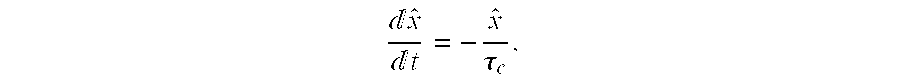Patents
Literature
299 results about "Loop bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
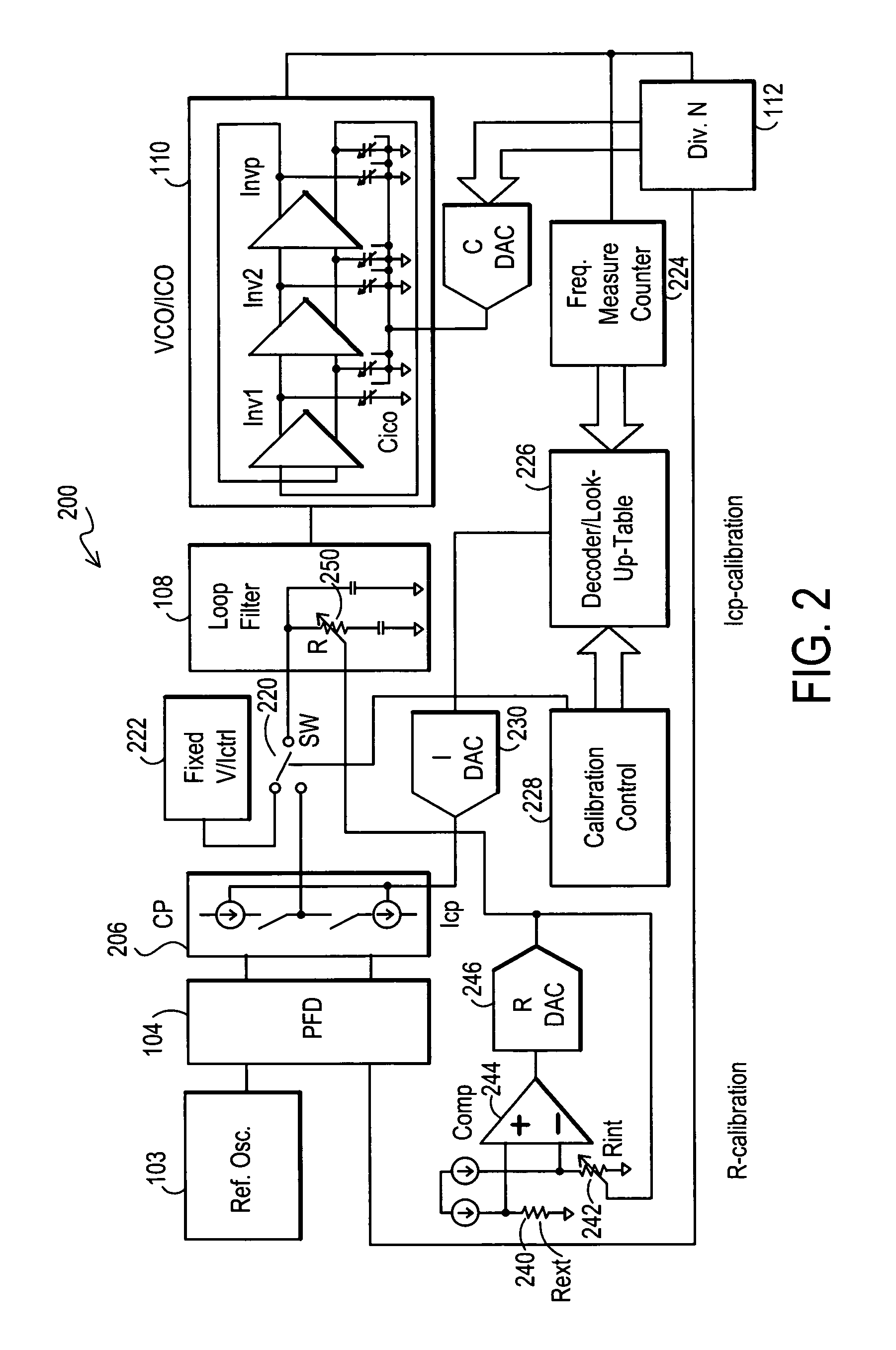
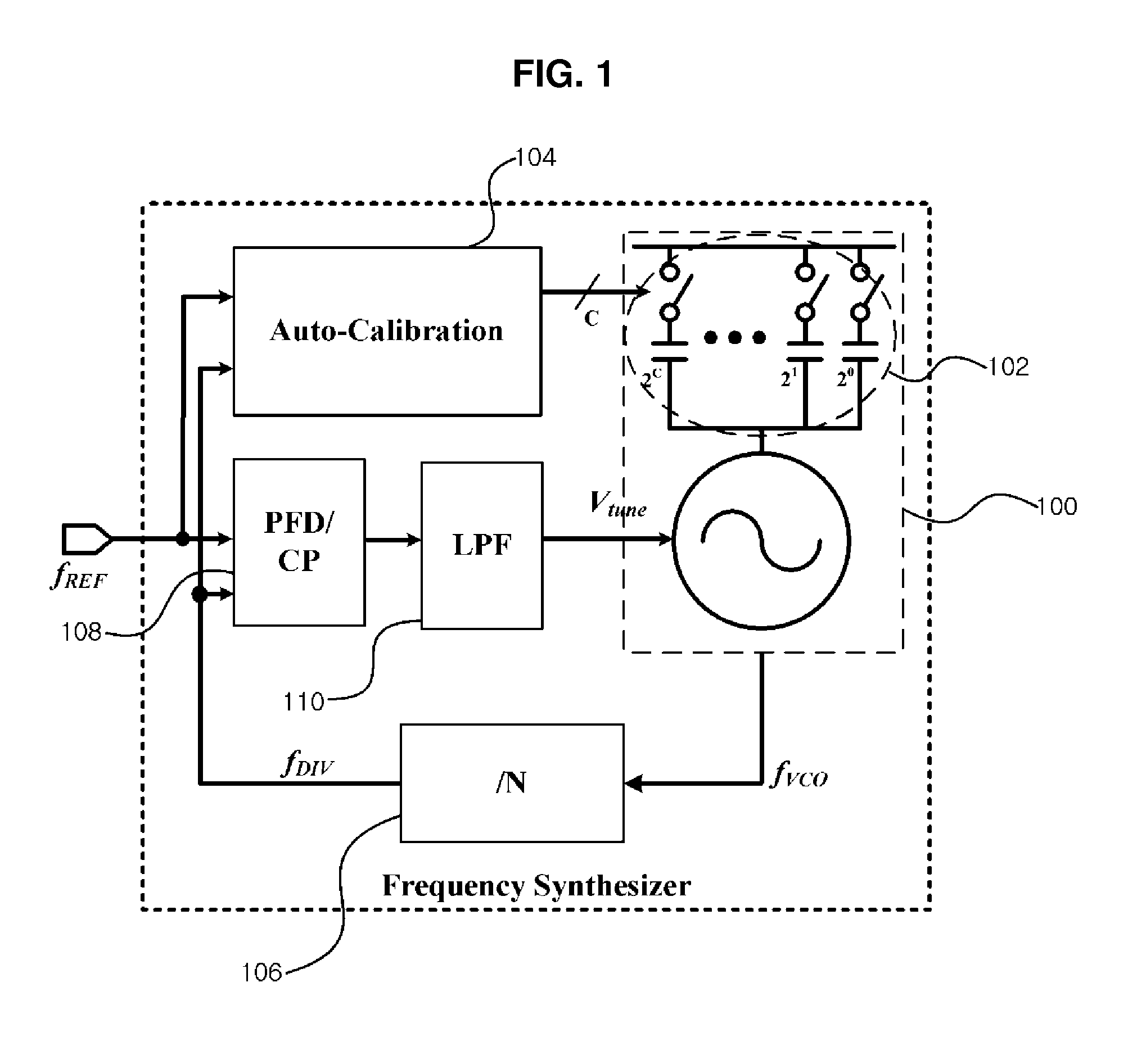
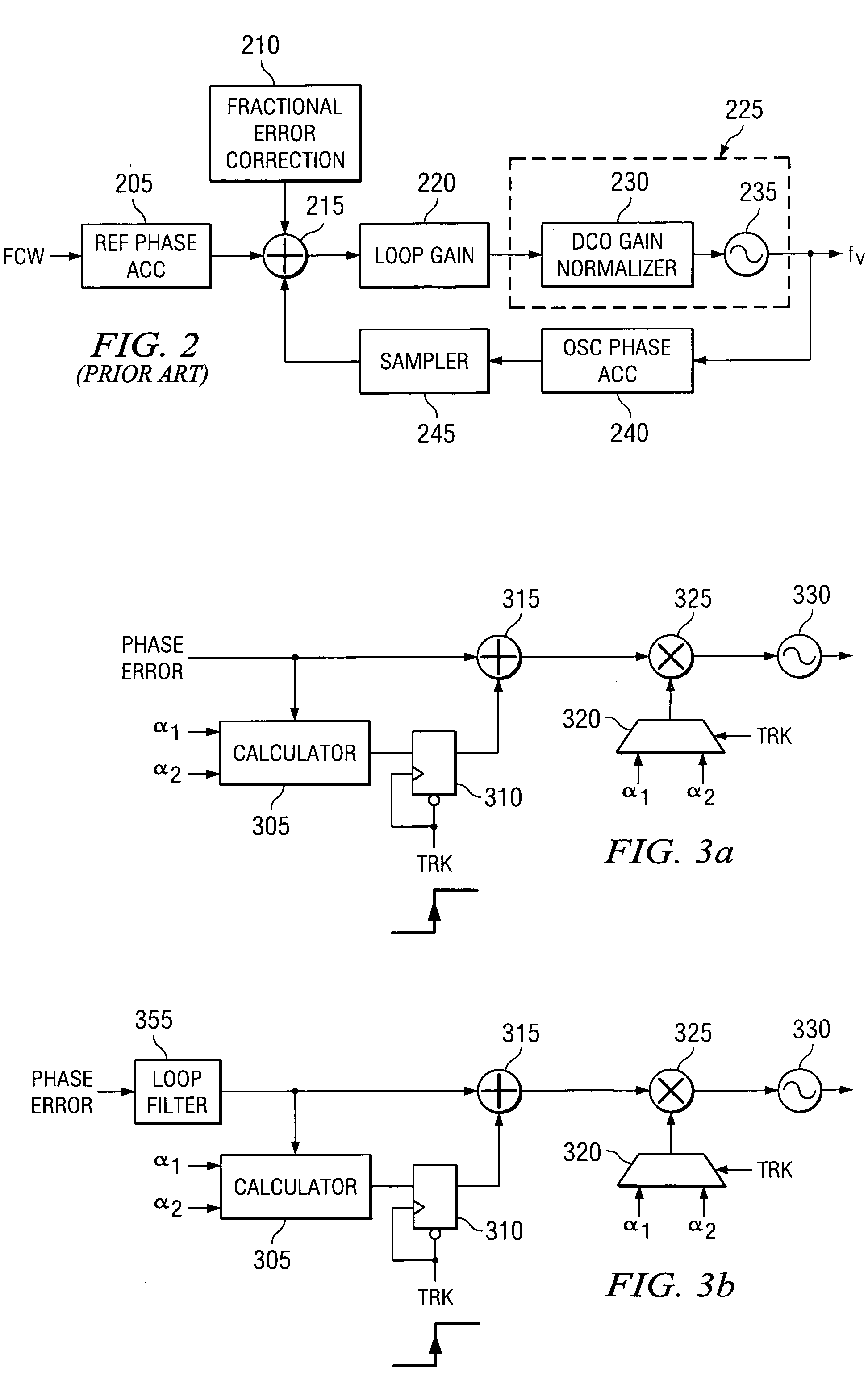
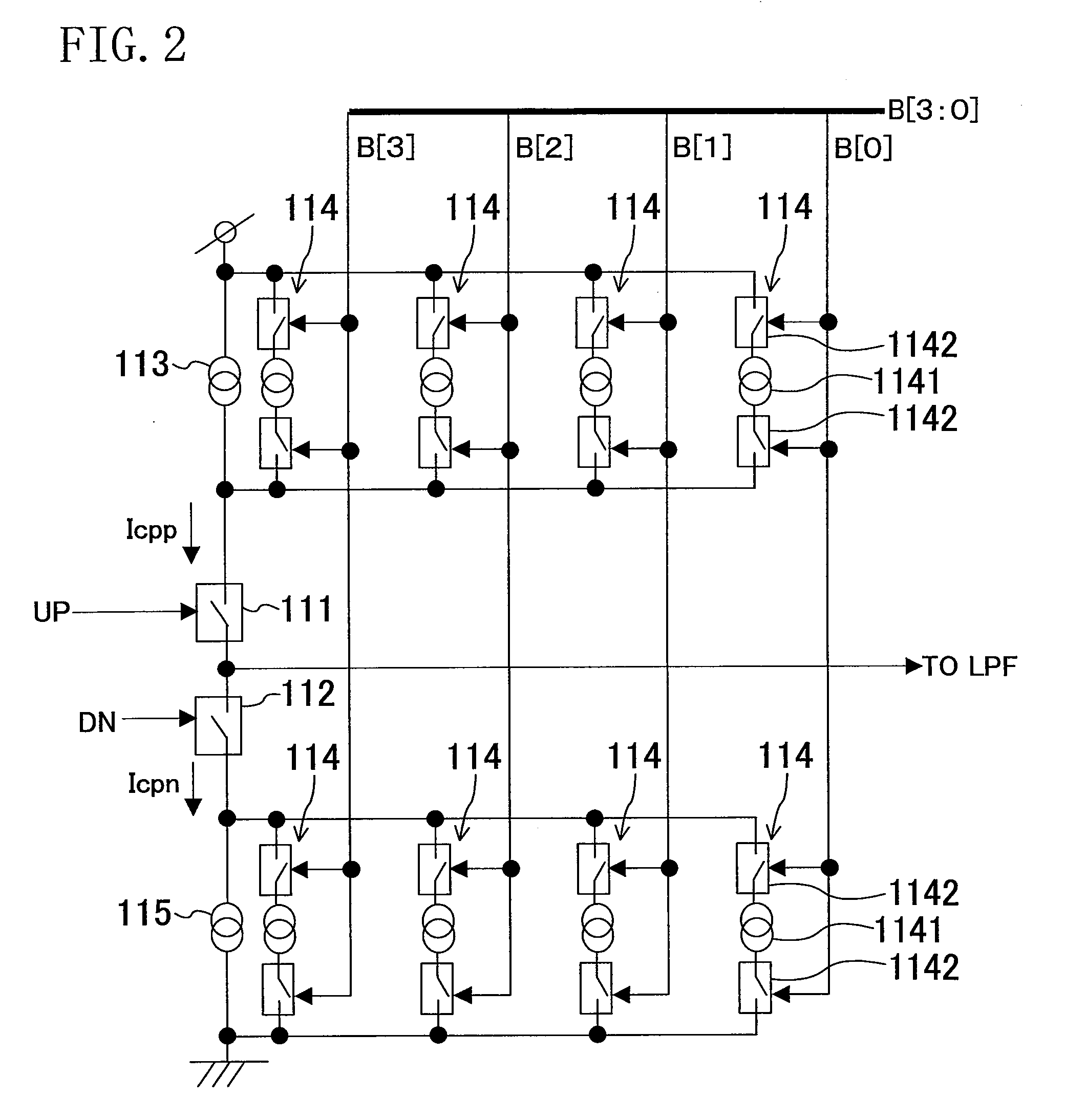
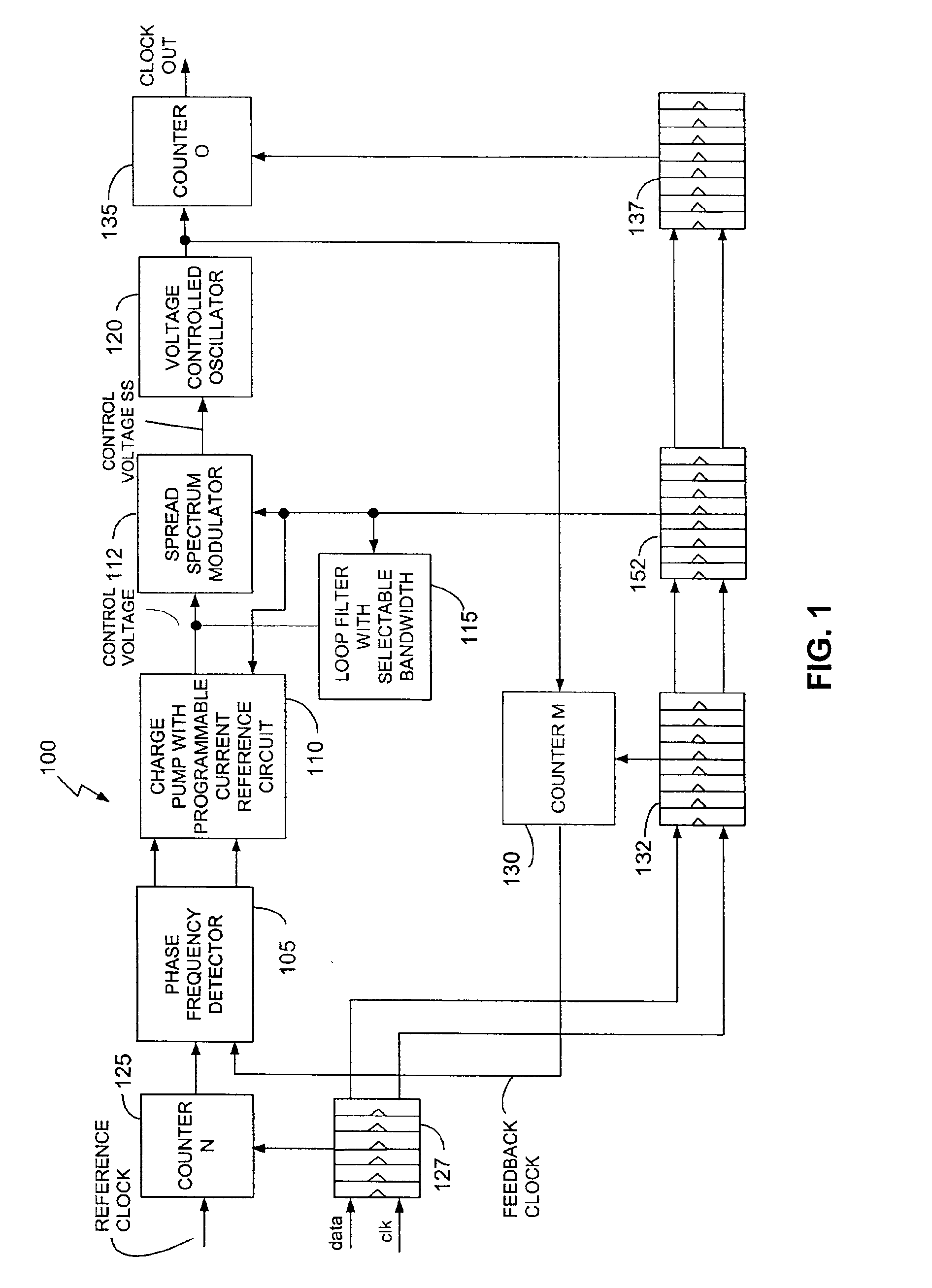
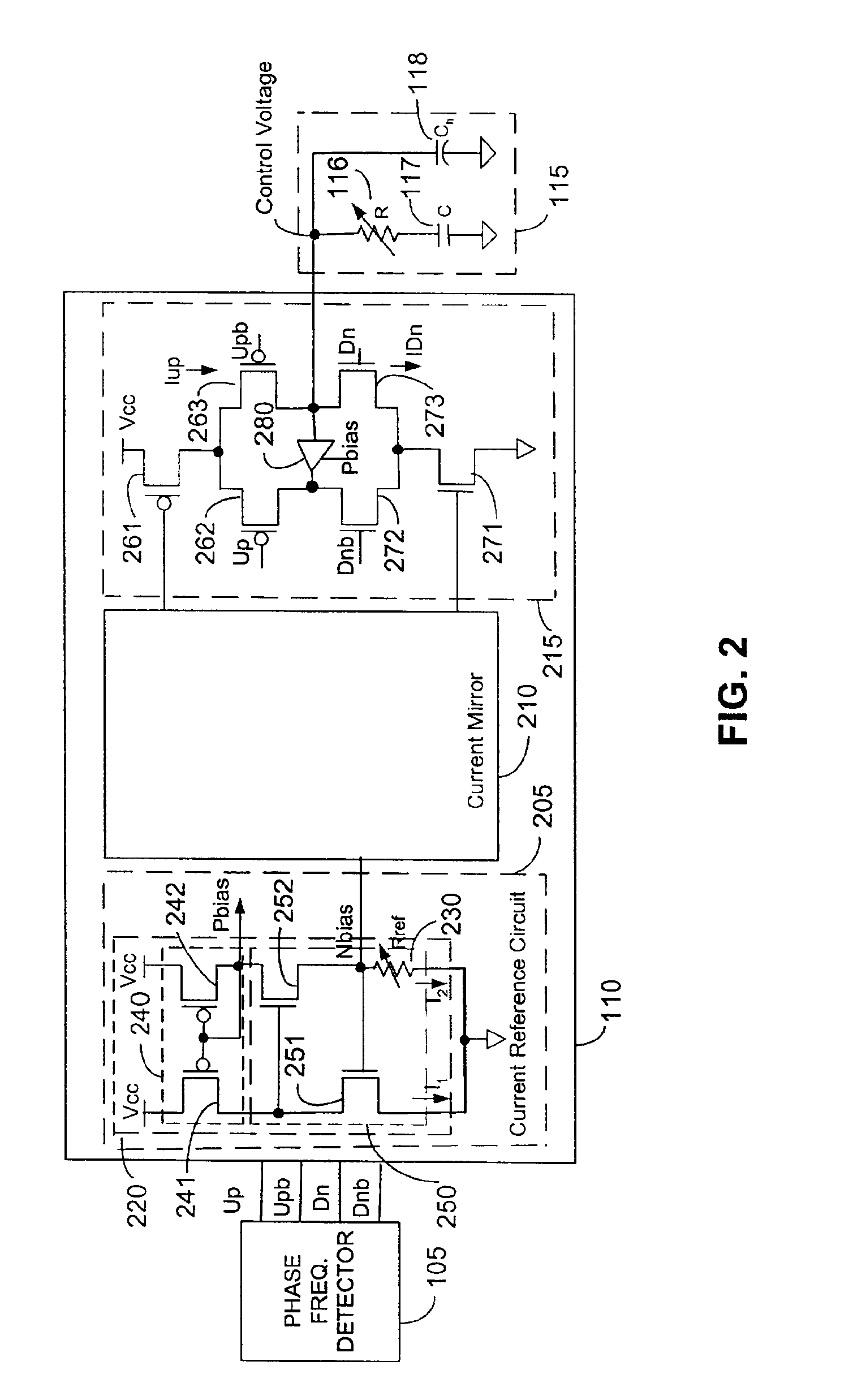
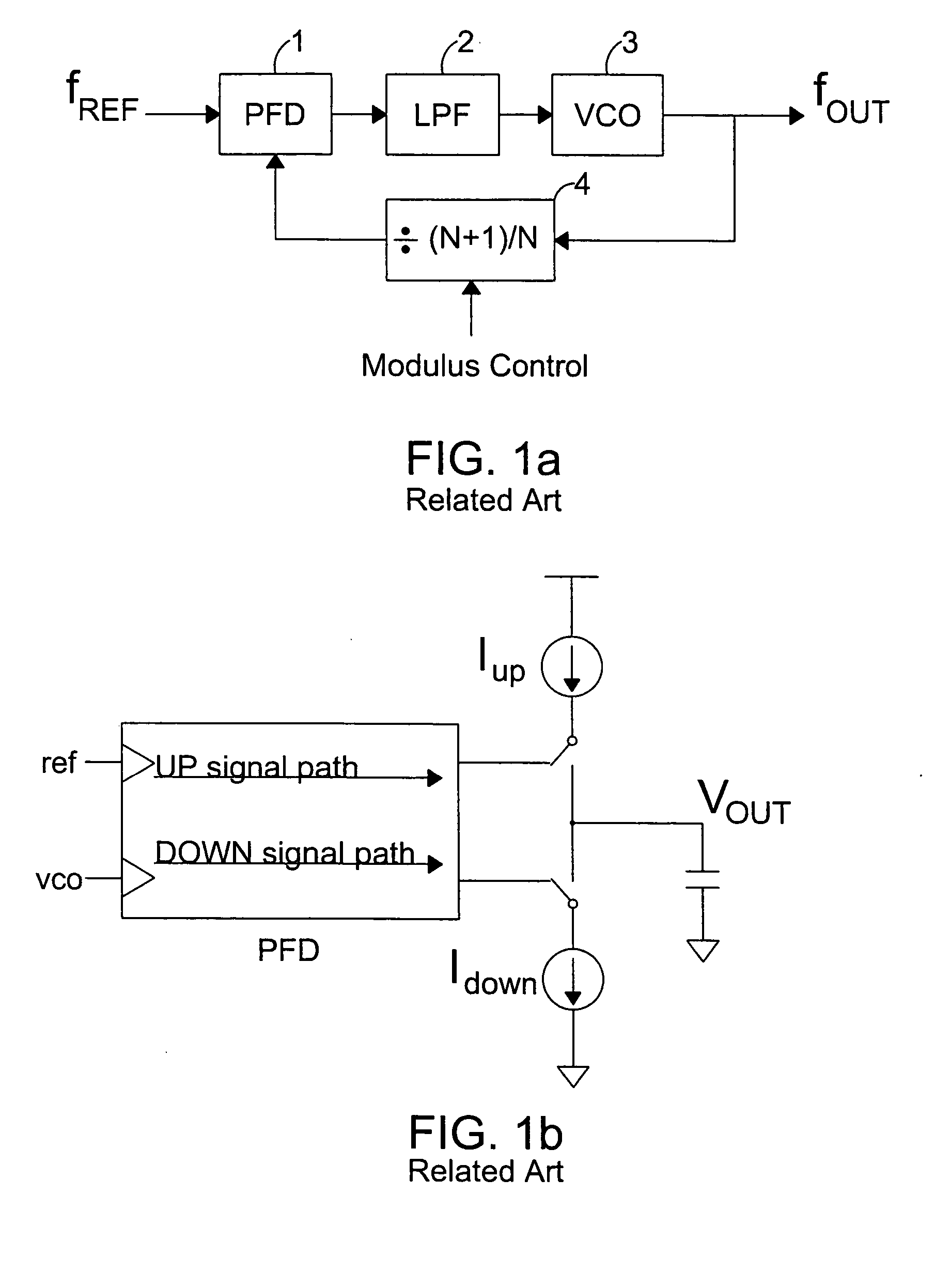
Apparatus and method for phase lock loop gain control using unit current sources
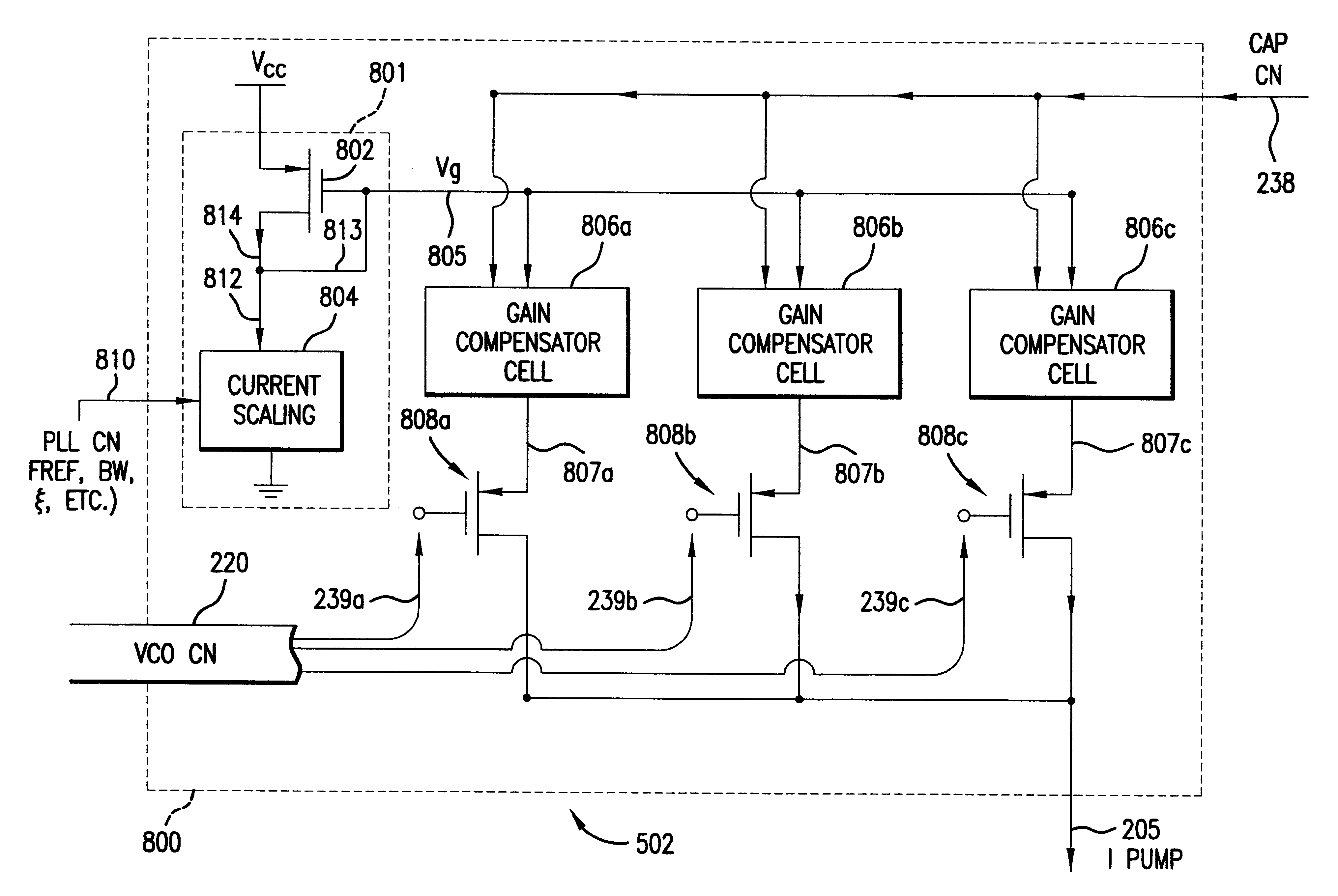
InactiveUS6583675B2Pulse automatic controlDiscontinuous tuning for band selectionFixed capacitorReference current
A gain compensator compensates for the gain variation of a varactor-tuned voltage tuned oscillator (VCO) in a phase lock loop (PLL). The VCO includes a parallel LC circuit having multiple fixed capacitors that can be switched-in or switched-out of the LC circuit according to a capacitor control signal to perform band-select tuning of the VCO. The gain compensator compensates for the variable VCO gain by generating a charge pump reference current that is based on the same capacitor control signal that controls the fixed capacitors in the LC circuit. The gain compensator generates the charge pump reference current by replicating a reference scale current using unit current sources. The number of times the reference scale current is replicated is based on the fixed capacitance that is switched-in to the LC circuit and therefore the frequency band of the PLL. The reference scale current is generated based on a PLL control that specifics certain PLL characteristics such as reference frequency, loop bandwidth, and loop damping. Therefore, the reference pump current can be efficiently optimized for changing PLL operating conditions, in addition to compensating for variable VCO gain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
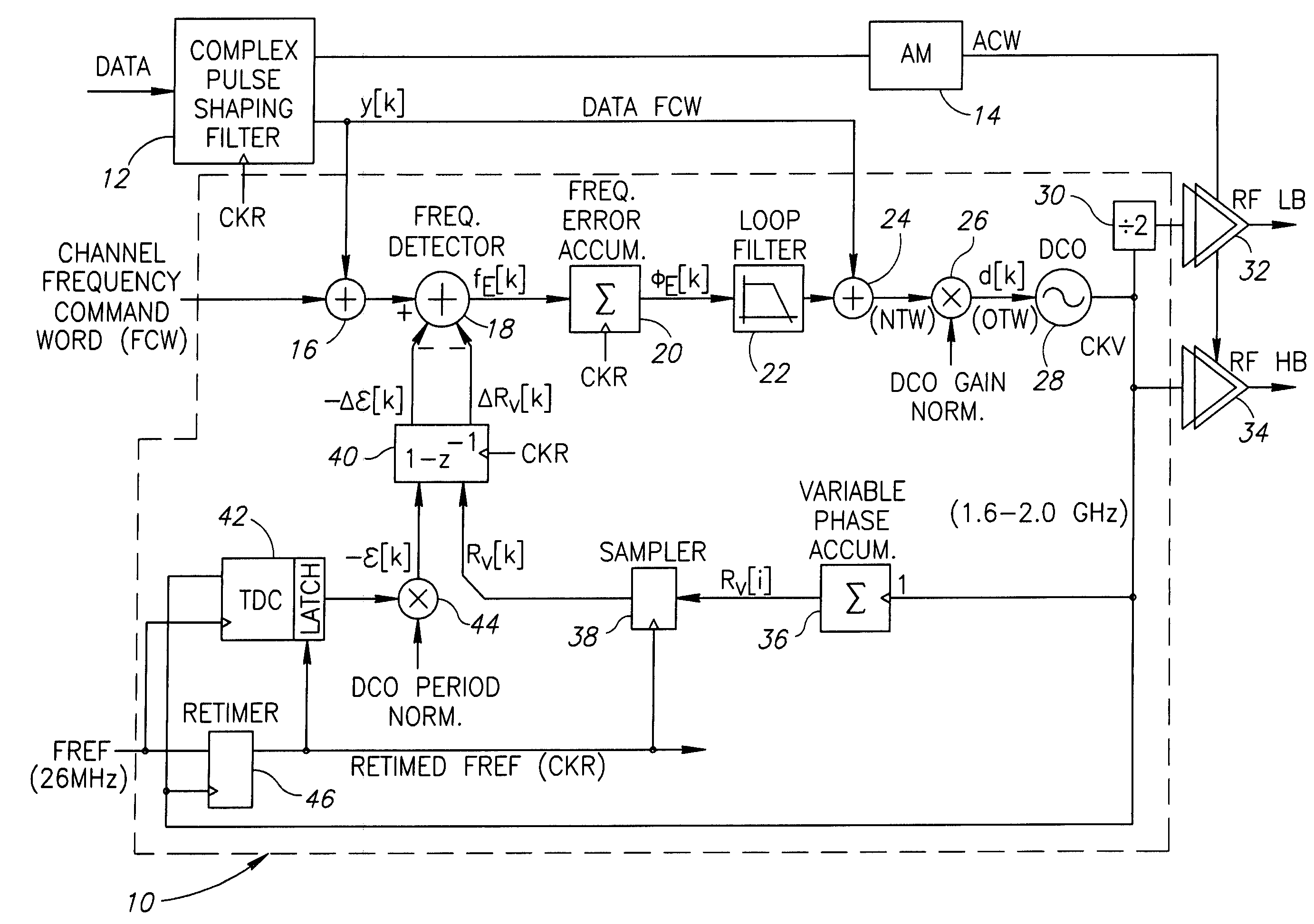
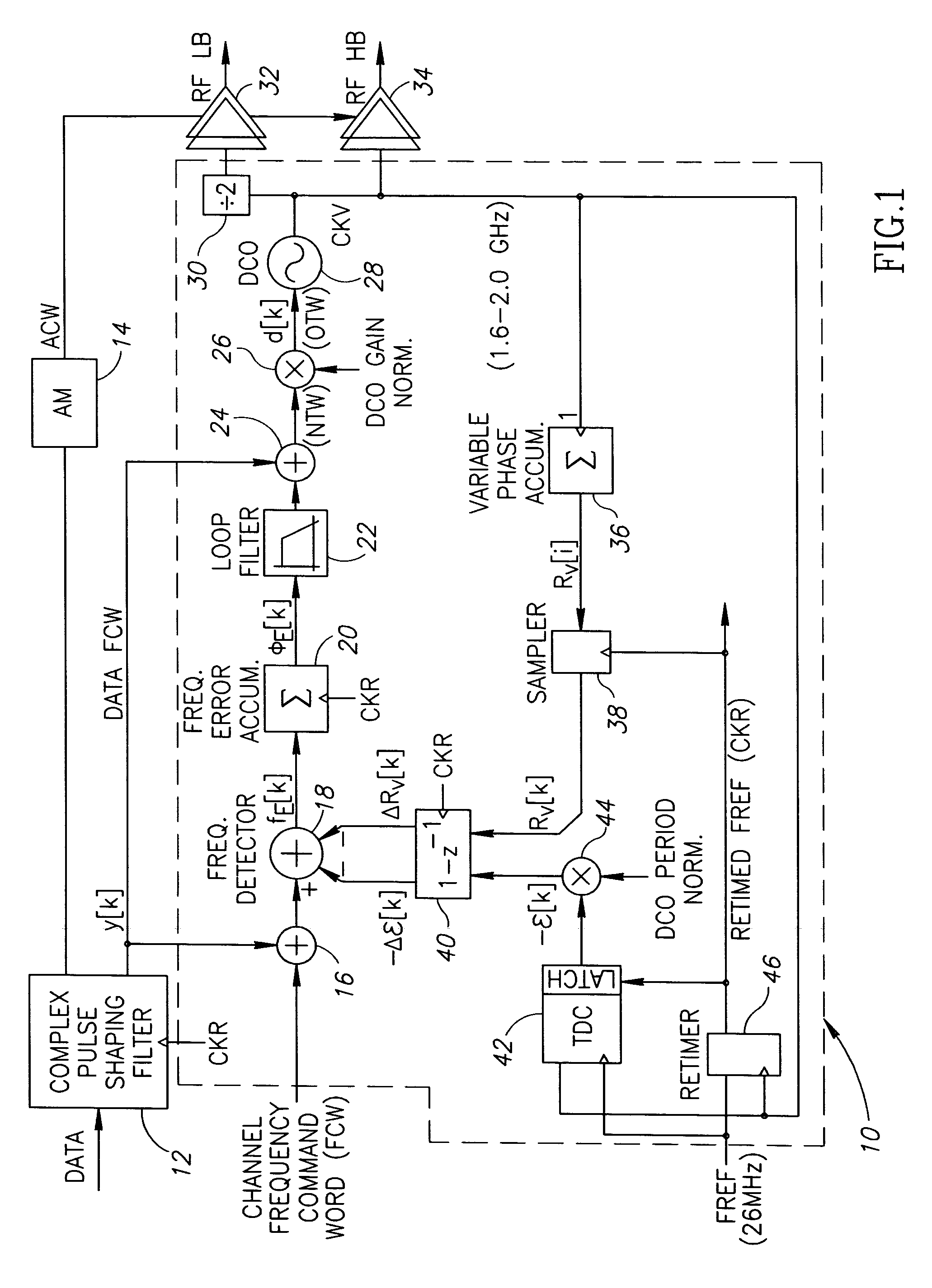
Gain calibration of a digital controlled oscillator
ActiveUS20060033582A1Good estimateImprove performancePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsSteep descentDigital control oscillator
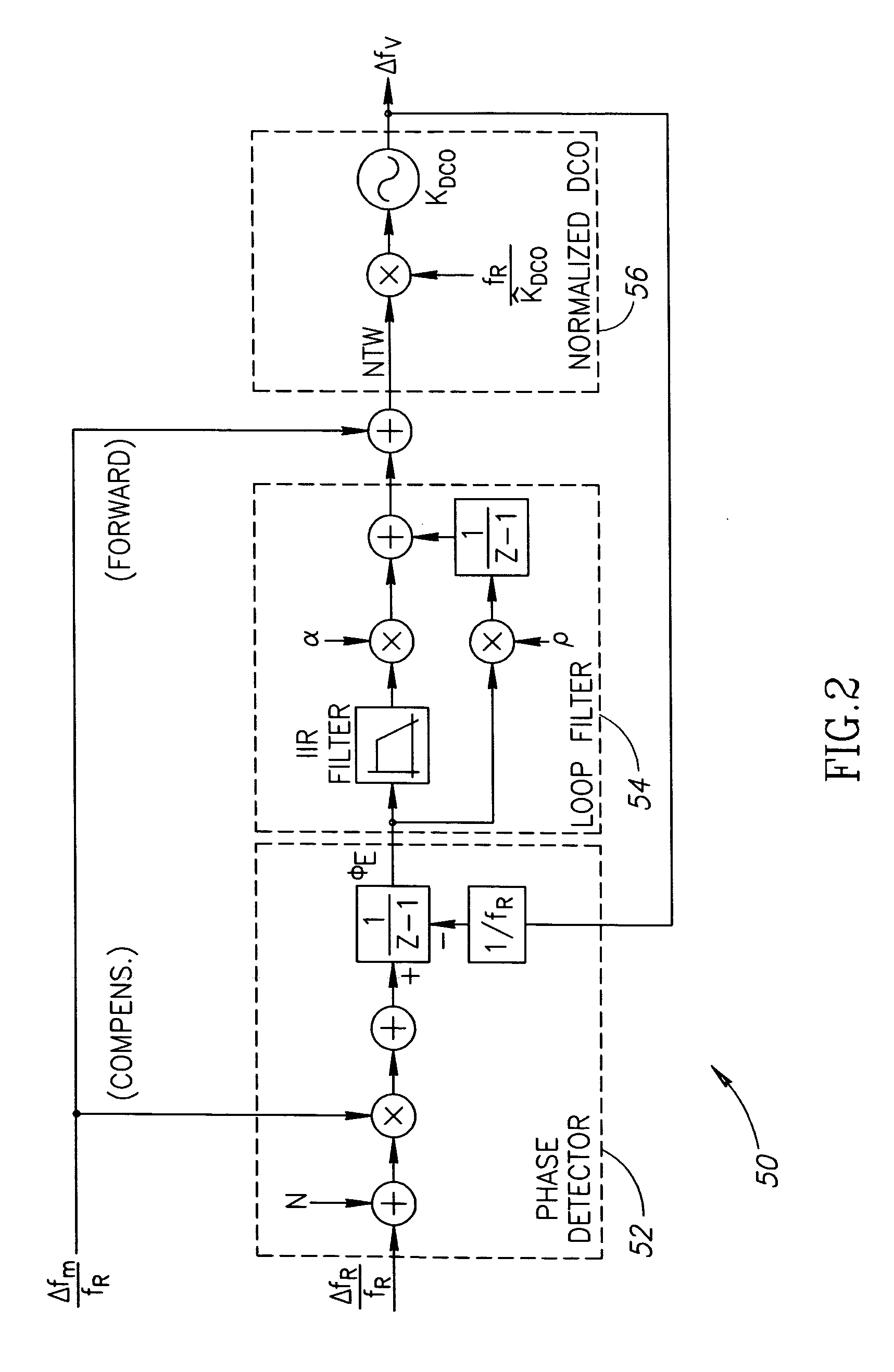
A novel apparatus for and a method of estimating, calibrating and tracking in real-time the gain of a radio frequency (RF) digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) in an all-digital phase locked loop (ADPLL). Precise setting of the inverse DCO gain in the ADPLL modulating path allows direct wideband frequency modulation that is independent of the ADPLL loop bandwidth. The gain calibration technique is based on a steepest descent iterative algorithm wherein the phase ADPLL error is sampled and correlated with the modulating data to generate a gradient. The gradient is then scaled and added to the current value of the DCO gain multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus to achieve a process, temperature and divider modulus independent PLL loop bandwidth and damping factor using open-loop calibration techniques
InactiveUS7095287B2Reduce complexityImprove accuracyPulse automatic controlFrequency analysisDamping factorProportional control
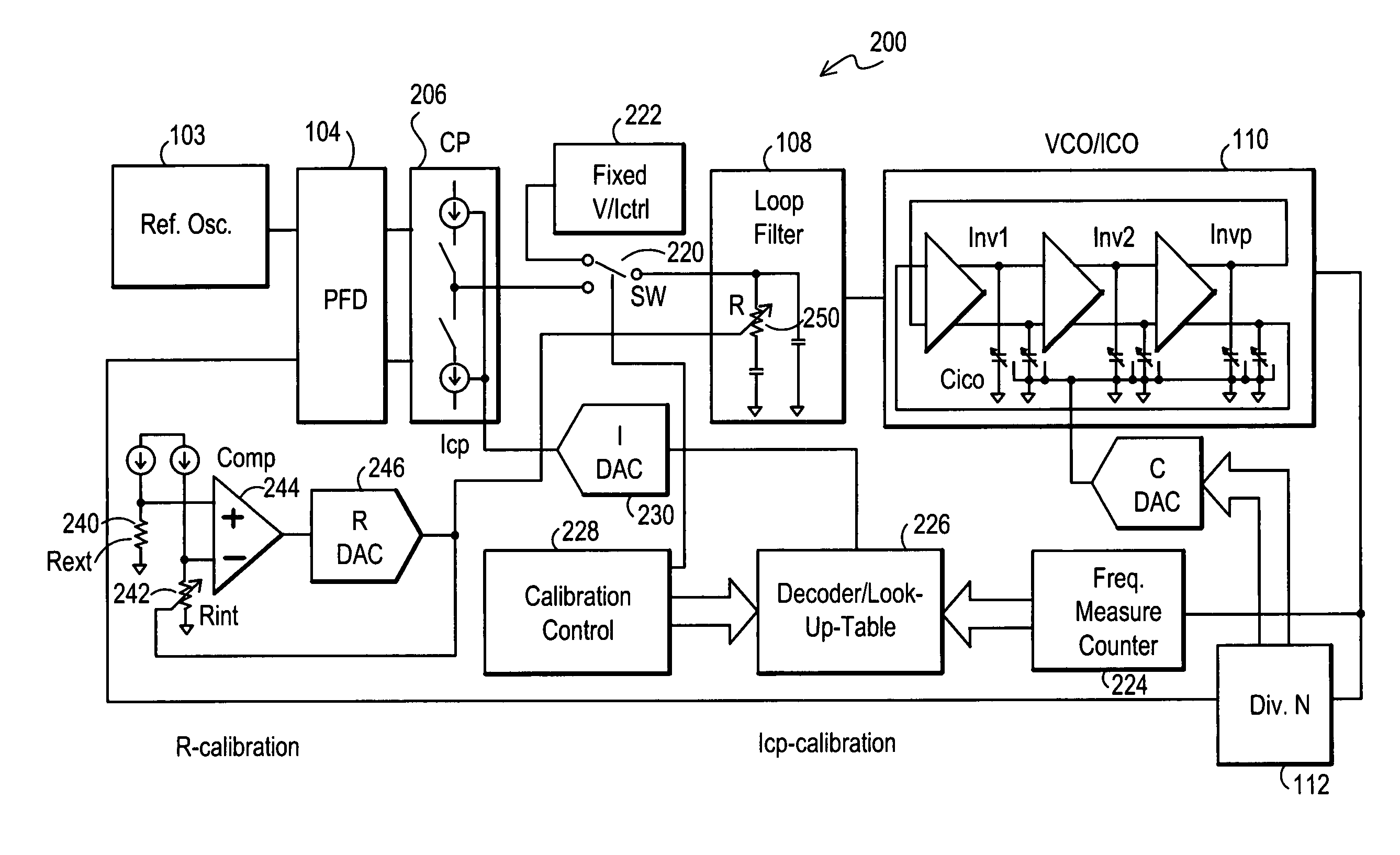
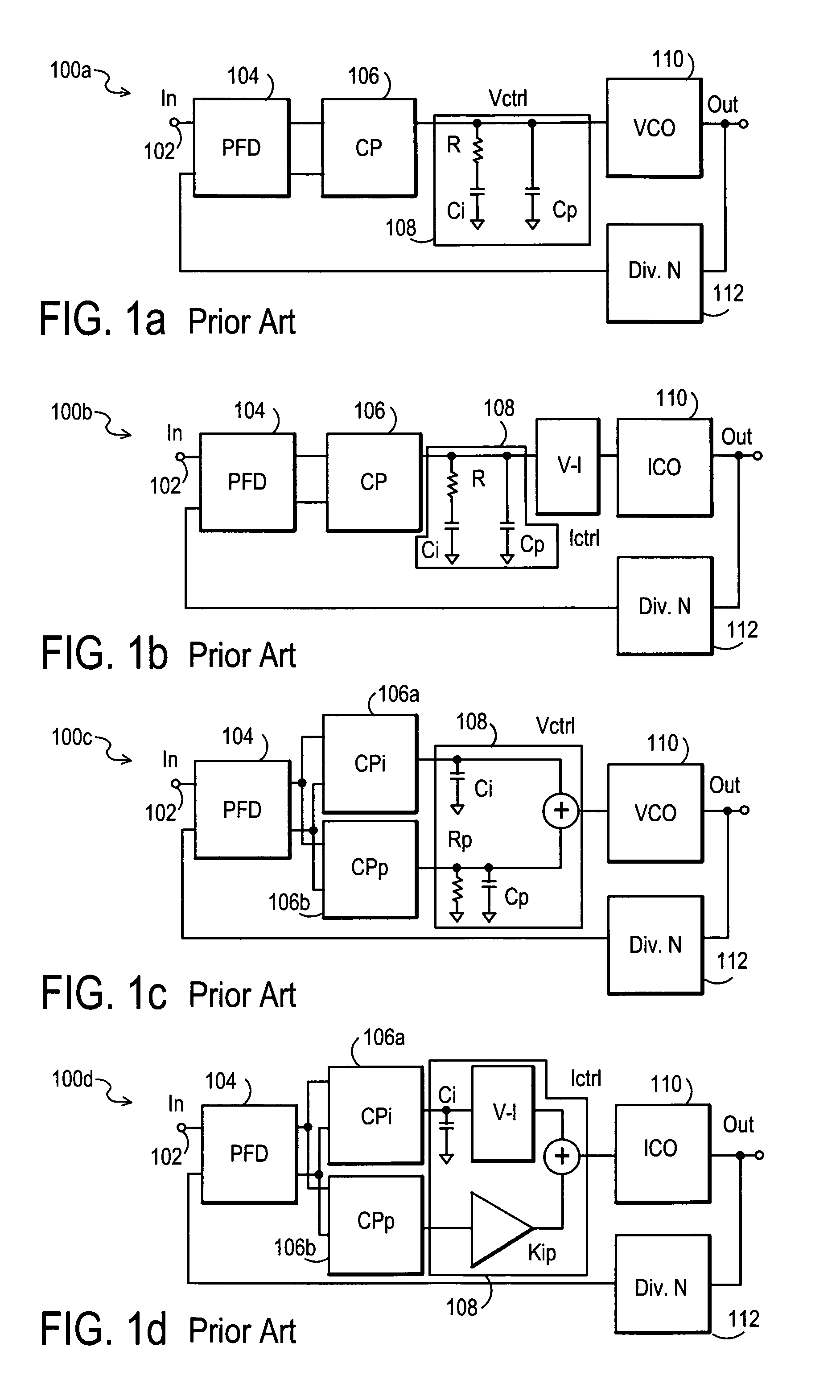
Several open-loop calibration techniques for phase-locked-loop circuits (PLL) that provide a process, temperature and divider modulus independence for the loop bandwidth and damping factor are disclosed. Two categories of open-loop techniques are presented. The first method uses only a single measurement of the output frequency from the oscillator and adjusts a single PLL loop element that performs a simultaneous calibration of both the loop bandwidth and damping factor. The output frequency is measured for a given value of the oscillator control signal and the charge-pump current is adjusted such that it cancels the process variation of the oscillator gain. The second method uses two separate and orthogonal calibration steps, both of them based on the measurement of the output frequency from the oscillator when a known excitation is applied to the open loop signal path. In the first step the loop bandwidth is calibrated by adjusting the charge-pump current based on the measurement of the forward path gain when applying a constant phase shift between the two clocks that go to the phase frequency detector, while the integral path is hold to a constant value. During the second step the damping factor is calibrated by adjusting the value of the integral loop filter capacitor based on the measurement of the oscillator output frequency when excited with a voltage proportional with the integral capacitor value, while the proportional control component is zeroed-out.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Apparatus and method for freezing the states of a receiver during silent line state operation of a network device
