Patents
Literature
56 results about "Leg prosthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
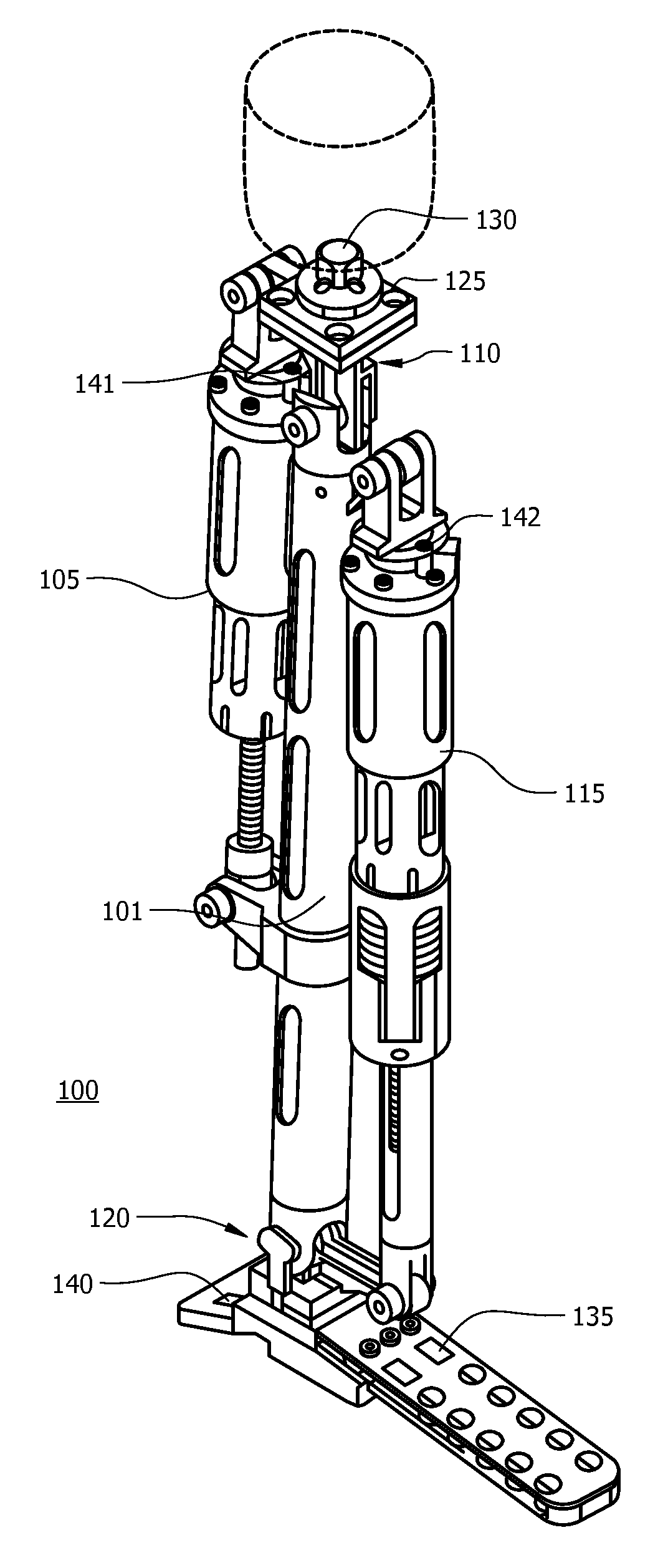
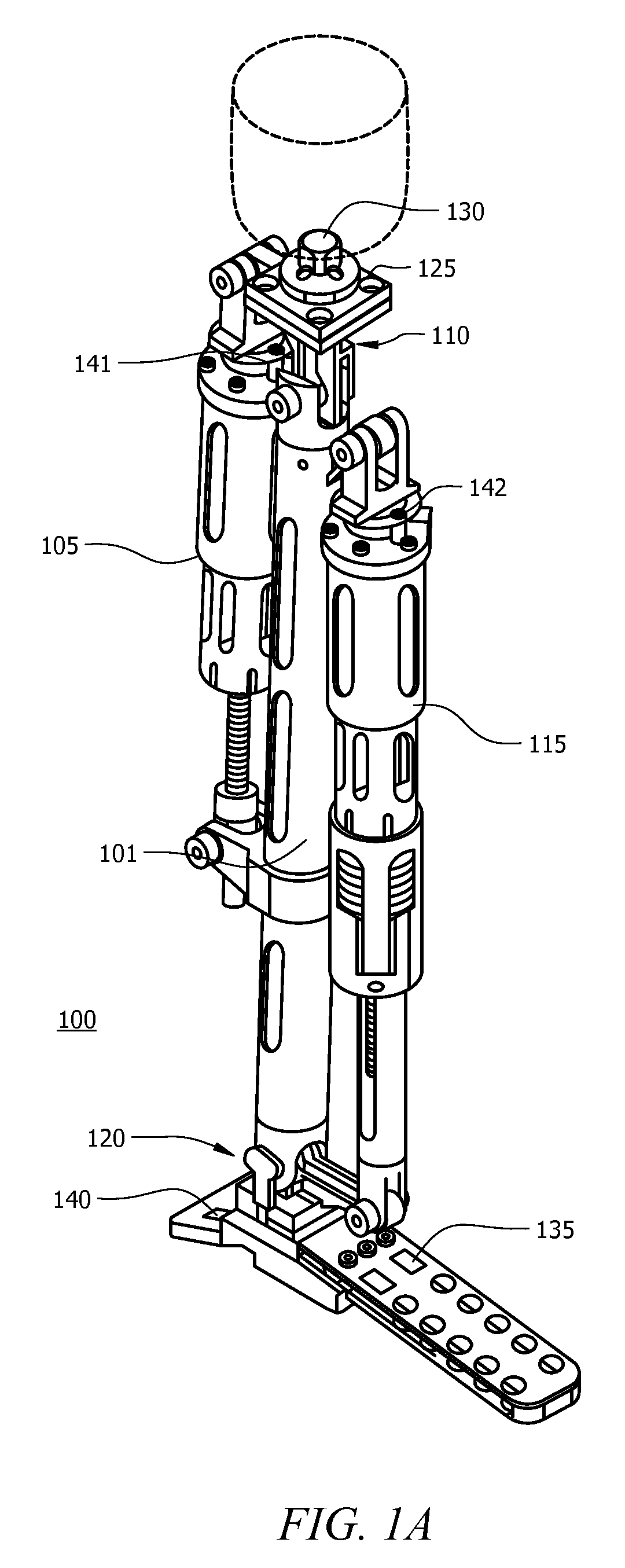
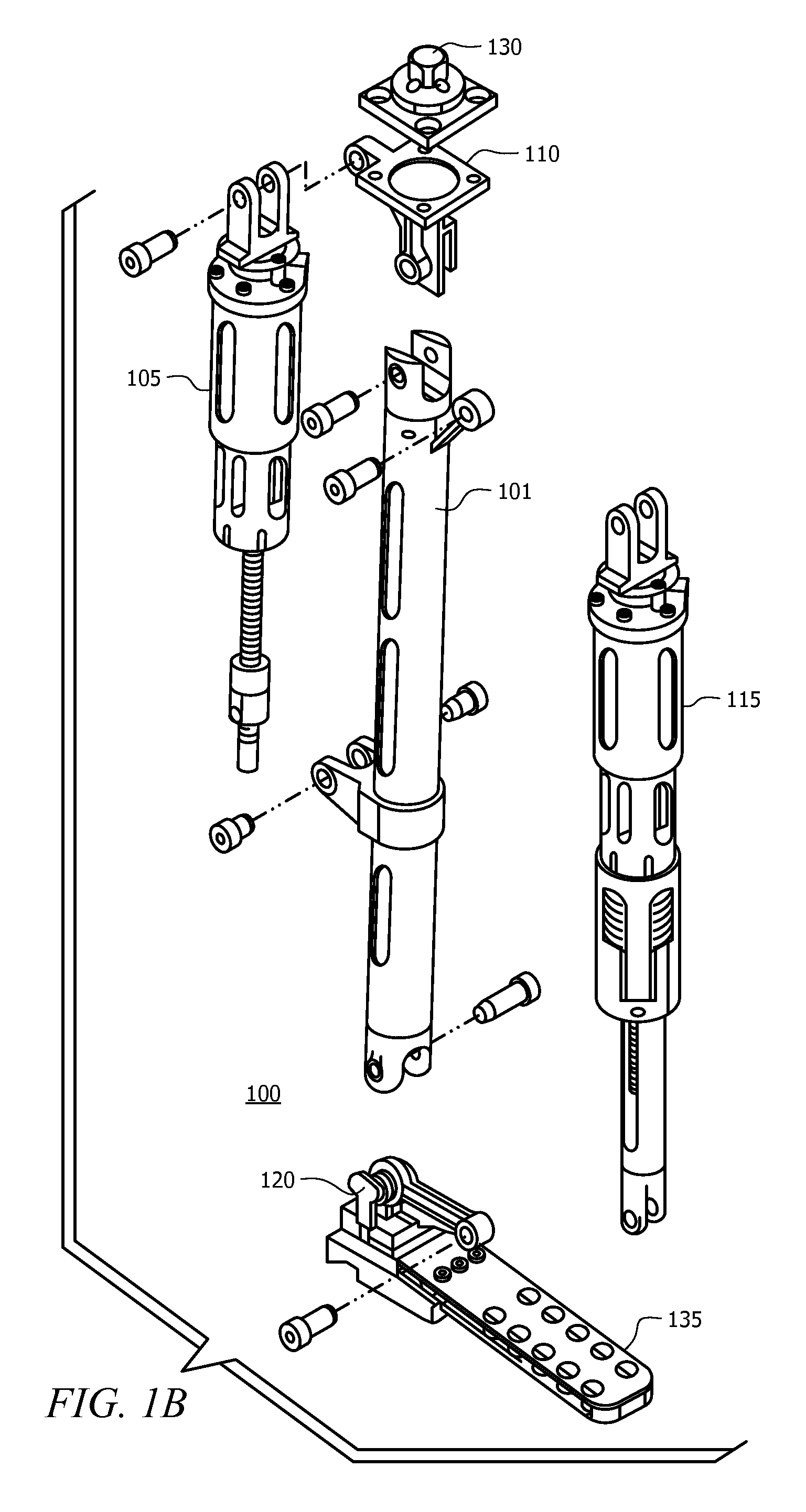
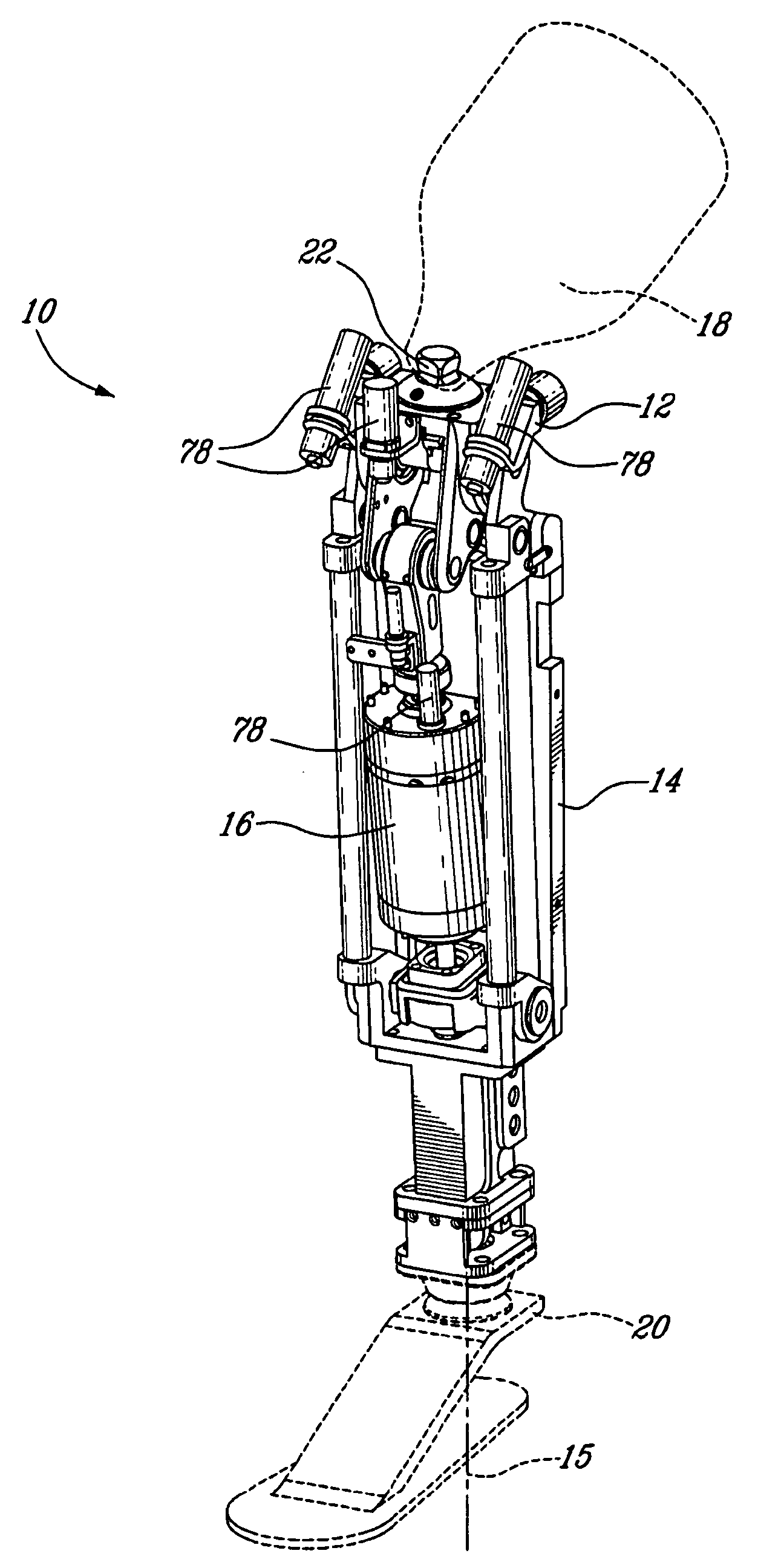
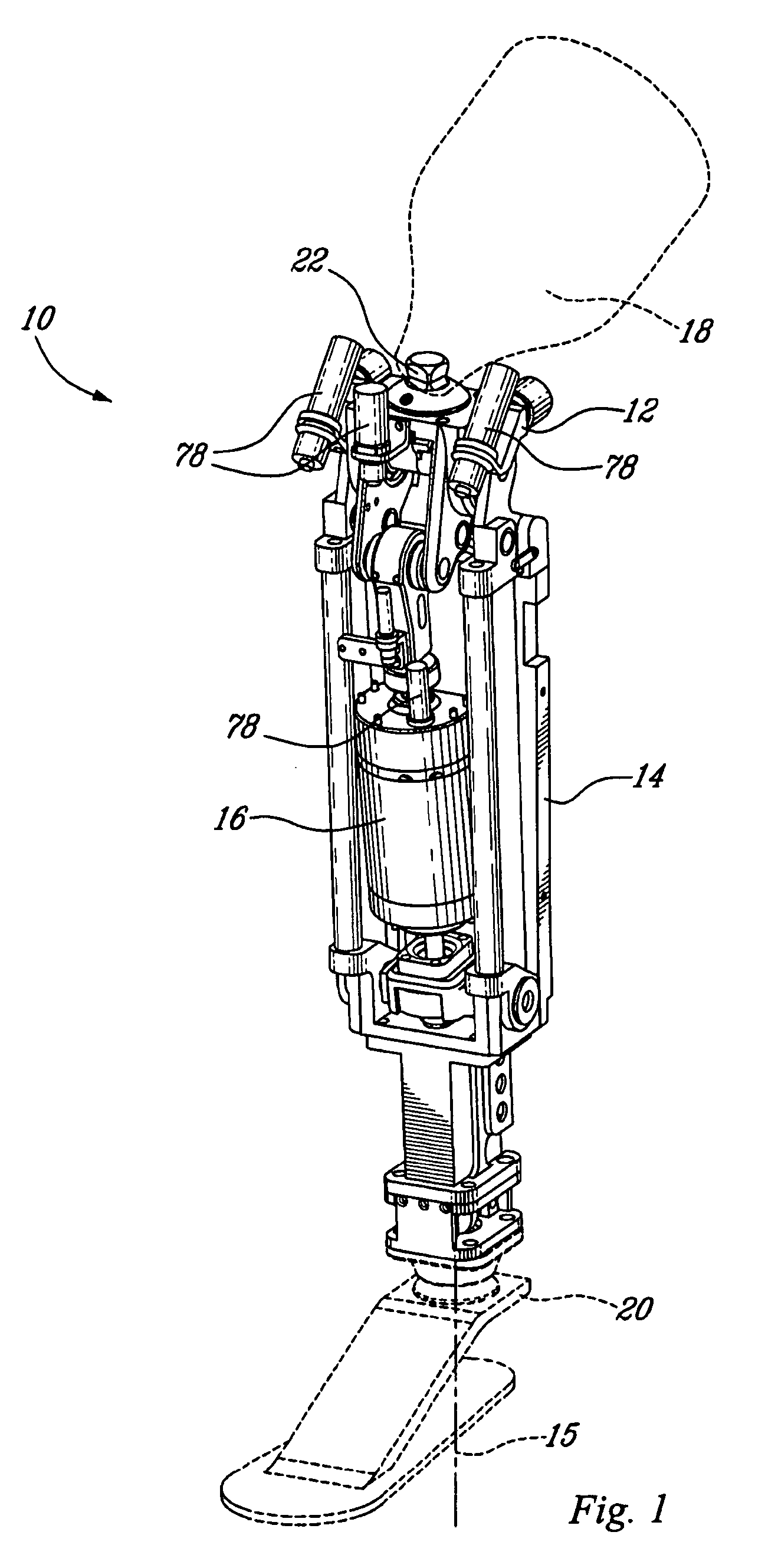
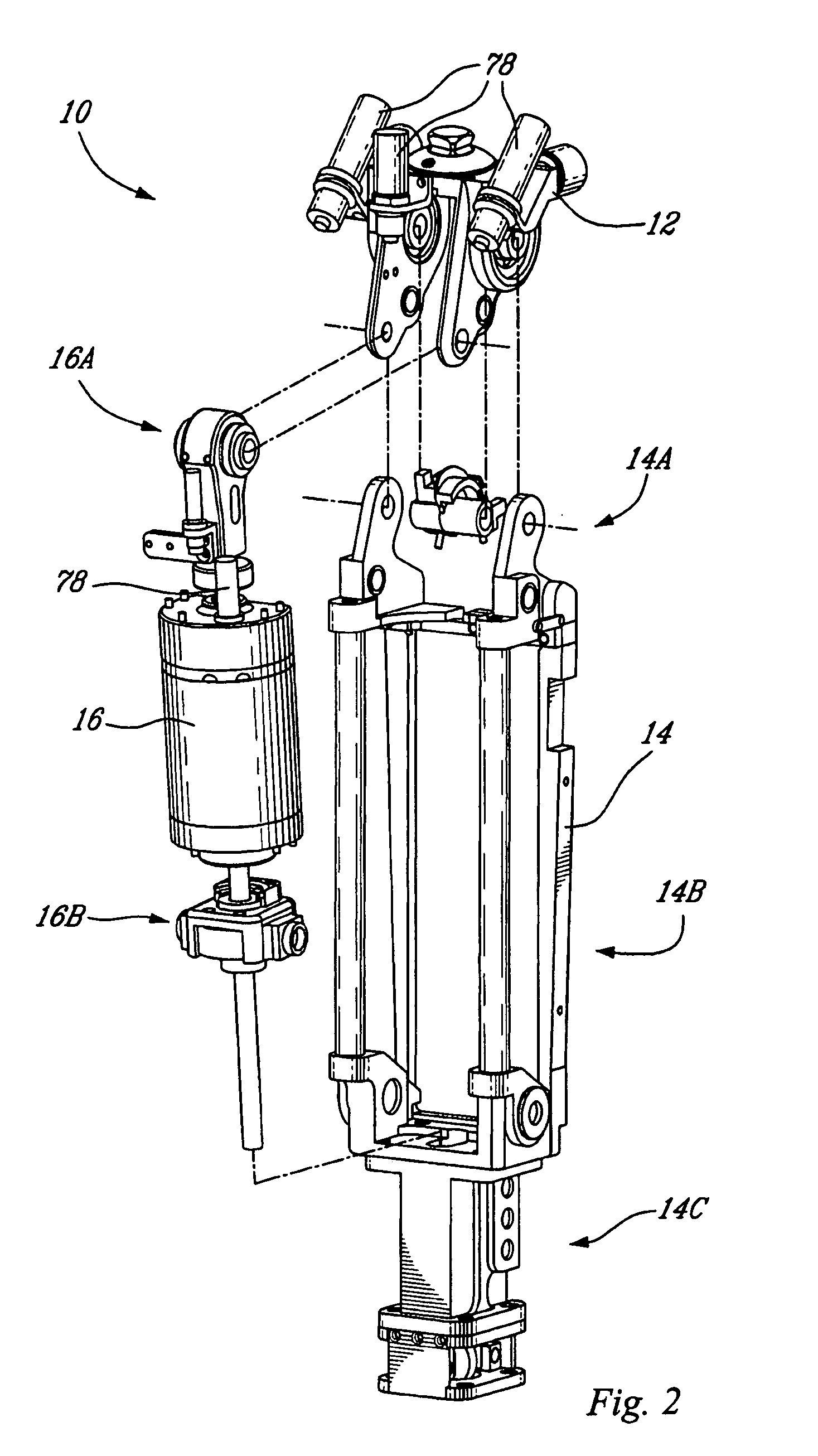
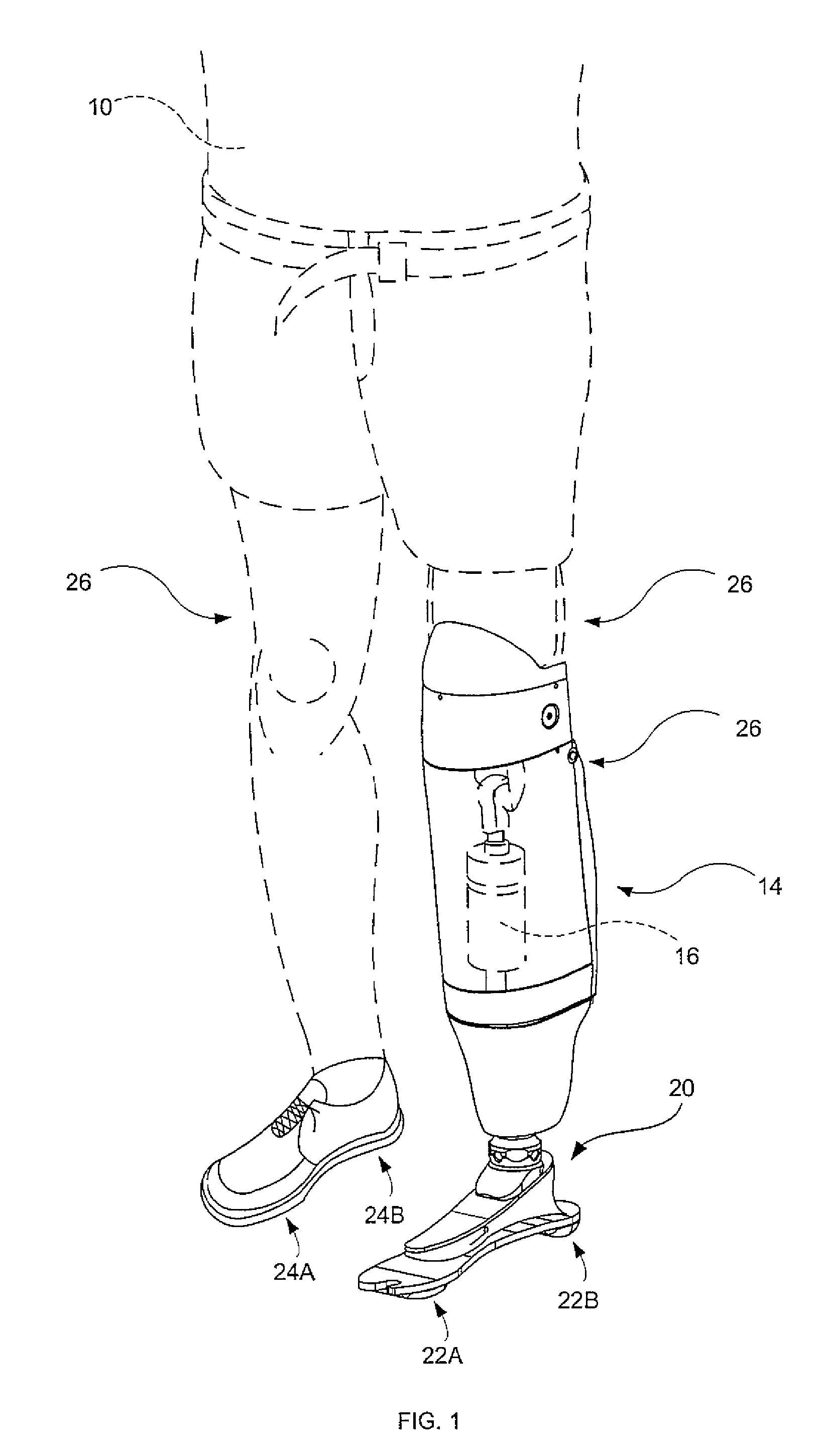
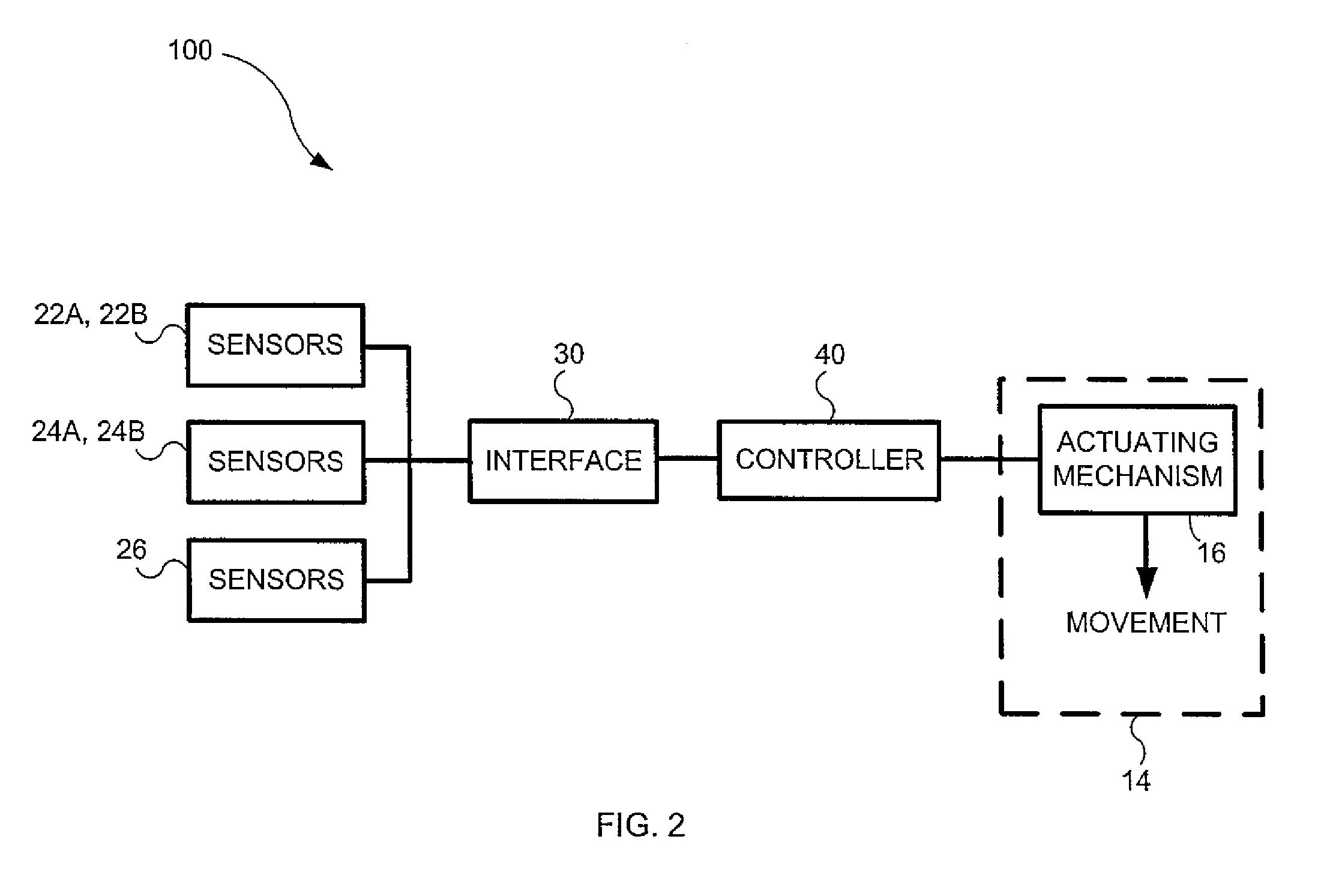
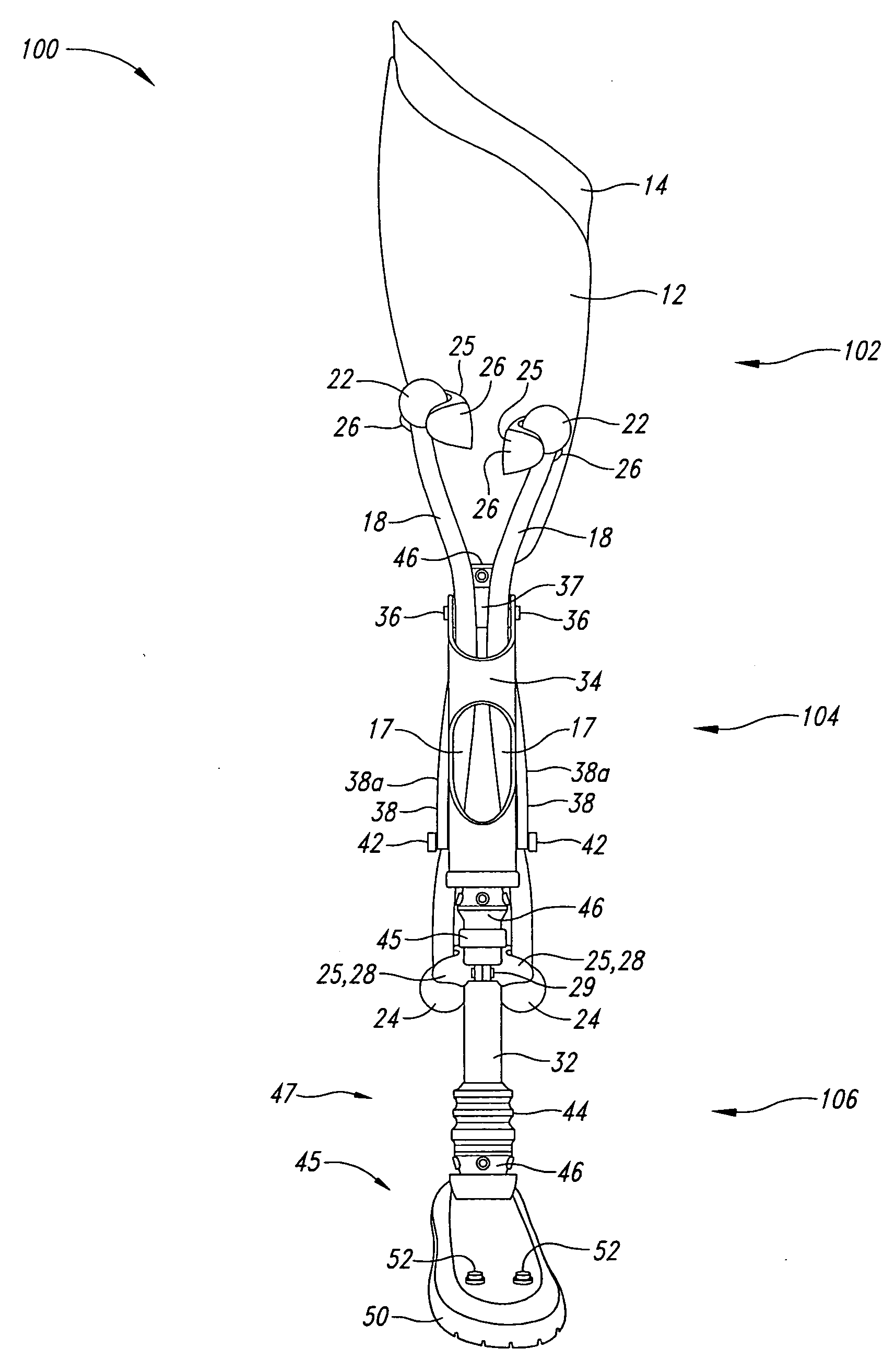
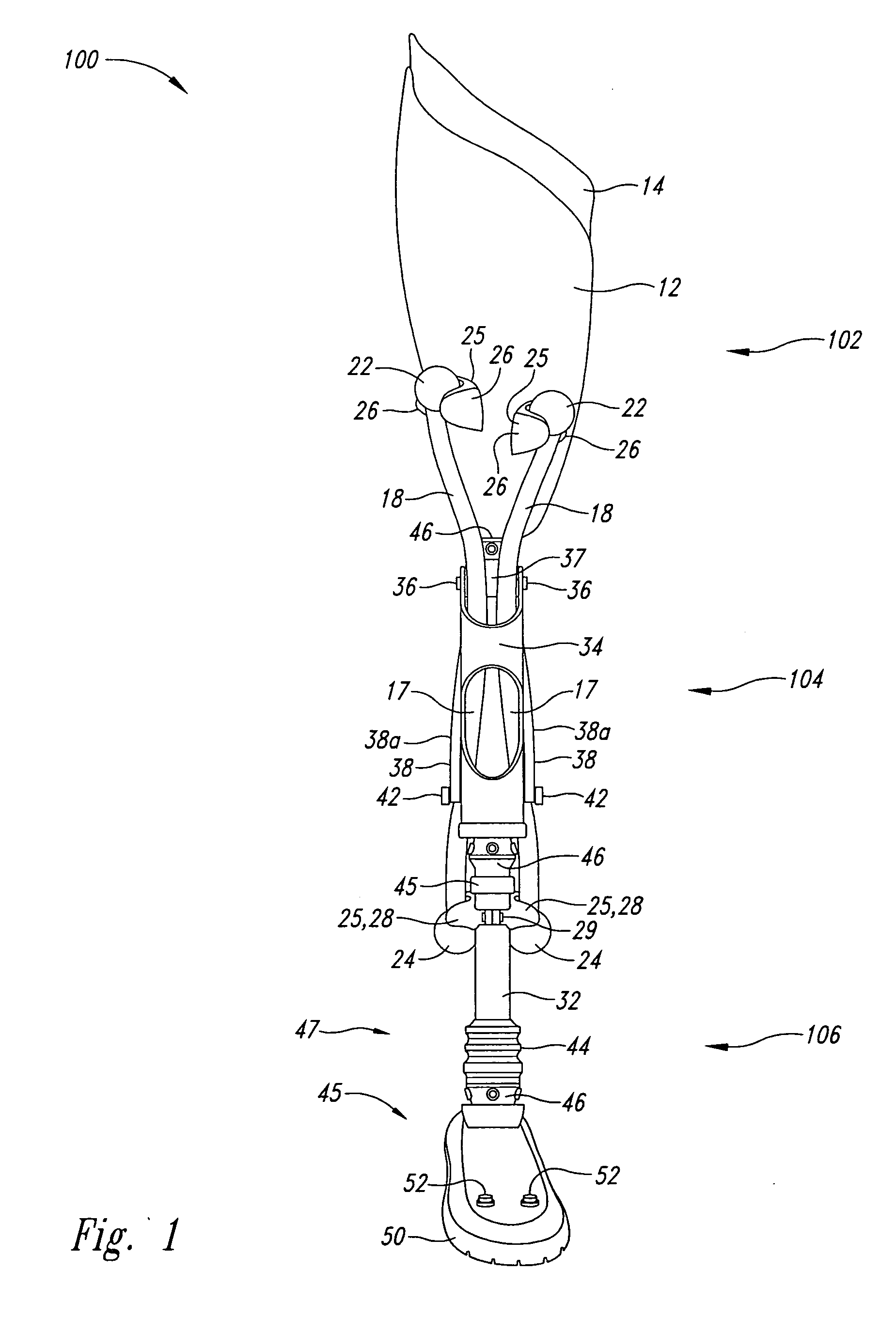
Powered leg prosthesis and control methodologies for obtaining near normal gait
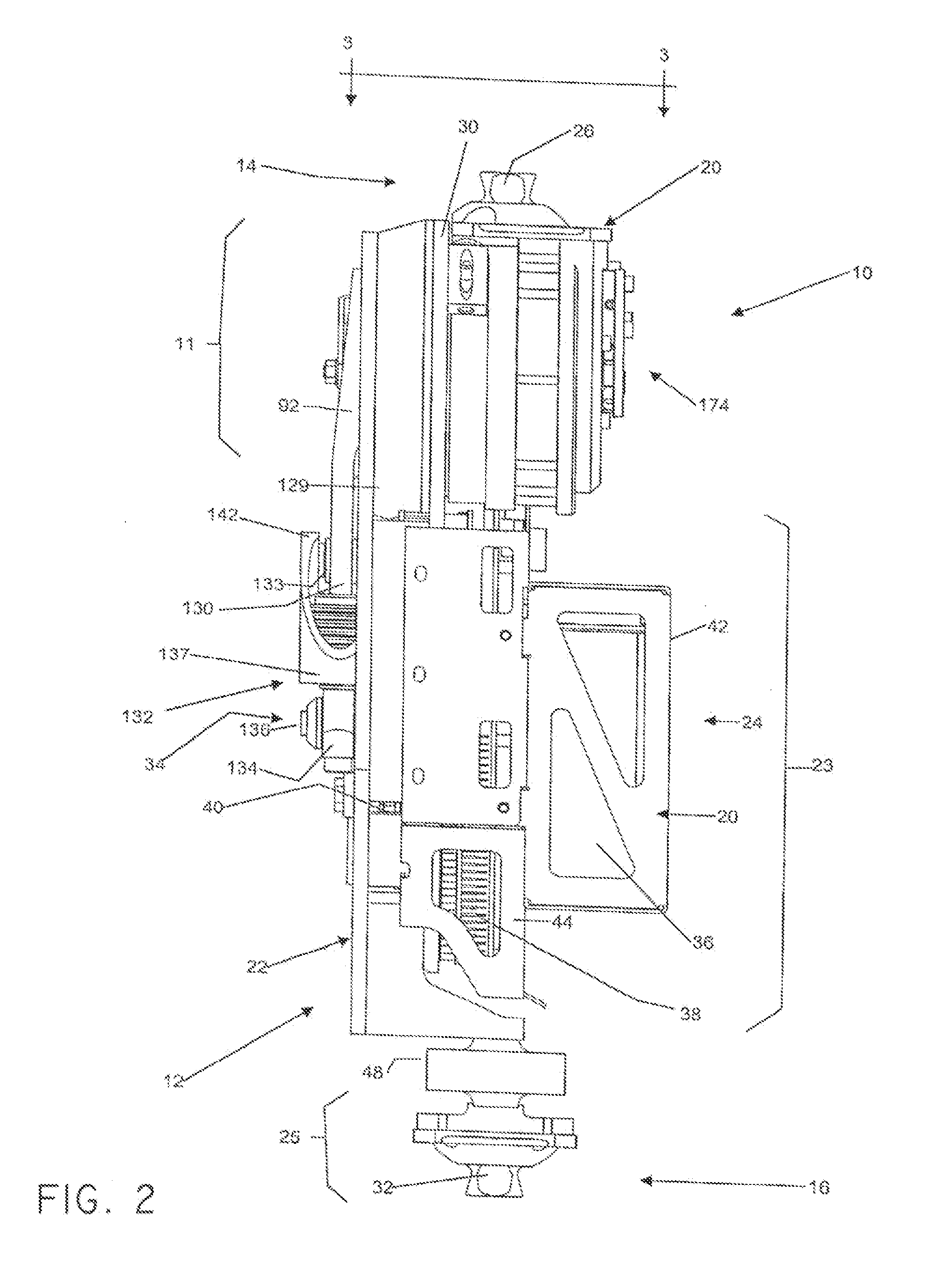
A powered leg prosthesis includes powered knee joint comprising a knee joint and a knee motor unit for delivering power to the knee joint. The prosthesis also includes a prosthetic lower leg having a socket interface coupled to the knee joint and a powered ankle joint coupled to the lower leg opposite the knee joint comprising an ankle joint and an ankle motor unit to deliver power to the ankle joint. The prosthesis further includes a prosthetic foot coupled to the ankle joint, at least one sensor for measuring a real-time input, and at least one controller for controlling movement of the prosthesis based on the real-time input.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
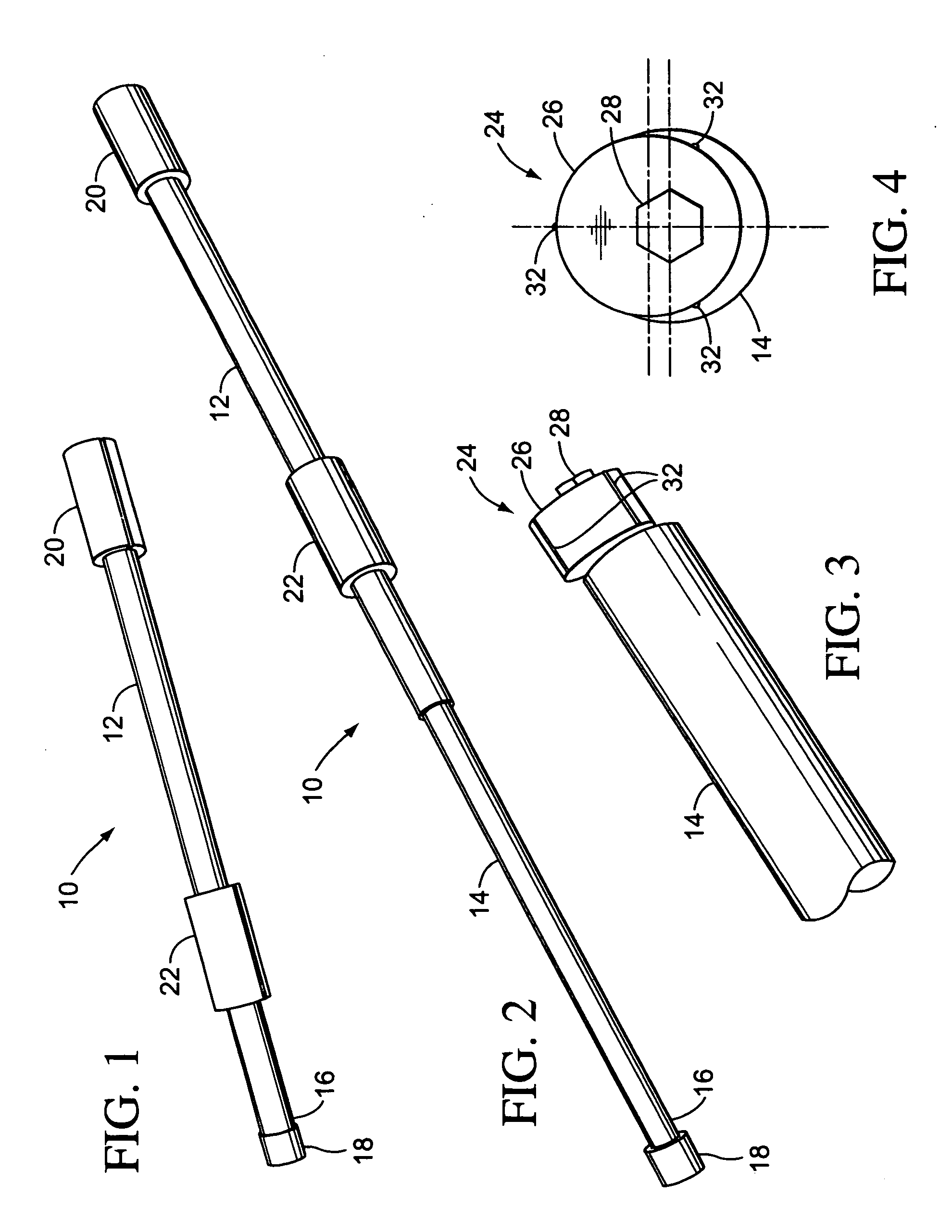
Device in a leg prosthesis
InactiveUS6855170B2Simple geometryReduce manufacturing costArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationLeg prosthesis
A device in a leg prosthesis which via a pivot axle is connected to the leg prosthesis, wherein first means are arranged to permit a limited rotation of the foot with respect to the leg prosthesis from an initial position, in which the leg prosthesis and the foot have a certain angle with respect to each other and second means are arranged to permit a stepless adjustment of the angle between the prosthesis and the foot in the initial position.
Owner:GRAMTEC INNOVATION
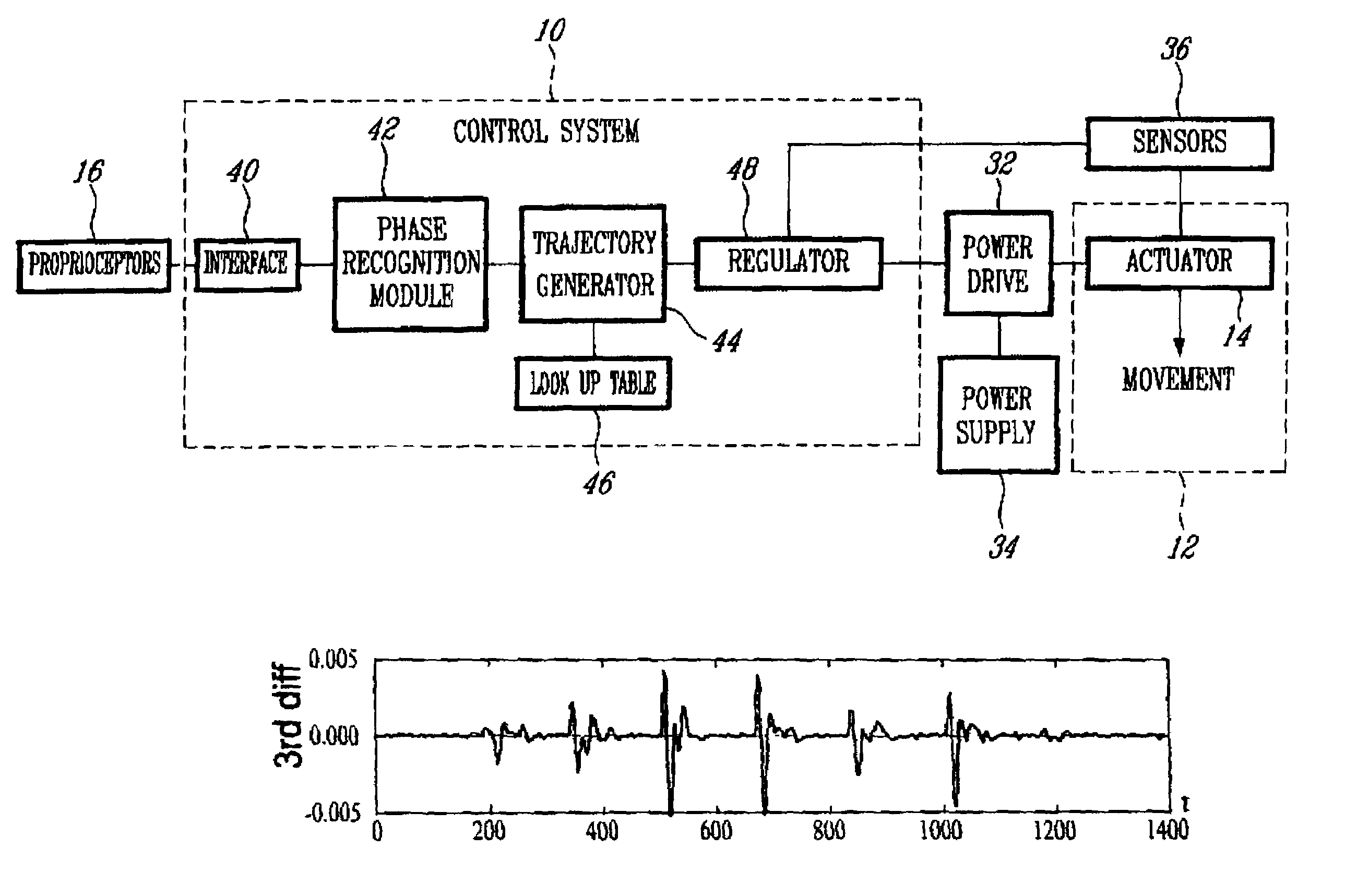
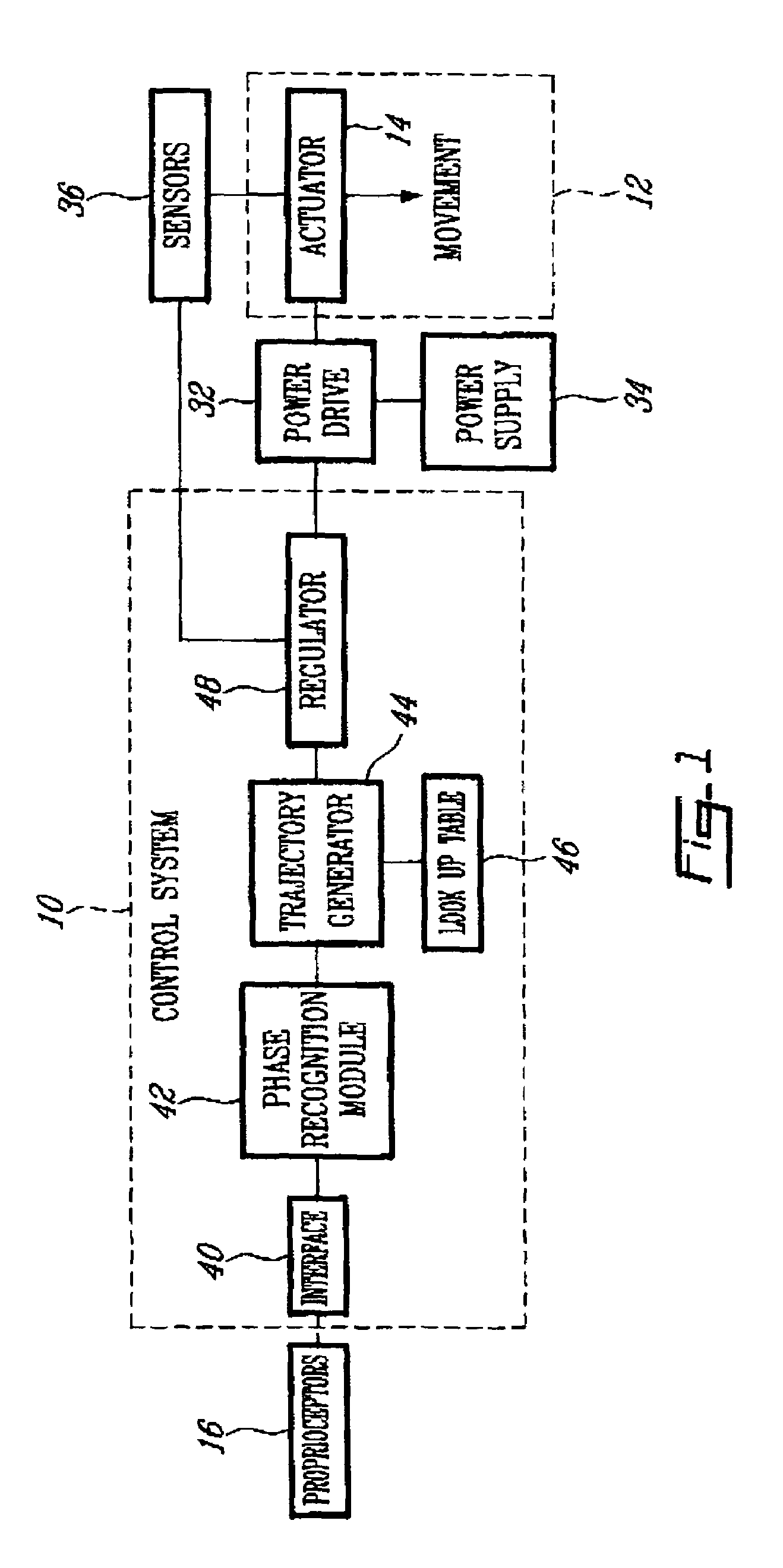
