Patents
Literature
571 results about "Leg length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Leg length difference (LLD) is primarily when the hips are not level, causing a limp from side to side. Most practitioners divide LLD into anatomical or functional. Anatomical is when there is a true difference in the length of the tibia/fibula or the femur bone, or both.
Method and apparatus for positioning a bone prosthesis using a localization system
InactiveUS20080051910A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceLocalization systemCoxal joint
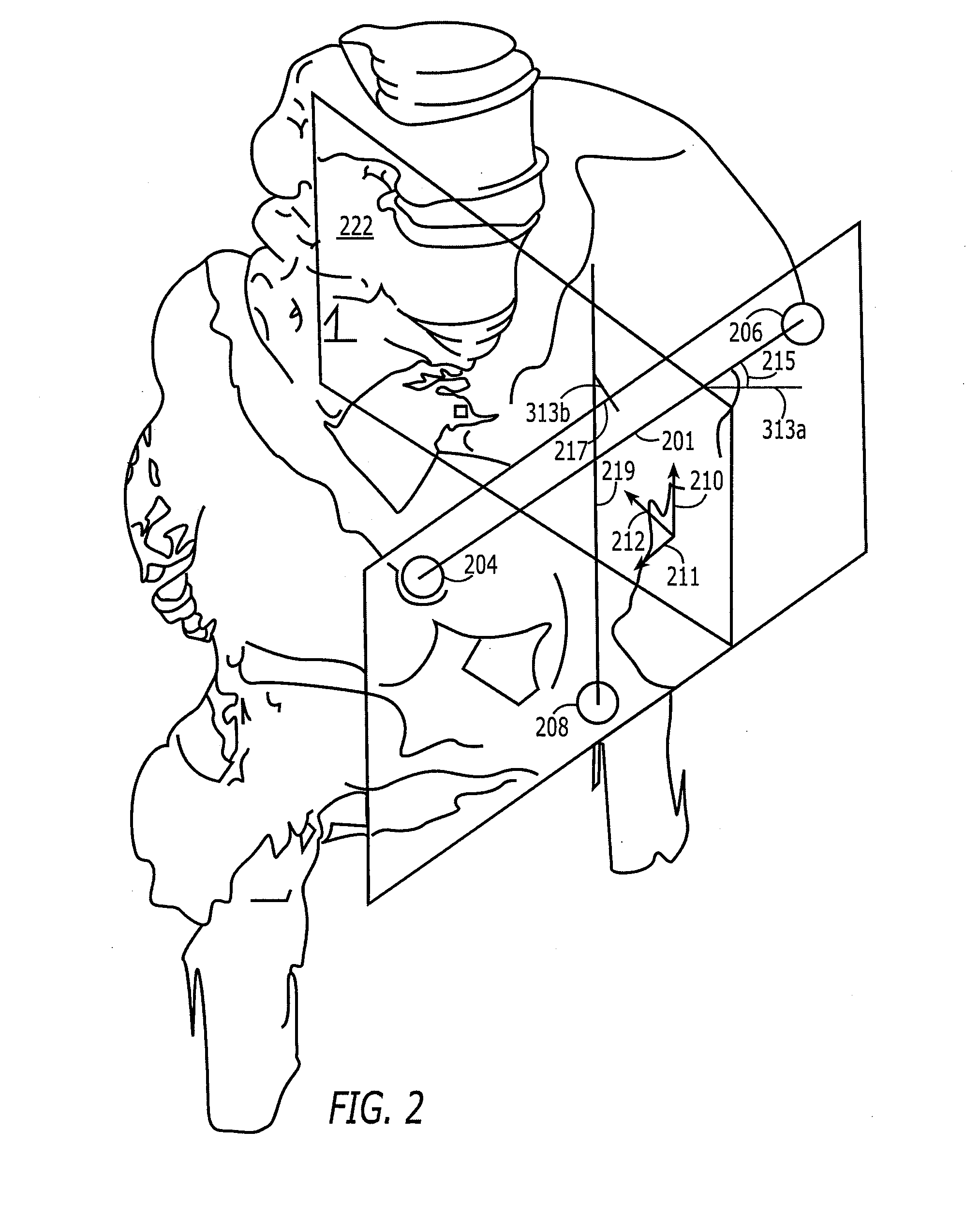
Methods and apparatus using a surgical navigation system to position the femoral component of a prosthetic hip during hip joint replacement surgery without separately affixing a marker to the femur. The navigation system acquires the center of rotation of the hip joint as well as at least one point on the femur in the pelvic frame of reference. From these two points, the navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the hip joint and the point on the femur. Optionally, a second point on the femur that is not on the first line is palpated. The system can calculate the position and length of a second line that is perpendicular to the first line and that runs from the first line to the second palpated point on the femur. The prosthetic cup is implanted and its center of rotation is recorded. A tool for forming the bore within which the stem of the femoral implant component will be placed is tracked by the navigation system. While the tool is fixed to the femur, the surgeon re-palpates the same point(s) on the femur that were previously palpated. The navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the prosthetic cup and the re-palpated first point. If a second point on the femur was re-palpated, the navigation system also calculates the position and length of a perpendicular line between the first line and the second point. The surgical navigation system uses this information to calculate and display to the surgeon relevant information about the surgery, such as change in the patient's leg length and / or medialization / lateralization of the joint.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
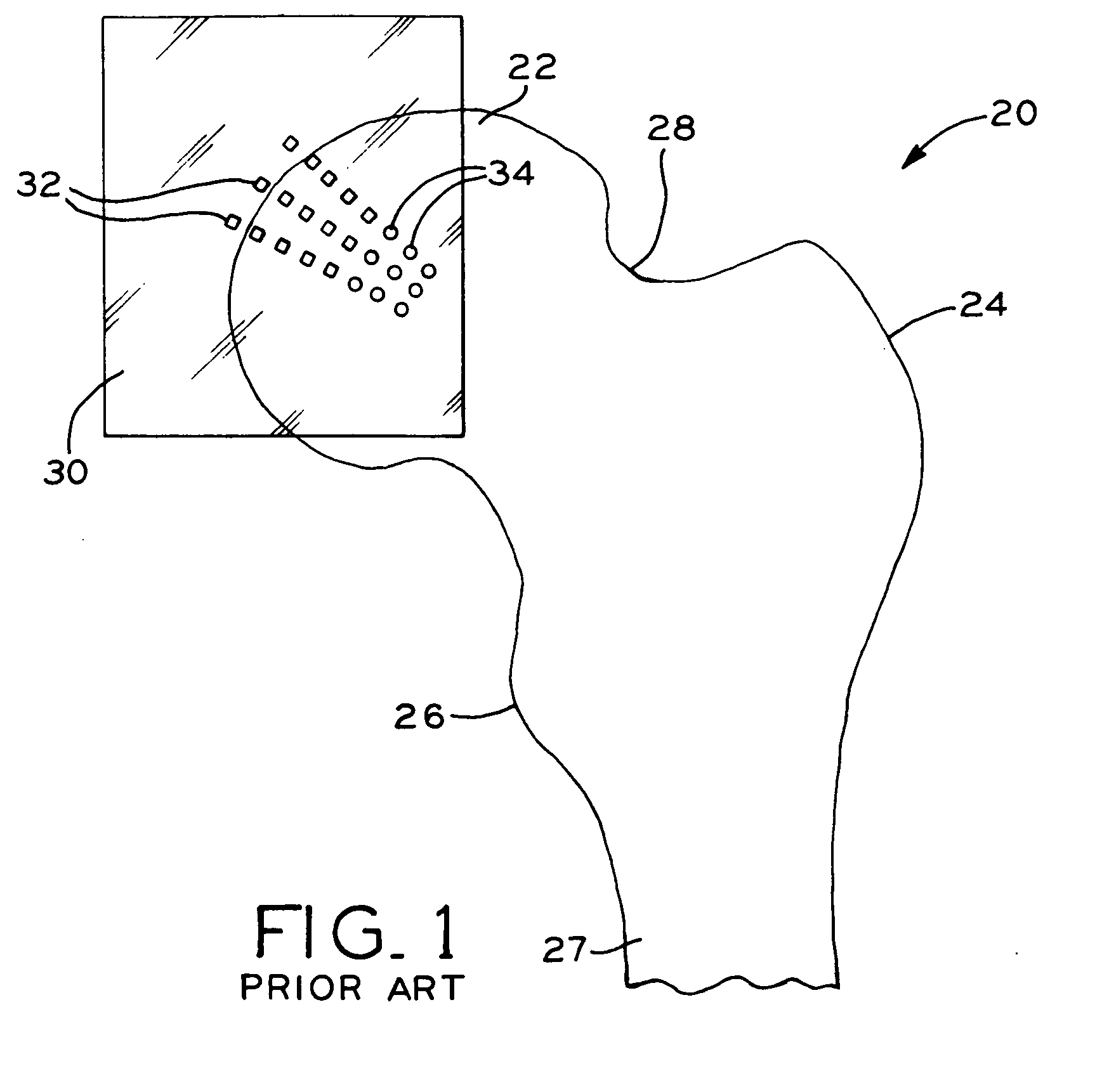
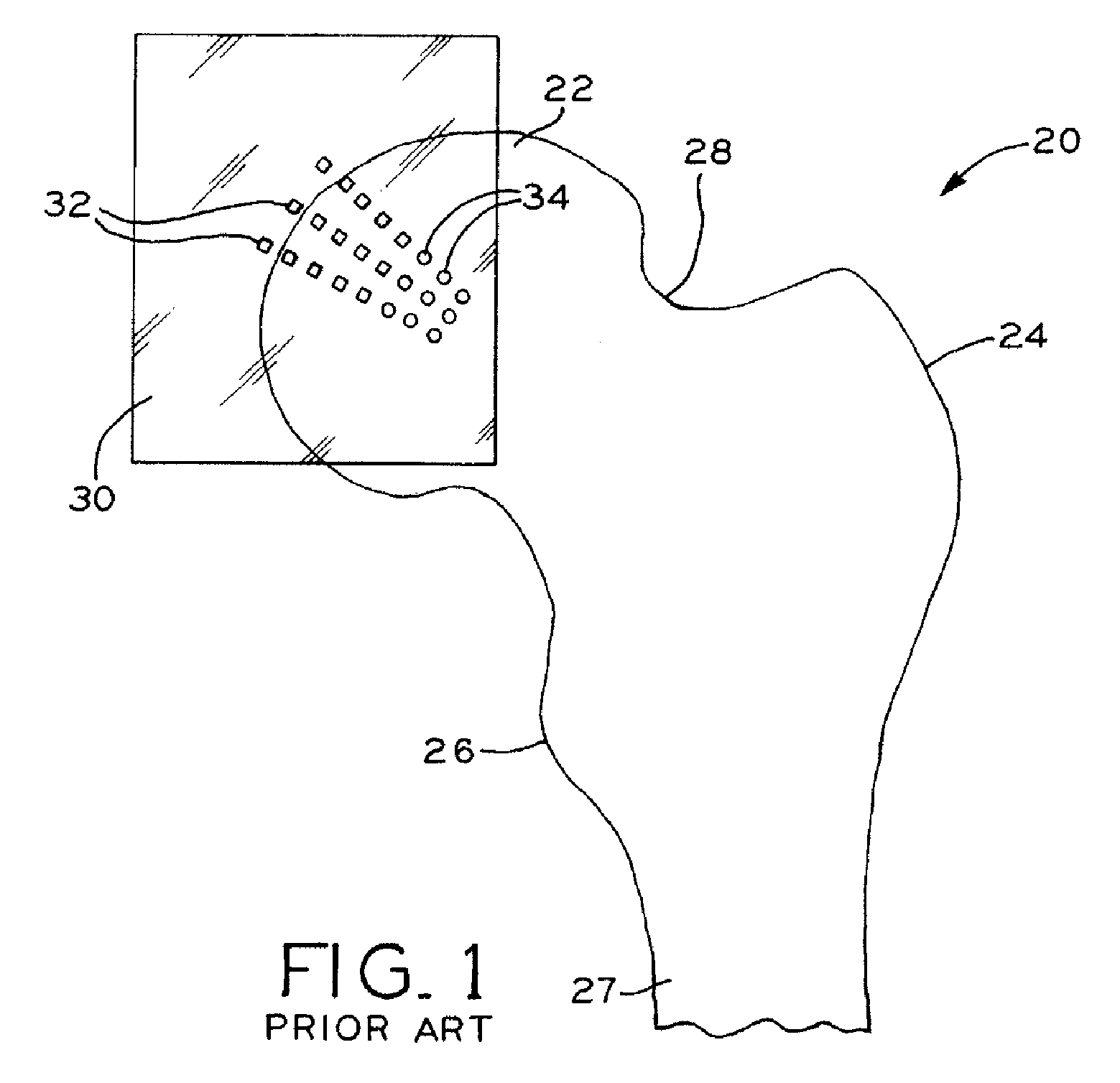
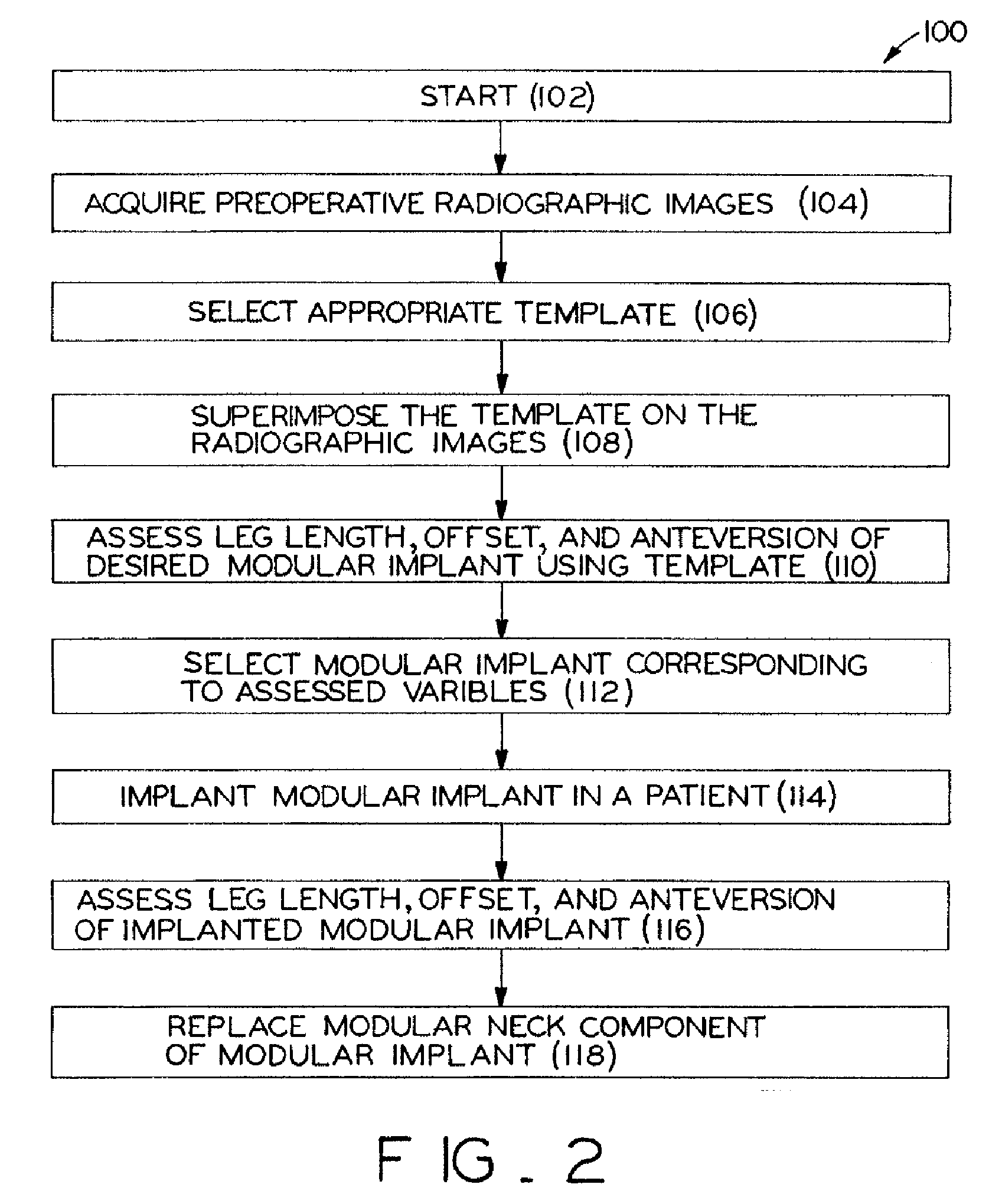
Method for selecting modular implant components
InactiveUS20080021299A1Easy and quick selectionProvide goodSurgical furnitureJoint implantsPresent methodModularity
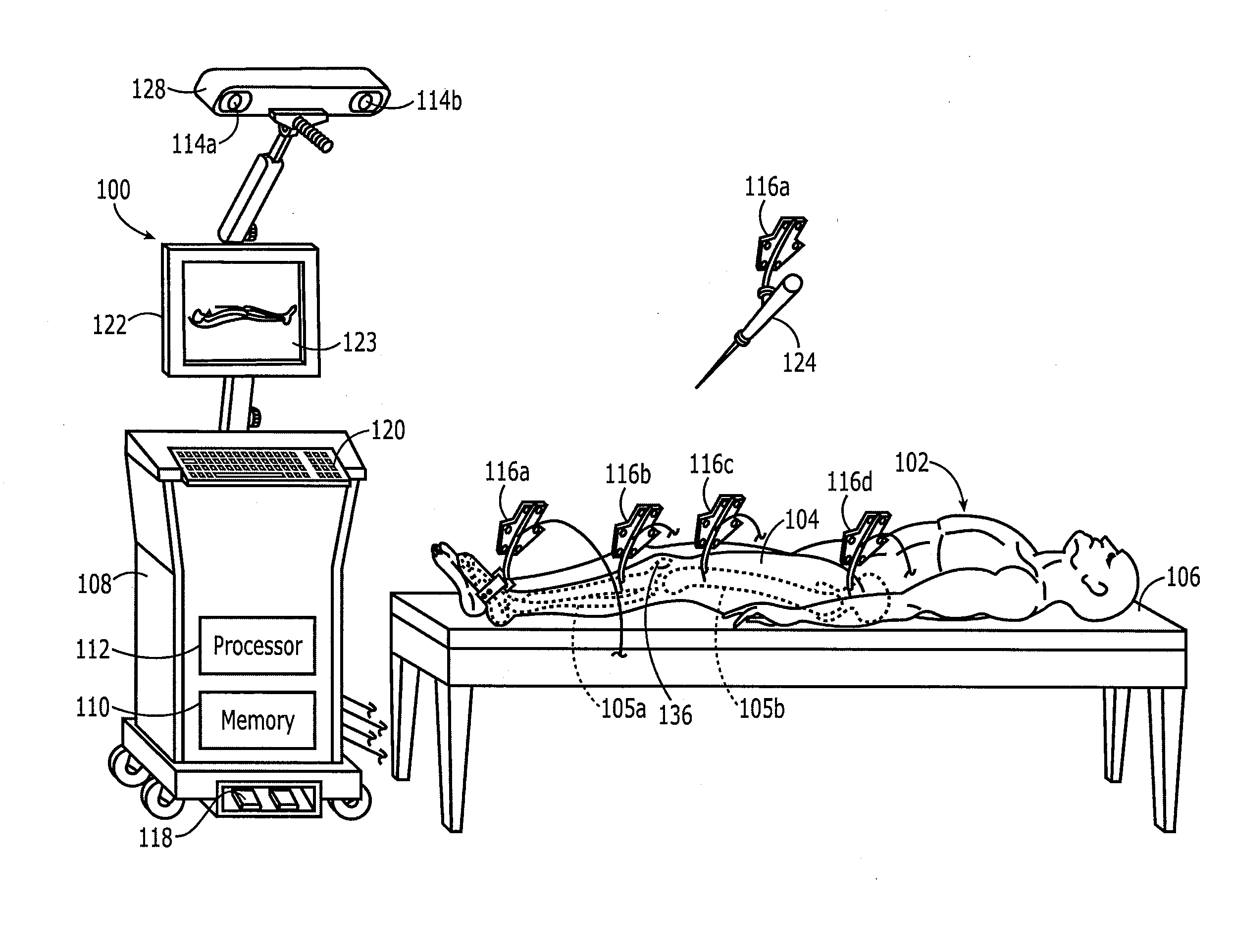
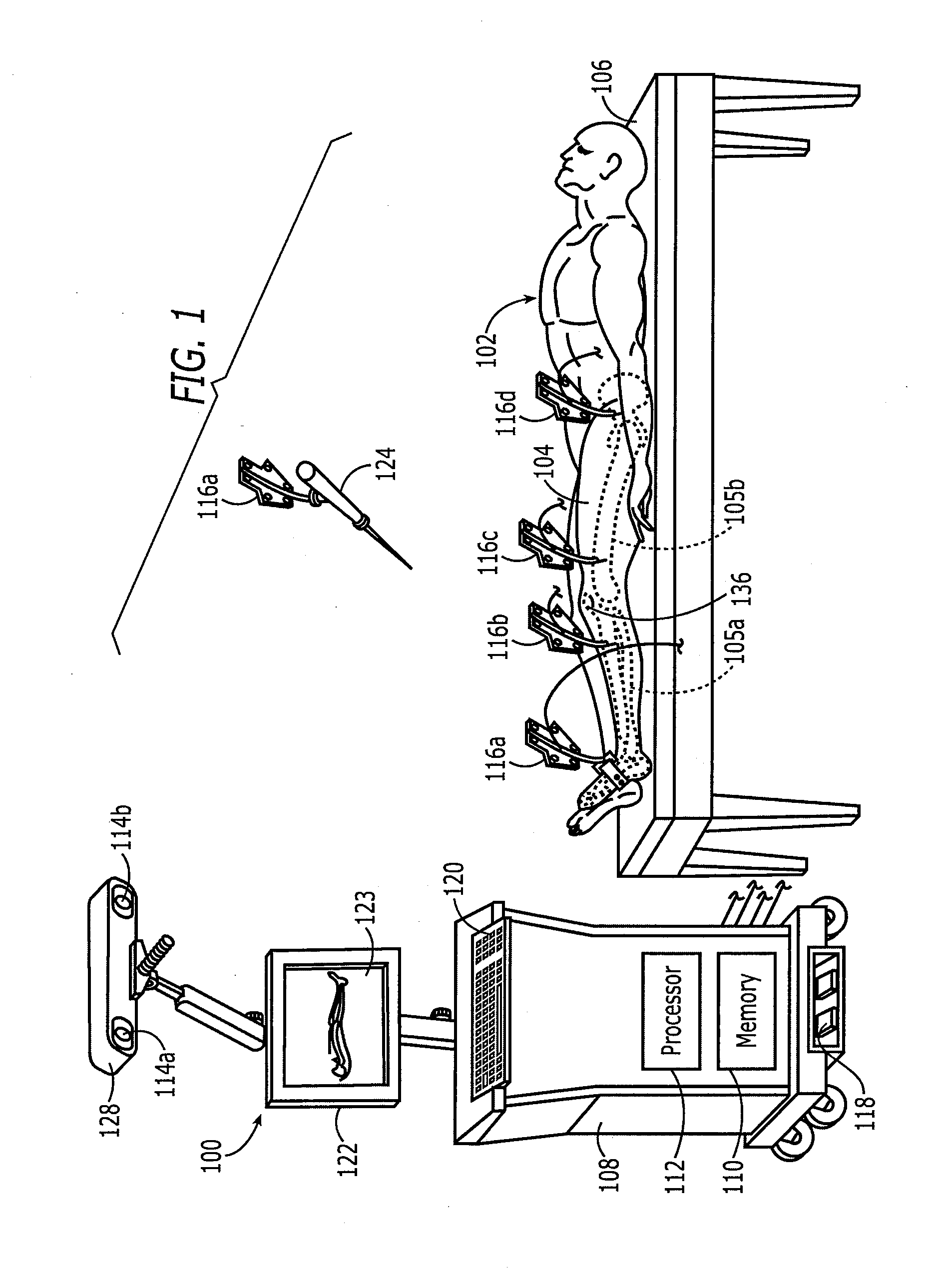
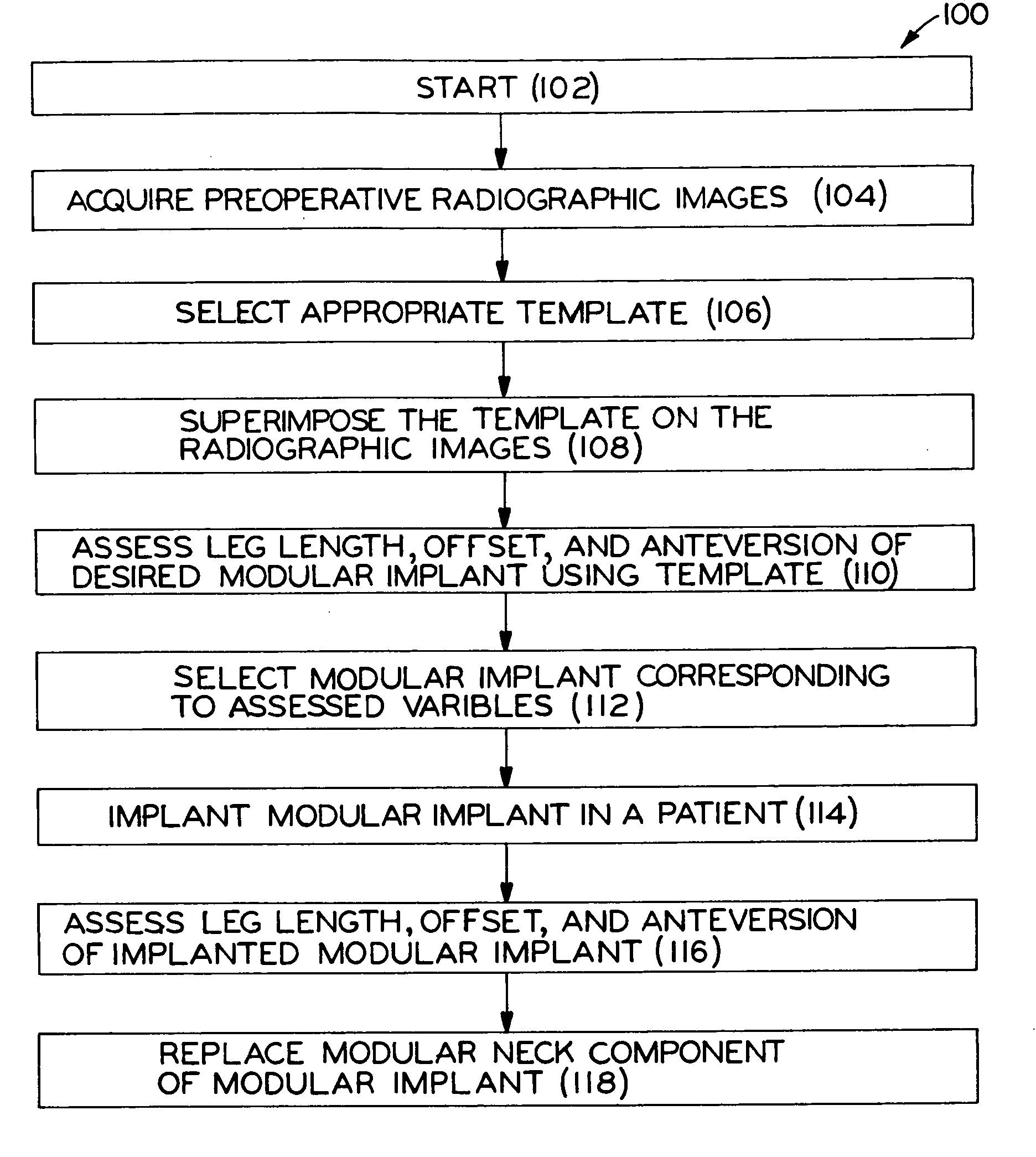
A method for selecting modular neck components for hip implants based on independent variables associated with physical characteristics of the implant, including leg length, offset, and anteversion. During surgery, the surgeon may be confronted with a need to change a preoperatively-chosen modular neck. For example, the surgeon may desire a change in at least one of the variables, e.g., leg length, offset, and / or anteversion. The present method allows the surgeon to quickly and easily select a different modular neck based on an evaluation of one of the variables without requiring reevaluation of the other variables. The method may include preoperative planning in which a template including a grid coordinate system is used.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