InactiveUS7327754B2Reduce the required powerAvoid data lossEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementMostly TrueLoop bandwidth
A method for maintaining the states of a receiver during the silent line state of a network device operating in a low power link suspend mode is presented. Accordingly, a method of freezing the states of the equalizer and keeping the receiver clock locked to a frequency that is approximately equal to that of the input data while providing for rapid adjustment to the phase and thus recovery of the input data is presented. During Silent Line State (SLS), the receiver states are frozen using methods that avoid parasitic decay. Also, the receive clock phase lock loop is locked onto the local transmit clock since the local transmit clock has a frequency approximating the incoming data frequency. During the SLS, the transmitter of the remote network device may have been turned off to conserve power therefore the receiver has no way of immediately knowing the phase of an incoming data. Thus, in order to prevent loss of data, the receiver loops of the receiving network device are trained to the frequency of the transmitting remote network device using periodic Link Suspend packets. Thus, in most cases, only the phase of the incoming signal need be acquired when data arrives. The phase may be quickly acquired using loop bandwidth shift methods whereby the receive clock phase lock loop bandwidth is increased to a value that aids rapid acquisition of the input clock and then, after acquisition, the bandwidth is shifted to a low value to enhance noise rejection during tracking.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Self calibrating receive path correction system in a receiver
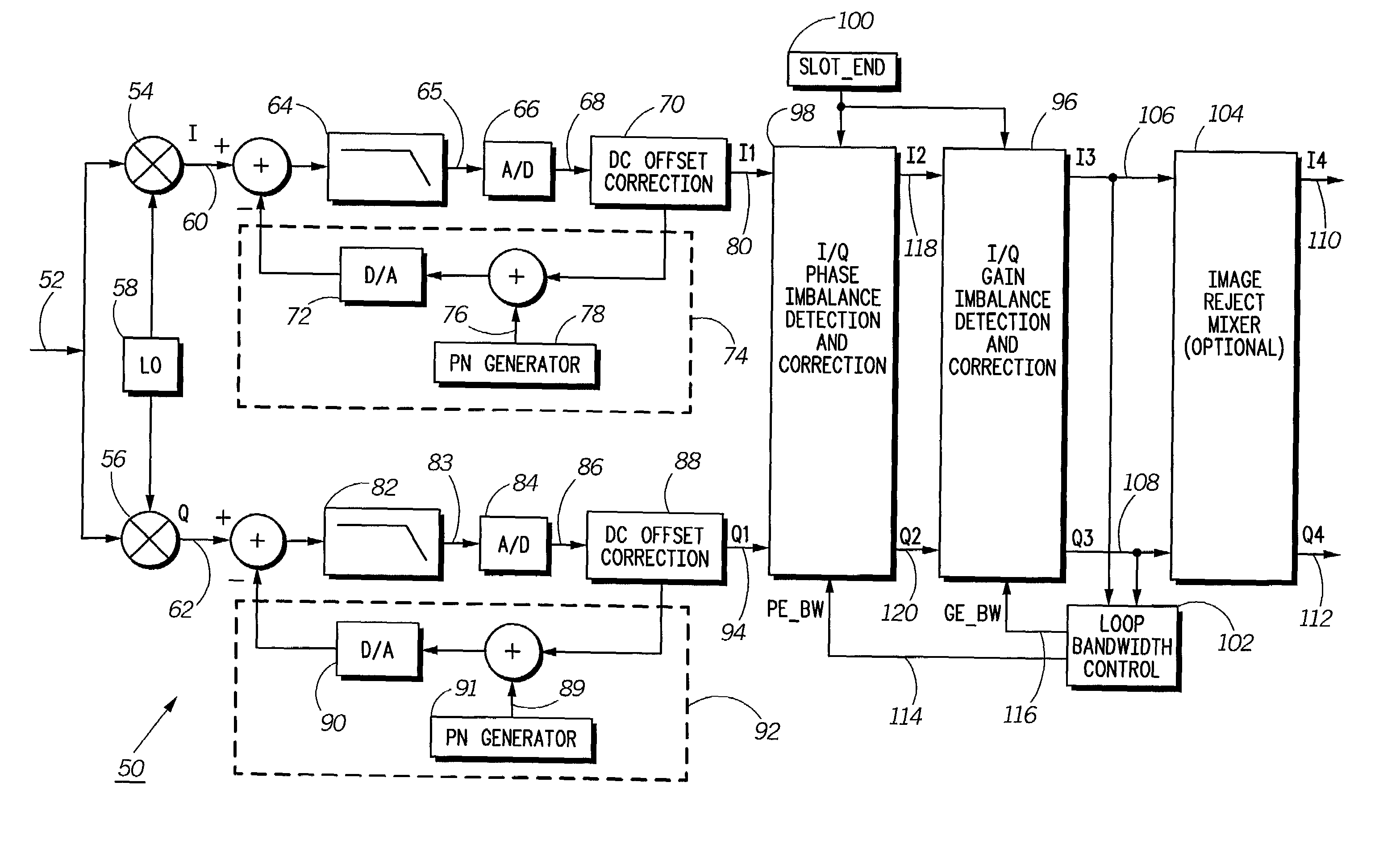
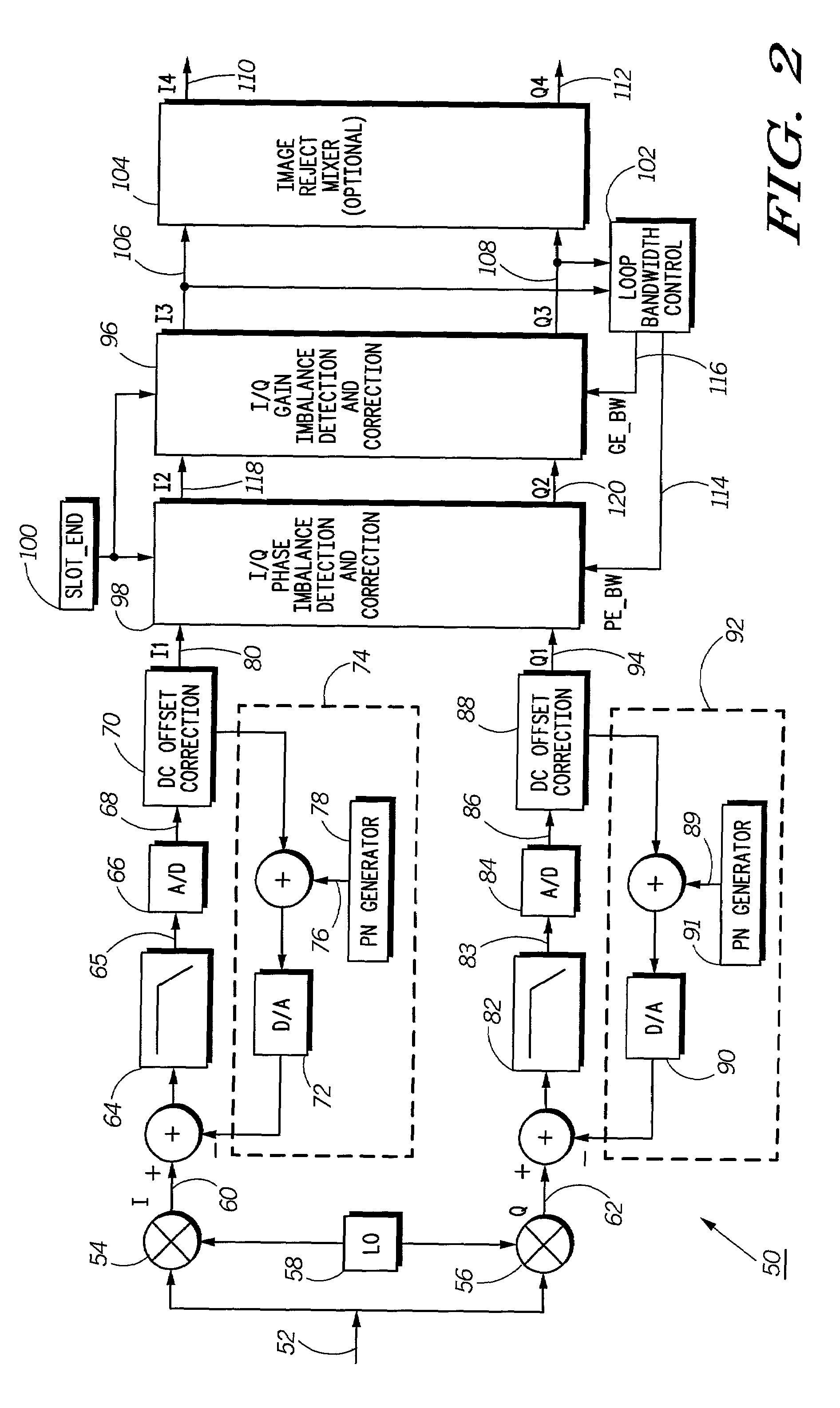
ActiveUS7130359B2Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationPhase imbalanceRelative phase
A receiver (50) includes a self-calibrating receive path correction system for correction of I / Q gain and phase imbalances in a radio frequency signal. The system includes a signal-processing block (53), an I / Q phase imbalance detection and correction circuit (98), an I / Q gain imbalance detection and correction circuit (96), and an adaptive loop bandwidth control circuit (102). The I / Q phase imbalance detection and correction circuit (98) equalizes for the relative phase imbalance and the I / Q gain imbalance detection and correction circuit (96) equalizes for the relative gain imbalance between the I and Q channels created by the analog portion of a quadrature receiver. The adaptive loop bandwidth control circuit (102) dynamically adjusts at least one loop bandwidth for the I / Q gain imbalance detection and correction circuit (96) and the I / Q phase imbalance detection and correction circuit (98) on a slot boundary.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
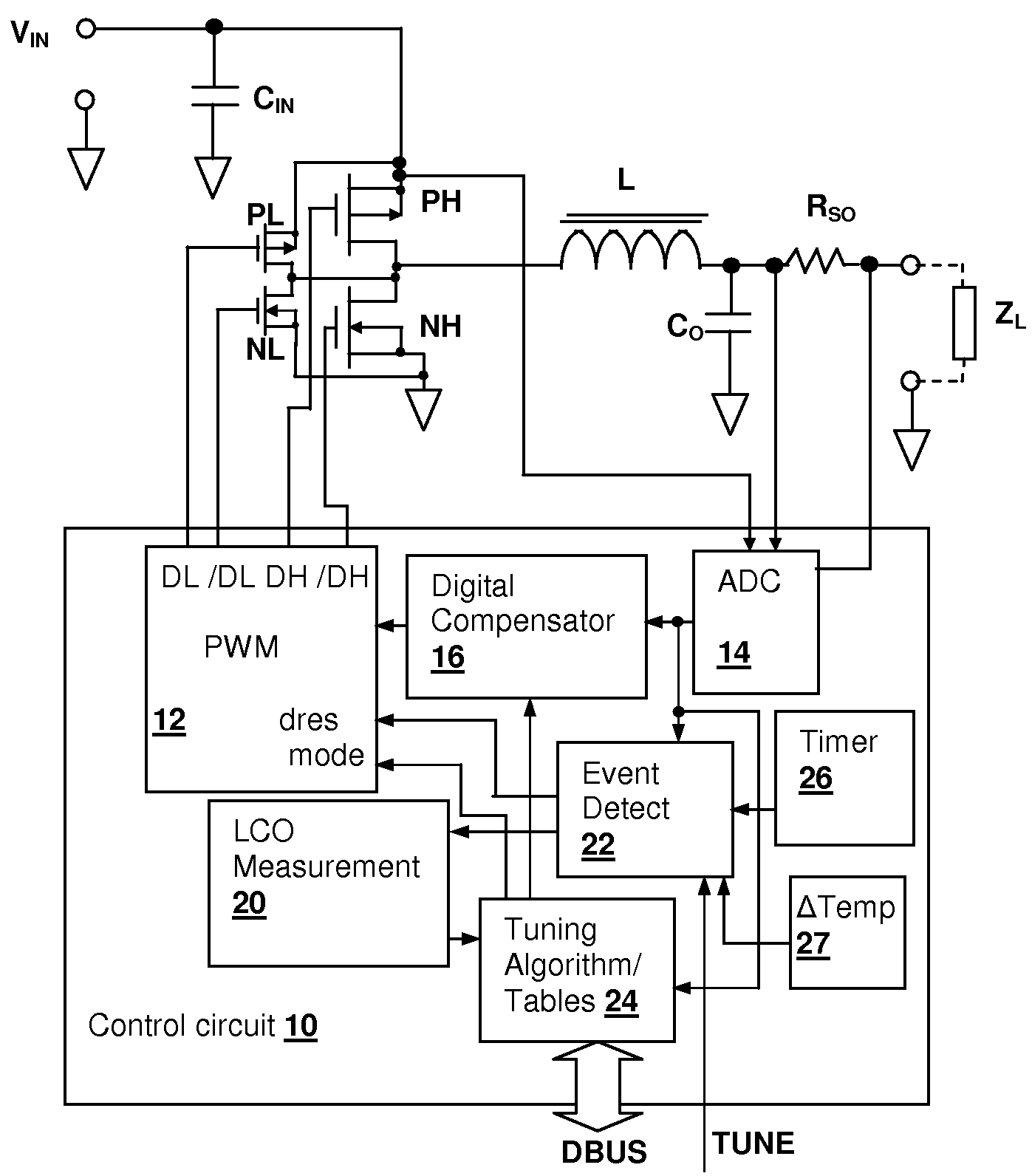
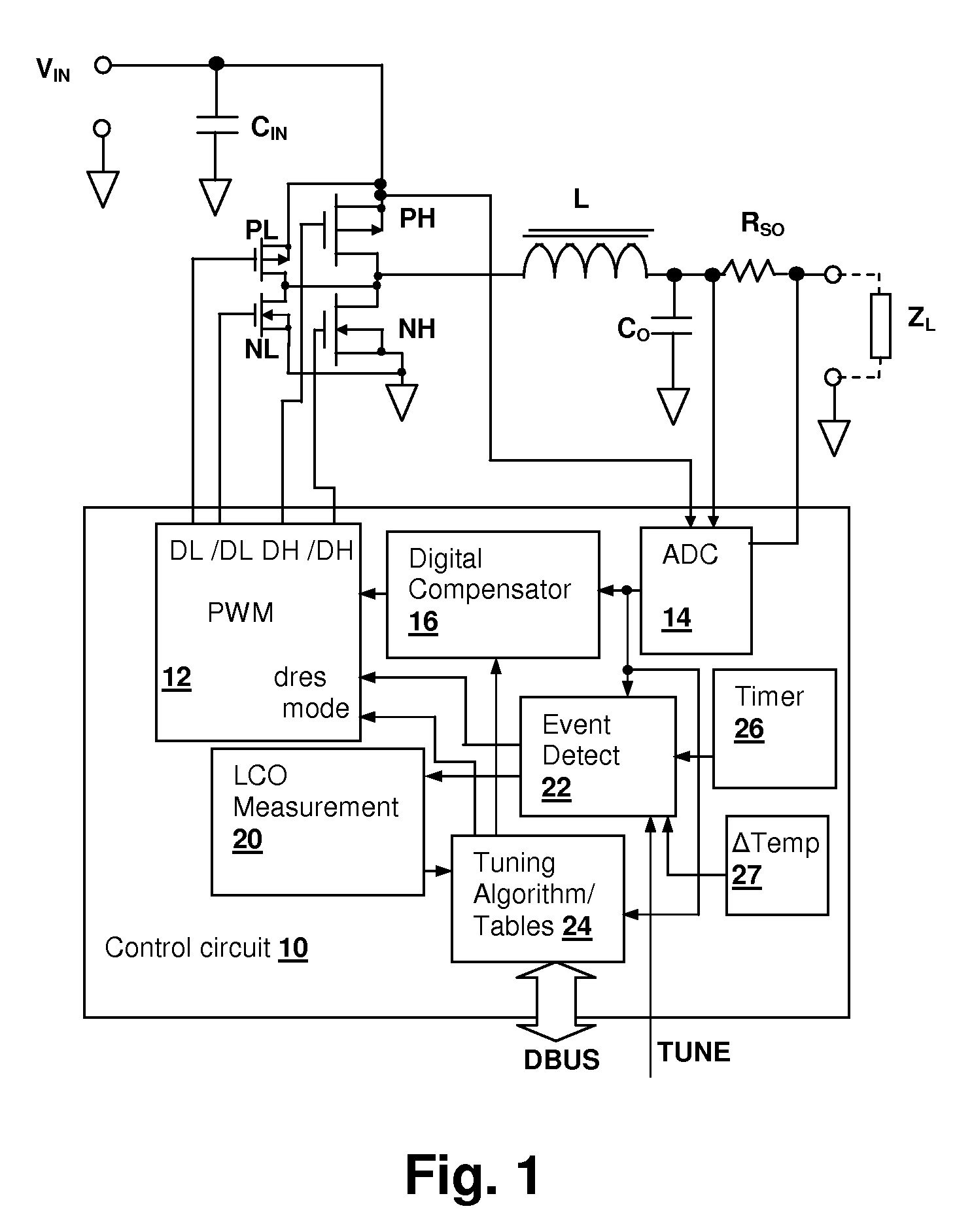
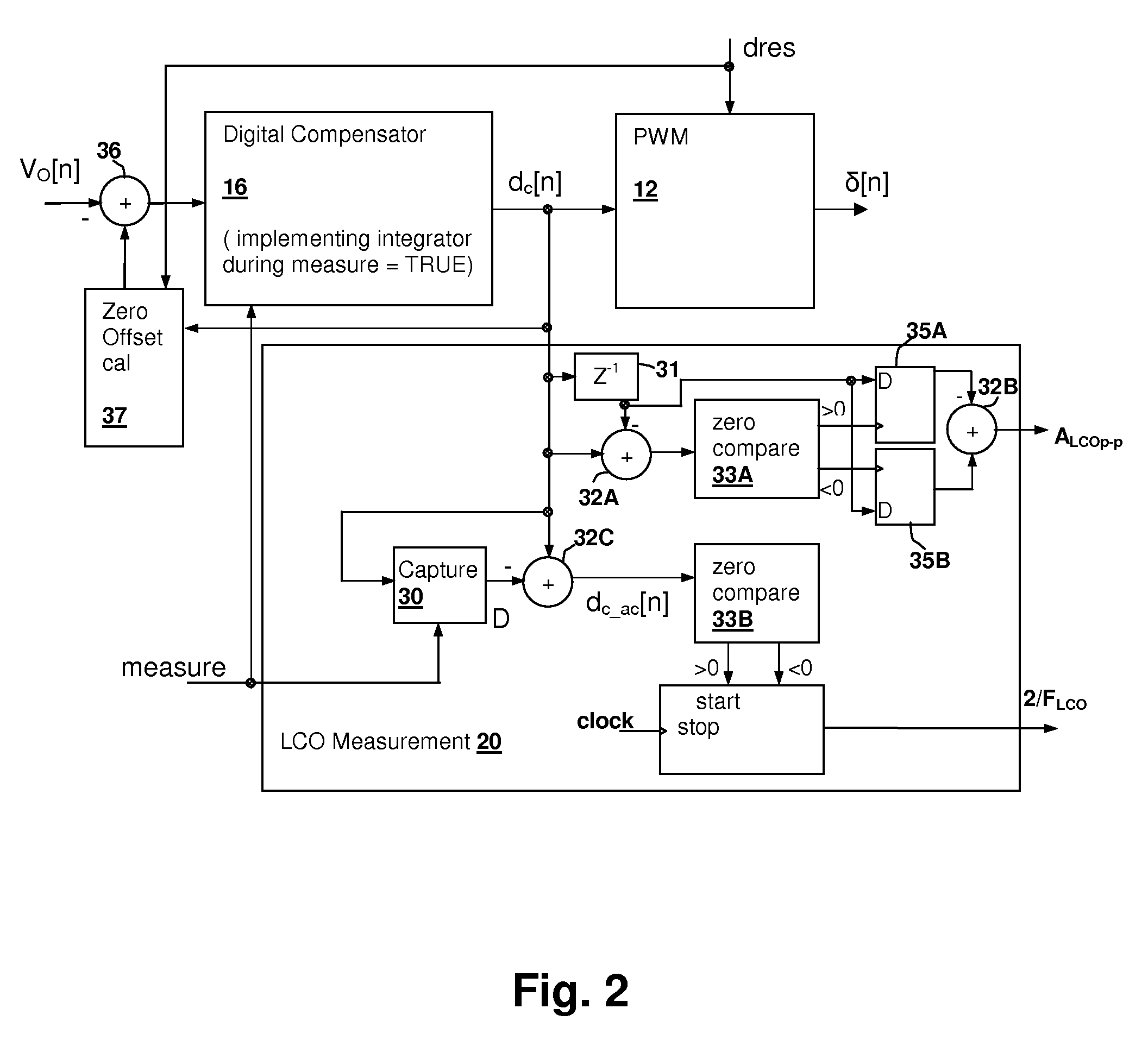
Switch-mode power supply (SMPS) with auto-tuning using limit-cycle oscillation response evaluation
A switch-mode power supply (SMPS) with auto-tuning using limit-cycle oscillation response evaluation provides optimized performance with reduced capacitance and inductance requirements for a given design. During operation of the SMPS, parameters of the converter are extracted, and the feedback and / or feed-forward compensation is adjusted to either hold the loop bandwidth of the converter near the critical bandwidth of the output capacitors, or maintain output voltage transients within a specified limit. The compensator response is either periodically updated, or is updated in response to an event, such as detection of a transient voltage spike having a characteristic that exceeds one or more predetermined thresholds.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Gain calibration of a digital controlled oscillator
