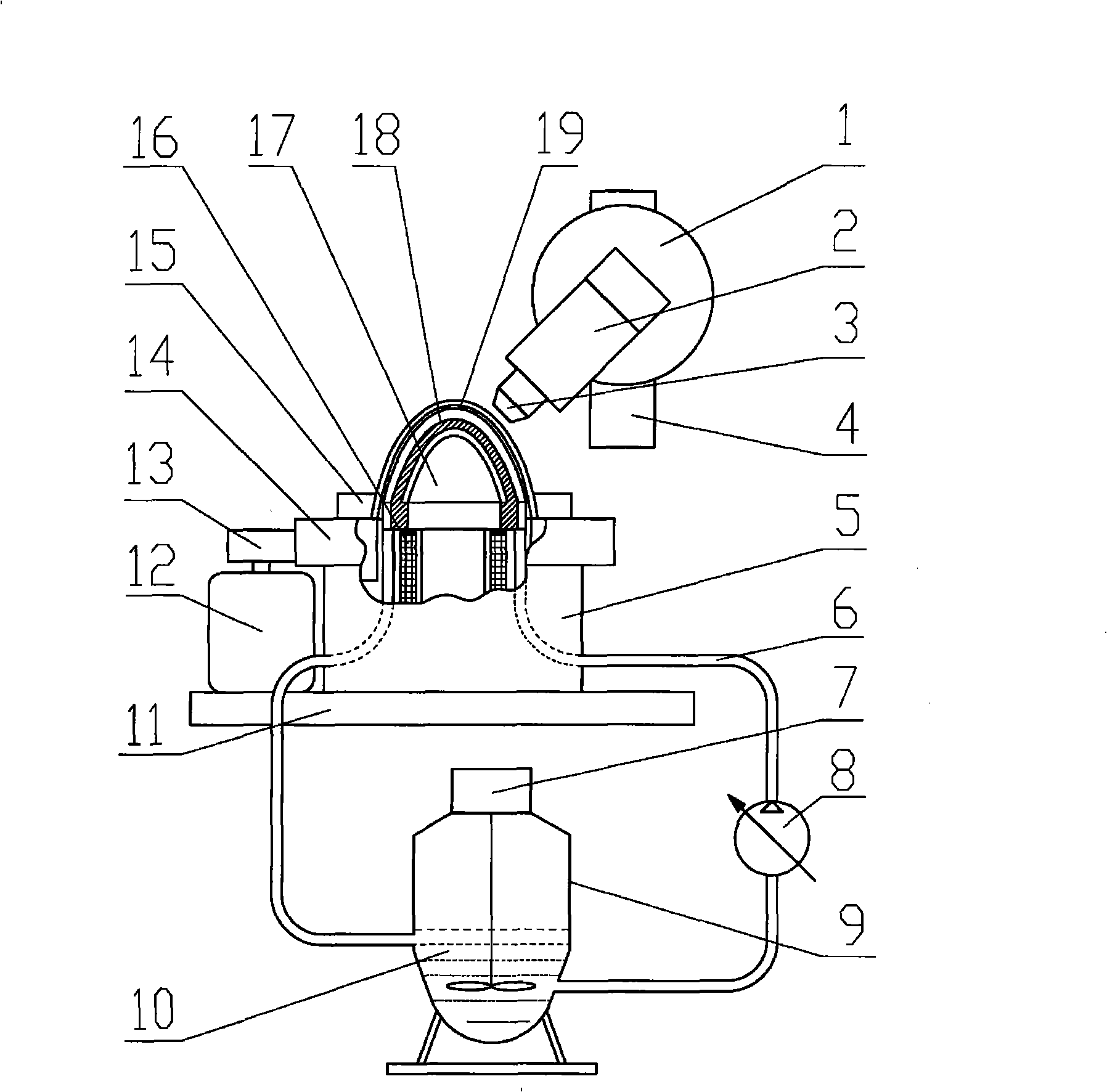
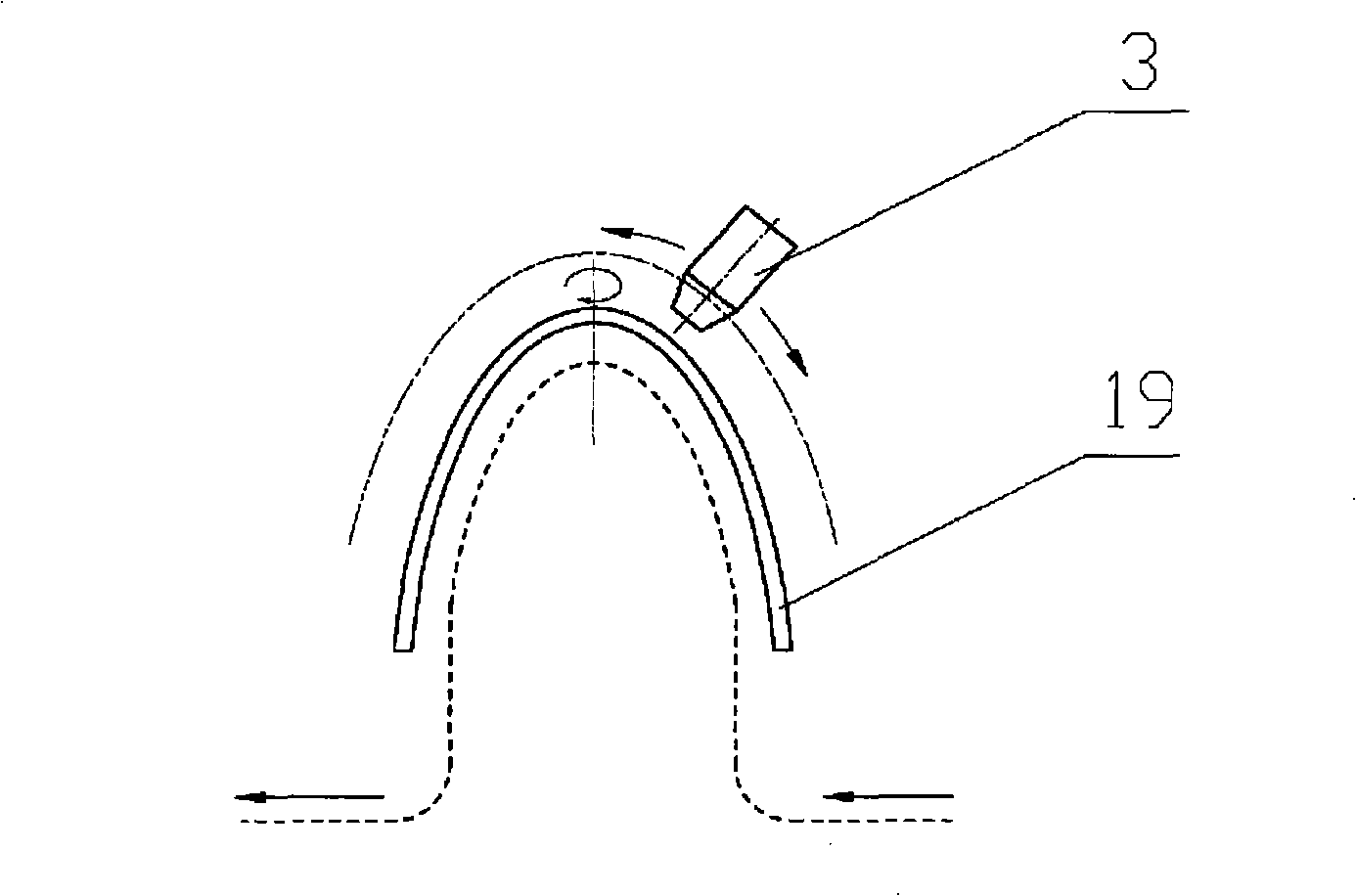
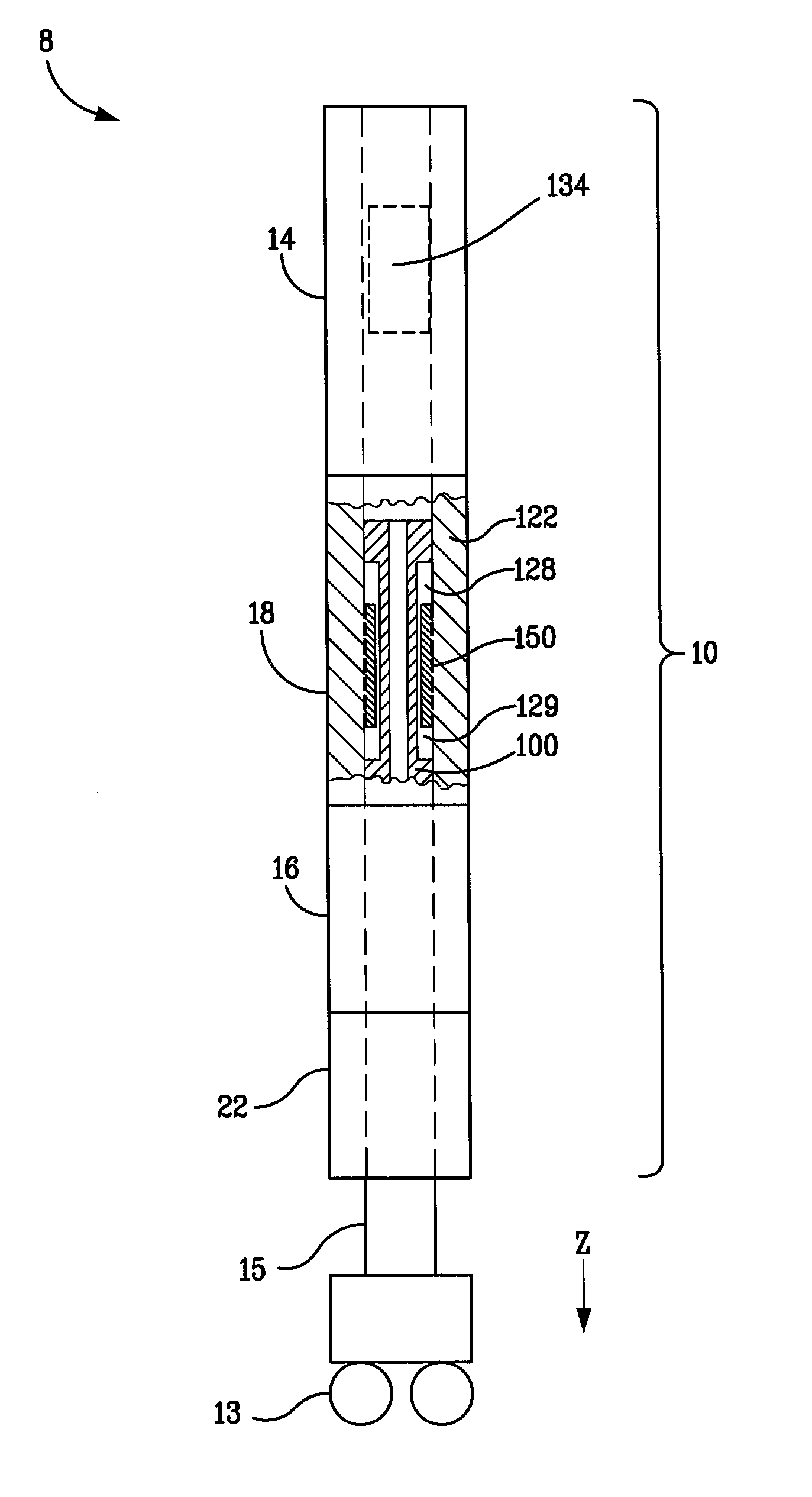
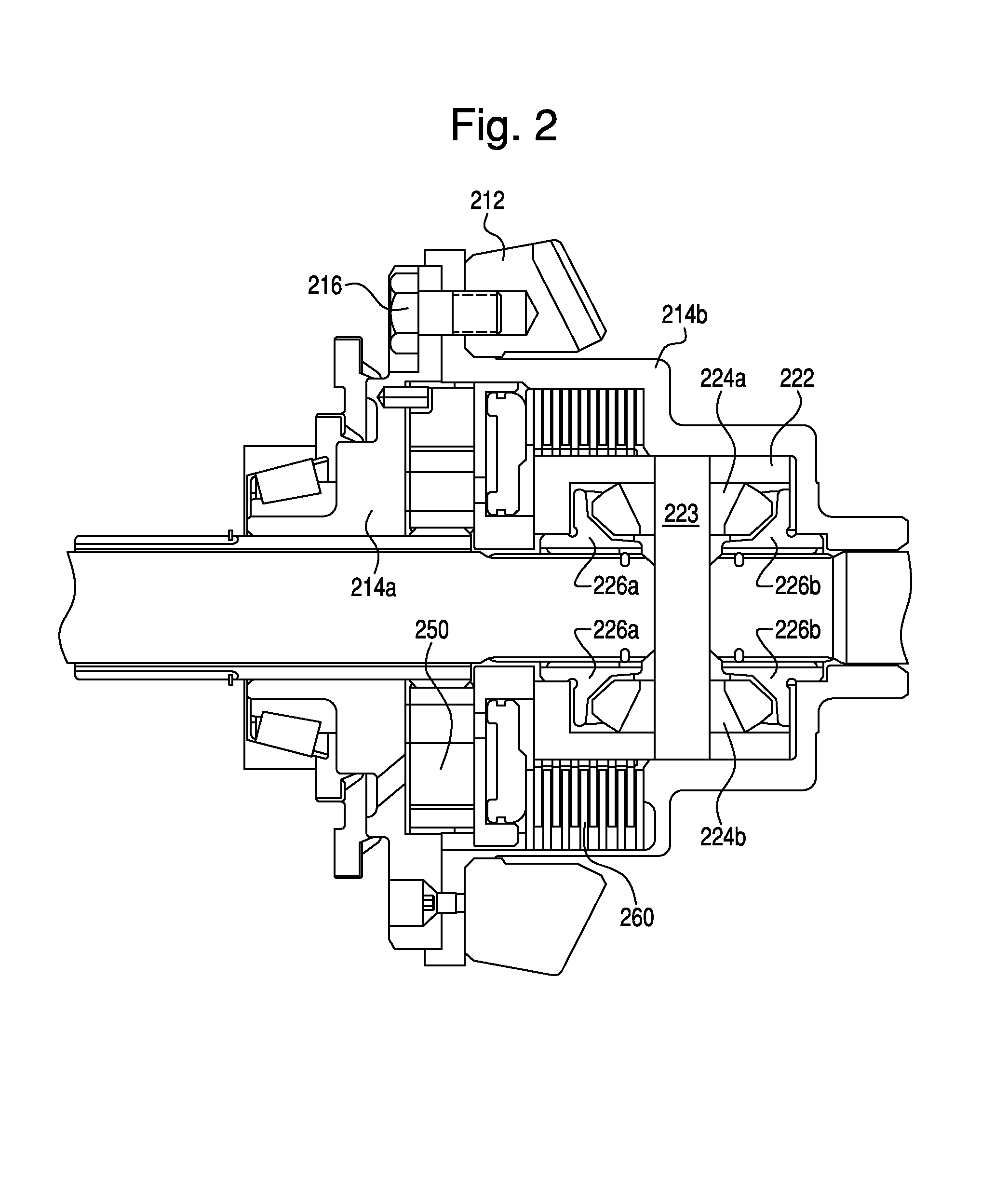
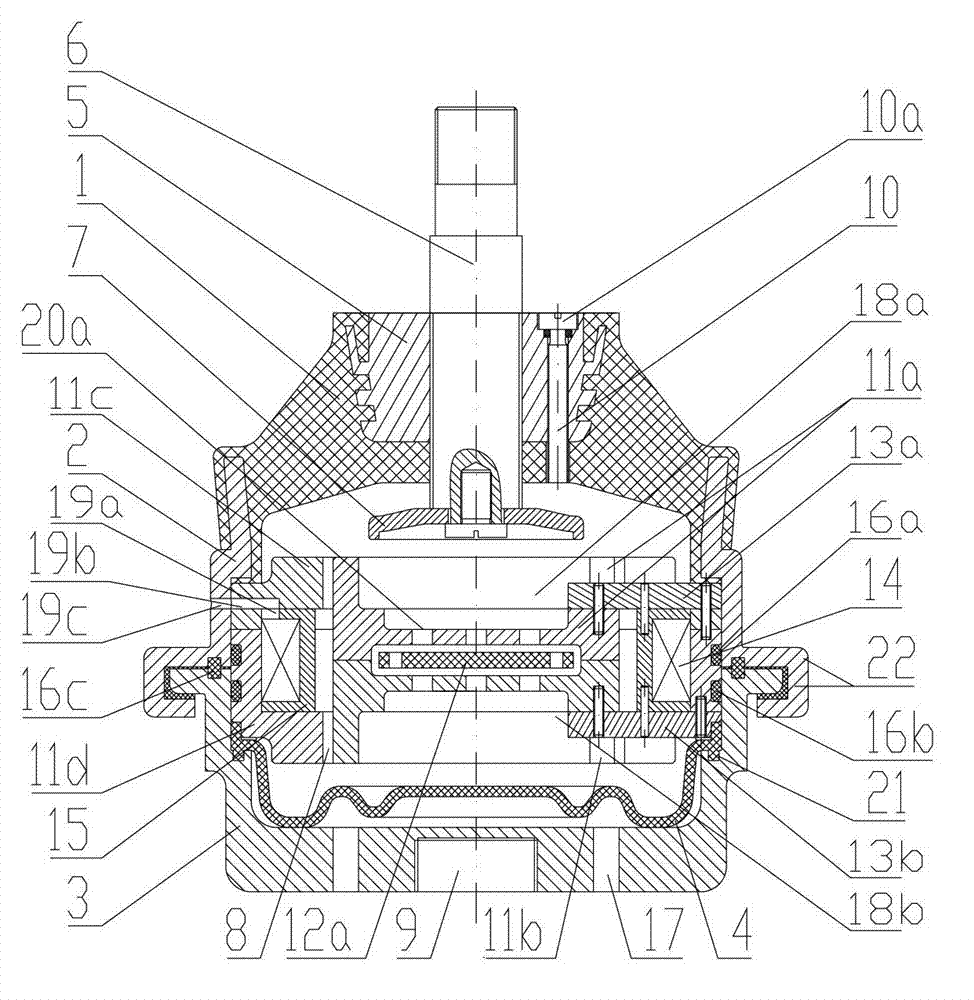
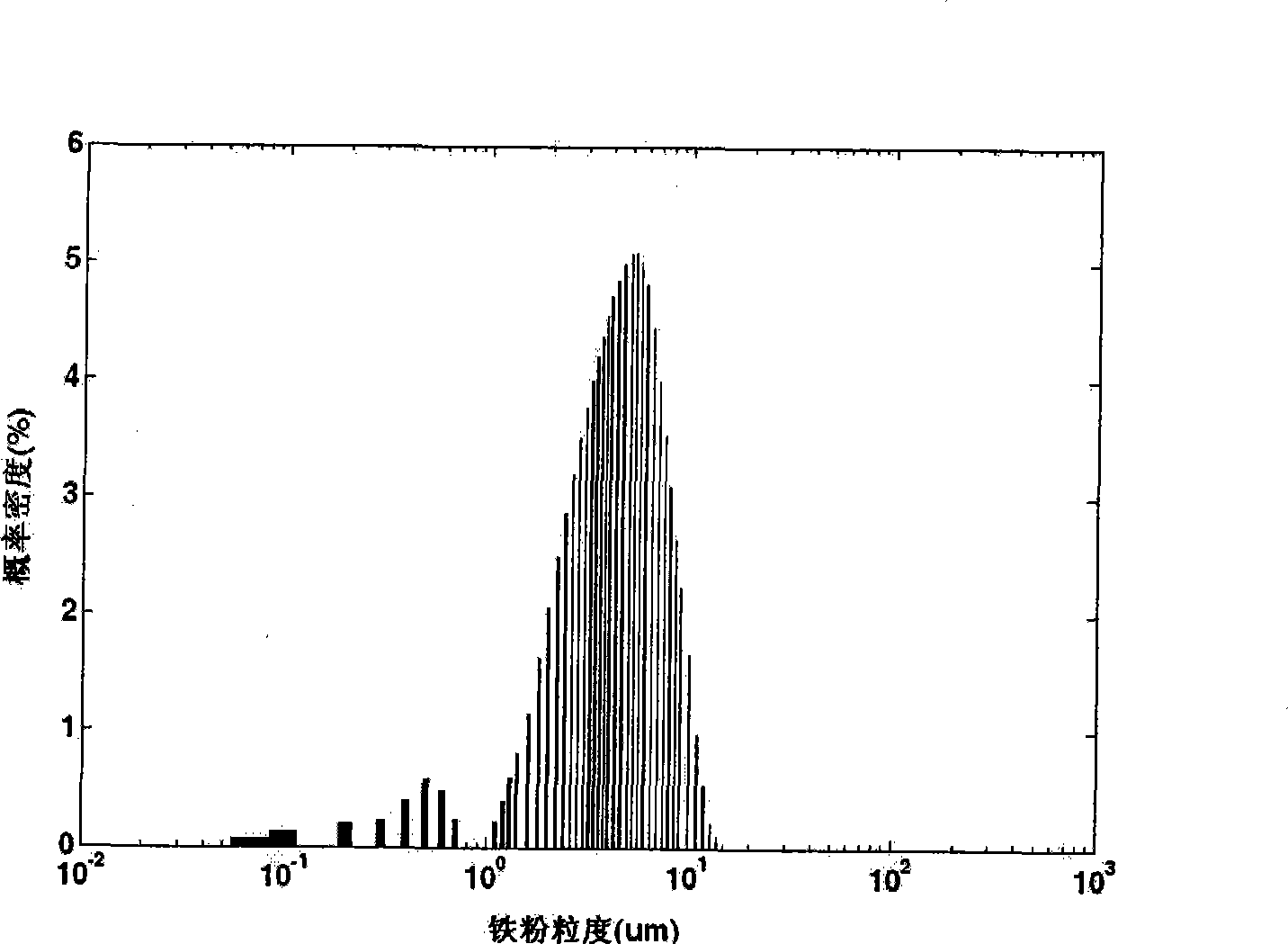
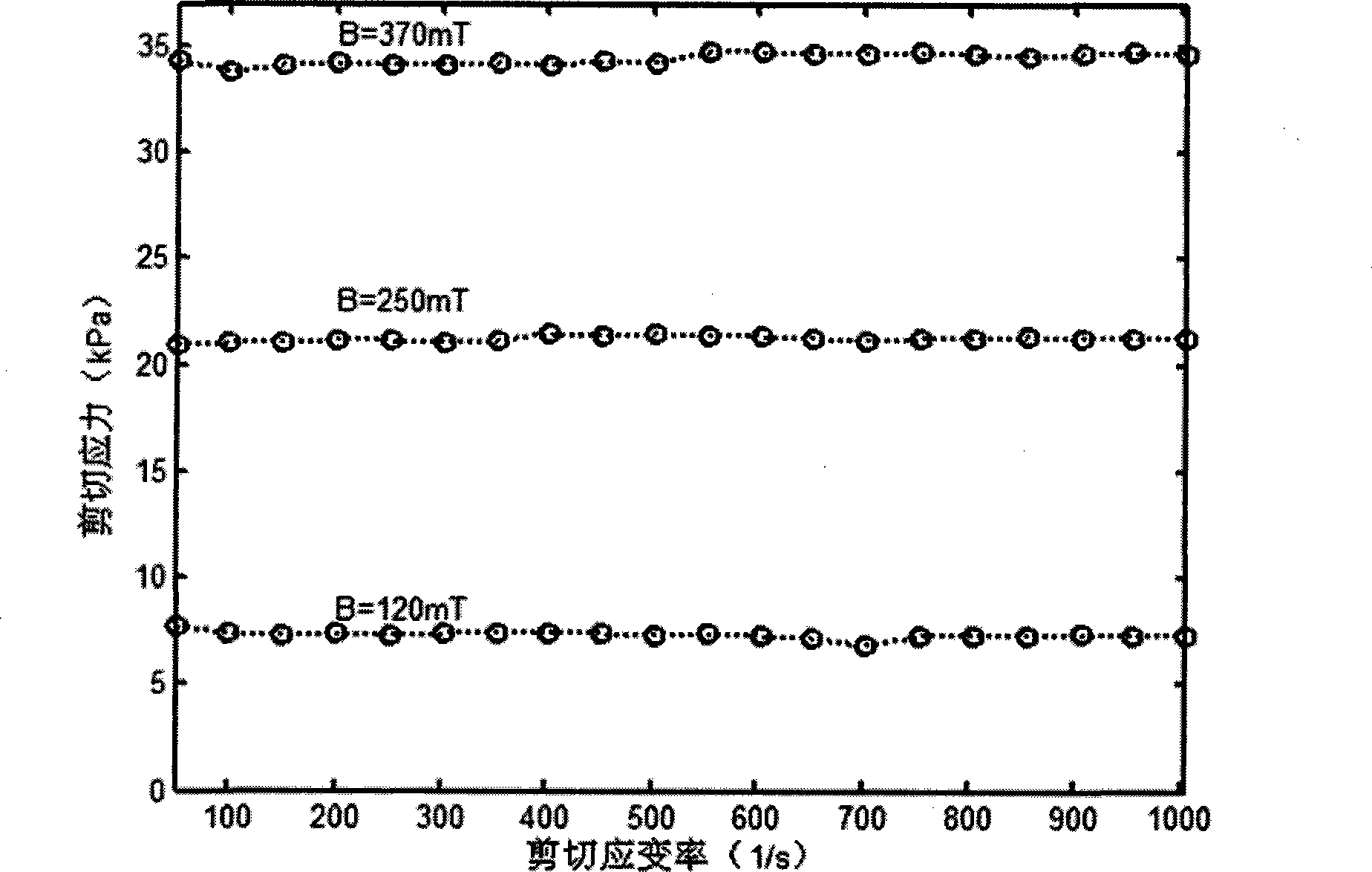
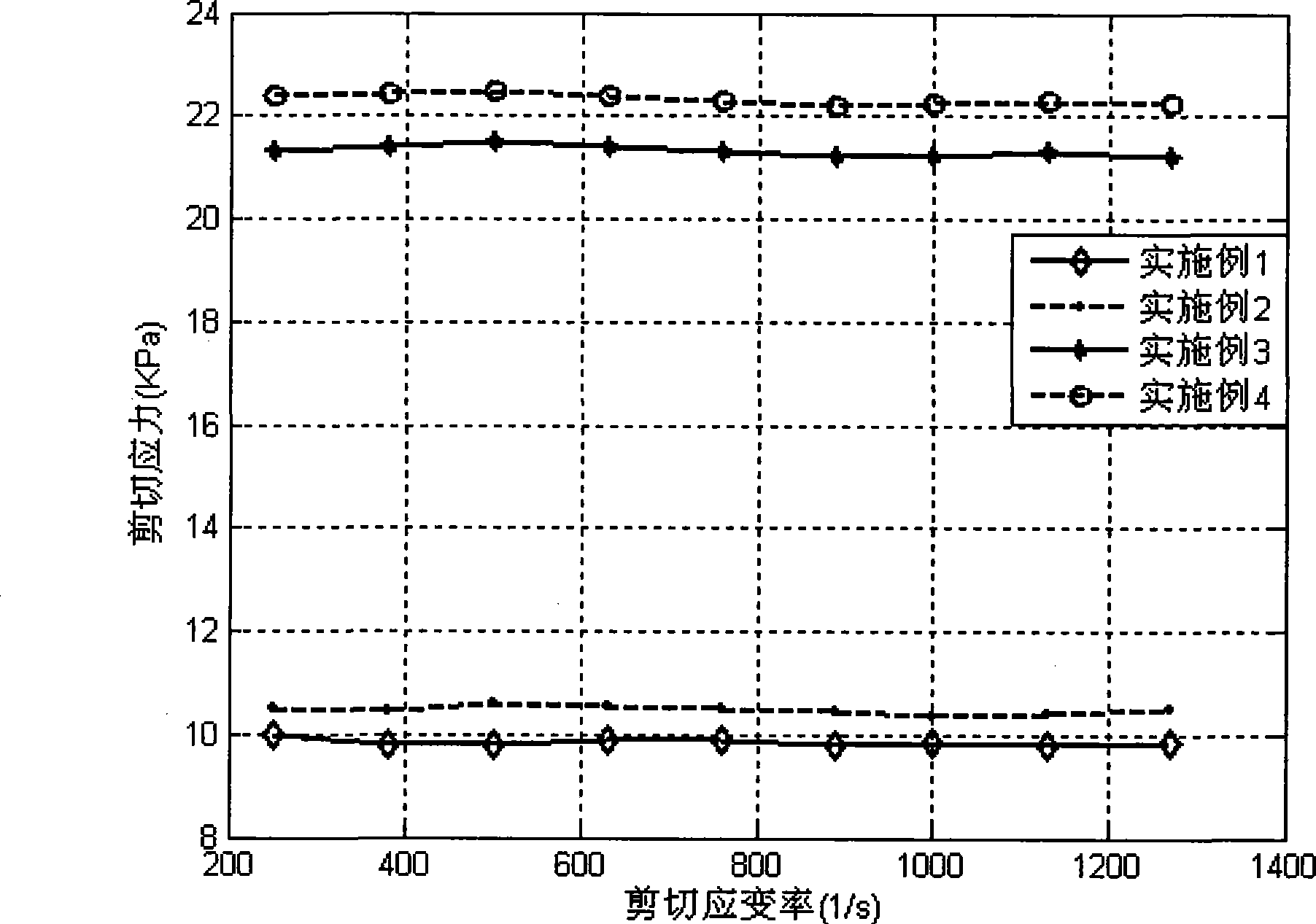
Patents
Literature
1797 results about "Magneto rheological" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magneto Rheological Fluid Market - Overview. Magneto rheological fluid (MR fluid or MRF) can be defined as smart and controllable fluids. It is a non-colloidal mixture of ferromagnetic particles randomly dispersed in oil or water, along with surfactants used to avoid the settling of suspended particles.
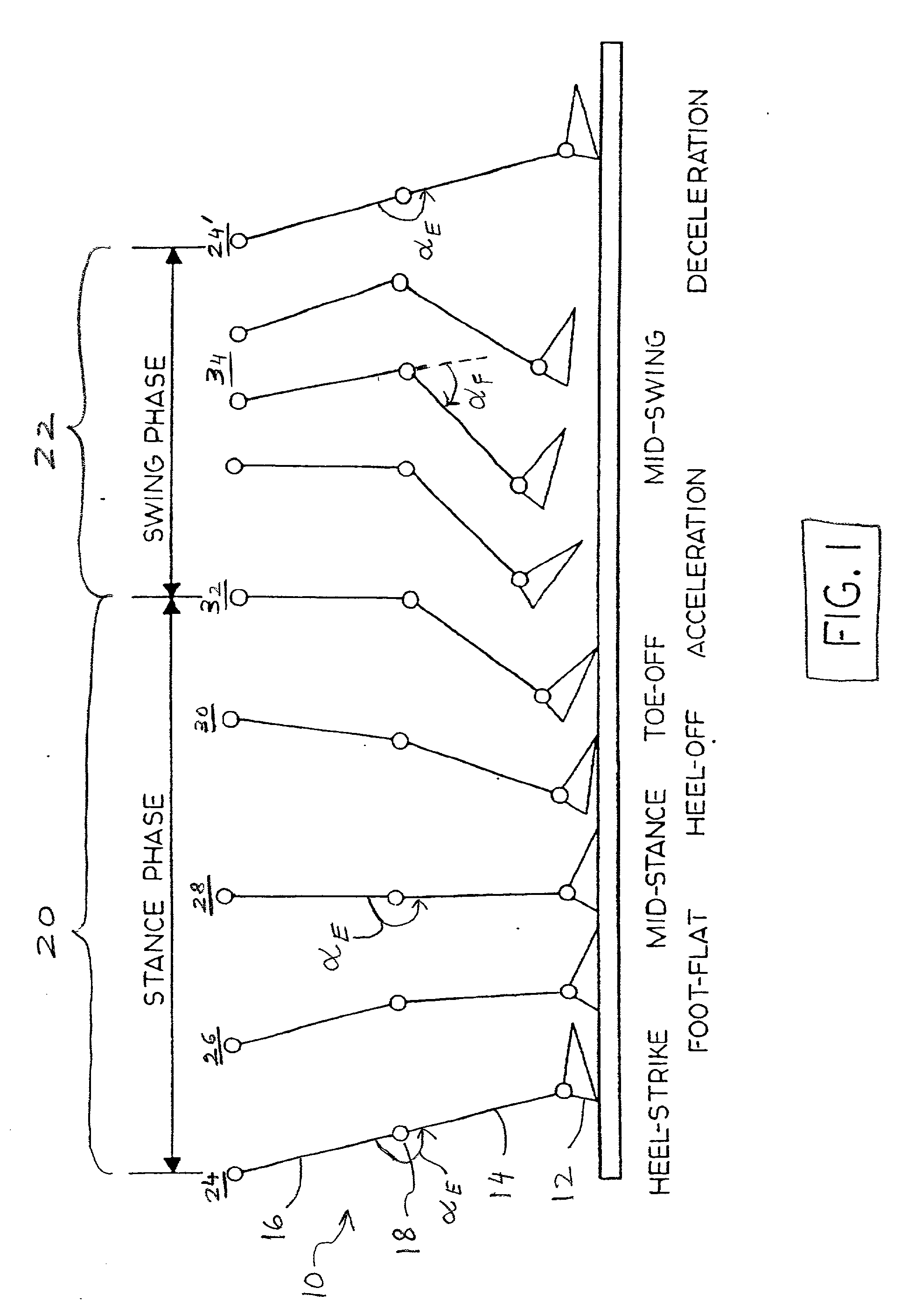
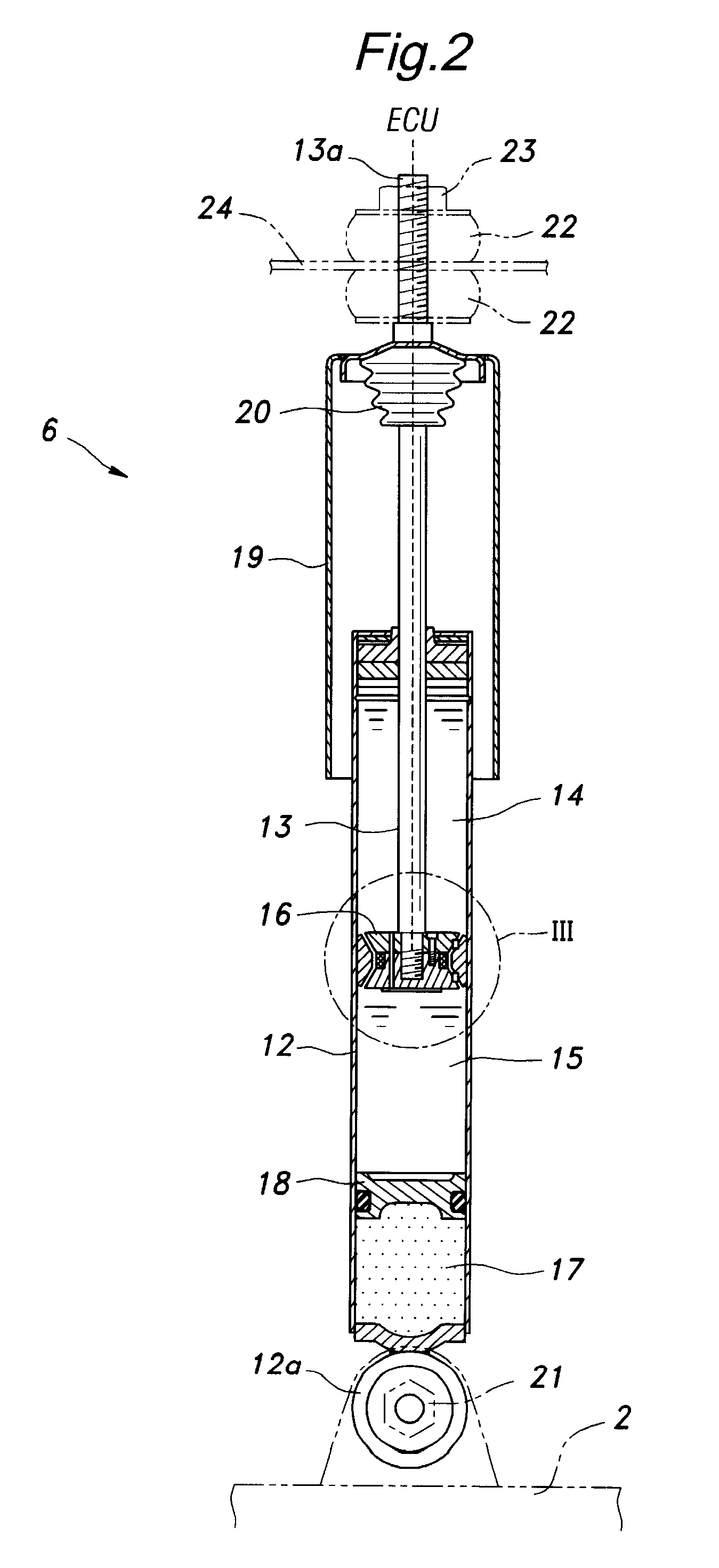
Electronically controlled prosthetic knee
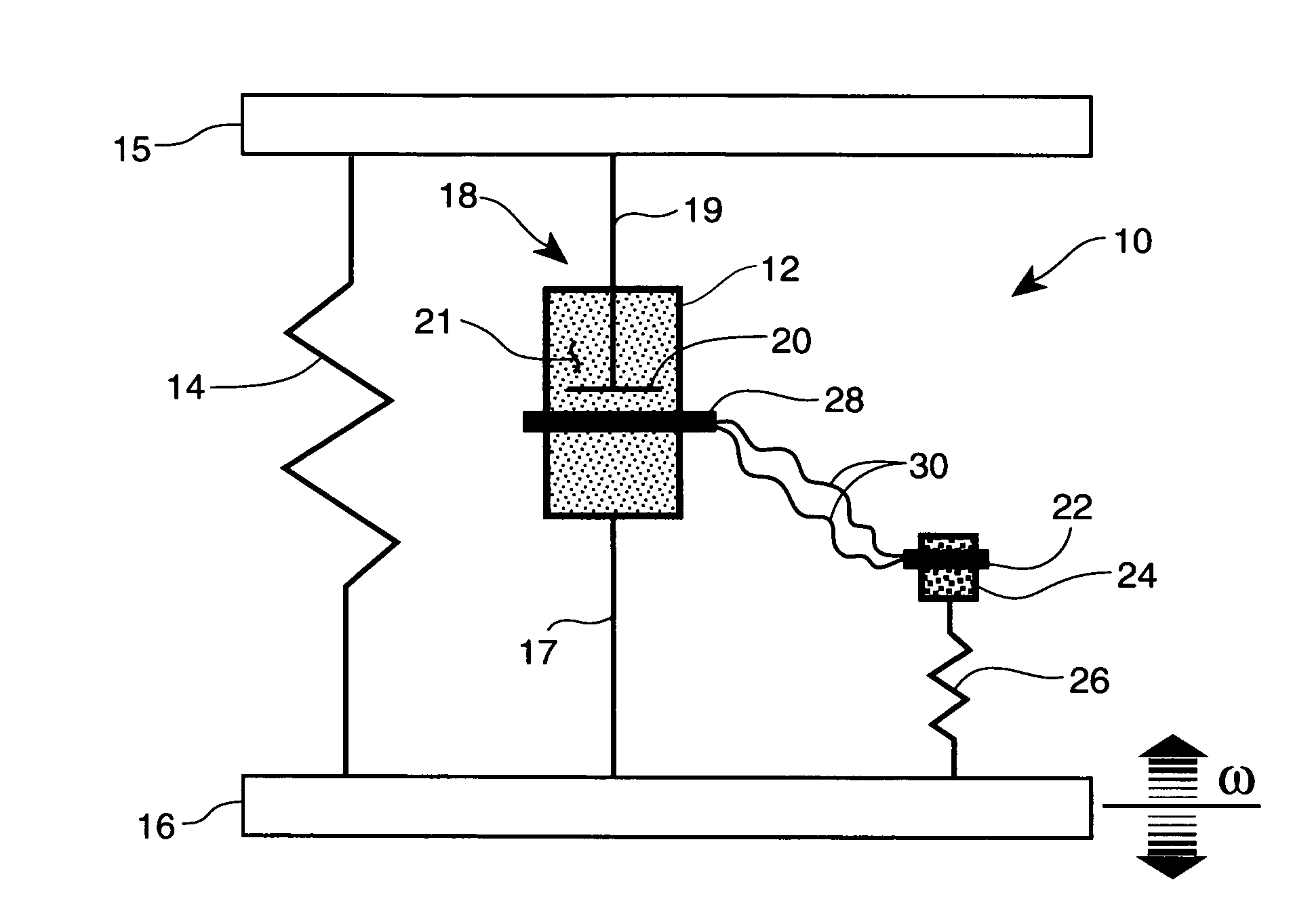
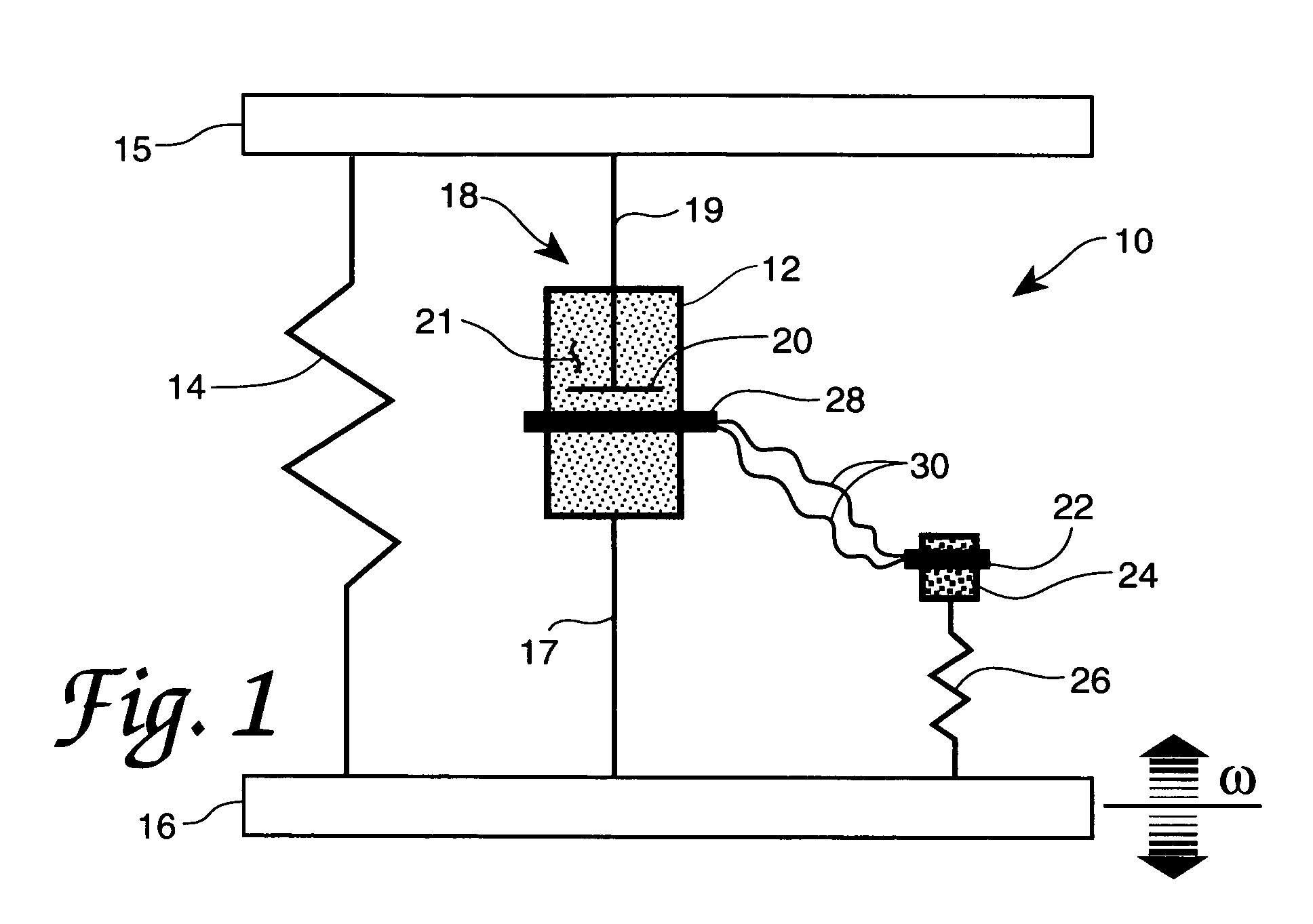
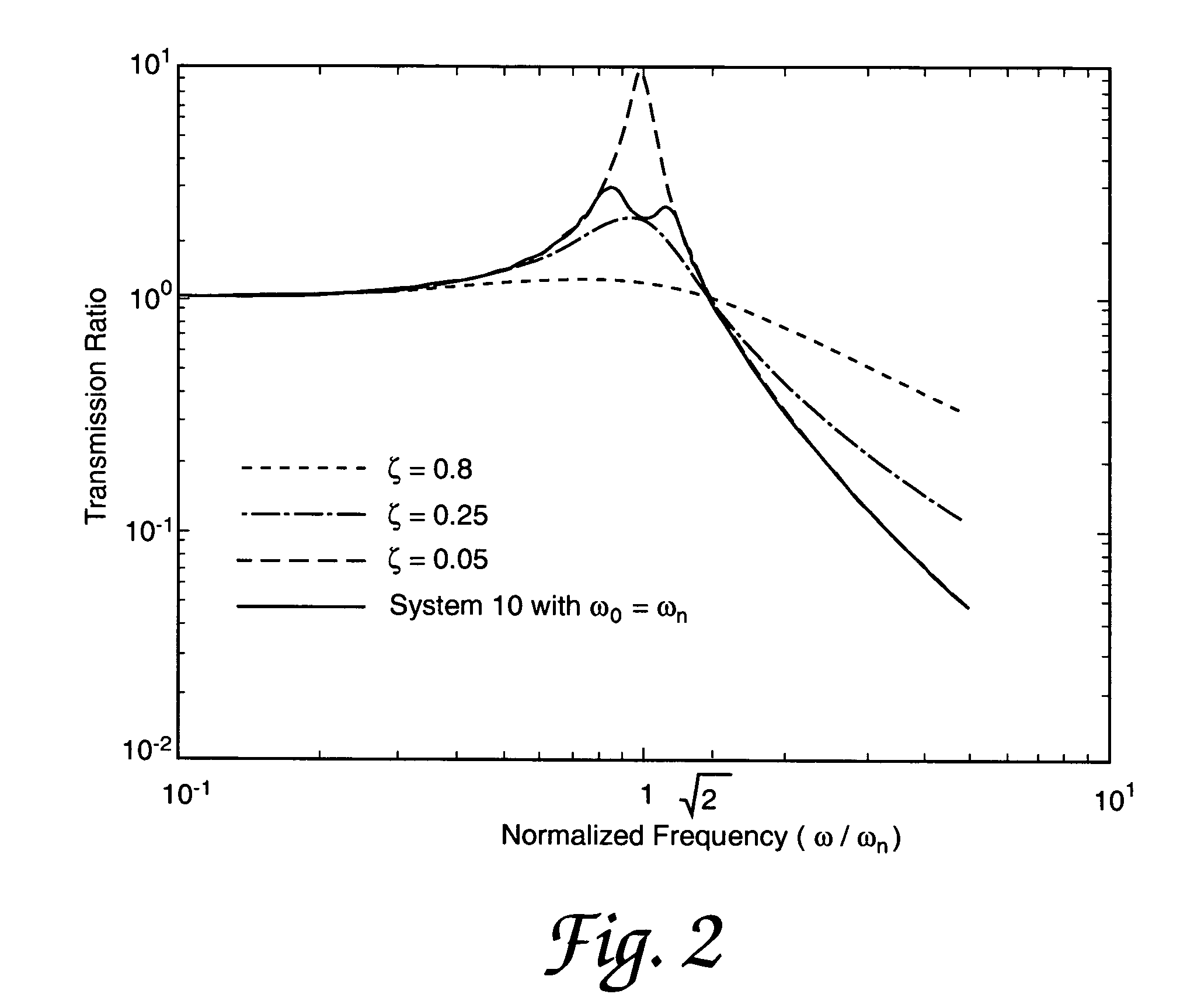
InactiveUS20010029400A1Move and/or adapt comfortably and safelyImprove efficiencySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionFriction torqueMagnetorheological fluid
