Patents
Literature
2222 results about "Magnetorheological fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A magnetorheological fluid (MR fluid, or MRF) is a type of smart fluid in a carrier fluid, usually a type of oil. When subjected to a magnetic field, the fluid greatly increases its apparent viscosity, to the point of becoming a viscoelastic solid. Importantly, the yield stress of the fluid when in its active ("on") state can be controlled very accurately by varying the magnetic field intensity. The upshot is that the fluid's ability to transmit force can be controlled with an electromagnet, which gives rise to its many possible control-based applications. Extensive discussions of the physics and applications of MR fluids can be found in a recent book.
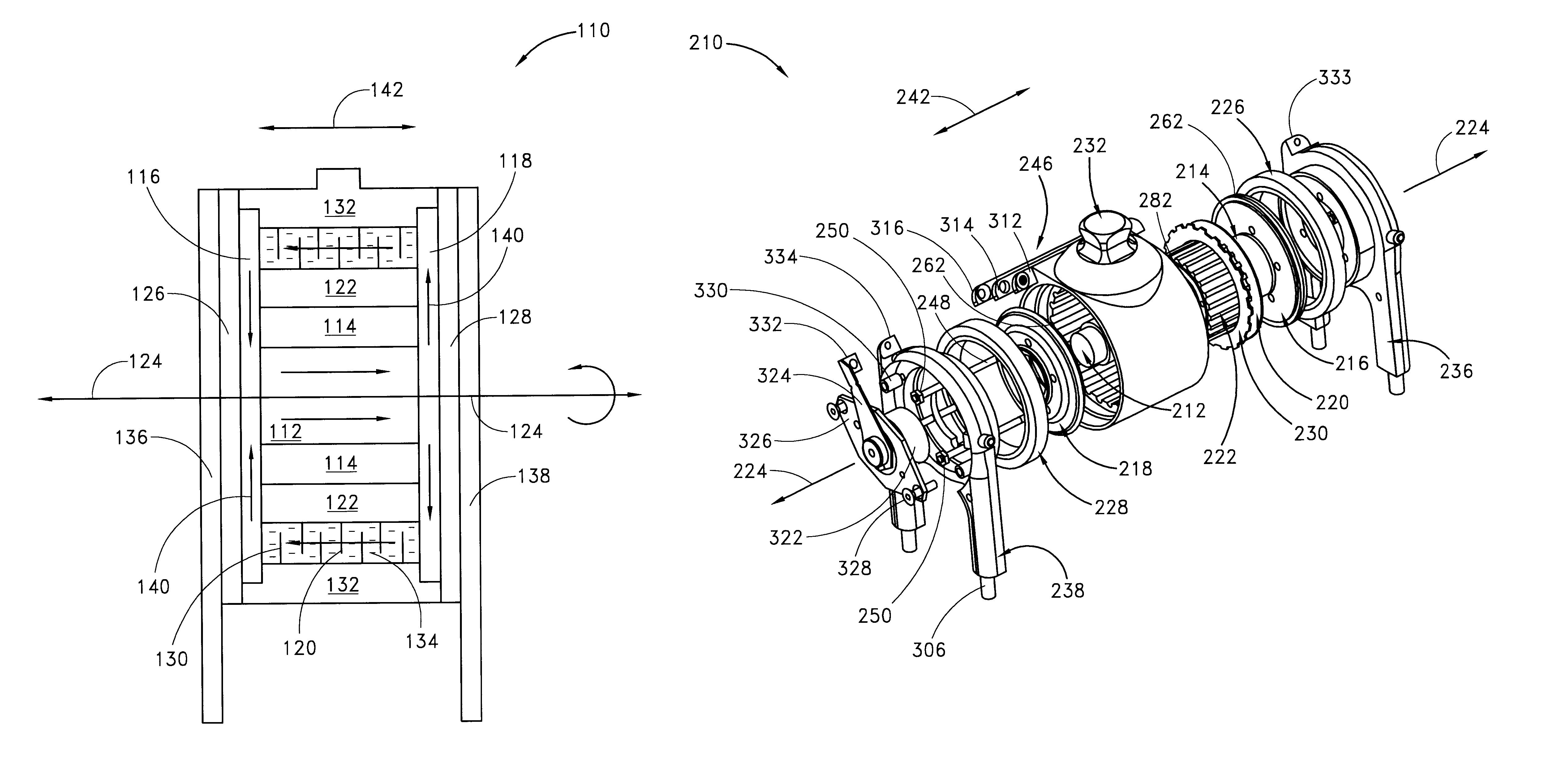
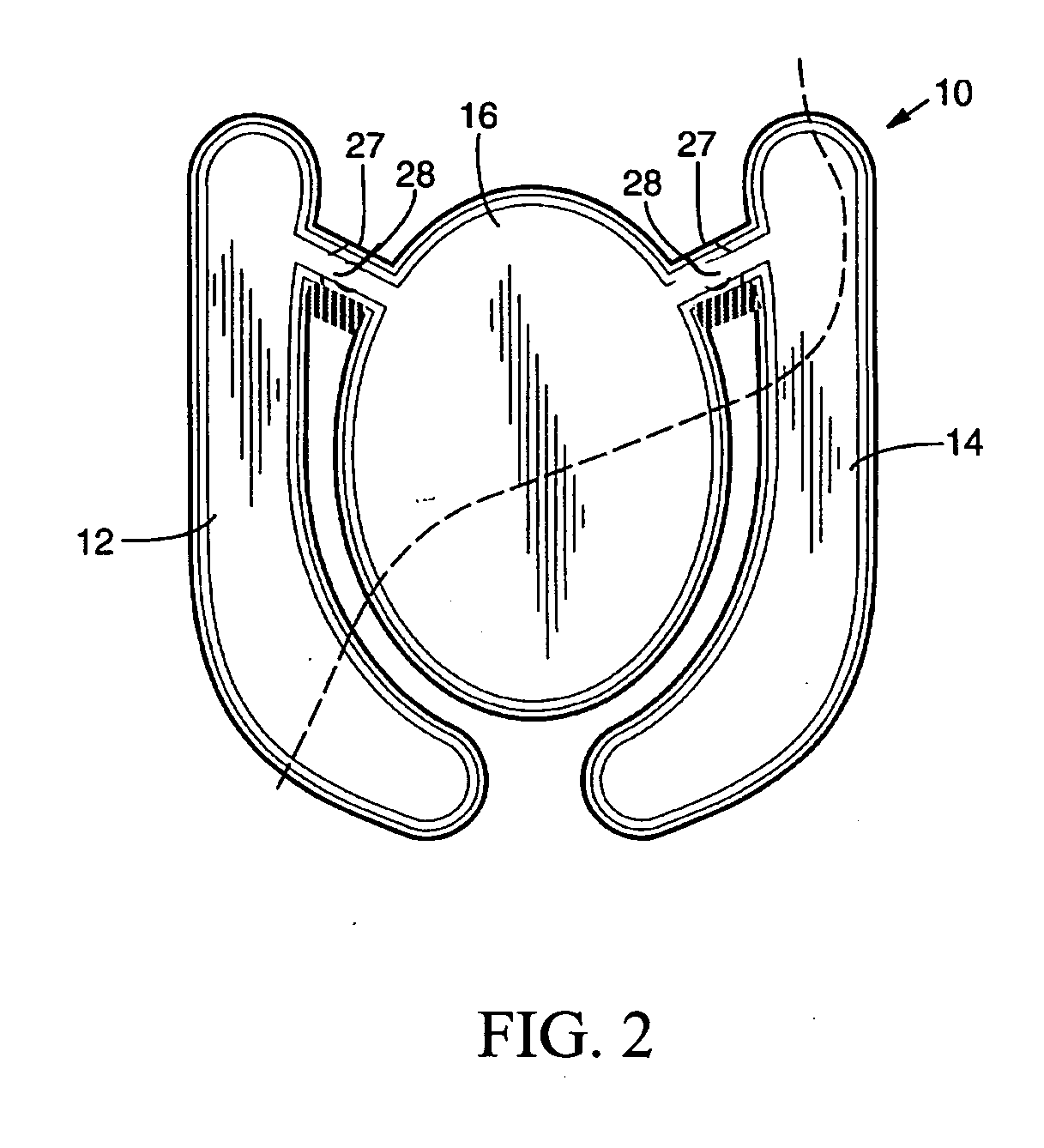
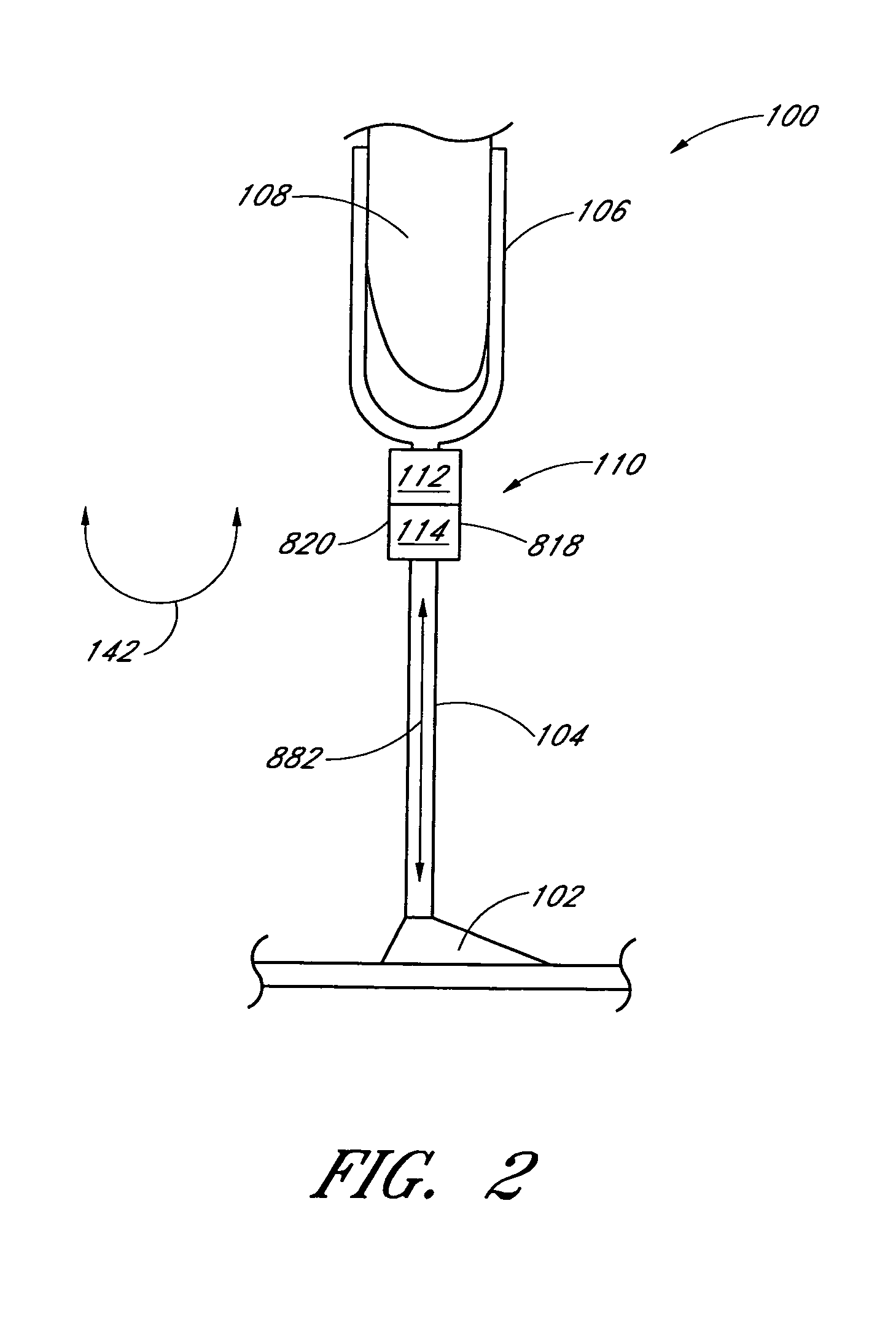
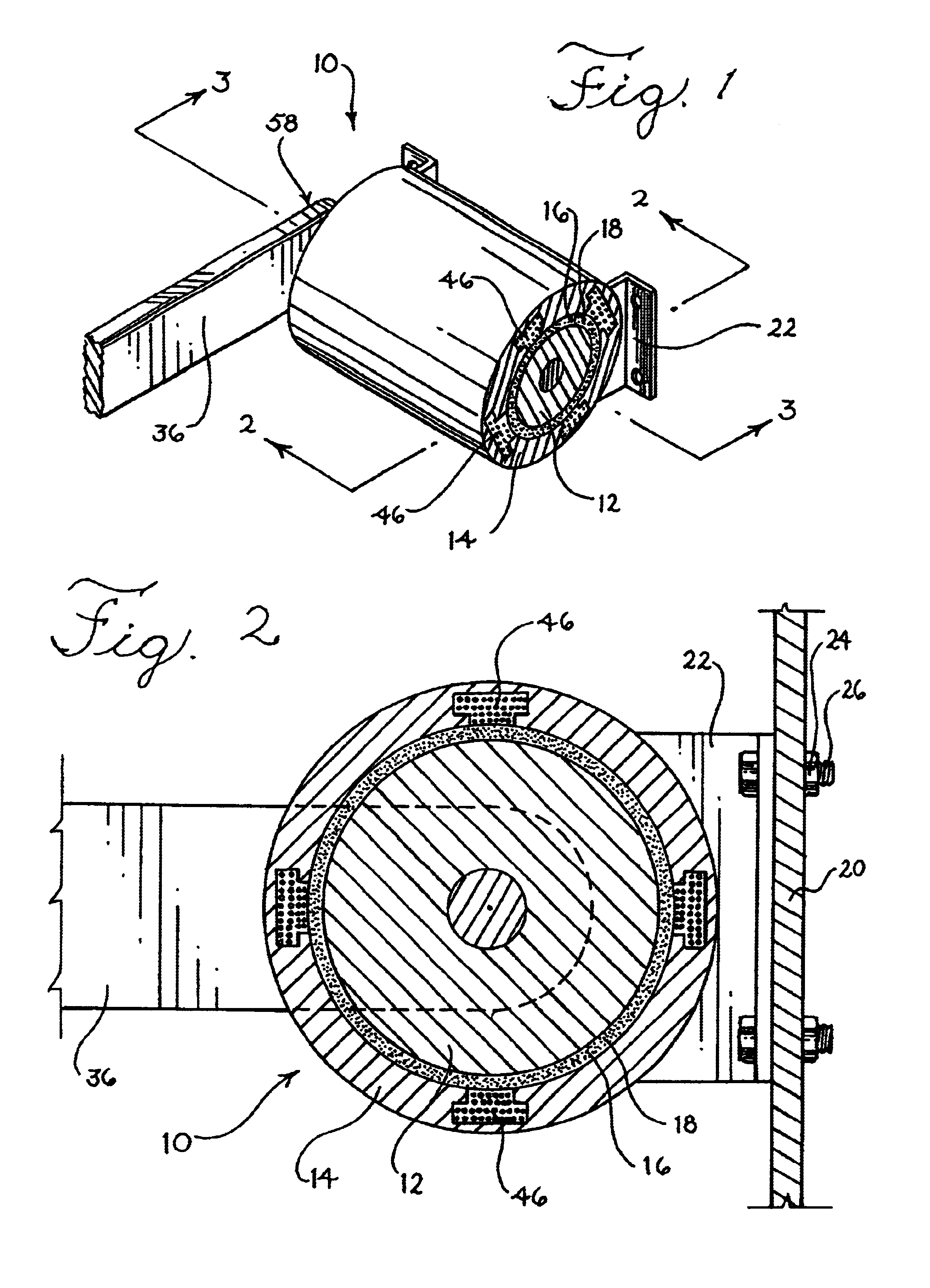
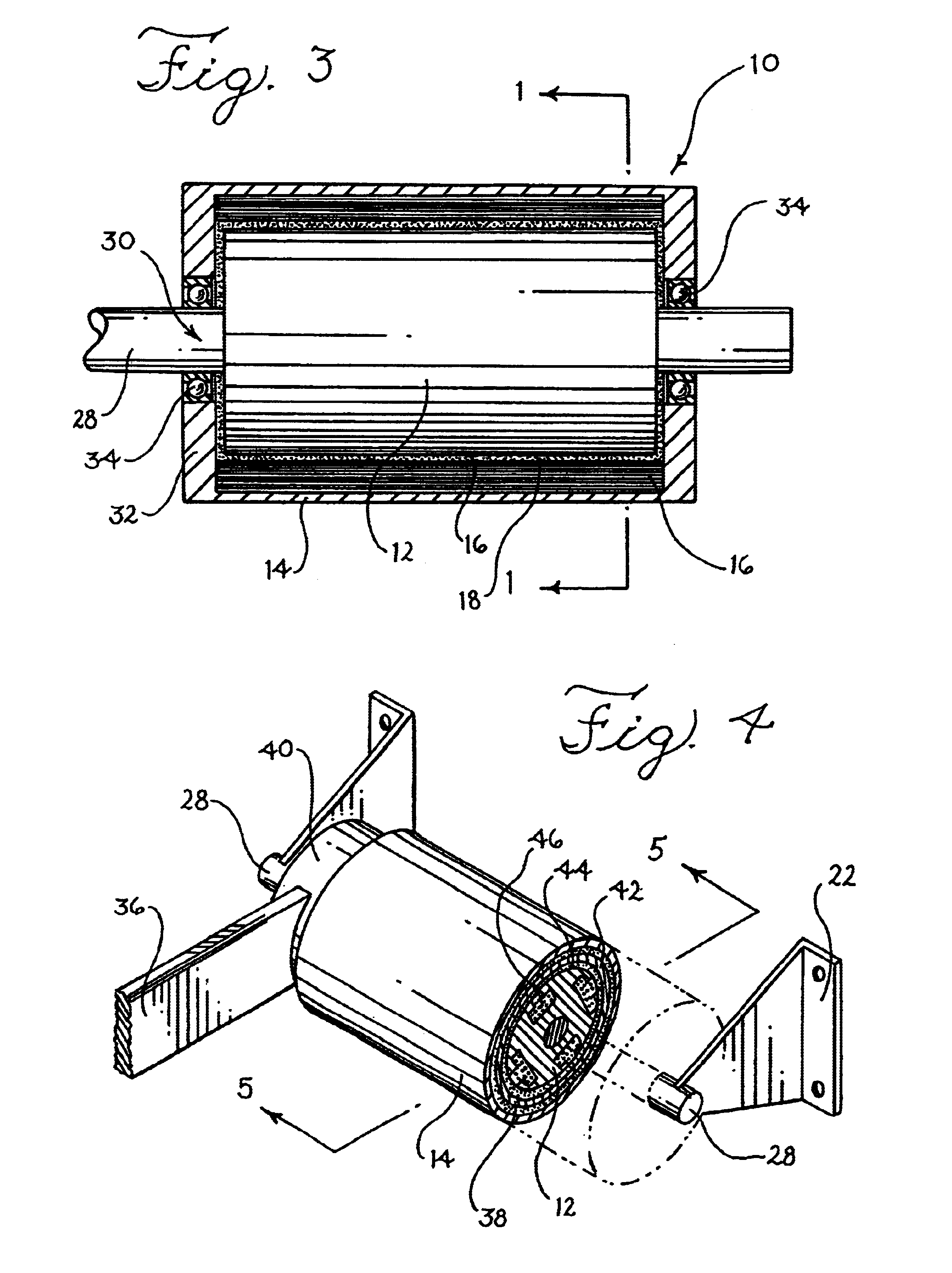
Electronically controlled prosthetic knee
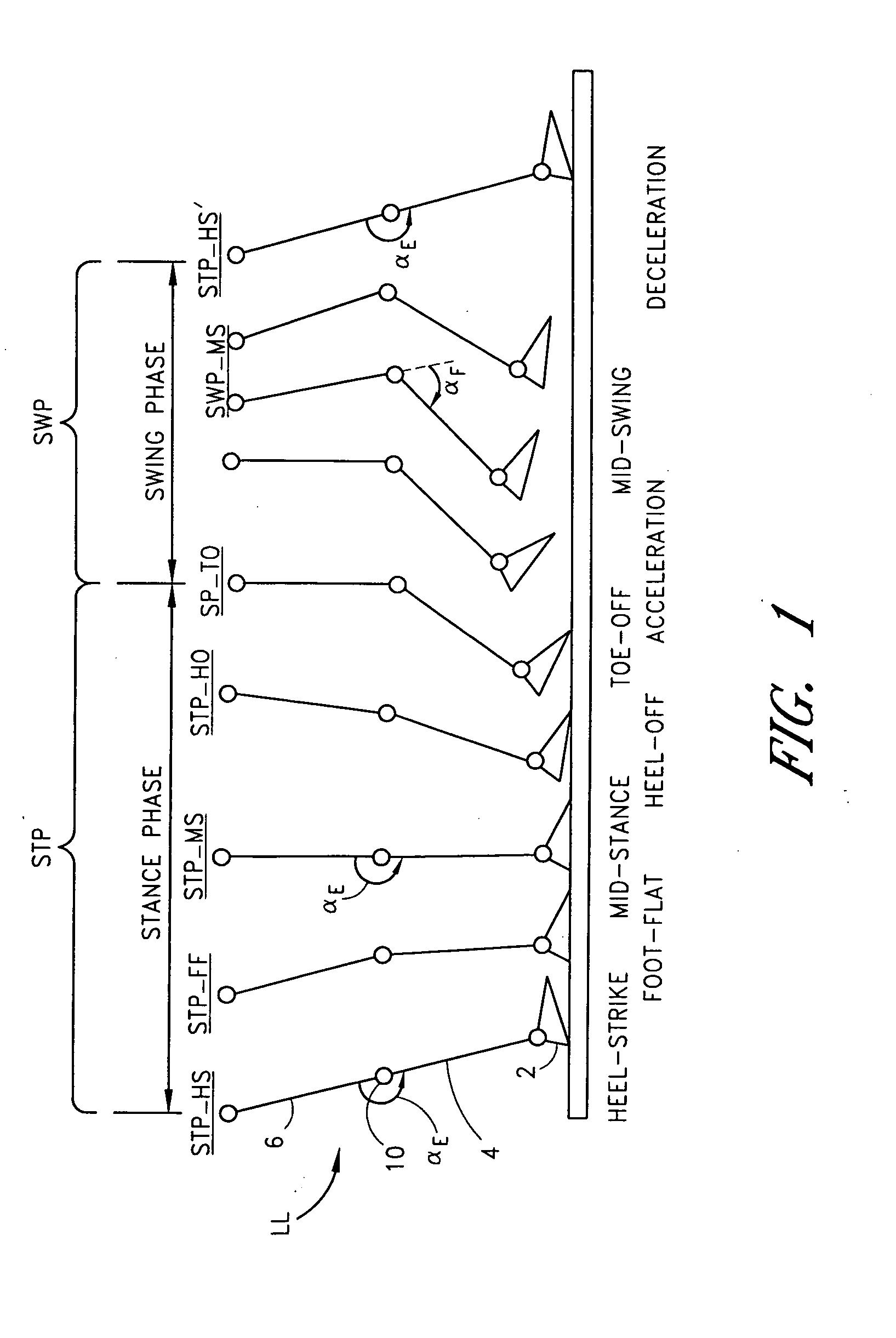
InactiveUS6764520B2Improve efficiencyImprove practicalitySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionLow speedMagnetorheological fluid
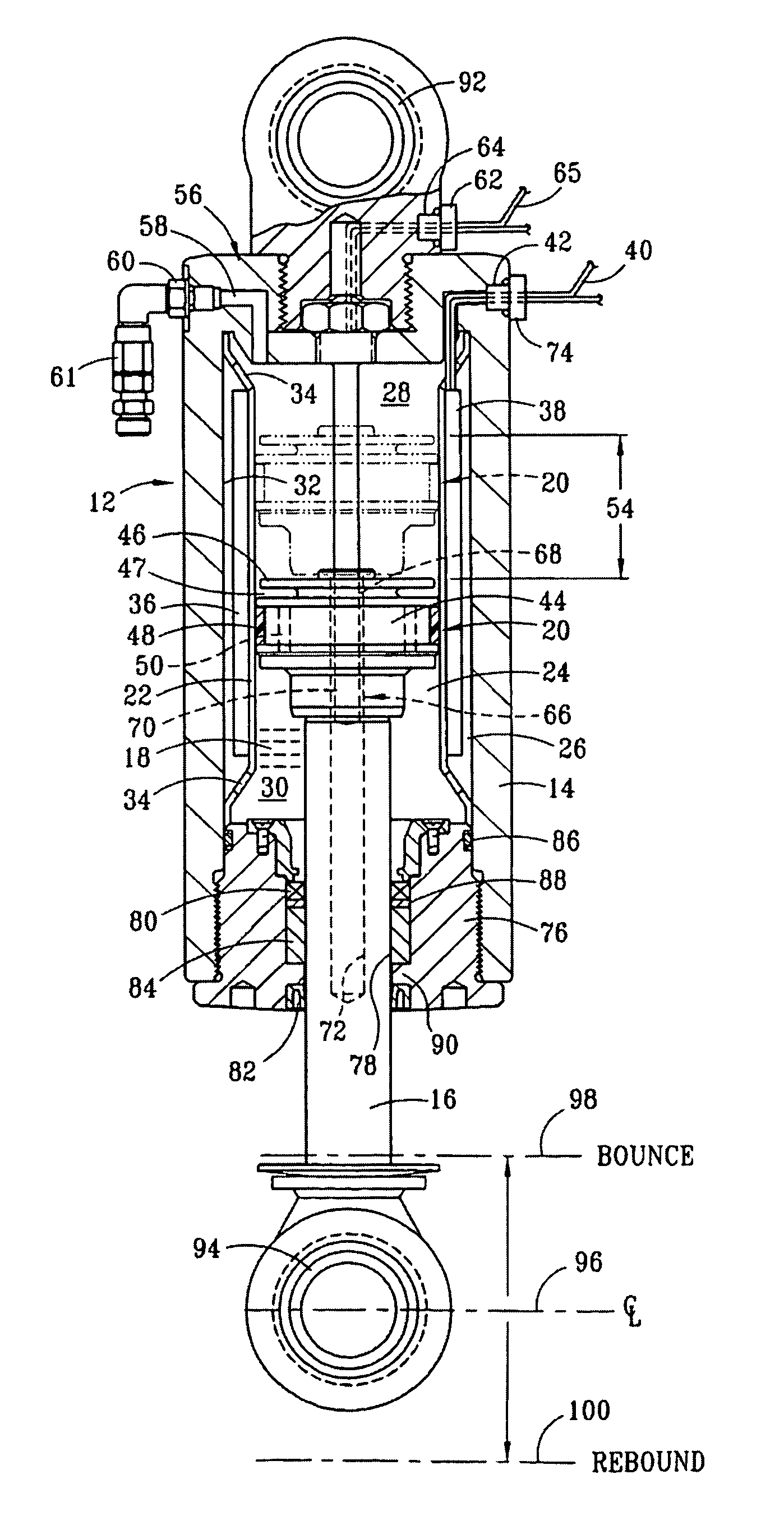
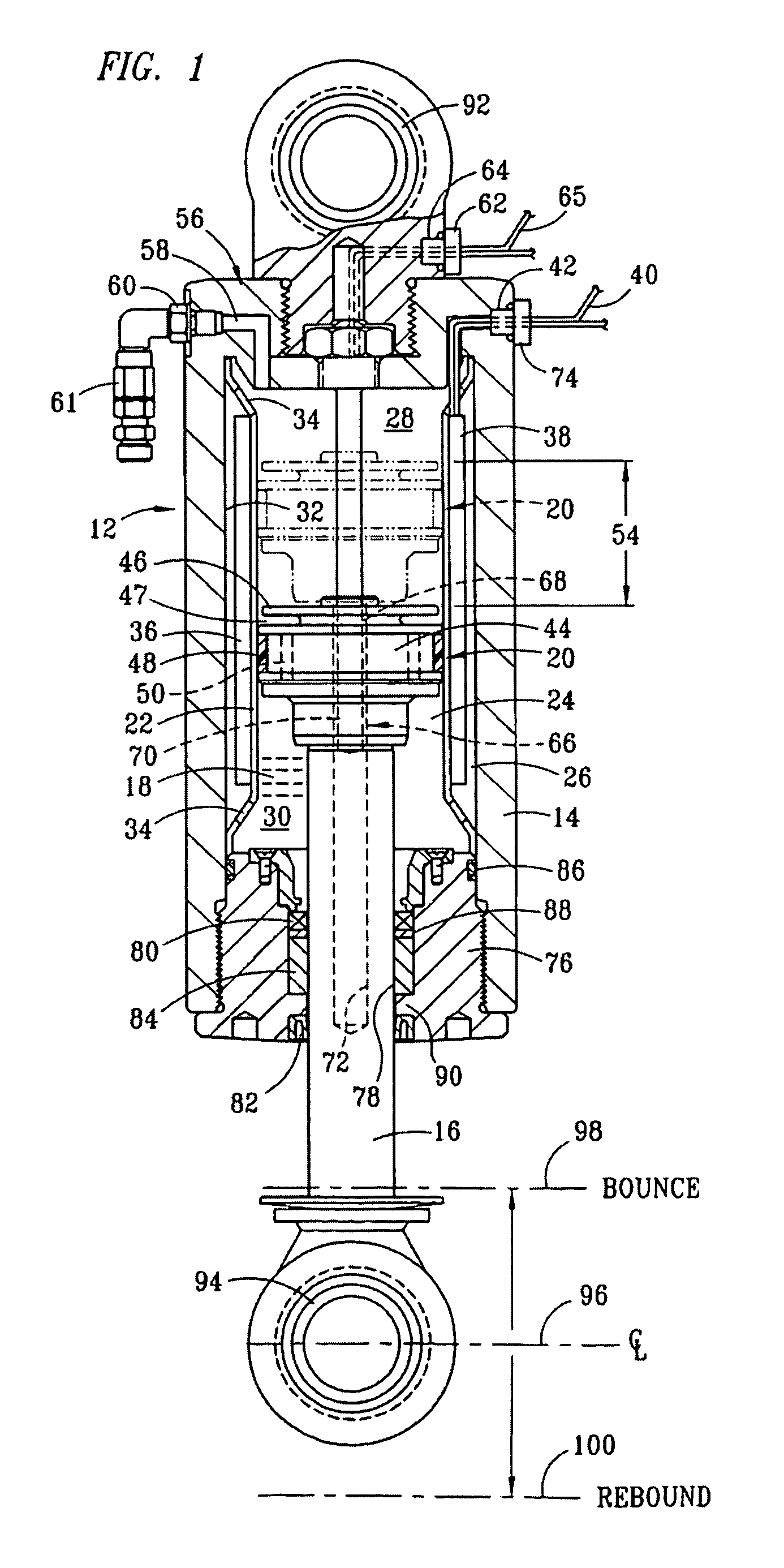
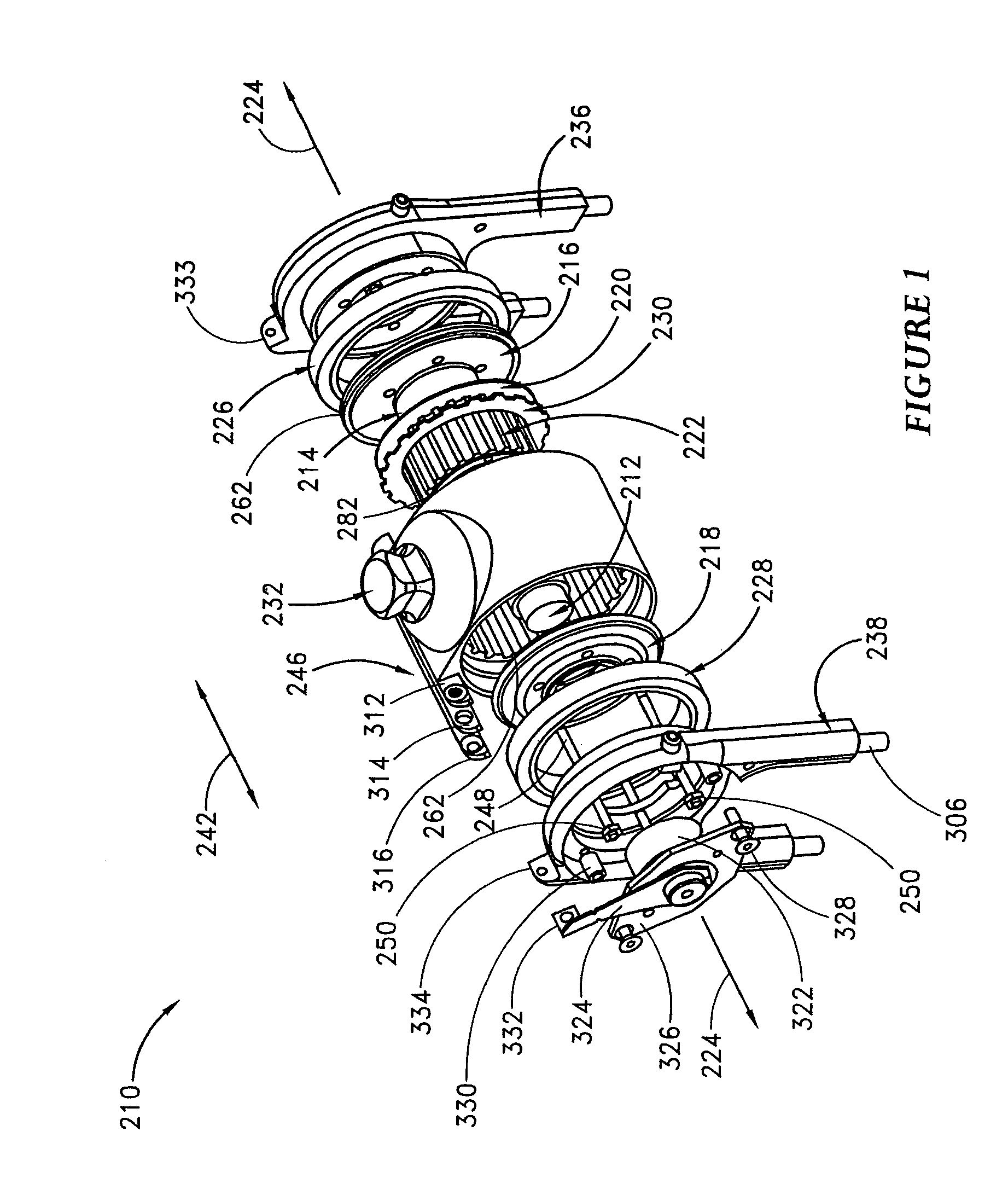
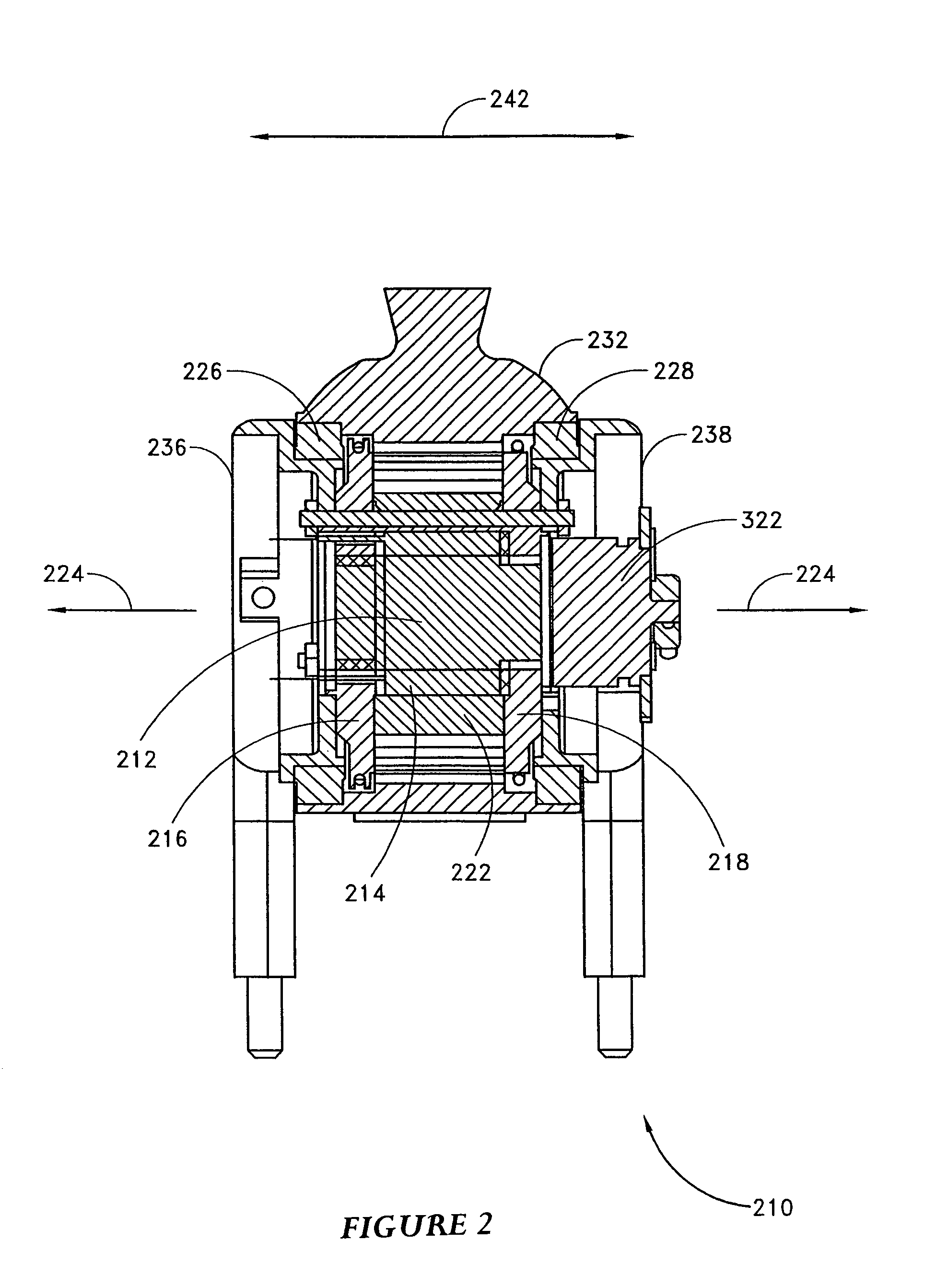
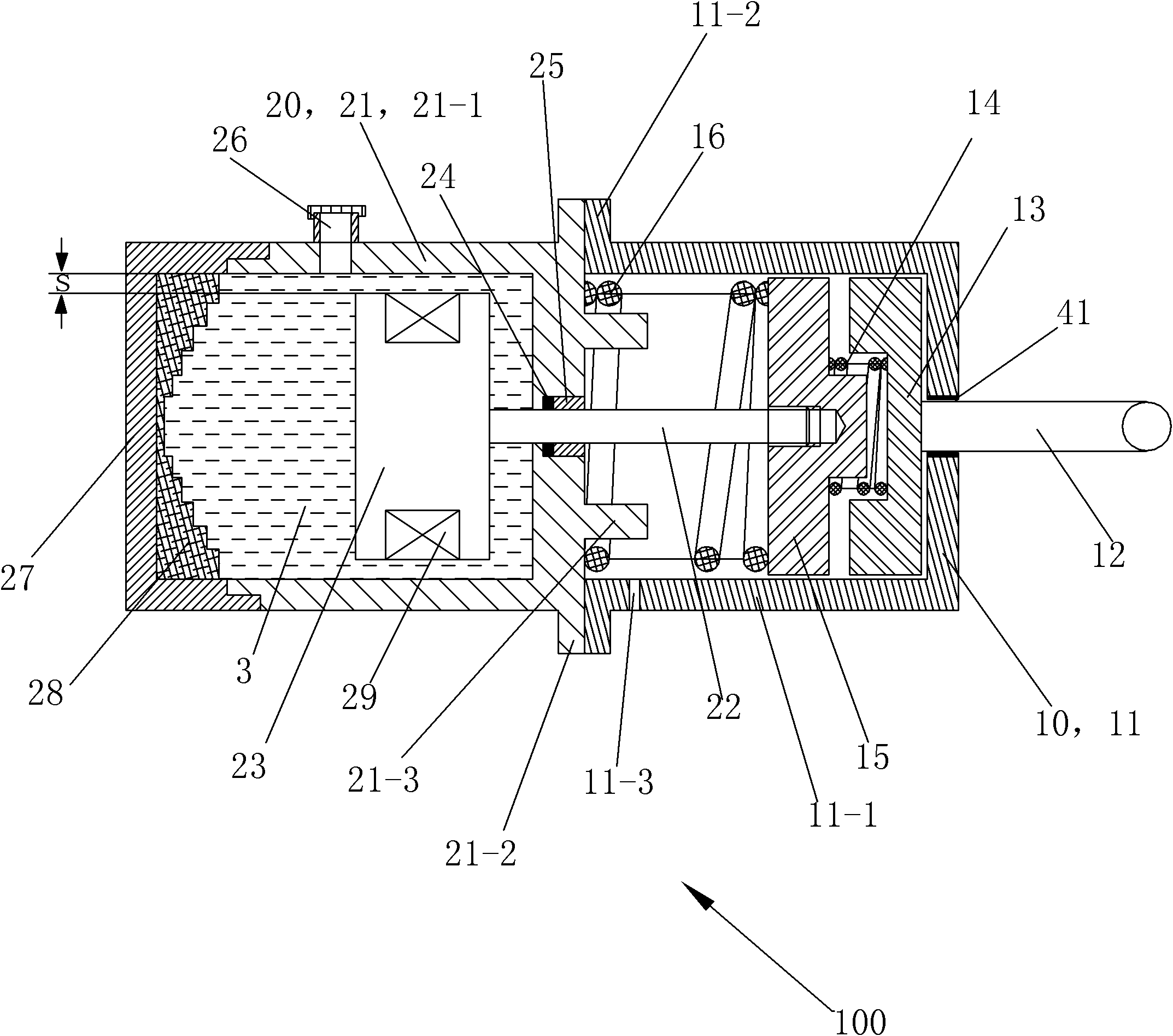
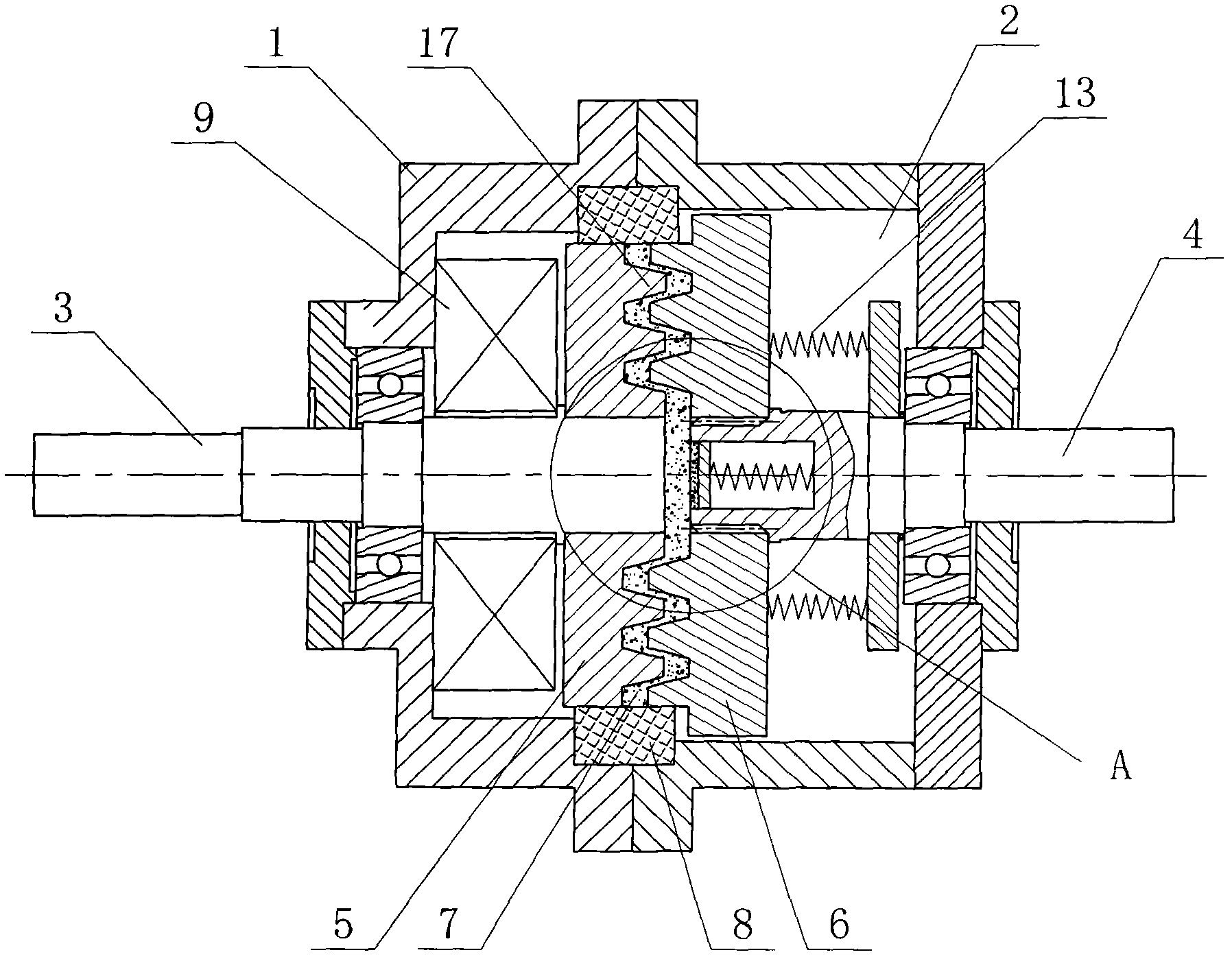
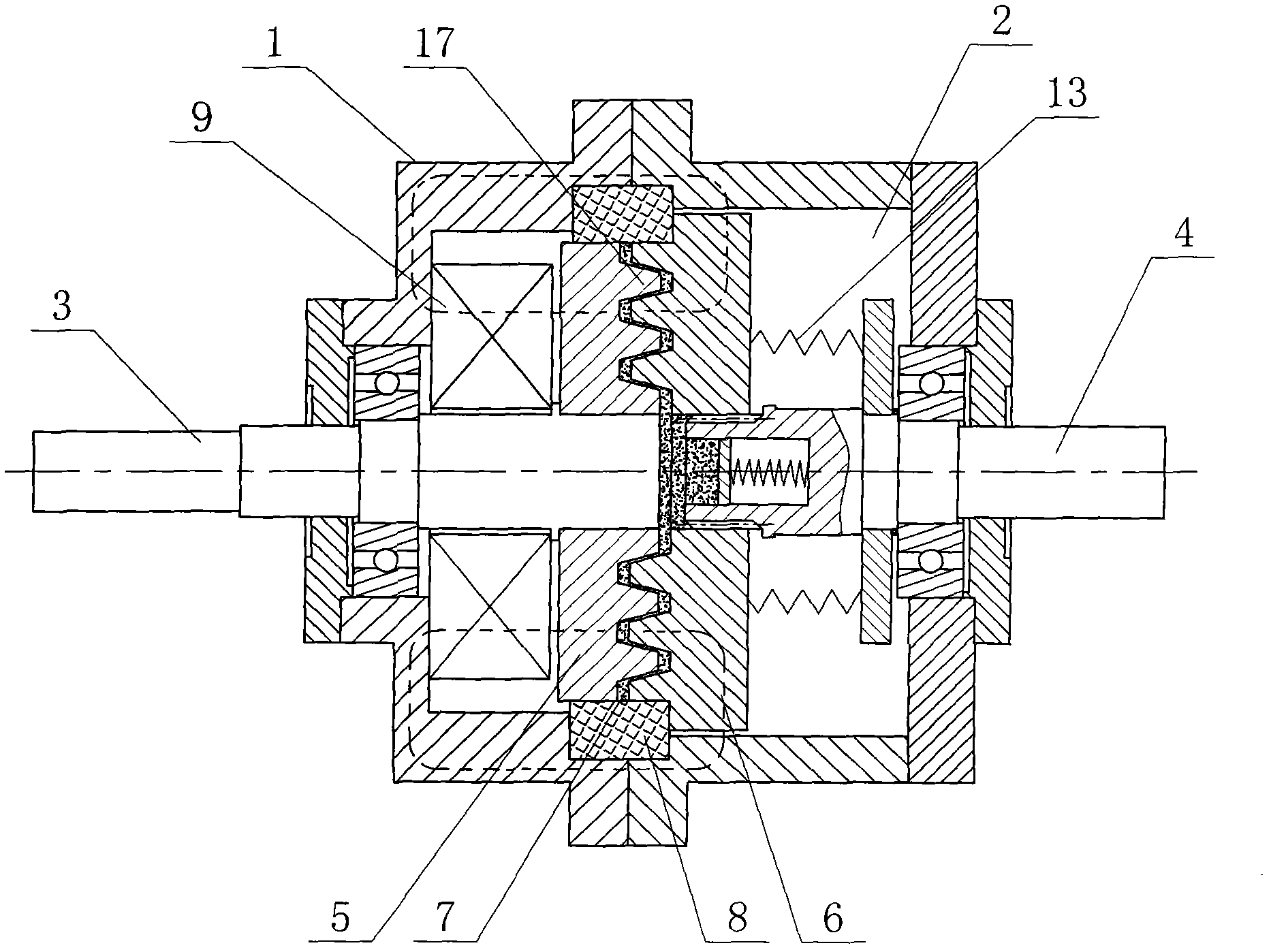