ActiveUS7183860B2Good estimatePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsSteep descentDigital control oscillator
A novel apparatus for and a method of estimating, calibrating and tracking in real-time the gain of a radio frequency (RF) digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) in an all-digital phase locked loop (ADPLL). Precise setting of the inverse DCO gain in the ADPLL modulating path allows direct wideband frequency modulation that is independent of the ADPLL loop bandwidth. The gain calibration technique is based on a steepest descent iterative algorithm wherein the phase ADPLL error is sampled and correlated with the modulating data to generate a gradient. The gradient is then scaled and added to the current value of the DCO gain multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
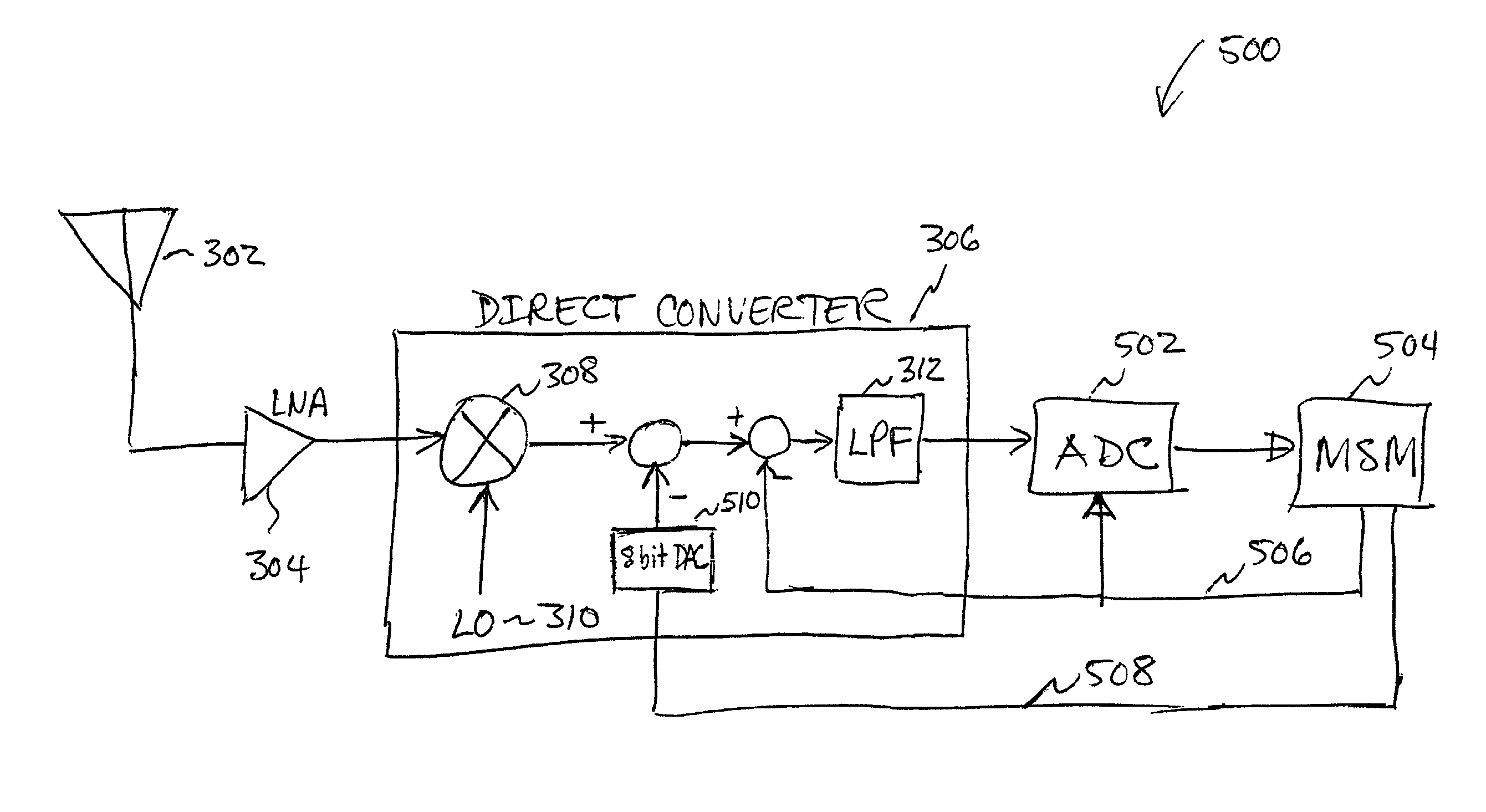
Direct current offset cancellation for mobile station modems using direct conversion
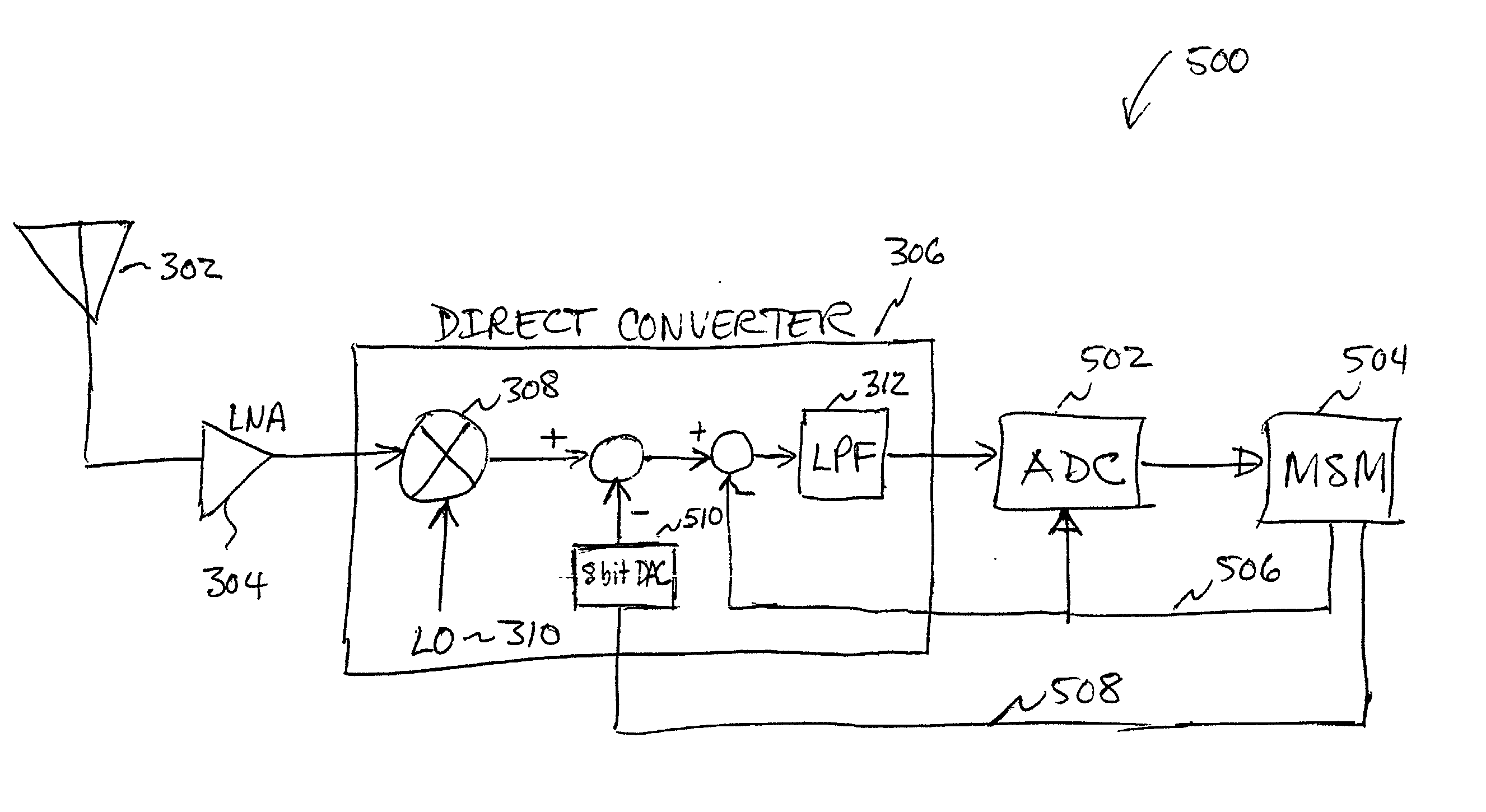
InactiveUS20030199264A1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionRadio transmissionModem deviceOffset cancellation
A system and method for canceling DC offset for Mobile Station Modems having direct conversion architectures. The present invention is a fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block that provides rapid and accurate DC offset estimates and cancellation techniques to support direct conversion architectures. The fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block combines four mechanisms to rapidly acquire and remove a DC offset estimate after power up, temperature changes, receiver frequency changes, and gain setting changes by increasing high pass loop bandwidth and adjusting DC offset levels at baseband. After removing the DC offset in large portions, the high pass loop bandwidth is decreased to fine tune the previous estimate and to remove any small variation in DC offset due to receiver self-mixing products.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
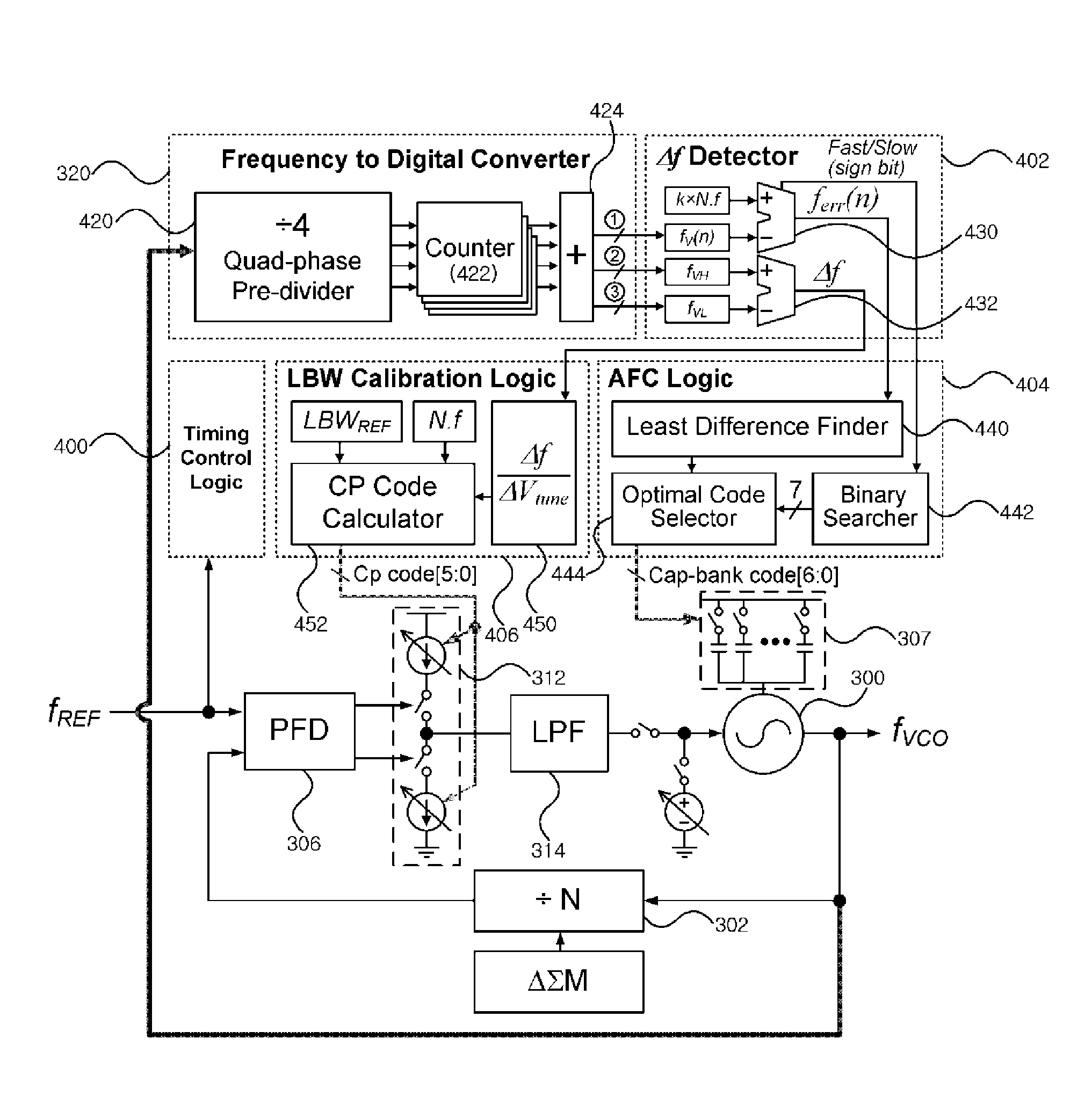
Frequency synthesizer and high-speed automatic calibration device therefor
ActiveUS8008956B1Reduce frequency calibration timeConstantPulse automatic controlOptimal controlLoop bandwidth
A frequency synthesizer and an automatic calibration device are disclosed. An automatic calibration device for a phase-locked loop based frequency synthesizer includes: a frequency-to-digital converter for converting a frequency of a signal outputted from a voltage controlled oscillator into a first digital value; a frequency difference detector for calculating a difference between the first digital value outputted from the frequency-to-digital converter and a second digital value corresponding to a target frequency; an automatic frequency calibration logic for selecting an optimal control code for a capacitor bank such that an output frequency of the voltage controlled oscillator is closer to the target frequency; and a loop bandwidth calibration logic for tuning a charge pump gain such that a loop bandwidth is kept constant in the optimal control code using the frequency-to-digital converter. Thus, the calibration speed can be increased, and the loop bandwidth can be kept constant within the output frequency range.
Owner:KWANGWOON UNIV IND ACADEMIC COLLABORATION FOUND
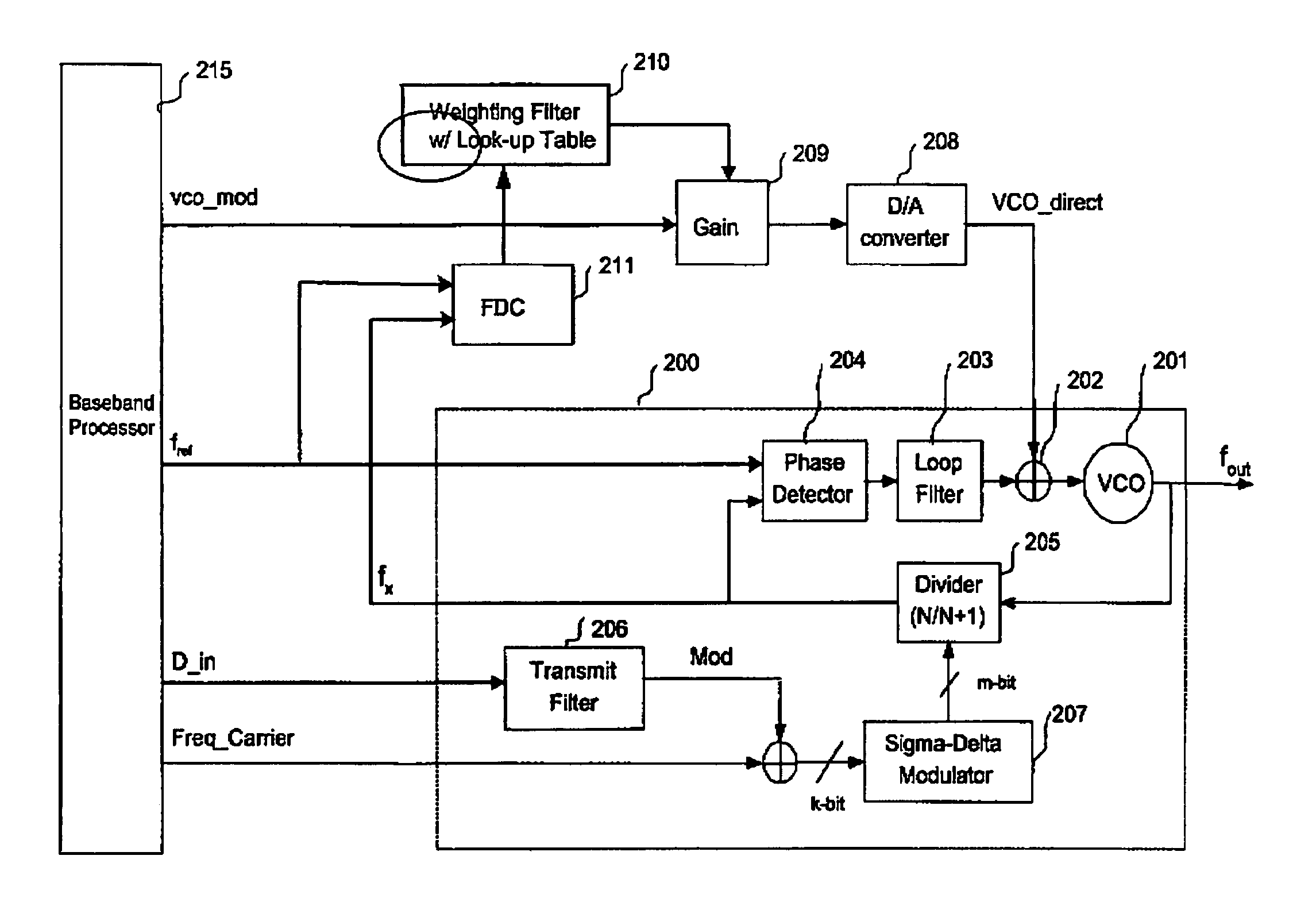
Direct modulation of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) with adaptive gain control
InactiveUS7015738B1Reduce output noiseWide bandwidthPulse automatic controlAngle modulationLoop filterDigital analog converter
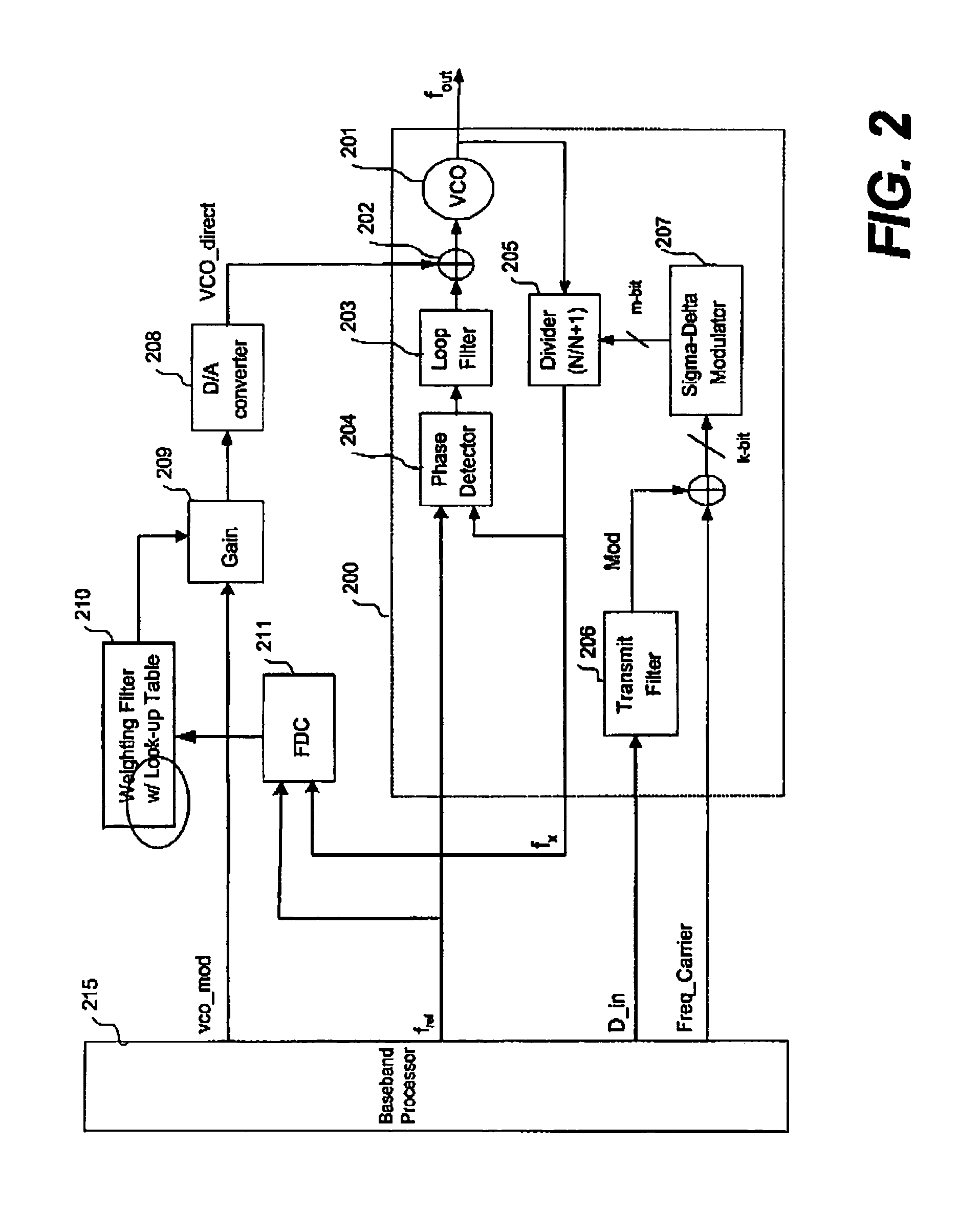
Techniques for direct modulation of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) with adaptive digital gain control for wideband wireless applications are disclosed. A digital adaptive gain control loop is used to directly modulate the VCO, and a phase-locked loop (PLL) to track the frequency drift and other nonlinear effects of the VCO. As the PLL is applied to track the carrier frequency without passing the modulation signal into the PLL loop filter, the PLL can be implemented with a narrow loop bandwidth. The wideband frequency modulated signal is directly up-converted to the radio frequency (RF) signal by directly modulating the VCO through a digital-to-analog converter which is digitally controlled by an adaptive gain control loop. Thus, both wide bandwidth and low output noise for a frequency synthesizer and modulator can be achieved.
