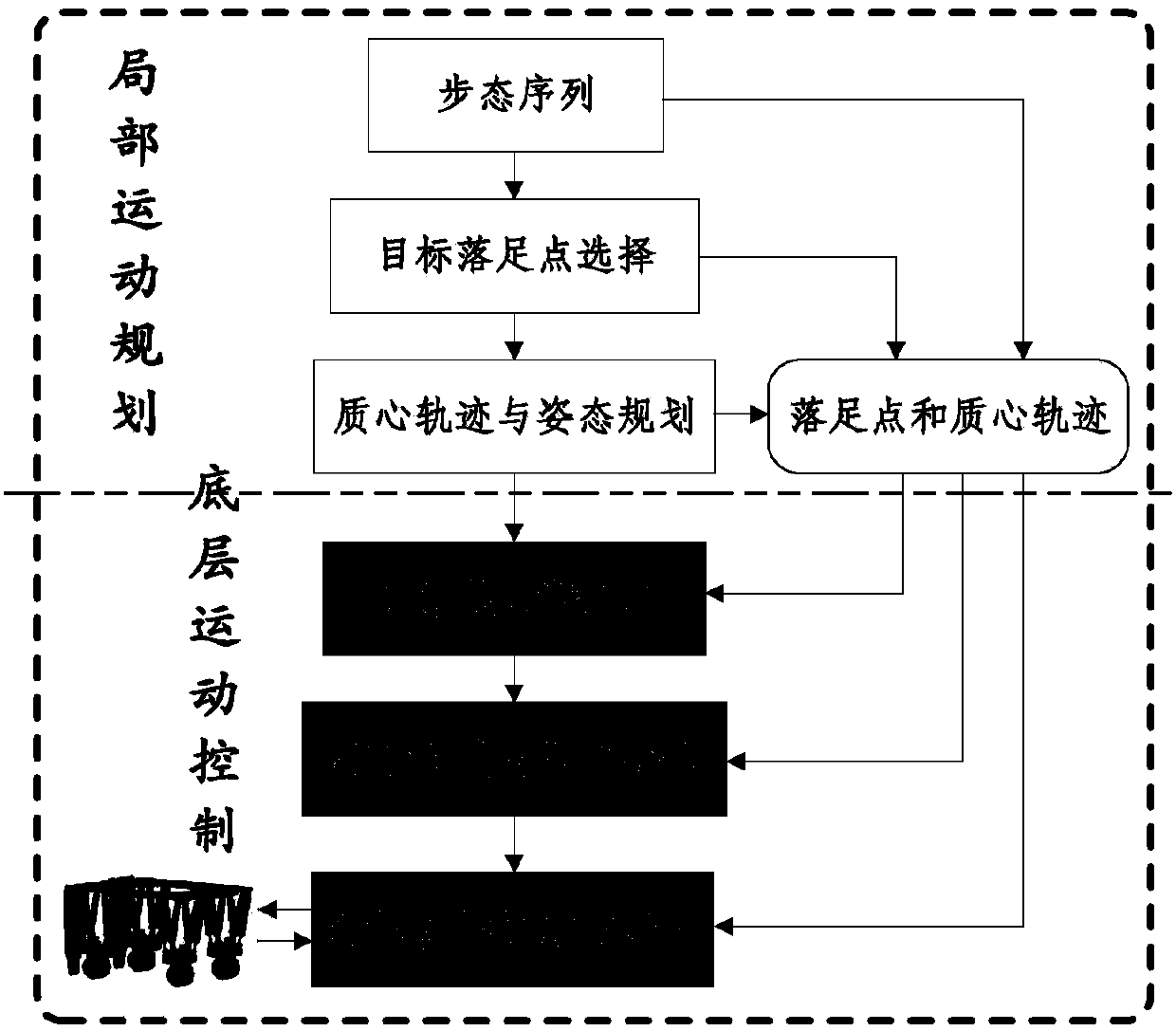
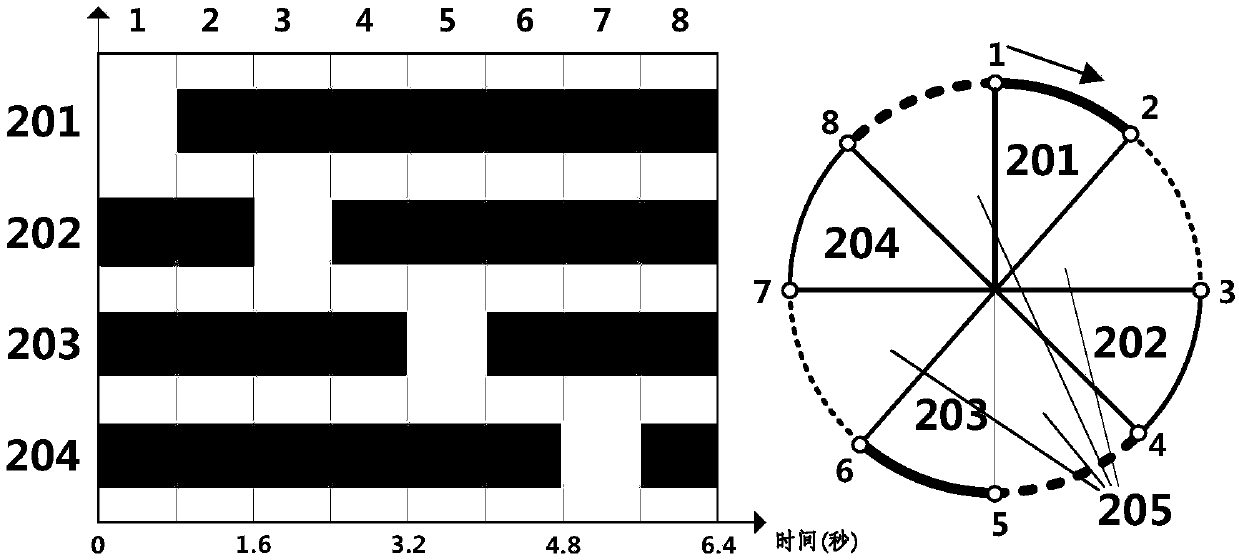
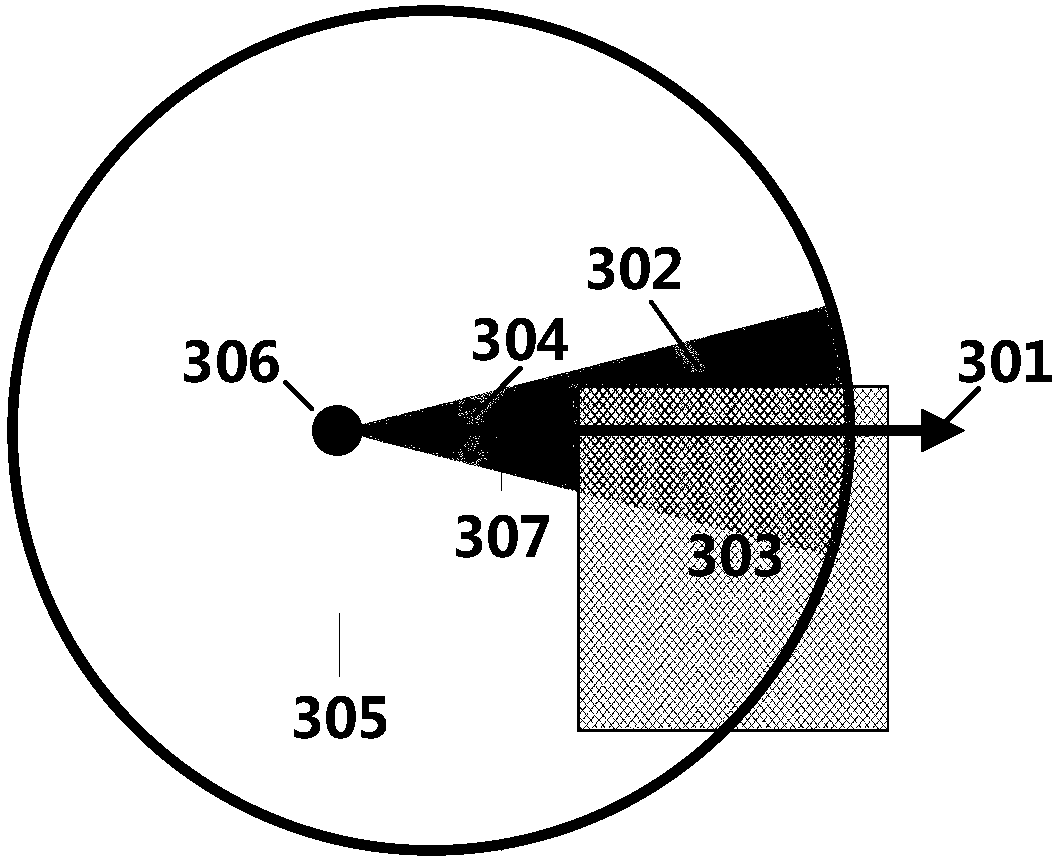
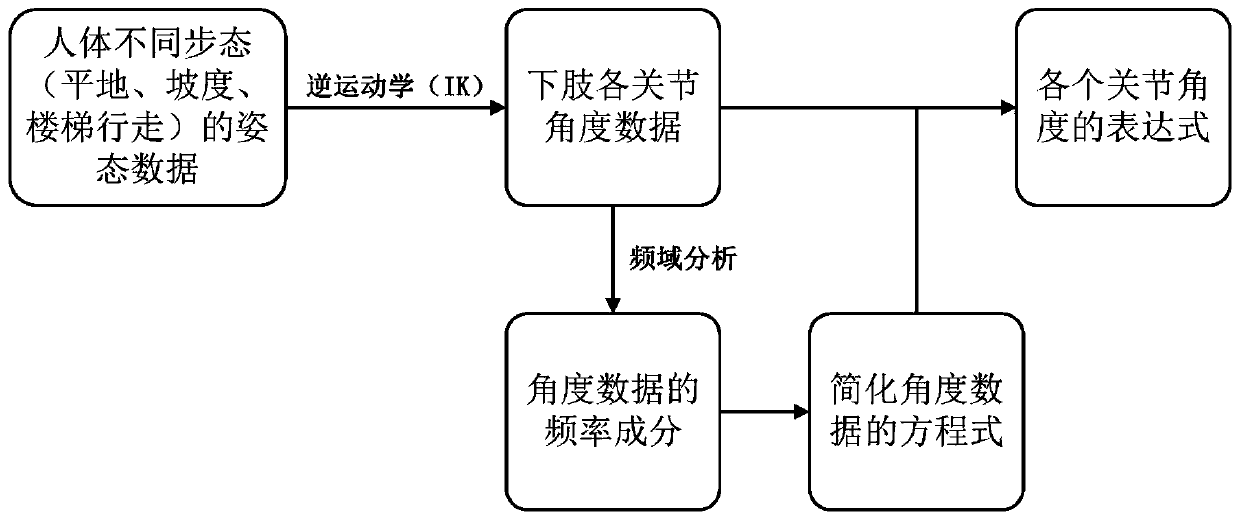
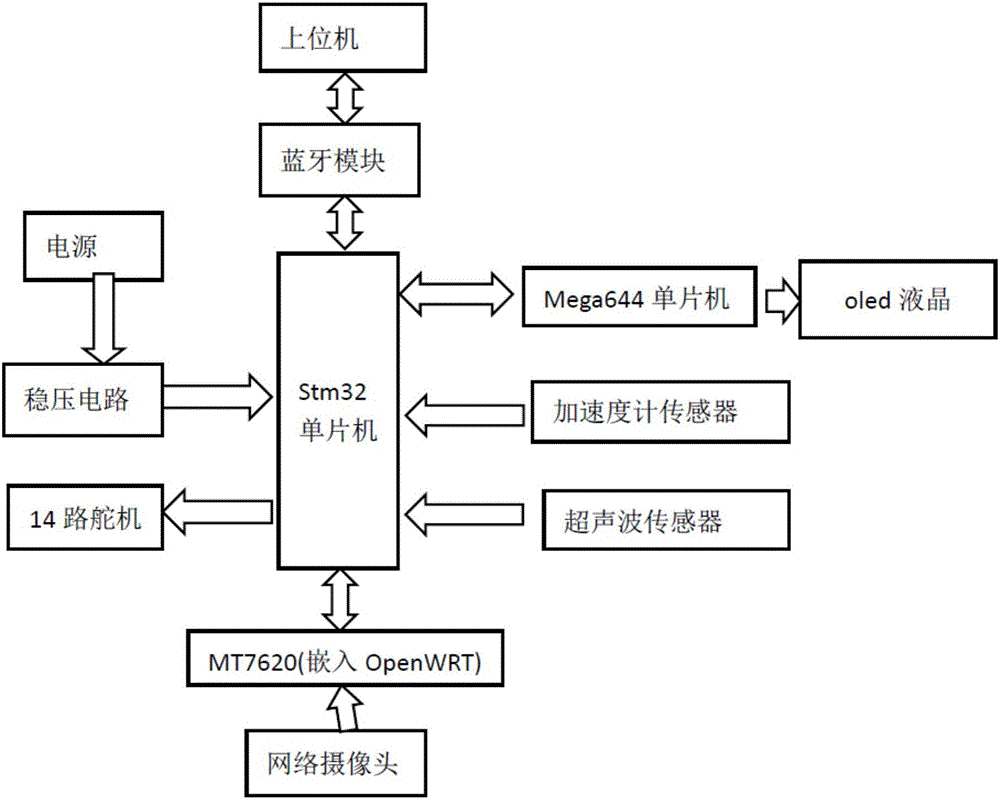
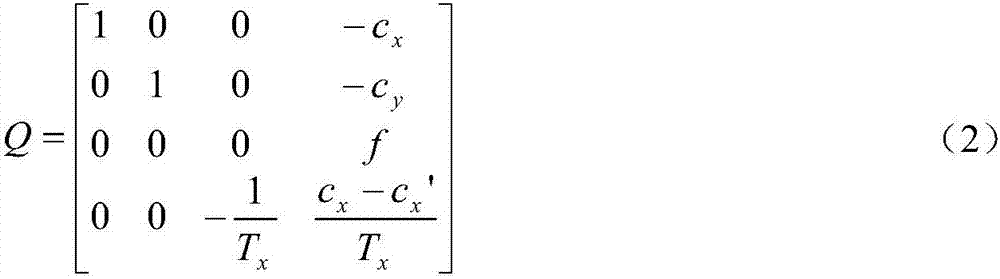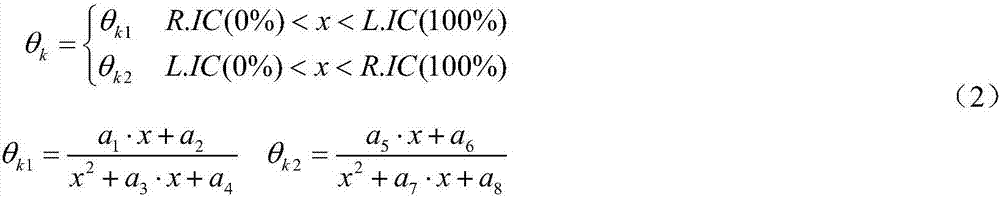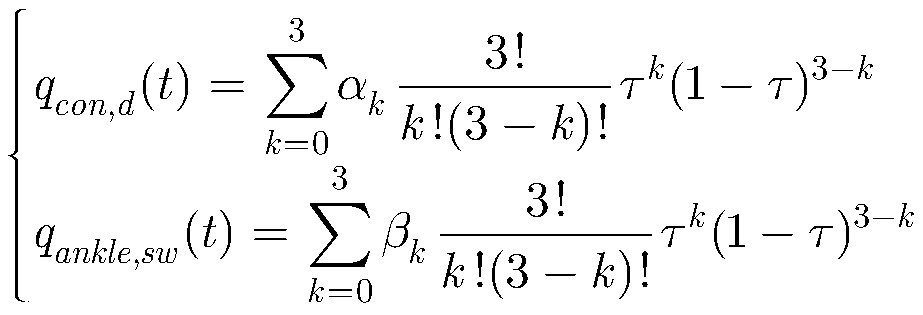Patents
Literature
160 results about "Gait planning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
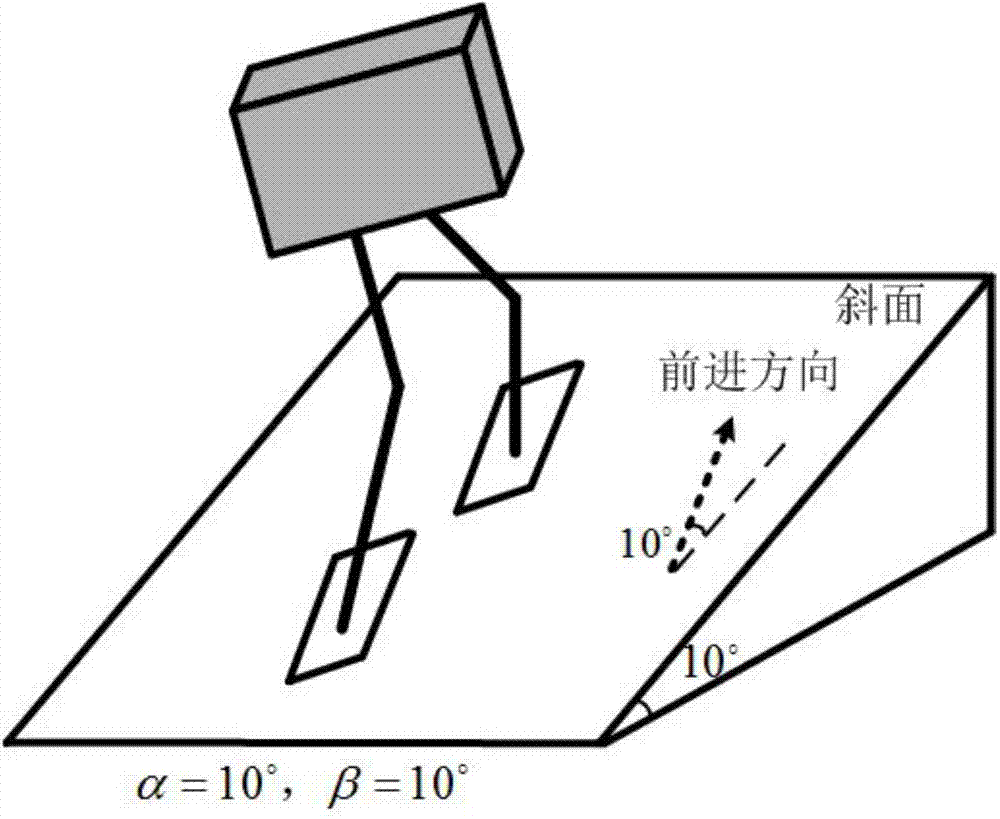
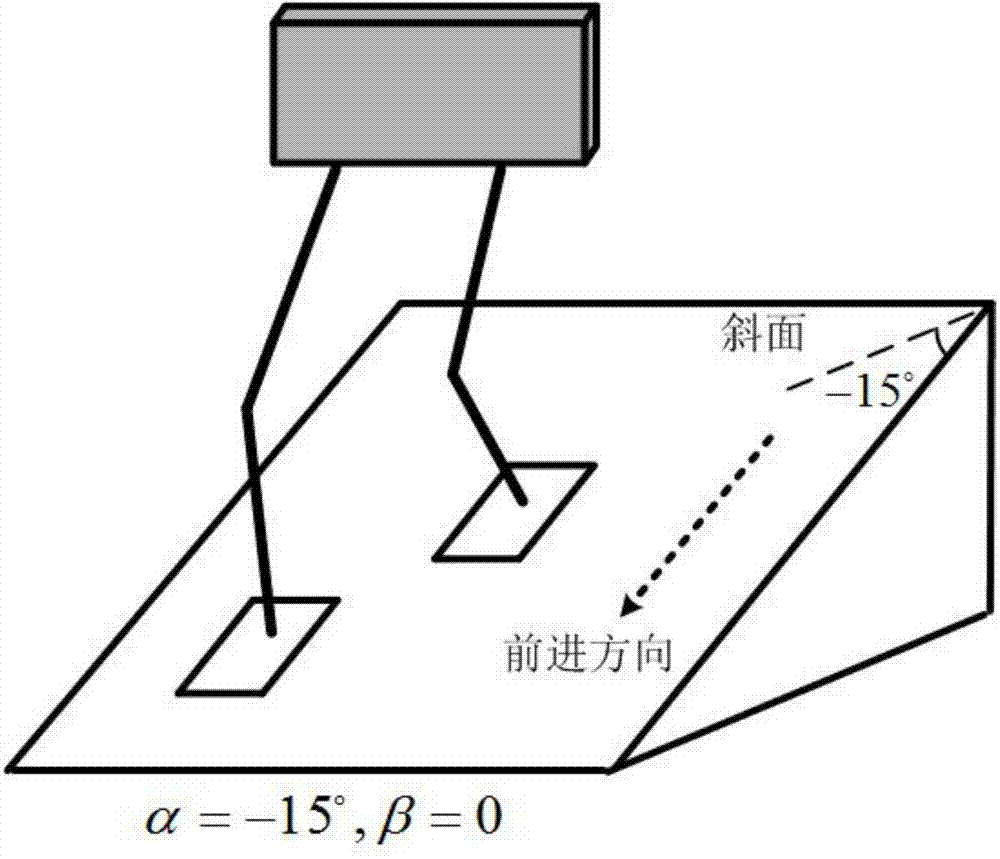
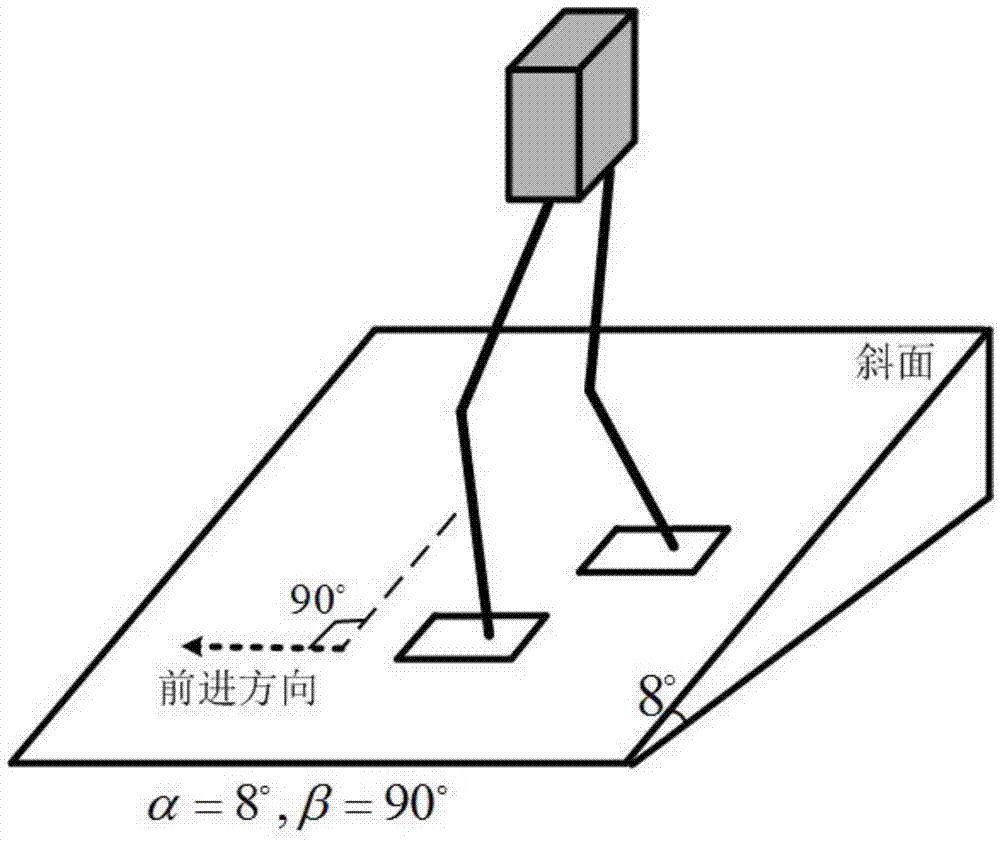
Gait planning method for walking of biped robot along slope
ActiveCN104331081AImprove environmental adaptabilityMovement coordination and natureAttitude controlCoronal planeDecomposition
The invention discloses a gait planning method for walking of a biped robot along a slope, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The method contains two core theories, namely, non-orthogonal decomposition and synthesis of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum and gait planning based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum. The method comprises the steps of gait parameter configuration, non-orthogonal decomposition of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum, foot trajectory planning based on three times of spline interpolation, centroid trajectory planning of a sagittal plane and a coronal plane based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum, non-orthogonal synthesis of the centroid trajectories of the sagittal plane and the coronal plane, and solving of joint trajectories of a robot based on inverse kinematics. By adopting the method of the invention, stable walking of a biped robot along all directions of a slope can be effectively achieved. The method is universal, simple in algorithm and high in practicality.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Hexapod-robot real-time gait planning method based on deep reinforcement learning
InactiveCN107450555AEnables real-time gait planningFast convergencePosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationGait
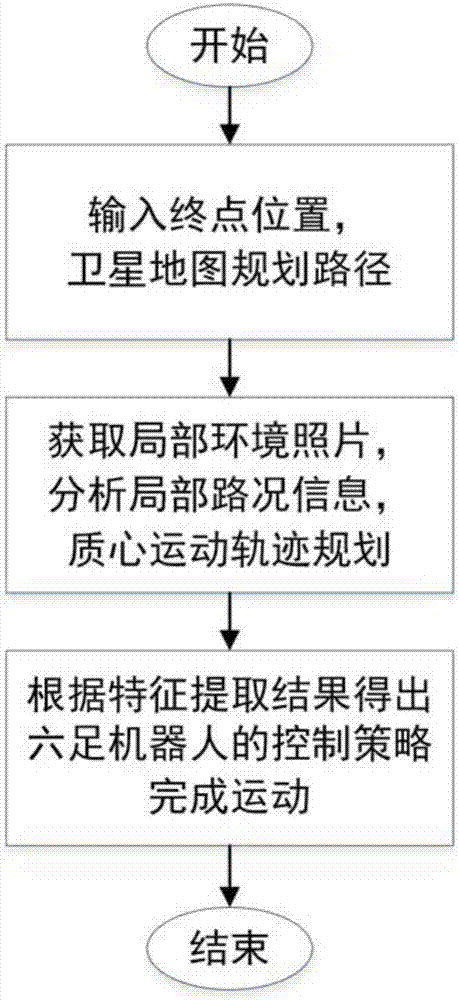
The invention provides a hexapod-robot real-time gait planning method based on deep reinforcement learning. The method comprises the following steps of using a hexapod robot to acquire environment road condition information and making an integral movement track; through a camera, acquiring an environment photograph, according to the photograph, using a binocular range finding method to calculate road condition information of a target track, and using the calculated road condition information of the track in robot center of mass movement track navigation; in a foot end swinging space range of robot legs, taking photographs of a road condition environment, and through a trained deep reinforcement learning network based on a depth determinacy policy gradient (DDPG), carrying out data dimension reduction and feature extraction on the photograph; and according to a feature extraction result, acquiring a control policy of a hexapod robot, wherein the hexapod robot controls foot laying of a robot according to the control policy so that real-time walking of the hexapod robot is realized. By using the gait planning method, a complex and non-structural environment of a road condition can be planned in real time. The method has an important meaning for increasing an environmental adaptive capacity of the hexapod robot.
Owner:唐开强
Hexapodous biomimetic wet-sucking wall-climbing robot
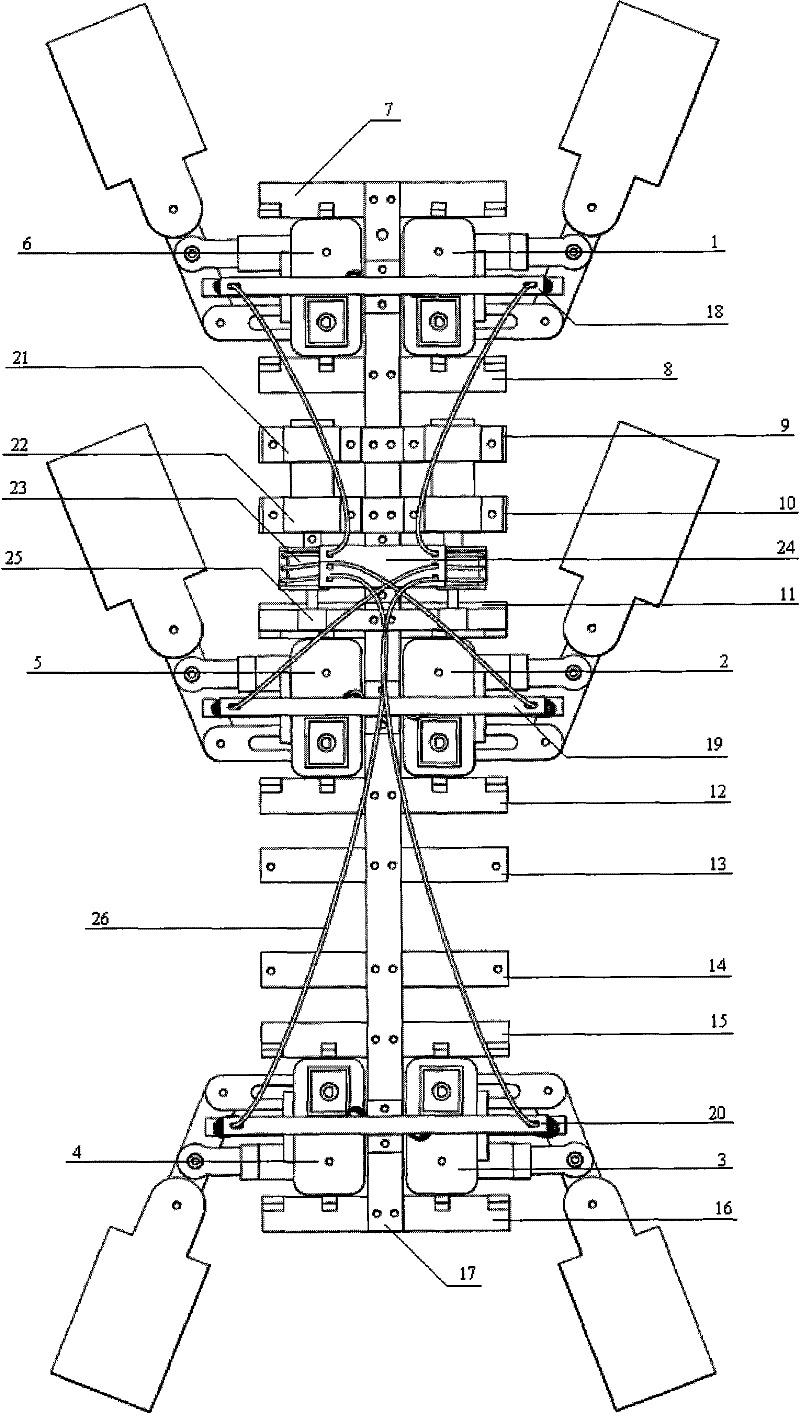
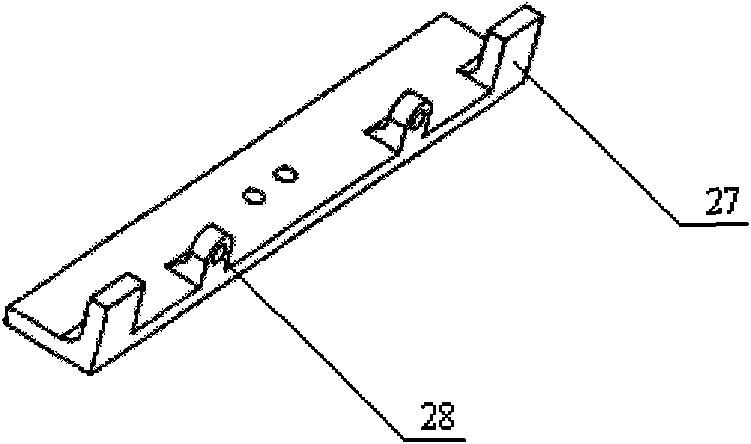
