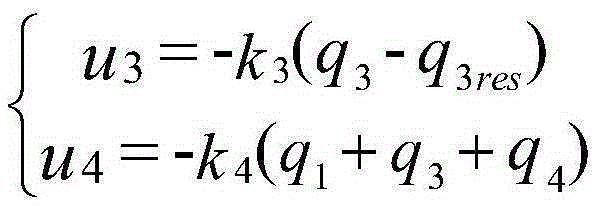Patents
Literature
368 results about "Biped robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Product presentation robot
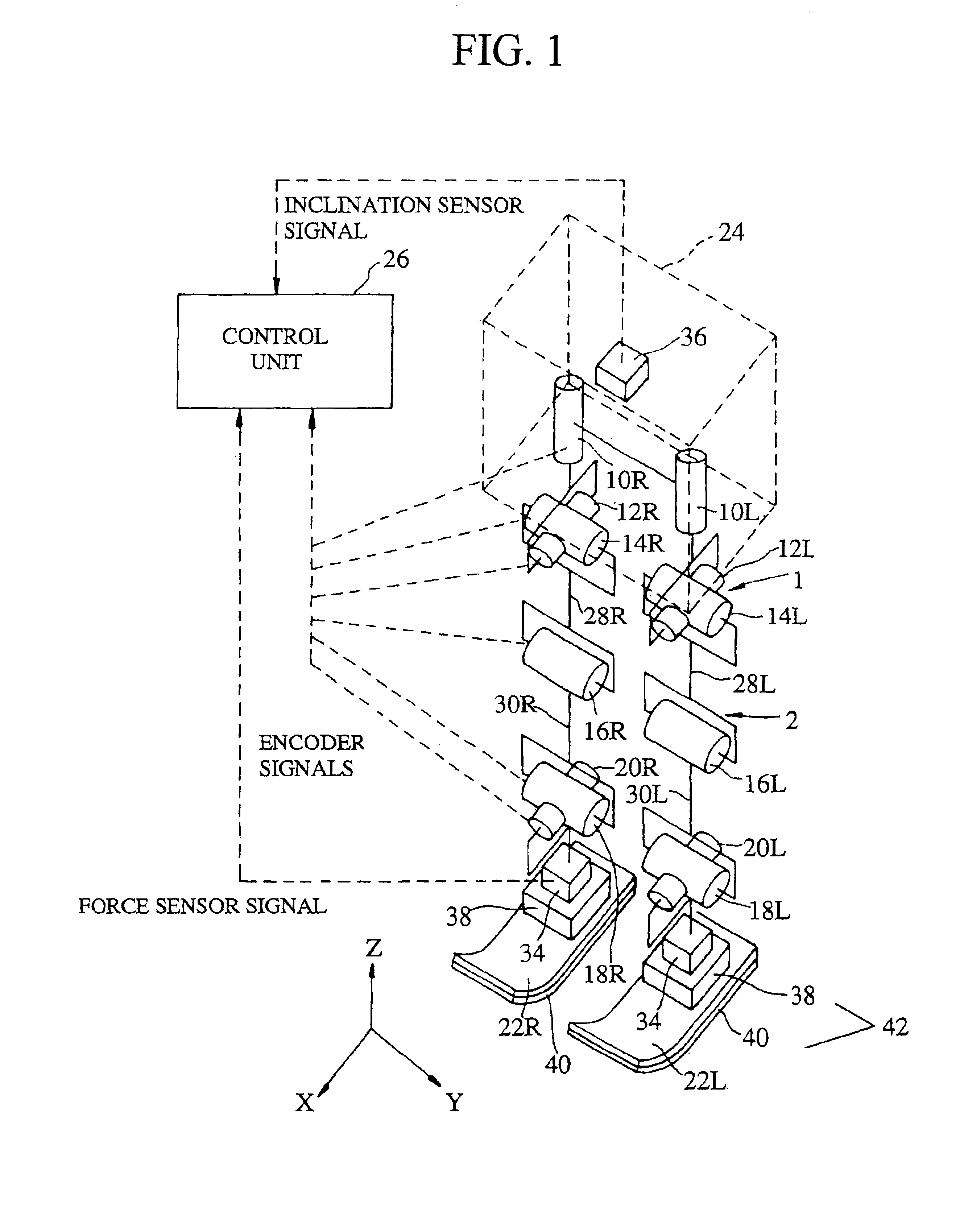
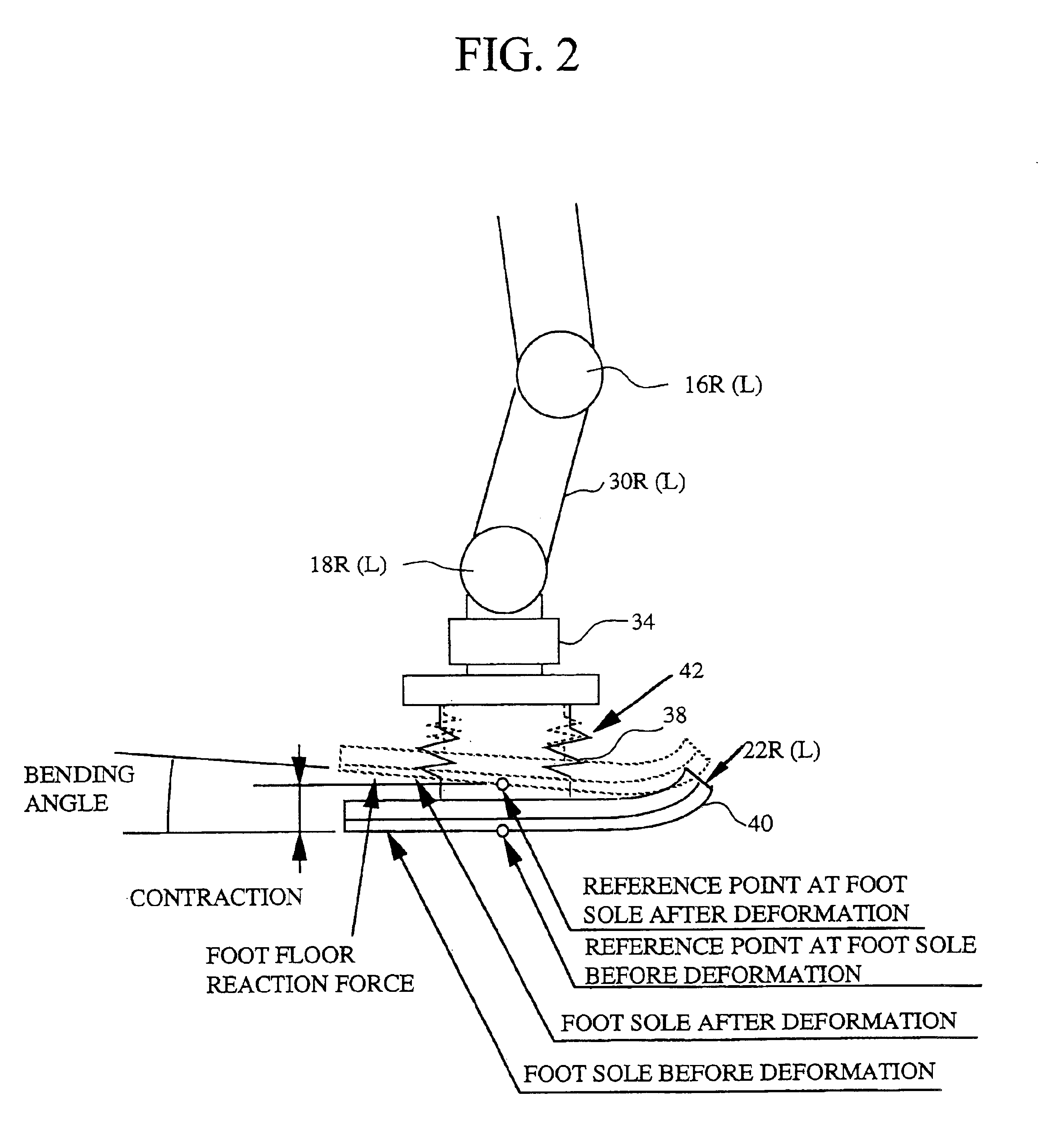
ActiveUS7636045B2Work lessElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunication unitData needs
A product presentation biped robot implementing presentation of products such as vehicles through explanation of at least one among performance, specifications and operation of the products, is provided. The robot has a communication unit being capable of communicating with a database located externally of the robot and storing information including at least data needed for implementing the presentation of the products, a data acquirer accessing the database through the communication unit to acquire the data needed for implementing the presentation of one from among the products interested by a customer, and a product presentation implementor implementing the presentation of the one from among the products to the customer based on the acquired data presentation robot that implements product presentation, thereby enabling to ease the work of a salesperson.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
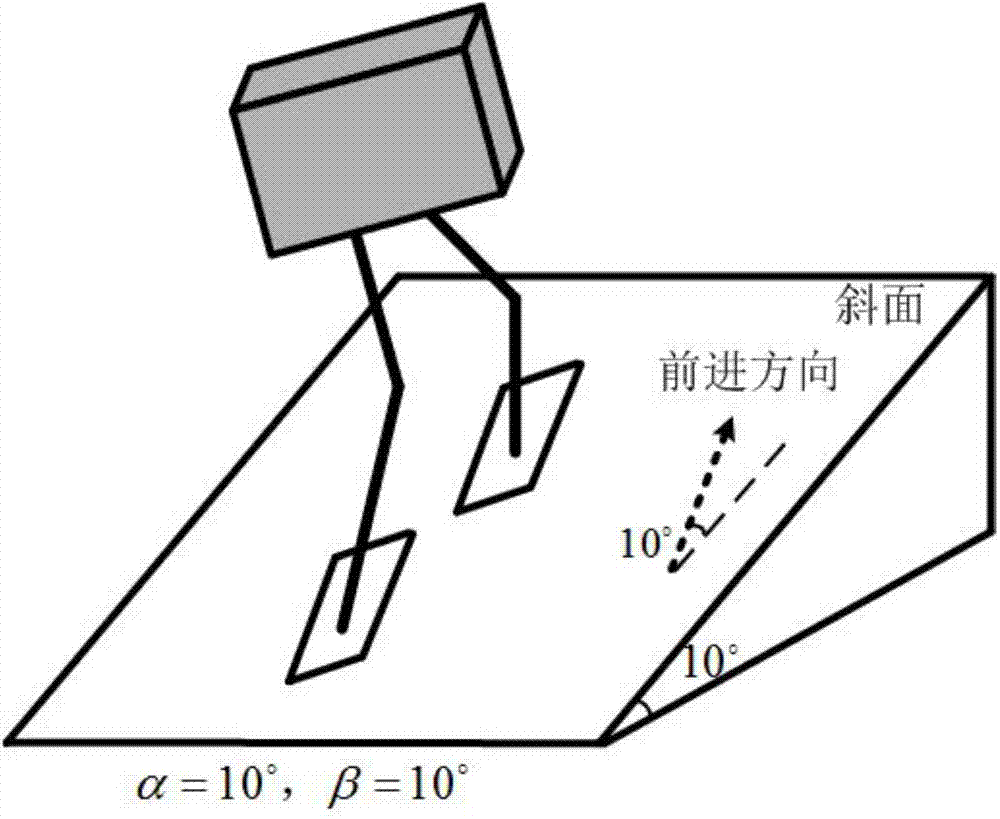
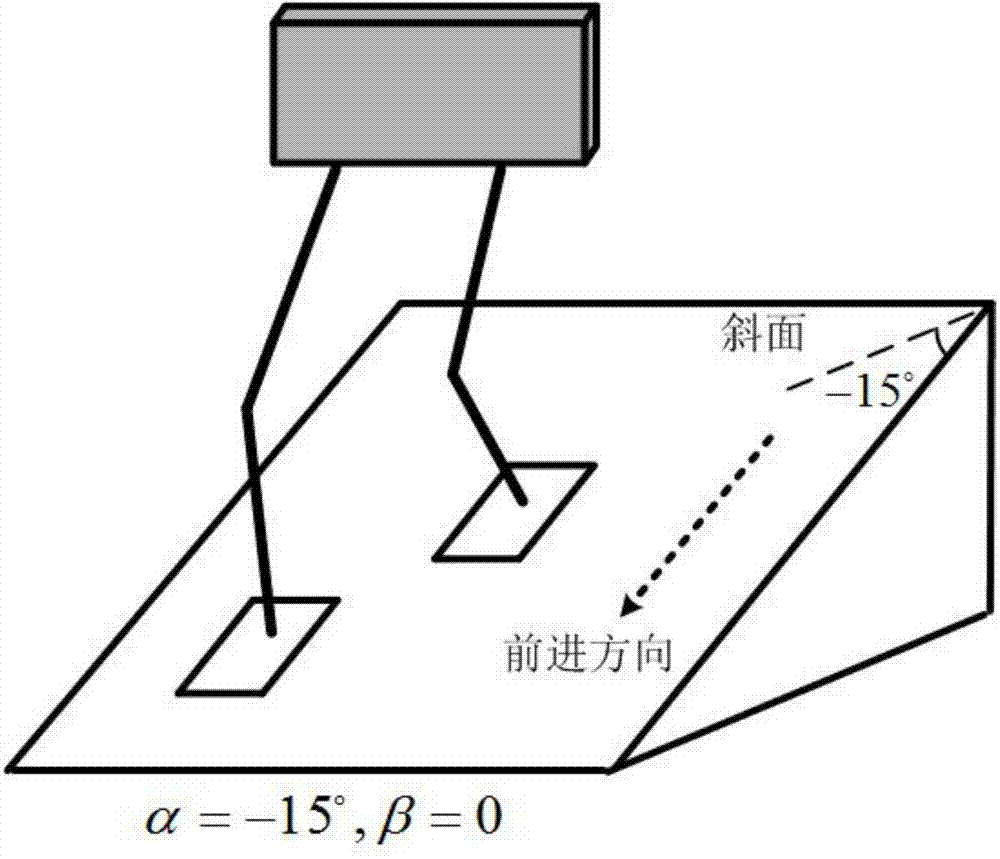
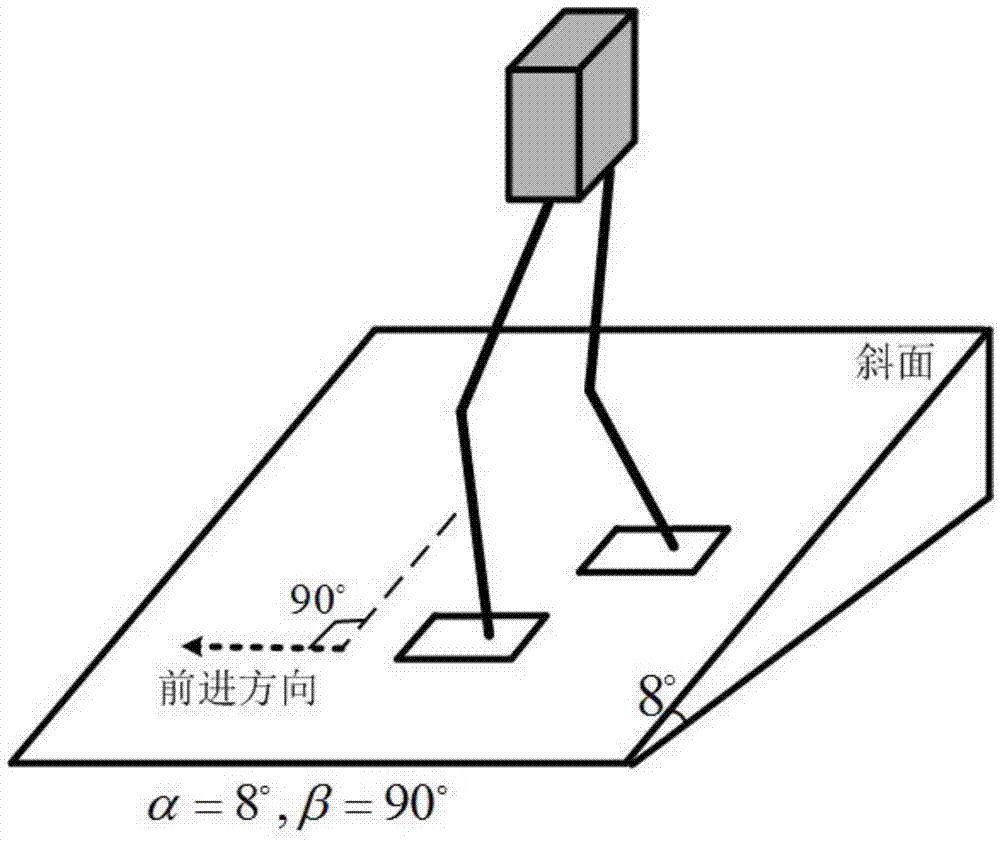
Gait planning method for walking of biped robot along slope
ActiveCN104331081AImprove environmental adaptabilityMovement coordination and natureAttitude controlCoronal planeDecomposition
The invention discloses a gait planning method for walking of a biped robot along a slope, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The method contains two core theories, namely, non-orthogonal decomposition and synthesis of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum and gait planning based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum. The method comprises the steps of gait parameter configuration, non-orthogonal decomposition of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum, foot trajectory planning based on three times of spline interpolation, centroid trajectory planning of a sagittal plane and a coronal plane based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum, non-orthogonal synthesis of the centroid trajectories of the sagittal plane and the coronal plane, and solving of joint trajectories of a robot based on inverse kinematics. By adopting the method of the invention, stable walking of a biped robot along all directions of a slope can be effectively achieved. The method is universal, simple in algorithm and high in practicality.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
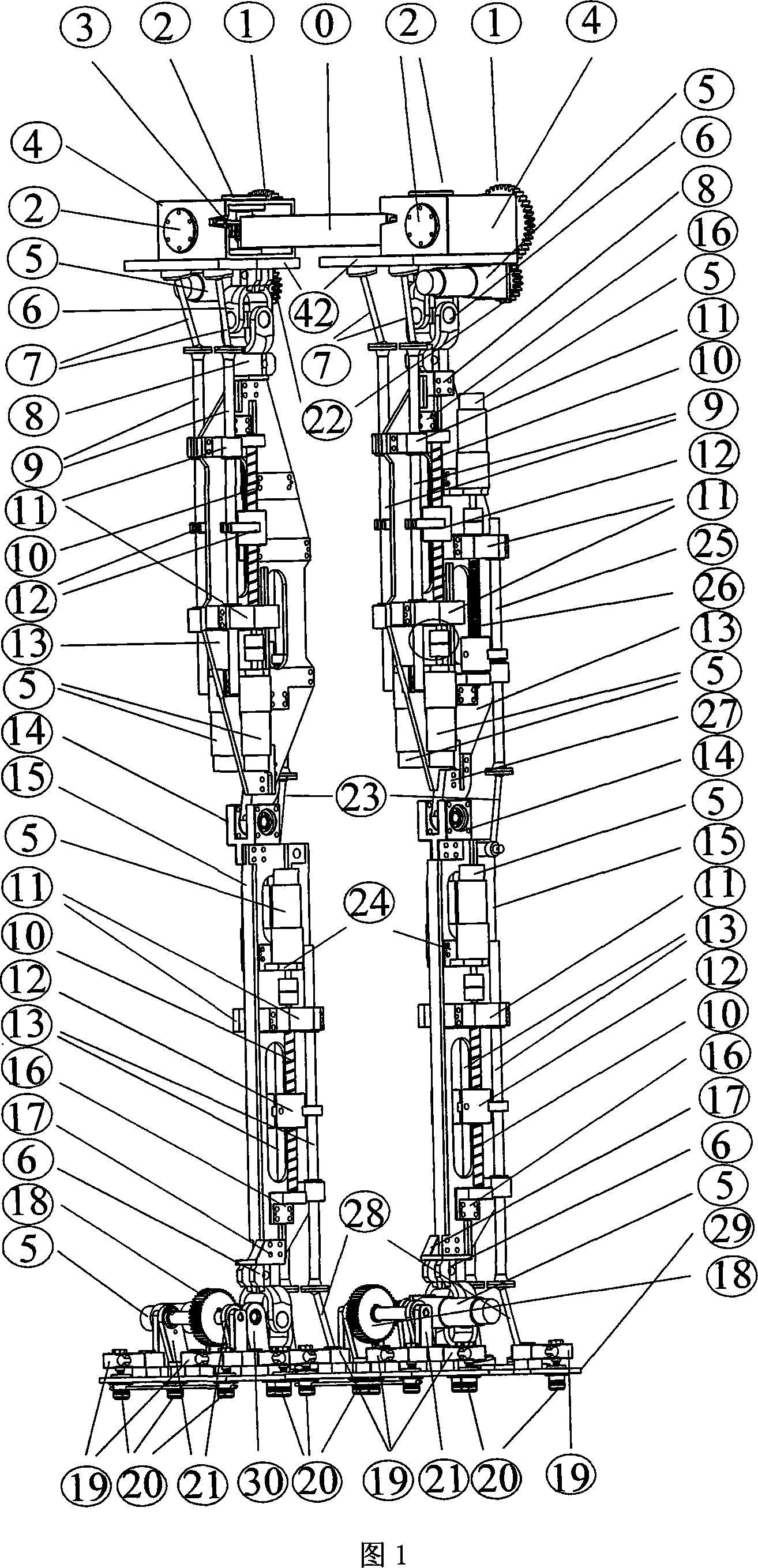
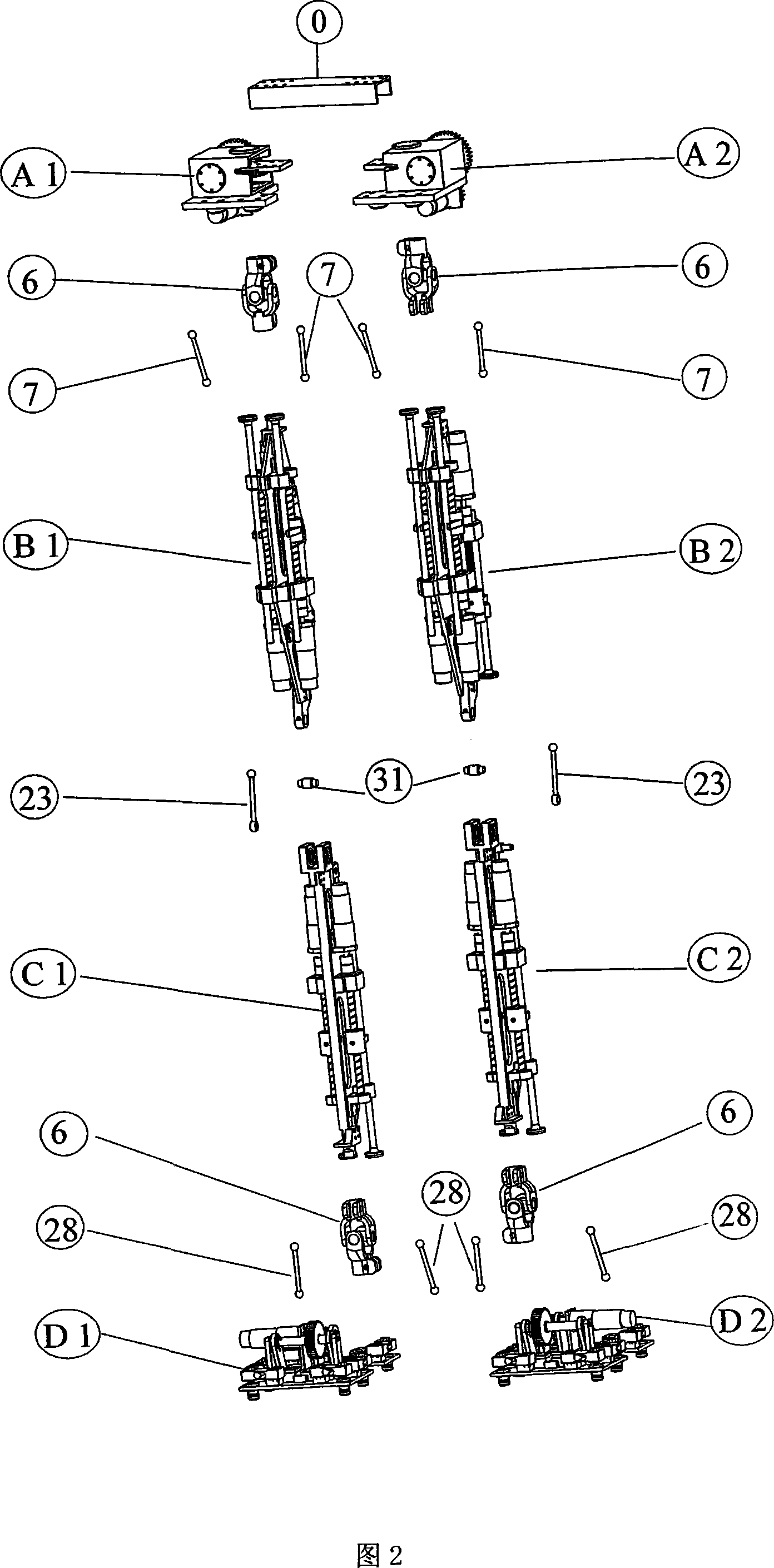
Double-foot robot lower limb mechanism with multiple freedom degree
InactiveCN101121424ARealize anthropomorphic gait walkingMany degrees of freedomSelf-moving toy figuresArtificial legsKnee JointGait
The invention provides a lower limb mechanism of a biped robot with multiple degrees of freedom. It includes the waist, thigh, calf and foot, the thigh includes the right thigh and the left thigh, the calf includes the right calf and the left calf, and the foot includes the right foot and the left foot; the waist is composed of two parts, the right hip joint and the left hip joint, connected through the waist Board connection composition; the right hip joint and left hip joint, right thigh and left thigh, right calf and left calf, right foot and left foot are symmetrical structures; the hip joint and thigh are connected in parallel through a Hooke hinge and two connecting rods The thigh and the lower leg are connected through the knee joint connecting rod and the knee joint shaft; the lower leg and the foot are connected in parallel through the Hooke hinge and two ankle joint connecting rods. The invention has the characteristics of many degrees of freedom, and can realize the humanoid gait walking of the biped robot to the greatest extent. The structure is simple, the principle is clear, and the economy is feasible. Large load capacity, compact structure, low cost, low design difficulty, strong feasibility, suitable for biped robot mechanism design requirements.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Lower limb mechanism of biped robot
InactiveCN101229826ASolve problems such as limited range of motion of jointsImprove athletic abilitySelf-moving toy figuresArtificial legsCoxal jointKnee Joint
