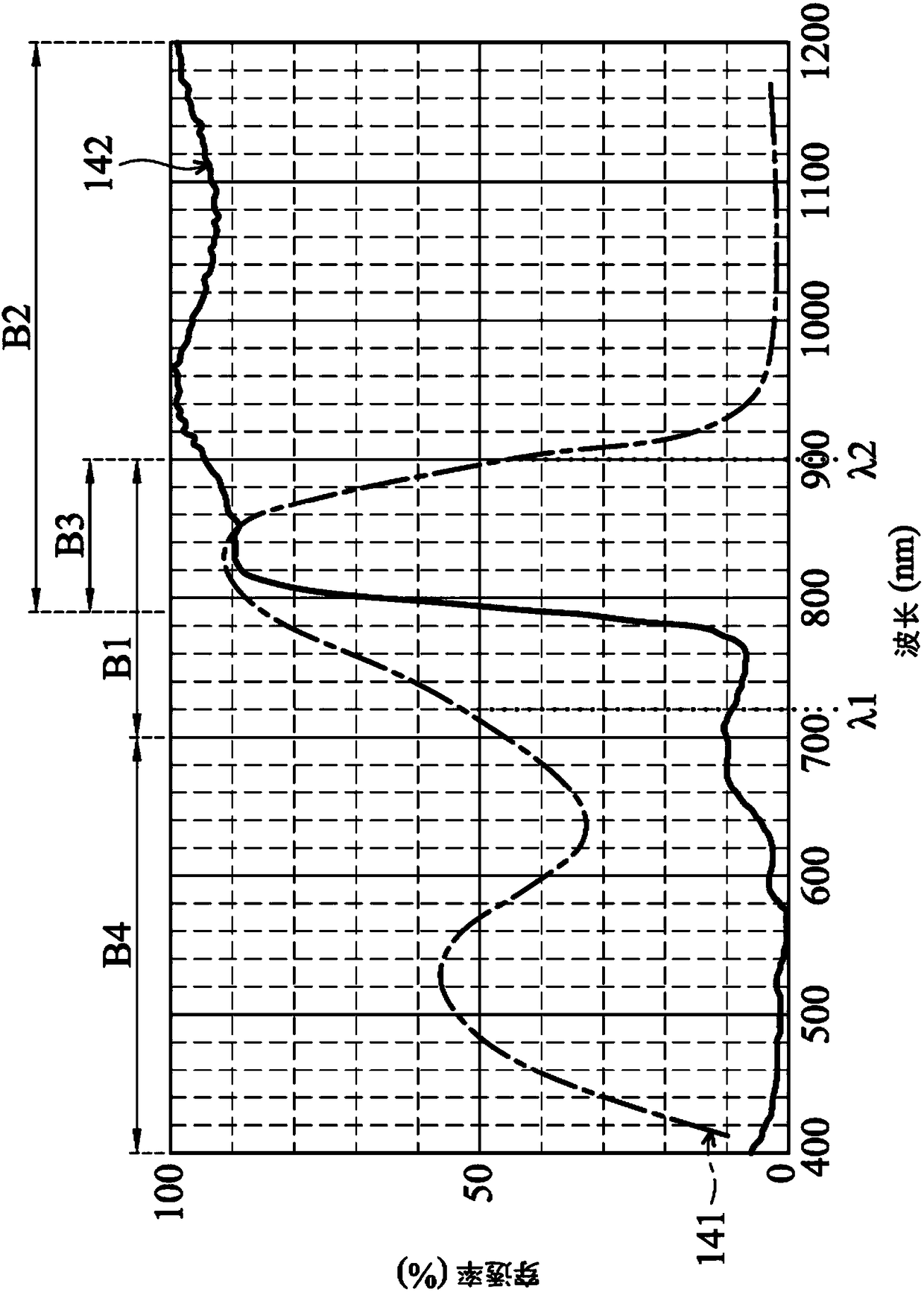
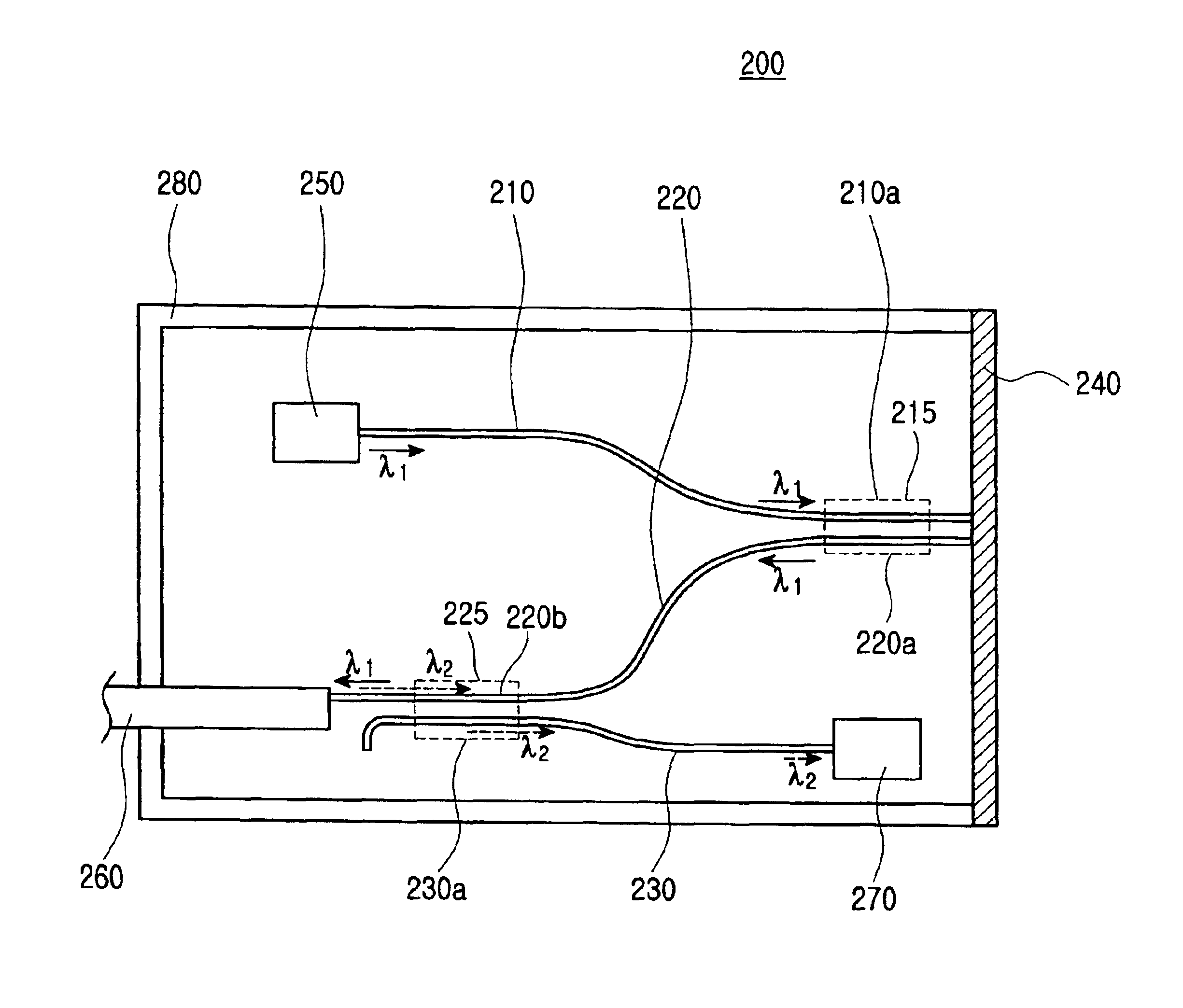
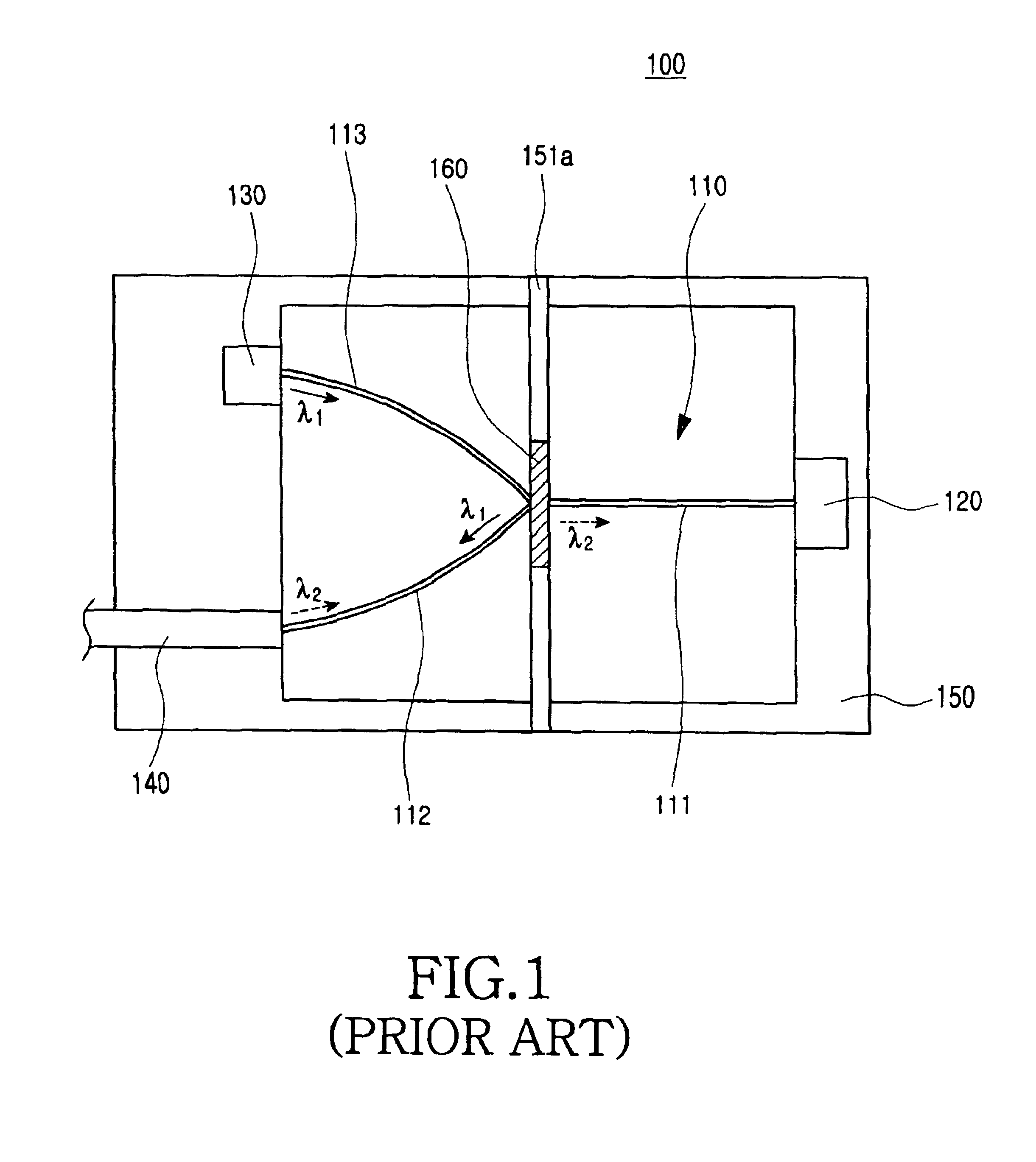
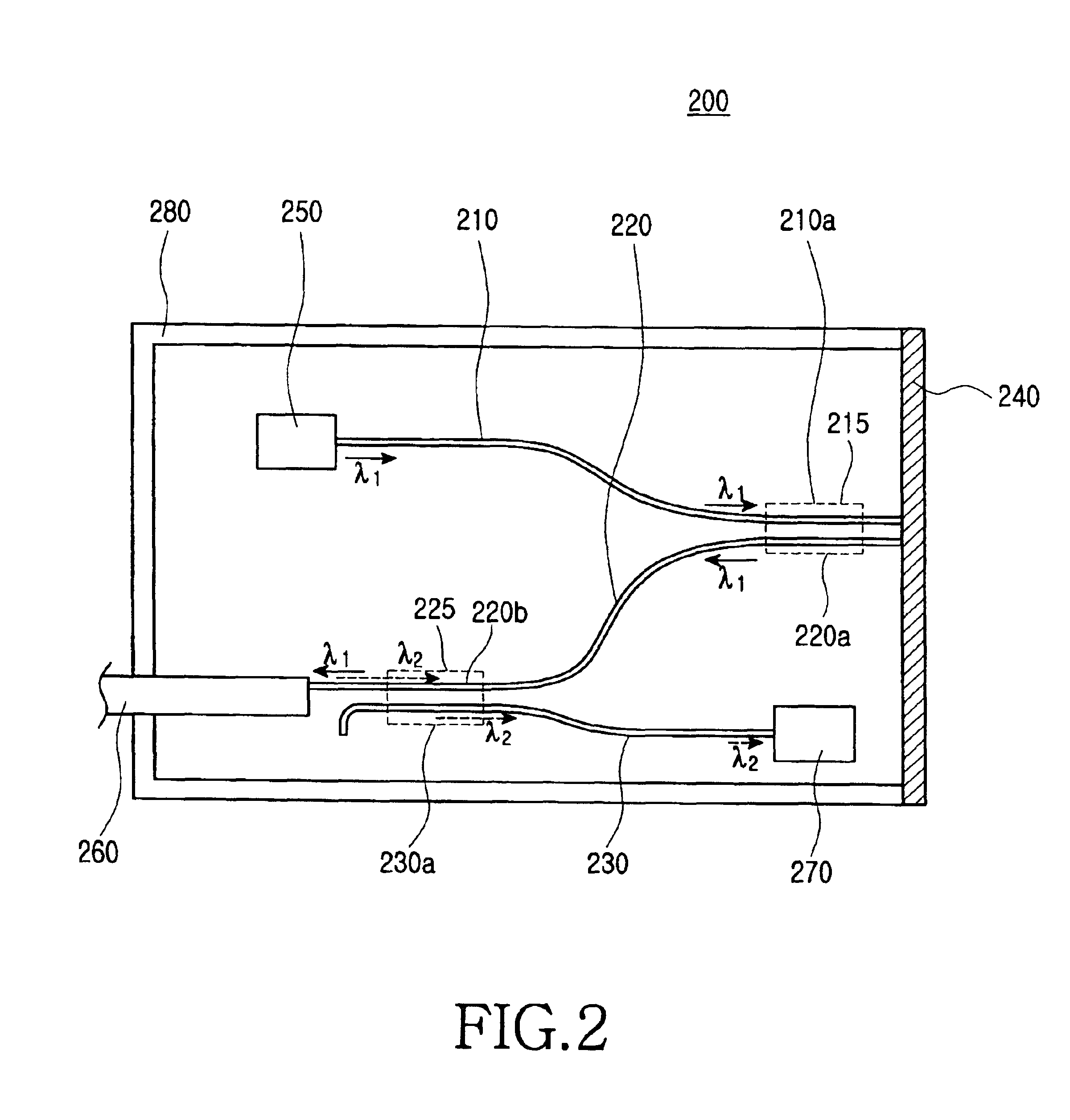
Patents
Literature
86 results about "Third wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
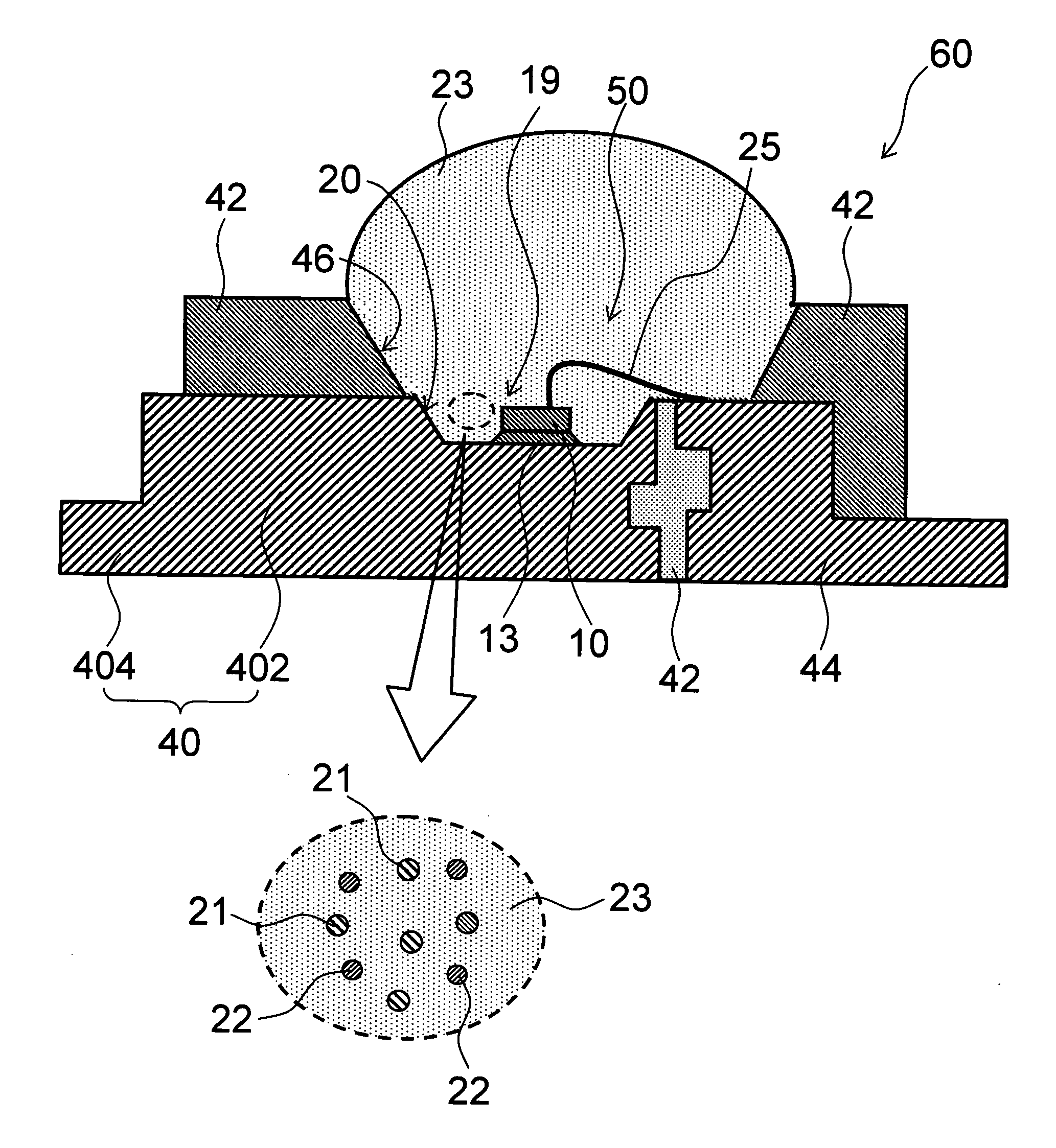
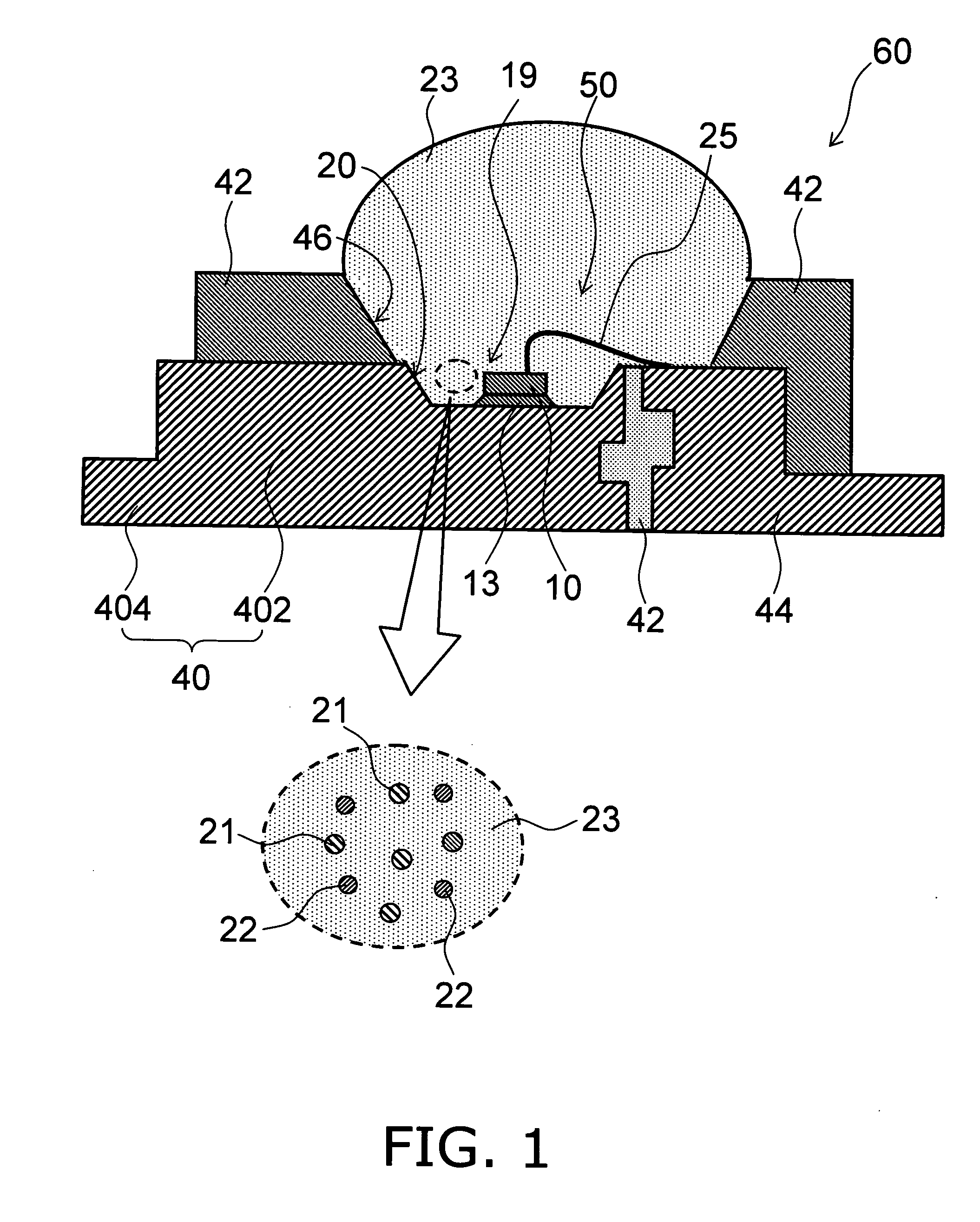
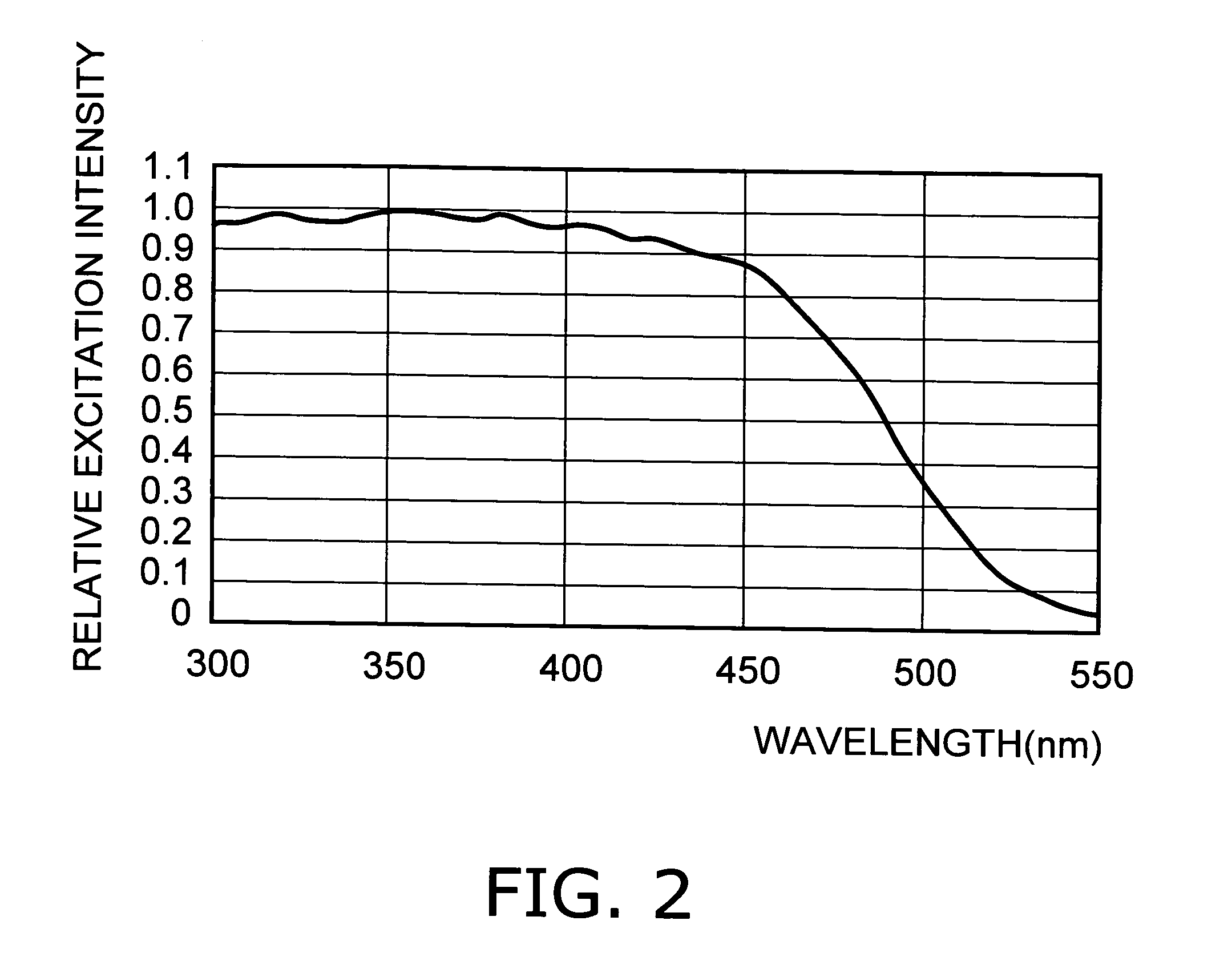
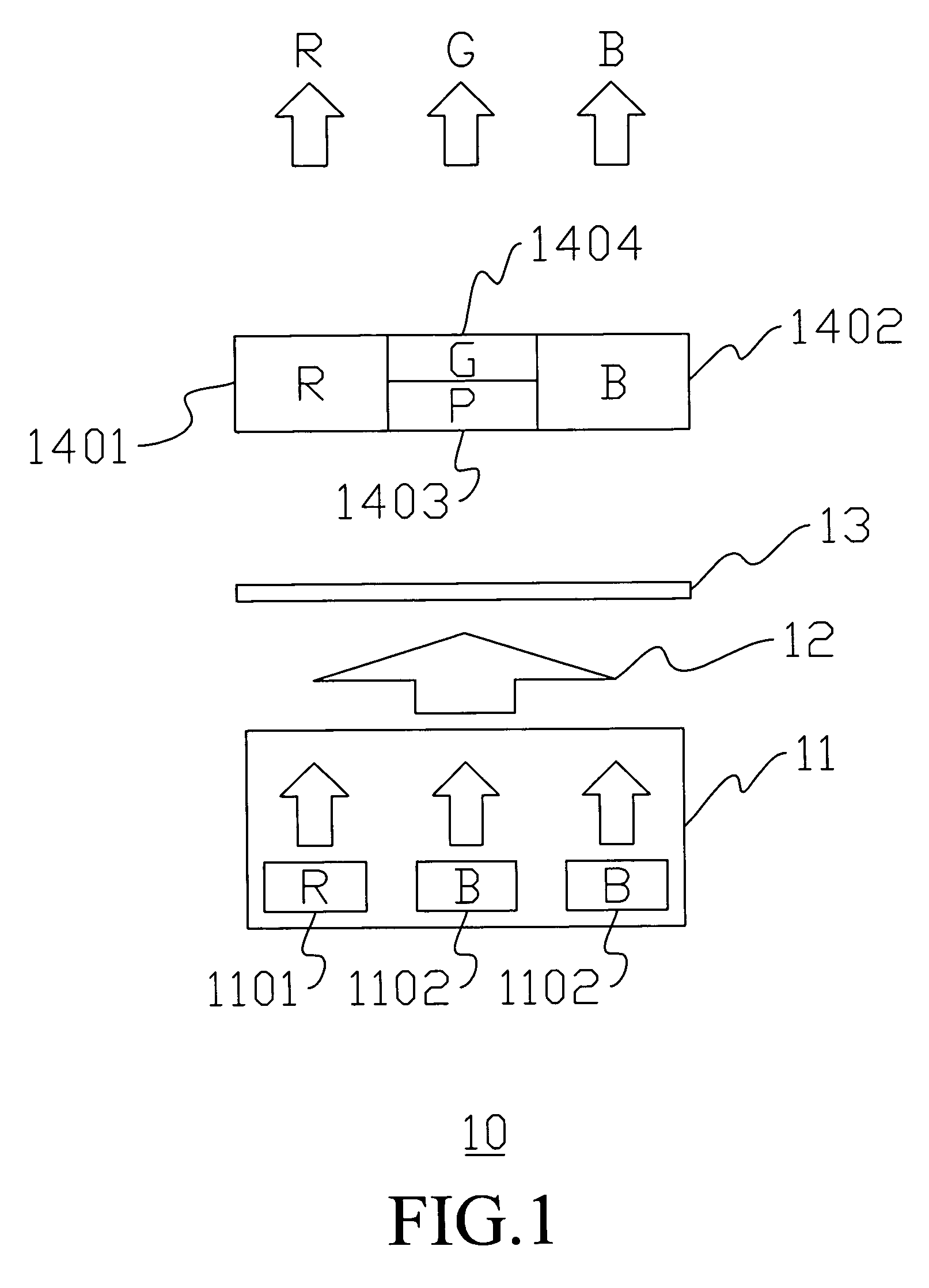
Semiconductor light emitting device
A semiconductor light emitting device comprises: a semiconductor light emitting element that emits first wavelength light; a first fluorescent material that absorbs the first wavelength light and emits second wavelength light having a longer wavelength than the first wavelength light; and a second fluorescent material that absorbs the first wavelength light and emits third wavelength light having a longer wavelength than the second wavelength light. The first fluorescent material and the second fluorescent material are represented by a common chemical composition formula. The first wavelength light, the second wavelength light, and the third wavelength light are combined into light emission of mixed color.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Two-stage adiabatically coupled photonic systems
ActiveUS20160131837A1Well formedCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideThird waveInterposer
In an example, a coupled system includes a first waveguide, at least one second waveguide, and an interposer. The first waveguide has a first refractive index n1 and a tapered end. The at least one second waveguide each has a second refractive index n2. The interposer includes a third waveguide having a third refractive index n3 and a coupler portion, where n1>n2>n3. The tapered end of the first waveguide is adiabatically coupled to a coupler portion of one of the at least one second waveguide. A tapered end of one of the at least one second waveguide is adiabatically coupled to the coupler portion of the third waveguide of the interposer. The coupled system is configured to adiabatically couple light between the first waveguide and the at least one second waveguide and between the at least one second waveguide and the third waveguide.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Two-stage adiabatically coupled photonic systems
In an example, a coupled system includes a first waveguide, at least one second waveguide, and an interposer. The first waveguide has a first refractive index n1 and a tapered end. The at least one second waveguide each has a second refractive index n2. The interposer includes a third waveguide having a third refractive index n3 and a coupler portion, where n1>n2>n3. The tapered end of the first waveguide is adiabatically coupled to a coupler portion of one of the at least one second waveguide. A tapered end of one of the at least one second waveguide is adiabatically coupled to the coupler portion of the third waveguide of the interposer. The coupled system is configured to adiabatically couple light between the first waveguide and the at least one second waveguide and between the at least one second waveguide and the third waveguide.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
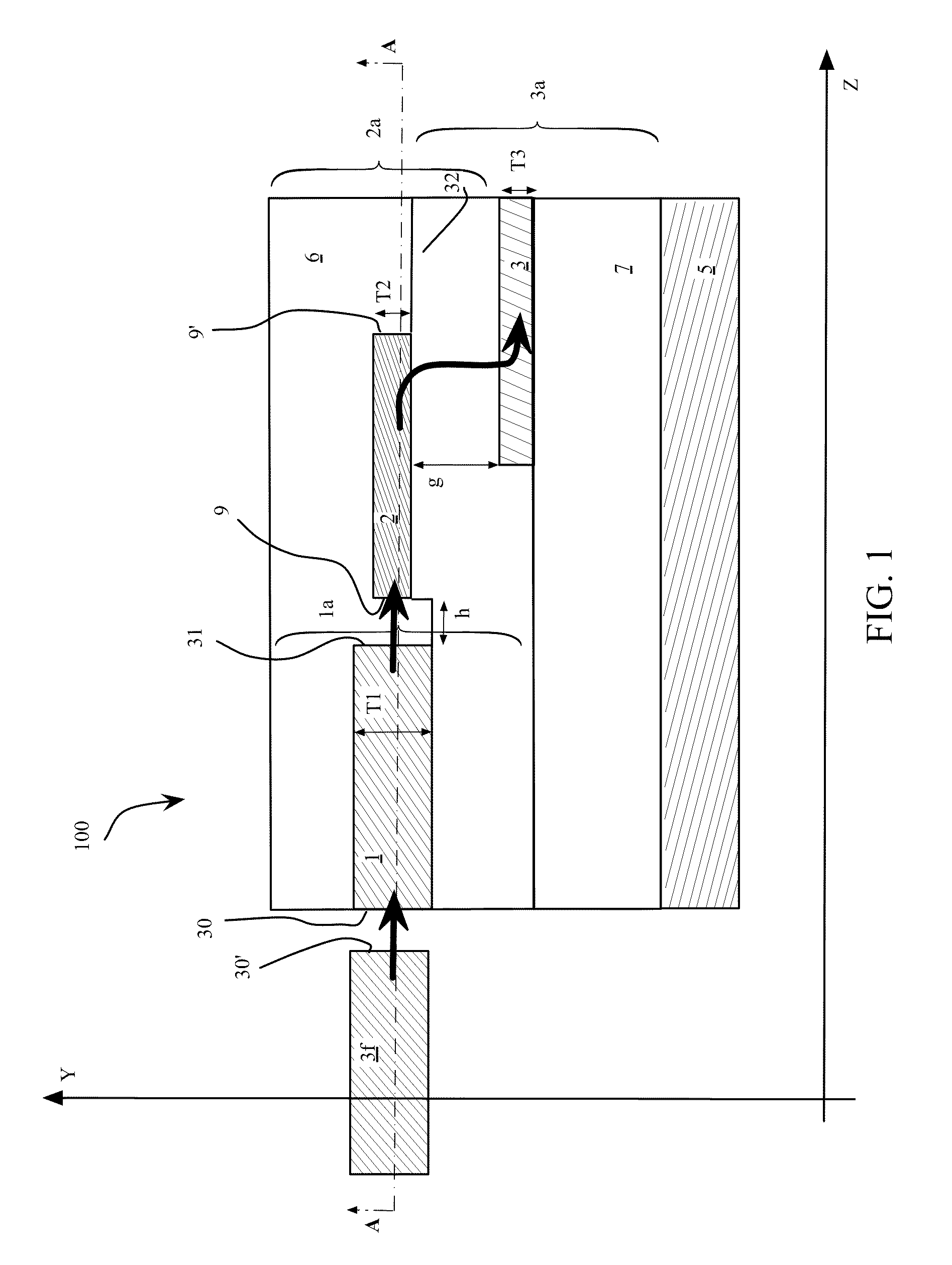
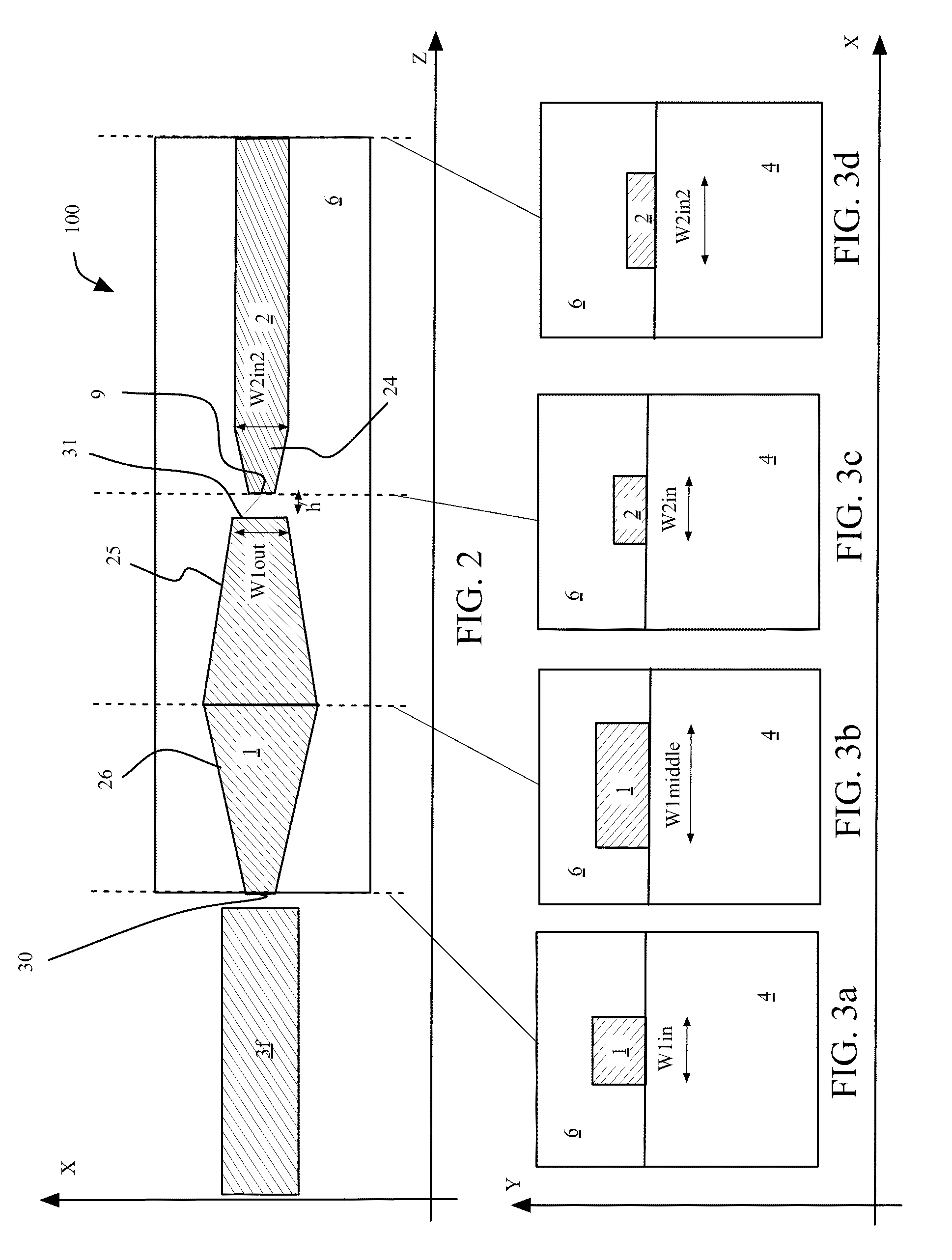
Optical mode transformer, in particular for coupling an optical fiber and a high-index contrast waveguide
InactiveUS20110116741A1Efficient couplingHigh indexCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideThird waveRefractive index contrast
An optical mode transformer comprises a first waveguide including a first core, a first cladding and an end facet configured to be coupled to an optical fiber. The transformer further includes a second waveguide comprising a second core, a second cladding and an end directly coupled to an end of the first waveguide. A third waveguide comprises a third core and a third cladding, and is arranged with respect to the second waveguide so as to realize an evanescent optical coupling with the second waveguide. The third core includes a tapered region wherein evanescent coupling takes place, and wherein a refractive index contrast of the first waveguide is less than a refractive index contrast of the second waveguide, the refractive index contrast of the second waveguide is less than a refractive index contrast of the third waveguide, and the refractive index contrast of the third waveguide is not less than 18%.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
