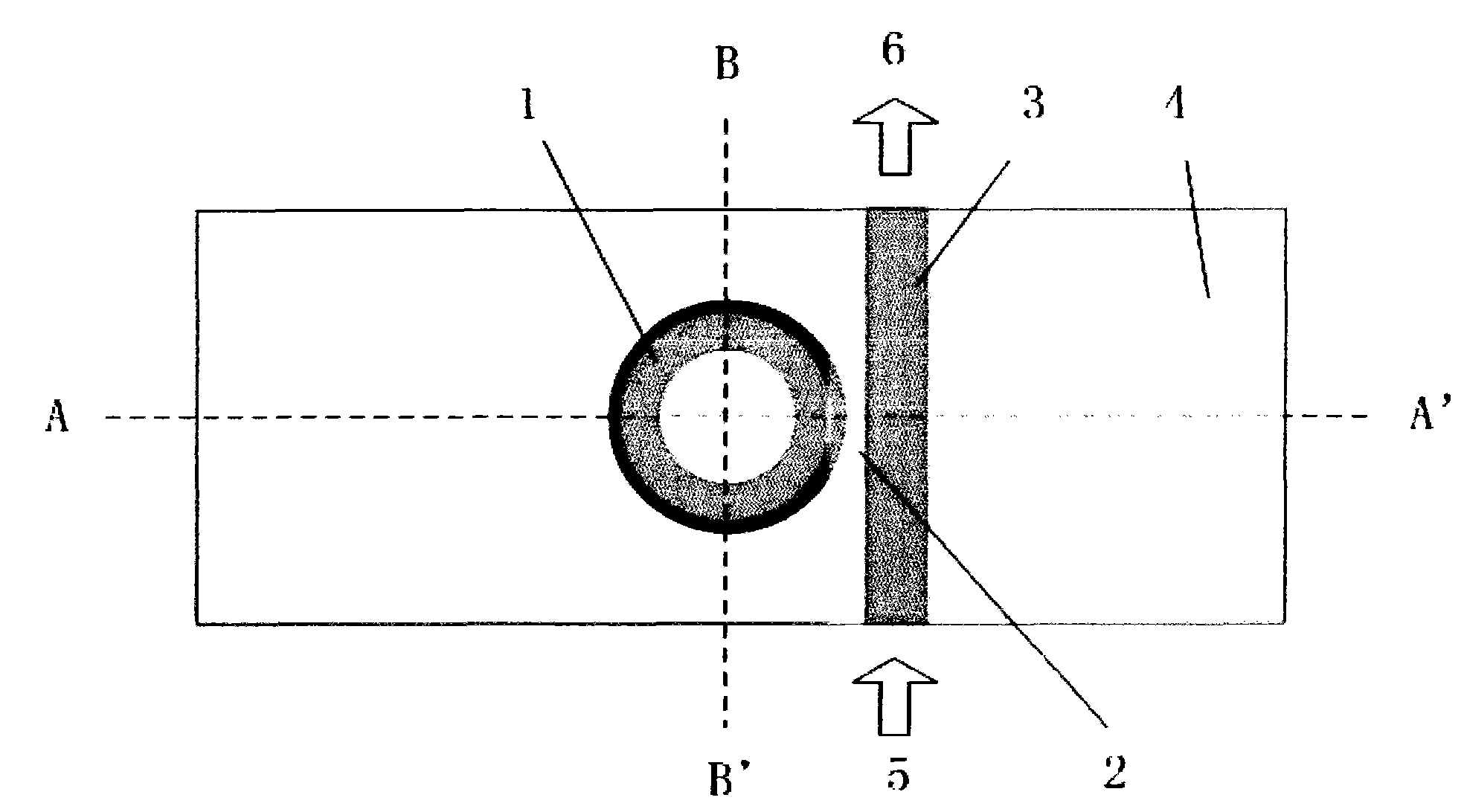
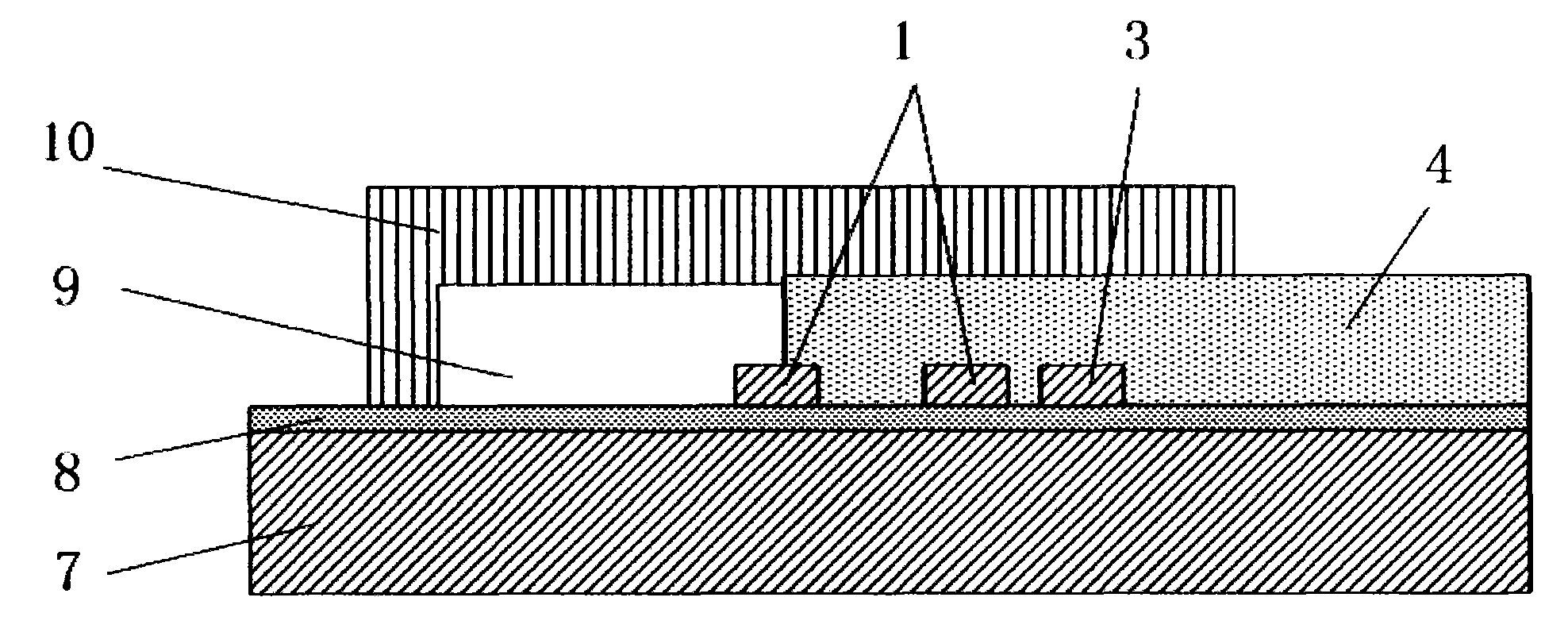
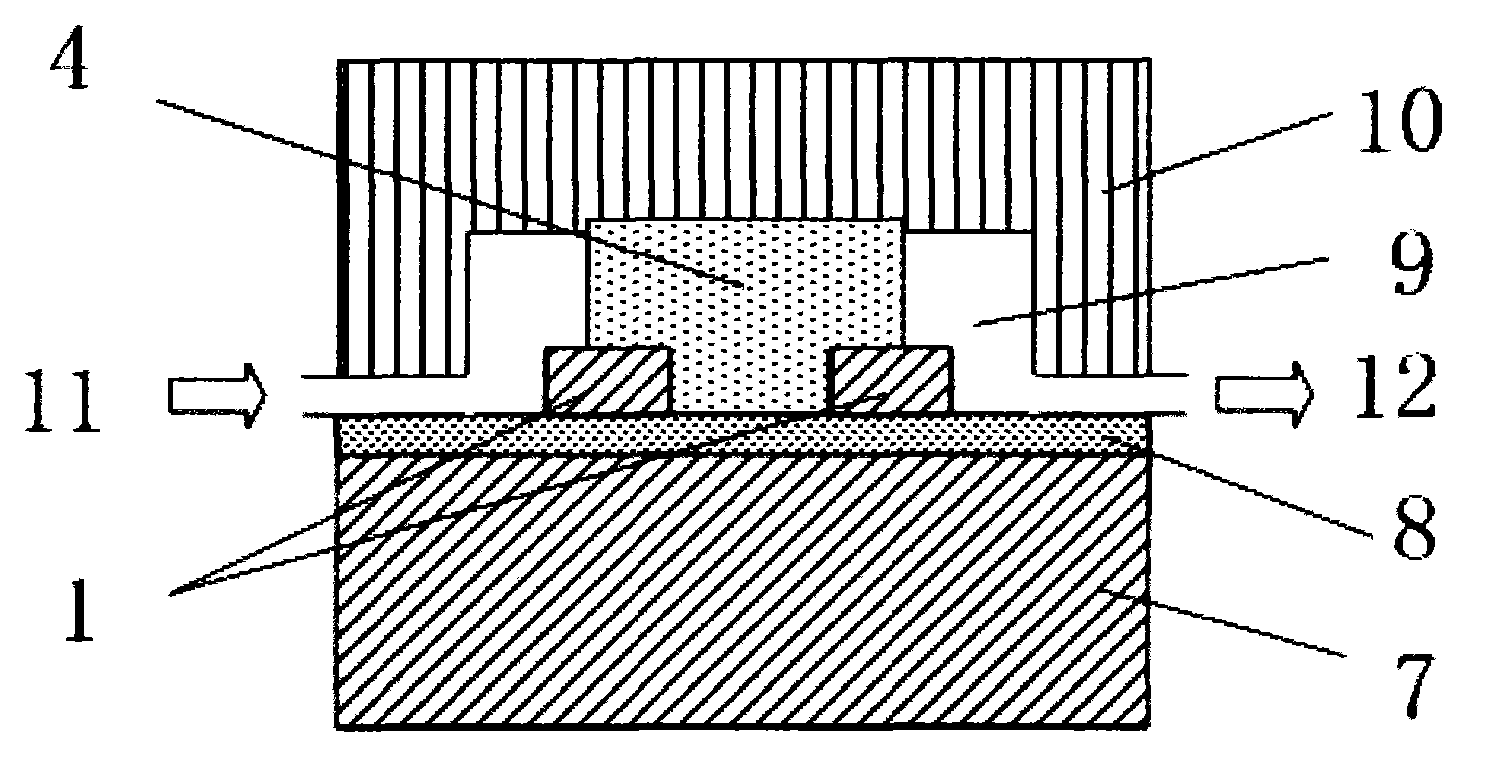
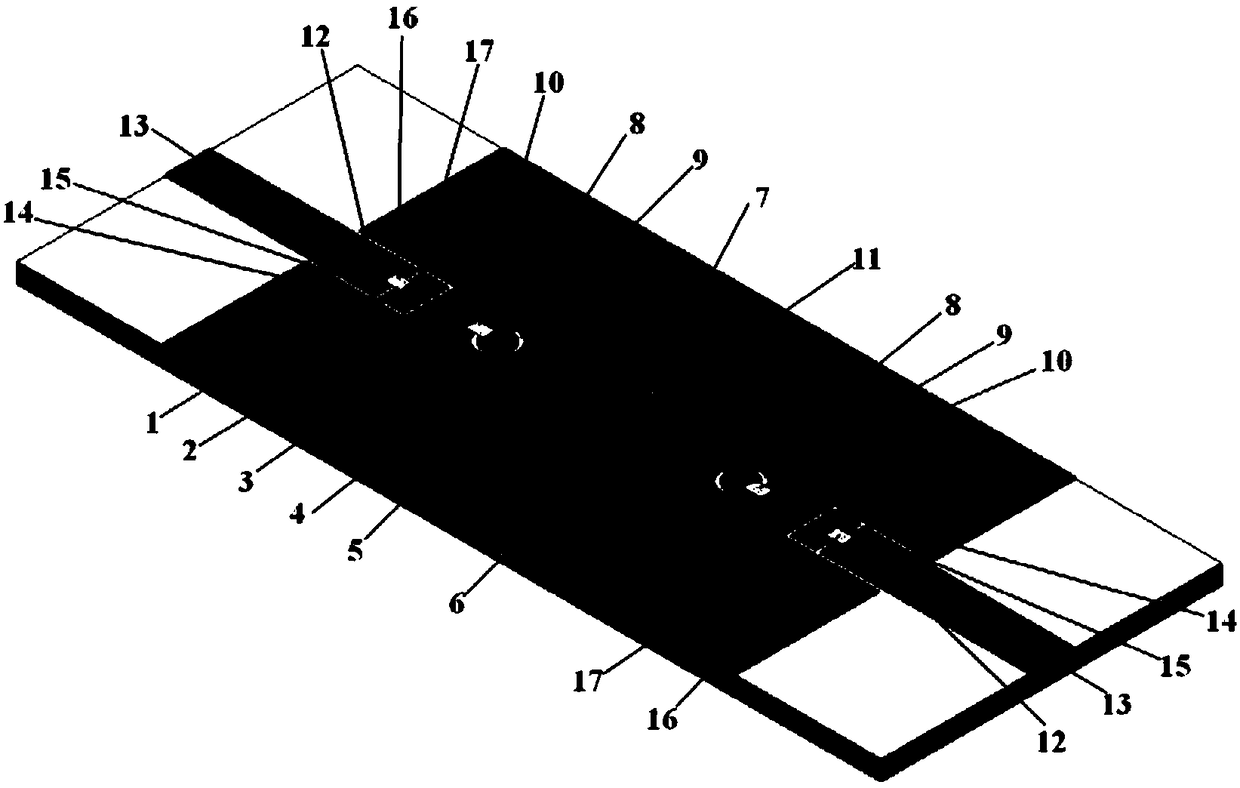
Patents
Literature
140 results about "Waveguide resonator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
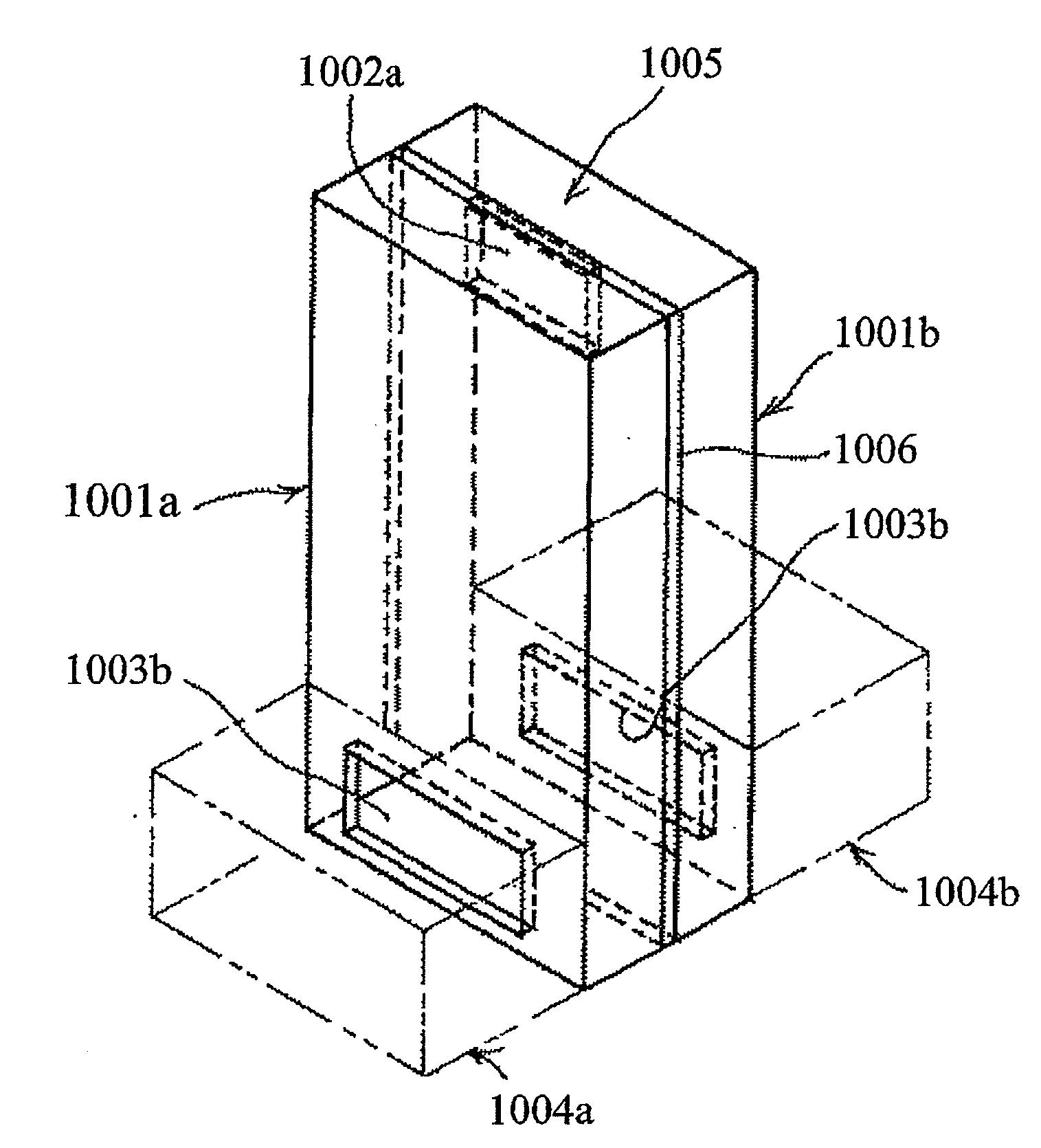
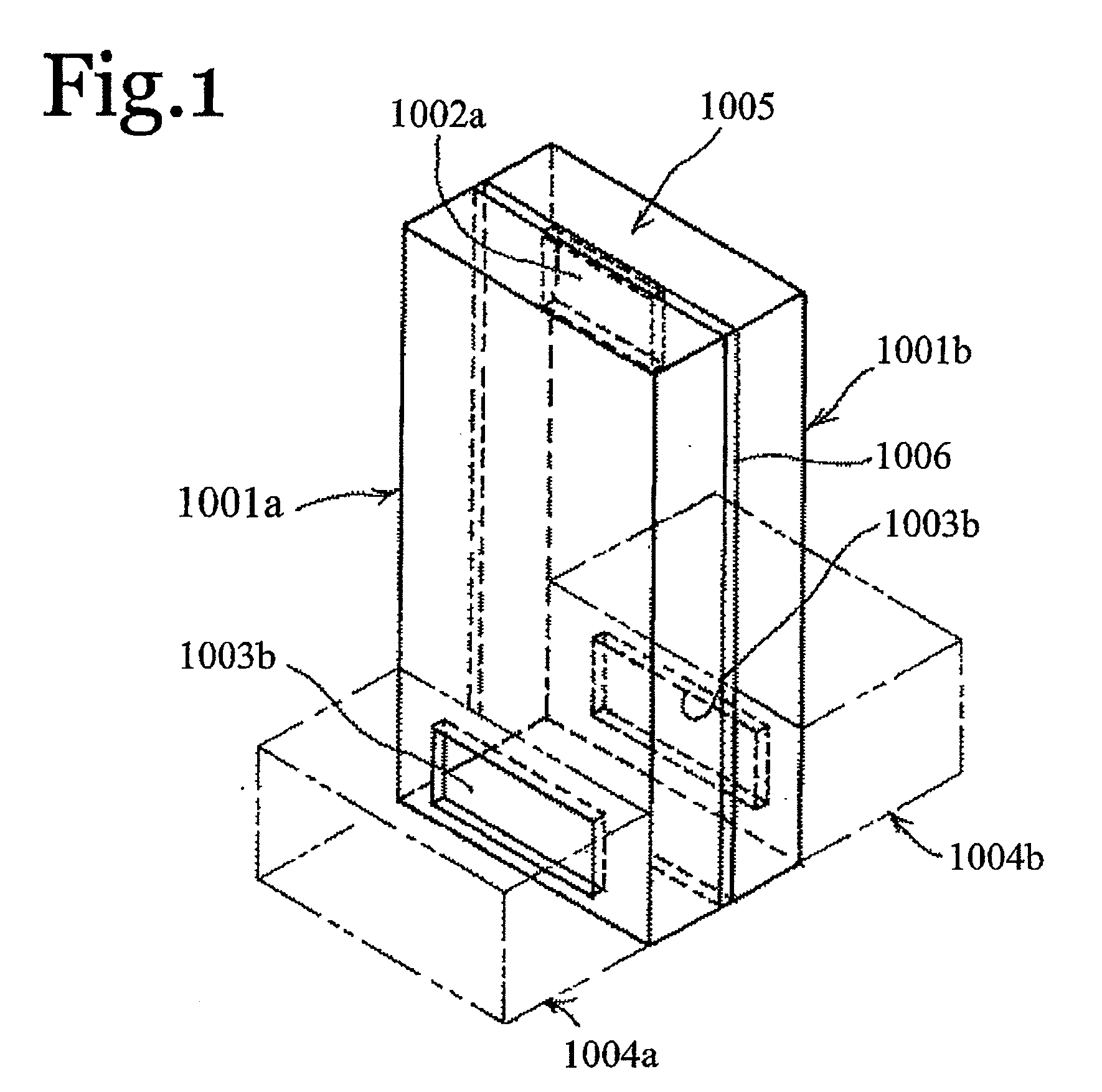
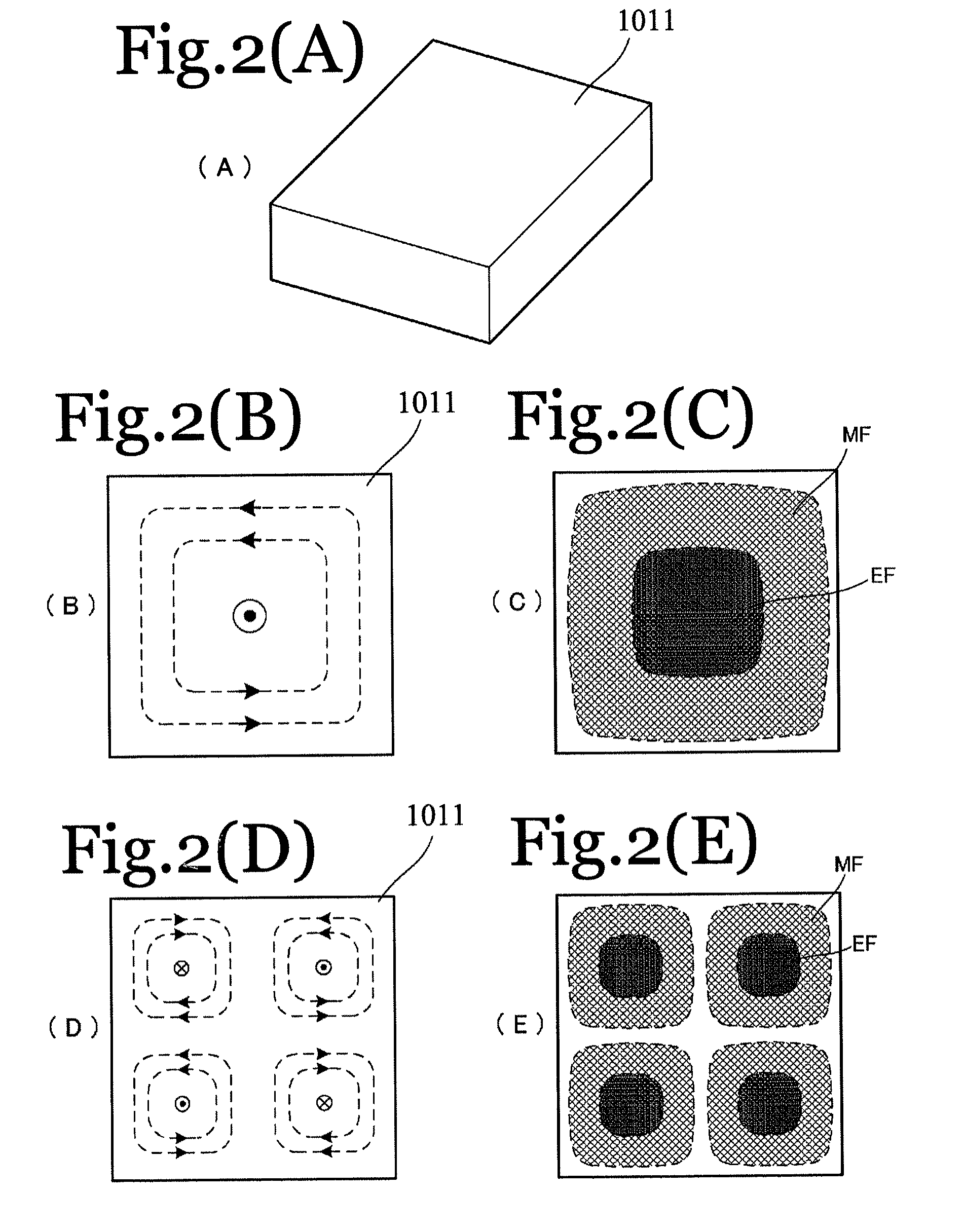
Monolithic microwave integrated circuit (MMIC) waveguide resonators having a tunable ferroelectric layer
ActiveUS7570137B2Improve scalabilityEasy to integrateResonatorsOscillations generatorsElectromagnetic couplingResonant cavity
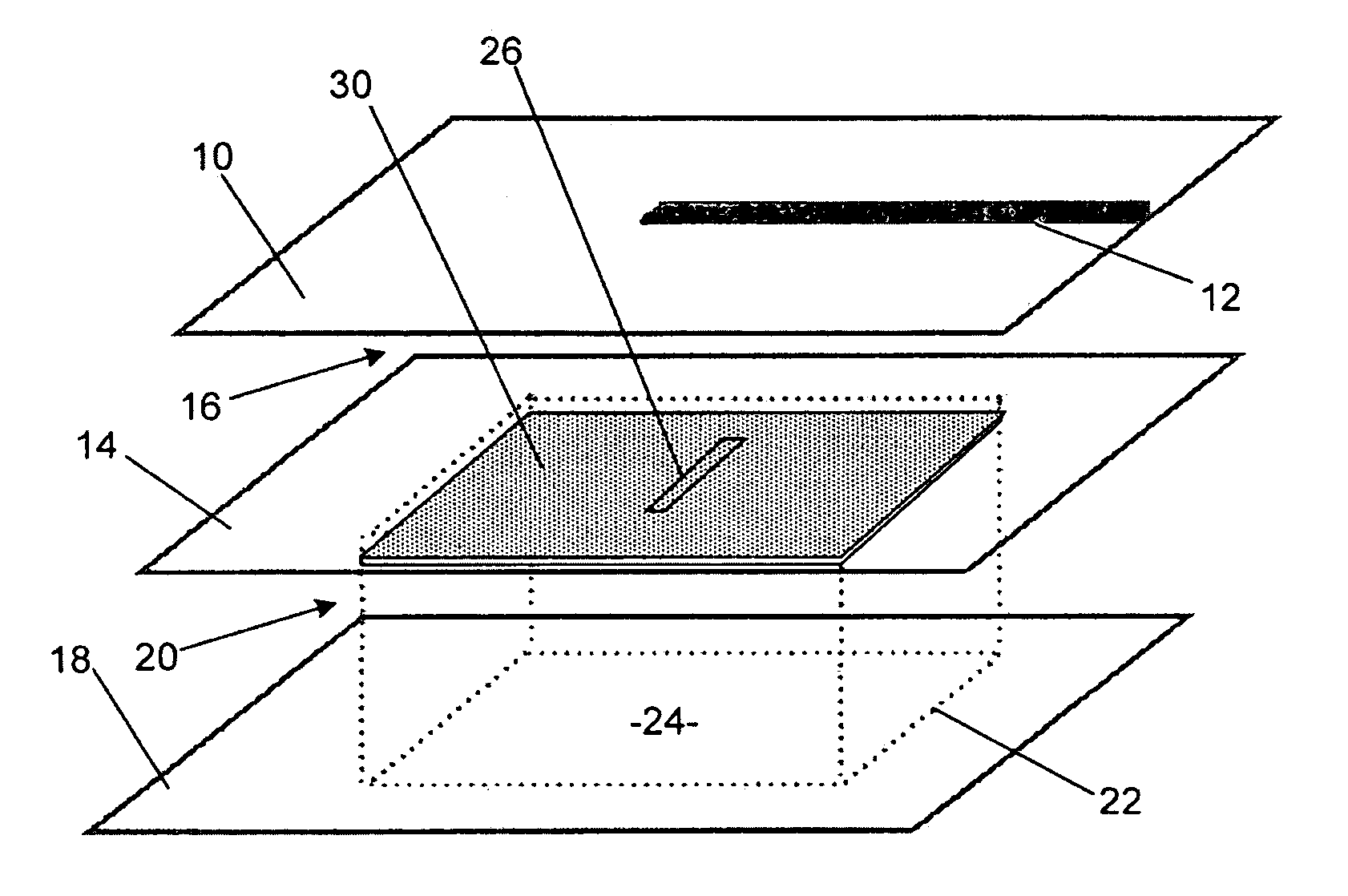
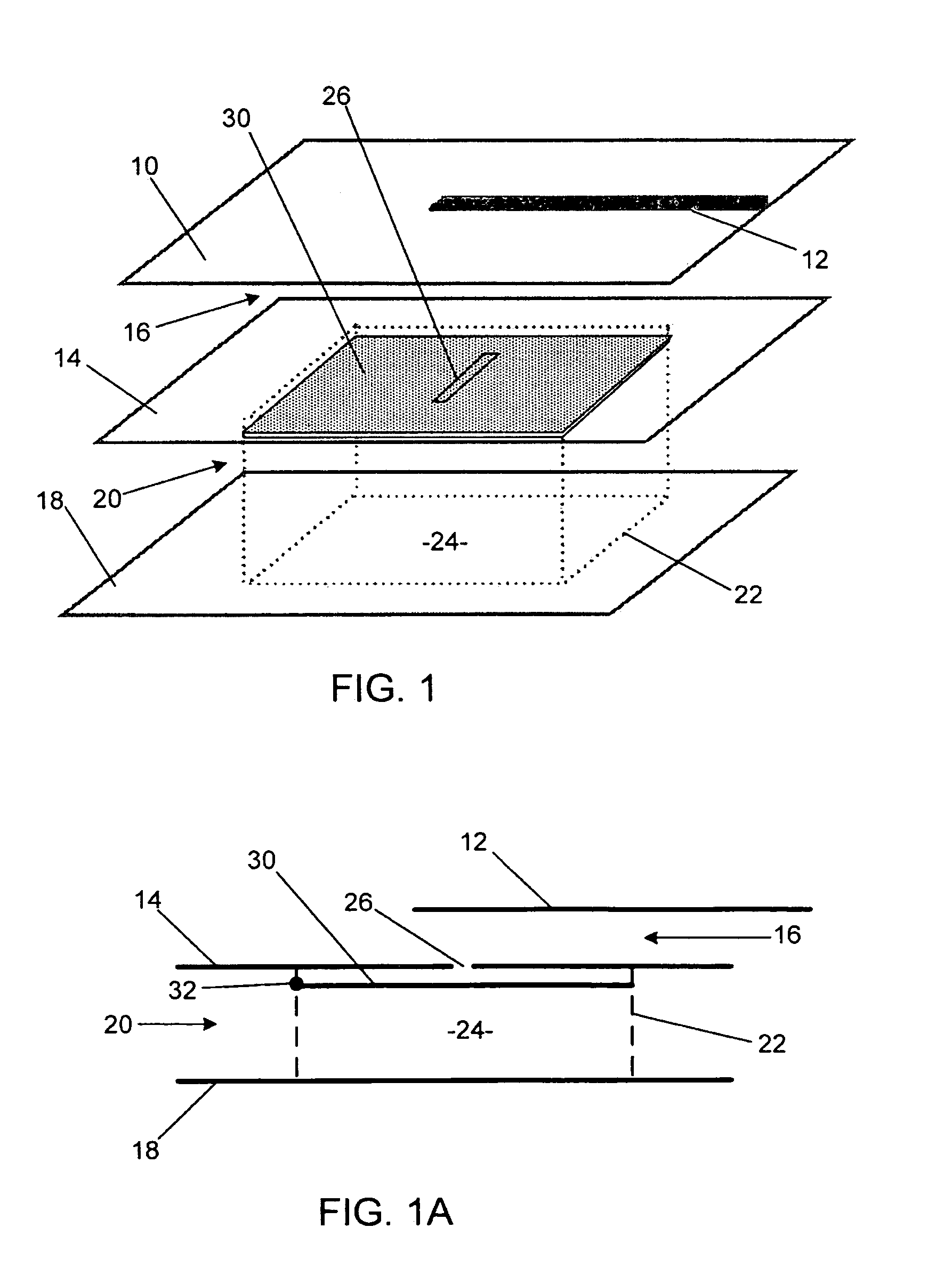
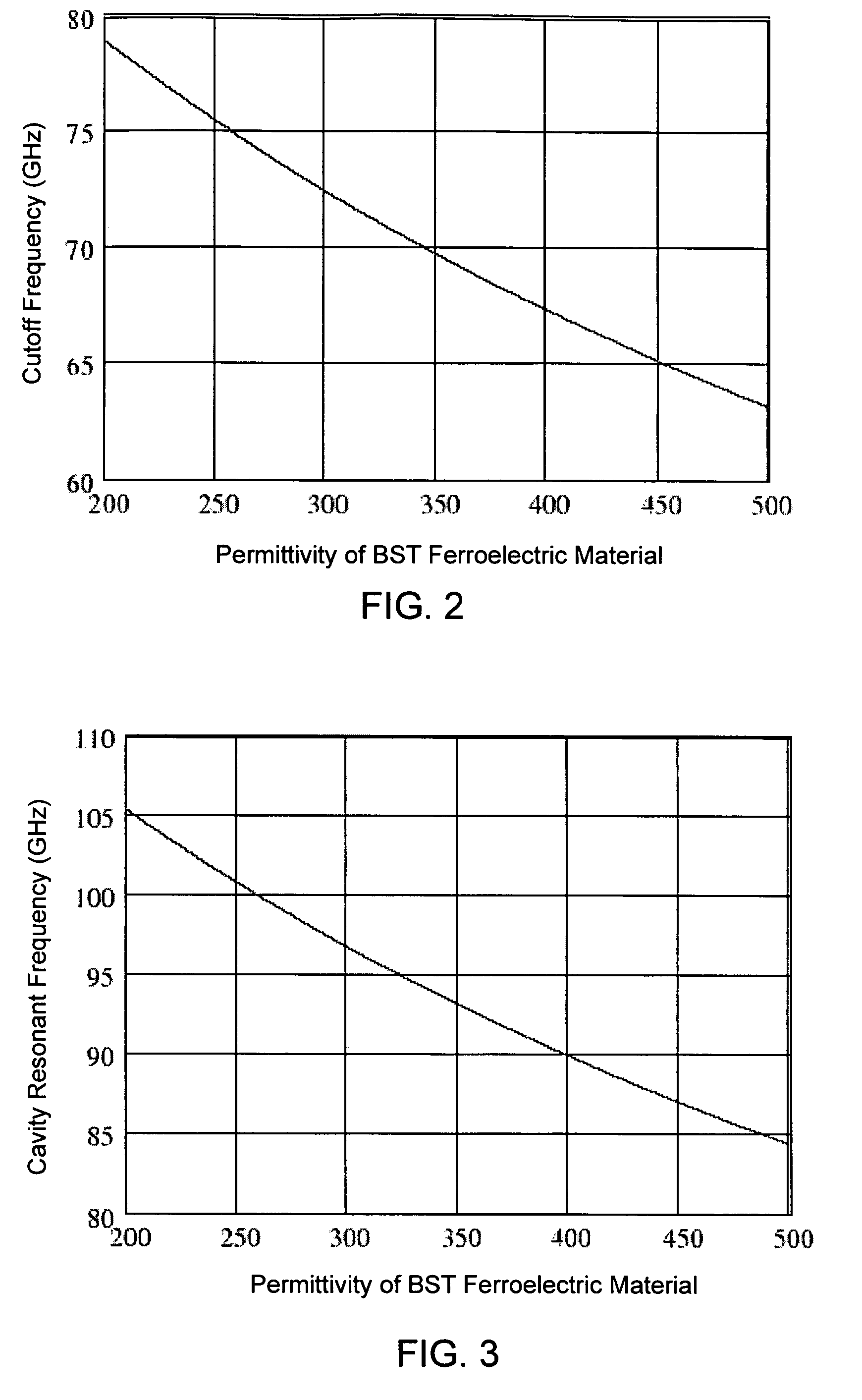
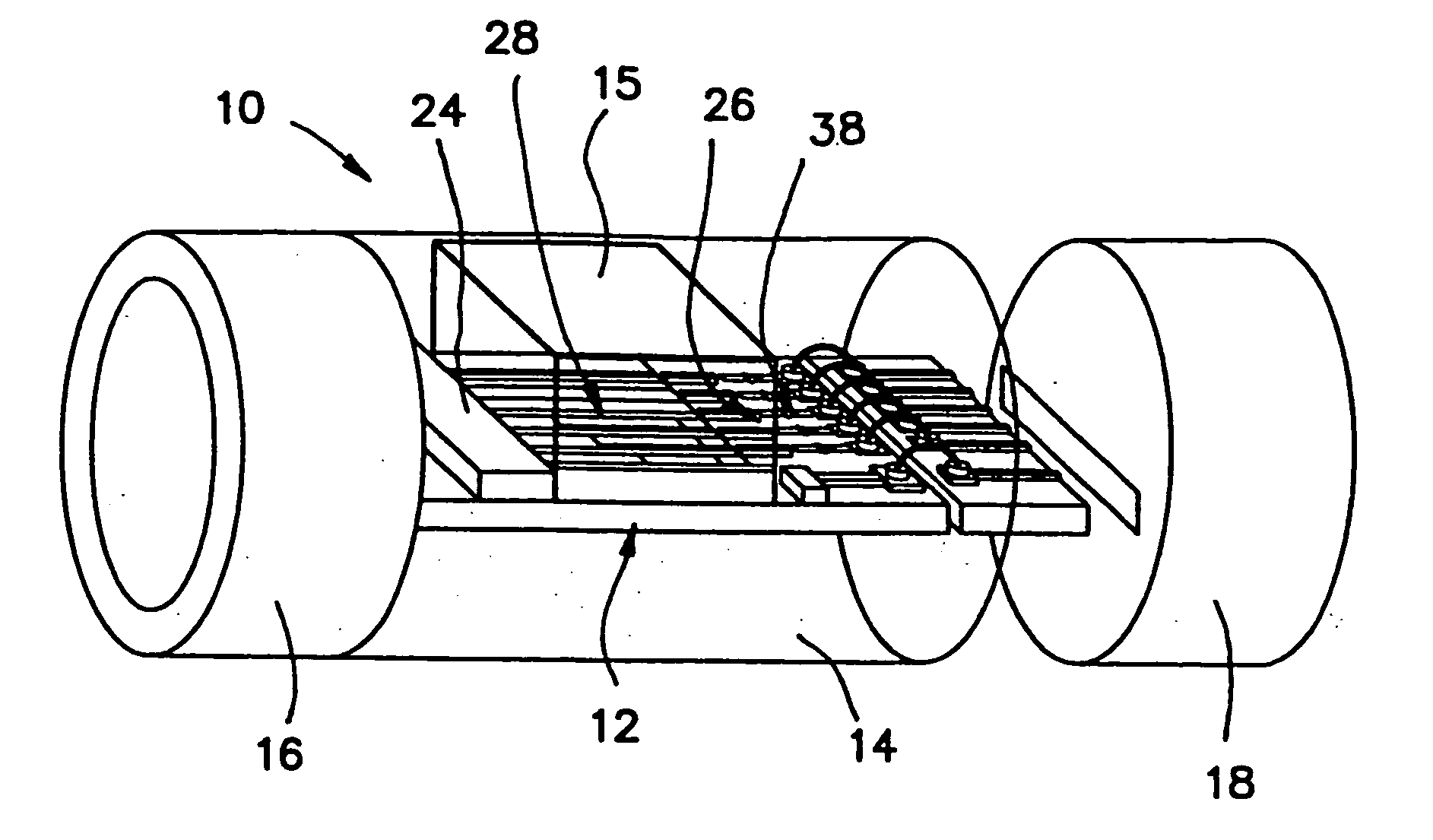
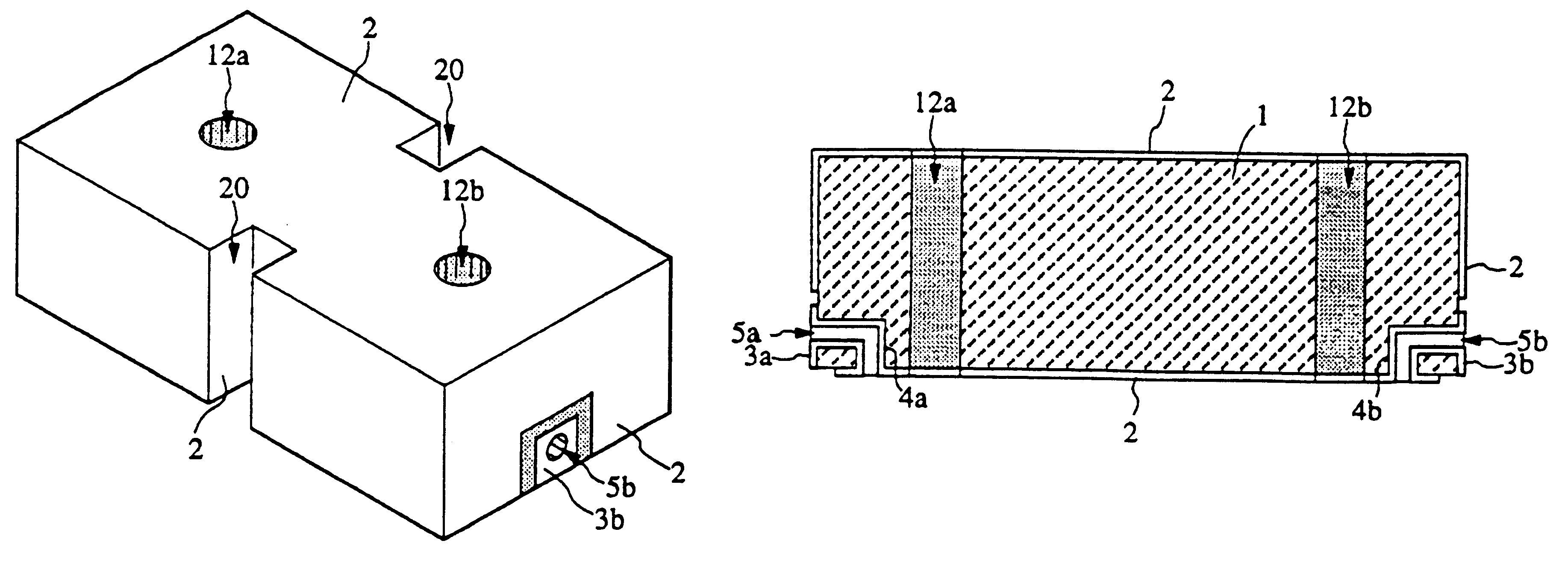
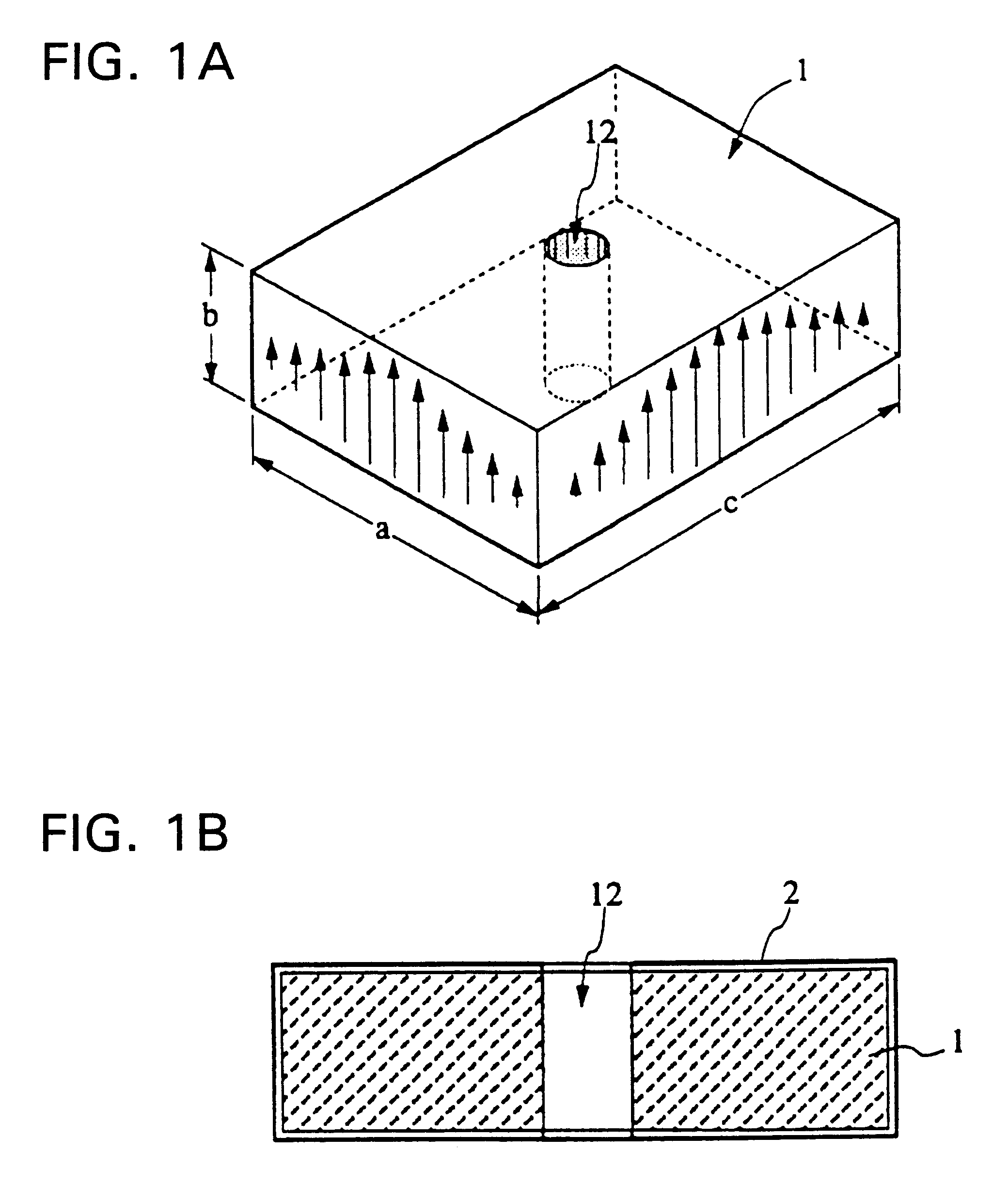
A ferroelectric loaded waveguide resonator capable of operation at microwave, millimeter-wave and higher frequencies and suitable for integration into a three-dimensional monolithic microwave integrated circuit (3D MMIC) is disclosed. The resonator includes a resonator cavity, which, in one form of the invention, is formed by two parallel metal layers and a metallized wall structure extending between the metal layers. The cavity is filled with dielectric material and includes a layer of ferroelectric material, which is used to control the resonant frequency by varying a voltage bias applied to the ferroelectric layer. The cavity includes a slot in one of the metal layers and a coupling strip formed adjacent to the slot to provide electromagnetic coupling to other components, such as a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). The invention can also be applied to other multi-metal semiconductor or wafer level packaging technologies.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Optical waveguide vibration sensor for use in hearing aid
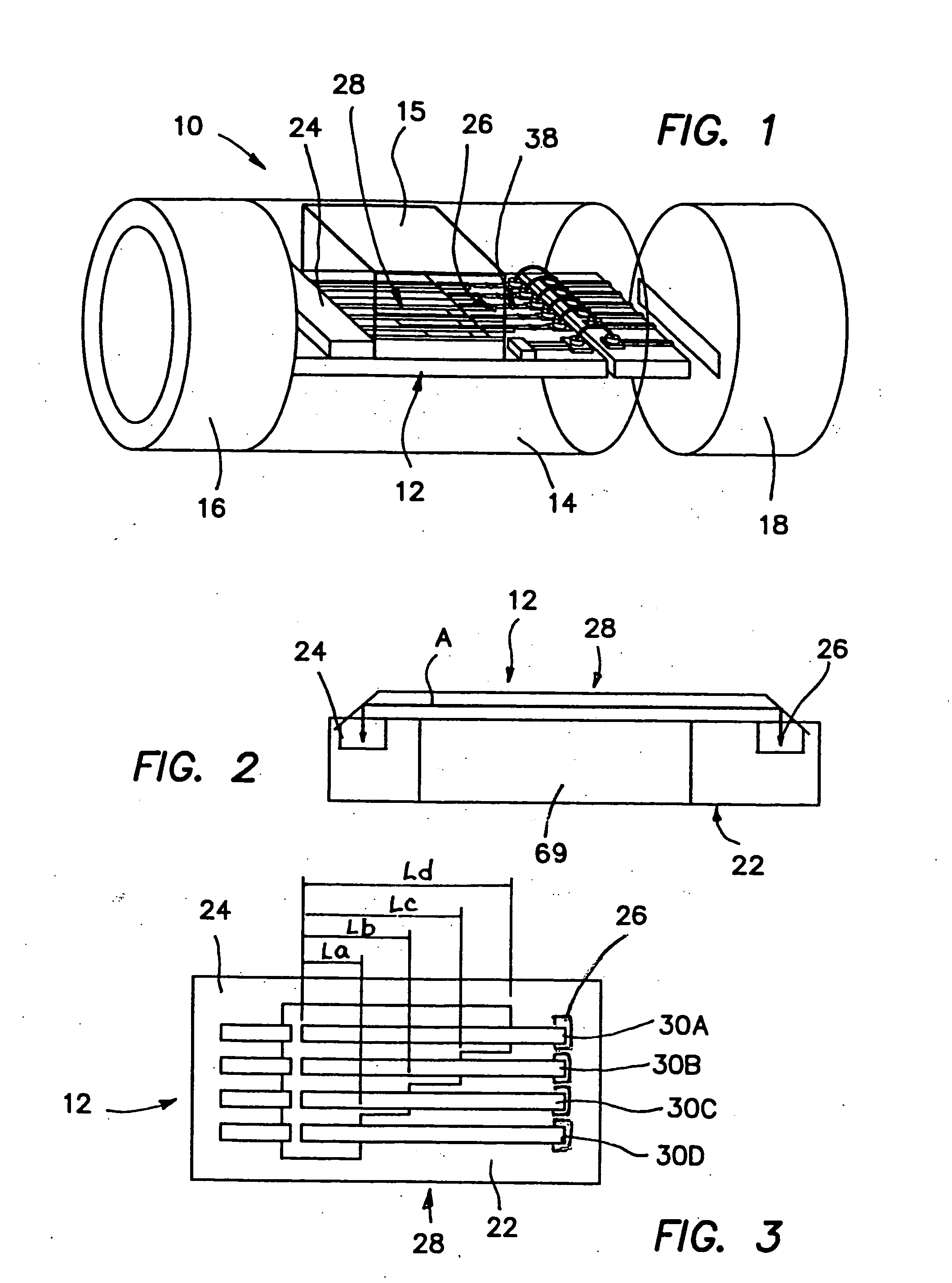
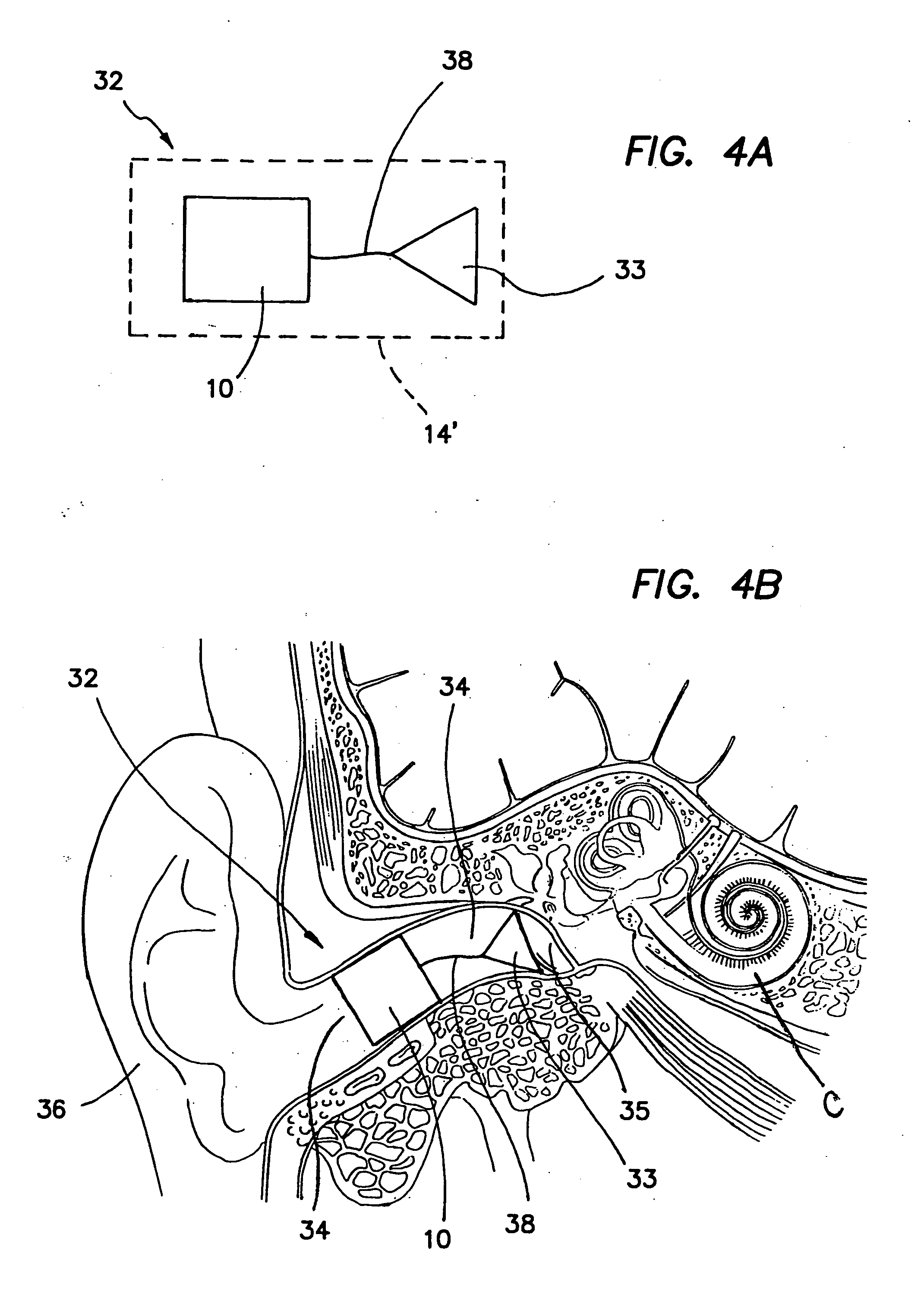
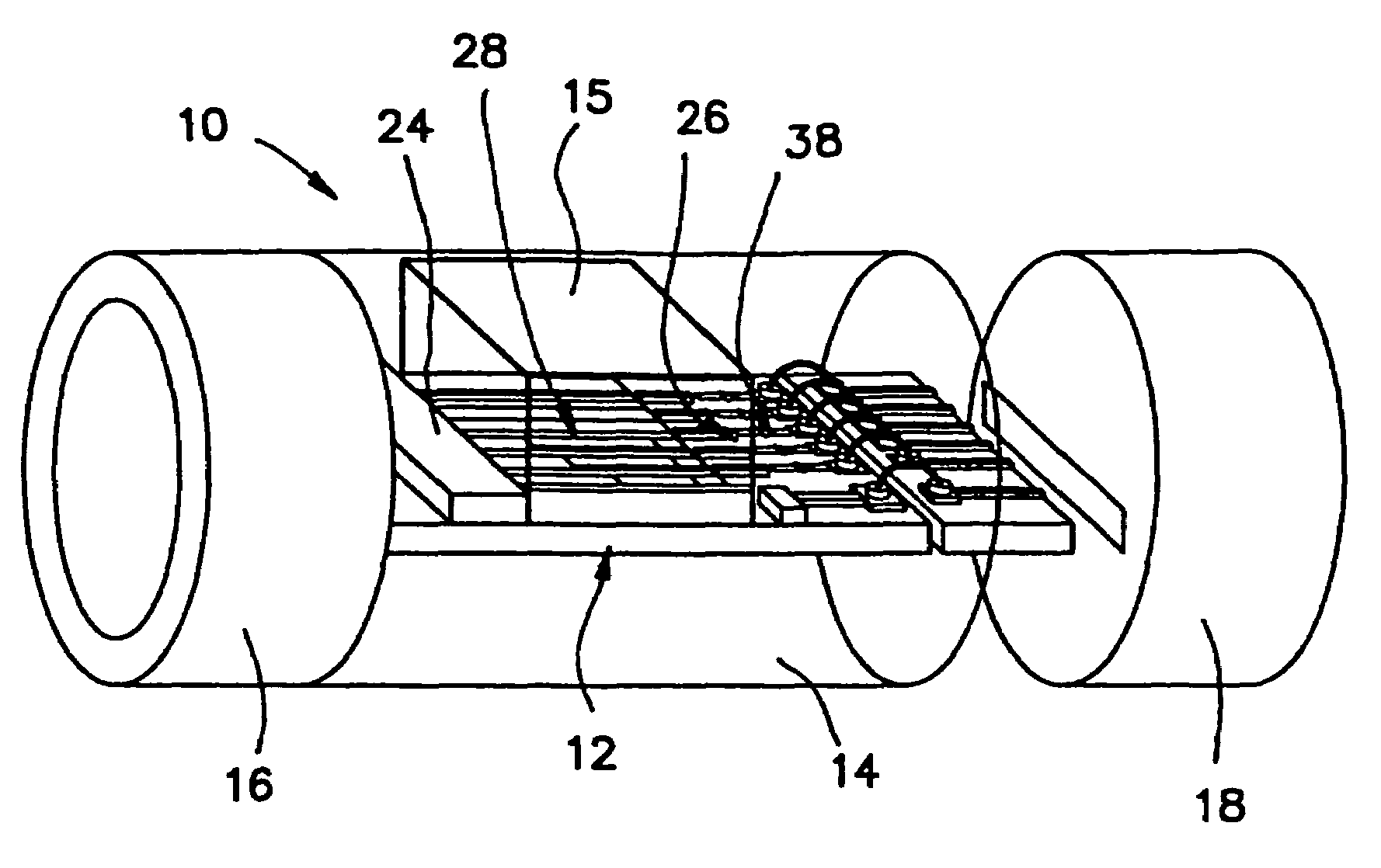
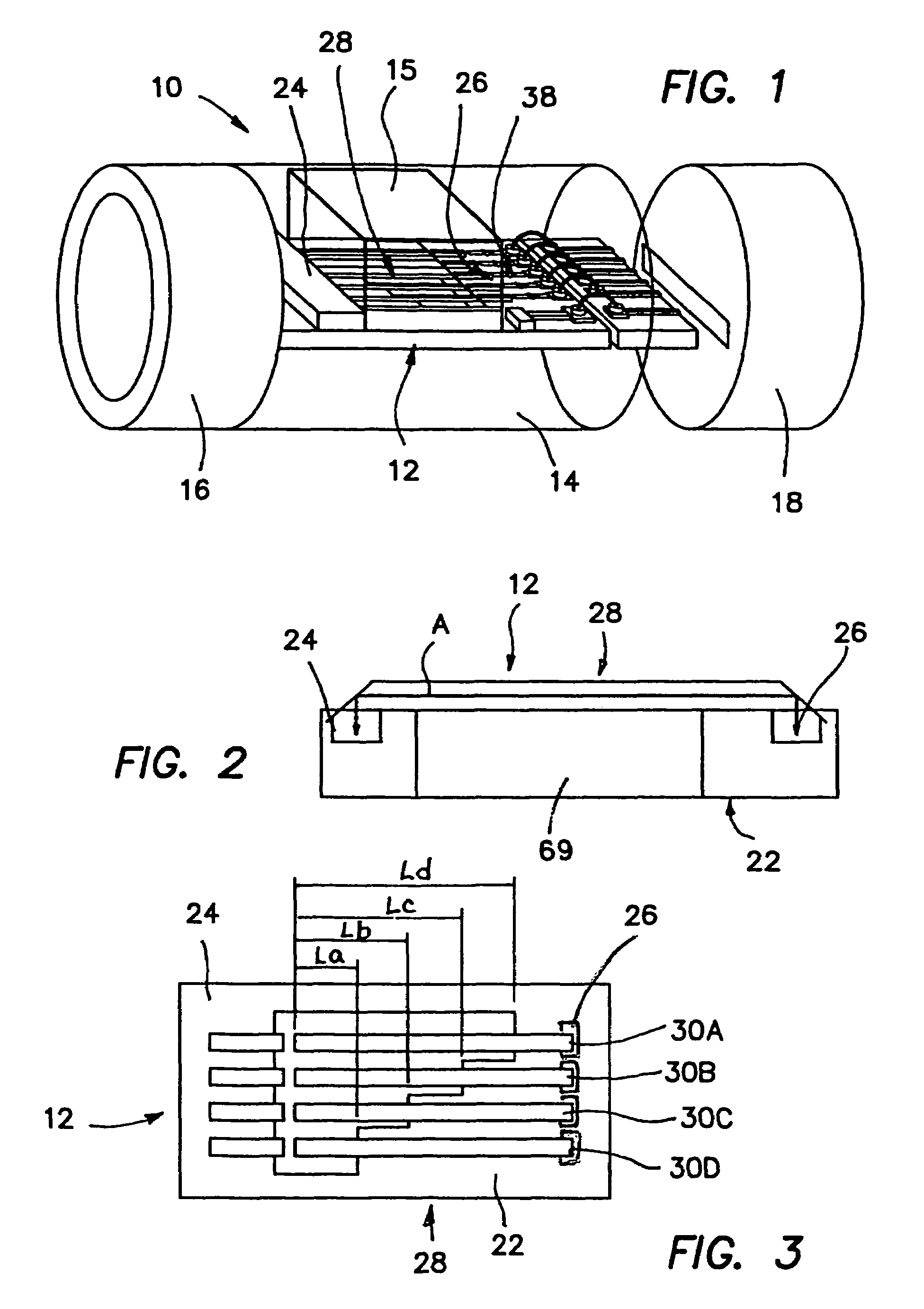
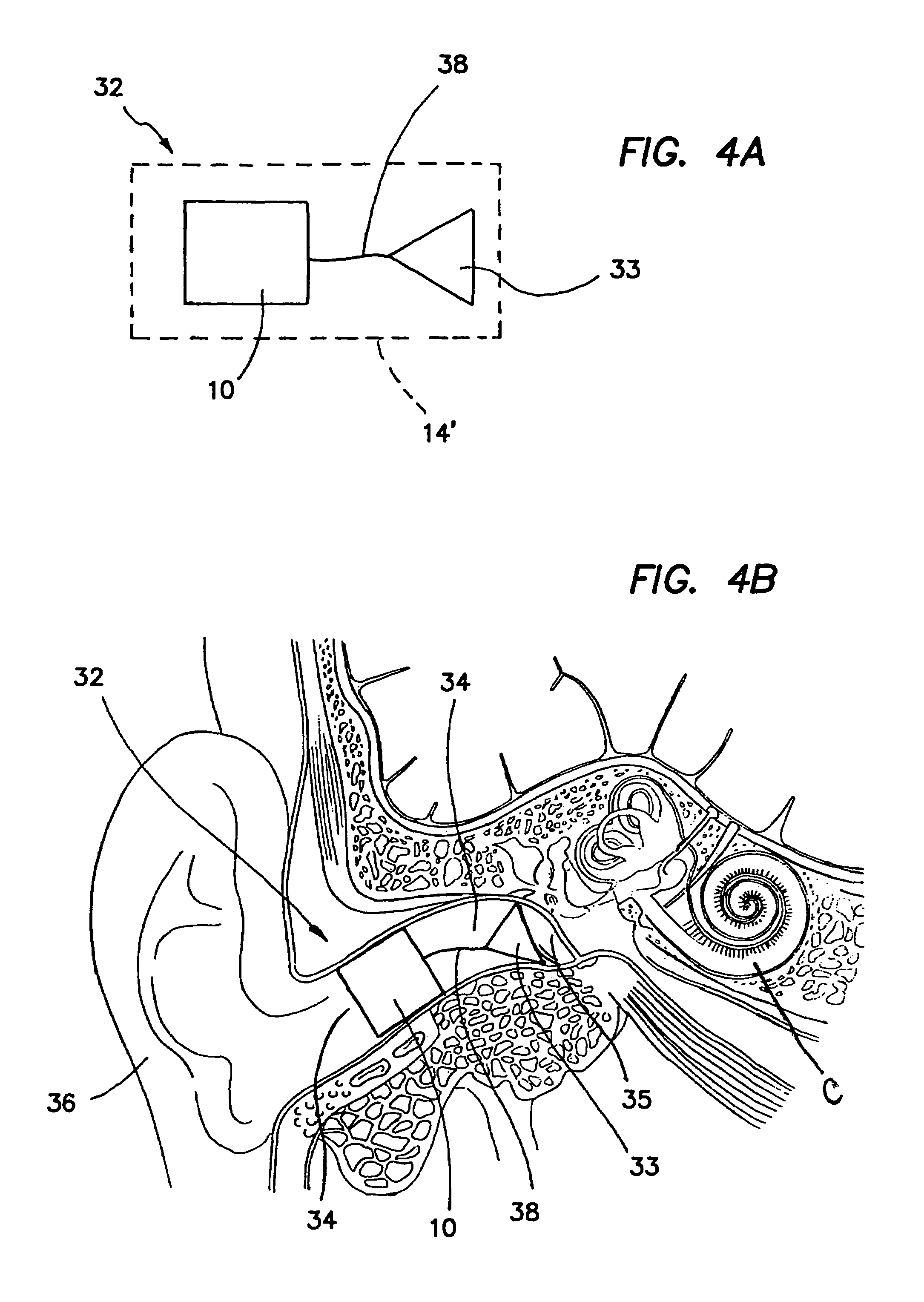
InactiveUS20060107744A1Improve hearingVibration measurement in solidsRecord carriersPolymer optical waveguideLoudspeaker
