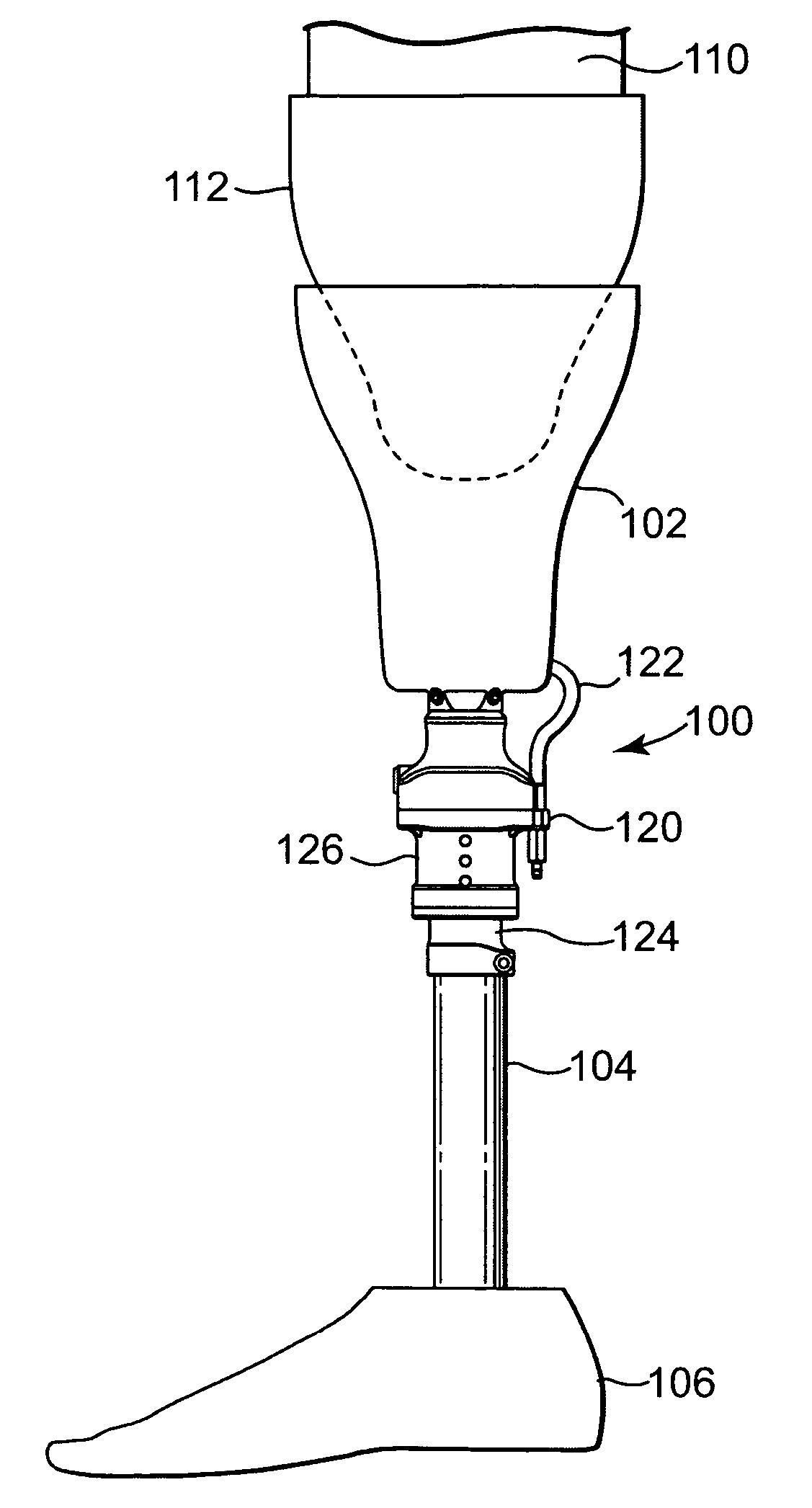
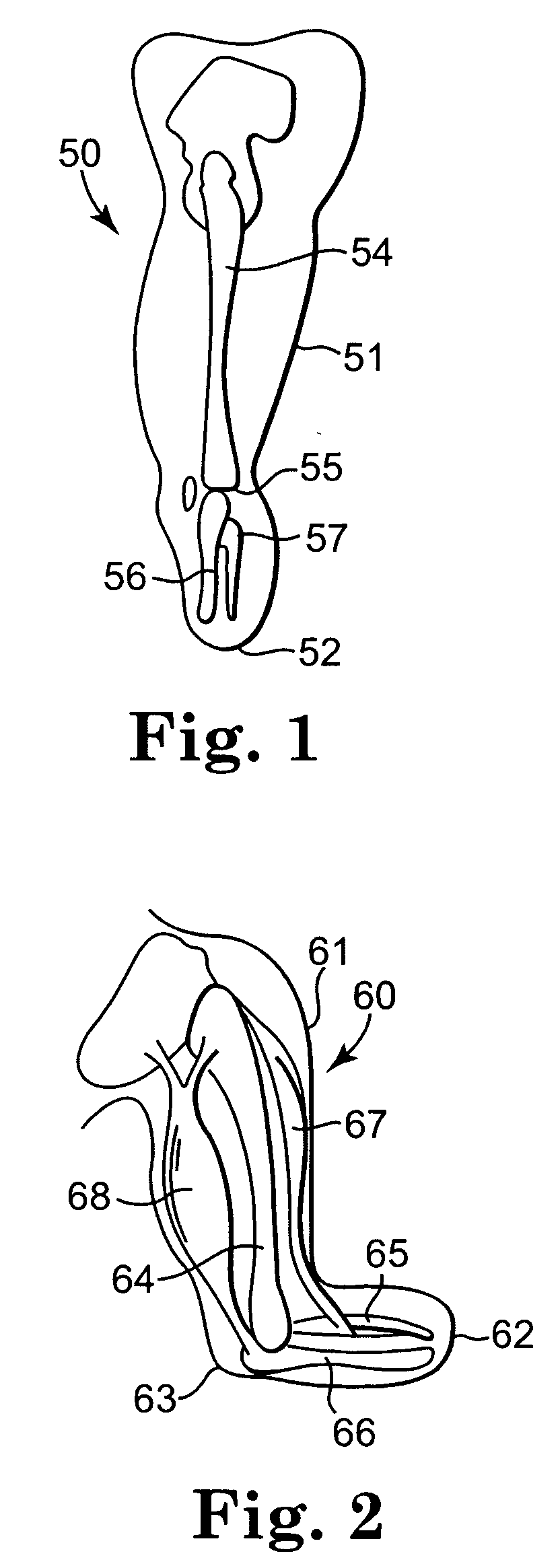
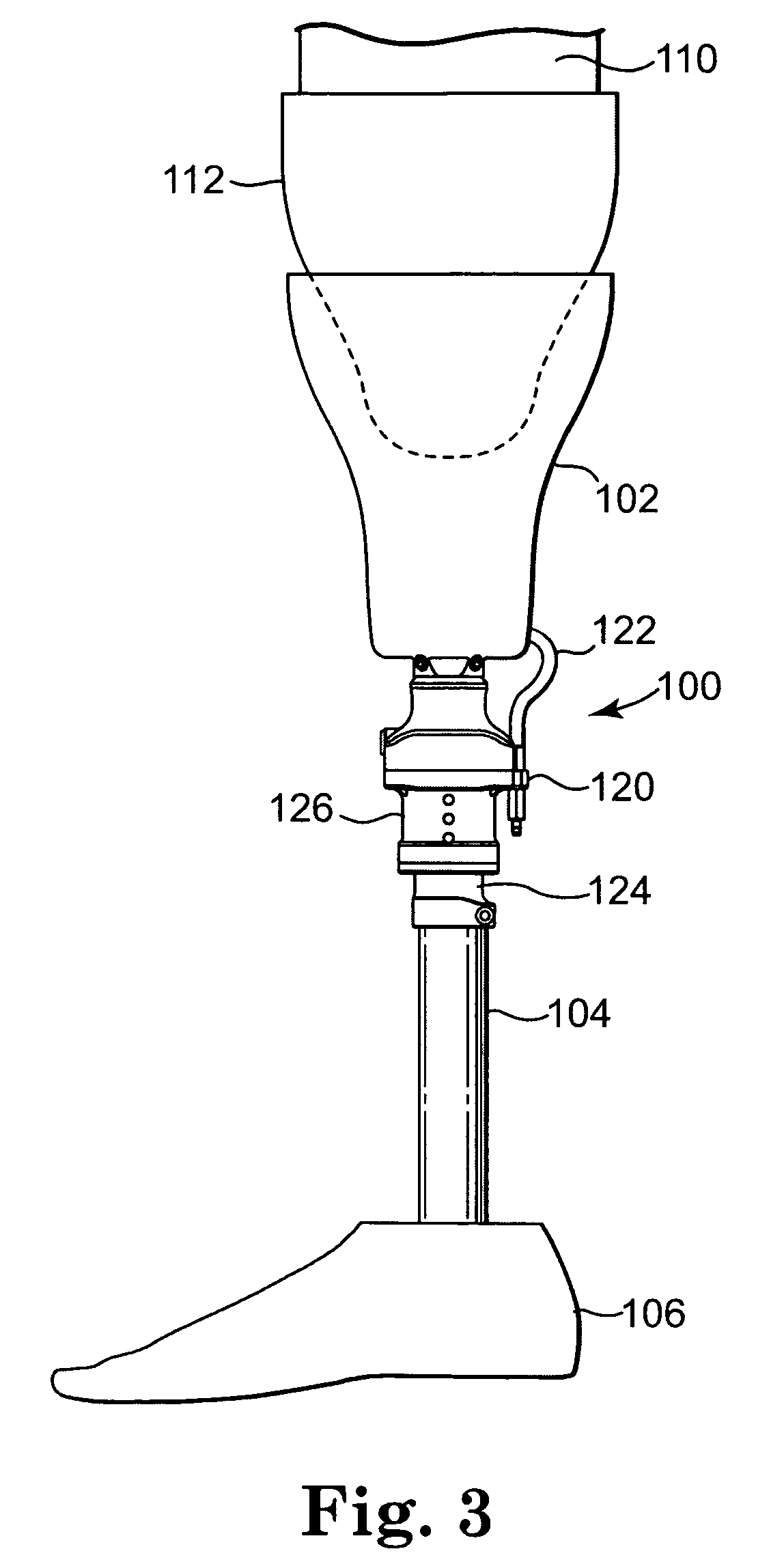
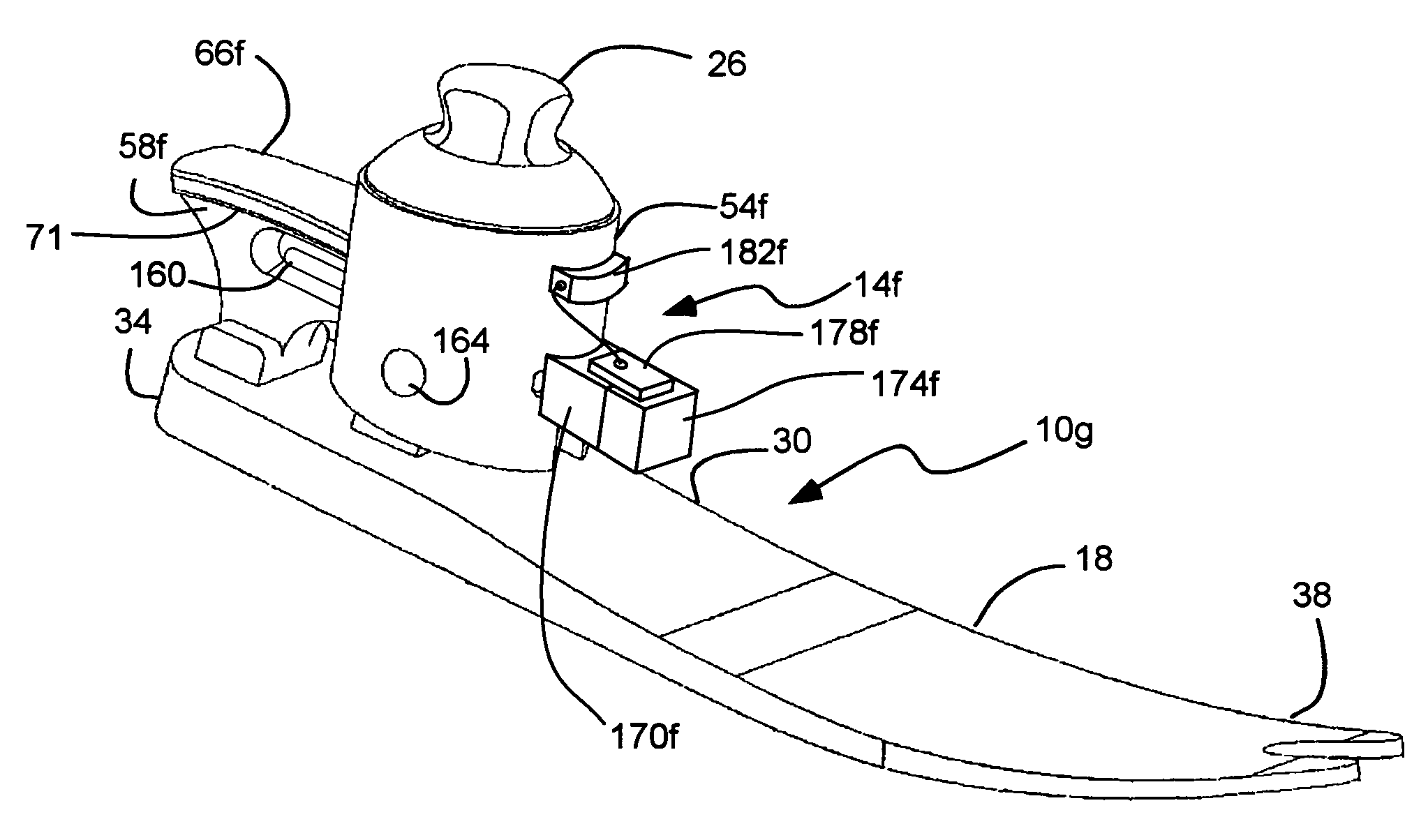
Patents
Literature
252 results about "Prosthetic feet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Powered leg prosthesis and control methodologies for obtaining near normal gait
A powered leg prosthesis includes powered knee joint comprising a knee joint and a knee motor unit for delivering power to the knee joint. The prosthesis also includes a prosthetic lower leg having a socket interface coupled to the knee joint and a powered ankle joint coupled to the lower leg opposite the knee joint comprising an ankle joint and an ankle