Owner:CAO WEIXUN
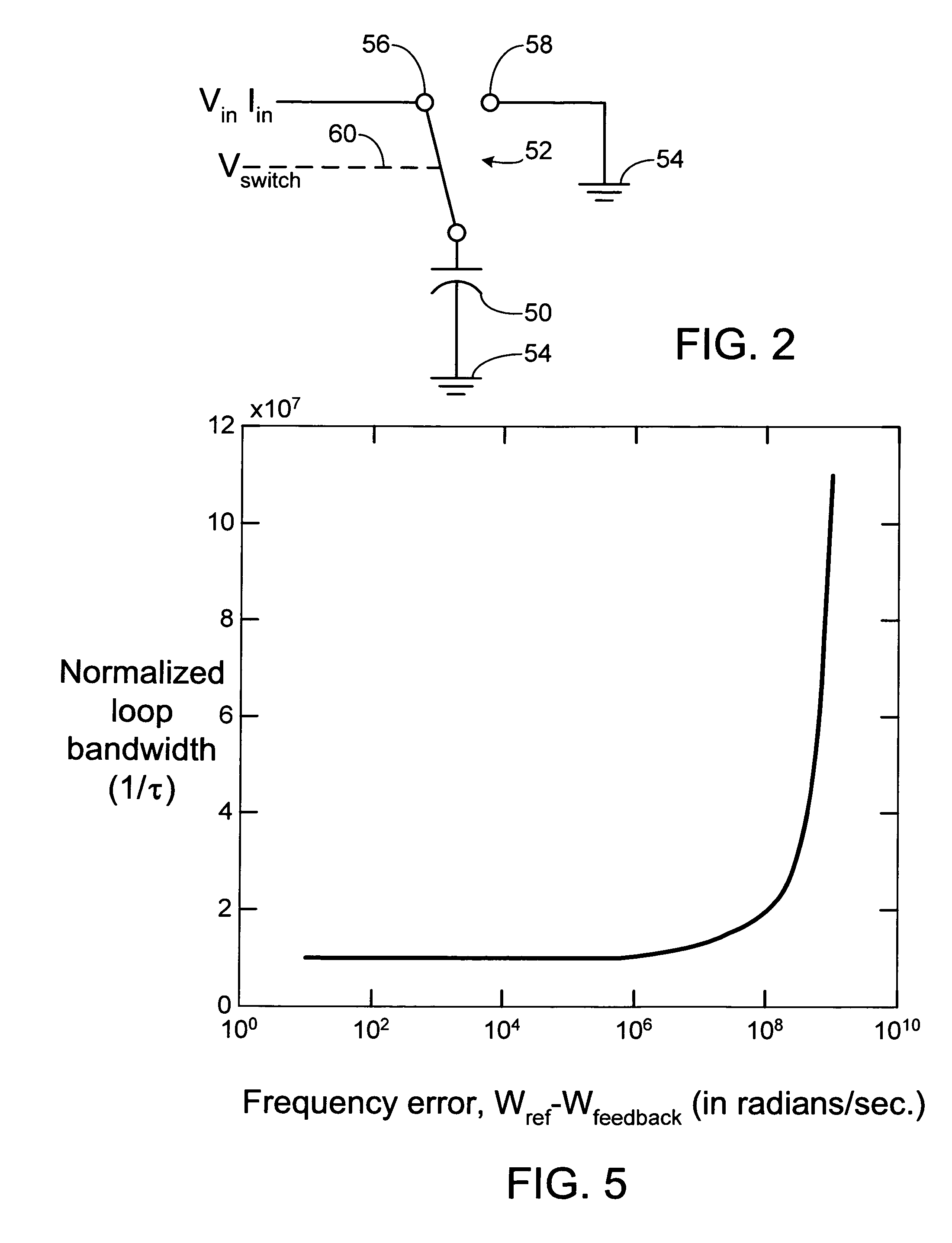
Adaptive method and apparatus to control loop bandwidth of a phase lock loop
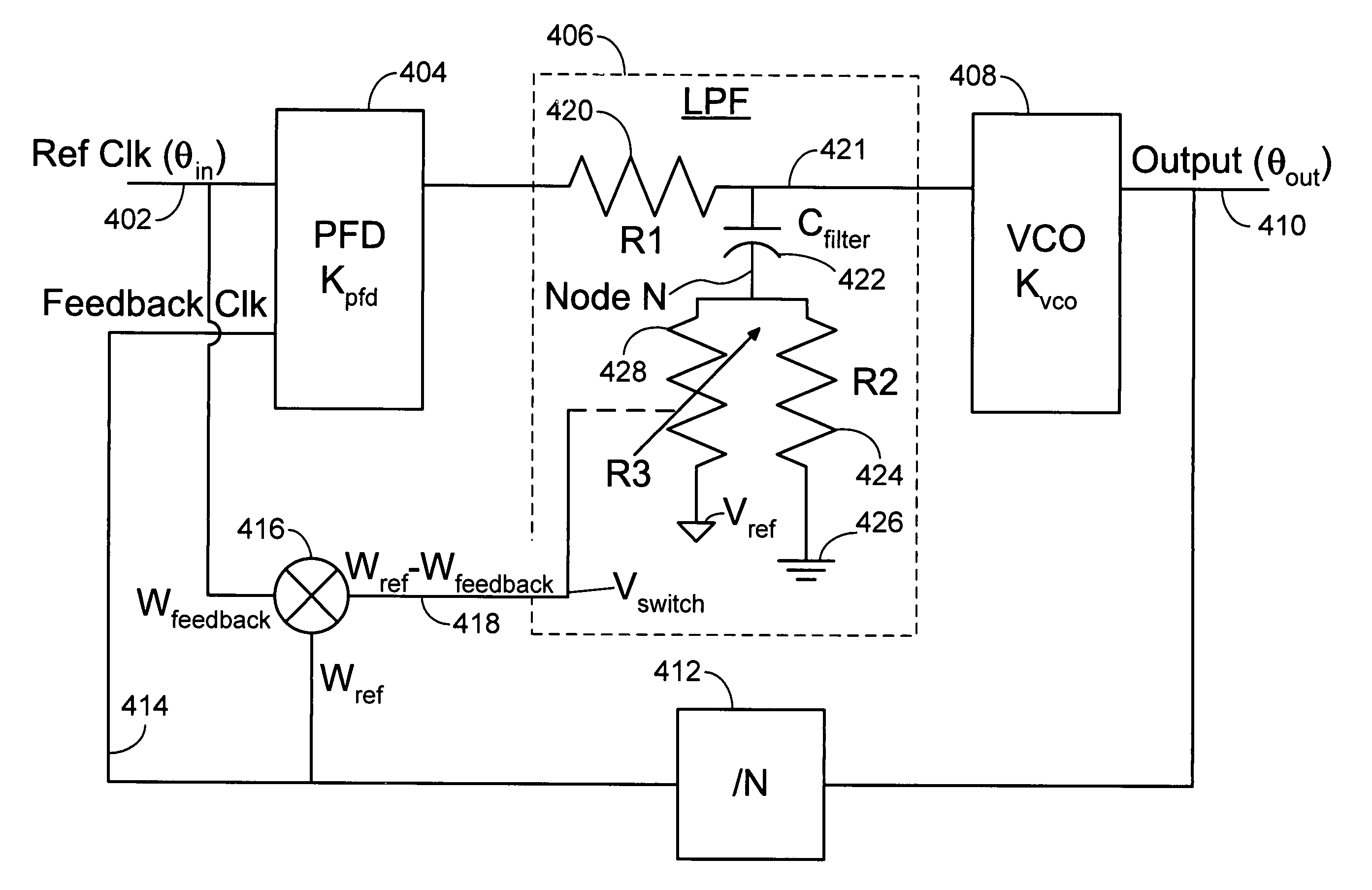
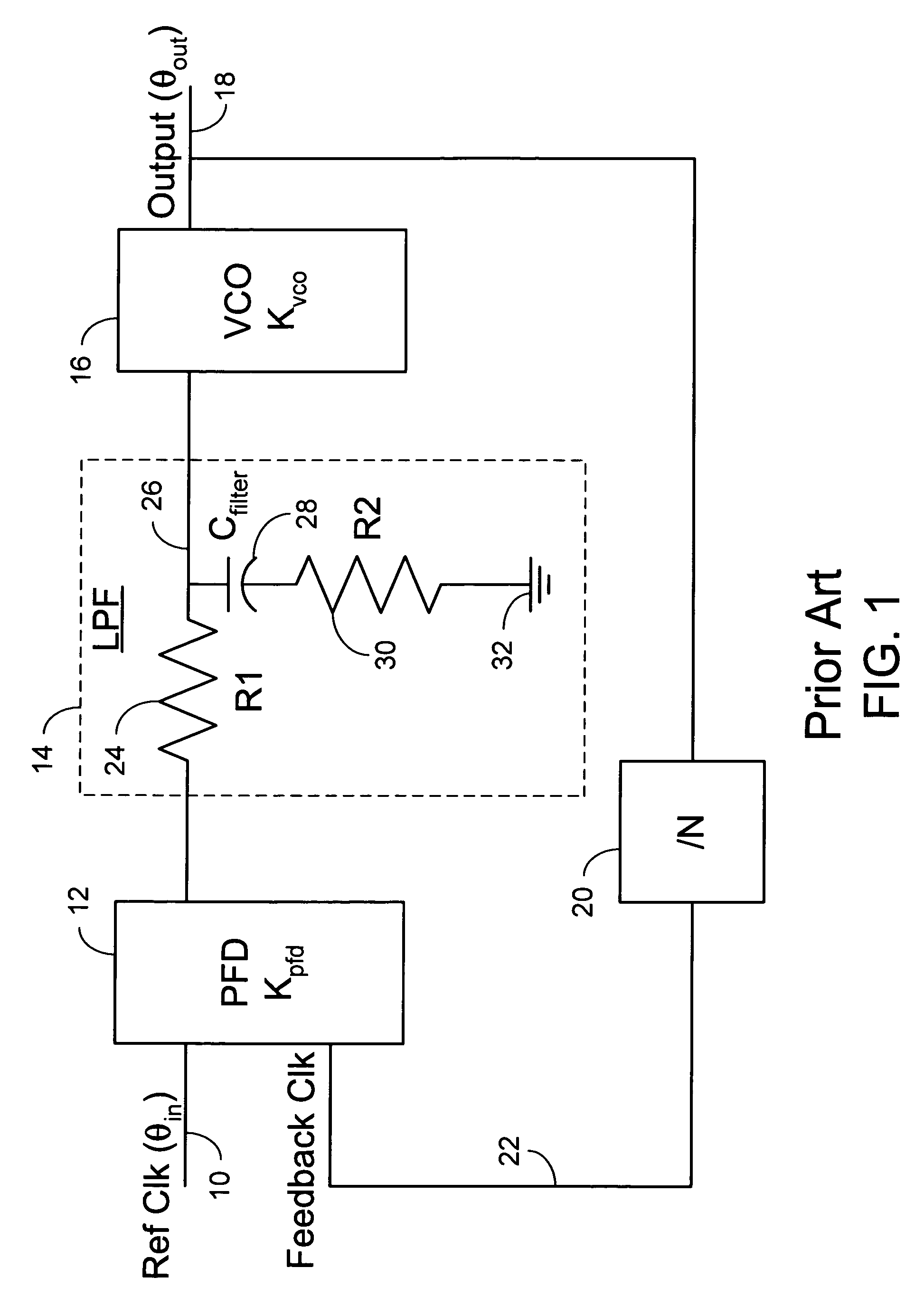
Disclosed is a PLL (Phase Lock Loop) reducing the lock-in-time of the phase lock loop by altering the impedance of the damping resistor portion of the included LPF (Low Pass Filter) as a function of the difference in frequency or phase between a PLL applied reference frequency and the output frequency provided by the VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) portion of the PLL. This variable impedance is accomplished by introducing a feed forward path that switches a capacitor in and out of the circuit in accordance with the difference frequency. One embodiment uses a mixer to provide the difference frequency signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
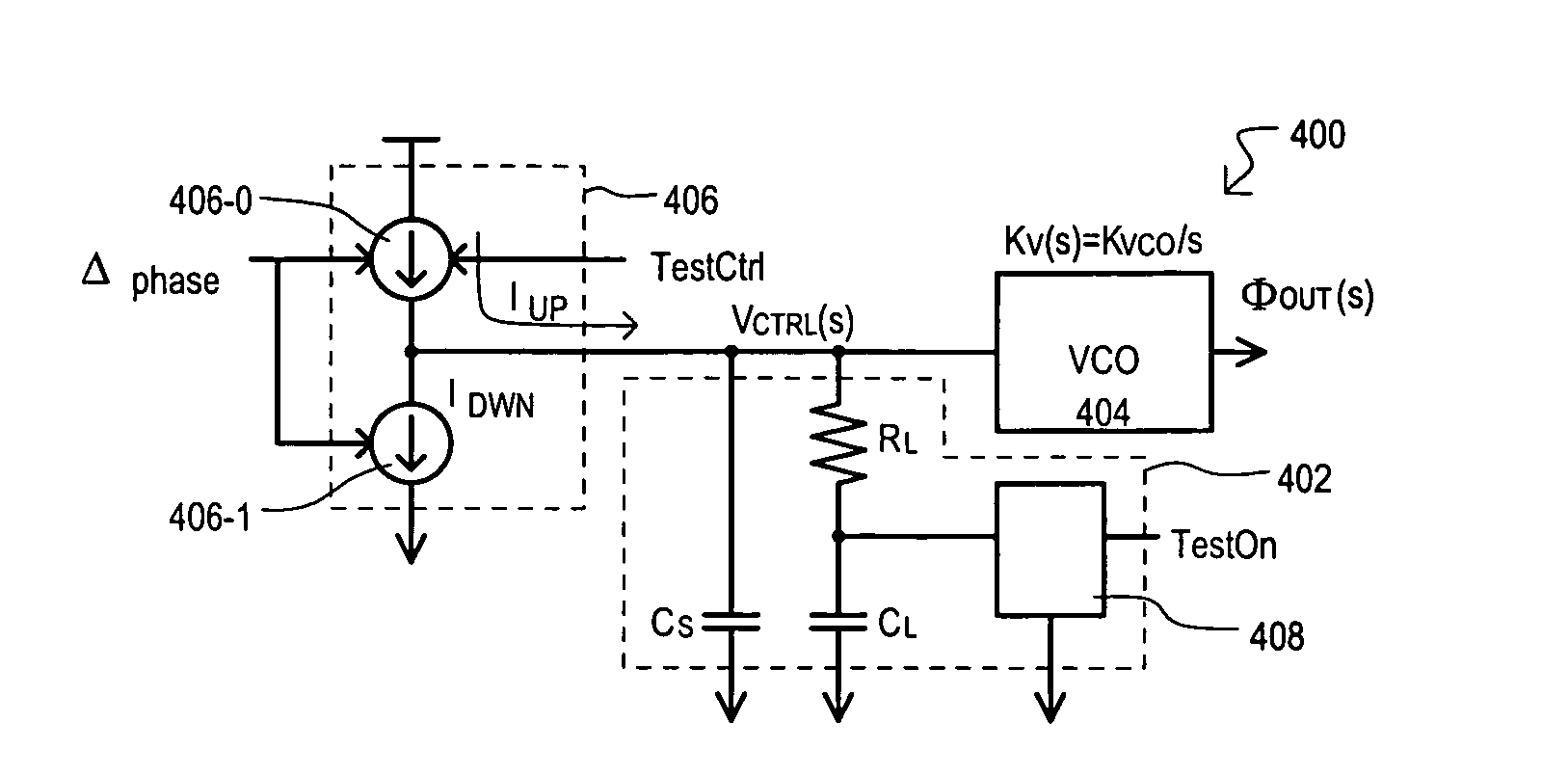
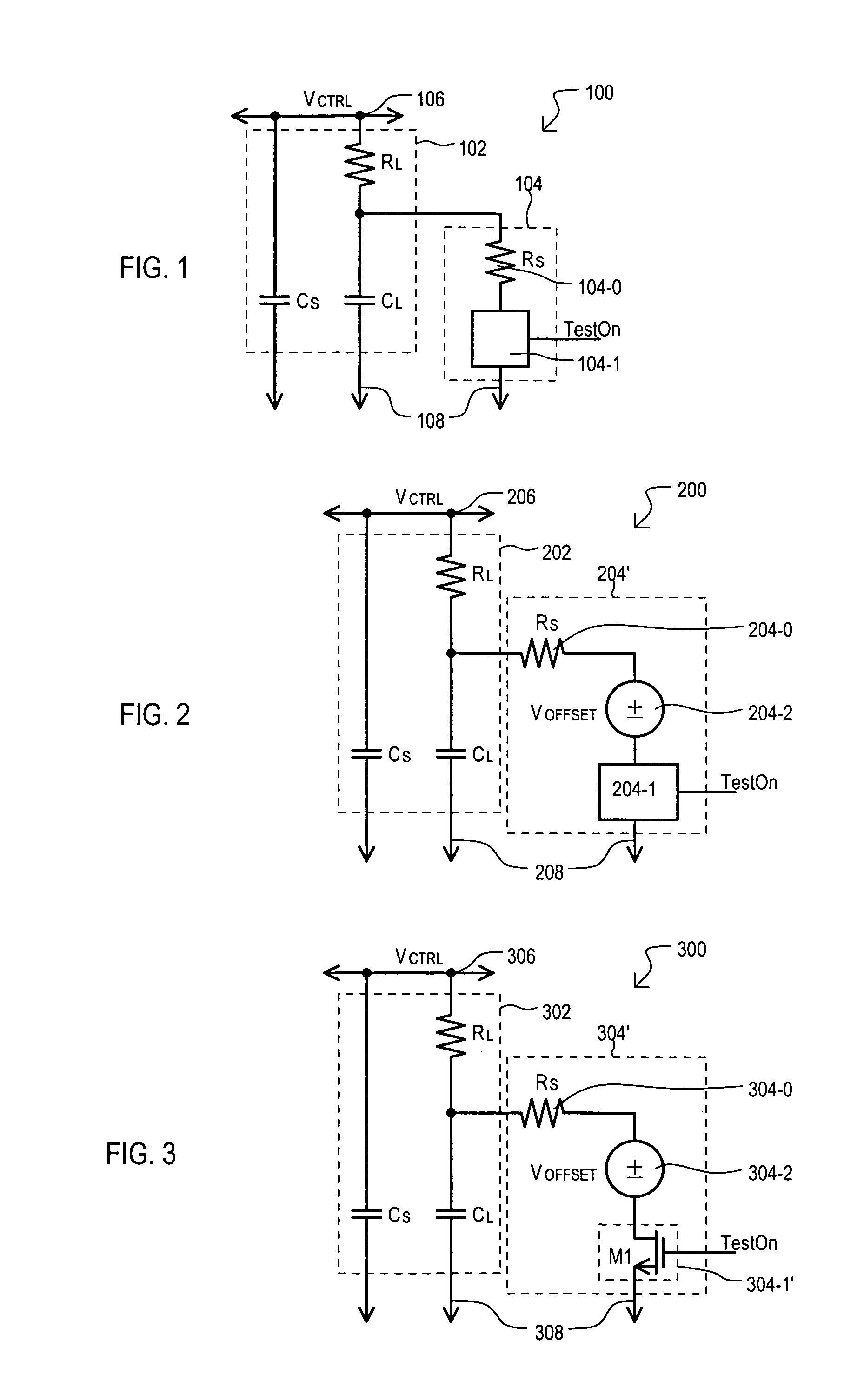
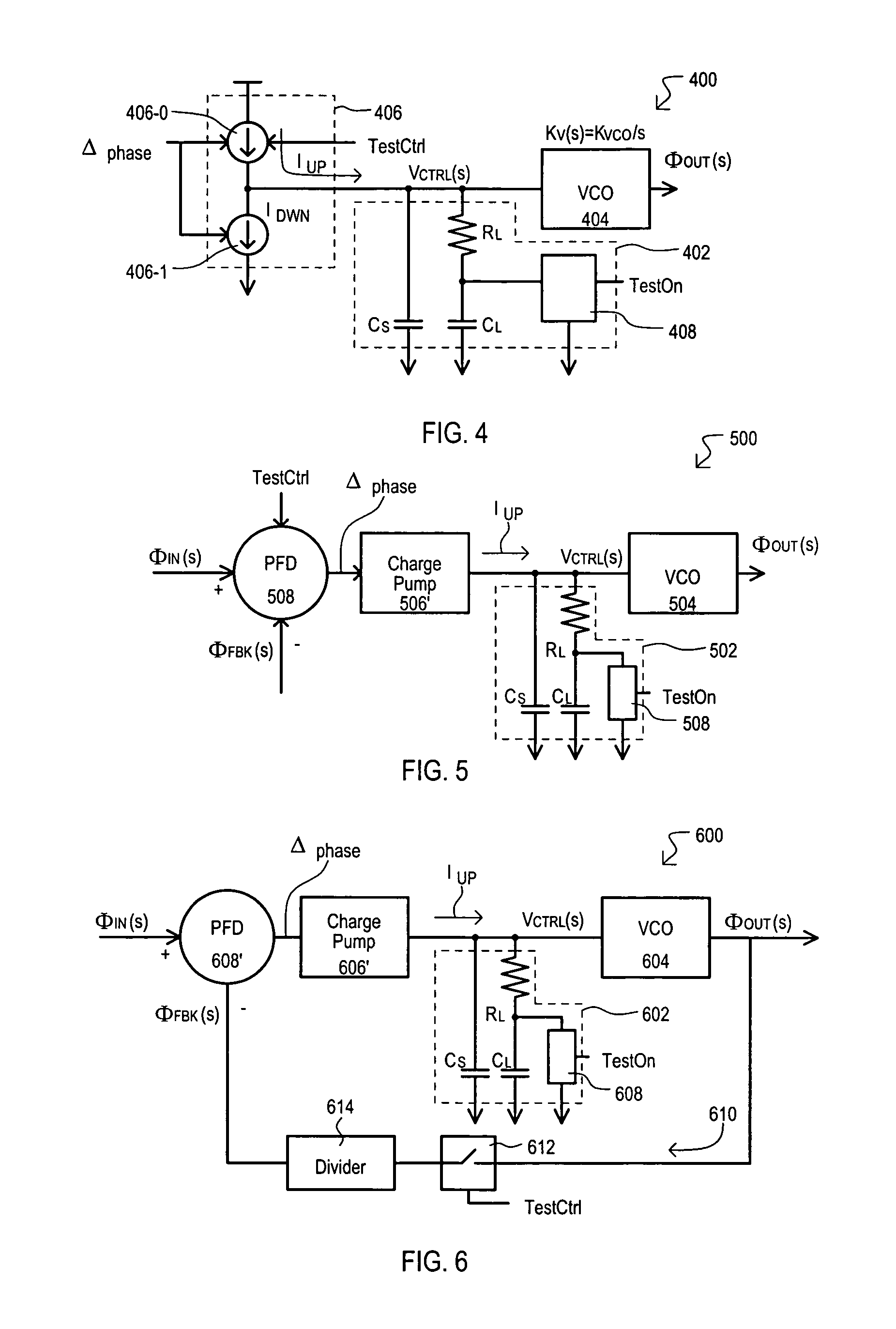
Open loop bandwidth test architecture and method for phase locked loop (PLL)
A phase locked loop (PLL) can include a test loop filter (100) that generates a control voltage (VCTRL) for input to a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). In a test mode, a control voltage can be varied and resulting output frequencies recorded, from which an open loop bandwidth can be determined. A control voltage can be varied by enabling a switch element (104-1) that can provide a current path through load resistance (RL) of test loop filter (100). Current provided to the test loop filter can be varied according to test signals to provide a variable control voltage (VCTRL).
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Low power digital phase lock loop circuit
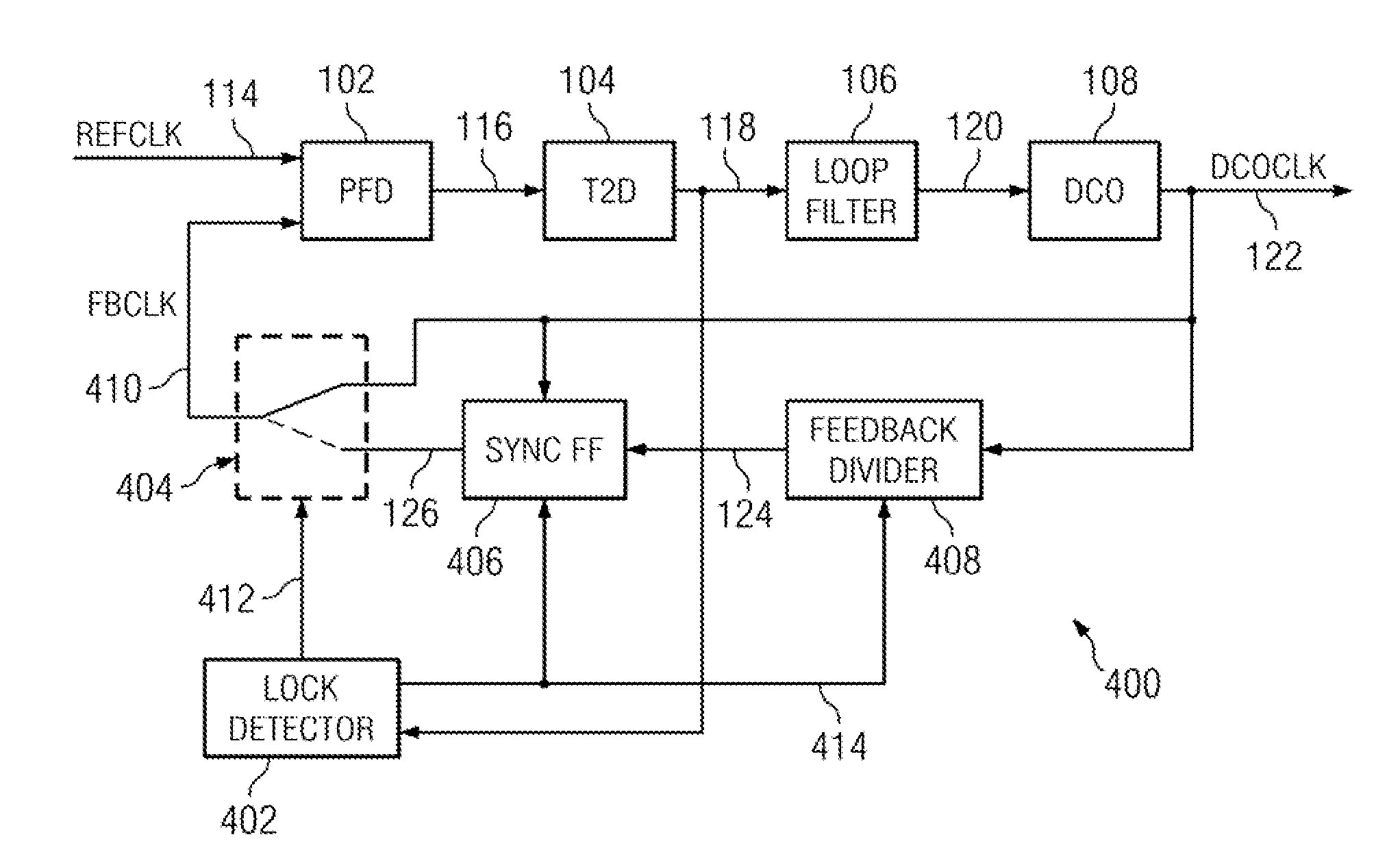
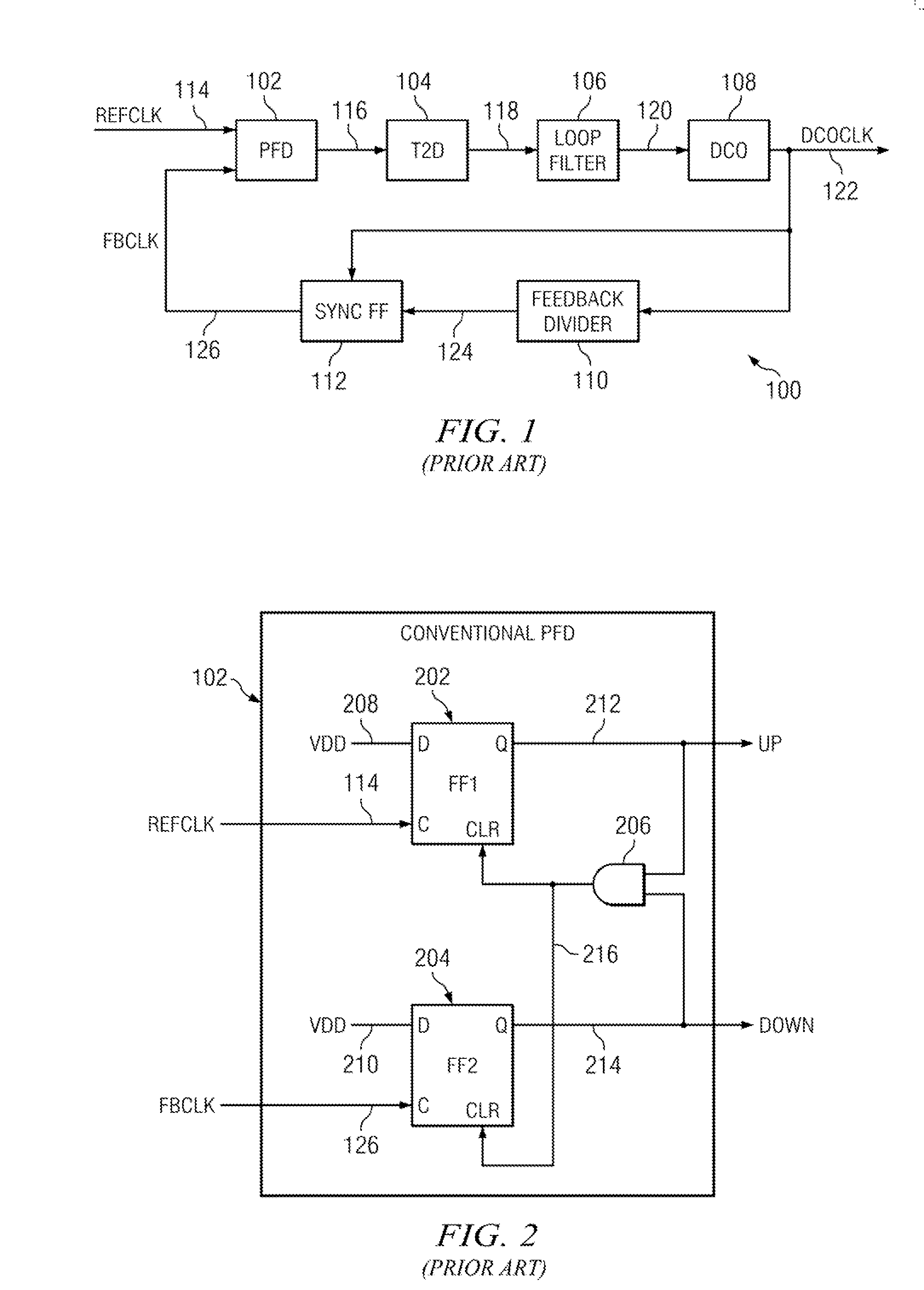
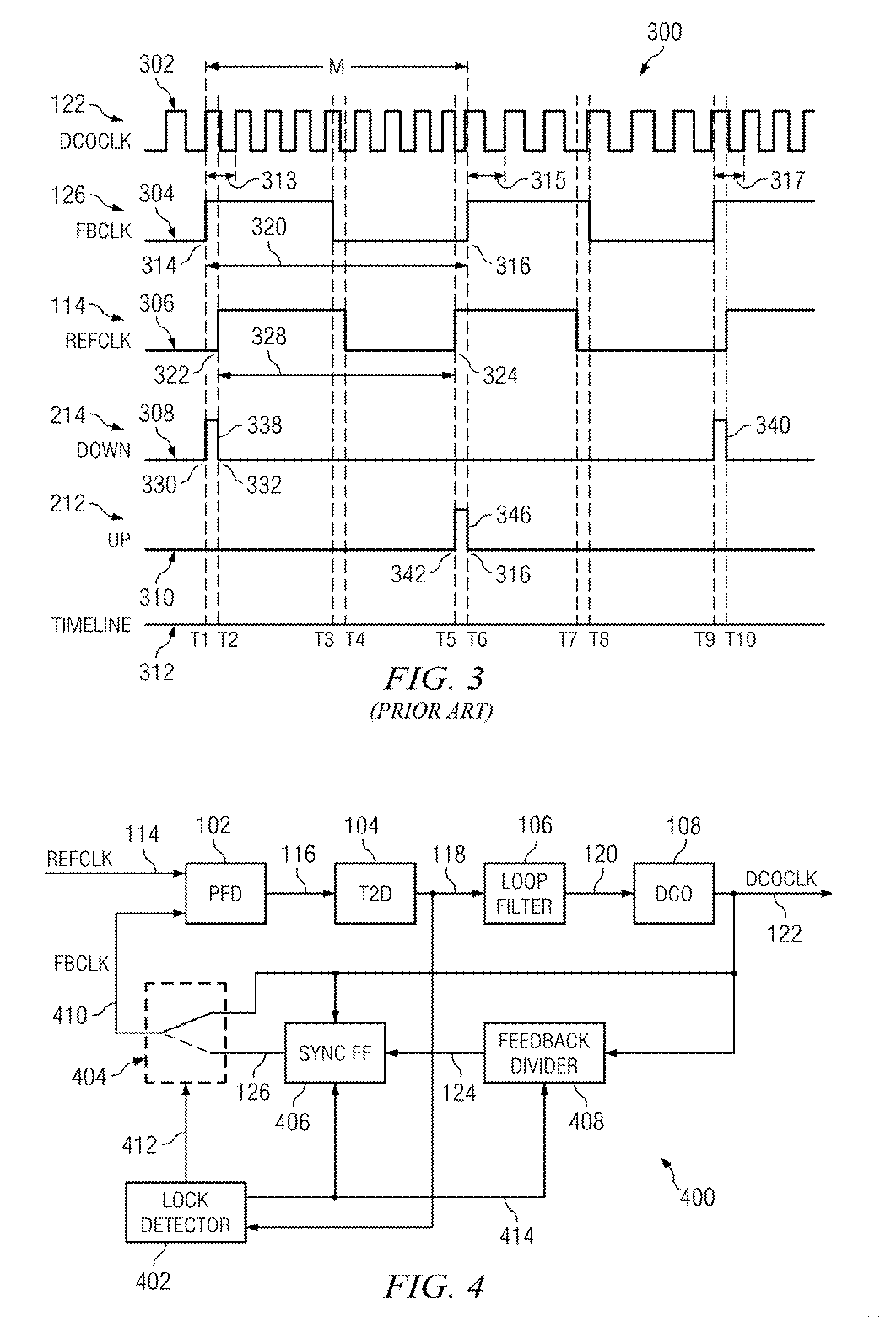
ActiveUS20110273210A1Increase power usageSufficient powerPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase locked loop circuitClock rate
A digital phase lock loop circuit, where under certain conditions the phase error is derived from phase comparison between a reference clock edge and the next oscillator clock edge rather than a feedback clock edge. This technique can be used to significantly reduce digital phase lock loop circuit power by disabling feedback divider and sync FF once initial frequency lock is established, provided phase jitter of digital phase lock loop circuit is low enough so that there is no cycle slip. This technique can also be used to multiply the effective reference clock frequency of digital phase lock loop circuits to increases the loop bandwidth, thus reducing the phase noise. Both the applications of this technique can be combined in some circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
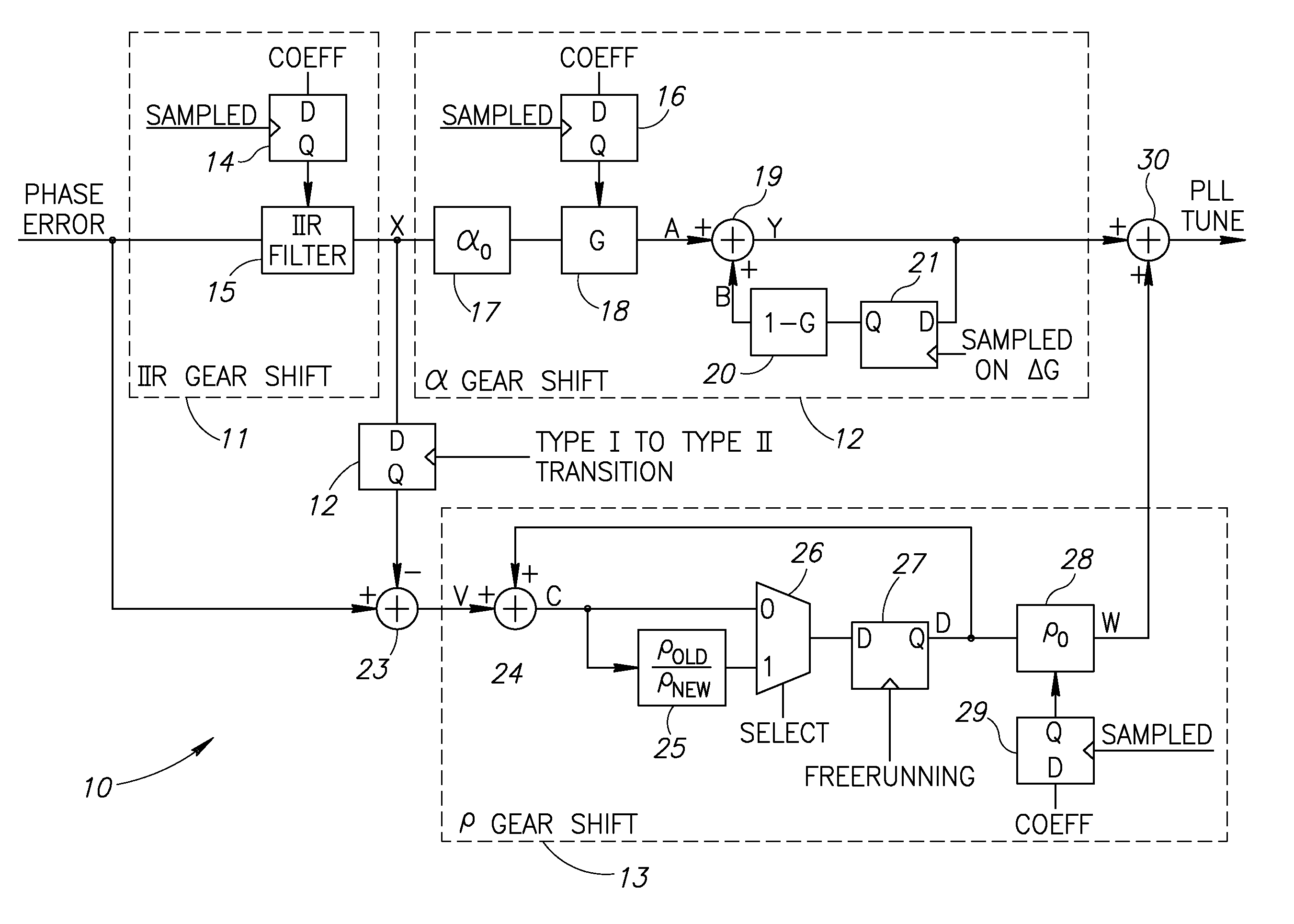
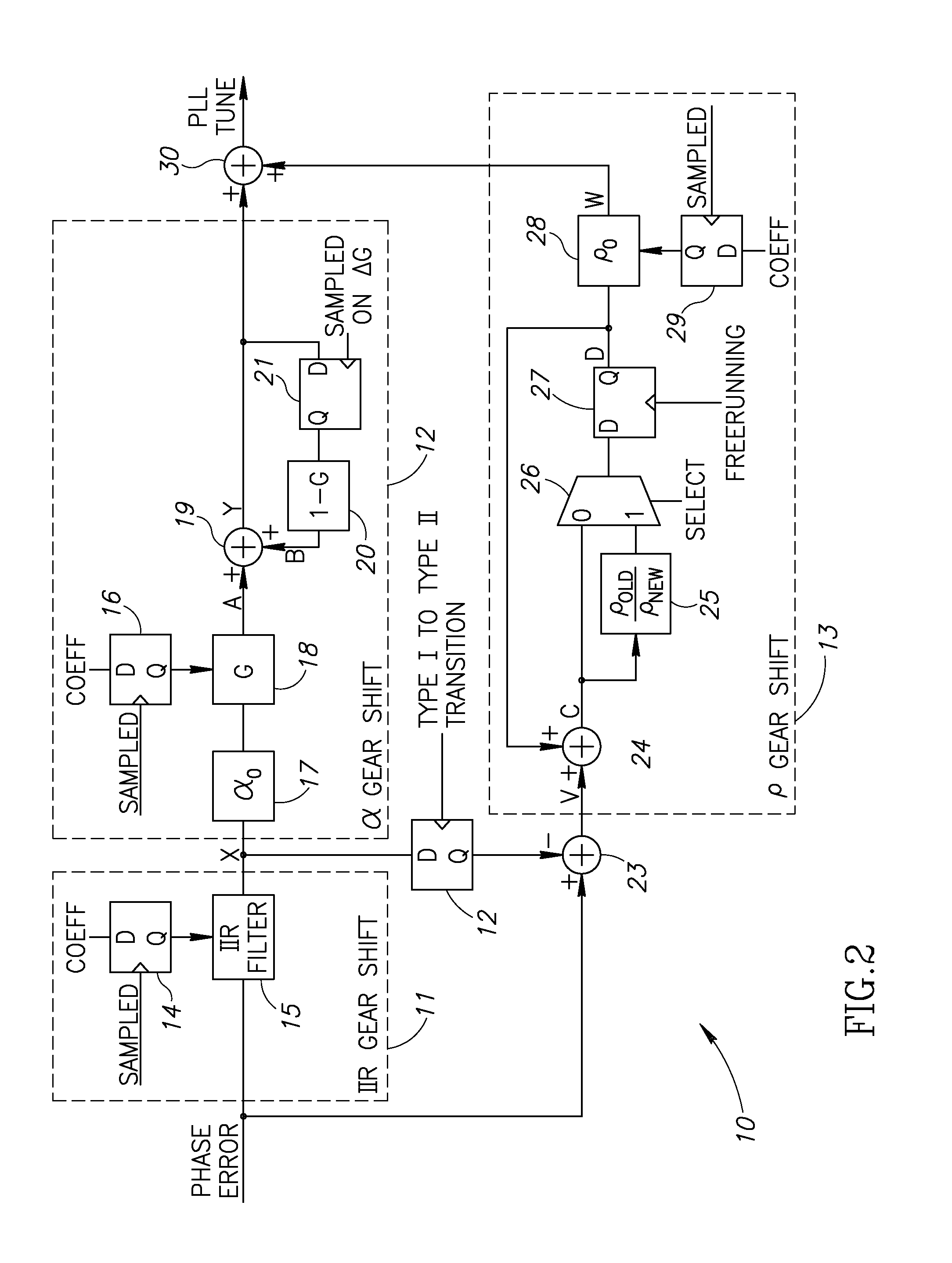
Continuous reversible gear shifting mechanism
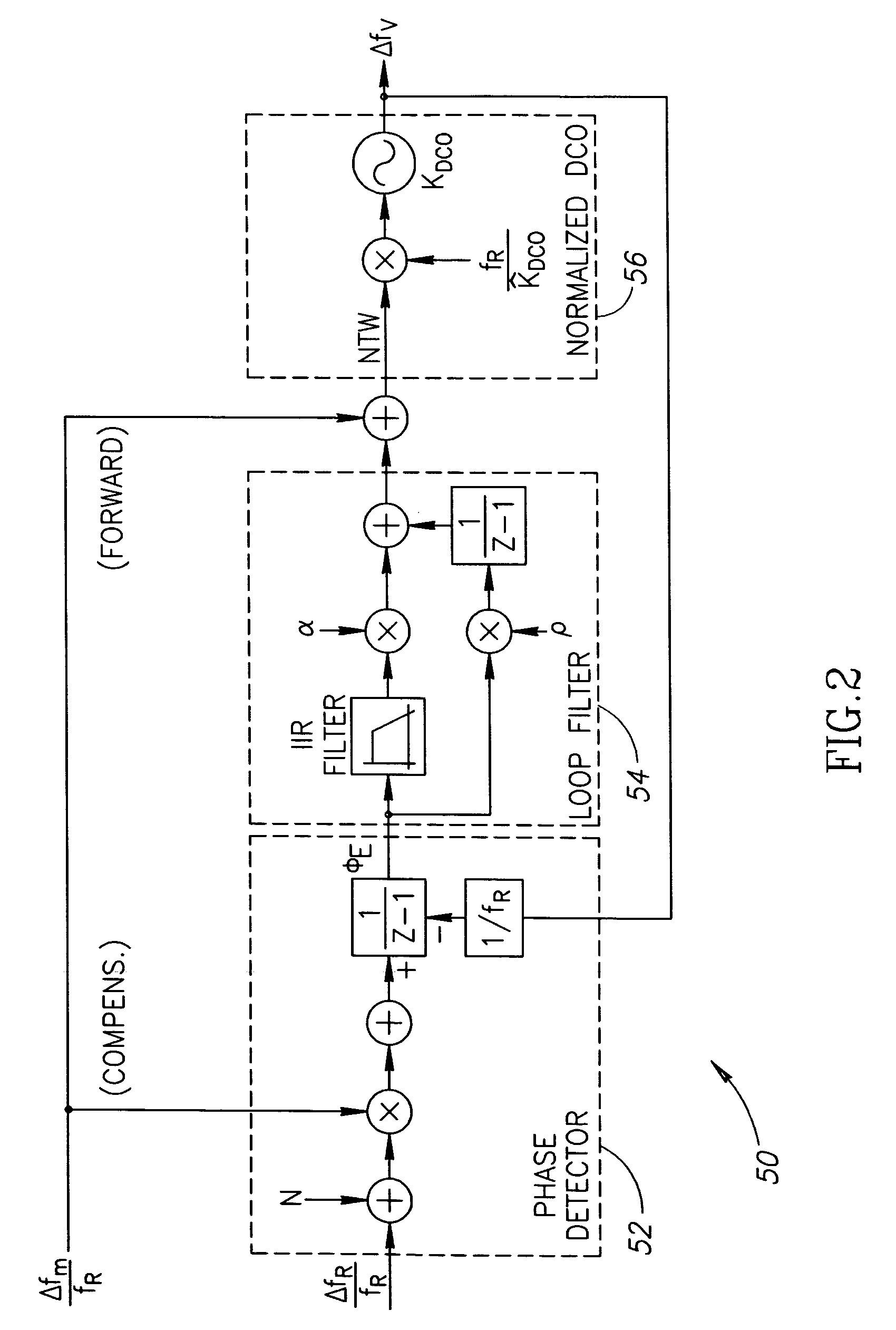
ActiveUS20070085622A1High bandwidthLoop gain can be increasedPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsPhase locked loop circuitLoop bandwidth
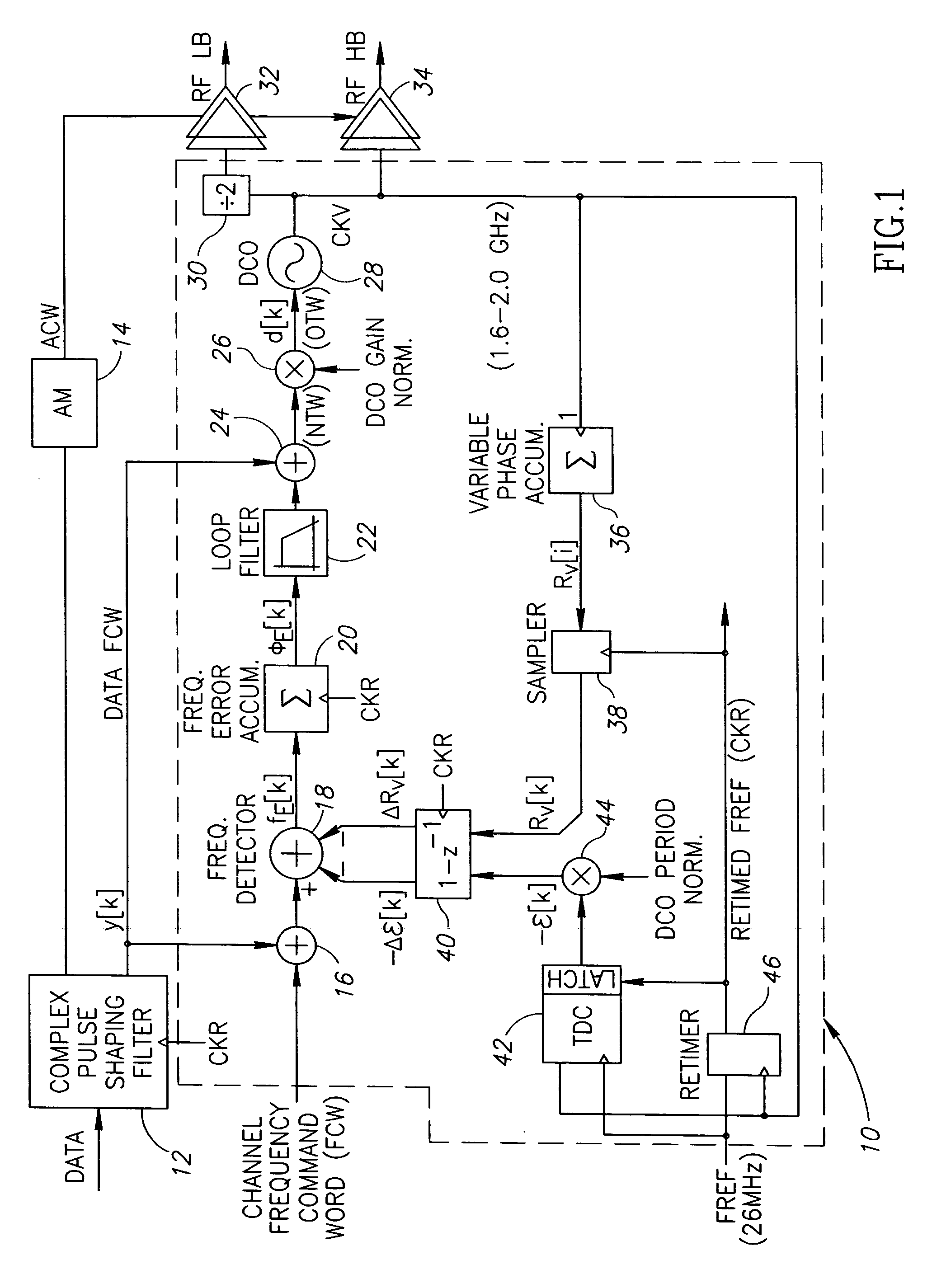
A novel gear shifting mechanism operative to adjust the loop gain of a phase locked loop (PLL) circuit in a continuous and reversible manner. The loop gain can be increased to widen the bandwidth of the loop and can also be decreased to narrow the loop bandwidth. The mechanism incorporates an α gear shift circuit, a p gear shift circuit and an optional IIR gear shift circuit. The α gear shift circuit comprises a infinite impulse response (IIR) filtering which enables hitless operation of the PLL loop at the occurrence of gear shift events. The α gear shift circuit comprises an accumulator whose output is multiplied by the gain value ρ. The invention enables multiple gear shifts in either positive or negative direction to be achieved by configuring the loop gain variables α and ρ which may be accomplished in software.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
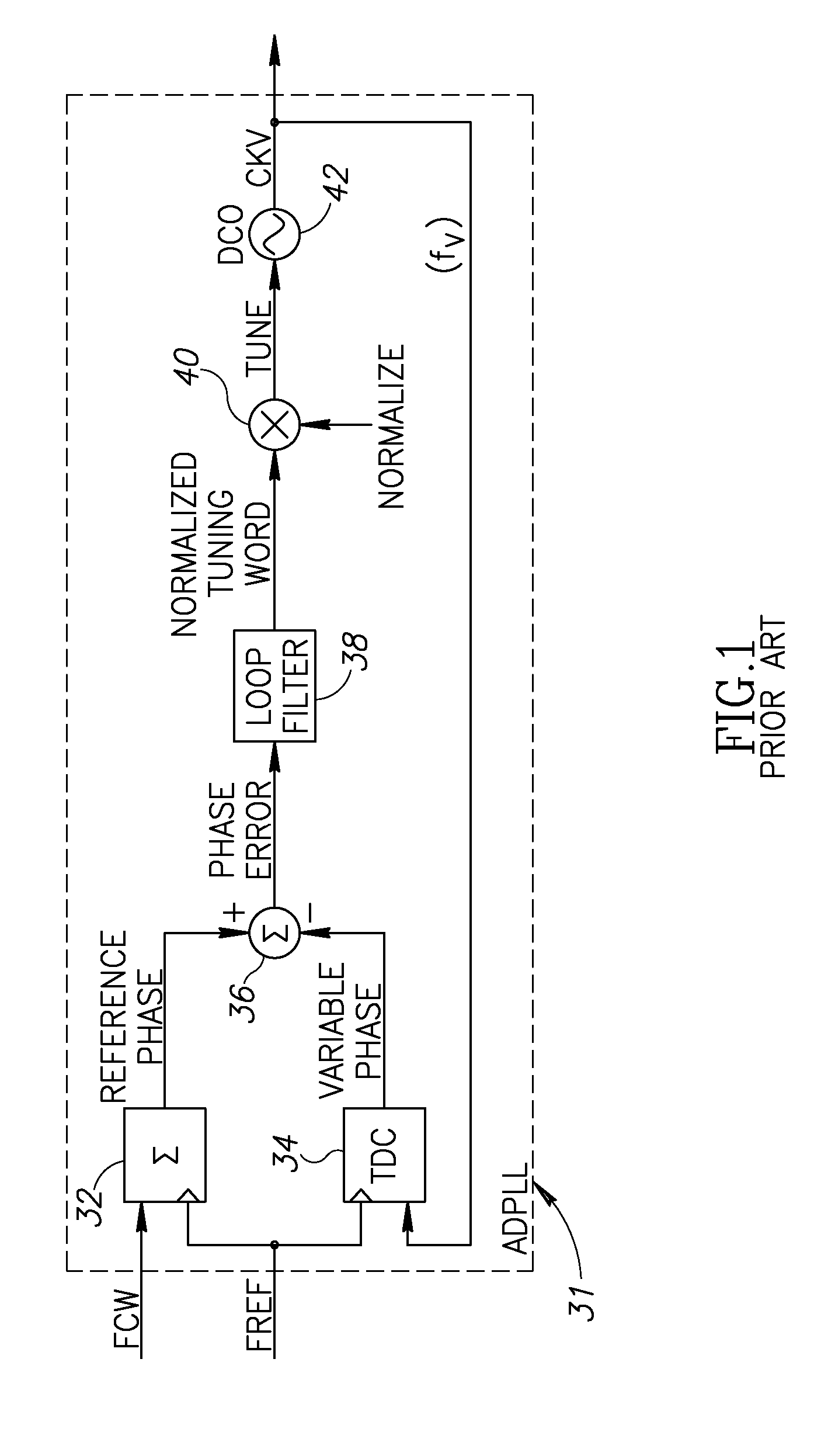
Type-II all-digital phase-locked loop (PLL)
InactiveUS7145399B2Improving signal acquisition performanceFast signal acquisitionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPulse automatic controlLoop filterLoop bandwidth