A directionally-sensitive device for detecting and processing vibration waves includes an array of polymeric optical waveguide resonators positioned between a light source, such as an LED array, and a light detector, such as a photodiode array. The resonators which are preferably oriented substantially perpendicularly with respect to incoming vibration waves, vibrate when a wave is detected, thus modulating light signals that are transmitted between the light source and the light detector. The light detector converts the modulated light into electrical signals which, in a preferred embodiment, are used to drive either the speaker of a hearing aid or the electrode array of a cochlear implant. The device is manufactured using a combination of traditional semiconductor processes and polymer microfabrication techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical waveguide vibration sensor for use in hearing aid
InactiveUS7444877B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPolymer optical waveguideLoudspeaker
A directionally-sensitive device for detecting and processing vibration waves includes an array of polymeric optical waveguide resonators positioned between a light source, such as an LED array, and a light detector, such as a photodiode array. The resonators which are preferably oriented substantially perpendicularly with respect to incoming vibration waves, vibrate when a wave is detected, thus modulating light signals that are transmitted between the light source and the light detector. The light detector converts the modulated light into electrical signals which, in a preferred embodiment, are used to drive either the speaker of a hearing aid or the electrode array of a cochlear implant. The device is manufactured using a combination of traditional semiconductor processes and polymer microfabrication techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Miniaturized antennas based on negative permittivity materials
ActiveUS20060022875A1High sensitivitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsResonatorMicrowave electromagnetic radiation
An antenna comprises a resonator and a waveguide. The resonator comprises at least one body having a negative effective electrical permittivity or a negative magnetic permeability when a resonance is excited therein by electromagnetic radiation lying in some portion of the microwave spectrum. A termination of the waveguide is situated adjacent the resonator. The resonator is conformed such that at the resonance, there is efficient coupling between the resonator and the waveguide.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS
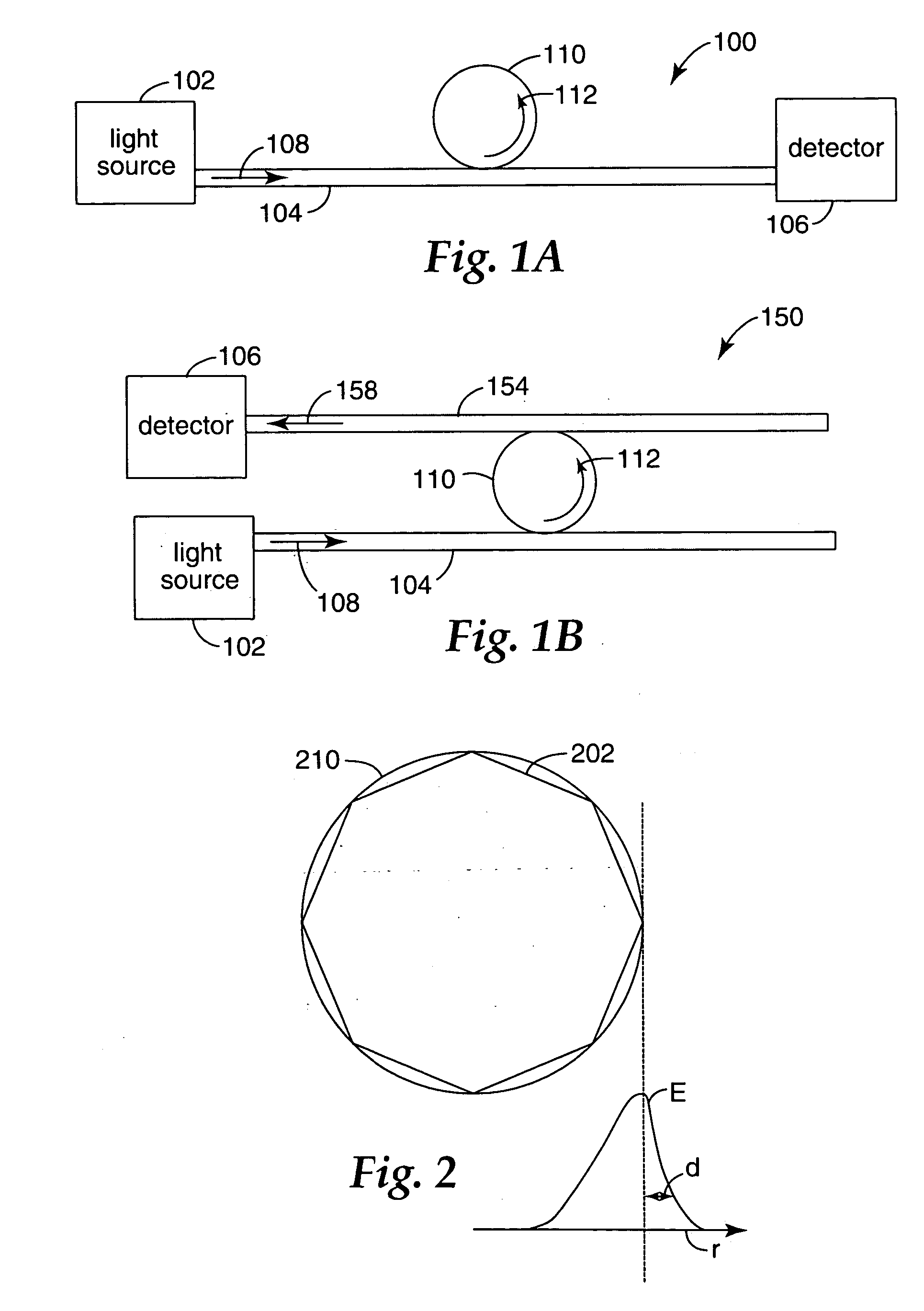
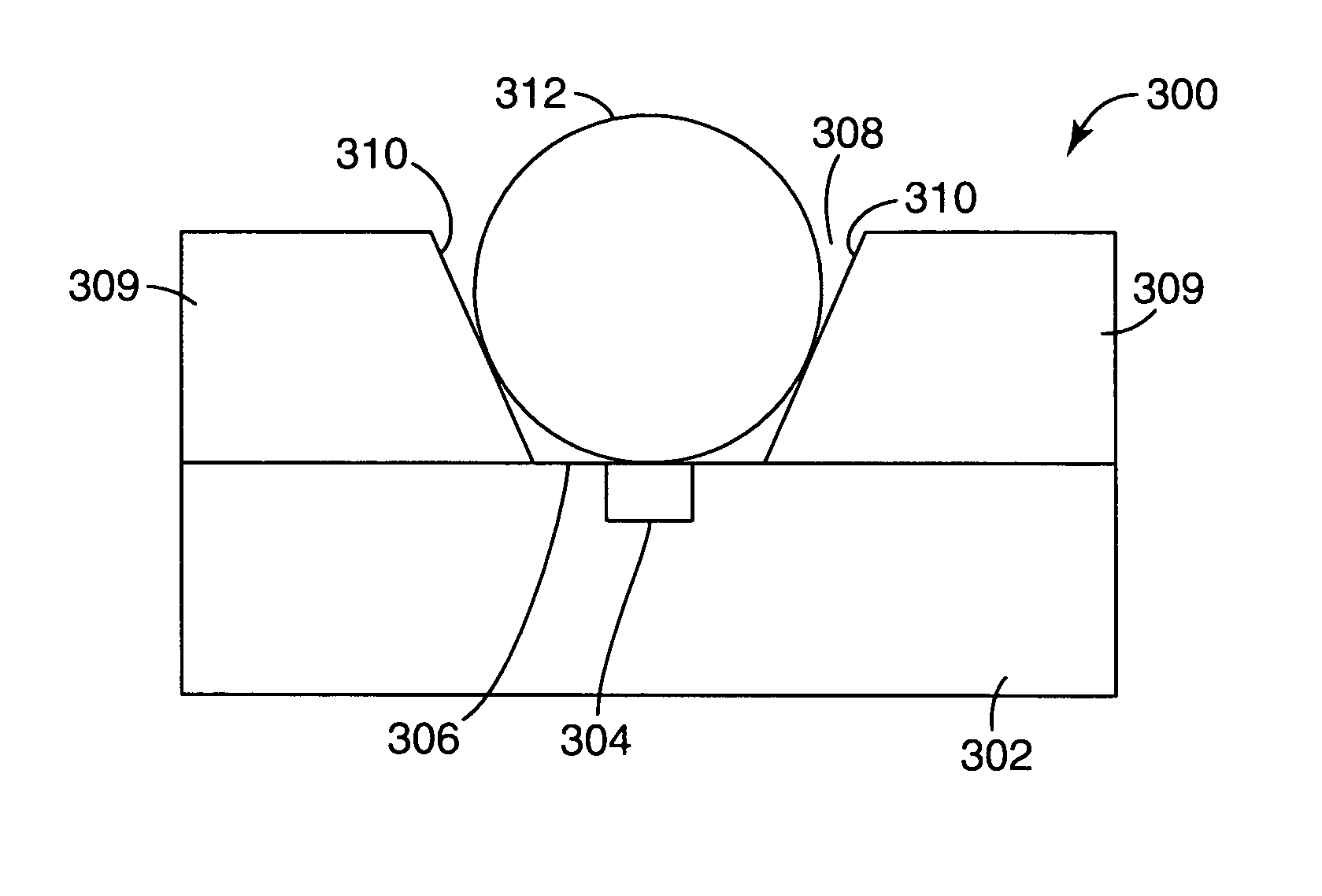
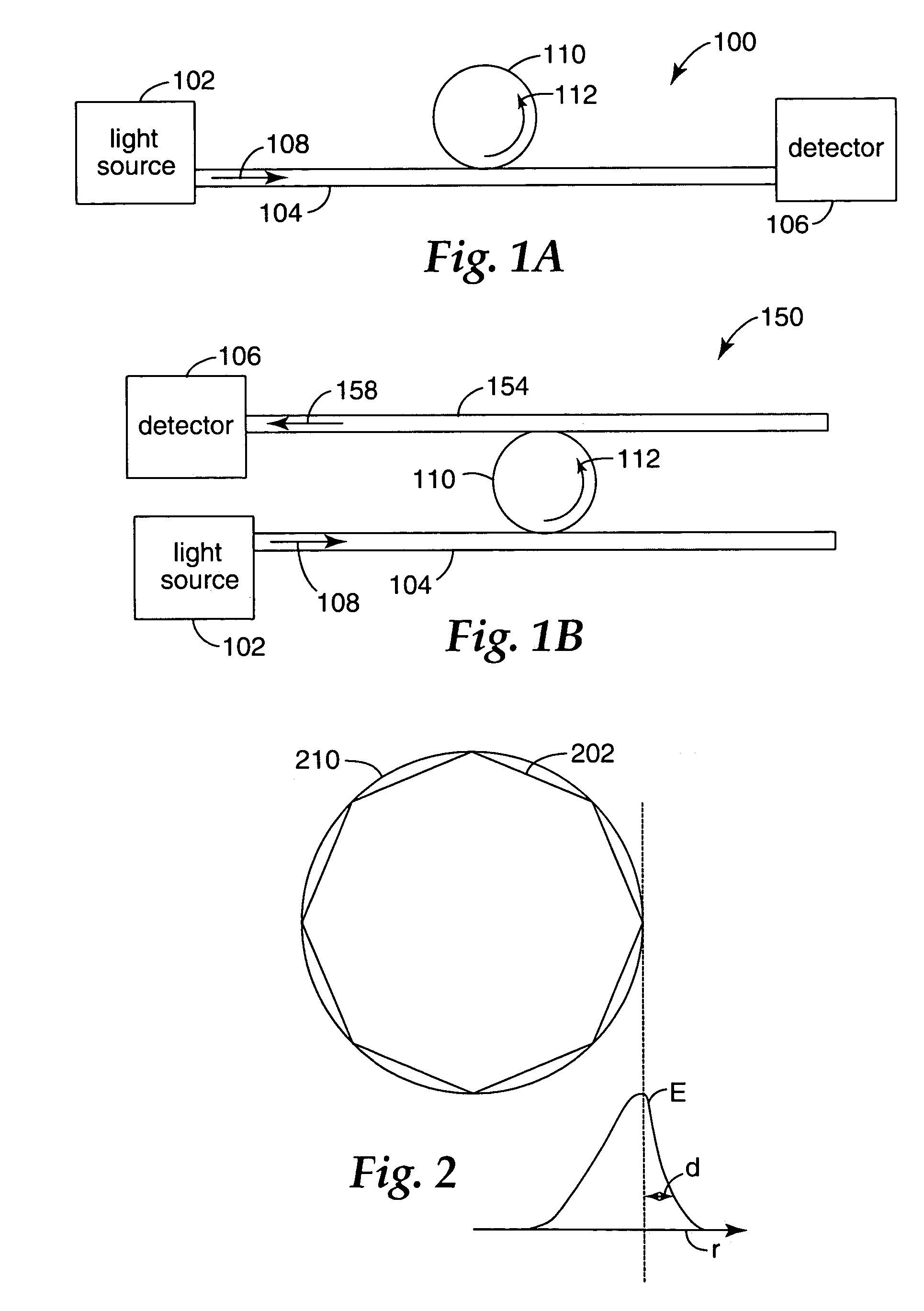
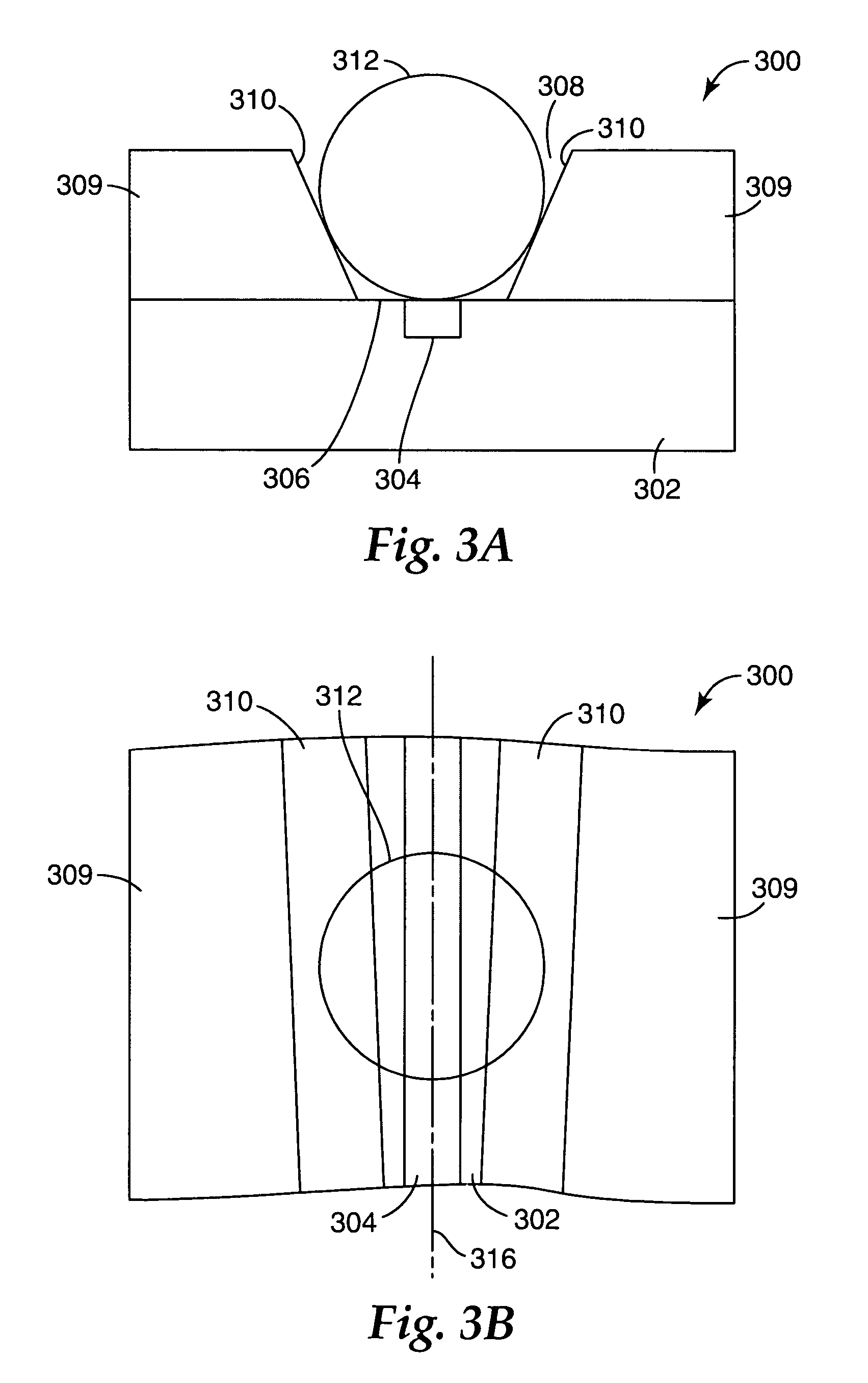
Hybrid sphere-waveguide resonators
InactiveUS20050077513A1Improve stabilityHigh cavity Q and ease of launchingRoof coveringCladded optical fibreCouplingMicrosphere
Microresonators, such as a microsphere resonators and planar microresonators, are optically coupled to waveguides for input and output of light. It is important that the relative positions of the microresonator and the waveguide are maintained stable, while still maintaining high cavity Q and ease of launching and extracting the optical beams. Structures are provided on a substrate that are useful for maintaining the position of the microresonator relative to the waveguide. The structures provide for vertical or horizontal coupling between the waveguide and the microresonator.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
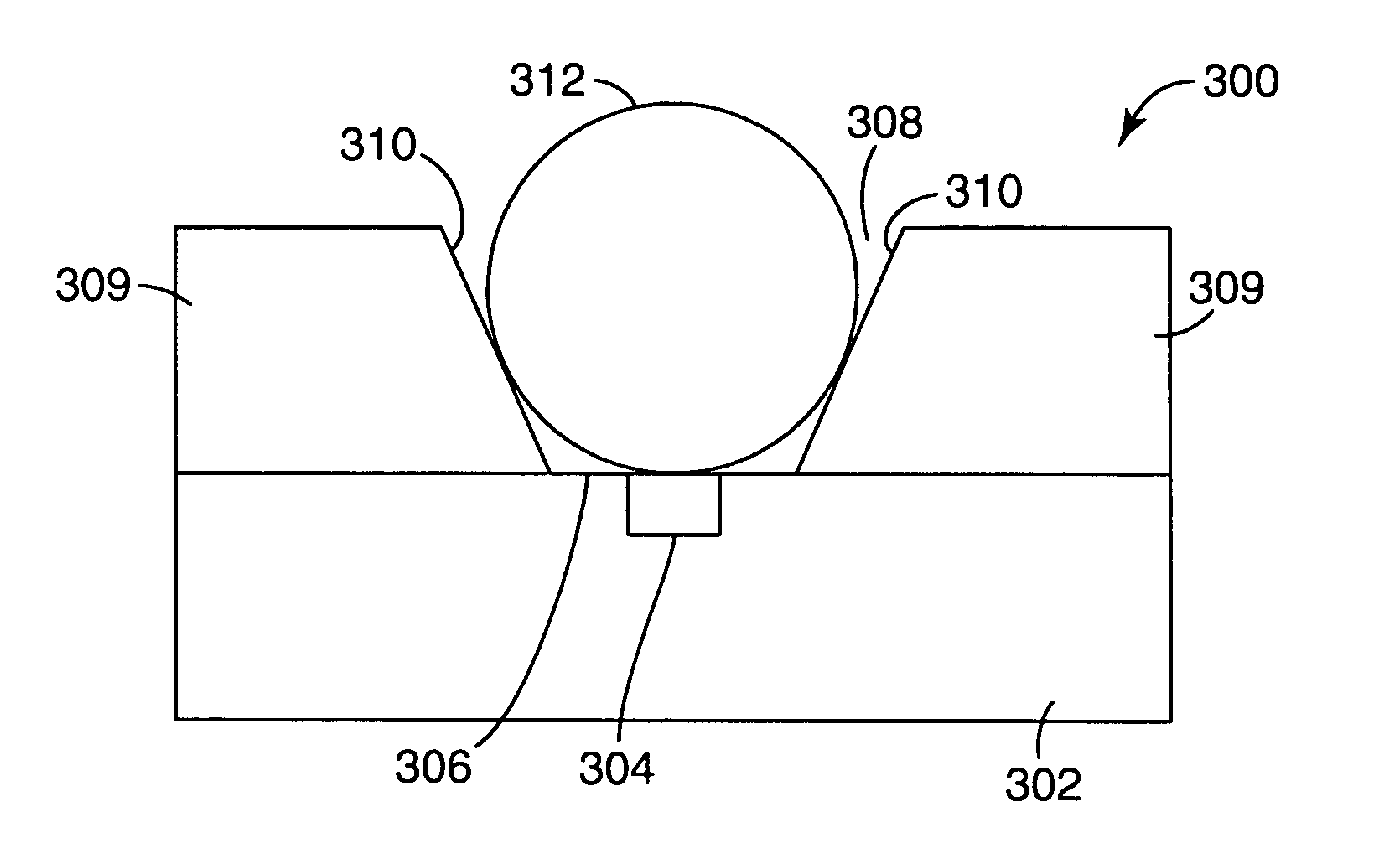
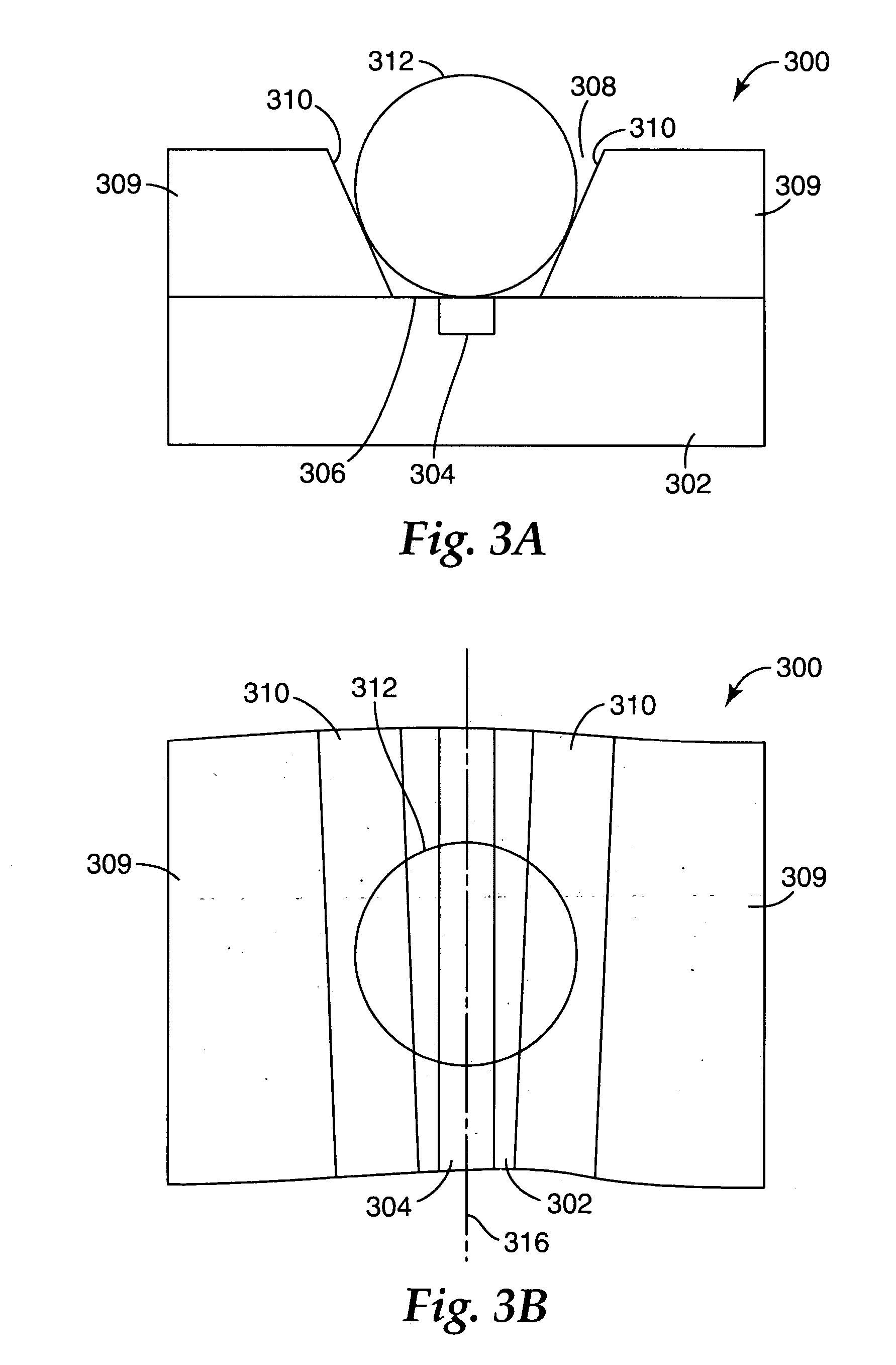
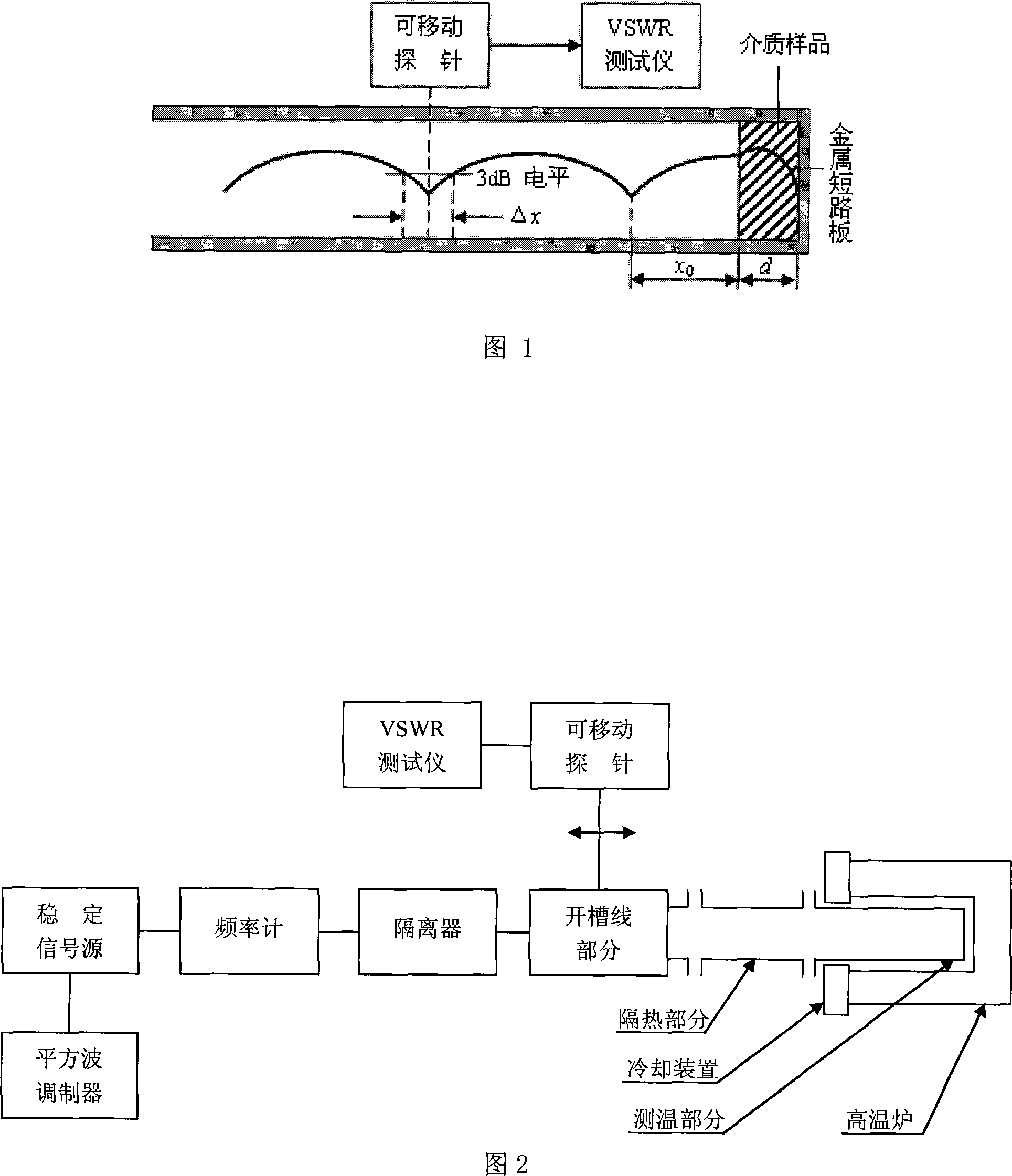
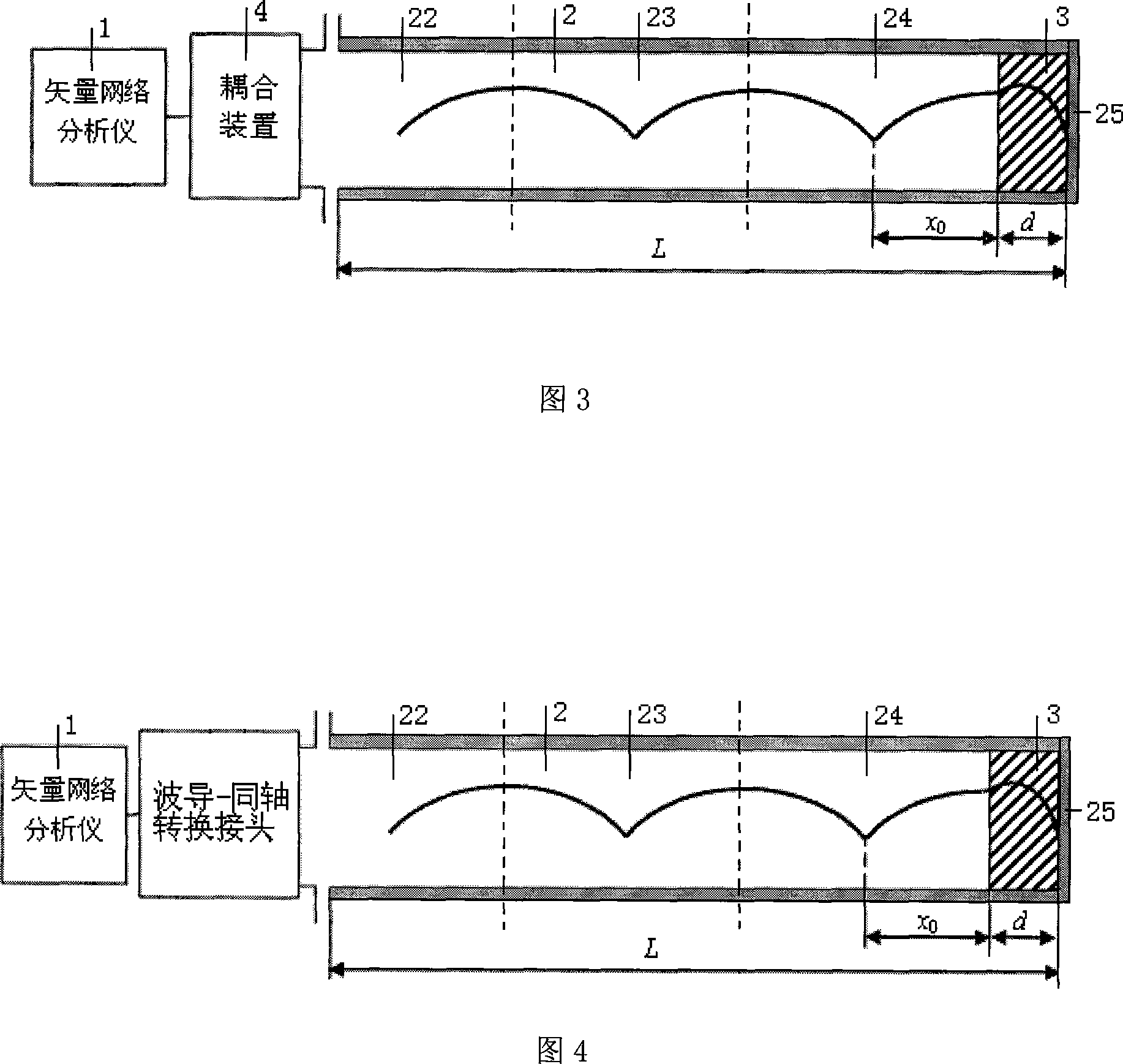
Dielectric materials high-temperature complex dielectric constant measurement method based on terminal short circuit method
InactiveCN101158702AImprove test accuracyReduce mistakesResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingResonant cavityElectricity
The present invention provides a medium material high-temperature complex permittivity measurement method based on terminal short circuit and pertains to technology of microwave and millimeter wave dielectric material complex permittivity measurement. When the present invention adopts the terminal short circuit for measurement of high-temperature medium material complex permittivity, a heat dissipation wave guide, a heat insulation waveguide, a high-temperature waveguide with a certain length, and a coupling device, a short circuit board are together constitute a reactive type resonator, and dimensions and microwave loss of the resonator under different