Control device and system for controlling an actuated prosthesis
A method and a control system are used for determining a portion of locomotion and a phase of locomotion portion in view of controlling an actuated prosthesis in real time. The method comprises receiving a data signal from a plurality of main artificial proprioceptors, obtaining a first and a second derivative signal for each data signal, obtaining a third derivative signal for at least one of the data signals, using a set of first state machines to select one state among a plurality of possible states for each artificial proprioceptor with the corresponding data and derivative signals, generating the phase of locomotion portion using the states of the main artificial proprioceptors; and using a second state machine to select the portion of locomotion among a plurality of possible portions of locomotion using events associated to the data signals. It is particularly well adapted for an actuated, above-knee leg prosthesis.
Owner:NATIONAL BANK OF CANADA
Control system and method for controlling an actuated prosthesis
The method and the control system are used for determining a portion of locomotion and a phase of locomotion portion in view of controlling an actuated prosthesis in real time. Accordingly, the method comprises receiving a data signal from a plurality of main artificial proprioceptors, obtaining a first and a second derivative signal for each data signal, obtaining a third derivative signal for at least one of the data signals, using a set of a first state machines to select one state among a plurality of possible states for each artificial proprioceptor with the corresponding data and derivative signals, generating the phase of locomotion portion using the states of the main artificial proprioceptors; and using a second state machine to select the portion of locomotion among a plurality of possible portions of locomotion using events associated to the data signals. It is particularly well adapted for the control of an actuated leg prosthesis for above-knee amputees.
