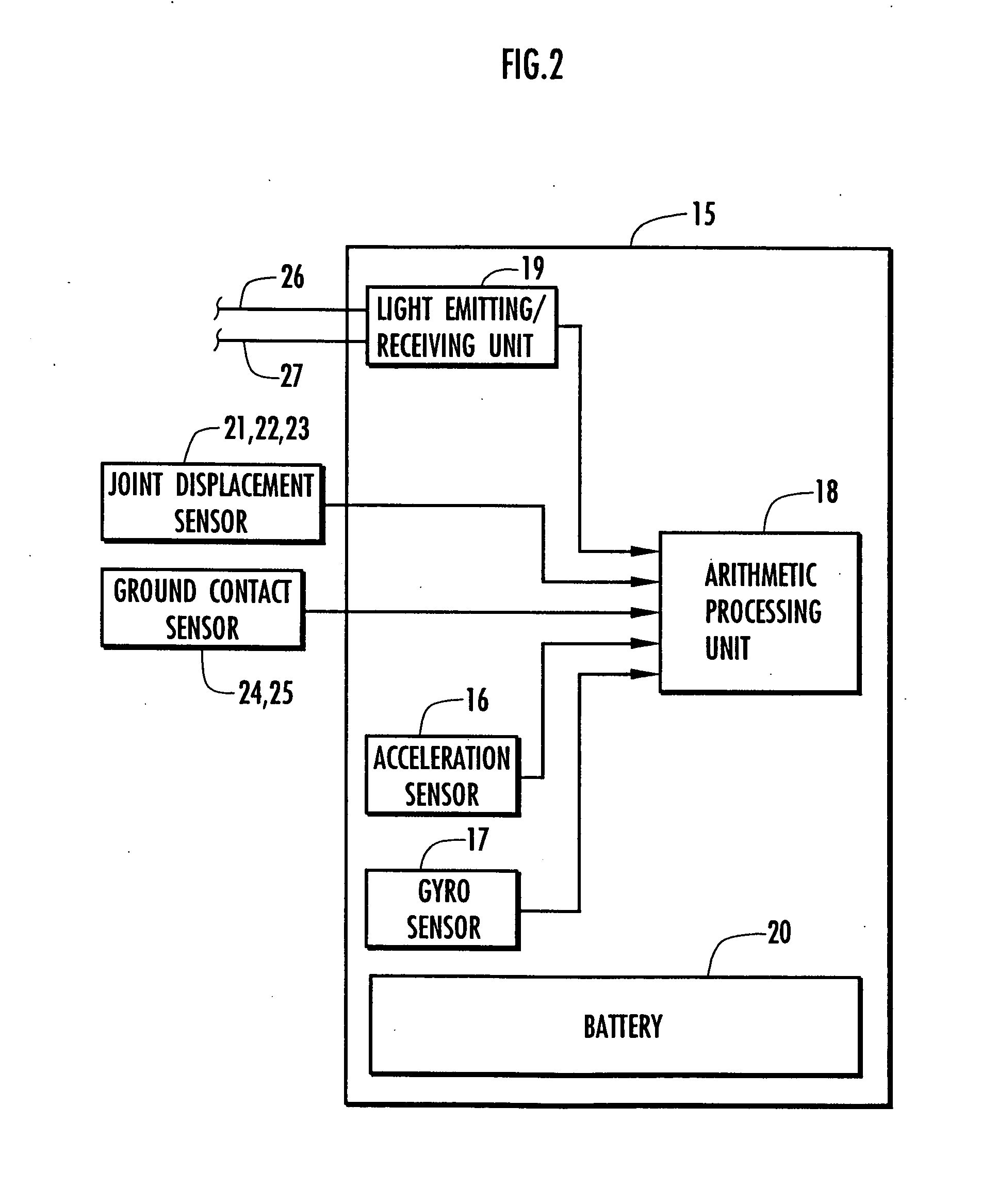
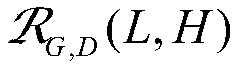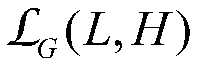Patents
Literature
141 results about "Inverse dynamics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
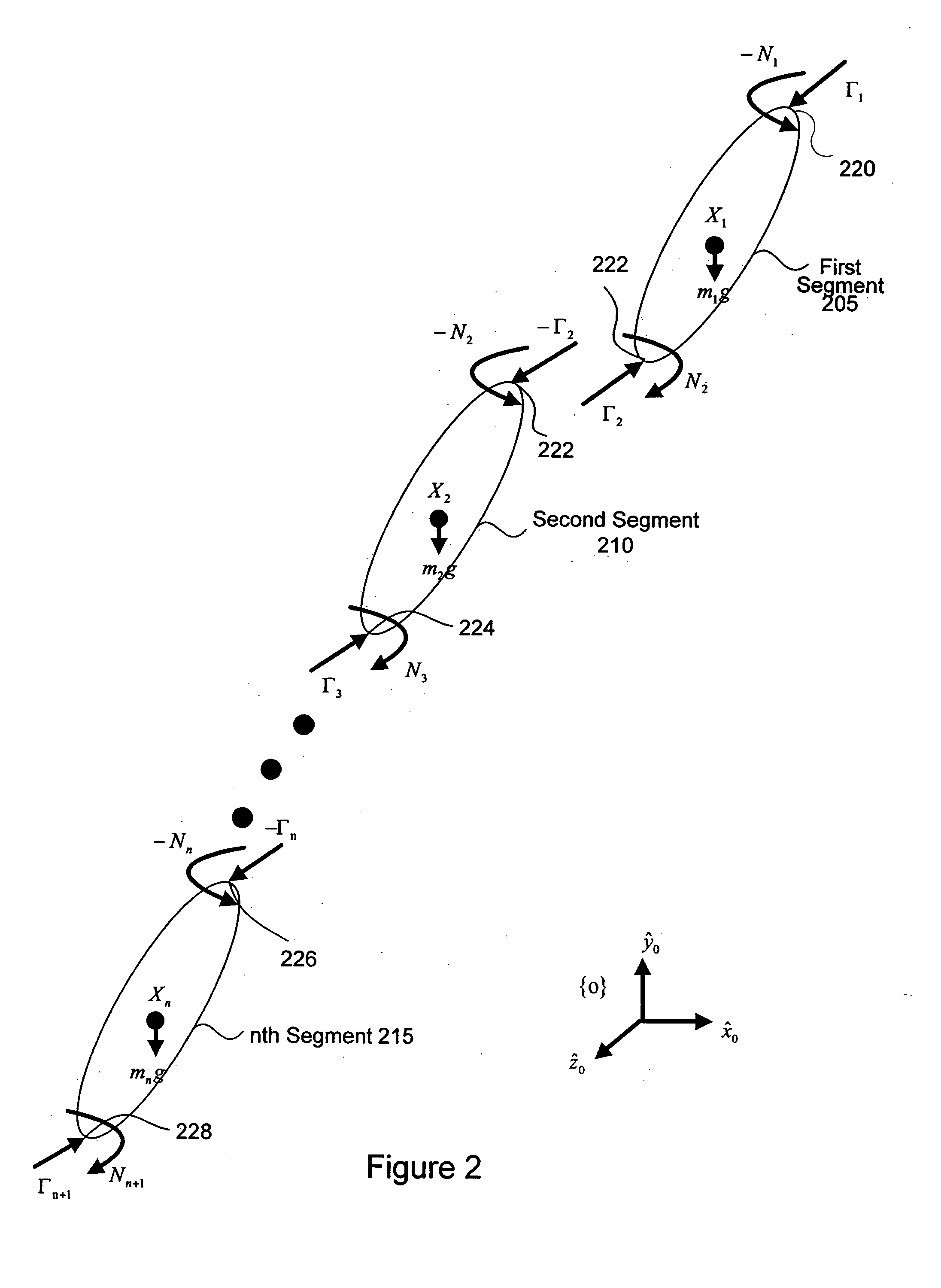
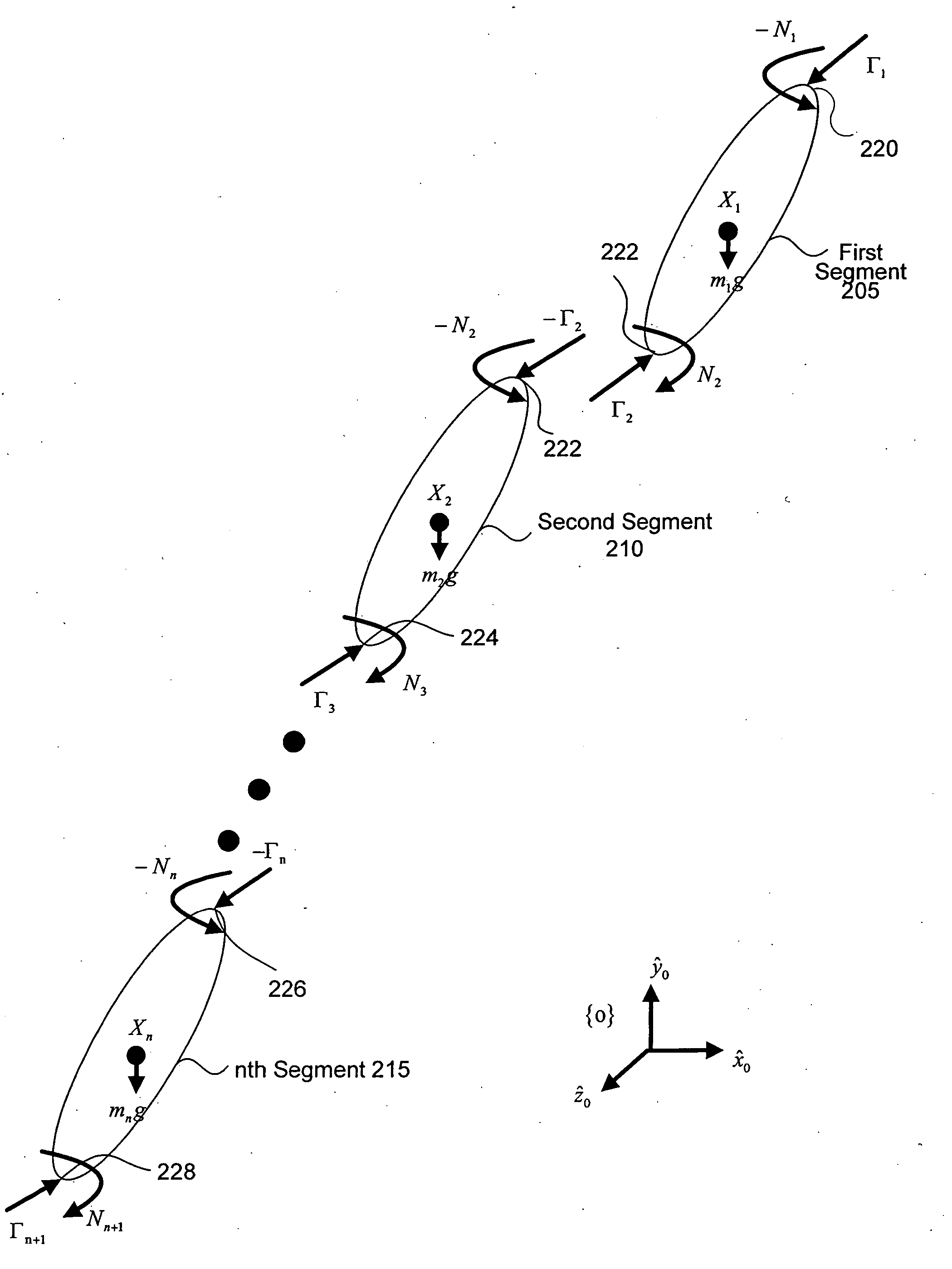
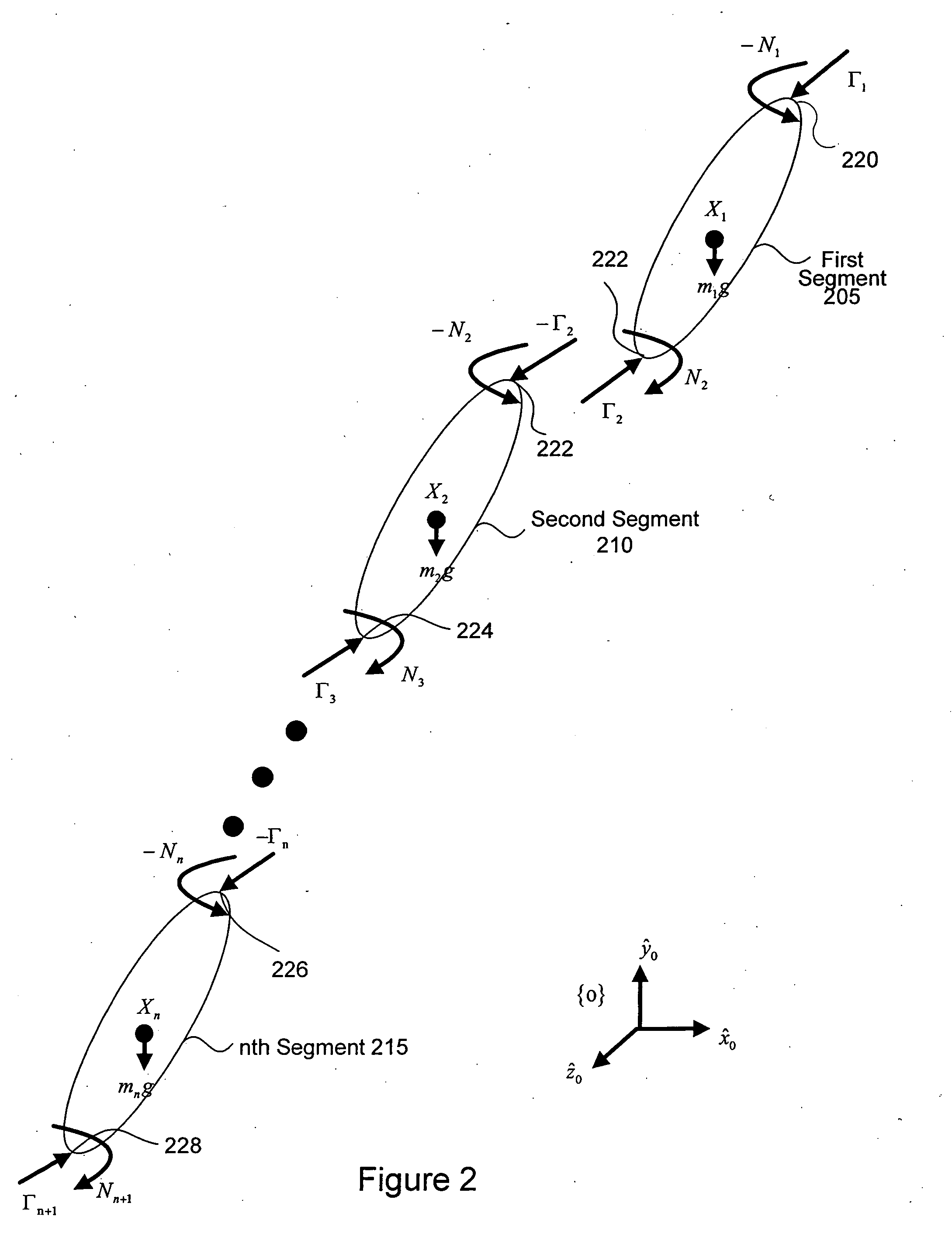
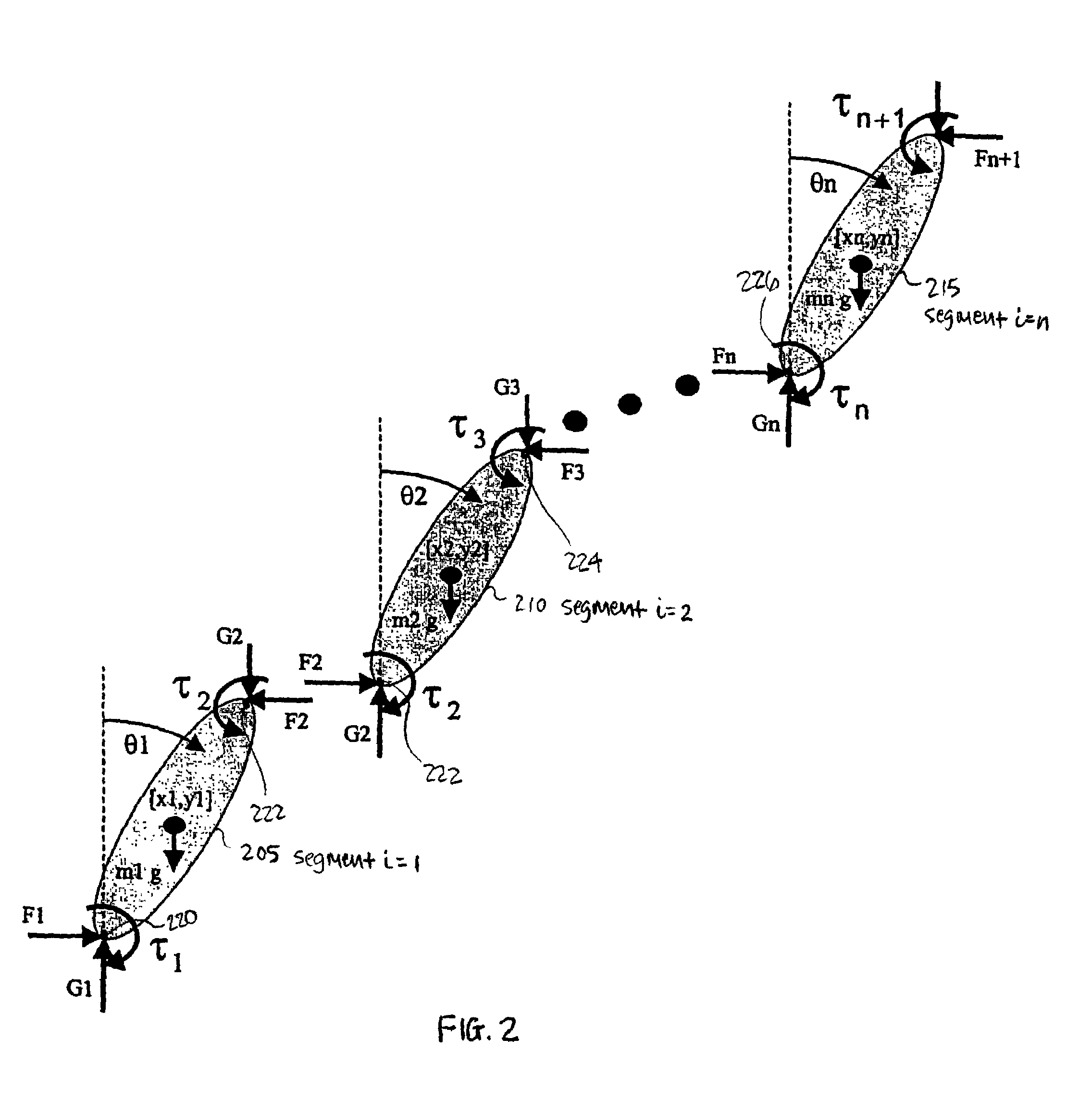
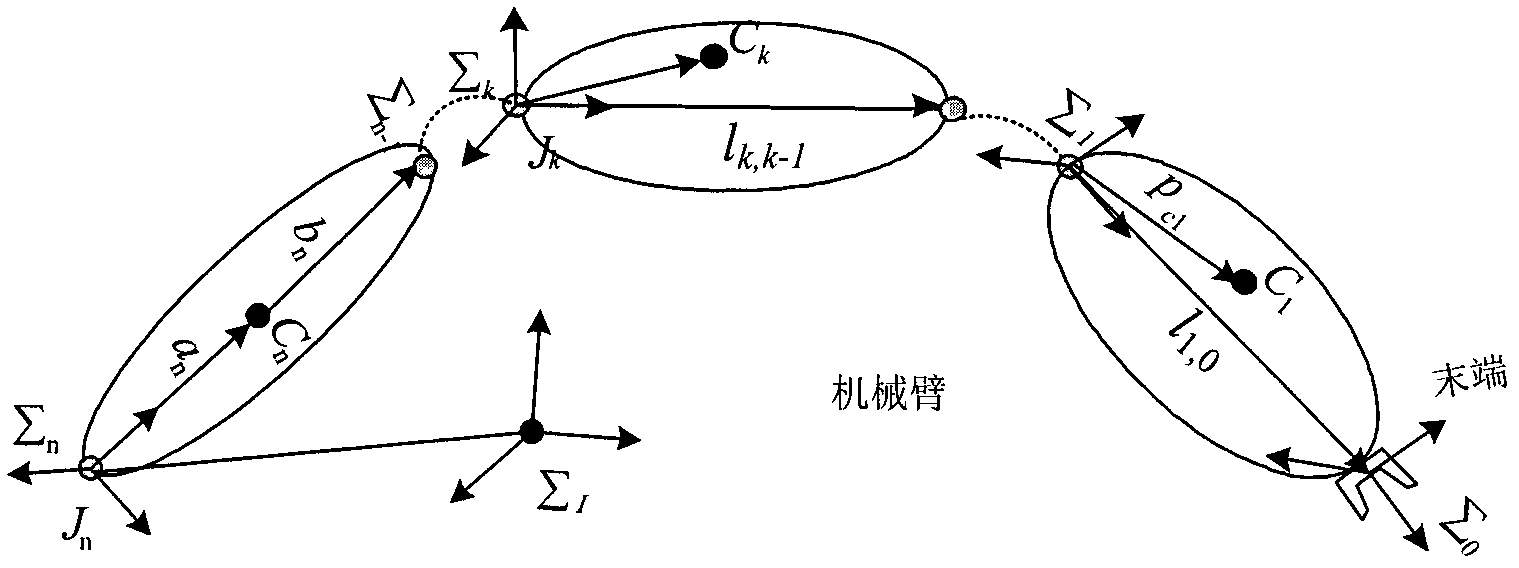
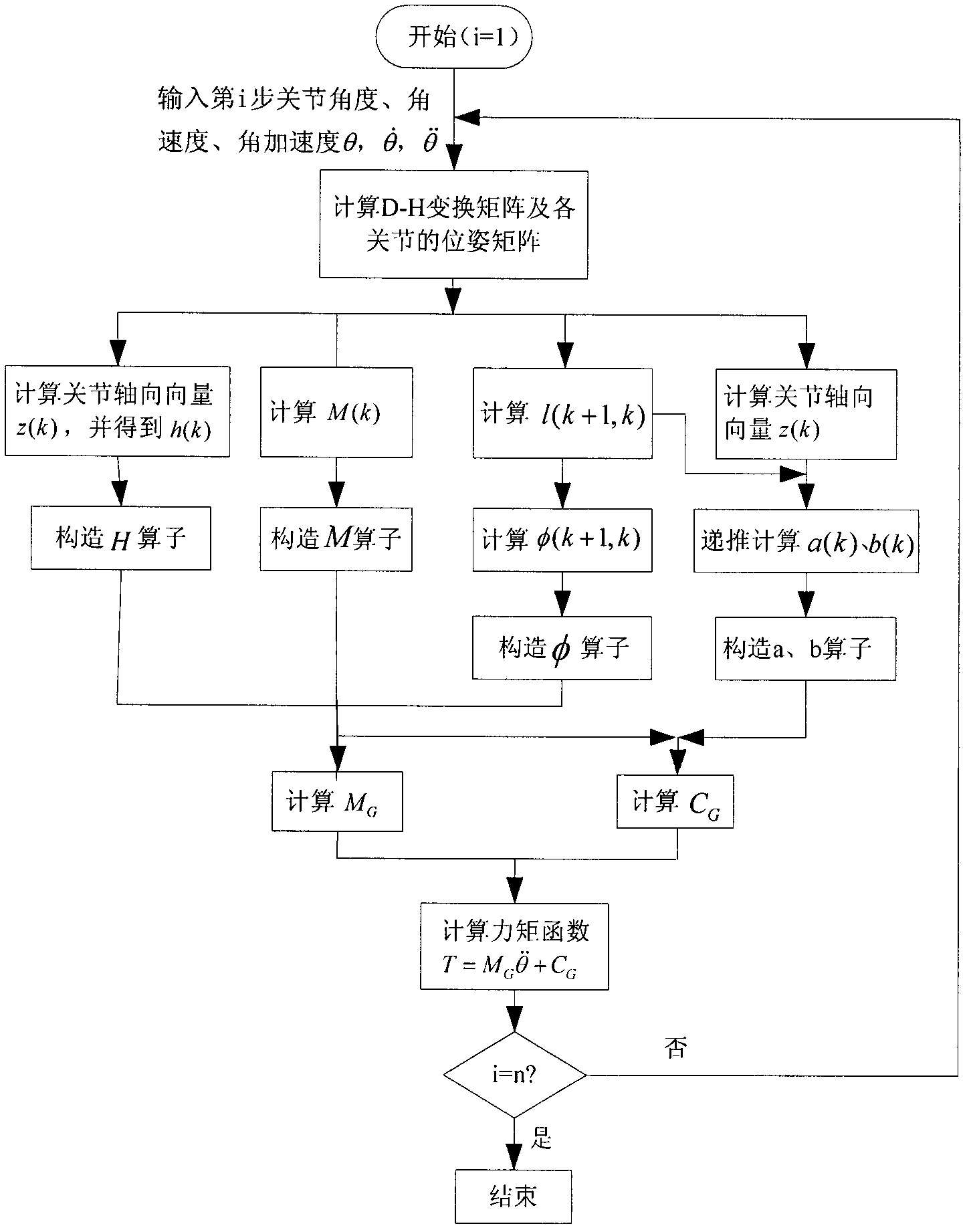
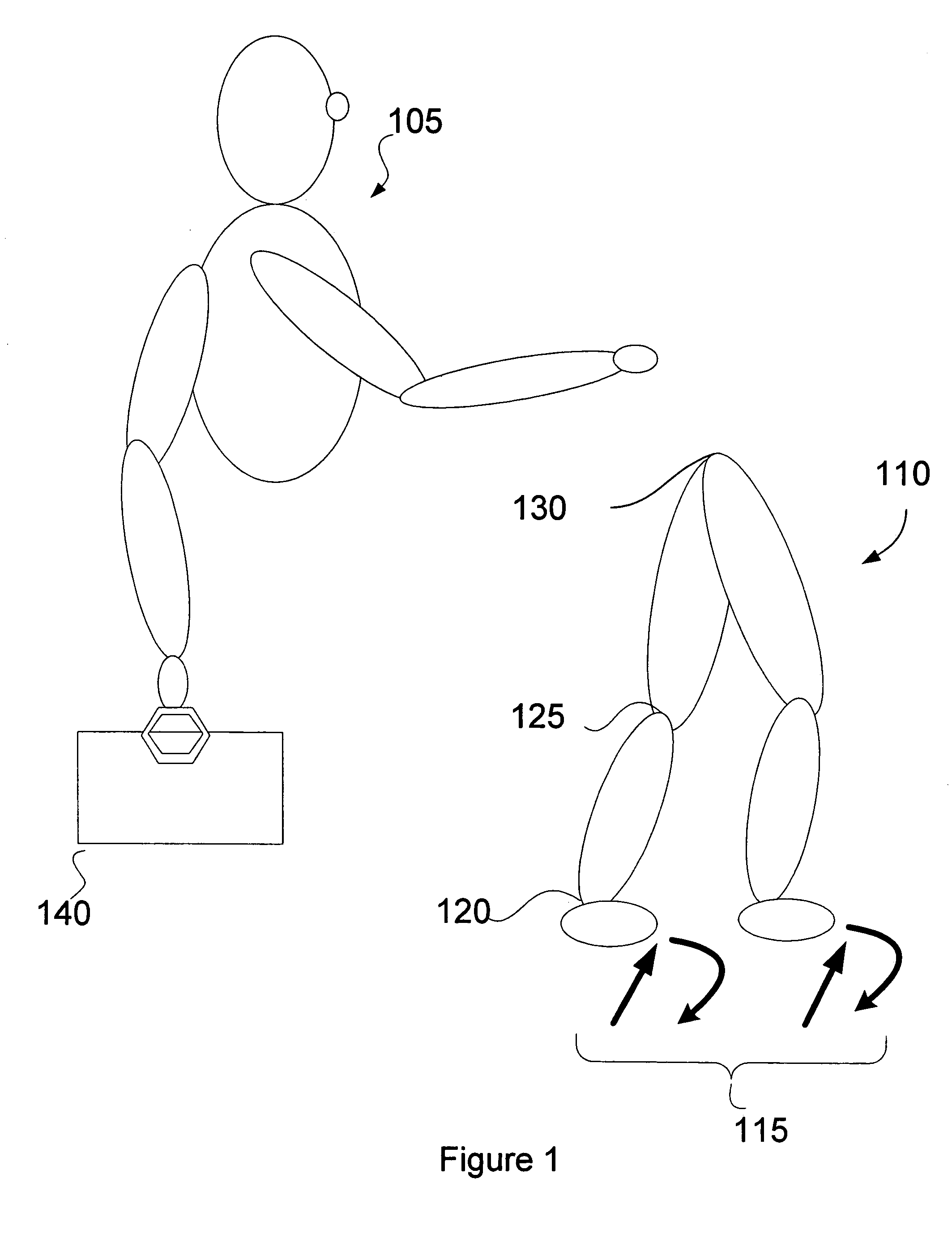
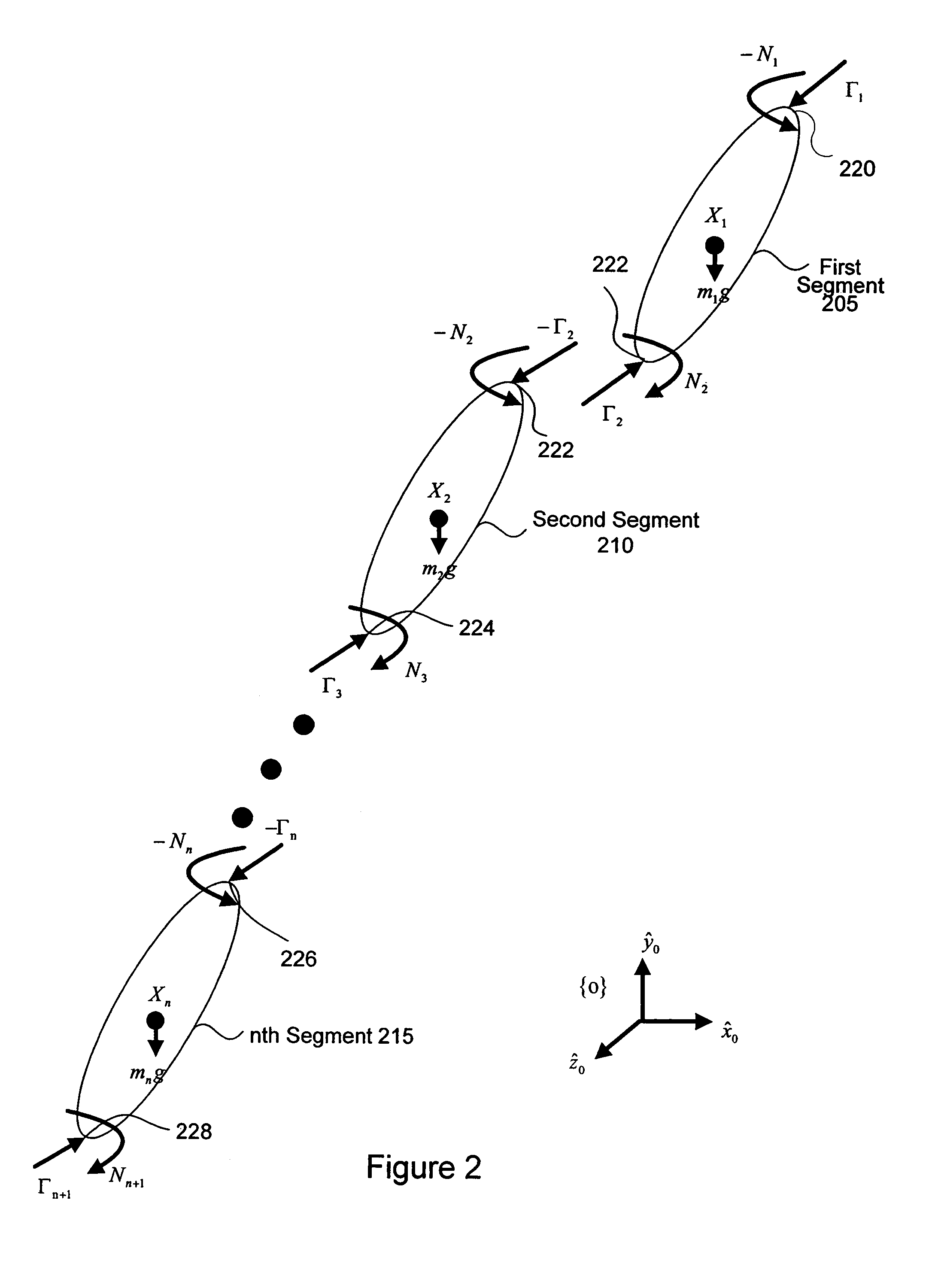
Inverse dynamics is an inverse problem. It commonly refers to either inverse rigid body dynamics or inverse structural dynamics. Inverse rigid-body dynamics is a method for computing forces and/or moments of force (torques) based on the kinematics (motion) of a body and the body's inertial properties (mass and moment of inertia). Typically it uses link-segment models to represent the mechanical behaviour of interconnected segments, such as the limbs of humans, animals or robots, where given the kinematics of the various parts, inverse dynamics derives the minimum forces and moments responsible for the individual movements. In practice, inverse dynamics computes these internal moments and forces from measurements of the motion of limbs and external forces such as ground reaction forces, under a special set of assumptions.
Motion control method of lower limb rehabilitative robot
InactiveCN102058464ARealize tracking controlEnhanced awareness of initiativeChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesEngineeringActive participation
The invention relates to a motion control method of a lower limb rehabilitative robot. In the method, aiming at different rehabilitation stages of a patient, two working modes of passive training and active training are carried out: under the mode of passive training, the patient is driven by controlling the robot to finish specific motions or motion according to a right physiological gait track; abnormal motions of the patient are completely restrained; and the patient passively follows the robot to do walking rehabilitation training; under the mode of active training, limited abnormal motions of the patient are restrained by the robot; through a real-time detection on joint driving forces generated when the patient acts on the robot in the motion process, human-computer interaction moment is extracted by utilizing an inverse dynamic model to judge the active motion intention of lower limbs of the patient; and the interaction moment is converted into correction value of gait track by utilizing an impedance controller to directly correct or generate the gait training track the patient expects through an adaptive controller, therefore, the purpose that the robot can provide auxiliary force and resistant force for the rehabilitation training can be indirectly realized. By means of the motion control method of the lower limb rehabilitative robot, rehabilitation training motions suitable for different rehabilitation stages can be provided for a dysbasia patient, thereby enhancing active participation degree of the rehabilitation training of the patient, building confidence of the rehabilitation and positivity of the motion, and then enhancing effect of the rehabilitation training.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Muscular Strength Acquiring Method and Device Based on Musculoskeletal Model
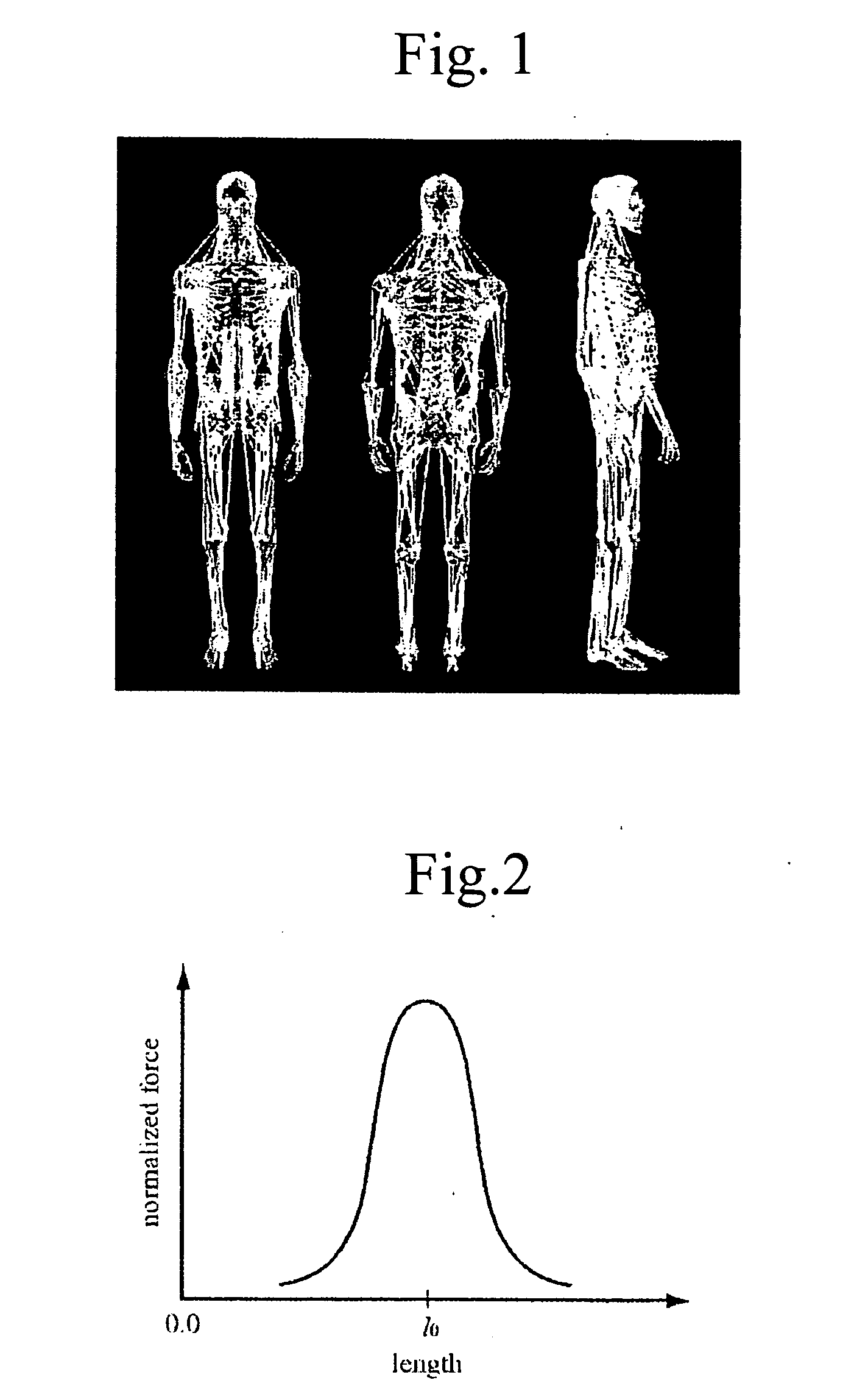
The present invention provides a method capable of acquiring a physically and physiologically valid muscular strength from motion data based on a musculoskeletal model. The present invention relates to a method for obtaining muscular tension by performing inverse dynamics calculation of a musculoskeletal model. The method comprises a step for optimizing a contact force τC received from an environment using acquired floor reaction force data and a step for optimizing the muscle tension ƒ using acquired motion data, acquired myogenic potential data, and optimized contact force. The motion data, reaction force data and myogenic potential data can be measured at the same time by a behavior capture system.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Method for generating a motion of a human type link system