temperature can be obtained by measurement of resonance frequency and quality factor of the resonator, and the complex permittivity of the medium material under the temperature can be further measured. The present invention is suitable for the measurement of the medium material high-temperature complex permittivity of various frequency band based on the terminal short circuit, and meanwhile the present invention can measure the dimension and the microwave loss of the waveguide resonator under different temperature. As the present invention considers the changing of the dimension and the microwave loss of the waveguide resonator caused by the influence of the temperature, the present invention has higher measurement accuracy and smaller error.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
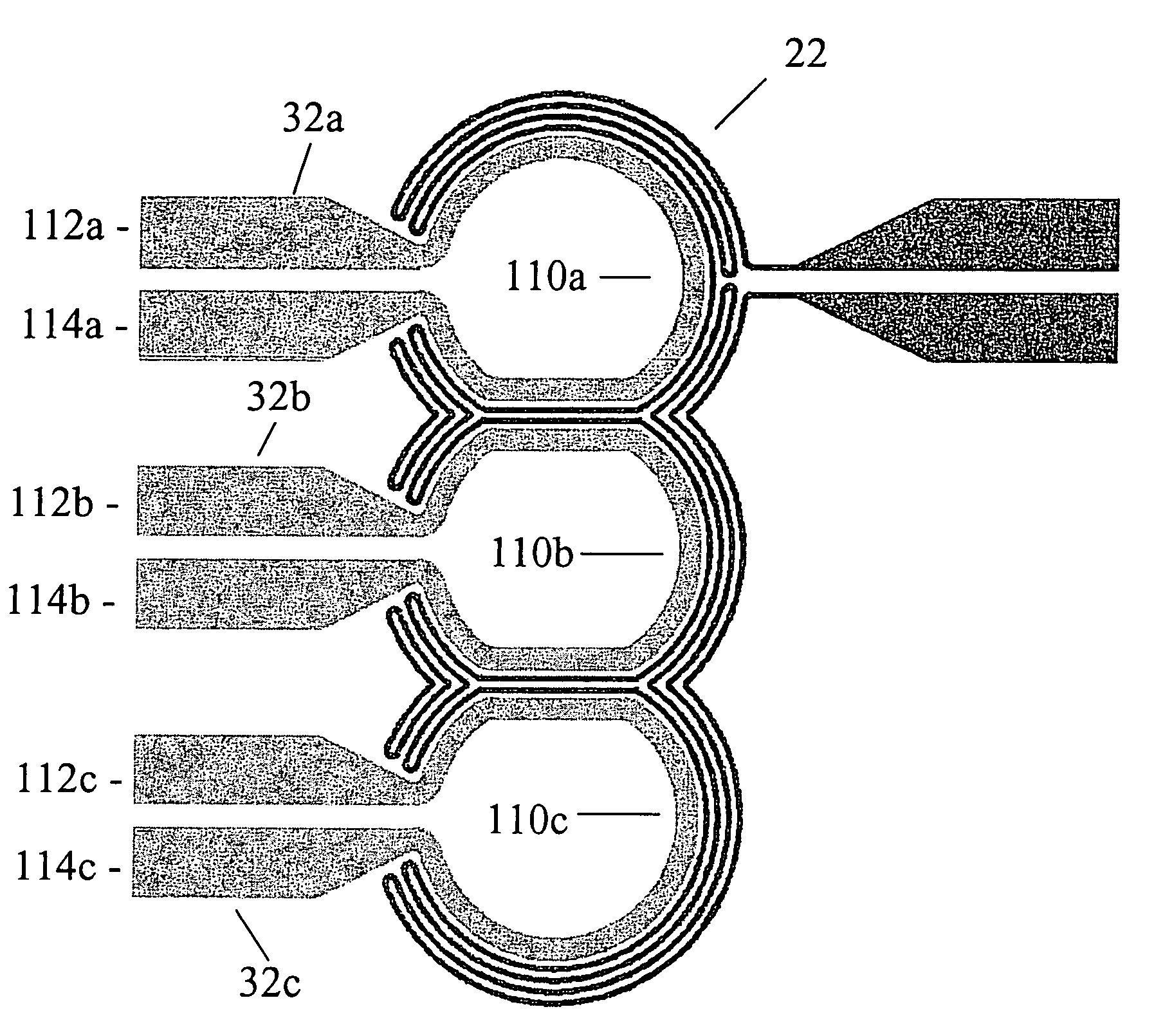
Coupled optical waveguide resonators with heaters for thermo-optic control of wavelength and compound filter shape
An integrated optical device is disclosed comprising a substrate, optical waveguide, and compound optical resonator having a temperature sensor, at least two coupled optical resonators, and a heater localized to each optical resonator. An optical input signal is coupled to one of the resonators making up the compound resonator to form an optical output signal. The center wavelength and shape of the output signal is optimized with a feedback loop using the temperature sensor to control the power dissipated in at least one of the localized heaters. The power dissipated in the remaining resonator heaters is set according to a predetermined function having as an input variable the power dissipated in the resonant heater under control of the said feedback loop
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Dielectric waveguide filter with cross-coupling
InactiveUS20070120628A1Suppress radiation lossSuppress broadband spuriousResonatorsWaveguidesThird waveCoupling
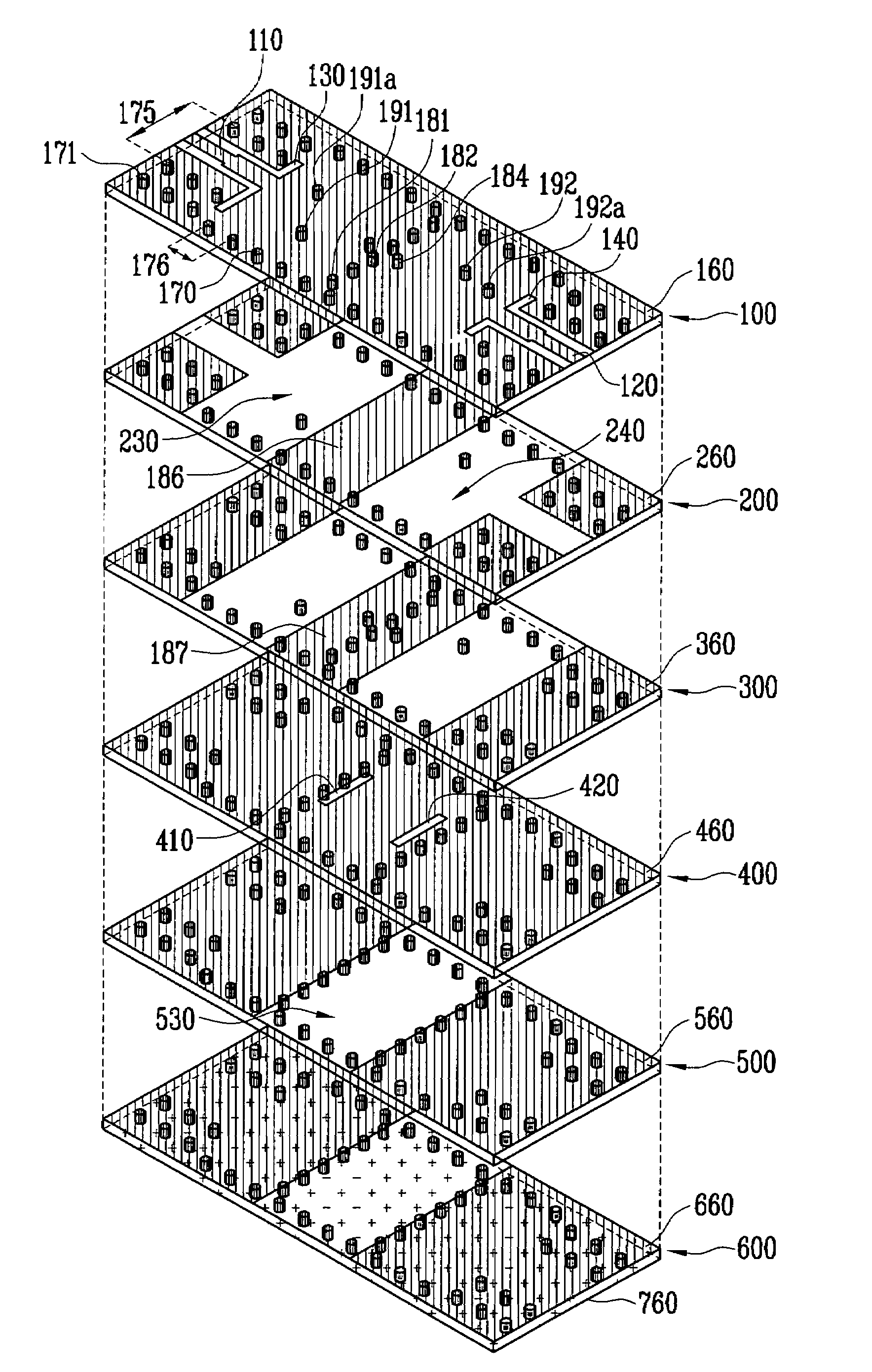
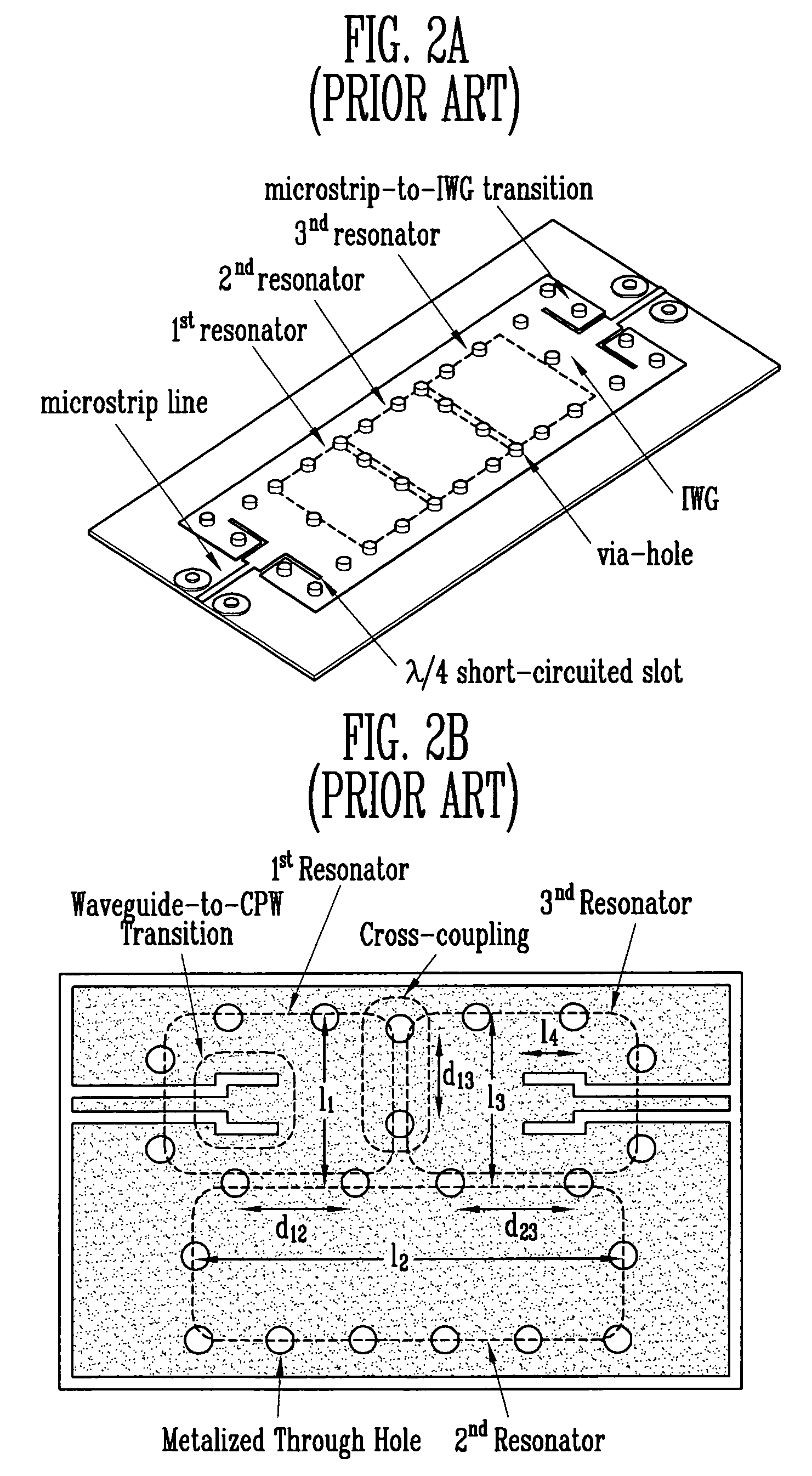