Owner:VICTHOM CORP +1
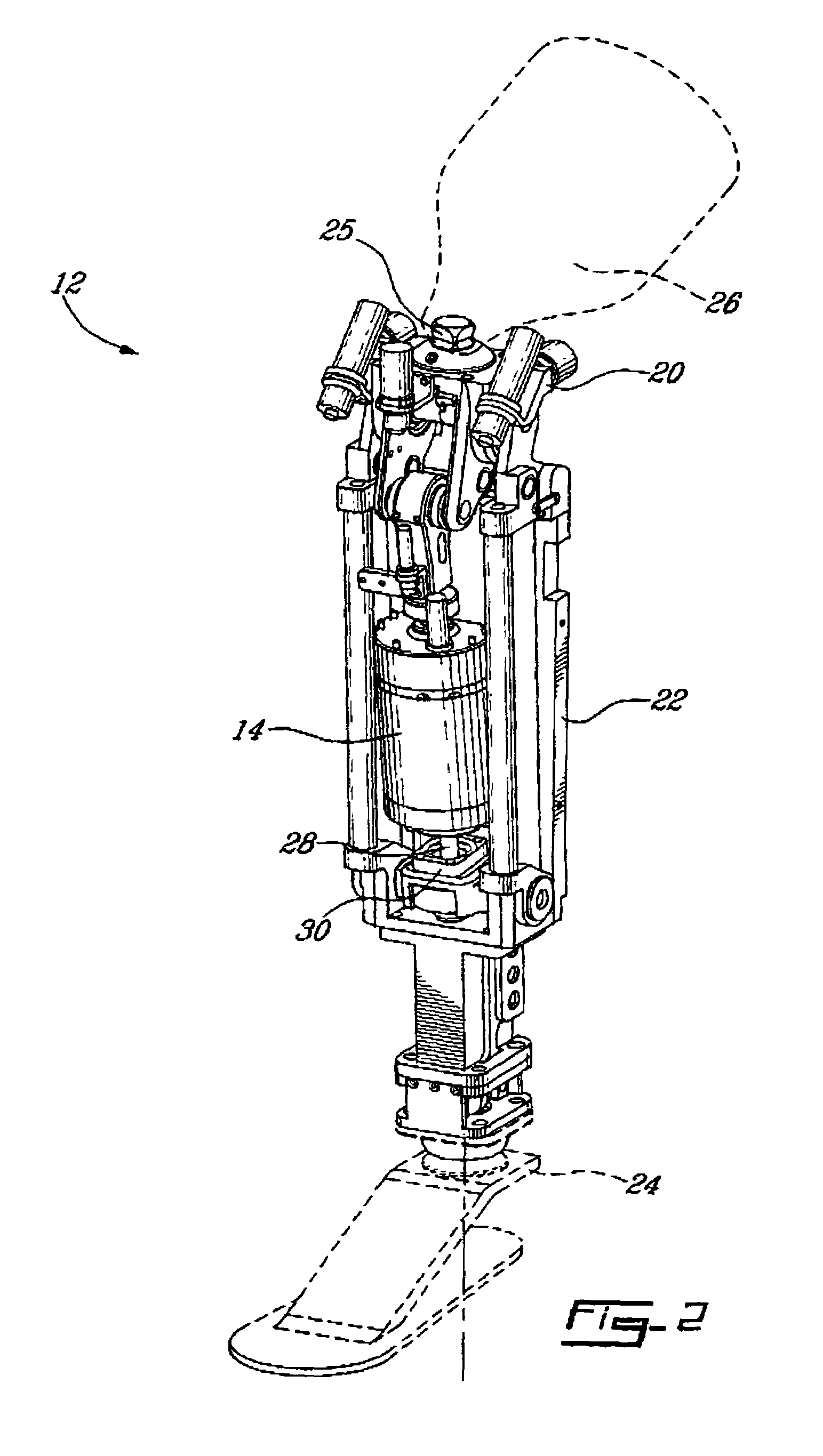
Leg prosthesis
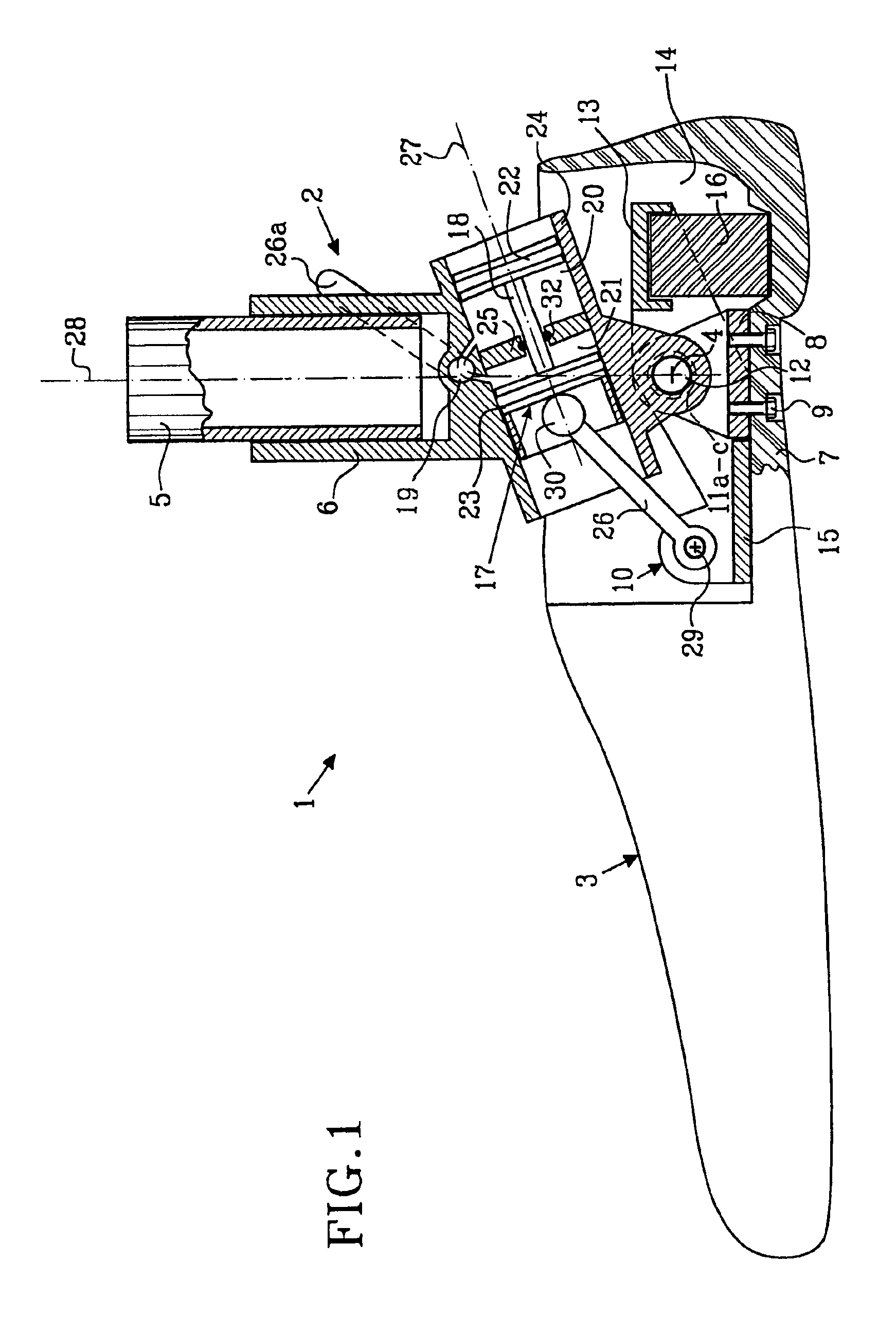
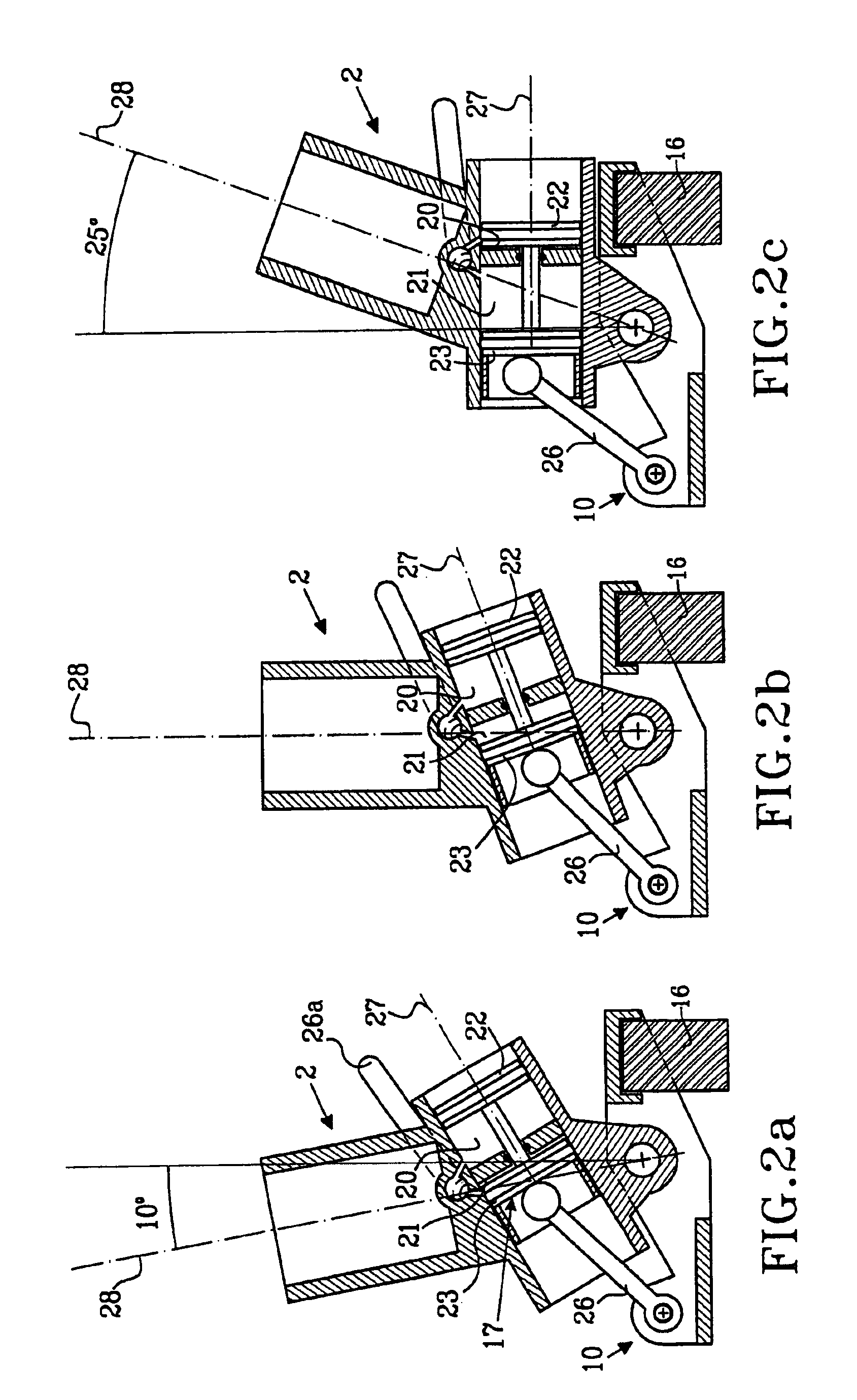
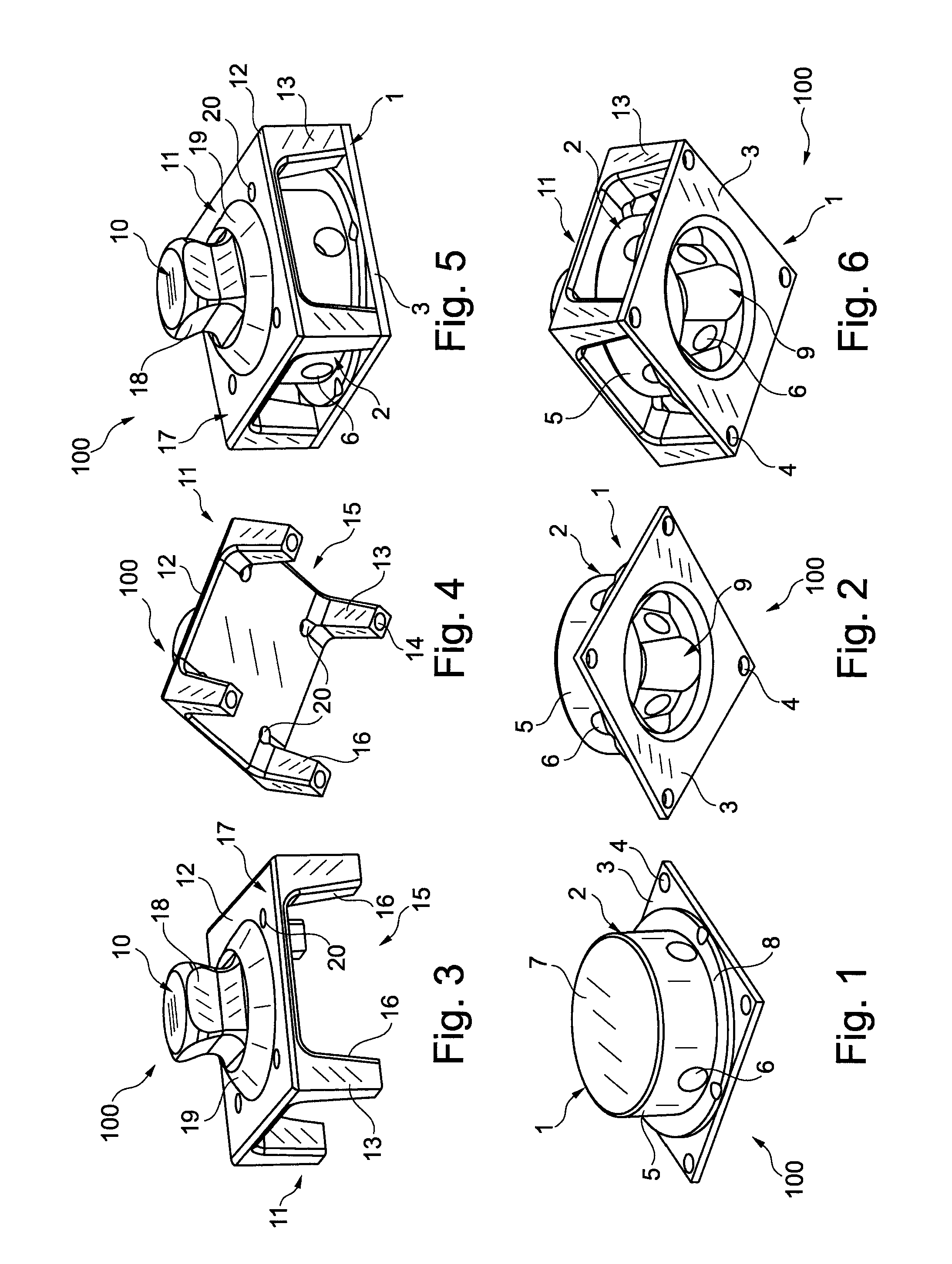
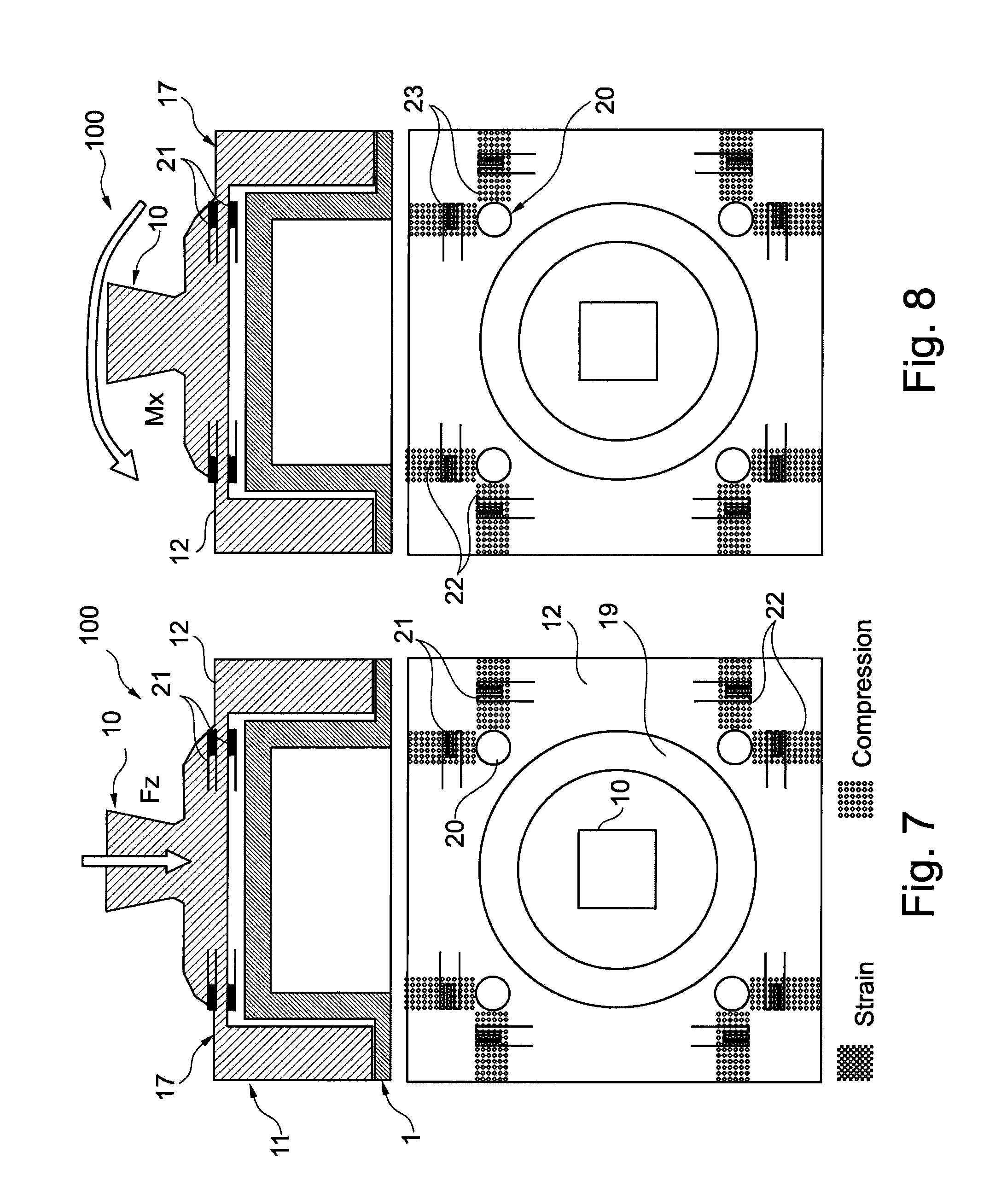
ActiveUS6955692B2Improve a leg prosthesisIncrease and decreases resistanceArtificial legsThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
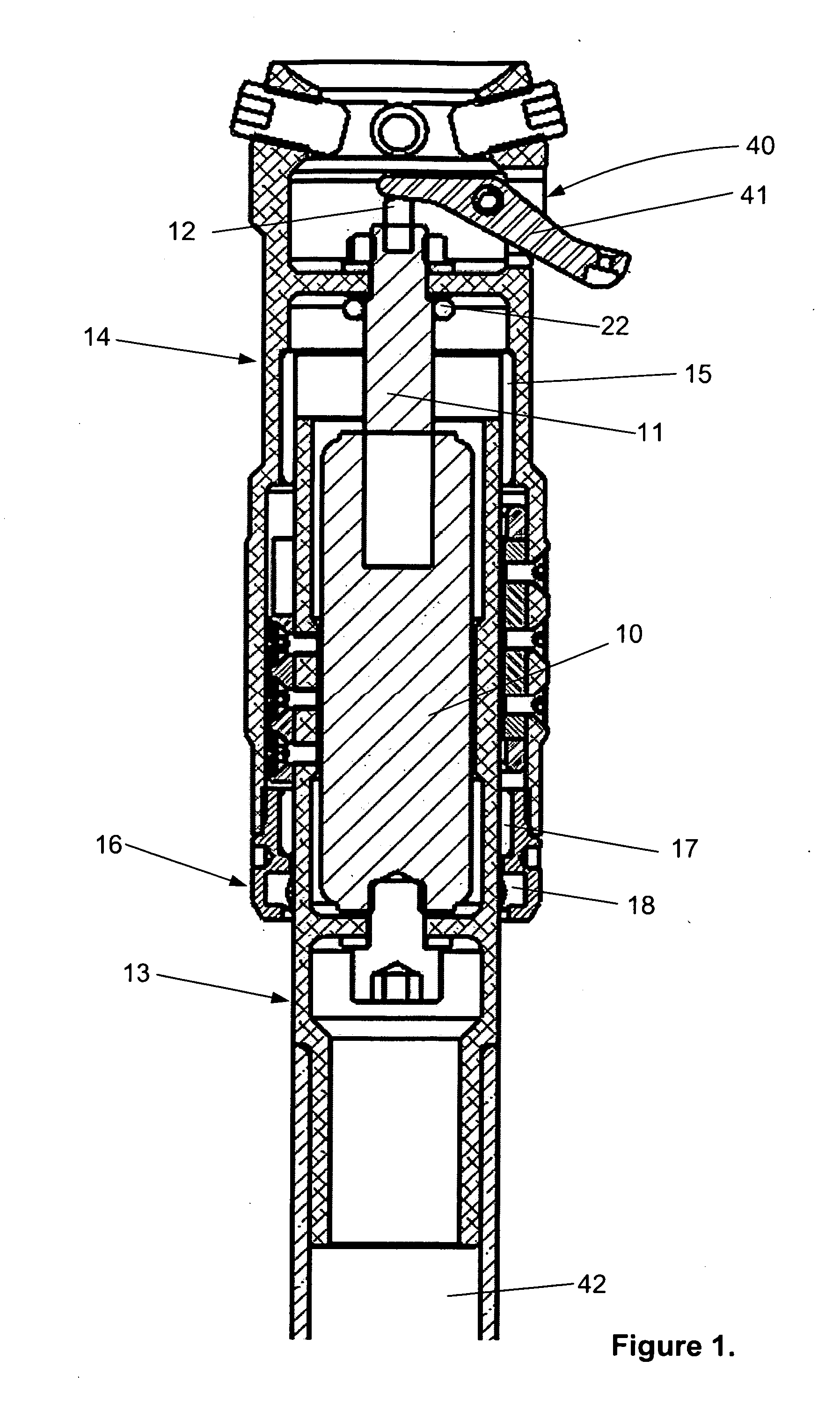
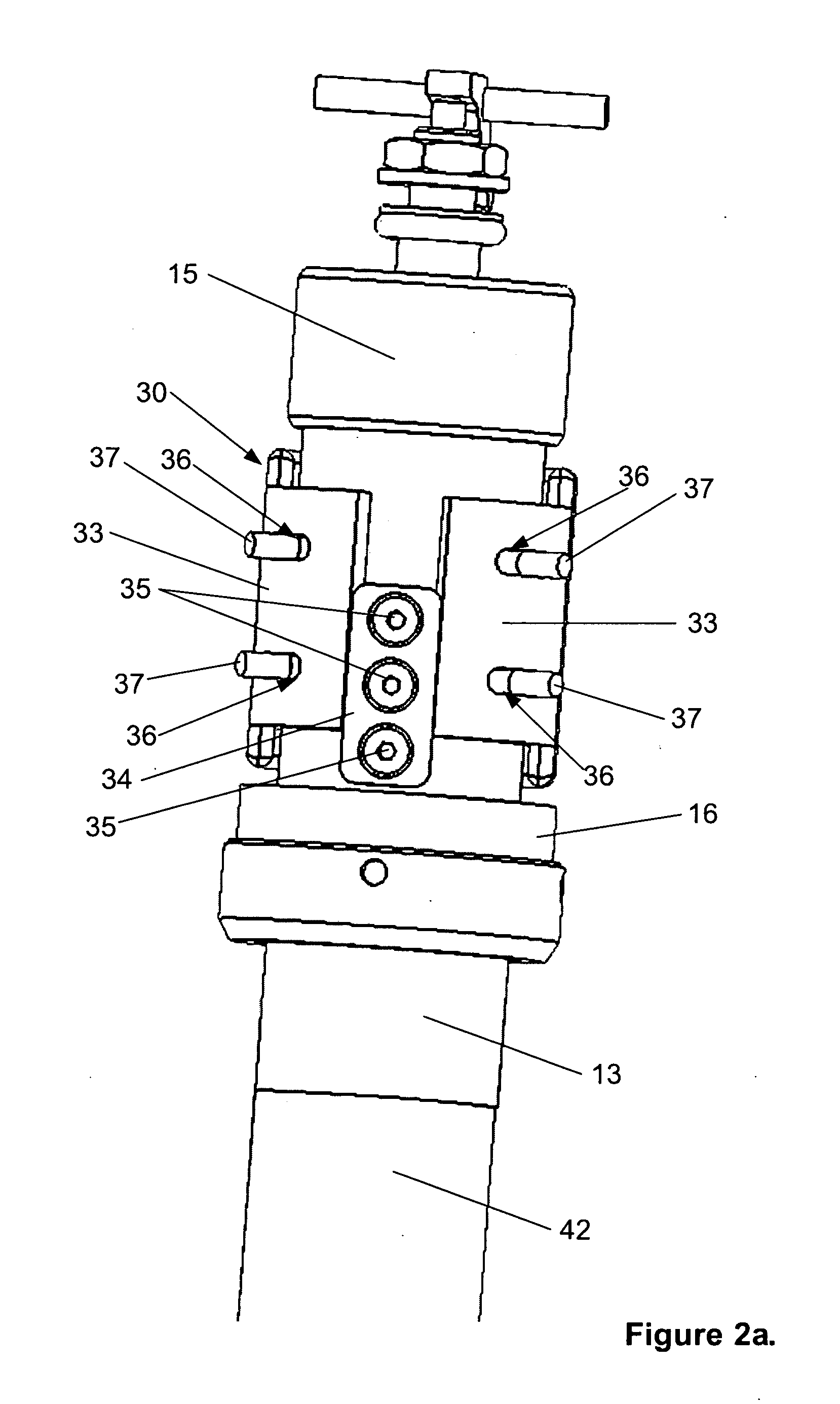
A leg prosthesis adapted to a thigh stump includes an adapter (2) for a knee joint (3), a knee joint (3) mounted on this adapter, and a prosthetic lower leg (4) coupled to the knee joint (3). A prosthetic foot (5) is attached to this prosthetic lower leg and can pivot into a toes-raised foot position. The knee joint (3) upon transition from the extended position to the bent position performs a combined rolling-sliding movement about a pivot axis (6). A force-transmitting element (8) moves the prosthetic foot (5) substantially from the toes-down foot position to the toes-raised foot position during bending of the knee joint (3). Each bending position of the knee joint is transformed by a converter into an unambiguous electrical signal, which is supplied to a programmable control device, which generates a signal used to control an electrically adjustable actuator, which increases or decreases the resistance of the knee joint against or for further bending according to the signal.
Owner:OSSEO PL GMBH
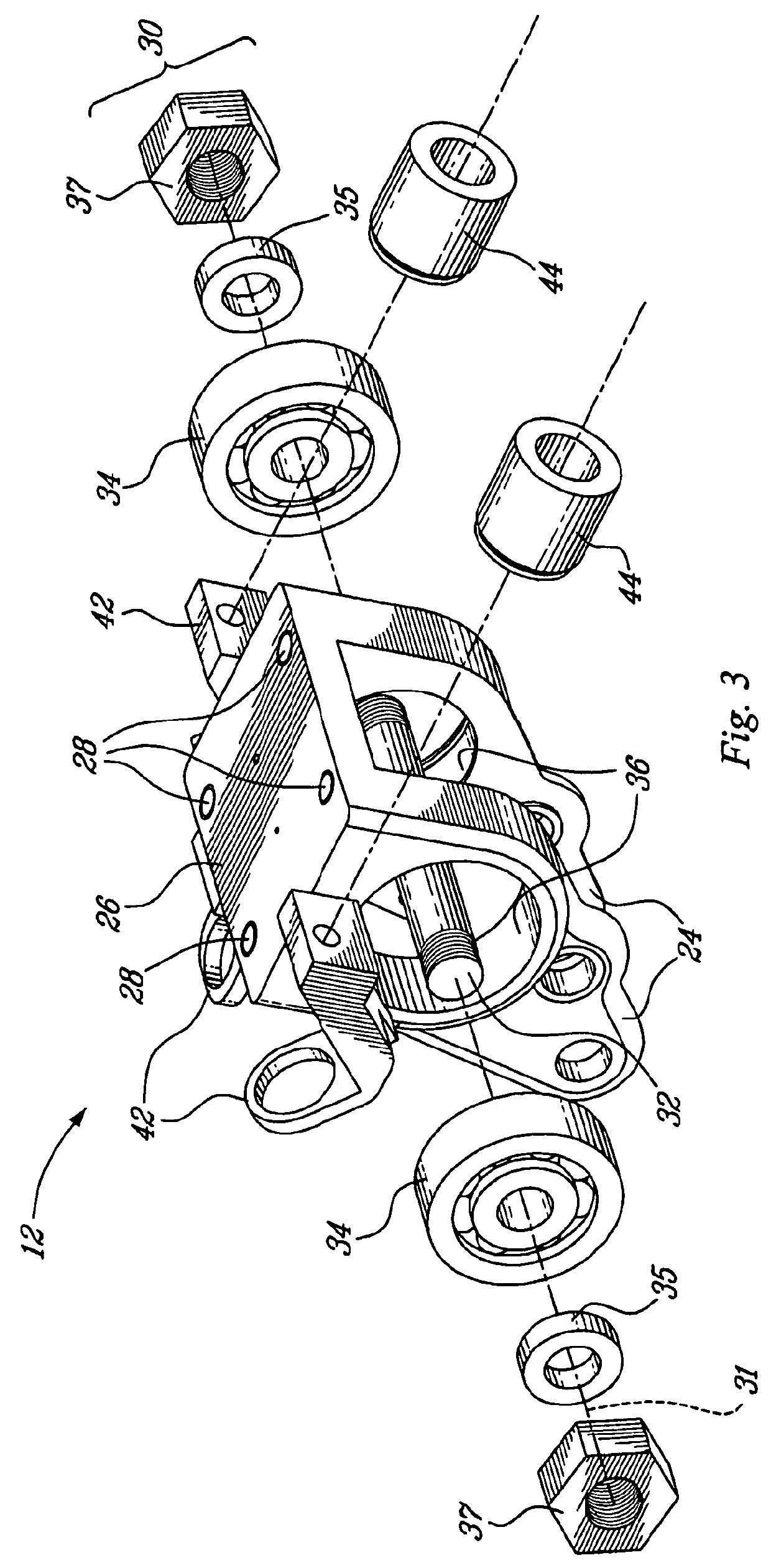
Connecting part between leg prosthesis components
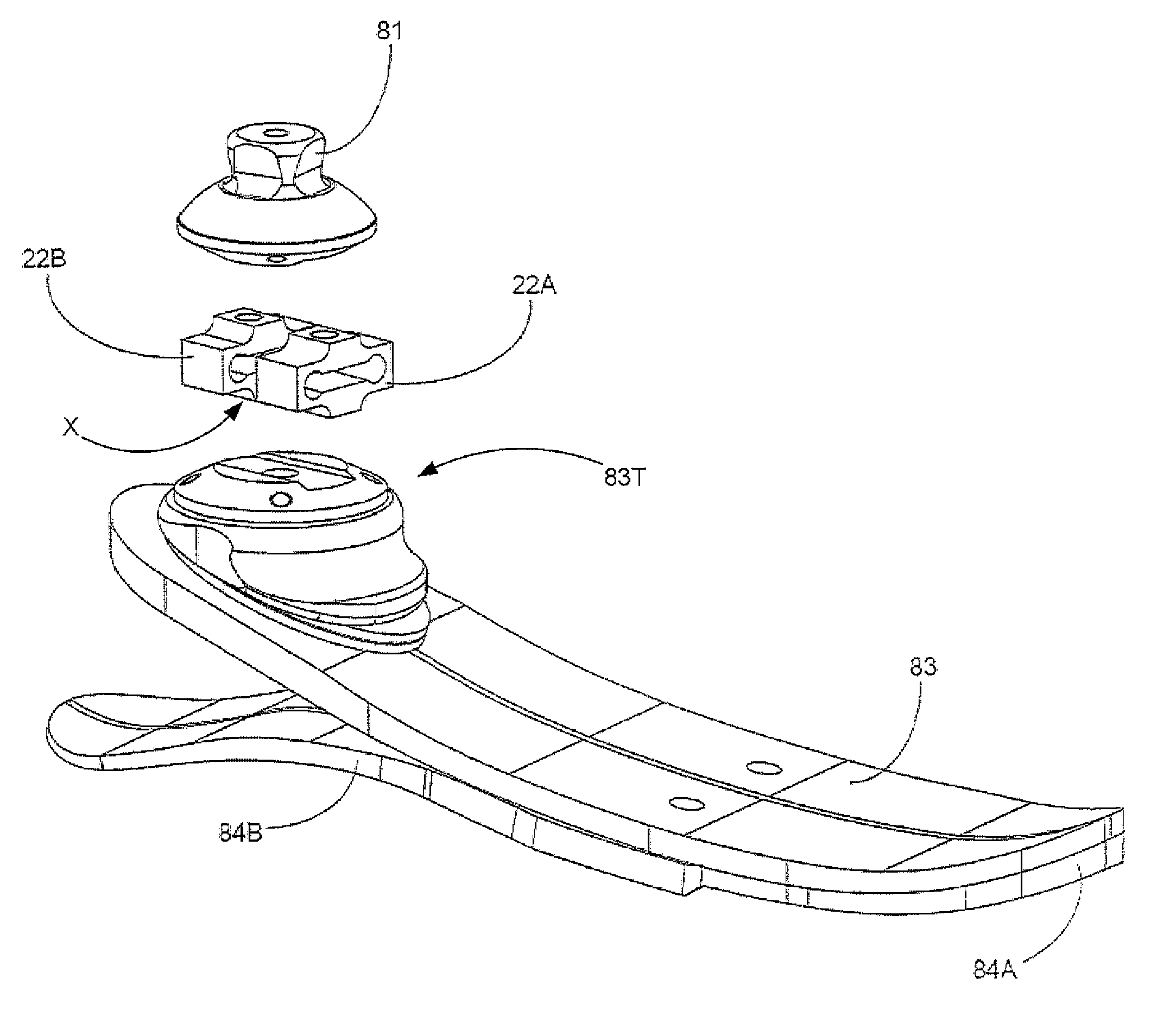
A connecting part of a ball joint between leg prosthesis components with a flange intended to fasten to the one component, the flange having an adjusting element position on it, consisting of a cup and a four-sided pyramid positioned centrally upon its point. To improve the adjustability of the connecting part, the flange is a rectangular flange with four holes, upon which the adjusting element is eccentrically positioned.