motor unit to deliver power to the ankle joint. The prosthesis further includes a prosthetic foot coupled to the ankle joint, at least one sensor for measuring a real-time input, and at least one controller for controlling movement of the prosthesis based on the real-time input.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
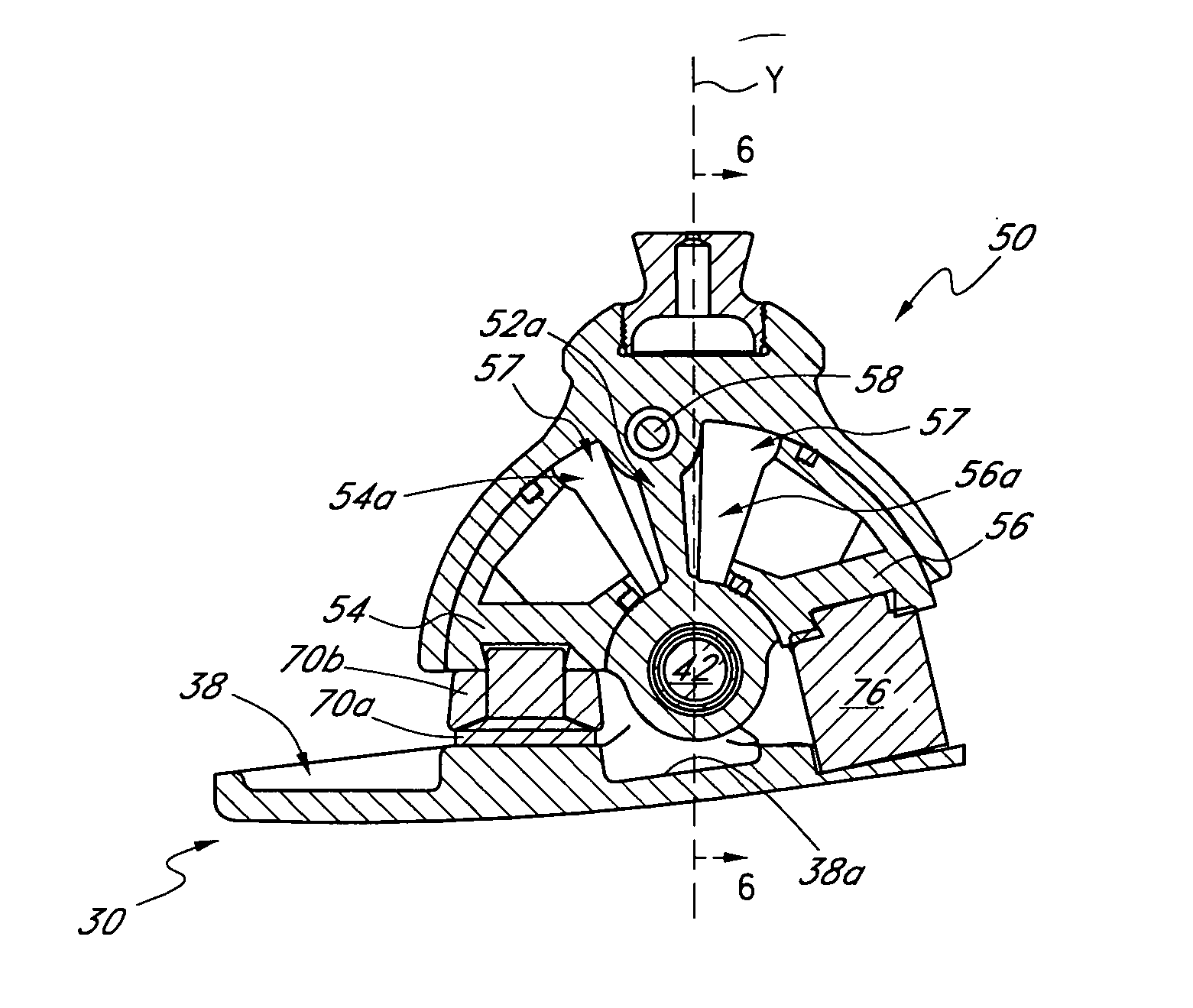
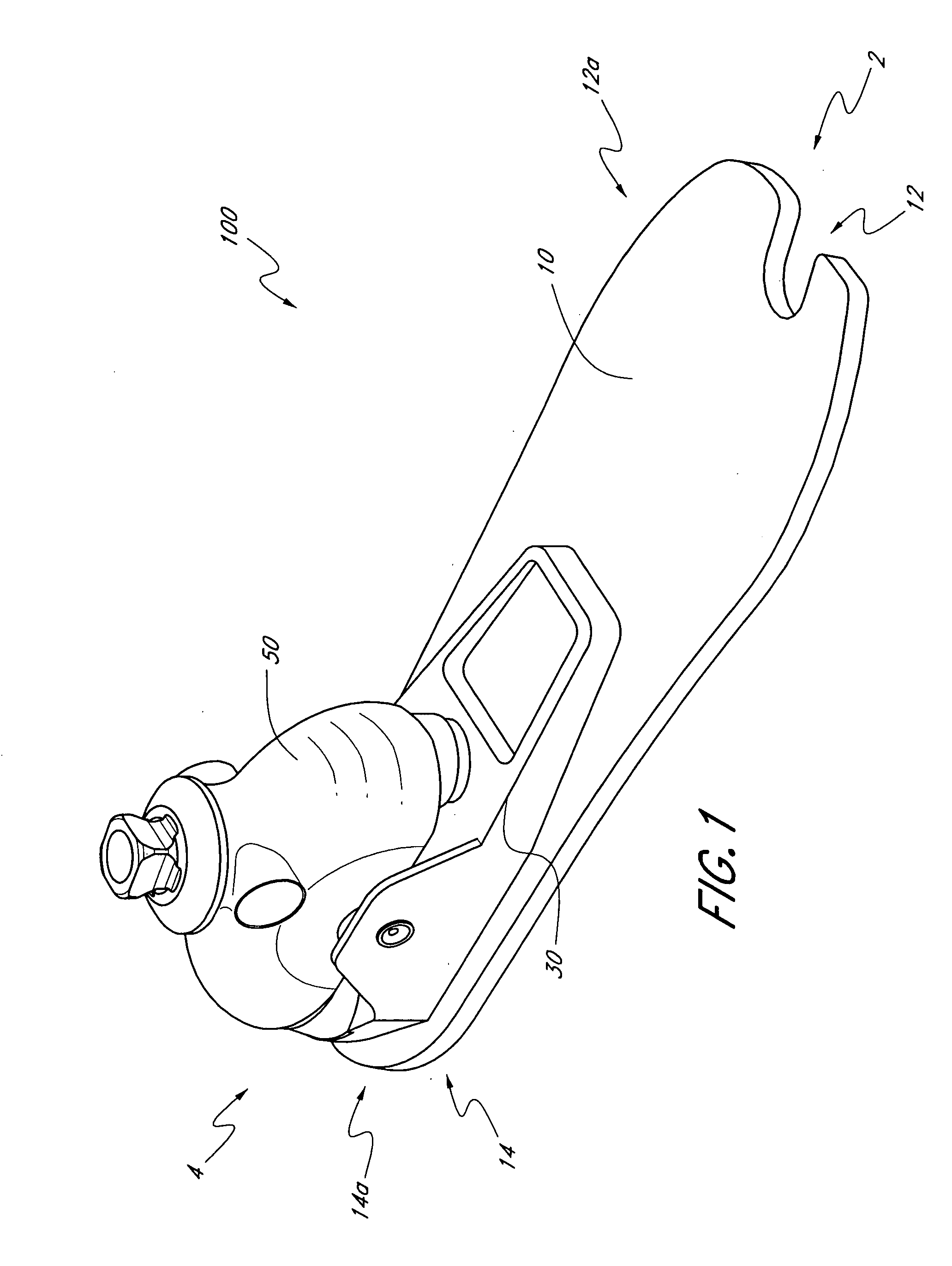
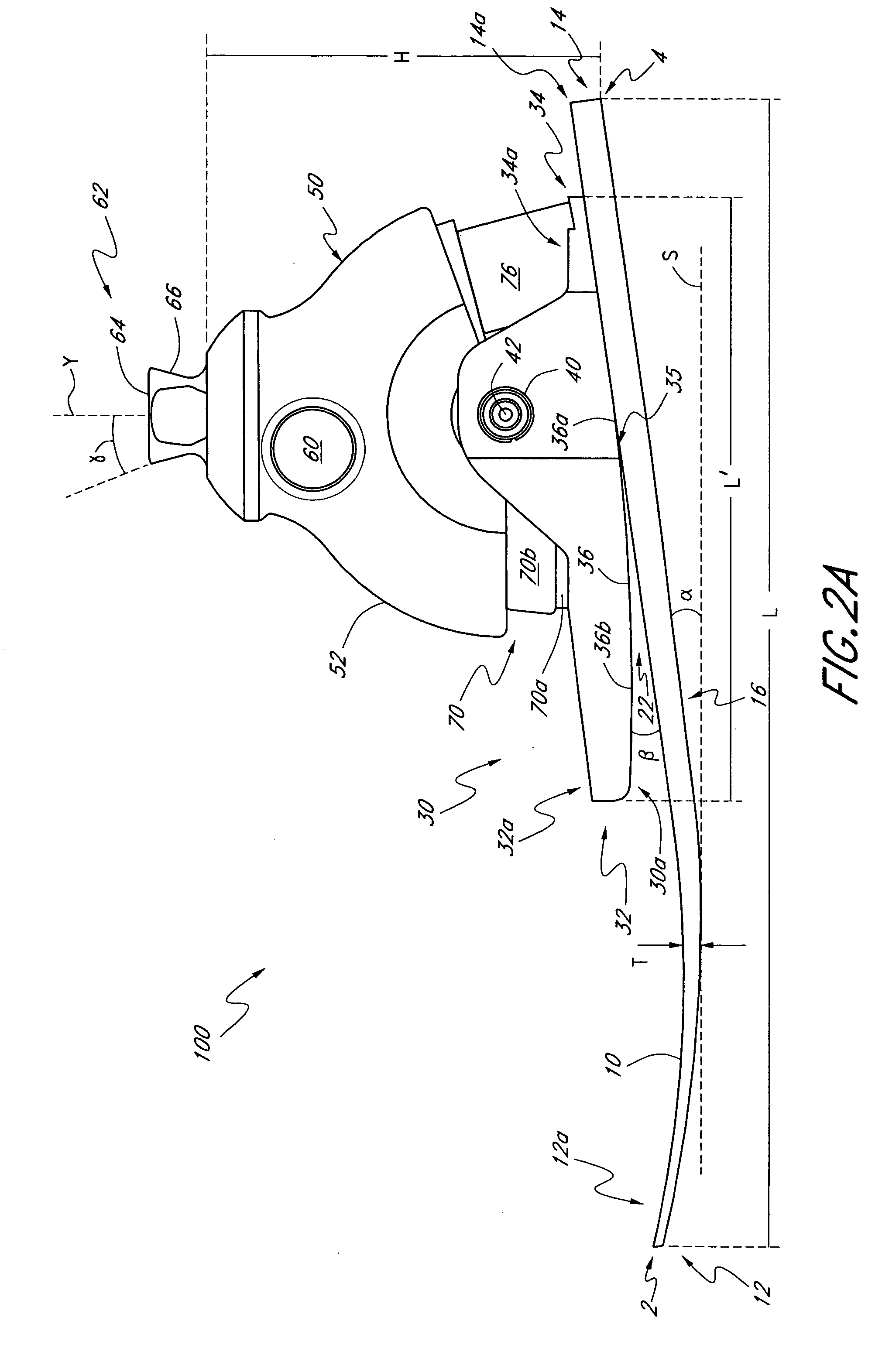
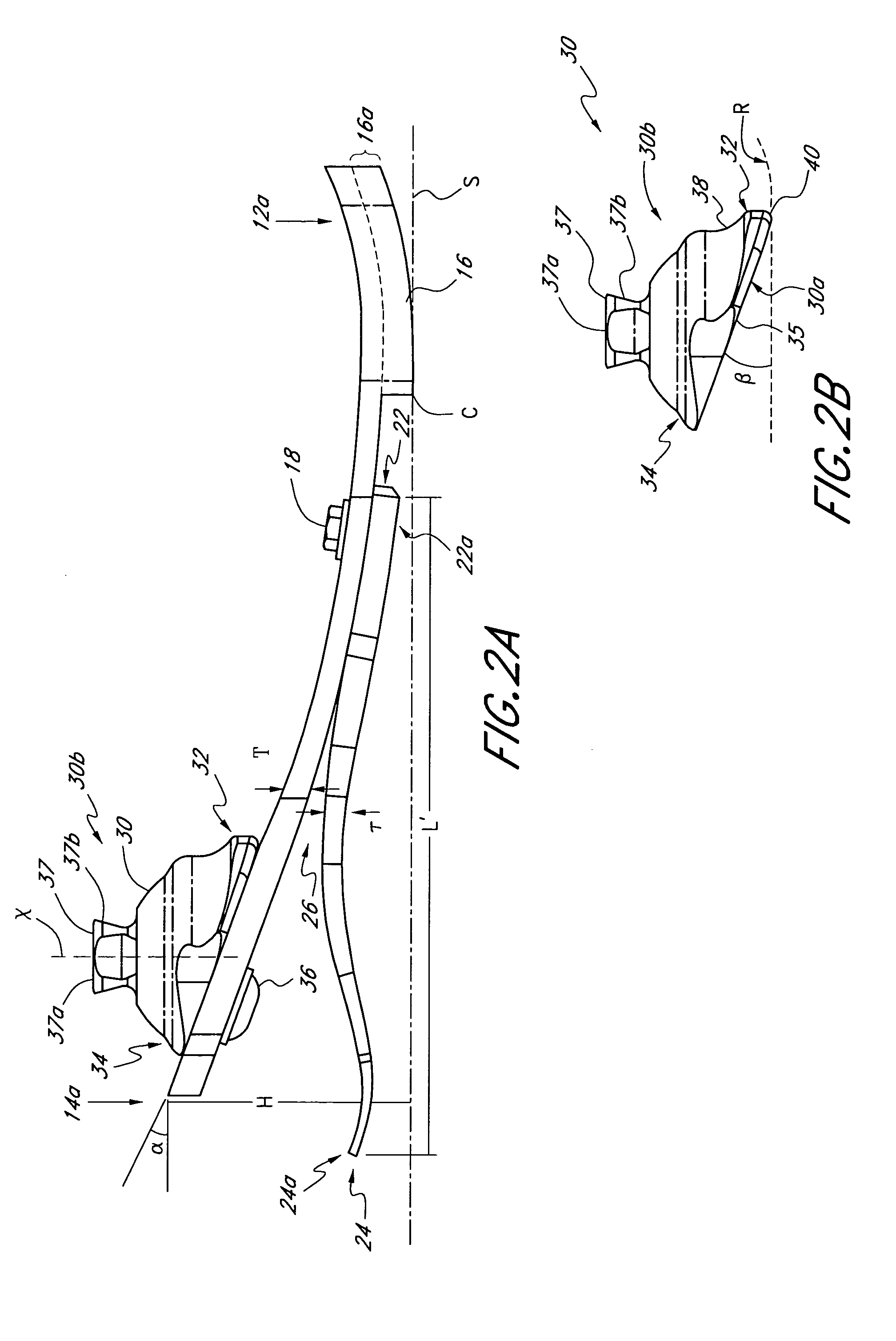
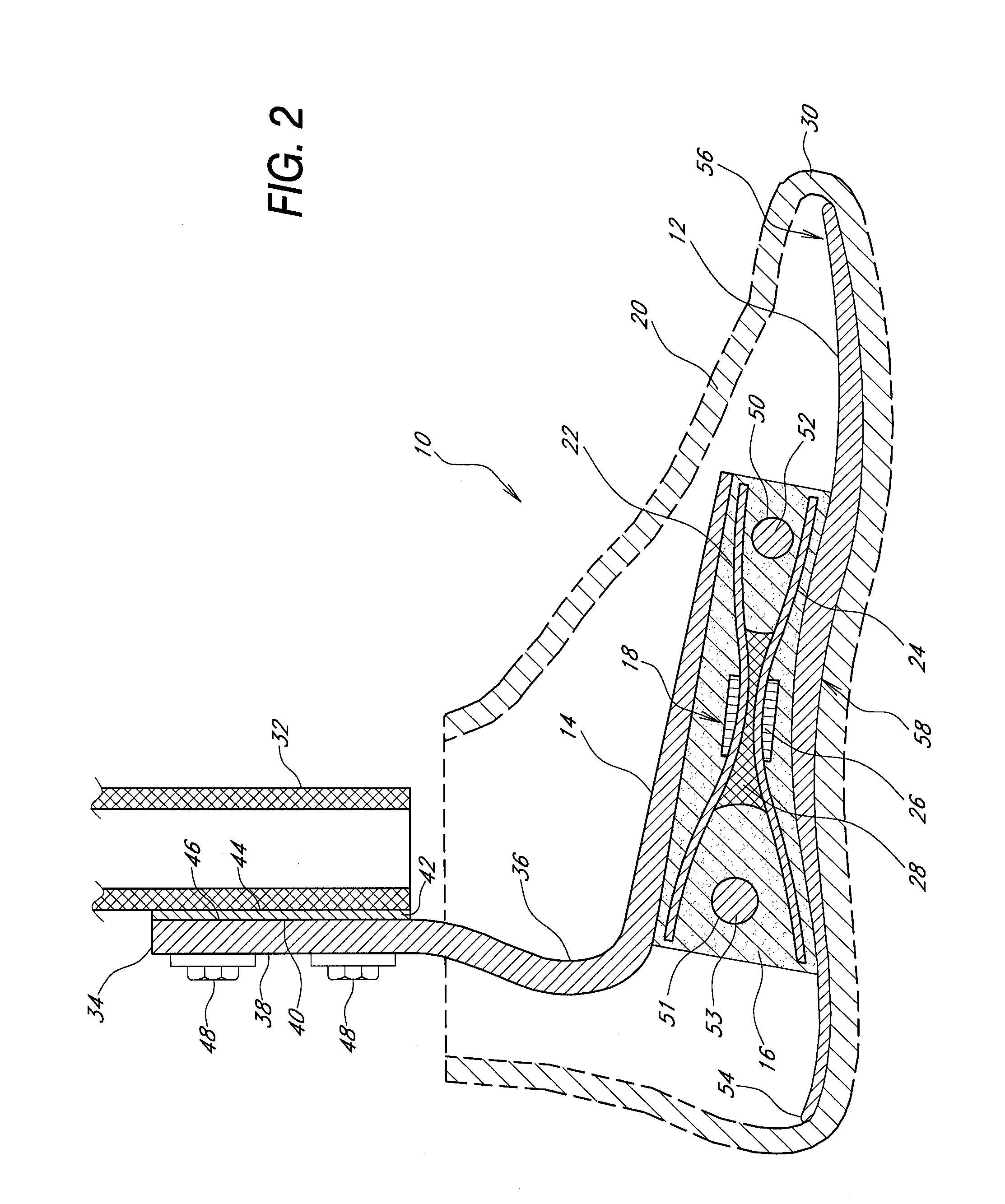
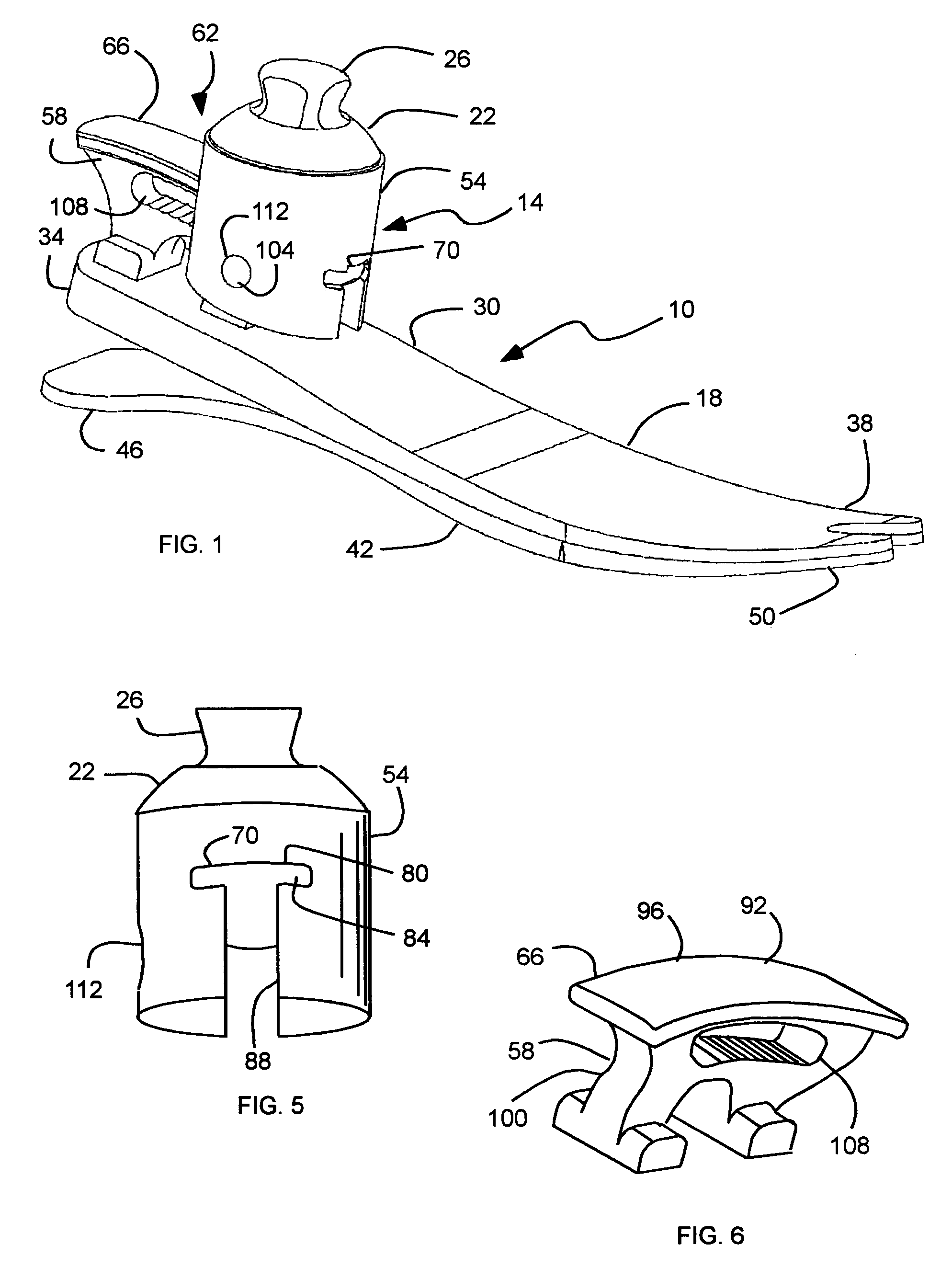
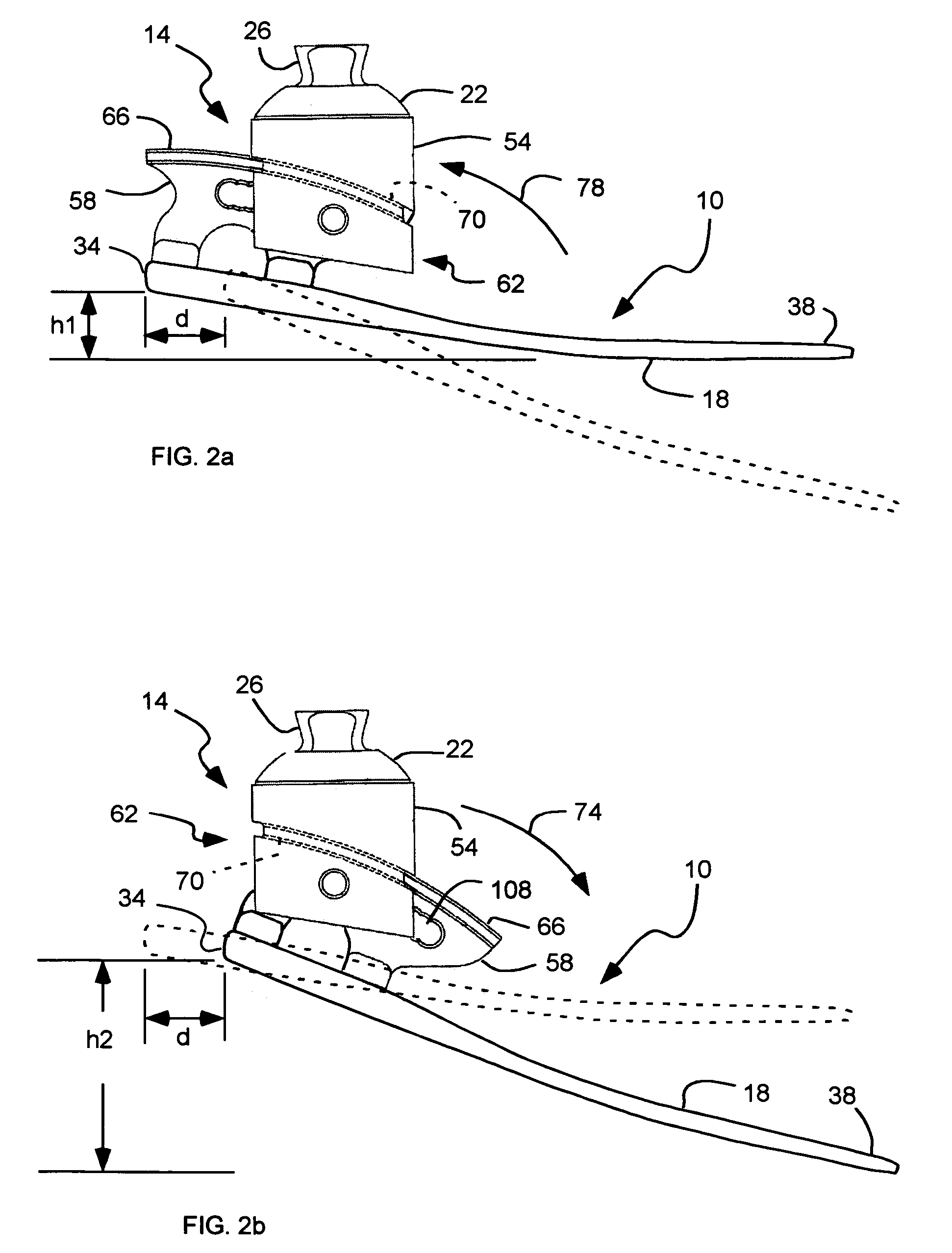
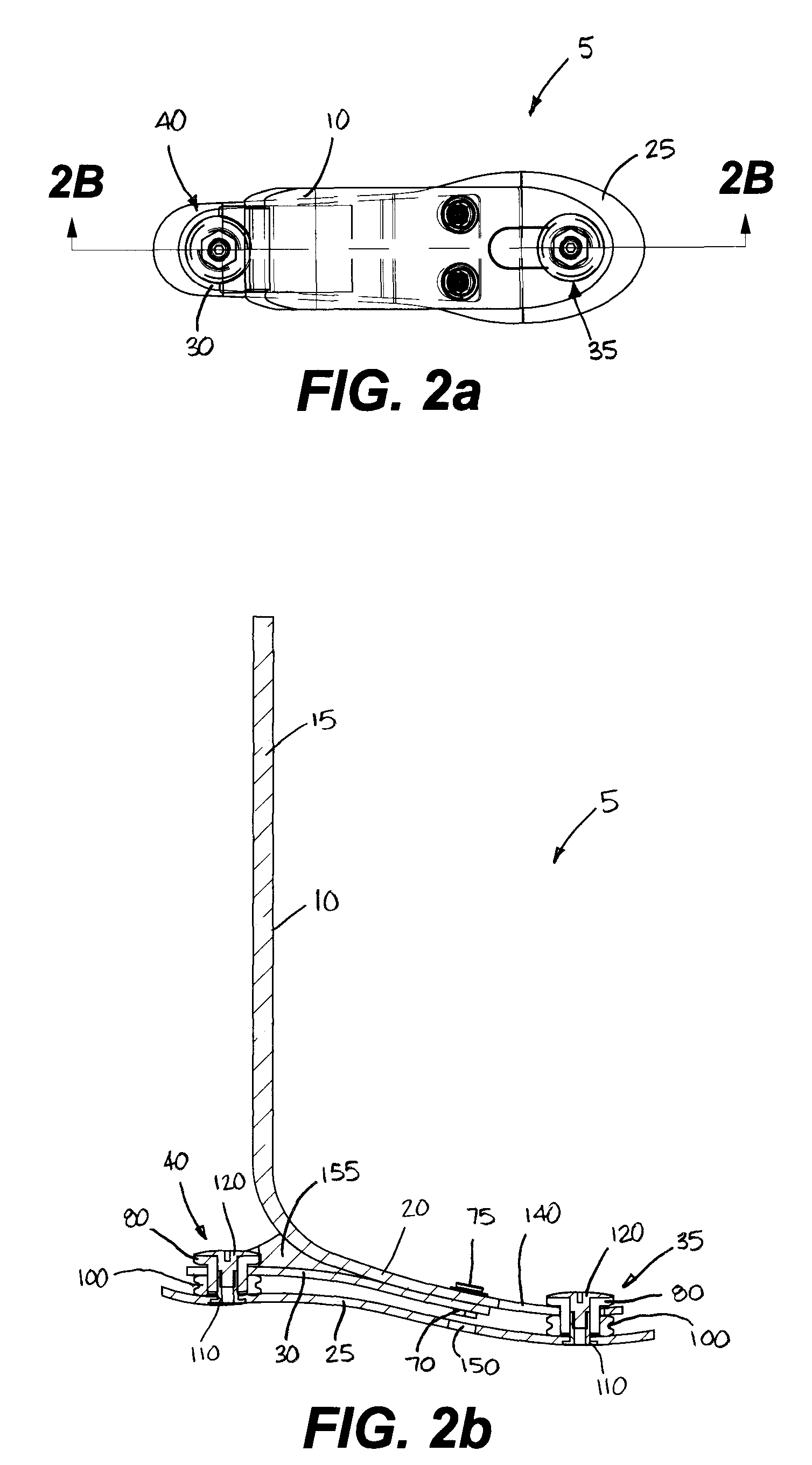
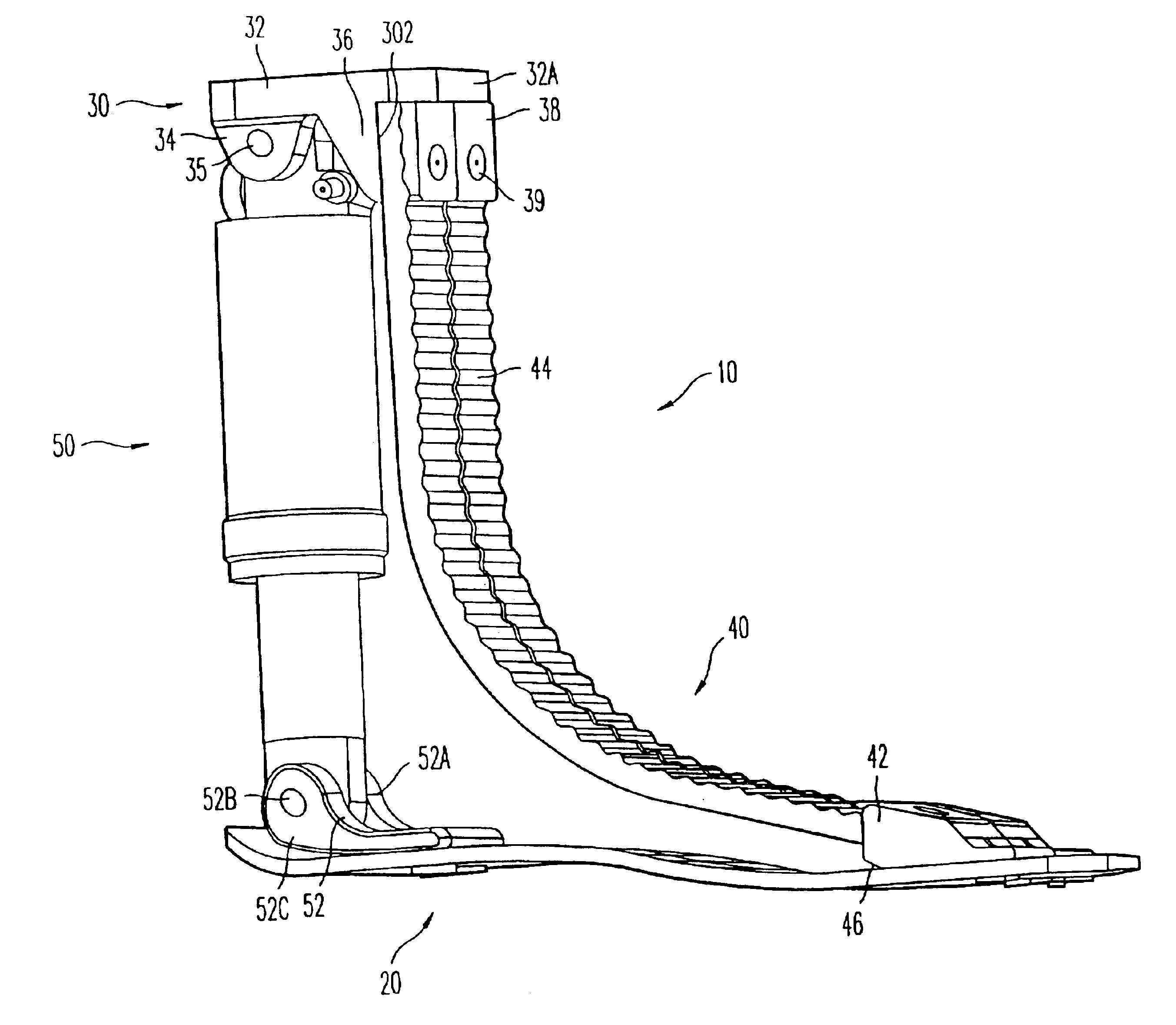
