Lower leg prosthesis
a lower leg and prosthesis technology, applied in the field of lower leg prosthesis, can solve the problems of limited upward deflection of the heel section of the foot plate, and achieve the effects of improving inversion/eversion compliance, and improving the dynamic feel of the heel strik
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
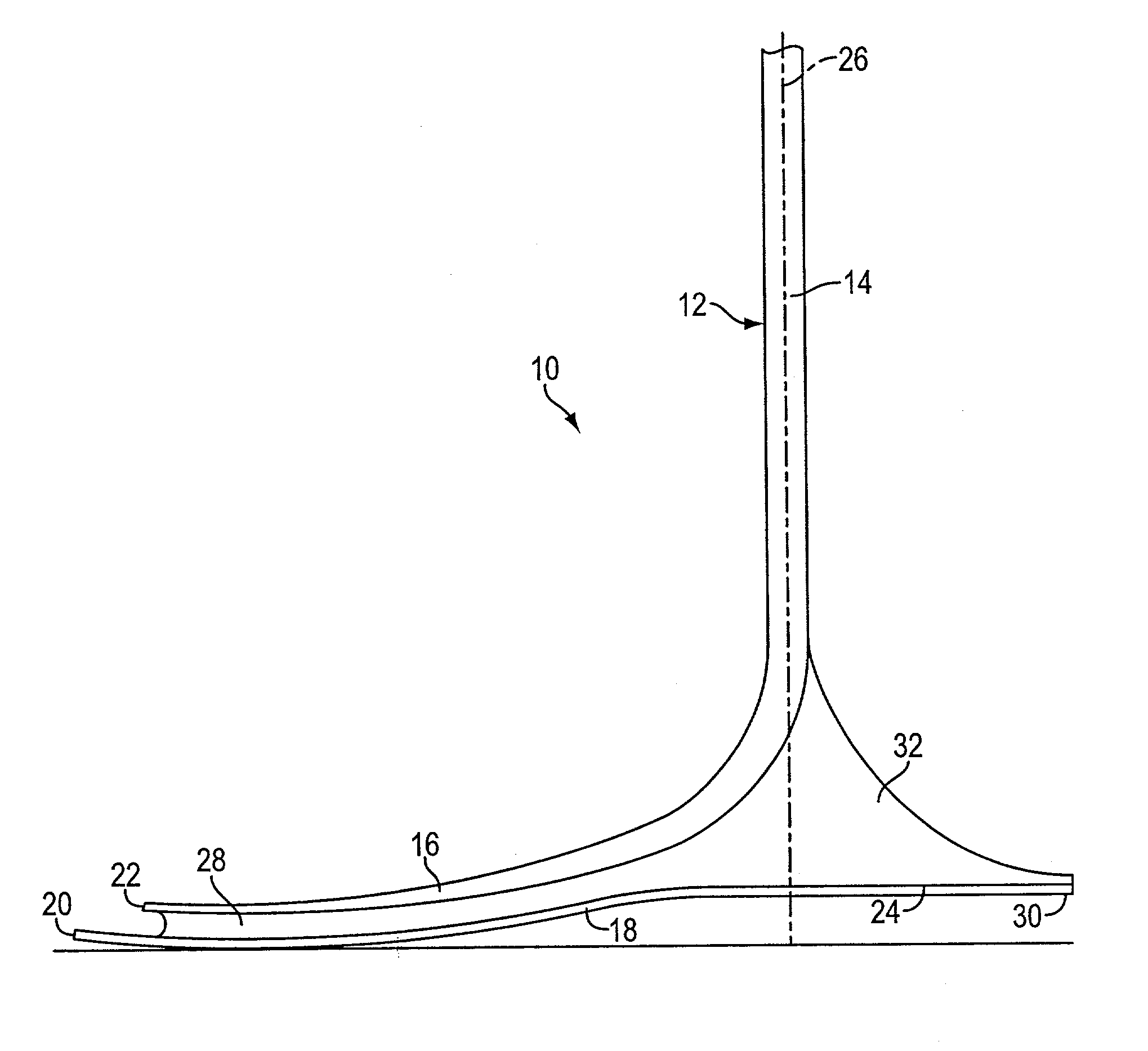
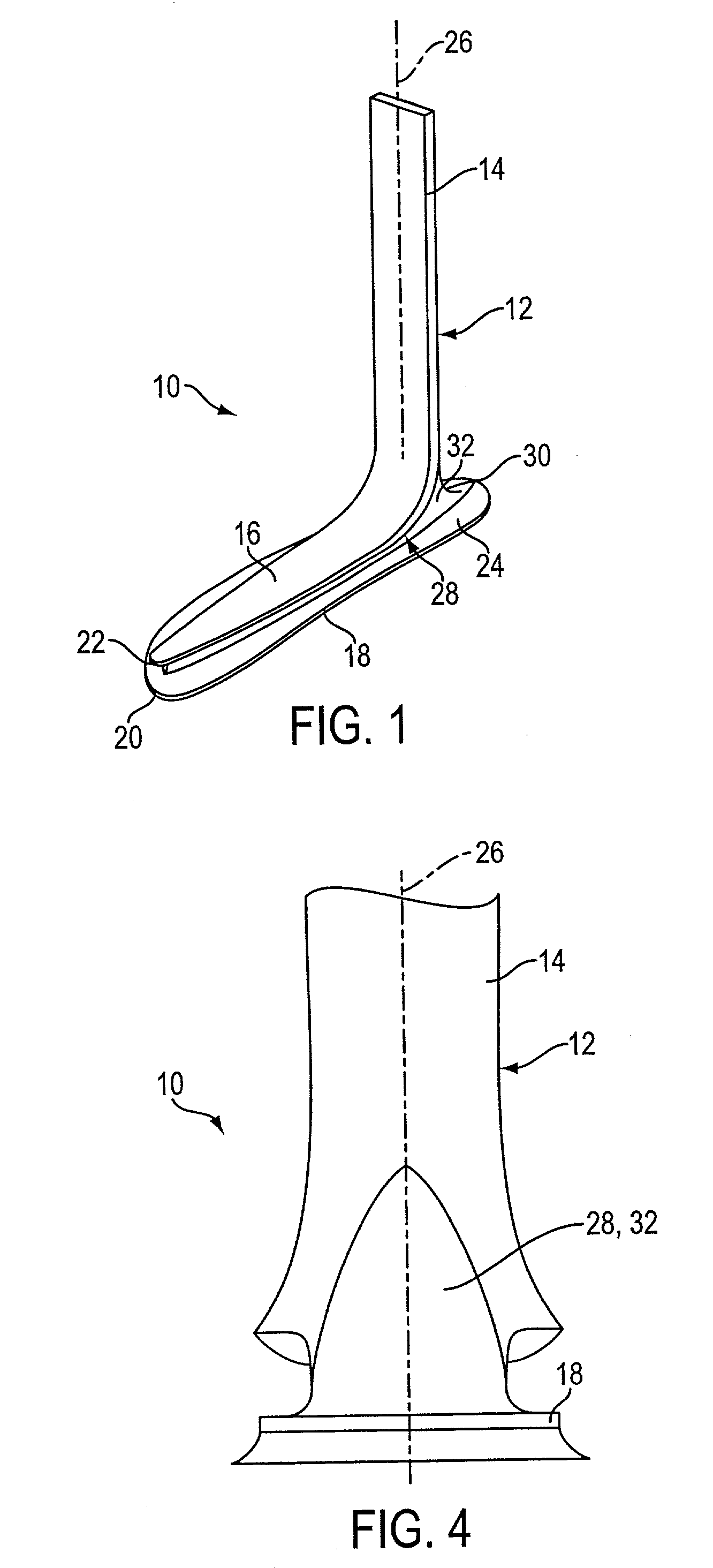
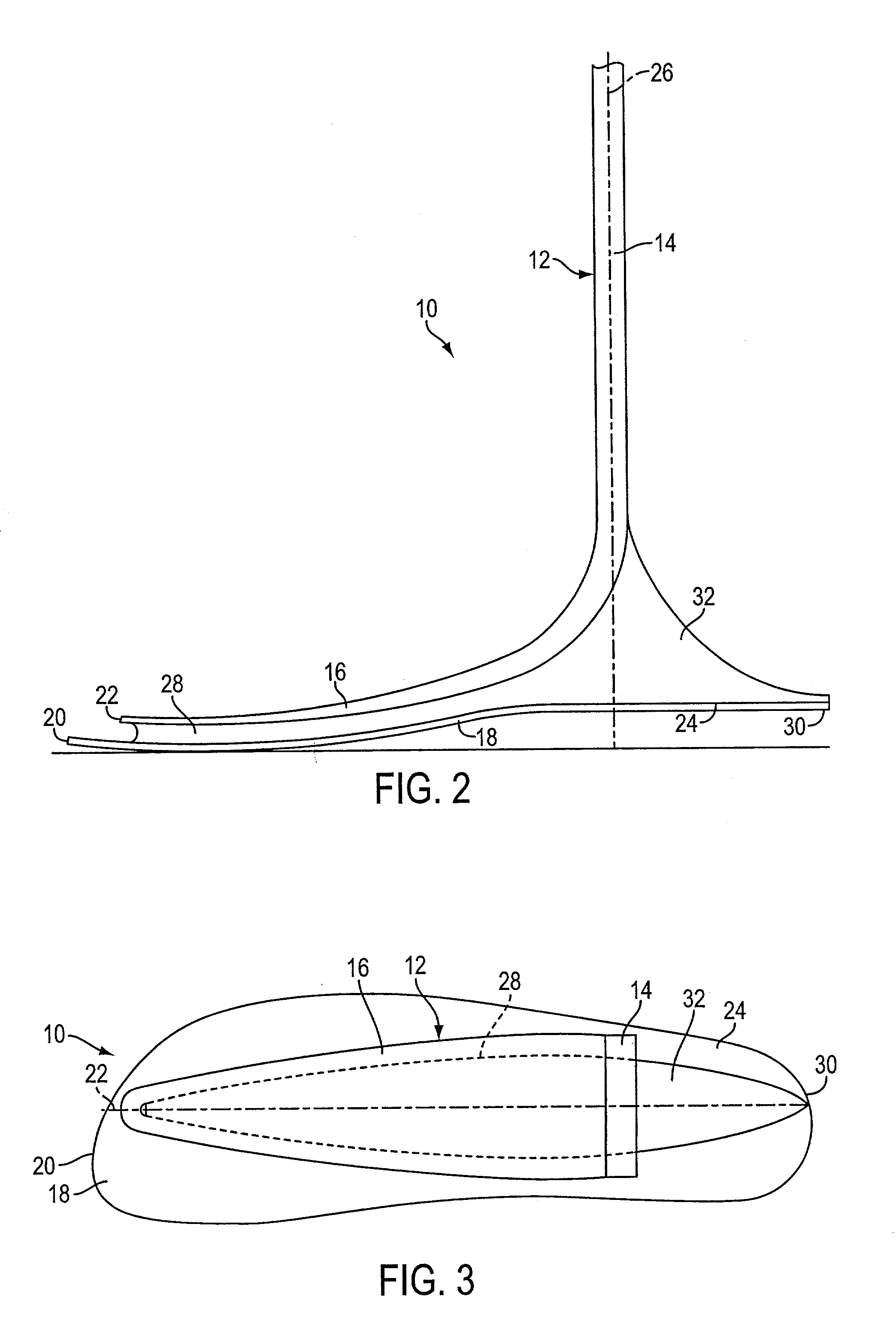
[0016] With reference now to the illustrative drawings, and particularly to FIGS. 1-4, there is shown a lower leg prosthesis 10 in accordance with the invention, the prosthesis incorporating an elongated pylon 12 having an upper, vertically oriented ankle / shin section 14 and a lower, forwardly oriented forefoot section 16, and further incorporating an underlying foot plate 18. As best shown in FIG. 2, the forward tip 20 of the foot plate is disposed substantially beneath the forward tip 22 of the pylon's forefoot section. In addition, the foot plate's rearward end defines a heel section 24 that projects rearwardly of a vertical axis 26 defined by the pylon's ankle / shin section. An elastomeric layer 28 extends along substantially the entire length of the foot-plate, or permanently attaching the foot plate to the pylon. The prosthesis duplicates the dynamic performance characteristics of the normal human foot, yet it is of simple construction and can be manufactured relatively inexpen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com