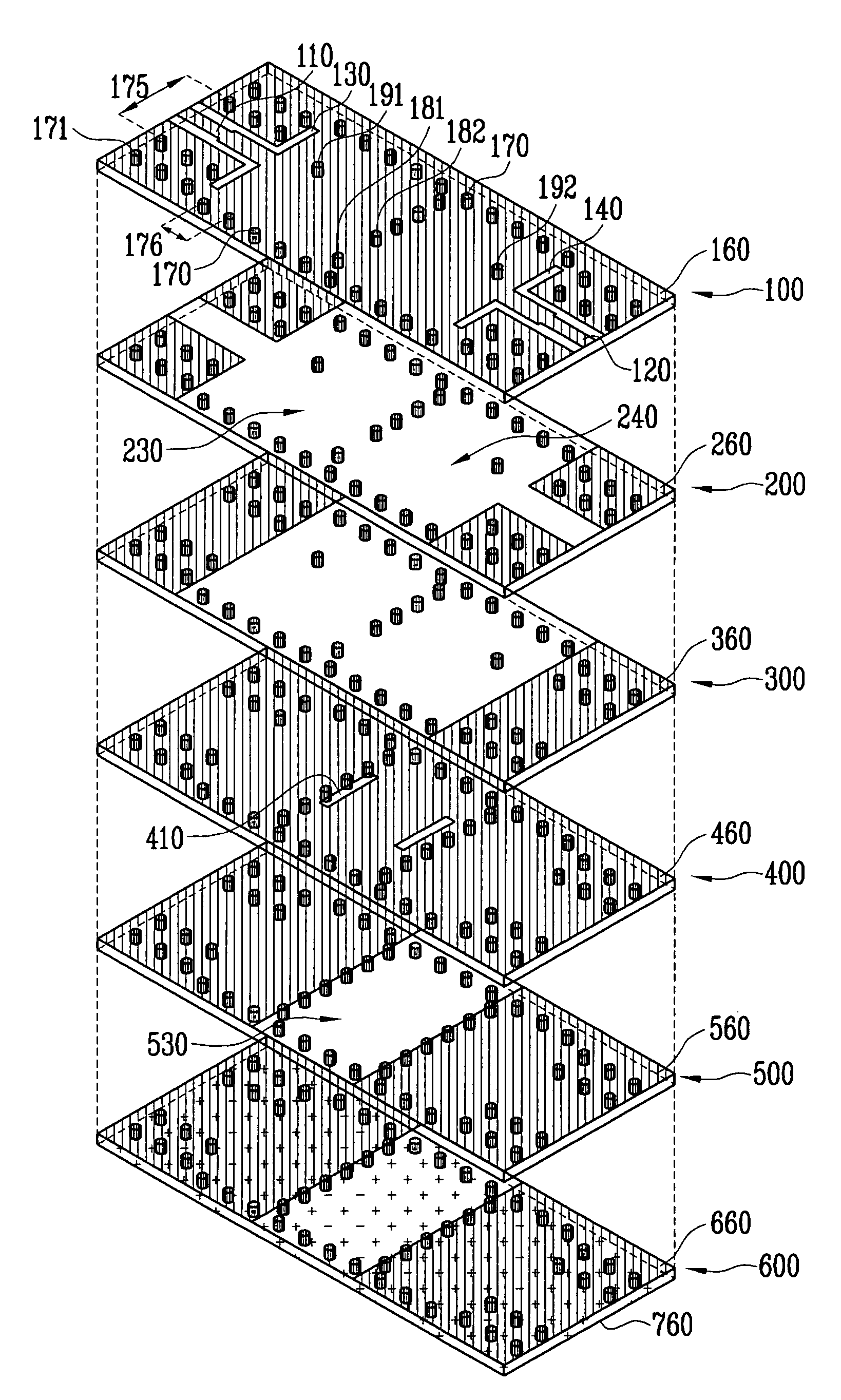
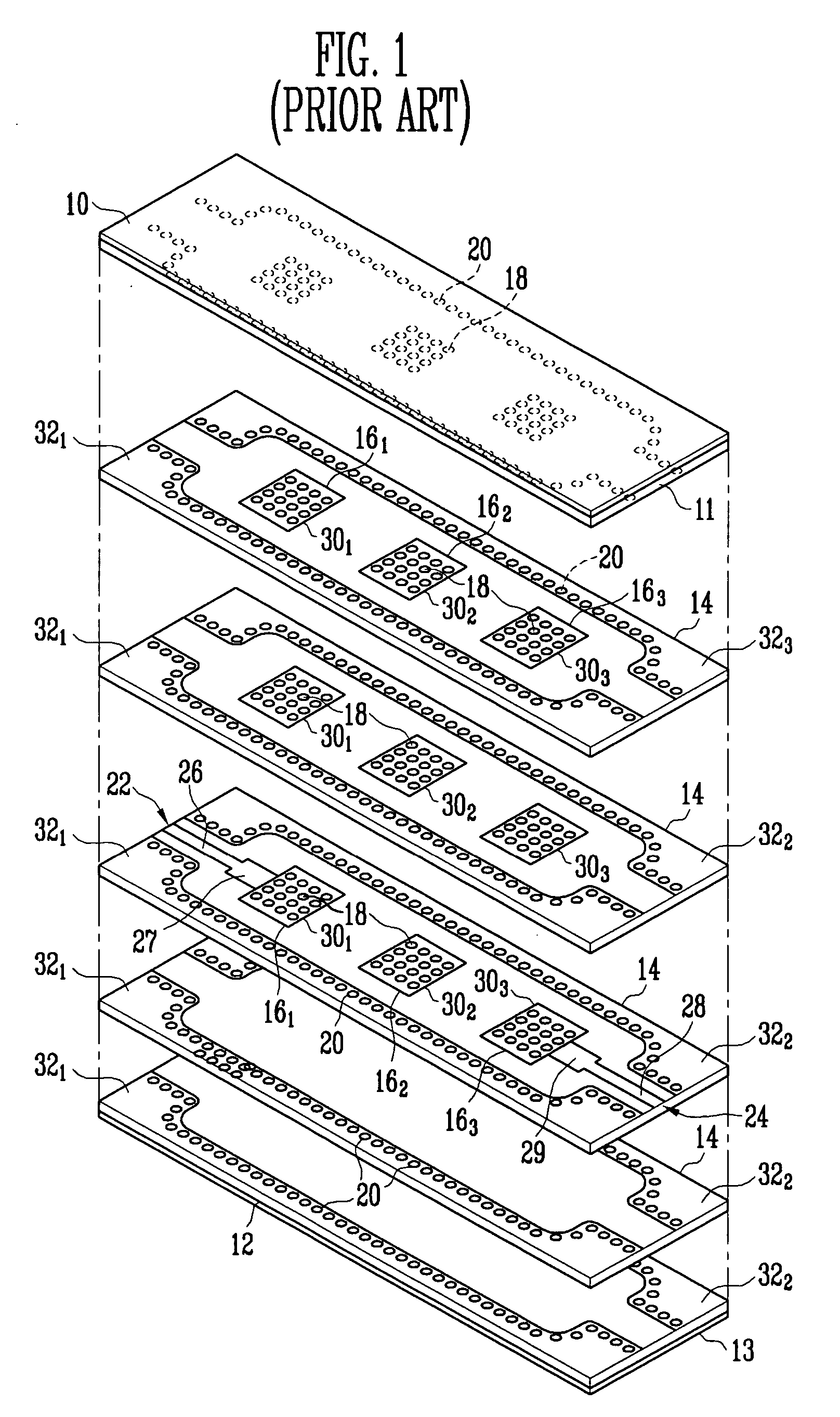
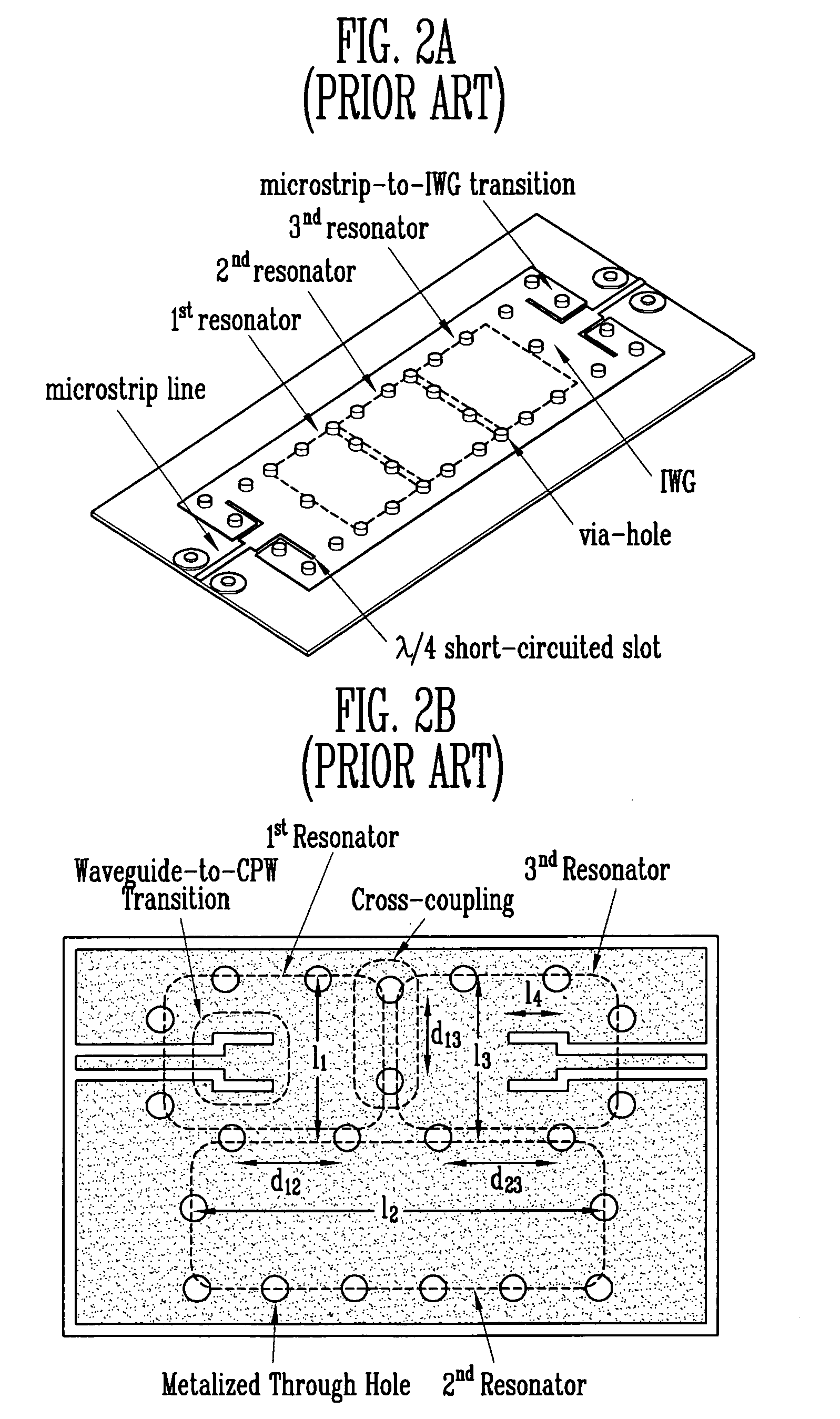
Dielectric waveguide filter with cross-coupling
InactiveUS20070120628A1Suppress radiation lossSuppress broadband spuriousResonatorsWaveguidesThird waveCoupling
Provided is a dielectric waveguide filter. The filter includes: a multi-layered structure of dielectric substrates having first and second ground planes at its top and bottom; first, second, and third waveguide resonators disposed at multiple layers within the multi-layered structure; converters for signal transition between input / output ports and the first and third waveguide resonators; first vias for forming the first, second, and third waveguide resonators; and second vias disposed at a boundary surface of the first waveguide resonator and the third waveguide resonator.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical mode transformer, in particular for coupling an optical fiber and a high-index contrast waveguide
InactiveUS8320721B2Efficient couplingIncrease contrastCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideThird waveRefractive index contrast
An optical mode transformer comprises a first waveguide including a first core, a first cladding and an end facet configured to be coupled to an optical fiber. The transformer further includes a second waveguide comprising a second core, a second cladding and an end directly coupled to an end of the first waveguide. A third waveguide comprises a third core and a third cladding, and is arranged with respect to the second waveguide so as to realize an evanescent optical coupling with the second waveguide. The third core includes a tapered region wherein evanescent coupling takes place, and wherein a refractive index contrast of the first waveguide is less than a refractive index contrast of the second waveguide, the refractive index contrast of the second waveguide is less than a refractive index contrast of the third waveguide, and the refractive index contrast of the third waveguide is not less than 18%.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
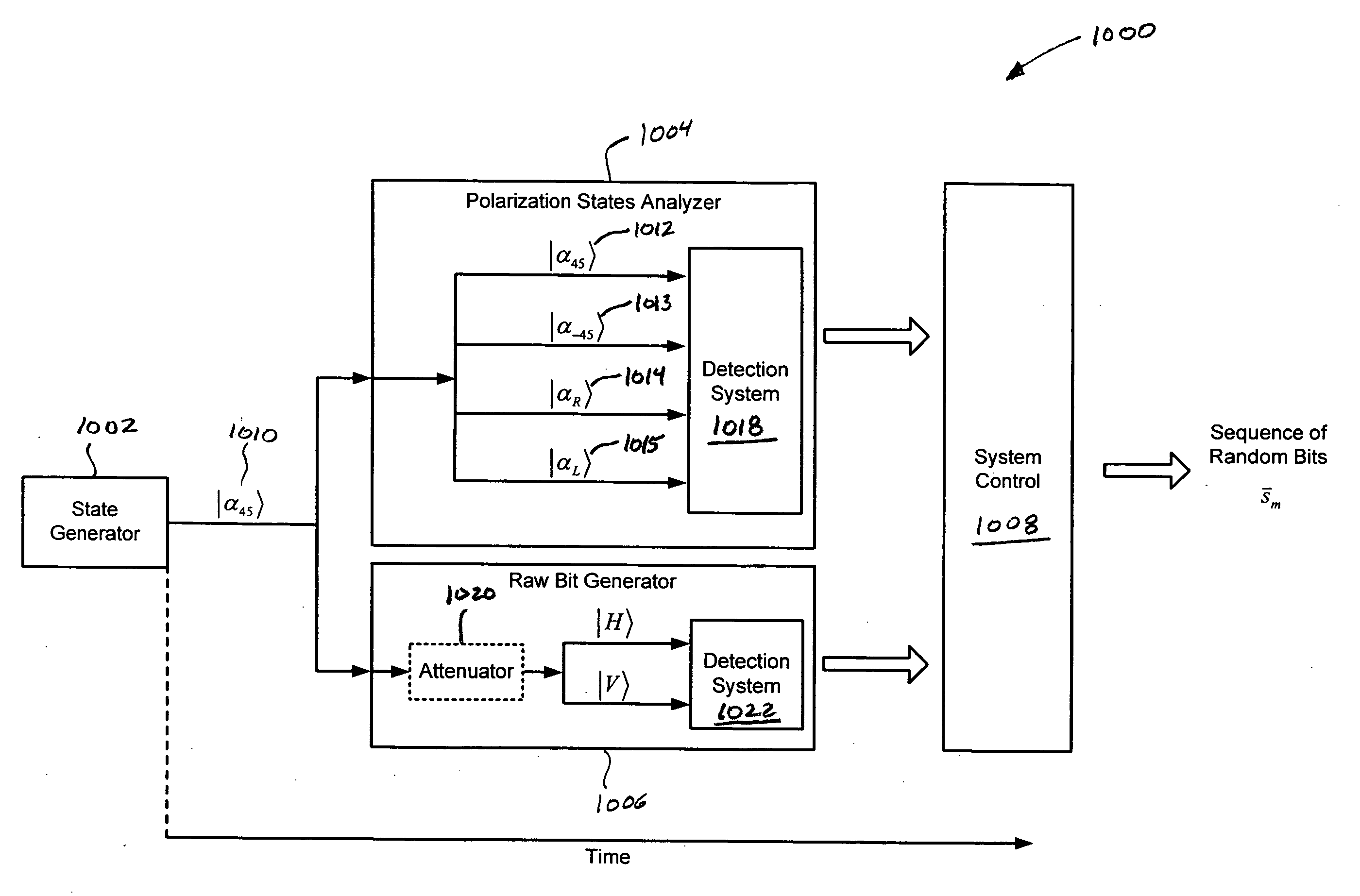
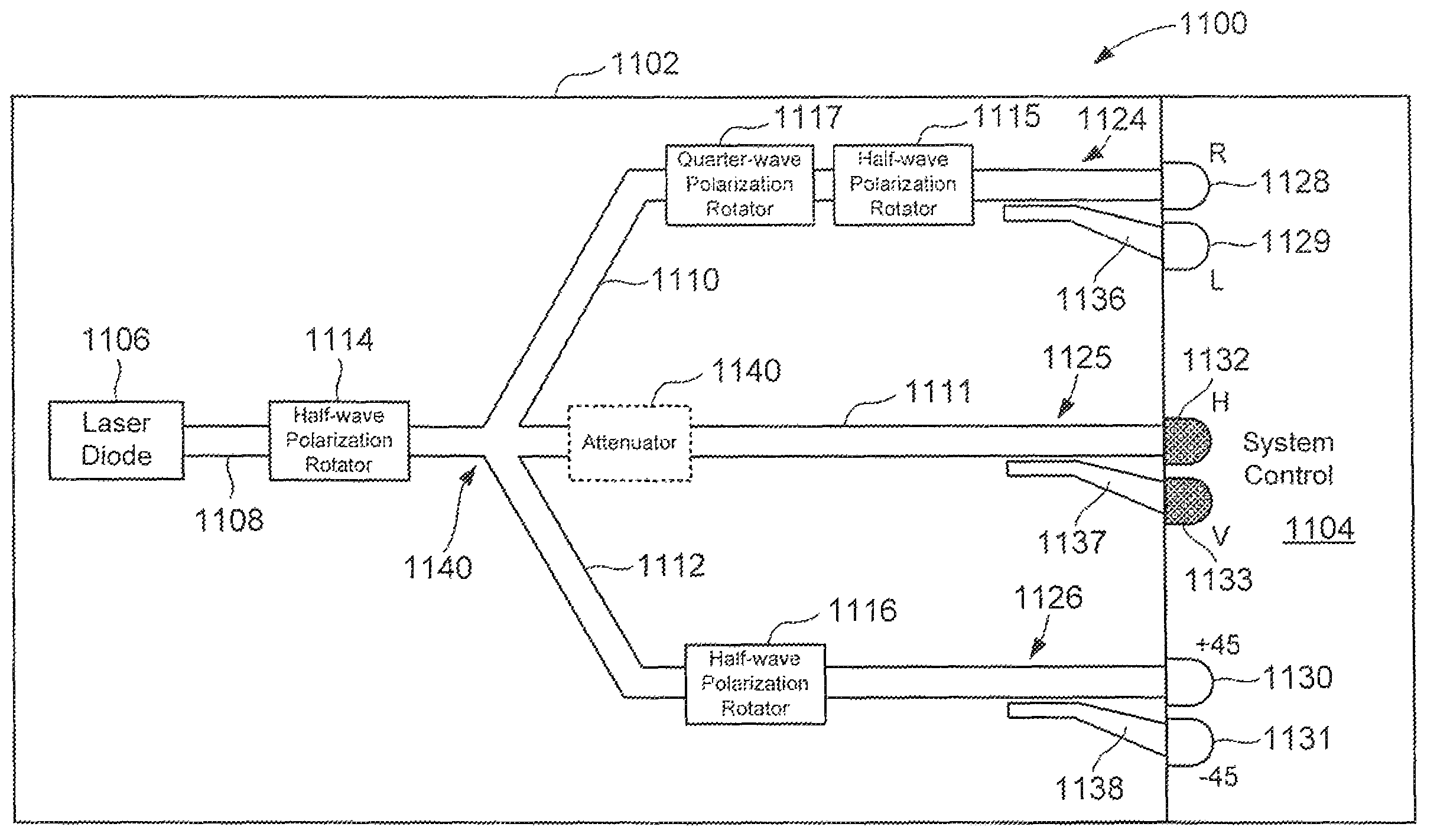
Self-authenticating quantum random bit generators
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to self-authenticating, quantum random bit generators that can be integrated into an optoelectronic circuit. In one embodiment, a quantum random bit generator comprises a transmission layer that includes an electromagnetic radiation source coupled to a waveguide branching into a first, second, and third waveguides. The radiation source generates pulses of electromagnetic radiation in a first polarization state. Polarization rotators are operably coupled to the second and third waveguides and rotate pulses transmitted in the second waveguide into a second polarization state and rotate pulses transmitted in the third waveguide into a third polarization state. The system control generates a sequence of bits based on polarization basis states of the pulses transmitted in the first waveguide, and tomographically authenticates randomness of the sequence based on polarization basis states of the second and third pulses.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method for monitoring forest fire by means of combination of infrared and multi-spectral wave bands
ActiveCN104240429AHighlight fire range featuresFire Range Characteristic PreservationRadiation pyrometryFire alarm radiation actuationImage resolutionData acquisition
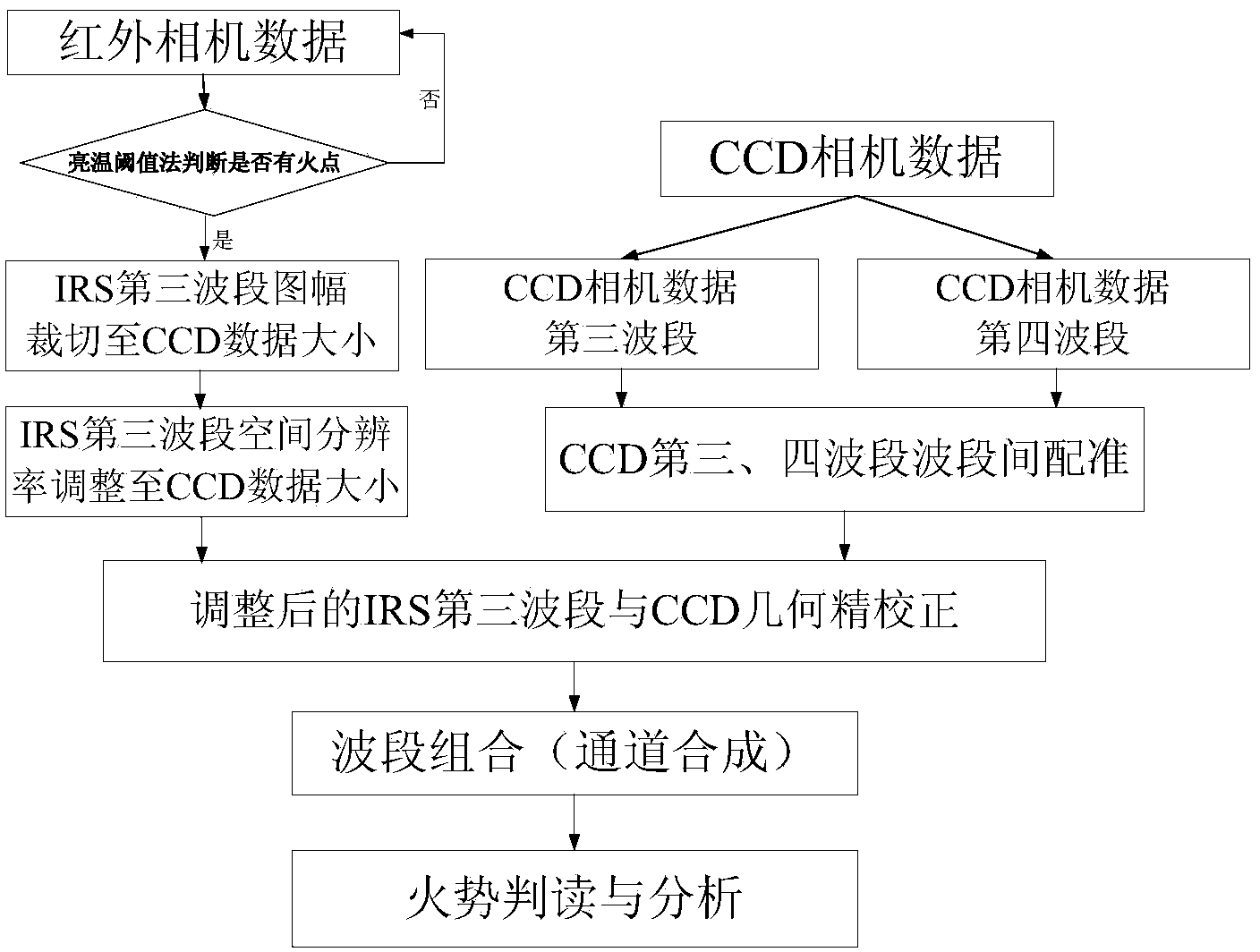
