Patents
Literature
63 results about "Subtalar joint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
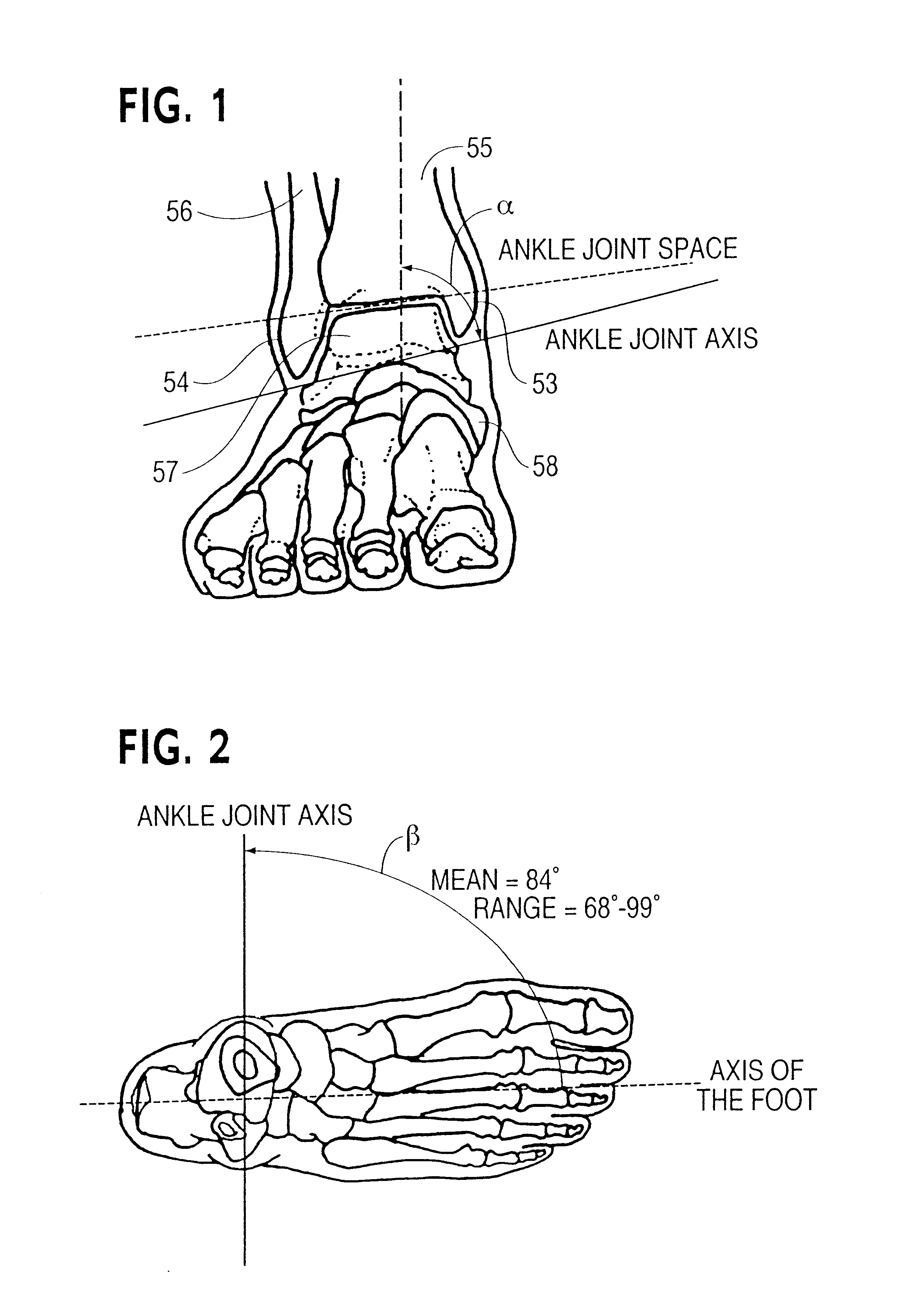
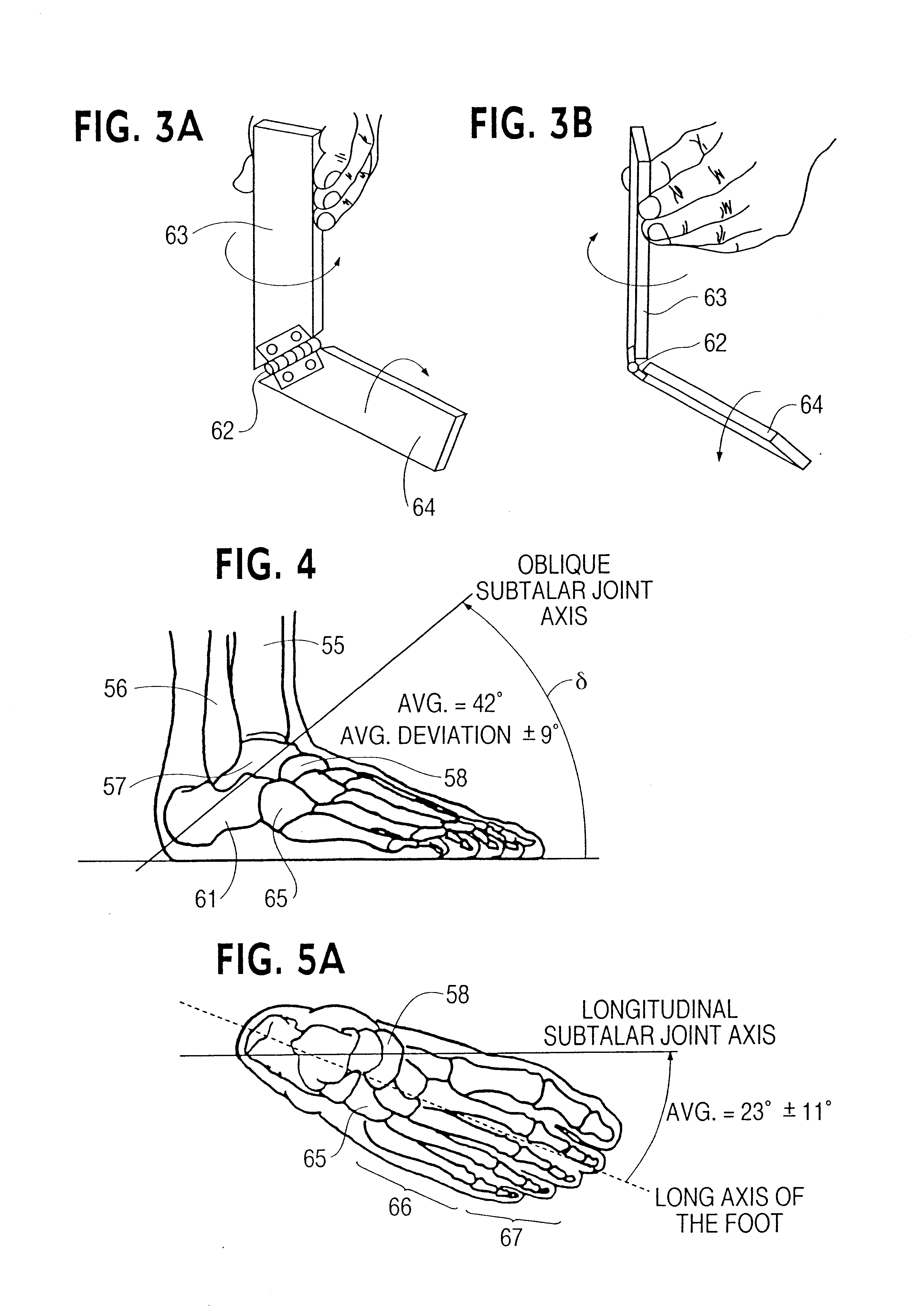
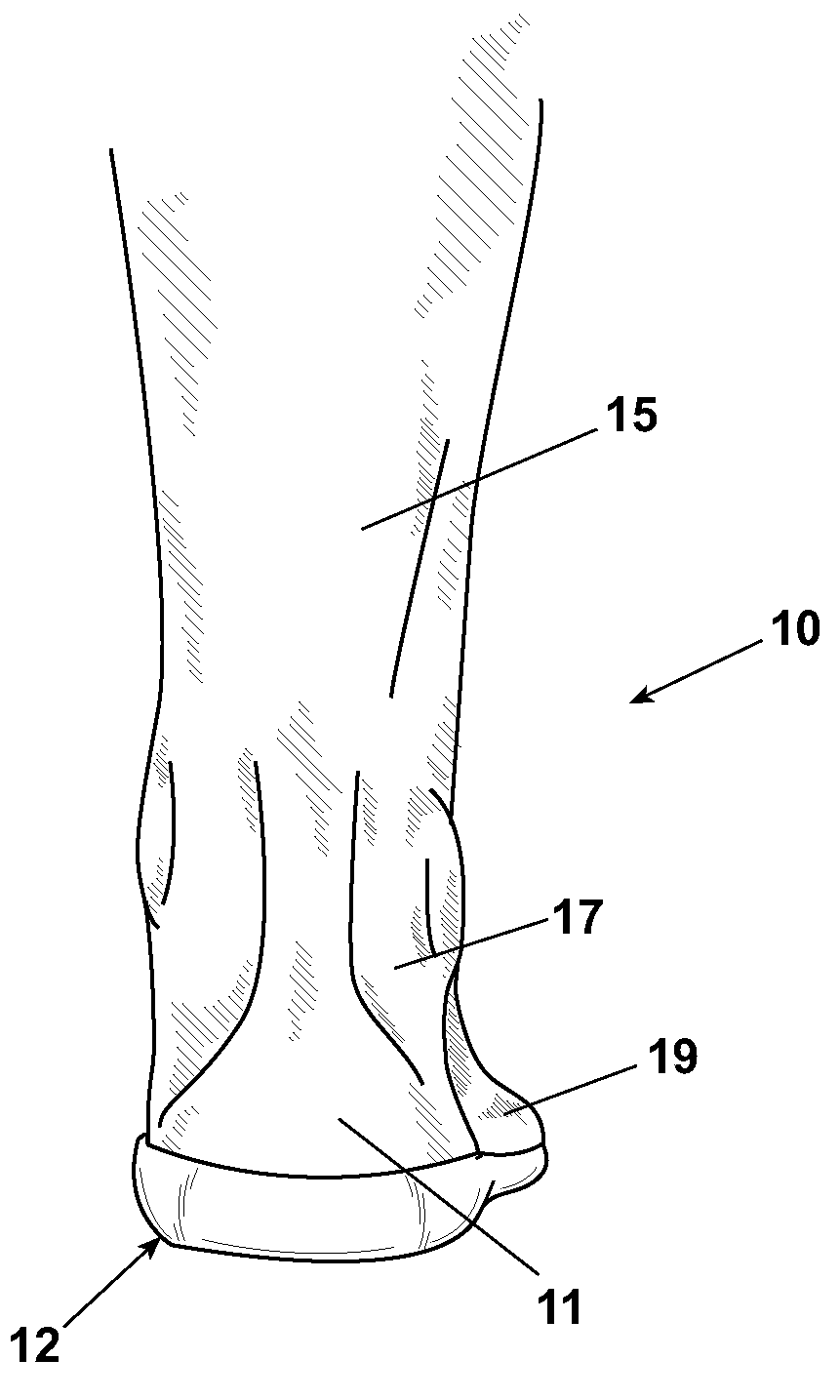
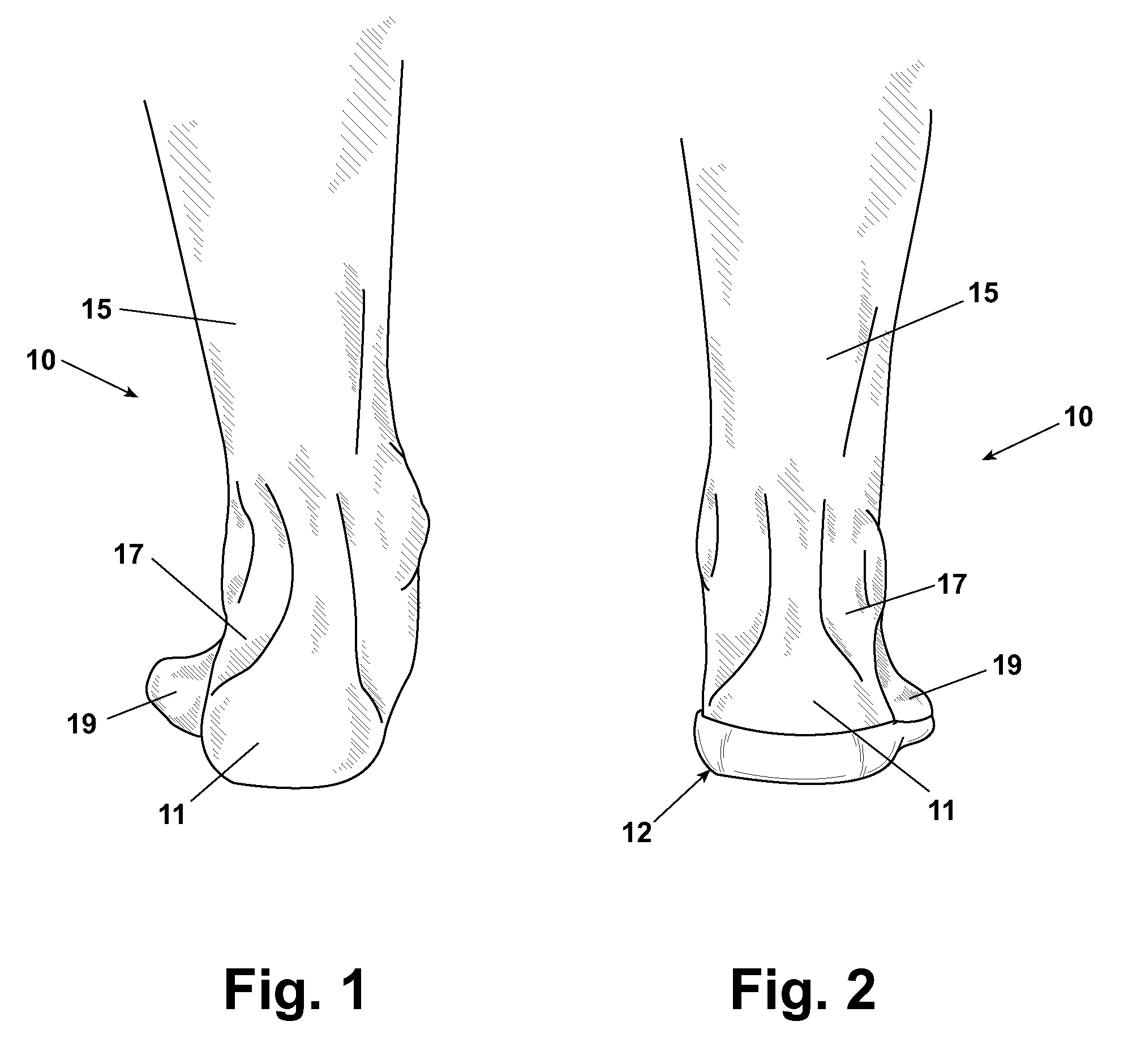
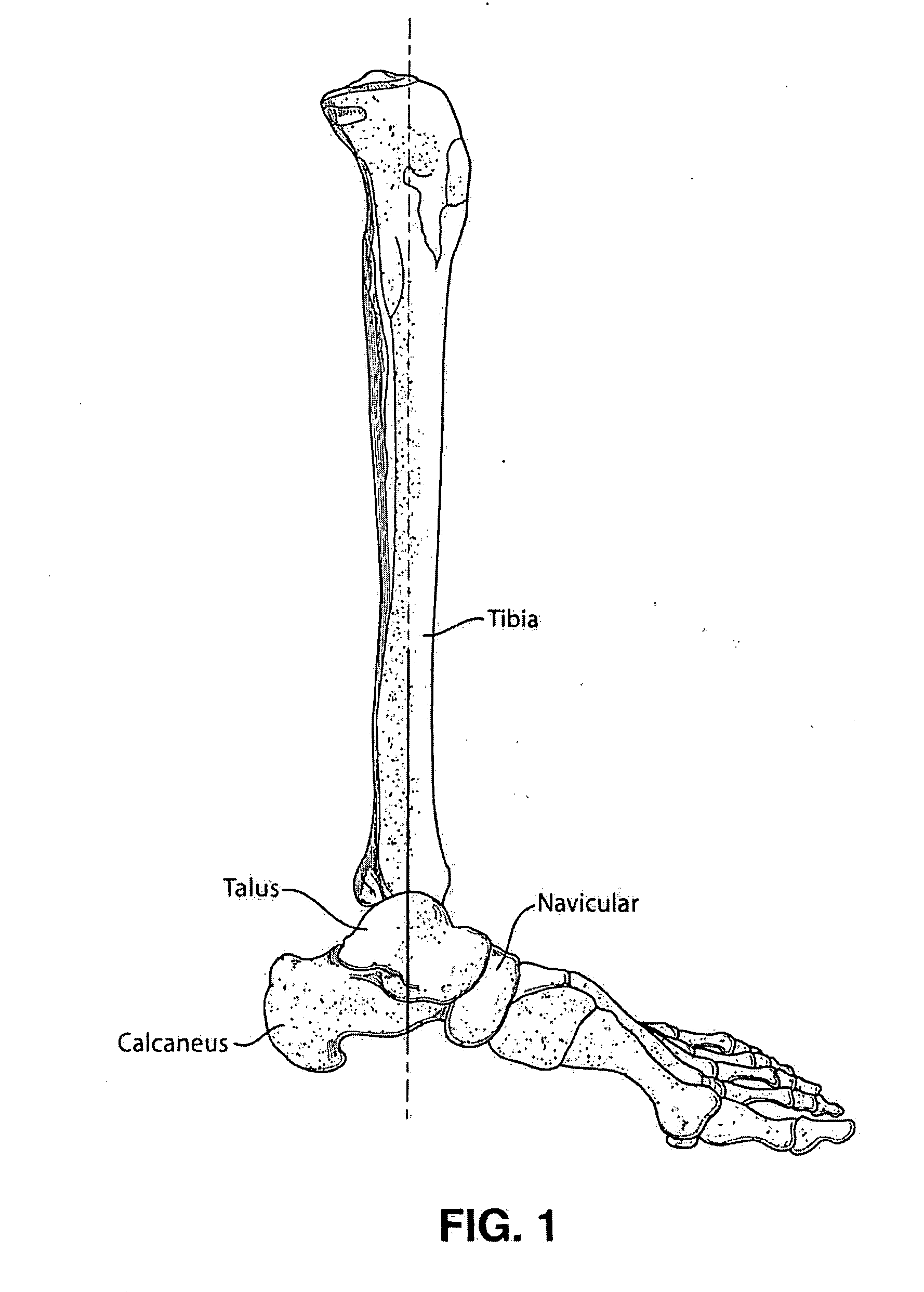
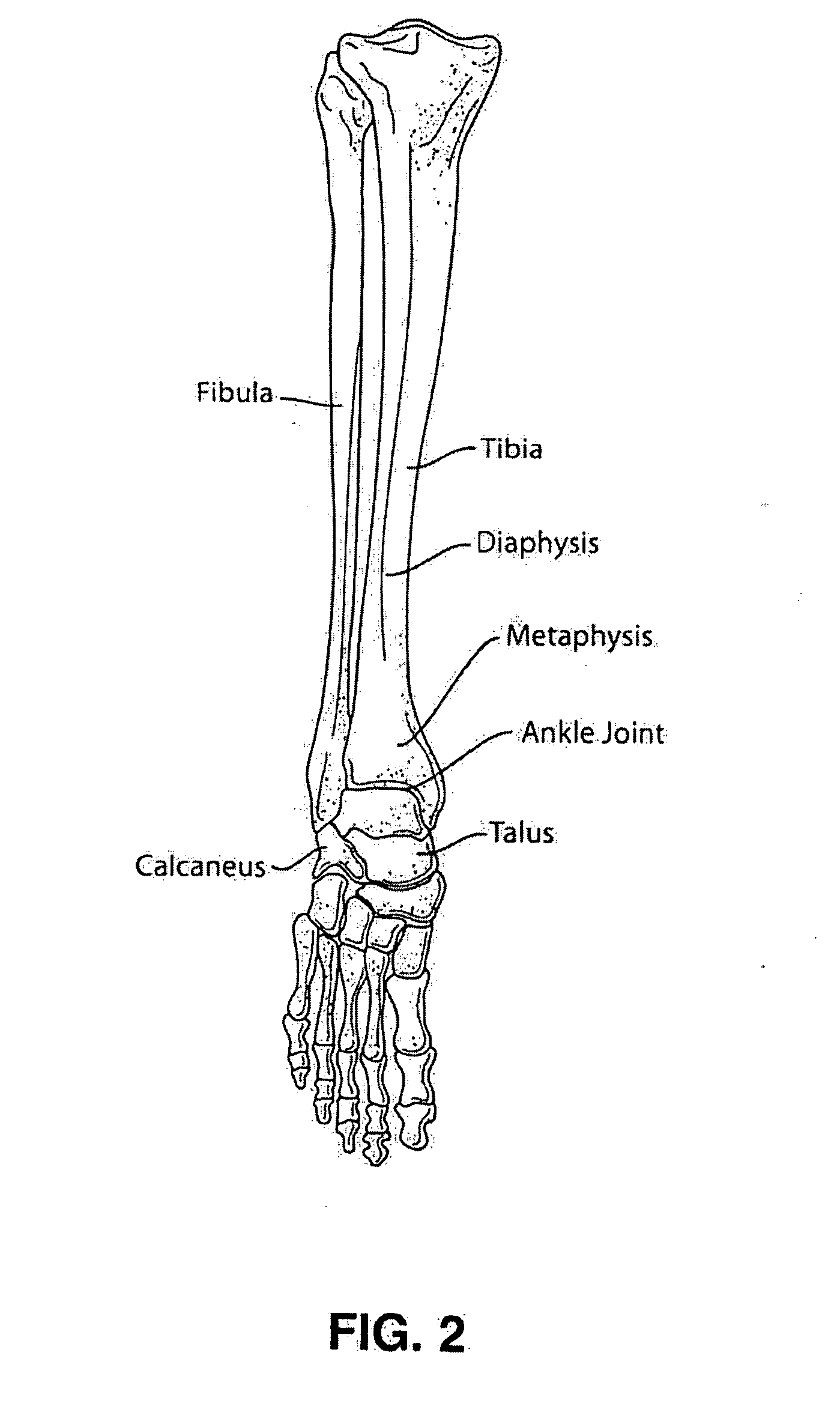
In human anatomy, the subtalar joint, also known as the talocalcaneal joint, is a joint of the foot. It occurs at the meeting point of the talus and the calcaneus. The joint is classed structurally as a synovial joint, and functionally as a plane joint.
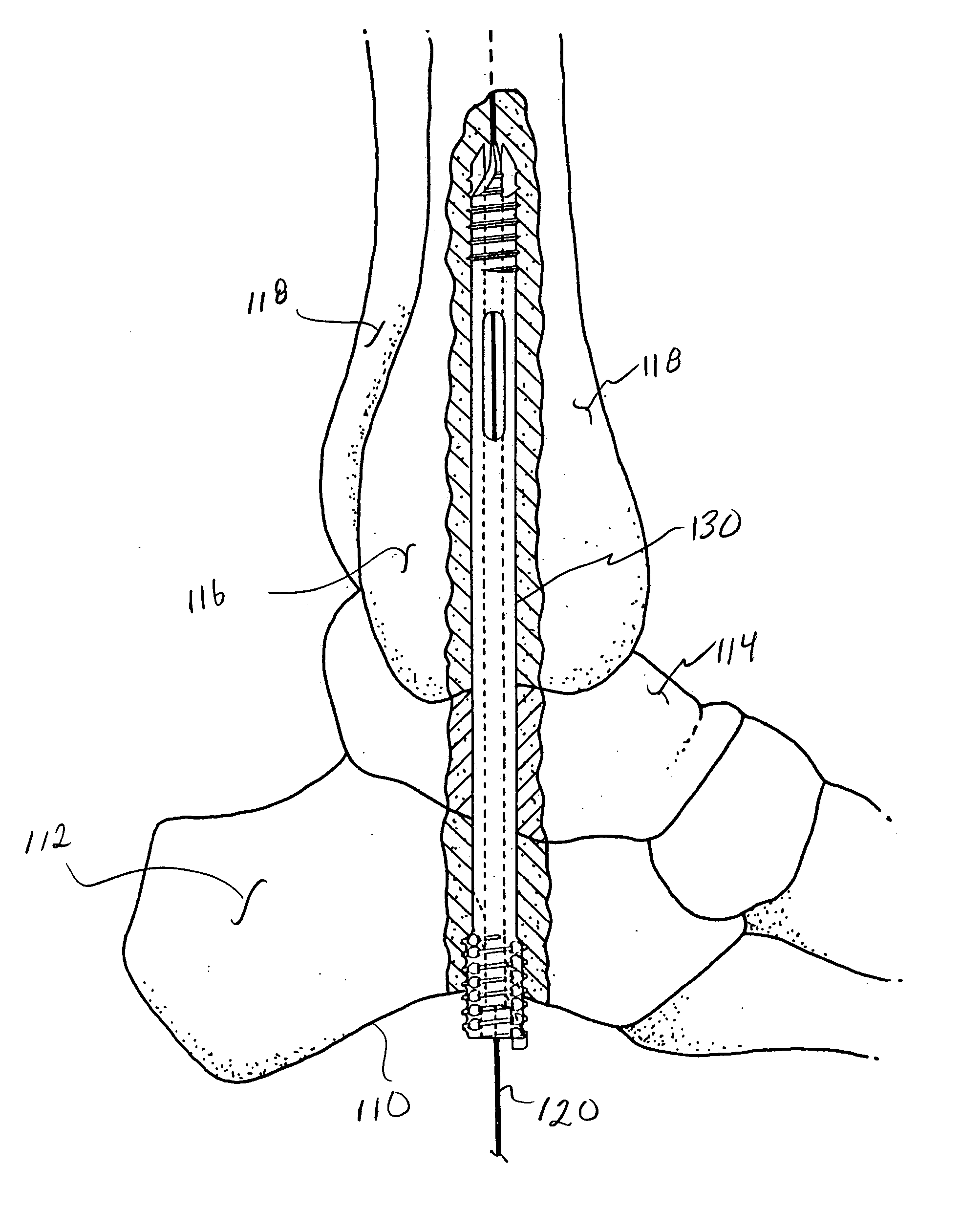
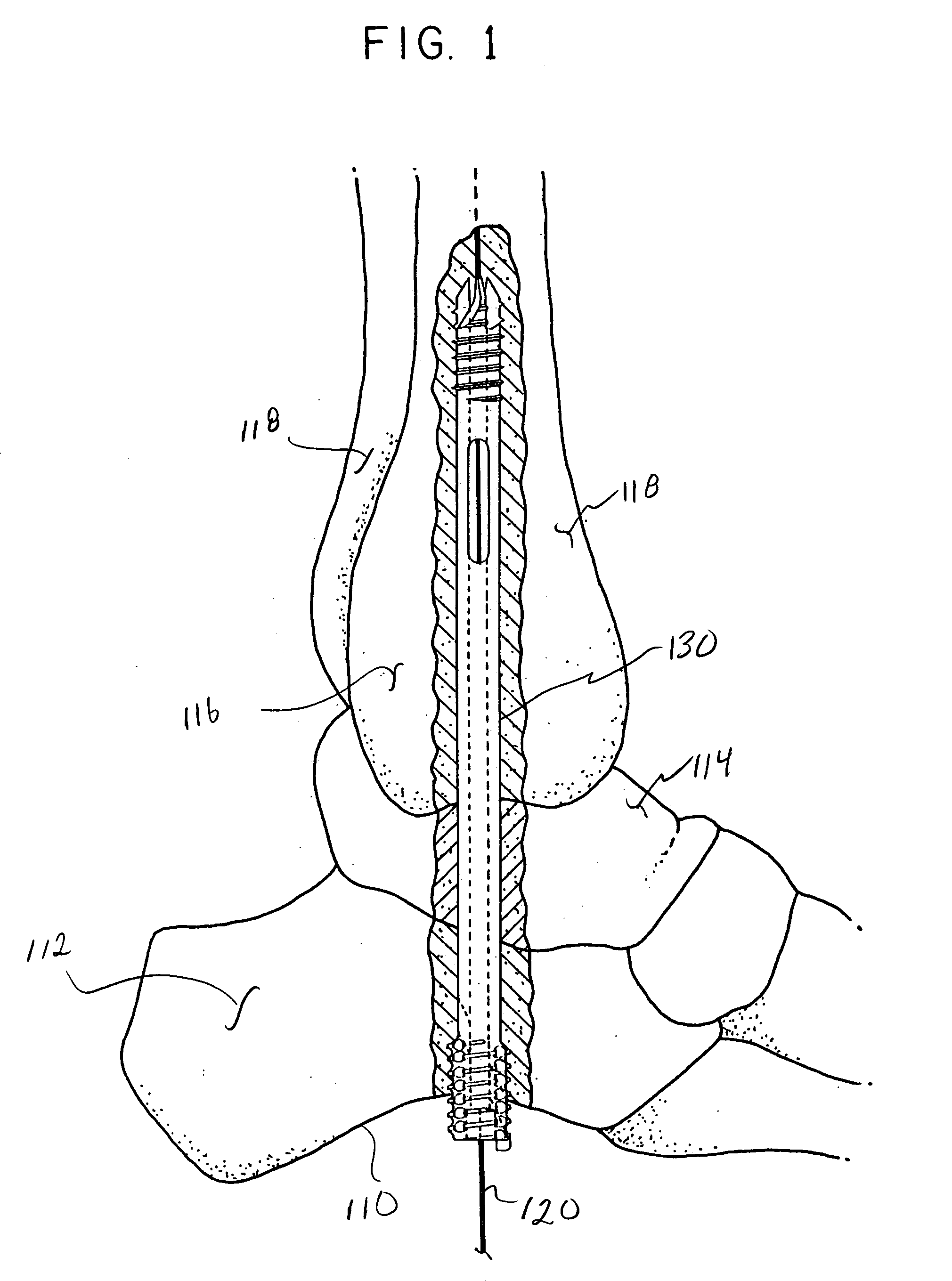
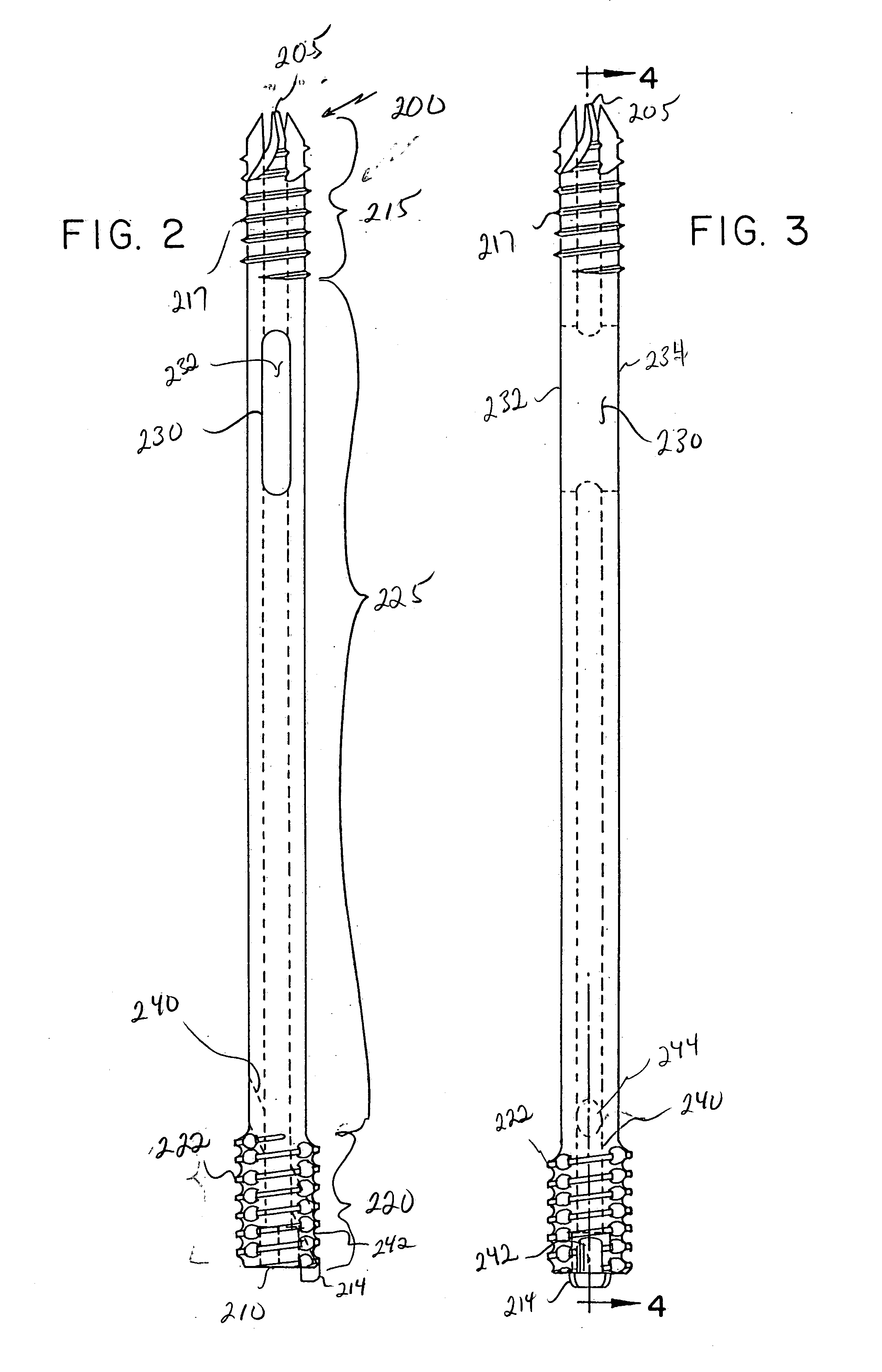
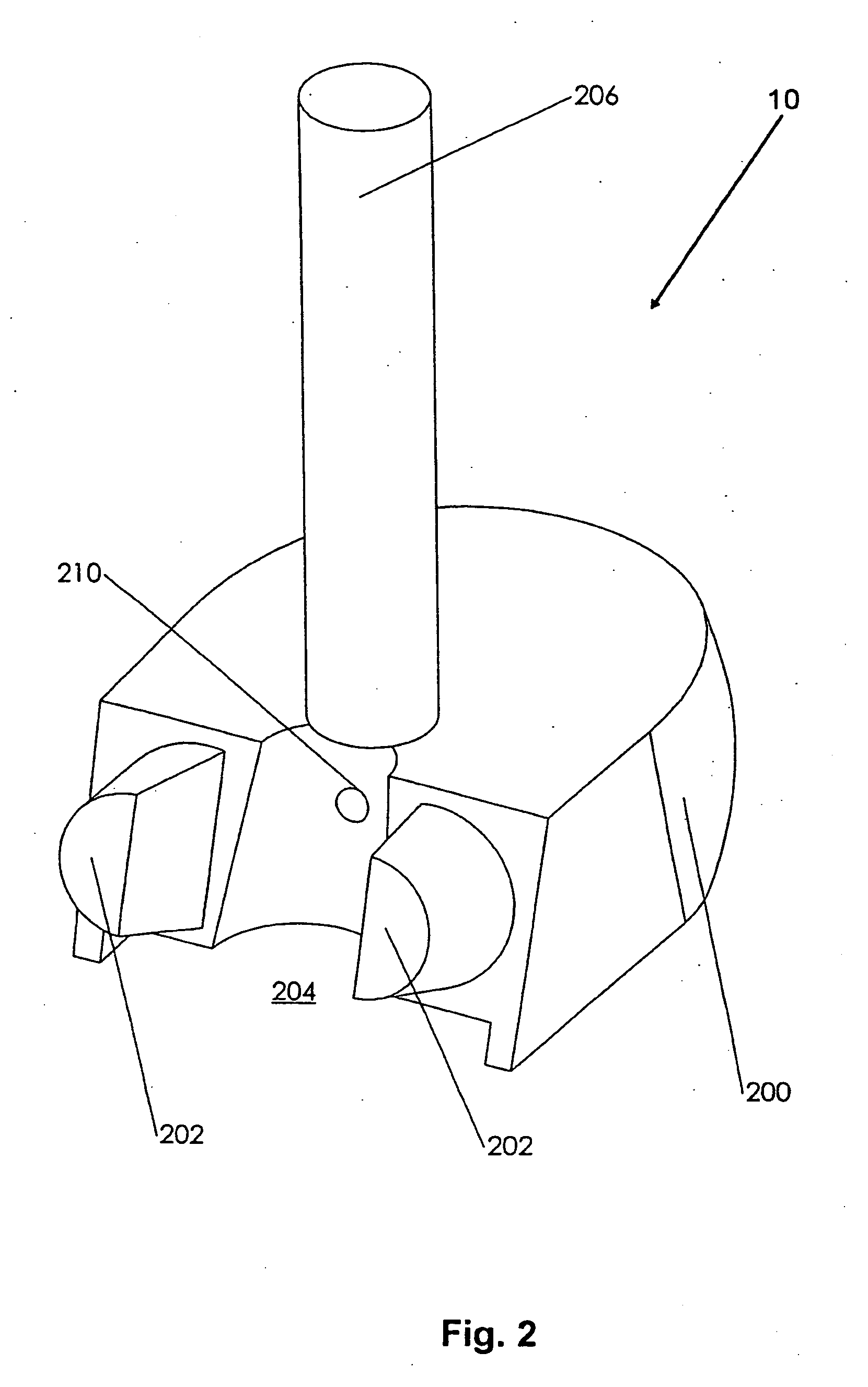
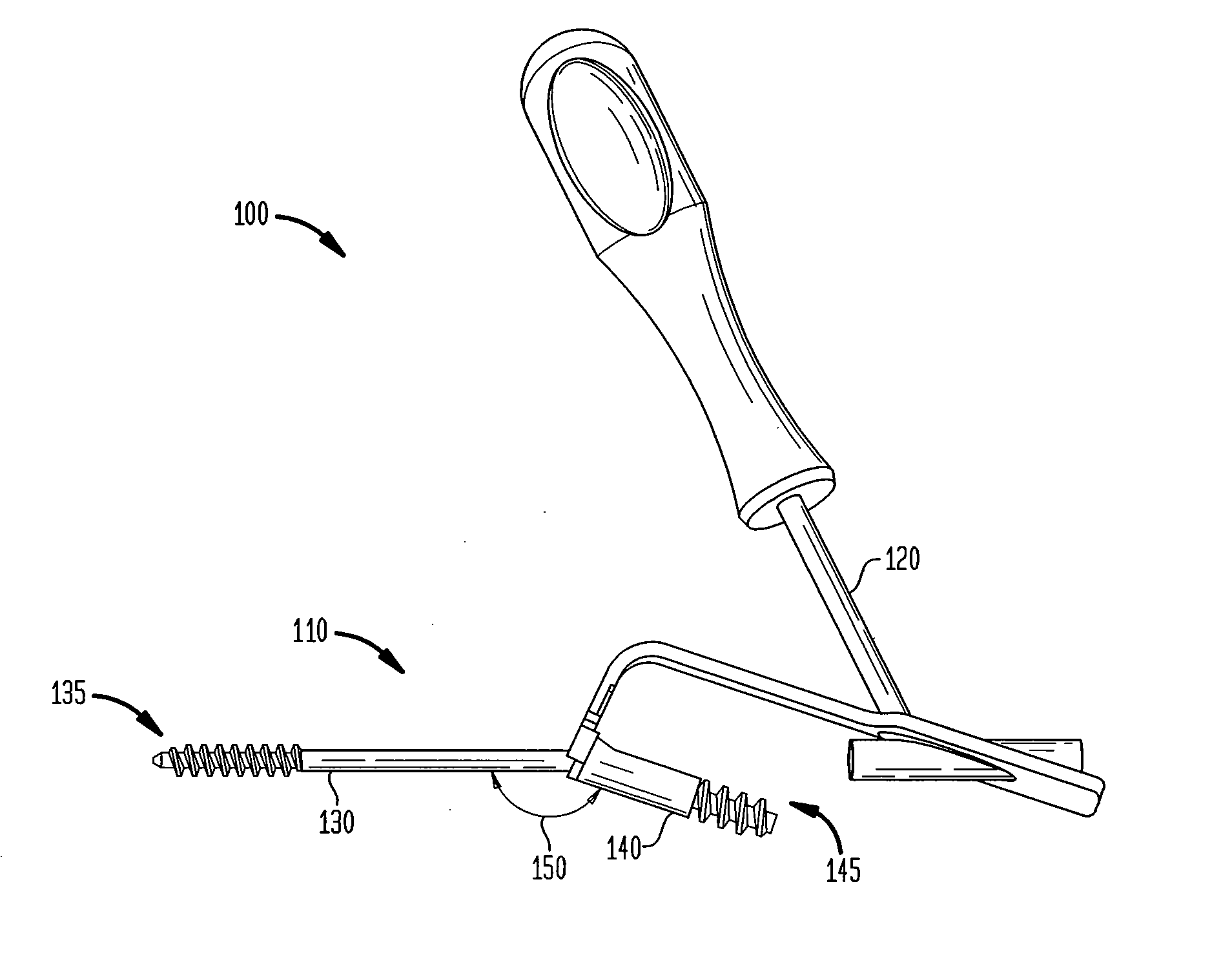
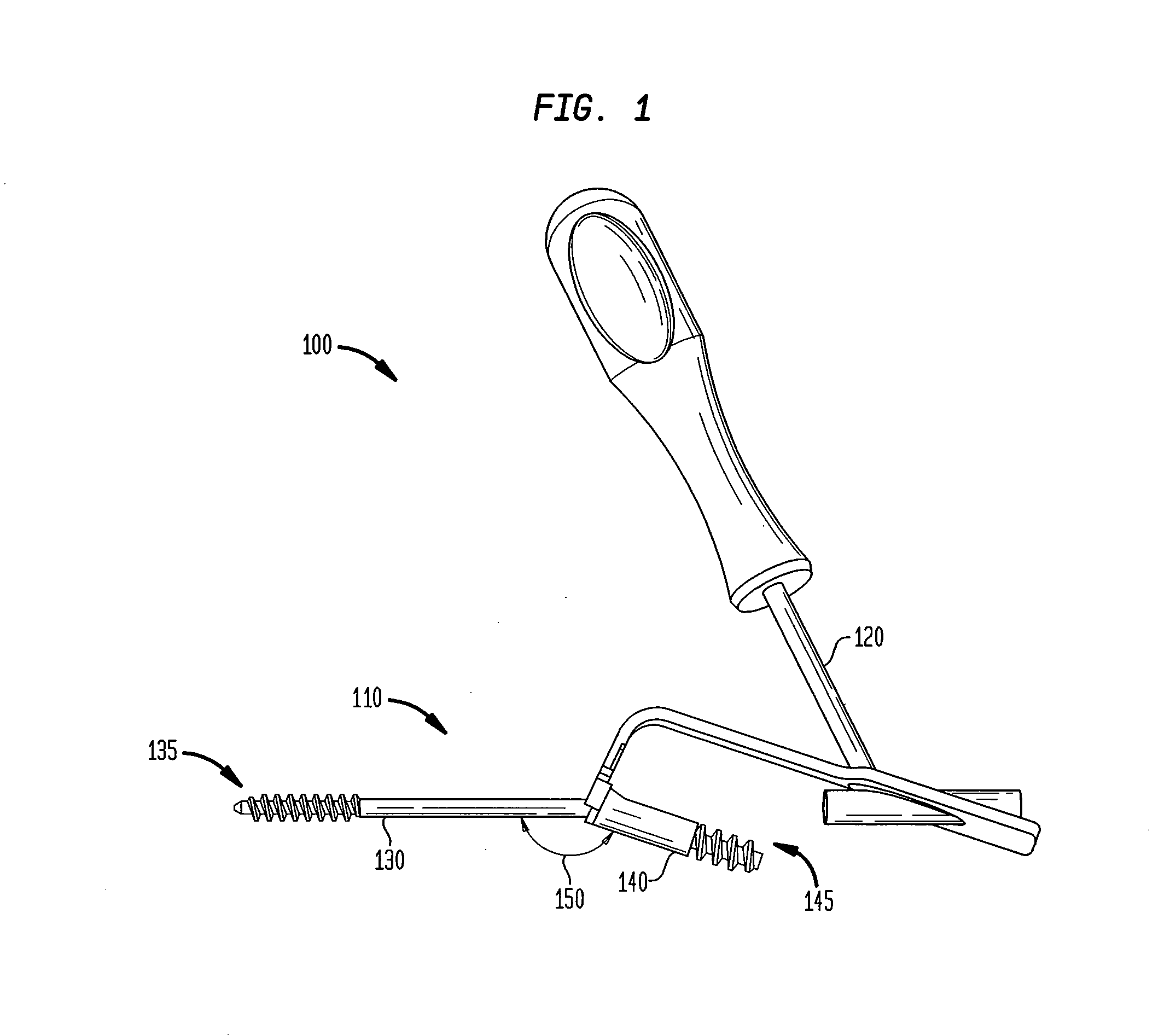
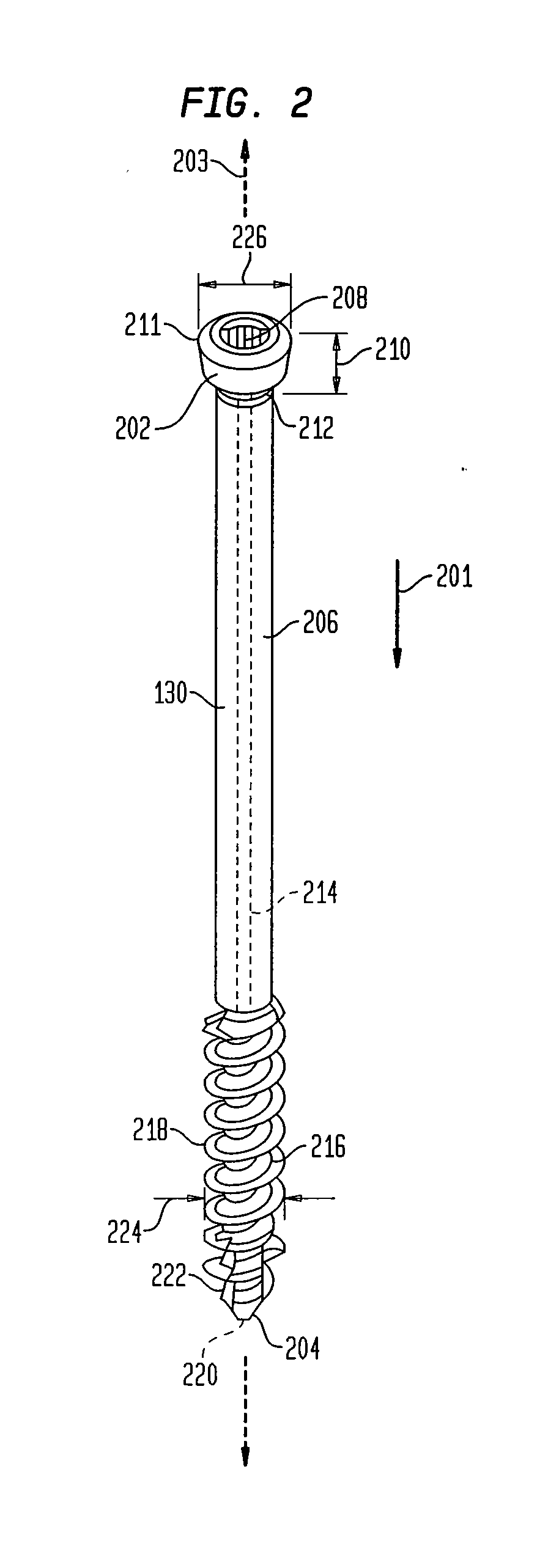
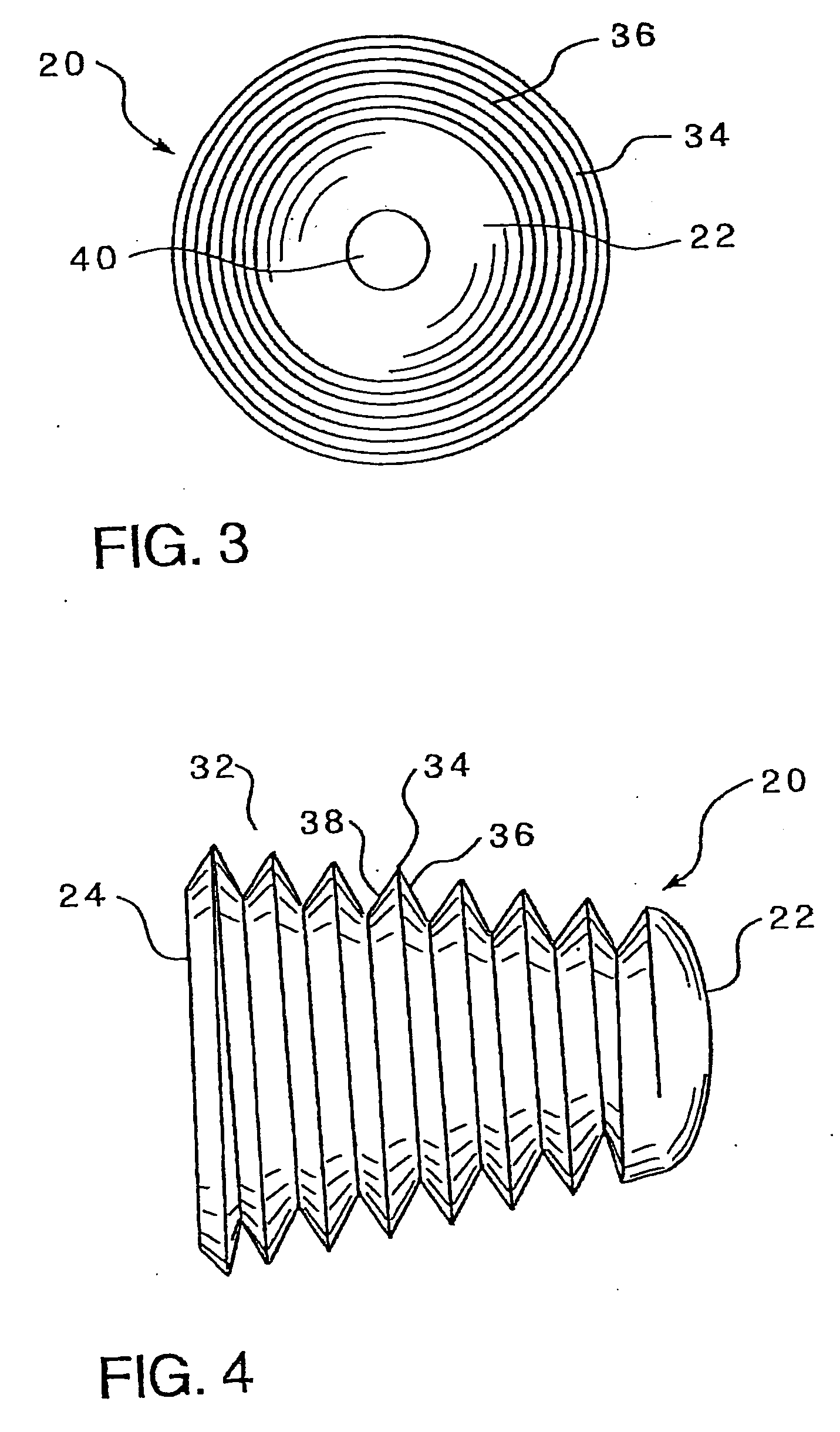
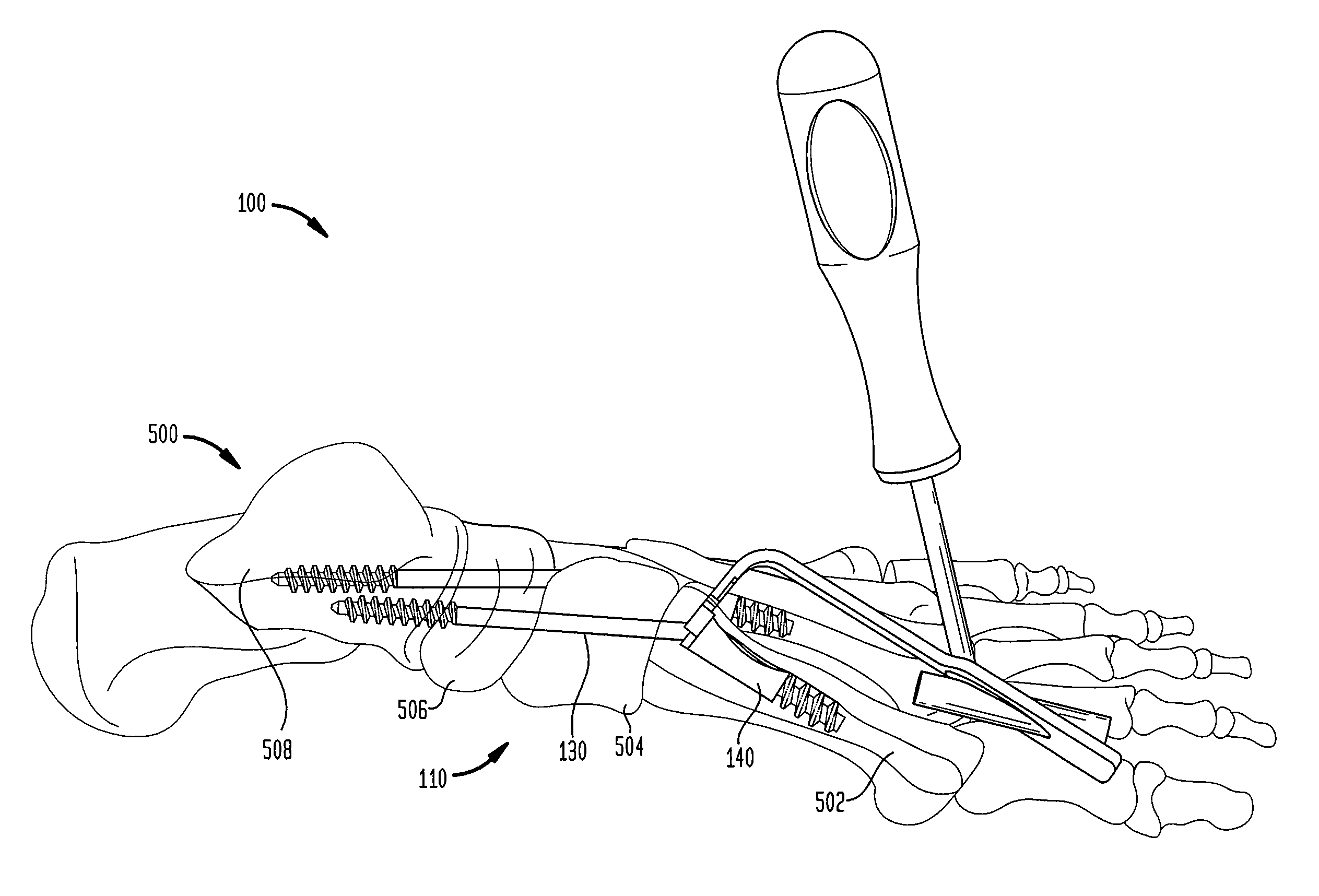
