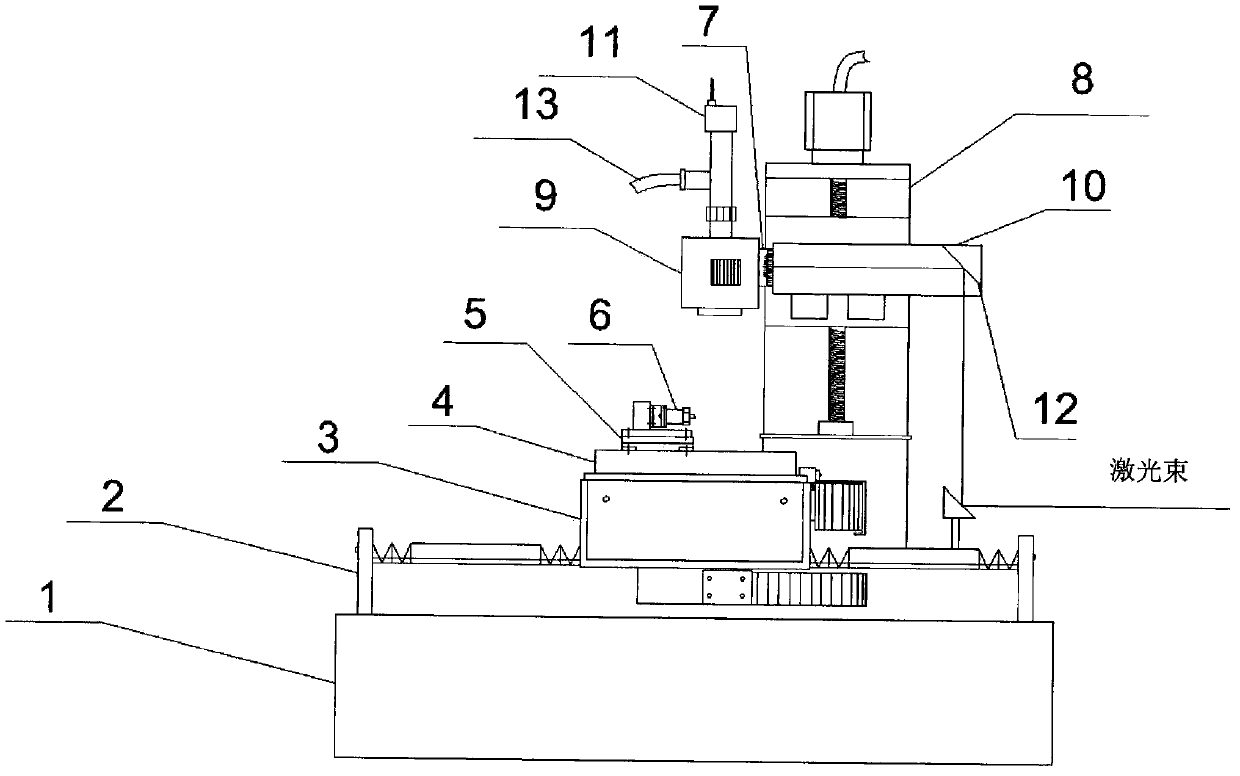
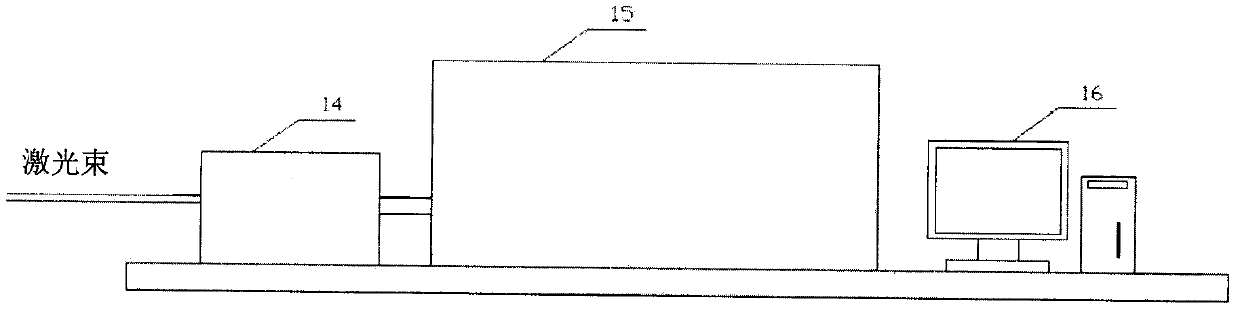
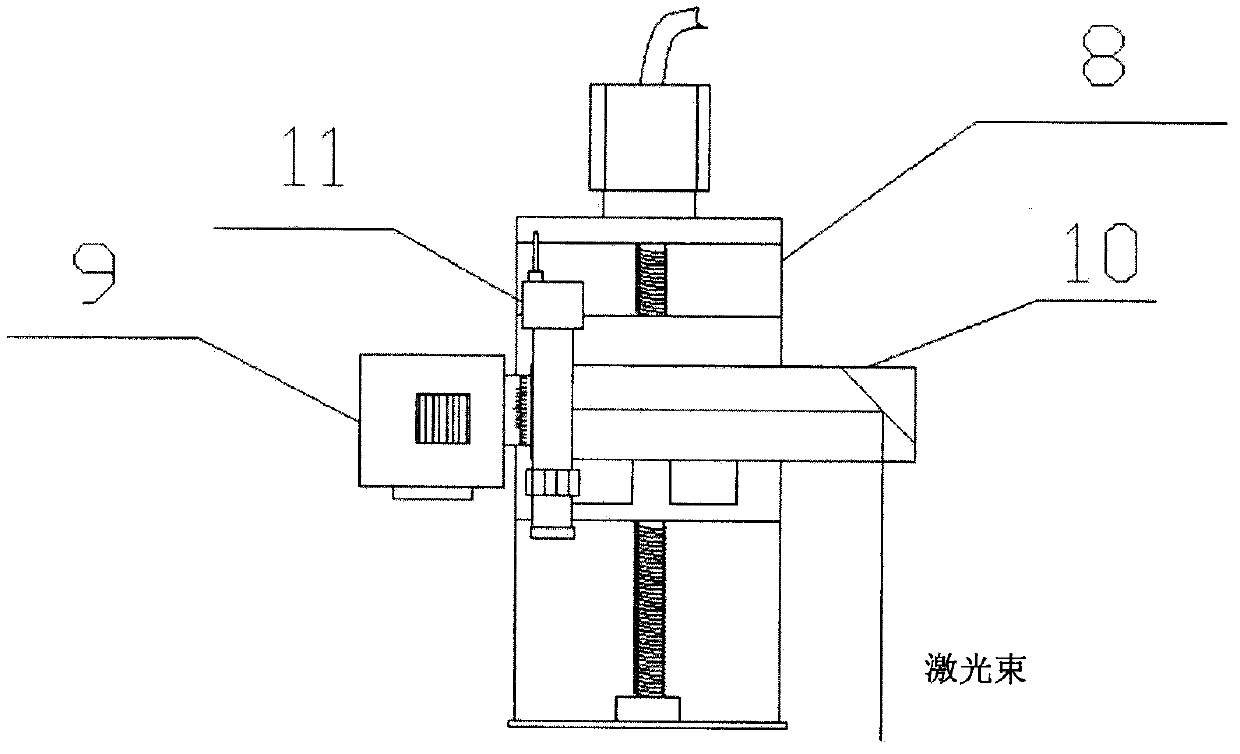
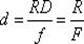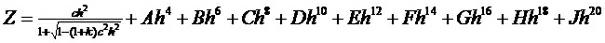Patents
Literature
131 results about "Diamond turning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diamond turning is turning with diamond as the cutting tool. It is a process of mechanical machining of precision elements using lathes or derivative machine tools (e.g., turn-mills, rotary transfers) equipped with natural or synthetic diamond-tipped tool bits. The term single-point diamond turning (SPDT) is sometimes applied, although as with other lathe work, the "single-point" label is sometimes only nominal (radiused tool noses and contoured form tools being options). The process of diamond turning is widely used to manufacture high-quality aspheric optical elements from crystals, metals, acrylic, and other materials. Plastic optics are frequently molded using diamond turned mold inserts. Optical elements produced by the means of diamond turning are used in optical assemblies in telescopes, video projectors, missile guidance systems, lasers, scientific research instruments, and numerous other systems and devices. Most SPDT today is done with computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools. Diamonds also serve in other machining processes, such as milling, grinding, and honing. Diamond turned surfaces have a high specular brightness and require no additional polishing or buffing, unlike other conventionally machined surfaces...
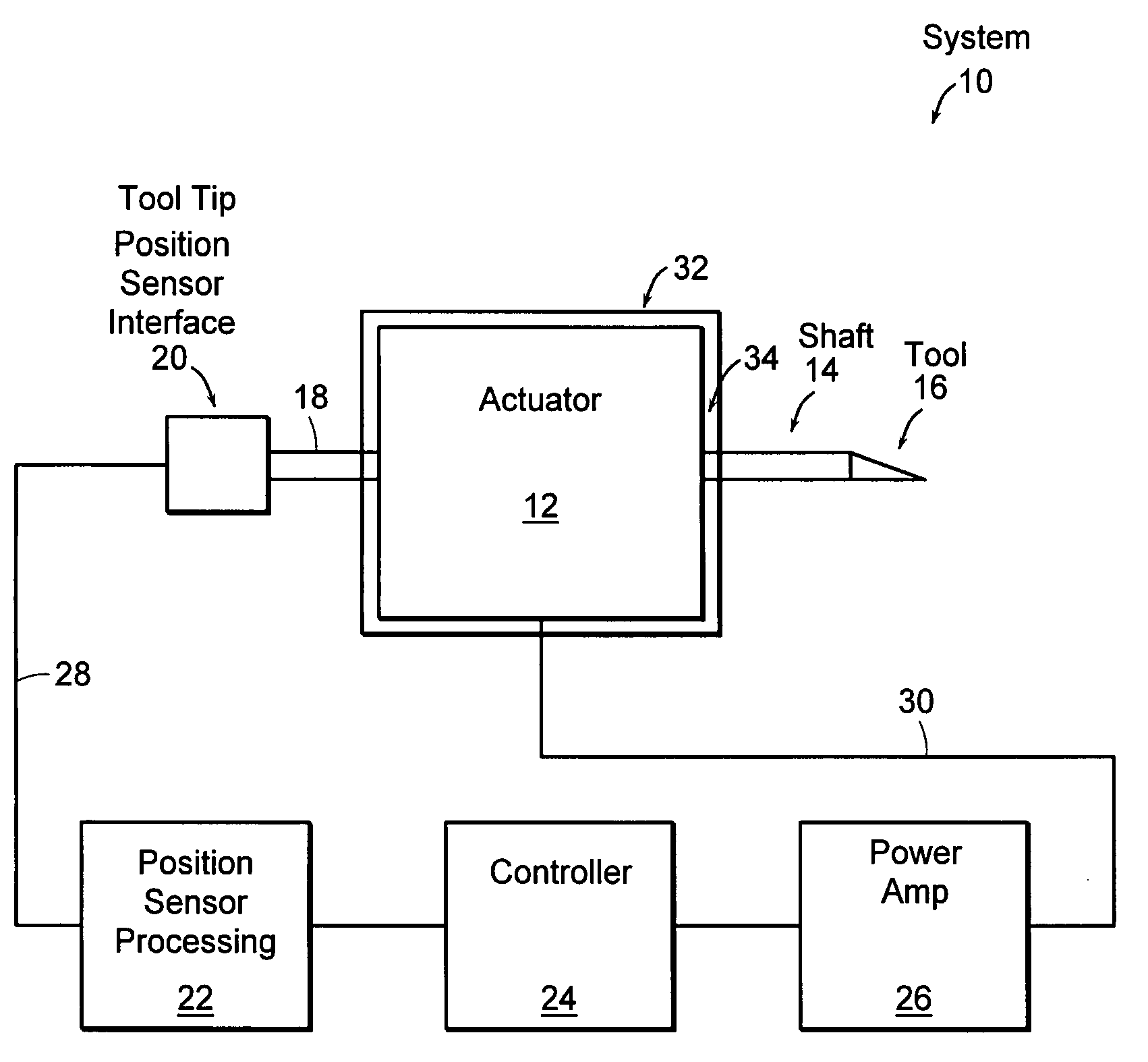
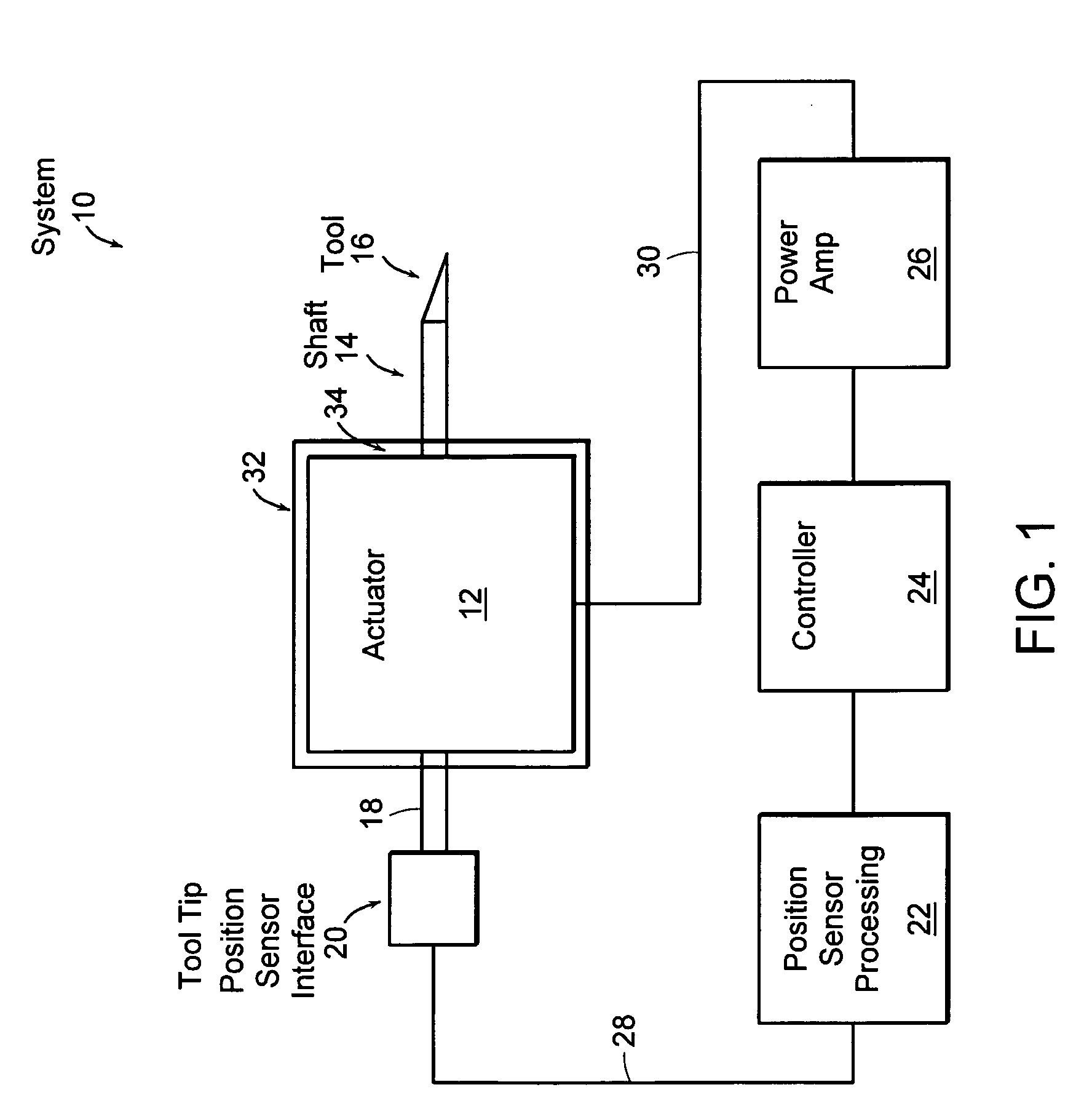
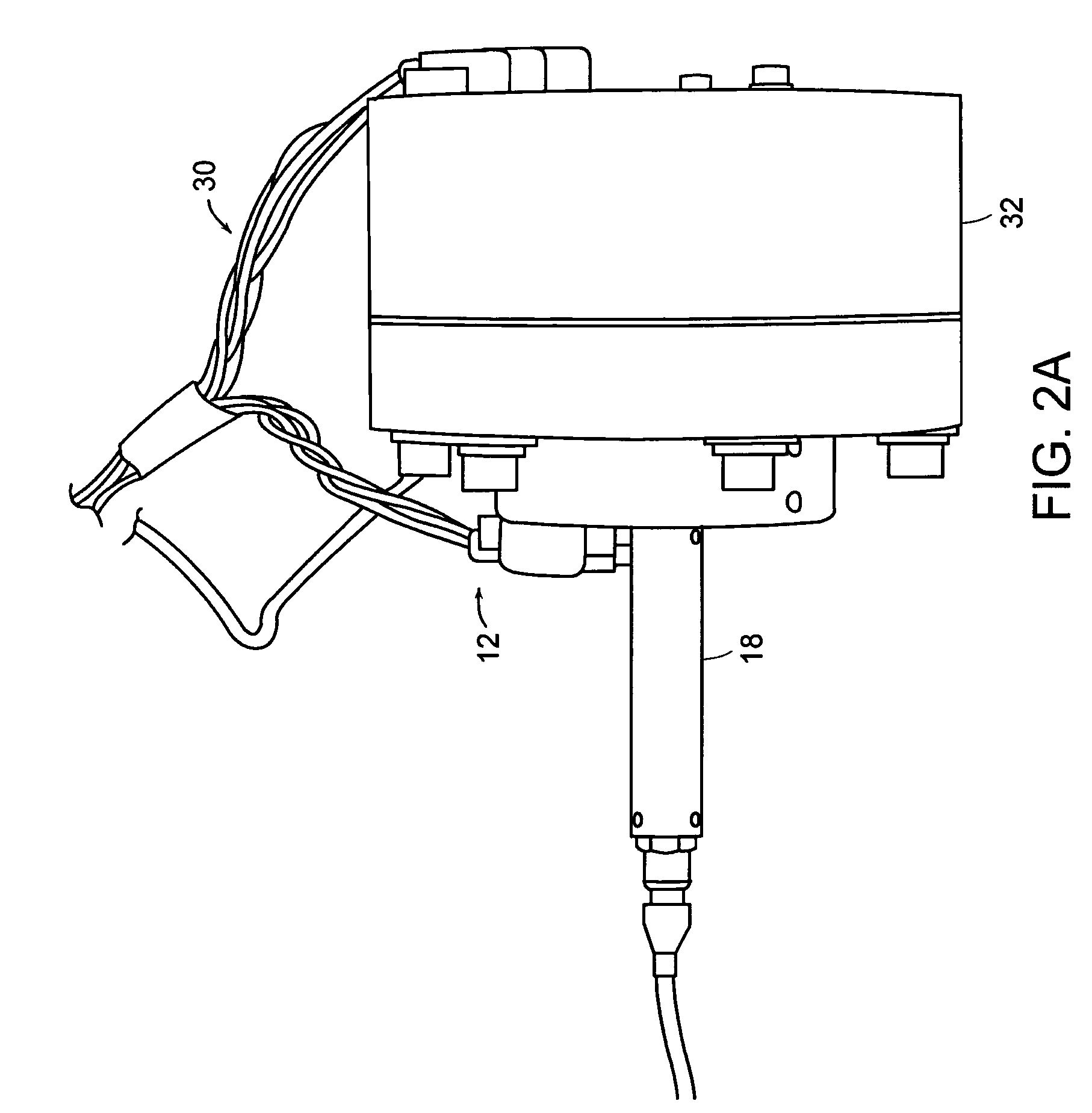
Variable reluctance fast positioning system and methods
InactiveUS20050223858A1Easy to operateElectromagnets without armaturesTurning machine accessoriesClosed loopLoop bandwidth
The preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to high bandwidth positioning systems such as fast tool servos (FTS). The applications of this invention include, for example, diamond turning of mold with structured surface for mass production of films for brightness enhancement and controlled reflectivity, diamond turning of molds for contact lens and micro-optical positioning devices. Preferred embodiments of the fast tool servo can have a closed-loop bandwidth of approximately 20±5 kHz, with acceleration of up to approximately 1000 G or more. The resolution or position error is approximately 1 nm root mean square (RMS). In a preferred embodiment, the full stroke of 50 μm can be achieved up tol kHz operation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
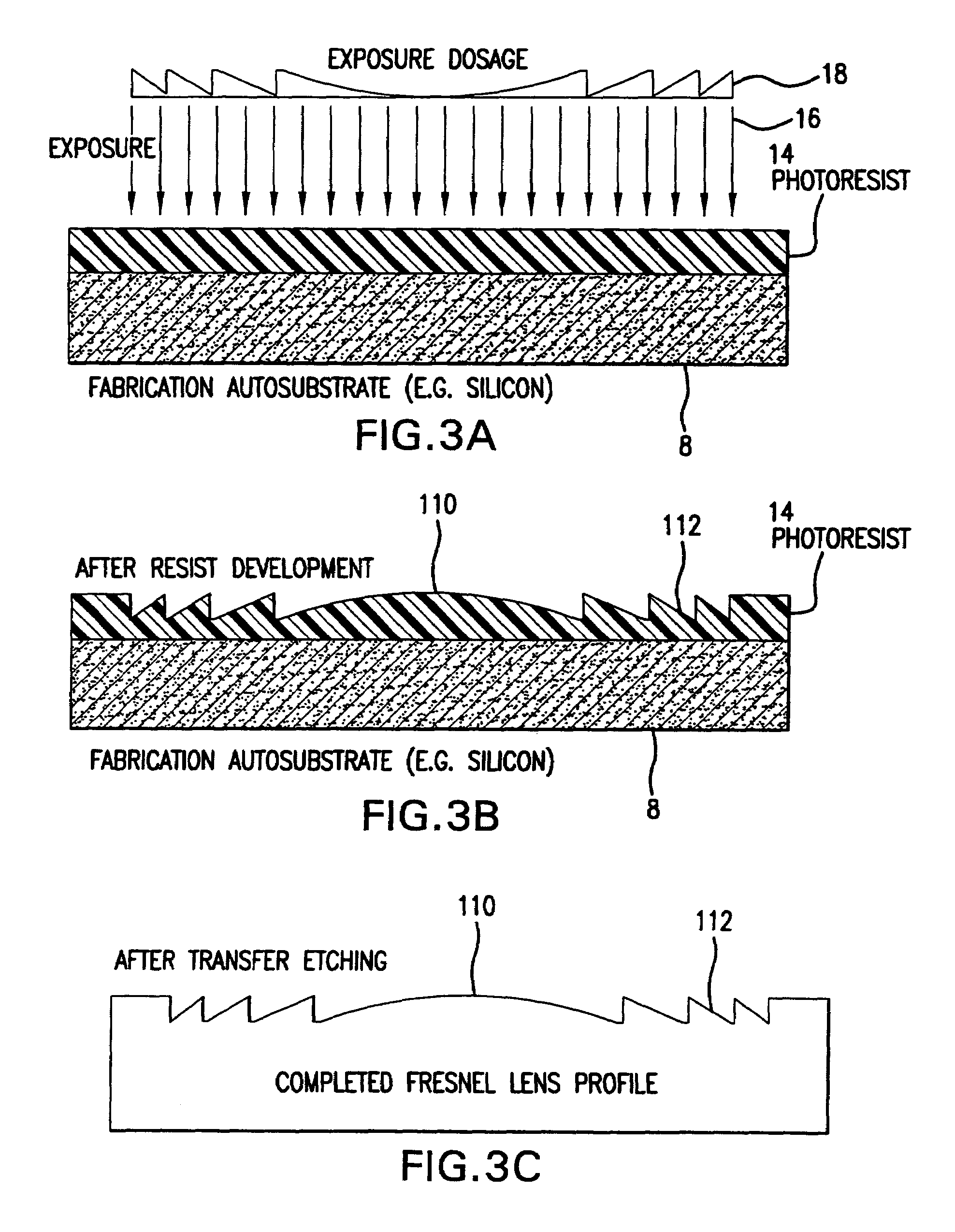
Fabrication Methods for Micro Compound Optics
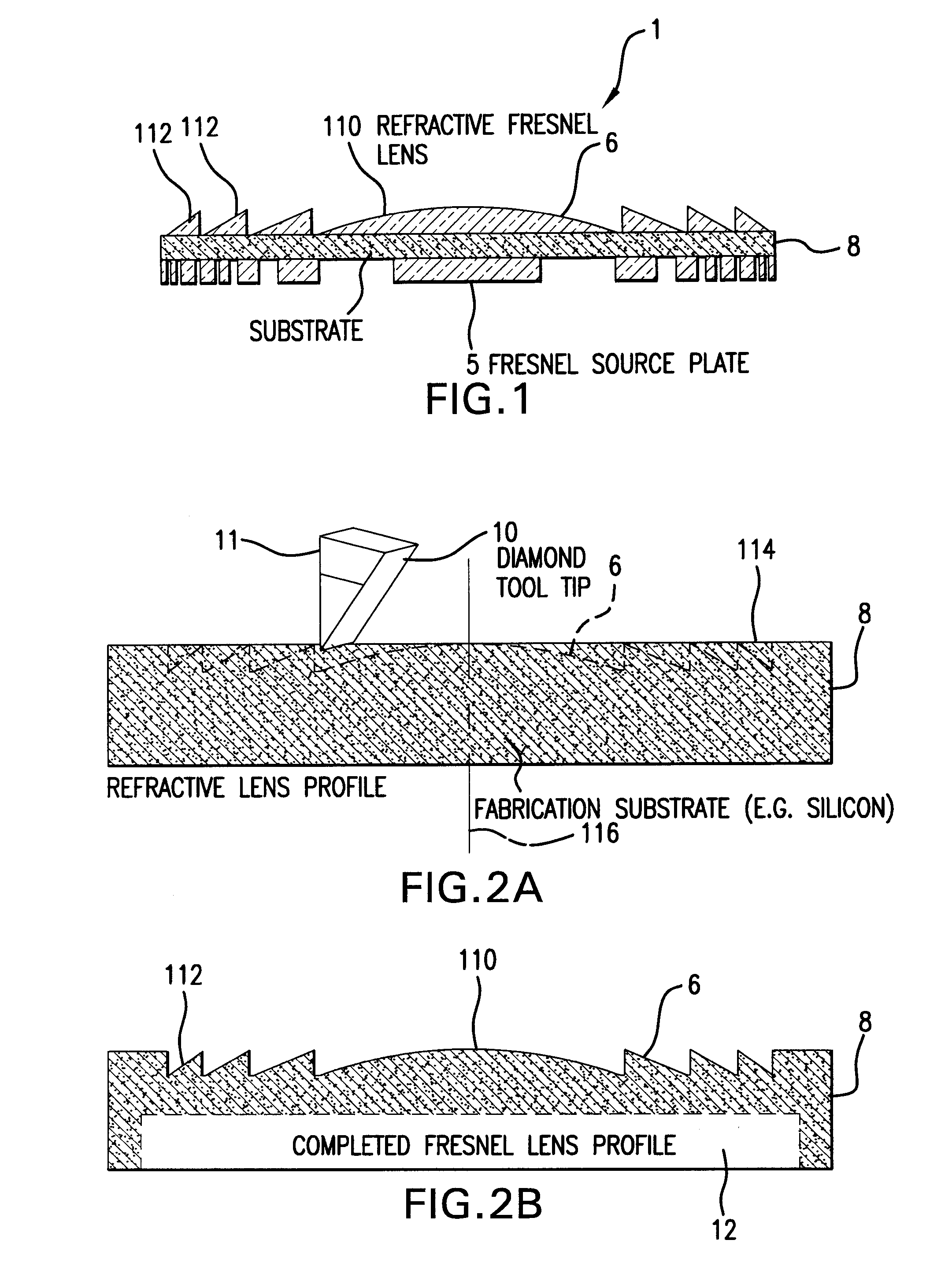
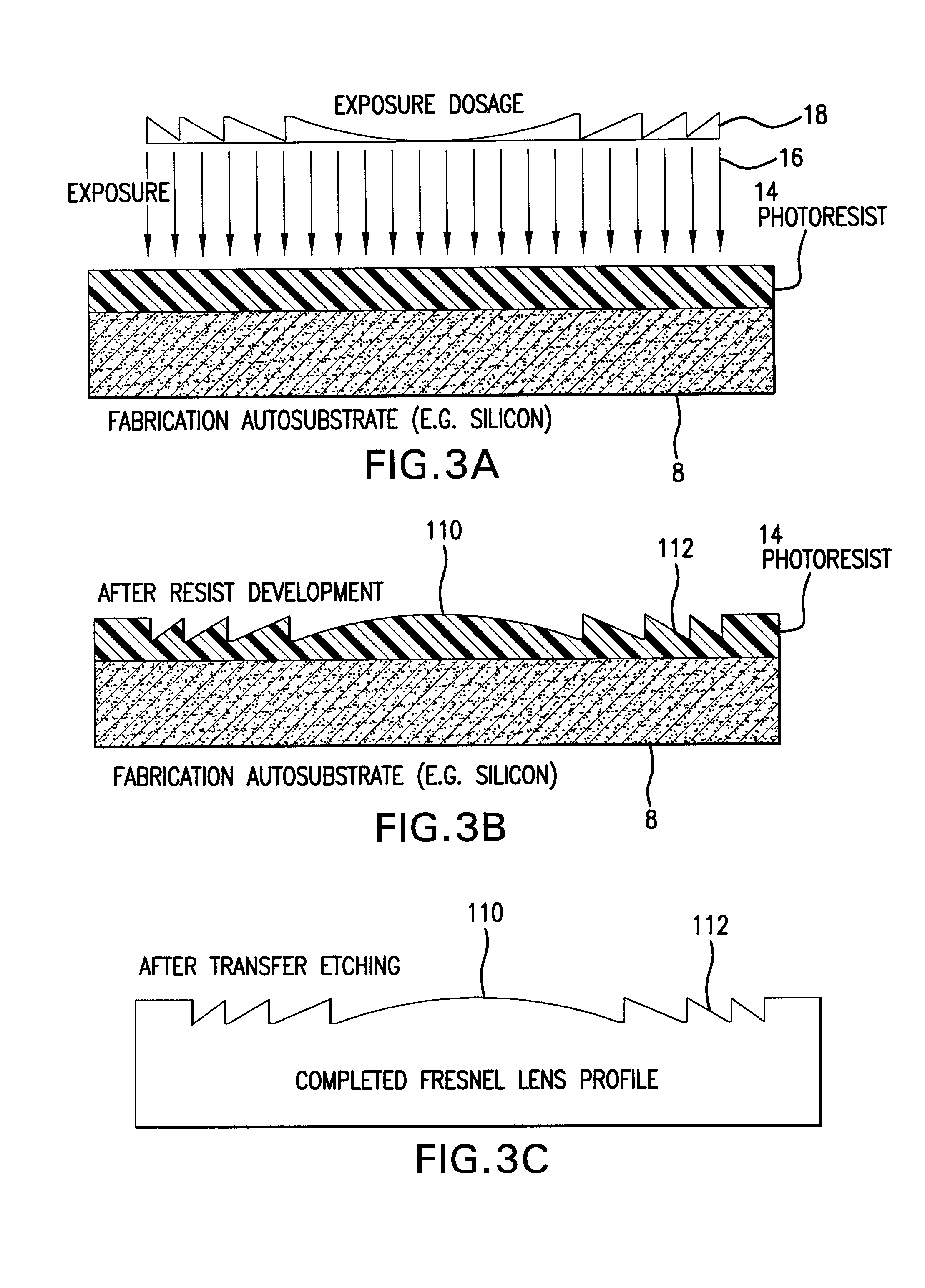
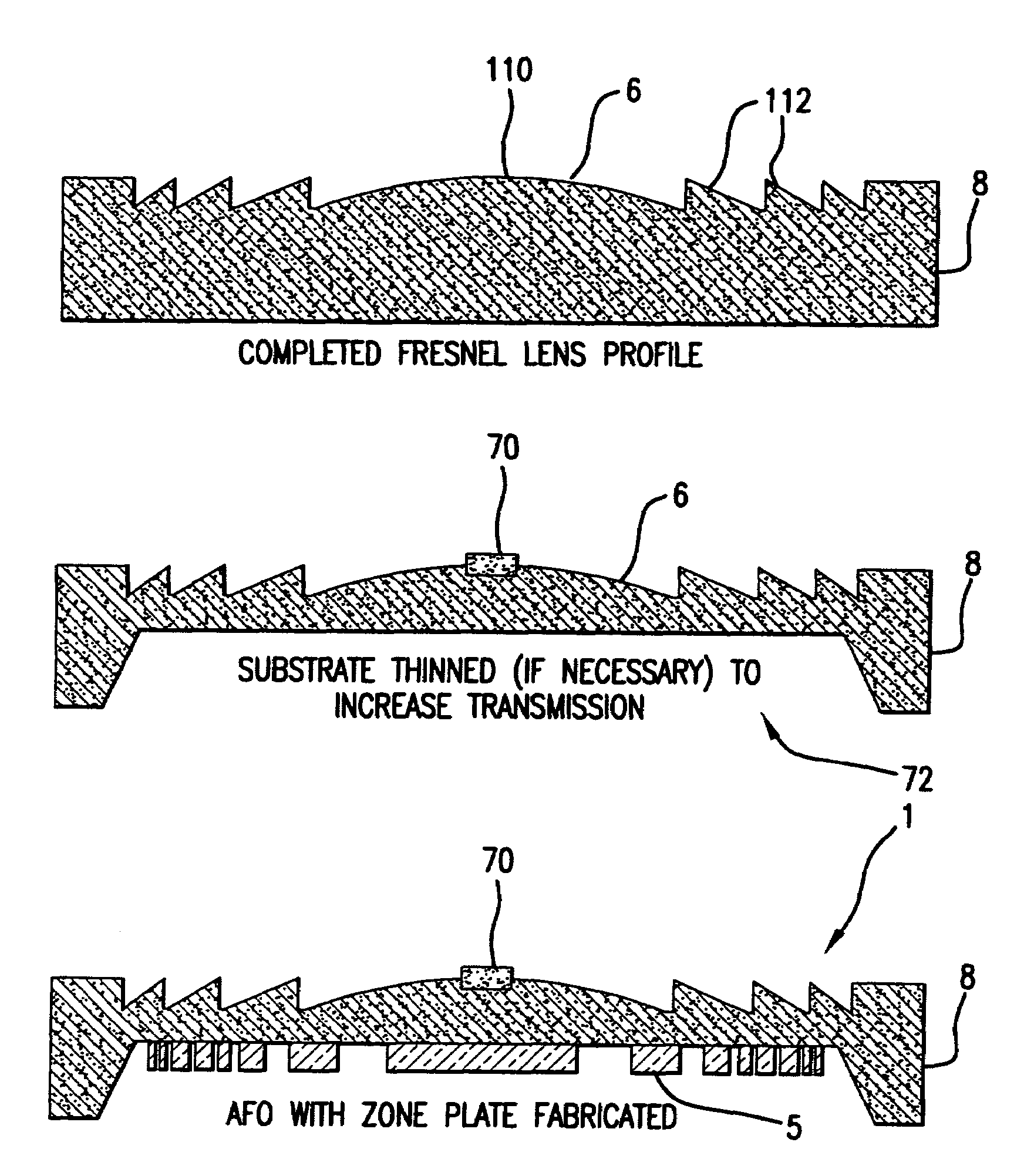
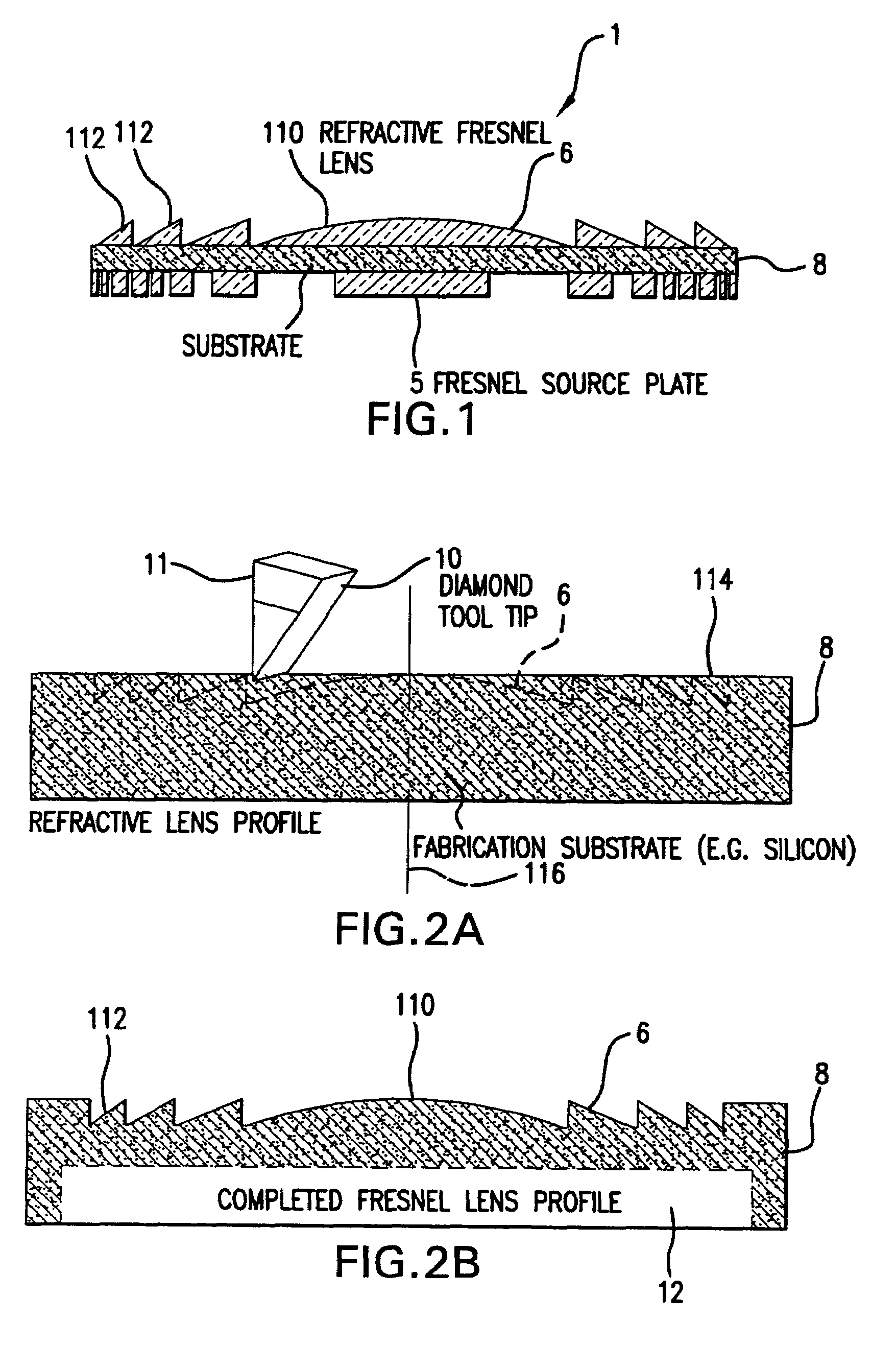
Methods for fabricating refractive element(s) and aligning the elements in a compound optic, typically to a zone plate element. The techniques are used for fabricating micro refractive, such as Fresnel, optics and compound optics including two or more optical elements for short wavelength radiation. One application is the fabrication of the Achromatic Fresnel Optic (AFO). Techniques for fabricating the refractive element generally include: 1) ultra-high precision mechanical machining, e.g,. diamond turning; 2) lithographic techniques including gray-scale lithography and multi-step lithographic processes; 3) high-energy beam machining, such as electron-beam, focused ion beam, laser, and plasma-beam machining; and 4) photo-induced chemical etching techniques. Also addressed are methods of aligning the two optical elements during fabrication and methods of maintaining the alignment during subsequent operation.
