Patents
Literature
136results about How to "Reduced propagation loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
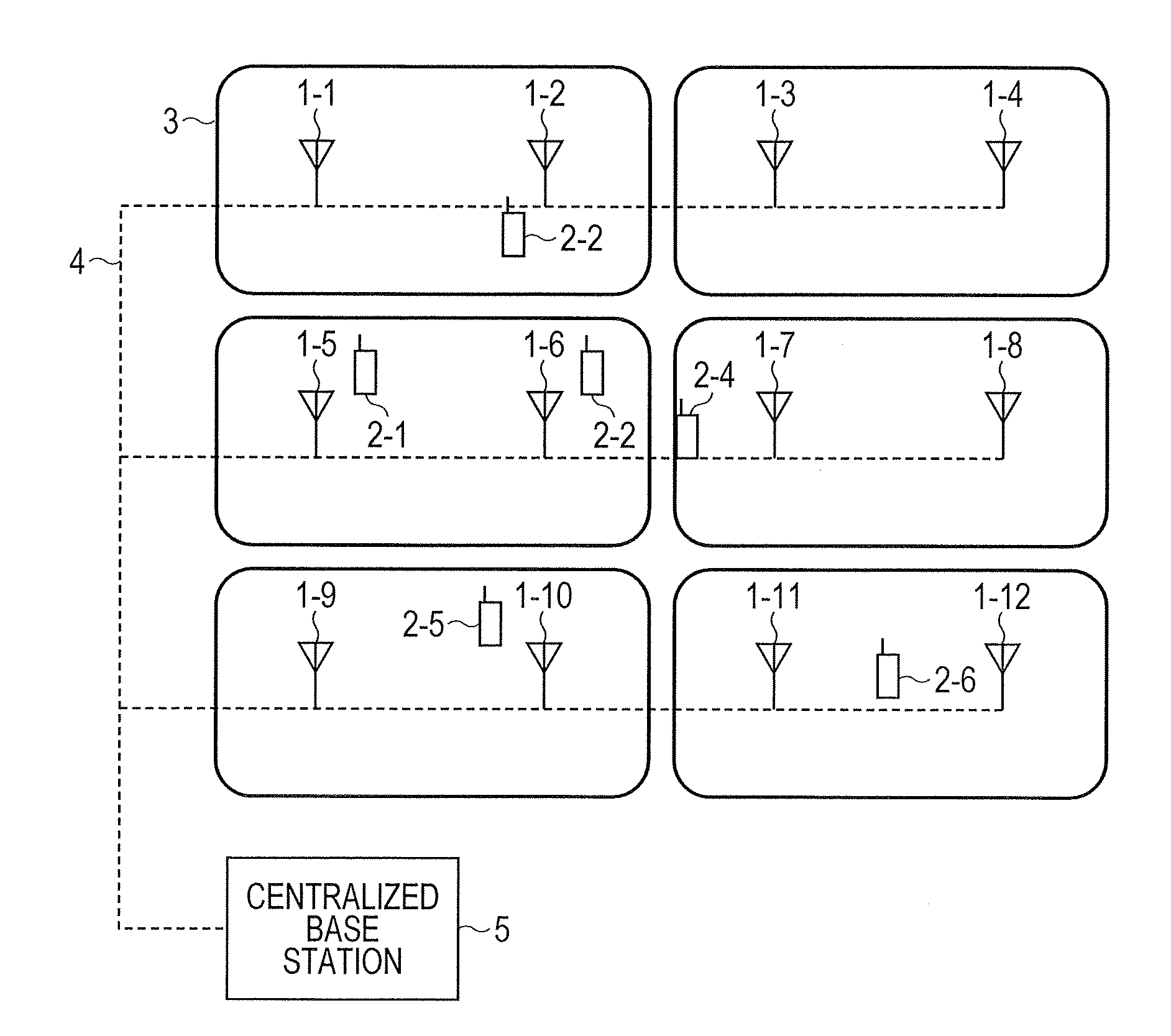
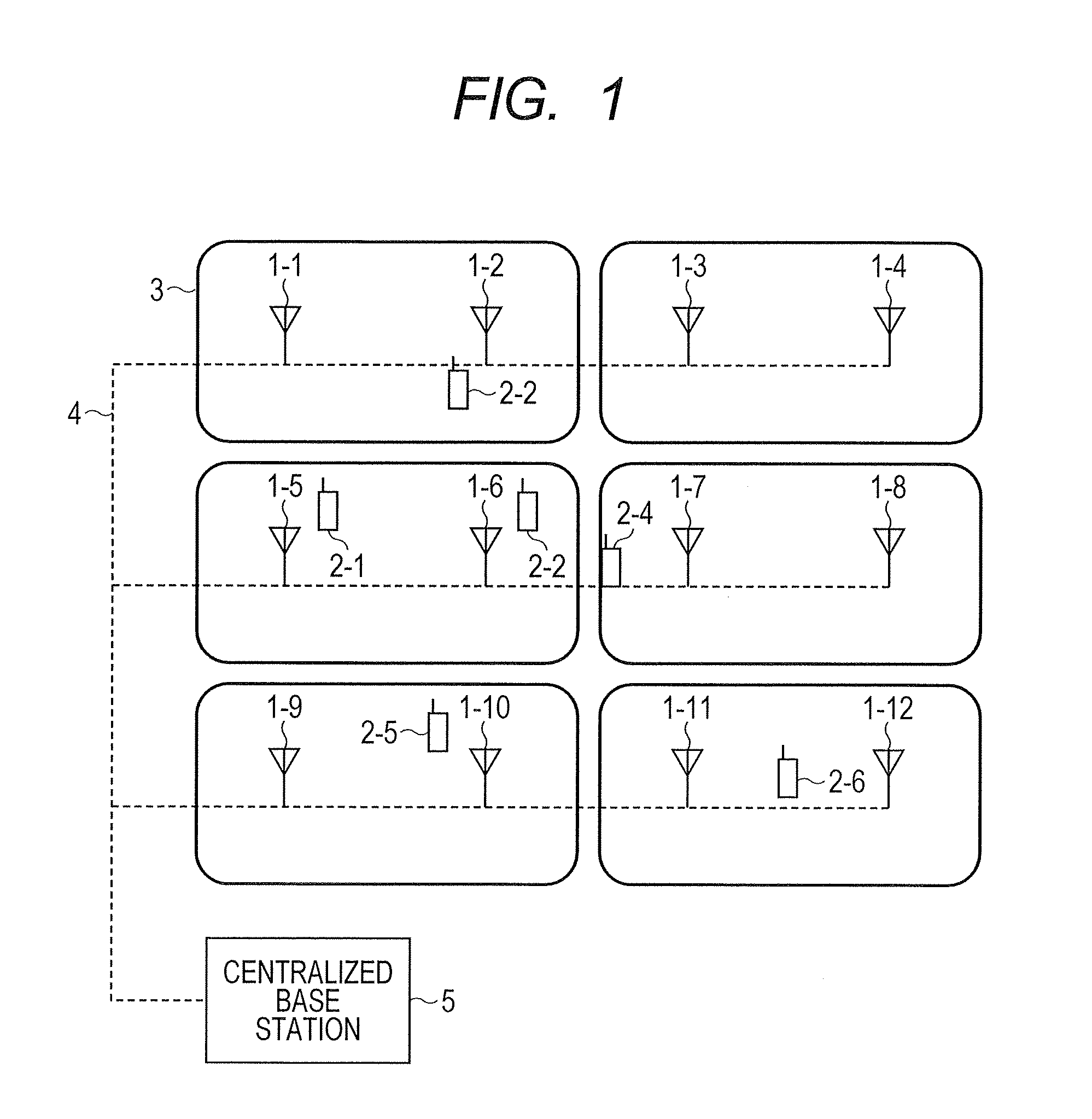
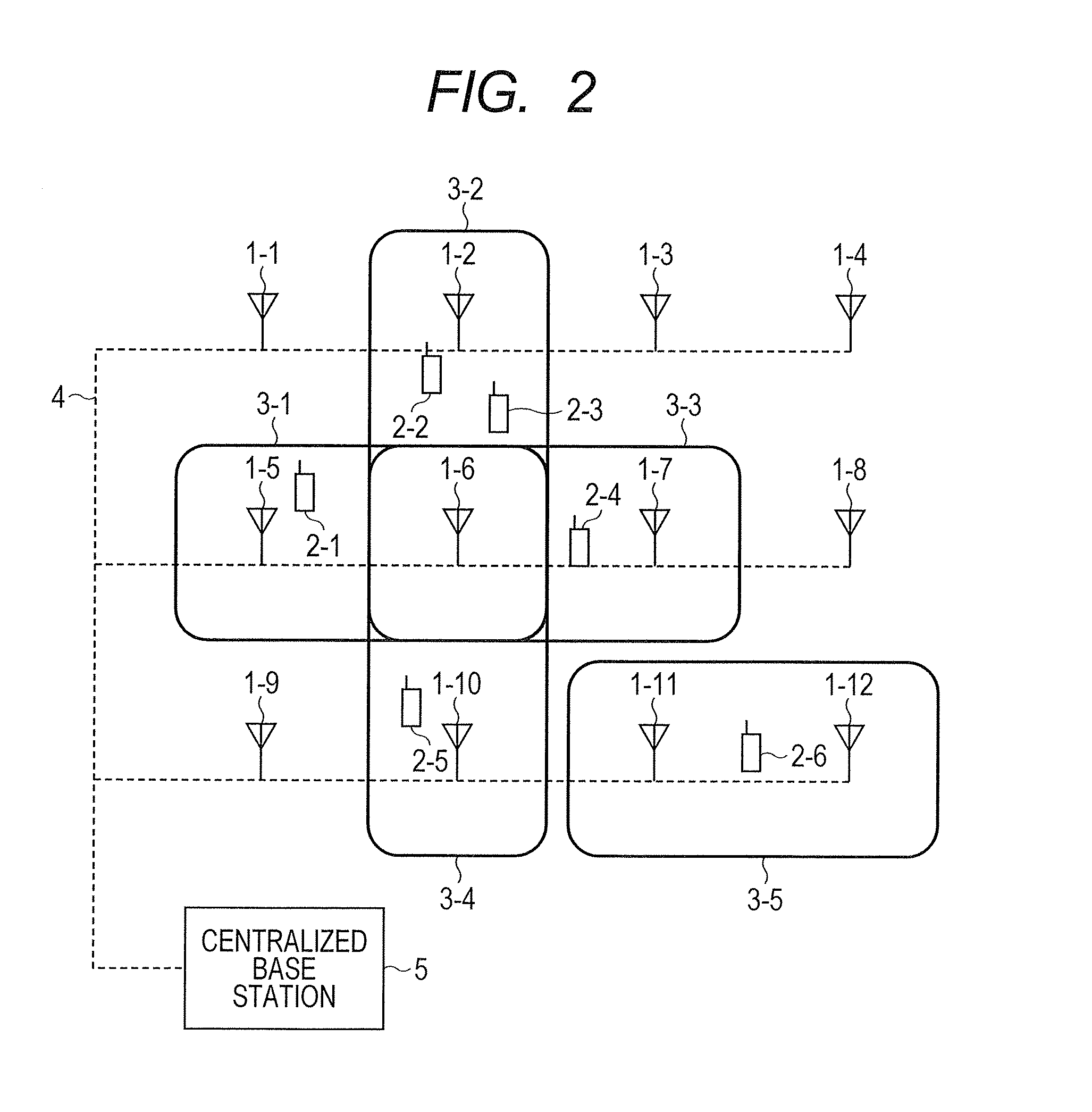
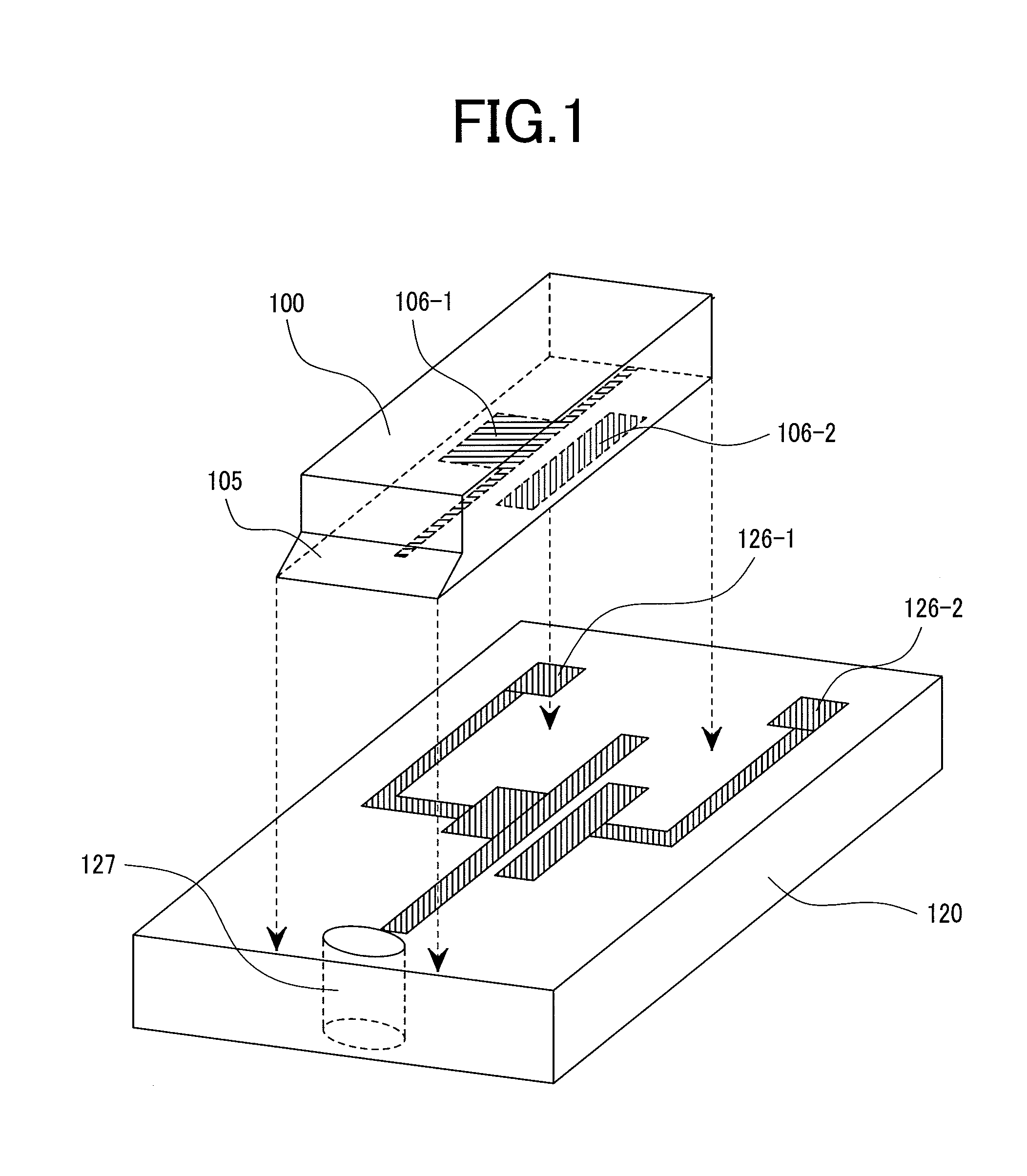
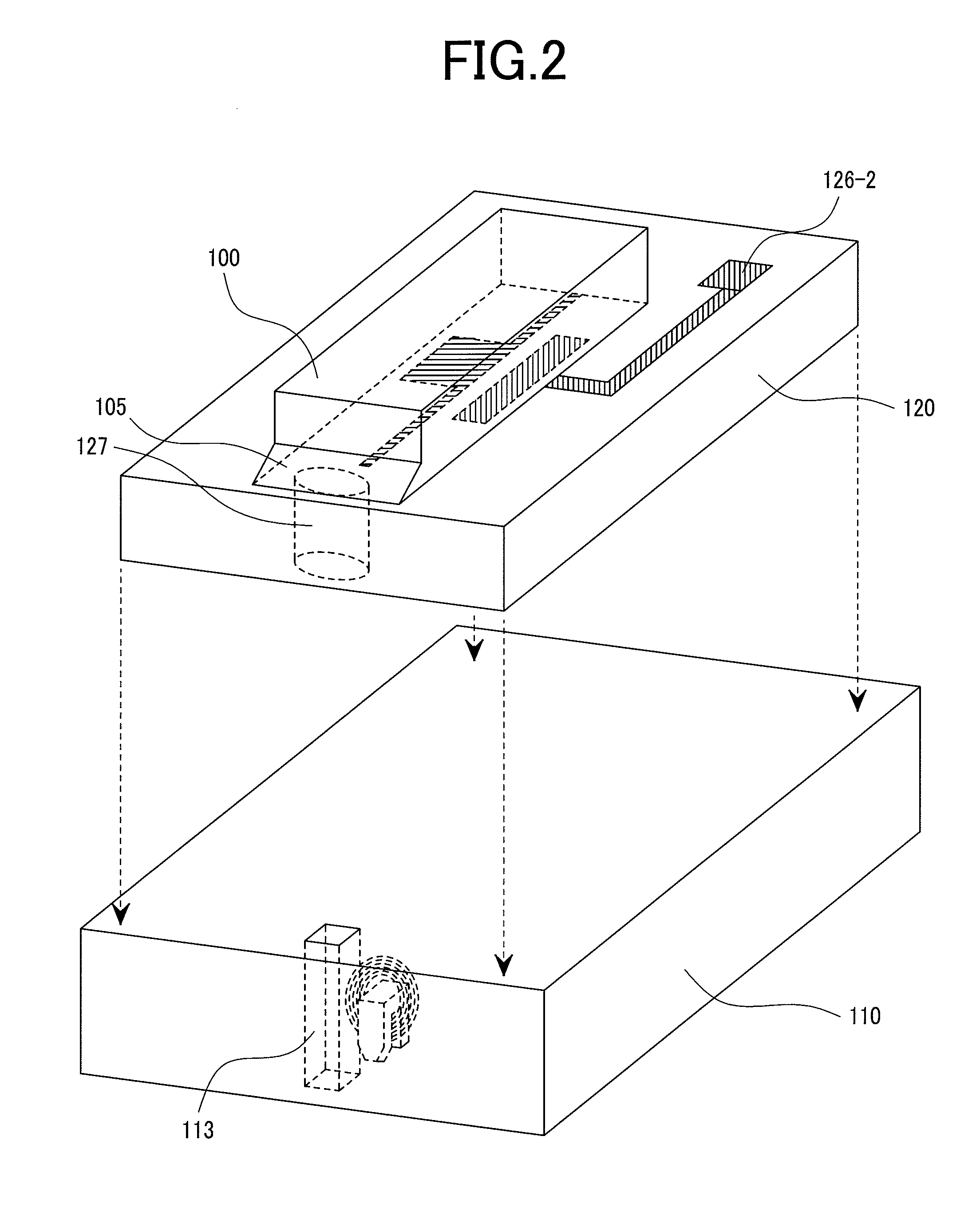
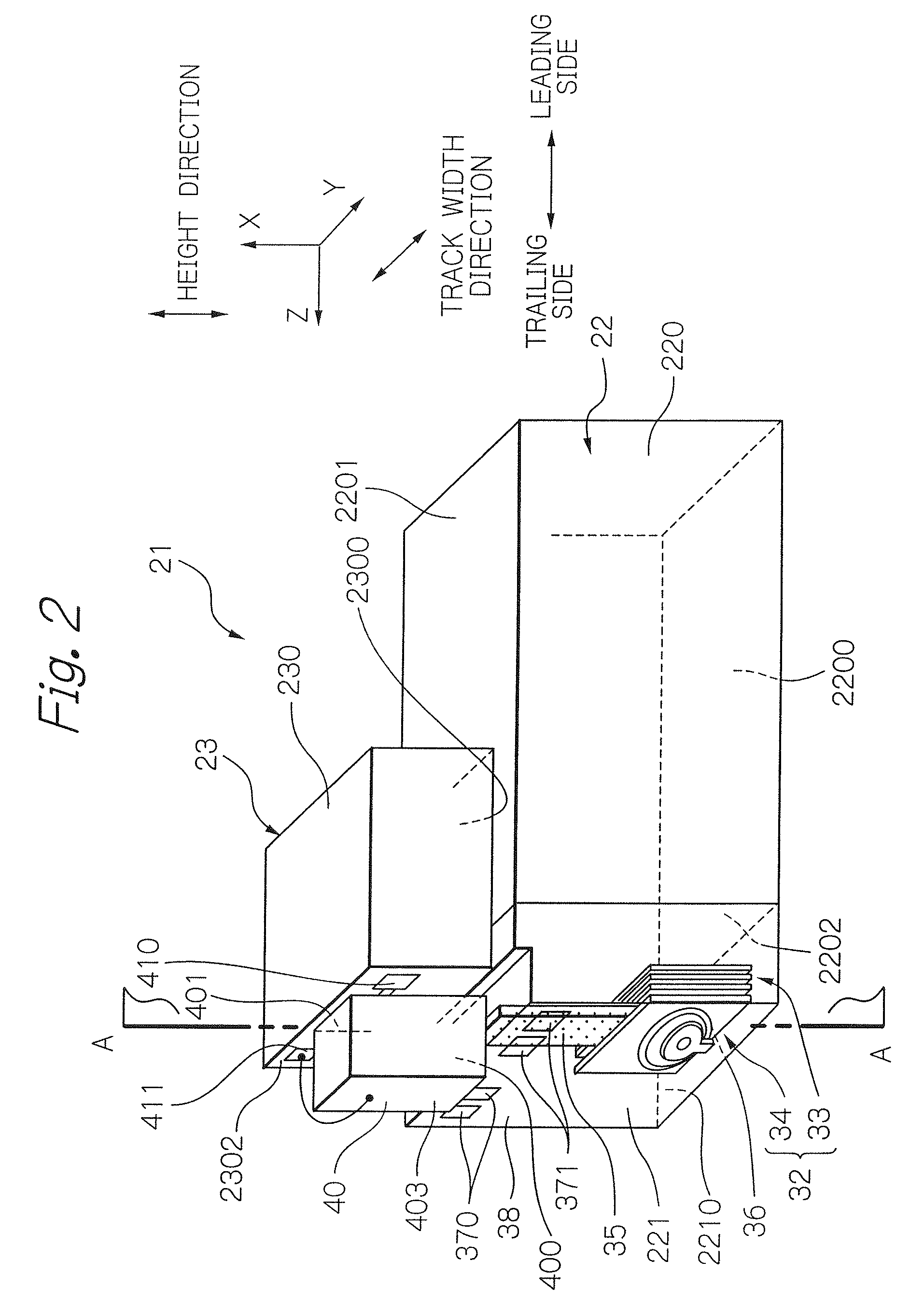
