Patents
Literature
436 results about "Gravity compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gravity compensation is a well-known technique in robot design to achieve equilibrium throughout the range of motion and as a result to reduce the loads on the actuator. Therefore, it is desirable and commonly implemented in many situations. Various design concepts for gravity compensation are available in the literature.
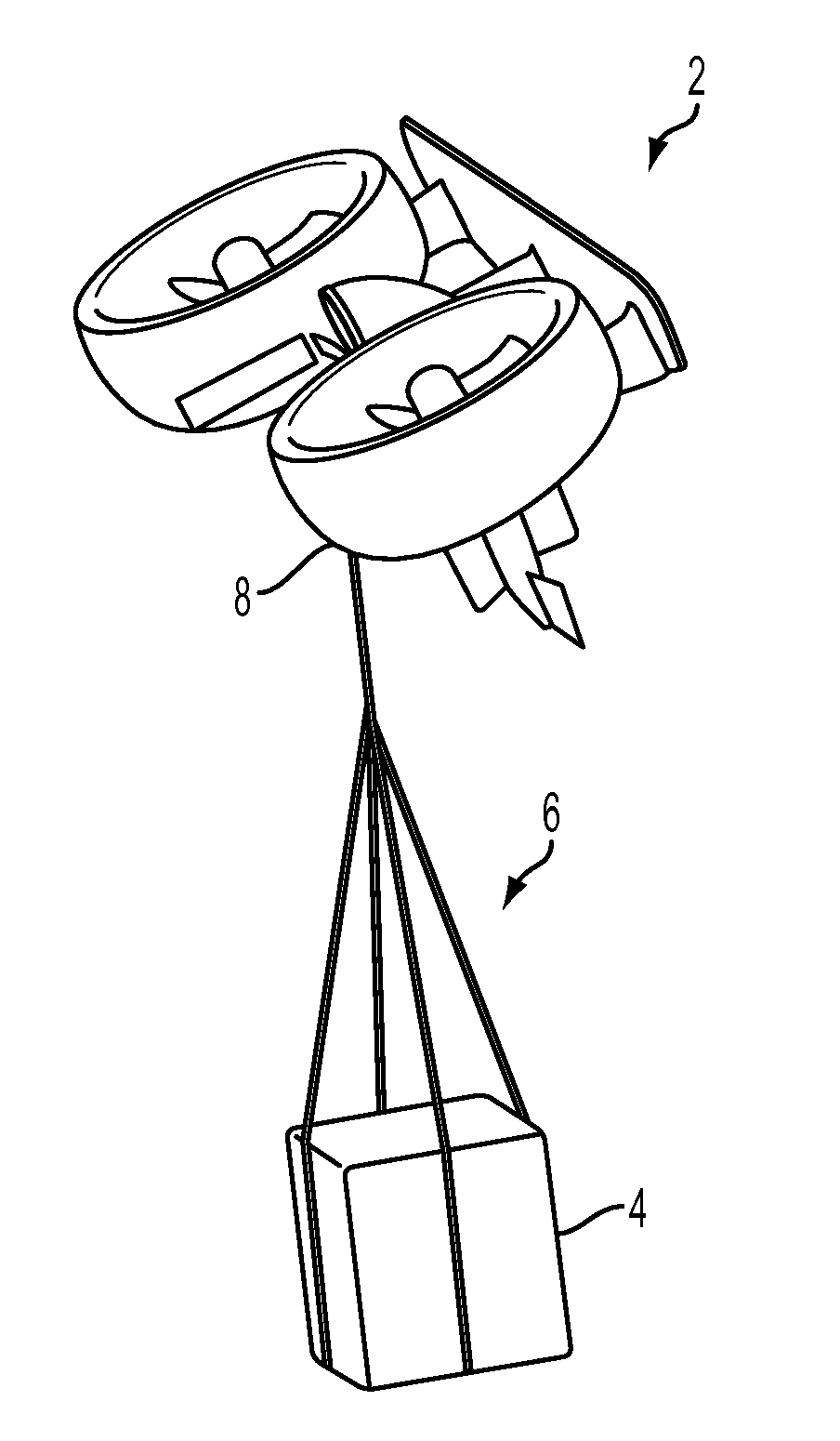
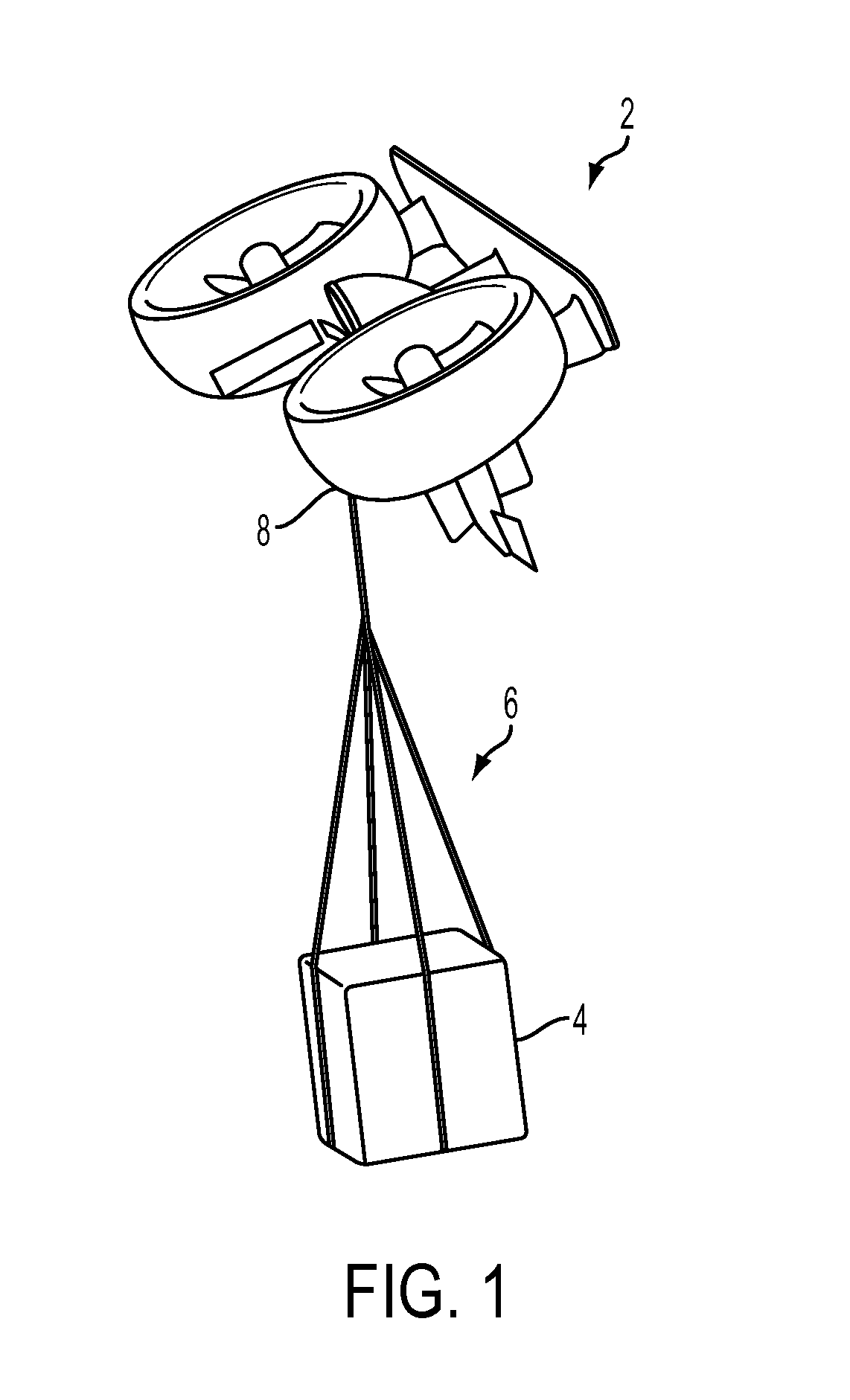
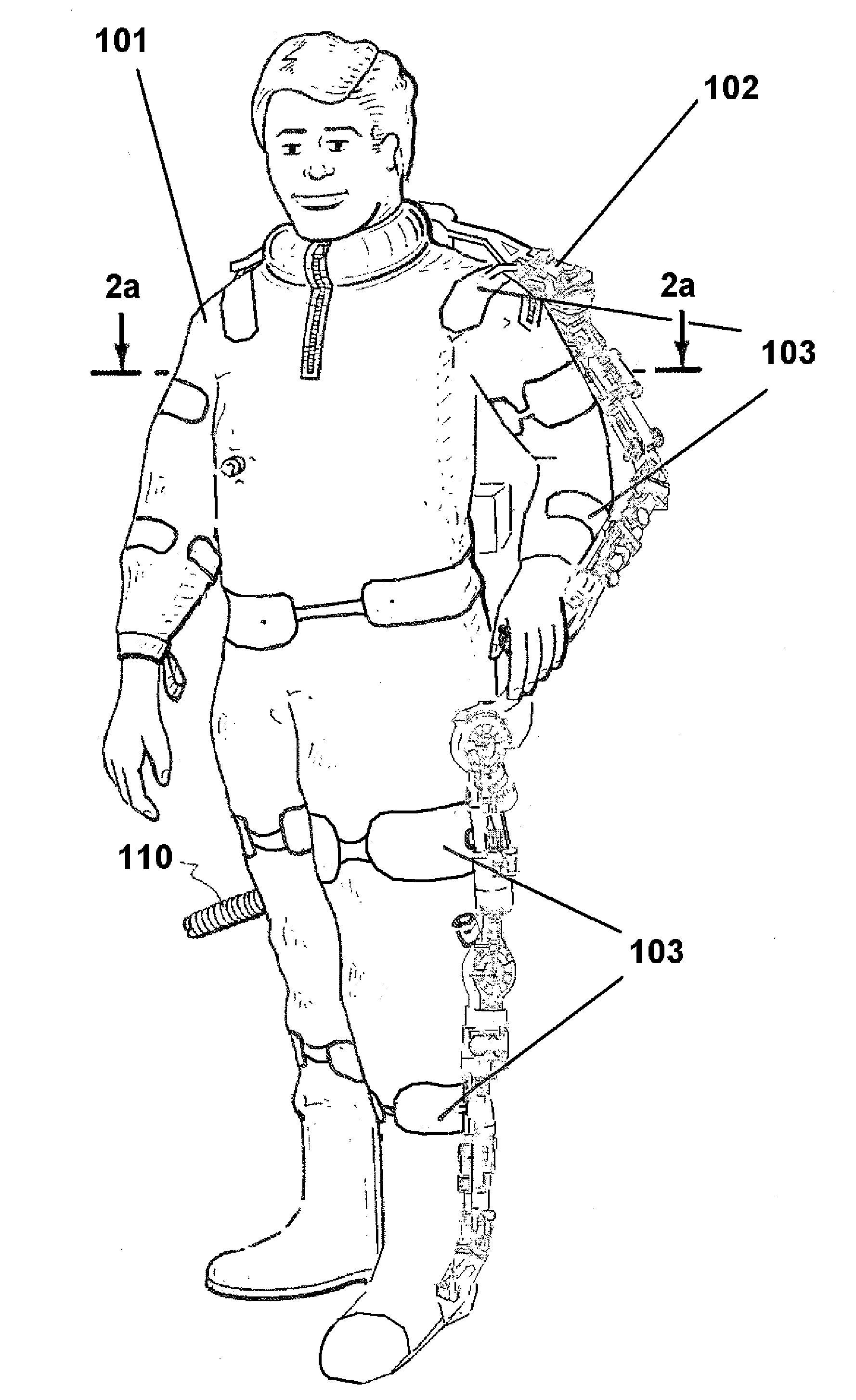
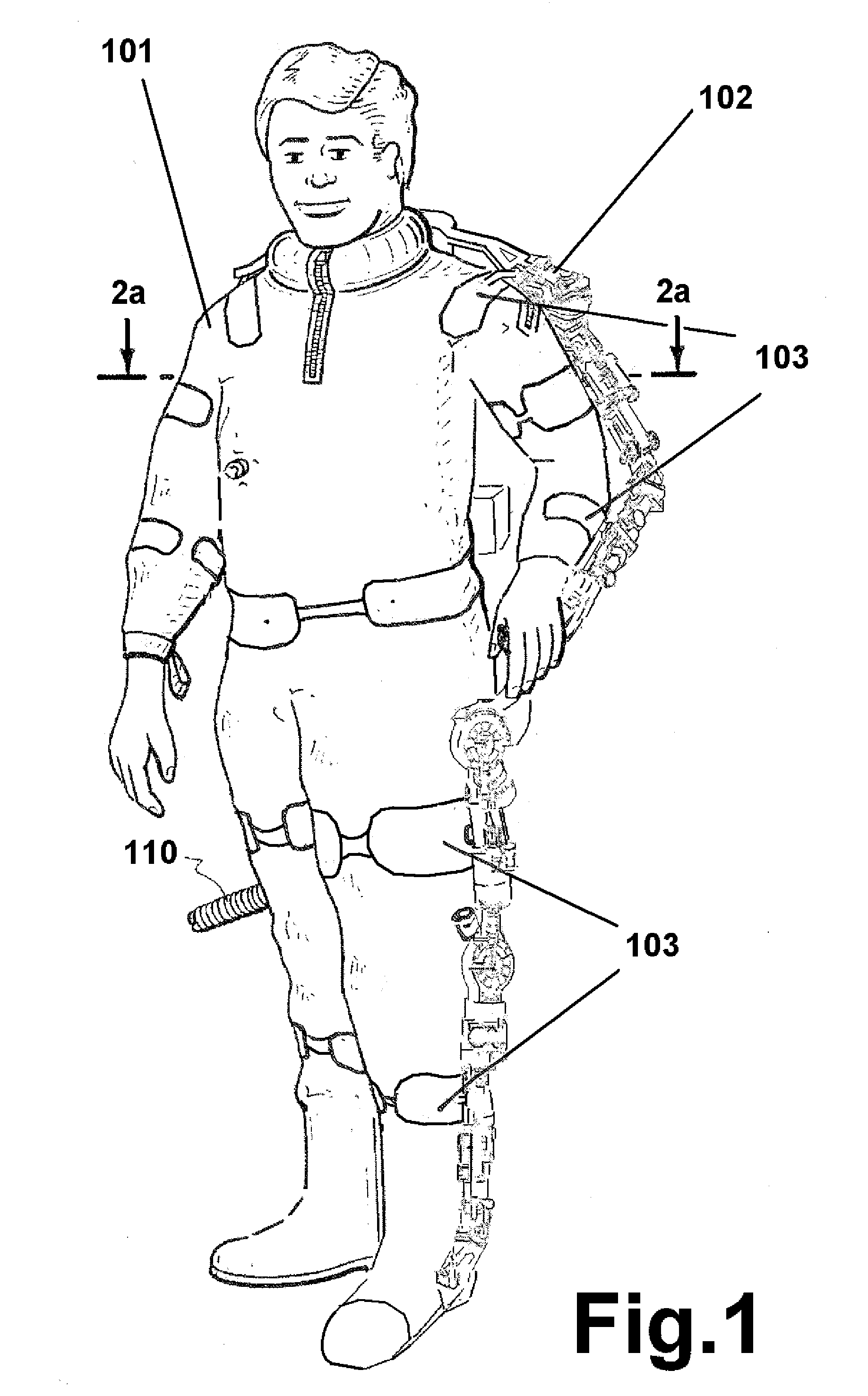
Autonomous Payload Parsing Management System and Structure for an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
InactiveUS20110084162A1Improve versatilityIncrease in sizeStatic/dynamic balance measurementRemote controlled aircraftManagement systemControl logic
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for making partial deliveries of cargo provisions includes a UAV having one or more ducted fans and a structural interconnect connecting the one or more fans to a cargo pod. The cargo pod has an outer aerodynamic shell and one or more internal drive systems for modifying a relative position of one or more cargo provisions contained within the cargo pod. Control logic is configured to, after delivery of a partial portion of the cargo provisions contained within the cargo pod, vary a position of at least a portion of the remaining cargo provisions to maintain a substantially same center of gravity of the UAV relative to a center of gravity prior to delivery of the partial portion. Other center of gravity compensation mechanisms may also be controlled by the control logic to aid in maintaining the center of gravity of the UAV.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Design method of unrestricted suspension type initiative gravity compensation system
ActiveCN103482089AOvercome the influence of microgravity horizontal directionHigh compensation accuracyCosmonautic condition simulationsTorque motorEngineering
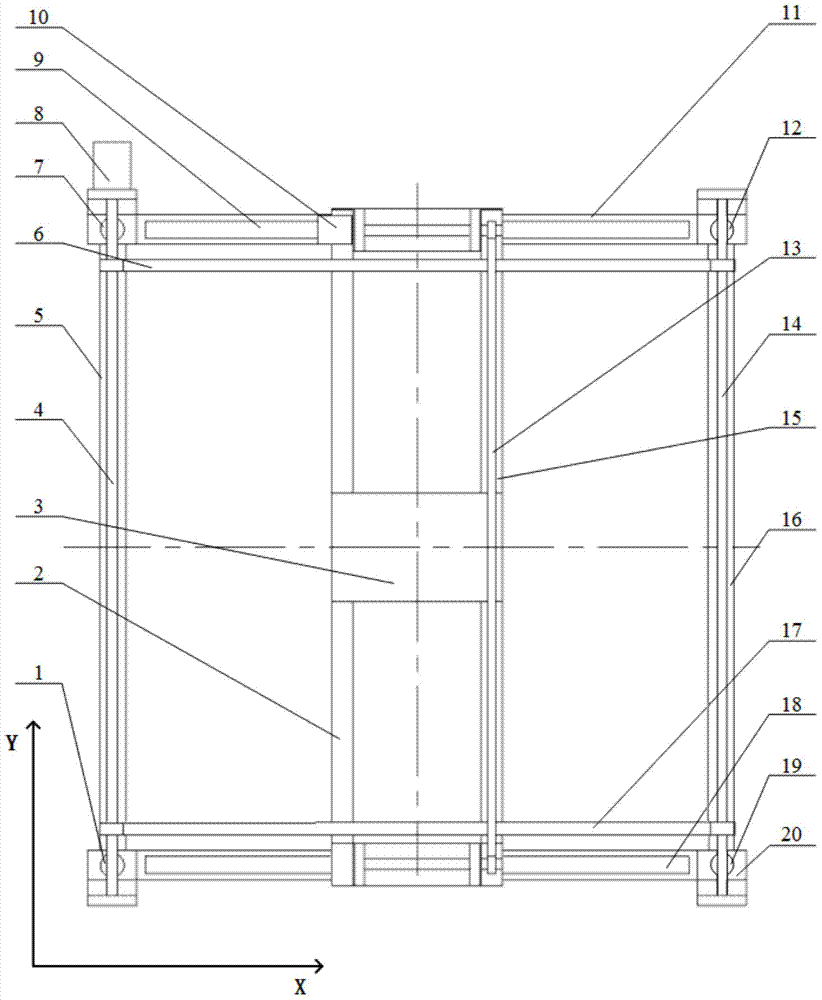
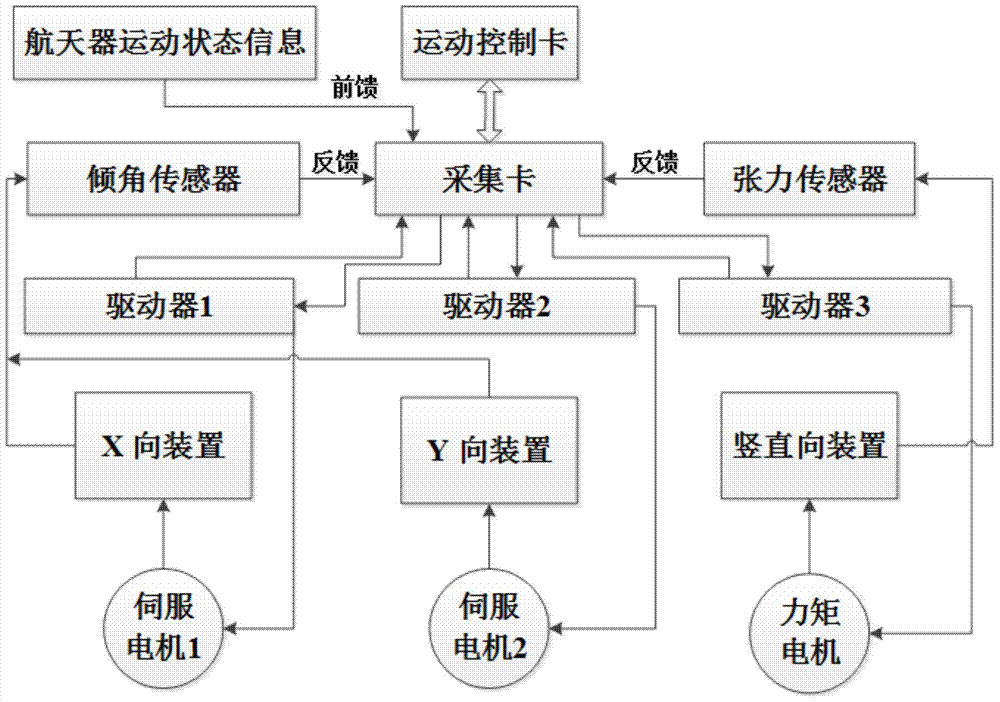
Provided is an unrestricted suspension type initiative gravity compensation system. The system is composed of an unrestricted connecting module, a vertical constant tension suspension module, a horizontal follow-up module and a control module. The unrestricted connecting module comprises a connecting sleeve, an outer mounting frame, a force applying piece and a low friction bearing, and enables a spacecraft to carry out approximate unrestricted rotation round a center of mass. The vertical constant tension suspension module comprises a torque motor, a pinion and rack, a suspension hanging spring and a tension sensor, and enable the tensile force borne by the spacecraft in movement is equal to gravity. The horizontal follow-up module comprises a servo motor, a guide rail, a synchronous belt and a tilt angle sensor, and the suspension module is made to carry out horizontal movement along with the spacecraft to