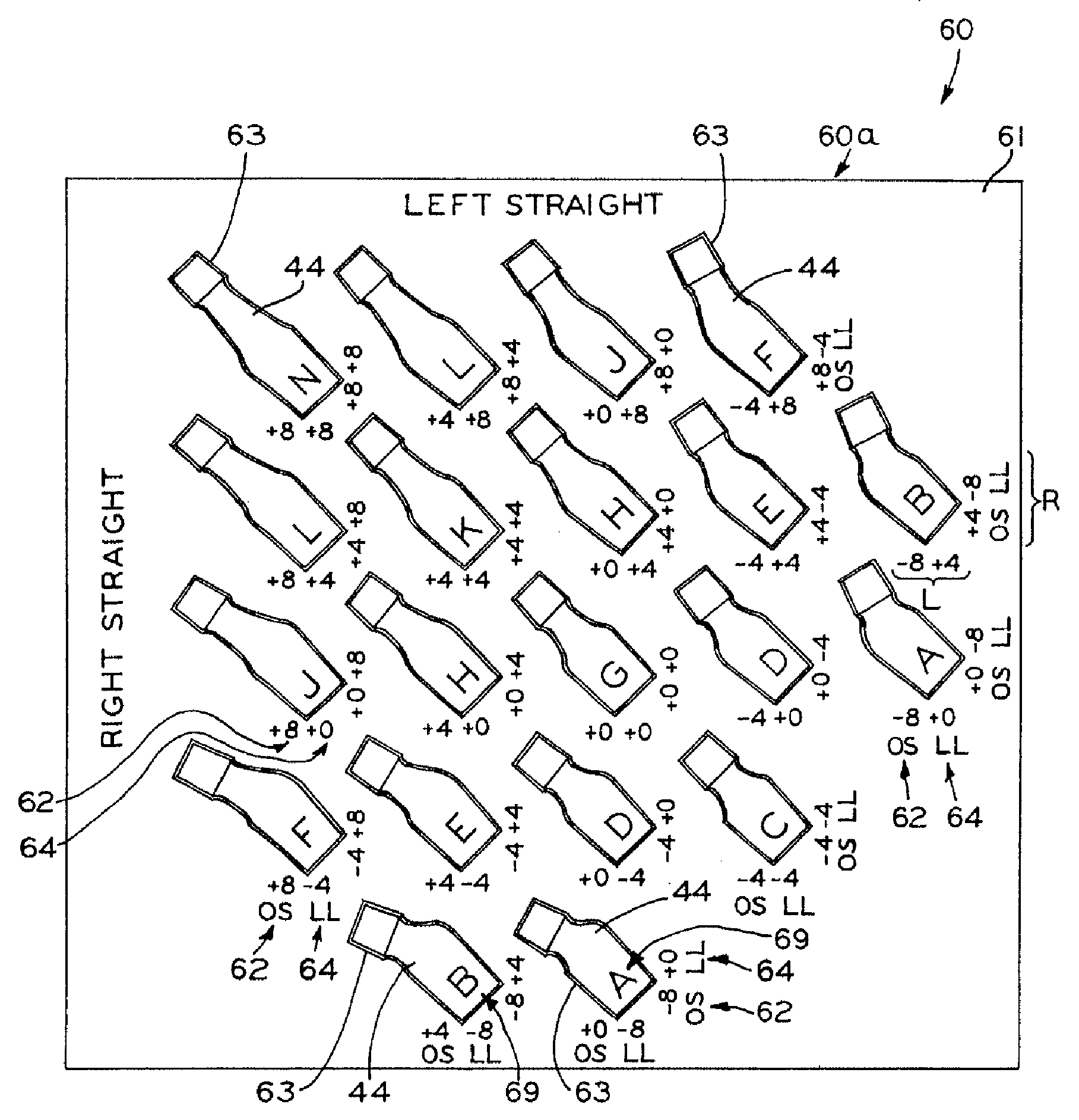
Modular orthopaedic component case
InactiveUS20080021567A1Easy and quick selectionProvide goodSurgical furnitureJoint implantsCoxal jointModularity
A case for modular neck components for hip implants. The case may include indicators based on independent variables associated with physical characteristics of the implant, including leg length, offset, and anteversion. During surgery, the surgeon may be confronted with a need to change a preoperatively-chosen modular neck. For example, the surgeon may desire a change in at least one of the variables, e.g., leg length, offset, and / or anteversion. The case allows the surgeon to quickly and easily select a different modular neck based on an evaluation of one of the variables without requiring reevaluation of the other variables. A method described herein may include preoperative planning in which a template including a grid coordinate system is used, which advantageously provides an intuitive system for the surgeon both preoperatively and during surgery.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
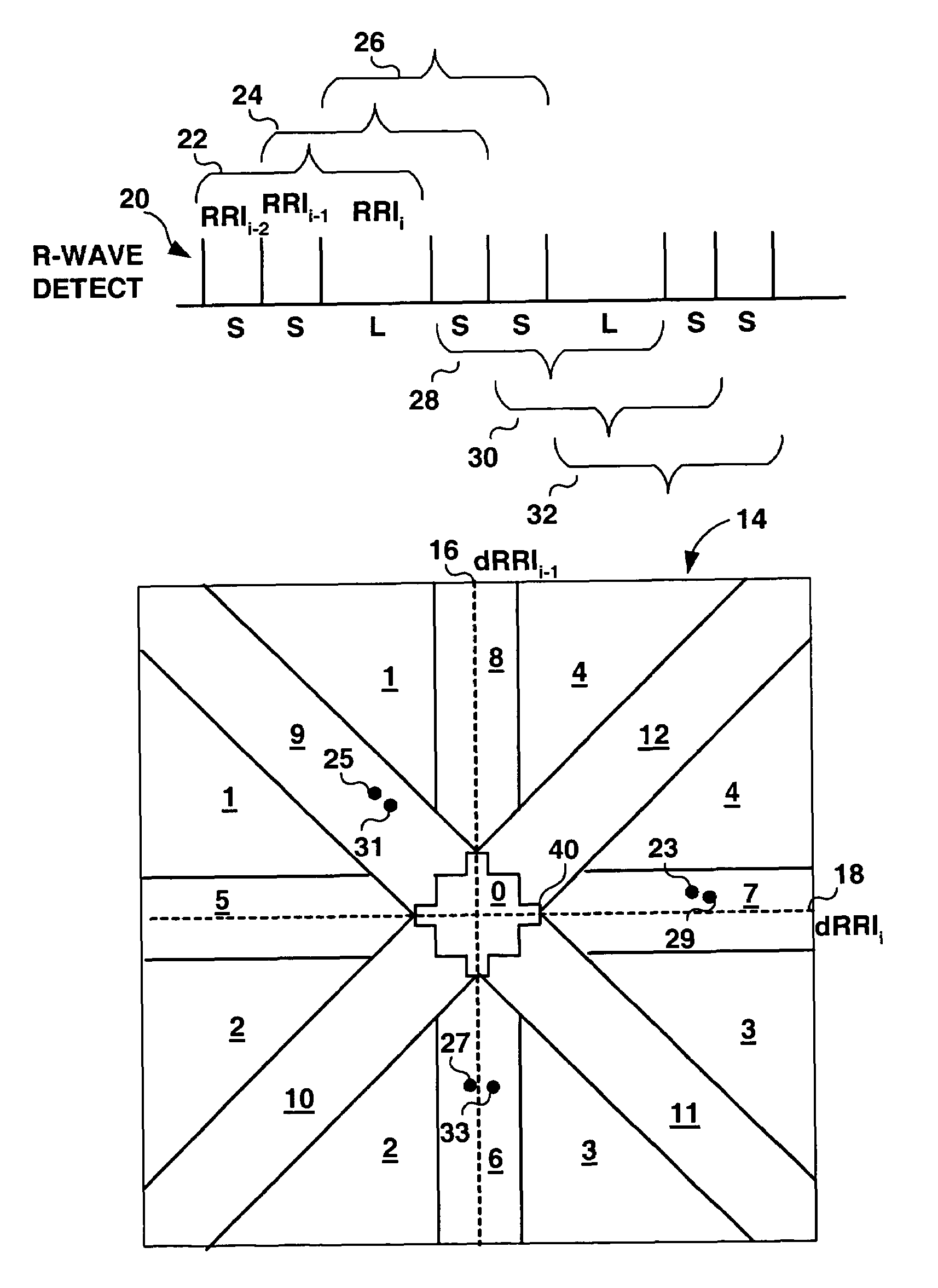
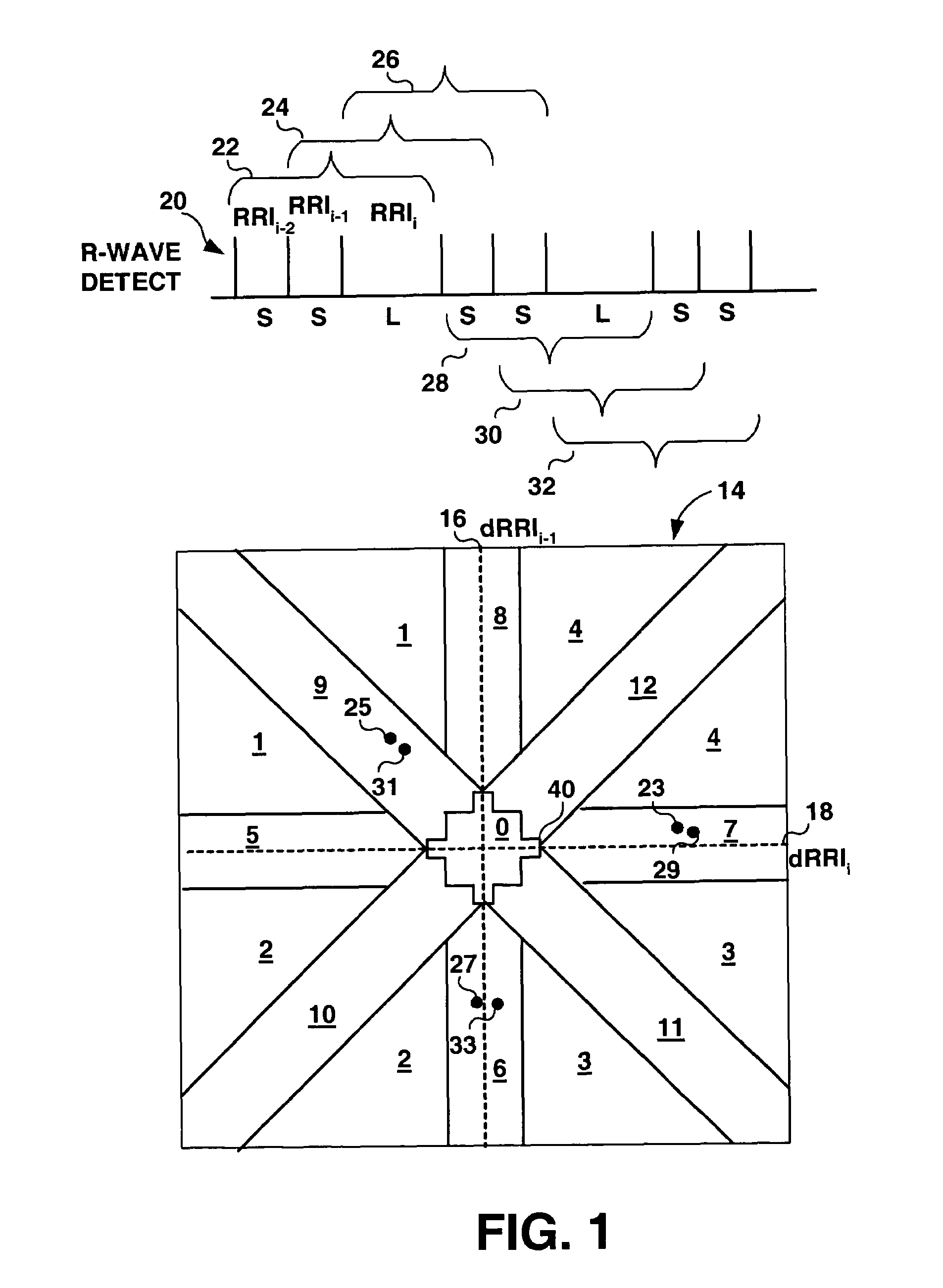
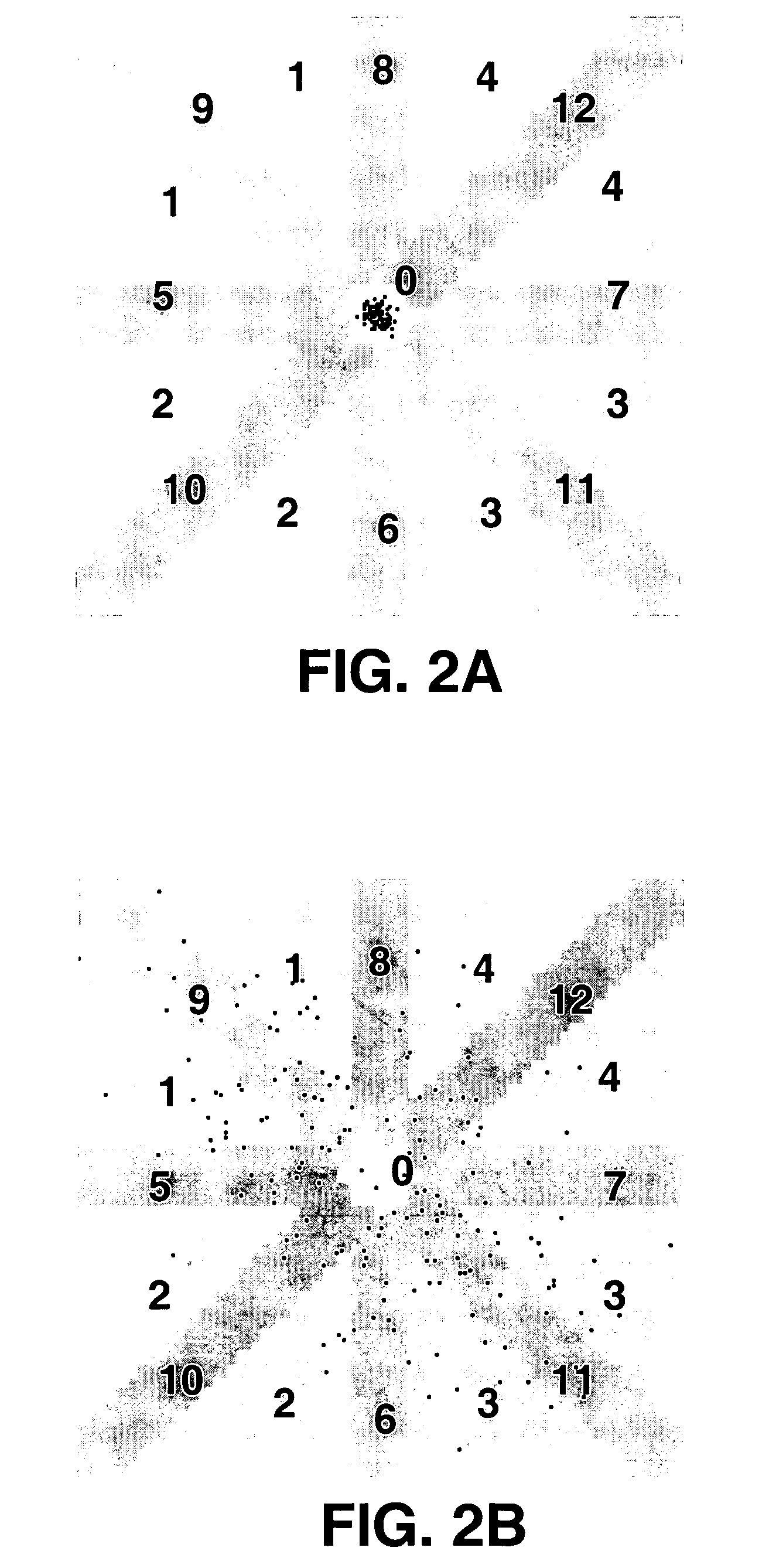
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
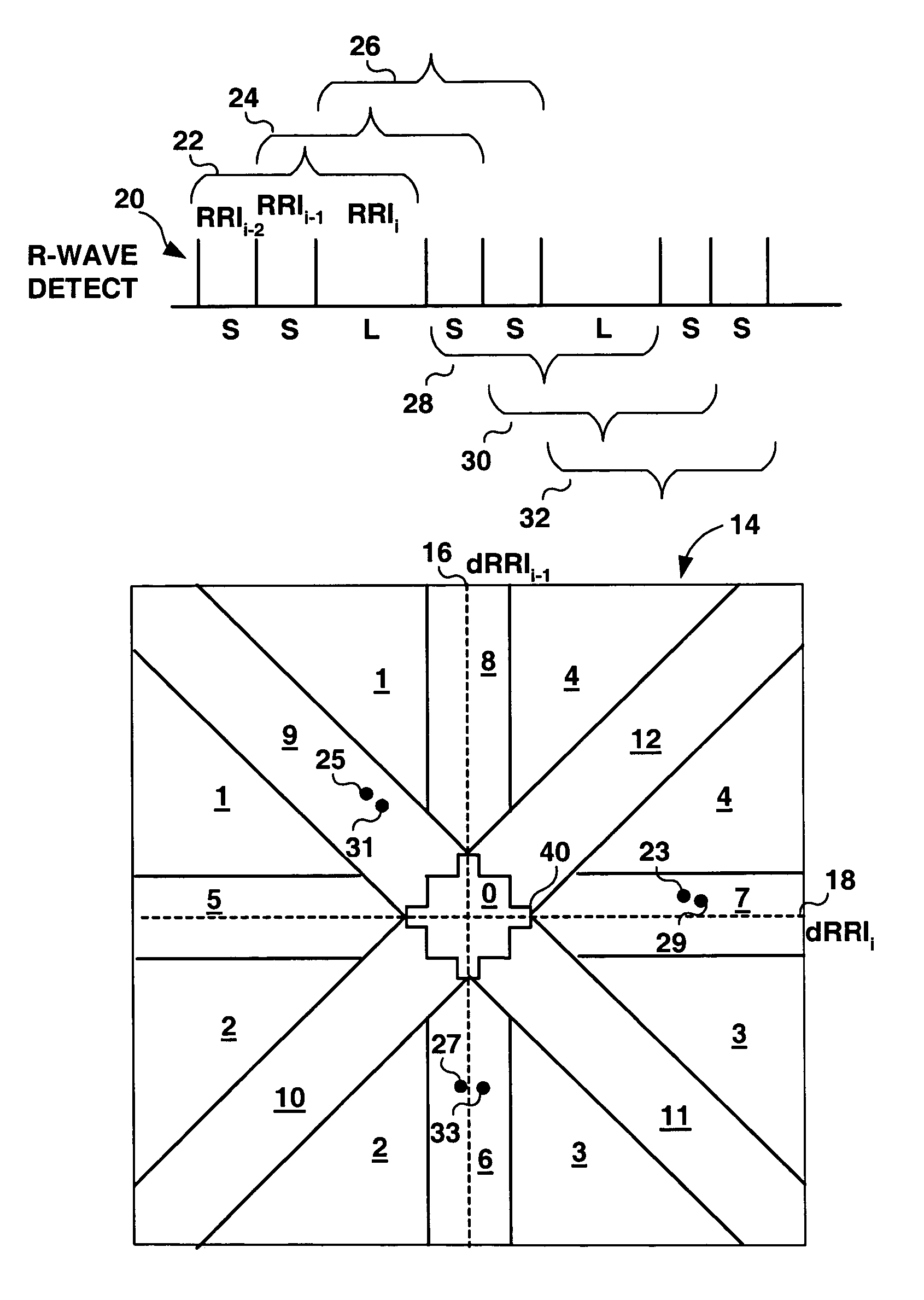
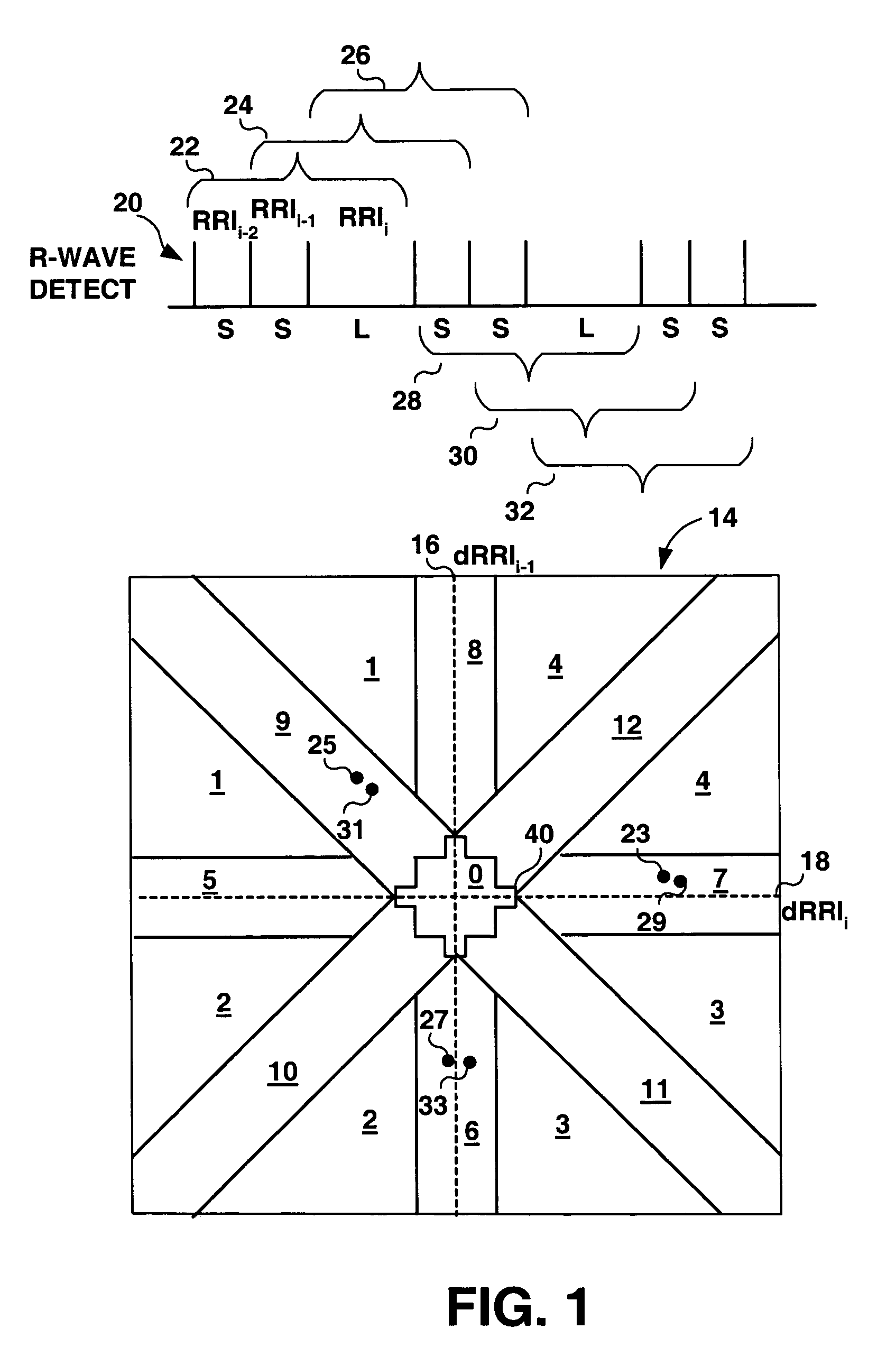
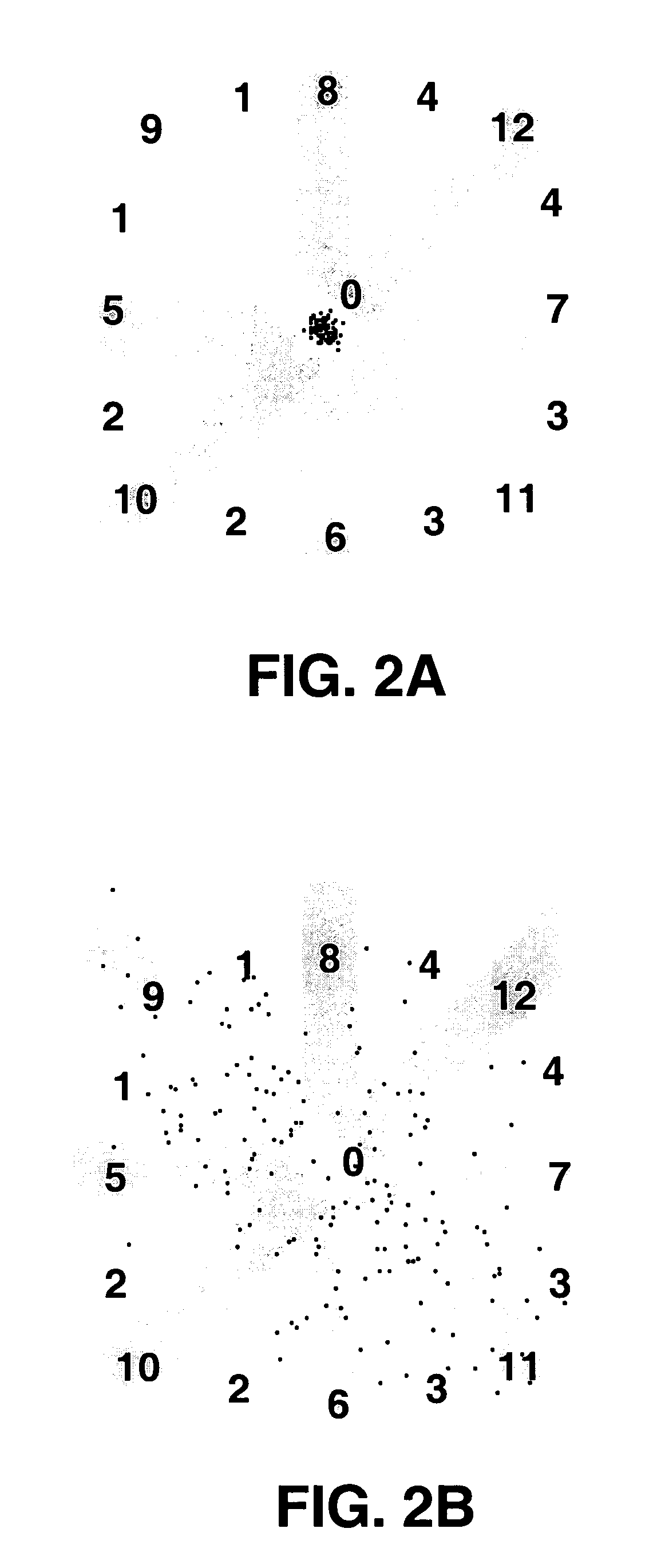
A method and apparatus for detecting atrial arrhythmias and discriminating atrial fibrillation (AF) and organized atrial tachycardia (OAT) that includes defining a threshold detection criteria for a cluster signature evidence metric corresponding to a Lorenz distribution of ventricular cycle lengths representative of AF or OAT. Using a signal containing VCL information, a number of consecutive ventricular cycle lengths are determined during a selected time interval for generating a one-dimensional or a two-dimensional histogram as a numerical representation of a Lorenz plot of VCLs. A number of cluster signature metrics are computed using the stored ventricular cycle length information, and a cluster signature evidence metric is computed from the cluster signature metrics. AF or OAT is detected if a comparative analysis of a corresponding cluster signature evidence metric meets a respective threshold detection criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
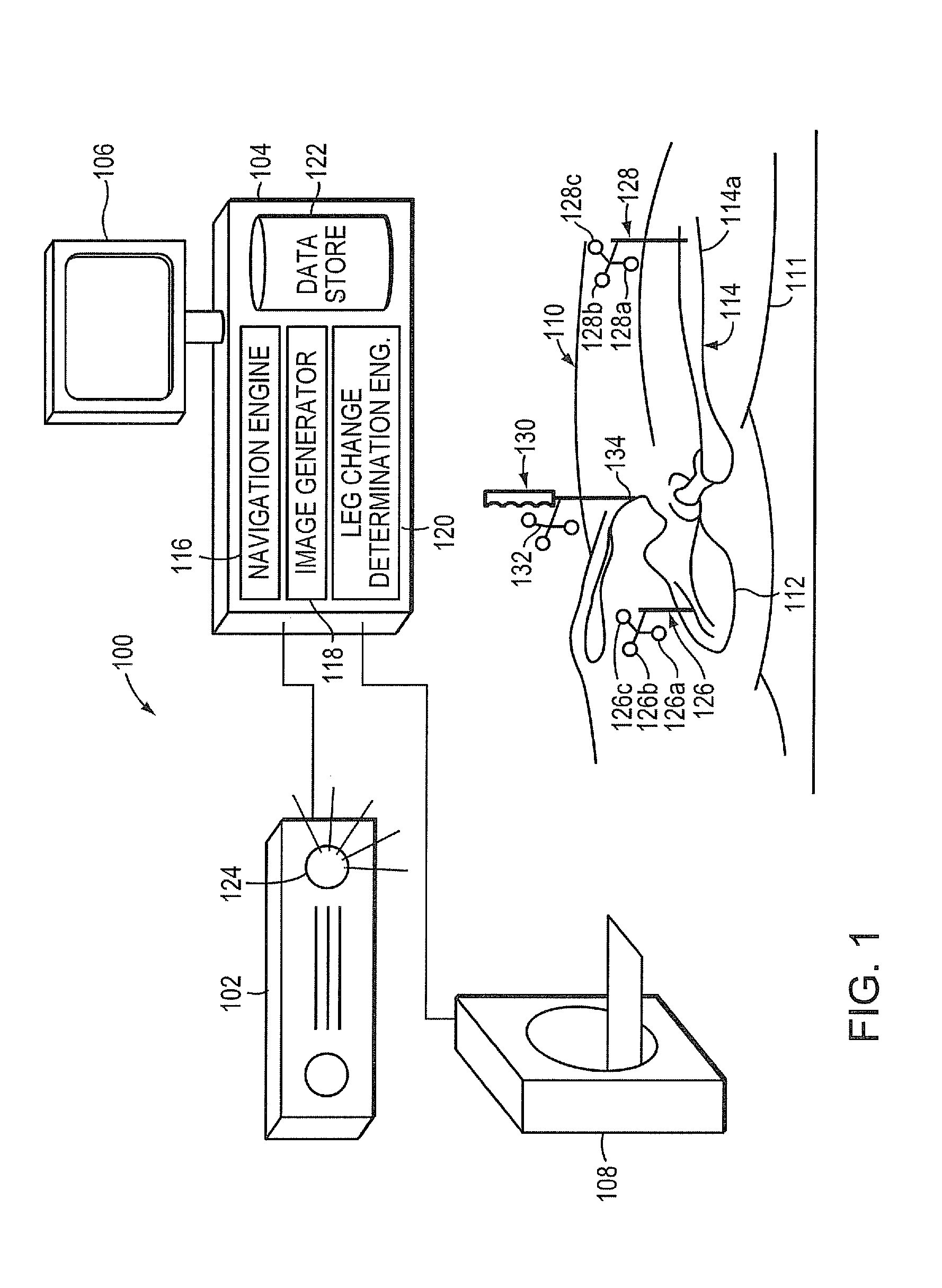
Hip implant registration in computer assisted surgery
ActiveUS20100261998A1Shorten the time to eliminateHigh precisionSurgical navigation systemsJoint implantsArray data structureCoxal joint
