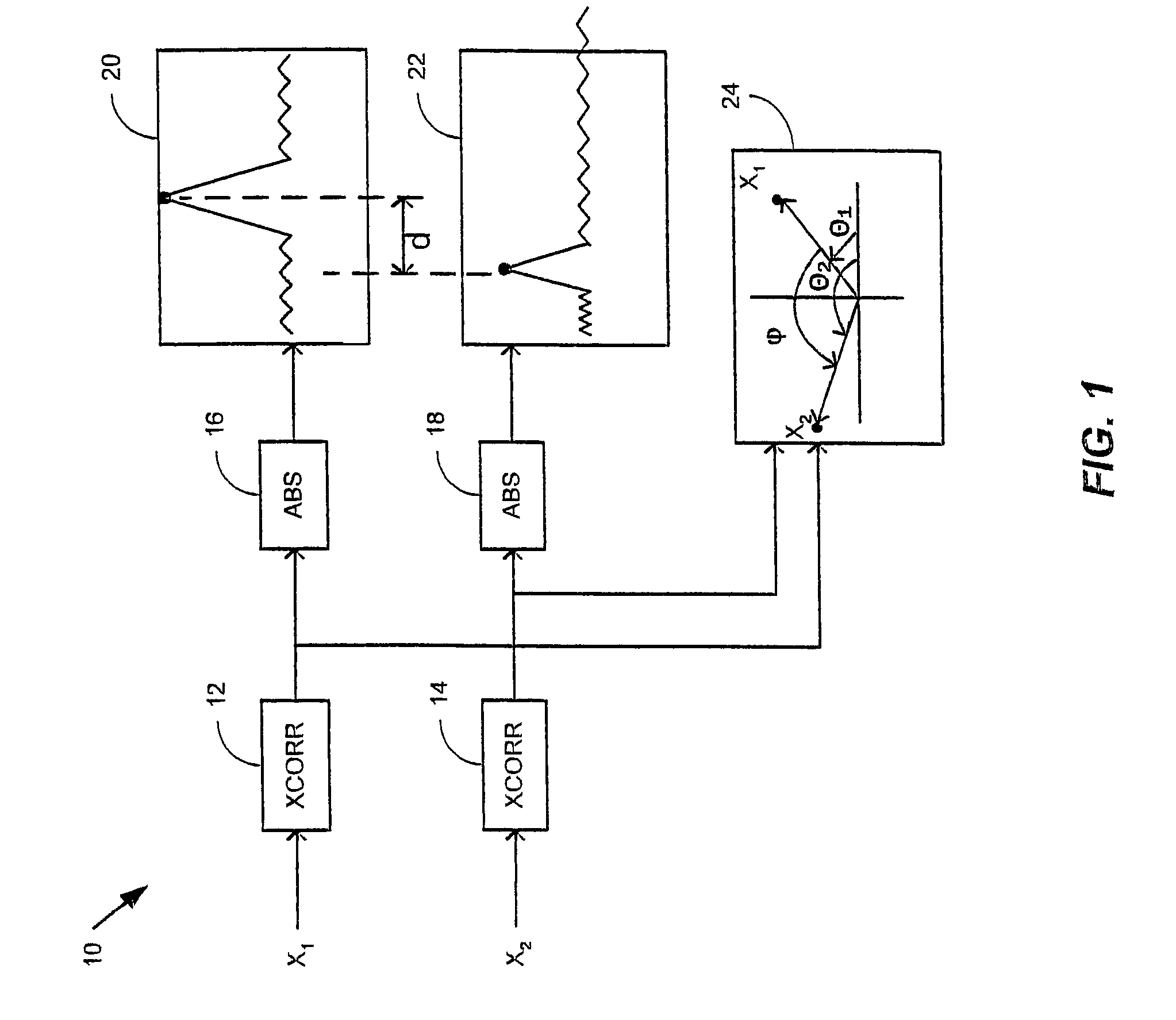
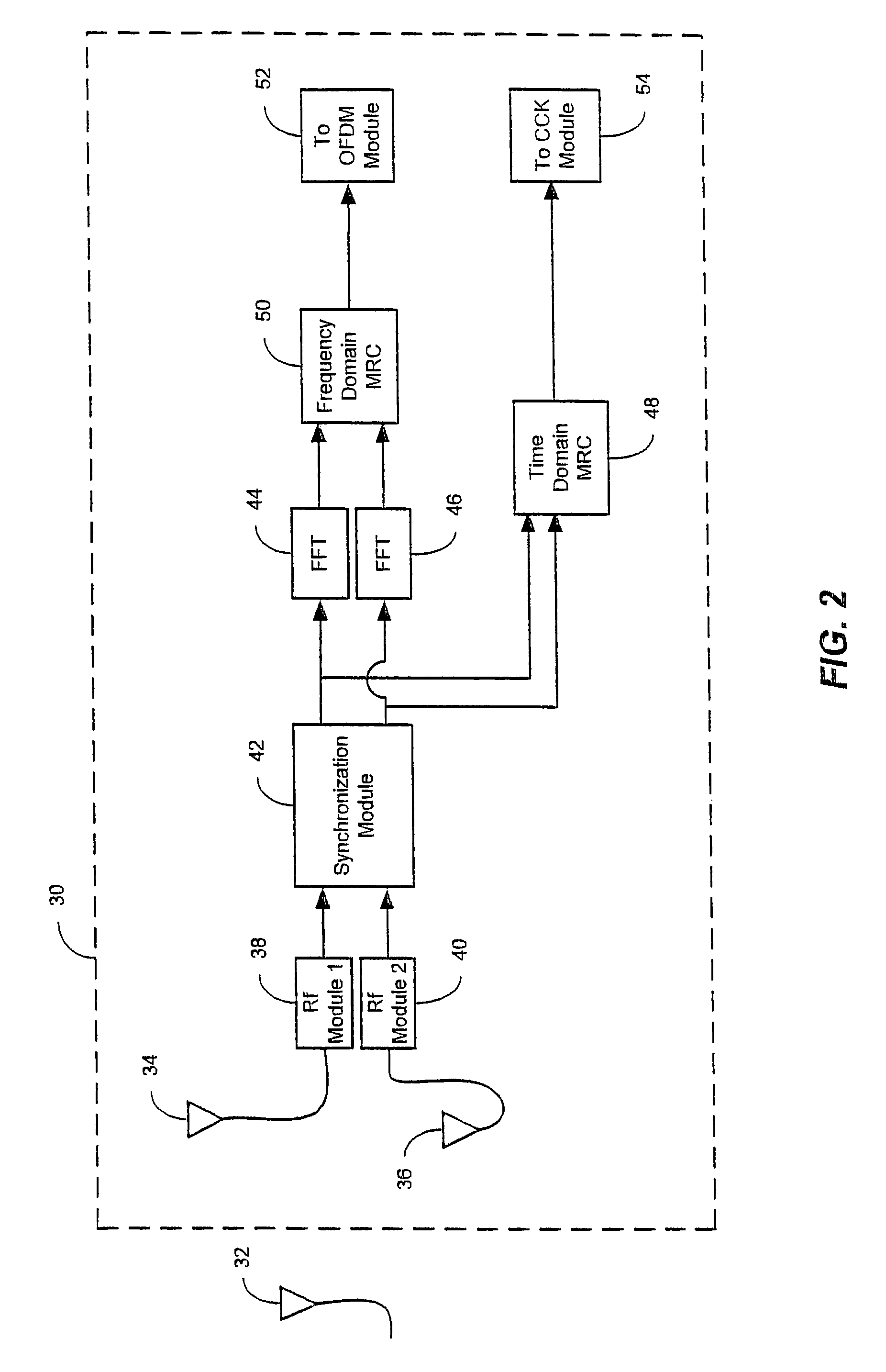
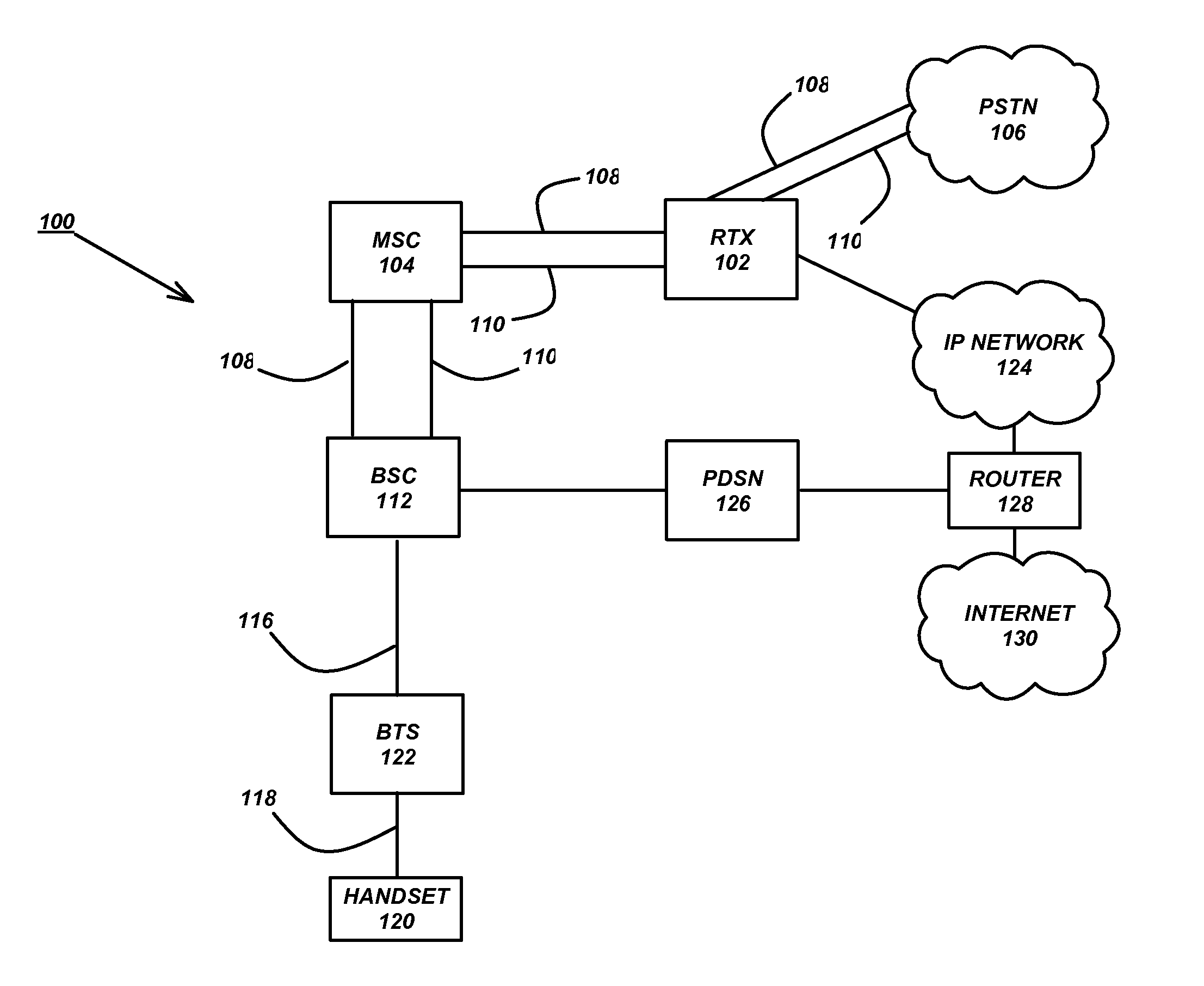
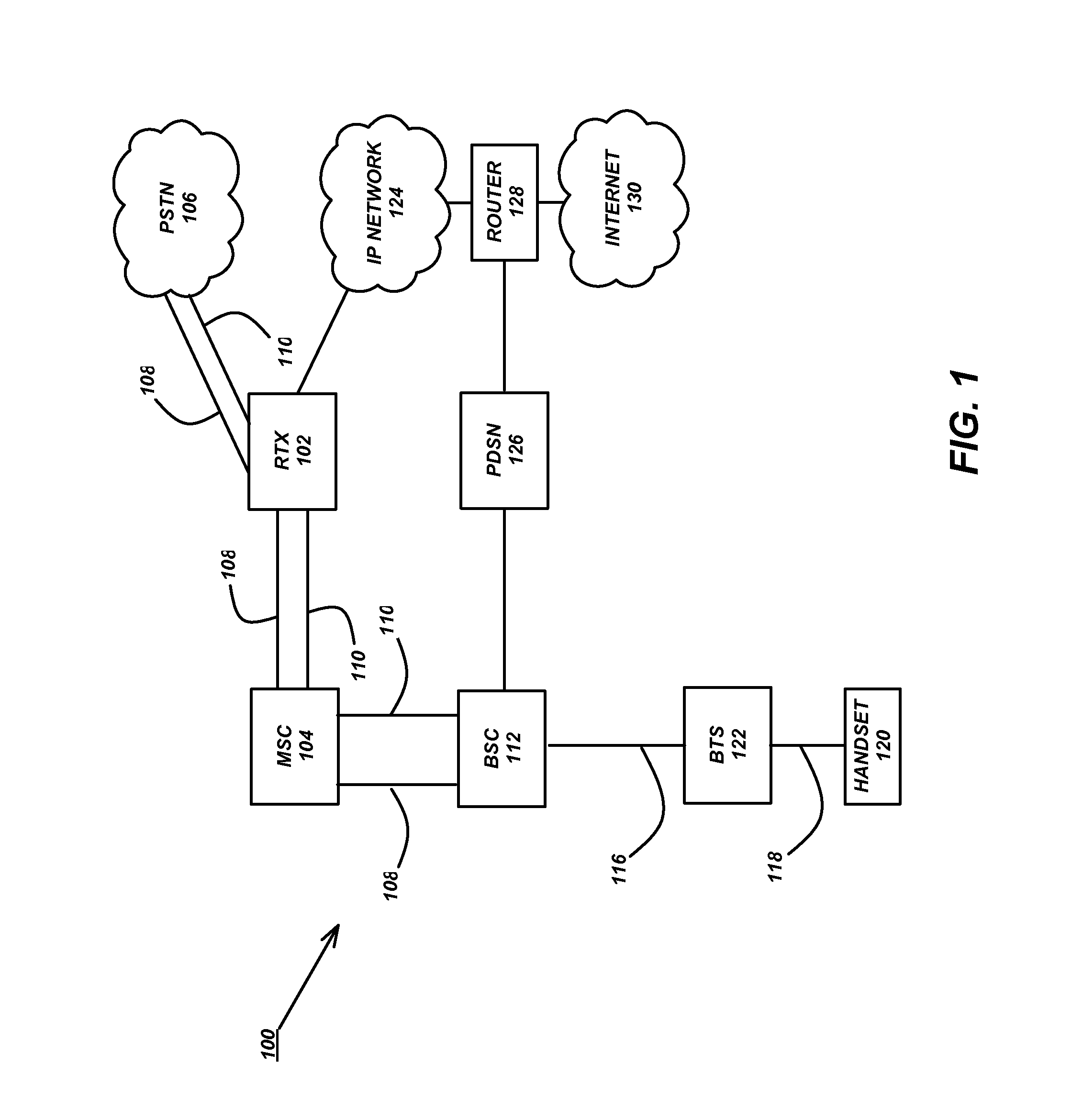
Patents
Literature
144 results about "In-band signaling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
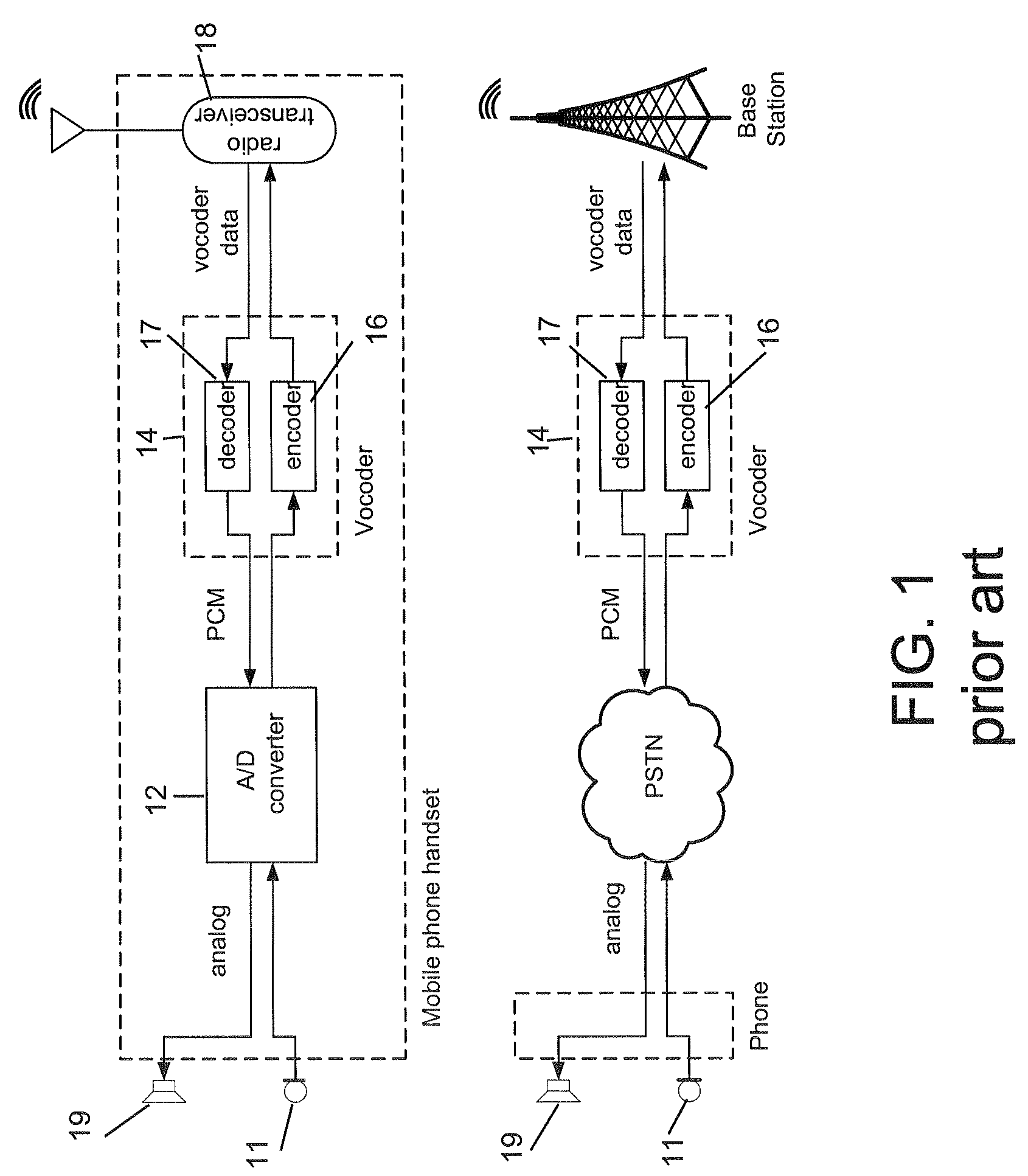
In telecommunications, in-band signaling is the sending of control information within the same band or channel used for data such as voice or video. This is in contrast to out-of-band signaling which is sent over a different channel, or even over a separate network. In-band signals may often be heard by telephony participants, while out-of-band signals are inaccessible to the user.
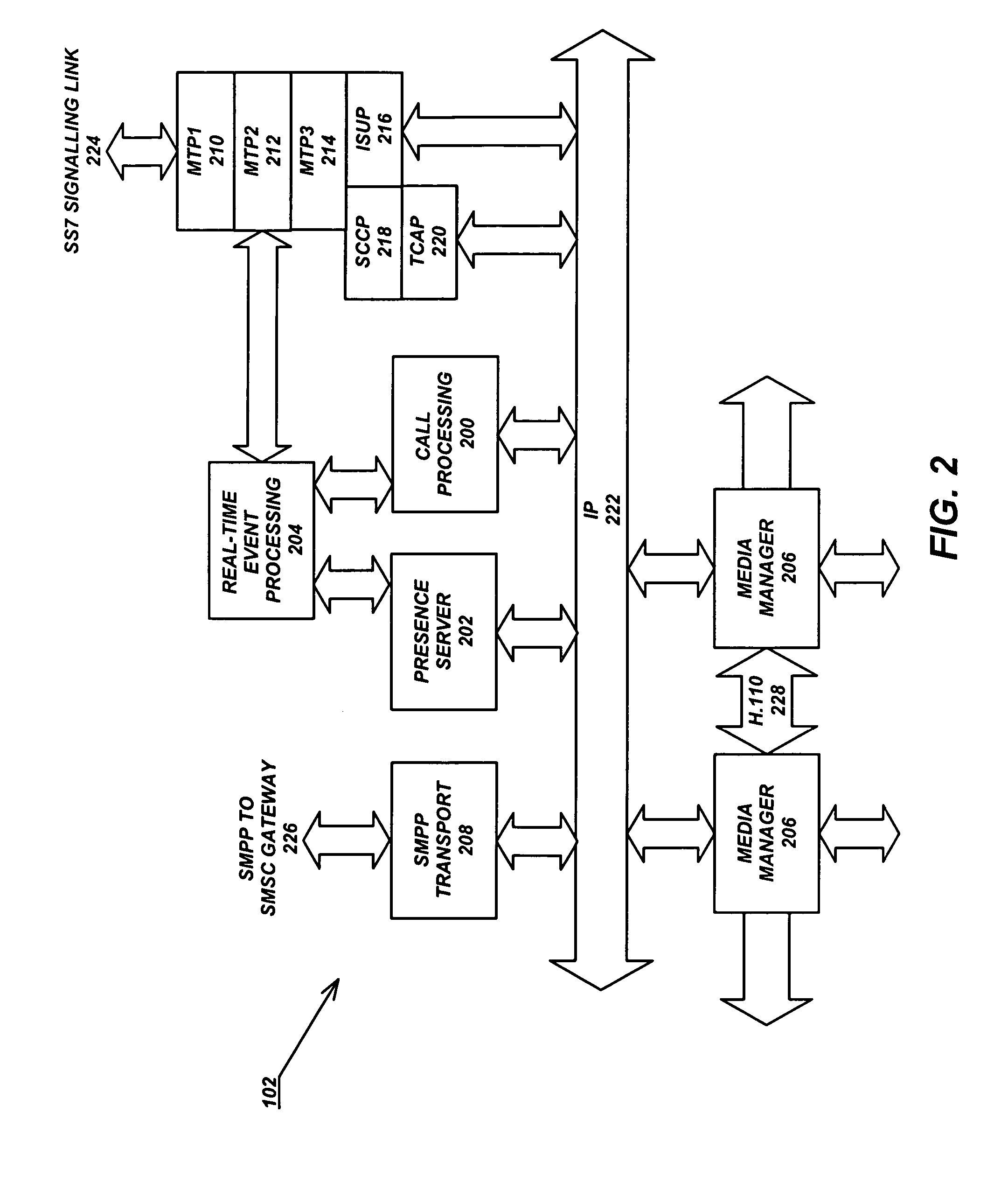
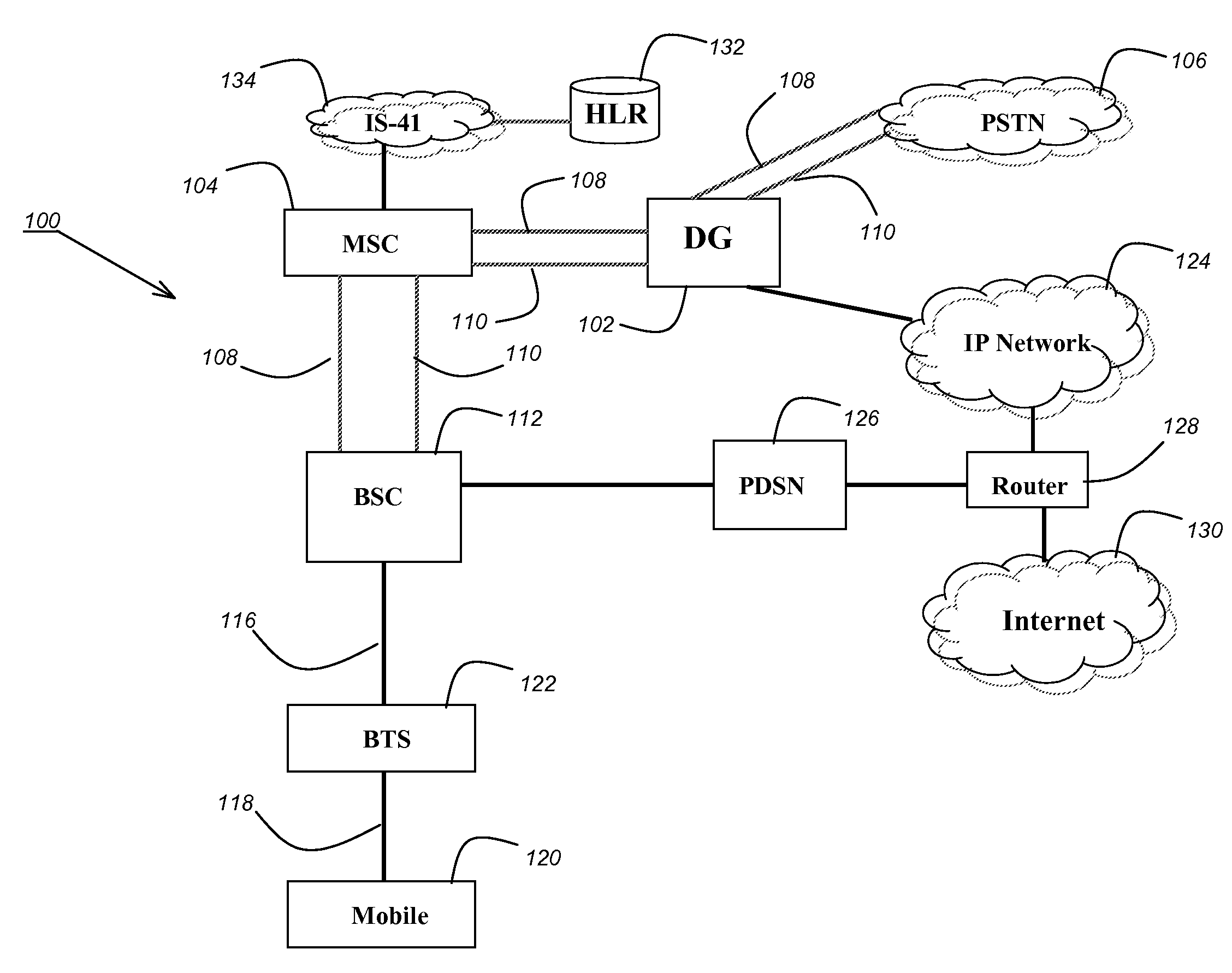
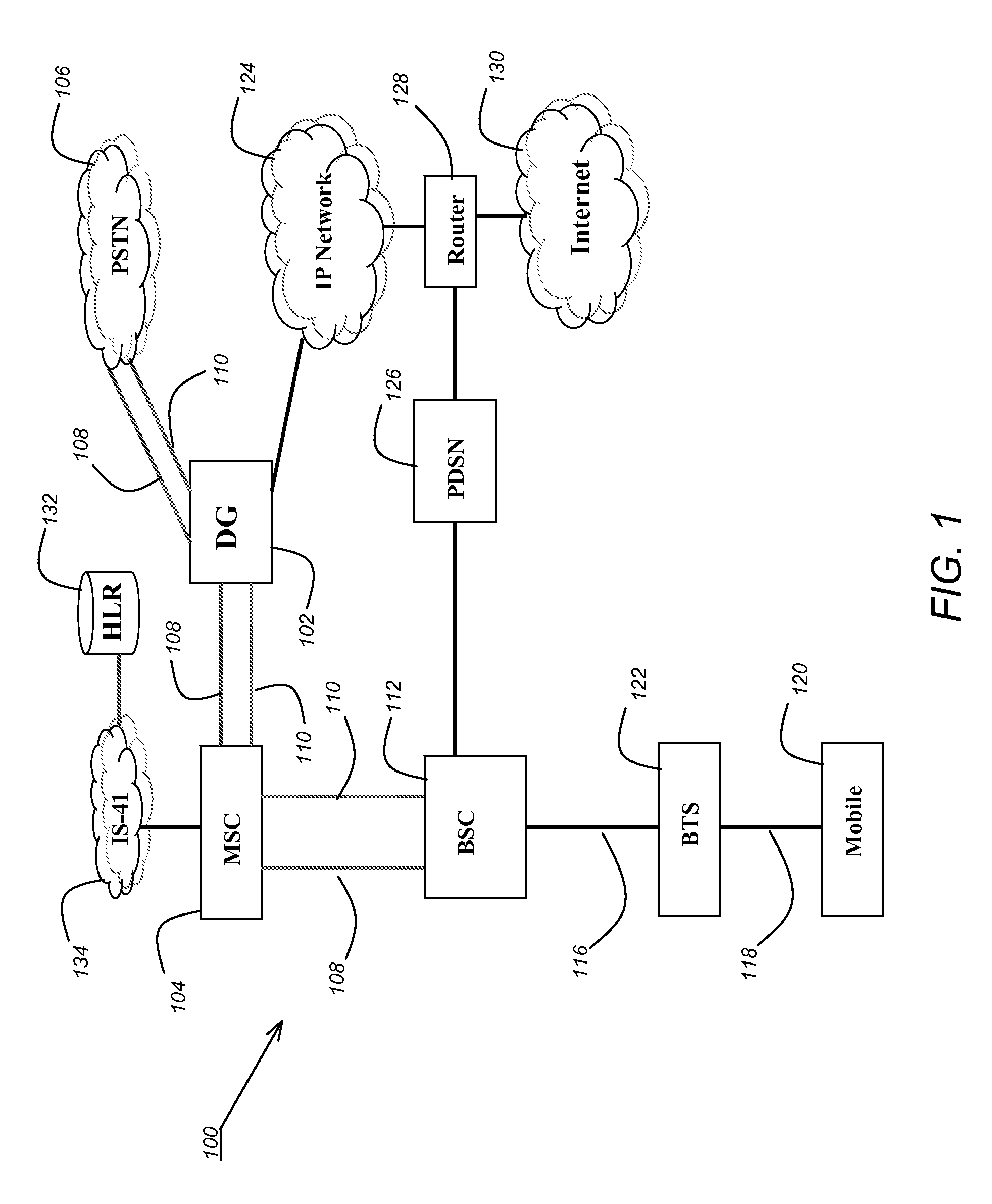
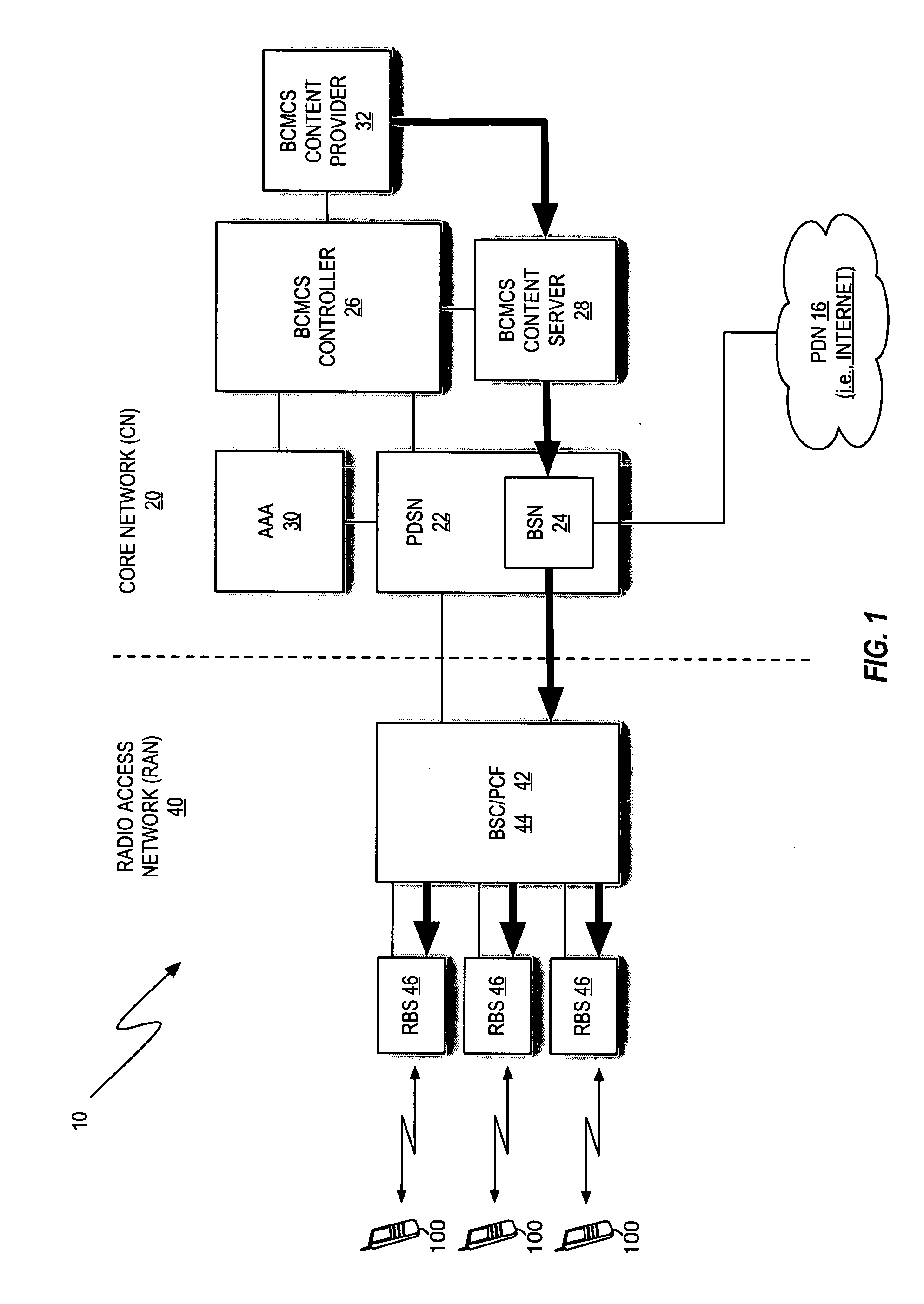
Premium voice services for wireless communications systems
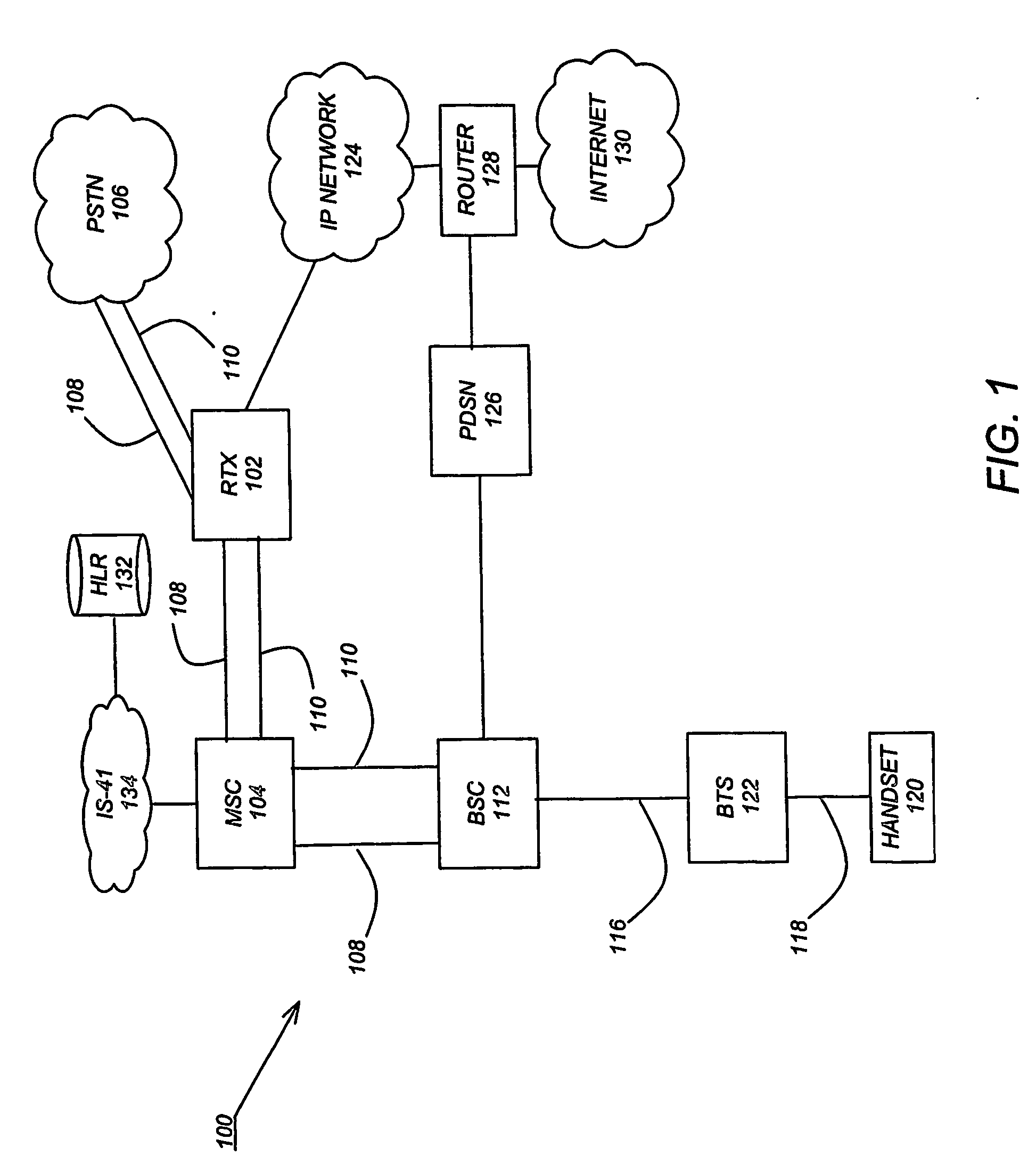
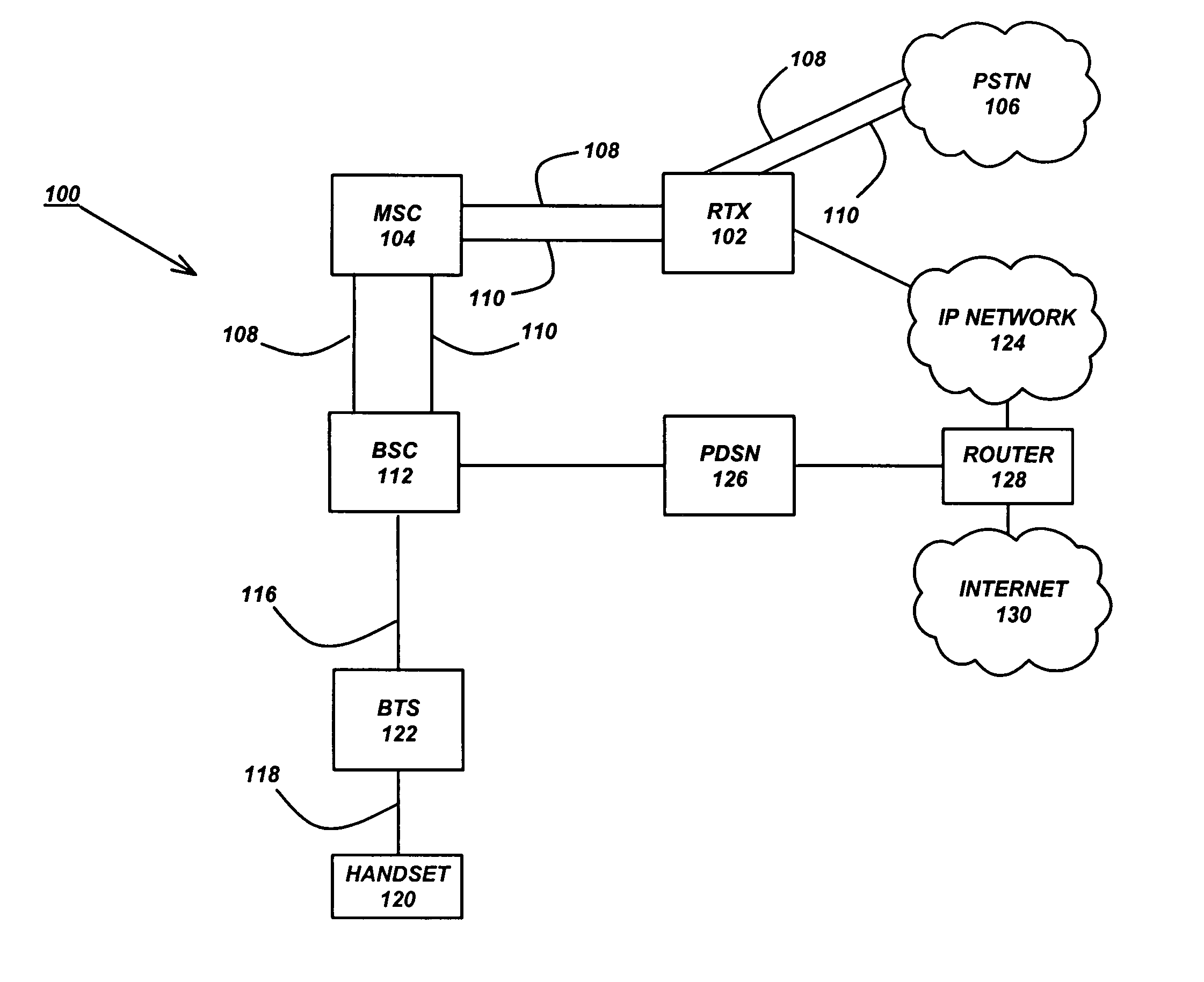
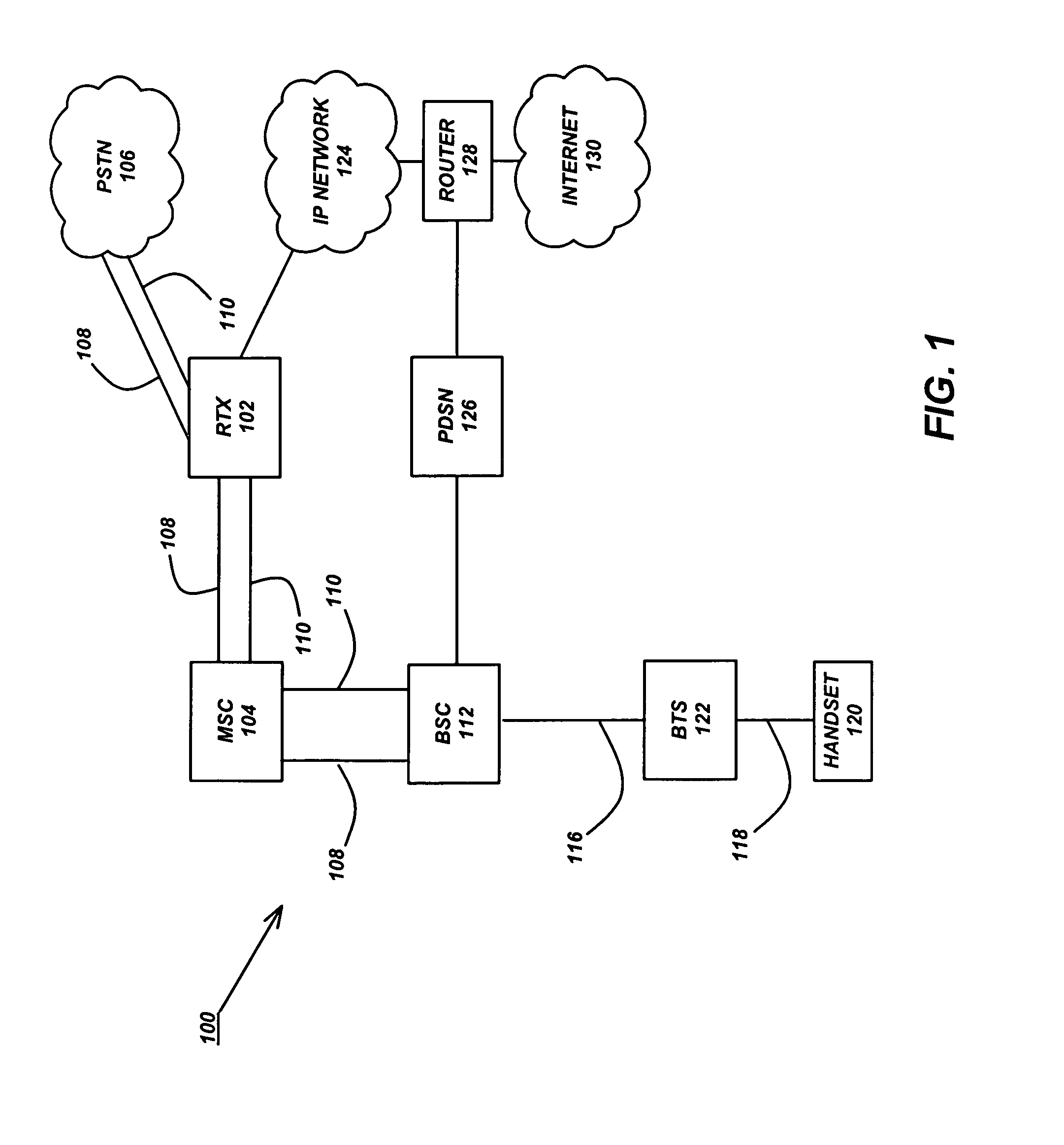
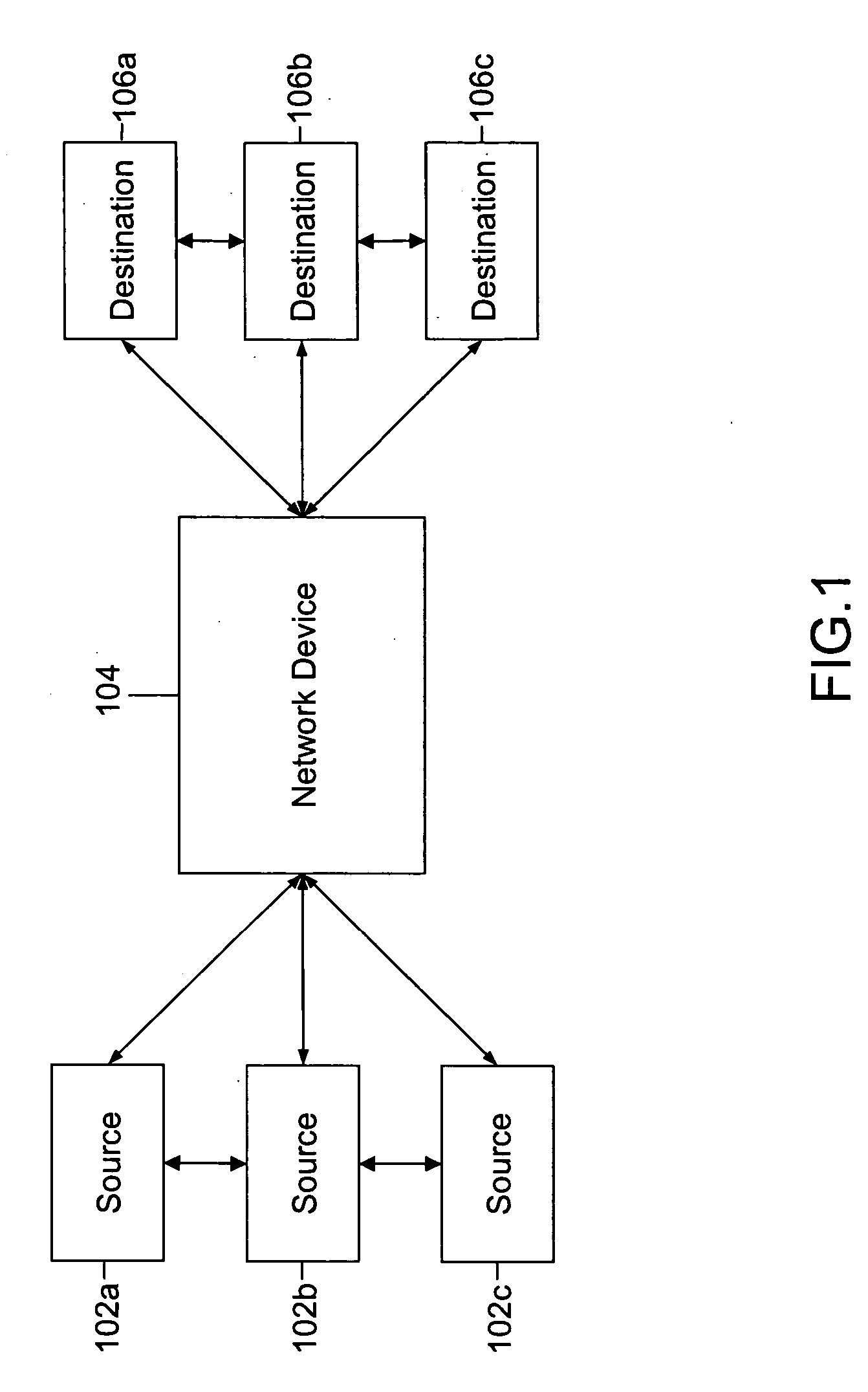
InactiveUS20060189337A1Improve experienceZero call-delayMultiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork topologiesNon real timeCommunications system
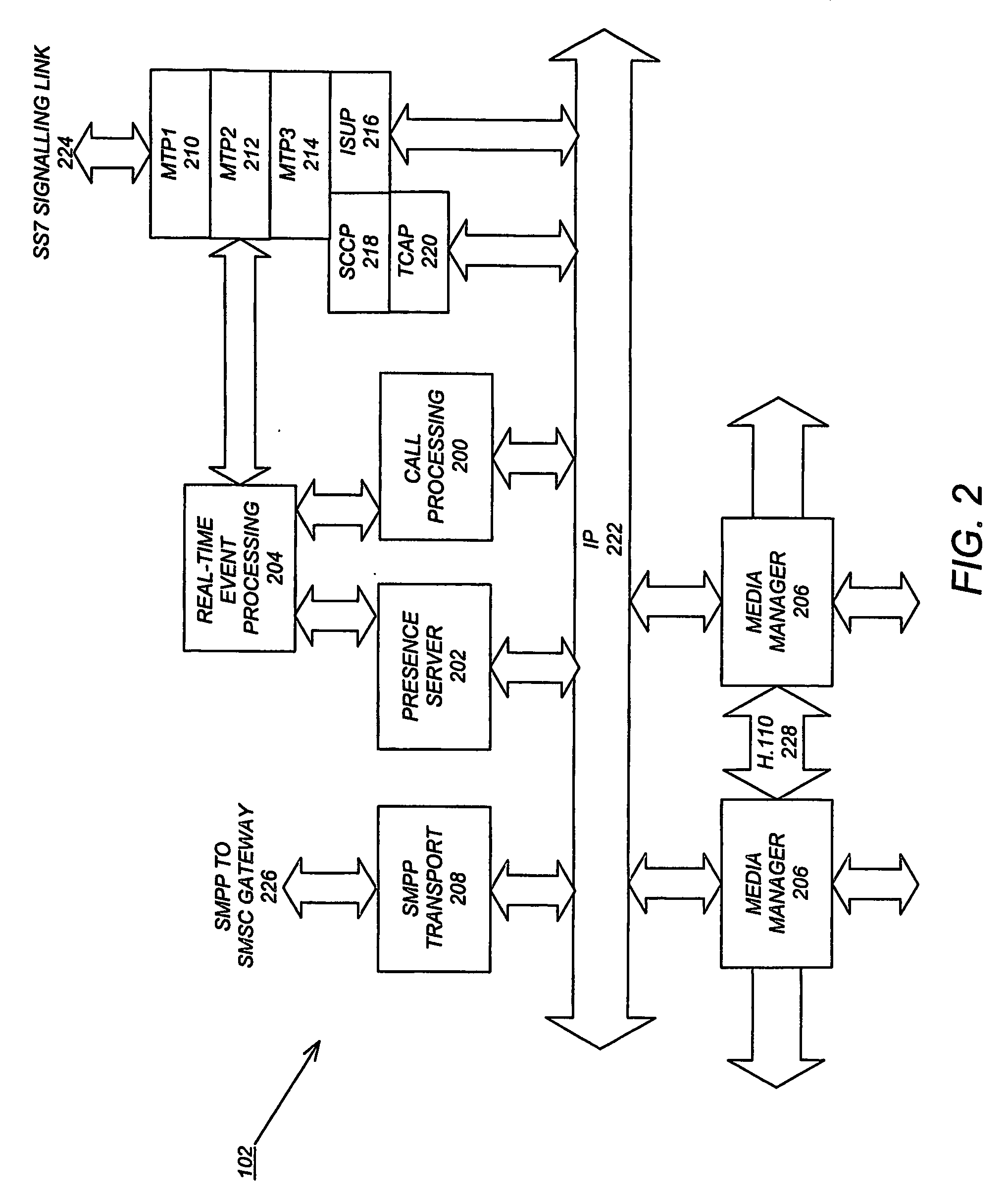
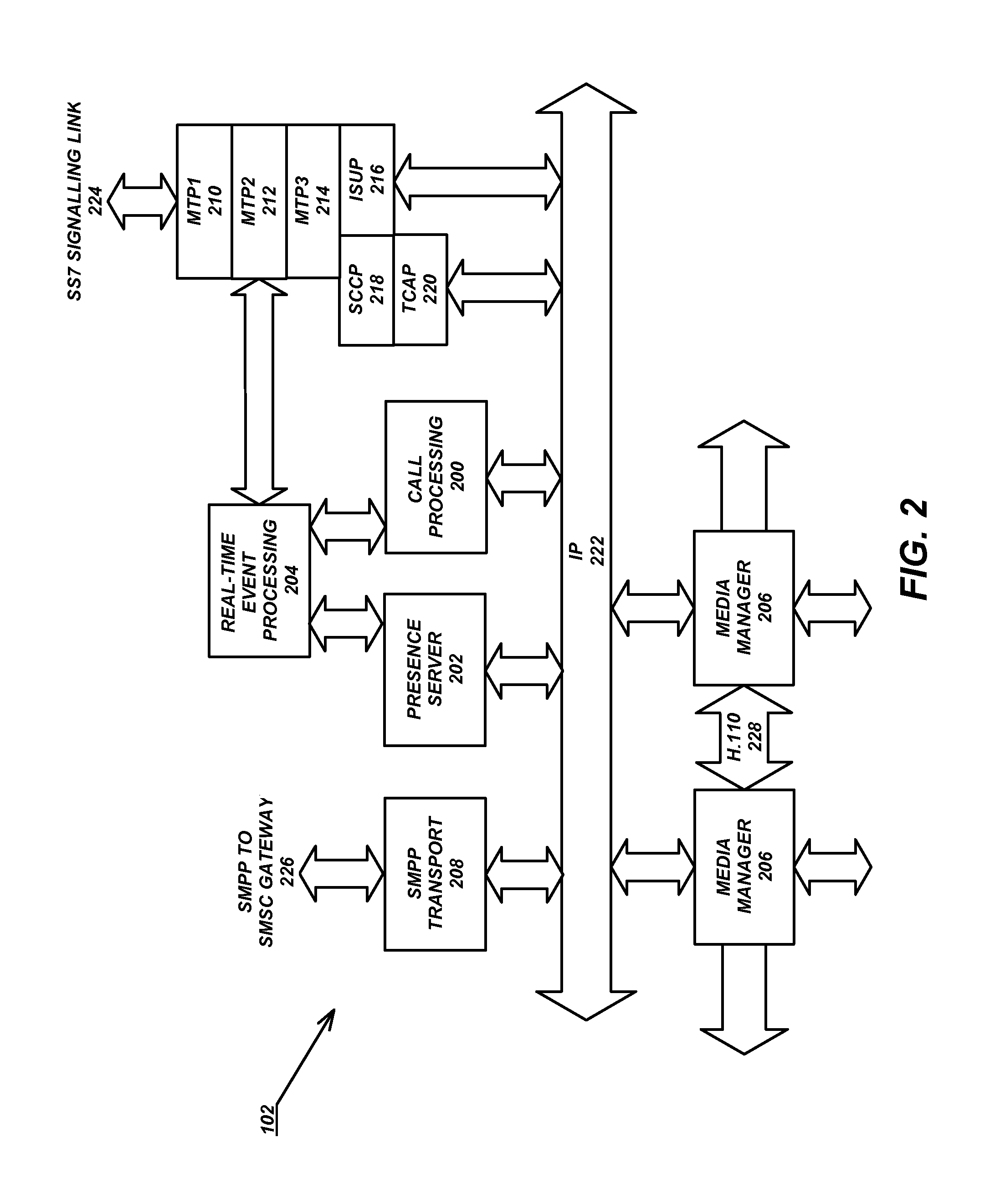
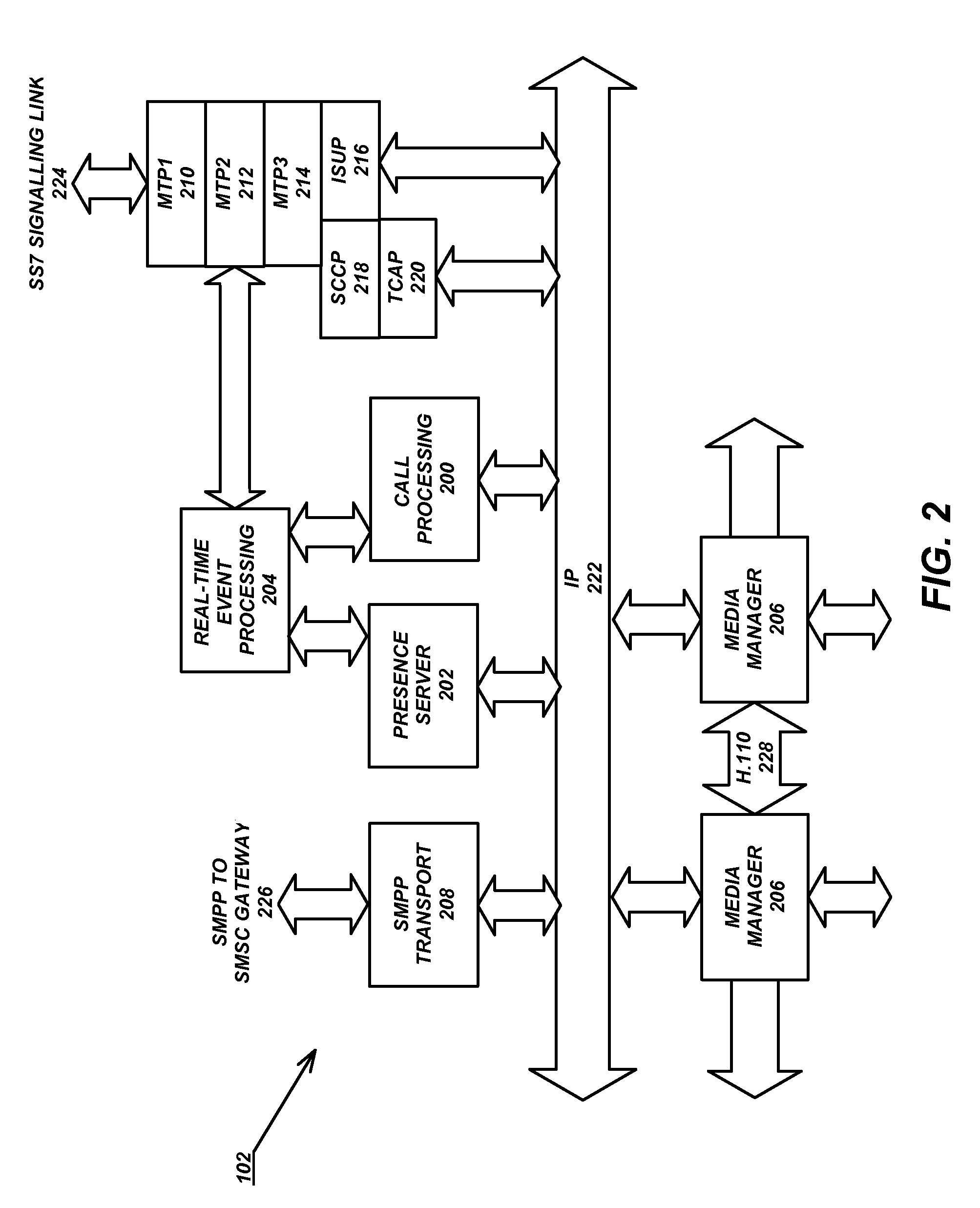
Two advanced group-based voice services, known as Push-to-Conference (P2C) and Push-to-Message (P2M) services are provided by a real-time exchange (RTX) that interfaces to the wireless network. The RTX provides a full-duplex Push-to-Conference (P2C) session between an initiator and two or more other participants, wherein the P2C session comprises a full-duplex conference call, and both the real time exchange and handsets participating in the P2C session communicate with each other using call setup and in-band signaling within the wireless network. The realtime exchange may be coupled to and work with a Push-to-Message (P2M) server to deliver multimedia messages in a non-real time manner from an originator to one or more recipients, without establishing voice paths between the originator and recipients, wherein the P2M server, and an optional Voice Mail Server, provide a message storage facility for the multimedia messages. Additionally, a technique based on handset speech buffering permits zero delay call set-ups to be achieved.
Owner:FARRILL CRAIG F +2
Architecture, client specification and application programming interface (API) for supporting advanced voice services (AVS) including push to talk on wireless handsets and networks