The invention relates to a lower limb structure of a two-leg robot, which belongs to the field of robot. Applying the characteristics of mechanical movement of parallel opposite sides in a parallel four-link, the invention designs the lower limb structure of the robot with two legs having ten degrees of freedom. Compared with the lower limb structure of the general two-leg robot having 12 degrees of freedom, two degrees of freedom of forward swinging on two ankle joints are decreased. In connection with the opposite driving method with two motors and the same axle applied by each forward swinging and sideward swinging, the invention increases a joint driving torque and decreases the rotation clearance when the mechanism is kept compact. Besides, two motors which realize the degrees of freedom of forward swinging on hip and knee joints are both designed and arranged at the knee joints, thus optimizing the quality distribution of leg mechanisms and reducing the design difficulty of the hip joints with 3 degrees of freedom. The invention uses the parallel four-link mechanism to realize the mechanism design of upper legs and lower legs of the robot, so bottoms of the two feet of the robot are always parallel with the ground during walking, and the effect on the walking stability of the robot due to the rotation clearance of output shafts of the motors is effectively decreased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Human-like biped robot foot structure
InactiveCN103738428AImproves upright walking stabilitySmooth landingVehiclesEngineeringDegrees of freedom
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Gait pattern generating device for legged mobile robot
InactiveUS6876903B2Drawback can be obviatedEvenly combinedProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlTurn angleDynamic models
A gait generation system of a legged mobile robot, in particular a biped robot that has the dynamic model expressing the relationship between the motion of the body and leg and the floor reaction force, and provisionally determines the current time gait parameters including at least parameters that determine leg trajectory and the like in response to a demand, supposes the parameters of a periodic gait, corrects the current time gait parameters such that the body trajectory determined from the dynamic model and the parameters of the current time gait, etc., converges to a body trajectory determined from the parameters of the periodic gait, and determines instantaneous values of the current time gait based on the corrected current time gait parameter. With this, the system can generates a gait of any stride, turning angle and walking period, including the floor reaction force acting on the legged mobile robot, that satisfies the dynamic equilibrium condition. Further, the system can generates a gait in such a manner that the displacement and velocity of each robot part are continues at the boundary of the generated gait and that succeeding thereto, can generate a gait that is high in the margin of stability, can predict future behavior of the robot and generate a gait such that no disadvantages such as posture divergence occurs.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
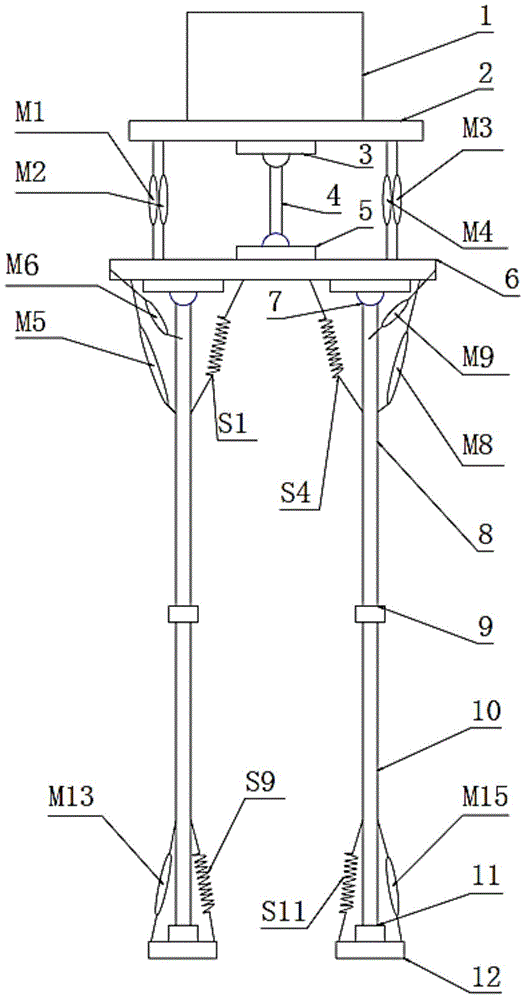
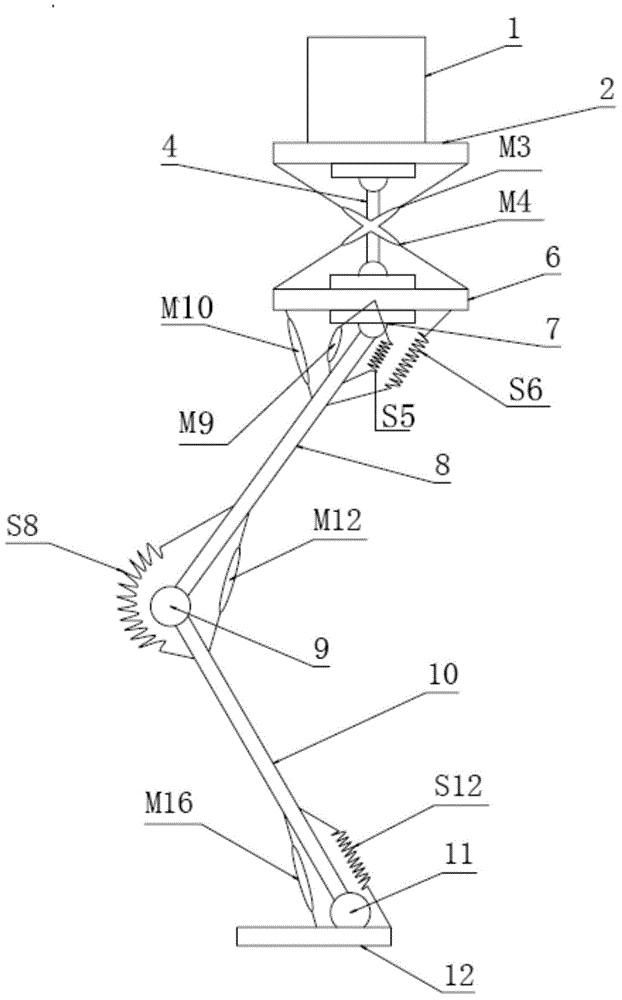
Novel biped humanoid robot system based on pneumatic artificial muscles
ActiveCN104401419AMeet the needs of multidisciplinary scientific research teachingUnique shapeVehiclesSystems designKnee Joint
The invention provides a novel biped humanoid robot system based on pneumatic artificial muscles, belongs to the technical field of robots, and in particular relates to a biped robot having powerful athletic ability and flexible humanoid characteristics. The biped humanoid robot system comprises a mechanical body and an electrical control system; the biped humanoid robot system is characterized in that the mechanical body is mainly composed of seven parts, namely a waist, a hip joint, thighs, knee joints, shanks, feet and the like, and has 13 degrees of freedom in total; in the 13 degrees of freedom, 3 degrees of freedom of the waist are realized by virtue of the cooperation of four pneumatic muscles and the waist spine, and the single degree of freedom of each of the hip joint, the knee joints and the ankle joints is realized by use of one pneumatic muscle and one spring which are pulled to each other to produce opposed rotating force. According to the design of the novel biped humanoid robot system, a control platform is provided; the system relates to the fields of control science and intelligent control in addition to robotics, and is capable of meeting the requirements of scientific research and teaching of a plurality of disciplines.
