Humanoid robot gait planning method and device and humanoid robot
A humanoid robot and gait planning technology, which is applied in the field of humanoid robots, can solve the problems of robot state mutation, instability, and inability to guarantee trajectory tracking accuracy, and achieve the effect of ensuring walking speed and dynamic stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
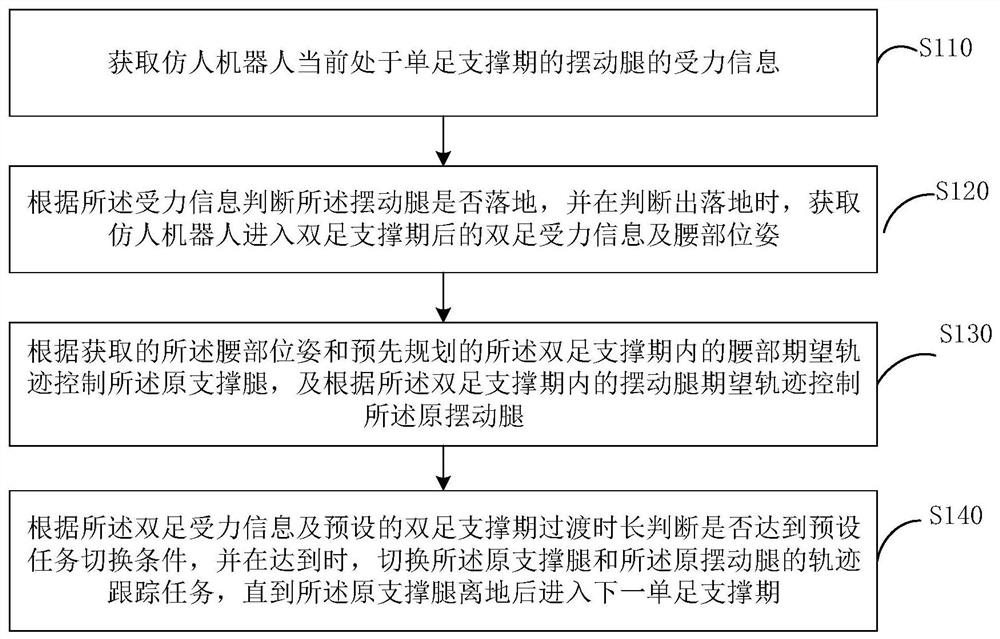
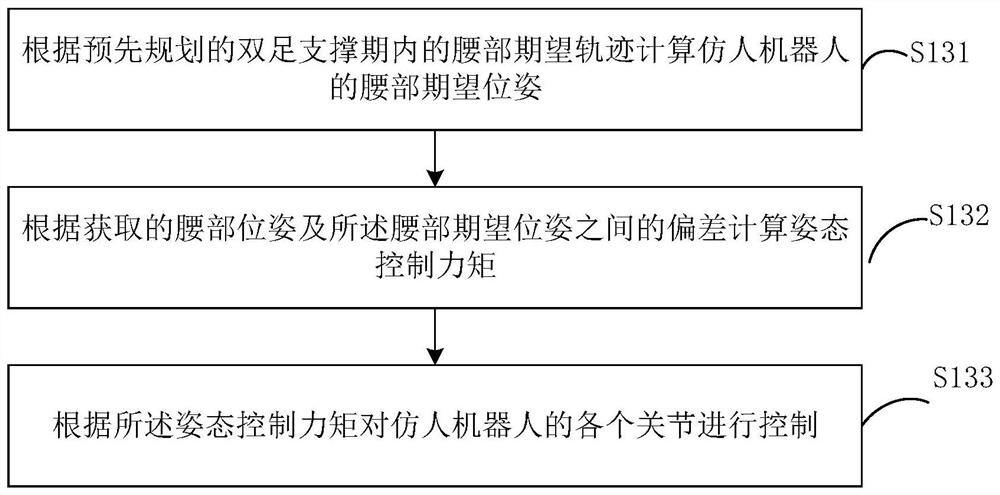
[0061] Please refer to figure 1 , this embodiment proposes a gait planning method for a humanoid robot, which can realize smooth alternate switching between the supporting leg and the swinging leg, and then realize steady and fast walking.