Owner:OTTO BOCK ORTHOPADISCHE IND BESITZ & VERW
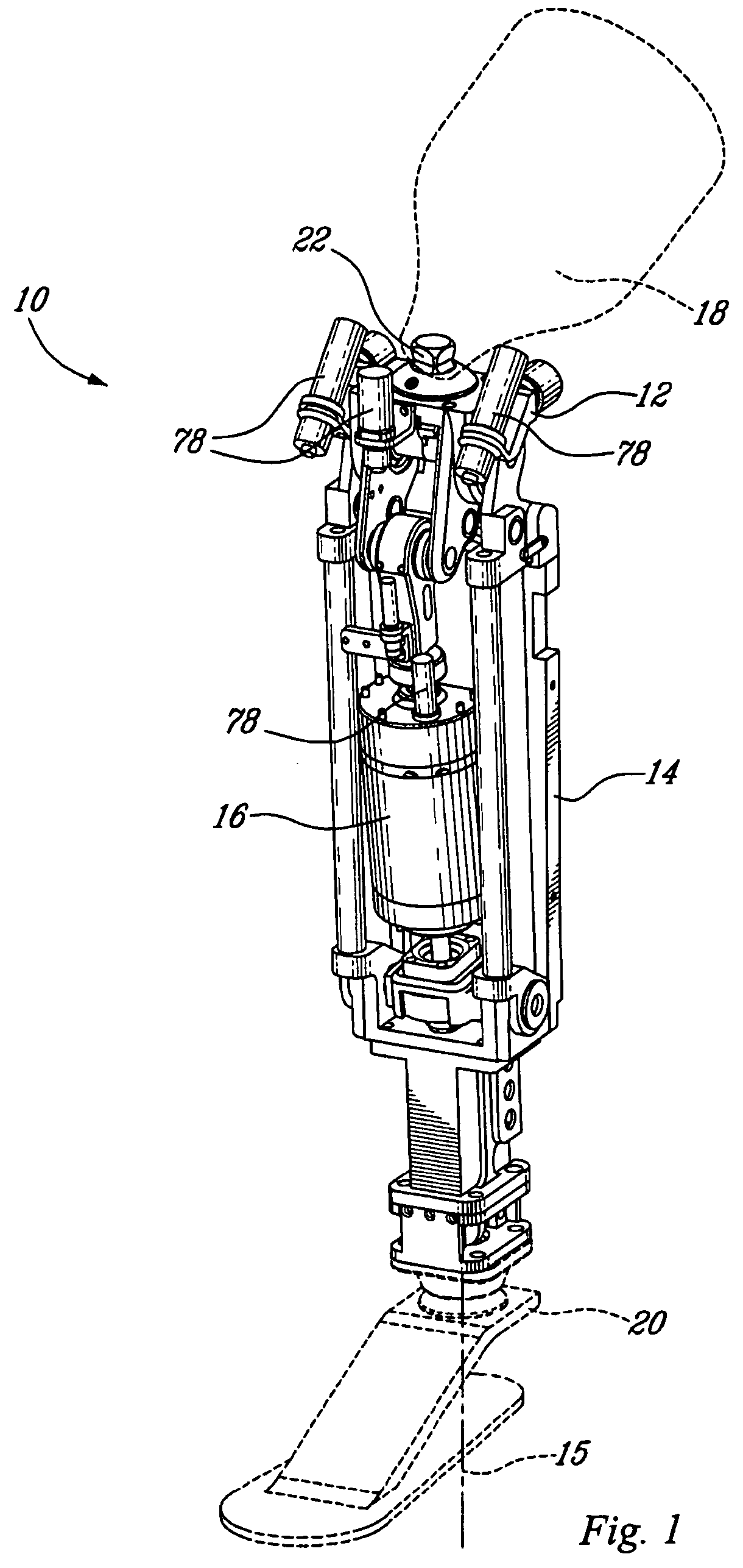
Actuated prosthesis for amputess
The actuated leg prosthesis comprises a knee member, a socket connector provided over the knee member, an elongated trans-tibial member having a bottom end under which is connected an artificial foot, and a linear actuator. A first pivot assembly allows to operatively connect the trans-tibial member to the knee member. A second pivot assembly allows to operatively connect an upper end of the actuator to the knee member. A third pivot assembly allows to operatively connect a bottom end of the actuator to the bottom end of the trans-tibial member. The prosthesis can be provided as either a front actuator configuration or a rear actuator configuration.
Owner:NATIONAL BANK OF CANADA
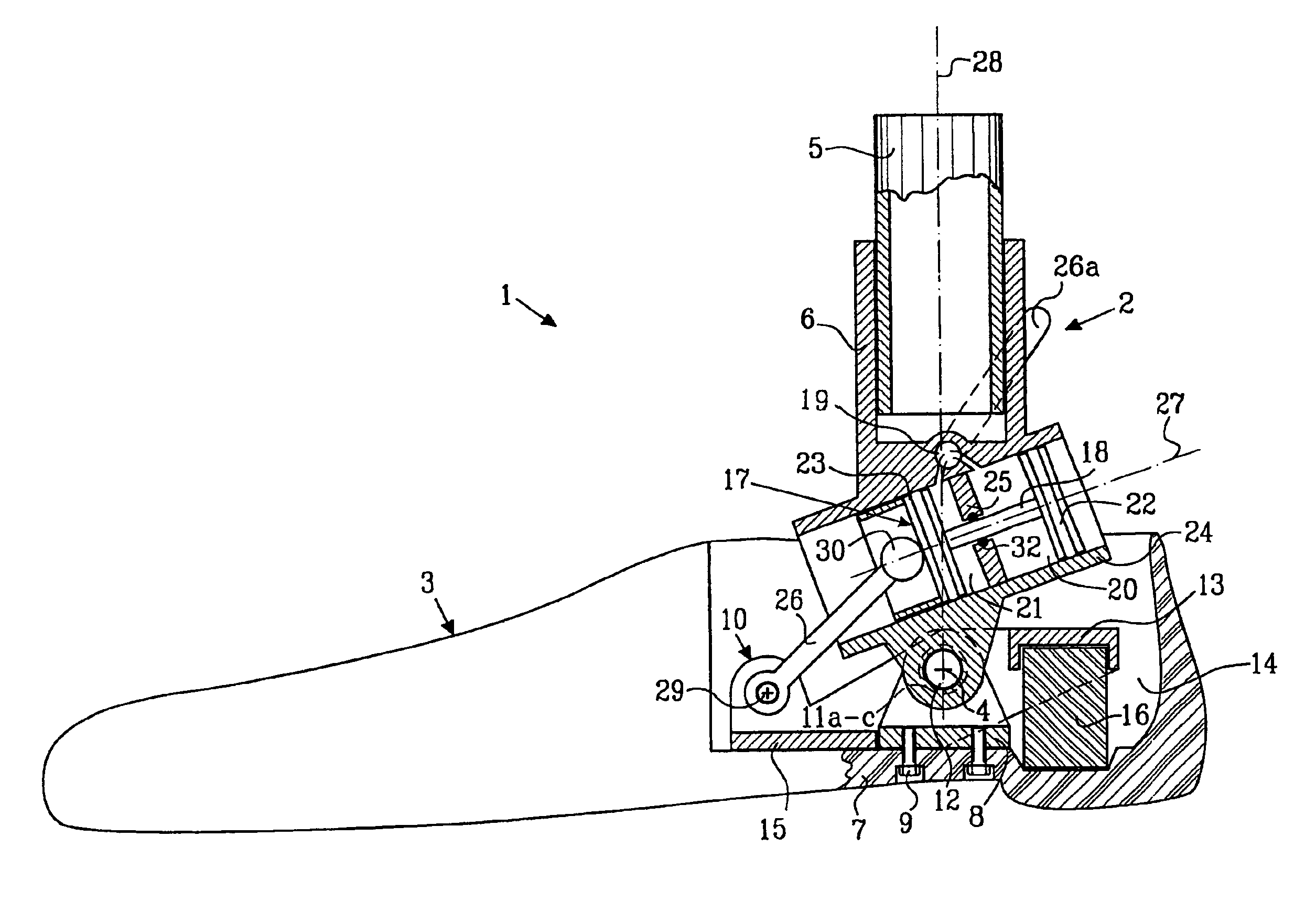
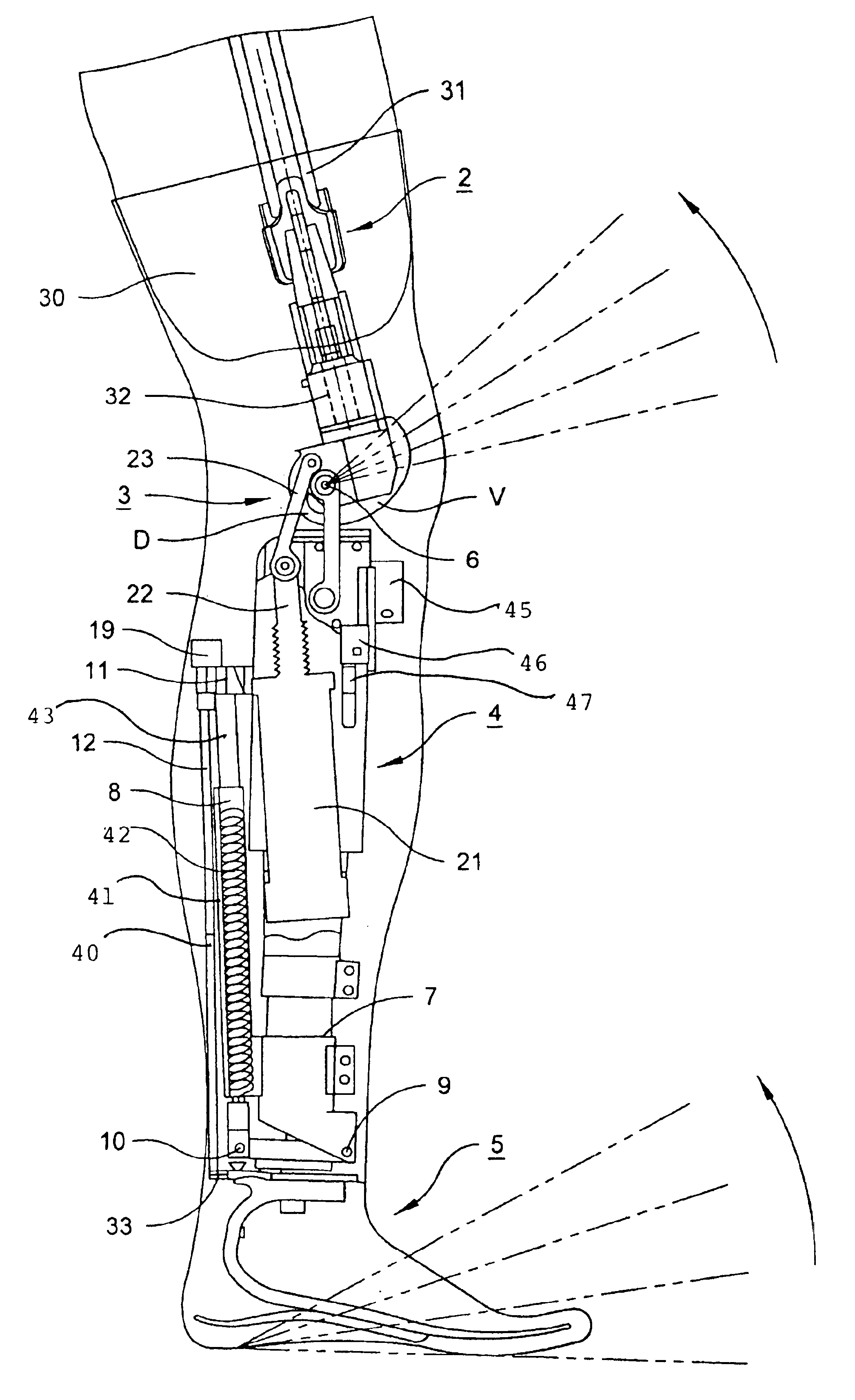
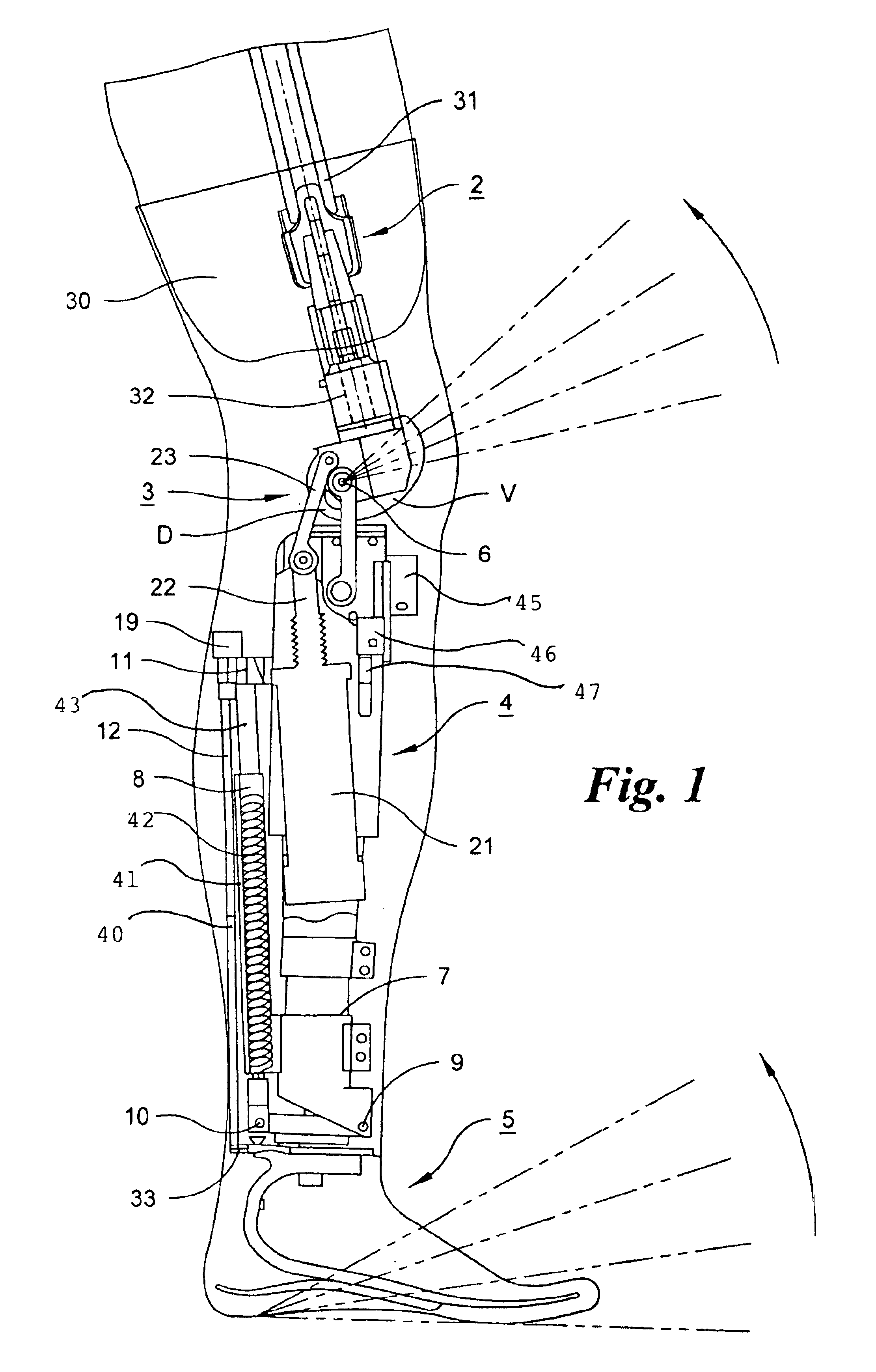
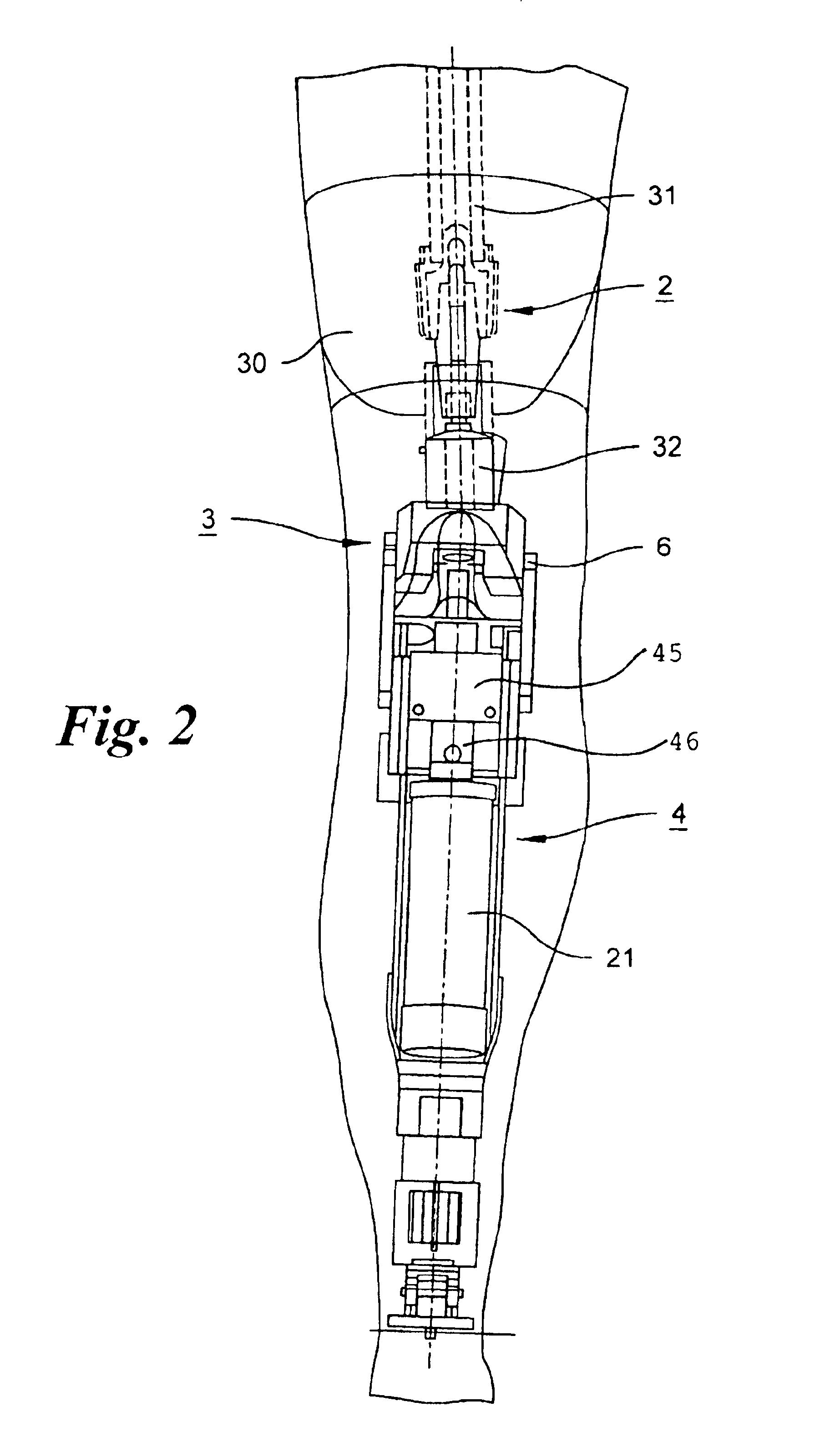
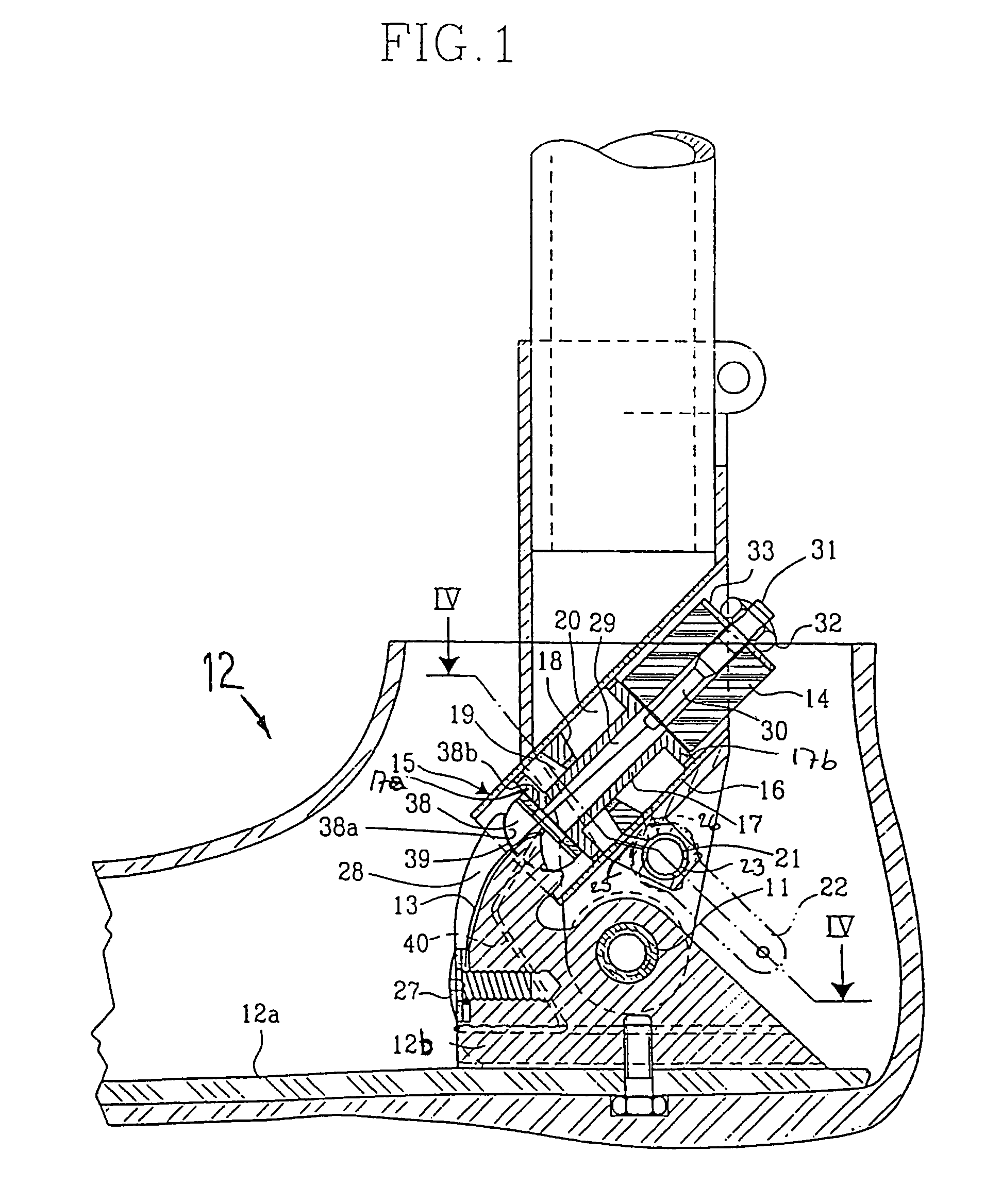
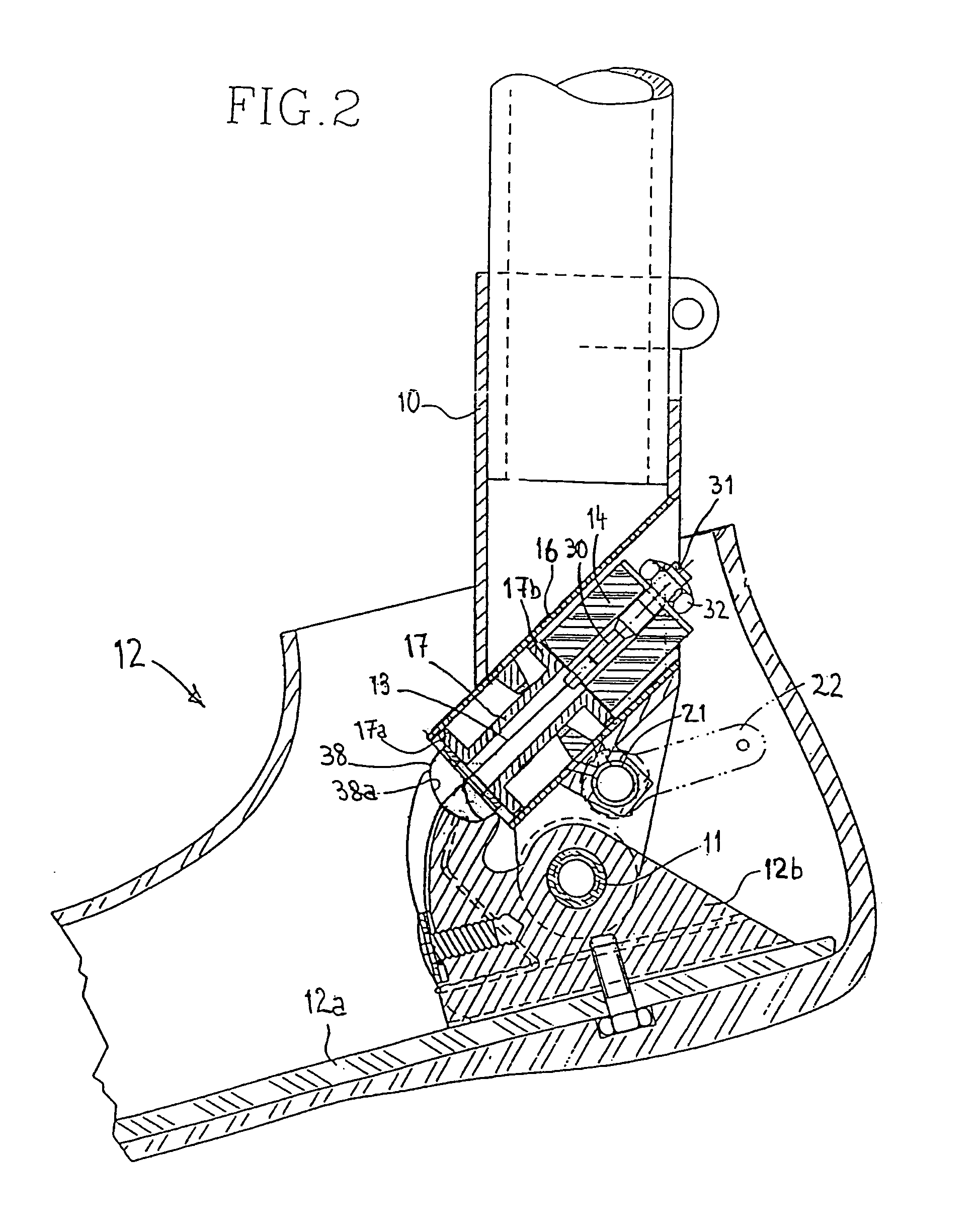
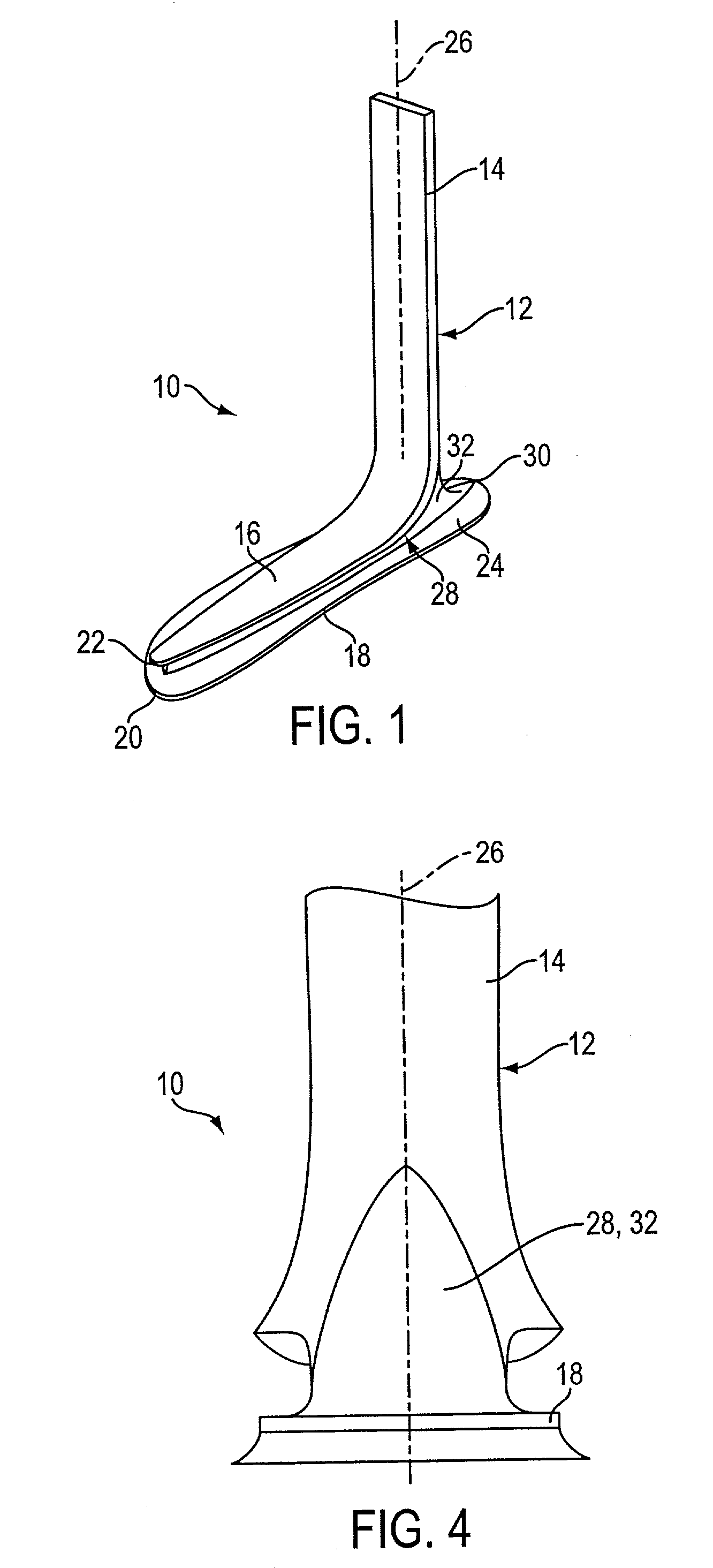
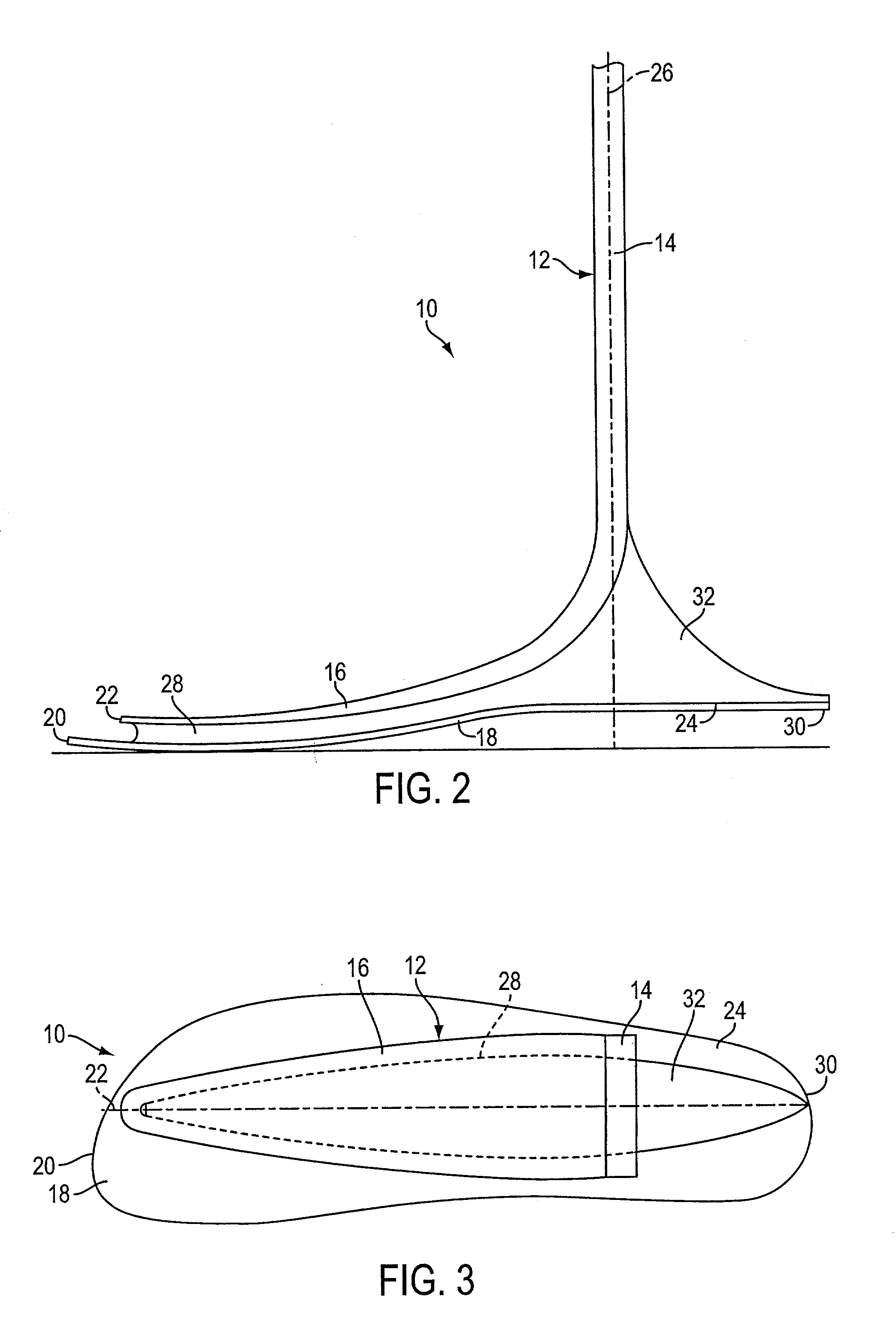
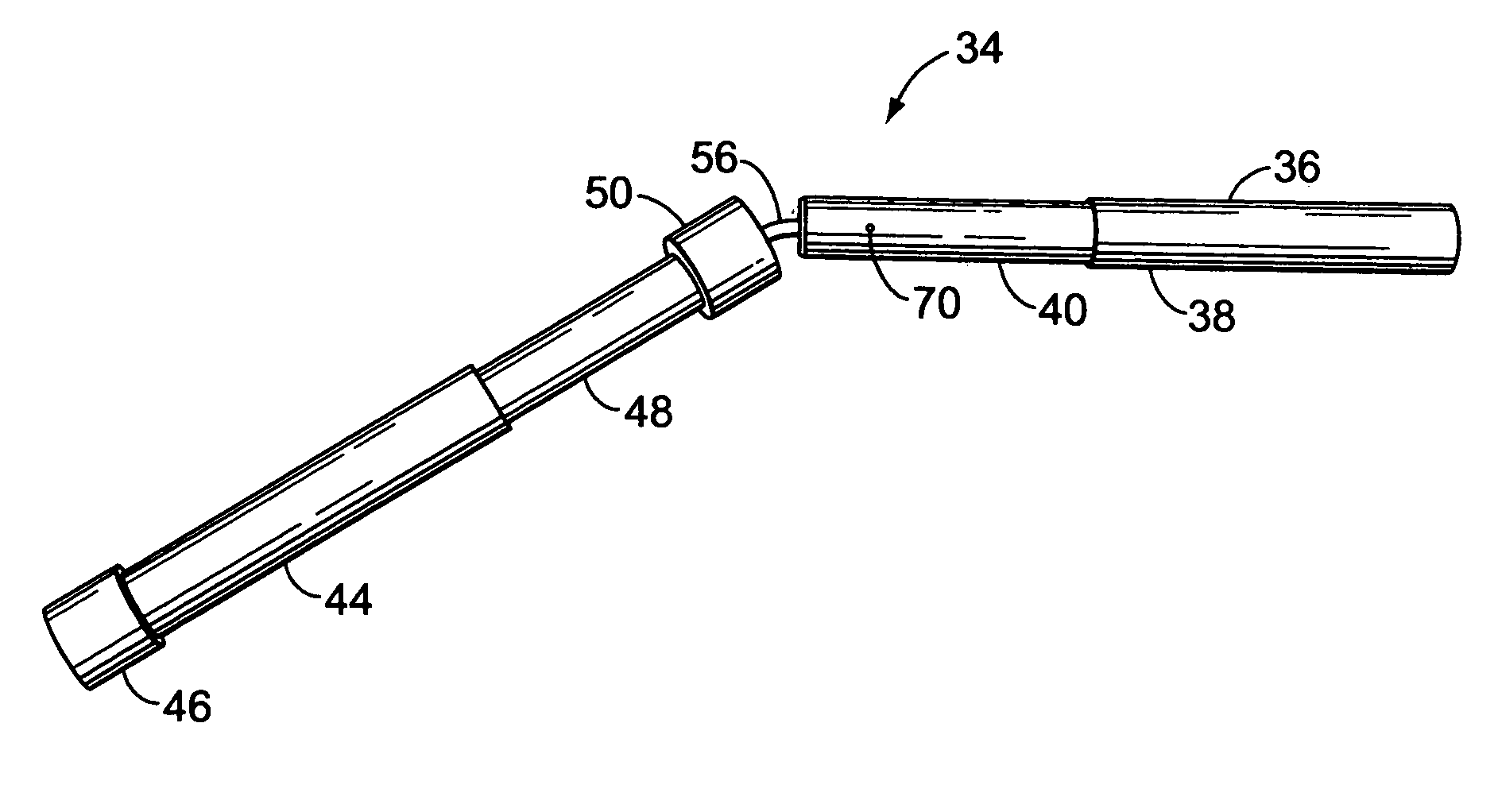
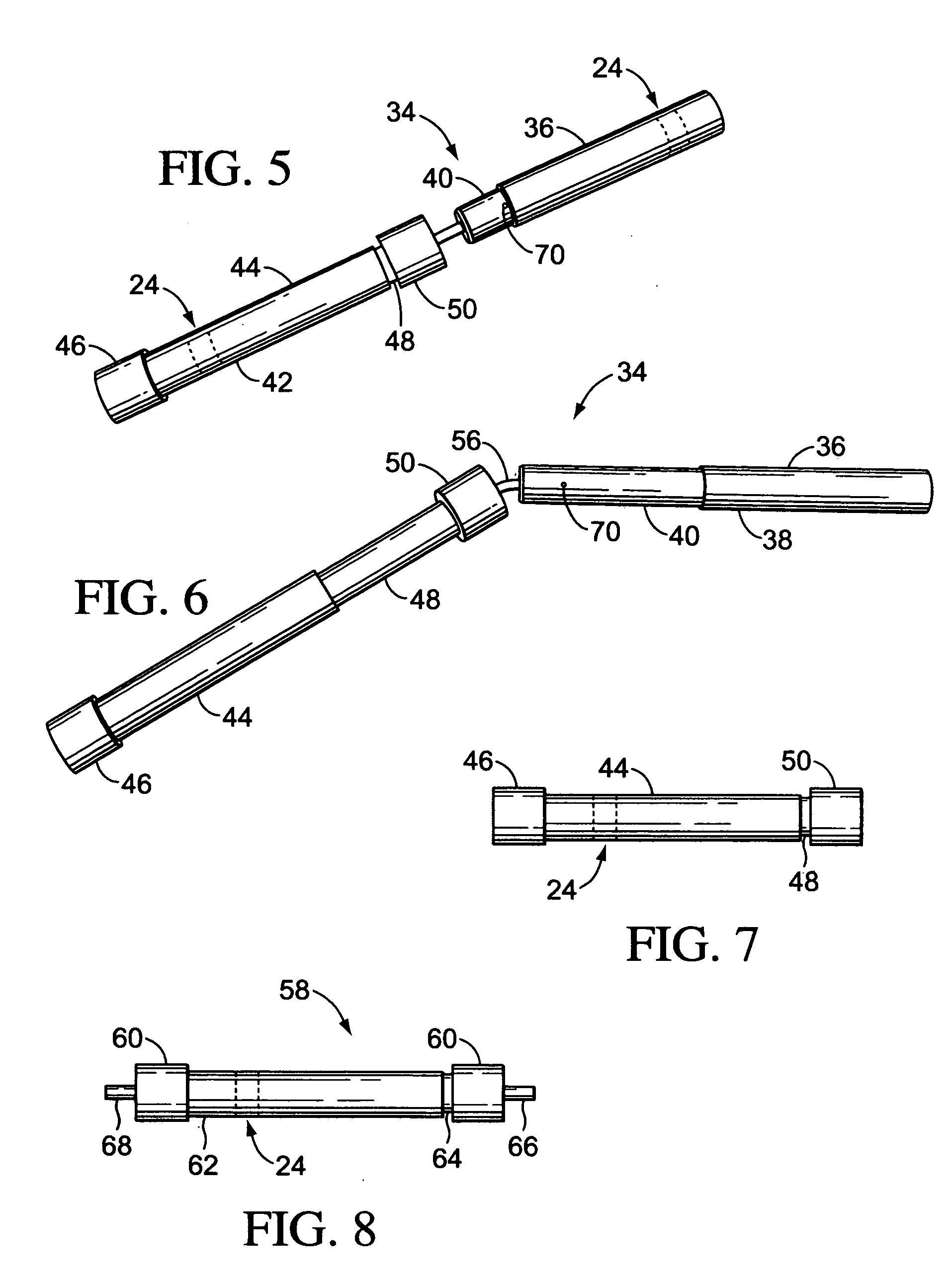
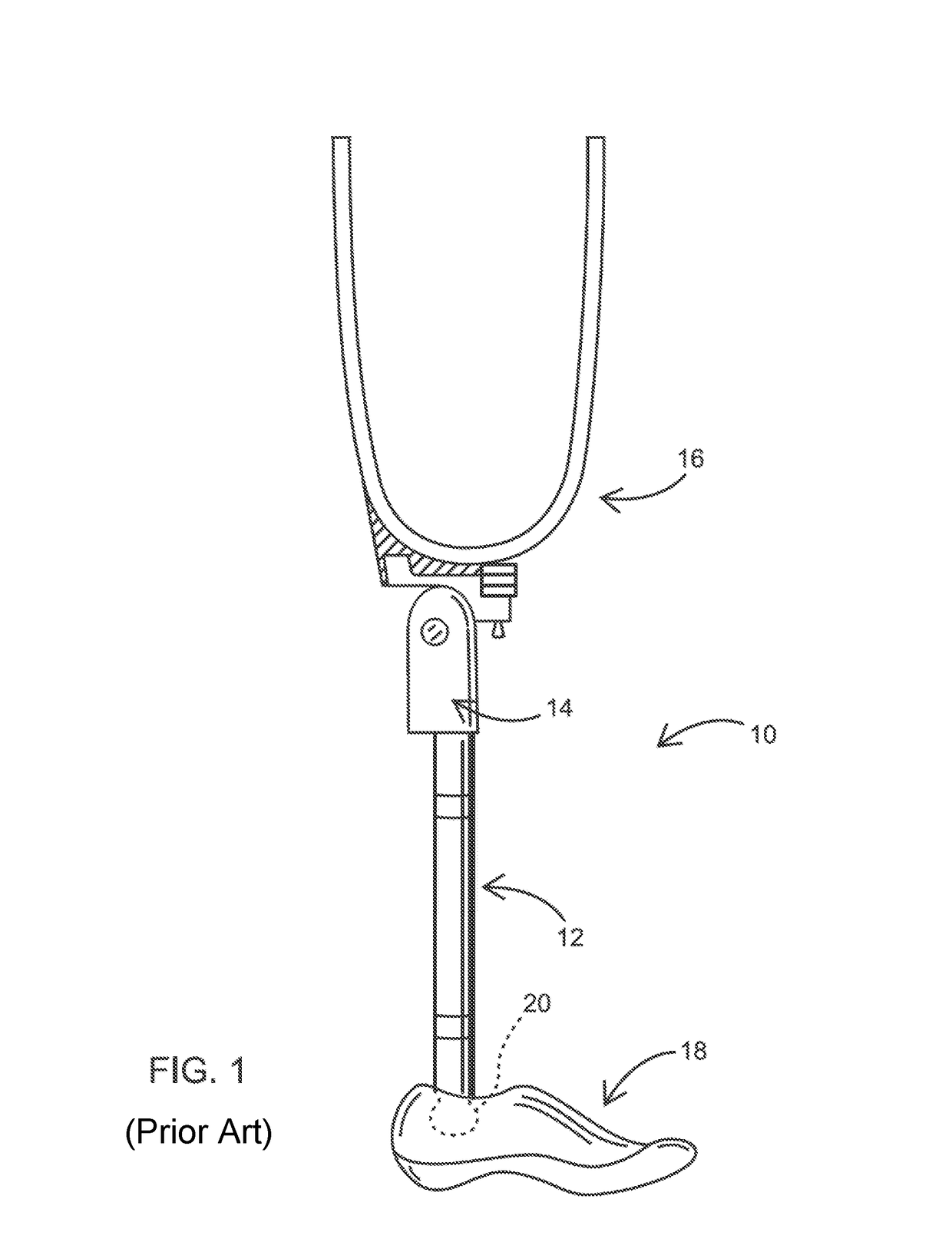
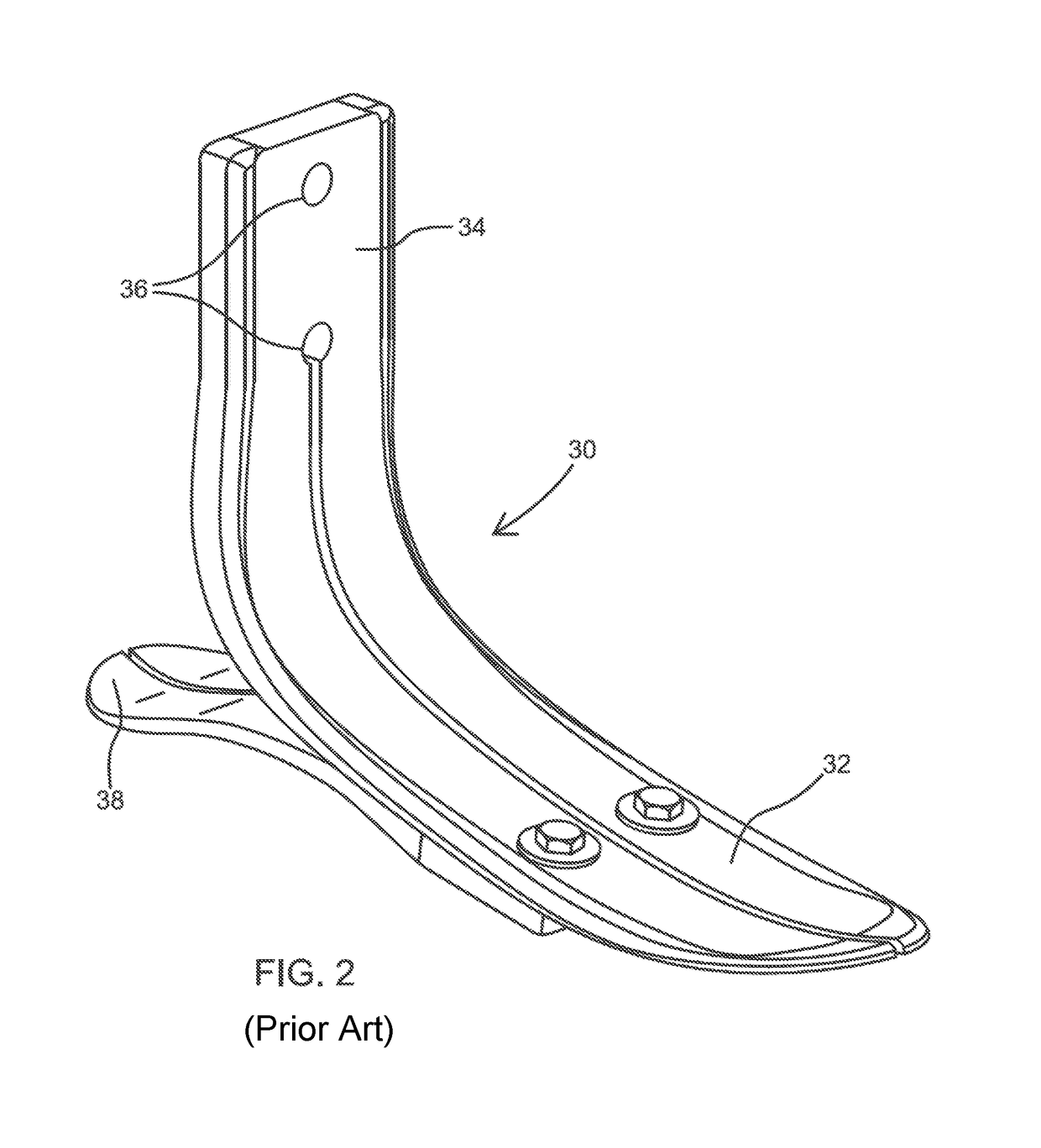
Prosthetic leg and foot apparatus
The present invention relates to an arrangement for a leg prosthesis (10) provided with a foot (12), which is connected to the leg prosthesis via an articulated axle (11), whereby first means (13, 14, 16–18, 30–33, 38) are arranged to provide a limited rotation of the foot relative the leg prosthesis from an initial position, in which position the leg prosthesis and the foot have a fixed angle relative each other, and second means (16–26) are arranged to provide a step-less adjustment