guarantee that the hanging spring is in a vertical state. The control module comprises an acquisition card, a driver and a motion control card. The design method of the unrestricted suspension type initiative gravity compensation system can compensate the gravity of the spacecraft in a ground test environment, further is used for reproducing the real movement of the spacecraft in the interspace microgravity environment, has the advantages of being stable in running, through in compensation and the like, and can provide the approximate unrestricted microgravity environment for movements with six degrees of freedom.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
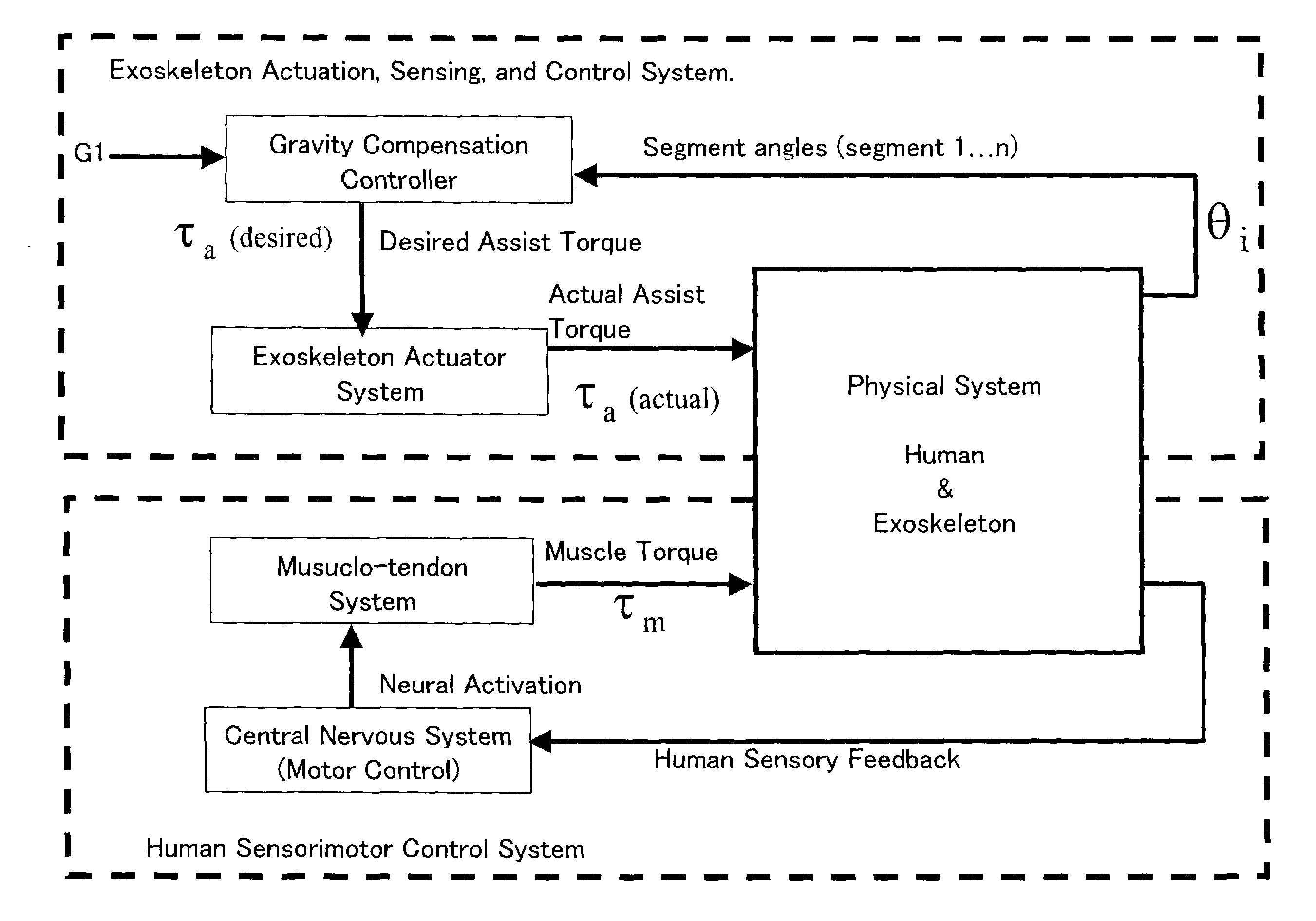
Human assist system using gravity compensation control system and method using multiple feasibility parameters
ActiveUS7390309B2Reduce interfaceReduce loadProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationControl systemMechanical energy
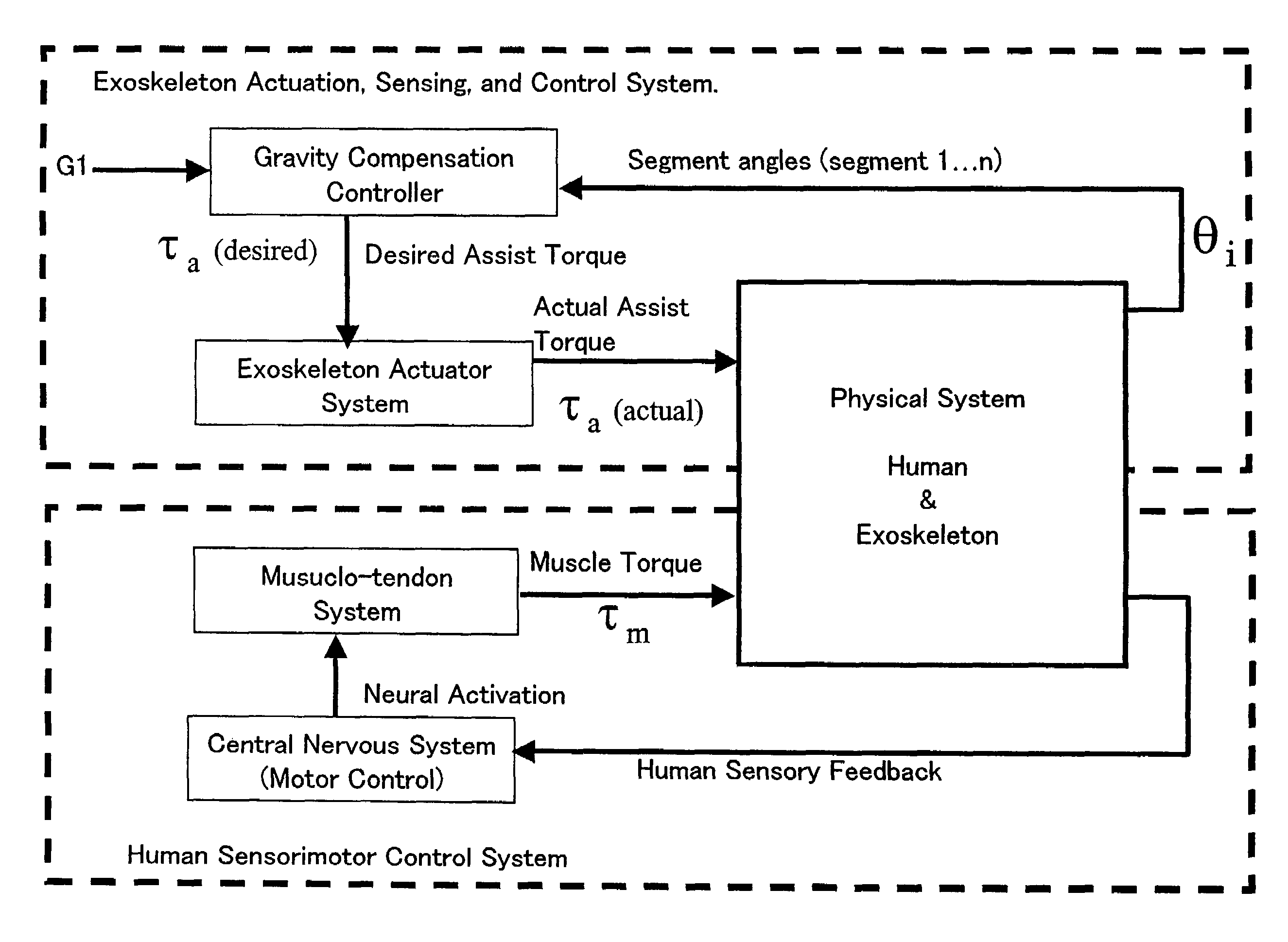
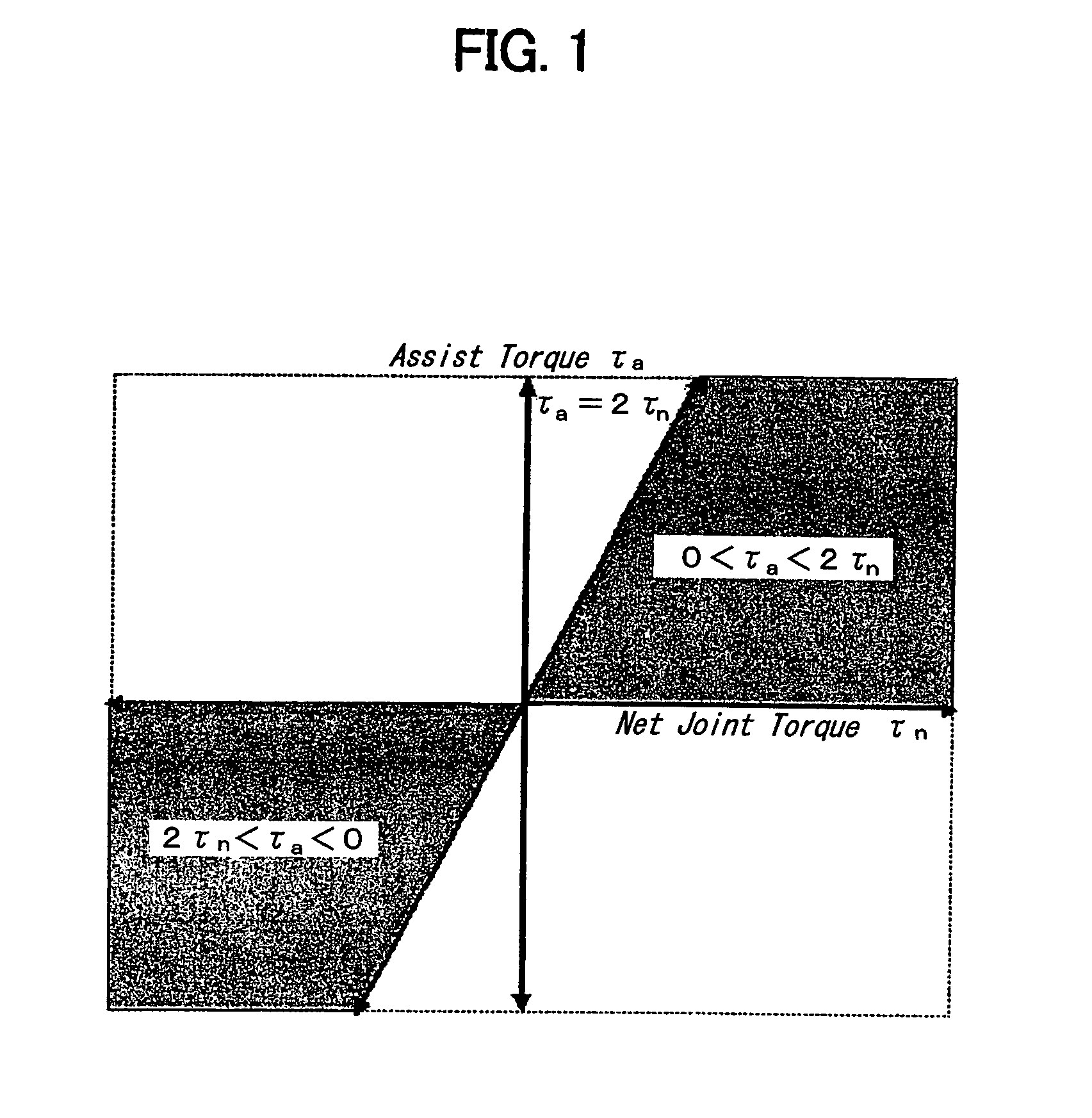
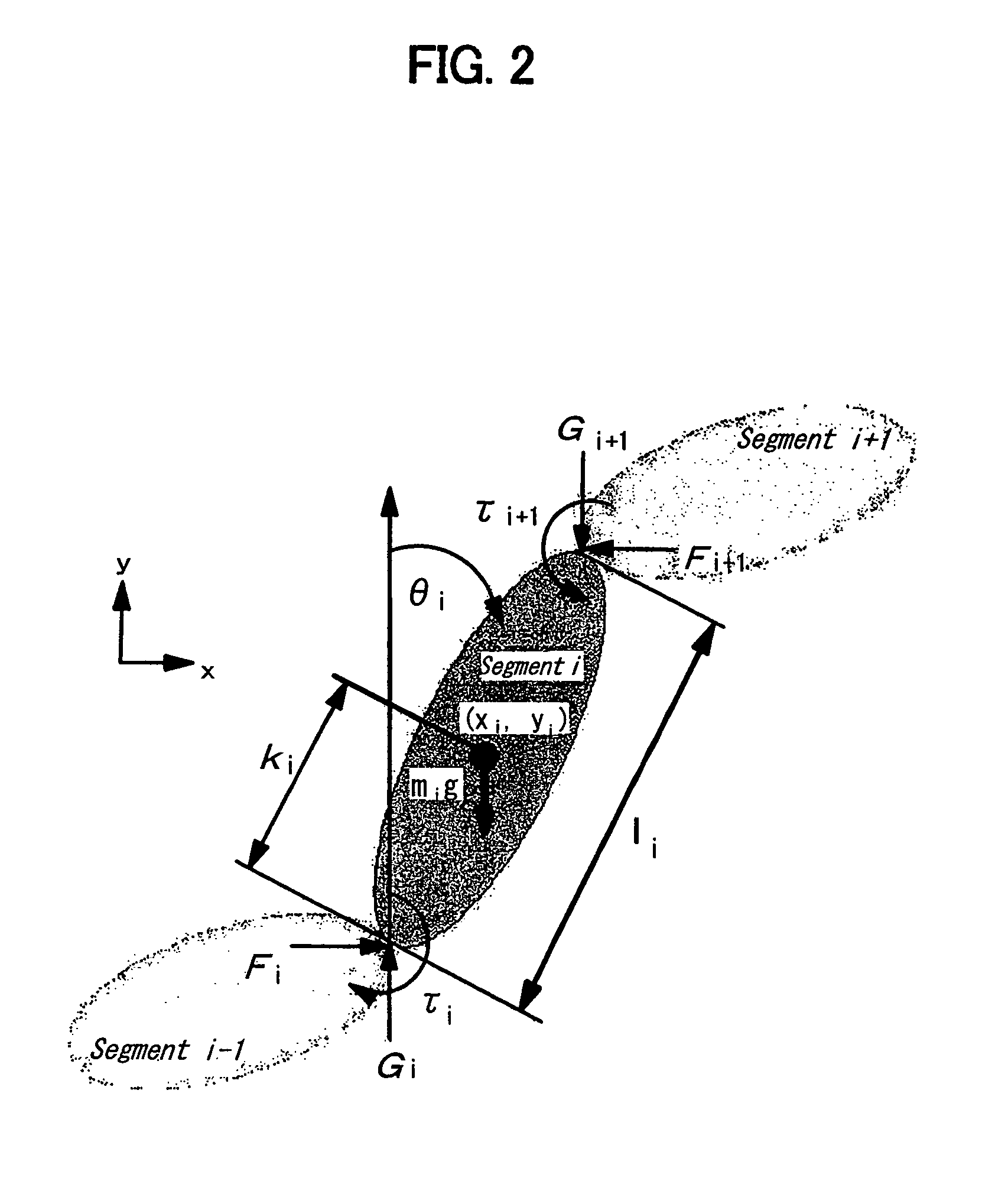
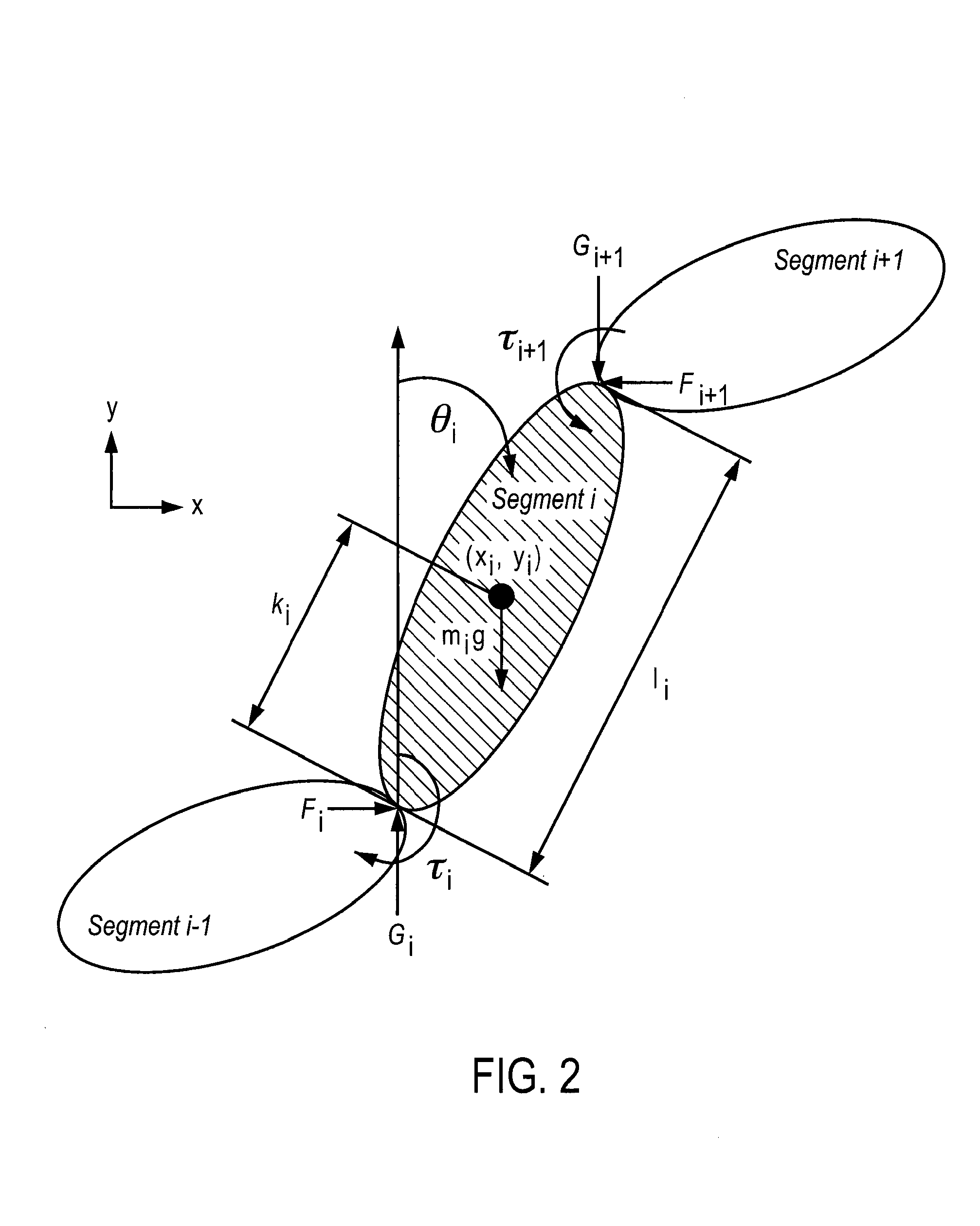
A method for obtaining an assist torque to be applied to a human joint, in a human assist system in order to reduce the load on muscles, according to the present invention comprises the step of obtaining a moment due to gravity, acting on a joint of each human segment, based on equations of force and moment balance on each segment. The method further comprises the step of obtaining an assist torque to be applied to the joint to compensate for the moment due to gravity, acting on the joint. In one embodiment of the present invention, various criteria are used such as mechanical energy, metabolic energy and / or a stability / equilibrium factor. In addition, the present invention can account for the situation where there is substantially no relative motion between segments of a given joint and thus, where the mechanical energy component of gravity compensation is approximately zero.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Hand movement tracking system and tracking method
ActiveCN106679649AAttitude Calculation ImprovementsAccurate solutionNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsHand movementsLow-pass filter
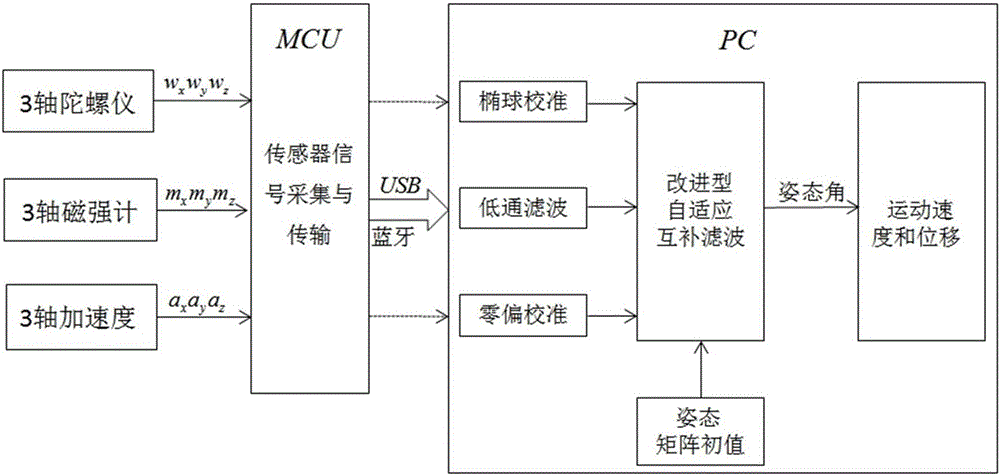
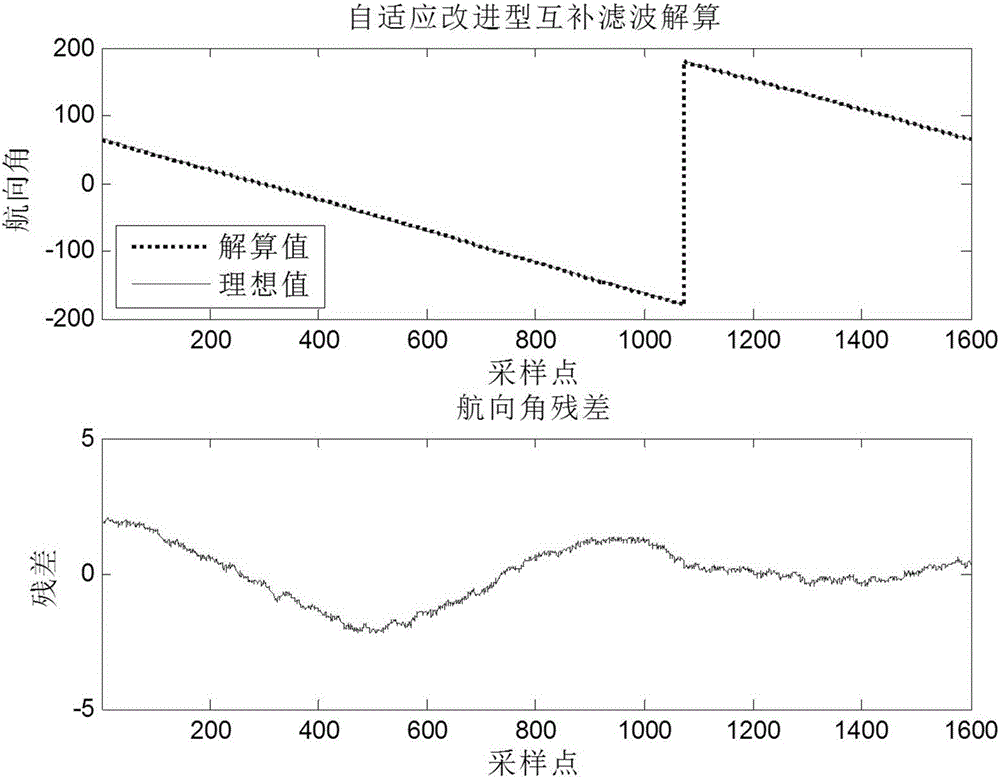
The invention discloses a hand movement tracking system and a hand movement tracking method. The invention comprises an attitude and heading reference system based on an accelerometer, a gyroscope and a magnetic sensor, and a hand movement tracking method based on the attitude and heading reference system. The hand movement tracking method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining a triaxial acceleration measured by the accelerometer, a triaxial angular velocity measured by the gyroscope and a triaxial magnetic-field component measured by the magnetic sensor, performing error compensation on the magnetic sensor by adopting a least square method to establish an