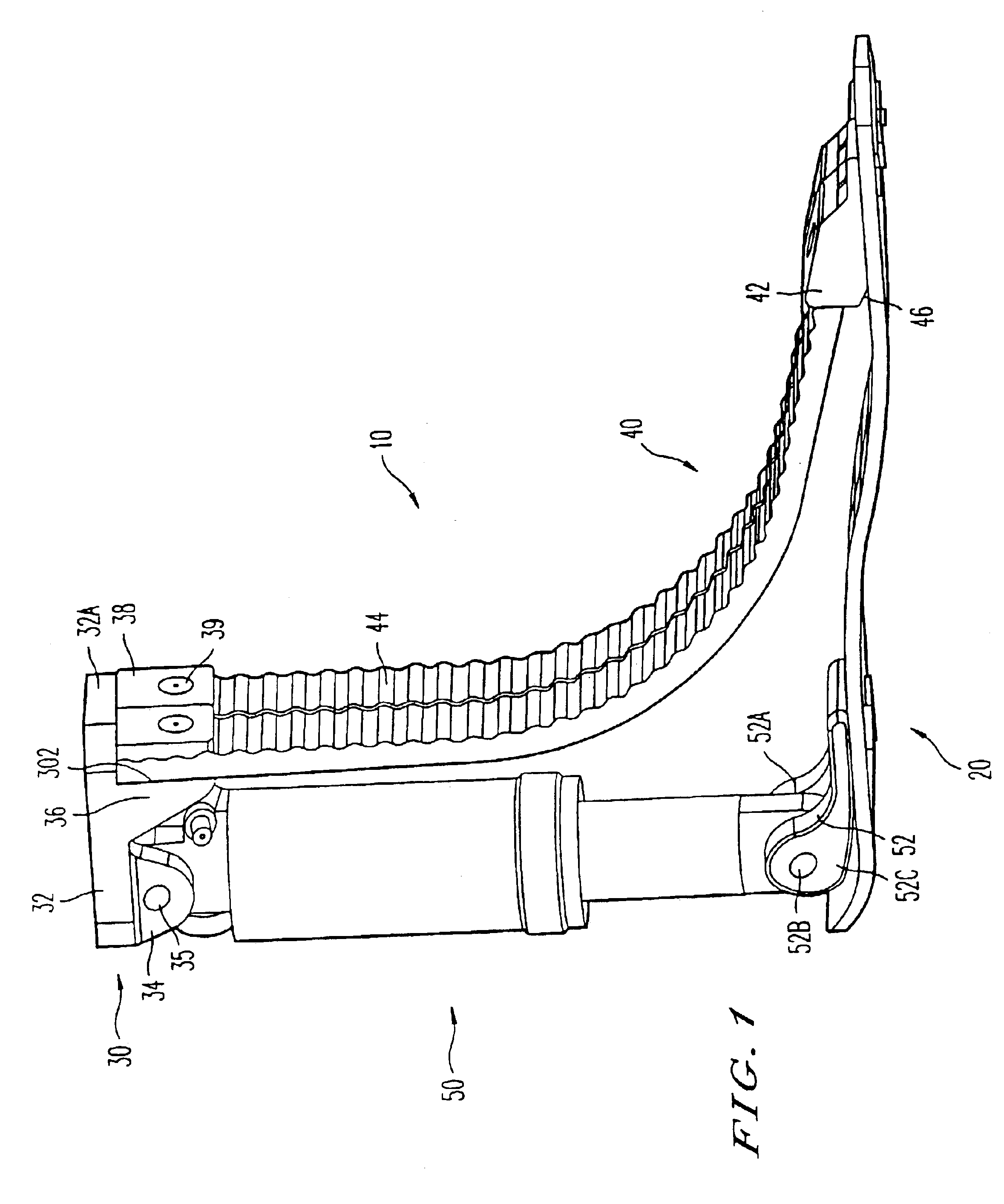
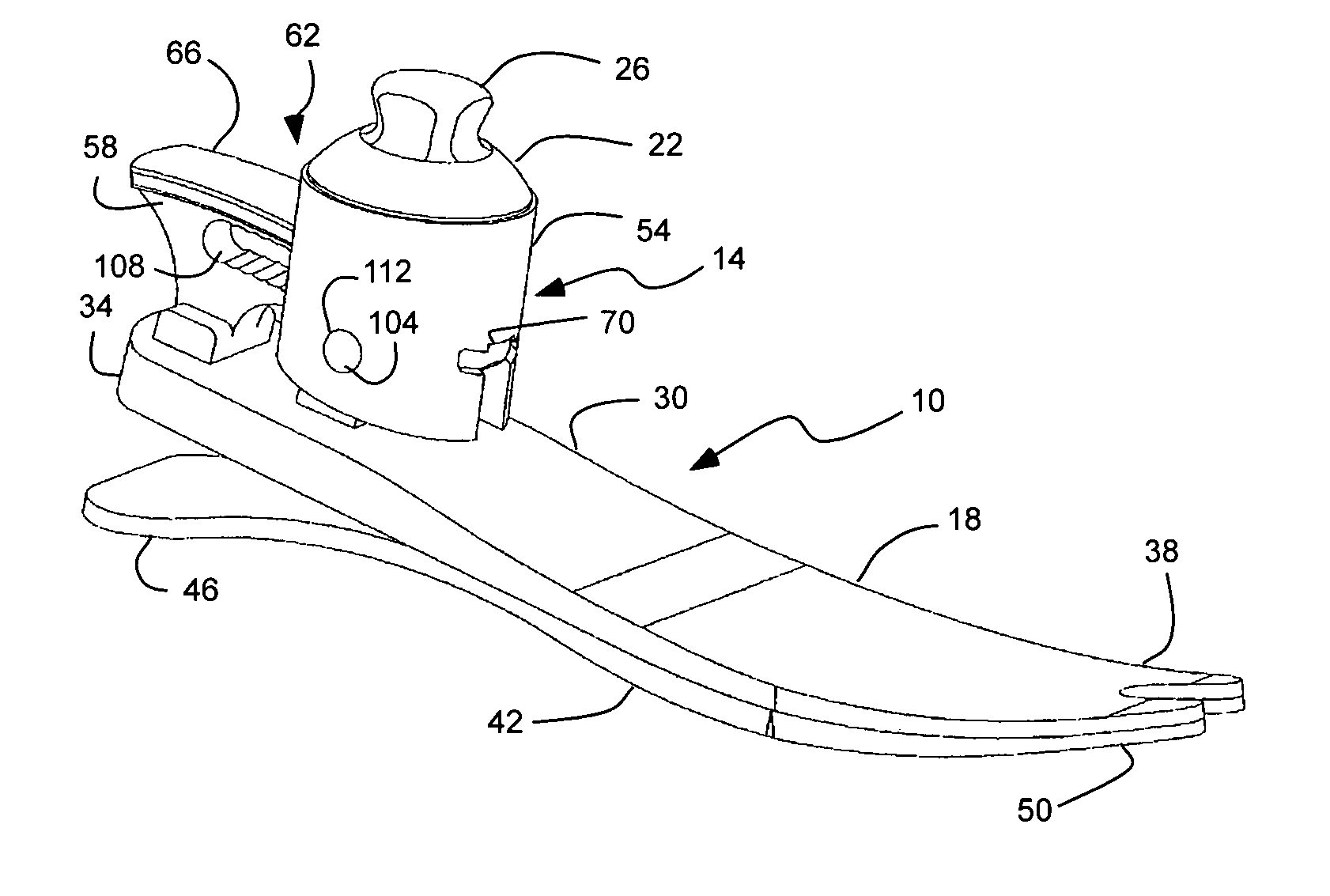
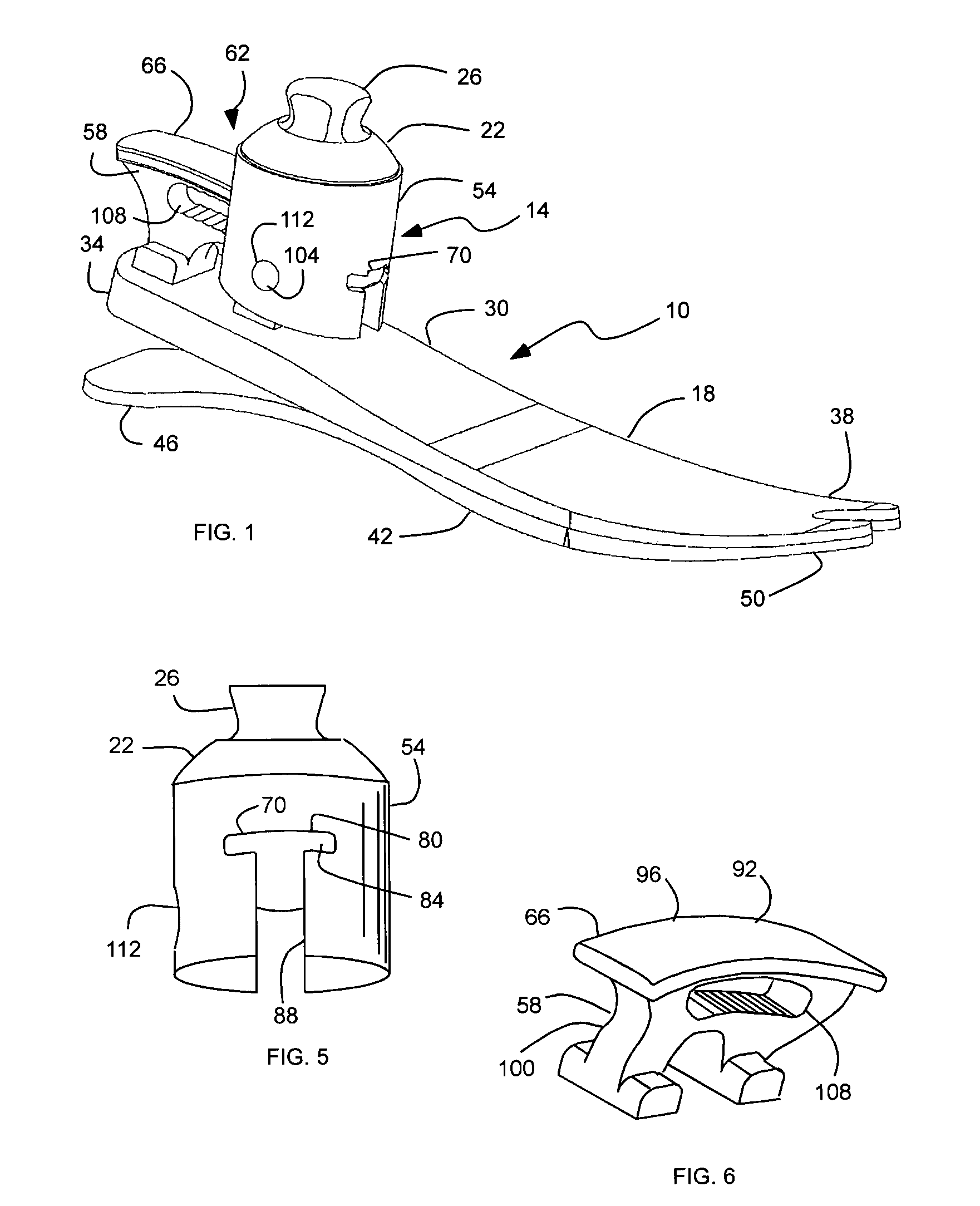
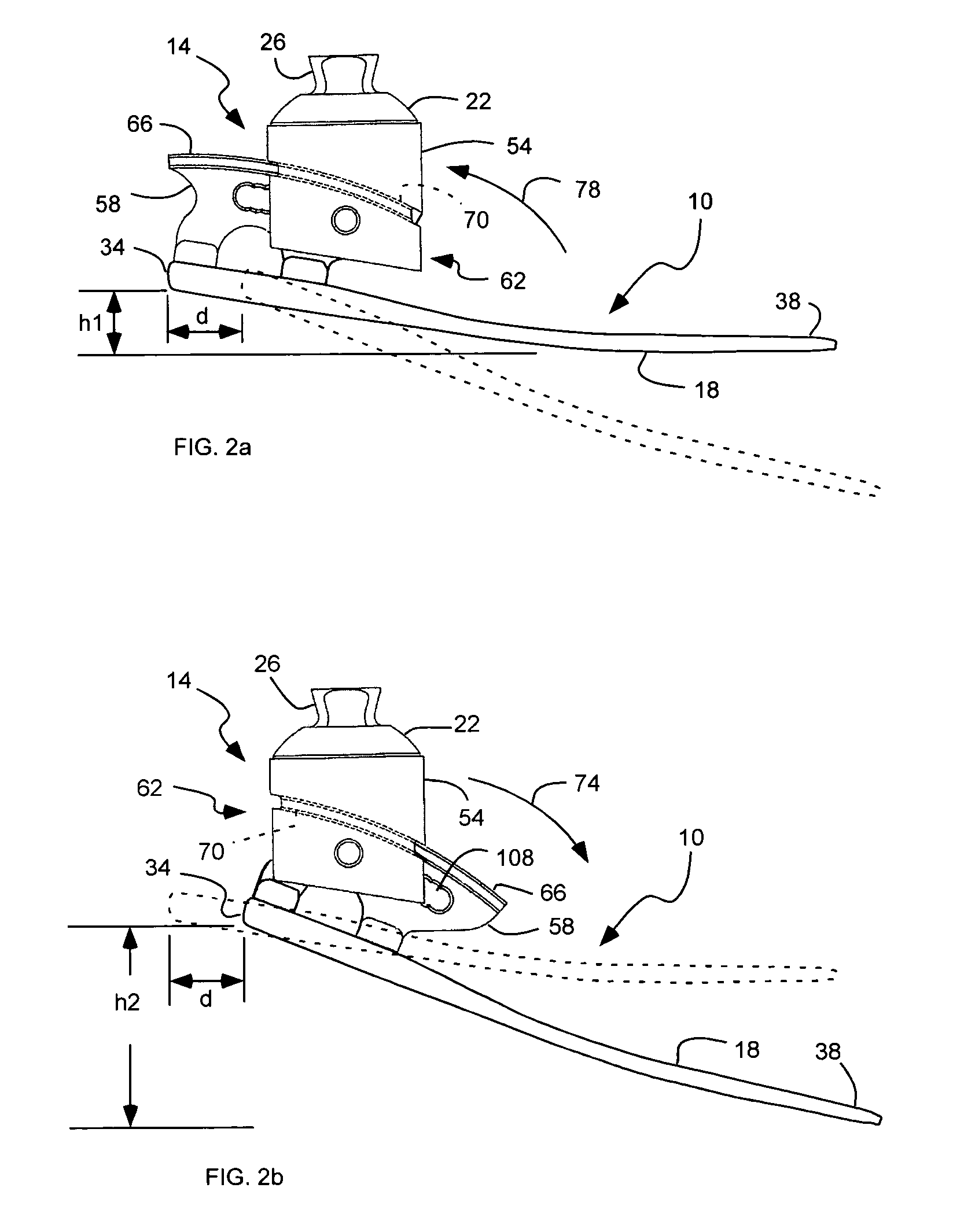
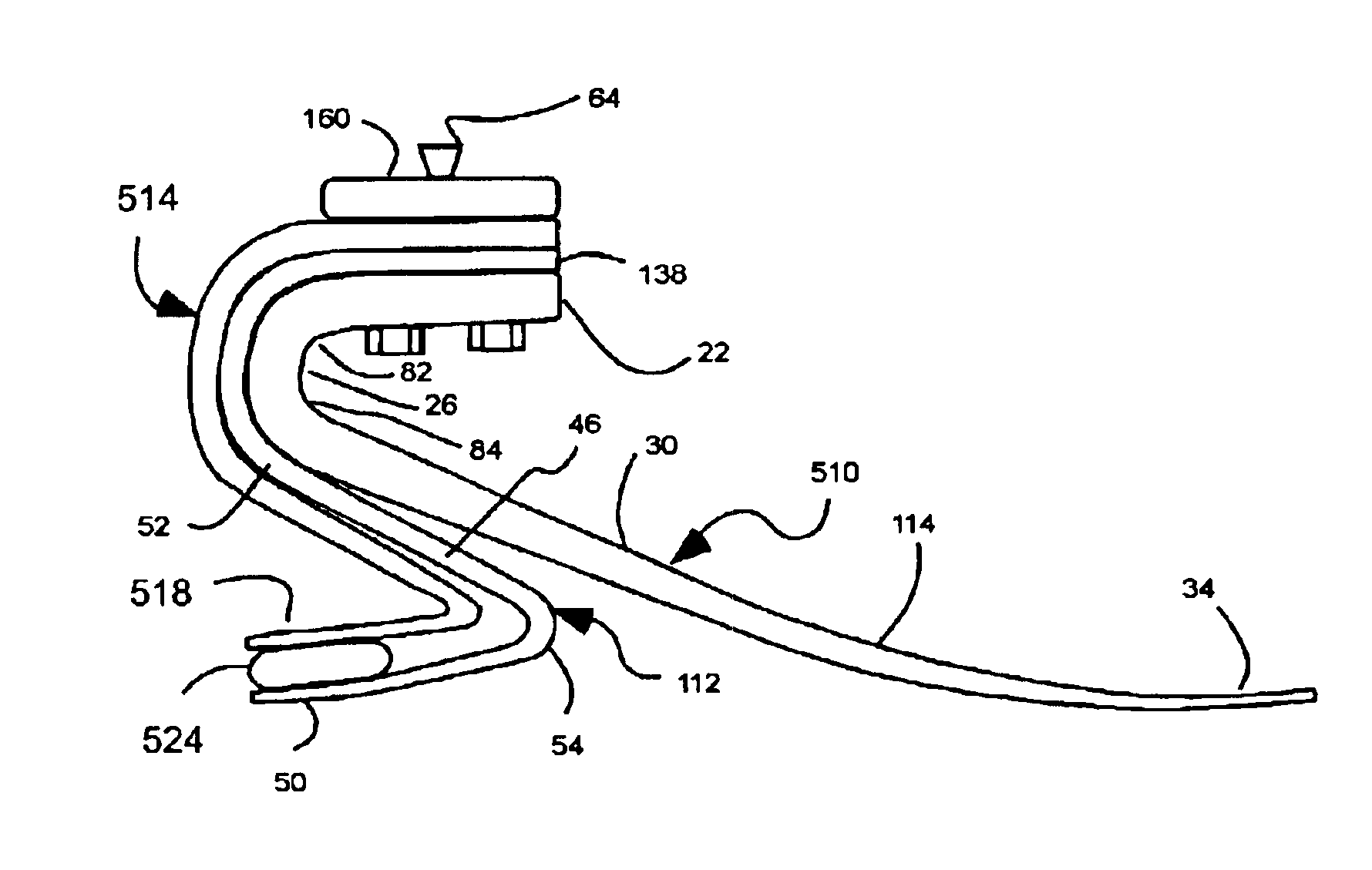
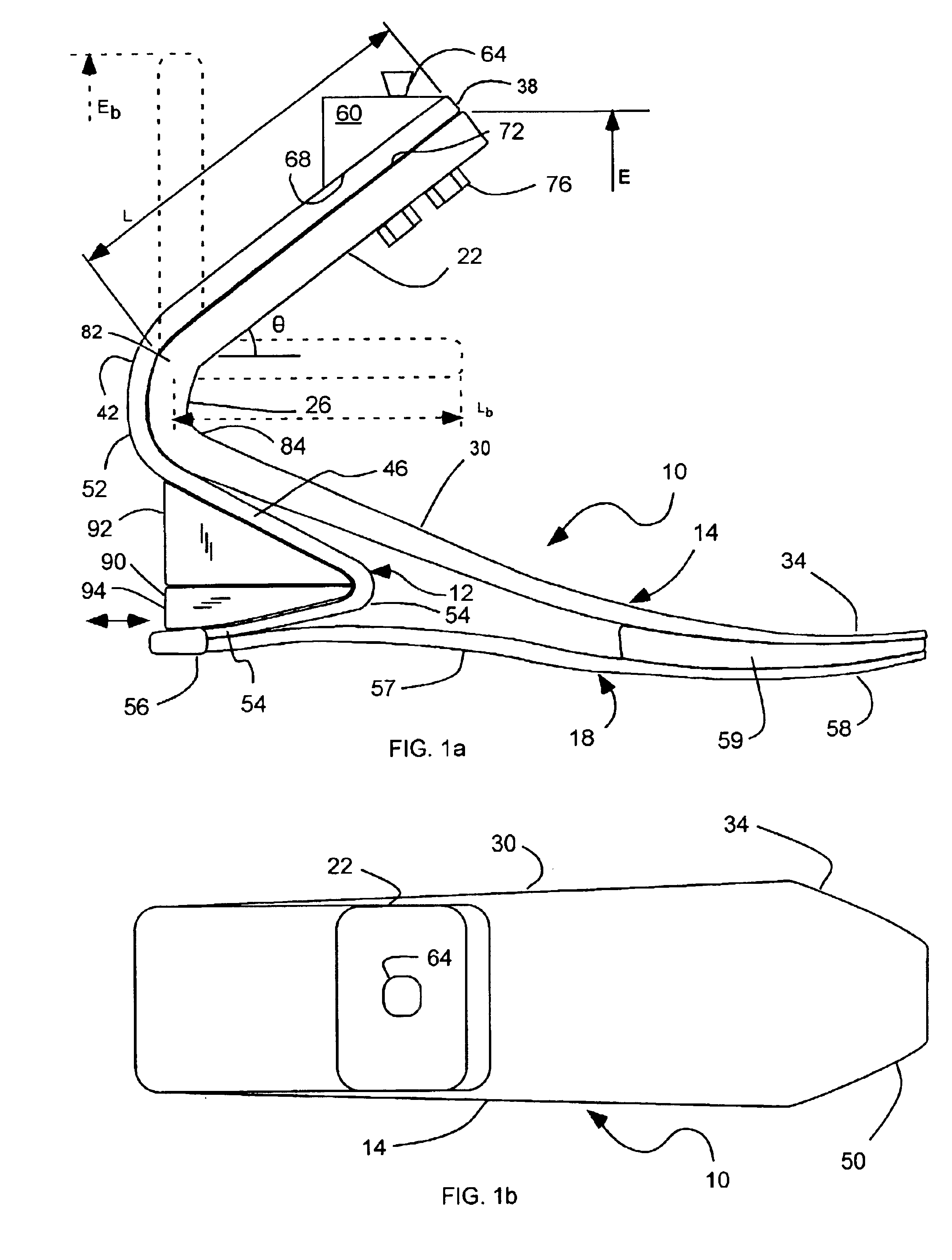
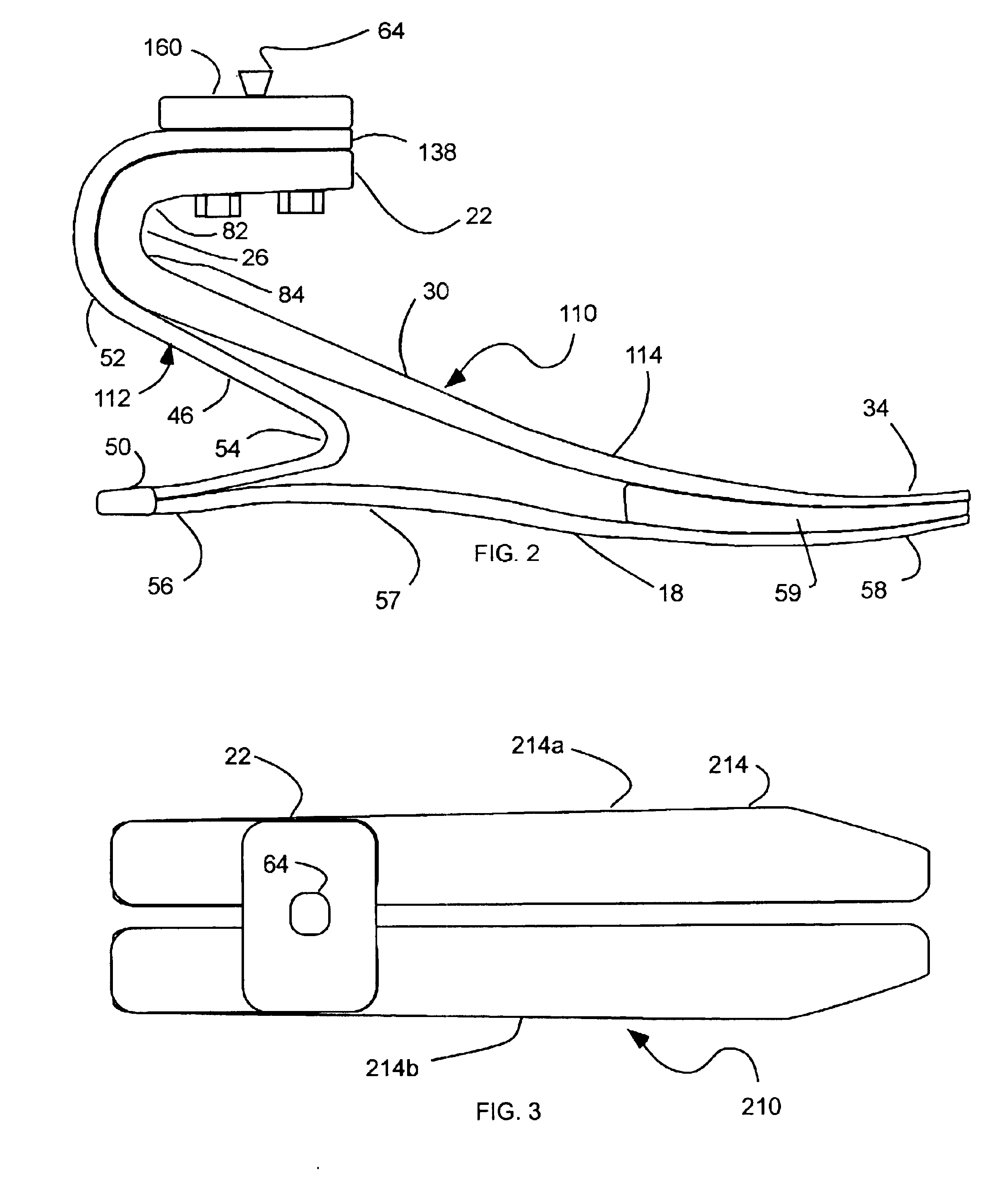
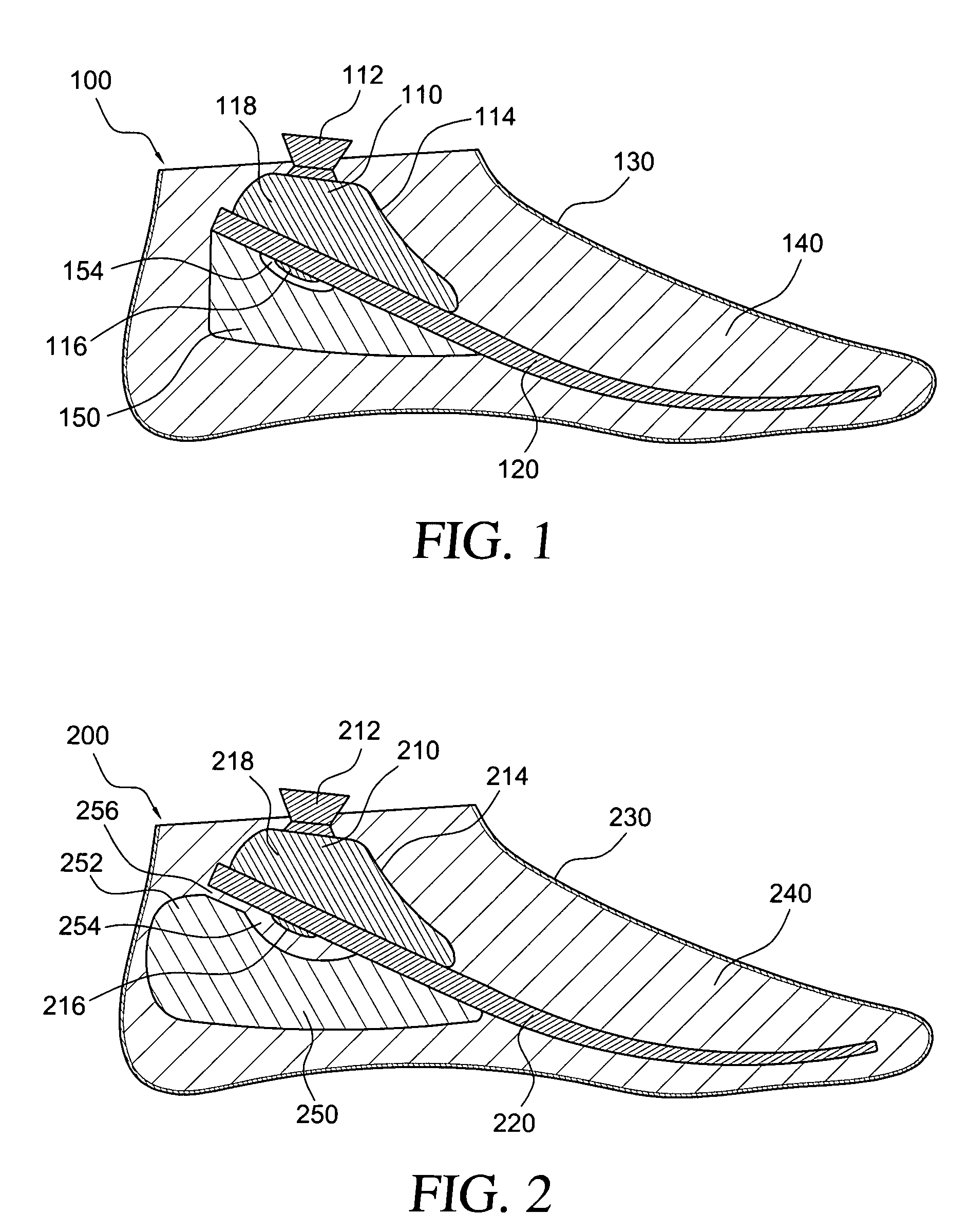
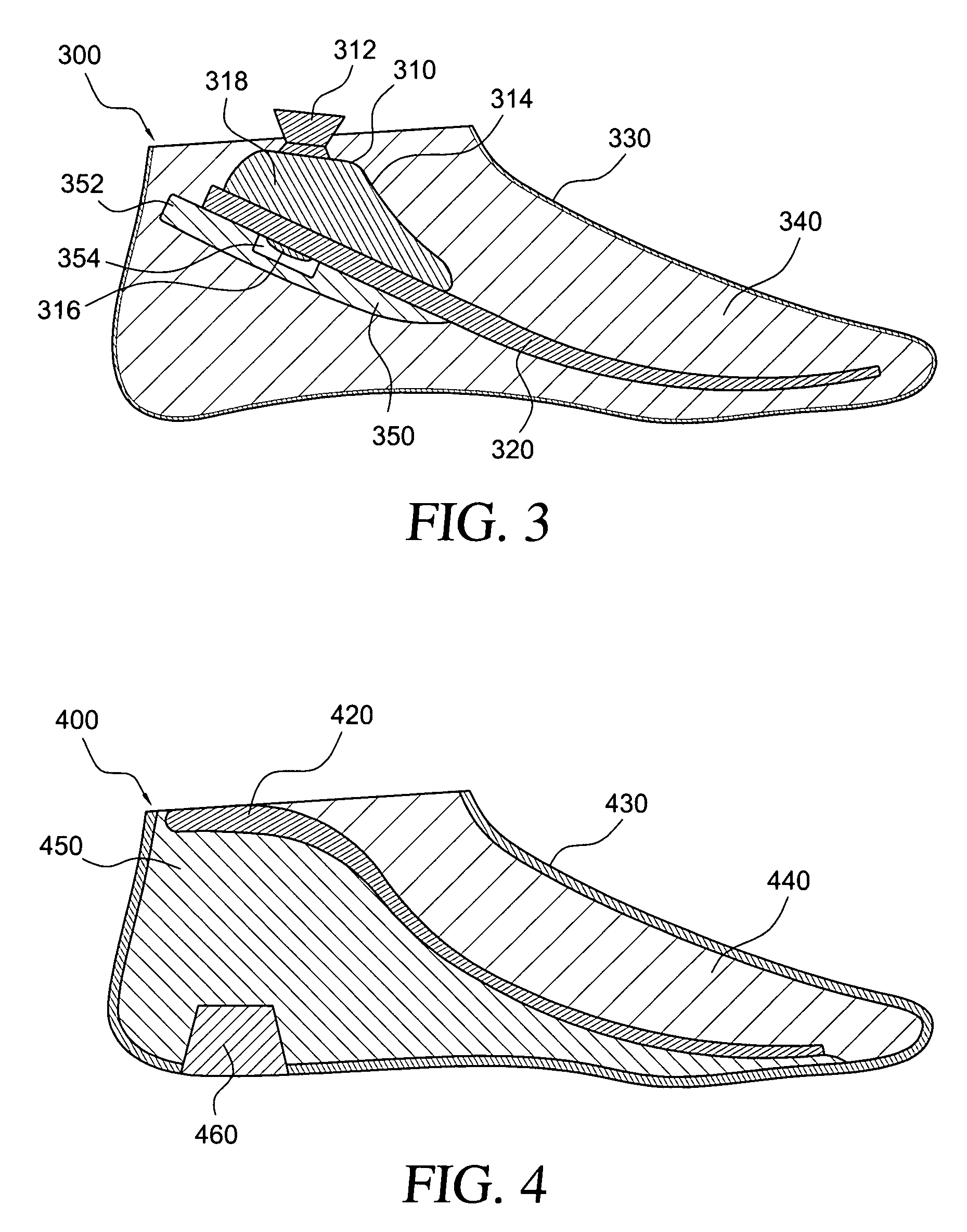
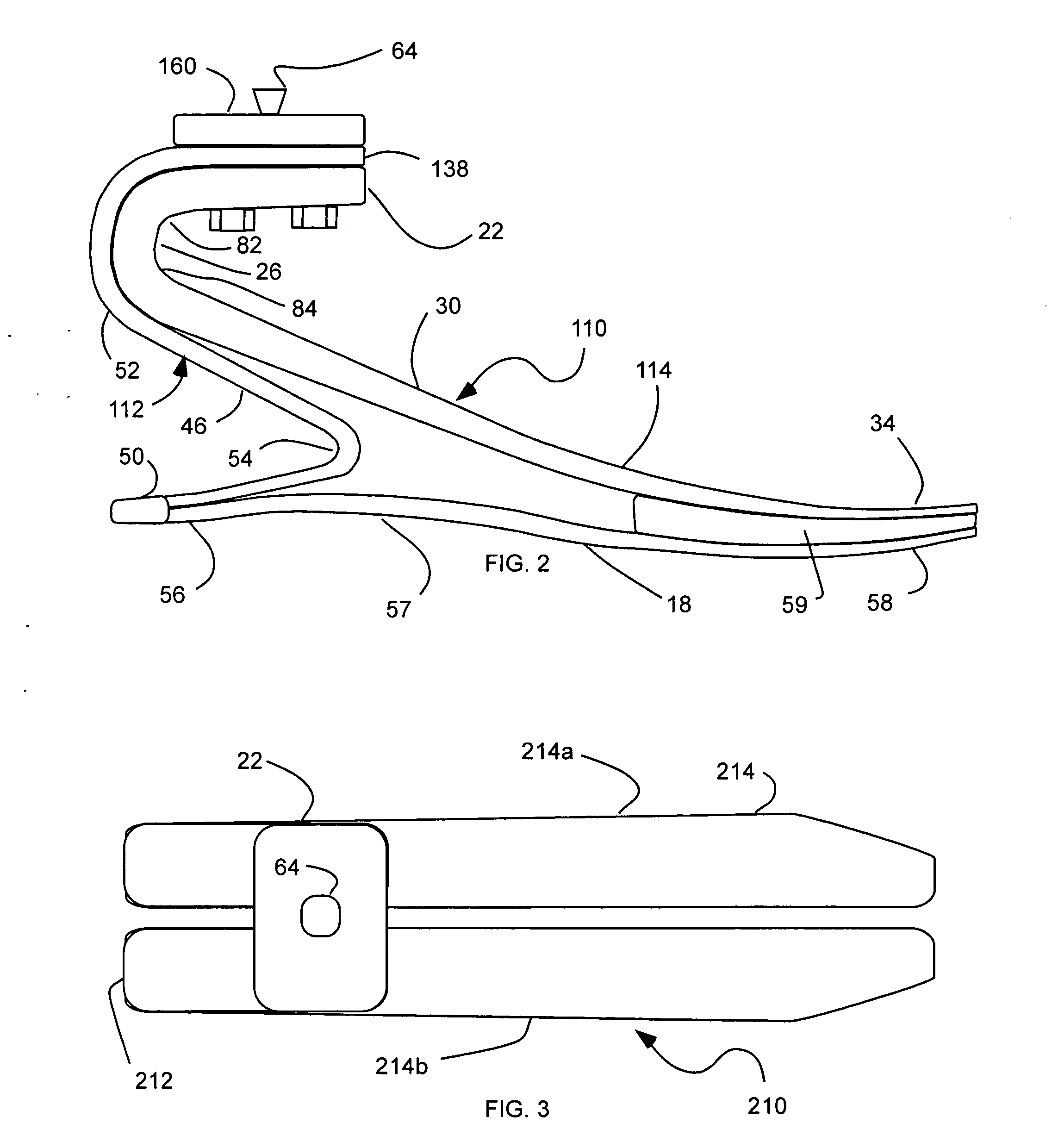
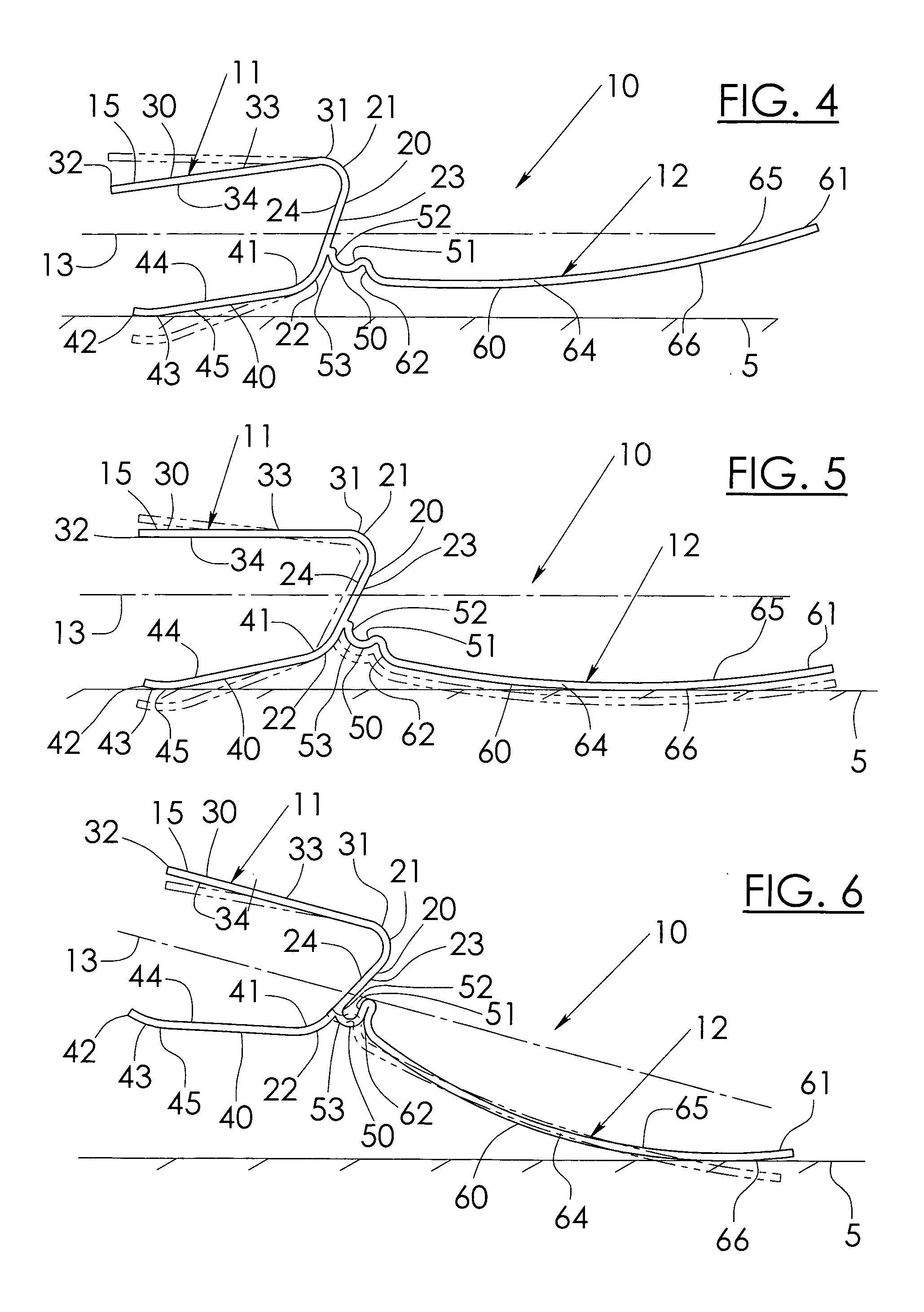
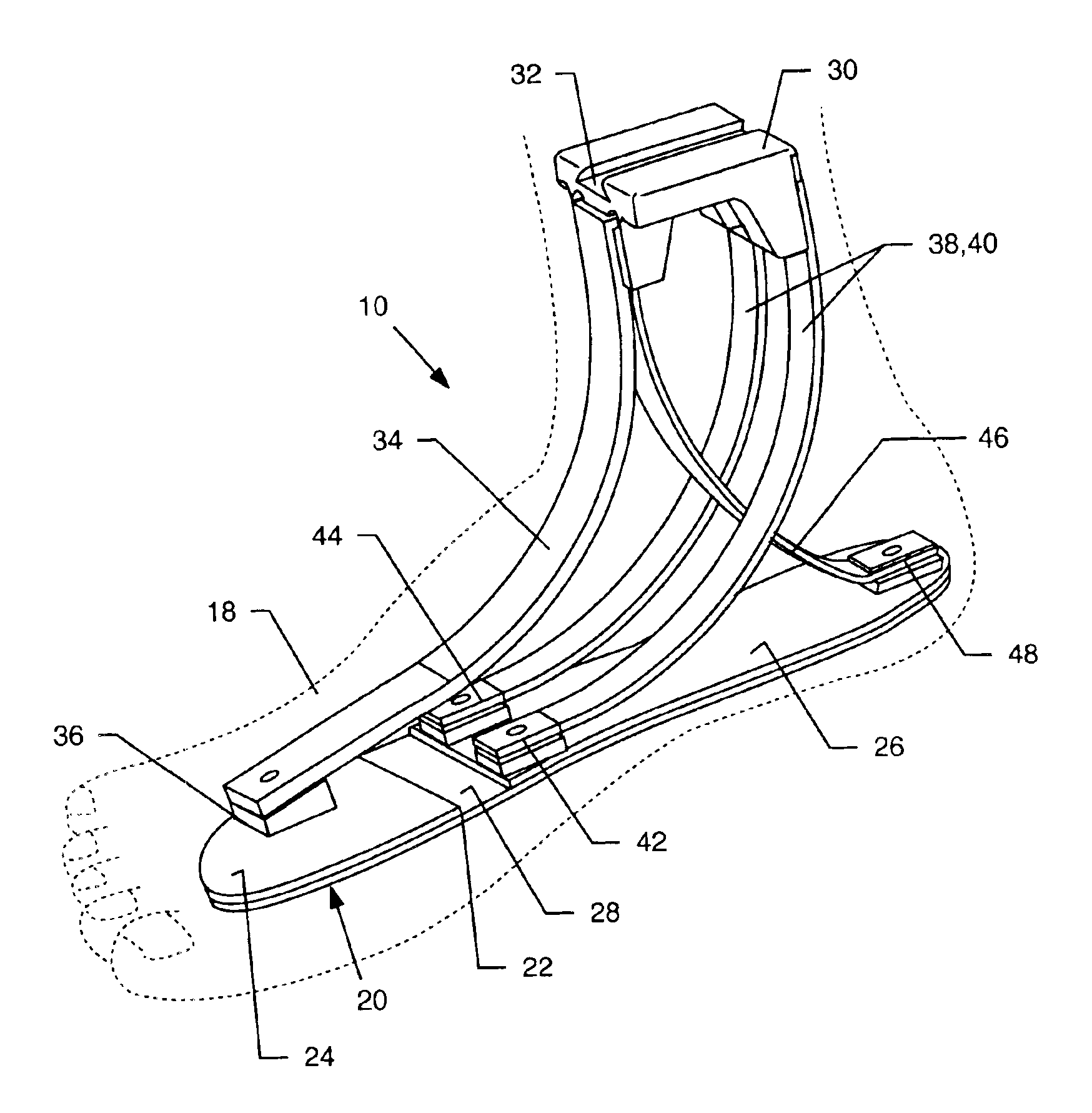
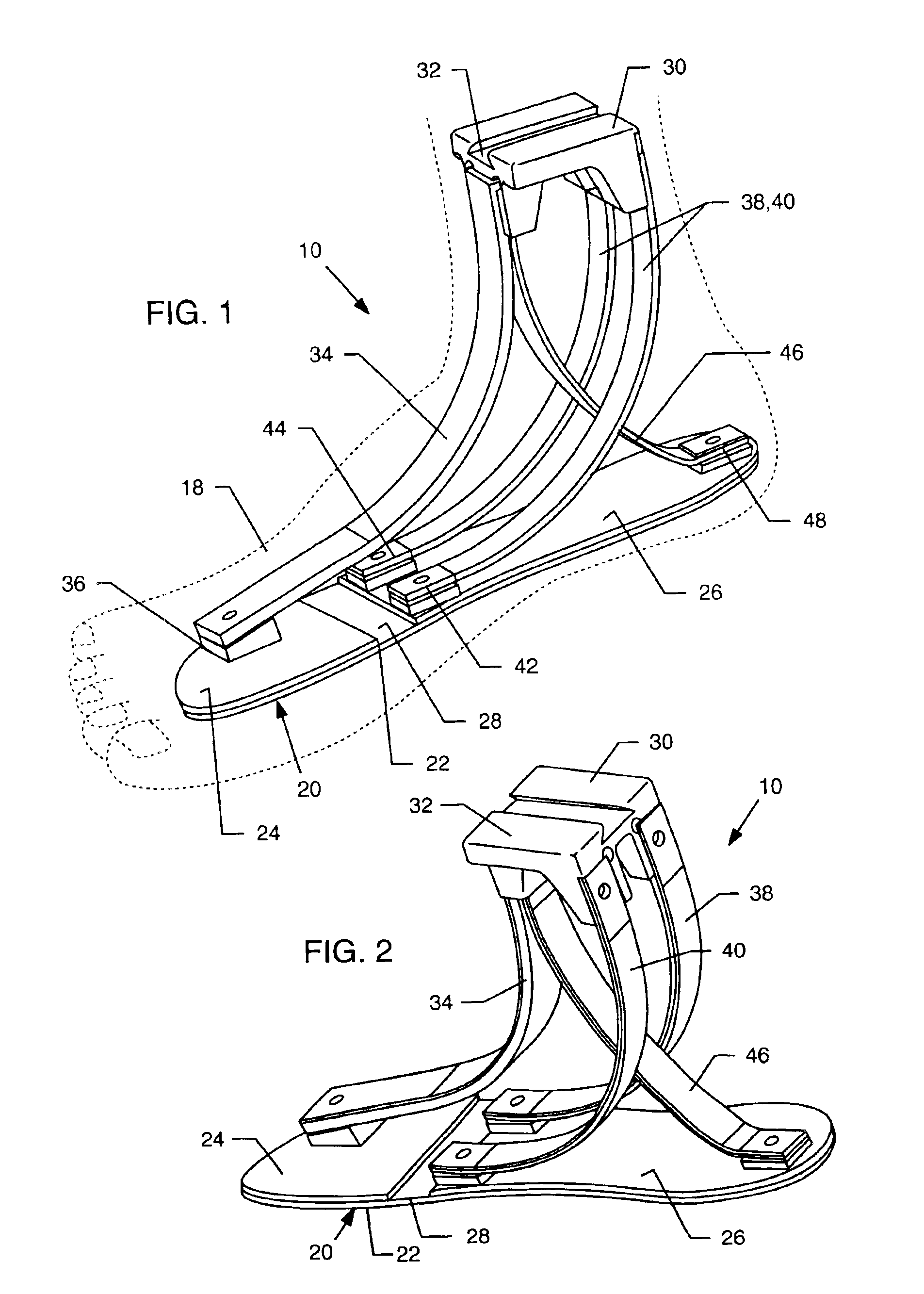
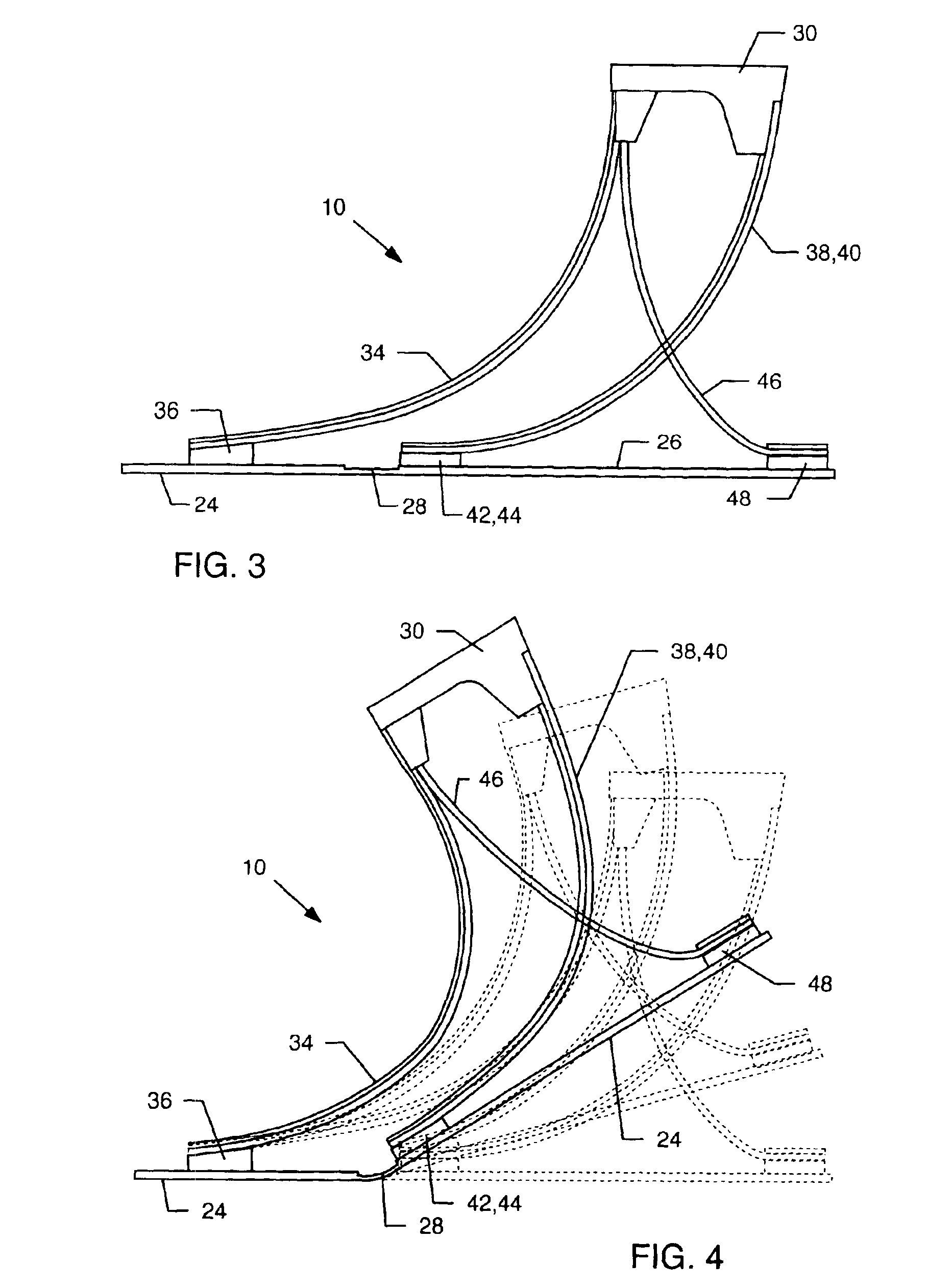
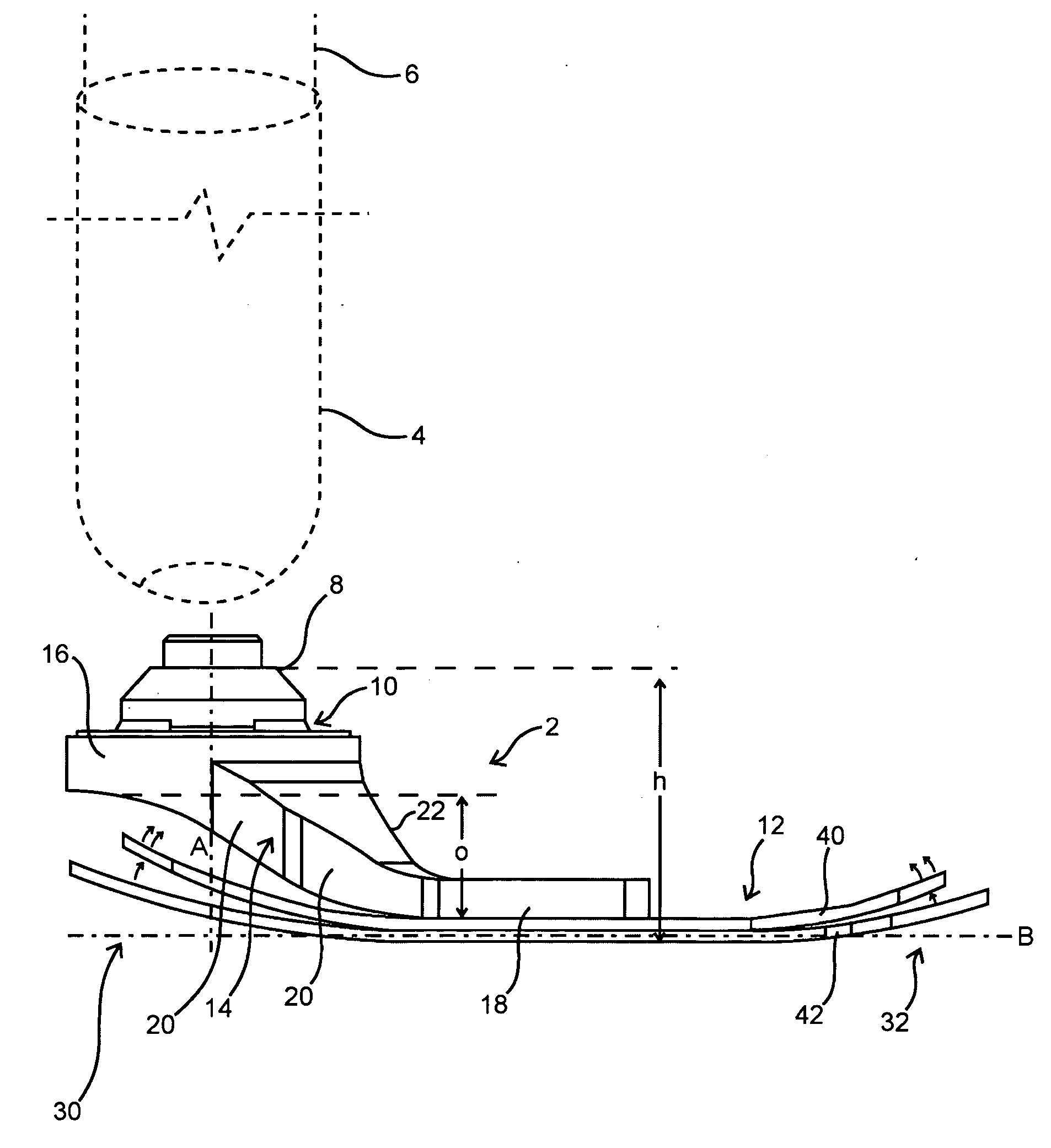
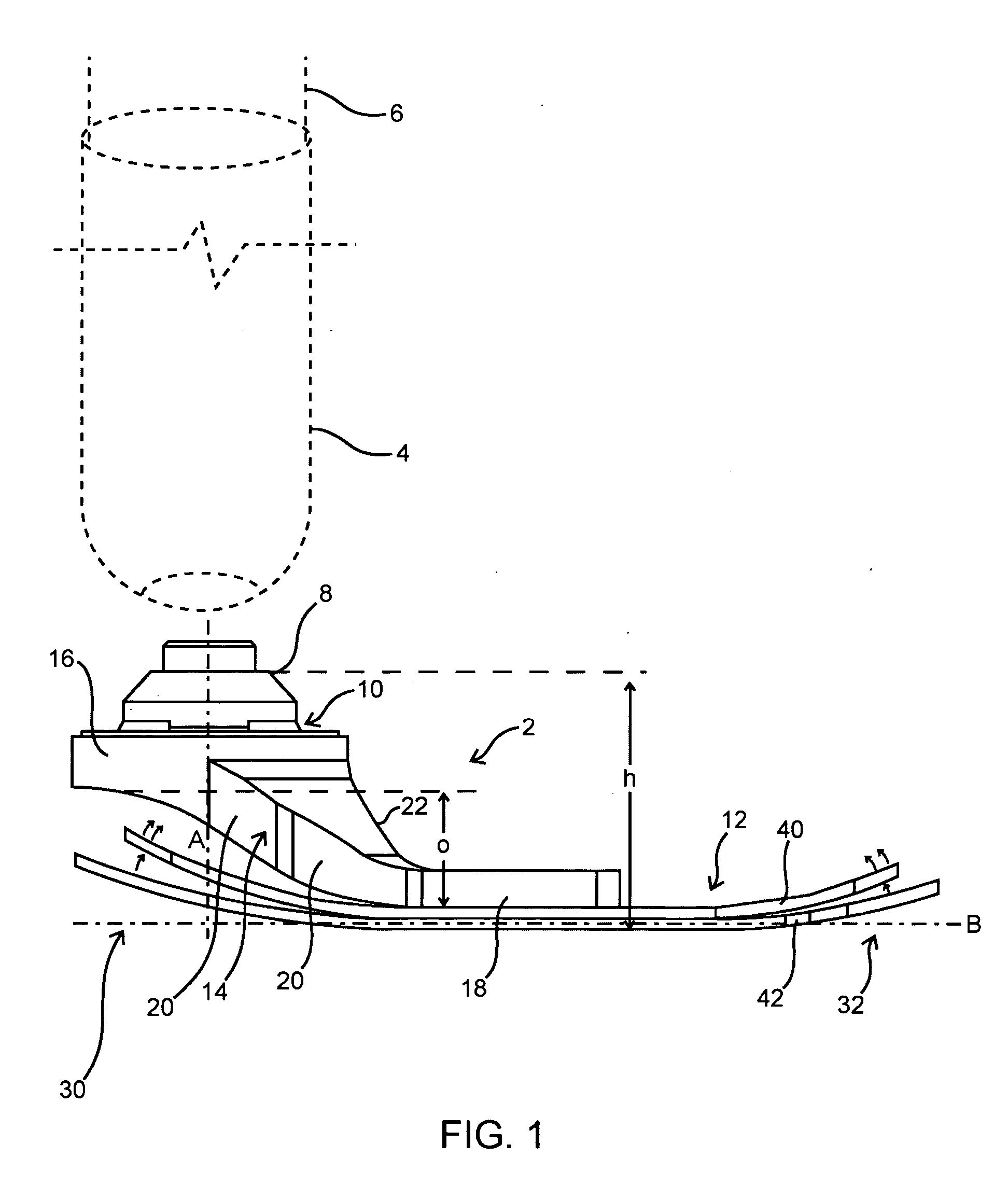
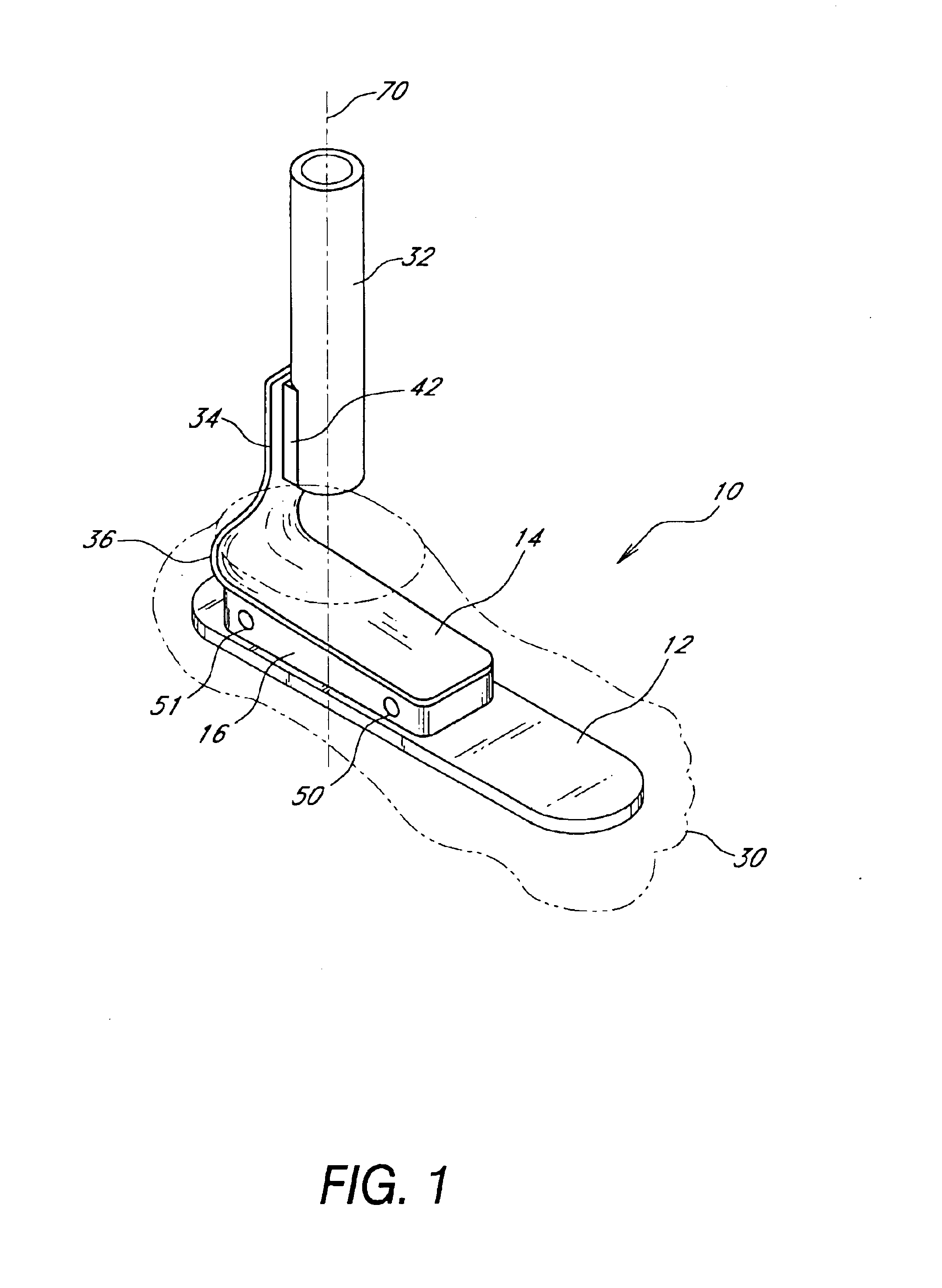