Owner:廊坊市奥联科技有限公司
Biped robot capable of walking rapidly
ActiveCN104228993ASimplify the control problemSimplified Motion AlgorithmVehiclesRatchetControl engineering
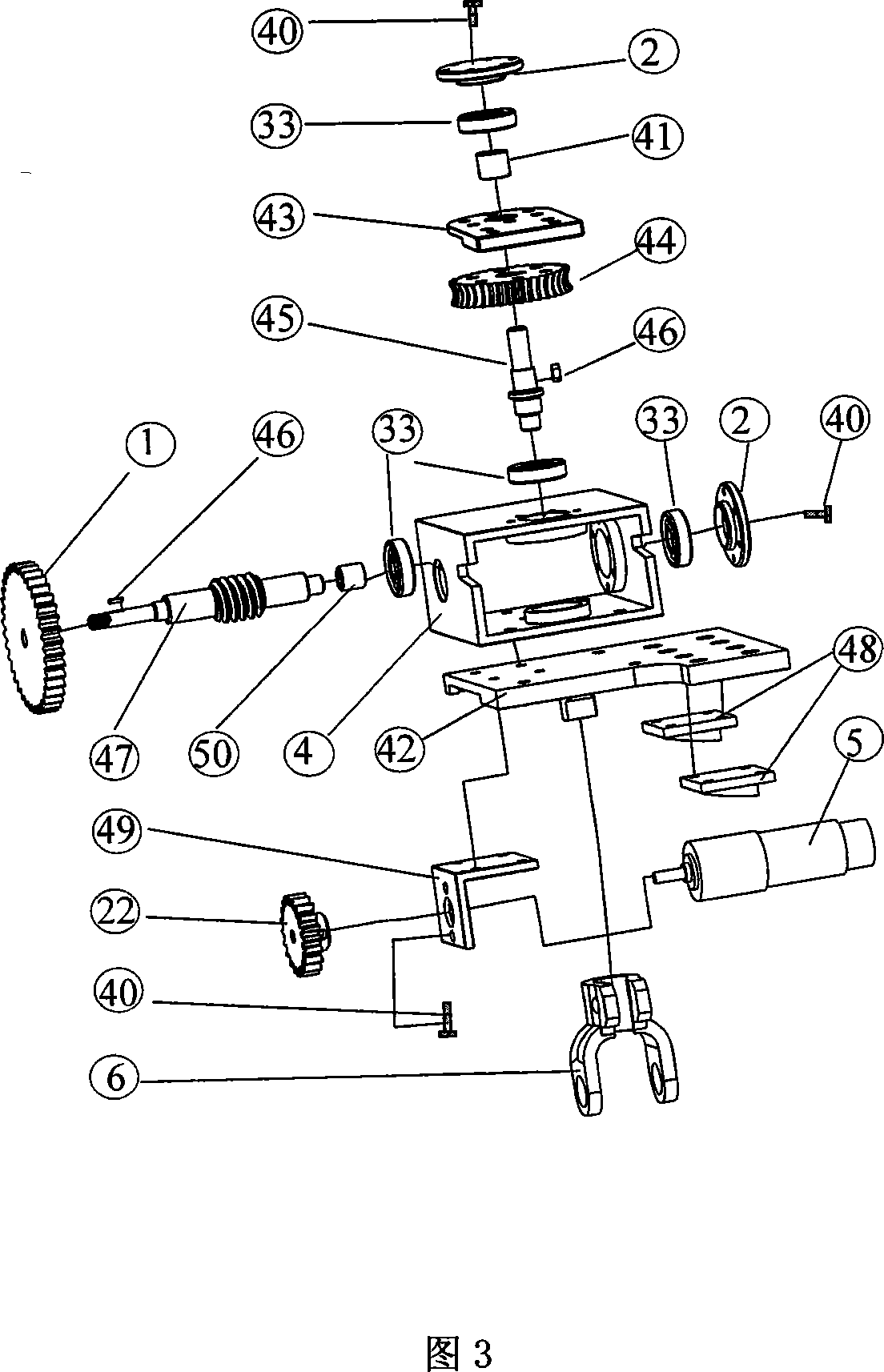
The invention discloses a biped robot capable of walking rapidly. The biped robot is composed of a servo motor, a motor support, a driving bevel gear, driven bevel gears, check pawls, ratchet wheel cam sets, ratchet wheel connecting pins, a driving pawl, oscillating bars, roller connecting pins, rollers, shanks, compression springs, screws, thighs and feet. The servo motor drives the driving bevel gear to rotate so as to drive the symmetrically-arranged driven bevel gears to rotate oppositely and the thighs to swing forwards and backwards; the shanks always make contact with cams in the ratchet wheel cam sets through the compression springs and supporting legs are longer than swinging legs through telescopic motion of the shanks. Compared with the prior art, the biped robot has the advantages that the robot can be driven by one servo motor, so that the robot is convenient to control and high in control accuracy; except for the servo motor, other structures of the robot are all mechanical structures, so that motion cooperation is convenient; the structure is simple, machining and installation are convenient, and the robot can walk rapidly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Power type walking method of dual-foot robot
A power-typed walking method for a biped robot belongs to the technical field of robot walking control. The method is characterized in that the robot realizes fully power-typed walking similar to passive walking by rapidly swinging two legs and controlling landing collision of the swinging legs in a gait cycle T which is more than 0.2s and less than 0.5s, the robot creates a virtual slope by bending the knee joint of a swinging leg and supplements energy by straitening the knee joint of a supporting leg, each gait of the gait cycle is determined by three key frames and described by four parameters, a first derivative continuous smooth curve connects the key frames. In the experiment, single gait of the robot reaches a relative walking speed of 4.48 leg lengths per second, which improves by 29 percent compared with the record created by RunBot; moreover, a plurality of gaits of the robot realizes continuous variable speed walking from 1.24 leg lengths per second to 3.88 leg lengths per second.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Biped robot walking plan and control method
InactiveCN105608309AReal-time computingRealize horizontal movement speed switchingSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsPhase changeGait
The invention provides a biped robot walking plan and control method. The method comprises the steps of establishing an equivalent model of a robot; determining a phase change graph meeting the requirement of the equivalent model; determining a phase change graph of a single-step horizontal movement track according to a human gait walking formula, namely, calculating a relationship between the speed of a single step and the step length / period of the single step; calculating a foothold according to the horizontal movement track of the single step; and controllably converting the position of the calculated foothold into an angle required for finishing motion of each joint. According to the method, the human gait formula is associated with the relationship between the walking speed and the step length / period of the single step, so that the calculation of the step length / period of the single step can be simplified; the period of the single step serves as a trigger event of single-step starting and ending, so that the end speed of the single step can be well predicted and the real-time calculation and adjustment of the foothold can be facilitated; and based on the motion description of the phase change graph, the analysis of a motion law of the biped robot can be more visual.