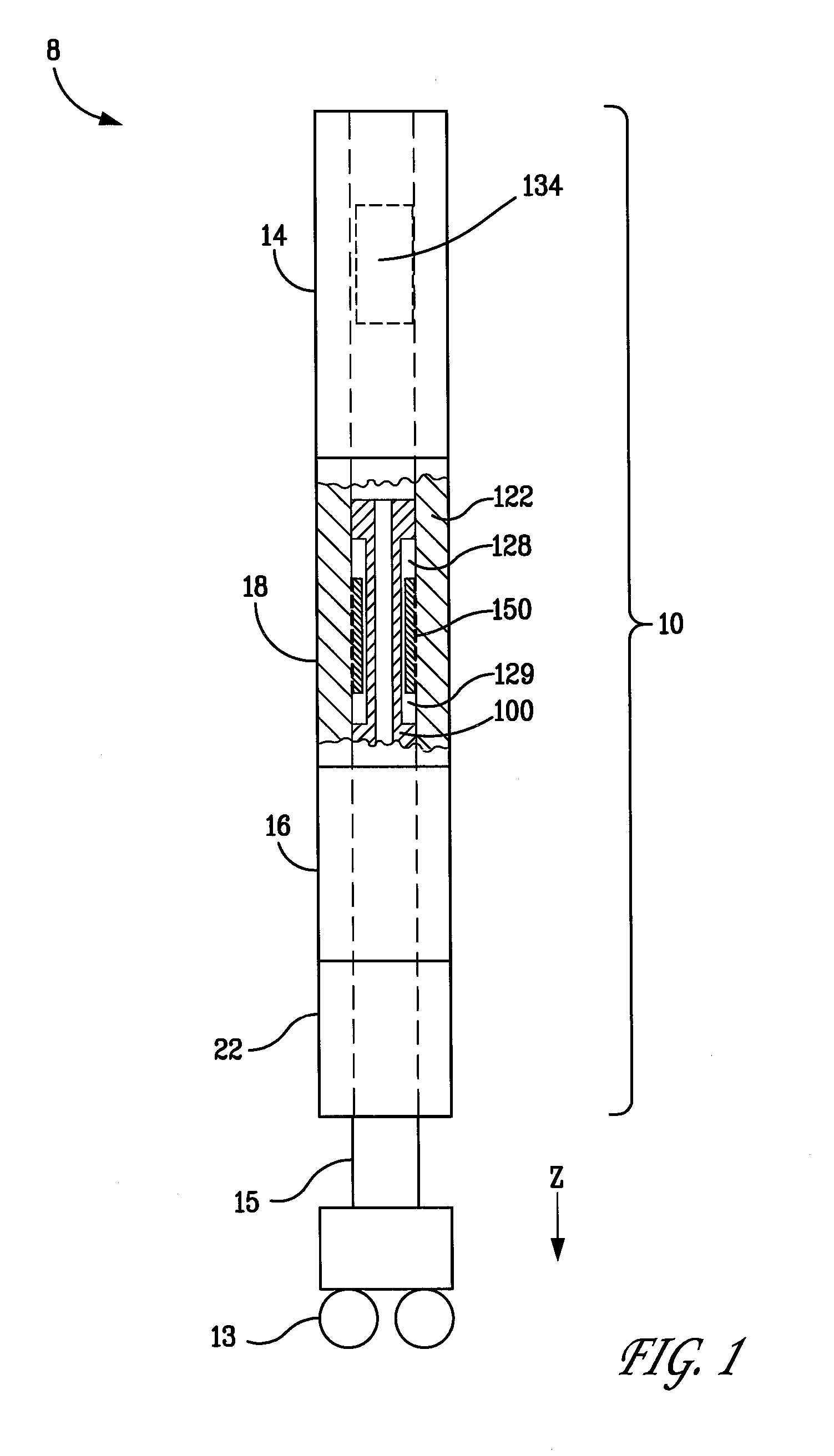
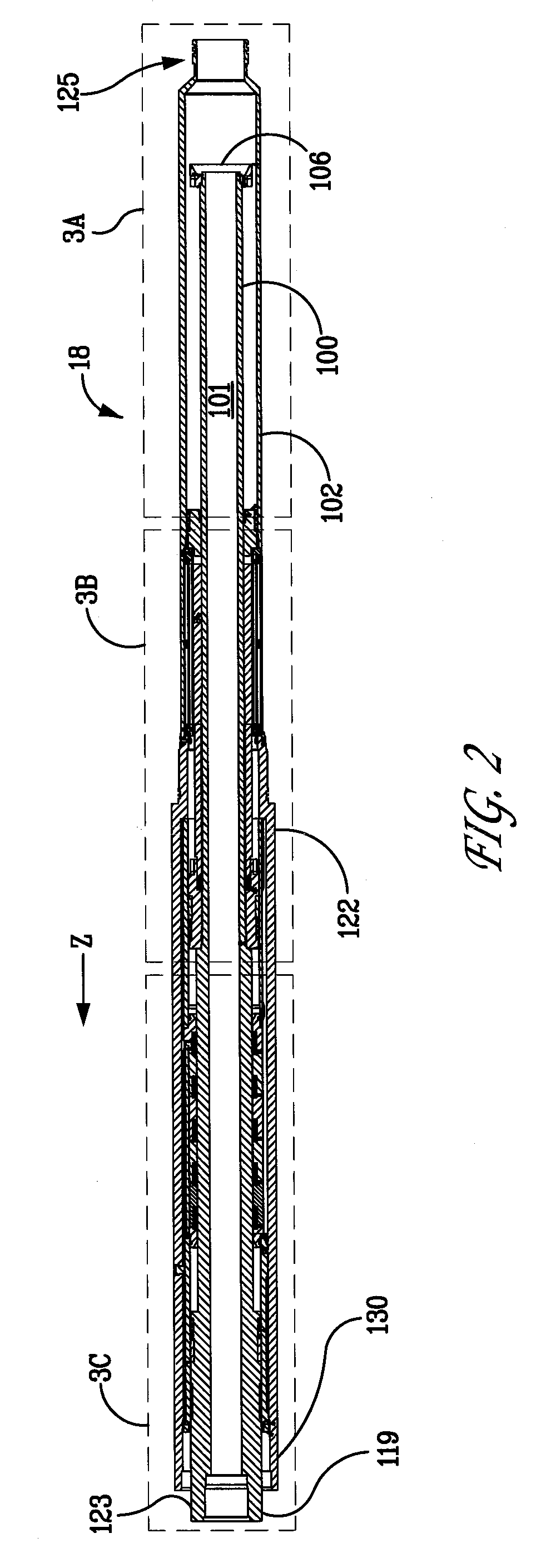
The present invention relates to a variable-torque magnetorheologically actuated prosthetic knee which utilizes a plurality of interspersed and alternating rotors and stators to shear magnetorheological fluid in gaps formed therebetween. Advantageously, by operating in the "shear mode" there is substantially no or negligible fluid pressure buildup or change. Moreover, the multiple MR fluid gaps or flux interfaces desirably allow for the production of a large torque at low speed-eliminating the need for a transmission-and also for a wide dynamic torque range. One embodiment of the invention allows the rotors and / or stators to close the gaps therebetween to create a frictional torque component, thereby forming a "hybrid" braking system which provides a total torque or damping which is a combination of viscous torque and frictional torque.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
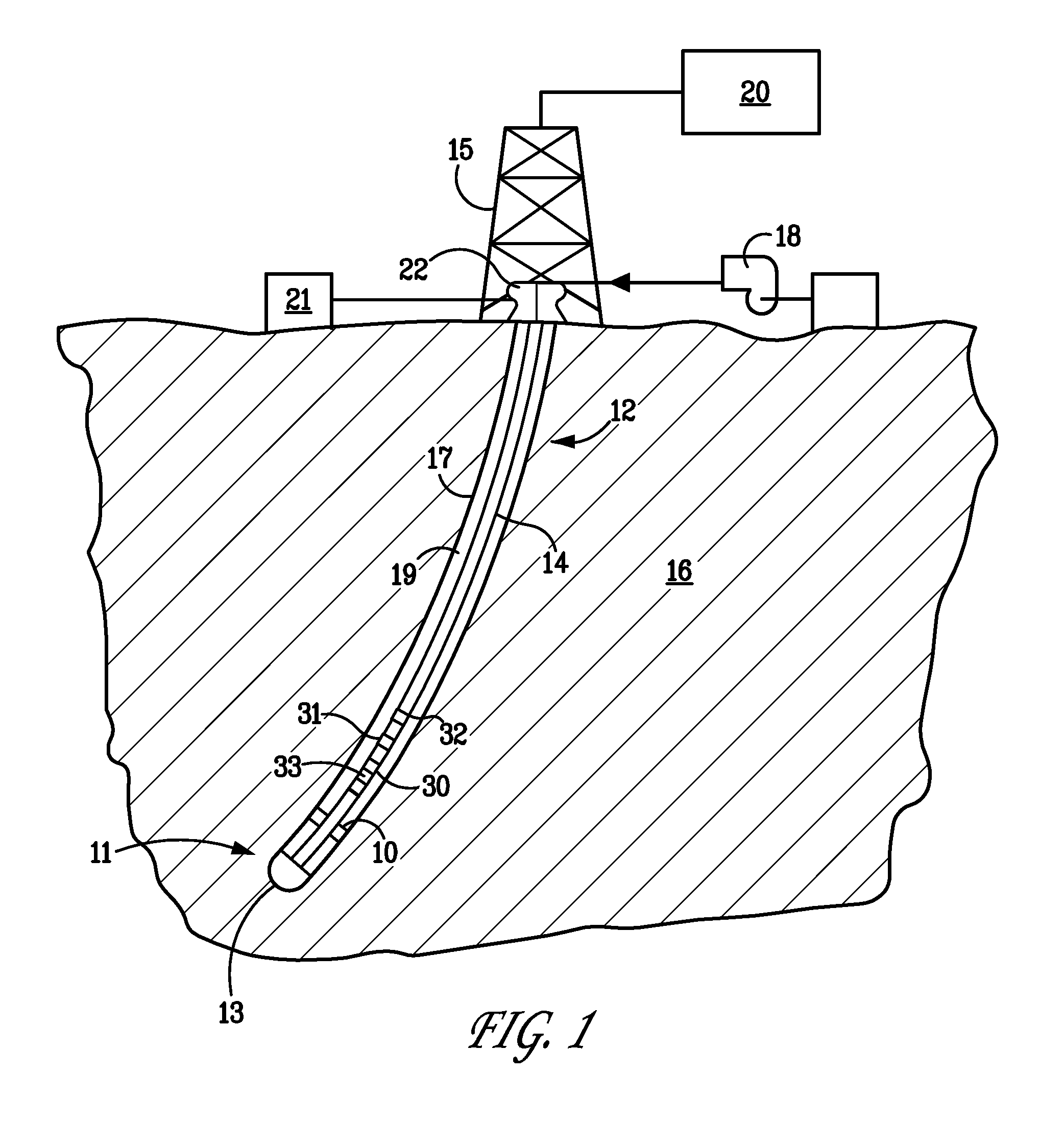
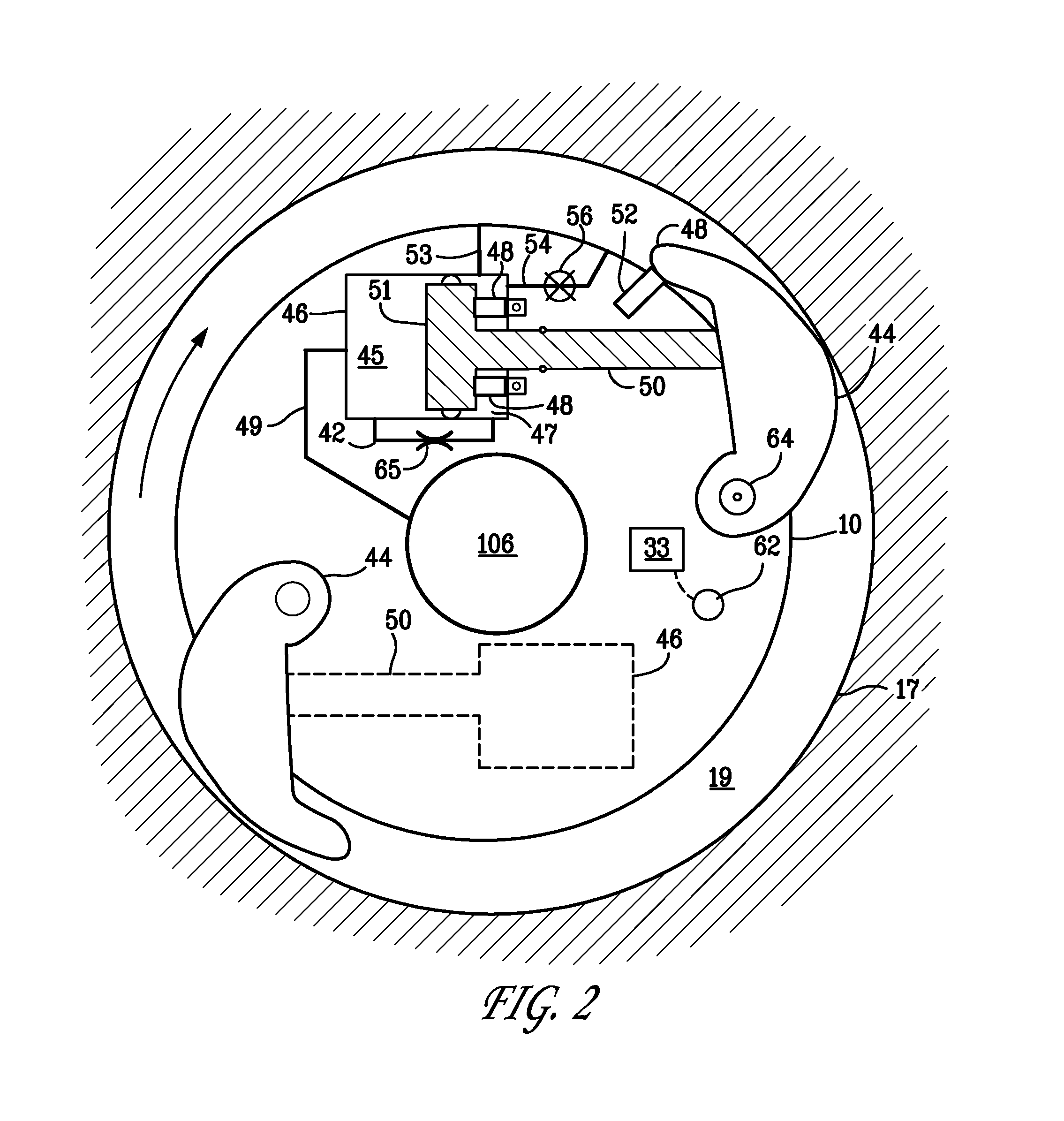
Apparatus And Method For Damping Vibration In A Drill String
