Parameter offline identification method for permanent magnet synchronous motor under condition of rest
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, static state technology, applied in the control of generator, motor generator control, electronic commutation motor control and other directions, can solve the problems of long identification time, poor consistency of results, poor practicability, etc., and the process is simple and easy. Line, eliminate influence, high consistency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
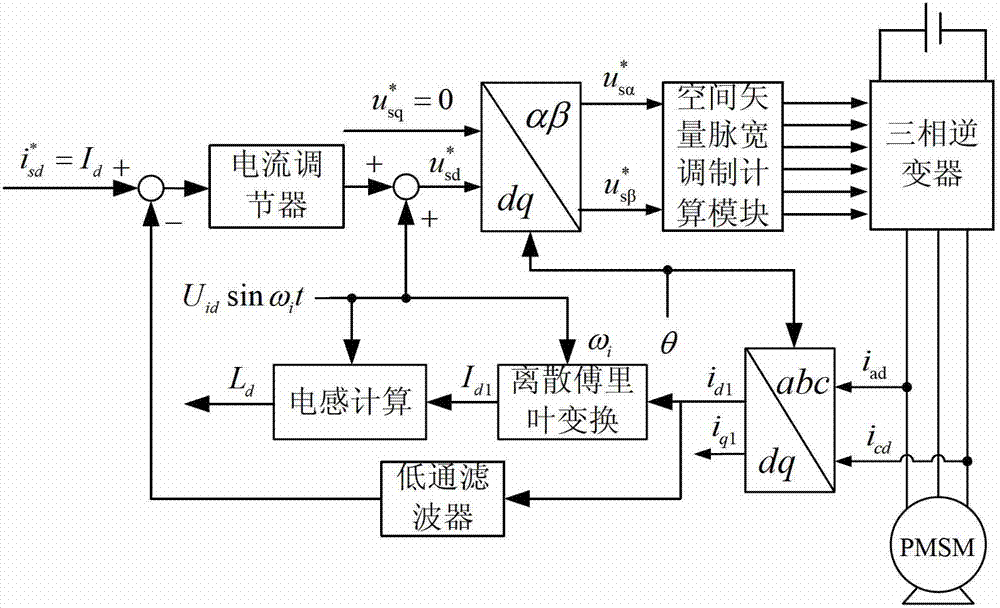
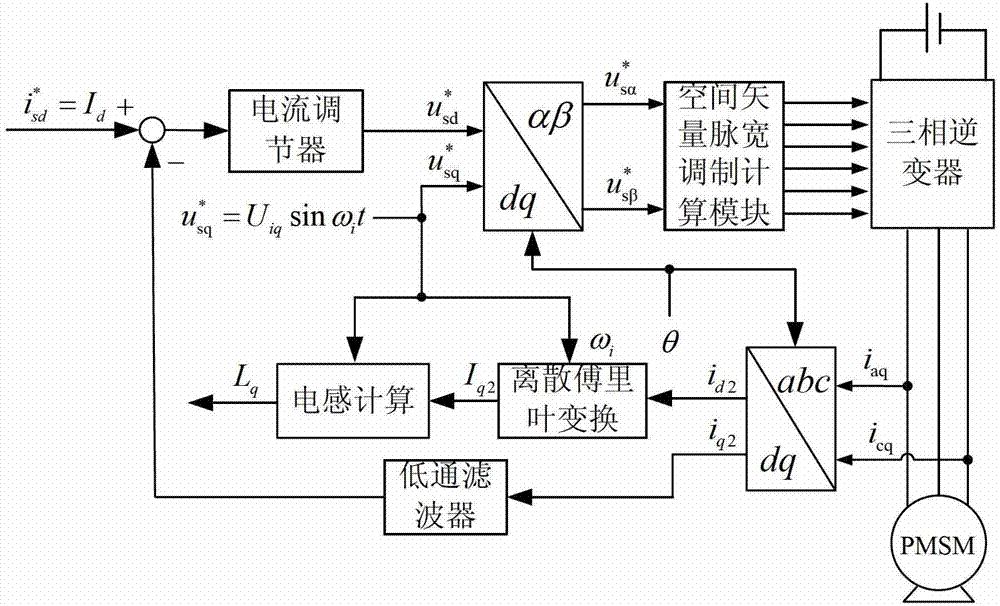
[0035] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination Figure 1 to Figure 5 Describe this embodiment, the parameter off-line identification method under the static state of permanent magnet synchronous motor described in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0036] Step 1. Obtain the rotor initial position angle θ of the permanent magnet synchronous motor by injecting high-frequency rotating voltage and pulse voltage into the stator winding of the permanent magnet synchronous motor;
[0037] Step 2: Stop injecting voltage, adopt open-loop control mode, and inject amplitude U into the direct axis of the stator winding of the permanent magnet synchronous motor under test id , the angular frequency is ω i Direct-axis sinusoidal high-frequency voltage vector signal;
[0038] At the same time, the three-phase current value of the stator winding of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is collected, and the direct-axis high-frequency current component is obtained through ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0048] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the parameter offline identification method of the permanent magnet synchronous motor in the static state described in Embodiment 1 is that the discrete Fourier transform pair described in step 2 is used to obtain the direct-axis high-frequency current amplitude. The value is processed, and then calculated to obtain the direct axis inductance L d The specific process is:
[0049] Step 21. Generate the amplitude U through the look-up table method id , the angular frequency is ω i The direct-axis sinusoidal high-frequency voltage vector signal U id sin ω i t,
[0050] Step 22. Calculate the current of the B-phase winding by collecting the obtained current of the A-phase winding and the current of the C-phase winding,
[0051] Step two and three, using the transformation formula from the three-phase stationary coordinates to the two-phase rotating coordinate system, to obtain the direct-axis current value and th...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0054] Specific Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and the parameter offline identification method of the permanent magnet synchronous motor in the static state described in the specific embodiment 1 is that the quadrature-axis high-frequency current amplitude is obtained by using the discrete Fourier transform described in step 3. , and then calculate the quadrature axis inductance L q The specific process is:
[0055] Step 31. Generate an amplitude value of U through the look-up table method iq , the angular frequency is ω i The direct-axis sinusoidal high-frequency voltage vector signal U iq sin ω i t,
[0056] Step 32: Calculate the current of the B-phase winding by collecting the obtained current of the A-phase winding and the current of the C-phase winding,
[0057] Step 33, using the transformation formula from the three-phase stationary coordinates to the two-phase rotating coordinate system to obtain the direct axis current value and the quadrat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com