ActiveUS20050202807A1Interconnection arrangementsServices signallingWireless handheld devicesCommunications system
An architecture, client specification and application programming interface (API) for supporting advanced voice services (AVS) for use in handsets in order to support advanced voice services (AVS) for wireless communications systems. The handset or mobile unit executes a client application therein for performing the call setup and in-band signaling with the wireless network for the group voice services, and executes a presence / group management application therein for performing presence and group management functions related to the group voice services in the mobile unit.
Owner:KODIAK NETWORKS
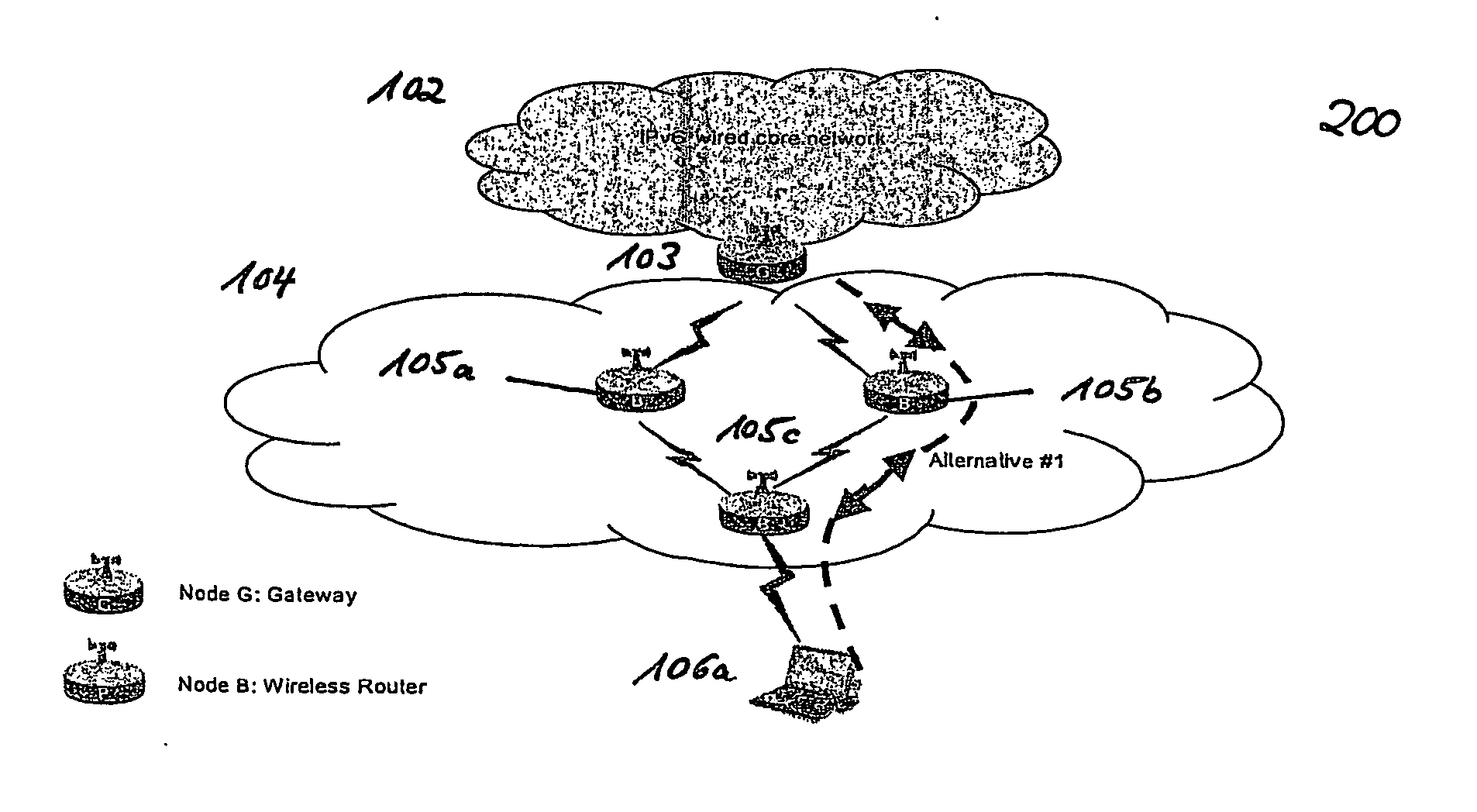
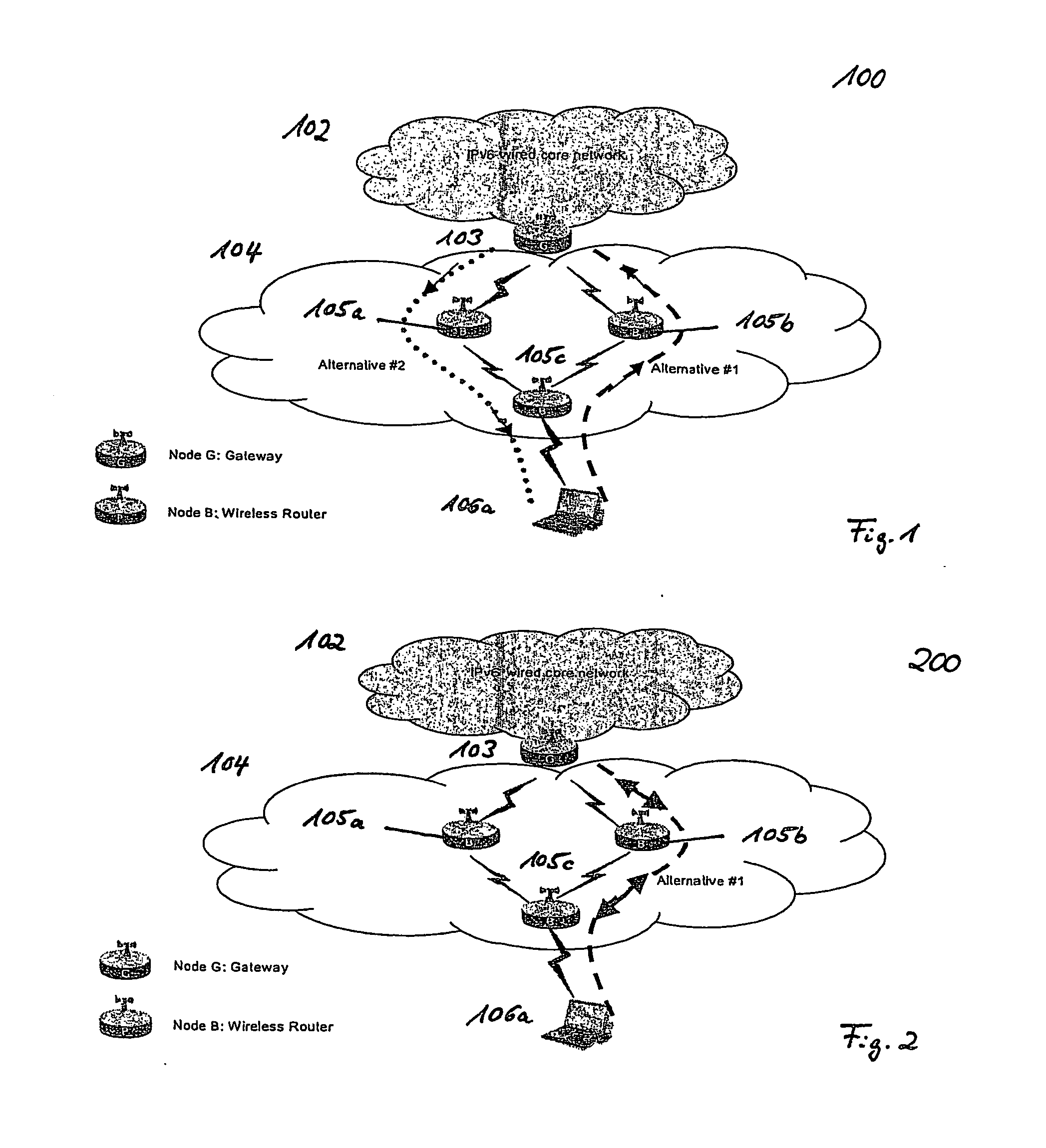
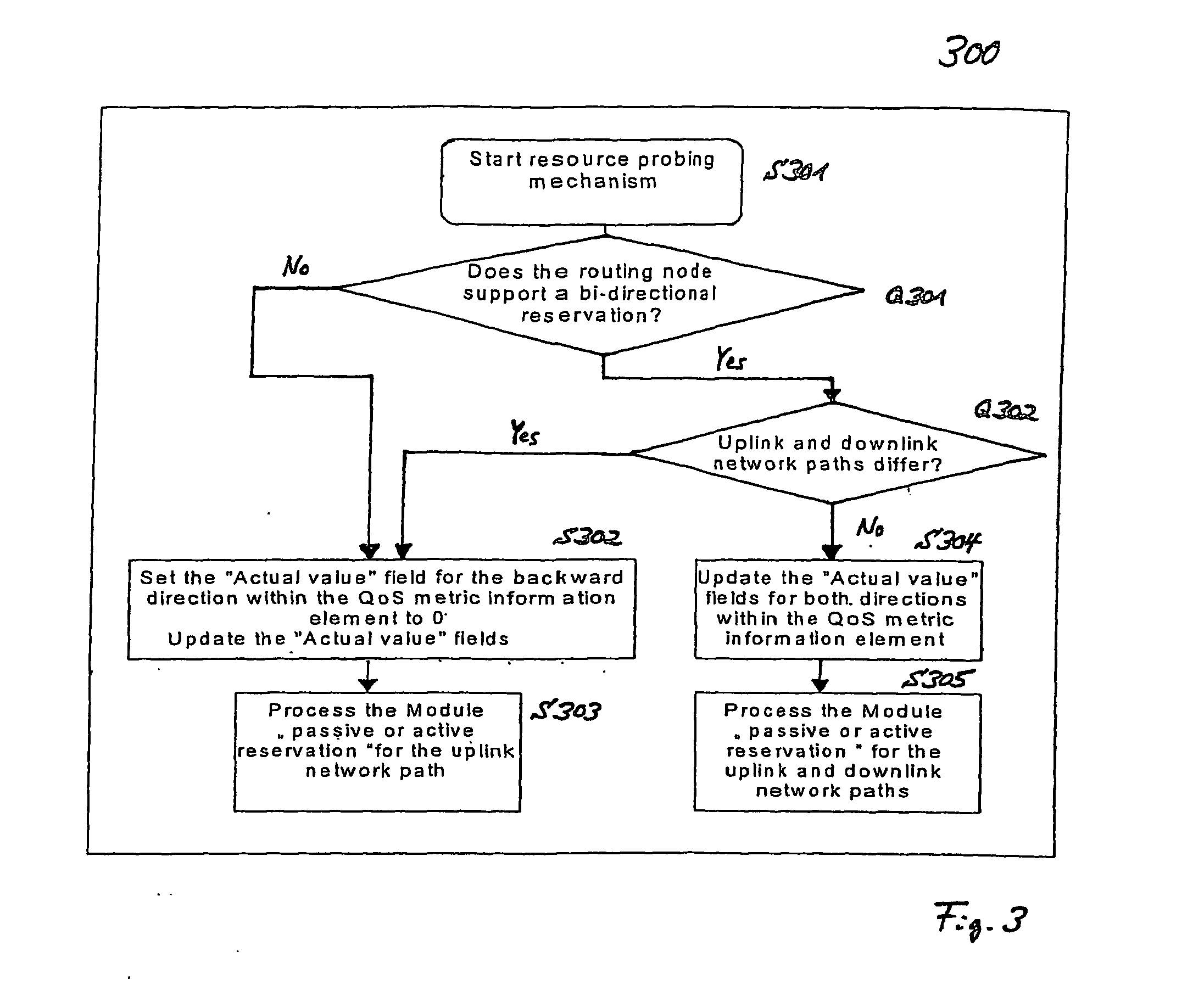
Bidirectional Qos Reservation Within an in-Band Signaling Mechanism
InactiveUS20070217406A1Optimize networkImprove network utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesReal time servicesWireless ad hoc network
A mechanism for a bidirectional reservation procedure within an in-band signaling mechanism gives symmetric real-time services running on mobile devices, which are used to support different access technologies in dynamic, mobile, wireless IP networks where the quality of the node connectivity can sometimes be unpredictably time-varying, the possibility to mutually reserve, monitor and adapt resources and service parameters for upstream and downstream direction along a communication path. The mechanism optimizes reservation mechanisms, especially for adaptive real-time services in wireless and wireless ad-hoc networks, by making use of a dynamic bidirectional reservation in-band signaling approach.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG +1
Dispatch service architecture framework
ActiveUS7787896B2Network topologiesSpecial service for subscribersWireless mesh networkTelecommunications
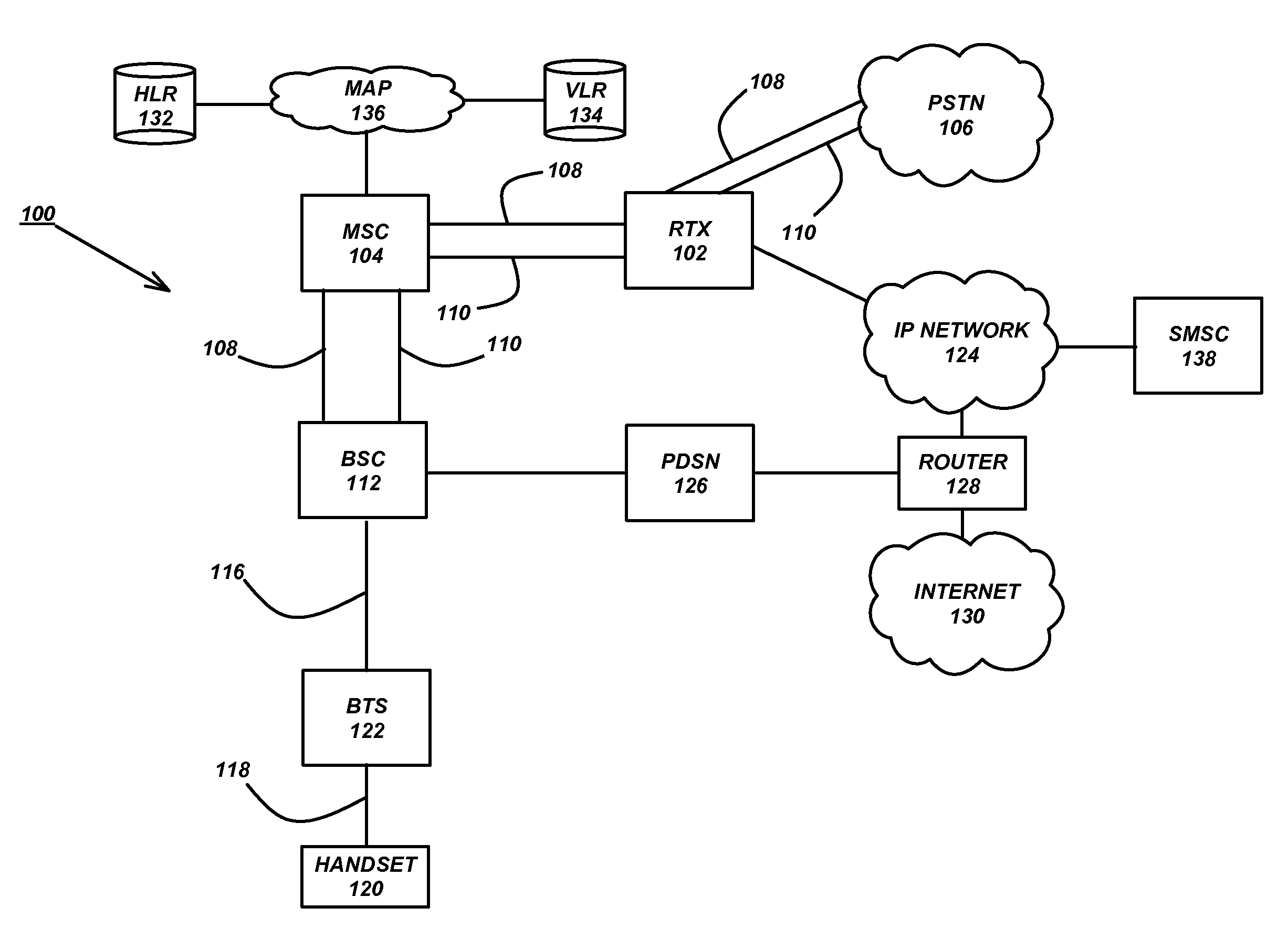
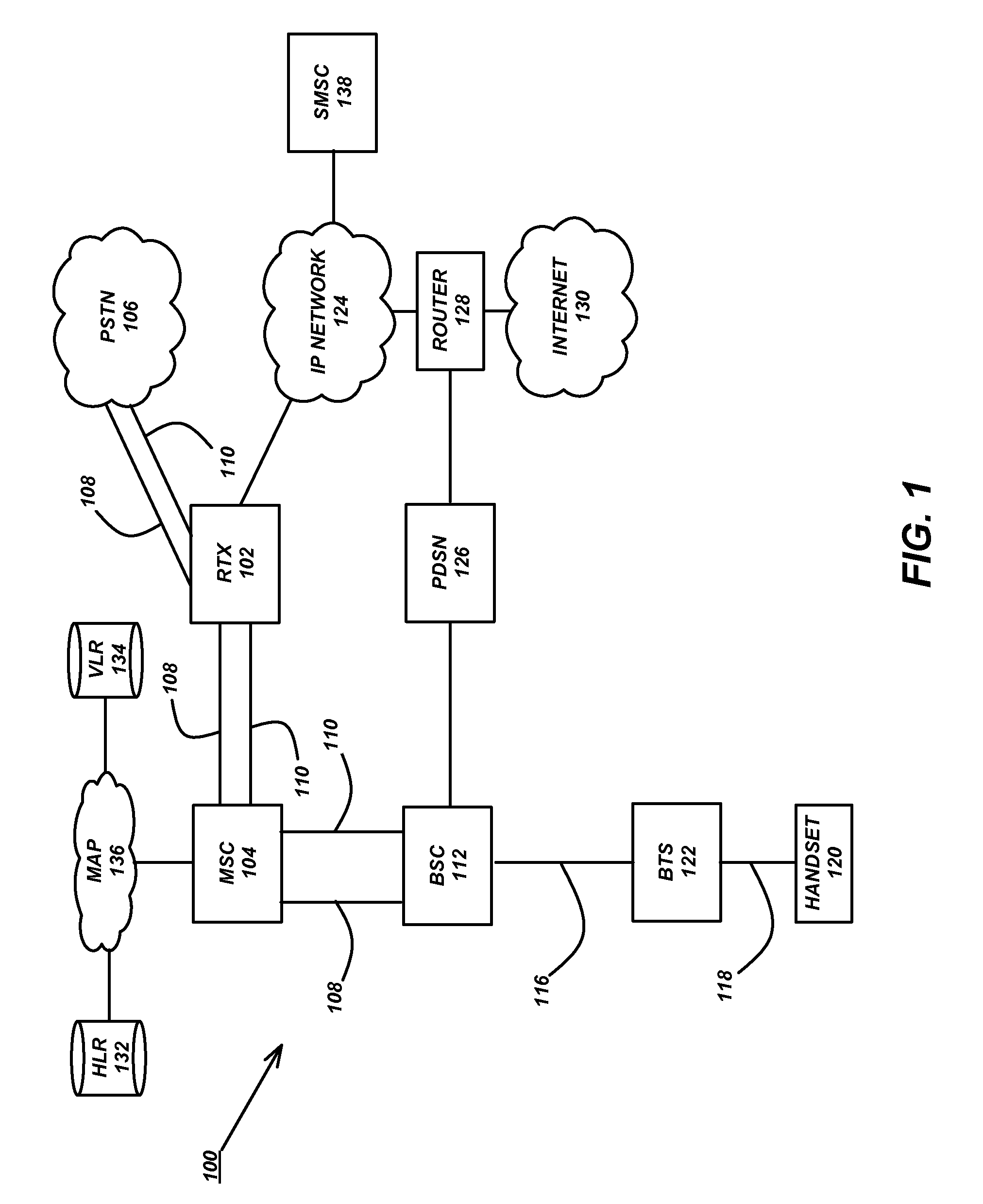
Group voice services are provided in a wireless network, such as a cellular telephone network (104, 108, 116), by a dispatch gateway (102) that interfaces to the wireless network to provide the group voice services therein, wherein both the dispatch gateway and mobiles (120) that use the group voice services communicate with each other using cell setup and in-band signaling within the wireless network.