Provided is a dielectric waveguide filter. The filter includes: a multi-layered structure of dielectric substrates having first and second ground planes at its top and bottom; first, second, and third waveguide resonators disposed at multiple layers within the multi-layered structure; converters for signal transition between input / output ports and the first and third waveguide resonators; first vias for forming the first, second, and third waveguide resonators; and second vias disposed at a boundary surface of the first waveguide resonator and the third waveguide resonator.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
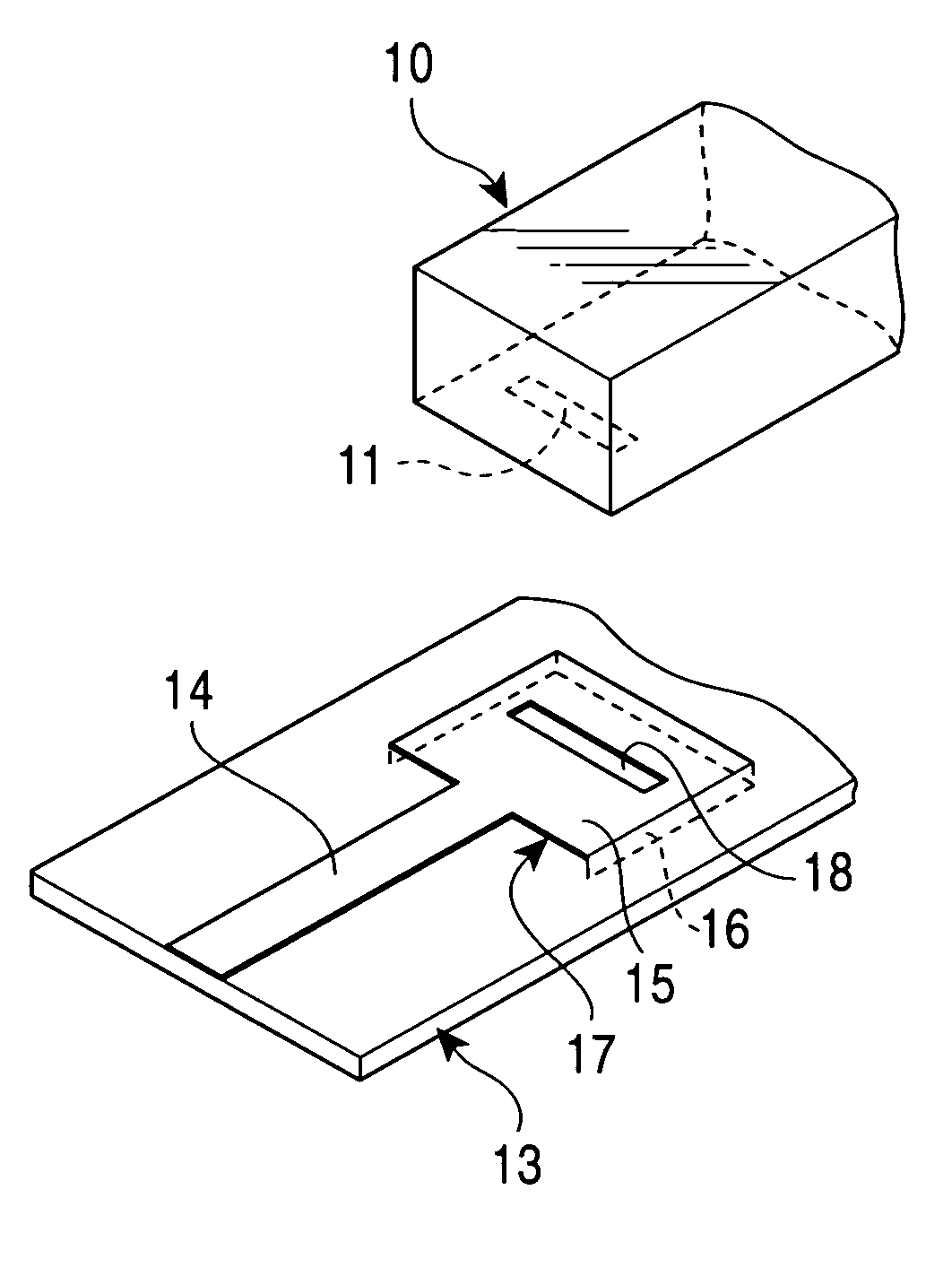
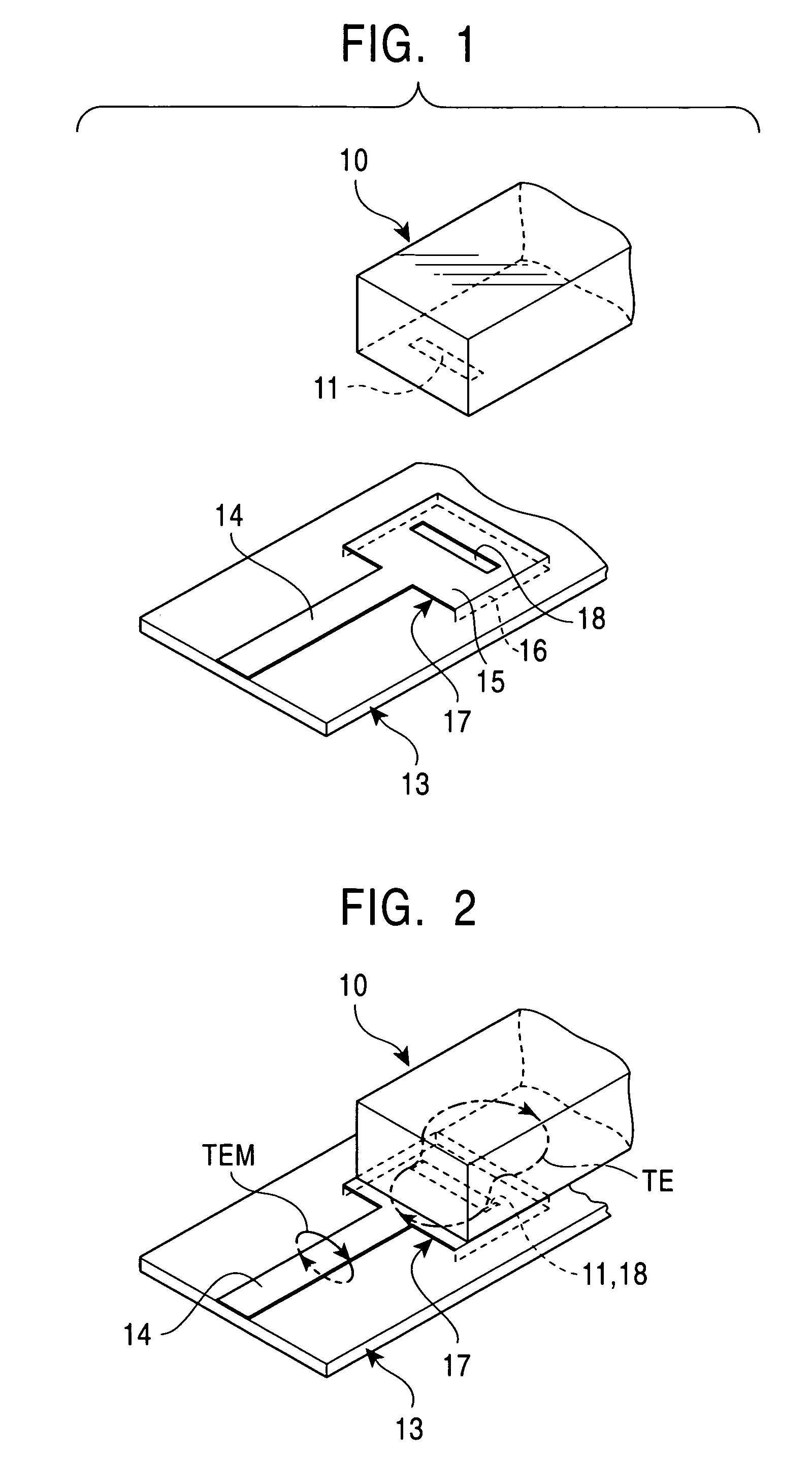
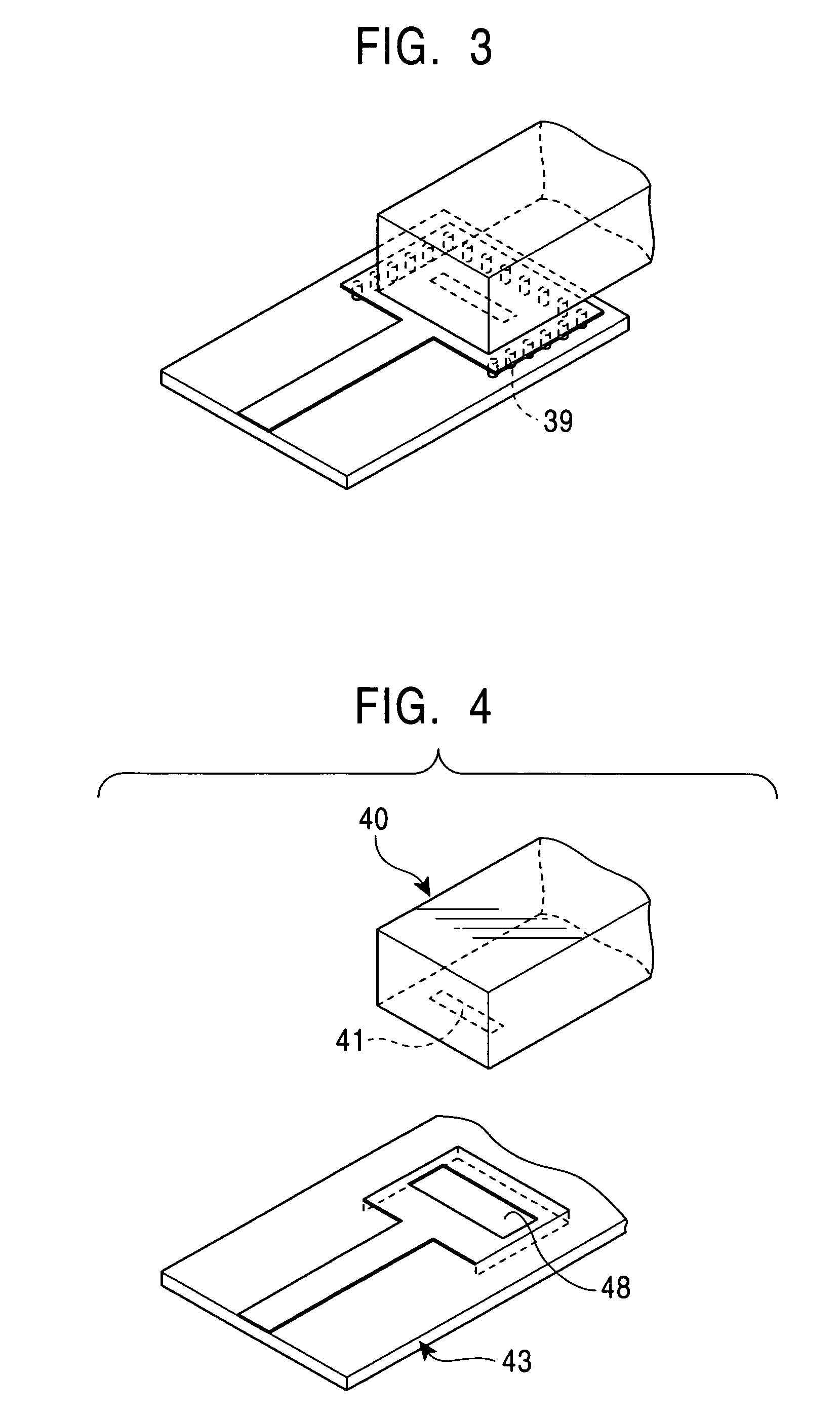
Input/output coupling structure for dielectric waveguide resonator
Disclosed is an input / output coupling structure for a dielectric waveguide resonator to be mounted on a printed circuit board, which comprises; a region defined in the printed circuit board and surrounded by a first conductive film formed on the front surface of the printed circuit board and connected to a microstrip line on the printed circuit board, a second conductive film formed on the back surface of the printed circuit board, and a conductive wall connecting the respective peripheries of the first and second conductive films; a first slot formed in the front surface of the region; and a second slot formed in a surface of the dielectric waveguide resonator which is disposed to be opposed to the region of the printed circuit board. The first and second slots are adapted to be disposed in opposed relation to one another. The coupling structure can achieve the connection between a dielectric waveguide resonator and a microstrip line without forming any input / output electrode on the resonator, to facilitate the application of the dielectric waveguide resonator to an electronic circuit even if it is intended to be used in millimetric-wave band.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
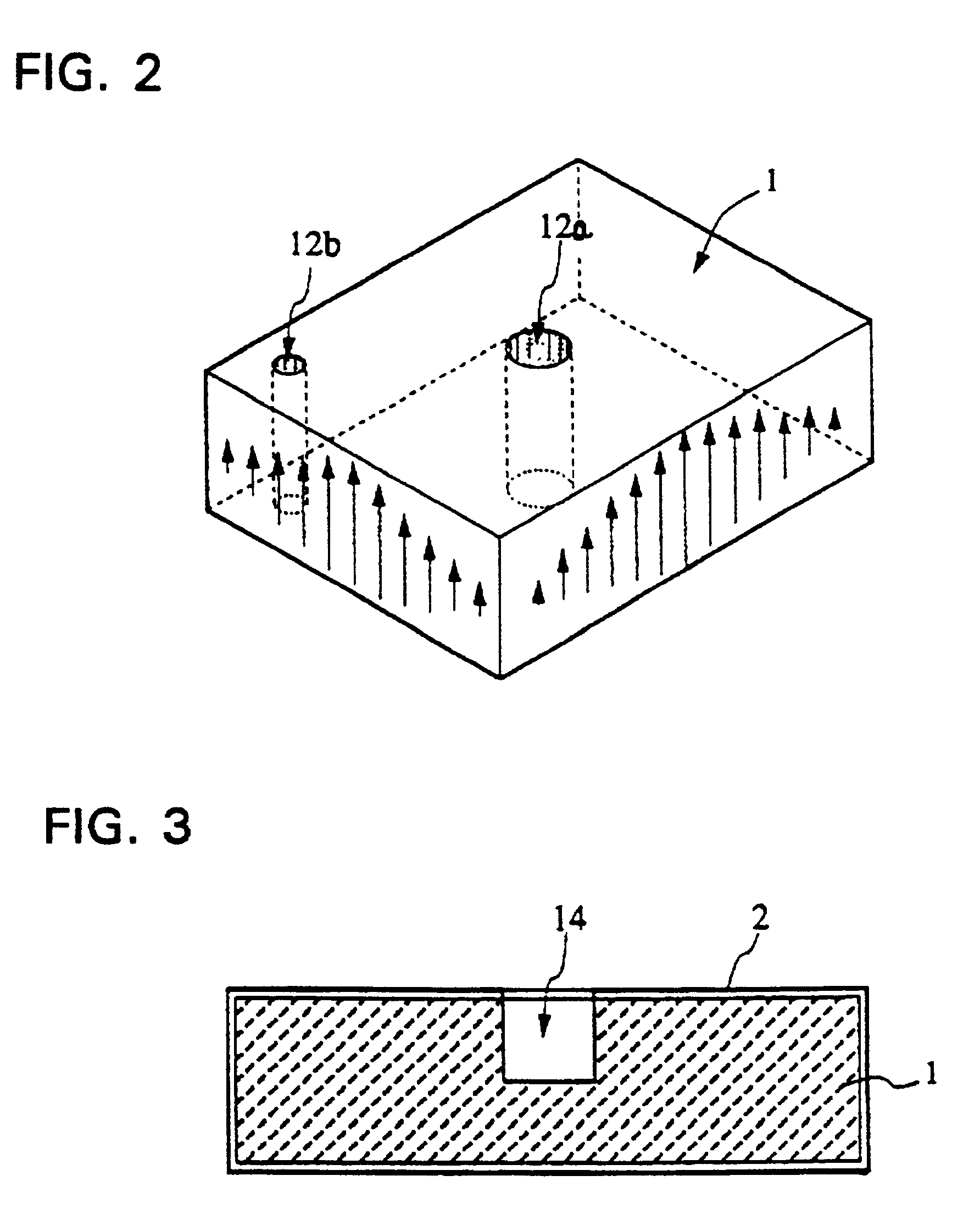
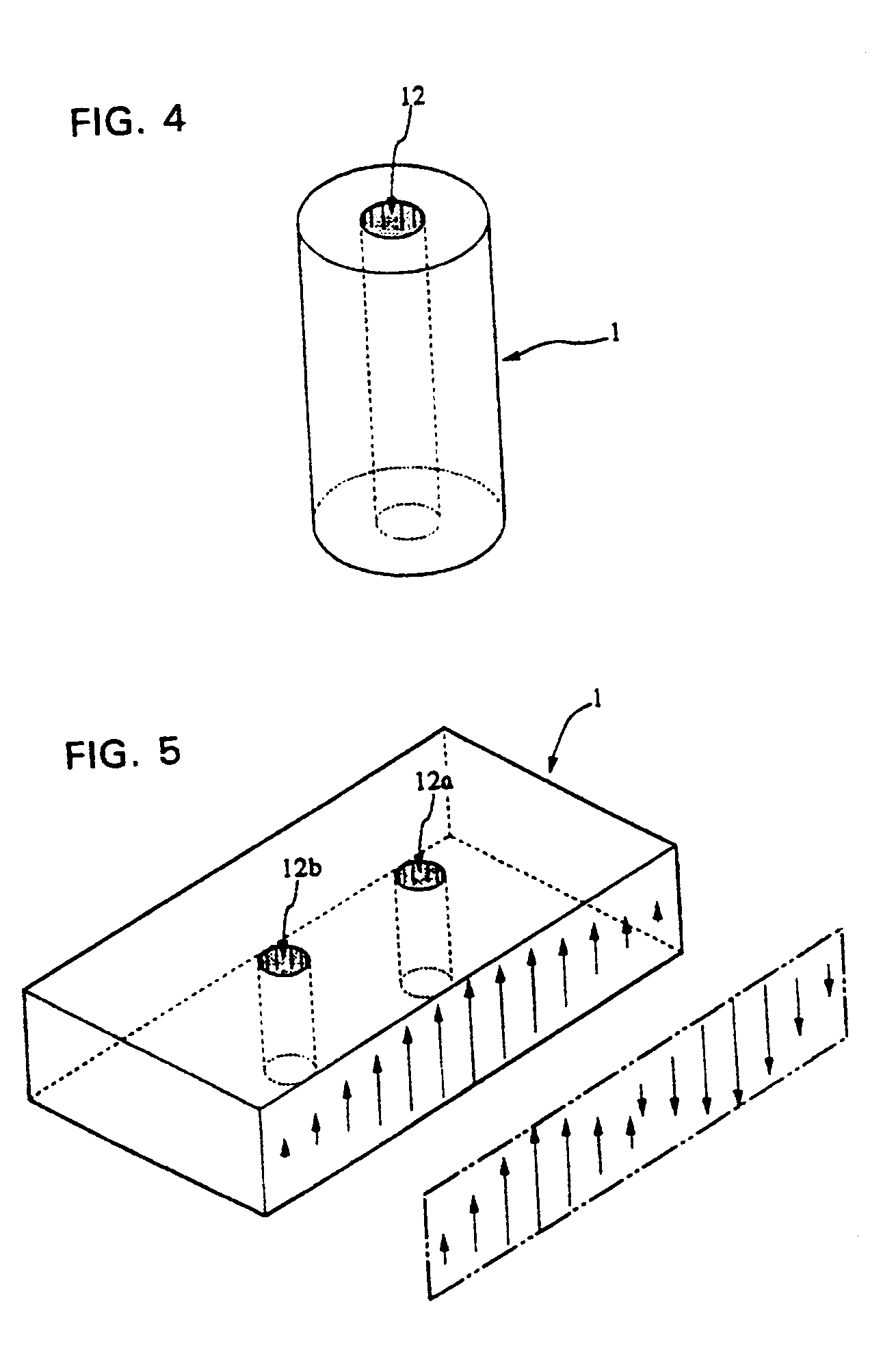
Dielectric waveguide resonator, dielectric waveguide filter, and method of adjusting the characteristics thereof
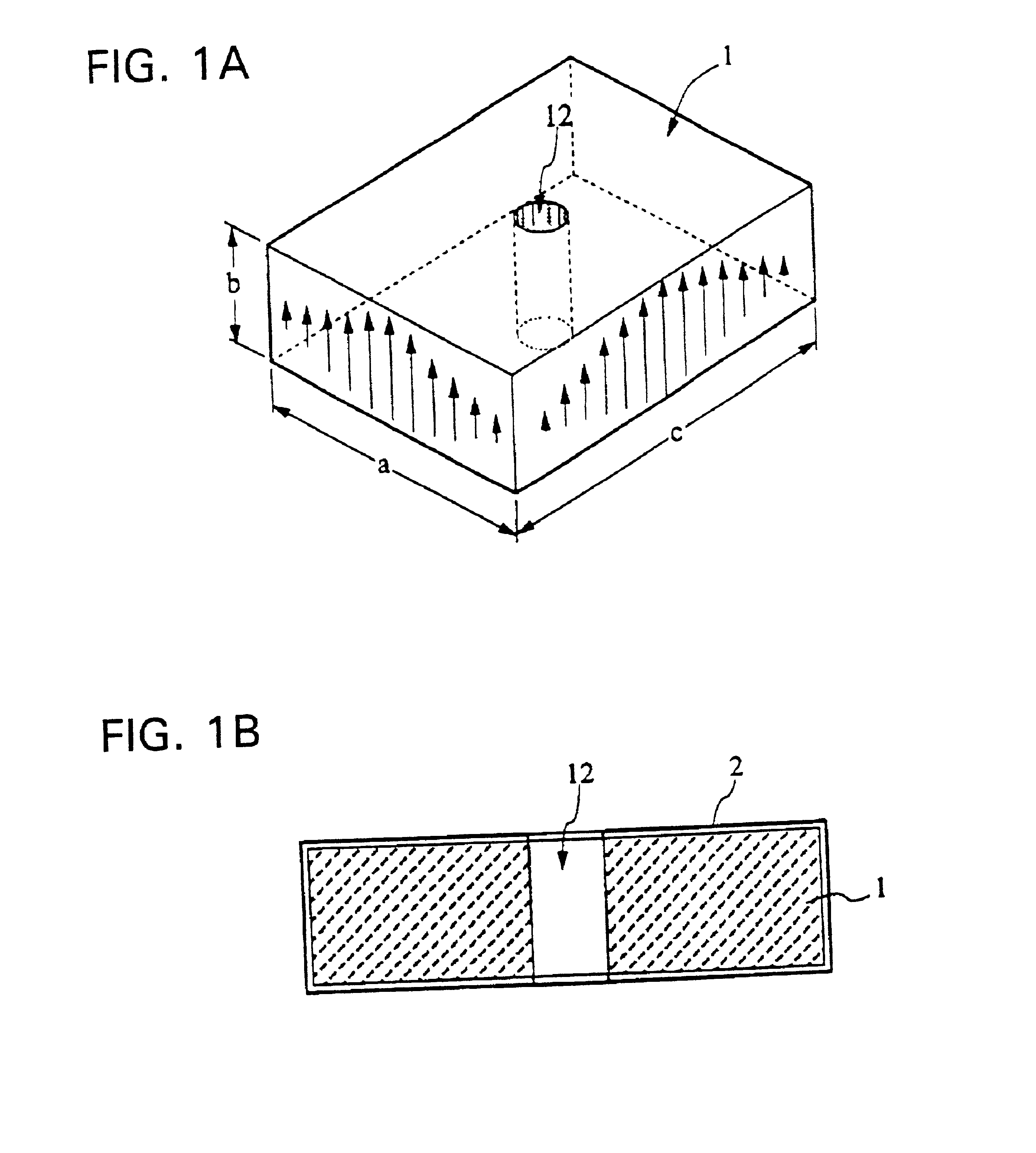
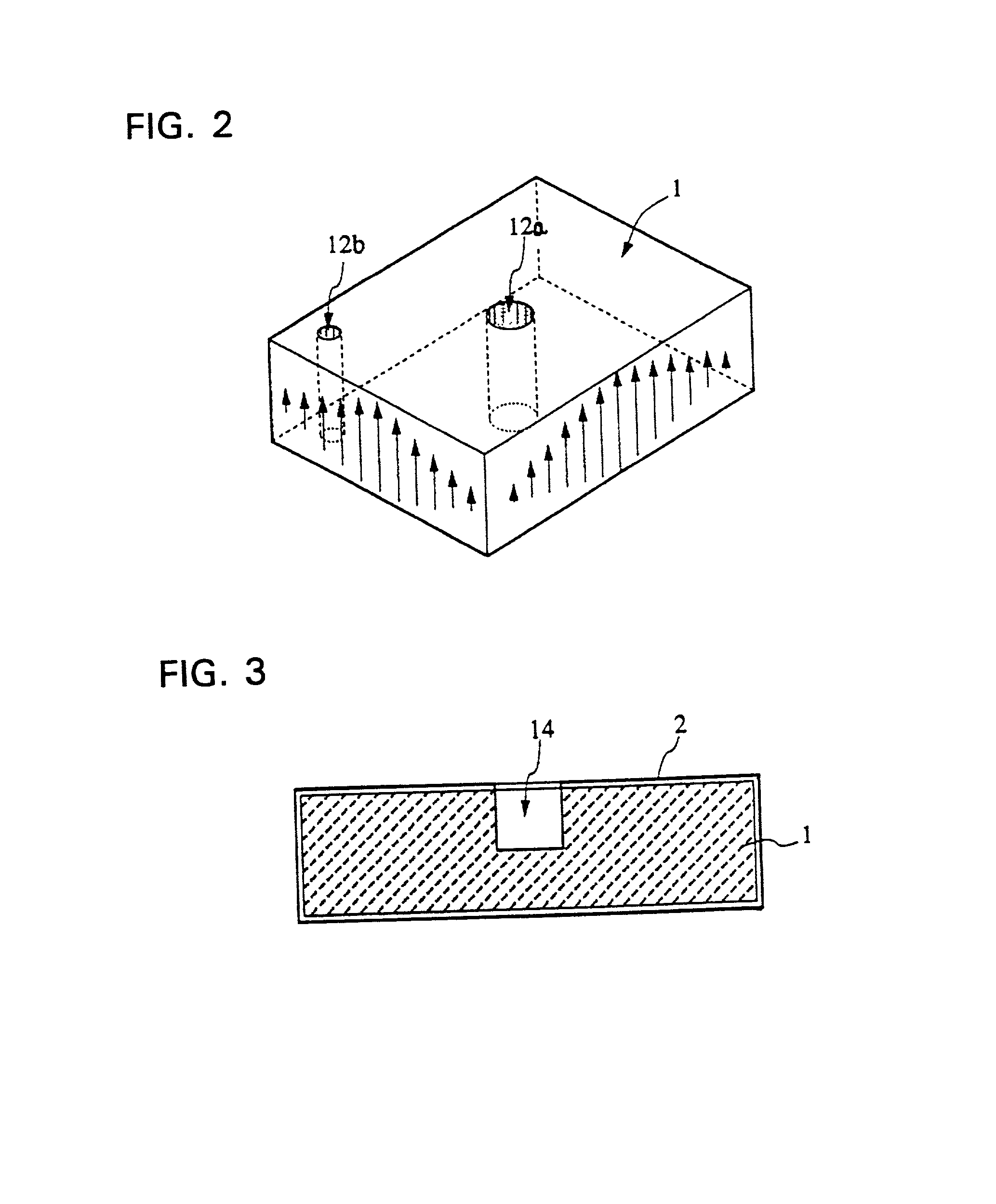
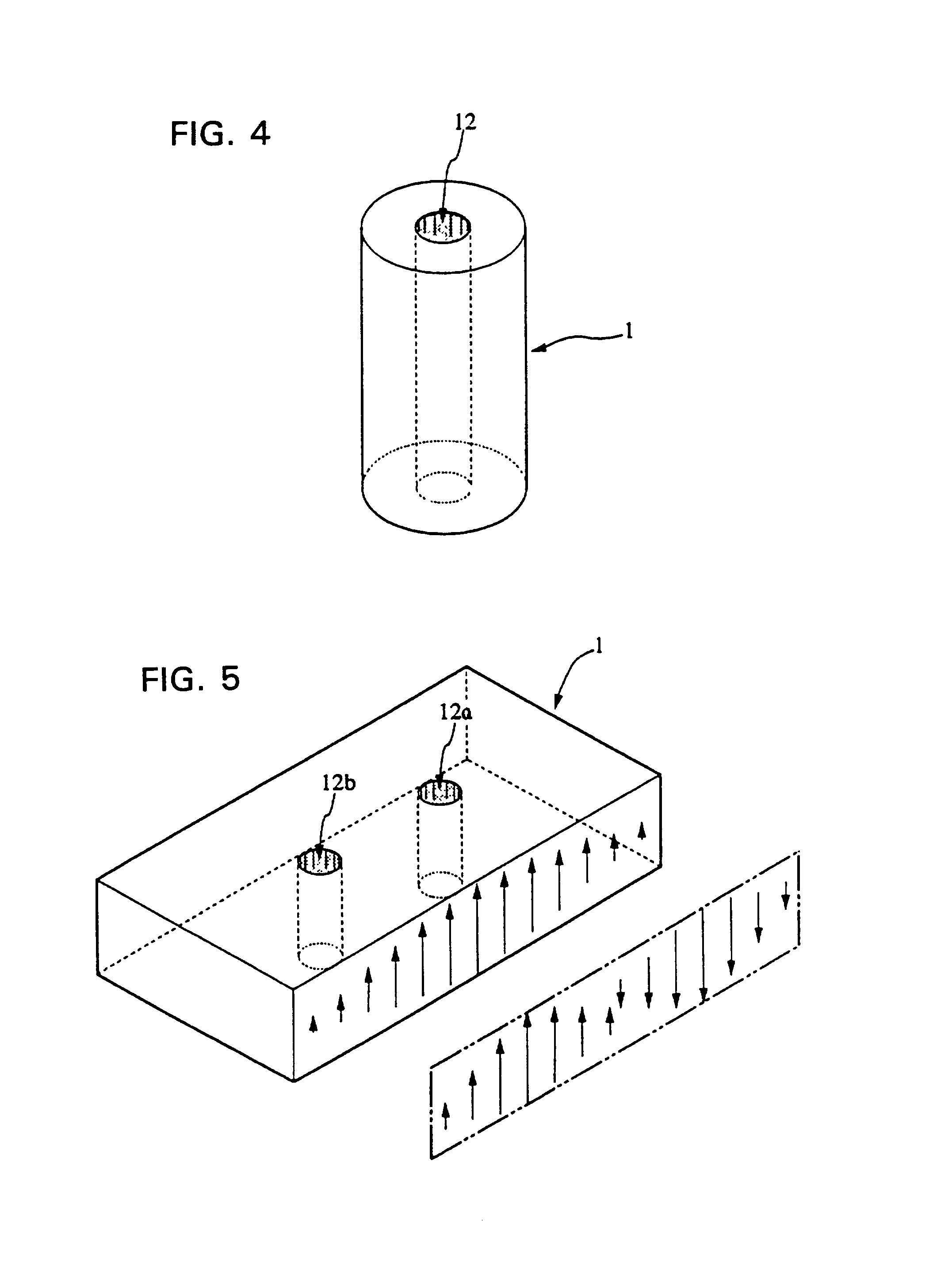