Owner:NANJIANG ROBOT
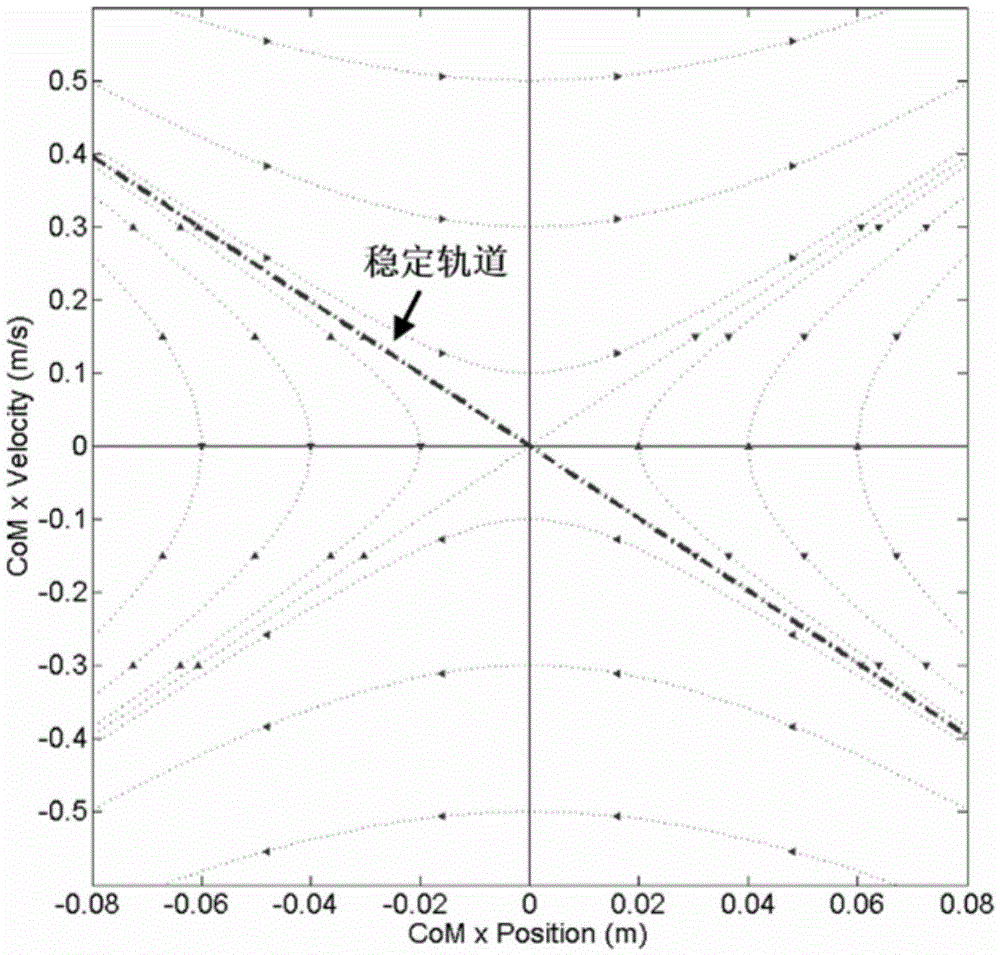
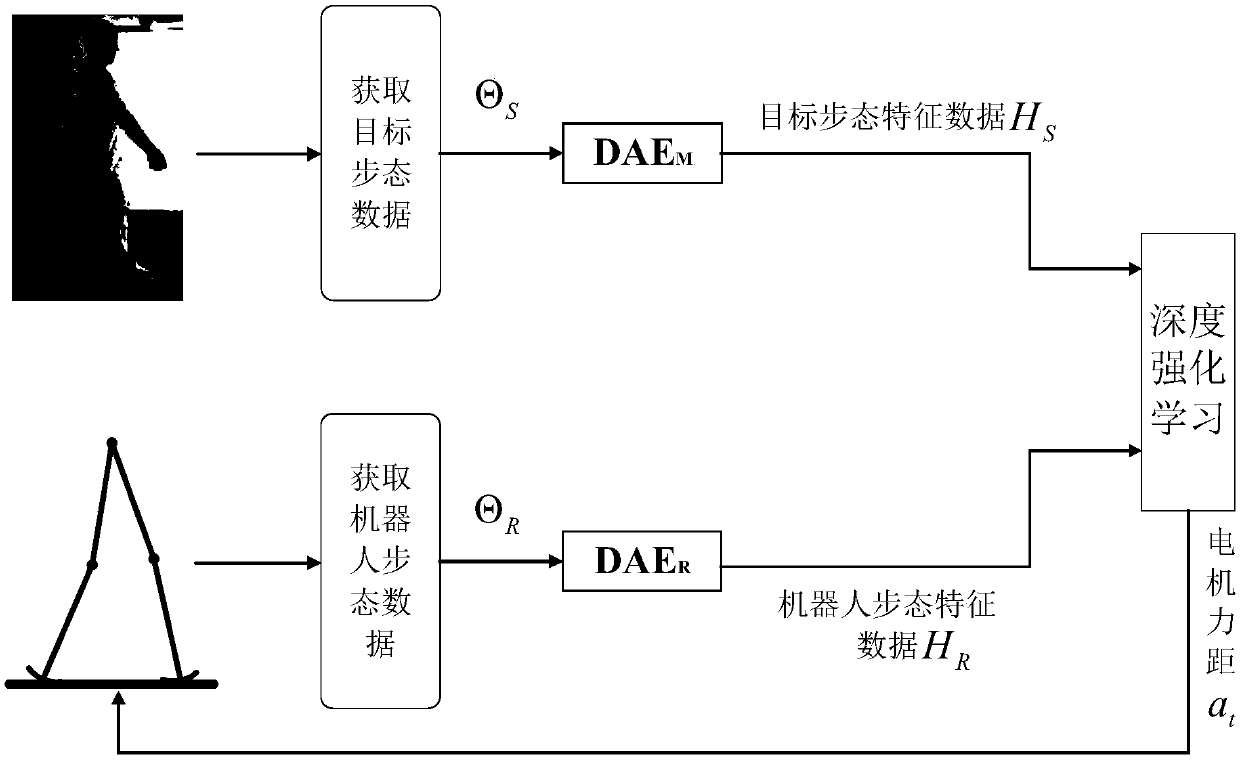
Gait planning method for biped robot based on deep reinforcement learning
The invention discloses a gait planning method for a biped robot based on deep reinforcement learning, and the method utilizes the stability and flexibility of human gait and combines deep reinforcement learning to effectively control the gait of the biped robot. The method includes the following steps: 1), establishing a passive biped robot model; 2), acquiring and processing human gait data andtarget gait data; 3), extracting the implicit features of the gait data of the biped robot and human gait data through using a noise reduction auto-encoder; 4), learning the gait characteristics of ahuman body through using deep reinforcement learning, and then planning the gait of the biped robot. The method combines deep reinforcement learning with human gait data to control the biped robot towalk as stable and compliant as a human.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Gait generation and optimization method for biped robot
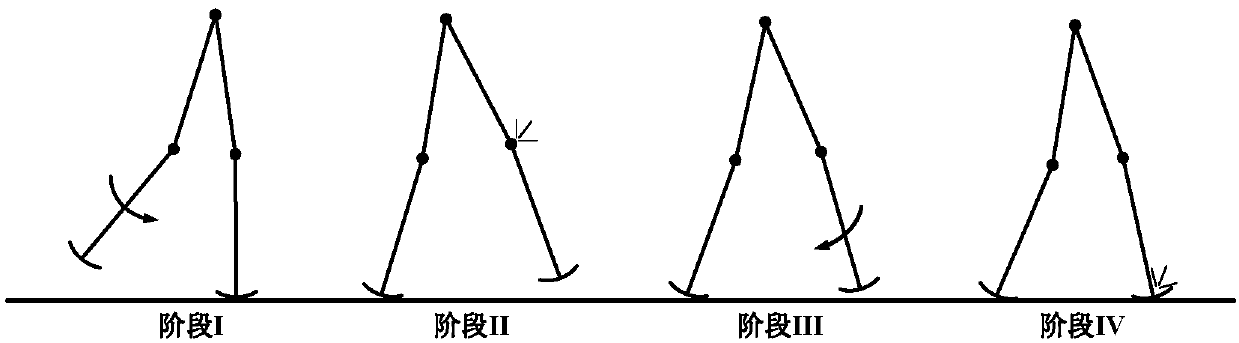
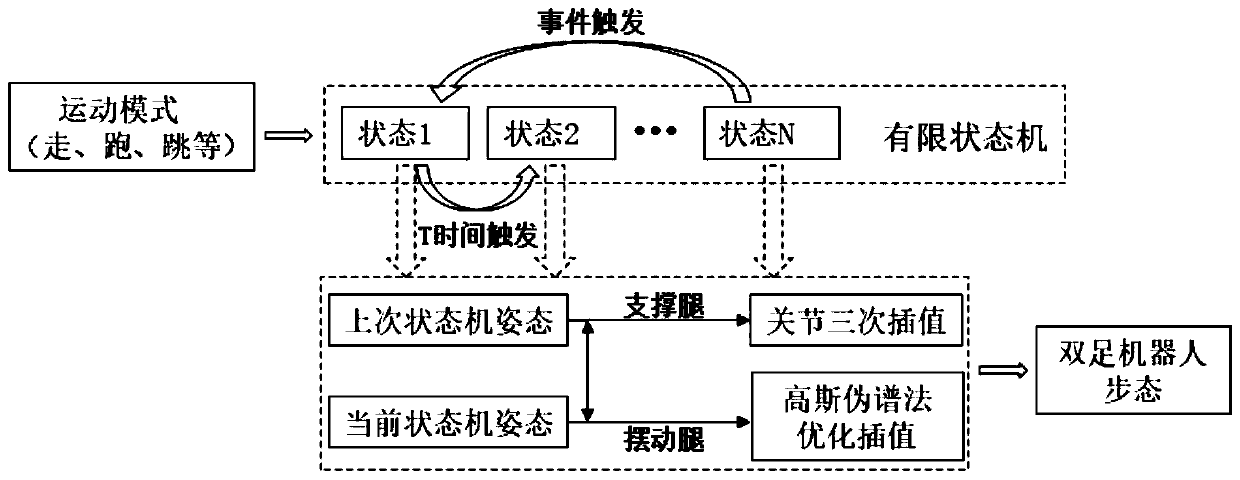
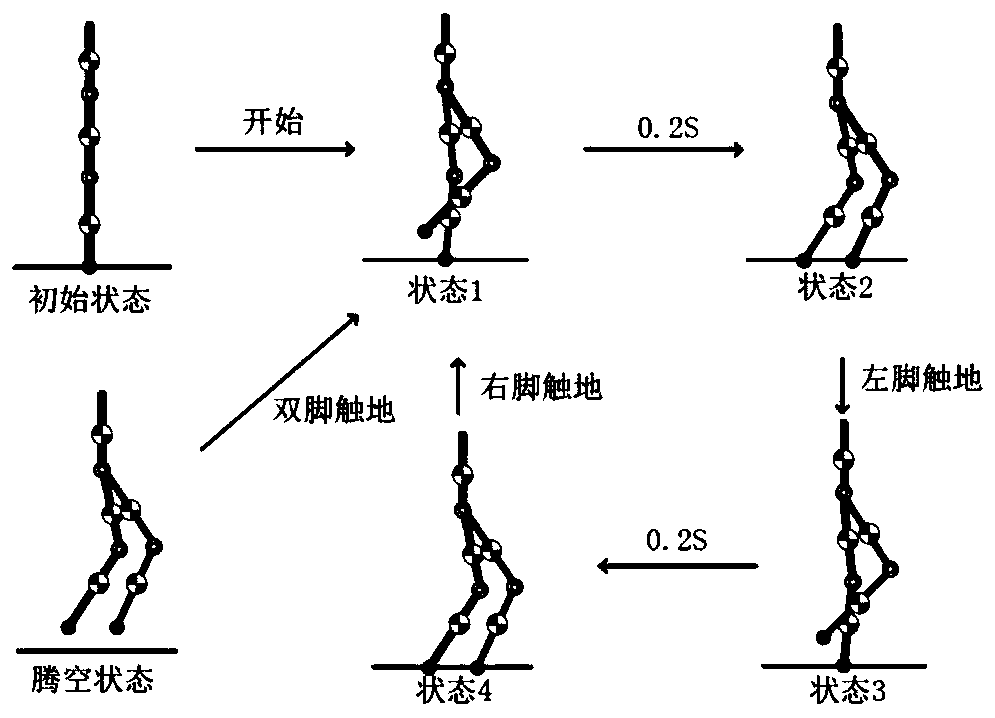
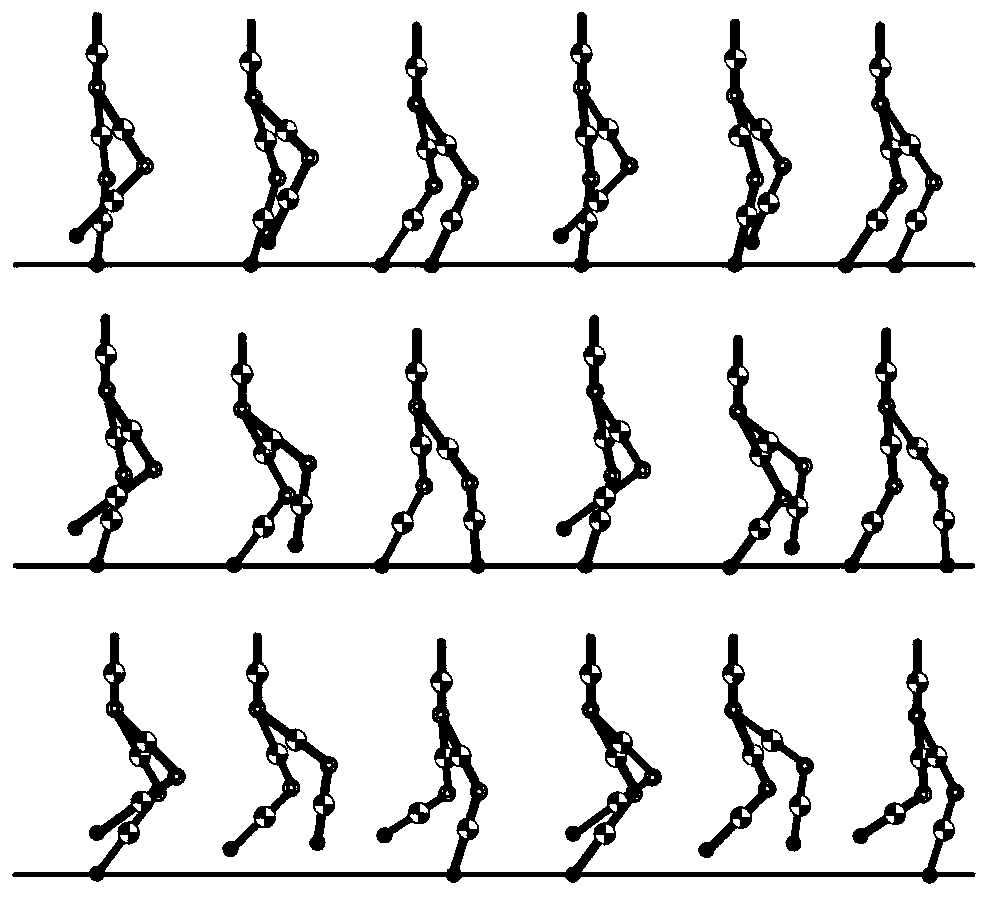
ActiveCN110315543AReduce energy lossAvoid errorsProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesSimulationState switching
The invention discloses a gait generation and optimization method for a biped robot. The method is characterized in that a gait library of the biped robot is constructed in a finite state machine according to a target pose of the state of the biped robot; mutual switching conditions among all states of the robot are set and triggered; in each state switching process, a joint cubic interpolation method is used for planning the movement track of support legs, and a gauss pseudo-spectral method is used for optimizing the movement track of swing legs; and finally, the gait of the biped robot in different motion modes is generated by the finite state machine. According to the gait generation and optimization method for the biped robot, the constraint of ZMP is not considered, and all the bipedrobots with or without the sole edges of the feet can generate the walking track by the method; and the planning process is simple and operable and is more suitable for online generation, and the biped walking robot can stably walk and finish walking, running, jumping and other actions by matching with a simple control strategy.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Biped robot lower limb mechanism driven hydraulically
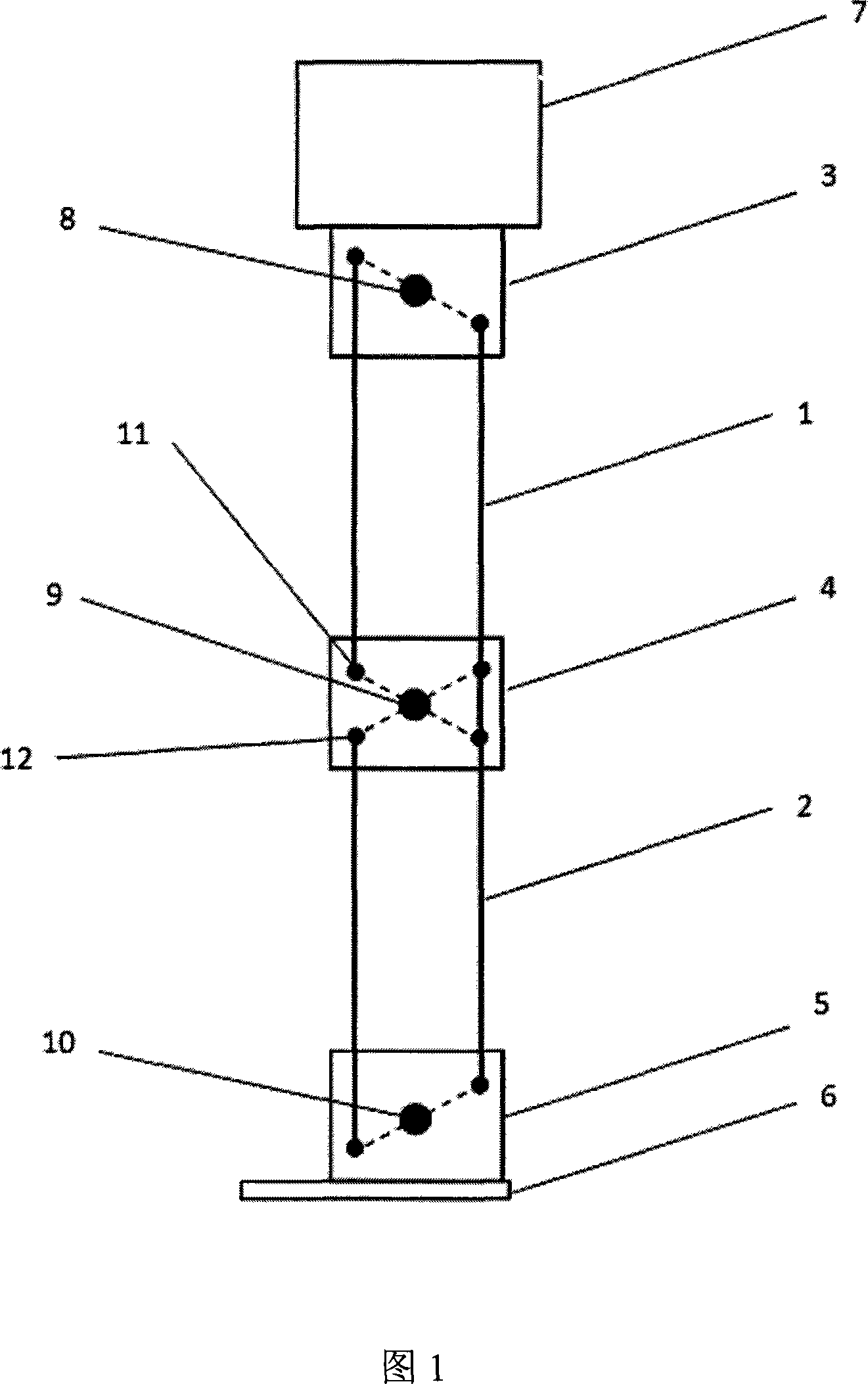
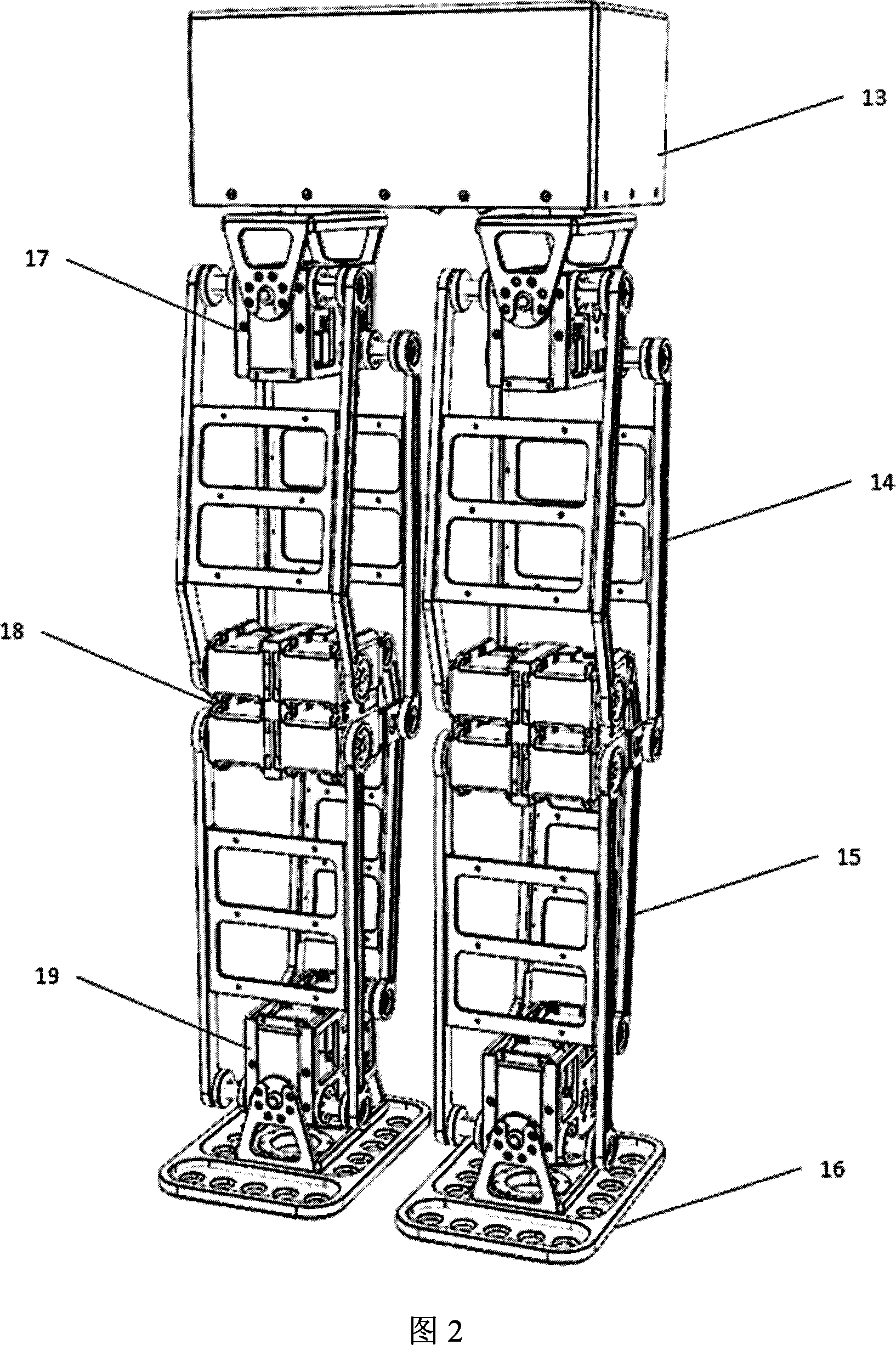
The invention relates to a biped robot lower limb mechanism, in particular to a biped robot lower limb mechanism driven hydraulically. The problems that an existing electrically-driven robot is small in loading capacity, low in specific power and poor in anti-interference performance are solved. The biped robot lower limb mechanism comprises a body, an oil distributor, a left leg and a right leg, the oil distributor is arranged on the upper surface of the body, the left leg and the right leg are arranged on the lower surface of the body side by side, and are of the same structure, and the left leg comprises a foot, a shank, a thigh, a hip joint forward swing hydraulic cylinder servo unit, a hip joint twisting hydraulic cylinder servo unit, a hip joint, a knee joint forward swing hydraulic cylinder servo unit, an ankle joint, two ankle joint hydraulic cylinder servo units, a hip joint side swing hydraulic cylinder servo unit and a body upper end swing connecting piece. The biped robot lower limb mechanism belongs to the field of robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot
The invention relates to a flexible biped robot, in particular to a pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot. The problems that linkage between joint flexibility and a dynamic response characteristic of existing flexible biped robots is poor, the walking efficiency of the robots is low and the dynamic stability of the robots is poor are solved. The pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot comprises a left leg, a right leg and a pelvis. The left leg and the right leg each comprise a thigh, a shank, a foot, a hip joint, a knee joint and an ankle joint. Each hip joint comprises a one-way series-connection elastic driver and a hip joint transmission mechanism. Each one-way series-connection elastic driver comprises a motor, a motor seat, a torsion spring, a first hub, a second hub, a first clamping ring, a second clamping ring and a hip joint driving shaft. Each hip joint transmission mechanism comprises a driving belt wheel, a driven belt wheel, a driving belt and a hip joint driven shaft. The driving belt wheels are mounted on the hip joint driving shafts correspondingly. Each knee joint comprises a knee joint driving mechanism and a knee joint transmission mechanism. The pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot belongs to the field of humanoid robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Biped robot gait energy efficiency optimization method
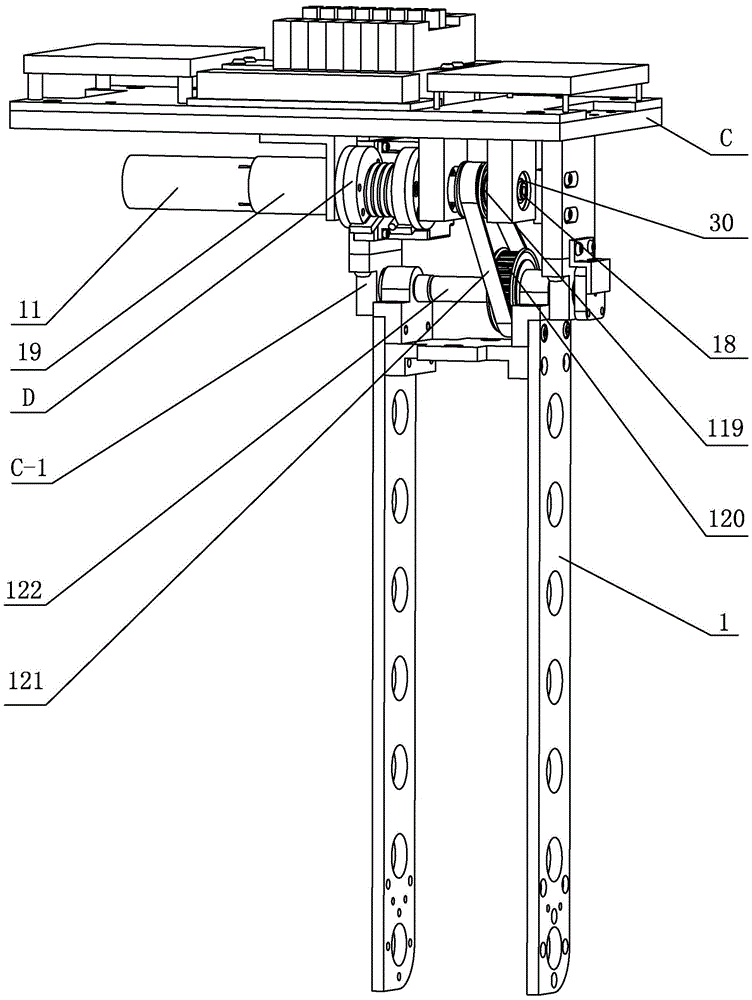
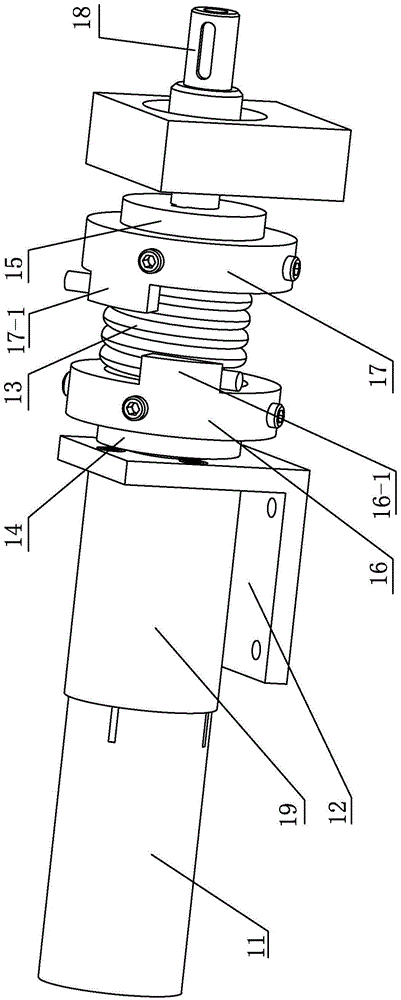
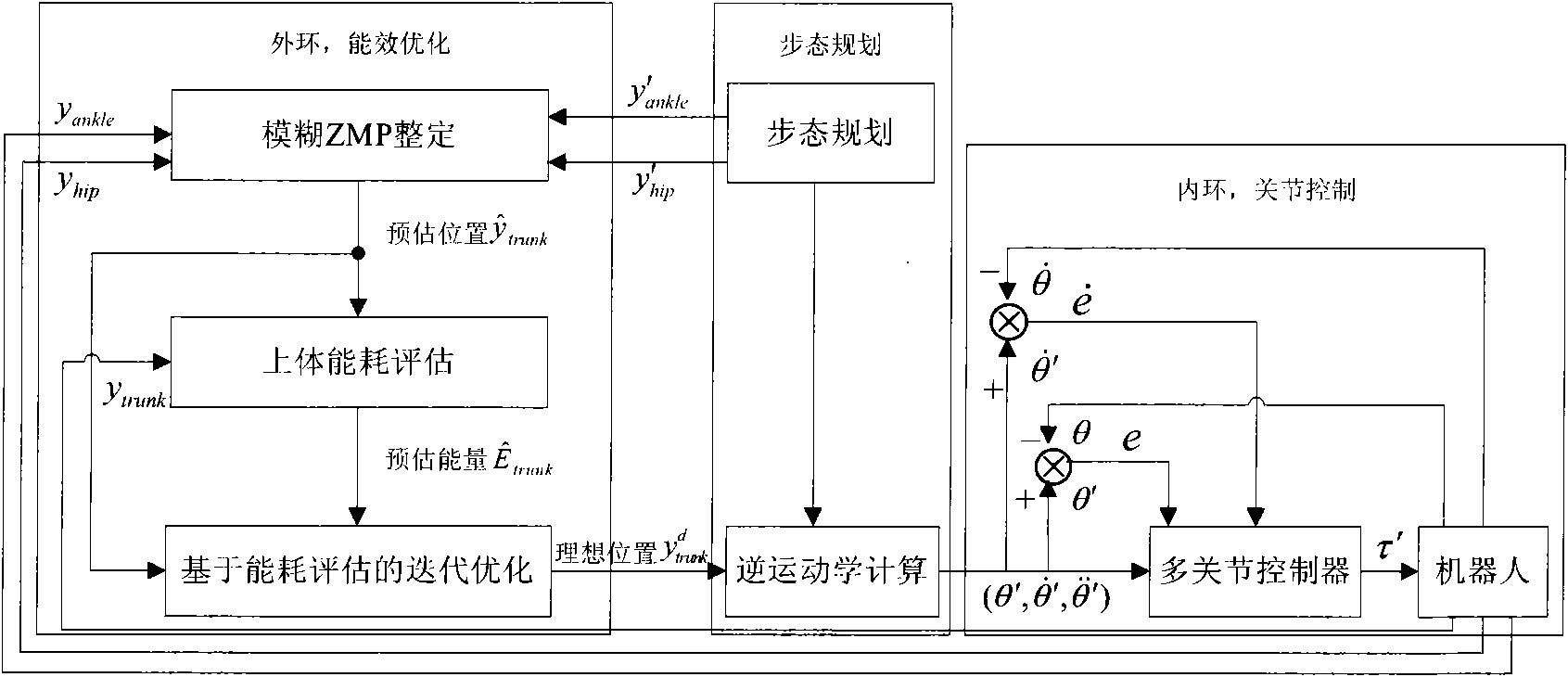
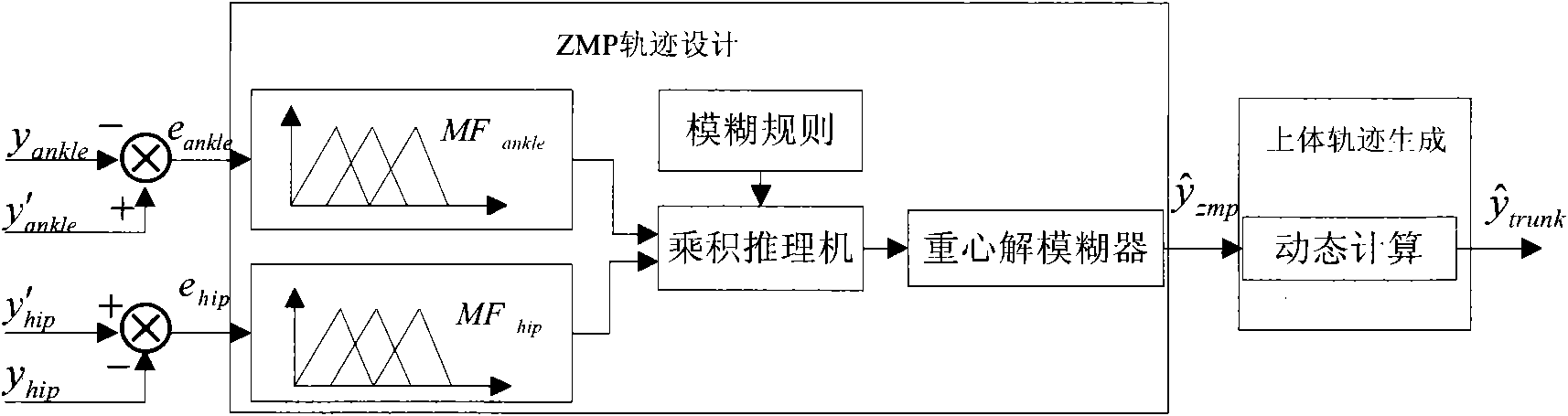
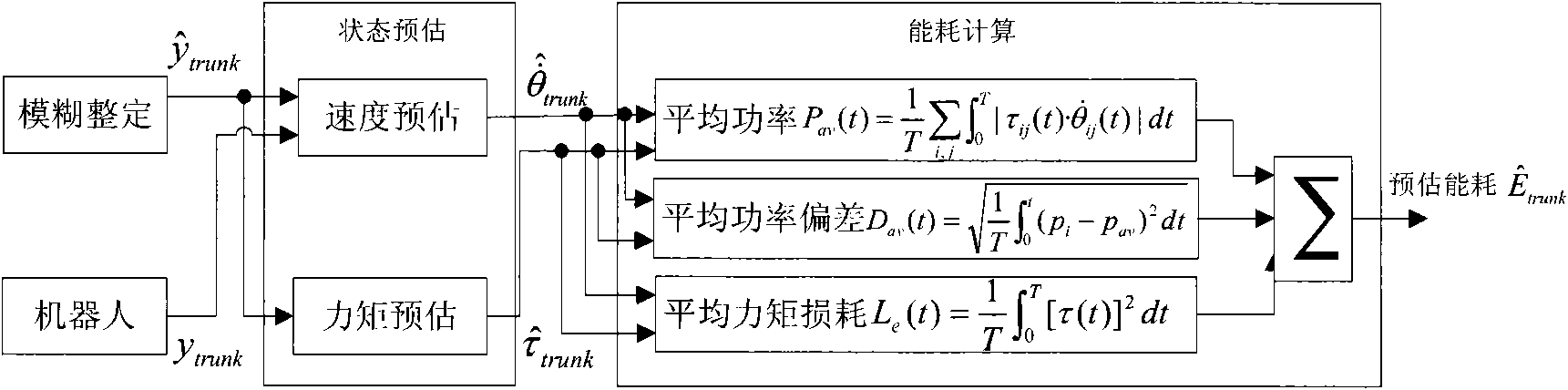
InactiveCN101847009AStable energy consumptionReduce energy consumptionVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlHigh energySimulation
The invention provides a biped robot gait energy efficiency optimization method, including that: (1) planning is carried out to obtain the track of the lower limb of the biped robot; (2) energy optimization is carried out to obtain the ideal gait of the robot; (3) the robot is controlled by a single joint controller; wherein the step of obtaining the ideal gait of the robot by energy efficiency optimization concretely includes fuzzy ZMP adjusting, upper body energy consumption evaluation and iteration optimization step based on energy consumption evaluation. The invention provides a biped robot gait energy efficiency optimization method based on fuzzy logic, aiming at solving the high energy consumption problem in the biped robot walking process. The method can effectively reduce robot energy consumption and maintains stability thereof.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
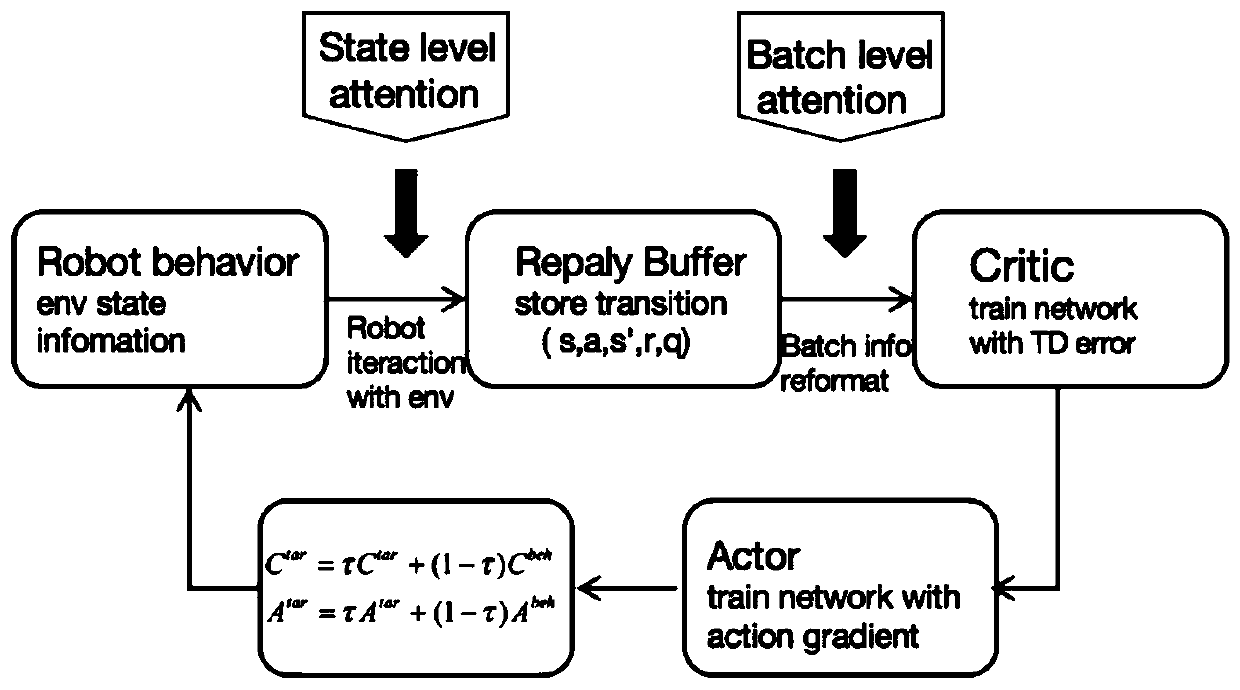
Biped robot adaptive walking control method based on deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN110262511AForced walking stabilityFast convergenceNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsSimulationNetwork model
The invention relates to a biped robot adaptive walking control method based on deep reinforcement learning. The method comprises the steps that 1) a simulation platform is established; 2) a network model based on a deep reinforcement learning method introducing an attention mechanism is constructed; 3) the network model is trained according to the interaction information of a biped robot in the environment of the simulation platform, and the interaction information is stored in a playback pool; and 4) the network model which completes training is used to realize adaptive control of walking of the biped robot. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of fast convergence speed, good fitting effect, high walking stability and the like.