Owner:XRADIA
Fabrication methods for micro compounds optics
InactiveUS7365909B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDiamond turningLithographic artist
Methods for fabricating refractive element(s) and aligning the elements in a compound optic, typically to a zone plate element. The techniques are used for fabricating micro refractive, such as Fresnel, optics and compound optics including two or more optical elements for short wavelength radiation. One application is the fabrication of the Achromatic Fresnel Optic (AFO). Techniques for fabricating the refractive element generally include: 1) ultra-high precision mechanical machining, e.g,. diamond turning; 2) lithographic techniques including gray-scale lithography and multi-step lithographic processes; 3) high-energy beam machining, such as electron-beam, focused ion beam, laser, and plasma-beam machining; and 4) photo-induced chemical etching techniques. Also addressed are methods of aligning the two optical elements during fabrication and methods of maintaining the alignment during subsequent operation.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
High-efficiency and high-precision detection device for circular arc roundness of cutter point of diamond cutter
ActiveCN103234481AOvercome the defect of small measurement rangeSolving Precision Measurement ProblemsUsing optical meansDiamond turningThree dimensional measurement
The invention provides a high-efficiency and high-precision detection device for circular arc roundness of a cutter point of a diamond cutter and belongs to the technical field of cutter detection devices. A precision air flotation shafting is vertically arranged at the center of a vibration isolation platform; a fine-aligning device is fixedly arranged at the upper end part of the precision air flotation shafting; a cutter fixture is fixedly arranged at the upper part of the fine-aligning device; a stereoscopic microscope system is arranged above the cutter fixture; and an atomic force microscope (AFM) system is arranged above one side of the cutter fixture. According to the high-efficiency and high-precision detection device disclosed by the invention, the stereoscopic microscope system assists the fine-aligning device in aligning, so that the aligning precision is increased, the defect that the measurement range of the AFM is narrow is overcome, and three-dimensional measurement with high measurement precision is realized; the problem of precision measurement of the circular arc roundness of the cutter point of the diamond cutter with a circular arc edge can be solved; and measurement data of the circular arc roundness can be used for reflecting dynamic characteristic of a cutter grinding machine, evaluating the cutter grinding quality of the cutter and providing data support for cutter compensation in the numeric control single-point diamond turning.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and device for femtosecond laser preparation of diamond tool
PendingCN109926731ANo macro forceNo macro force, no high requirements on machine tool rigidityLaser beam welding apparatusTool bitNumerical control
The invention relates to a method and device for femtosecond laser preparation of a diamond tool, and belongs to the field of laser processing and machining. According to the method, a numerical control platform designed specially is used for mounting and positioning the diamond tool, and the angle and height position of a femtosecond laser galvanometer can be adjusted simultaneously, so that cutting and polishing requirements of the diamond tool are met. In the process, the machining position of the tool can be adjusted through a precision multi-axis positioning system on a machine tool, so that the machining precision is guaranteed. The method and device are applicable to laser processing of arc-blade diamond tool, laser cutting and polishing machining of an arc blade of a diamond tool bit can be realized through deflection of the laser galvanometer and constant-speed rotation of a tool base, and a sharp and complete tool cutting edge can be obtained. The method and device are applicable to cutting and polishing preparation of traditional diamond turning and milling tools and diamond micro milling and turning tools simultaneously. The special device comprises three parts including a tool clamping device, a multi-axis laser processing system and a femtosecond laser.
Owner:夏浥
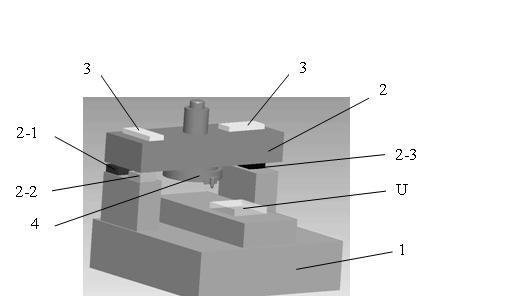
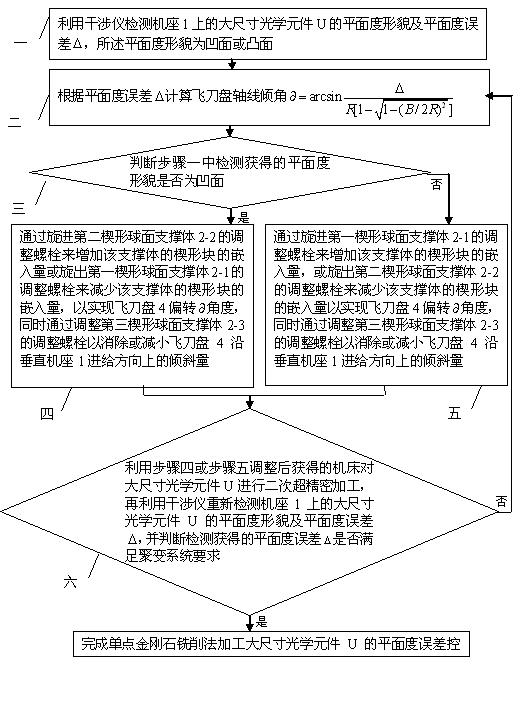
Flatness error control method for single-point diamond turning method machining large-sized optical elements
InactiveCN101870002AGuaranteed to be always verticalAvoid repeated processingAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusDiamond turningControl theory
The invention relates to a flatness error control method for the single-point diamond turning method machining large-sized optical elements, which relates to the field of the ultraprecision machining of large-sized fragile optical elements. The invention solves the problems that: when the conventional SPDT method machines a large-sized optical element, the flatness error is high, and the surface figure precision can be hardly guaranteed. The flatness error control method first utilizes an interferometer to detect the flatness topography and the flatness error Delta of a large-sized optical element on a bed, the inclination angle of the axis of a fly-cutter head is then calculated according to the flatness error Delta, three wedged spherical supporting bodies are adjusted according to the detected flatness topography, so that the angle of the fly-cutter head can be deflected, the adjusted machine tool is finally utilized to carry out the secondary ultraprecision machining of the optical element, the interferometer is utilized again to redetect the flatness topography and the flatness error Delta, and when the flatness error Delta meets the requirement of a fusion system, flatness error control is fulfilled for the single-point diamond turning method machining the large-sized optical element. The invention is applicable to the machining of the surface figures of large-sized optical elements.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
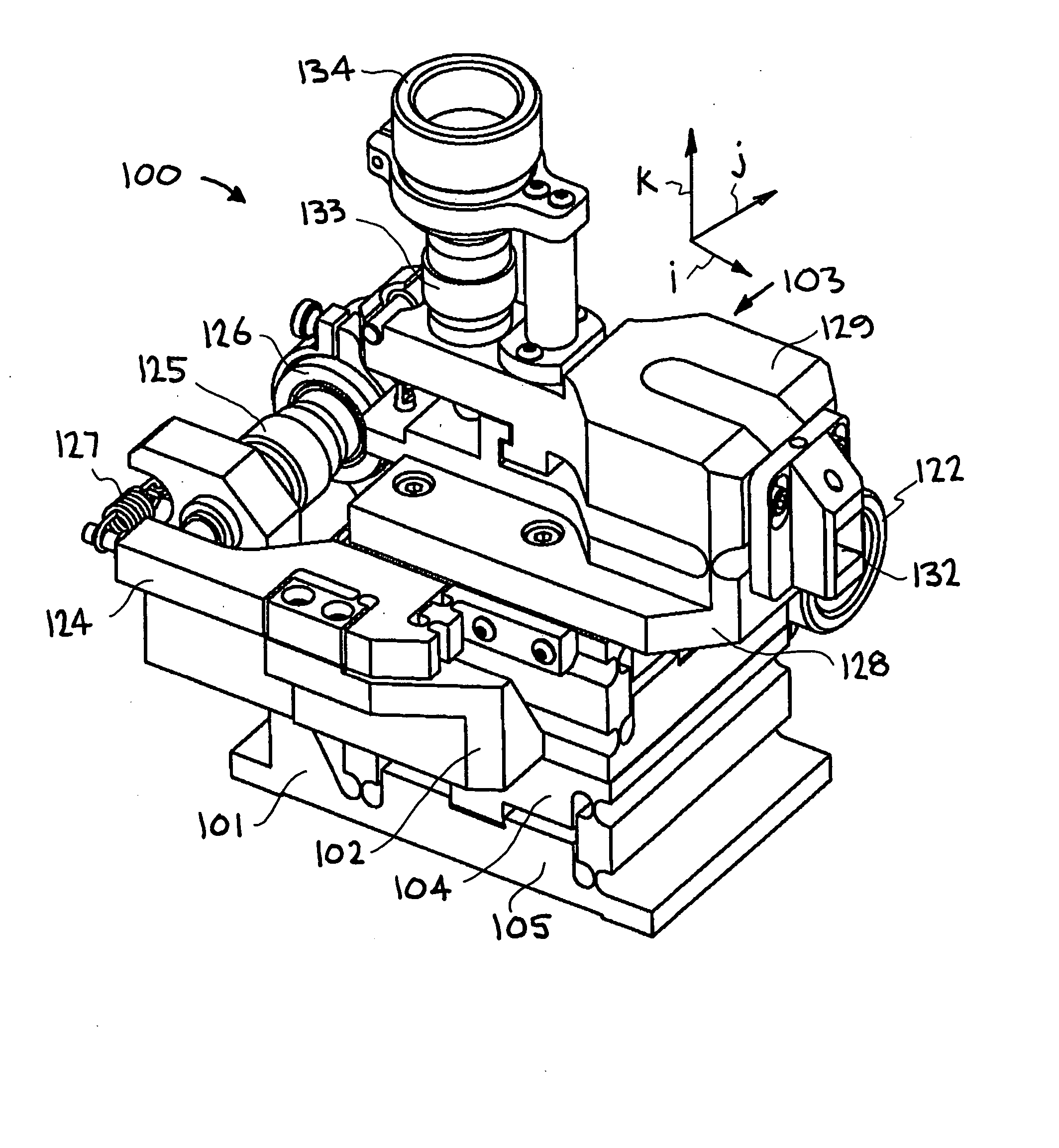
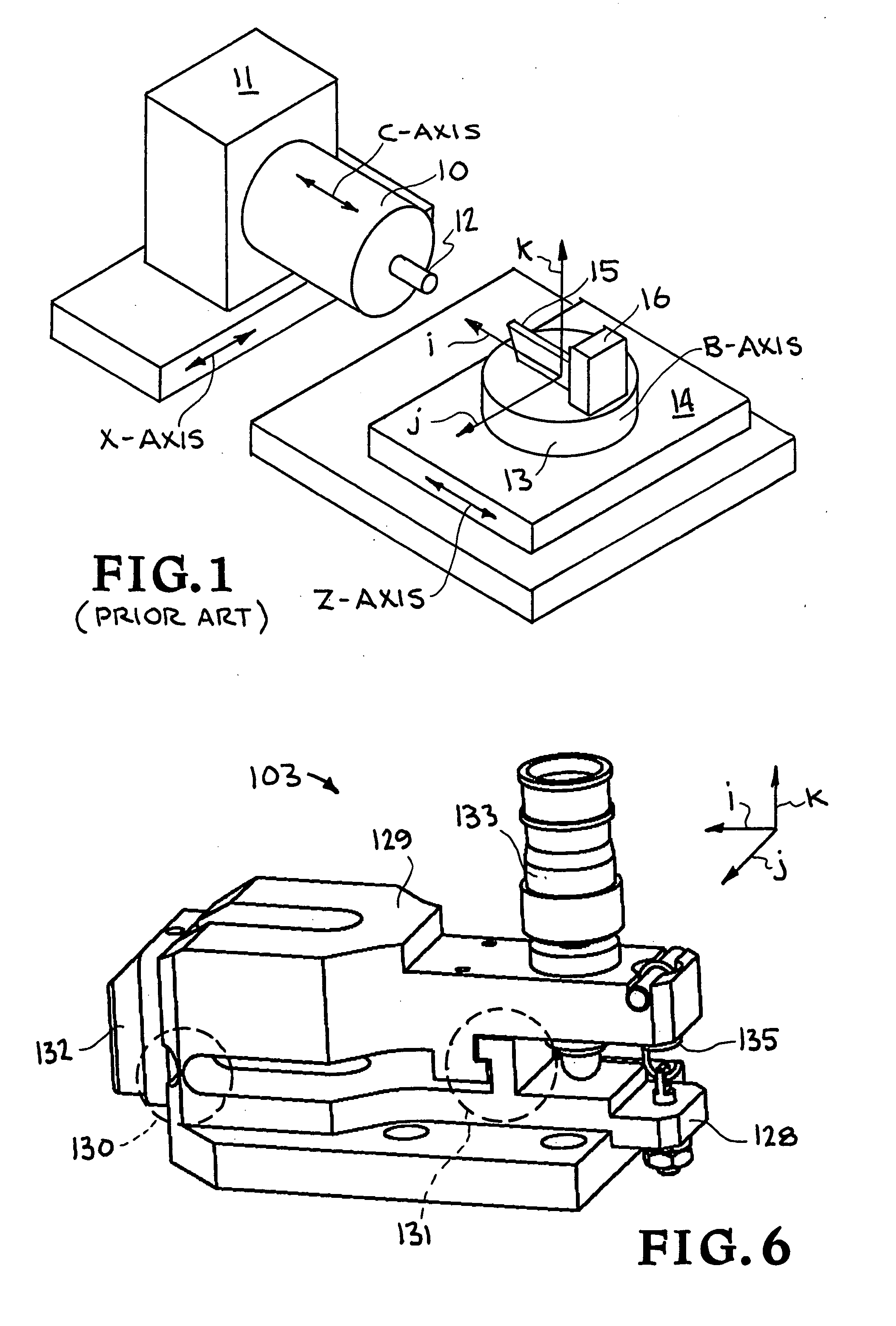
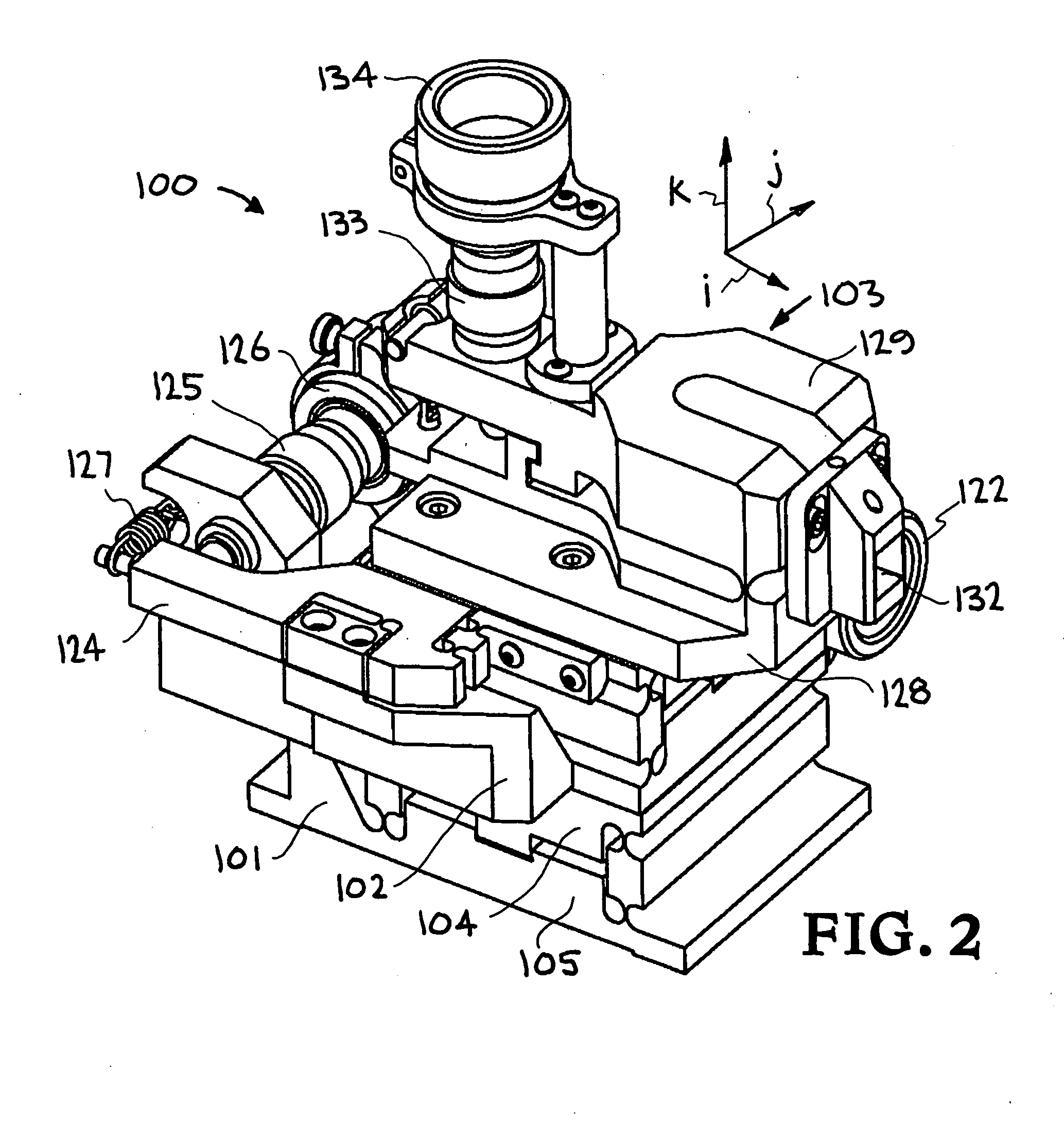
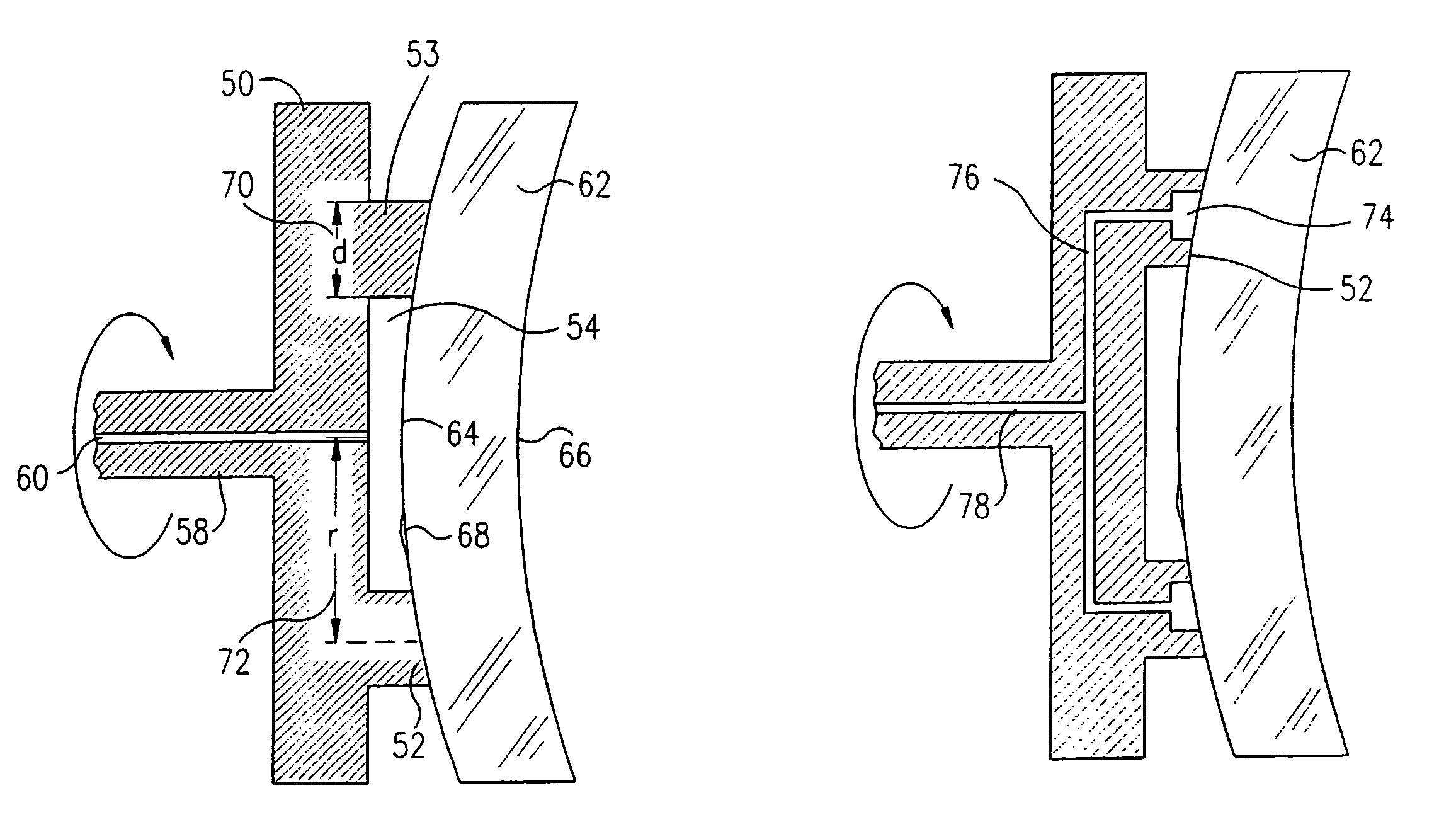
Precision tool holder with flexure-adjusted, three degrees of freedom for a four-axis lathe
InactiveUS20070261522A1Precise positioningMinimum errorLathesAutomatic/semiautomatic turning machinesDiamond turningThree degrees of freedom