ActiveUS20120228028A1Reducing drill string torsional vibrationLimiting maximum angular velocityDrilling rodsDirectional drillingMagnetorheological fluidAngular velocity
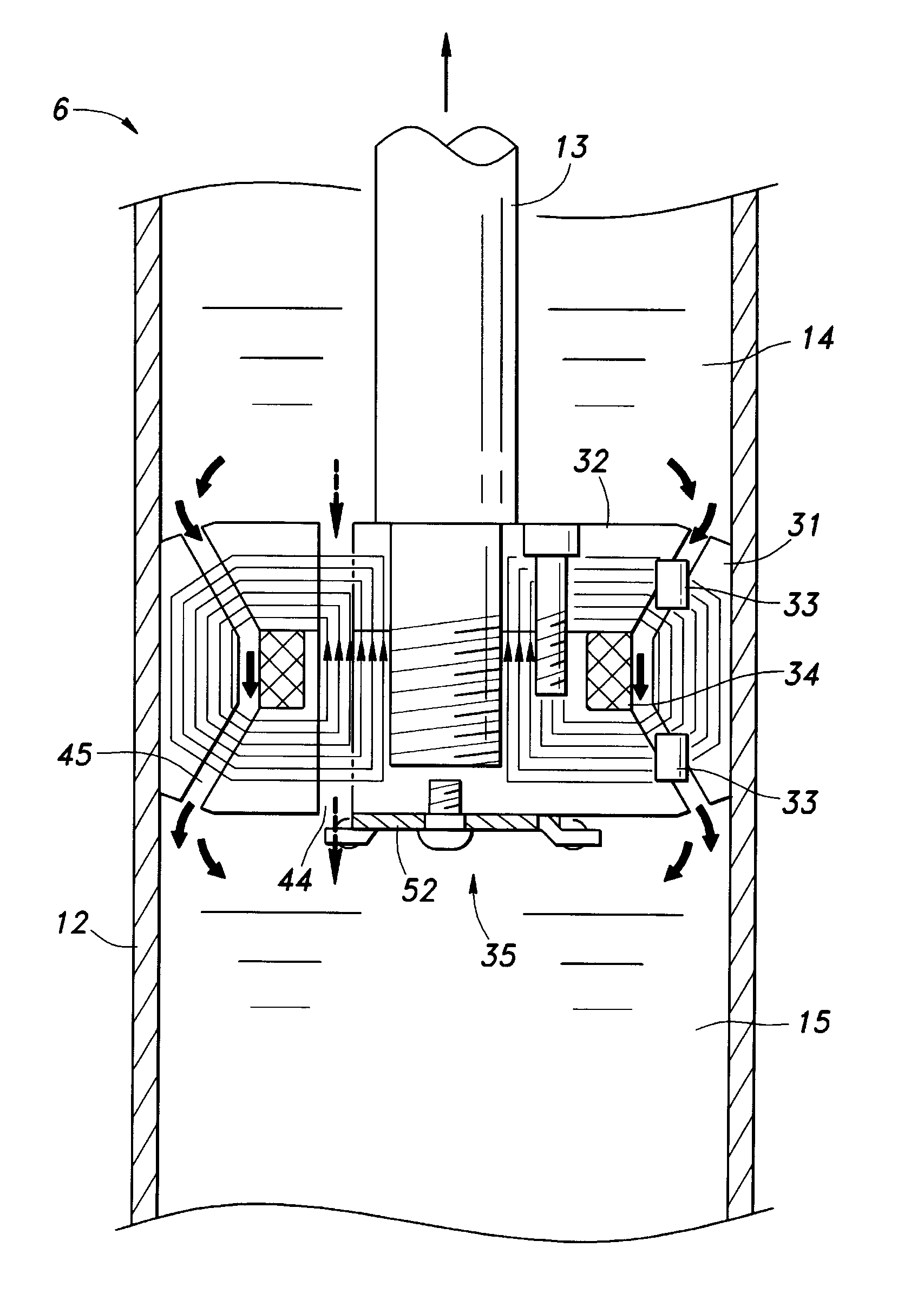
An apparatus and method for damping vibration, especially torsional vibration due to stick-slip, in a drill string, Sensors measure the instantaneous angular velocity of the drill string at one or more locations along the length of the drill string. One or more vibration damping modules are also spaced along the length of the drill string. When torsional vibration above a threshold is detected, the damping module imposes a reverse torque on the drill that dampens the torsional vibration. The reverse torque can be created by imparting a frictional resistance to the rotation of the drill string. The frictional resistance can be created externally, by extending friction pads from the damping module so that they contact the bore hole wall and drag along the bore hole as the drill string rotates, or internally by anchoring a housing mounted on the drill string to the wall of the bore hole and then imposing frictional resistance on a fluid, such as a magnetorheological fluid, flowing within the drill string.