The present invention relates to a variable-torque magnetorheologically actuated prosthetic knee which utilizes a plurality of interspersed and alternating rotors and stators to shear magnetorheological fluid in gaps formed therebetween. Advantageously, by operating in the "shear mode" there is substantially no or negligible fluid pressure buildup or change. Moreover, the multiple MR fluid gaps or flux interfaces desirably allow for the production of a large torque at low speed-eliminating the need for a transmission-and also for a wide dynamic torque range. One embodiment of the invention allows the rotors and / or stators to close the gaps therebetween to create a frictional torque component, thereby forming a "hybrid" braking system which provides a total torque or damping which is a combination of viscous torque and frictional torque.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
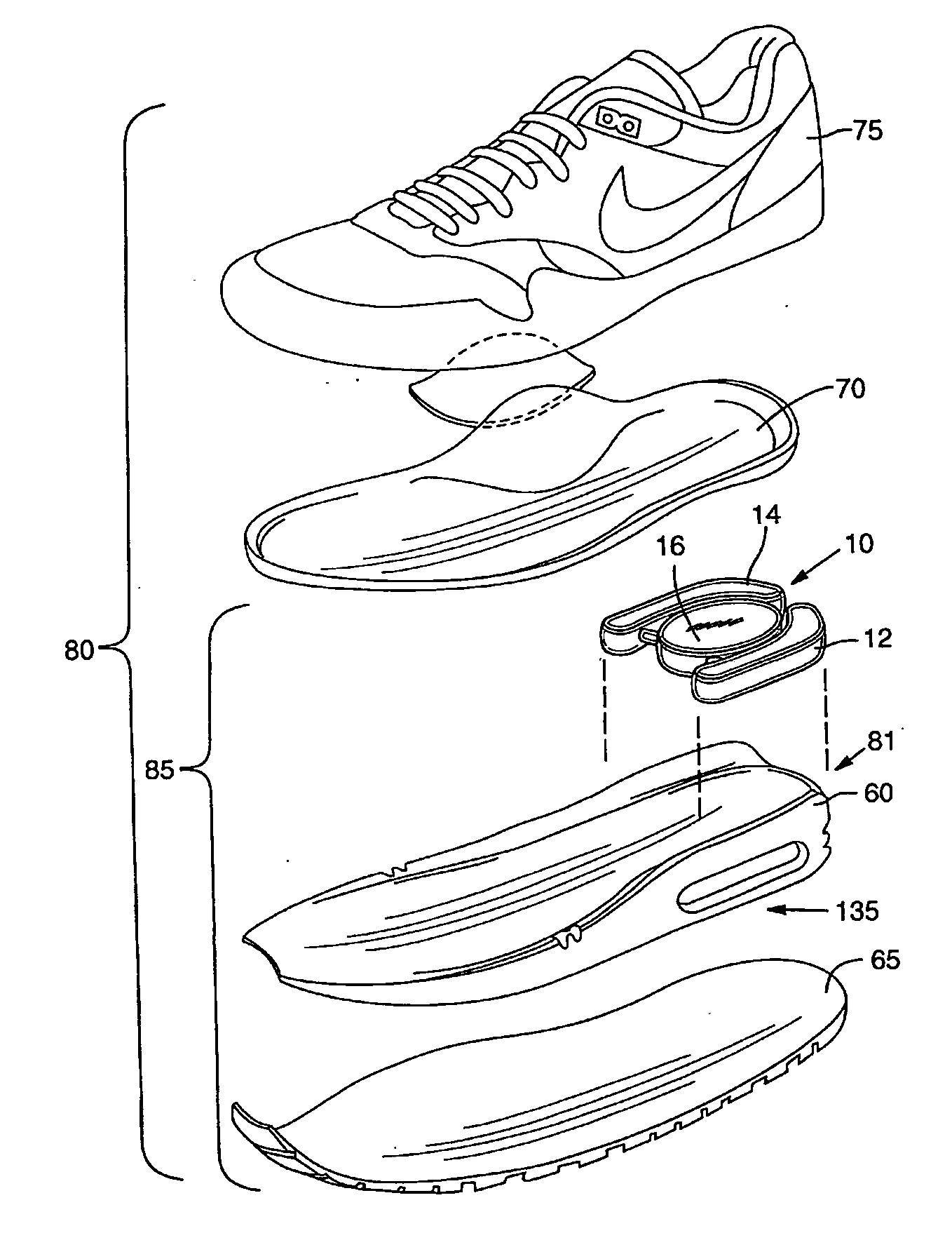
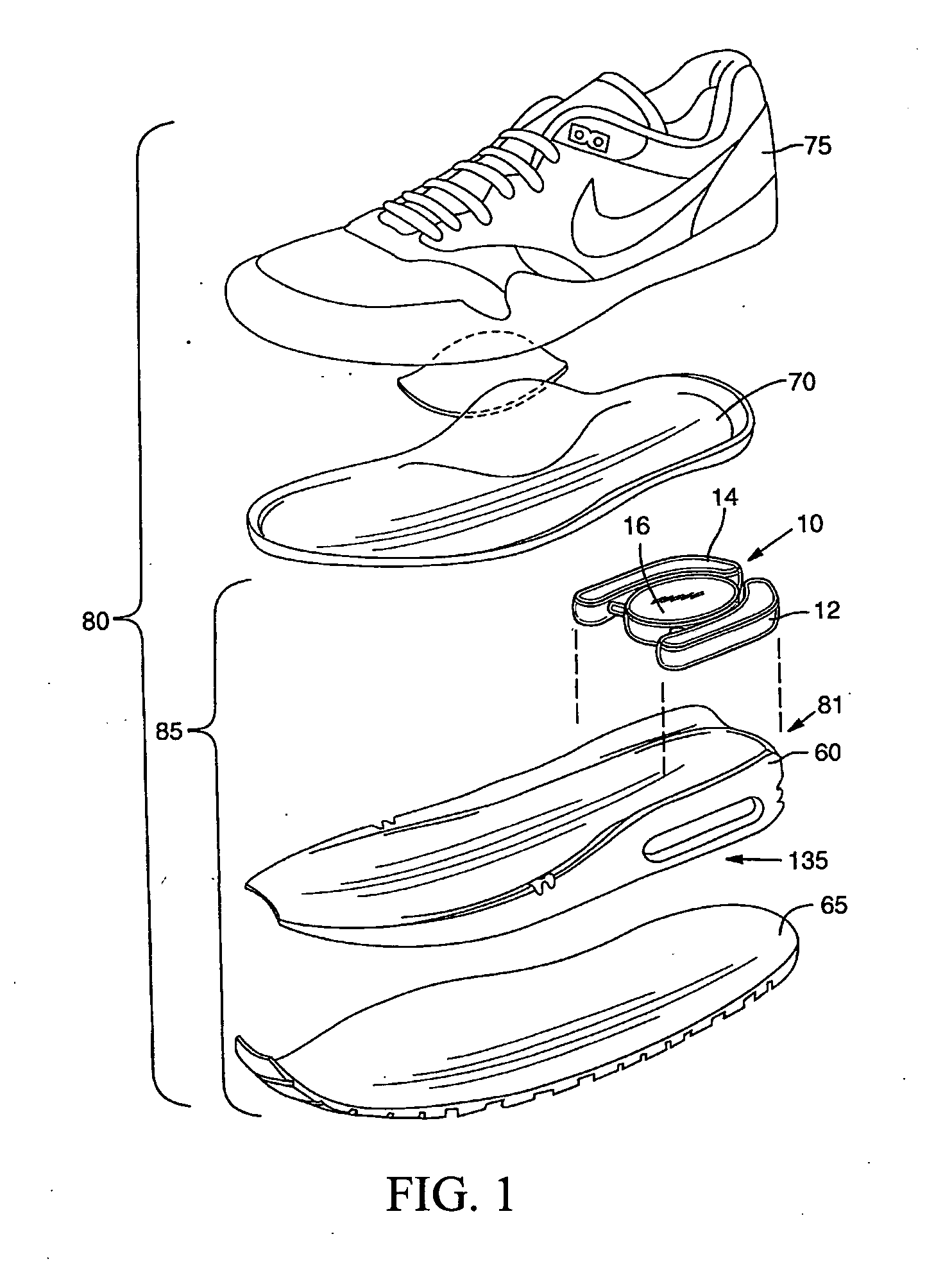
Variable support footwear using electrorheological or magnetorheological fluids
A variable footwear support system includes at least one rheological body within a sole of an article of footwear, control electronics within the article of footwear, and at least one E / M field generator coupled to the control electronics and arranged operably proximate to at least one rheological body. The sole is formed of a resilient material and the rheological body contains a Theological fluid having a viscosity that is variable in the presence of an energy field. The control electronics is adapted to generate at least one control signal. The at least one E / M field generator is adapted to generate an energy field corresponding to a control signal generated by the control electronics upon the rheological body.