The invention provides a method for monitoring a forest fire by means of combination of infrared and multi-spectral wave bands. The method includes the steps that (1) CCD camera data and infrared camera data collected by an environment satellite on the same day are selected; the third wave band namely an infrared wave band and the fourth wave band namely a near infrared wave band of a CCD camera and the third wave band namely an infrared wave band of an infrared camera are selected; (2) radiation brightness calculation is carried out on the collected infrared camera data, whether fire points exist is judged primarily, if the answer is positive, the step (3) is carried out and otherwise, the step (1) is carried out again for data collection; (3) data of the third wave band of the infrared camera are adjusted so that the infrared camera can keep consistent with the CCD camera in mapsheet and space resolution ratio; (4) precise geometric rectification is carried out on the adjusted CCD camera data and the adjusted infrared camera data; (5) the third wave band of the CCD undergoing precise geometric rectification serves as a new first wave band, the fourth wave band serves as a new second wave band, the third wave band of the infrared camera serves as a new third wave band and the forest fire is monitored by means of a newly obtained image.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Bonded helical compression spring
A bonded helical compression spring. The spring includes a plurality of layers having successive wave crests and troughs. First crests and first troughs of a first layer are aligned with respective second troughs and second crests of an adjacent second layer and with respective third troughs and third crests of an adjacent third layer. The first crests of the first layer are bonded to the second troughs of the adjacent second layer and the first troughs of the first layer are bonded to the third crests of the adjacent third layer. As the crests and troughs of adjacent layers are bonded together, friction between the crests and troughs is eliminated.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
Optical Signal Amplifying Triode And Optical Signal Transfer Method, Optical Signal Relay Device, And Optical Signal Storage Device Using The Same
ActiveUS20060008203A1Optical signal enhancementAvoid attenuationLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsThird waveAudio power amplifier
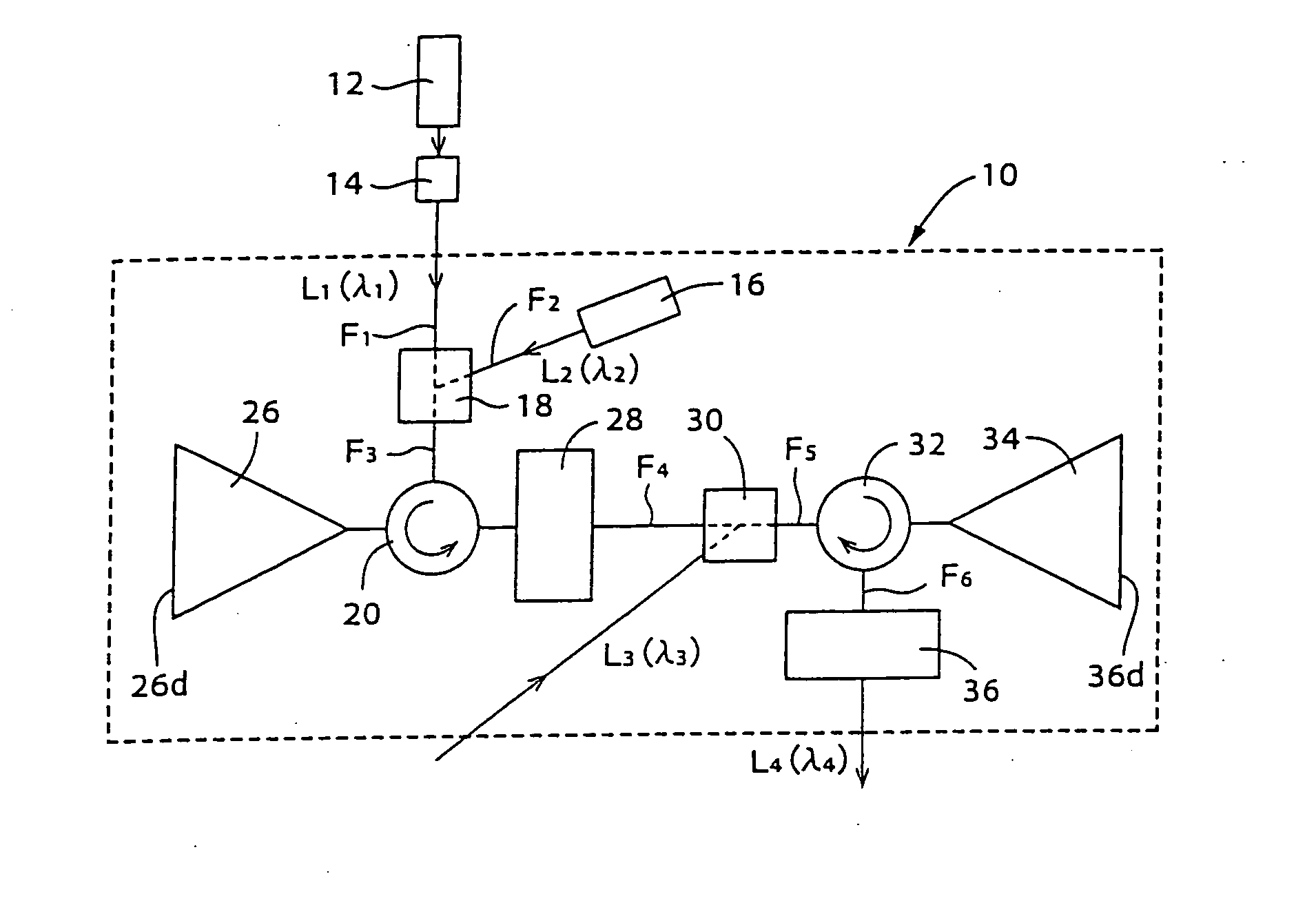
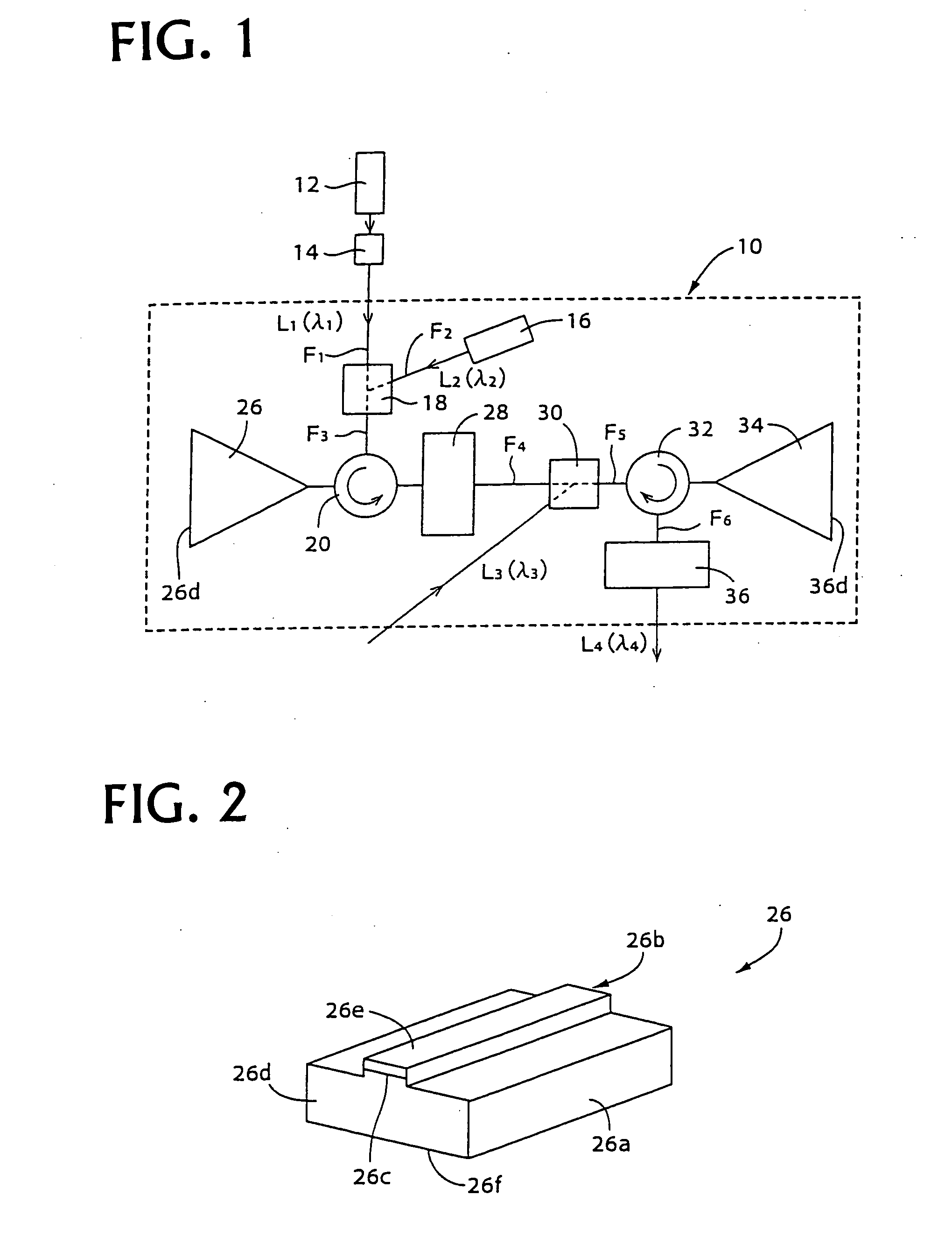
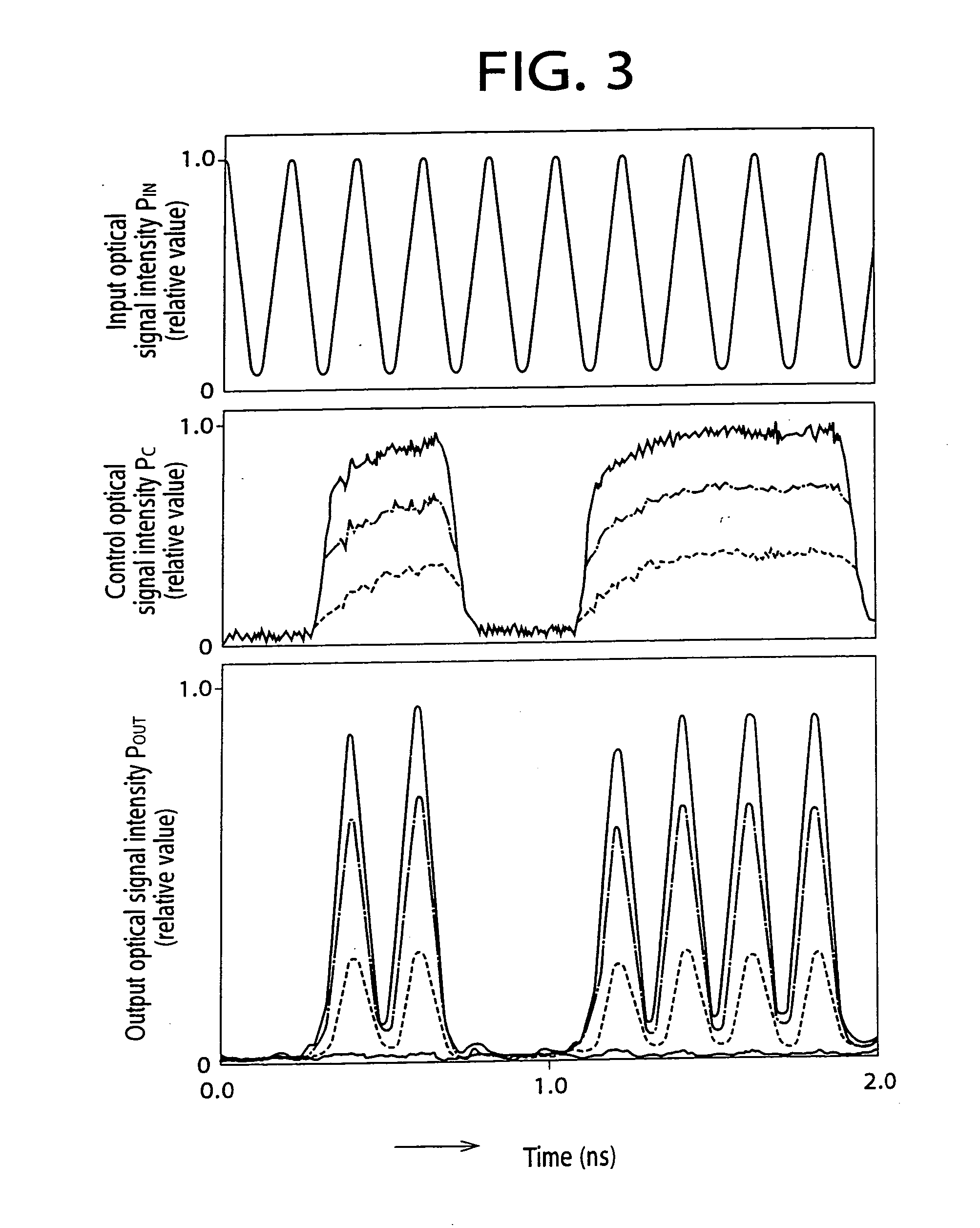
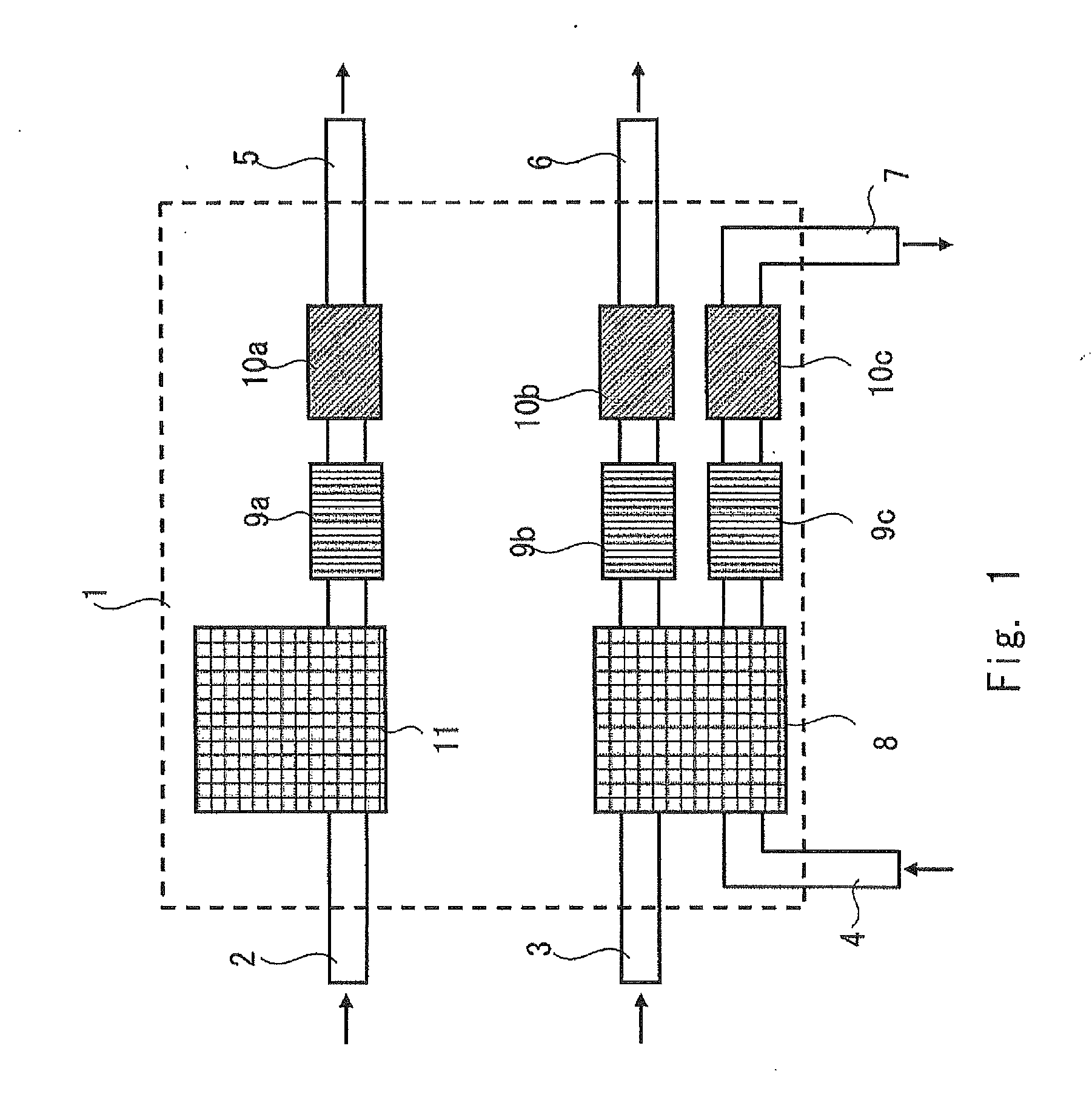
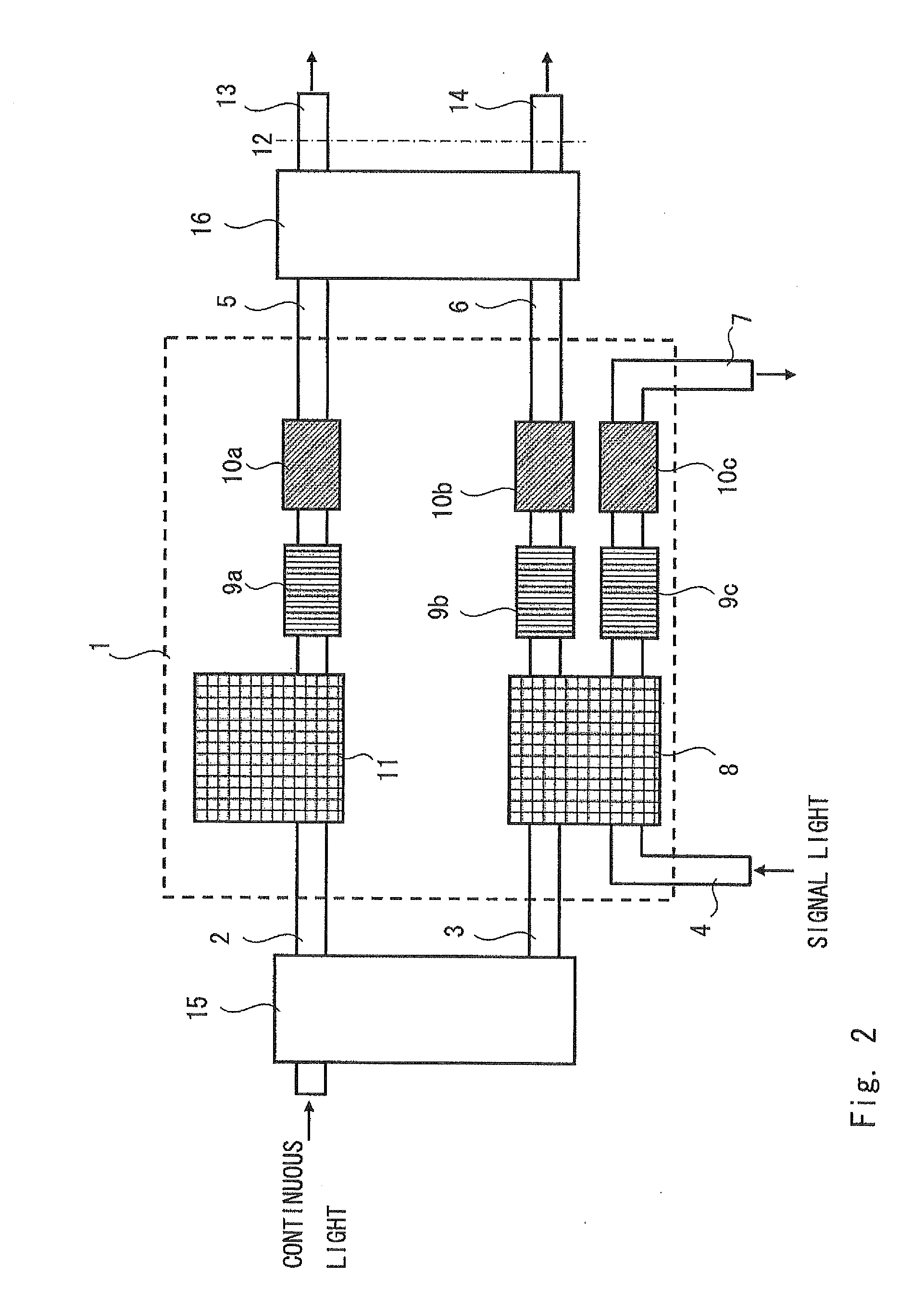
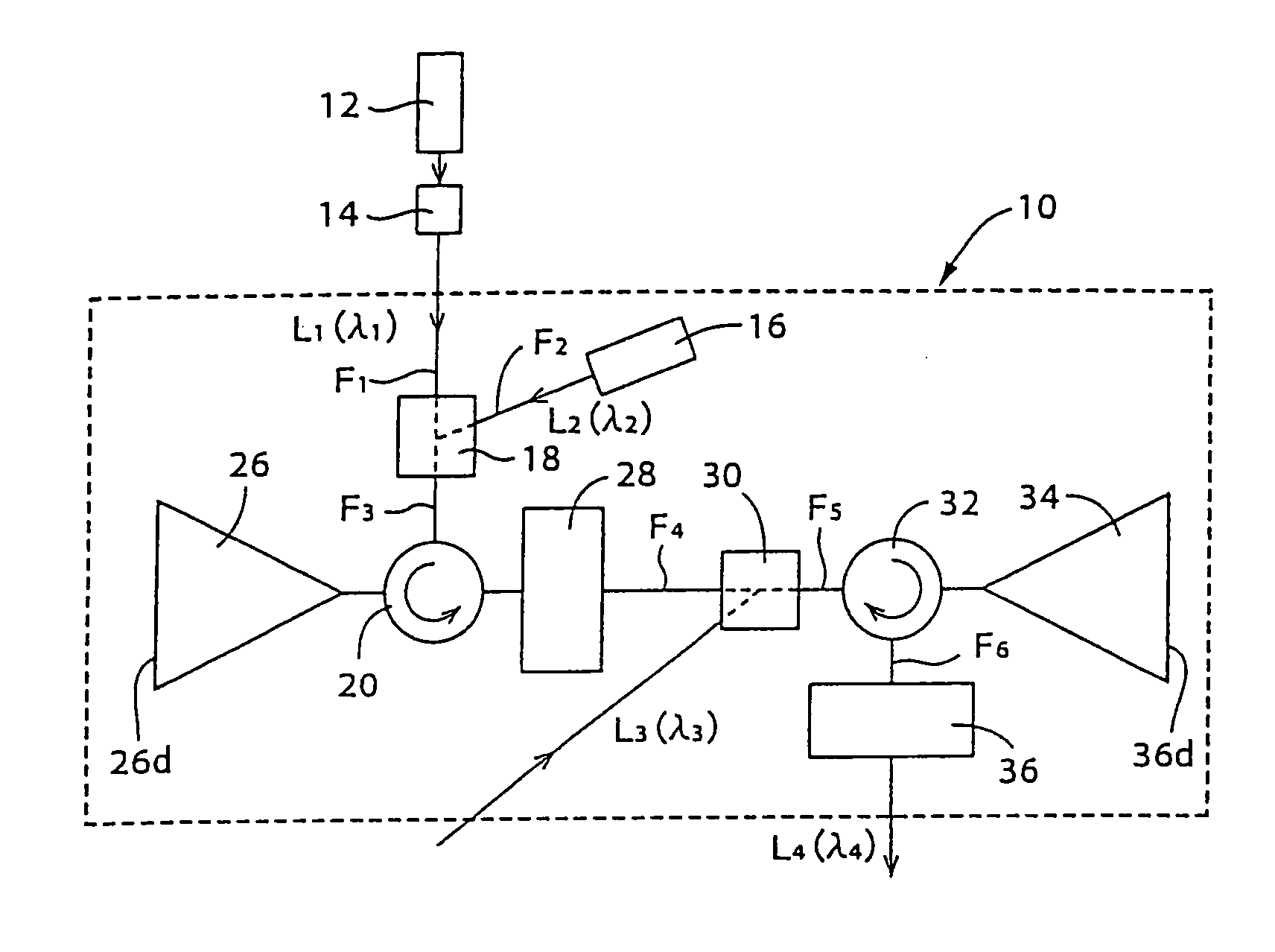
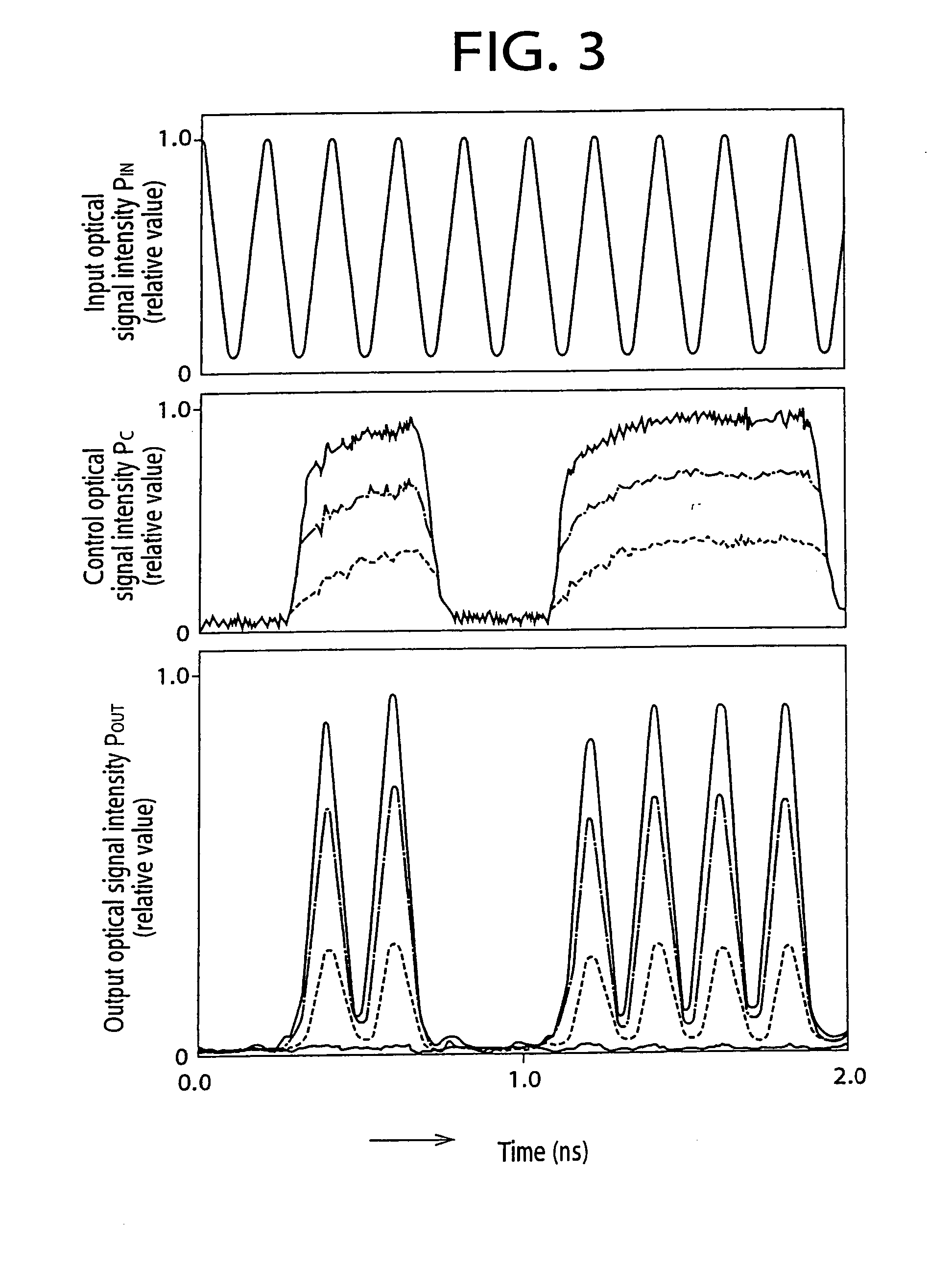
When in an optical signal amplifying triode 10, light of a second wavelength λ2, selected from among light from a first optical amplifier 26, into which a first input light L1 of a first wavelength λ1 and a second input light L2 of second wavelength λ2 have been input, and a third input light (control light) L3of a third wavelength λ3 are input into a second optical amplifier 34, an output light L4 of the third wavelength λ3, selected from among the light output from the second optical amplifier 34, is light that is modulated in response to the intensity variation of one or both of the first input light L1 of the first wavelength λ1 and the third input light L3 of the third wavelength λ3 and is an amplified signal, with which the signal gain with respect to the third input light (control light) L3 of the third wavelength λ3 is of a magnitude of 2 or more. An optical signal amplifying triode 10, which can directly perform an optical signal amplification process using control input light, can thus be provided.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
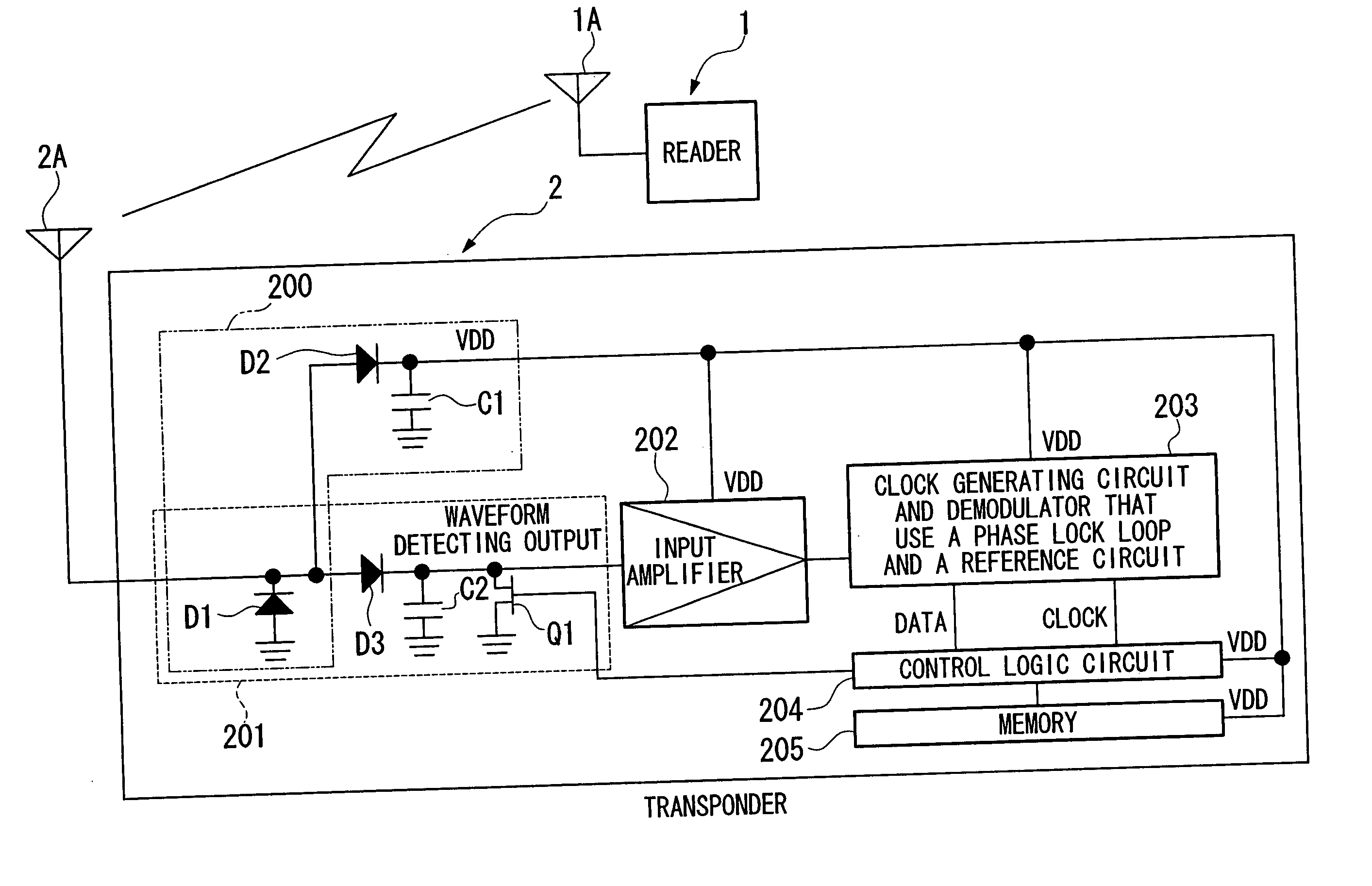
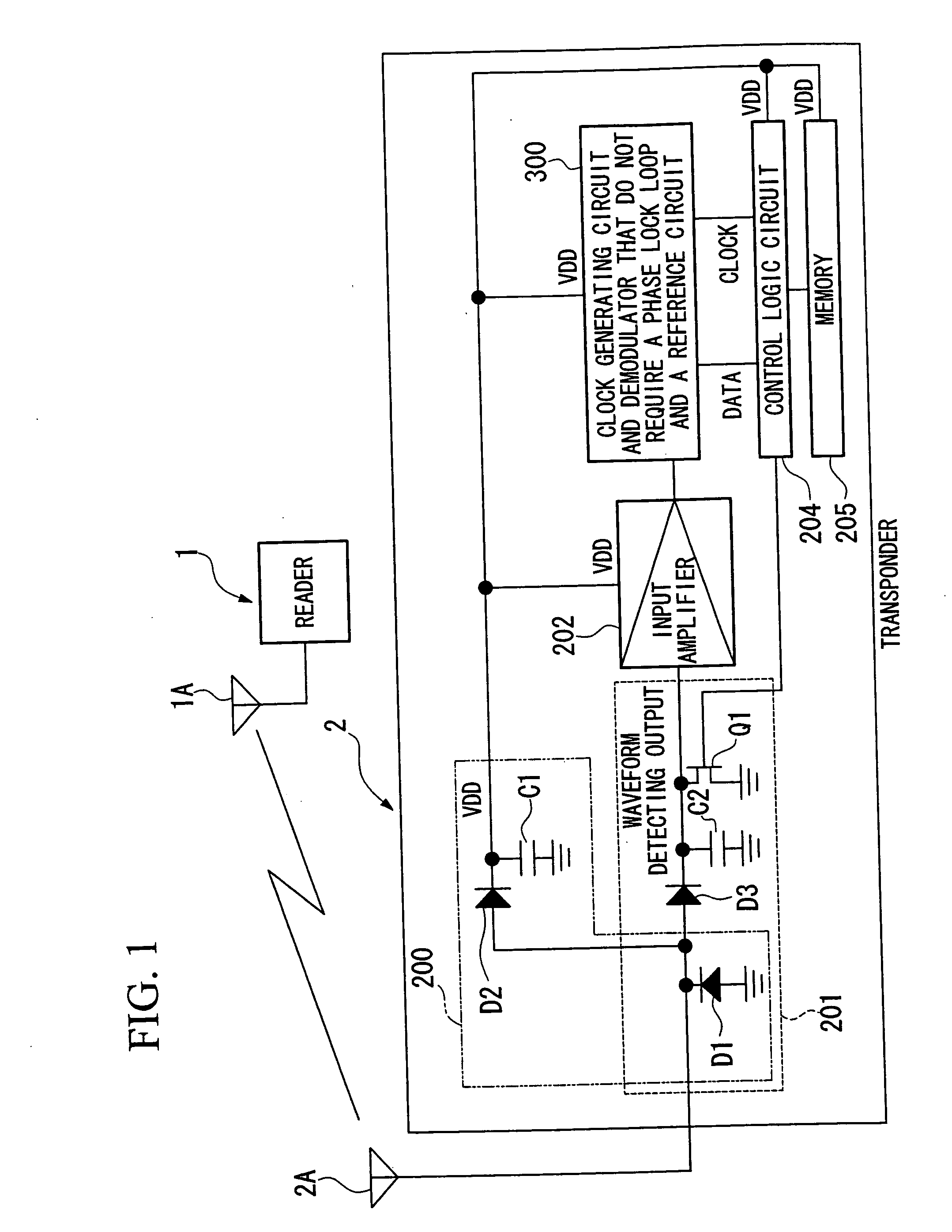
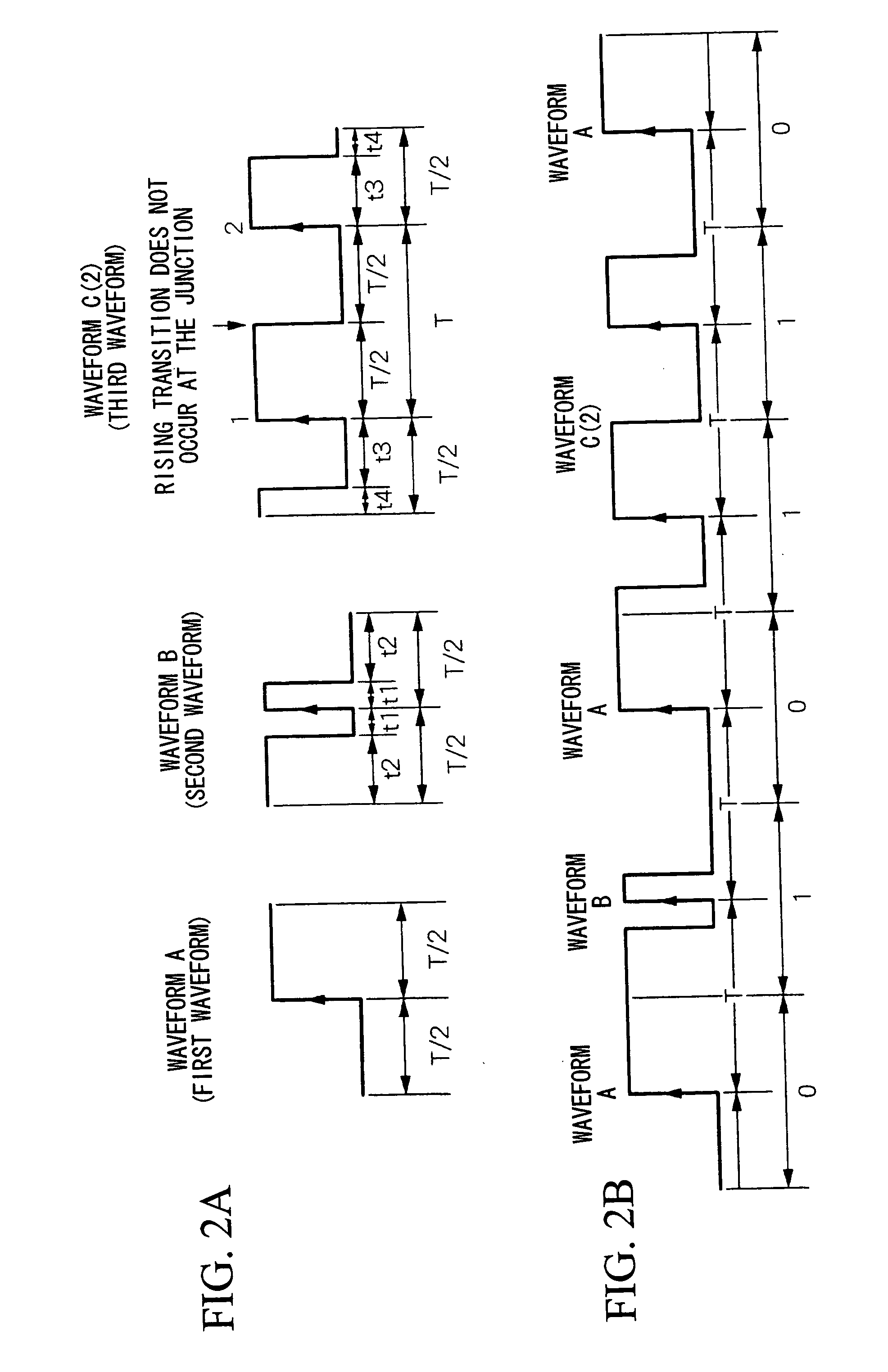
Non-contact rf id system communication method, non-contact rf id system, transmitter, and receiver
InactiveUS20050253716A1Easily clock signalPromote generationElectric signal transmission systemsEqual length code transmitterWave shapeEngineering