Owner:KODIAK NETWORKS
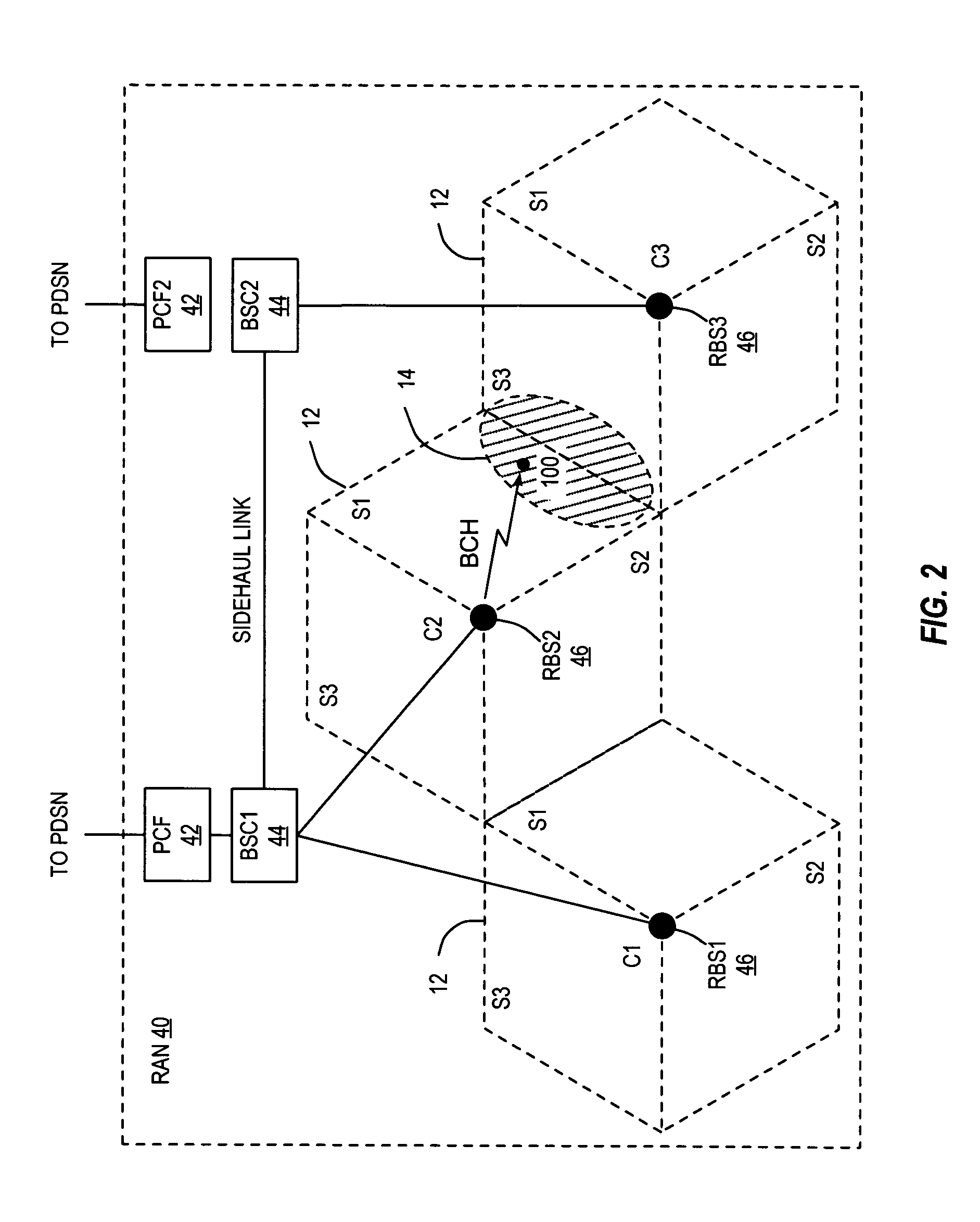
In-band signaling within broadcast stream and support for mixed flows
InactiveUS20050118946A1Special service provision for substationBroadcast with distributionBroadcast channelsMobile station
A base station inserts an overhead message into a broadcast stream transmitted to a mobile station. To support autonomous soft handoff by the mobile station, the base station inserting the overhead message sends a notification message to one or more of the base stations transmitting the same broadcast stream. The notification message indicates the time when the overhead message will be sent and the duration and / or length of the overhead message. The broadcast channel may be divided into multiple time slots to support mixed flows. Base stations supporting a mobile station in soft handoff can agree on the time slots allocated for a designated broadcast stream.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
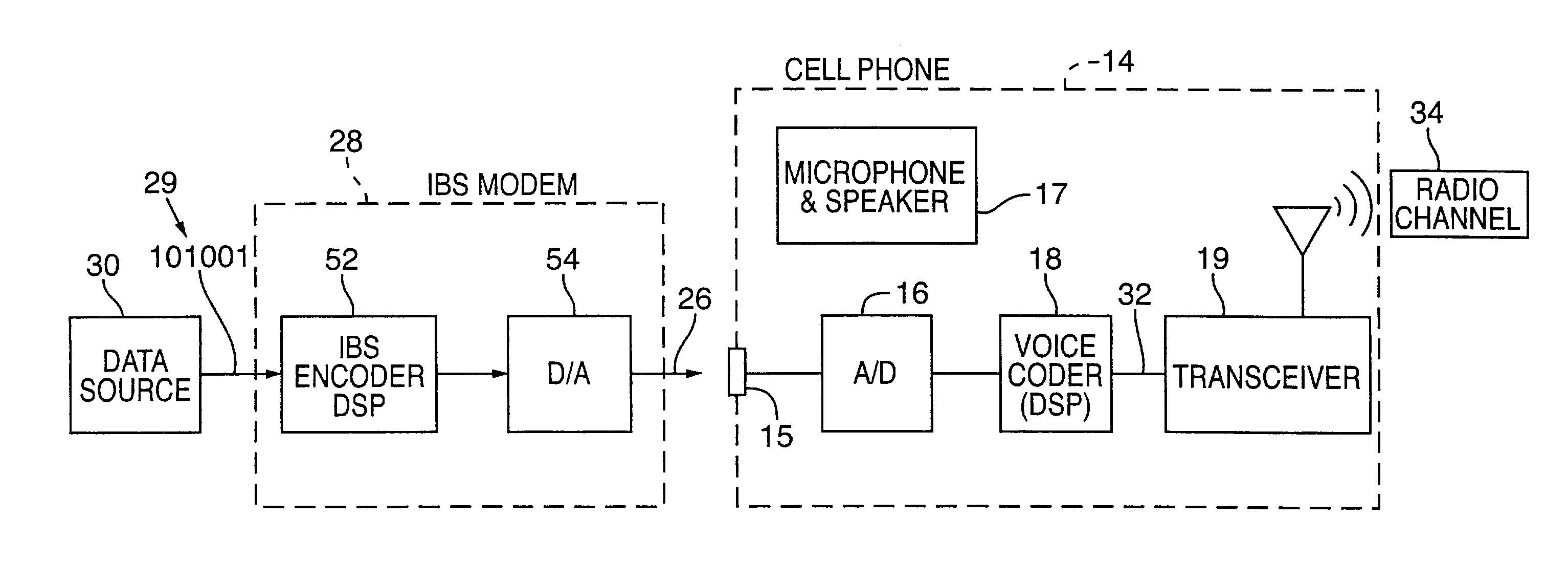
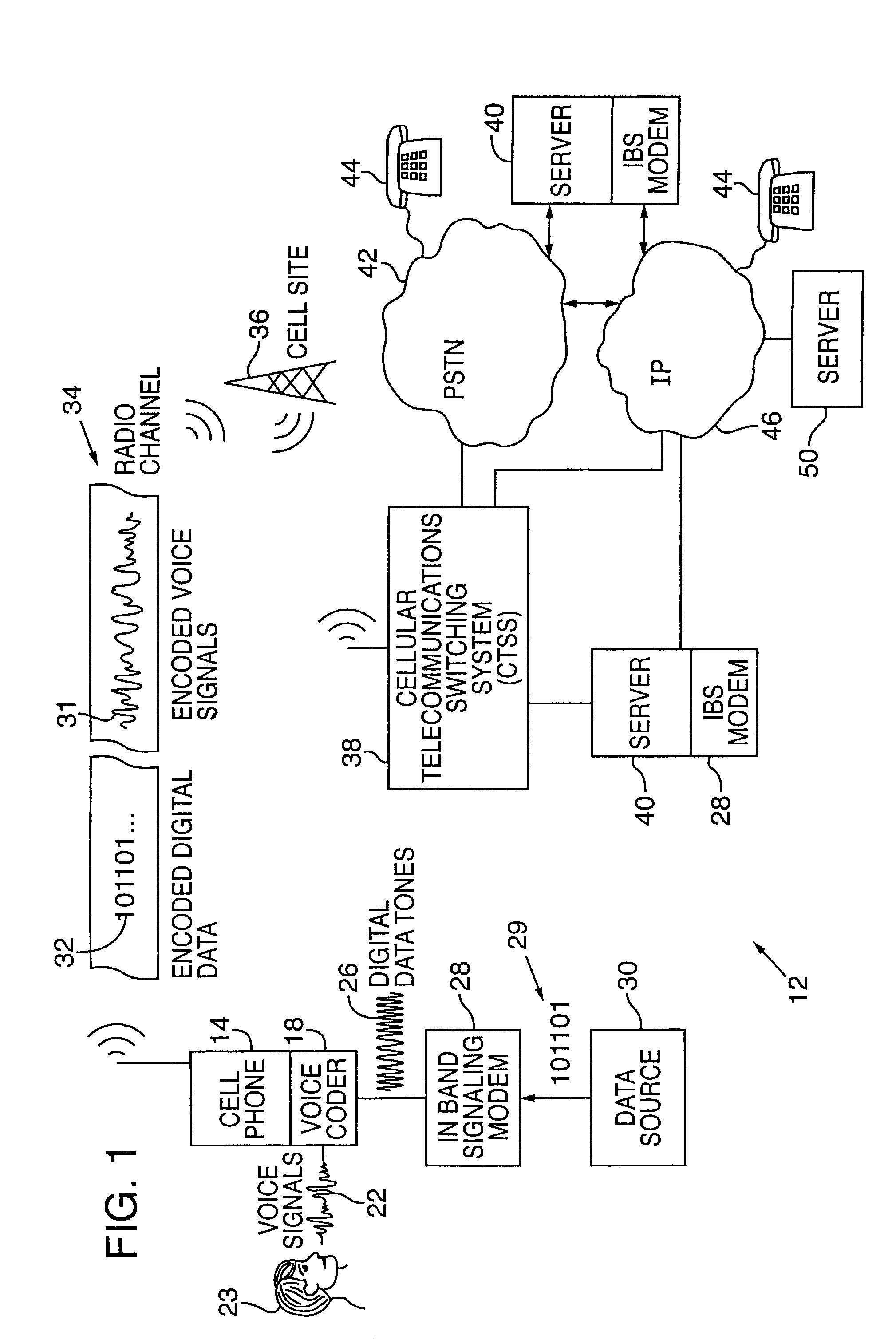
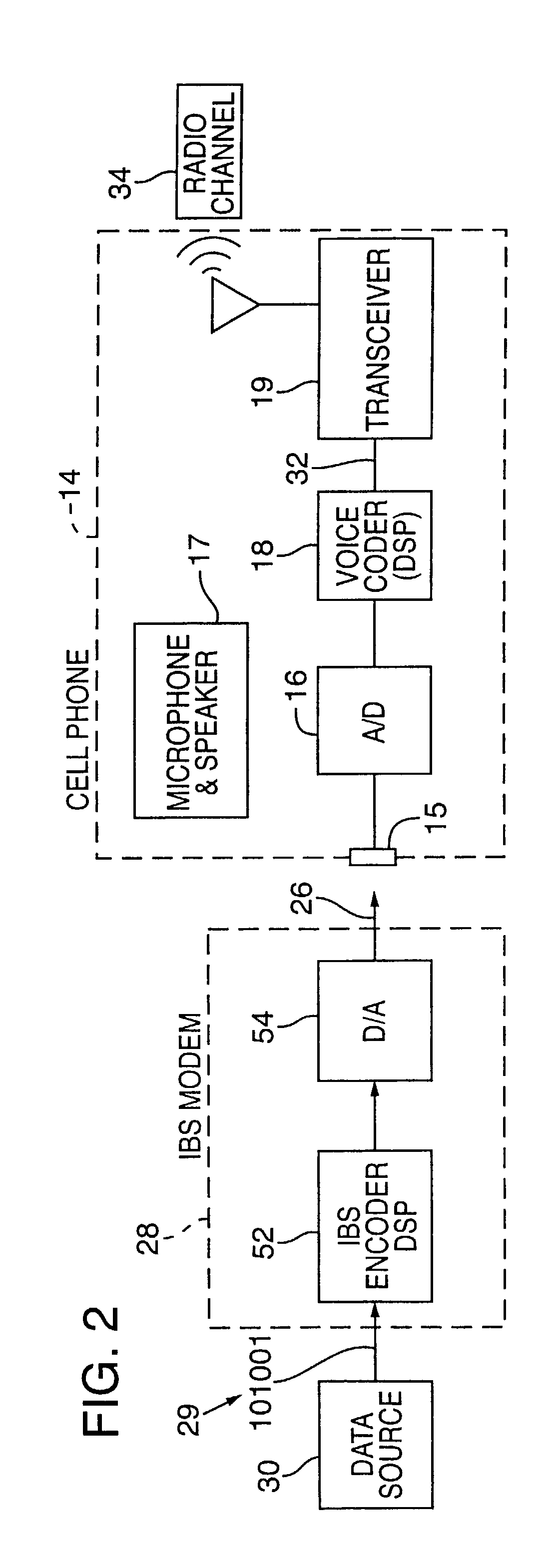
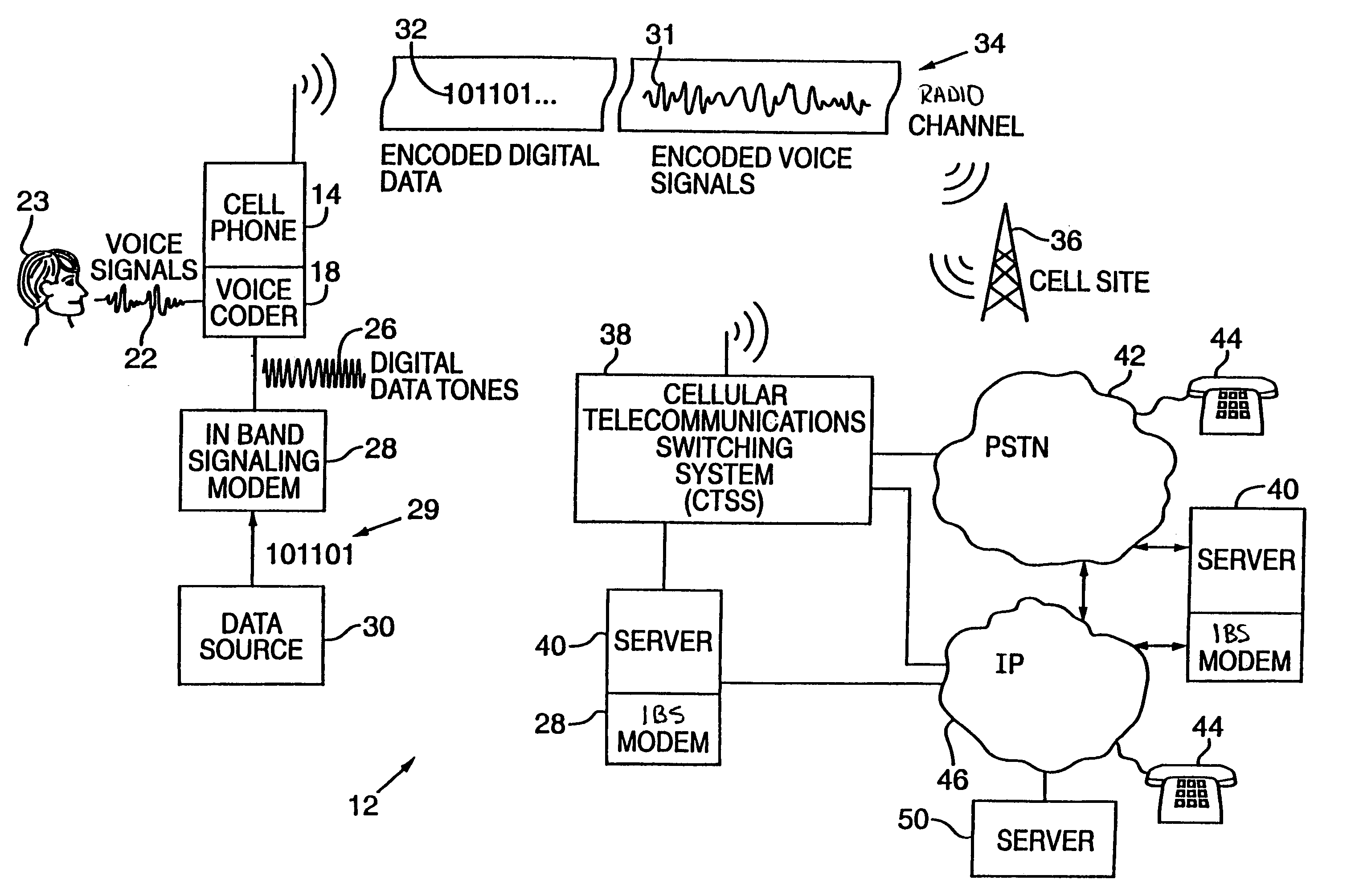
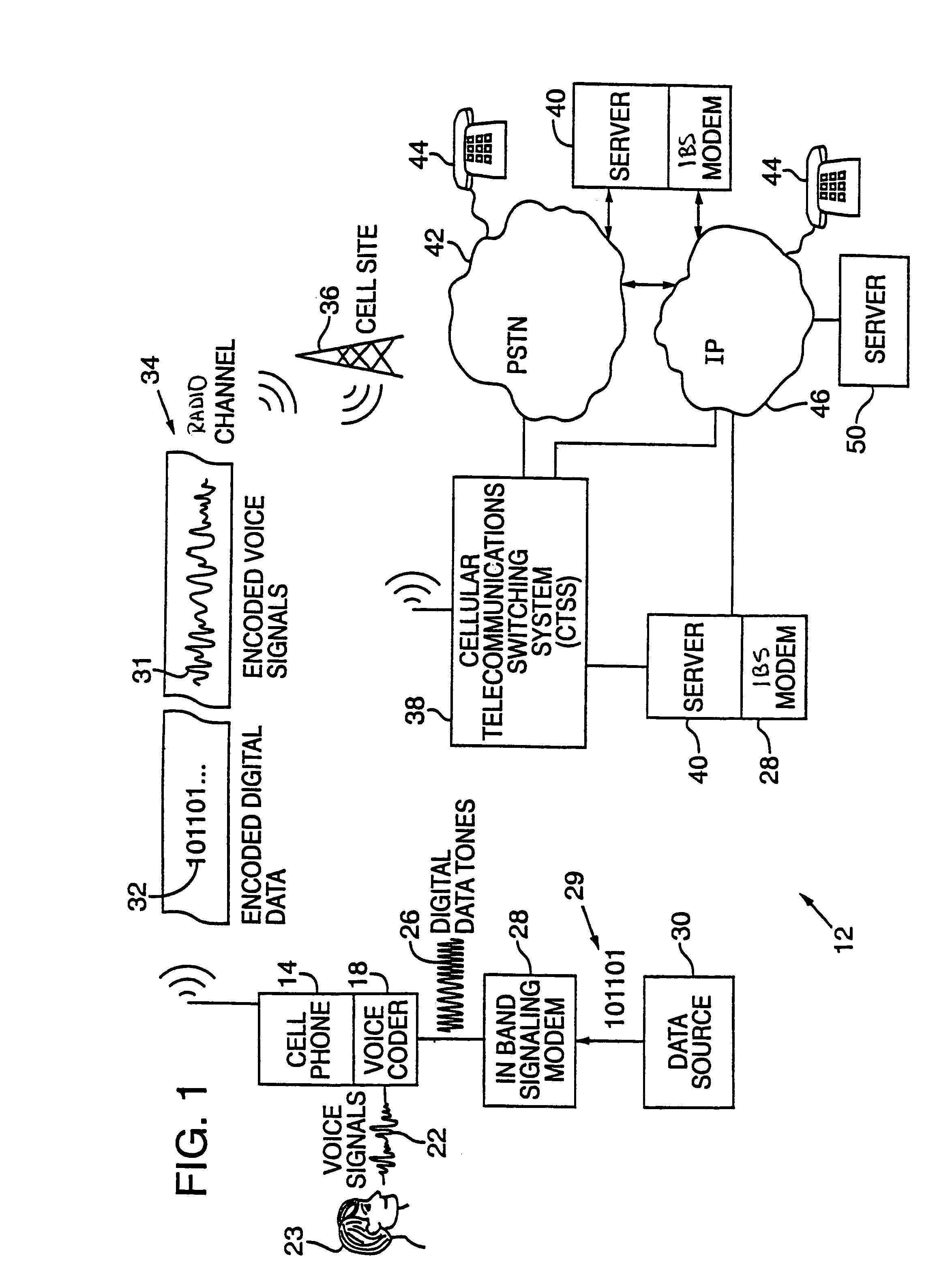
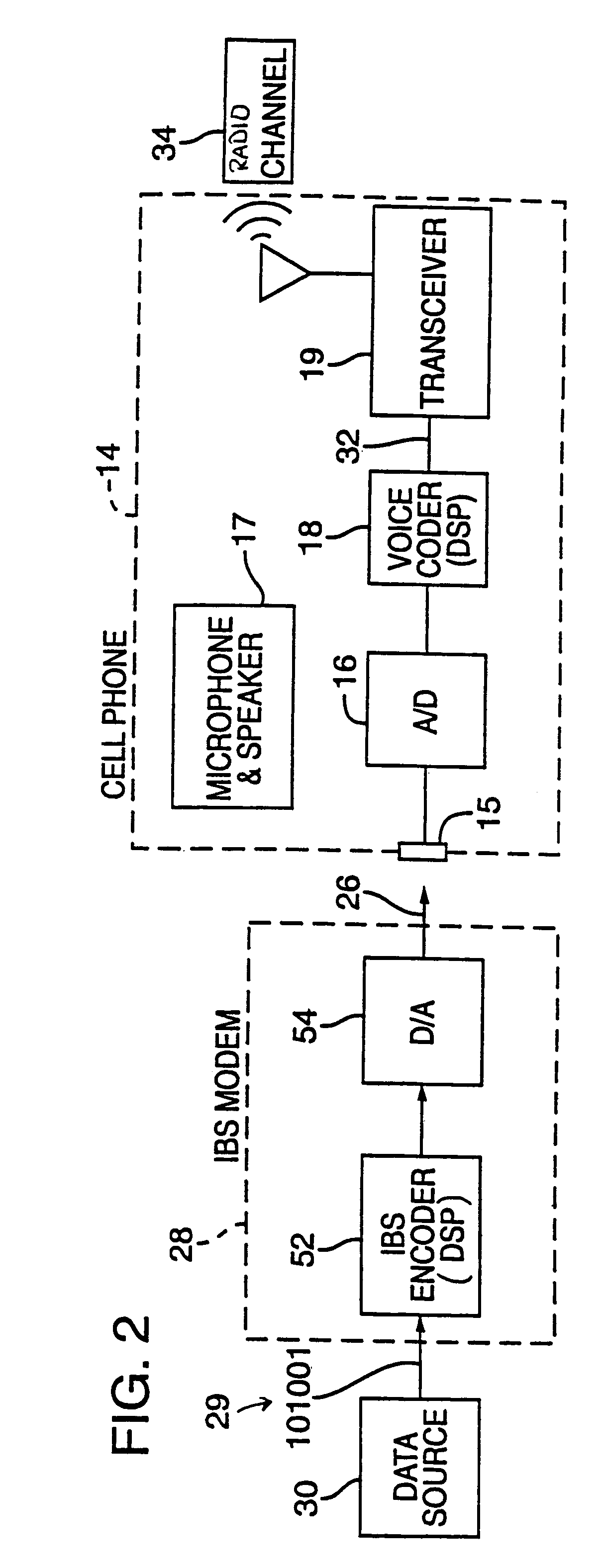
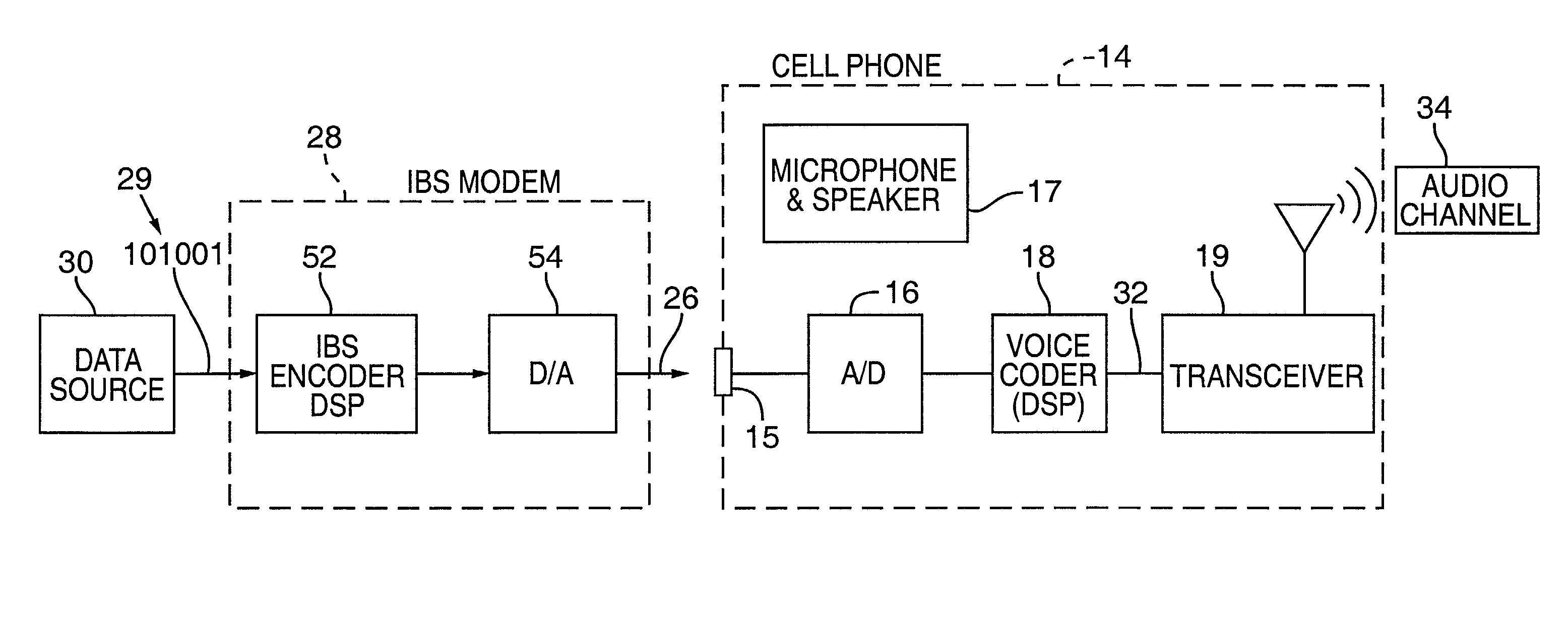
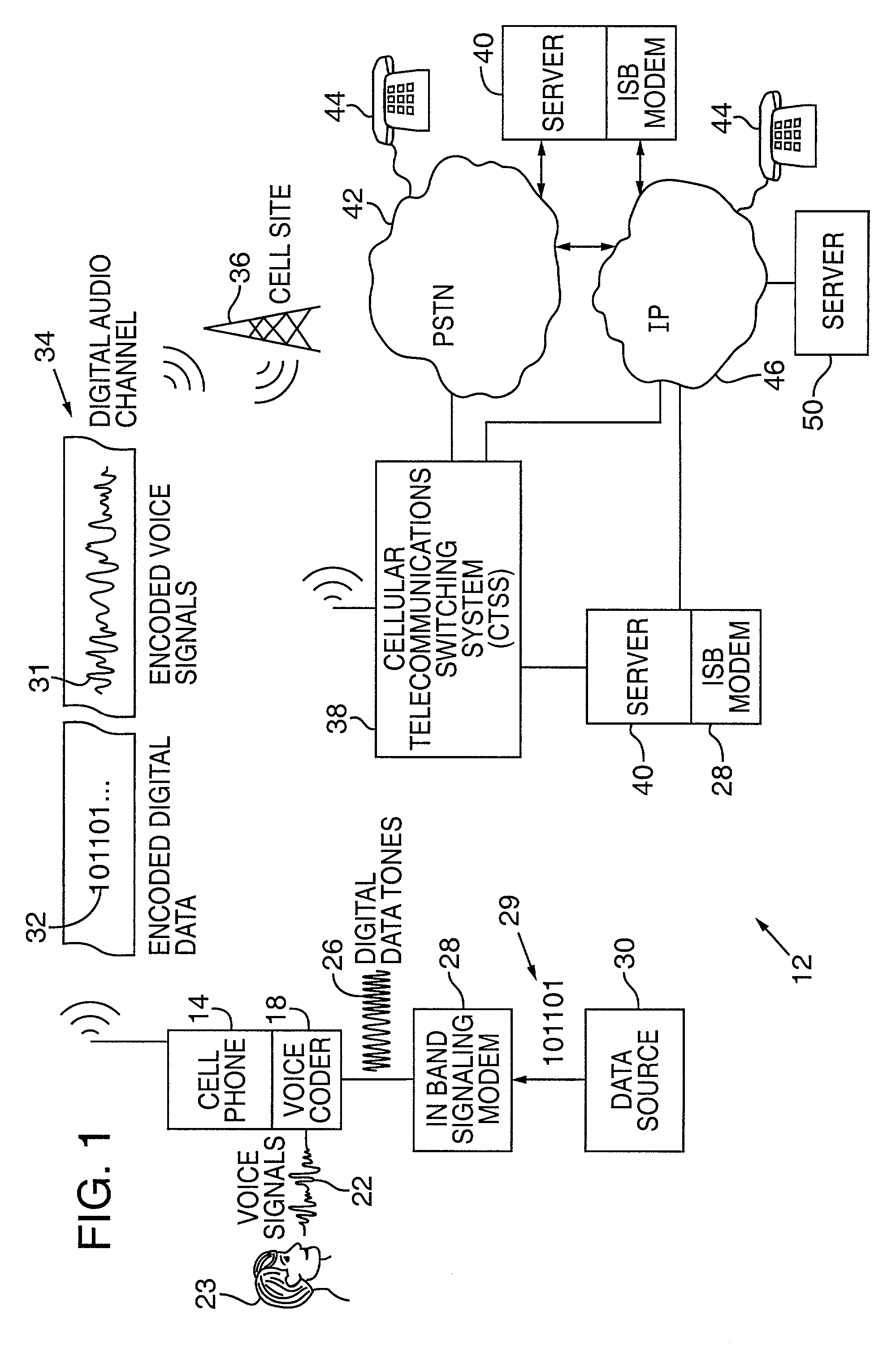
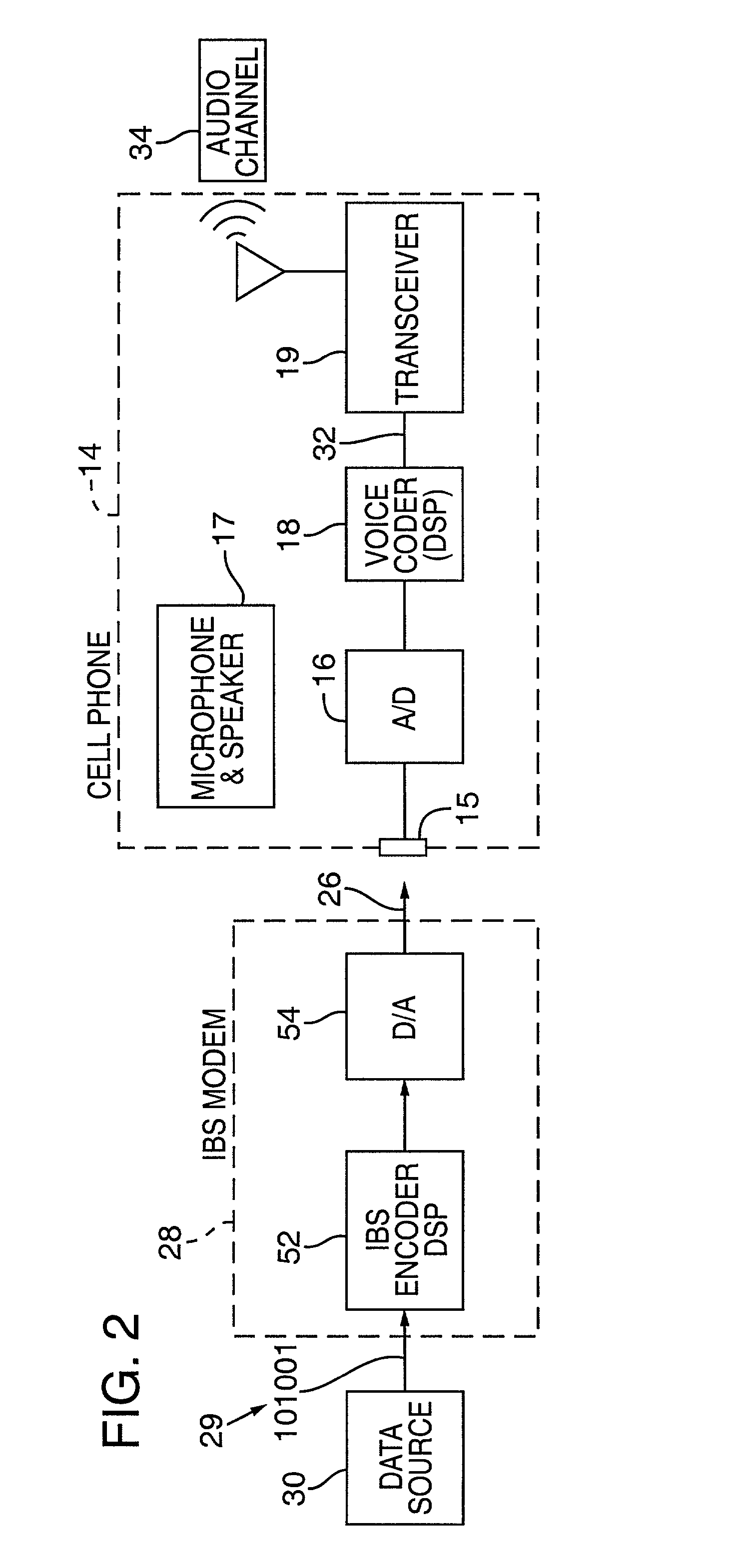
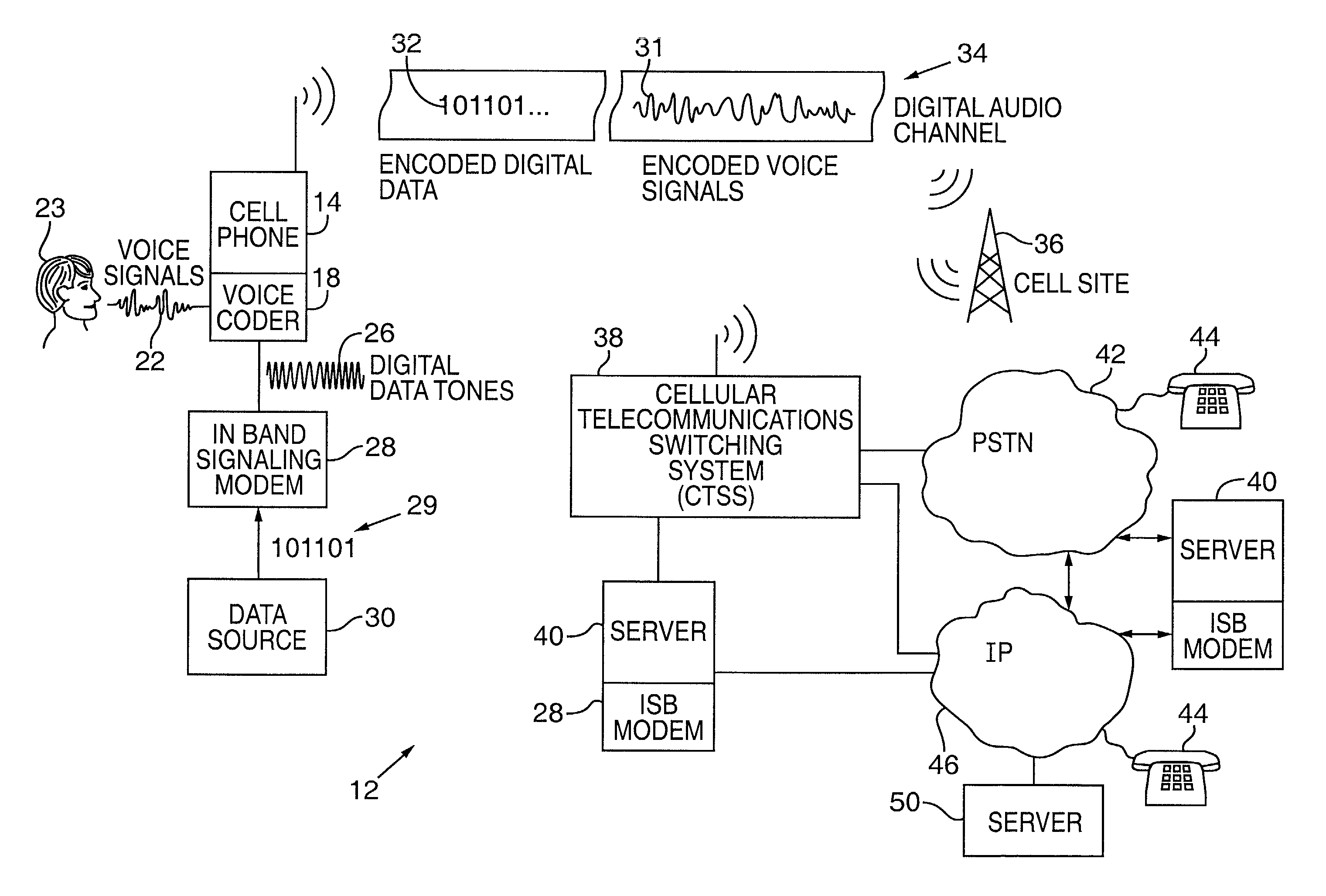
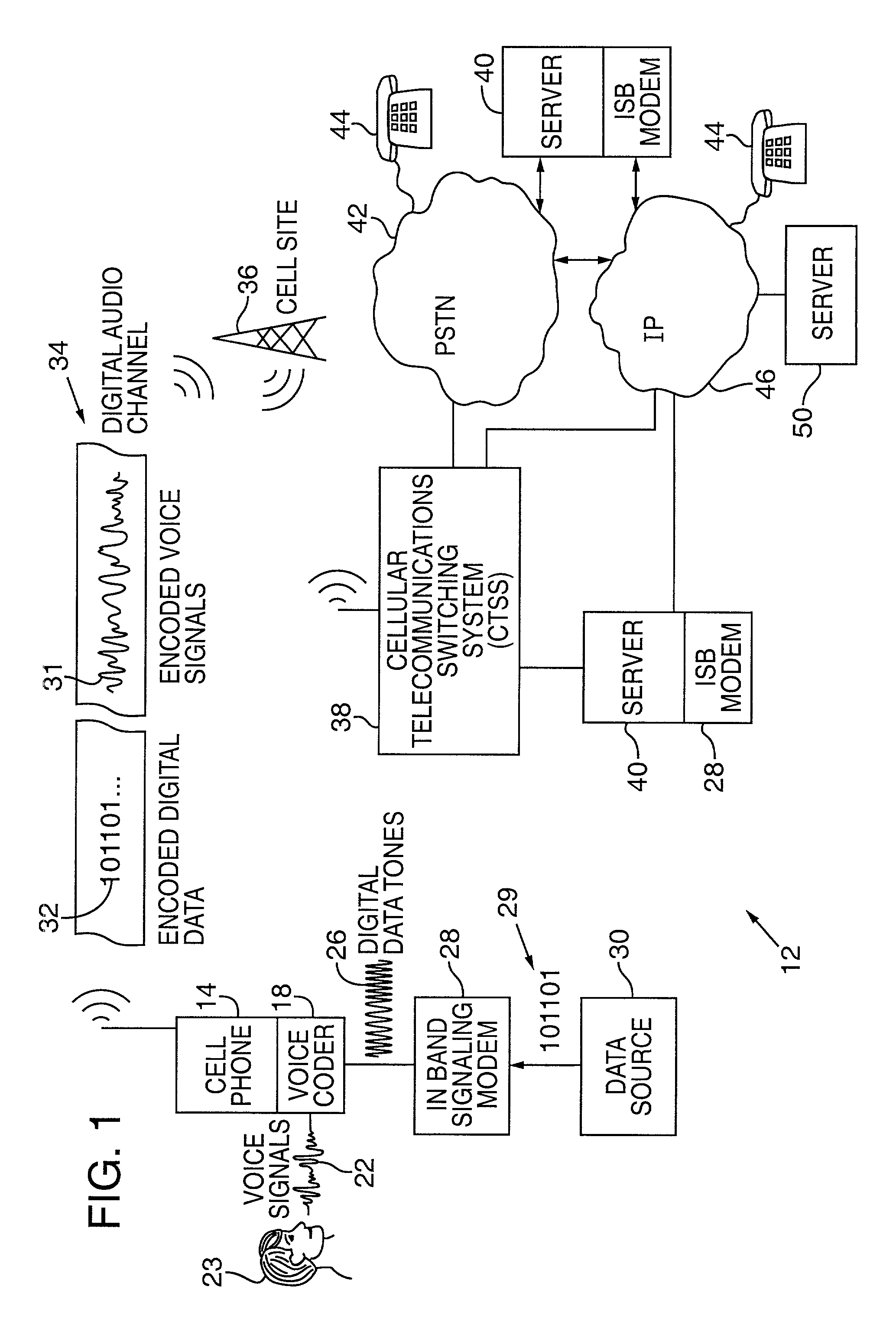
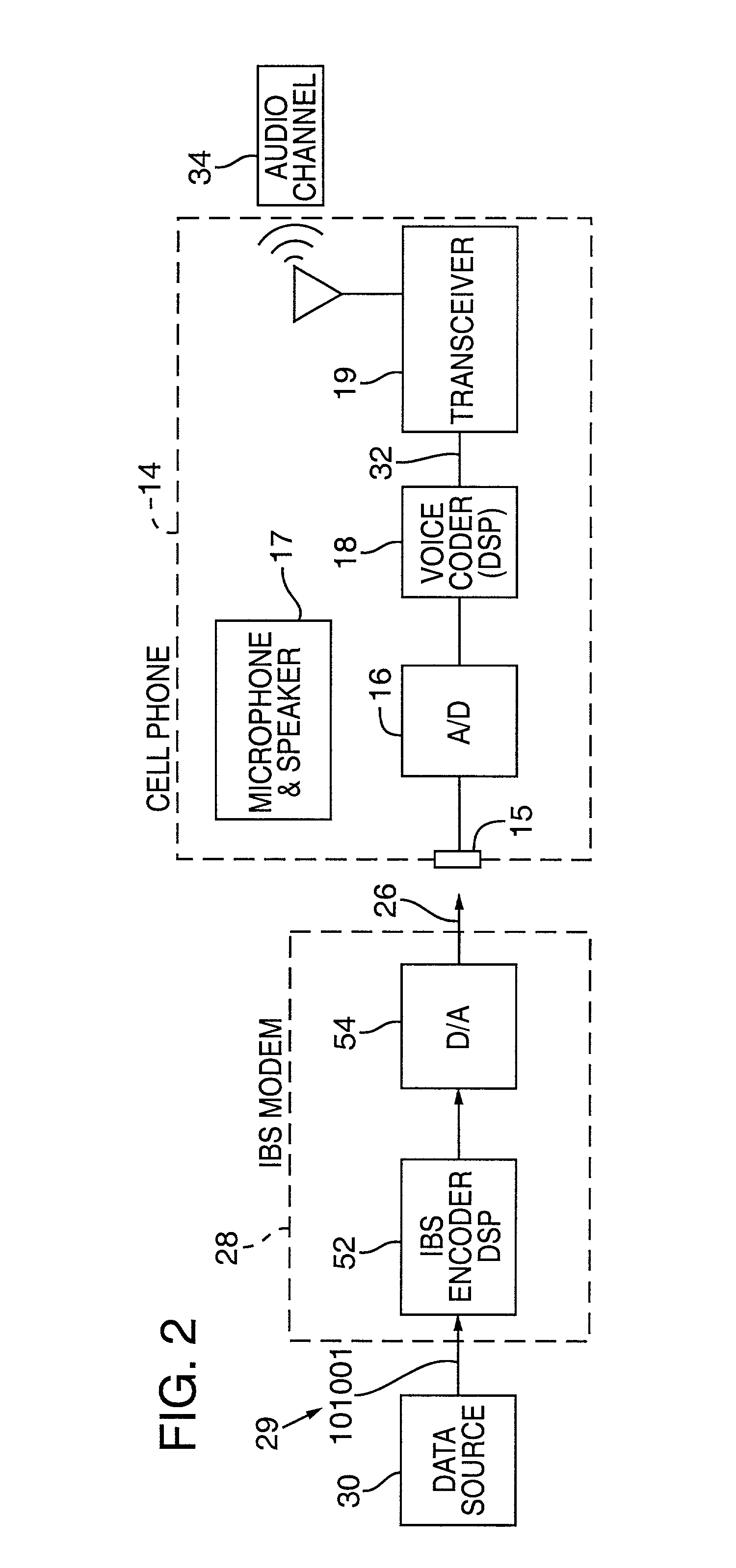
Synchronizer for use with improved in-band signaling for data communications over digital wireless telecommunications networks
InactiveUS7286522B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlDigital dataTelecommunications network
An inband signaling modem communicates digital data over a voice channel of a wireless telecommunications network. An input receives digital data. An encoder converts the digital data into audio tones that synthesize frequency characteristics of human speech. The digital data is also encoded to prevent voice encoding circuitry in the telecommunications network from corrupting the synthesized audio tones representing the digital data. An output then outputs the synthesized audio tones to a voice channel of a digital wireless telecommunications network.
Owner:AIRBIQUITY INC
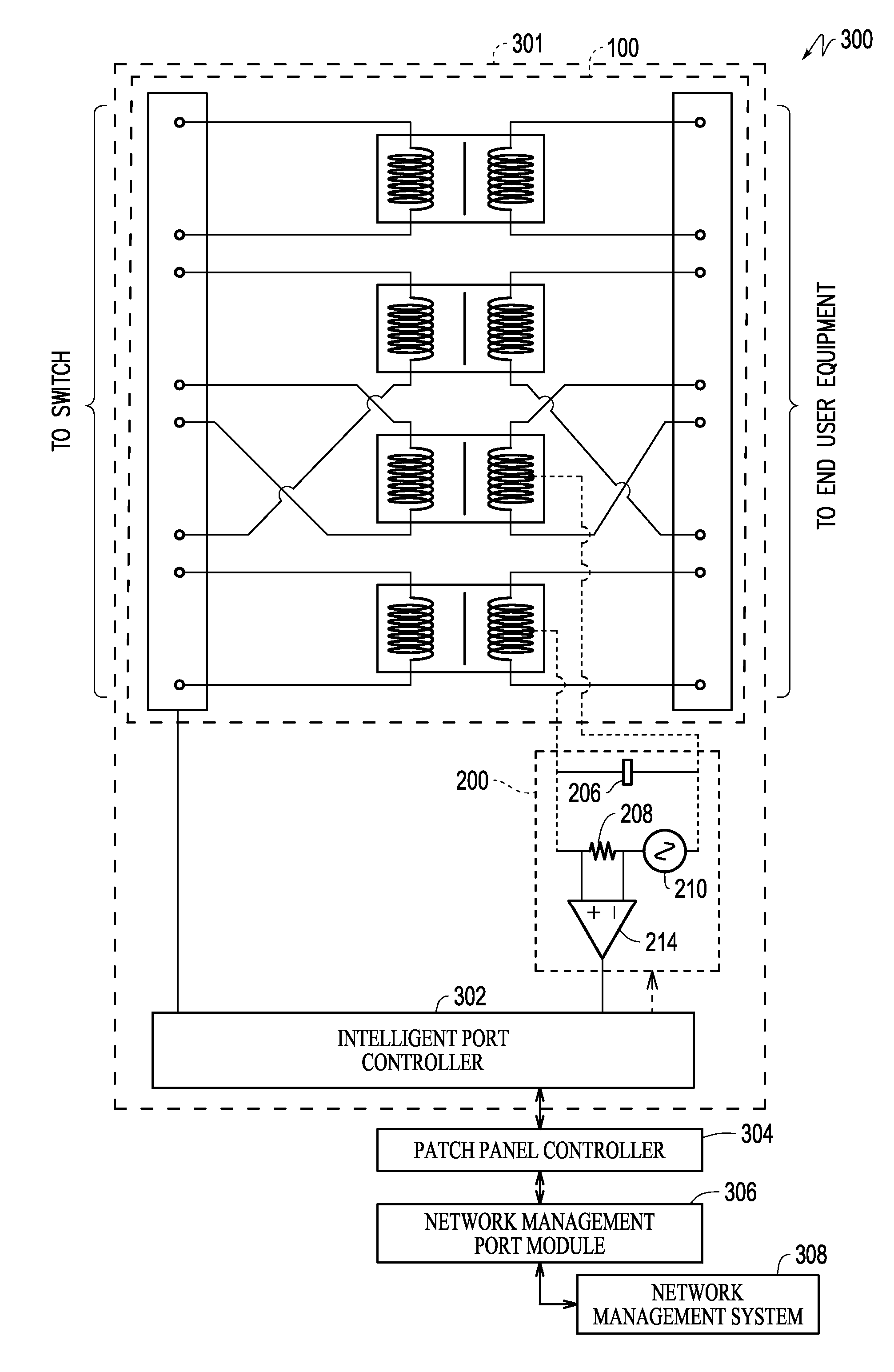
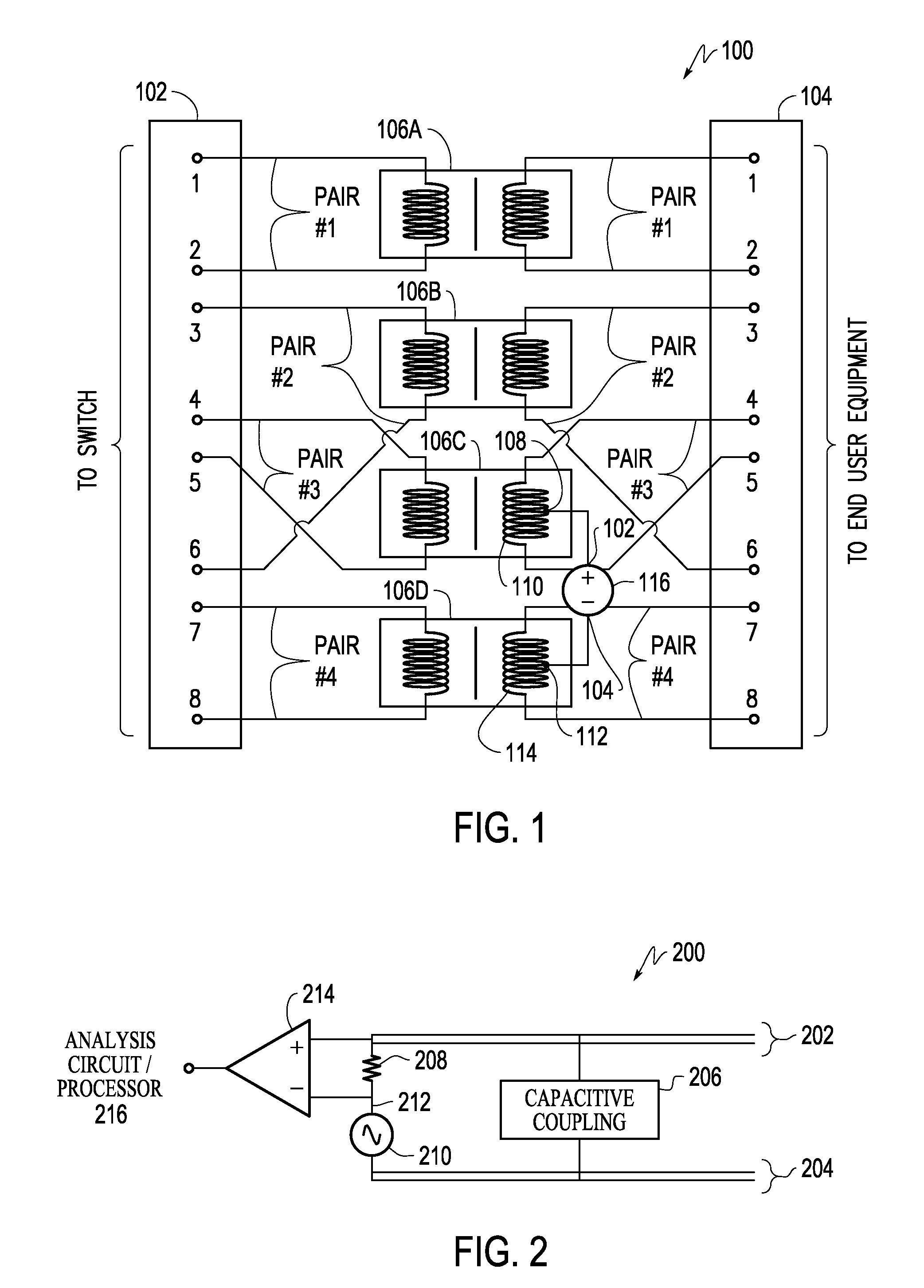
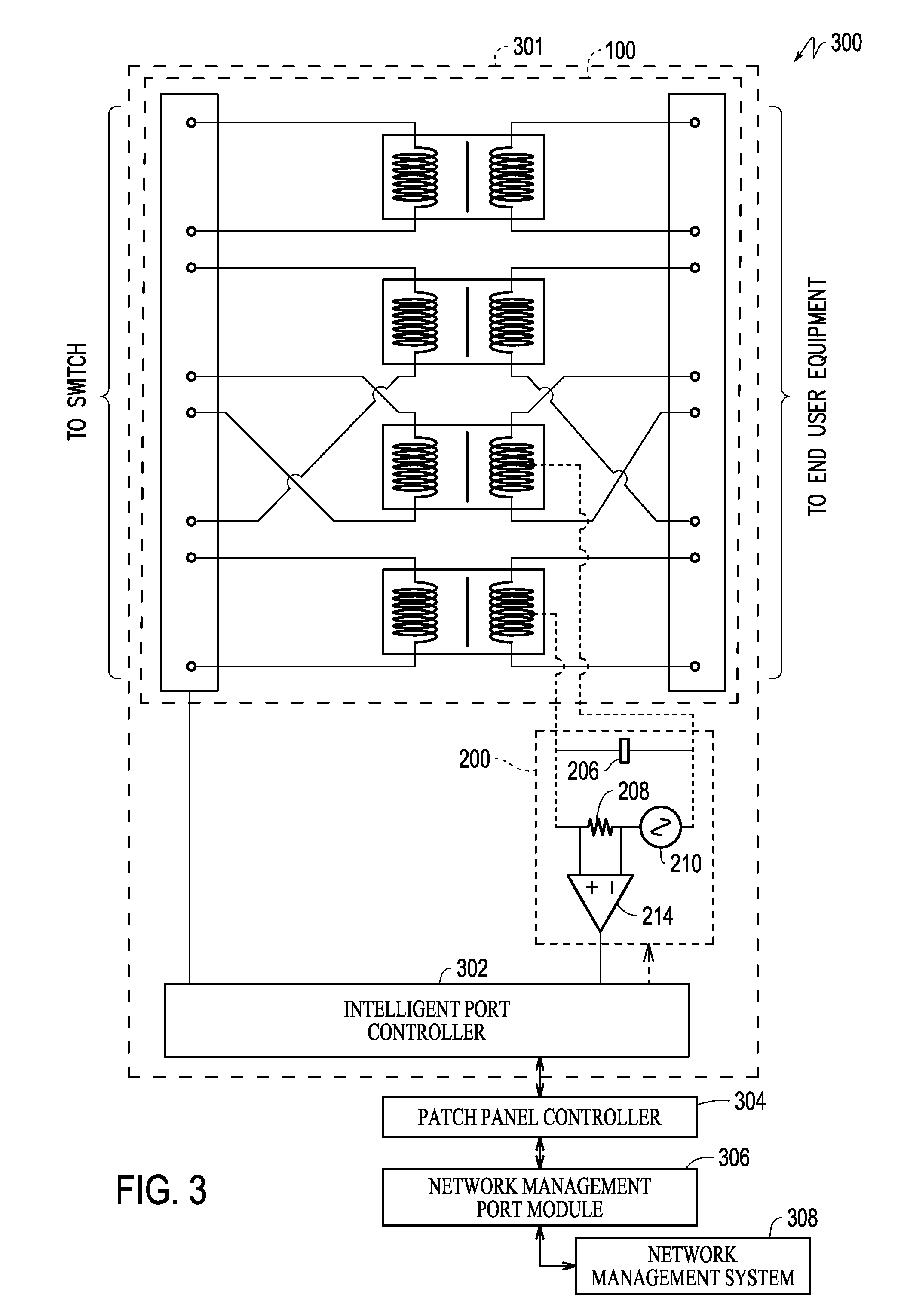
Power patch panel with guided mac capability