Owner:APS TECH
Magneto-rheological damper with ferromagnetic housing insert
InactiveUS20020130000A1Improve performanceDecreased damping capacitySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagneto rheologicalControl theory
A magneto-rheological ("MR") damper having a damper body tube containing an MR fluid. A piston assembly is disposed in the damper body tube and forms an annular flow gap between the piston assembly and the damper body tube. The piston assembly has a piston core containing ferrous material and an electromagnetic coil mounted on the piston core for generating a magnetic field. The damper further includes a ferromagnetic member positioned outside of the damper body tube substantially adjacent the piston assembly for providing at least a part of a magnetic flux return path for the magnetic field.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC +1
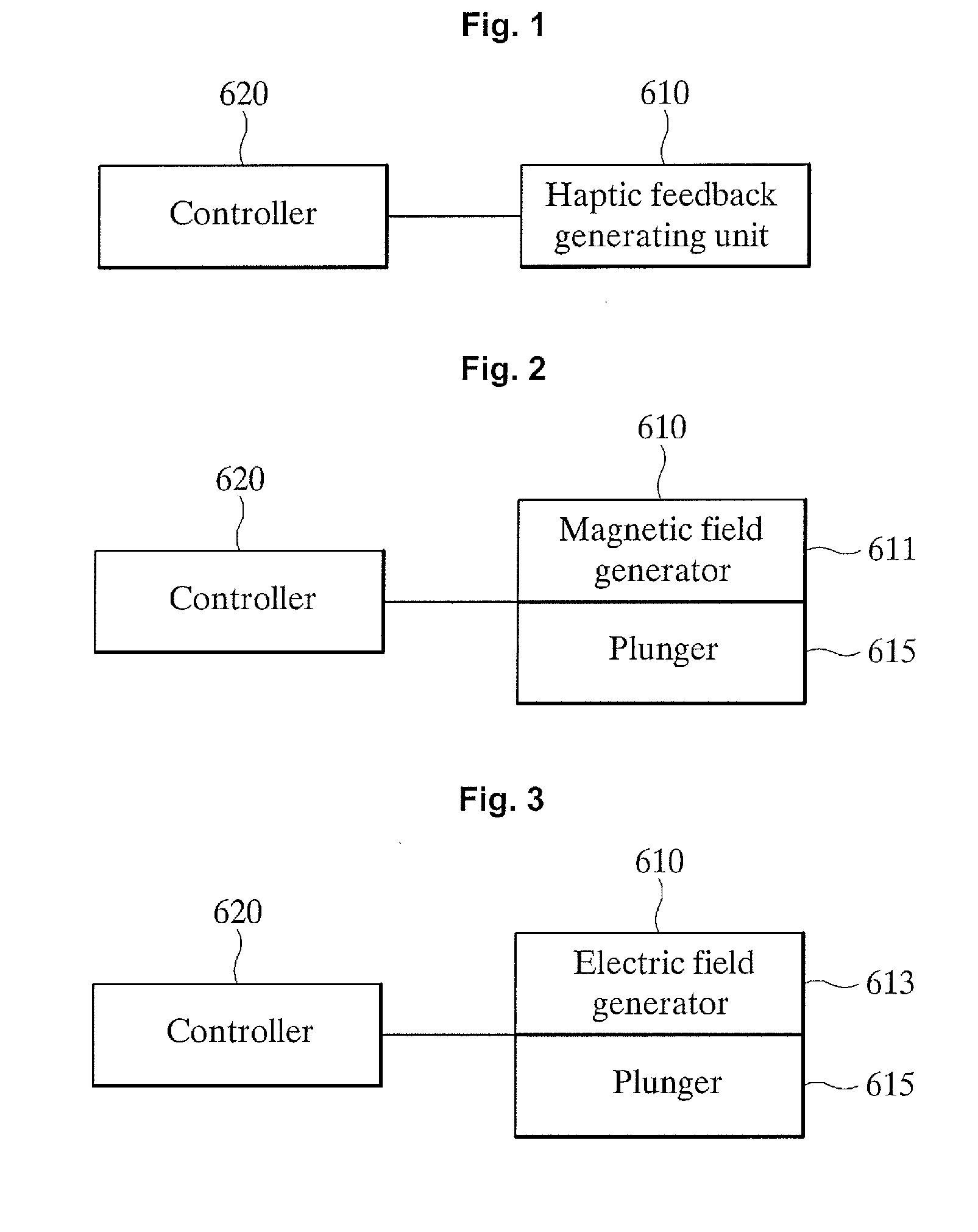
Haptic feedback generator, portable device, haptic feedback providing method using the same and recording medium thereof
InactiveUS20120112894A1Resistance may varyChange resistanceRepeater circuitsInput/output processes for data processingControl signalMagnetorheological fluid
An apparatus and a method for generating haptic feedback and a portable device having the apparatus are provided. The haptic feedback generator changes the property of a magneto-rheological fluid or an electro-rheological fluid using a magnetic field or an electric field and transmits haptic feedback using the property variation. The haptic feedback generator includes a controller 620 outputting a control signal for providing a haptic feedback based on application information selected by a user and a haptic feedback generating unit 610 generating the haptic feedback based on the control signal and providing the haptic feedback in response to an external force Fin of the user.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Controllable magneto-rheological elastomer vibration isolator
InactiveUS20050011710A1Expand the scope of operationIncrease its stiffness sensitivityMachine framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionElastomerControl system
A tunable vibration isolation device comprising a magneto-rheological elastomer (MRE), and methods of using such a device, are provided. By manipulating a magnetic field within the MRE the device's stiffness is controlled. The vibration isolator can be constructed to provide shock absorption in one, two and three dimensions. Coupling the tunable device to a sensor feedback and a control system provides fast and accurate vibration isolation and energy dissipation for shock events in a variety of applications.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT NEVADA SYST OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF NEVADA RENO
Power-off damping in MR damper
InactiveUS6419057B1High than minimum level of dampingMore operating rangeSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionElectricityEngineering
A magneto-rheological (MR) damper provides a higher than minimum level of damping when a power source to the MR damper is not supplying a control current. The present invention damper includes magnets positioned to direct a magnetic flux across a MR fluid path. The fluid path is created when a rod and piston assembly stroke the fluid though a control valve assembly attached to a damper chamber causing a resistance to MR fluid flow. An electric coil cancels an effect of the permanent magnets when the control current is available to allow a control circuit more operating range. The permanent magnets allow for damping when no control current is available.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC +1
Fluid haptic interface with improved haptic rendering using a torque or load sensor
ActiveUS9898032B2Improved haptic renderingReduce, or even suppress, a spatial and time delay in the control of the interfaceControlling membersSpringsMagnetic currentLow speed
A haptic interface, including: a button which can be rotated by a user; an interaction element interacting with a magnetorheological fluid, secured to the button; a mechanism measuring a current position of the button; a brake including a magnetorheological fluid and a generation system to generate a magnetic field in the fluid; a controller configured to generate orders for the system to generate a magnetic fluid to modify a value of the magnetic field; and a mechanism to detect torque exerted by a user on the button to know direction of the torque and whether the torque is greater than a given value for a given direction, the controller controlling generation of a magnetic field based on obtained information about the torque at least when the button indicates zero or low speed.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Magnetic nanoparticles decorated activated carbon nanocomposites for purification of water