A communication method for a noncontact RF ID system that uses a first waveform, a second waveform, and a third waveform, wherein the first waveform and the second waveform are formed by a basic waveform having one of a rising or falling state transition at the approximate center of the waveform, the third waveform is formed by a plurality of basic waveforms that have one state transition at the approximate center part of the waveform, and the third waveform generates one state transition only at the approximate center of the plurality of basic waveforms. In addition, communication is carried out by using the third waveform in place of the first waveform and the second waveform in the case in which communication is carried out using a first waveform and a second waveform and one state transition is generated outside the approximate center part of the basic waveform.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Flat light-emitting apparatus
ActiveUS20070091599A1Improve lighting efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectric circuit arrangementsThird waveLength wave
A flat light-emitting apparatus includes a light-emitting element for radiating visible light consisting of a first-wavelength light with a wavelength substantially not less than 600 nm and a second-wavelength light with a wavelength substantially not greater than 480 nm, a wavelength conversion material for generating a third-wavelength light when irradiated by the second-wavelength light, a first color filter for the passing of the first-wavelength light, a second color filter for the passing of the second-wavelength light, and a third color filter for the passing of the third-wavelength light.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Self-authenticating quantum random bit generators
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to self-authenticating, quantum random bit generators that can be integrated into an optoelectronic circuit. In one embodiment, a quantum random bit generator comprises a transmission layer that includes an electromagnetic radiation source coupled to a waveguide branching into a first, second, and third waveguides. The radiation source generates pulses of electromagnetic radiation in a first polarization state. Polarization rotators are operably coupled to the second and third waveguides and rotate pulses transmitted in the second waveguide into a second polarization state and rotate pulses transmitted in the third waveguide into a third polarization state. The system control generates a sequence of bits based on polarization basis states of the pulses transmitted in the first waveguide, and tomographically authenticates randomness of the sequence based on polarization basis states of the second and third pulses.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Image sensor having improved light utilization efficiency
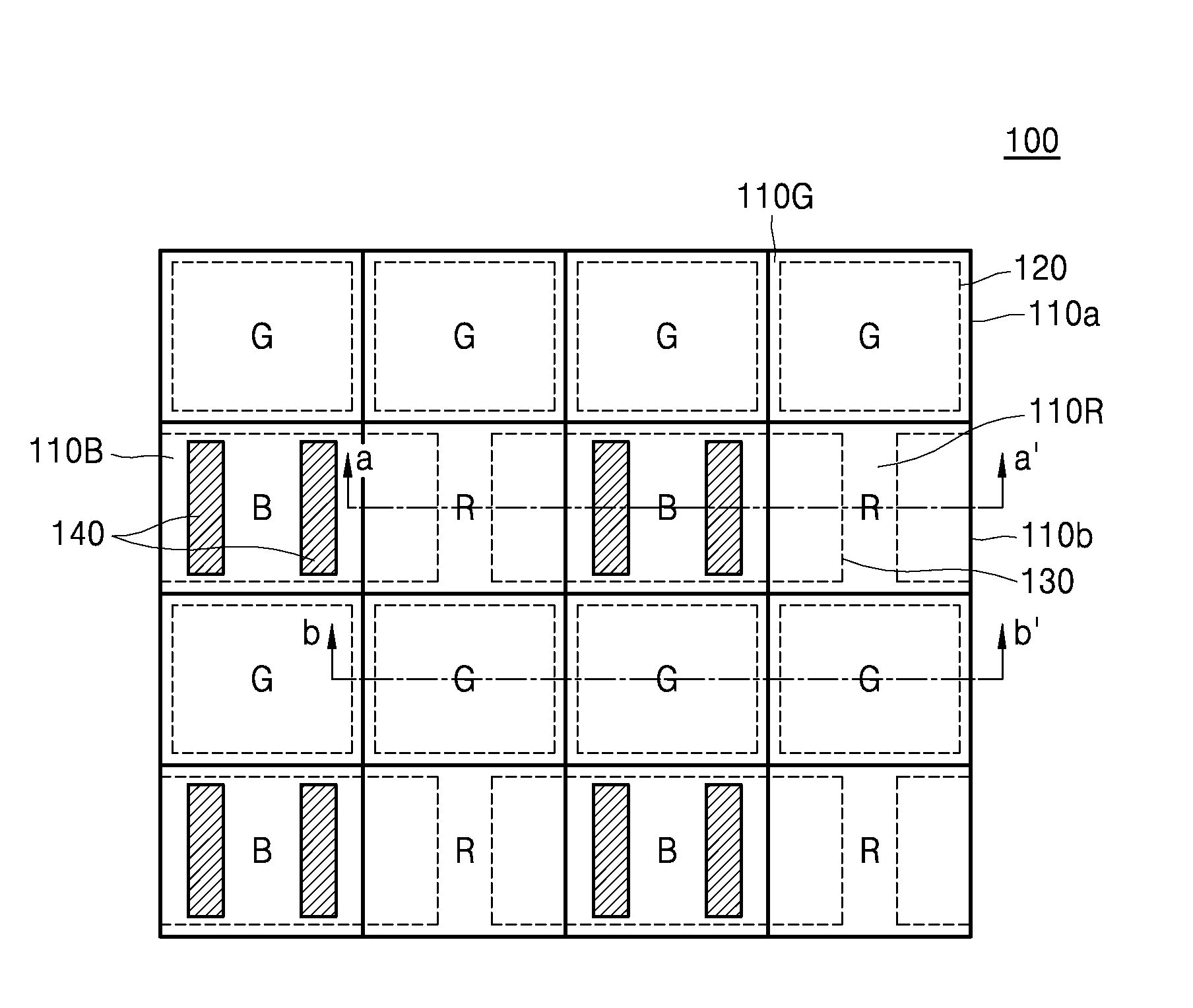
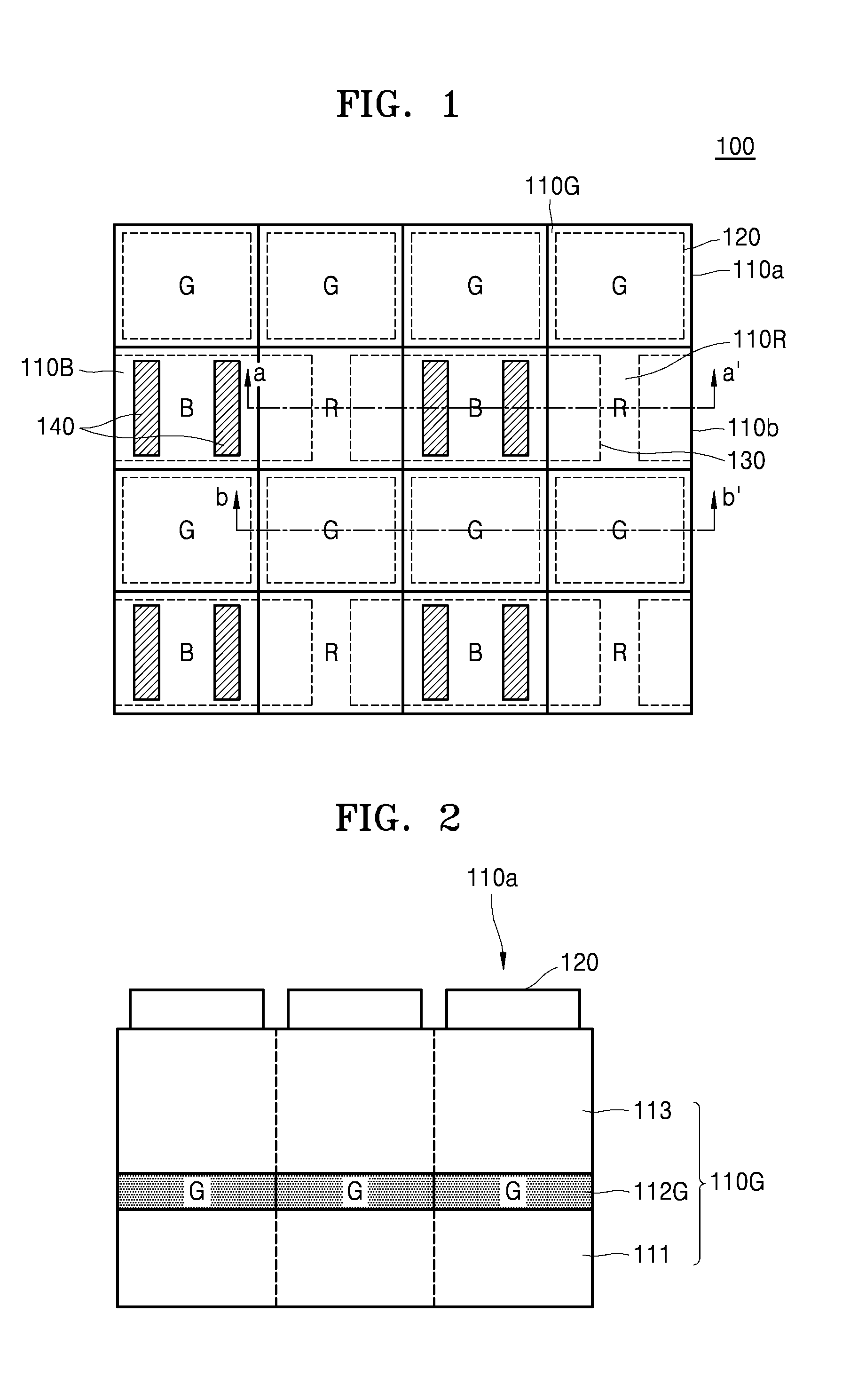
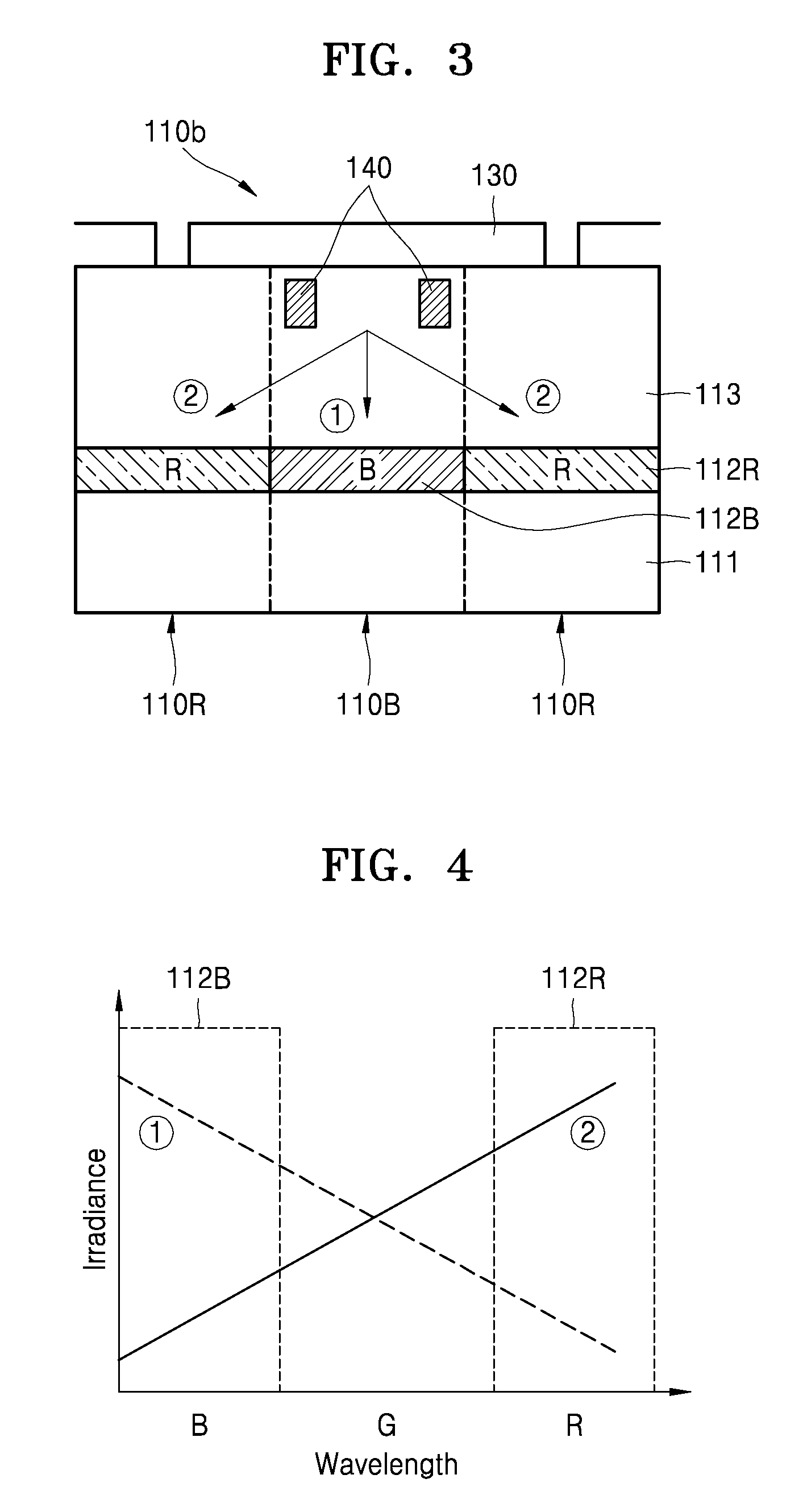
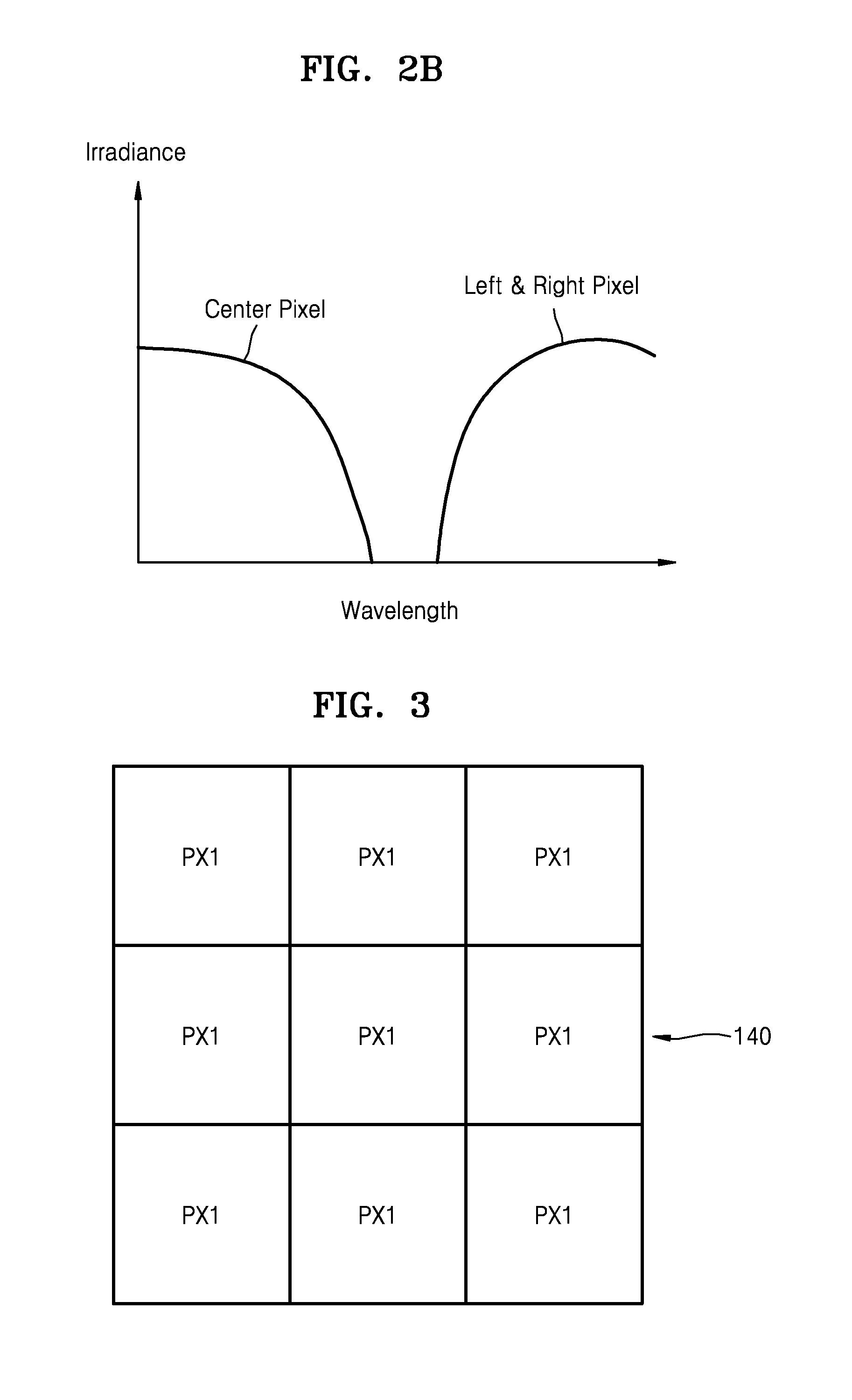
ActiveUS20150318318A1Raise the ratioSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesThird waveLength wave
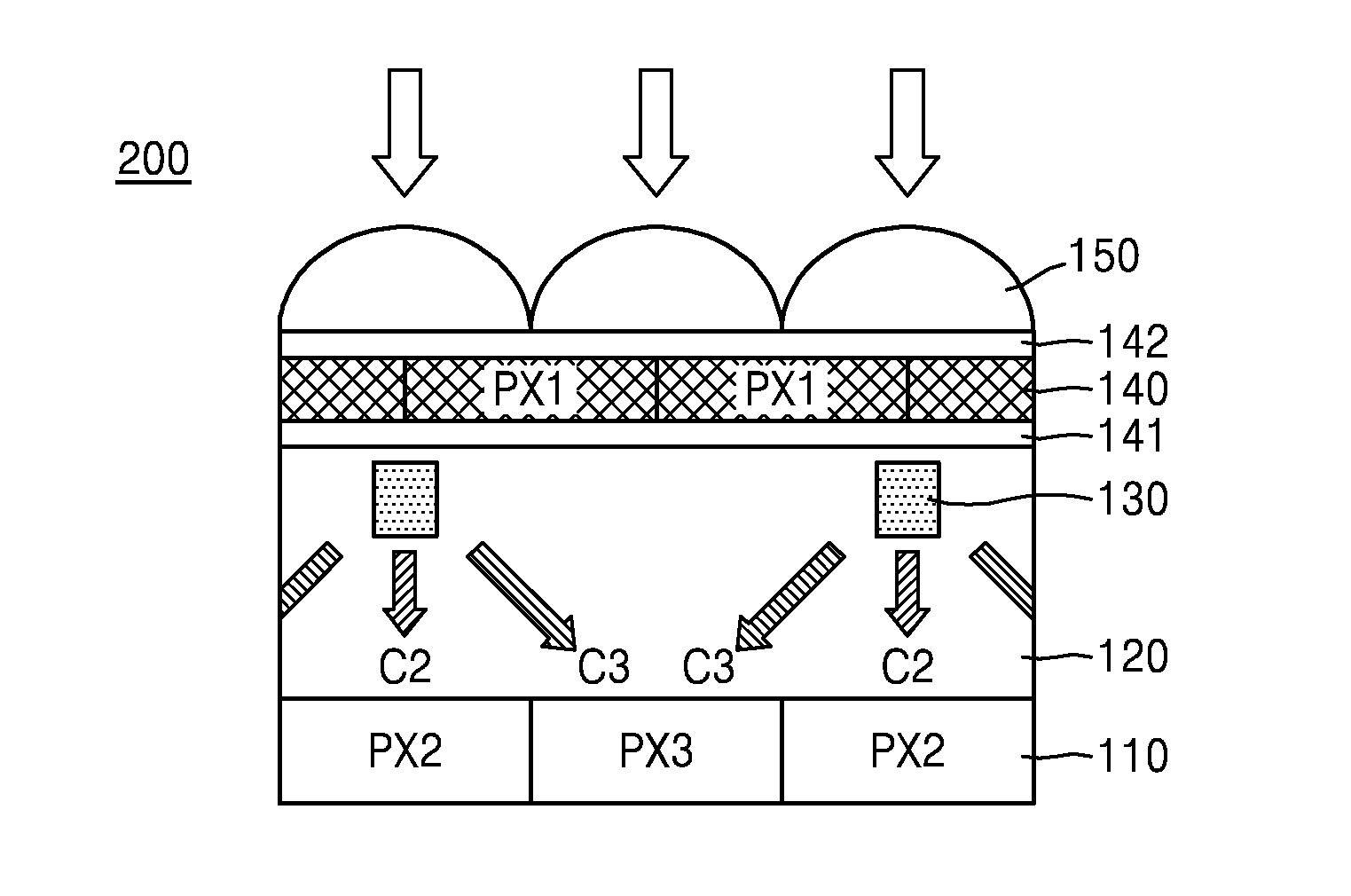
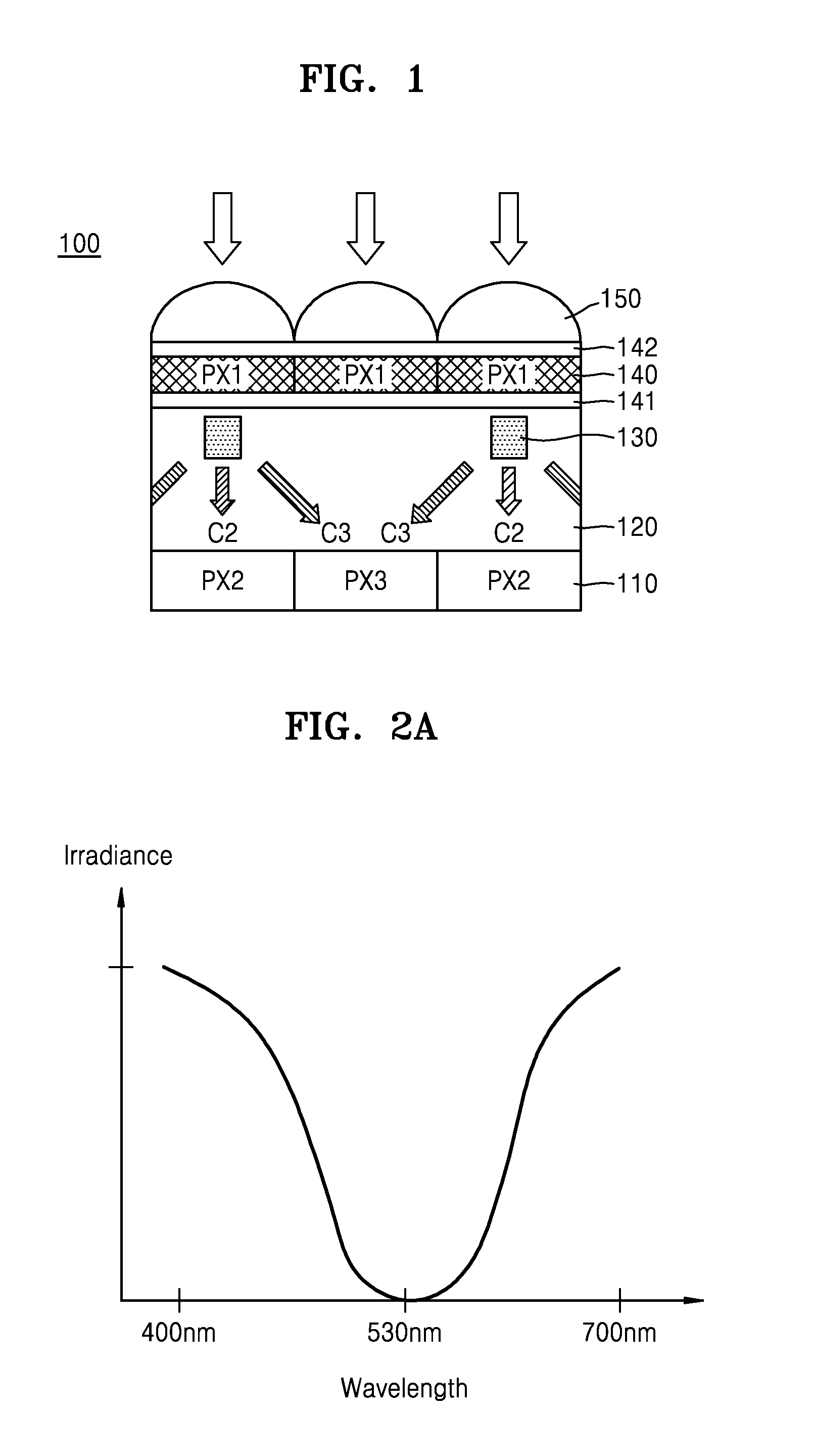
An image sensor includes a first pixel row including a plurality of first pixels configured to sense first wavelength light, the first wavelength light having a first wavelength, a second pixel row adjacent to the first pixel row, the second pixel row including a plurality of second pixels configured to sense second wavelength light and a plurality of third pixels configured to sense third wavelength light, the plurality of second pixels and the plurality of third pixels being alternately arranged, the second wavelength light having a second wavelength and the third wavelength light having a third wavelength and a plurality of first color separation elements in the plurality of second pixels, respectively, the plurality of separation elements configured to change a spectrum distribution of incident light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Integrateable band filter using waveguide grating routers
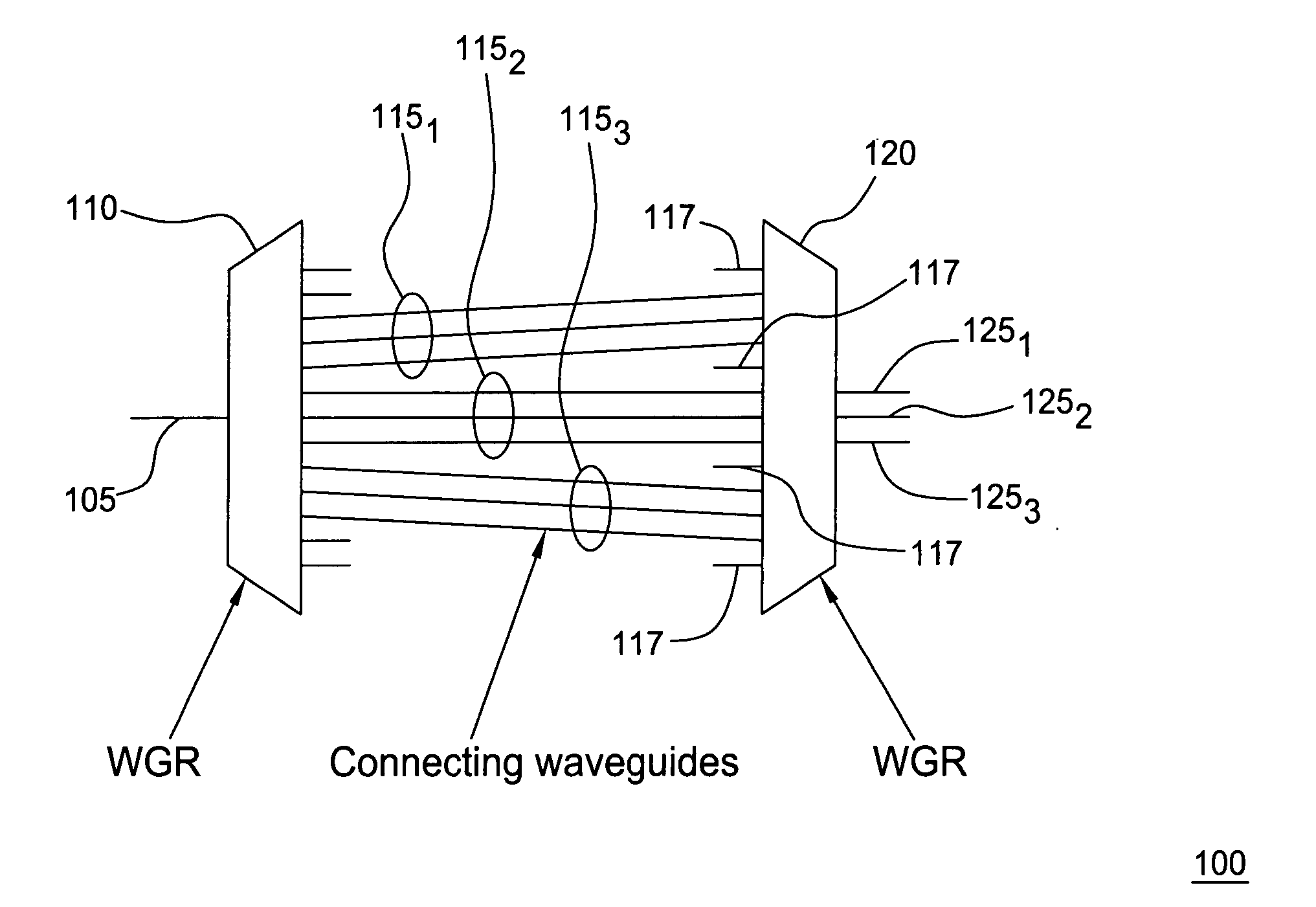
ActiveUS20050053332A1Easy to makeReduce rippleCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsThird wavePath length