A computer assisted surgical navigation system and method is disclosed for registering the position of prosthetic hip joint components. Elements are applied to the pelvis and femur, generating a three-dimensional array. These two arrays combine to derive a reference point representing the native joint. A tracking device with a pre-determined shape and dimensions that precisely articulate with an acetabular cup component generates a third three-dimensional array. The device has a further shape and dimensions that independently articulate precisely with a neck portion of a femoral component, which represents a prosthetic joint center that is independently registered in the system. The tracking device concurrently registers the three dimensional positions of the femoral and acetabular prosthetic components, along with the prosthetic joint center and the native joint center, respectively enabling alterations in three dimensional location of the leg length and offset prior to reduction of the prosthetic joint.
Owner:BLUE ORTHO
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A multi-layer method for detecting atrial arrhythmias using ventricular cycle length information that includes performing a base layer algorithm for detecting the onset and offset of an atrial tachyarrhythmia. The multi-layer method further includes one or more higher layer algorithms executed in response to a base layer detection to confirm or reject the base layer detection. The base layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia and the higher layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity and high specificity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Individualizable convenience system for drivers
A method and system for automatically adjusting a driver seat, steering wheel, pedals, mirrors, and other components of a vehicle, based on information about the size of the driver. The method uses basic information about the driver's size—including standing height, sitting height, and gender—in a model which estimates all anthropometric data for the driver. The anthropometric data for the driver—including upper and lower arm and leg lengths, torso length, and other dimensions—is used in inverse kinematic calculations to determine optimal positions and orientations for the adjustable components of the vehicle's cockpit. The method then pre-adjusts the components before the driver enters the vehicle, and makes compatible adjustments to the mirrors and other components if the driver adjusts the driver seat.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
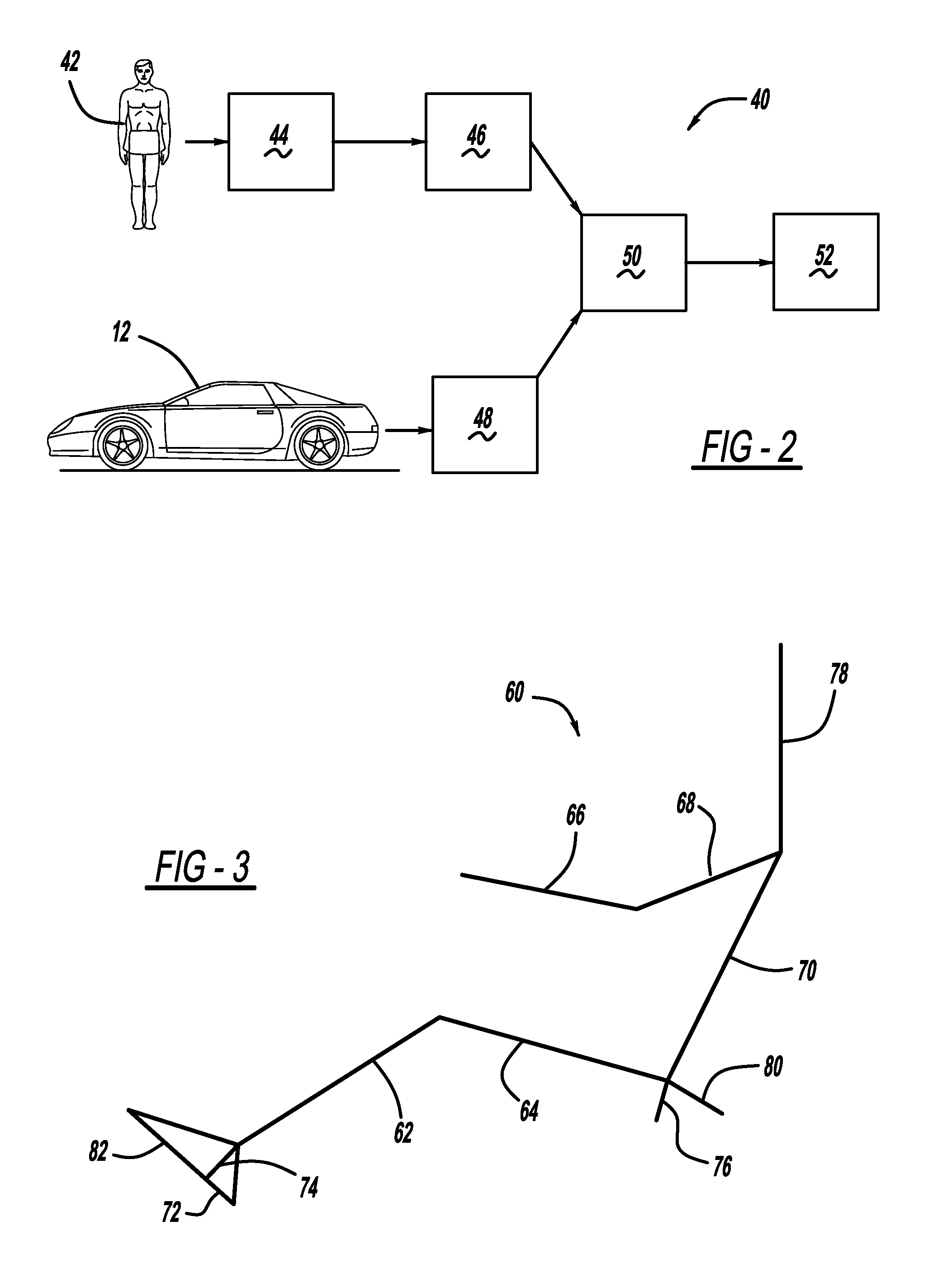
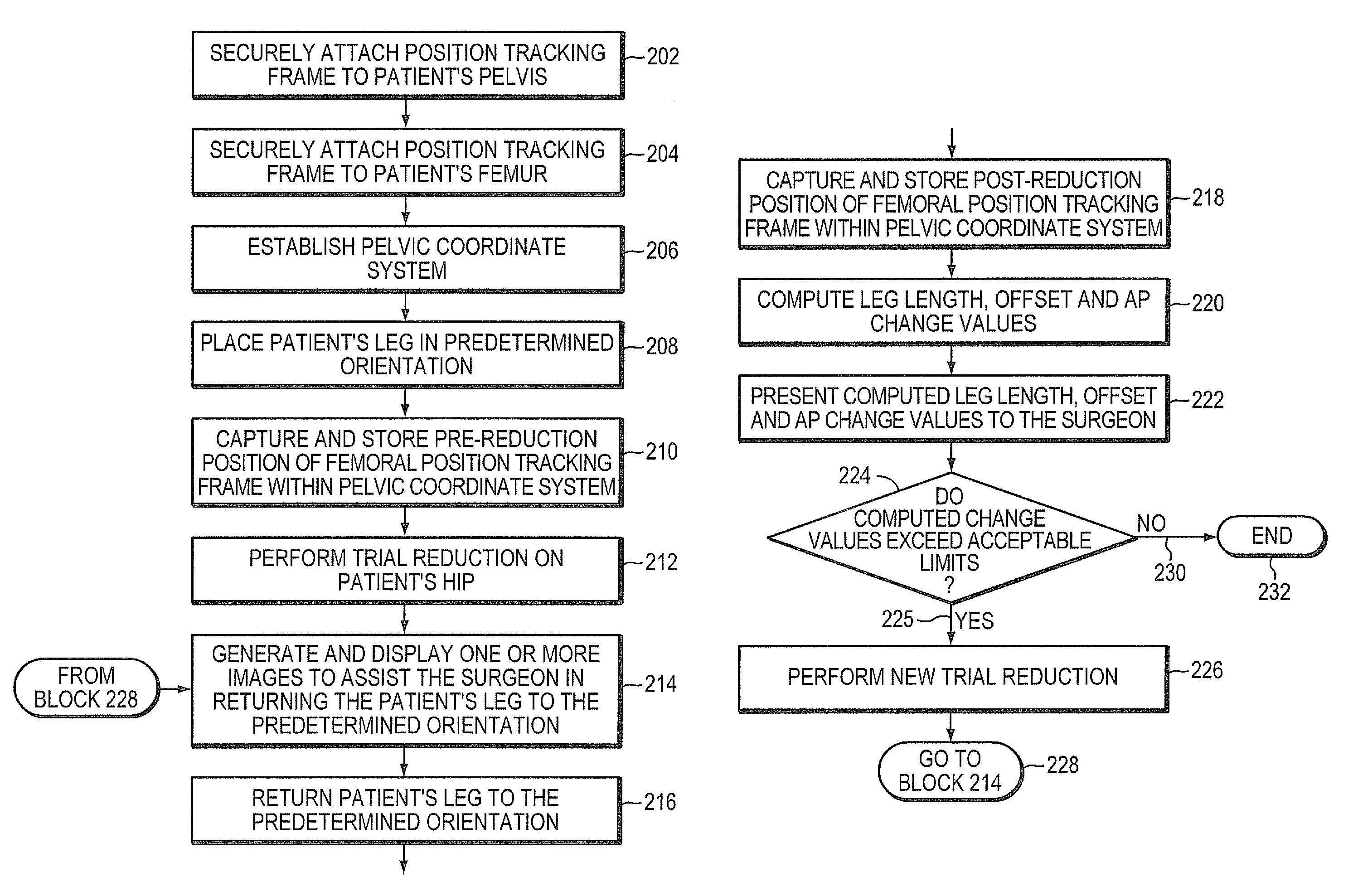
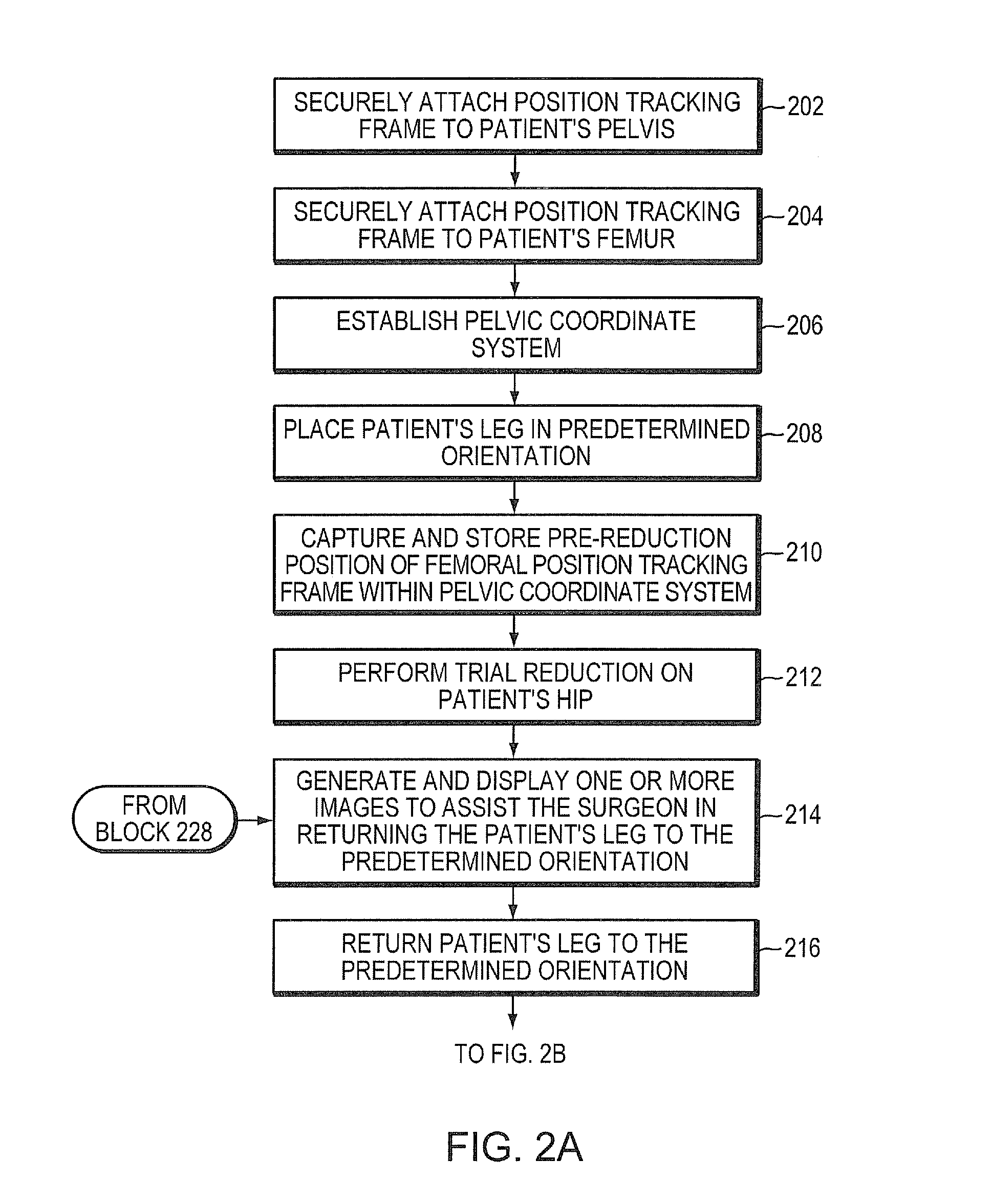
System and method for facilitating hip surgery
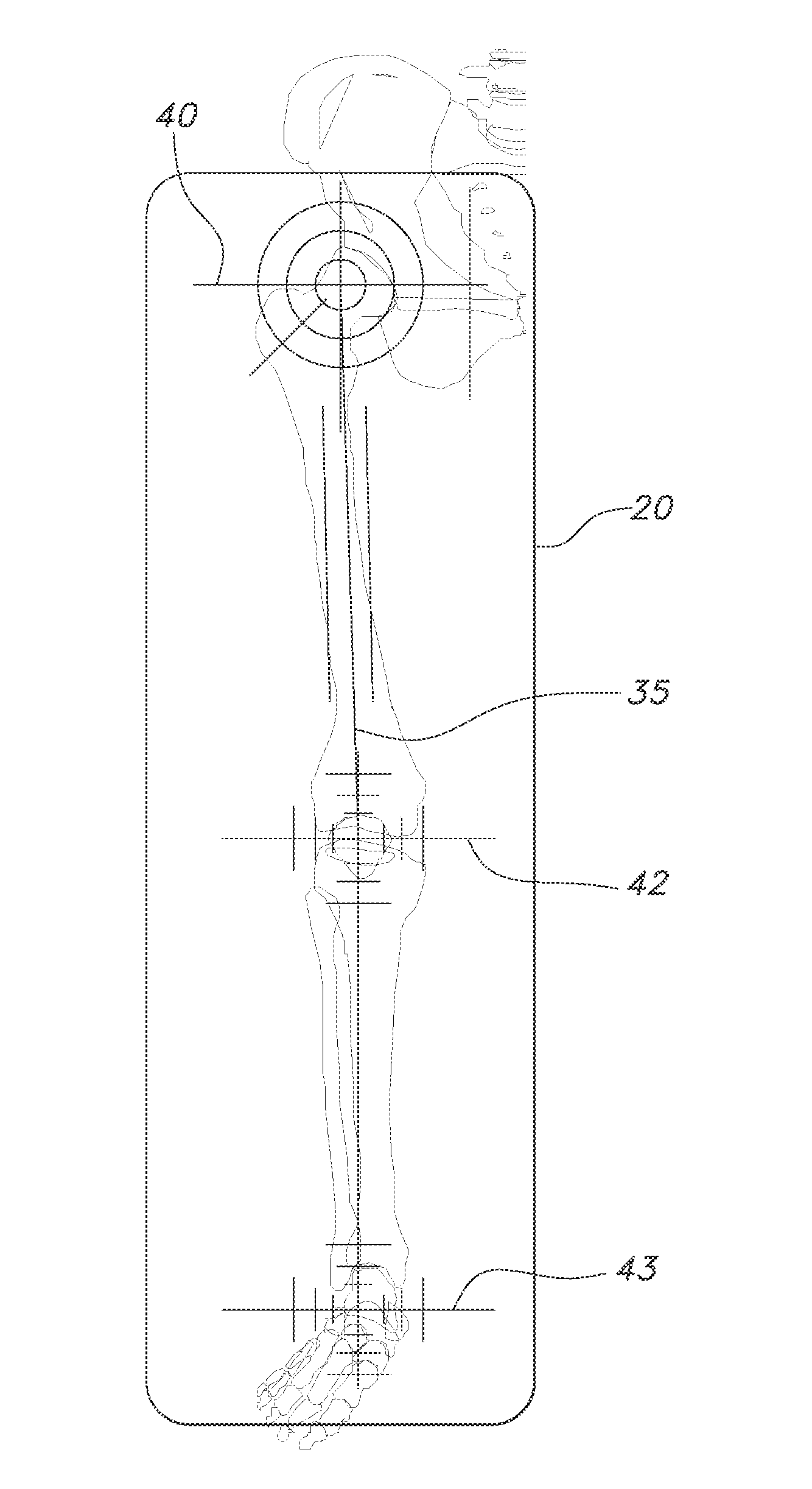
ActiveUS7885705B2Simplifying and reducing timeMeasurement devicesSurgical navigation systemsLeg lengthPelvis