A precision tool holder for precisely positioning a single point cutting tool on 4-axis lathe, such that the center of the radius of the tool nose is aligned with the B-axis of the machine tool, so as to facilitate the machining of precision meso-scale components with complex three-dimensional shapes with sub-μm accuracy on a four-axis lathe. The device is designed to fit on a commercial diamond turning machine and can adjust the cutting tool position in three orthogonal directions with sub-micrometer resolution. In particular, the tool holder adjusts the tool position using three flexure-based mechanisms, with two flexure mechanisms adjusting the lateral position of the tool to align the tool with the B-axis, and a third flexure mechanism adjusting the height of the tool. Preferably, the flexures are driven by manual micrometer adjusters. In this manner, this tool holder simplifies the process of setting a tool with sub-μm accuracy, to substantially reduce the time required to set the tool.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Optical component surface cleaning method based on ion beam polishing
The invention discloses an optical component surface cleaning method based on ion beam polishing. The method comprising the following steps of: machining the surface of a machining object by adopting an ion beam polishing method based on a low-energy ion sputtering principle by taking an optical component subjected to single-point diamond turning or magnetorheological polishing as the machining object; during the machining process, controlling ion beams to uniformly sweep the surface of the optical component; and after the machining is concluded, cleaning the surface of the optical component. The optical component surface cleaning method disclosed by the invention is simple and practicable, low in requirements on equipment, and capable of reducing the surface roughness of the optical surface component and removing the surface impurities of the optical component.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
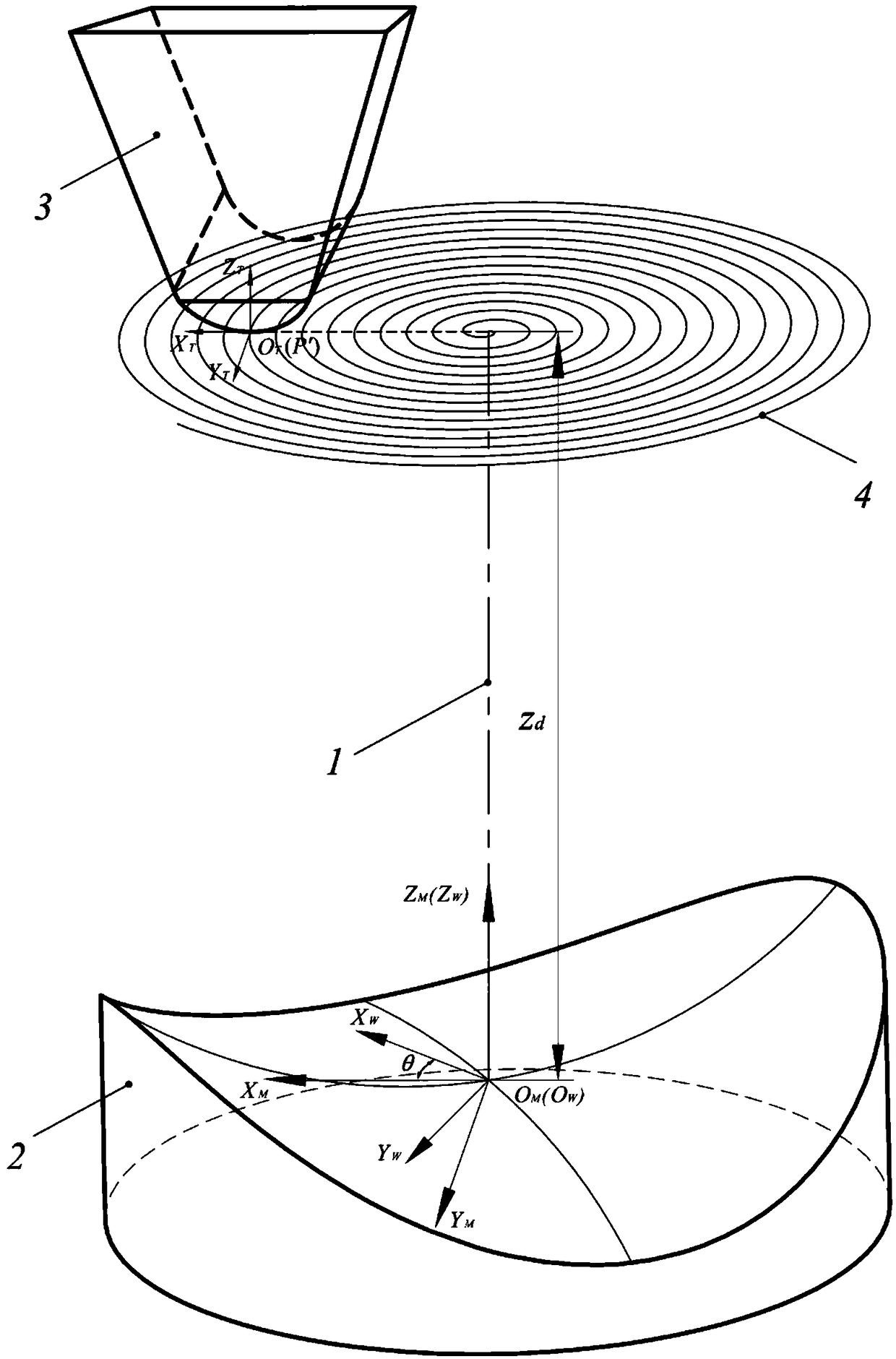
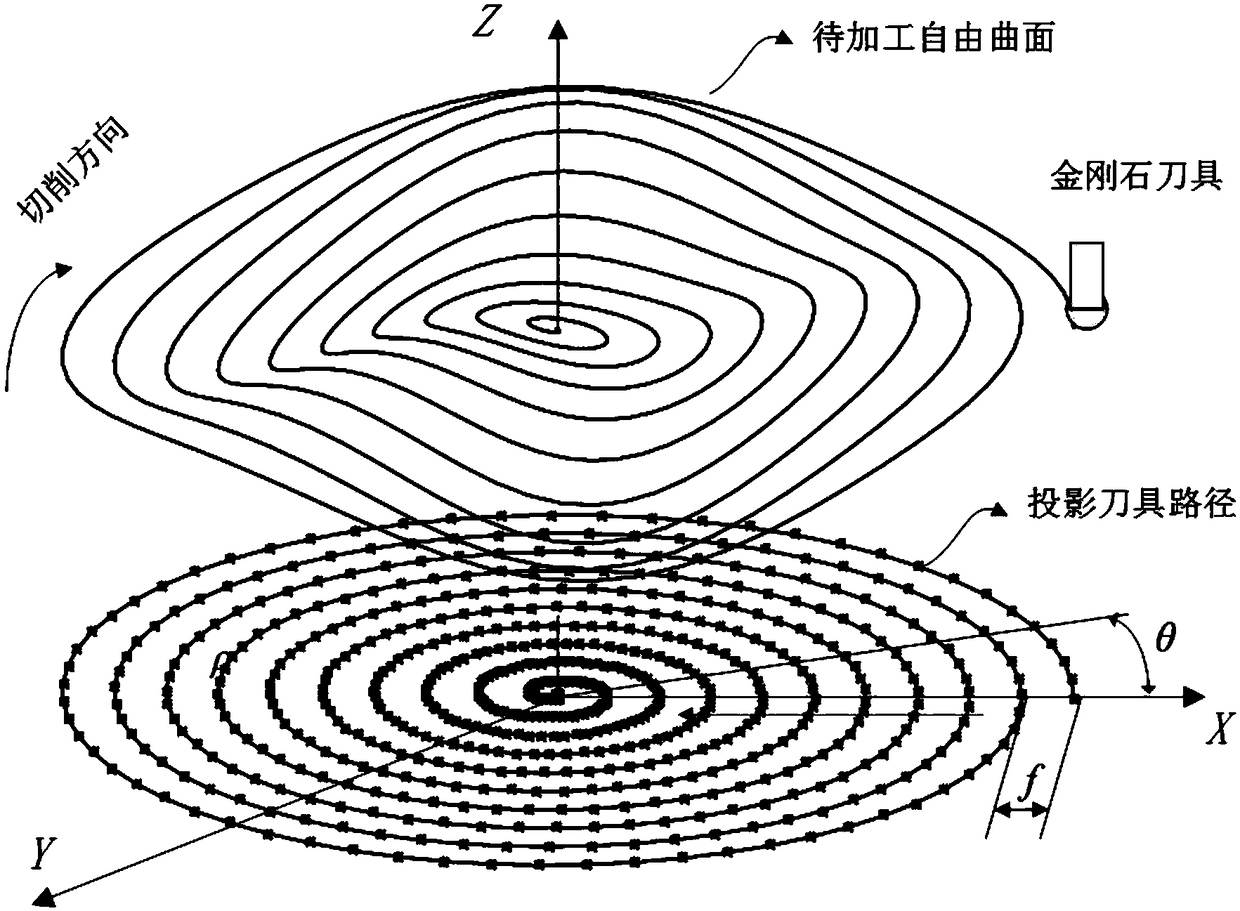
Method for generating free-form surface turning tool path through control point drive projection
The invention relates to a method for generating a free-form surface turning tool path through a control point drive projection. The method comprises the steps that a plane perpendicular to the Z axisof a workpiece coordinate system is built at the position zd away from the top of the to-be-processed free-form surface in the workpiece coordinate system, an equidistant spiral line is generated inthe plane and discretized, discretized points are converted into a cylindrical coordinate system (rho, theta, zd), the to-be-processed free-form surface is rotated by the angle theta around the Z axis, the smallest distance delta between each point of the tool edge curve on the equidistant spiral line and the rotated to-be-processed free-form surface is calculated, and therefore the coordinate (rho, 0, zd-delta) of the tool control point is obtained, wherein a tool is a cylindrical turning tool. The projection driving track of the tool control point is preferentially generated, and stability of feeding movement of the tool in the X direction is ensured. By means of the method, a universal model of cylindrical diamond turning tools rather than only zero degree front angle tools is built, and the defects of traditional tool path design methods are overcome.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
The Processing Method of Improving the Center Deviation Precision of Aspheric Lens
InactiveCN102269830AHigh precisionGuaranteed coincidenceOptical surface grinding machinesLensDiamond turningOptical axis
The invention discloses a processing method for improving a central deviation precision of a non-spherical lens. When processing is carried out, an excircle of a lens is not directly ground to a completed size and a certain allowance is left; after processing by a spherical surface of a point diamond turning and an optimum fitting spherical surface, surface shape of a spherical surface is refined, so that a surface shape precision of the spherical surface is improved. When the surface shape of the spherical surface is being refined, a point diamond turning mode is changed, so that a central deviation is ensured. After the refinement, a reflective centering edging operation is added to correct the central deviation. Firstly, it is ensured that an optical axis of the spherical surface is superposed with a symmetric axis of the excircle of the lens and a platform is perpendicular to the optical axis; and secondly, positioning is carried out according to the processed excircle and the platform and a non-spherical surface shape that satisfies a precision requirement is made by utilizing the changed point diamond turning mode, so that a non-spherical optical axis is consistent with symmetric axis of the excircle of the lens. Because the reflective centering operation is reasonably arranged, an eccentric error caused during refinement and polishing of the surface shape of the spherical surface is improved and thus a central deviation precision of the non-spherical lens is enhanced.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
High-precision large-stroke triaxial fast cutter servo device
ActiveCN102069411AInhibition of lateral movementLarge non-rotational symmetryMeasurement/indication equipmentsFeeding apparatusDiamond turningGrating
The invention discloses a high-precision large-stroke triaxial fast cutter servo device, which belongs to the technical fields of ultra-precision processing, optical component processing and the like, and is suitable for turning and generating a free-form surface diamond with larger non-rotational symmetry. The device is provided with two voice coil motors respectively driving a flexible hinge mechanism so as to make a diamond cutter quickly reciprocate respectively in an X direction and a Z direction, and a fine adjustment mechanism is driven by a piezoelectric stack actuator so as to eliminate additional motion in a Y direction; and two linear gratings are used for respectively detecting the displacements of the diamond cutter in the X direction and the Y direction, and a capacitance sensor is used for detecting the additional displacement in the Y direction. The invention has the advantage of realizing high-precision large-stroke fast reciprocating motion simultaneously in the X direction and the Z direction.