InactiveUS7136722B2Easy to understandSimple interfaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlInverse dynamicsClassical mechanics
A human-type link system, such as a humanoid robot having a dynamically feasible motion of the link system that is generated when a reference joint acceleration that is only calculated from a kinematical constraint condition is determined not feasible by an evaluation of external force computed based on an inverse dynamics calculation, or is generated by calculating from a dynamic constraint condition and a kinematical constraint condition simultaneously, the dynamic constraint condition is formulated by using an actuation space inverse inertial matrix that represents the relation of force acting on the link system and the acceleration of the link system caused by the force.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Control device for mobile robot
ActiveUS20110160906A1Ensure stable implementationImprove stabilityComputer controlSimulator controlMobile robot controlMomentum
A control device for a mobile robot, in which the desired value of a motion state amount of a mobile robot includes at least the desired value of a vertical component of a first-order differential value of the translational momentum of the entire mobile robot. The desired value is determined by a state amount desired value determiner such that the observed value of the vertical position of an overall center-of-gravity point of the mobile robot is converged to a predetermined desired value according to a feedback control law. A control input determiner carries out the processing of inverse dynamics calculation, using the desired value of the motion state amount thereby to determine the desired driving force for each joint. The operation of an actuator is controlled on the basis of the determined desired driving force.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method of estimating joint loads in a three-dimensional system
ActiveUS20050209535A1Eliminate errorsProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsInverse dynamicsForward dynamic
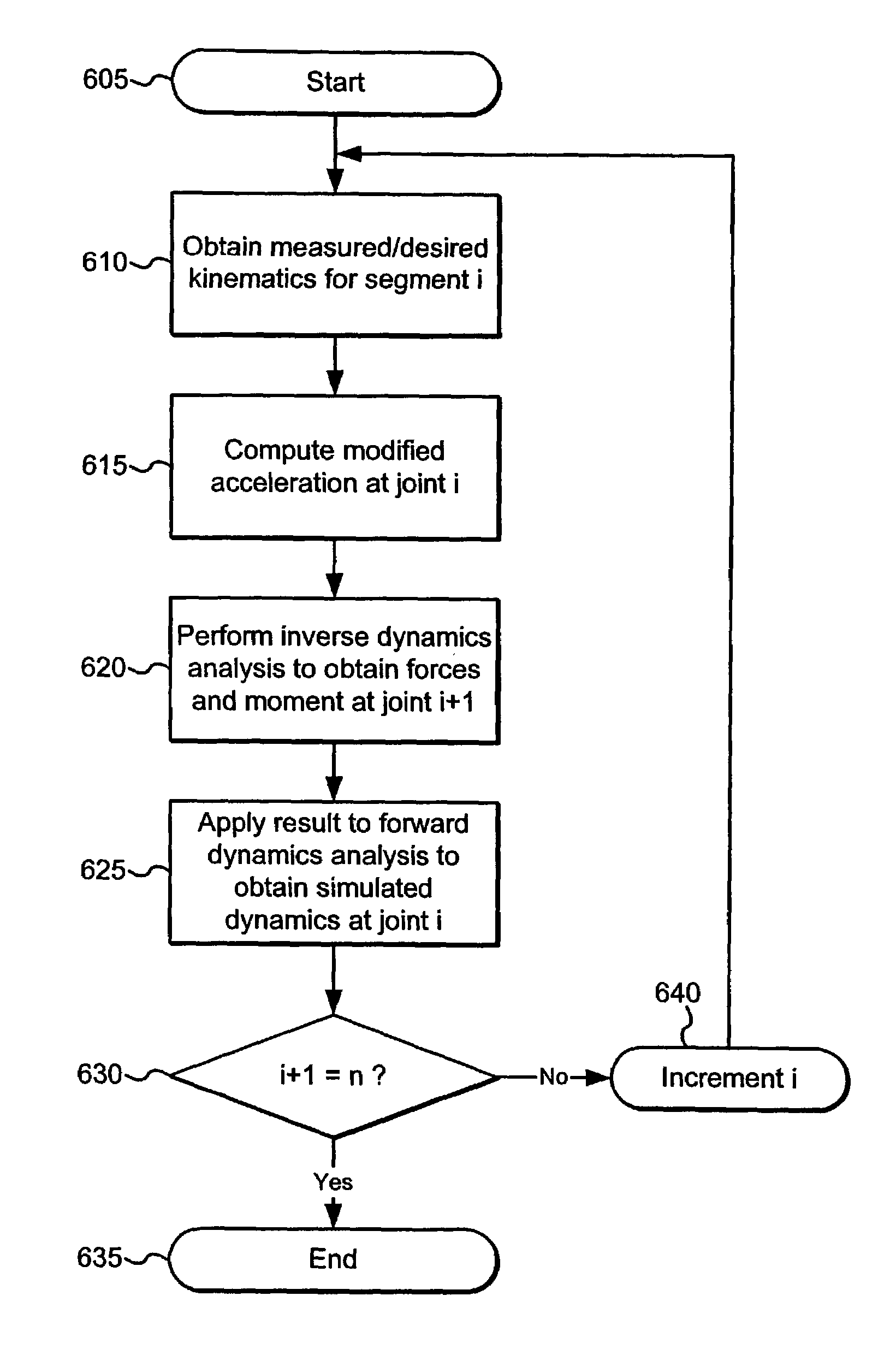
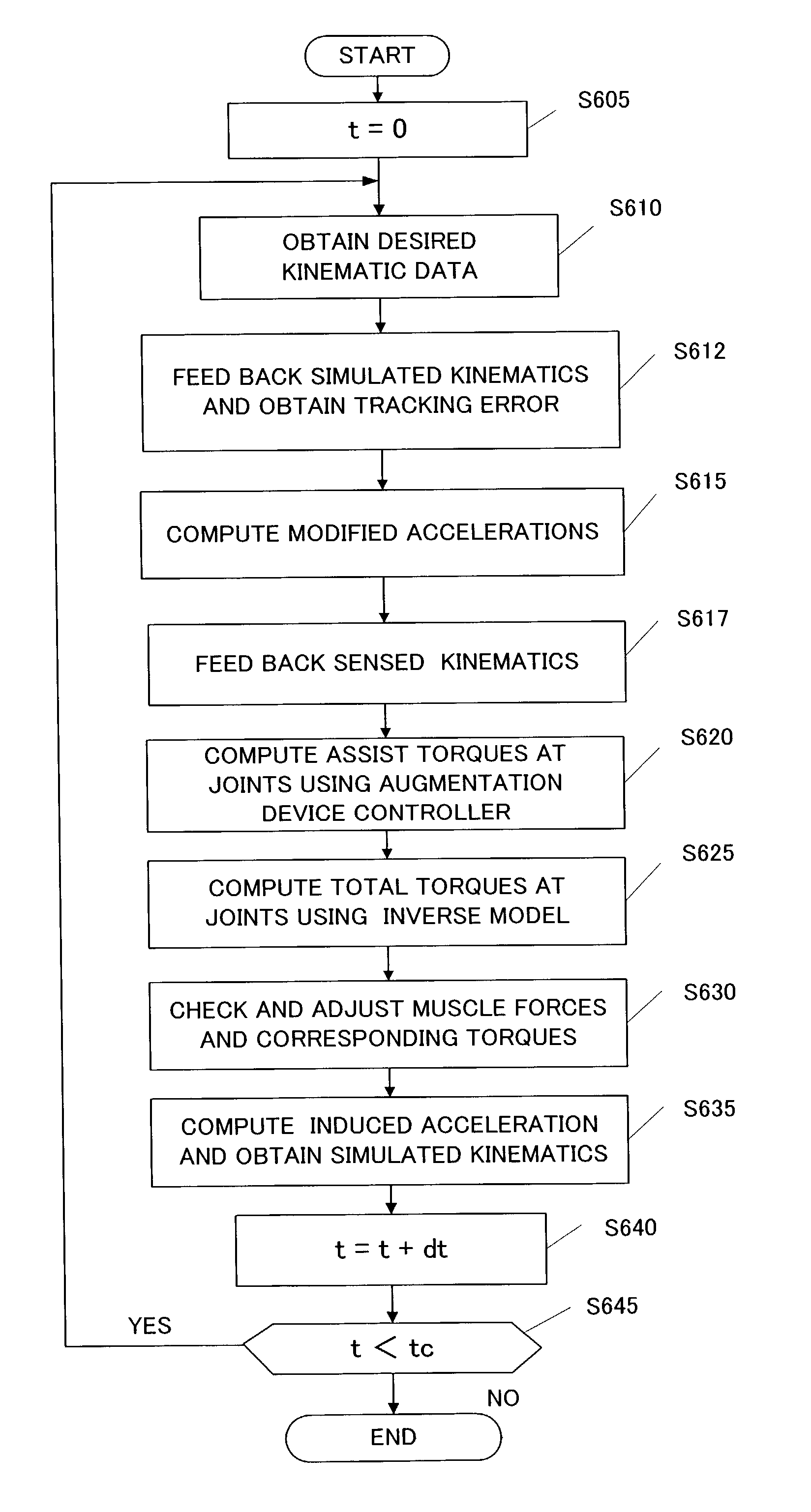
A method for estimating joint load at a joint of a segment. The method comprises the steps of receiving kinematic data, determining a modified acceleration using at least the kinematic data, estimating a joint load using at least the modified acceleration; and determining simulated kinematic data for the segment using at least the joint load. The present invention thus addresses the problems with conventional inverse dynamics analysis by providing a forward dynamics solution for estimation of joint loads that is stable, guaranteed to converge, computationally efficient, and does not require acceleration computations. According to one embodiment of the present invention, a joint load is estimated recursively.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
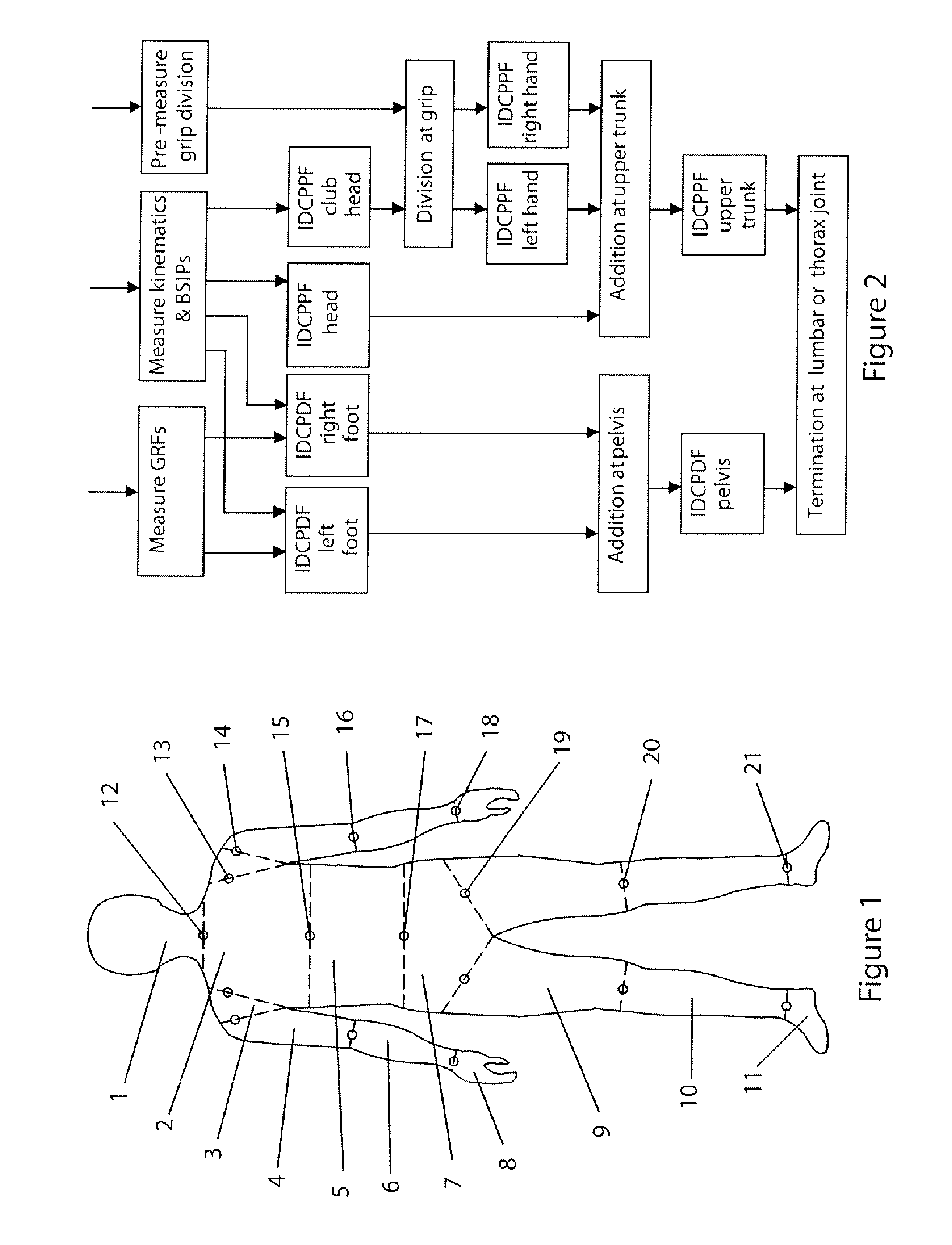
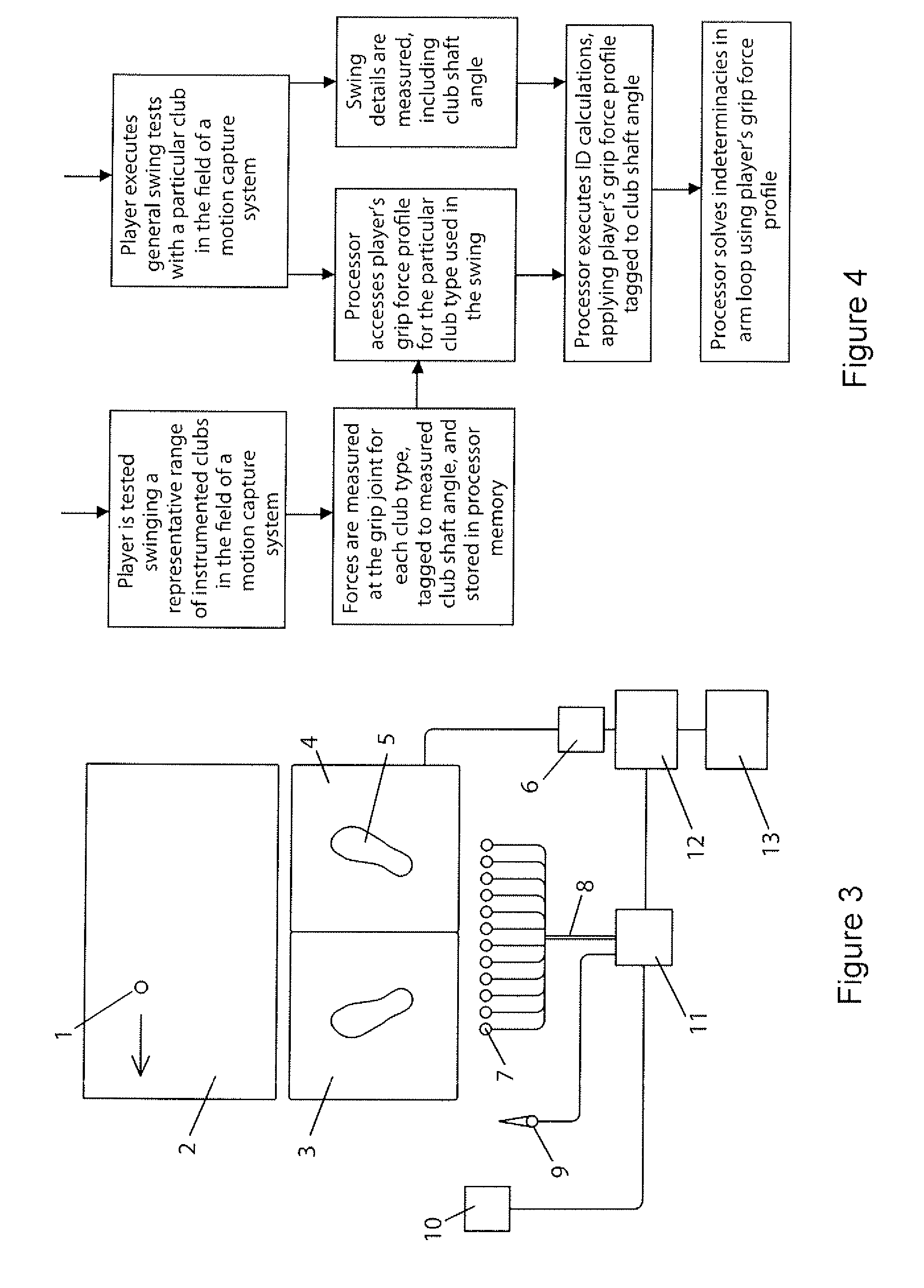
Apparatus and method for analysing a golf swing
ActiveUS20140342844A1Gymnastic exercisingCharacter and pattern recognitionInverse dynamicsHighly skilled
The system analyses a golf swing, determining individual joint powers generated in a player's body with high levels of accuracy, using inverse dynamics and detailed modelling of the player's body. A depth camera is used to measure body segment shapes and a magnetic motion capture system and 3D force plate system used to measure swing parameters. The system produces an expeditious analysis without the need for highly skilled technical personnel and is suitable for individual coaching and compilation of large golf swing databases.