A method and apparatus are provided for incorporating guided network cable Move / Add / Change (MAC) work order capability into a power patch panel. MAC work orders may be controlled and monitored using in-band signaling using, e.g., standard RJ-45 patch cords. Cable detection is performed at a port level on a real-time basis. Coordination of guided MAC operations may be performed by the patch panel, independently, or in conjunction with, or under the control of, a remote Network Management System. The patch panel may be in either an interconnect or cross-connect configuration.
Owner:PANDUIT
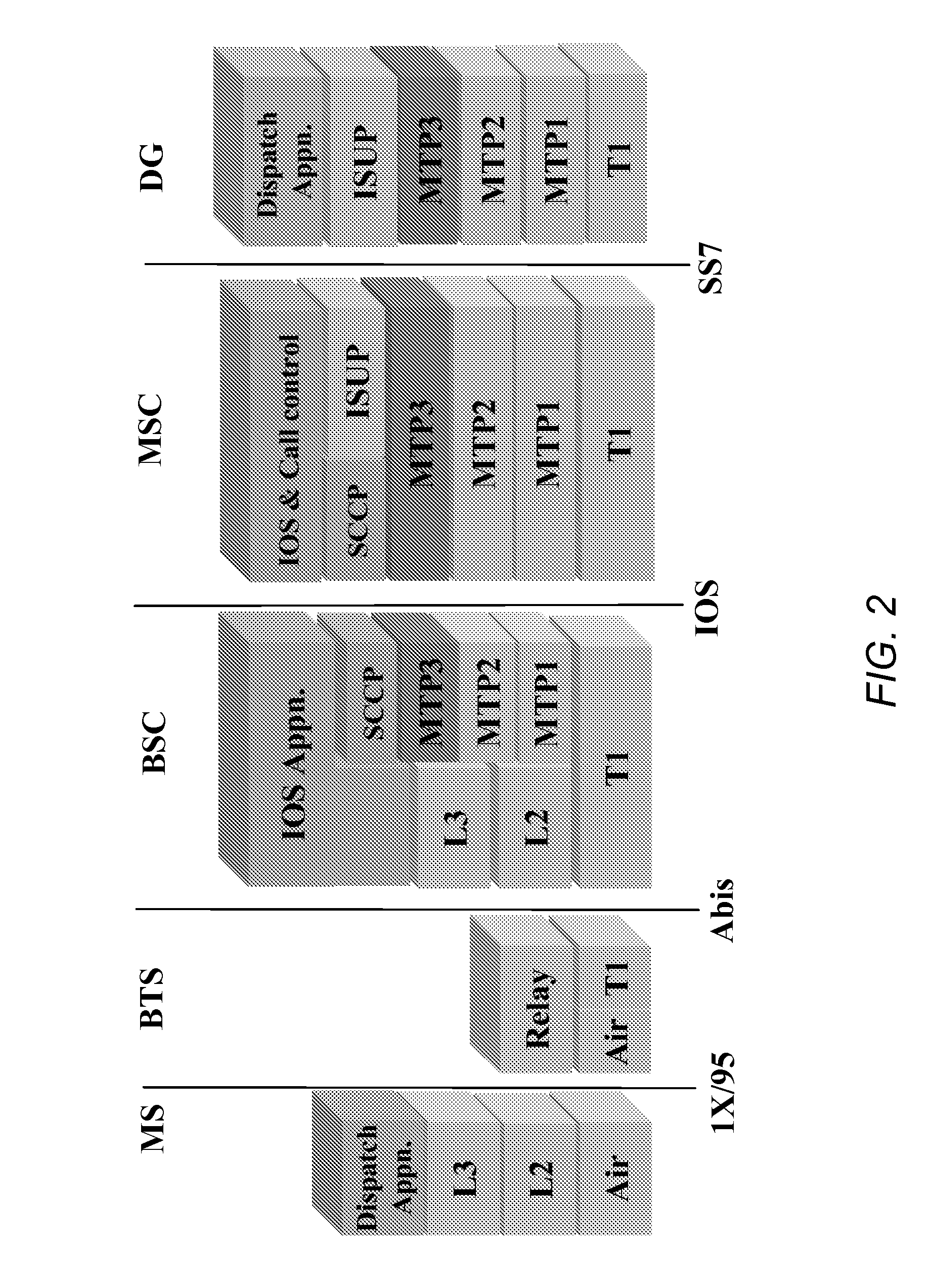
Methods and systems for call routing and codec negotiation in hybrid voice/data/internet/wireless systems
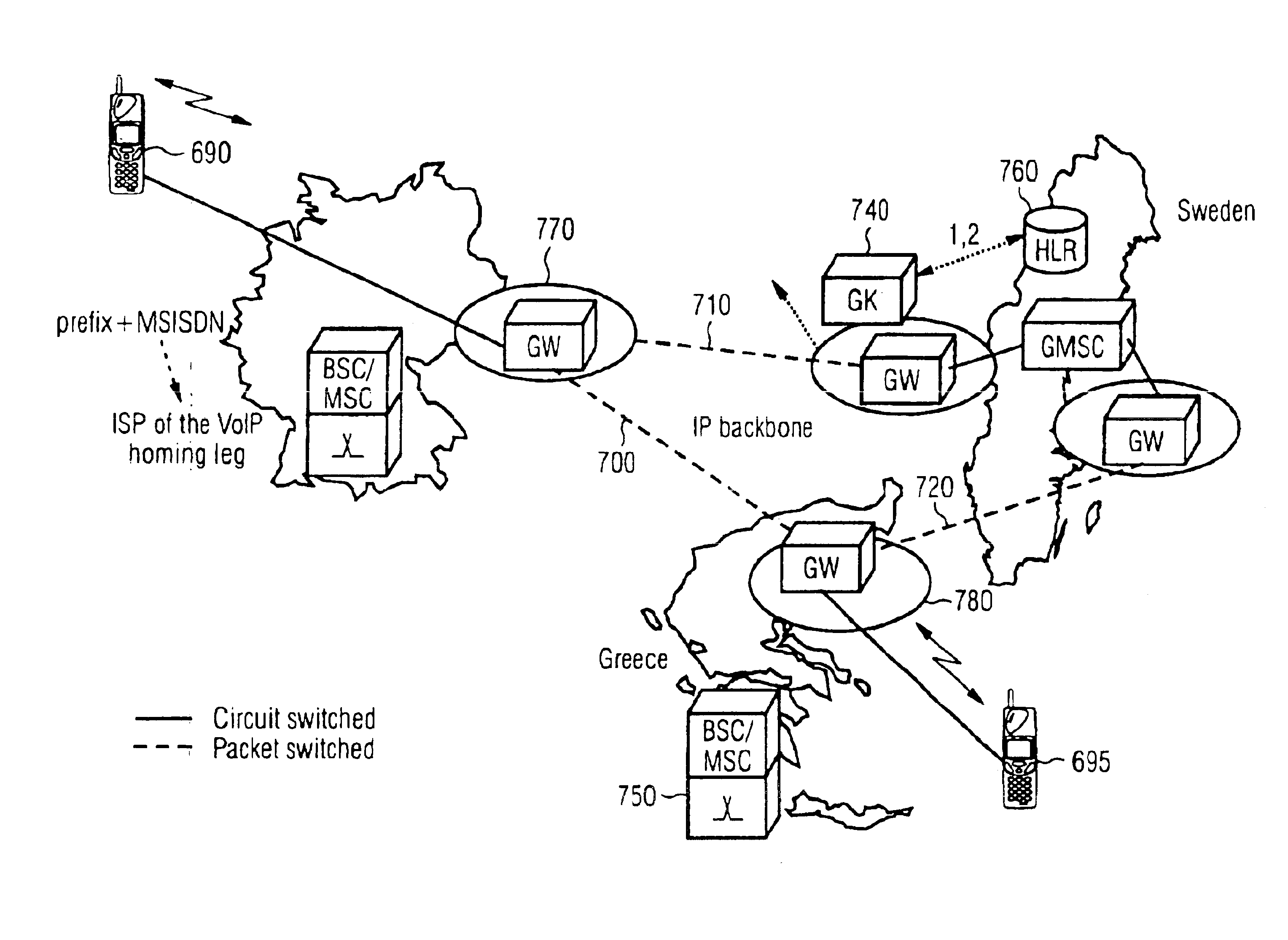
InactiveUS6856612B1Minimize delayMinimize the numberInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsThe InternetTranscoding
A method and system for communicating information includes evaluation regarding routing of calls performed at a call control point in an ITSP and / or wireless network. A PIC identity associated with another party's preferences is acquired and sent to the call control point. The PIC identity identifies the type of the carrier network (e.g., circuit switched or VoIP) and is used to make further routing decisions. If a circuit-switched carrier is identified, the IP homing leg is terminated at the voice gateway in the recipient's HPLMN and information is sent over to the GMSC where normal, circuit-switched routing procedures. If a VoIP carrier is identified then the called user's roaming number is retrieved from the HLR, and the call is further routed directly over the IP domain towards a voice gateway at the visited network minimizing the number of transcodings. Additional transcoding steps can be avoided if a single encoding is agreed upon according to “tandem free operation” (TFO). Combining inband signaling through the telephony exchanges and out-of-band signaling in the IP network it is possible to achieve, for a mobile subscriber, one encoding and one decoding of a voice.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
In-band signaling for data communications over digital wireless telecommunications networks
InactiveUS7151768B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlDigital dataTelecommunications link
An inband signaling modem communicates digital data over a voice channel of a wireless telecommunications network. An input receives digital data. An encoder converts the digital data into audio tones that synthesize frequency characteristics of human speech. The digital data is also encoded to prevent voice encoding circuitry in the telecommunications network from corrupting the synthesized audio tones representing the digital data. An output then outputs the synthesized audio tones to a voice channel of a digital wireless telecommunications network.