The invention relates to a hexapodous biomimetic wet-sucking wall-climbing robot, which belongs to the technical field of bionics. The robot comprises a body framework, biomimetic podites, motors, a driving circuit, a pre-compression structure, a cam structure and a pull rope structure, wherein all the components are installed on the body framework. The body framework comprises a support and a crossbeam which is installed in the groove of the body framework; each biomimetic podite comprises a base seat, a femur, a tibia, a spring steel sheet and a flexible structure, one end of the femur and the flexible structure is connected with the base seat, the other end thereof is connected with the tibia, and the spring steel sheet is installed on the tibia; the driving circuit performs joint control to the motors, the motors are vertically installed in the motor grooves and horizontally installed on the crossbeam; the pre-compression structure comprises a podite support and a T-shaped femur extension support which are connected through a spring; the cam structure comprises a cam and a cam fixing support, one end of the cam is fixed on the motor shafts, and the other end is connected with the cam fixing support; the pull rope structure comprises a pull rope support, pull ropes and brake lines, and the pull ropes are connected with the biomimetic podites through the pull rope support. The hexapodous biomimetic wet-sucking wall-climbing robot has the advantages of simple structure, part modularization and standardization, convenient processing and assembly, hollow structure, light overall weight, multi-motor driving, easy gait planning, and easy realization of stable and reliable operation of the hexapodous wall-climbing robot.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
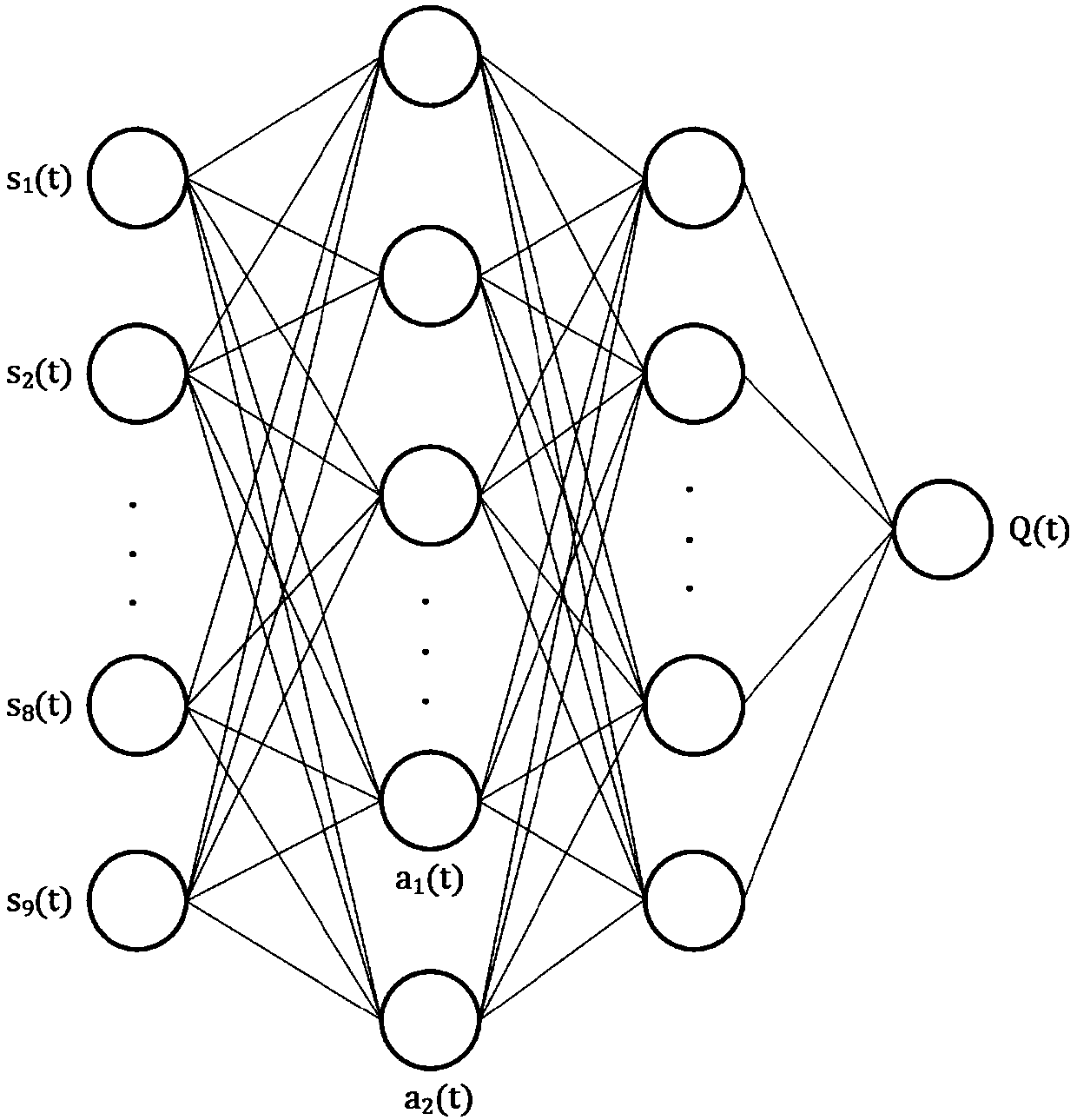
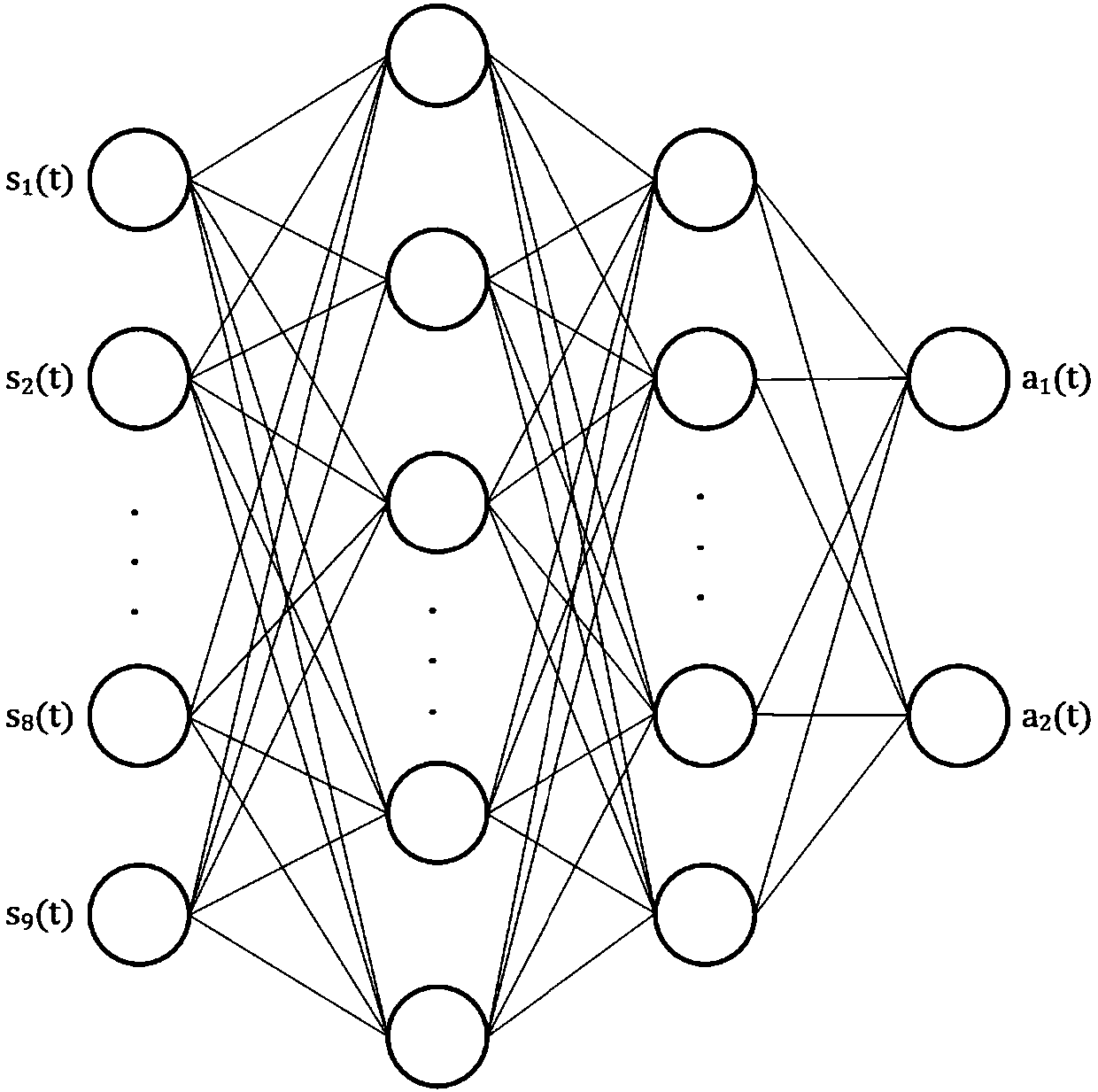
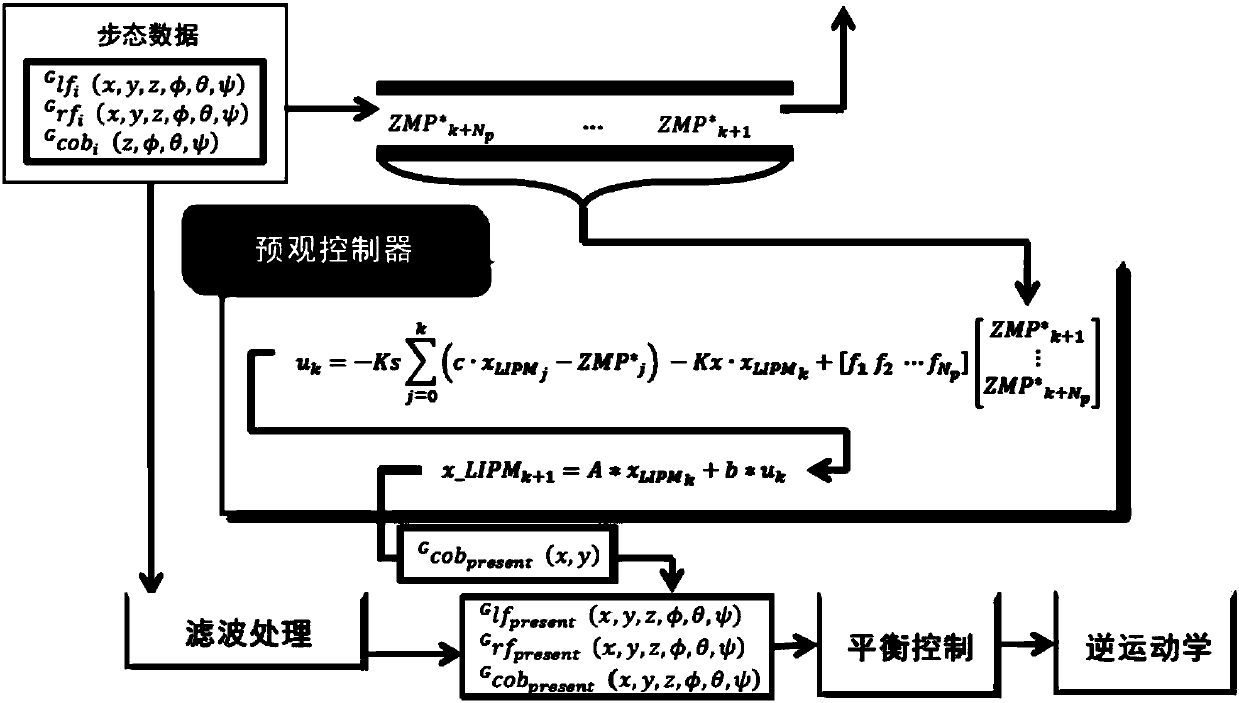
Previewing control humanoid robot gait planning method based on deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN108549237AFast convergenceTimely adjustment for walkingAdaptive controlChannel state informationGait planning
The invention discloses a previewing control humanoid robot gait planning method based on deep reinforcement learning. The method comprises steps of 1) acquiring state information through a sensor assembled on a humanoid robot; 2) improving a current deep reinforcement learning network, and defining totally new states, action vectors and awarding functions; 3) using the defined action vectors to correct output of a previewing controller, calculating the angle of each steering engine of the feet of the humanoid robot and guiding the humanoid robot to walk; and 4) during walking processes of thehumanoid robot, using values of the states, the action vectors and the awarding functions to update the improved deep reinforcement learning network. According to the invention, the walking problem of the humanoid robot under a complex environment can be effectively solved; and a test is carried out on a simulation platform and a real robot to verify the validity of the method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Gait planning method for biped robot based on deep reinforcement learning
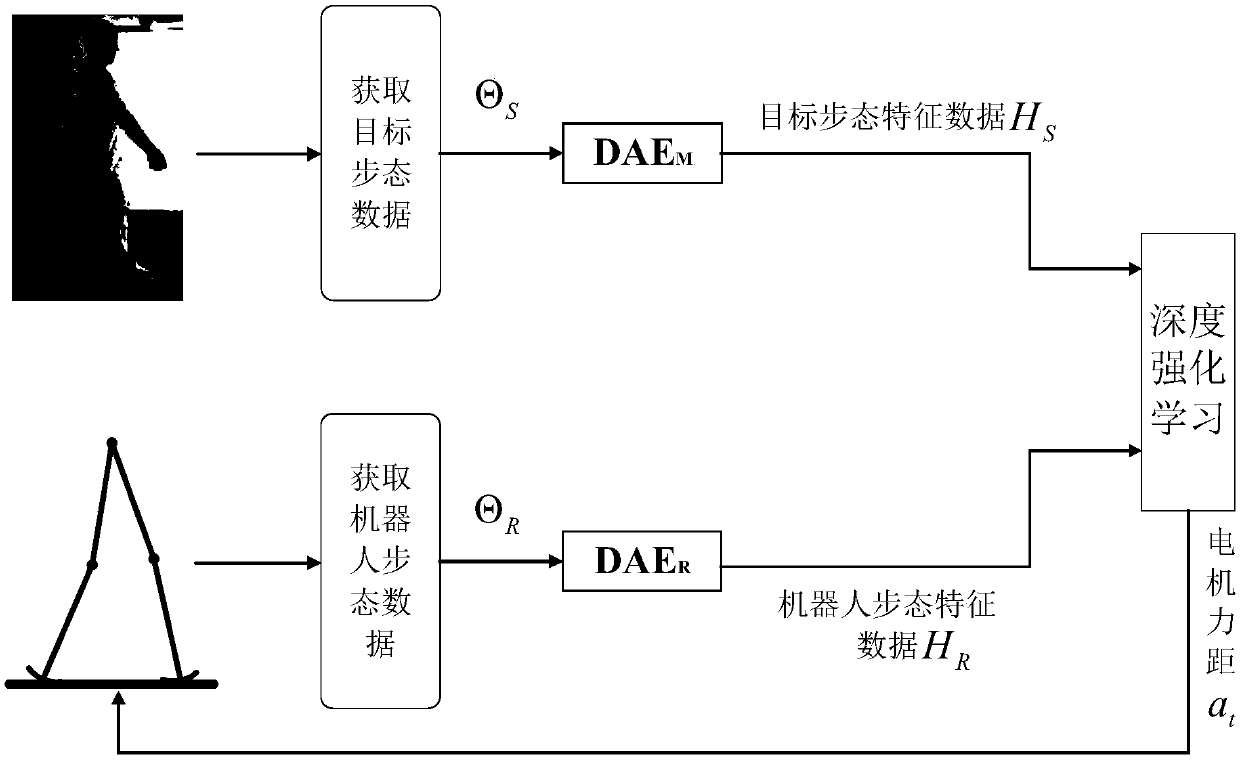
The invention discloses a gait planning method for a biped robot based on deep reinforcement learning, and the method utilizes the stability and flexibility of human gait and combines deep reinforcement learning to effectively control the gait of the biped robot. The method includes the following steps: 1), establishing a passive biped robot model; 2), acquiring and processing human gait data andtarget gait data; 3), extracting the implicit features of the gait data of the biped robot and human gait data through using a noise reduction auto-encoder; 4), learning the gait characteristics of ahuman body through using deep reinforcement learning, and then planning the gait of the biped robot. The method combines deep reinforcement learning with human gait data to control the biped robot towalk as stable and compliant as a human.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Hexapod robot gait planning method based on depth reinforcement learning
