Variable reluctance fast positioning system and methods
a positioning system and resistance technology, applied in the direction of magnets, manufacturing tools, magnets, etc., can solve the problems of hysteresis loss, imposing limits on the type, quality and rate at which the intended surface can be produced, and piezoelectrically actuated fts's also have significant disadvantages
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
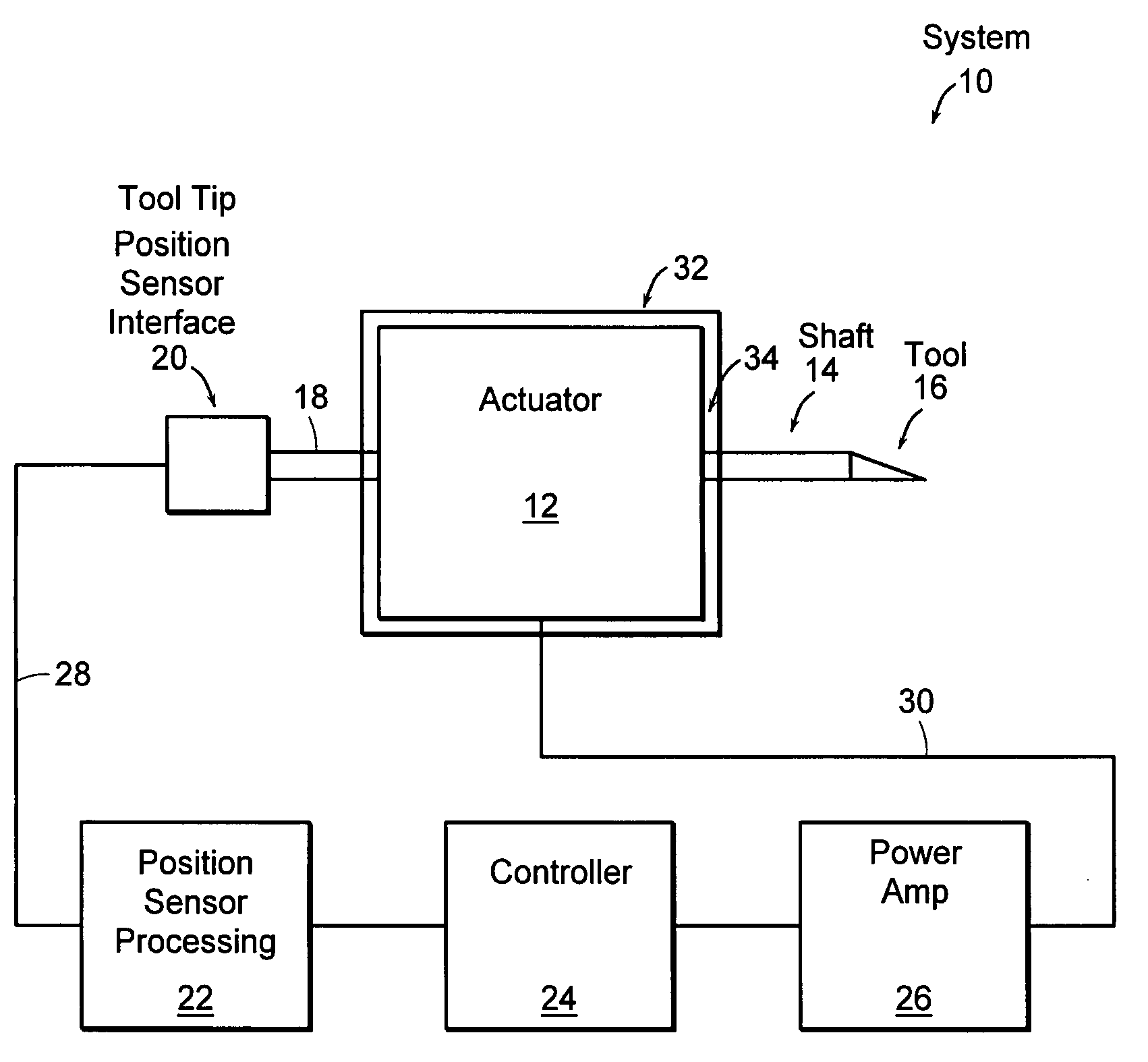
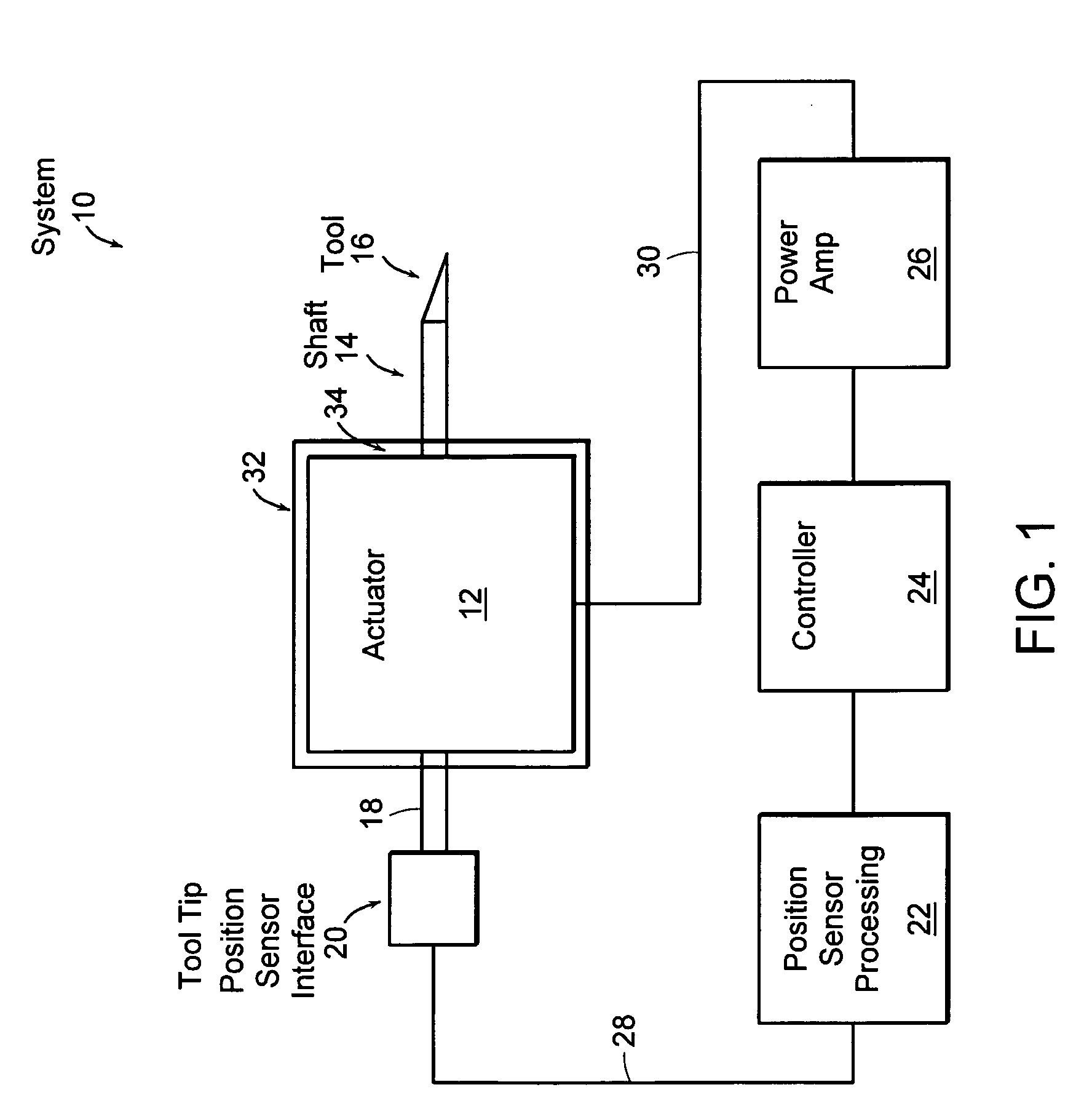
[0045]FIG. 1 illustrates a schematic representation of a system 10 consisting of linear fast tool servo (linear FTS) 12 having a shaft 14 and tool 16, a tool tip position sensor 18 having a position sensor interface 20 and a position sensor control and processing module 22, a controller 24 and a power amplifier 26. FTS 12 is an electromagnetic device that operates at very high speeds while allowing extremely precise control of tool tip 16. In fact, embodiments of FTS can operate at speeds on the order of 20 kHz while providing tool position accuracies on the order of 1 nanometer (nm).
[0046] Position sensor 18 is communicatively coupled to shaft 14 in a manner allowing the position of tool 16 to be monitored with respect to a reference. The reference may be a face 34 of a housing 32 surrounding components making up FTS 12, or the reference may be a gap between magnetic components, a point located external to housing 32, etc. Position sensor 18 may also include an interface 20 and co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com