of the fixed angle between the leg prosthesis and the foot in the initial position. According to the invention the first means (13, 14, 16–18, 30–33, 38) comprise a resilient element (14), which first end thereof is connected to the foot (12) via an elongated element (13) and which second end is connected to the leg prosthesis so that the leg prosthesis can be rotated relative the foot against the effect of the spring force of the resilient element.
Owner:GRAMTEC INNOVATION
Combined Active and Passive Leg Prosthesis System and a Method for Performing a Movement With Such a System
ActiveUS20090299489A1The process is simple and effectiveEliminate the problemArtificial legsEngineeringSacroiliac joint
A combined active and passive leg prosthesis system is disclosed, and a method of performing a gait cycle by a leg prosthesis system is disclosed, for replacing a missing lower extremity of an individual to perform a gait cycle by the leg prosthesis system and / or the method. In at least one embodiment, the leg prosthesis system includes at least one movable joint, and a disconnectable active drive unit to drive the movable joint and a passive brake unit to brake the movable joint when the drive unit is disconnected.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Instrumented prosthetic foot
The present invention discloses an instrumented prosthetic foot for use with an actuated leg prosthesis controlled by a controller, the instrumented prosthetic foot comprising a connector to connect the instrumented prosthetic foot to the leg prosthesis, an ankle structure connected to the connector, a ground engaging member connected to the ankle, at least one sensor for detecting changes in weight distribution along the foot, and an interface for transmitting signals from the sensor to the controller.