A conducting film is formed on a dielectric block in a dielectric waveguide resonator, and a through-hole is formed in the dielectric block. The unloaded Q is set by selecting the outside dimensions of the dielectric block. The resonance frequency is set by selecting the size and location of the through-hole as well as the outside dimensions of the dielectric block. A terminal electrode is formed on the outer surface of the dielectric block. A coupling hole is formed in the dielectric block and a coupling electrode is formed on the inner surface of the coupling hole. One end of the coupling electrode is connected to the terminal electrode and the other end of the coupling electrode is either connected to the conducting film formed on the outer surface of the dielectric block or terminated inside the dielectric block. The above structure allows an increase in the degree of freedom in the design of the characteristics including the resonance frequency and unloaded Q of the dielectric waveguide resonator. The invention also provides a dielectric waveguide filter with a simple coupling mechanism whereby it is possible to couple to an external circuit without having to use an additional member and without electromagnetic leakage.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Dielectric waveguide filter with cross-coupling
InactiveUS7659799B2Simple manufacturing processLow costResonatorsWaveguidesCouplingDielectric substrate
Provided is a dielectric waveguide filter. The filter includes: a multi-layered structure of dielectric substrates having first and second ground planes at its top and bottom; first, second, and third waveguide resonators disposed at multiple layers within the multi-layered structure; converters for signal transition between input / output ports and the first and third waveguide resonators; first vias for forming the first, second, and third waveguide resonators; and second vias disposed at a boundary surface of the first waveguide resonator and the third waveguide resonator.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical Chemical Detector and Method
ActiveUS20100149523A1Expand the detection areaLittle changeLaser optical resonator constructionPhase-affecting property measurementsAnalyteRefractive index
An apparatus and method for optically detecting the presence of an analyte in a solution is presented. An embodiment comprises a waveguide resonator that is optically coupled to a fluid in a fluidic conduit so that the resonant wavelength of the waveguide resonator is based on the refractive index of the fluid.