System and method for providing type-II (and higher order) phase-locked loops (PLLs) with a fast signal acquisition mode. A preferred embodiment comprises a loop filter with a proportional loop gain path (proportional loop gain circuit 1115) and an integral loop gain block (integral loop gain block 1120). The proportional loop gain path is used during signal acquisition to provide large loop bandwidth, hence fast signal acquisition of a desired signal. Then, during the PLL's signal tracking phase, the integral loop gain block is enabled and its output is combined with output from the proportional loop gain path to provide higher order filtering of the desired signal. An offset that may be present due to the use of the proportional loop gain path can be measured and subtracted to help improve signal tracking settling times.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
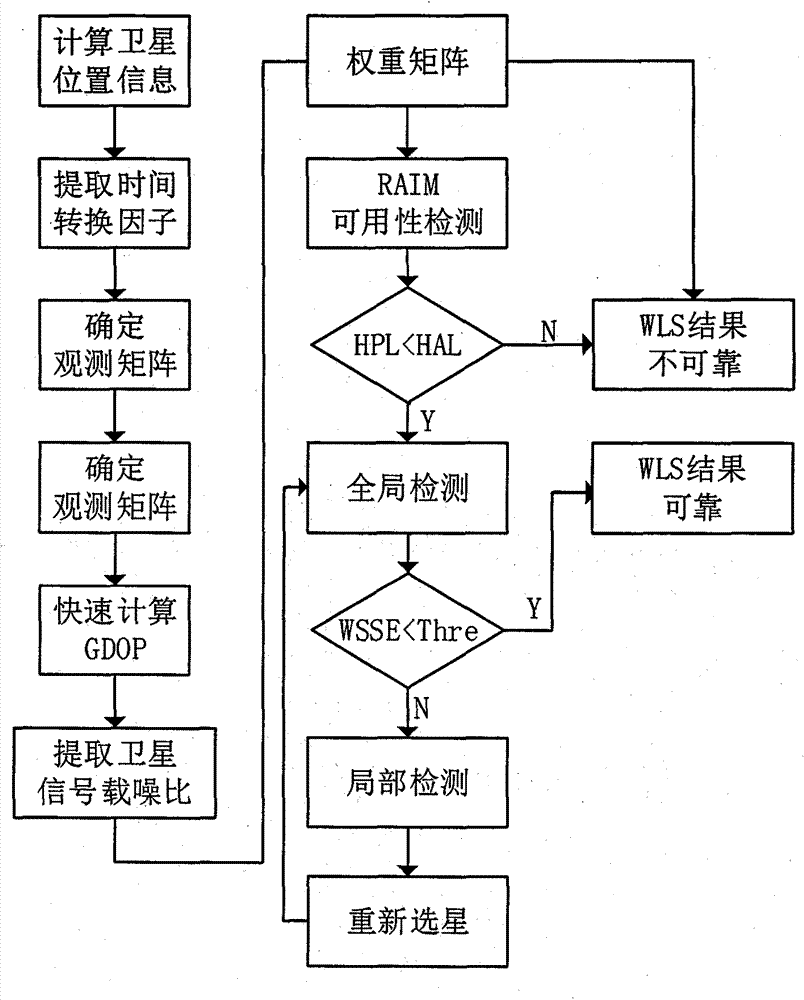
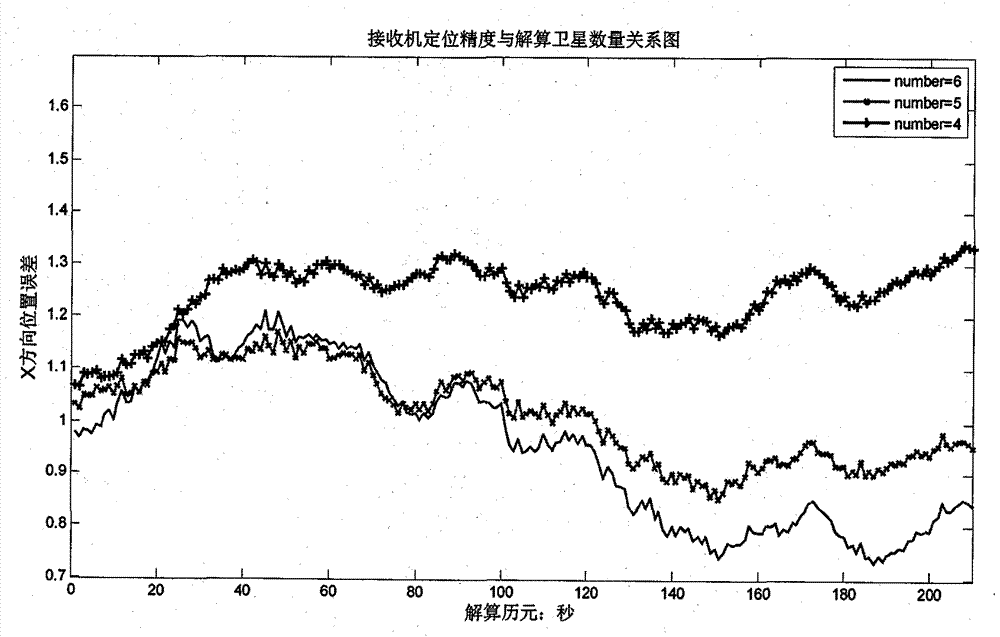
New method for RAIM (receiver autonomous integrity monitoring) based on satellite selecting algorithm in multimode satellite navigation system
InactiveCN103592658AReduce operational complexityHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingLoop bandwidthClock correction
The invention discloses a new method for RAIM (receiver autonomous integrity monitoring) based on a satellite selecting algorithm in a multimode satellite navigation system. The method comprises the steps of first determining space position information of satellites according to a navigation message and eliminating satellites with a small elevation angle according to a shielding angle; determining an observation matrix including only one clock correction item according to clock correction conversion factors in the navigation message; selecting p satellites from N visible satellites so as to be used for positioning calculation of a receiver, acquiring a satellite combination, which enables the GDOP (geometric dilution of precision) to be minimum, through the satellite selecting algorithm to act as calculating satellites, and determining a weight matrix in WLS (weighted least squares) according to parameters such as the carrier-to-noise ratio, the loop bandwidth, pre-check integral time and the like of satellite signals; carrying out RAIM availability detection according to a false alarm rate and a missed alarm rate which are preset by the receiver, and calculating a pseudo-range residual error threshold value after positioning according to the false alarm rate and a degree of freedom in Chi-squared distribution; carrying out global detection at first, then carrying out local monitoring in a circumstance that a fault satellite exists, determining calculation satellites again through satellite selection, and finally carrying out positioning calculation through selecting satellite combinations within the threshold value. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, high in fault recognition rate, not only applicable to multi-mode and multi-fault satellite navigation systems, but also applicable to single-mode and multi-fault satellite navigation systems, thereby providing new ideas for carrying out RAIM by a modern GNSS (global navigation satellite system).
Owner:PEKING UNIV
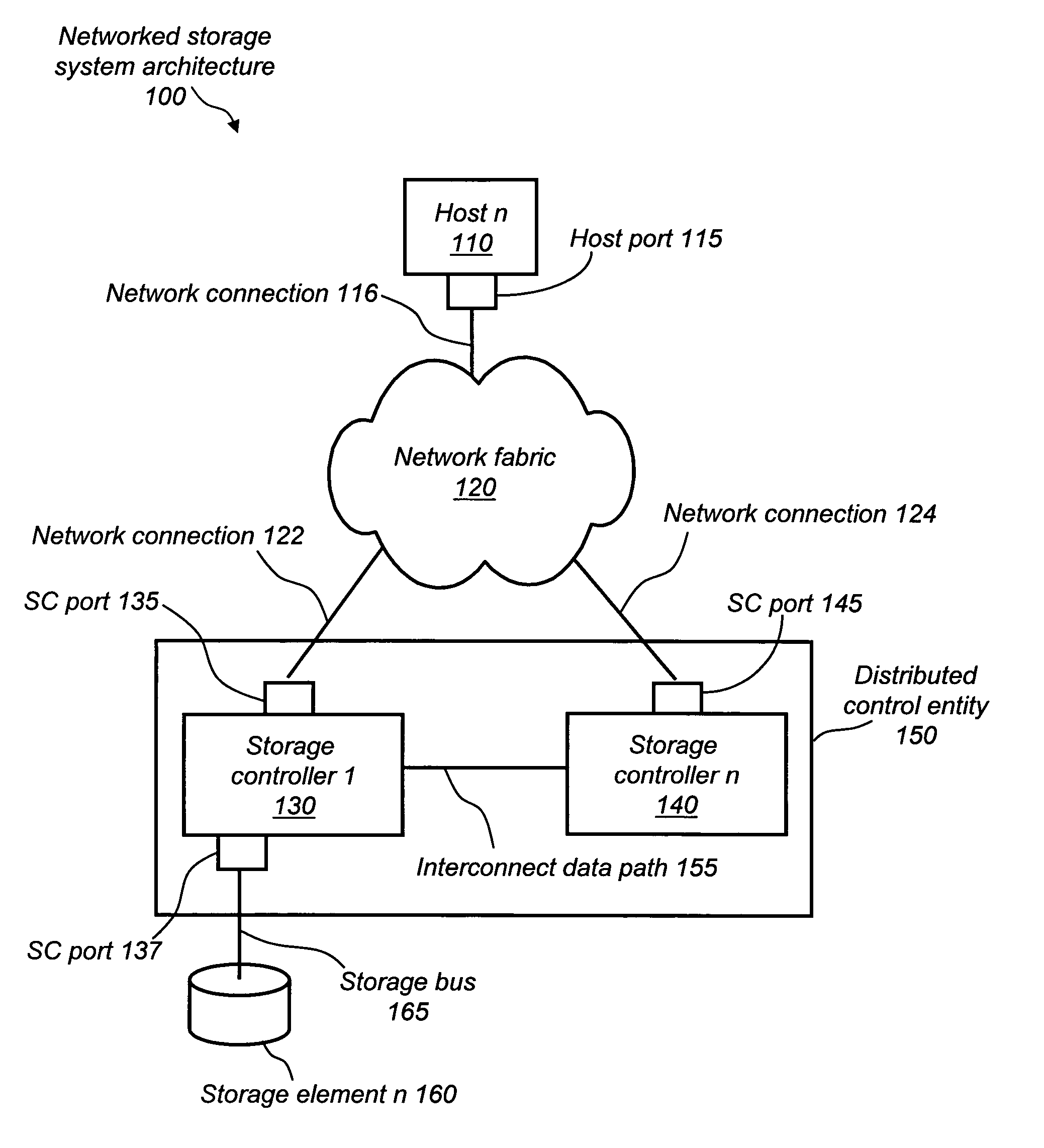
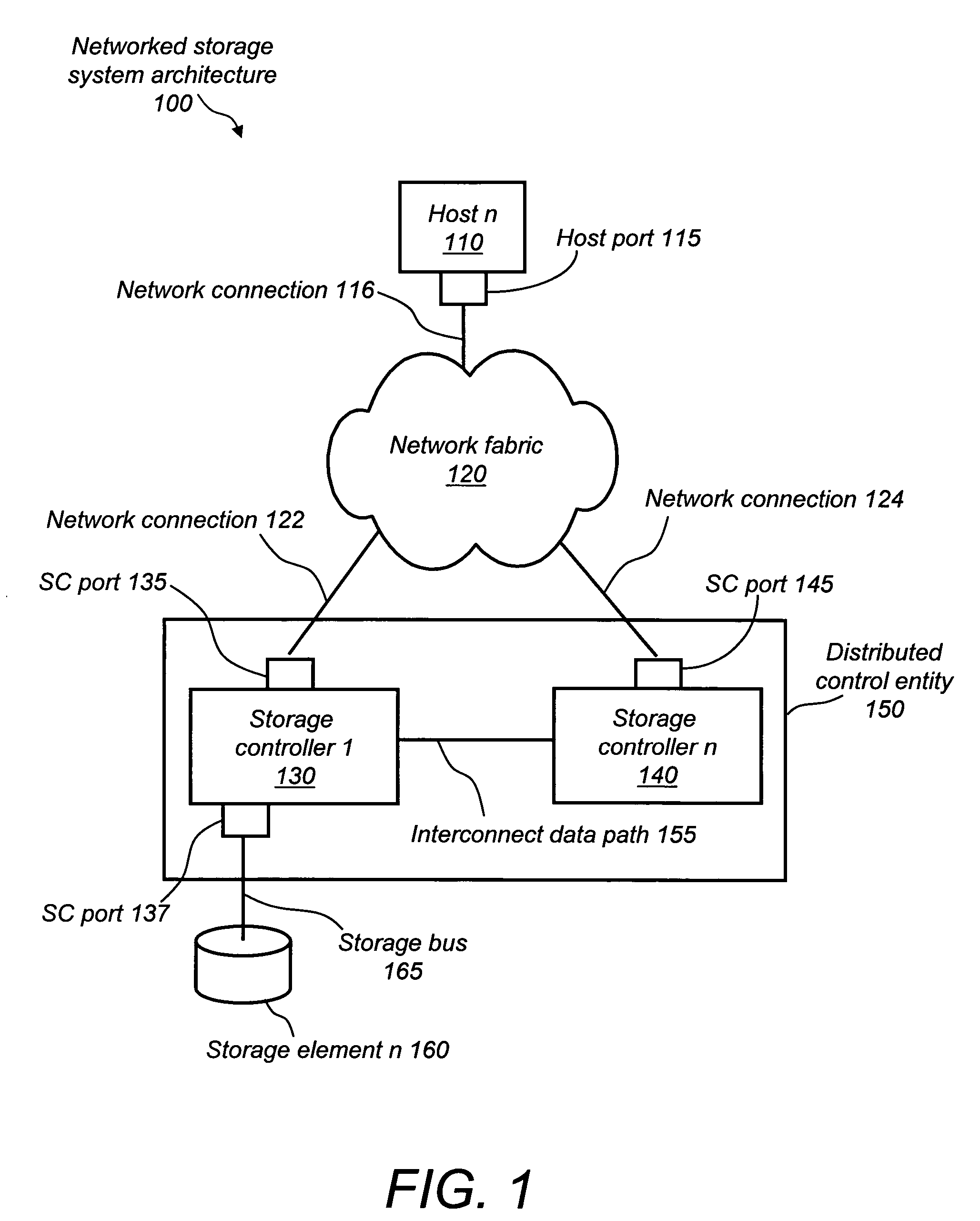
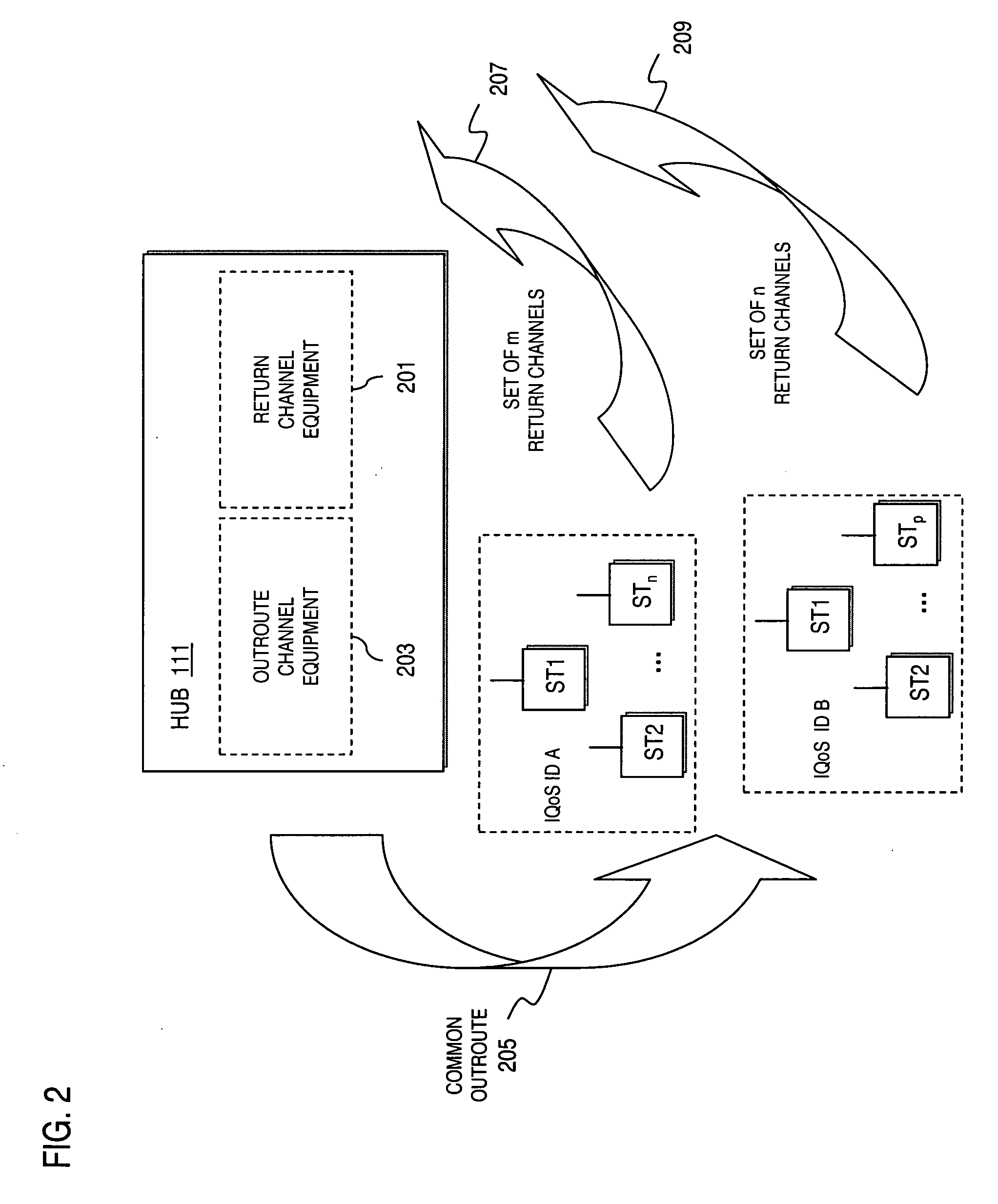
Optimized port selection for command completion in a multi-ported storage controller system
InactiveUS20050091426A1Good choiceInput/output to record carriersTransmissionStorage area networkLoop bandwidth
A multi-ported storage area network (SAN) controller system with command completion that utilizes optimal port selection. The system determines the optimal port for command completion based on criteria such as loop bandwidth utilization or port throughput maximization, and allows data and response information to occur via the optimal port regardless of the receiving port. This is accomplished through port aliasing (spoofing) of port identities, in which the receiving port identity is substituted into a sending port identity by a distributed control entity. In this way, any port within the SAN may return data or status to the originating host.