Owner:NATIONAL BANK OF CANADA
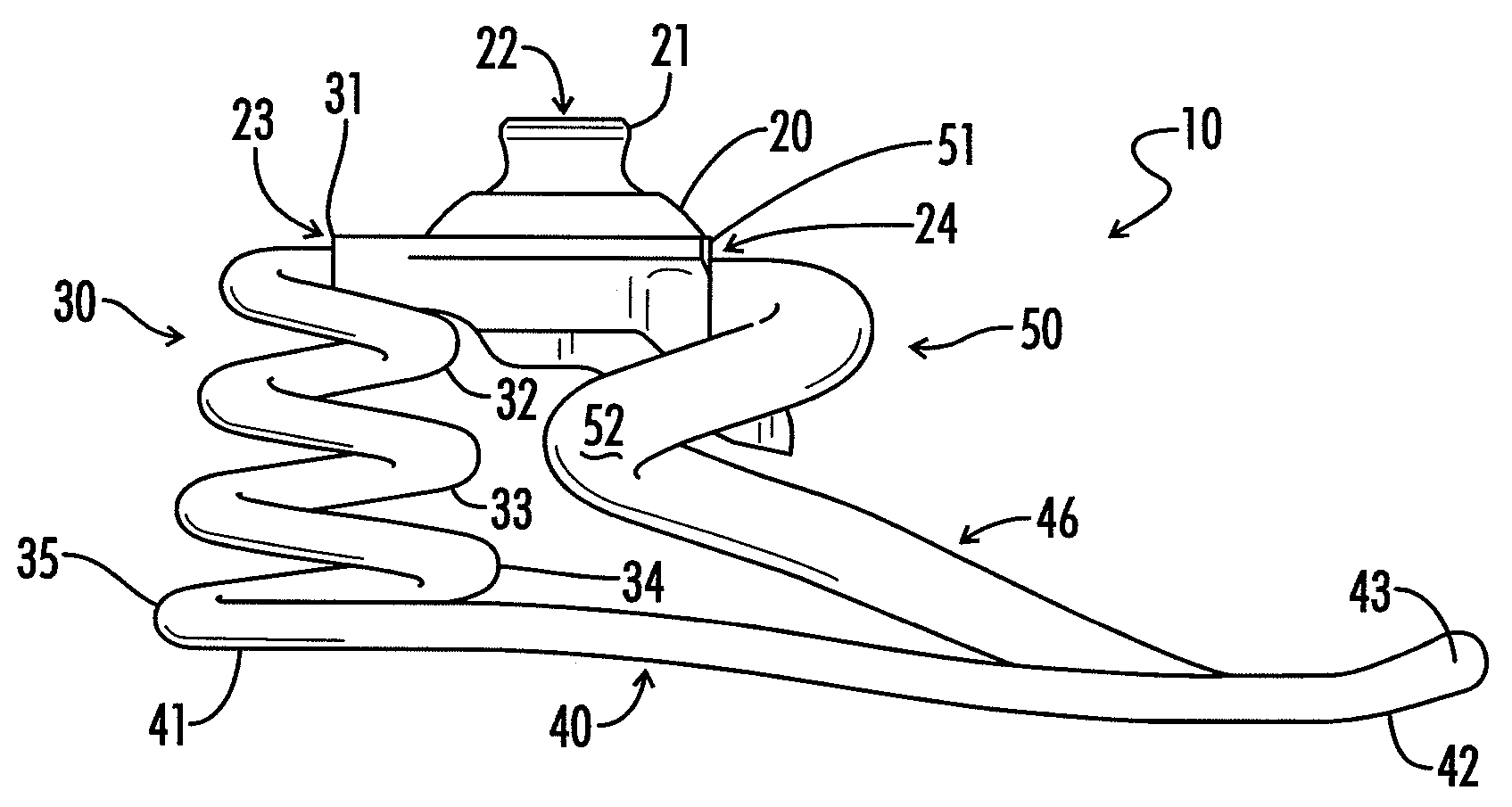
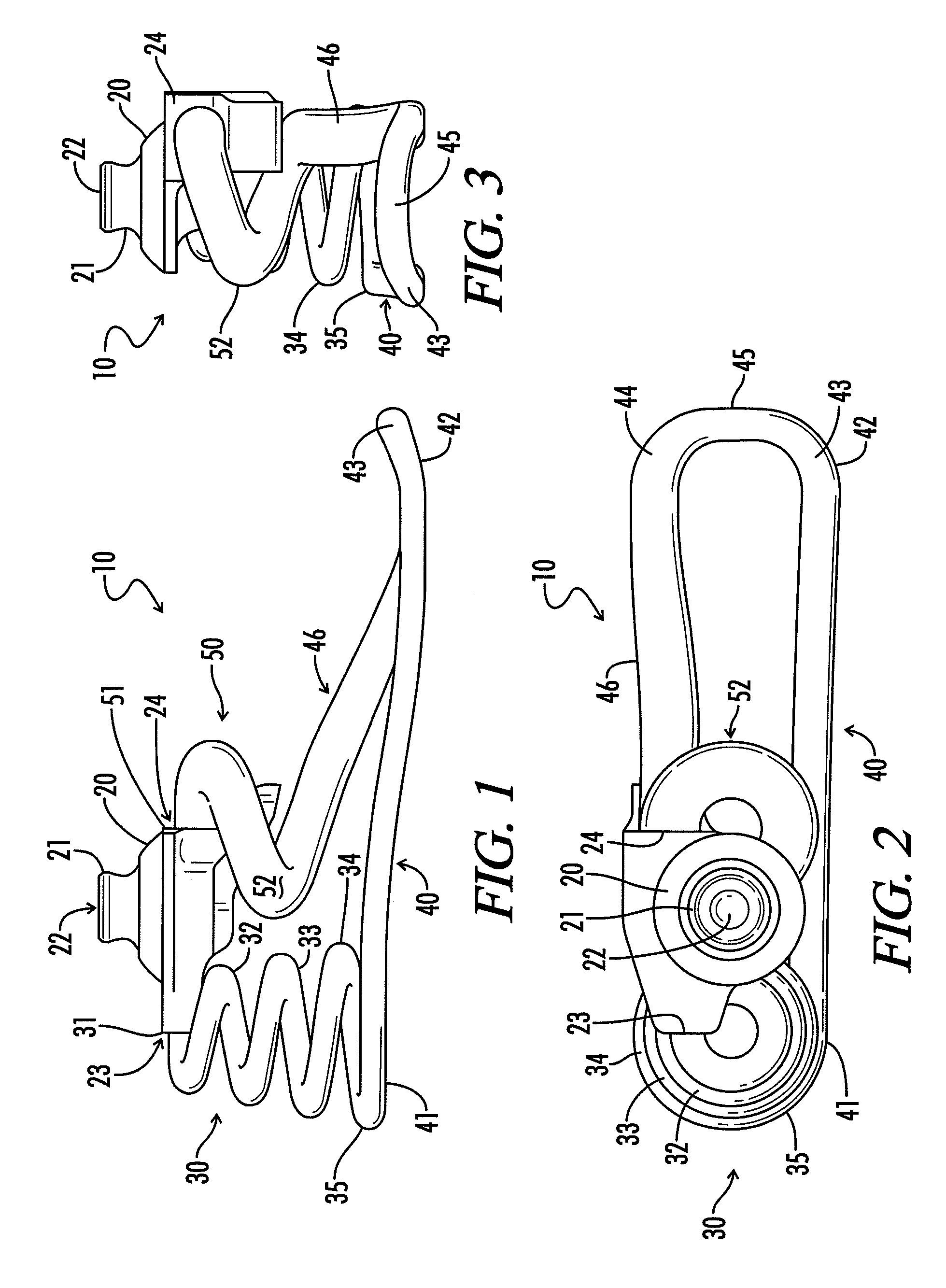
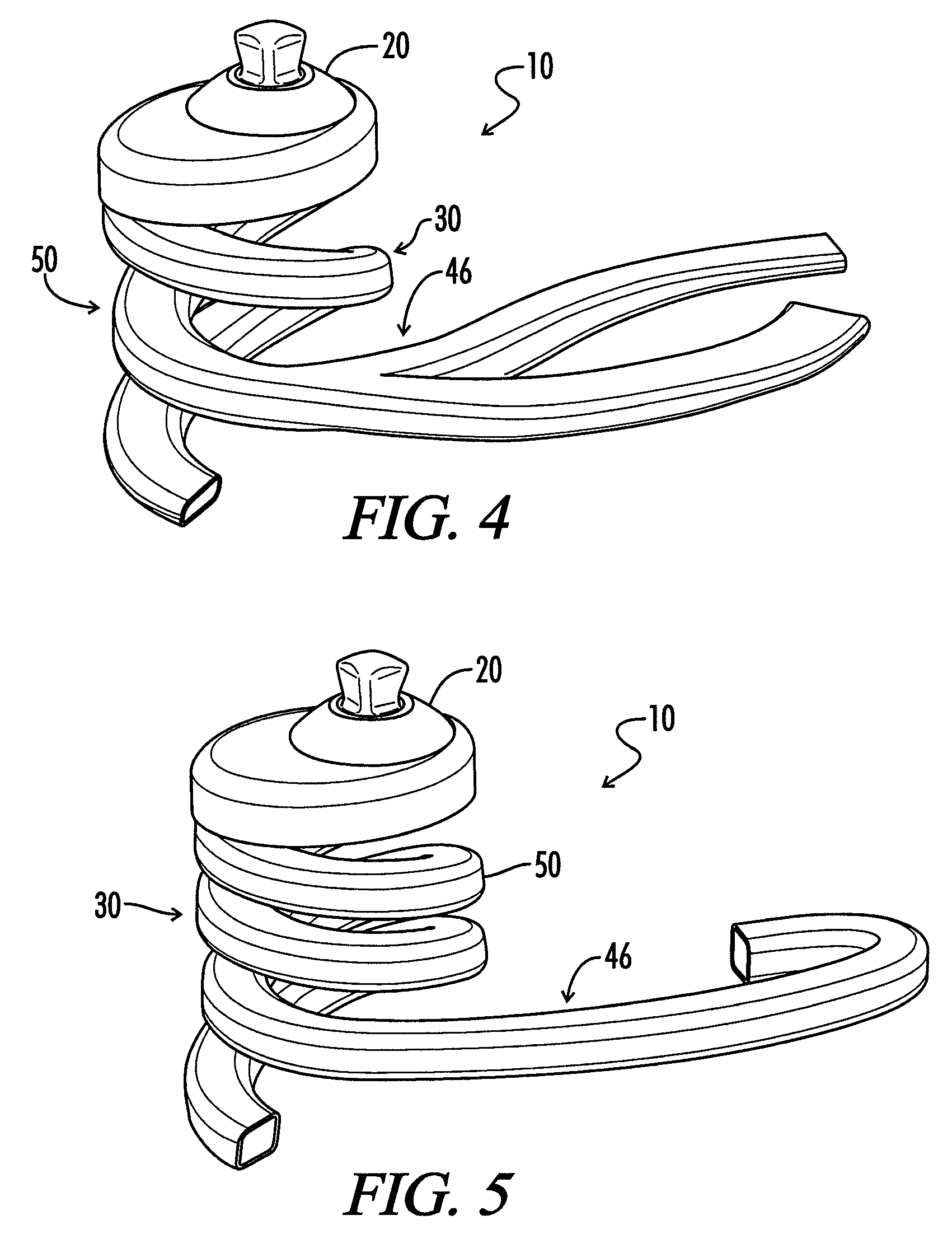
Composite Prosthetic Foot
InactiveUS20080228288A1High torsionalHigh radial tensile loadDomestic articlesArtificial legsMedicineCoil spring
A prosthetic foot is provided with an ankle plate for attachment to a lower leg prosthesis and supporting a composite frame having a hollow composite biasing structure, preferably in the form of a generally helical spring curved about a vertical axis.
Owner:CLOSEDMOLD COMPOSITES
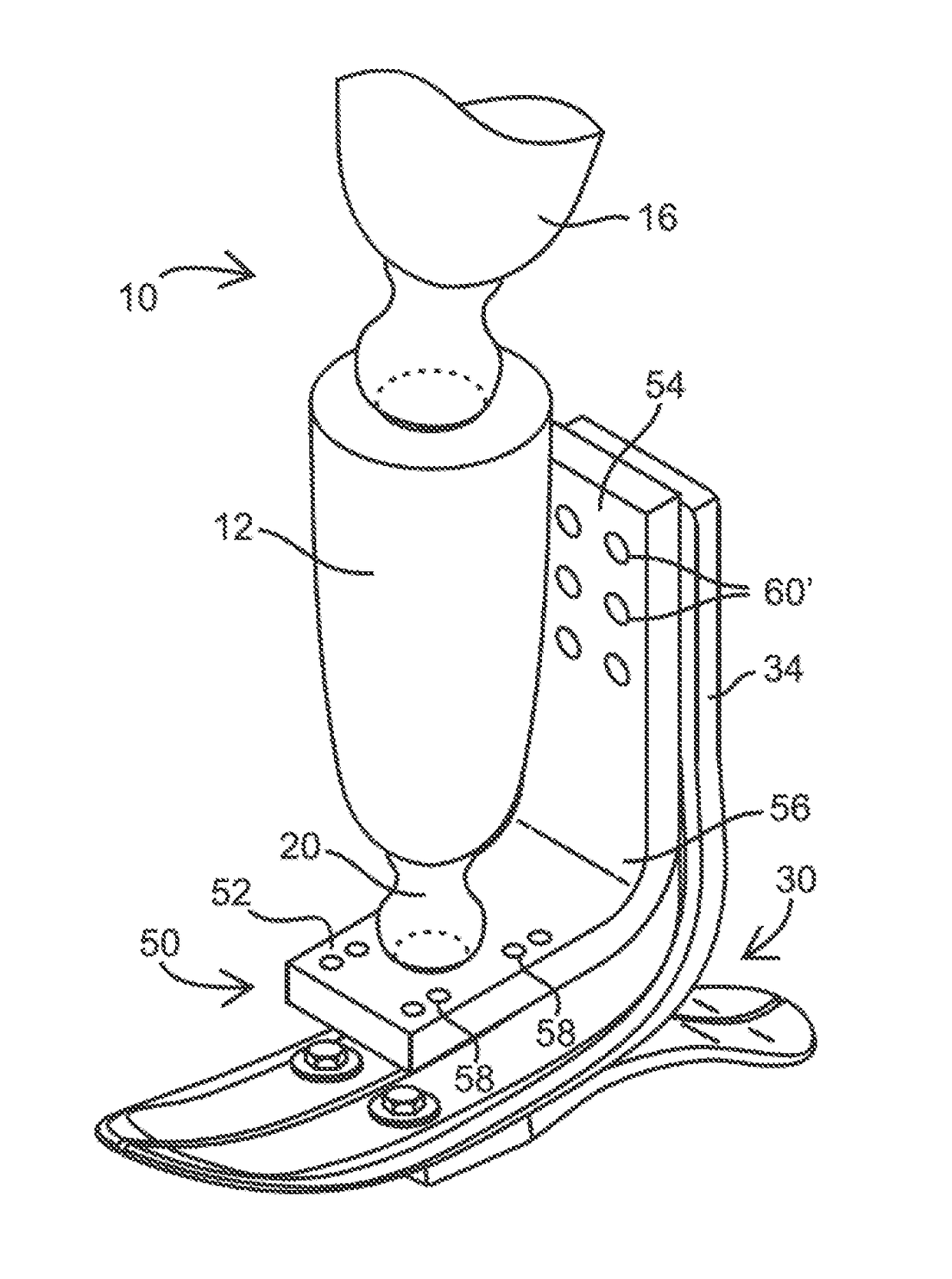
Lower leg prosthesis
An improved lower leg prosthesis is disclosed that, during use, provides an improved dynamic feel at heel strike and that provides improved inversion / eversion compliance. The prosthesis includes an elongated pylon having an upper, generally vertical section and a lower, forwardly oriented foot section, and it further includes a generally horizontally oriented foot plate disposed beneath the pylon and including a heel section projecting a substantial distance rearwardly of a vertical pylon axis. An elastomeric layer is interposed between the pylon and the foot plate, extending along substantially the entire length of the heel section of the foot plate, for attaching the pylon and foot plate together. During use of the prosthesis, at heel strike, upward deflection of the foot plate's heel section is limited in substantial part both by the stiffness of the heel section, itself, and by compression of the portion of the elastomeric layer disposed rearwardly of the vertical pylon axis.
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE IP GMBH & CO KG
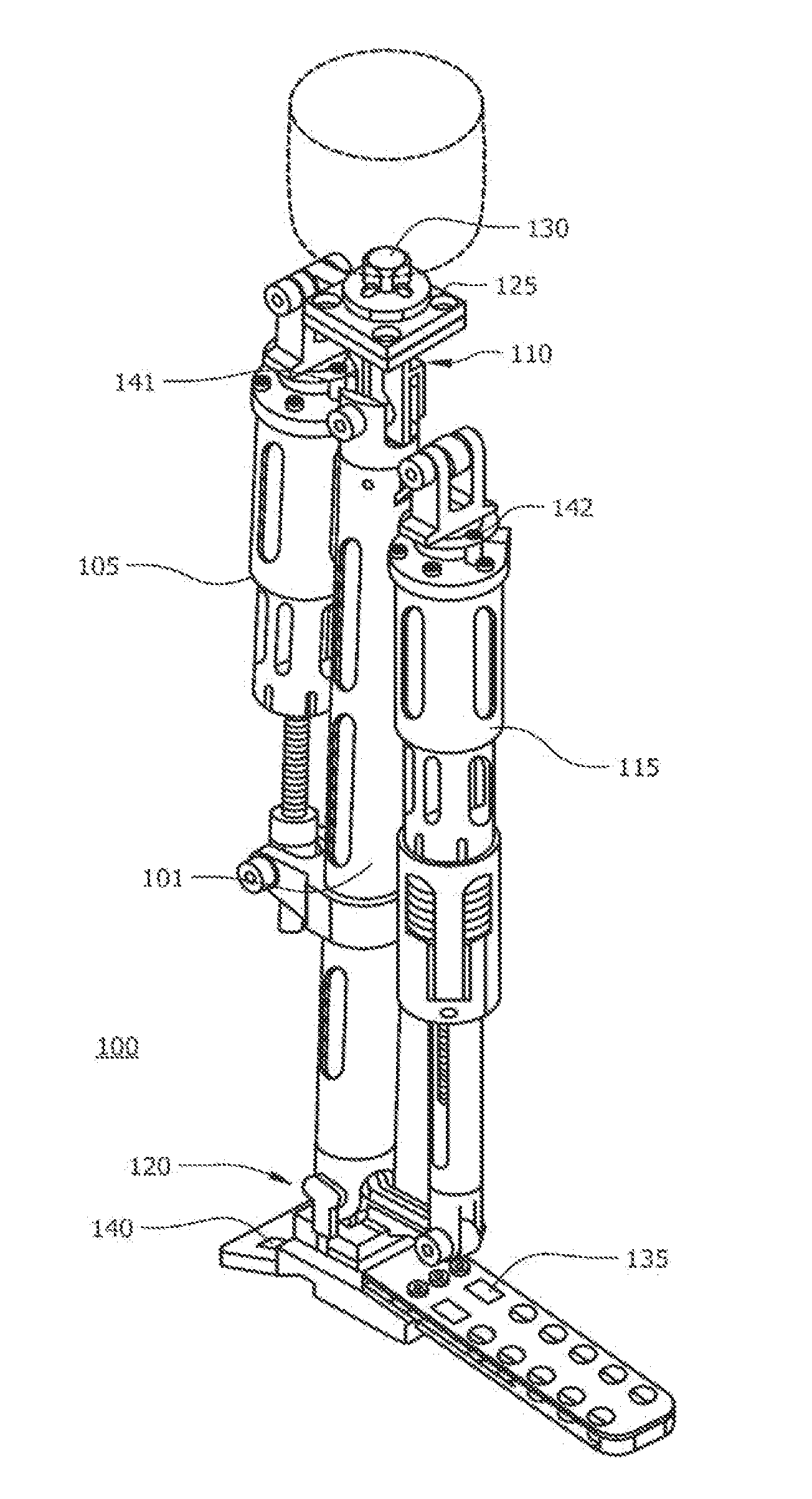
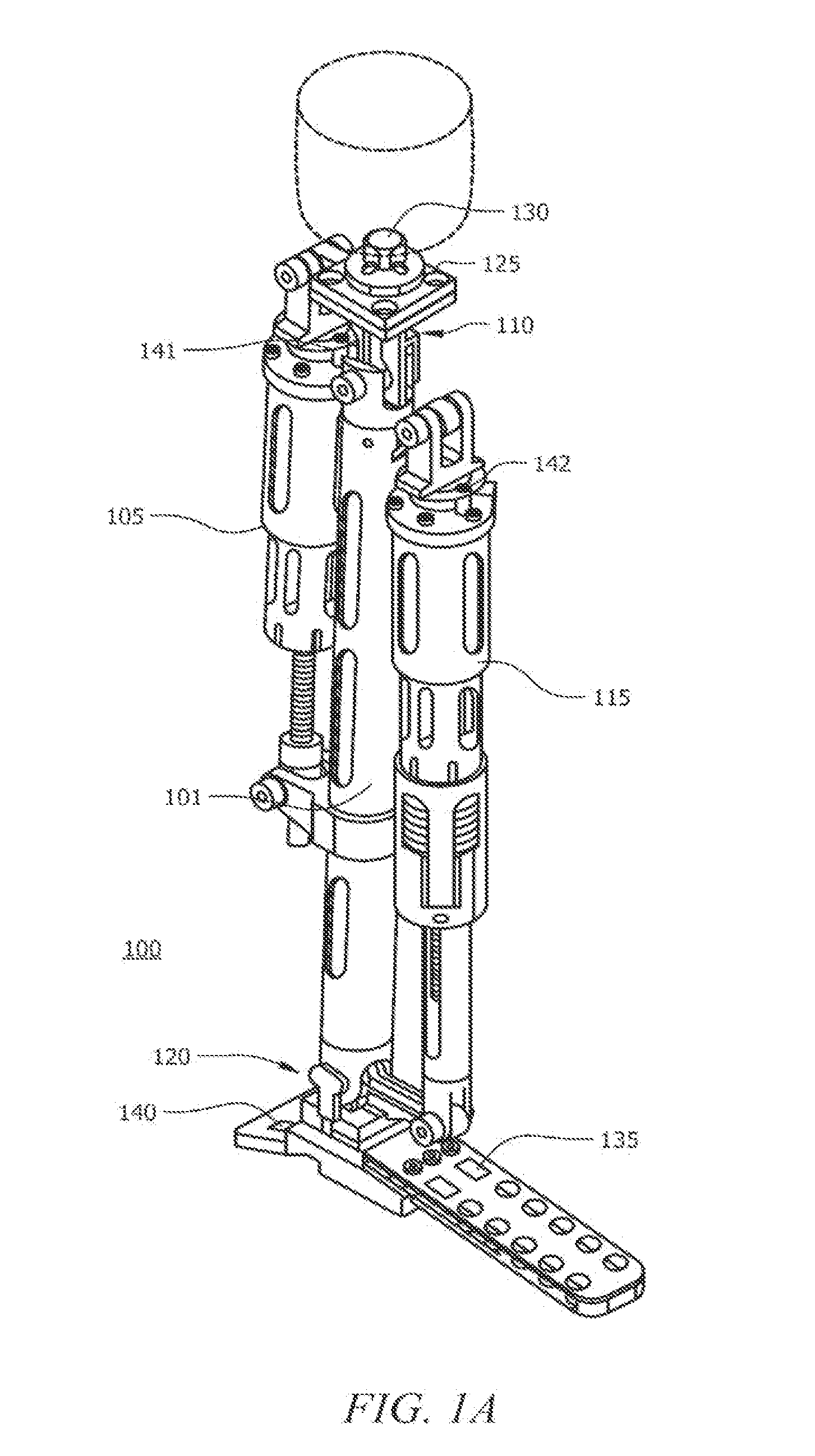
Actuated leg prostheses for amputees
ActiveUS20130268093A1ResilienceRestores natural dynamics and adaptation to a user's gaitWork measurementNon-surgical orthopedic devicesStretch exerciseAbsorbed energy
A prosthetic or orthotic device can include at least one device portion and a joint portion for providing for the at least one device portion to pivot between flexion and extension movements relative to another adjacent device portion or an adjacent limb segment of a user. In some embodiments, a prosthetic or orthotic device can include a compliant transmission assembly in operational communication with the joint portion. The compliant transmission assembly can include a compliant member and a pivot. The pivot can be interposed between the compliant member and the joint portion. In some embodiments, the compliant member absorbs energy when a torque is applied.
Owner:NATIONAL BANK OF CANADA
Combined active and passive leg prosthesis system and a method for performing a movement with such a system
ActiveUS20130204395A1The process is simple and effectiveEliminate the problemArtificial legsMedicineHydraulic fluid
A lower limb prosthesis system and a method of controlling the prosthesis system to replace a missing lower extremity of an individual and perform a gait cycle are disclosed. The prosthesis system has a controller, one or more sensors, a prosthetic foot, and a movable ankle joint member coupled to the prosthetic foot. The movable ankle joint member comprises a hydraulic damping system that provides the ankle joint member damping resistance. The controller varies the damping resistance by providing volumetric flow control to the hydraulic damping system based on sensor data. In one embodiment, the hydraulic damping system comprises a hydraulic piston cylinder assembly, hydraulic fluid, and a valve to regulate the fluid. In one embodiment, the controller alters the damping resistance by modulating the valve to vary the hydraulic fluid flow within the hydraulic piston cylinder assembly of the movable ankle joint member based on sensor data.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Instrumented prosthetic foot
The present invention discloses an instrumented prosthetic foot for use with an actuated leg prosthesis controlled by a controller, the instrumented prosthetic foot comprising a connector to connect the instrumented prosthetic foot to the leg prosthesis, an ankle structure connected to the connector, a ground engaging member connected to the ankle, at least one sensor for detecting changes in weight distribution along the foot, and an interface for transmitting signals from the sensor to the controller.
Owner:NATIONAL BANK OF CANADA
Actuated prosthesis for amputees
The actuated leg prosthesis comprises a knee member, a socket connector provided over the knee member, an elongated trans-tibial member having a bottom end under which is connected an artificial foot, and a linear actuator. A first pivot assembly allows to operatively connect the trans-tibial member to the knee member. A second pivot assembly allows to operatively connect an upper end of the actuator to the knee member. A third pivot assembly allows to operatively connect a bottom end of the actuator to the bottom end of the trans-tibial member. The prosthesis can be provided as either a front actuator configuration or a rear actuator configuration.
Owner:NATIONAL BANK OF CANADA
Powered leg prosthesis and control methodologies for obtaining near normal gait
A powered leg prosthesis includes powered knee joint comprising a knee joint and a knee motor unit for delivering power to the knee joint. The prosthesis also includes a prosthetic lower leg having a socket interface coupled to the knee joint and a powered ankle joint coupled to the lower leg opposite the knee joint comprising an ankle, joint and an ankle motor unit to deliver power to the ankle joint. The prosthesis further includes a prosthetic foot coupled to the ankle joint, at least one sensor for measuring a real-time input, and at least one controller for controlling movement of the prosthesis based on the real-time input.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
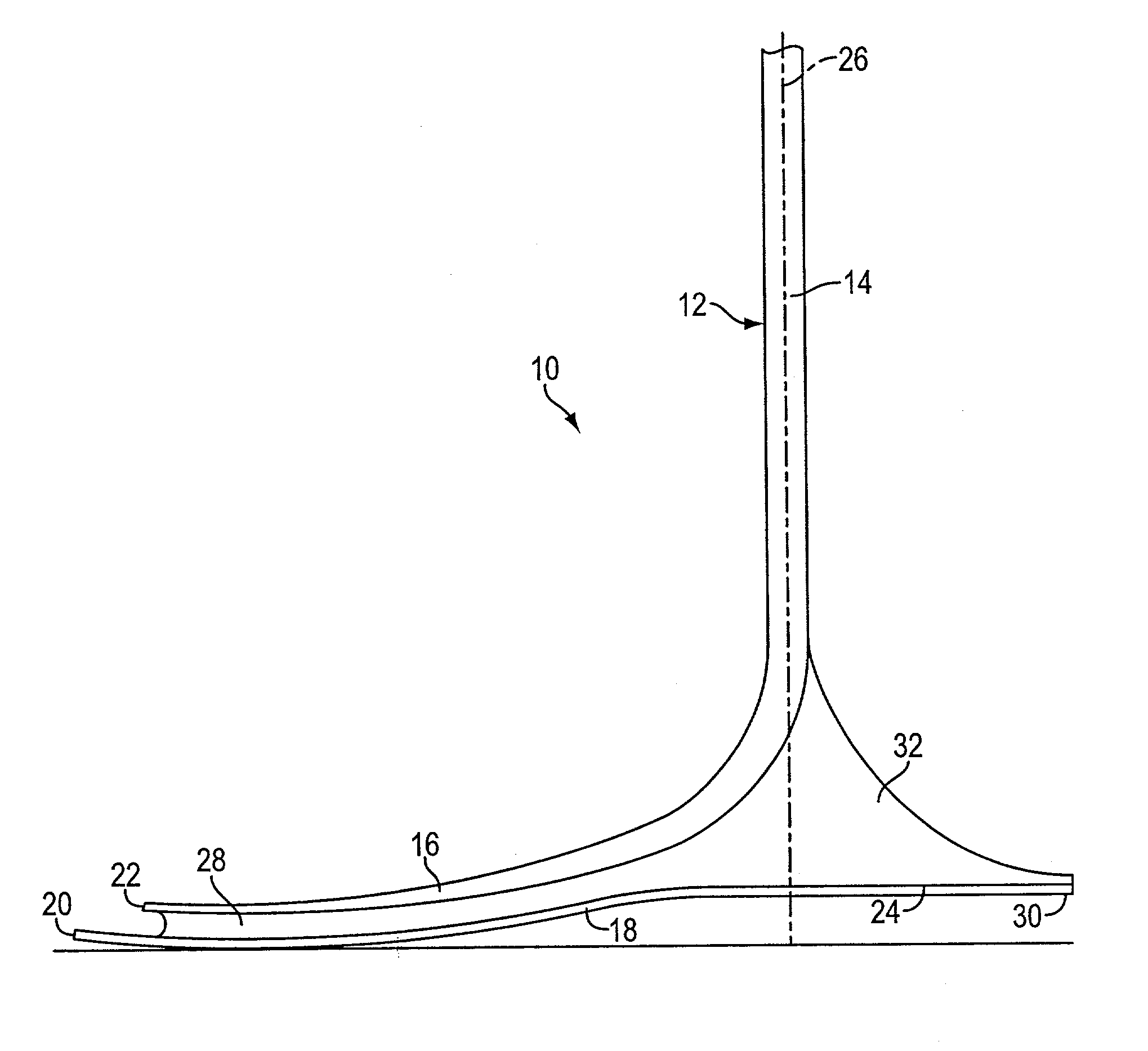
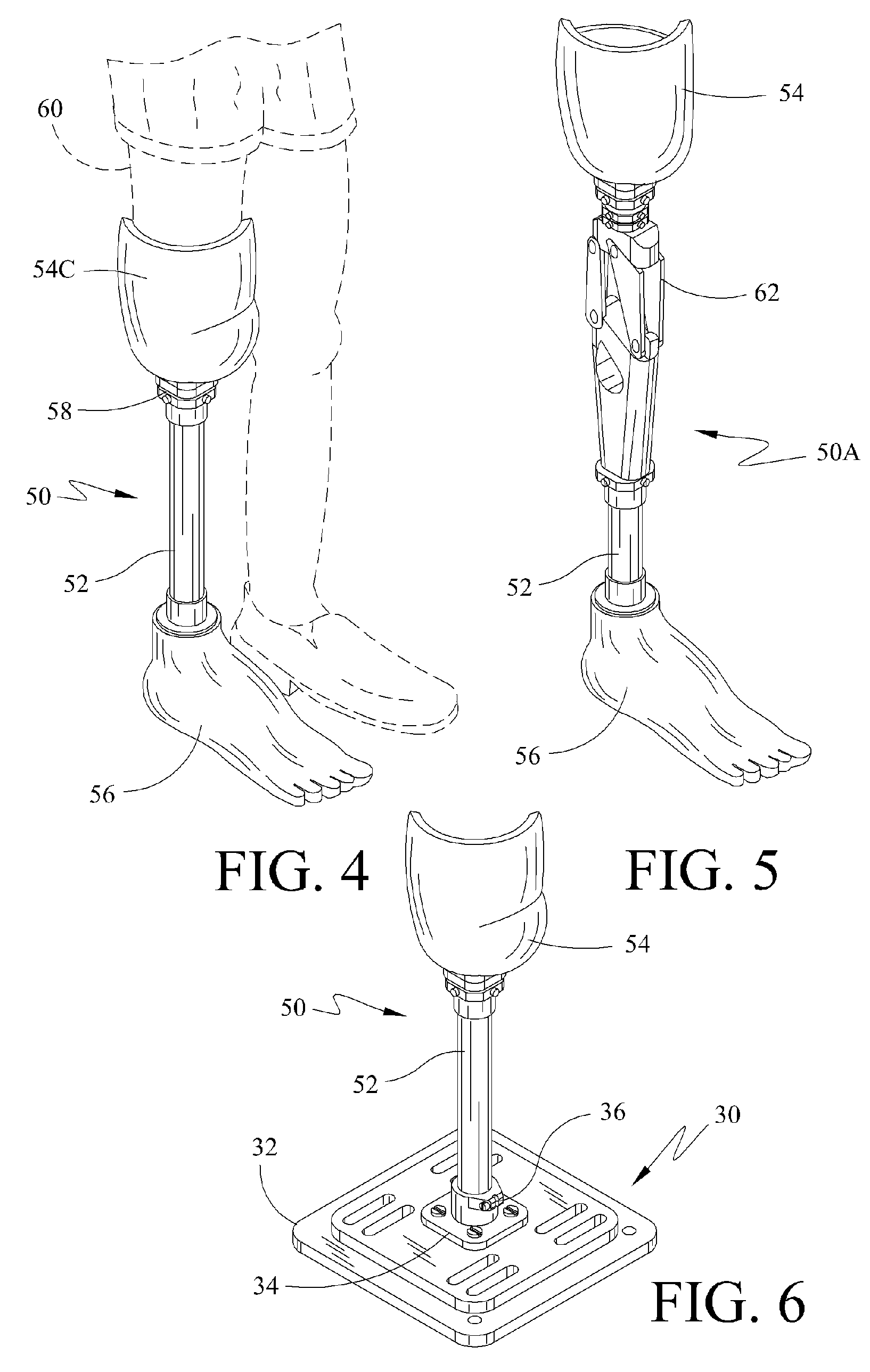
Leg Prosthesis
A lower limb prosthesis for a transfemoral amputee, having a shin portion, ankle portion and a forefoot part of the foot portion formed as an integral fibre-reinforced plastics leaf spring component. This integral component is adjustably mounted to a knee joint which has a knee chassis, a cradle pivotally connected to and depending from the knee chassis, and a flexion control unit in the form of a piston and cylinder assembly interconnecting the knee chassis and the cradle. The shin portion has an elongate resilient section of constant cross-section oriented substantially vertically. The connection of this resilient section to the knee joint cradle and the arrangement of the cradle is such that the vertical distance between the knee axis of rotation and the location of the connection is less than 25% of the vertical distance between the knee axis and the lowest weight-bearing surface of the foot portion.