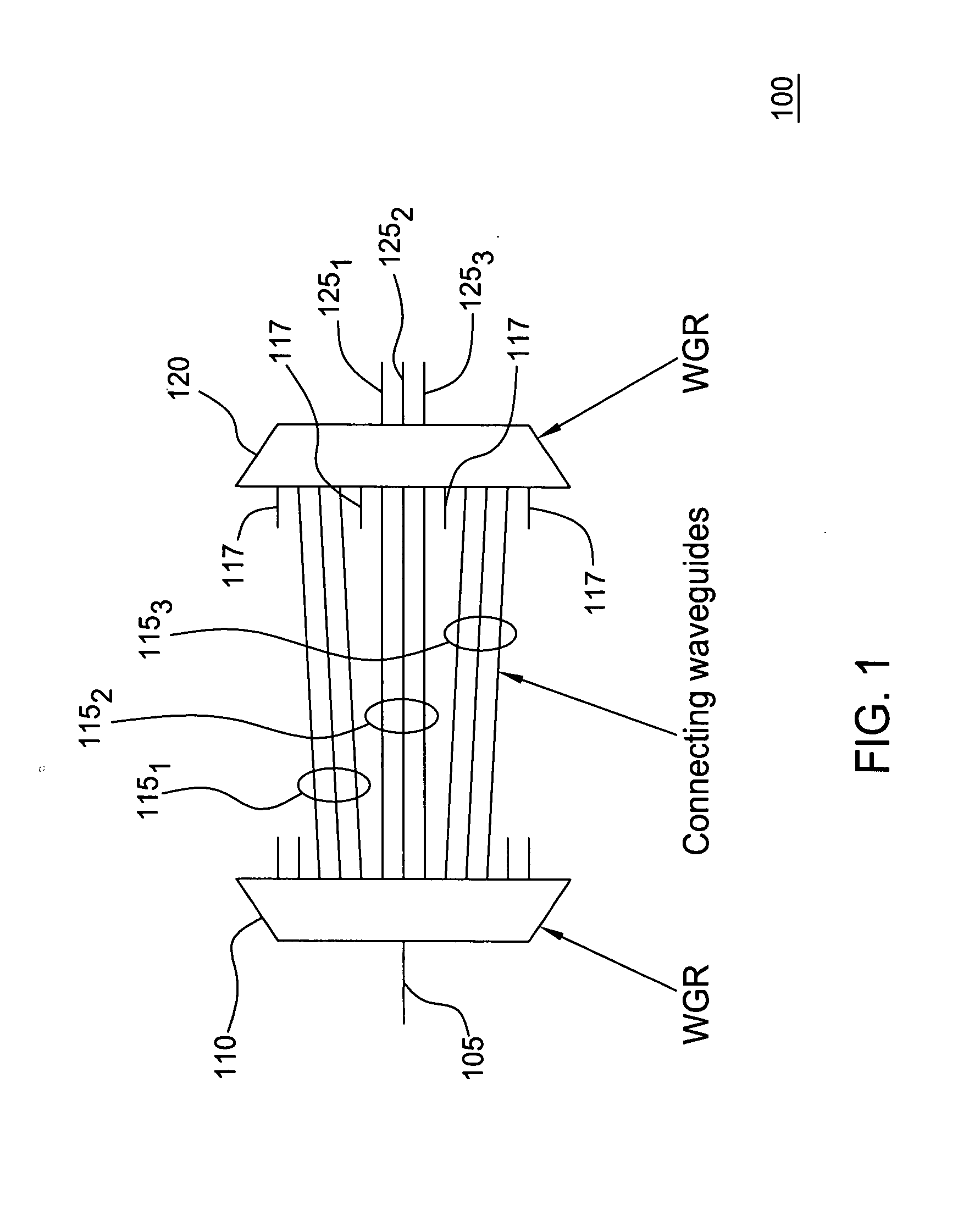
The inventors propose herein a novel band filter design for planar lightwave circuits. In one embodiment of the present invention, the band filter includes two waveguide grating routers interconnected by a third waveguide grating, wherein waveguides comprising the third waveguide grating have unequal path lengths. In addition, the waveguides in the third grating are partitioned into sets of adjacent waveguides wherein each set corresponds to a particular wavelength band for the filter. The individual sets of waveguides are spaced at their connection to the second waveguide grating router such that optical signals within predetermined, different optical wavelength bands are routed to different output ports of the band filter. Some of the advantages of this novel band filter include compactness, sharp passband corners, low spectral ripple, and a lack of chromatic dispersion.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
System and method for providing failure protection in optical networks
ActiveUS20080063405A1Improve reliabilityImprove robustnessWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringThird waveOptomux
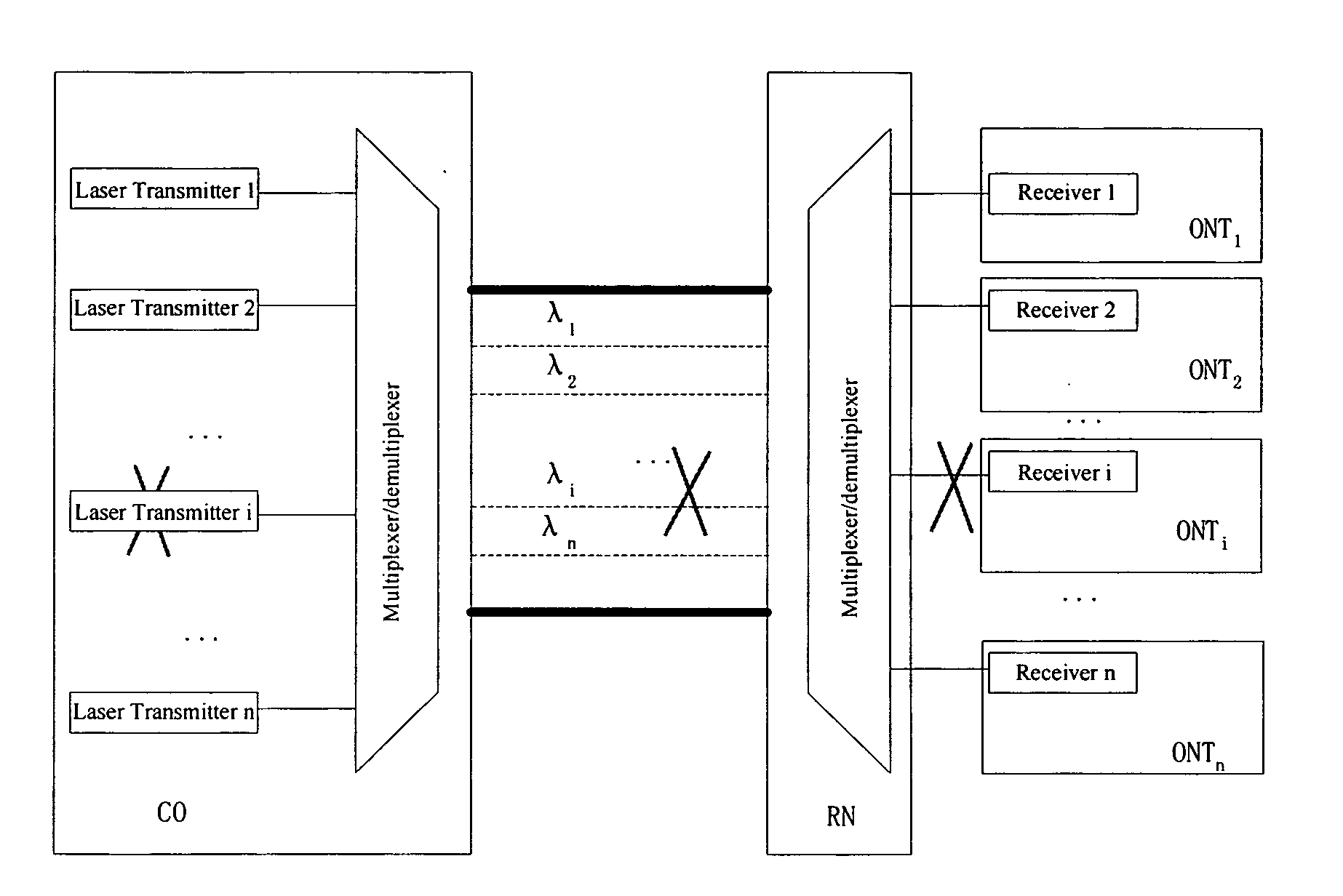
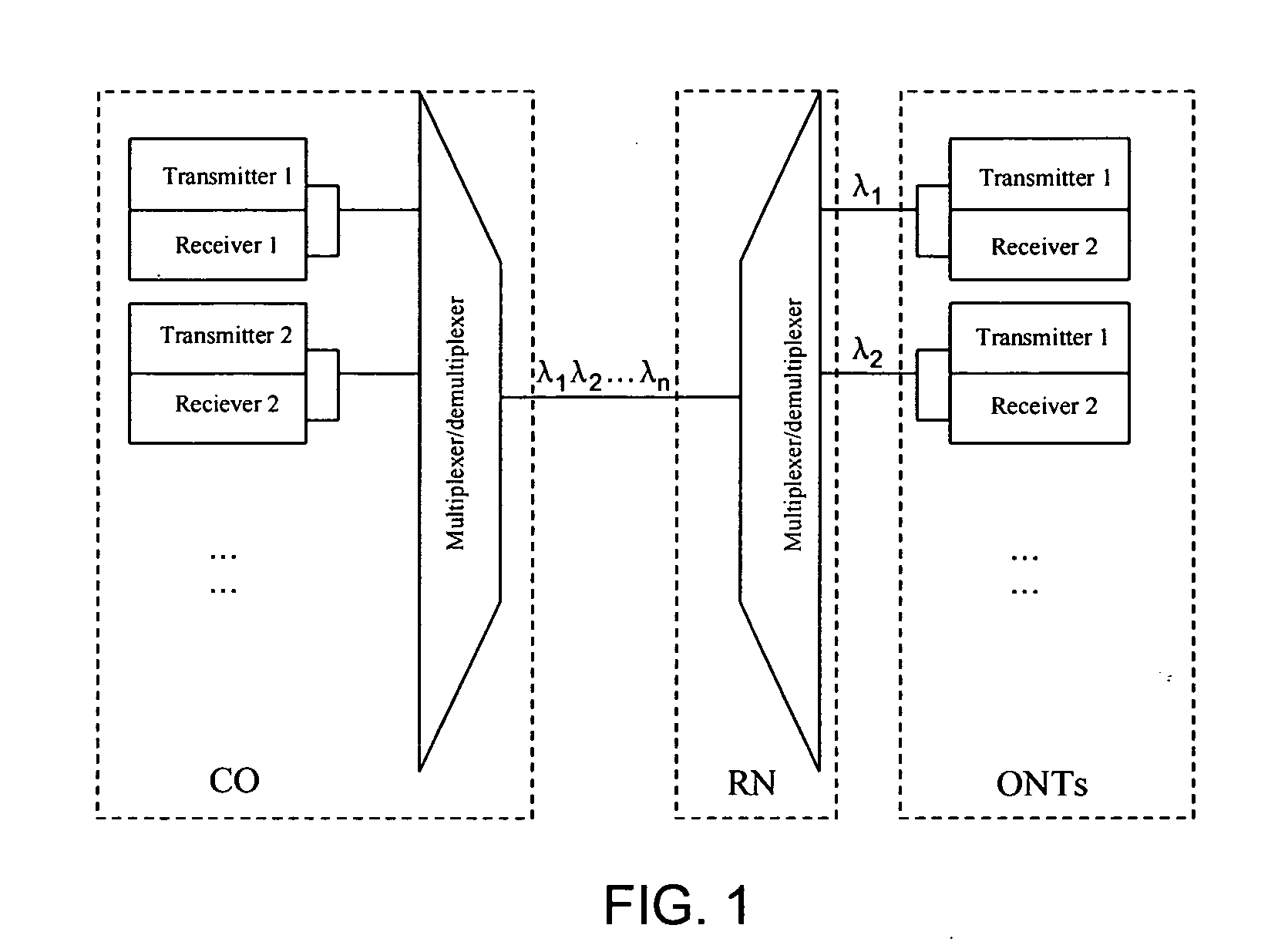
A system and method for transmitting an optical signal. The system includes a first optical transmitter capable of transmitting a first optical signal under one or more first operating conditions, and the first optical signal corresponds to a first wavelength. Additionally, the system includes a second optical transmitter capable of transmitting a second optical signal under one or more second operating conditions, and the second optical signal corresponds to a second wavelength. Moreover, the system includes an optical multiplexer coupled to the first optical transmitter and the second optical transmitter and capable of generating a multiplexed optical signal, a detection component configured to determine at least whether the first optical transmitter satisfies one or more predetermined conditions, and a tunable optical transmitter capable of transmitting a third optical signal. The third optical signal corresponds to a third wavelength.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Planar light wave circuit and optical performance monitoring module using the same
A planar light wave circuit is disclosed, which comprises: a first waveguide for receiving optical signals from an outside; a second waveguide having a first end surface and a second end surface, so that lights outputted from the first waveguide are partially reflected by the first end surface and are partially incidented into the first end surface and then outputted through the second end surface; a third waveguide for receiving the light reflected by the first end surface; and a common region bordering each end surface of the first to the third waveguides and having an index of refraction different from an index of refraction of the second waveguide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Integrated feed horn device
An integrated feed horn device including three sets of integrally formed feed horn devices is provided. The integrated feed horn device may receive satellite signals reflected by a single parabolic reflector antenna, wherein the satellite signals are transmitted by three satellites separated by small angles. The integrated feed horn device may comprise a first waveguide, a second waveguide and a third waveguide, wherein the first waveguide, the second waveguide and the third waveguide may be adopted for receiving a first satellite signal, a second satellite signal, and a third satellite signal. Each of the satellite signals described above is transmitted by different satellites.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Optical intensity-to-phase converter, mach-zehnder interferometer, optical a/d converter, and method of constructing optical intensity-to-phase converter
ActiveUS20130113641A1Simple configurationElectric signal transmission systemsOptical analogue/digital convertersMultiplexingThird wave