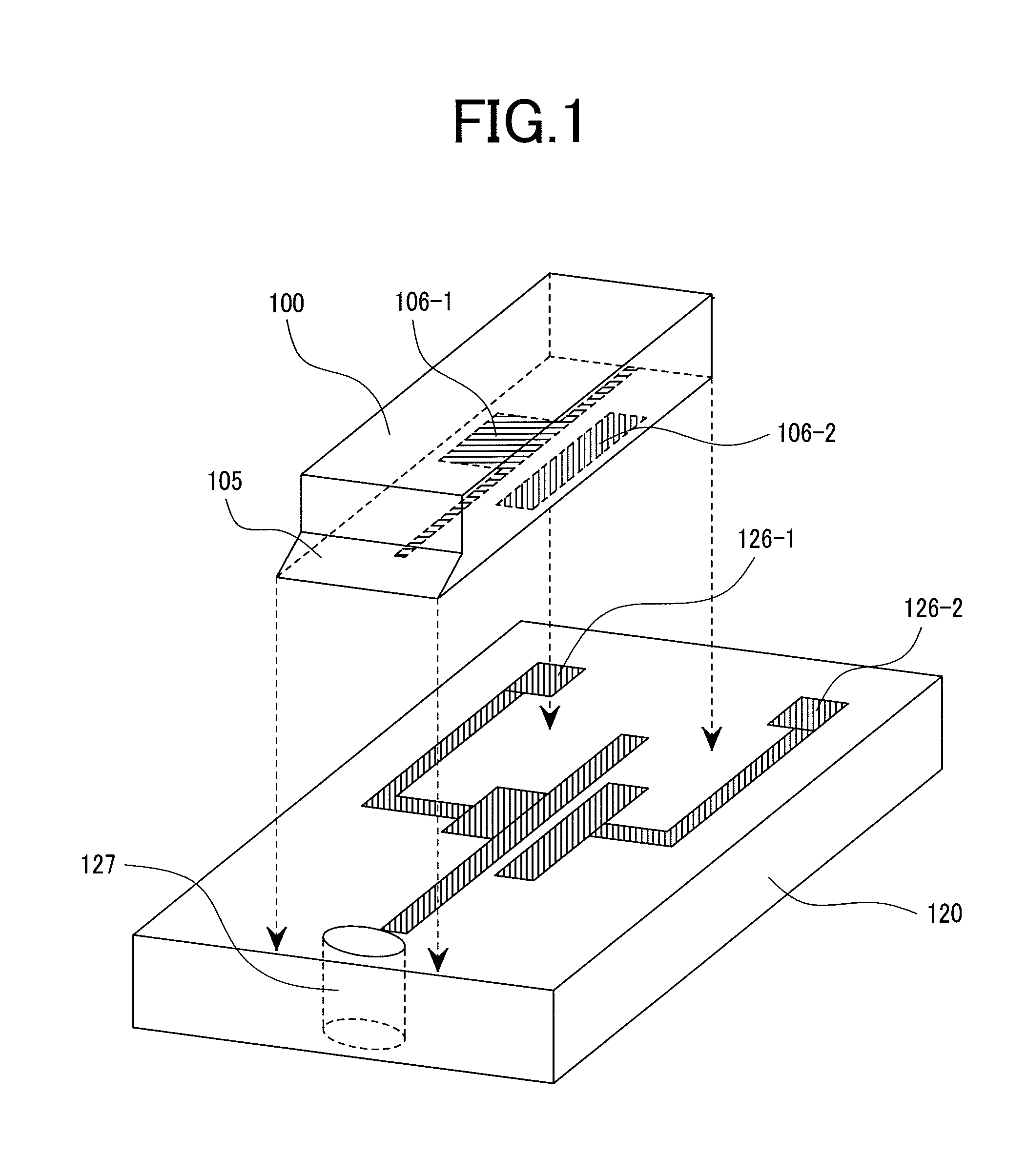
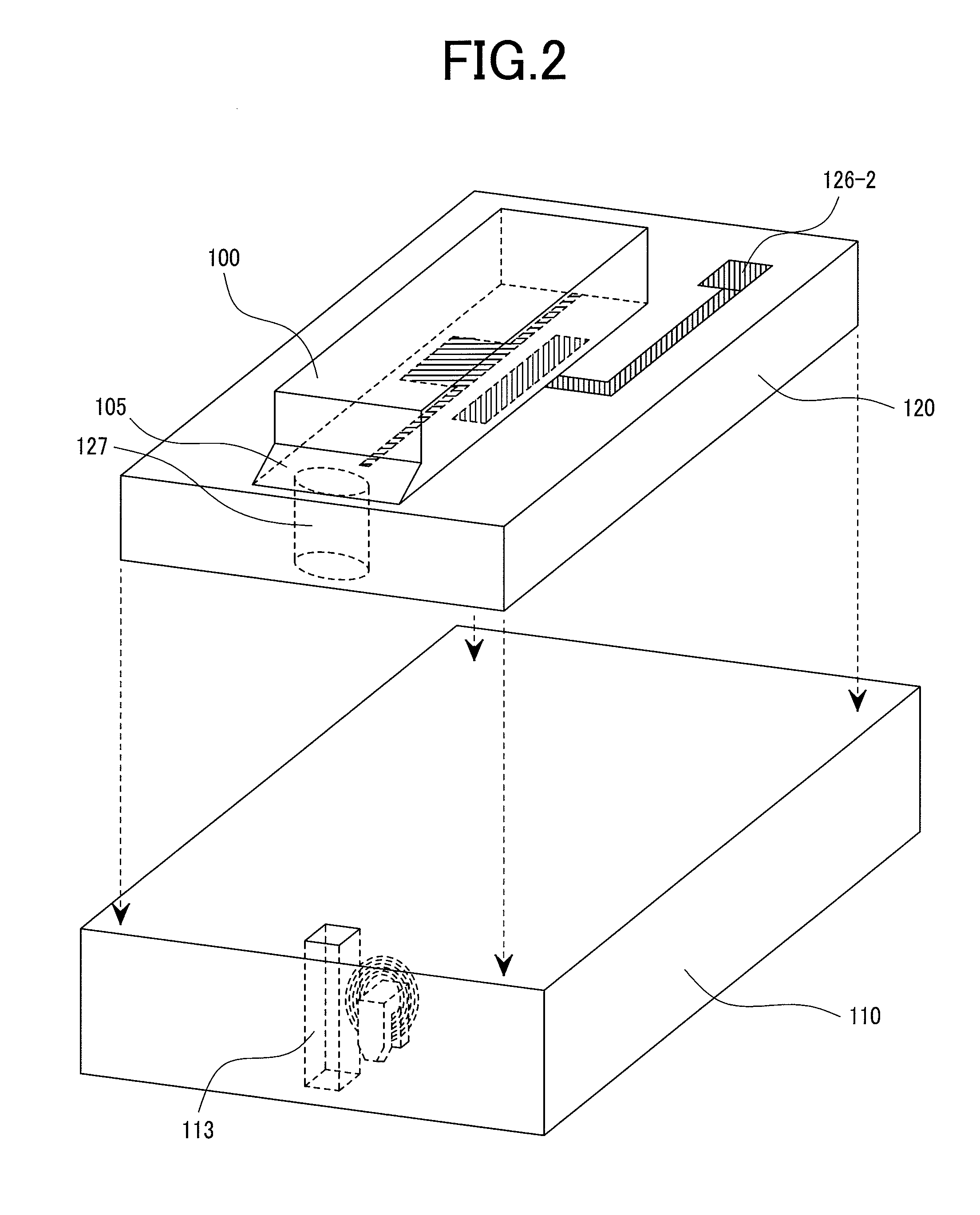
Distributed antenna system base station and radio resource control method
InactiveUS20120208581A1Improve communication qualityReduce variationSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionCommunication qualityEngineering