Owner:BLATCHFORD PRODS
Leg prosthesis system and method
A prosthesis system can have an advantageous use over conventional prostheses in certain activities, including, but not limited to certain sports activities: The system includes, elastic member(s) that can store and release energy. The storing and releasing of energy in the elastic members happens during the movements made by the user and with the application of the user's own body weight while performing an activity. Implementations can also include a variety of routing configurations for the elastic member(s), as well as a variety of mounting points to integrate the elastic member(s) into the system, and / or a variety of adjustable anti-hyperextension members, and / or a variety of interchangeable shoes used for applicable activities.
Owner:BARTLETT BRIAN
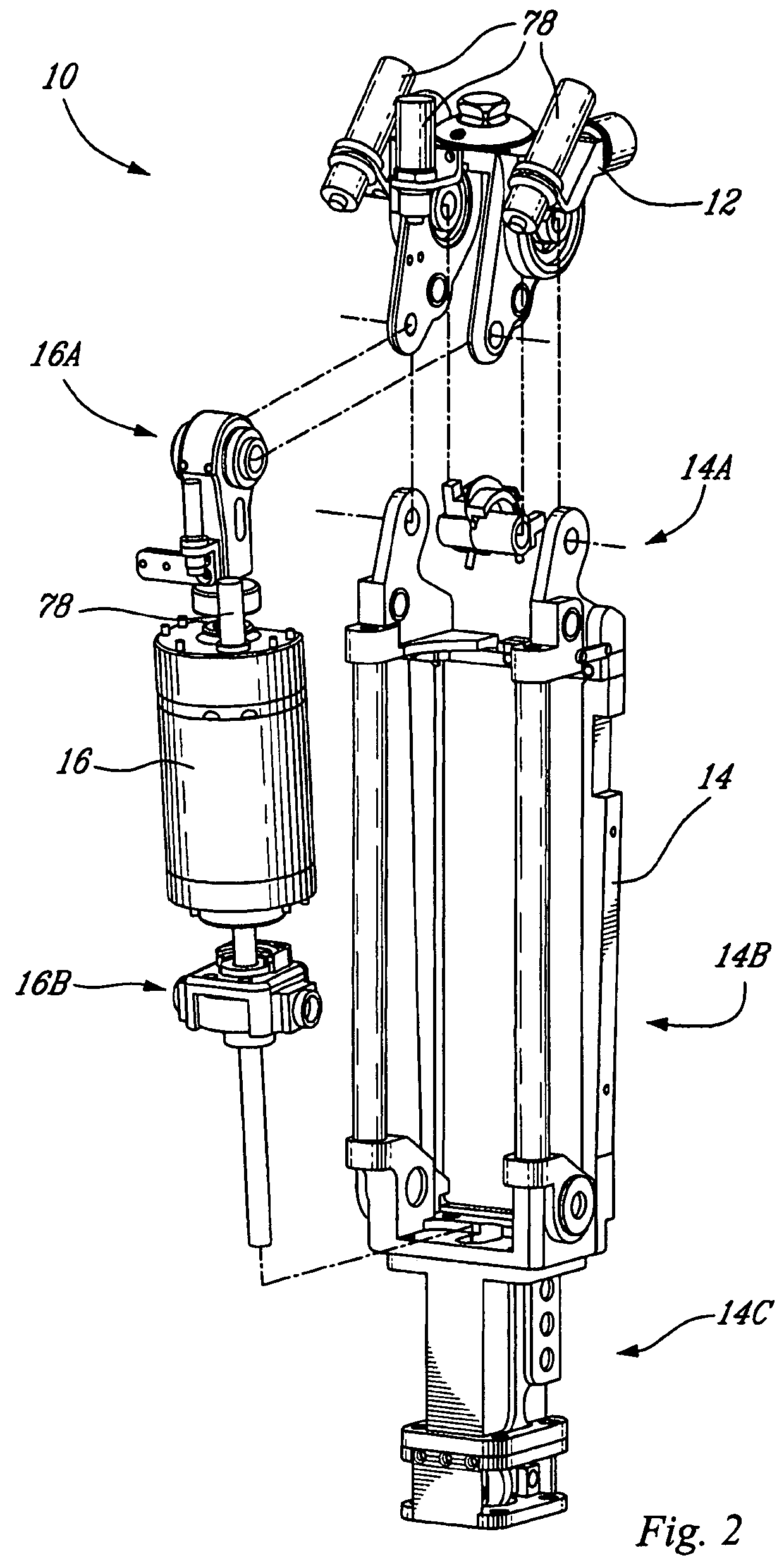
Leg prosthesis
Leg prosthesis including a cylinder with a piston and a piston rod, the piston rod being led out of one end of the cylinder and attached to an outer tube of the prosthesis, with the lower part of the cylinder being attached to an inner tube of the prosthesis. The outer tube and the inner tube may be connected to parts of the leg prosthesis, and the cylinder may contain a pneumatic or hydraulic medium. The inner tube and the outer tube provide a cavity for the arrangement of a torsion device, where the outer tube can rotate in both directions in relation to the inner tube and vice versa. The torsion device includes an elastomer fixed to the outer tube, elastomer supports fixed to the outer tube and an elastomer end stop fixed to the inner tube.
Owner:INLIEU
Structure of leg prosthesis
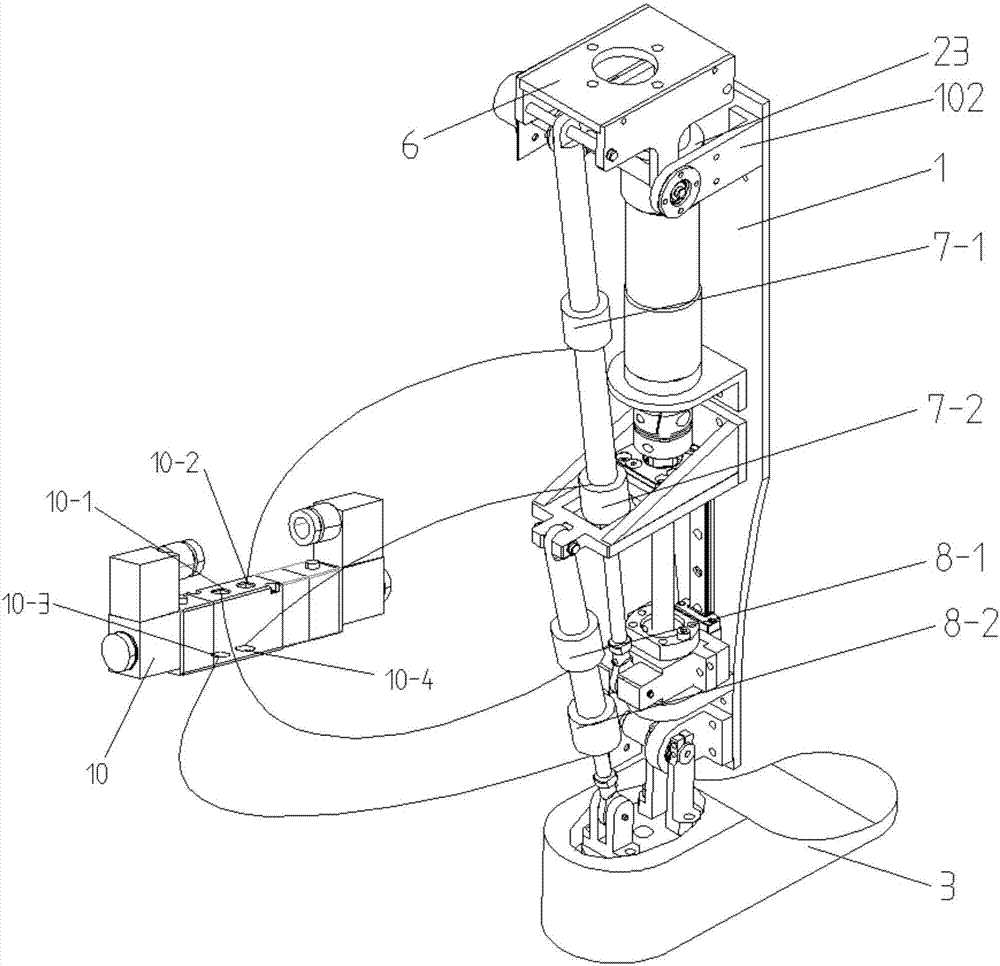
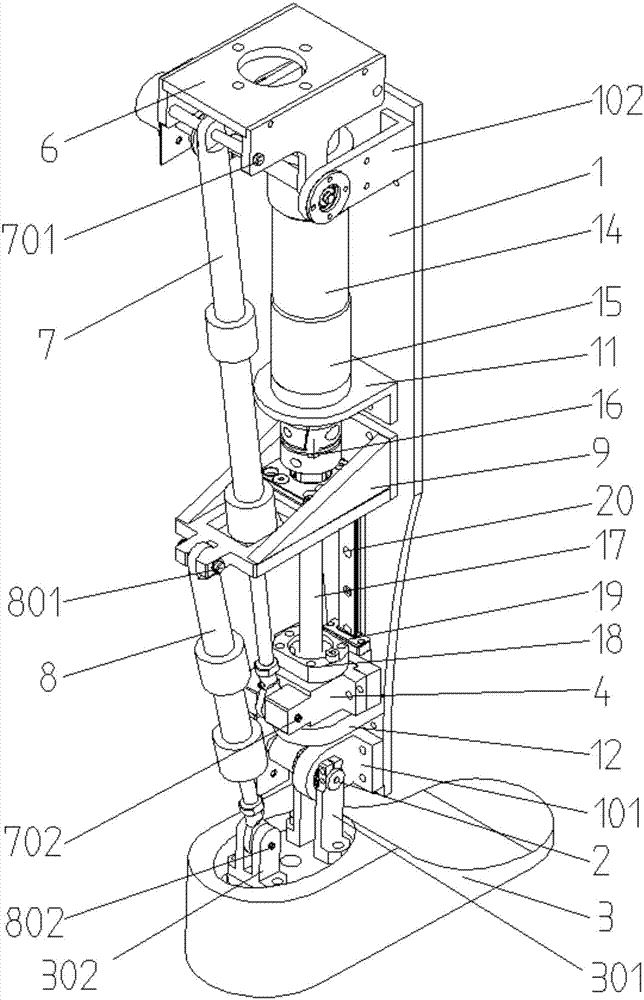
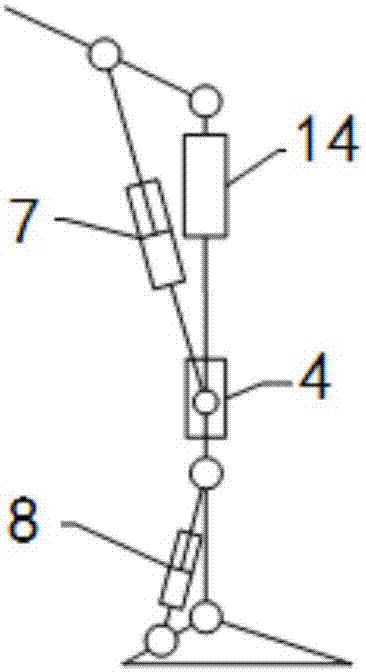
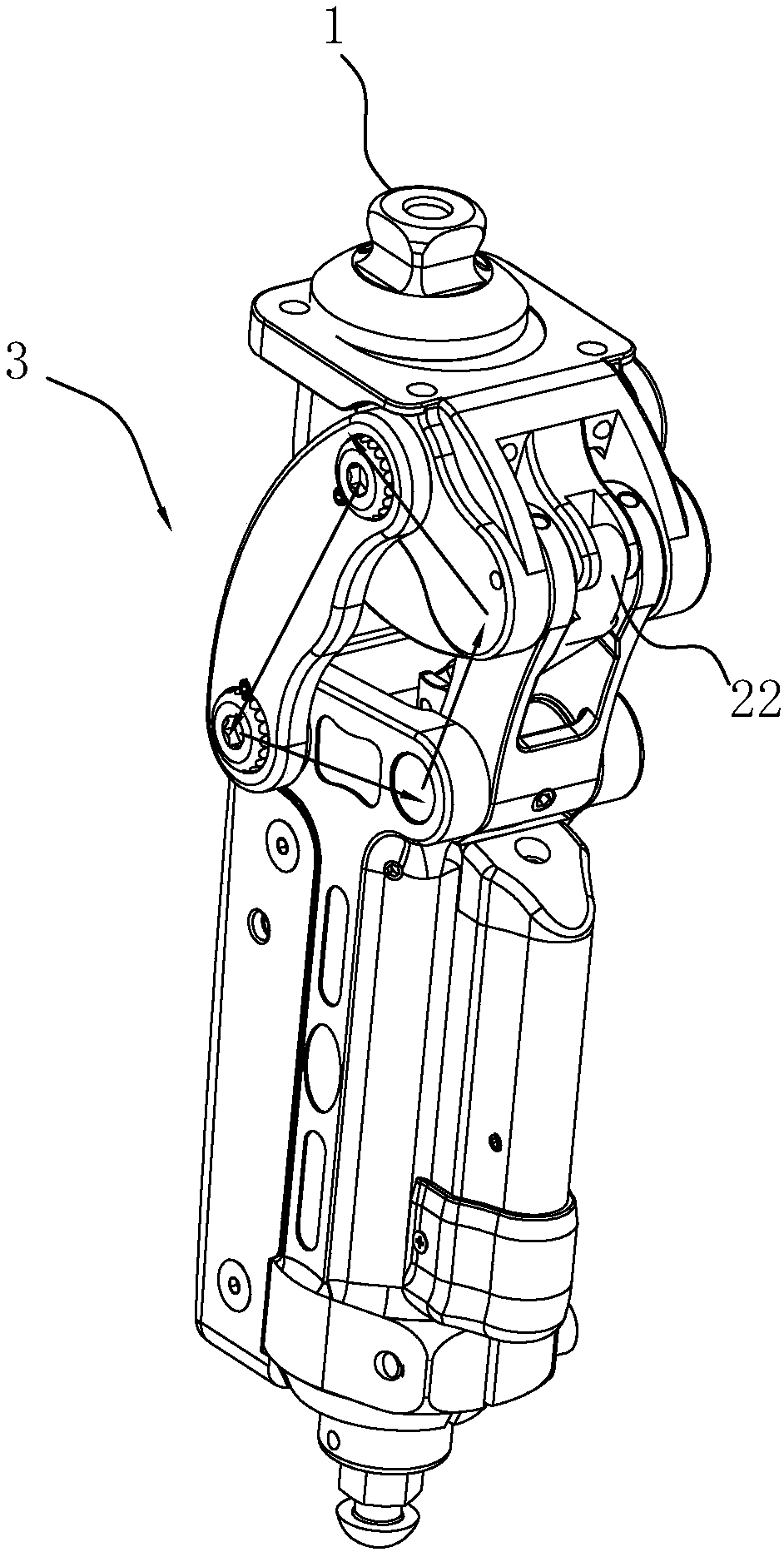
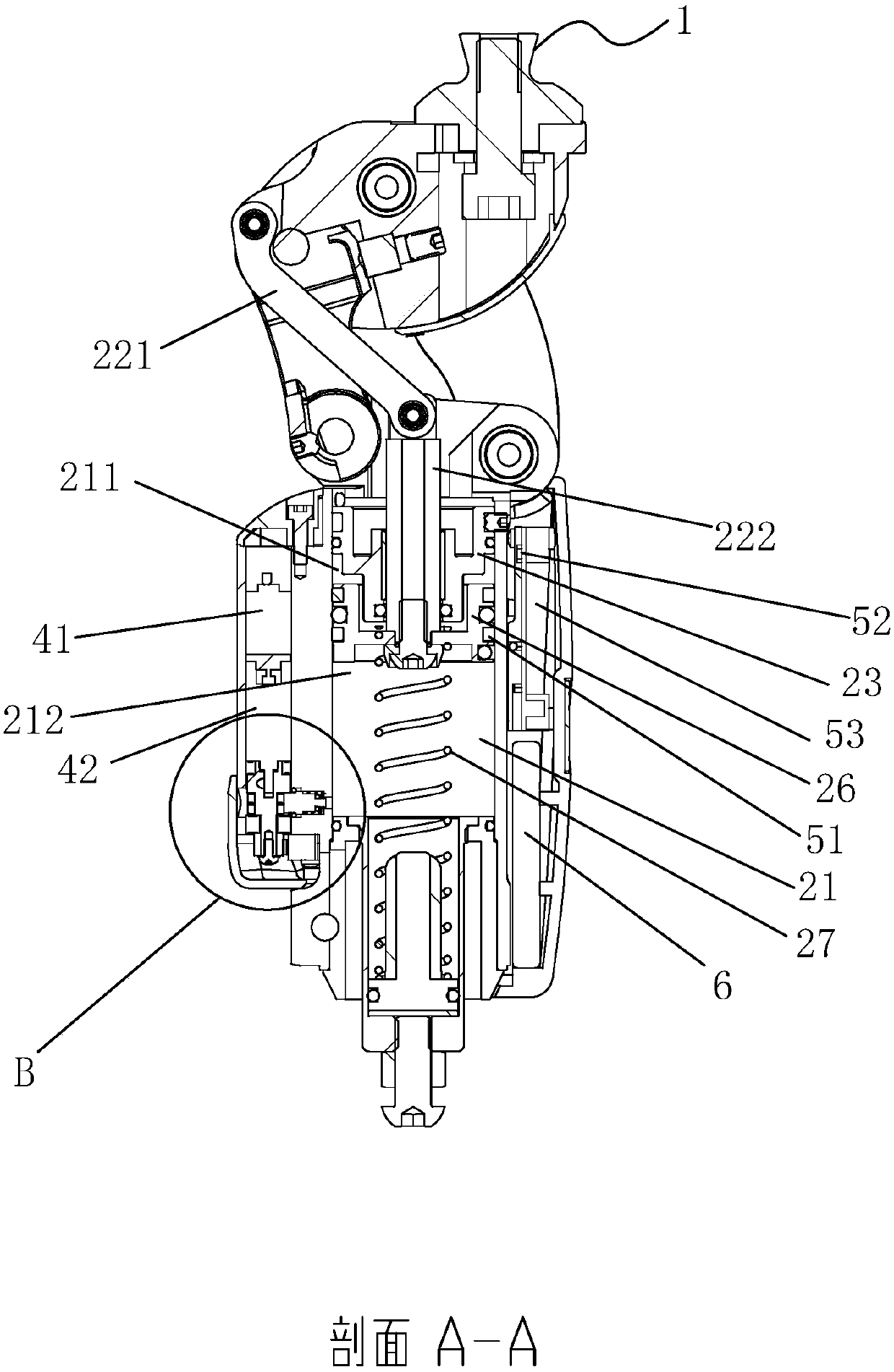
ActiveCN107361886ATo achieve the purpose of couplingMeet the needs of active torqueArtificial legsEngineeringDevice prosthetic
The invention relates to a structure of a leg prosthesis. The structure comprises a base plate, a foot plate which is rotatably connected to the base plate by virtue of a first rotating shaft and a driving mechanism which is arranged on the base plate, and further comprises a first transmission mechanism and a second transmission mechanism, wherein the driving mechanism comprises a moving piece which is capable of moving up and down along the base plate; an adapter block is additionally rotatably connected to the upper end of the base plate by virtue of a second rotating shaft; the upper end of the first transmission mechanism is rotatably connected to the adapter block by virtue of a first axial line; the lower end of the first transmission mechanism is rotatably connected to the moving piece by virtue of a second axial line; the upper end of the second transmission mechanism is rotatably connected to a first supporting seat on the base plate by virtue of a third axial line; and the lower end of the third transmission mechanism is rotatably connected to the foot plate by virtue of a fourth axial line. According to the leg prosthesis structure, by simultaneously arranging the driving mechanism and the transmission mechanisms, driving and driven hybrid driving can be implemented on the lower extremity leg prosthesis, so that different gait control effects can be achieved.
Owner:苏州普瑞川传动科技有限公司
Prosthetic knee with gravity-activated lock
InactiveUS20100082115A1Increase flexibilityEncourages normal movementArtificial legsPediatric patientPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Disclosed is a prosthetic knee appliance having upper and lower leg elements with a single-axis, articulating joint therebetween controllable with an electric knee-lock mechanism. A tilt-switch located within the prosthetic knee can facilitate activation of the electric knee-lock to lock or unlock the joint when the lower leg element is in a pre-determined position. A remote control can provide external locking control of the articulating joint. A pressure switch can ensure that the free-knee is locked only when the lower leg element is sufficiently extended relative to the upper leg element. The mobility of a free-knee system combined with the stability of a straight-leg prosthesis can be advantageous for pre-ambulatory pediatric patients.
Owner:SHRINERS HOSPITALS FOR CRIPPLED CHILDREN
Light duty consumable prosthesis
A light duty consumable prosthesis for use in replicating leg bones, arm bones and spinal column vertebra in a cadaver is constructed of largely consumable products to enable the prosthesis to be incinerated in the event that the host cadaver is cremated. The leg prosthesis is telescoping such that it is length adjustable to be sizable in cadavers of different leg lengths. The arm prosthesis is also of a telescoping design that includes a bendable hinge between an upper arm portion and a lower arm portion. The spinal column prosthesis is similar to the upper arm prosthesis and includes rods to assist in securing it in location.