Owner:ARISTOS LOGIC
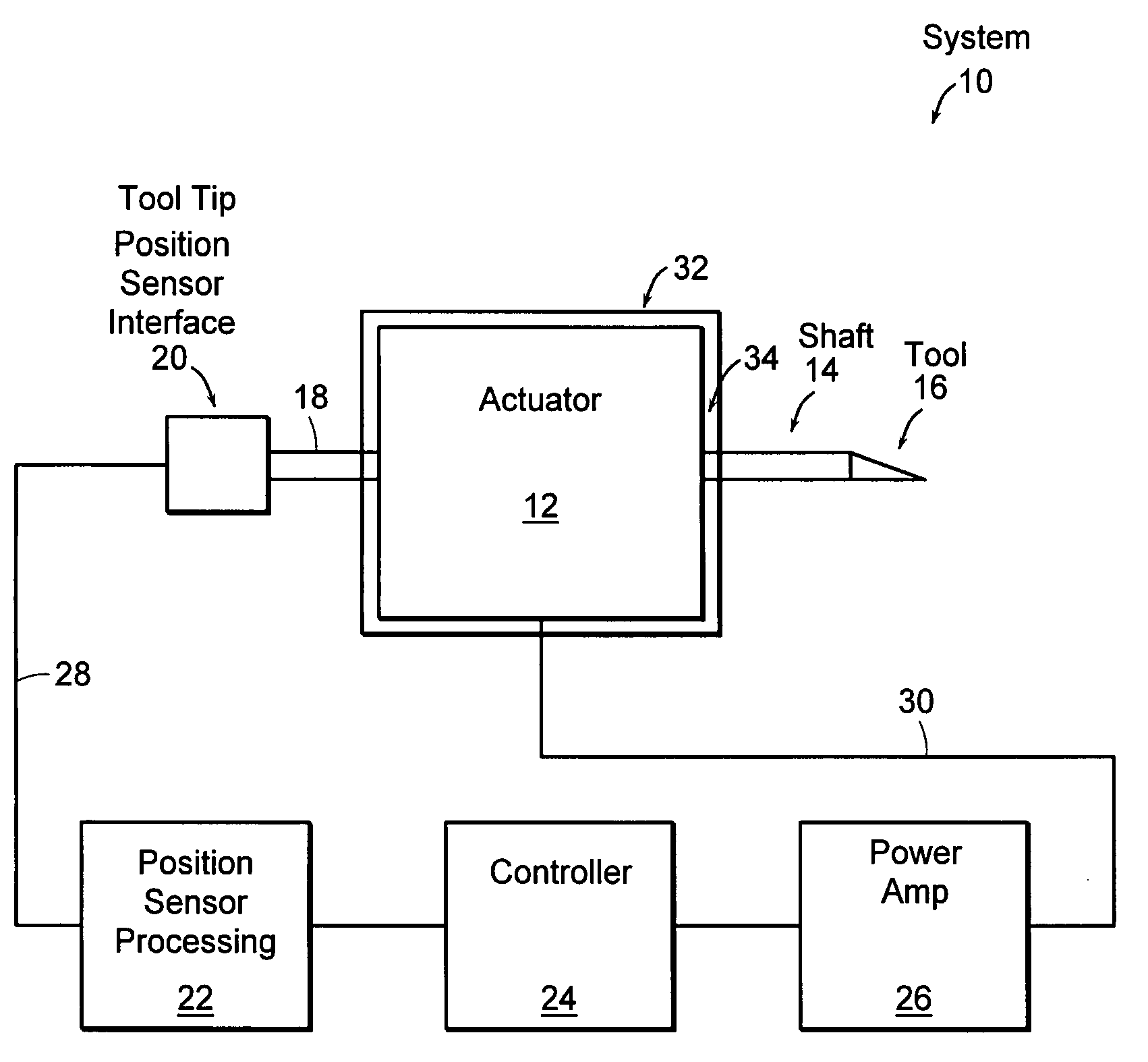
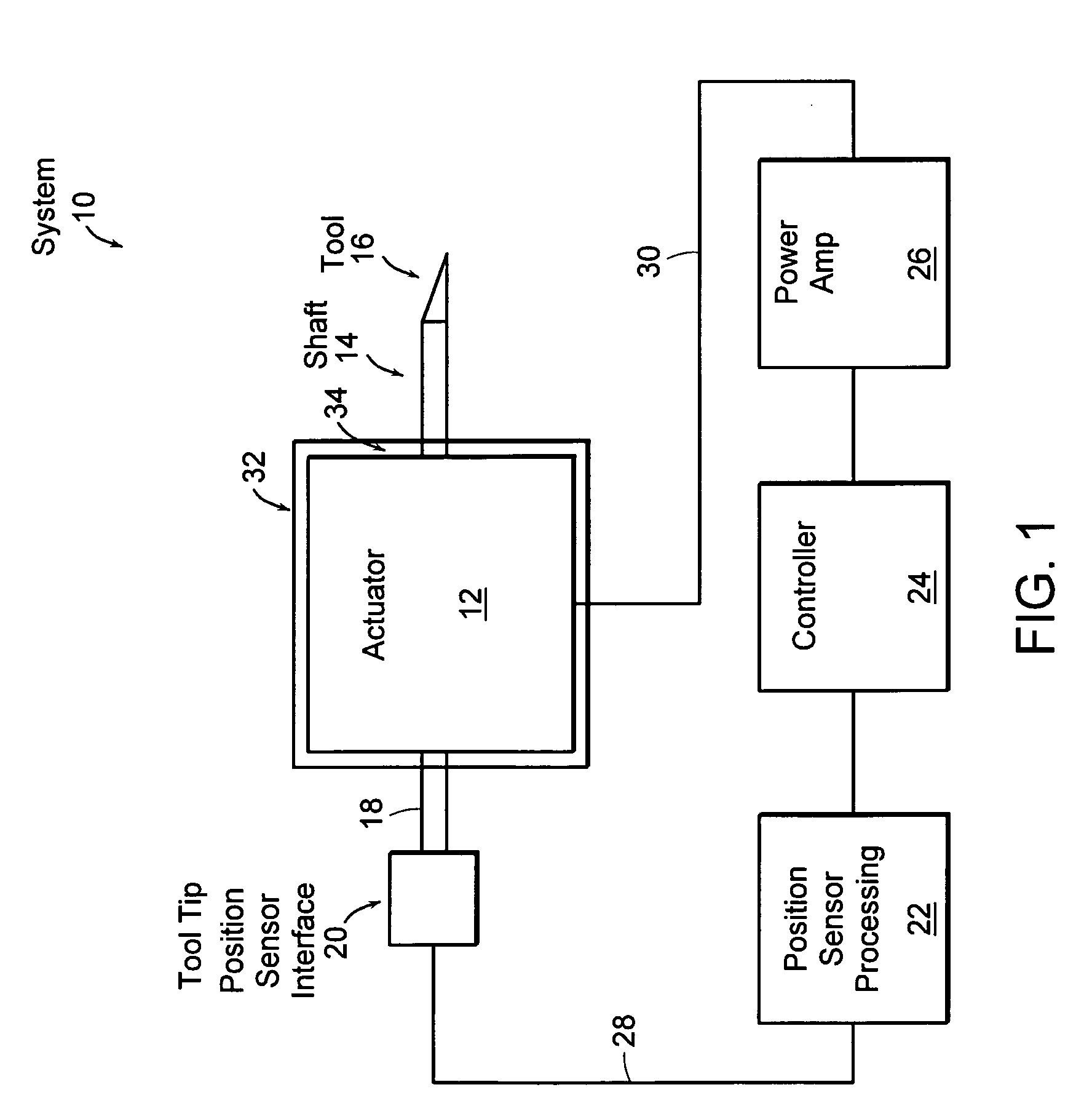
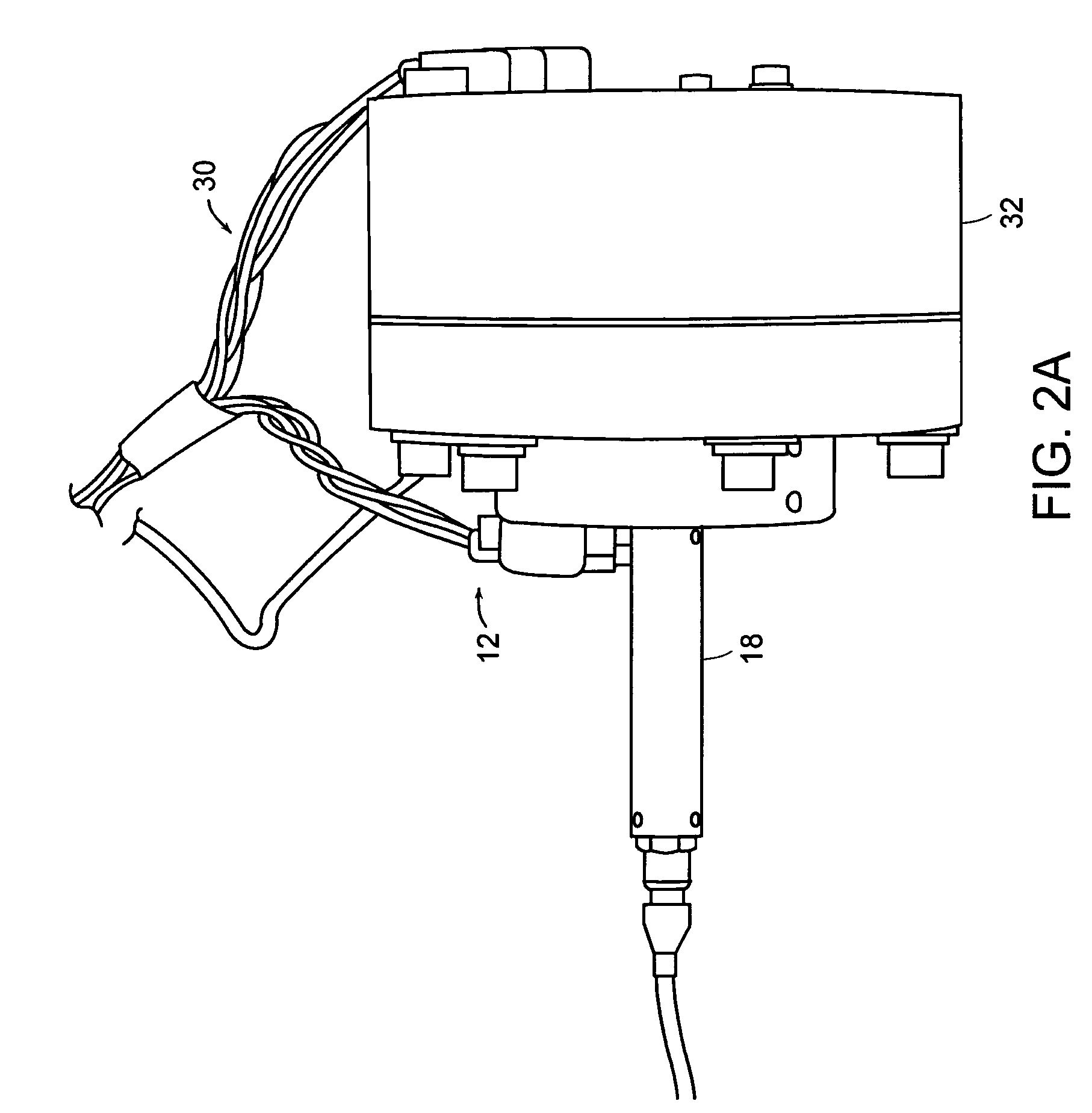
Variable reluctance fast positioning system and methods
InactiveUS20050223858A1Easy to operateElectromagnets without armaturesTurning machine accessoriesClosed loopLoop bandwidth
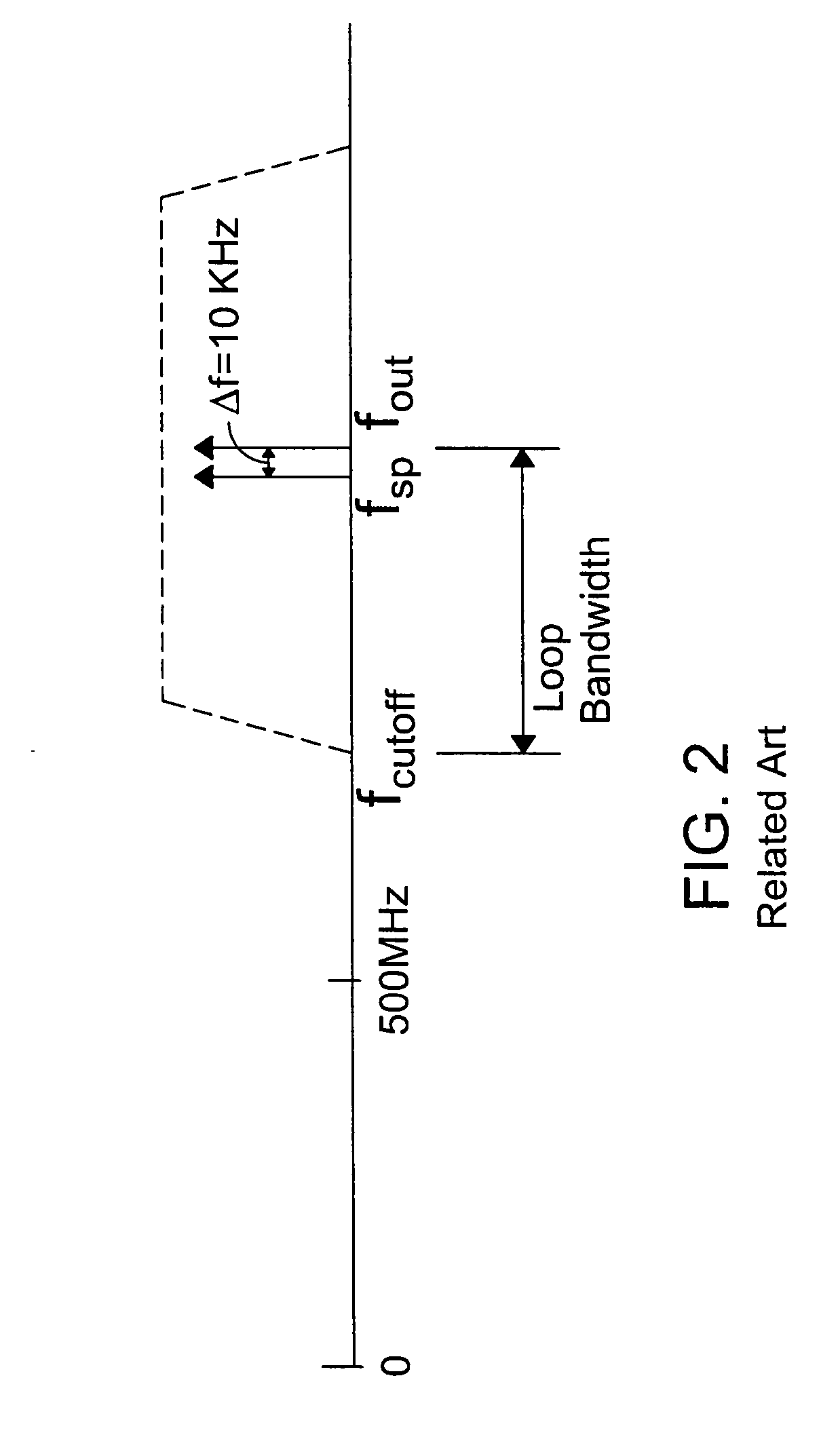
The preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to high bandwidth positioning systems such as fast tool servos (FTS). The applications of this invention include, for example, diamond turning of mold with structured surface for mass production of films for brightness enhancement and controlled reflectivity, diamond turning of molds for contact lens and micro-optical positioning devices. Preferred embodiments of the fast tool servo can have a closed-loop bandwidth of approximately 20±5 kHz, with acceleration of up to approximately 1000 G or more. The resolution or position error is approximately 1 nm root mean square (RMS). In a preferred embodiment, the full stroke of 50 μm can be achieved up tol kHz operation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
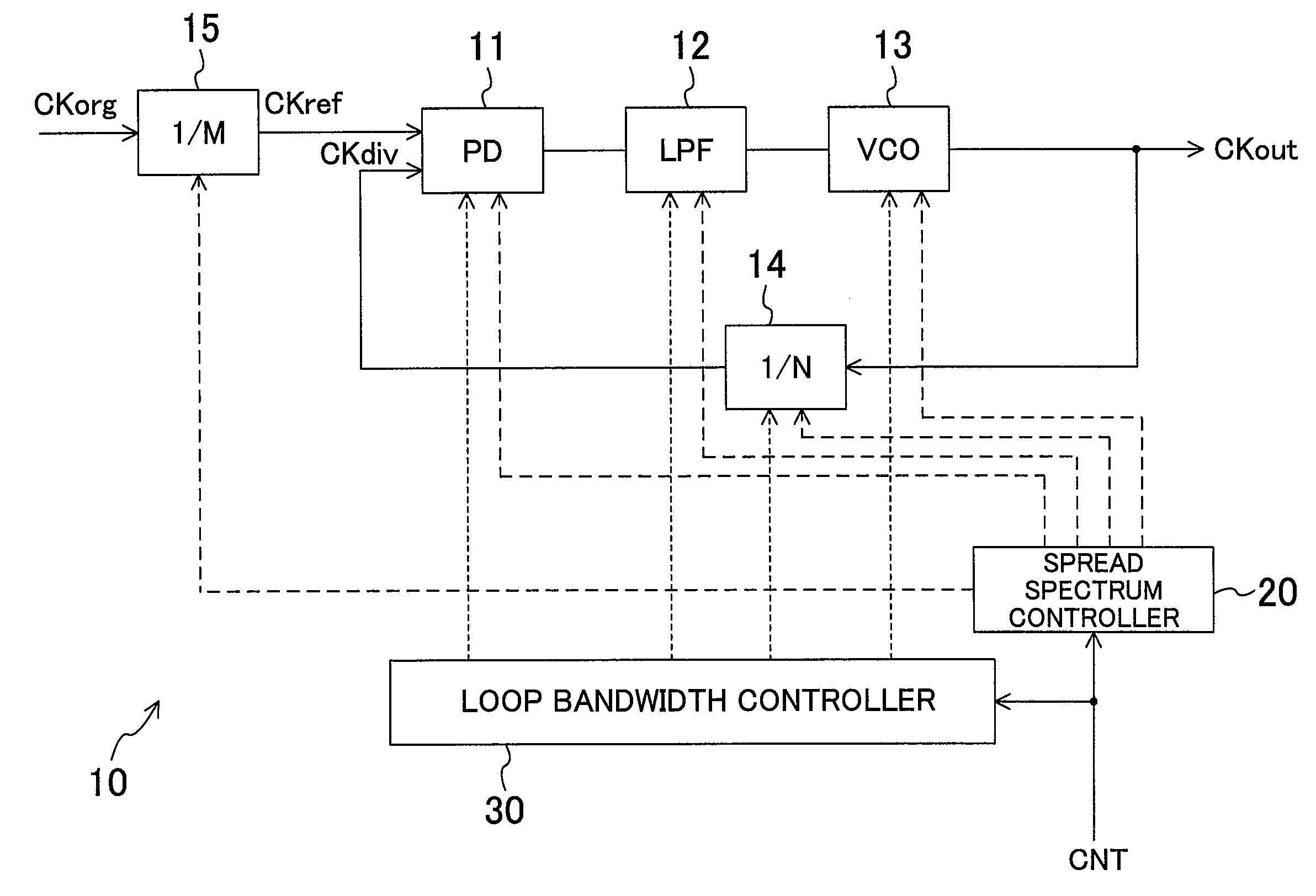
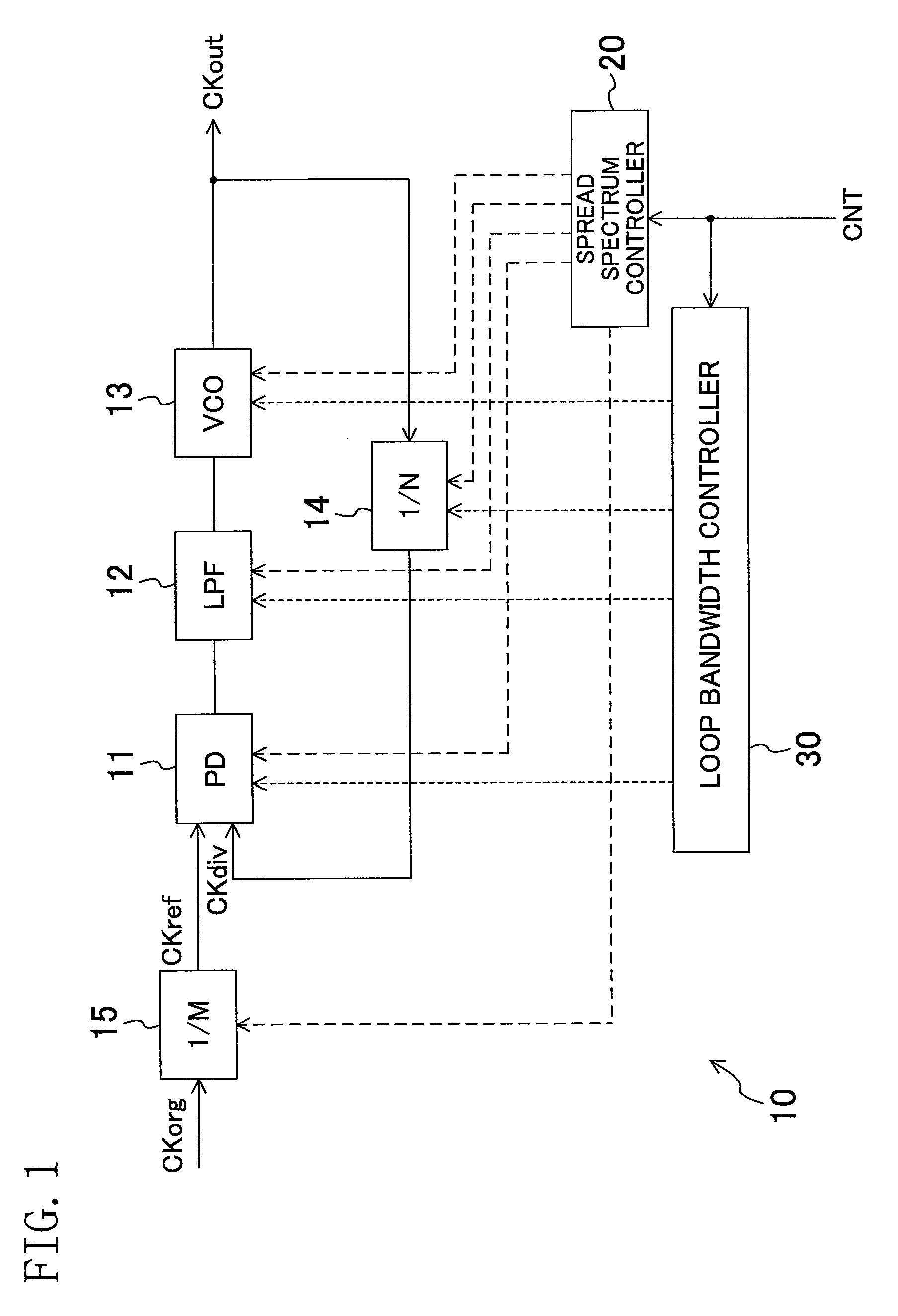
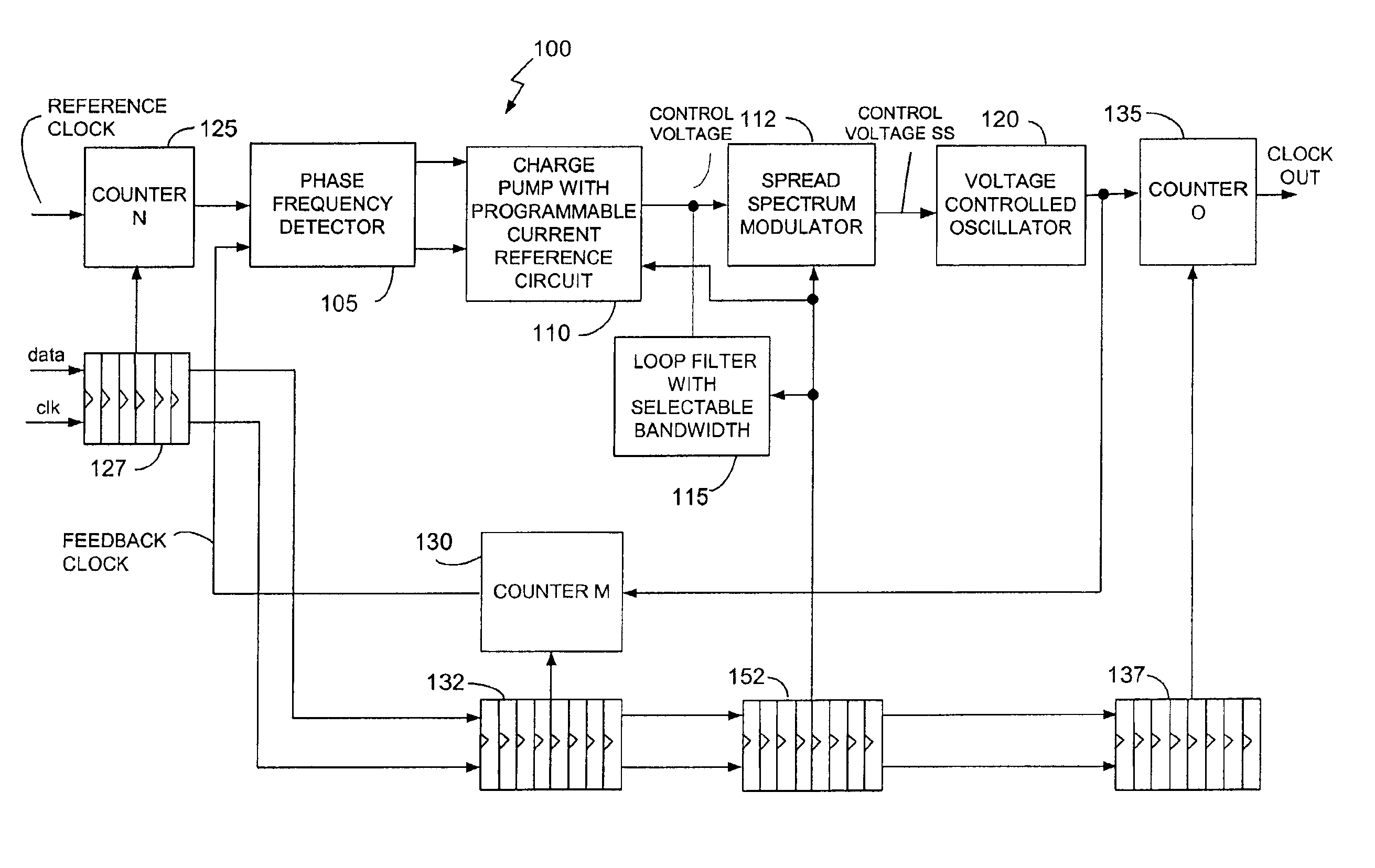
Spectrum spread clock generation device
ActiveUS20100214031A1Improve propertiesPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsLoop filterPhase detector
A spread spectrum controller (20) controls a PLL (10) so that the PLL outputs a spread-spectrum processed clock signal. A loop bandwidth controller (30) controls at least one of a phase detector (11), a loop filter (12), a voltage-controlled oscillator (13), and a frequency divider (14) in the PLL (10) during operation of the spread spectrum controller (20) to change a loop bandwidth of the PLL (10).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Direct current offset cancellation for mobile station modems using direct conversion
InactiveUS6985711B2Easy accessRapid and accurate DC offset estimates and cancellation techniquesDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionRadio transmissionModem deviceOffset cancellation
A system and method for canceling DC offset for Mobile Station Modems having direct conversion architectures. The present invention is a fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block that provides rapid and accurate DC offset estimates and cancellation techniques to support direct conversion architectures. The fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block combines four mechanisms to rapidly acquire and remove a DC offset estimate after power up, temperature changes, receiver frequency changes, and gain setting changes by increasing high pass loop bandwidth and adjusting DC offset levels at baseband. After removing the DC offset in large portions, the high pass loop bandwidth is decreased to fine tune the previous estimate and to remove any small variation in DC offset due to receiver self-mixing products.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
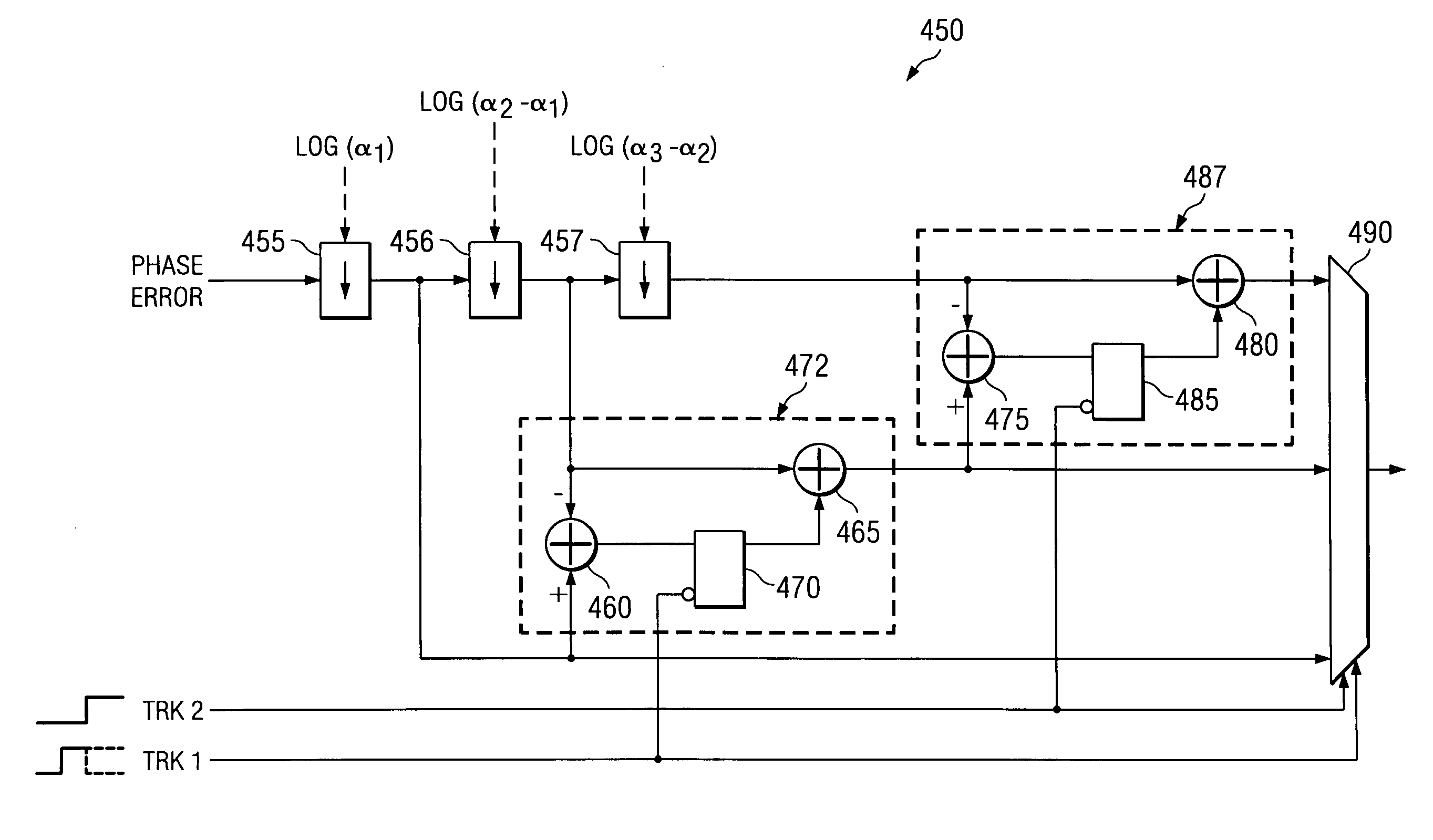
Bandwidth control in a mostly-digital pll/fll
InactiveUS20090108891A1Minimize disturbanceFaster frequency switching timePulse automatic controlLoop filterLoop bandwidth
Methods and apparatus for controlling a controlled oscillator using a phase-locked loop (PLL) or frequency-locked loop (FLL) having a digital loop filter with programmable filter parameters. An exemplary PLL (or FLL) includes a digital loop filter having one or more of the programmable filter parameters, which are changed by increments during operation in order to minimize disturbances (e.g., settling transients) as the loop bandwidth of the PLL is varied from a narrow loop bandwidth to a wide loop bandwidth, or vice versa. By changing the loop filter parameters in increments the loop bandwidth can be varied with substantially no perturbation. The end result is a much faster frequency switching time, improved settling dynamics, and predictable and stable loop operating performance. According to another aspect of the invention, one or more of the programmable filter parameters are changed in order to oppose a change in tuning sensitivity of the controlled oscillator (e.g., in order to maintain a constant loop bandwidth). By holding the loop bandwidth constant, switching time is maintained substantially constant under all conditions. This allows design and production margins to be reduced in a frequency agile system, and also relaxes the tuning sensitivity linearity requirements of the controlled oscillator.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Programmable loop bandwidth in phase locked loop (PLL) circuit
A PLL circuit is described. The PLL circuit includes: a feedback loop and a loop filter coupled to the feedback loop, where the loop filter is programmable to provide one of a plurality of bandwidths. In one embodiment, the loop filter is programmable to provide one of a plurality of resistances, each resistance of the plurality of resistances corresponding to one of the plurality of bandwidths. In one embodiment, the feedback loop includes a detector and a signal generator coupled to the detector.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