Owner:苏州市利恒精工机械有限责任公司
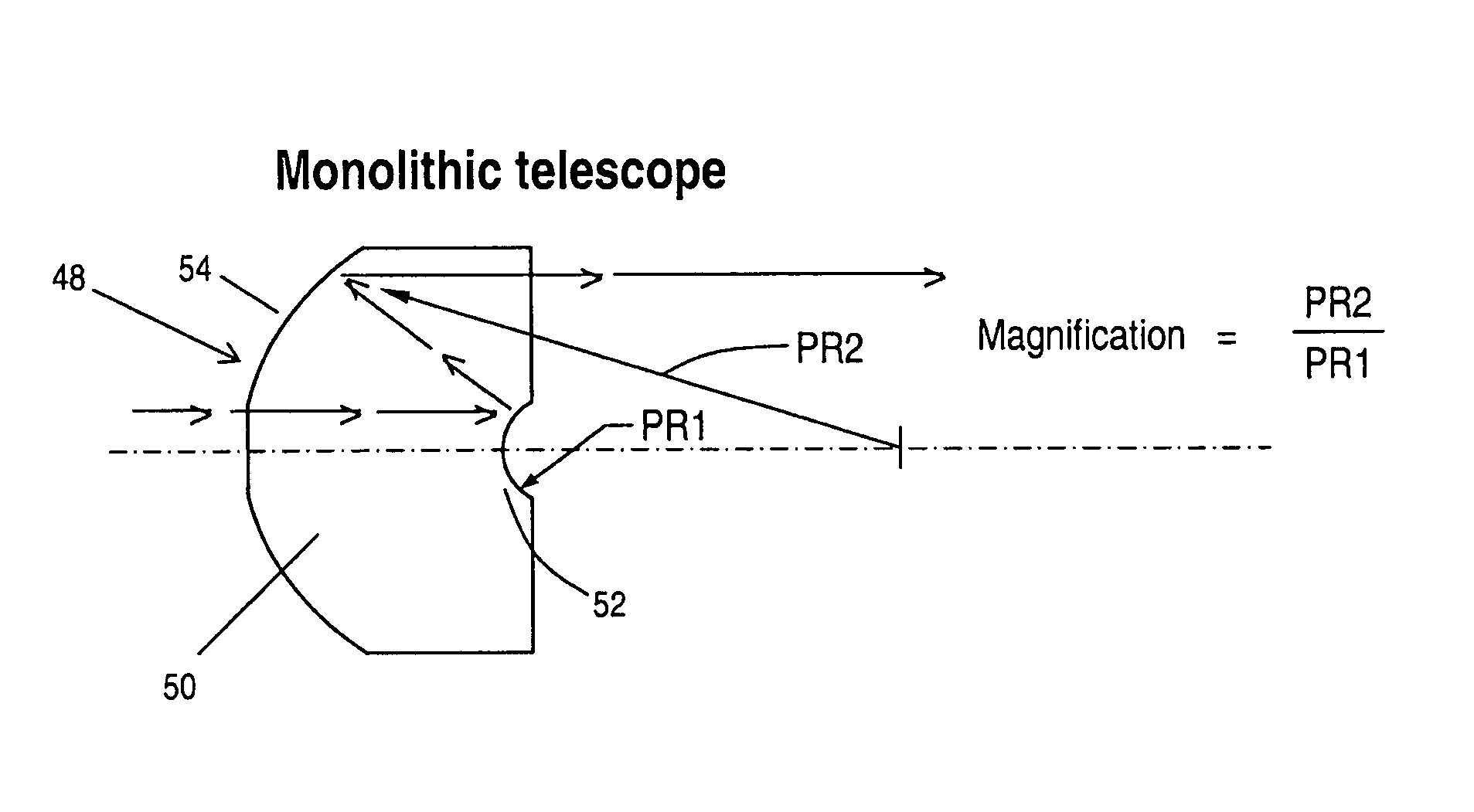
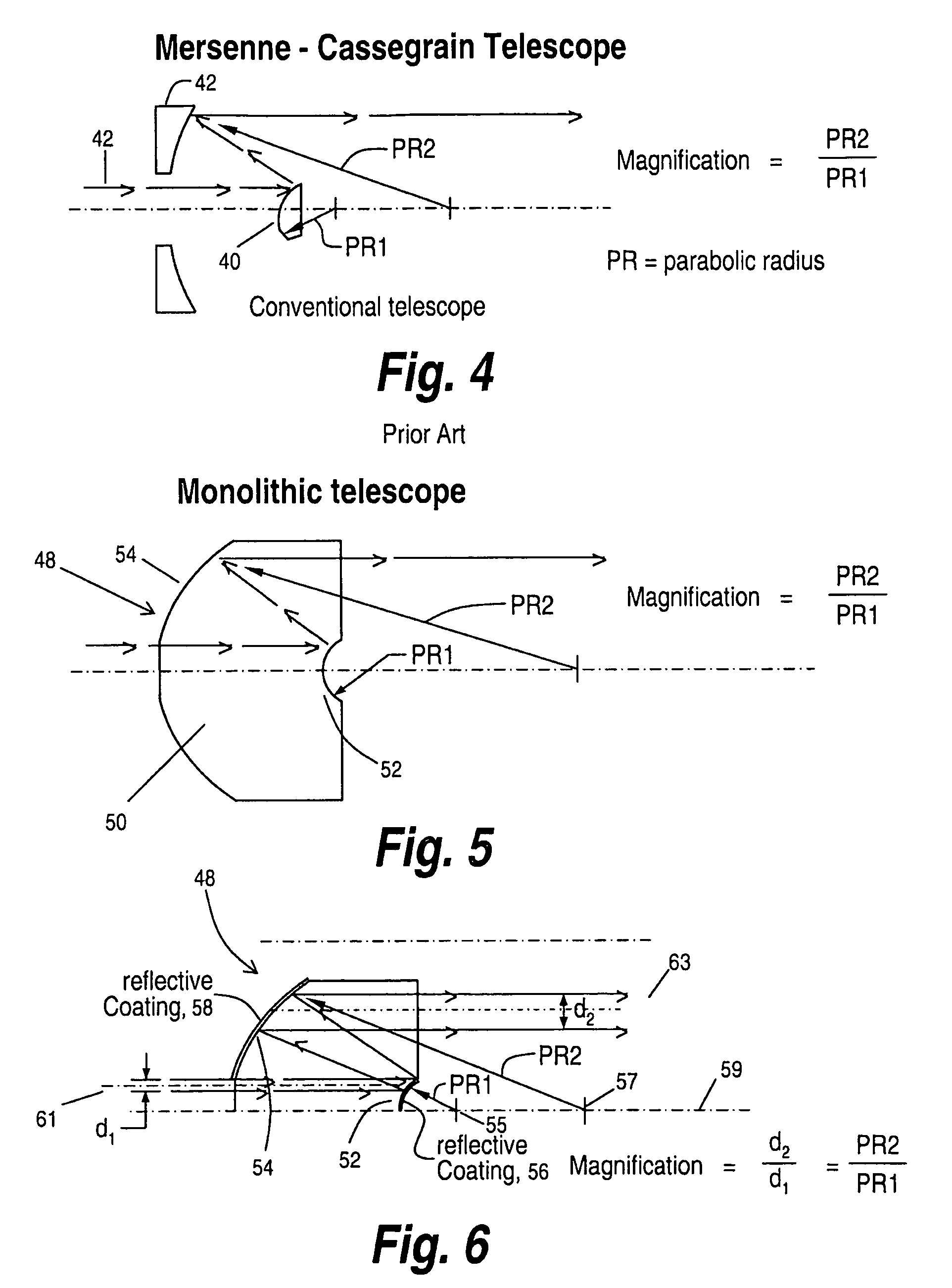
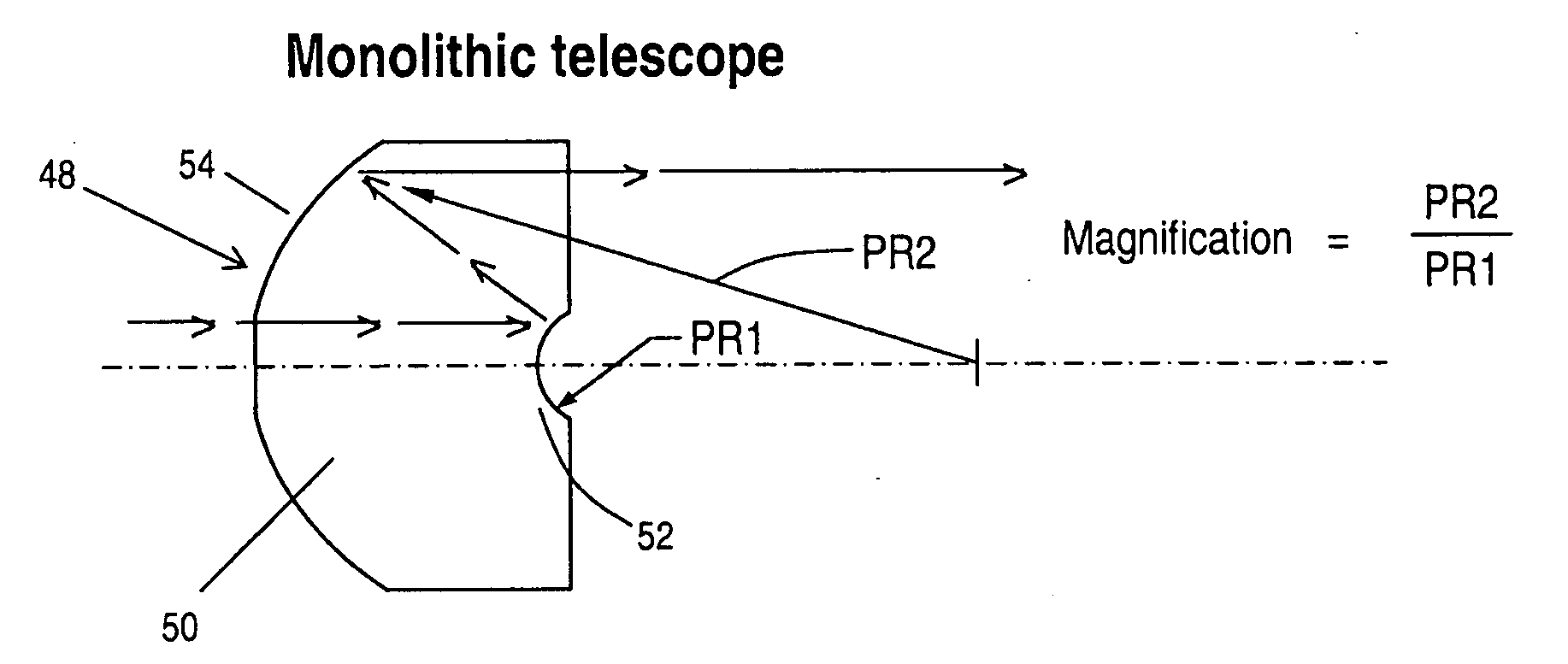
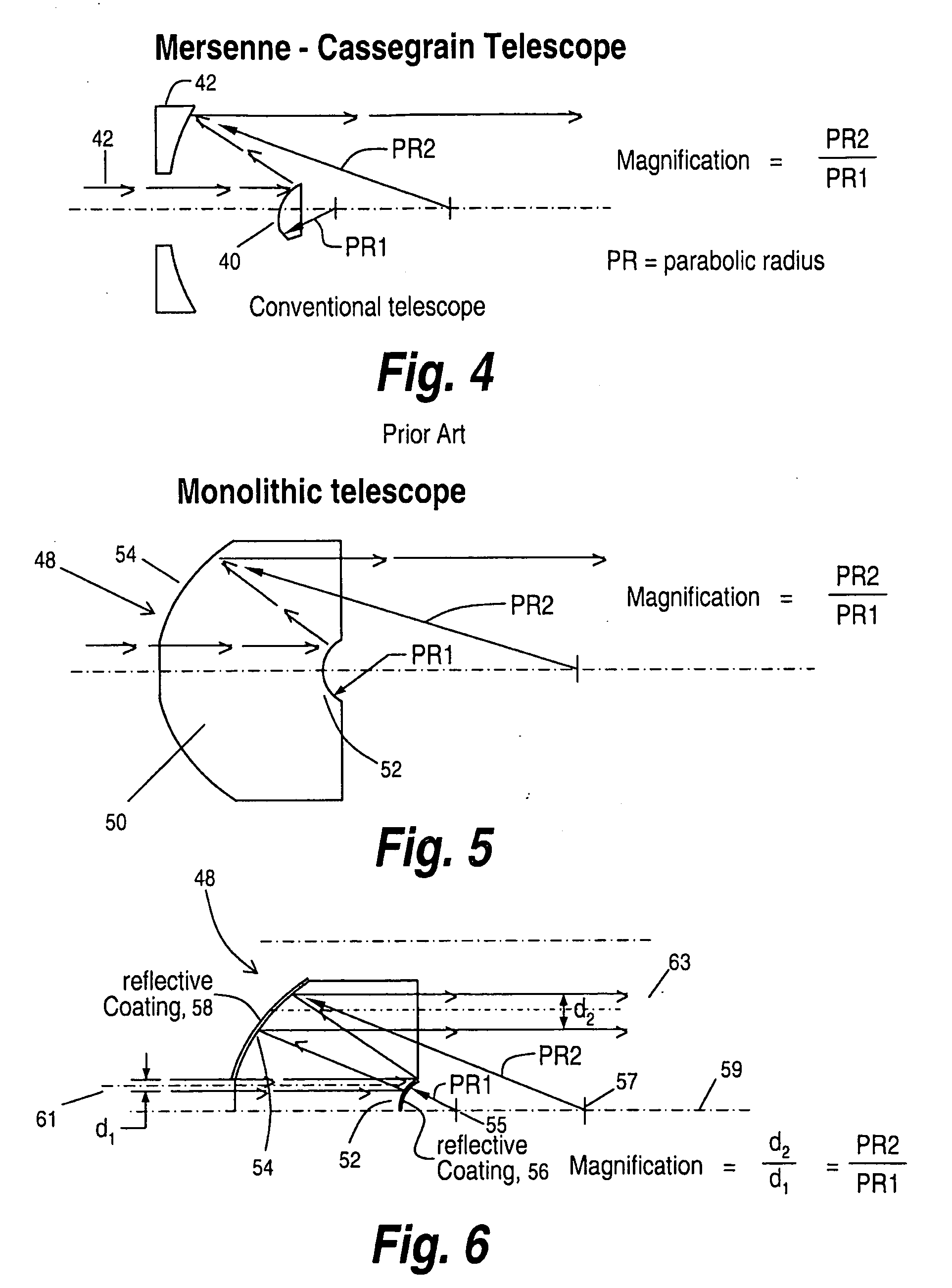
Monolithic eccentric Mersenne-Cassegrain telescope
ActiveUS8134778B2Stable meteringNot be contaminated or scratchedMirrorsTelescopesDiamond turningThermal coefficient
A Mersenne-Cassegrain telescope provided in a single block of glass in which opposed parabolic elements are precision milled through diamond turning of a glass boule, with the magnification power of the telescope determined by the differences in focal length between the two parabolas. The result is a volumetrically small telescope with pre-aligned surfaces that are maintained by the structural rigidity of the glass itself and in which thermal coefficients of expansion, vibration and the like have no effect due to the single glass element structure.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
Pin based method of precision diamond turning to make prismatic mold and sheeting
A system, and corresponding method for use, for providing a mass-producible retroreflective material, or sheeting, featuring full cube corner pins is presented. The full cube corner shaping may be provided with the use of a diamond turning tool. The diamond turning tool may be used to simultaneously manufacture a number of pins. The pins may be used to form a mold featuring a triangular or full cube corner surface formation.
Owner:ORAFOL AMERICAS
Machining trajectory generation method for machining Fresnel microstructural arrays by precise lathe
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Precision double-sided aspheric element
InactiveUS7028595B2Low costSaving in sizeTurning machine accessoriesOptical surface grinding machinesDiamond turningSystems design
A precision optical element is described, such as is used in thermal imaging systems in the infra-red, manufactured by means of single point machining, with both of its surfaces having an aspheric form, with or without the addition of a diffractive optics pattern. The element is produced while held in a novel vacuum chuck, whose support surface has a width in the radial direction significantly less than the size of the element, and which is aspherically machined to match the aspheric first surface of the element. A method whereby such an element can be produced by means of single point machining, such as diamond turning or fly cutting, is also described. Also described are new optical system designs and applications using such double-sided aspheric elements, thereby providing significant improvement over currently available optical systems.
