Patents
Literature
1129results about How to "Efficient reception" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
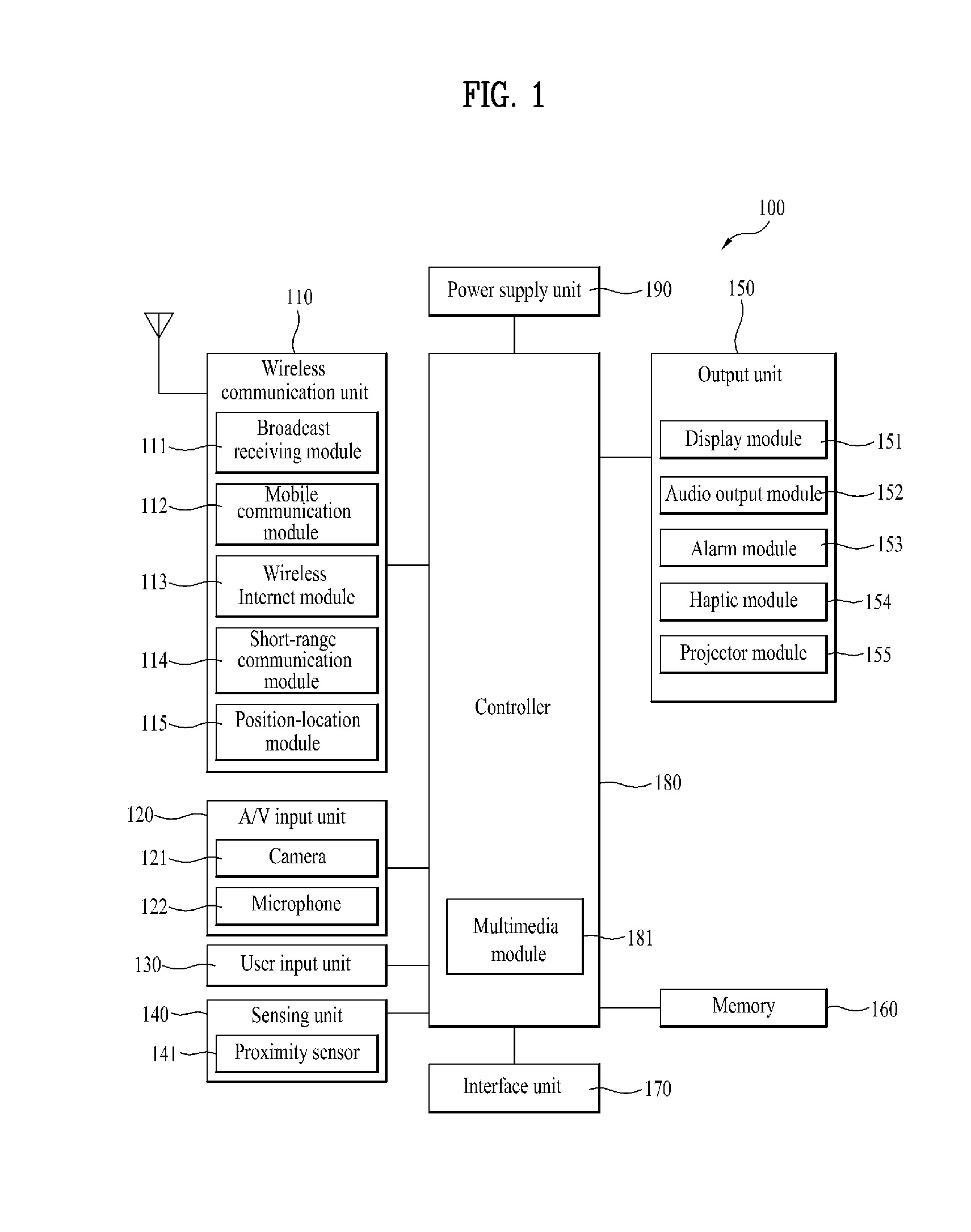
Radio frequency identification tag and radio frequency identification tag antenna
InactiveUS8098201B2Efficiently receiving electromagnetic wave transmittedMaximize readable rangeResonant long antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsTag antennaRadio frequency
An RFID tag includes an antenna and a chip, and the antenna includes a first polygonal dielectric material, first and second microstrip lines partially formed in the first dielectric material, a second polygonal dielectric material stacked on the first dielectric material, and a third microstrip line partially formed in the second dielectric material. According to the present invention, the RFID tag can efficiently receive electromagnetic waves to thereby maximize a readable range.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
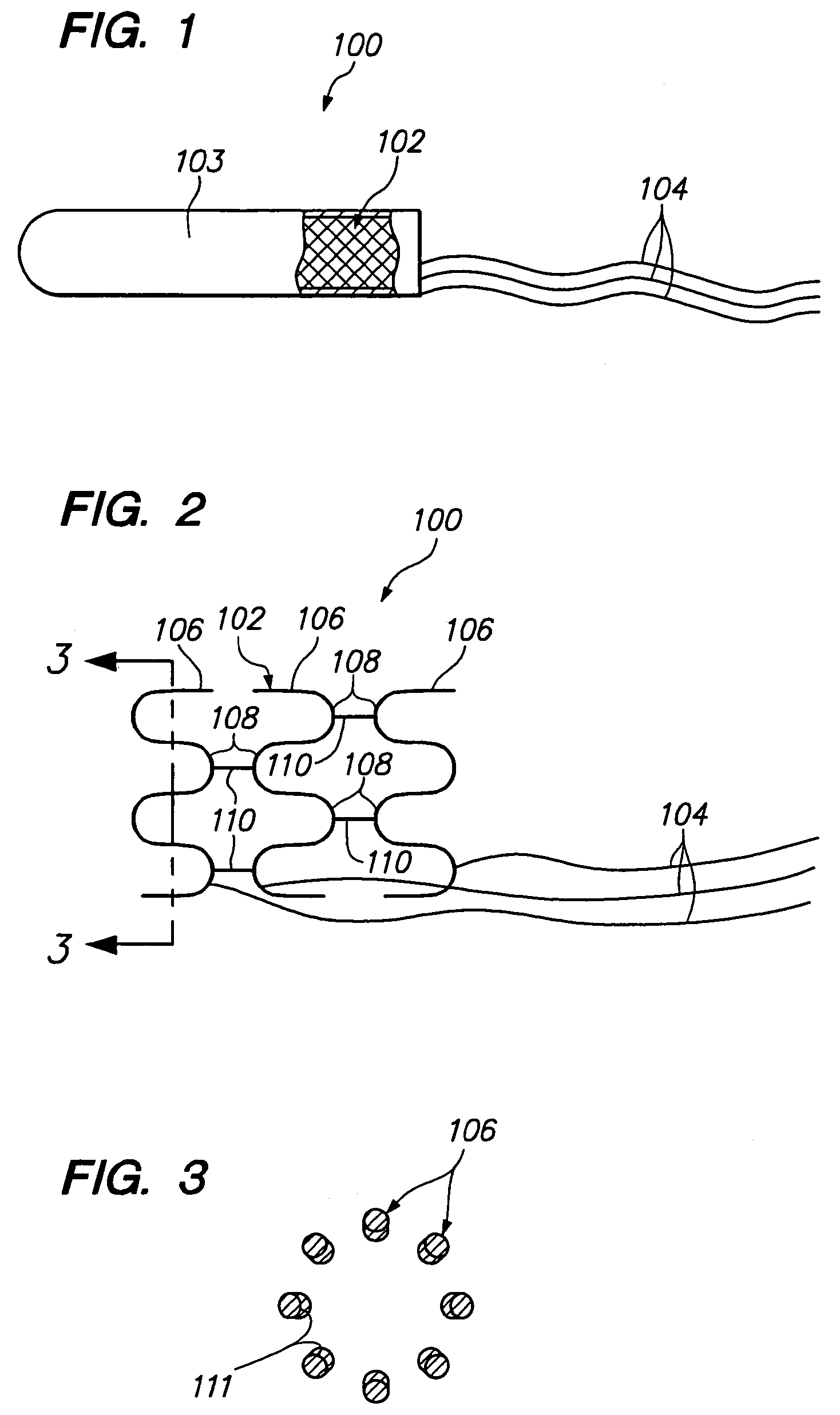
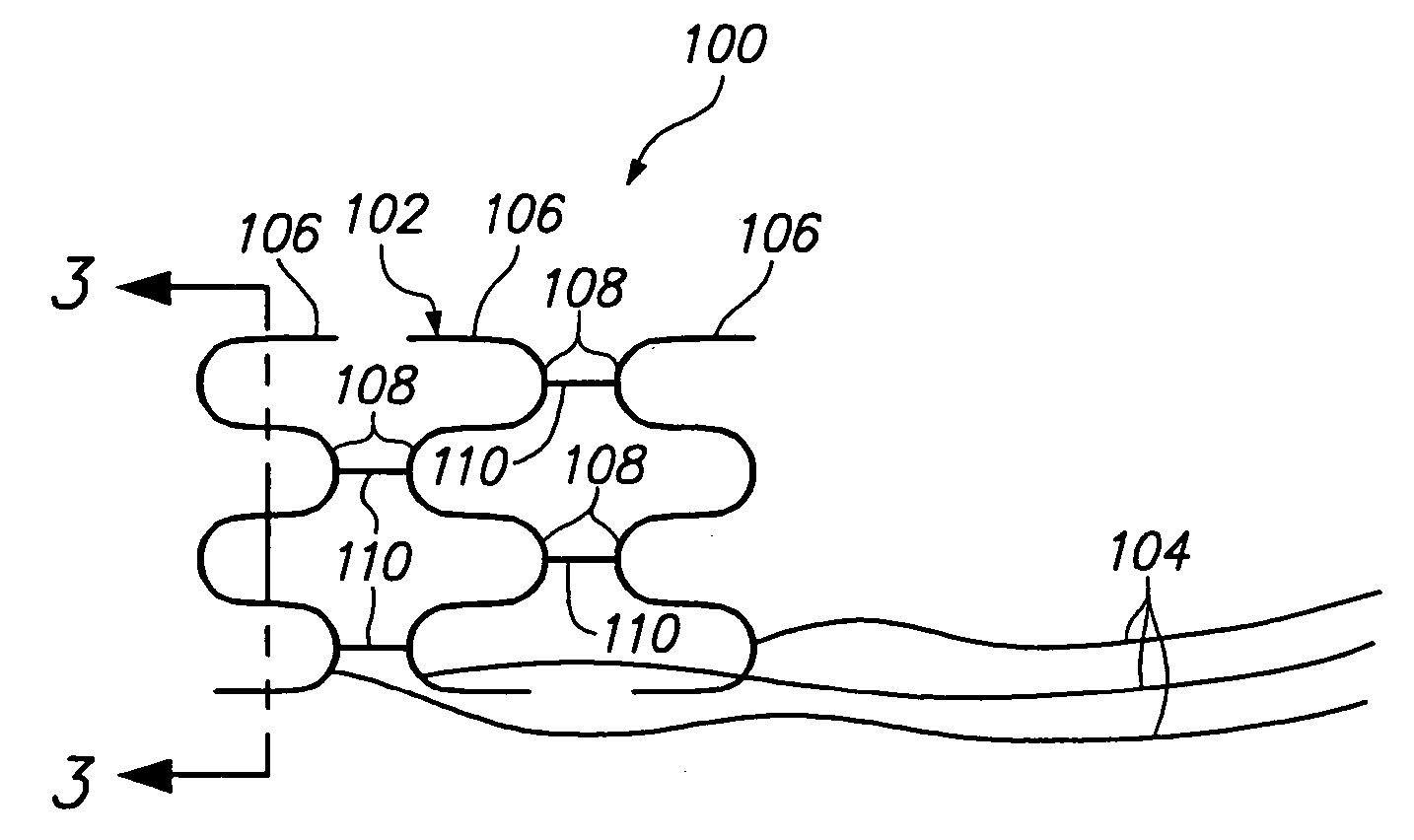
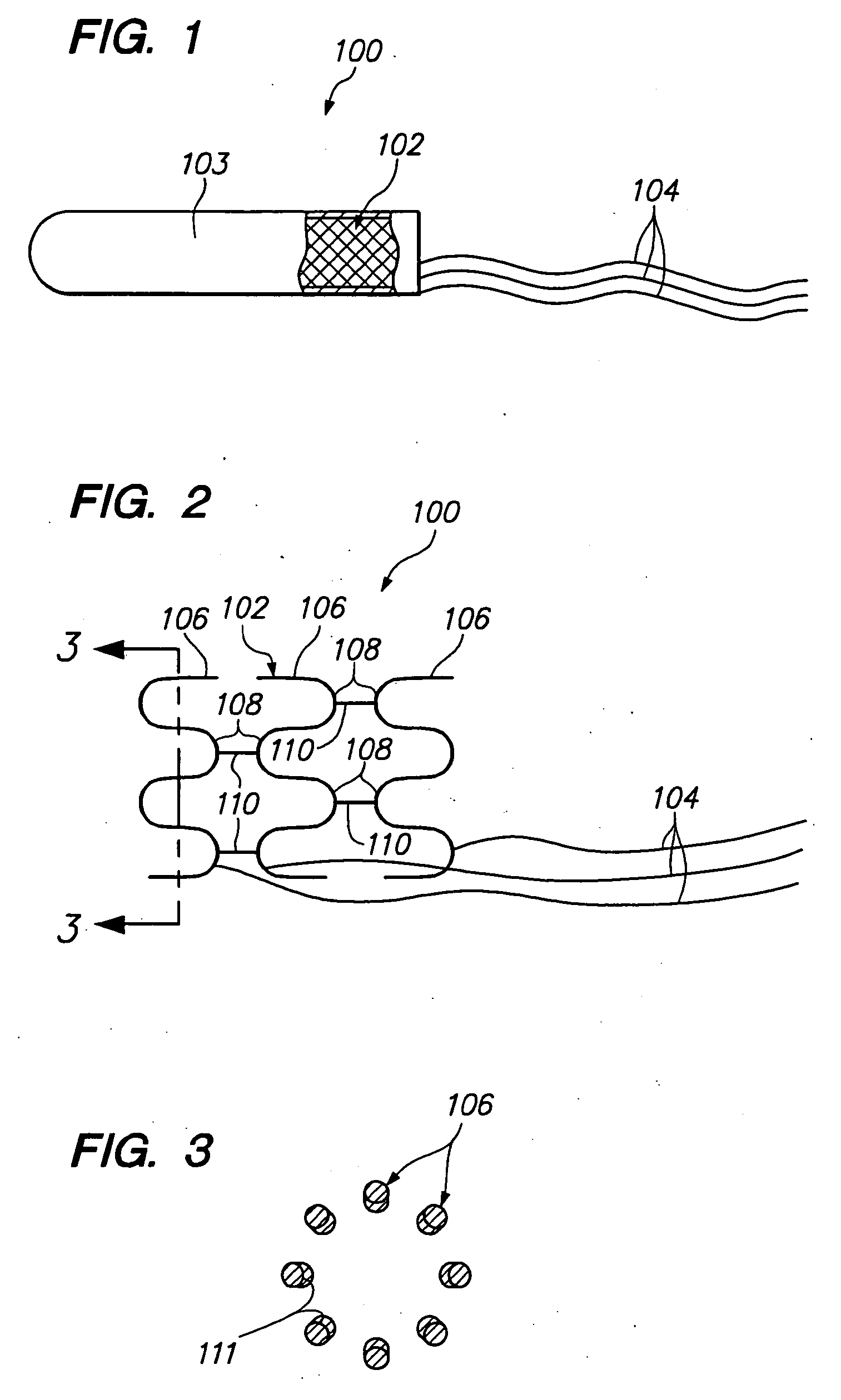
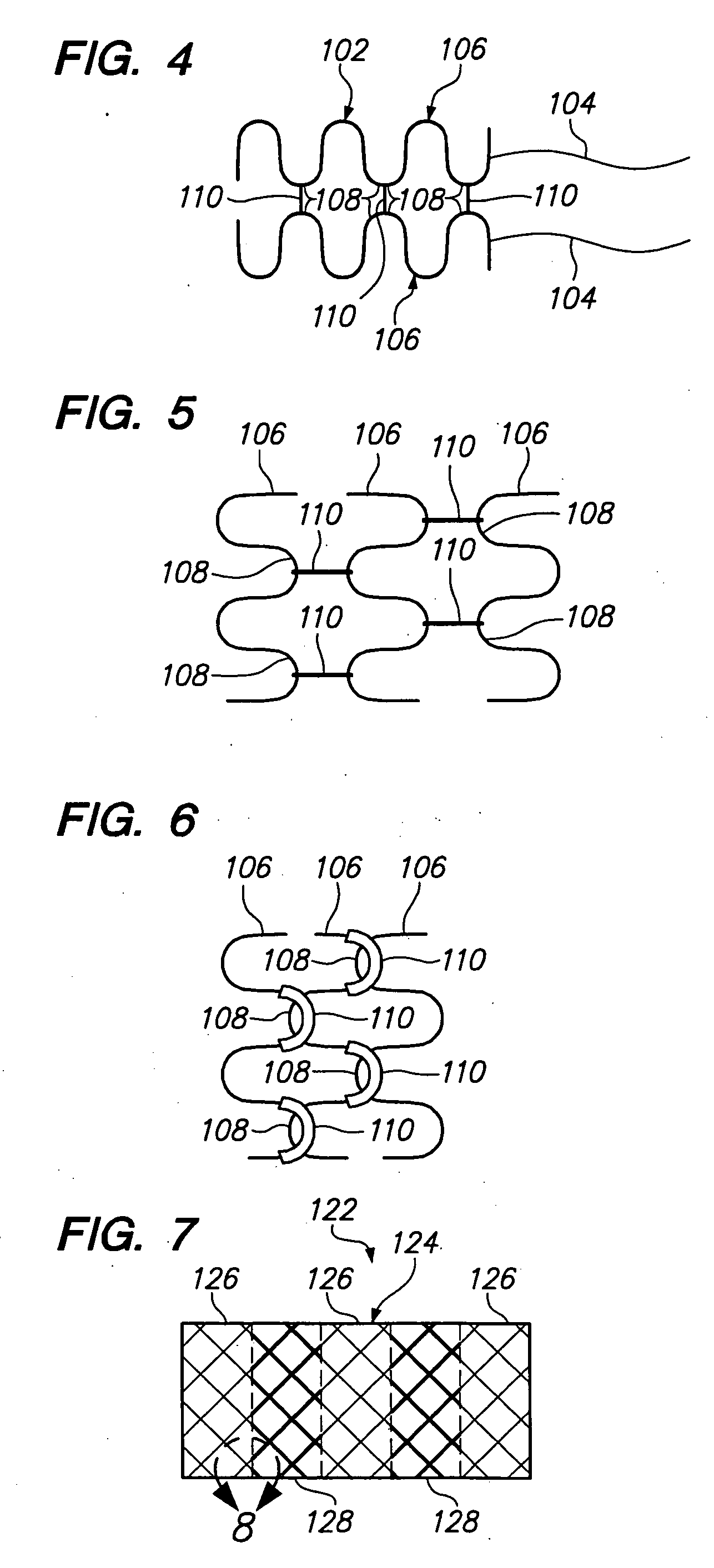
Intravascular self-anchoring electrode body with arcuate springs, spring loops, or arms
InactiveUS7231260B2Efficient receptionGuaranteed normal transmissionStentsTransvascular endocardial electrodesMedicineMedical device
An expandable intravascular medical device comprises an arcuate spring configured to be expanded into contact with the inner surface of a blood vessel. Another medical device comprises an electrode support structure, e.g., a non-tubular arcuate structure or a cylindrical member, and a plurality of resilient spring loops laterally extending from the support structure. The contact created between the loops and a blood vessel is sufficient to anchor the medical device within the blood vessel. In another embodiment, the medical device comprises an elongated member and two resilient spring arms extending distally from the elongated member. The arms are configured to be laterally moved towards each other to place the medical device in a collapsed geometry, and configured to be laterally moved away from each into contact with an inner surface of a blood vessel to place the medical device an expanded geometry.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
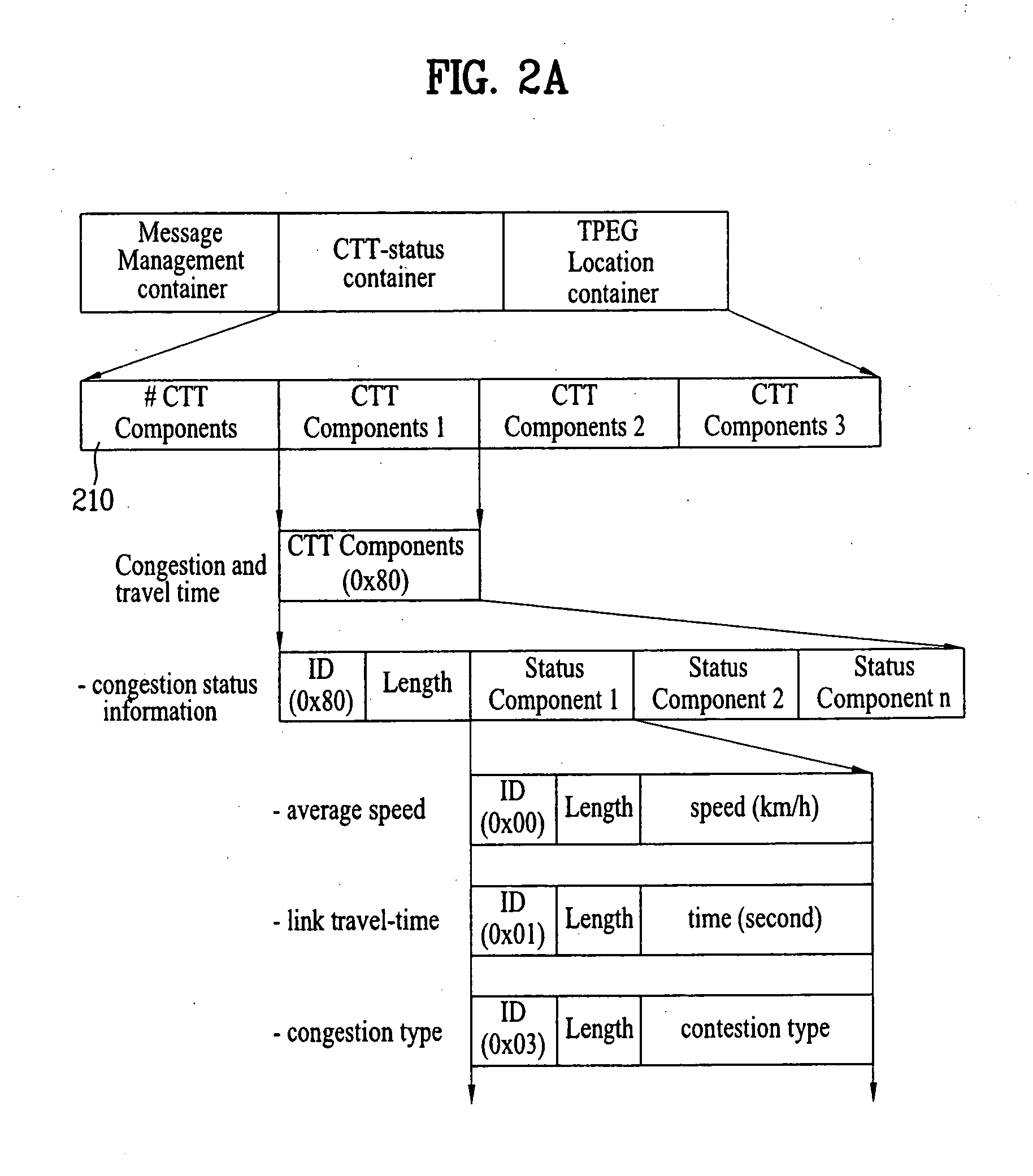
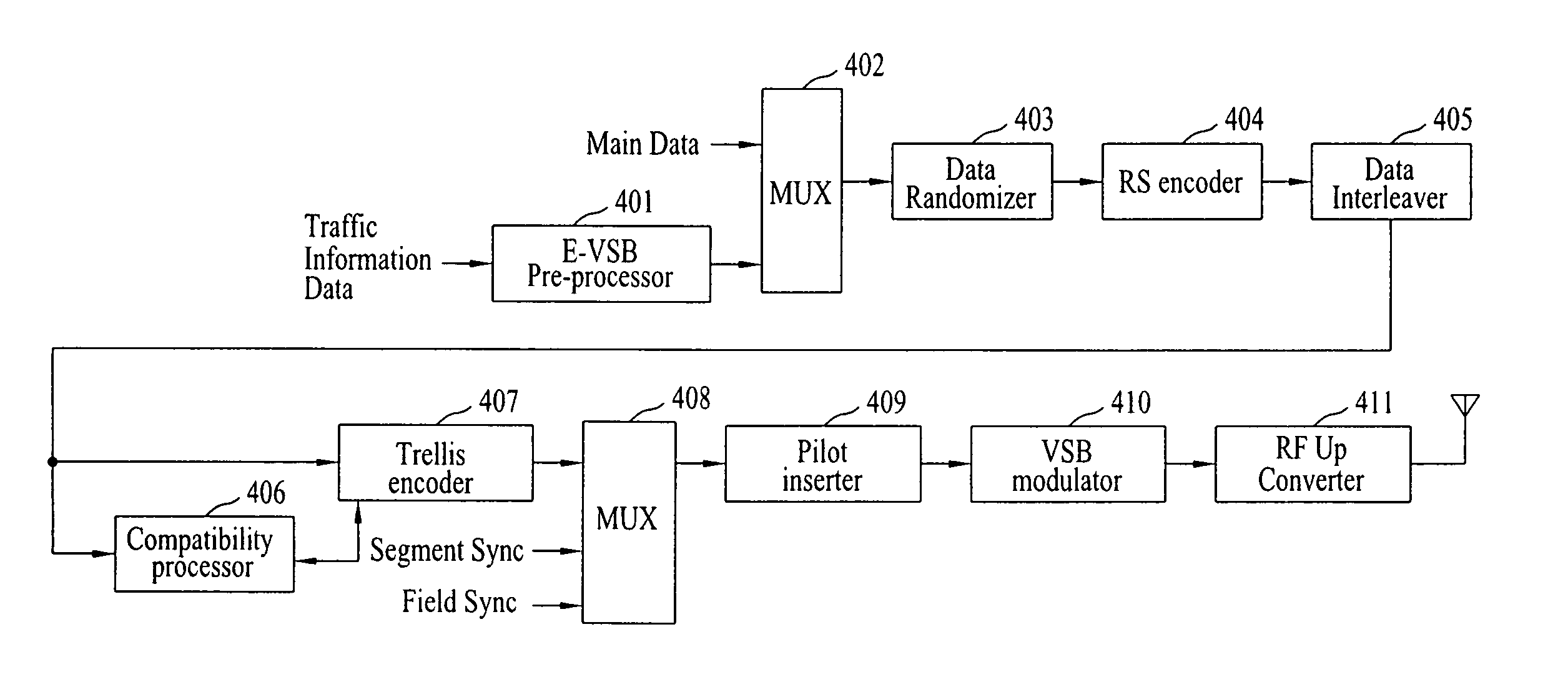
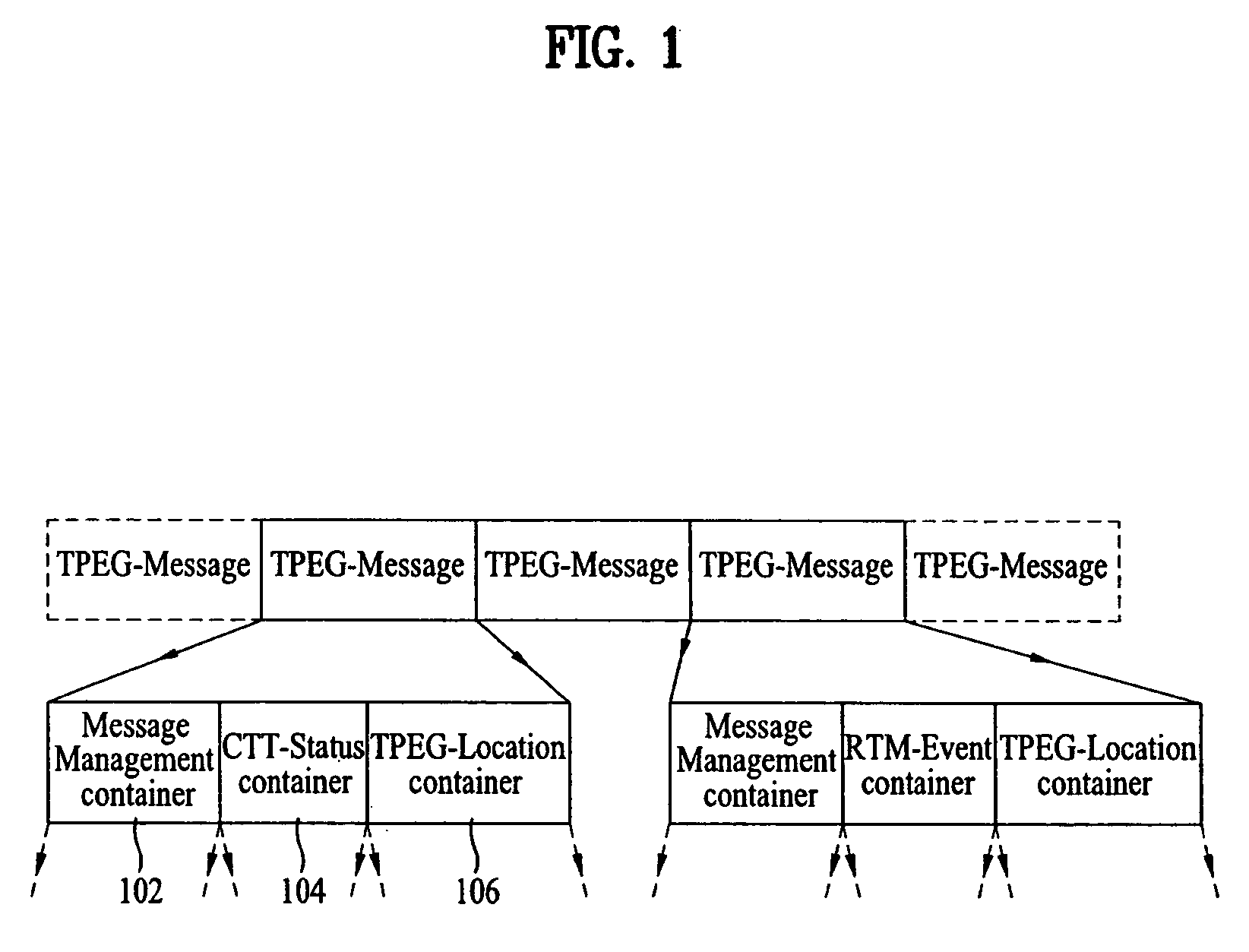
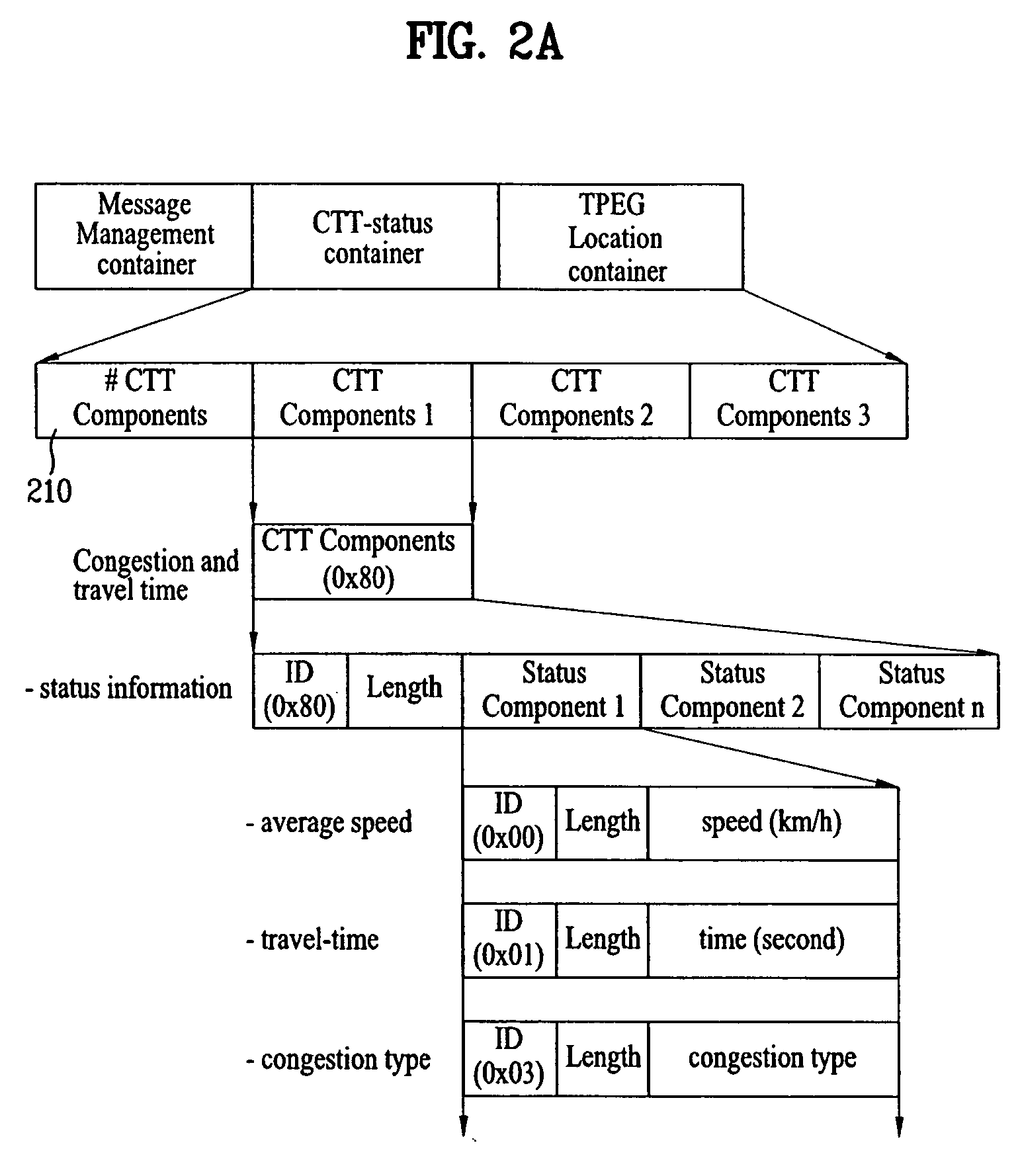
Method of processing traffic information and digital broadcast system
ActiveUS20070086488A1Noise robustData augmentationBroadcast specific applicationsModulation with suppressed carrierMultiplexingDigital broadcasting
A digital broadcast transmitting / receiving system and a method for processing data are disclosed. The method for processing data may enhance the receiving performance of the receiving system by performing additional coding and multiplexing processes on the traffic information data and transmitting the processed data. Thus, robustness is provided to the traffic information data, thereby enabling the data to respond strongly against the channel environment which is always under constant and vast change.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
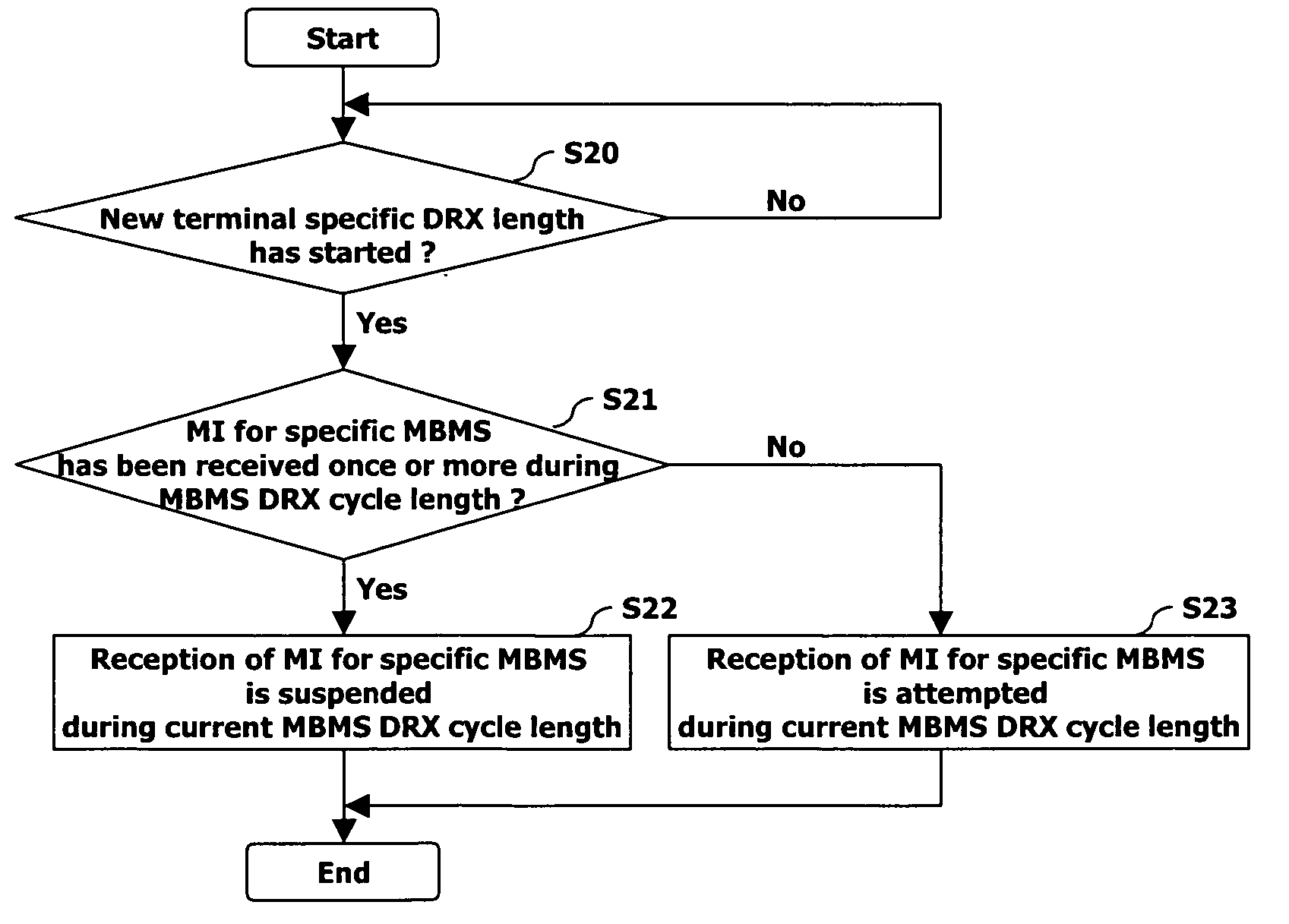
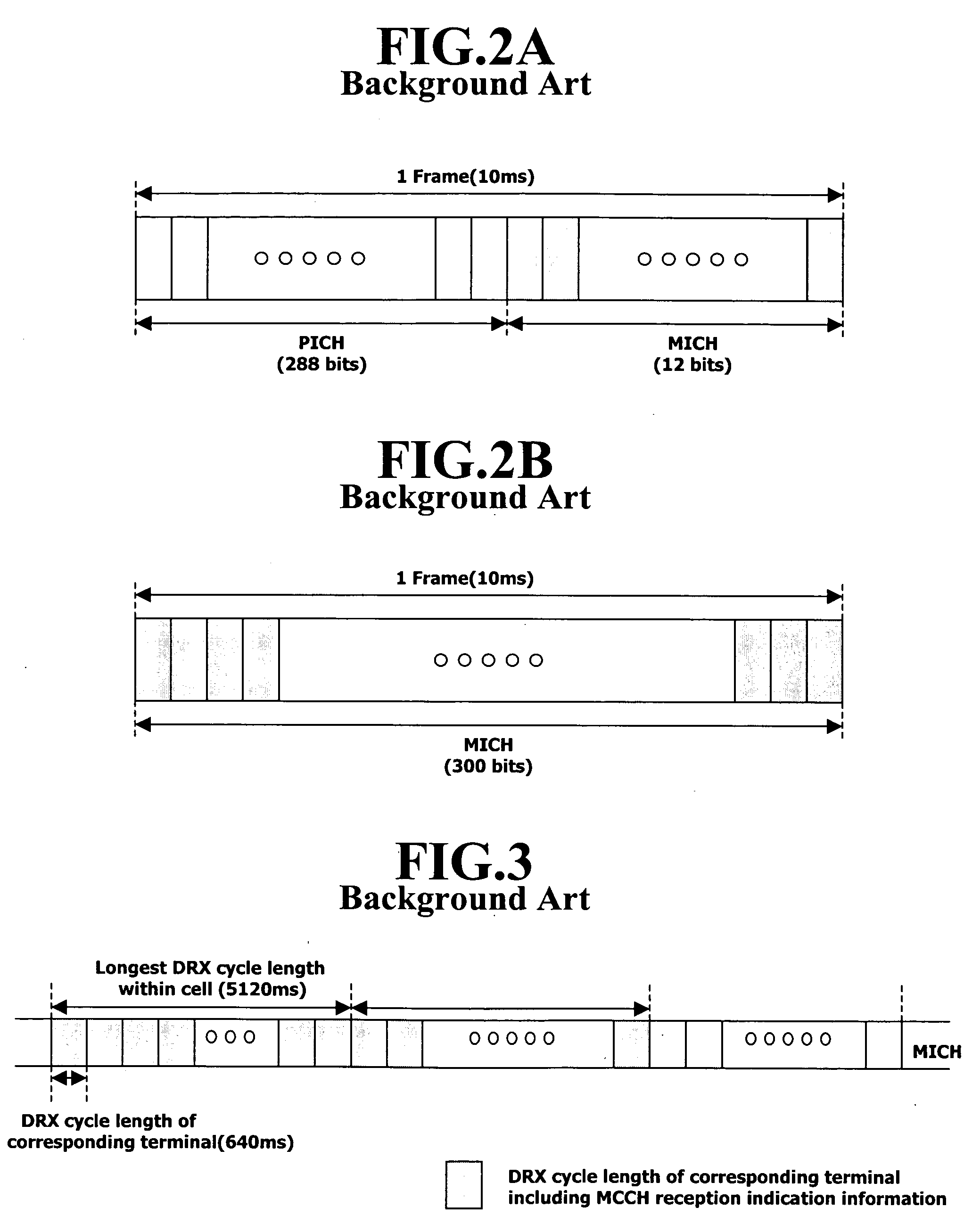
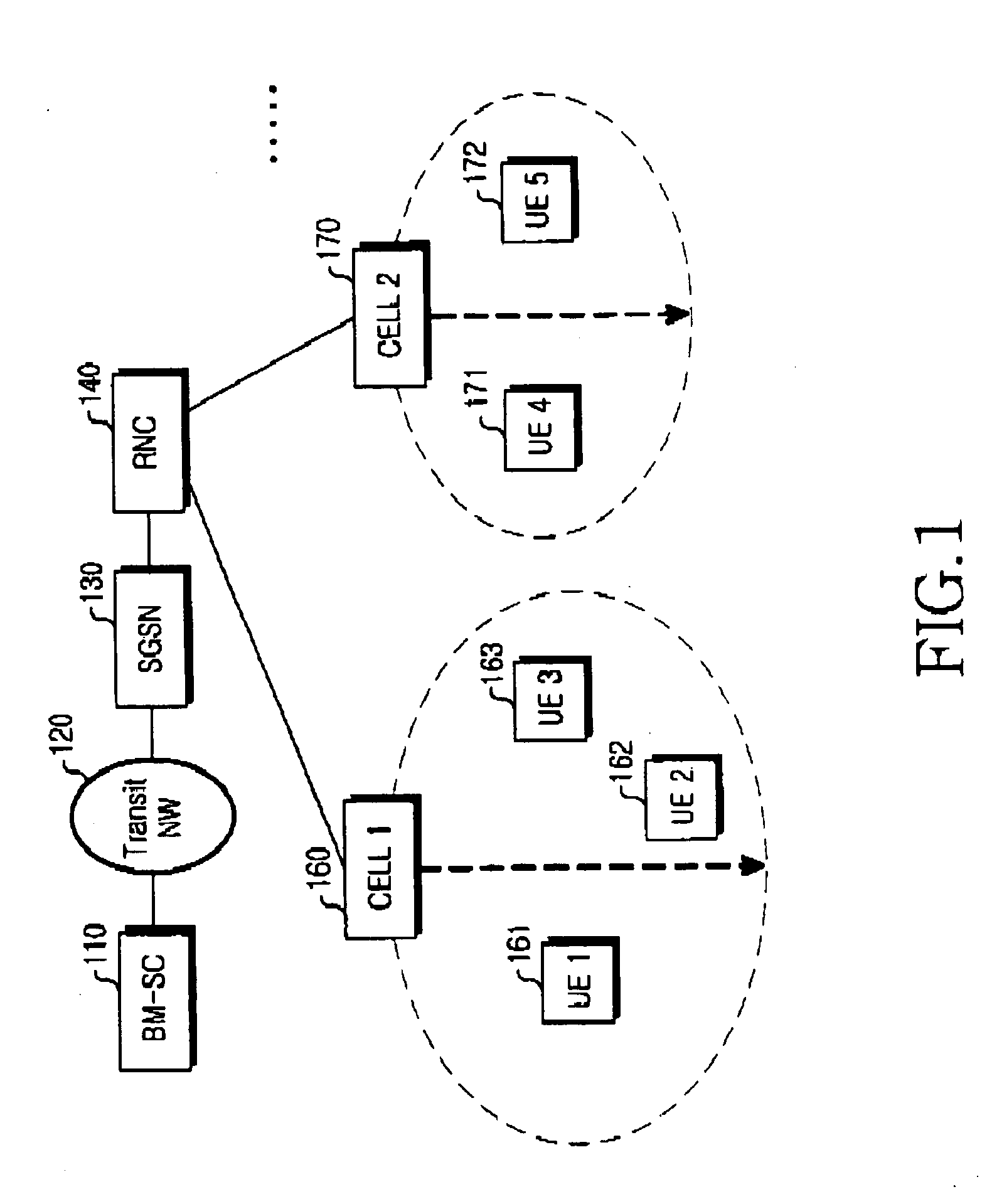
Apparatus and method for discontinuously receiving MBMS notification indicator in mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050176474A1Efficient receptionAssess restrictionSpecial service for subscribersMobile communication systemsComputer science