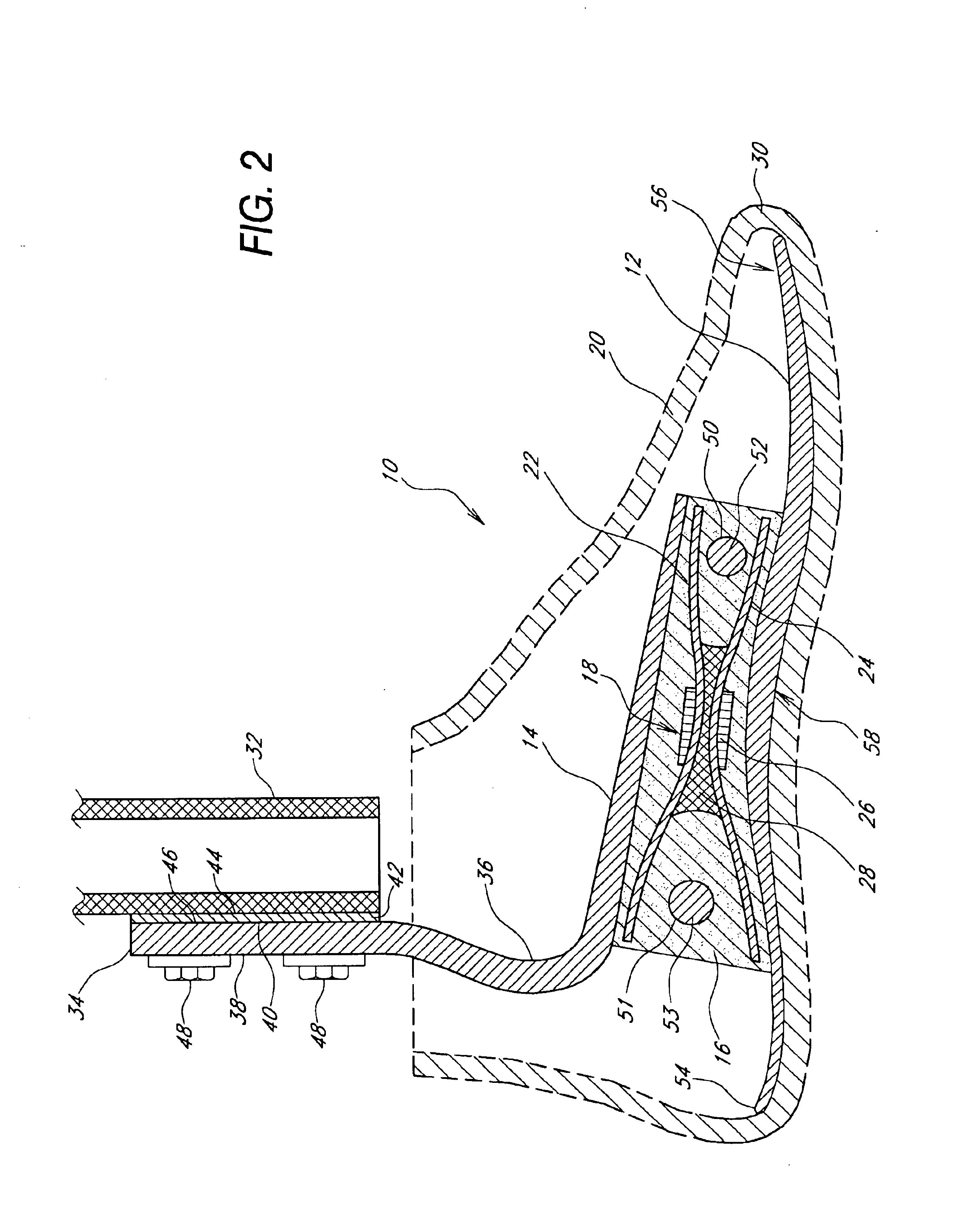
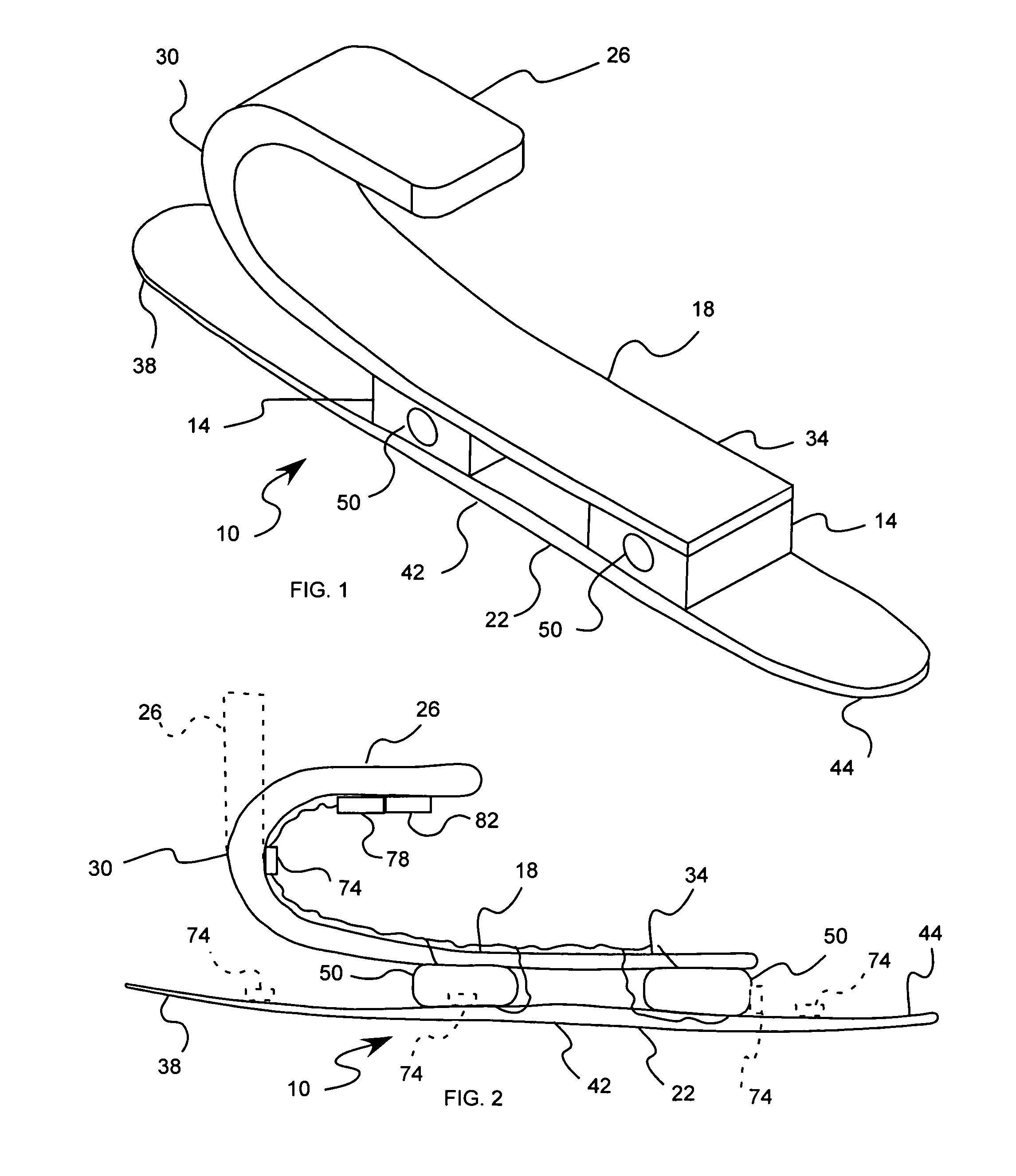
Prosthetic foot with rocker member
InactiveUS20050137717A1Easy introduction intoEasy to removeArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationCantilever
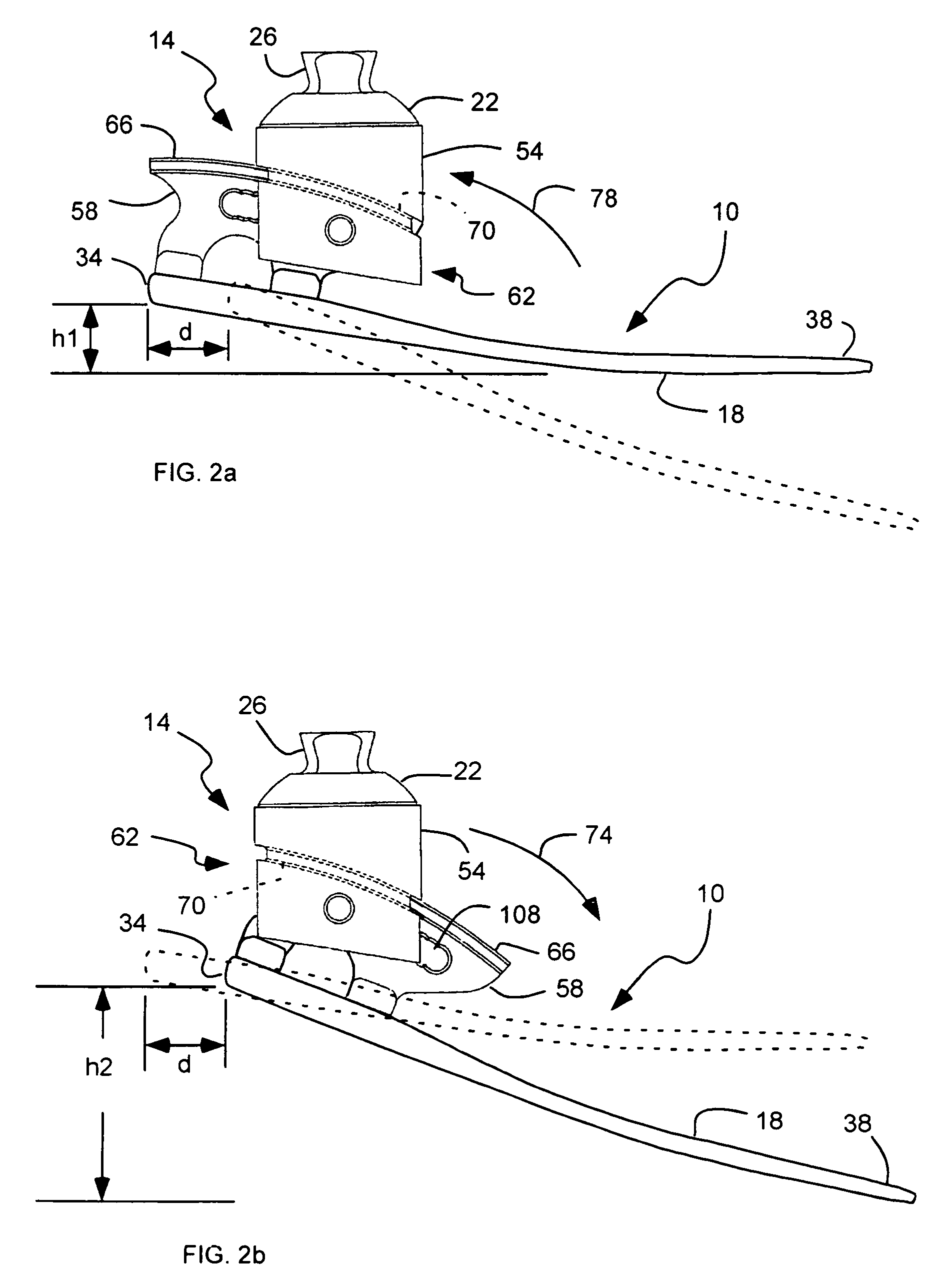
A prosthetic foot comprises a foot member, a rocker member connected in cantilever fashion to the foot member, and an ankle module movably connected to the rocker member about an axis, wherein an anterior section of the rocker member is configured to roll-up onto the foot member an amount corresponding to the load applied on the foot, and wherein the foot member is configured to facilitate the initial roll-up of the rocker member.