ActiveCN107562052AGood for gait planningEasy to walkPosition/course control in two dimensionsGait planningSimulation
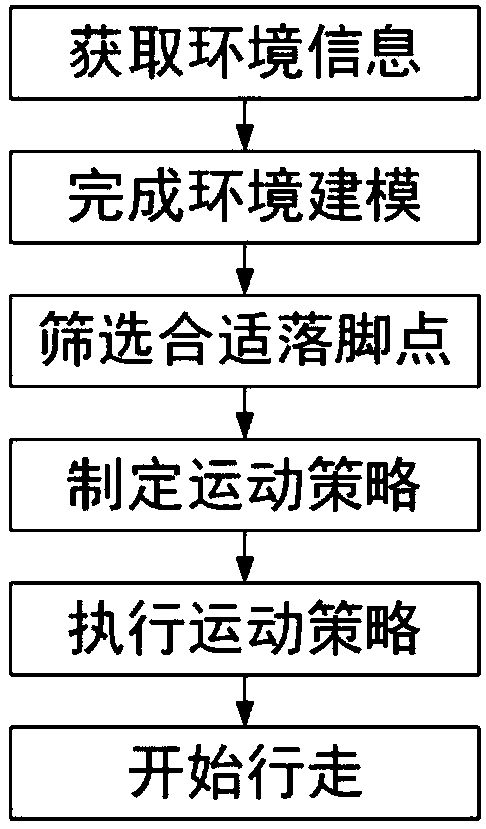
The invention provides a hexapod robot gait planning method based on depth reinforcement learning. The method comprises the steps of environment information acquiring, environment modeling, anchor point screening, upper-level exercise policy formulating, lower-level policy executing and robot movement drive. Through the hexapod robot gait planning method, a hexapod robot uses a depth learning andreinforcement learning algorithm to acquire the optimal path by solving a quincuncial pile maze problem abstracted from an environment, and can select the suitable anchor point according to the optimal path to realize efficient walking in a non-structural environment.
Owner:唐开强
Humanoid robot gait planning method based on human body teaching
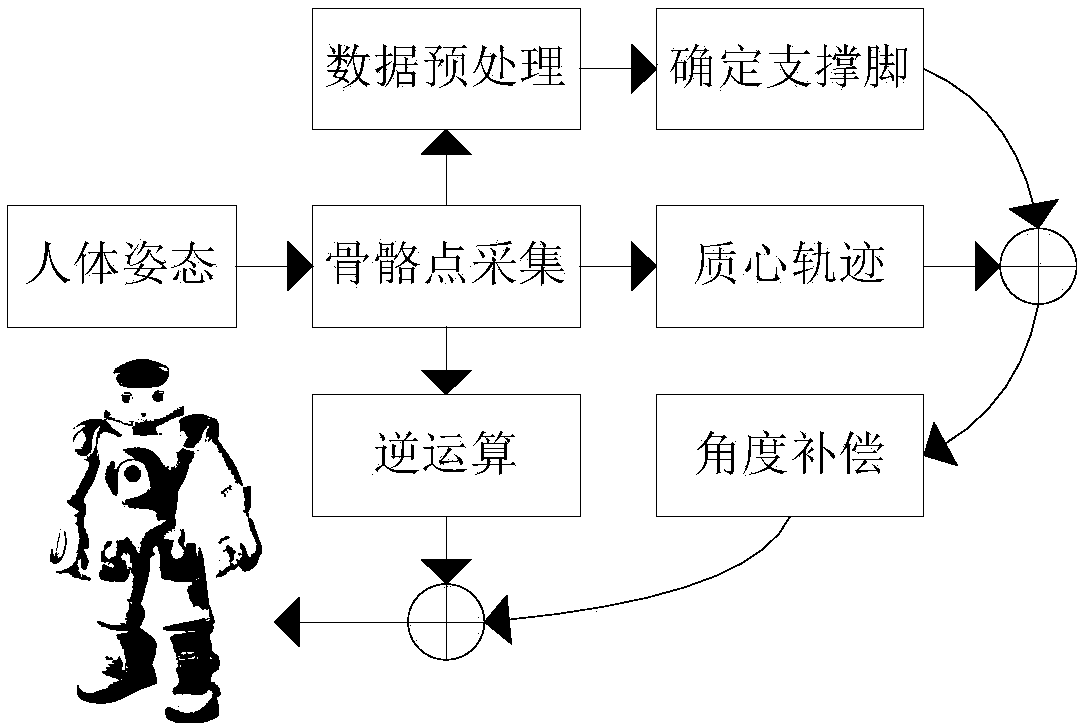
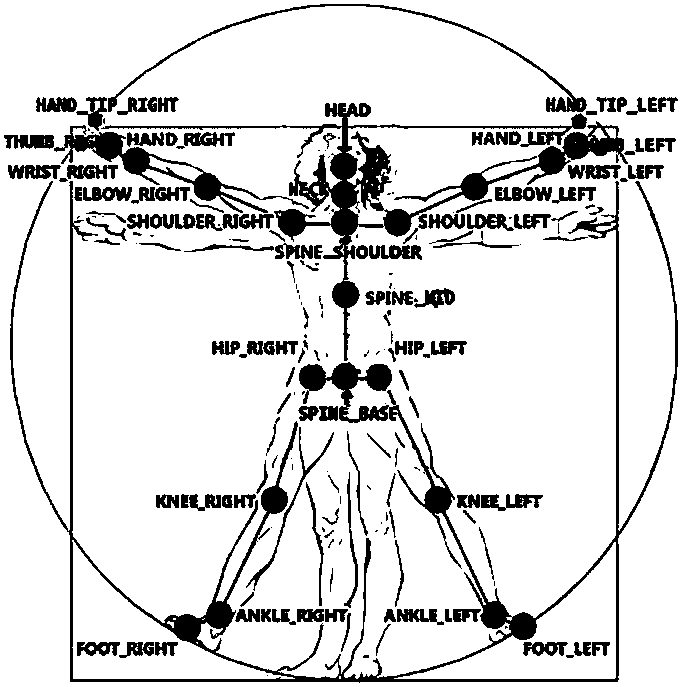
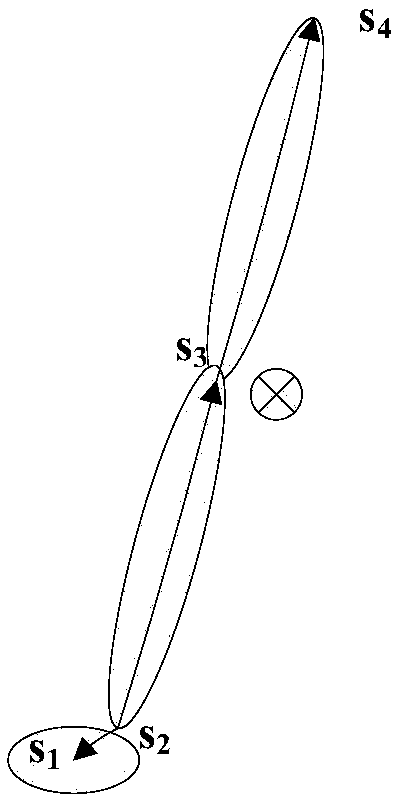
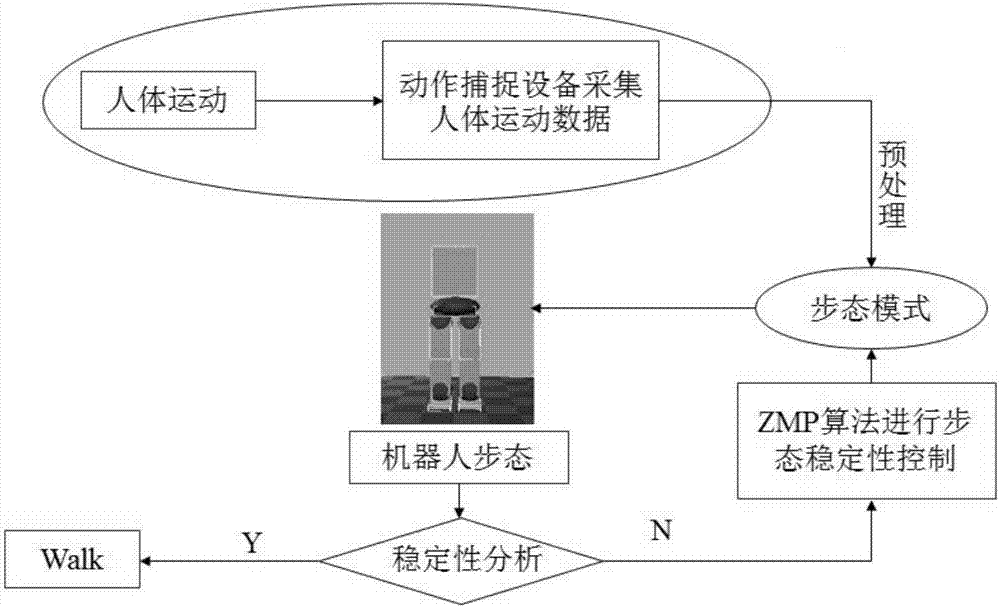
The invention discloses a humanoid robot gait planning method based on human body teaching. Human body movement information is used for gait planning of a humanoid robot. The joint driving angle of the robot is obtained through inverse operation of skeleton information during human body movement. The mass center track information of the robot is estimated through human body teaching data in orderto meet the stability during movement of the humanoid robot. Compensation control is conducted on the driving angle of the robot by combining a ZMP criterion and a robot mass center-angle jacobi matrix. In selection of supporting feet, switching of the supporting feet during human body teaching is judged through a hysteretic curve, so that selection of the supporting feet of the robot is determined. The humanoid robot gait planning method based on human body teaching greatly simplifies the complexity of humanoid robot gait planning, and the movement process of the robot is more personified through the gait planning based on human body teaching.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
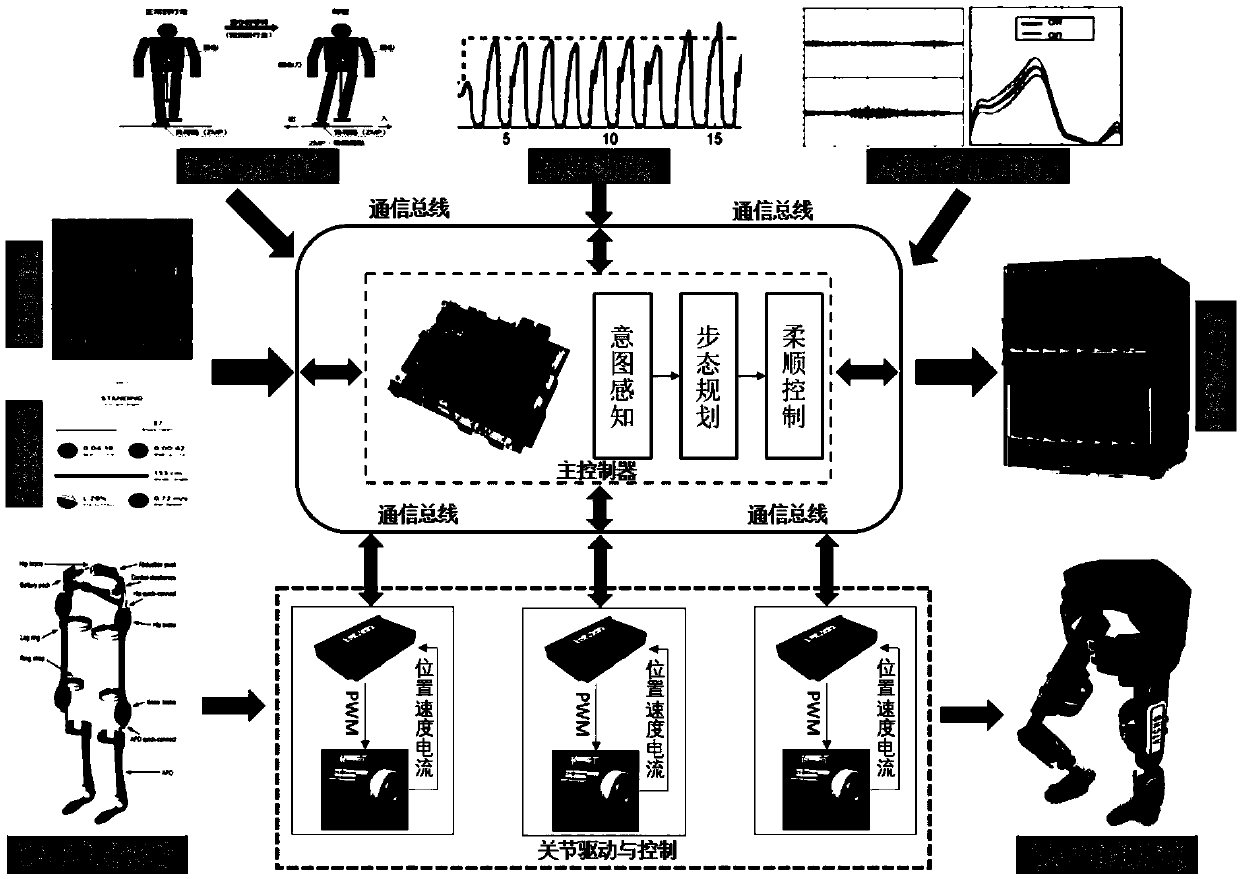
Power-assisted exoskeleton control system and method
ActiveCN110303471AReduce the risk of fallingImprove adaptabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemGait planning
The invention relates to a power-assisted exoskeleton control system and method, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The system comprises a sensing communication execution subsystem and a processing planning decision subsystem. The sensing communication execution subsystem is used for sensing the motion intention, the motion state and the physiological information, and a computing main control platform makes a command decision on the basis of the man-machine coupling information and drives a joint of a robot to timely and appropriately assist; and the processing planning decision subsystem is used for realizing human-machine information interaction mode and human-machine consciousness fusion on the basis of a motion intention identification method and a bioelectrical signal analysis technology, realizing gait planning on the basis of a multi-variable depth learning gait planning method and ensuring overall comfort and safety of the control system on the basis of variable impedance control, so that a user achieves the optimal use effect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
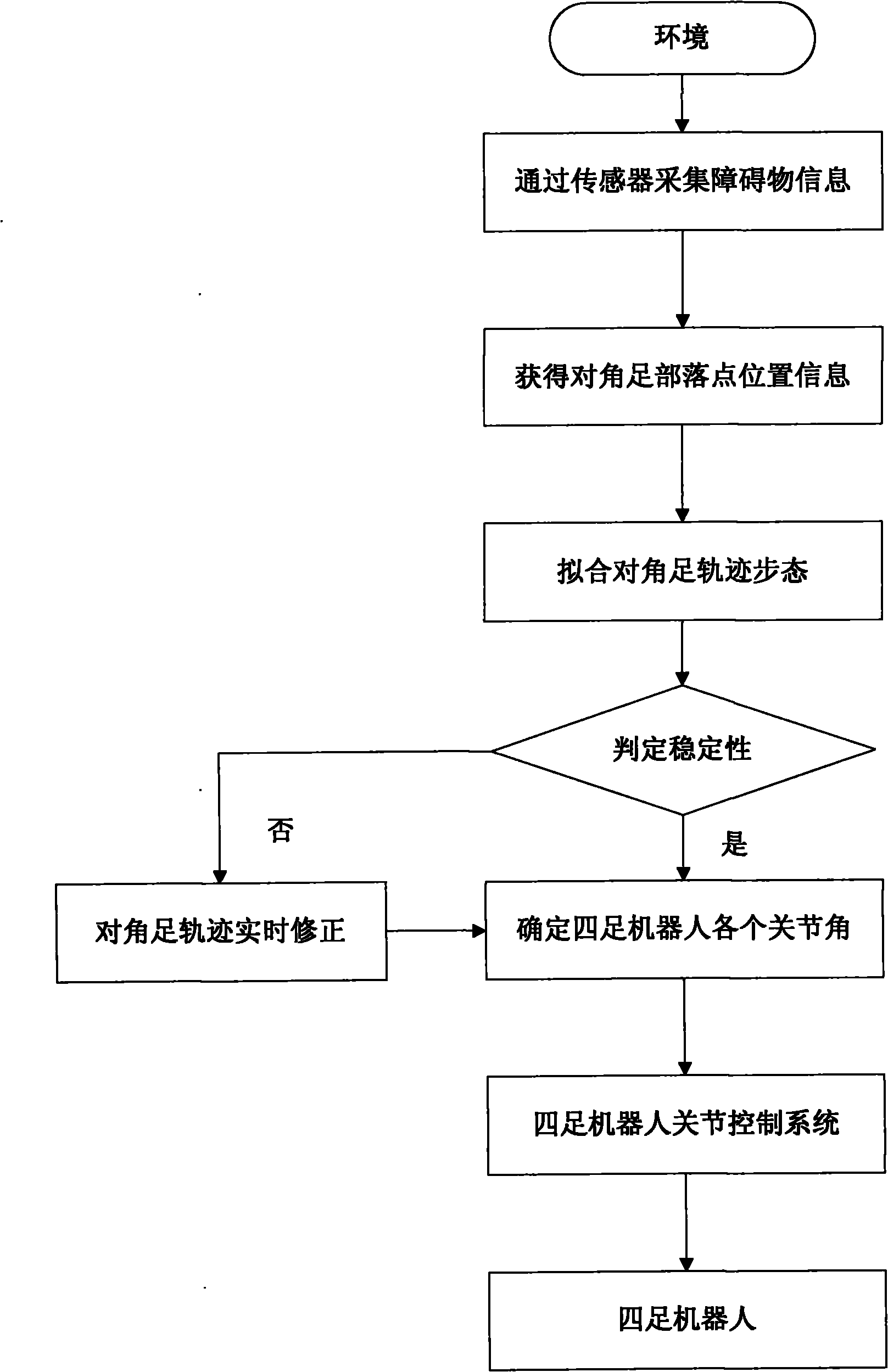
Self-adaptive control method for diagonal gait of four-footed robot
InactiveCN102156484AImprove execution efficiencyClear division of laborControl without using feedbackTerrainEngineering