An apparatus and method for receiving an MBMS (Multimedia Multicast / Broadcast Service) notification indicator is disclosed to discontinuously receive an MBMS notification indicator in a mobile communication system. A mobile terminal receives and stores a terminal-specific DRX (Discontinuous Reception) cycle length and the longest DRX cycle length broadcasted in a cell. The mobile terminal discontinuously receives a notification indicator for a specific MBMS during a terminal-specific DRX cycle length of the longest DRX cycle length by using the stored terminal-specific DRX cycle length and the longest DRX cycle length used in a cell.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method of processing traffic information and digital broadcast system
InactiveUS20070076584A1Noise robustData augmentationPulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast information characterisationInformation processingMultiplexing
A digital broadcast transmitting / receiving system and a method for processing data are disclosed. The method for processing data may enhance the receiving performance of the receiving system by performing additional coding and multiplexing processes on the traffic information data and transmitting the processed data. Thus, robustness is provided to the traffic information data, thereby enabling the data to respond strongly against the channel environment which is always under constant and vast change.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
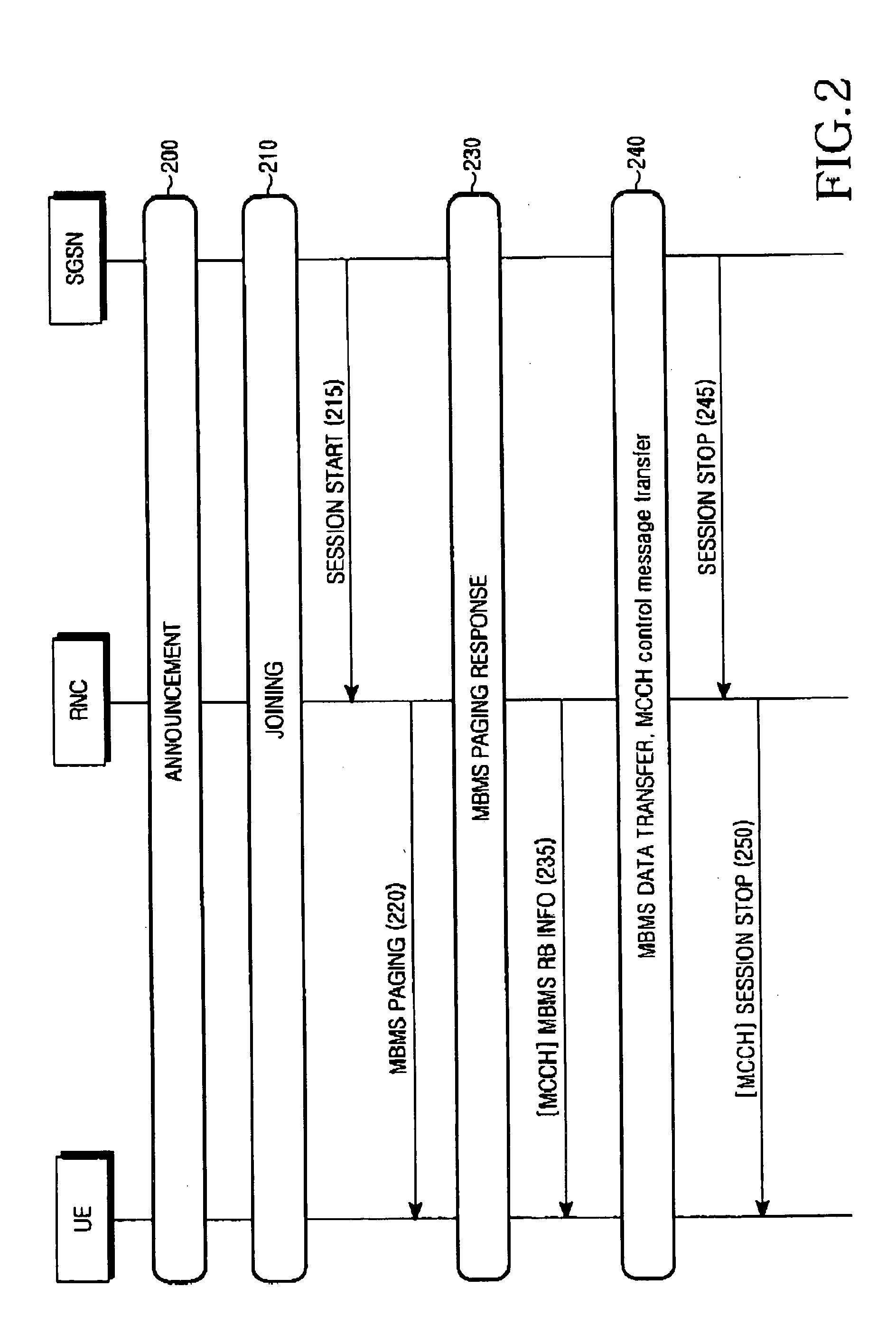
Method for providing requested MBMS service to UEs that failed to receive paging message in a mobile communication system supporting MBMS service
InactiveUS20050096017A1Efficiently receive MBMS serviceEfficient receptionSpecial service provision for substationSpecial service for subscribersTelecommunicationsMobile communication systems
Disclosed is a method for providing an MBMS service in a mobile communication system, which enables a UE to receive a specific MBMS service when the UE failed to receive a corresponding MBMS call message after requesting the specific MBMS service. After receiving period information for confirming information indicating whether the MBMS service is available in a cell where the UE is located, the UE receives the MBMS service by periodically receiving a control message including the information indicating whether the MBMS service available, according to the period information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting HARQ ack/nack
ActiveUS20150215079A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient receptionError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsComputer science
Provided is a method and apparatus for transmitting an HARQ ACK / NACK. The method includes: recognizing, from a PDCCH or an EPDCCH, a 2-bit uplink (UL) downlink assignment index (DAI) field configured in a UL downlink control information (DCI) format; receiving a PDSCH transmission through the second serving cell; generating an HARQ response signal based on the number of PDSCHs scheduled in the downlink subframes indicated by the UL DAI field and the number of total downlink subframes associated with one uplink subframe; and transmitting the HARQ response signal through a PUSCH in the one uplink subframe.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD +1
Signal transmission/reception method and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS20150173048A1Efficient receptionGuaranteed normal transmissionError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementCommunications systemVIT signals