error model after an upper computer receives sensor data, eliminating high-frequency noise of the triaxial acceleration by virtue of a window low-pass filter, and establishing an error model for the gyroscope so as to perform error compensation on random drift of the gyroscope; secondly, effectively integrating the gyroscope, the accelerometer and the magnetic sensor by virtue of an improved adaptive complementary filtering algorithm to obtain an attitude angle and a path angle; and finally, performing gravity compensation and discrete digital integration on acceleration signals to obtain a velocity and a track of a hand movement. The tracking system and the tracking method disclosed by the invention can be applied to a man-machine interactive system, is convenient to operate, and is strong in experience feeling.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Seven-degree-of-freedom exoskeletal rehabilitation robot for upper limbs
ActiveCN104490565AImprove training efficiencyExact training parametersGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesEngineeringDegrees of freedom
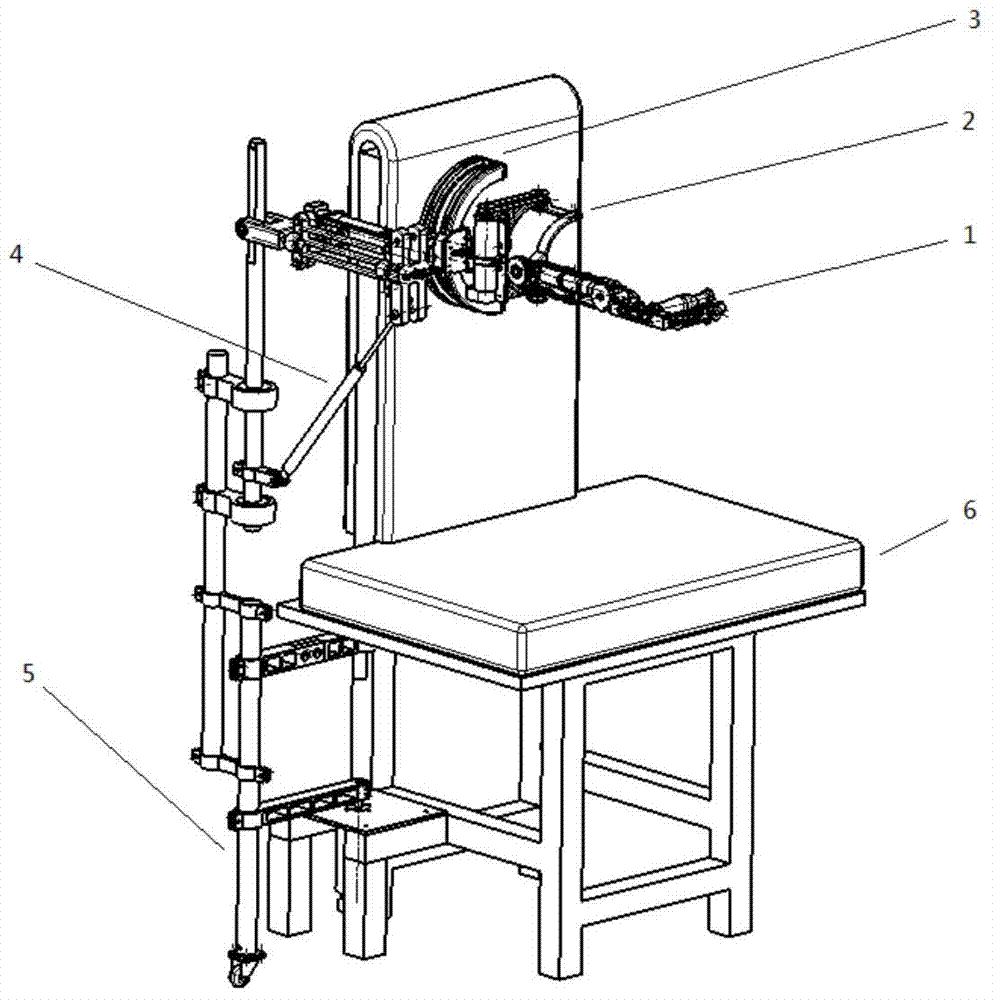
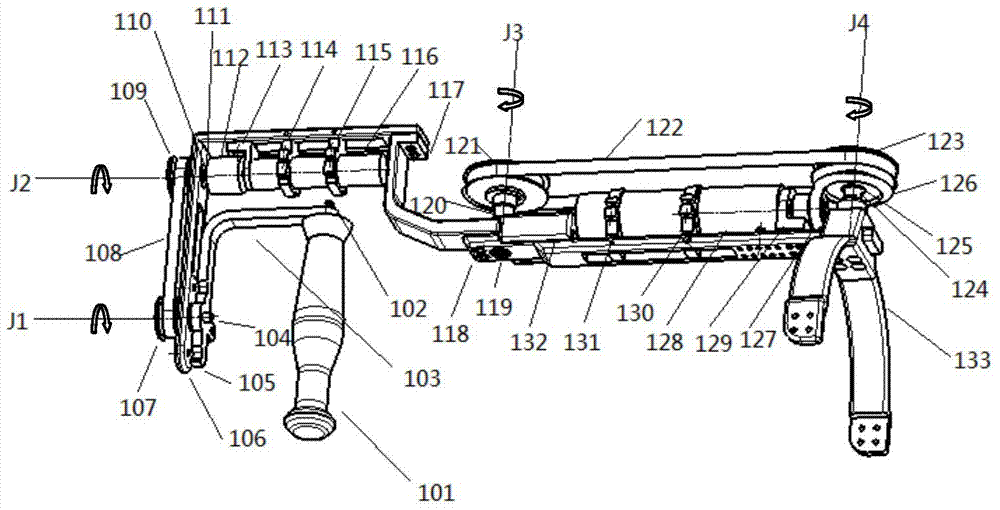
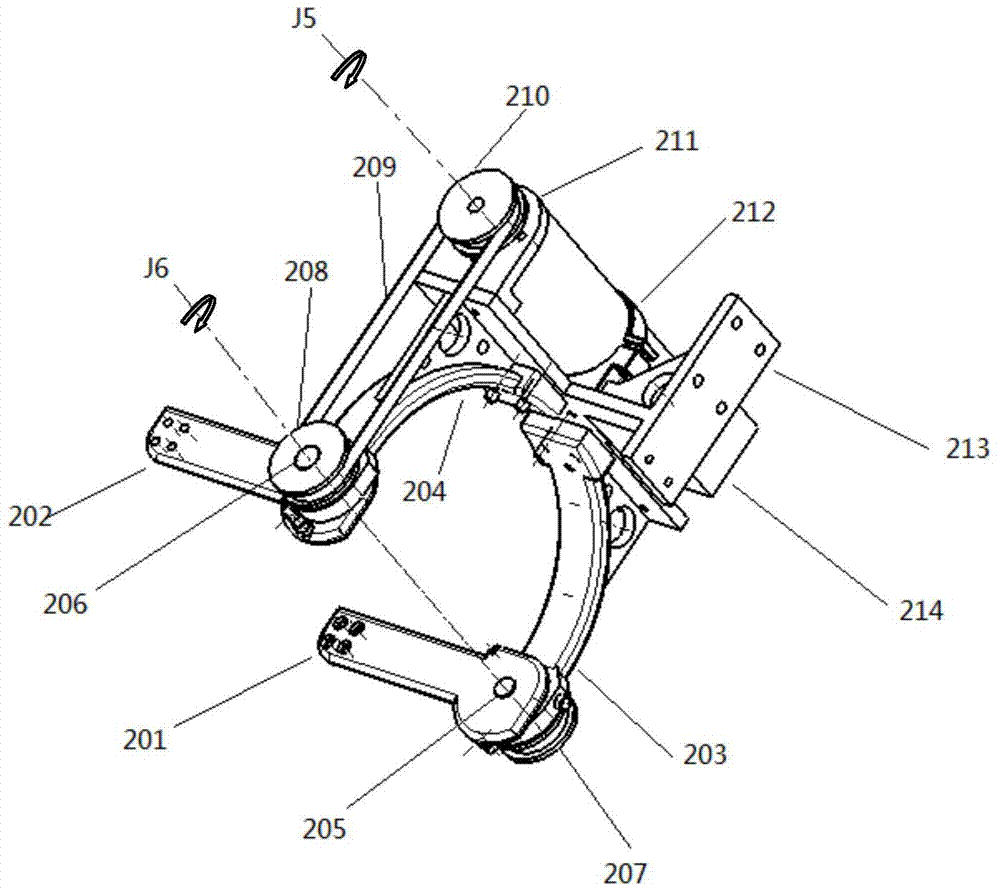
The invention provides a seven-degree-of-freedom exoskeletal rehabilitation robot for upper limbs. The seven-degree-of-freedom exoskeletal rehabilitation robot for upper limbs comprises a front arm and wrist joint movement mechanism, an elbow joint movement mechanism, an upper arm movement mechanism, a gravity compensation movement mechanism, a shoulder joint movement mechanisms and a chair mechanism which are sequentially connected. The seven-degree-of-freedom exoskeletal rehabilitation robot for upper limbs is driven and controlled by a motor to help a hemiplegic patient do active and passive training for upper affected limbs, including bending / stretching of wrist joints, adduction / abduction movement of the wrist joints, inward / outward rotating movement of the front arms, bending / stretching of elbow joints, bending / stretching of shoulder joints, inward / outward rotating movement, and outward swinging / adduction movement.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Haptic Device Gravity Compensation
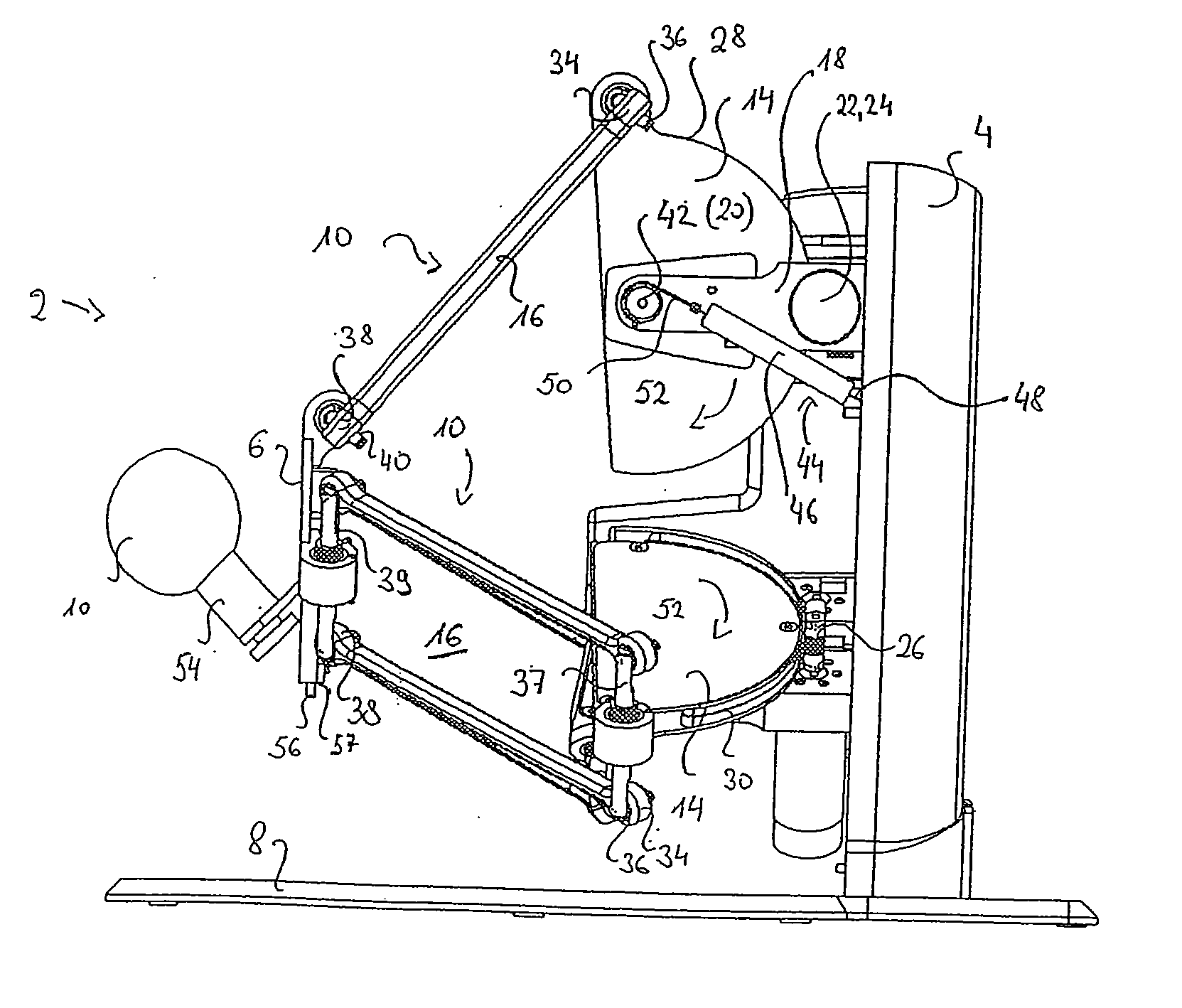
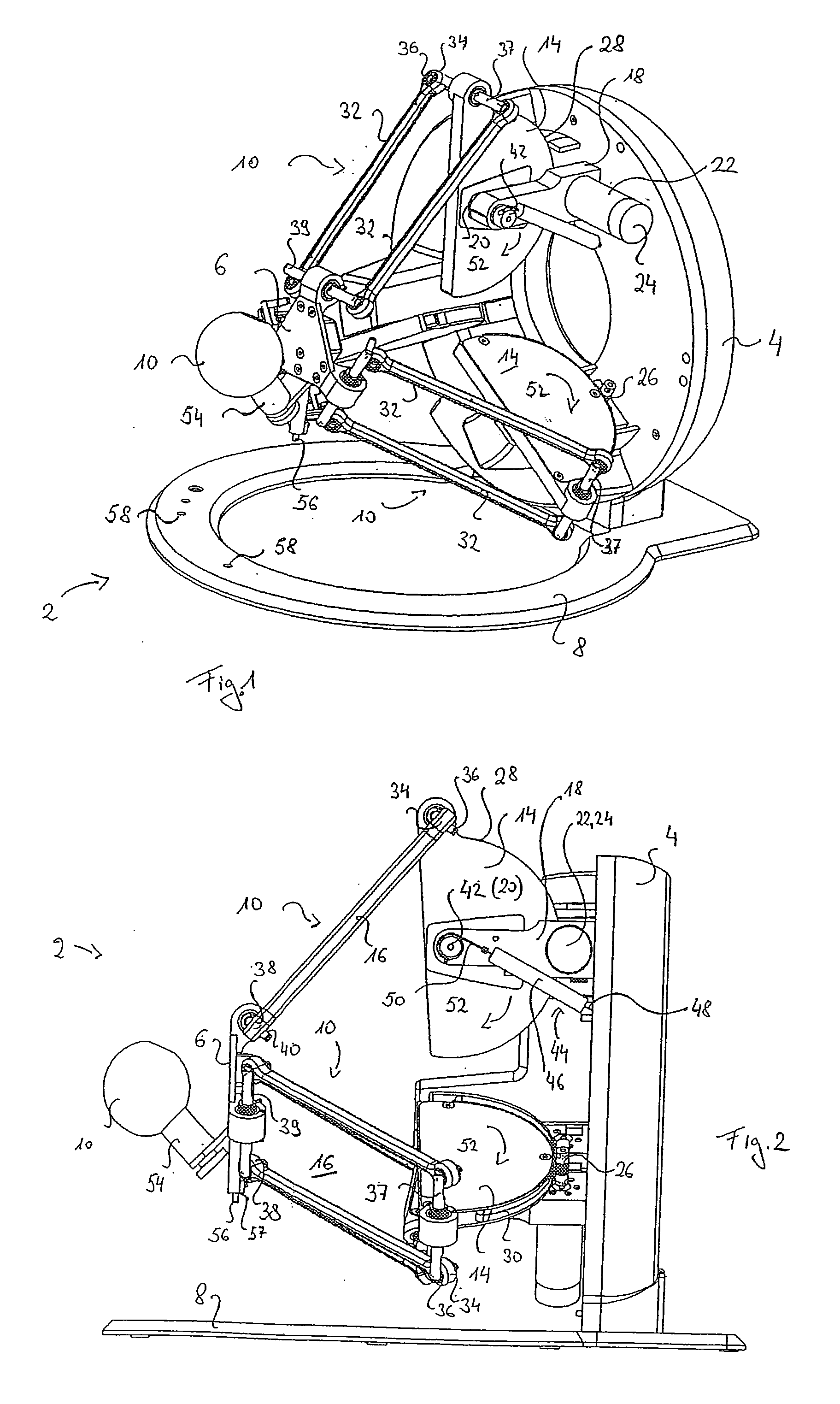
ActiveUS20100019890A1Manual control with multiple controlled membersRepeater circuitsThree degrees of freedomParallel kinematics
A haptic device comprising a base member (4), an end-effector (6), a parallel kinematics structure arranged between the base plate and the end-effector and providing at least three degrees of freedom including at least three translational degrees of freedom in relation to the end-effector, and at least one passive gravity compensation means being adapted to exert forces and / or torques on the parallel kinematics structure for at least partial compensation of gravity related forces and / or torques acting in at least one of the three translational degrees of freedom.