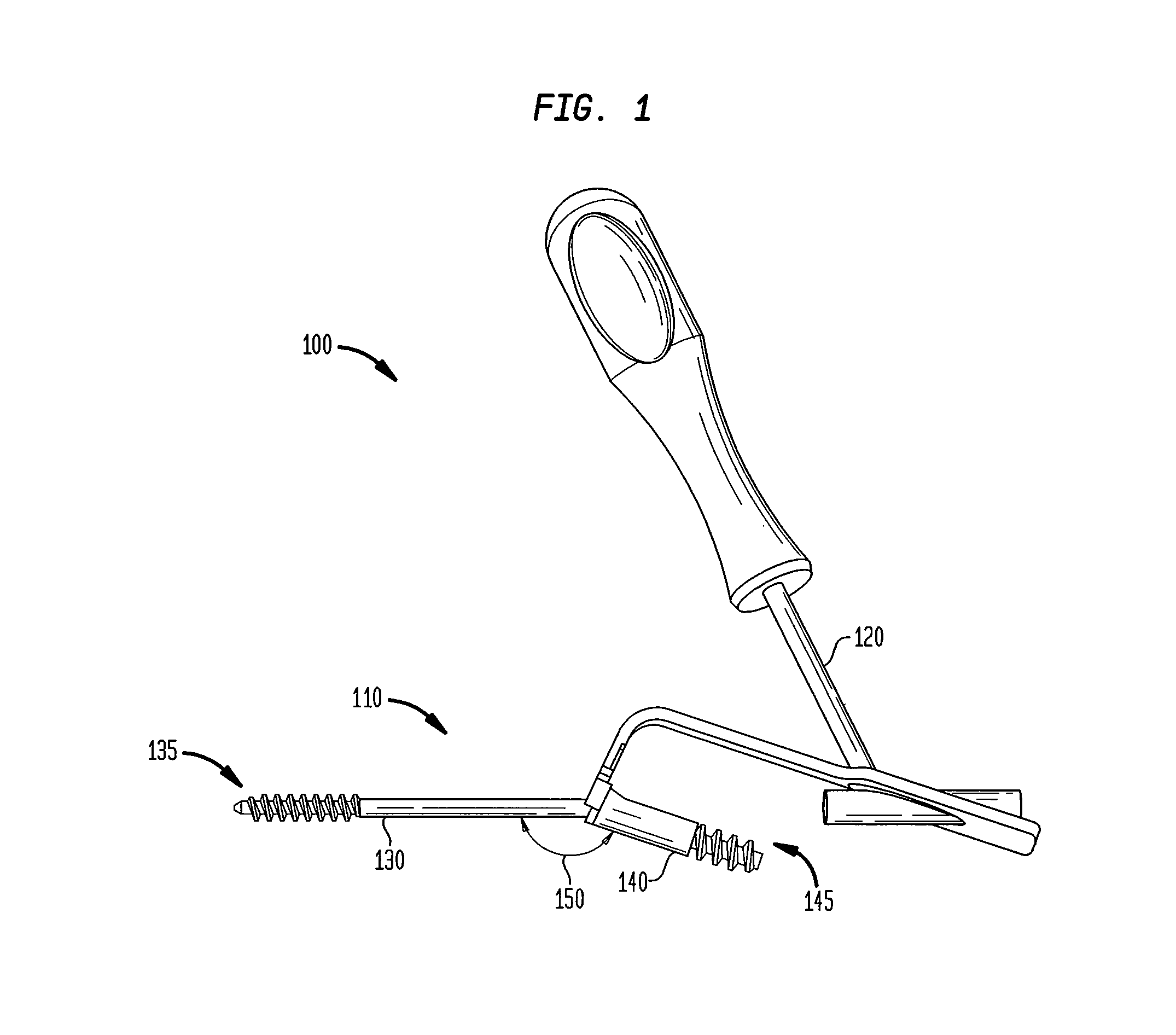
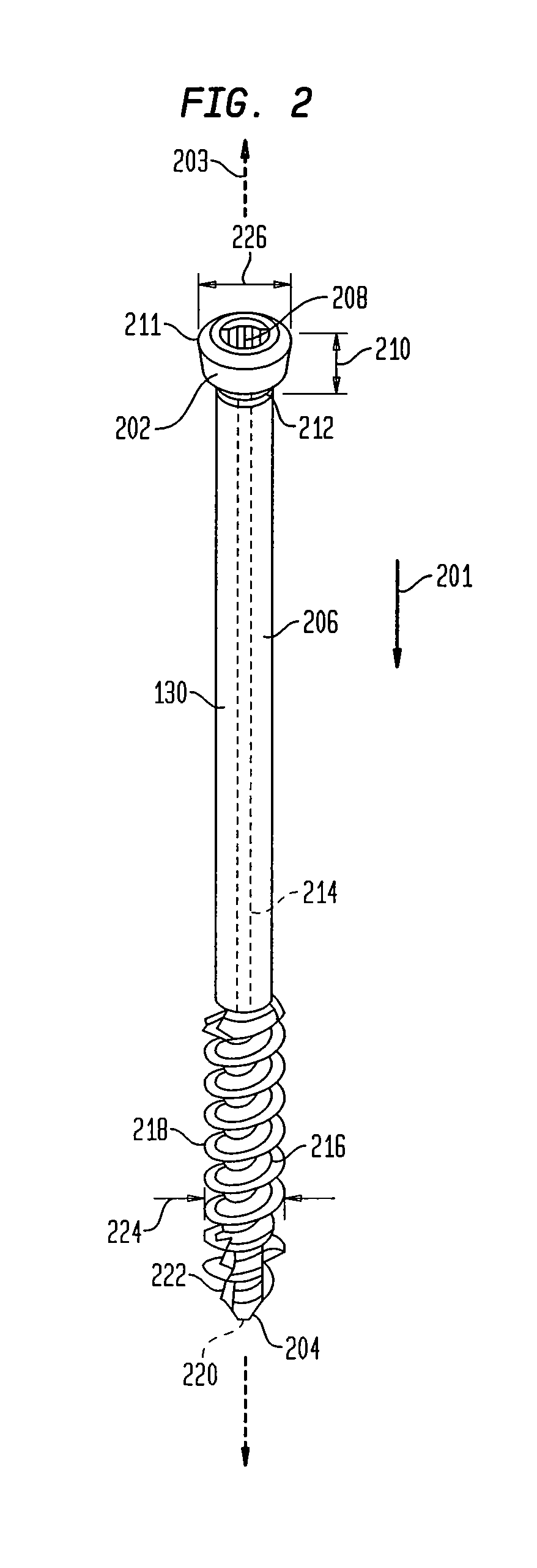
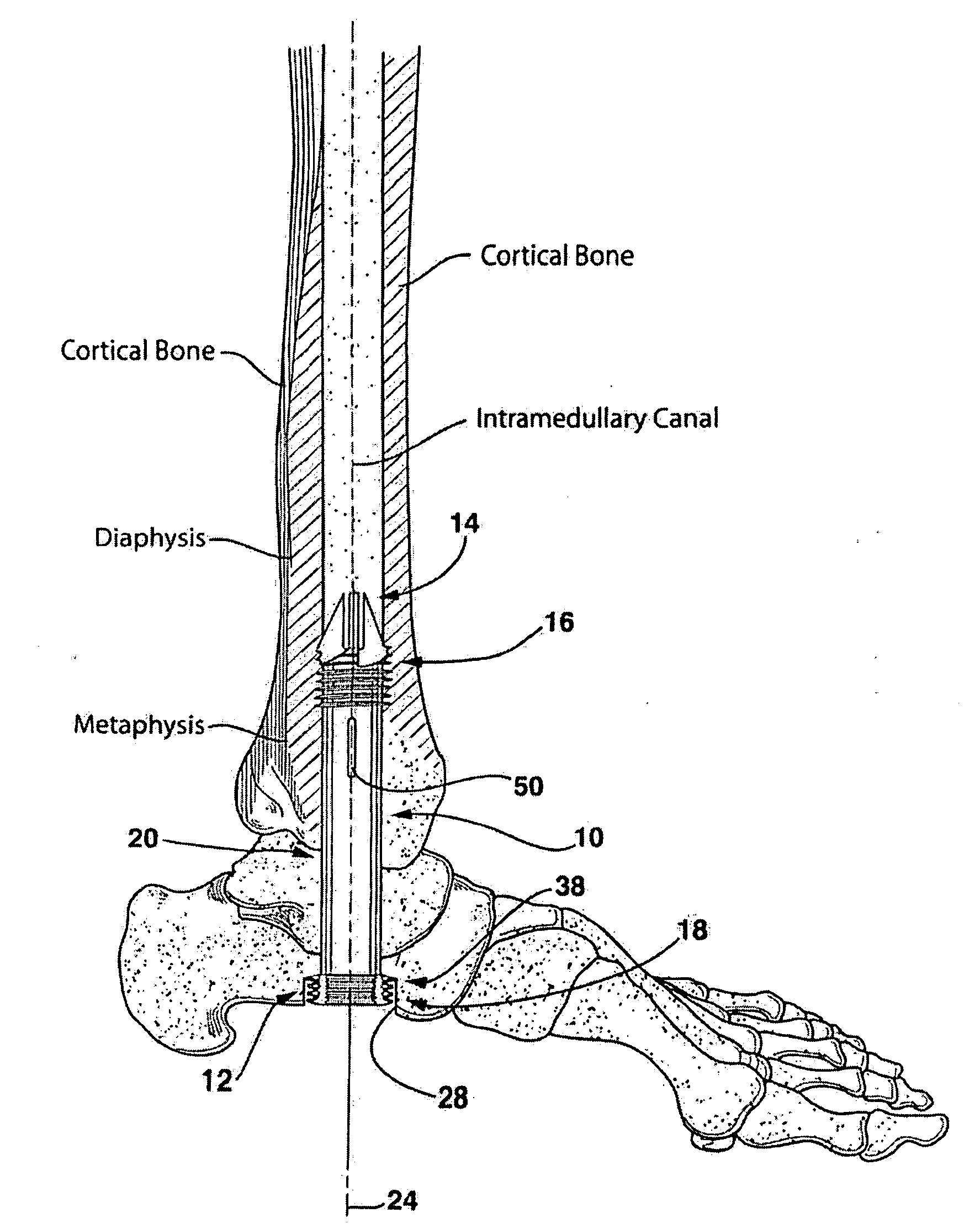
Intramedullary locked compression screw for stabiliziation and union of complex ankle and subtalar deformities
InactiveUS20050107791A1Easy to installReduce exposureInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsJOINT MALFORMATIONEngineering
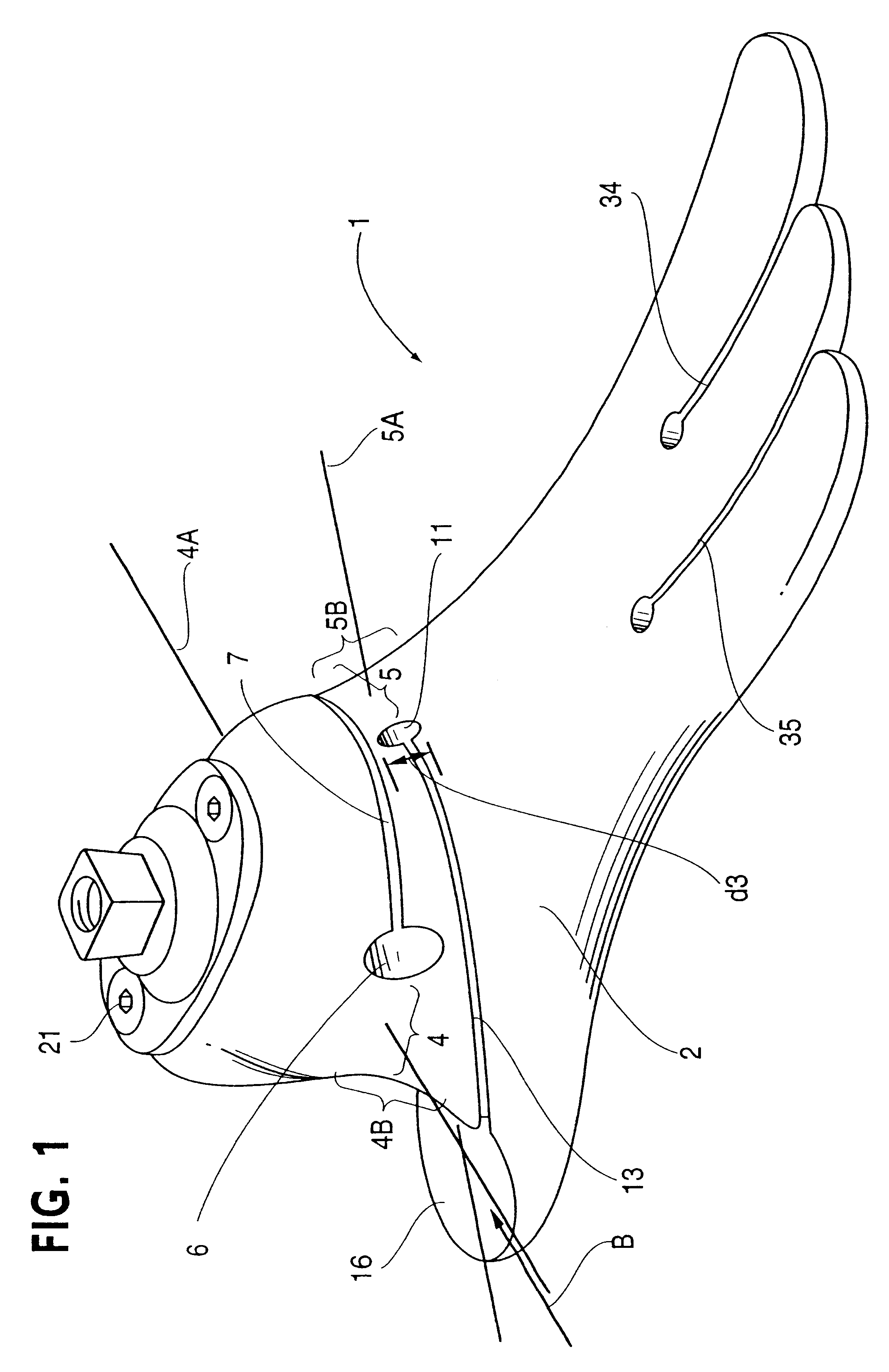
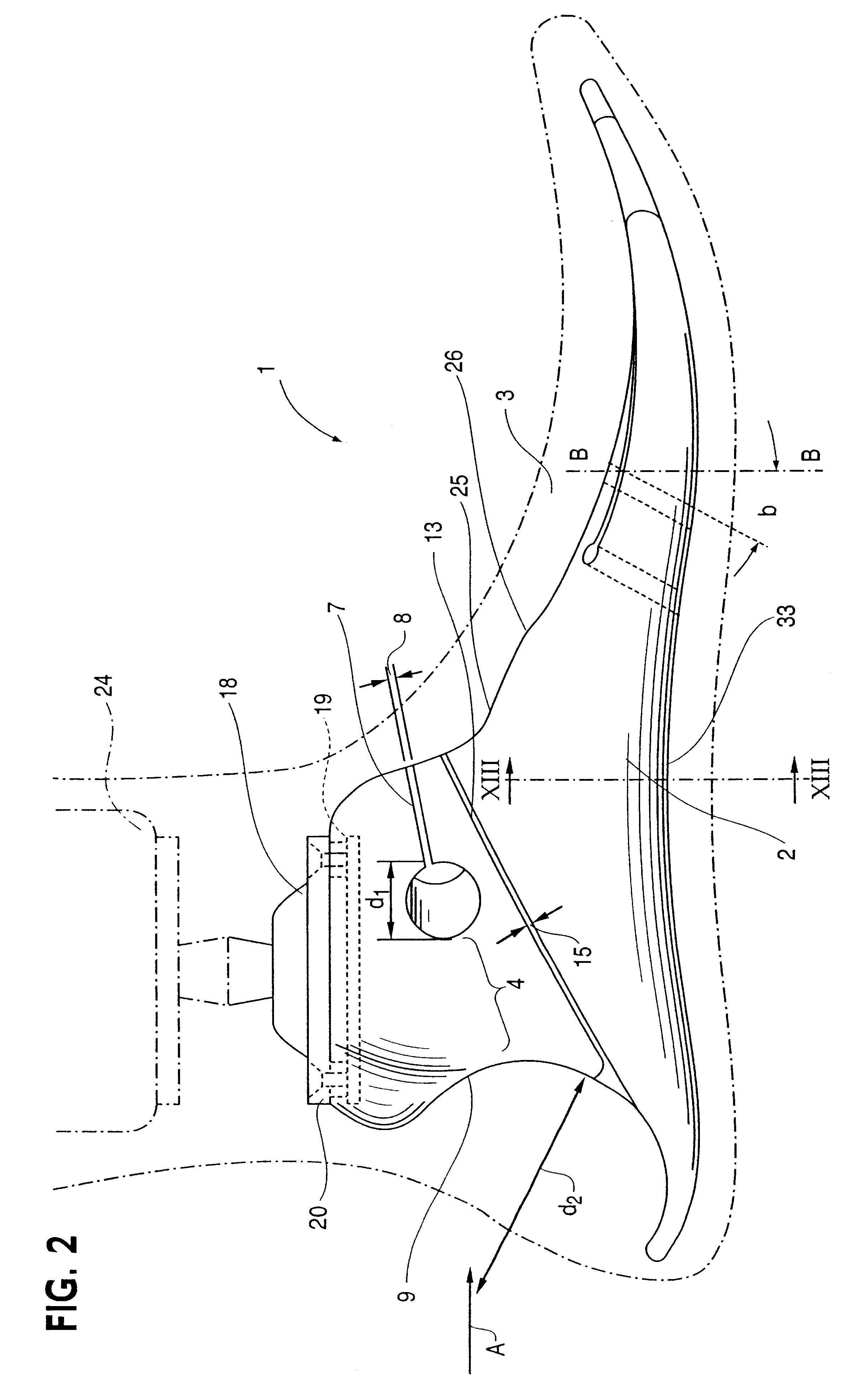
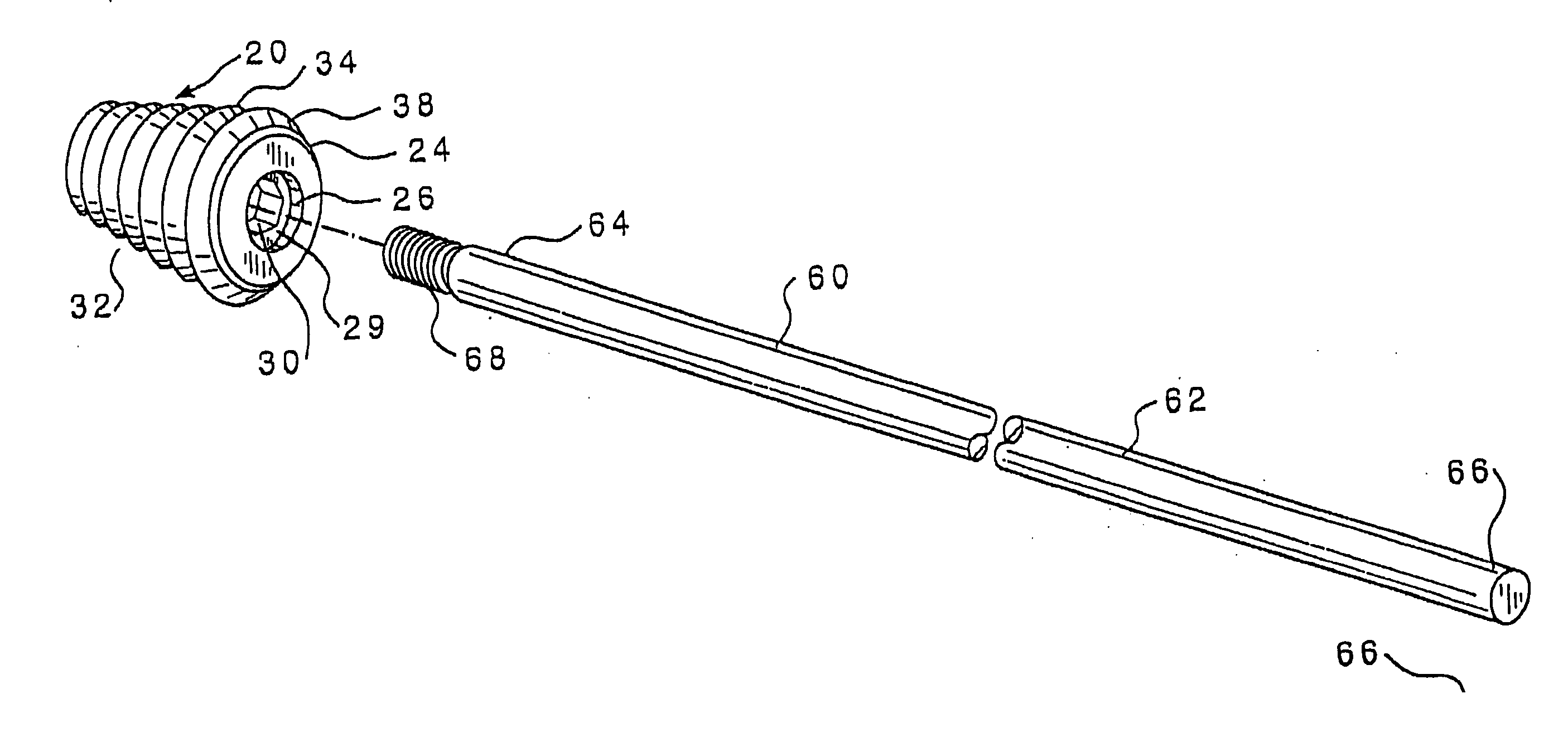
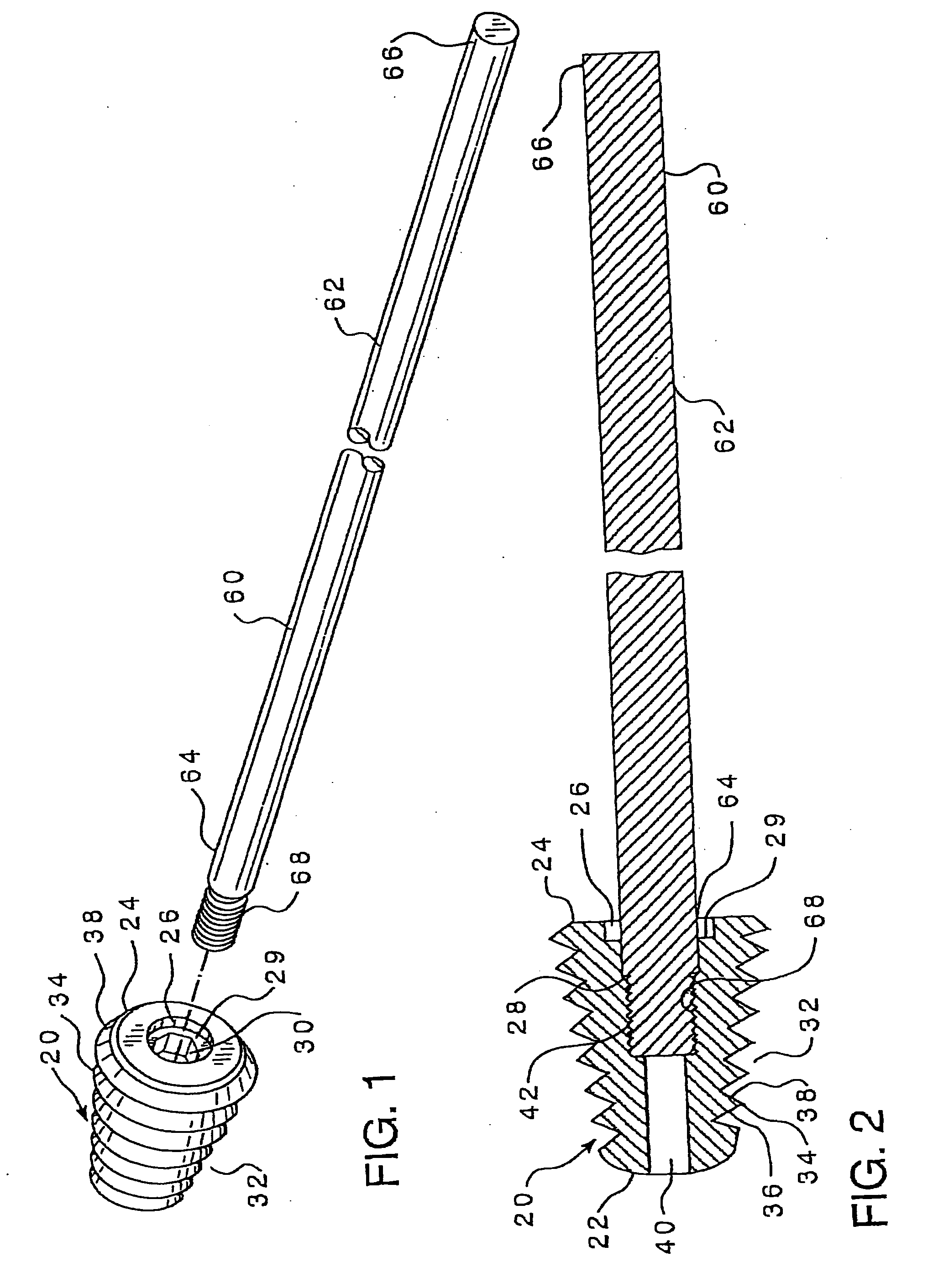
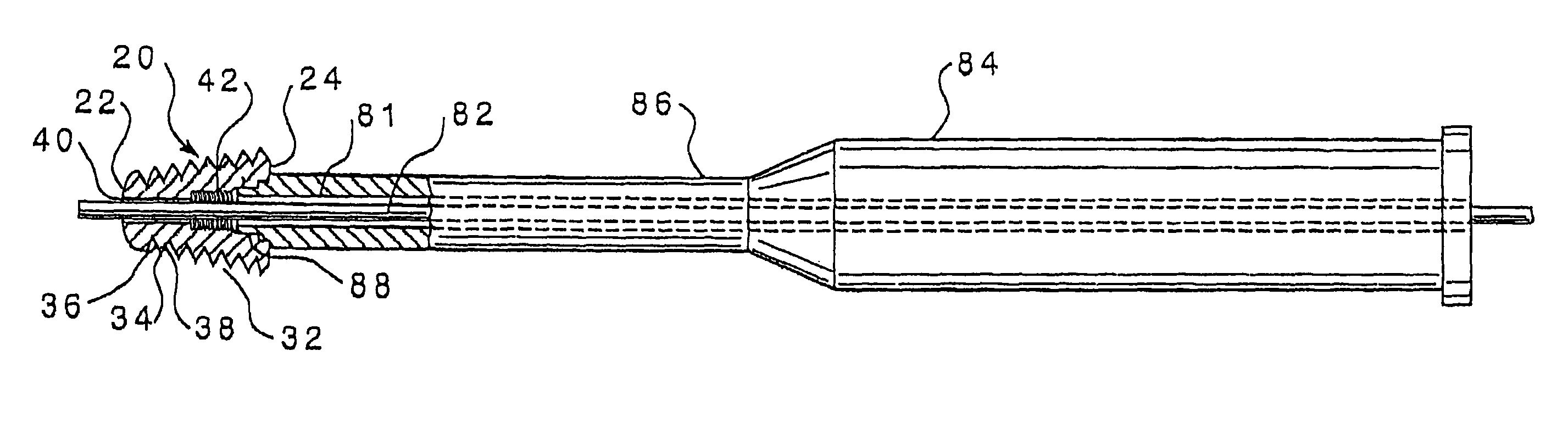
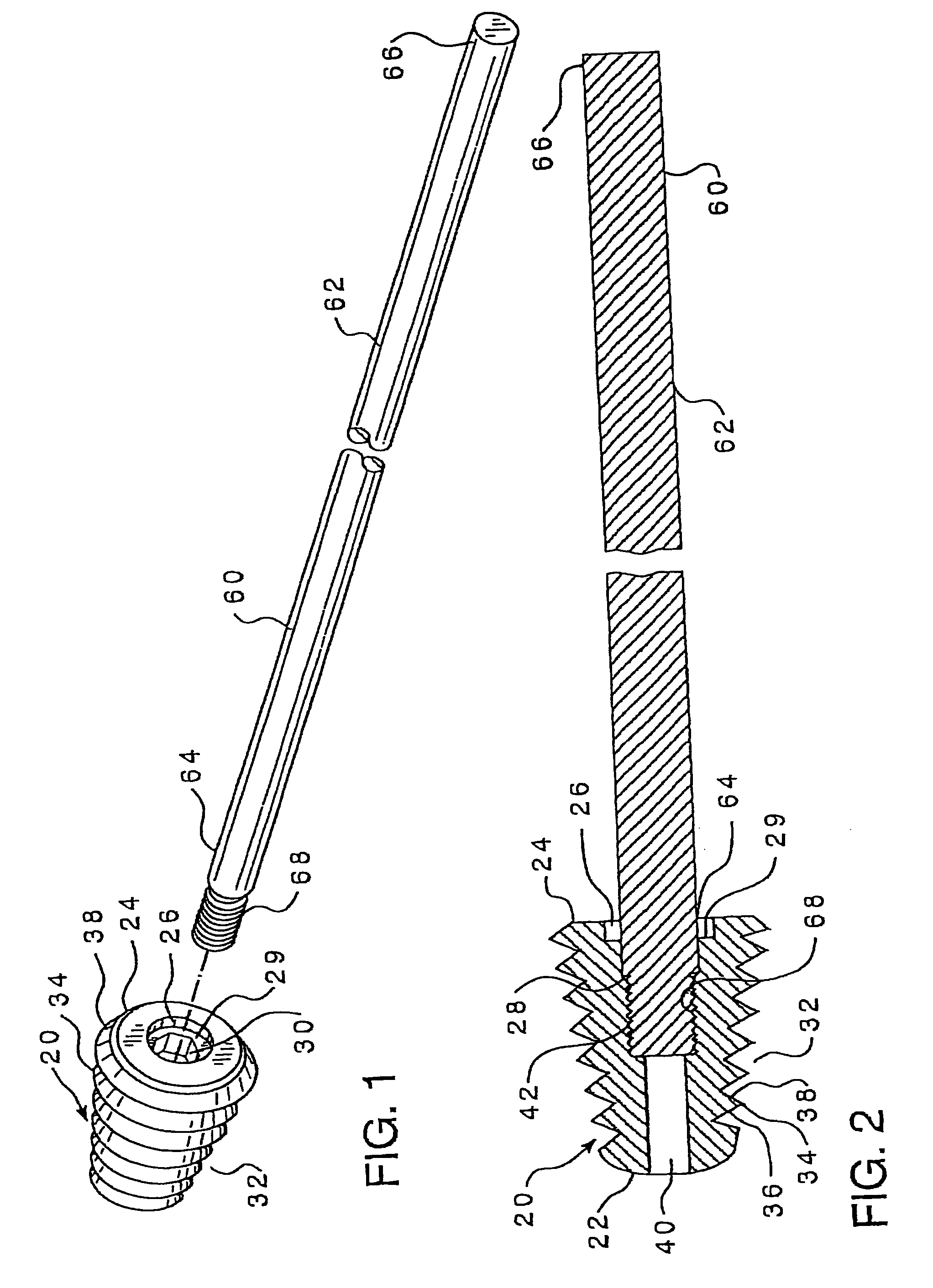
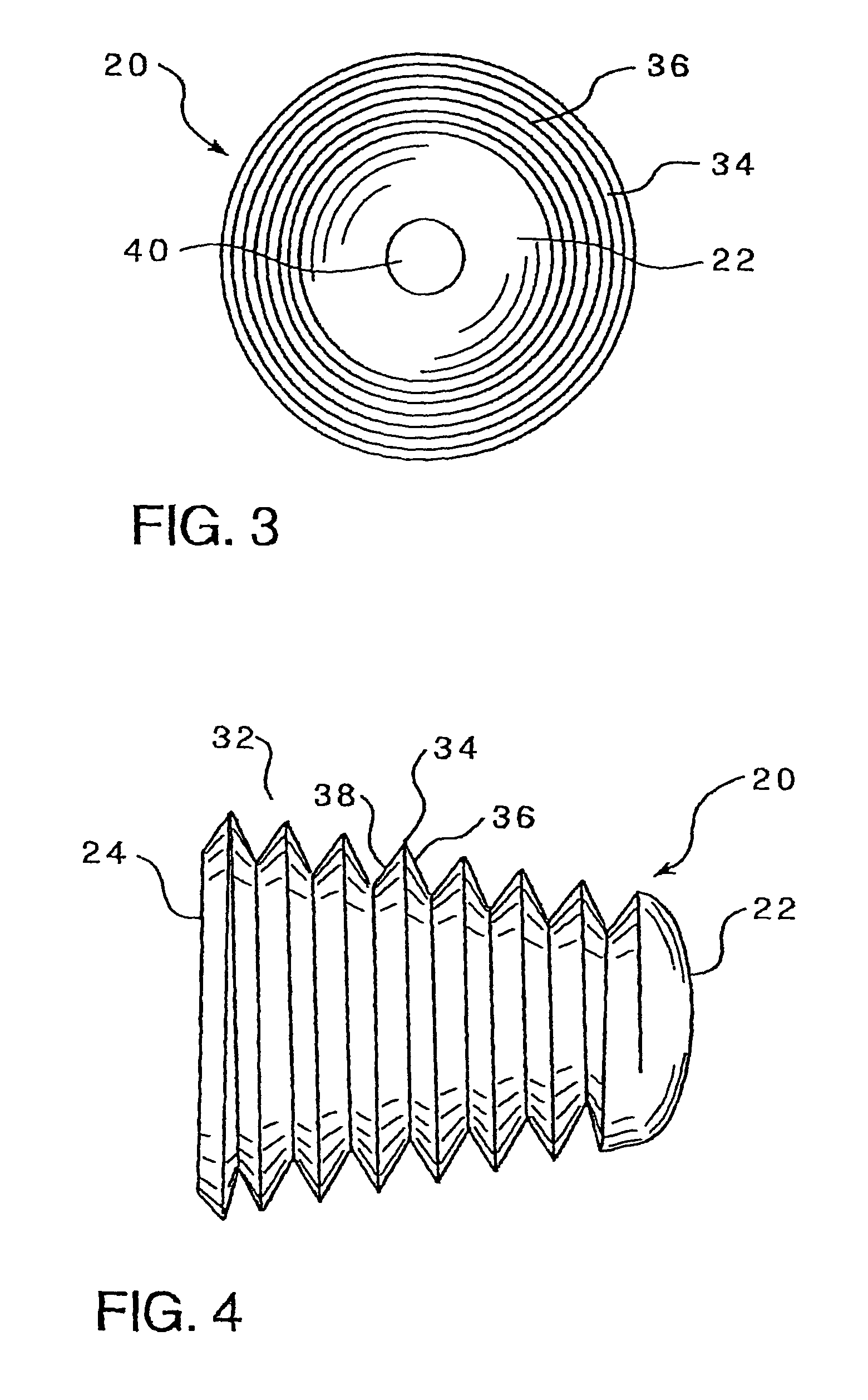
An intramedullary lockable compression screw for stabilization and reconstruction of deformities of the ankle and subtalar joints, and which is particularly suitable for stabilization and fusion of the tibiotalar, talocalcaneal, tibiocalcaneal and / or tibiotalocalcaneal, is provided. The compression screw includes an elongated tubular member extending along a substantially straight first longitudinal axis between the leading end and the trailing end of the member. The tubular member includes a threaded leading end portion proximate the leading end, a threaded trailing end portion proximate to the trailing end, and an unthreaded shaft portion interconnecting the threaded leading end and the threaded trailing end portions. The diameter of the threaded leading end portion is smaller than the diameter of the threaded trailing end portion. A through-hole extends along a straight second longitudinal axis between a first opening, in a first area of an outer periphery of the tubular member proximate to the trailing end, and a second opening, in a second area of the outer periphery of the tubular member distal to the trailing end. The through hole is formed such that the second longitudinal axis intersects the first longitudinal axis at an angle of other than 90 degrees and so as to accommodate a locking screw.