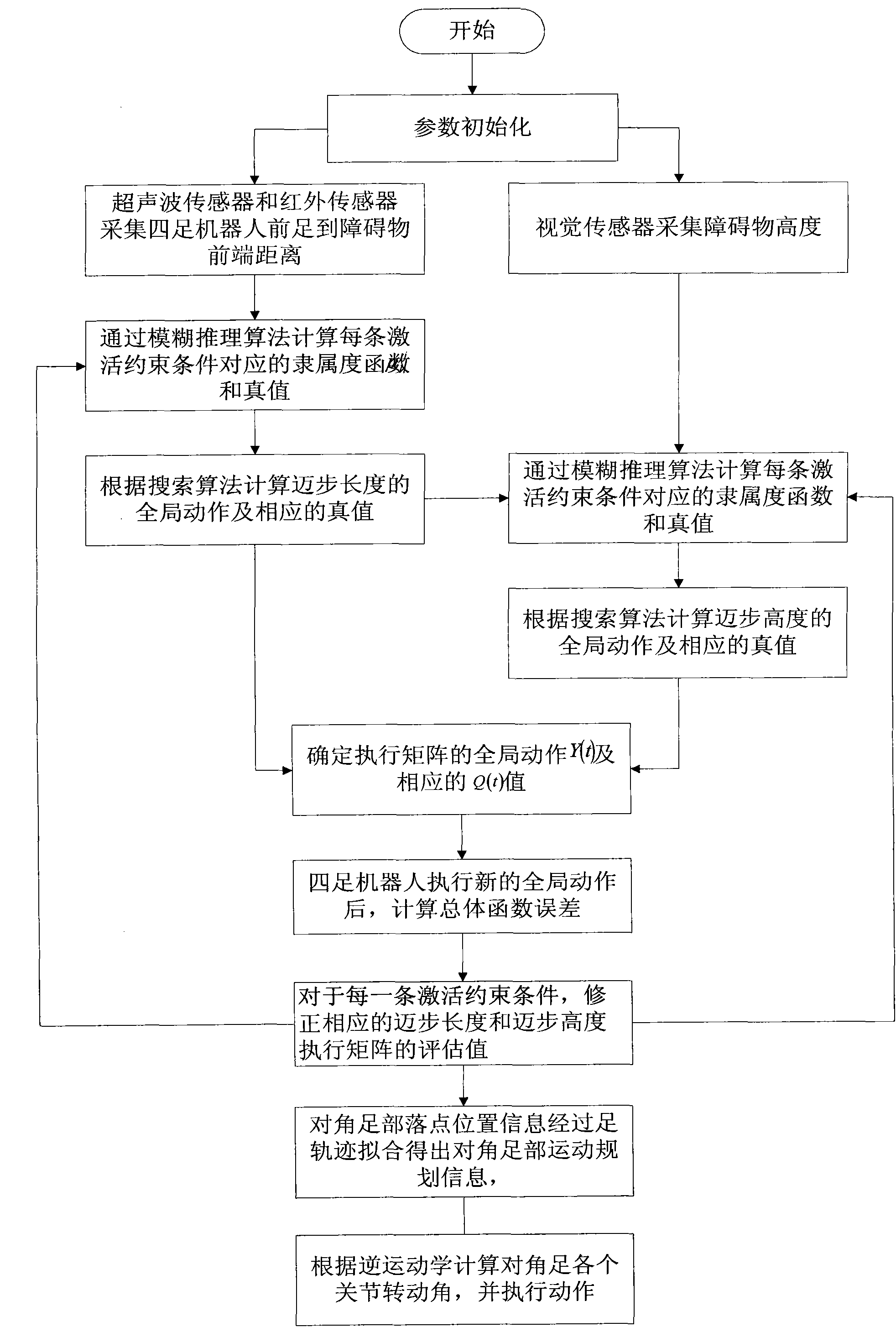
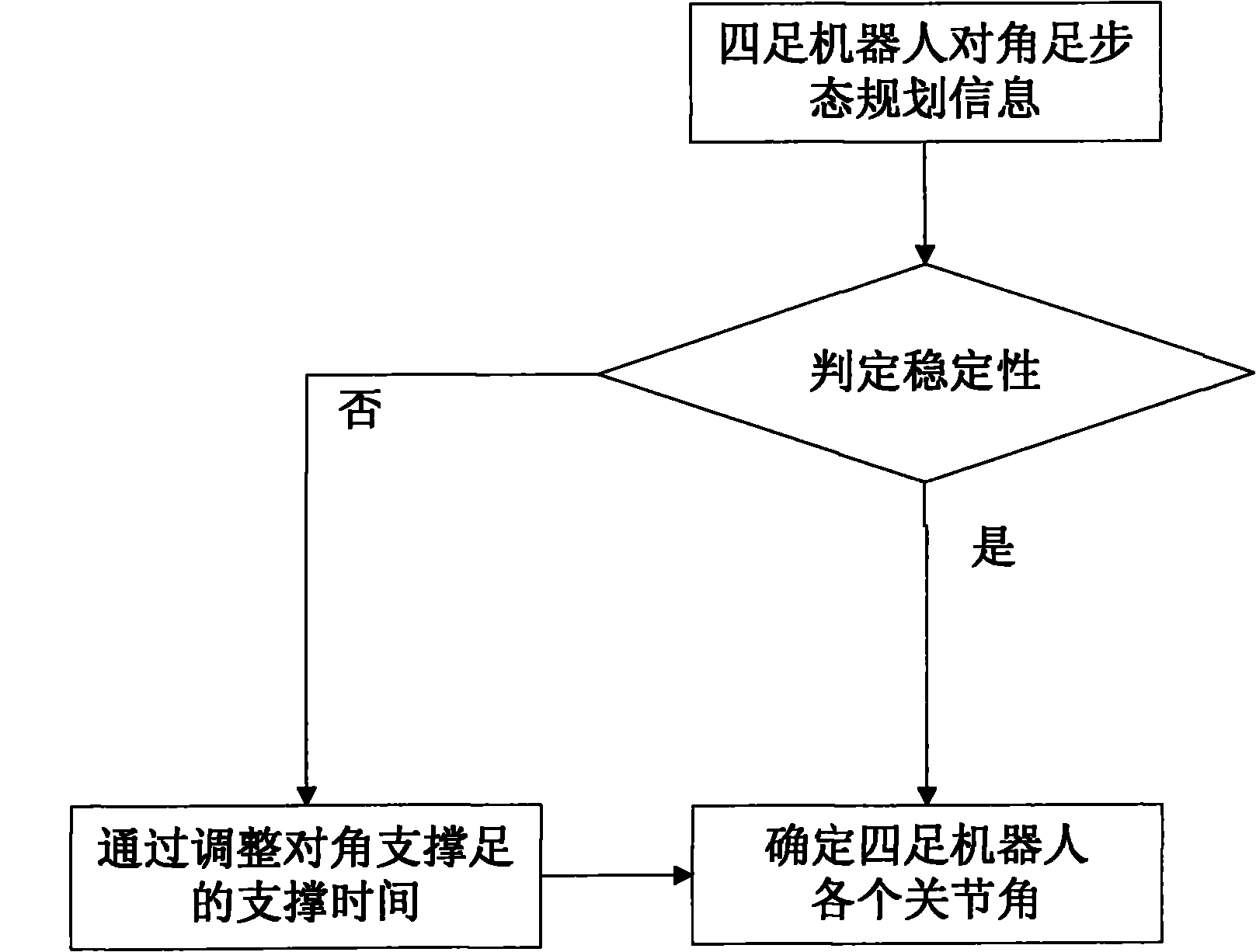
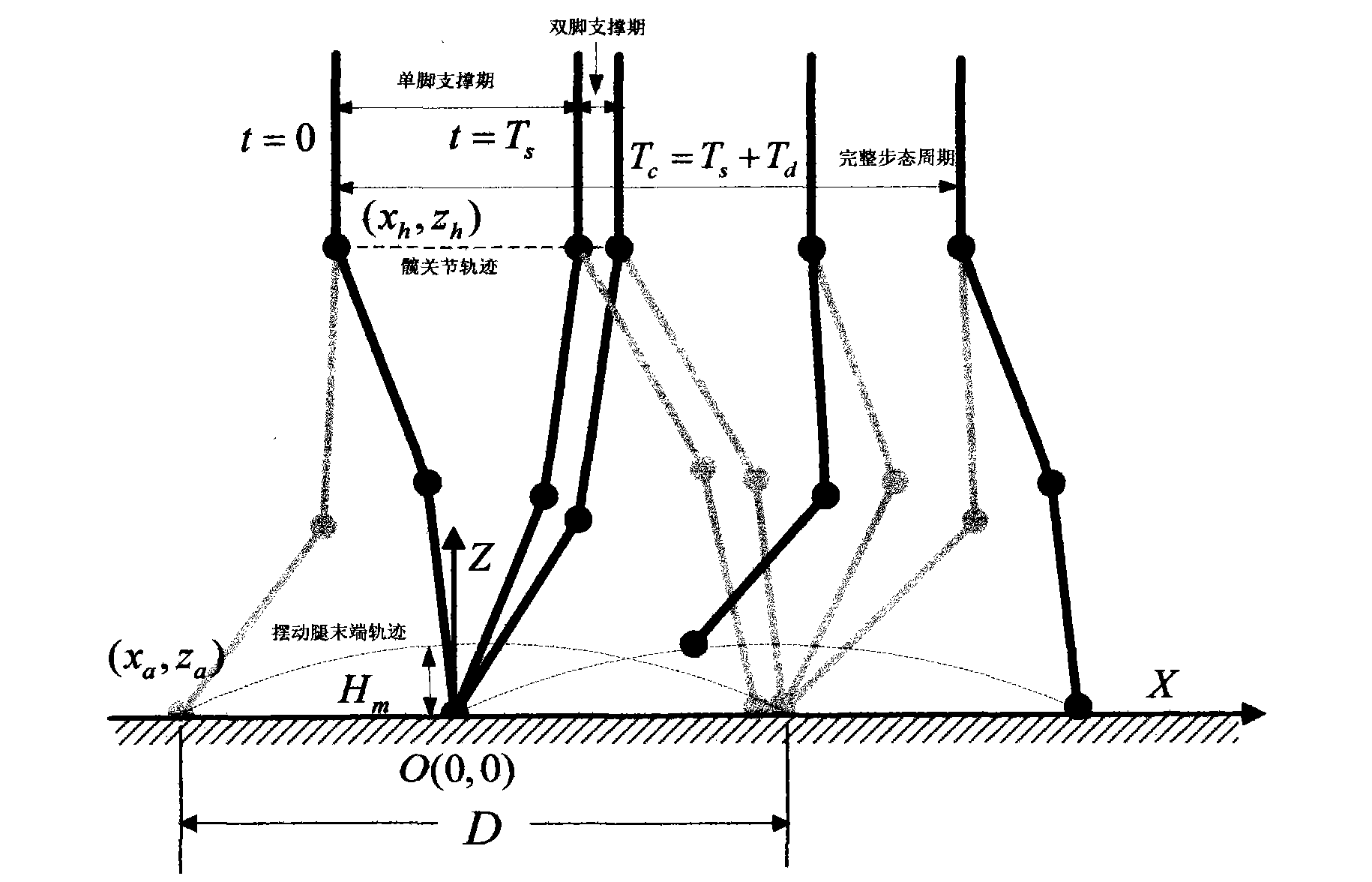
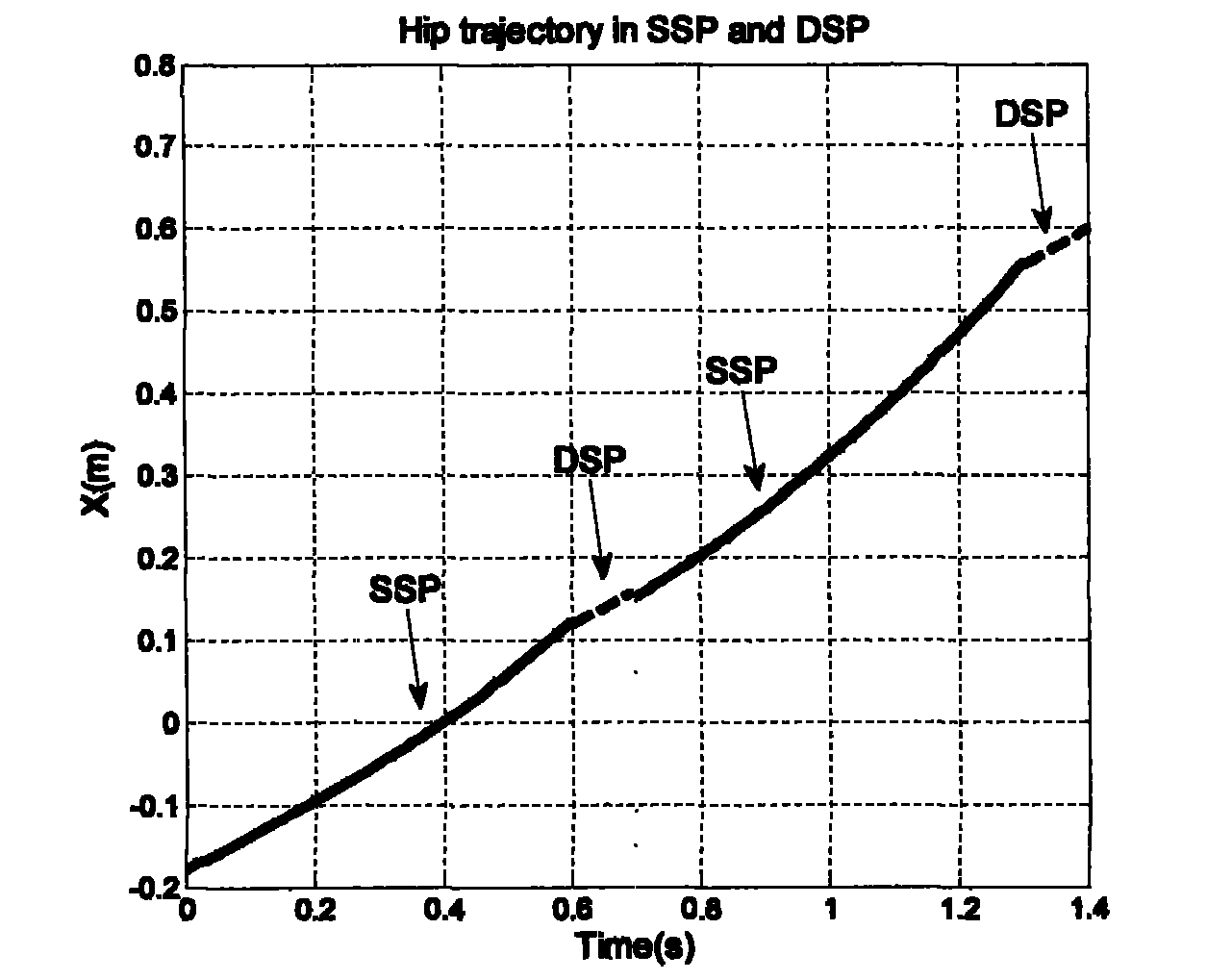
The invention discloses a self-adaptive control method for diagonal gait of a four-footed robot, which is used for self-adaptively controlling the walking of the four-footed robot in the nonstructural terrain with the diagonal gait. The self-adaptive control method bases on a fuzzy reasoning learning method and a foot trajectory real-time correction method and takes the diagonal gait as the motion mode so as to comprehensively control a robot body to adapt for the nonstructural environment. The gait planning is carried out on the environmental information collected by the sensor through the fuzzy reasoning learning method; the stability judgment is carried out on the gait planning information; if the planned four-footed robot has stable diagonal gait, the joint corner information is sent to a control system; if not, the supporting time of the diagonal feet is corrected by the foot trajectory real-time correction method so that the four-footed robot has better stability when walking under the changed gait in the nonstructural terrain. The self-adaptive control method is used for correcting foot trajectory planning and walking stability under changed gait when the four-footed robot walks diagonally in a dynamic way, thus realizing the self-perception, self-correction and self-adjustment of the four-footed robot.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Gait planning and synthetic method for humanoid robot
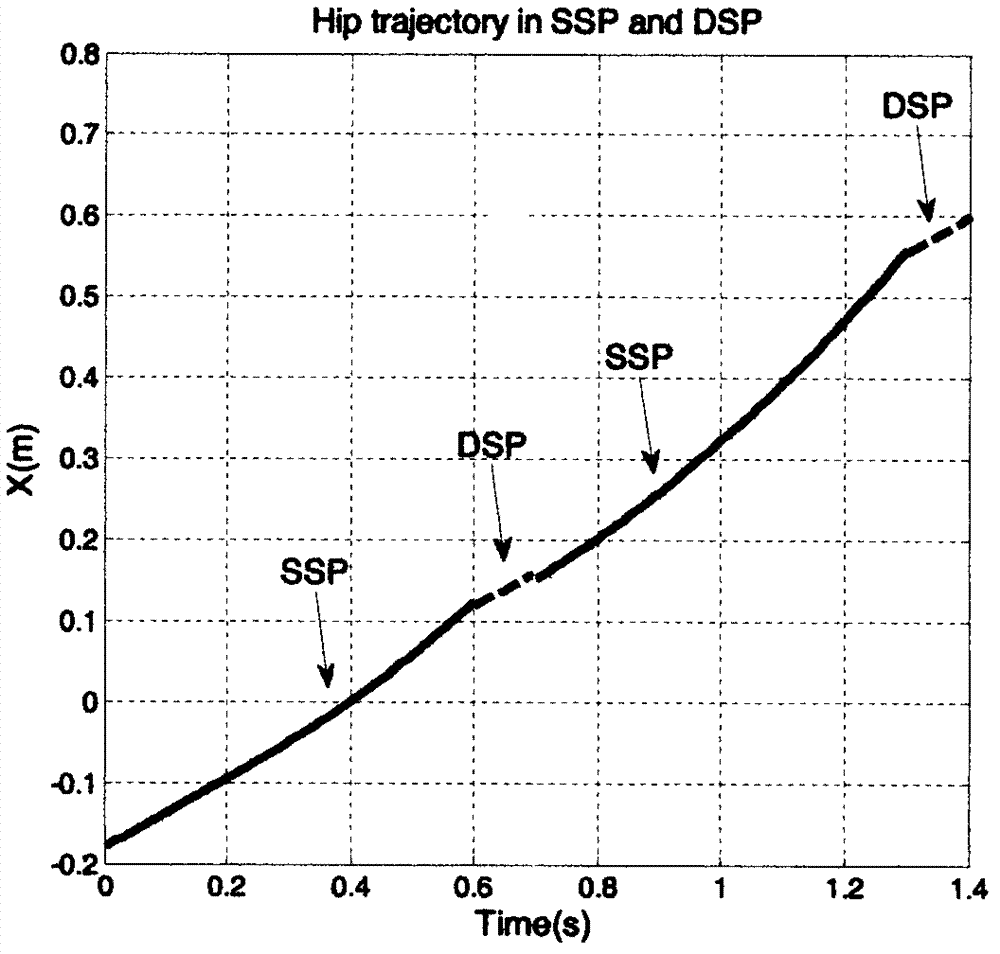
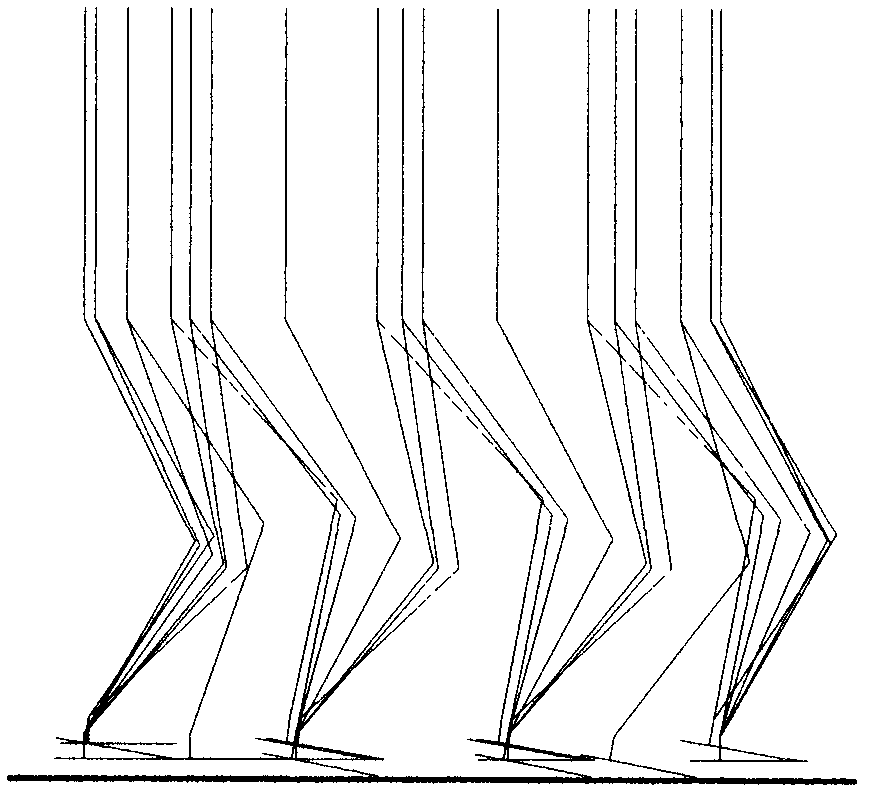
The invention discloses a gait planning and synthetic method for a humanoid robot, and belongs to the technical field of motion planning of the humanoid robot. The method comprises the steps of adopting a polynomial function to show the track of a hip joint and the track of the tail end of a swing leg of the robot, respectively planning gaits of the single-leg supporting period and the double-leg supporting period in robot walking according to constraint conditions in humanoid robot walking, such as geometric constraint, the largest crossing height of the tail end of the swing leg, the influences of periodicity and collision of the gaits, and motion of the hip joint, then conducting synthesis on the planned gaits, and judging whether the obtained gait track is stable or not according to zero moment criterion. According to the method, the gaits of the single-leg supporting period and the double-leg supporting period of the robot are planned and synthesized into the complete gait, the problem of the influence of the collision of the legs and the ground on walking stability in robot walking is solved, the walking stability of the robot is improved, and meanwhile the important effect of the gaits of the robot in the double-leg supporting period on the complete gait period is achieved.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
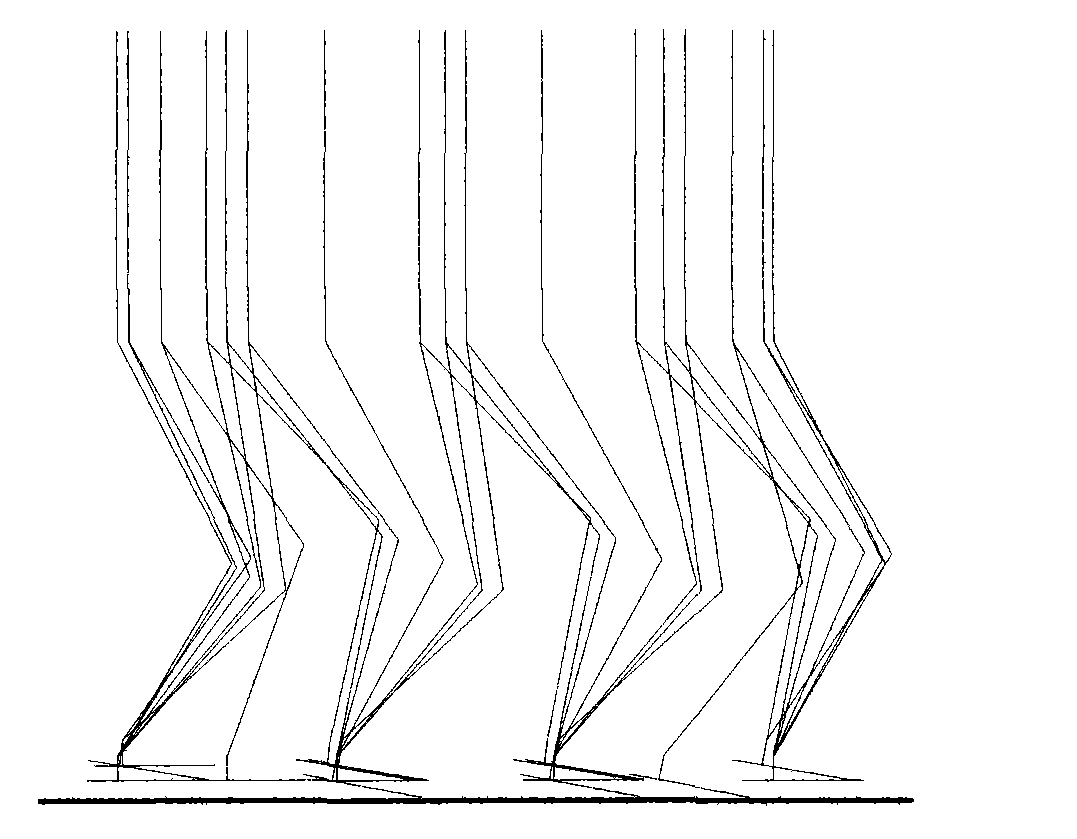
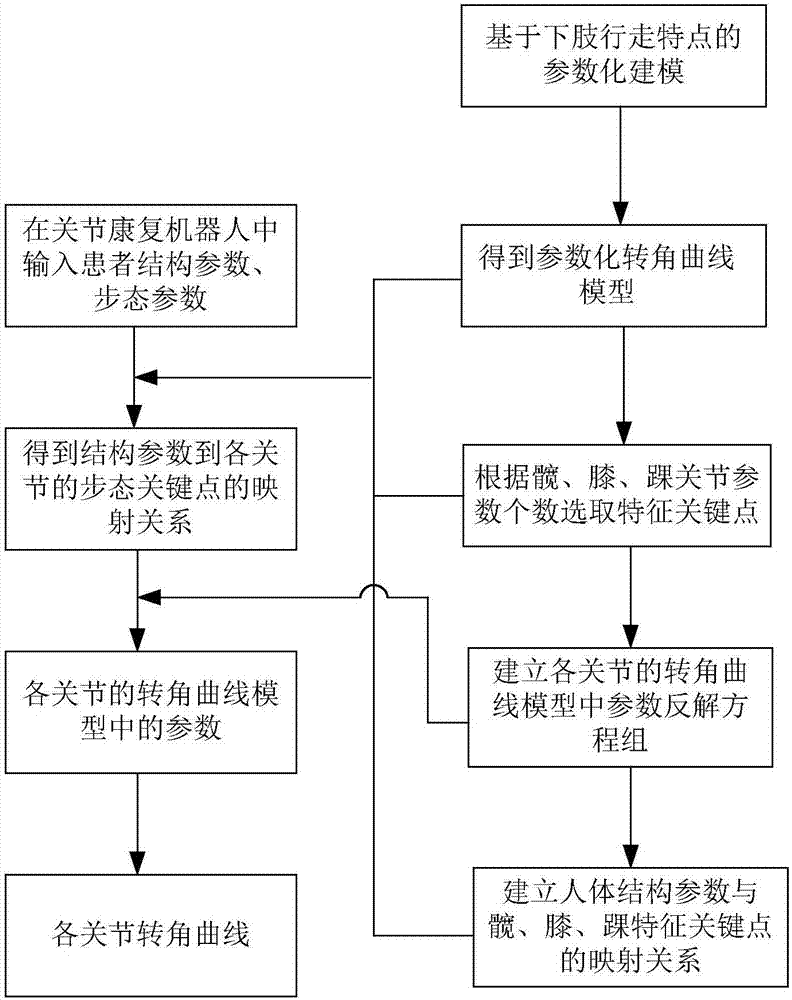
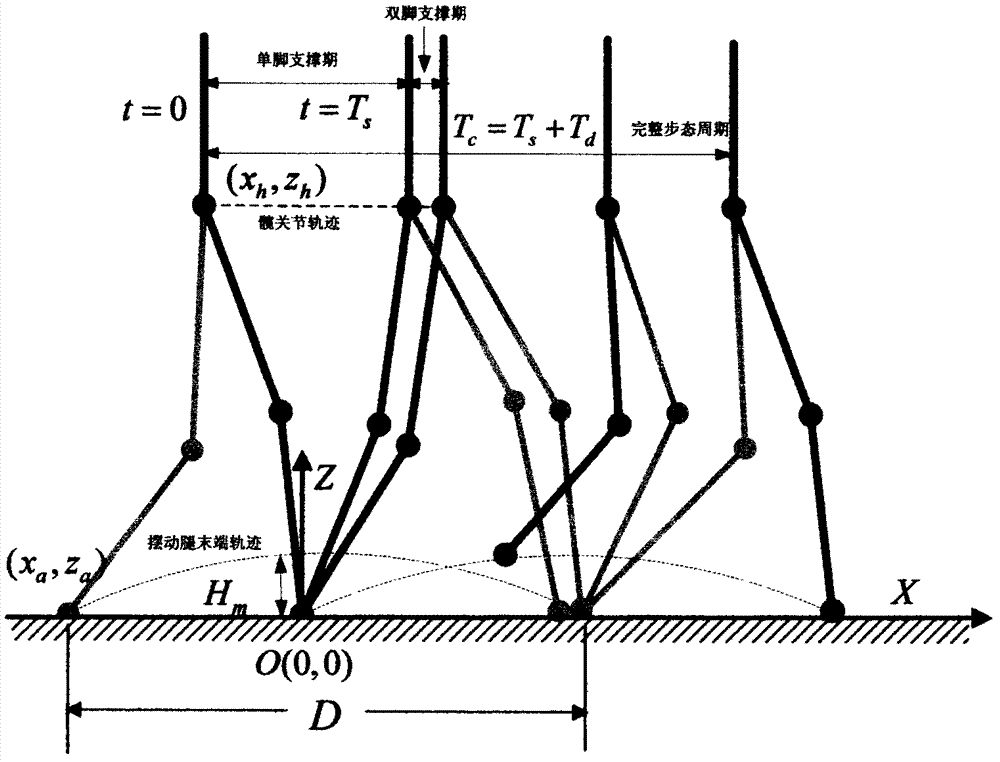
Lower limb rehabilitation robot gait planning method based on lower limb walking characteristics
ActiveCN107273611AIn line with the law of lower limb movementRealize motion trajectory customizationWalking aidsDesign optimisation/simulationHuman bodyGait