Owner:MOONEY BRIAN FRANCIS
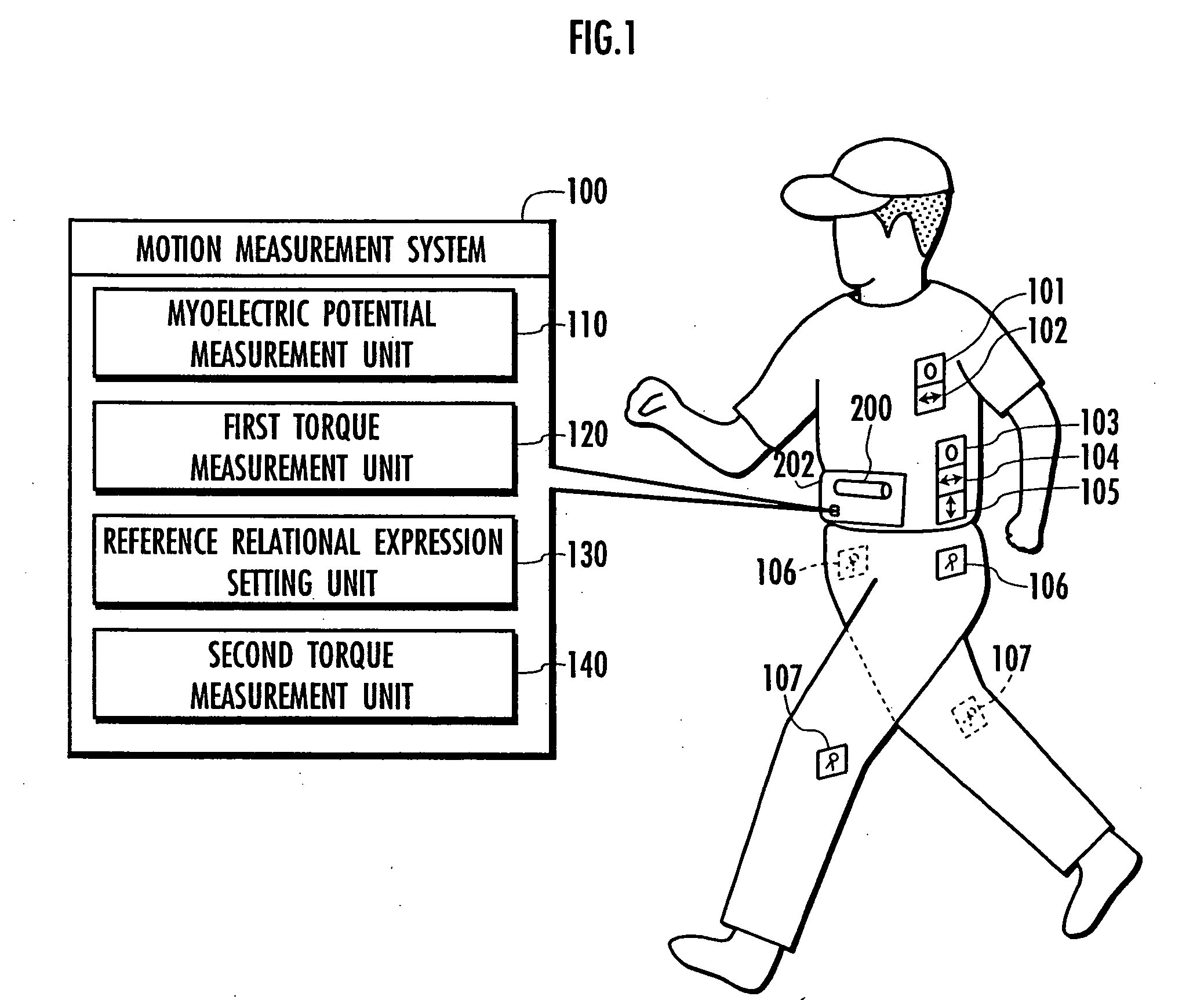
Motion measurement method, motion measurement system, and motion measurement program
InactiveUS20060004299A1Accurate measurementAvoid disagreementElectromyographyPerson identificationInverse dynamicsKnee Joint
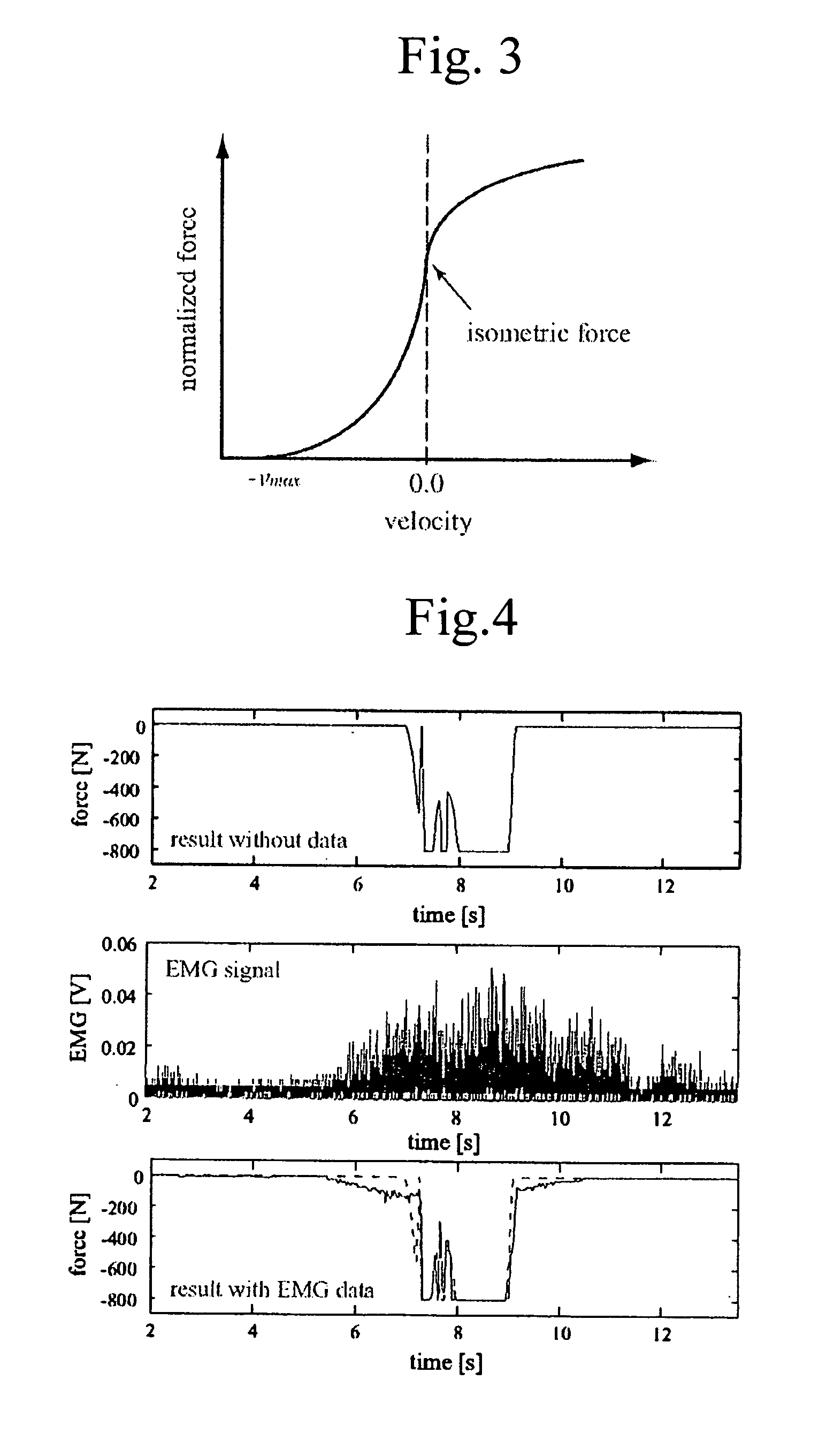
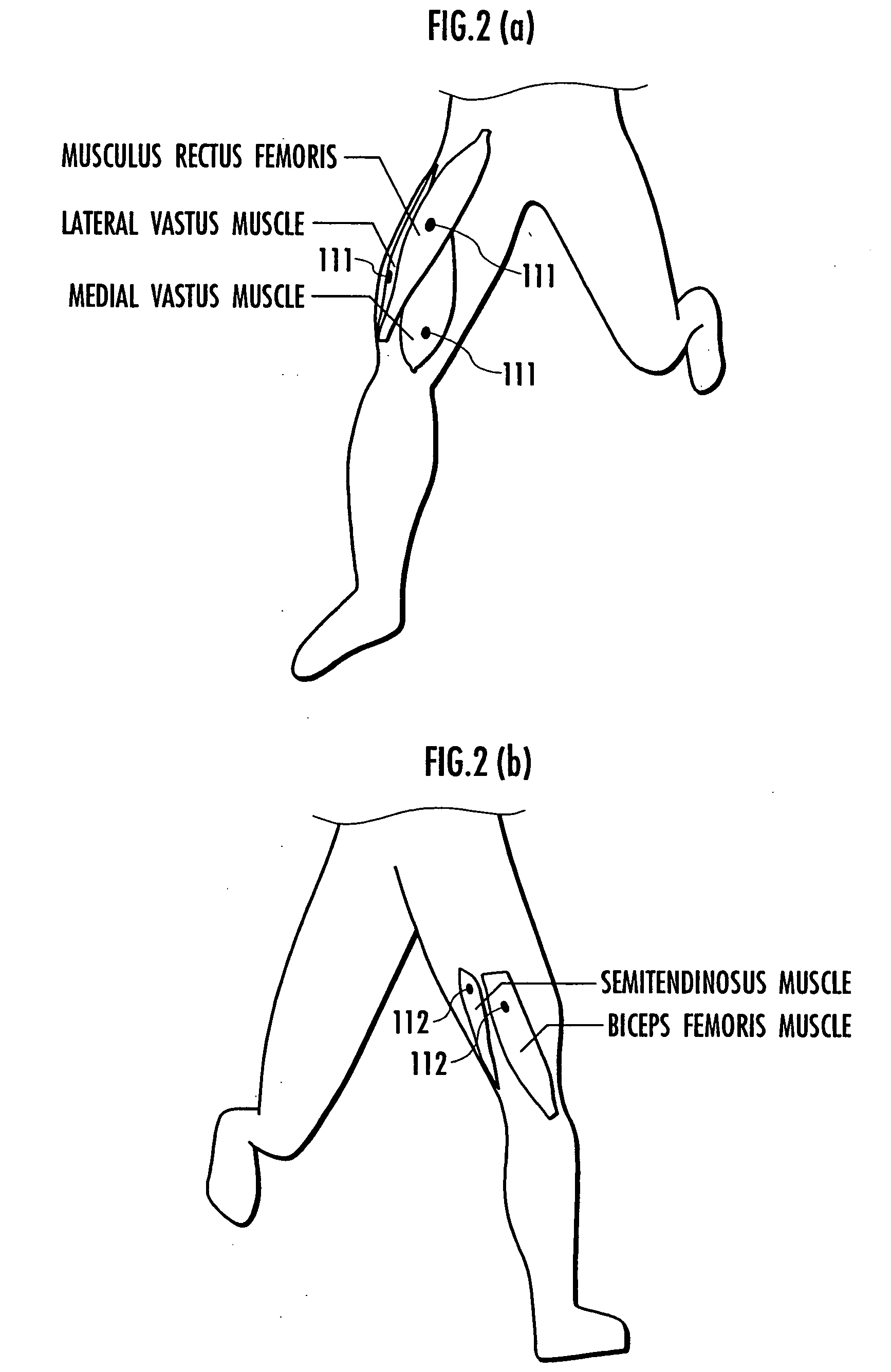
A method, system, and program enabling a variable varying with animal's motions such as a joint torque to be accurately measured in a series of the animal's motions. First, a reference relational expression representing a relation between myoelectric potentials and a knee joint torque is set on the basis of the myoelectric potentials and the knee joint torque (variable) measured by using an inverse dynamics model. Then, the knee joint torque is measured on the basis of the measured myoelectric potentials and according to the reference relational expression. For example, if an animal makes first and second motions continuously, first a reference relational expression is set on the basis of myoelectric potentials measured in the first motion and a knee joint torque corresponding to the first motion. Then, a knee joint torque corresponding to the second motion is measured on the basis of the myoelectric potentials measured in the second motion and according to the reference relational expression. The first and second motions are arbitrary and the animal is not forced to make a given motion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
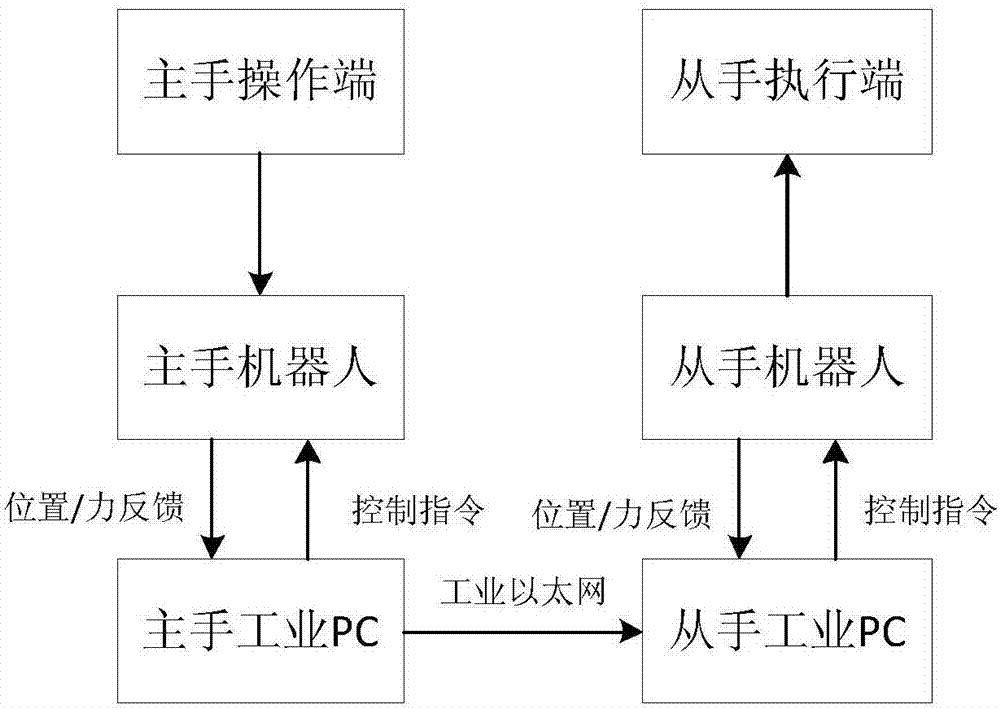
Novel master-salve mode surgical robot control method
The invention discloses a novel master-slave mode surgical robot control method. The method comprises the first step of conducting calculating to obtain an iteration equation of force and torque between each connection rod and joint; the second step of calculating a gravity compensation coefficient of each connection rod, and mapping the effect of force and torque of gravity to each joint to each joint; the third step of conducting calculating to obtain expecting torque to each joint through inverse dynamics, and leading in an inner ring / outer ring control framework according to current actual force feedback information which is fed back in real time to conduct control; the fourth step of calculating the iteration equation of force and torque between each connection rod and joint; the fifth step of obtaining in real time force feedback information from a hand execution end, and leading in the inner ring / outer ring control framework to conduct control. According to the novel master-slave mode surgical robot control method, kinematics and dynamics modeling of a master hand and a slave hand and theoretical derivation of a mapping relation between the master hand and the slave hand are achieved, a gravity compensation and inner ring / outer ring control strategy is adopted, a modularized procedural framework is adopted to complete the achievement of a control algorithm, and a master-slave mode teleoperation surgical robot system is efficiently achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
System and method of estimating joint loads using an approach of closed form dynamics
ActiveUS20050209536A1Eliminate errorsProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsDynamic methodInverse dynamics
A method for estimating joint load at a joint of a segment. The method comprises the steps of receiving kinematic data, determining a modified acceleration using at least the kinematic data, estimating a joint load using at least the modified acceleration; and determining simulated kinematic data for the segment using at least the joint load. The present invention thus addresses the problems with conventional inverse dynamics analysis by providing a forward dynamics solution for estimation of joint loads that is stable, guaranteed to converge, computationally efficient, and does not require acceleration computations. According to one embodiment, a joint load is estimated using an approach of closed form dynamics.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Industrial robot dragging teaching method without adopting torque sensor