The present invention relates to a radio communication system which supports device-to-device (D2D) communication. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for transmitting a D2D semi-persistent scheduled (SPS) signal in a radio communication system which supports D2D communication, and an apparatus therefor, the method comprising the steps of: receiving priority information of a D2D SPS signal from a base station; determining whether to send the D2D SPS signal or a signal intended for the base station, on the basis of the priority information, in a case where there is a clash, in a particular sub-frame, between the transmission of the D2D SPS signal and the signal intended for the base station; and transmitting the D2D SPS signal to a second terminal if the priority information of the D2D SPS signal has a higher priority than the signal intended for the base station.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
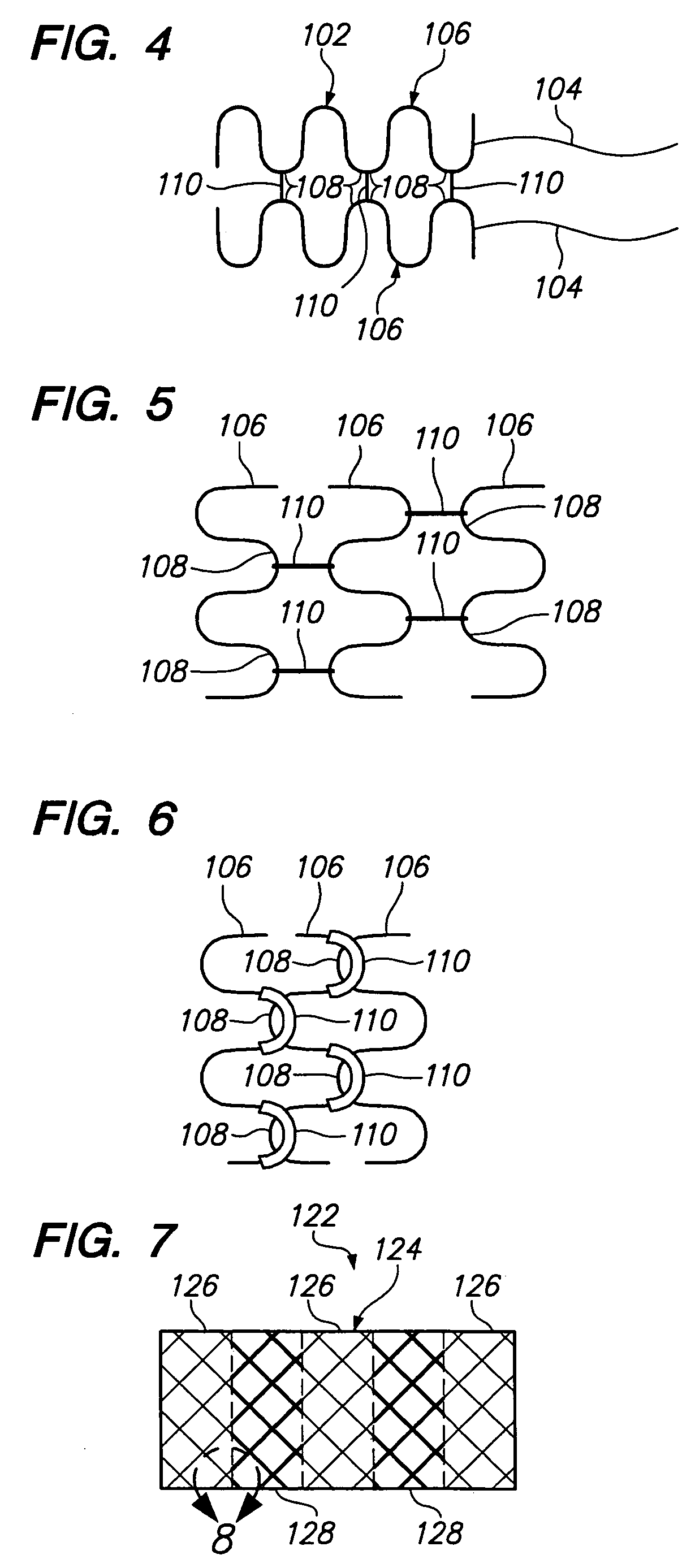
Intravascular self-anchoring electrode body with springs loops or arms
InactiveUS20050251239A1Guaranteed normal transmissionMinimize occlusionStentsTransvascular endocardial electrodesMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
An expandable intravascular medical device is provided. The medical device comprises an arcuate spring configured to be expanded into firm contact with the inner surface of a blood vessel. The medical device further comprises at least one electrode associated with the arcuate spring. For example, the electrode(s) can be discrete elements that are bonded to the arcuate spring, electrically conductive layers disposed on the arcuate spring, or the arcuate spring, itself, can form the electrode(s). The inner surface of the arcuate spring may optionally be electrically insulative. An intravascular medical device is provided. In one embodiment, the medical device comprises an electrode support structure, e.g., a non-tubular arcuate structure or a cylindrical member, and a plurality of resilient spring loops laterally extending from the support structure. The contact created between the loops and a blood vessel are sufficient to anchor the medical device within the blood vessel. In another embodiment, the medical device comprises an elongated member and two resilient spring arms extending distally from the elongated member. The arms are configured to be laterally moved towards each other to place the medical device in a collapsed geometry, and configured to be laterally moved away from each into contact with an inner surface of a blood vessel to place the medical device an expanded geometry. The contact created between the respective arms and the blood vessel are sufficient to anchor the medical device within the blood vessel. In either embodiment, the medical device further comprises an electrode associated with the electrode support structure or the spring arms.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method of processing traffic information and digital braodcast system
InactiveUS20070076721A1Noise robustData augmentationPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionMultiplexingDigital broadcasting
A digital broadcast transmitting / receiving system and a method for processing data are disclosed. The method for processing data may enhance the receiving performance of the receiving system by performing additional coding and multiplexing processes on the traffic information data and transmitting the processed data. Thus, robustness is provided to the traffic information data, thereby enabling the data to respond strongly against the channel environment which is always under constant and vast change.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
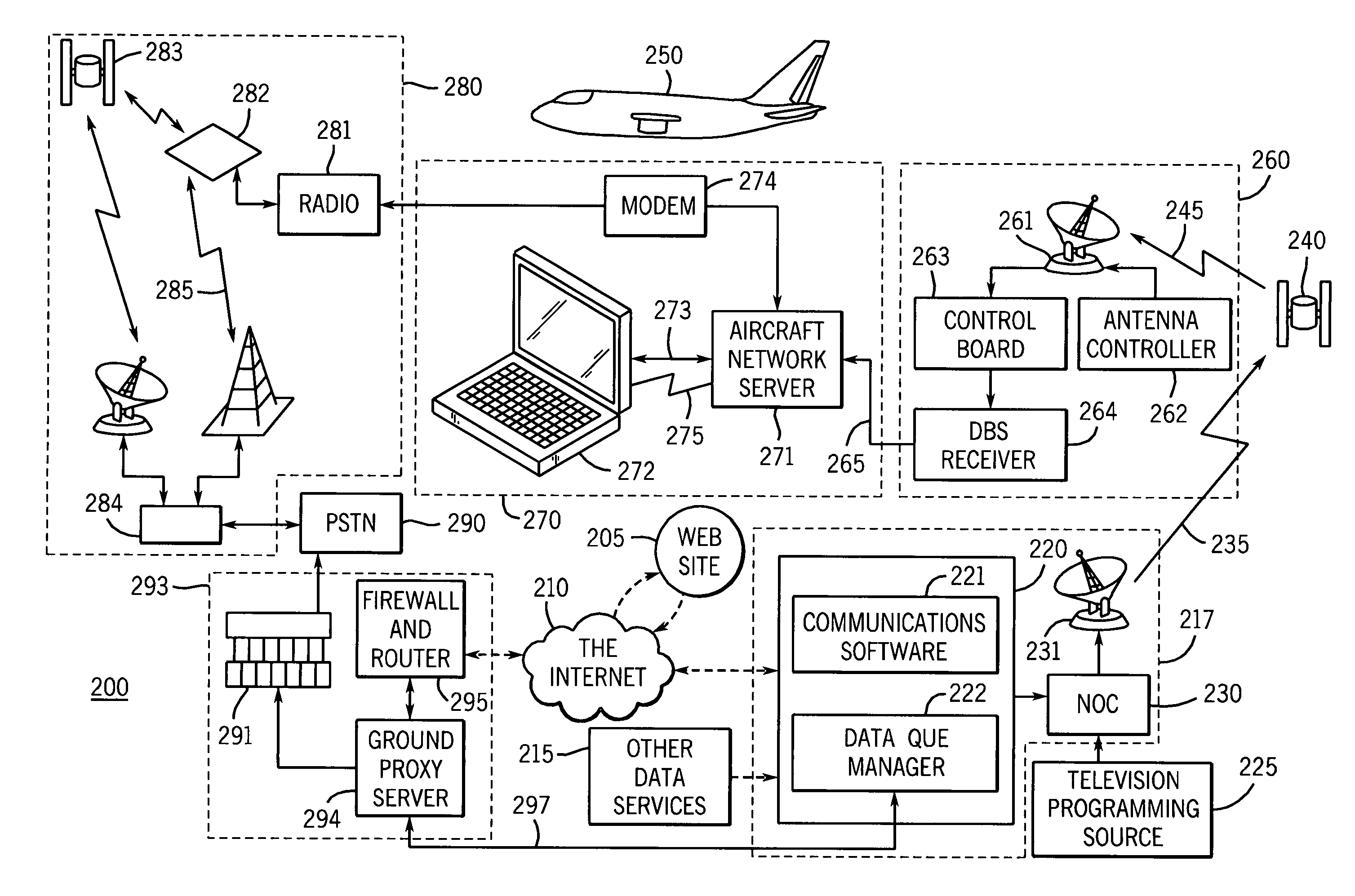
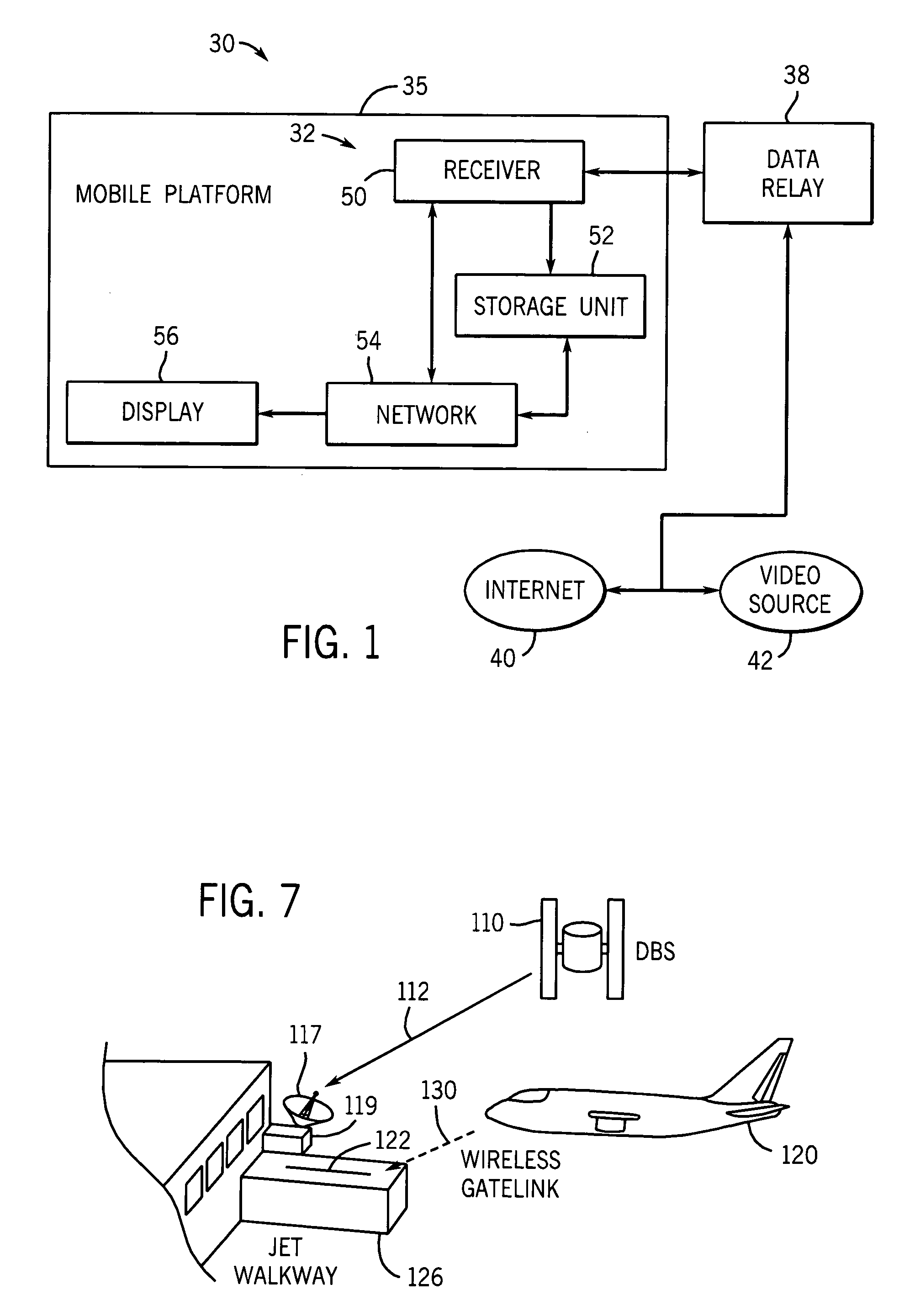
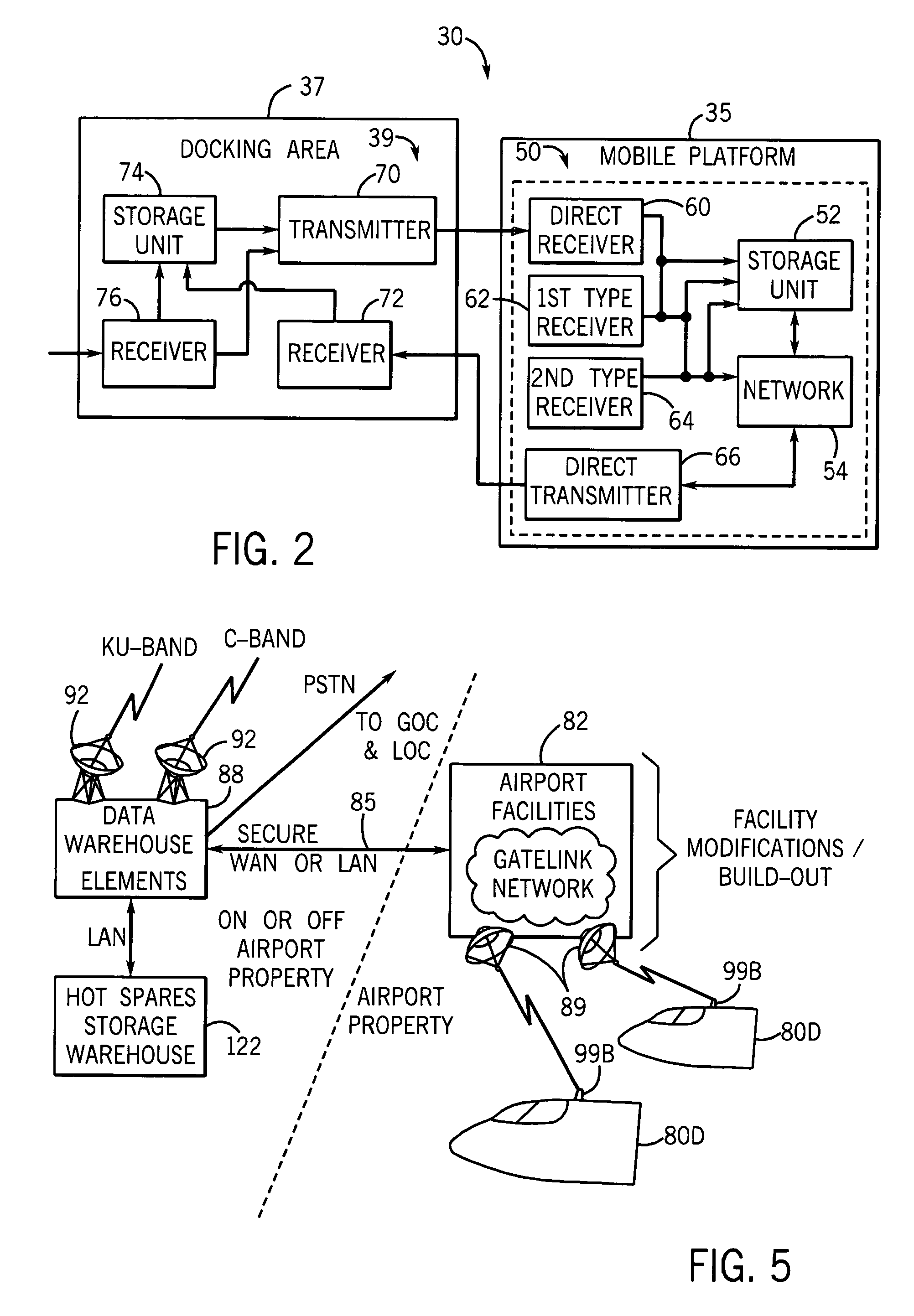
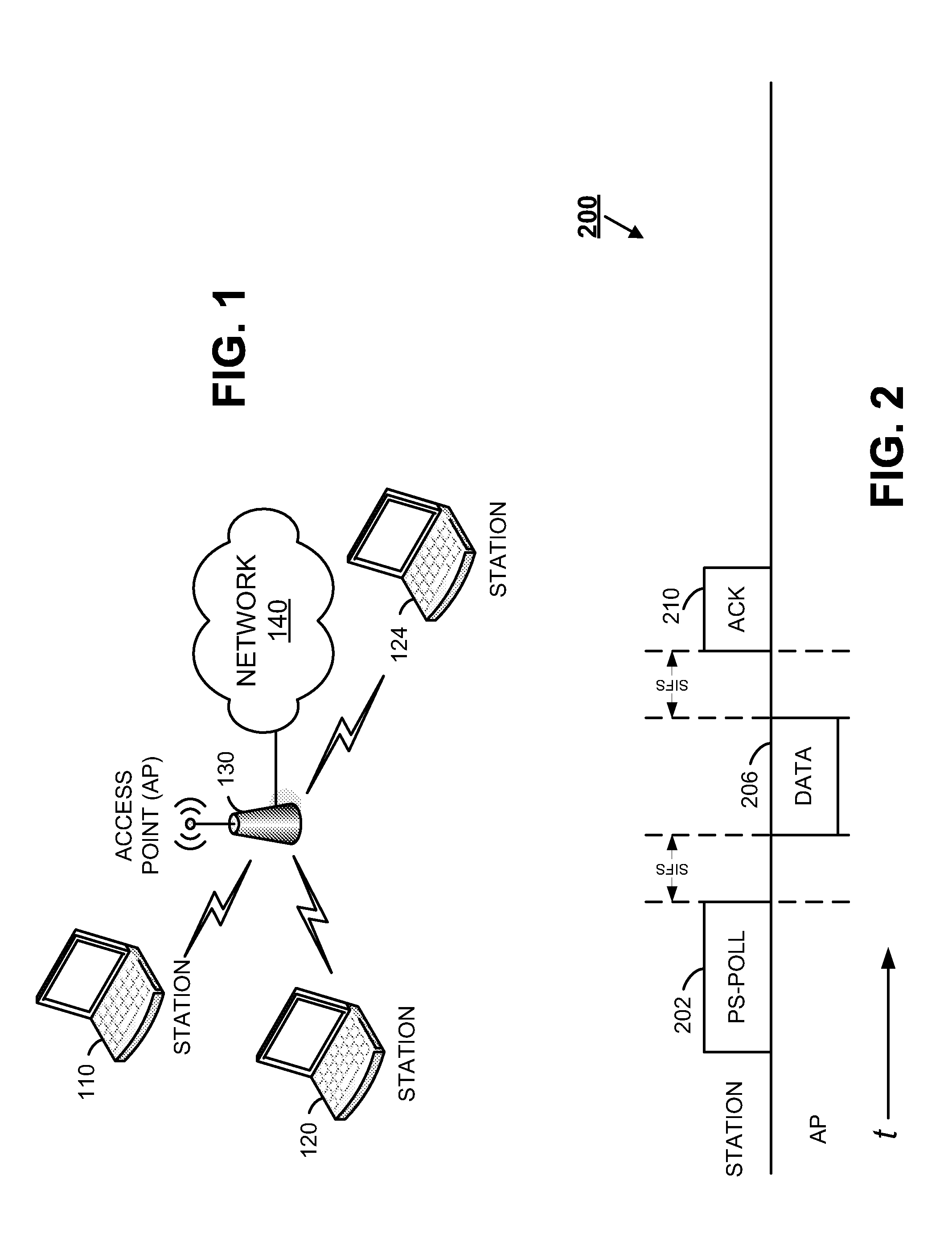
System and method for internet access on a mobile platform