Owner:TONGJI ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE RES INST SUZHOU CO LTD
Under-actuated biped robot walking control method
InactiveCN103204193AControl is fast and smoothControlling the biped robot quickly and smoothly achieves stabilityVehiclesTrial and errorBiped robot
The invention discloses an under-actuated biped robot walking control method aiming at the problem of planar walking control of a biped robot. By adopting a MACCEPA flexible actuator and utilizing self dynamic characteristics of the biped robot, quick walking is achieved effectively. In continuous interaction of the robot with the ground, the robot learns walking independently in a trial and error mode by fully utilizing trial-and-error learning capability of a Q learning method; and stable, natural and periodical quick walking of the robot is achieved, and the method has high application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hydraulic-drive lower-limb mechanism with load bearing capability of biped robot
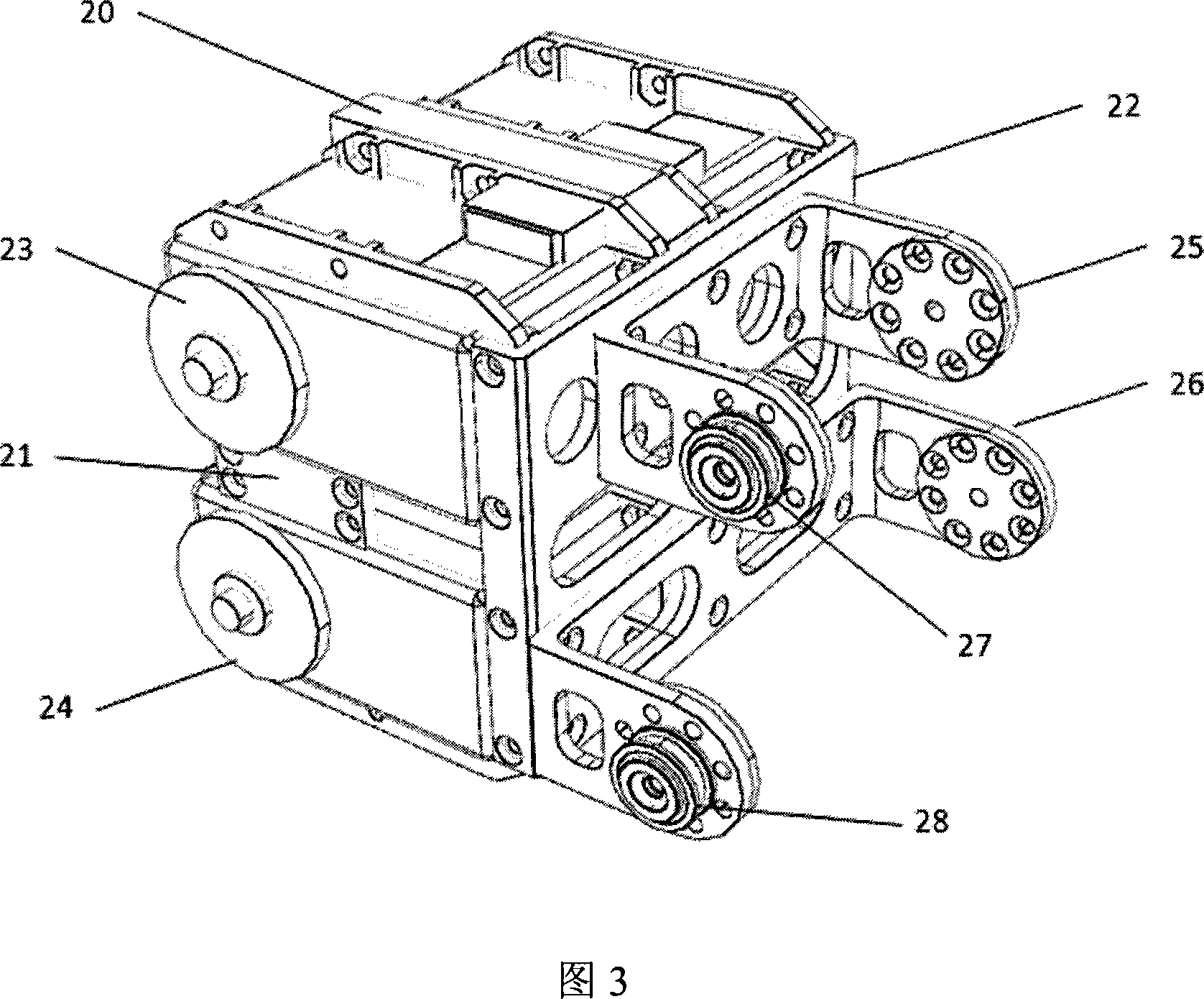
The invention discloses a hydraulic-drive lower-limb mechanism with load bearing capability of a biped robot, which comprises two robot legs. The upper portion of each robot leg is connected with a robot steering mechanism, the robot steering mechanisms are arranged on the body of a robot, the lower portion of the each robot leg is connected with a robot foot, and each robot leg, each robot steering mechanism and each robot foot are driven hydraulically. A driving rotation freedom-degree rotation pair I utilizing the normal direction of the body of the robot as the axis, a lateral driving freedom-degree rotation pair II and a lateral driven freedom-degree rotation pair VI are arranged on one robot leg, one robot steering mechanism and one robot foot, and three front driving freedom degrees include the rotation pair II, the rotation pair IV and a rotation pair V. The hydraulic-drive lower-limb mechanism is simple in structure, capable of steering, easy to maintain and high in dynamic response capability and has obstacle detouring performance and the load bearing capability.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
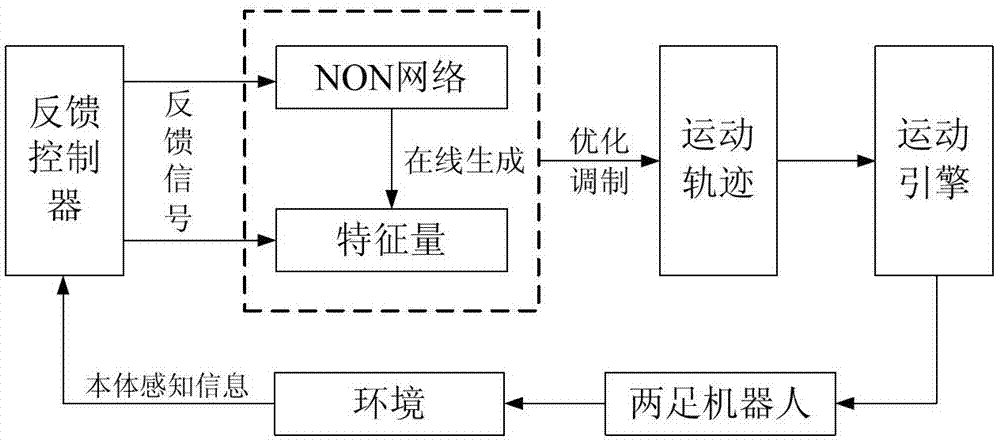
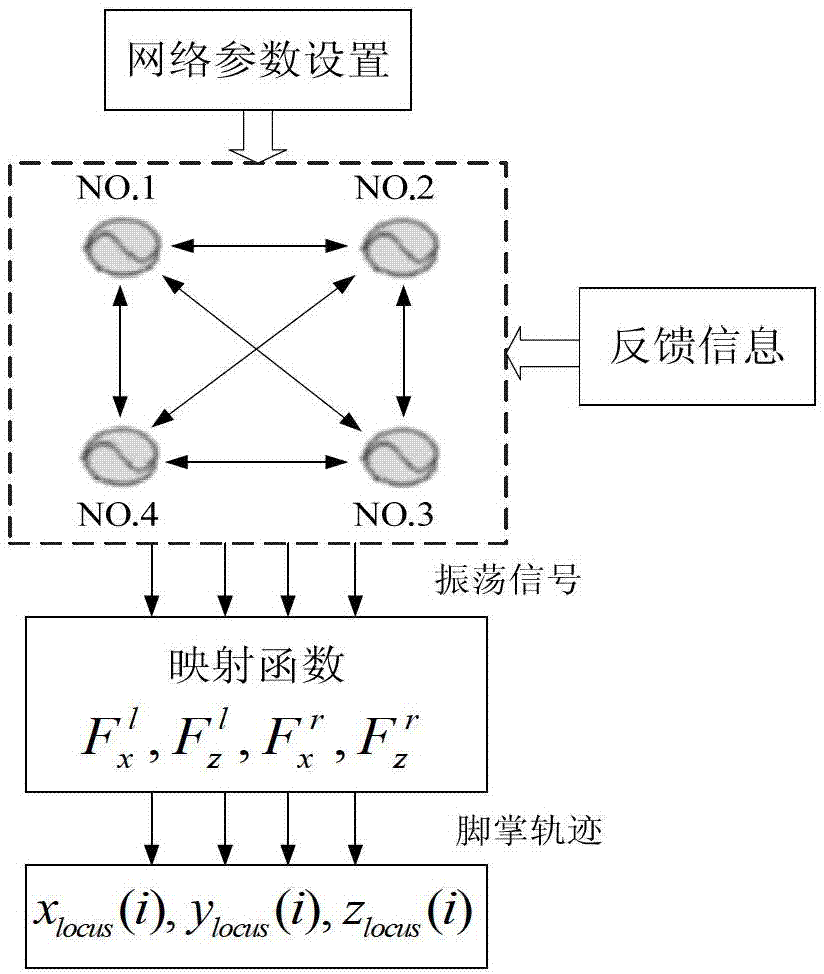
Method for generating real-time gait path of biped robot
ActiveCN103116354AImprove real-time performanceImprove robustnessPosition/course control in two dimensionsOscillator networkControl system
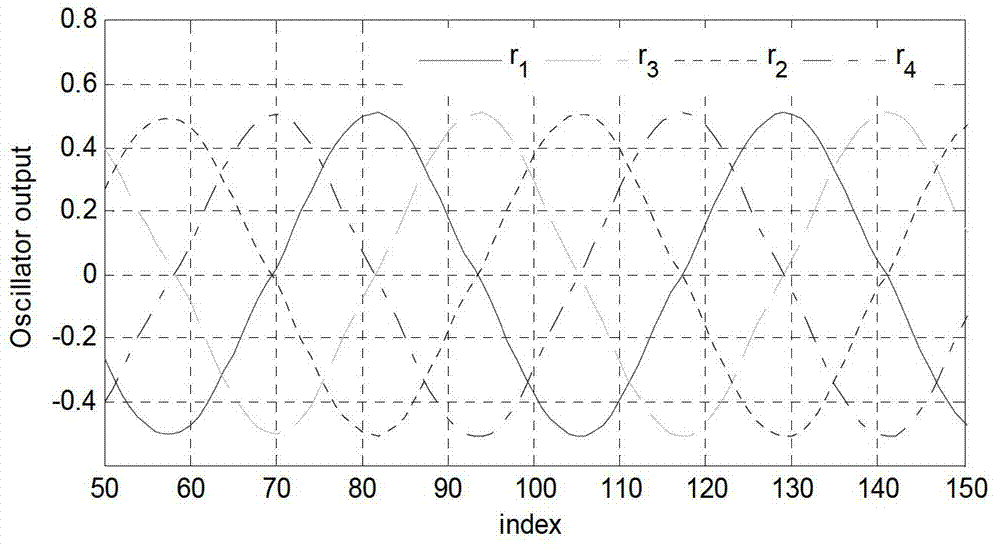
The invention relates to a method for generating a real-time gait path of a biped robot. The method includes steps of forming an oscillator network by means of omni-directionally coupling four oscillator neural units, designing mapping functions and generating sole paths of the biped robot in an online manner; forming a gravity center path generator by three oscillator neural units and generating three-dimensional gravity center paths of the robot in an online manner; enabling sensors to detect environmental information, creating a feedback circuit, and adjusting the sole paths and the gravity center paths in real time to obtain the gait paths with environmental adaptability; and optimizing parameters of a control system by a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm to obtain the optimal gait path. The oscillator network can output four channels of oscillator signals with adjustable phase relations. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that abundant dynamic characteristics and the characteristic of capabilities of coupling walking environments and feeding information of the oscillator neural network are sufficiently utilized, so that the gait path generated in an online manner is adaptable to the walking environments to a certain degree.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Bionic foot capable of improving gait naturality and stability of biped robot
ActiveCN105292297AIncrease the elastic deformation rangeReduce adverse outcomesVehiclesEngineeringGait
The invention discloses a bionic foot capable of improving the gait naturality and stability of a biped robot. The bionic foot comprises a bionic foot body and a bionic ankle. The bionic foot body comprises bionic arches, extension springs, a compression spring, a viscoelastic material layer and rubber non-slip mats. Part of impact borne by the bionic foot can be consumed by the viscoelastic material layer, and the rest of the impact is absorbed by the elastic deformation of the bionic arches, the extension springs and the compression spring. Due to the fact that the rubber non-slip mats are adopted, the non-slip performance of the bionic foot can be improved. The bionic ankle comprises a first ankle joint connecting piece, a first ankle joint platform, a second ankle joint connecting piece and a second ankle joint platform. The bionic ankle can do inward turnover and outward turnover movement through the rotation of the first ankle joint platform around a third pin shaft, and can do back bending and toe bending movement through the rotation of the second ankle joint platform around a fourth pin shaft. By means of the bionic foot, the harmful effect caused by the impact can be effectively reduced, meanwhile, the walking mode of human beings can be imitated, and the gait of the robot can be more natural.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
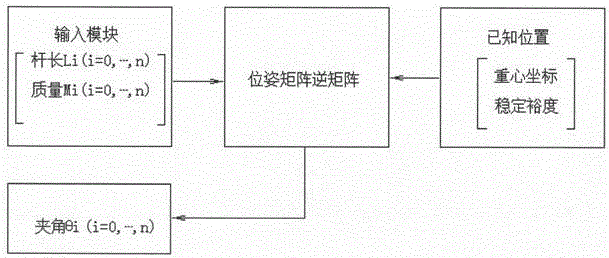
Humanoid biped robot walking posture control method based on genetic algorithm
InactiveCN105965506AAchieve stable anthropomorphic walkingAvoid complexityProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsTime response
The invention discloses a walking posture control method of a humanoid biped robot based on a genetic algorithm. A mathematical model of a biped robot is established based on the ZMP control theory and a pose matrix, and the basic gait of a human is simulated. V, height H, arm swing R, body center up and down swing C, body center left and right swing A These six parameters plan the robot's gait, and select optimized T, V, H, R through genetic algorithm The six parameters of , C, and A are brought into the inverse operation of the pose matrix to obtain the values of other joint coordinates of the robot, and solve the method of generating data that stably controls the gait of the robot. It overcomes the problem of large amount of calculation and low efficiency in inverse operation of pose matrix, improves the real-time response ability of the system, and uses the data generated by this method in the humanoid biped robot system to achieve a good control effect.
Owner:北京格分维科技有限公司
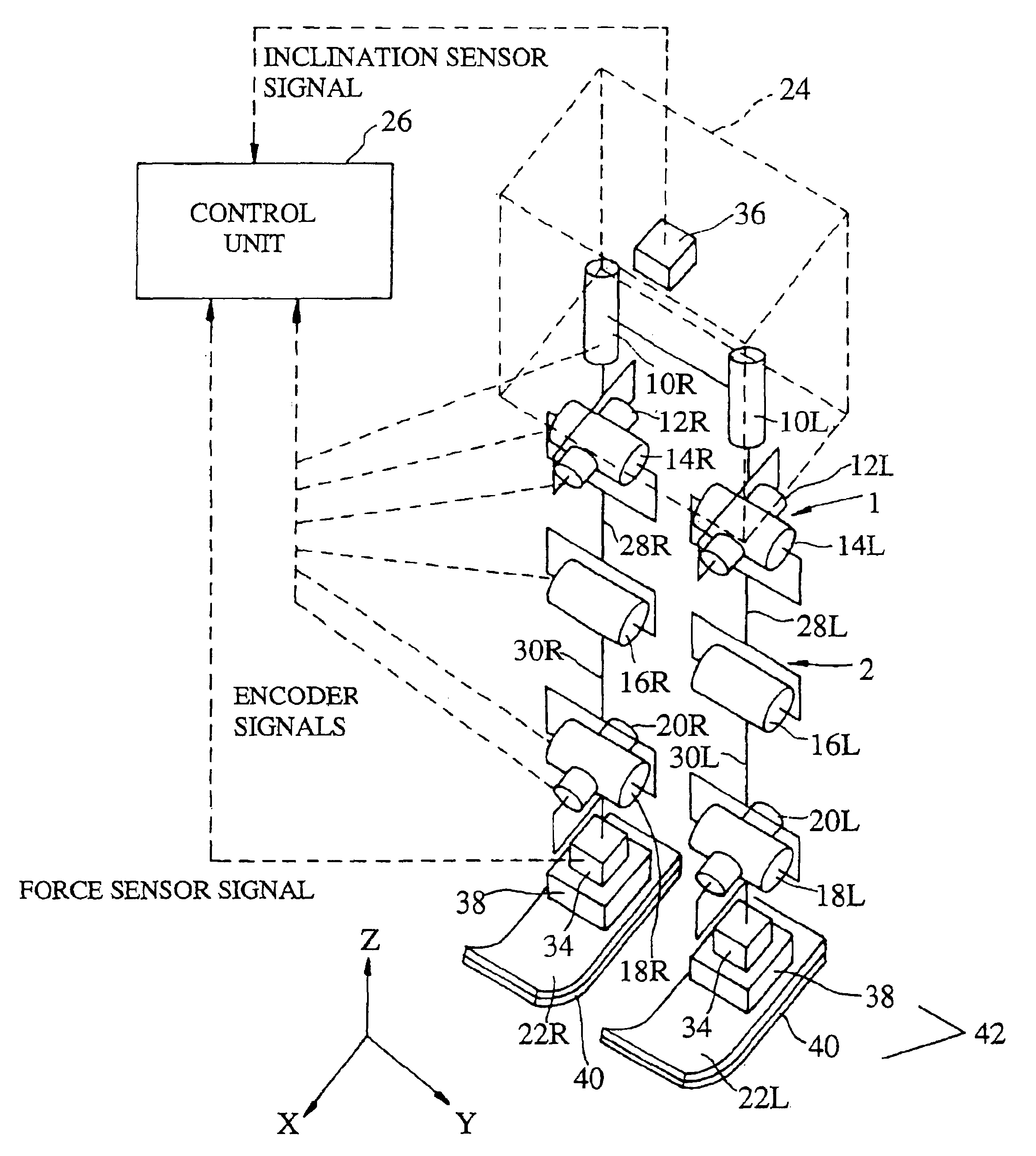
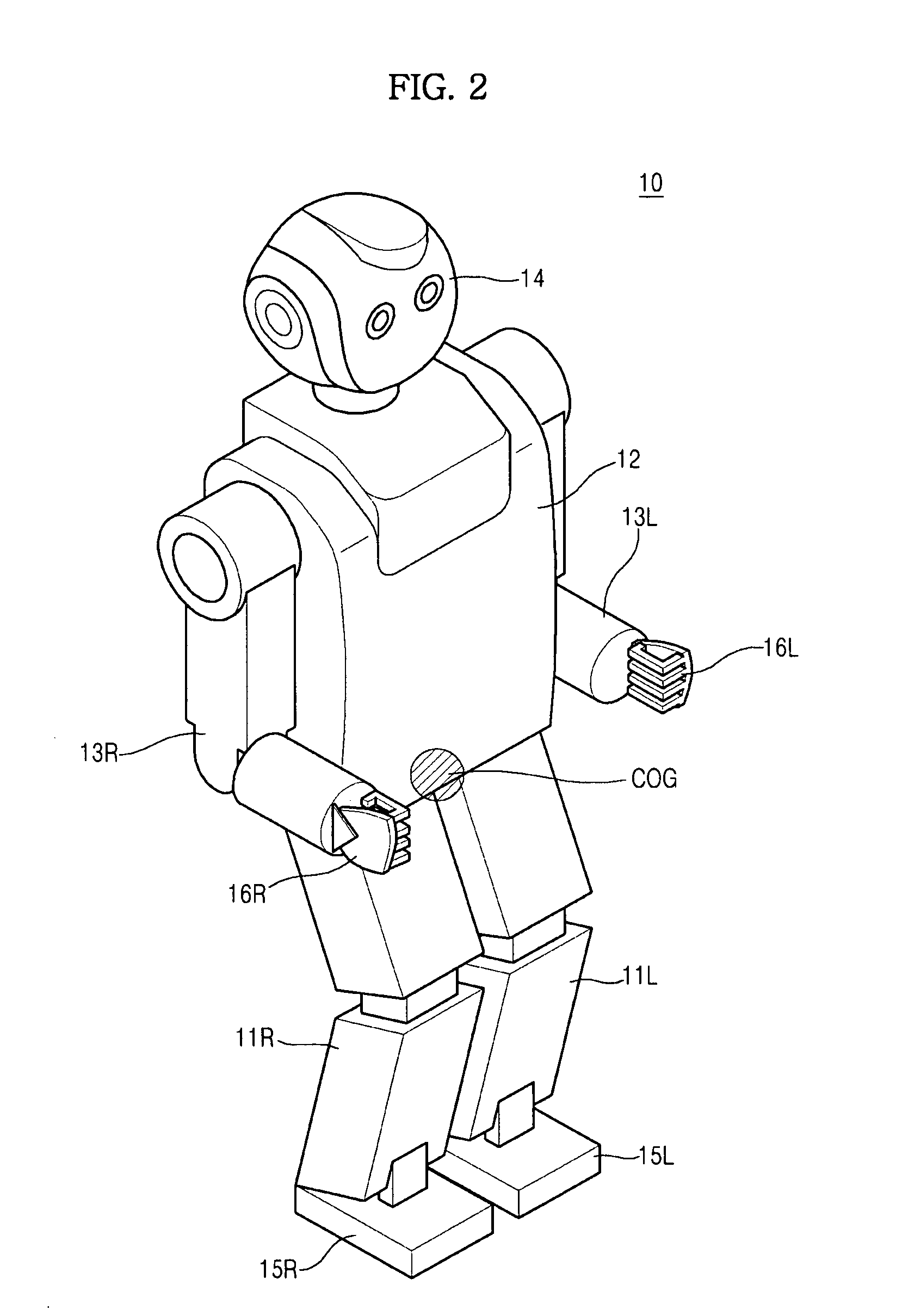
Robot and method of controlling balance thereof
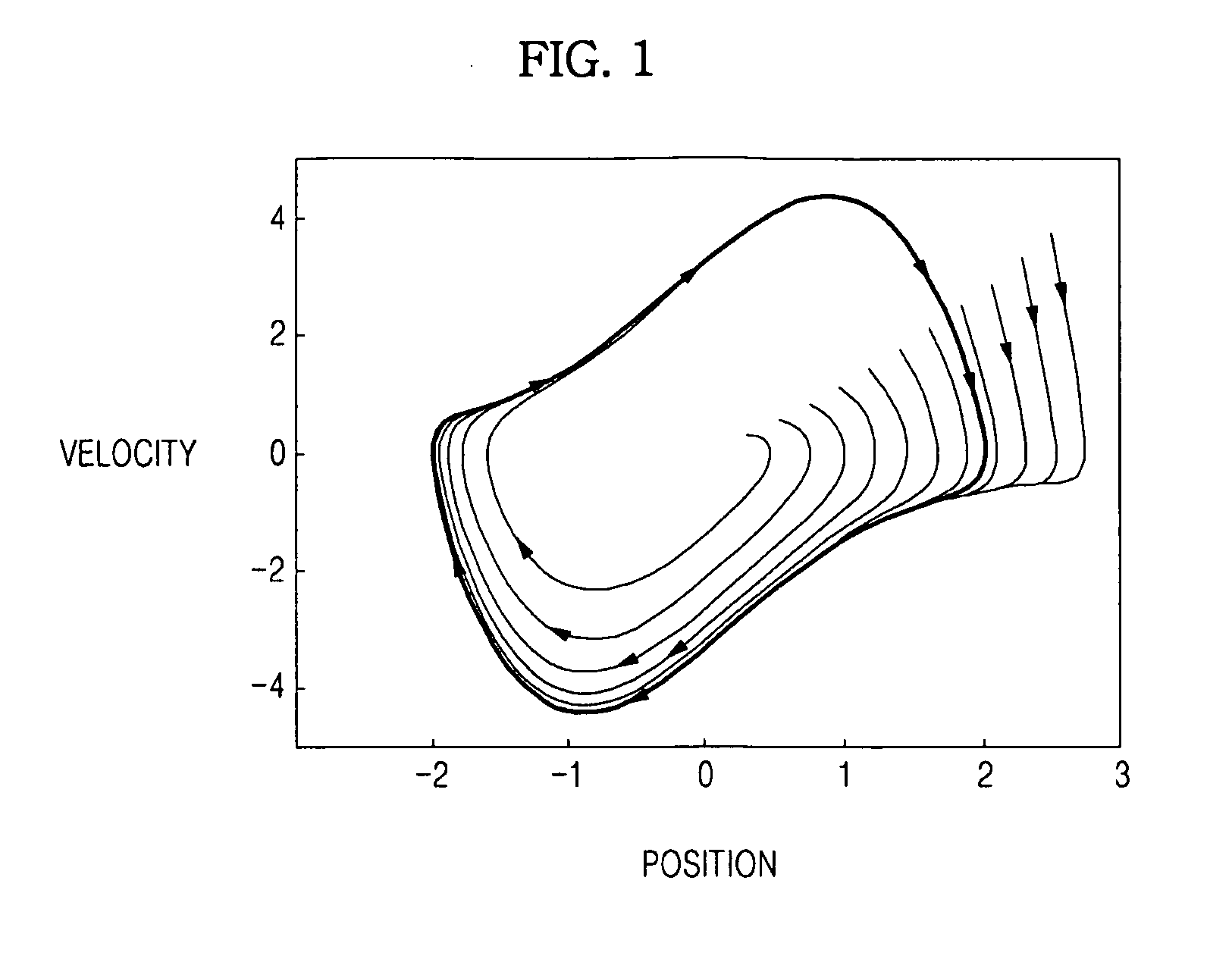
ActiveUS20100161116A1Reduce maximum rightLimited rangeProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlFinite-state machineControl theory