Disclosed is a distributed antenna system that selects an antenna in accordance with the position of a mobile terminal and reduces the variation in the total number of mobile terminals using each antenna while maintaining adequate communication quality. In the distributed antenna system in which a large number of antennas are distributively disposed, an antenna group including antennas having good communication quality is selected in accordance with the position of a mobile terminal. Further, in accordance with the communication quality and load status of a current antenna group and with the communication quality and load status of a post-change antenna group, which is obtained by changing some antennas in the current antenna group, the post-change antenna group is formed by changing some antennas in the current antenna group with which a mobile terminal using a heavily loaded antenna communicates.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
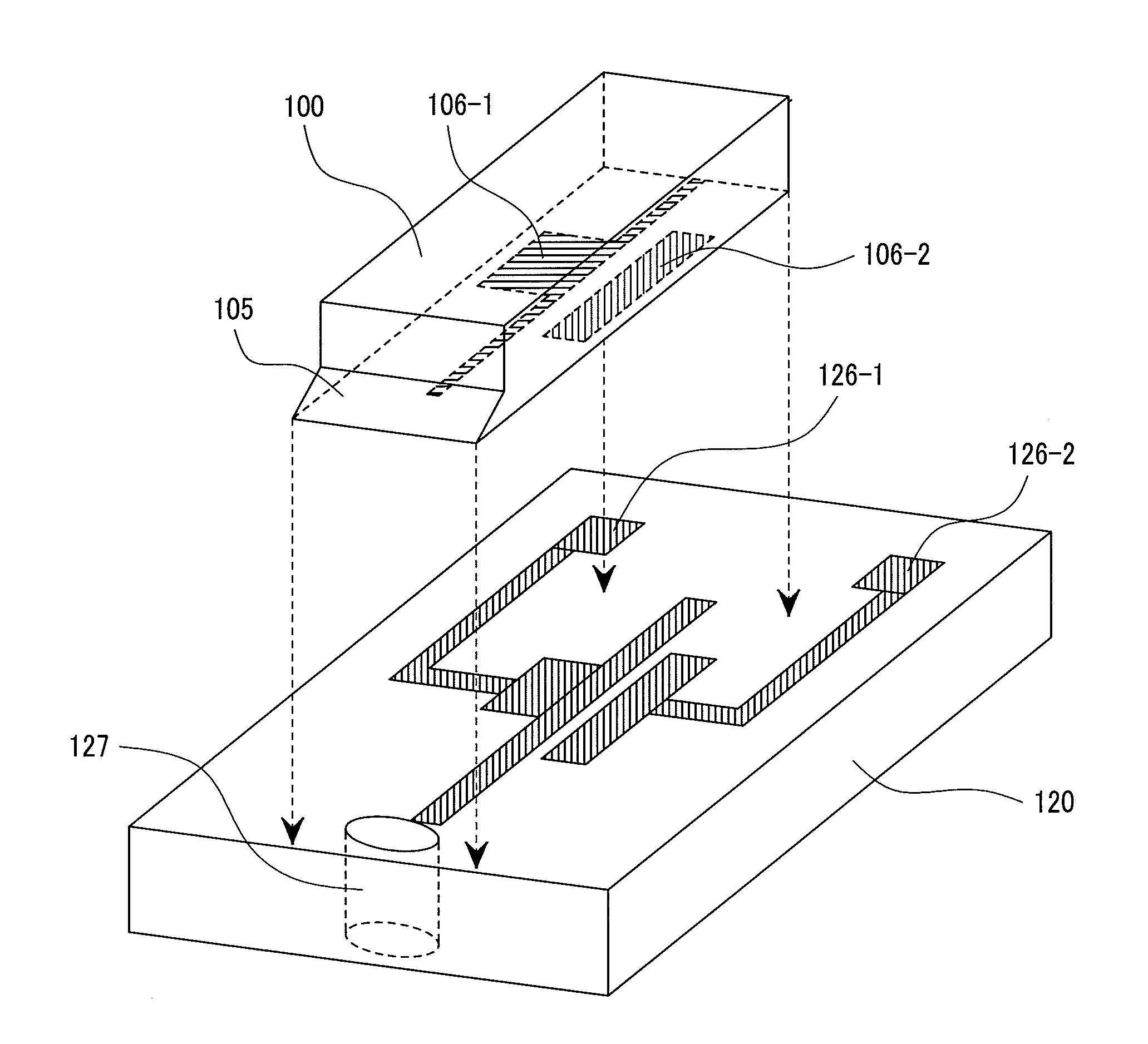
Optical device integrated head
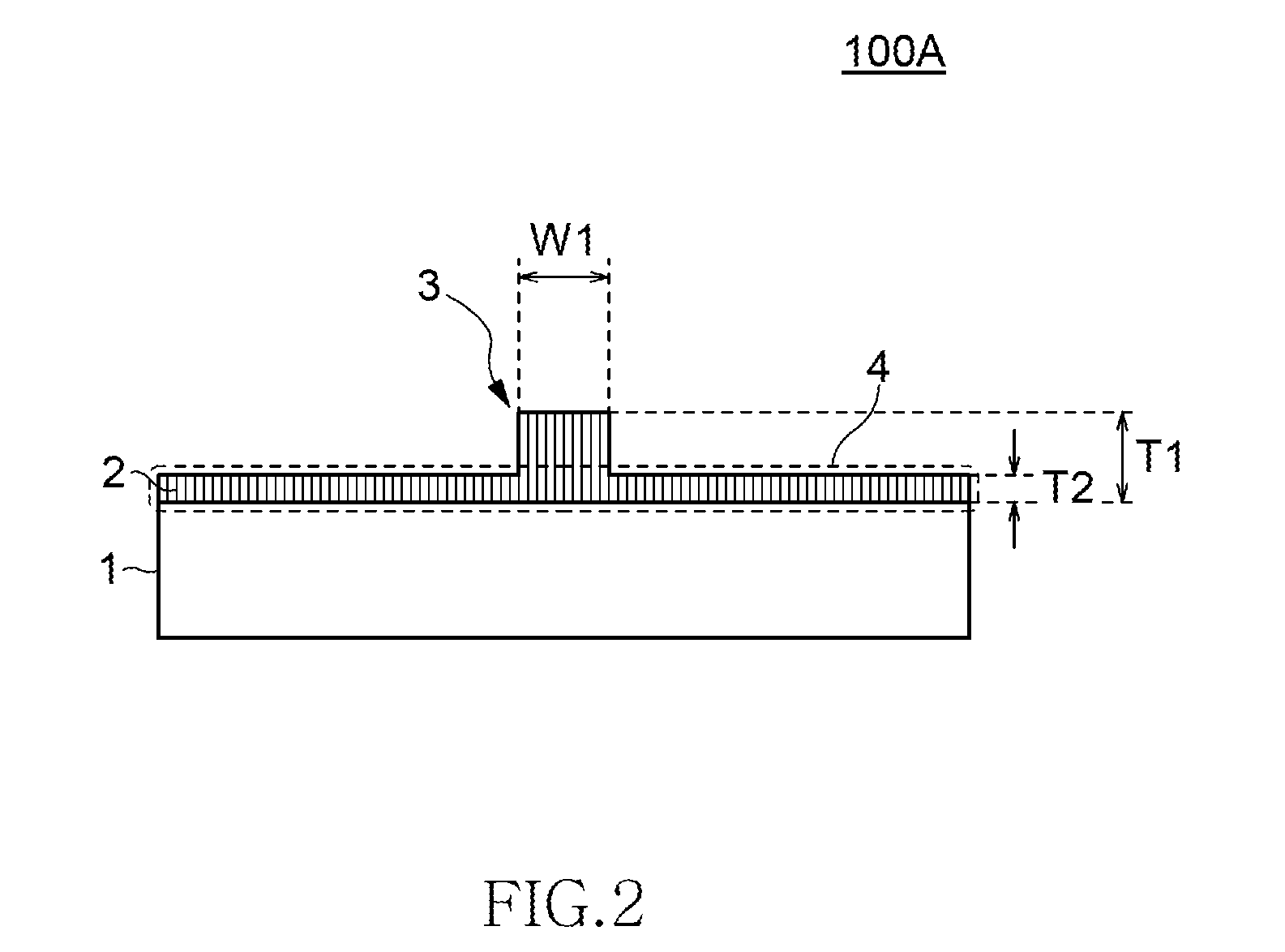
InactiveUS20080316872A1Reduce light lossReduce power consumptionCombination recordingRecord information storageWaveguideLaser