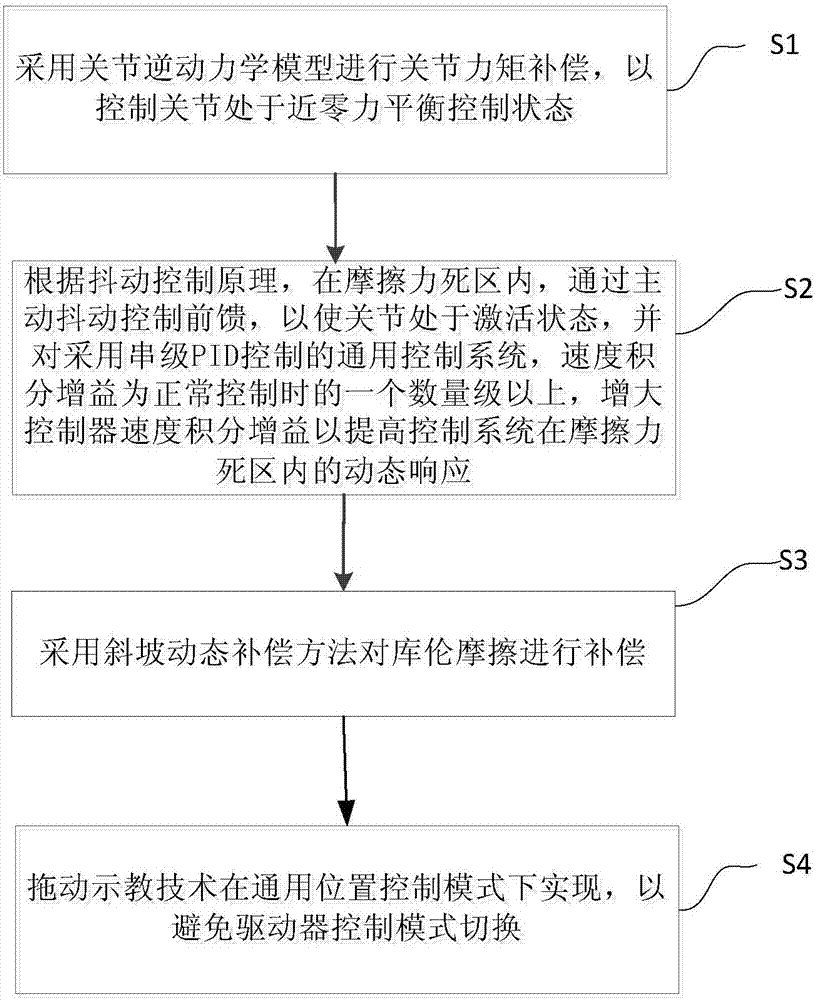
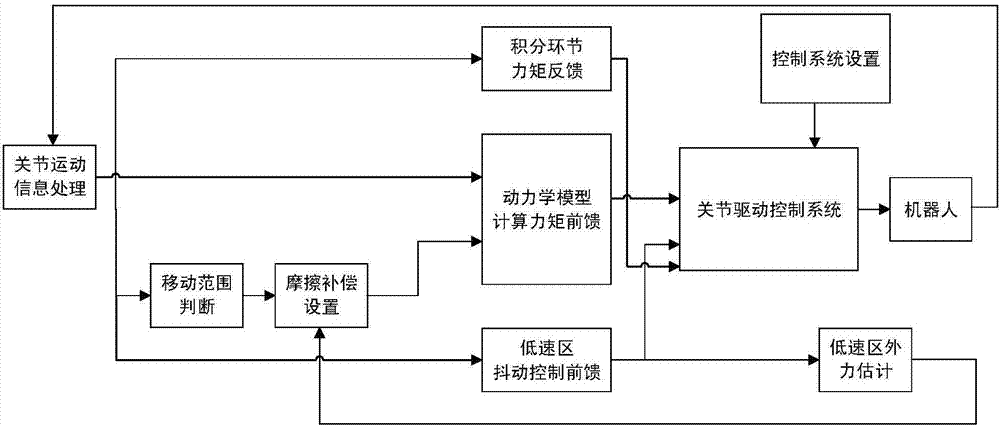
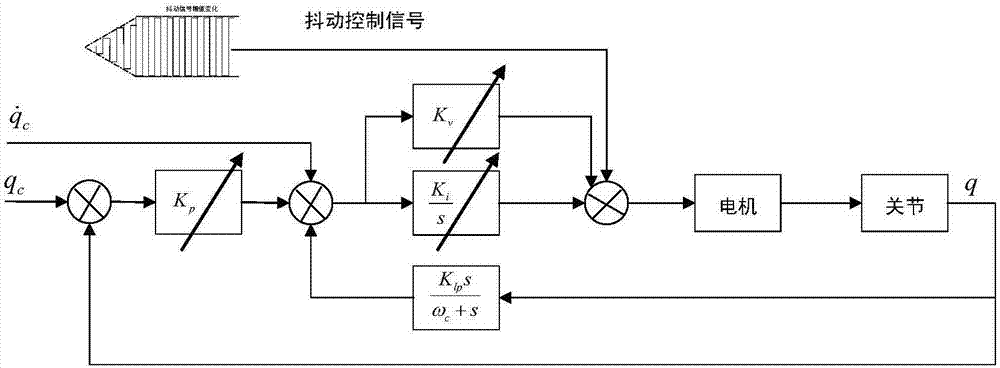
The invention provides an industrial robot dragging teaching method without adopting a torque sensor. The method comprises the steps that a joint inverse dynamic model is adopted for joint moment compensation, so that a joint is controlled to be in a near-zero force balanced control state; according to a jitter control principle, feedforward is controlled through drive jitter within a dead zone of friction force, so that the joint is in an activated state, velocity integral grain of a universal control system adopting serial PID control is one order of magnitudes that of a system adopting normal control, and the controller velocity integral gain is increased to improve the dynamic response of the control system in the dead zone of the friction force; a slope dynamic compensation method is adopted for compensating coulomb friction; and a dragging teaching technology is achieved in a universal position control mode, so that switching of a control mode of a driver is avoided. According to the dragging teaching method adopted in the invention, the torque sensor is not needed, and the cost is low.
Owner:ROKAE SHANDONG INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
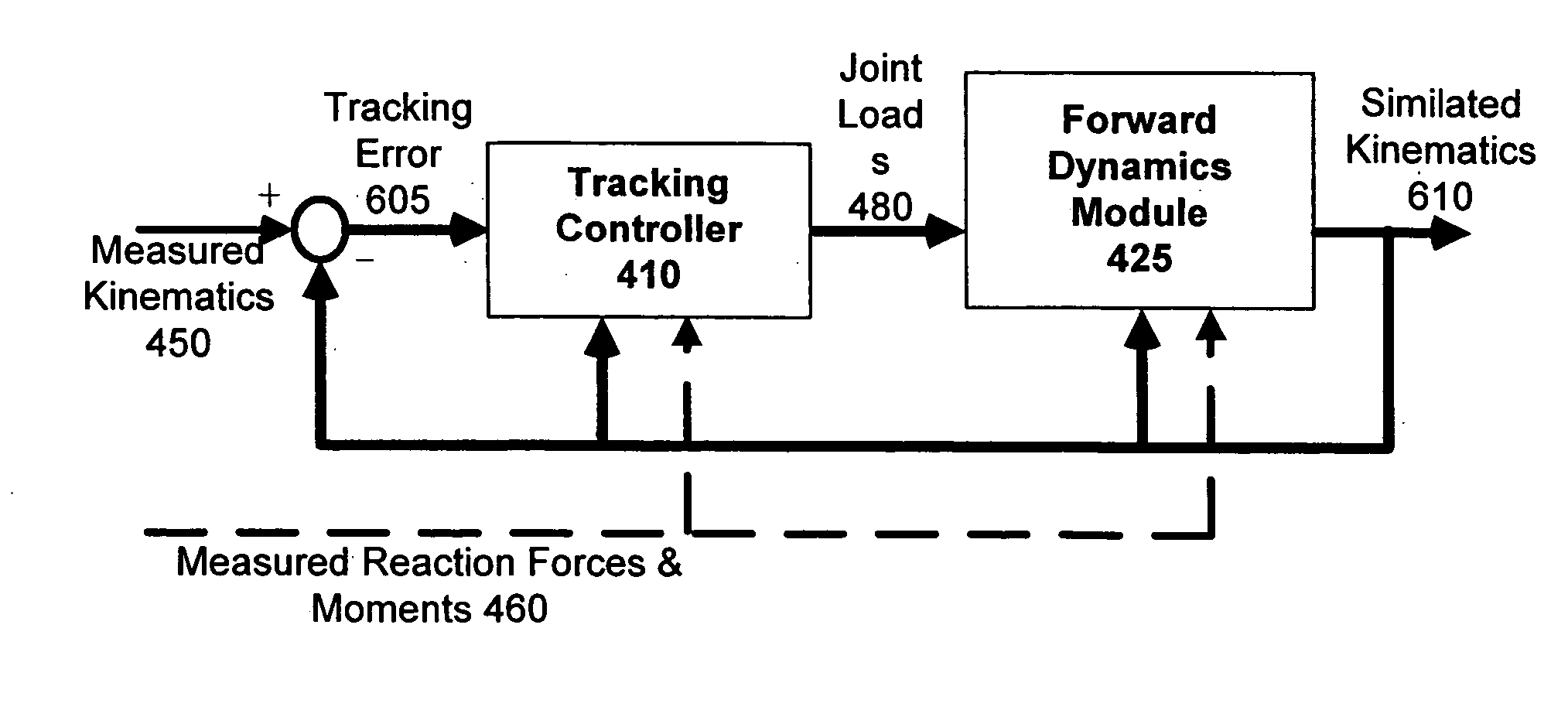
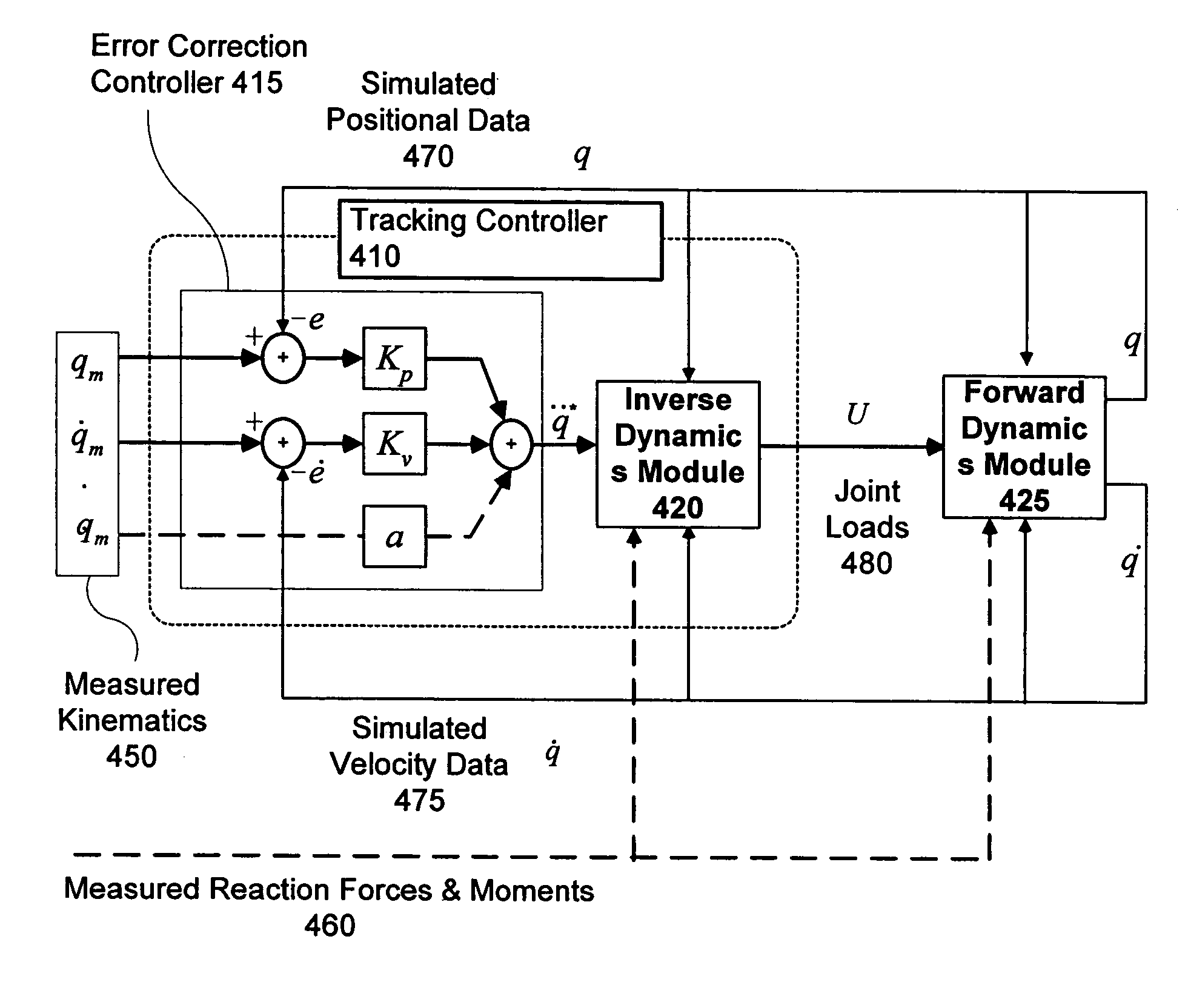
Feedback estimation of joint forces and joint moments
ActiveUS7135003B2Reduce sourceHigh precisionPerson identificationAnalogue computers for chemical processesInverse dynamicsControl theory
Apparatus and methods are provided for estimating joint forces and moments in human beings. A forward dynamics module determines simulated kinematic data. An error correction controller forces tracking error between the simulated kinematic data and measured (or desired) kinematic data to approach zero. The error correction controller generates a modified acceleration for input into an inverse dynamics module. The estimated joint forces and moments track the measured (or desired) kinematics without the errors associated with computing higher order derivatives of noisy kinematic data.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Model inverse dynamic algorithm for extreme power of power battery pack
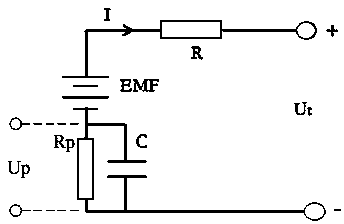
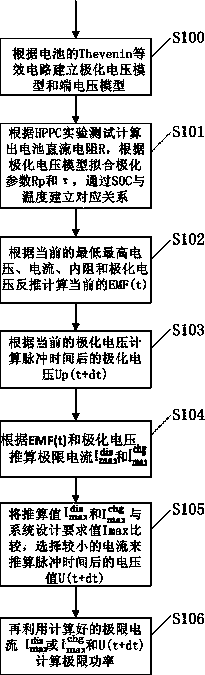
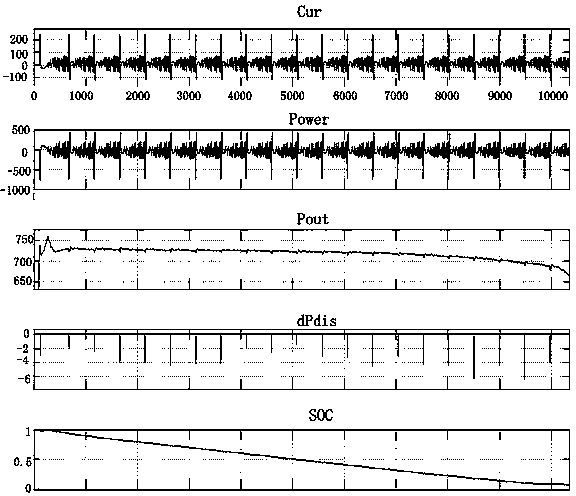
ActiveCN104298793ASolve the problem that the valuation is affected by the accuracy of the SOCReduce estimation errorSpecial data processing applicationsSystems designTerminal voltage
The invention discloses a model inverse dynamic algorithm for the extreme power of a power battery pack, and aims to avoid the influence of the state of charge (SOC) accuracy of a battery on an extreme power estimated value due to calculation of the electrodynamic potential of the battery through a mathematical model. The model inverse dynamic algorithm comprises the following steps: establishing a polarization voltage model of a single battery and a terminal voltage model of the single battery by adopting a Thevenin equivalent circuit; computing the direct-current resistance R, polarization parameter Rp and tau of the battery according to an HPPC (Hybrid Pulse Power Characterization) experiment, and establishing a corresponding relation through the SOC and a temperature; computing current EMF(t) by using a current sampled voltage value U(t) and current I(t); computing a polarization voltage Up(t+dt) after pulse time according to Up(t); calculating extreme current according to EMF(t) and Up(t+dt); comparing the extreme current with a system design required value Imax, and selecting lower current for calculating a voltage value U(t+dt) after the pulse time; and computing extreme power and charging extreme power.