Owner:OUTLAND RES
Electronically controlled prosthetic knee
InactiveUS20010029400A1Move and/or adapt comfortably and safelyImprove efficiencySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionFriction torqueMagnetorheological fluid
The present invention relates to a variable-torque magnetorheologically actuated prosthetic knee which utilizes a plurality of interspersed and alternating rotors and stators to shear magnetorheological fluid in gaps formed therebetween. Advantageously, by operating in the "shear mode" there is substantially no or negligible fluid pressure buildup or change. Moreover, the multiple MR fluid gaps or flux interfaces desirably allow for the production of a large torque at low speed-eliminating the need for a transmission-and also for a wide dynamic torque range. One embodiment of the invention allows the rotors and / or stators to close the gaps therebetween to create a frictional torque component, thereby forming a "hybrid" braking system which provides a total torque or damping which is a combination of viscous torque and frictional torque.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fluid damper having continuously variable damping response
ActiveUS20050121269A1Reduce manufacturing costLower the volumeSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetorheological fluidEngineering
An improved damping apparatus that utilizes a fluid having a viscosity that may be varied by the application of an electromagnetic field, such as a magnetorheological fluid or an electrorheological fluid, to provide the damping response. The damping apparatus includes a linear to rotary conversion mechanism which comprises a translatable member that is adapted for linear translation in a forward and a reverse direction and a rotatable member comprising a rotatable shaft that is rotatably coupled to the translatable member; wherein translation of the translatable member in one of the forward or the reverse directions produces a forward or a reverse rotation of the rotatable member and shaft, respectively. The damping apparatus also includes a damping mechanism which comprises a hub that is fixed to the shaft, a means for generating a variable electromagnetic field in response to an applied electrical signal that may be continuously varied in response to an input signal that is representative of a desired damping force and a fluid having a viscosity that may be continuously varied by application of the electromagnetic field that is in touching contact with the hub. Application of the variable electromagnetic field to the fluid produces changes in the viscosity of the fluid that in turn provides variable resistance to rotation of the hub and resistance to translation of the translatable member, thereby providing a damping apparatus with a continuously variable damping response.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Force feedback devices using fluid braking