Owner:AIRBIQUITY INC
Software code for improved in-band signaling for data communications over digital wireless telecommunications networks
InactiveUS7206305B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlDigital dataTelecommunications link
An inband signaling modem communicates digital data over a voice channel of a wireless telecommunications network. An input receives digital data. An encoder converts the digital data into audio tones that synthesize frequency characteristics of human speech. The digital data is also encoded to prevent voice encoding circuitry in the telecommunications network from corrupting the synthesized audio tones representing the digital data. An output then outputs the synthesized audio tones to a voice channel of a digital wireless telecommunications network.
Owner:AIRBIQUITY INC
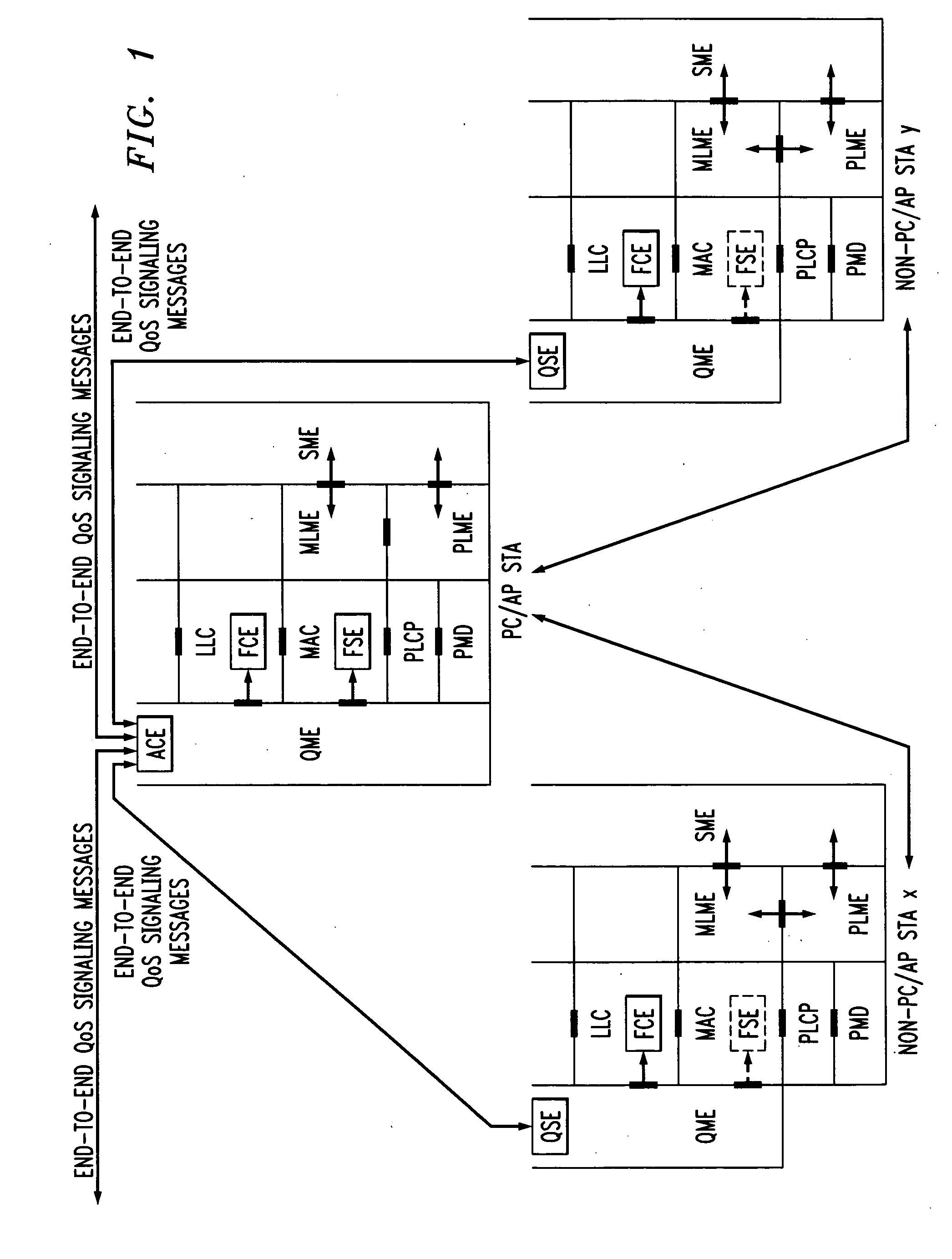
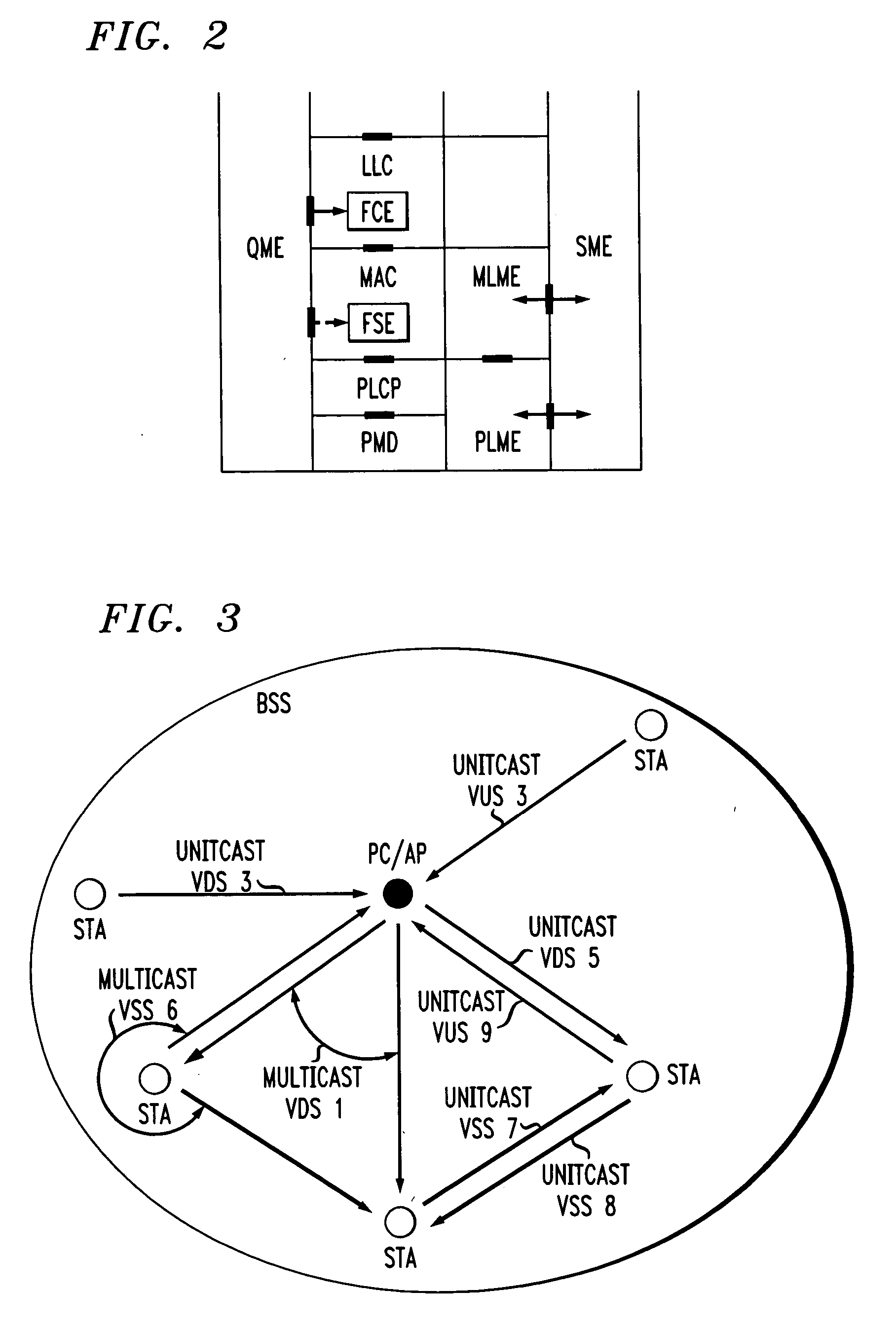
In-band QoS signaling refernce model for QoS-driven wireless lans
InactiveUS20050041670A1Function increaseError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceFrame based
A station, such as a point coordinator (PC) or a non-PC station, in a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) is disclosed. The station includes a frame classification entity (FCE), a frame scheduling entity (FSE) and a QoS management entity (QME). The FCE is logically located in a logical link control (LLC) layer of the station and has a classification table containing at least one classifier entry. Each classifier entry contains a virtual stream identifier (VSID) and a frame classifier associated with a user session. The FCE receives a data frame associated with the user session, which can be one of a voice session, a video session, a data session and a multimedia session. The data frame contains in-band quality of service (QoS) signaling information for the user session. The FCE classifies the received data frame to a selected VSID contained in a classifier entry in the classification table based on a match between an in-band frame classification information contained in the received frame and the frame classifier contained in the classifier entry. The FSE is logically located in a medium access control (MAC) sublayer of the station and has a frame scheduling table containing at least one entry. Each entry in the frame scheduling table contains a VSID and a QoS parameter set associated with a user session identified by the VSID. The FSE is responsive to the classified data frame by scheduling a transmission opportunity (TO) for the classified data frame based on the at least one QoS parameter value associated with the VSID and characterizing the user session. The QME interfaces with the FCE and The FSE.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Cellular telephone having improved in-band signaling for data communications over digital wireless telecommunications networks
InactiveUS7221669B2Road vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationDigital dataTelecommunications link
Owner:AIRBIQUITY INC
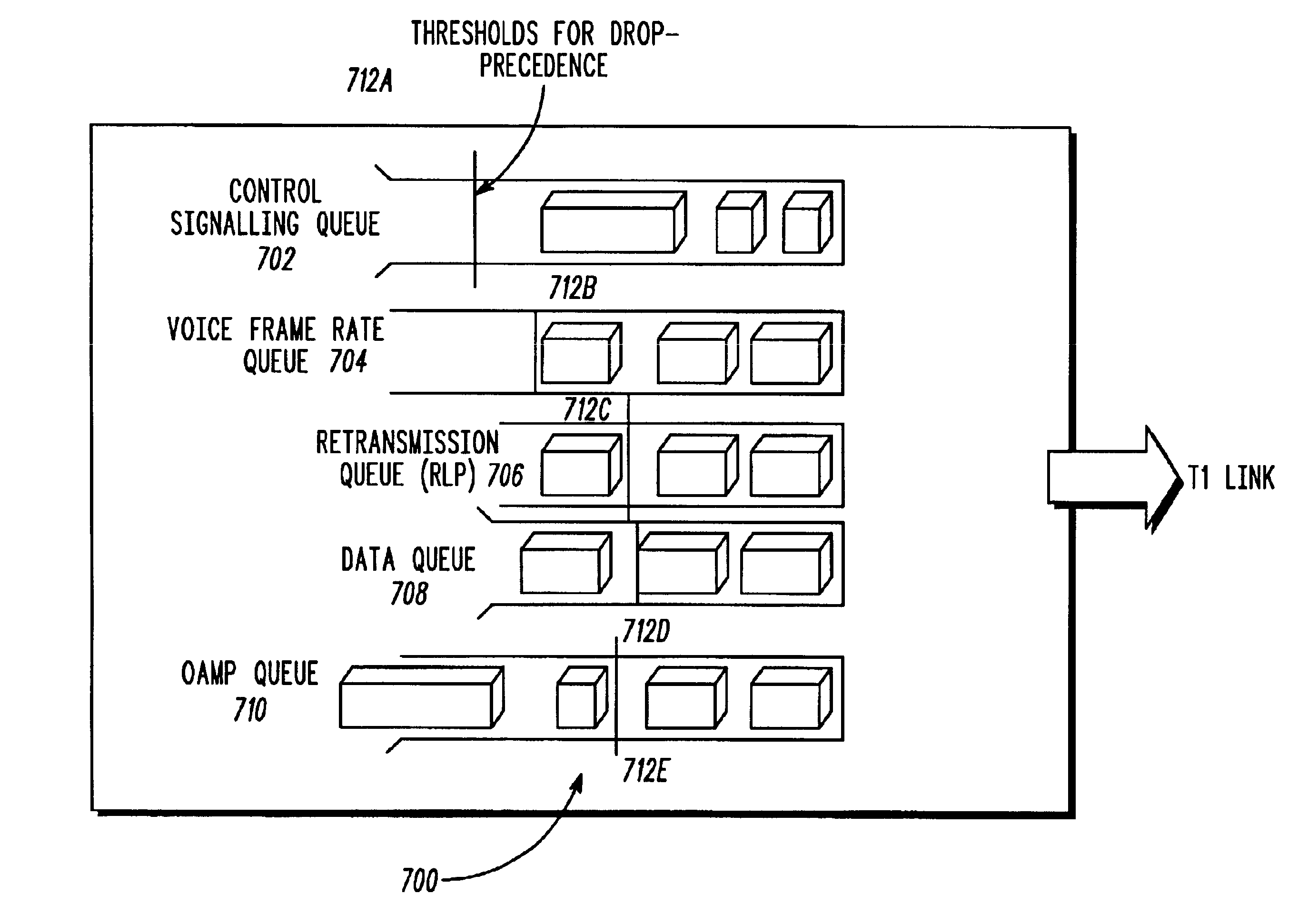
Method and apparatus for enhancing the quality of service of a wireless communication
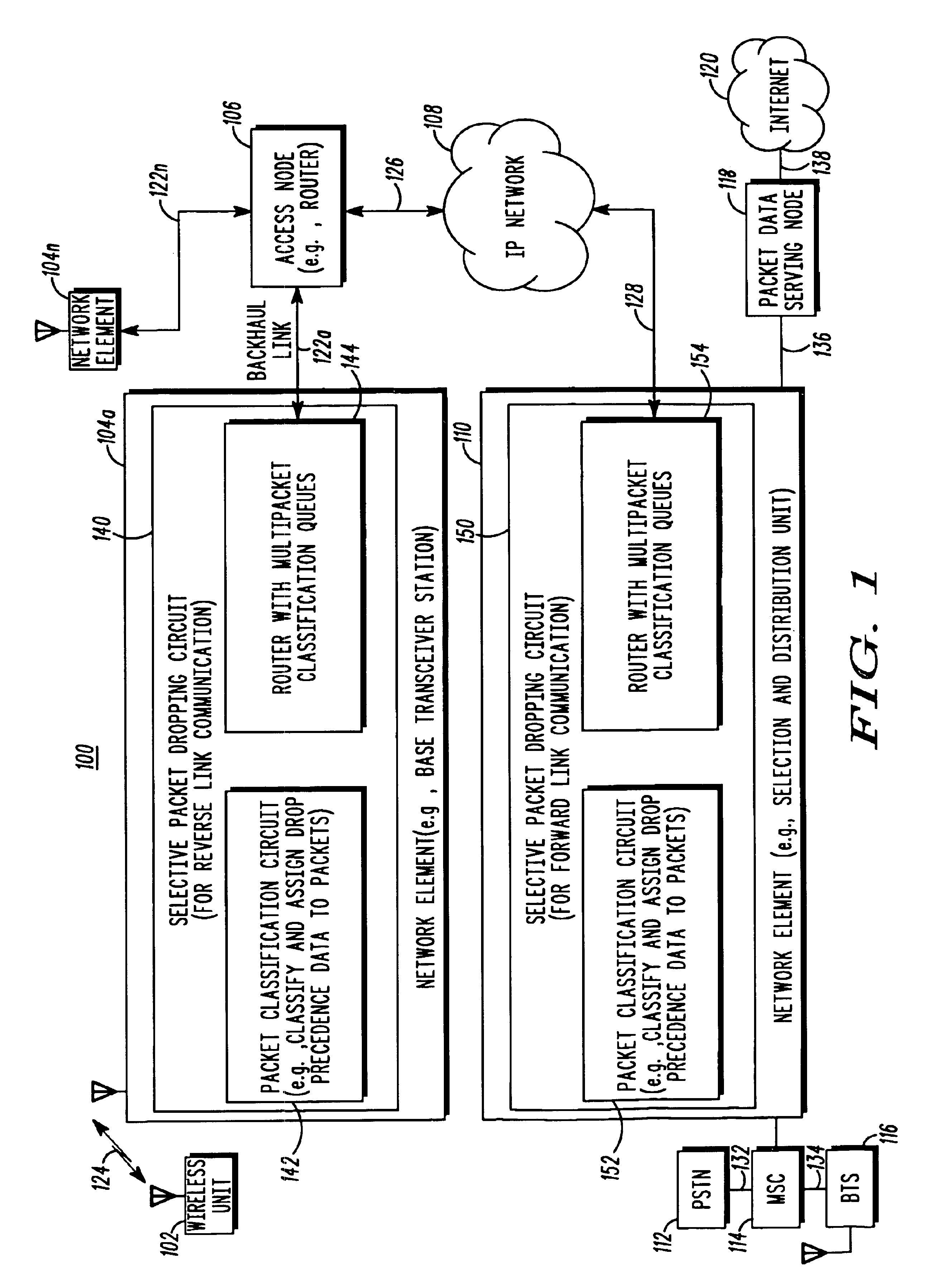
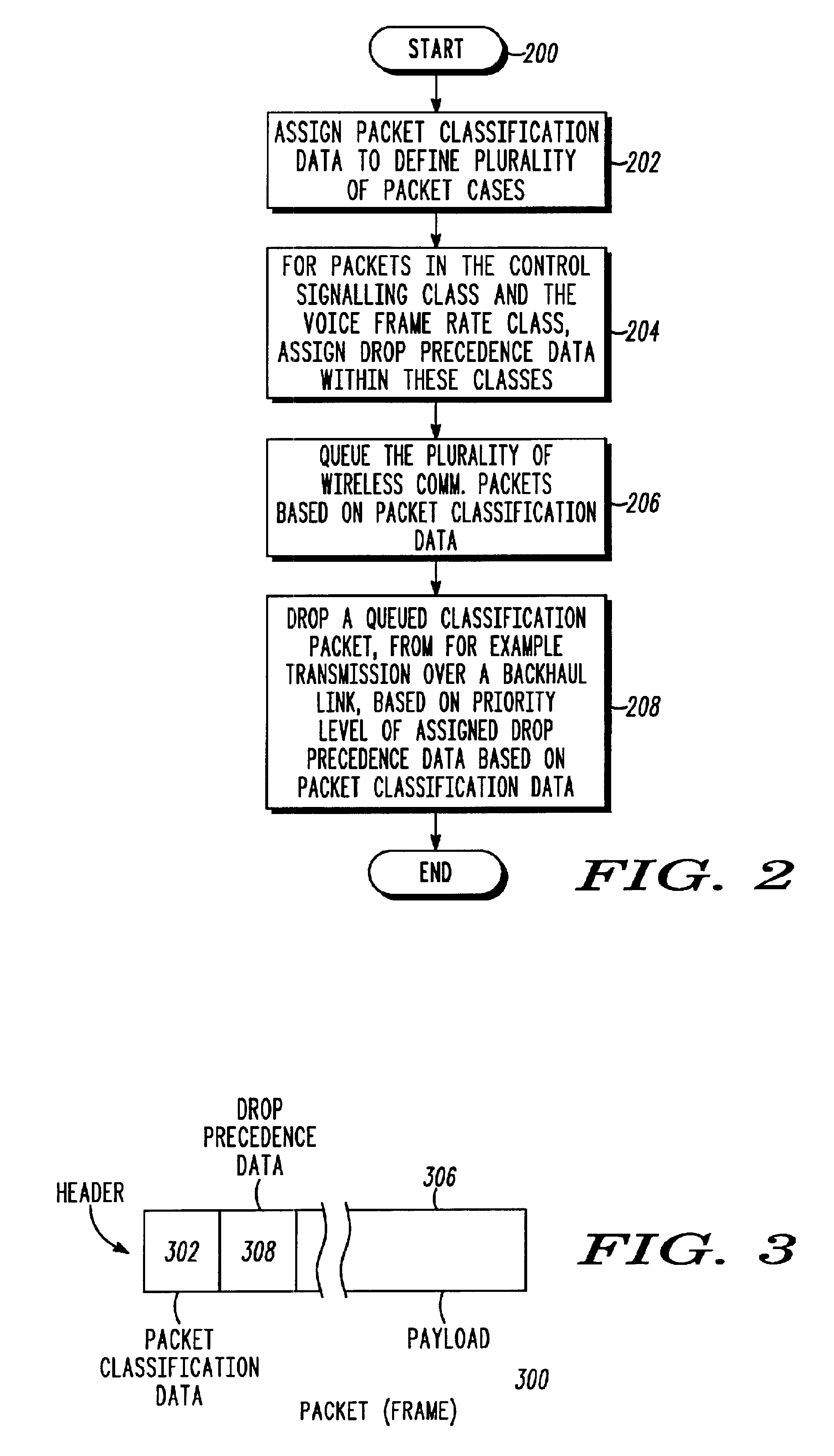
A communication system and method assigns, such as by marking headers of wireless communication packets, packet classification data to packets to define at least one of the following classes: a control signaling class, such as in-band signaling and control packets, a voice class, a data retransmission class, OAMP class and a data class and wherein each class represents a different transmission priority over a backhaul link. For wireless communication packets associated with the control signaling class and the voice class, the method and apparatus assigns each of the wireless communication packets with additional drop precedent data wherein the drop precedence data defines a further packet drop priority within the control signaling class and the voice class. The apparatus and method drops a queued classified wireless communication packet based on a priority level of assigned drop precedent data and based on the packet classification data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