A finite state machine (FSM)-based biped robot, to which a limit cycle is applied to balance the robot right and left on a two-dimensional space, and a method of controlling balance of the robot. In order to balance an FSM-based biped robot right and left on a two-dimensional space, control angles to balance the robot according to states of the FSM-based biped robot are set. The range of the control angles is restricted to reduce the maximum right and left moving distance of the biped robot and thus to reduce the maximum right and left moving velocity of the biped robot, thereby reducing the sum total of the moments of the biped robot and thus allowing the ankles of the biped robot to balance the biped robot to be controlled, and causing the soles of the feet of the biped robot to parallel contact the ground.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
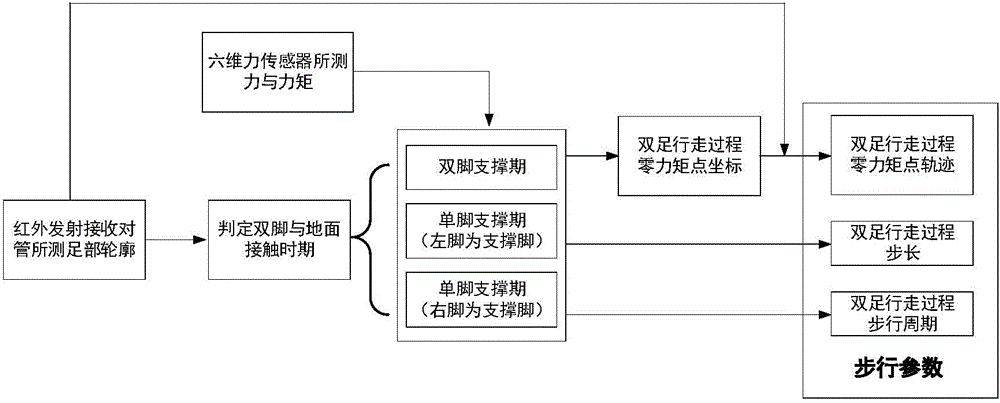
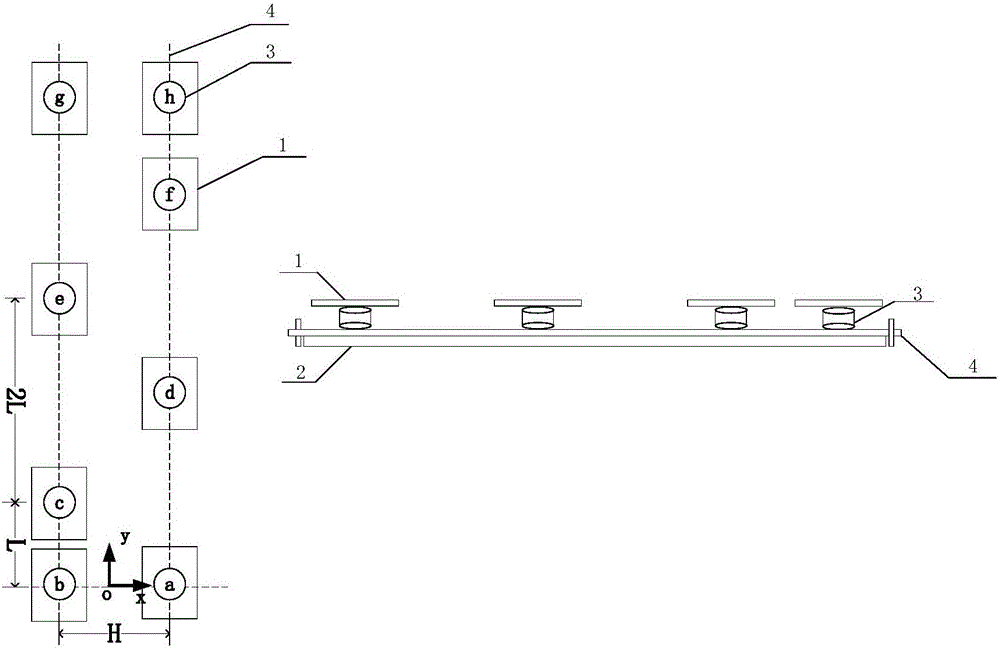
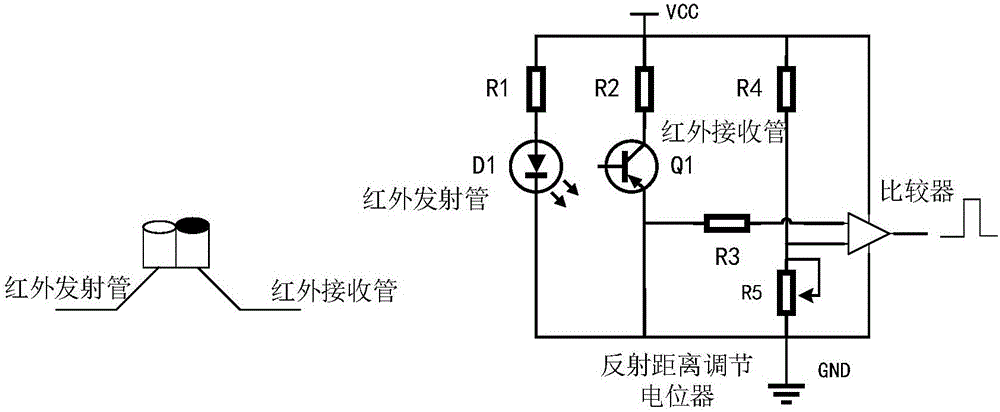
Biped walking parameter measuring method and apparatus
ActiveCN105973143AWalking smoothlyDiagnostic recording/measuringUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceState parameter
The invention provides biped walking parameter measurement and belongs to the technical field of robots. A biped walking parameter measuring apparatus is provided and comprises a zero moment point measuring system, a foot contour measuring system and a walking parameter calculating system. A biped walking parameter measuring method provided can accurately and effectively measure biped walking parameters including stand state parameter before walking, step, step period, zero moment point track, and the contours of feet contacting the ground. The method for measuring biped walking parameters of a human being is of great importance to analysis of walking gaits of the human being, thereby providing important basis for planning track of a biped robot. The method is used for measuring the walking parameters of a biped robot, and feedback parameters of biped robot walking gaits, walking track on-line adjusting, and enclosed control of a host computer and each joint of leg portions are provided. The method is of great significance to stable walking of a biped robot.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
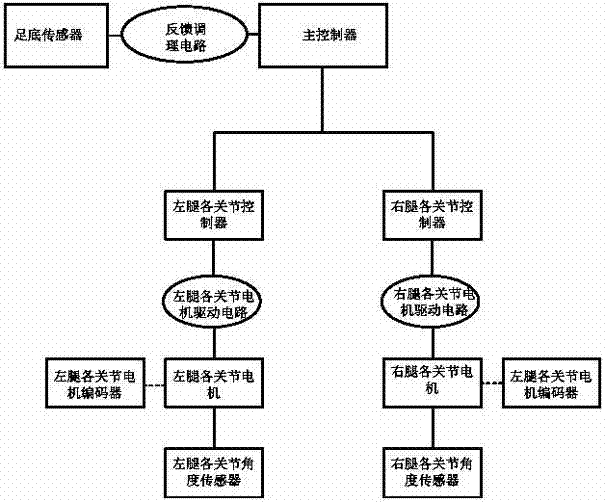
Control system of humanoid biped robot
InactiveCN105446345AFast operationEasy to controlAttitude controlAdaptive controlGyroscopeAngular degrees
The invention provides a control system of a humanoid biped robot. The robot comprises two leg parts and 12 degrees of freedom, each degree of freedom is corresponding to one joint motor. The control system comprises a main controller installed on the body of the robot, and joint controllers, motor driving circuits, motor encoders, joint angle sensor and feedback conditioning circuits which are respectively corresponding to the joint motors, and plantar pressure sensors and plantar gyroscopes installed on soles of two feet of the robot. The control system is characterized in that the main controller receives information feedback of the plantar pressure sensors and gyroscopes, plans a path and transmits motion instructions to each joint controller; and the joint controllers control joint motors to execute the motion instructions, receive information fed back by the motor encoders and the joint angle sensors and utilize a fuzzy self-adaptation PID control method to precisely control the motors according to the feedback information, so that the robot is enabled to walk precisely according to the ground condition.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
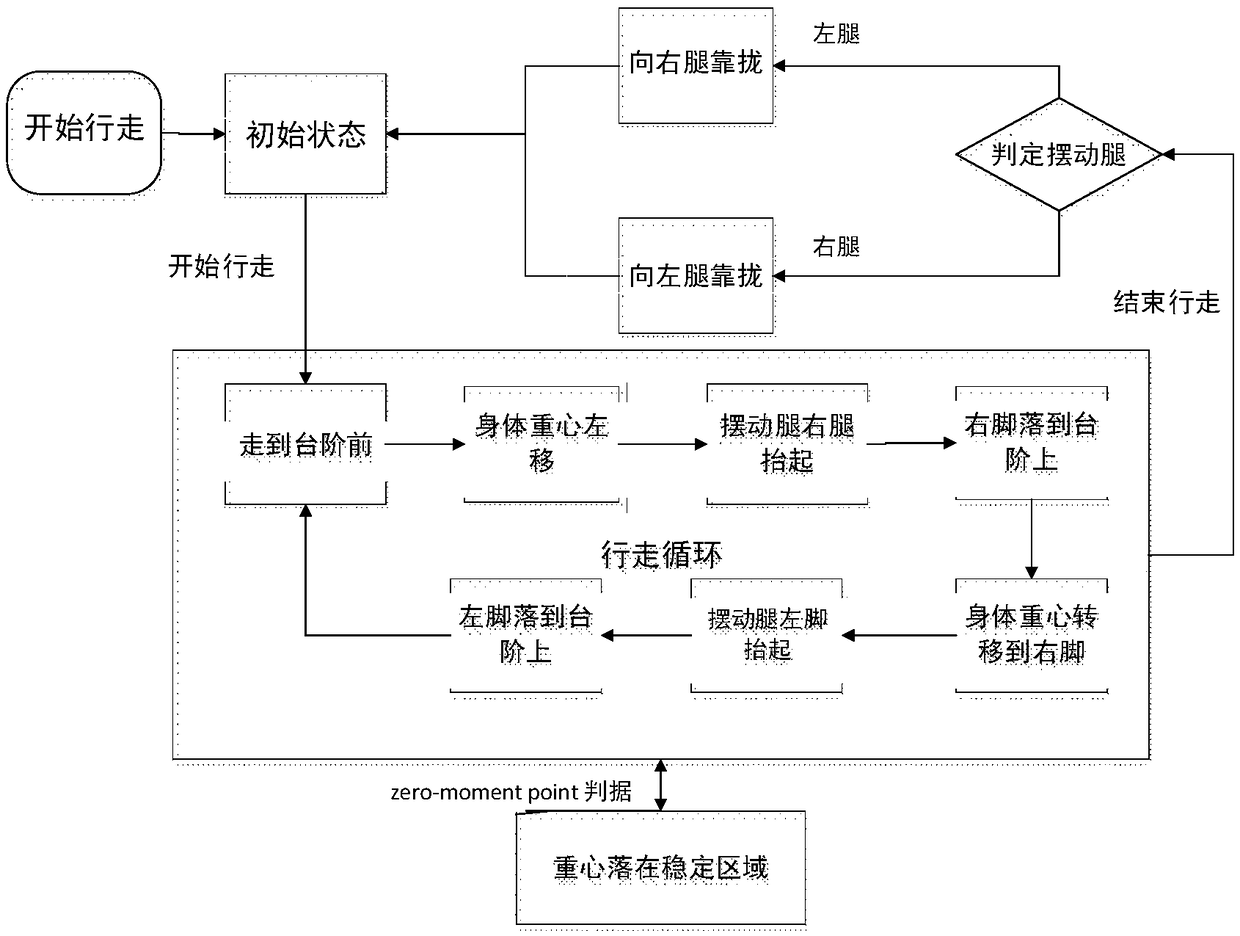
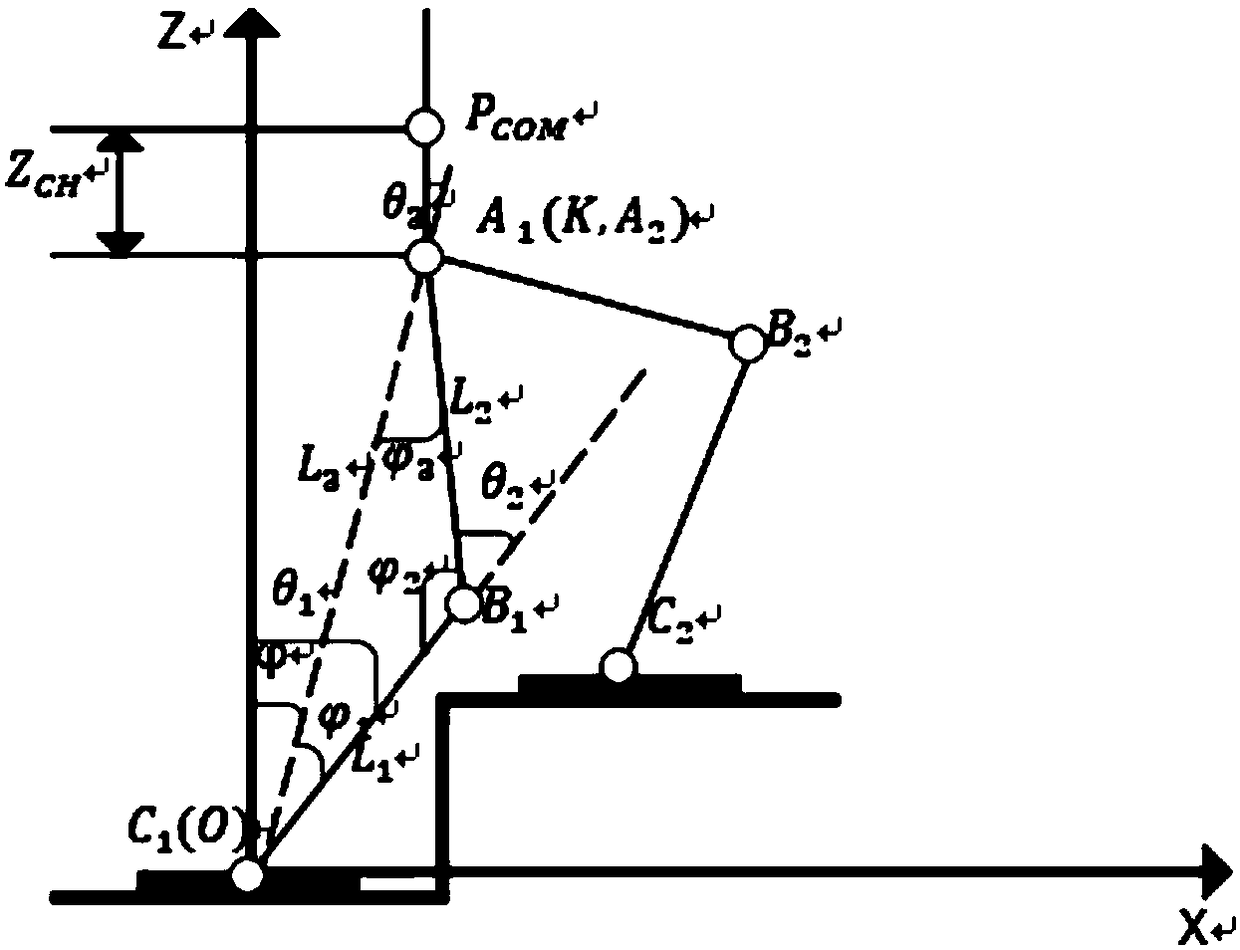
Biped robot climbing stair gait planning method and device and robot
InactiveCN109202901AWalk freelyProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesGait planningPlanning approach
The invention discloses a biped robot climbing stair gait planning method and device and a robot. The biped robot climbing stair gait planning method comprises the steps that in the stair climbing process, a variable-length first-order inverted pendulum model is adopted to carry out trajectory planning on a forward gait, the motion trajectory of an ankle joint is constrained according to preset constraint conditions, and a first-order linear inverted pendulum model is adopted to carry out trajectory planning on a lateral gait to realize stair climbing of a biped robot; the process is that whenfacing the first stair, the center of gravity of a body is controlled to move to the left; a right foot of a swing leg is lifted to drop the right foot onto the stair; the center of gravity of the body is moved to the right foot, and the left foot of the swing leg is lifted so that the left foot falls onto the stair; the steps are repeated until the first stair is the last stair; whether the center of gravity falls within a stable region or not is judged; if yes, the walking is finished; and if not, the two legs are controlled to close and return to the starting state. Based on the biped robot climbing stair gait planning method and device and a robot, an effective application of a robot walking mode can be realized, so that the robot can walk on the stairs as freely as a human.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV OF TECH
Method for constructing central pattern generator (CPG) control network topology structure of biped robot
ActiveCN103203746AReasonable structureReduce complexityProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl signalCoupling
The invention relates to a method for constructing central pattern generator (CPG) control network topology structure of biped robot. The method comprises the steps of separating a CPG control network into a body network portion for controlling hip joints and a leg network portion for controlling leg joints to achieve symmetry of control signals for left and right leg joints and control over reasonable phase relations of left and right legs; optimizing coupling connection modes among neuron units in the CPG control network to reduce the complexity of the CPG control network; and performing parameters setting on the CPG control network to construct an optimal network topology structure. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of being low in complexity, reasonable in control network structure and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Biped robot with obstacle crossing function
ActiveCN105774938AFlexible walkingWith obstacle avoidance functionVehiclesVertical planeCross device
The invention discloses a biped robot with an obstacle crossing function. The biped robot comprises a walking device and an obstacle crossing device. The walking device comprises a vertically arranged frame, a motor arranged in the frame, an output gear connected to the motor and a transmission gear engaged with the output gear. A transmission shaft is arranged in the center of the transmission gear and mounted on a shaft frame, the two ends of the transmission shaft are each provided with a crank extending in the radial direction of the transmission shaft, and a rotating shaft vertically and outwards extends from the other end of each crank. Supporting shafts outwards extend from the two outer sides of the frame and located above the rotating shafts. The rotating shafts and the supporting shafts are located in the same vertical plane. The difference between the rotational angles of the two cranks is 180 degrees. The biped robot can flexibly walk, has the obstacle crossing function, is wide in application and has practicability.