A system and method for use during hip surgery includes a position frame that is removably secured to the patient's femur. The system further includes a tracking unit and navigation engine that establish a pelvic coordinate system and, with the patient's leg placed in a predetermined orientation, capture the location of the femoral position frame within the pelvic coordinate system. The system further includes an image generator configured to display one or more images for directing the surgeon to return the patient's leg to the predetermined orientation following a trial reduction based upon the previously captured position. A leg change determination engine compares the current, post-reconstruction position of the femoral position tracking frame with the previously captured, pre-reconstruction position to derive leg length, offset, and anterior-posterior change values. The change values are then provided to the surgeon for evaluating the suitability of the trial reduction.
Owner:MURPHY STEPHEN B
Viscous oil inflow control device for equalizing screen flow
A flow balancing system for long screen sections particularly useful in high viscosity hydrocarbon production features an annular flow path whose height and length can be varied to provide a predetermined resistance to a given flow rate of a material of a given viscosity. In assembling a long length of screen sections, greater resistance configurations are placed closer to the wellhead end of the screen section with the more remote sections having progressively less restriction until the furthest section of the screen string where low or no resistance to flow internally to the screen section is offered.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A multi-layer method for detecting atrial arrhythmias using ventricular cycle length information that includes performing a base layer algorithm for detecting the onset and offset of an atrial tachyarrhythmia. The multi-layer method further includes one or more higher layer algorithms executed in response to a base layer detection to confirm or reject the base layer detection. The base layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia and the higher layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity and high specificity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Long length imaging using digital radiography
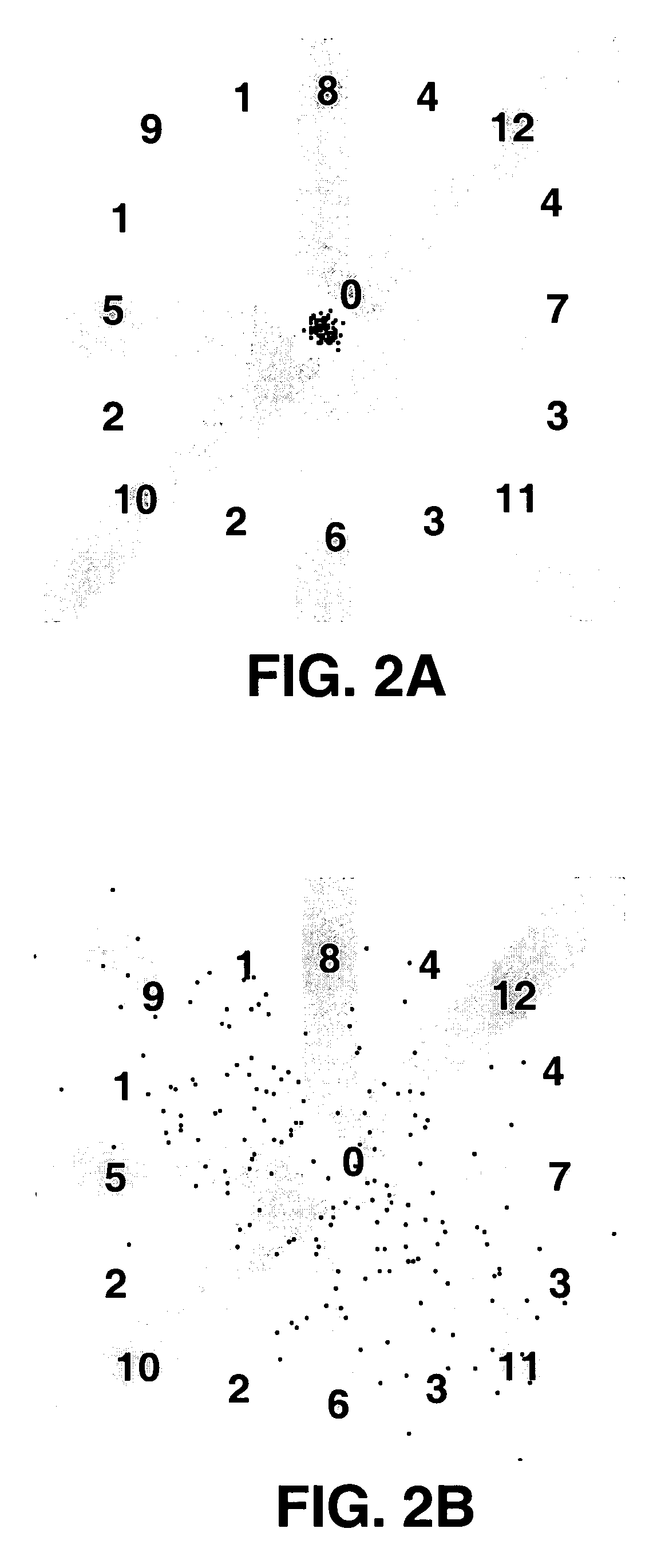
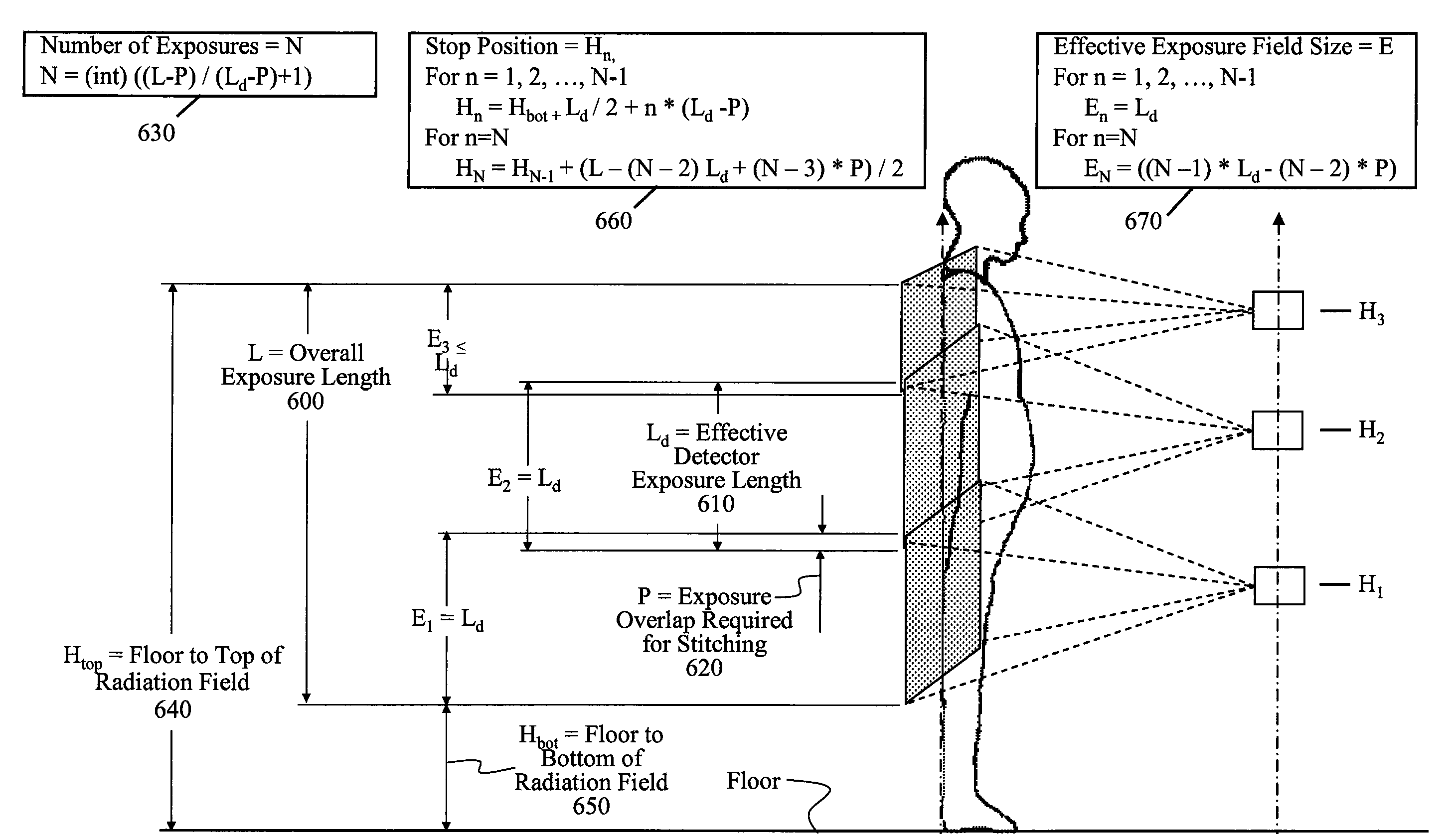
InactiveUS7555100B2Reduce needSimplifies the long length imaging processTelevision system detailsTomographyLeg lengthDigital radiography
A method for long length imaging with a digital radiography apparatus. Setup instructions are obtained for the image and a set of imaging positions is calculated for an exposure series according to the setup instructions. An operator command is obtained to initiate an imaging sequence. The imaging sequence is executed for each member of the set of imaging positions in the exposure series by automatically repeating the steps of positioning a radiation source and a detector at a location corresponding to the specified member of the set of imaging positions and obtaining an image from the detector at that location and storing the image as a partial image. The long length image is generated by combining two or more partial images.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Vertical fore grip with bipod
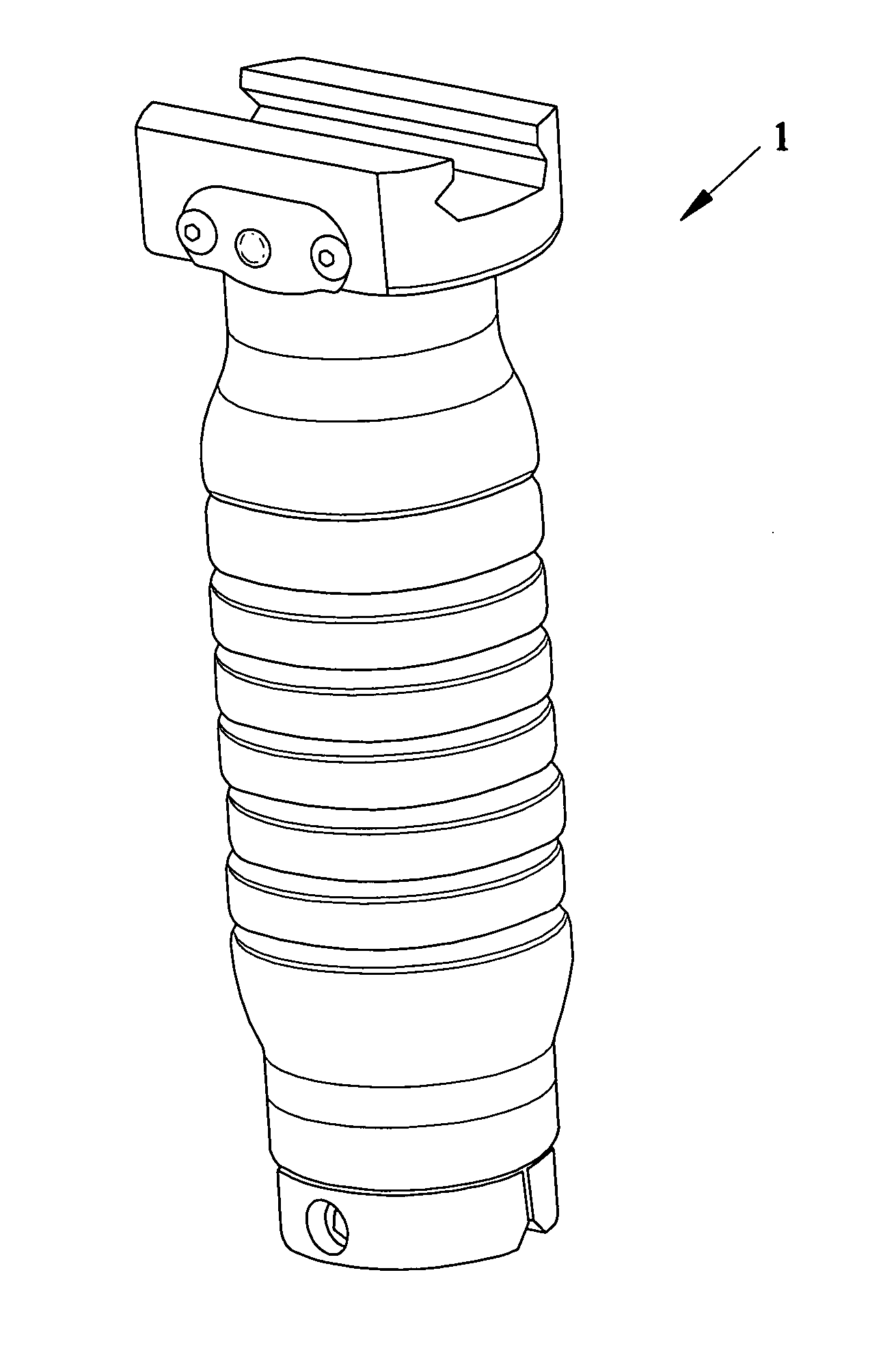