Owner:OPHIR OPTRONICS SOLUTIONS
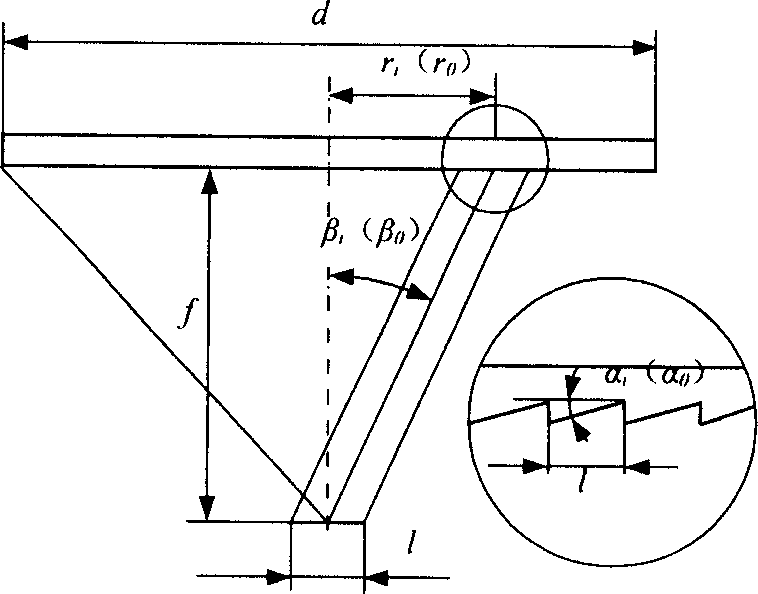
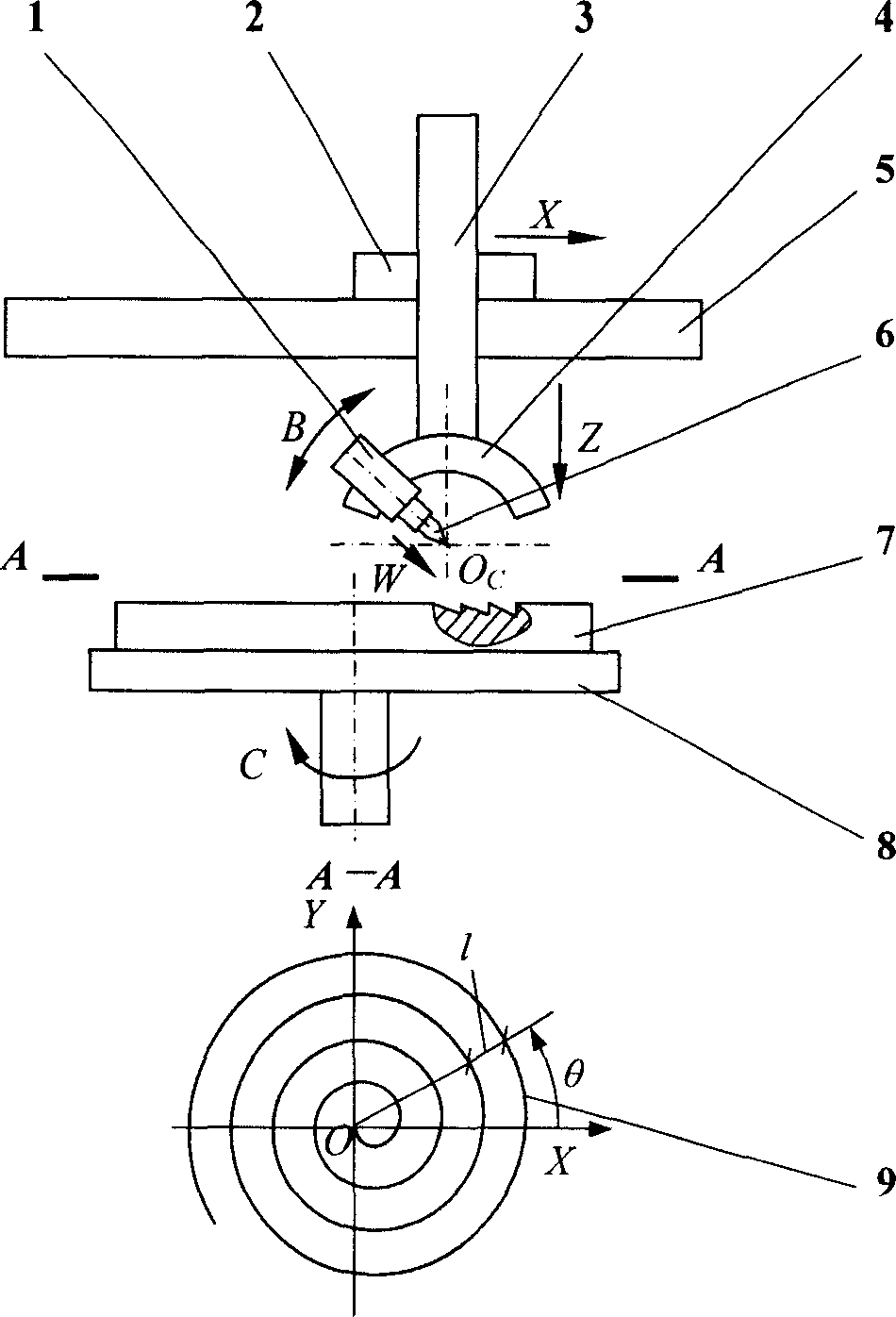
Diamond turning method and device for Archimedean spiral type Fresnel lens
The present invention belongs to the field of precise machining technology, and is especially diamond turning method and apparatus for Archimedean spiral type Fresnel lens. The present invention has X axis ram on guide track on bed for X axis motion, Z axis ram on guide track on the X axis ram for Z axis motion, arced direct driving motor on Z axis ram for B axis motion, precise linear motor on the mover of the arced direct driving motor, and diamond cutter on the precise linear motor for W axis motion. During machining, the diamond cutter has the motion path as the synthesis of the X axis motion, the B axis motion and the W axis motion, and the work piece on the bench rotates around C axis, so that the diamond cutter moves along Archimedean spiral in the surface of the work piece. The present invention has continuous cutting, less damage of the cutter, short machining period and raised machining precision of Fresnel lens.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Aspheric surface processing method of high-precision CVD ZnSe lens
ActiveCN105467480AEffective controlNo problem of scratching the surface of optical componentsLensDiamond turningMachine tool
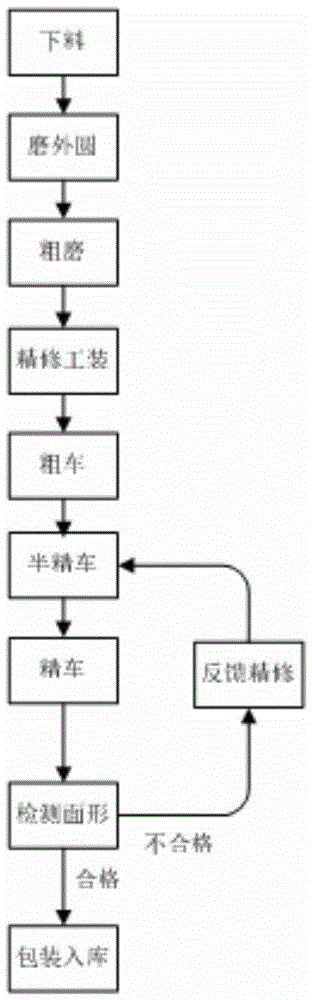
The invention belongs to the single-point-diamond super-precision cutting technology field and mainly relates to a single point diamond turning processing method of a high-precision CVD ZnSe lens. The invention aims at providing the processing method which can be used to guarantee technology indexes of CVD ZnSe lens aspheric surface shape precision, surface imperfection, decentration and the like. The method is mainly characterized in that a single point diamond turning machine tool and a diamond arc knife are used to carry out super-precision turning processing on the CVD ZnSe lens; and a technological method processing flow mainly comprises blanking, external grinding, rough grinding, processing tooling, rough turning, semi-finishing turning and finish turning. The method has the advantages that an external grinding process is taken as a first process; through finish machining of a blank excircle, rough grinding technology index control and precision turning processing tooling, a lens center deviation technology index is guaranteed; simultaneously, a single point diamond turning process step is divided into the semi-finishing turning and the finish turning so that damaged layers when rough turning is performed on a blank material are effectively reduced, and the surface imperfection and a surface shape technology index are guaranteed.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG INST OF TECH PHYSICS
Combined technology method suitable for efficient processing of calcium fluoride convex cone mirror
InactiveCN105269412AImprove processing efficiencyAccurate surface shape accuracyOptical surface grinding machinesStone-like material working toolsDiamond turningMagneto rheological
The invention discloses a combined technology method suitable for efficient machining of a calcium fluoride convex cone mirror. The material characteristics of calcium fluoride crystals and the characteristics of a convex cone surface special-shaped structure are fully considered, a machining process is divided into three links of forming, surface figure accuracy increasing and roughness increasing, three combined technologies of a milling forming technology, a diamond turning technology and a magneto-rheological polishing technology are adopted for machining, and the technological difficulties of the cone angle, surface figure accuracy, roughness and the like of a calcium fluoride convex cone are broken through one by one. Machining efficiency is high, the cone angle accuracy is high, the surface figure accuracy and roughness are controllable and stable, the technological difficulty that the special-shaped curved surface of the calcium fluoride convex cone cannot be machined in domestic existing technologies is broken through, and technological guarantees are provided for our country to carry out development of photoetching machine projection exposure optical systems.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-contact precise tool setting gauge of ultra-precise diamond turning tool and tool setting method
PendingCN108942413AAvoid the disadvantage of poor repeat positioning accuracyGuaranteed positional relationshipAutomatic control devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsDiamond turningTool wear
The invention relates to a non-contact precise tool setting gauge of an ultra-precise diamond turning tool and a tool setting method. The tool setting gauge comprises a supporting ring body, lenses inthe X direction and the Y direction, CCDs and a lighting source in the X direction. The lens in the X direction and the CCD of the lens in the X direction are arranged at the position, correspondingto the X-axis direction of the lathe coordinates, of the supporting ring body, the lens in the Y direction and the CCD of the lens in the Y direction are arranged at the position, corresponding to theY-axis direction of the lathe coordinates, of the supporting ring body, the lenses in the X direction and the Y direction are located on the inner side of the supporting ring body, the CCDs in the Xdirection and the Y direction are located on the outer side of the supporting ring body, and the lighting source is arranged at the position, facing the lens in the X direction, of the inner side of the supporting ring body. The tool setting gauge and the tool setting method thereof replace a traditional trial cutting method, ultra-precise machining tool high-precision optical online detection isachieved, the problems that an ultra-precise machining tool is long in position adjusting period, and tool wear is hard to avoid are solved, machining efficiency is greatly improved, the tool is freeof wear, and the wide application prospects and the large popularization value are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for predicting surface roughness in single-point diamond turning