Owner:FORCE DIMENSION S A R L
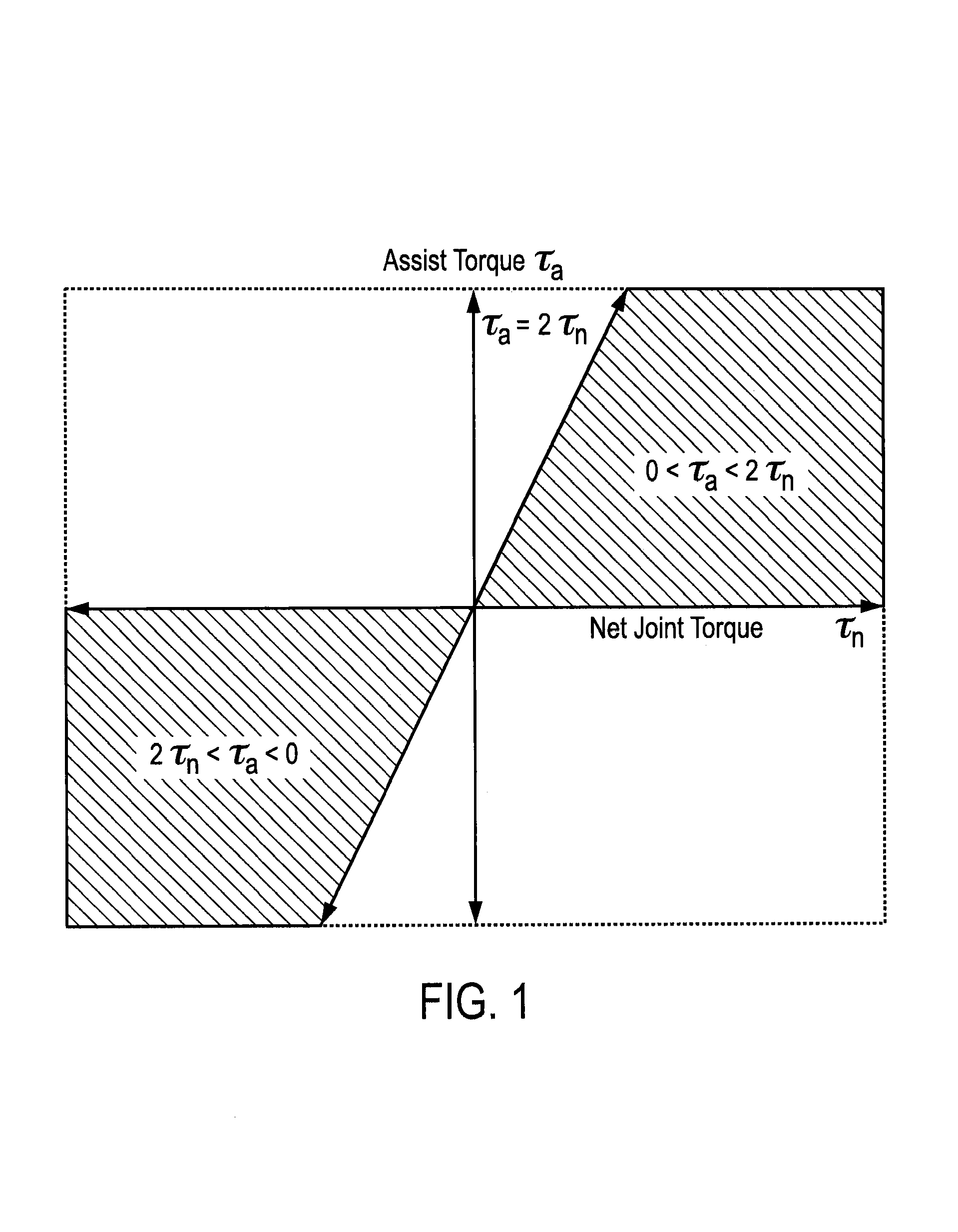
Gravity compensation method in a human assist system and a human assist system with gravity compensation control
ActiveUS7217247B2Reduce distractionsReliably carry-outProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationGravitational forceEngineering
A method for obtaining an assist torque to be applied to a human joint, in a human assist system for applying an assist torque to the human joint to reduce load of muscles, and the human assist system are provided. The method comprises the step of obtaining a moment due to gravity, acting on a joint of each human segment, based on equations of force and moment balance on each segment. The method further comprises the step of obtaining an assist torque to be applied to the joint to compensate for the moment due to gravity, acting on the joint. The human assist system comprises a motor for delivering an assist torque to a joint and a motor driver for driving control of the motor. The system further comprises a controller for determining a desired value of an assist torque, comprising a processor and a memory. The controller is configured to obtain a moment due to gravity, acting on a joint of each human segment, based on equations of force and moment balance on each segment and then to obtain an assist torque to be delivered to the joint to compensate for the moment due to gravitational acceleration at the joint.The method provides a natural subdivision between the voluntary actuators which are responsible for forward progression of motion and the assist actuators which are responsible for preserving static equilibrium. This subdivision may mitigate the interference between voluntary control and artificial control.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
7-DOF (degree of freedom) space manipulator ground microgravity hybrid simulation method
InactiveCN103144104ASmall footprintRealize three-dimensional space movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringDegrees of freedom
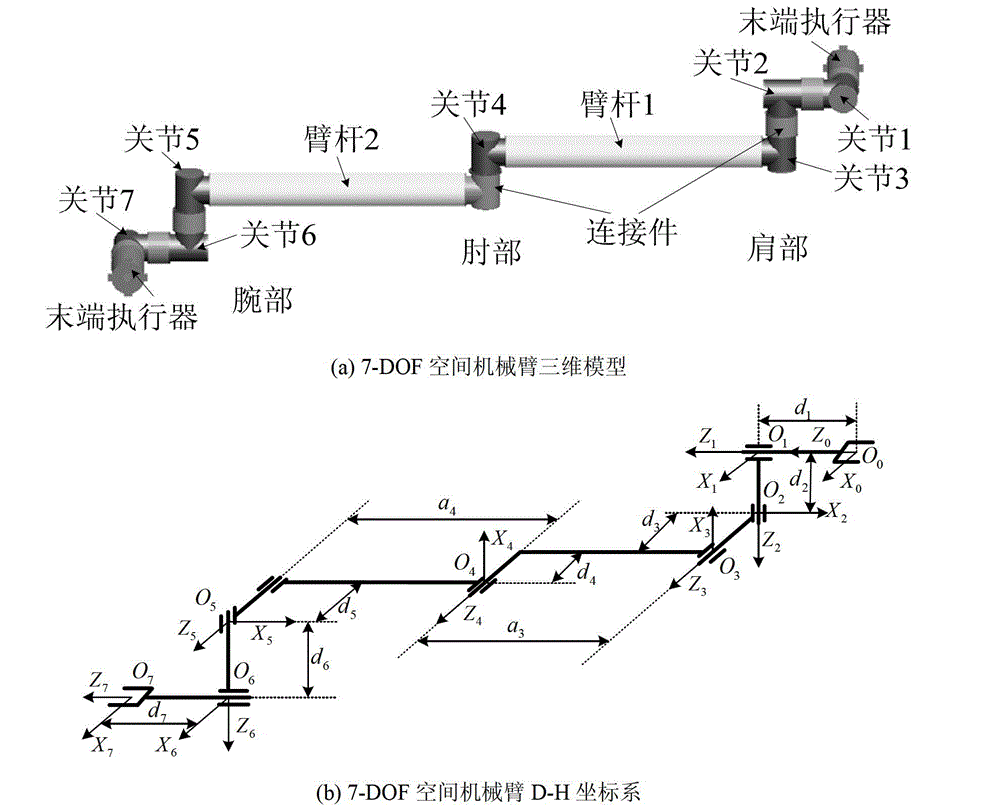
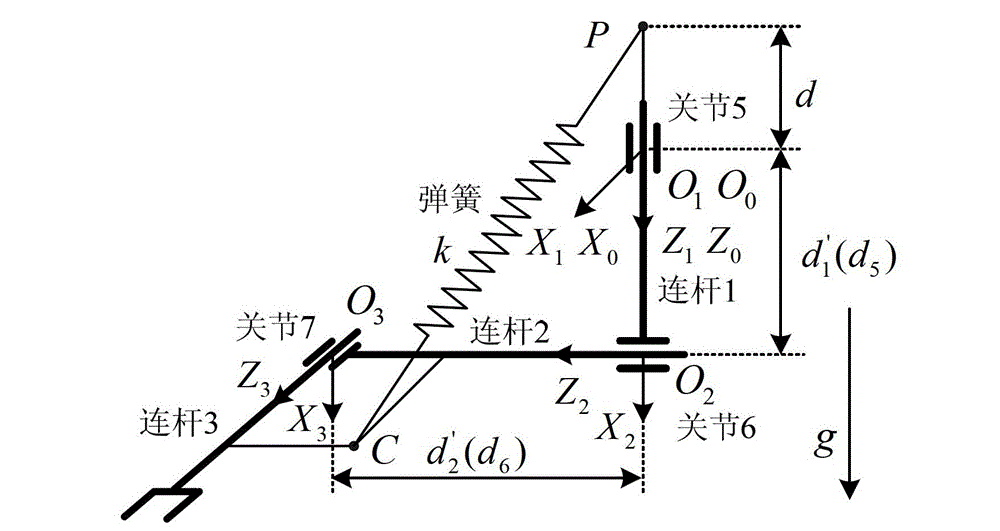
The invention discloses a space manipulator ground microgravity hybrid simulation method, and particularly relates to a realization method for ground-based simulation of a space microgravity environment by a 7-DOF space manipulator. Gravity compensation is realized at the middle part of the 7-DOF space manipulator by adopting the gas flotation method; the middle part of the 7-DOF space manipulator is supported on two gas flotation feet; shoulder parts and wrist parts at two ends as well as an end effector adopt static balance mechanisms to realize gravity compensation; two static balance mechanisms are designed, respectively named as a shoulder part static balance mechanism and a wrist part static balance mechanism, and used for realizing gravity compensation for a 2-DOF manipulator formed by a shoulder joints 1 and 2 and the end effector as well as gravity compensation for a 3-DOF manipulator formed by wrist joints 5, 6 and 7 and the end effector, as a result, gravity compensation for the whole space manipulator system is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
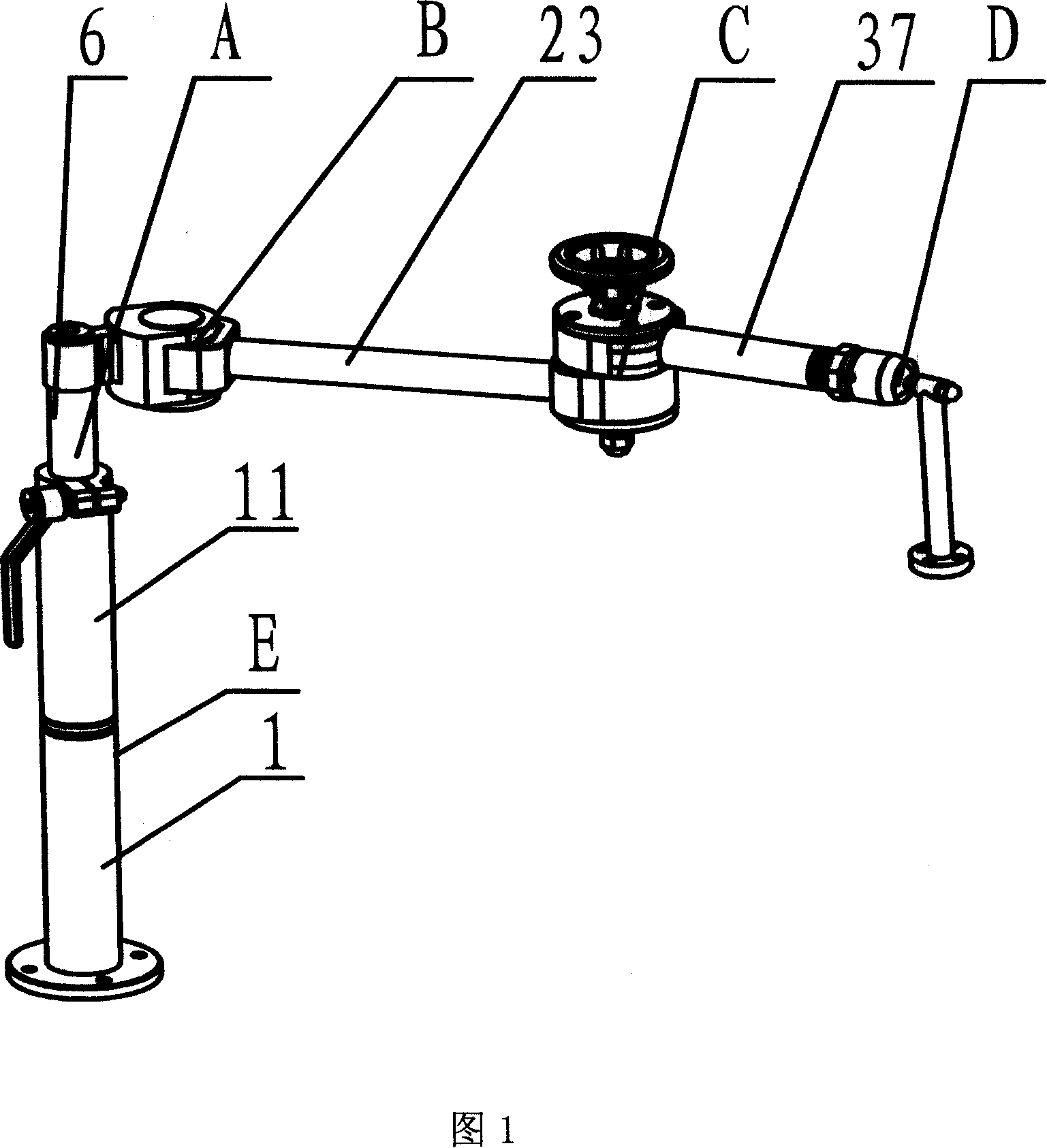
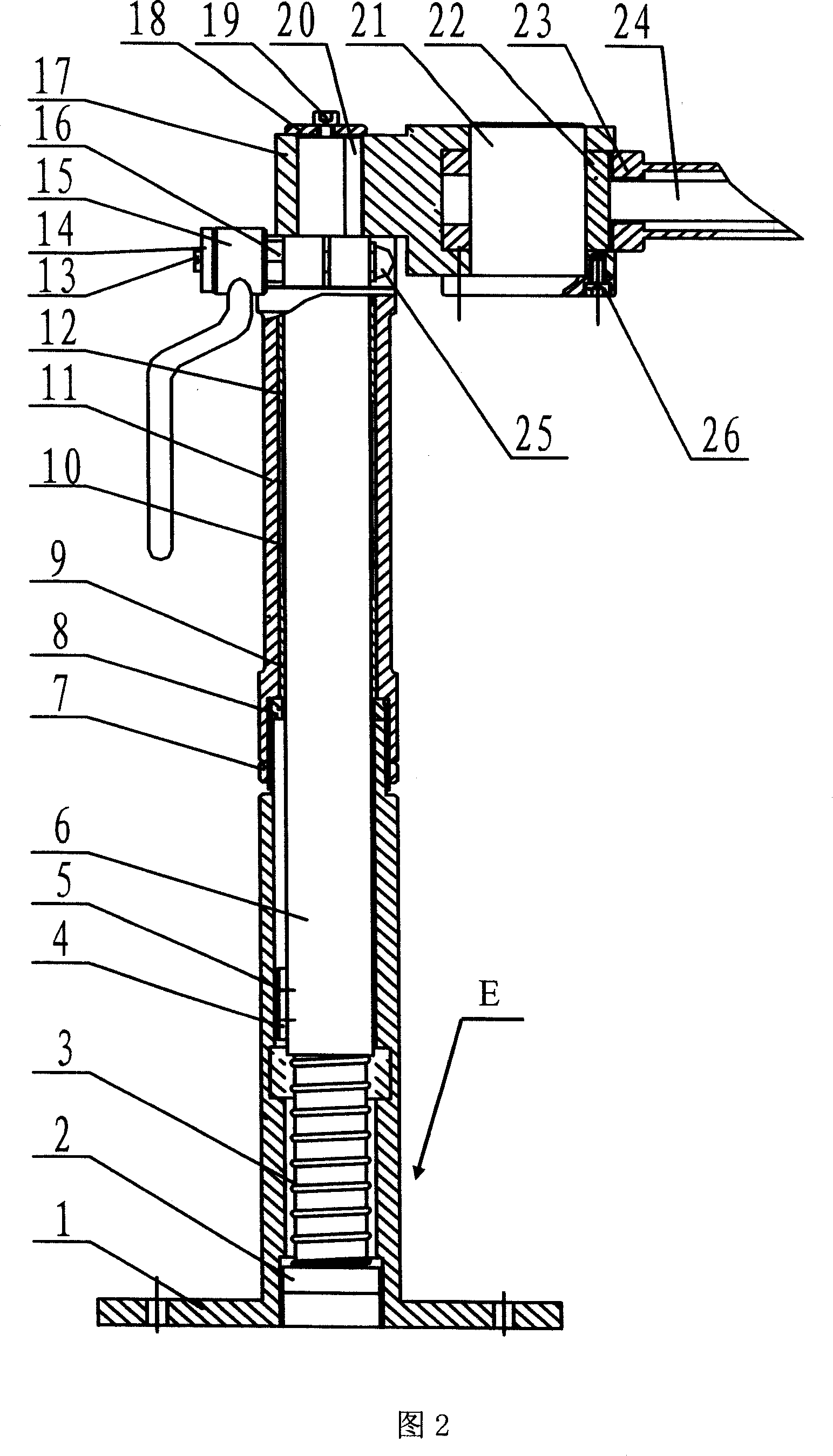
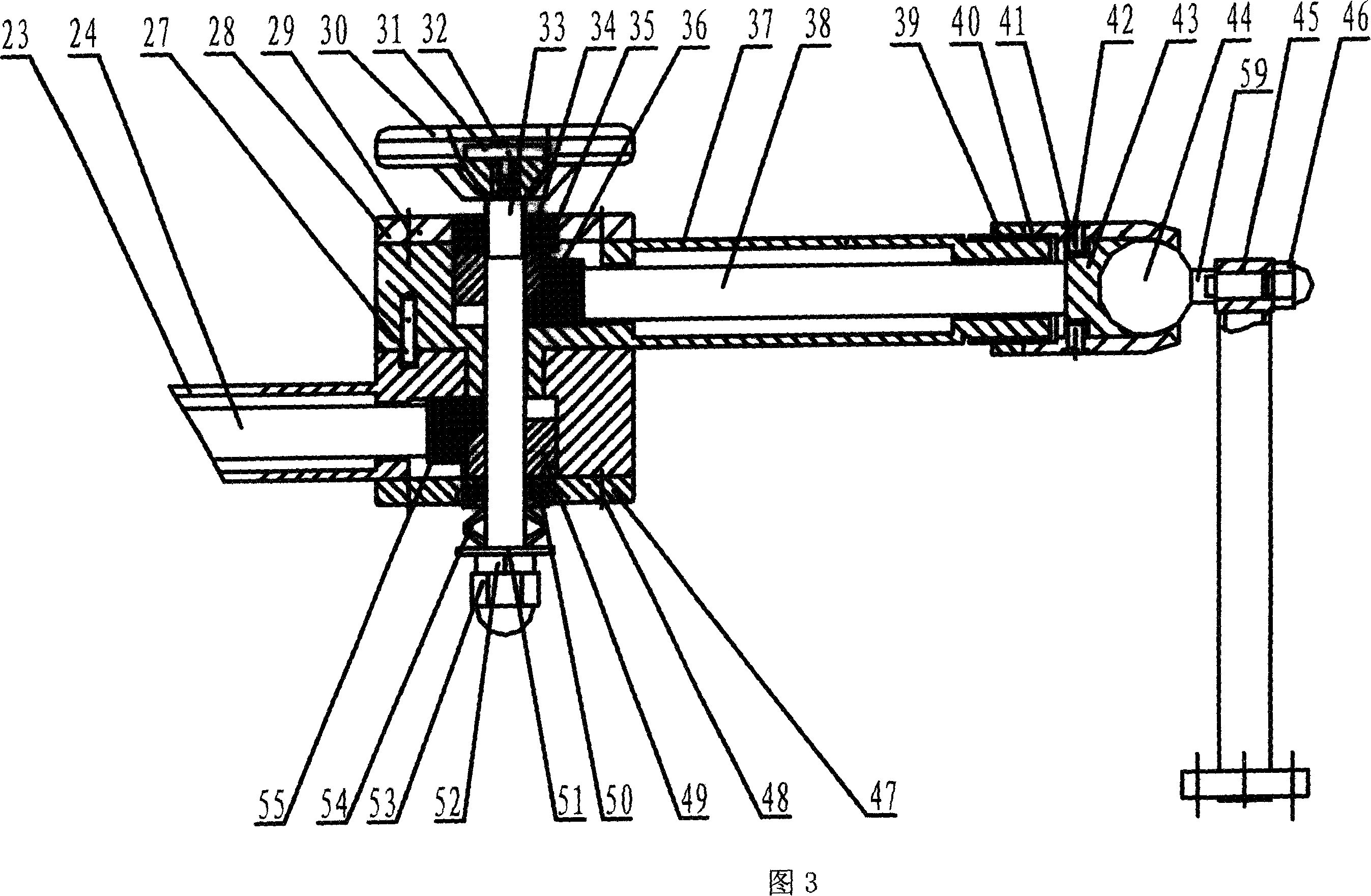
Passive manual locking bracket having gravity compensation function
ActiveCN1969772AWith gravity compensation functionMeet the positioning requirementsSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringShoulder joint capsule
The invention discloses a negative hand locking rack with gravity supplement function, which comprises the following parts: gravity supplement mechanism, straight-line joint mechanism, shoulder joint mechanism, middle joint mechanism and ball joint mechanism, wherein the straight-line joint mechanism is set on the gravity supplement mechanism with top connecting one end of shoulder joint mechanism vertically through small arm; the other end of shoulder joint mechanism connects one end of middle joint mechanism through big arm; the other end of middle joint mechanism connects ball joint mechanism through front arm; The negative hand locking rack possesses six freedom degrees, which satisfies the orientation need of operation mechanics.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIGAO SURGICAL ROBOT CO LTD
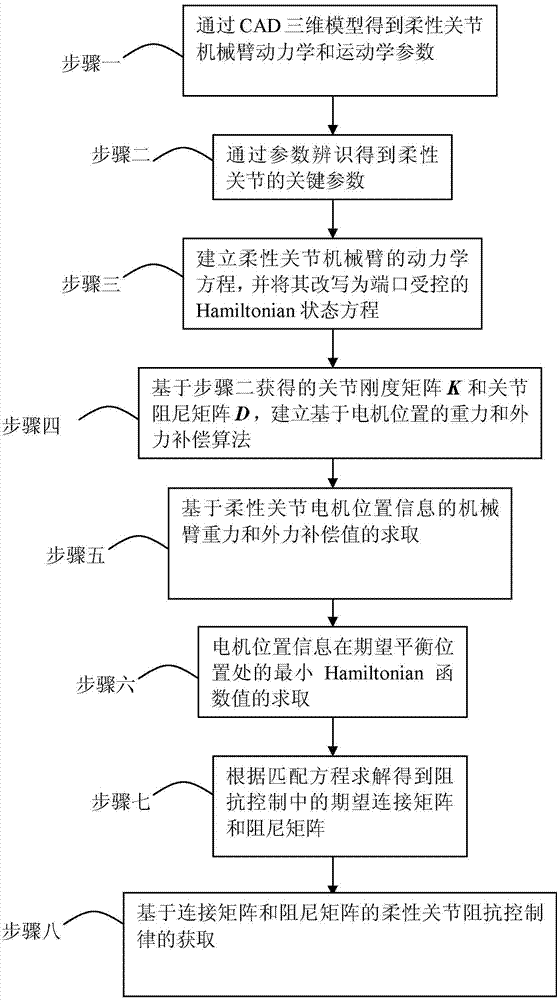
Impedance control method for flexibility joint mechanical arm based on connection and damping configuration
ActiveCN104723340AReduce computationSimple designProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsMedical robot
The invention provides an impedance control method for a flexibility joint mechanical arm based on a connection and damping configuration, and belongs to the technical field of robot controlling. The problem in a traditional mechanical arm control method that during the flexibility joint mechanical arm control process, due to the fact that the residual oscillation is large, the aim of stable control cannot be achieved is solved. The technical points are that according to a CAD three-dimensional model, a kinetic parameter and a kinematic parameter of the flexibility joint mechanical arm are obtained; according to the parameter identification, a key parameter of a flexibility joint is obtained; a kinetic equation of the flexibility joint mechanical arm is established; a gravity compensation algorithm and an external force compensation algorithm based on the motor position are established; a gravity compensation value and an external force compensation value of the mechanical arm are calculated and obtained; a minimum Hamiltonian function value on the expectation balance position of motor position information is calculated and obtained; an expectation connection matrix and a damping matrix in the impedance control are calculated; an impedance control rule of the flexibility joint based on the connection matrix and the damping matrix are obtained. The impedance control method for the flexibility joint mechanical arm based on the connection and the damping configuration can be used for controlling service robots, medical robots and space robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
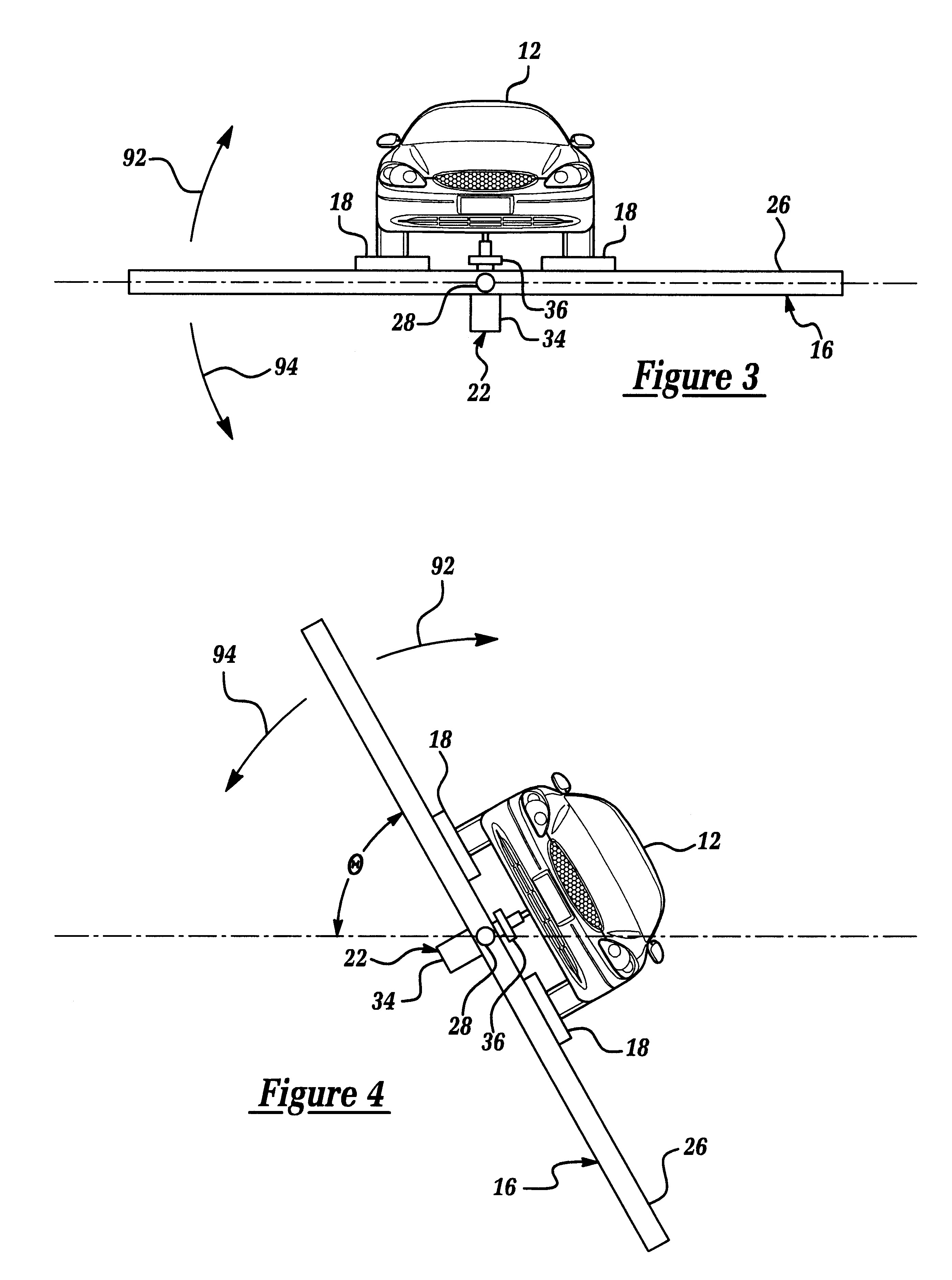
Method and apparatus for measuring the rollover resistance and compliance characteristics of a vehicle
InactiveUS6327526B1Accurate resistanceAccurate measurementVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRolloverDynamic compliance
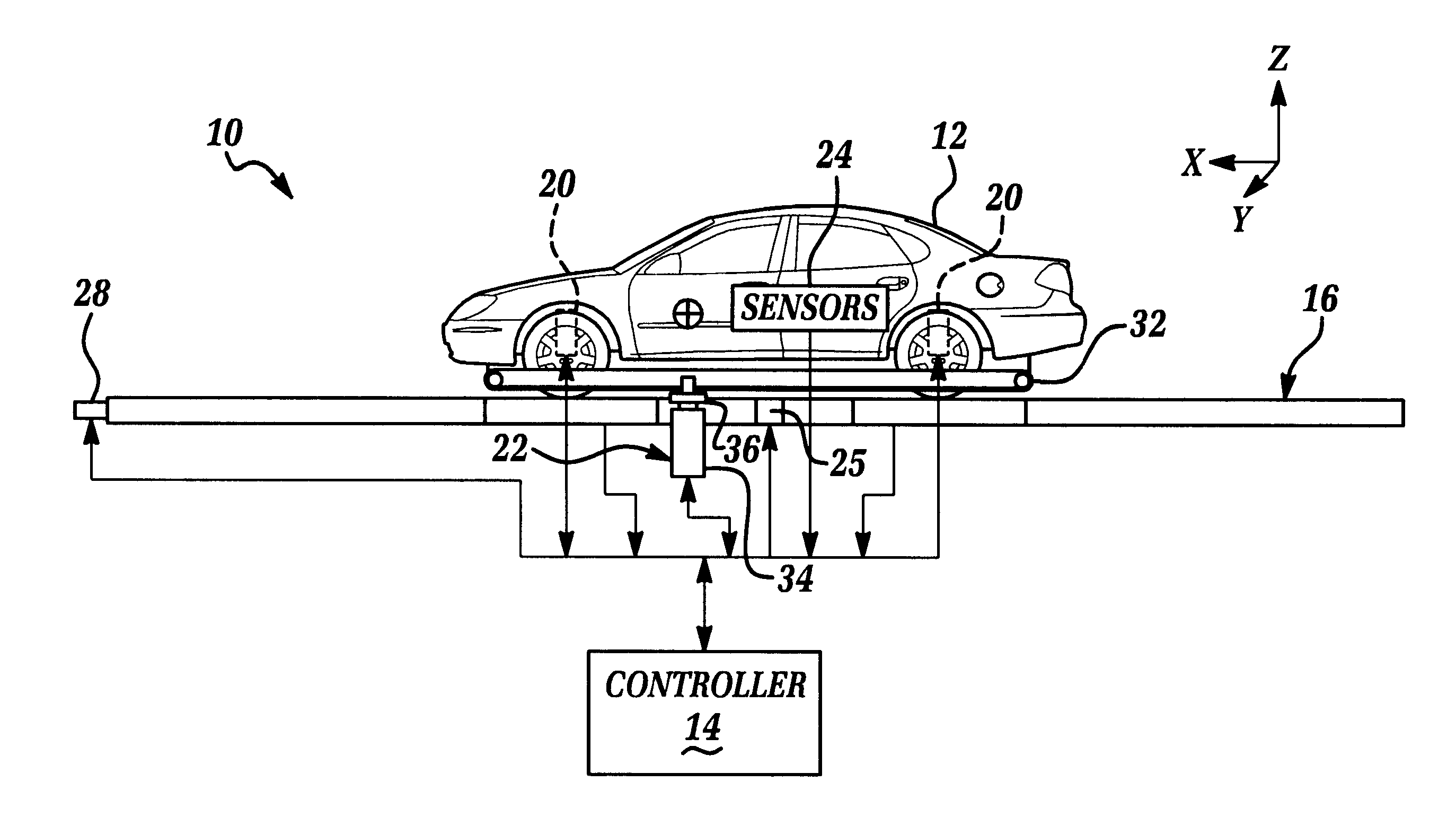
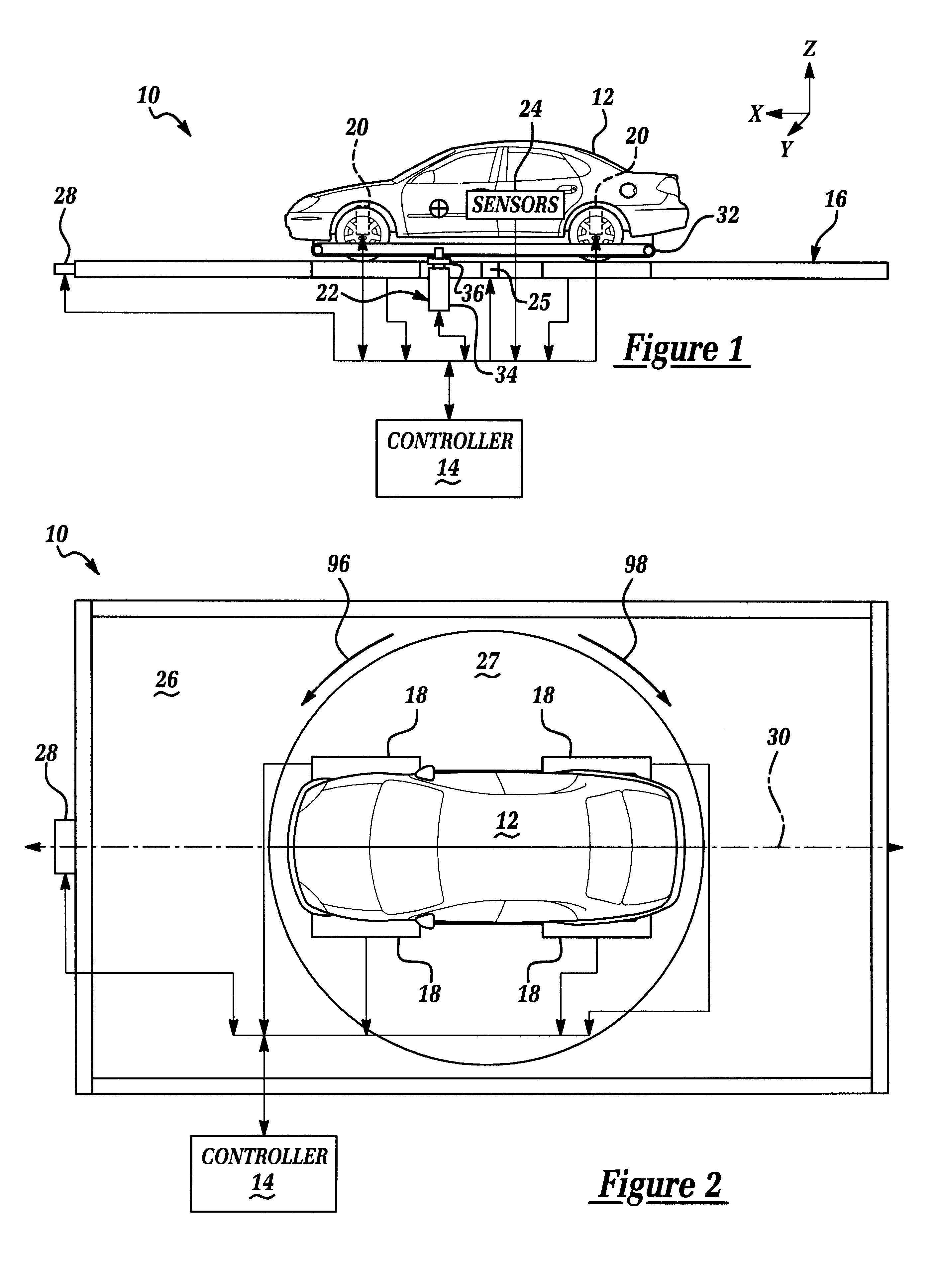
An apparatus 10 for measuring and / or analyzing the rollover resistance and dynamic compliance characteristics of a vehicle 12. Apparatus 10 includes a controller 14, a selectively rotatable test bed assembly 16, several load sensors 18 which are disposed upon test bed assembly 16, suspension jacks or actuators 20, a gravity compensation assembly 22, and various vehicle sensors 24. Controller 14 is communicatively coupled to test bed assembly 16, sensors 18, actuators 20, gravity compensation assembly 22, and vehicle sensors 24. Controller 14 generates signals to test bed assembly 16, actuators 20, and assembly 22, effective to cause test bed assembly 16, actuators 20 and assembly 22 to replicate certain inertial conditions or events. Controller 14 further receives signals from sensors 18 and 24, and processes and utilizes the received signals to analyze and / or measure the resistance of vehicle 12 to rollover and dynamic compliance characteristics of vehicle 12 during the replicated inertial conditions or events.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