InactiveUS7113166B1High strengthLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInherent safetyFluid viscosity
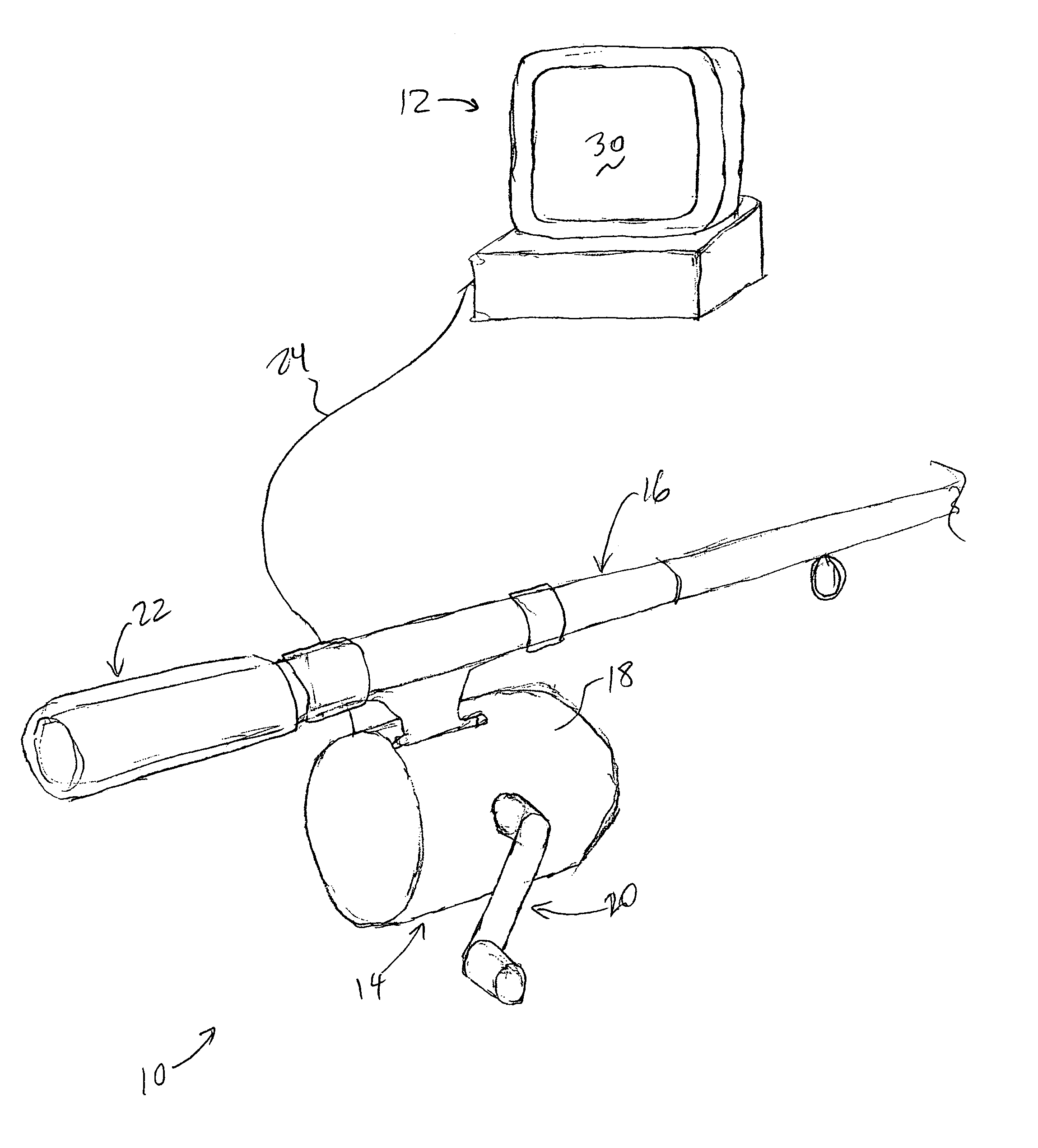
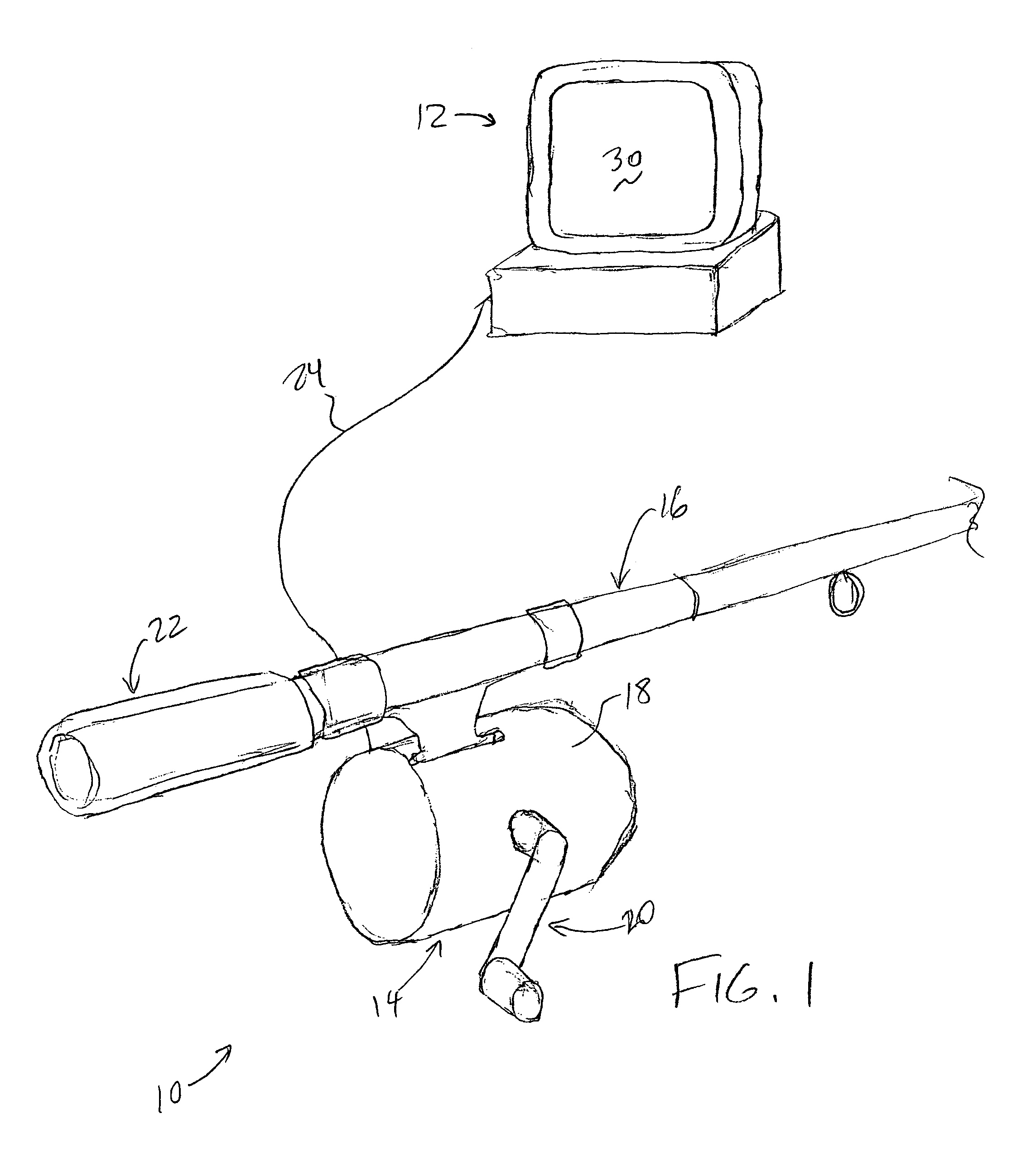
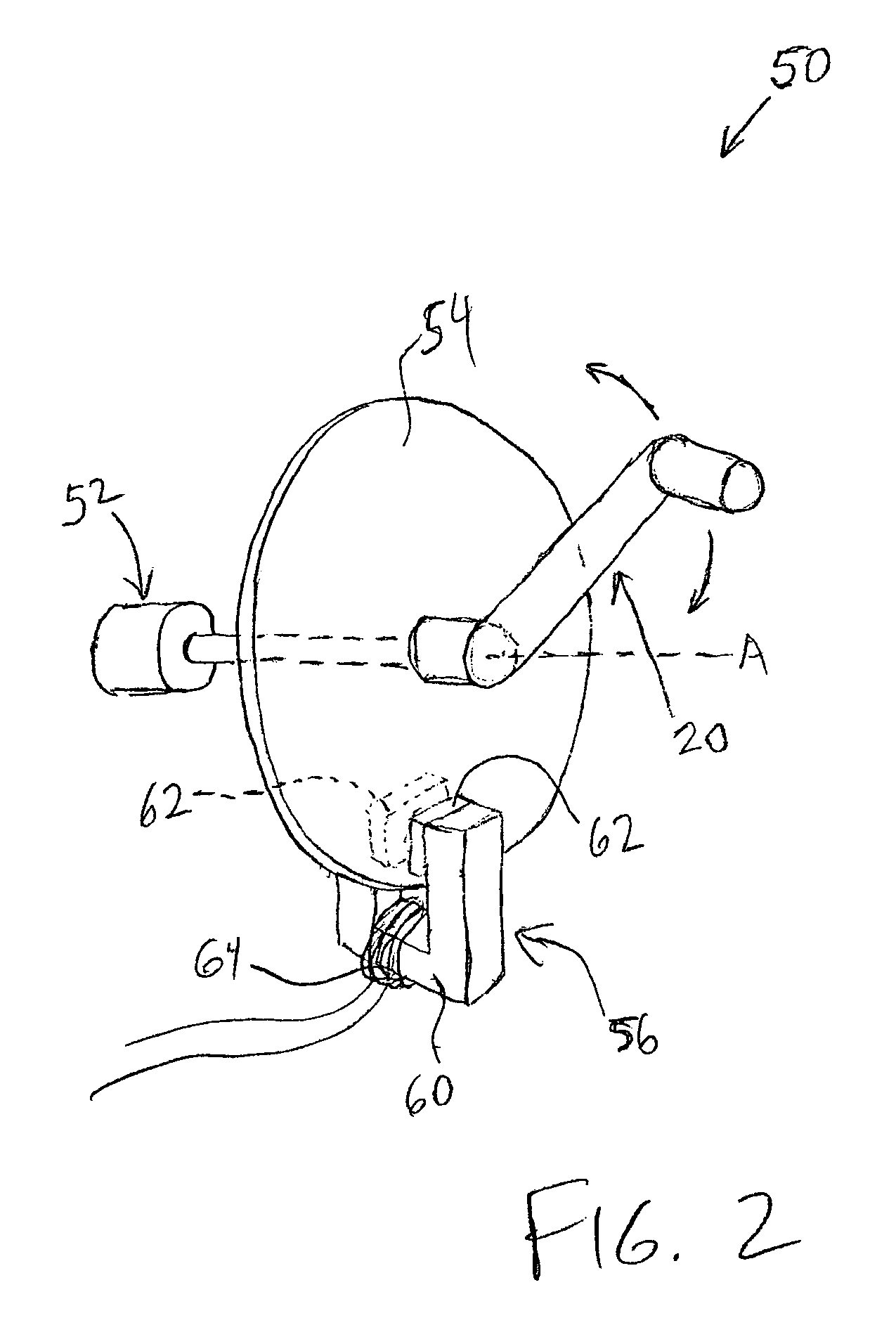
A haptic feedback device including a fluid viscosity-controlled brake that outputs high forces to the device user at low cost while maintaining inherent safety. An interface device includes a manipulandum physically contacted by the user. A sensor senses a position of the manipulandum and outputs a sensor signal. The interface device also includes a brake including a field-controlled fluid having a viscosity that can be controlled by controlling an electric current in a coil, where a resistive force or drag on the manipulandum is controlled by controlling the fluid's viscosity. The fluid can be an electrorheological fluid controlled by an electric field or a magnetorheological fluid controlled by a magnetic field. In one preferred embodiment, the resistive force is controlled by adjusting a degree of contact of the brake with the manipulandum based on the fluid's viscosity. Disclosed embodiments include fishing devices, bicycle simulators, and control knobs.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Pump drivetrain damper system and control systems and methods for same
ActiveUS10316832B2Reduce vibrationLiquid resistance brakesPositive displacement pump componentsControl signalDrivetrain
Owner:SPM OIL & GAS INC
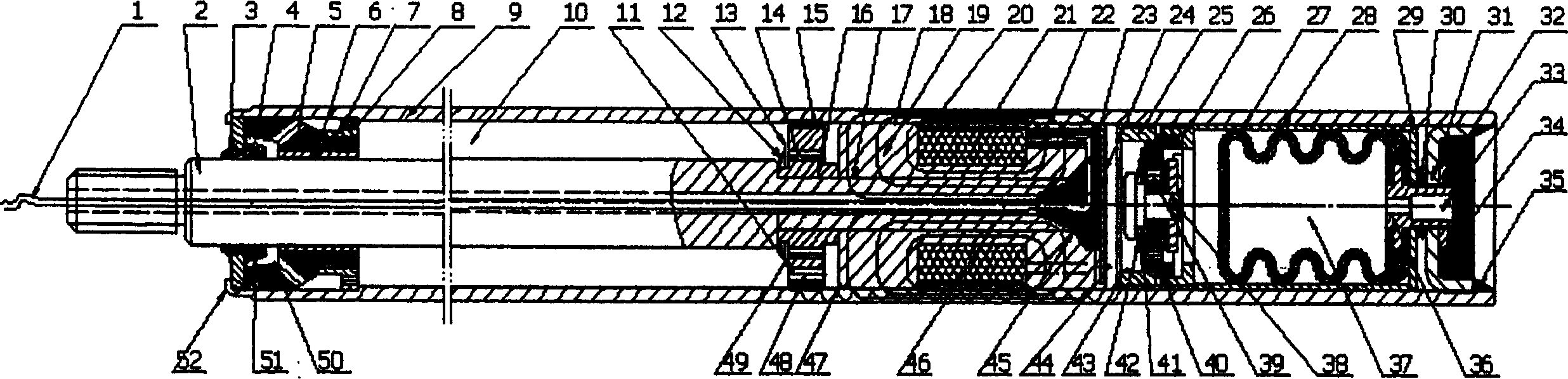
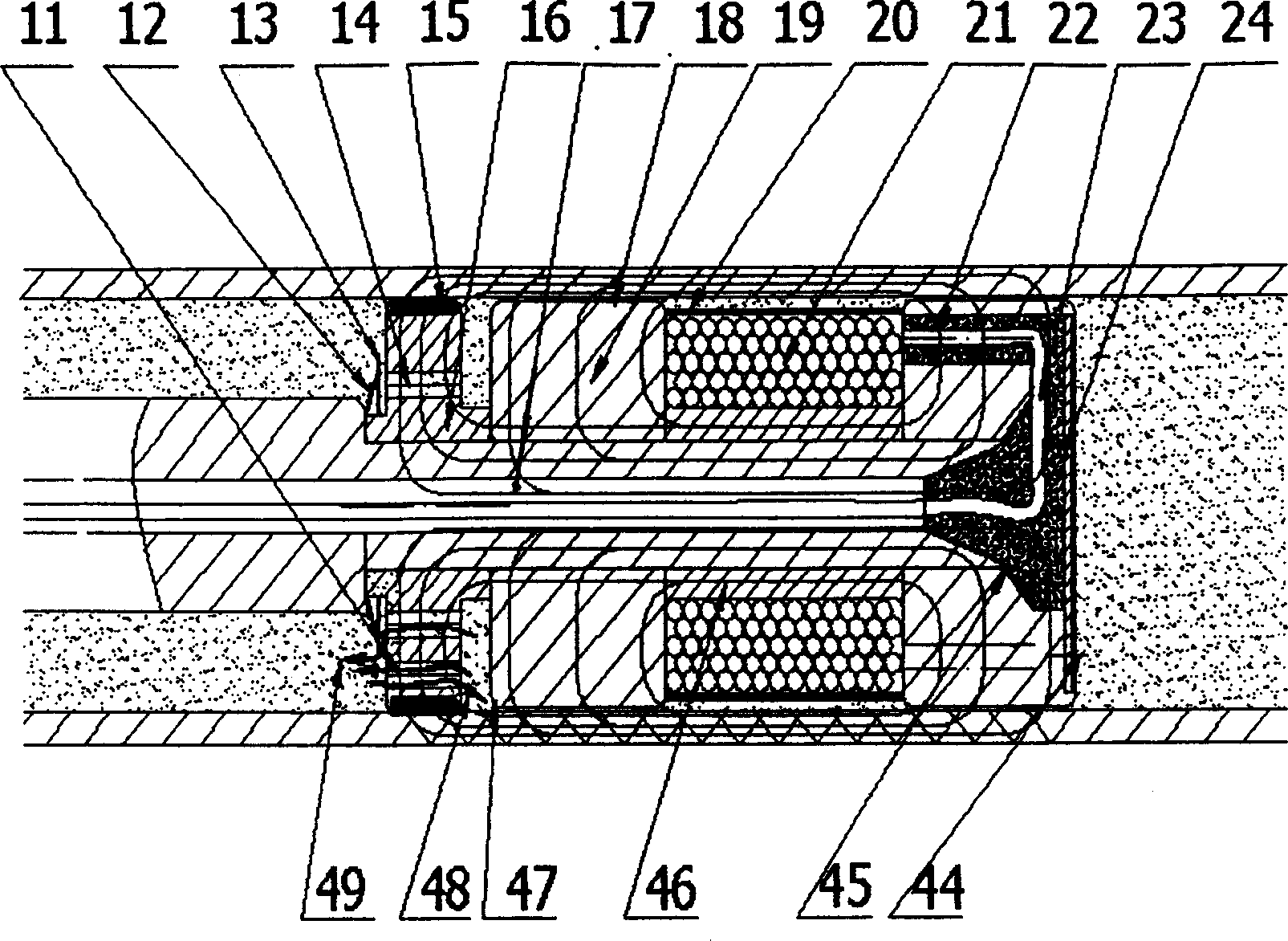
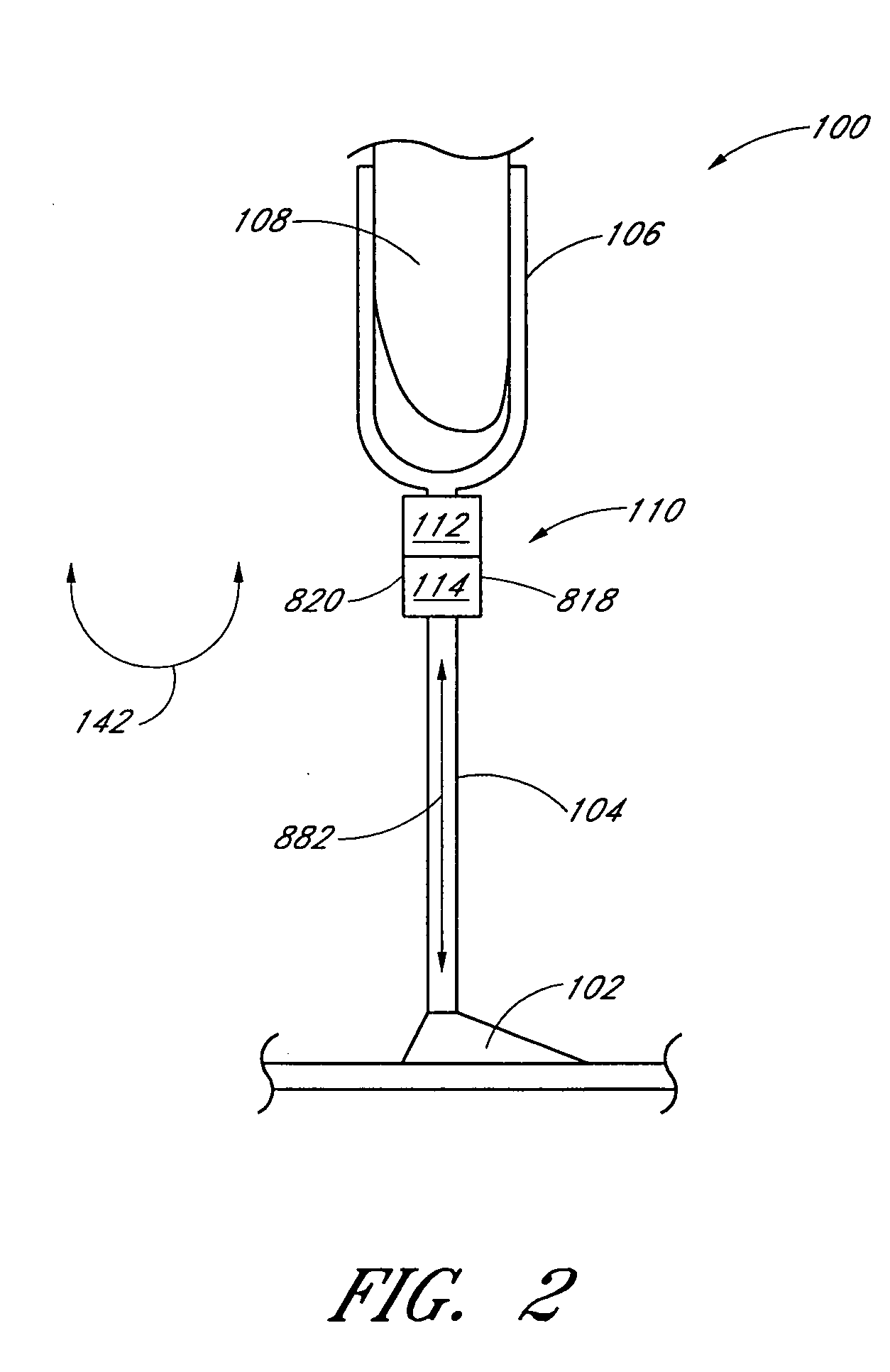
Systems and methods of loading fluid in a prosthetic knee
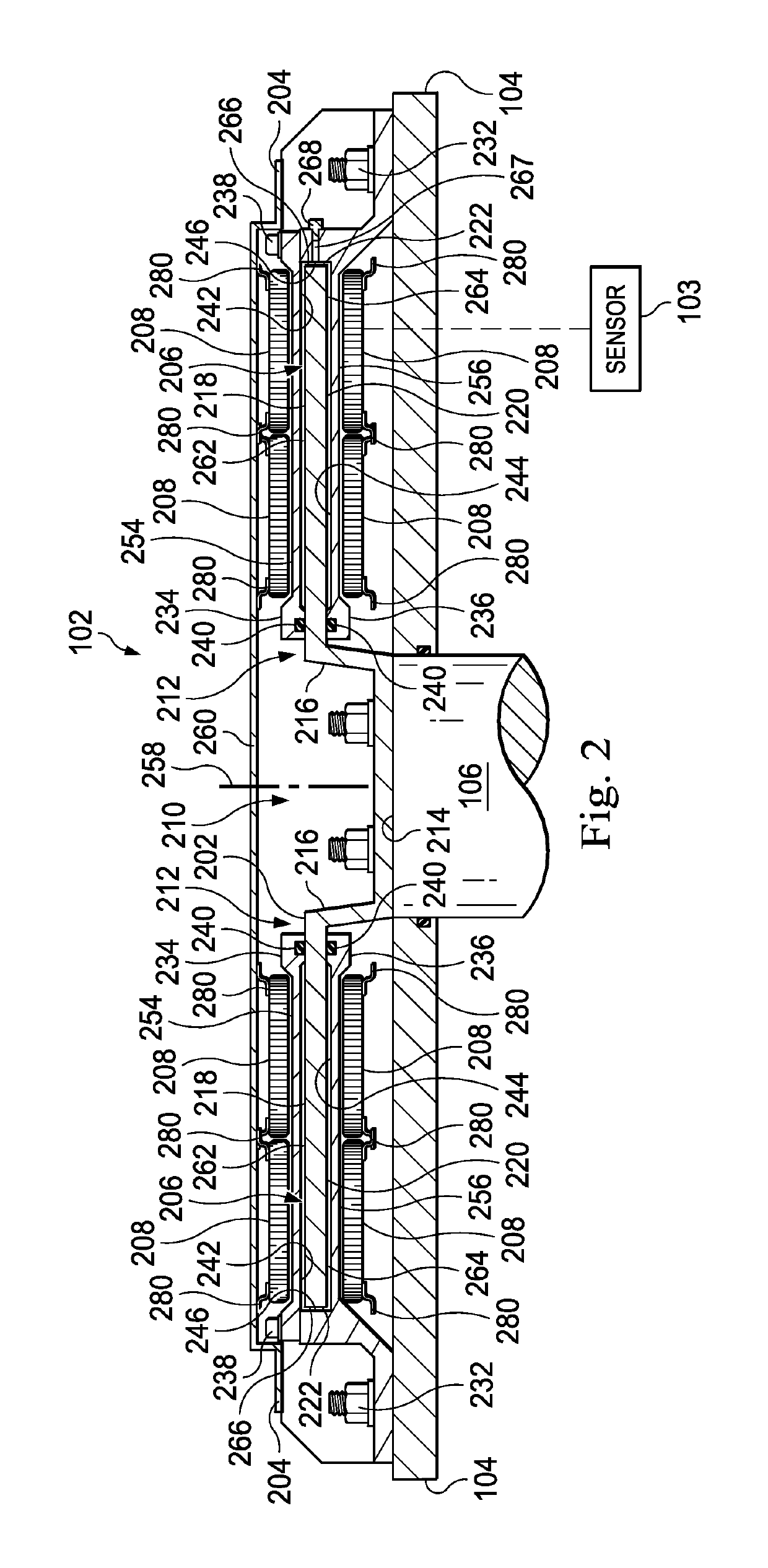
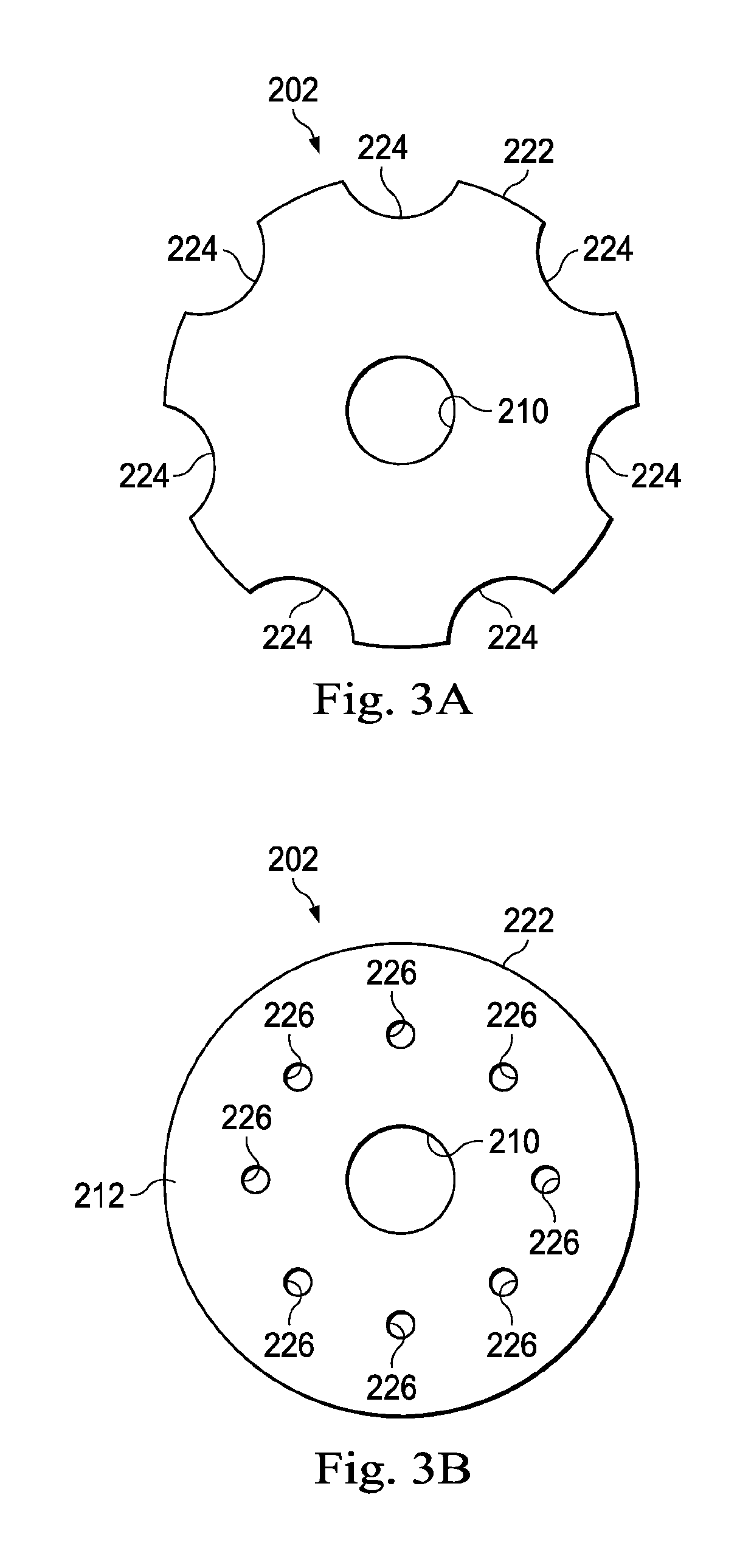
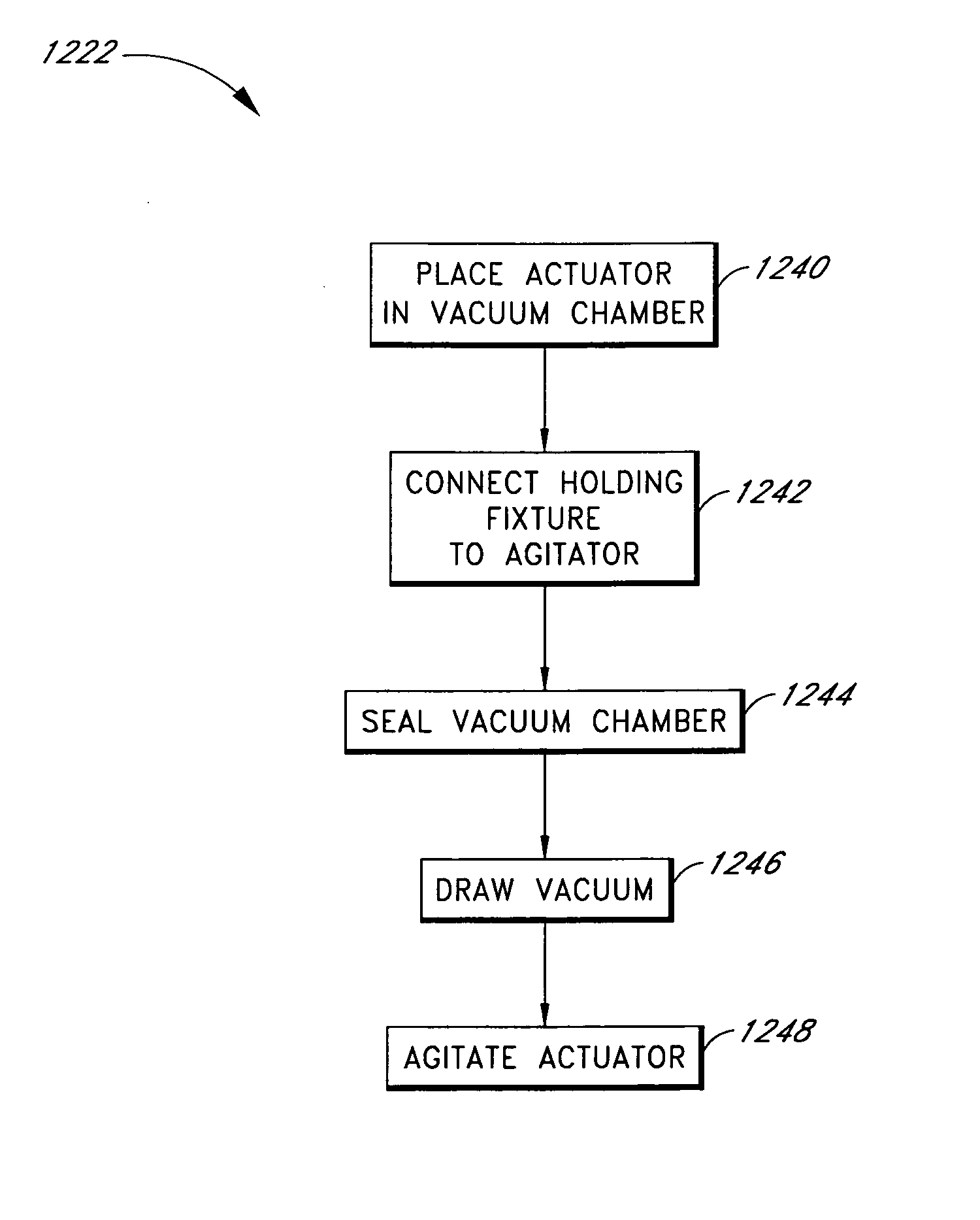
InactiveUS7198071B2Efficient loadingIncrease speedLiquid fillingOther chemical processesMagnetorheological fluidEngineering
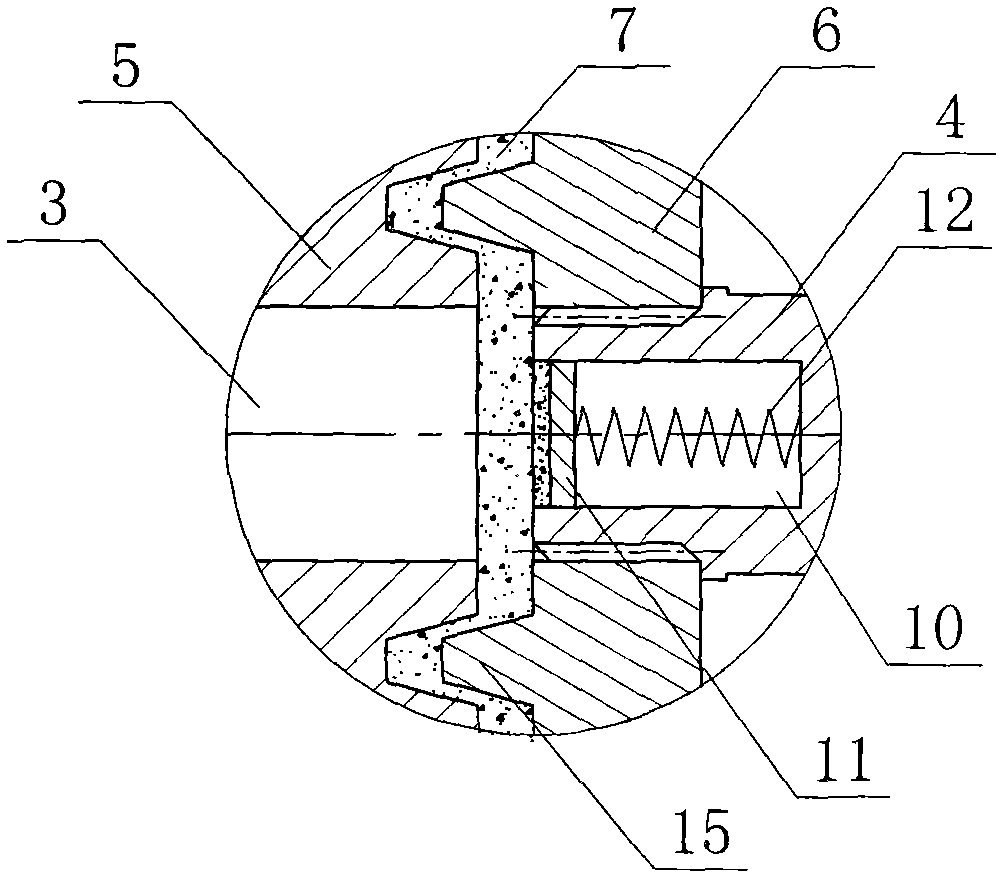
The invention in some embodiments relates to systems and methods of loading fluid in a prosthetic knee. A vacuum fill technique is utilized in one embodiment to load magnetorheological fluid within small gaps in a chamber of a prosthetic knee. Advantageously, this allows for an efficient loading scheme thereby desirably allowing for faster manufacturing speed. Another advantage is that the magnetorheological fluid is substantially uniformly distributed within the small gaps thereby desirably providing consistent production.
Owner:OSSUR HF
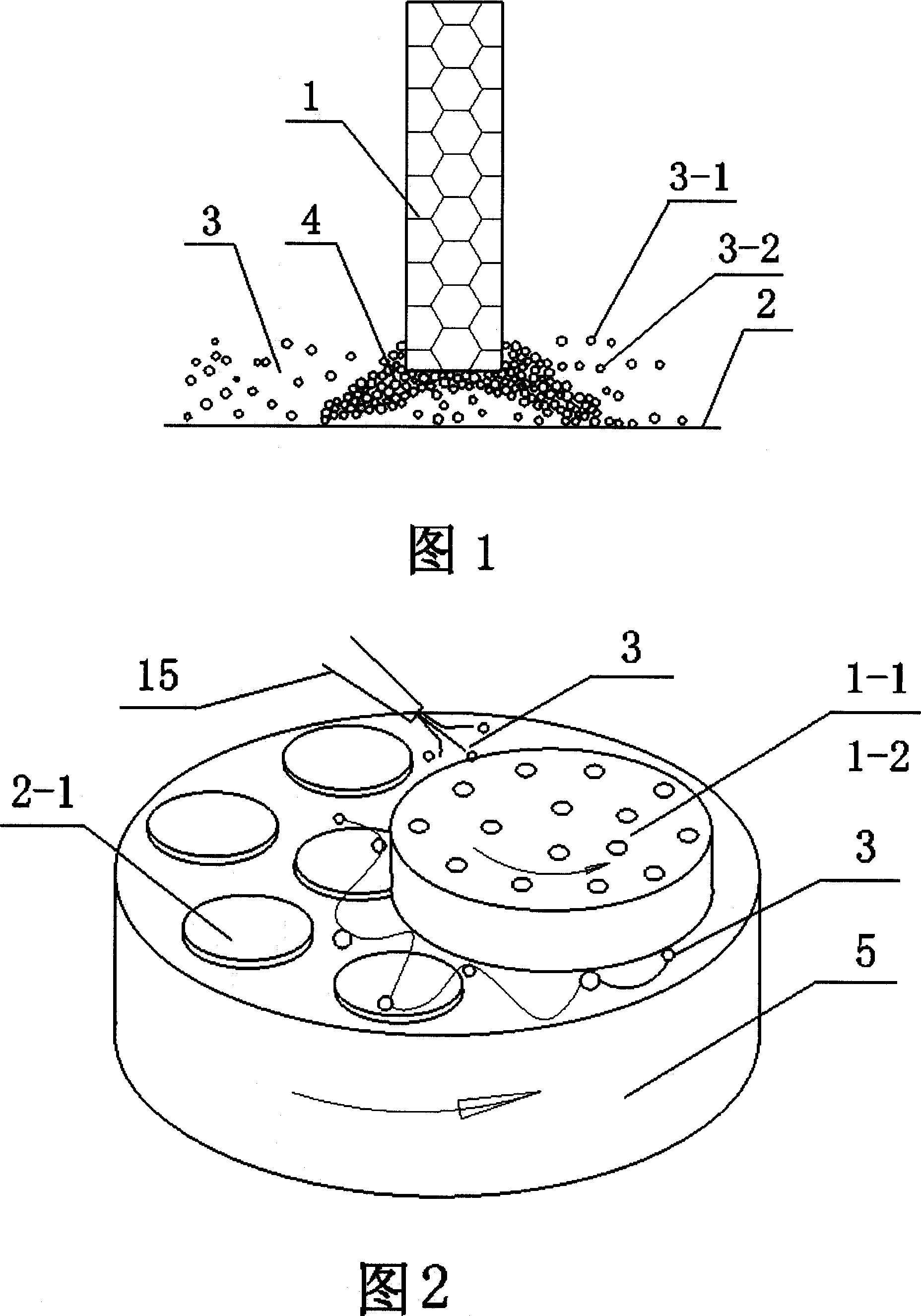
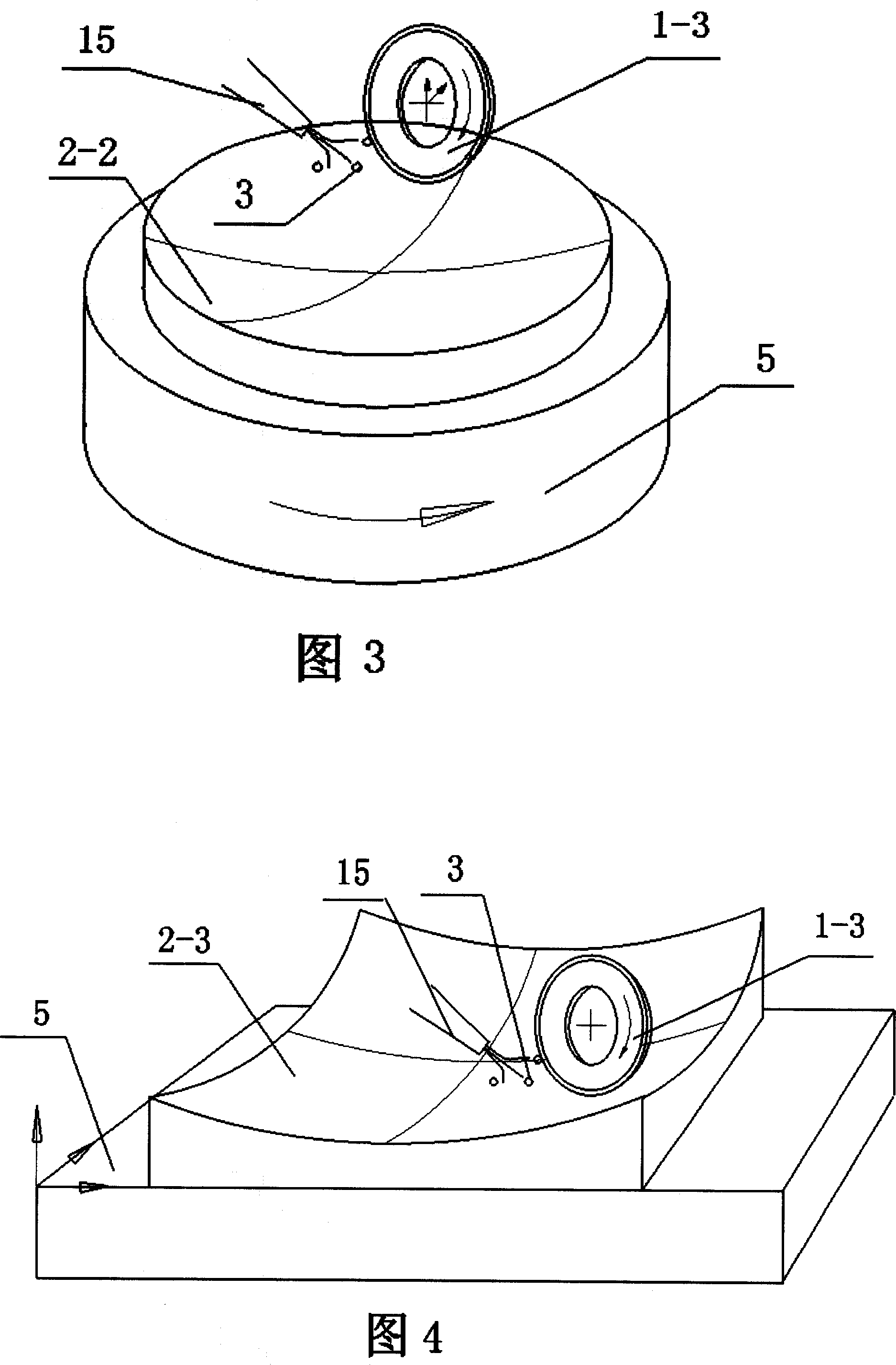