Owner:WANXIANG 123 CO LTD
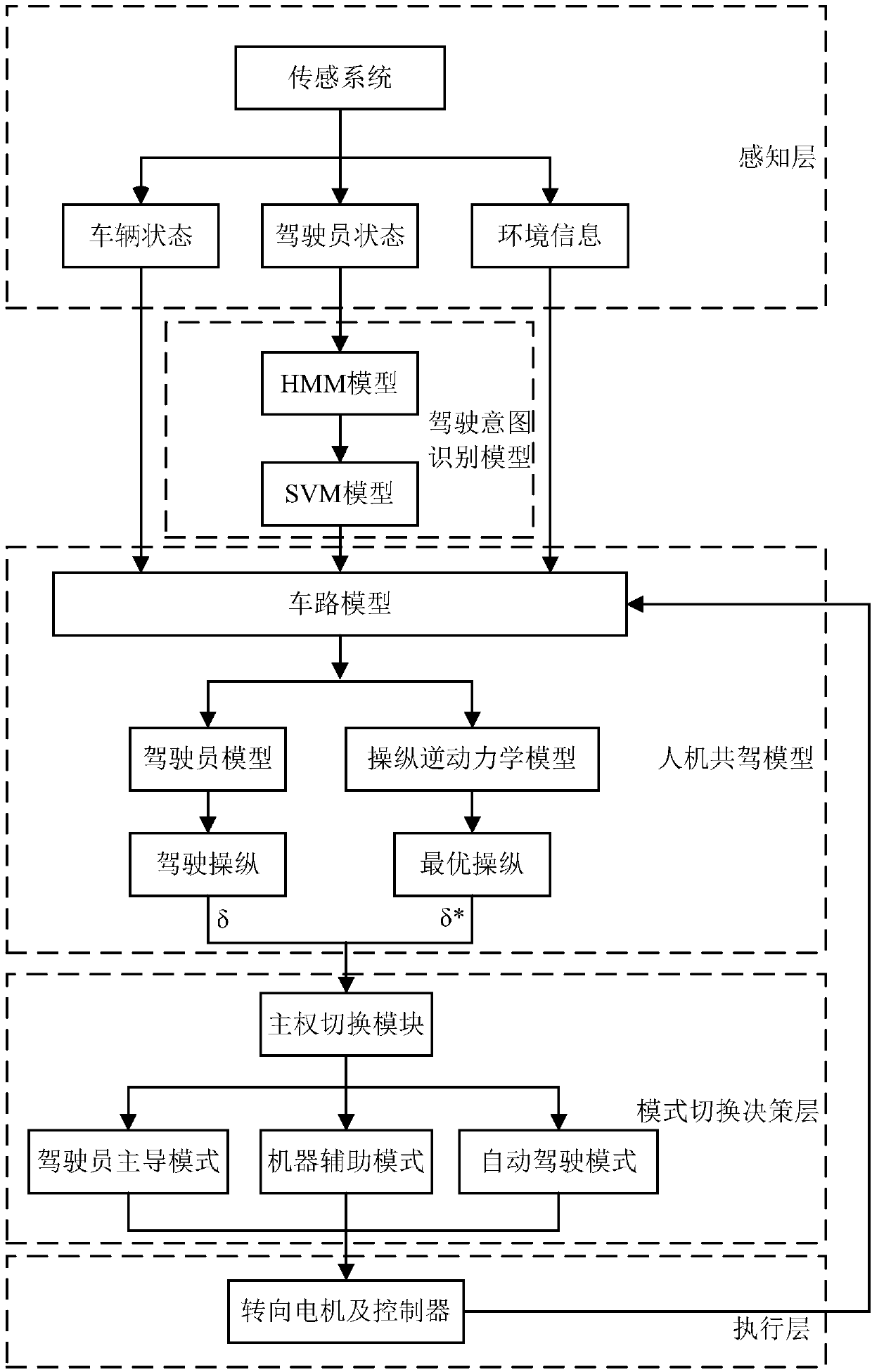
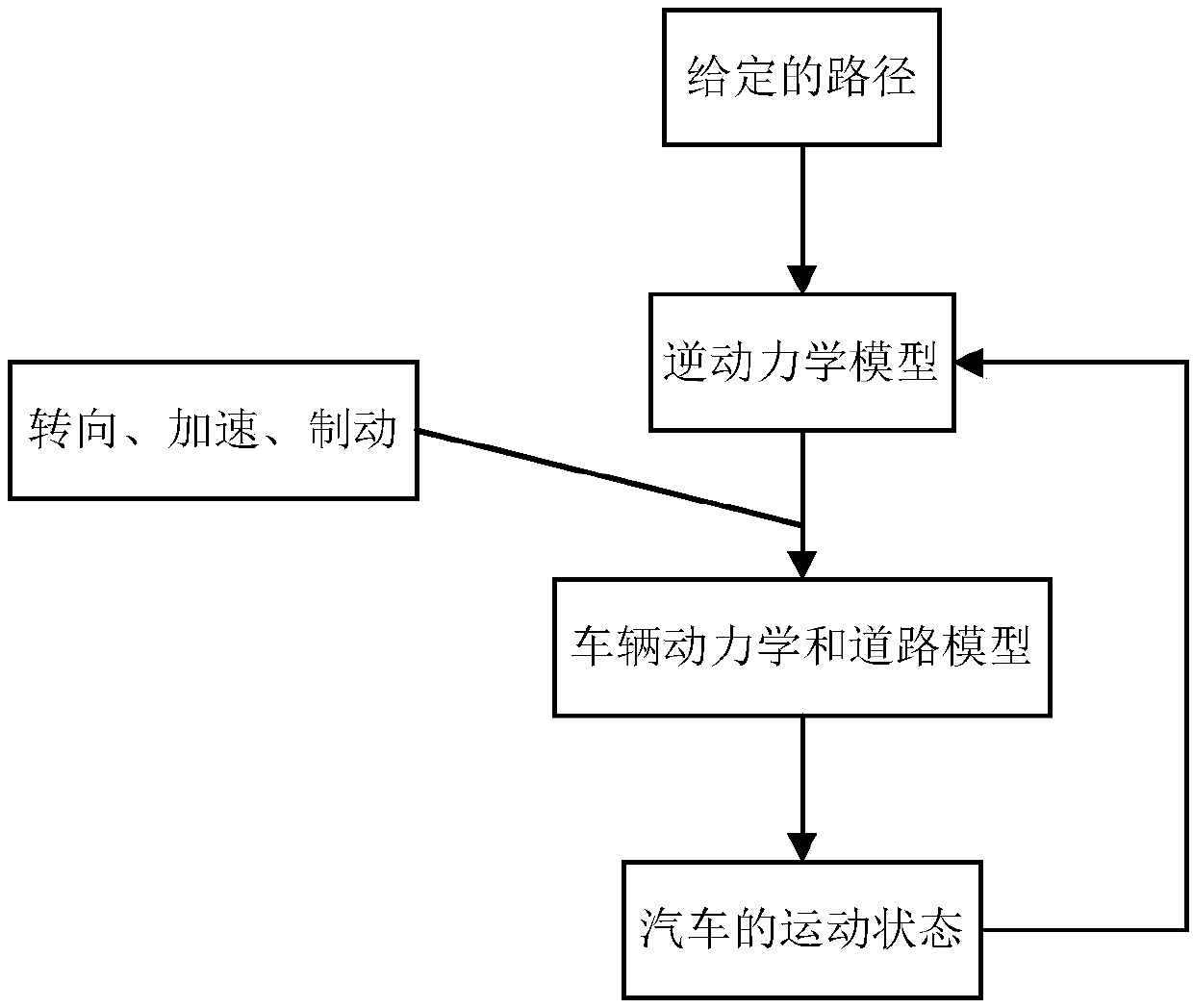
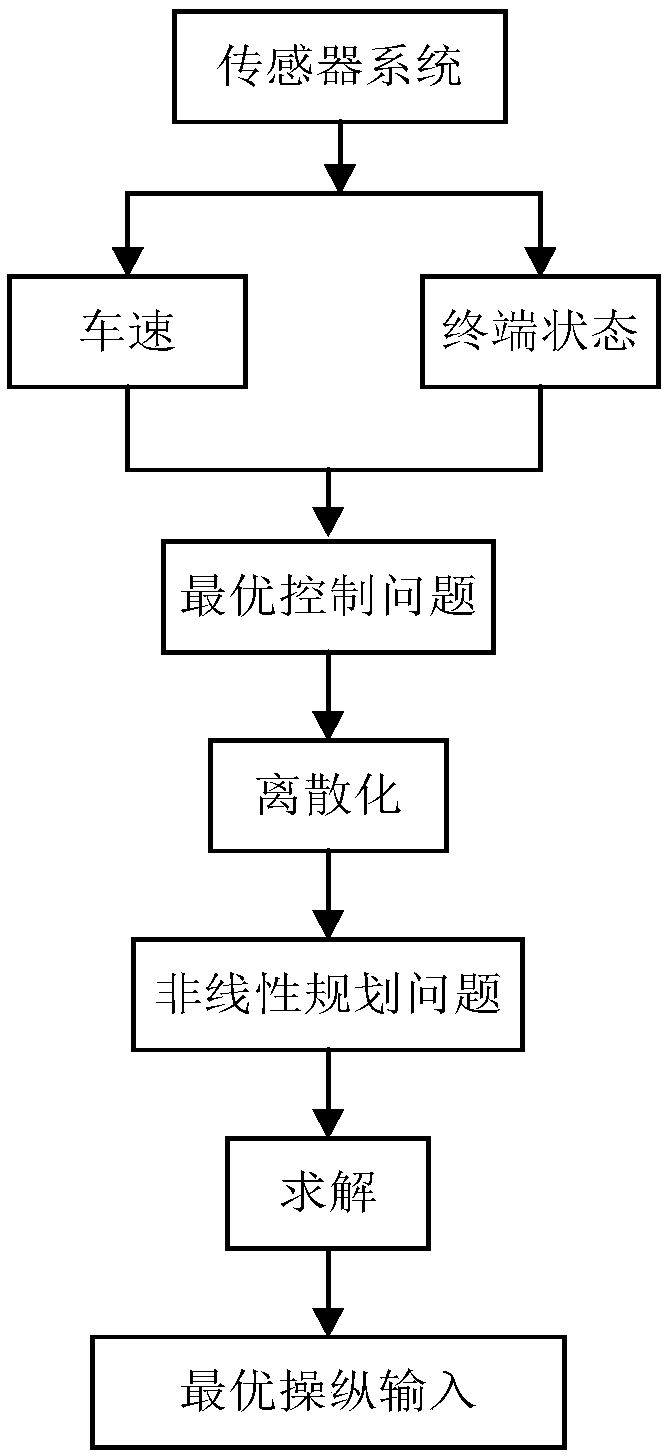
Man-machine co-driving control system based on driver model and handling inverse dynamics and switching mode of man-machine co-driving control system
PendingCN108725453AIncrease freedomRealize cooperative drivingElectrical steeringControl devicesInverse dynamicsControl system
The invention discloses a man-machine co-driving control system based on a driver model and handling inverse dynamics and a switching mode of the man-machine co-driving control system. The man-machineco-driving control system comprises a sensor system, a driving intention recognition model, a man-machine co-driving model, a right switching control system and an executive system. The method comprises the following steps: monitoring driving environment information, vehicle state information and driver state information by the sensor system, wherein a driver state signal is transferred to the driving intention recognition model; establishing a man-machine co-driving model based on the handling inverse dynamics and the driver model, and calculating expected control input and control input ofthe driver; performing necessary correction by the system on the basis of understanding the driving intention of the driver based on the established man-machine co-driving switching law, and performing full authority control by the other party when the driver temporarily loses control ability or the auxiliary system temporarily loses auxiliary operational capability to avoid unnecessary man-machine interference. According to the man-machine co-driving control system disclosed by the invention, the operating burden of the driver is reduced, and man-machine alternative disharmony is avoided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
System and method of estimating joint loads using an approach of closed form dynamics
ActiveUS7684896B2Eliminate errorsProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsDynamic methodForward dynamic
A method for estimating joint load at a joint of a segment. The method comprises the steps of receiving kinematic data, determining a modified acceleration using at least the kinematic data, estimating a joint load using at least the modified acceleration; and determining simulated kinematic data for the segment using at least the joint load. The present disclosure thus addresses the problems with conventional inverse dynamics analysis by providing a forward dynamics solution for estimation of joint loads that is stable, guaranteed to converge, computationally efficient, and does not require acceleration computations. According to one embodiment, a joint load is estimated using an approach of closed form dynamics.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Lower limbs rehabilitation robot motion control system
InactiveCN104688486AAbnormal motor inhibitionActively adjust in real timeGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesEngineeringGait
The invention discloses a lower limbs rehabilitation robot movement control system which comprises a passive training mode and an active training mode these two working modes according to different rehabilitation effects at different restoration stages of a patient, wherein in the passive training mode, the patient is driven by mechanical legs to move according to a predetermined physiological gait trajectory, the generated abnormal movement is completely inhibited; in the active training mode, limited abnormal movement of the patient is inhibited by the mechanical legs, the joint driving force generated by the action of the patient on the mechanical legs is extracted by a man-machine inverse dynamics model through real-time detection of man-machine interaction, the active movement intent of the patient is acquired, so that the patient can initiatively adjust the gait trajectory in real time, and the enthusiasm of the patients initiatively participating in the rehabilitation training is improved. The lower limbs rehabilitation robot movement control system is suitable for the lower limbs rehabilitation training movement at different restoration stages, enhances the initiative of patients participating in the rehabilitation training, and establishes the rehabilitation confidence and the movement enthusiasm of the patients, so as to enhance the effect of rehabilitation training.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Efficient dynamic modeling method for multi-degree of freedom (multi-DOF) mechanical arm
InactiveCN102207988AReduce computational complexityImproving the efficiency of positive dynamics calculationsSpecial data processing applicationsComputational problemInertial mass
The invention discloses an efficient modeling method for a multi-degree of freedom (multi-DOF) mechanical arm. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: describing speed, acceleration, force and moment of each joint of the mechanical arm by using the screw theory; performing inverse dynamic modeling on the mechanical arm by using the spatial operator algebraic theory; and obtaining a generalized inertial mass matrix of the mechanical arm and a factorization form of the inverse matrix of the mechanical arm by using a Kalman filter smoothing method so as to obtain an efficient lower dynamic model. According to the method, the efficient dynamic calculation problem of the multi-DOF mechanical arm is solved, and the calculation efficiency of the method is first power magnitude order of the degree of freedom of the mechanical arm; meanwhile, the method has strong theoretical property, intuitive expression form and definite physical significance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
System and method of estimating joint loads in a three-dimensional system
ActiveUS7623944B2Eliminate errorsProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsForward dynamicInverse dynamics
A method for estimating joint load at a joint of a segment. The method comprises the steps of receiving kinematic data, determining a modified acceleration using at least the kinematic data, estimating a joint load using at least the modified acceleration; and determining simulated kinematic data for the segment using at least the joint load. The method addresses the problems with conventional inverse dynamics analysis by providing a forward dynamics solution for estimation of joint loads that is stable, guaranteed to converge, computationally efficient, and does not require acceleration computations. According to one embodiment, a joint load is estimated recursively.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Quaternion-based five-coordinate spline interpolation control method
InactiveCN101738984ASolve the fitting problemSmooth feed rateNumerical controlQuaternionInverse dynamics
The invention discloses a quaternion-based five-coordinate spline interpolation control method, and relates to a numerical control system. In order to solve the problems that the transfer error between a CAD / CAM system and CNC, the discontinuity between segments destroys the track precision, and the movement speed becomes nonuniform and discontinuous, the quaternion-based five-coordinate spline interpolation control method comprises the following implementing processes: 1, CAM software reads track data on a curve of a parts design drawing, and establishes a CAM tool path; 2, the CAM tool path is converted into a numerical control code format of the five-coordinate spline interpolation, wherein the numerical control code format of the five-coordinate spline interpolation is divided into three formats: a linear-translation numerical control code format of the five-coordinate spline interpolation, a linear-rotation numerical control code format of the five-coordinate spline interpolation, and a universal numerical control code format of the five-coordinate spline interpolation; 3, converting the three numerical control code formats of the five-coordinate spline interpolation into a joint movement program through an inverse dynamics transformation formula; and 4, finishing processing parts. The quaternion-based five-coordinate spline interpolation control method is widely applied to the field of numerical control systems.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Rehabilitation robot and human-machine cooperative interaction force control method thereof
