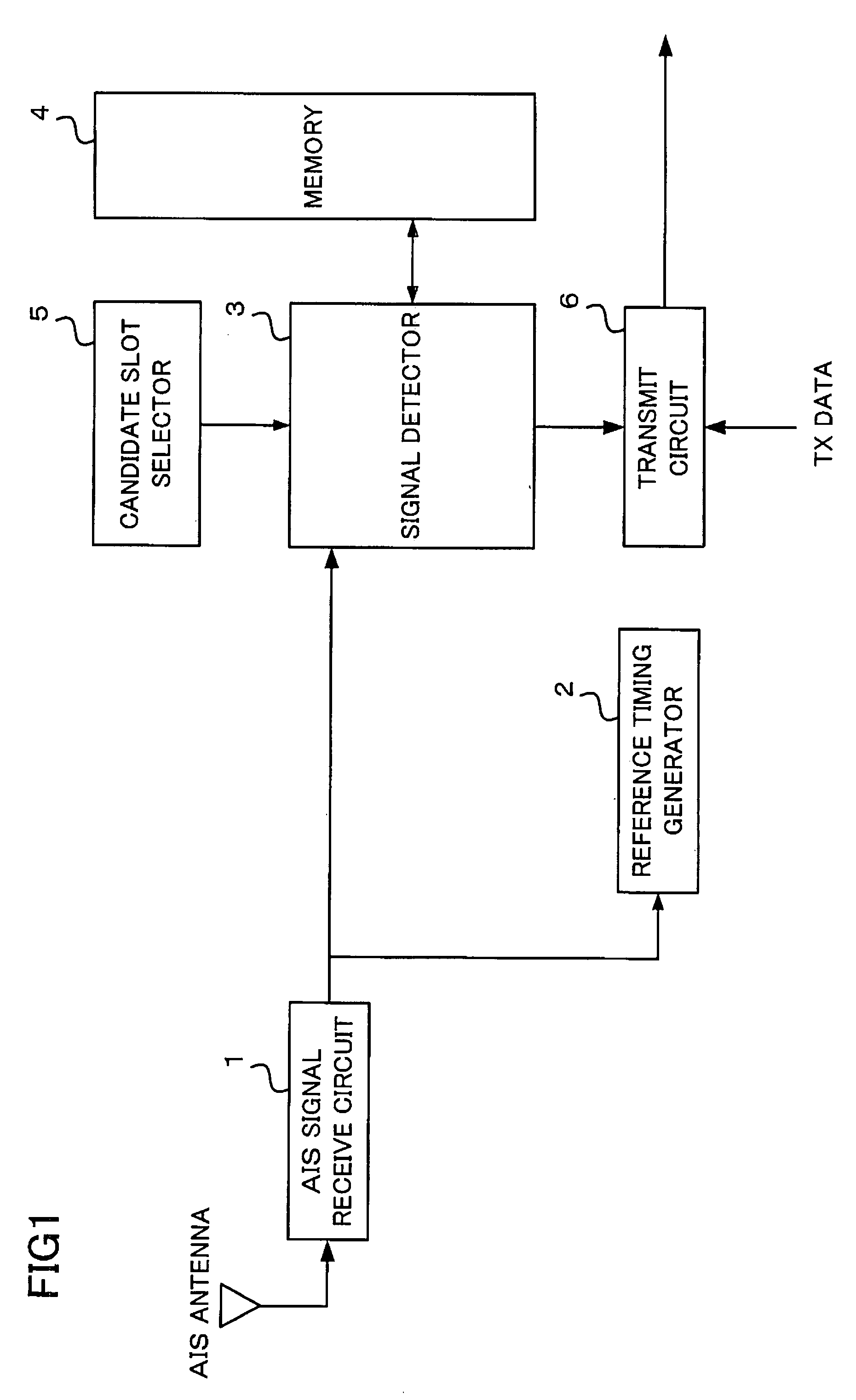
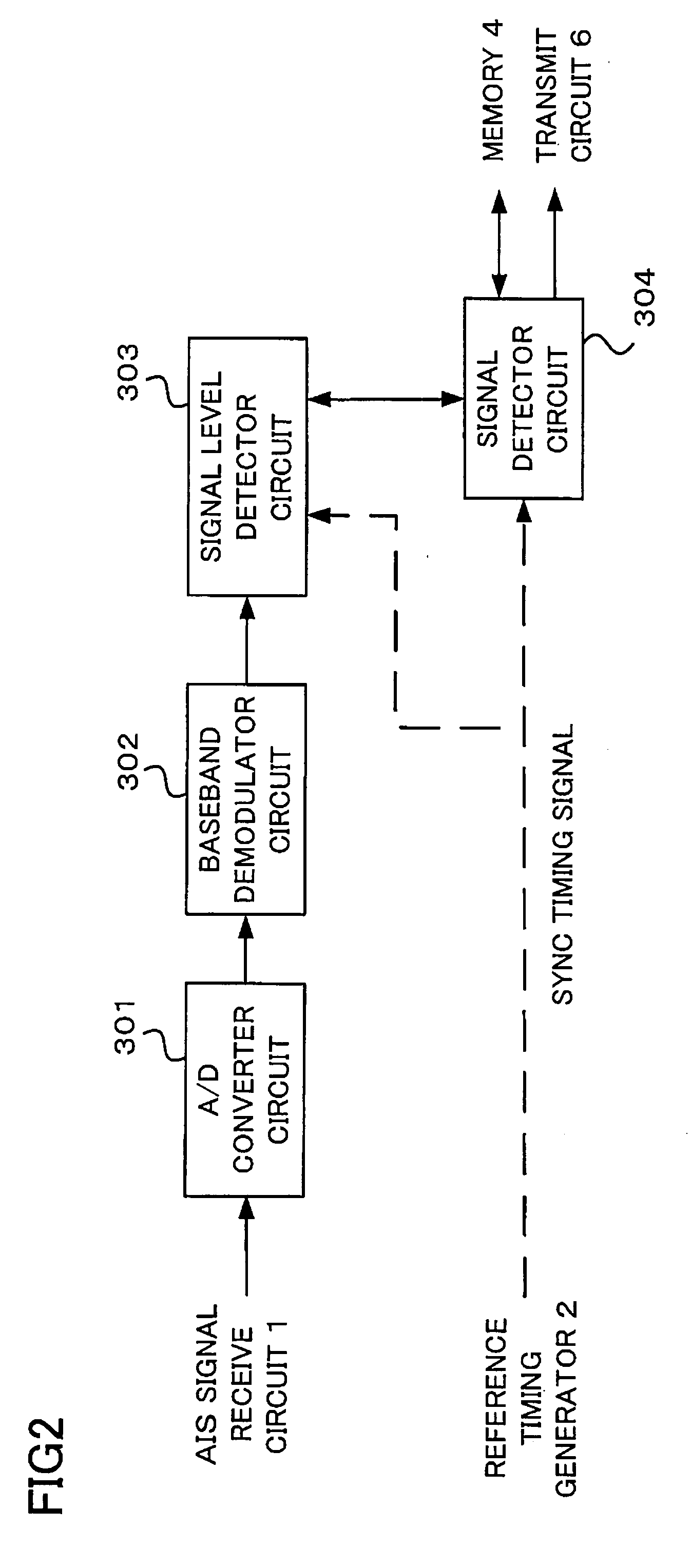
InactiveUS20070194979A1Reliable and accurate fashionShorten the timeSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexSupport vector machineSignal on
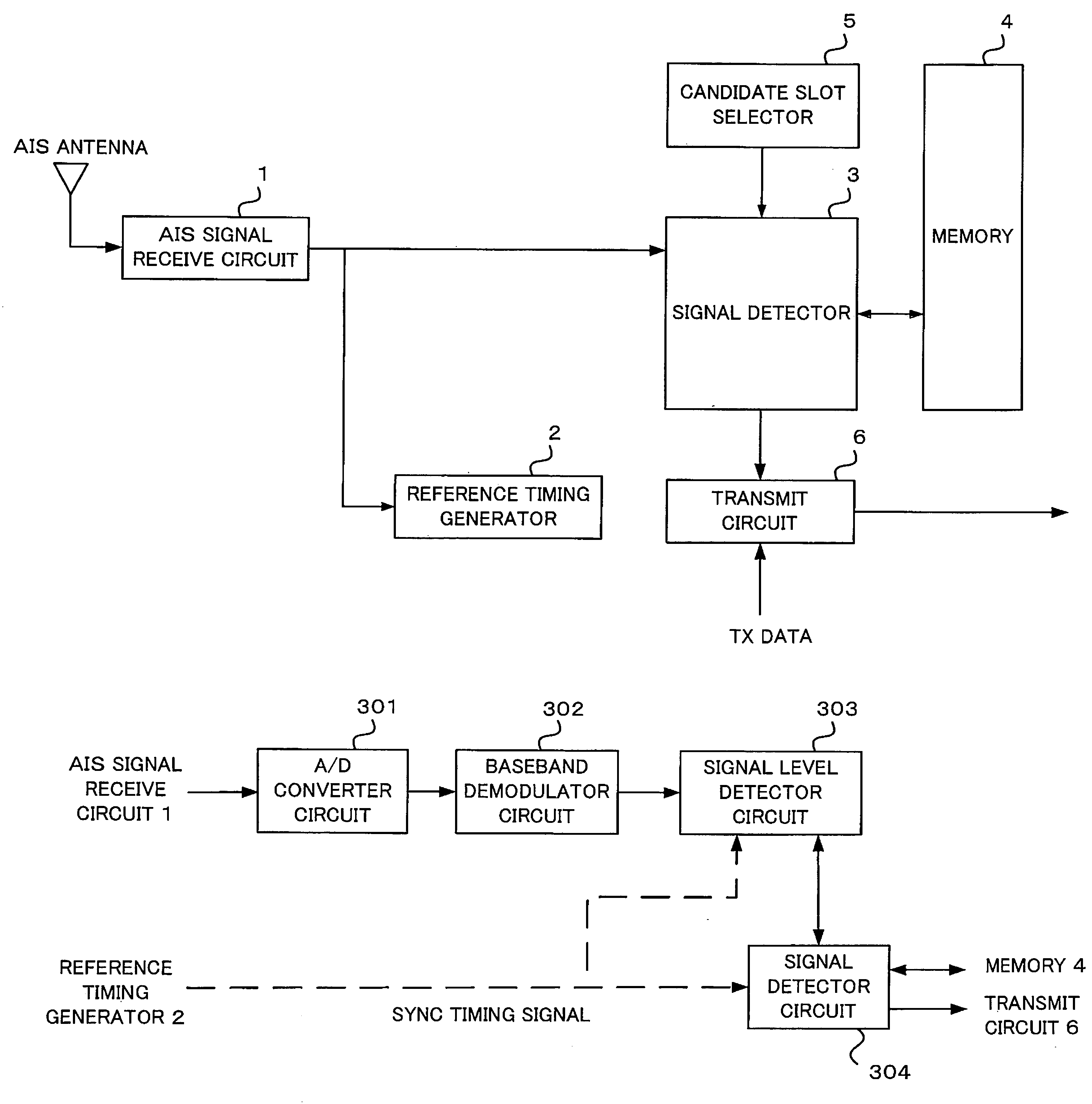
A navigational aid for use as an AIS apparatus includes a memory for storing information about previous use of individual time slots synchronized with transmission schedules of other stations and a signal detector for judging whether an information signal exists in a time slot specified in accordance with a synchronization timing signal based on the information stored in the memory and a result of monitoring of the behavior of a baseband signal obtained from a received