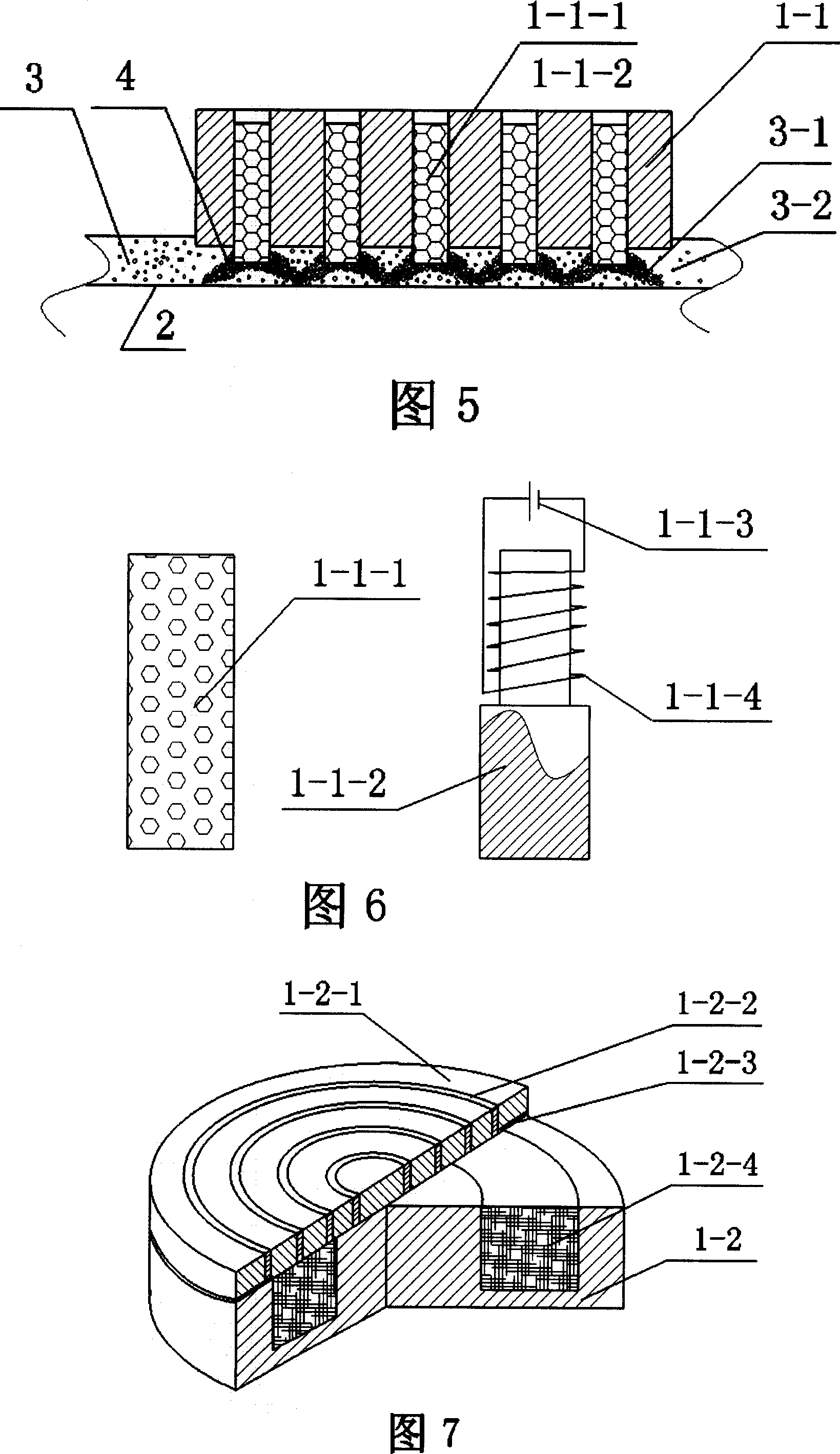
Grinding polishing method based on magnetic rheology effect and its polishing device
InactiveCN100999061AReduce removal rateReduce machining accuracyPolishing machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesMagnetorheological fluidMaterials science
The present invention discloses a grinding-polishing method based on magnetorheological effect. Said method is characterized by that in the magnetorheological fluid a kind of free abrasive material is added, used as grinding-polishing liquor and injected into the between of magnetic body and workpiece surface, under the action of magnetic field the ferromagnetic particles in the magnetorheological fluid can be arranged by strings to cover the abrasive material pacticles and can be constrained in the end face of magnetic body to form magnetic grinding brush, said magnetic grinding brush can be used for grinding-polishing workpiece surface. Said invention also provides a grinding-polishing device for implementing said grinding-polishing method. Said device includes grinding tool mounted on main shaft connected with motor and working table for mounting workpiece.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
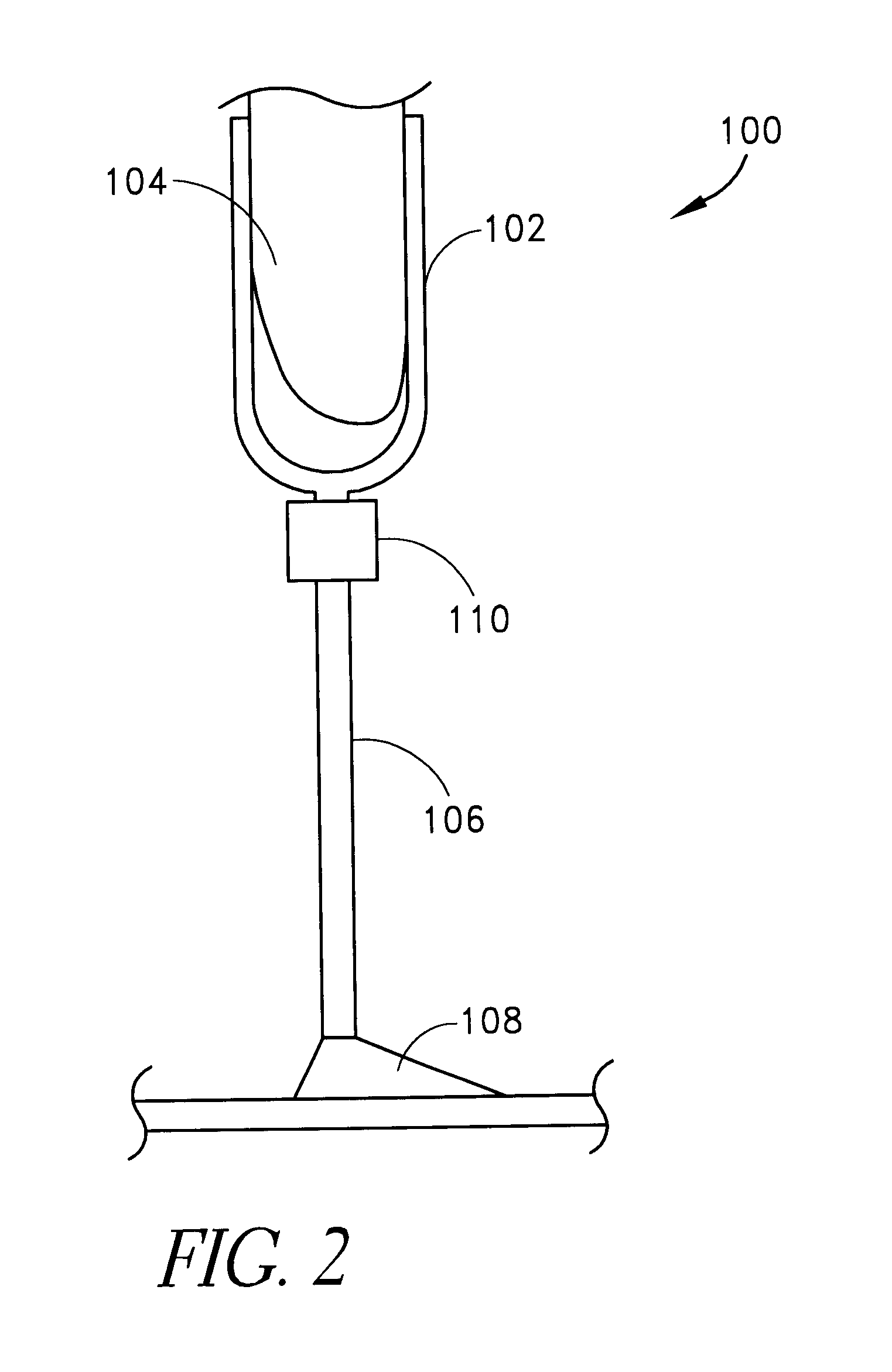
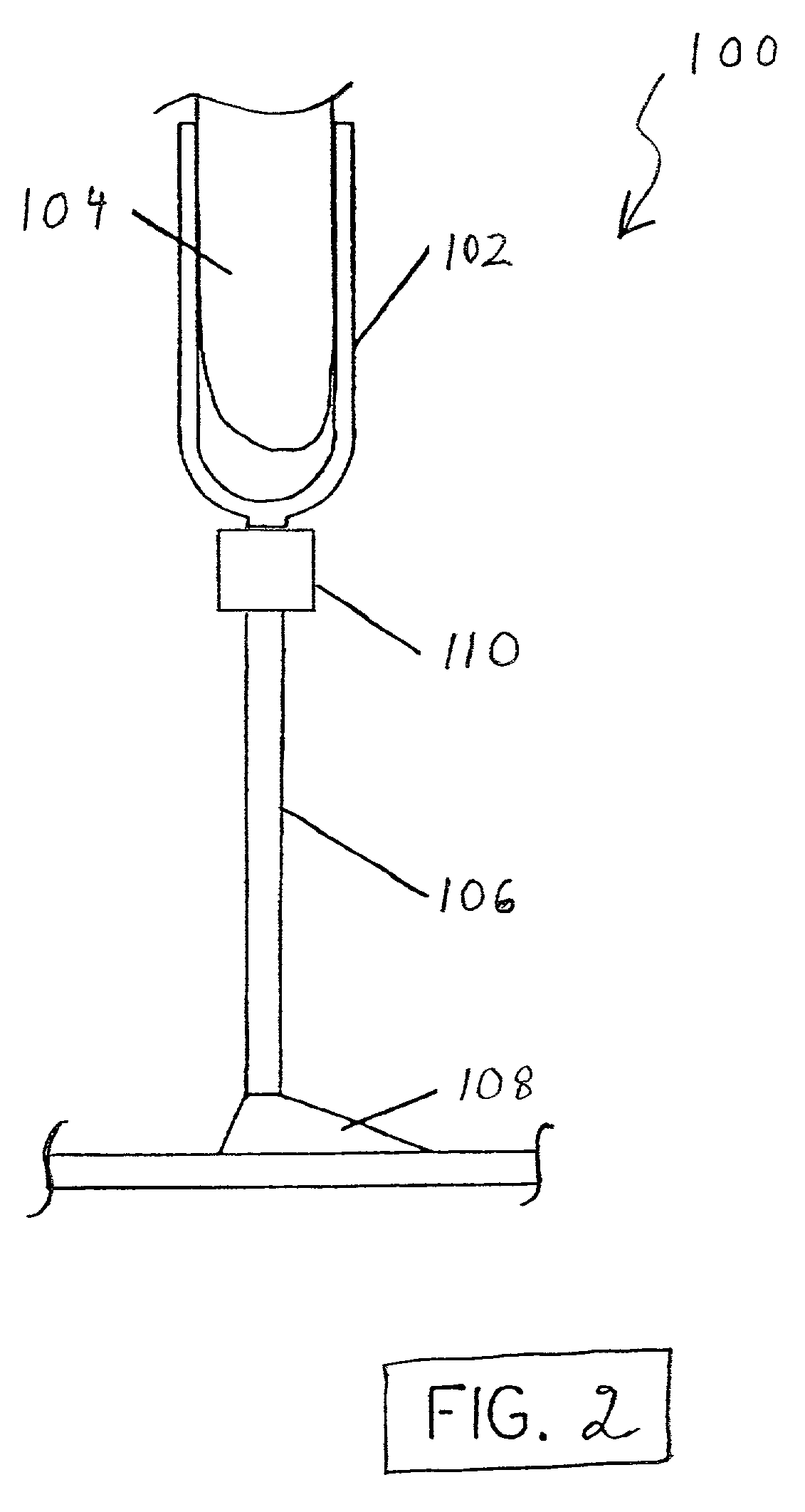
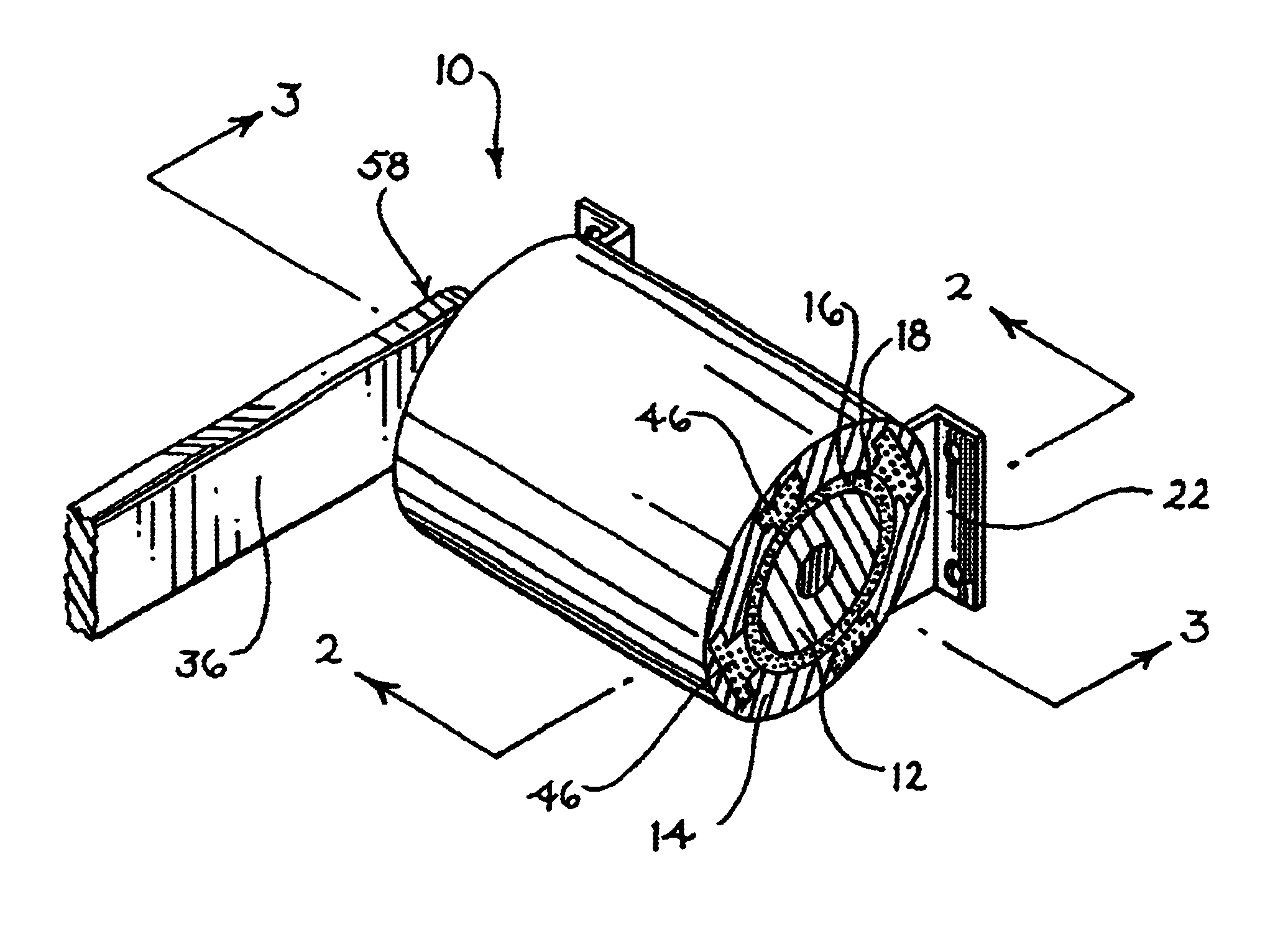
Suspension strut for use with a compressible magnetorheological fluid
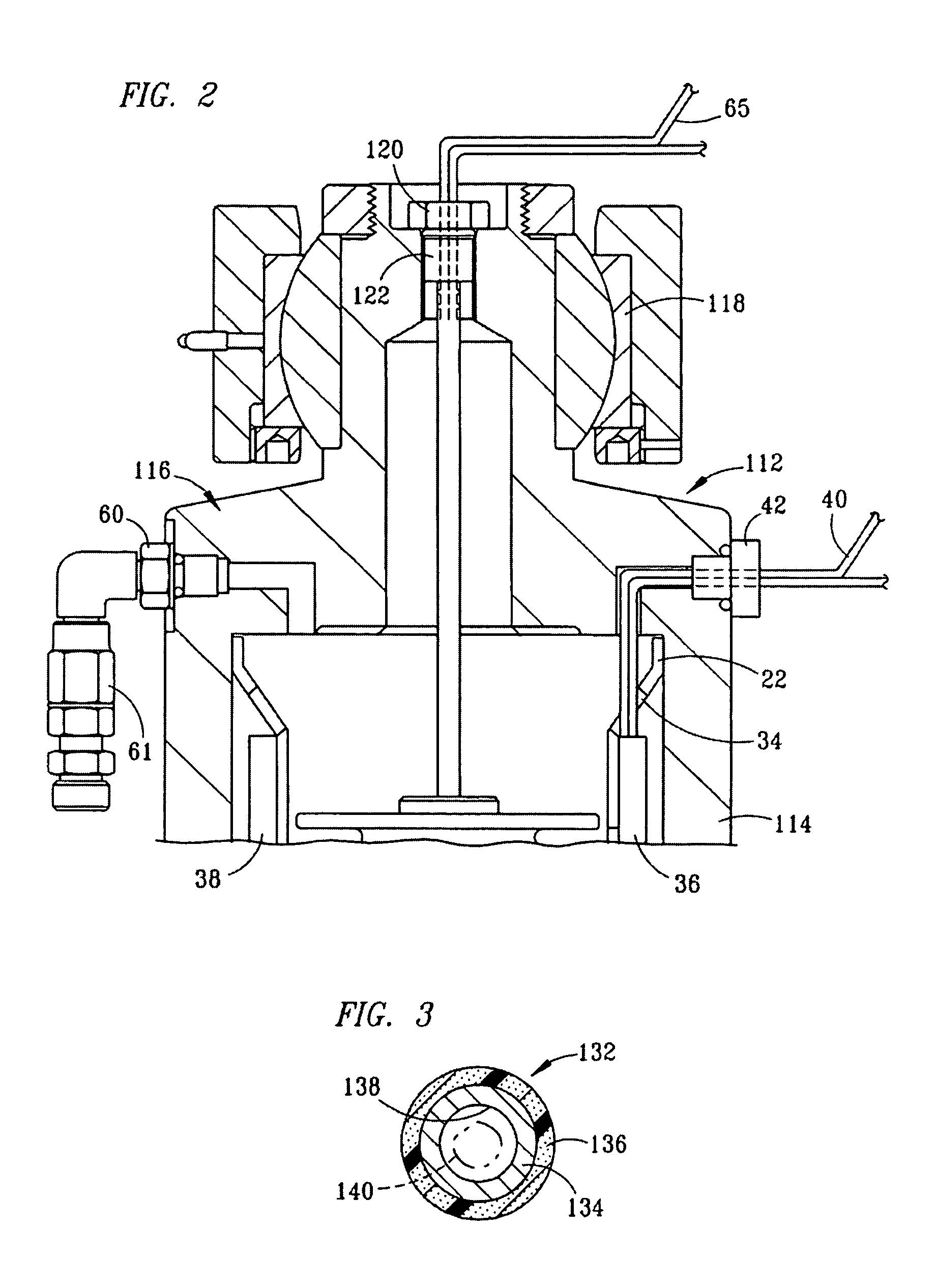
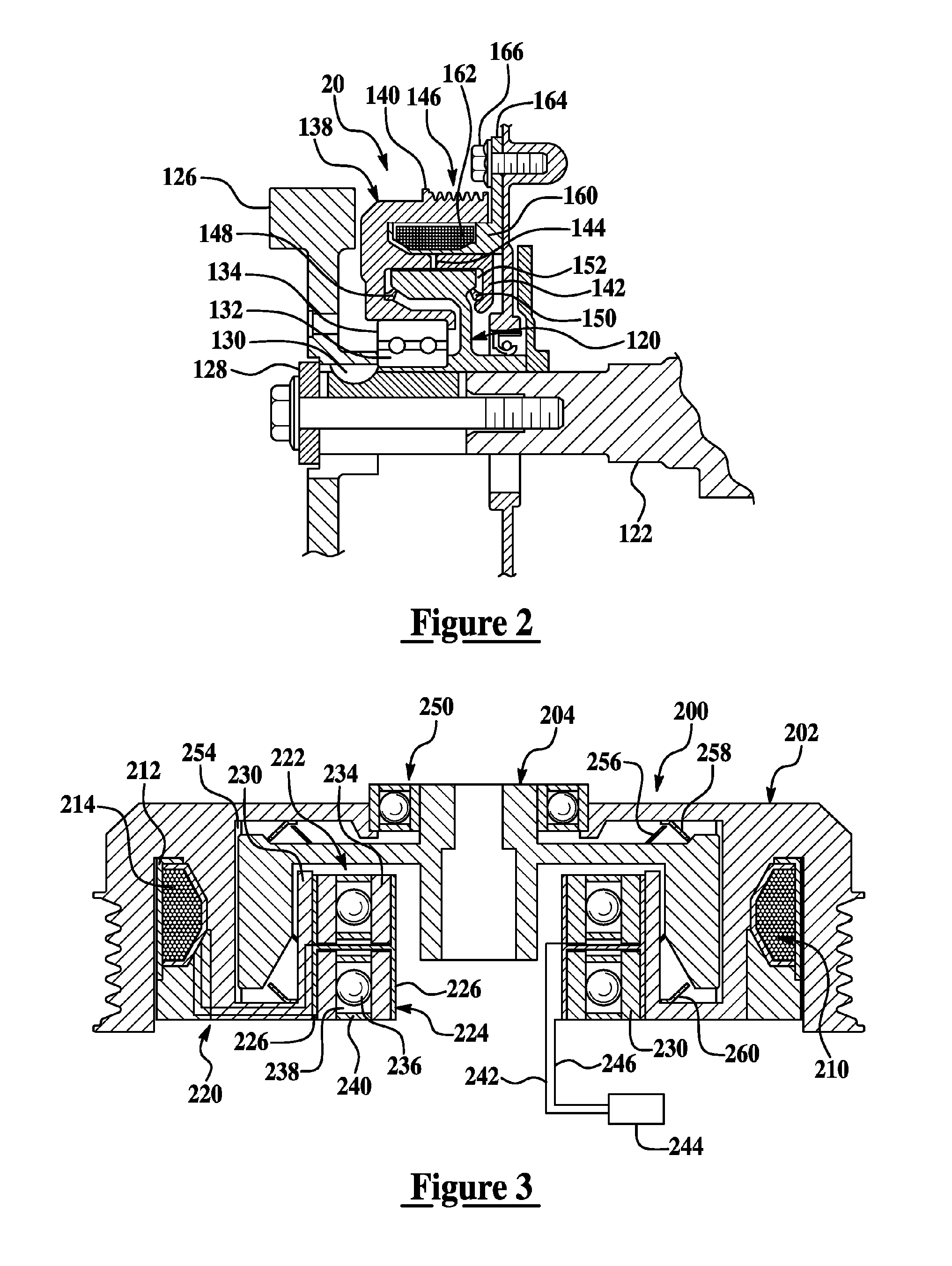
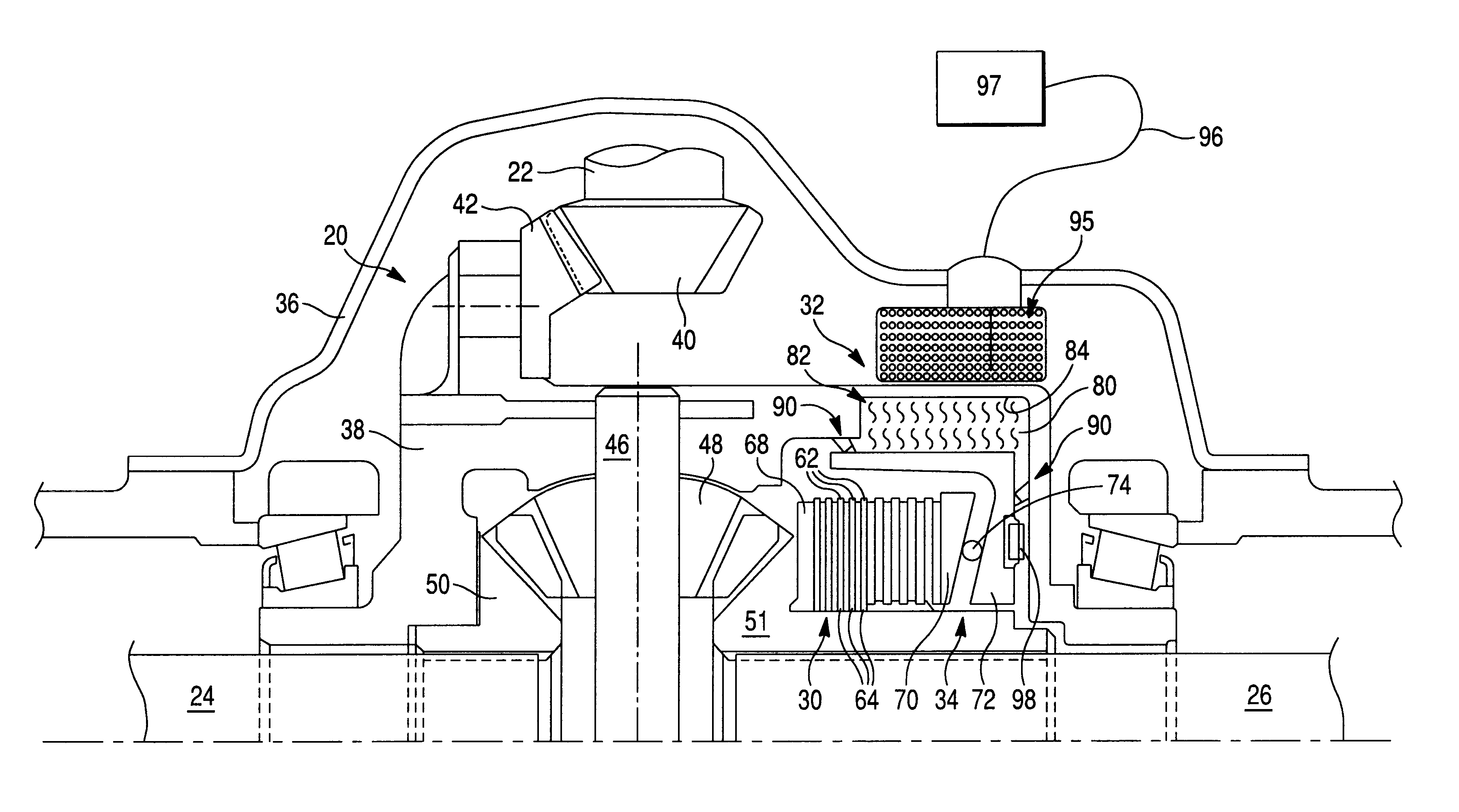
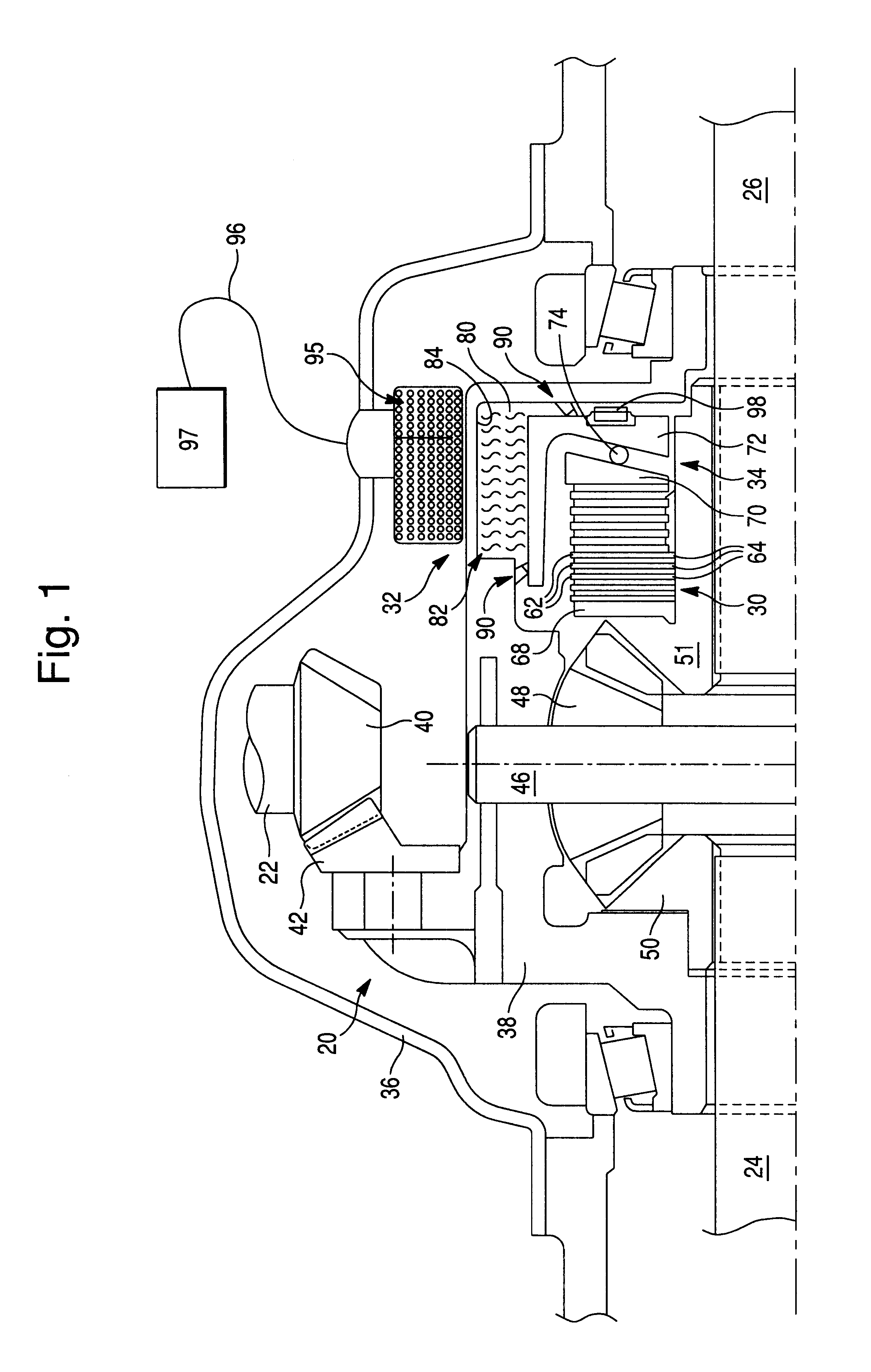
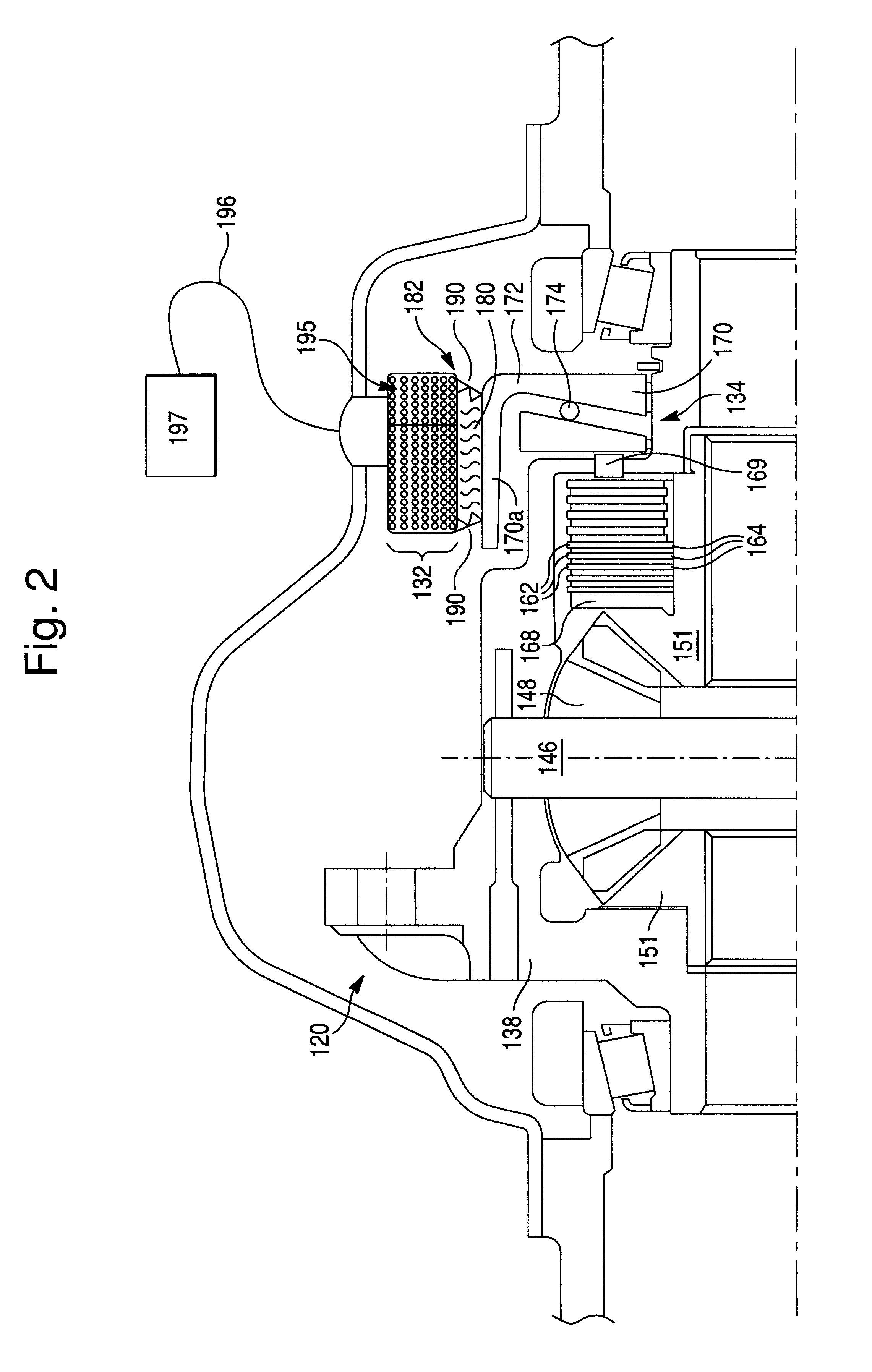
ActiveUS7770701B1Prevent precipitationStay flexibleSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetorheological fluidVolumetric Mass Density
A strut (12) is configured for an active suspension system (142) which provides electronic control for both the force applied by the strut (12) and the dampening characteristics of the strut (12). A compressible fluid (18) is used within the strut (12), and preferably includes a compressible base fluid and electromagnetic field responsive particles (132) which are suspended in the compressible base fluid. The electromagnetic field responsive particles (132) are preferably closely matched in density and modulas of elasticity to that of the compressible base fluid to prevent sedimentation of the particles (132) and to maintain the elasticity of the compressible fluid (18). The amount compressible fluid (18) within the strut (12) is electronically controlled to determine the force applied by the strut (12) and a field strength applied to the compressible fluid in a fluid flow passage is electronically controlled to determine the dampening characteristics of the strut (12).