InactiveUS20160243523A1Material nanotechnologyOther chemical processesSorbentMagnetite Nanoparticles
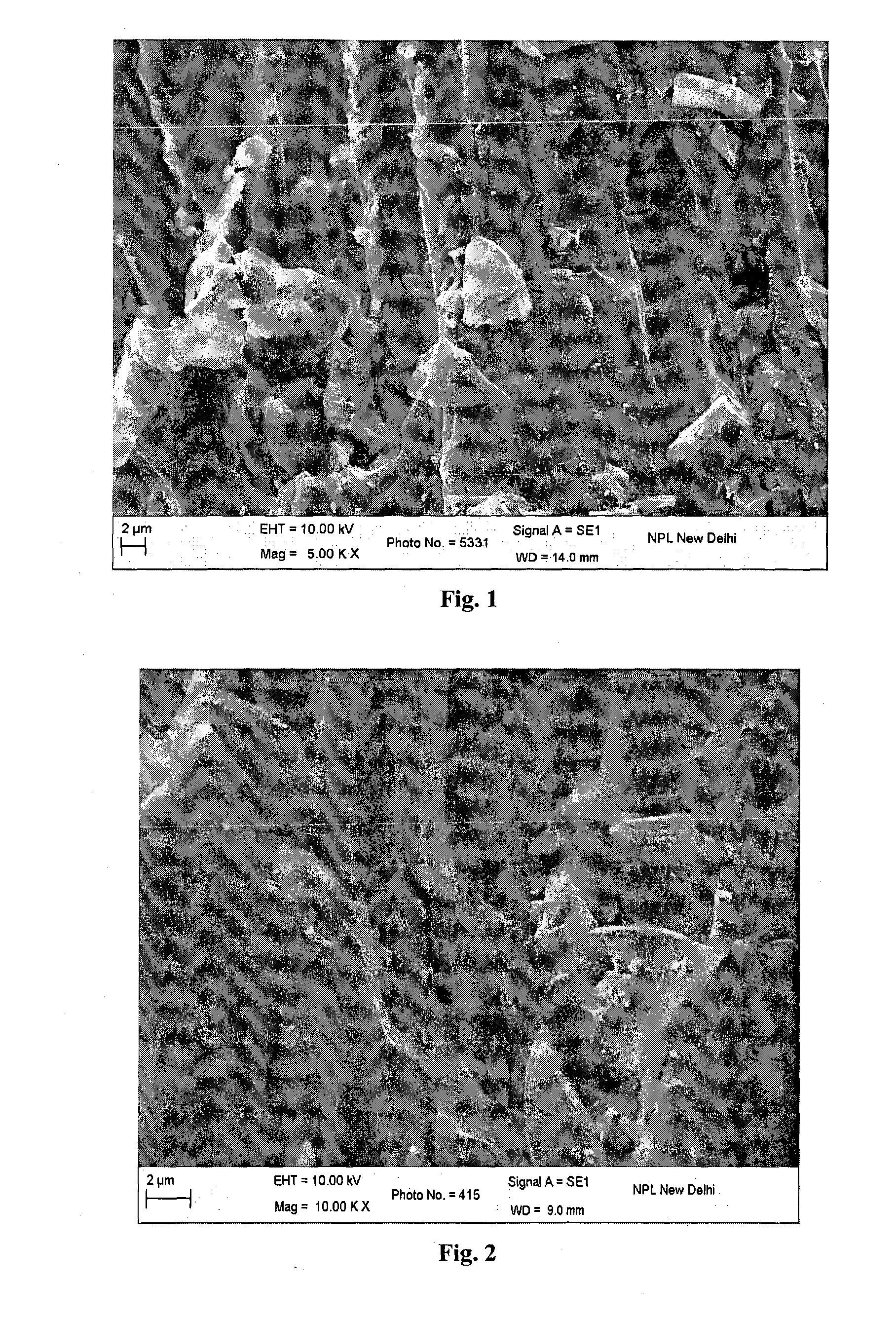
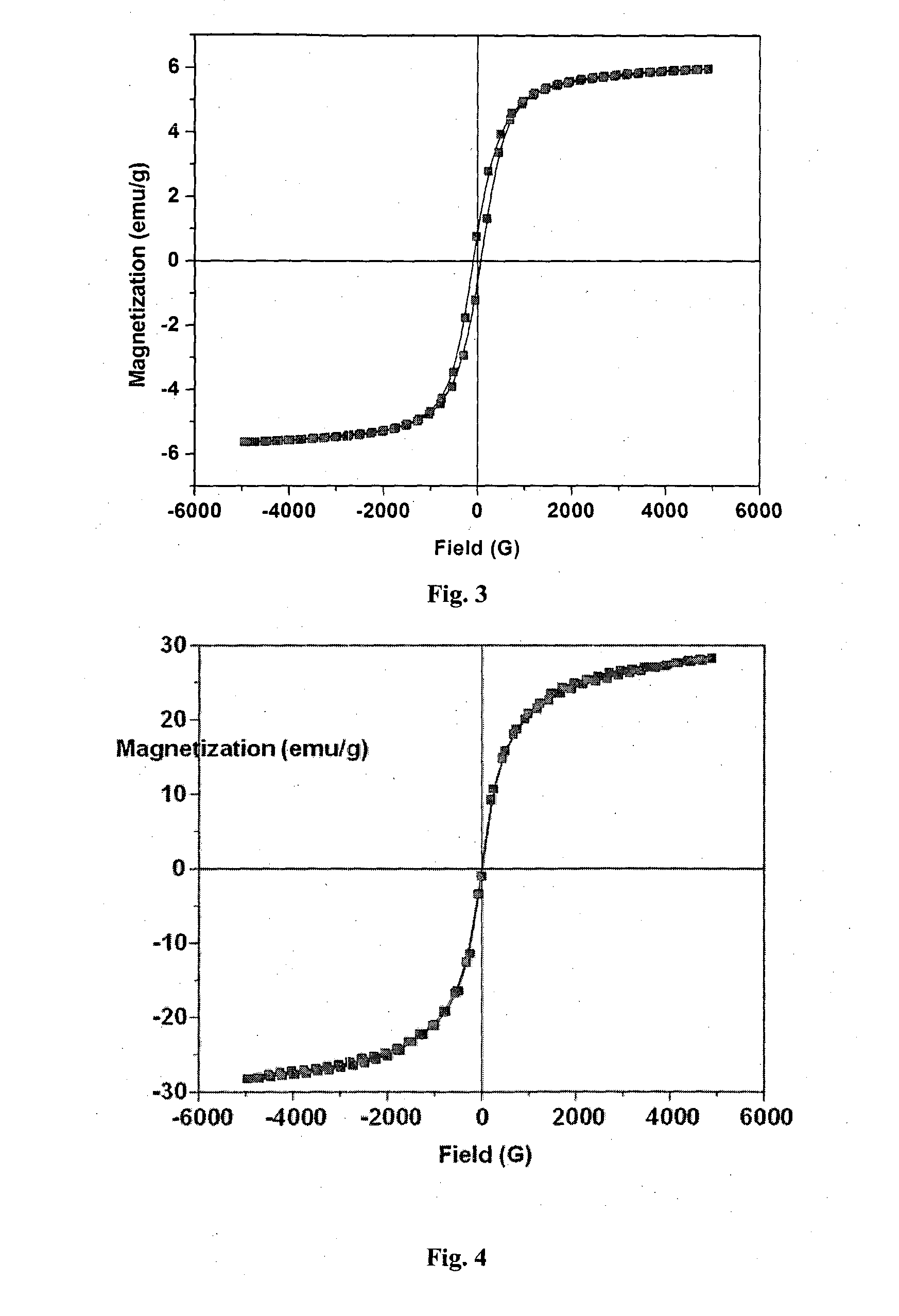
The present invention relates to the development of water purifying compositions based on magnetic nanoparticles decorated activated carbon nanocomposites which display both magnetic character as well as adsorbent characteristics. The addition of adsorbent to impure water containing dye as pollutant enables the fast adsorption of dye leading to discoloration of water whereas magnetic properties facilitates the rapid isolation of pollutant adsorbed nanocomposites powder from the purified water with the aid of a magnet. The present invention also provides a process for the development of such multifunctional adsorbent using a process which enables decoration of adsorbent with 5-50 weight % of magnetic nanoparticles, the enables the realization of magnetic adsorbent having saturation magnetization in the range 0.09 to 28.3 emu / g, dye removal efficiency of >99%, rapid decolourization of methylene blue (MB) / methyl orange (MO) dye polluted water in less than 1 min, magnetic separation time in the range <0.2 to 60 min and dye sorption capacity in the range of 3.3×10−4 to 116.3×10−4 mol of MB and 3.6×10−4 to 148.6×10−4 mol of MO dye per 100 gram of nanocomposite powder in a rapid adsorption (<1 min) and magnetic separation process. Besides, these nanocomposites could also be useful for other of applications e.g. as separation of catalytic residues from the products, for removal of oil from water, filler for development of thermally / electrically conducting magneto-rheological fluids or for handling of electromagnetic pollution.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Haptic feedback device
InactiveUS20060197741A1Quick changeManual control with multiple controlled membersLimiting/preventing/returning movement of partsSteering wheelMagneto rheological
Owner:ULTRA ELECTRONICS LTD
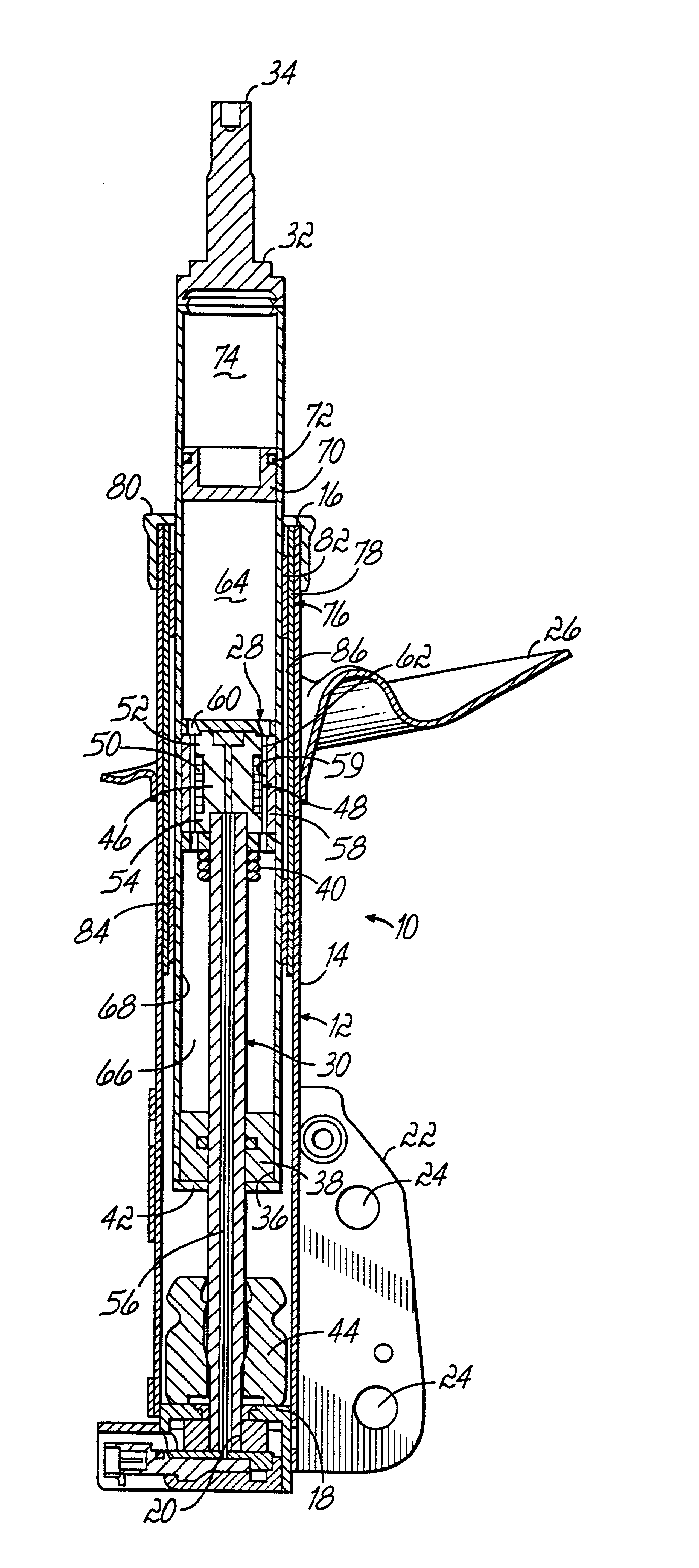
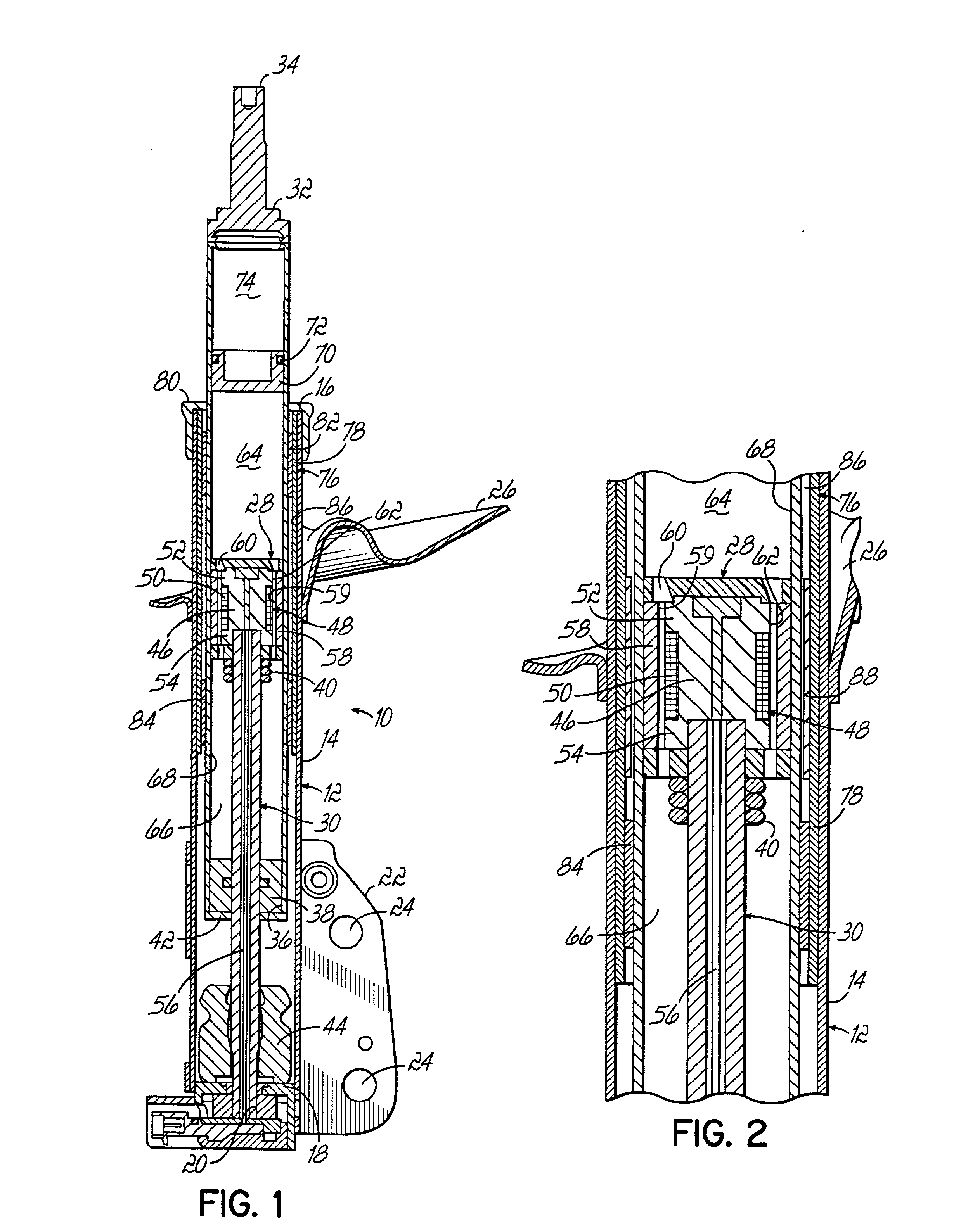
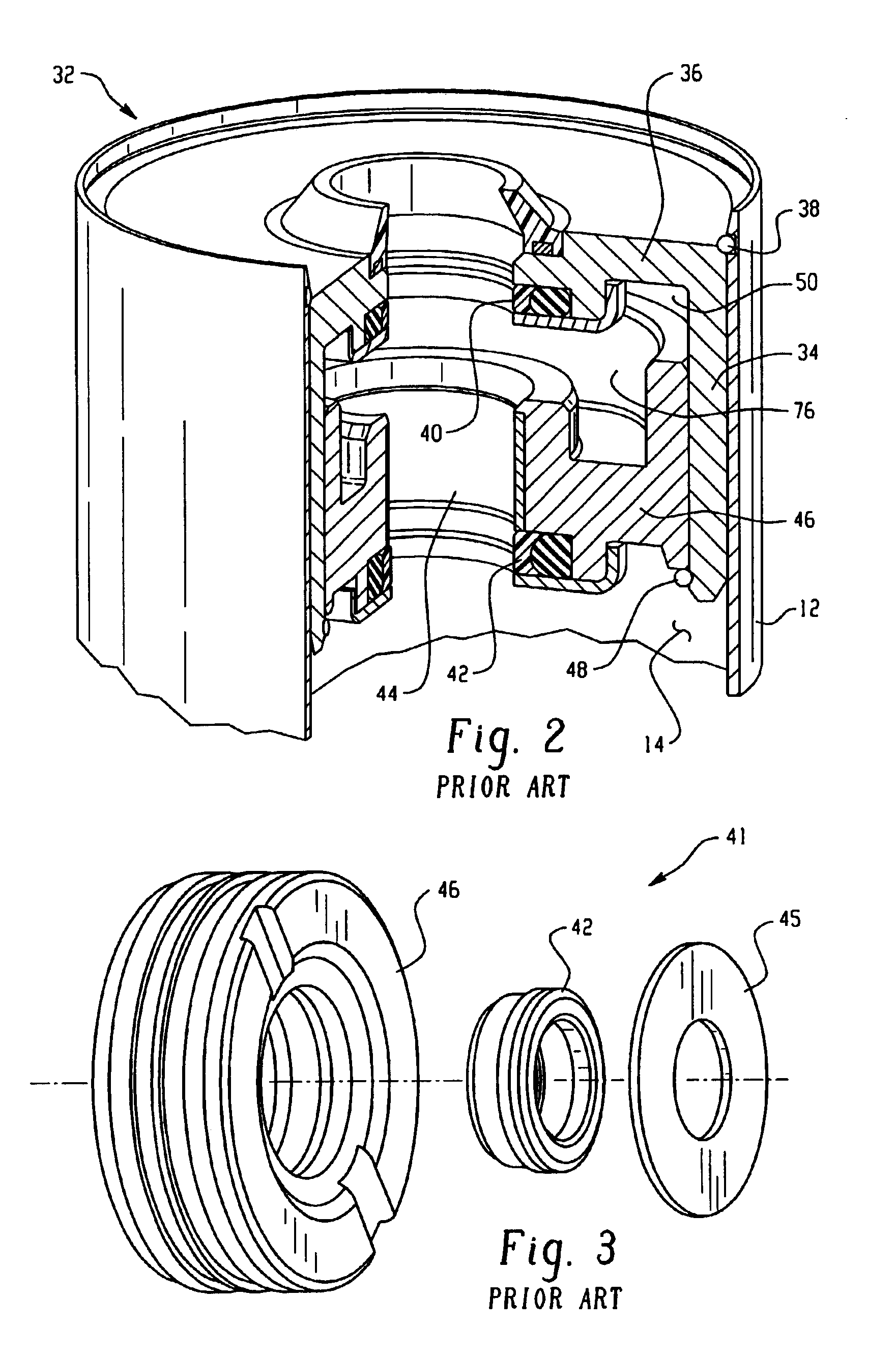
Closing system for a magneto-rheological damper
A closing system for use with a magneto-rheological (MR) damper. The closing system provides lubrication for a piston rod without a need for periodic replenishment. According to an embodiment of the present invention, a lubrication chamber of the closing system utilizes a carrier fluid portion of MR fluid present in a fluid reservoir of the damper as lubricant for a piston rod guide and the piston rod. A seal retainer comprised of a porous material acts as a selective barrier to the micro-particles in the MR fluid in the fluid reservoir, allowing the MR carrier fluid portion to pass through the porous seal retainer to the lubrication chamber while restraining the micro-particles in the fluid reservoir. The seal retainer thus acts as a filter to segregate the abrasive particles of the MR fluid and allows the MR carrier fluid portion of the MR fluid to continuously replenish the lubrication chamber and lubrication passage to lubricate the piston rod guide and piston rod.
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA +1
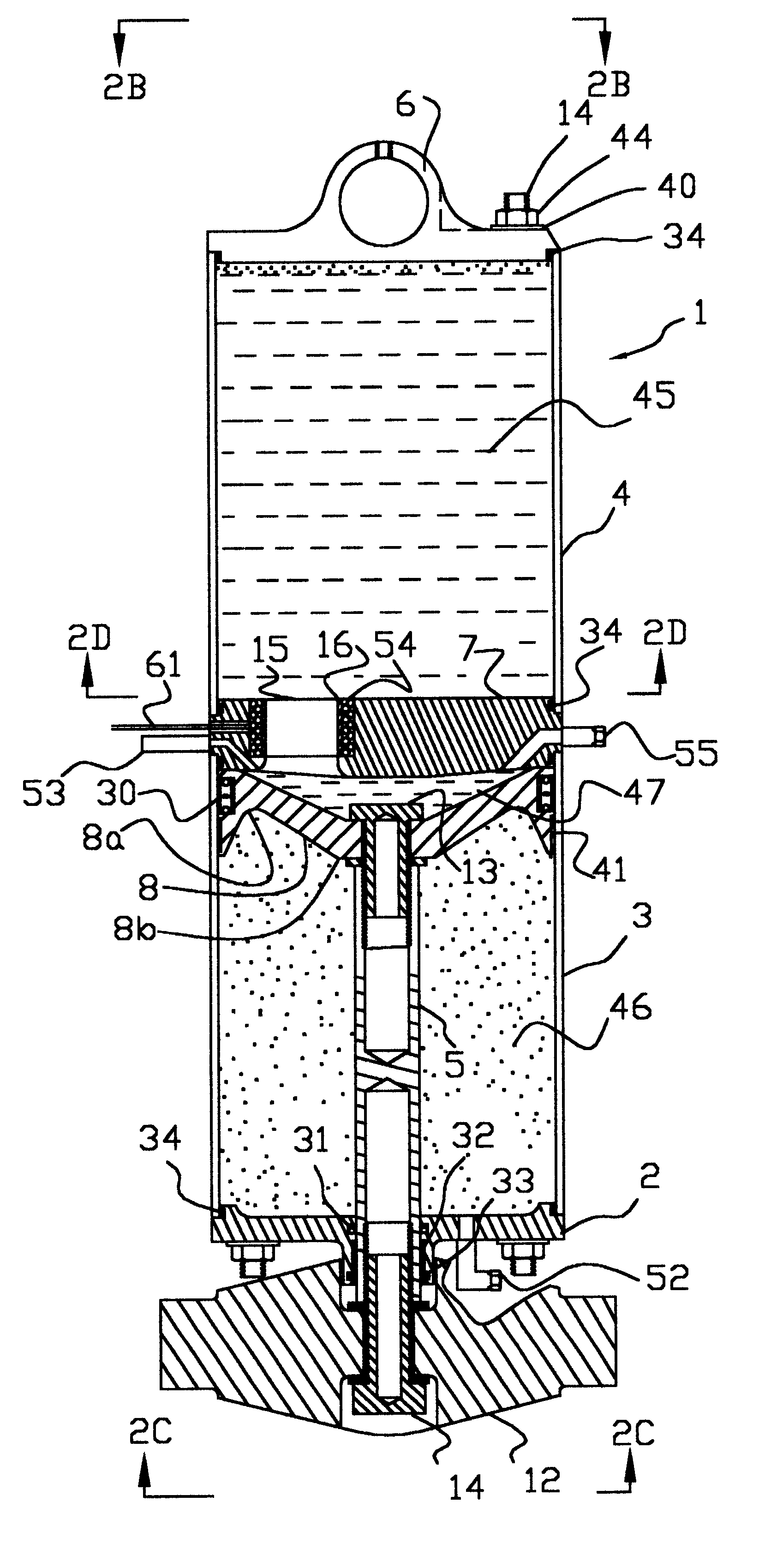
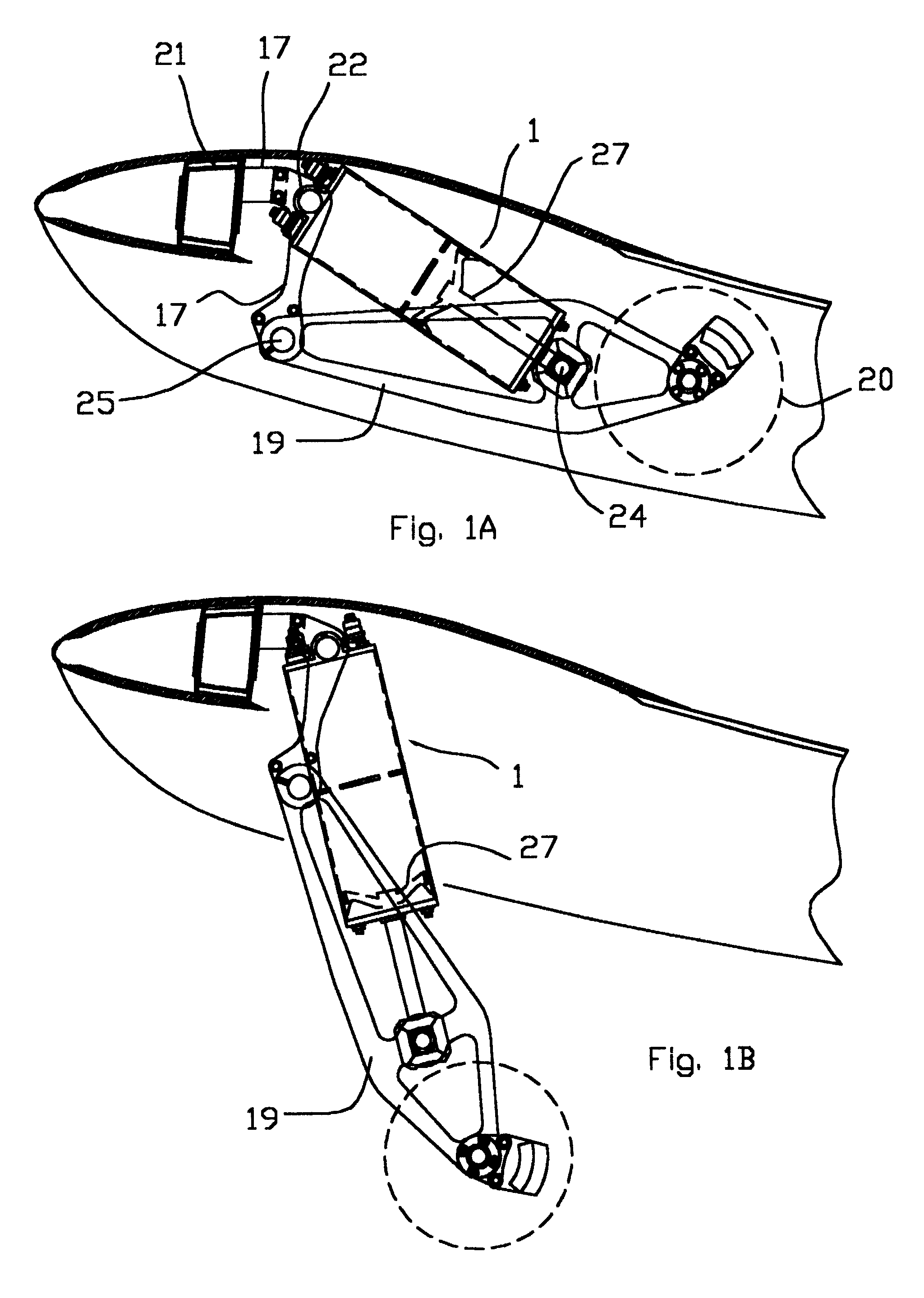
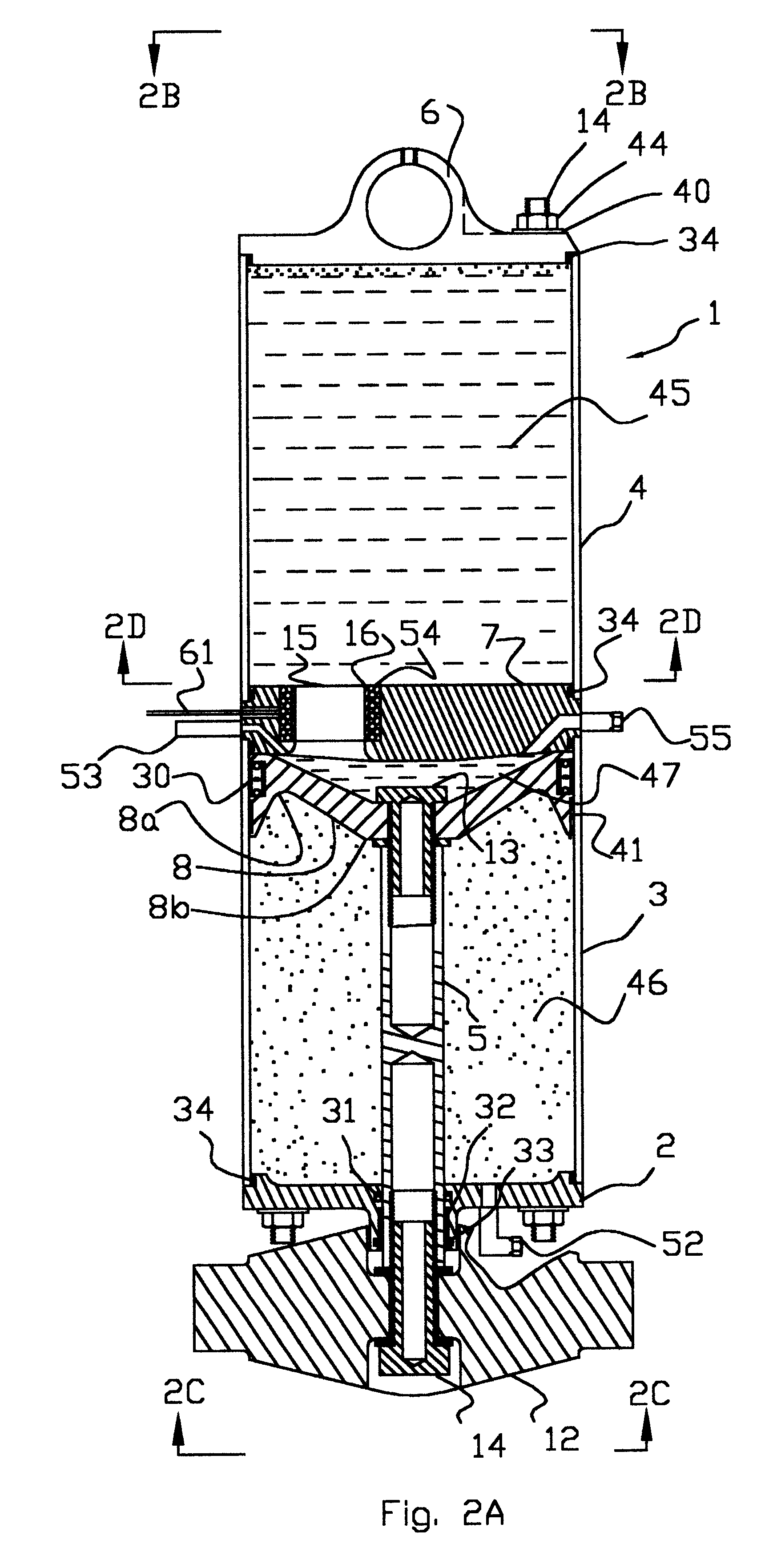
Landing gear shock absorber with variable viscosity fluid
An aircraft landing gear includes a sealed cylinder divided by a cylinder head to define an upper chamber and a lower chamber. The lower chamber is further divided by a piston having a piston rod passing in a sealed manner through the lower cylinder end. The cylinder head includes one or more orifices, the opening of each containing an electromagnetic coil configured to control the viscosity of the magneto-rheological oil passing therethrough. The electrical current through the electromagnetic coil is continually controlled by a microcomputer with attached sensors for piston position and pressure between the desired piston and the cylinder head, such that the pressure between the piston and the cylinder head decelerates the aircraft evenly throughout the desired piston stroke. The pressure also is limited to a desired maximum level so that, in a severe crash, the shock absorber will absorb significant energy before it fails structurally.