Owner:OCTROLIX
Highly miniaturized substrate integrated waveguide resonator
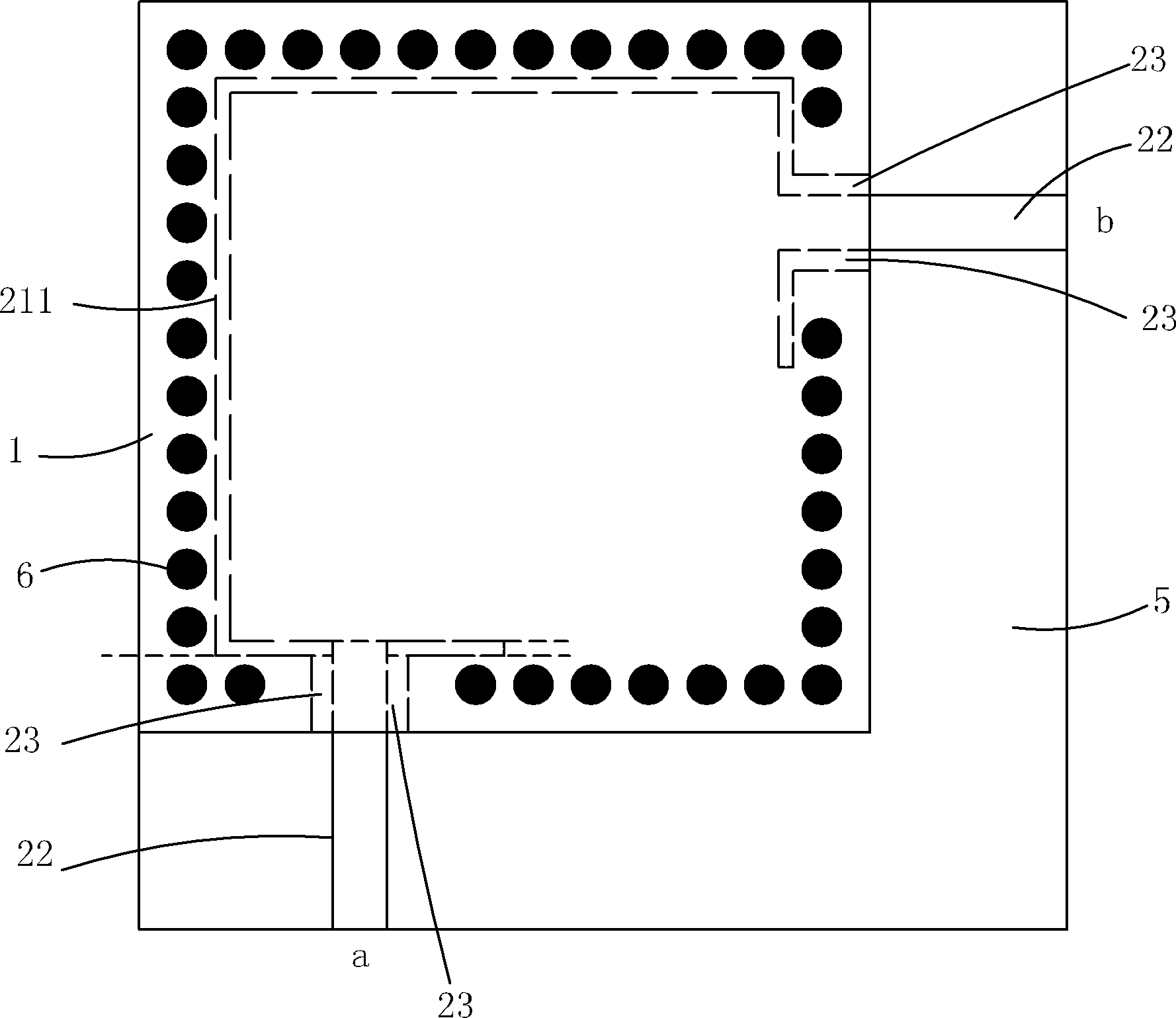
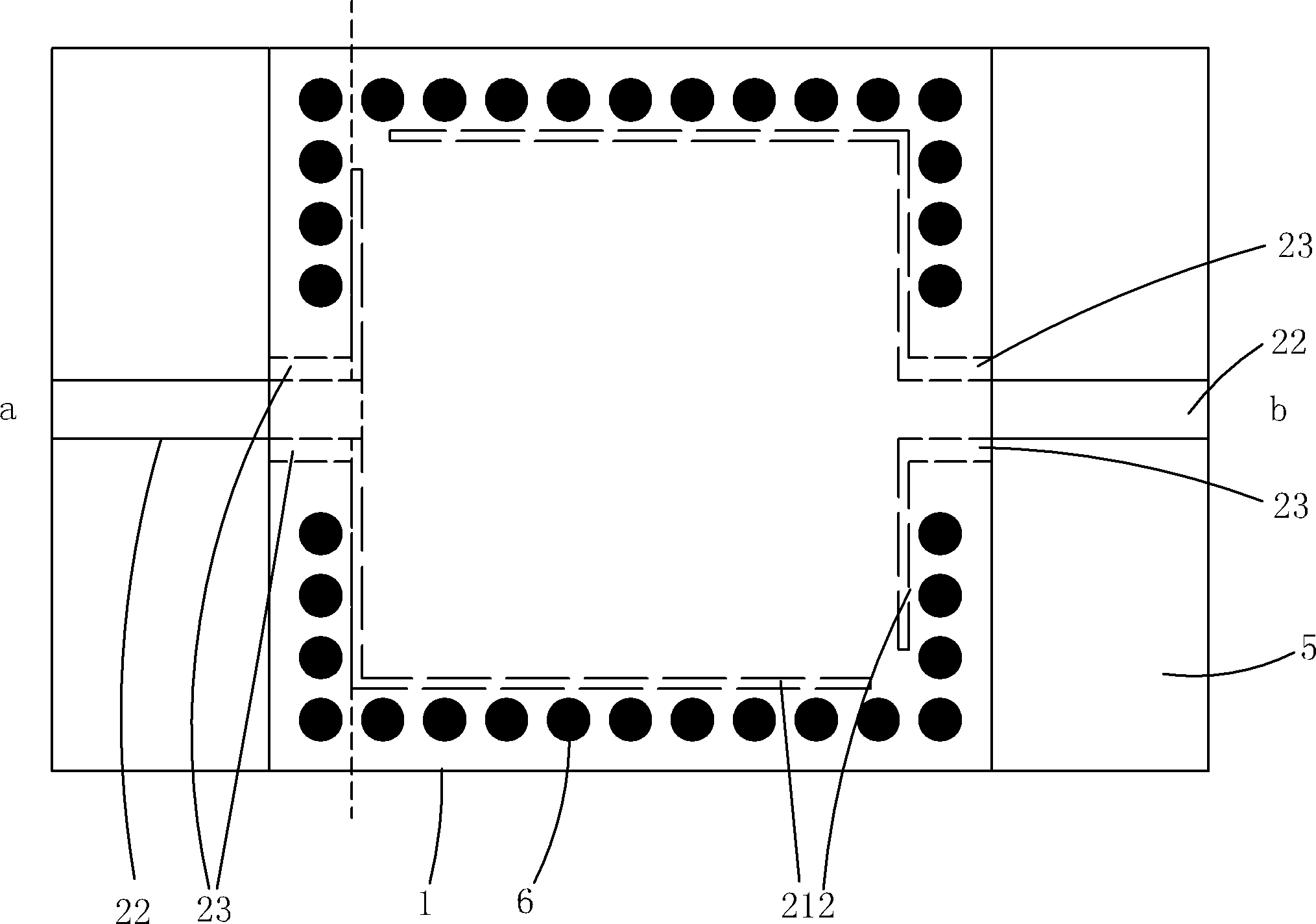
The invention relates to a highly miniaturized substrate integrated waveguide resonator which comprises a first metal copper-coated layer, a first medium layer, a second metal copper-coated layer, a second medium layer and a third metal copper-coated layer which are successively overlaid from top to bottom, wherein a metalizing through hole is connected with the third metal copper-coated layer after successively penetrating through the above interlayer to form an upper group of overlaid square cavities and a lower group of overlaid square cavities; in the second metal copper-coated layer, one group of C-shaped slots penetrating through the second metal copper-coated layer is arranged close to the metalizing through hole corresponding to the position of the square cavities; two microstrip lines are respectively connected close to two ends of the C-shaped slots; two sides of the microstrip line, which are close to one ends of the C-shaped slots, are respectively provided with a coupling slot penetrating through the second metal copper-coated layer; the coupling slot is connected with the C-shaped slots; and the metalizing through hole is broken on the positions of the microstrip lines and the coupling slots. The high-density miniaturized substrate integrated waveguide resonator has the beneficial effect that the traditional substrate integrated waveguide resonator structure is folded so as to greatly reduce the circuit area of the existing resonator, and highly miniaturization is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Dielectric waveguide resonator, dielectric waveguide filter, and method of adjusting the characteristics thereof
A conducting film is formed on a dielectric block in a dielectric waveguide resonator, and a through-hole is formed in the dielectric block. The unloaded Q is set by selecting the outside dimensions of the dielectric block. The resonance frequency is set by selecting the size and location of the through-hole as well as the outside dimensions of the dielectric block. A terminal electrode is formed on the outer surface of the dielectric block. A coupling hole is formed in the dielectric block and a coupling electrode is formed on the inner surface of the coupling hole. One end of the coupling electrode is connected to the terminal electrode and the other end of the coupling electrode is either connected to the conducting film formed on the outer surface of the dielectric block or terminated inside the dielectric block. The above structure allows an increase in the degree of freedom in the design of the characteristics including the resonance frequency and unloaded Q of the dielectric waveguide resonator. The invention also provides a dielectric waveguide filter with a simple coupling mechanism whereby it is possible to couple to an external circuit without having to use an additional member and without electromagnetic leakage.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
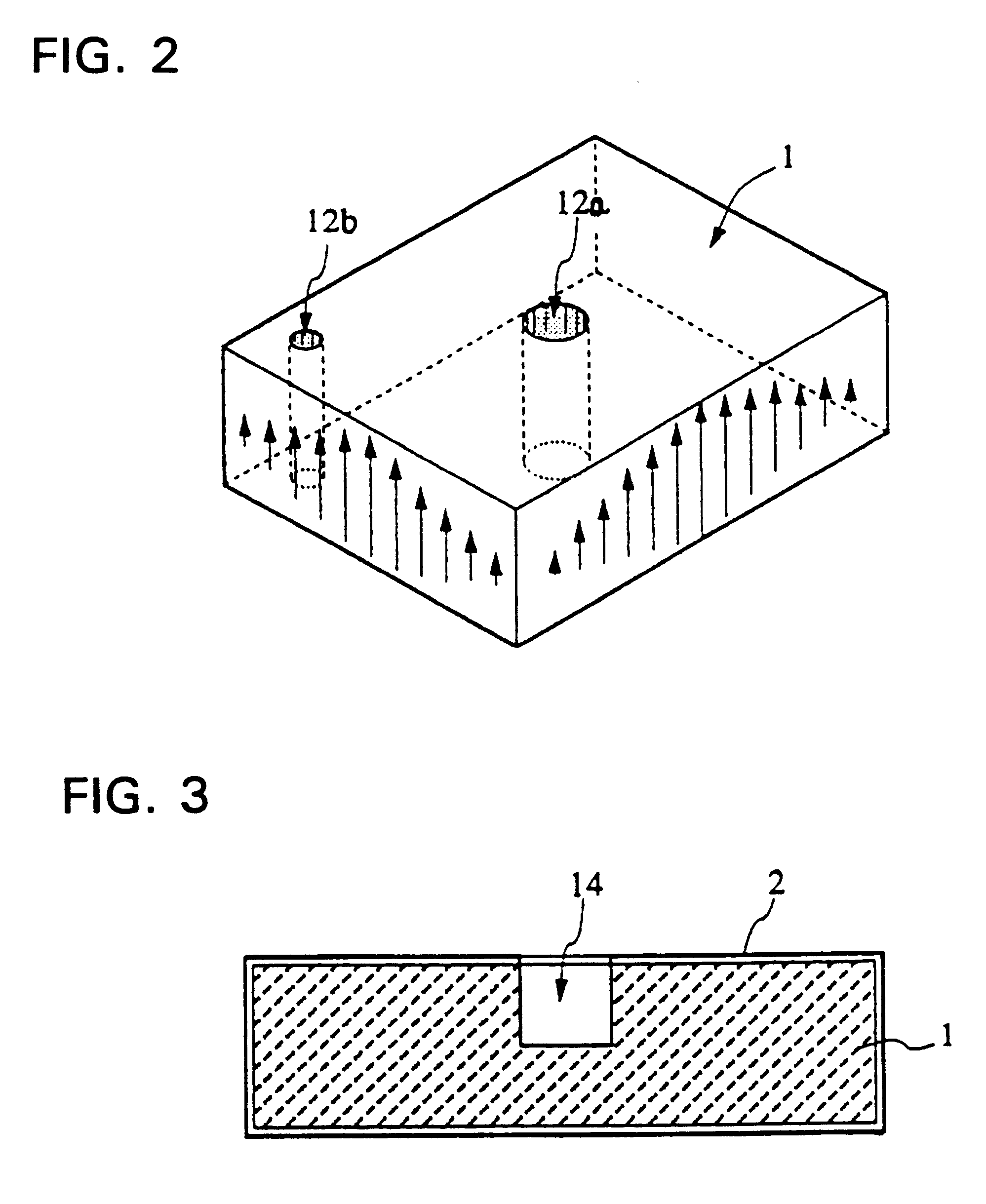
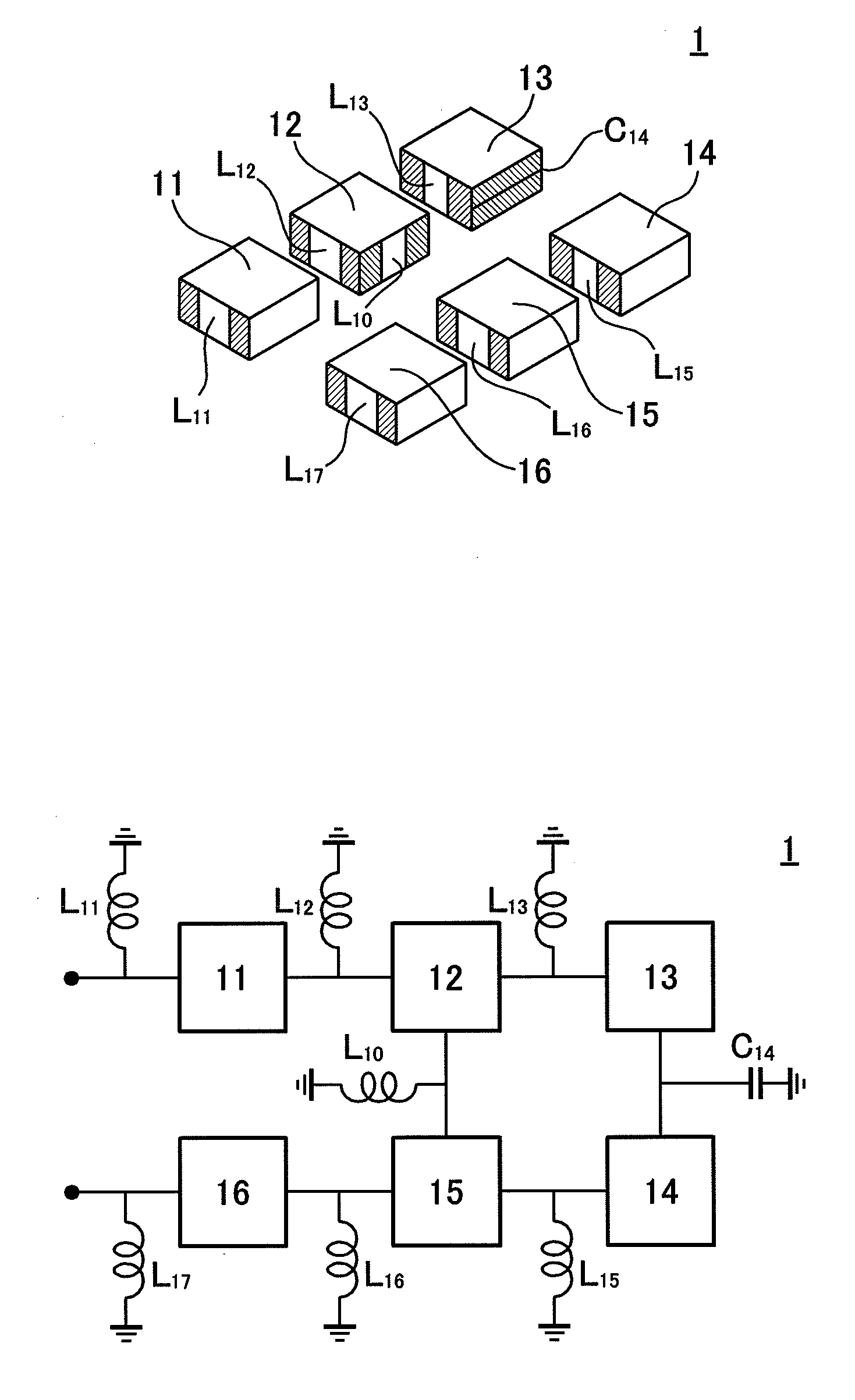
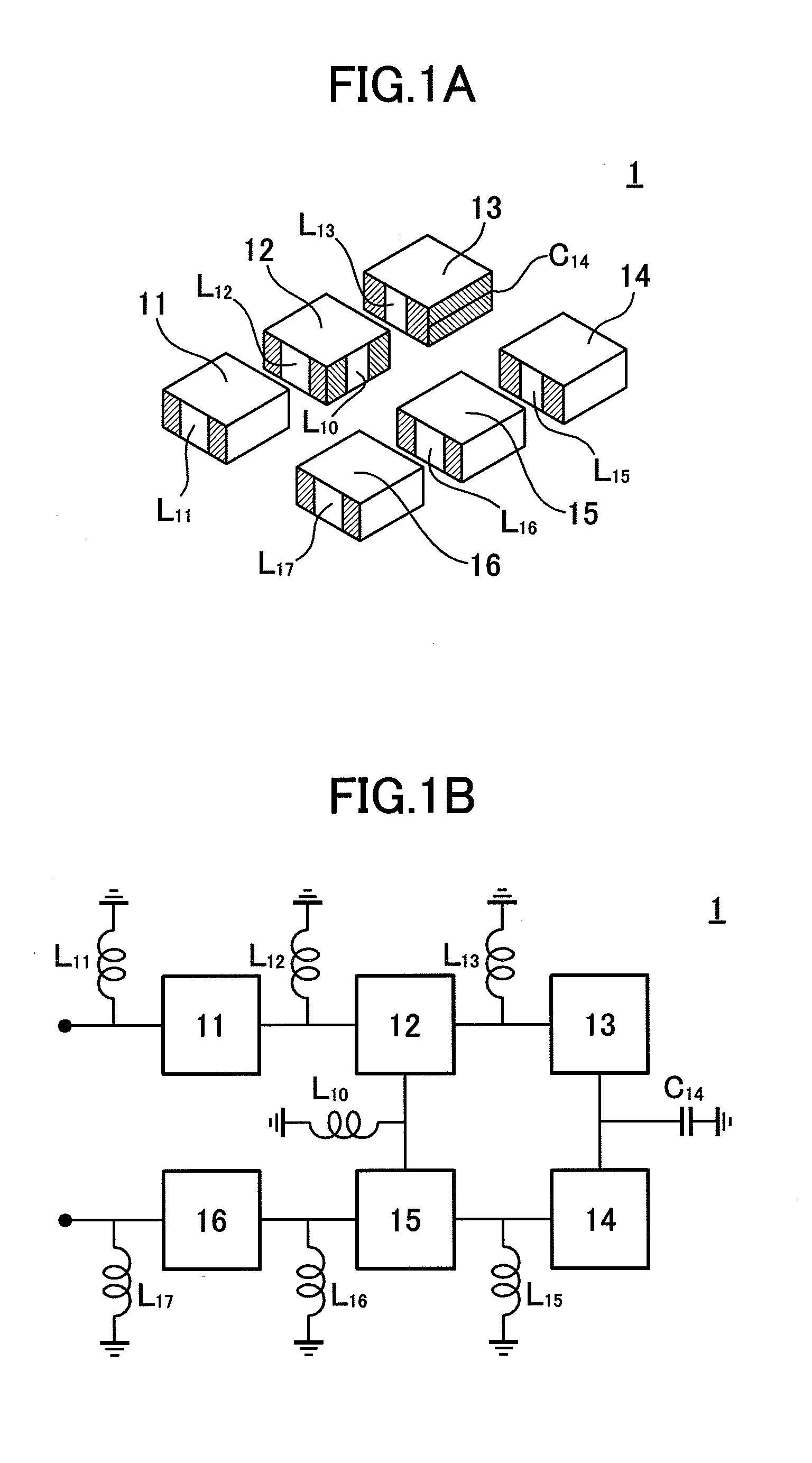
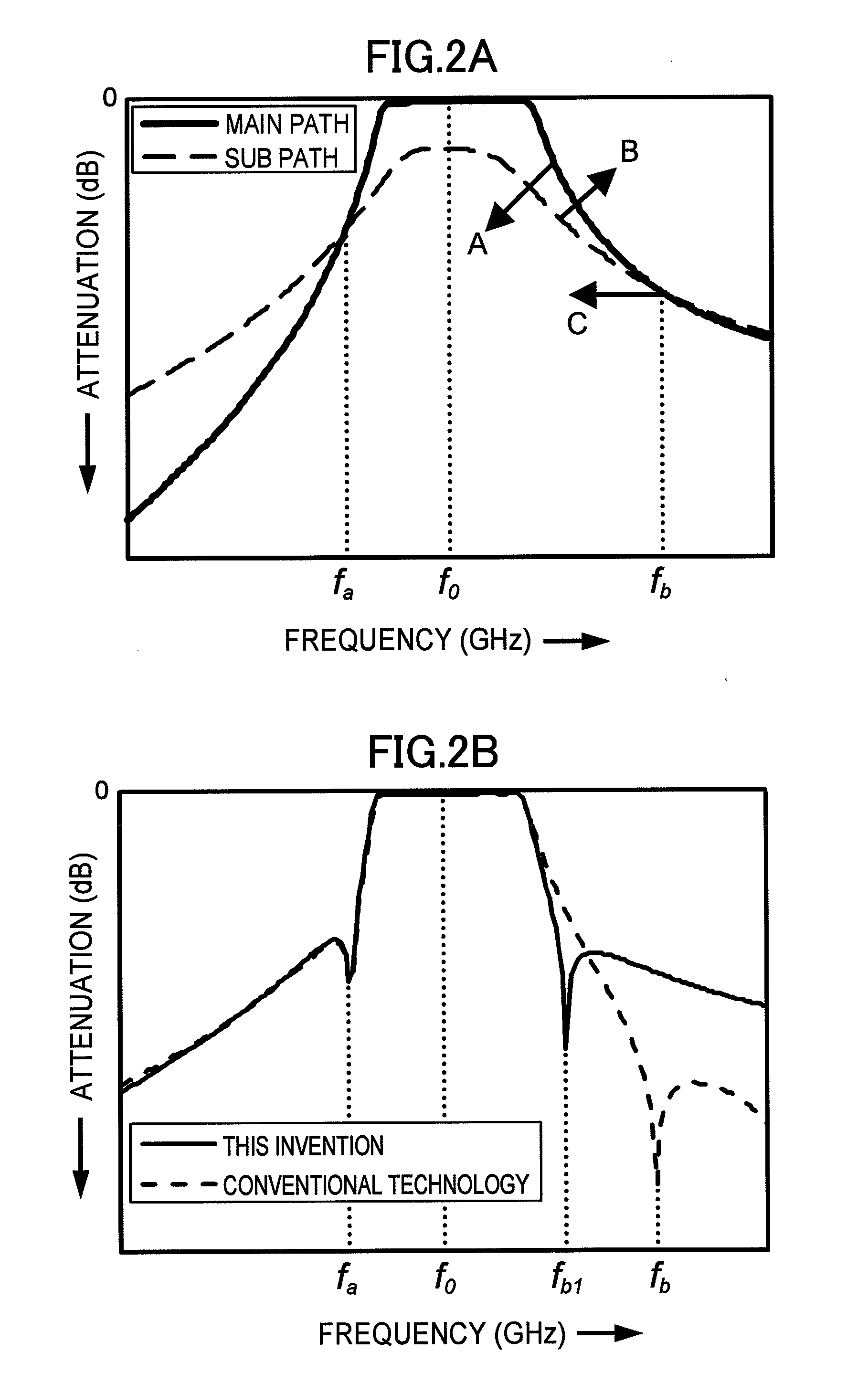
Dielectric Waveguide Filter
InactiveUS20120229233A1Reduced characteristicsIncrease distanceResonatorsWaveguidesCapacitanceUltrasound attenuation
[OBJECT]It is an object to provide a dielectric waveguide filter with attenuation poles, which is capable of suppressing deterioration in a high band-side attenuation characteristic with respect to a low band-side attenuation characteristic.[SOLUTION]A dielectric waveguide filter comprises a plurality of dielectric waveguide resonators each having a rectangular parallelepiped-shaped dielectric block, periphery of which is covered by a conductor film. The dielectric waveguide resonators are configured to form a main coupling path, and a sub coupling path bypassing a part of the main coupling path. The part of the main coupling path bypassed by the sub coupling path includes at least one capacitive coupling path.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
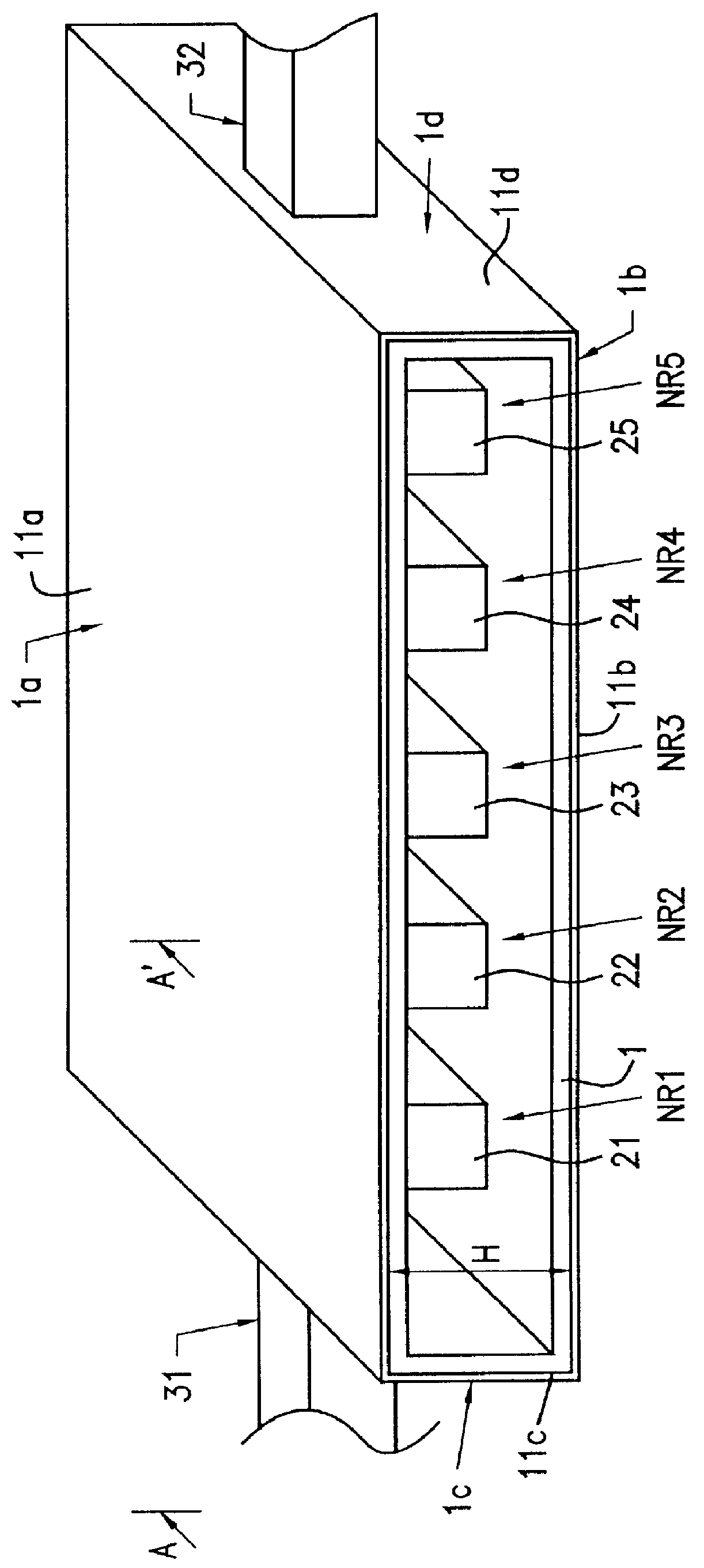
Harmonic suppression resonator, harmonic propagation blocking filter, and radar apparatus
A harmonic suppression resonator comprises a plurality of waveguide resonators that resonate in TE mode, in which harmonic suppression resonator, adjoining resonators are coupled via a plurality of coupling windows. Four coupling windows 33bc1, 33bc2, 33bc3 and 33bc4 are provided between a resonant region 51b and a resonant region adjoining the resonant region 51b. These coupling windows allow fundamental wave modes of the adjoining resonators to be coupled mainly by magnetically coupling. The coupling windows 33bc3 and 33bc4 allow second harmonic modes of the adjoining resonators to be electrically coupled, and the coupling windows 33bc1 and 33bc2 allow the second harmonic modes of the adjoining resonators to be magnetically coupled. By causing the amount of the electrically coupling and the amount of the magnetically coupling to be substantially equal, the coupling of the second harmonic modes is negated, whereby propagation of the second harmonic is blocked.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Coupled optical waveguide resonators with heaters for thermo-optic control of wavelength and compound filter shape
An integrated optical device is disclosed comprising a substrate, optical waveguide, and compound optical resonator having a temperature sensor, at least two coupled optical resonators, and a heater localized to each optical resonator. An optical input signal is coupled to one of the resonators making up the compound resonator to form an optical output signal. The center wavelength and shape of the output signal is optimized with a feedback loop using the temperature sensor to control the power dissipated in at least one of the localized heaters. The power dissipated in the remaining resonator heaters is set according to a predetermined function having as an input variable the power dissipated in the resonant heater under control of the said feedback loop.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Triangle substrate-integrated waveguide resonator-based planar slot antenna
InactiveCN105958197AImprove radiation efficiencyEasy to integrateRadiating elements structural formsSlot antennasIsoetes triquetraDielectric plate
The invention discloses a planar slot antenna based on a triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity, which is fed by a coplanar waveguide on the lower surface of a dielectric plate by slotting in the edge region of the upper surface of an equilateral triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity. electricity, so that the antenna works in model. A rectangular slit is opened on the edge of the equilateral triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity, and made parallel to one side of the equilateral triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity, so that a displacement current will be generated on the slit, and electromagnetic waves will be radiated. The antenna retains the advantages of better radiation performance of the traditional cavity-backed slot antenna. At the same time, the entire antenna, including the radiation structure, feed structure and back cavity, is completely fabricated on a single-layer dielectric board, which greatly reduces the processing complexity and reduces the processing time. The cost also makes planar circuit integration easier.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Microwave low-band high-selectivity cavity medium filter and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103811835AGuaranteed filter indexAchieve miniaturization goalsWaveguide type devicesState of artSputtering
The invention discloses a microwave low-band high-selectivity cavity medium filter and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises designing the size of a cylindrical circular waveguide medium according to the index requirements, wherein the longitudinal direction of the circular waveguide medium is provided with frequency adjustment holes which are communicated in the longitudinal direction; heating the circular waveguide medium in a vacuum environment; generating circular waveguides after metal layer sputtering treatment is performed on the circular waveguide medium; enabling the circular waveguides to form the cavity medium filter. According to the microwave low-band high-selectivity cavity medium filter and the manufacturing method thereof, a metal layer is sputtered on a filling medium directly on the basis of the prior art that a circular waveguide resonator is filled with medium materials to enable the metal layer to coat the medium materials closely and accordingly an air layer which is formed between the metal layer and the filling medium is avoided, the occupied space of the metal layer is narrowed, filter indicators of the filter are ensured, and meanwhile the miniaturization purpose of the filter is achieved.
Owner:庄昆杰 +1
Optical waveguide immunosensor and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101846674ASimple structureAccurate Immune Response DetectionColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingMagnetic beadAntibody antigen reactions
The invention discloses an optical waveguide immunosensor and a detection method thereof. The optical waveguide immunosensor basically comprises an optical waveguide resonator cavity, a magnetic needle and an immunologic reaction tank. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out surface specificity modification to nano magnetic particles; capturing a substance to be detected by utilizing an antibody-antigen reaction; orderly limiting the nano magnetic particles on the surface of the circular or disc-shaped optical waveguide resonator cavity by utilizing the magnetic needle; sensing refraction index change before and after an immunologic reaction by utilizing an evanescent field; and analyzing corresponding resonance spectrum change to acquire the content of the substance to be detected in a sample. The optical waveguide immunosensor has simple structure. Based on the circular or disc-shaped optical waveguide resonator cavity with compact structure, the nano particles after immunologic specificity modification are absorbed to the optical waveguide surface by the magnetic needle to measure the offset of a resonance frequency and accurately and sensitively detect the immunologic reaction, and the device can be repeatedly used so that the invention has favorable application prospects.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH
Electromagnetic two-dimensional reconfigurable filter with adjustable frequency bandwidth
ActiveCN108808190AImproved waveform retentionChange the resonant frequencyResonatorsCapacitanceMulti band