Owner:HORSTMAN
Magnetorheological fluid compositions and prosthetic knees utilizing same
The present invention relates in one embodiment to magnetorheological fluids utilized in prosthetic joints in general and, in particular, to magnetorheological fluids utilized in controllable braking systems for prosthetic knee joints. Preferred magnetorheological fluids of the present invention comprises polarizable iron particles, a carrier fluid, and optionally an additive. Preferred additives include, but are not limited to functionalized carrier fluids as well as derivatized fluoropolymers. Preferred carrier fluids include, but are not limited, to perfluorinated polyethers.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Active pressure relief valves and methods of use
ActiveUS20050199845A1Efficient changeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCheck valvesElastomerElectricity
Active pressure relief valves and methods of use for regulating atmospheric conditions within an interior compartment of a vehicle generally include an active material to effect movement of a flap relative to an opening. The active material has the ability to remember its original at least one attribute such as dimension, shape, and / or flexural modulus, which can subsequently be recalled by applying or removing an external stimulus, as will be discussed in detail herein. Suitable active materials include, without limitation, shape memory alloys, ferromagnetic shape memory alloys, shape memory polymers, piezoelectric materials, electroactive polymers, magnetorheological fluids and elastomers, electrorheological fluids, composites of one or more of the foregoing materials with non-active materials, combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing materials, and the like. Depending on the particular active material, the activation signal can take the form of, without limitation, an electric current, a temperature change, a magnetic field, a mechanical loading or stressing, or the like.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Apparatus And Method For Damping Vibration In A Drill String
ActiveUS20120228028A1Reducing drill string torsional vibrationLimiting maximum angular velocityDrilling rodsDirectional drillingMagnetorheological fluidAngular velocity
An apparatus and method for damping vibration, especially torsional vibration due to stick-slip, in a drill string, Sensors measure the instantaneous angular velocity of the drill string at one or more locations along the length of the drill string. One or more vibration damping modules are also spaced along the length of the drill string. When torsional vibration above a threshold is detected, the damping module imposes a reverse torque on the drill that dampens the torsional vibration. The reverse torque can be created by imparting a frictional resistance to the rotation of the drill string. The frictional resistance can be created externally, by extending friction pads from the damping module so that they contact the bore hole wall and drag along the bore hole as the drill string rotates, or internally by anchoring a housing mounted on the drill string to the wall of the bore hole and then imposing frictional resistance on a fluid, such as a magnetorheological fluid, flowing within the drill string.
Owner:APS TECH
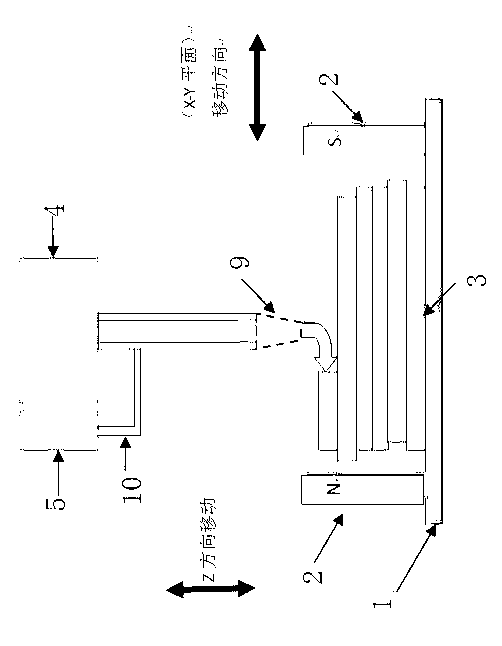
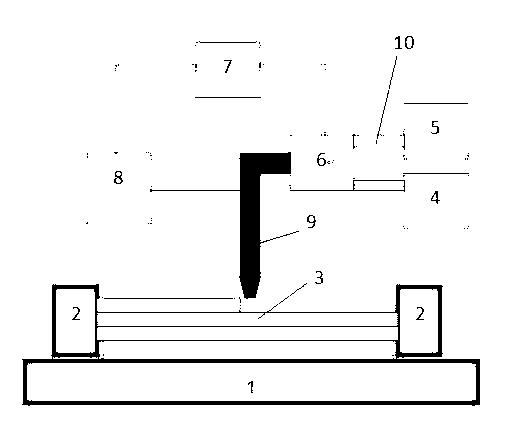
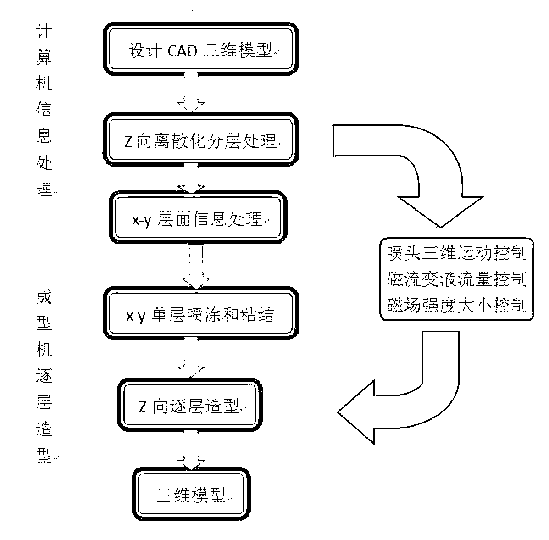
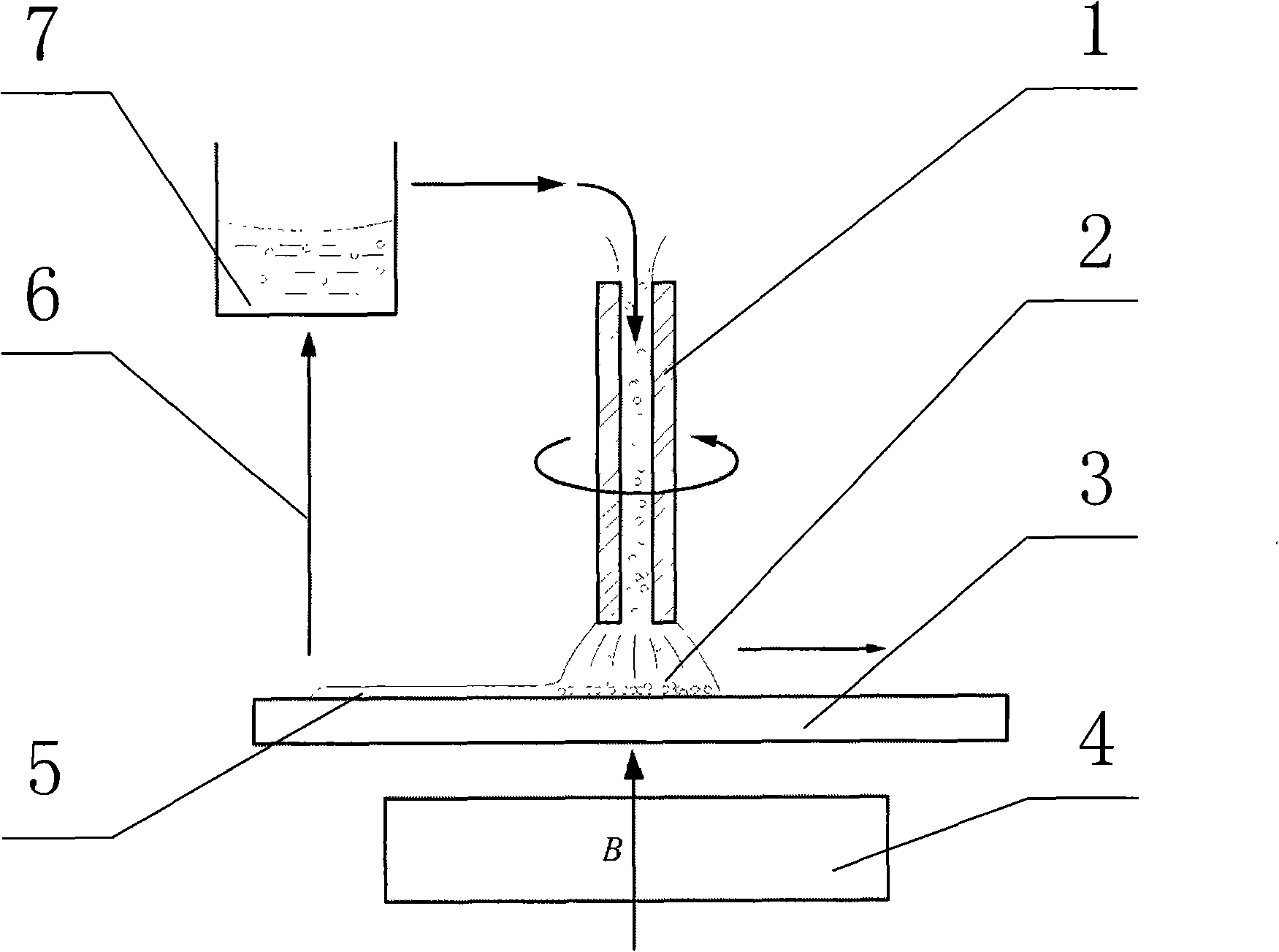
Magnetorheological-material-based 3D (Three-Dimensional) printing type rapid prototyping device and method
The invention relates to a magnetorheological-material-based 3D (Three-Dimensional) printing type rapid prototyping method and device. According to the principle of magnetorheological effect, a magnetorheological material is used as a 3D printing raw material; and a 3D solid model is constructed by spraying the magnetorheological material on a workbench with a magnetic field, rapidly solidifying and prototyping the sprayed magnetorheological material, and then depositing the treated material layer by layer. A computer is provided with three control circuits; one circuit is used for controlling the flow of a driving pump, namely the flow at a spray head; another circuit is used for controlling the 3D motion of the spray head through a servo mechanism; and the rest circuit is used for controlling colour mixing and allocating of a colourized ink box. The magnetorheological material is solidified and prototyped by utilizing the magnetic field generated by an electromagnet. According to the magnetorheological effect of the magnetorheological material, a temperature control module in the traditional melting, spraying and rapid prototyping type 3D printing method is replaced by the magnetic field; in addition, the device disclosed by the invention is also different from a high-pressure electric field required by an electrorheological fluid effect, has the advantages of being simple in structure, low in energy consumption and cost, capable of realizing the microminiaturization and the like, and can be applicable to the fields of process design, art and entertainment, prosthesis model and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
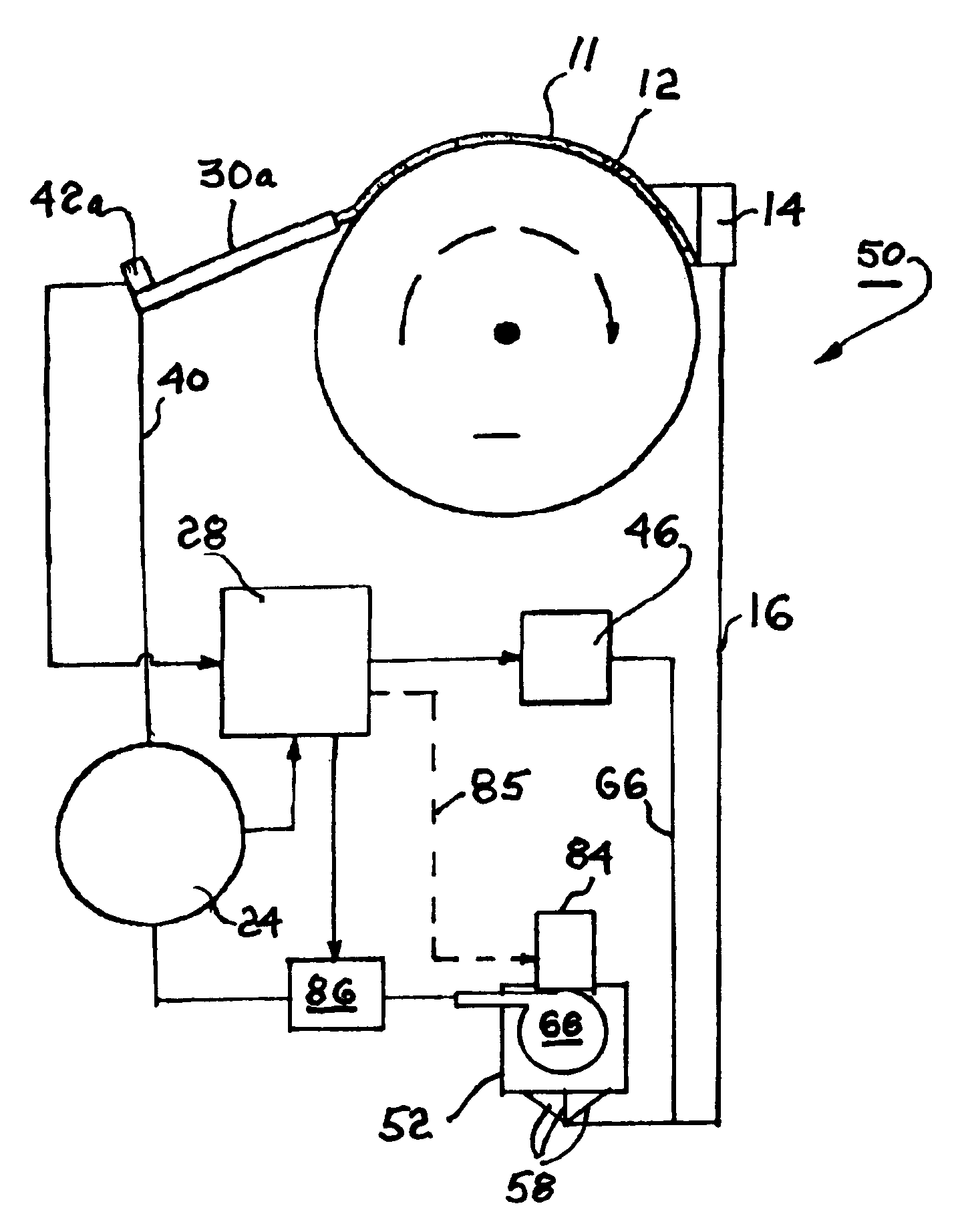
Magnetorheological fluid-controlled vehicle suspension damper
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Magnetorheological suspensions damping device for automobile suspension system
InactiveCN1603651AReduce power consumptionSmall currentSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetorheological fluidEngineering
The invention involving a magnetorheological fluid damping device for automobile suspension system.The magnetic field generator of this damping device consists of permanent magnet and electromagnetic coil.On the top of the damping device,there are guide apparatus and damping regulator,the function of which is that to ensure the damping channel is uniform annular duct and to meet the high-damp requirement in the restoration process and low-damp requirement in the compression process of damper seperately.The current in the electromagnetic coil designs of bi-directional and this controls the magnetic field intersity of the damping channel,decreases the excitation current of the electromagnetic coil,reduces energy consumption and decreases damper fever.On the non-controlling conditions,this damping device has the equivalent characteristics of the traditional shock absorber and can instead the passive shock absorber,after equiping corresponding current controller,this device can regulate the damping characteristics of suspension system,which improves the automobile driving safety and ride comfort.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Tunable vehicle structural members and methods for selectively changing the mechanical properties thereto