The invention provides a lower limb rehabilitation robot gait planning method based on lower limb walking characteristics. Firstly, parameterized modeling is performed based on the lower limb walking characteristics, wherein parameterized mathematic models of the lower limb hips, knees and ankle turn angles of the human body are established, and the forms of function curves of the models and required parameter number are determined; secondly, a mathematic inverse solution equation set of curve parameters is established; thirdly, the linear and nonlinear mapping relation of human body structure parameters and characteristic key point positions is found; finally, human body structure parameters are measured, the characteristic key points of a patient are found according to the mapping relation between the human body structure parameters and the characteristic key points, the curve parameters are inversely solved to obtain a specific curve expression, kinematic positions and corresponding lower angles of a robot are solved according to the specific structure and configuration of the lower limb rehabilitation robot to generate a joint movement instruction corresponding to the robot. The lower limb rehabilitation robot gait planning method conforms to a human body lower limb movement rule and can also reveal the mechanism of human body lower limb movements.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Humanoid robot gait planning and synthesizing method
The invention discloses a humanoid robot gait planning and synthesizing method, and belongs to the technical field of humanoid robot motion planning. The humanoid robot gait planning and synthesizing method comprises the following steps that a polynomial function is adopted to represent tracks of hip joints and the tail ends of swing legs of a robot, a one-foot support period gait and a double-feet support period gait are respectively planned when the robot walks according to constraint conditions including geometric constraints, maximum stride height of the tail end of each swing leg, gait periodicity, impact effect, hip joint motions and the like when the humanoid robot walks, then the planned gaits are synthesized, and whether obtained gait tracks are stable is judged according to a zero moment point criterion. According to the humanoid robot gait planning and synthesizing method, the one-foot support period gait and the double-feet support period gait of the robot are planned and synthesized into a complete gait, the problem that collisions between legs of the robot and ground affect walking stability when the robot walks is solved, walking stability of the robot is improved, and an important effect, of the double-feet support period gait of the robot, on a complete gait period is explained at the same time.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
Robot component based on parallel mechanism, optimum design method and robot
InactiveCN101564840AImprove stabilityLarge space for exerciseProgramme-controlled manipulatorHumanoid robot naoGait planning
The invention discloses a robot component based on a parallel mechanism, an optimum design method and a robot; the robot component comprises at least two parallel mechanisms; adjacent parallel mechanisms are connected with each other by an output converter; each parallel mechanism is provided with a fixed platform and a movable platform which moves correspondingly to the fixed platform, wherein the fixed platform of one parallel mechanism is movably connected with a motor. The robot with the parallel mechanism adopts the robot component and conducts optimum analysis and forward kinematics analysis on the initially selected parallel mechanism by inverse kinematics analysis to validate and debug the analysis results in the above steps so as to determine the component structure finally. By adjusting the motion types of the parallel mechanism, the space motion track of the robot in the motion process is realized, a genetic arithmetic is used to conduct the computation of inverse kinematics and gait planning to the parallel mechanism, the trajectory planning and motion form of the humanoid robot is improved, and the stability of the robot is improved during the motion process.