Owner:MANDERSON EASTON L
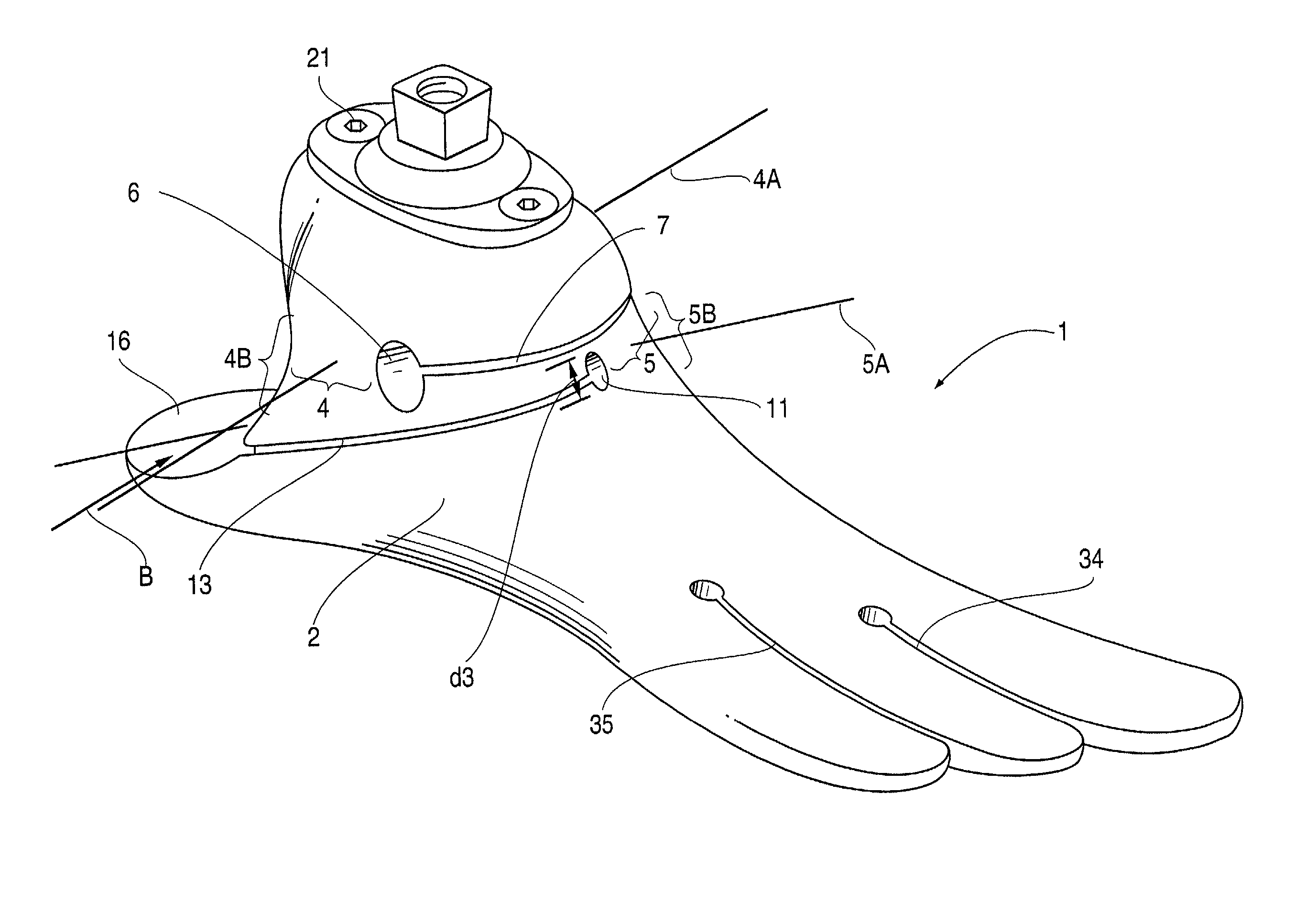
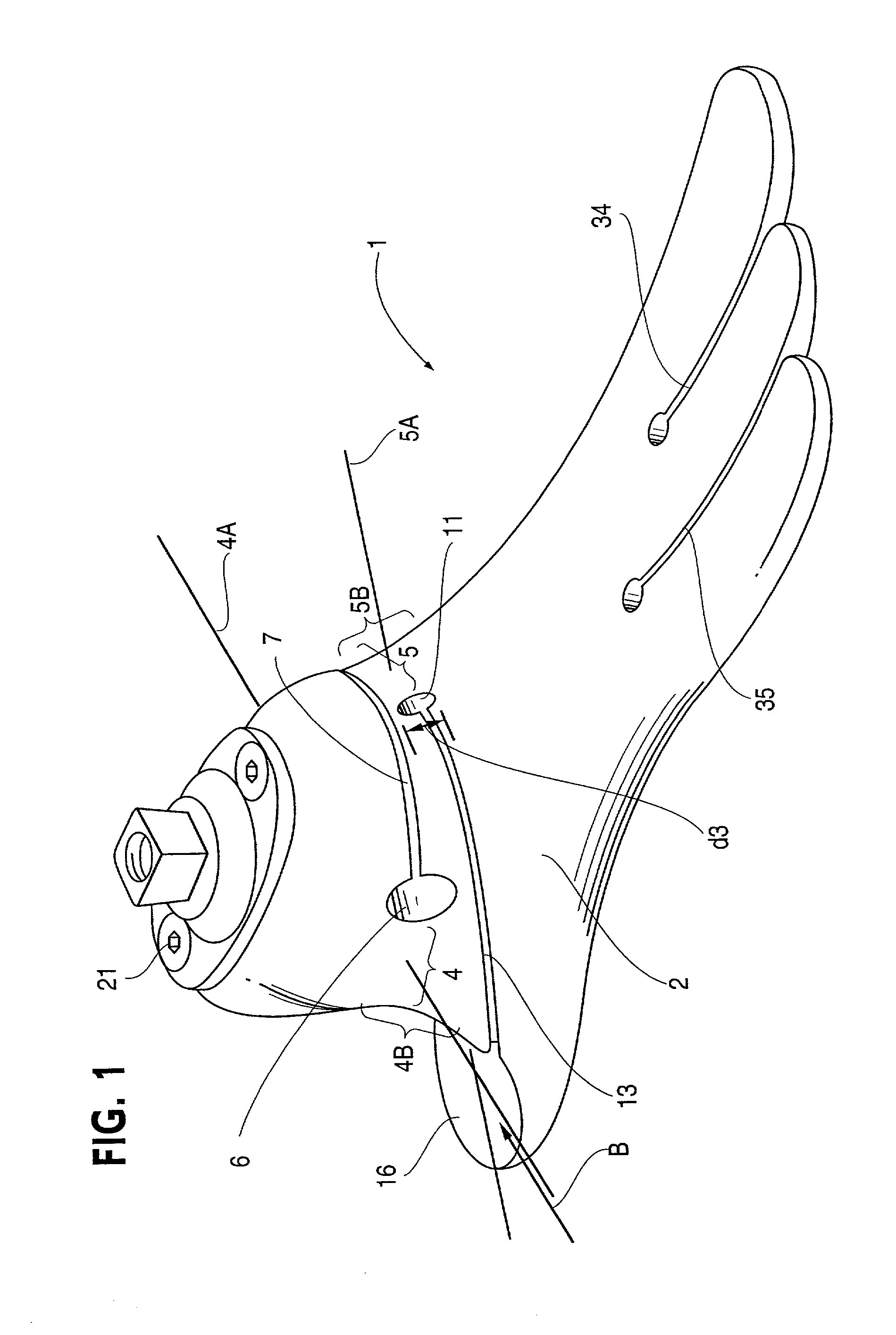
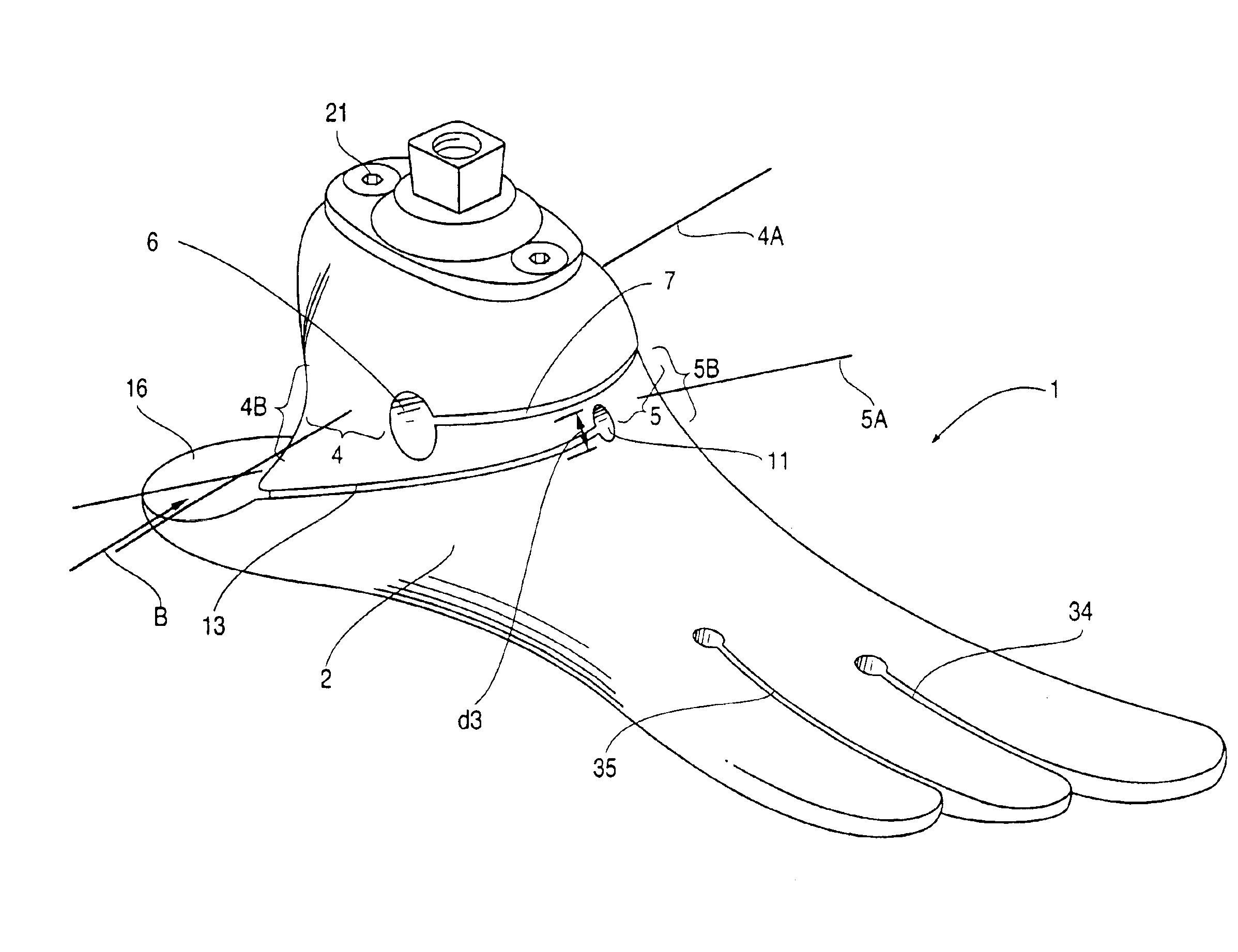
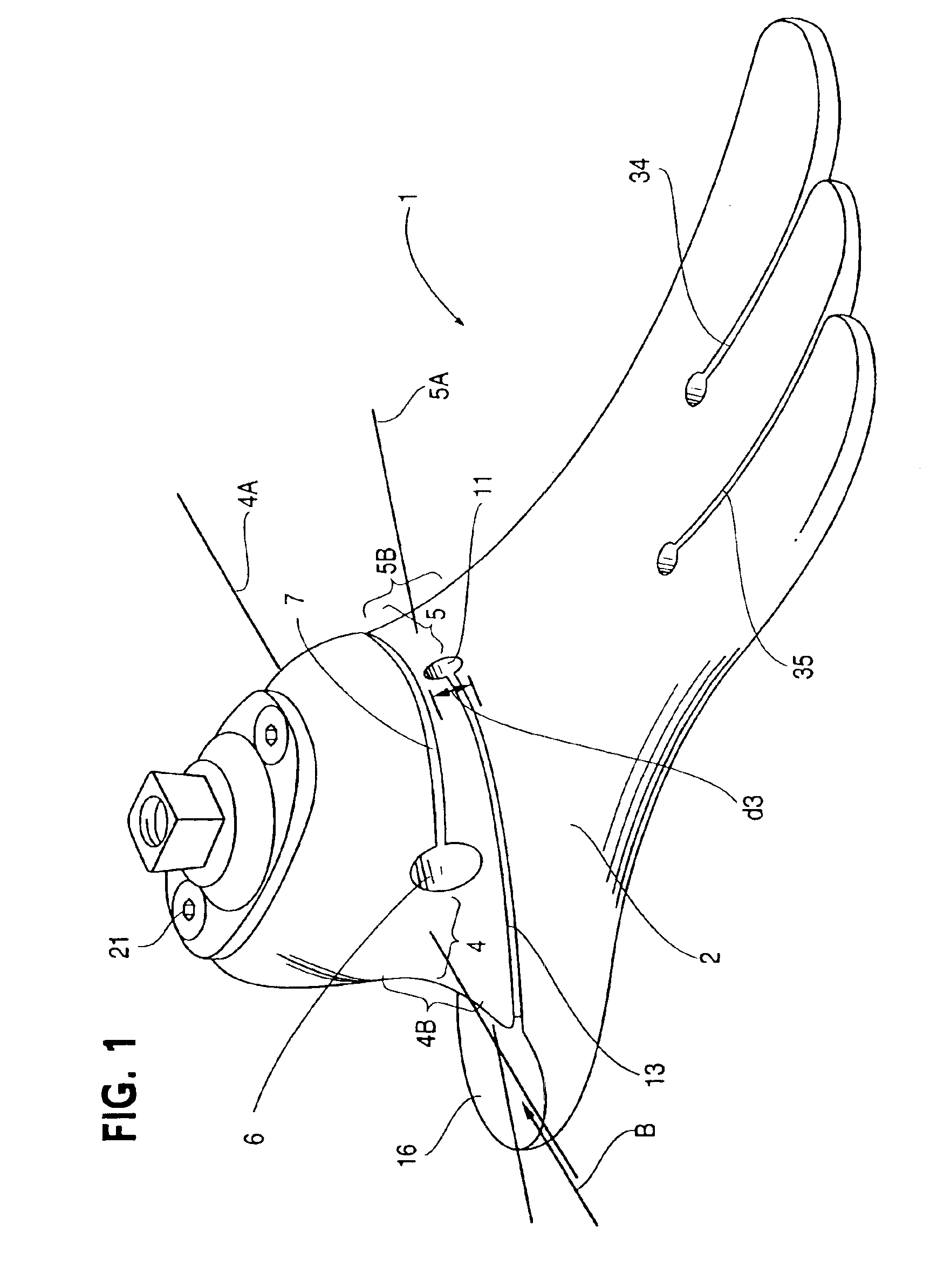
Prosthetic foot
InactiveUS6443995B1Improve the quality of lifeImproves footArtificial legsSagittal planePlantar surface
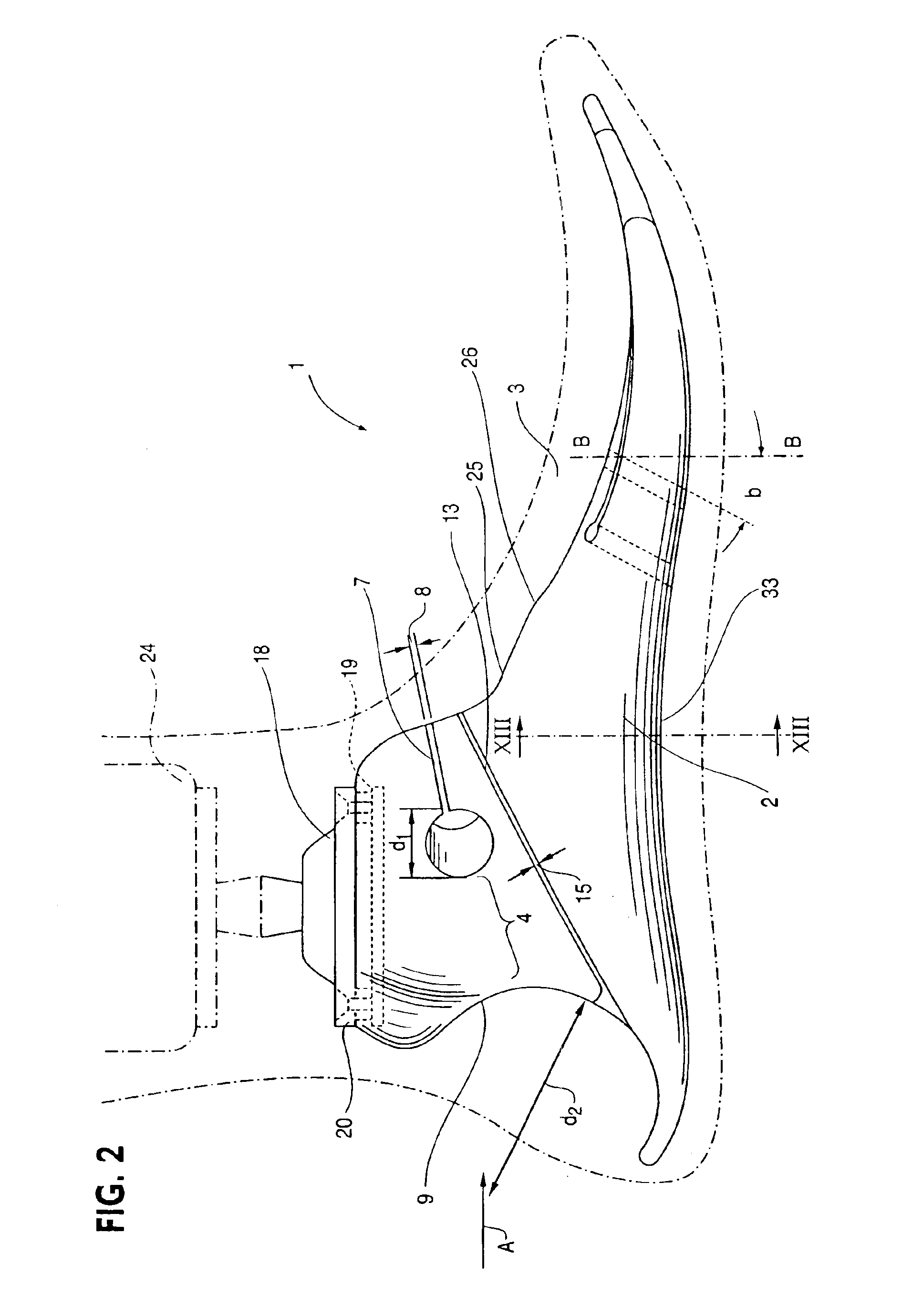
An ankle joint and a subtalar joint provided in a hindfoot permit closed kinetic chain motion of the foot. The ankle and subtalar joints are preferably formed integrally with the hindfoot by respective struts of resilient material of the hindfoot. An arch in the midfoot creates frontal and sagittal plane motion capabilities. The forefoot includes at least one expansion joint hole extending therethrough between dorsal and plantar surfaces. An expansion joint extends forward from the hole to the anterior edge of the forefoot to form plural expansion struts that create improved biplanar motion capability of the forefoot. Concavities and convexities on the surface of the hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot encourage desired motions and motion directions so that the foot functions and feels like a normal foot to the amputee.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
Tensegrity joints for prosthetic, orthotic, and robotic devices
Embodments of the invention relate to a prosthetic, orthotic, or robotic foot having at least two joints. One joint is located in a position analogous to the human MTP joint, and the other is located in a position analogous to the human subtalar joint. Motions of these two joints are mechanically couples. Furthermore, these joints are created using “tensegrity” design principals, where connections between the compression members are made by a network of tension members. These tension members create axes of motion, and limitations on those axes of motion. Actuators or linear elastic “springs” are use to alter the torque / angular deflection response curve of these joints, so that the rollover profile of the human foot can be duplicated by this invention.
Owner:TENSEGRITY PROSTHETICS
Intramedullary fixation screw, a fixation system, and method of fixation of the subtalar joint
An intramedullary screw and fixation system for intraosseous bone fusion of the subtalar joint includes a lag screw member, a reamer for reaming an internal surface of each of the calcaneus and talus medullary canals, and targeting guide assembly for alignment with the subtalar joint. The lag screw member includes an elongated body, a first threaded portion at a first end and a bulbous portion at a second end. The targeting guide assembly receives a cutting blade in an elongated rod for reaming the articulating surfaces of the calcaneus and talus intramedullary canals, where the cutting blade is inserted through a percutaneous incision into the elongated rod.
Owner:EXTREMITY MEDICAL
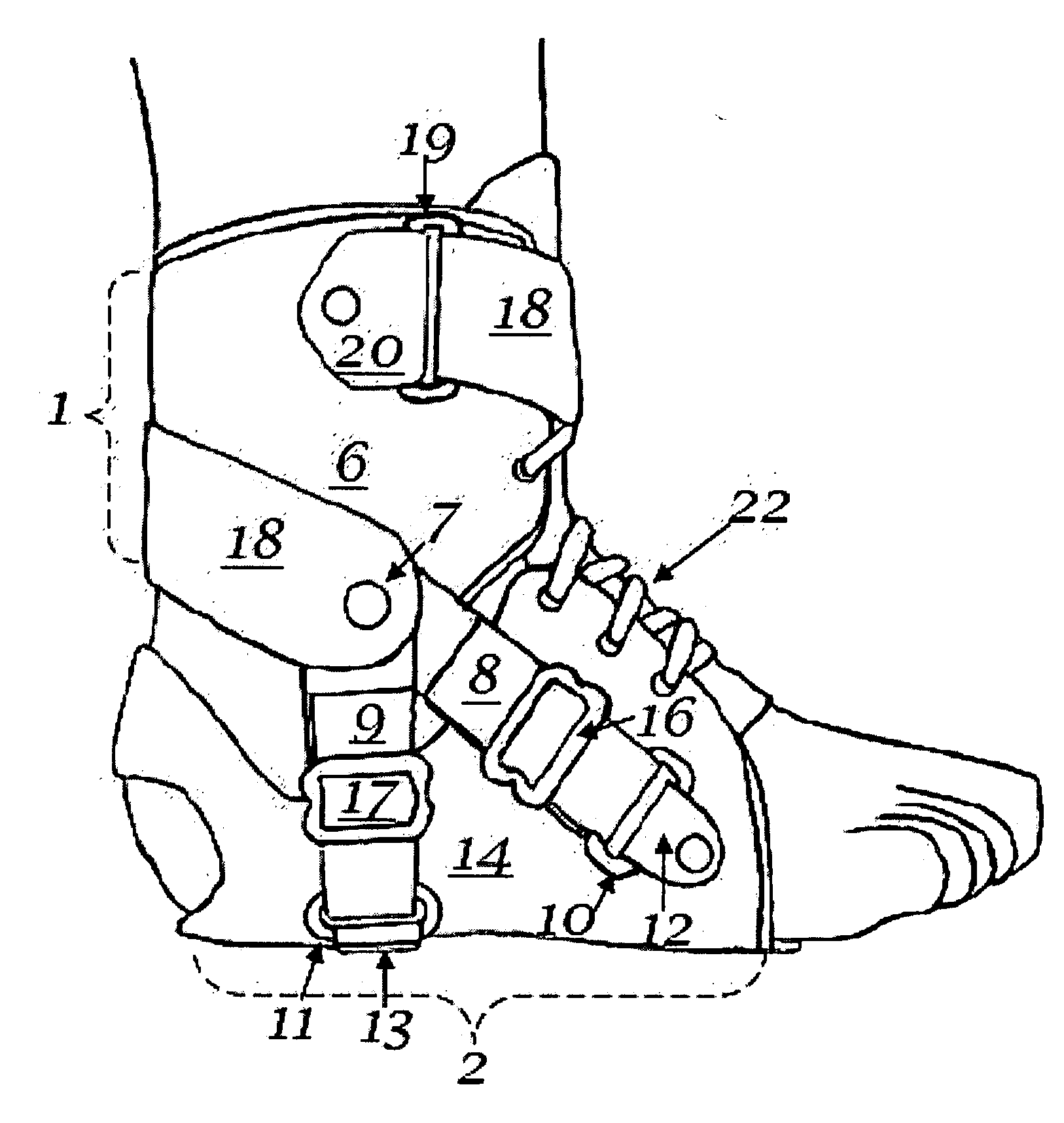
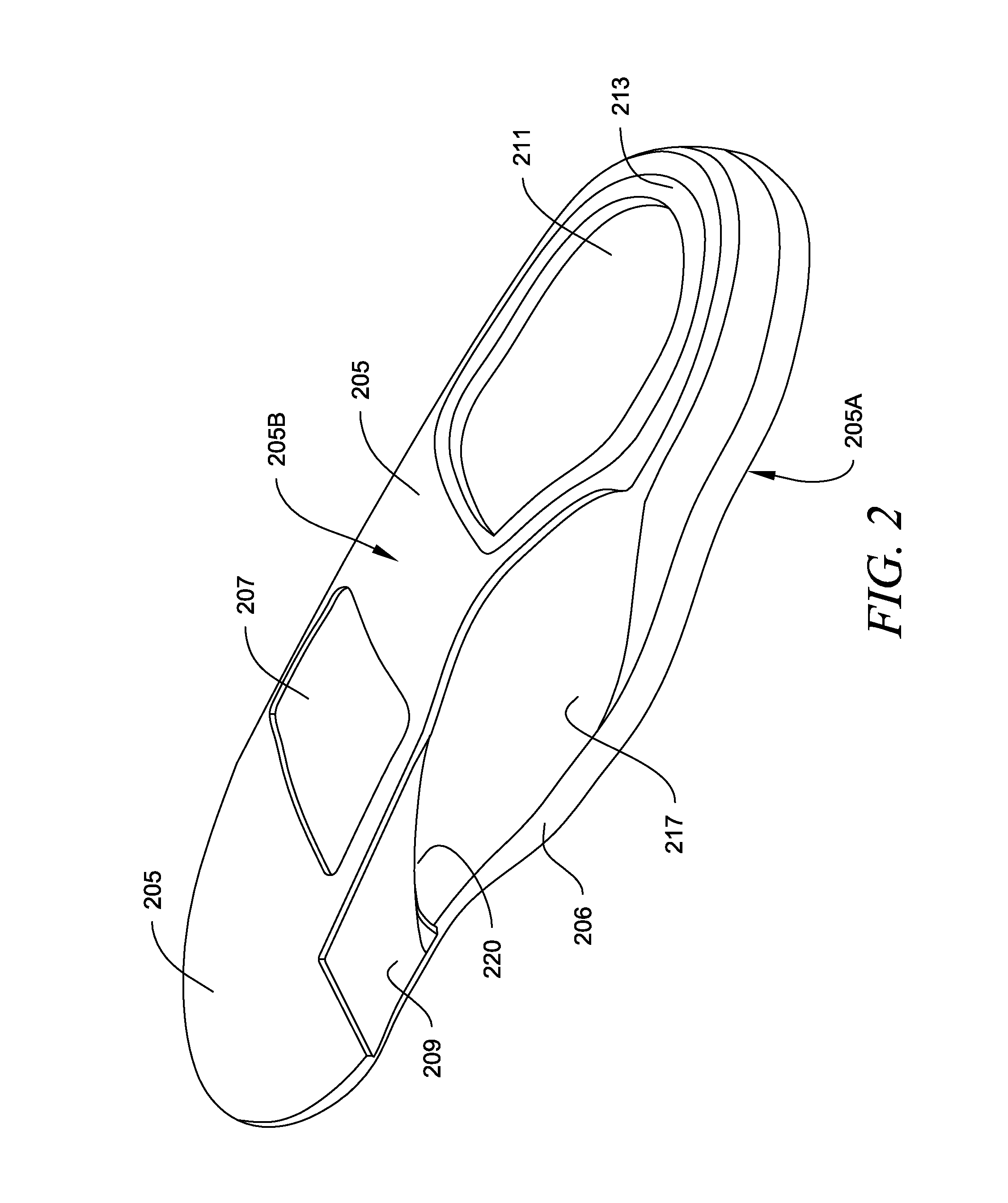
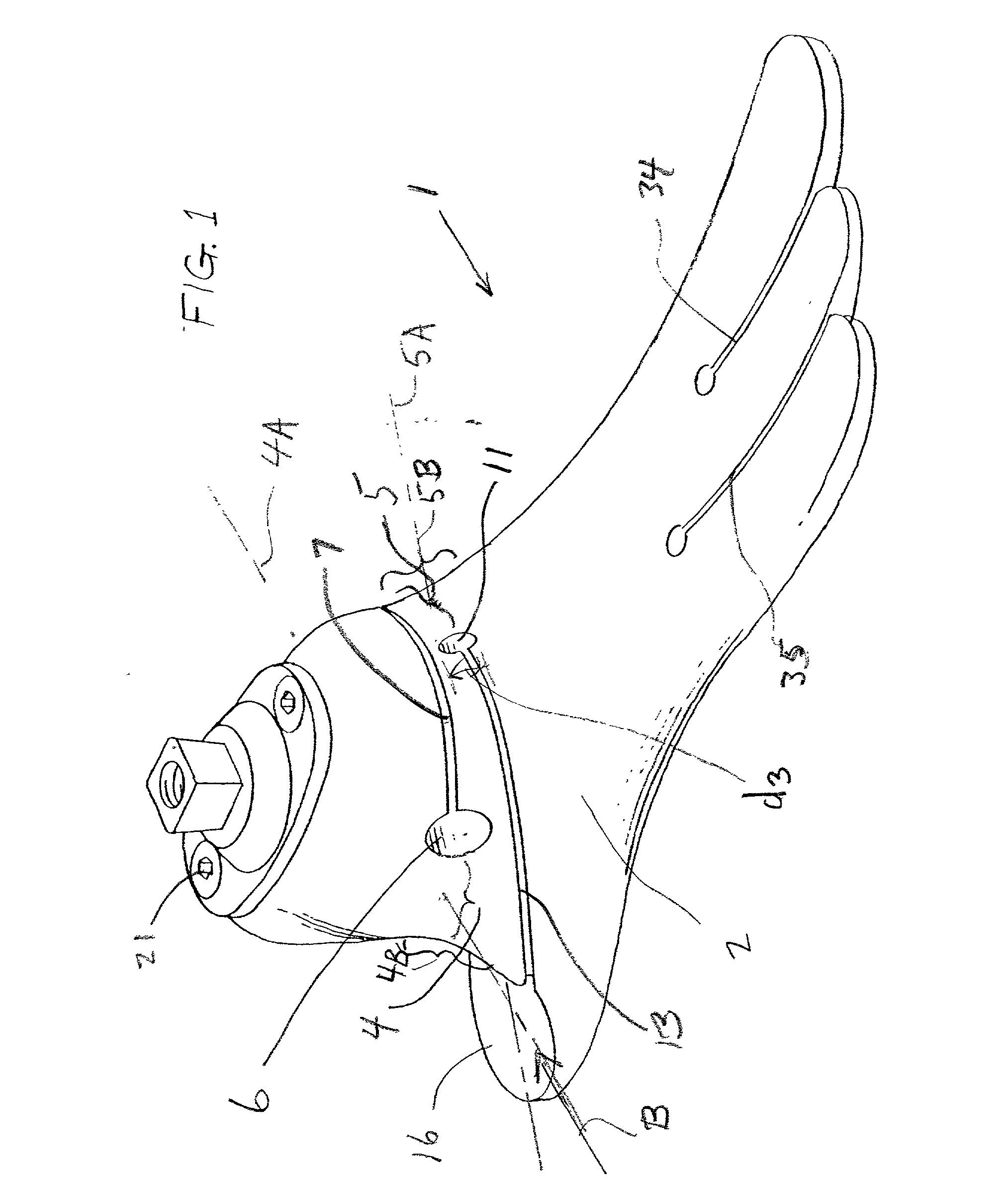
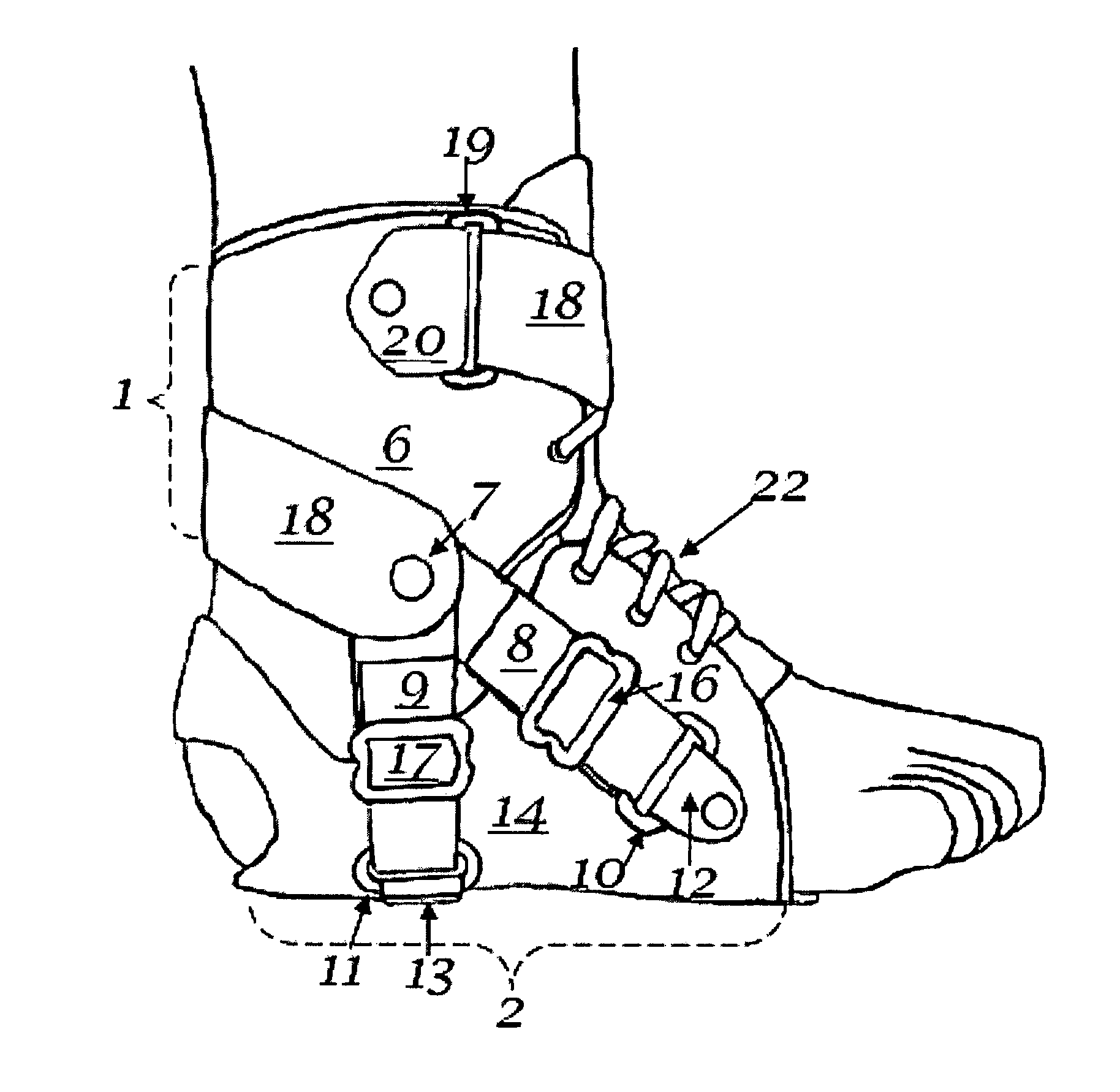
Shoe, ankle orthosis and method for protecting the ankle
InactiveUS6692454B1Ankle protectionRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesRolloverFoot/ankle orthoses
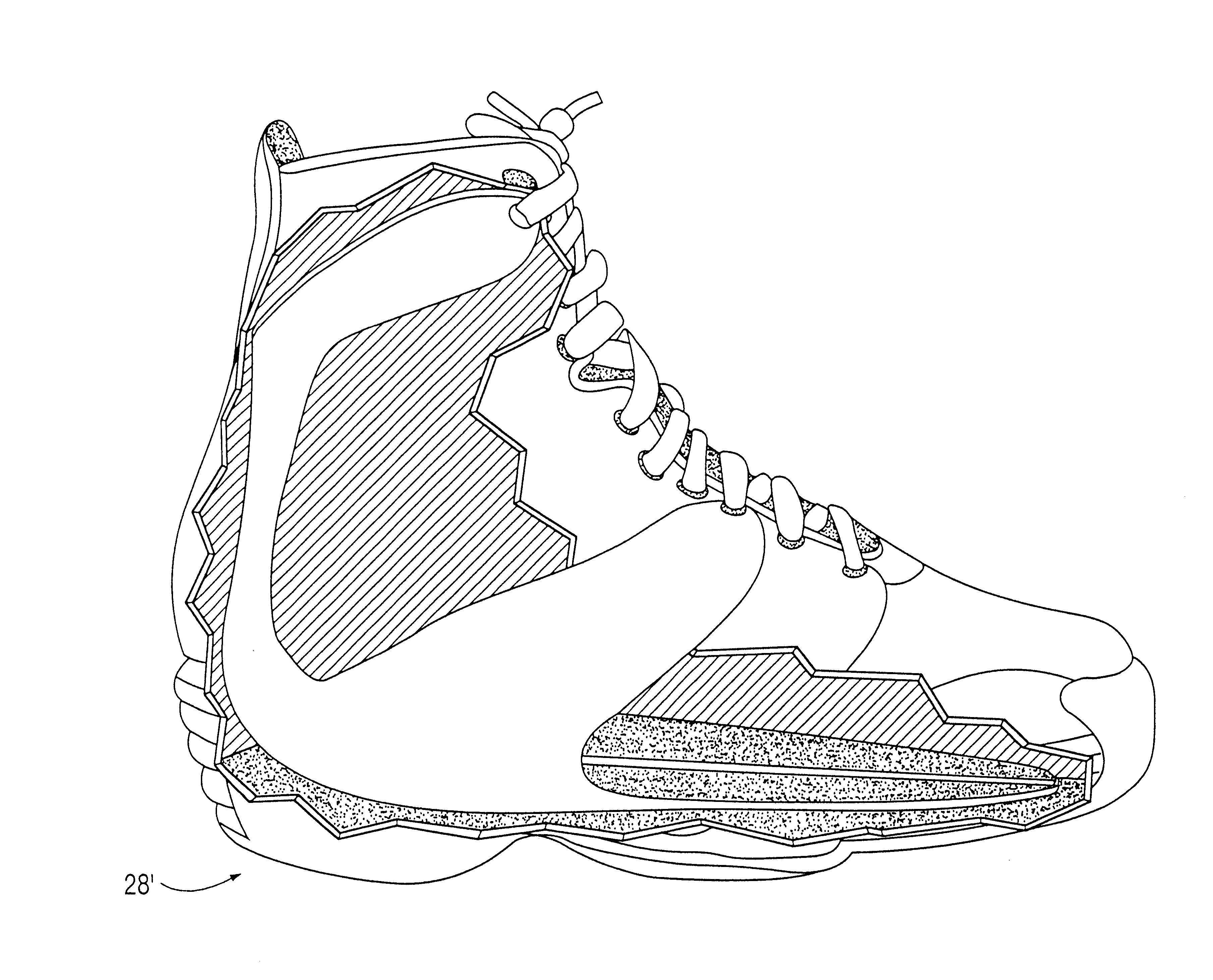
A method for protecting the ankle against injury, limit subtalar joint motion of the ankle by controlling the motions of segments of the subtalar joint fore and aft of the subtalar joint while permitting motion of the foot about the ankle joint with an improved athletic shoe, ankle orthosis. A supporting structure a part of or connected to the shoe or orthosis is preferably in the form of a heel-sole counter provided about the heel and at least a portion of the foot forward of the subtalar joint which includes a split toe sole extension. The supporting structure has a semi-rigid shape retaining character which is not collapsible vertically and which together with the shoe or orthosis limits torsional movement of the foot about the longitudinal axis of the subtalar joint as seen in a top plan view thereof by an upwardly extending portion thereof which acts as a torsion bar that is, in turn, secured to the lower leg. Preferably, the torsion bar has directional properties for resisting bending which are most rigid in a direction orthogonal or nearly orthogonal to the longitudinal axis of the subtalar joint. In a disclosed embodiment of the shoe motion of the midtarsal joint is also limited by the supporting structure to aid in limiting subtalar joint motion and shoe rollover. The shoe is secured to the foot by way of a strap arrangement which applies a force to the foot in a direction which, together with the heel-sole counter opposes the subtalar joint motion in supination.
Owner:TOWNSEND BARRY W +1
Correcting foot alignment
A component system of footwear corrective alignment insoles provides adjustment of the alignment of a human foot based upon evaluation and measurement of structural anomalies in the foot. A subtalar joint goniometer measures the angular alignment of the foot with a patient's leg properly inclined with respect thereto. A database contains data with selected relationships between the degree of a patient's foot pronation and supination and a variety of corrective pads for use with an insole for correcting pronation and supination. The foot pronation and supination is corrected by first measuring a patient's foot pronation and supination, comparing the measured pronation or supination with a database that correlates degrees of pronation and supination with a variety of corrective pads for use with a corrective alignment insole, selecting corrective pads from the database that correspond to the measured pronation or supination, and mounting the selected corrective pads to a base insole.