Tunable structural member for a vehicle generally comprises an active material adapted to selectively undergo a change in at least one attribute in response to an activation signal. The change in the at least one attribute results in a change in the mechanical properties of the tunable structural member. Active materials generally include shape memory alloys, shape memory polymers, magnetorheological fluids and elastomers, piezoelectrics, electroactive polymers, and the like.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Active pressure relief valves and methods of use
Active pressure relief valves and methods of use for regulating atmospheric conditions within an interior compartment of a vehicle generally include an active material to effect movement of a flap relative to an opening. The active material has the ability to remember its original at least one attribute such as dimension, shape, and / or flexural modulus, which can subsequently be recalled by applying or removing an external stimulus, as will be discussed in detail herein. Suitable active materials include, without limitation, shape memory alloys, ferromagnetic shape memory alloys, shape memory polymers, piezoelectric materials, electroactive polymers, magnetorheological fluids and elastomers, electrorheological fluids, composites of one or more of the foregoing materials with non-active materials, combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing materials, and the like. Depending on the particular active material, the activation signal can take the form of, without limitation, an electric current, a temperature change, a magnetic field, a mechanical loading or stressing, or the like.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
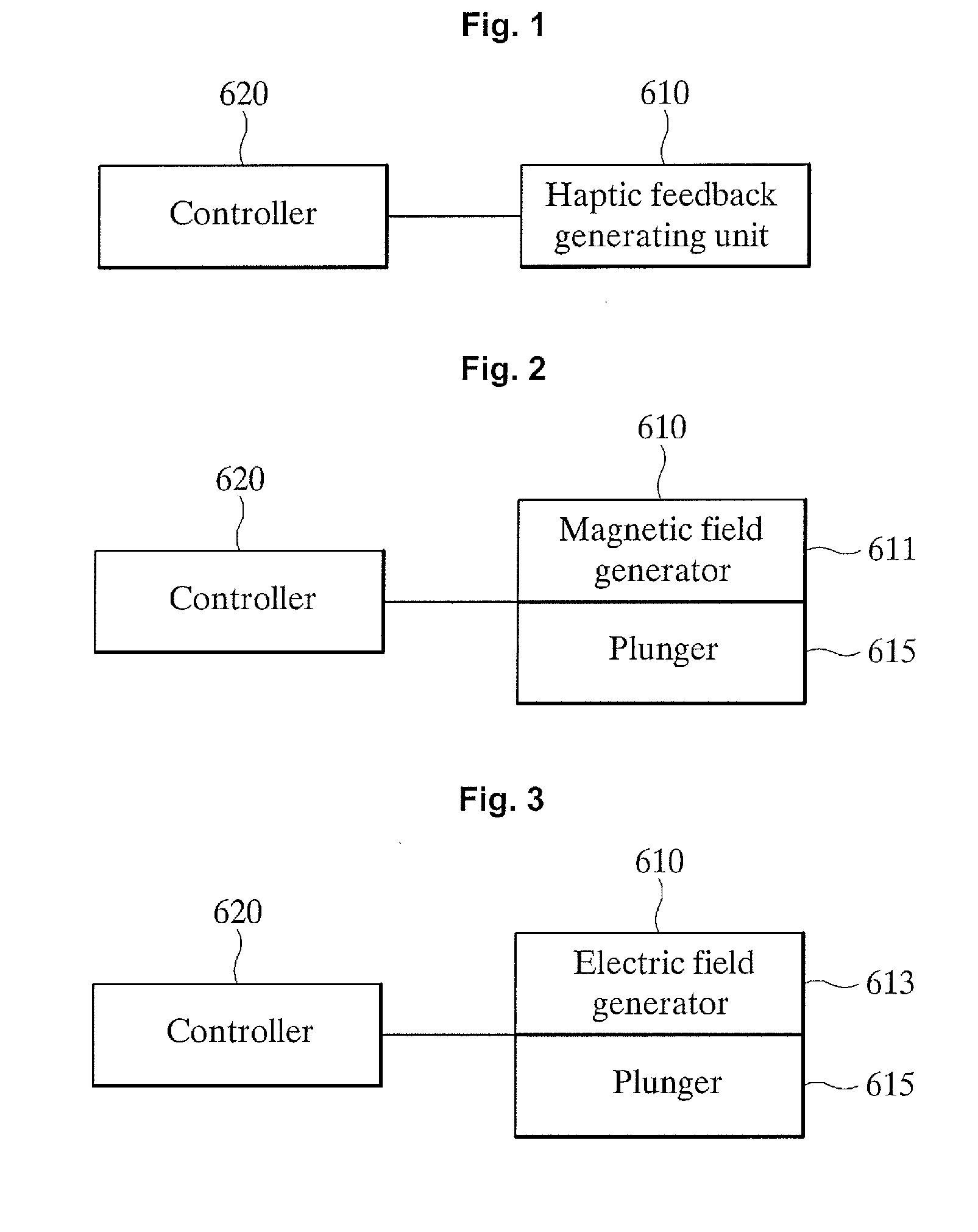
Haptic feedback generator, portable device, haptic feedback providing method using the same and recording medium thereof
InactiveUS20120112894A1Resistance may varyChange resistanceRepeater circuitsInput/output processes for data processingControl signalMagnetorheological fluid
An apparatus and a method for generating haptic feedback and a portable device having the apparatus are provided. The haptic feedback generator changes the property of a magneto-rheological fluid or an electro-rheological fluid using a magnetic field or an electric field and transmits haptic feedback using the property variation. The haptic feedback generator includes a controller 620 outputting a control signal for providing a haptic feedback based on application information selected by a user and a haptic feedback generating unit 610 generating the haptic feedback based on the control signal and providing the haptic feedback in response to an external force Fin of the user.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
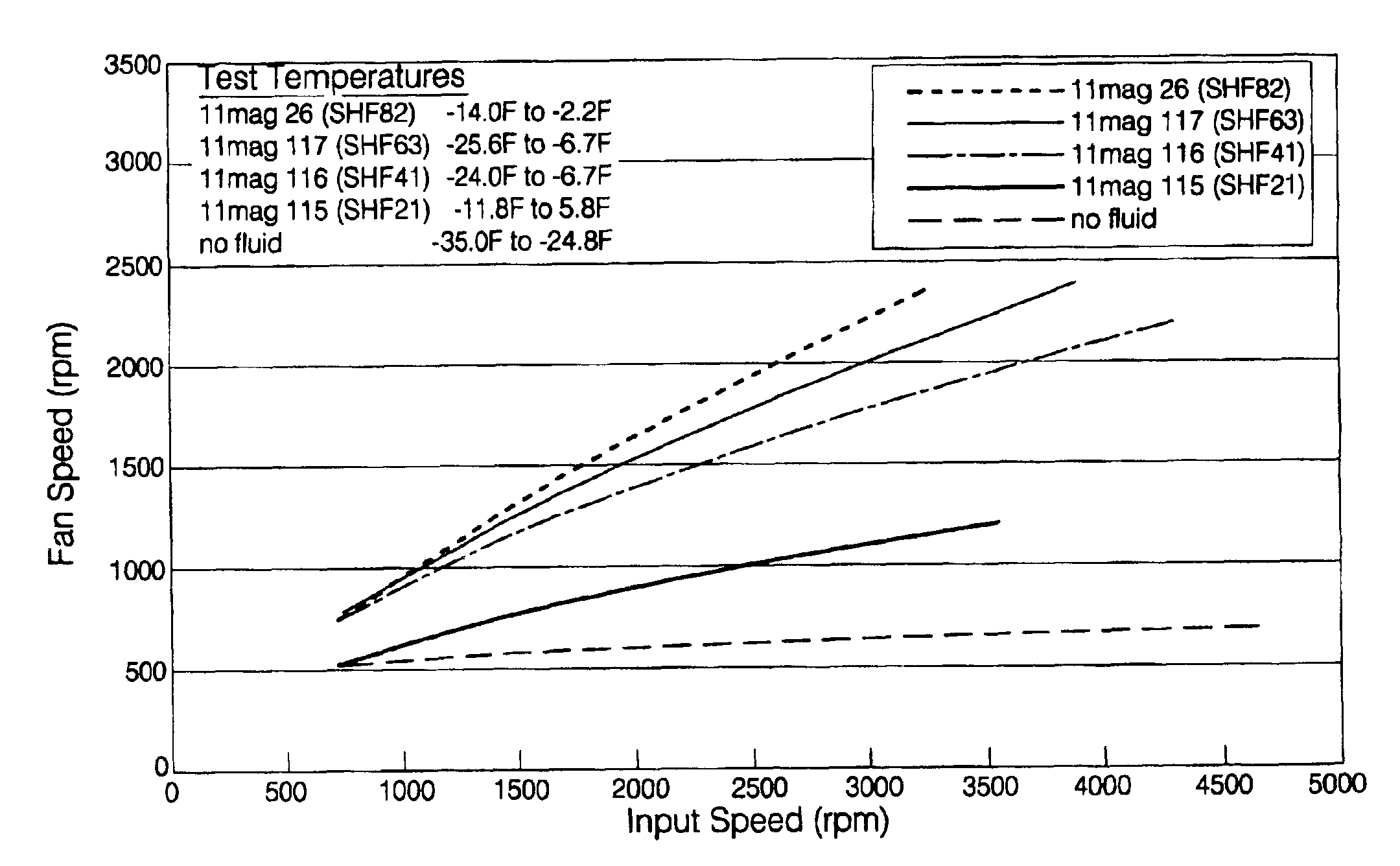
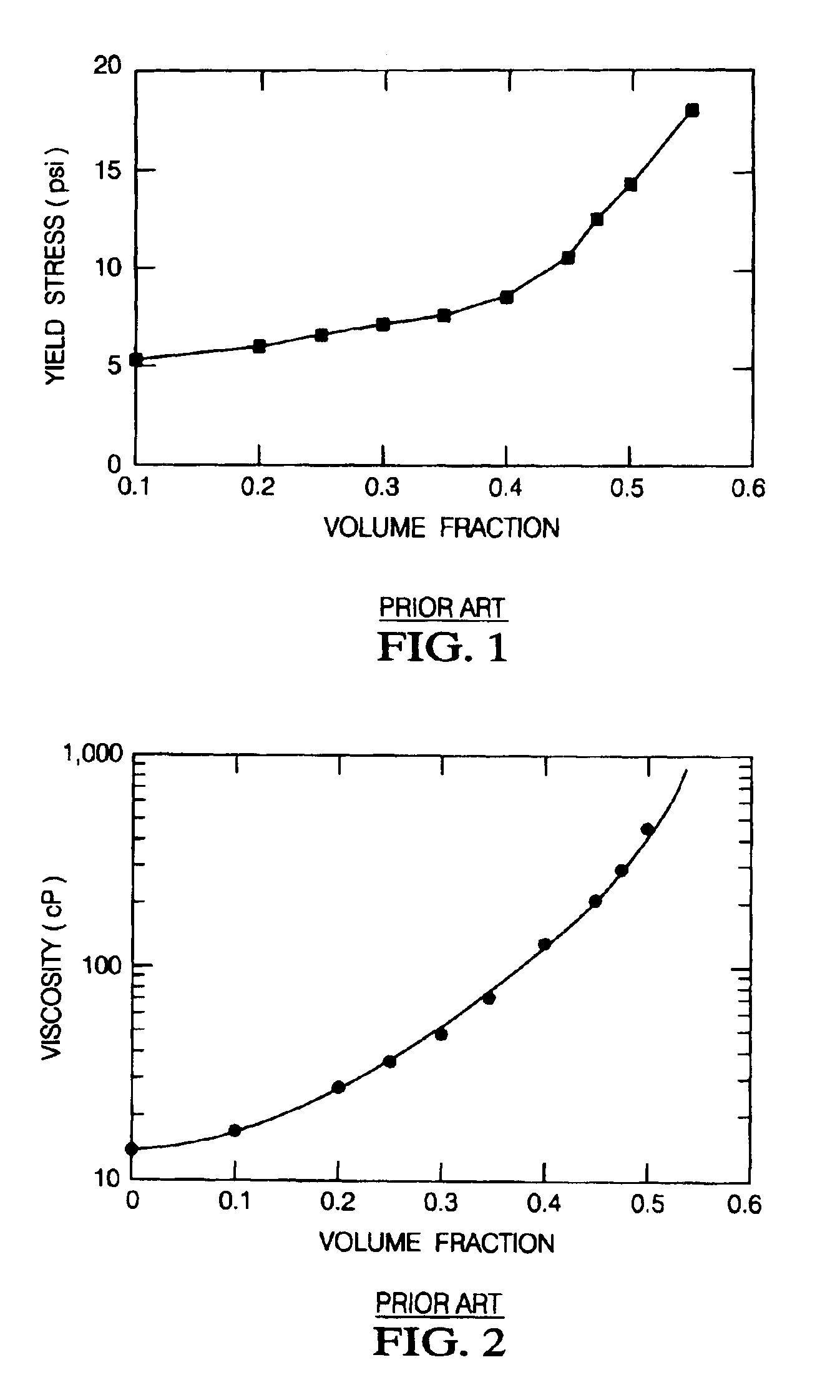
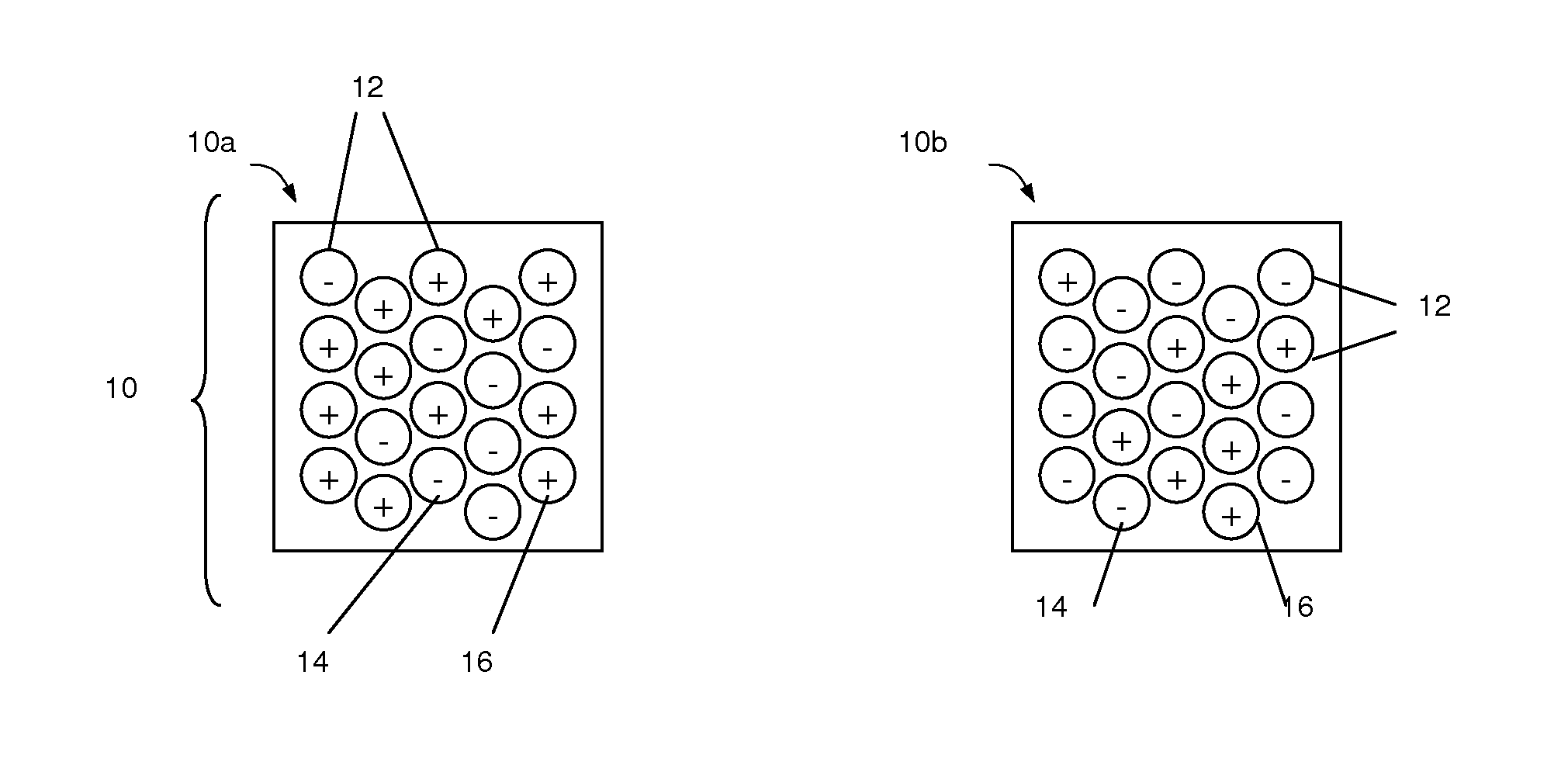
Magnetorheological fluids
InactiveUS6932917B2Increased durabilityLow viscosityOther chemical processesMagnetic liquidsMagnetorheological fluidCentrifugal force
One embodiment of the invention includes an MR fluid of improved durability. The MR fluid is particularly useful in devices that subject the fluid to substantial centrifugal forces, such as large fan clutches. A particular embodiment includes a magnetorheological fluid including 10 to 14 wt % of a hydrocarbon-based liquid, 86 to 90 wt % of bimodal magnetizable particles, and 0.05 to 0.5 wt % fumed silica.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Well Tractor With Active Traction Control
ActiveUS20130068479A1Prevent slippingAdjustable viscosityConstructionsFluid removalWorking fluidMagnetorheological fluid
A downhole tool that includes a tractor for assisting movement of the tool through deviated portions of a wellbore. The tractor includes a working fluid that damps vibrations in the tractor by adjusting the viscosity in the fluid. In an example, the working fluid is a magnetorheological fluid that has a viscosity that changes in response to applied electrical energy. The working fluid, which may be used for powering actuators on the tractor, may contain a suspension of magnetic particles.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Automobile brake pedal mechanism and pedal feel simulator thereof
Owner:南通特力锻压机床有限公司 +1
Dynamic seals for a prosthetic knee
The invention in some embodiments relates to a dynamic seal for a prosthetic knee. The dynamic seal in one embodiment is utilized to seal a magnetorheological fluid comprising a liquid and solid particles within a chamber of the knee. The dynamic seal embodiments are specially configured with a pre-loaded tensioned garter spring which has a coil spacing that is at least as large as the size of the particles or maximum size of the particles in the magnetorheological fluid. Desirably, this allows the magnetorheological fluid particles to flow in and out of the dynamic seal without clogging the seal and advantageously provides for a reliable dynamic seal.
Owner:OSSUR HF
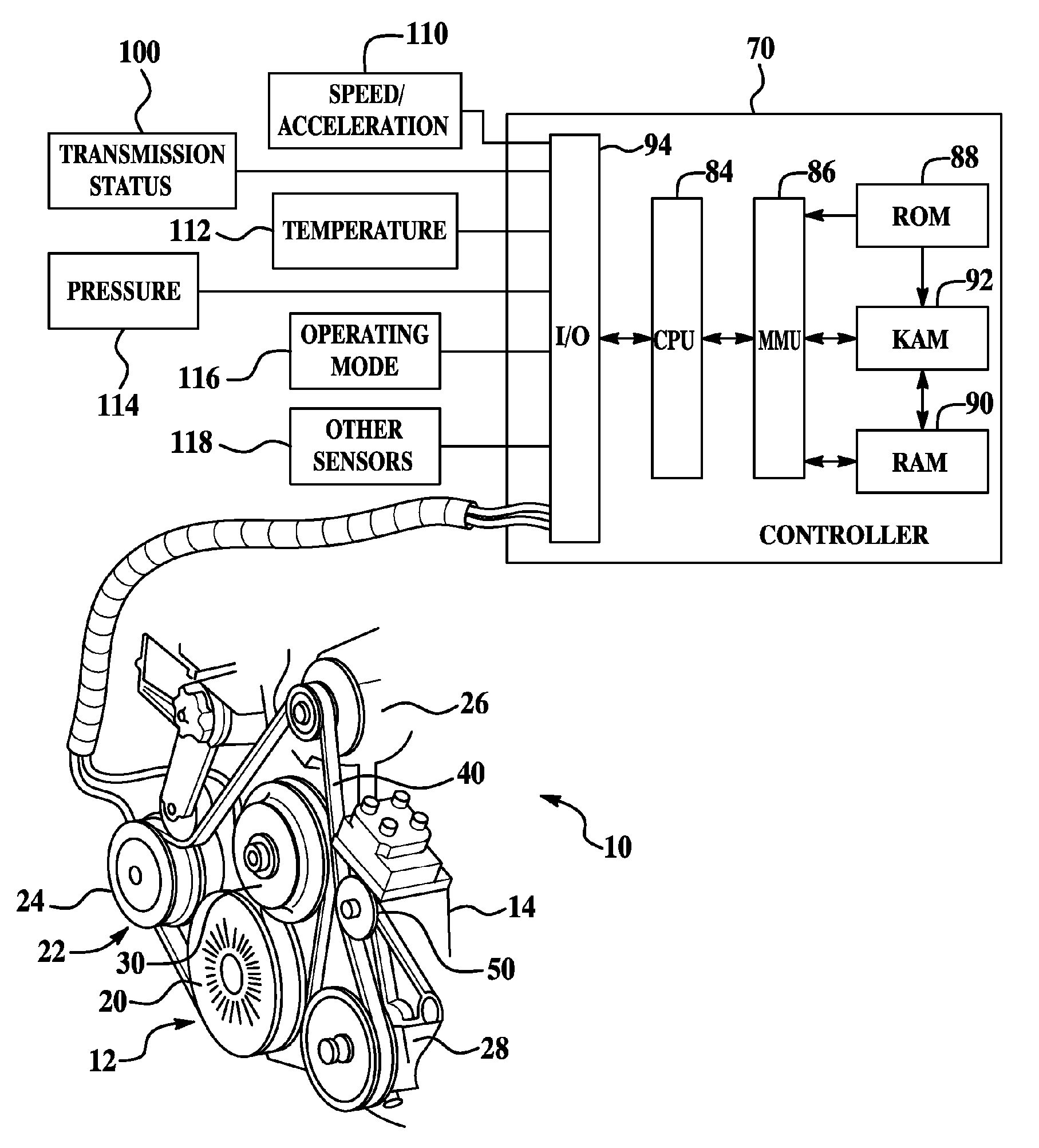
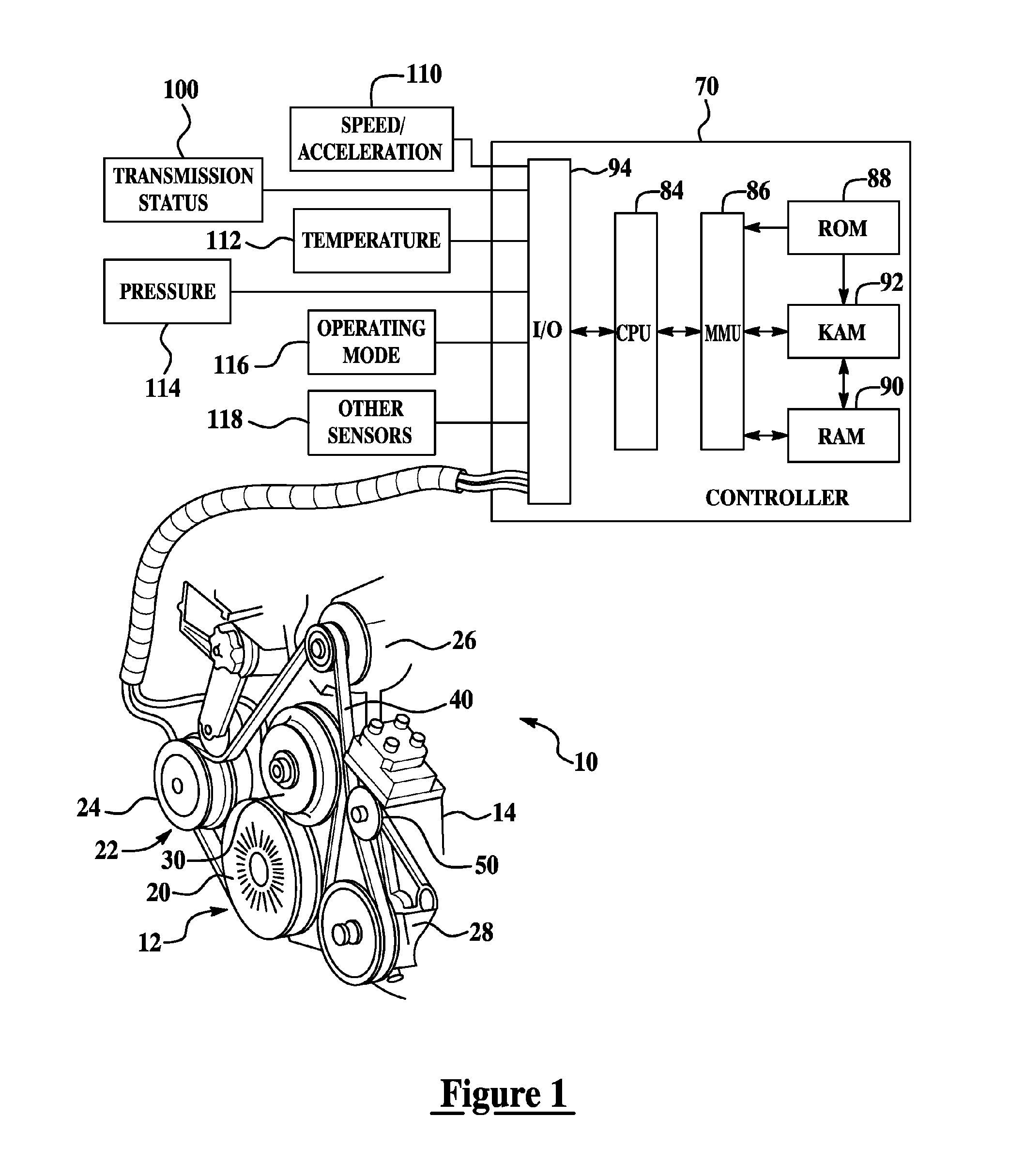
Electromagnetic coupling device for engine accessories
InactiveUS20070080037A1Reduce and eliminate powerEnhance engine/vehicle responseGearingMagnetically actuated clutchesElectromagnetic couplingAlternator
A system and method for controlling a plurality of accessories associated with a multiple cylinder internal combustion engine having the accessories coupled to an engine crankshaft by an electromagnetic coupling device with a flowable magnetic material disposed between a driving member and a driven member include selectively supplying power to the electromagnetic coupling device in response to at least one operating condition to simultaneously engage or disengage the plurality of engine accessories. Embodiments include a magnetic particle clutch or magnetorheological fluid clutch connected to an engine crankshaft and a plurality of engine accessories that may include an air conditioning compressor, water pump, power steering pump, alternator, and / or supercharger, for example.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Locking differential with clutch activated by magnetorheological fluid
InactiveUS6428441B1Magnetically actuated clutchesFriction clutchesElectromagnetic couplingLimited-slip differential
A limited slip differential includes a friction clutch mechanism, an electromagnetic coupling, and a camming mechanism disposed between the friction clutch mechanism and the electromagnetic coupling. The camming mechanism converts shearing forces within the electromagnetic coupling to an axial force applied to engage the clutch mechanism. The camming mechanism includes annular discs having axially inclined ramps, and a roller bearing for movement along the ramps to provide for variable spacing between the annular discs, wherein increased spacing is used to apply the axial force.