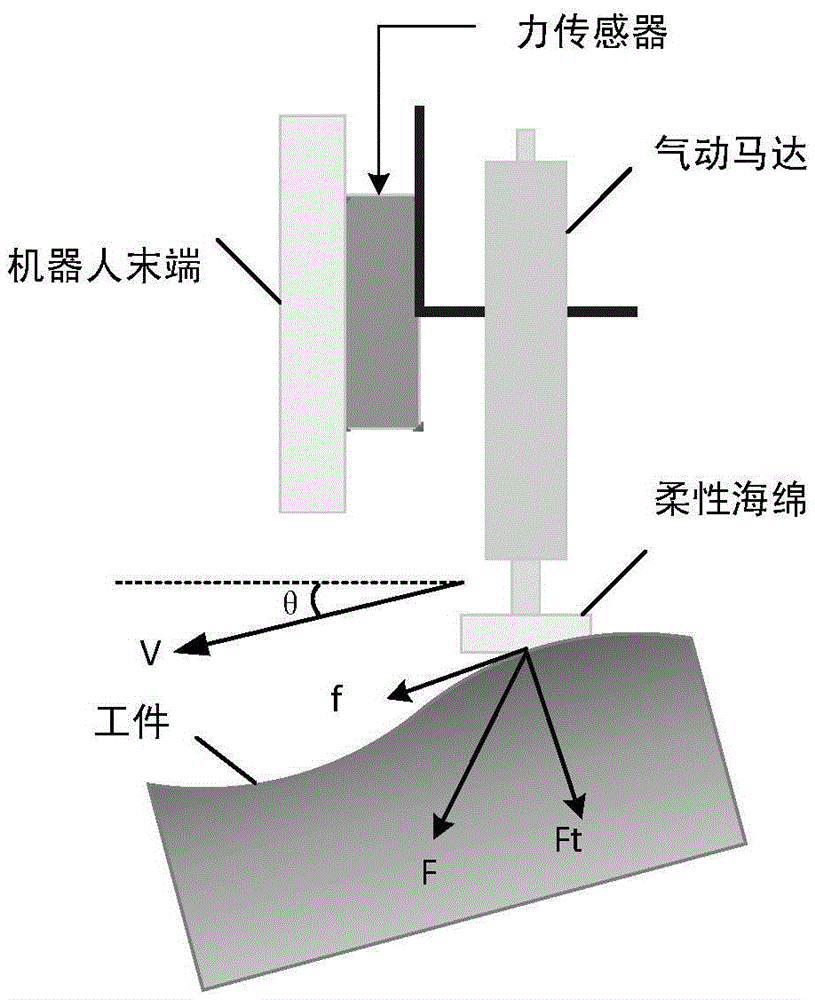
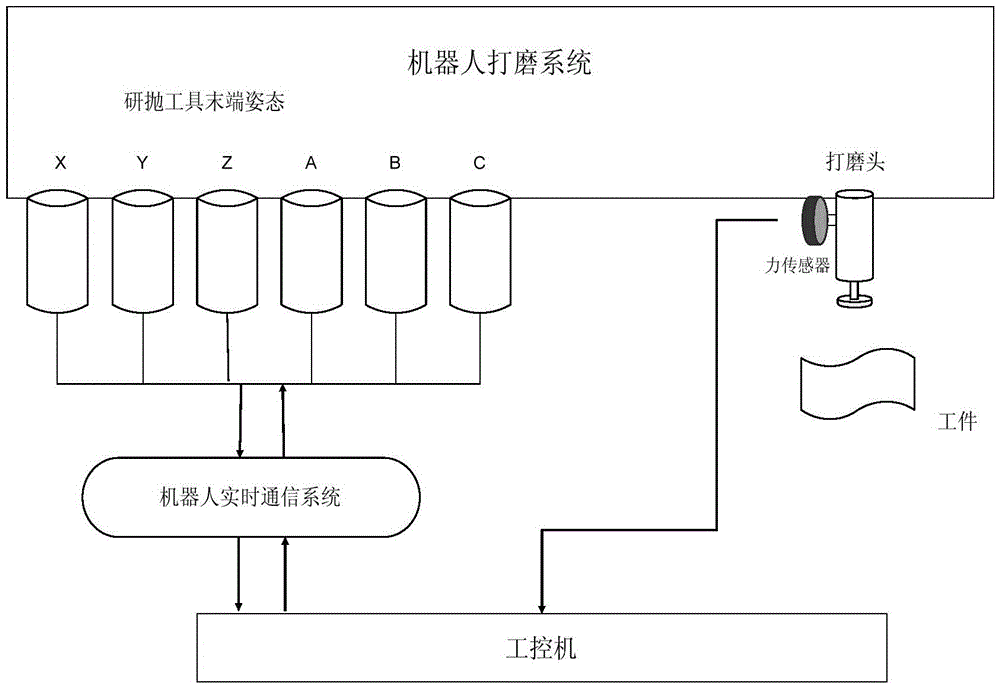
Polishing method of portal lifting robot based on force control
InactiveCN105500147AImprove machining accuracyEasy to processAutomatic grinding controlGrinding machinesPersonal computerRobot machining
The invention relates to a polishing method of a portal lifting robot based on force control. The polishing method comprises the following steps: an industrial personal computer generates an offline path according to a workpiece model, and the robot processes a workpiece according to the offline path; a force sensor acquires force information at the tail end of the robot in real time to return to the industrial personal computer, and the industrial personal computer obtains returned force through gravity compensation according to the force information; the industrial personal computer obtains a difference between a set force target value and the returned force, and obtains a position corrected quantity through a force controller; and the sum of the position corrected quantity and a present position of the robot is obtained, and an impedance controller obtains a control quantity to control polishing acting force in robot processing. The polishing method eliminates the disturbance of tool gravity on the polishing acting force in the polishing process to guarantee the detecting and control precision of the polishing acting force, and is high in sensor measuring precision, high in robot control precision and excellent in processing effect.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
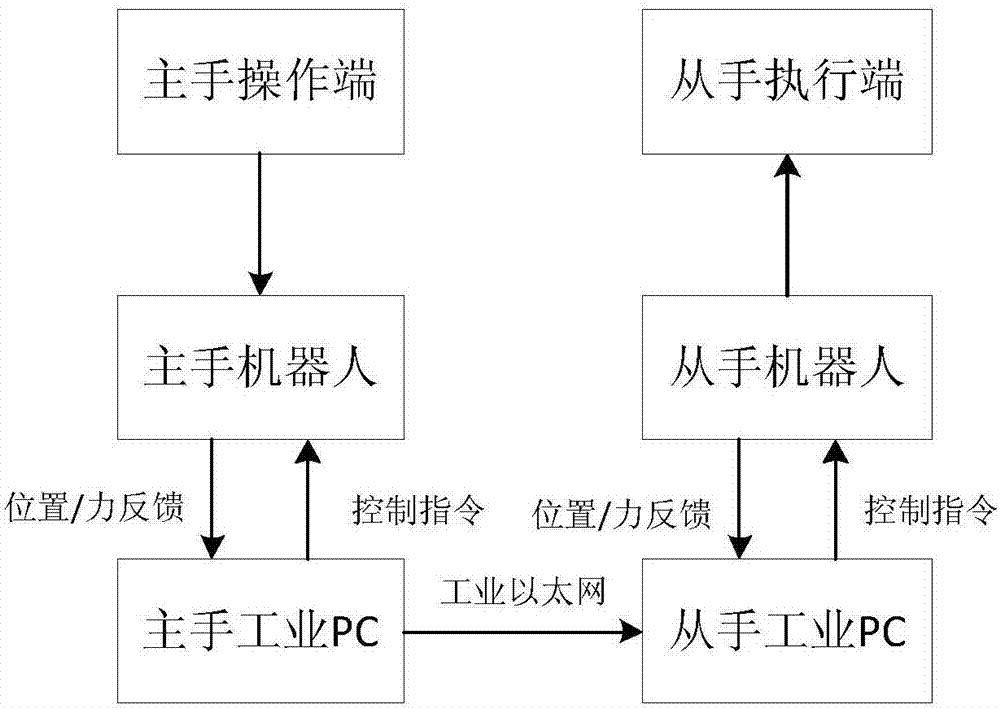
Novel master-salve mode surgical robot control method
The invention discloses a novel master-slave mode surgical robot control method. The method comprises the first step of conducting calculating to obtain an iteration equation of force and torque between each connection rod and joint; the second step of calculating a gravity compensation coefficient of each connection rod, and mapping the effect of force and torque of gravity to each joint to each joint; the third step of conducting calculating to obtain expecting torque to each joint through inverse dynamics, and leading in an inner ring / outer ring control framework according to current actual force feedback information which is fed back in real time to conduct control; the fourth step of calculating the iteration equation of force and torque between each connection rod and joint; the fifth step of obtaining in real time force feedback information from a hand execution end, and leading in the inner ring / outer ring control framework to conduct control. According to the novel master-slave mode surgical robot control method, kinematics and dynamics modeling of a master hand and a slave hand and theoretical derivation of a mapping relation between the master hand and the slave hand are achieved, a gravity compensation and inner ring / outer ring control strategy is adopted, a modularized procedural framework is adopted to complete the achievement of a control algorithm, and a master-slave mode teleoperation surgical robot system is efficiently achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Six-freedom remote control arm with gravity compensation and length regulation
The present invention relates to data arm mechanism for remote operation job of robot. The data arm mechanism is one mechanical arm with six rotating joints, and each of rotating joints is provided with one potentiometer as angle sensor. The data arm has gravitational compensation mechanism and may be worn by operator for leading motion or may be drawn to required state without being worn, and it may stop in any position without need of auxiliary outside force. The data arm has length regulating mechanism for person of different arm length to wear. The present invention can detect the rotation angles of total six freedoms of the shoulder joint, elbow joint and wrist joint of the operator, and is suitable for control platform of remote operated robot and for being worn onto arm of the operator.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
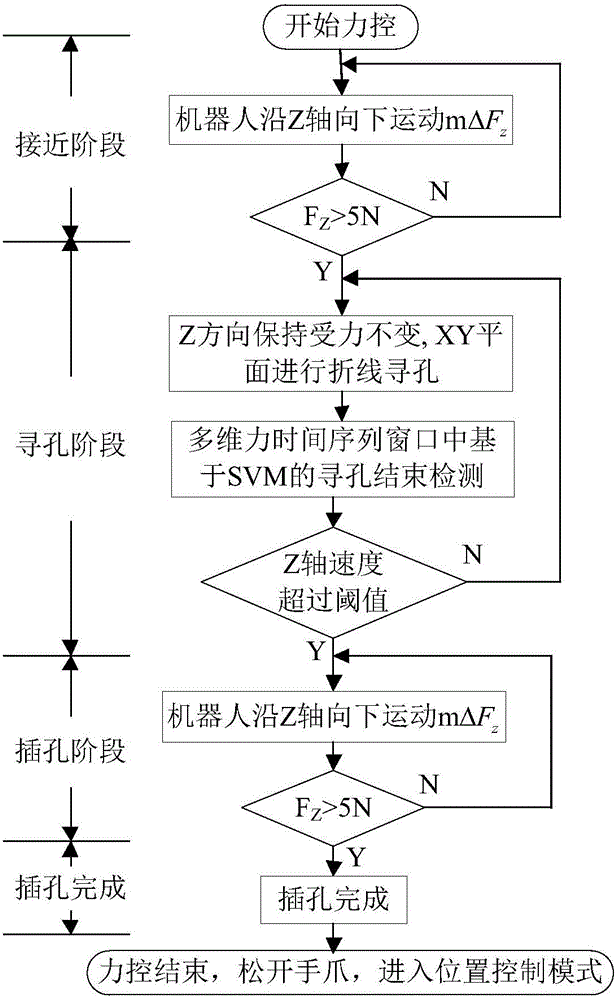
Total-space smooth hole insertion control method applied to assembly robot and based on real-time force control
ActiveCN106335057AAvoid misalignmentImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorSupport vector machineControl system
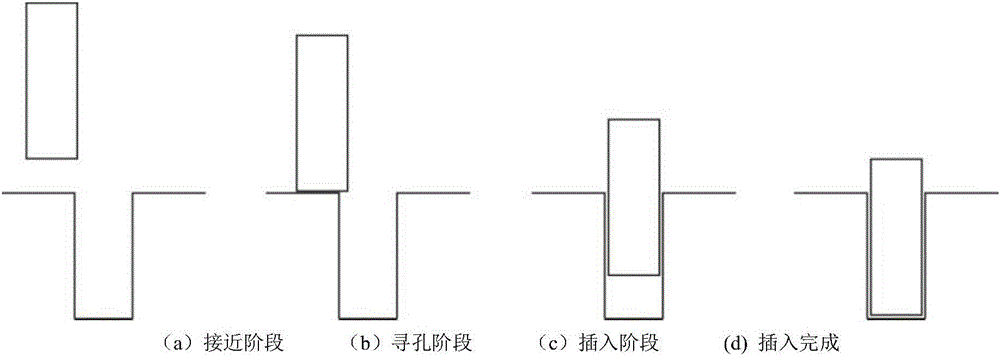
The invention discloses a total-space smooth hole insertion control method applied to an assembly robot and based on real-time force control. The total-space smooth hole insertion control method applied to the assembly robot and based on real-time force control comprises the steps that a bolt hole insertion real-time force control system of the assembly robot is established by means of a six-dimensional wrist force sensor, a real-time communication software package and the like; the influence of the gravity component on the reading of the six-dimensional wrist force sensor during total-space work of the robot is eliminated through a gravity compensation method based on the standard position; and the common phenomena of jamming and excessive clamping in the bolt hole insertion process are avoided through the design of a stress analysis and force / position hybrid control strategy in the approaching stage, the hole searching stage, an insertion stage and an insertion completing stage of a hole insertion task, thus the insertion success rate of the robot is increased, and the insertion efficiency of the robot are improved; and a detector based on a support vector machine is arranged in a multi-dimensional force time sequence window, so that automatic detection of the hole searching completion state is achieved, and accurate switching between the hole searching subtask and the hole insertion subtask is guaranteed. By adoption of the total-space smooth hole insertion control method applied to the assembly robot and based on real-time force control, control over high-efficiency and high-accuracy chamfer-free smooth hole insertion assembly work can be achieved through a conventional rigid joint robot.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Force feedback system and actuator power management
InactiveUS7345672B2Input/output for user-computer interactionProgramme controlTouch PerceptionConstant force