Owner:AVIC POWER SCI & TECH ENG
Switching control system and method for gaits of humanoid biped robot
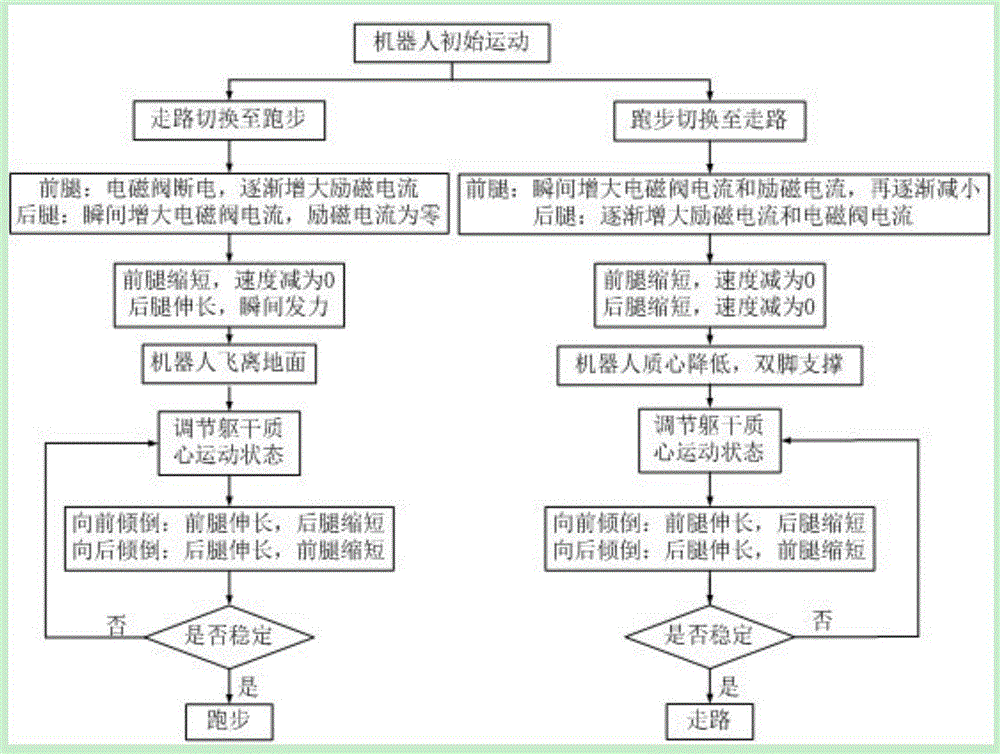
The invention relates to a switching control system and method for gaits of a humanoid biped robot based on the magneto-rheological technology. The control system comprises a plurality of compliance controllers, and the compliance controllers comprise magneto-rheological units, length adjusting units and feedback circuit units. The switching method for the gaits comprises the steps that interpolation is carried out on walking (running) final states and running (walking) initial states planned in advance into a continuous, smooth and derivable curve, meanwhile, the motion track of a gait switching instant joint is repeatedly optimized and calculated online, the mass center positions, speed and accelerated speed of rods of the robot are changed by controlling the reciprocating movement of pistons of the compliance controllers, and when the robot tends to incline forwards, a front leg is lengthened, a rear leg is shortened, and the mass center of the robot is adjusted backwards; and when the robot tends to incline backwards, the front leg is shortened, the rear leg is lengthened, the mass center of the robot is adjusted forwards, the stability of the robot is controlled, and free switching of walking and running of the robot is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gait planning method of 3D (3 dimensional) underactuated biped robot jumping motion
ActiveCN105599816AJumping movement achievedSpecial data processing applicationsVehiclesBody angleGait planning
The invention relates to a gait planning method of a 3D (3 dimensional) underactuated biped robot jumping motion. The bionic characteristics of the gait planning method are mainly embodied in two aspects of: (1) simulating the jumping motion of human, namely, in the process of jumping, a robot supports leg knee joints to quickly stretch, and the hip joint of the robot simultaneously moves so that the included angle between the body of the robot and the vertical direction of gravity is quickly reduced; (2) meeting the joint constraints in the jumping motion of human, mainly including crotch angle constraint, body angle constraint, and knee joint angle constraint. Thus, compared with the previous jumping motion gait planning method, the gait planning method provided by the invention can not only realize the jumping motion of robots but also embody the humanoid gait characteristics. Furthermore, the invention also provides a set of program design scheme of effectively realizing the gait planning of 3D underactuated biped robot jumping motion.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
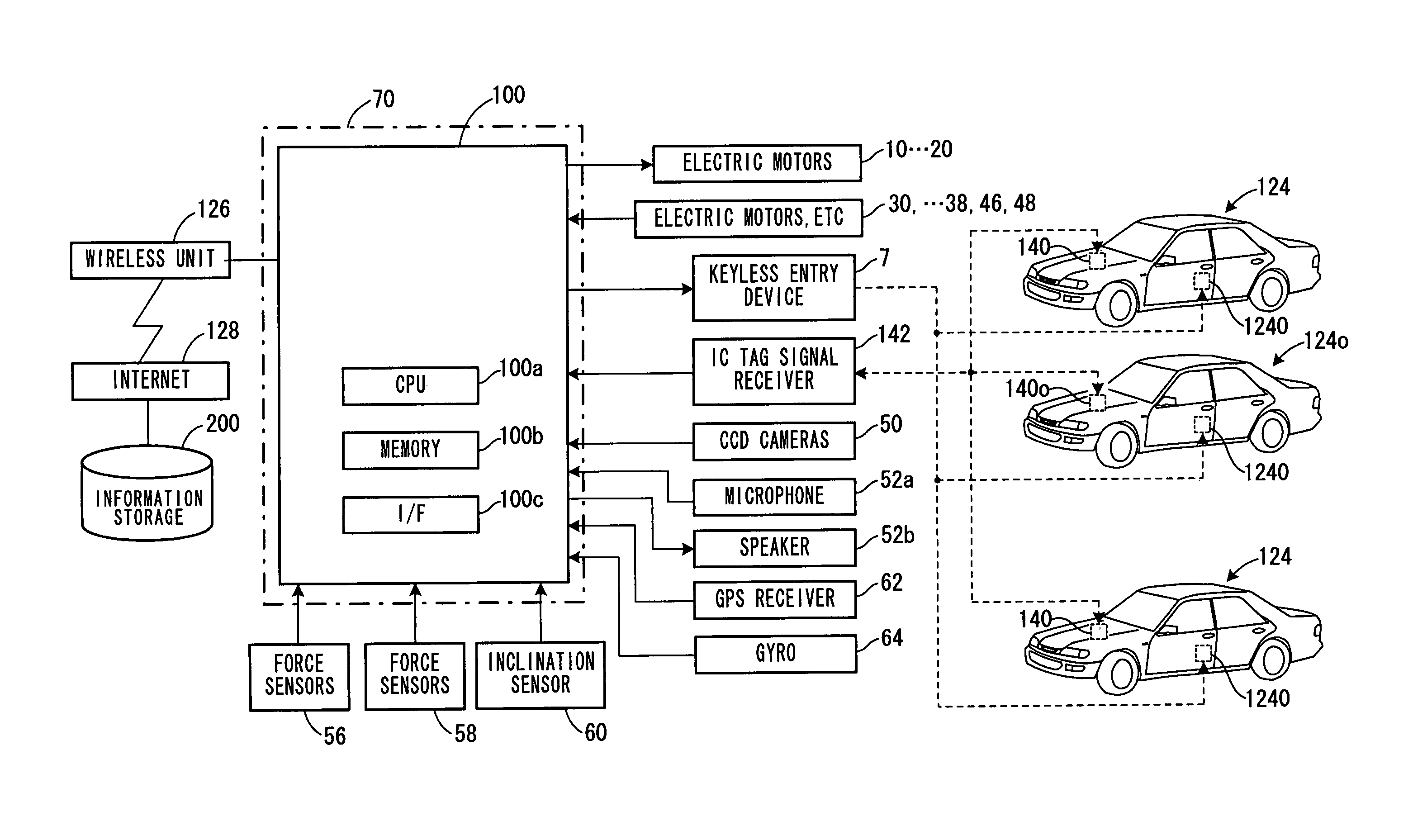
Biped robot control system
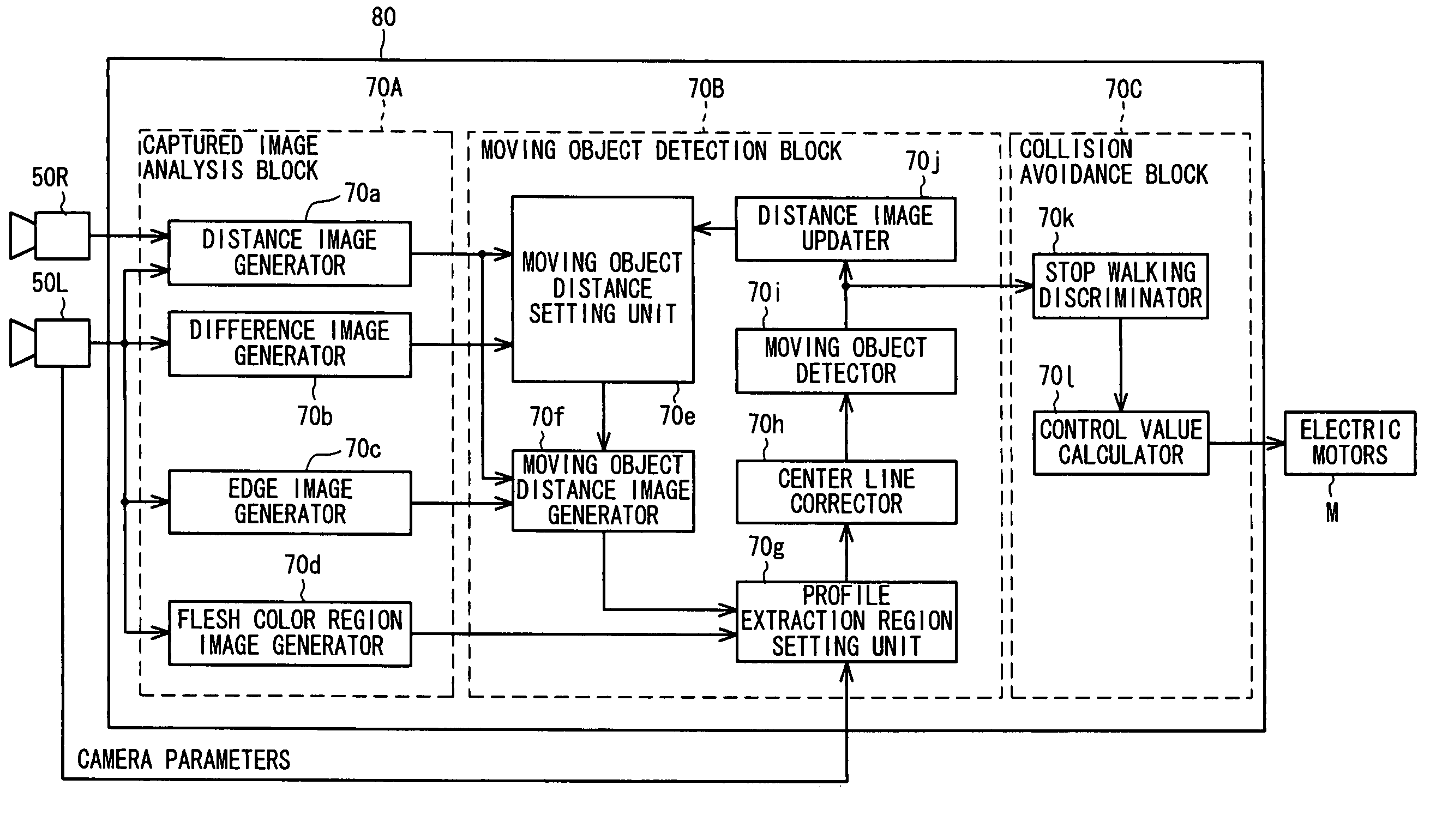
ActiveUS7398136B2Avoid collisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage analysisControl systemSimulation
In a biped robot control system, stereoscopic images captured by CCD cameras are analyzed, the analyzed images are then utilized to detect presence of any moving object around the robot and if it present, to calculate moving object information, and based on the calculated moving object information, it is determined whether or not walking of the robot needs to be stopped. If it is determined to be stopped, the robot is controlled to stop within a period that brings the travel distance at stopping (distance moved between image capture by the CCD cameras and stopping of robot walking) to within a predetermined distance. With this, when the robot approaches a moving object during walking, it can be stopped within the predetermined distance to avoid collision with the moving object.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com