Owner:SHANGHAI XPARTNER ROBOTICS
Four-foot robot static gait planning method based on terrain fuzzy self-adaption
ActiveCN110328670AAvoid Loss of Stability SituationsCausing a loss of stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesTerrainGait planning
Disclosed is a four-foot robot static gait planning method based on terrain fuzzy self-adaption. The four-foot robot static gait planning method based on terrain fuzzy self-adaption comprises the following steps of (1) calculating a trunk pitching angle according to foot falling position information of a robot; (2) planning a trunk movement track, and ensuring the stability of the robot in a nextstepping stage; (3) estimating the complexity of walking terrain by using the time of ground touching of two feet of the robot, and automatically adjusting parameters of truck moving track planning onthe basis of a fuzzy algorithm; and (4) completing a complete gait cycle and repeating the whole process. By means of the method, the pitching angle of a trunk can be automatically adjusted accordingto the terrain fluctuation in the walking process of the fur-foot robot, and the height and the terrain adaptability of the four-foot robot swinging feet across an obstacle are effectively increasedand improved respectively; the situation that the robot loses stability due to the fact that the speed or the acceleration is suddenly changed is effectively avoided; the self-adaption of the four-foot robot to the terrain is realized, and the terrain adaptability of the four-foot robot is effectively improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
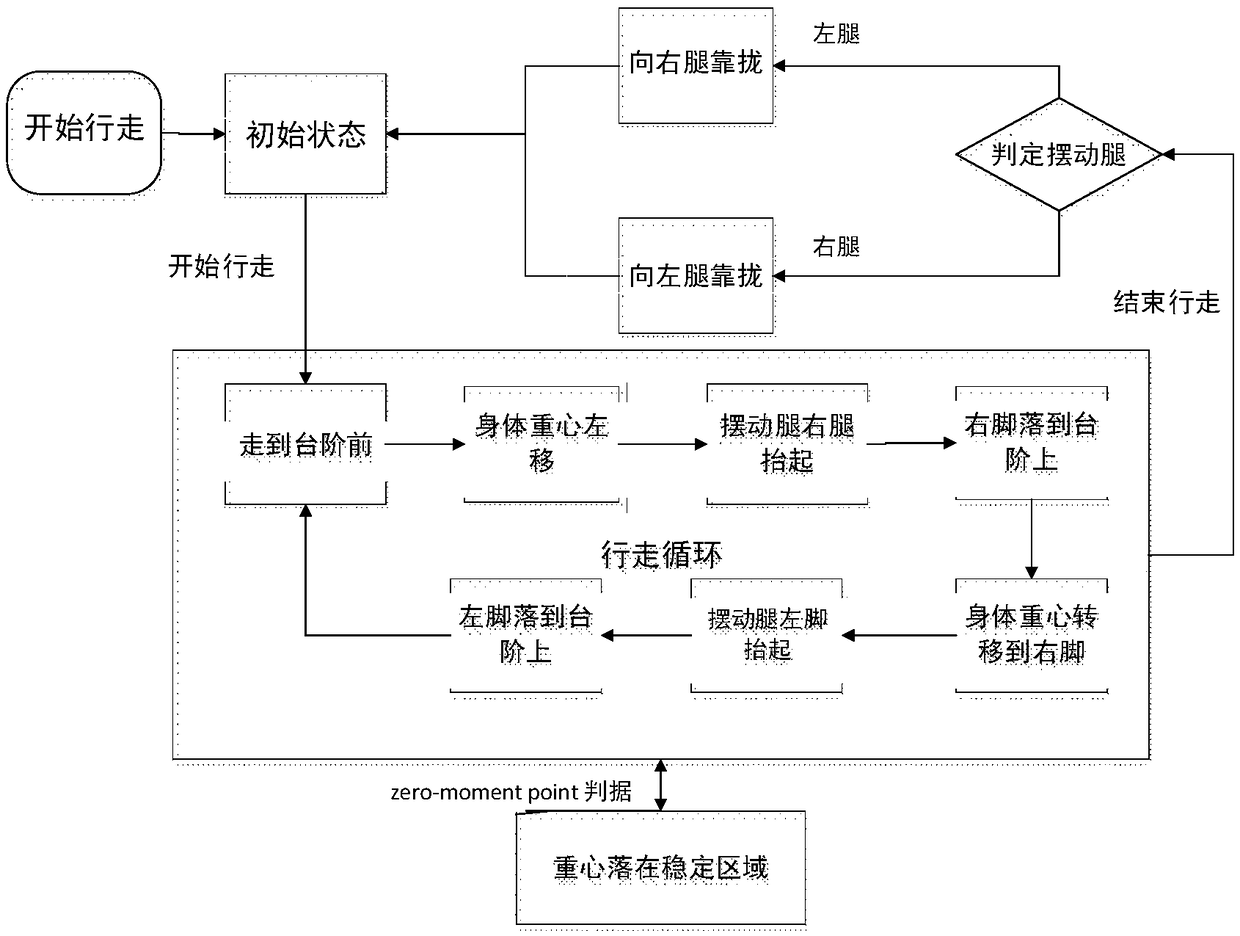
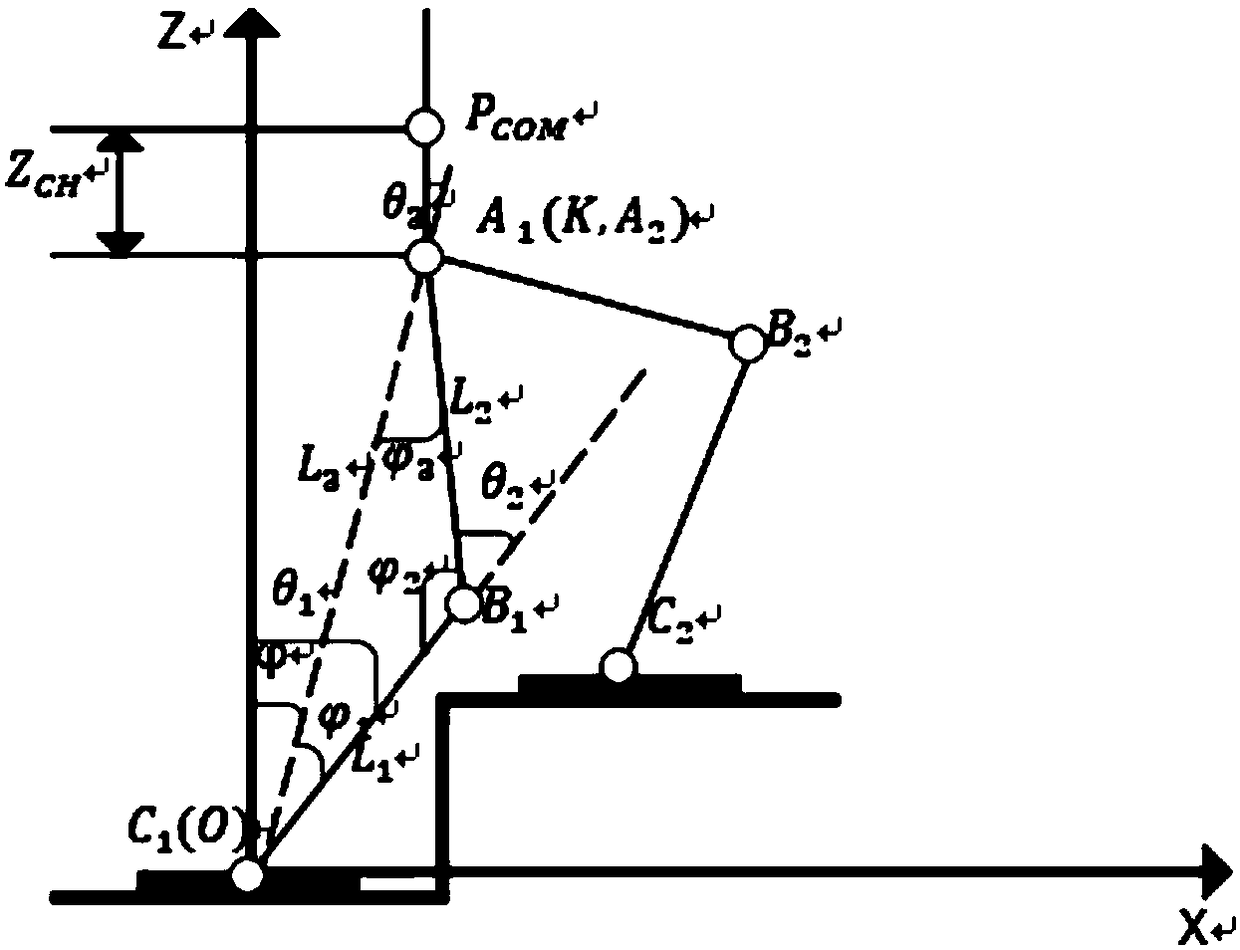
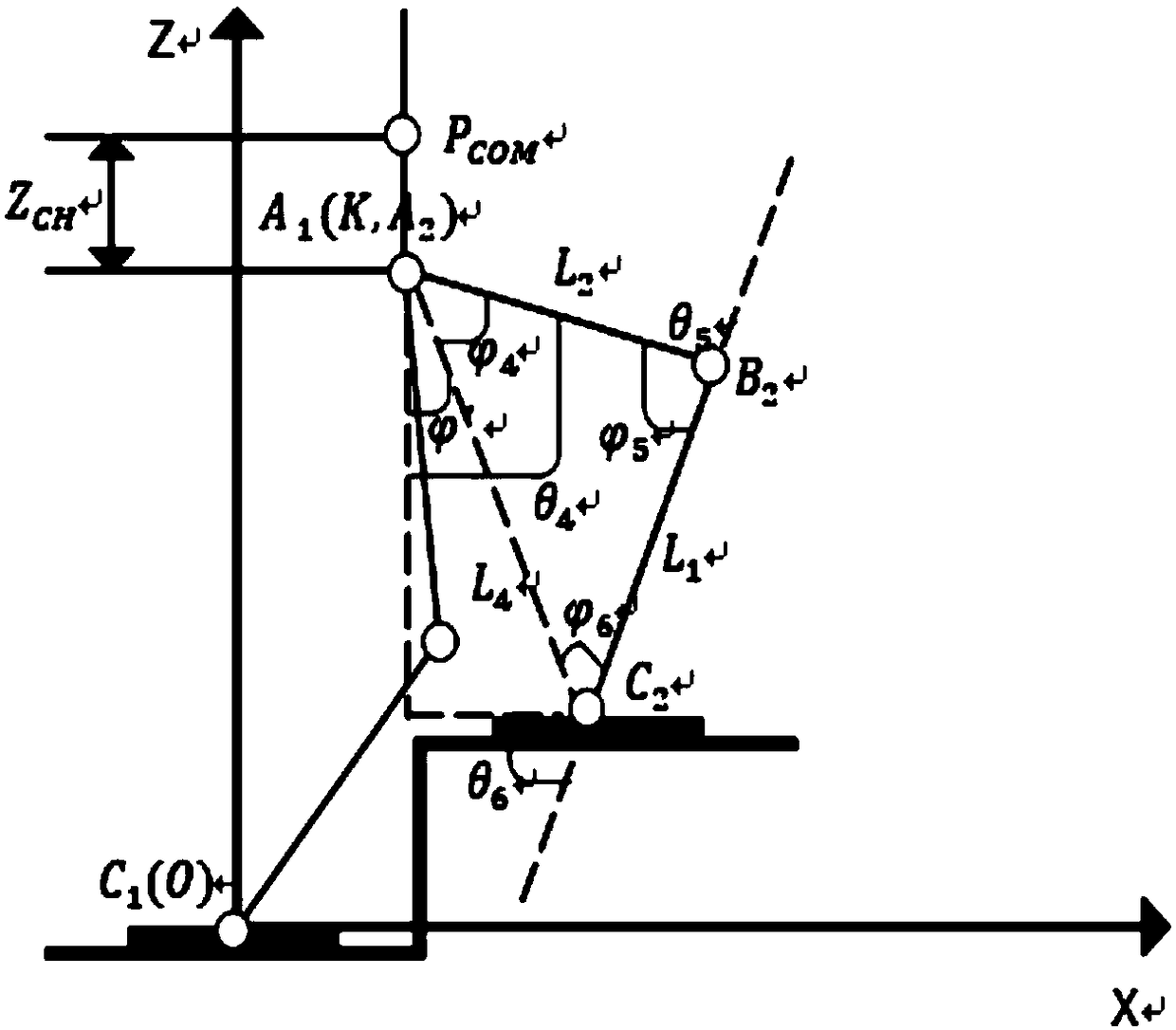
Biped robot climbing stair gait planning method and device and robot
InactiveCN109202901AWalk freelyProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesGait planningPlanning approach
The invention discloses a biped robot climbing stair gait planning method and device and a robot. The biped robot climbing stair gait planning method comprises the steps that in the stair climbing process, a variable-length first-order inverted pendulum model is adopted to carry out trajectory planning on a forward gait, the motion trajectory of an ankle joint is constrained according to preset constraint conditions, and a first-order linear inverted pendulum model is adopted to carry out trajectory planning on a lateral gait to realize stair climbing of a biped robot; the process is that whenfacing the first stair, the center of gravity of a body is controlled to move to the left; a right foot of a swing leg is lifted to drop the right foot onto the stair; the center of gravity of the body is moved to the right foot, and the left foot of the swing leg is lifted so that the left foot falls onto the stair; the steps are repeated until the first stair is the last stair; whether the center of gravity falls within a stable region or not is judged; if yes, the walking is finished; and if not, the two legs are controlled to close and return to the starting state. Based on the biped robot climbing stair gait planning method and device and a robot, an effective application of a robot walking mode can be realized, so that the robot can walk on the stairs as freely as a human.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV OF TECH
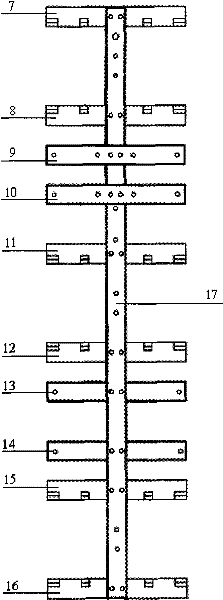
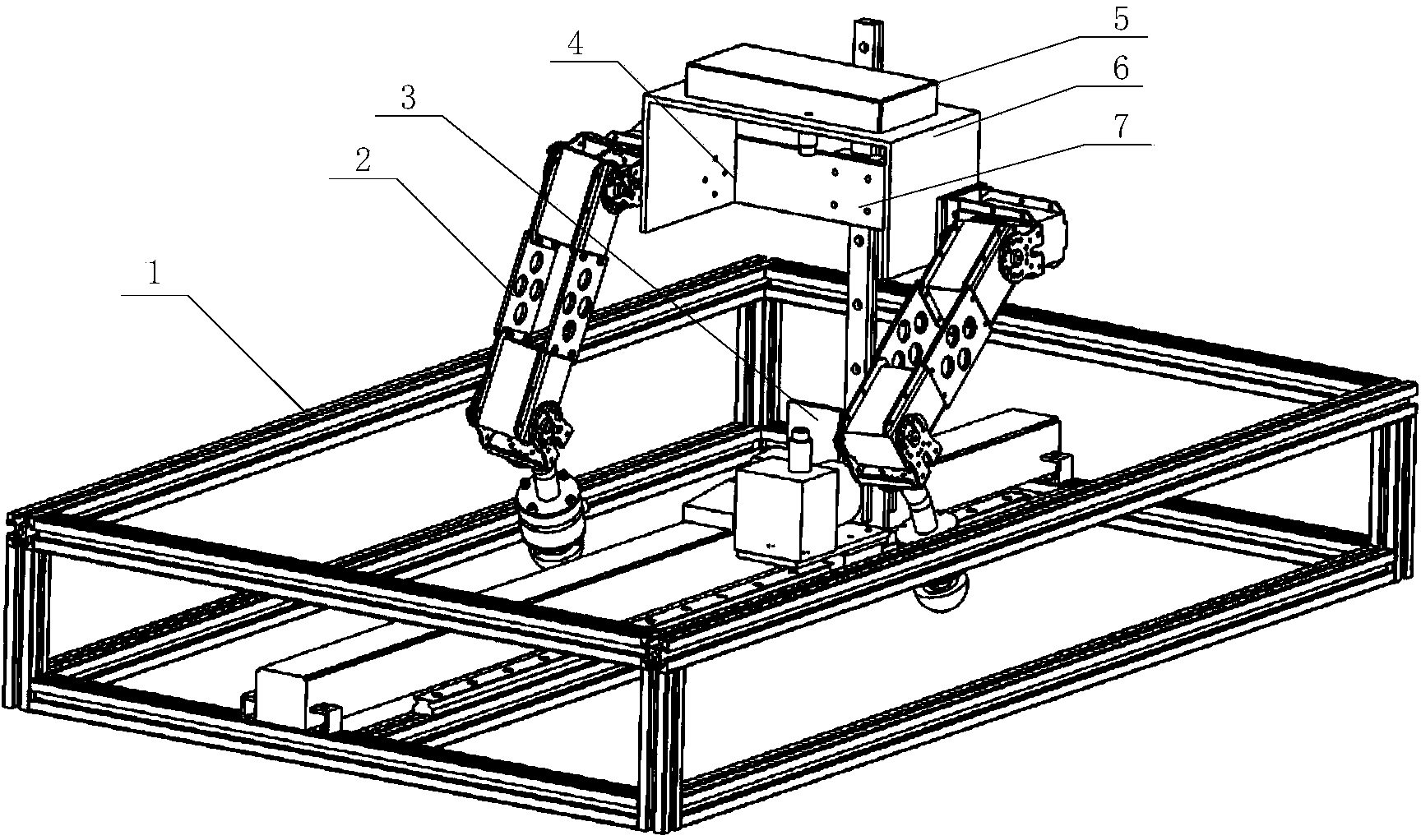
Doubleleg strength test experimental platform of foot type walking robot
InactiveCN103885446AEasy to buildLow costPosition/course control in two dimensionsTerrainControl system
The invention discloses a double leg strength test experimental platform of a foot type walking robot. The experimental platform is composed of a robot double leg experimental platform frame, robot single leg assemblies, a robot double leg connector, a robot double leg experimental mechanism and a robot double leg controller. The two robot single leg assemblies are connected through the robot double leg connector, and the robot double leg experiment mechanism is connected with the robot double leg connector through a sliding block on a vertical guide rail. The robot double leg control system is used for collecting and processing data of the robot double leg experiment platform by setting communication of an upper computer and a lower computer and performing planning control over movement strategies. The double leg strength test experimental platform is suitable for controlling single leg strength and double leg strength of the foot type walking robot, walking tests on different terrain, load distribution and gait planning and suitable for early-stage study and control strategy verification of researchers of the foot type walking robot and has the advantages of being low in cost, easy to manufacture and accurate and reliable in experimental result.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
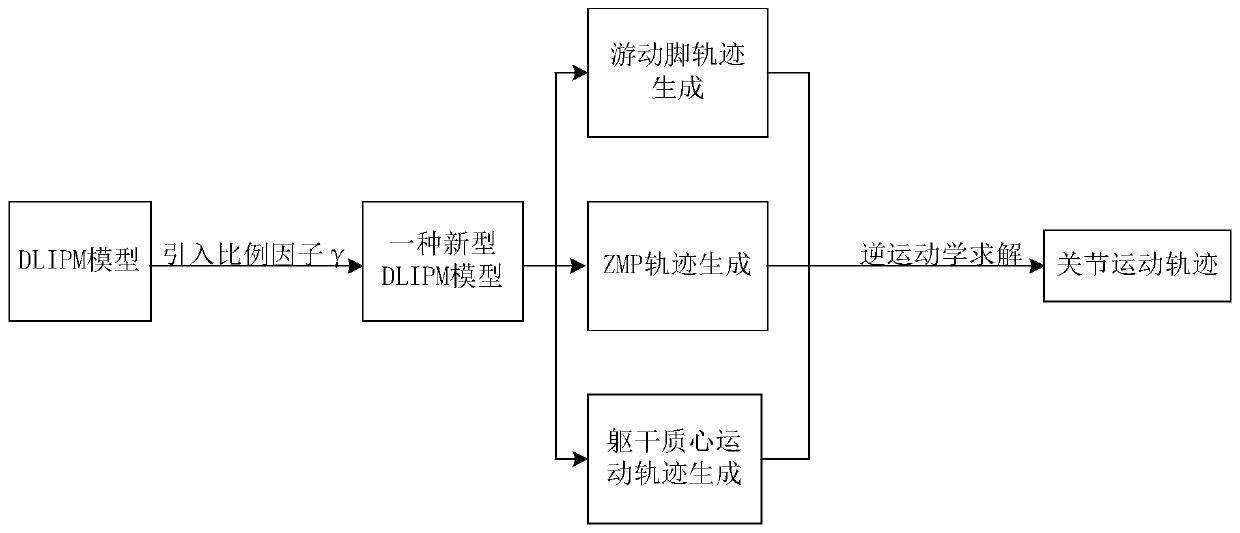
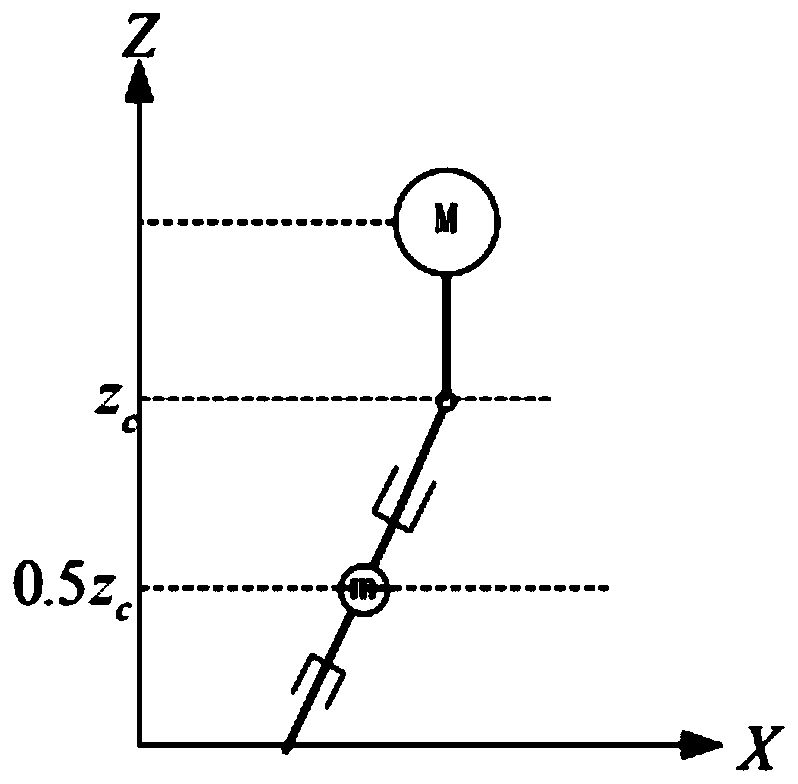
Linear inverted pendulum model-based robot gait planning method
InactiveCN110286679AImprove stabilityConform to gait processPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesGait planningPlanning approach
The invention discloses a linear inverted pendulum model-based robot gait planning method. The linear inverted pendulum model-based robot gait planning method comprises the following steps of building a linear inverted pendulum model, in which a proportion factor Gamma is introduced on the basis of a dual-connection rod inverted pendulum model (DLIPM) to build a new linear inverted pendulum model; and performing robot gait planning, in which zero-torque point track, trunk mass center motion track and free foot planning track are generated on the basis of the linear inverted pendulum model, and each joint gait motion curve is solved by inverse kinematics. The linear inverted pendulum model built by the method more conforms to actual mass distribution condition of a humanoid robot, the zero-torque point track, the trunk mass center motion track and the feet foot planning track which are generated on the basis of the model and the each solved joint gait motion curve linear are more reasonable and more conform to the gait process of a natural person dual-foot robot, and the gait planning accuracy is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gait planning method of 3D (3 dimensional) underactuated biped robot jumping motion
ActiveCN105599816AJumping movement achievedSpecial data processing applicationsVehiclesBody angleGait planning
The invention relates to a gait planning method of a 3D (3 dimensional) underactuated biped robot jumping motion. The bionic characteristics of the gait planning method are mainly embodied in two aspects of: (1) simulating the jumping motion of human, namely, in the process of jumping, a robot supports leg knee joints to quickly stretch, and the hip joint of the robot simultaneously moves so that the included angle between the body of the robot and the vertical direction of gravity is quickly reduced; (2) meeting the joint constraints in the jumping motion of human, mainly including crotch angle constraint, body angle constraint, and knee joint angle constraint. Thus, compared with the previous jumping motion gait planning method, the gait planning method provided by the invention can not only realize the jumping motion of robots but also embody the humanoid gait characteristics. Furthermore, the invention also provides a set of program design scheme of effectively realizing the gait planning of 3D underactuated biped robot jumping motion.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Rugged-terrain-oriented four-foot robot double-layer structure gait planning method
ActiveCN108333931AAchieve quadrupedal movementImprove computing efficiencyAdaptive controlTerrainGait planning