A system and method for providing a tactile virtual reality to a user is present. The position and orientation of the user is utilized to generate a virtual reality force field. Forces are in turn generated on the user as a function of this force field. A six-axis manipulator is presented for providing a user interface to such a system. This manipulator provides a unique kinematic structure with two constant force springs, which provide gravity compensation so that the manipulator effectively floats.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
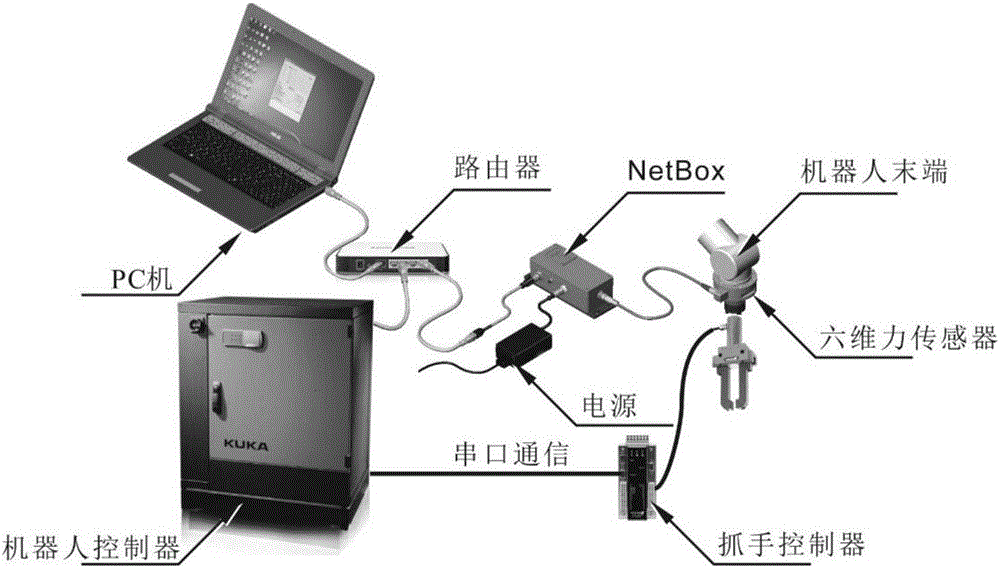
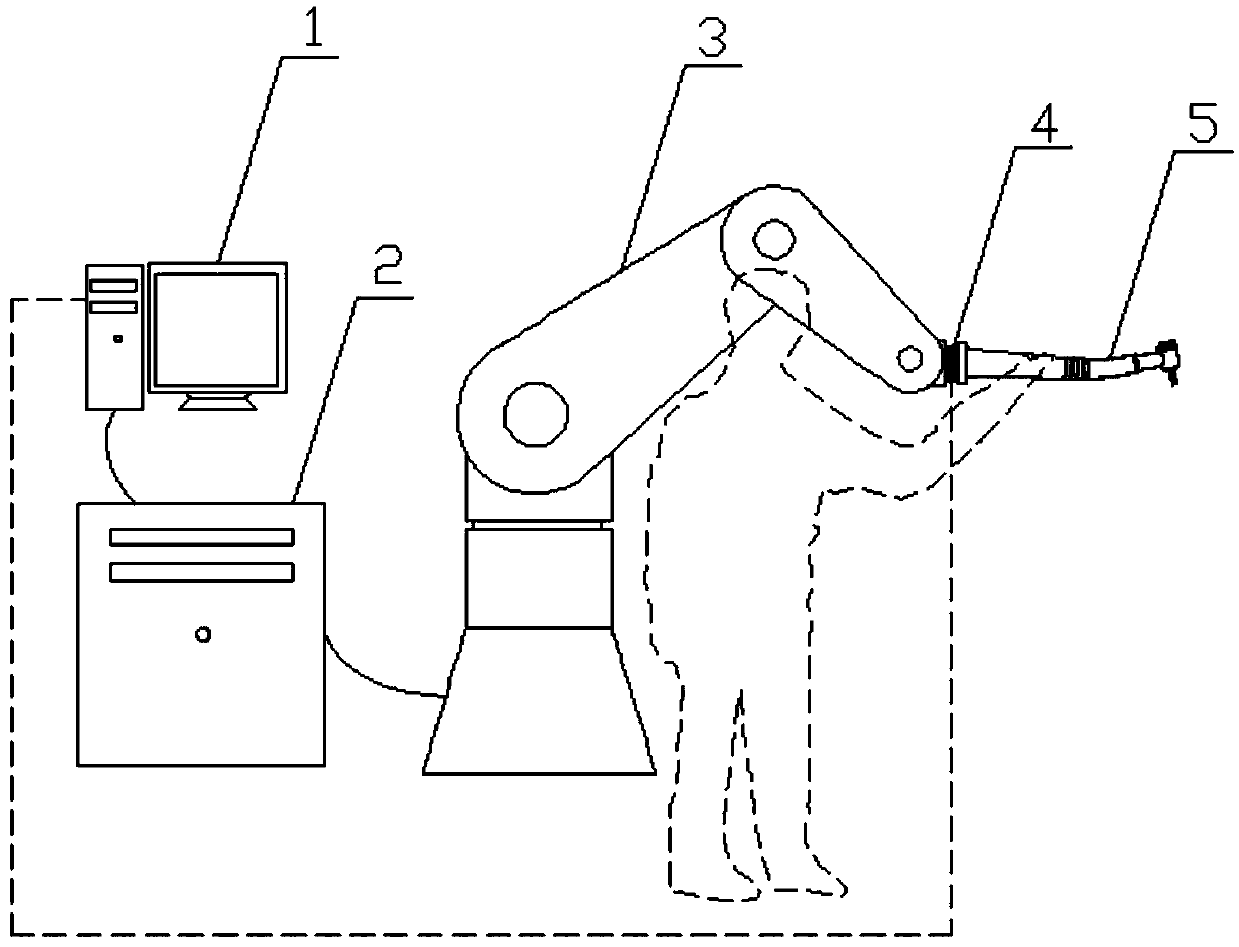
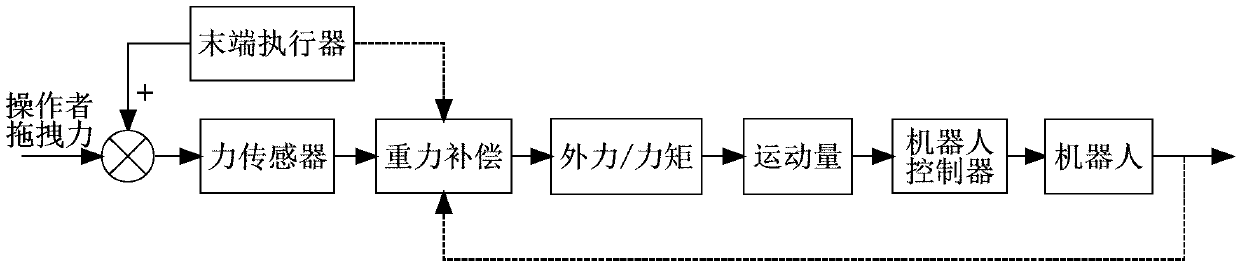
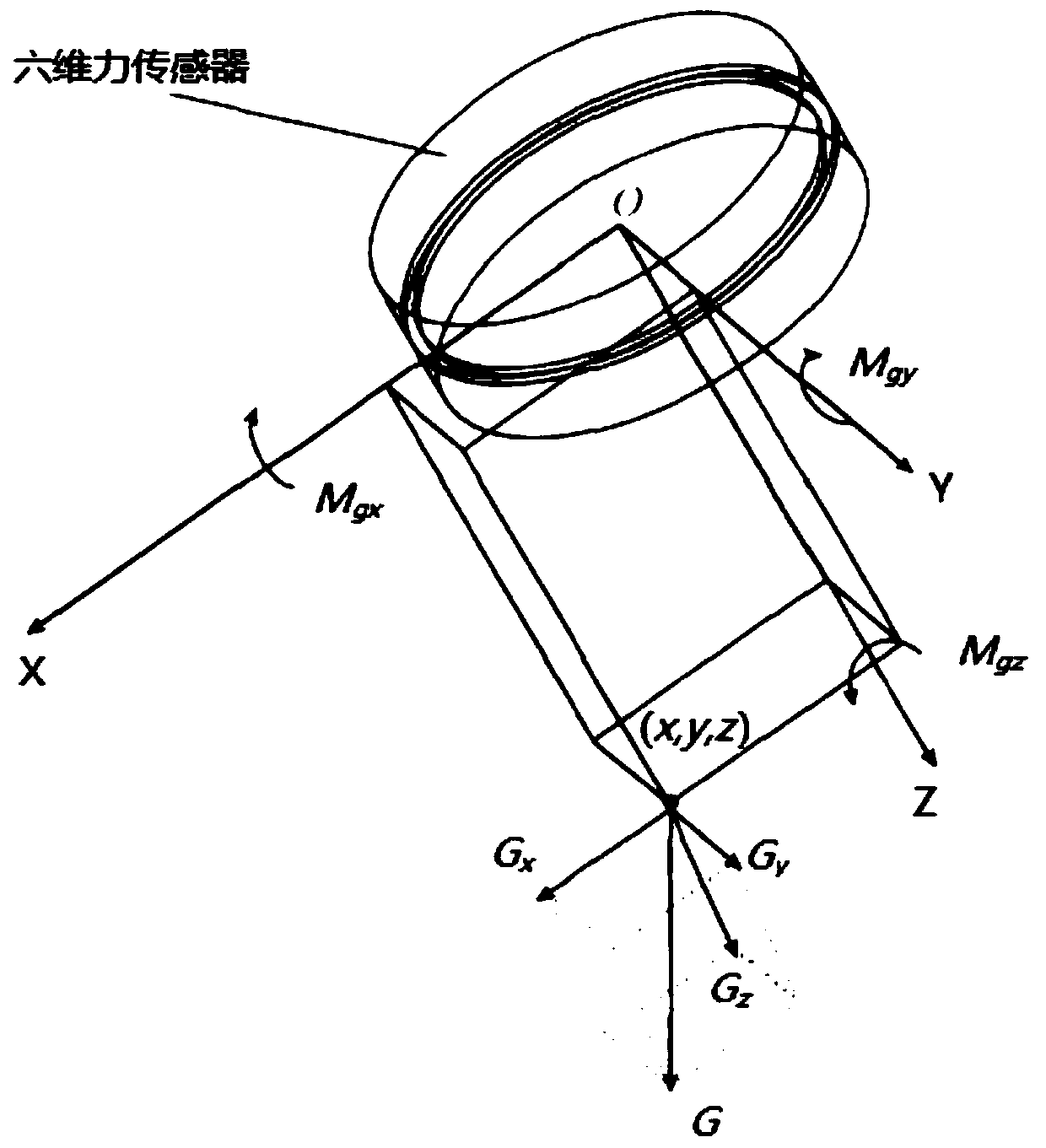
Direct dragging teaching system and method based on force sensor
ActiveCN108789363AEliminate the effects of gravityAccurate perceptionProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical operationEngineering
The invention provides a direct dragging teaching system and method based on a force sensor and used in the surgical operation. The system comprises an industrial personal computer, a robot controller, a robot, the six-dimensional force sensor and a tail end executor; the six-dimensional force sensor is used for collecting stress information of the tail end executor when a doctor drags the tail end executor to do motion, the industrial personal computer carries out gravity compensation on the stress information, collected by the six-dimensional force sensor, of the tail end executor, the external force when the doctor drags the tail end executor to carry out motion is obtained, the industrial personal computer generates robot motion instructions according to the external force generated when the doctor drags the tail end executor to carry out motion, and the robot controller controls the robot to move according to the motion instructions. The multidimensional force sensor is additionally arranged on the tail end of the robot to transmit teaching intentions of the doctor, the robot is guided to move, through the gravity compensation, the gravity influence of the tail end executor isremoved, the doctor hand action force can be accurately perceived, and the flexible and accurate dragging teaching in the operation process is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING YAKEBOT TECH CO LTD
Hybrid maglev gravity compensation apparatus
ActiveCN102200689AImplement static gravity compensationAchieve horizontalPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusComputer moduleHorizontal and vertical
The invention discloses a hybrid maglev gravity compensation apparatus comprising a static gravity compensation module. The static gravity compensation module comprises: an intermediate moving component, an exterior fixed component arranged around the intermediate moving component, and a bottom fixed component arranged below the intermediate moving component. The intermediate moving component is in a radially suspended state with the magnetic forces between the exterior fixed component and the intermediate moving component, such that a vertical guiding to the intermediate moving component is carried out. Static gravity compensating between the exterior fixed component and the intermediate moving component can be carried out with adjustable magnetic forces. According to the invention, non-contact displacement between relatively moving objects can be achieved with maglev forces. Meanwhile, gravity compensation, horizontal and vertical decoupling of a wafer supporting stage can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD +1
Joint type manipulator low gravity compensation system
ActiveCN104175331AAchieve coordinated movementGuaranteed accuracyCosmonautic condition simulationsManipulatorControl systemRobotic arm
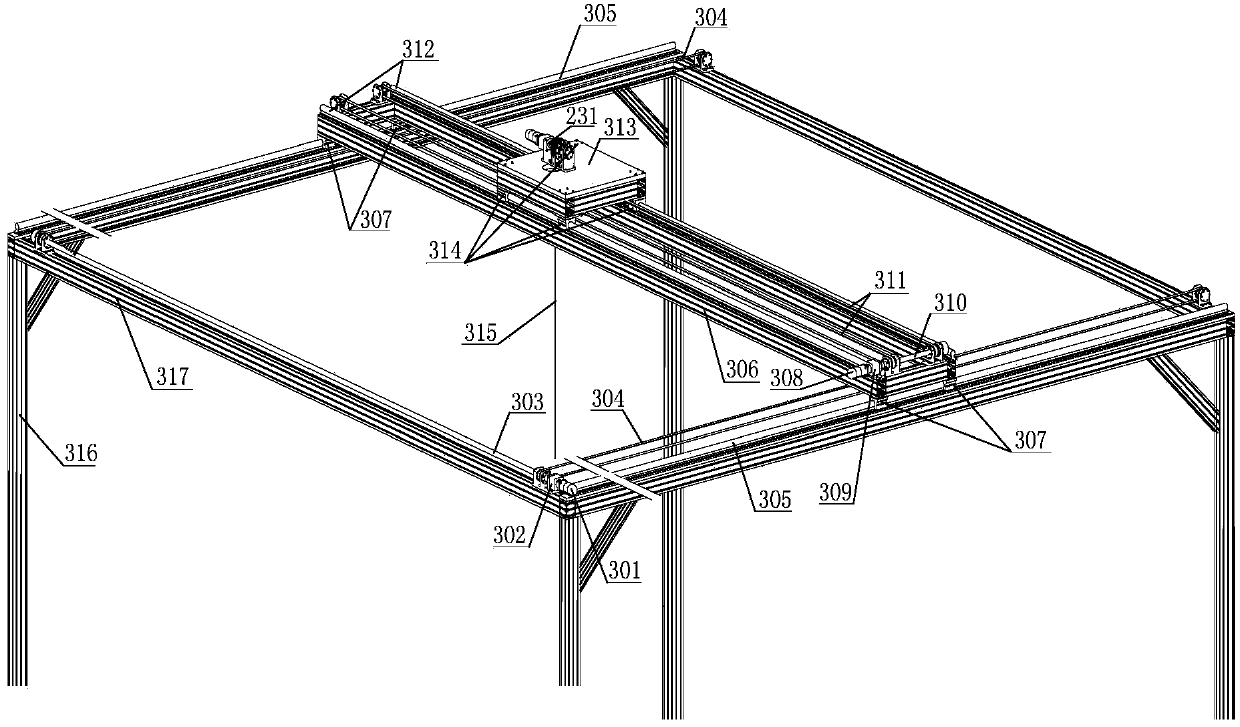
The invention provides a joint type manipulator low gravity compensation system comprising a support, an upper platform, a right-angle type tracking platform, a polar-coordinate type tracking platform, a gravity compensation system body, a suspending device and a control system. The upper platform is mounted on the support, the right-angle type tracking platform is capable of moving corresponding to the X and Y directions of the upper platform, the polar-coordinate type tracking platform is mounted below the right-angle type tracking platform and is capable of rotating around the Z-axis of the right-angle type tracking platform or moving in the X and Y directions with the polar-coordinate type tracking platform, the gravity compensation system body is mounted on the top of the right-angle type tracking platform and the bottom of the polar-coordinate type tracking platform, the suspending device is connected between the gravity compensation system body and a joint type manipulator, and the control system is use for monitoring and controlling the components. The right-angle type tracking platform and the polar-coordinate type tracking platform are combined, multiple joint manipulator complex movement tracking is implemented, the system can be adaptive to movement tracking of manipulators of carriers with different postures, multiple manipulator suspension and multiple suspending point coordinated movement are implemented, gravity compensation is low, and accuracy is high.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROSPACE ELECTROMECHANICAL EQUIP RES INST
Experimental system and ground experimental method for gecko-inspired robot under micro-gravity environment
ActiveCN104859746ASmooth motionIncrease passive degrees of freedomCosmonautic condition simulationsVehiclesVolumetric Mass DensityOperability
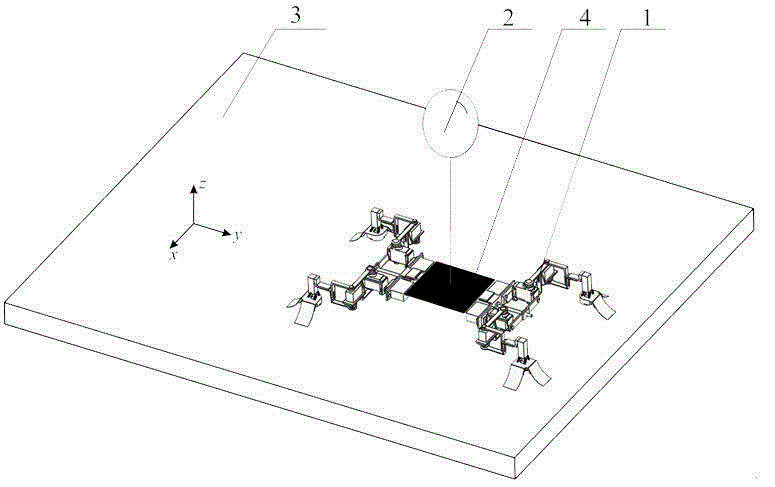
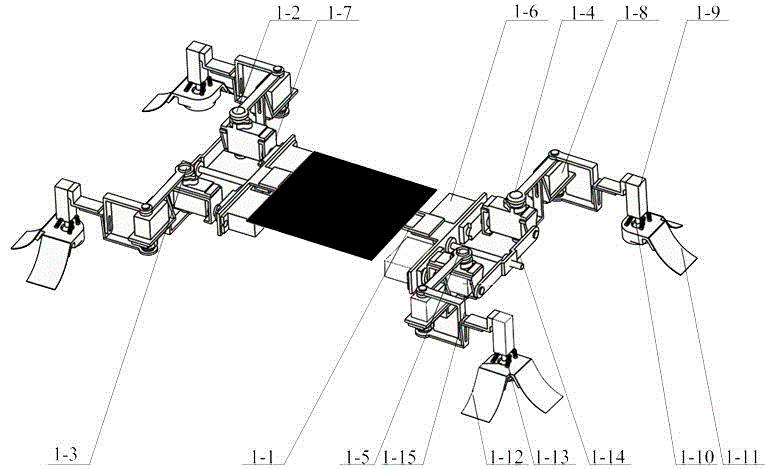
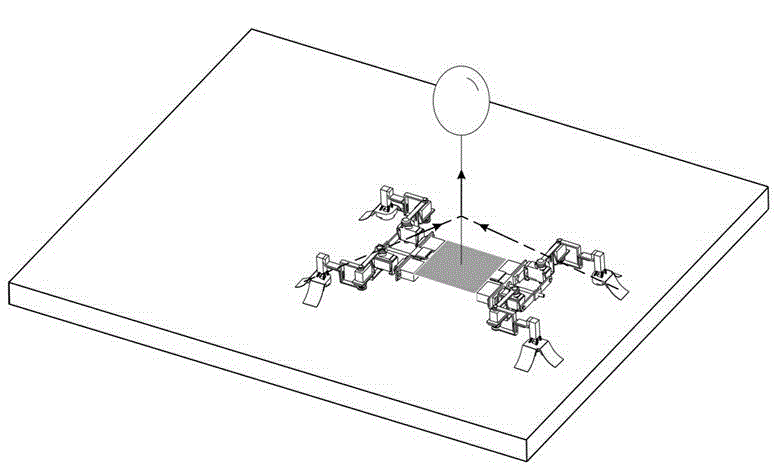
The invention discloses an experimental system for a gecko-inspired robot under a micro-gravity environment, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The experimental system comprises a gecko-inspired robot mechanism, an air balloon, a three-freedom motion platform and a motion control unit, wherein the air balloon is used for providing gravity compensation to the gecko-inspired robot mechanism; the motion control unit is used for controlling the gecko-inspired robot mechanism to operate; the gecko-inspired robot mechanism comprises a machine body and four limbs of the same structure, which are connected with the machine body, and any two adjacent limbs are symmetrical; and the density of gas filled in the air balloon is smaller than the air density. According to the experimental system, the micro-gravity environment is simulated by the air balloon with the filled gas density smaller than the air density, and the gravity compensation of a micro robot under a three-dimensional space is realized, so that the experimental system is low in cost, high in operability and high in reliability in comparison with a conventional method. The invention further provides an experimental method for the gecko-inspired robot under the micro-gravity environment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
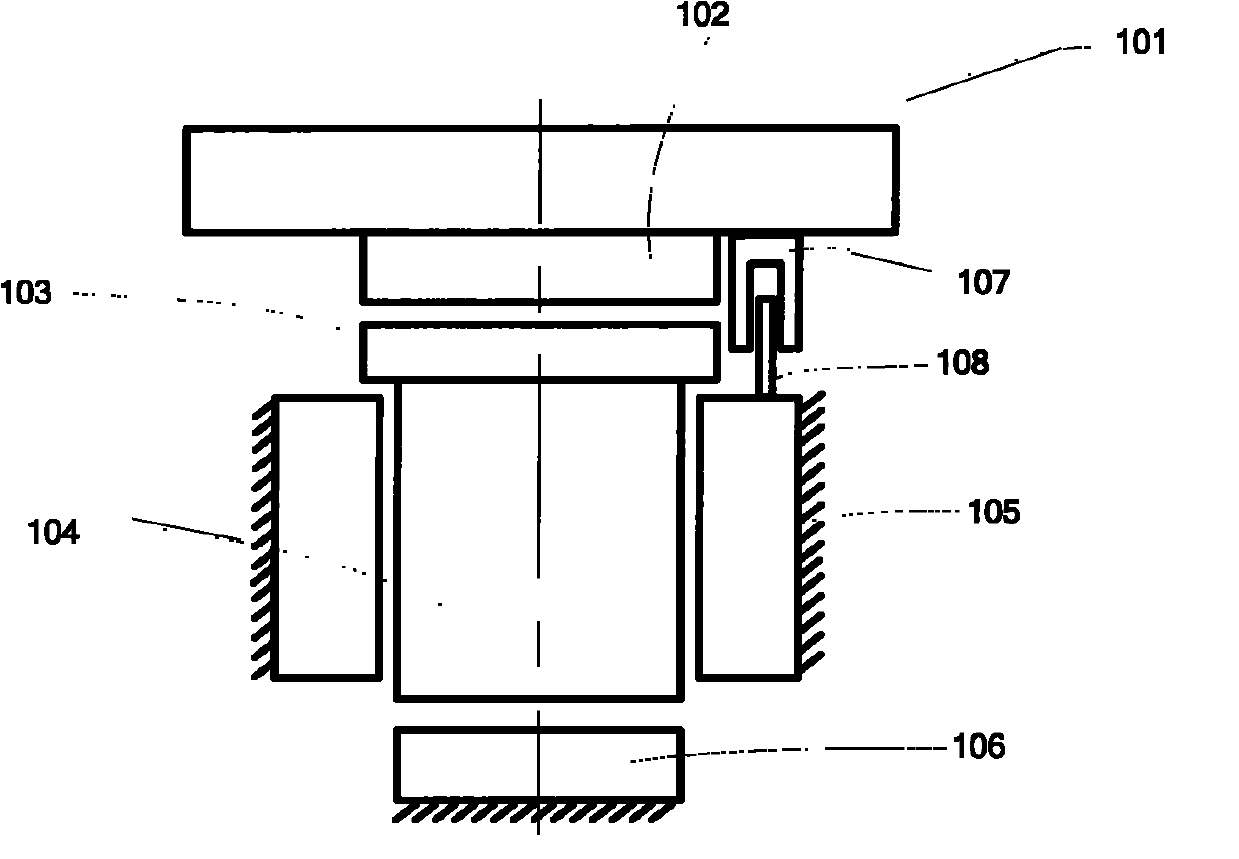
Gravity compensation device
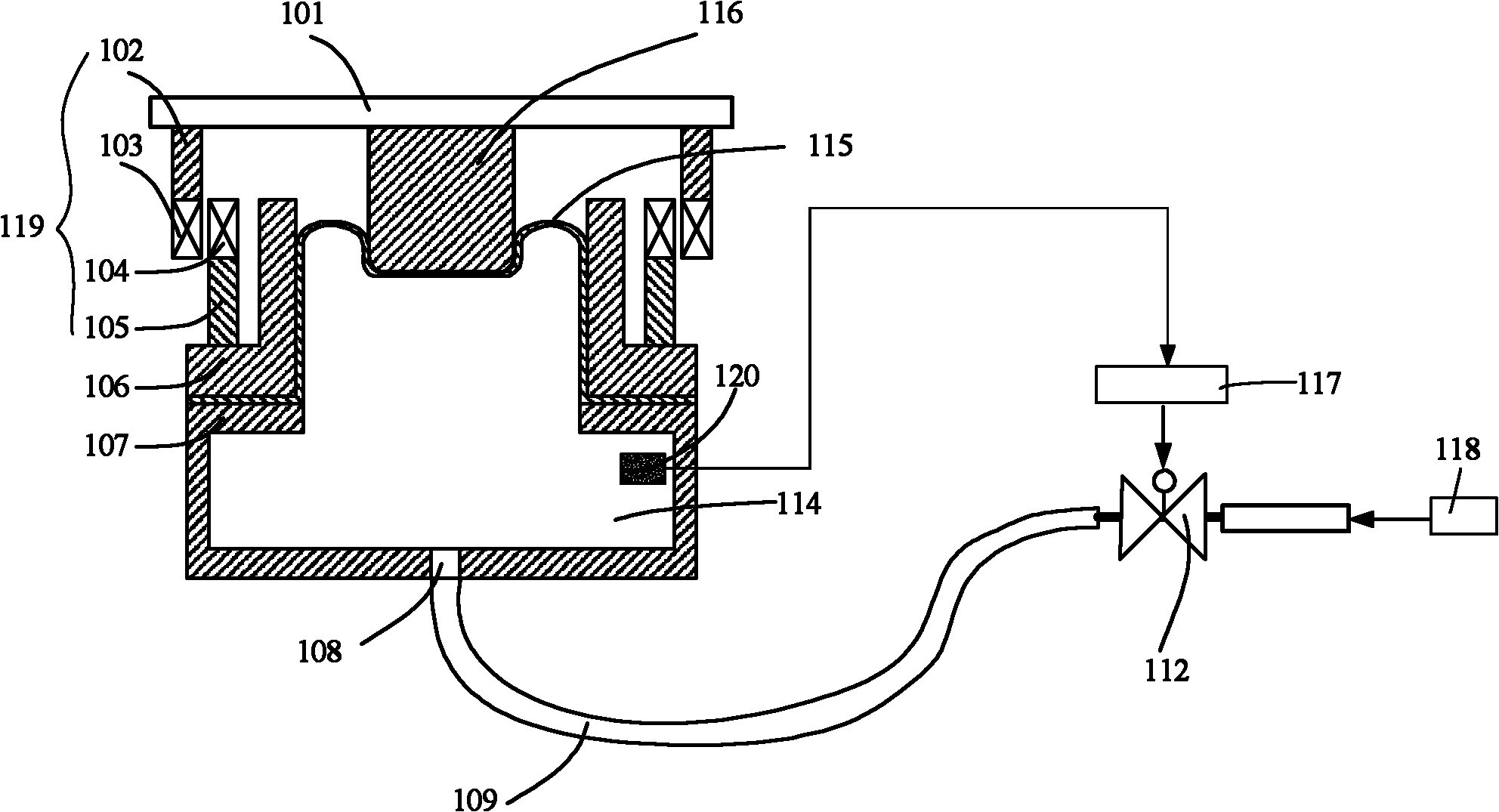
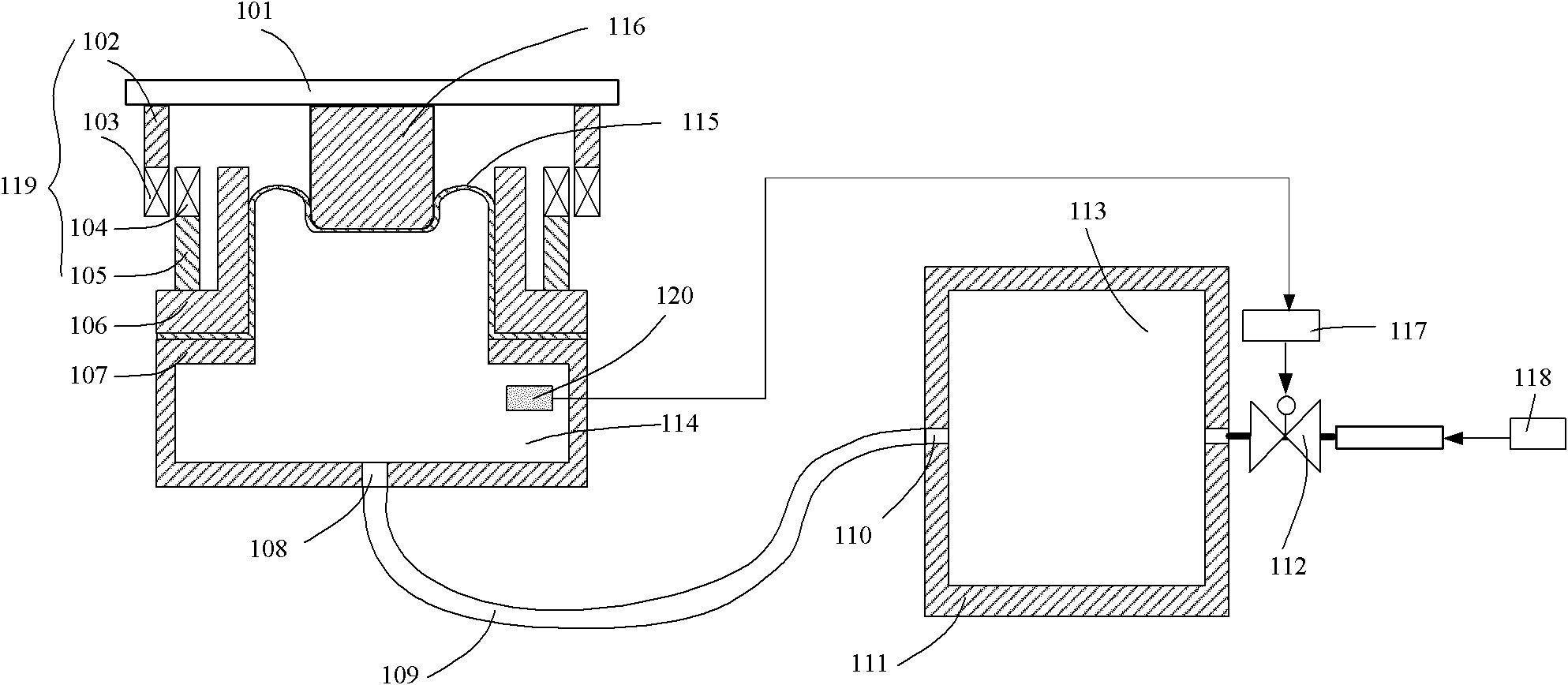
ActiveCN102486215AEliminate errorsReduce structural stiffnessPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringReticle
The invention discloses a gravity compensation device which is used for supporting a micropositioner of a worktable and a reticle stage in a photoetching machine and is communicated with a gas circuit of a gas supplying gas source. The gravity compensation device comprises a first gas chamber, a piston, a supporting plate and a pneumatic valve, wherein the piston is supported by the first gas chamber; the supporting plate is used for supporting the micropositioner, is positioned above the piston and is fixedly connected with the piston; and the valve is communicated with the first gas chamber and is used for adjusting the air pressure of the first air chamber. The gravity compensation device has the advantages that: firstly, the gravity compensation device has a simple structure; secondly, the gravity compensation device has lower rigidity so as to isolate low-frequency vibration; thirdly, the gravity compensation device has certain damping so as to reduce resonance; thirdly, the gravity compensation device has no action of exhausting gas to the environment and can be applied to a vacuum environment; and fourthly, when a load changes, the error of a static position of the reticle stage can be eliminated by adjusting the air pressure of the first gas chamber.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Gravity compensation device for solar wing low temperature unfolding experiment
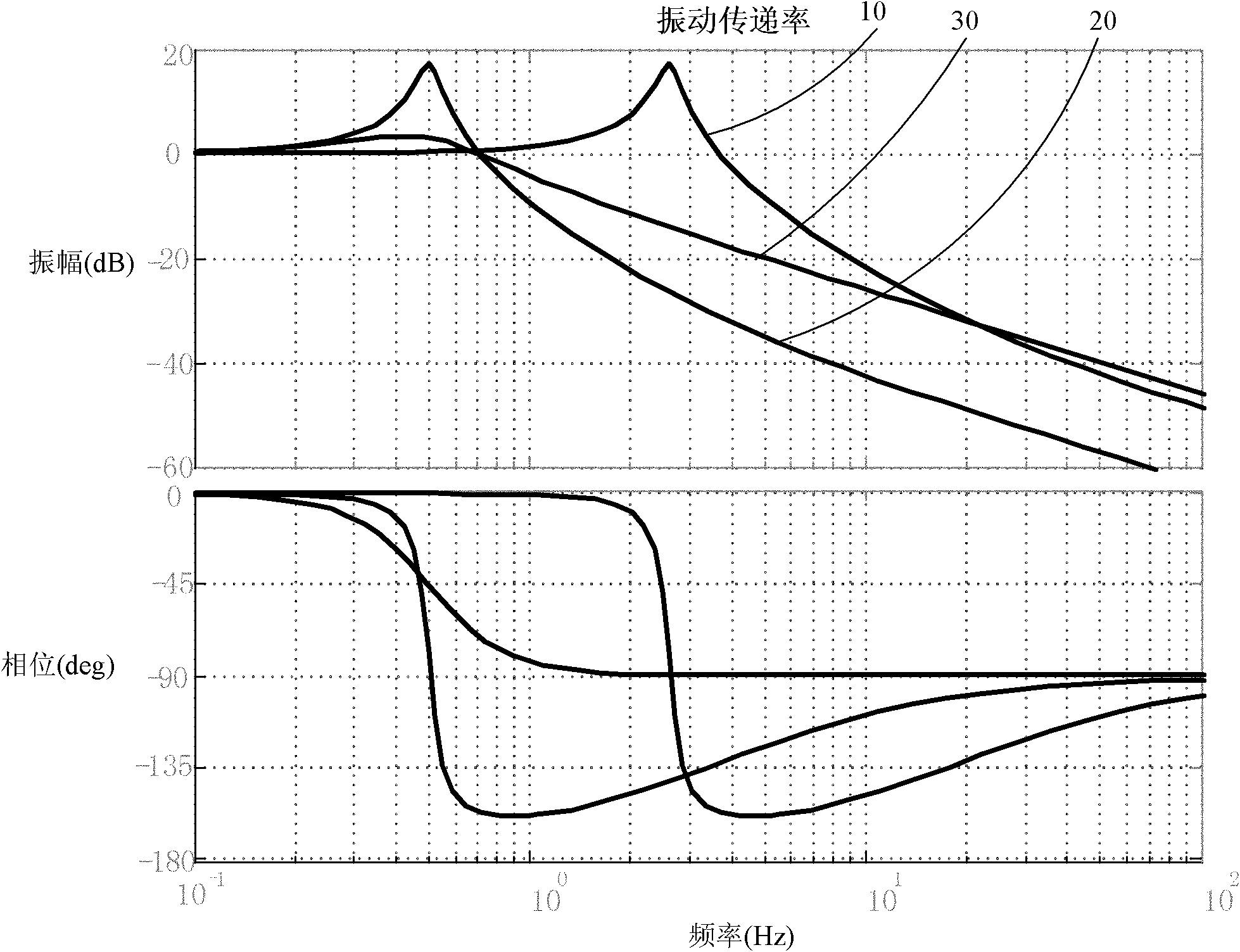
ActiveCN104326368ASolve the problem of crack failureLight in massTravelling cranesZero gravityMotion resistance
A gravity compensation device for solar wing low temperature unfolding experiment is capable of realizing one sixth gravity compensation and zero gravity compensation of solar wing at a temperature of -120 DEG C. The device also can carry out solar wing multi-angle repeated unfolding and folding experiments in a limit position by simulating a landing situation when the included angle between the moon surface and the horizontal plane is 15 degrees. A balance rod is adopted in the device to carry out gravity compensation, and is completely made of metals so as to adapt to the low temperature environment. The three-dimensional trace movement of the mass center of a solar wing is completed by the swinging of a guide rail and a suspension rod; the conventional bidirectional guide rail structure composed of a solar wing vertical guide rail and a solar wing horizontal guide rail is broken through, thus the system complexity is reduced, and the movement reliability is improved. A horizontal rotation assembly is adopted to enable the main beam to freely rotate in a horizontal plane, and the gravity compensation technology is broken through when the included angle between a solar wing and the horizontal plane is 15 degrees namely the extreme working condition. A pulley and a pulley structure are adopted to reduce the movement resistance. A main beam having an I-shaped aluminum structure is adopted, the weight of movable parts is reduced, and thus the inertia force during the folding and unfolding process of a solar wing is effectively reduced.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE MFG FACTORY
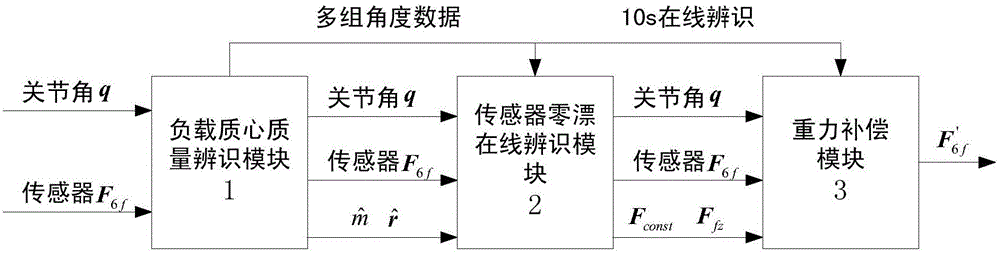
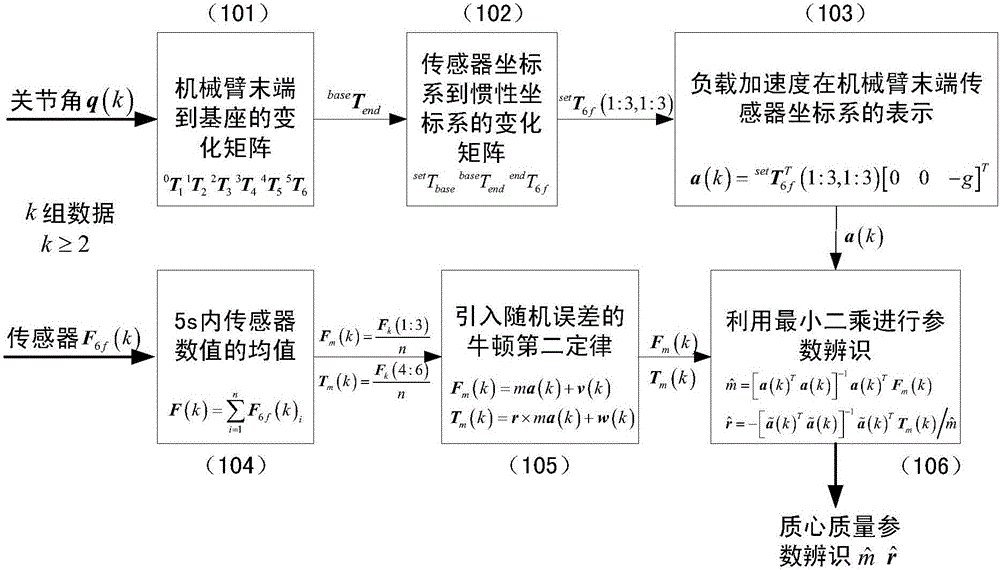
Gravity compensation method for mechanical arm load mass and sensor null drift online recognition
ActiveCN107433590AFunction increaseRealize online identificationProgramme-controlled manipulatorGravitational forceEngineering
The invention provides a gravity compensation method for mechanical arm load mass and sensor null drift online recognition. The gravity compensation method comprises the steps that S1, a load mass center and mass recognition module is adopted for obtaining and recognizing the mass center and mass of loads at the tail end of a mechanical arm, and the recognized mass center and the recognized mass of the loads are obtained; S2, a sensor null drift recognition module is adopted for reading the numerical value of a sensor, calculation is performed according to the recognized mass center and the recognized mass, and sensor null drift is obtained; and S3, a gravity compensation module is adopted for performing gravity compensation on the numerical value of the sensor according to the sensor null drift. By means of the method, the problem that due to the additional force and torque introduced by the loads of the tail end of the mechanical arm to the tail-end six-dimensional force sensor by the gravity effect and the presence of sensor null drift errors, the numerical value of the sensor is inaccurate and the final force control effect is affected can be solved, and uncertainty of the sensor null drift determines the necessity of online recognition of the sensor null drift.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
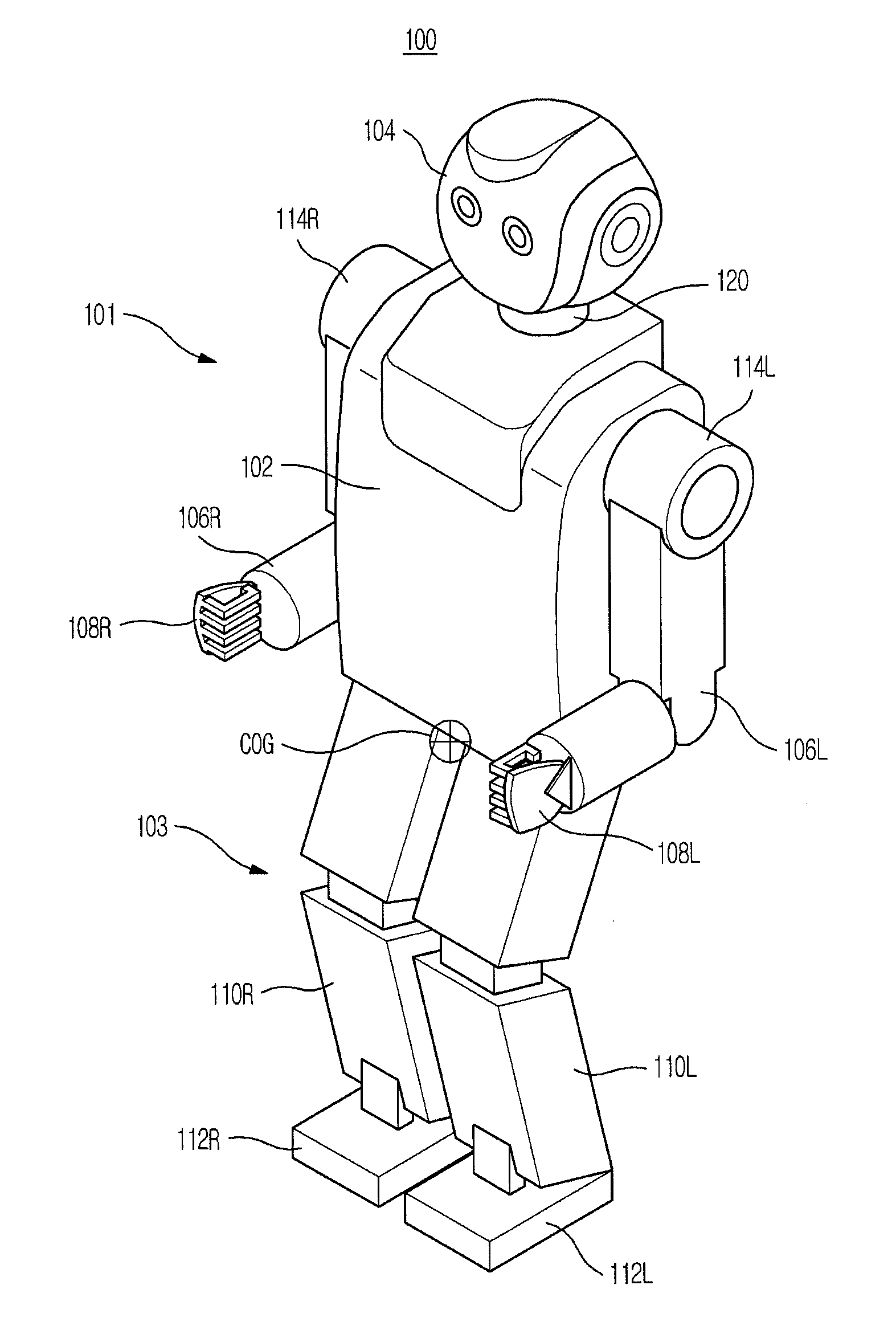
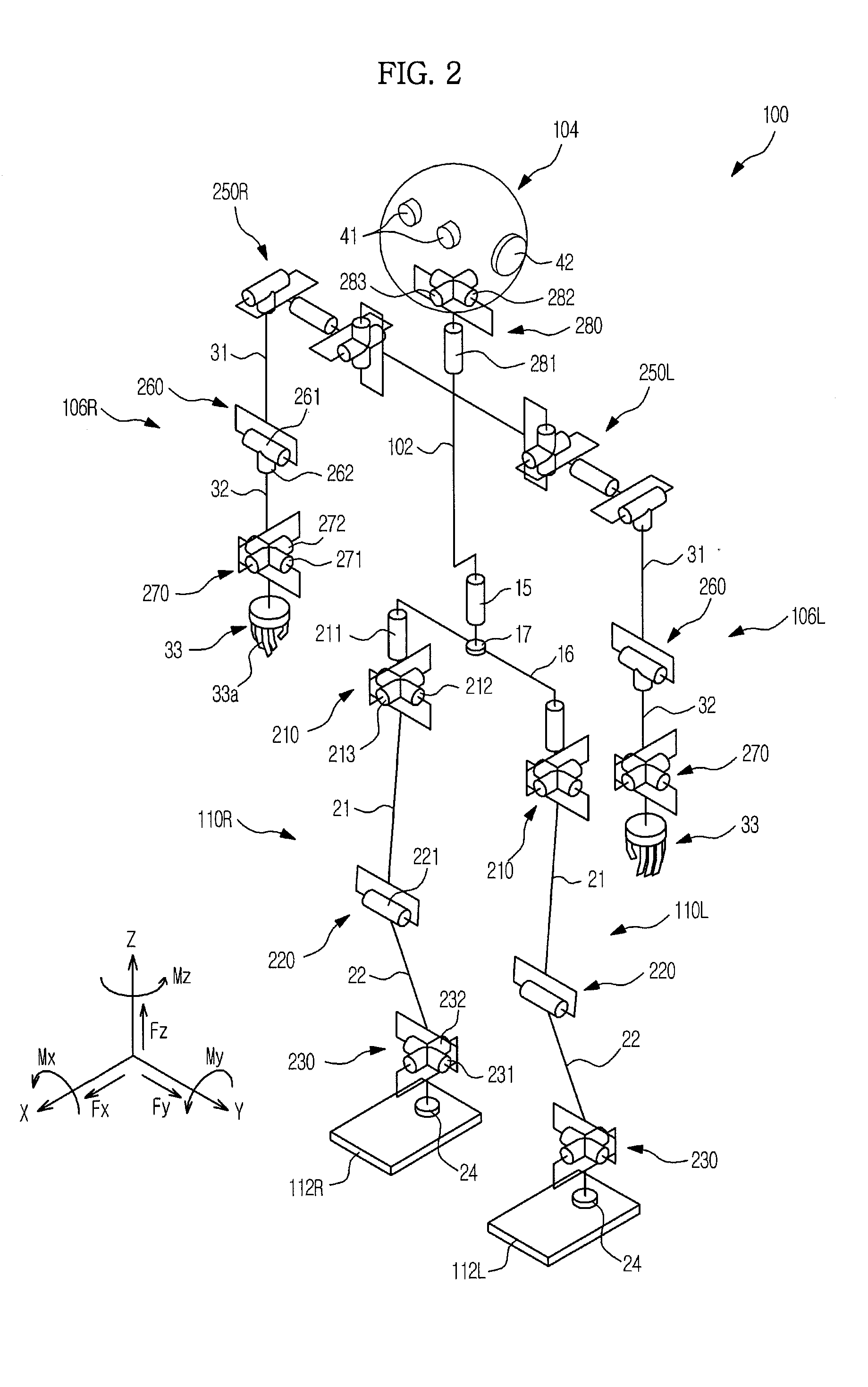
Walking robot and pose control method thereof
ActiveUS20120158181A1Increase valueProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorBody angleAttitude control
A walking robot, respective joints of which are operated through torque servo control to achieve stable pose control, and a pose control method thereof. A virtual acceleration of gravity is calculated using the COG of the robot and gravity compensation torques to apply force to links are calculated from the calculated acceleration of gravity so as to actively cope with external changes including external force or a tilt of the ground, thereby allowing the robot to stably maintain an erect pose and a desired upper body angle. Further, the robot maintains the erect pose with respect to the direction of gravity even under the condition that data regarding whether or not the ground is level or tilted are not given in advance, and maintains uniform poses of an upper body and legs while actively changing angles of ankle joints even if the ground is gradually tilted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus of variable g force experience and create immersive VR sensations
InactiveCN102656091AImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorCosmonautic condition simulationsEngineeringZero gravity
A variable zero gravity simulation system is provided. A variable zero gravity condition is achieved by substantial immersion in a fluid environment by buoyancy means (101) and using robotic displacement devices such as exoskeleton (102) to help user's movement / gravity compensation and / or relief or change loads on the subject's torso and limbs that caused by the weight and shape of the buoyancy means (101), so that user can experience the effect of the variable gravity environment being simulated, such as zero gravity in which situation user could move effortlessly in a weightless environment. When combine with VR related technology, this can create vivid immersive simulations for extraterrestrial scenes and can be widely used for entertainment, game, training, healing and etc.
Owner:肖泉
Mechanical arm collision detection and response method based on six-dimensional force sensor
InactiveCN104626171AImprove detection accuracyQuick responseManipulatorCollision detectionForce constant