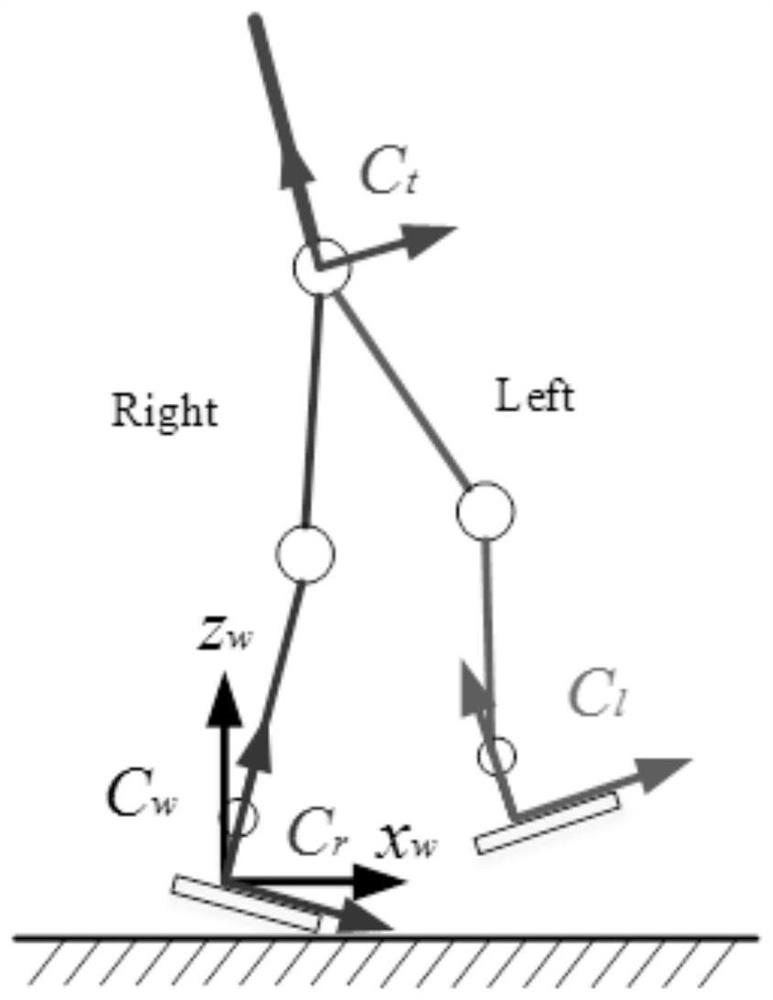
[0062] Typically, when a humanoid robot is walking, the two legs will alternately make contact with the contact surface. In the process of walking, it mainly includes two periods, which are the single-foot support period and the double-foot support period, and these two periods appear in sequence. Among them, the two-foot support period mainly refers to the transition period when the two legs are switched alternately, and can also be called the two-foot transition period. It can be understood that the contact surface here may refer to any supporting ground that is not restricted by the slope or a platform with a supporting function.
[0063] Whether in the single-foot support period or the double-foot support period, the sole of the leg ...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Please refer to Figure 4 , based on the method of the above-mentioned embodiment 1, the gait planning method of the humanoid robot proposed in this embodiment also includes, performing gravity compensation in the single-foot support period and the double-foot support period, specifically including:
[0107] Step S210, when the humanoid robot enters the single-foot support period, perform gravity compensation on the support leg.
[0108] Exemplarily, for the single-foot support period, the total amount of gravity compensation is F g =[0,0,mg], where mg is the gravity of the humanoid robot, and the total amount of gravity compensation is applied to the supporting legs.
[0109]It can be understood that the above-mentioned step S210 usually occurs when entering the single-foot support period, so the execution order of some steps in the method of the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is not specifically limited, for example, it can be executed in sequence with step S110 , or ...
Embodiment 3
[0119] Please refer to Figure 5 , based on the above-mentioned embodiment 1 or 2, the gait planning method of the humanoid robot proposed in this embodiment also includes adjusting the control torque during the single-foot support period, so as to effectively avoid the slipping and instability of the robot foot. Exemplarily, the method also includes:
[0120] Step S310, when the humanoid robot is in the single-foot support phase, calculate and control the scaling factor according to the force information of the current supporting leg and the gravity of the humanoid robot.
[0121] Exemplarily, the force information of the supporting legs mainly includes the component of the ground reaction force on the supporting legs in the vertical direction. The control scaling factor is mainly determined by the force on the sole of the supporting leg and the gravity on the robot.
[0122] In one embodiment, the calculating and controlling the scaling factor according to the force inform...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com