Variable support footwear using electrorheological or magnetorheological fluids
a technology of electrorheological or magnetorheological fluids and footwear, applied in the field of footwear articles, can solve the problems of foot and leg injuries of runners, stress on various joints, bones and soft tissues, and foot and leg injuries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The following description is not to be taken in a limiting sense, but is made merely for the purpose of describing the general principles of exemplary embodiments. The scope of the invention should be determined with reference to the claims.
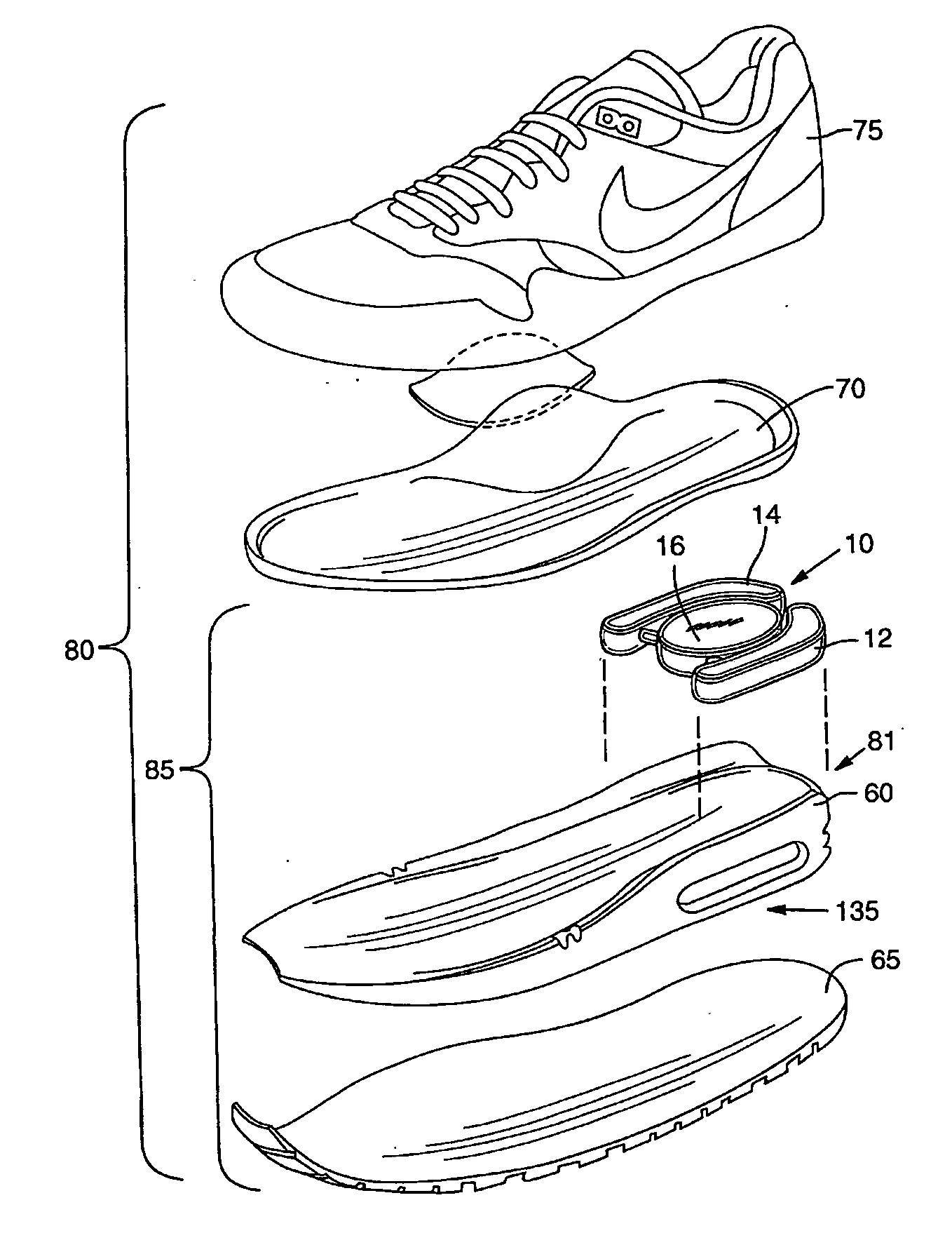
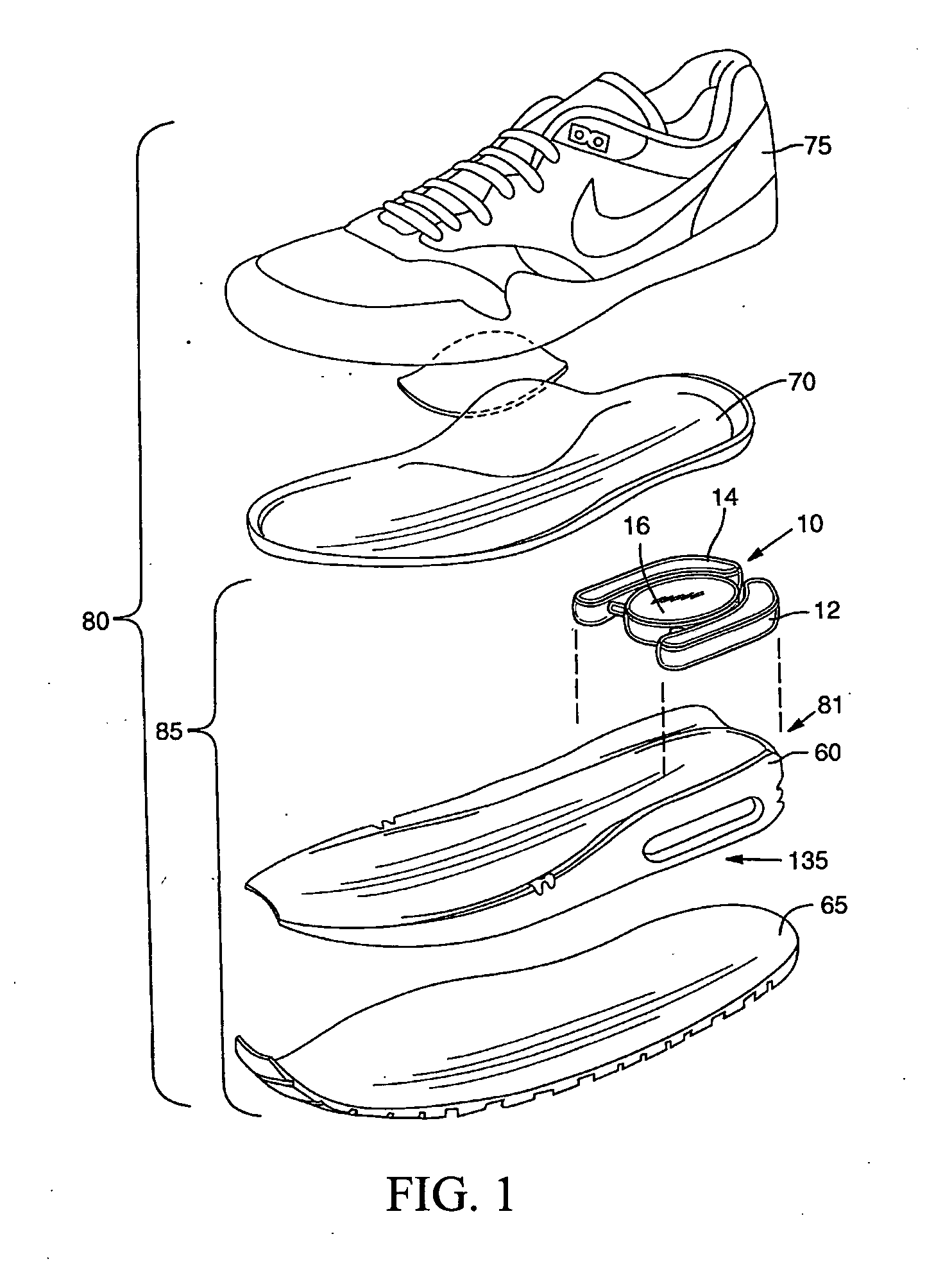
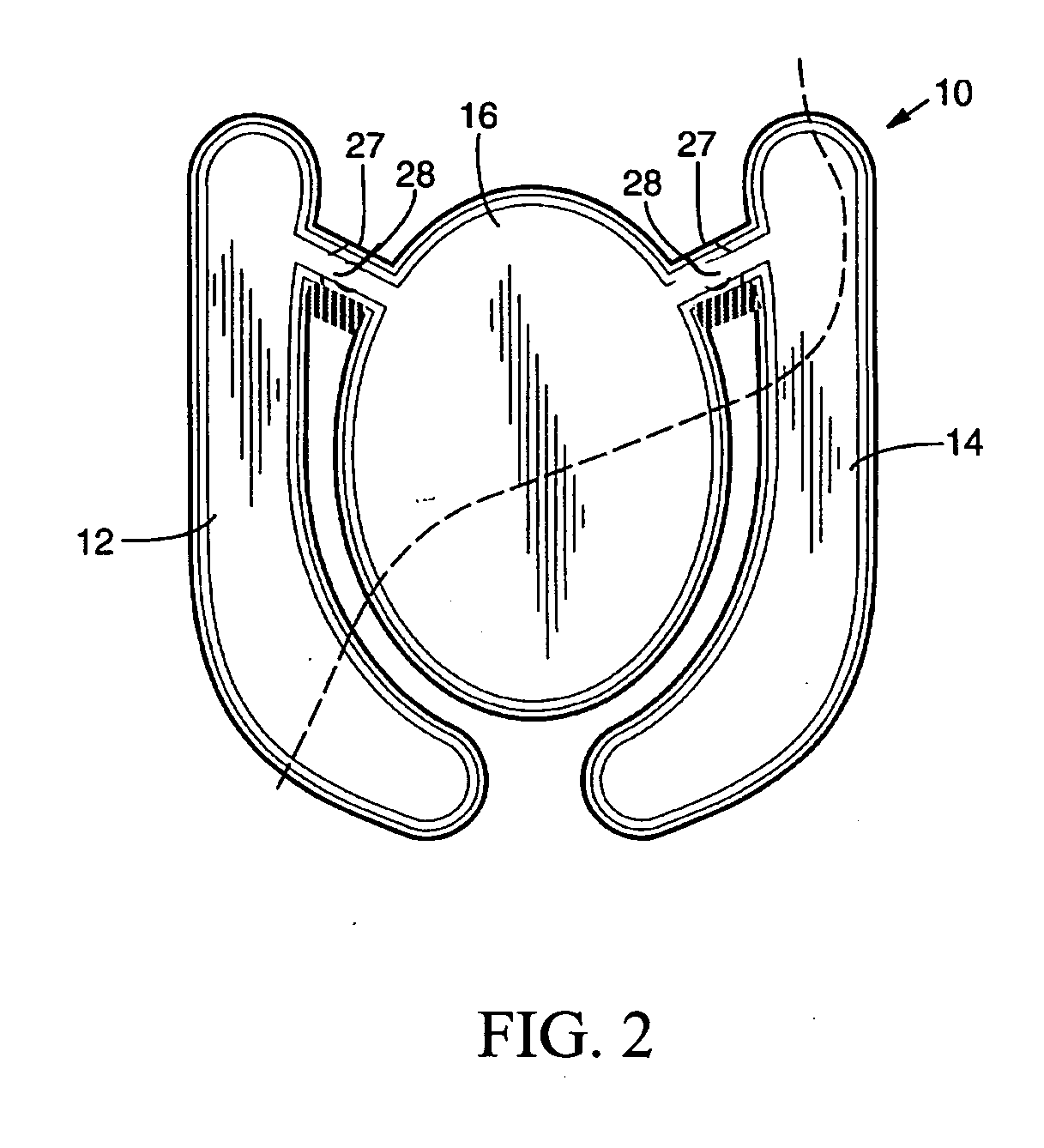
[0022]FIG. 1 illustrates an exploded view of an article of footwear incorporating a bladder system filled with MR or ER fluid, according to one embodiment. FIG. 2 illustrates a top view of the bladder system shown in FIG. 1, in accordance with one embodiment.
[0023] Referring to FIG. 1, an article of athletic footwear 80 is comprised of an upper 75 for covering a wearer's foot and a sole assembly 85. The upper 75 can include a sock liner 70 can be placed therein. The sole assembly 85 includes the bladder system 10, a midsole layer 60, and an outsole layer 65.
[0024] The outsole layer 65 is adapted to engage the ground and is secured to at least a portion of midsole layer 60. Depending upon the material forming the midsole layer 60 and upo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com