InactiveUS7599691B1Efficient receptionBroadcast specific applicationsNetwork topologiesAirplaneCable Internet access
A communication system is provided for use with a mobile platform. The communication system can be configured to store video data on-board to allow pseudo-live or live broadcasts to be played as the mobile platform traverses a number of broadcasts regions. The mobile platforms can be automobiles, aircraft, boats, ships, trains, or other vehicles. The communication system allows Internet access, movies, and other entertainment and business functions to be performed.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Method of processing traffic information and digital broadcast system
InactiveUS20070076758A1Noise robustData augmentationRoad vehicles traffic controlBroadcast specific applicationsInformation processingMultiplexing
A digital broadcast transmitting / receiving system and a method for processing data are disclosed. The method for processing data may enhance the receiving performance of the receiving system by performing additional coding and multiplexing processes on the traffic information data and transmitting the processed data. Thus, robustness is provided to the traffic information data, thereby enabling the data to respond strongly against the channel environment which is always under constant and vast change.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
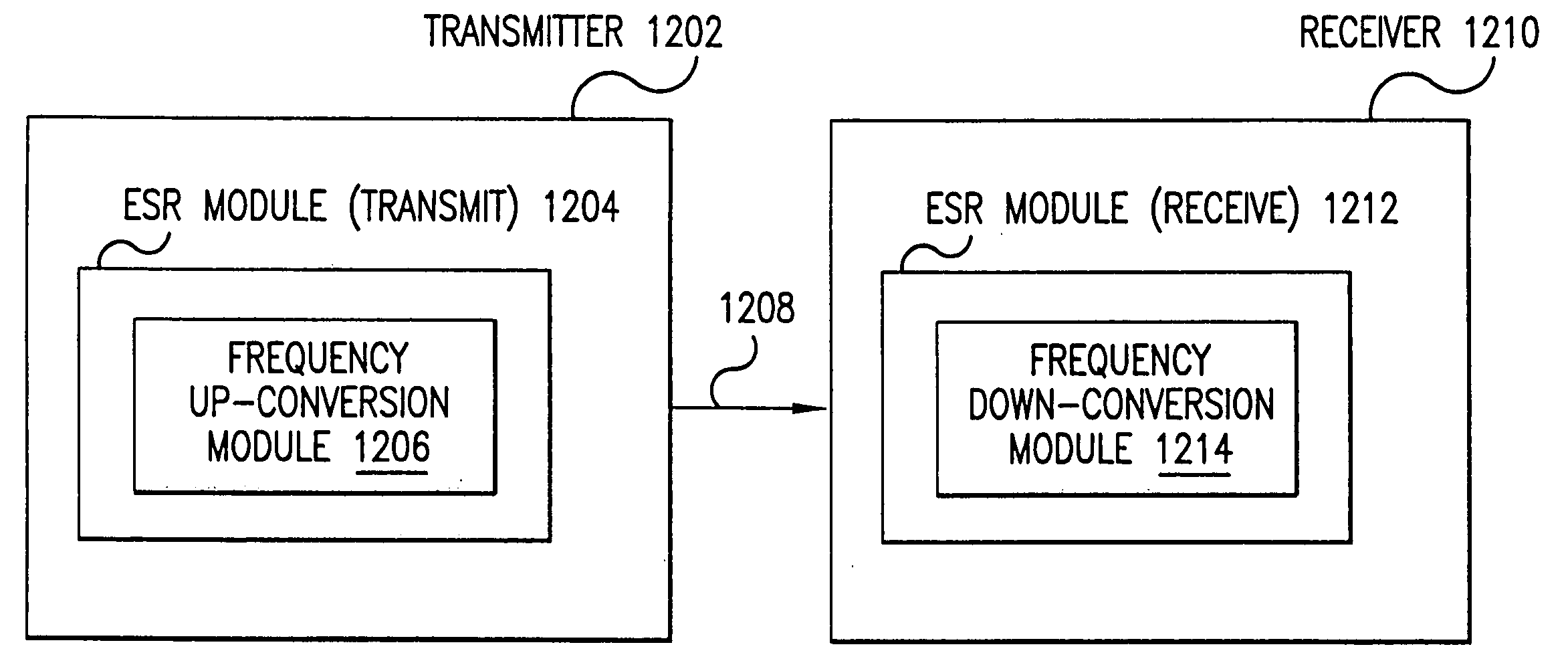
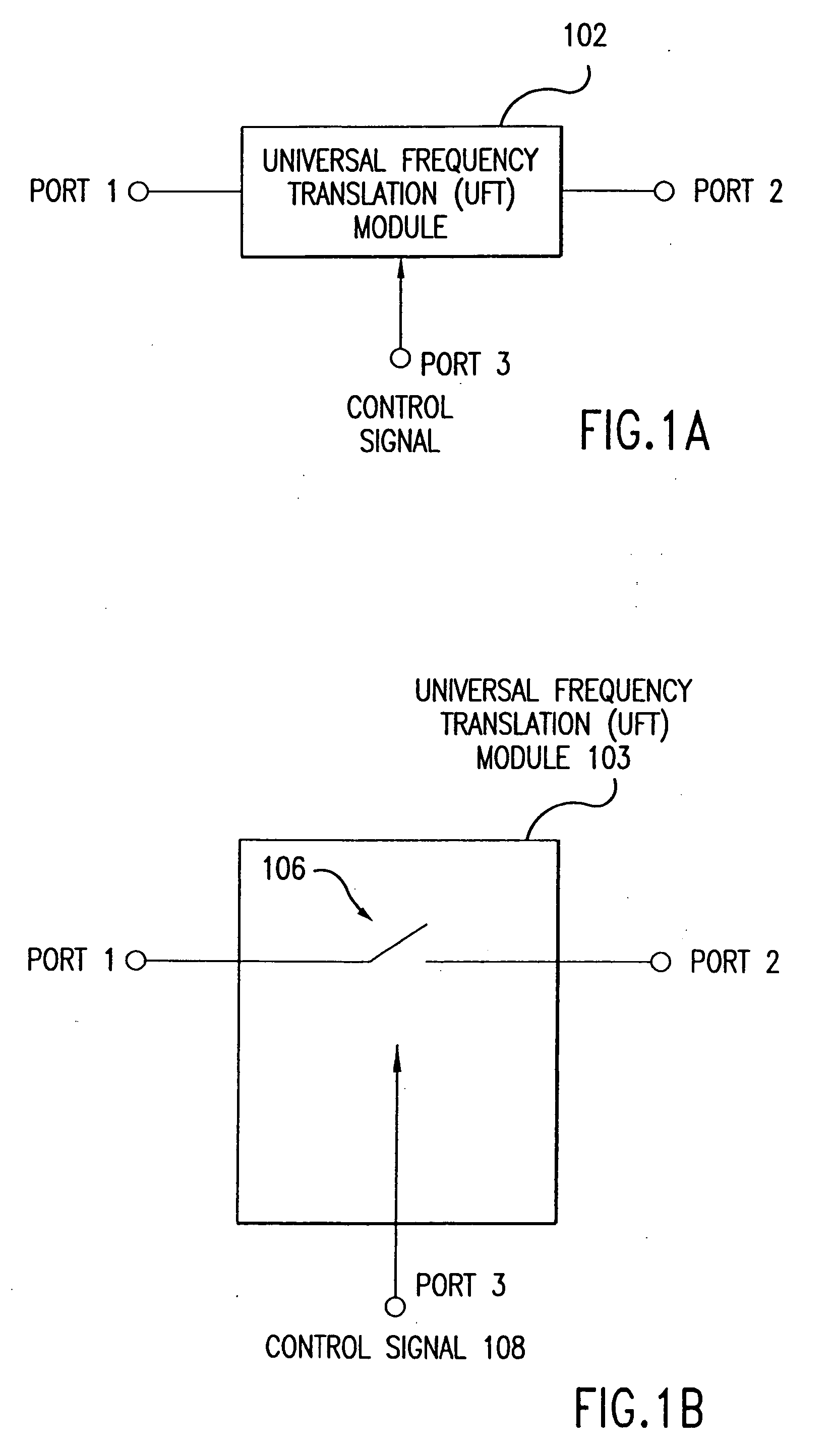
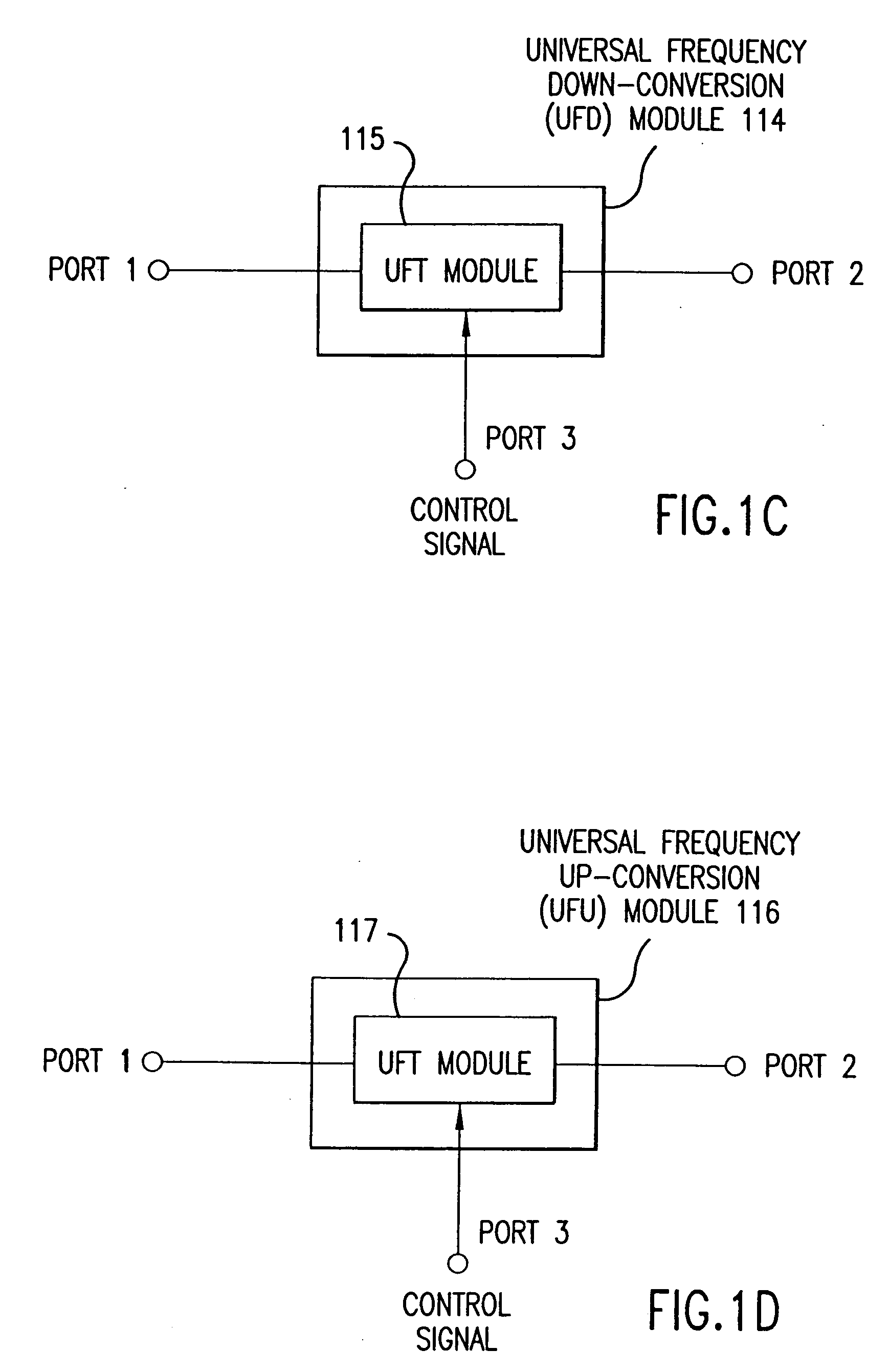
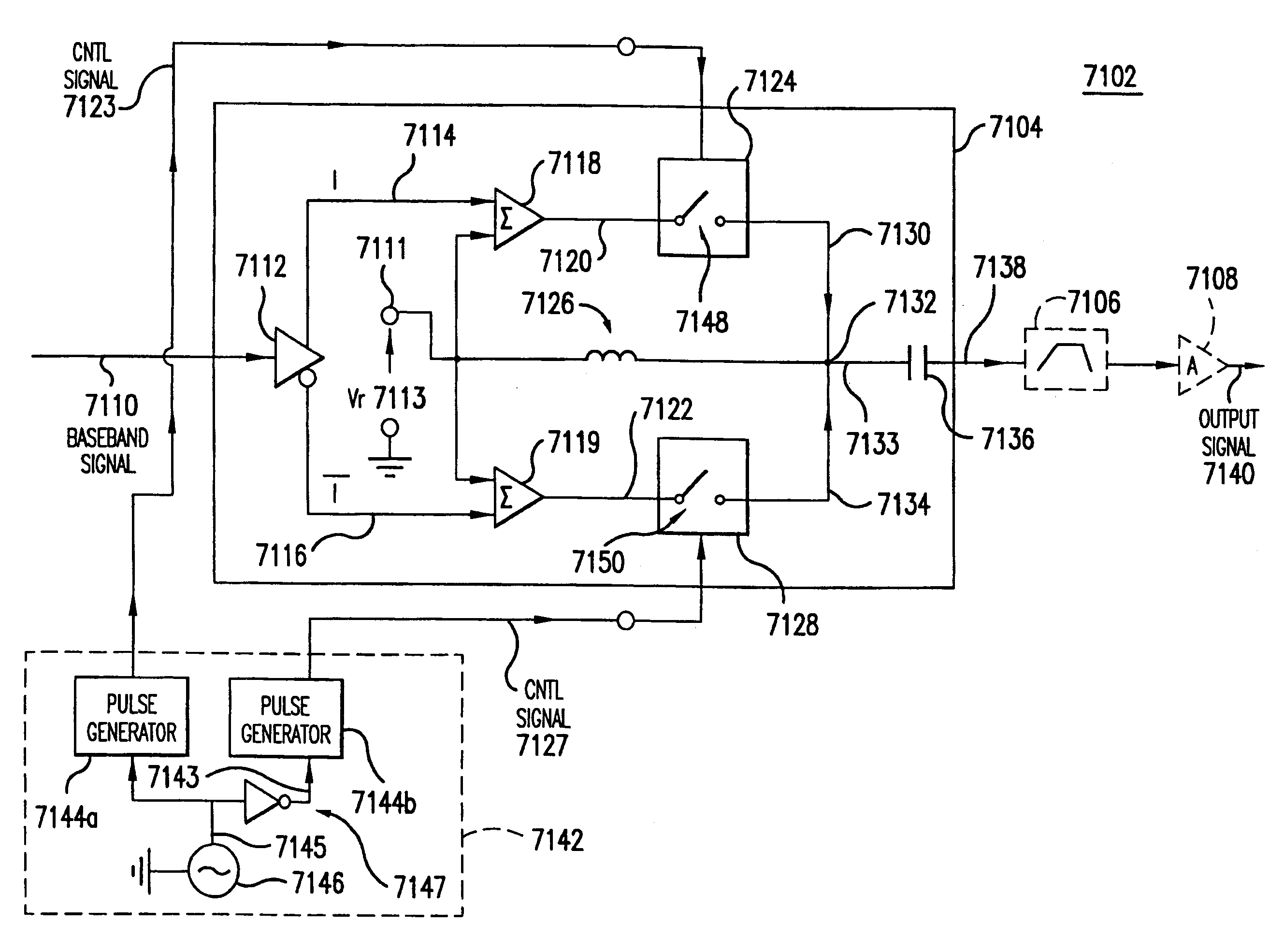
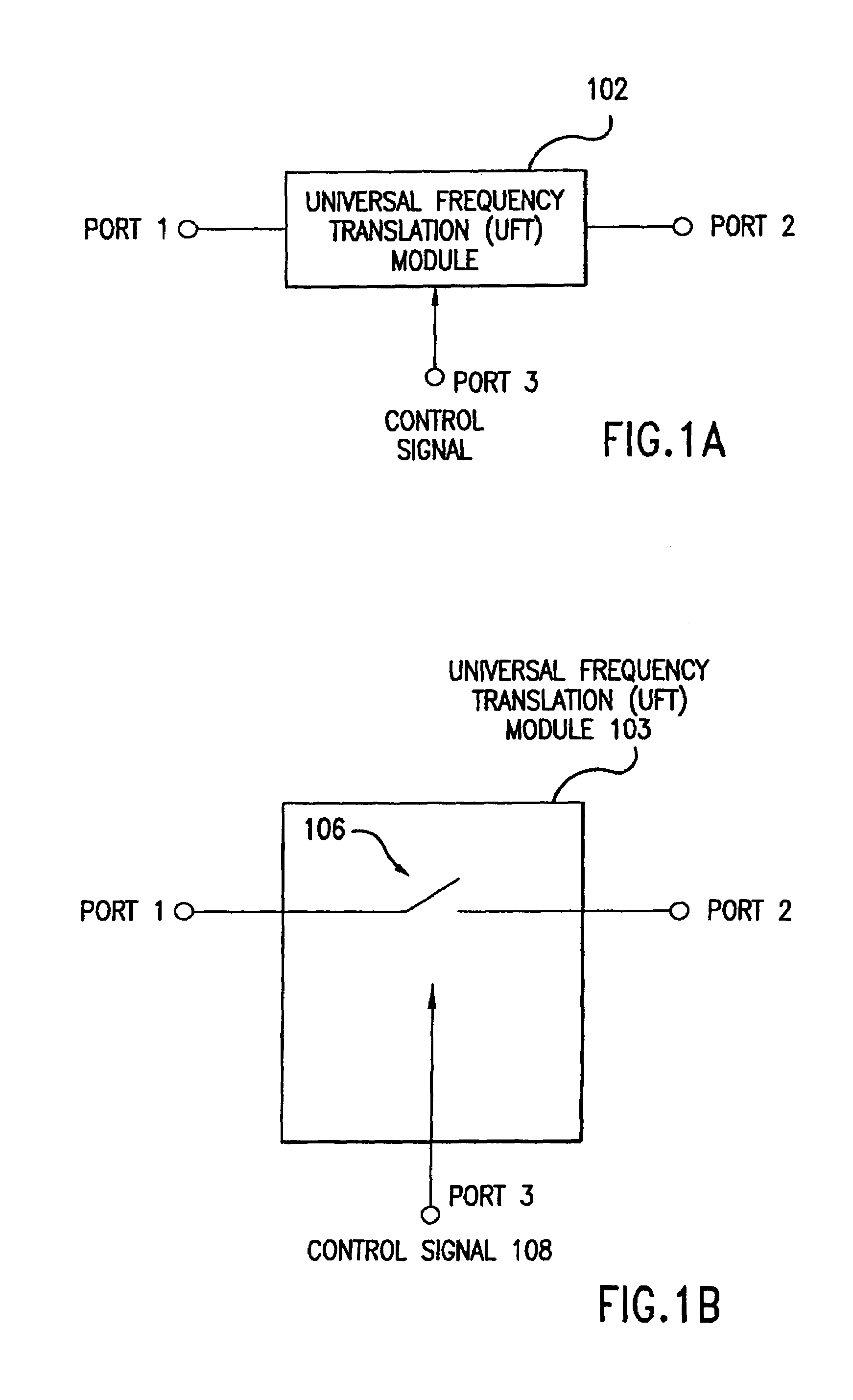
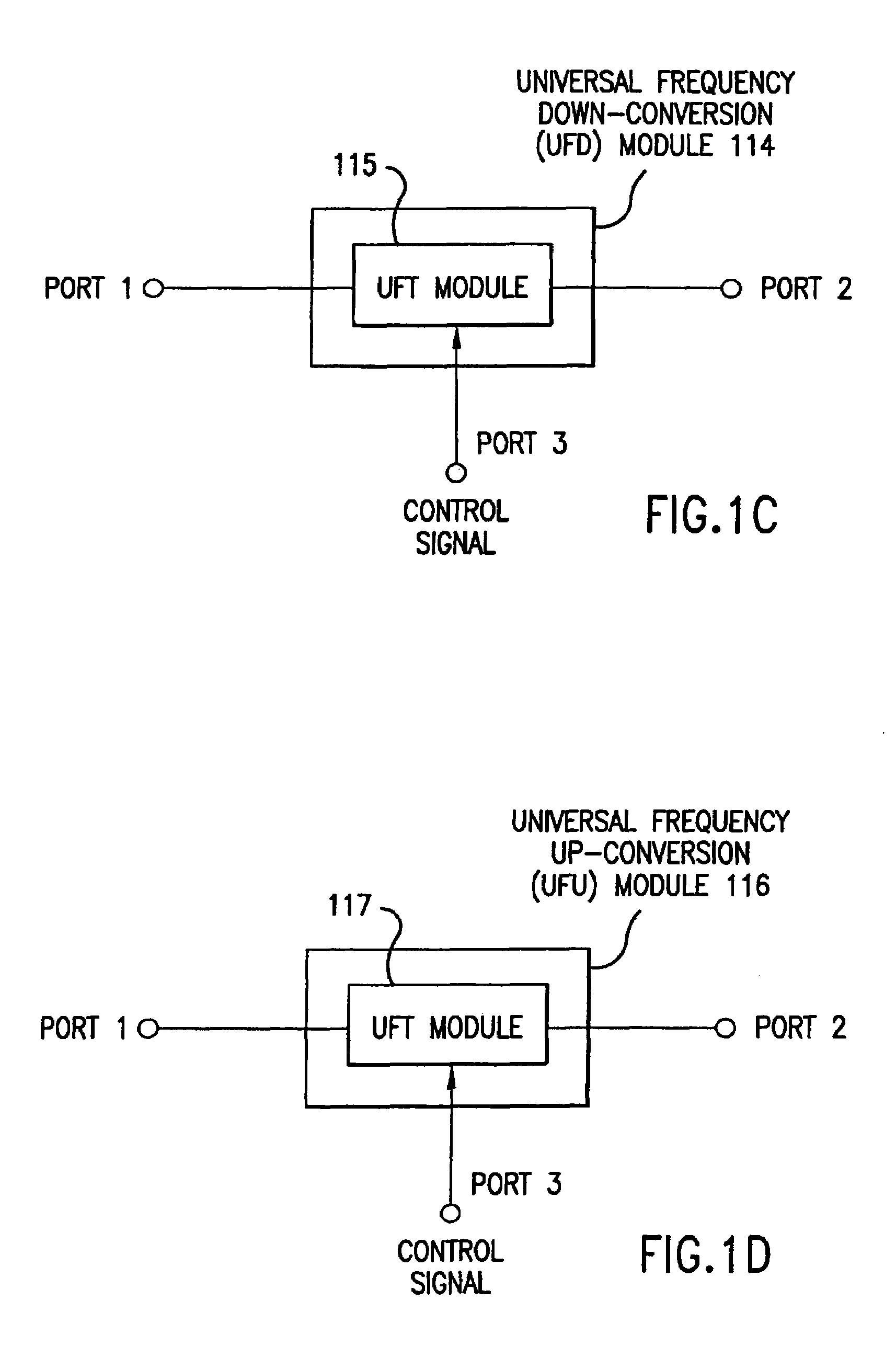
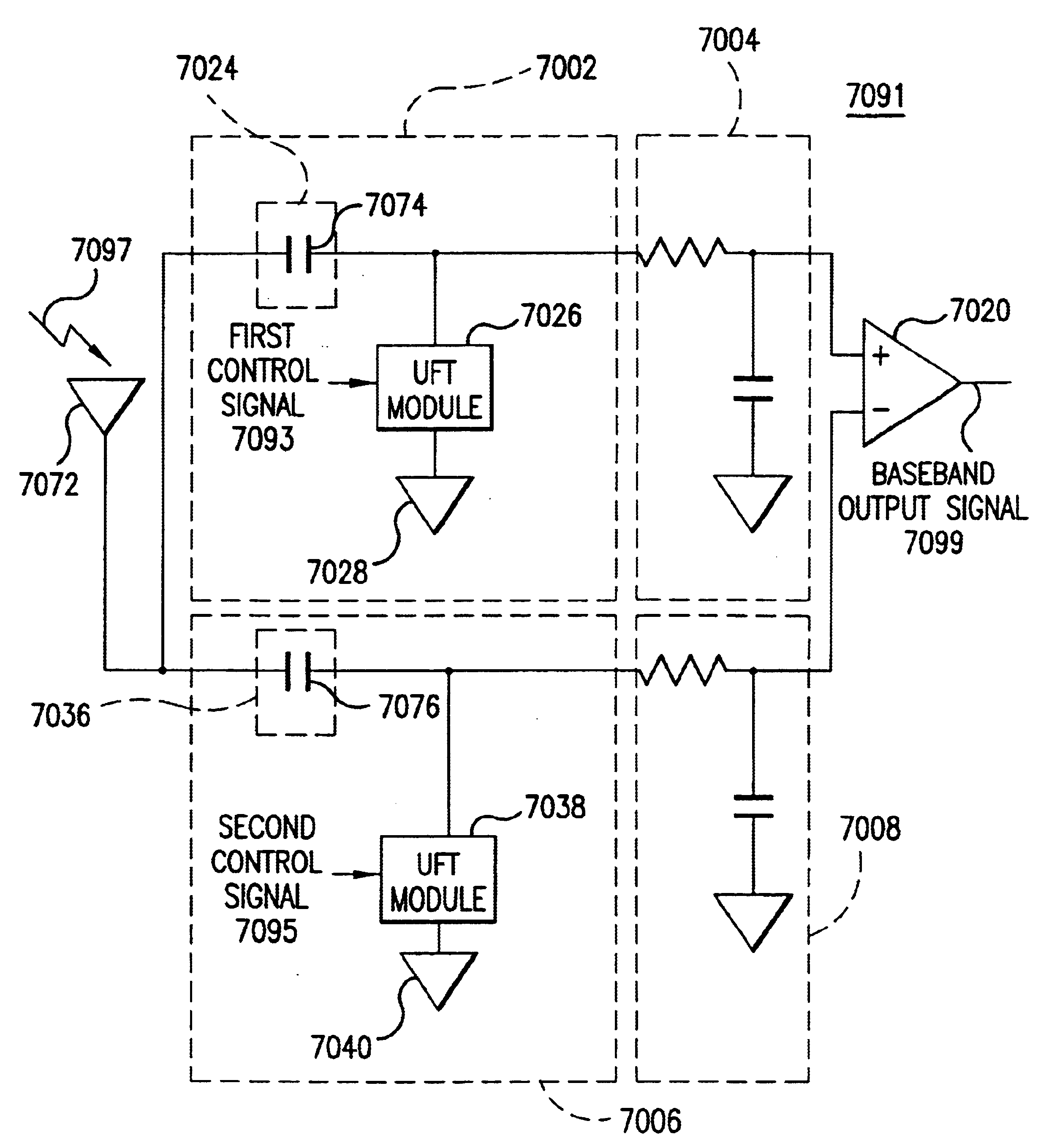
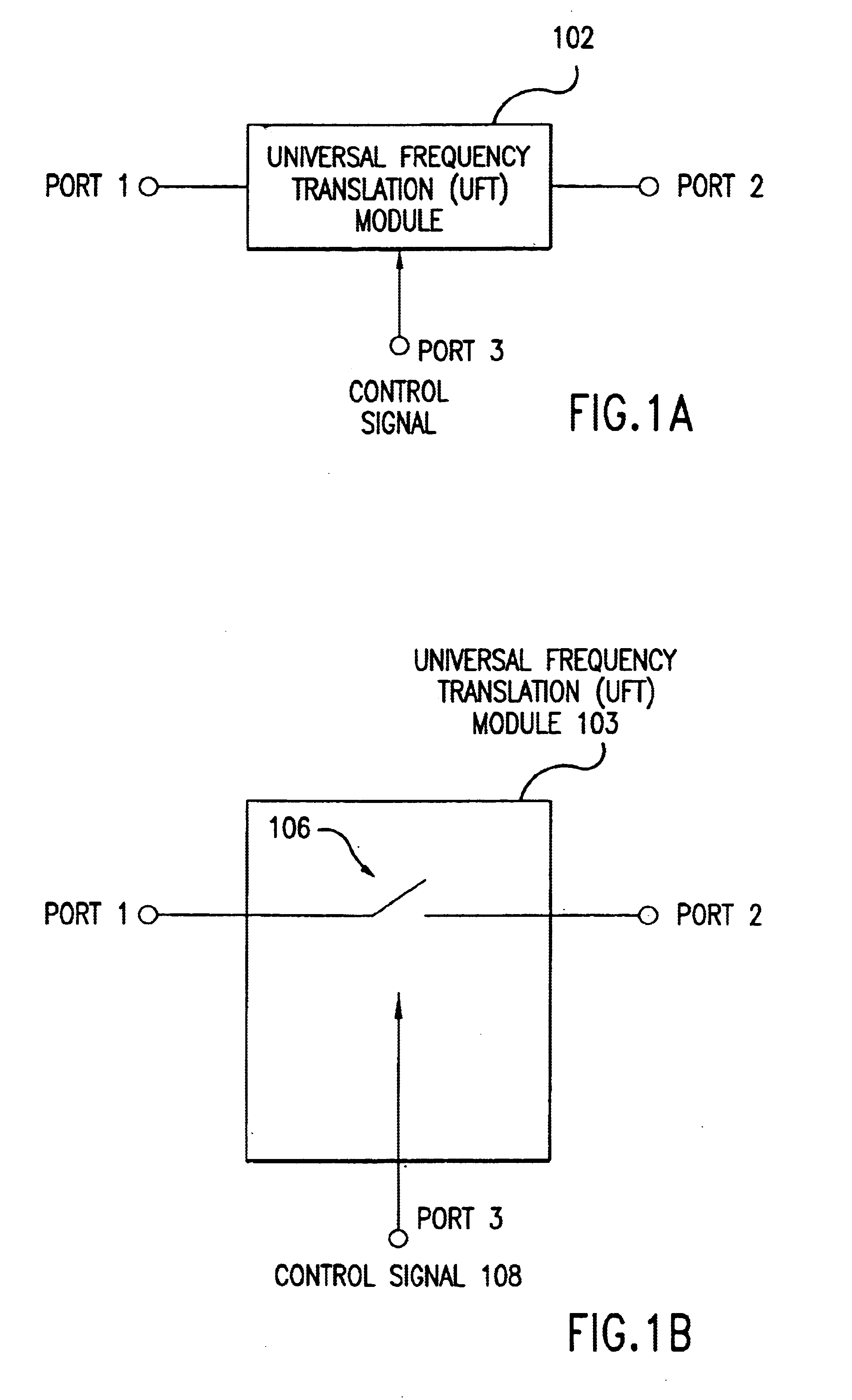
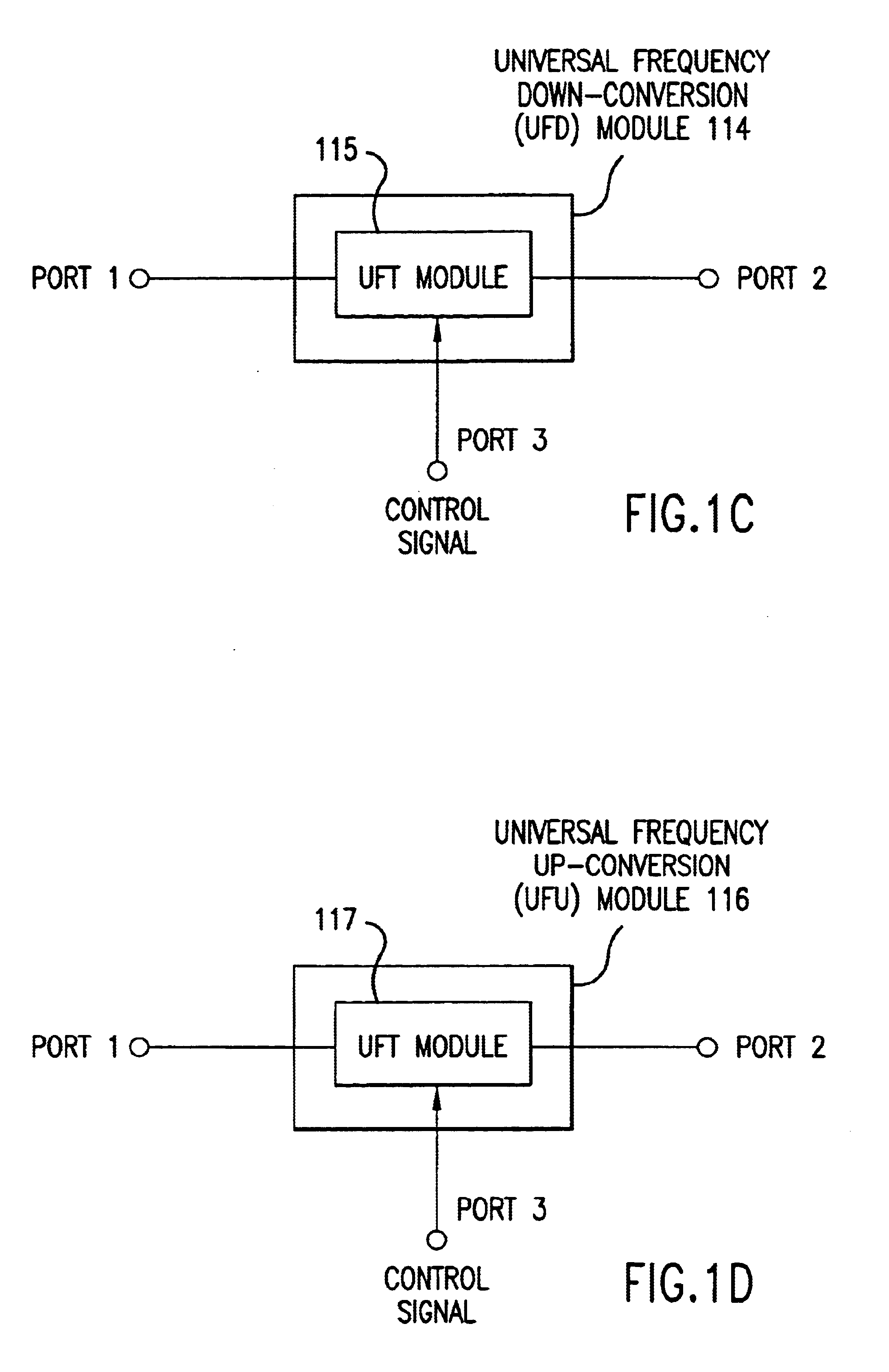
Wireless local area network (WLAN) using universal frequency translation technology including multi-phase embodiments and circuit implementations
InactiveUS20050123025A1Reduce and eliminate re-radiationReduce carrier insertionResonant long antennasNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumModem device
Frequency translation and applications of the same are described herein, including RF modem and wireless local area network (WLAN) applications. In embodiments, the WLAN invention includes an antenna, an LNA / PA module, a receiver, a transmitter, a control signal generator, a demodulation / modulation facilitation module, and a MAC interface. The WLAN receiver includes at least one universal frequency translation module that frequency down-converts a received EM signal. In embodiments, the UFT based receiver is configured in a multi-phase embodiment to reduce or eliminate re-radiation that is caused by DC offset. The WLAN transmitter includes at least one universal frequency translation module that frequency up-converts a baseband signal in preparation for transmission over the wireless LAN. In embodiments, the UFT based transmitter is configured in a differential and multi-phase embodiment to reduce carrier insertion and spectral growth.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Method for allocating multiple radio communication periods
ActiveUS20100135256A1Interference minimizationReliable communicationAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexWi-FiBluetooth