The invention discloses a rugged-terrain-oriented four-foot robot double-layer structure gait planning method. During upper layer movement planning, landing points of swing legs under each swing phaseare planned according to a gait sequence, and centroid track planning of a robot trunk is carried out on each supporting phase to form the optimal target movement state of each step till the finishing point of a given planned path is reached, wherein the landing points are planned in the mode that a sector search area of the current swing legs in the four-foot robot is built in a grid map, and coordinates of the optimal target landing points are found in a passable area of the sector search area. By using method, the calculation efficiency and the terrain adaptability of the robot are improved under the condition that the movement speed and stability of the robot are not reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Complex environment-oriented lower limb robot gait planning method
ActiveCN109991979AGood fitSignificant reductionPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesHuman bodyGait planning
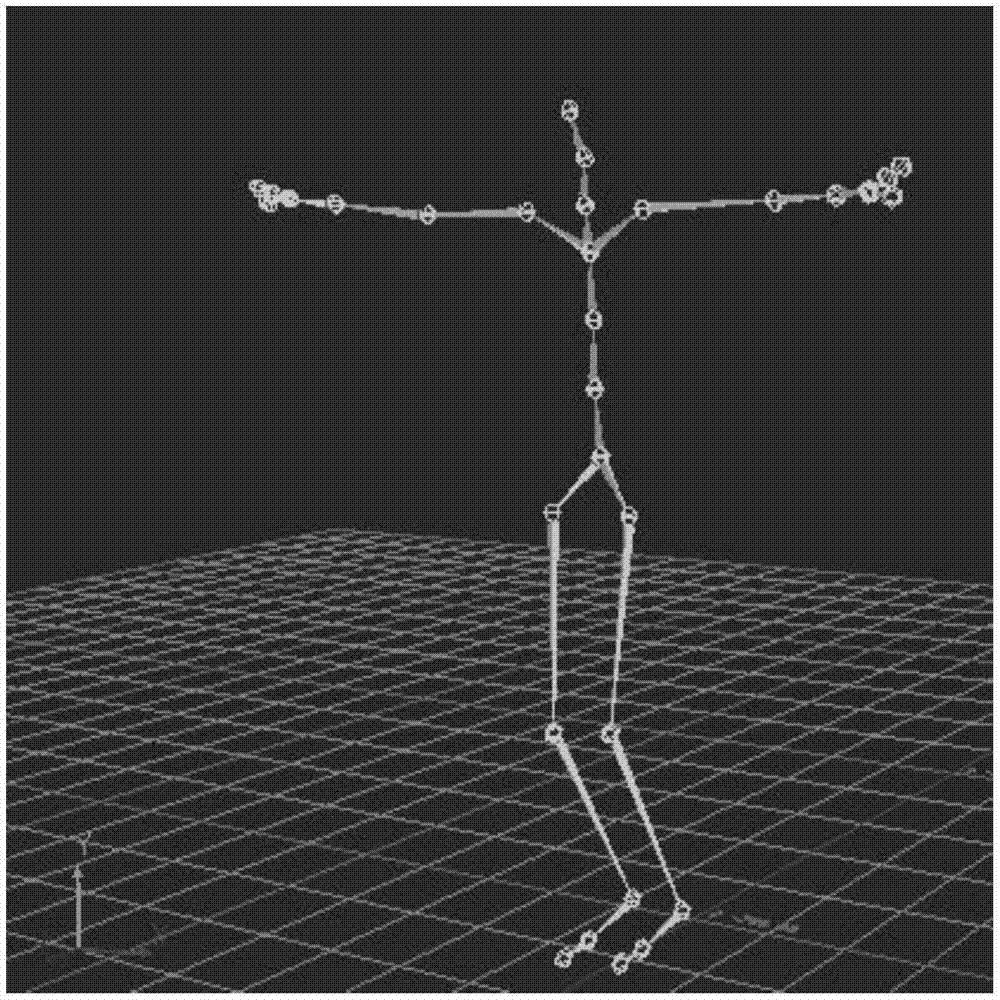
The invention belongs to the field of robots, and specifically discloses a complex environment-oriented lower limb robot gait planning method. The method comprises the steps of: setting mark points onthe lower limbs of a human body, and obtaining static posture data and moving posture data of the human body through a motion capture system; carrying out inverse kinematic calculation on a human body model according to the moving posture data so as to obtain angle data of each joint in the moving process; and establishing a fitting function according to a relationship between the angle data of each joint and a period, and carrying out lower limb robot gait planning according to the fitting function. According to the method, the discrete joint angle data is serialized, so that the change of the joint angle data in the gait period can be basically restored; experiences prove that the method has relatively fitting results, is capable of enabling the lower limb robots to restore the motionsof the human bodies to the greatest extent, and can be suitable for complex walking environments such as walking, climbing hills and climbing stairs.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Humanoid gait planning method of biped robot
ActiveCN111240339AImprove walking energy efficiencyImprove battery lifePosition/course control in two dimensionsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationGait planning
The invention discloses a humanoid gait planning method for a biped robot, and the method enables the movement characteristics of human walking to be integrated into the gait planning of the biped robot, so as to improve the walking energy efficiency of the robot and improve the endurance of the robot. The humanoid gait planning method comprises double-foot support phase planning and single-foot support phase planning, in the biped support phase, the robot enables the mass center of the robot to move forwards by means of the thrust of the ankle, meanwhile the mass center of the robot gets close to the supporting legs in a forward plane, so that the landing time is provided to the single-foot supporting phase; and in the single-foot supporting phase, the degree of freedom of the single-footsupporting phase and the degree of freedom of the lateral plane of the robot supporting ankle joint are in a passive state, the mass center of the robot moves forwards naturally under the action of gravity, and the swinging foot moves to the foot falling point quickly within the estimated landing time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
Human body motion capture data-based humanoid robot gait planning method
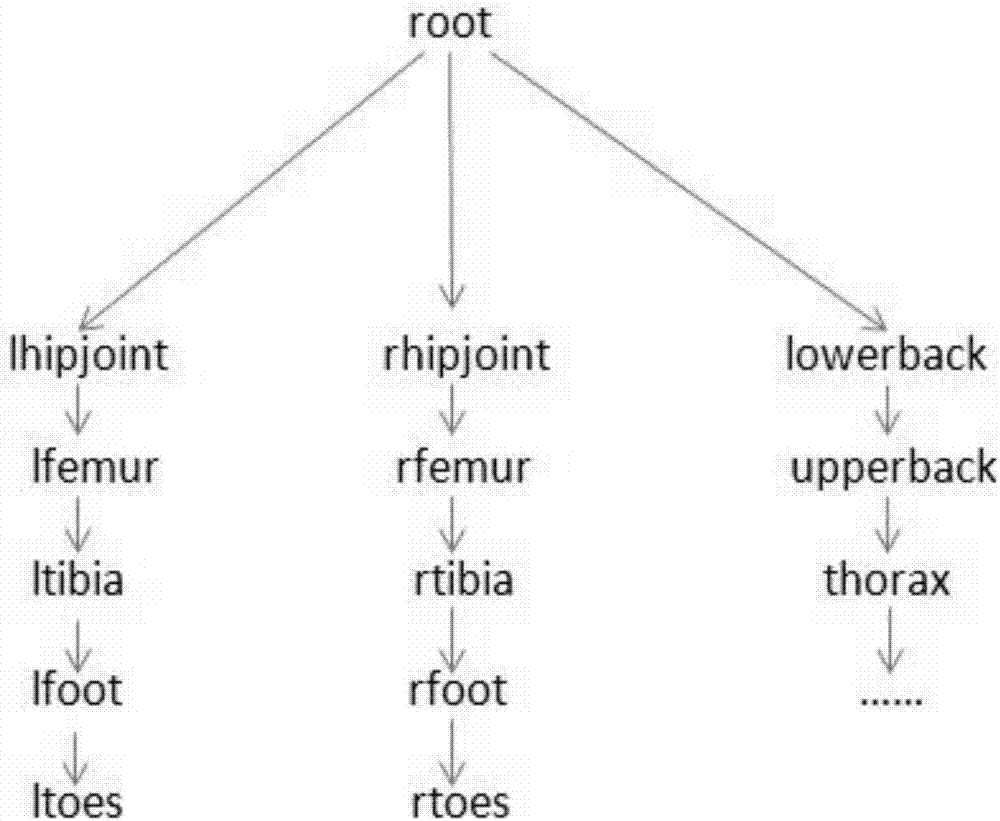
The invention relates to a human body motion capture data-based humanoid robot gait planning method. The method includes the following steps that: human body gait modes are extracted, angle curves of the six degrees of freedom of a single leg are obtained, wherein the human body gait modes include hip joint roll, hip joint pitch, hip joint yaw, knee joint pitch, ankle joint pitch and ankle joint roll; format conversion and mathematical optimization are performed on the human body gait mode data, so that the data can be applied to a human simulating robot; and a ZMP control algorithm is introduced to finely adjust the joint angles of a humanoid robot to improve the robustness of the humanoid robot. With the human body motion capture data-based humanoid robot gait planning method of the invention adopted, the gait planning difficulty of the humanoid robot can be simplified, the humanoid property and stability of the gait of the humanoid robot can be improved, and a foundation can be provided for the complex action planning of the humanoid robot. Compared with a traditional humanoid robot gait planning method, the human body motion capture data-based humanoid robot gait planning method has outstanding advantages and has a bright prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Biped walking simulation evaluation system and method of robot based on six-degree-of-freedom legs
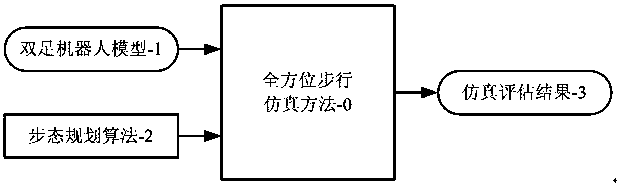
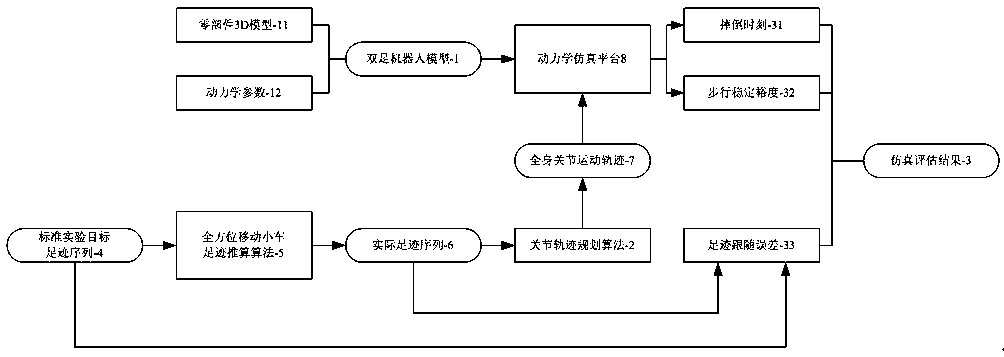
ActiveCN108058758ASolving Omnidirectional Walking Motion OptimizationShorten the development cycleDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEvaluation resultWhole body
The invention provides a biped walking simulation evaluation system and method of a robot based on six-degree-of-freedom legs. The system comprises a biped robot model and a gait planning algorithm, the biped robot model-1 and the gait planning algorithm-2 are input of the simulation evaluation system, the biped robot model contains the shape and dynamics parameters of the robot, and the gait planning algorithm can be used for planning motion trajectories of more than 20 joints of the whole body according to expected staying footprints; the simulation evaluation system outputs a simulation evaluation result used for evaluating the robot structure and the performance of the gait planning algorithm. Through a computer simulation mode, the purpose of omnidirectional walking motion optimization with more complex parameters and more involved factors is achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA INNOVATION CENT IN DONGGUAN
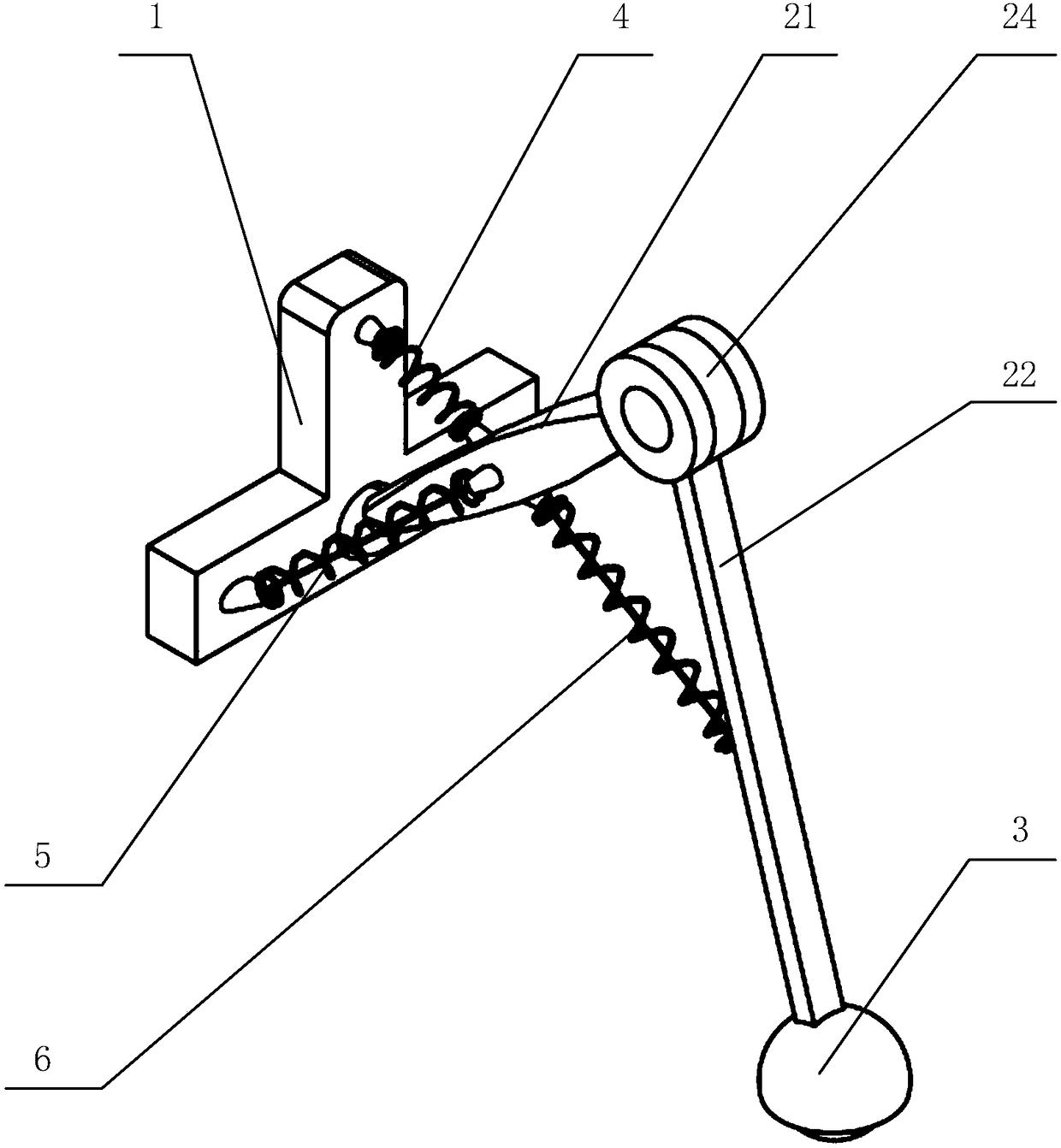
Shape memory alloy-driving bionic wall climbing robot leg unit and robot
The invention discloses a shape memory alloy-driving bionic wall climbing robot leg unit. The shape memory alloy-driving bionic wall climbing robot leg unit comprises bionic legs, a foot module, a shock absorption spring, a bi-directional shape memory alloy driving device and a single-directional shape memory alloy driving device, wherein the front-back and left-right movement of the bionic legs are driven by virtue of the bi-directional shape memory alloy driving device and the single-directional shape memory alloy driving device. The invention also discloses a shape memory alloy-driving bionic wall climbing robot driven by shape memory alloy. The bionic wall climbing robot comprises the bionic wall climbing robot leg unit. The shape memory alloy driving device adopts a bionic structure,so that the wall climbing movement of the robot on a medium surface is realized; the driving device is simple in structure, light in weight and flexible in movement; and the foot module adopts an ironmagnetic ball body, no surplus leg raising and re-absorption action is needed in the movement process of the bionic leg, the leg can provide a stable supporting force and absorption adsorption force,the supporting point is stable, the center of gravity of the robot is slight in change, and the gait planning is simple.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Quadruped robot and gait planning method thereof
The invention discloses a quadruped robot and a gait planning method thereof. The quadruped robot comprises a robotic trunk, wherein the upper part of the front end of the robotic trunk is connected with a robotic head through a robotic neck, and the lower part of the robotic trunk is connected with four legs of a first leg, a second leg, a third leg and a fourth leg; the first leg and the second leg are mounted at the front end of the robotic trunk, the third leg and the fourth leg are mounted at the rear end of the robotic trunk, and each leg comprises four parts of a shank part, a thigh part, a vertical rod part and a horizontal rod part which are sequentially connected from bottom to top; a control device is arranged on the trunk and used for controlling the robot to walk. The quadruped robot disclosed by the invention has the functions of walking smoothly and automatically avoiding obstacles.