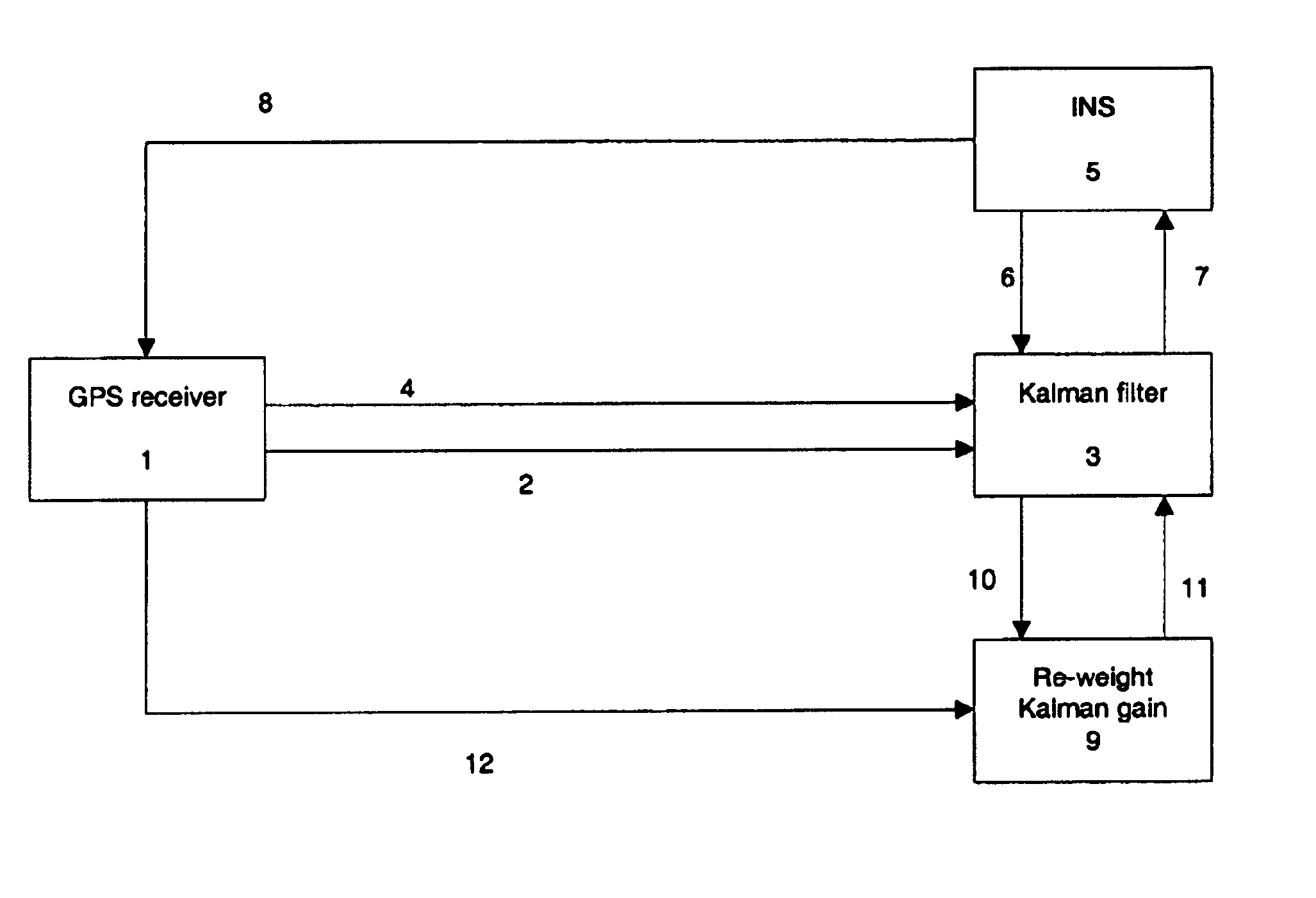
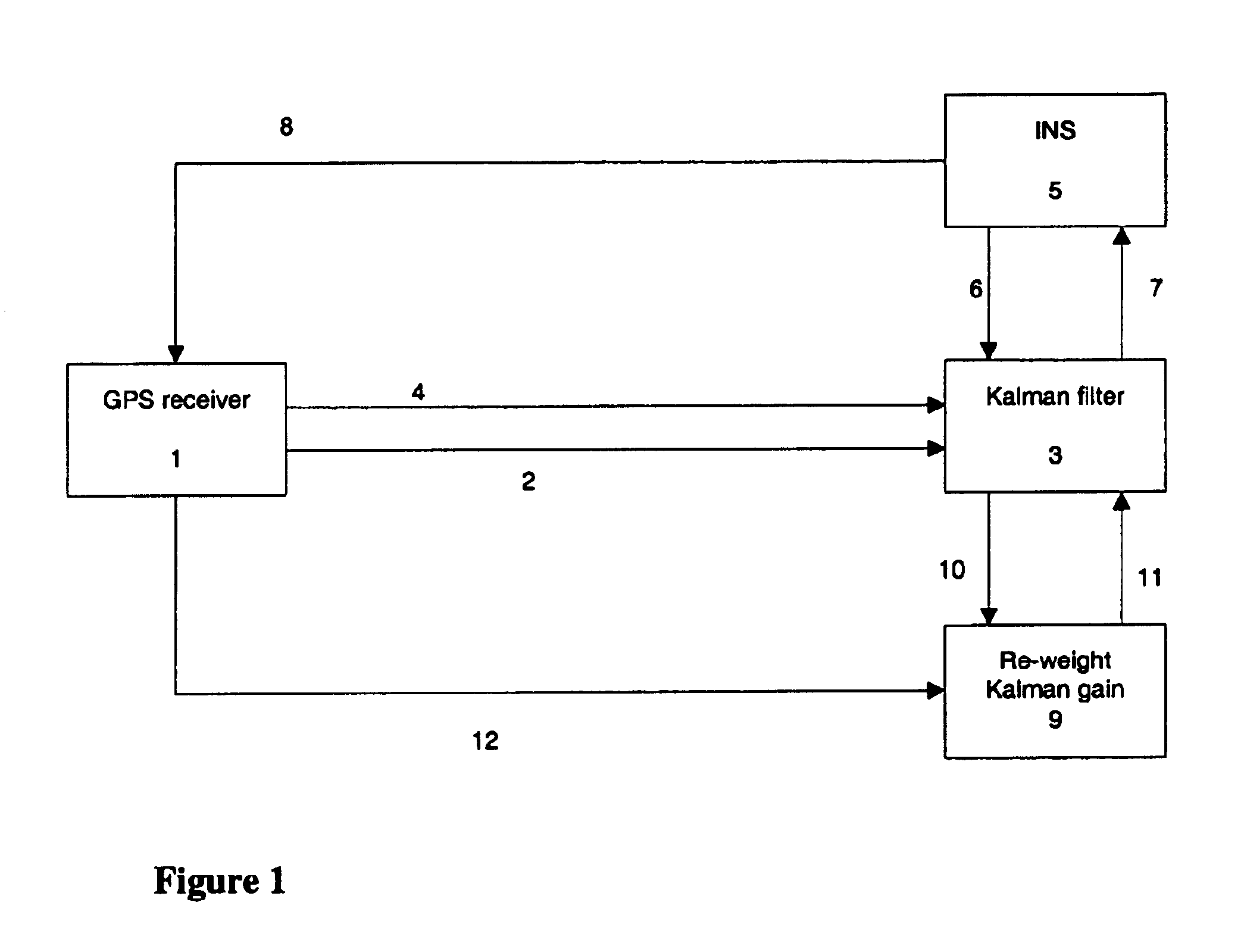
Adaptive GPS and INS integration system
InactiveUS6900760B2Increase weightImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationSatellite radioLoop bandwidth
This invention relates to the field of Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) and satellite navigation systems such as the Global Positioning System (GPS) and in particular relates to methods of integrating GPS and INS data in order to provide more accurate navigation solutions. The invention provides a method of improving the accuracy of a tightly coupled integrated INS and satellite radio navigation system in cases where the satellite navigation receiver has adaptive tracking loop bandwidths.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
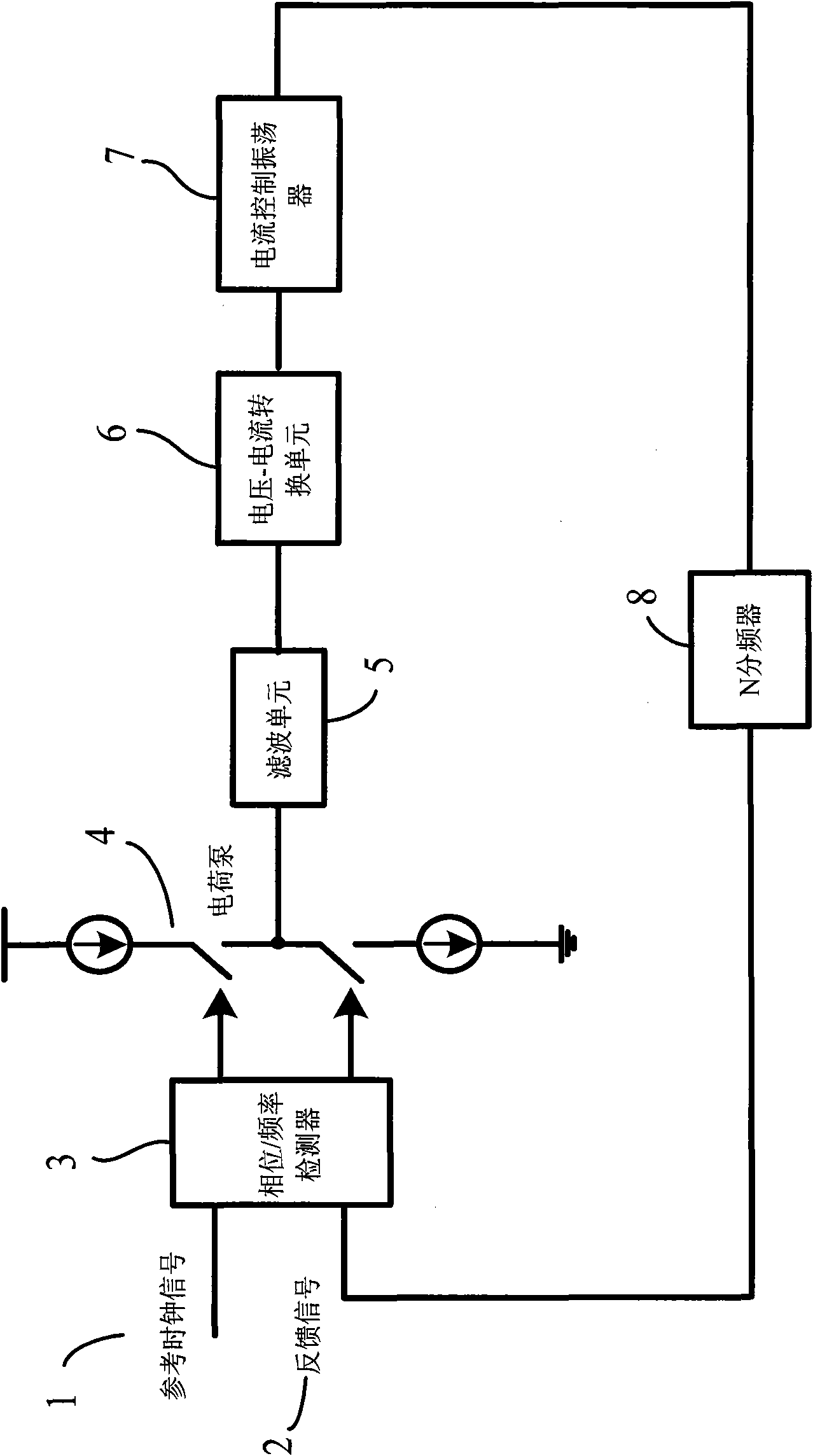
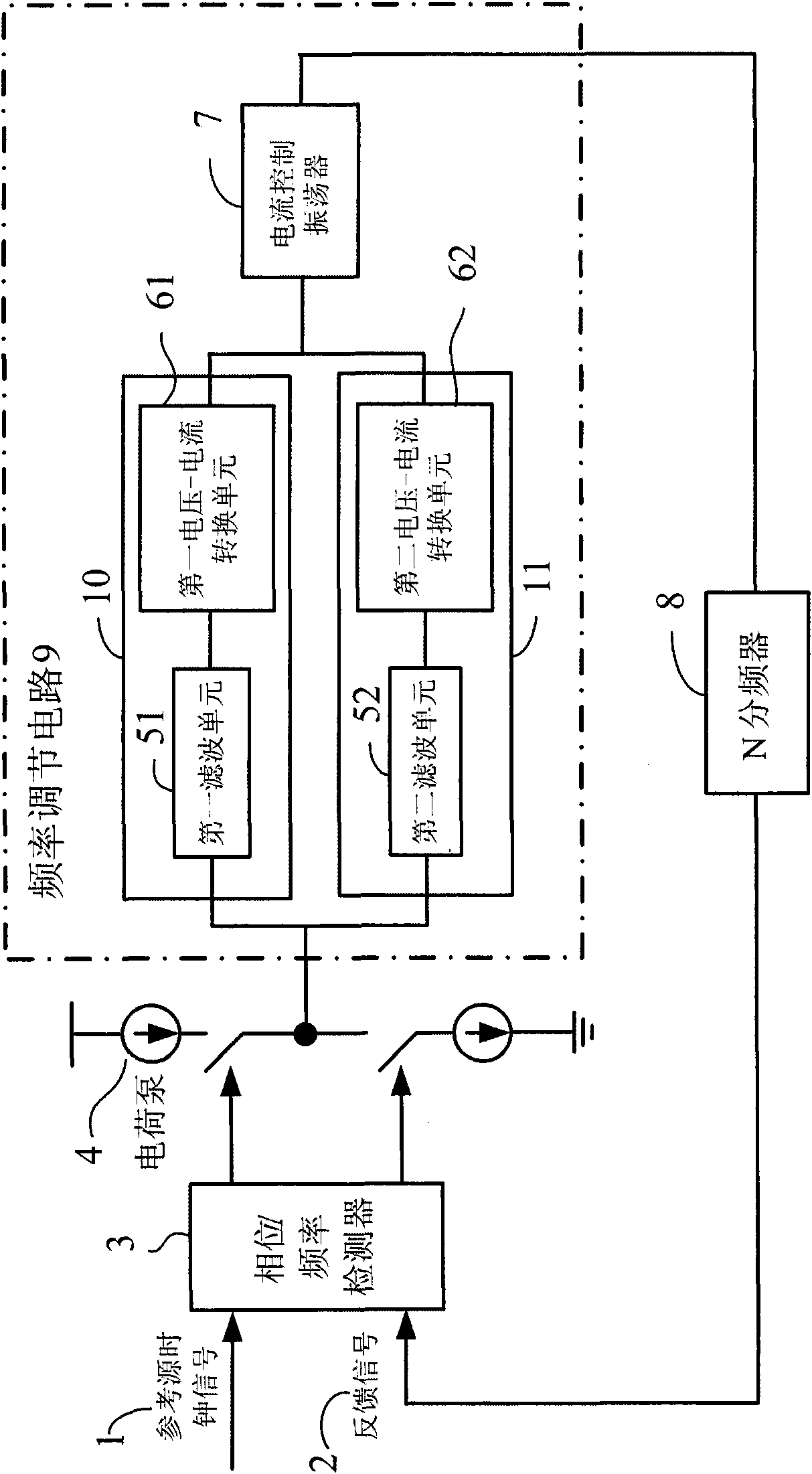
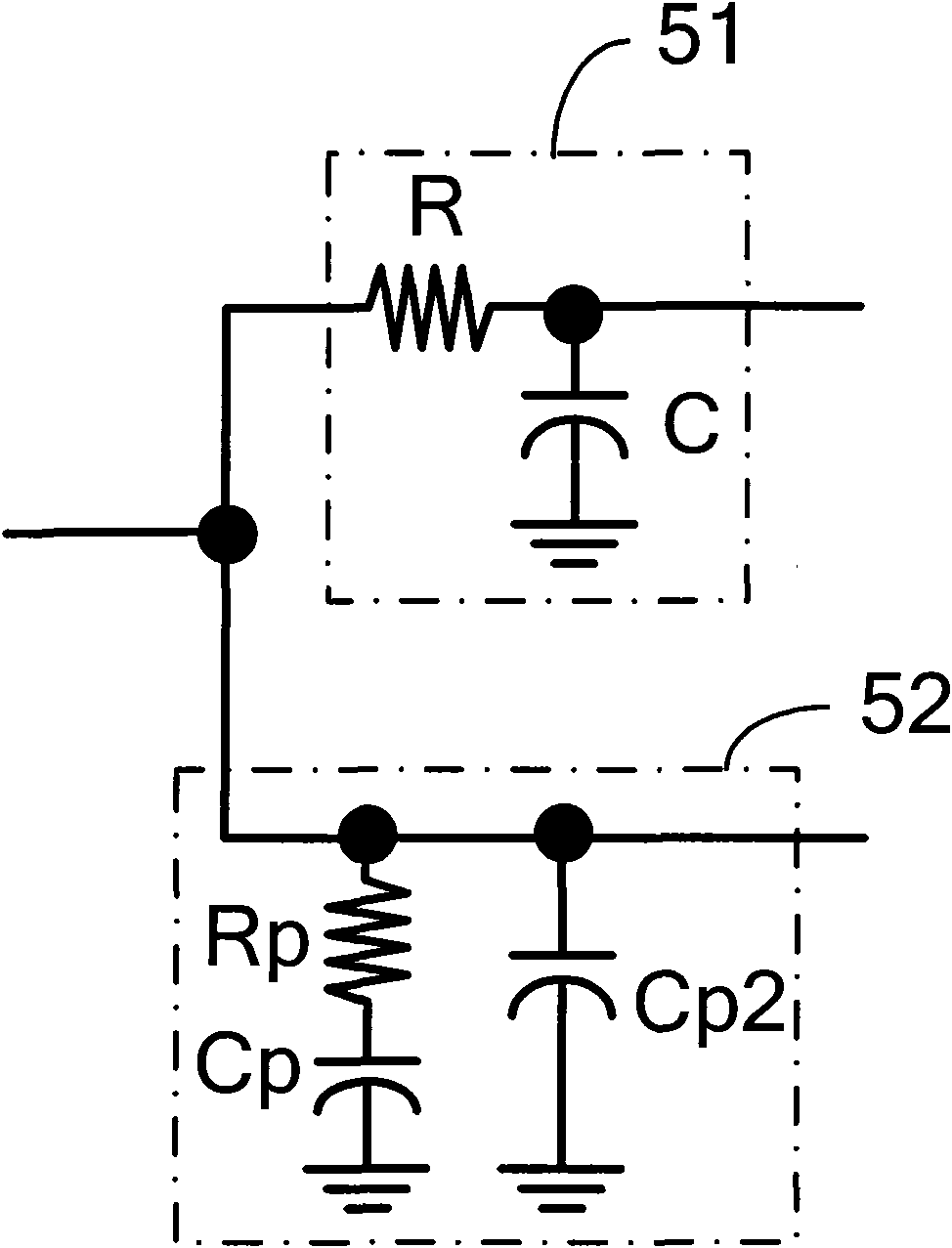
Double-phase-locked loop circuit and control method thereof
ActiveCN101944910AReduce Design ComplexityImprove performancePulse automatic controlPhase locked loop circuitDouble phase
The invention discloses a double-phase-locked loop circuit and a control method thereof. The double-phase-locked loop circuit comprises a phase / frequency detector, a charge pump, a frequency adjustment circuit and an N frequency divider. The frequency adjustment circuit comprises a coarse adjustment circuit, a fine adjustment circuit and a current-controlled oscillator, wherein the coarse adjustment circuit is used for coarse adjustment of frequency of output signals of phase-locked loops till approaching a target frequency; the fine adjustment circuit is used for fine adjustment of the frequency of the output signals of the phase-locked loops till the target frequency; and the current-controlled oscillator is coupled with the coarse adjustment circuit and the fine adjustment circuit and used for producing the output signals of the phase-locked loops, wherein the frequency of the output signals is the target frequency. The double-phase-locked loop circuit can effectively achieve the purpose of expanding the frequency adjustment range under the situation of keeping the loop bandwidth of the phase-locked loops smaller, realize the on-chip integration and further reduce the cost and the design complexity of the circuit.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
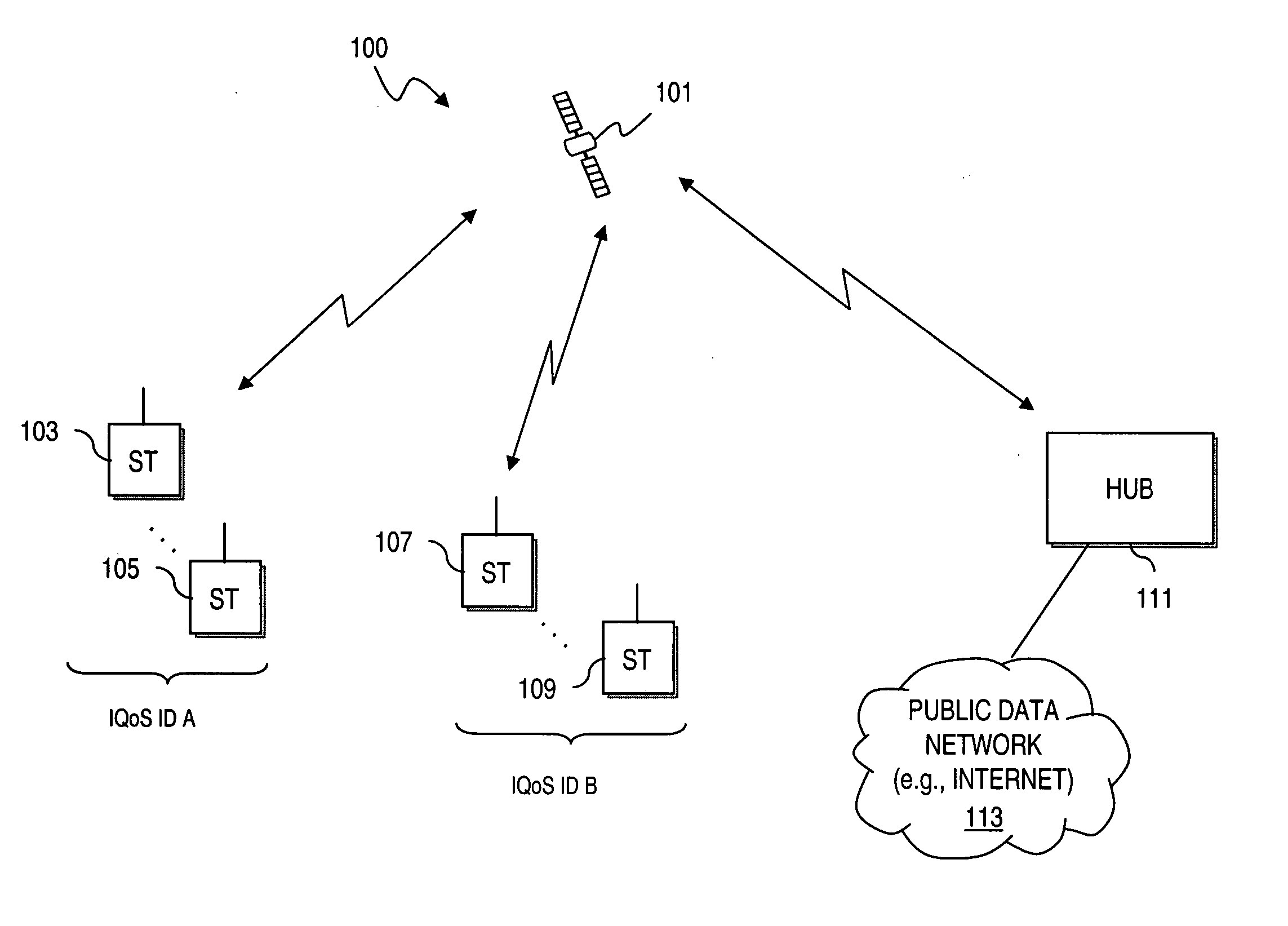
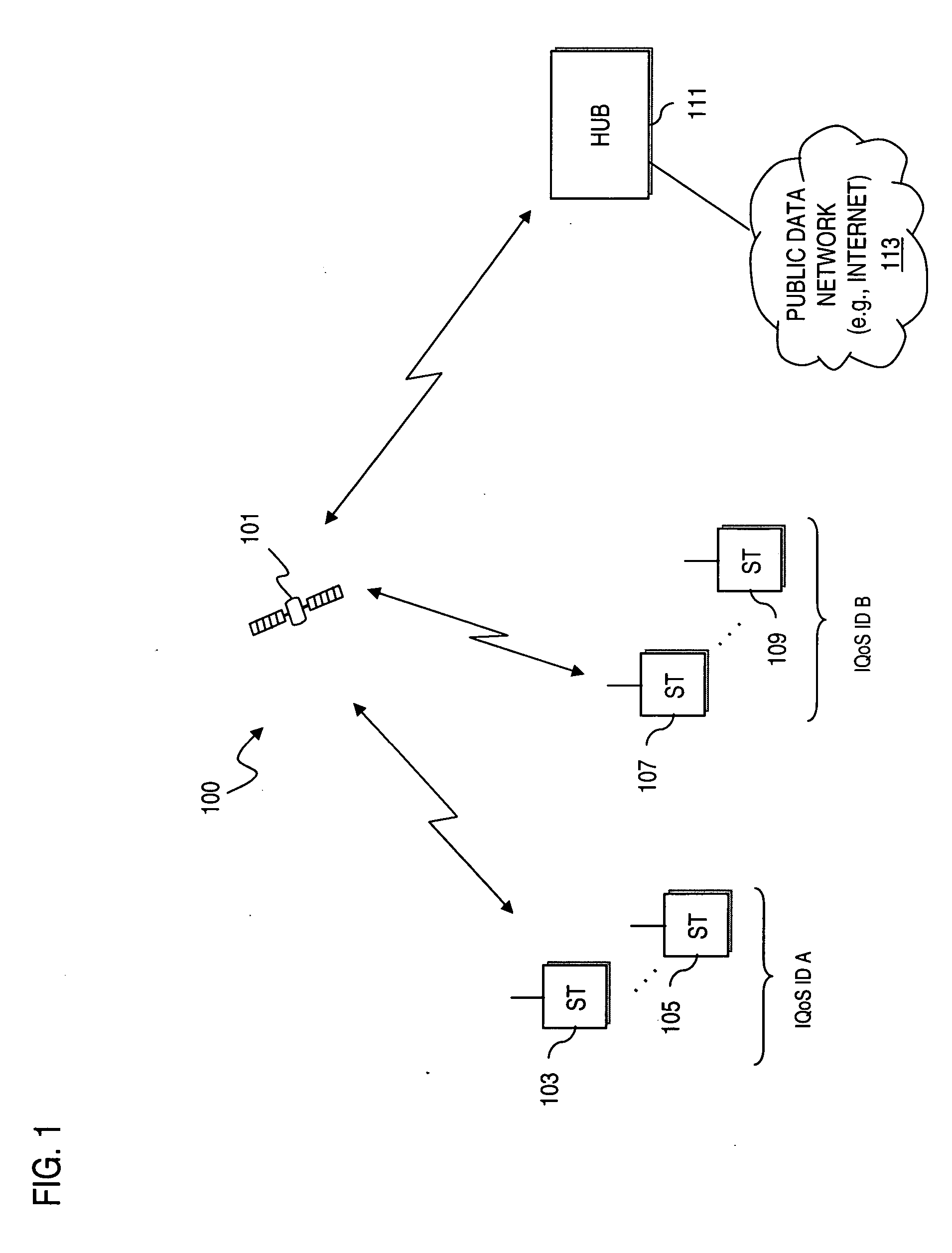
Method and apparatus for providing open loop bandwidth allocation
ActiveUS20060215628A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsLoop bandwidth
An approach for allocating bandwidth is disclosed. A request is detected from a terminal for capacity on a communication channel based on type of traffic transmitted from the terminal. A bandwidth allocation pattern designated for the terminal is retrieved, wherein the bandwidth allocation pattern is set based on a predetermined service plan associated with the terminal. Bandwidth over the communication channel is reserved for the terminal according to the bandwidth allocation pattern without feedback to the terminal. This arrangement has particular applicability to a satellite network that provides data communication services.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
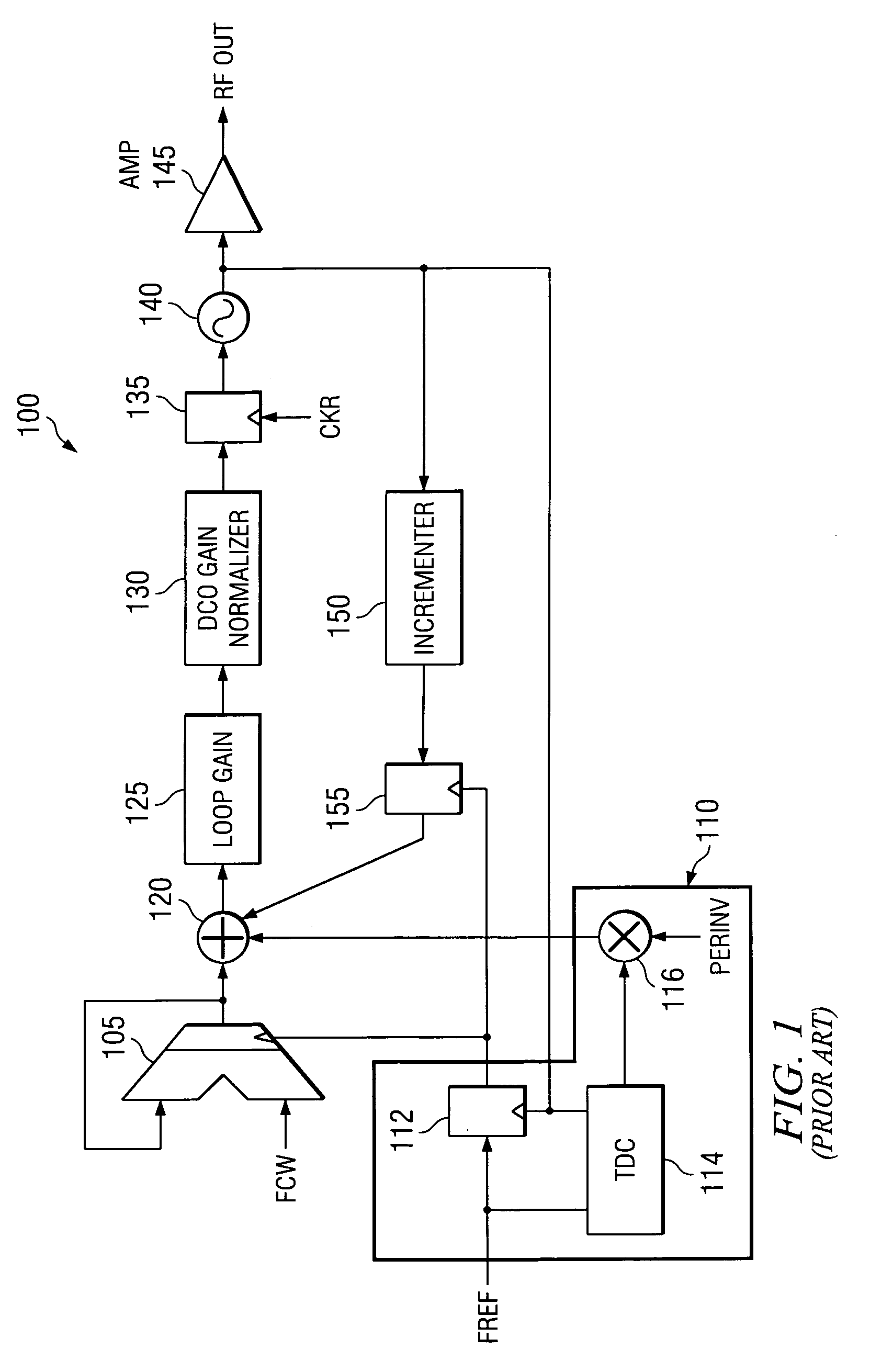
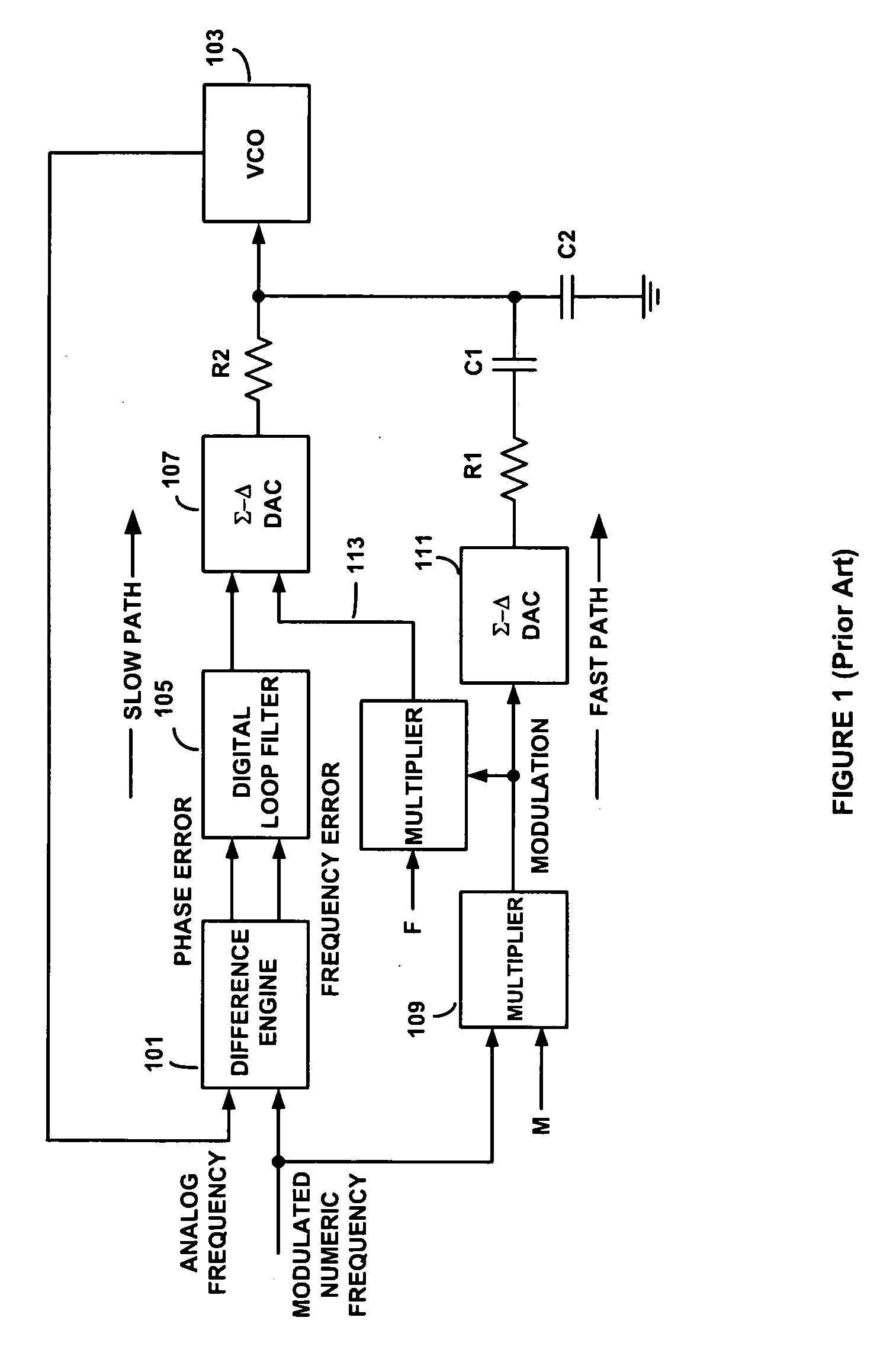
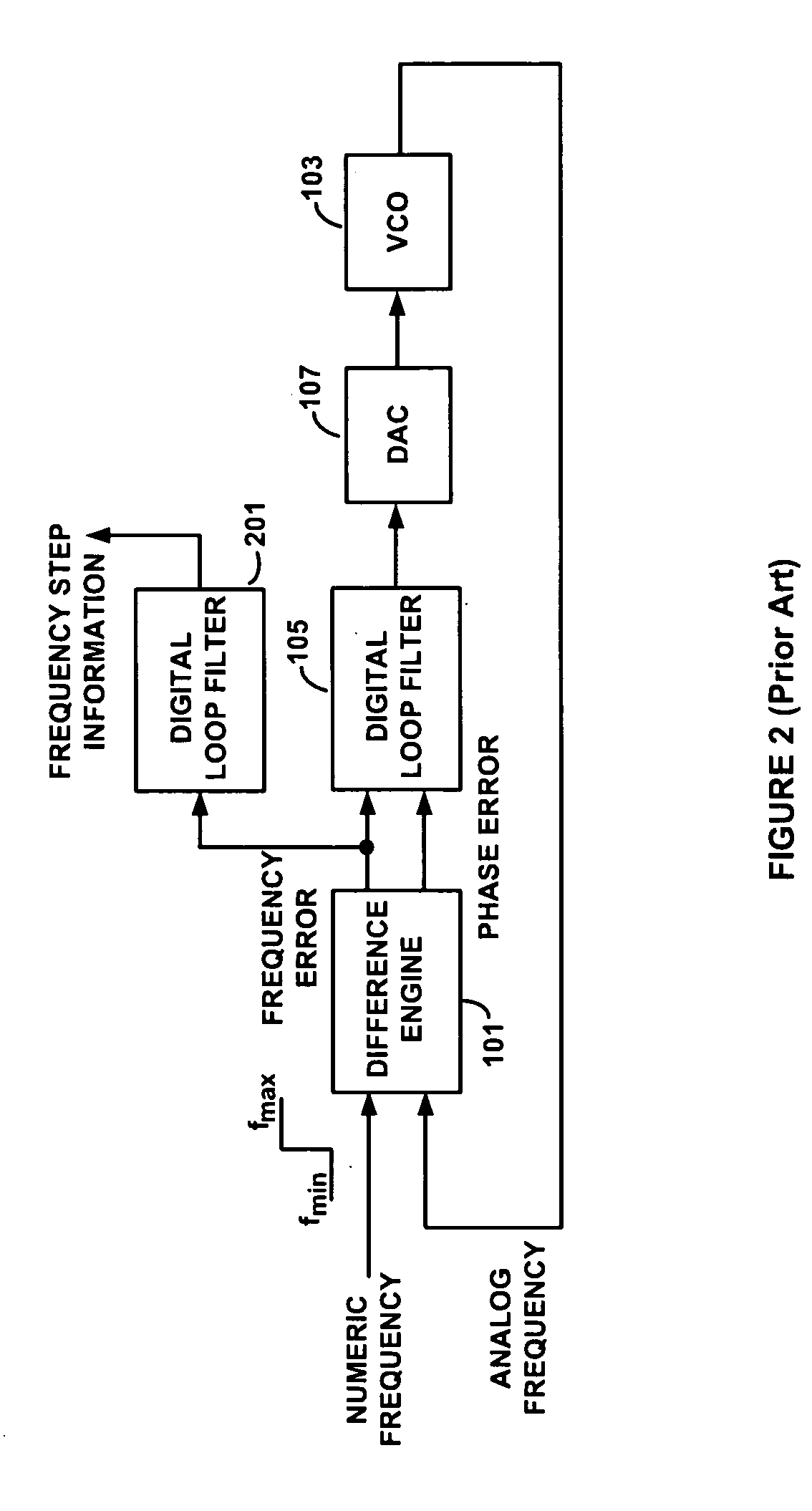
System and method for suppressing noise in a phase-locked loop circuit
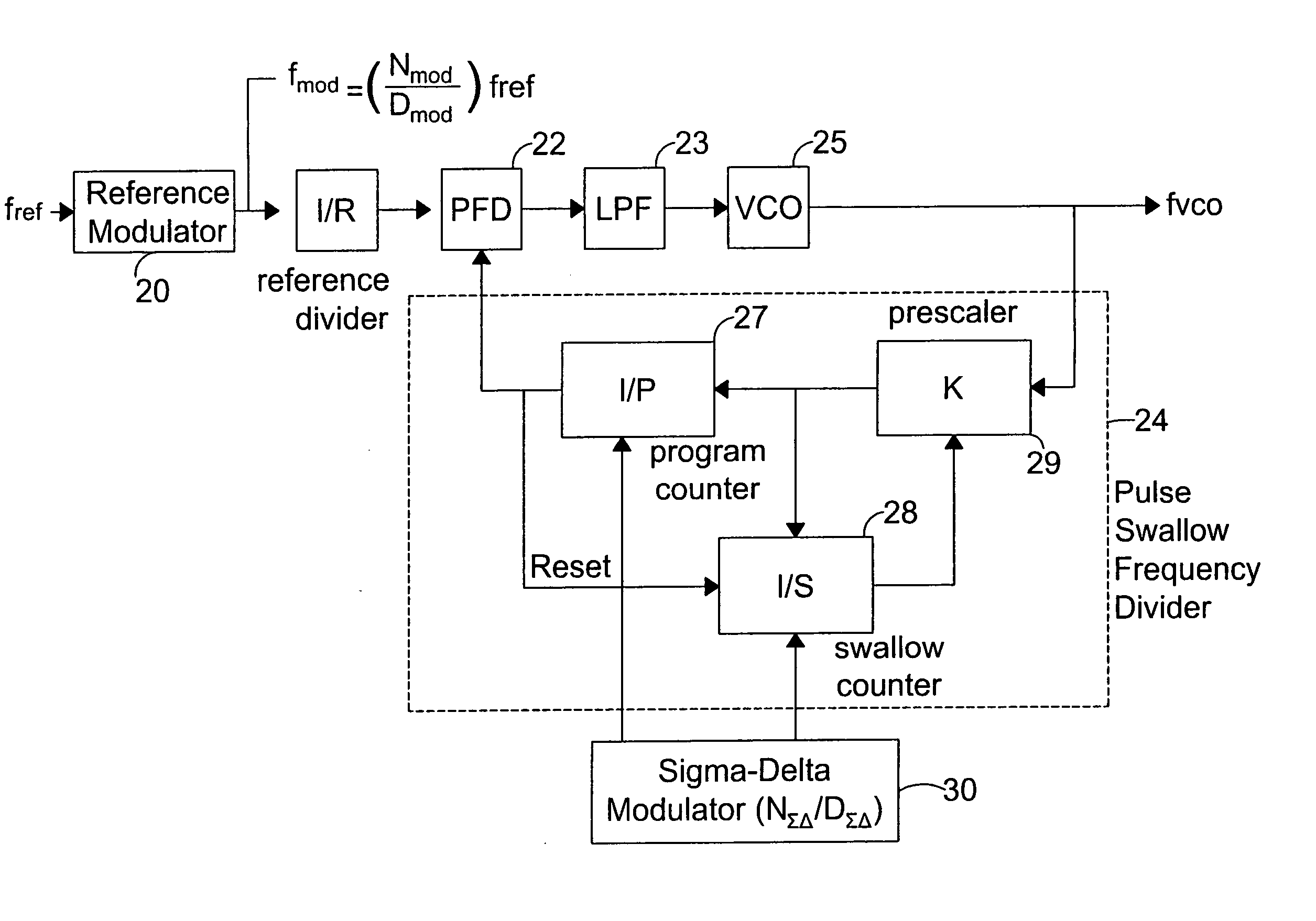
ActiveUS20040085103A1Pulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Phase locked loop circuit
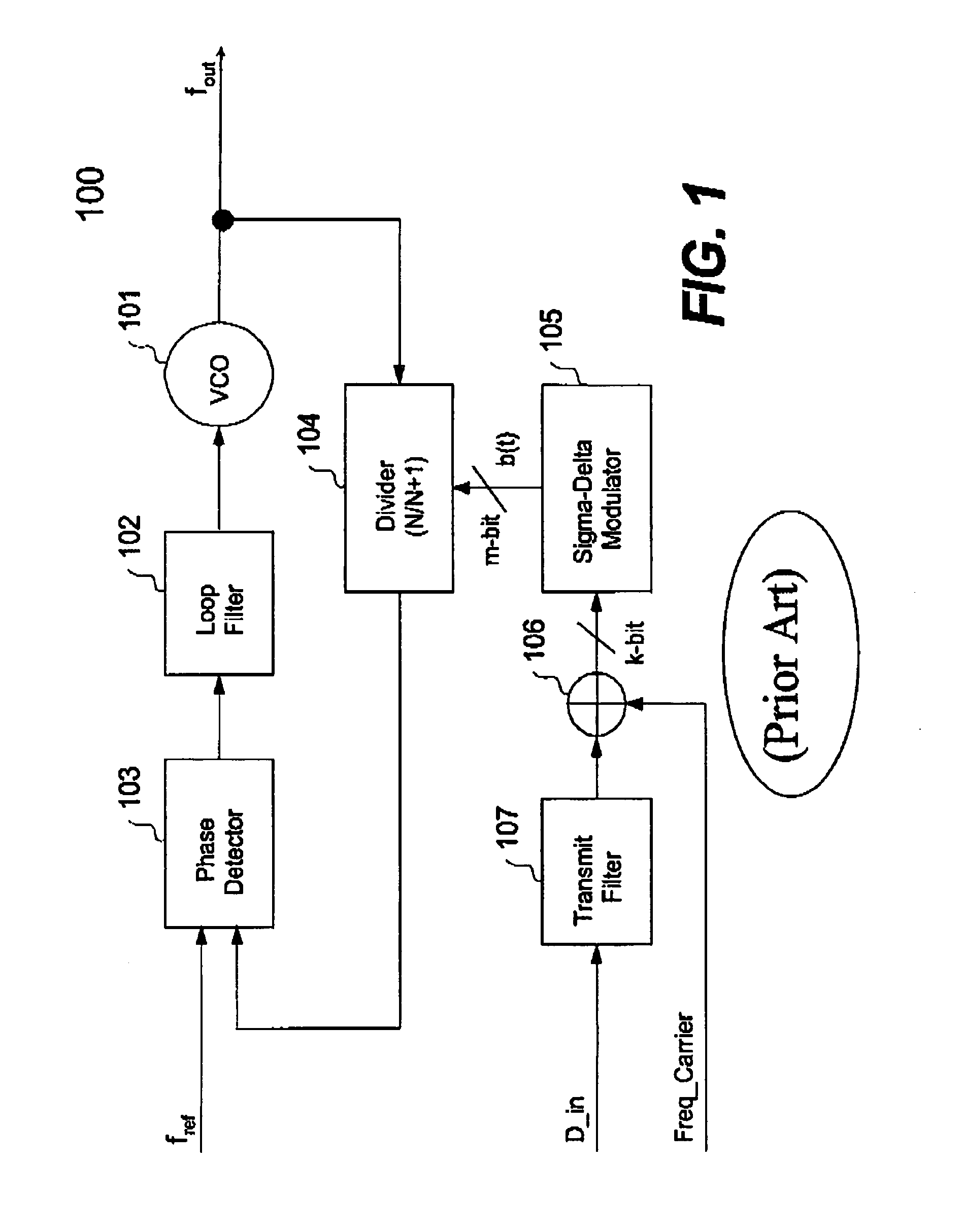
A system and method for improving the signal-to-noise ratio of a frequency generator suppresses phase noise and noise generated from mismatches in the internal generator circuits. This is accomplished using a modulation scheme which shifts spurious noise signals outside the loop bandwidth of the generator. When shifted in this manner, the noise signals maybe removed entirely or to any desired degree using, for example, a filter located along the signal path of the generator. In one embodiment, a Sigma-Delta modulator controls the value of a pulse-swallow frequency divider situated along a feedback path of a phase-locked loop to achieve a desired level of noise suppression. In another embodiment, a reference signal input into a phase-locked loop is modulated to effect noise suppression. In another embodiment, the foregoing forms of modulation are combined to accomplish the desired frequency shift. Through these modulation techniques, the signal-to-noise ratio of the frequency generator may be substantially improved while simultaneously achieving faster lock times.