An optical intensity-to-phase converter according to the present invention includes first and second waveguides to which a first input light is input, a third waveguide to which a second input light is input, and an interaction region that is provided in common on the second and third waveguides in which the first and second input lights are multiplexed and interact. The optical intensity-to-phase converter provides delay to output lights output from the first and second waveguides based on intensity of the first or second input light. Then, it is possible to provide an optical intensity-to-phase converter that enables simple configuration of an optical A / D converter.
Owner:NEC CORP
Stacked type image sensor including color separation element and image pickup apparatus including the stacked type image sensor
ActiveUS20150364521A1Improve light utilization efficiencySolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesThird waveLight sensing
A stacked type image sensor with improved optical characteristics, which may result from a color separation element, and an image pickup apparatus including this image sensor. The stacked type image sensor includes first and second light sensing layers arranged in a stacked manner, and color separation elements positioned between the first and second light sensing layers. Accordingly, the first light sensing layer absorbs and detects light of a first wavelength band, and the second light sensing layer detects light of second and third wavelength bands separated by the color separation elements.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical fiber amplifier and optical amplifying method employing it, laser oscillating method, laser amplifier and laser oscillator, and laser and laser machining apparatus both employing laser oscillator
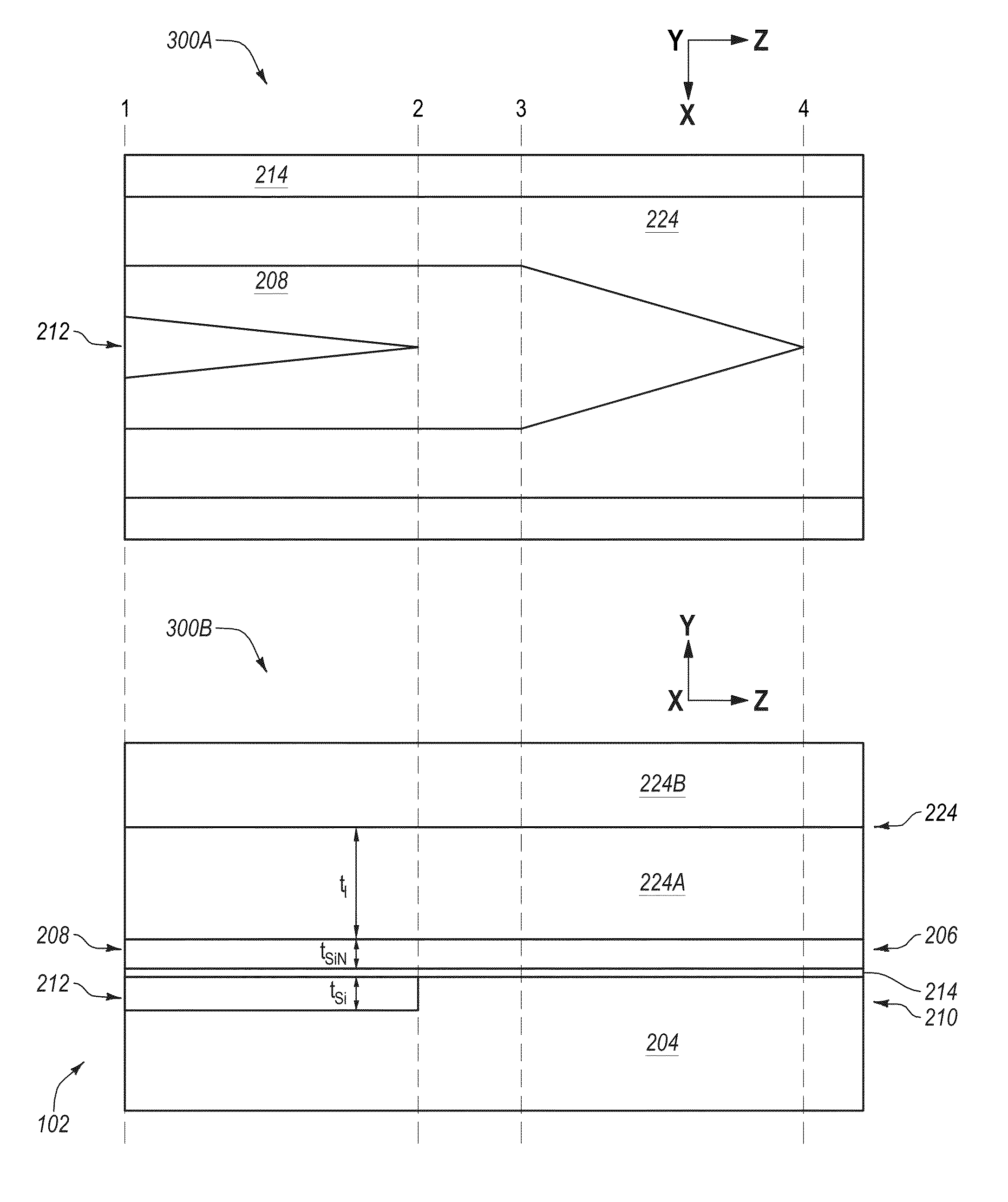
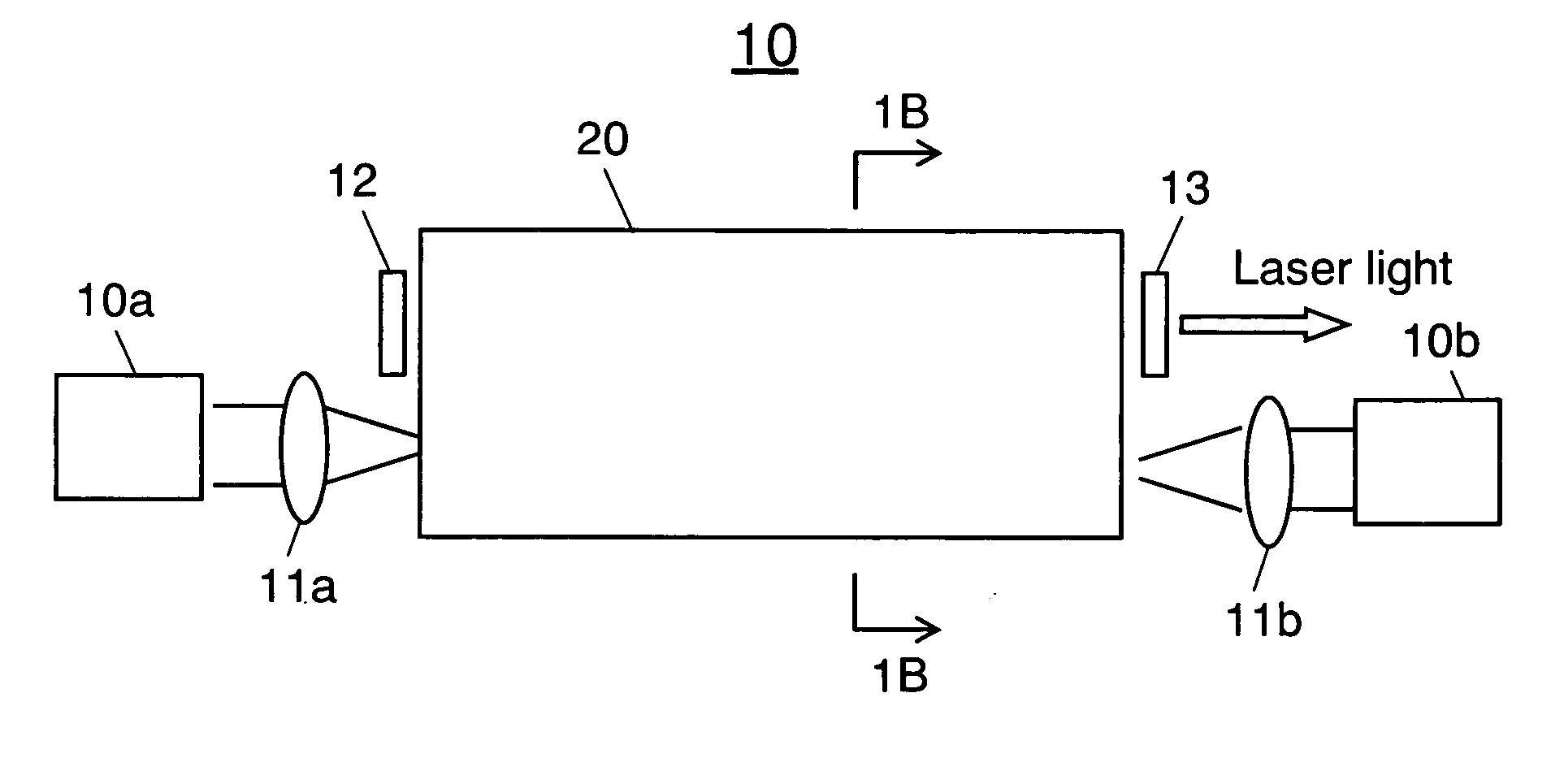
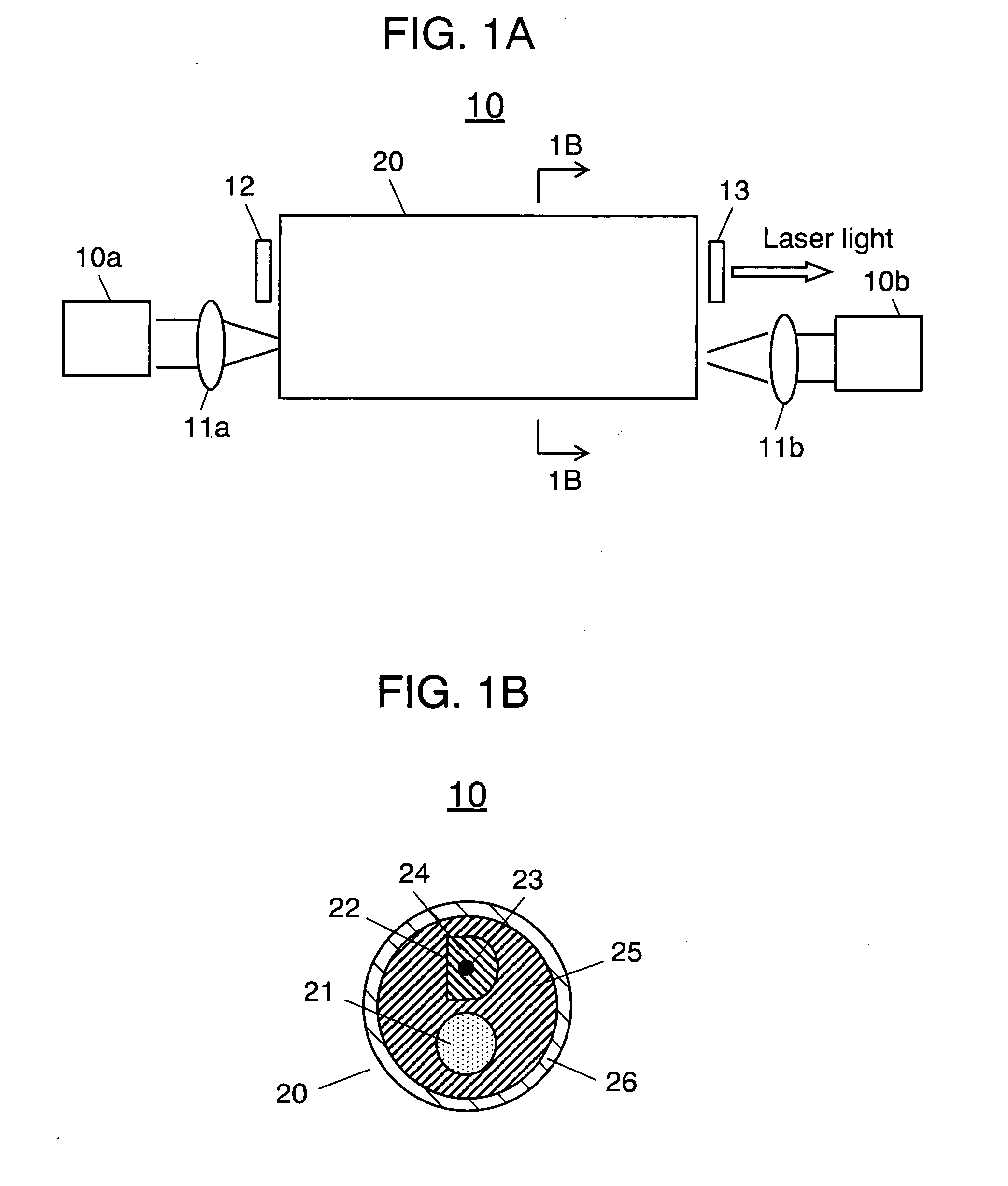
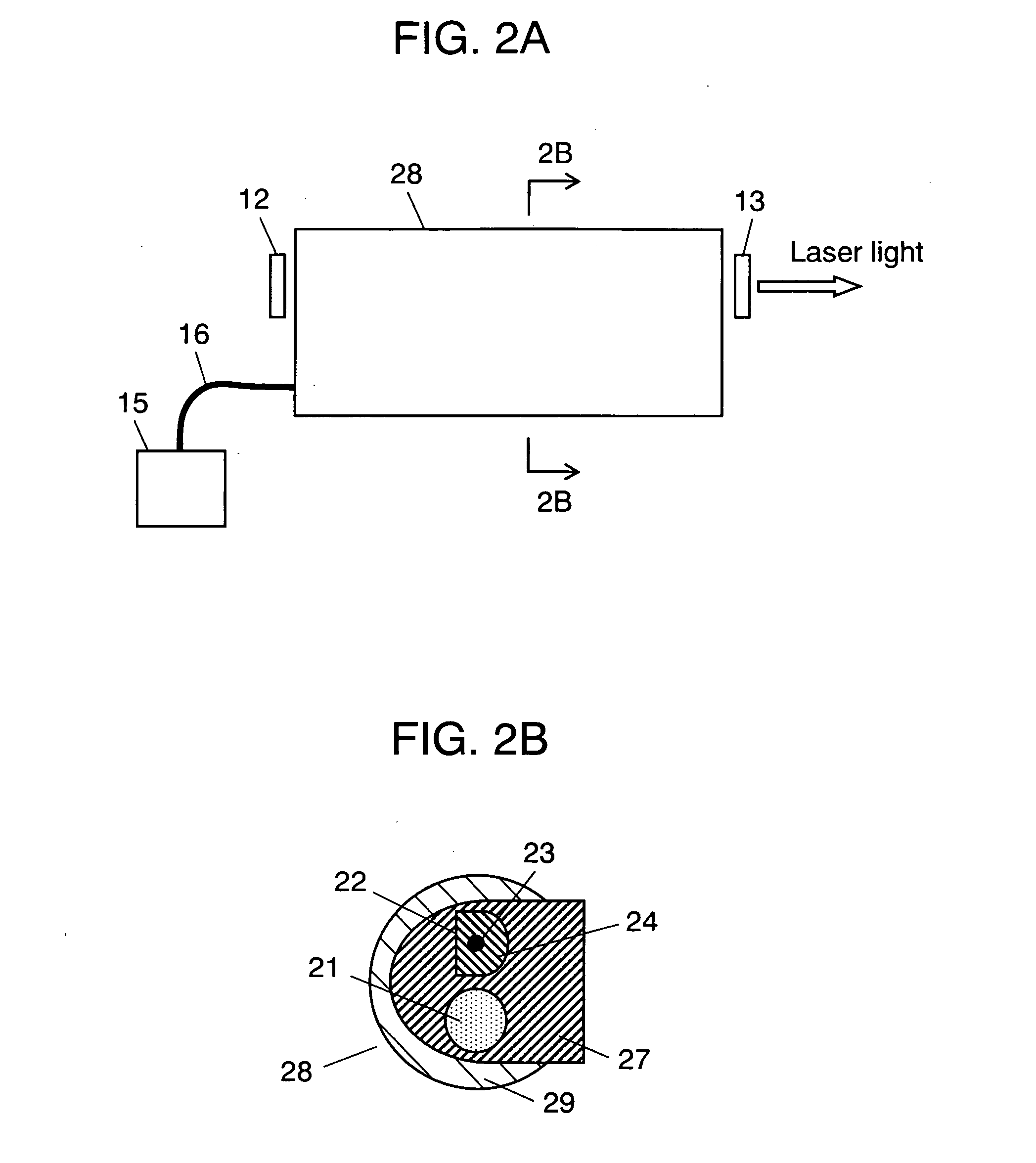
InactiveUS20060245704A1Efficient emissionsAvoid low lightCladded optical fibreFibre transmissionFiberThird wave
A small size and high efficiency laser oscillation apparatus capable of obtaining high output and high beam quality laser light is provided. First waveguide (21) (refractive index=n1) for transmitting excitation light, second waveguide (22) composed of core (23) (refractive index=n3) for generating laser light and clad (24) (refractive index=n2) for transmitting the excitation light, and third waveguide (25) (refractive index=n4) including first waveguide 21 and second waveguide 22 are provided. Light amplifying fiber (20), in which the refractive indices are set so as to satisfy the relation: n1<n4<n2<n3, is used and excised by semiconductor lasers (10a) and (10b).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Projection display apparatus
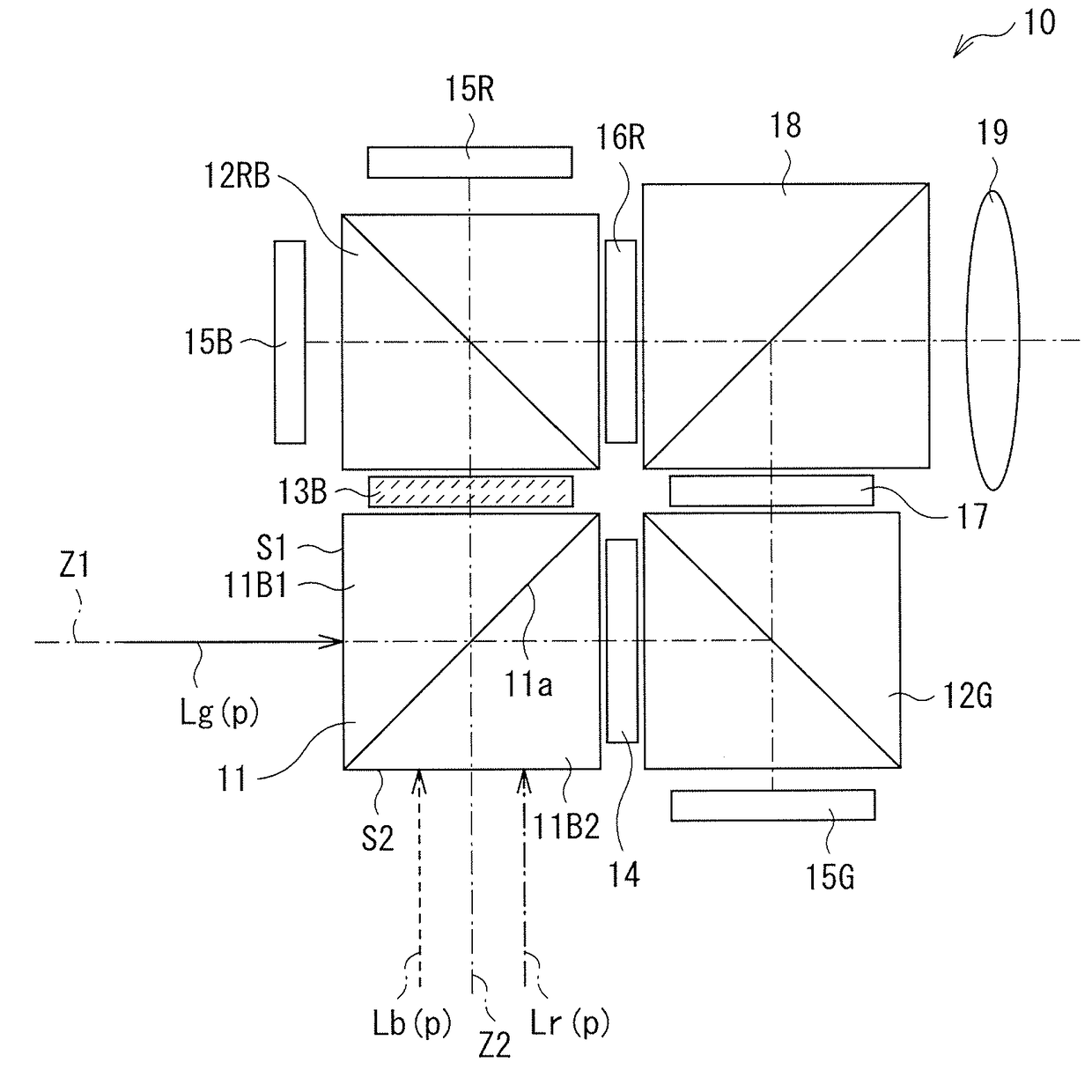
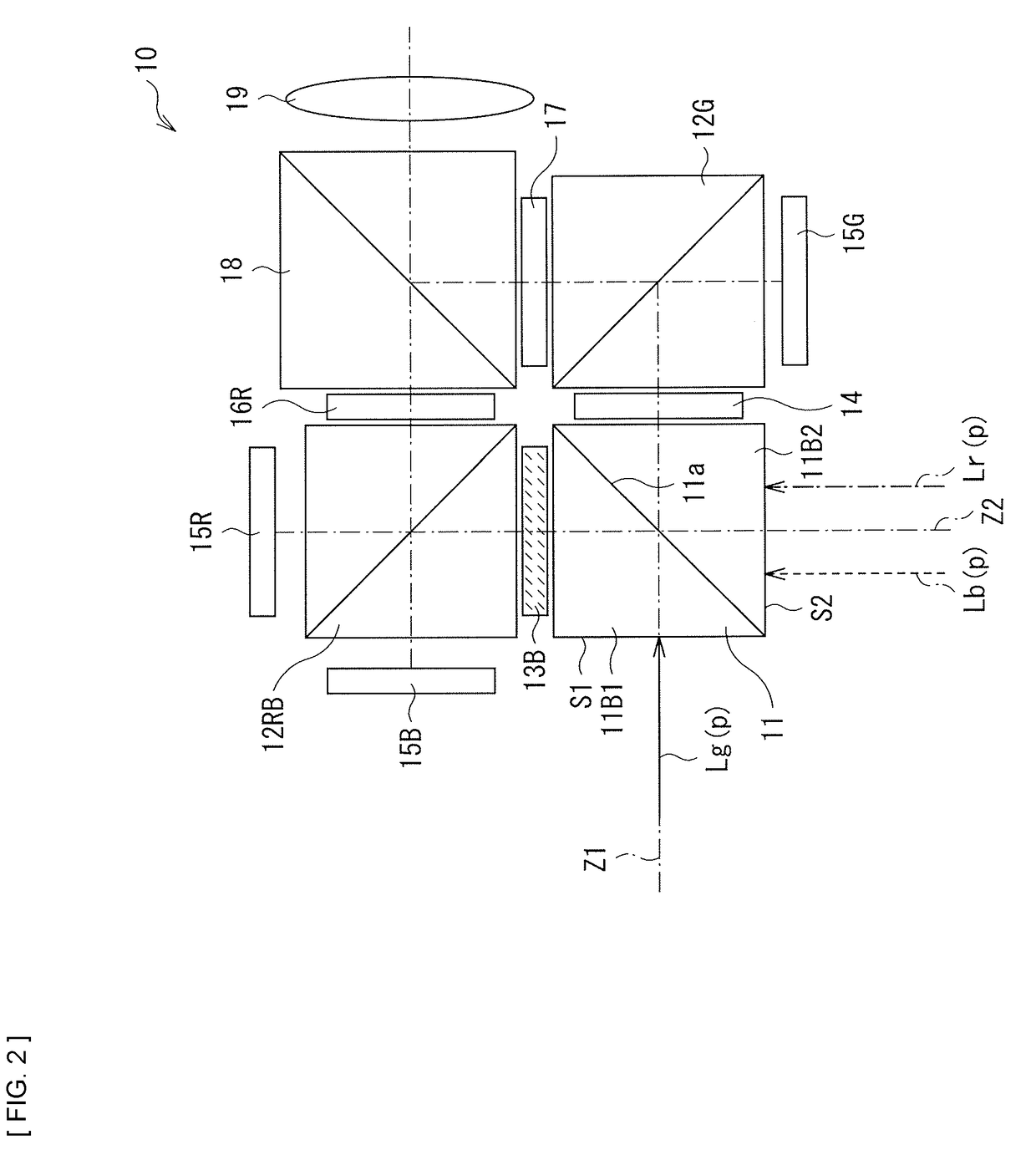
ActiveUS20180131917A1Inhibition decreasedReduce in quantityProjectorsColor photographyThird waveProjection display
A first projection display apparatus includes a color separator (41A) that has first and second incident surfaces (S1a and S1b), and allows light in first to third wavelength bands to pass therethrough or reflects the light in the first to third wavelength bands; first to third reflective light modulators (15); a first polarization splitter (12G); a second polarization splitter (12RB); and a projection optical system (19). Light in at least one of the first to third wavelength bands enters the first incident surface of the color separator as first polarized light, and light in the other wavelength bands enters the second incident surface of the color separator as second polarized light orthogonal to the first polarized light.
Owner:SONY CORP
Enhanced hybrid-tee coupler
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Light filter structure and image sensor