Owner:JAUNT AIR MOBILITY LLC
Active seat suspension for watercraft
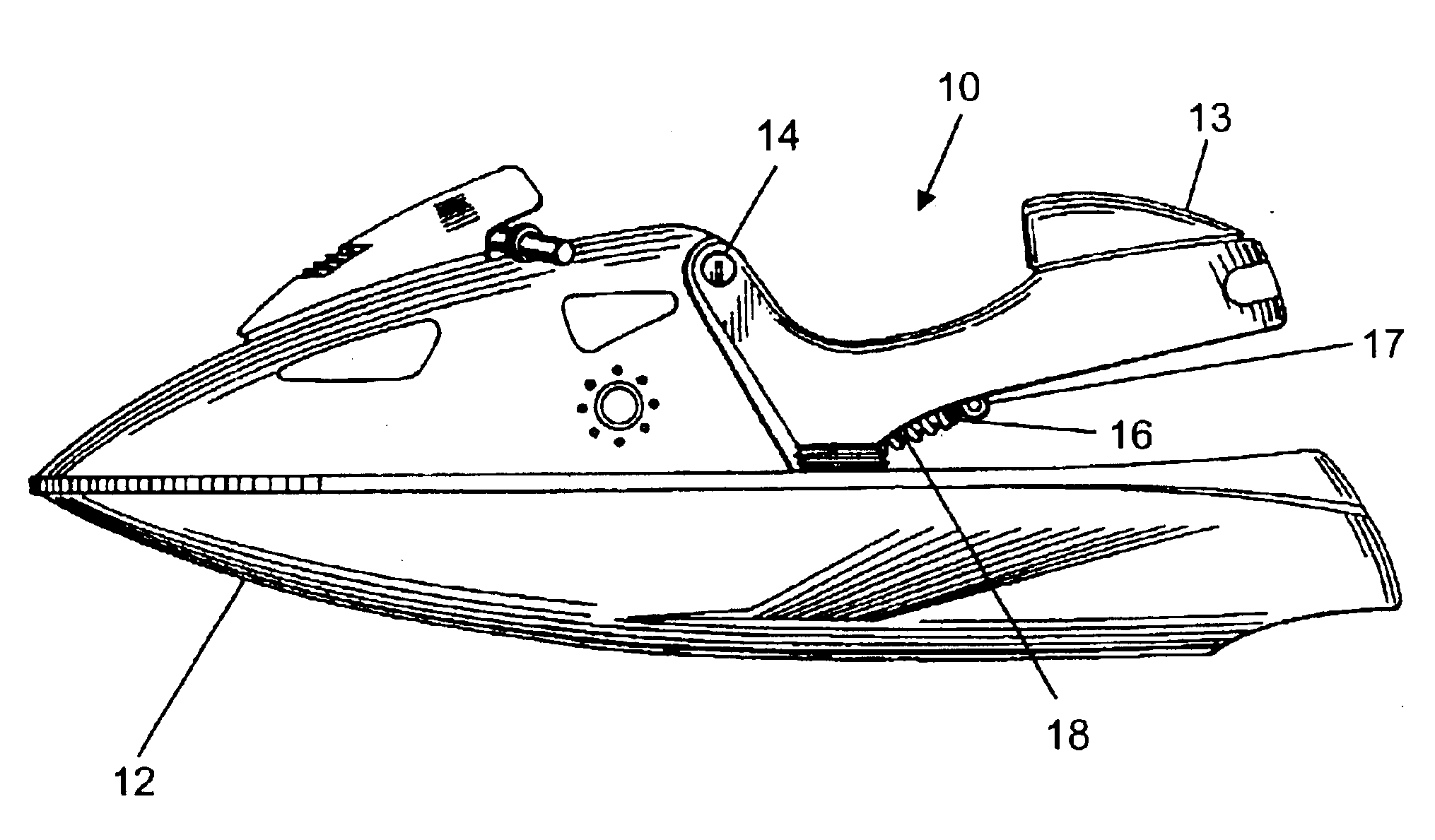
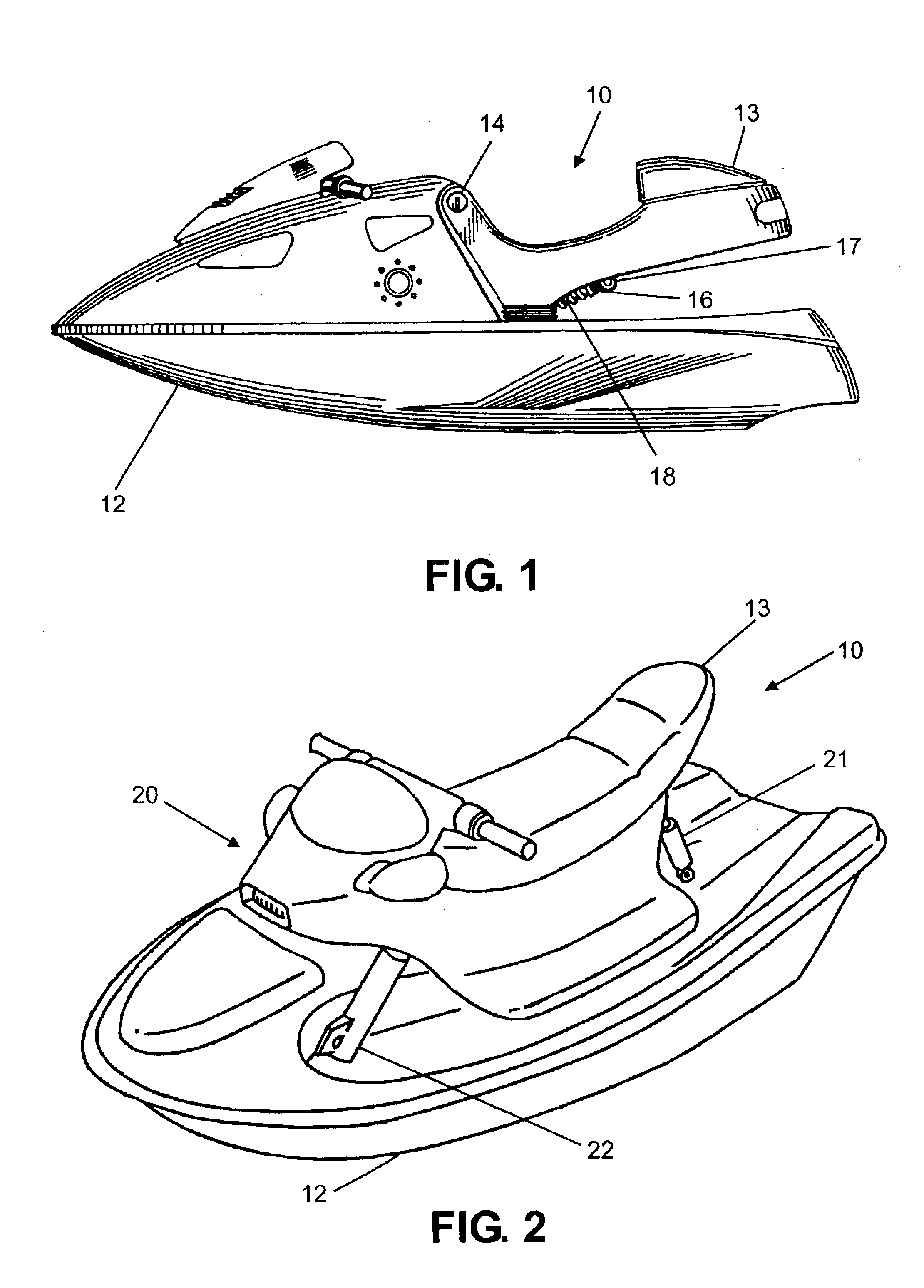
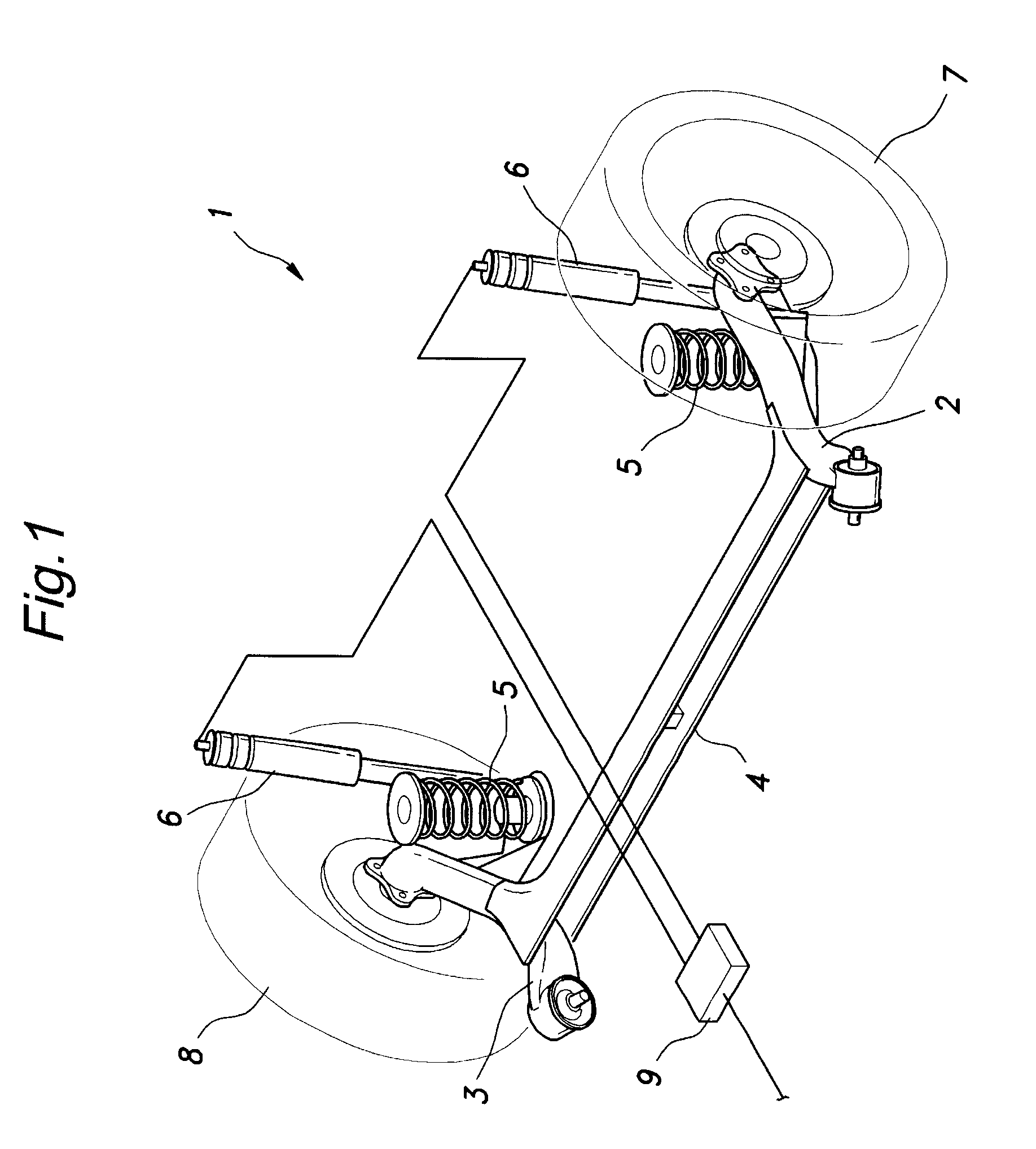
InactiveUS6880483B2Low costEasy maintenanceMachine framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionElectrical conductorMagnetorheological fluid
A watercraft seat suspension includes a damper mounted between a watercraft seat and the watercraft hull. The damper includes an electrically actuated mechanism controlling fluid flow from a first chamber to a second chamber within the damper. A sensor senses motion of the seat relative to the hull. A control unit interpolates the sensor signal and develops an actuating signal controlling the electrically actuated mechanism. In one arrangement, the electrically actuated mechanism is a solenoid actuated by the actuating signal to effect one of two different damping modes. In another arrangement, the electrically actuated mechanism includes a conductor coil and flux ring generating a magnetic field proportional to the actuating signal to vary the viscosity of magneto-rheological fluid in the damper.
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA
Article of footwear with variable support structure
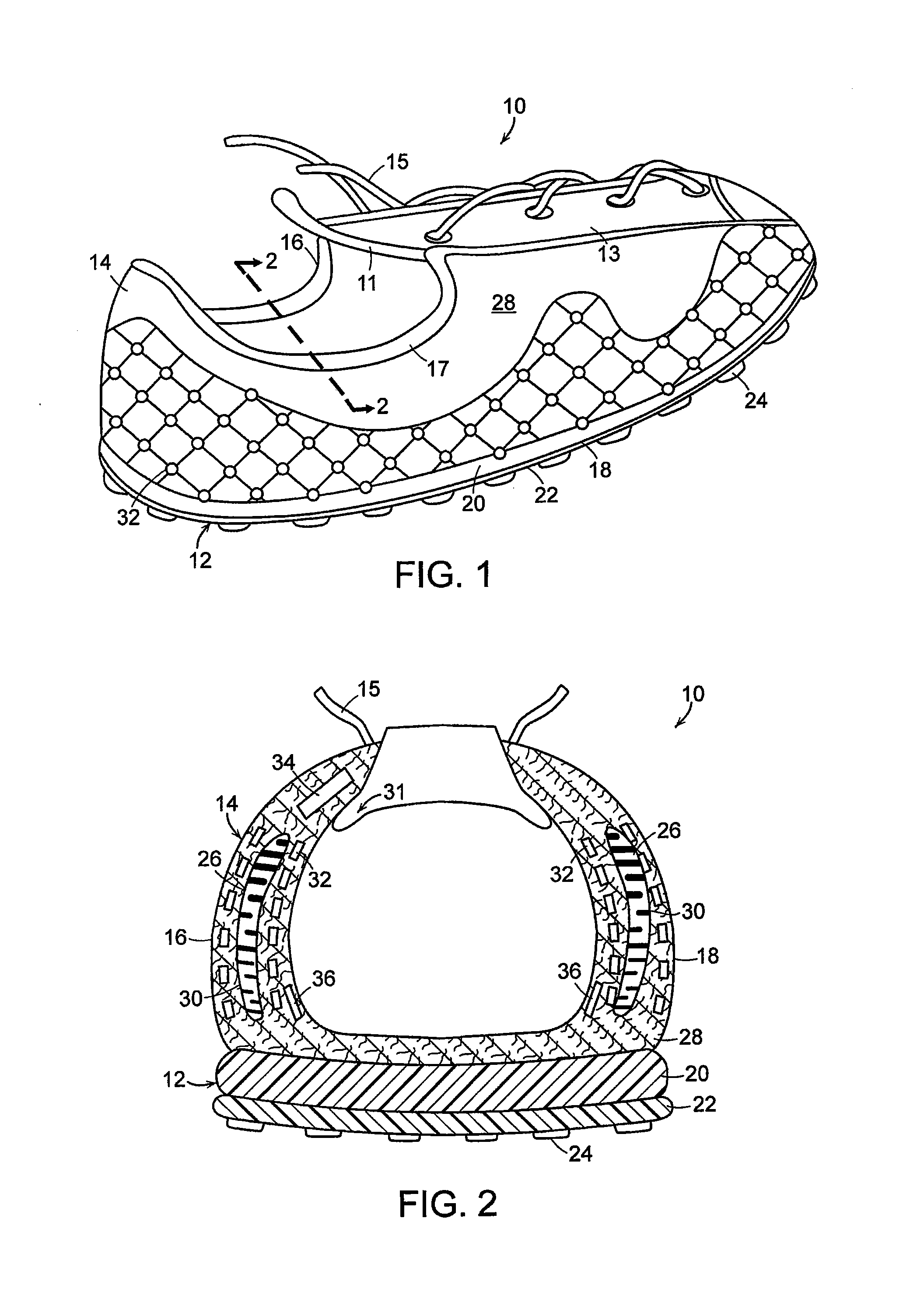
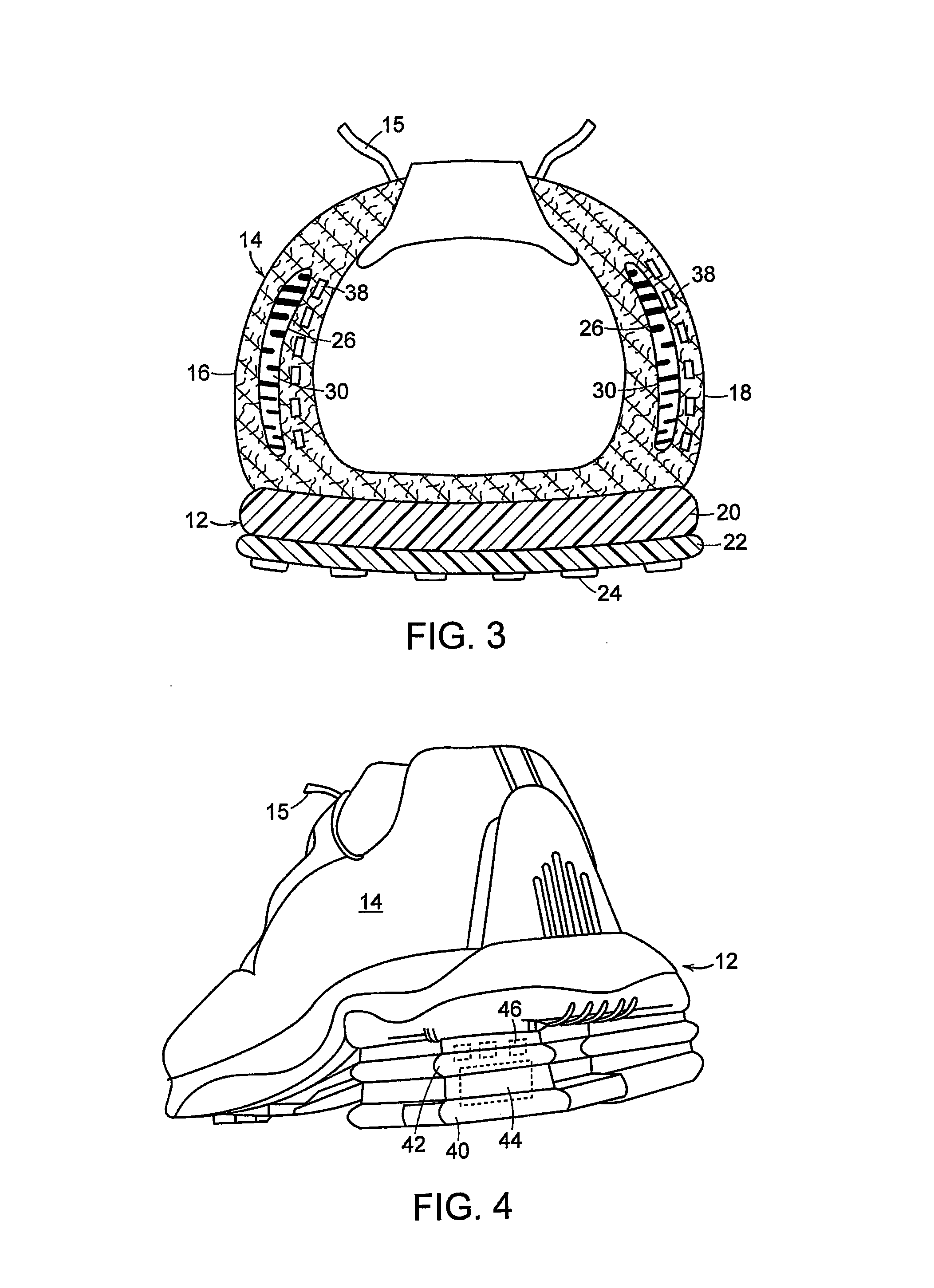
ActiveUS7254908B2Additional resistance and supportBig advantageSolesHeelsMagnetorheological fluidEngineering
An article of footwear having a variable support structure includes a sole structure and an upper secured to the sole structure. At least one reservoir of magneto-rheological fluid is positioned in at least one of the upper and the sole structure. A magnet assembly is positioned proximate each reservoir, and a magnetic field produced by the magnet assembly transforms the magneto-rheological fluid from a fluid state to a near-solid state.