Owner:MUZZILLO SEAN A
Method for carrying out a functional analysis of an artificial extremity
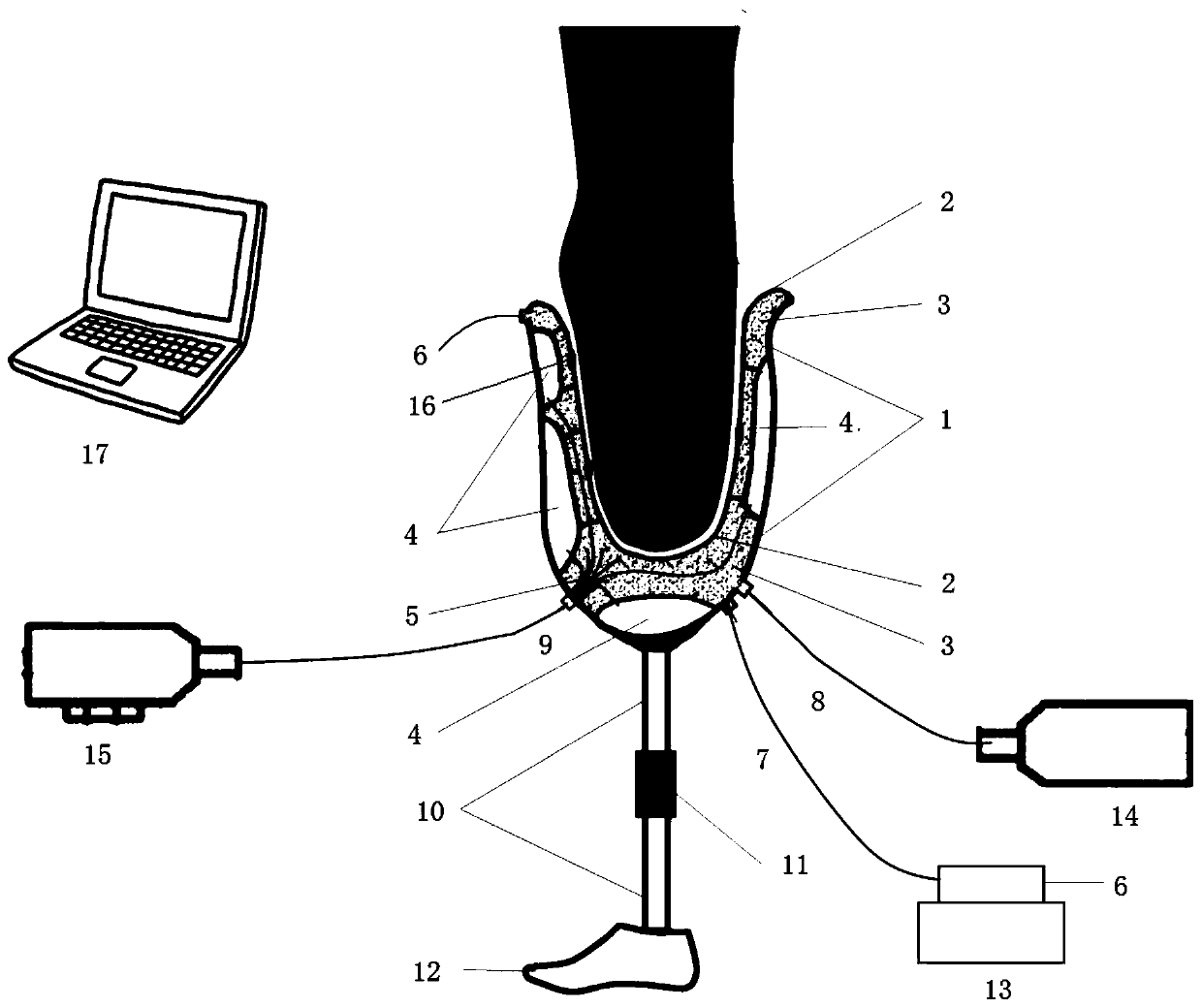
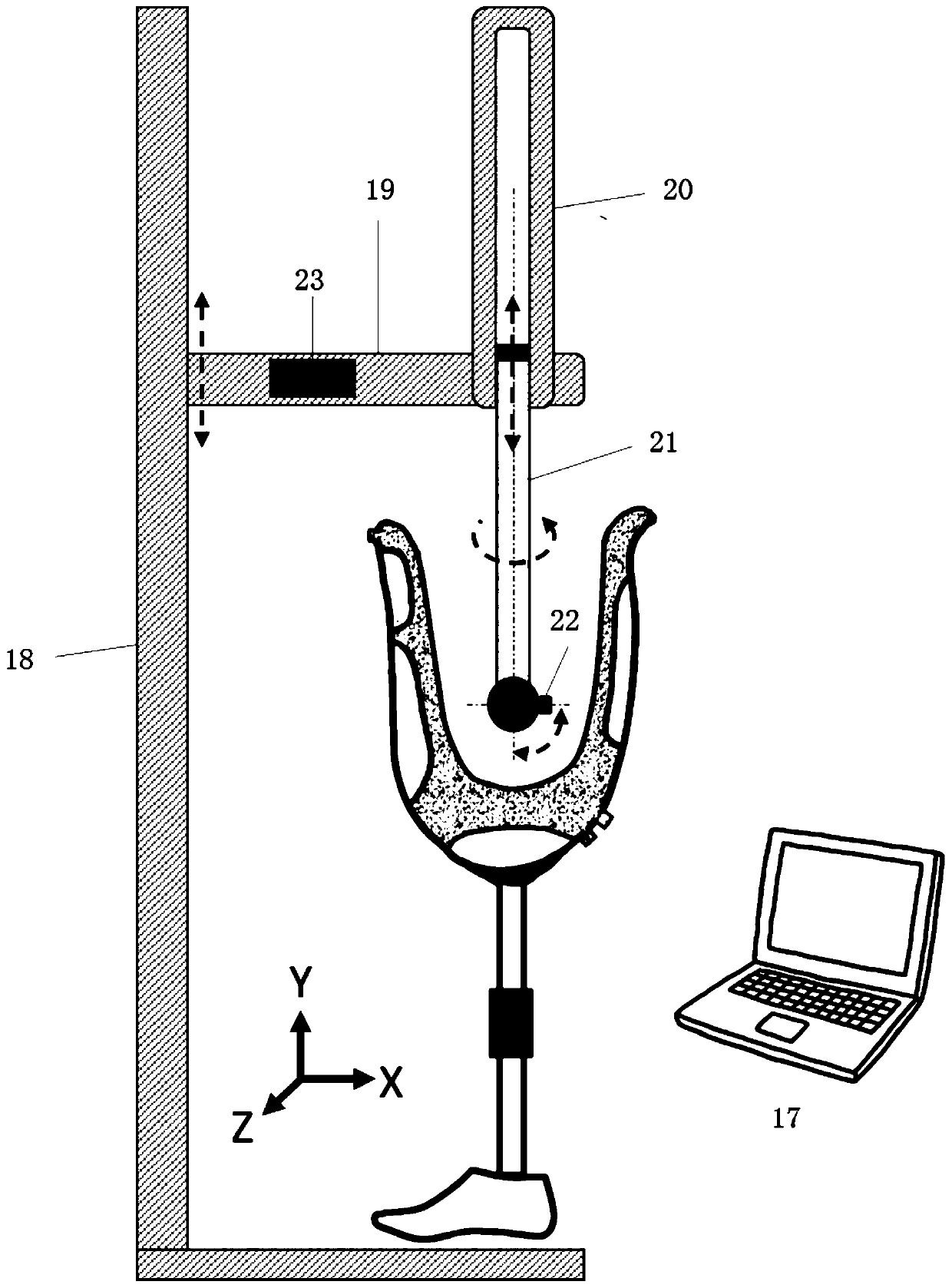
ActiveUS8251928B2Cutting pieceDifferent setWave based measurement systemsPerson identificationEngineeringDevice prosthetic
A method for carrying out a functional analysis on a person equipped with an artificial extremity having adjustable settings. The method includes the steps of providing a sensor assembly configured as a replacement for a part of the artificial extremity and installing the sensor assembly in place of the part. Forces, accelerations and / or torques are then measured with the sensor assembly during use of the artificial extremity by the person and the settings of the artificial extremity are optimized based on these measurements. The sensor assembly is removed and the replaced part is installed back into the artificial extremity, while retaining the optimized settings. In one embodiment, the artificial extremity is a leg prosthesis having an artificial knee joint with a rotational adaptor mounted above it. The sensor assembly then replaces the rotational adaptor.
Owner:OTTOBOCK SE & CO KGAA
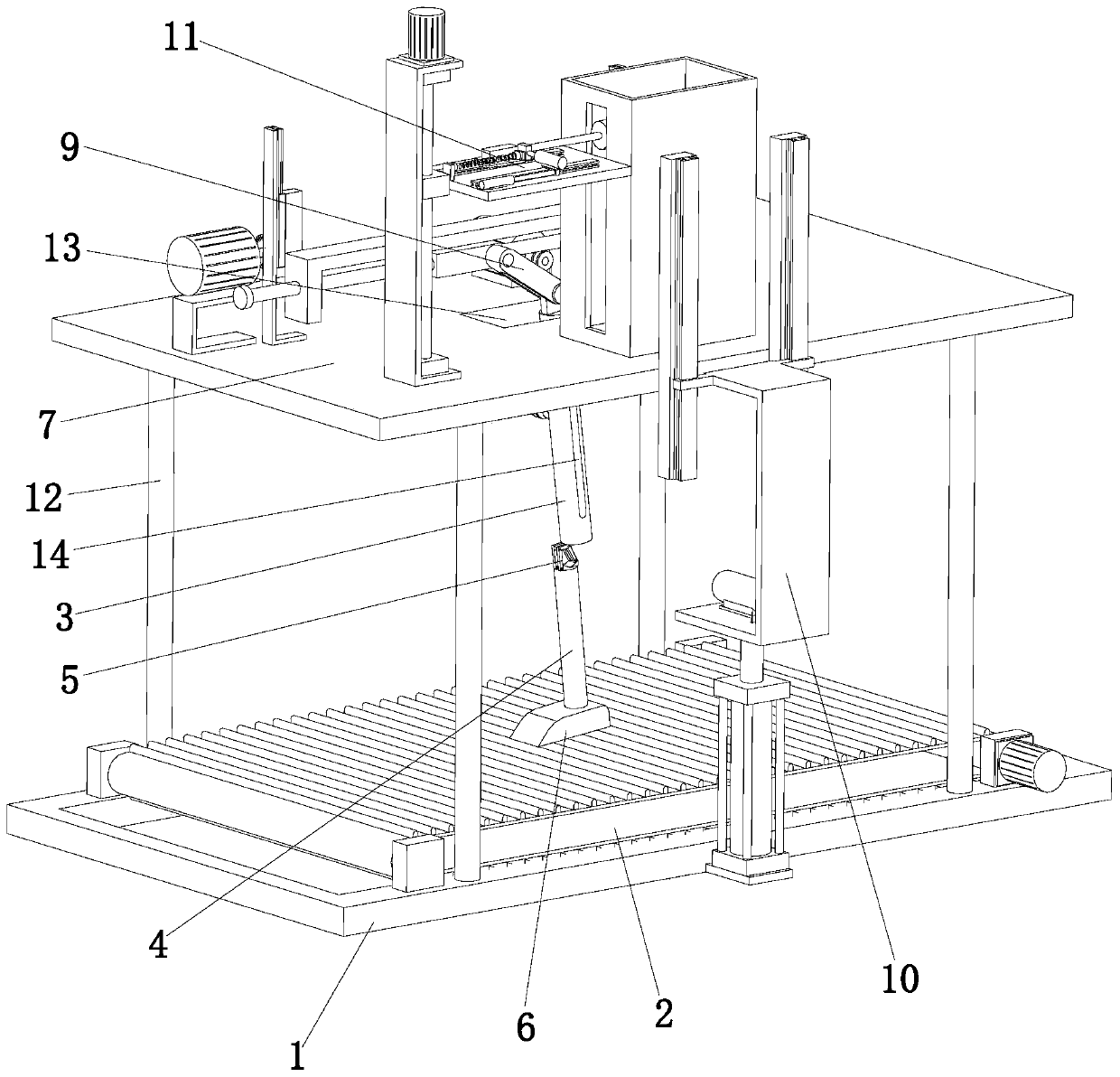
Method and Apparatus for Restoring Alignment of the Support Socket in the Manufacture of Leg Prostheses
InactiveUS20060106465A1Easy to adjustFast preparationAutomatic control devicesAssembly machinesOrthotic deviceMechanical engineering
An apparatus for restoring the alignment of the support socket with other structural components during the fabrication of a leg prosthesis comprising a stand with base, a means to secure the lower aspect of the leg prosthesis to the stand base, and a laser source attached to the top of the stand that emits visible cross-beams downward onto the leg prosthesis when the prosthesis is mounted on the stand base. The method of the invention uses the described apparatus with leg prosthesis mounted thereon to mark points on the inside of a check or test socket that coincide with the laser cross-beams; transferring these marks from the check socket to the permanent support socket; and re-aligning the permanent support socket with the lower aspect prosthetic components by mounting the leg prosthesis with permanent support socket on the alignment apparatus and matching the marks to the laser cross-beams. A removable base plate allows for a number of leg prostheses to be fabricated concurrently, using the same alignment apparatus. The method and apparatus of the present invention reduces the time and expense of orthotic fabrication while increasing the accuracy of alignment of the finished prosthetic product.
Owner:HIKICHI YUICHI
Intelligent bionic knee joint
PendingCN107550606ADamping to achieve adjustmentJoint implantsKnee jointsThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An intelligent bionic knee joint is used for being connected between an above-knee prosthesis and a below-knee prosthesis and comprises a connector, a knee joint simulation device, a first air pressure damping device, a detection device and a second air pressure damping device. The connector is fixedly connected with the above-knee prosthesis, the knee joint simulation device is fixedly arranged below the connector and used for simulating a human prosthesis, the first air pressure damping device cooperates with the knee joint simulation device in operation, the detection device is used for detecting a current moving state, and the second air pressure damping device responds to the detection device to adjust air pressure damping. Therefore, real-time adjustment of knee joint movement statesaccording to human walking speeds can be realized.
Owner:北京精博现代假肢矫形器技术有限公司
Clearance enhancer for lower limb prosthesis
A lower limb prosthesis for a person is provided that comprises a foot prosthesis having a heel plate for contacting the ground and an ankle plate extending vertically from the heel plate when the heel plate is in ground contact, a leg prosthesis having an upper end portion mountable to the body of the person and a lower end portion, and a clearance enhancer. The clearance enhancer is in the form of a generally L-shaped plate, the plate including a base plate and an upper plate extending generally perpendicularly from the base plate. The base plate is configured to be connected to the lower end of the leg prosthesis. The upper plate includes a number of mounting openings to receive a corresponding number of fasteners for connecting the upper plate to the ankle plate of the foot prosthesis so that the lower portion of the leg prosthesis overlaps the ankle plate of the foot prosthesis.
Owner:PALMER JEFFREY RAY
Prosthesis testing equipment
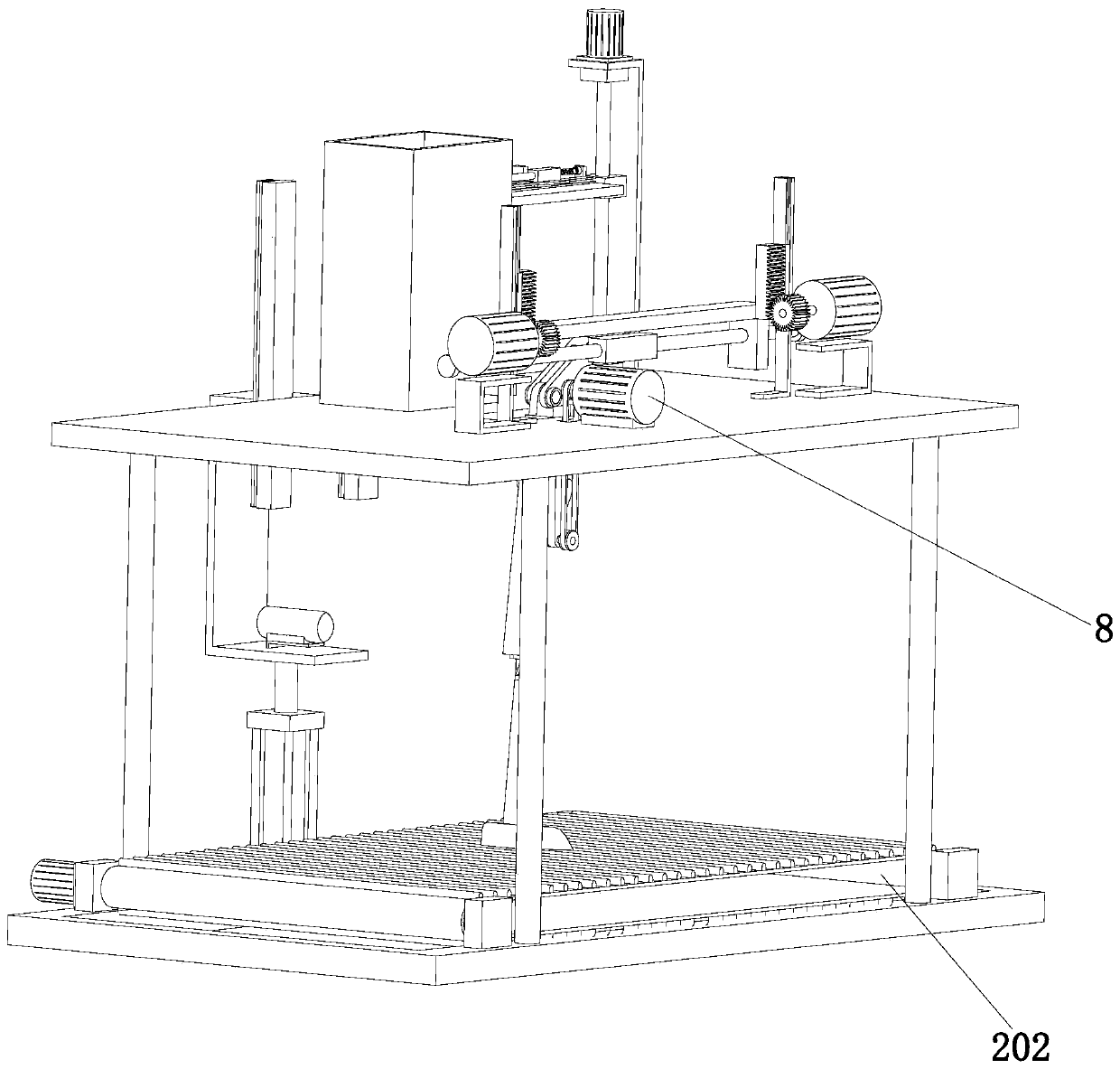
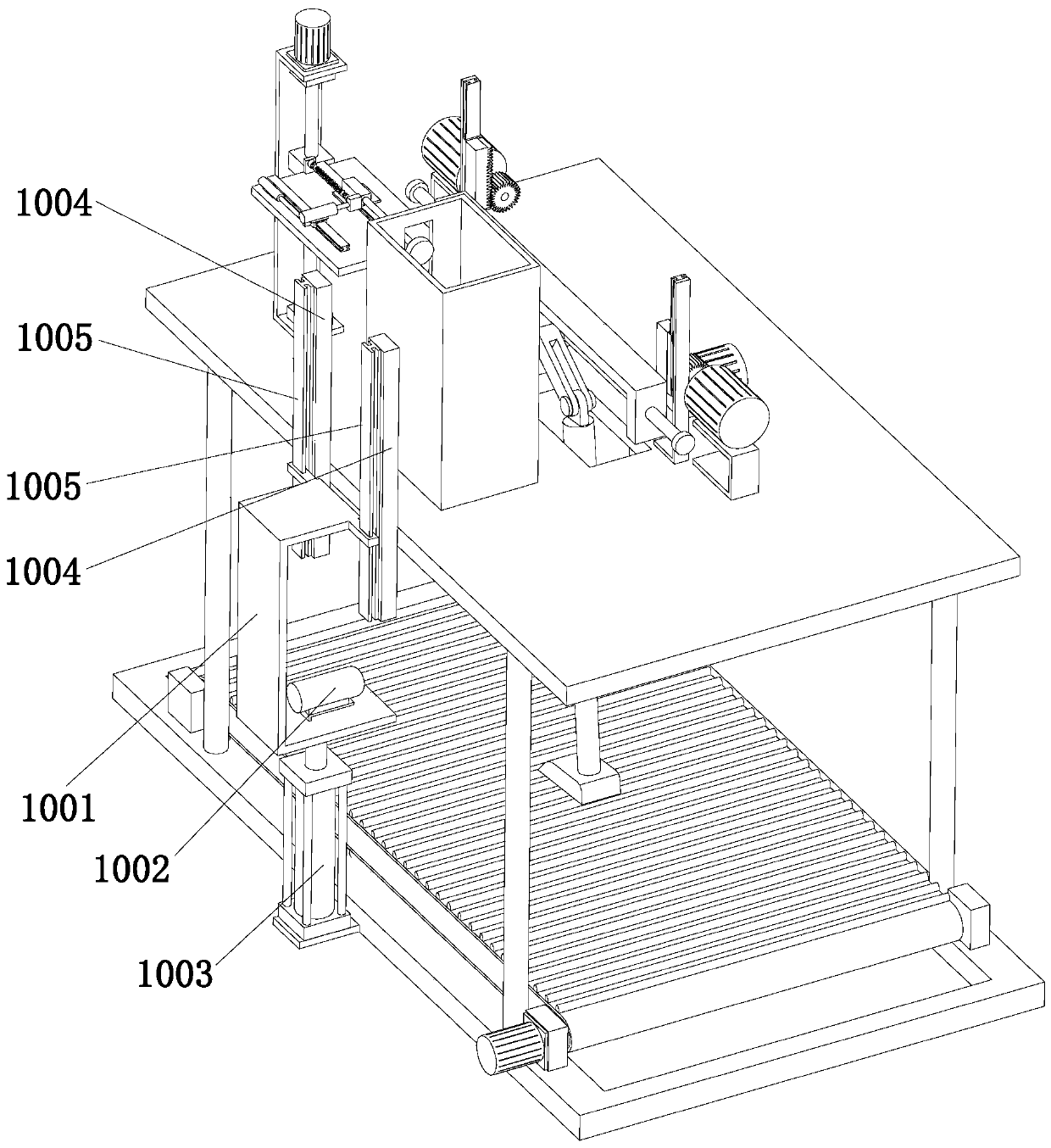
ActiveCN110897766AAccurate walking performanceEasy slow-motion analysisProsthesisShock testingThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses prosthesis testing equipment and belongs to the technical field of prosthesis testing. The equipment includes a bottom plate, a ground transmission assembly, a thigh prosthesis, a crus prosthesis, a knee joint, a sole of the foot, a mounting plate, a driving assembly, a lifting assembly, a monitoring assembly, a collision assembly and four supporting columns. The ground transmission assembly is mounted at the top of the bottom plate. The four supporting columns are distributed at the top of the bottom plate in a rectangular shape. The mounting plate is fixedly connectedwith the top of the four supporting columns, and a rectangular groove is arranged on the mounting plate. The lifting assembly is arranged at the top of the mounting plate. The top end of the thigh prosthesis is hinged to the lifting assembly. The driving assembly is arranged on the mounting plate. The top of the crus prosthesis is connected to the bottom of the thigh prosthesis through the knee joint. The sole of the foot is connected with the bottom end of the crus prosthesis. The monitoring assembly is arranged on the bottom plate and the outer side wall of the mounting plate. The collisionassembly is arranged on the top of the mounting plate. The problem that the test result of existing prosthesis testing equipment cannot truly feedback performance of the knee joint is solved in the invention.
Owner:人民非物质文化传播有限公司
Method and system applied to loading modeling of crus prosthetic socket
PendingCN111494071AImprove comfortSimplify the manufacturing processProsthesisEngineeringProsthetic socket
The invention relates to a method and system applied to loading modeling of a crus prosthetic socket. A negative pressure modeling system is used for acquiring the geometrical shape of a socket of a stump in a loading state and correcting the geometrical shape of a socket supporting interface; the corrected geometrical shape of the socket supporting interface is obtained by using a socket three-dimensional scanning system; a supporting interface geometric model of the socket is generated automatically by combining the geometrical shape of the socket supporting interface with a crus socket database and a final digital model of the crus socket is generated in a manner of translating to construct an entity with a specific thickness. Quantitative control over the geometrical morphology of thesupporting interface can be conducted according to the biomechanical property of the stump and the bearing capacity of each area, geometrical modeling of the crus socket of the loading position is achieved, finally digital reconstruction of the socket is achieved through a three-dimensional scanning method, and the three-dimensional scanning method is applied to digital design of the crus socket.
Owner:国家康复辅具研究中心
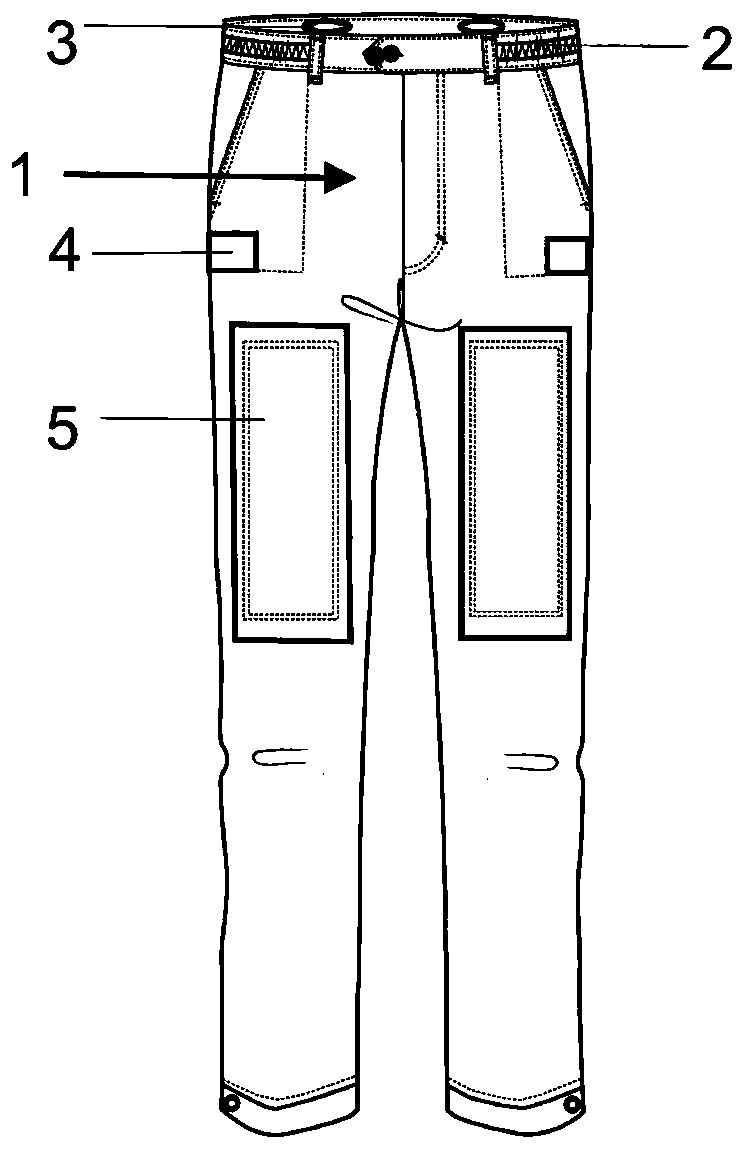
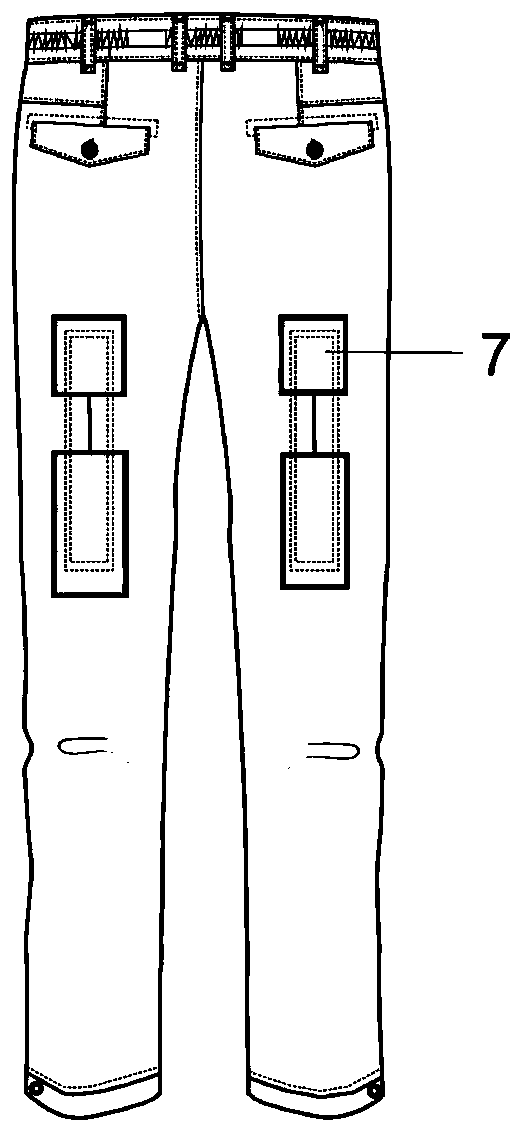
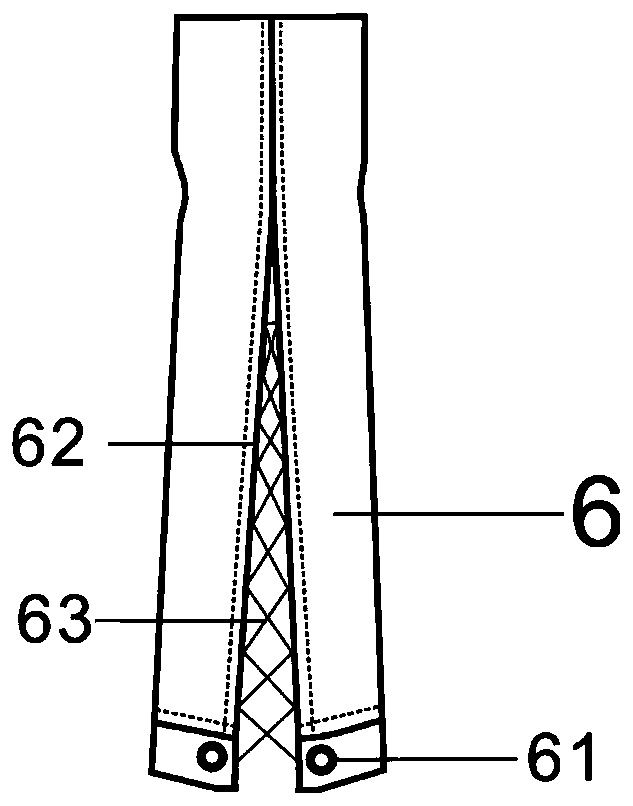
Automatically-fastened split type physiotherapy trousers convenient for artificial limb to put on and take off and use method of automatically-fastened split type physiotherapy trousers convenient for artificial limb to put on and take off
InactiveCN110694182AEasy on and offEffectively hideElectrotherapyLight therapyPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
The invention discloses automatically-fastened split type physiotherapy trousers convenient for artificial limb to put on and take off and a use method of the automatically-fastened split type physiotherapy trousers convenient for artificial limb to put on and take off. The girth of trouser openings of conventional trousers is small, so that a single lower limb handicapped person puts on and takesoff an artificial limb alone extremely difficultly. An automatic fastening module is arranged on each of two trouser legs of a trouser body. Each automatic fastening module comprises driving motors and binding tapes. Splits are formed in the bottoms of outer side seams of two trouser legs of the trouser body. Thread loops for fastening buttons, which are sequentially arrayed, are arranged on twosides of the splits of the trouser legs. One ends of two binding tapes are fixed to the tops of the splits of the trouser legs, and penetrate through the thread loops for fastening buttons on two sides of the splits of the trouser legs in a crossing manner. Rehabilitation health-care devices of physiotherapy electrode pieces, far infrared heating pieces and the like are arranged on the waist and the legs of the trouser body. According to the automatically-fastened split type physiotherapy trousers convenient for artificial limb to put on and take off disclosed by the invention, automatically-fastened split trouser feet are arranged, so that the disabled person that need putting on below-knee prosthesis can easily put on and take off the artificial limb, and after the artificial limb is puton, trouser leg splits can be automatically superimposed, and the artificial limb can be effectively hidden. In addition, the split degree can be autonomously controlled according to the requirementsof the user.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com