Owner:GRAMTEC INNOVATION +1
Prosthetic foot
InactiveUS6443995B1Improve the quality of lifeImproves footArtificial legsSagittal planePlantar surface
An ankle joint and a subtalar joint provided in a hindfoot permit closed kinetic chain motion of the foot. The ankle and subtalar joints are preferably formed integrally with the hindfoot by respective struts of resilient material of the hindfoot. An arch in the midfoot creates frontal and sagittal plane motion capabilities. The forefoot includes at least one expansion joint hole extending therethrough between dorsal and plantar surfaces. An expansion joint extends forward from the hole to the anterior edge of the forefoot to form plural expansion struts that create improved biplanar motion capability of the forefoot. Concavities and convexities on the surface of the hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot encourage desired motions and motion directions so that the foot functions and feels like a normal foot to the amputee.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
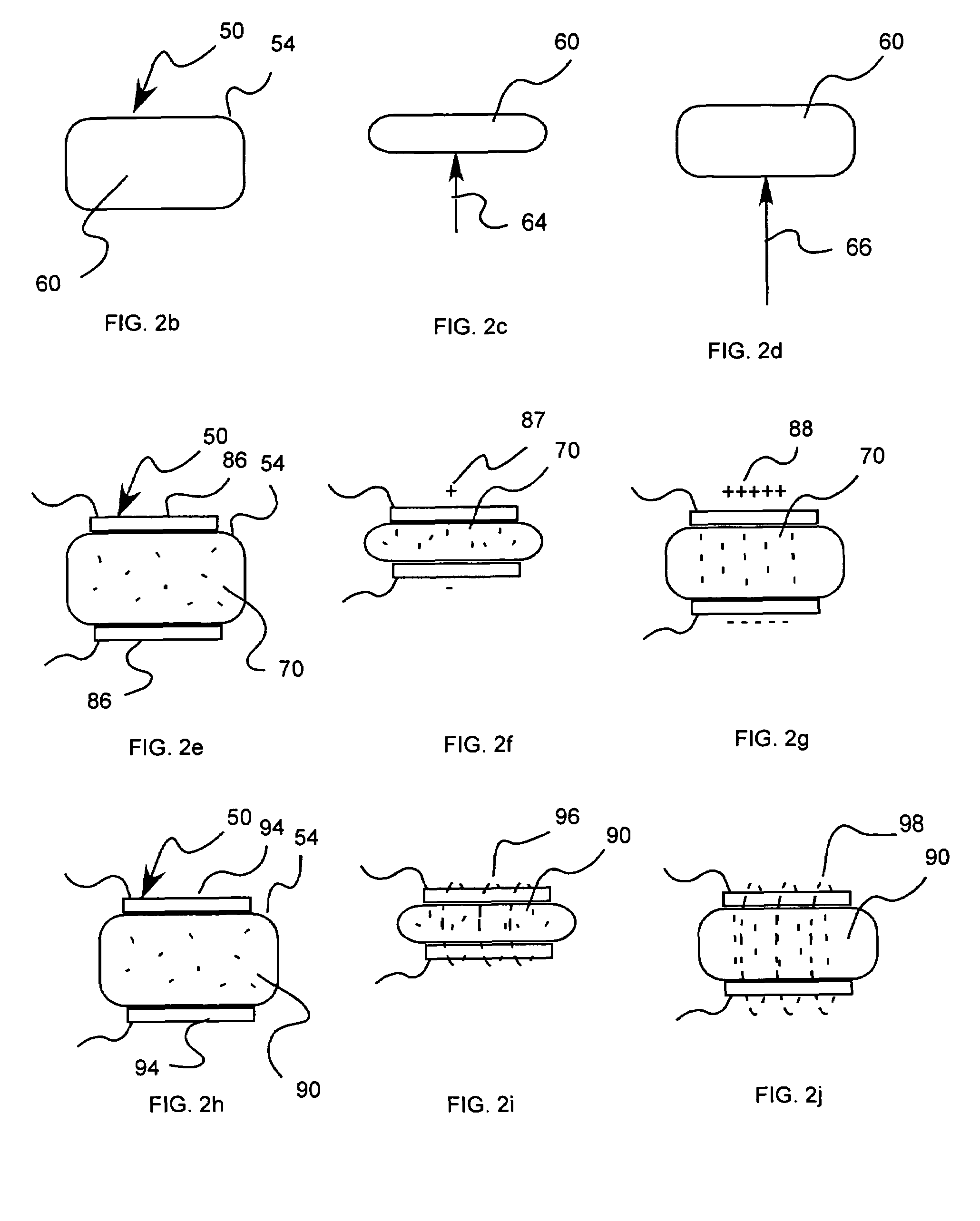
Foot prosthesis having cushioned ankle
InactiveUS7063727B2Improve rigidityHigh degreeArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMedicine
A simple, inexpensive prosthetic foot is provided incorporating a cushioned ankle including an ankle block formed of a resilient material or bladder having desired compliance and energy return characteristics. The ankle block is sandwiched between a foot element and an ankle element. One or more openings extends through the ankle block with a substantially transverse orientation relative to a forward walking motion. The size and shape of these openings, as well as the insertion of different types of stiffeners therein, provide desired performance characteristics to the ankle block. When the ankle block takes the form of one or more inflatable bladders, the pressure within these bladders is individually controlled by valves to provide desired performance characteristics to different portions of the prosthetic foot. A pump system can also be used to control and generate fluid pressure into these bladders. A preferred pump system generates fluid pressure based upon the movement of the amputee onto two telescoping pylons that are connected to the prosthetic foot.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Shock absorbing prosthetic foot for use with prosthetic ankle
InactiveUS20050038525A1Efficient energy transferImprove stabilityArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDuring ambulation
A low profile prosthetic foot designed for use with a prosthetic ankle. The prosthetic foot includes at least one toe spring and at least one heel spring. The prosthetic foot is able to absorb shocks generated during ambulation of a user of said foot. When a prosthetic ankle is attached to the prosthetic foot, the position (height) of the ankle preferably approximates the position (height) of a typical human ankle.
Owner:THE OHIO WILLOW WOOD CO INC
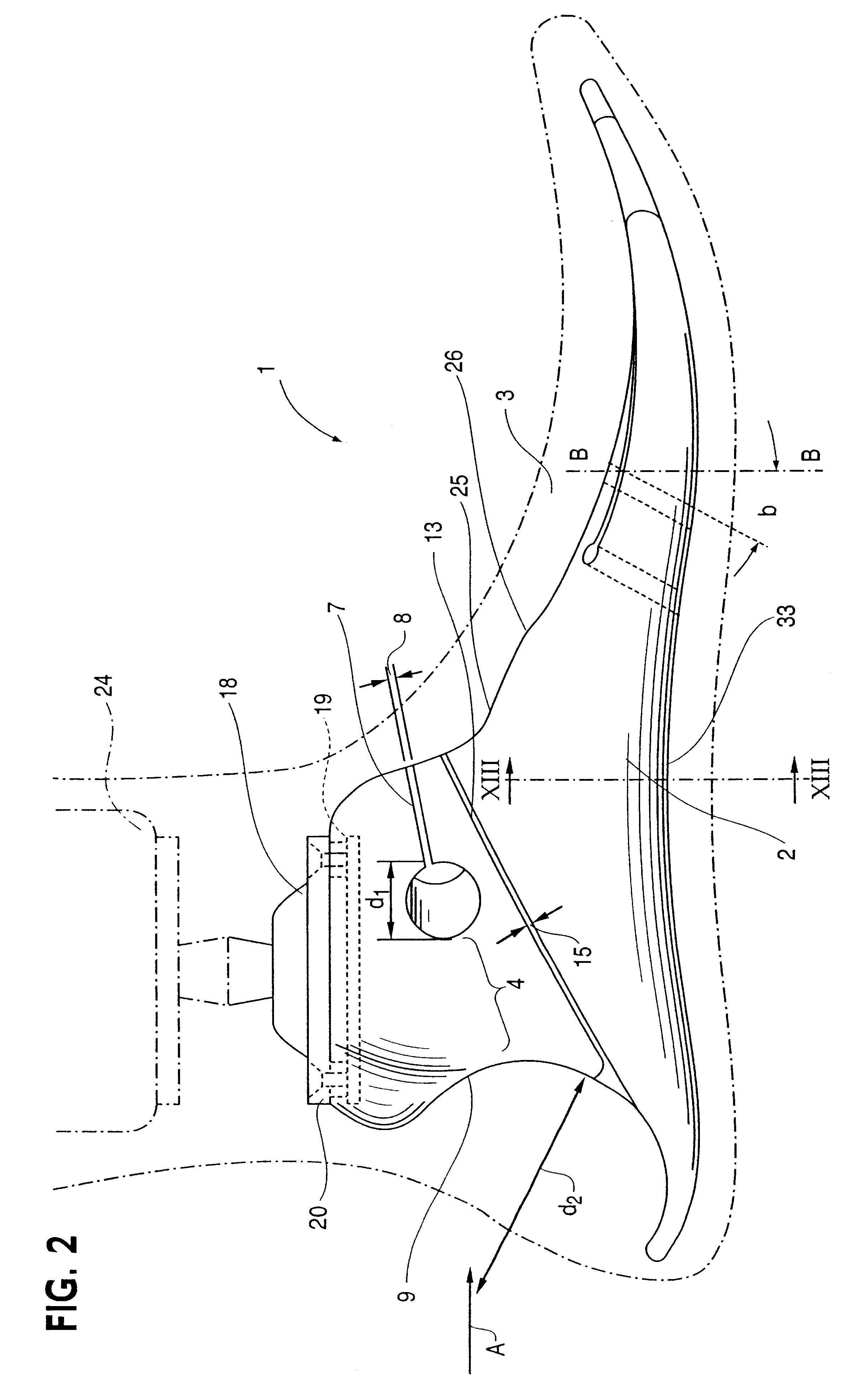
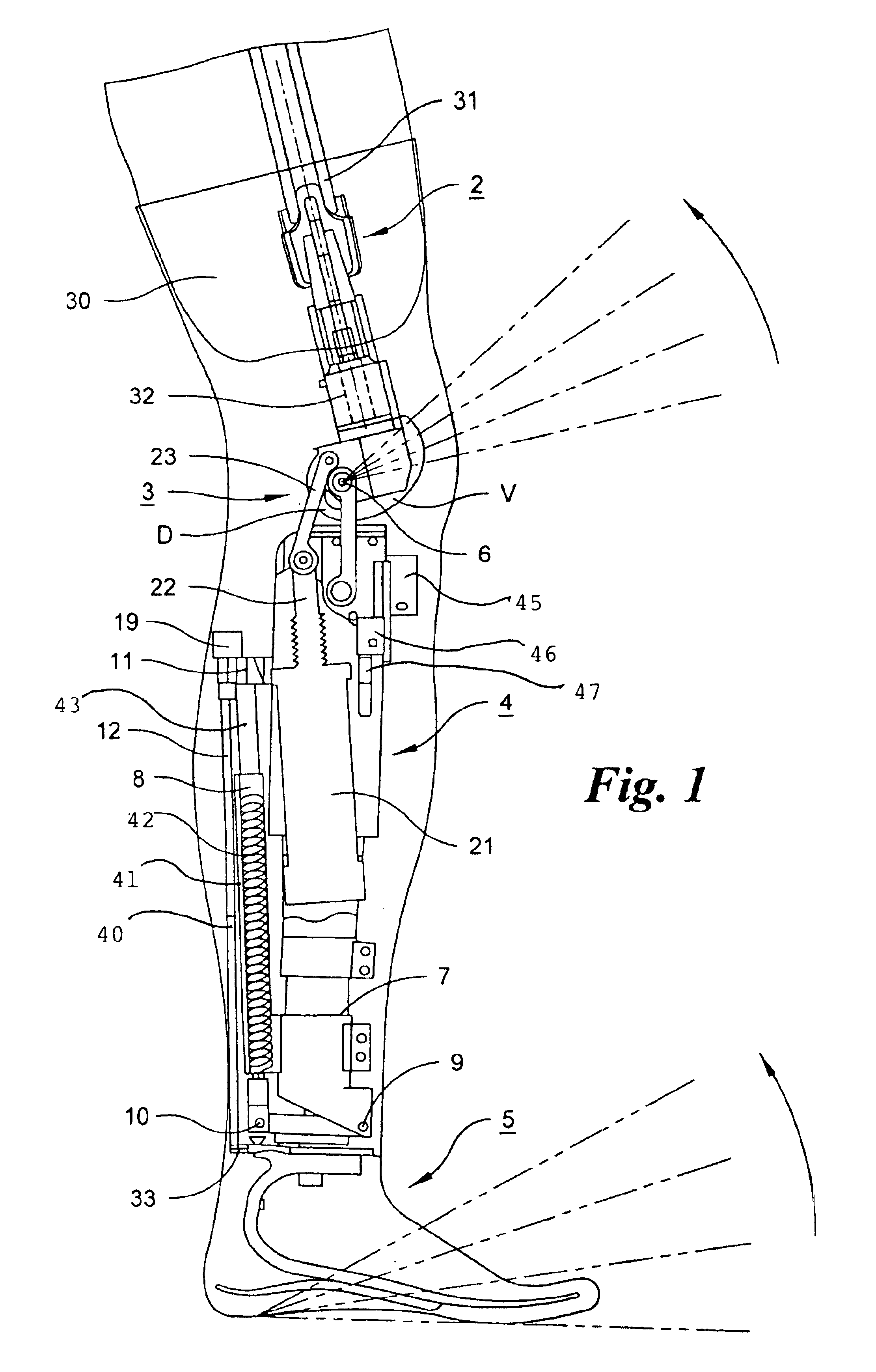
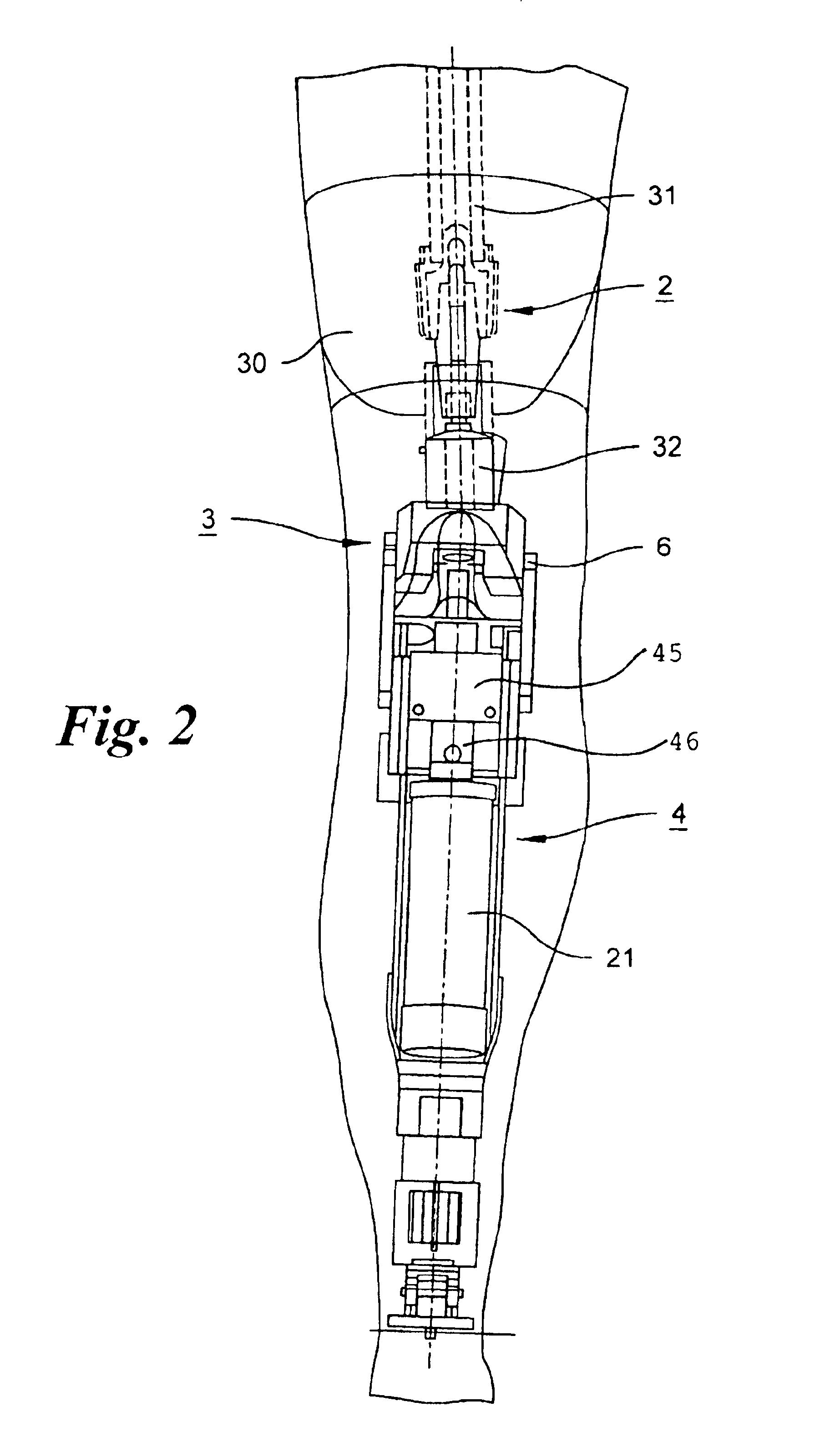
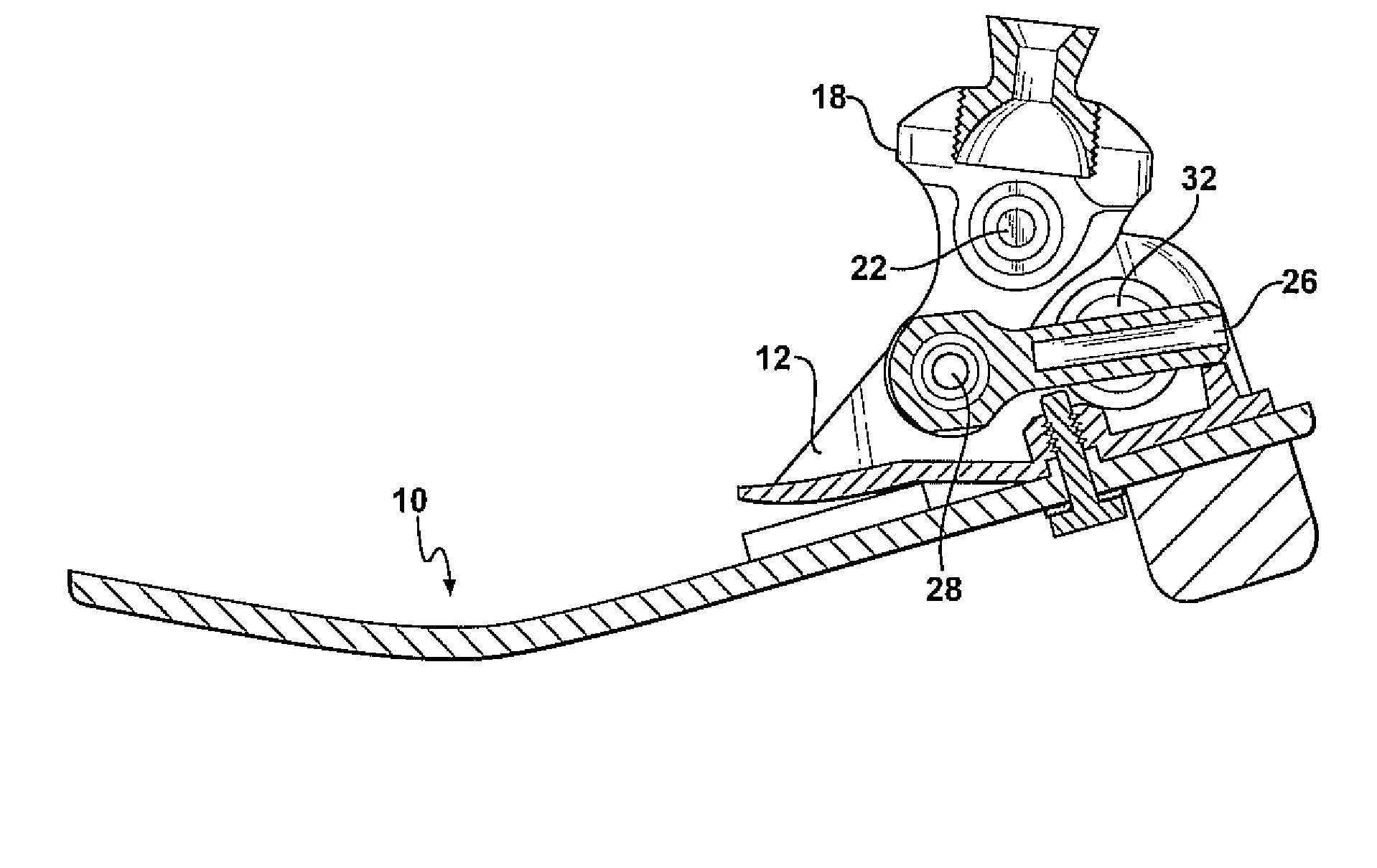
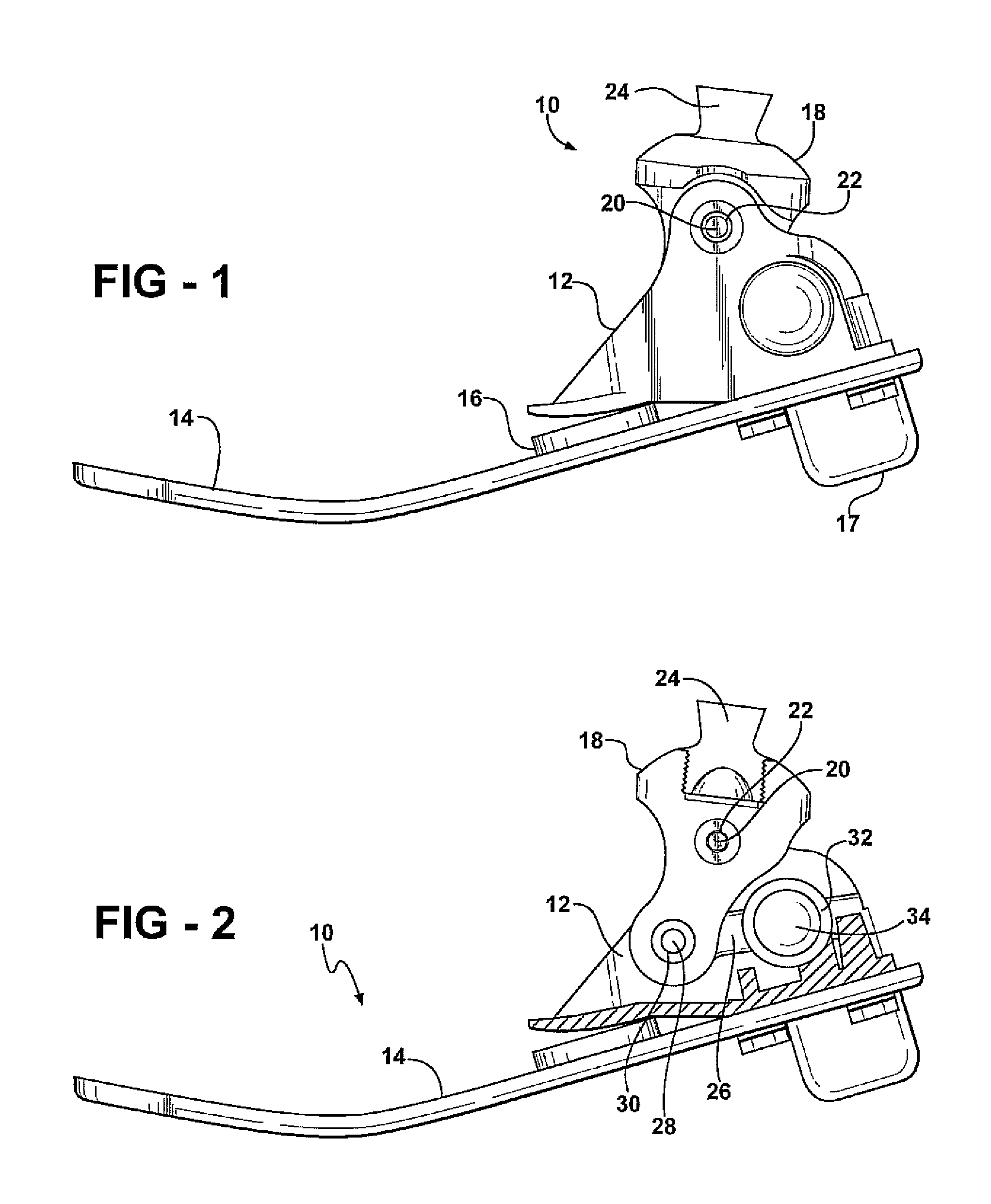
Leg prosthesis
ActiveUS6955692B2Improve a leg prosthesisIncrease and decreases resistanceArtificial legsThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
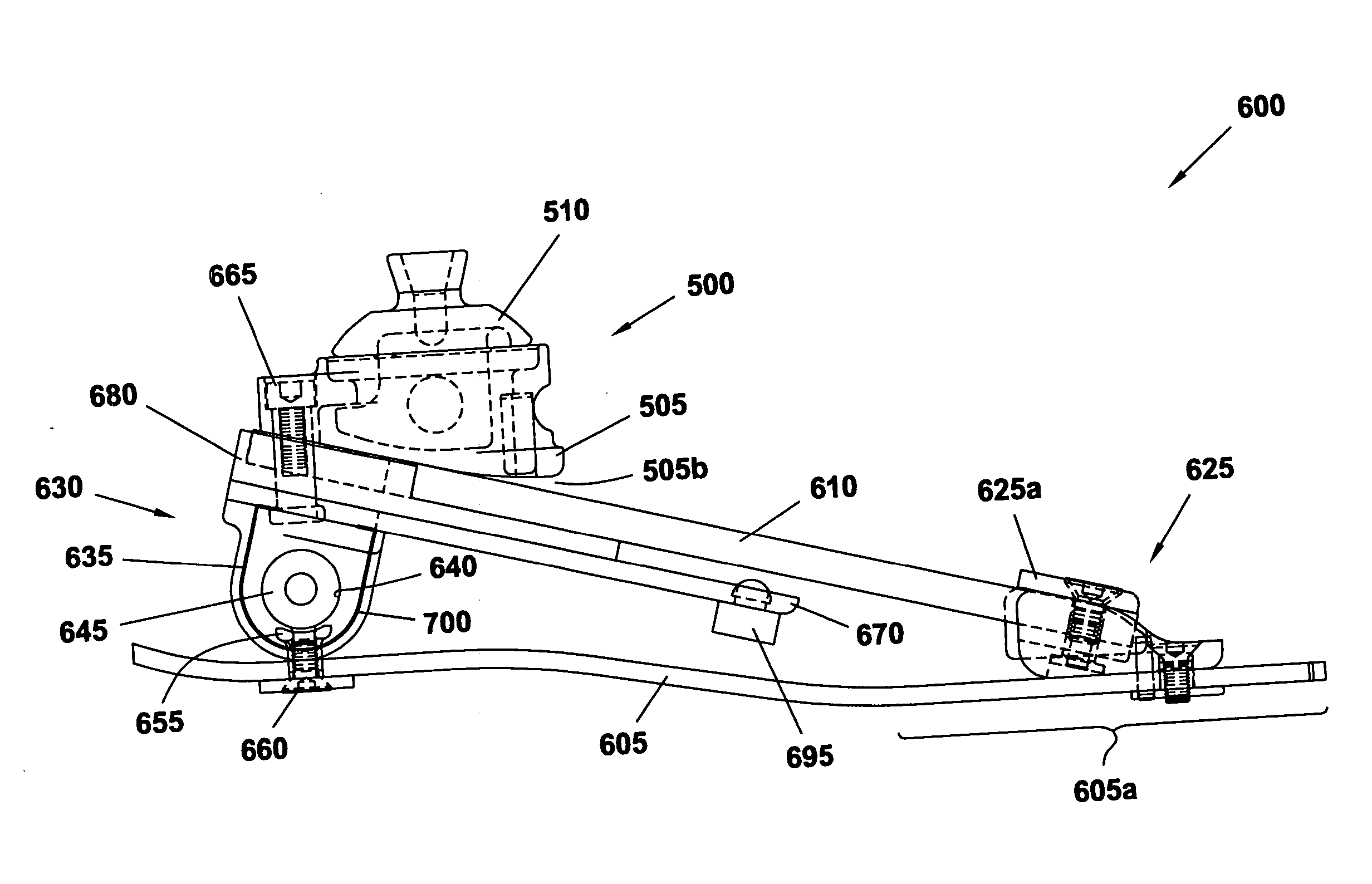
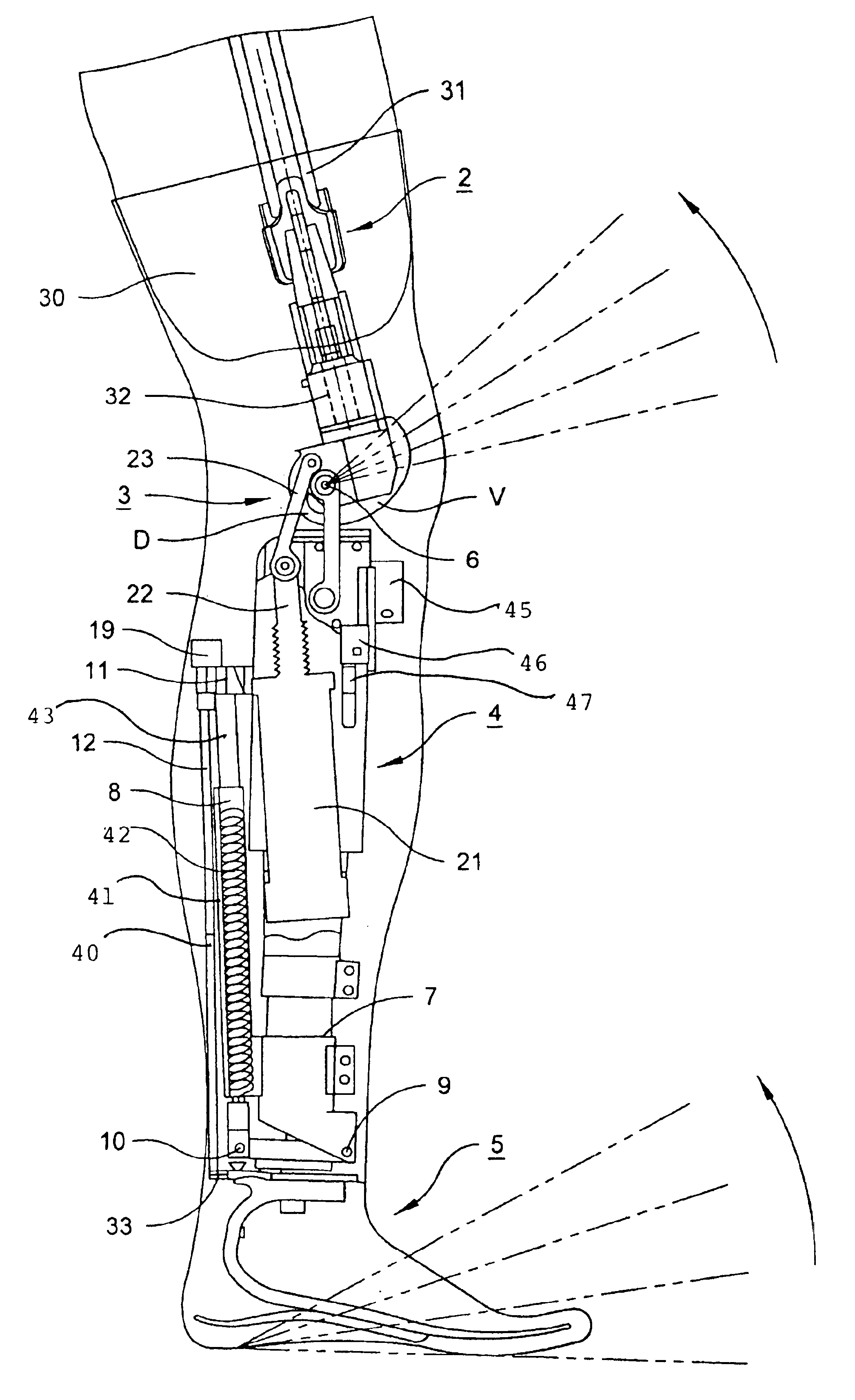
A leg prosthesis adapted to a thigh stump includes an adapter (2) for a knee joint (3), a knee joint (3) mounted on this adapter, and a prosthetic lower leg (4) coupled to the knee joint (3). A prosthetic foot (5) is attached to this prosthetic lower leg and can pivot into a toes-raised foot position. The knee joint (3) upon transition from the extended position to the bent position performs a combined rolling-sliding movement about a pivot axis (6). A force-transmitting element (8) moves the prosthetic foot (5) substantially from the toes-down foot position to the toes-raised foot position during bending of the knee joint (3). Each bending position of the knee joint is transformed by a converter into an unambiguous electrical signal, which is supplied to a programmable control device, which generates a signal used to control an electrically adjustable actuator, which increases or decreases the resistance of the knee joint against or for further bending according to the signal.
Owner:OSSEO PL GMBH
Low profile prosthetic foot
InactiveUS20050038524A1Increased strength and resilienceEasy to disassembleArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDevice prosthetic
Owner:OSSUR HF
Foot prosthesis having cushioned ankle
InactiveUS20030093158A1Improve rigidityDegree of improvementArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTransverse orientation
Abstract of Disclosure A simple, inexpensive prosthetic foot is provided incorporating a cushioned ankle including an ankle block formed of a resilient material or bladder having desired compliance and energy return characteristics. The ankle block is sandwiched between a foot element and an ankle element. One or more openings extends through the ankle block with a substantially transverse orientation relative to a forward walking motion. The size and shape of these openings, as well as the insertion of different types of stiffeners therein, provide desired performance characteristics to the ankle block. When the ankle block takes the form of one or more inflatable bladders, the pressure within these bladders is individually controlled by valves to provide desired performance characteristics to different portions of the prosthetic foot. A pump system can also be used to control and generate fluid pressure into these bladders. A preferred pump system generates fluid pressure based upon the movement of the amputee onto two telescoping pylons that are connected to the prosthetic foot.