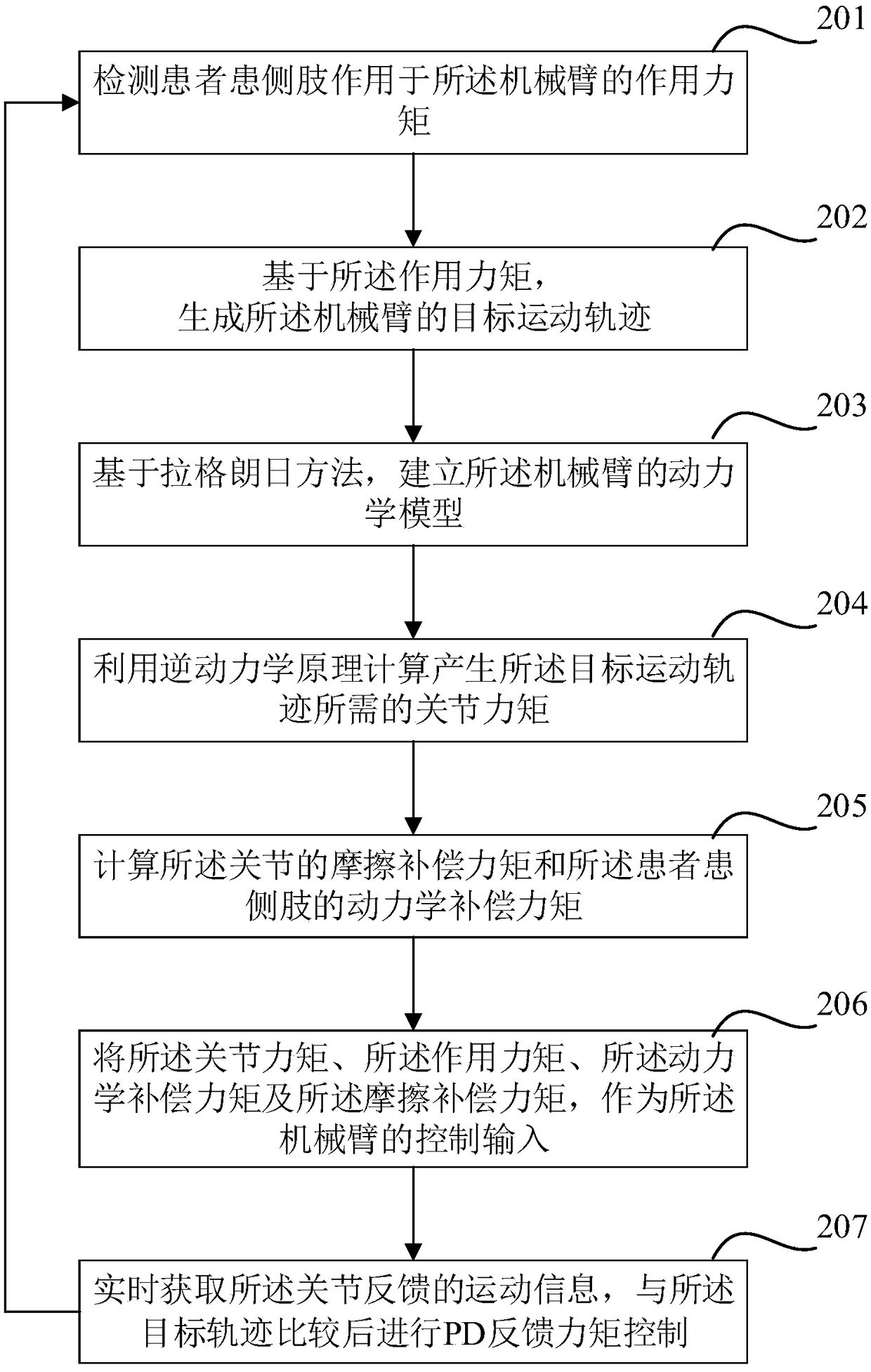
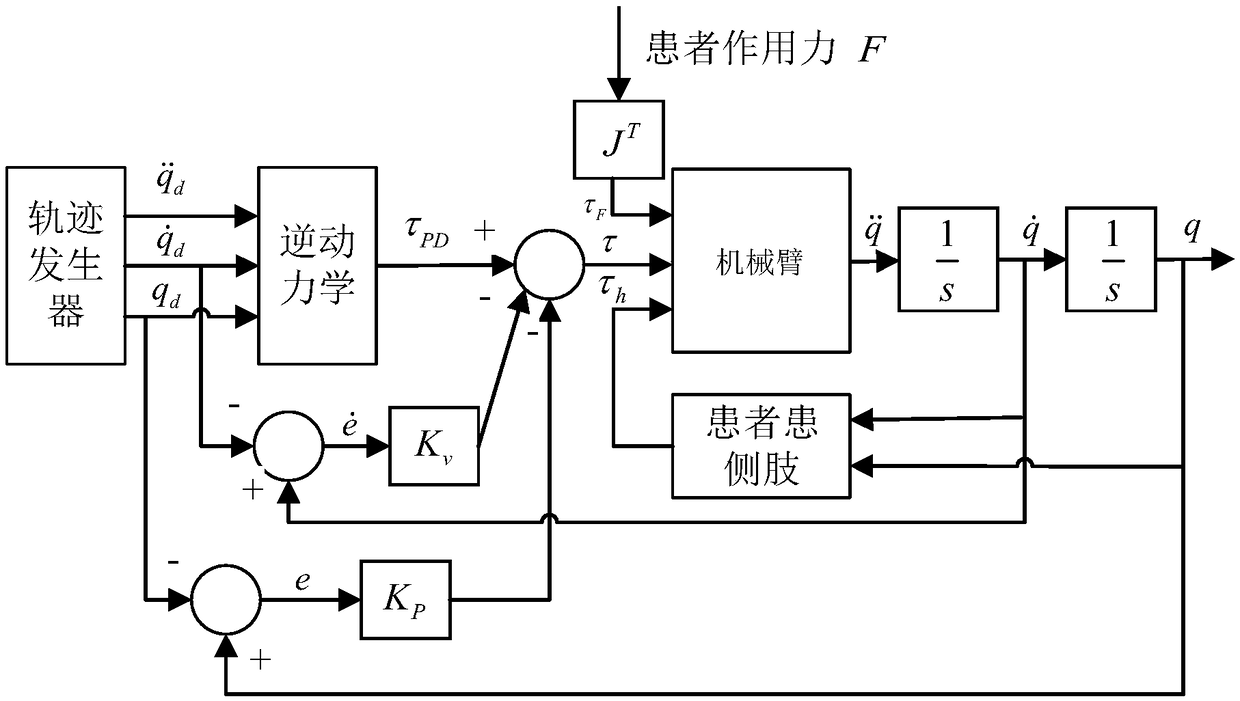
ActiveCN109223444AImprove movement flexibilityIncrease flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesInverse dynamicsDynamic models
The invention discloses a rehabilitation robot and a human-machine cooperative interaction force control method thereof. The rehabilitation robot comprises a robot arm with at least one joint. The method for controlling the human-machine interaction force of the rehabilitation robot comprises the following steps: detecting an action moment of a patient's affected side limb acting on the robot arm;Generating a target motion trajectory of the manipulator; Establishing a dynamic model of the manipulator; Calculating a joint moment required for generating the target motion trajectory by using aninverse dynamics principle; Calculating a friction compensation torque of the joint and a dynamic compensation torque of the affected side limb of the patient; The joint torque, the action torque, thedynamics compensation torque, and the friction compensation torque are used as control inputs to the manipulator. The robot can provide the compliant force interactive control between the patient andthe rehabilitation robot arm, provides complete dynamic compensation, improves the equipment motion starting ability and flexibility, and is favorable for improving the experience degree of the patient to the auxiliary rehabilitation training. The invention can provide the compliant force interactive control between the patient and the rehabilitation robot arm, provides complete dynamic compensation, and improves the equipment motion starting ability and flexibility.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRICGROUP CORP
Automobile engine thermal management system modeling and control method
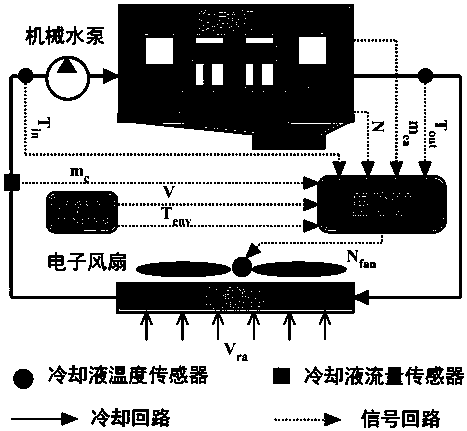
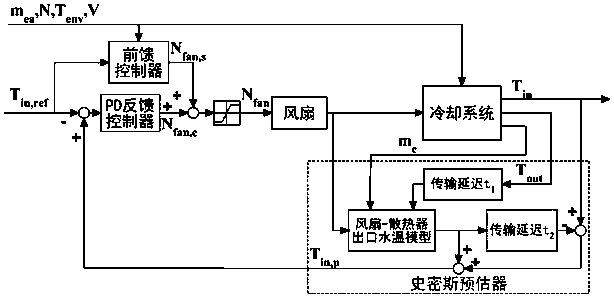
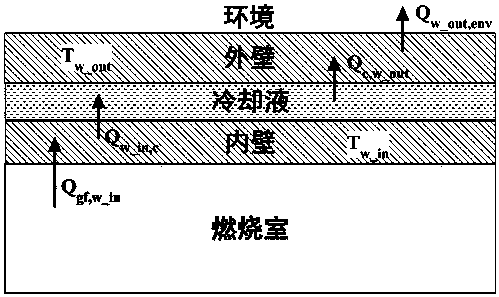
ActiveCN107869383ASolving Modeling Problems of Forced Convection Heat Transfer CoefficientsHigh control precisionGeometric CADCoolant flow controlDynamic modelsSystem dynamics model
The invention relates to an automobile engine thermal management system modeling and control method, and belongs to the technical field of control. The aim is to provide an engine thermal management system dynamic modeling method and a water temperature control method. In the system dynamic modeling method, an accurate heating power model of an air cylinder to an inner wall, a heat exchange coefficient model of a water jacket and cooling liquid and a radiating power model of a radiator are built. The research method of the method comprises the following steps that according to the structure, the principle and measurable signals of an engine thermal management system, a system dynamic model is built; seen from the heat convection heat exchange and radiation heat exchange mechanisms, three intermediate variables in the dynamic model are derived; a system inverse dynamic model is derived according to the system dynamic model; a Smith predictor is designed according to the system dynamic model; and a PD feedback controller is designed. The dynamic model of the engine thermal management system is accurately built, and the control accuracy is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Generative adversarial network-based high dynamic range inverse tone mapping method and system
InactiveCN108681991AImprove visual effectsIntegrity guaranteedImage enhancementImage analysisStandard dynamic rangeData set
The present invention provides a generative adversarial network-based high dynamic range inverse tone mapping method and system. The method includes the following steps that: an original high dynamicrange video is read, and the original high dynamic range video is cut and converted into data sets which can be used for training and are corresponding to a standard dynamic range and a high dynamic range respectively; a generative adversarial network is established based on a convolutional neural network and a hopping type connection is established, and standard dynamic range images are convertedinto high dynamic range images, namely inverse tone mapping is performed; and the entire generative adversarial network is continuously optimized according to a set comprehensive objective function,and a finally obtained network can complete mapping from the standard dynamic range to the high dynamic range. With the method of the invention adopted, the problems such as non-linearity insufficiency and complicated parameter adjustment of an existing non-learning method can be solved; the one-dimensional characteristic and gradient characteristic of the high dynamic range images are considered,so that inverse dynamic mapping of the high dynamic range can be better realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method of estimating joint moment of bipedal walking body
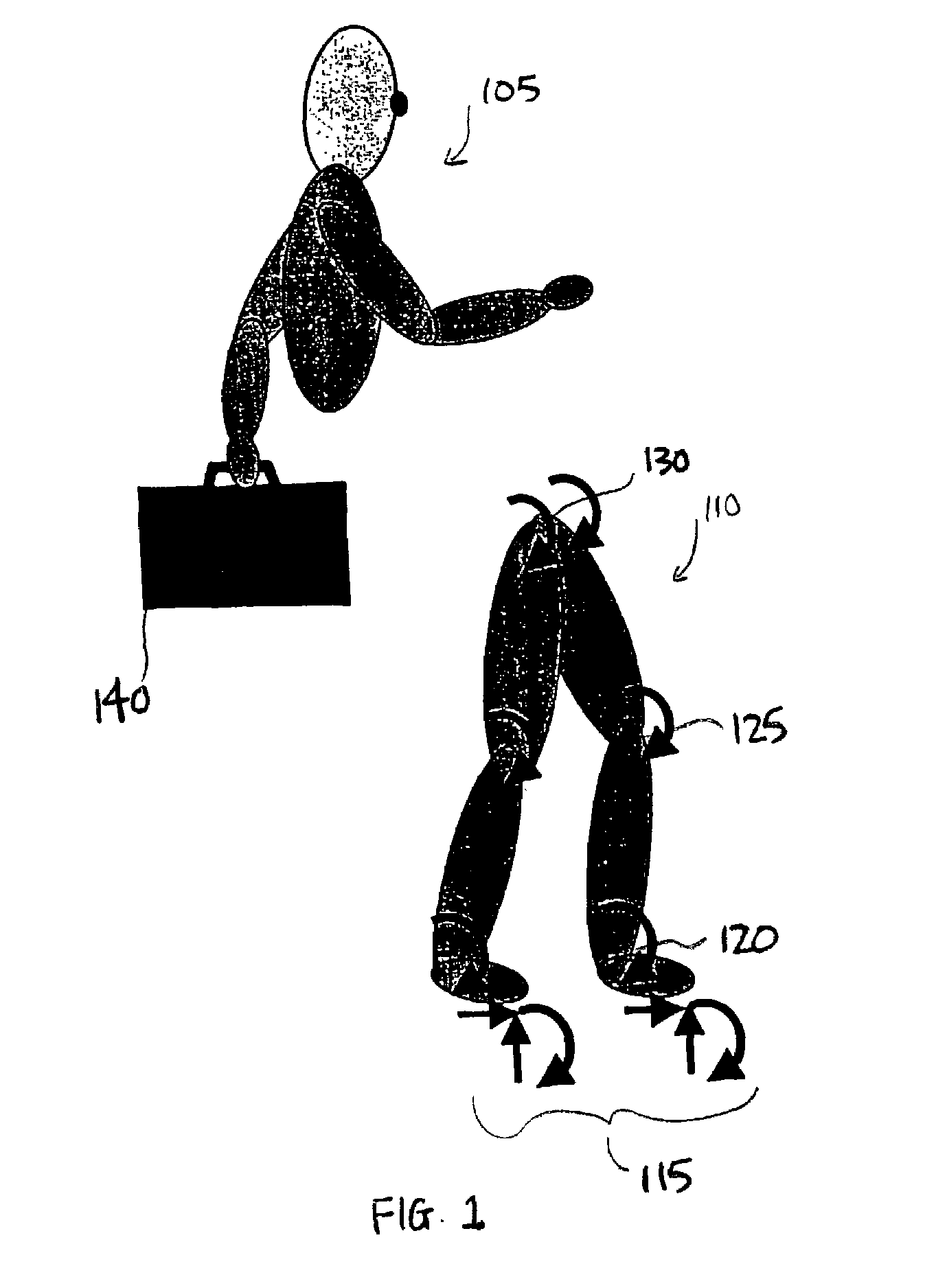
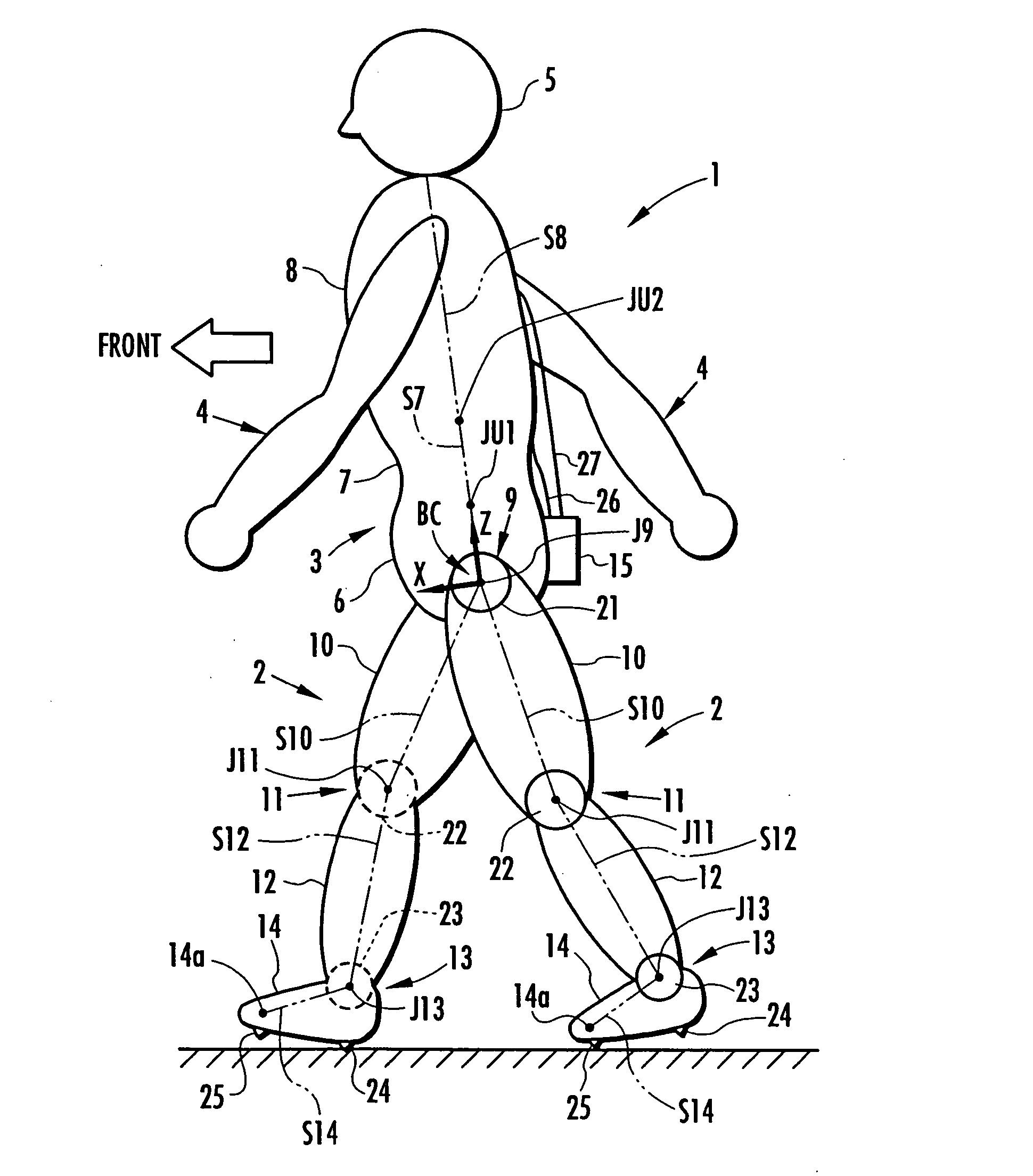
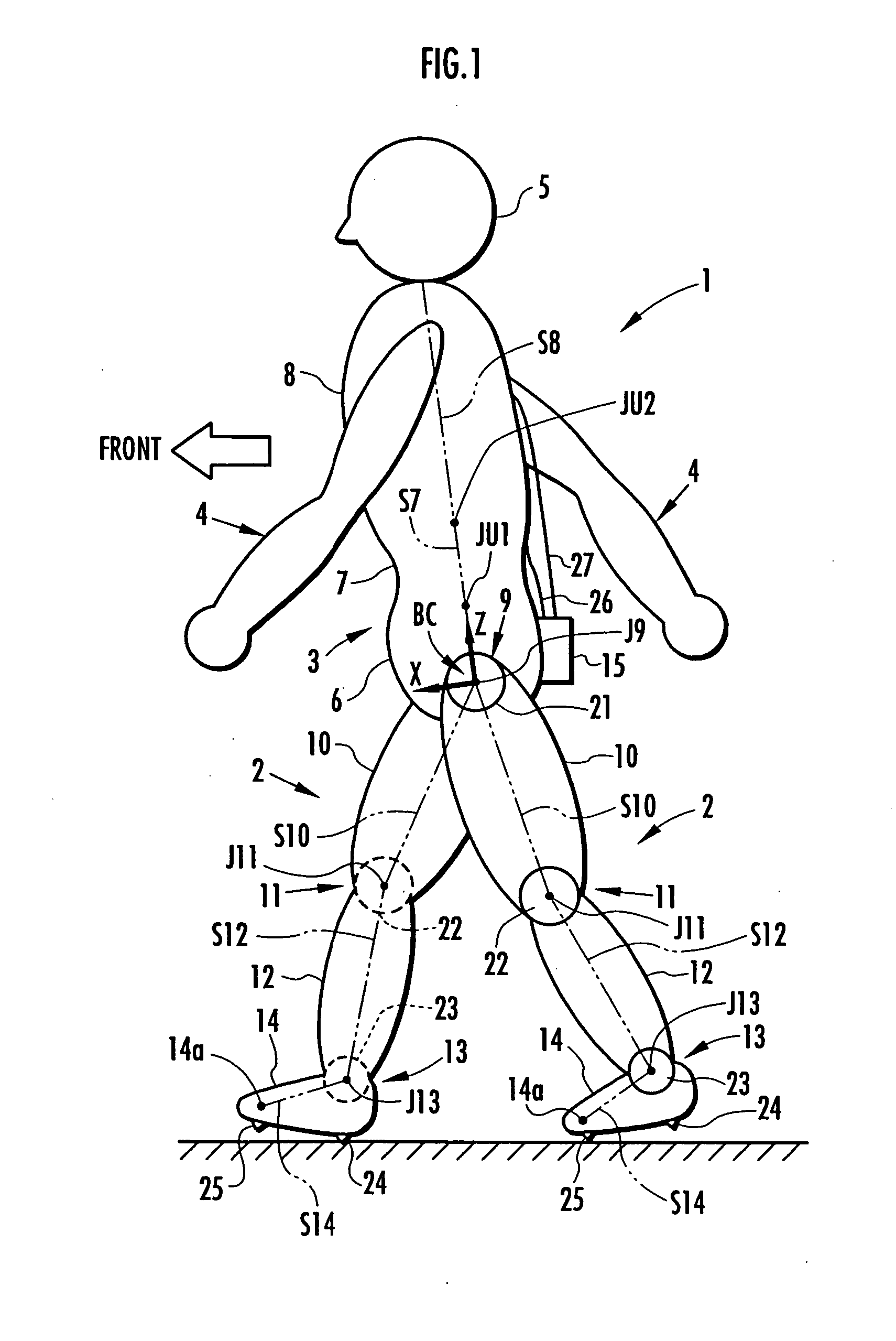
InactiveUS20070084278A1Improve estimation accuracyImprove accuracyPerson identificationWalking aidsInverse dynamicsEngineering
The joint rotational angles of joints 9, 11 and 13 of each leg 2 of a bipedal walking body 1 are detected to grasp the positions / postures of the corresponding rigid bodies 10, 12 and 14 of each leg 2 on a leg plane passing the joints 9, 11 and 13 of each leg 2. At the same time, the acceleration of a reference point (the origin of a body coordinate system BC) of the bipedal walking body 1, the floor reaction force acting on each leg 2 and the position of an acting point thereof are grasped in terms of three-dimensional amounts. Two-dimensional amounts obtained by projecting the acceleration, the floor reaction force and the position of the acting point thereof, and the positions / postures of the corresponding rigid bodies of each 2 onto the leg plane are used to estimate the moments acting on joints of each leg on the basis of an inverse dynamic model. The stability of the estimated values of joint moments can be improved while securing the accuracy of estimating the joint moments in the bending and stretching directions of each leg, considering three-dimensional motions of the bipedal walking body.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
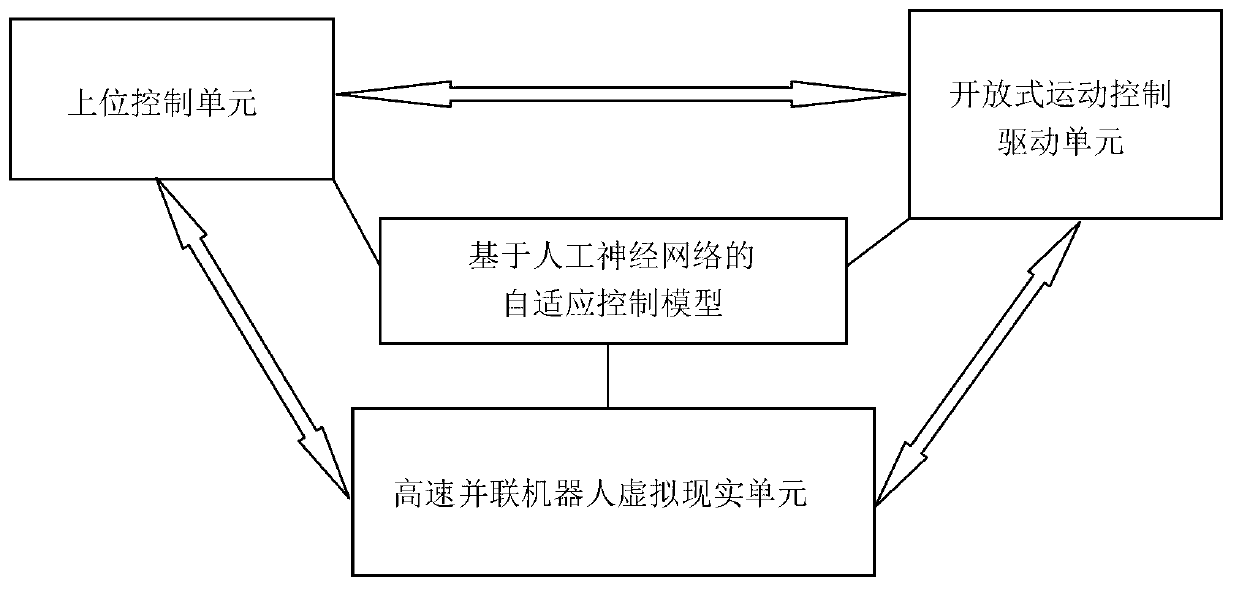
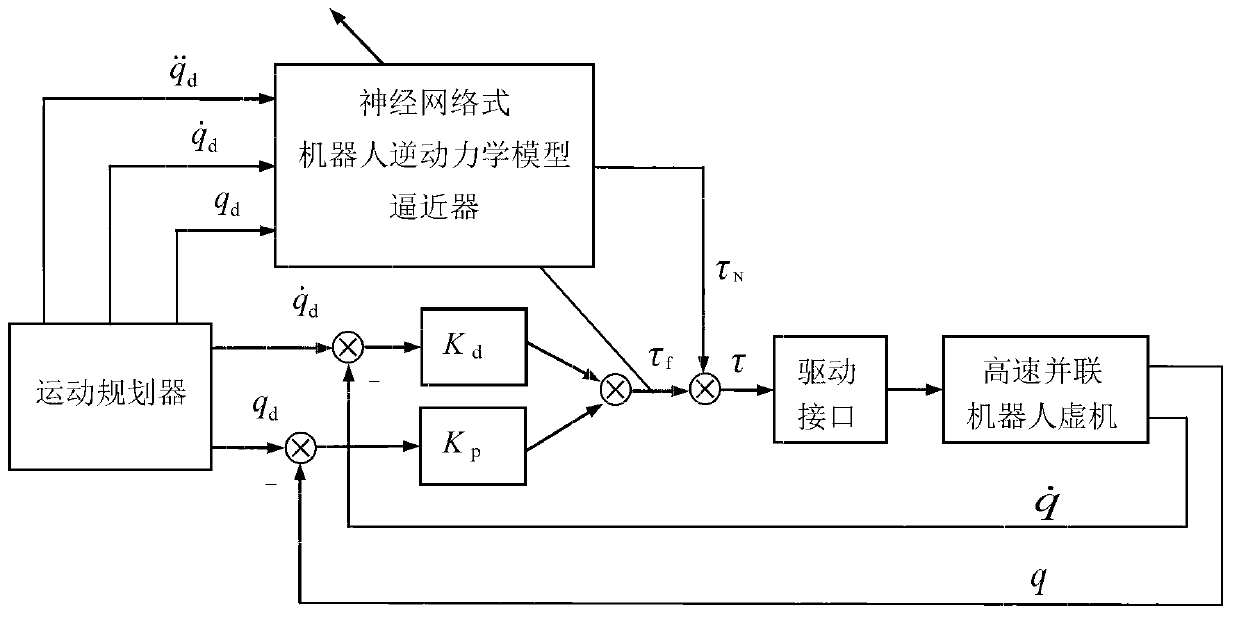
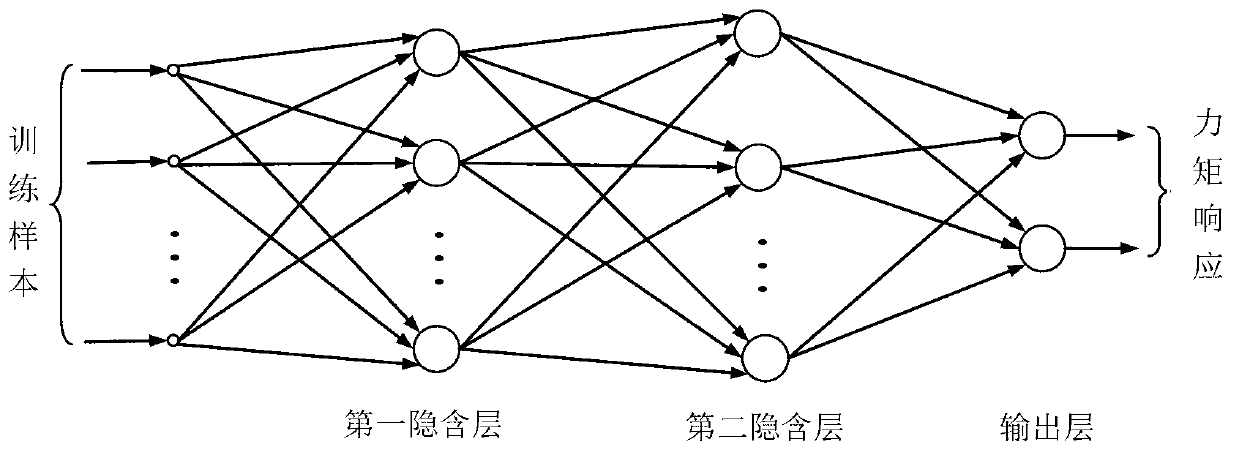
Robot neural network type computed torque controller training platform and training method
InactiveCN103279039AAvoid economyAvoid investing timeMechanical power/torque controlSimulator controlSystems designData acquisition
The invention discloses a robot neural network type computed torque controller training platform and training method, belonging to the technical field of robot control. The training platform consists of an upper control unit, an open type motion control driving unit, a high-speed parallel robot virtual reality unit, a data acquisition and communication unit and an artificial neural network-based adaptive control model, wherein motion planning and process monitoring are finished by the upper control unit; the open type motion control driving unit is an actual electrical part which finishes a control command of the upper control unit to convert to electrical control driving; the high-speed parallel robot virtual reality unit is used for realizing construction of a high-speed parallel robot virtual machine and a related three-dimensional scene; the data acquisition and communication unit realizes data communication and can collect a training sample required by the artificial neural network; and the artificial neural network-based adaptive control model consists of a neural network type robot inverse dynamic model approximator and a linear proportional differential feedback controller which work in parallel. The robot neural network type computed torque controller training platform and training method can realize trace tracking control of the high-speed parallel robot and have the characteristics of wide fitness, low system design cost and the like.