Owner:NIKE INC
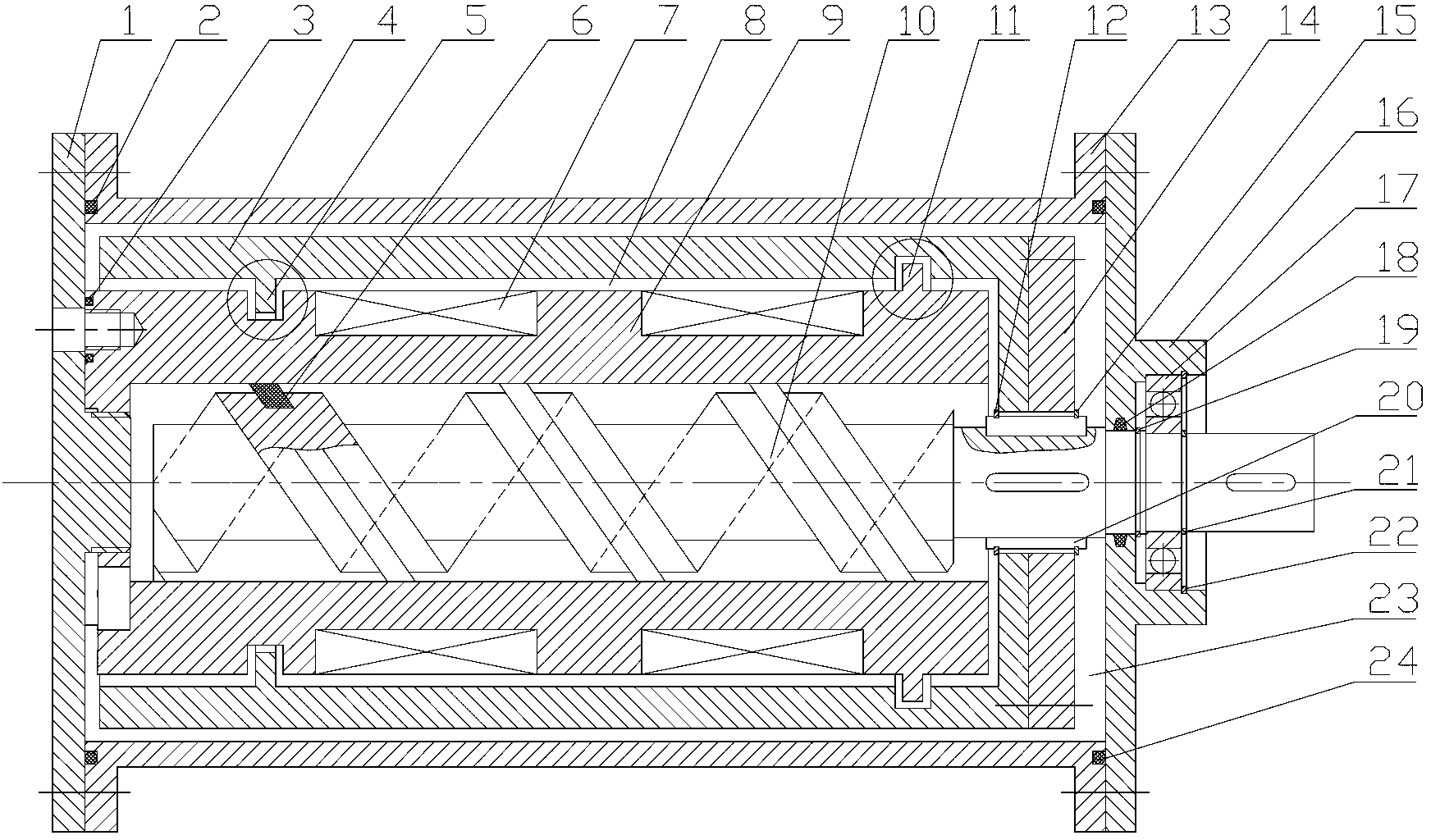
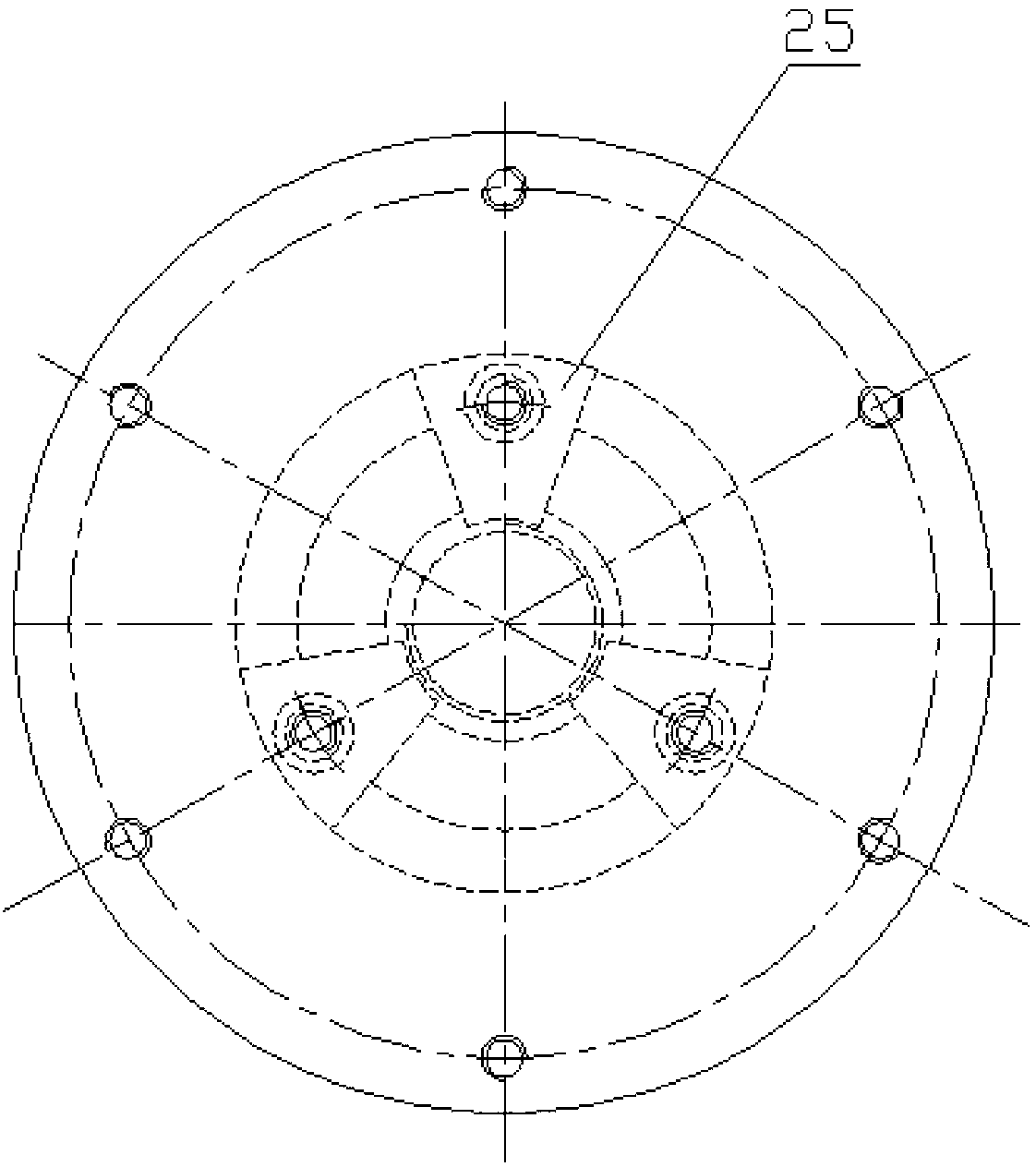
Magneto-rheological torsion damper
ActiveCN103016602ASimple structureLarge damping forceNon-rotating vibration suppressionFluid shearCoupling
The invention relates to a magneto-rheological torsion damper, which mainly comprises a stator, a rotor, a spiral propulsion rod and a shock absorber cylinder body, wherein the input end of the magneto-rheological torsion damper is connected with loading equipment via a coupler; the stator is wound with multiple stages of electromagnetic coils; a groove or a bulge matched with the rotor is processed on the outer wall of the stator; a certain gap is formed between the outer wall of the stator and an inner sleeve; a bulge or groove matched with the stator is processed on the inner wall of a rotor cylinder; the propulsion rod with a spiral propulsion structure, the rotor and the spiral propulsion rod are mutually connected via a terminal pad; the shock absorber cylinder body consists of an outer sleeve, a sealing bearing, a left cover plate and a right cover plate; a certain gap is formed between the shock absorber cylinder body and the inner sleeve; and the gap between the stator and the shock absorber cylinder body as well as the gap between the shock absorber cylinder body and the rotor is full of magneto-rheological fluid. According to the magneto-rheological torsion damper disclosed by the invention, two working modes of magneto-rheological fluid shearing and flowing are fully utilized, and the magneto-rheological torsion damper has the advantages of compact structure, big adjustable damping force and wide dynamic range and can be widely applied to the occasion of torsional vibration control.
Owner:SUZHOU SHIHAO BUILDING MATERIAL NEW TECH ENG
Method for polishing inner concave surface of optical elements as well as device
InactiveCN101352826AImprove controllabilityHigh utility valueOptical surface grinding machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesMagnetic polesHigh surface
The invention belongs to the technical field of precision optical polish finish, in particular to a polishing method of the inner concave surface of optical elements and a polishing device. A core mould with a tank circuit and inosculating with the shape of the inner concave surface to be processed is fixed below the inner concave surface of a work piece to be processed, and the work piece rotates around the own rotary shaft, keeps a micro clearance from the core mould and applies magnetic fields to processing regions by an external magnetic pole tool head and an internal magnetic pole exciting coil. When magneto-rheological fluids with polishing abrasives flow through the processing region along the tank circuit, a flexible polishing head is formed under the action of magnetic field and absorbed on the inner concave surface and polishing effects are generated. The polishing method and the device can realize the inner concave surface polishing of conformal optical elements with small curvature radiuses or deep cavity structure and other cyclically symmetric high gradient aspheric surfaces, and can remove distribution by utilizing computer-controlled polishing, and besides the polishing method and the device have the polishing surface shape control ability and both the advantages of high precision and high surface quality.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System and method for damping vibration in a drill string using a magnetorheological damper
ActiveUS20100224410A1Change viscosityReduce induced remanent magnetic fieldSurveyDrilling rodsAlternatorEngineering
A system for damping vibration in a drill string can include a magnetorheological fluid valve assembly having a supply of a magnetorheological fluid, a first member, and a second member capable of moving in relation to first member in response to vibration of the drill bit. The first and second members define a first and a second chamber for holding the fluid. Fluid can flow between the first and second chambers in response to the movement of the second member in relation to the first member. The valve assembly can also include a coil for inducing a magnetic field that alters the resistance of the magnetorheological fluid to flow between the first and second chambers, thereby increasing the damping provided by the valve. A remanent magnetic field is induced in one or more components of the magnetorheological fluid valve during operation that can be used to provide the magnetic field for operating the valve so as to eliminate the need to energize the coils during operation except temporarily when changing the amount of damping required, thereby eliminating the need for a turbine alternator power the magnetorheological fluid valve. A demagnetization cycle can be used to reduce the remanent magnetic field when necessary.
Owner:APS TECH
Variable damper
InactiveUS20080251982A1Compact designImprove damping performanceMachine framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic valveControl theory
In a variable damper using magneto-rheological fluid that comprises a cylinder (12) filled with the fluid, a piston (16) slidably received in the cylinder and including an inner yoke (32; 62; 126), an outer yoke (31; 64, 65; 140) and a coil (34; 130), a piston rod (13) having an inner end attached to the piston and an outer end extending out of the cylinder and a magnetic valve formed in a gap between the inner and outer yokes, at least one of the outer yoke and inner yoke consisting of at least two parts that are joined to each other in an axial direction. The two piece arrangement of the inner yoke or outer yoke allows the end plates to be omitted because the gap spacer can be installed without requiring end plates, and this contributes to a compact design and a favorable damping property. Also, the manufacturing and servicing of the damper can be simplified. When end plates (134) are used, the freedom in the positioning of the coil is increased.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
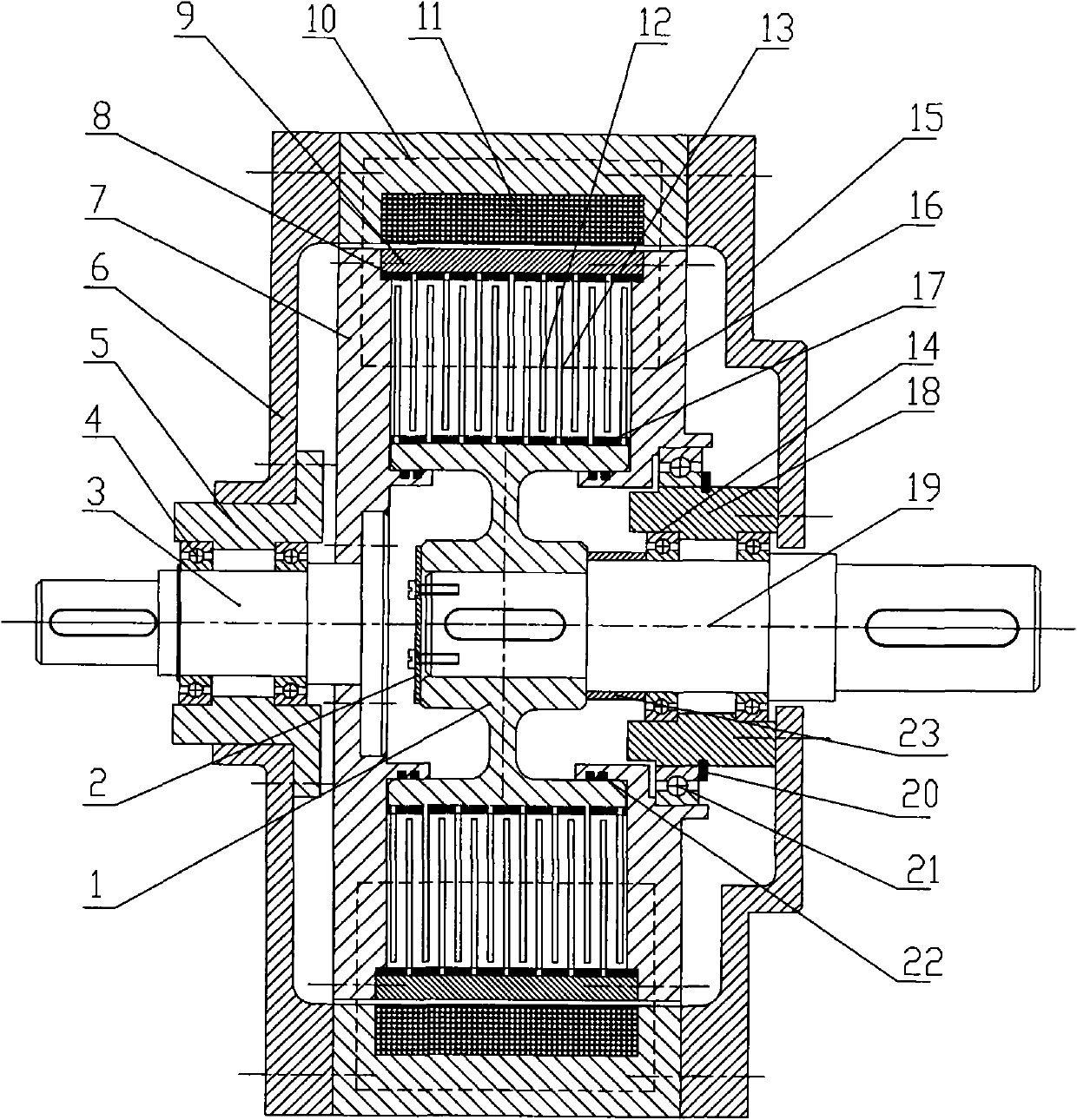
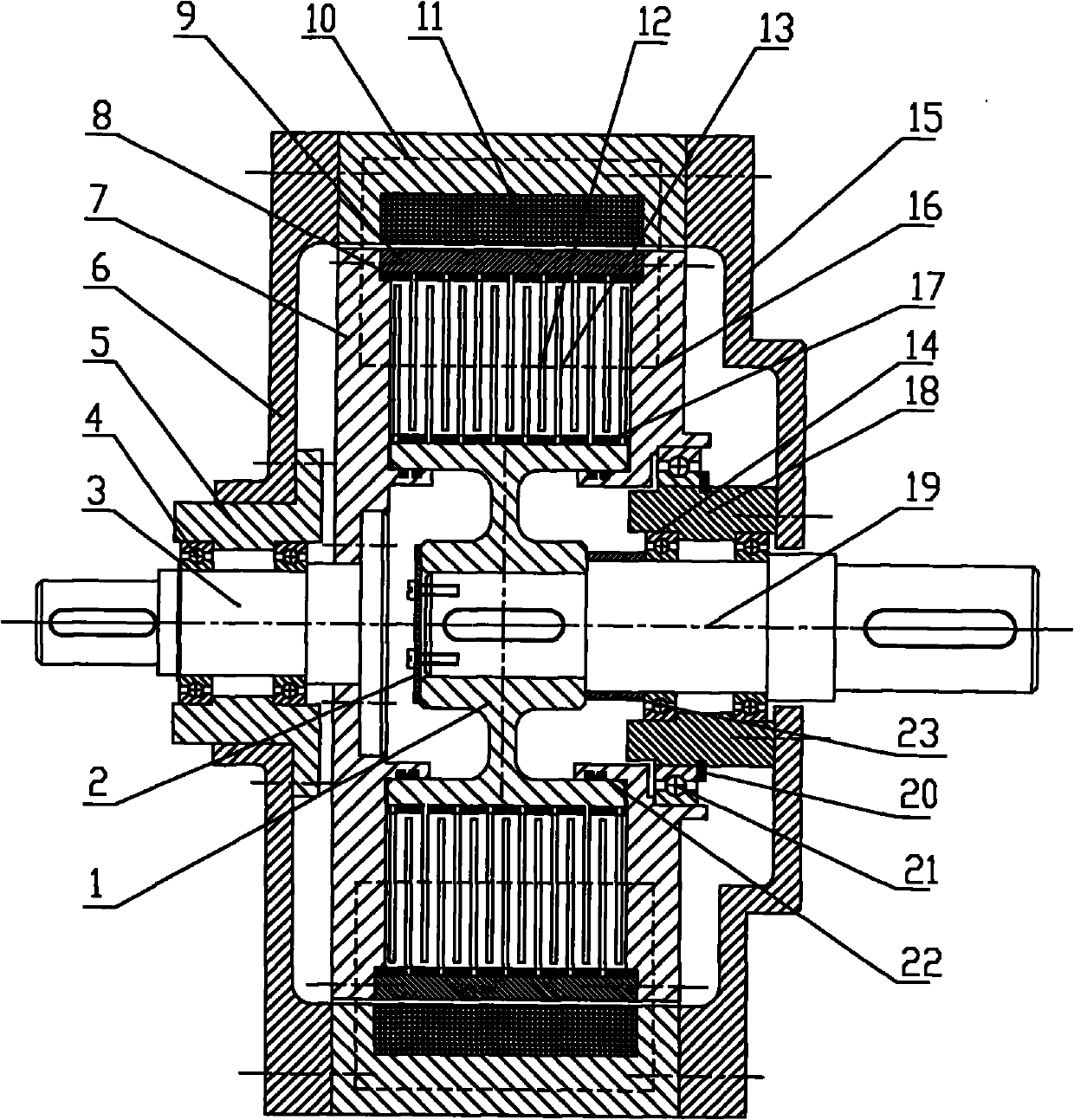
Magneto-rheological stepless speed changer
InactiveCN101793312AIncrease or decrease quantityChange speed differenceFriction gearingsDrive shaftMagneto rheological
The invention relates to a multi-disc type magneto-rheological stepless speed changer which mainly comprises a magnetic isolation hub, an input shaft, an output shaft, a driving friction plate, a driven friction plate, magnetic exciting coils and magnetic isolation rings; wherein the driving friction plate and the driven friction plate are respectively fixed on an outer magnetic isolation circular ring and the magnetic isolation hub through the magnetic isolation rings; a right magnetic conducting lateral plate is connected with the input shaft through a big magnetic isolation circular ring and a left magnetic conducting lateral plate; the output shaft is connected with the driven friction plate and the magnetic isolation hub; magneto-rheological fluid is sealed between the driving friction plate and the driven friction plate through a seal ring; the magnetic exciting coils are fixed on two bearing seats through a magnetic conducting shell, the left magnetic isolation lateral plate and the right magnetic isolation lateral plate in a motionless way, and the driving friction plate and the driving friction plate are in interleaved matching and isolated through the magnetic isolation rings. The shear yield stress of the magneto-rheological fluid can be changed by adjusting the electric current of the magnetic exciting coils, therefore, the speed difference between a driving shaft and a driven shaft is changed, and the stepless speed change is further realized. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, no electric sparks, high transmission torque and large transmission power.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
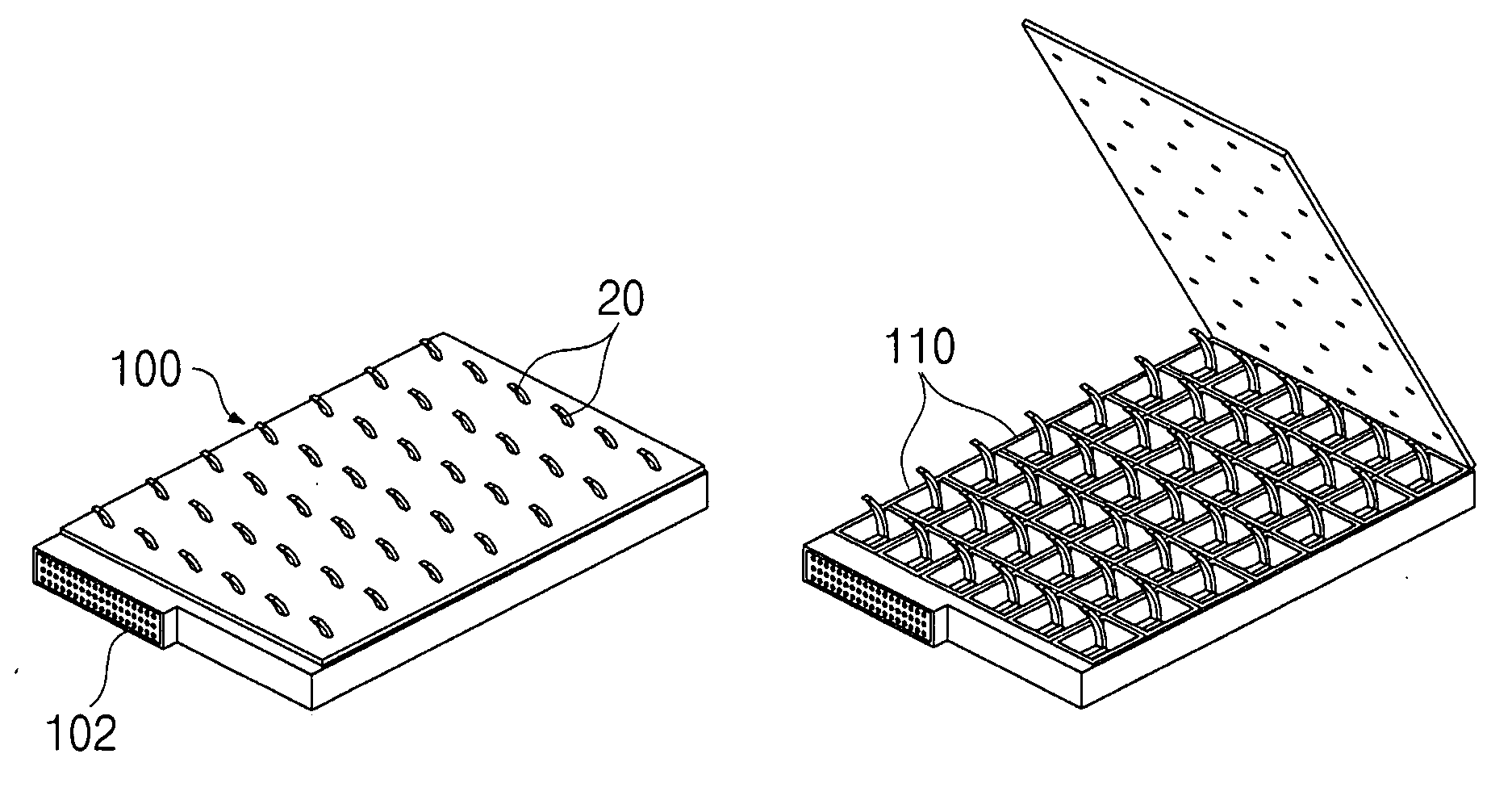
Device and method for transmitting shape information of image through tactile sensation using rheological fluid
InactiveUS20070211032A1Simple structureCathode-ray tube indicatorsTeaching apparatusTactile sensationMiniaturization
The tactile transmission device includes a plurality of cells arranged at regular intervals, each having a storage space therein. A contact member is installed in each of the cells, an upper portion of the contact member protruding out of the cell. An elastic member is installed in each of the cells, and biases the contact member upwards. A sensor is installed in each of the cells, and measures displacement of the contact member. A magneto-rheological fluid is contained in each of the cells. A coil is installed in each of the cells and generates a magnetic field in the cell. A control means compares a shape information value of the image with a displacement value of the contact member output from the sensor, thus controlling a quantity of current applied to the coil. According to the present invention, the shape information of an image displayed on a screen is corrected to be suitable for a user's characteristics, thus more precisely transmitting the shape information on the screen to the user. Further, a transmission medium for transmitting a tactile sensation to a user has a simple construction, so that miniaturization of the tactile transmission device is very easily realized.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Externally actuated torque coupling for drivetrain
A torque-coupling device comprising a hydraulically actuated friction clutch pack and a gerotor pump provided for generating hydraulic pressure actuating the friction clutch pack. The gerotor pump is selectively actuated by a device external to the gerotor pump and the friction clutch pack, such as an electric motor, friction brake, electro-magnetic clutch, friction mechanism utilizing a magneto-rheological fluid, electro-magnetic brake, etc. The externally driven gerotor pump may be further provided with torque-multiplication gearing, and / or an electronic controller to modulate the actuation of the pump in order to provide flexible control of the hydraulic pressure generated by the gerotor pump.