A method for allocating multiple radio communication periods to an MS supporting co-existence mode is disclosed. The method includes transmitting a co-existence mode request message to a BS by the MS, receiving information about the position of a start frame for the co-existence mode by a co-existence mode response message as a response to the co-existence mode request message from the BS by the MS, and receiving information about an allocated Wi-Fi beacon reception period by an unsolicited co-existence mode response message in the start frame from the BS by the MS. A frame allocation pattern for allocating periods for communications with a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi system using a frequency band adjacent to that of an IEEE 802.16m system can be provided according to an IEEE 802.16m frame structure, and an MS with multiple radio interfaces can communicate with each system reliably, while minimizing interference between systems.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
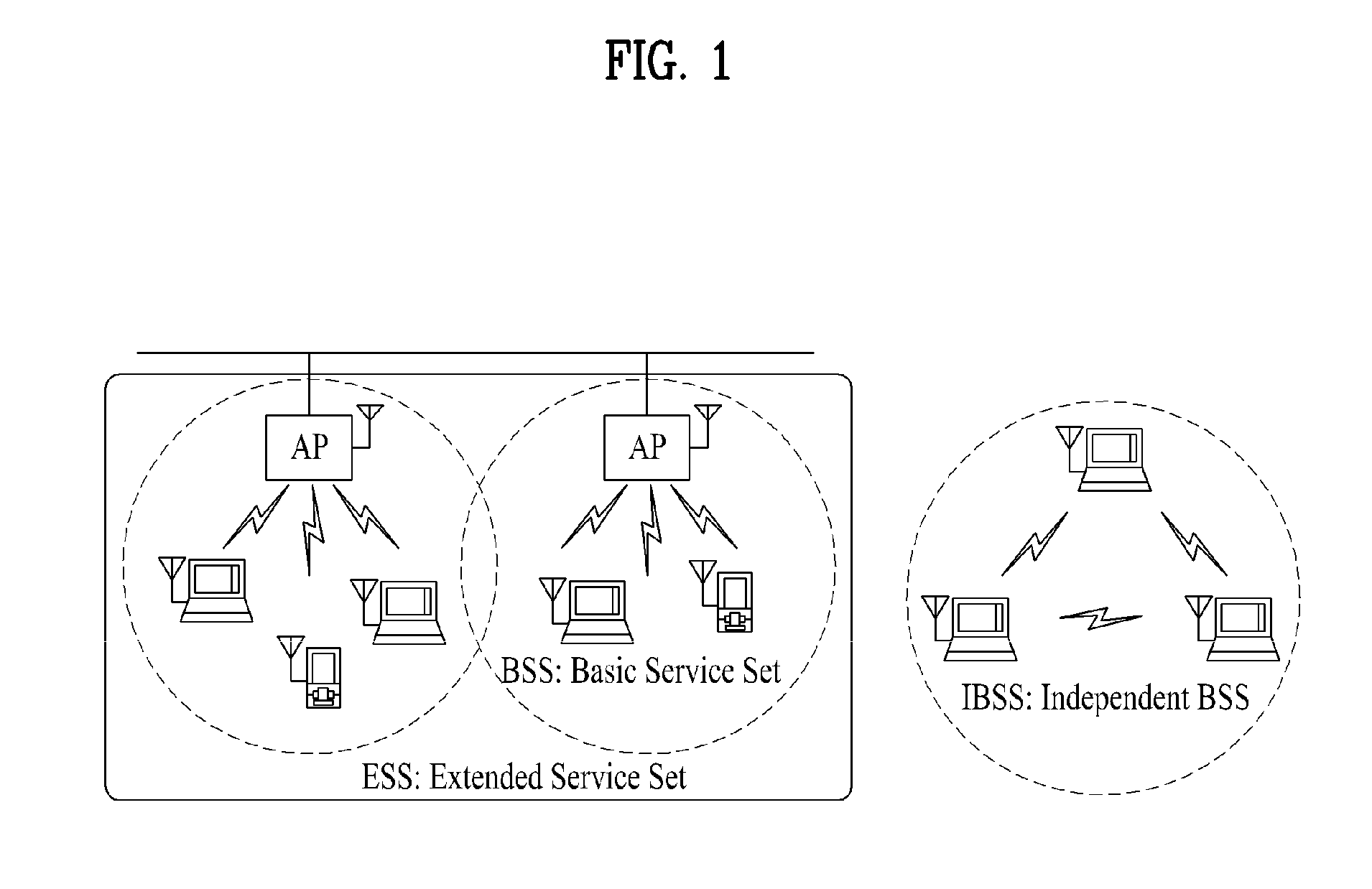
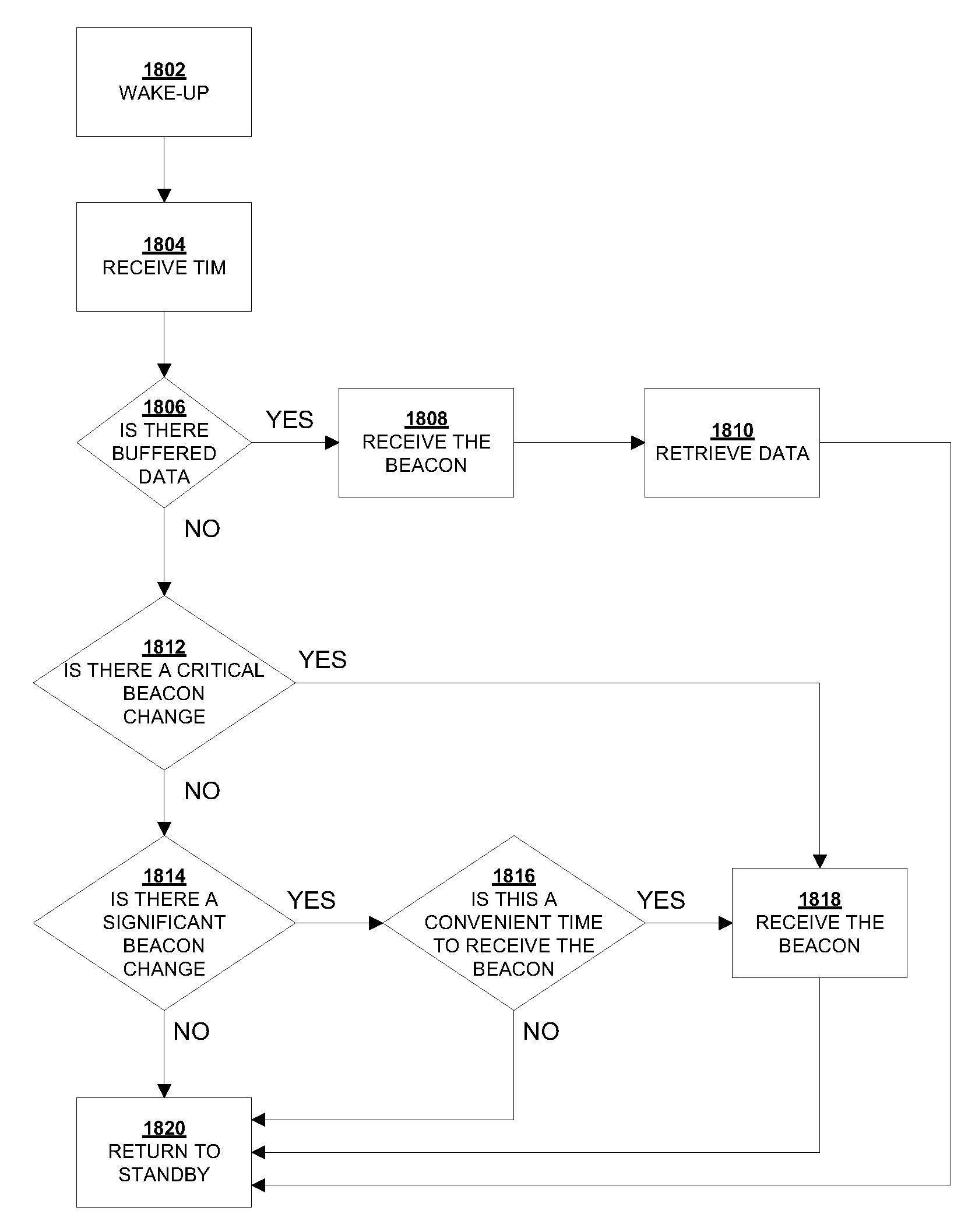
Systems and Methods for Indicating Buffered Data at an Access Point Using an Embedded Traffic Indication Map
ActiveUS20090010191A1Efficiently receiveIncreased timePower managementTransmission systemsTraffic volumeTraffic capacity
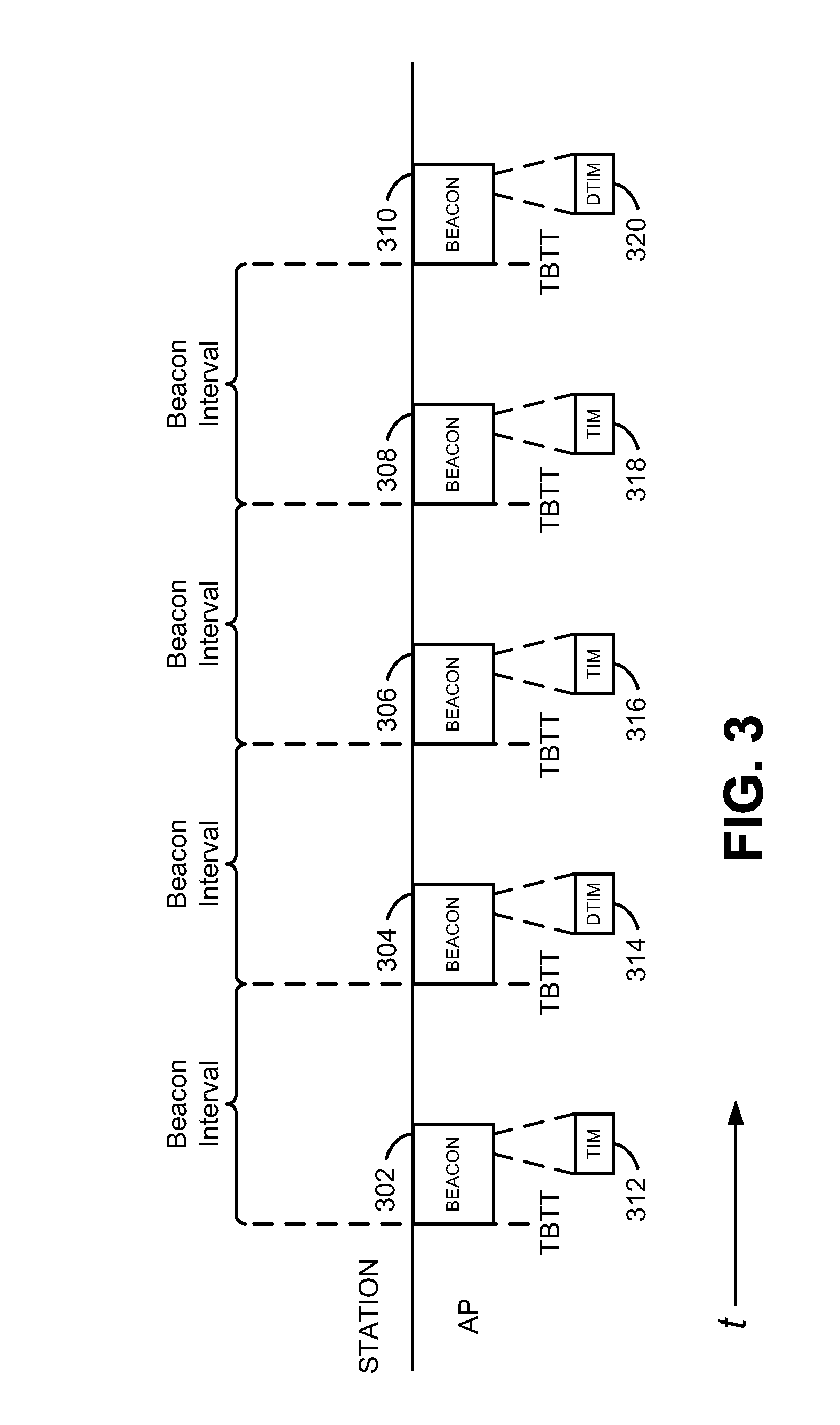
Stations in standby mode periodically wake up to check for buffered data at the access points. Traditionally, the information is available by checking the periodic beacon frame for a traffic indication map (TIM). Unfortunately, the length of beacons has steadily increased with the progression of the various wireless standards requiring stations to wake up for longer periods to merely check for buffered data. Several approaches are disclosed which address this shortcoming, including the broadcast of TIM frames, the partial reception of beacon frames and the use of an embedded TIM frame within a beacon frame.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Transceiver with closed loop control of antenna tuning and power level
InactiveUS6978126B1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient receptionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsDetector circuitsTransceiver
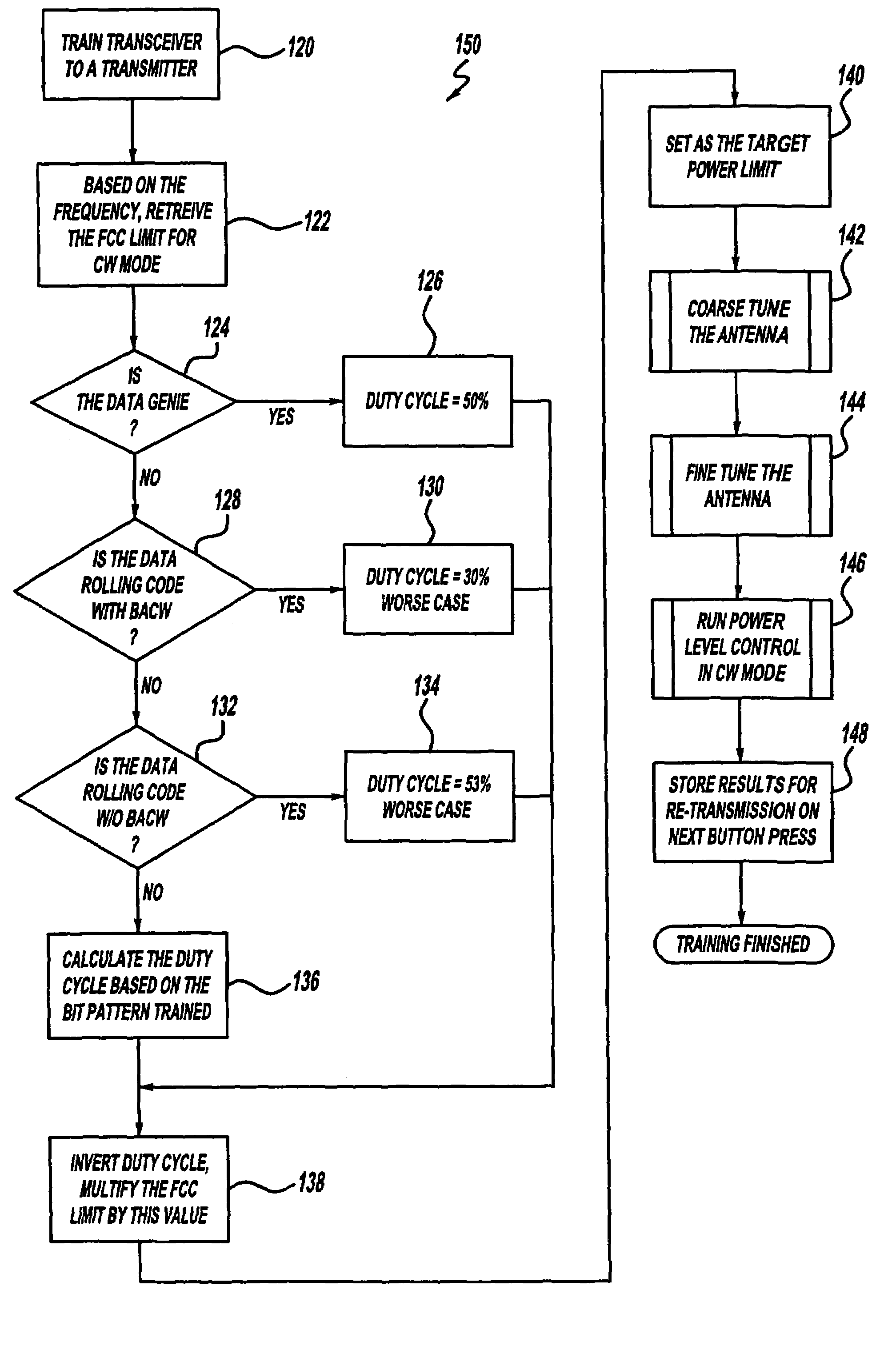
A trainable transceiver for learning and transmitting an activation signal that includes an RF carrier frequency modulated with a code for remotely actuating a device, such as a garage door opener. The trainable transceiver preferably includes a controller, a signal generator, and a dynamically tunable antenna having a variable impedance that may be selectively controlled in accordance with a detector circuit signal. The detector circuit provides a measurement of the transmission power and is also used to vary the applied transmission power of the transceiver in response to operating and environmental parameters.
Owner:GENTEX CORP +1
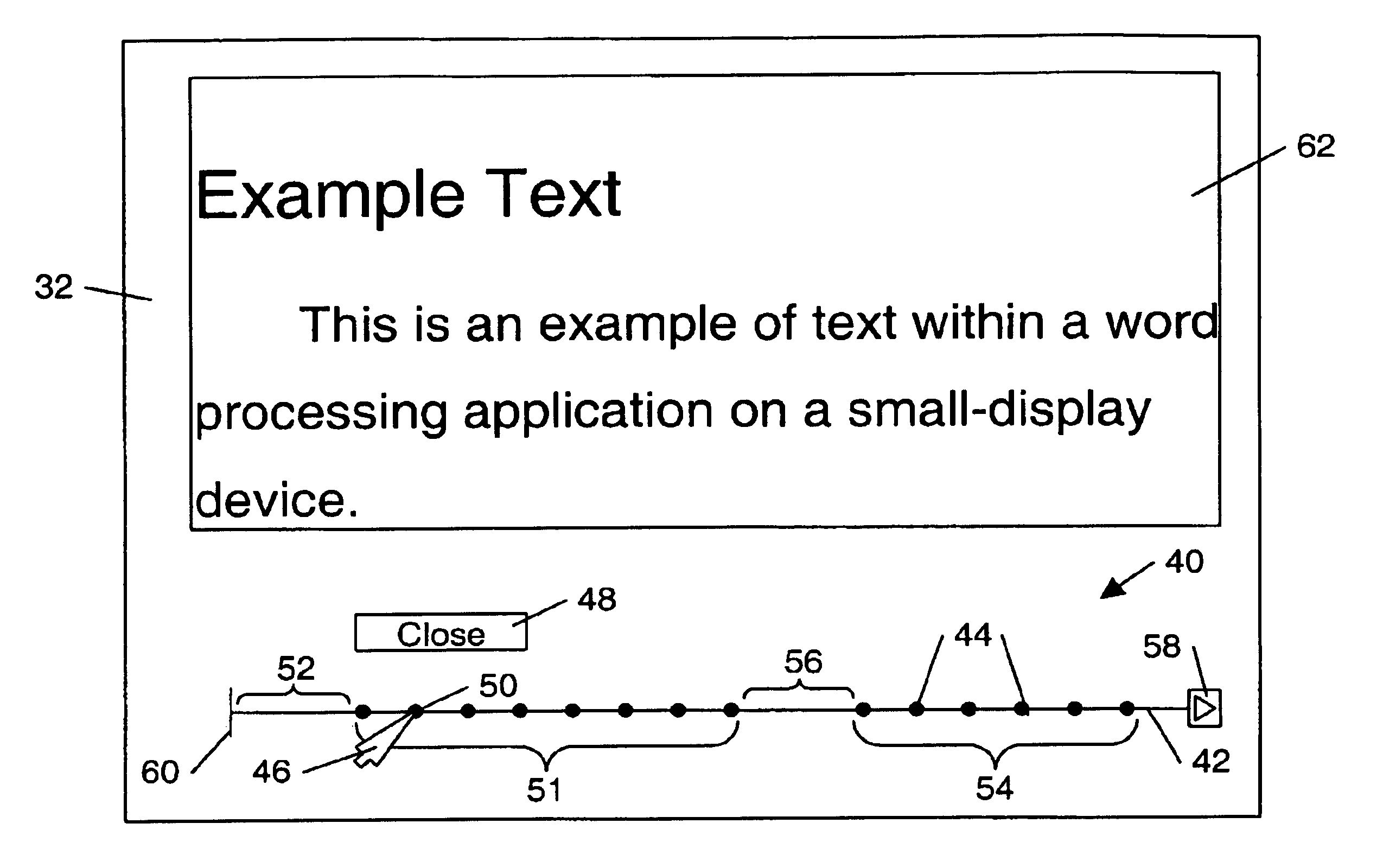
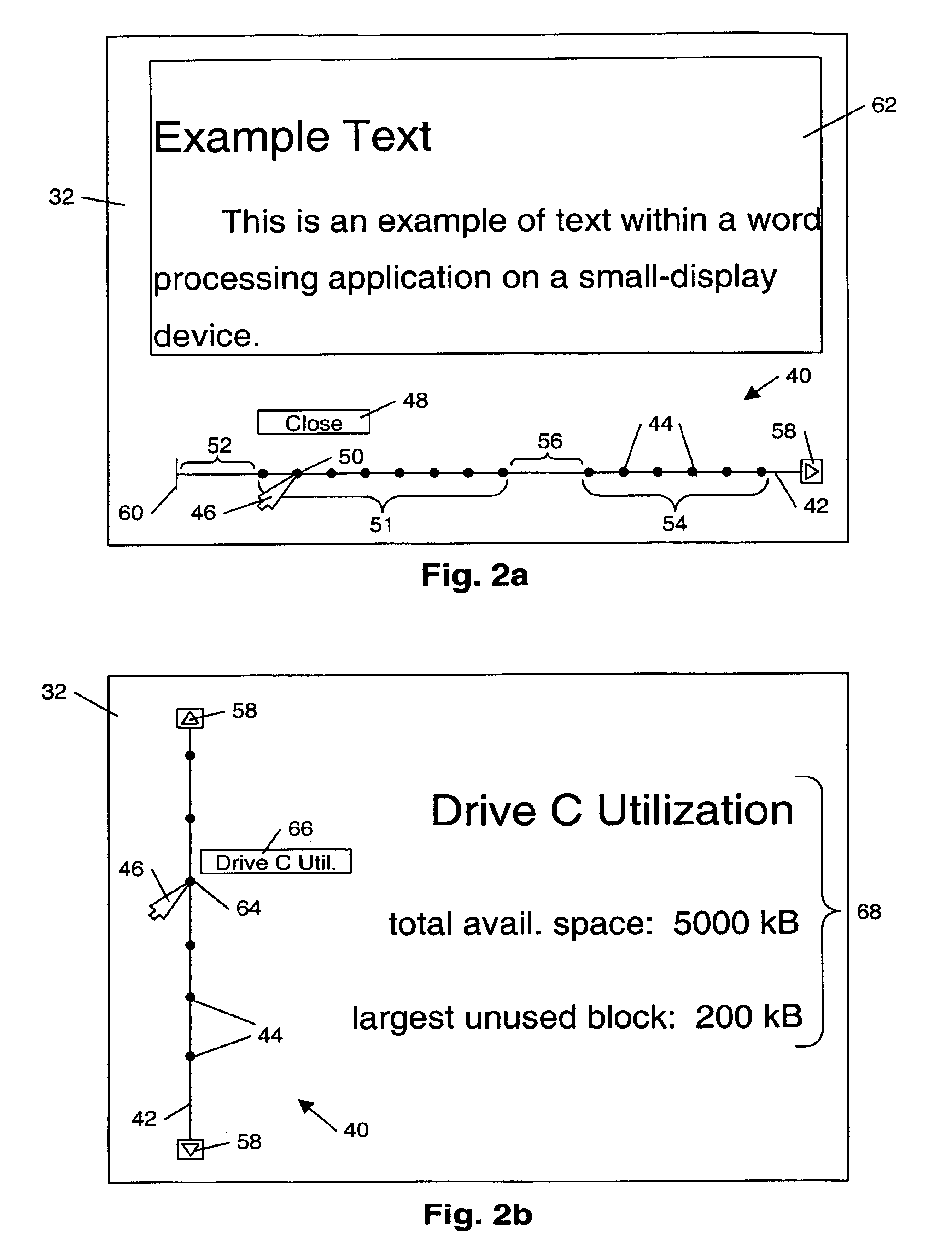
Arrangement of information into linear form for display on diverse display devices
InactiveUS6924797B1Make fastEasy accessDigital output to display deviceGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method of display with a graphical user interface includes arranging selectable navigation points along a line configured on a display screen. In some embodiments, the selectable points correspond to pieces of information to be displayed, such that selection of a selectable point causes the corresponding piece of information to be displayed. The selectable points may be arranged along the line according to a priority sequence of the corresponding pieces of information. In other embodiments, the selectable points correspond to functions useful in using an application program. Selection of a selectable point in this embodiment causes the corresponding function to be executed. The line with selectable navigation points may therefore be used in place of other display tools such as toolbars or pull-down menus, and may allow rapid selection of desired options, commands, or information while using a minimum amount of screen space.