Owner:BIOCORRECT
Subtalar implant and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20070173954A1Facilitate proper positioningAnkle jointsJoint implantsAnatomical structuresSacroiliac joint
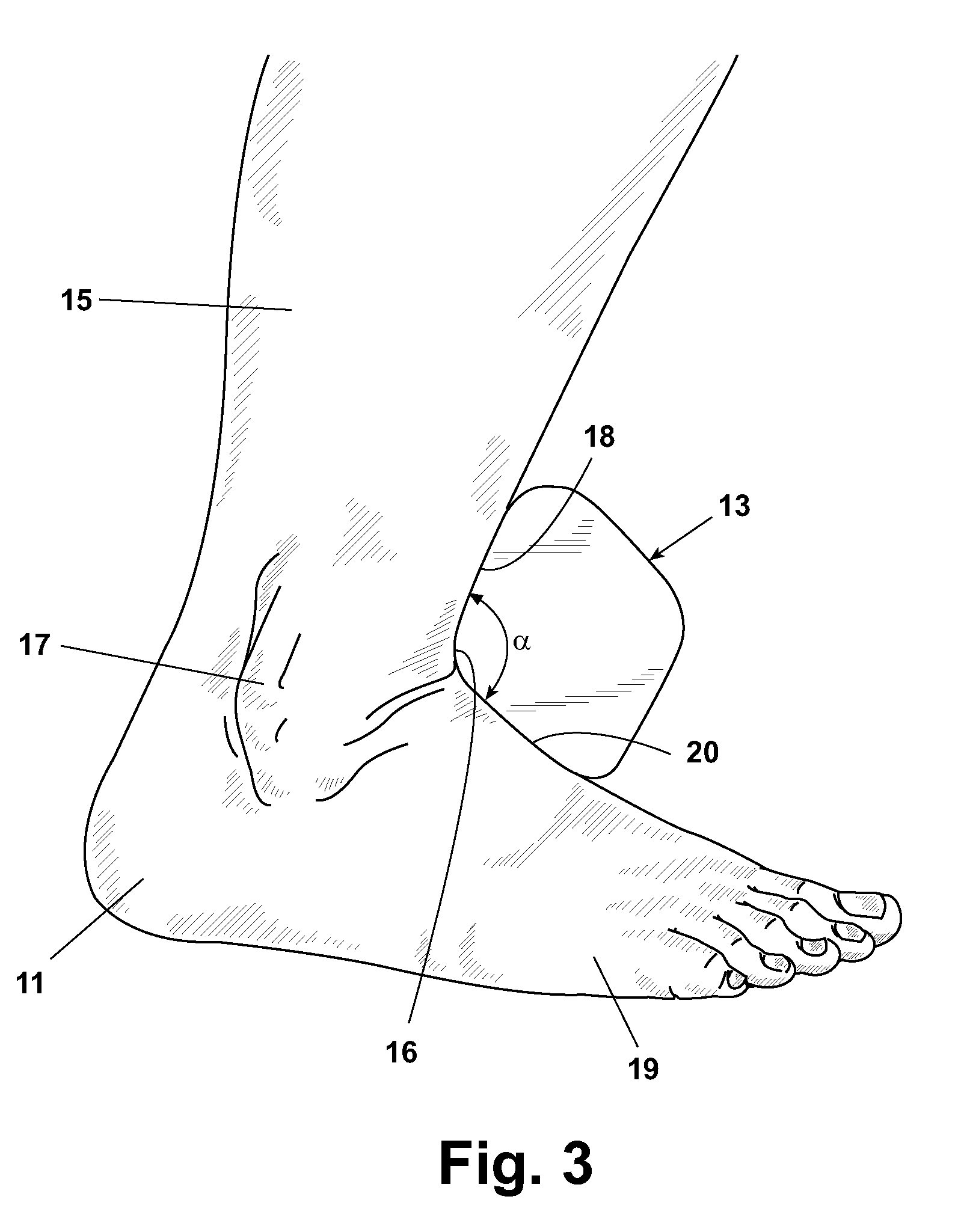
The present invention provides a subtalar implant as well as methods of use thereof for the purpose of correcting podiatric disorders such as various types of flat foot conditions relating to the subtalar joint. The subtalar implant is capable of threaded engagement with a positioning element used to position and manipulate the implant during surgical implantation in the sinus tarsi of the foot. The implant is cannulated to receive a guide rod to facilitate final positioning of the implant. Once implanted, the subtalar implant provides anatomical fit with the subtalar joint anatomical structure without the need for indentations to receive osseous tissue growth to anchor the subtalar implant.
Owner:VILEX LLC
System and method for non-binding allograft subtalar joint implant
Provided is a system and method for providing a non-binding allograft subtalar joint implant for surgical implant into a person's foot proximate to the ankle. This system for repair includes at least one sterile non-binding allograft subtablar joint implant provided as a pre-formed allograft rod plug “ARP” having a diameter about equal to an average width of a canal between a person's talus and calcaneus bones, the ARP being resiliently compressible and flexible. When snuggly disposed between the person's talus and calcaneus bones, the ARP compresses during normal use of the person's foot and maintains the canal in an anatomically correct alignment and reduces a tendency for abnormal motion between the person's talus and calcaneus bones. An associated method of use is also provided.
Owner:ARTHROSURFACE
Intramedullary fixation screw, a fixation system, and method of fixation of the subtalar joint
An intramedullary screw and fixation system for intraosseous bone fusion of the subtalar joint includes a lag screw member, a reamer for reaming an internal surface of each of the calcaneus and talus medullary canals, and targeting guide assembly for alignment with the subtalar joint. The lag screw member includes an elongated body, a first threaded portion at a first end and a bulbous portion at a second end. The targeting guide assembly receives a cutting blade in an elongated rod for reaming the articulating surfaces of the calcaneus and talus intramedullary canals, where the cutting blade is inserted through a percutaneous incision into the elongated rod.
Owner:EXTREMITY MEDICAL
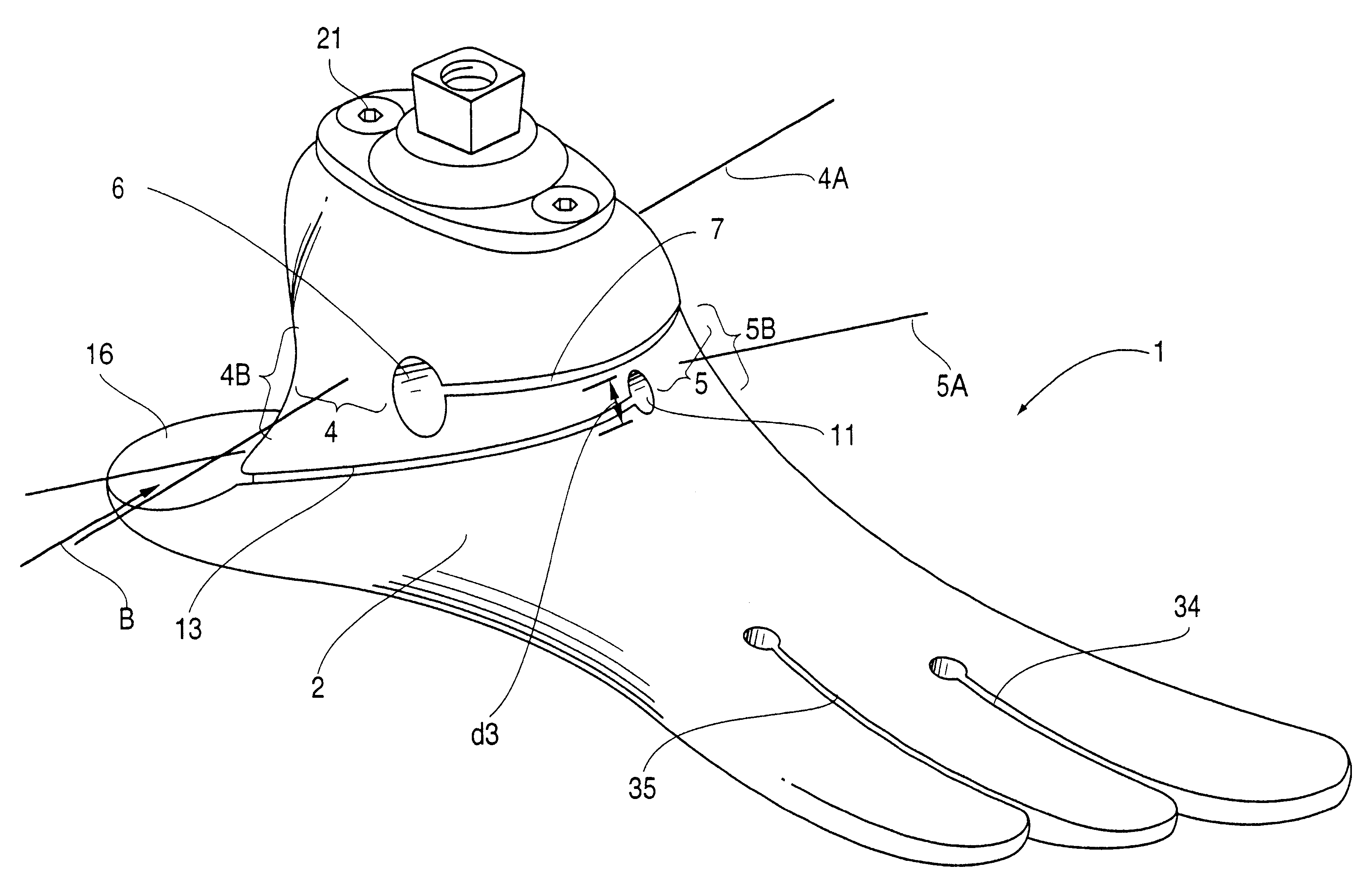
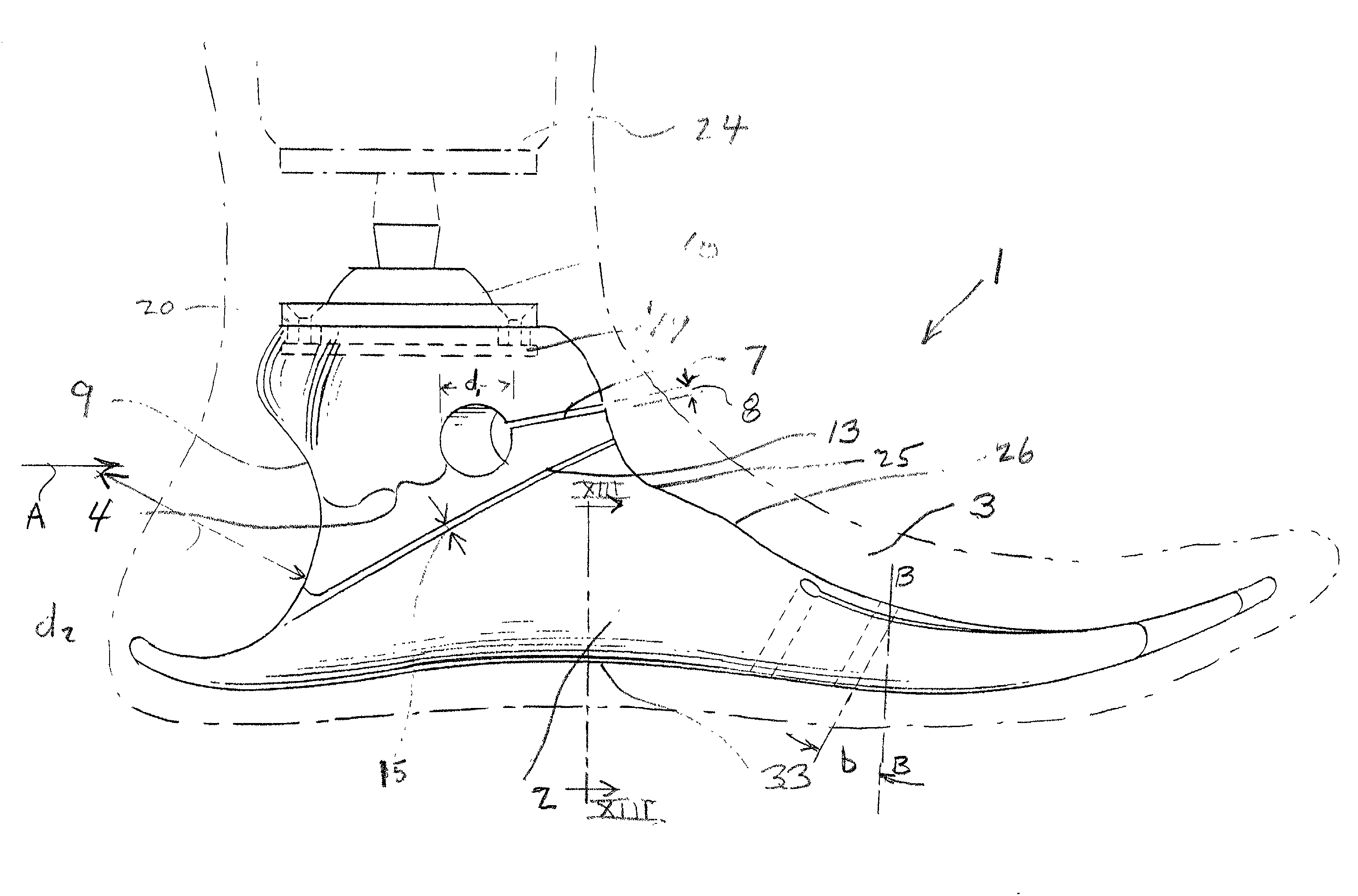
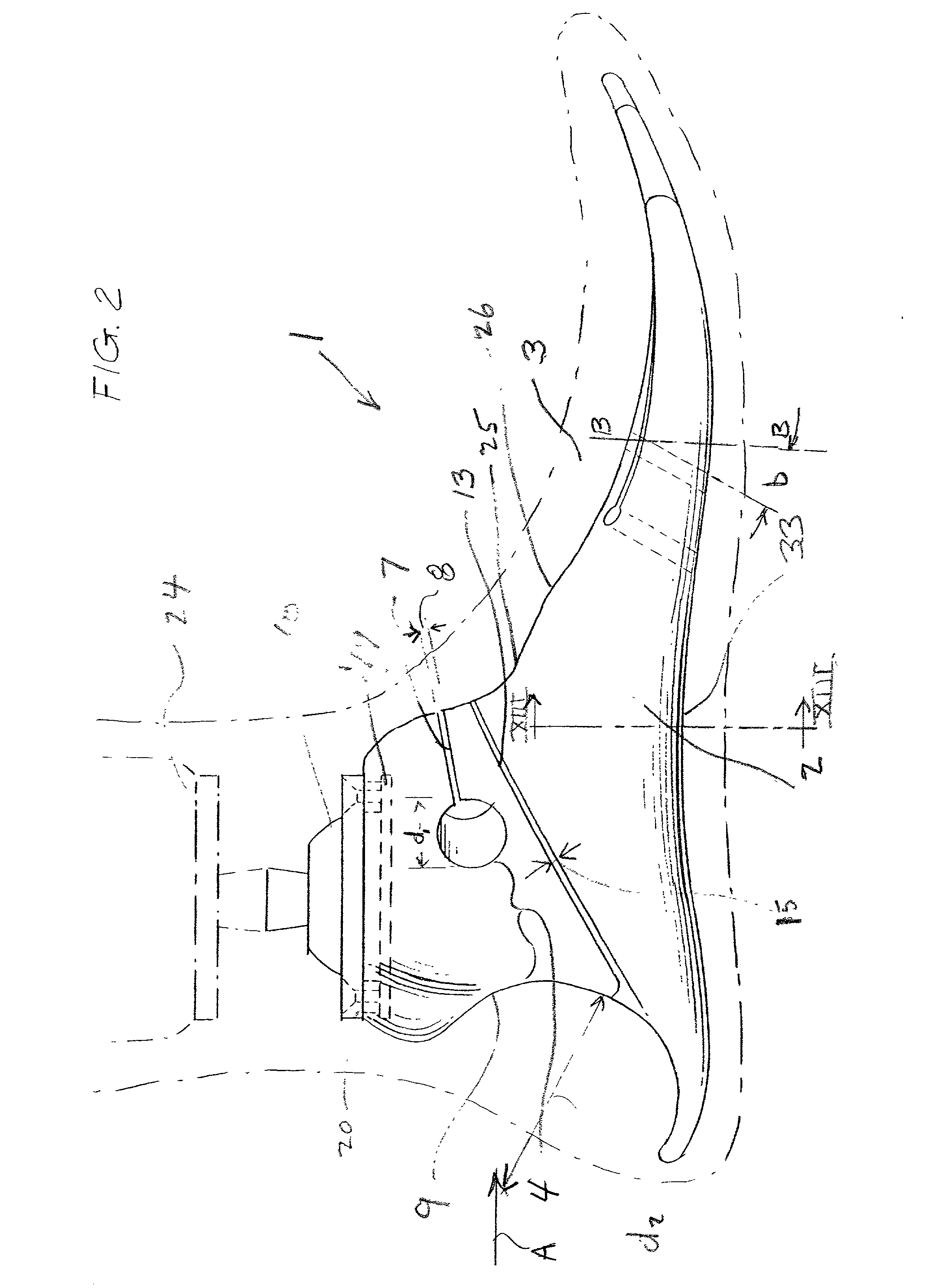
Ankle Derotation and Subtalar Stabilization Orthosis
ActiveUS20080082034A1Prevent reversalEffective in inversionFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisFrenulum
The invention is an ankle derotation and subtalar stabilization system that incorporates a pivoting adjustable-tension oblique tether strap that is anchored to both a forefoot component and leg component, and that is contiguous with pivoting adjustable-tension derotation strap that passes behind the leg and that is secured to a leg component. The system restrains oppositely directed rotation between the foot and the leg, and can actually after the normal biochemical relationship in a manner that produces foot rotation in a direction opposite to that which is normally coupled with leg rotation, without restriction of upward and downward foot movement. The primary application for the system is restraint of excessive subtalar joint inversion, leg external rotation, and anterolateral rotary displacement of the talus, but it can also be configured to restrain subtalar eversion and leg internal rotation through its incorporation into the structure of an ankle orthosis or shoe.
Owner:WILKERSON GARY BLAINE
Customizable Component Insole System
This invention provides for individualized adjustment to a user's specific needs through the use of multiple variable size, thickness and rigidity components that can be placed or integrated into an insole. The current invention is an insole that incorporates, but is not limited to: (1) a base layer with various depressions, (2) a metatarsal dome, (3) a first metatarsal head pad, (2) a forefoot wedge to create a pronation moment around the midfoot joint, (3) a heel cushion, (4) a heel lift to raise the heel area of the foot, (5) a rearfoot wedge to increase the supination moments around the subtalar joint, and (6) an arch support of a specific stiffness or with varying stiffness.
Owner:IMPLUS FOOTCARE
Prosthetic foot
InactiveUS20020082713A1Improves footDecrease residual limb to socket shear forceArtificial legsPlantar surfaceSubtalar joint
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
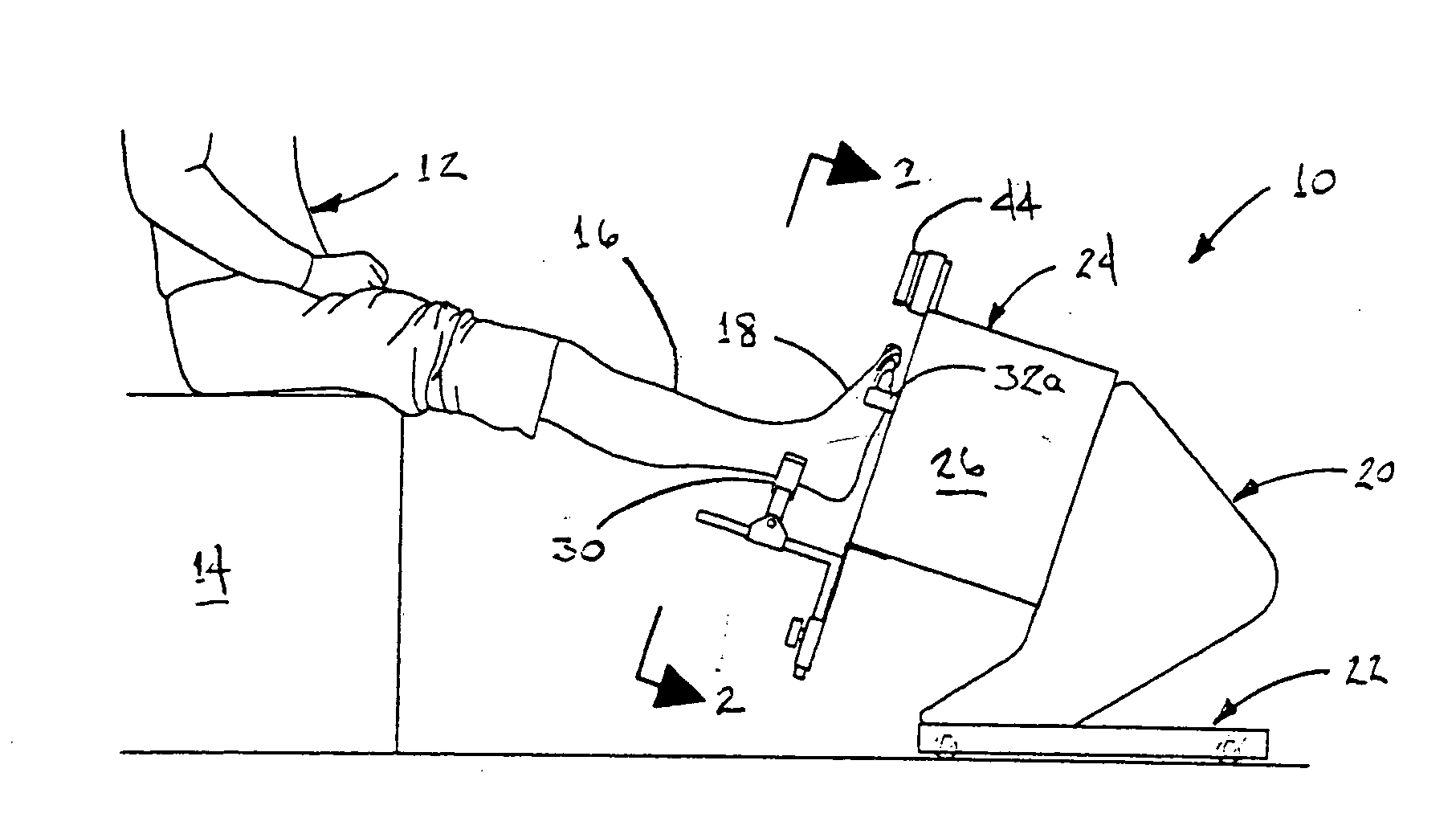
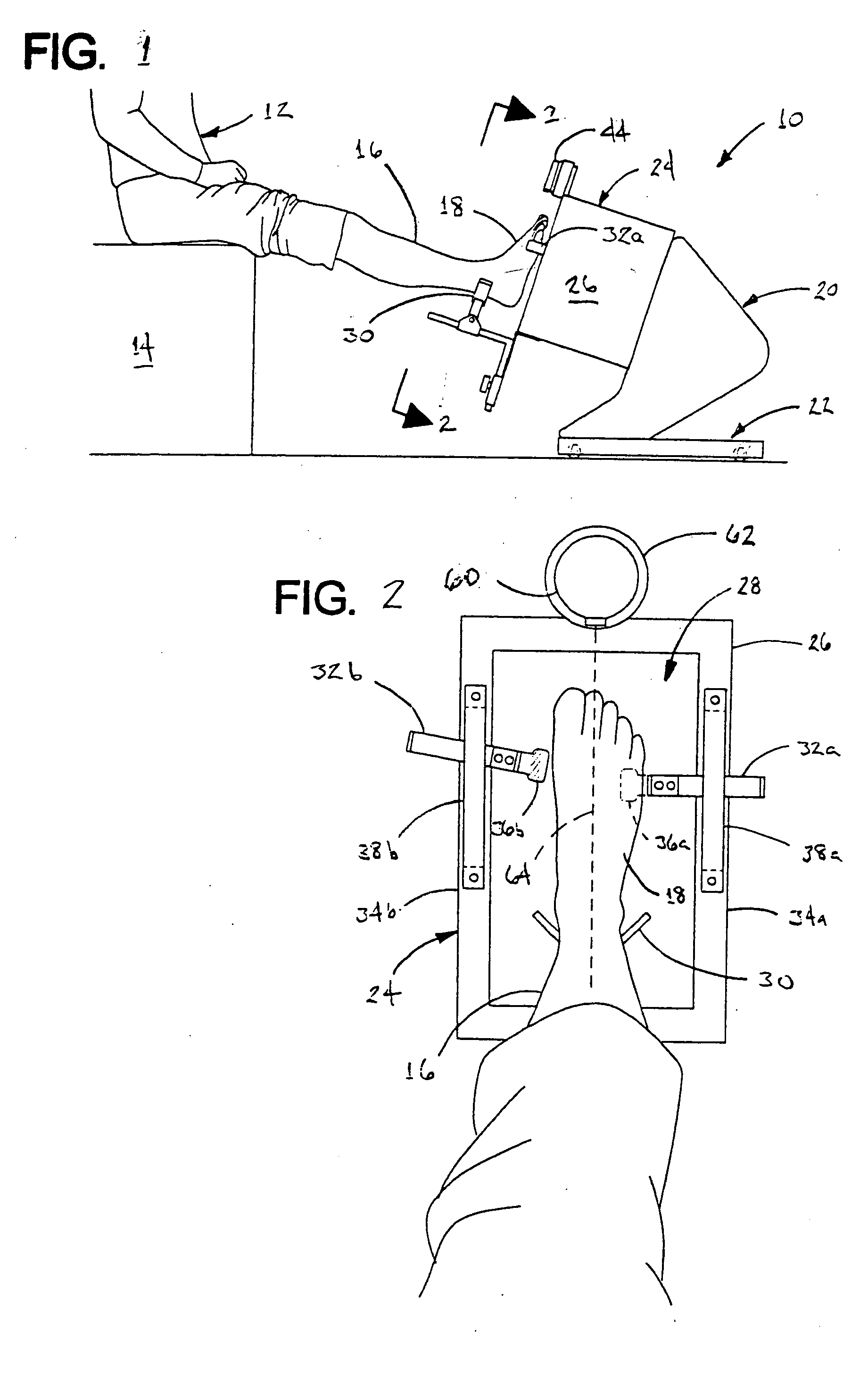
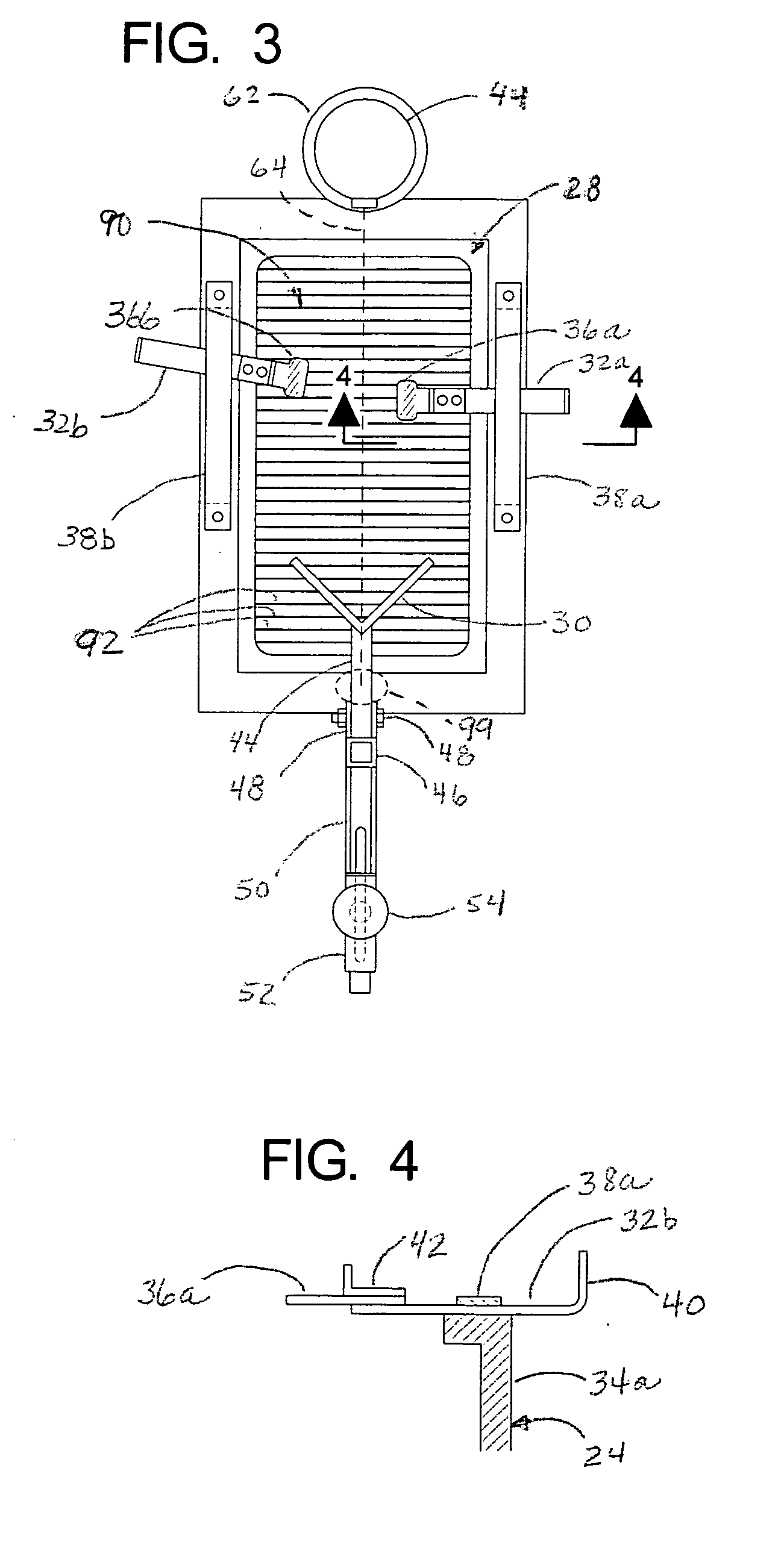
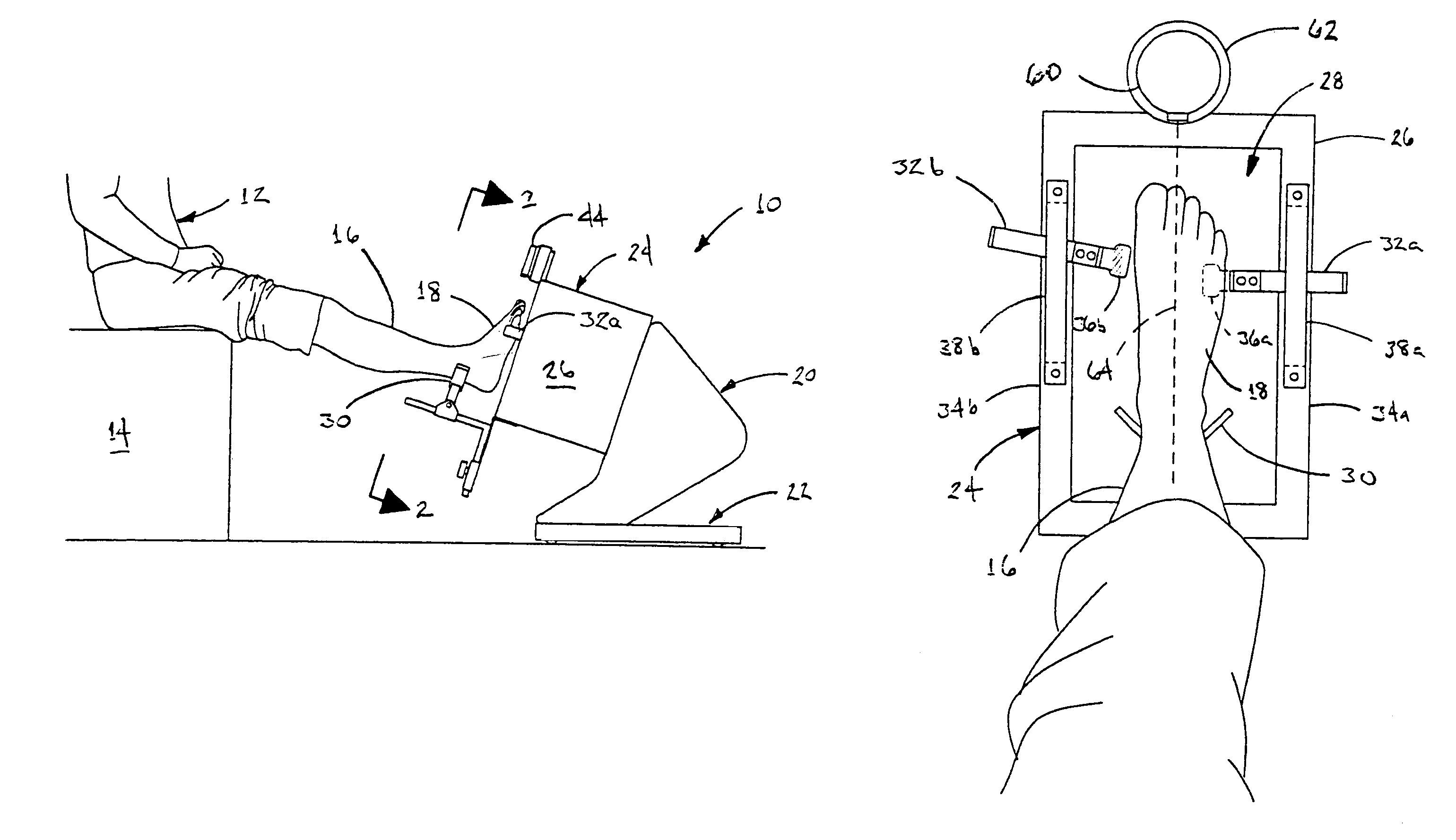
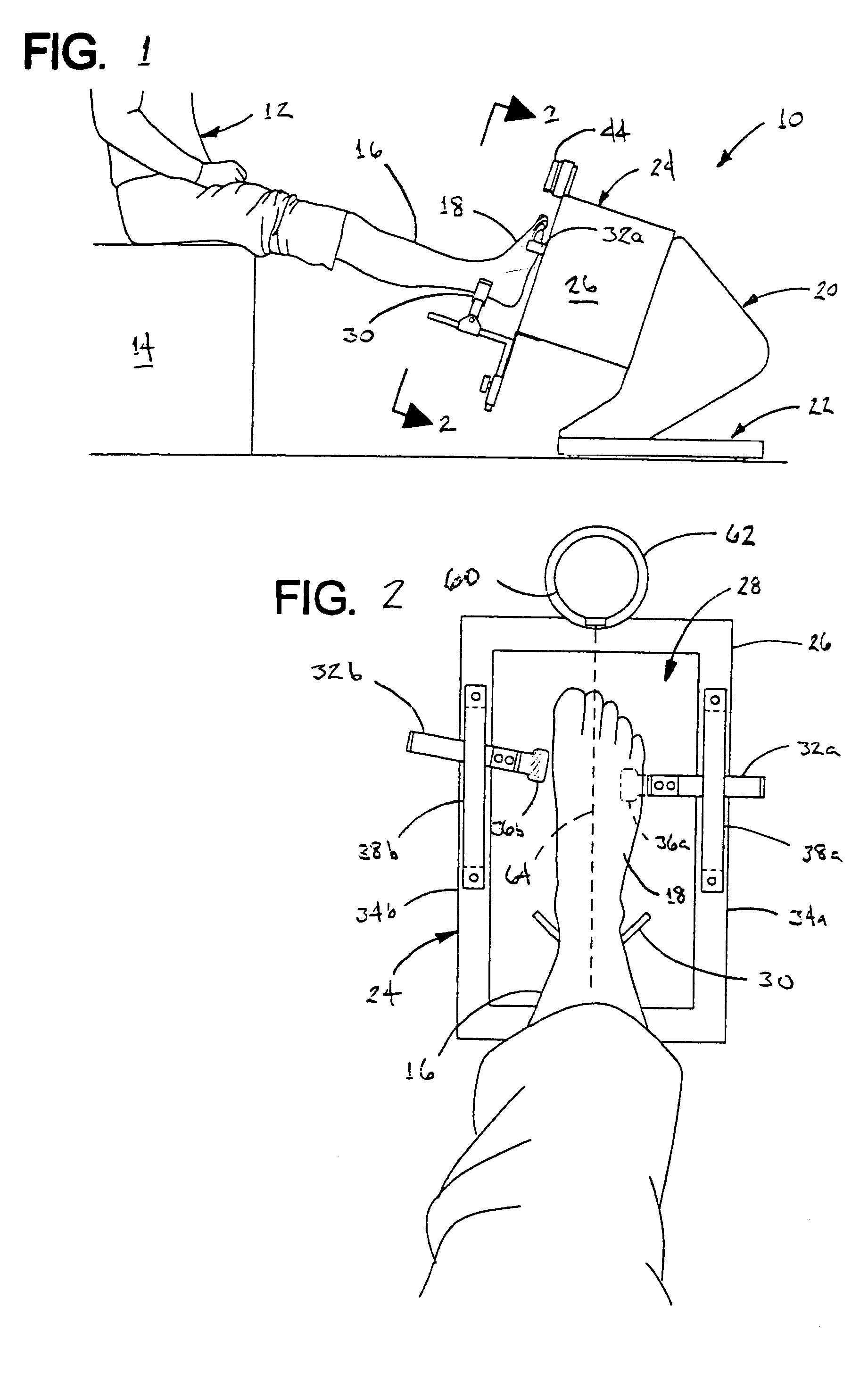
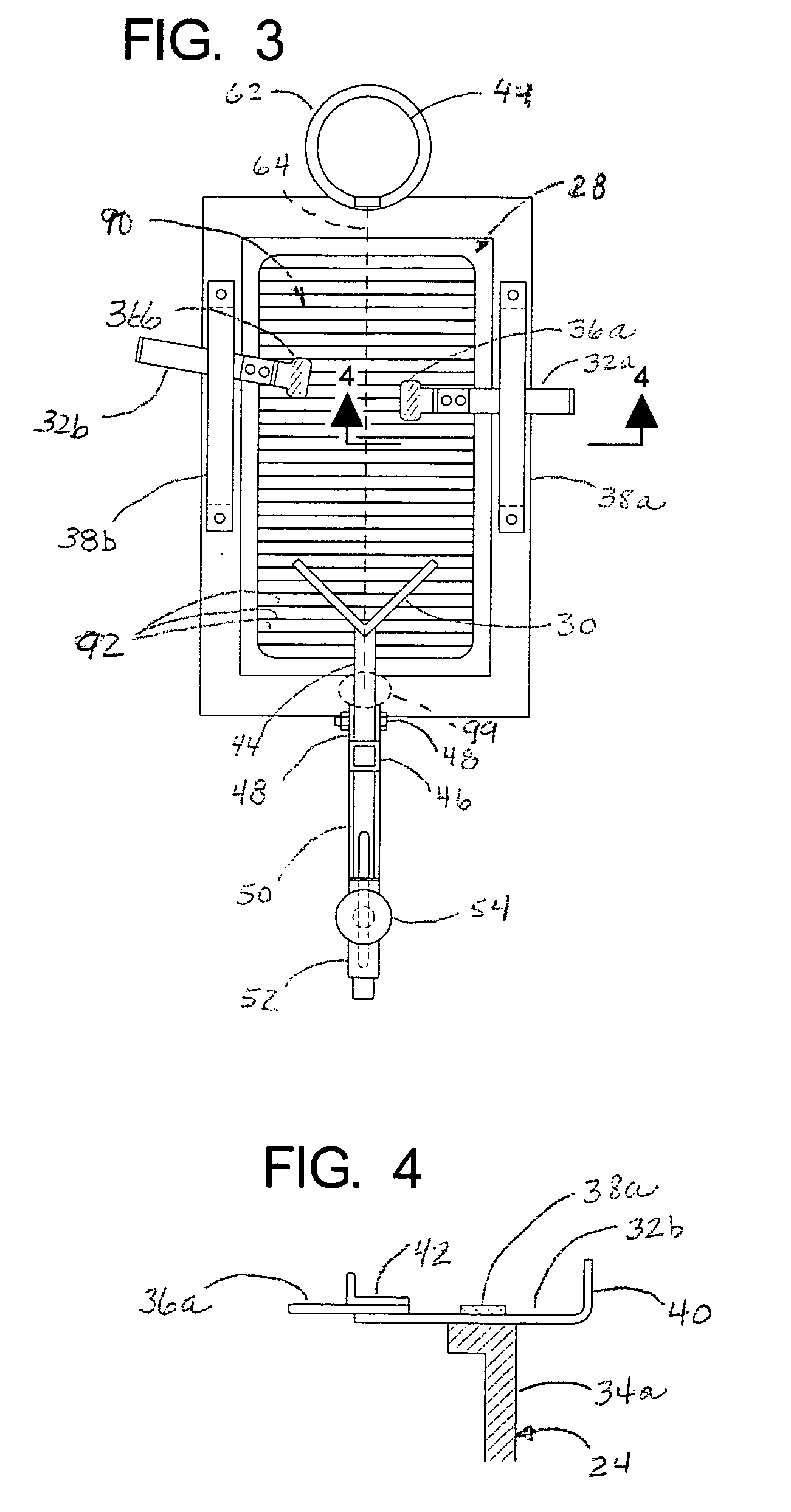
Apparatus and method for imaging feet
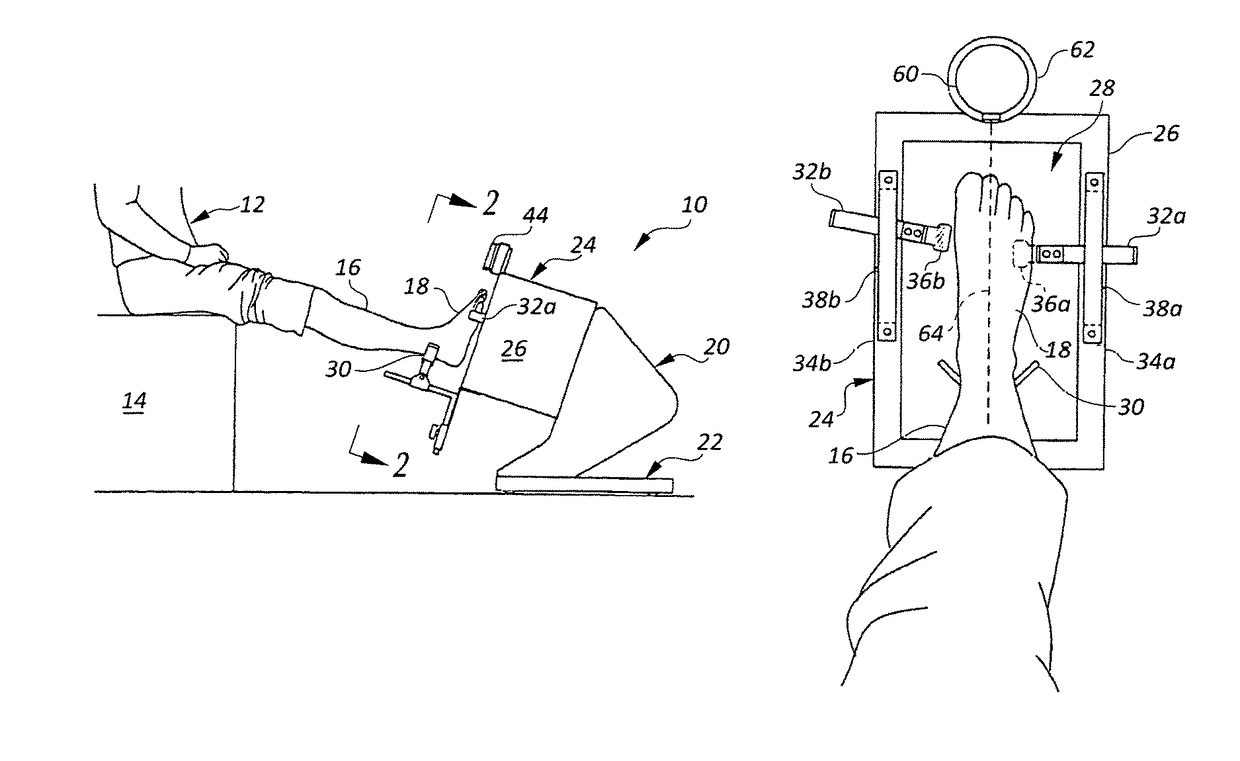
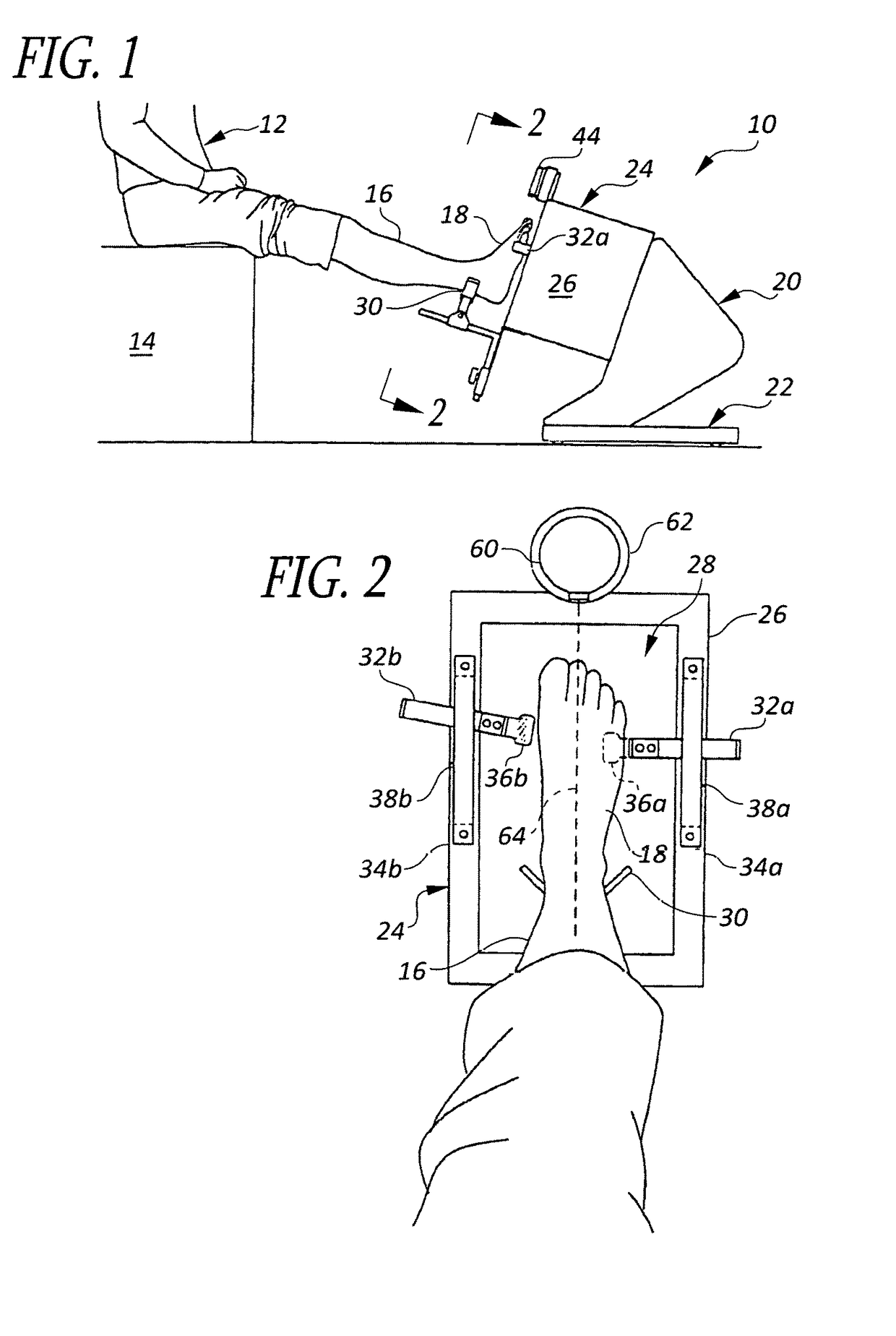
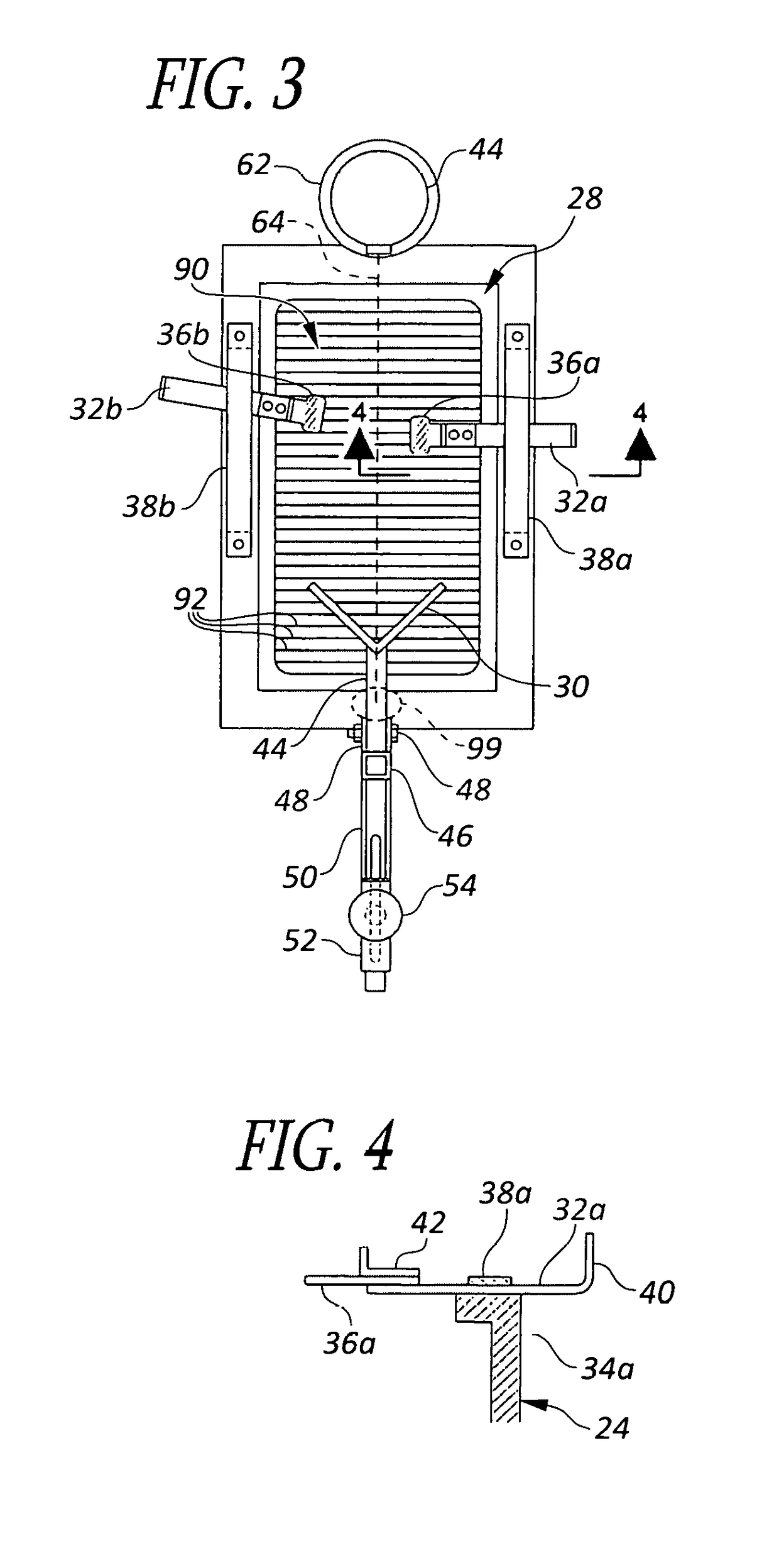
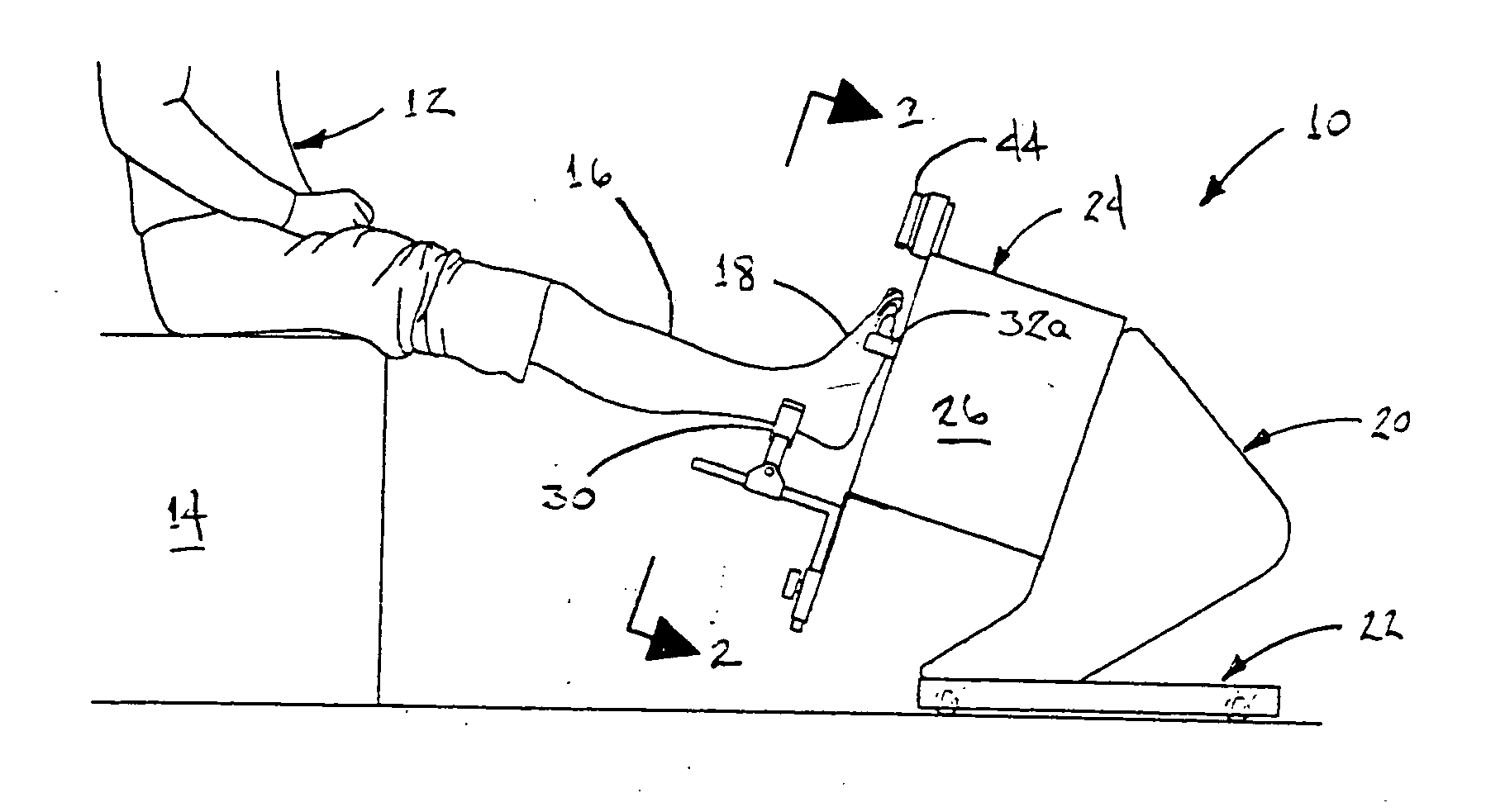
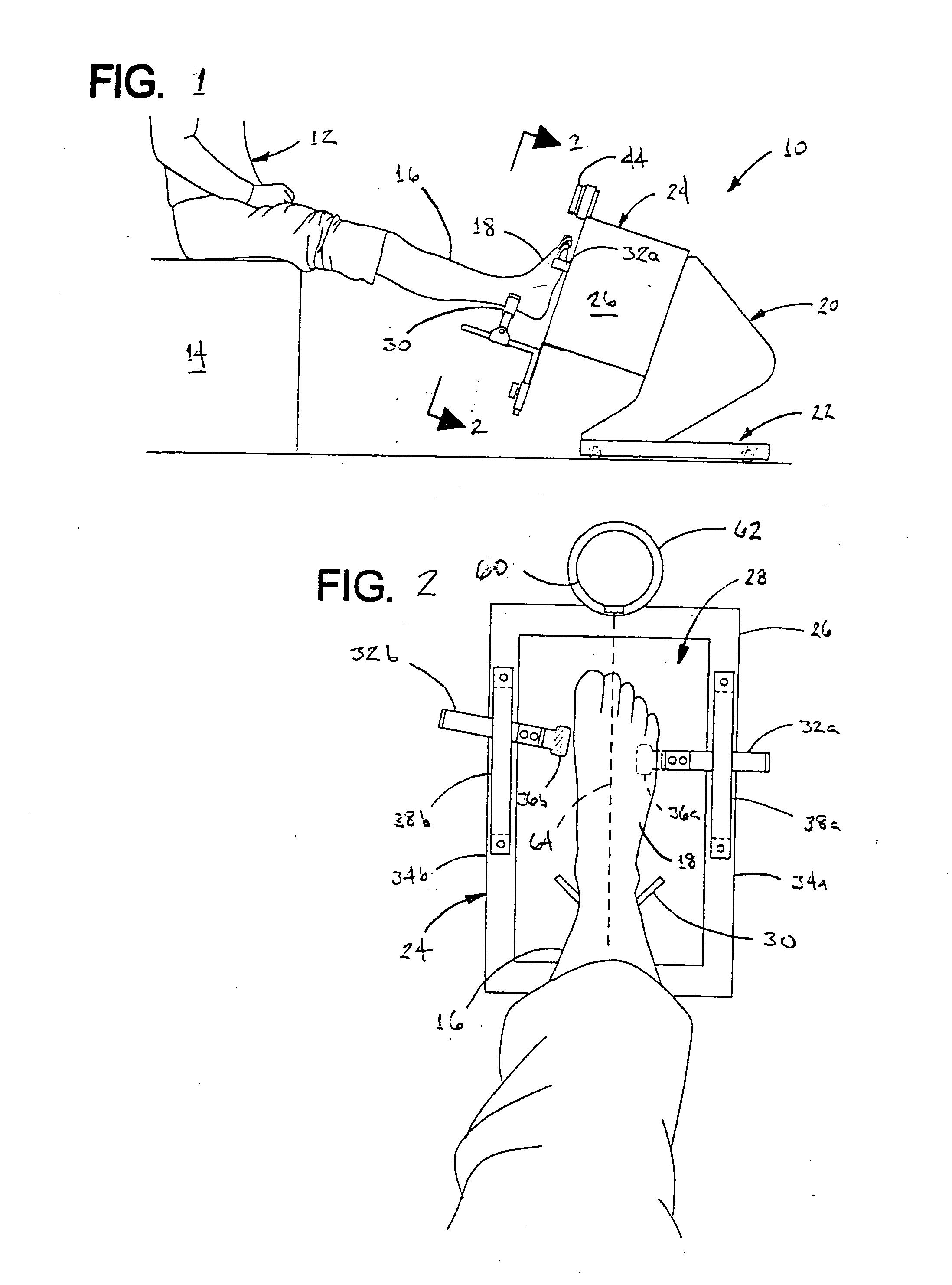
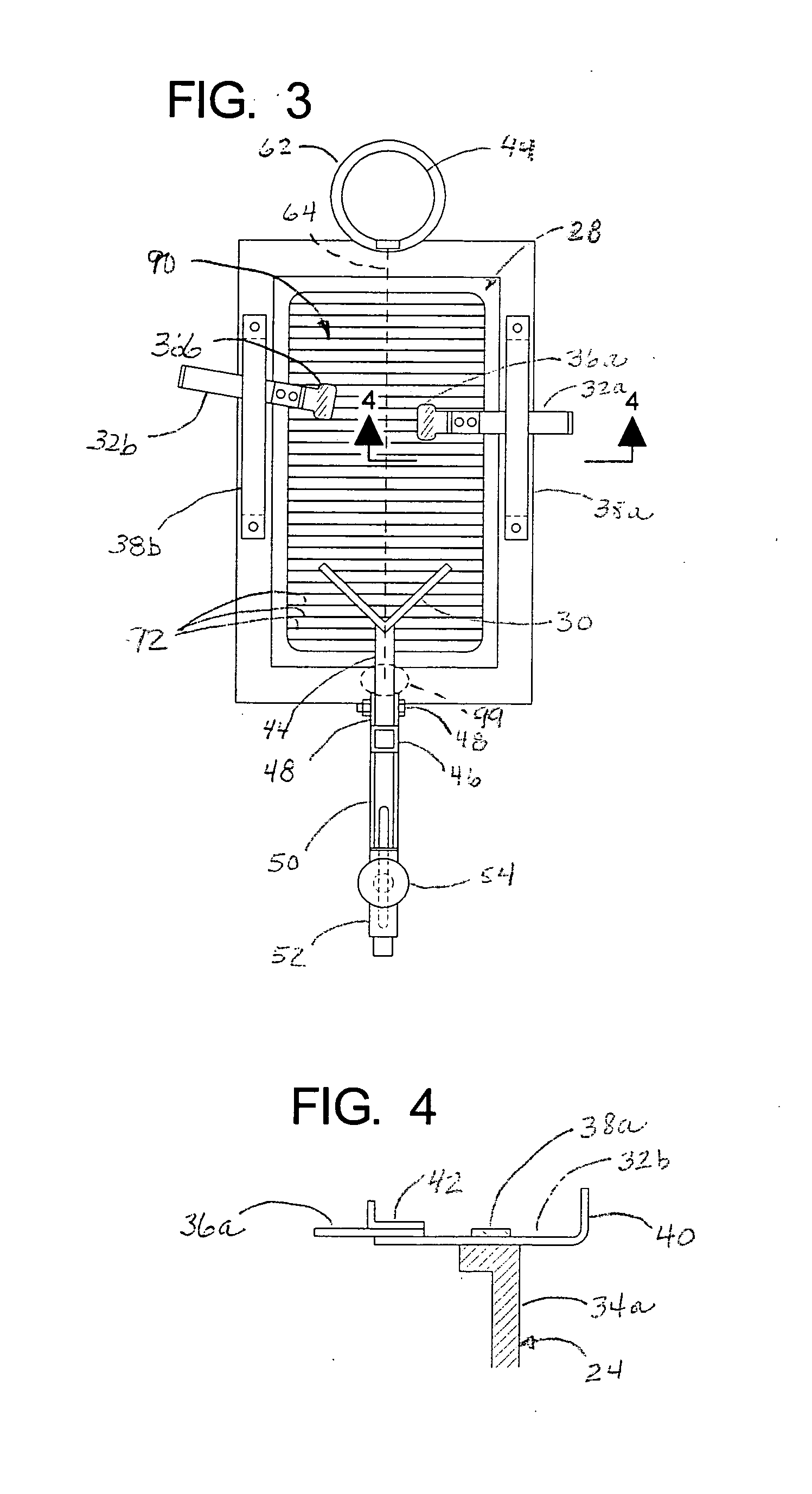
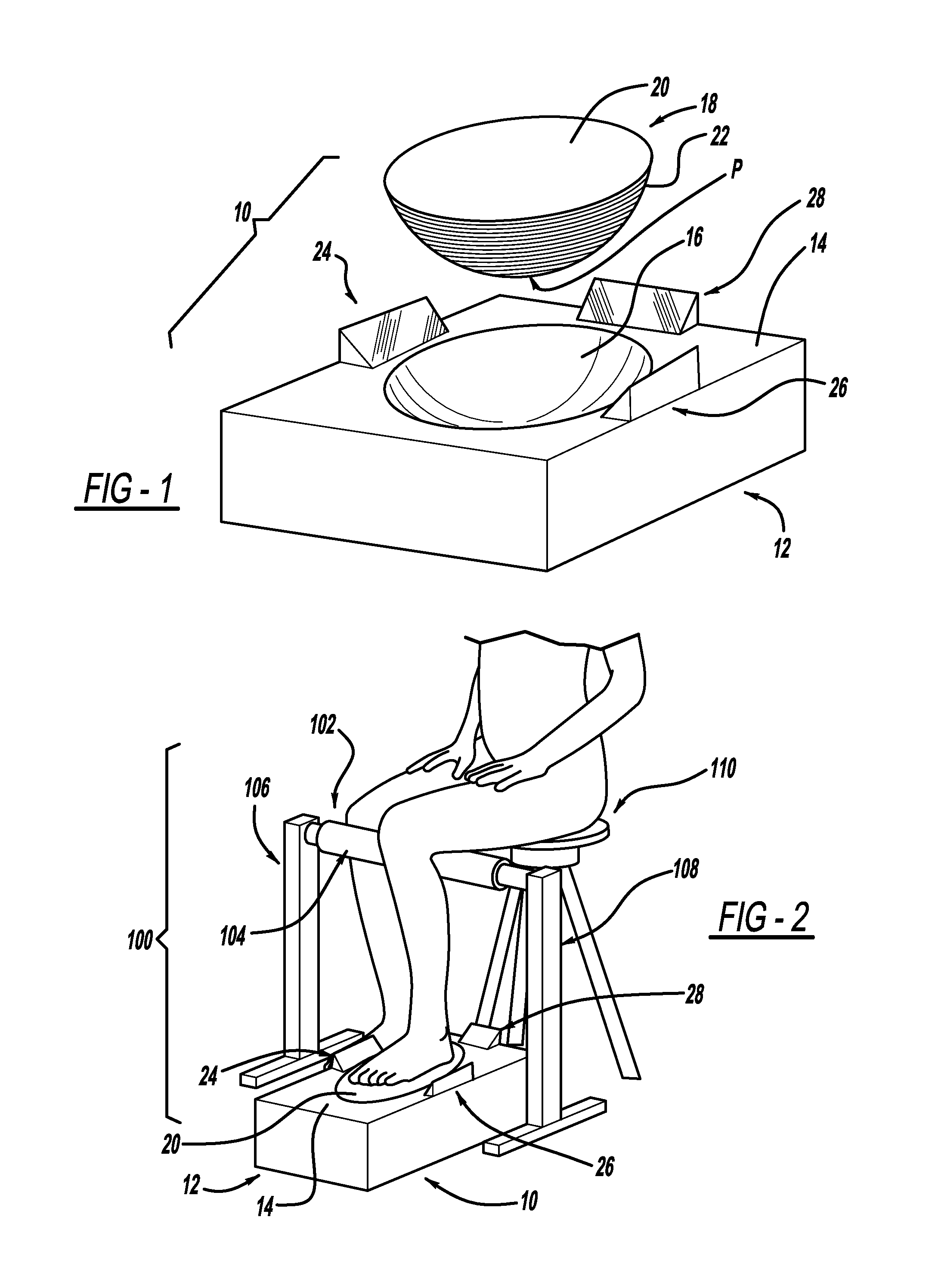
ActiveUS20120053490A1Without distortionWithout of structureFoot measurement devicesPerson identificationBone structurePlantar surface
An apparatus and method for determining contours of a patient's foot. The apparatus includes an alignment section that orientates the foot relative to an optical imaging section. The alignment section includes at least one support member located proximate a focal length of the imaging section, that engages the plantar surface substantially only in the immediate area of the fifth metatarsal head of the foot. The support generates a dorsally-directed load that locks the midtarsal joint. The alignment section further includes a heel stirrup and a laser beam or other reference line for aligning the second metatarsal head with the distal one-third of the lower leg, to place the subtalar joint in a neutral condition. The foot is thus suspended in space such that the imaging section is able to obtain an accurate measurement of the plantar surface without distortion of the soft tissues or bone structure of the foot.