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
Combination machining method for removing high-frequency errors in optical elements
ActiveCN102848287AImprove high frequency errorOptical surface grinding machinesEngineeringSpectral density
The invention discloses a combination machining method for removing high-frequency errors in optical elements. The combination machining method includes measuring surface shape errors of an optical element to be machined by an interferometer, carrying out PSD (power spectral density) analysis, and determining distribution characteristics of the medium and high-frequency errors on the basis of a DSD curve; acquiring an optimized removal function model according to predetermined machining time and machining precision, and acquiring an amplitude spectral line of a removal function; acquiring cut-off frequency of the removal function according to the amplitude spectral line; machining by a magneto-rheological finishing process if correctable medium and high-frequency errors with the frequency lower than the cut-off frequency exist according to the frequency distribution of the medium and high-frequency errors; and machining by a computer controlled optical surfacing process if uncorrectable medium and high-frequency errors with the frequency higher than the cut-off frequency exist according to the frequency distribution of the medium and high-frequency errors. By the combination machining method, technical advantages of MRF (magneto-rheological finishing) and technical advantages of CCOS (computer controlled optical surfacing) can be sufficiently combined, efficient uniform convergence of all-band errors of the optical element can be realized, and performance of the optical element is effectively improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Inerter and damping controllable magneto-rheological inerter device and control method thereof
ActiveCN103644248ASolve the problem that dynamic adjustment of inertia cannot be realizedTo overcome the shortcomings of only dynamically adjusting the dampingNon-rotating vibration suppressionSemi activeInertial effect
The invention relates to an inerter and damping controllable magneto-rheological inerter device and a control method thereof. The device comprises a cylinder, a piston, a piston rod, long and thin pipes, a thick pipe, a magneto-rheological fluid, switch valves, MR (magnetic resonance) conductors and a damping hole. According to the inerter and damping controllable magneto-rheological inerter device and the control method thereof, an apparent viscosity changing process of the magneto-rheological fluid is a continuous, stepless and reversible magneto-rheological effect under the action of an applied magnetic field, simultaneously, the low viscosity of the magneto-rheological fluid without the applied magnetic field and an inertial effect of the magneto-rheological fluid flowing in the long and thin pipes are utilized, the two effects are integrated in one device, further, the switch valves are adopted to control switching on and off of the long and thin pipes which have different pipe diameters and are filled with the magneto-rheological fluid, then the inerter is adjusted in a stepping manner,; and damping is adjusted steplessly by changing the magneto-rheological viscosity through the applied magnetic field simultaneously According to the invention, requirements for semi-active control when dynamical combination adjustment of inerter and damping is applied to a vibration isolation device for engineering are met, so that mounting and using are facilitated, the cost is reduced, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method and device for polishing magneto-rheological inclined shaft
InactiveCN101564824AReduce size requirementsAvoid interferenceOptical surface grinding machinesEngineeringMagneto rheological
A method and a device for polishing a magneto-rheological inclined shaft relate to the technical field of precise finishing machining. A polishing tool head and the axial direction of a workpiece have an angle so that the normal of the working arc of the polishing tool head is coincident with the polishing surface normal of the workpiece; the shell of the polishing tool head rotates; furthermore, the rear end of the shaft in the shell passes through the hollow shaft of an adjustable speed motor and is fixedly connected with a machine body; the fixed shaft is provided with an excitation device; one part of the small front area of the shell of the polishing tool head is provided with a magnetic field and the other part thereof has no magnetic field or has weak magnetic field, thus facilitating updating the magneto-rheological liquid; the contact point of the workpiece and the magneto-rheological point is always the normal direction of the polishing area of the workpiece; the shell of the polishing tool head rotates and the magneto-rheological body generates a high shearing force at the clearance between the polishing tool head and the workpiece, thus removing trace of the material. By adopting the inclined shaft polishing, the interference is prevented from being generated; by planning path and controlling relevant parameters, the specific ultra-precise polishing process can be carried out to the surfaces of minitype non-spherical optical parts, dies and workpieces of general dimensions.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Magneto-rheological clutch with sensors measuring electromagnetic field strength
Systems and methods relating to a clutch system for use in controllably transmitting torque from an input shaft to an output shaft. The clutch system has a torque transmission fluid that has a viscosity that changes based on the strength of an electromagnetic field passing through the fluid. A number of sensors are placed at different radial locations on the torque transmission disks to detect the strength of the electromagnetic field. Based on the strength of the electromagnetic field, the amount of torque being transmitted from the input shaft to the output shaft can be adjusted. Also disclosed is a distributed actuation architecture that uses this clutch system. The distributed actuation architecture allows for the use of a single drive motor in conjunction with multiple instances of the clutch system to actuate a mechanical linkage, such as a robotic arm.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
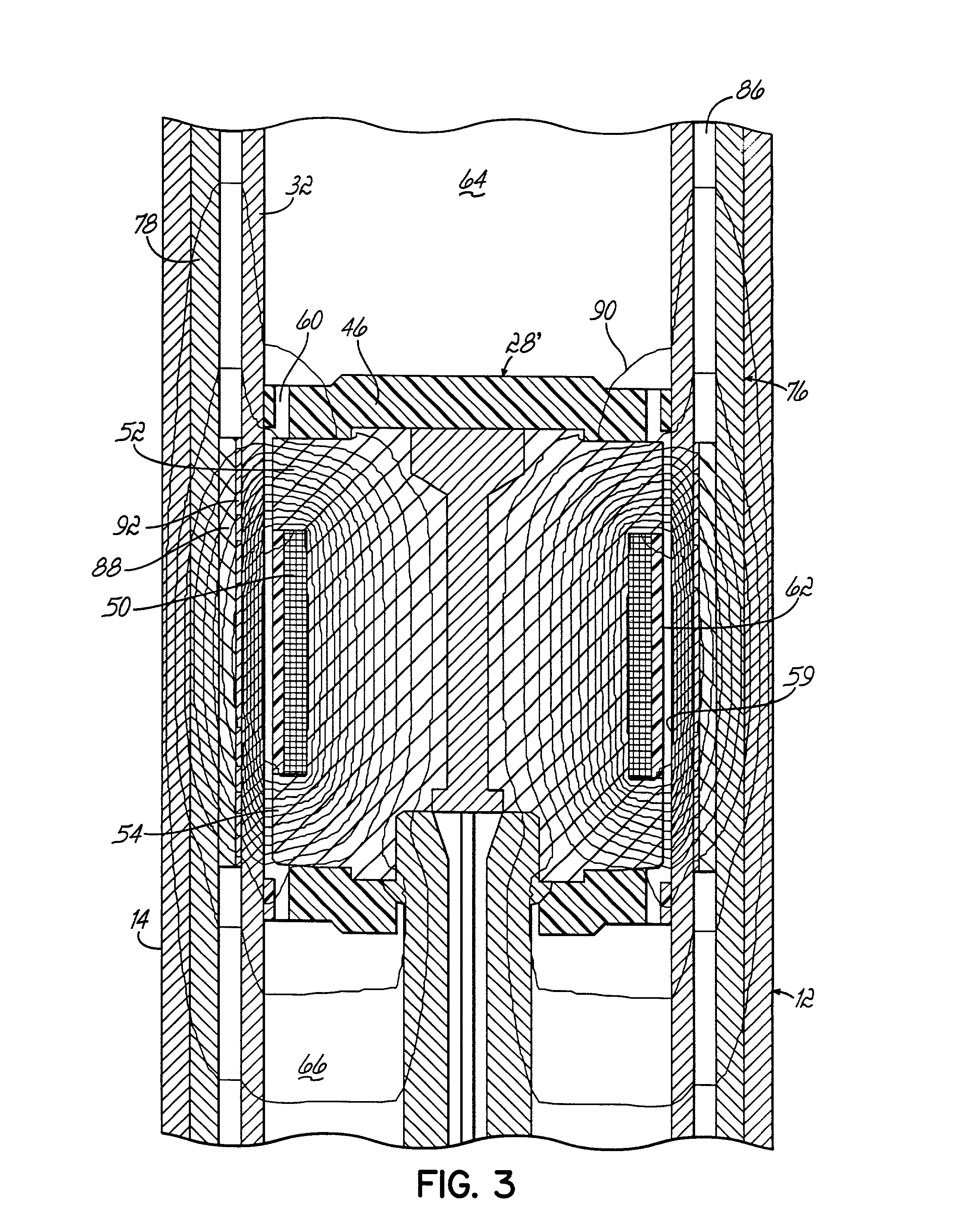
Passive magneto-rheological vibration isolation apparatus
InactiveUS7445094B1High viscosityIncrease dampingMachine framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionSnubberMagneto rheological
A fixture is isolated from the transmission of vibration emanating from a vibration source by a damper containing magneto-rheological (“MR”) fluid and a plunger mechanically coupling the damper and the fixture. The isolation apparatus is mechanically coupled to the vibration source. The viscosity of the MR fluid contained in the damper is controlled by a magnetic field produced by the vibration of an isolation system responsive to the vibration of the vibration source. The resonant frequency of the isolation system is adjusted to approximate that of the fixture.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Non-newtonian flow fluid-locking mechanism for vehicles
InactiveUS7165786B1Shorten manufacturing timeLow costSpringsSteering columnsSteering columnUser input
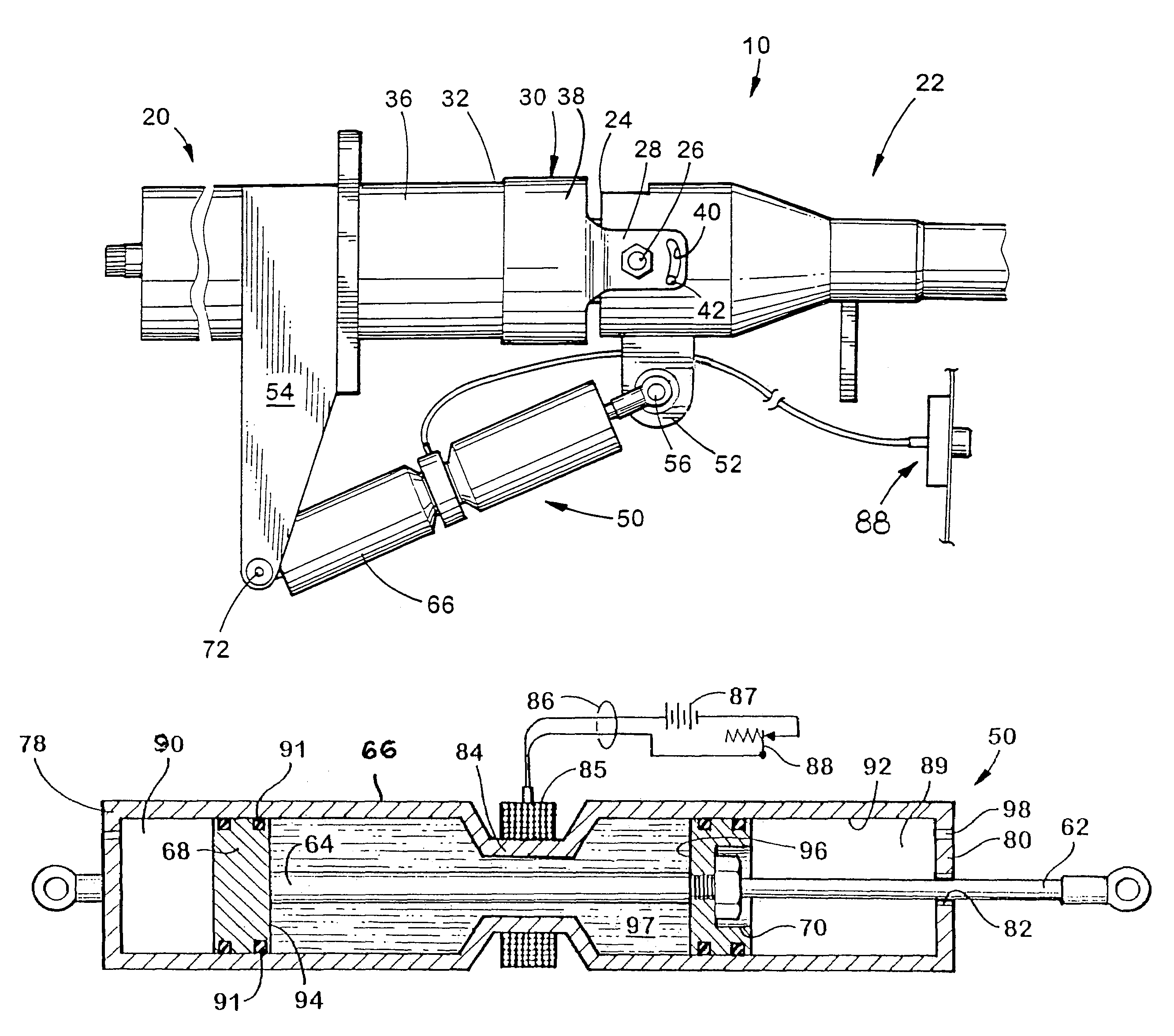
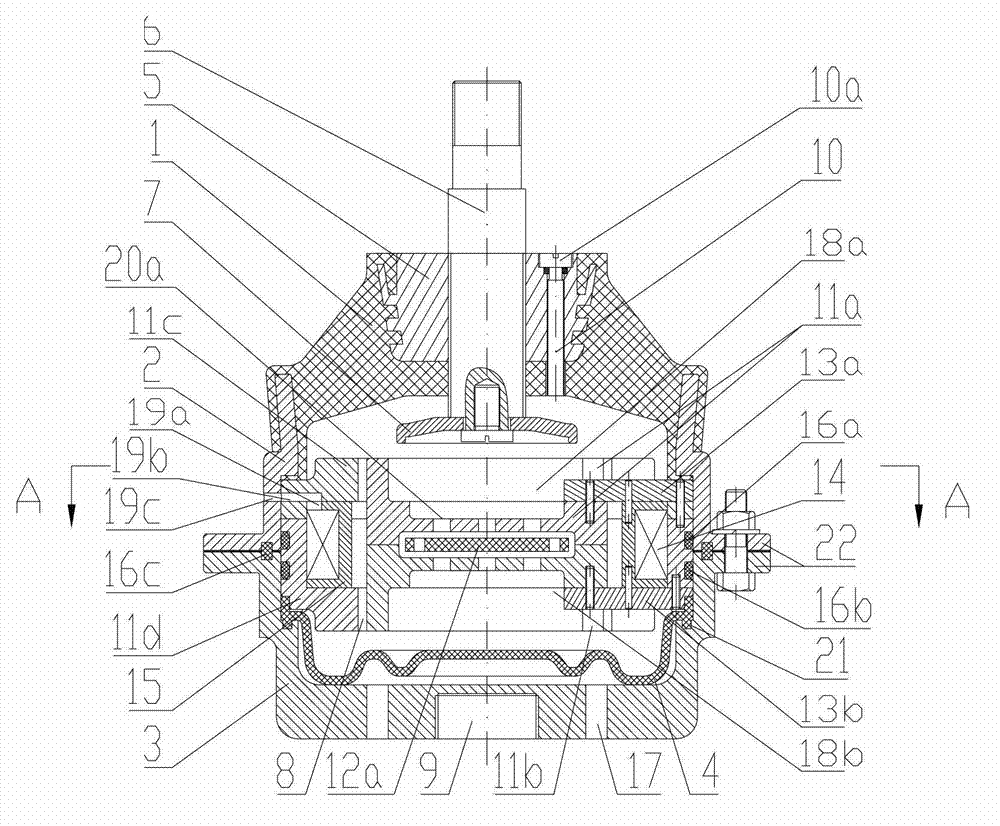
An assembly is provided for fixing the position of an adjustable component (22) of a vehicle, comprising in combination a fixed reference frame (20) within the vehicle such as a dash or a firewall, an adjustable component (22) also disposed in the vehicle such as an adjustable steering column (10), pedals, or a seat. Interconnecting the fixed reference frame (20) and the adjustable component (22) is a fluid locking mechanism (50) which permits selective positioning of the adjustable component relative to the fixed reference frame (20) and holds the adjustable component (22) in position. The fluid locking mechanism (50) is preferably a non-Newtonian flow fluid locking mechanism which uses a magneto-rheological fluid (97) to fix the position of the adjustable component (22) in place once the desired position is selected. To provide additional safety for the vehicle occupants, the fluid locking mechanism may be controlled by an electrical microprocessor (556) or circuit which adjusts the locking strength of the fluid locking mechanism (50) based upon user inputs and dynamic events.
Owner:DOUGLAS AUTOTECH
Magneto-rheological damper of automobile engine suspension system
InactiveCN102829127ASuppression of high frequency dynamic hardeningImprove the vibration isolation effectNon-rotating vibration suppressionPower flowExcitation current
The invention discloses a magneto-rheological damper of an automobile engine suspension system, comprising a main rubber spring, a throttling disk, a magnetic core assembly and a decoupling film, wherein the damper is used for regulating the magnetic induction intensity at a magneto-rheological liquid channel in the magnetic core assembly through controlling the excitation current of an electromagnetic coil and then regulating the viscosity of magneto-rheological liquid at the magneto-rheological liquid channel to achieve the optimal damping effect. When the magneto-rheological damper is used, the turbulence level of the magneto-rheological liquid in a liquid feeding chamber can be increased through the throttling disk, the high-frequency dynamic hardening of the damper can be effectively inhibited, and the effectively damping frequency range can be widened. The damper has a more ideal dynamic characteristic and meets the use requirement for damping the automobile engine suspension system with high rotating speed; in addition, the damping capacity, the work stability and the convenience in assembly of the damper are improved through improving a floating decoupling film type decoupler, a sealing structure of the magnetic core assembly, a liquid injection hole structure and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Water-based magneto-rheological polishing liquid for optical processing and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101250380ALow magnetic field viscositySuitable for recyclingMagnetic liquidsPolishing compositions with abrasivesWater basedIron powder
The invention relates to a water-based magnetorheological polishing solution for optical manufacture, which is formed by the following volume components, water-based remixed carrier liquid 25%-75% and additive component 25%-75%, wherein the additive component is dispensed by the following volume percentage, carbonyl iron powder 80%-90%, nanometer iron powder 4%-10% and polishing powder 4%-10%, the water-based remixed carrier liquid which is measured according to volume percentage comprises deionized water 85%-90%, dispersing agent 3%-5%, wetting agent 2%-5% and thixotropic agent 3%-5%, the method for preparing comprises the following steps: mixing deionized water and thixotropic agent, stirring in indoor temperature for 1-2 hours, and adding dispersing agent, stirring in indoor temperature for 0.5-1 hour, and then adding wetting agent, stirring in indoor temperature for 0.5-1 hour, getting water-based remixed carrier liquid, mixing additive component and water-based remixed carrier liquid, adding into a ball-milling tank, adding into a steel ball according to mass ratio which is 1:10, grinding for 3-5 hours in the speed which is 20-30r / m, separating out a steel ball, and getting products. The polishing solution of the invention has the advantages of excellent stability, high rheological property, excellent oxidation resistance property and simple and environmental-friendly preparation technology.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Controllable vibration isolator based on magnetic current change elastic element and damping element coupled action
InactiveCN101324257AMeet the requirements of the suspension parametersImproves sealing reliabilityNon-rotating vibration suppressionElastomerMagnetic current
The invention relates to an engine vibration isolation device of a magneto-rheological fluid damper in extrusion mode and a magneto-rheological elastomer in shearing mode for supporting static loads. The vibration isolation device comprises two pars of a damping adjusting unit and a rigidity adjusting unit; the damping adjusting unit is connected with the rigidity adjusting unit through a rigid connecting rod; the vibration of an engine causes the connecting rod to move upwards and downwards, so that the magneto-rheological fluid in the damping adjusting unit flows in radial direction and shearing occurs to the magneto-rheological elastomer in the rigid adjusting unit; a magnetic field generated by two exciting coils can be respectively adjust damping parameters and rigidity parameters of a vibration isolator. The magneto-rheological vibration isolator can meet the independent adjustment of the damping parameters and the elastic parameters of the vibration isolator under different vibrational excitation conditions, and achieve the coupling control of the transmission of engine vibration energy, and has great realistic significance in improving the technical level and market competence of special vehicles.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Flexible mechanical arm vibration reduction device and method based on magneto-rheological technology
InactiveCN103029139ATheoretical basis is scientific and simple and feasibleFully absorb vibration energyArmsElastomerVibration control
The invention relates to a flexible mechanical arm vibration reduction device and method based on a magneto-rheological technology, which belongs to the technical field of flexible mechanical arm vibration control. The vibration reduction device comprises a rigid-flexible coupled mechanical arm, a magneto-rheological elastomer vibration reduction device and a feedback control loop, wherein the rigid-flexible coupled mechanical arm comprises a rigid mechanical arm, a motor mounting plate, a servo motor, a harmonic reducer, a flexible mechanical arm mounting base and a flexible mechanical arm; the magneto-rheological elastomer vibration reduction device comprises an iron core, a guide rod, a fixed seat, a magneto-rheological elastomer, a permanent magnet and an electromagnetic coil; and the feedback control loop comprises two acceleration sensors, a charge-amplifier, a data acquisition system, a PC (Personal Computer) upper computer and a programmable power supply. The PC upper computer is used for regulating the supply voltage of two ends of the electromagnetic coil through the analyzing and processing the feedback signals of the two acceleration sensors so as to change the rigidness of the magneto-rheological elastomer, thereby meeting the resonance requirement in a system. The flexible mechanical arm vibration reduction device has the characteristics of obvious vibration reduction effect and less energy consumption and is suitable for large amplitude vibration reduction.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com