The invention discloses a mechanical arm collision detection and response method based on a six-dimensional force sensor. The six-dimensional force sensor is arranged between a flange at the tail end of a mechanical arm and a load, and the measurement data of the sensor are continuously acquired according to set sampling frequency; a control system of the mechanical arm obtains the force (see the specification for the symbol) and moment (see the specification for the symbol) on the load of the mechanical arm under external action through gravity compensation of the load; collision detection is conducted according to a preset force constant threshold value Fs and a preset moment constant threshold value Ms when the mechanical arm drives the load to make translation movement or rotation movement, and corresponding motions are controlled according to the relative directions of the preset linear velocity / angular velocity of the mechanical arm and external force / moment. By adopting the six-dimensional force sensor for collision detection, detection precision is high, and respond speed is high; by eliminating the influences of load gravity and load posture, sensitive collision detection can still be conducted on heavy loads; motions making collision worse can be stopped instantly once collision occurs, motions in the opposite directions are allowed, and the method is reasonable and practical.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Double arm coordination acceleration control method based on impedance model under rigidity condition
ActiveCN106475999ASimple two-arm handling applicationVersatilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorAngular accelerationJoint spaces
The invention discloses a double arm coordination acceleration control method based on an impedance model under the rigidity condition. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a robot controller collects information of a six-dimensional force sensor, filtering treatment is conducted on the collected information, then gravity compensation is conducted, and finally expected force deviation value data or expected torque value deviation value data are obtained; secondly, the force deviation value data or the torque value deviation value data are converted into the moving acceleration and the pivoting angular acceleration of a robot tail end in the Cartesian space; thirdly, a corresponding position function, a corresponding speed function, a corresponding acceleration function and a corresponding jerk function are obtained; fourthly, a joint angle function in the joint space is obtained according to the inverse kinematics; and fifthly, after isochronic synchronous interpolation of the joint space is conducted on the joint angle function, the joint angle function is sent to a servo driver through a bus of the controller, and then the action of a robot is controlled. By means of the double arm coordination acceleration control method, the real-time force tracking effect can be achieved, and the movement of the robot is smooth during following.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Mobility vehicle and power-assisting system
ActiveUS20160059928A1Save human effortGood adhesionDigital data processing detailsWheelchairs/patient conveyanceGyroscopeAngular velocity
A mobility vehicle includes a personal mobility vehicle having at least one wheel body and a power-assisting system. The power-assisting system includes an actuation unit, a sensing unit and a signal processing unit. The actuation unit has a motor and a power amplifier geared with the motor. The sensing unit includes a motor rotation speed sensor, a multi-axis accelerometer and a multi-axis gyroscope, so as to sense the velocity, acceleration and the absolute angular velocity of the mobility vehicle in motion in real time. The signal processing unit is connected to the actuation unit and the sensing unit, so as to process the signals of the sensing unit. Then, the actuation unit performs inertia compensation, damping compensation and gravity compensation to the mobility vehicle through a dynamic signal-conditioning algorithm. When the mobility vehicle is actuated by human-power, the power-assisting system assists the power automatically to save human labor.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
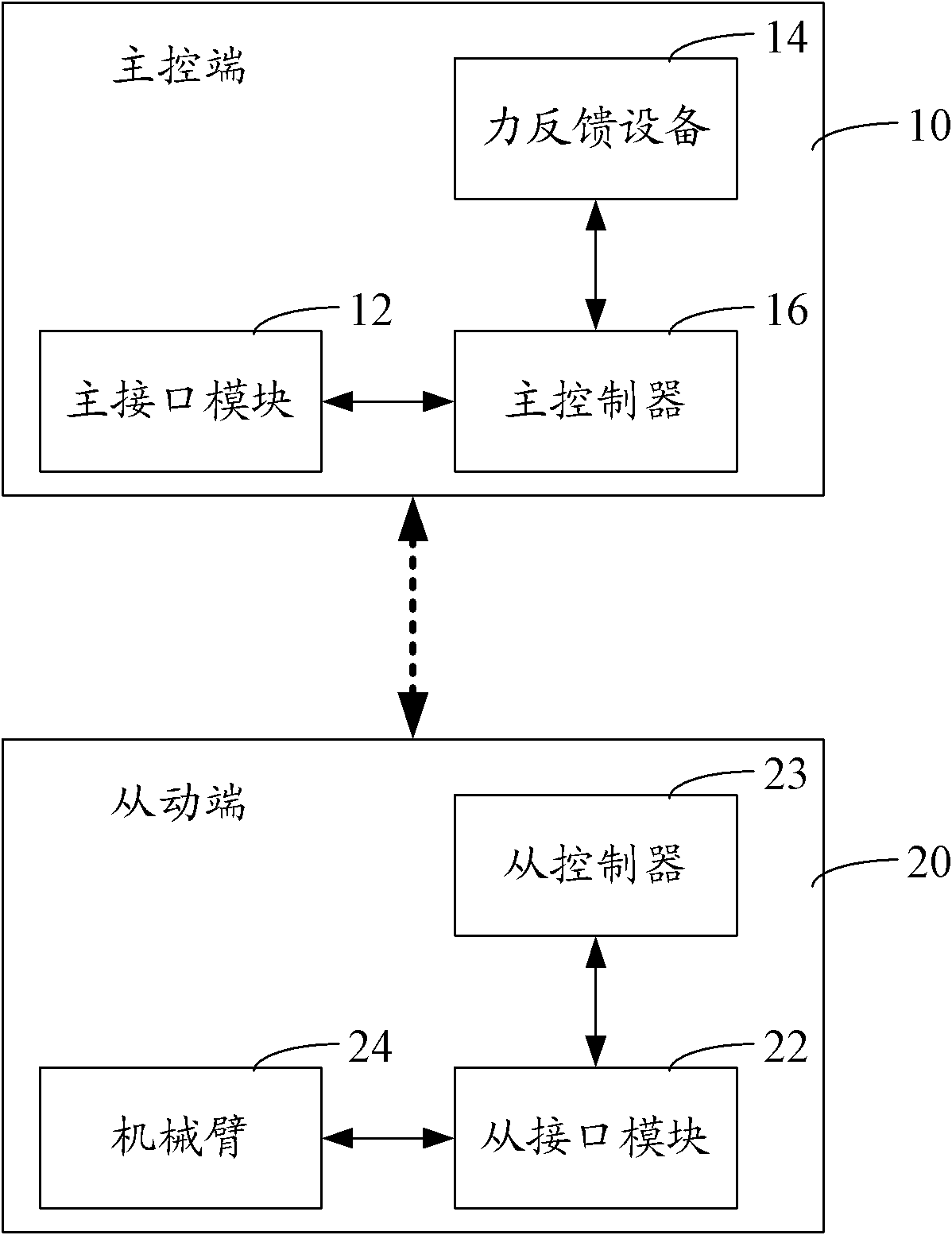
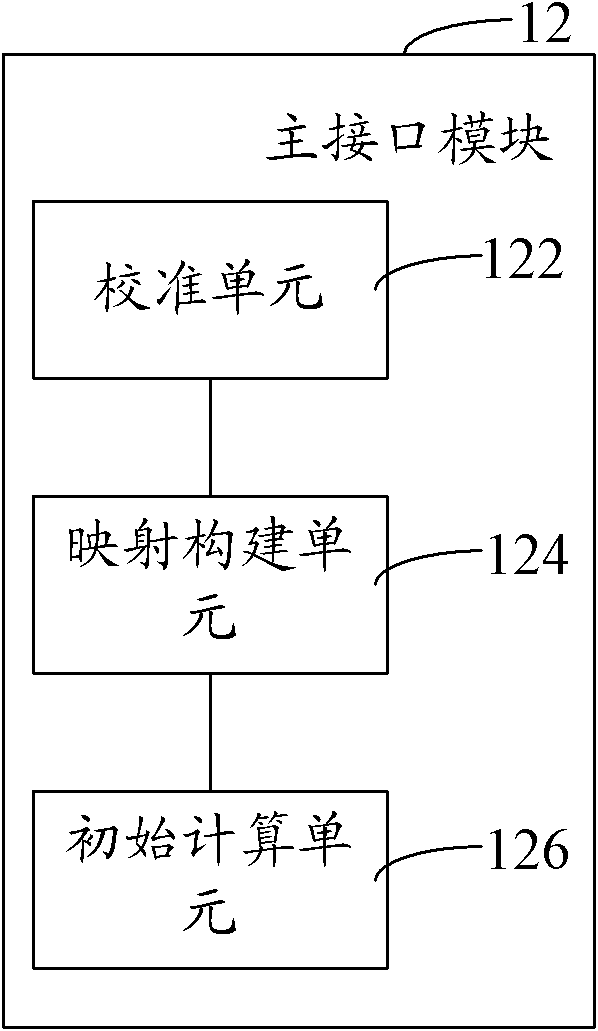
Remote operating system and method
ActiveCN102085663AFlexible and smooth movementEasy to operateManipulatorVirtual spaceComputer module
The invention relates to a remote operating system, comprising a master terminal and a slave terminal, wherein the master terminal creates a master terminal operating space to acquire an operation instruction; and the slave terminal creates a slave terminal operating space and collides with an operational object in the slave terminal operating space according to the operational instruction and then feeds back. The master terminal comprises a master interface module which is used for creating the master terminal operating space and mapping the slave terminal operating space and the master terminal operating space into a virtual space, a force feedback device which is used for acquiring the operational instruction and moving in the master terminal operating space according to the operational instruction to obtain a motion state, a master controller which is used for calculating according to the motion state and carrying out gravity compensation to obtain a control force; and the slave terminal comprises a slave interface module used for creating the slave terminal operating space according to the position of a mechanical arm, a slave controller used for controlling the mechanical arm according to the control force and the mechanical arm used for colliding the operation object in the slave terminal operating space. The remote operating system carries out the gravity compensation, thus the mechanical arm operates easily under the condition of heavy load, and the aim of easy operation is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for Variable G force experience and creating immersive VR sensations
InactiveUS20110067157A1Improve accuracyAdd funProgramme-controlled manipulatorCosmonautic condition simulationsEngineeringZero gravity
The present invention relates to variable low / zero gravity simulation systems. variable low / zero gravity condition is achieved by substantial immersion in a fluid environment (“buoyancy means”) and using power assist means / robotic displacement devices such as exoskeleton to help user's movement / gravity compensation and / or relief or change loads on the subject's torso and limbs that caused by the weight and shape of the “Buoyancy means”, so that user can experience the effect of the (variable) gravity environment being simulated, such as Zero gravity in which situation user could move effortlessly in a weightless environment. When combine with VR related technology, this can create vivid immersive simulations for extraterrestrial scenes and can be widely used for entertainment, game, training, healing and etc.
Owner:SOAREALM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com