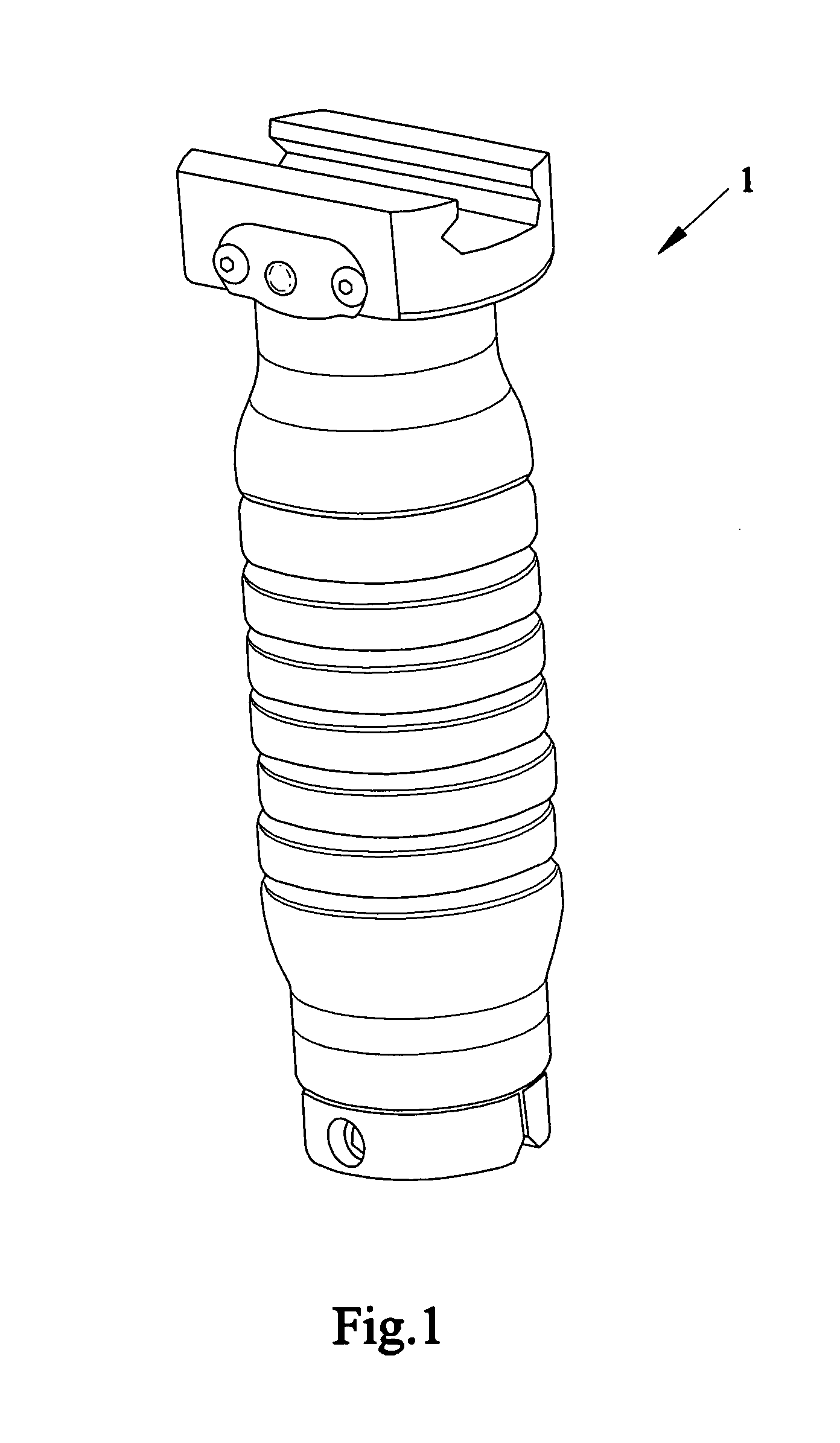
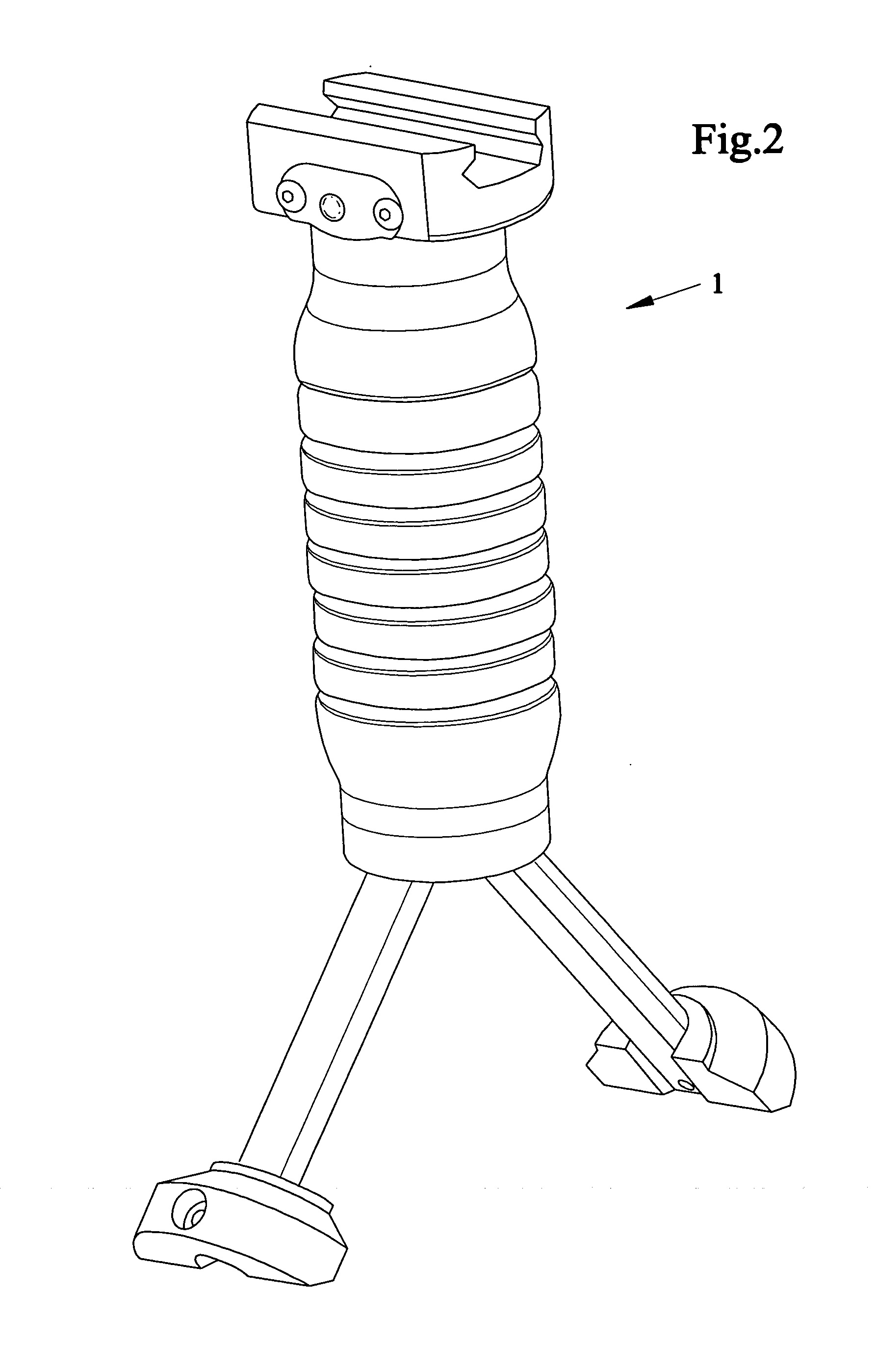
ActiveUS20060277809A1Self containedSimple attachmentAmmunition loadingStands/trestlesTerrainLeg length
Devices, systems and methods of using an ergonomic fore grip / gun handle with a concealable and collapsible bipod. One version can have a tubular recess consisting of a first cylindrical cutout housing the bipod legs when concealed and a sliding piston that deploys the legs and a second cylindrical cutout housing a release mechanism and a void space for other accessories. The release mechanism has a compression spring positioned between the piston assembly and the bottom of the first cylindrical cutout and the compression spring. The legs are connected to the bottom of the piston assembly via a hinge and spring that when released from confinement within the fore grip, causes the legs to expand outward until fully deployed. Telescoping legs allow adjustment of leg length for use on uneven terrain. The grip portion has an outer surface with a flat surface on sides of the grip to provide a more stable grip, assist in orienting the mounted weapon and support pressure pads for lights.
Owner:GRIP POD SYST INT
Method and apparatus for limiting growth of eye length
ActiveUS20110313058A1Prevent and ameliorate and reverse effectInhibiting further degradation of visionBiocideSenses disorderProbable CaseLeg length
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN
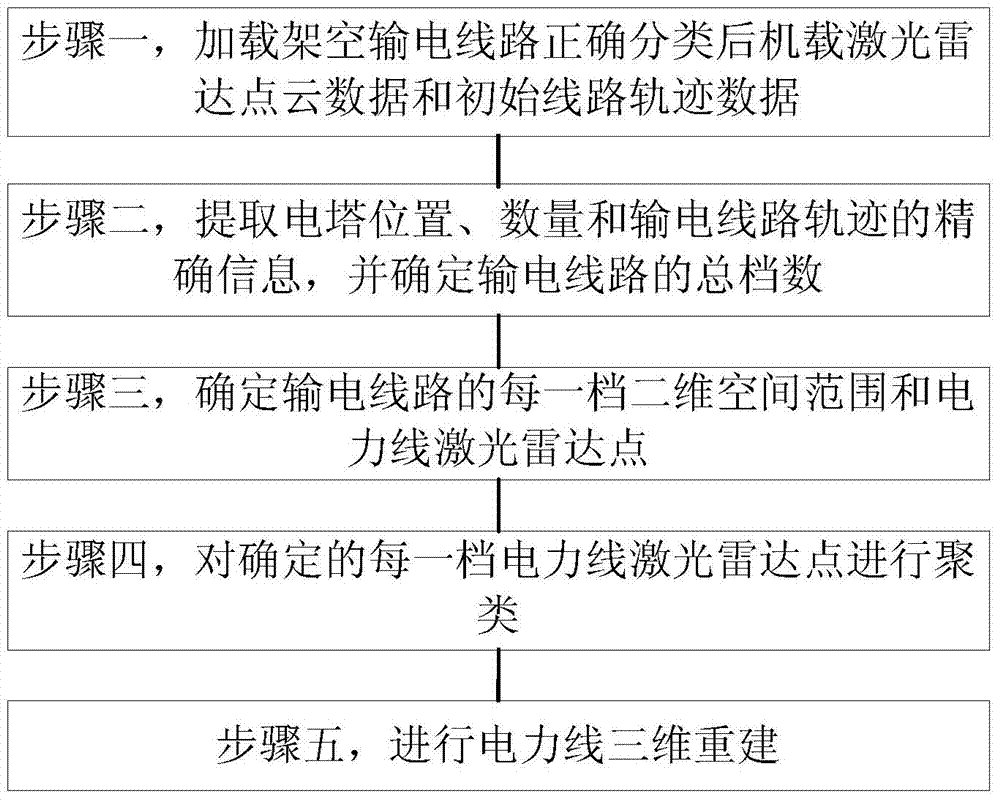
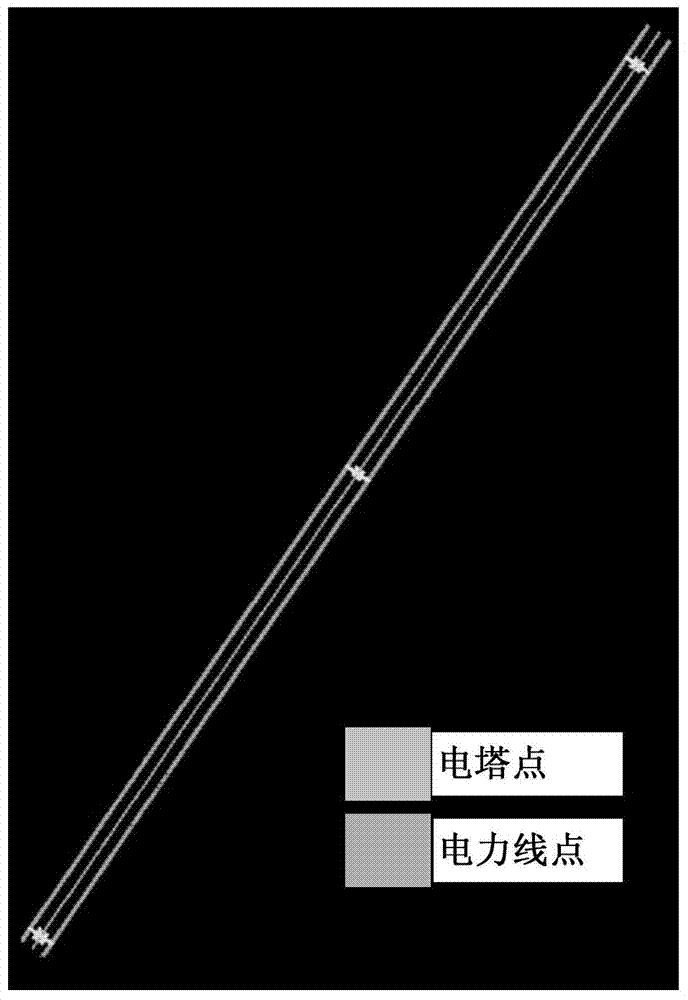
Power line three-dimensional reconstructing method based on airborne laser radar point cloud
InactiveCN104732588AHigh precisionImprove reconstruction accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiation3D modellingElectric powerLine length
The invention discloses a power line three-dimensional reconstructing method based on airborne laser radar point cloud. Data of the airborne laser radar point cloud have been correctly classified. The method includes the following steps: 1, loading the correctly-classified data of the airborne laser radar point cloud and initial line track data of an overhead transmission line; 2, extracting accurate information of the positions and the number of electric towers and the track of the power transmission line, and determining the total number of spans of the power transmission line; 3, determining the two-dimensional space range and power line laser radar points of each span of the power transmission line; 4, clustering the determined power line laser radar points of the spans; 5, carrying out power line three-dimensional reconstruction. According to the power line three-dimensional reconstructing method, the number of required parameters is small, the automation degree is high, robustness and universality are better, and the power line three-dimensional reconstructing method has the advantage of being insensitive to the factors such as the number of power lines, the types of the power lines, the power line space arrangement structure, gross error points, point-cloud irregular breaking and the line length; in addition, a reconstruction model has the high reconstruction accuracy.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