Owner:IBM CORP
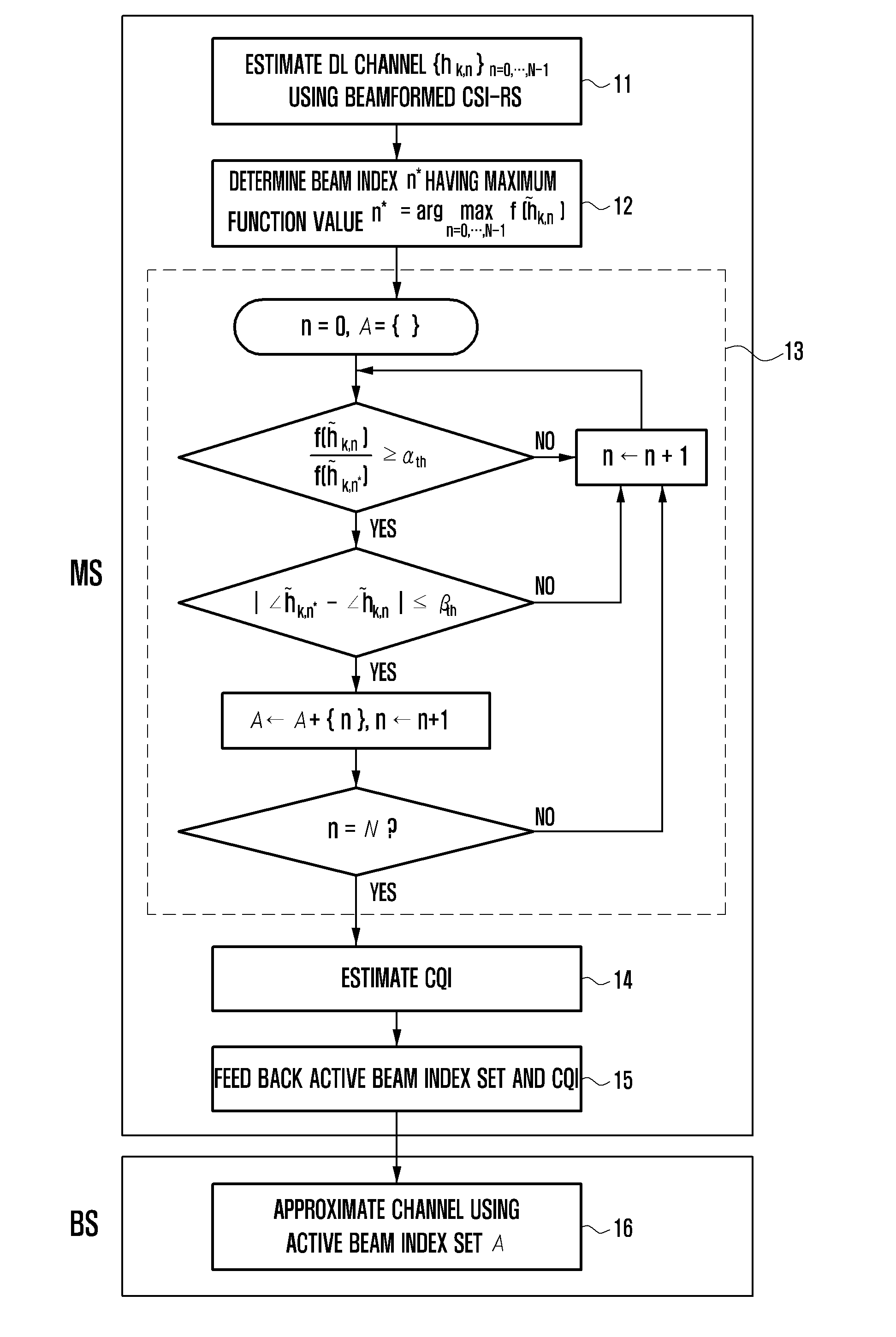
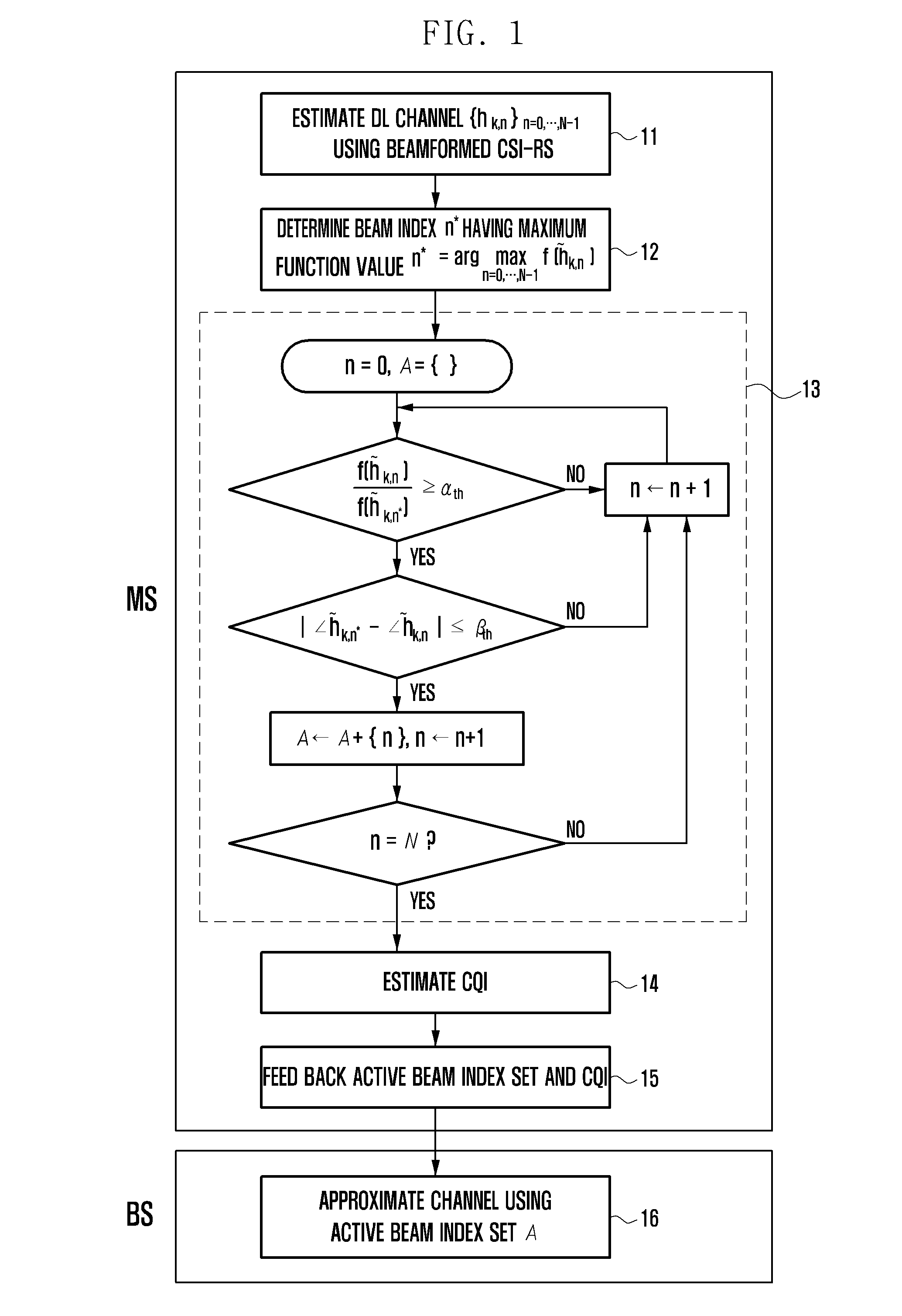
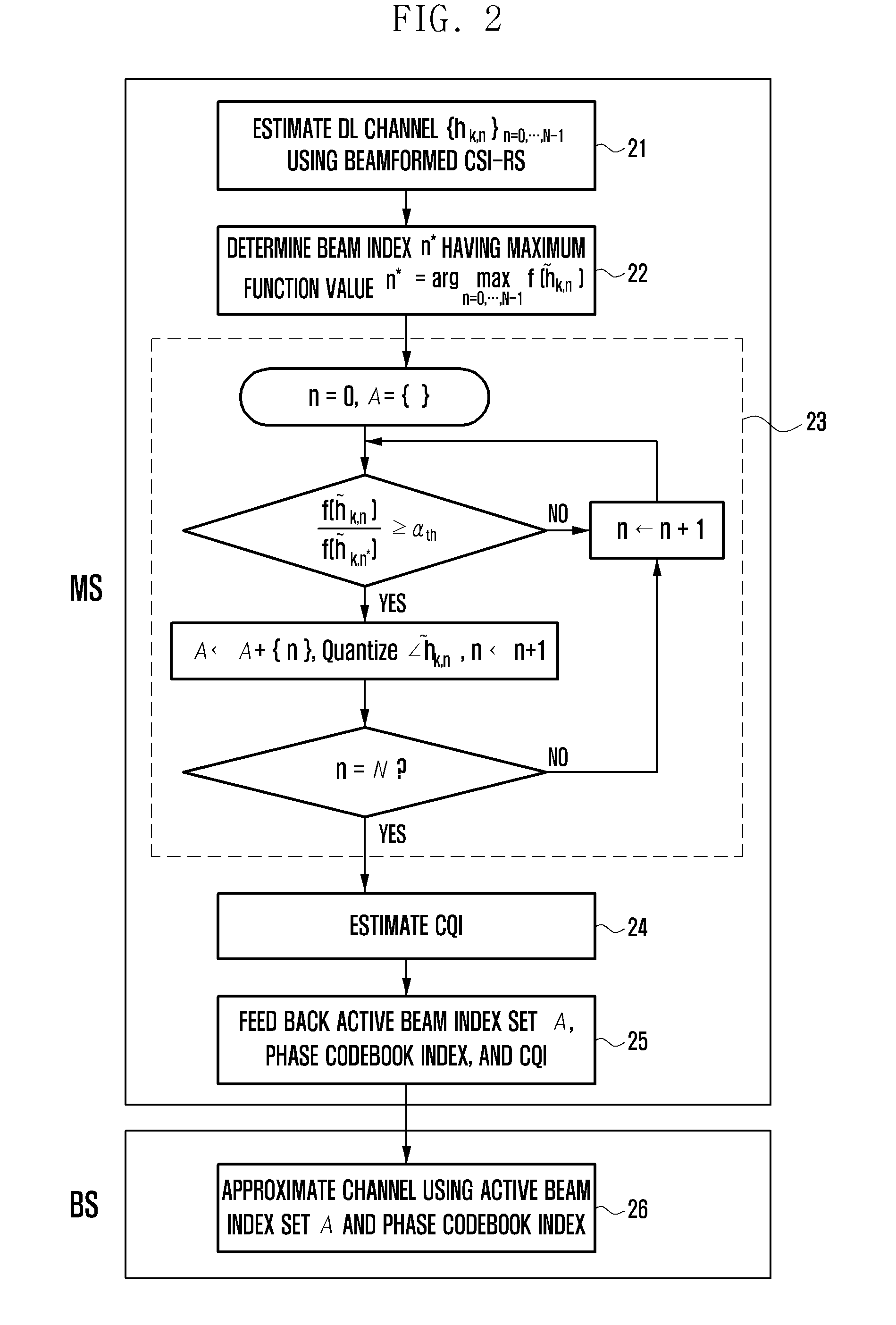
Channel state information feedback apparatus and method in wireless communication system operating in fdd mode
ActiveUS20130163457A1Efficient receptionFeedback information efficientlyError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemMobile station
A Channel State Information (CSI) feedback method and apparatus is provided for transmitting, at a base station, the CSIs for plural transmit antennas with a limited amount resource and receiving, at a mobile station, the CSIs efficiently in a massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) system operating in the Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
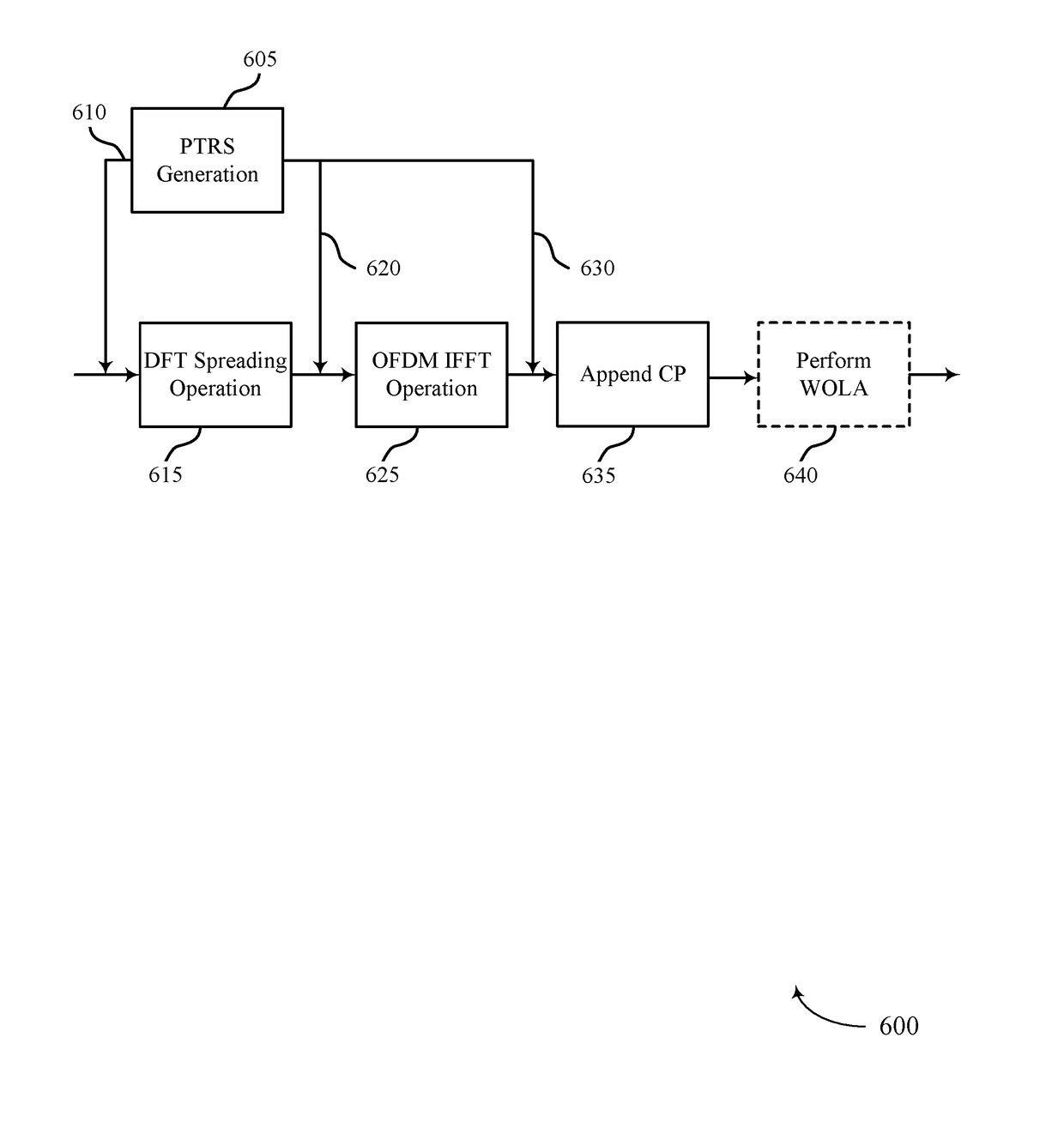
Enhancements to phase-noise compensation reference signal design and scrambling
ActiveUS20180091350A1Efficient receptionIncrease flexibilityNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionTime domainPhase noise
Methods, systems, and devices for wireless communication are described. In one example, phase-noise compensation tracking signals (PTRS) may be transmitted using sets of resource blocks (RBs), where a frequency for each PTRS within the sets RBs is different from a frequency corresponding to a direct current (DC) tone. In another example, a time-domain-based PTRS may be used, where a discrete Fourier transform (DFT)-spread-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (DFT-s-OFDM) symbol may include a cyclic prefix and a PTRS inserted in the DFT-s-OFDM symbol. Additionally or alternatively, a guard-interval-based DFT-s-OFDM symbol may include a PTRS that replaces part or all of a guard interval. In some examples, subsets of tones used for PTRS across a system bandwidth may be transmitted using a scrambled modulation symbol, where at least one antenna port may be used for the transmission of PTRS.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Apparatus and method for freezing the states of a receiver during silent line state operation of a network device
InactiveUS7327754B2Reduce the required powerAvoid data lossEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementMostly TrueLoop bandwidth
A method for maintaining the states of a receiver during the silent line state of a network device operating in a low power link suspend mode is presented. Accordingly, a method of freezing the states of the equalizer and keeping the receiver clock locked to a frequency that is approximately equal to that of the input data while providing for rapid adjustment to the phase and thus recovery of the input data is presented. During Silent Line State (SLS), the receiver states are frozen using methods that avoid parasitic decay. Also, the receive clock phase lock loop is locked onto the local transmit clock since the local transmit clock has a frequency approximating the incoming data frequency. During the SLS, the transmitter of the remote network device may have been turned off to conserve power therefore the receiver has no way of immediately knowing the phase of an incoming data. Thus, in order to prevent loss of data, the receiver loops of the receiving network device are trained to the frequency of the transmitting remote network device using periodic Link Suspend packets. Thus, in most cases, only the phase of the incoming signal need be acquired when data arrives. The phase may be quickly acquired using loop bandwidth shift methods whereby the receive clock phase lock loop bandwidth is increased to a value that aids rapid acquisition of the input clock and then, after acquisition, the bandwidth is shifted to a low value to enhance noise rejection during tracking.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Wireless local area network (WLAN) using universal frequency translation technology including multi-phase embodiments
InactiveUS7072390B1Reduce and eliminate re-radiationReduce carrier insertionInformation formatNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumModem device
Frequency translation and applications of the same are described herein, including RF modem and wireless local area network (WLAN) applications. In embodiments, the WLAN invention includes an antenna, an LNA / PA module, a receiver, a transmitter, a control signal generator, a demodulation / modulation facilitation module, and a MAC interface. The WLAN receiver includes at least one universal frequency translation module that frequency down-converts a received EM signal. In embodiments, the UFT based receiver is configured in a multi-phase embodiment to reduce or eliminate re-radiation that is caused by DC offset. The WLAN transmitter includes at least one universal frequency translation module that frequency up-converts a baseband signal in preparation for transmission over the wireless LAN. In embodiments, the UFT based transmitter is configured in a differential and multi-phase embodiment to reduce carrier insertion and spectral growth.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
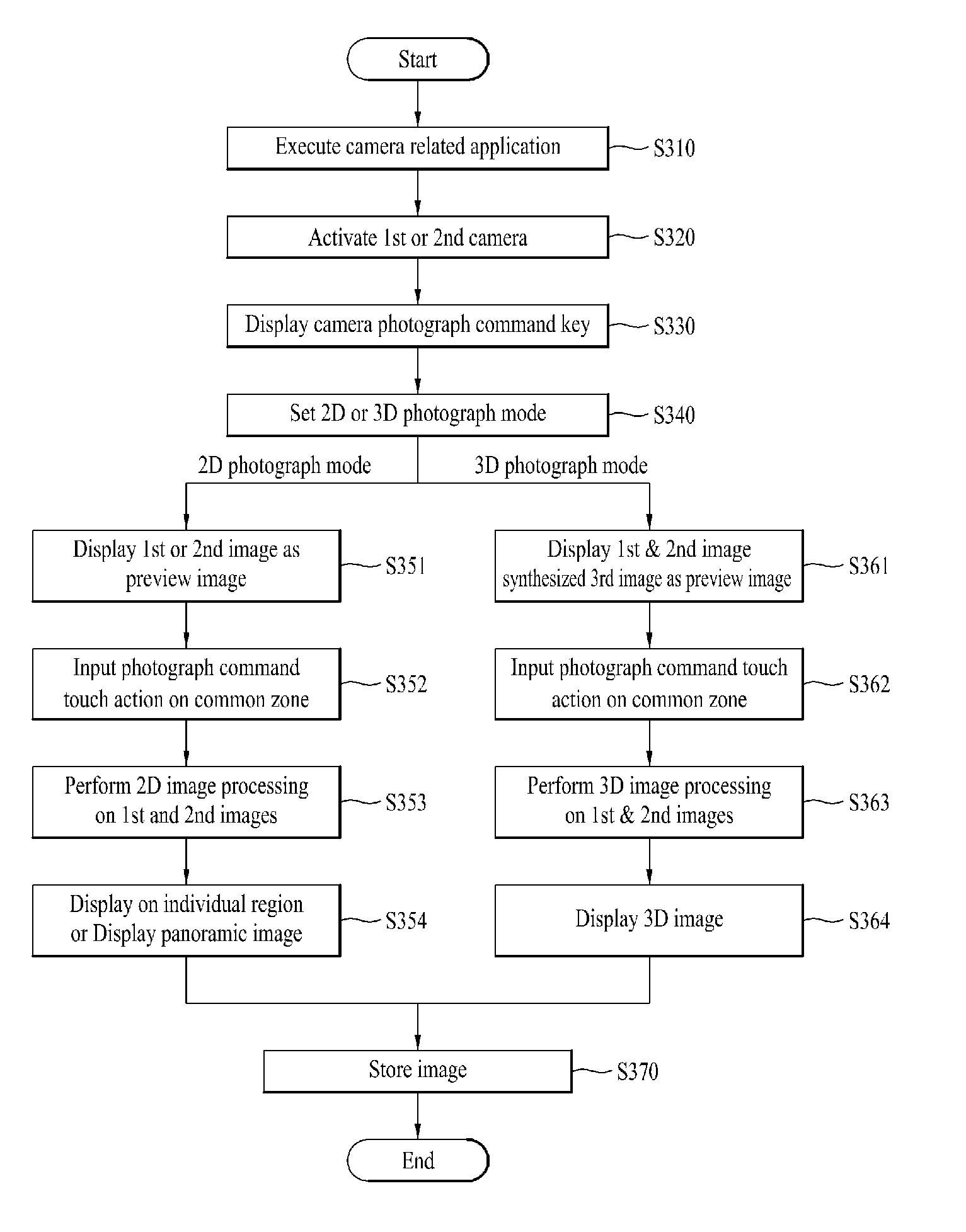
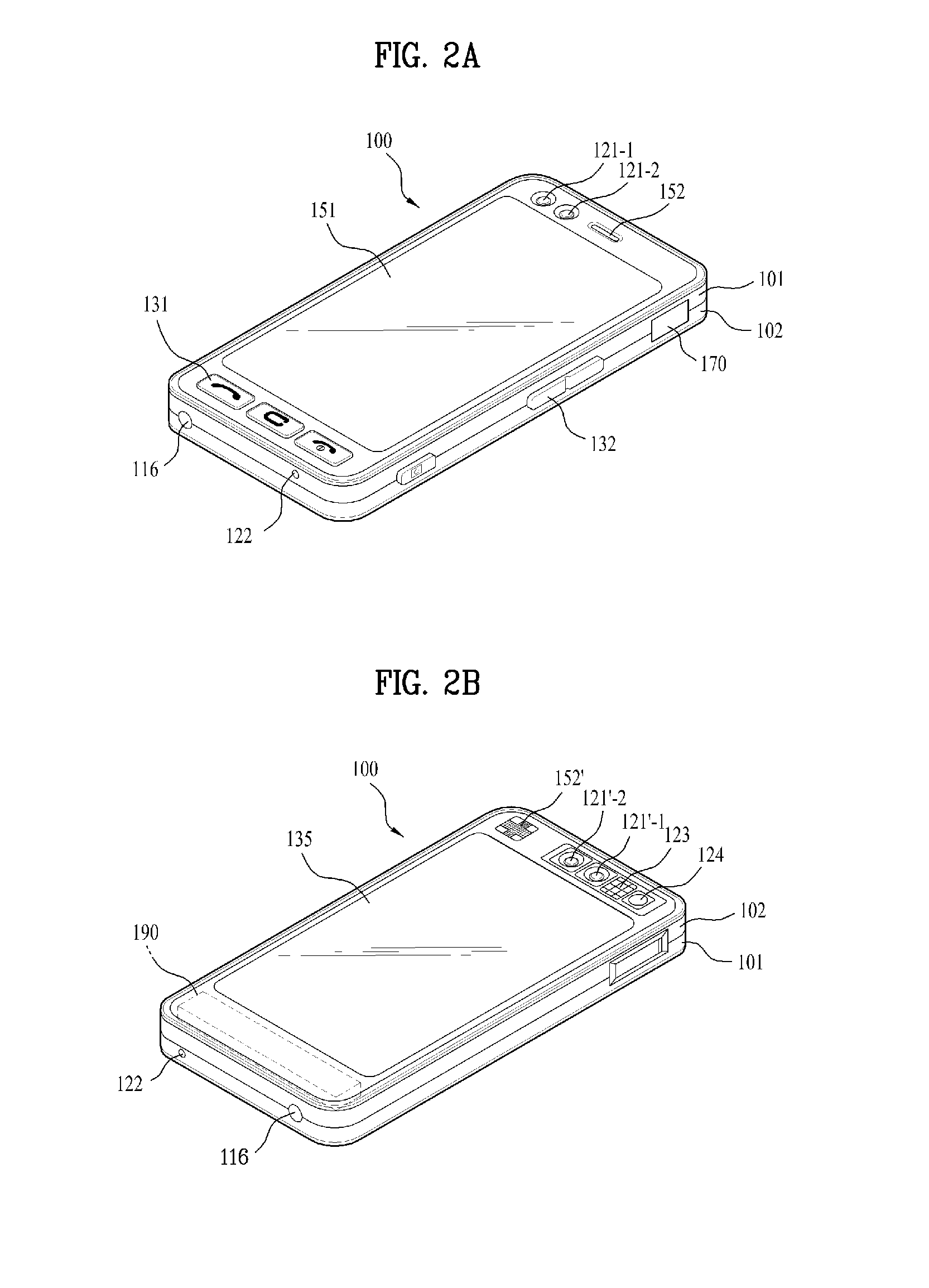
Mobile terminal and method of controlling an image photographing therein
InactiveUS20120113216A1Efficient inputEfficient receptionTelevision system detailsSubstation equipmentTouchscreen3d image processing
A mobile terminal including a first camera configured to receive an input of a first image; a second camera configured to receive an input of a second image; a touchscreen configured to display a photograph command key including a first zone, a second zone and a common zone; and a controller configured to set a photograph mode selected from a 3D photograph mode and a 2D photograph mode, to control the first and second cameras to respectively capture the first and second images upon receiving a photograph command touch action on the common zone, and to perform either a 3D image processing or a 2D image processing on the photographed first and second images according to the set photograph mode.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
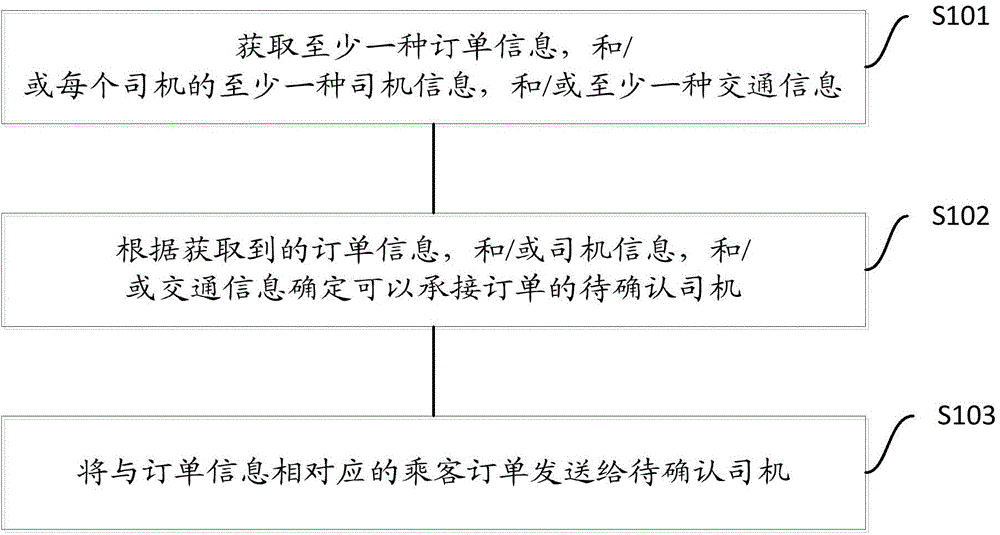
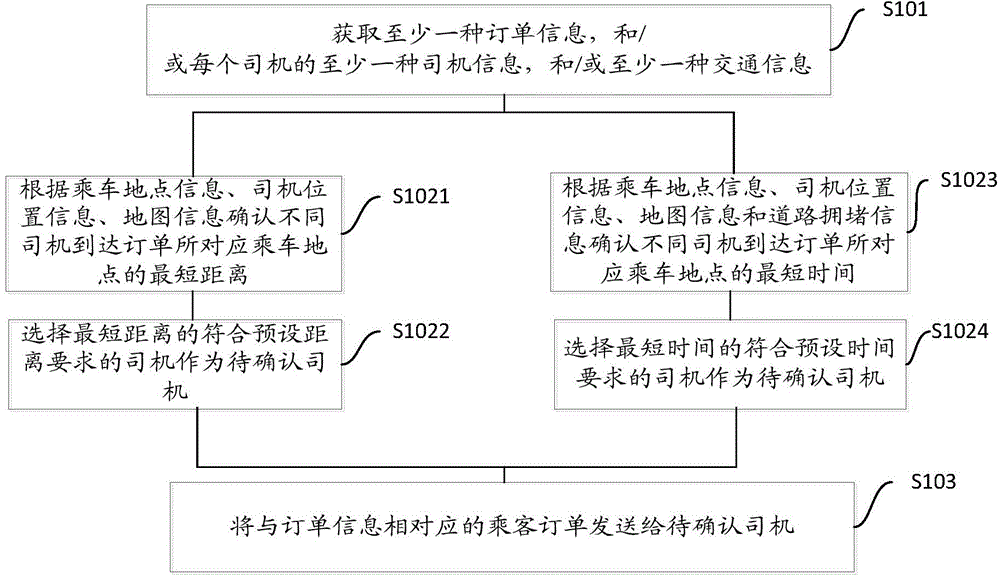
Order pushing method and order confirmation method for network taxi taking
InactiveCN104463509AReduce wasteEfficient receptionResourcesCommerceResource informationThe Internet
The invention provides an order pushing method and an order confirmation method for network taxi taking and particularly relates to the internet field. According to the order pushing method for network taxi taking, various kinds of resource information are comprehensively matched; compared with the situation that orders are sent to all drivers within a certain range regardless of order conditions, driver conditions and road conditions and consequently system resources are wasted in the prior art, various kinds of resource information such as order information, driver information and traffic information are obtained in advance, specific contents in the three kinds of the information are matched and calculated, a driver who possibly can receive an order is confirmed within a certain range to serve as a driver to be confirmed, the order sent by a passenger is sent to the driver to be confirmed so that order pushing can be finished, it is guaranteed that the order of the passenger can be effectively received, and meanwhile system resource waste caused by invalid passenger order pushing to a system is reduced.