Owner:NORTHWEST PODIATRIC LAB
Apparatus and method for imaging feet
ActiveUS8567081B2Without distortionWithout of structureFoot measurement devicesPerson identificationBone structurePlantar surface
An apparatus and method for determining contours of a patient's foot. The apparatus includes an alignment section that orientates the foot relative to an optical imaging section. The alignment section includes at least one support member located proximate a focal length of the imaging section, that engages the plantar surface substantially only in the immediate area of the fifth metatarsal head of the foot. The support generates a dorsally-directed load that locks the midtarsal joint. The alignment section further includes a heel stirrup and a laser beam or other reference line for aligning the second metatarsal head with the distal one-third of the lower leg, to place the subtalar joint in a neutral condition. The foot is thus suspended in space such that the imaging section is able to obtain an accurate measurement of the plantar surface without distortion of the soft tissues or bone structure of the foot.
Owner:NORTHWEST PODIATRIC LAB
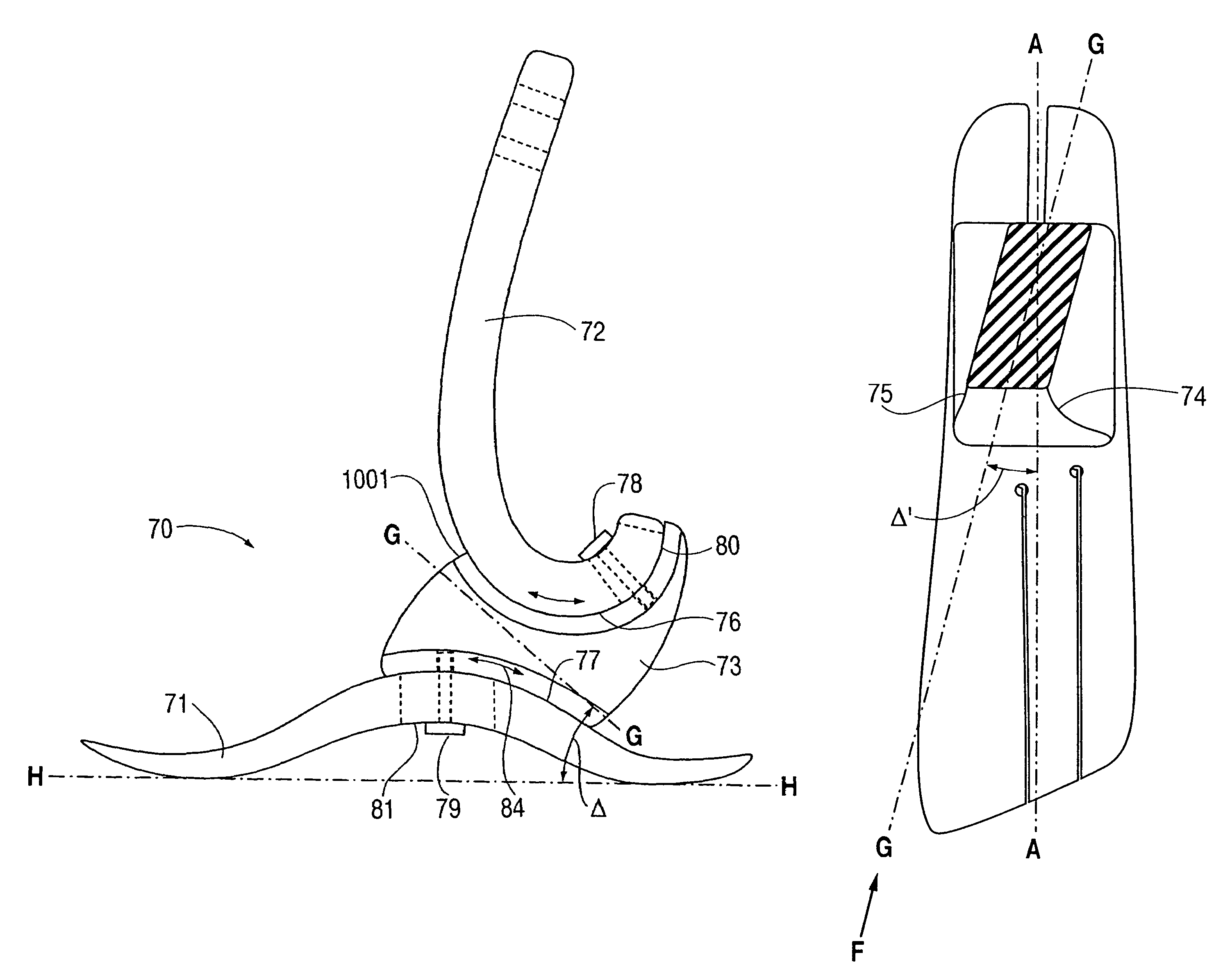
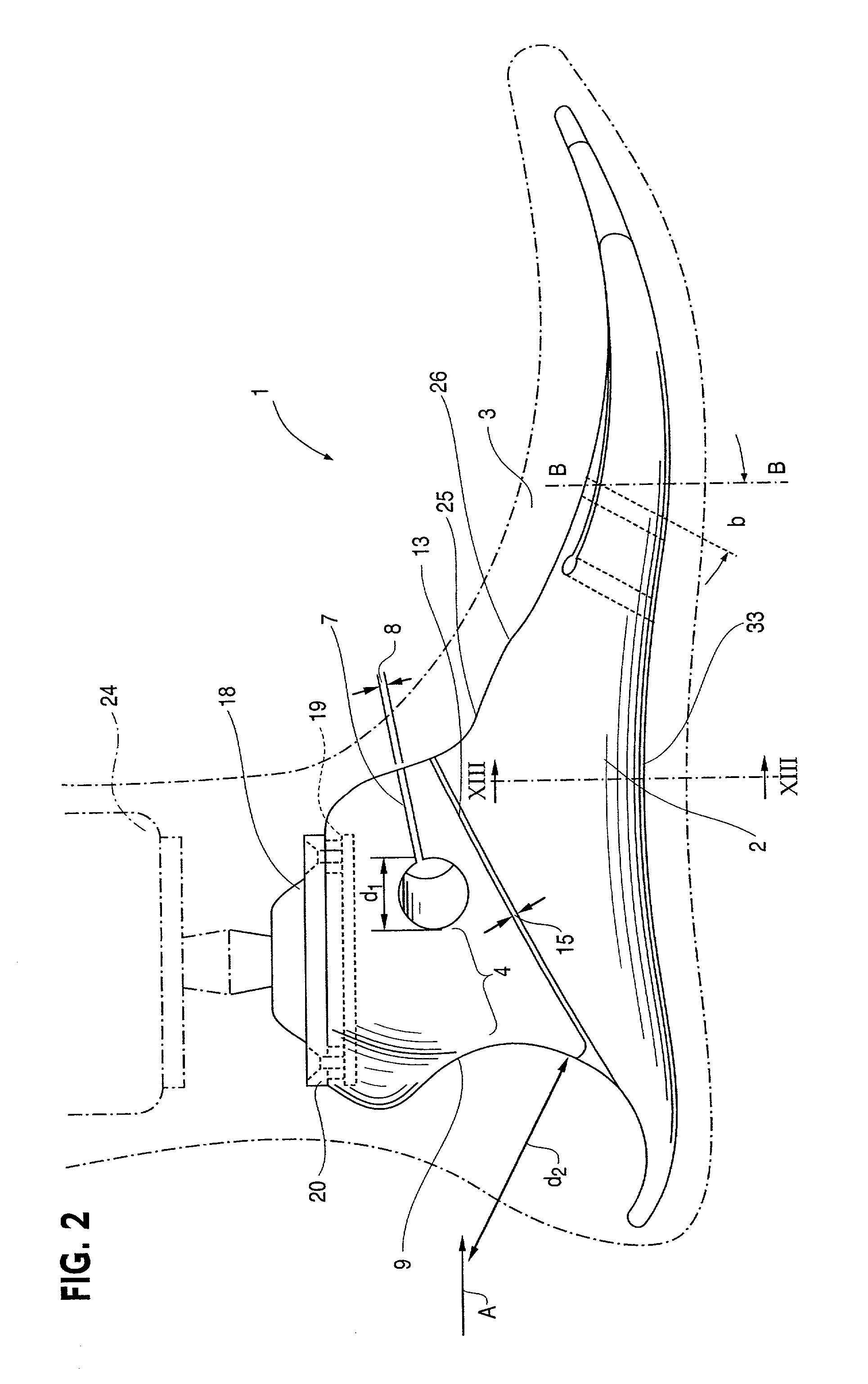
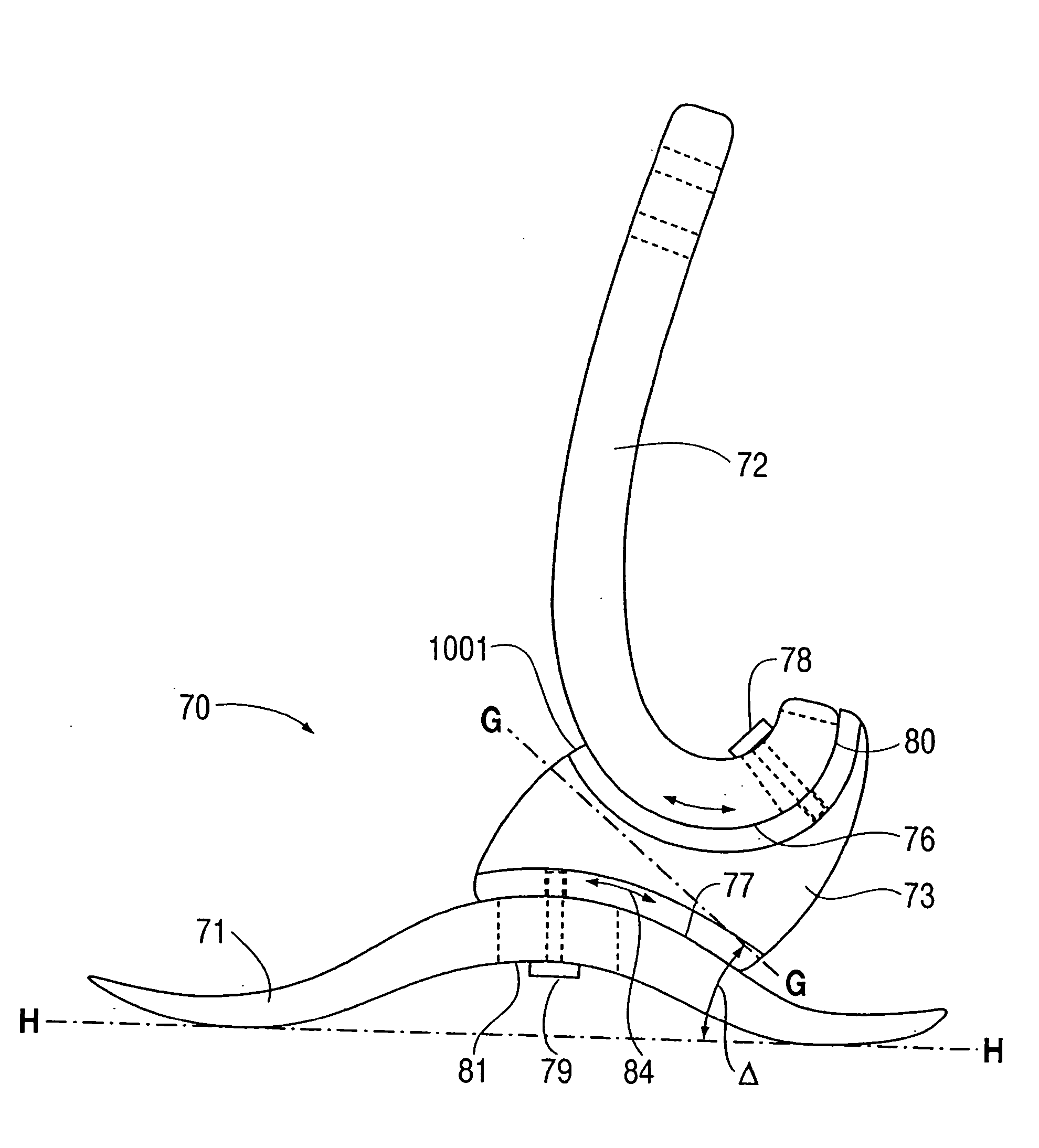
Prosthetic foot with tunable performance
A prosthetic foot (70) incorporates a foot keel (71) and a calf shank (72) connected to the foot keel to form an ankle joint area of the prosthetic fool. The foot keel has forefoot and hindfoot portions and an upwardly arched midfoot portion extending between the forefoot and midfoot portions. The calf shank includes a downward convexly curved lower end which is adjustably attached at a portion thereof to the foot keel by way of a releasable fastener arrangement which includes a coupling element (73) intermediate the calf shank and foot keel. The coupling element includes a resilient material forming a joint permitting subtalar joint-like motion of the prosthetic foot in gait.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
Forefoot wedge insert for footwear
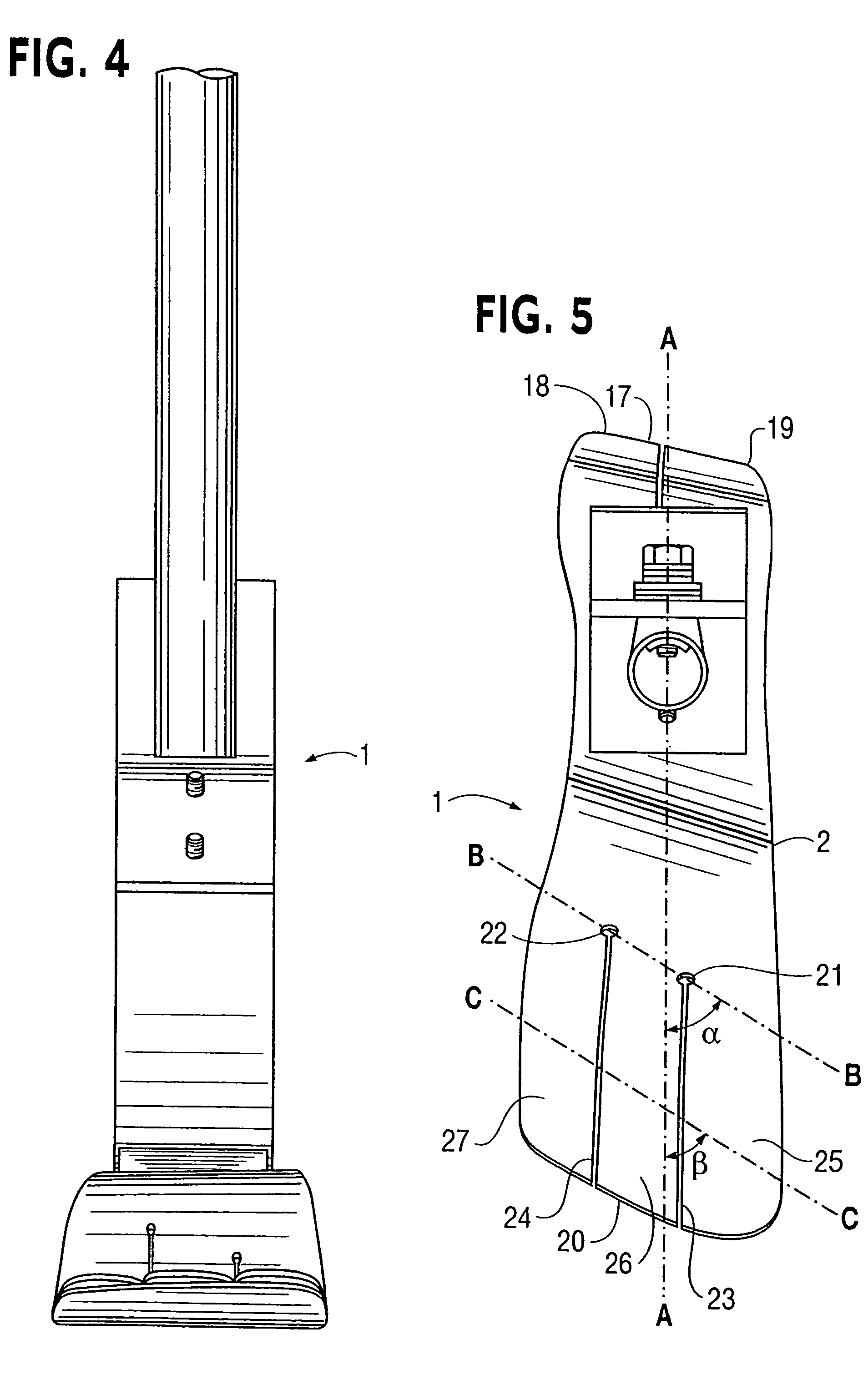
A forefoot wedge insert, and methods for forming same, are described for a piece of footwear, such as but not limited to ice skating boots, or a shoe, such as but not limited to exercise, therapeutic, or physiological footwear, for correcting a pronation and / or supination condition wherein the insert permits the subtalar joint of the affected foot to be placed and / or maintained in a neutral position. In this manner, the insert can provide the corrected foot with adequate balance relative to the skate blade during typical ice skating maneuvers. Also described is a skating boot, or shoe, having an adjustable toe cap portion that is selectively operable to be raised up to accommodate the uplifted forefoot portion of the wearer when the forefoot wedge insert is being used.
Owner:SMIRMAN MARIE
Prosthetic foot
A prosthetic foot is disclosed for improving the gait and comfort qualities of the amputee that participates in walking, running and jumping activities. An ankle pylon component attached to a foot keel of the foot allows hindfoot triplanar motion. An ankle joint and a subtalar joint provided in the hindfoot ankle pylon component permit closed kinetic chain motion of the foot. The ankle and subtalar joints are formed by respective struts of resilient material of a single piece of material of the ankle pylon component. The ankle pylon component can be used as a functional upgrade component to an existing low profile prosthetic foot, for example.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
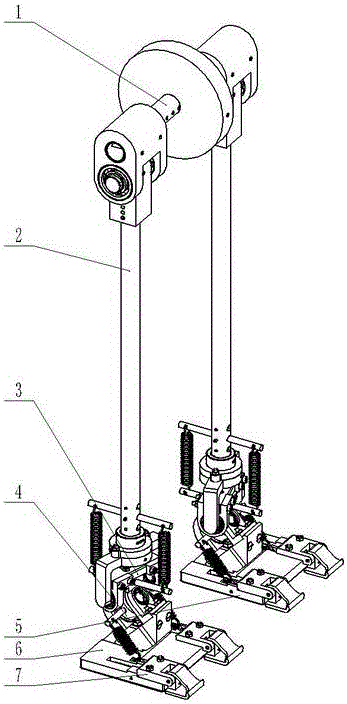
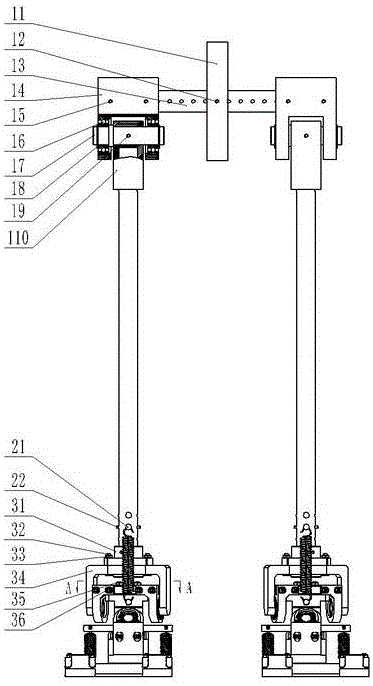
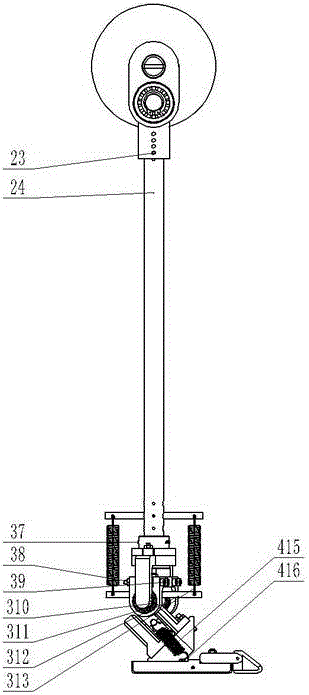
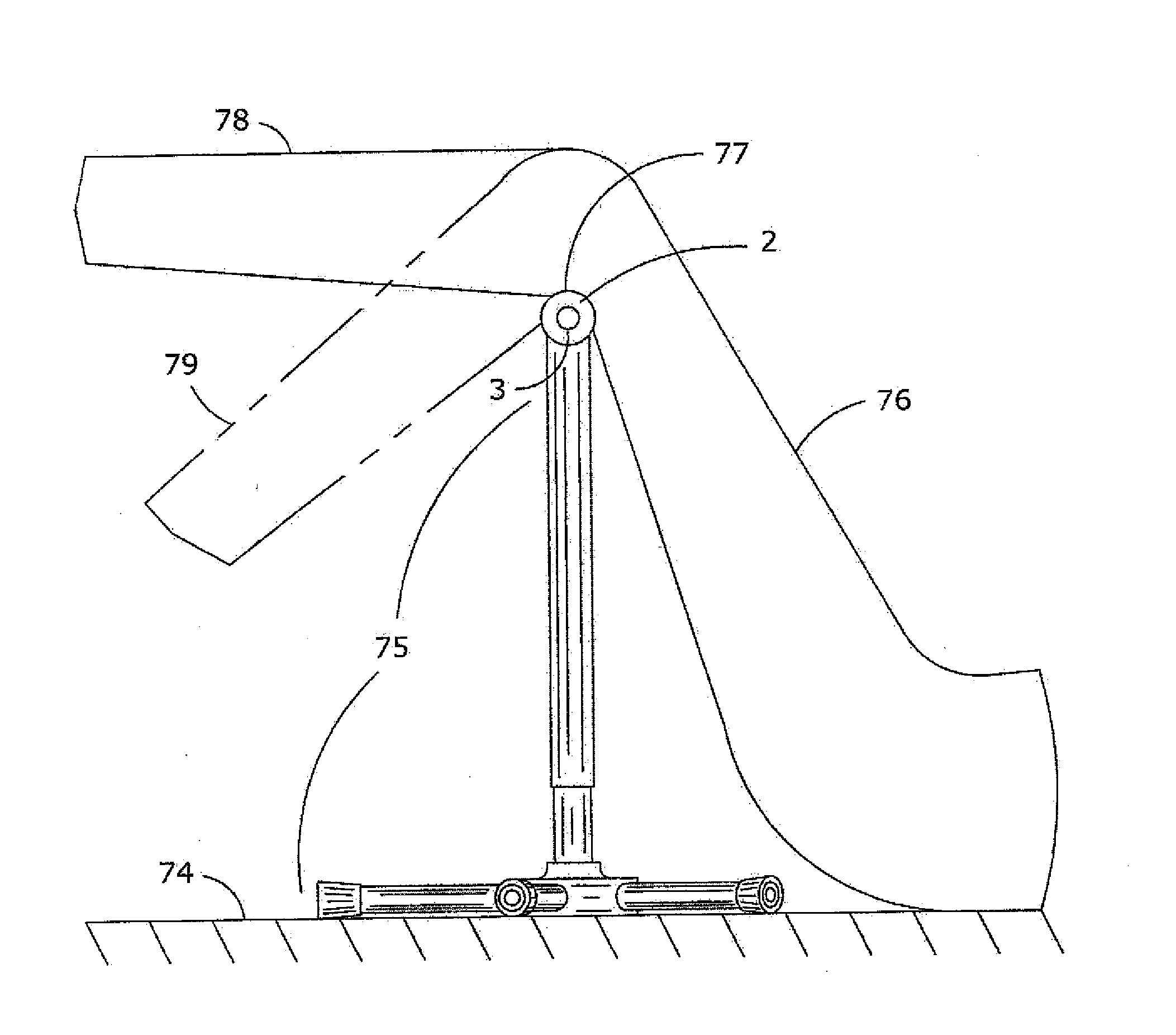
Completely passive both-foot walking machine with bionic ankle and subtalar joints
The invention discloses a completely passive both-foot walking machine with bionic ankle and subtalar joints, comprising a hip assembly, leg assemblies, ankle joint assemblies, subtalar joint assemblies, a left foot, a right foot and toe assemblies, wherein each leg assembly is arranged between the hip assembly and the ankle joint assembly, and a main body of the walking machine is constructed; each subtalar joint assembly is arranged between the ankle joint assembly and a foot, the toe assemblies are distributed at two sides of each foot. Foot joints disclosed by the invention comprise the ankle joint assemblies and the subtalar joint assemblies, the foot joints of the walking machine are designed by simulating the physiological angles of the ankle joints and the subtalar joints of a human in the space. Meanwhile, toes can realize an elastic start in the walking process under the effect of springs. According to the walking machine disclosed by the invention, the beneficial effects of the optimal walking energy efficiency, improvement of walking stability and naturality of the both-foot walking machine are achieved according to the passive walking principle and the introduction of the bionic ankle and subtalar joints.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Prosthetic foot
A prosthetic foot is disclosed for improving the gait and comfort qualities of the amputee that participates in walking, running and jumping activities. An ankle pylon component attached to a foot keel of the foot allows hindfoot triplanar motion. An ankle joint and a subtalar joint provided in the hindfoot ankle pylon component permit closed kinetic chain motion of the foot. The ankle and subtalar joints are formed by respective struts of resilient material of a single piece of material of the ankle pylon component. The ankle pylon component can be used as a functional upgrade component to an existing low profile prosthetic foot, for example.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
Subtalar implant and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS8628582B2Facilitate proper positioningSuture equipmentsAnkle jointsAnatomical structuresSacroiliac joint
The present invention provides a subtalar implant as well as methods of use thereof for the purpose of correcting podiatric disorders such as various types of flat foot conditions relating to the subtalar joint. The subtalar implant is capable of threaded engagement with a positioning element used to position and manipulate the implant during surgical implantation in the sinus tarsi of the foot. The implant is cannulated to receive a guide rod to facilitate final positioning of the implant. Once implanted, the subtalar implant provides anatomical fit with the subtalar joint anatomical structure without the need for indentations to receive osseous tissue growth to anchor the subtalar implant.
Owner:VILEX LLC
Apparatus and method for imaging feet
ActiveUS9778027B1Optimally positioned and configuredWithout distortionFoot measurement devicesCannulasBone structurePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An apparatus and method for determining contours of a patient's foot ankle and lower leg. The apparatus includes an alignment structure that orientates the foot for imaging. The alignment structure includes at least one support member that engages the plantar surface of the foot substantially only in the immediate area of the lateral metatarsal heads of the foot, preferably the fifth metatarsal head. The support generates a dorsally-directed force that locks the midtarsal joint. The alignment structure further includes a saddle that engages the rearfoot and a laser beam for aligning the second metatarsal head with the distal one-third of the lower leg to place the subtalar joint in a neutral condition. The foot is thus suspended in space such that imaging is able to produce an accurate measurement of the subject areas of the foot, ankle and lower leg without distortion of the soft tissues or bone structure.
Owner:NORTHWEST PODIATRIC LAB
Apparatus and method for imaging feet
ActiveUS20140055590A1Without distortionWithout of structureFoot measurement devicesColor television detailsBone structurePlantar surface
An apparatus and method for determining contours of a patient's foot. The apparatus includes an alignment section that orientates the foot relative to an optical imaging section. The alignment section includes at least one support member located proximate a focal length of the imaging section, that engages the plantar surface substantially only in the immediate area of the fifth metatarsal head of the foot. The support generates a dorsally-directed load that locks the midtarsal joint. The alignment section further includes a heel stirrup and a laser beam or other reference line for aligning the second metatarsal head with the distal one-third of the lower leg, to place the subtalar joint in a neutral condition. The foot is thus suspended in space such that the imaging section is able to obtain an accurate measurement of the plantar surface without distortion of the soft tissues or bone structure of the foot.