Pedal stroke adjuster for bicycles or the like
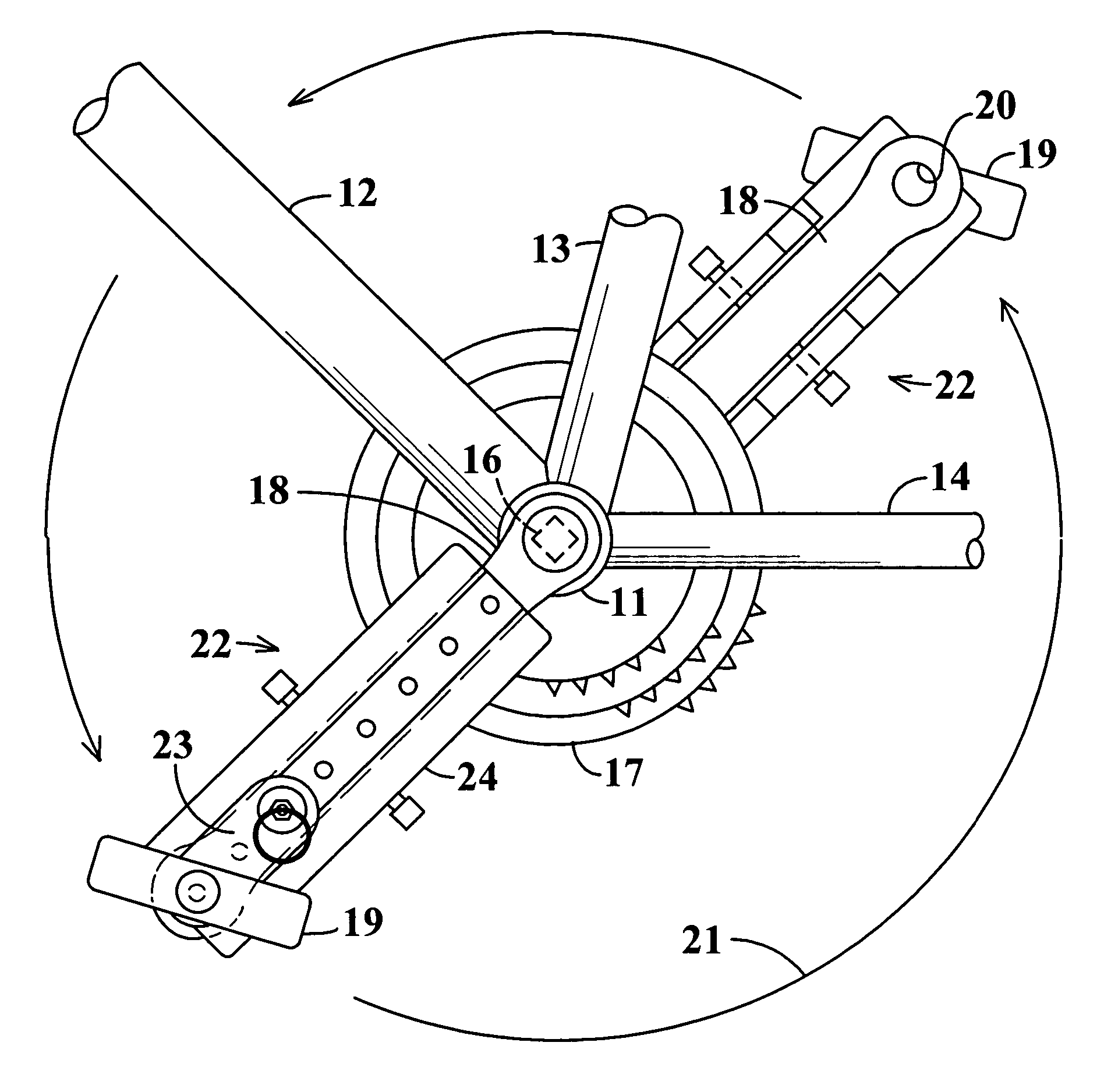
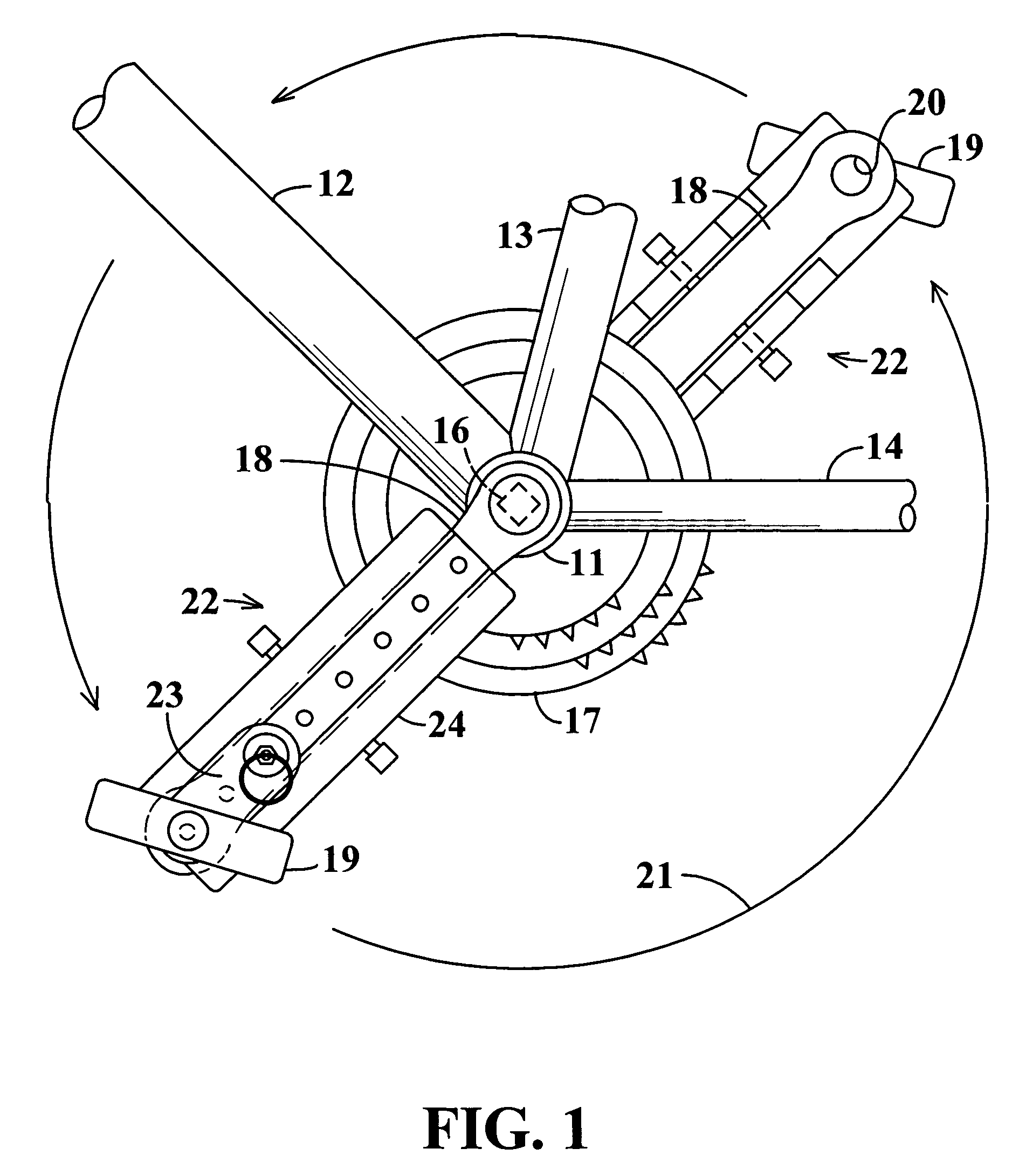
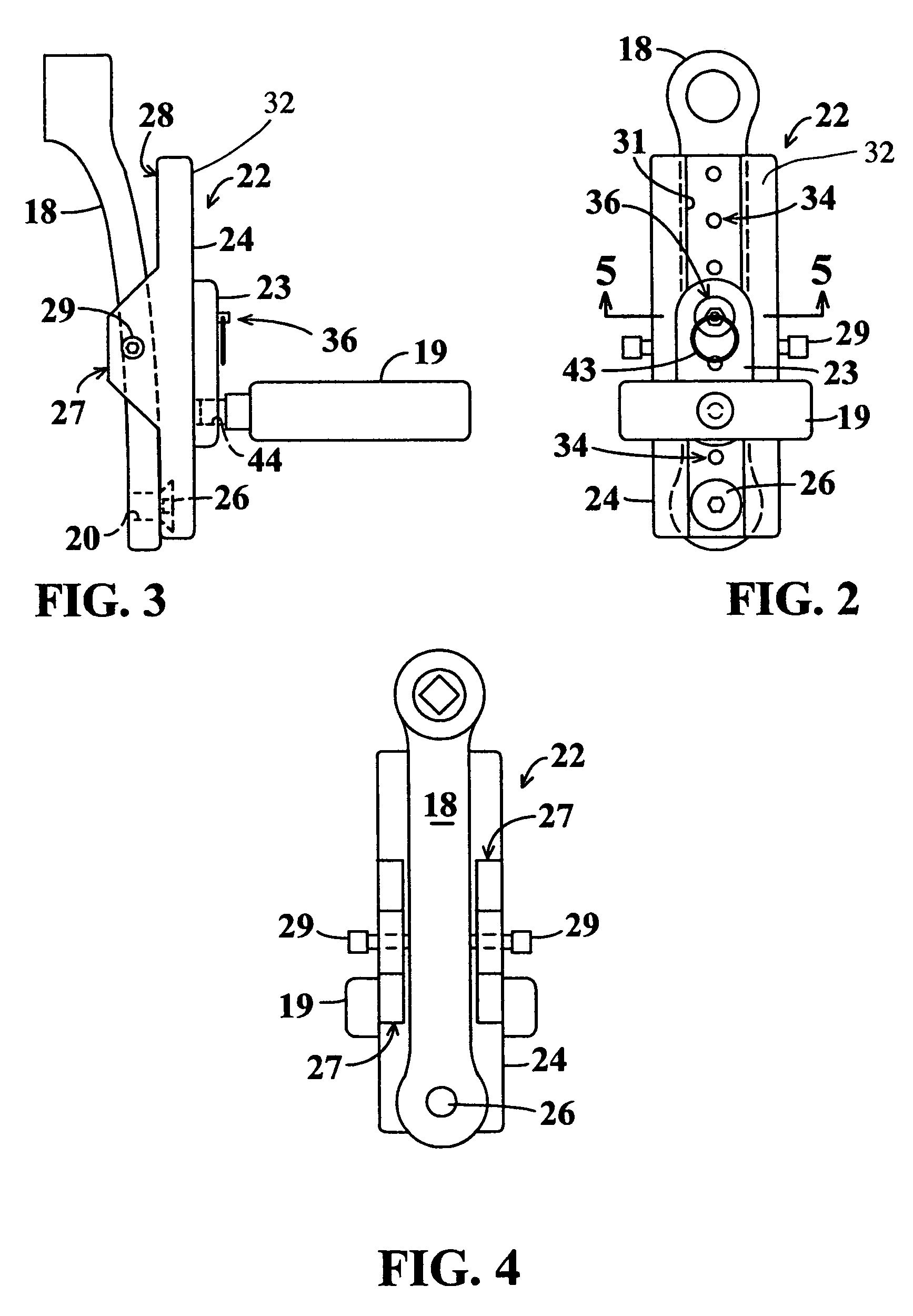
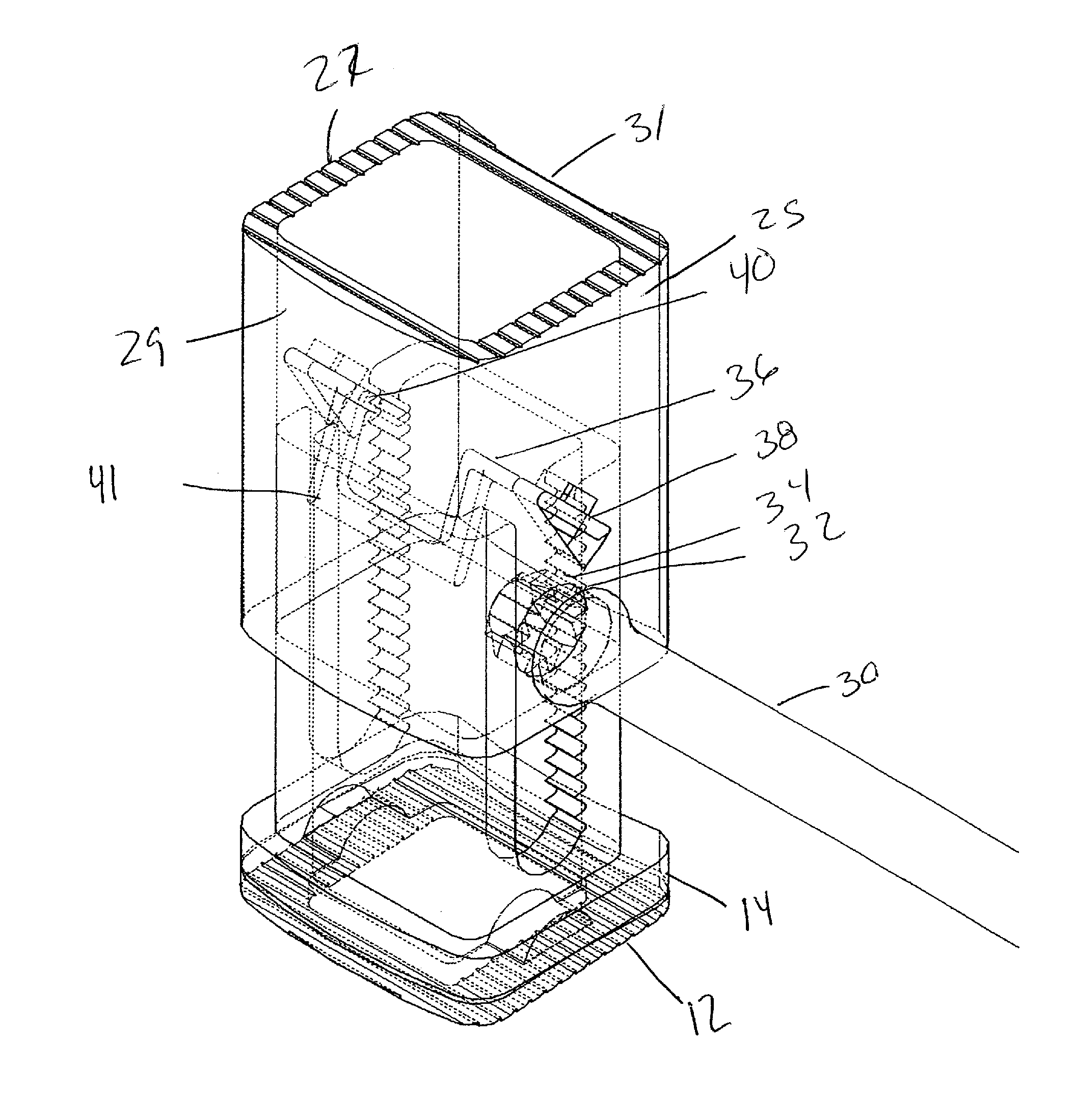
InactiveUS7204788B2Easy to processImprove distributionControlling membersMechanical apparatusLeg lengthEngineering
Owner:ANDREWS RONALD A
Expandable corpectomy device
The instant invention is a longitudinally adjustable corpectomy device which fits within the intervertebral distracted channel. A ratchet mechanism allows for an extendable member to adjust to a longer length to accommodate a distracted channel. The ratchet type mechanism allows the members to move in a unidirectional movement to prevent the two members from contracting once expanded.
Owner:ATLAS SPINE
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A method and apparatus for detecting atrial arrhythmias and discriminating atrial fibrillation (AF) and organized atrial tachycardia (OAT) that includes defining a threshold detection criteria for a cluster signature evidence metric corresponding to a Lorenz distribution of ventricular cycle lengths representative of AF or OAT. Using a signal containing VCL information, a number of consecutive ventricular cycle lengths are determined during a selected time interval for generating a one-dimensional or a two-dimensional histogram as a numerical representation of a Lorenz plot of VCLs. A number of cluster signature metrics are computed using the stored ventricular cycle length information, and a cluster signature evidence metric is computed from the cluster signature metrics. AF or OAT is detected if a comparative analysis of a corresponding cluster signature evidence metric meets a respective threshold detection criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
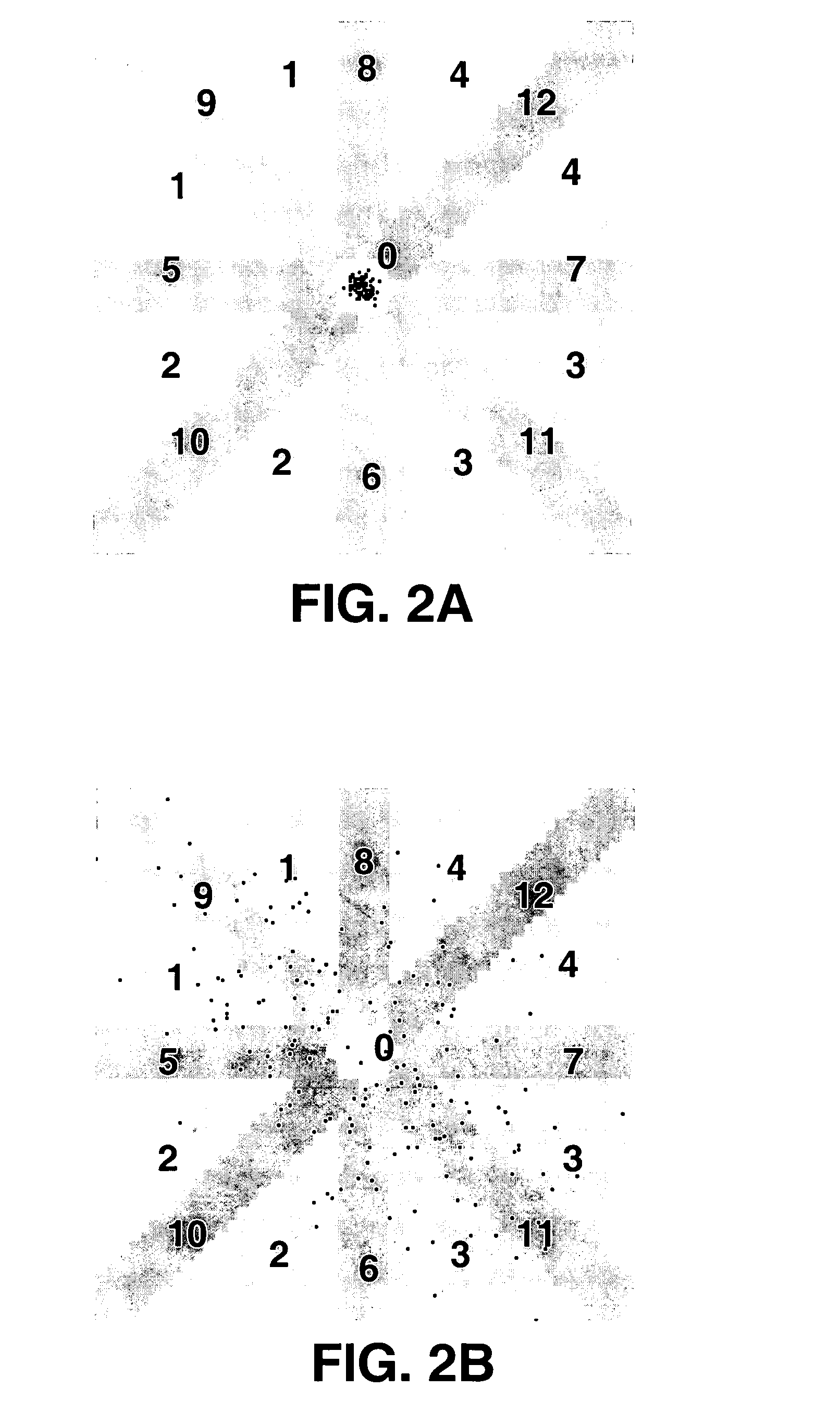
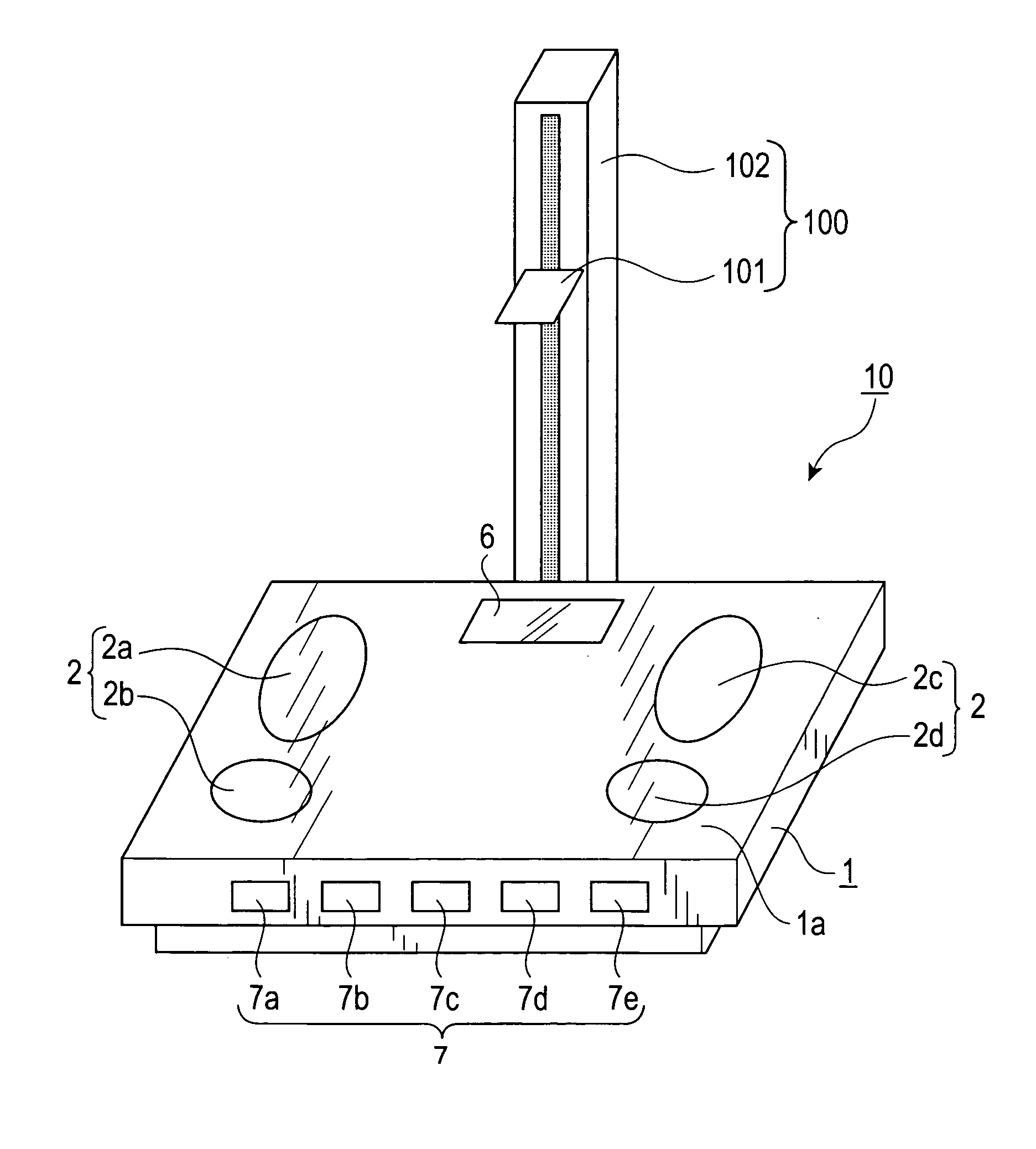
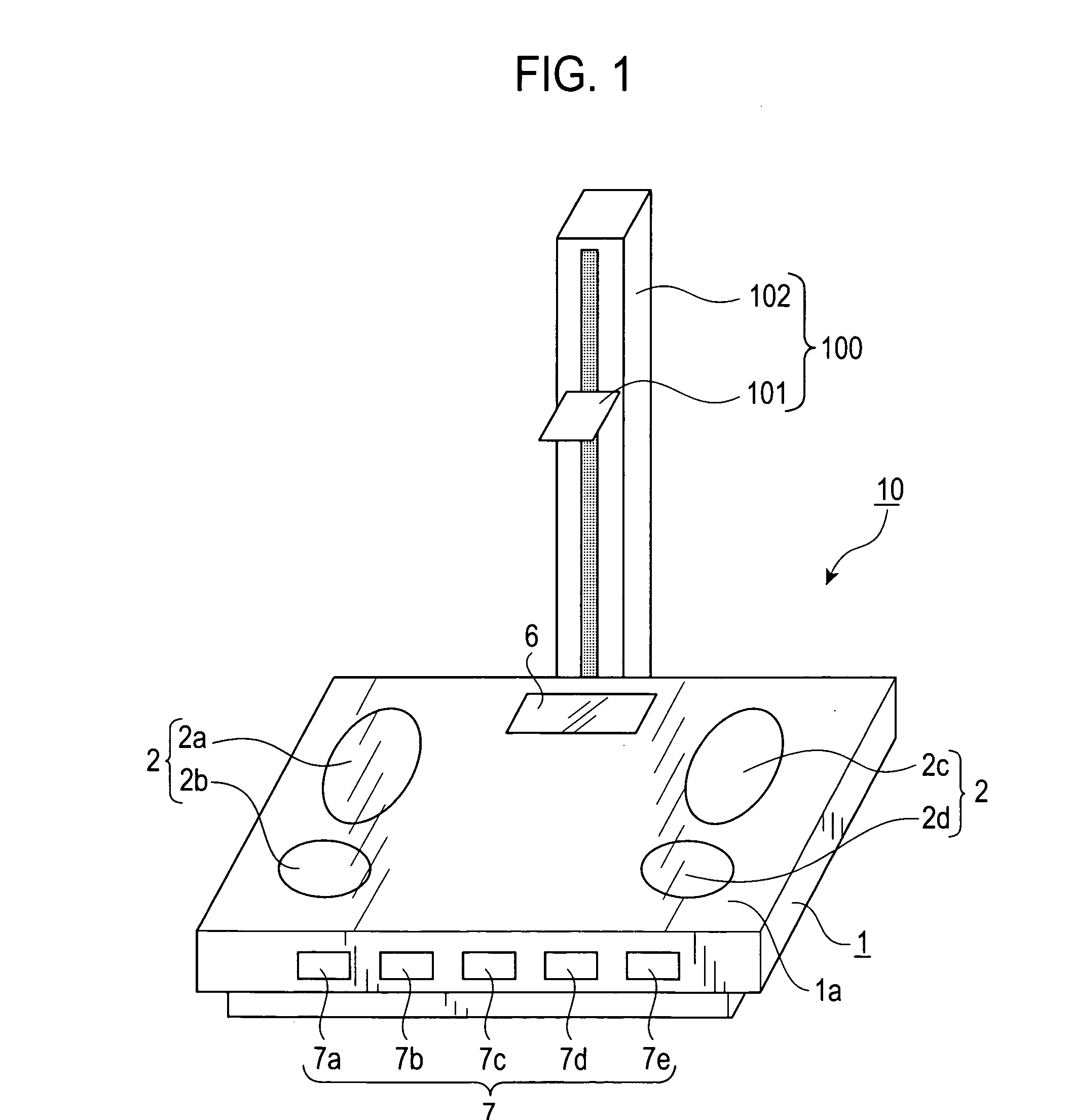
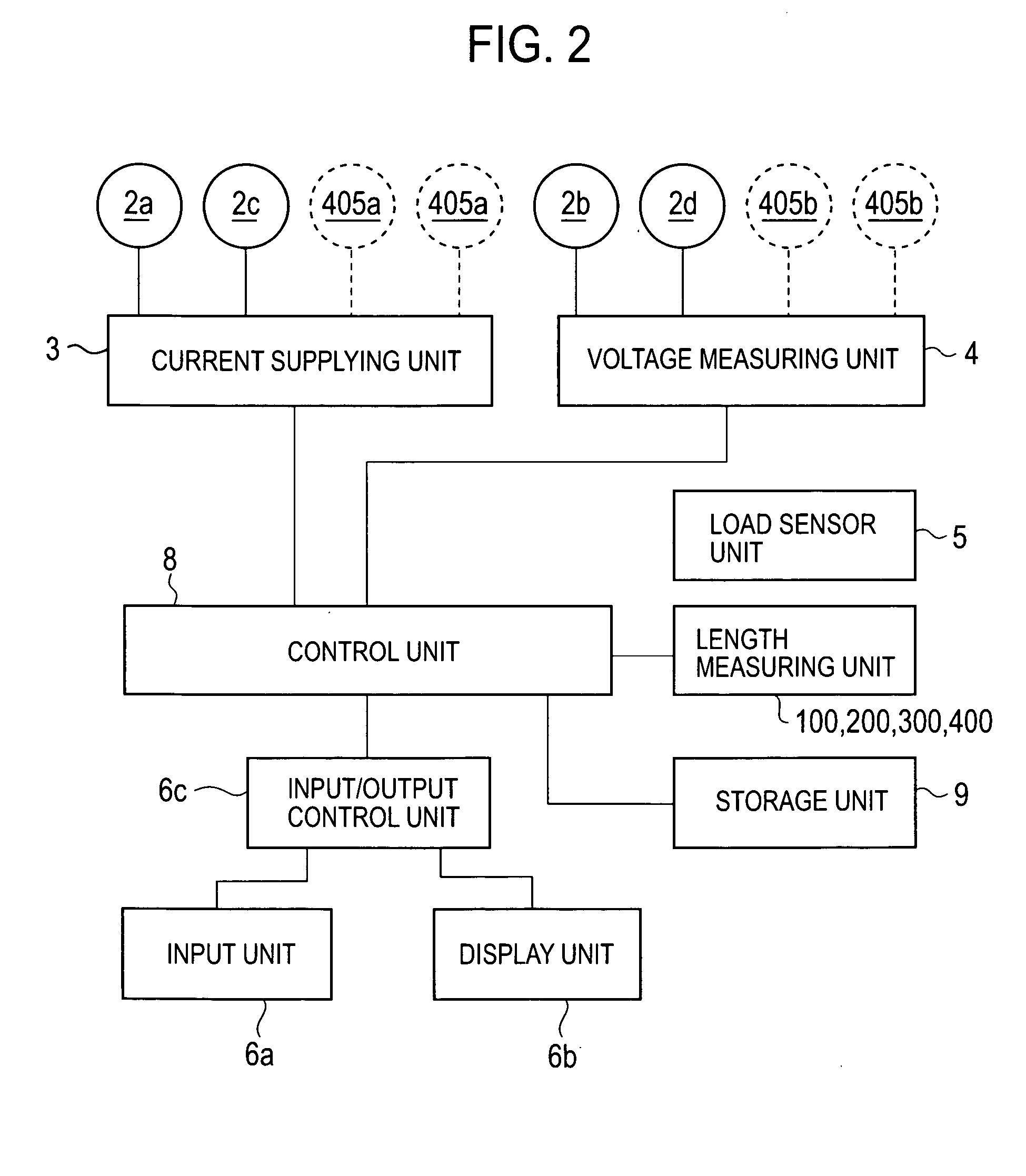
Body composition data acquiring apparatus
InactiveUS20050059902A1Little changeAccurate estimatePerson identificationUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansElectrical resistance and conductanceLeg length
A body composition data acquiring apparatus has a main unit comprising: bioelectrical impedance measuring means, body weight measuring means, leg length measuring means, and body composition data calculating means wherein the bioelectrical impedance measuring means measures a bioelectrical impedance between both feet by use of a group of electrodes which make contact with the bottoms of the feet of a subject, the bodyweight measuring means measures the body weight of the subject, the leg length measuring means measures the leg length of the subject, and the body composition data calculating means calculates the body composition data of the subject based on at least the bioelectrical impedance, body weight and leg length measured by these measuring means.