Owner:XIANFENG ZHIDAO BEIJING TECH CO LTD
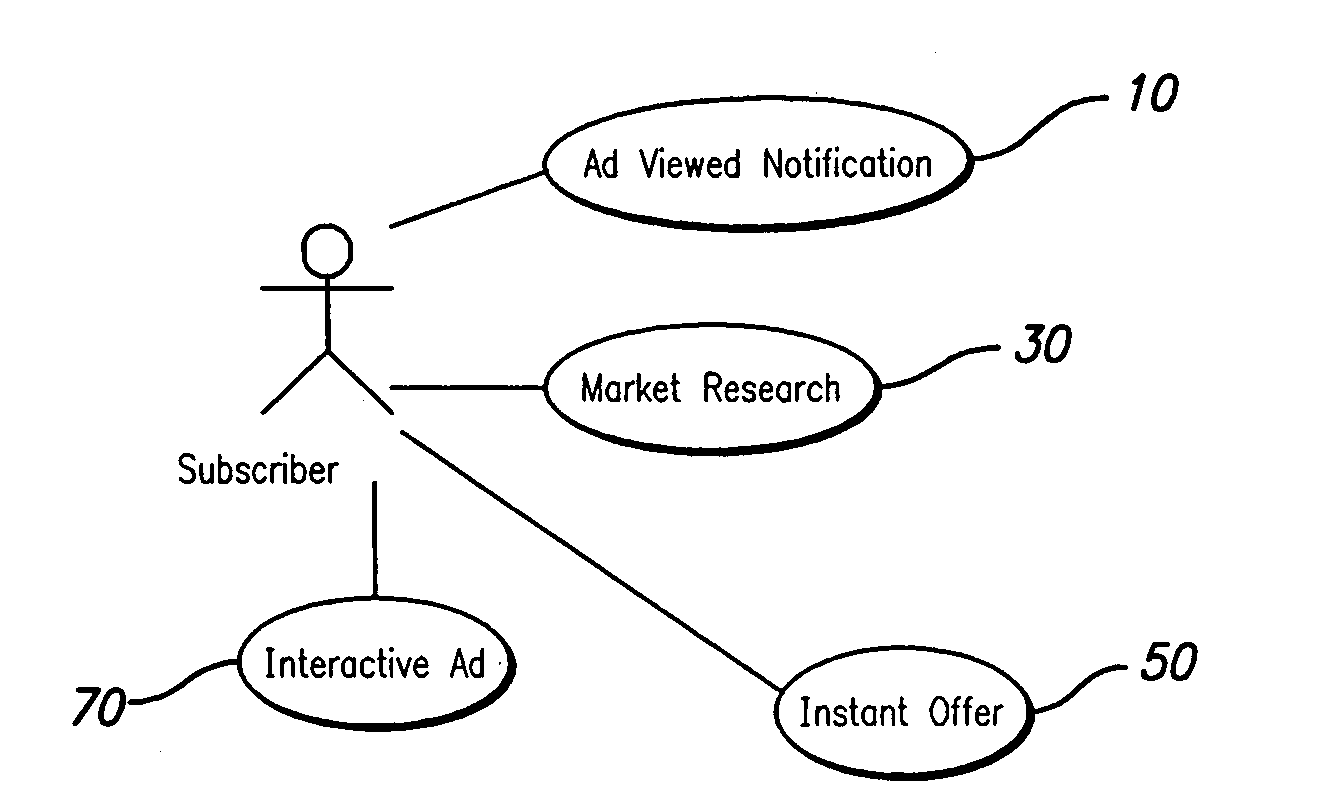
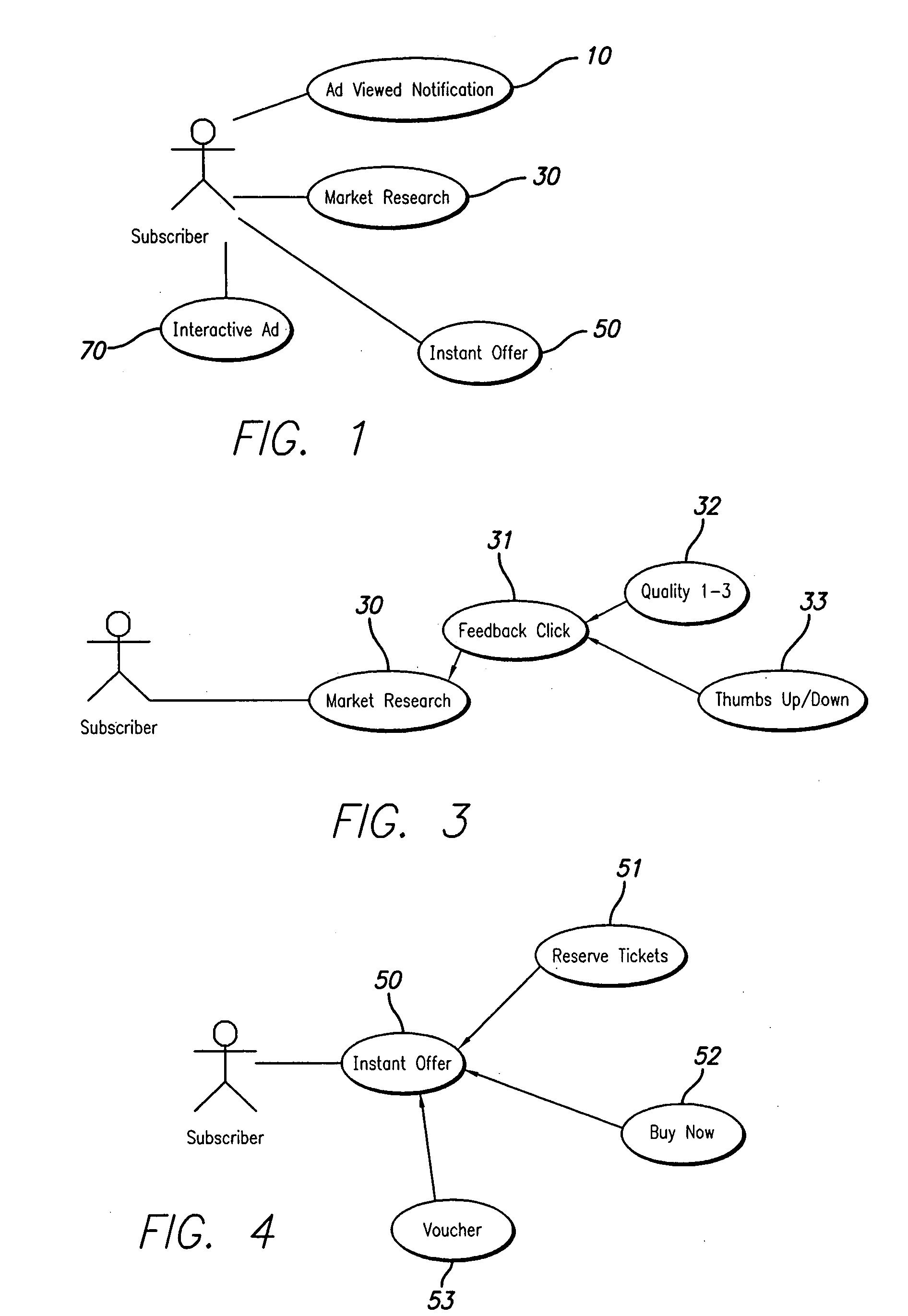
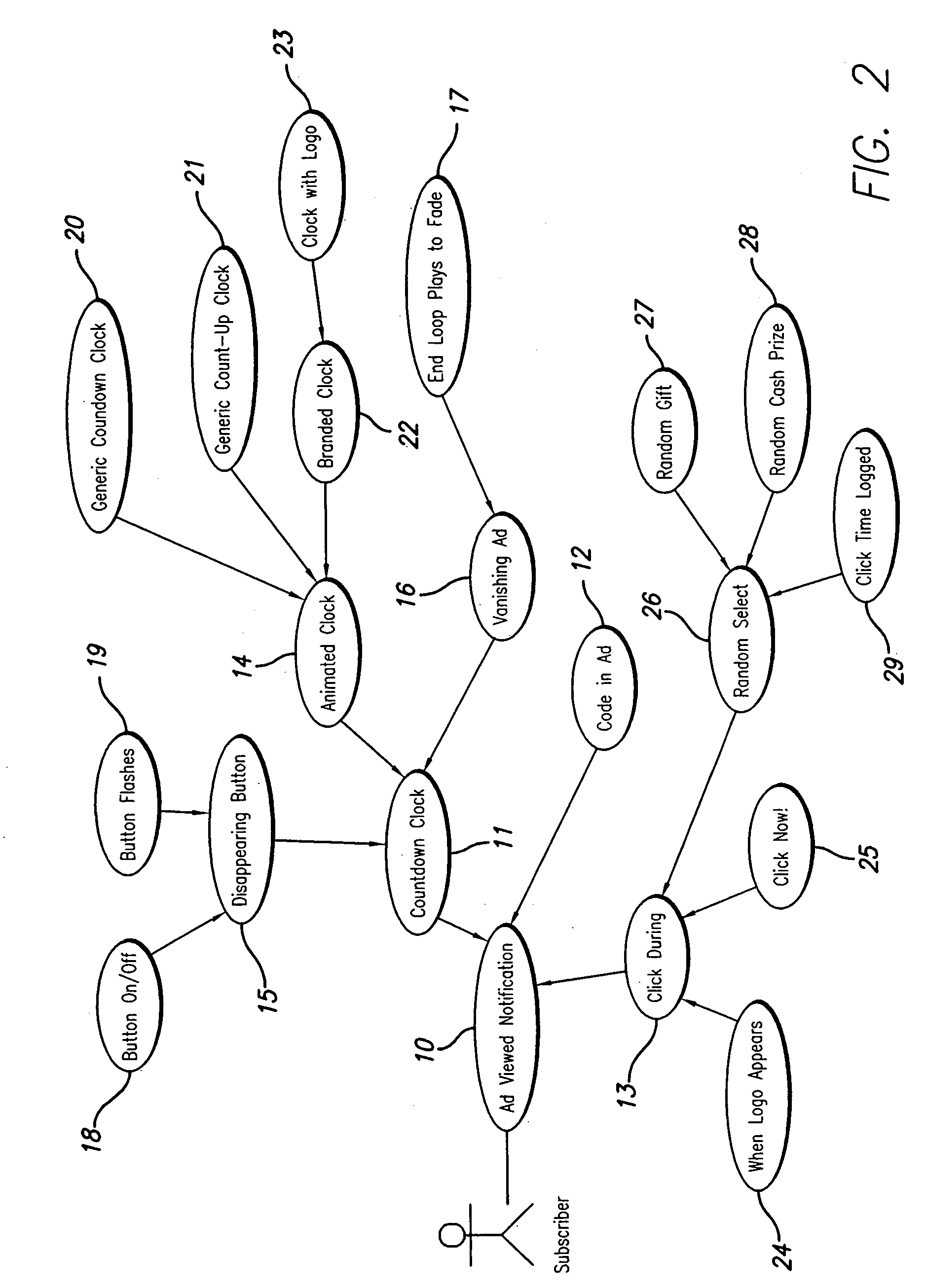
System and method for advertising
The present invention is directed to method and system for presenting advertisement messages, marketing surveys, invitation to instant offers, interactive media, or electronic voucher to a user of a remote communication device, such as a cellular telephone or a television set top box. In accordance with the preferred embodiments of the present invention, executable multimedia files are transmitted to one or more remote devices (e.g., a mobile phone), which is caused to execute the multimedia files either upon receiving the file or at a later time. Upon execution of the multimedia file, a user is prompted to interact with the remote device (e.g., by pressing one ore more buttons on a phone), preferably within a specified time period. Upon receiving input signals from the user, a notification signal is generated and transmitted by the remote device.
Owner:BLOWFISH WORKS
Wireless local area network (WLAN) using universal frequency translation technology including multi-phase embodiments and circuit implementations
InactiveUS7110444B1Reduce carrier insertion and spectral growthReduce and eliminate re-radiationModulation transferenceNetwork topologiesModem deviceFrequency spectrum
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Money transfer systems and methods for travelers
InactiveUS7104440B2Easy transferEfficient receptionComplete banking machinesFinanceComputerized systemRemote computer
One method involves payment of money to a recipient traveling to one or more foreign countries by entering into a remote computer money transfer information from a sender. The money transfer information comprises recipient identification information, at least one country where the money is to be received, and a payment amount in an originating currency. The money transfer information is transmitted to a host computer system. When ready to receive payment in the designated country, recipient identification information along with a request to withdraw a portion of a possible payment amount is entered into a payout computer. The recipient identification information and the request to withdraw is transmitted to a host computer system, and the requested withdrawal is provided to the recipient in the local currency.