Owner:NORTHWEST PODIATRIC LAB
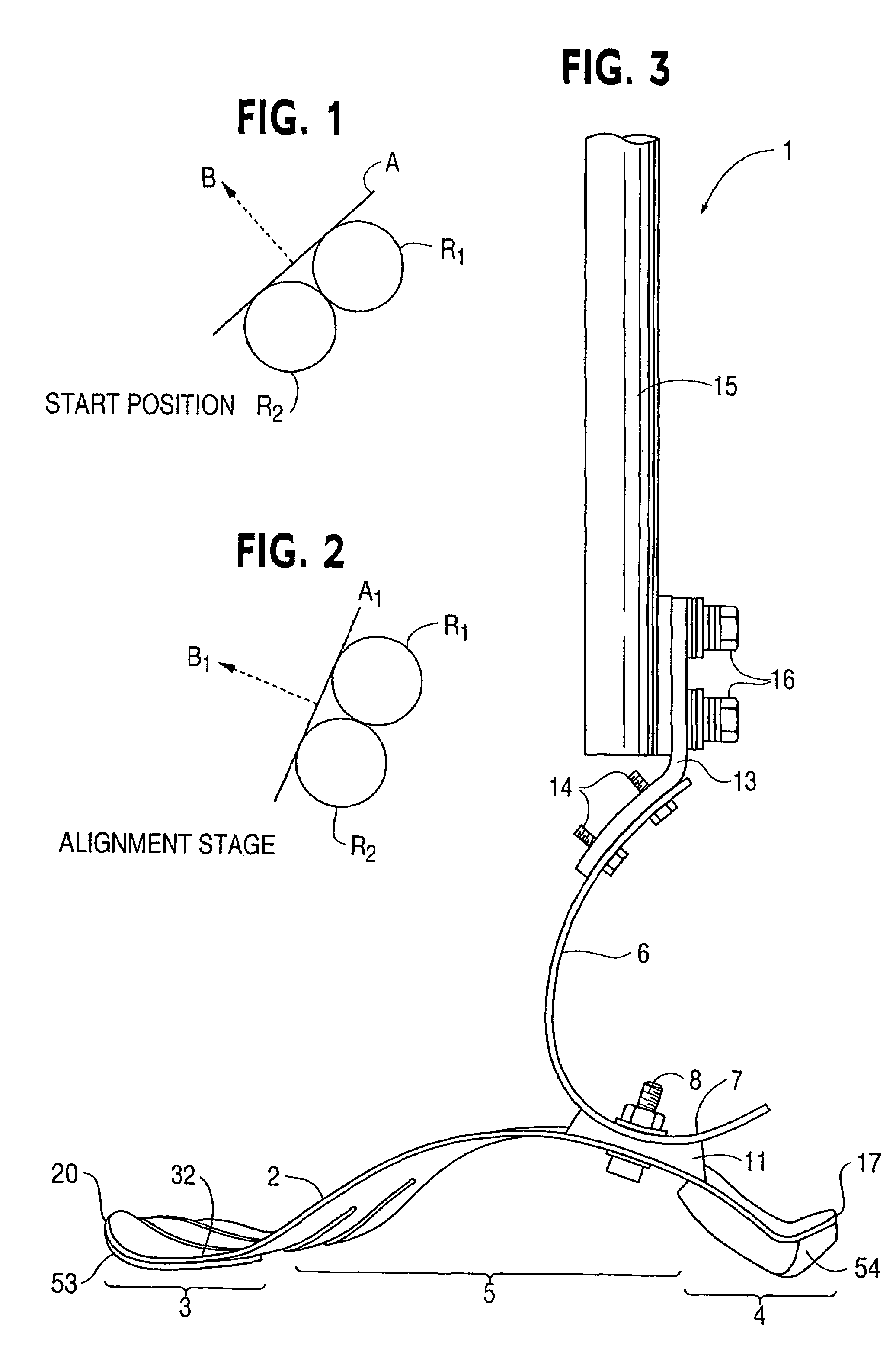
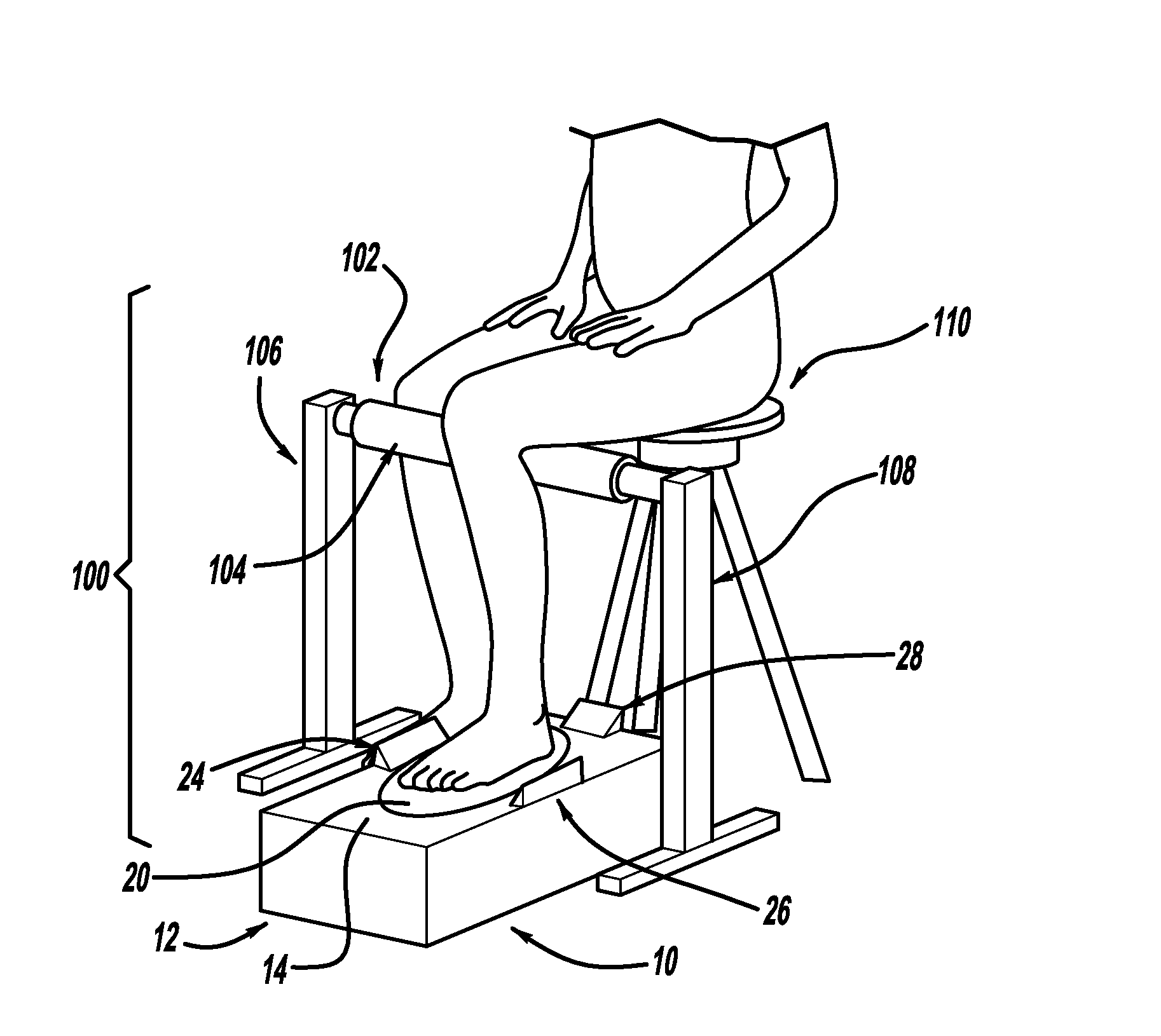
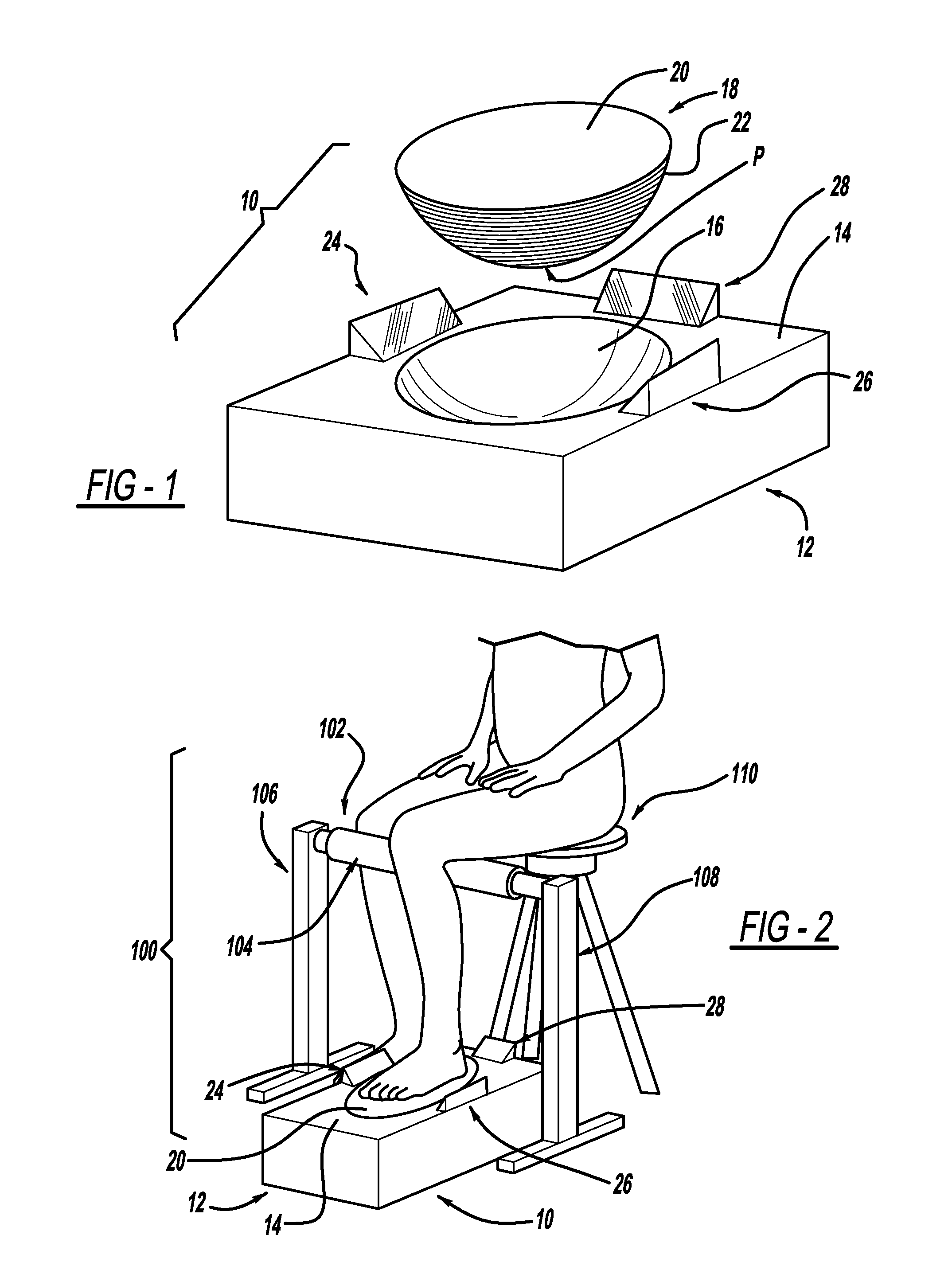
Measurement system for varus/valgus angles in feet
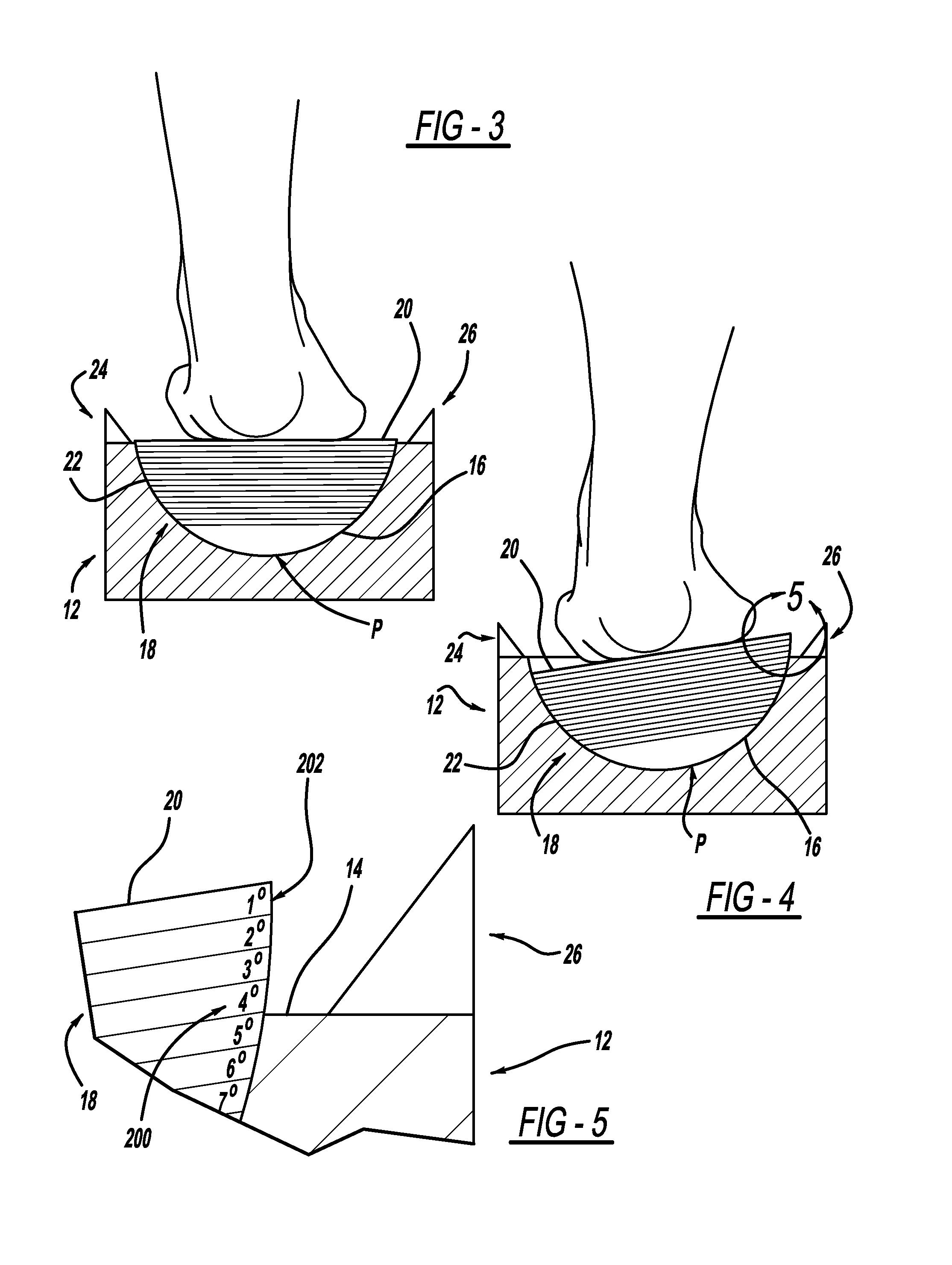
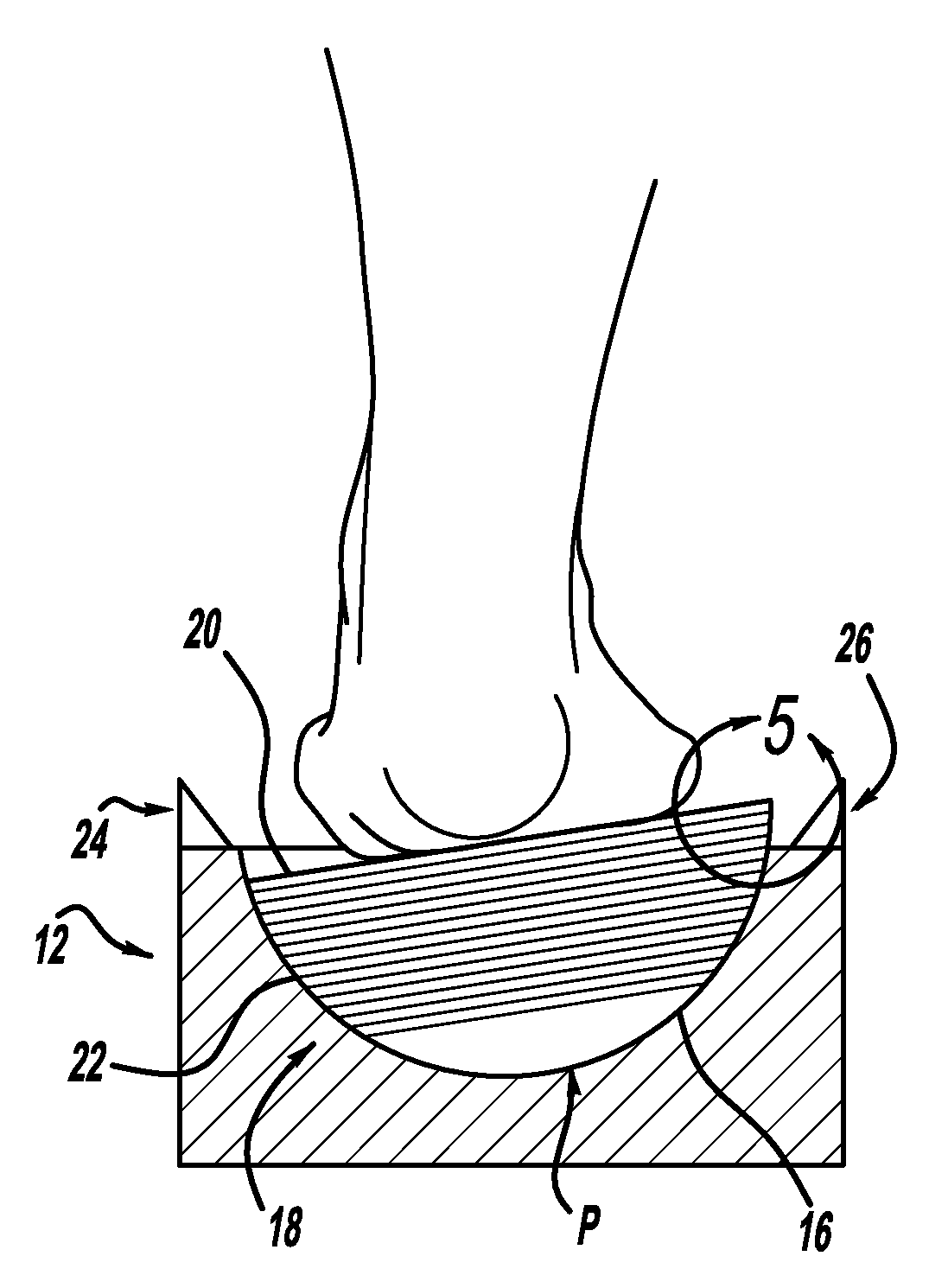
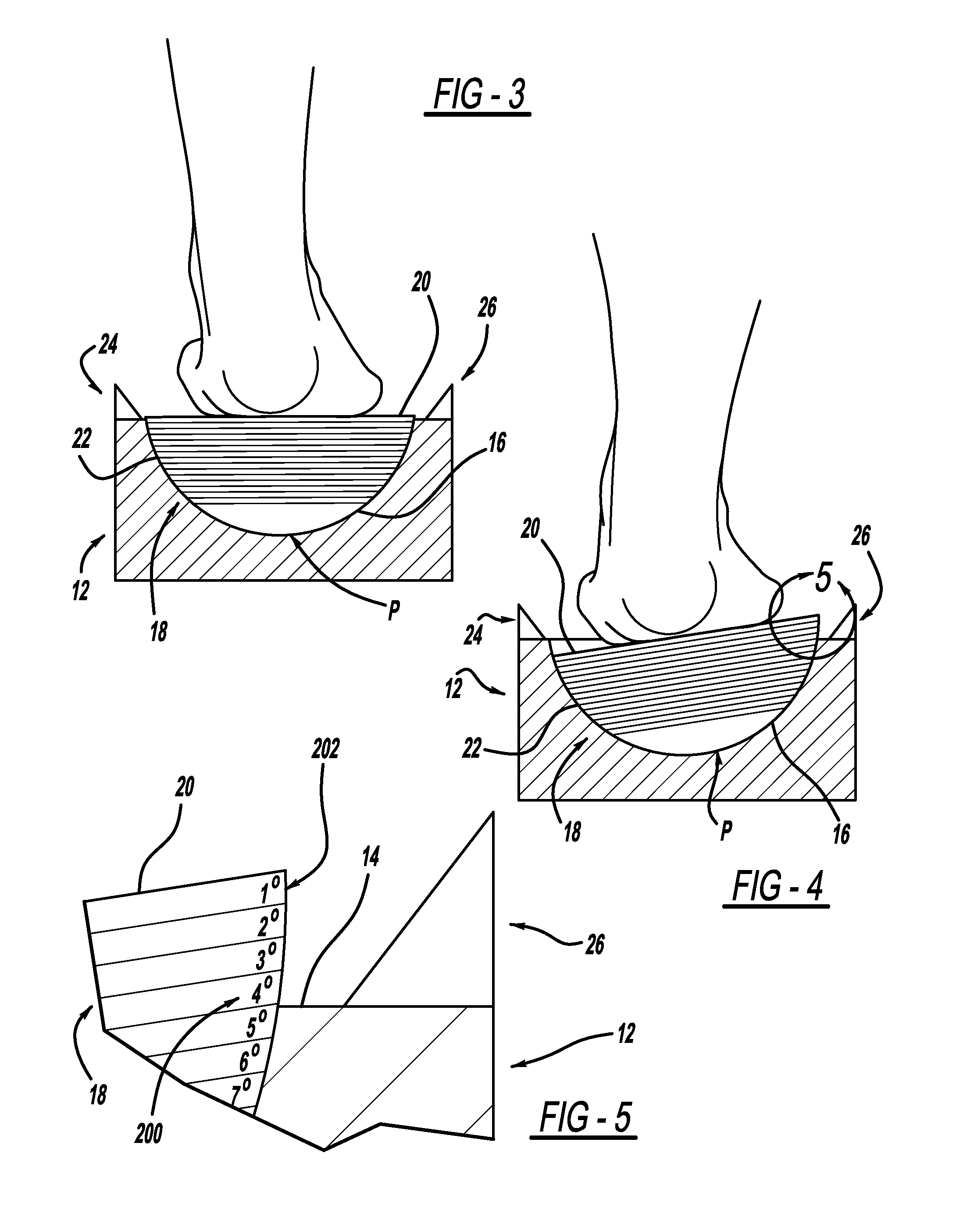
InactiveUS20130276317A1Larger (although more accurate) varus/valgus anglesPerson identificationSensorsPronationsAngular degrees
A measurement system is described for determining the varus and / or valgus angles of a pronating and / or supinating foot, especially when the subtalar joint of the foot is placed and / or maintained in a neutral position. When the user's foot is maintained in the subtalar joint neutral position, it causes a platform member to rotate relative to a correspondingly shaped depression formed in a base portion such that a top surface of the platform member is no longer in a substantially coplanar relationship with a top surface of the base portion. When this occurs, a bottom surface of the platform member is exposed. As a result, indicia are exposed which correspond to degree markings disposed on the bottom surface of the platform member. The degree markings indicate the angle that corresponds to the varus and / or valgus angles, and thus the amount of pronation and / or supination, of the user's foot.
Owner:SMIRMAN MARIE
Measurement system for varus/valgus angles in feet
InactiveUS20120079733A1Larger (although more accurate) varus/valgus anglesPerson identificationSensorsPronationsEngineering
A measurement system is described for determining the varus and / or valgus angles of a pronating and / or supinating foot, especially when the subtalar joint of the foot is placed and / or maintained in a neutral position. When the user's foot is maintained in the subtalar joint neutral position, it causes a substantially hemispherically shaped platform member to rotate relative to a correspondingly shaped depression formed in a base portion such that a top surface of the platform member is no longer in a coplanar relationship with a top surface of the base portion. When this occurs, a bottom surface of the platform member is exposed. As a result, indicia are exposed which correspond to degree markings disposed on the bottom surface of the platform member. The degree markings indicate the angle that corresponds to the amount of pronation and / or supination of the user's foot.
Owner:SMIRMAN MARIE
Passive Knee Joint and Knee Extension Device
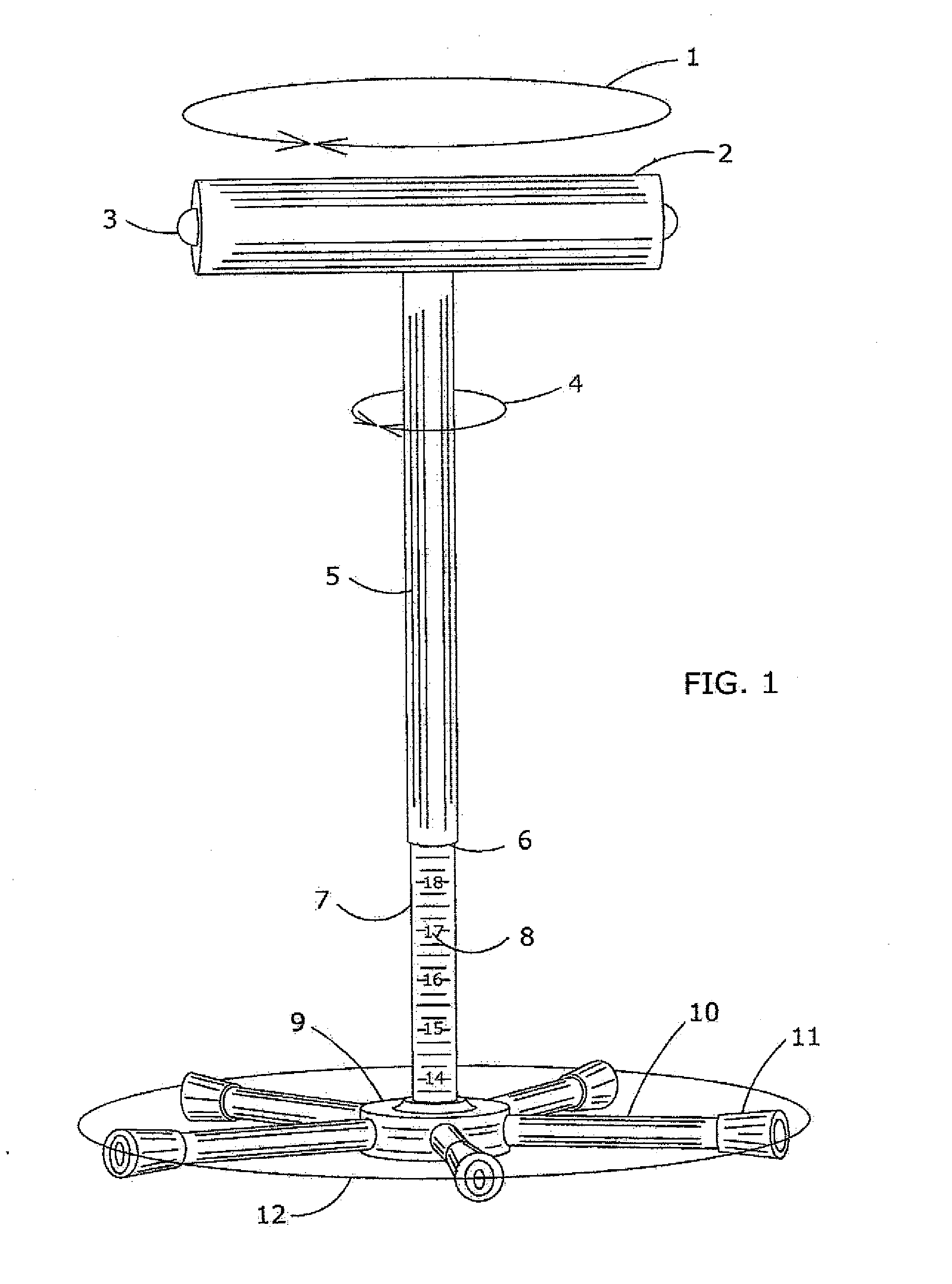
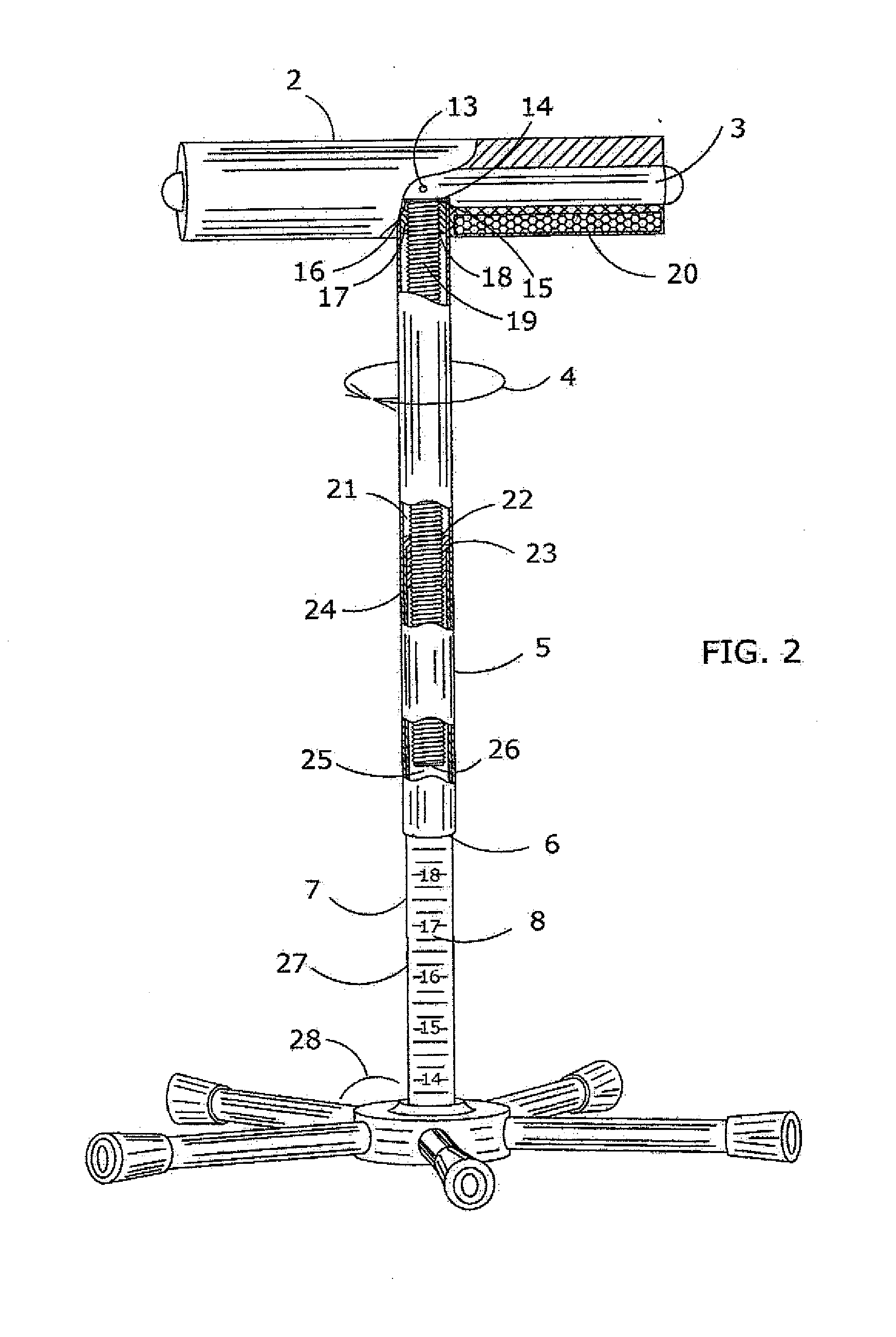
Disclosed is a passive gravity assist flexion and / or extension device, principally for regaining knee joint range of motion flexibility; having such arrangement to provide appropriate content vertically stable elevated under knee support of the posterior intersection, concerning the femur and tibia of an impaired knee joint and / or concerning the subtalar joint (ankle); whereby promoting gravity assist passive flexion and / or extension towards gradual content knee joint muscle stretching. The disclosed device arrangement, being comprised of a padded solitary horizontal support bar, capable of desired lateral rotational movement, while firmly affixed mid-span atop a vertical linear traveling wholly enclosed height adjustable threaded rod. Whereby adjustable rod thread engagement means, establishes and maintains desired horizontal support bar height position. Furthermore, the disclosed device utilizes a center base foundation arrangement providing a resolute perpendicular stable knee support means.
Owner:LUTZ DAVID C
Detachable talus prosthesis
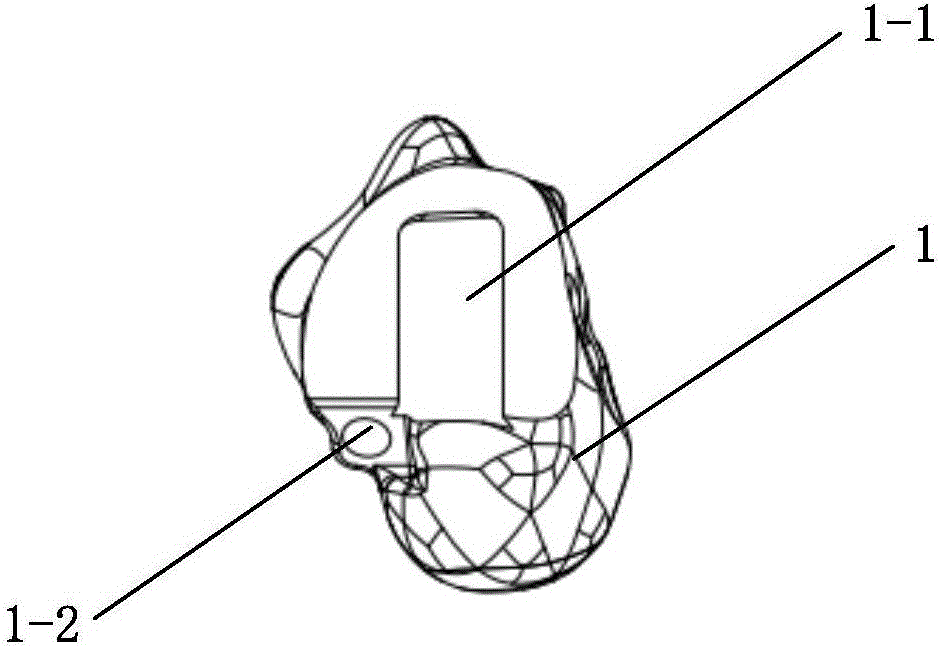
InactiveCN106618807AHas a biological functionEasy to manufactureAnkle jointsJoint implantsAnkle boneTibiotalar joint
The invention discloses a detachable talus prosthesis which comprises a talonavicular subtalar joint assembly and a tibiotalar joint assembly. On one hand, the detachable talus prosthesis is formed by combining the talonavicular subtalar joint assembly and the tibiotalar joint assembly and is easy to manufacture; on the other hand, the subtalar joint surface and talonavicular joint surface are of porous structures, and the detachable talus prosthesis has a biological function and facilitate rapid fusion and growth of prosthesis and calcaneus and scaphoid bone.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Foot shape analysis and shoe pad customization system
The invention discloses a foot shape analysis and shoe pad customization system, and relates to the technical field of foot treatment. A manufacturing method comprises the following steps: acquiring data of soles and heels of a patient through an optical foot detection instrument; photographing the feet and knees of the patient by the system, and capturing pictures to obtain a detection report; selecting the type of shoe pads and a yardage which are suitable for a customer according to the report, and putting the shoe pads into a special heater for heating; placing non-shaped customized shoe pads on a special shaping pillow for shaping; keeping ankles and subtalar joints in a correct biological power line; after the two shoe pads are shaped, checking whether the shoe pads are suitable for arches of the feet of the customer precisely or not; performing simple tailoring on the widths according to shoes of the customer to ensure that the shoe pads are perfectly matched with the shoes. The foot shape analysis and shoe pad customization system can make a quick diagnosis according to the shapes of the feet, the shapes of knee joints, the shapes of the arches of the feet, excessive intortion, insufficient intortion, hallux valgus, high and low feet, paint points, proper shoe styles and the like to customize assorted correction shoe pads, and is convenient and practical.
Owner:广州隆达医疗器械有限责任公司
Intramedullary locked compression screw for stabilization and union of complex ankle and subtalar deformities
This invention describes an implant to fuse the bones of the ankle and subtalar joints together. The method includes steps of producing an implant to apply compressive forces across the bones of the ankle or the bones of the subtalar joint. In one embodiment, the invention includes a method that uses images such as radiographs preoperatively to determine the length and width of the disclosed implant or any other implant based on each patient's unique anatomy, that will properly allow coaptation of the ends of the prepared tibia and talus at the ankle joint or the prepared talus and the calcaneus at the subtalar joint. The implant is inserted from the bottom of the foot through a predetermined hole in the calcaneus extending through the talus into the diaphysis of the tibia. When properly seated in the bones, the implant is locked to the bones by screws.
Owner:MANDERSON EASTON L
Ankle derotation and subtalar stabilization orthosis
ActiveUS8202239B2Effective in inversionEffective movementFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisOrthotic device
The invention is an ankle derotation and subtalar stabilization system that incorporates a pivoting adjustable-tension oblique tether strap that is anchored to both a forefoot component and leg component, and that is contiguous with pivoting adjustable-tension derotation strap that passes behind the leg and that is secured to a leg component. The system restrains oppositely directed rotation between the foot and the leg, and can actually after the normal biochemical relationship in a manner that produces foot rotation in a direction opposite to that which is normally coupled with leg rotation, without restriction of upward and downward foot movement. The primary application for the system is restraint of excessive subtalar joint inversion, leg external rotation, and anterolateral rotary displacement of the talus, but it can also be configured to restrain subtalar eversion and leg internal rotation through its incorporation into the structure of an ankle orthosis or shoe.
Owner:WILKERSON GARY BLAINE
Prosthetic foot with tunable performance
InactiveUS20050177250A1High level of performanceImproved applied mechanicArtificial legsTibiaCoupling
A prosthetic foot (70) incorporates a foot keel (71) and a calf shank (72) connected to the foot keel to form an ankle joint area of the prosthetic fool. The foot keel has forefoot and hindfoot portions and an upwardly arched midfoot portion extending between the forefoot and midfoot portions. The calf shank includes a downward convexly curved lower end which is adjustably attached at a portion thereof to the foot keel by way of a releasable fastener arrangement which includes a coupling element (73) intermediate the calf shank and foot keel. The coupling element includes a resilient material forming a joint permitting subtalar joint-like motion of the prosthetic foot in gait.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com