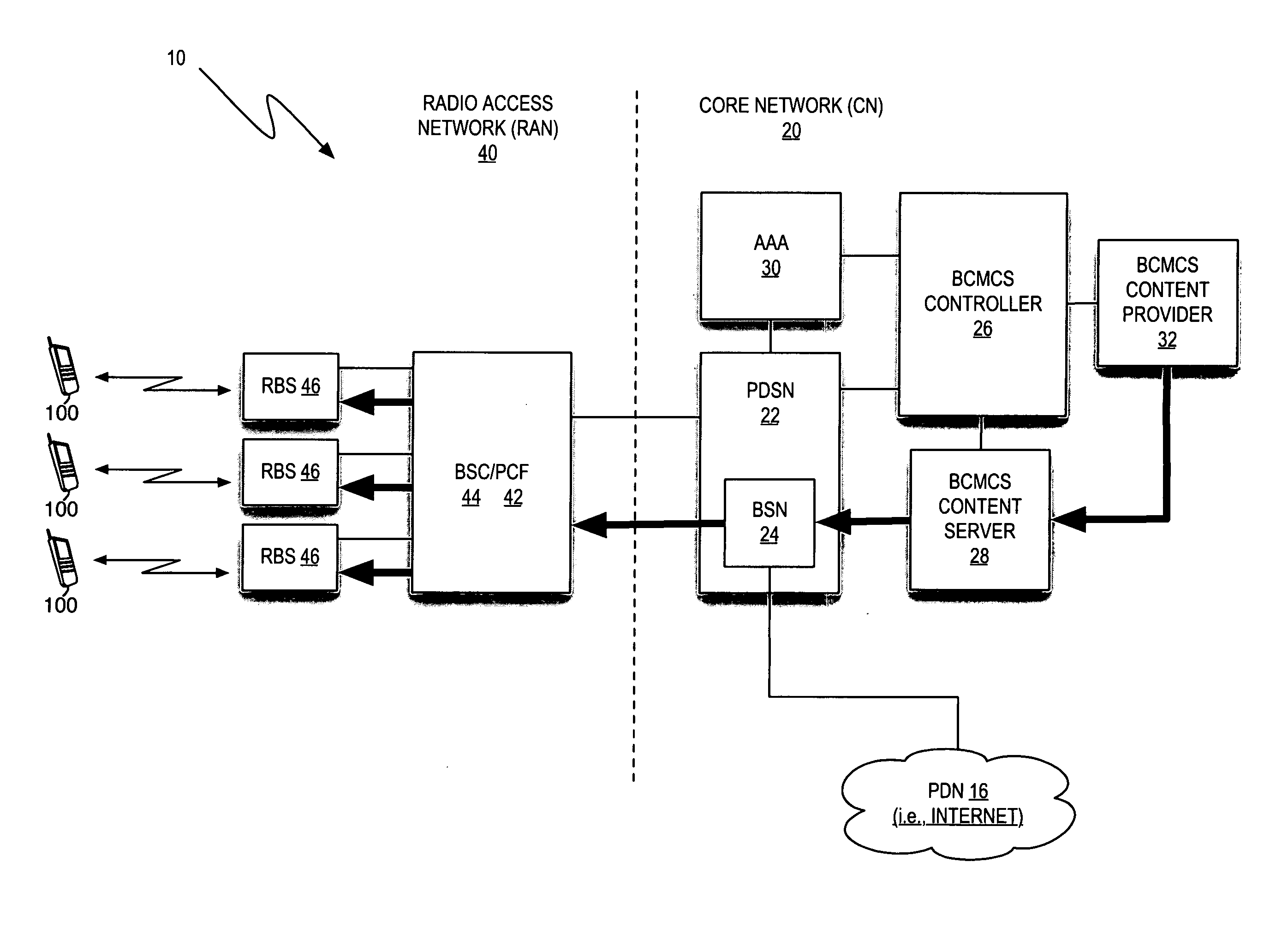
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving a frame including control information in a broadcasting system
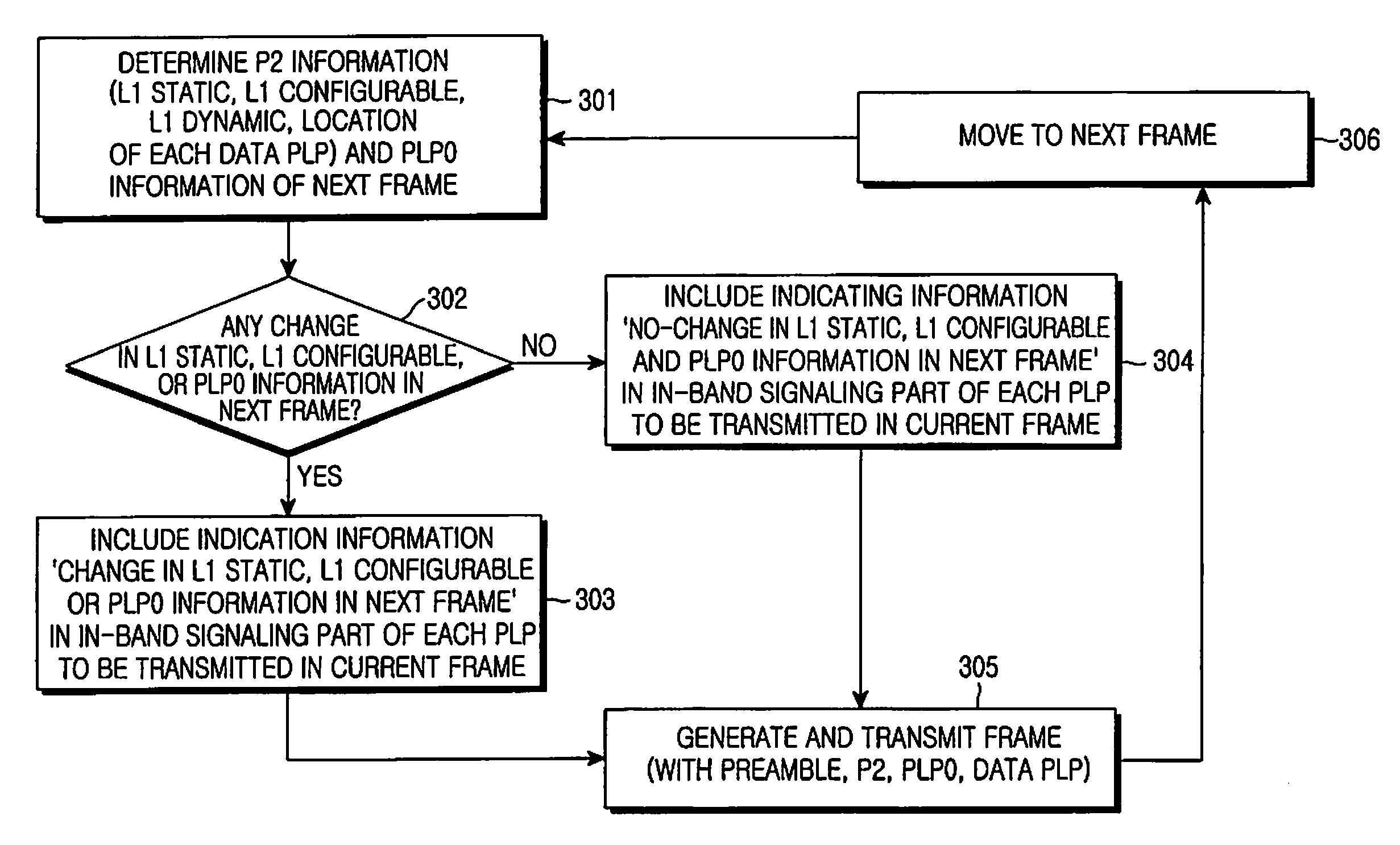
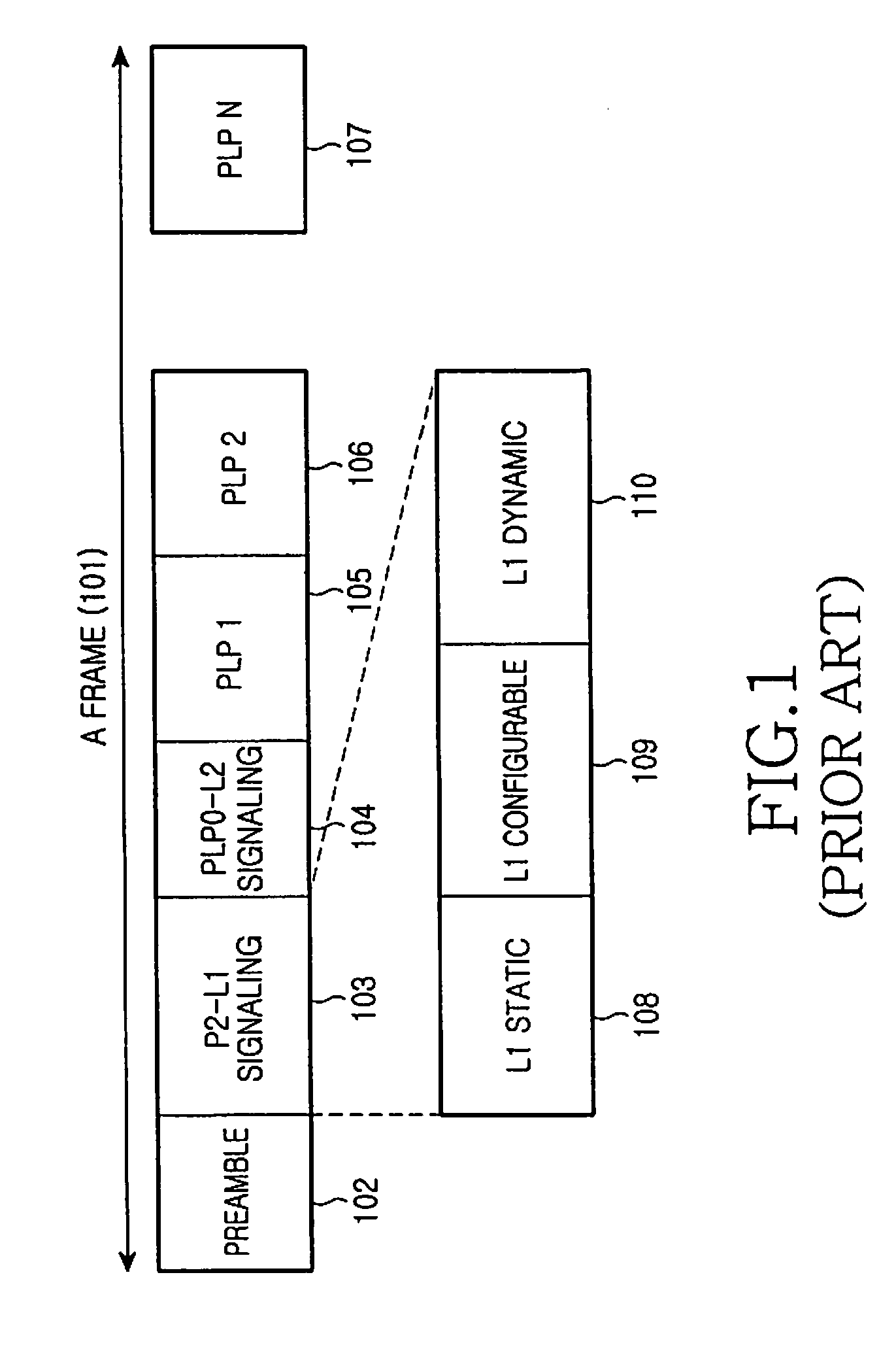
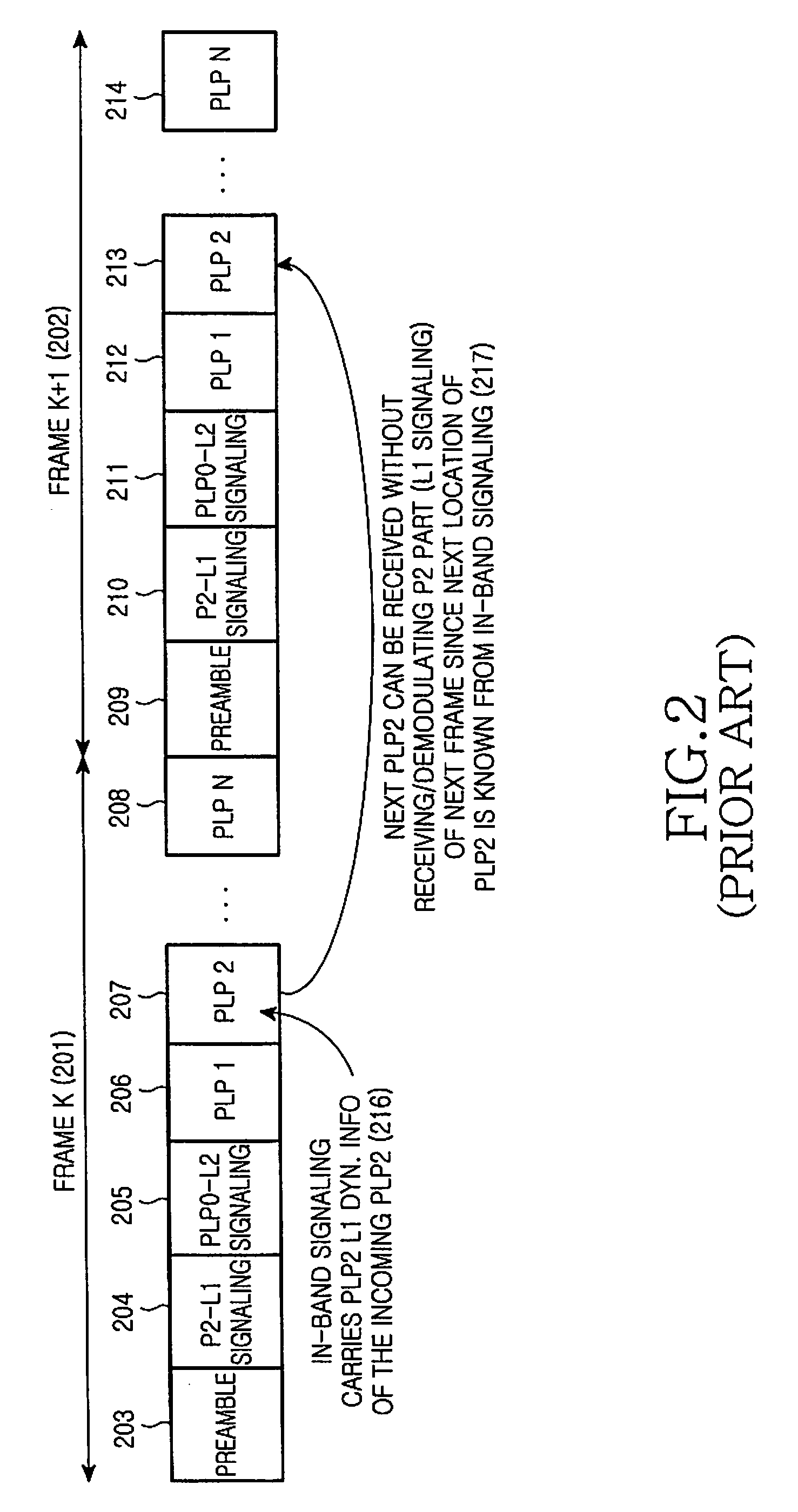
ActiveUS20090213853A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient receptionBroadcast information characterisationResource management arrangementsIn-band signalingBroadcast service
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving a frame including control information in a broadcasting system. A frame for a broadcast service is generated using an in-band signaling scheme, and includes location information of control information in a next frame and indication information indicating a change / no-change in the control information in the next frame. The new frame structure minimizes power consumption of a receiver supporting the broadcast service.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
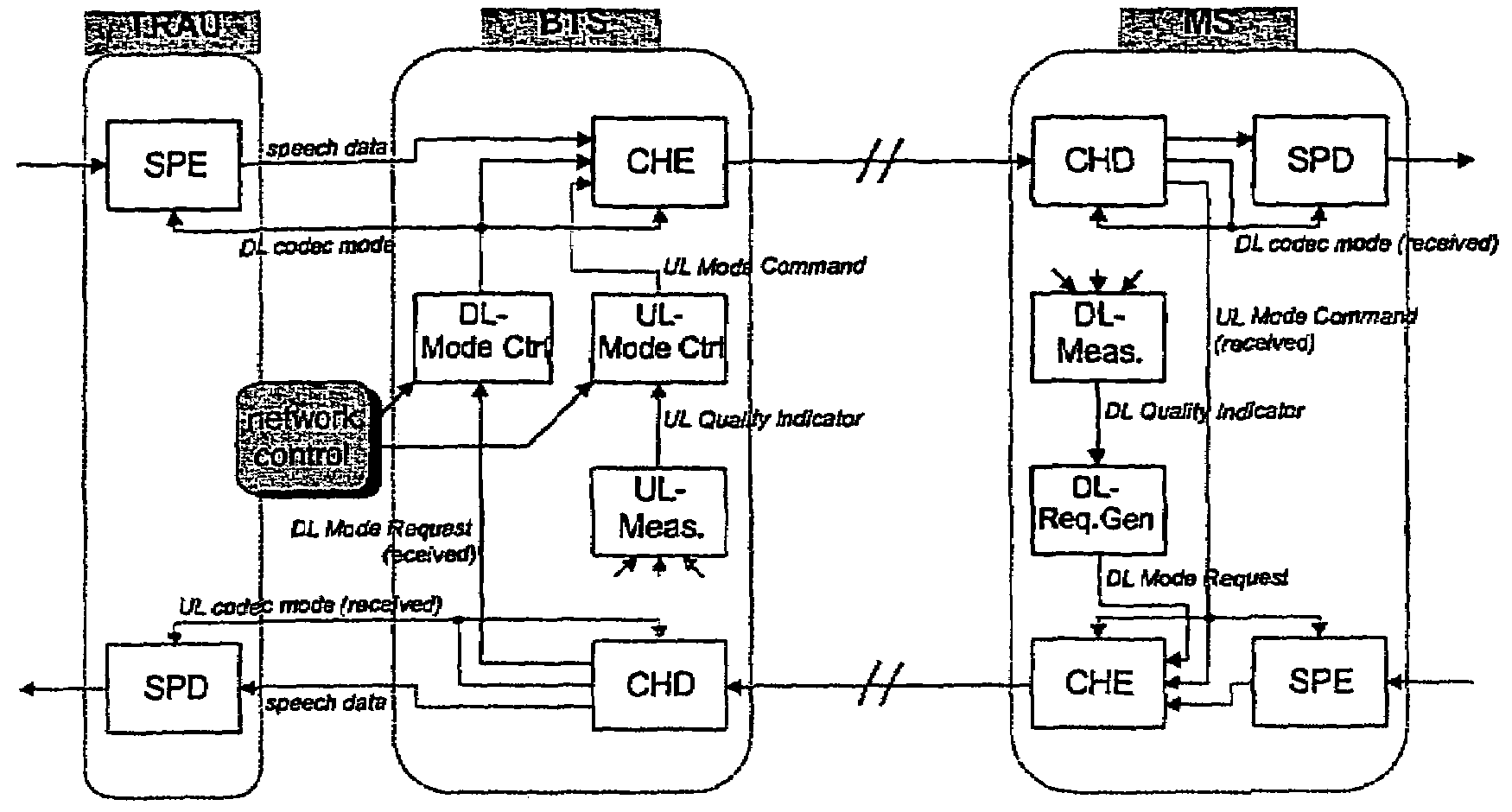
Integrated power control and link adaptation
InactiveUS20100279701A1Accurate and timely sub-channel transmission power controlMaximize speech qualityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorModulated-carrier systemsSignal qualityControl channel
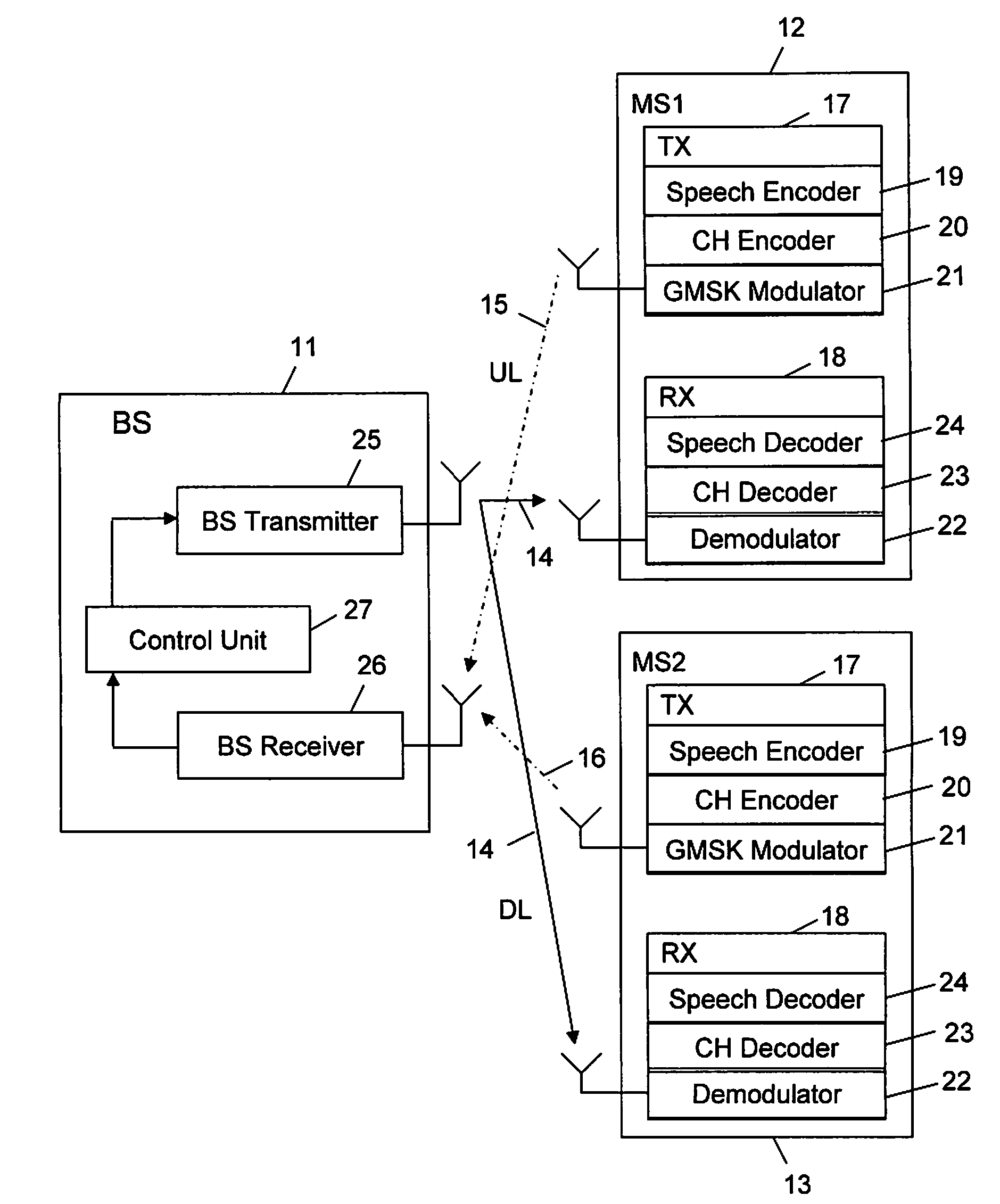
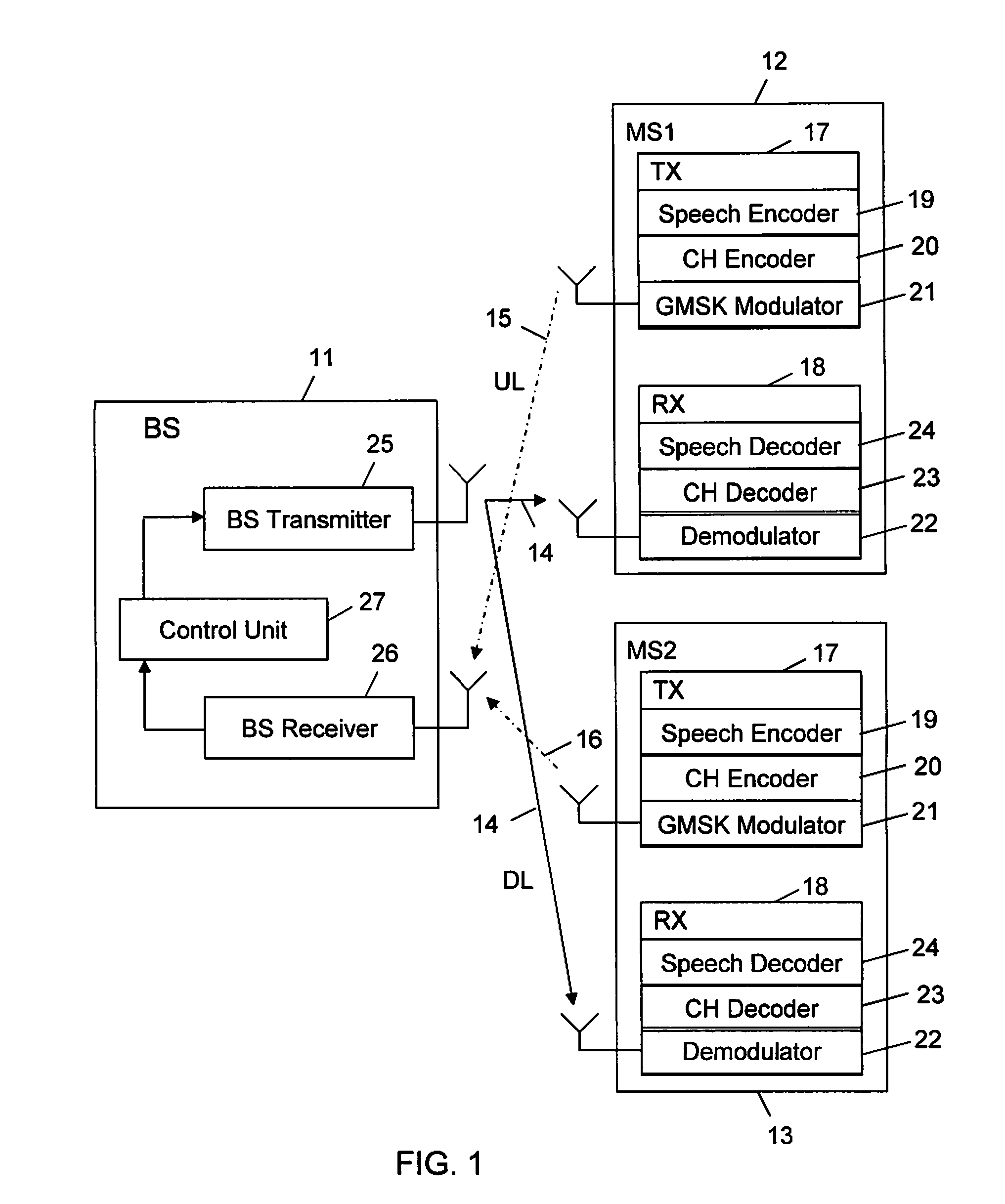
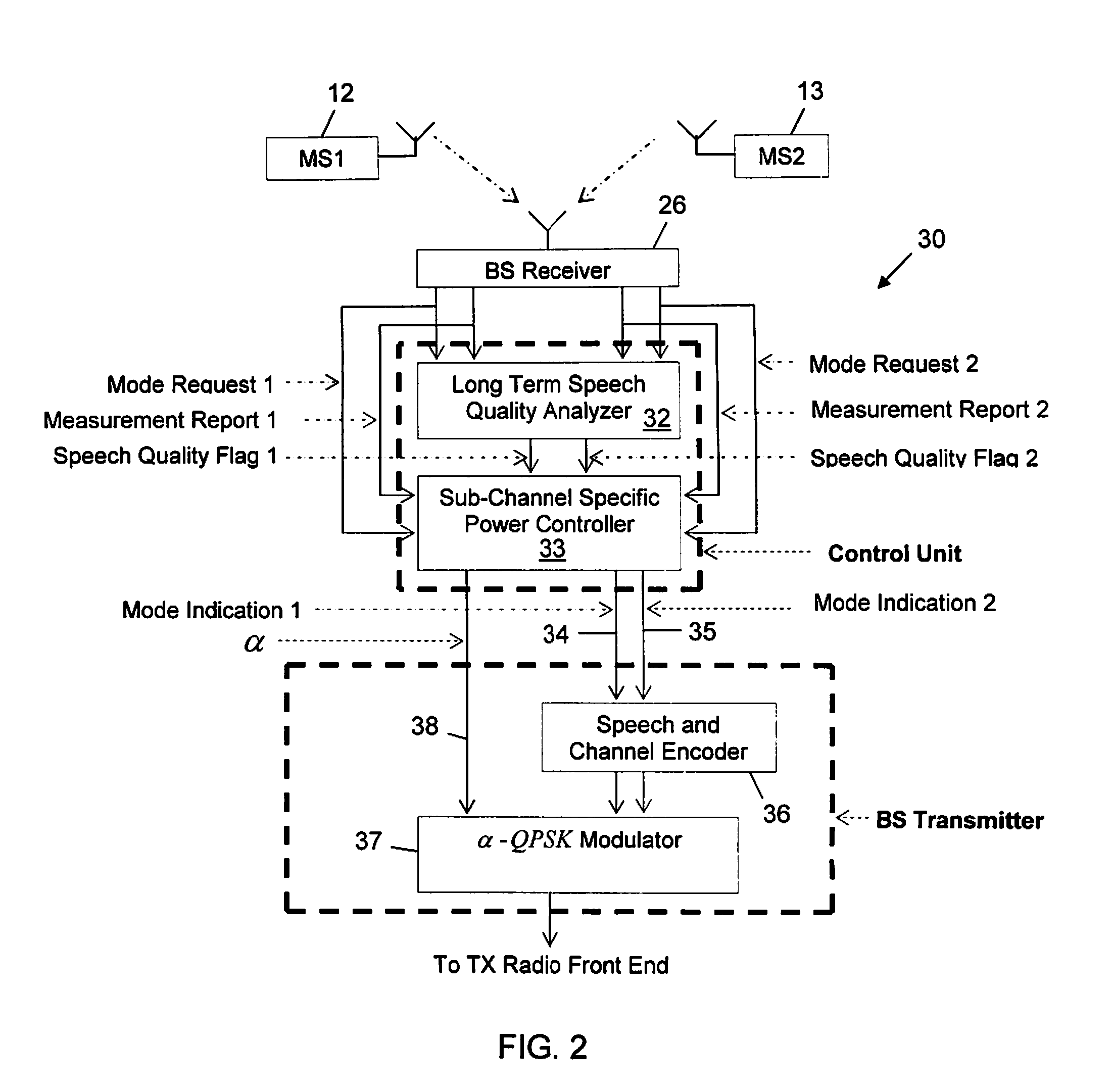
A method and apparatus in a base station for jointly controlling sub-channel transmission power and assigned codec modes for a first and second mobile station utilizing Voice services over Adaptive Multi-user channel on One Slot (VAMOS). The base station receives signal quality information reports from the mobile stations every 480 ms using the Slow Associated Control Channel (SACCH), and receives codec mode requests from the mobile stations every 40 ms using Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) in-band signaling. The base station associates the requested codec modes with estimated levels of speech quality currently being experienced by the first and second mobile stations. The base station then allocates sub-channel transmission power and assigns codec modes to the first and second mobile stations based on the estimated levels of speech quality associated with the requested codec modes and the signal quality reports.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
In-band signaling for point-multipoint packet protection switching
A method and system provide in-band protection switch signaling in a communication system arranged as a point-to-multipoint tree. The point-to-multipoint tree includes a root node communicatively coupled to a plurality of leaf nodes through both a working link and a protection link. Data is transferred through a current link of the point-to-multipoint tree. The current link is either the working link or the protection link. A fault is detected in the current link in the point-to-multipoint tree. Each leaf node in the point-to-multipoint tree is notified of the fault using the current link. Upon receiving the notification, the root node and each leaf node switch to the other link of the working link and the protection link.
Owner:CIENA
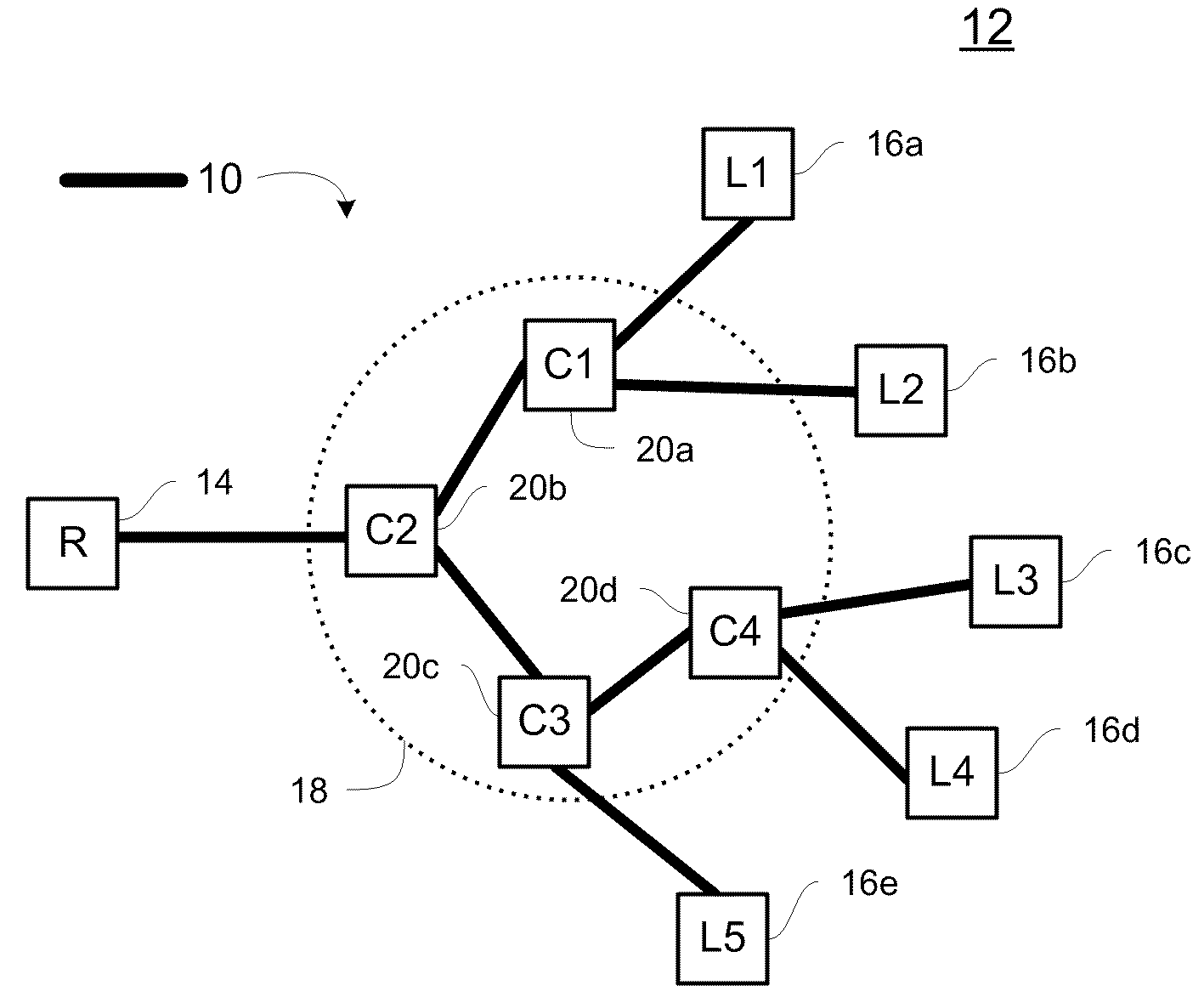
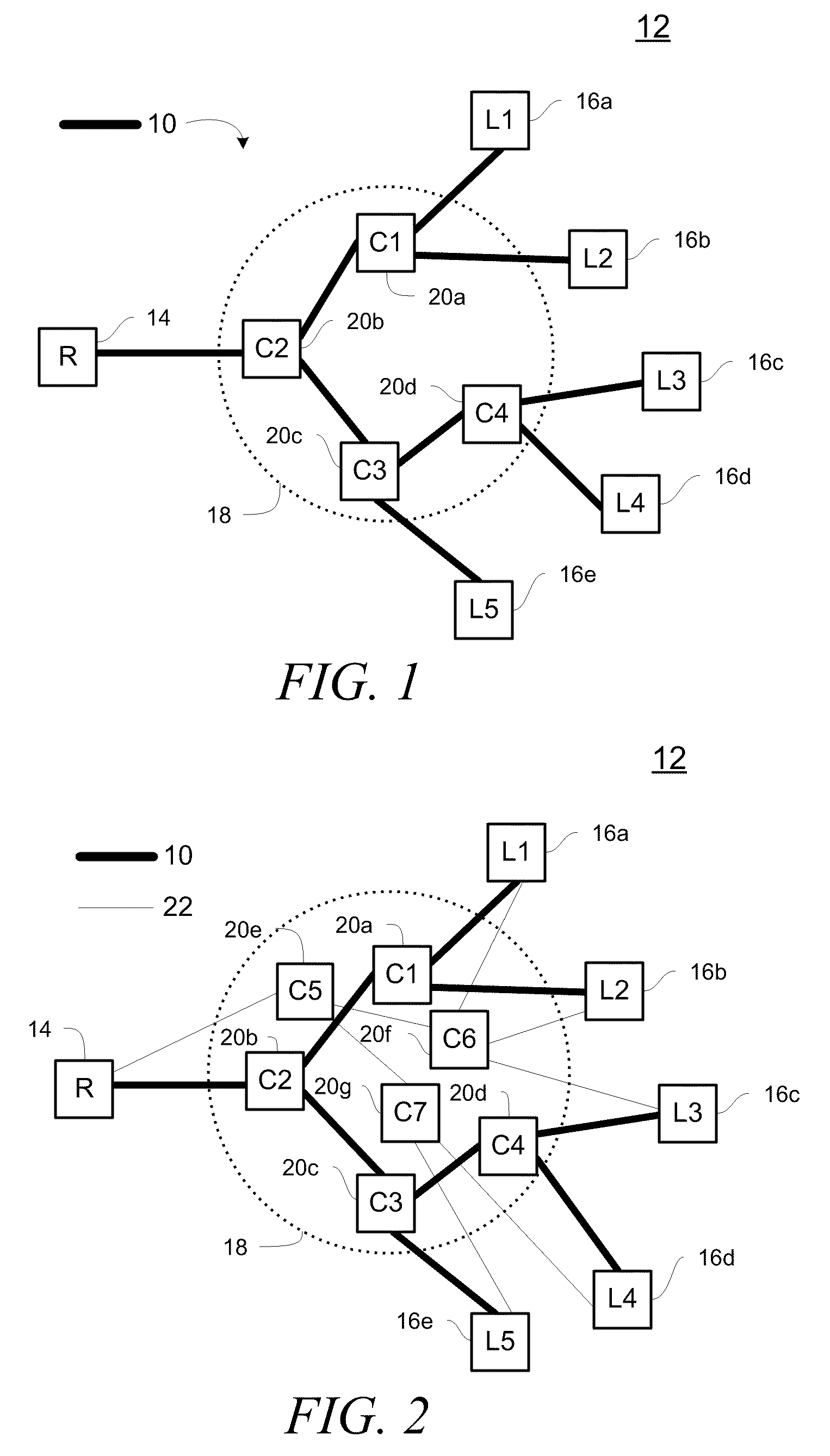
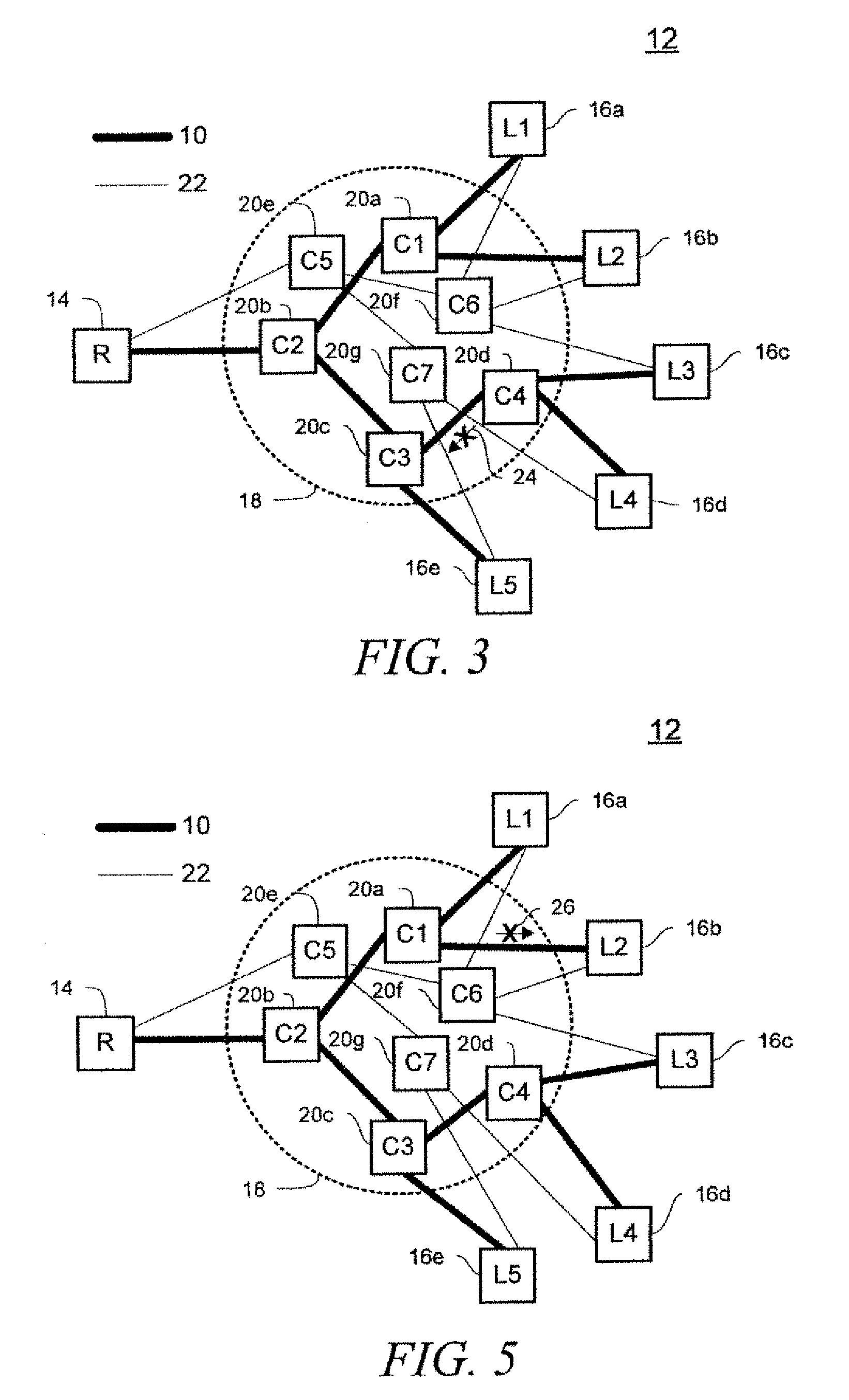
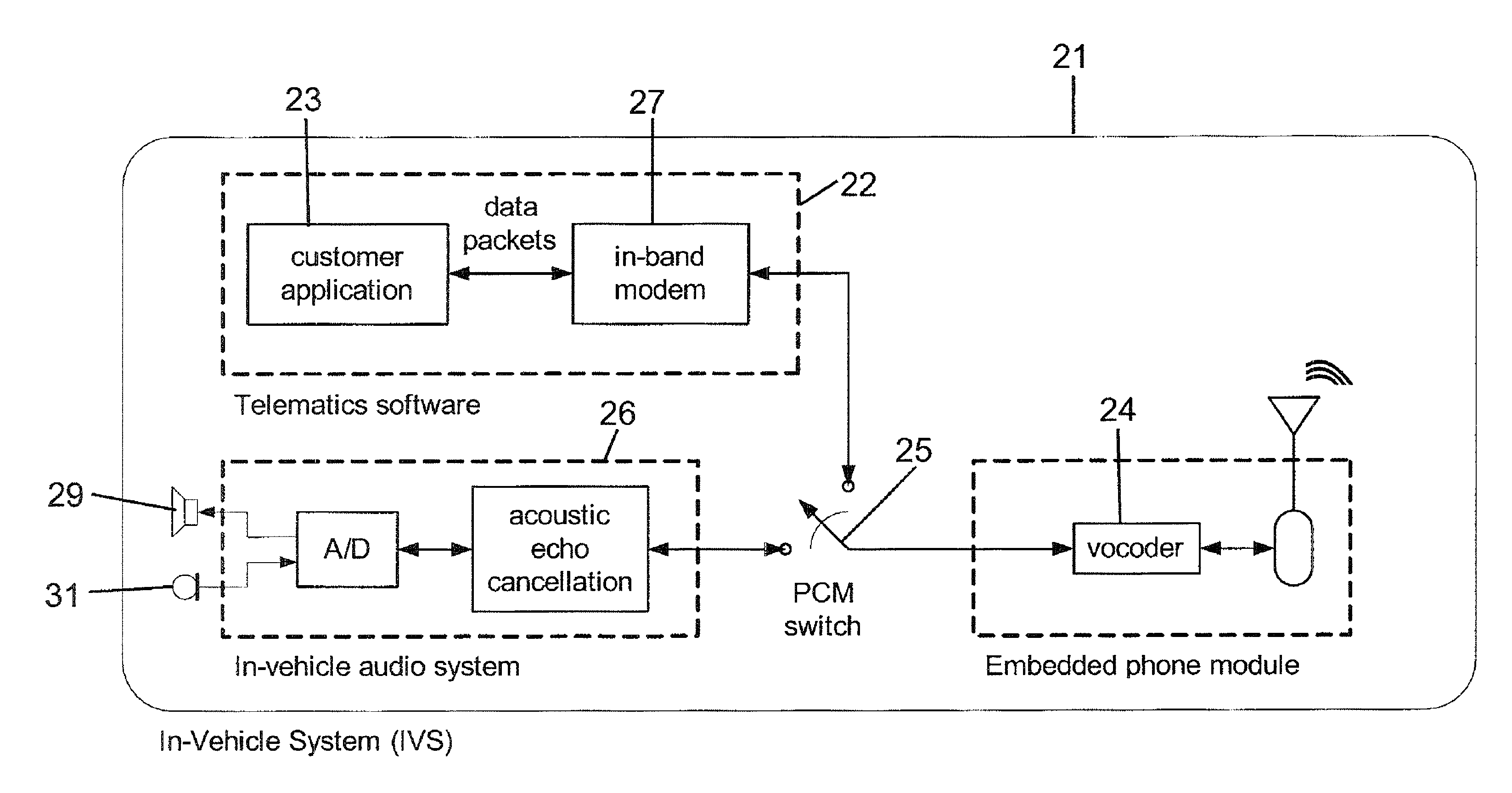
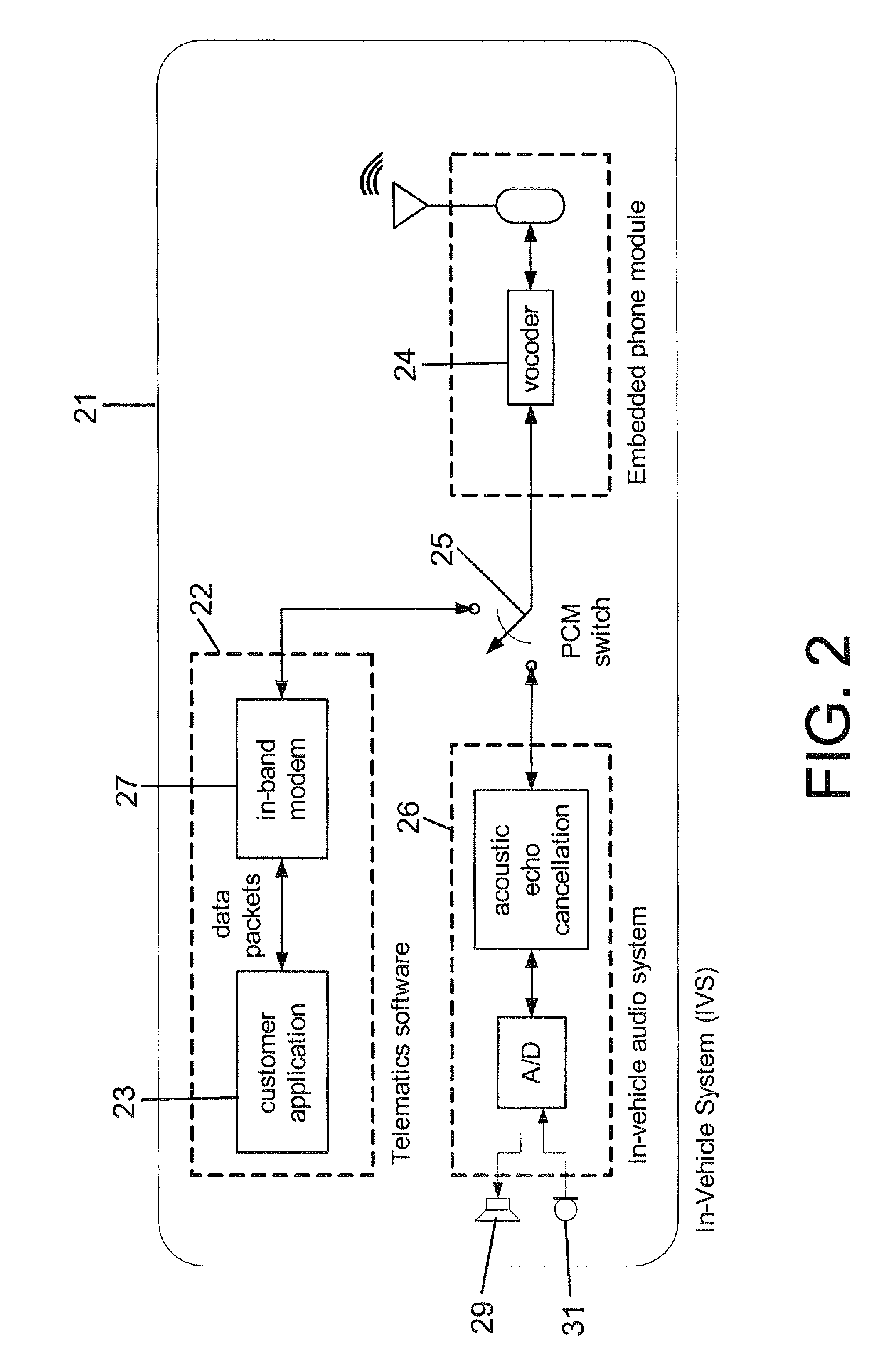
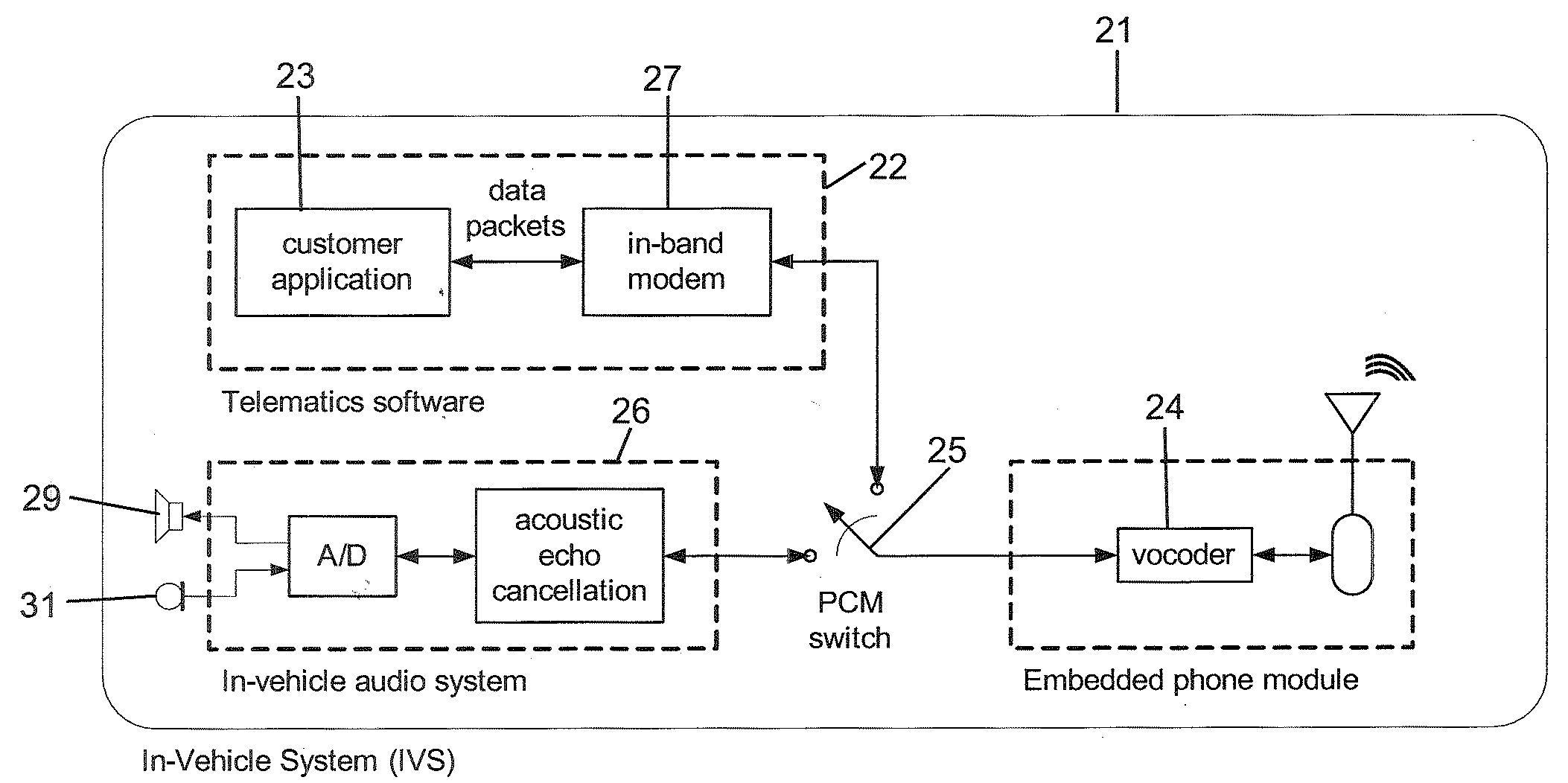
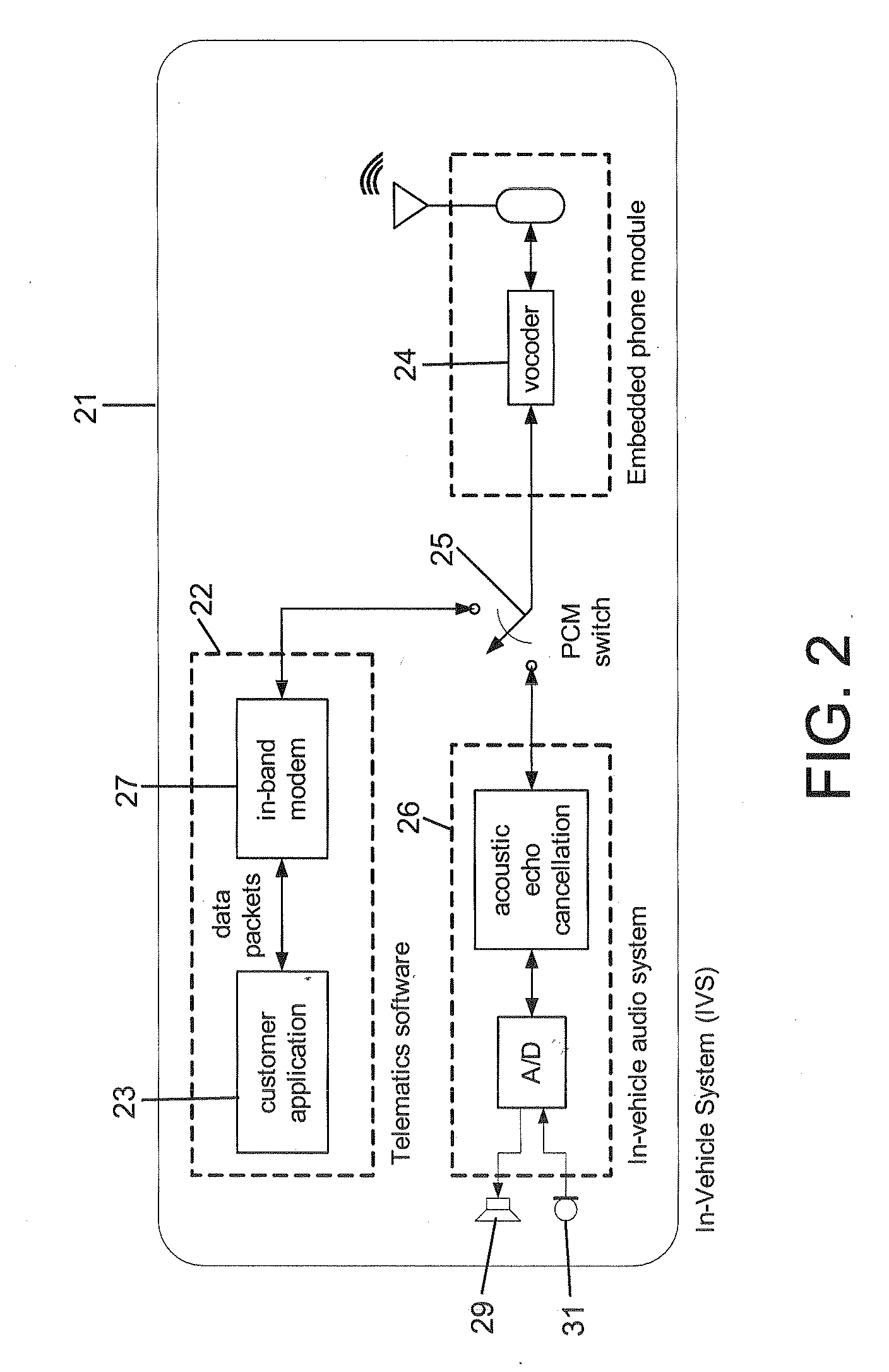
Wireless in-band signaling with in-vehicle systems
ActiveUS7979095B2Registering/indicating working of vehiclesSpecial service for subscribersTelecommunications networkIn vehicle
This invention pertains to methods and apparatus for data communications from vehicles, to obtain emergency, concierge and other services, using a voice channel of a digital wireless telecommunications network. Signaling is described for commencing data sessions after establishing a voice channel call. The call may be initiated from the vehicle automatically, and the call taker location may be unattended. Signaling methods are selected for traversing both newer and legacy vocoders for ubiquitous operation.