Owner:OSSUR HF
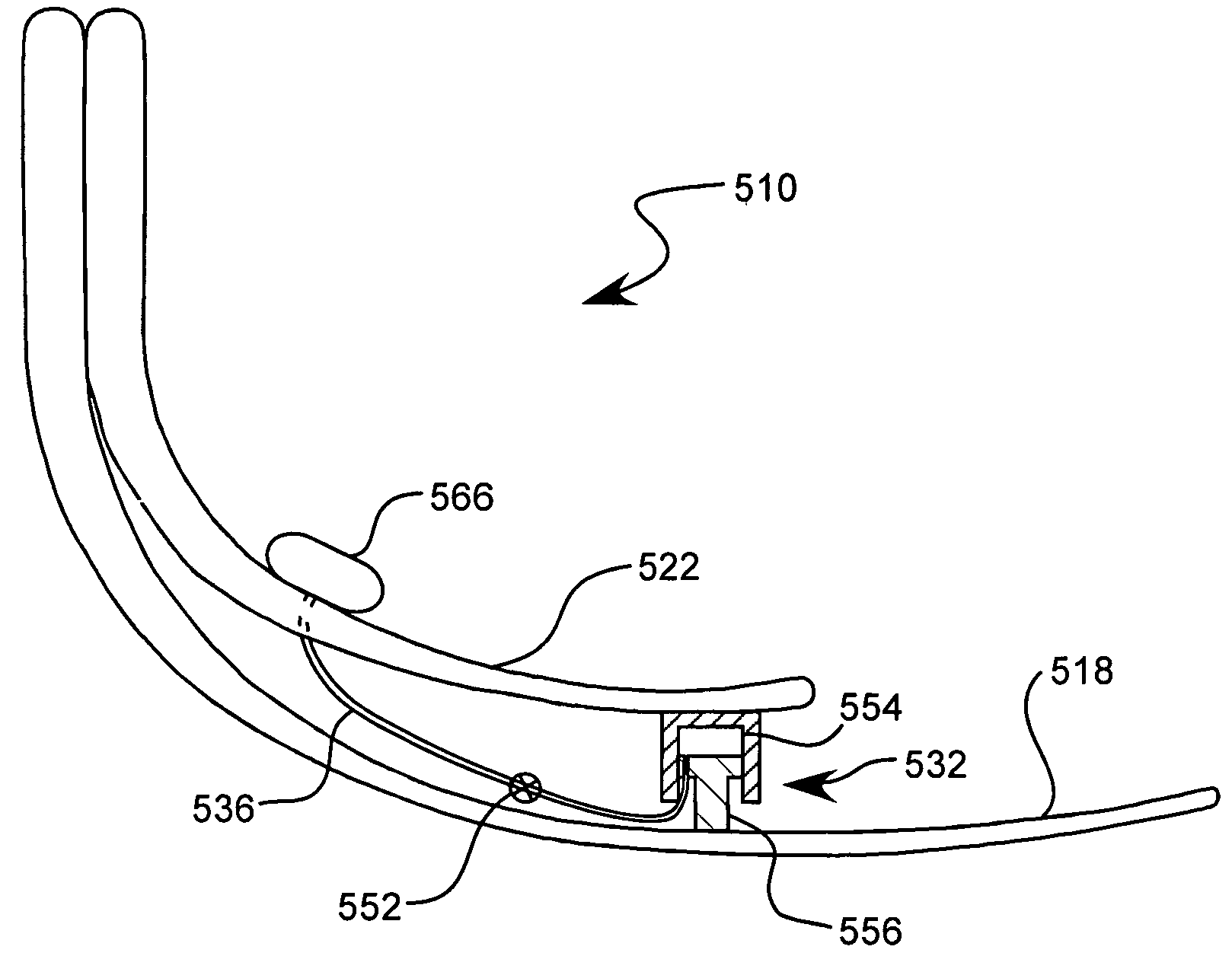
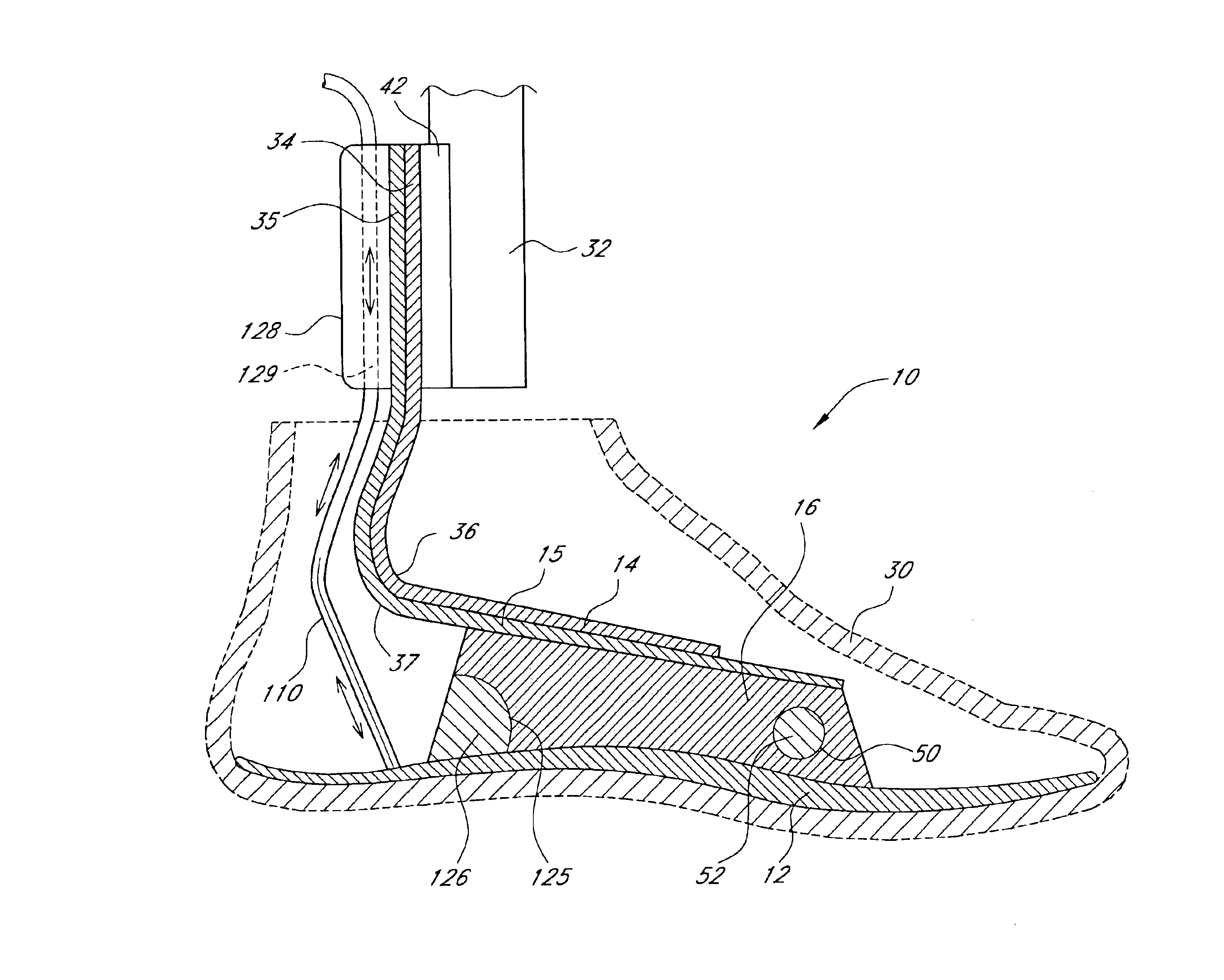
Vacuum pump with shock absorption and controlled rotation for prosthetic devices
ActiveUS20050240282A1Positive displacement pump componentsPositive-displacement liquid enginesReciprocating motionPump chamber
A vacuum pump having shock absorption and controlled rotation for use in an artificial limb. The pump includes a housing having a first chamber, and a shaft configured to be received by and to reciprocate within the first chamber, the housing and shaft forming a pump chamber. A piston may be coupled to the shaft and positioned within the pump chamber, and intake and exhaust ports are fluidly coupled to the pump chamber. Rotational structure is mounted with respect to the pump to provide controlled rotation of the shaft relative to the housing, and shock absorption structure is included within the pump to provide shock absorption for the shaft. Both a pneumatic spring and a mechanical spring element may be provided for the shock absorption structure. An optional adapter couples the shaft to the pylon of an integral pylon prosthetic foot.
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE IP GMBH & CO KG
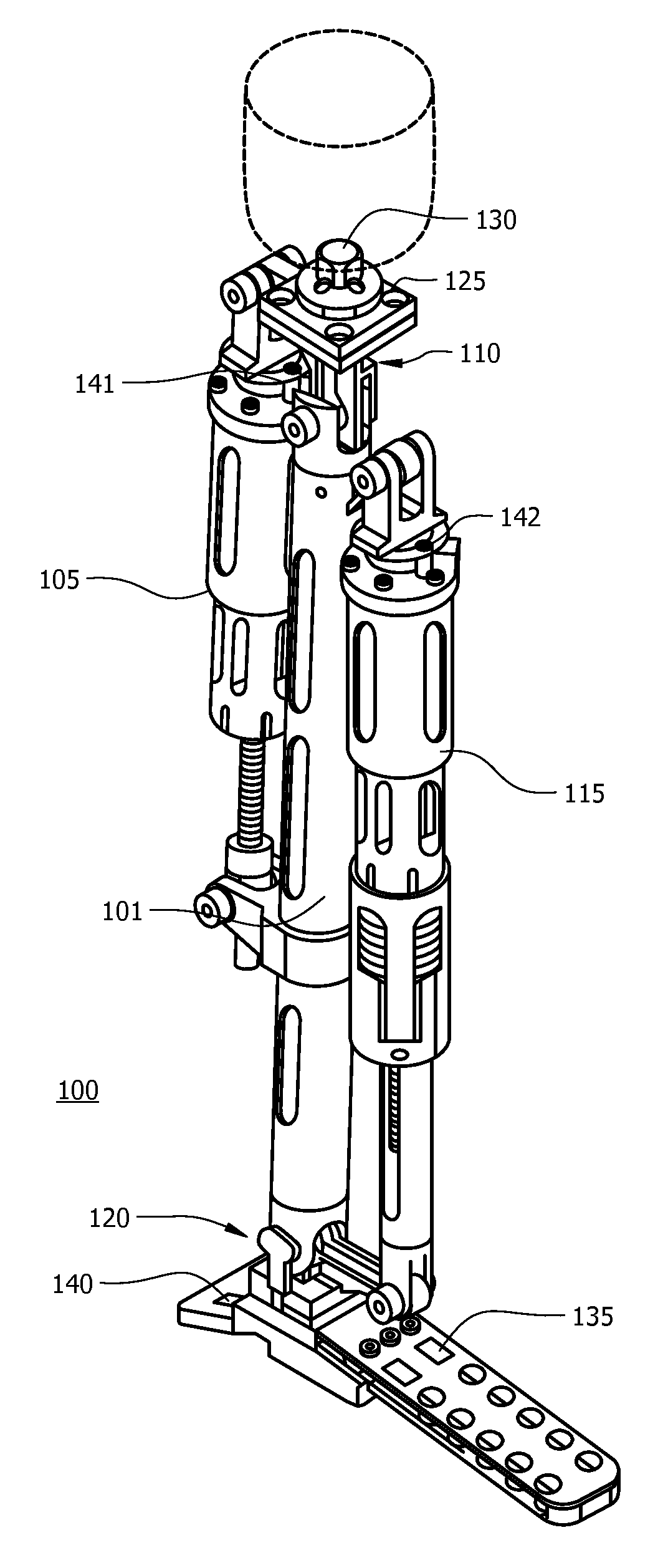
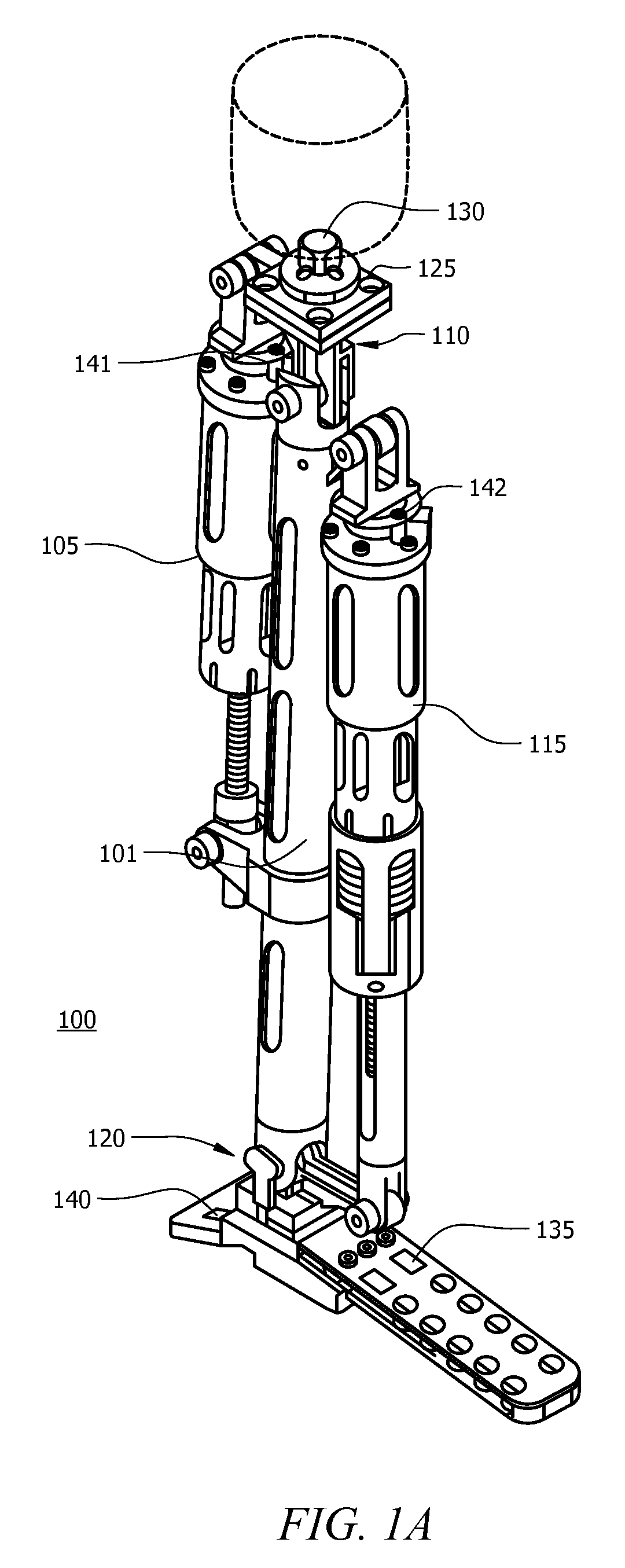
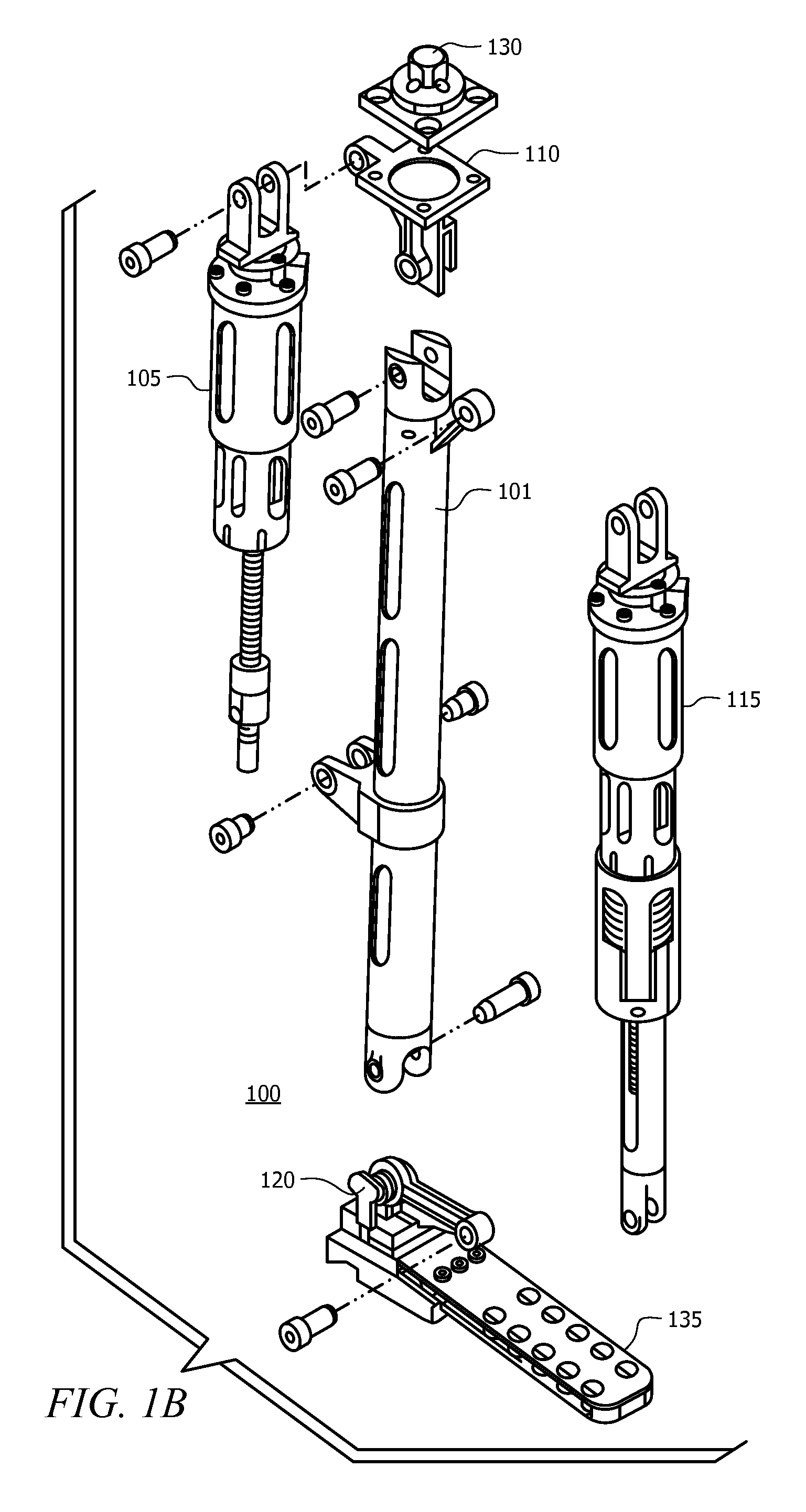
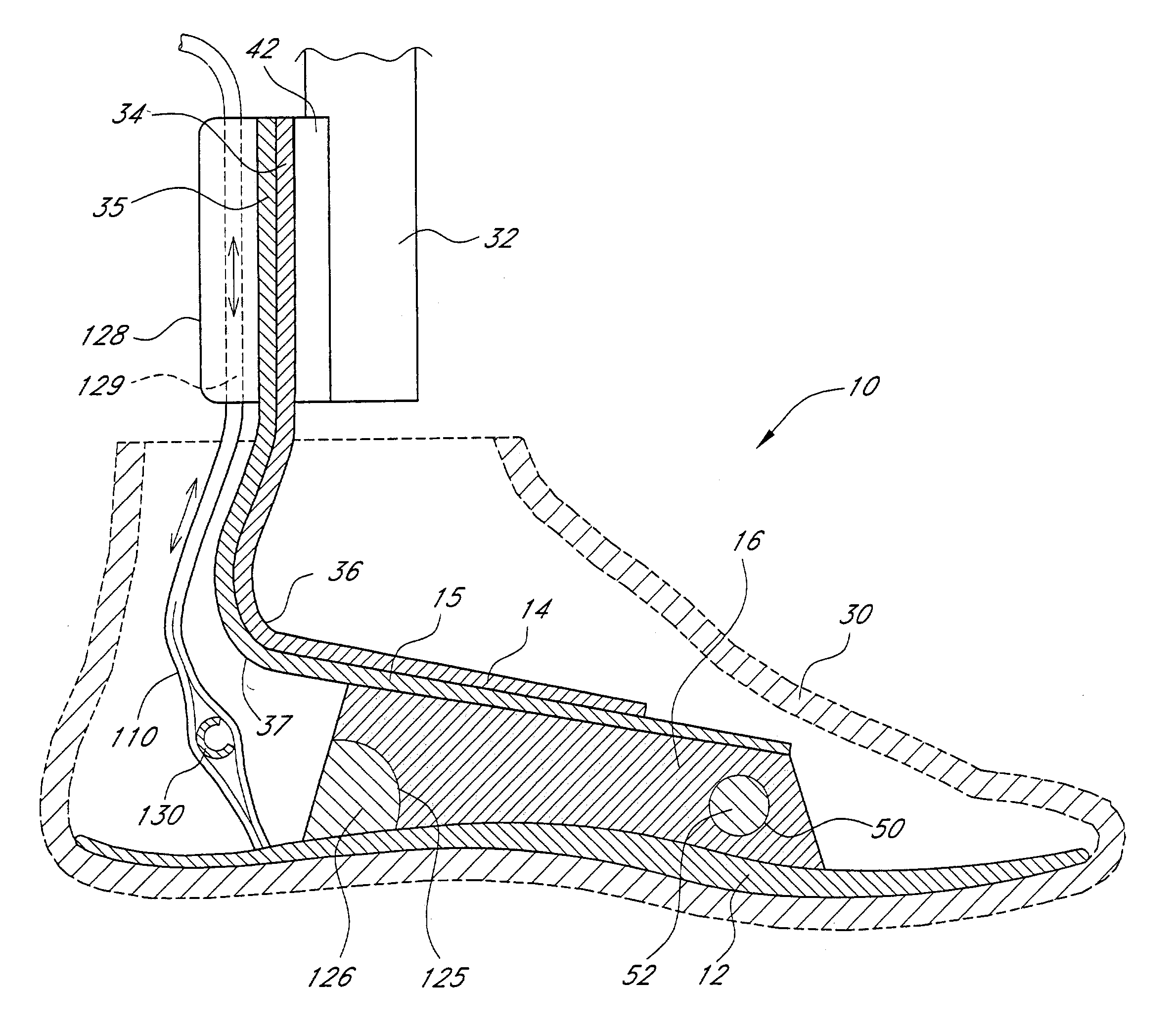
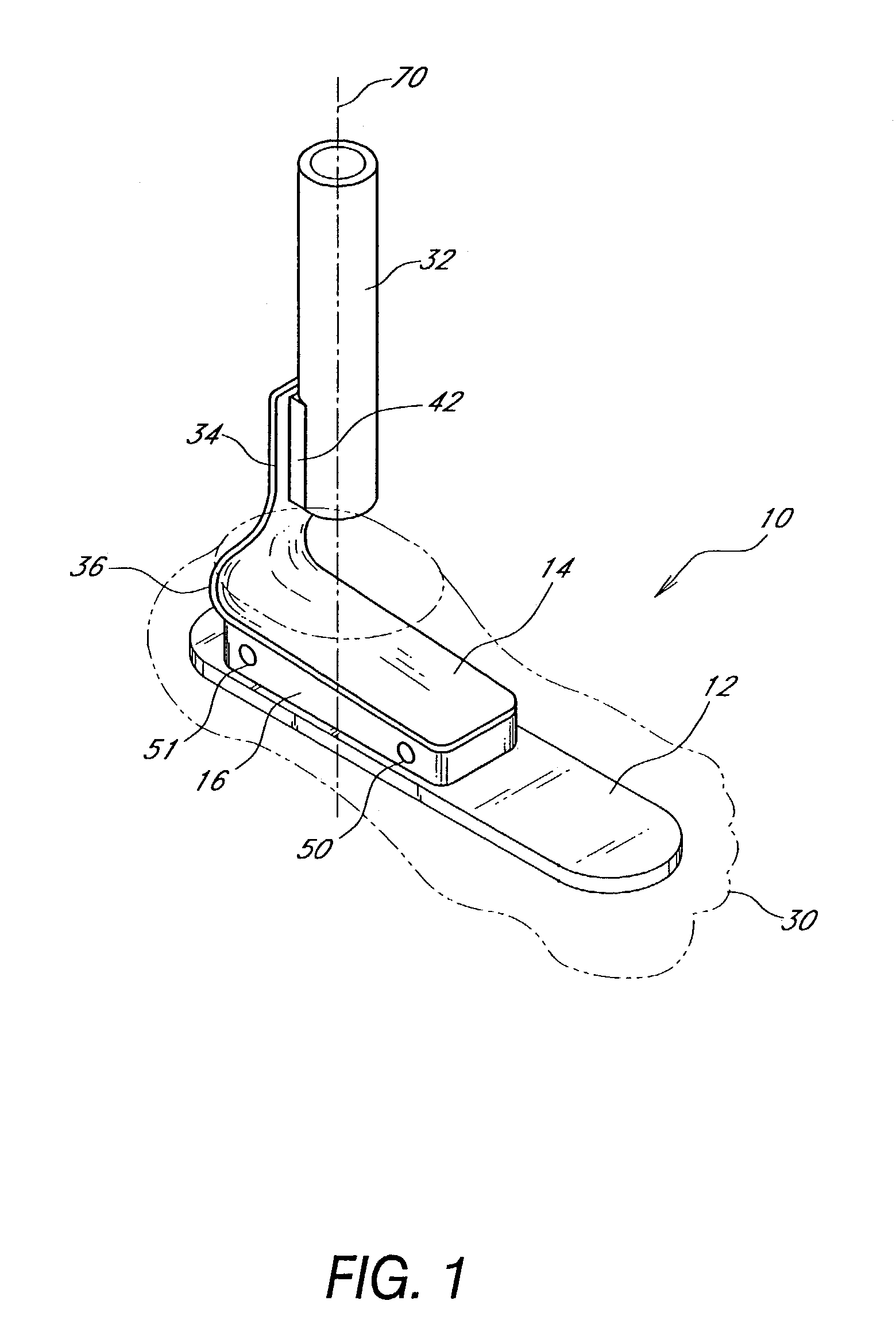
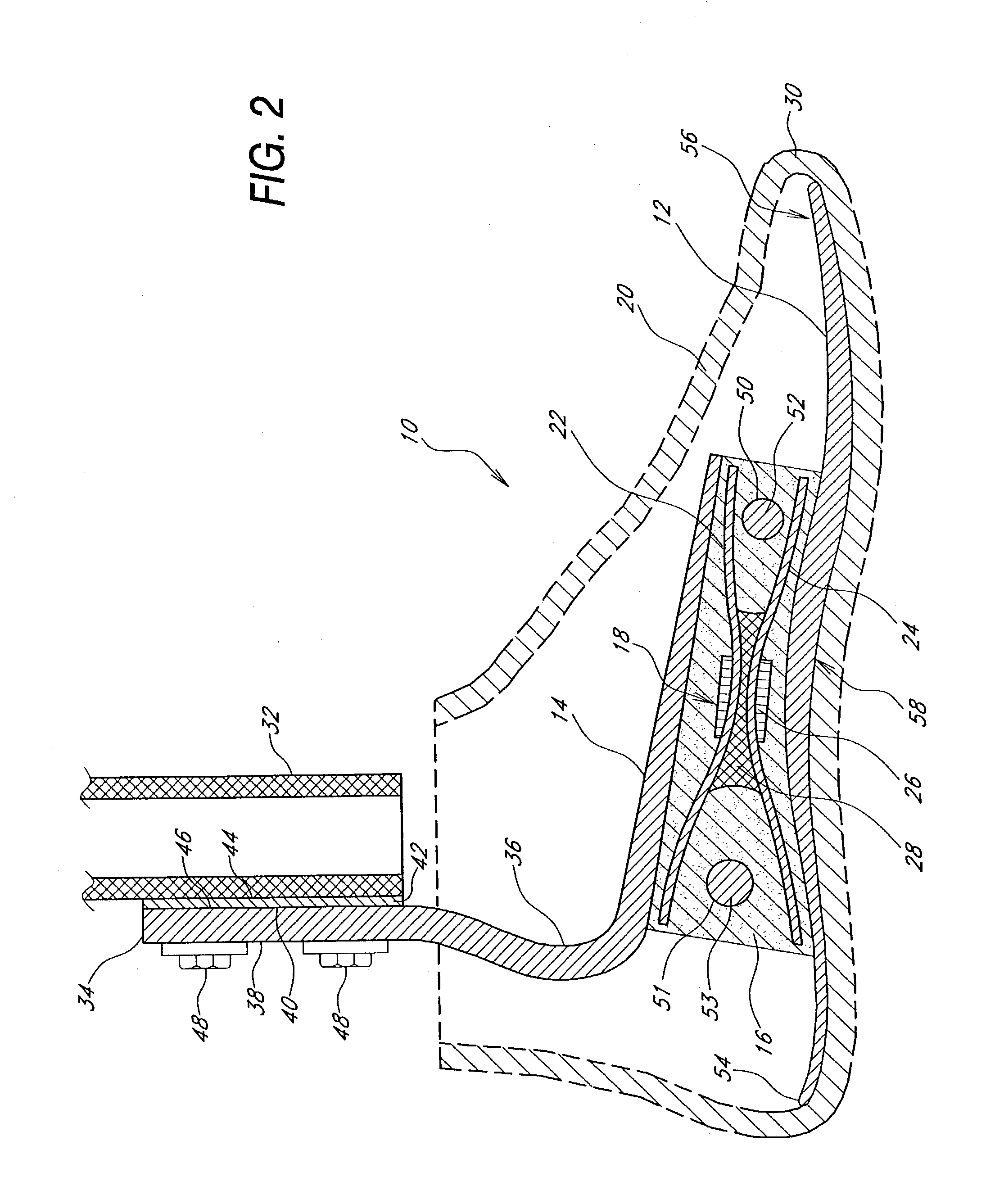
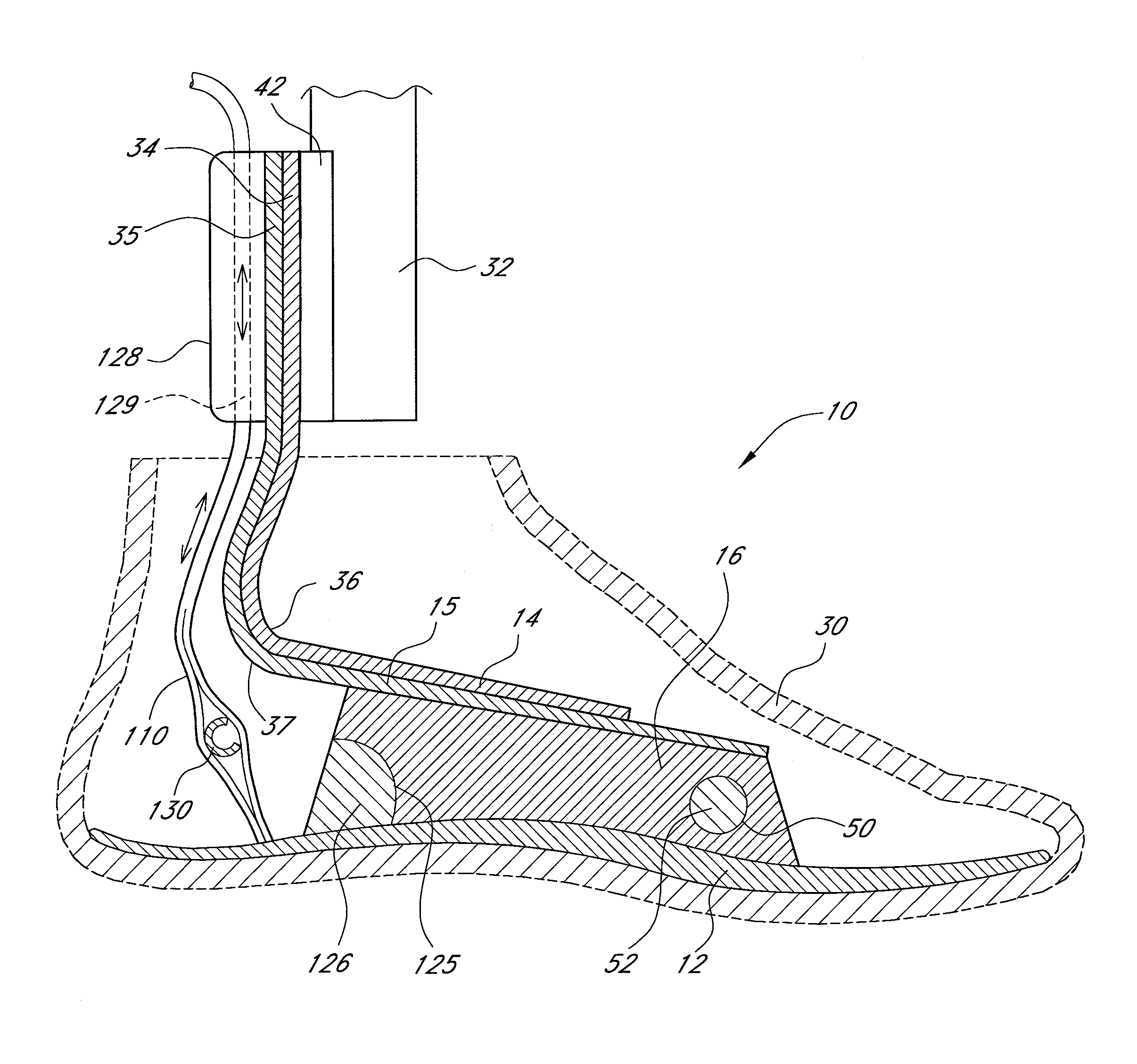
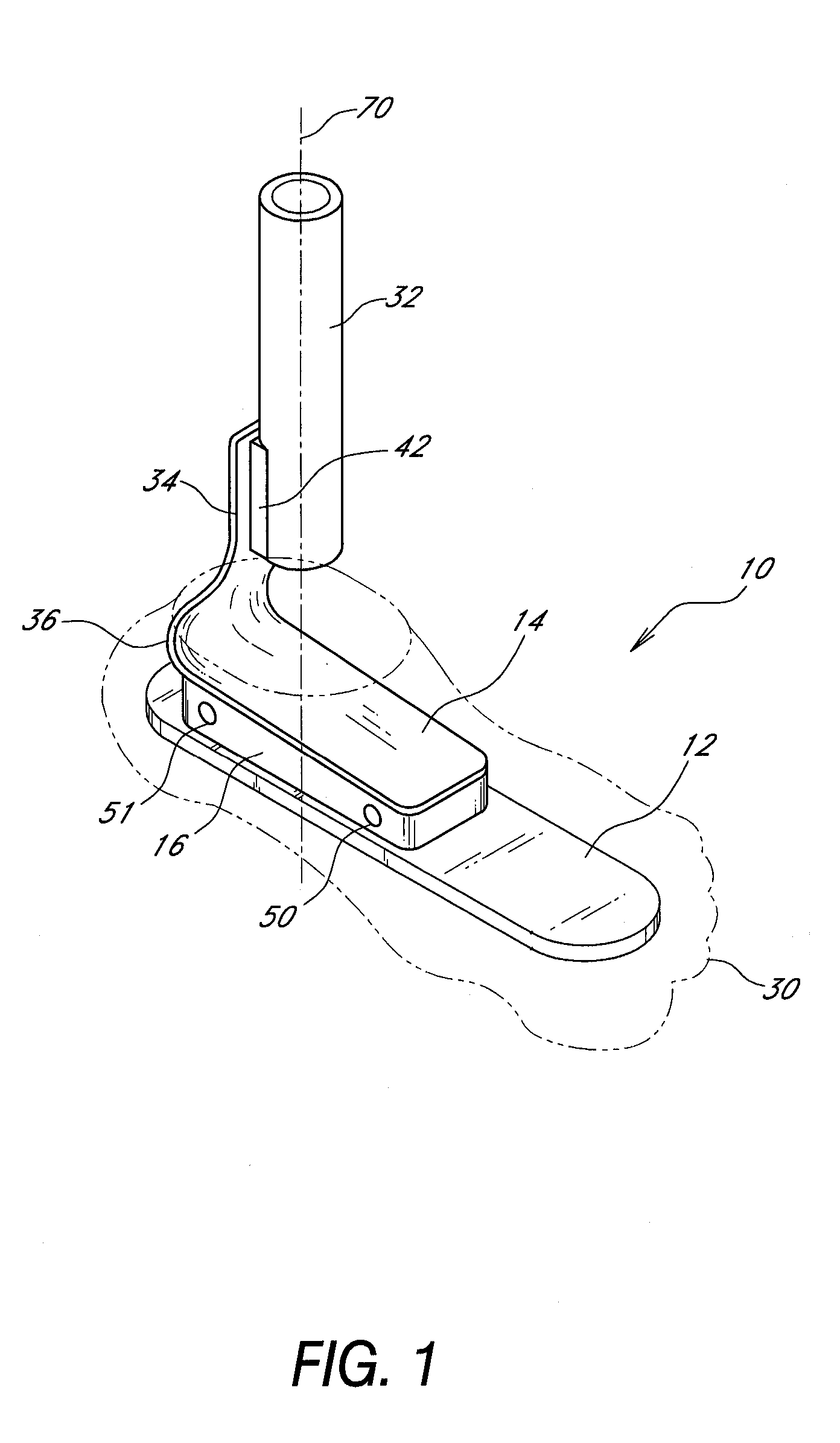
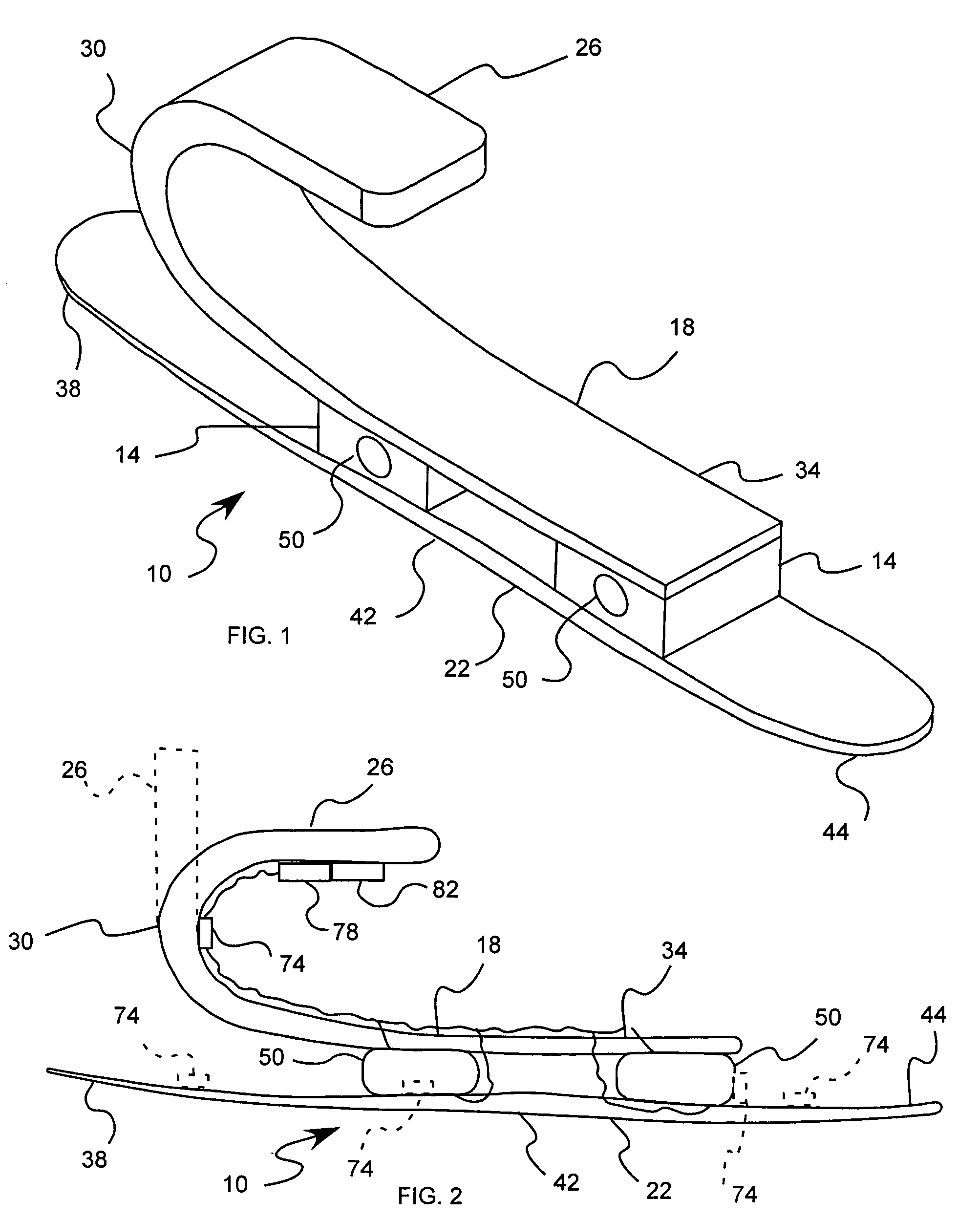
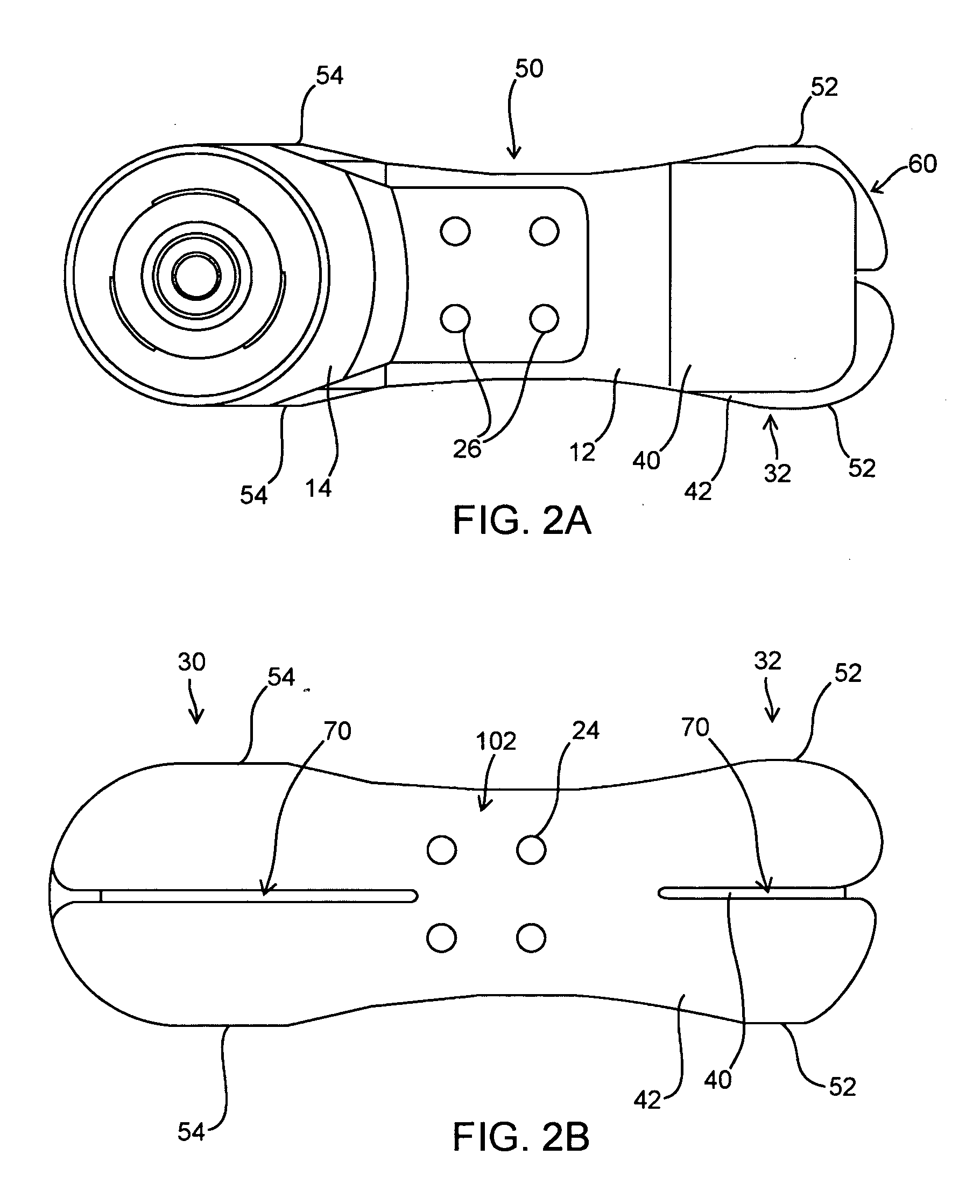
Prosthetic foot with an adjustable ankle and method
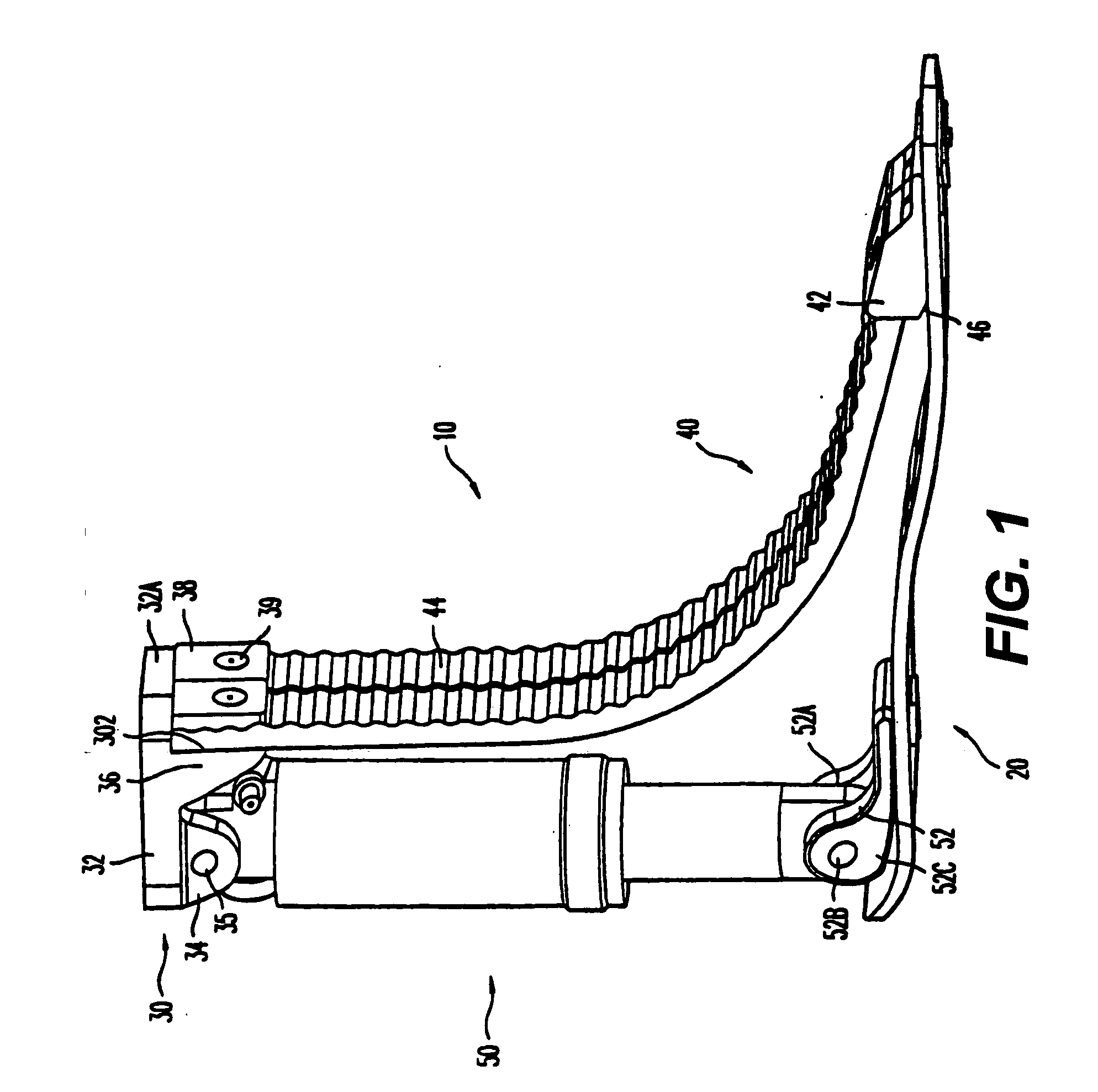
A prosthetic foot with an adjustable ankle includes an upper portion coupled to a socket of an amputee. A lower portion is adjustably coupled to the upper portion, and is attached to a foot member with heel and toe sections. A movable coupling is disposed between the upper and lower portions, and includes a displacement member slidably coupled to a displacement track. The movable coupling allows the toe section to pivot downward and the heel section to simultaneously displace forward. The adjustable ankle can be adjusted with an actuator coupled to a tractor bolt coupled between the upper and lower portions. A sensor is associated with the upper portion or the lower portion to sense frequency of contact, force of contact, or orientation of the upper portion or the lower portion, and to output a corresponding output signal.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Prosthetic foot
ActiveUS20100042228A1Improve energy transferIncreased spring lengthArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationHeel strike
A stable shock absorbing prosthetic foot that transfers energy between heel strike and toe-off. A toe plate is separated from one or more other plates by a bumper assembly located at each of the toe end and heel end of the foot. Certain embodiments of the shock absorbing foot of the present invention are designed for use with a prosthetic ankle. A torsion adapter may also be used to attach a prosthetic foot of the present invention to the remainder of a prosthesis.
Owner:WILLOWWOOD GLOBAL LLC
Low profile prosthetic foot
ActiveUS20070027557A1Increased strength and resilienceEasy to disassembleArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMedicine
Owner:OSSUR HF
Prosthetic foot having shock absorption
InactiveUS6863695B2Efficiently transferring energyAbsorb energyArtificial legsEngineeringTubes types
A prosthetic foot includes an adapter element securable to a residual limb, a foot plate having a heel portion and a toe portion along the length thereof, at least one toe spring connected between the adapter element and the toe portion of the foot plate, and a heel spring connected between the adapter element and the heel portion. The heel spring may be a leaf spring or a tube type shock absorber. The concave side of the leaf spring exhibits a plurality of transverse ribs. Alternatively, a tubular pylon may have a collar mounted thereon for movement along the length of the pylon. A toe spring and a heel spring extend from the collar to form toe and heel portions of the prosthetic foot. A further heel spring is connected between the heel portion and another end of the pylon, and a non-extensible band extends between the heel portion and the collar. As another alternative, a tubular pylon has one end securable to a residual limb, and a collar is mounted to the pylon for movement along the length of the pylon. At least one toe spring is connected between the collar and the toe portion of a foot plate, while a heel spring is connected between the heel portion of the foot plate and another end of the pylon.
Owner:THE OHIO WILLOW WOOD CO INC
Prosthetic foot with an adjustable ankle and method
A prosthetic foot with an adjustable ankle includes an upper portion coupled to a socket of an amputee. A lower portion is adjustably coupled to the upper portion, and is attached to a foot member with heel and toe sections. A movable coupling is disposed between the upper and lower portions, and includes a displacement member slidably coupled to a displacement track. The movable coupling allows the toe section to pivot downward and the heel section to simultaneously displace forward.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Prosthetic foot with adjustable heel height
A prosthetic foot having an adjustable height heel includes a frame portion with an ankle link pivotally supported on the frame portion at a first pivot axis. A detent rod is pivotally connected to the ankle at a second pivot axis, and a detent member is pivotally affixed to the frame portion at a third pivot axis. The detent member is selectively operable to receive and releasably retain a length of the detent rod therein so that the length of the detent rod extending between the second and third pivot axes may be selectably adjusted. When the length of the rod is so adjusted, the angular relationship of the frame portion and the ankle link is changed thereby changing the heel height of the foot. The detent mechanism may be activated by various means including fluidic means, mechanical means, electromechanical means, and the like.