Owner:GCT SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Method of establishing an oscillator clock signal
InactiveUS20060267640A1Easy to controlLow costPulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsFrequency spectrumCycle control
A hybrid numeric-analog clock synchronizer, for establishing a clock or carrier locked to a timing reference. The clock may include a framing component. The reference may have a low update rate. The synchronizer achieves high jitter rejection, low phase noise and wide frequency range. It can be integrated on chip. It may comprise a numeric time-locked loop (TLL) with an analog phase-locked loop (PLL). Moreover a high-performance number-controlled oscillator (NCO), for creating an event clock from a master clock according to a period control signal. It processes edge times rather than period values, allowing direct control of the spectrum and peak amplitude of the justification jitter. Moreover a combined clock-and-frame asynchrony detector, for measuring the phase or time offset between composite signals. It responds e.g. to event clocks and frame syncs, enabling frame locking with loop bandwidths greater than the frame rate.
Owner:TRAVIS CHRISTOPHER JULIAN
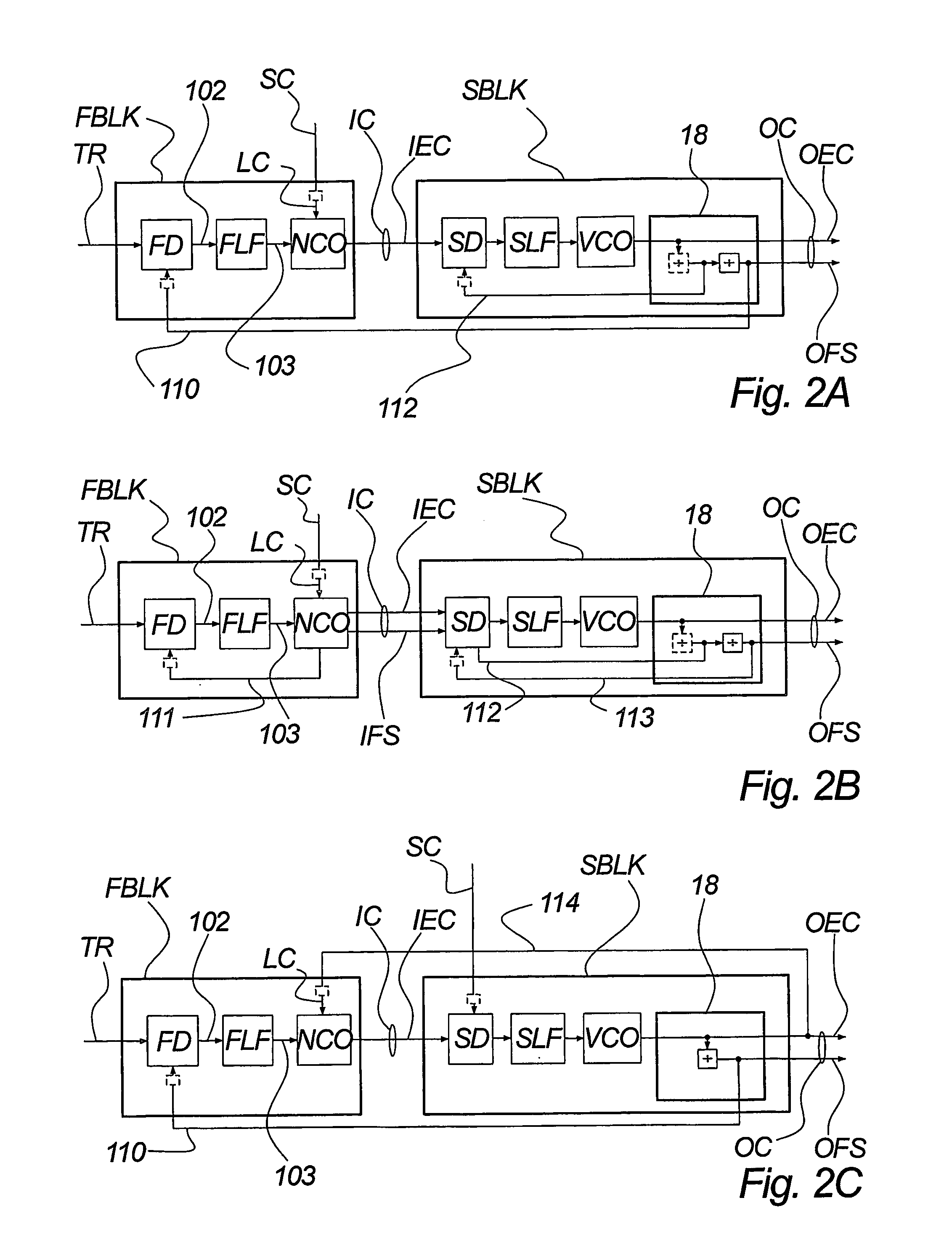
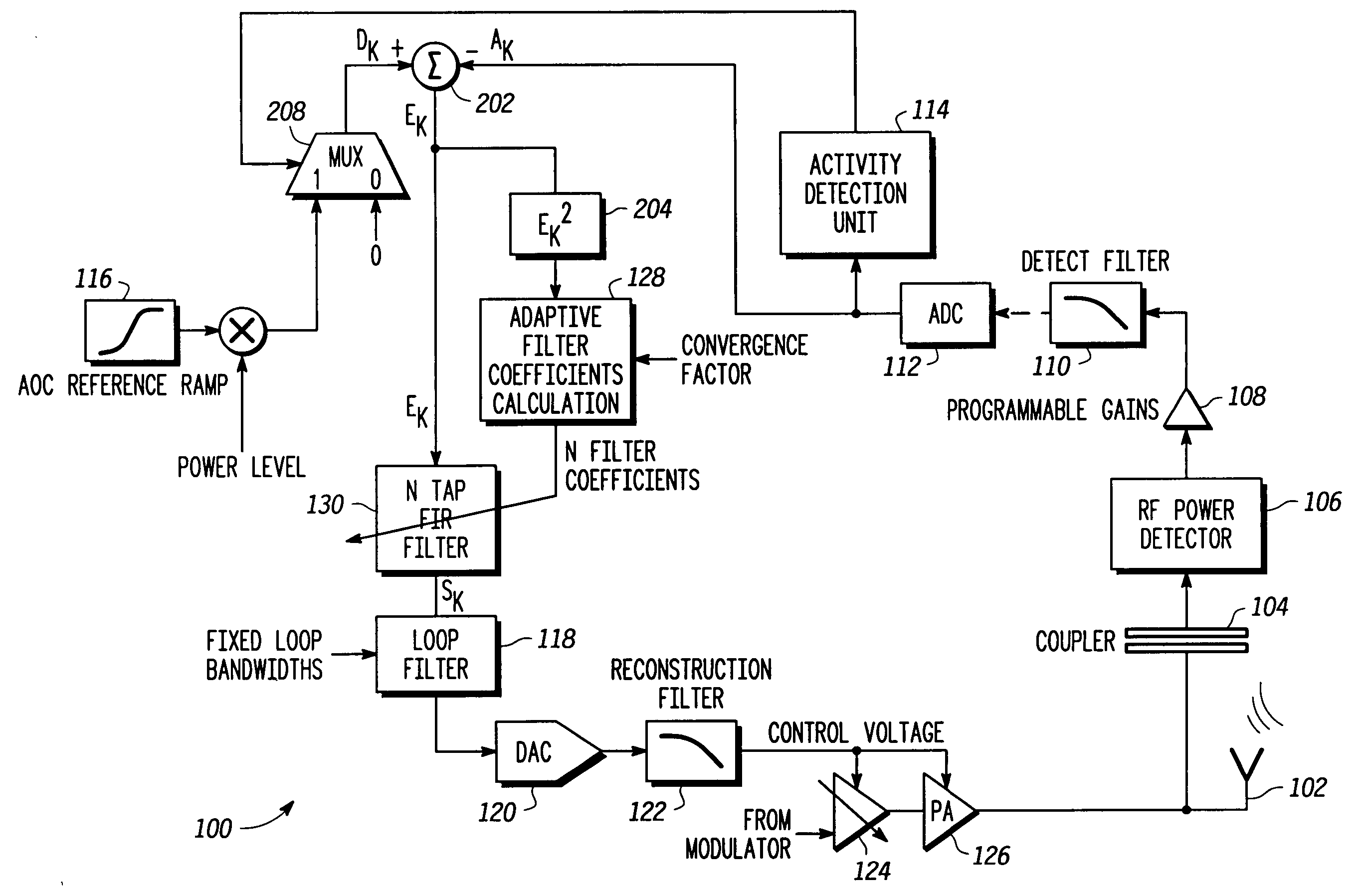
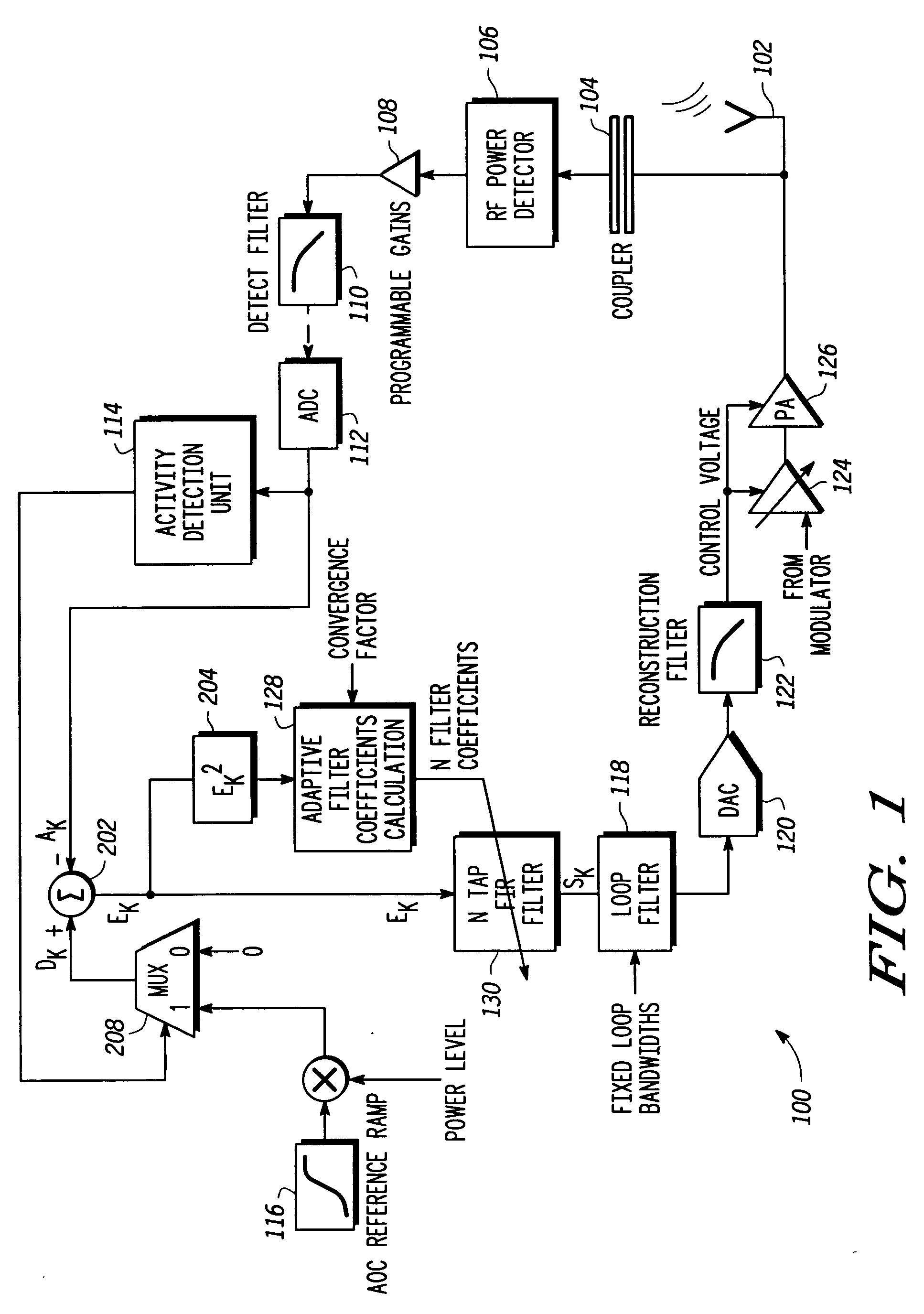
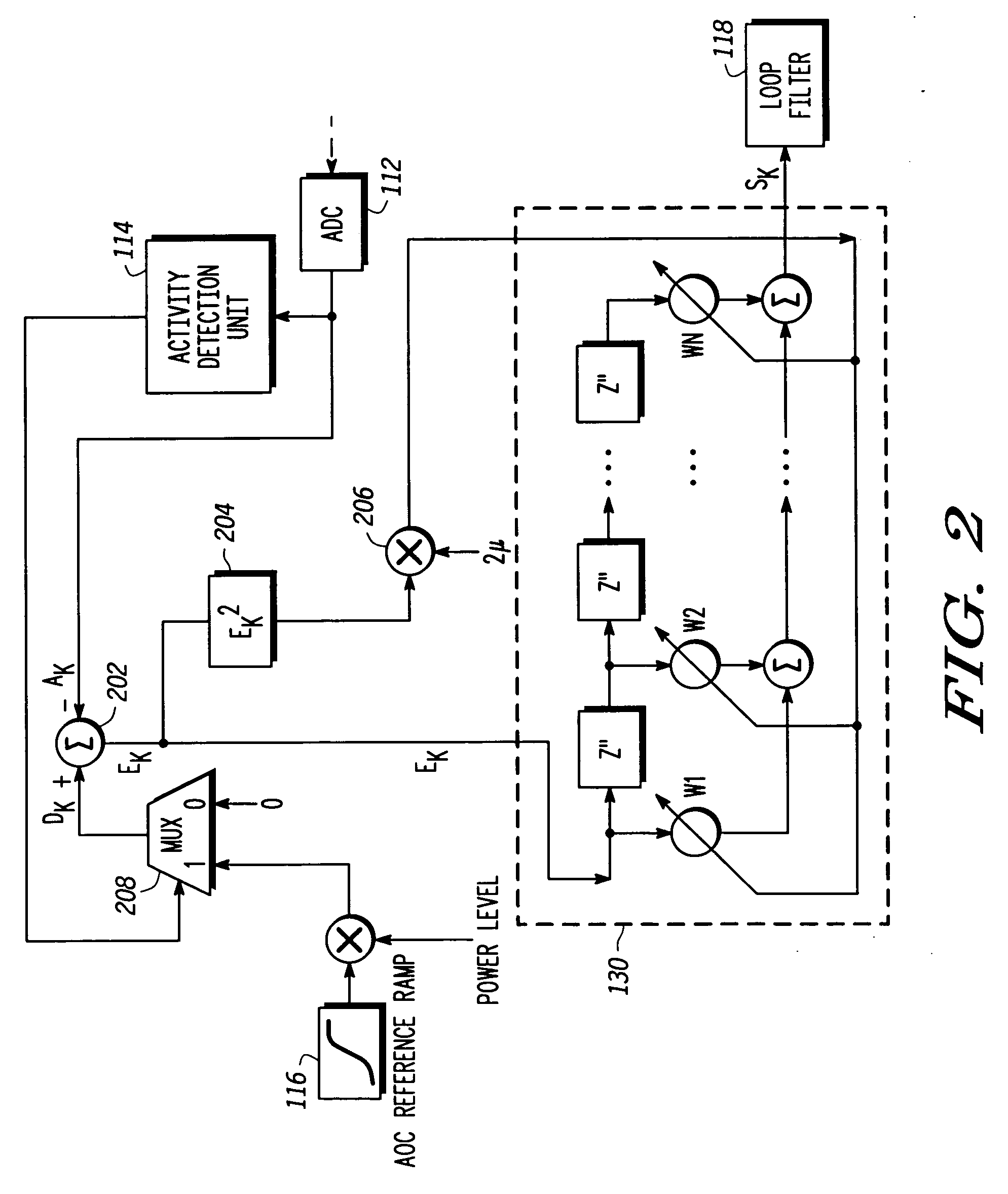
Adaptive transmit power control system
InactiveUS20050122166A1Resonant long antennasTransmission systemsDigital signal processingPower control system
An adaptive closed loop transmit power control system which does not require extensive factory calibration of power control loop bandwidths and feedback detect path gain settings over the power transition ranges, frequency bands of operation, temperature, and supply voltage is disclosed. The system automatically compensates for any gain or slope variations in the analog feedforward and feedback paths to maintain system stability and meet performance specifications. The system achieves this by using an adaptive digital signal processing (DSP) system architecture within the feedback path of this closed loop power control system. The system eliminates the need for extensive factory calibration of such parameters as loop bandwidths and feedback detect path gain settings over power transition ranges, frequency bands of operation, temperature, and supply voltage.
Owner:APPLE INC
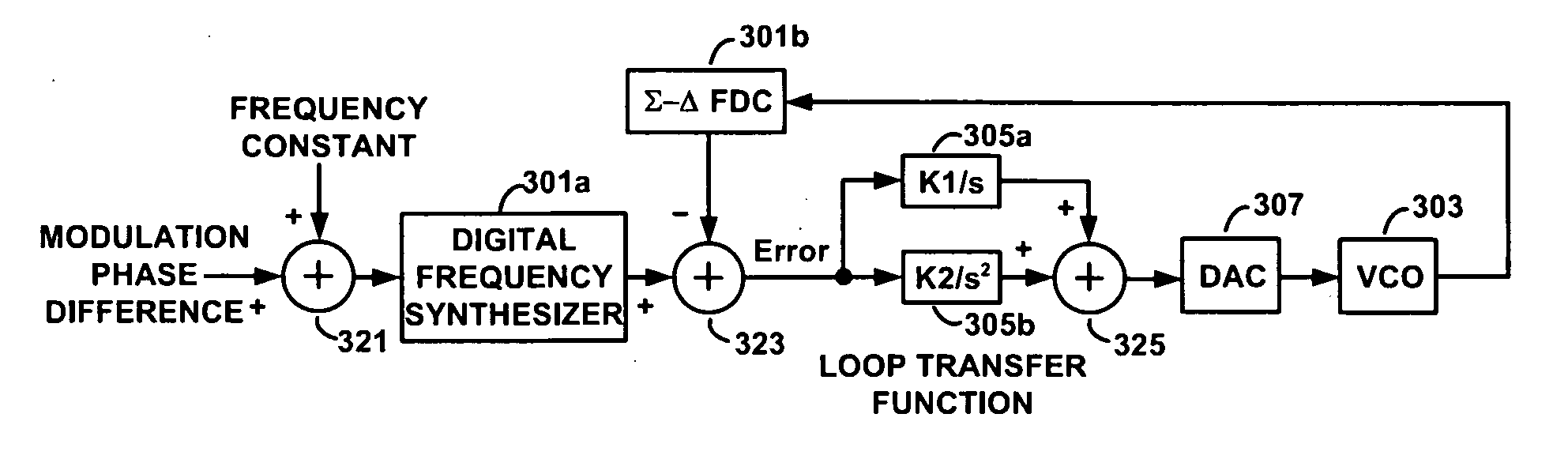
Loop bandwidth enhancement technique for a digital PLL and a HF divider that enables this technique
ActiveUS20080043893A1Pulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersLoop bandwidthPhase-locked loop
A method of operating a phase locked loop (FIG. 5) for a wireless receiver is disclosed. The method includes receiving a reference signal (503) having a first and a second plurality of cycles and receiving a feedback signal (512) having the first and the second plurality of cycles. The feedback signal is compared (504) to the reference signal. A plurality of phase errors is produced for each cycle of (UP, FIG. 10A) the first plurality of cycles in response to the step of comparing.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
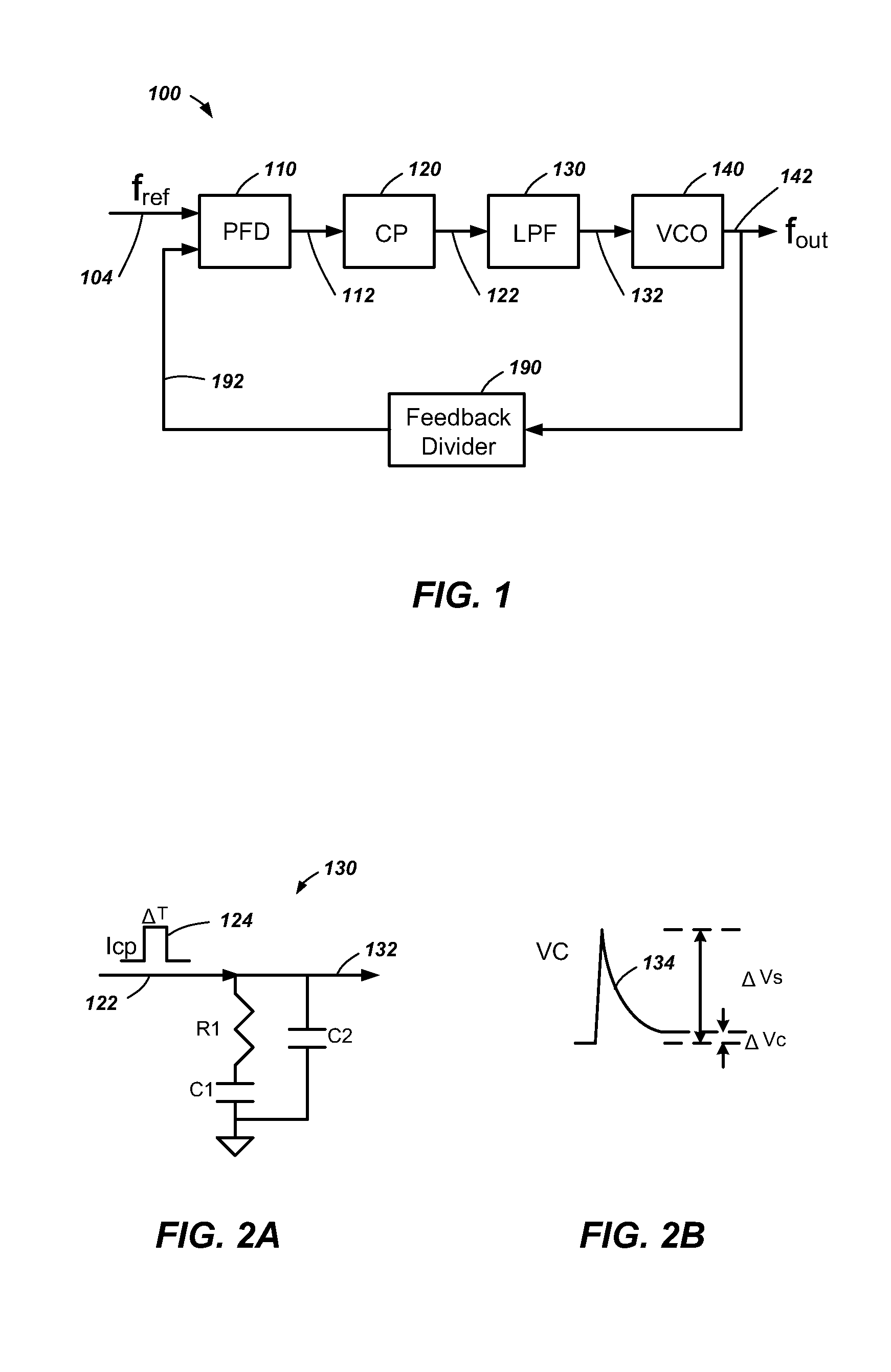
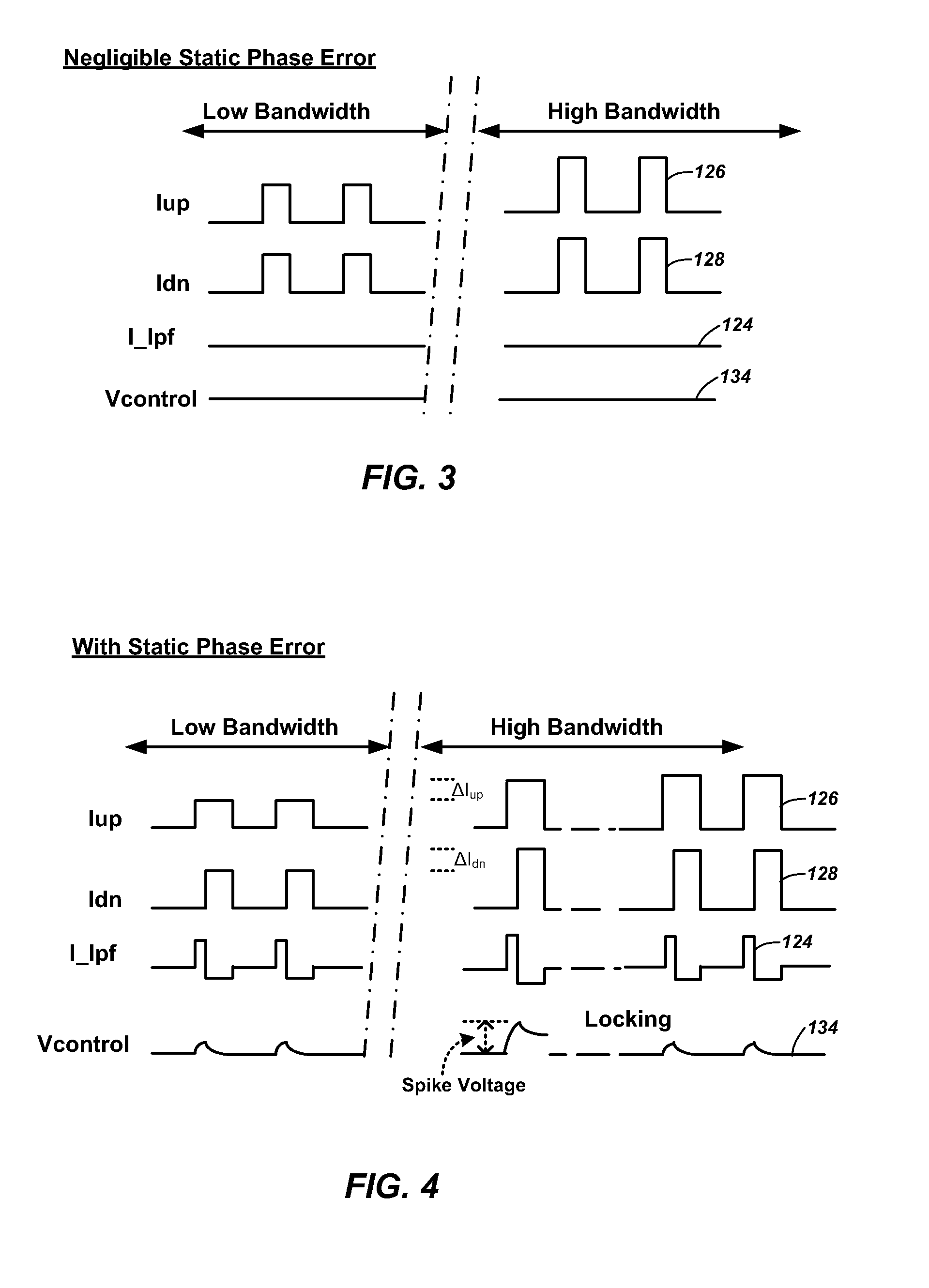
Methods and apparatuses for incremental bandwidth changes responsive to frequency changes of a phase-locked loop
In a phase-locked loop, a desired change in frequency is indicated. The phase-locked loop locks to the new frequency and a loop bandwidth of the phase-locked loop is changed. In changing the loop bandwidth, a frequency adjustment signal to a voltage-controlled oscillator may include a voltage spike. The voltage spike is reduced by detecting a lock when the reference clock and a feedback clock reach a same frequency, then waiting for a time delay after the detecting the lock, and adjusting a current level of a charge pump pulse by an incremental amount to achieve a fractional portion of a new loop bandwidth. The charge pump pulse is filtered to generate the frequency adjustment signal and the frequency spike reduction process is repeated until the new loop bandwidth is achieved.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com