Owner:SHANDONG YOUBAOTE INTELLIGENT ROBOTICS CO LTD
Humanoid robot gait planning method and device and humanoid robot
PendingCN111880544AGuaranteed walking speedGuaranteed dynamic stabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationGait planning
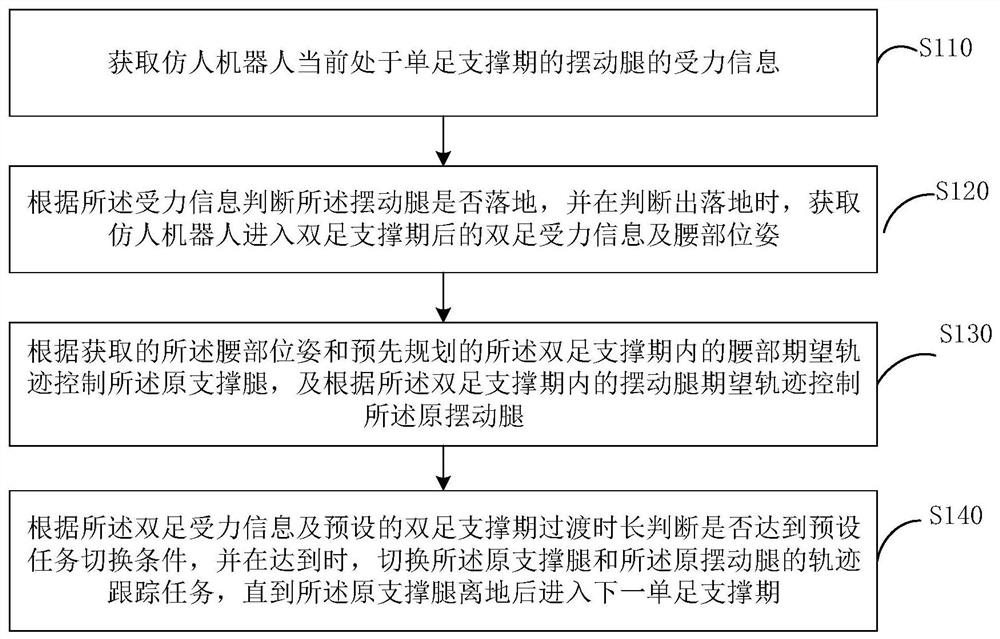
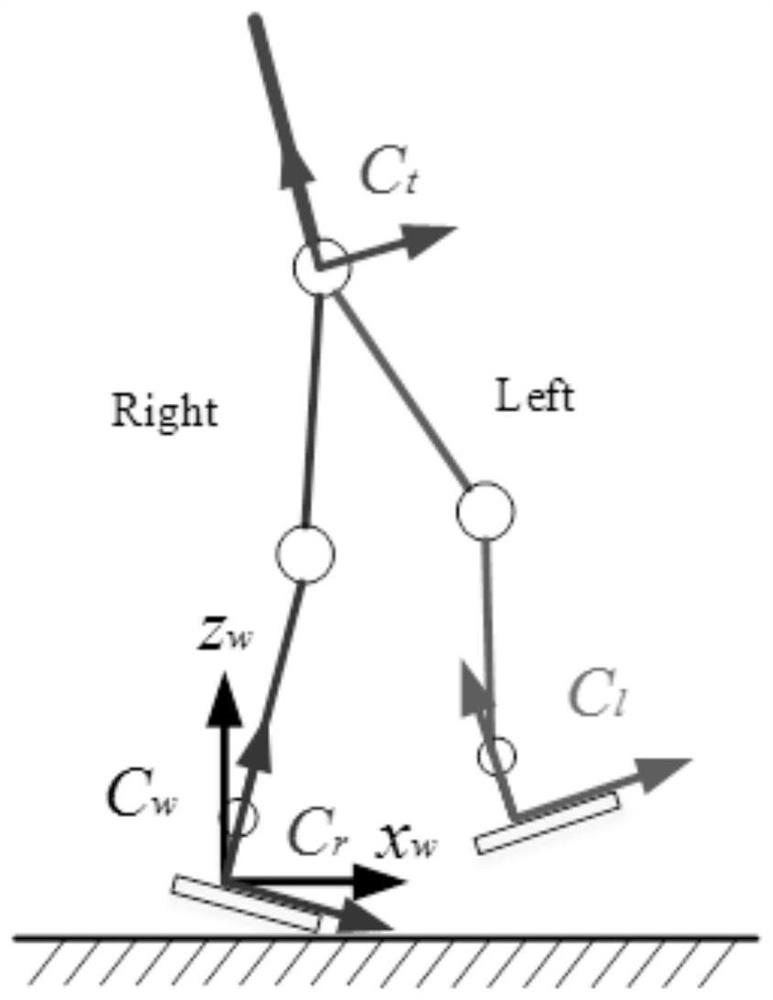
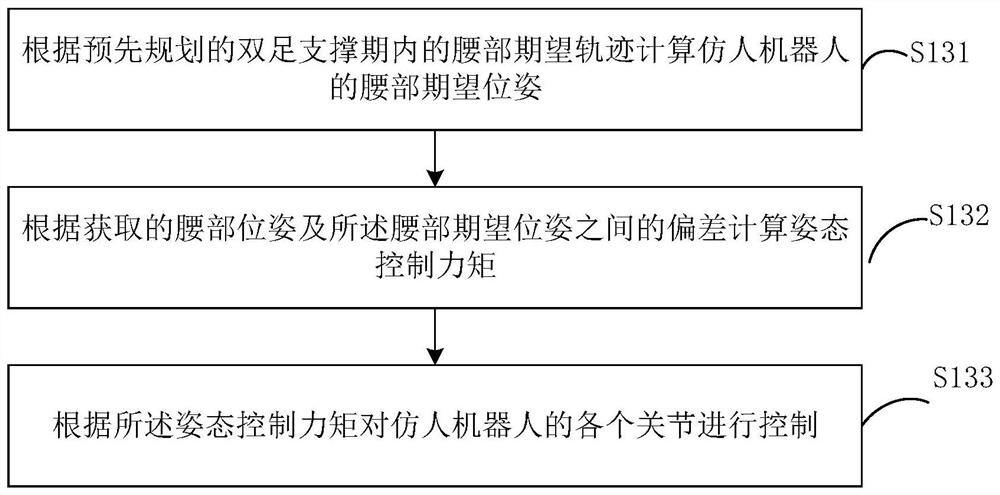
The embodiment of the invention discloses a humanoid robot gait planning method, a humanoid robot gait planning device and a humanoid robot. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring stressinformation of a swinging leg of the humanoid robot in a single-foot supporting period at present; judging whether the swinging legs fall to the ground or not according to the stress information, andacquiring biped stress information and waist poses of the humanoid robot after the humanoid robot enters a biped supporting period when it is judged that the swinging legs fall to the ground; controlling an original supporting leg according to the waist pose and the expected waist track in the biped supporting period, and controlling an original swinging leg according to the expected swinging legtrack; and judging whether a preset task switching condition is met or not according to the biped stress information and the biped supporting period transition duration, and switching the trajectory tracking tasks of the original supporting leg and the original swinging leg when the preset task switching condition is met. According to the technical scheme, smooth alternate switching of the supporting legs and the swinging legs can be achieved in the rapid walking process of the humanoid robot, and the dynamic stability and the like of the posture and the speed of the humanoid robot are guaranteed.
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
Biped robot kinematic analysis method based on toddler gait extraction
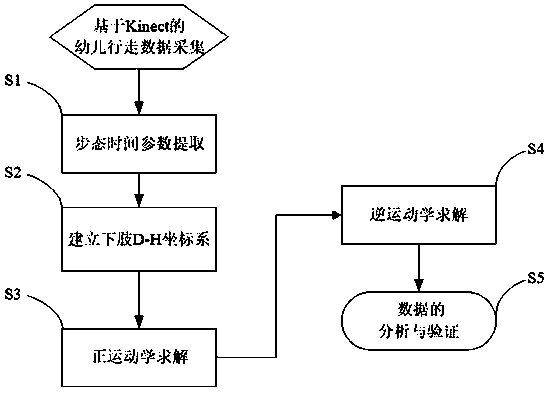
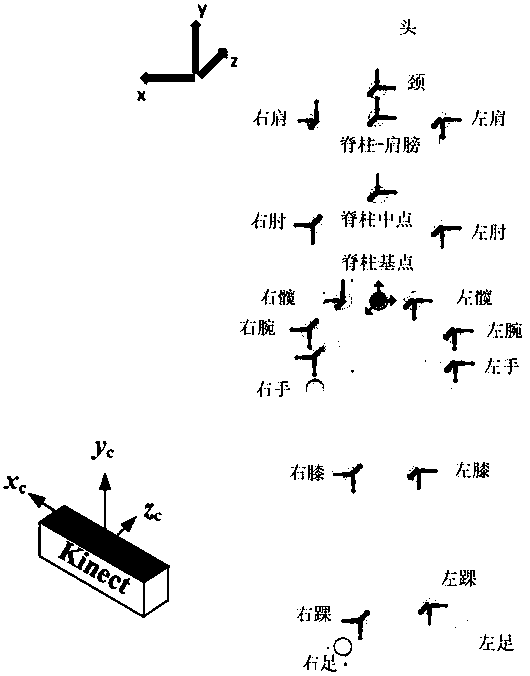
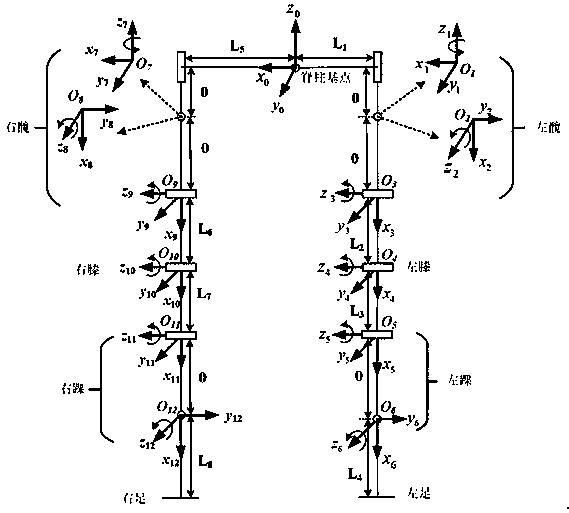
InactiveCN108388887ACharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationCurve fittingInverse kinematics
The invention discloses a biped robot kinematic analysis method based on toddler gait extraction. The method comprises the following steps: (1) walking videos of a toddler in different months are acquired, and corresponding supporting phases, oscillating phases, uniped or biped supporting phases, a gait cycle and a step frequency are extracted; (2) based on a D-H pose conversion method, a human lower limb coordinate system is built, skeletons of thighs, lower legs and soles are regarded as connecting rods, parts driving the skeletons to move are regarded as joints connecting the connecting rods, and a corresponding D-H parameter table is solved; (3) a forward kinematic model and an inverse kinematic model of the lower limb are solved; and (4) change values of joint angles are subjected tocurve fitting to analyze the spatial characteristics of a toddler walking gait. On the basis of acquiring the toddler walking data and extracting the gait time parameters, the forward kinematic modeland the inverse kinematic model of the lower limb are deduced based on the D-H pose conversion method, a toddler gait development space parameter change law is thus acquired, and a theoretical supportcan be provided for gait planning for the biped robot.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Humanoid robot walking control method
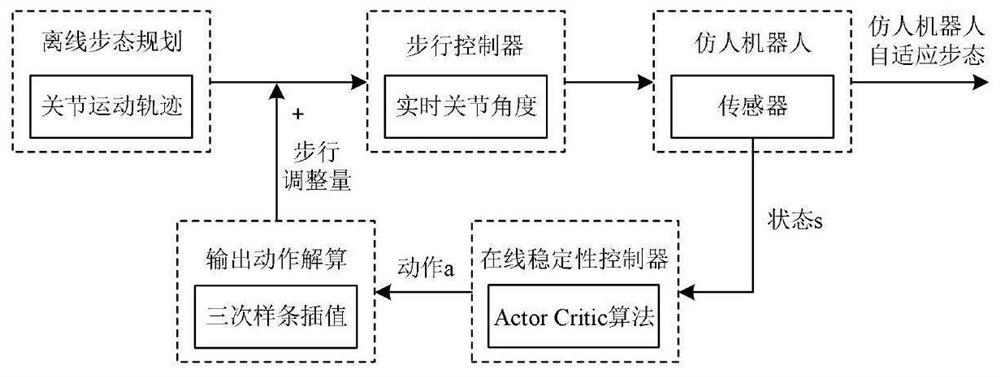
The invention discloses a humanoid robot walking control method, belongs to the field of humanoid robots, and provides the following technical scheme in order to solve the problem of improving the stability and balance ability of a humanoid robot in the walking process: the humanoid robot walking control method performs offline gait planning on the humanoid robot, so a joint movement track generated by the humanoid robot in an off-line tracking mode has the walking capacity; state information in the walking process of the humanoid robot is collected in real time, the walking posture of the humanoid robot is adjusted on line in real time in response to a stability controller of the state information, the humanoid robot can walk on an uneven road surface, and the effect is that walking control over the humanoid robot is achieved in the mode of combining offline gait planning and line stability control, and the humanoid robot has the effect that the humanoid robot has the capability of adapting to complex environments.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
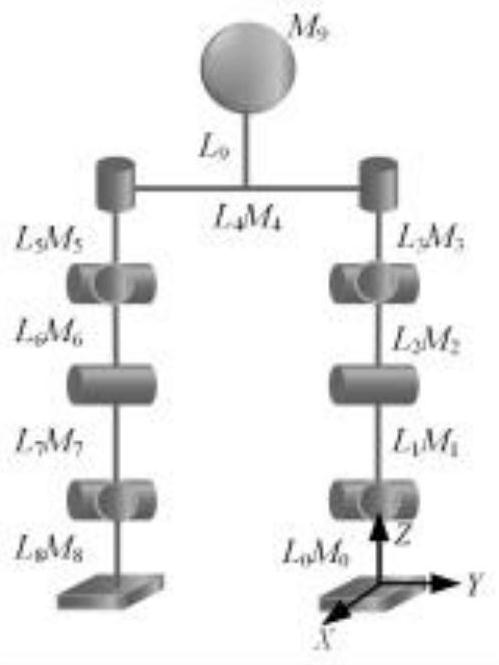
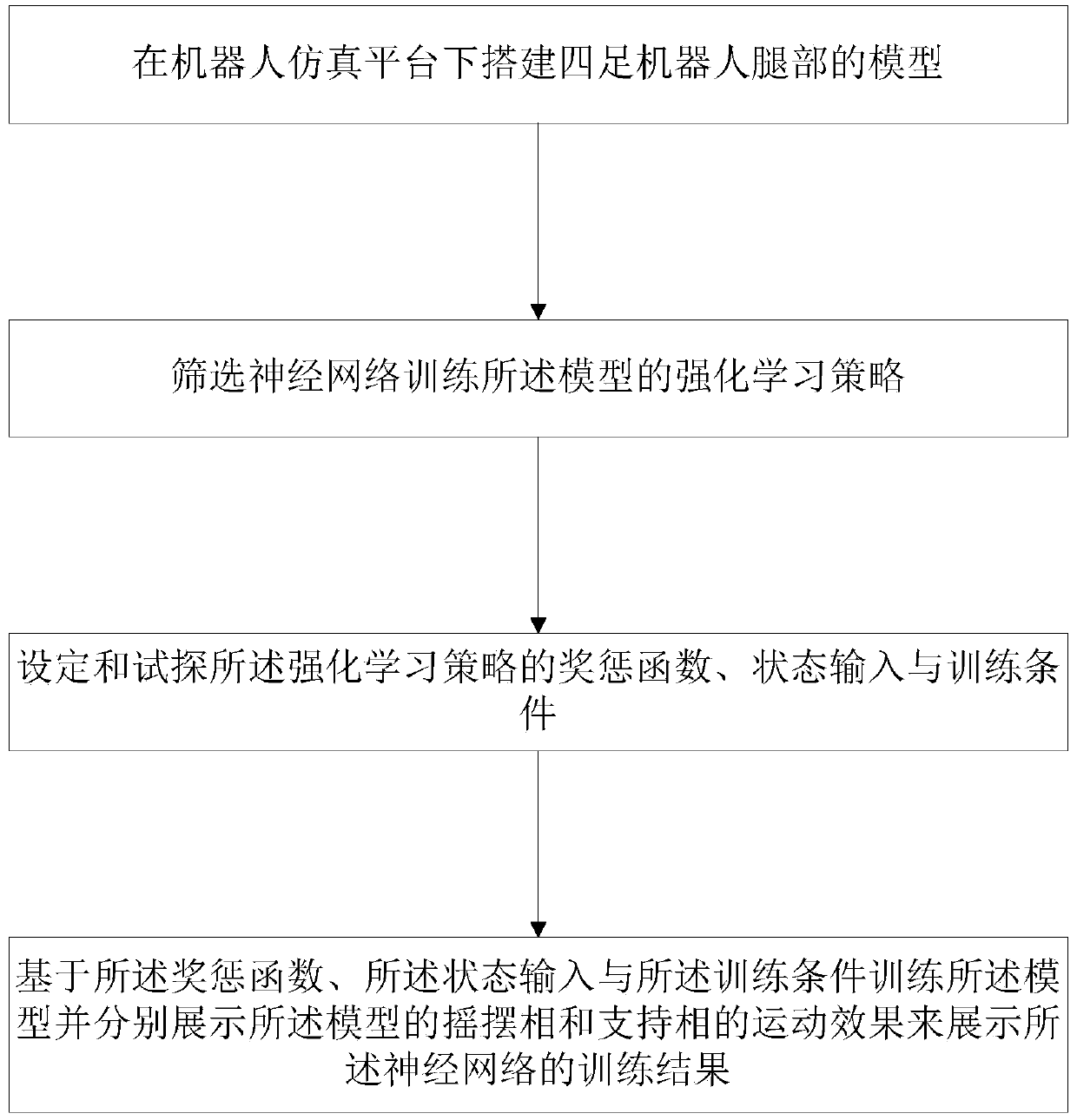
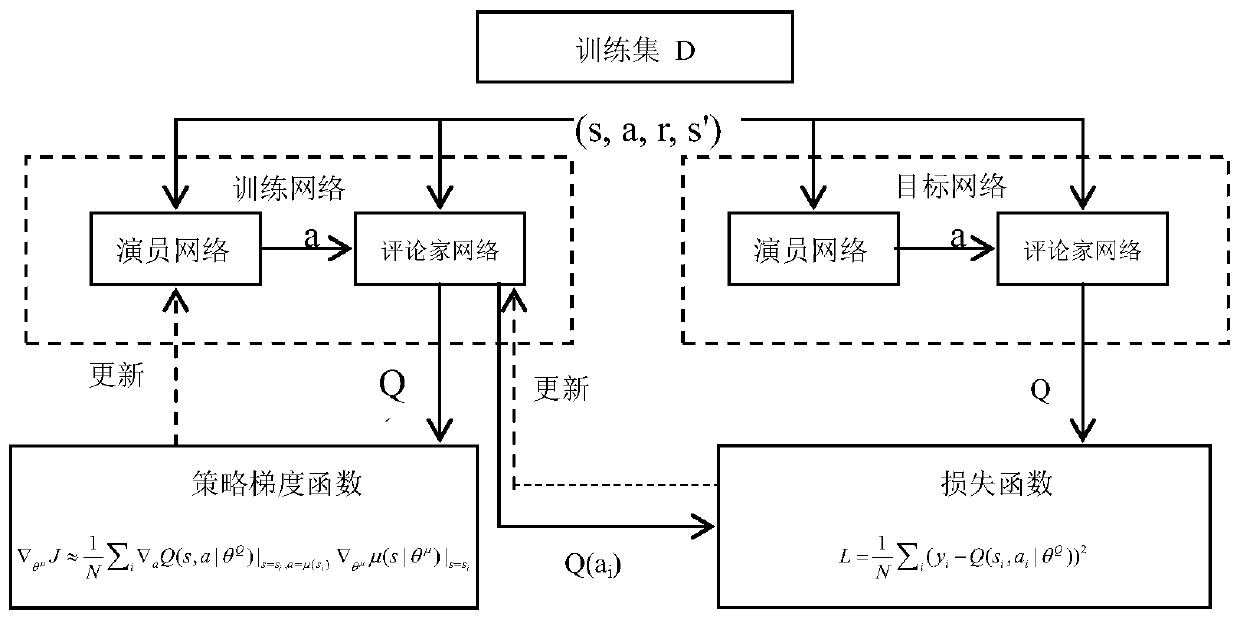
Gait planning method for leg movement of four-legged robot
The invention provides a gait planning method for leg movement of a four-legged robot. The gait planning method comprises the following steps that S1, models of legs of the four-legged robot are constructed under a robot simulation platform; S2, enhanced learning strategies for training the models by a neural network are screened; S3, reward and punishment functions, state input and training conditions of the enhanced learning strategies are set and sounded out; and S4, the models are trained on the basis of the reward and punishment functions, state input and the training conditions, and themotion effects of swing phases and supporting phases of the models are displayed respectively to display training results of the neural network. By adopting an enhanced learning algorithm and utilizing a heuristic learning training scheme, leg kinematics is planned, and the robot can be made to adaptively adjust gaits under the algorithm network.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Pipeline detection robot
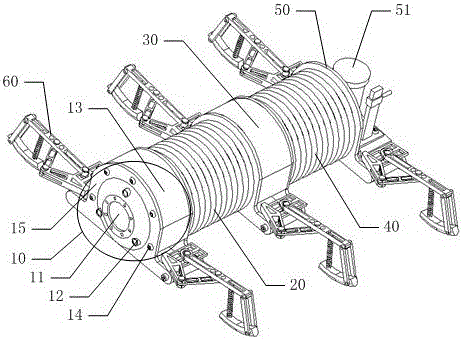
The invention discloses a pipeline detection robot. The pipeline detection robot comprises a robot head, a robot middle portion connected with the robot head through a first elastic connecting body and a robot tail connected with the robot middle portion through a second elastic connecting body. A bionic leg for traveling is arranged on each of the left sides and the right sides of the robot head, the robot middle portion and the robot tail. A camera for camera-shooting and multiple ultrasonic sensors for detecting obstacles are arranged on the robot head. A circuit control board for controlling the traveling gait of the robot and receiving detection signals is arranged on the robot middle portion. A winder for take-up and pay-off of cables is arranged at the robot tail. According to the pipeline detection robot, a body of the pipeline detection robot has certain scalability and flexibility, meanwhile has flexible gait planning capability and can adapt to the application needs of cornering, crawling, obstacle avoidance and detection in different pipeline environments; and due to the fact that detection signal transmission is stable and reliable, the pipeline failure detection efficiency of the robot is higher.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com