Owner:AIRBIQUITY INC
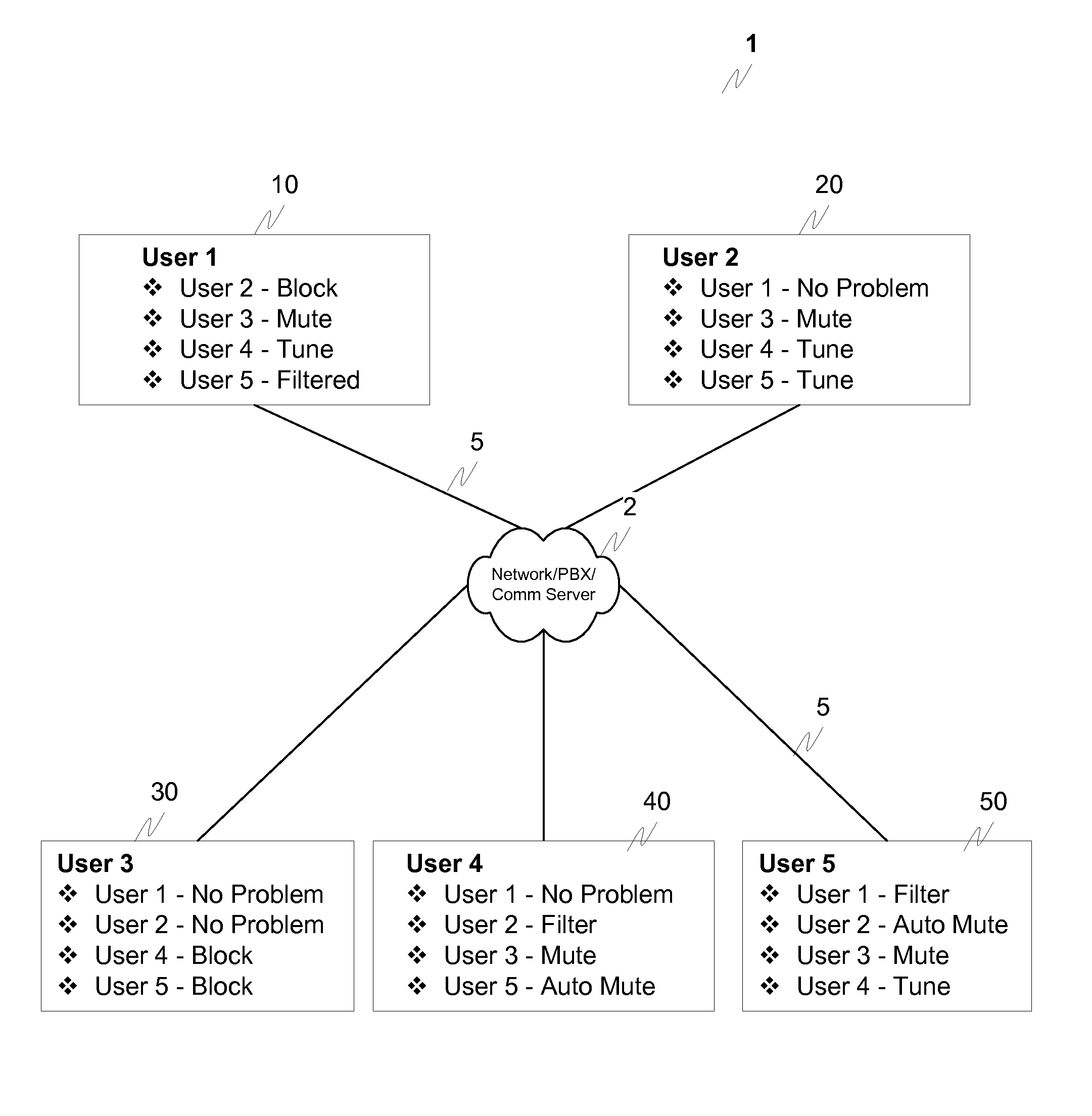
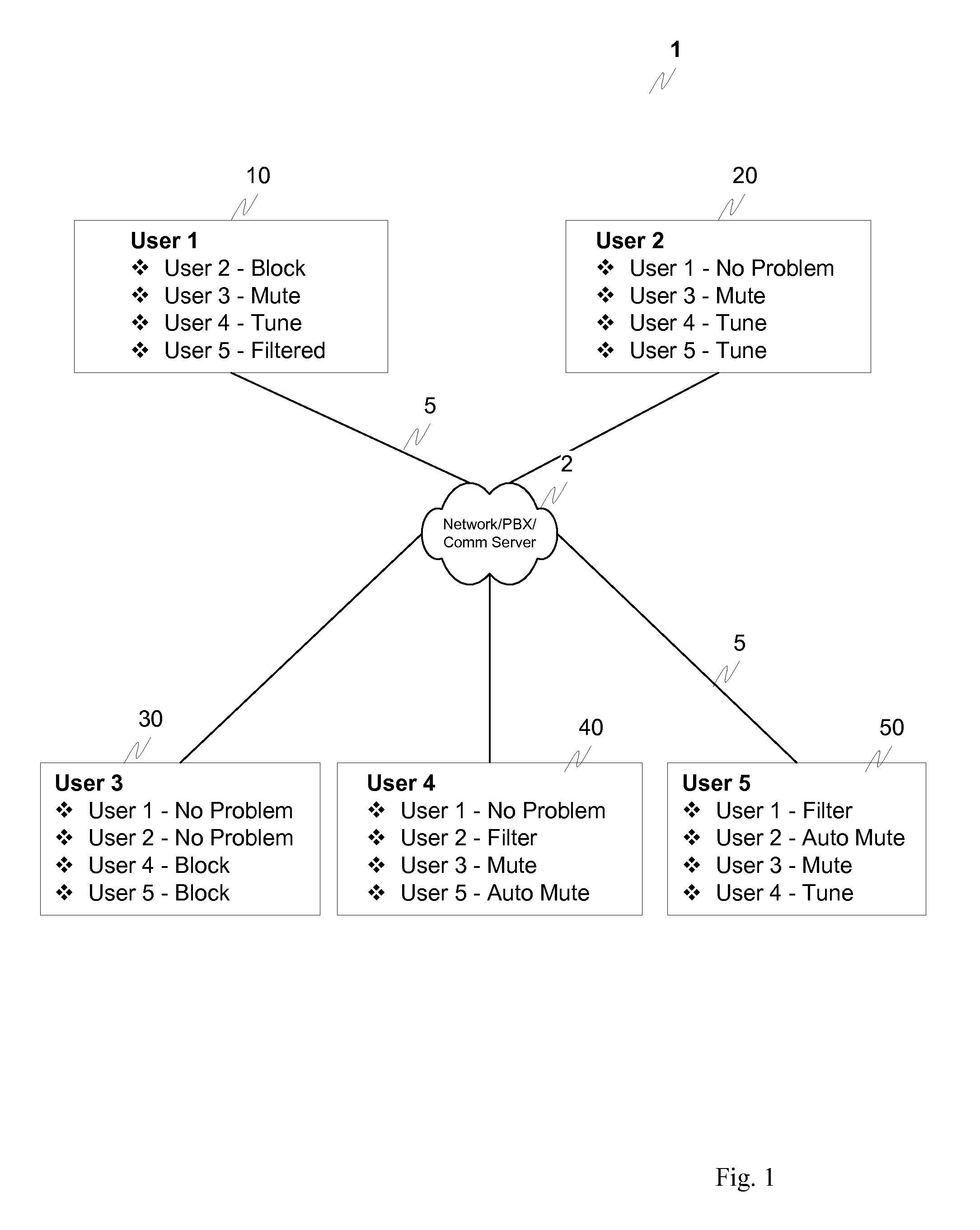
Method and apparatus for identifying and eliminating the source of background noise in multi-party teleconferences
ActiveUS20100080374A1Exercise controlReduce noiseSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsIn-band signalingTeleconference
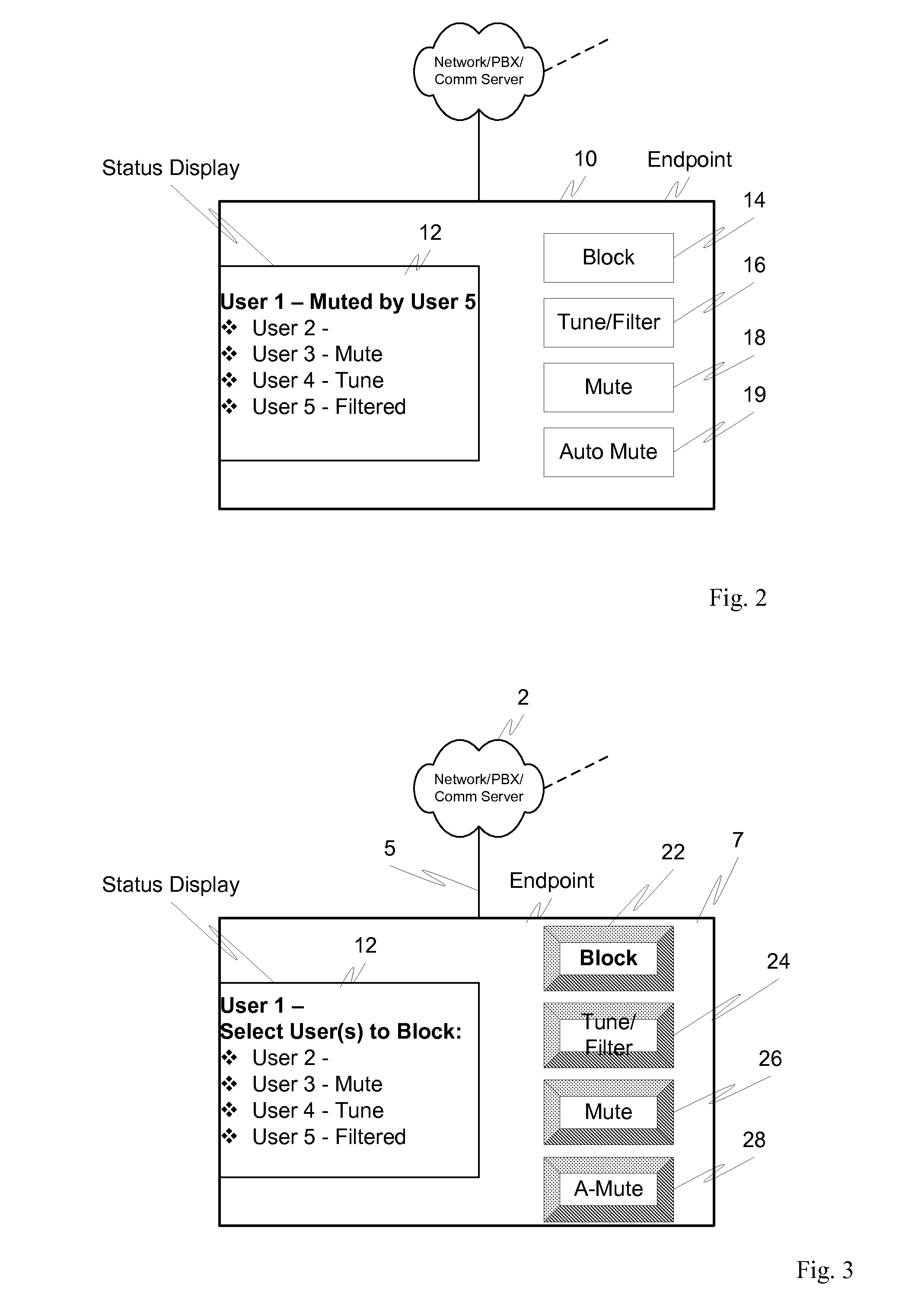
A mechanism is provided that allows participants on the conference call to identify, and then mute or filter, a participant(s) responsible for introducing the noise, regardless of whether the noise is caused by transmission impairments or by the participant(s) being in a noisy location. For example, individual users could be able to press a “test” button that could block each of the participants one at a time. This would allow the source of the noise to be identified. This “test button” could be one or more of provided at the endpoint(s), be enabled through a web interface or, for example, through a dedicated conference call interface at the endpoint(s) or at the conference bridge. The blocking of each participant could occur through interaction with the main PBX using, for example, in-band signaling to the PBX. Once the source(s) of the noise is identified, noise mitigation can be applied as needed.
Owner:AVAYA INC
On hold call retrieval & routing
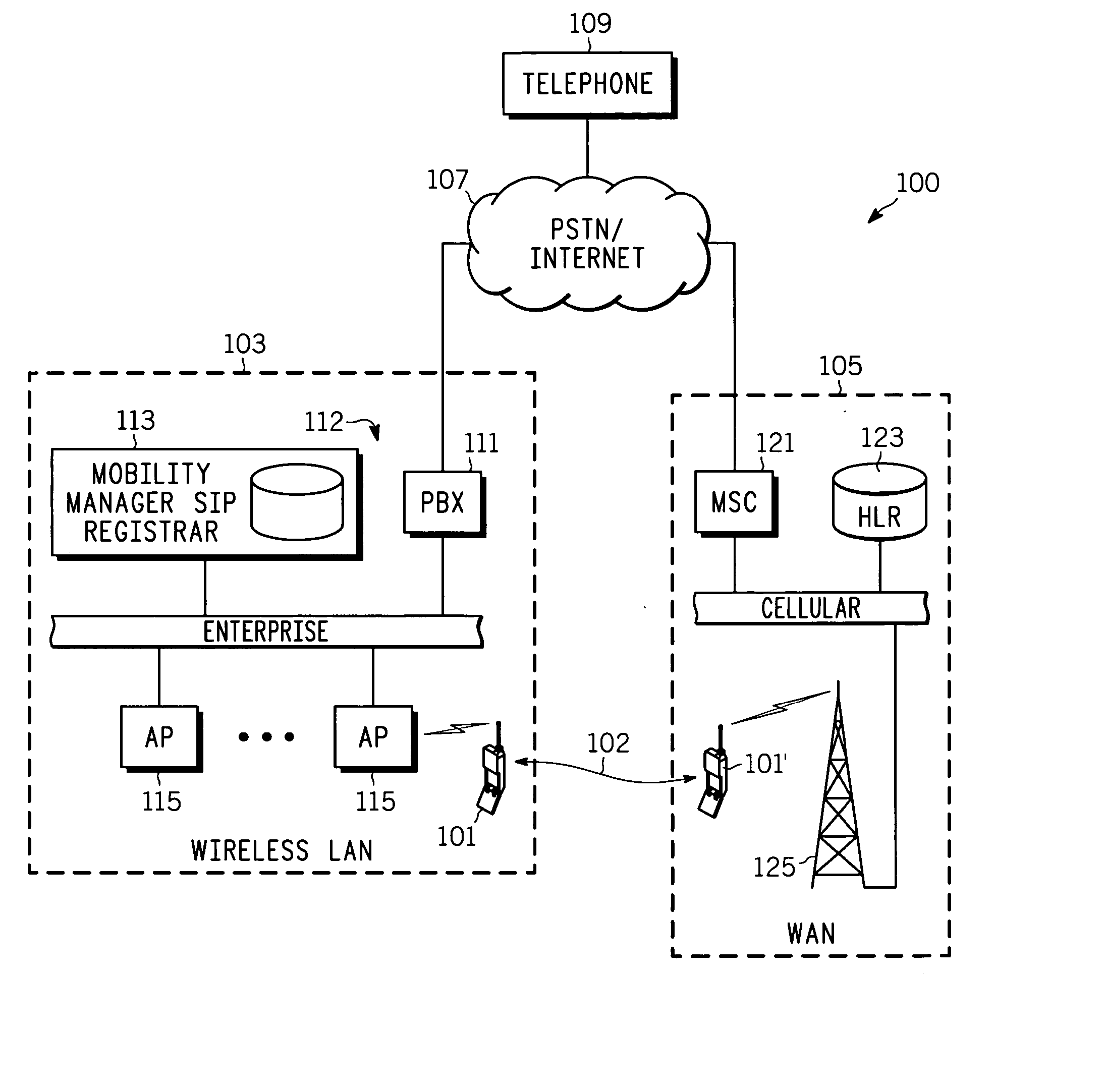
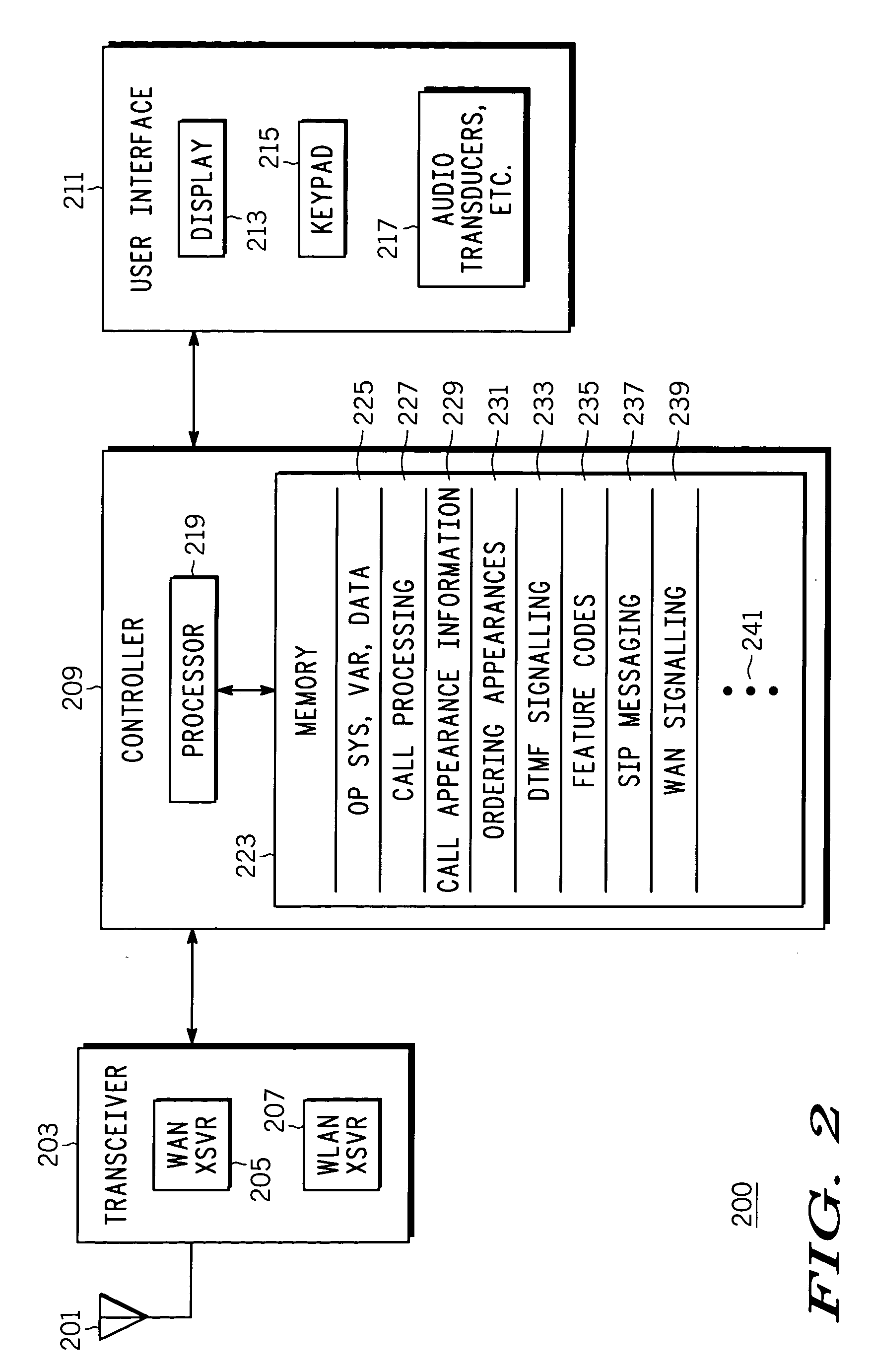
ActiveUS20050124326A1Special service for subscribersDevices with wireless LAN interfaceTransceiverCommunication unit
A wireless communication unit (101, 200, 401), network switch (112, 300, 407) and corresponding methods facilitate retrieval, routing, and management of on-hold calls (FIG. 4-FIG. 7) within a first communication network (103) when the unit is operating in a second communication network (105) that is loosely coupled to the first. The communication unit comprises a transceiver (203) configured to support an air interface with the first and the second communication network; and a controller (209) arranged to cooperatively operate with the transceiver to retrieve an on-hold call from the first network via a call leg established to support a handout to and while the unit is operating in the second network. A user interface (211) and in band signaling over the call leg facilitates management, connecting, disconnecting, etc., of the on-hold calls by the communication unit.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Flexible and in-band signaling for nested preamble
InactiveUS20100316094A1Modulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityMulti inputTransport layer
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
Flexible and in-band signaling for nested preamble
InactiveUS7738538B1Modulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityMulti inputTransport layer
A multi input multi output (MIMO) receiver is disclosed for transmitting and receiving packets having a preamble format of a packet of information and having a short training sequence (STS), a long training sequence (LTS) and signal (SIG) for training receivers, in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. The packets having a preamble format for allowing data to be piggy-backed, e.g. transmitted and received using the physical layer rather than the transport layer of networking layers.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
Architecture, client specification and application programming interface (API) for supporting advanced voice services (AVS) including push to talk on wireless handsets and networks
ActiveUS7738892B2Interconnection arrangementsBroadcast transmission systemsWireless handheld devicesCommunications system
An architecture, client specification and application programming interface (API) for supporting advanced voice services (AVS) for use in handsets in order to support advanced voice services (AVS) for wireless communications systems. The handset or mobile unit executes a client application therein for performing the call setup and in-band signaling with the wireless network for the group voice services, and executes a presence / group management application therein for performing presence and group management functions related to the group voice services in the mobile unit.