Owner:ANHUI HUACHUANG INTELLIGENT EQUIP
Method and device for attenuating interbed multiples during process of processing marine seismic data
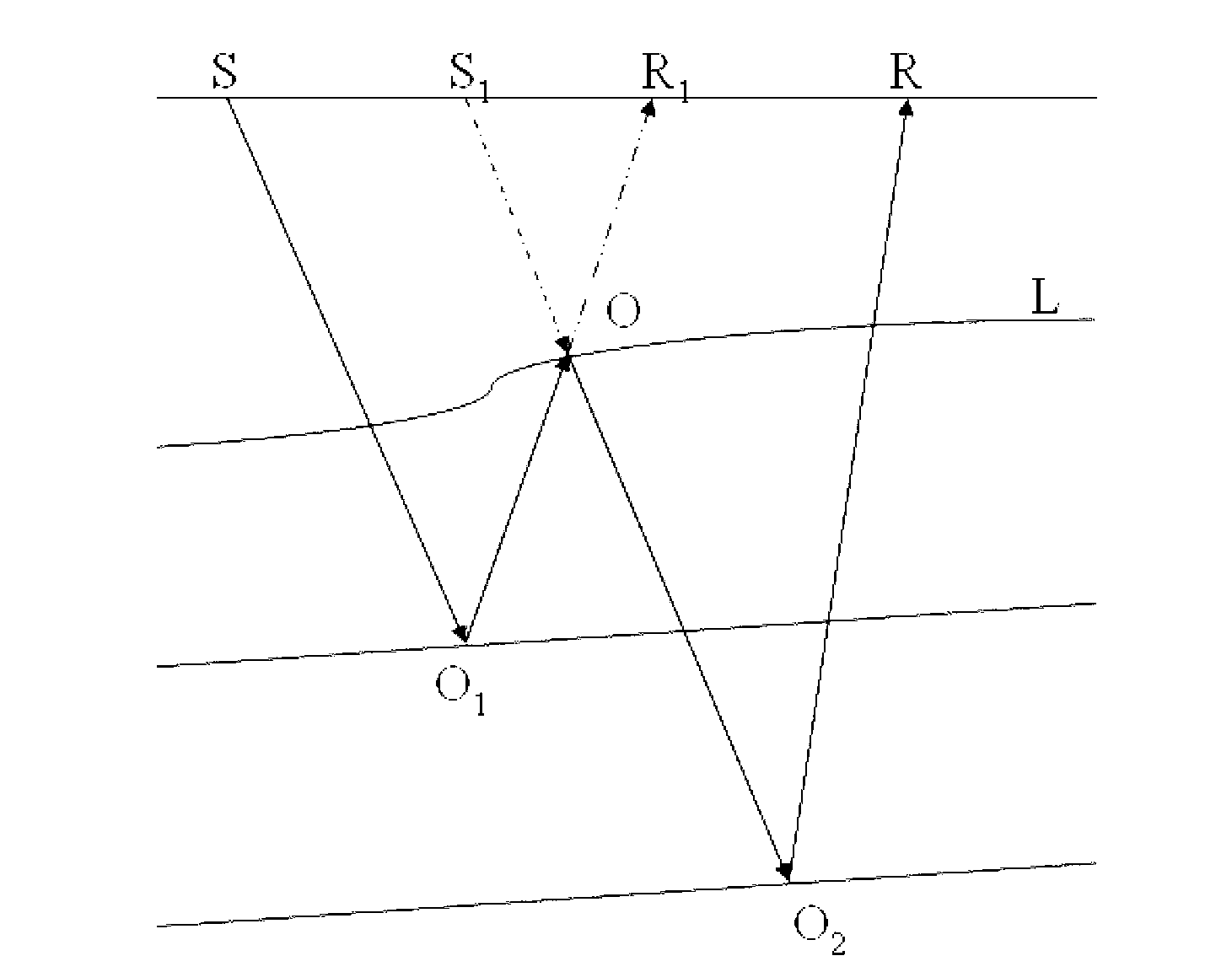
The invention provides a method and a device for attenuating interbed multiples during the process of processing marine seismic data. The method comprises the following steps of preprocessing original seismic records to obtain preprocessed seismic records PPR (x, z0; t); overlapping the dynamically-corrected seismic records and obtaining the location of a strong reflecting interface L in which the interbed multiples are generated on the overlapped section; picking up primary reflection waves generated by the interface L from the dynamically-corrected seismic records, and correcting the primary reflection waves inversely and dynamically to obtain a second wave field item P2 (x, z0; t); deleting a reflected wave field above the interface L from the dynamically-corrected seismic records according to the location of the interface L, and carrying out inverse dynamic correction to obtain a first wave field item P1 (x, z0; t); setting a third wave field item P3 (x, z0; t) to be equal to the first wave field item; carrying out calculation according to the first wave field item P1 (x, z0; w), the second wave field item P2 (x, z0; w) and the third wave field item P3 (x, z0; w) to obtain the interbed multiples PLM (x, z0; w) relevant with the interface L; and attenuating the interbed multiples PLM (x, z0; t) of a time domain from the preprocessed seismic records PPR (x, z0; t) to obtain the records PME (x, z0; t) of the attenuated interbed multiples. By the adoption of the method and the device for attenuating the interbed multiples during the process of the processing marine seismic data, as the interbed multiples are predicted and attenuated only through data driving, independent of the precision of a velocity field, the processing quality of the marine seismic data is improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
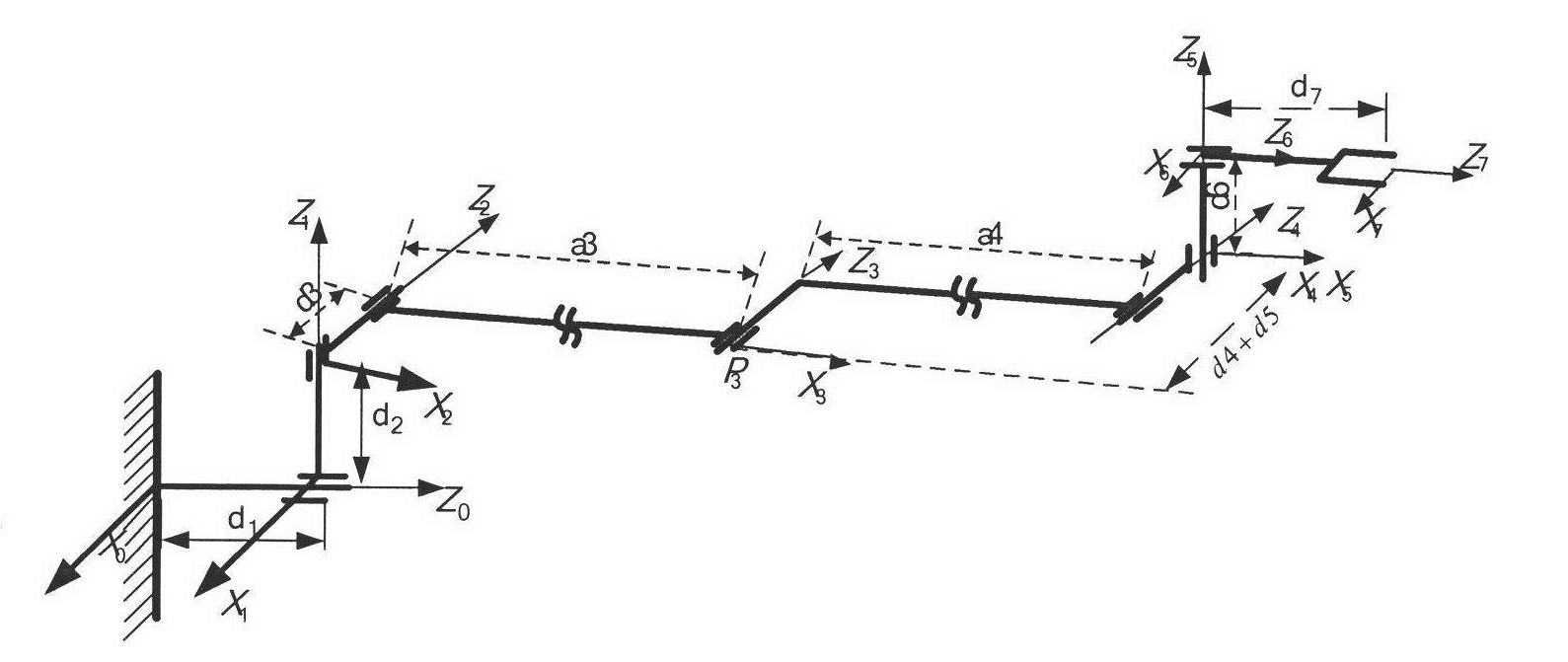
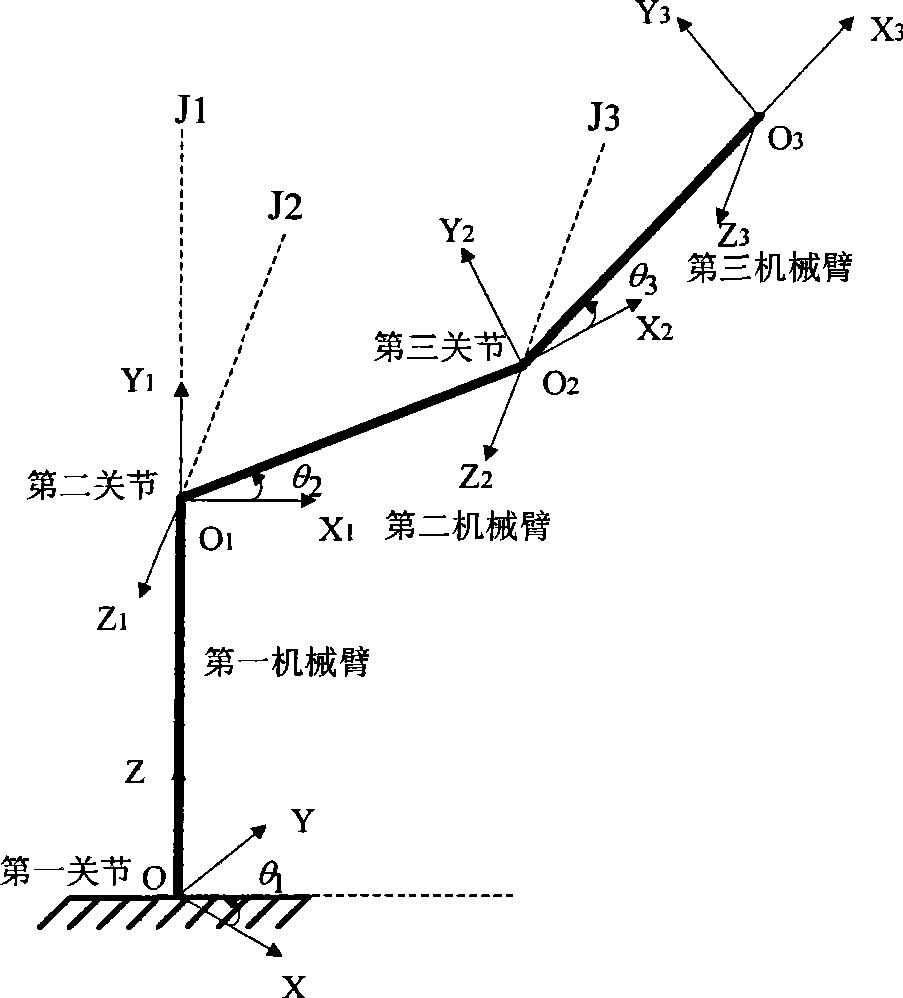
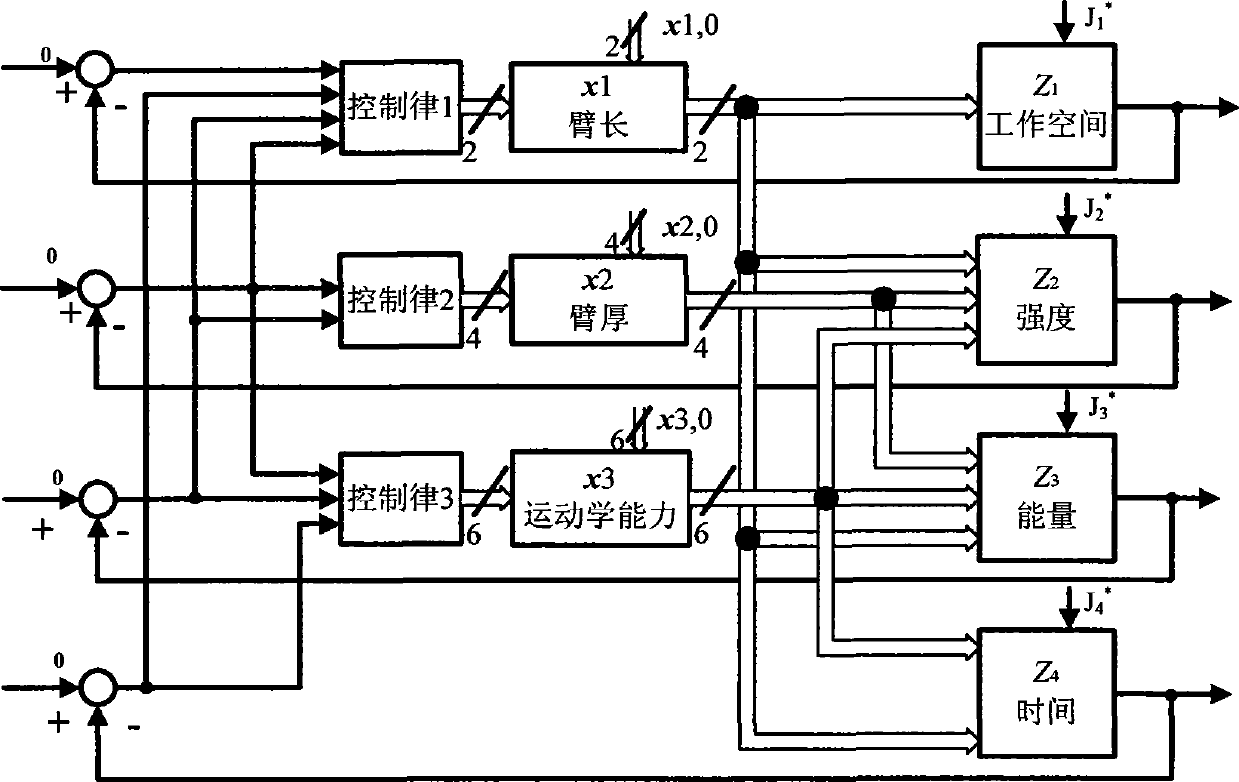
Acquisition method of three freedom-degree transportation industrial robot multiple-objective optimization design parameter
InactiveCN101508112AOptimize workspace performanceHigh strengthProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsClosed loop
The invention relates to a method for multiobjective optimization design of industrial robots, which consists of three steps: firstly, obtaining four performance indexes representing mechanical arm working space, strength, control energy and control time and a computing method thereof through establishment of a mechanical arm kinematics model, a strength analysis model, a dynamic model based on an electromechanical coupling system and a systemic closed-loop model controlled by inverse dynamics; secondly, selectively optimizing robot design parameters related to the four performance indexes to establish a multiobjective optimization design model; and finally, through a control method, adjusting mechanical arm design parameters, optimizing four objectives parallelly, and finally obtaining design values of the design parameters meeting the four performance requirements simultaneously so as to provide a method for overall improving the performance of the industrial robots.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Guidance law of multi-constraint aircraft based on Bezier curve
InactiveCN103245257AAchieve precision strikesMeet the requirements of the end collision angleAiming meansInverse dynamicsEngineering
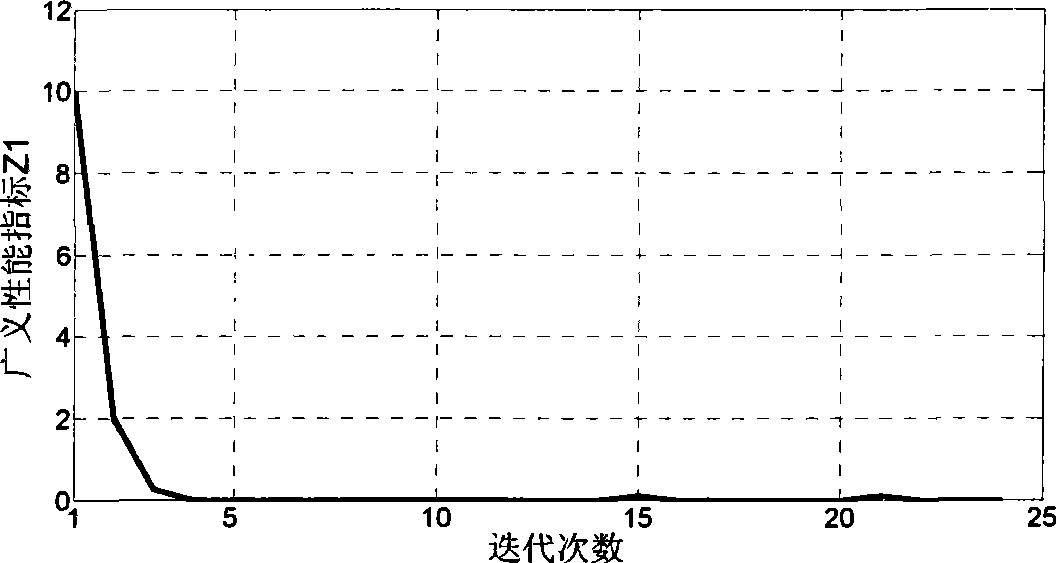
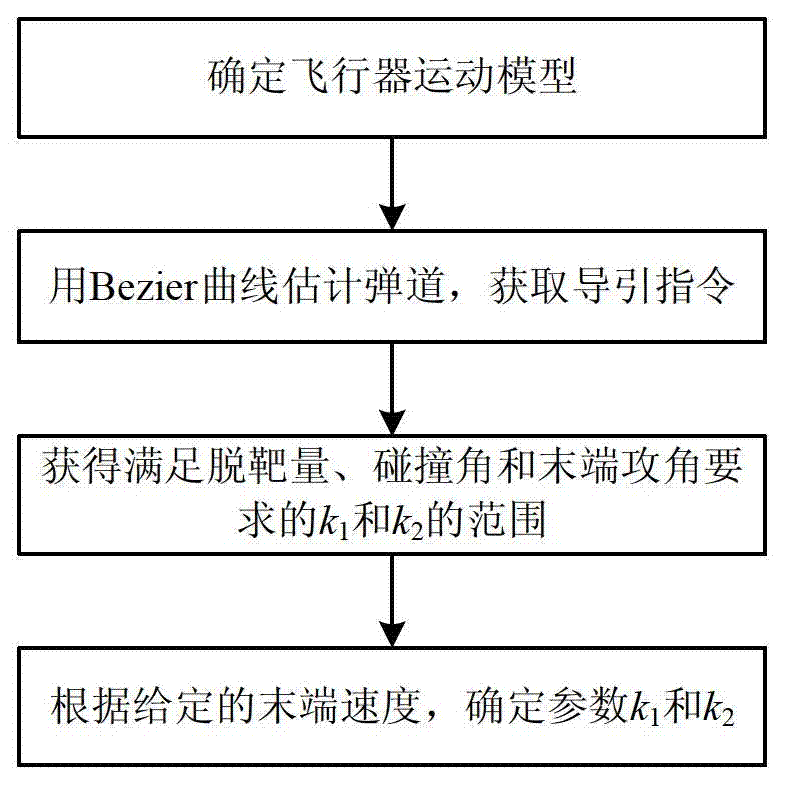
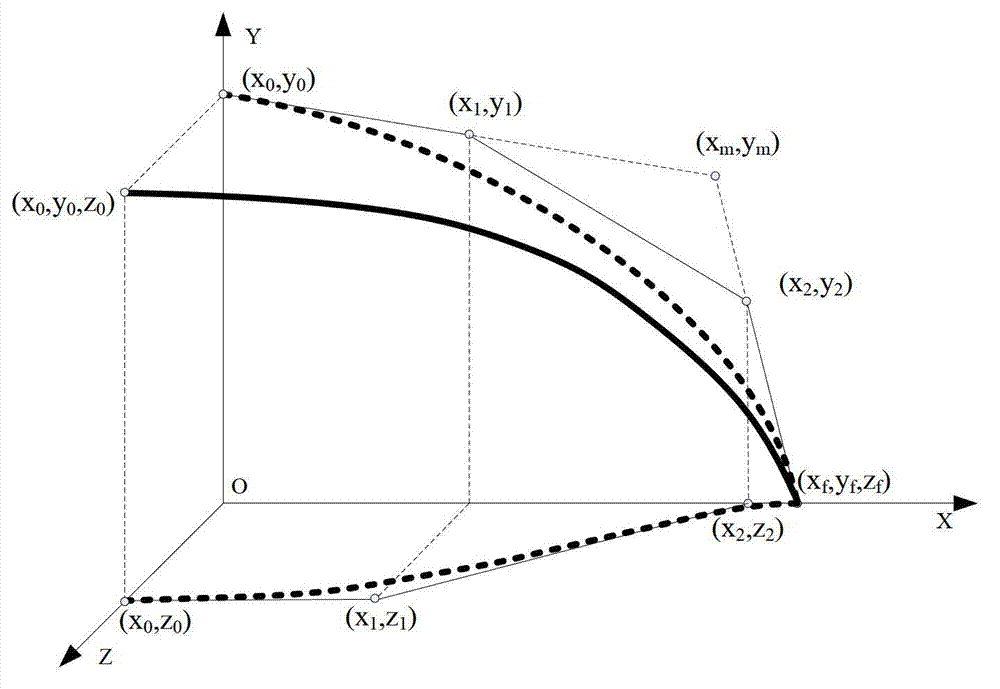
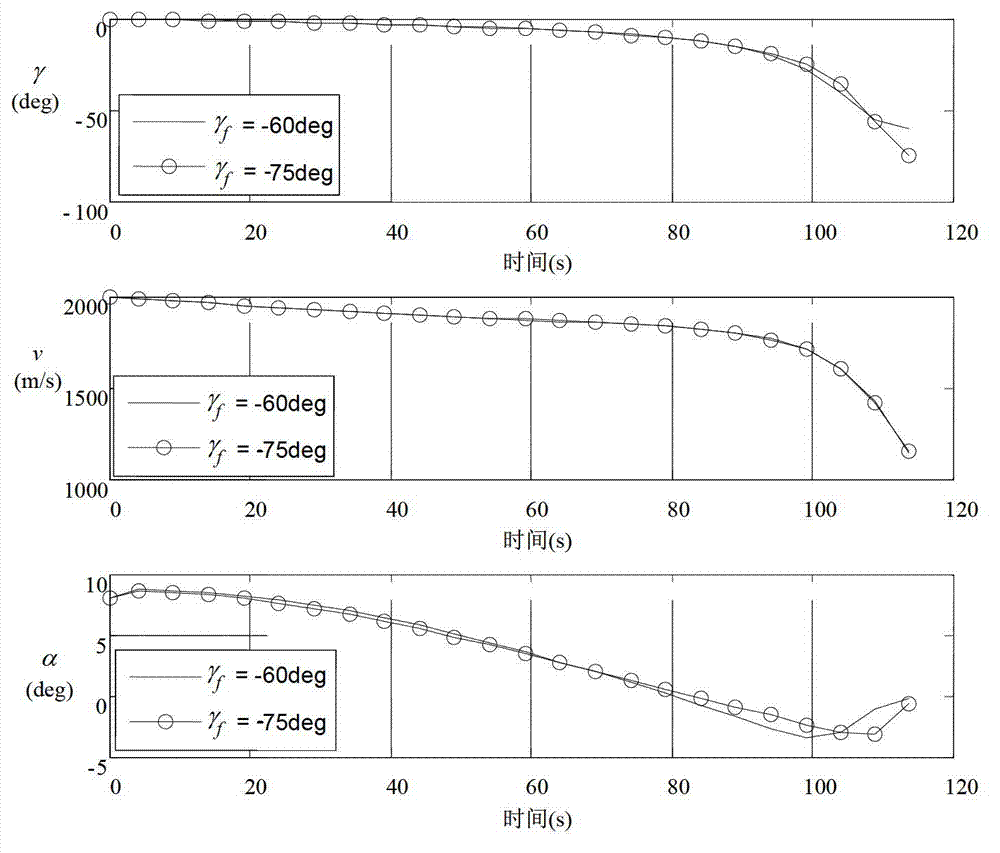
The invention provides a guidance law of a multi-constraint aircraft based on a Bezier curve, and belongs to the technical field of aircraft dynamics and guidance. According to a specified aircraft motion model and a three-order Bezier curve equation simulative ballistic trajectory, an attack angle and a heeling angle of the aircraft are determined by four controlling points with two middle controlling points described by parameters k1 and k2; a range of the parameters k1 and k2 meeting requirements of miss distance, collision angle and terminal attack angle is acquired through optimization; values of k1 and k2 corresponding to terminal speed maximum and terminal speed minimum are figured out; and according to a given terminal speed, the parameters of k1 and k2 are determined. Based on inverse dynamics, the terminal collision angle, the attack angle and speed constraint are all considered, requirements on the collision angle, the terminal attack angle and terminal collision speed can be met, and accurate attacks on fixed targets are achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Simulation system, method and computer-readable medium for human augmentation devices
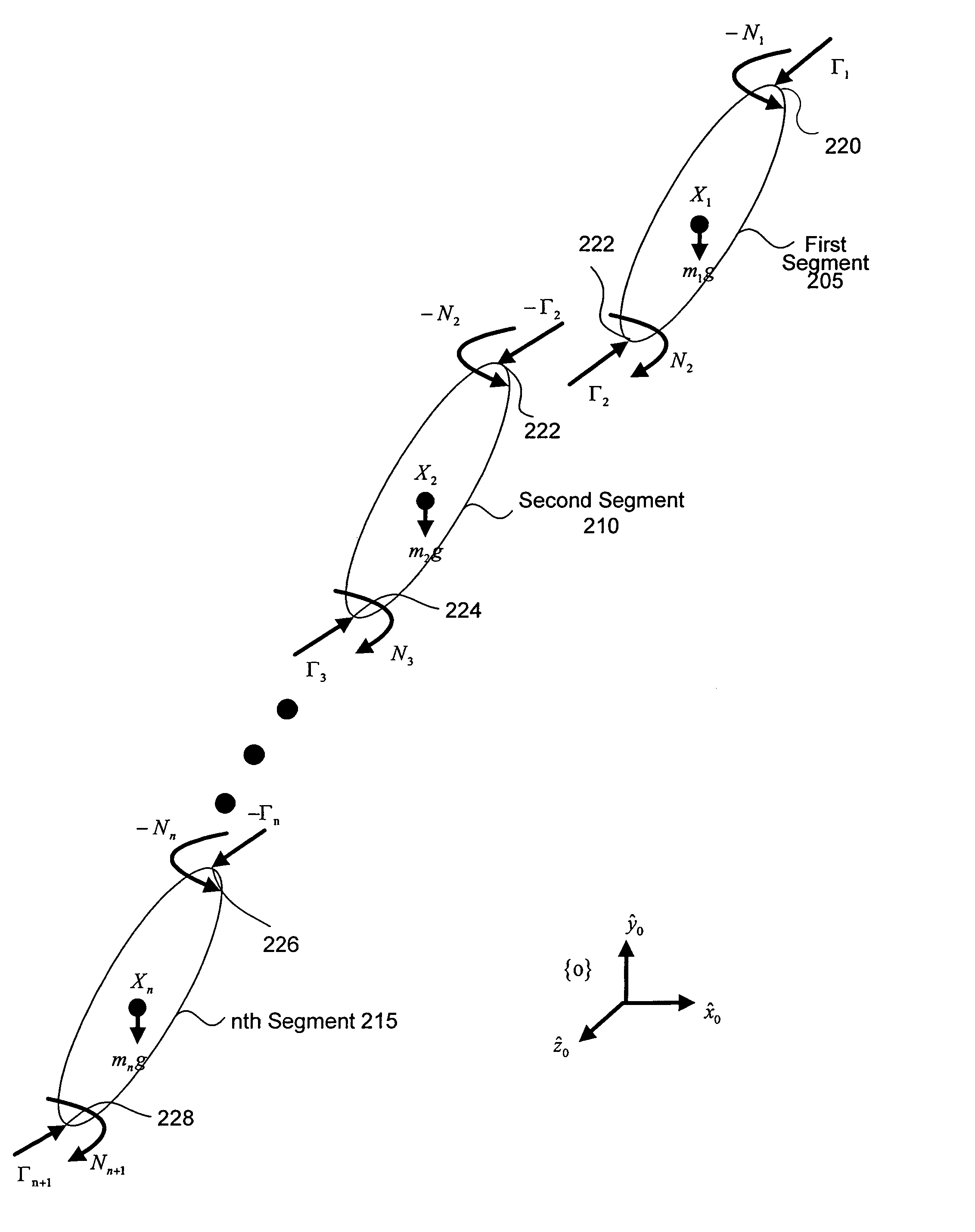
InactiveUS7251593B2Physical therapies and activitiesDigital data processing detailsMuscle forceInverse dynamics