Owner:TORQUE TRACTION TECH INC
Method and device for polishing magnetic field auxiliary flexible rotary brush for optical element
InactiveCN101559571ACompact structureImprove removal efficiencyOptical surface grinding machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesFree formMagnetorheological fluid
The invention belongs to the technical field of precise optical polishing processing, and in particular relates to a method and a device for polishing a magnetic field auxiliary flexible rotary brush for an optical element. The method comprises that a ferromagnetic main shaft capable of rotating at a high speed drives a magnetorheological fluid which can be updated circularly to be adsorbed on a finished surface under certain pressure and the action of a magnetic field to form a flexible rotary polishing grinding head which finishes the polishing processing of a whole concave surface in a composite motion mode of self rotation and workpiece rotation. The device is applicable to polishing the concave surface of a conformal optical element; and the method has the characteristic of flexible fine machining and stable polishing removal, can adopt a computer to control the polishing removal distribution, is capable of controlling a polished surface shape, has the advantages of high precision and high surface quality, and is applicable to polishing aspheric surface and free-form surface elements with thin-walls and high gradients.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Magnetorheological fluid-based device and method for use
InactiveUS20130186473A1Reduce sedimentation rateSpringsFluid dynamicsMagnetorheological fluidEngineering
A magnetorheological fluid-based device and method may include the use of magnetorheological (MR) fluid, a primary magnetic field to control the viscosity of the fluid, and a secondary magnetic field to reduce clumping of ferromagnetic particles.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
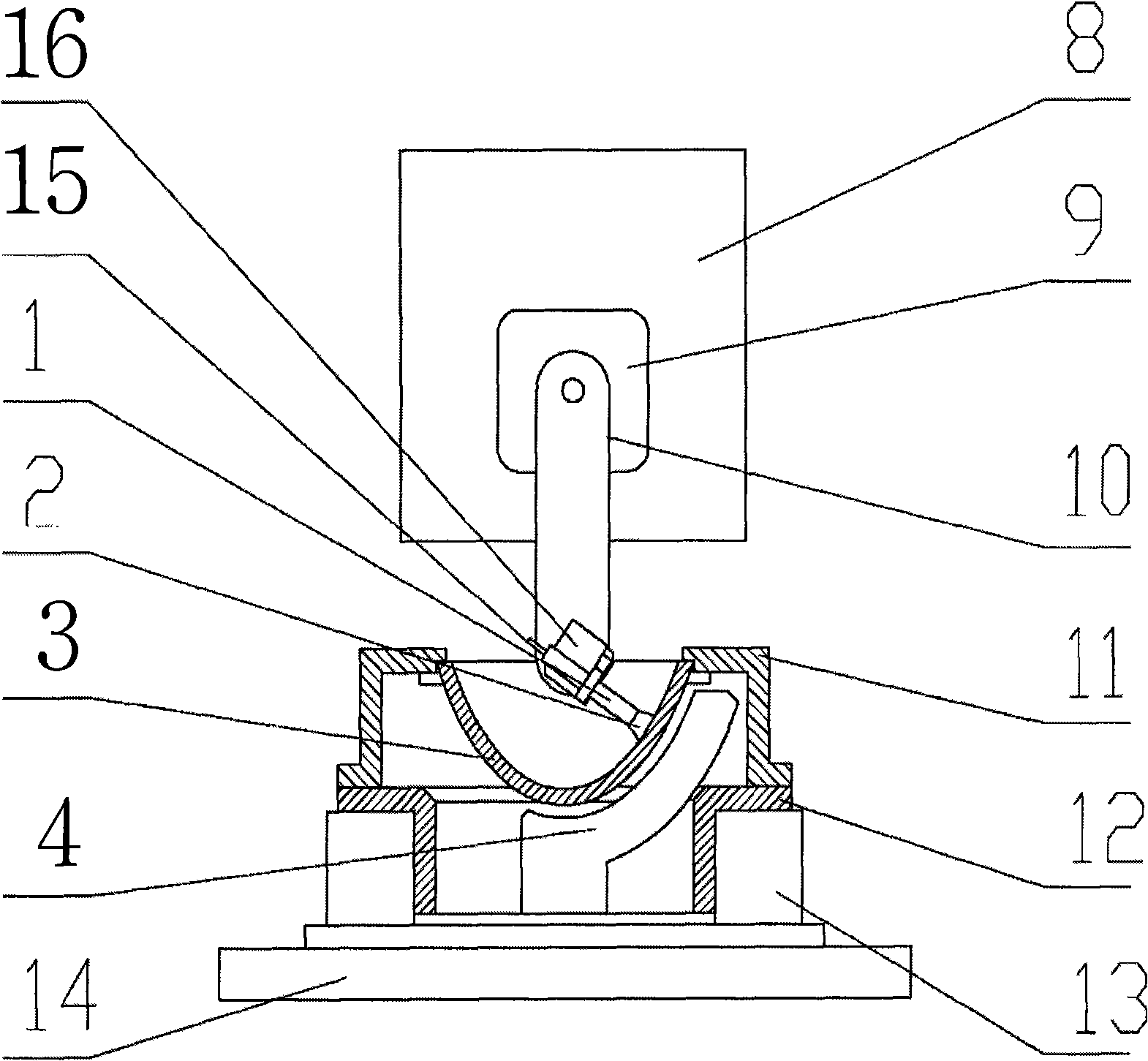
Fluid haptic interface with improved haptic rendering using a torque or load sensor
ActiveUS9898032B2Improved haptic renderingReduce, or even suppress, a spatial and time delay in the control of the interfaceControlling membersSpringsMagnetic currentLow speed
A haptic interface, including: a button which can be rotated by a user; an interaction element interacting with a magnetorheological fluid, secured to the button; a mechanism measuring a current position of the button; a brake including a magnetorheological fluid and a generation system to generate a magnetic field in the fluid; a controller configured to generate orders for the system to generate a magnetic fluid to modify a value of the magnetic field; and a mechanism to detect torque exerted by a user on the button to know direction of the torque and whether the torque is greater than a given value for a given direction, the controller controlling generation of a magnetic field based on obtained information about the torque at least when the button indicates zero or low speed.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
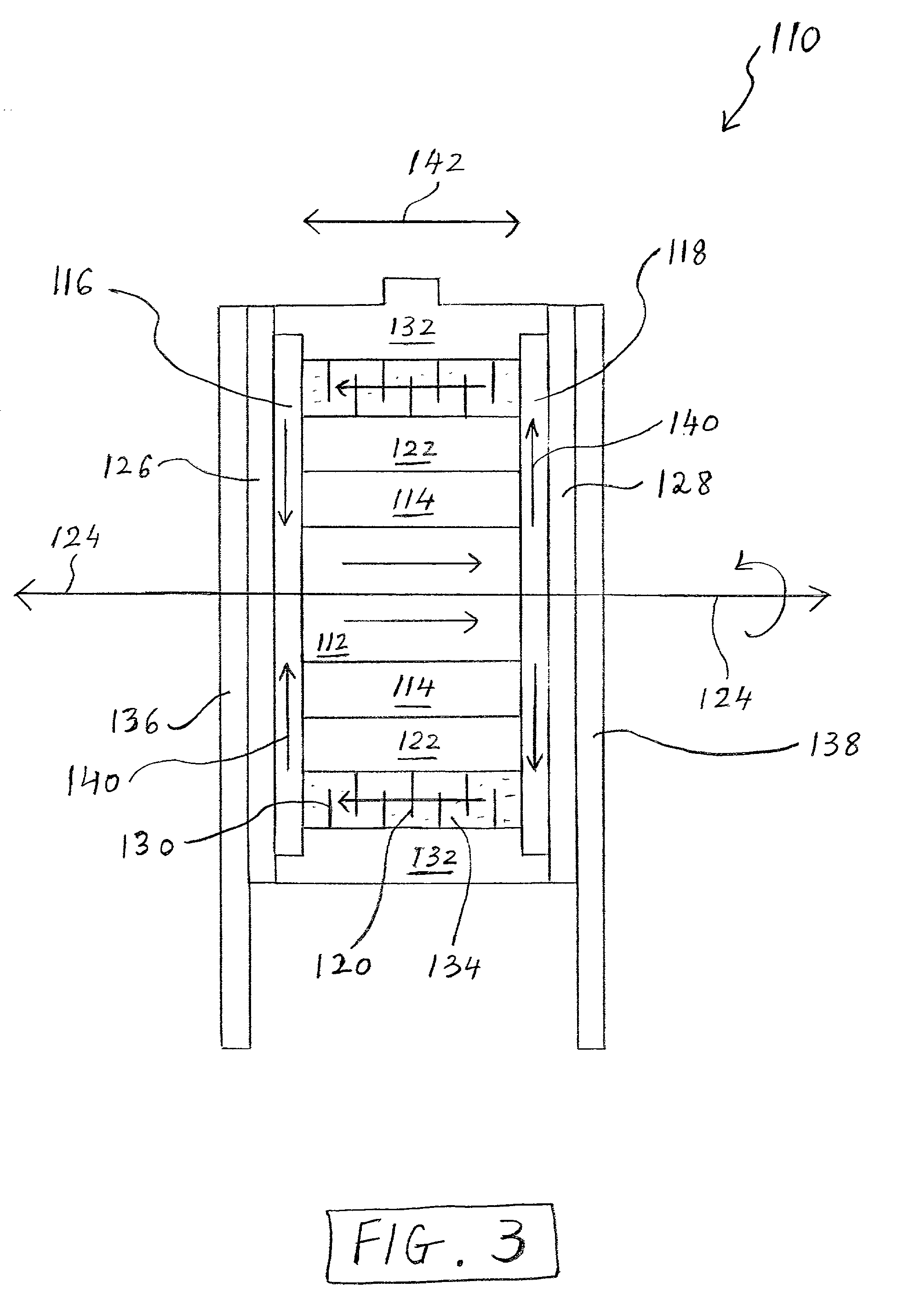
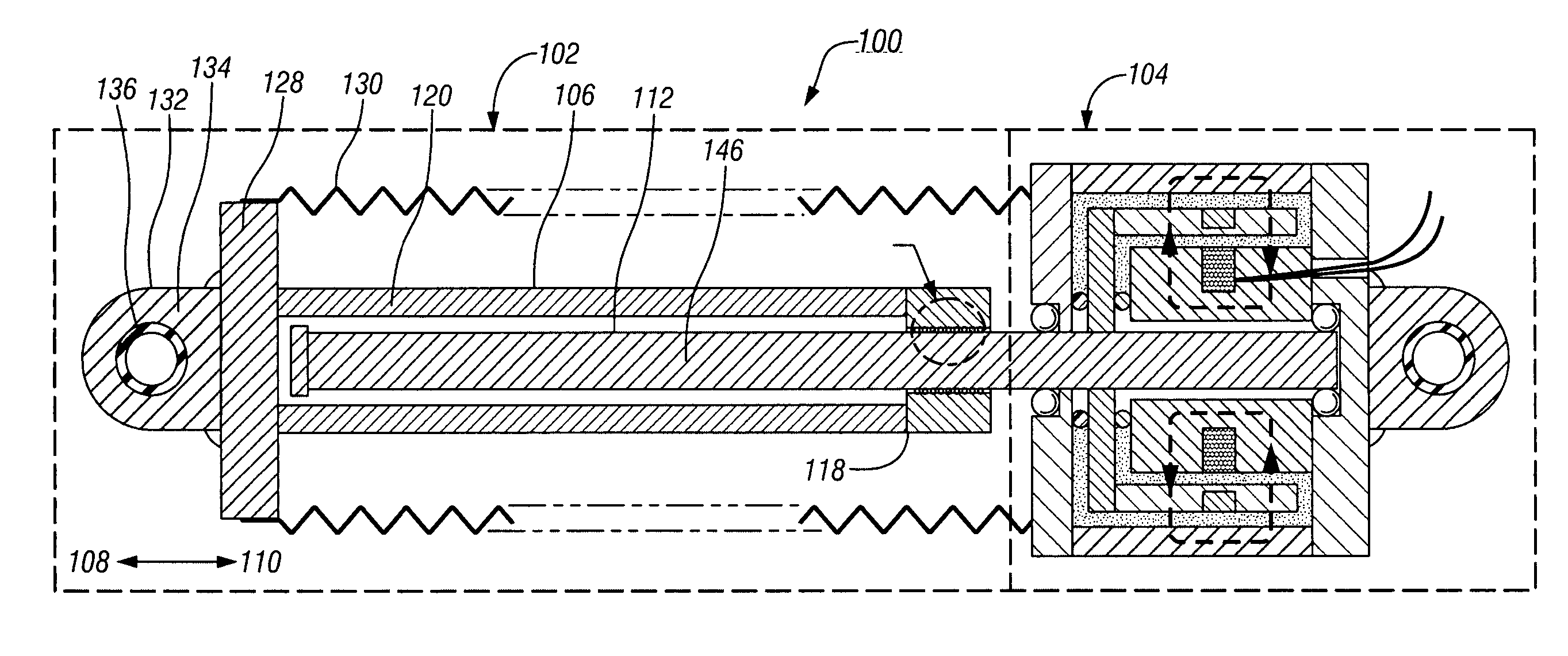
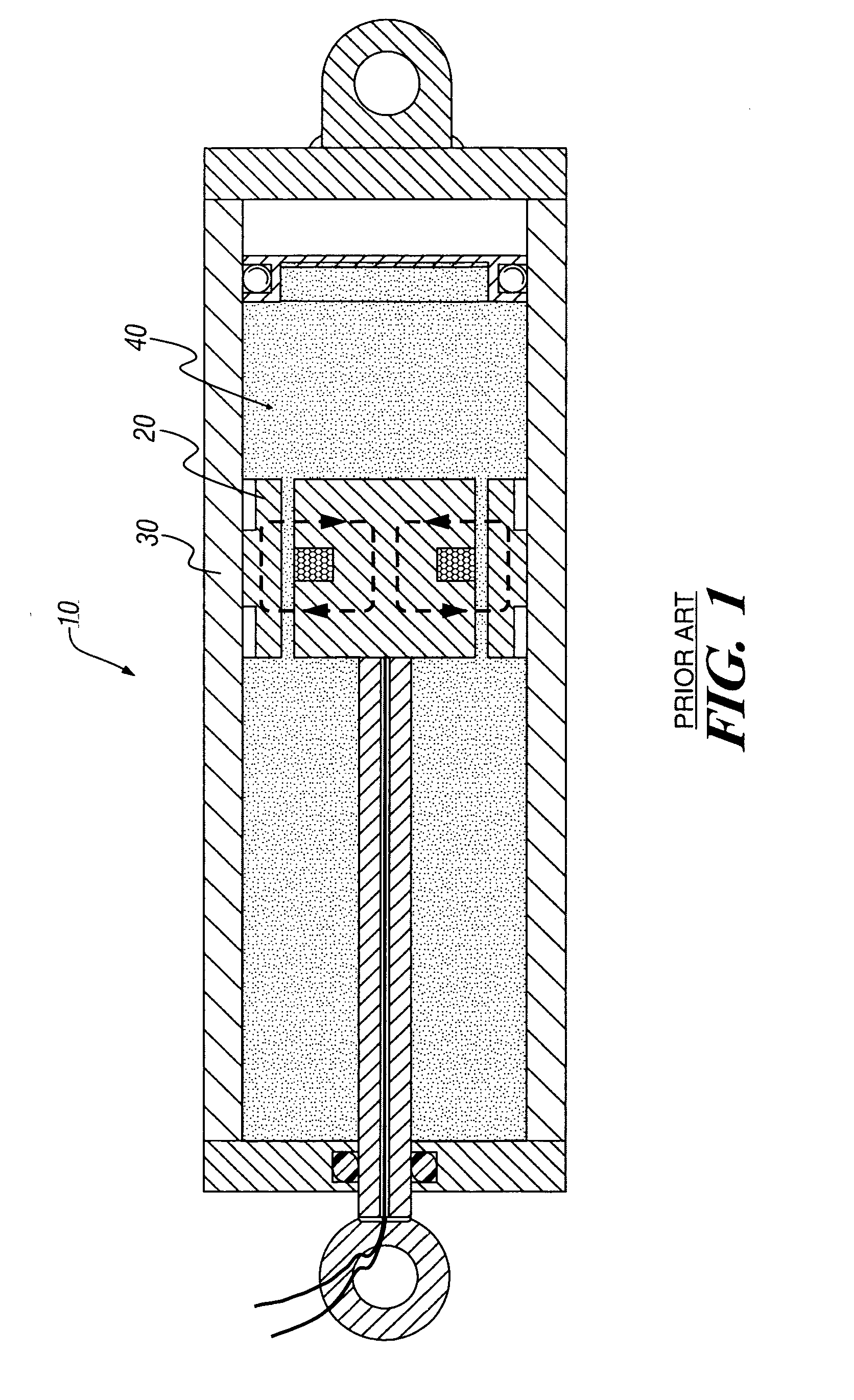
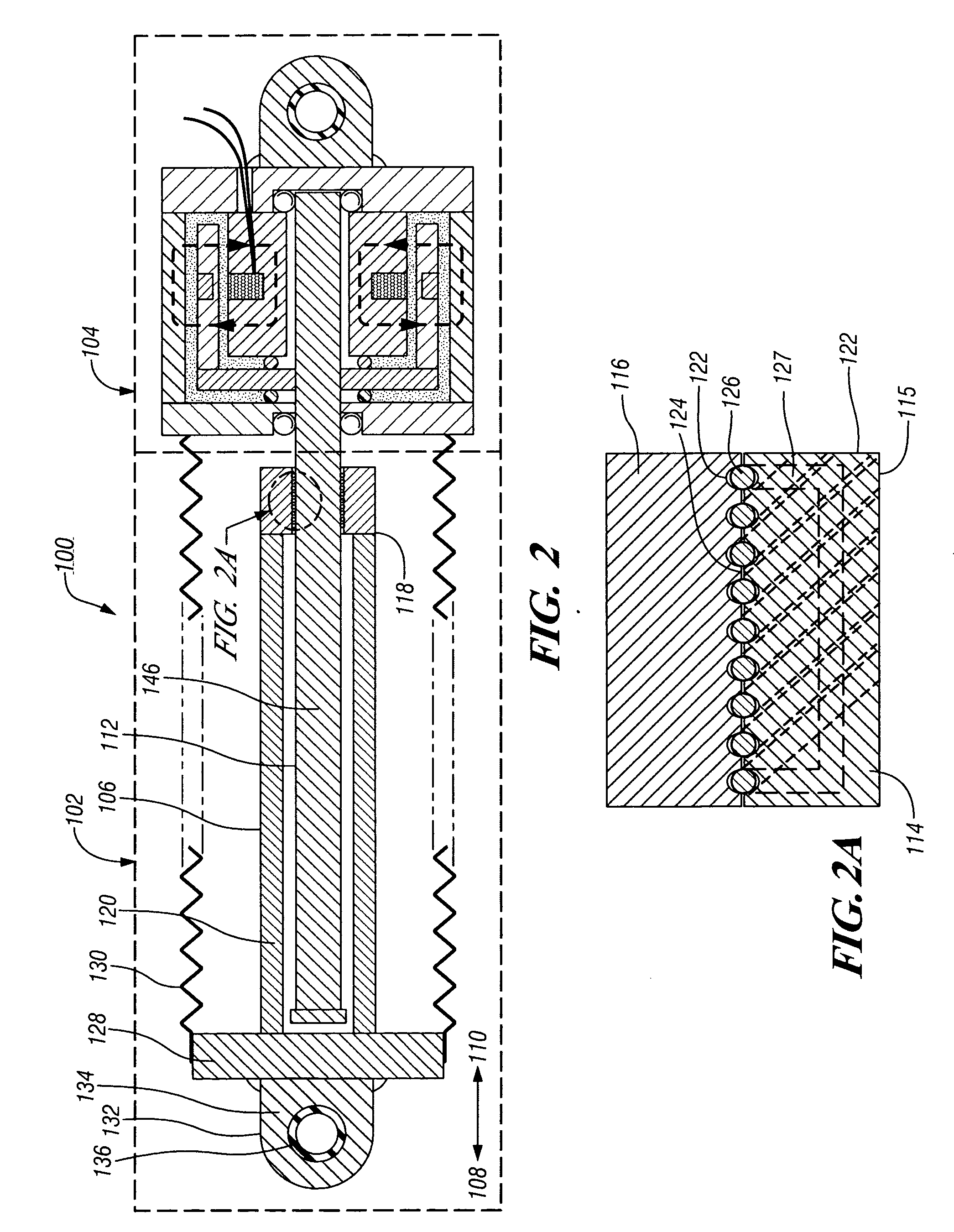
System and method for self-powered magnetorheological-fluid damping
InactiveUS20080053763A1SpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionHydraulic cylinderMagnetorheological fluid
A system and method for self-powered magnetorheological-fluid damping of mechanical vibrations includes a hydraulic cylinder. The hydraulic cylinder is configured for at least partially disposing magnetorheological fluid therein. A piston head is disposed within the hydraulic cylinder. The piston head has first and second sides and is configured to be in sliding engagement with the hydraulic cylinder. A piston rod is at least partially disposed within the hydraulic cylinder and is connected to the piston head on the first side. The system also includes a vibration absorber assembly having housing. The vibration absorber assembly is configured to transduce mechanical vibrations of the piston rod to electric current.
Owner:WERELEY NORMAN +1
Conical extrusion-shearing type magnetorheological clutch
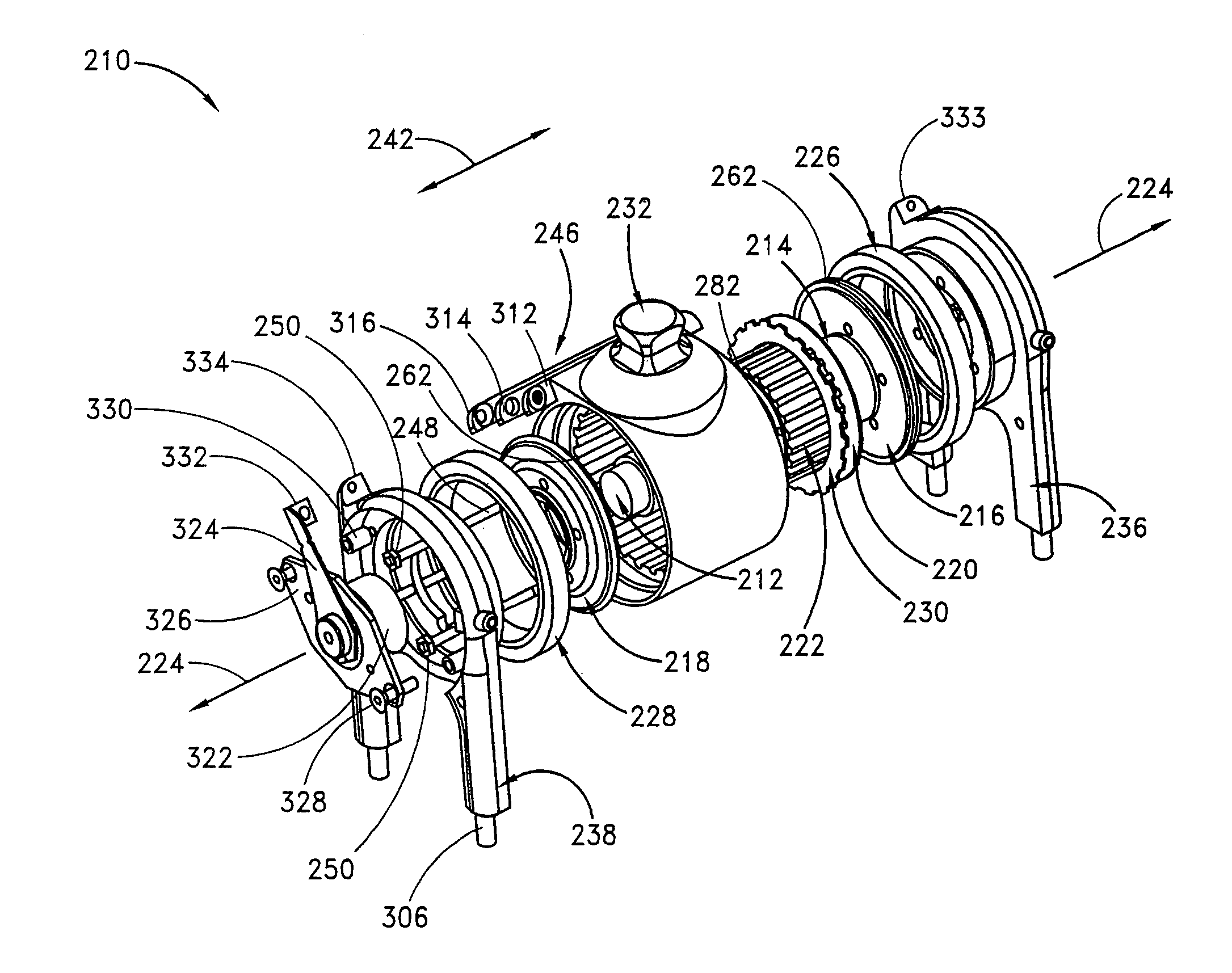
The invention discloses a conical extrusion-shearing type magnetorheological clutch. An iron core input disc is fixed at a front end of an input shaft and an armature output disc sliding axially is arranged at a front end of an output shaft, or the armature output disc sliding axially is arranged at the front end of the input shaft and the iron core output disc is fixed at the front end of the output shaft; a containing cavity is formed between the iron core input disc and the armature output disc; magnetorheological fluid is filled in the containing cavity; a sealing ring for sealing the magnetorheological fluid in the containing cavity is arranged on the periphery of the containing cavity; a coil for driving the armature output disc to move axially to the iron core input disc is further arranged in a working cavity; and an adjusting device for adjusting the volume of the containing cavity is further arranged between the iron core input disc and the armature output disc. The conical extrusion-shearing type magnetorheological clutch has the advantages that: when the clutch is in the working state, through attraction to the armature output disc by a magnetic field generated by the coil, the volume of the containing cavity is reduced, and meanwhile, an extrusion and shearing force is generated against the magnetorheological fluid, so as to transfer a greater torque; in addition, the conical extrusion-shearing type magnetorheological clutch is small in volume, reliable in performance, compact in structure, and good in effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Delivery system for magnetorheological fluid
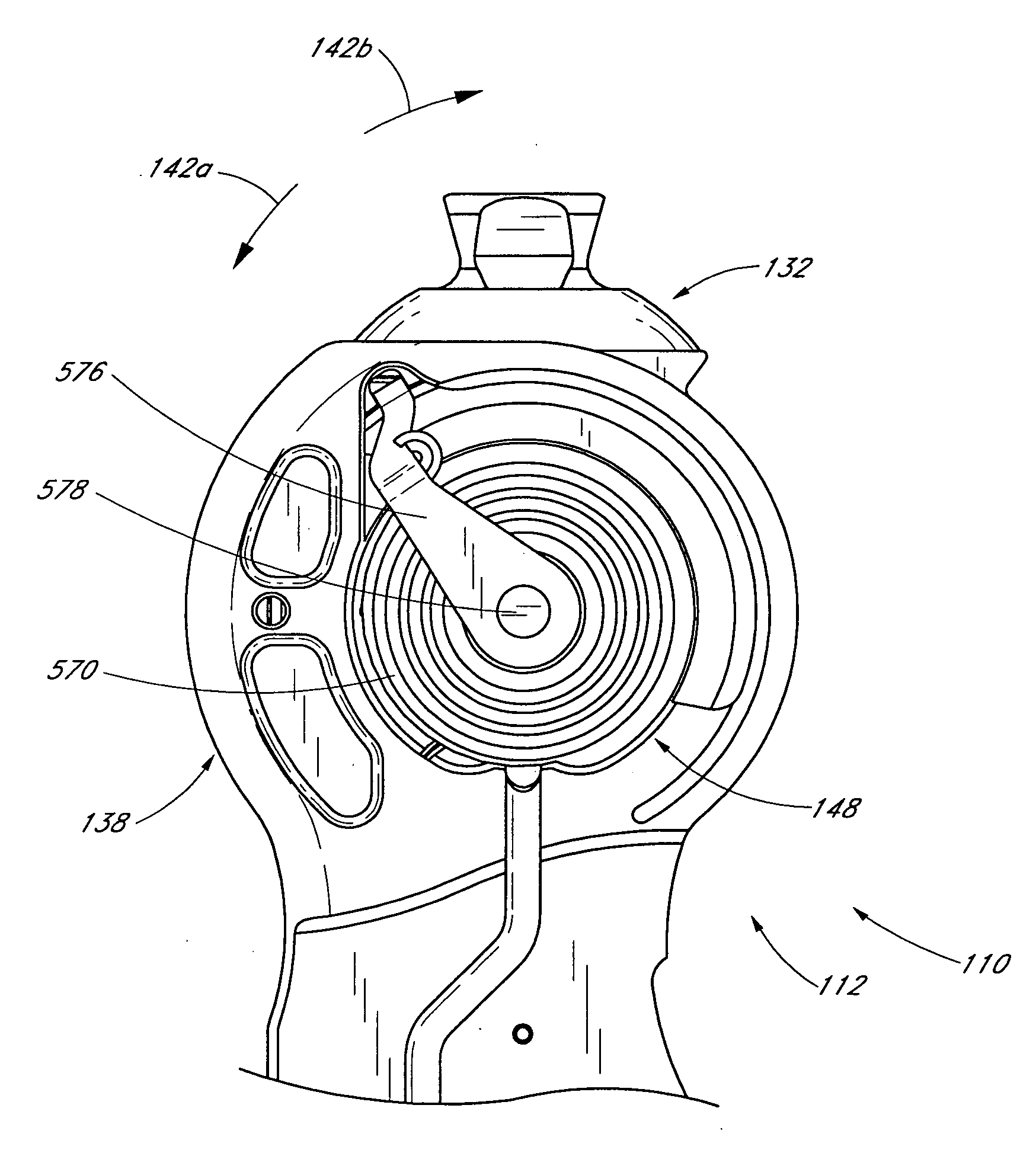
A magnetorheological fluid delivery system includes a mixing and tempering vessel. Fluid is admitted to the vessel via a plurality of tangential ports, creating a mixing of the fluid in the vessel and promoting homogeneity. Fluid may be reconstituted in the vessel by metered addition of carrier fluid. A fixed-speed centrifugal pump disposed in the vessel pressurizes the system. Fluid is pumped through a magnetic-induction flowmeter and a magnetic flow control valve having solenoid windings whereby MR fluid is magnetically stiffened to restrict flow. A closed-loop feedback control system connects the output of the flowmeter to performance of the valve. A nozzle having a slot-shaped bore dispenses MR fluid for re-use in the work zone. A planar-diaphragm flush-mounted pressure transducer at the entrance to the nozzle and flowmeter inferentially measure relaxed viscosity and provide signals to a computer for dispensing metered amounts of carrier fluid into the mixing vessel to assure correct composition of the reconstituted fluid as it is dispensed.
Owner:QED TECH INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com