Owner:KODIAK NETWORKS
Prepaid billing solutions for push-to-talk in a wireless communications network
ActiveUS8369829B2Accounting/billing servicesSpecial service for subscribersReal-time chargingMobile phone operator
Owner:KODIAK NETWORKS
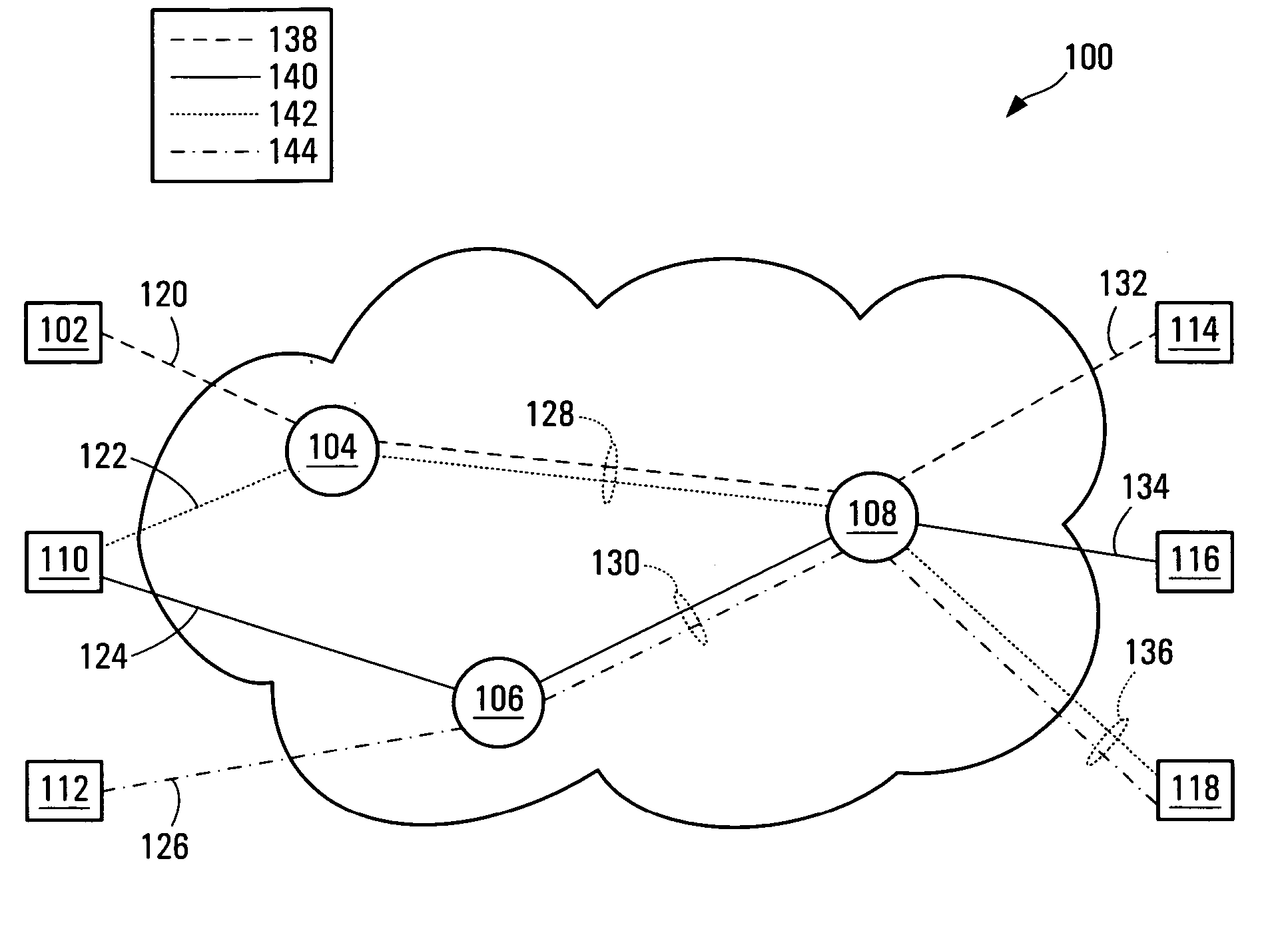
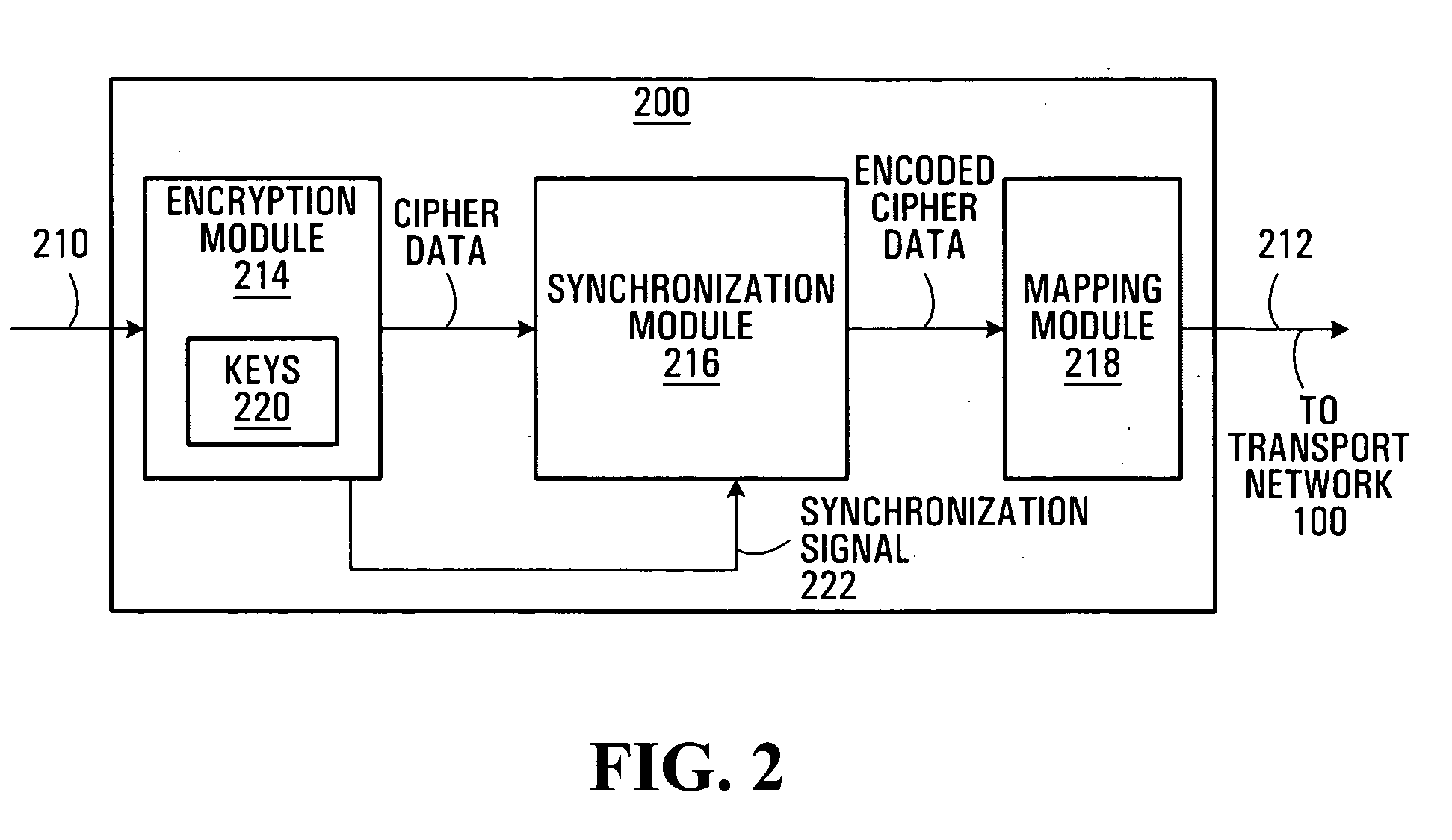
Method and system for transmitting signaling information over a data transport network
InactiveUS20060045273A1Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesMultiple keys/algorithms usageData transportDatapath
A method for transmitting signaling information, such as cryptographic key synchronization information, over a data path of a network, the data path having an originating end and a terminating end. The method uses in-band signaling to transmit the signaling information from the originating end of the data path to the terminating end of the data path without consuming any bandwidth of the data path. More specifically, the method includes the steps of receiving user data to be transmitted over the data path and encrypting this user data with a cryptographic key, thereby generating cipher data. The method next includes processing the cipher data such that the cipher data includes the signaling information, and mapping the cipher data including the signaling information into a traffic unit for transmission over the data path.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
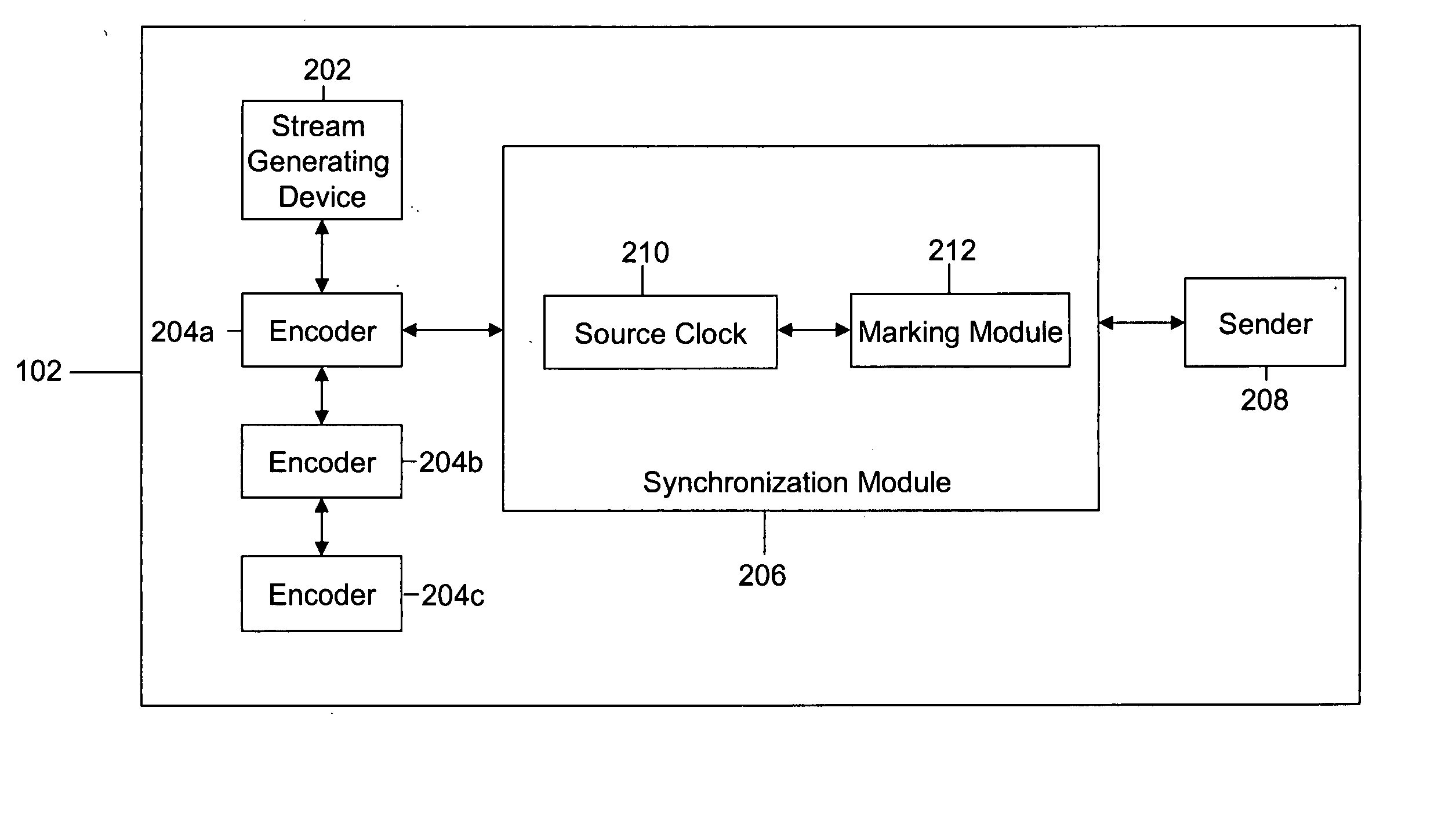
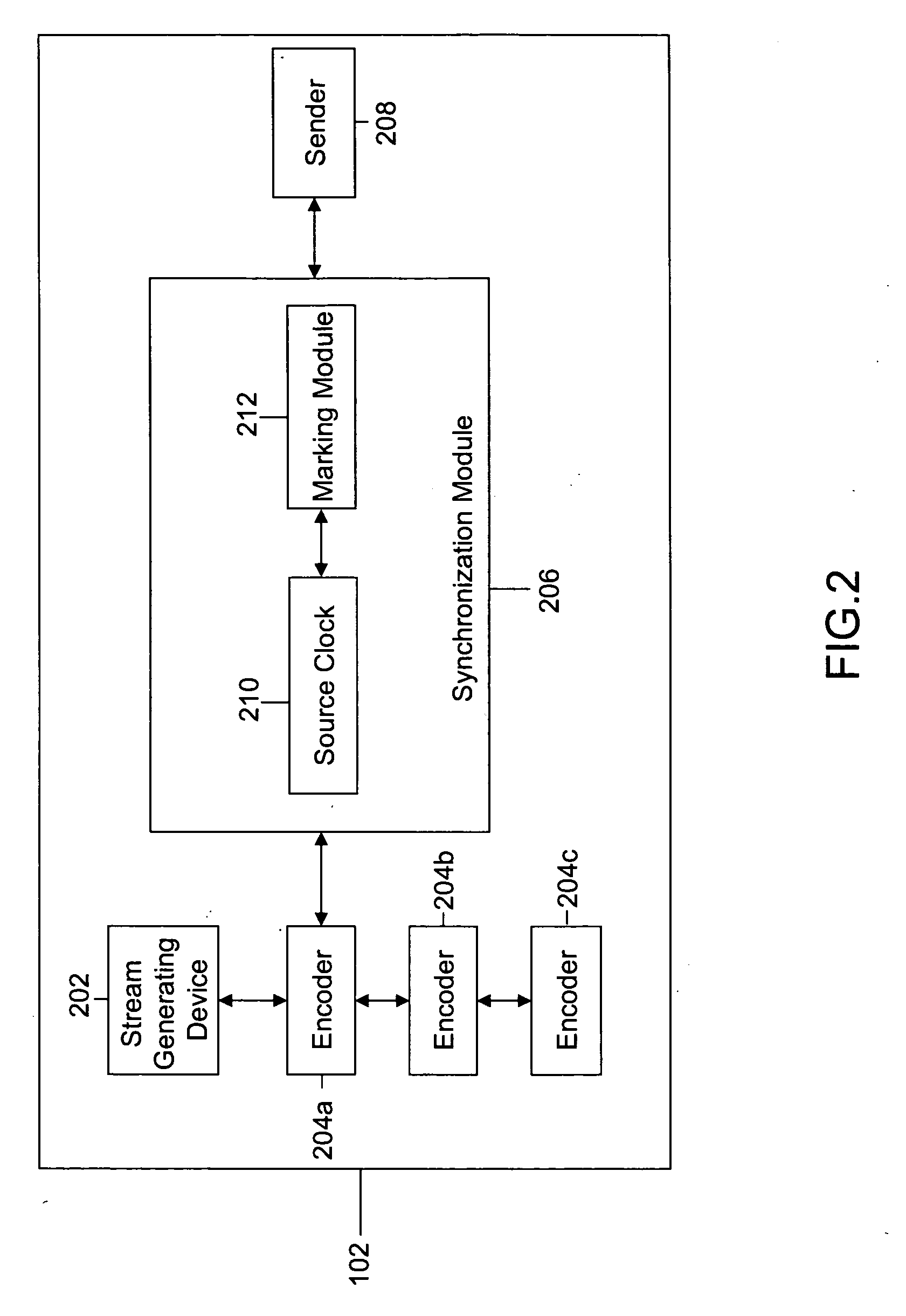
Method and system for in-band signaling of multiple media streams
ActiveUS20070110107A1Channel dividing arrangementsTime-division multiplexComputer networkIn-band signaling
Methods and systems are provided for in-band signaling of at least two simultaneous digital media streams in a network, the two simultaneous streams being a part of a media session. Each of the at least two simultaneous streams is generated from a corresponding source. The generated simultaneous streams are synchronized by using a unique marker packet. Each synchronized stream is transmitted to a destination corresponding to each source.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
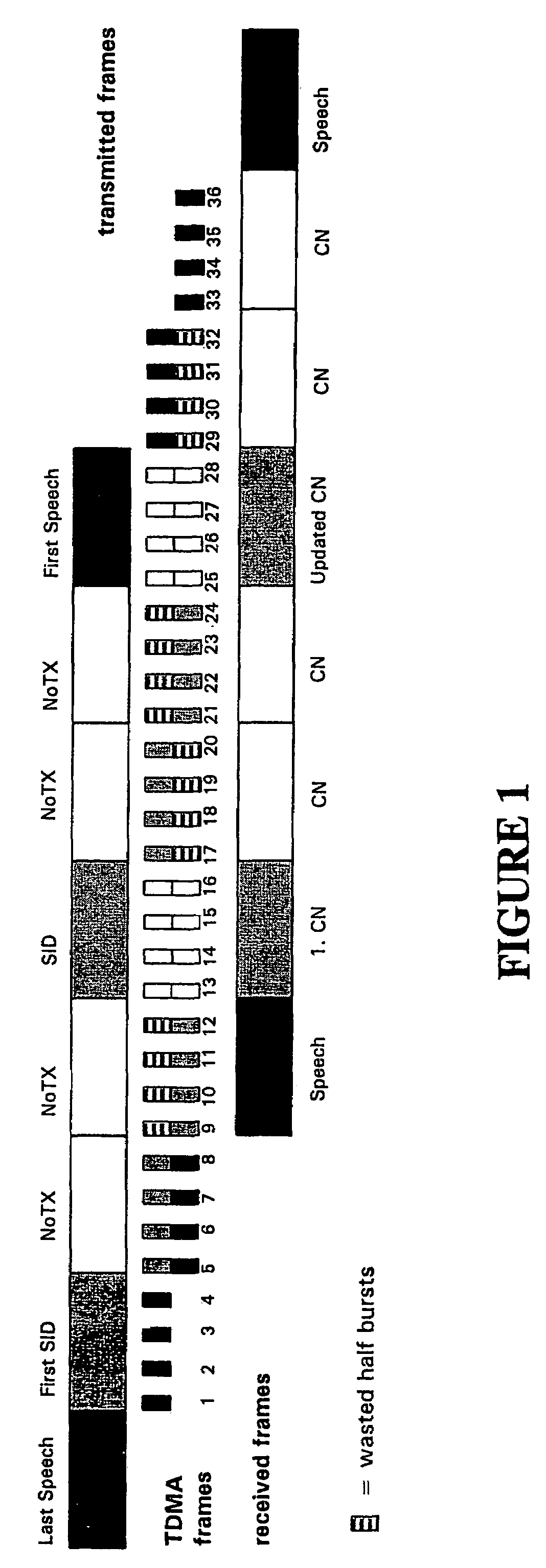
Efficient in-band signaling for discontinuous transmission and configuration changes in adaptive multi-rate communications systems
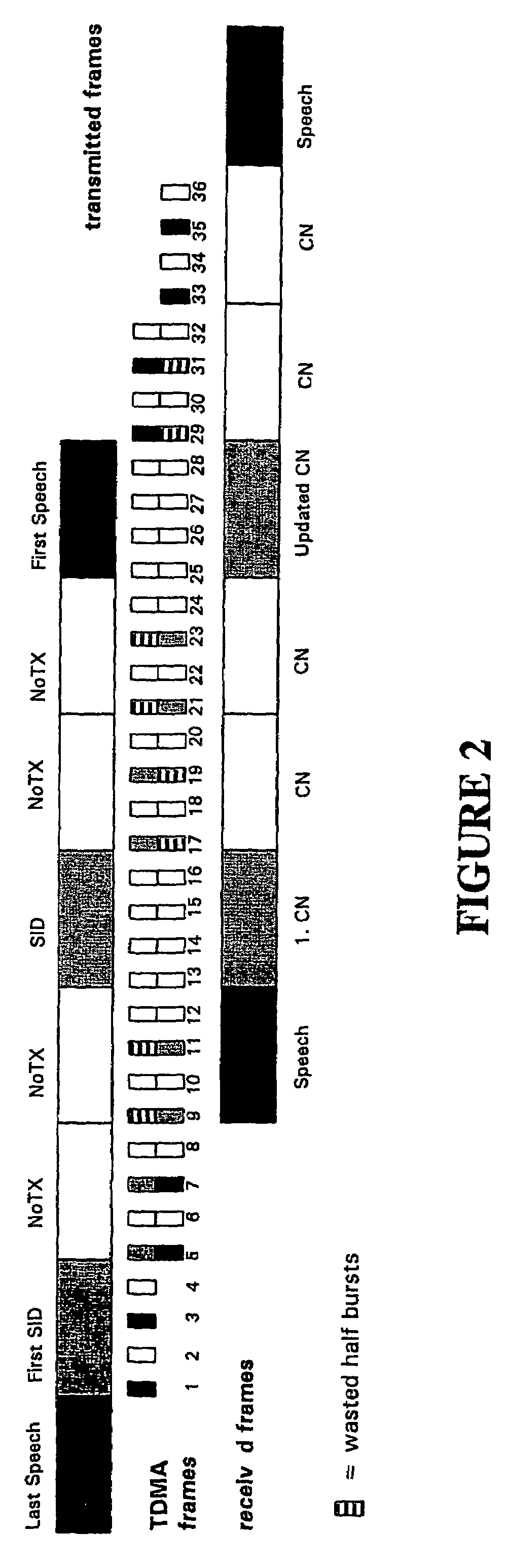
Techniques for discontinuous transmission (DTX) and fast in-band signaling of configuration changes and protocol messages in speech communications systems provide cost efficiency in terms of radio transmission capacity, in terms of fixed line transmission, and in terms of implementation effort. An exemplary method for performing discontinuous transmission (DTX) in a communications system in which source data is interleaved for transmission from a first component in the system to a second component in the system includes the steps of detecting periods of source data inactivity, and transmitting silence descriptor (SID) frames from the first to the second component during the periods of source data inactivity, certain of the transmitted SID frames being interleaved using a different interleaving algorithm as compared to that used for source data. For example, the source data can be block diagonally interleaved, and certain of the SID frames can be block interleaved. An exemplary method for effecting configuration changes in a communications system includes the step of transmitting an escape frame in place of a speech data frame, the escape frame including a gross bit pattern to distinguish the escape frame from speech data frames and conveying a configuration change indication. The escape frame can further include a data field to indicate a particular configuration change to be made. For example, where the communications system is an AMR system, an escape frame can be used to change an active codec mode set. Alternatively, an escape frame can be used to change a phase of codec information.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Digital video guard
InactiveUS20110264922A1Simple in-line pathHigh bandwidthUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
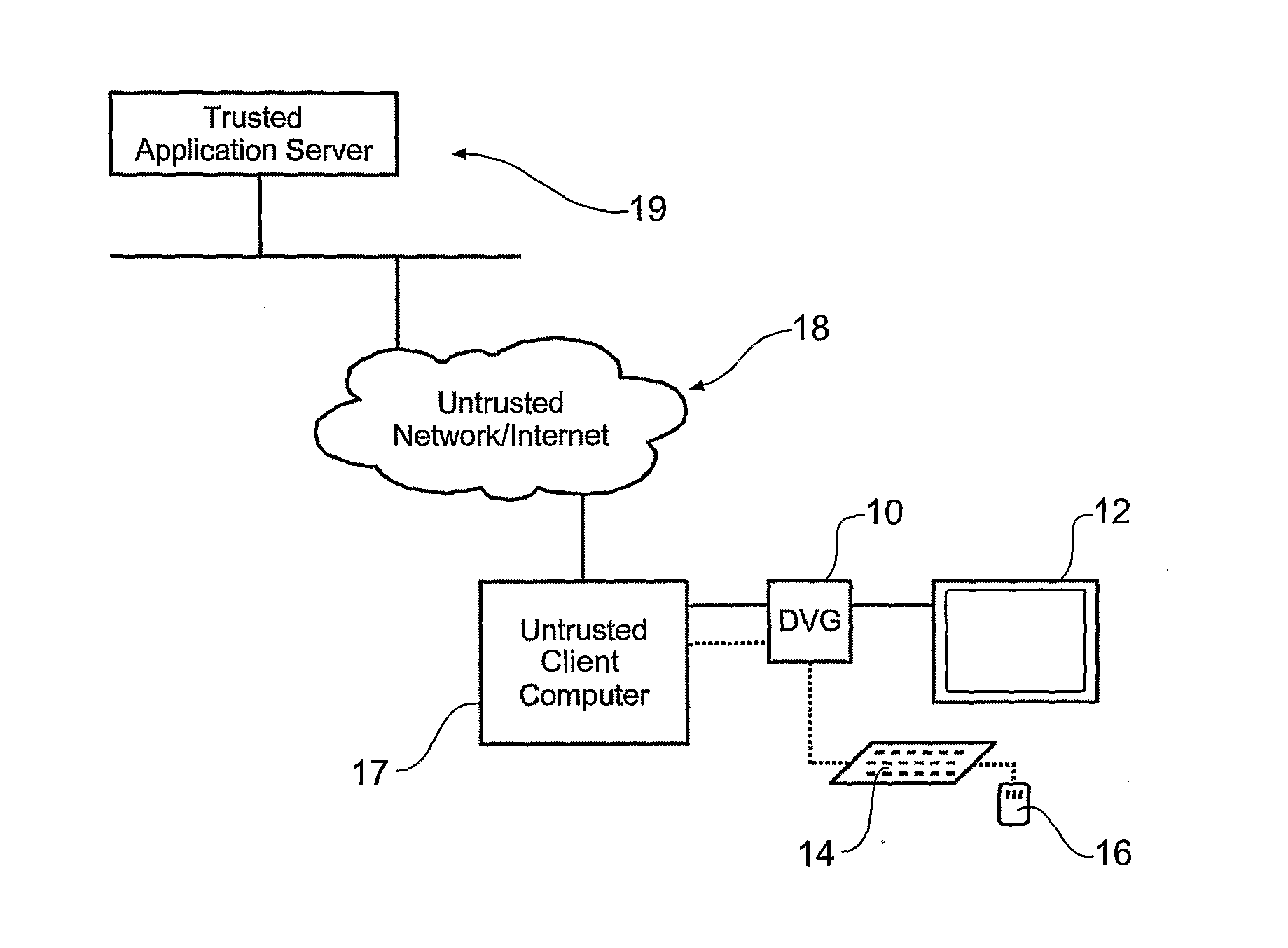
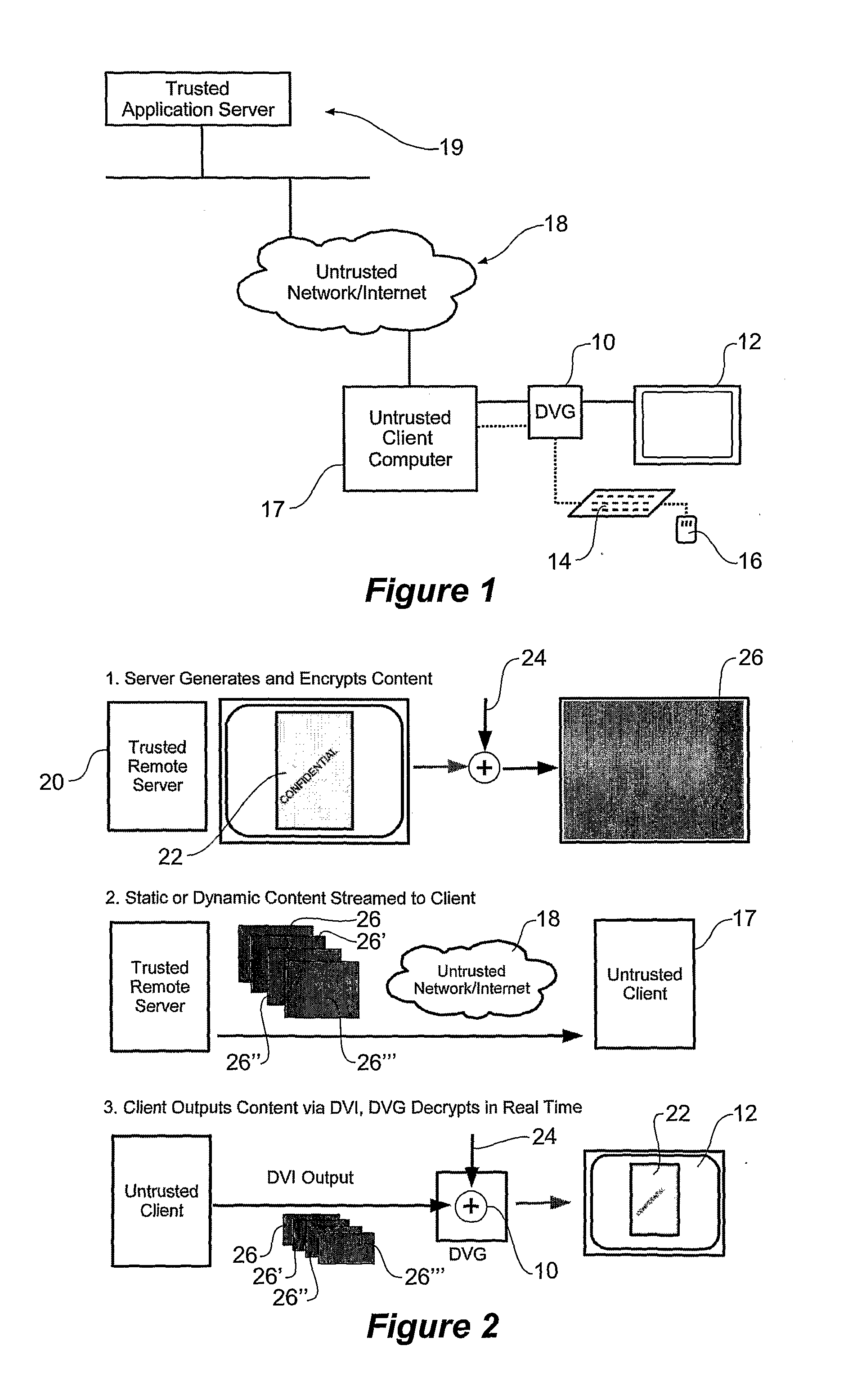
This invention relates to the veracity of information that is displayed to a user of a computer and can also relate to the veracity of information provided to a computer by human input devices such as pointing devices and keyboards. A digital video guard device is a peripheral that is retrofitted to commodity computer device. The digital video guard device provides trust in specific information presented on a digital display. The digital video guard device resides in-line with a digital display and enables secure end-to-end interactions between a user and a displayed (usually remote) application. In-band signalling within the digital video stream is used to carry encrypted information from a remote source, over untrusted network infrastructure through the digital video guard device to a user for viewing. The creation of encrypted digital video content can be achieved by either local or remote applications, and is effected by manipulating what is to be rendered on a computer's display, i.e. encrypting data that will at some time form part of a digital display stream and be output from an information device to a digital display. The digital video guard device can decrypt and verify the integrity of the digital video content as it is sent to a digital display. The integrity of the displayed information is indicated by a trusted LED on the digital video guard device hardware. Part or the entire video signal may be designated as trusted, depending on what data within the video signal has been encrypted, signed, or otherwise labelled as being trustworthy.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA
Wireless in-band signaling with in-vehicle systems
ActiveUS20090117947A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesSpecial service for subscribersTelecommunications networkIn vehicle
This invention pertains to methods and apparatus for data communications from vehicles, to obtain emergency, concierge and other services, using a voice channel of a digital wireless telecommunications network. Signaling is described for commencing data sessions after establishing a voice channel call. The call may be initiated from the vehicle automatically, and the call taker location may be unattended. Signaling methods are selected for traversing both newer and legacy vocoders for ubiquitous operation.
Owner:AIRBIQUITY INC
Mesh restoration in optical transport networks
The present disclosure provides mesh restoration systems and methods with Optical Transport Network (OTN) links using a signaling and routing protocol, such as Optical Signaling and Routing Protocol (OSRP), Automatically Switched Optical Network (ASON), Generalized Multi Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS), and the like. The present invention includes an optical node, network, and method using the signaling and routing protocol for OTN lines of differing bandwidth granularities. The present invention utilizes OTN overhead for in-band signaling and may include capability for supporting SONET / SDH lines as well as OTN lines in the same system using the signaling and routing protocol.
Owner:CIENA
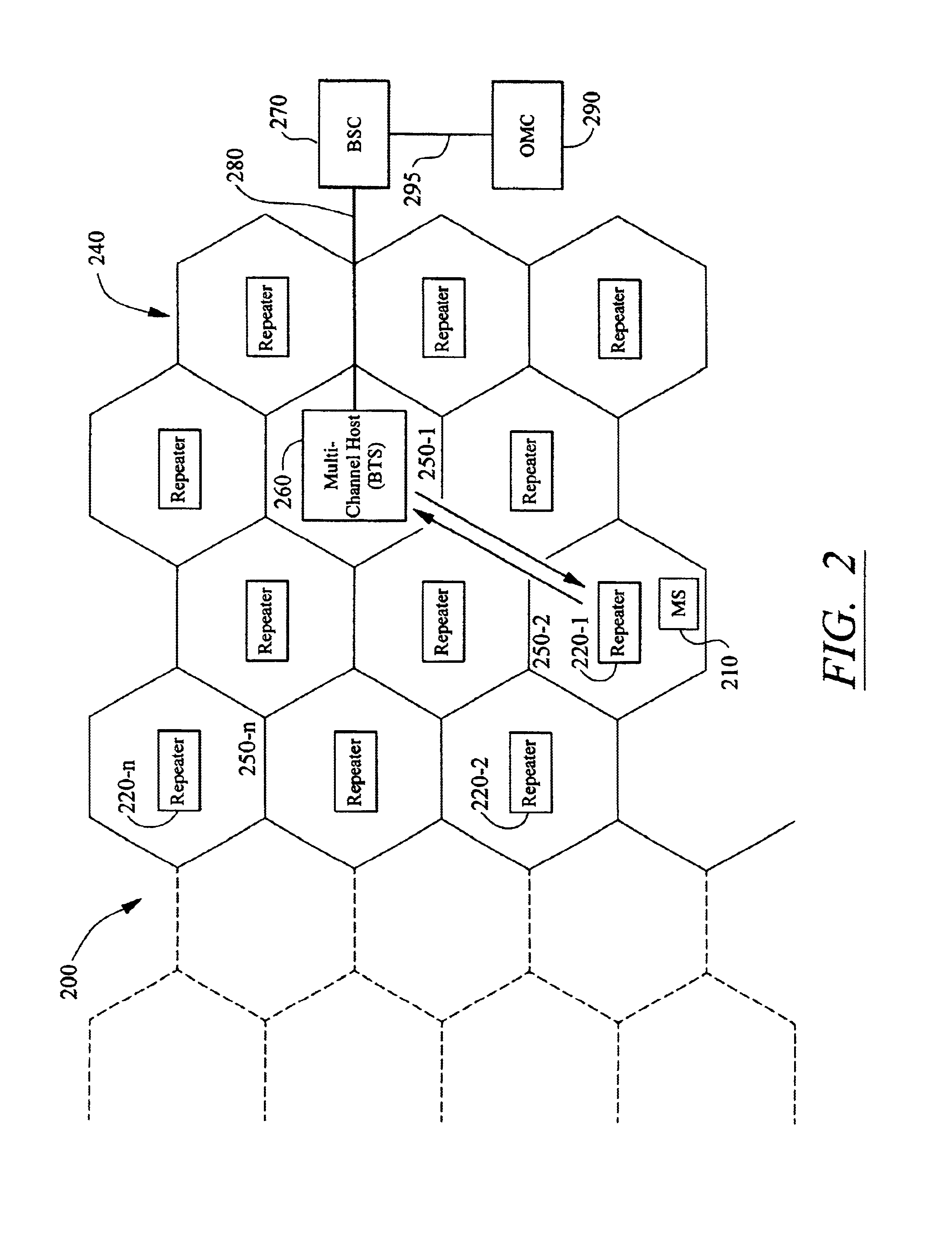
Method and apparatus employing wireless in-band signaling for downlink transmission of commands and uplink transmission of status for a wireless system repeater
InactiveUS6690662B1Accurate timingPulse transformerActive radio relay systemsIn-band signalingTransceiver
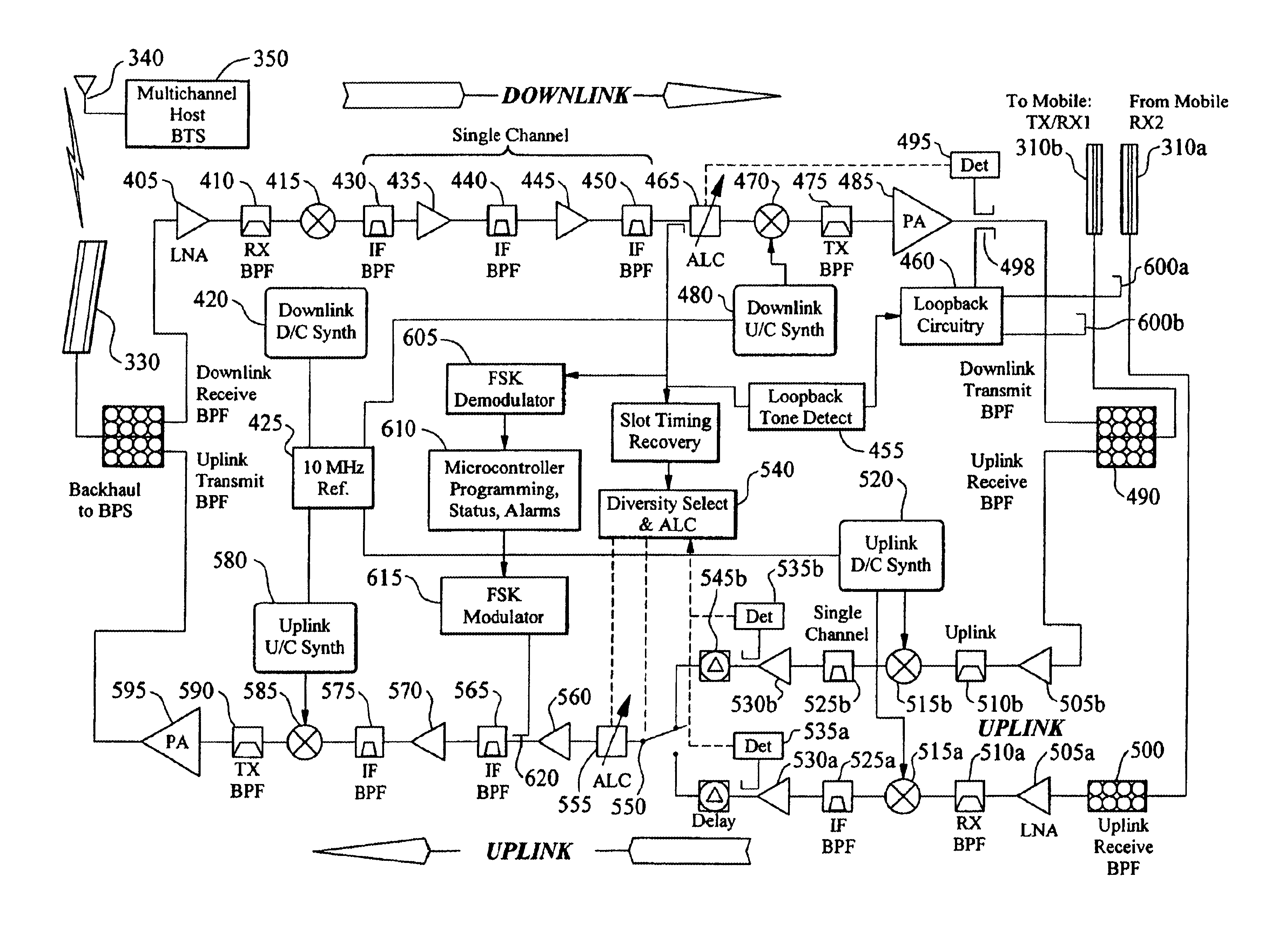
An approach to improving TDMA system operation is disclosed wherein in-band translator components are located in the center of remote cells which would normally contain a base transceiver system (BTS). The in-band. translators employ wireless in-band signaling for downlink transmission of commands from an operation and maintenance center (OMC) and uplink transmission of status-indicating and alarm signal data. The remotely located repeaters of the present invention have frequency shift key detection and demodulation capability incorporated in the downlink path, while also incorporating FSK modulation capability into the uplink path. This allows the repeater to extract commands from the serving BTS downlink signal and act on them. It also allows for the repeater to transmit status-indicating signals and alarms to the OMC via the uplink path to the serving BTS.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com