InactiveCN102172990AImprove forecast accuracyAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusDiamond turningSurface roughness
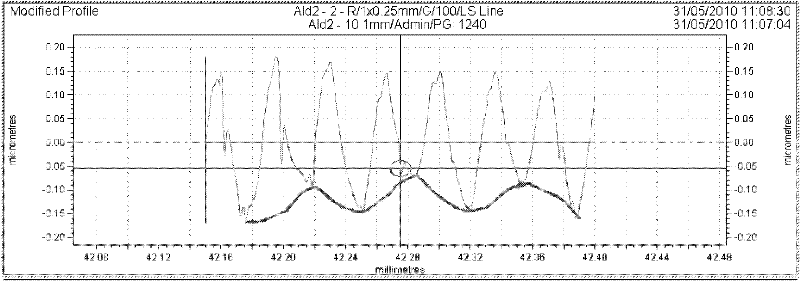
The invention relates to a method for predicting surface roughness, in particular to a method for predicting surface roughness in single-point diamond turning. The method solves the problem that the conventional method for predicting the surface roughness has high predication error. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting amplitude information of relative vibration between a cutter and a workpiece in the processing process from the detection result of a processed surface, establishing corresponding relationships between the main shaft revolving speed and the material property and between the relative vibration and the expansion effect, calculating a profile curve of the processed surface after the expansion effect happens, finding the corresponding equivalent amplitude according to the specific processing material and the main shaft revolving speed so as to obtain equivalent relative vibration between the cutter and the workpiece, superposing the equivalent relative vibration and the profile curve of the processed surface after the expansion effect happens to obtain a new surface profile curve, performing data processing on the new curve and calculating the surface roughness. The method is used for predicting the surface roughness in the single-point diamond turning.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Monolithic Eccentric Mersenne-Cassegrain Telescope
ActiveUS20100284099A1Stable meteringNot be contaminated or scratchedMirrorsTelescopesDiamond turningThermal coefficient
A Mersenne-Cassegrain telescope provided in a single block of glass in which opposed parabolic elements are precision milled through diamond turning of a glass boule, with the magnification power of the telescope determined by the differences in focal length between the two parabolas. The result is a volumetrically small telescope with pre-aligned surfaces that are maintained by the structural rigidity of the glass itself and in which thermal coefficients of expansion, vibration and the like have no effect due to the single glass element structure.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
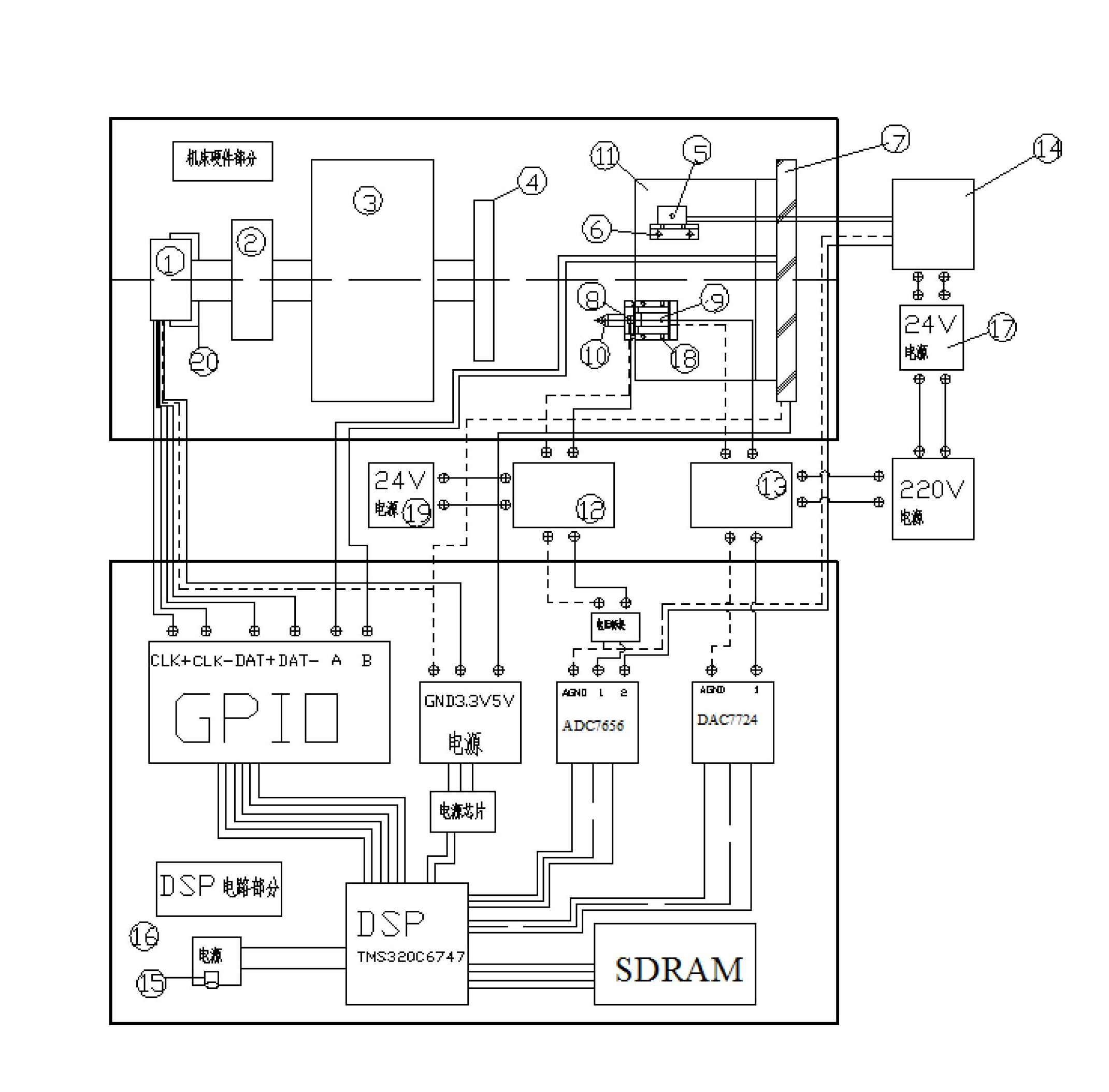
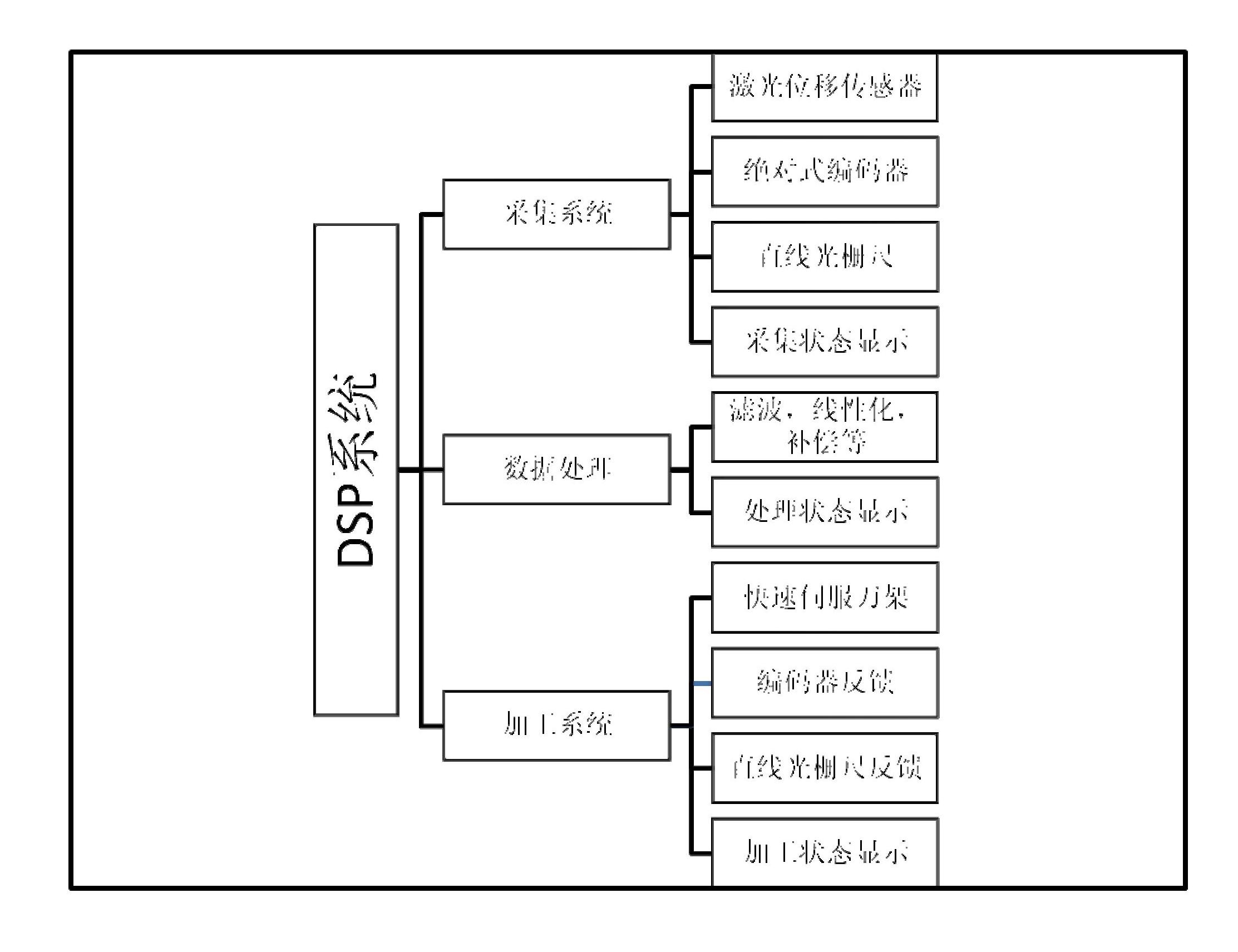
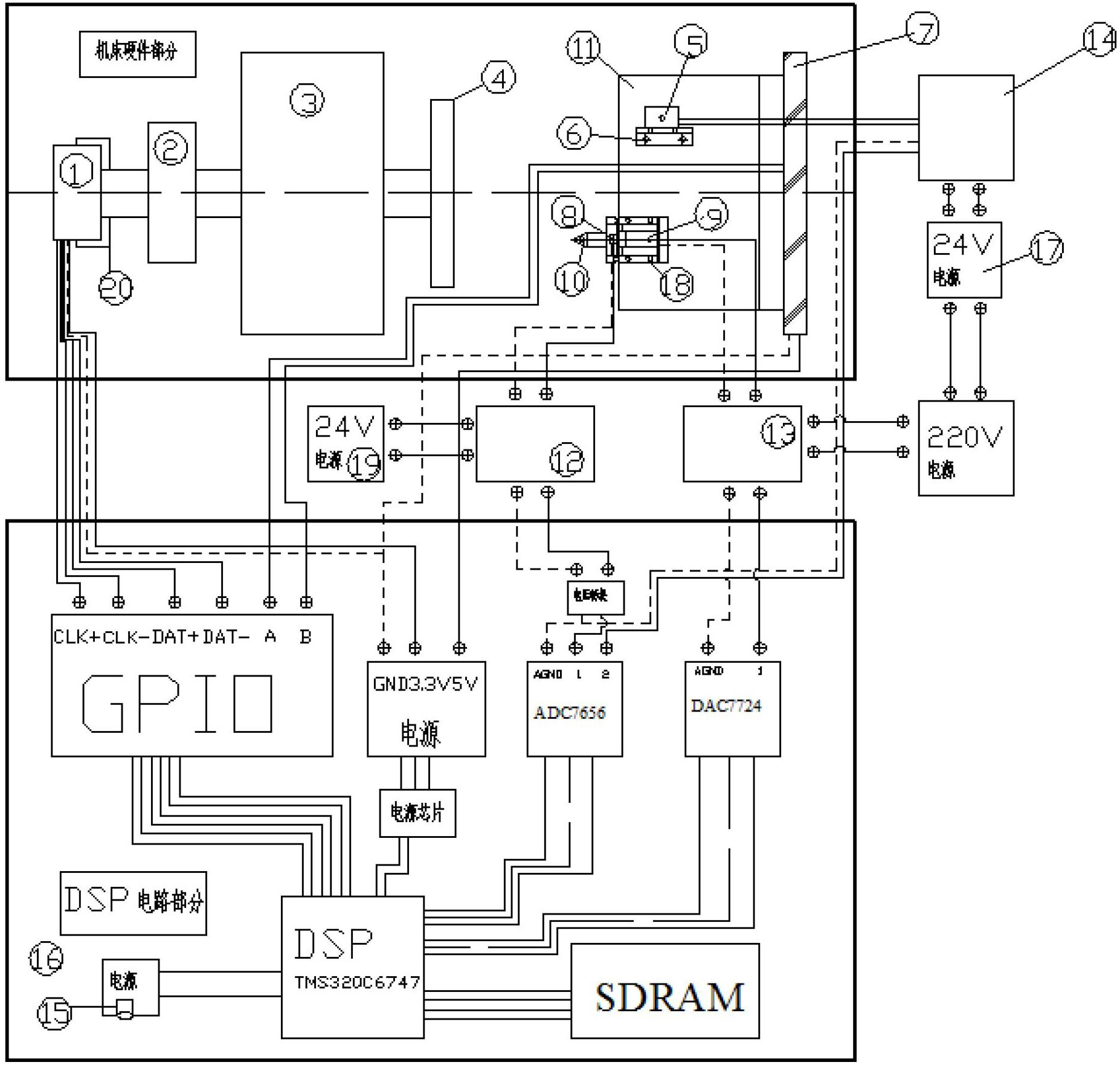
System for measuring surface topography of aerospace thin-wall disc part and machining fixture based on digital signal processor (DSP)
ActiveCN102672540AQuick measurementFast preparationAutomatic control devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsDigital signal processingGrating
The invention relates to a system for measuring the surface topography of an aerospace thin-wall disc part and machining a fixture based on a digital signal processor (DSP). The system consists of a TMS320C6747 chip, and a DSP development board, a DSP development board 5V power supply, a quick servo tool rest, a piezoelectric ceramic displacement driver, a piezoelectric ceramic power amplifier, a capacitive sensor measuring head, a capacitive sensor signal amplifier, a capacitive sensor power supply, an absolute encoder, a linear grating ruler, a laser displacement sensor measuring head, a laser displacement sensor measuring head retainer, a laser displacement sensor controller, a laser displacement sensor power supply, an absolute encoder bracket, an elastic coupling, a monocrystalline diamond turning tool, a thin-wall workpiece, a fixture mounting platform and an experiment platform which are based on the chip. The system has the functions of quickly measuring the surface topography and manufacturing the fixture at high accuracy, has practical value in the field of machining, and can solve the problems that the deformation of the thin-wall part is large, new deformation is generated in each machining process, accuracy is difficult to ensure, and the fixture cannot meet the clamping requirement in each process.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High quality optically polished aluminum mirror and process for producing
InactiveUS6966820B1Improve accuracyEliminate the problemEdge grinding machinesOptical surface grinding machinesDiamond turningSurface roughness
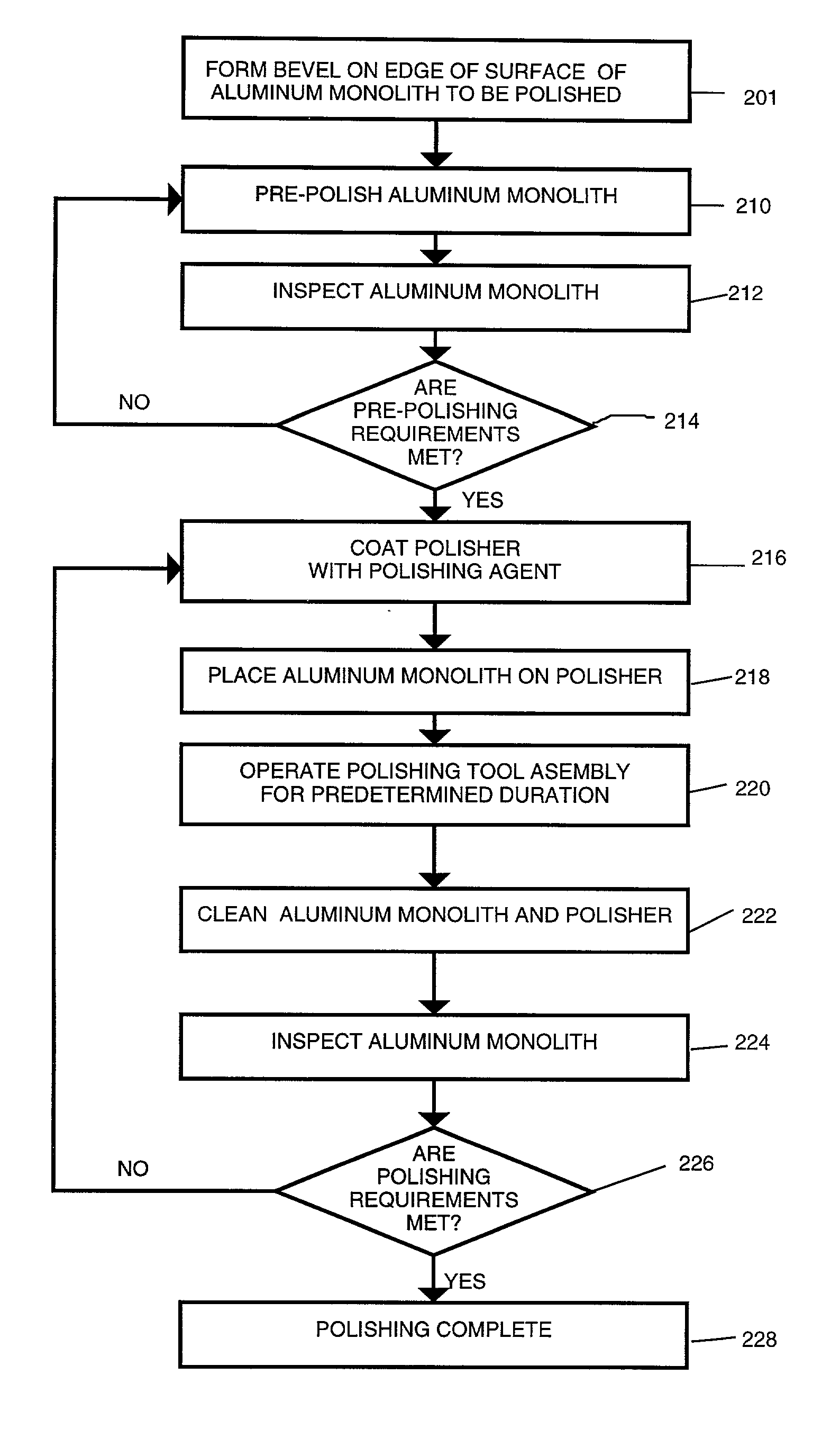
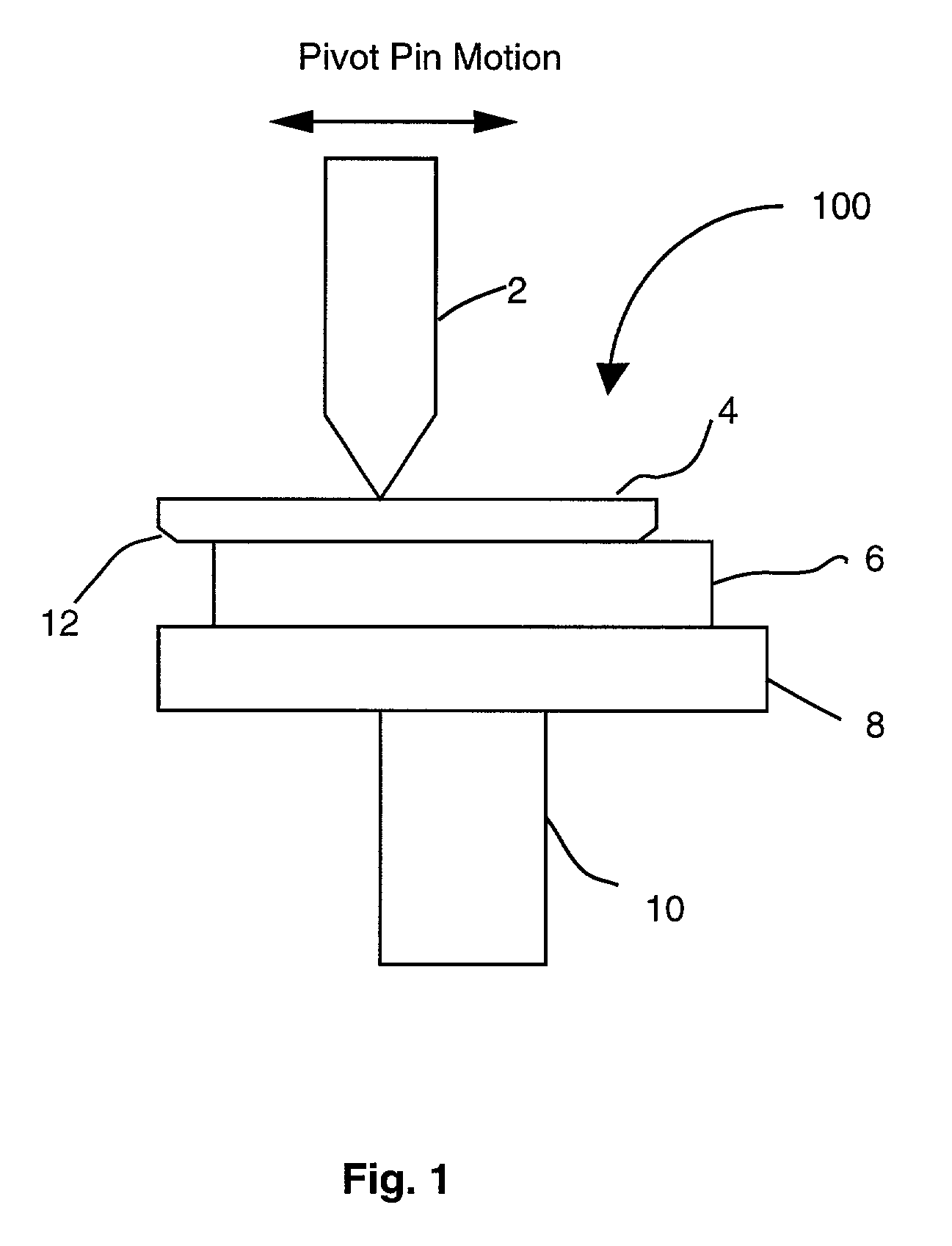
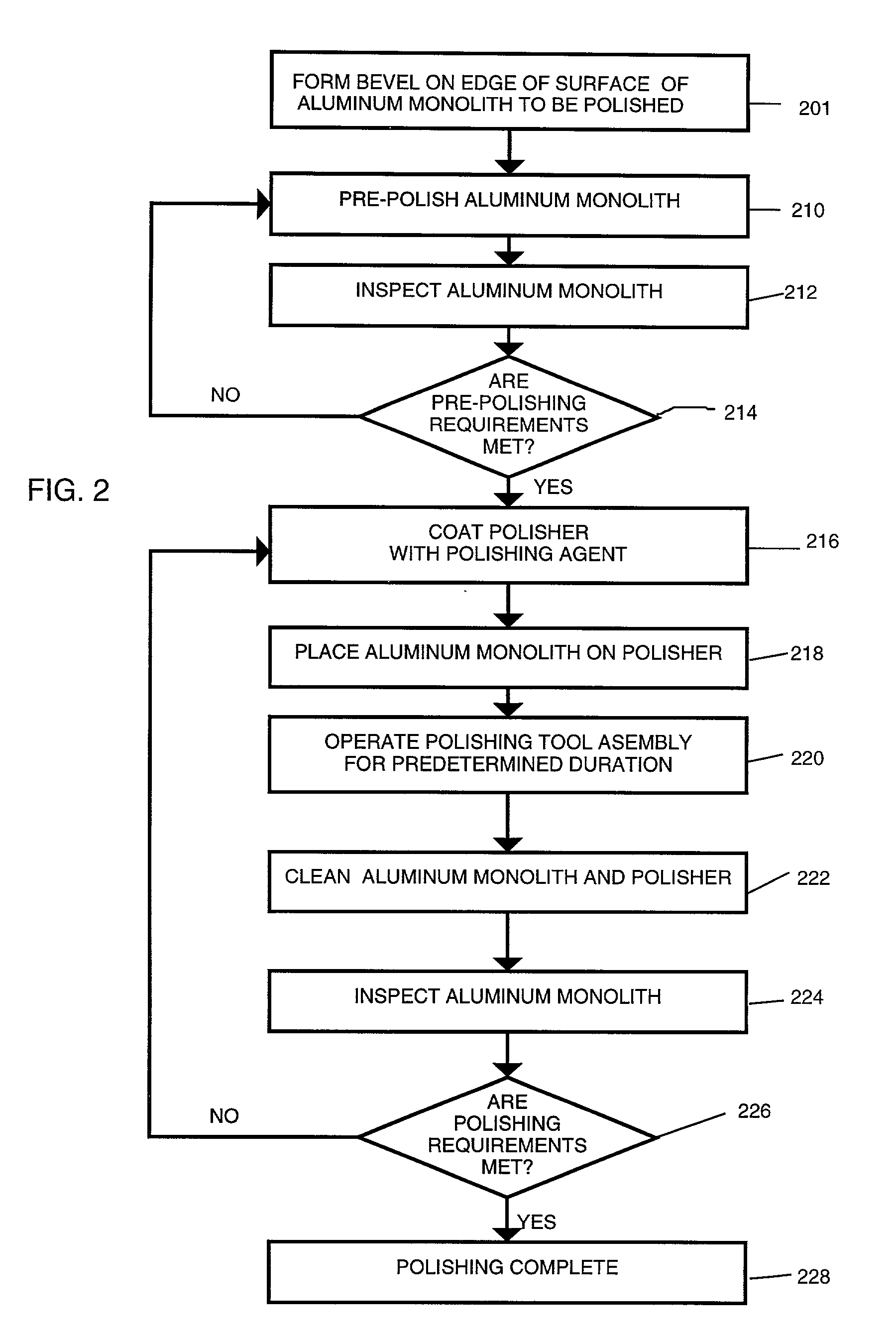
A new technical advancement in the field of precision aluminum optics permits high quality optical polishing of aluminum monolith, which, in the field of optics, offers numerous benefits because of its machinability, lightweight, and low cost. This invention combines diamond turning and conventional polishing along with india ink, a newly adopted material, for the polishing to accomplish a significant improvement in surface precision of aluminum monolith for optical purposes. This invention guarantees the precise optical polishing of typical bare aluminum monolith to surface roughness of less than about 30 angstroms rms and preferably about 5 angstroms rms while maintaining a surface figure accuracy in terms of surface figure error of not more than one-fifteenth of wave peak-to-valley.