Owner:TANITA CORP
Power type walking method of dual-foot robot
A power-typed walking method for a biped robot belongs to the technical field of robot walking control. The method is characterized in that the robot realizes fully power-typed walking similar to passive walking by rapidly swinging two legs and controlling landing collision of the swinging legs in a gait cycle T which is more than 0.2s and less than 0.5s, the robot creates a virtual slope by bending the knee joint of a swinging leg and supplements energy by straitening the knee joint of a supporting leg, each gait of the gait cycle is determined by three key frames and described by four parameters, a first derivative continuous smooth curve connects the key frames. In the experiment, single gait of the robot reaches a relative walking speed of 4.48 leg lengths per second, which improves by 29 percent compared with the record created by RunBot; moreover, a plurality of gaits of the robot realizes continuous variable speed walking from 1.24 leg lengths per second to 3.88 leg lengths per second.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Pedal stroke adjuster for bicyles or the like
InactiveUS20050020411A1Easy to processImprove distributionControlling membersMechanical apparatusLeg lengthEngineering
A stroke adjusting attachment for bicycles or the like enables selective changing of the diameter of the orbit which is traveled by a foot pedal to adapt a particular bicycle to persons having different leg lengths or who may have physical impairments which limit foot movement. The pedal is fastened to the attachment rather than being directly secured to a crank arm of the bicycle in the conventional manner. A track member is secured to the bicycle crank arm and the pedal is fastened to a slider which is travelable to any of a plurality of different locations along the track member. Blades extend from the track member adjacent to opposite surfaces of the crank arm thereby maintaining the attachment in a fixed orientation relative to the crank arm. A particular attachment of this form can be fitted onto a variety of crank arms of different sizes and shapes.
Owner:ANDREWS RONALD A
Method of calculating step length
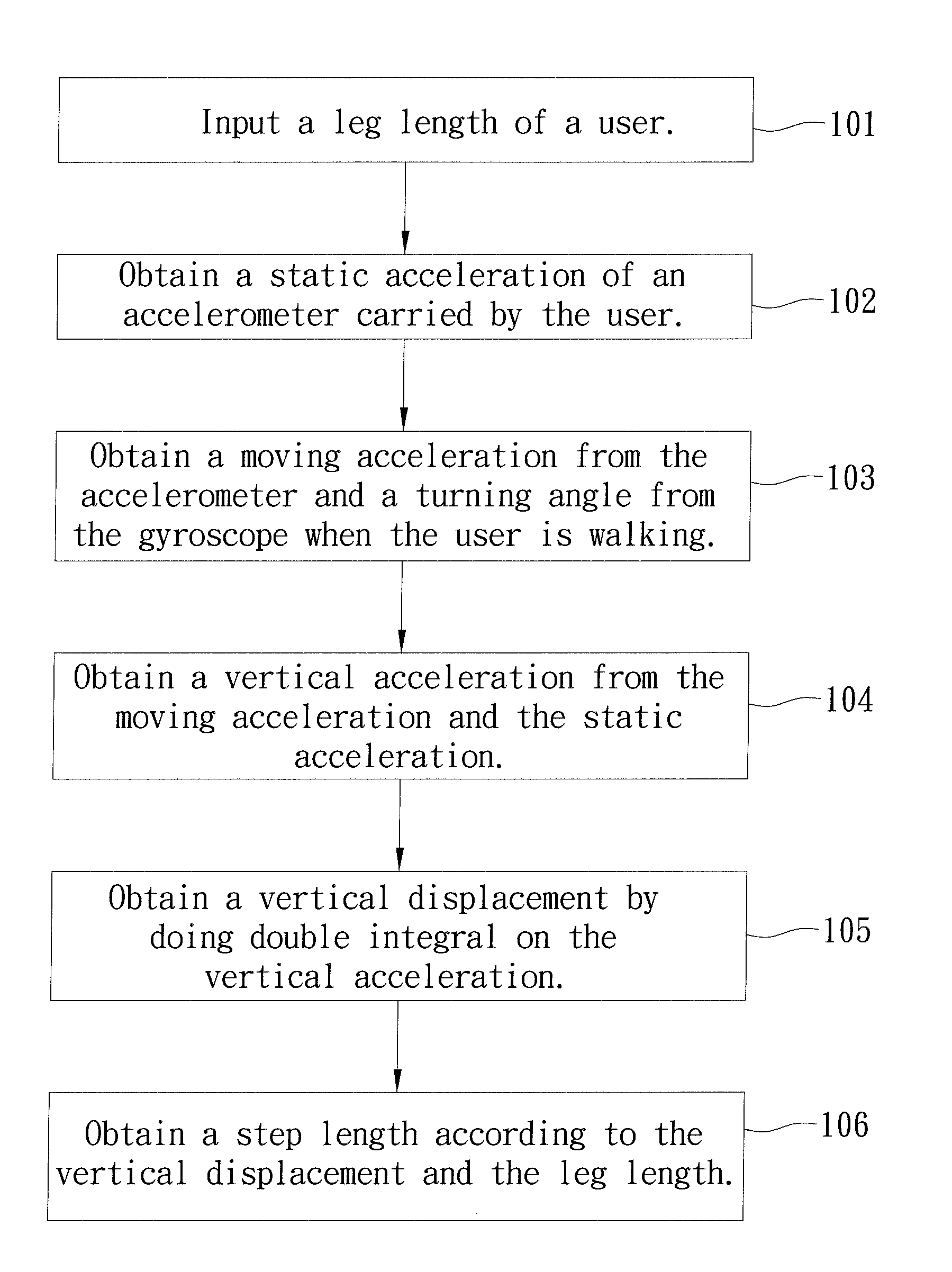
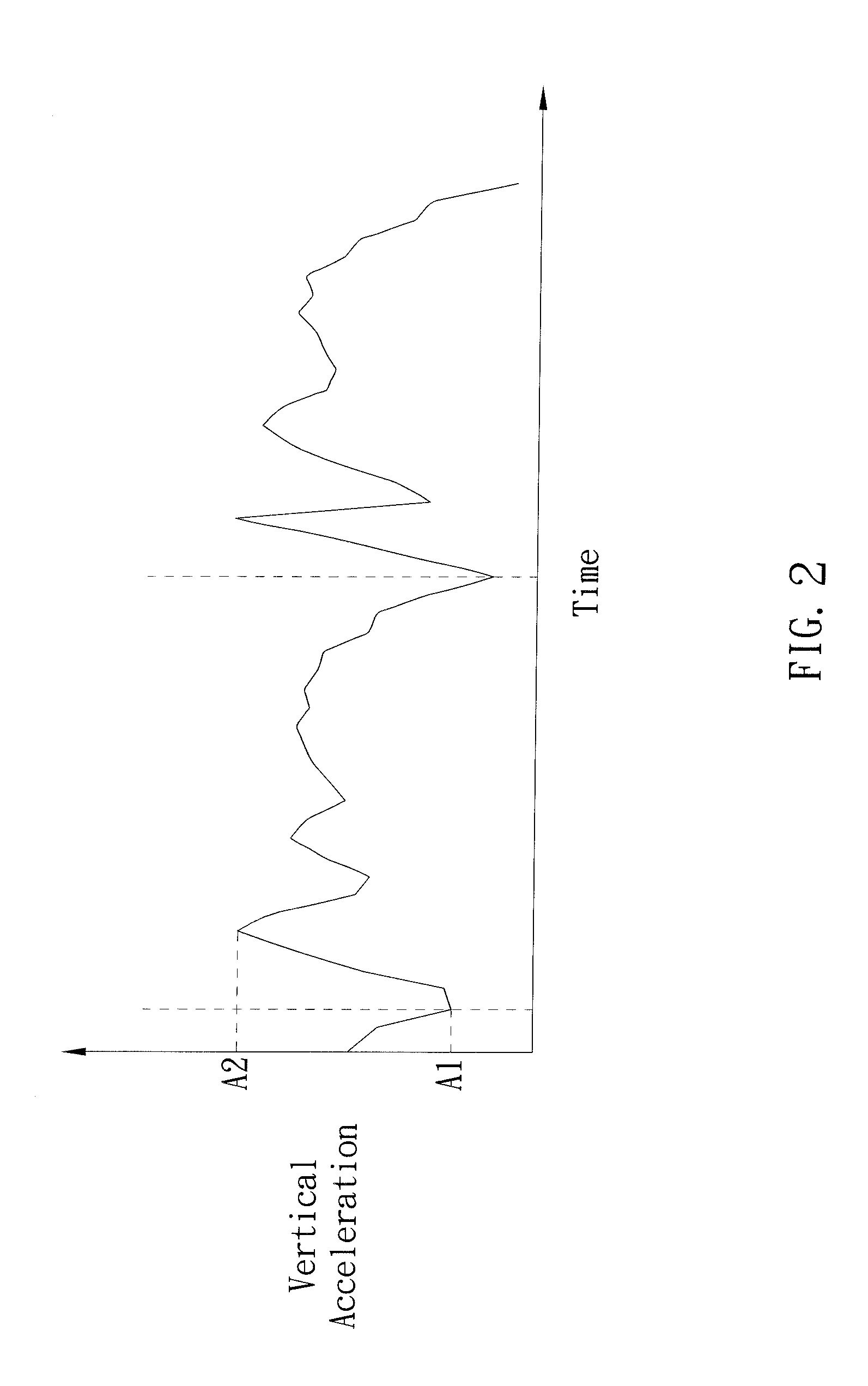
InactiveUS20140019082A1Precise NavigationNavigational calculation instrumentsDigital computer detailsAccelerometerLeg length
A method of calculating a step length of a user, which comprises the steps: input a leg length of the user; obtain a vertical acceleration when the user is walking, wherein the vertical acceleration is sensed by an accelerometer and then removed the effect of gravity; do double integral on the vertical acceleration to obtain a vertical displacement for one step of the user; calculate a step length according to the vertical displacement and the leg length by applying Pythagorean theorem.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Method for precision forming of concave-bottom and thin-wall cylindrical part with large length and diameter ratio
The invention discloses a method for precision forming of a concave-bottom and thin-wall cylindrical part with large length and diameter ratio. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, calculating the size of a plate blank; then, forming the concave bottom, performing deep drawing and spinning to form a cylindrical blank, and performing spinning and thinning on the blank to reach the specified size; performing subsequent universal processing to meet the requirement of part size; in the deep drawing and spinning process of the cylindrical blank, turning the blank with the formed concave bottom, fixing between a tail jack and a code die, preparing a common spinning track by a common spinning track preparation method, enabling a main shaft to drive the blank to rotate, enabling a rotary wheel to feed according to the prepared track under the drive action of a numerical control system, using the first 6-8 passes of the spinning track as the simple reciprocating spinning, using the subsequent passes of the spinning track as the spinning track combined with the reciprocating travel, and performing the deep drawing and spinning on the blank to form the cylindrical part. The method has the advantages that by utilizing multiple times of deep drawing and spinning, the cylindrical blank is obtained, and then the spinning and thinning are performed on the blank to reach the specified size; by utilizing the characteristics of strong spinning and high accuracy, the wall thickness of the manufactured part is uniform, the surface quality is high, the compactness is good, and the number of defects is fewer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
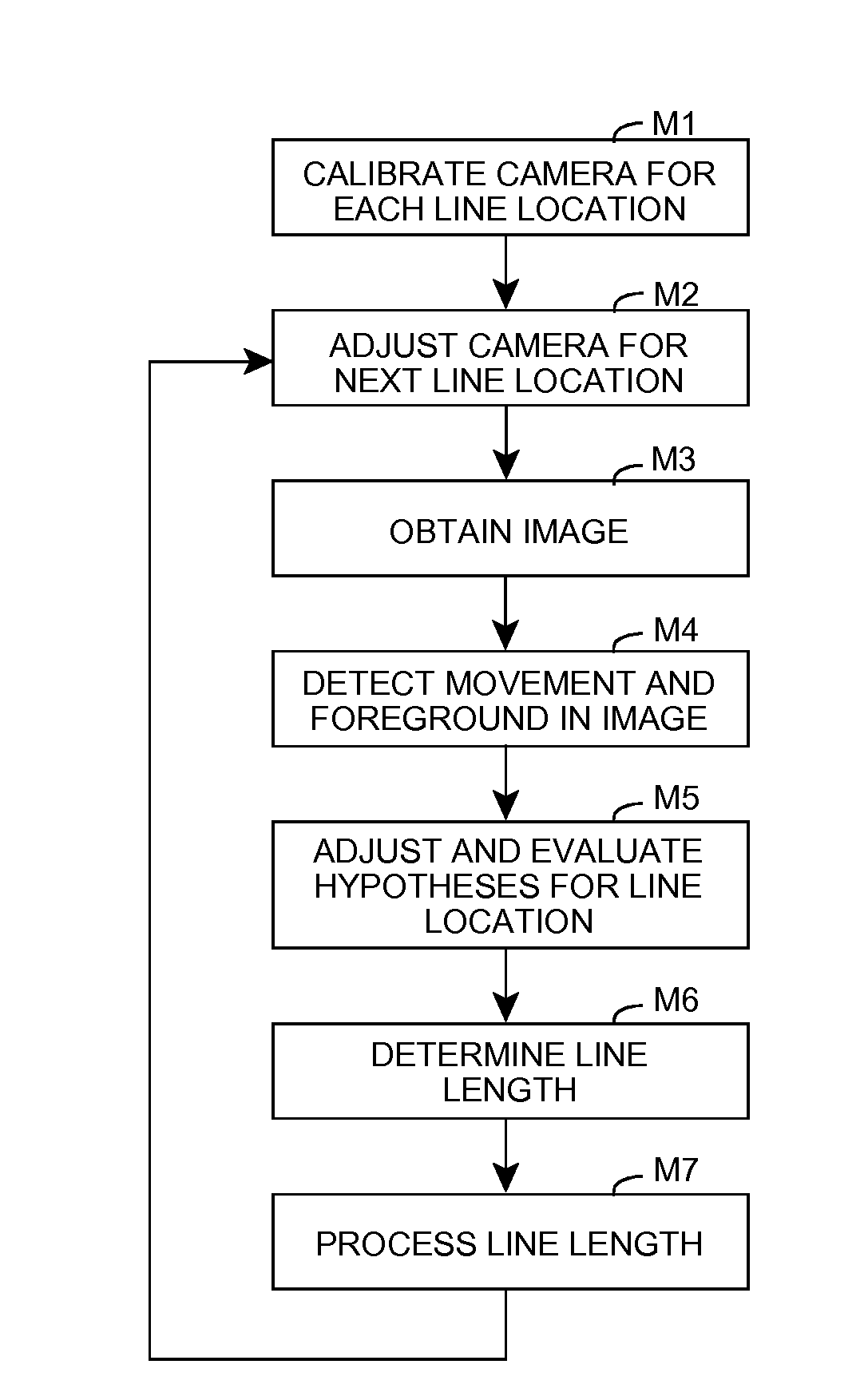
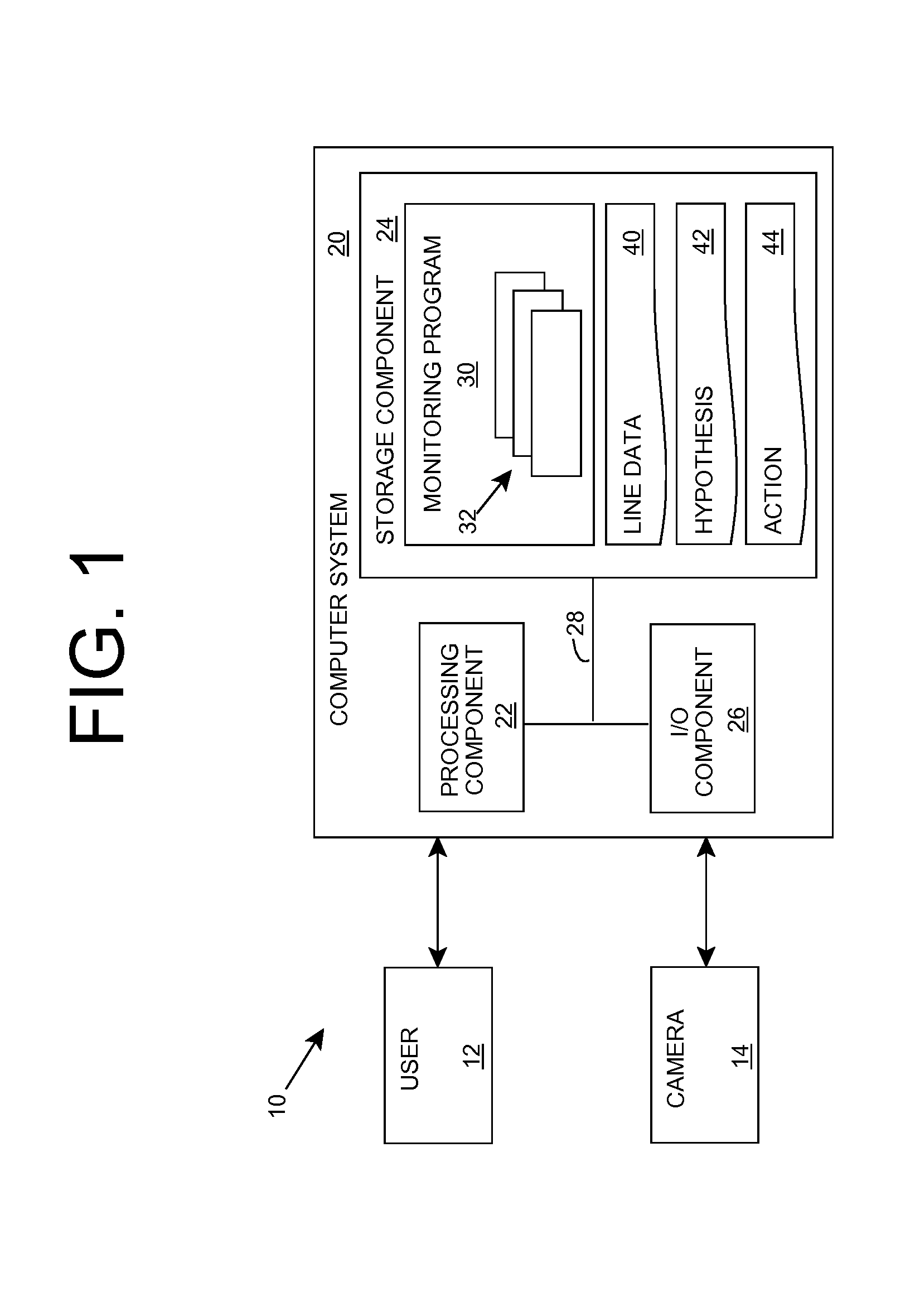
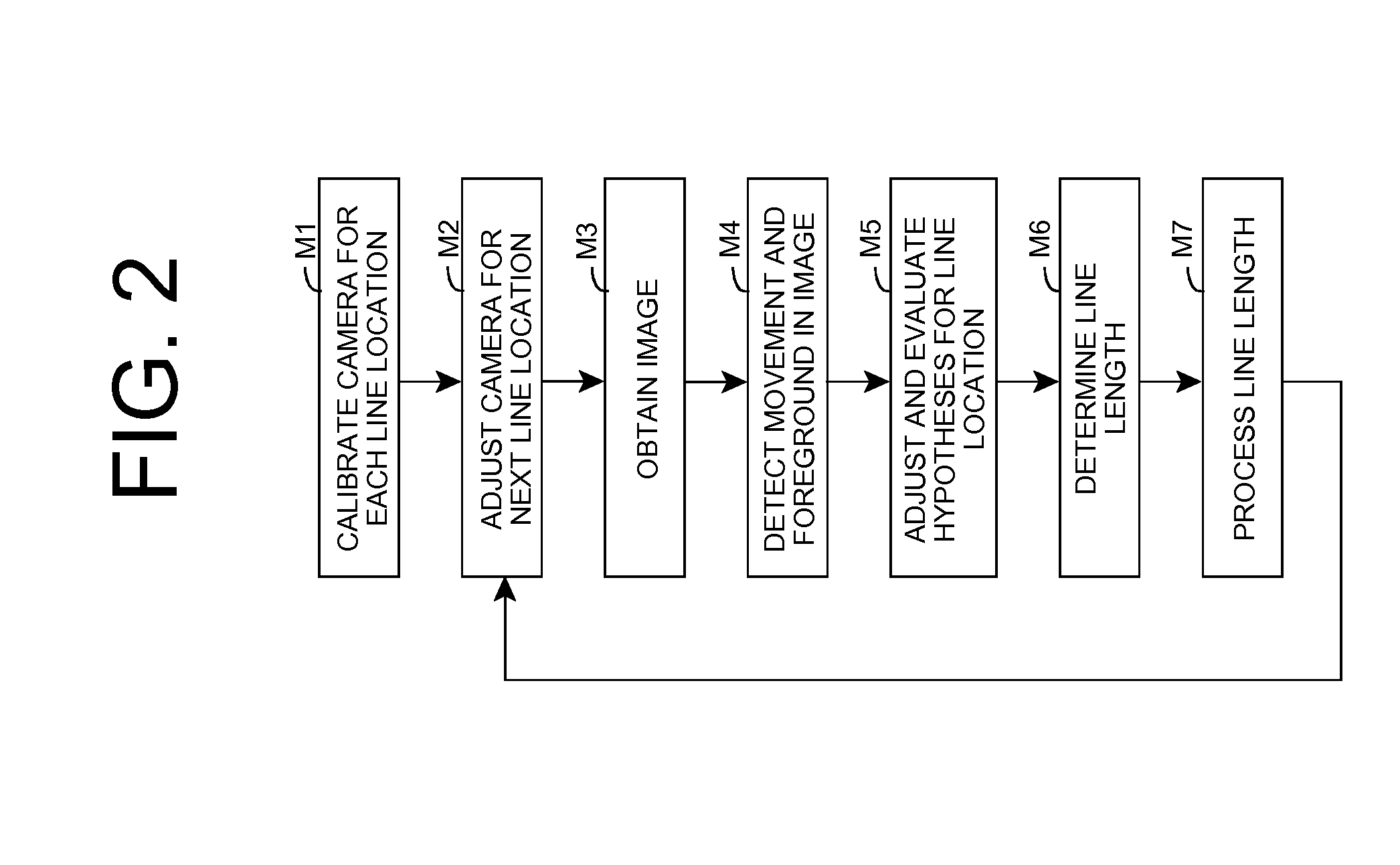
Line length estimation
A solution for monitoring an area is provided. At least one image of a physical area corresponding to a line is obtained and a set of hypotheses are evaluated based on the image(s). For one or more hypotheses, an estimated length of the line is extracted, and an estimated line length is generated based on the estimated length(s) and the corresponding evaluation(s) of the set of hypotheses. In this manner, a length of a line of people, customers, vehicles, and / or the like, can be estimated. The estimation can be stored for later use, utilized to generate one or more alerts, and / or the like. The invention also provides for the use of a single camera to monitor multiple lines and / or perform other monitoring functions.