According to the embodiment of the invention, the present invention provides a light filter structure is provided. The light filter structure includes a first filter layer disposed over the substrate.The first filter layer has a transmittance greater than 50% in a first waveband, wherein the first filter layer is an interference-type filter. The light filter structure further includes a second filter layer disposed over the substrate. The second filter layer has a transmittance greater than 50% in a second waveband, wherein the second filter layer is an absorption-type filter. The first waveband partially overlaps the second waveband at the wavelength in a third waveband, and the third waveband is in an IR region. Furthermore, an image sensor used as a time-of-flight image sensor is alsoprovided.
Owner:VISERA TECH CO LTD
Bi-directional optical transceiver module
InactiveUS6950582B2Easy to makeLow production costLaser detailsCoupling light guidesThird waveTransceiver
In a bi-directional optical transceiver module, a first waveguide transmits a optical signal received from a light source to a high reflection layer formed on a waveguide substrate. A second waveguide extends from the optical fiber to the high reflection layer. With a first mode coupling region formed by ends of the first and second waveguides near the high reflection layer, the second waveguide transmits the transmission optical signal mode-coupled from the first waveguide to the optical fiber and receives the reception optical signal from the optical fiber. A third waveguide extends from the optical detector to near an end of the optical fiber. With a second mode coupling region formed by an end of the third waveguide and the other end of the second waveguide, the third waveguide transmits the reception optical signal mode-coupled from the second waveguide to the optical detector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Phase measuring device for laser interference photoetching system and using method thereof
ActiveCN110837213AImprove laser utilizationSimple structureDiffraction gratingsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusThird waveOptical instrumentation
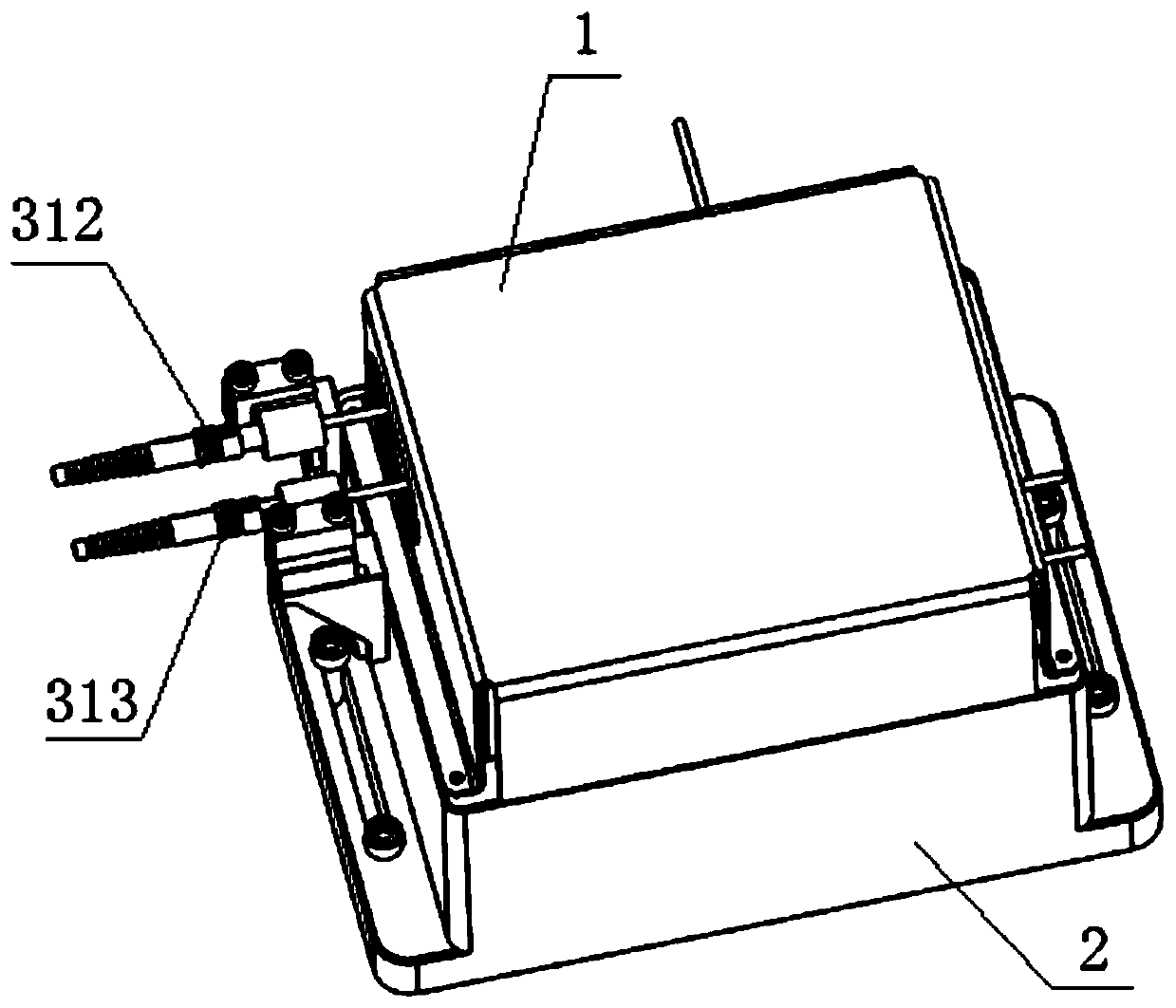
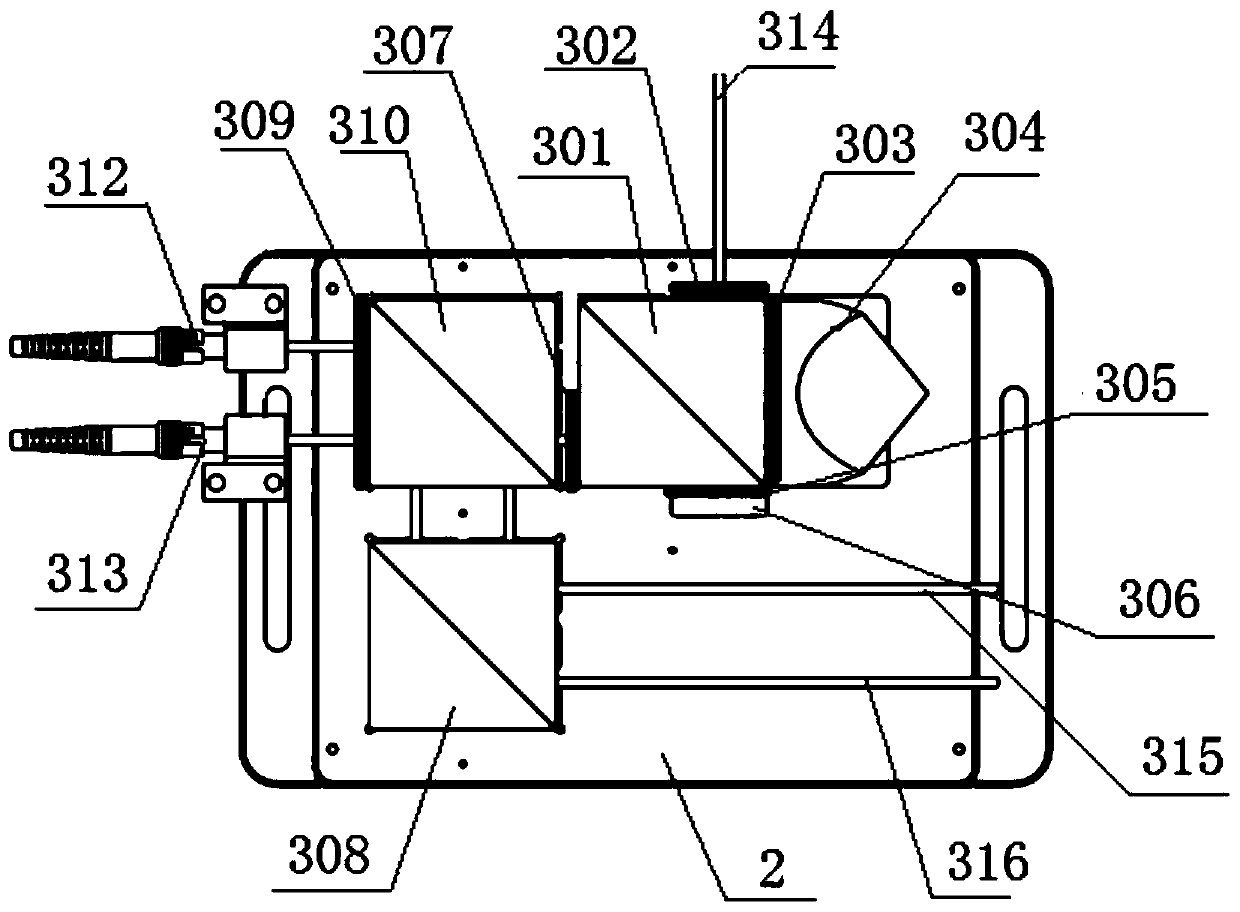
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical instruments and meters, and provides a phase measuring device for a laser interference photoetching system and a using method thereof. The phasemeasuring device comprises a first wave plate, a first polarization splitting prism, a fourth wave plate, a backward reflecting mirror, a third wave plate, a reflecting mirror, a second wave plate, apolarizing film, a second polarization splitting prism, a third polarization splitting prism, a first photoelectric detector, a second photoelectric detector and a base, wherein the first polarization splitting prism, the second polarization splitting prism, the third polarization splitting prism, the first photoelectric detector and the second photoelectric detector are fixed on the base; the first wave plate, the second wave plate, the third wave plate and the fourth wave plate are respectively arranged around the first polarization splitting prism; the polarizing film and the emergent surface of the third polarization splitting prism, the backward reflecting mirror outside the fourth wave plate, and the reflecting mirror outside the third wave plate form a light path system for phase measurement. An interference measurement signal is resolved to obtain a measurement light phase, and the device and the method are used for fringe control of variable-period interference exposure.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for detecting ultraviolet ray intensity by panel and its display device
The invention discloses a method for detecting ultraviolet ray strength by a panel and a display device using the same. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, a first detection unit, a second detection unit and a third detection unit are configured on the panel and used for detecting and converting the light source strengths of a first wave band, a second wave band and a third wave band into a first current, a second current and a third current; then, a processing unit is provided for receiving and processing the first current, the second current and the third current in order to acquire a strength value of the ultraviolet rays.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Optical signal amplifying triode and optical signal transfer method, optical signal relay device, and optical signal storage device using the same