Owner:UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATIO OF THE NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION
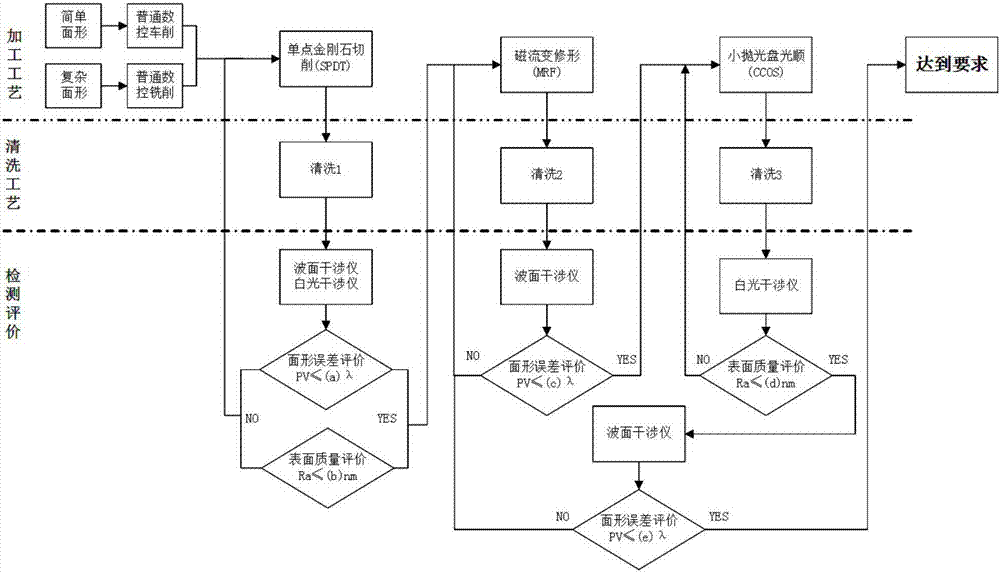
Combined polishing method of aluminum alloy reflecting mirrors
ActiveCN107953151AImprove surface qualitySolve the associated turning textureNumerical controlDiamond turning
The invention discloses a combined polishing method of aluminum alloy reflecting mirrors. The method comprises the following implementation steps: the numerical control milling rough machining and thesingle-point diamond turning are performed on workpieces to be machined to obtain aluminum alloy reflecting mirror surfaces which meet initial surface shapes and surface quality requirements; then, magnetorheological shape correction is iteratively performed; and a small grinding head is used for polishing until the aluminum alloy reflecting mirror surfaces of the workpieces to be machined meet index requirements. The method can solve associated turning lines in the cutting process of the aluminum alloy reflecting mirrors, and overcomes the problems of weak shape correction of complex curvedsurfaces and weak surface quality improvement in a traditional aluminum alloy reflecting mirror polishing technology; and the polishing method can perform high-precision certain shape correction on the aluminum alloy reflecting mirrors, meanwhile, obtains higher-quality polishing surfaces, further improves low-defect manufacturing capacity of optical parts, and develops a new path for ultra-precise machining of the optical parts.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method of accurate location of diamond turning tool in micro-turning process
InactiveCN103170877AGuaranteed machining accuracyHigh positioning accuracyAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusDiamond turningImage system
The invention discloses a method of accurate location of a diamond turning tool in a micro-turning process, and belongs to the field of micro-manufacture. The method of accurate location of the diamond turning tool in the micro-turning process is characterized by comprising extracting an image of a tool through a high-precision charge coupled device (CCD) measuring technology, calculating a coordinate position of a tool nose in a CCD image system, detecting a three-dimensional locating error of the diamond turning tool, comparing a position, obtained through measurement, of the tool nose with an original position of the tool nose, carrying out error compensation on line by being matched with an accurate locating platform of a tool system, and improving locating accuracy of the tool nose. The method of accurate location of the diamond turning tool in the micro-turning process is a non-contact type detection method which is capable of achieving location accuracy, in a submicron level, of the diamond turning tool, and meanwhile is simple in needed equipment, and convenient to implement.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Diamond turning free-form surface route generation method and system and related components
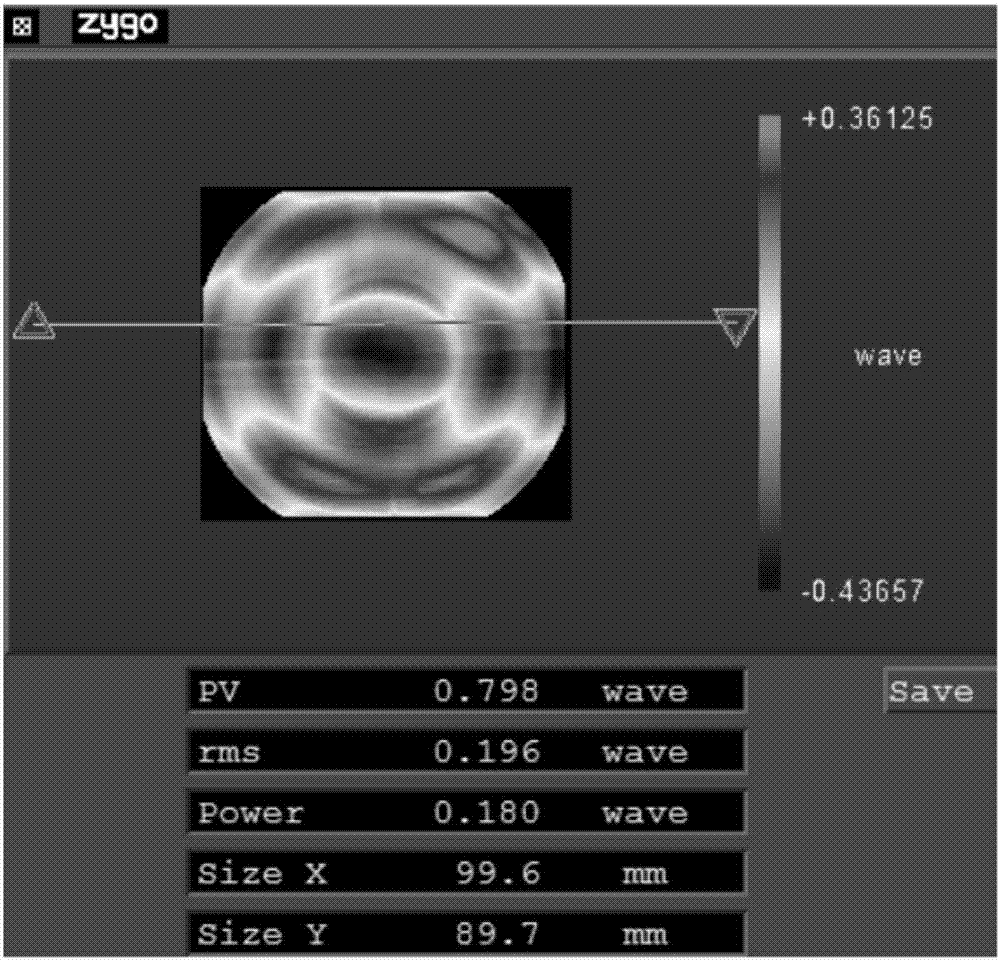
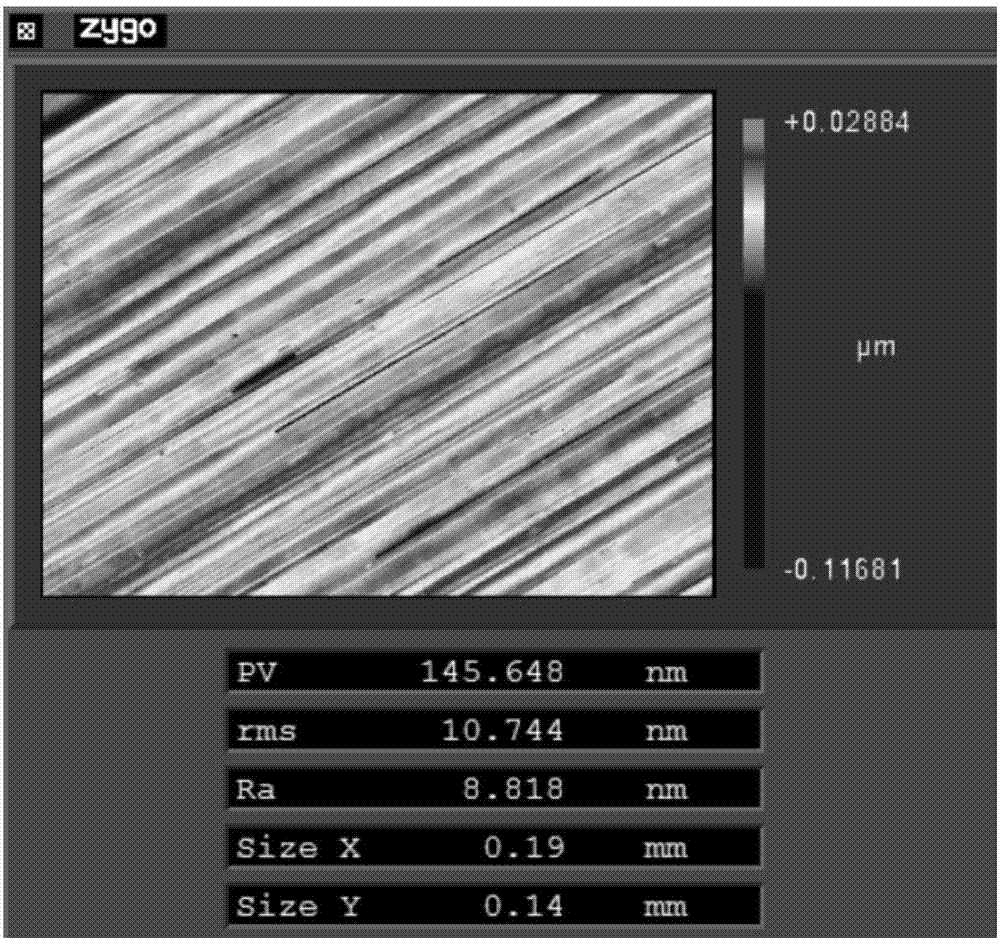
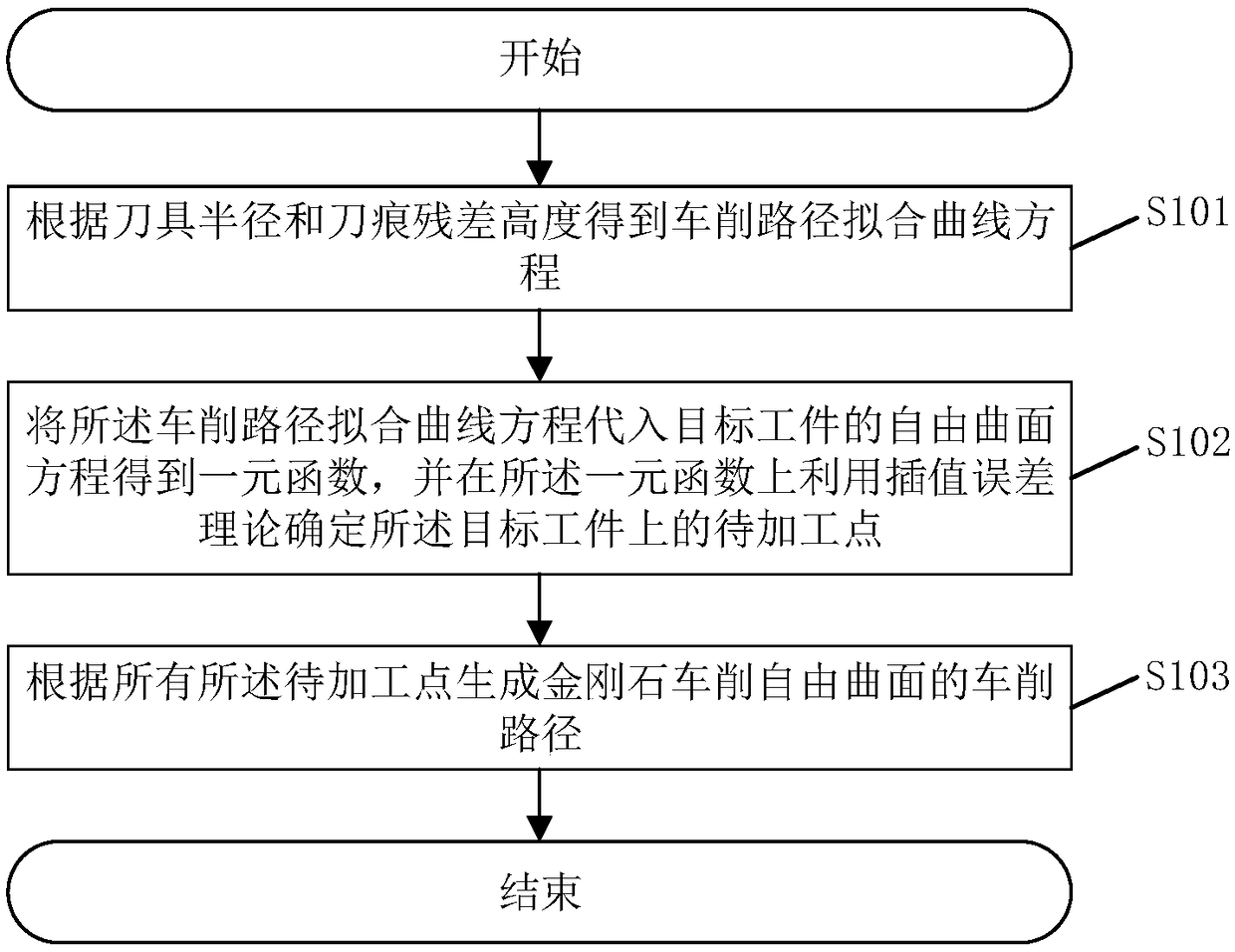
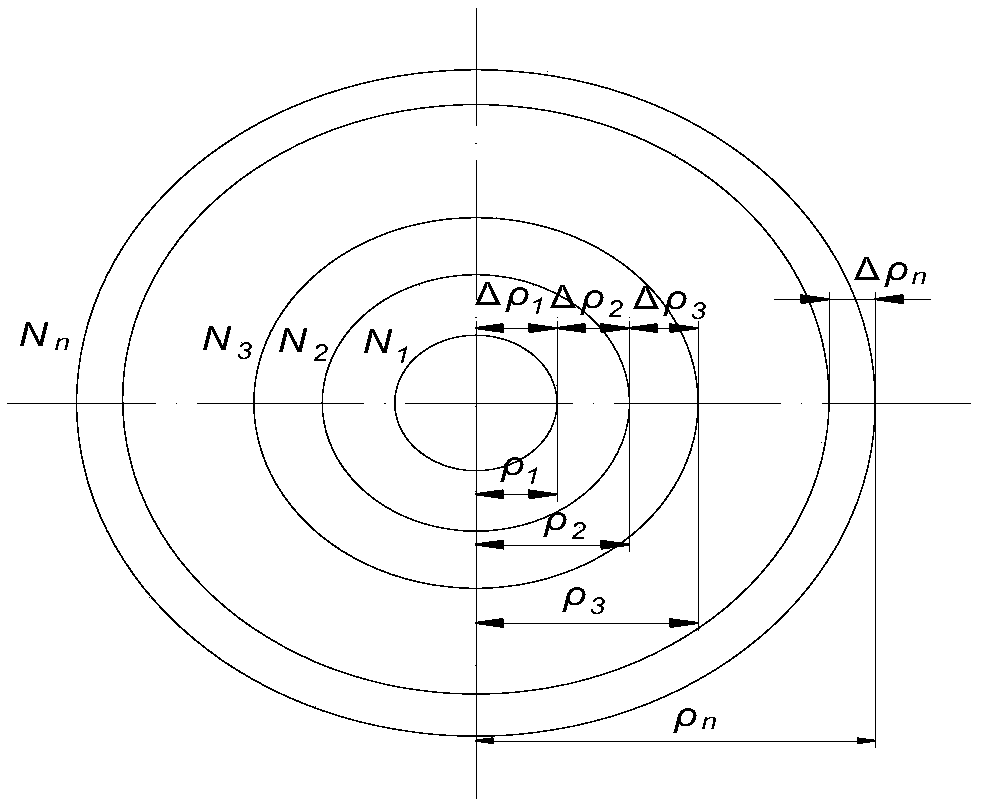
The invention discloses a diamond turning free-form surface route generation method. The method includes the following steps: firstly, obtaining a fitting curve equation of helix coil numbers and helix radiuses according to a tool radius and a tool mark residual height; substituting the obtained fitting curve equation into a free-form surface equation of a target workpiece to obtain a function ofone variable, and determining to-be-processed points on the target workpiece on the function of one variable by using an interpolation error theory; and finally, obtaining all tool locations by tool radius compensation and generating a turning route. The method can generate the processing route according to shape characteristics of the to-be-processed workpiece and processing error requirements, greatly reduce the number of data points, and make interpolation errors of all parts of the processed workpiece uniform, thereby improving the quality of turning processing. The invention also discloses a diamond turning free-form surface route generation system, a computer readable storage medium and diamond turning equipment which have the above beneficial effects.
Owner:长春国科精密光学技术有限公司
Techniques for reducing optical noise in metrology systems
InactiveUS20070121104A1Improved metrology system performanceReduce scattered lightMirrorsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationLow noiseDiamond turning
A first method for fabricating low-noise optical components for use in optical metrology systems includes shaping a glass substrate to obtain a desire shape and then coating the glass substrate with a reflective coating. A second method includes shaping a glass master die to a desired shape and then using the glass master to form a glass substrate to the desire shape. A third method includes diamond turning a substrate to a desired shape and then polishing the substrate to meet two surface conditions which in turn ensures that the scattered light is minimized and the metrology instruments performance is greatly increased. These conditions relate to a measurement of encircled energy compared to an ideal diffraction limited component of the same focal length and diameter.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Aluminum alloy material with high-precision super-smooth surface, polishing disk, polishing agent and polishing method
InactiveCN102941528ARealize fixed-point quantitative removalIncrease roughnessLapping machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesDiamond turningActive agent
The invention discloses a polishing method for an aluminum alloy material with a high-precision super-smooth surface and further discloses a polishing disk and a polishing agent. The polishing disk comprises a bottom disk body, a polishing pad, a polishing film and a compression piece, wherein the polishing film is coated outside the polishing pad, the compression piece hoops the edge of the polishing film and enables the polishing pad to be closely attached to the lower surface of the bottom disk body, and the polishing pad is made of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The polishing agent is mainly prepared by water, diadust, hydrogen peroxide and a surfactant. The polishing method includes performing primary polishing on the surface of the aluminum alloy material through a single-point diamond turning process and then performing secondary polishing on the surface after the primary polishing through a computer-control optical surface forming process, the polishing disk and the polishing agent. The aluminum alloy material with the high-precision super-smooth surface (the roughness Ra<=2nm and the root-mean-square (RMS) value<=lambda / 10) can be obtained according to the polishing disk, the polishing agent and the polishing method.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Super-precise turning method for free-form-surface prism
The invention relates to a super-precise turning method for a free-form-surface prism. The method comprises the steps that multiple inner reflection surfaces of the free-form-surface prism needing super-precise turning are positioned online through optical probes, and the processing curved-surface-shaped deviation is detected and compensated. Based on a two-axis single-point diamond turning latheof the X axis and the Z axis, an adjustable tool structure clamped single time is designed for assisting in processing the free-form-surface prism, several to-be-processed curved faces of the free-form-surface prism can be freely switched online and positioned, and a wedge with a standard angle is adopted for assisting in adjusting the angles of the processed curved faces. When the free-form-surface prism is detected online, an optical probe is adopted, and the surface-shaped deviation and processing allowance of the processed curved surfaces are detected and compensated. Compared with the prior art, the super-precise turning method has the advantages that the method is suitable for multiple kinds of sizes, the manufacturing cost is lowered, and the processing efficiency is improved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Diamond lathing cutter track tracing method
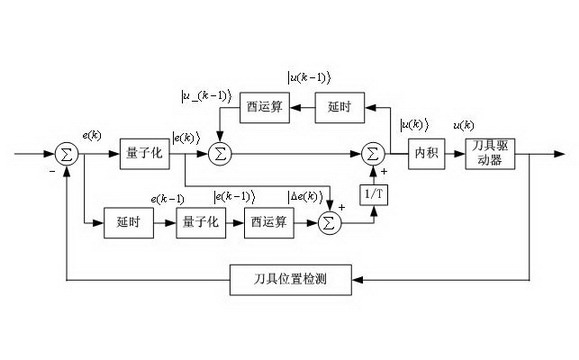
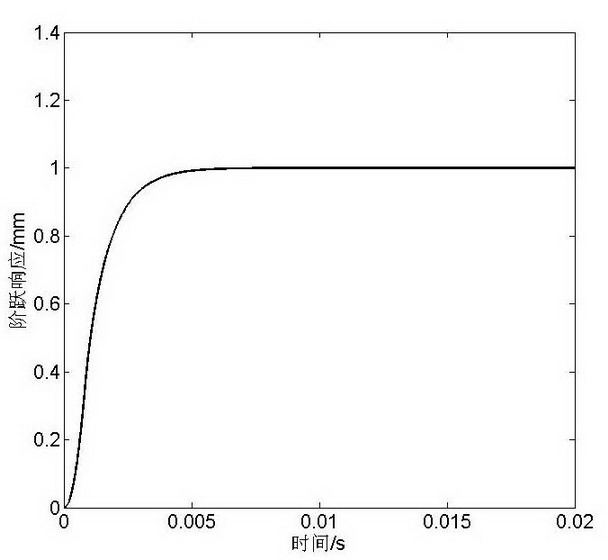
ActiveCN102063089ARealize high-precision trackingSimple methodTotal factory controlNumerical controlDiamond turningDigital control
The invention relates to a diamond lathing cutter track tracing method which belongs to the field of micronano processing and ultraprecise processing, in particular to a cutter track tracing method in the diamond lathing process. The diamond lathing cutter track tracing method comprises the following steps of: quantizing a tracing error; obtaining an entangled state quantum error; obtaining a quantum state historical control parameter; obtaining digital control amount; carrying out inner product operation on a quantum bit in a ground state and the quantum state control parameter to obtain a final control amount which is suitable for digital amount control; and acting on a driver of the cutter for finishing tracing on a cutter track. The method provided by the invention is simple, does not need complicated parameter design and selection, has certain generality and is convenient for application and popularization in industrial control.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com