A system, a method and a computer readable medium are provided for simulating a combined musculoskeletal and augmentation device system. The dynamics model of the combined musculoskeletal and augmentation device system receives computed torques at the joints as inputs and delivers simulated kinematic data of the segments as outputs. The augmentation device controller for control of the augmentation device, receives the simulated kinematic data as inputs and delivers assist torques as outputs. The inverse dynamics model for the musculoskeletal and augmentation device system, receives the simulated kinematic data, desired kinematic data of the segments and the assit torques as inputs and delivers the computed net joint torque and muscle torque. The muscle force and muscle capacity module for checking and adjusting the computed torques, receives the computed torques as inputs and delivers computed torques as outputs after the checking and adjustment.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
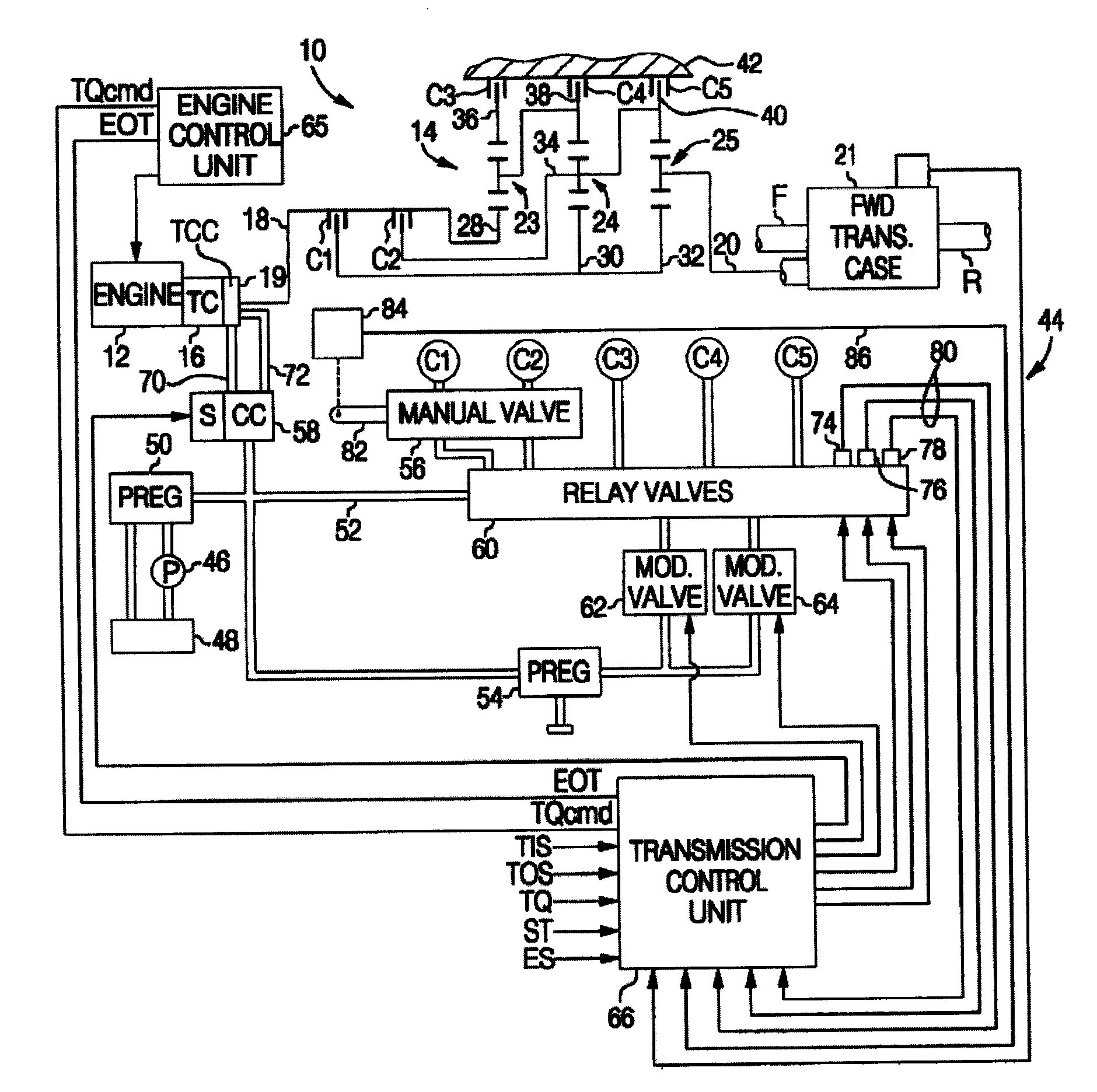
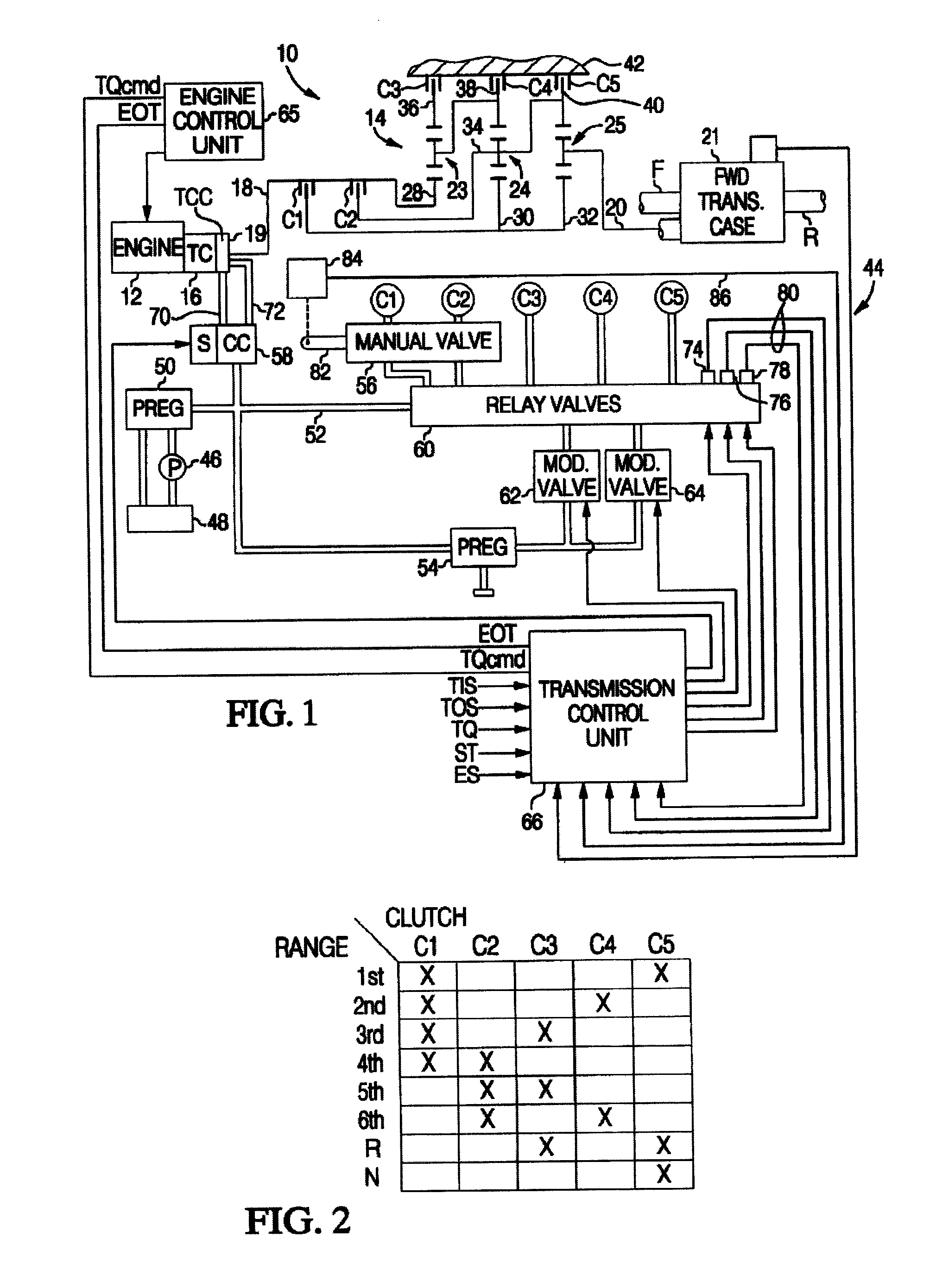
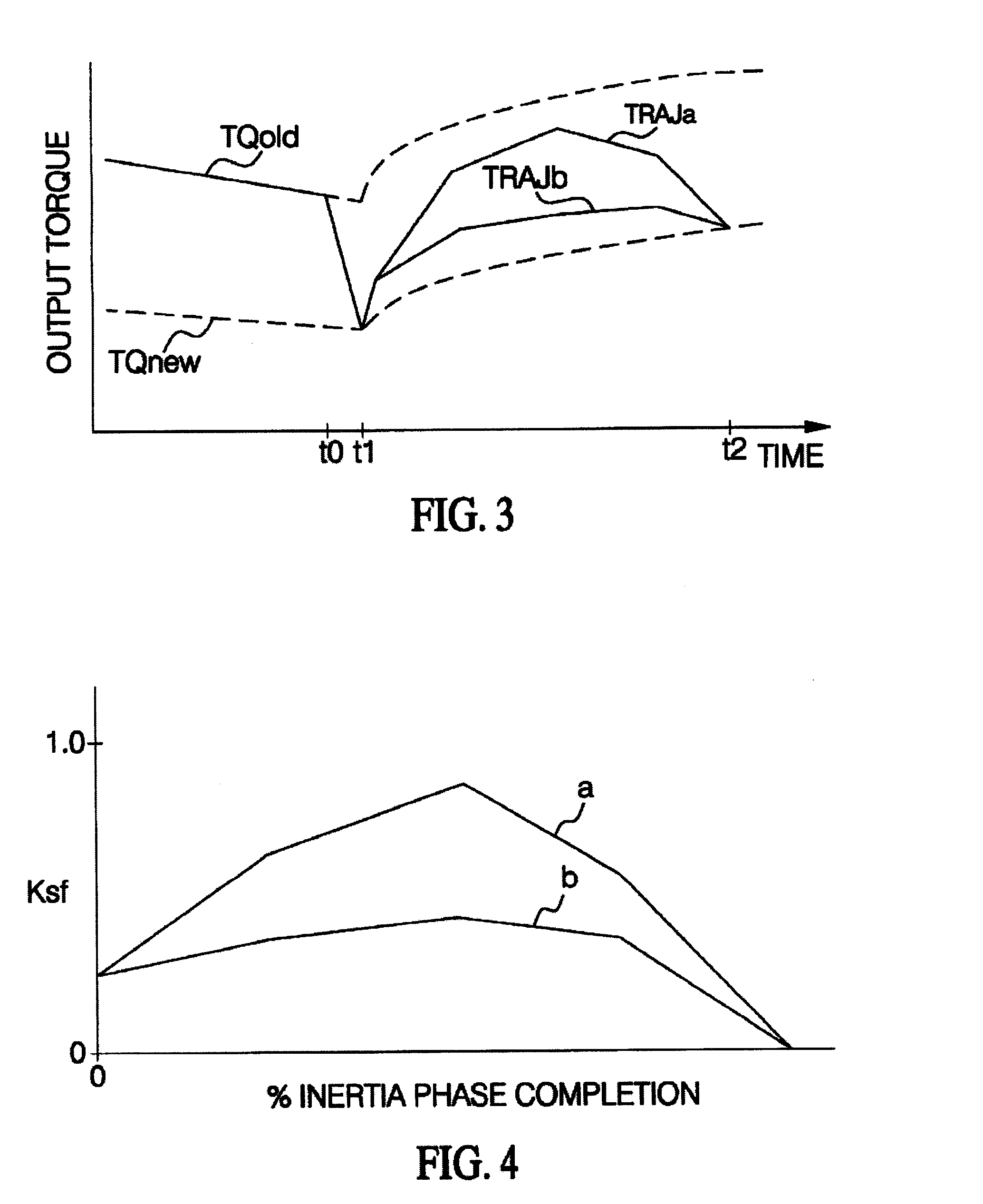
Control of engine torque reduction at upshift initiation
ActiveUS20080081735A1Excessive energy dissipationLess-intensive calibration effortInternal combustion piston enginesDigital data processing detailsDynamic modelsInverse dynamics
An improved control for an automatically shiftable transmission upshift, wherein the engine output torque and on-coming clutch pressure are coordinated during the shift based on an inverse dynamic model of the transmission to achieve a desired output torque trajectory. At the initiation of an upshift, the engine torque is commanded to decrease in a ramp-like or sloping fashion to and engine output torque value calculated using the dynamic model. This ramp-like or sloping decrease provides smooth shifting, while reducing the likelihood of tie-up between on-coming and off-going clutches within the automatically shiftable transmission.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
A flexible multi-body robot modeling and solving method based on multi-dimensional reconstruction and correction
ActiveCN109543264AAccurate descriptionAvoid the phenomenon of wrong iterative solutionsProgramme-controlled manipulatorDesign optimisation/simulationCorrection algorithmState parameter
The invention discloses a flexible multi-body robot modeling and solving method based on multi-dimensional reconstruction correction, This method is successively performed by: A mathematical model ofrigid component and a flexible component are respectively constructed and parameters are set, the holonomic constraint conditions of a flexible multi-body robot system are established, the static anddynamic equations of flexible multi-body robot system with holonomic constraints are obtained, According to the known state parameters of t-time, the state parameters of t + h-time are obtained by iterative solution of dynamic equations under complete constraints using multi-dimensional reconstruction and correction method, and the state parameters of t + h-time are obtained by repeated iterativeprocess until the end of the algorithm. The forward and inverse dynamic models of flexible multi-body robot with holonomic constraints are established by the modeling and solving method, and the dynamic equations are solved iteratively by using the multi-dimensional reconstruction and correction algorithm. The modeling is complete and the solving scale is small. Compared with the traditional solving method, the convergence condition is easier to be satisfied, and the efficiency of calculation and solution is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
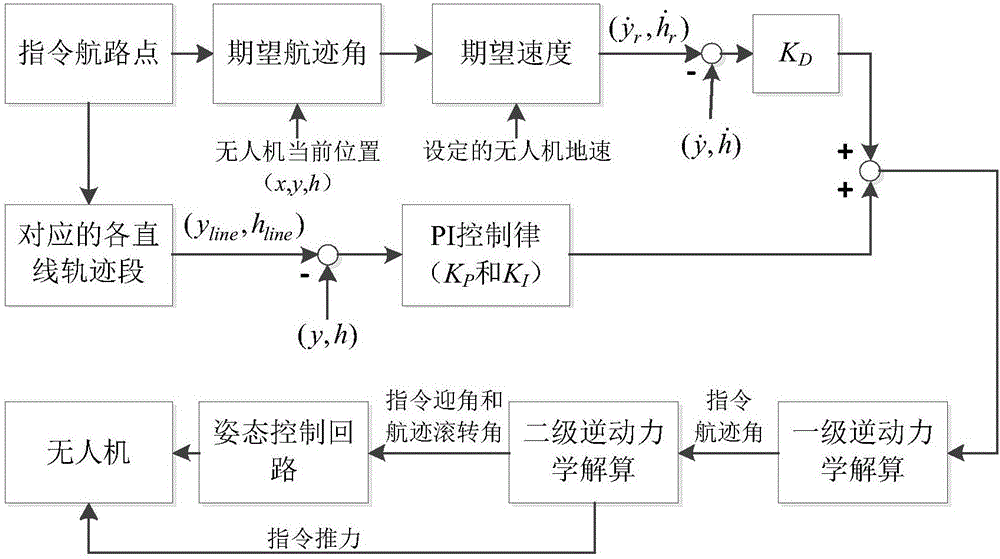
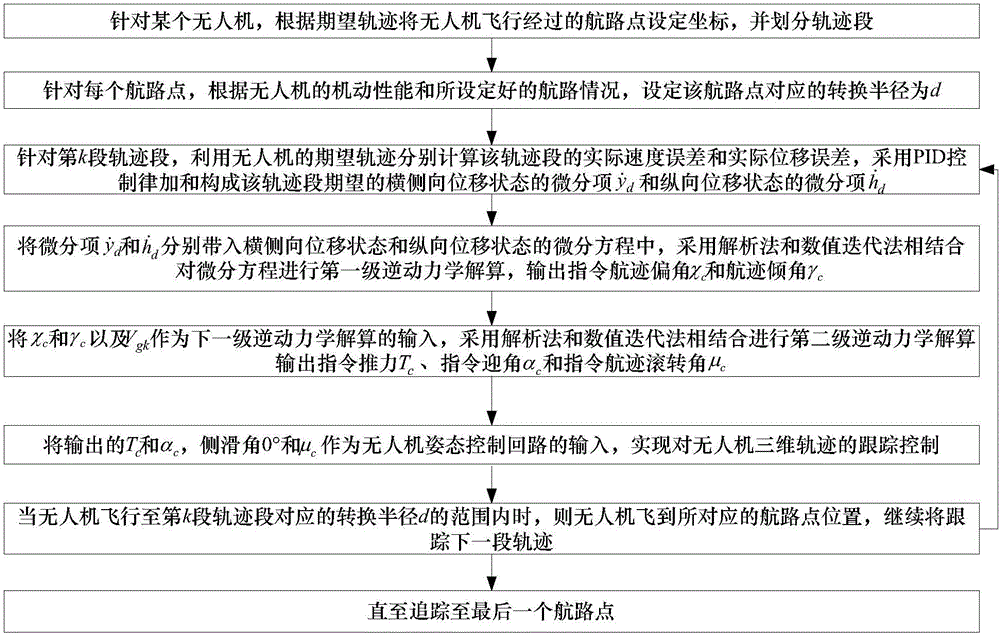
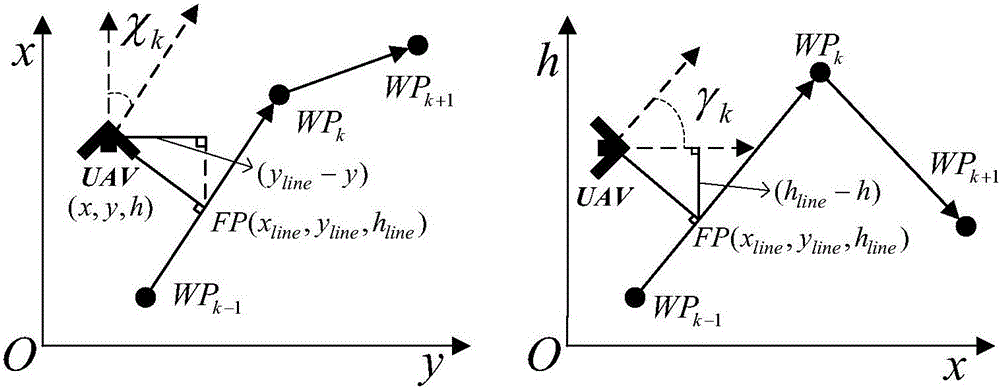
Unmanned aerial vehicle three-dimensional trajectory guidance method based on inverse dynamics
ActiveCN106774400AAdjust desired flight trajectory onlineReduce computing costPosition/course control in three dimensionsProportion integration differentiationInverse dynamics
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle three-dimensional trajectory guidance method based on inverse dynamics and belongs to the technical field of unmanned air vehicle navigation guidance and control. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing primary inverse dynamics resolving on position state equations of the unmanned aerial vehicle by combining an analytical method and a numerical iteration method at the aim of a certain trajectory section of a certain unmanned aerial vehicle, and performing secondary inverse dynamics resolving on ground velocity and track angle state equations of the unmanned aerial vehicle so as to obtain the command thrust, command attack angle and command track roll angle of the unmanned aerial vehicle; inputting the command quantities into the designed attitude control loop so as to control the actual ground velocity and position of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and enabling the actual position of the unmanned aerial vehicle to be convergent to a reference trajectory between way points by adopting PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) control. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the ground velocity and three-dimensional position of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be simultaneously and accurately controlled, the expected flight path of the unmanned aerial vehicle is adjusted on line, and the controller computing cost is low.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com