InactiveUS20070183712A1Increase signal gainSlow in the cross-gain modulation response timeWavelength-division multiplex systemsNanoopticsThird waveAudio power amplifier
When in an optical signal amplifying triode 10, light of a second wavelength λ2, selected from among light from a first optical amplifier 26, into which a first input light L1 of a first wavelength λ1 and a second input light L2 of second wavelength λ2 have been input, and a third input light (control light) L3 of a third wavelength λ3 are input into a second optical amplifier 34, an output light L4 of the third wavelength λ3, selected from among the light output from the second optical amplifier 34, is light that is modulated in response to the intensity variation of one or both of the first input light L1 of the first wavelength λ1 and the third input light L3 of the third wavelength λ3 and is an amplified signal, with which the signal gain with respect to the third input light (control light) L3 of the third wavelength λ3 is of a magnitude of 2 or more. An optical signal amplifying triode 10, which can directly perform an optical signal amplification process using control input light, can thus be provided.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) channel estimation to improve the smoothing process
ActiveUS20150319011A1Reduce edge distortionReduce distortion problemsTransmission path divisionChannel estimationTime domainThird wave
A method of processing communication signals, is described. The method includes receiving a communication signal in a time domain, converting the communication signal to a frequency domain, providing resource blocks, the resource blocks including a first resource block and a second resource block, the first having a first boundary and a second boundary, the first boundary being adjacent to the second resource block, the second boundary being non-adjacent to other resource blocks, the first resource block including pilot signals, generating a third resource block based on the one or more pilot signals, providing a first waveform based on the resource blocks and the third resource block, applying a smoothing filter against the first waveform to generate a second waveform, generating a third waveform using at least the first and third set of phase and amplitude differences, and converting the third waveform from the frequency domain to the time domain.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Organic luminous device
InactiveCN103531716ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThird waveRefractive index
The invention relates to an organic luminous device, which comprises a transparent base plate, a first electrode, an organic luminous layer, a middle layer and a second electrode, wherein the first electrode is positioned above the transparent base plate, the organic luminous layer is positioned above the first electrode and is used for sending out light in the first wave length, the second wave length and the third wave length, and the first wave length, the second wave length and the third wave length are mutually different. The middle layer is arranged between the transparent base plate and the first electrode in a clamping way, and the refractive index of the middle layer is in a range between the refractive index of the transparent base plate and the refractive index of the first electrode. The middle layer is provided with a first region, a second region and a third region ranged in a plane direction, the thicknesses d of the first region, the second region and the third region are respectively calculated according to the following formula that d=(2x+1) lambda / 4n, wherein x is 0 or an integer, lambda is respectively the first wave length, the second wave length and the third wave length, and n is the refractive index of the middle layer. The second electrode is positioned above the organic luminous layer.
Owner:华映视讯(吴江)有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com