signal on an IQ-plane. The navigational aid transmits information about own station based on a result of judgment by the signal detector. The monitoring of the behavior of the received baseband signal plotted on the IQ-plane can be accomplished by performing pattern recognition operation, for which a carrier sense technique, such as a support vector machine, subspace method or neural network, can be used.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for hybrid multicast and unicast transmissions in a data network
InactiveUS7423973B2Avoids costly re-broadcastsEfficient use ofSpecial service provision for substationError preventionTransmission scheduleNetwork method
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for prioritized information delivery with network coding over time-varying network topologies
ActiveUS20080225751A1Data switching by path configurationWireless communicationTraffic capacityNetwork code
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for information delivery with network coding over time-varying network topologies. In one embodiment, the method comprises decomposing a sequence of topology graphs that model a time-varying network topology into a plurality of virtual graphs, where each virtual graph of the plurality of virtual graphs corresponds to a distinct traffic class, and the virtual topology graph representing a partial topology of a time-varying network. The method also includes selecting a network code for each virtual graph in the plurality of the virtual graphs to meet requirements of the distinct traffic class corresponding to said each topology graph, where the network code is used to encode packets of the associated traffic class, and processing packets of each traffic class using the network code determined by its corresponding virtual topology and the requirements of said each traffic class, including using a virtual buffer system to implement the network code corresponding to each traffic class over the physical network topology. The method also includes using a scheduler to determine the transmission schedules for each output packet from the virtual buffer system of each traffic class where the scheduling decisions are based, at least in part, on the QoS requirements of each class.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Remote monitoring and diagnostic sytem