Owner:TERRACE LICENSING LLC
Machining method of porous thin-wall protective tube with large length-diameter ratio
The invention discloses a machining method of a porous thin-wall protective tube with a large length-to-diameter ratio. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly cutting a tube material at a desired length of the protective tube; heating to melt a low-temperature lead / tin alloy material into liquid and then pouring the molten alloy into the inner hole of the tube material; clamping a threaded plug at one end of the tube material by use of a dividing head chuck, compacting a threaded plug at the other end of the tube material by use of a miller center, and straightening and clampingthe two sides of the outer wall of the tube material by use of flat tongs; milling kidney-shaped holes which are uniformly distributed on the wall of the tube material by use of a milling cutter which is mounted on a numerically-controlled milling machine, and milling kidney-shaped holes which are arranged in rows in the axial direction of the tube material; and vertically hanging the tube material subjected to milling, and heating such that the low-temperature lead / tin alloy material is molten and breaks away from the inner hole of the tube material, thus obtaining the porous thin-wall protective tube with large length-to-diameter ratio. The process of machining the porous thin-wall protective tube with large length-to-diameter ratio by the method disclosed in the invention has the advantages that the rate of qualified products is high and is up to above 99%; the machining accuracy is increased and fully meets the design requirement on product accuracy; and the machining efficiency is increased by more than 50%.
Owner:湖北三江航天江北机械工程有限公司
Wearable lower limb rehabilitation training device
InactiveCN103622796AImprove comfortImprove the effect of rehabilitation trainingChiropractic devicesWalking aidsThighLeg length
The invention provides a wearable lower limb rehabilitation training device which comprises a base, a column, a waist bracket, knee-joint motion control units and hip joint motion control units, wherein the column is installed on the base, the waist bracket is installed at the top of the column and is provided with two protective frames, each protective frame is provided with the hip joint motion control unit and the knee-joint motion control unit, each hip joint motion control unit comprises a hip joint motor, a thigh rod, a thigh connecting rod, a thigh driving rod and a thigh layer board, and each knee-joint motion control unit comprises a knee-joint motor, a shank rod, a shank connecting rod, a shank driving rod and a pedal. The upper end of the shank rod is connected with the thigh rod through a thigh joint shaft. The device can realize lower limb rehabilitation training of patients or the old, improve a training effect, and further improve the comfort level of a user. Meanwhile, the device can be suitable for crowds in different body types by adopting a leg length, height and width adjusting mechanism.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Alignment plate apparatus and system and method of use
ActiveUS20150257846A1Easy to installContinuous measurementImage enhancementImage analysisFracture reductionLeg length
A computer implemented system for adjusting the placement of an implant in a patient through the use of a dimensioned grid template placed relative to patient anatomy on a fluoroscopic machine and a method to digitally quantify alignment parameters is provided. This system can be used for determining: 1) leg length, offset, and cup position during arthroplasty replacement surgery; 2) fracture reduction / correction position during trauma procedures and 3) an apparatus to be used for deformity correction planning is provided; 4) placement and positioning of instruments and implants relative to bone and anatomical architecture; 5) bone anatomy boundary parameter identification relative to reaming and cutting landmarks of bone.
Owner:ORTHOGRID SYST HLDG LLC
Hydraulic aerial cage control system and method
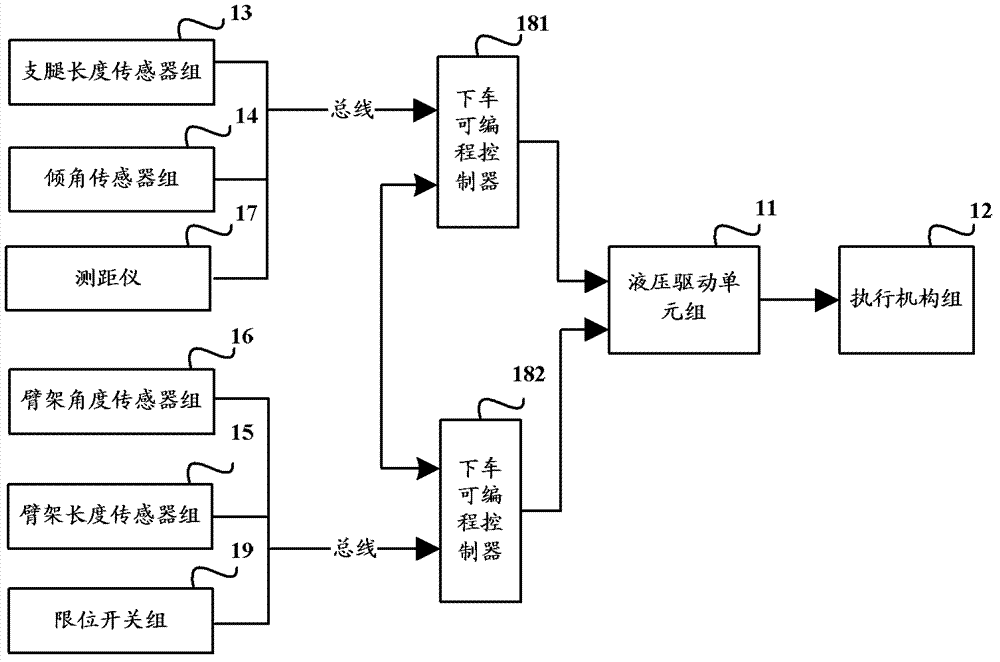
ActiveCN102849659AAvoid damageHigh control precisionSafety devices for lifting equipmentsControl systemLeg length
The invention relates to a control technique, and in particular relates to a control technique of a hydraulic aerial cage, aiming at realizing automatic rescue preparation and reclaiming of the hydraulic aerial cage. The embodiment of the invention also provides a control system of the hydraulic aerial cage. The control system comprises a landing leg length sensor of each landing leg, at least one inclination angle sensor, a cantilever crane length sensor of each cantilever crane, a cantilever crane angle sensor of each cantilever crane, a range finder, a get-off programmable controller and a get-on programmable controller. According to the automatic rescue preparation in high altitude reclaiming and a reclaiming control method provided by the embodiment of the invention, operating personnel does not need to do complex operation, and the system carries out the operation completely automatically, so that the control precision on the reclaiming at the high altitude is improved, and the intensity of manual operation is reduced; and the precise control is carried out by the sensors and detection signals of limiting switches, thereby avoiding the damage, caused by excessive operation, to machinery.
Owner:ZOOMLION INTELLIGENT ACCESS MASCH CO LTD
OLED substrate and display panel
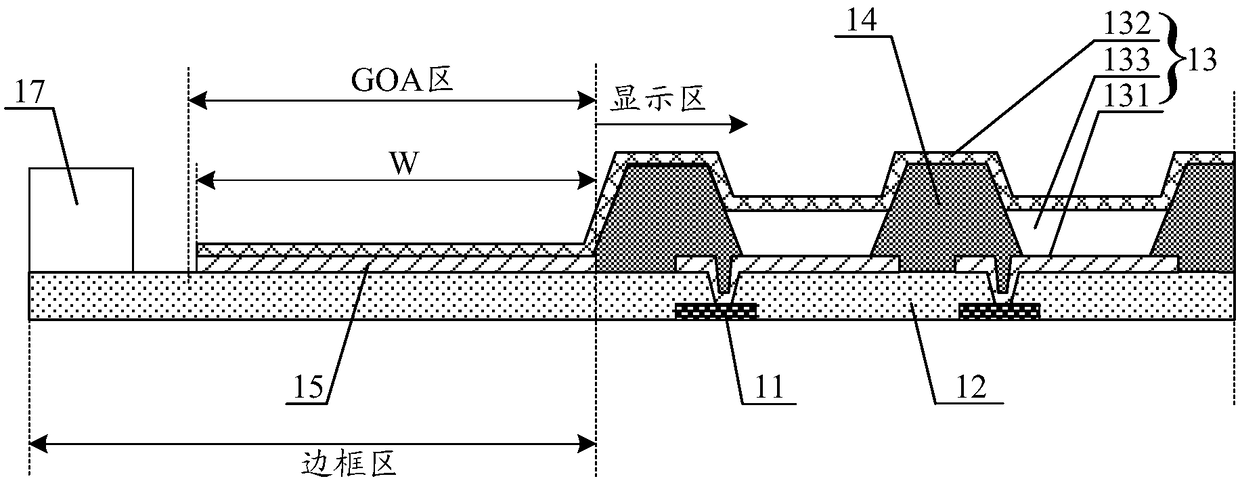
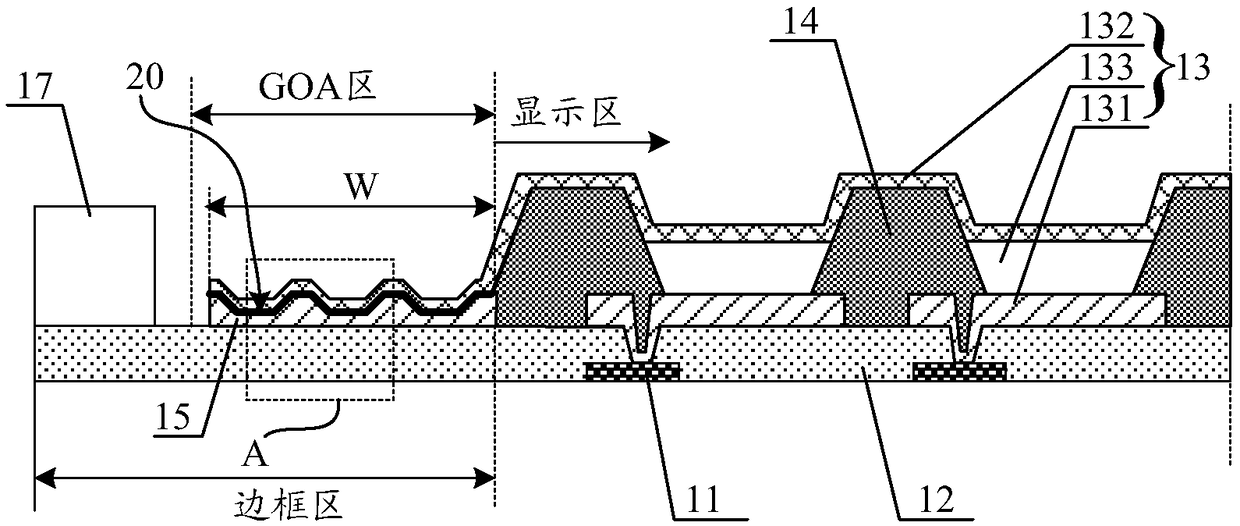
InactiveCN108649063AIncrease lap lengthIncrease the overlap areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLeg lengthElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention discloses an OLED substrate and a display panel. The OLED substrate comprises a display area and a GOA area located on the outer side of the display area,the GOA area is provided with asignal wiring layer,the display area is provided with an OLED pixel,a negative pole of the OLED pixel is in lap joint with the signal wiring layer,and the lap surface of the negative pole and the signal wiring layer is undulating. According to the OLED substrate,by arranging the lap surface of the negative pole and the signal wiring layer to be undulating,the lap length of the negative pole and the signal wiring layer is increased,and the lap area of the negative pole and the signal wiring layer is increased accordingly,in this way,on the basis that the lap length of the negative pole and thesignal wiring layer meets the requirement,the lap width of the negative pole and the signal wiring layer can be reduced,then the width of the GOA area is reduced,and narrow bezel design of the OLED display panel is facilitated.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Linear scale, linear motor, and linear motor controller
ActiveUS20110109252A1Continuous detectionDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlWave shapeLeg length
Disclosed is a linear scale for obtaining a distance from a reference point. A scale detection mechanism is adapted to output waveform signals of the same phase. Also the scale detection mechanism corresponds to a magnetic flux density generated by magnetic bodies of a scale element. The scale detection mechanism may be sensors. The sensors are arranged at even intervals corresponding to a scale length of the scale element. The sensors are adapted to output sine-wave signals having the same phase to continuously detect the scale element in a movement direction of the scale element. The scale element has opposite ends each has the same polarity and configured such that an output voltage of the single sensor detecting the end of the scale element is reduced to one-half of an output voltage of the single sensor detecting the remaining portion of the scale element.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
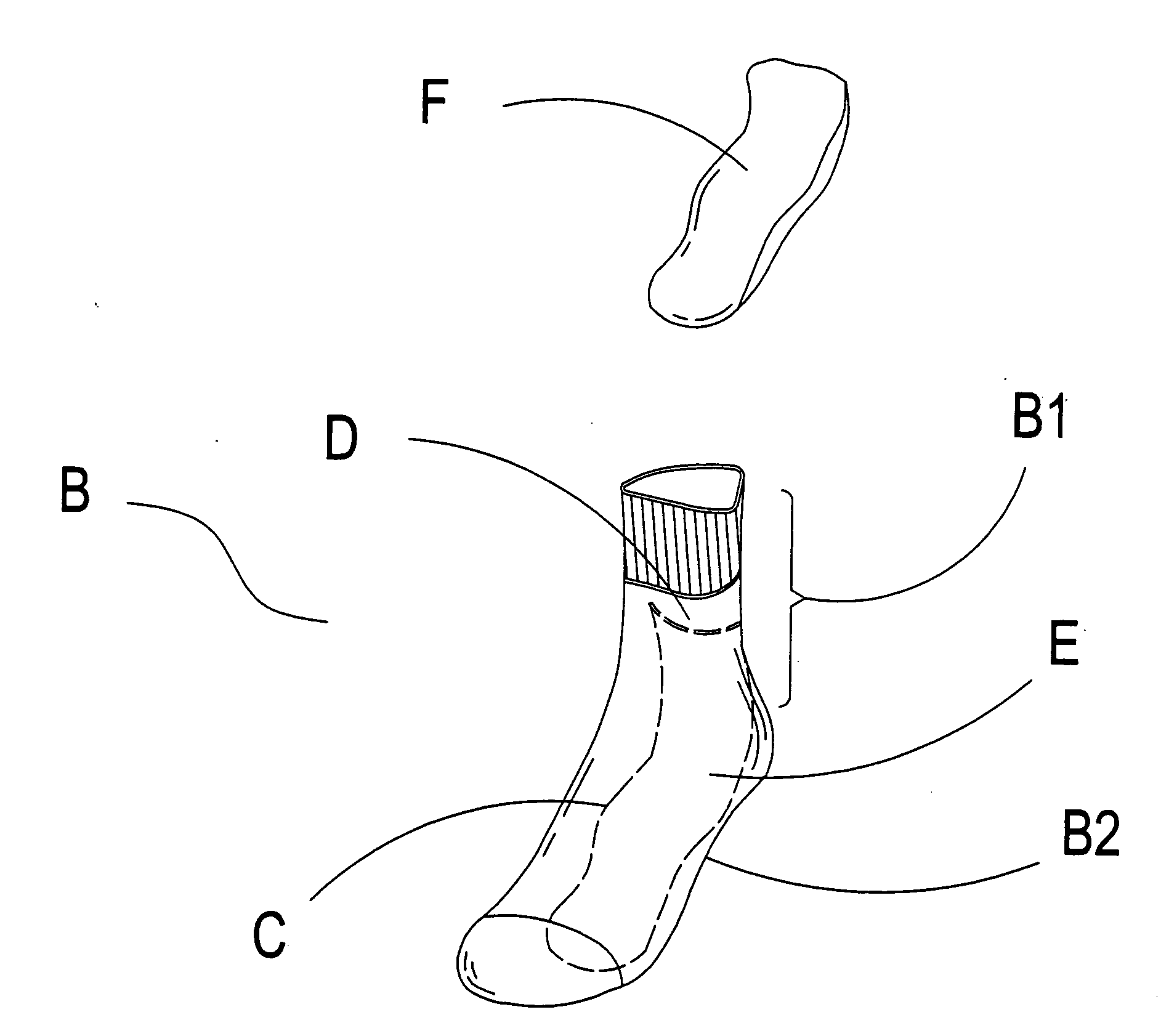
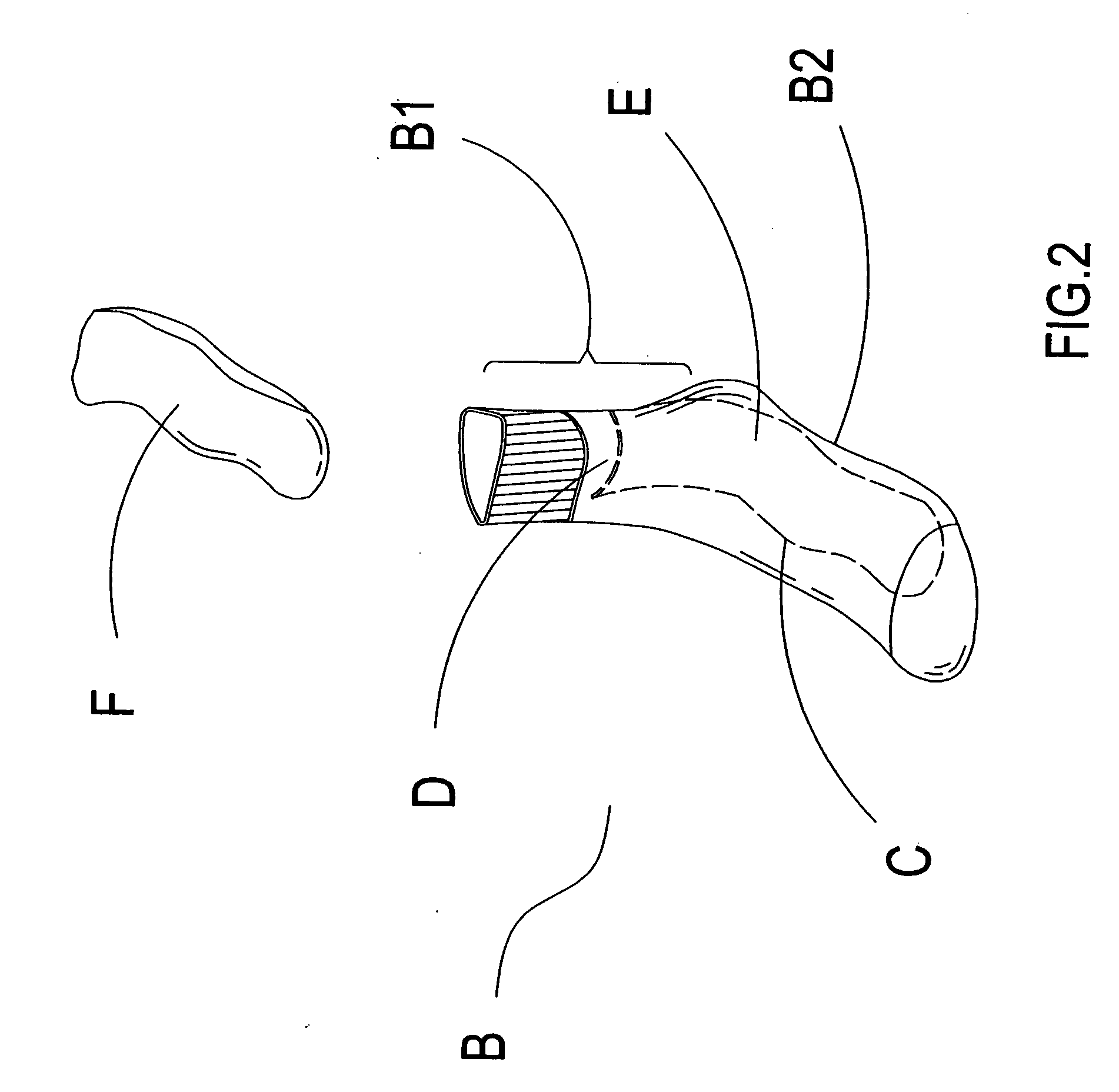
Leg length discrepancy corrective sock
InactiveUS20060253962A1Super softGood elastic propertiesInsolesPanty-hoseLower limb length discrepancyLeg length
The present invention provides a leg length discrepancy corrective sock, which has an elastic strip attached within a sock. A holding space formed between a sock body and a sock sole of the sock and the elastic strip provides for disposing a filler therein, and height of the filler achieves the objective of correcting the difference in length of the lower limbs of the leg length discrepancy sufferer. Hence, equalizing the difference in length of the lower limbs is easily achieved by wearing the leg length discrepancy corrective sock of appropriate thickness.
Owner:HUA WEI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com