Owner:COLLEGE PARK IND INC
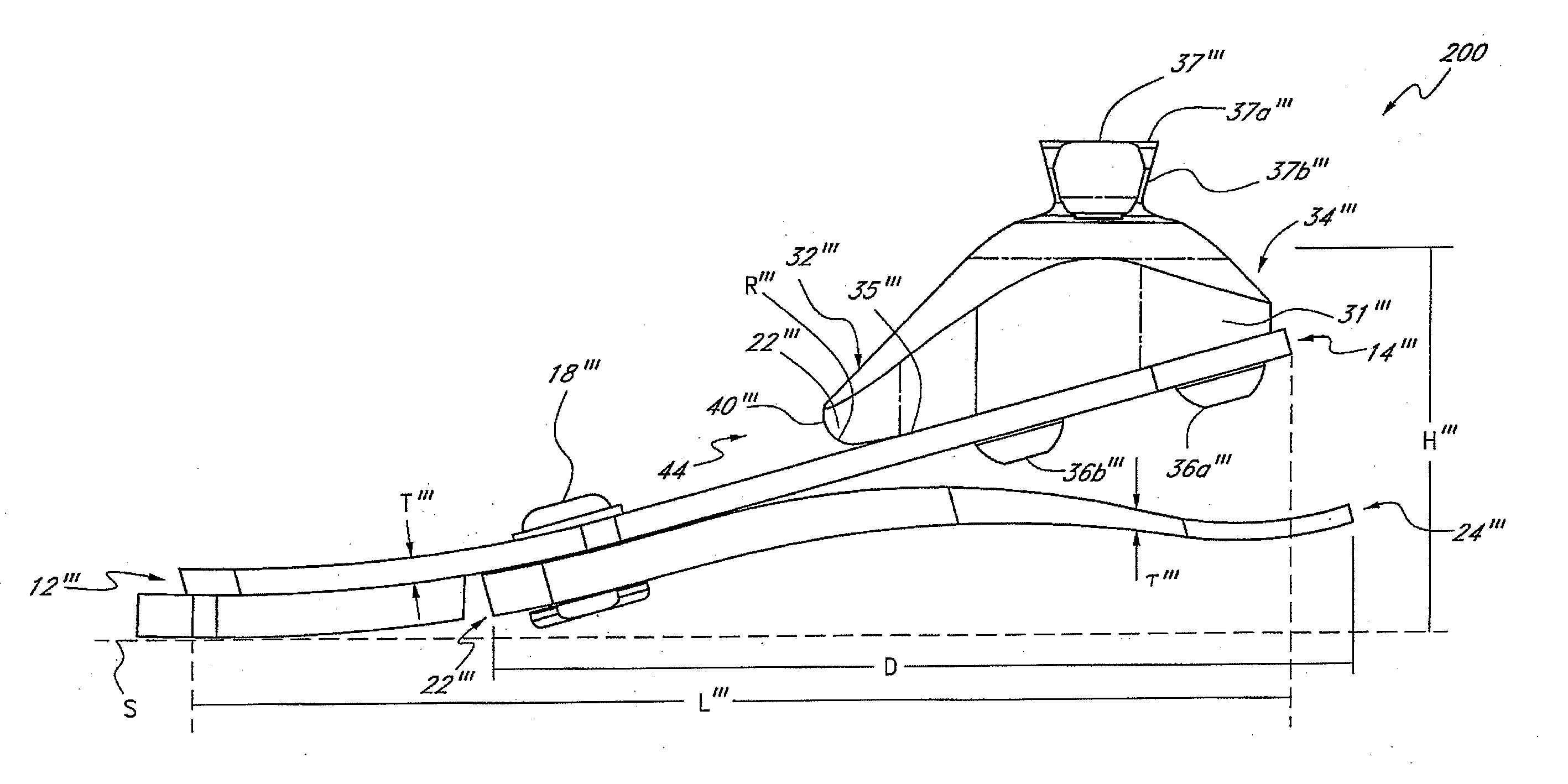
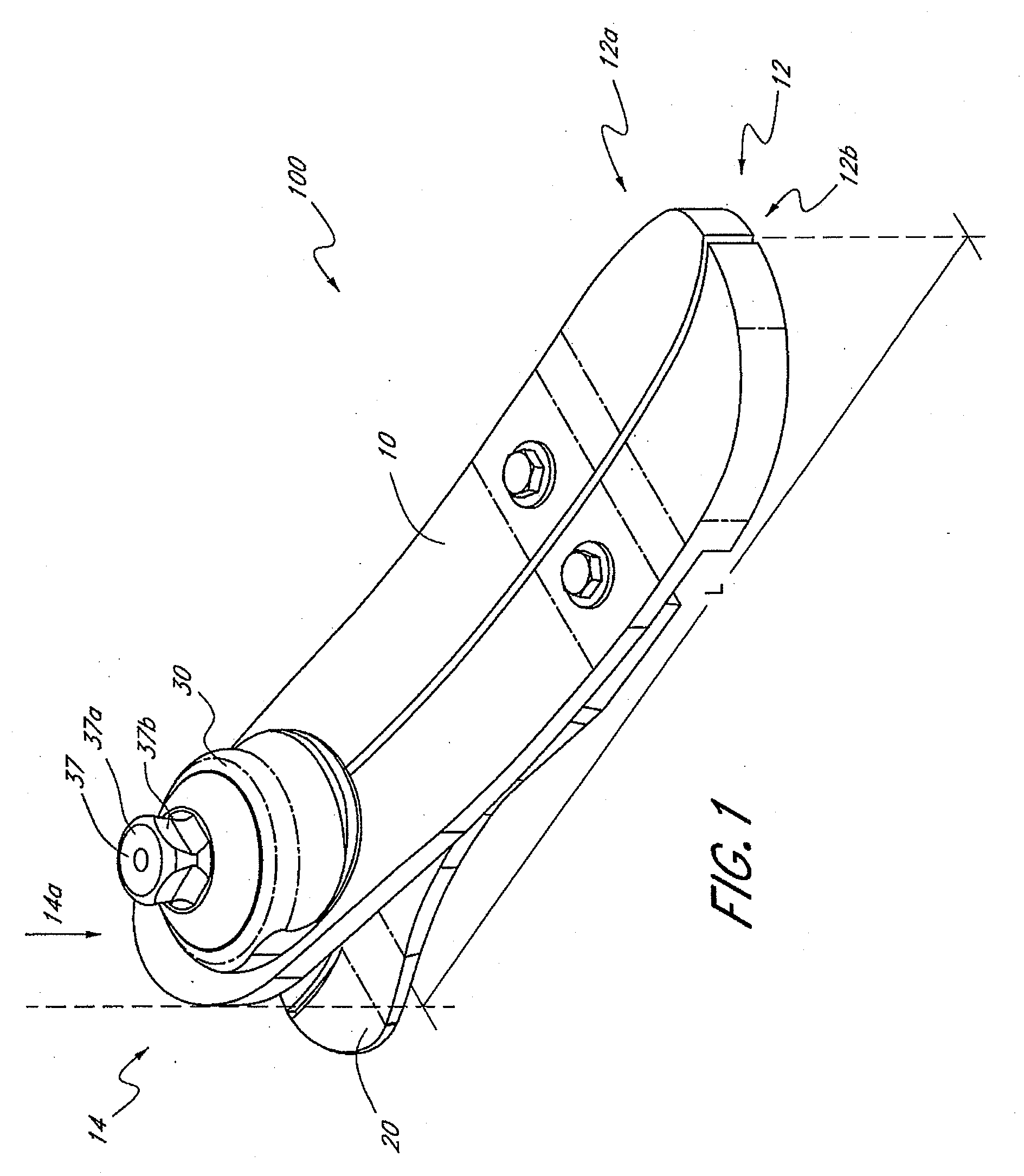
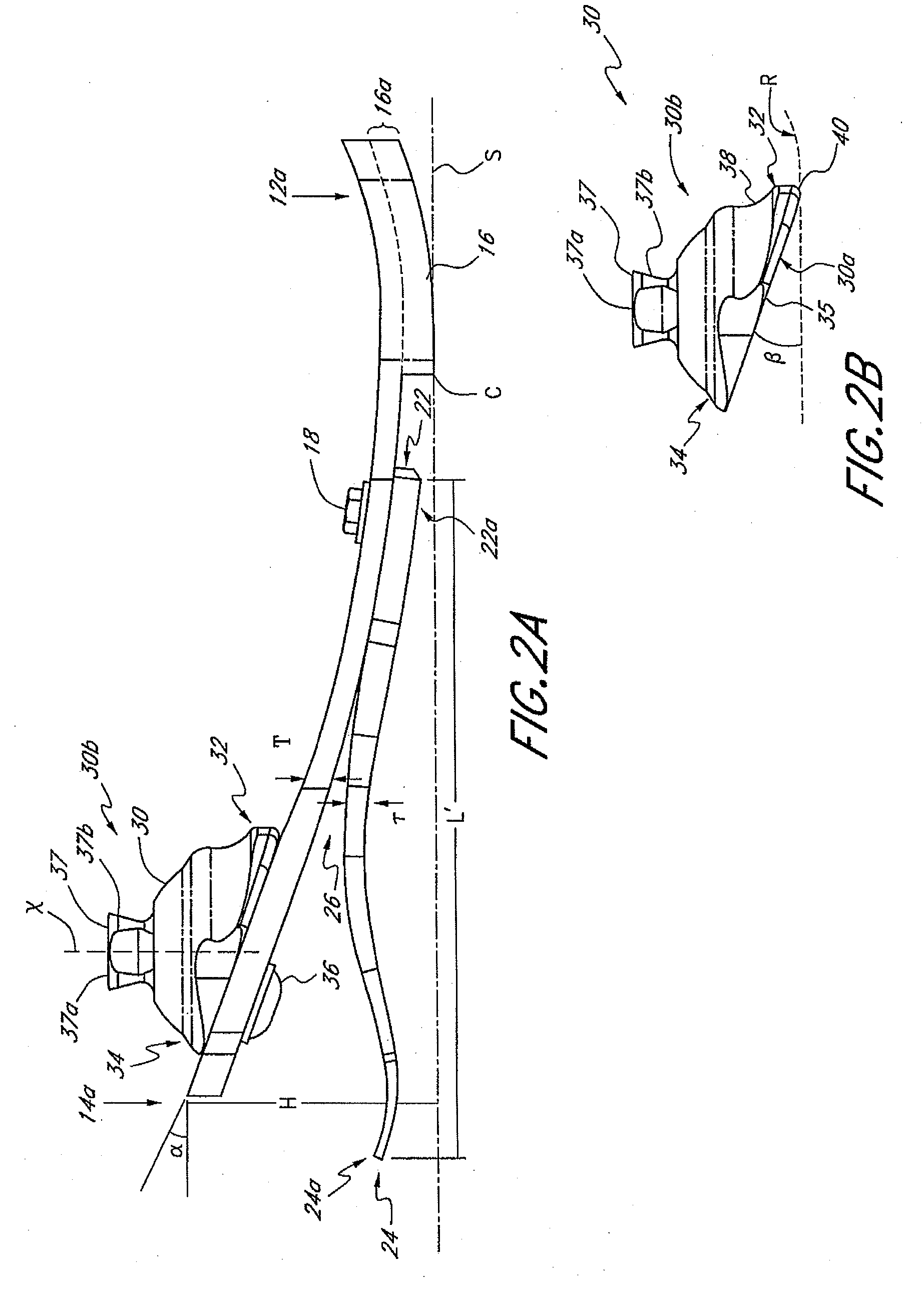
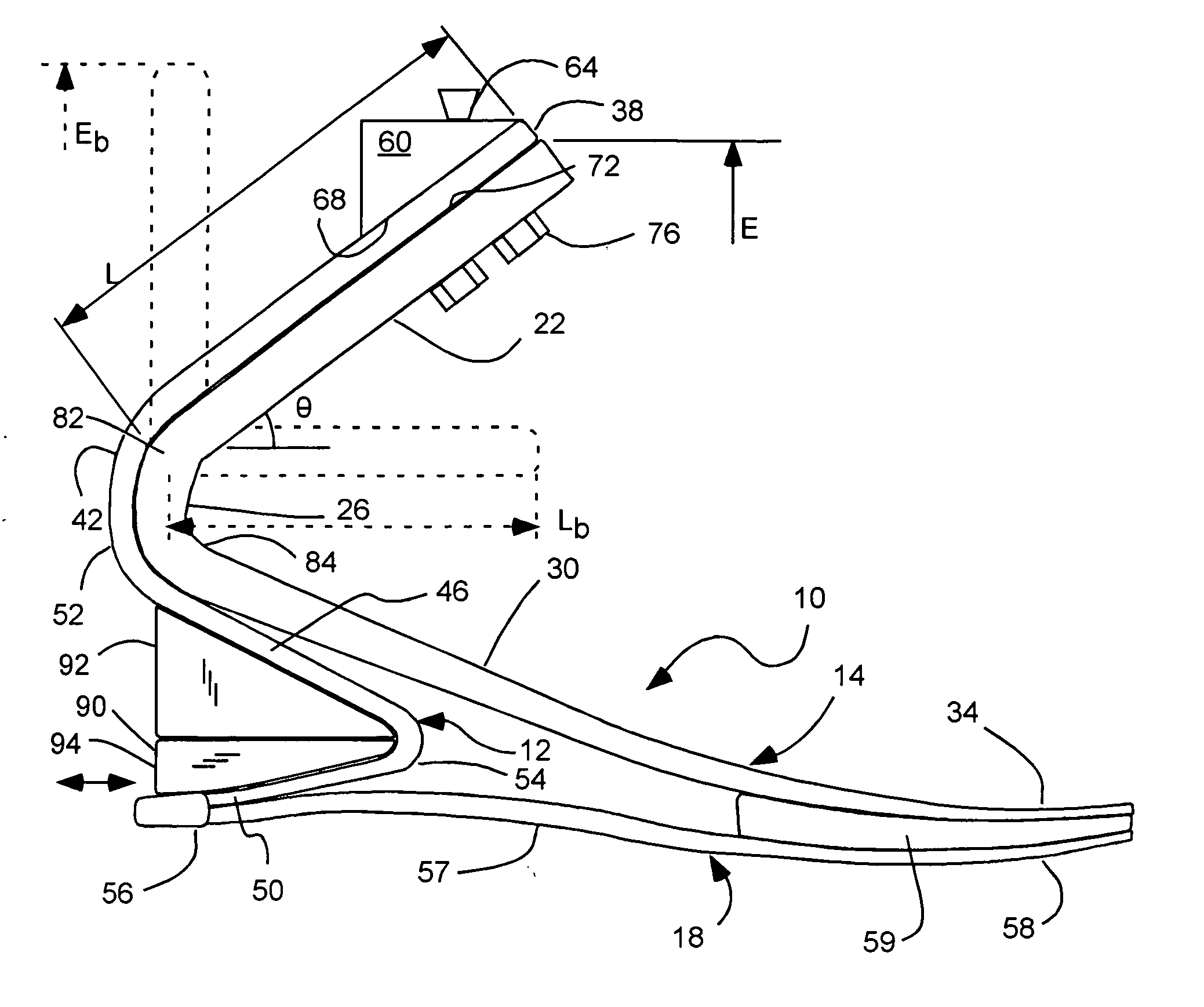
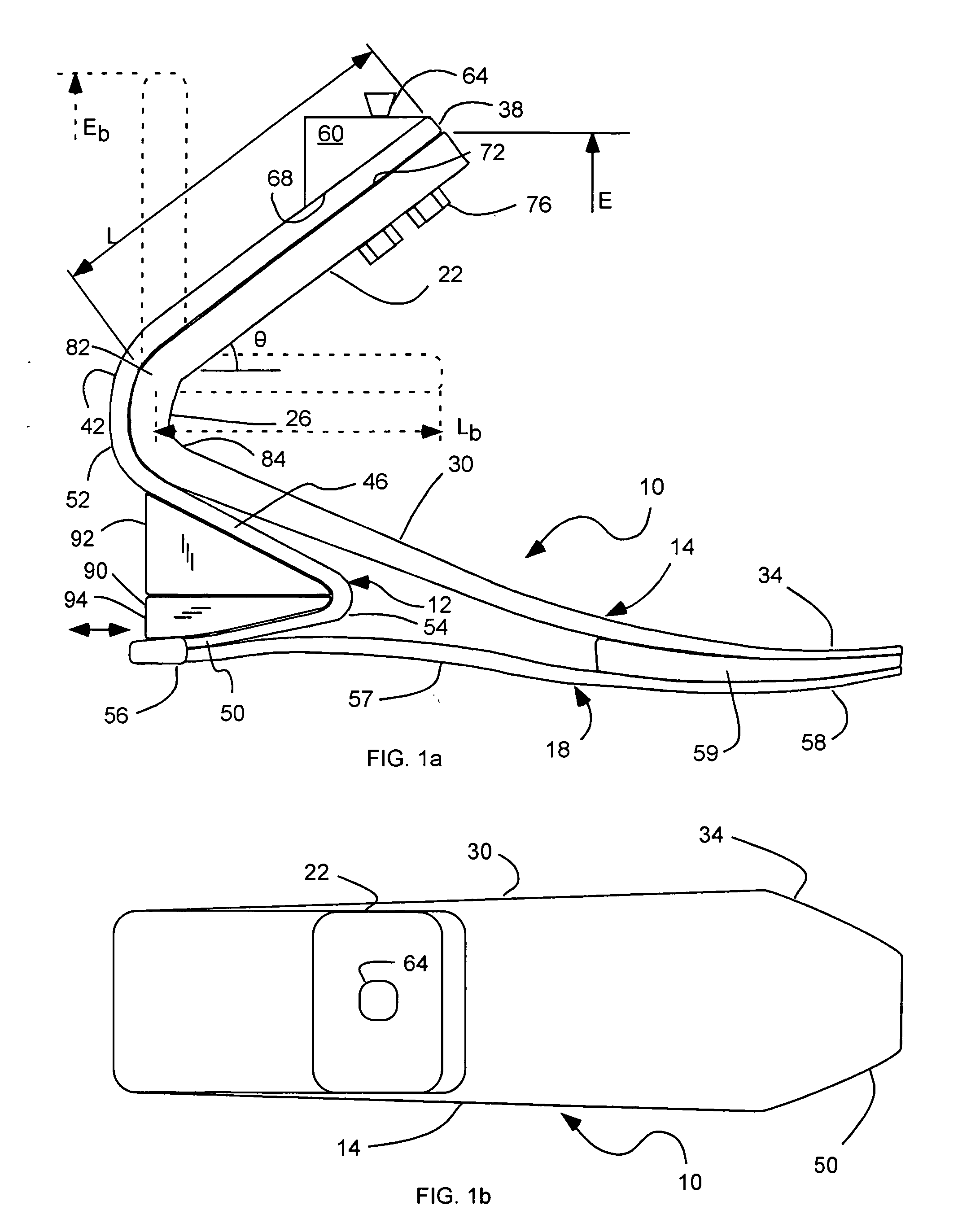
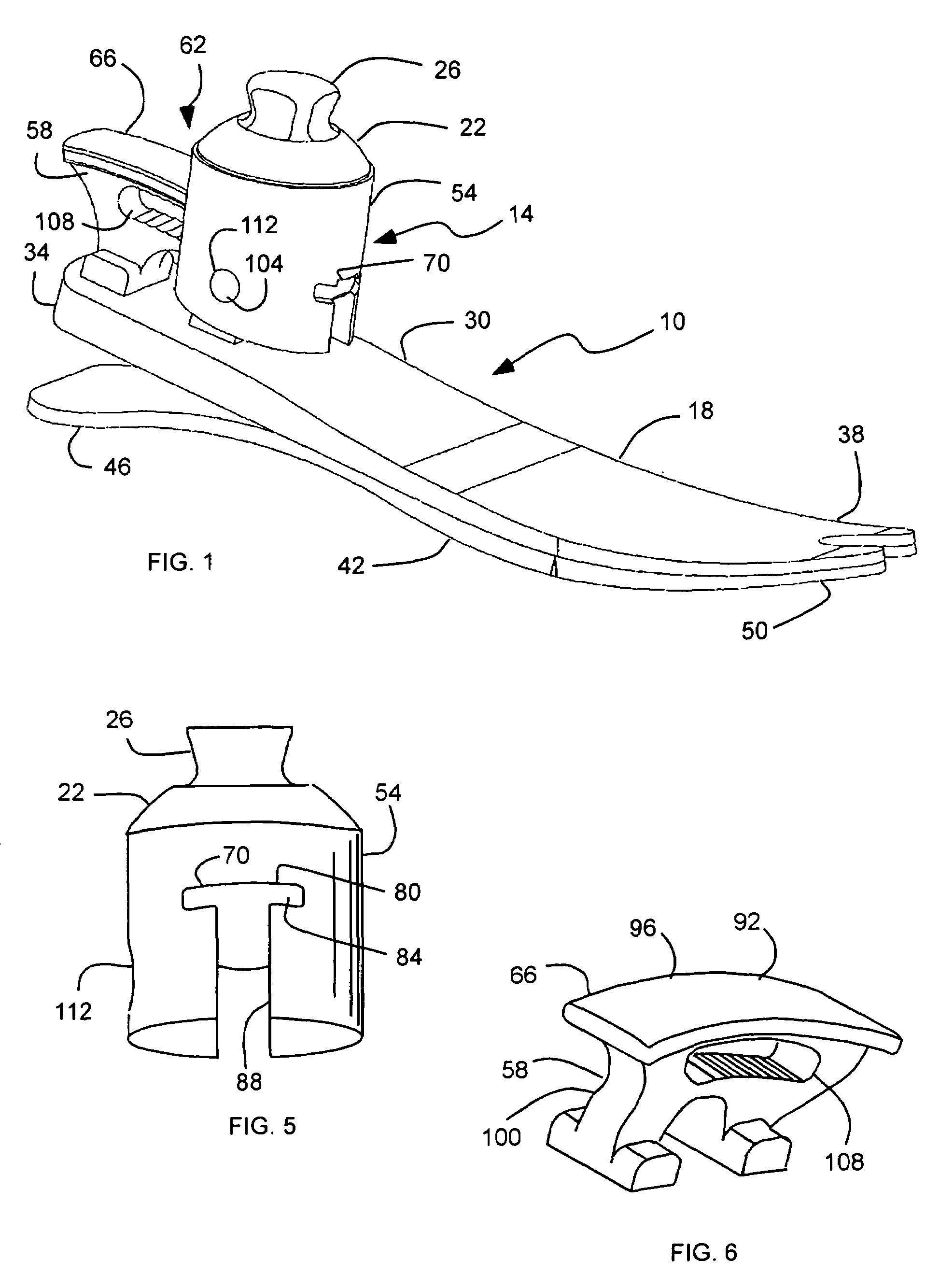
Prosthetic foot with cam
A prosthetic foot device includes an elongated continuous cantilever-spring, extending from an attachment section coupleable to a stump of an amputee to a toe section at a toe location of a natural foot. The cantilever-spring is elastically deformable under a load to store energy as the amputee steps onto the cantilever-spring and to release energy as the amputee steps off of the cantilever-spring. A cam is pivotally coupled to the cantilever-spring at a pivot. A resistance arm is coupleable to the stump of the amputee, and extends to a displaceable section engaging the cam. A lever arm is attached to the cantilever-spring and engages the cam. The cam operatively inter-couples the cantilever-spring and the resistance arm to elastically deform the resistance arm along with the cantilever-spring to collectively store more energy than the cantilever-spring alone.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Prosthetic foot with a resilient ankle
InactiveUS6929665B2Soft heelPromote absorptionArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationForefoot
A prosthetic foot device includes an elongated upper forefoot portion, an ankle portion, and a lower footplate. The forefoot portion can extend rearwardly through an upper attachment section, downwardly through an ankle section, forwardly through an arch section, and to a toe section. The ankle portion can attach to the forefoot portion, and can extend rearwardly through an upper attachment section, downwardly through an ankle section, forwardly under the ankle section of the forefoot portion, and rearwardly to a heel section, in a substantial s-shaped profile. The lower footplate can attach to the ankle or forefoot portion, and can extend through a heel section, an arch section, and to a toe section. The upper forefoot, the ankle portion, and the lower footplate each being flexible to store energy and resilient to return energy.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Prosthetic foot
ActiveUS7503937B2Low costImproved prosthetic feetArtificial legsHigh stiffnessBiomedical engineering
Embodiments of low cost prosthetic feet include a footplate with a connection mechanism embedded within a first foam element having a first stiffness. A second foam element is bonded to the footplate and has a recess in a proximal surface and a stiffness greater than the first foam element. The second foam element may have a portion extending past the terminal end of the footplate. A cosmesis encloses the components of the prosthetic foot. A third foam element that extends through the cosmesis into the second foam element may be provided. The third foam element may have a higher stiffness than the first and second foam elements.
Owner:KAUPTHING BANK
Prosthetic foot with a resilient ankle
A prosthetic foot device includes an elongated upper forefoot portion and a shock absorbing ankle portion. The forefoot portion can extend from an upper attachment section, downwardly through an ankle section, forwardly through an arch section, and to a toe section. The ankle portions can include at least two substantially straight sections including a first section extending downwardly and forwardly under the ankle section of the forefoot portion, and a second section extending downwardly and rearwardly to a heel section positioned at a heel location of a natural heel.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Prosthetic foot with energy transfer including variable orifice
A prosthetic foot device with variable stiffness response includes a variable energy transfer mechanism or variable resistance cell disposed between first and second foot members to transfer a variable amount of energy from the second member to the first member during use. The energy transfer mechanism or variable resistance cell includes a variable orifice with variable size to variably resist flow of fluid therethrough, and thus variably transfers energy between the first and second members to vary stiffness of the prosthetic foot device.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Prosthetic foot with an adjustable ankle and method
A prosthetic foot with an adjustable ankle includes an upper portion coupled to a socket of an amputee. A lower portion is adjustably coupled to the upper portion, and is attached to a foot member with heel and toe sections. A movable coupling is disposed between the upper and lower portions, and includes a displacement member slidably coupled to a displacement track. The movable coupling allows the toe section to pivot downward and the heel section to simultaneously displace forward. The adjustable ankle can be adjusted with an actuator coupled to a tractor bolt coupled between the upper and lower portions. A sensor is associated with the upper portion or the lower portion to sense frequency of contact, force of contact, or orientation of the upper portion or the lower portion, and to output a corresponding output signal.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Method of measuring the performance of a prosthetic foot
ActiveUS7581454B2Force measurementWork measurementPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDevice prosthetic
Owner:OSSUR HF
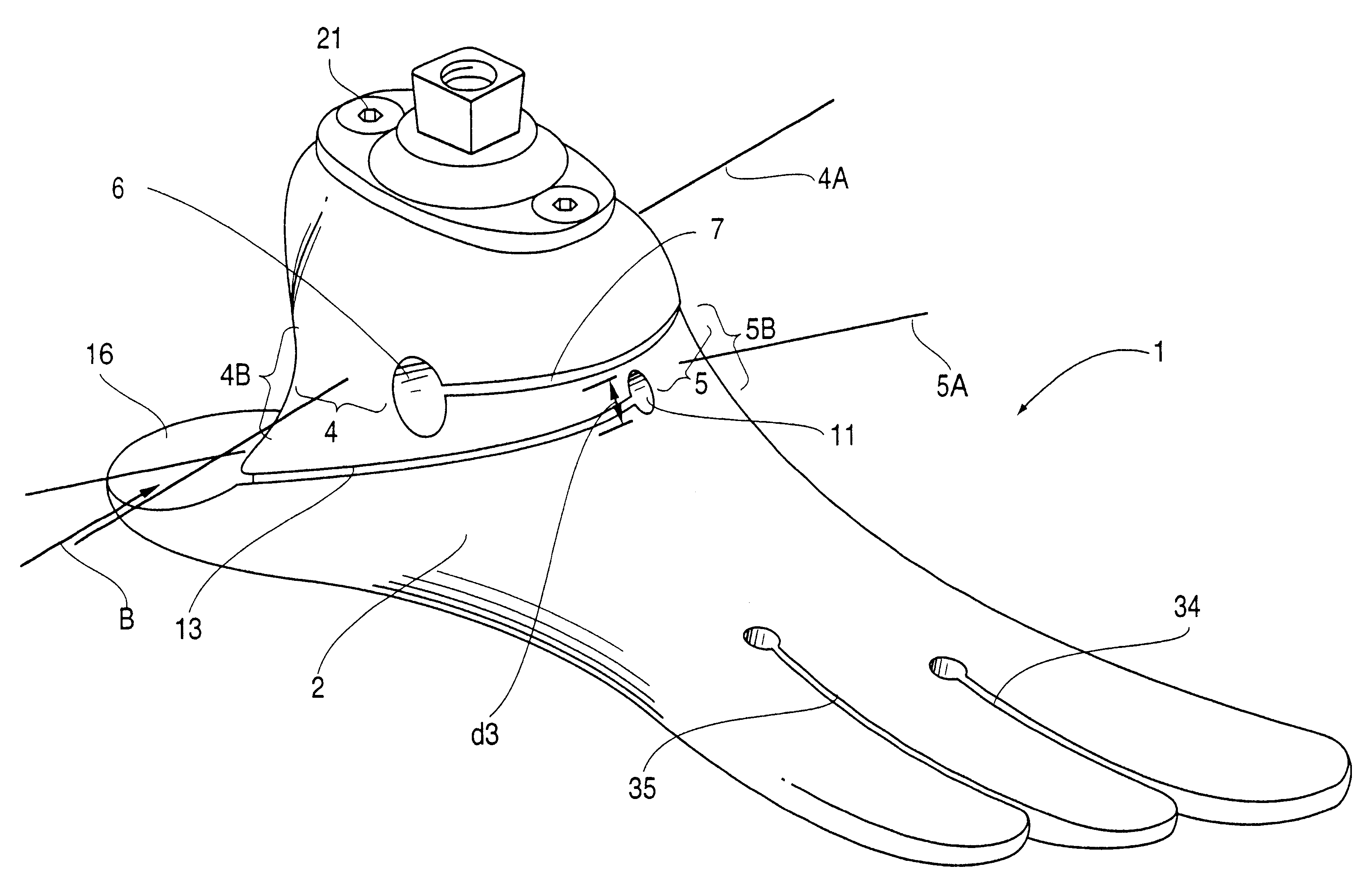
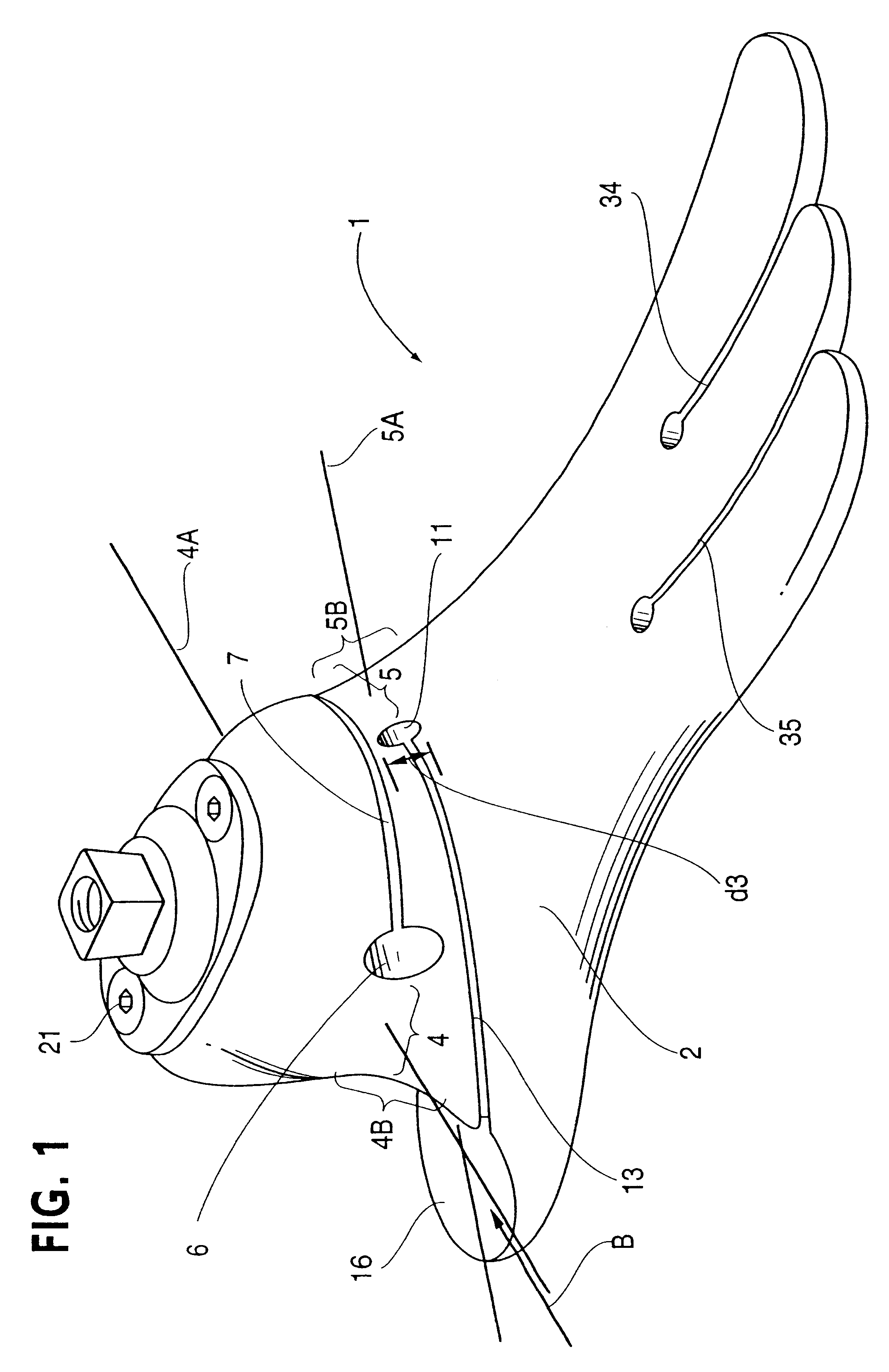
Energy returning prosthetic foot
InactiveUS20060212131A1Free from undesired noiseIncrease flexibilityArtificial legsMomentumHeel strike