The invention discloses an electromagnetic two-dimensional reconfigurable filter with an adjustable frequency bandwidth and belongs to the technical field of microwave and millimeter waves. Accordingto the reconfigurable filter, adjustable capacitors are loaded in a substrate integrated waveguide resonator to adjust the operating frequency of each cavity, the ferrite materials are loaded at thecoupling window of the substrate integrated waveguide filter to directly control the coupling strength between the substrate integrated waveguide resonators, the adjustable capacitance is loaded on the input-output feeder to adjust the external quality factor, then the frequency of the reconfigurable filter is adjusted and the bandwidth of the filter are flexibly controlled. Compared with the traditional single electrical reconfigurable substrate integrated waveguide filters, the filter realizes a flexible design of bandwidth, the waveform retention degree of the filter is greatly improved andthe future multi-band, miniaturization, intelligent wireless communication equipment and systems can be broadly applied in potential.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Echo wall mode resonator and preparation method thereof
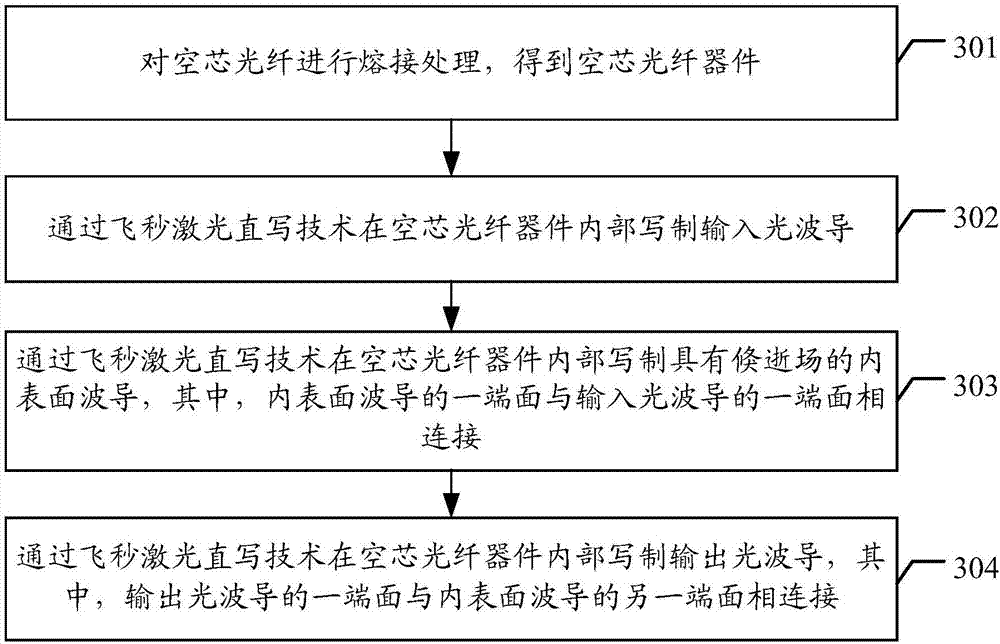
PendingCN107272116AStable structureEasy to integrateCoupling light guidesOptical integrationOptical coupling
The invention discloses an echo wall mode resonator and a preparation method thereof. The resonator comprises a hollow-core optical fiber, a waveguide, a waveguide resonator, a first single-mode optical fiber and a second single-mode optical fiber. The waveguide and the waveguide resonator are located in the hollow-core optical fiber. One end face of the first single-mode optical fiber is connected with one end face of the hollow-core optical fiber through welding. One end face of the second single-mode optical fiber is connected with the other end face of the hollow-core optical fiber through welding. The waveguide comprises an input optical waveguide, an inner surface waveguide and an output optical waveguide. Two end faces of the input optical waveguide are connected with one end face of the first single-mode optical fiber and one end face of the inner surface waveguide respectively. Two end faces of the output optical waveguide are connected with one end face of the second single-mode optical fiber and the other end face of the inner surface waveguide respectively. The inner surface waveguide is provided with an evanescent field. The echo wall mode resonator prepared by the connection method has a stable and simple structure. The optical coupling between the inner surface waveguide and the waveguide resonator is realized through the evanescent field of the inner surface waveguide, which is conducive to optical integration.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Hybrid sphere-waveguide resonators
InactiveCN1867844AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorScattering properties measurementsResonant cavityMicrosphere
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Hybrid sphere-waveguide resonators
InactiveUS7444045B2Improve stabilityHigh cavity Q and ease of launchingCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrosphereCoupling
Microresonators, such as a microsphere resonators and planar microresonators, are optically coupled to waveguides for input and output of light. It is important that the relative positions of the microresonator and the waveguide are maintained stable, while still maintaining high cavity Q and ease of launching and extracting the optical beams. Structures are provided on a substrate that are useful for maintaining the position of the microresonator relative to the waveguide. The structures provide for vertical or horizontal coupling between the waveguide and the microresonator.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Mini double-frequency band pass filter based on stacked substrate integrated waveguide
ActiveCN105070993AHigh Q valueIncreased power carrying capacityWaveguide type devicesDouble frequencyHigh isolation
The invention discloses a mini double-frequency band pass filter based on stacked substrate integrated waveguide (SIW). The filter comprises an upper SIW resonator, a middle SIW resonator and a lower SIW resonator which are stacked, and the upper and lower SIW resonator are the same in structure, arranged reversely, symmetrical by taking the filter as the center, and couple energy mutually via the middle SIW resonator. Compared with microstrip lines and the like, the mini double-frequency band pass filter is higher in the Q value and power capacity, lower in the passband insertion loss, higher in the echo loss and higher isolation degree among passband has steep edge selection feature, realizes the optimization aim of miniaturaization, and is convenient to process and test, simple in structure and low in cost.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Device and method for testing polarization extinction ratio of polarization maintaining fiber coupler based on resonant cavity technology
The invention discloses a device and method for testing polarization extinction ratio of a polarization-maintaining fiber coupler based on resonator technology. One output end and one input end of the polarization-maintaining fiber coupler are connected to form a fundamental annular resonator structure; a polarization axis alignment angle error of the polarization-maintaining fiber coupler is obtained by testing a resonance curve of an optical fiber annular resonator so as to obtain the polarization extinction ratio of the polarization-maintaining fiber coupler. The device for testing polarization extinction ratio of the polarization-maintaining fiber coupler comprises an optical fiber laser, a first isolator, an optical fiber annular resonator, a second isolator, a photoelectric detectorand an oscillograph which are connected in order; and the optical fiber annular resonator is arranged on a temperature-controlled panel. For an in separable optical waveguide resonator of the opticalfiber coupler, the device and method provided by the invention can test the polarization extinction ratio of the coupler constituting the resonator in non-destructive manner. The invention provides anovel and simple method for testing polarization extinction ratio of the polarization-maintaining fiber coupler with important scientific significance and application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Low loss microring resonator device
InactiveUS20070071394A1Reduced propagation lossMinimizing propagation lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexClosed loop
A low loss micro-ring resonator device which has a closed-loop resonator waveguide having a first refractive index, the resonator waveguide defining an inner and an outer region by an outer curved edge of the waveguide. The resonator waveguide is arranged on a substrate having a second refractive index, the refractive index difference between the first refractive index and the second refractive index is greater than 0.3. The device also has an upper cladding covering the inner region of the resonator waveguide having a third refractive index and a lateral cladding in contact with the outer curved edge and extending in the outer region, the lateral cladding having a fourth refractive index, the fourth refractive index being lower than the third refractive index. A method for reducing propagation losses of a resonator device is also described.
Owner:PIRELLI & C
Dielectric waveguide resonator, dielectric waveguide filter, and method of adjusting the characteristics thereof
A conducting film is formed on a dielectric block in a dielectric waveguide resonator, and a through-hole is formed in the dielectric block. The unloaded Q is set by selecting the outside dimensions of the dielectric block. The resonance frequency is set by selecting the size and location of the through-hole as well as the outside dimensions of the dielectric block. A terminal electrode is formed on a side surface of the dielectric block. A coupling hole is formed in the dielectric block and a coupling electrode is formed on the inner surface of the coupling hole. One end of the coupling electrode is connected to the terminal electrode and the coupling electrode extends toward the conducting film formed on the opposite side surface and one end surface of the dielectric block. The above structure allows an increase in the degree of freedom in the design of the characteristics including the resonance frequency and unloaded Q of the dielectric waveguide resonator. The invention also provides a dielectric waveguide filter with a simple coupling mechanism whereby it is possible to couple to an external circuit without having to use an additional member and without electromagnetic leakage.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Band-pass filter apparatus using superconducting integrated nonradiative dielectric waveguide
InactiveUS6011983AEasy constructionSmall sizeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectromagnetic couplingResonance
An NRD waveguide band-pass filter apparatus is provided which is simple in construction, which can be easily manufactured as well as being small in size and light in weight, and which operates in a single operating mode. The NRD waveguide band-pass filter apparatus includes a plurality of NRD waveguide resonators arrayed in such a way that each two adjacent NRD waveguide resonators are electromagnetically coupled to each other. A plurality of arrayed rectangular dielectric waveguides are interposed between an upper surface portion and a lower surface portion of a rectangular dielectric housing, which are parallel to each other. The upper surface portion and the lower surface portion and the plurality of arrayed rectangular dielectric waveguides are formed integrally, thus forming the housing. A first superconducting electrode and a second superconducting electrode are formed on the outer surfaces of the upper surface portion and the lower surface portion, respectively. By setting the spacing between the first and second superconducting electrodes at one-half or less of the wavelength of the resonance frequency in a vacuum of the present apparatus, the portions outside of each dielectric waveguide form cut-off regions.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Substrate integrated waveguide-type cavity filter
InactiveCN106025464AMiniaturizationHigh Q valueWaveguide type devicesMiniaturizationCoplanar waveguide
The invention provides a substrate integrated waveguide-type cavity filter, and belongs to the technical field of microwave communication devices. The substrate integrated waveguide-type cavity filter comprises an input feeder, an output feeder and m*n*p substrate integrated waveguide resonators, wherein m, n and p are numbers of the substrate integrated waveguide resonators in an x direction, a y direction and a z direction in a three-dimensional coordinate system; the input feeder, the output feeder and the substrate integrated waveguide resonators are coupled in coplanar waveguide and metal post manners; the adjacent substrate integrated waveguide resonators are coupled in a metal post manner or a windowing manner; and the stacked substrate integrated waveguide resonators are coupled in the windowing manner. The substrate integrated waveguide-type cavity filter provided by the invention is beneficial to achievement of miniaturization of the filter and integration of an active circuit; and meanwhile, the substrate integrated waveguide-type cavity filter also has the advantages of integral fabrication, high reliability and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com