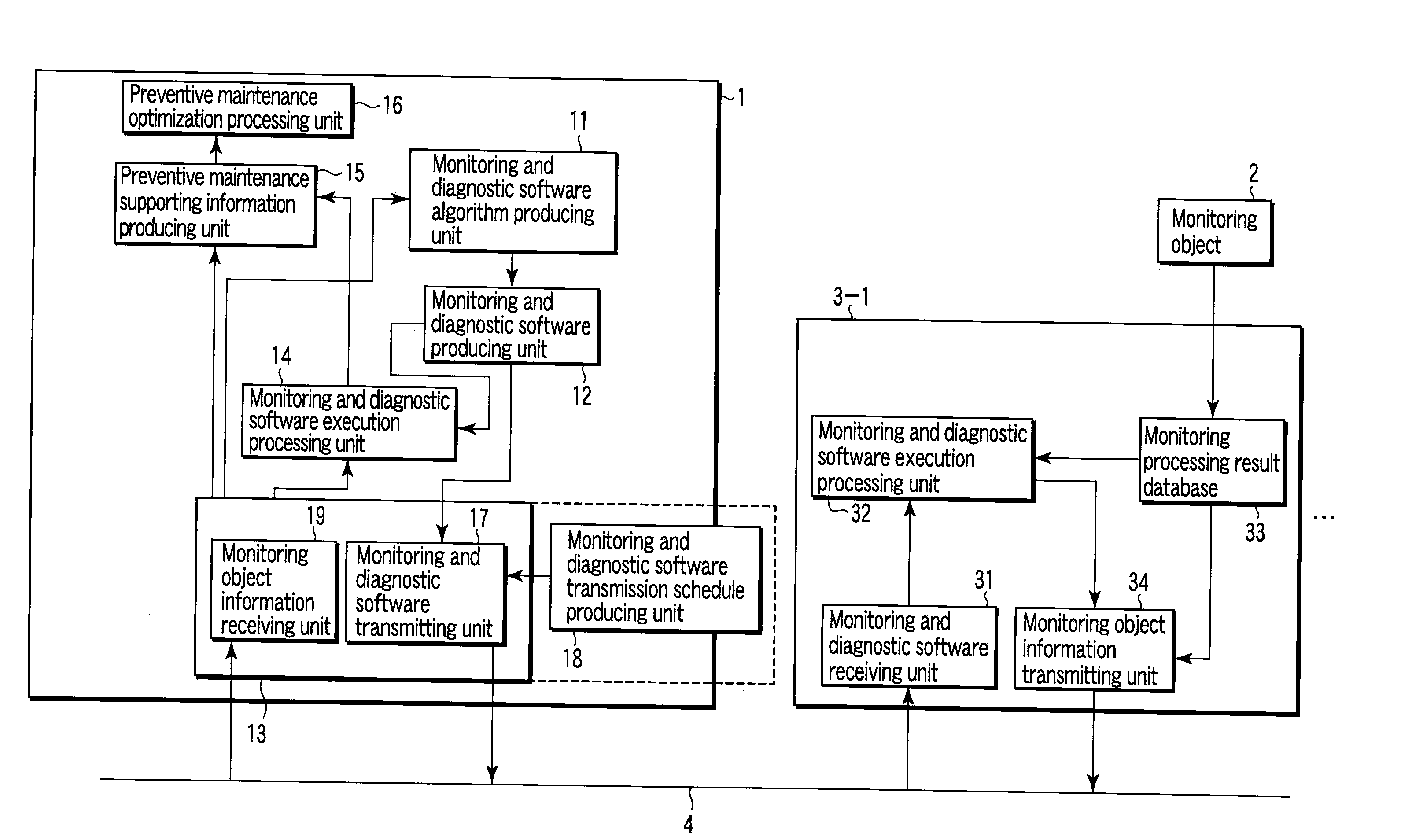
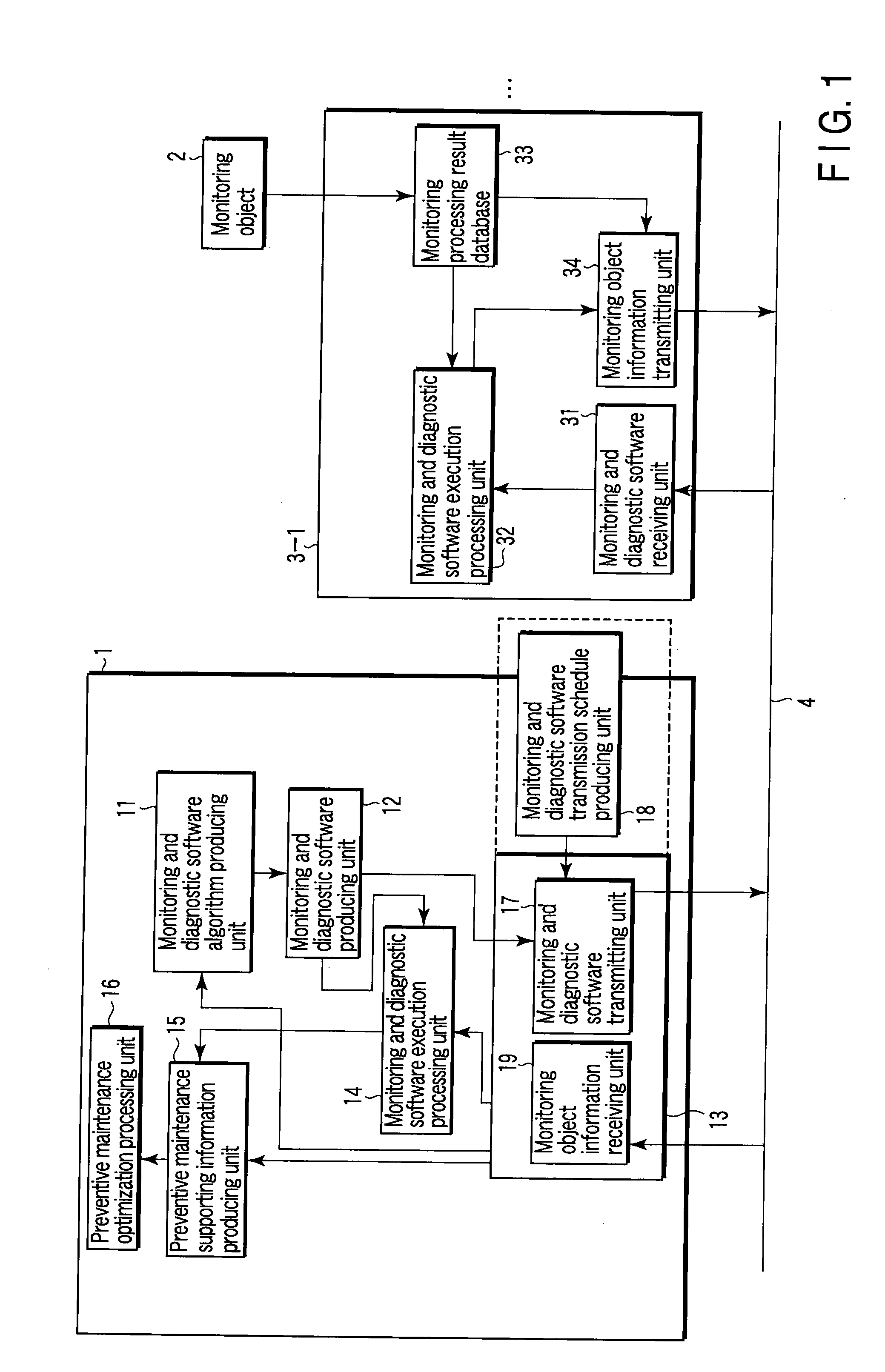
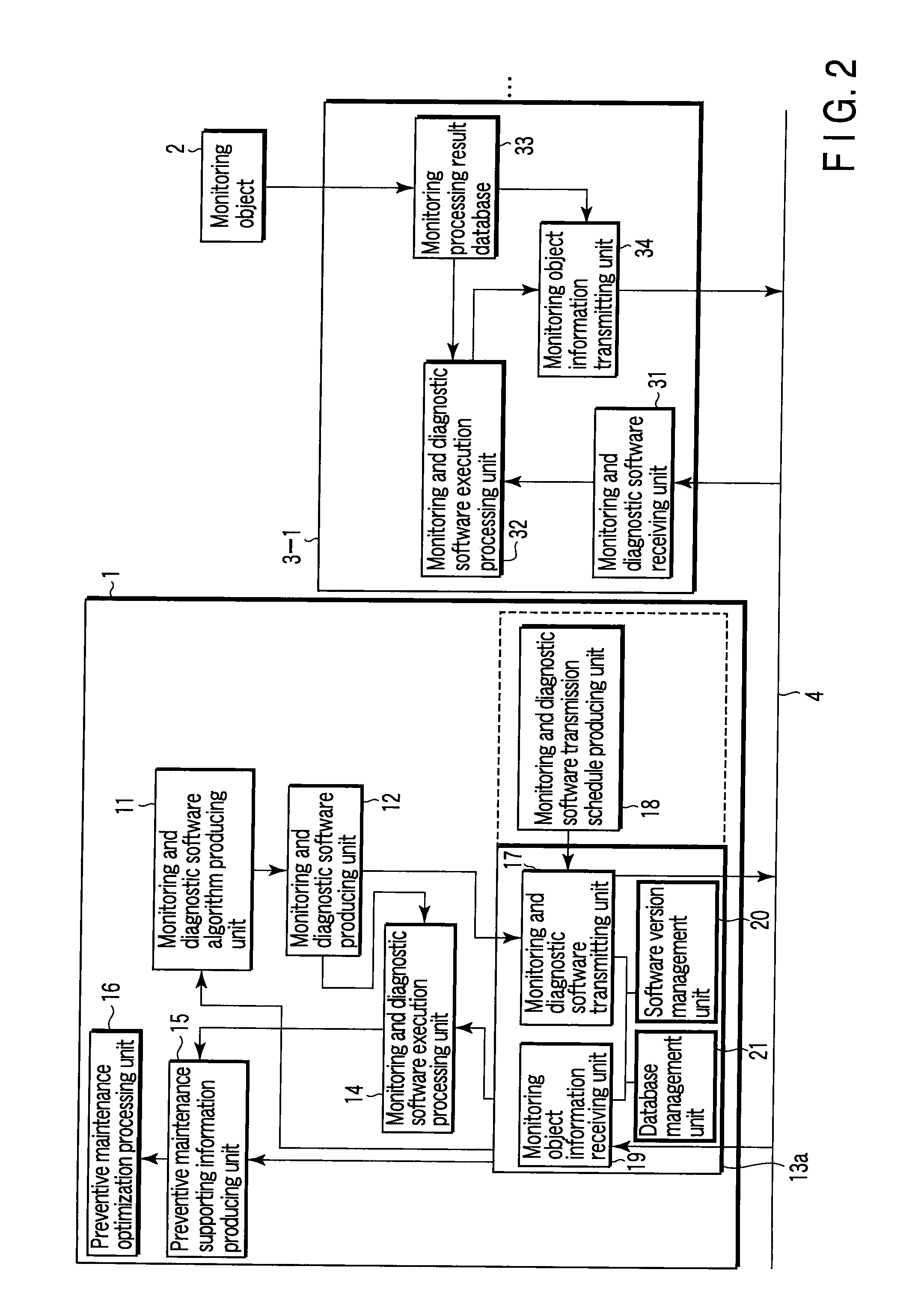
InactiveUS20090013311A1Efficient updateProgramme controlData processing applicationsComputer hardwareTransmission schedule
A center-side processing system and monitoring processing systems of monitoring objects are connected through a network. The center-side processing system includes a module for producing monitoring and diagnostic algorithms of the monitoring objects, software producing module for producing monitoring and diagnostic software from the monitoring and diagnostic algorithm, a module for producing a transmission schedule of the monitoring and diagnostic software, transmitting module for transmitting software according to the transmission schedule, a module for correcting and changing the monitoring and diagnostic software from data received from the monitoring processing system, and verification module for performing verification before the transmission of the monitoring and diagnostic software. Each of the monitoring processing systems includes a module for receiving the monitoring and diagnostic software, execution processing module for executing the monitoring and diagnostic software, a module for automatically verifying the monitoring and diagnostic software, and transmitting module.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com