Owner:THE WESTERN UNION CO
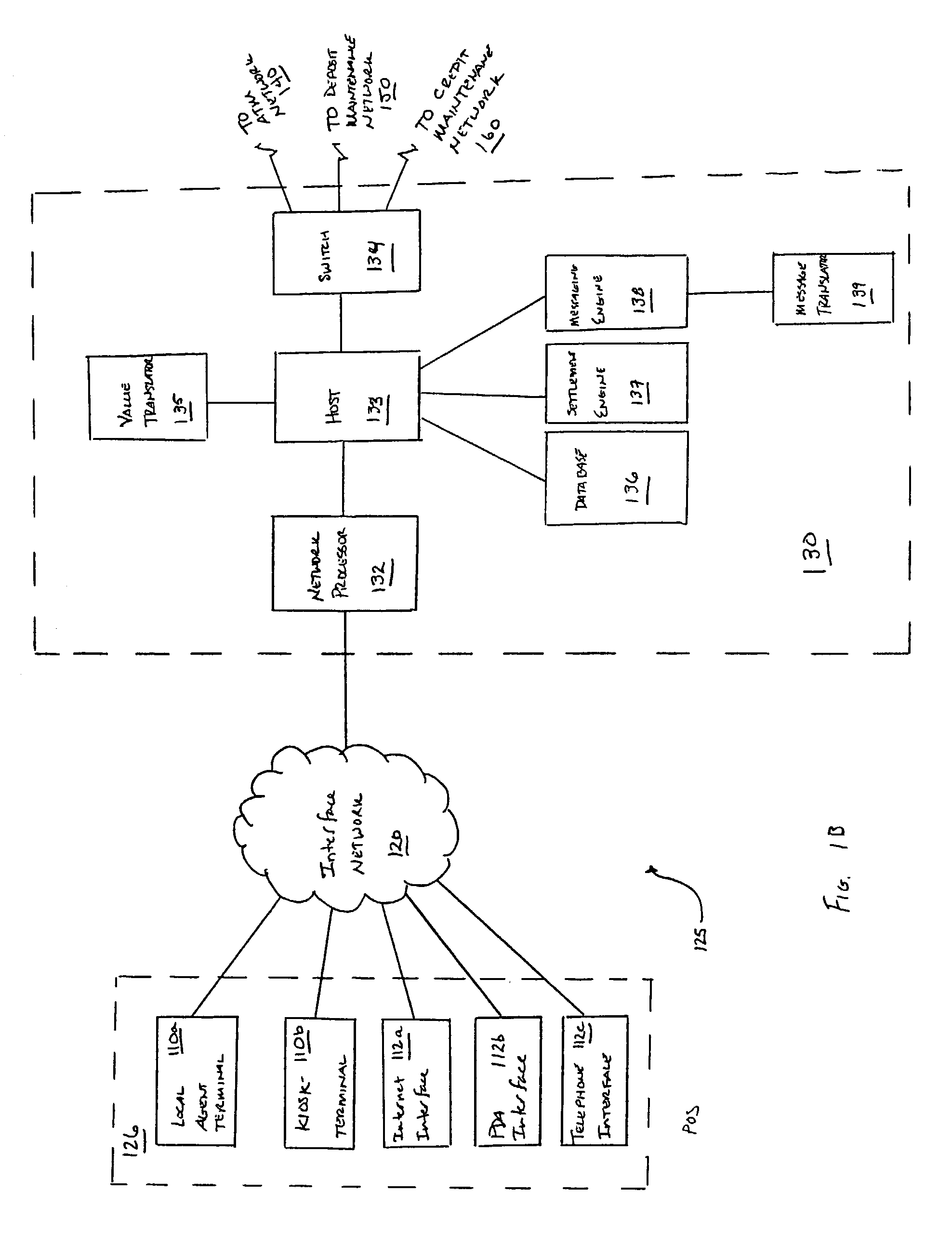
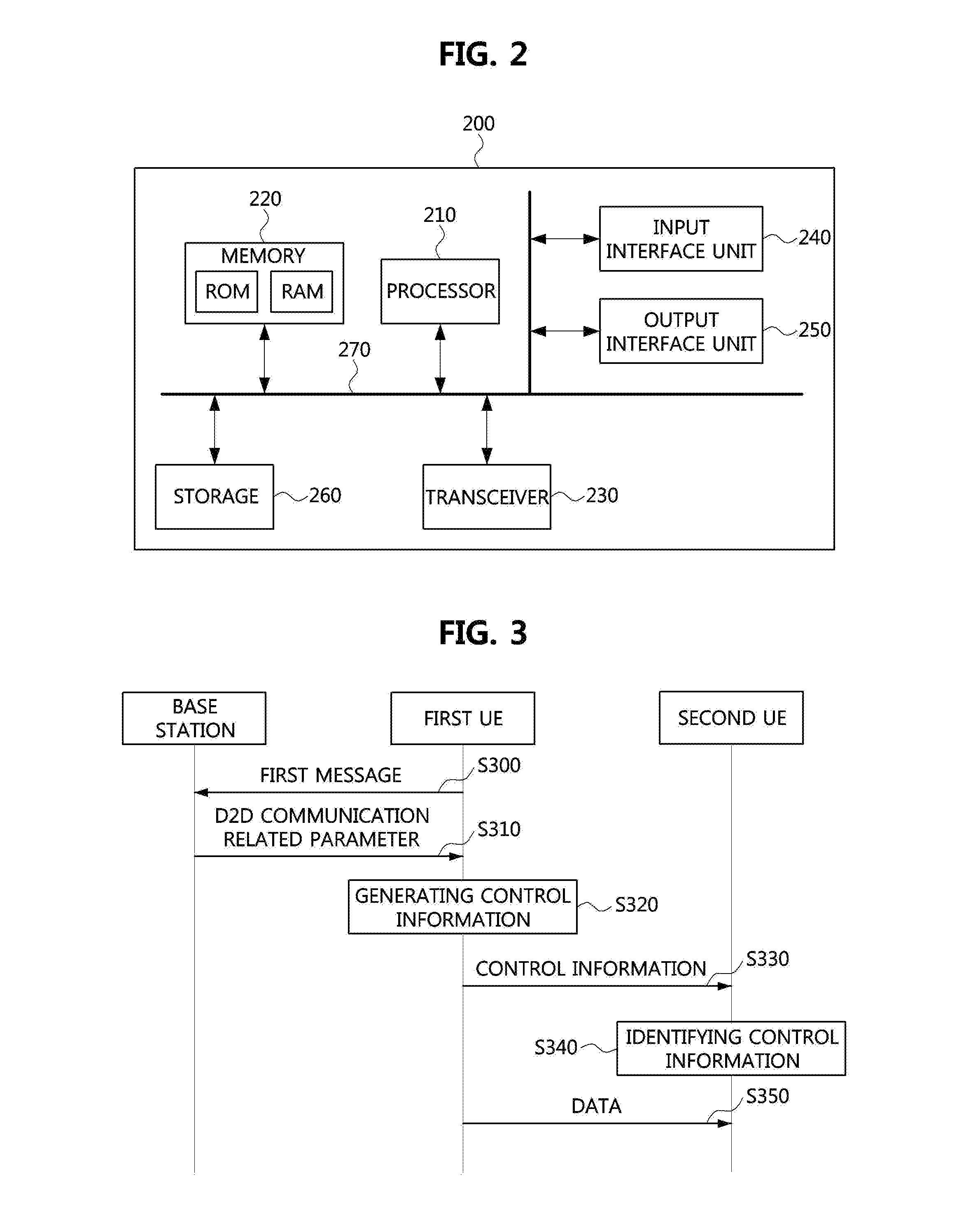
Operation method of communication node supporting direct communication in network
ActiveUS20170048905A1Efficient receptionGuaranteed normal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementSignal allocationTelecommunicationsControl channel
Disclosed are operation methods of communication node supporting direct communications in network. The operation method may comprise generating control information which includes parameters used for transmitting and receiving data; transmitting, to a second UE, the control information through a physical sidelink control channel (PSCCH); and transmitting, to the second UE, the data through a physical sidelink shared channel (PSSCH) based on the parameters. Therefore, a performance of the network can be enhanced.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and apparatus for setting up radio resource control connection
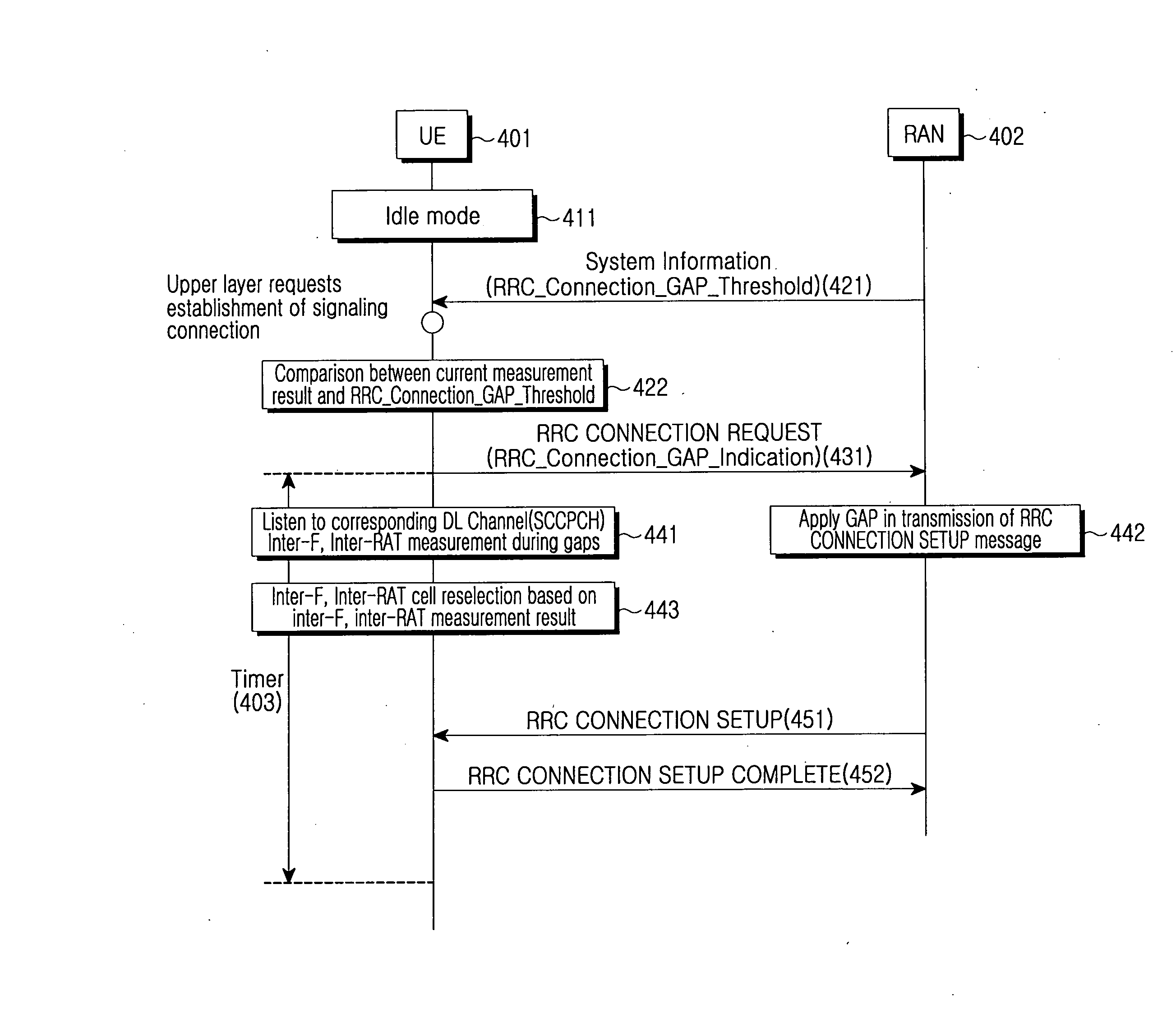
InactiveUS20080039094A1Efficiently receiveEfficient receptionConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsSignal strength
A method and apparatus for establishing an RRC connection are provided, in which a UE compares the strength of a signal received from a serving cell with a threshold, upon receipt of a request for RRC connection establishment, transmits an RRC connection request message to a RAN, measures the strengths of signals from neighbor cells during a first time period and monitors a downlink channel of the serving cell to receive a response message for the RRC connection request message during a second time period, if the signal strength of the serving cell is less than the threshold, and receives the response message from the RAN on the downlink channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving control information to randomize inter-cell interference in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20080212555A1Reduce Inter-Cell InterferenceEfficient receptionNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionTelecommunicationsControl channel
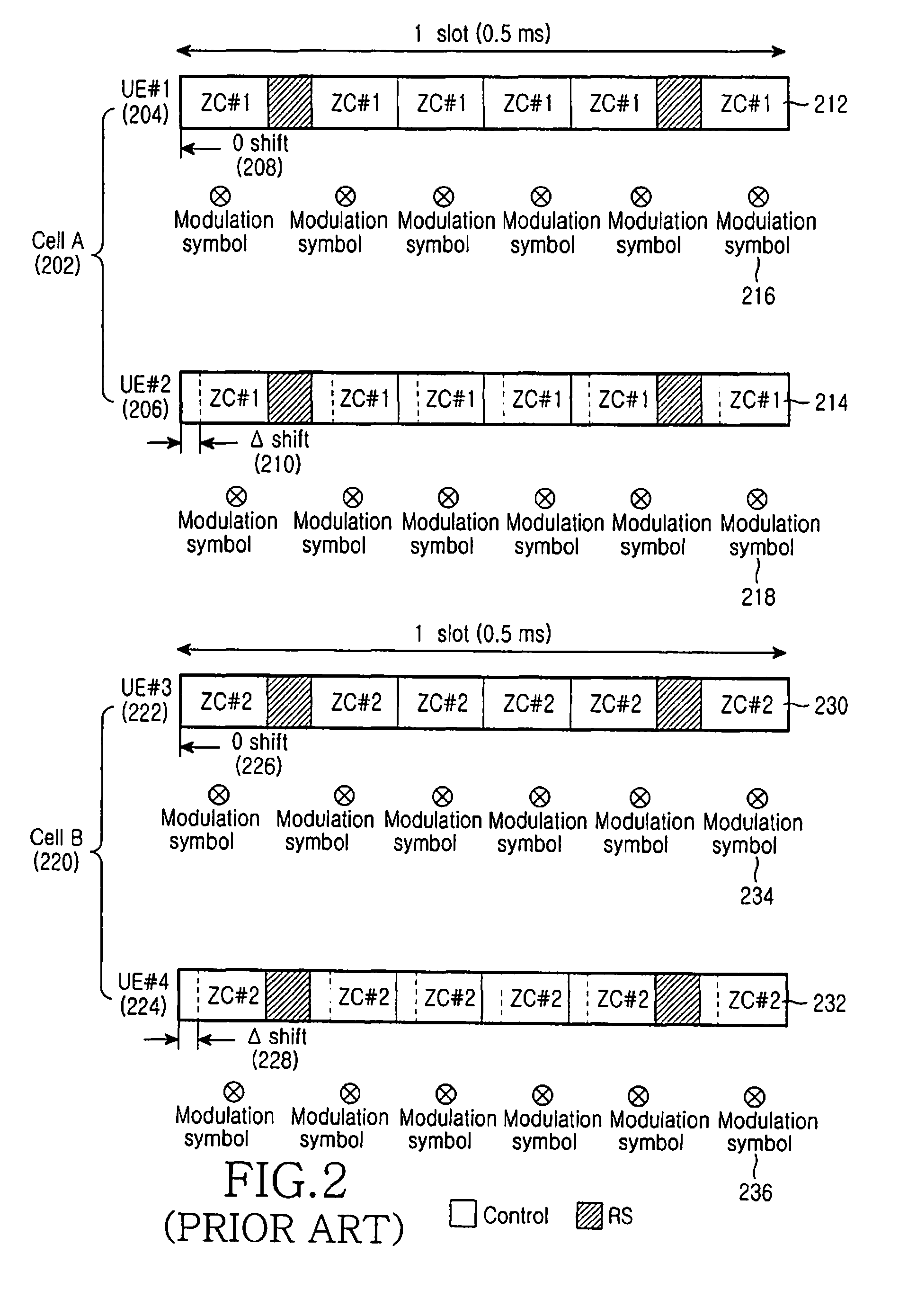
A method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving control information in an SC-FDMA system are provided, in which different cyclic shift values are generated for different SC-FDMA symbols in one of a slot and a subframe, a sequence allocated for CDM of control information is cyclically shifted by the cyclic shift values, and a control channel signal including the control information is combined with the cyclically shifted sequences on an SC-FDMA symbol basis and transmitted in the SC-FDMA symbols.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving a frame including control information in a broadcasting system
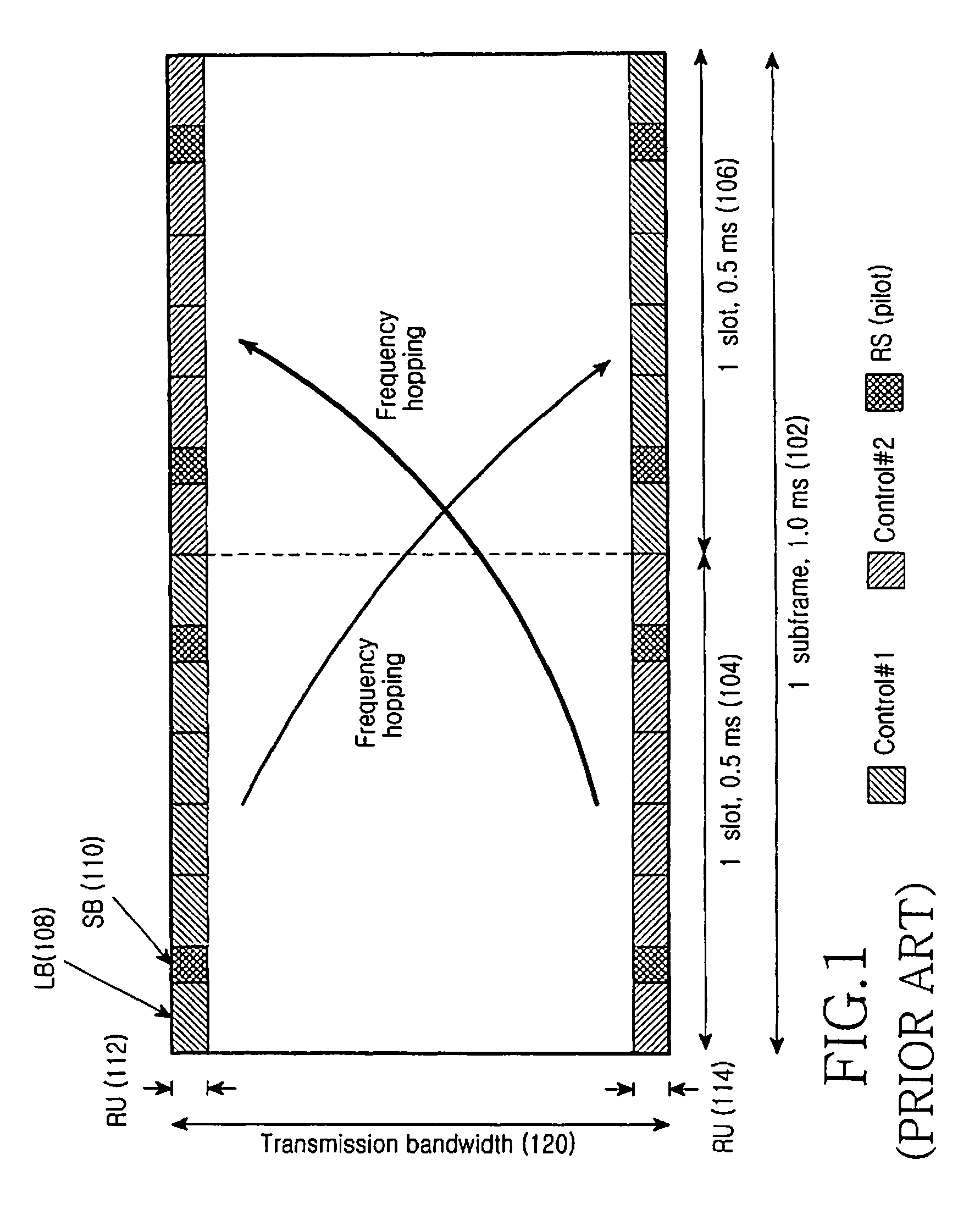
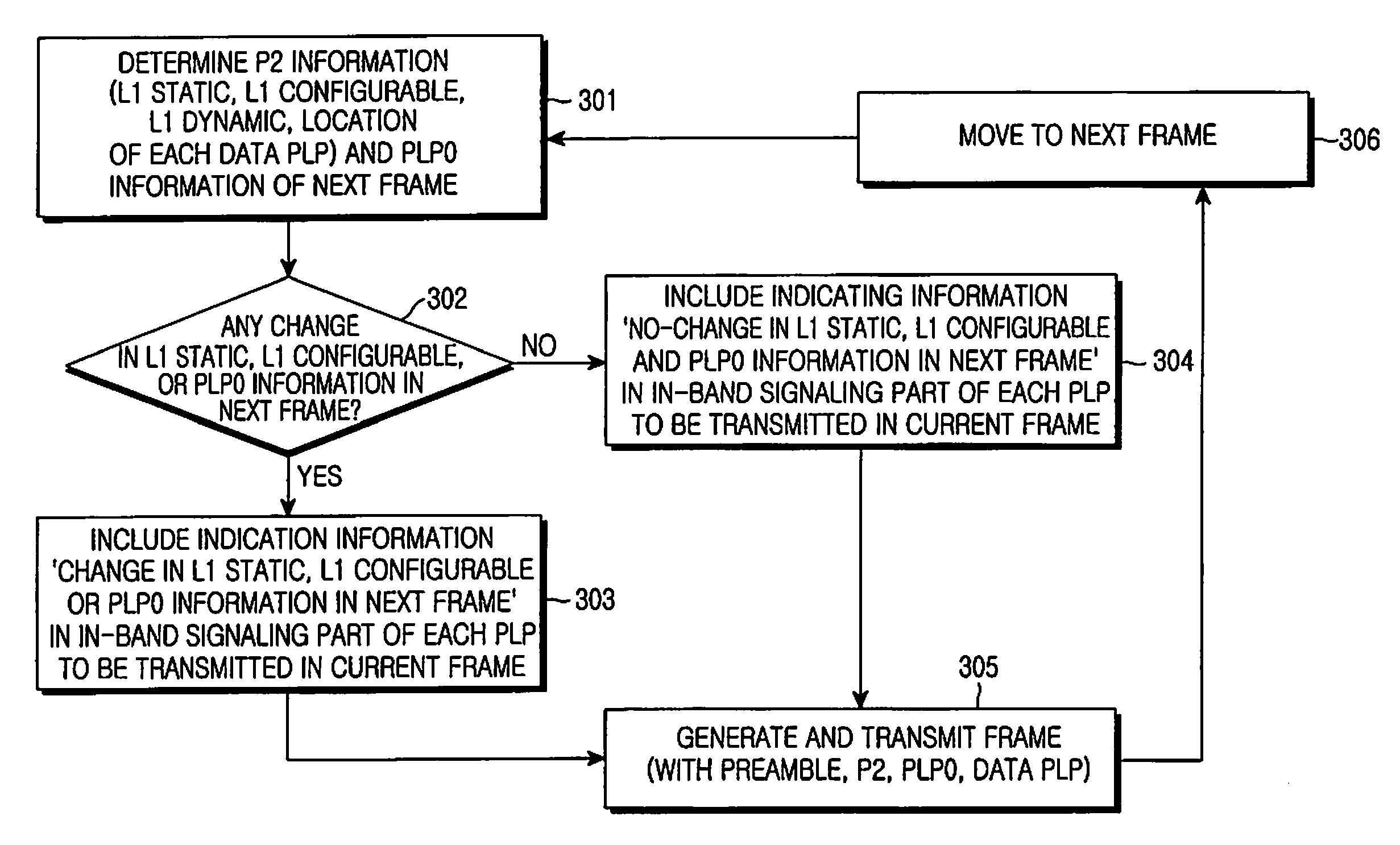
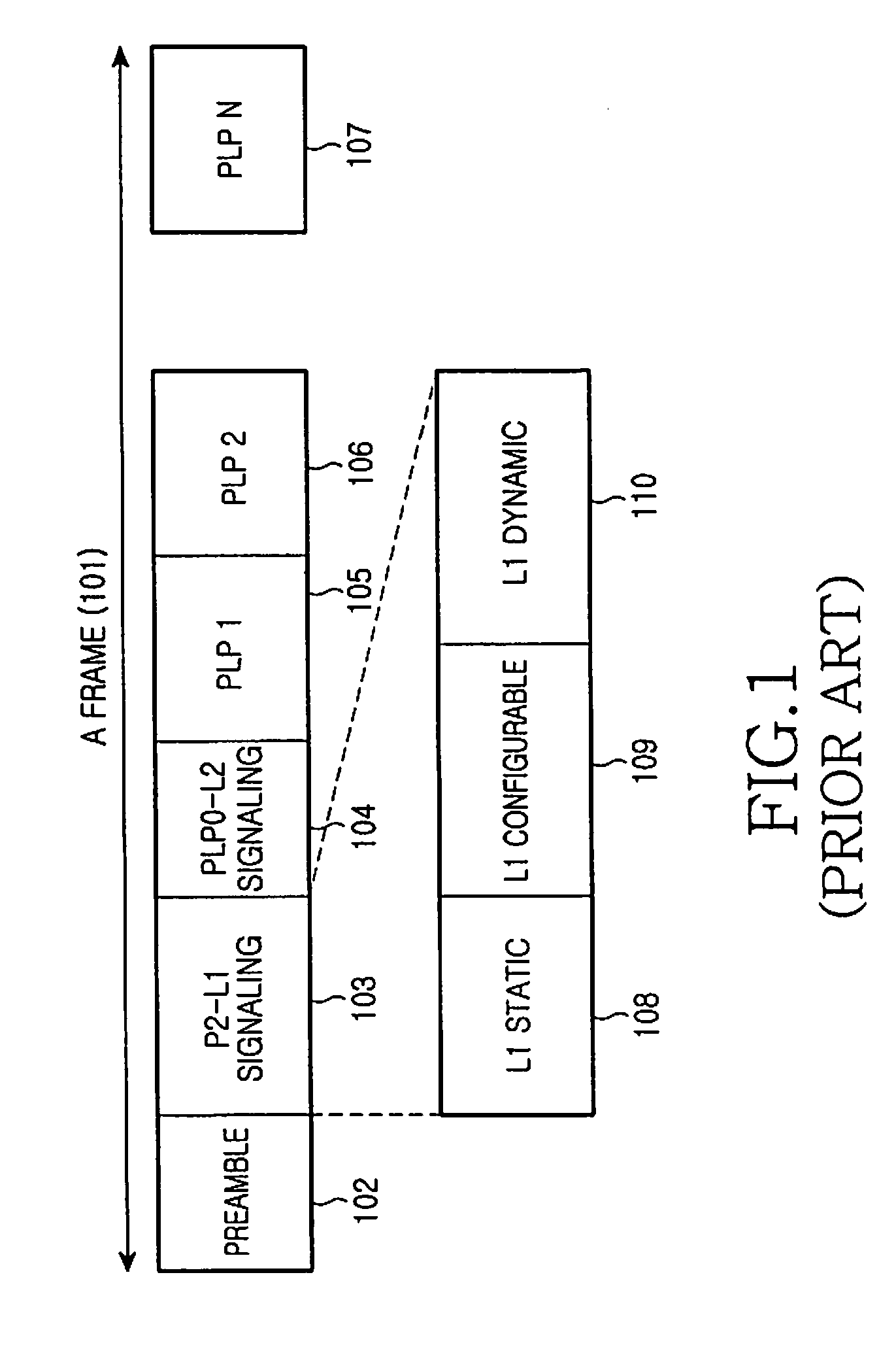
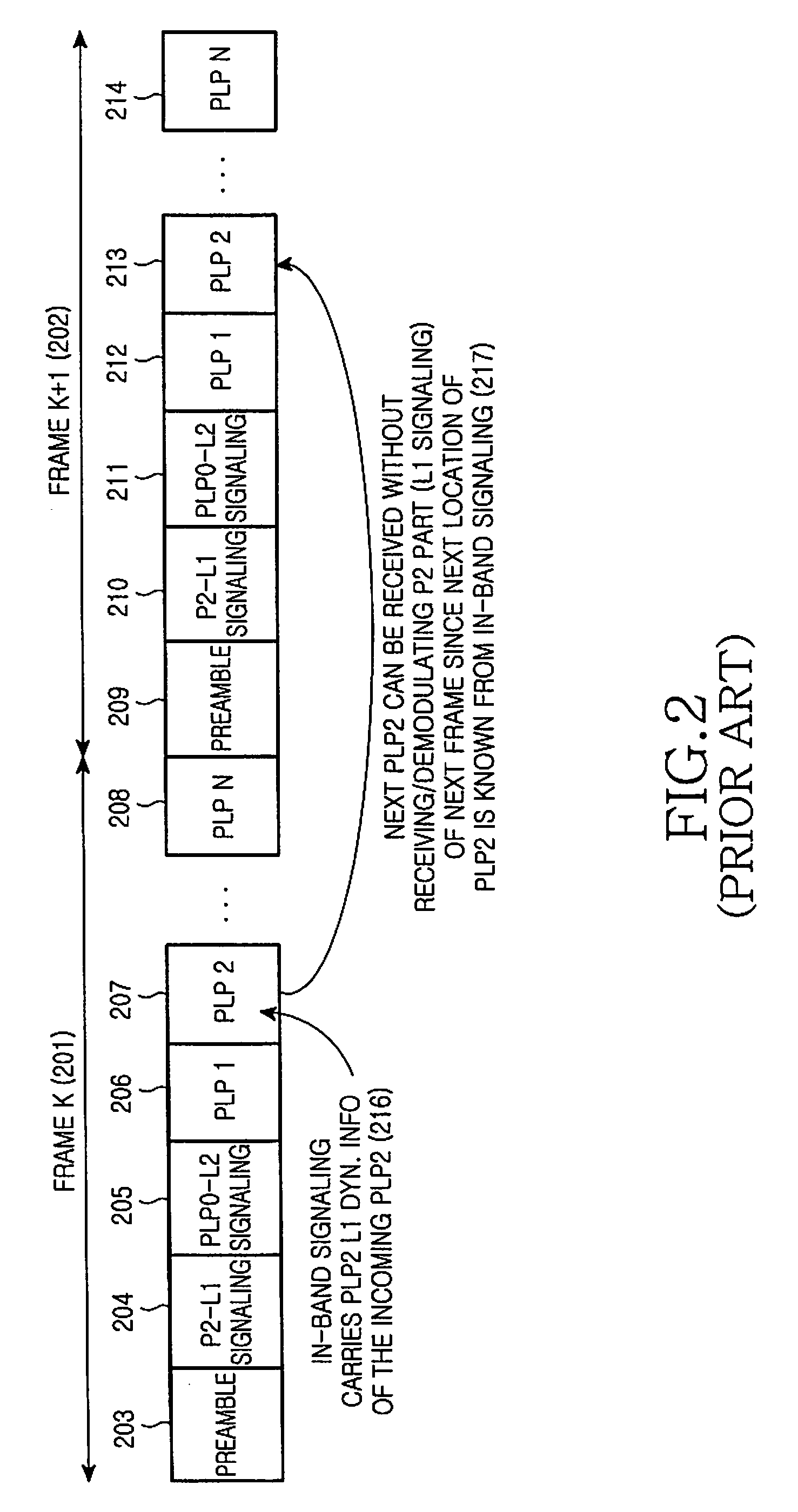
ActiveUS20090213853A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient receptionBroadcast information characterisationResource management arrangementsIn-band signalingBroadcast service
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving a frame including control information in a broadcasting system. A frame for a broadcast service is generated using an in-band signaling scheme, and includes location information of control information in a next frame and indication information indicating a change / no-change in the control information in the next frame. The new frame structure minimizes power consumption of a receiver supporting the broadcast service.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com