The present invention relates to a prosthetic foot comprising a rear foot portion having an attachment platform and a heel strike, and a front foot portion having a momentum interrupter and a toe plate. As the foot approaches toe-off, the toe plate flexibly deflects upwards and the momentum interrupter compresses. The amount of returned energy at toe-off is comprised from stored flexural energy of the toe plate and stored expansive energy of the momentum interrupter. The toe plate of the present invention can have a split toe design. Further, mechanically adjustable stiffeners can be incorporated into the design if desired.
Owner:AMERICAN PROSTHETIC COMPONENTS
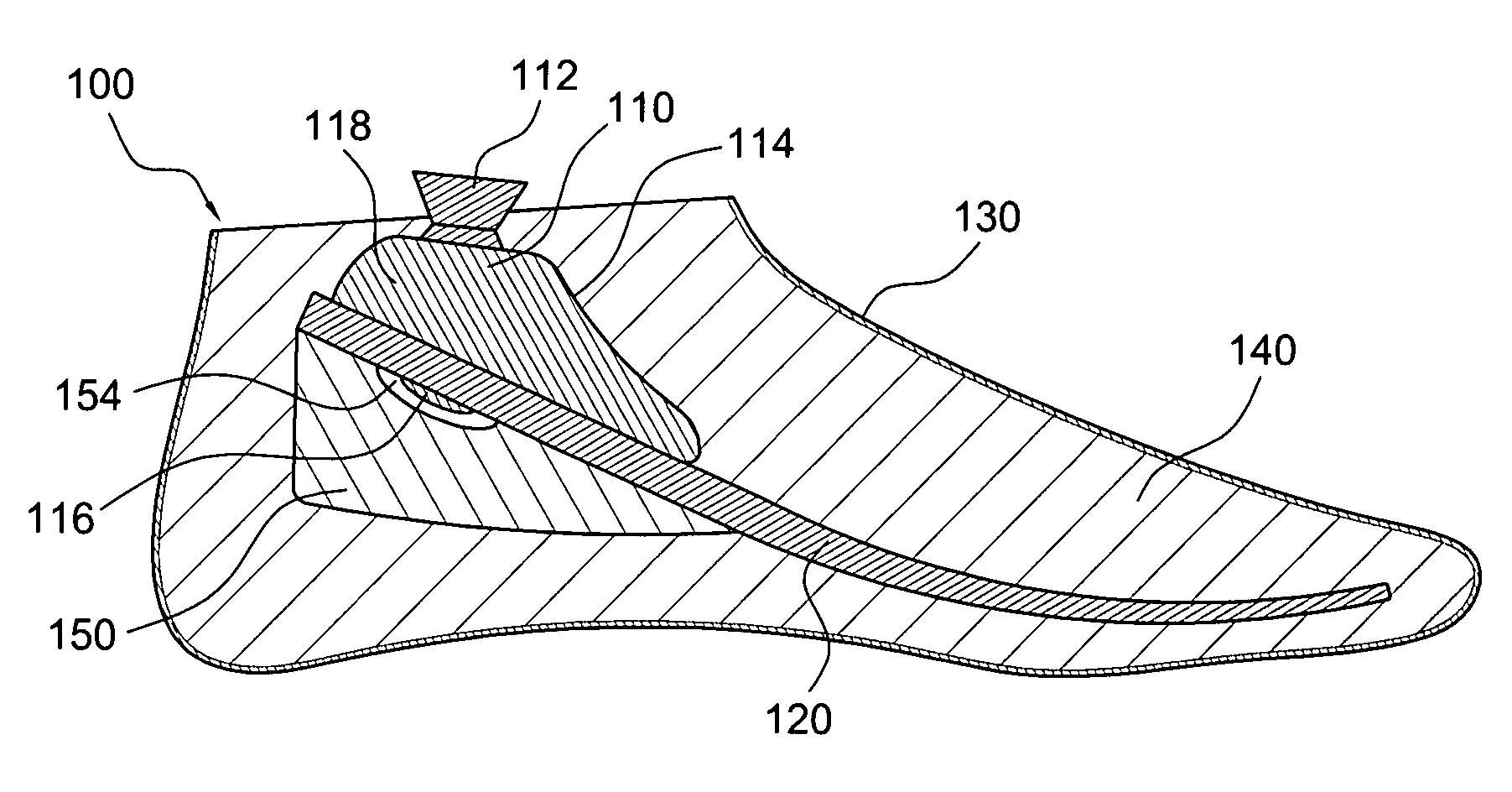
Prosthetic foot
InactiveUS6942704B2Easy constructionGreat freedom of movementArtificial legsEngineeringProsthetic feet
A prosthetic foot including a ground-engaging base in the form of a generally planar and resiliently flexible foot bed which extends between two or more platforms to form one or more flexible hinges therebetween. The platforms include a toe platform, a mid-section platform and a heel platform. A support shank is disposed above the platforms so as to be generally positioned above an ankle area of the foot. A first spring extends from the toe platform to the support shank. A second spring extends from the support shank to the mid-section platform. A third spring extends from the support shank to the heel platform. Typically, the springs are curvilinear springs.
Owner:COLLEGE PARK IND INC +1
Prosthetic foot
InactiveUS20050033451A1Facilitates iterative tuningNatural appearanceArtificial legsFeature completeEngineering
Features for a high performance prosthetic foot are provided in a package suitable for use with Symes and reverse-Symes amputees. The foot has a very low profile despite incorporating ankle-type torsional features complete with biasing. Other optional features are presented by way of a dual-rate padding spring system, that convincingly allow for both walking and running (together with related tasks like jumping) by way of a single prosthetic setup. Additional features may be provided in the padding springs directed toward more natural foot movement and response. The foot may be provided alone, in connection with a prosthetic socket and be bare or encased in order to appear more natural.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Foot prosthesis having cushioned ankle
InactiveUS6899737B1Improve rigidityDegree of improvementArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTransverse orientation
A simple, inexpensive prosthetic foot is provided incorporating a cushioned ankle including an ankle block formed of a resilient material or bladder having desired compliance and energy return characteristics. The ankle block is sandwiched between a foot element and an ankle element. One or more openings extends through the ankle block with a substantially transverse orientation relative to a forward walking motion. The size and shape of these openings, as well as the insertion of different types of stiffeners therein, provide desired performance characteristics to the ankle block. When the ankle block takes the form of one or more inflatable bladders, the pressure within these bladders is individually controlled by valves to provide desired performance characteristics to different portions of the prosthetic foot. A pump system can also be used to control and generate fluid pressure into these bladders. A preferred pump system generates fluid pressure based upon the movement of the amputee onto two telescoping pylons that are connected to the prosthetic foot.
Owner:FLEX FOOT
Prosthetic foot with an adjustable ankle and method
A prosthetic foot with an adjustable ankle includes an upper portion coupled to a socket of an amputee. A lower portion is adjustably coupled to the upper portion, and is attached to a foot member with heel and toe sections. A movable coupling is disposed between the upper and lower portions, and includes a displacement member slidably coupled to a displacement track. The movable coupling allows the toe section to pivot downward and the heel section to simultaneously displace forward. The adjustable ankle can be adjusted with a motor coupled to a tractor bolt coupled between the upper and lower portions. A level sensor can sense the orientation of the upper portion and send a signal to operate the motor to vertically orient the upper portion or level the foot.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Prosthetic foot with tunable performance and improved vertical load/shock absorption
InactiveUS7578852B2Improve performanceImproved applied mechanicCapsule deliveryArtificial legsTibiaKeel
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
Prosthetic foot with energy transfer
A prosthetic foot device with variable stiffness response includes a variable energy transfer mechanism disposed between first and second foot members to transfer a variable amount of energy between the members during use. A chamber is associated with one of the first and second foot members, and a piston is associated with another of the first and second foot members and is movable in the chamber. At least one aperture is formed between the piston and the chamber. A variable viscosity fluid is disposed in the chamber and displaceable through the at least one aperture between the piston and the chamber to allow fluid to flow within the chamber between opposite sides of the piston. The variable viscosity fluid has a viscosity that is variable to vary an ability of the variable viscosity fluid to flow through the at least one aperture.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Adjusting mechanism for a prosthetic
An adjusting mechanism alters the heel height on a prosthetic foot, and works independently of any articulating ankle joint or foot style, without changing the original dynamic alignment of a prosthetic leg. In a two chamber hydraulic closed system—a fluid material is allowed to flow through the two chambers by use of pistons that push the fluid material equally from one chamber to another until the desired heel height is obtained. Once the correct position is obtained, the ports are closed by use of a push button stop, which closes the ports and stops all transfer of fluid between the ports holding the heel in position during use.
Owner:THERMAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com