An optical device integrated head having high light utilizing efficiency by decreasing the propagation loss caused from an optical source to a recording medium, conducting by mounting according to compact active alignment method for efficiently guiding a light generated from a laser device to the top end of a head, in which a light source device mounted on a submount has a mirror portion having an inclinated surface to at least a portion of one edge thereof for reflecting an output light from the optical source device at the inclinated surface, a structural member including a lens structure for further allowing a light to pass through the submount, and an optical waveguide disposed passing through a slider for mounting the submount, and the optical source and the slider are positioned by using active alignment of light in a chip-on carrier structure having the optical source device mounted on the submount.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
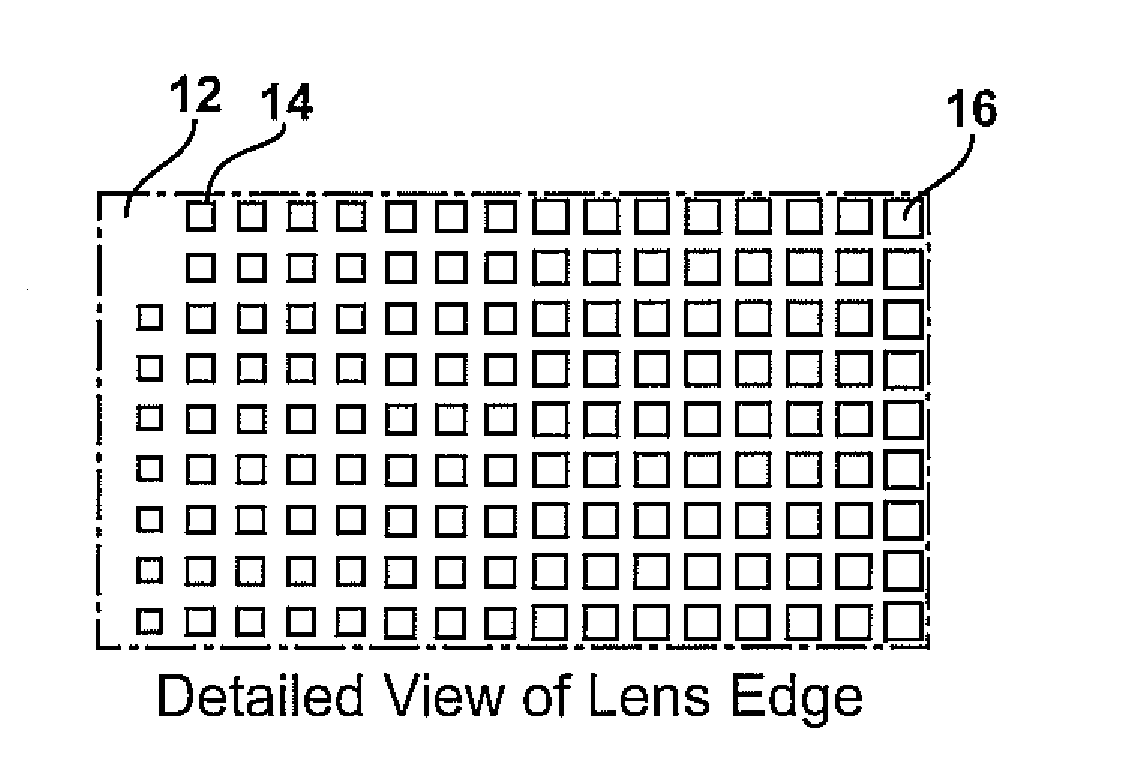
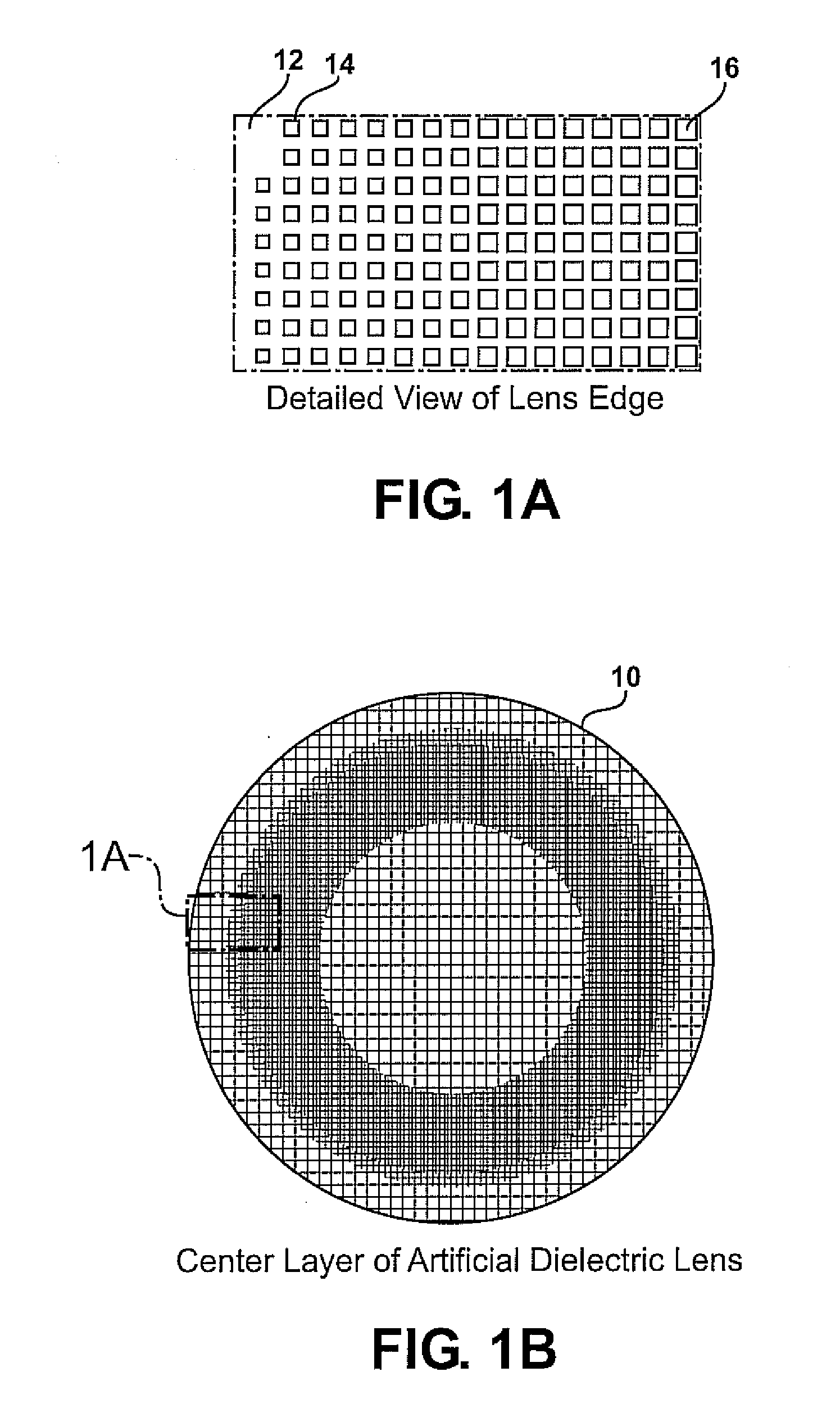
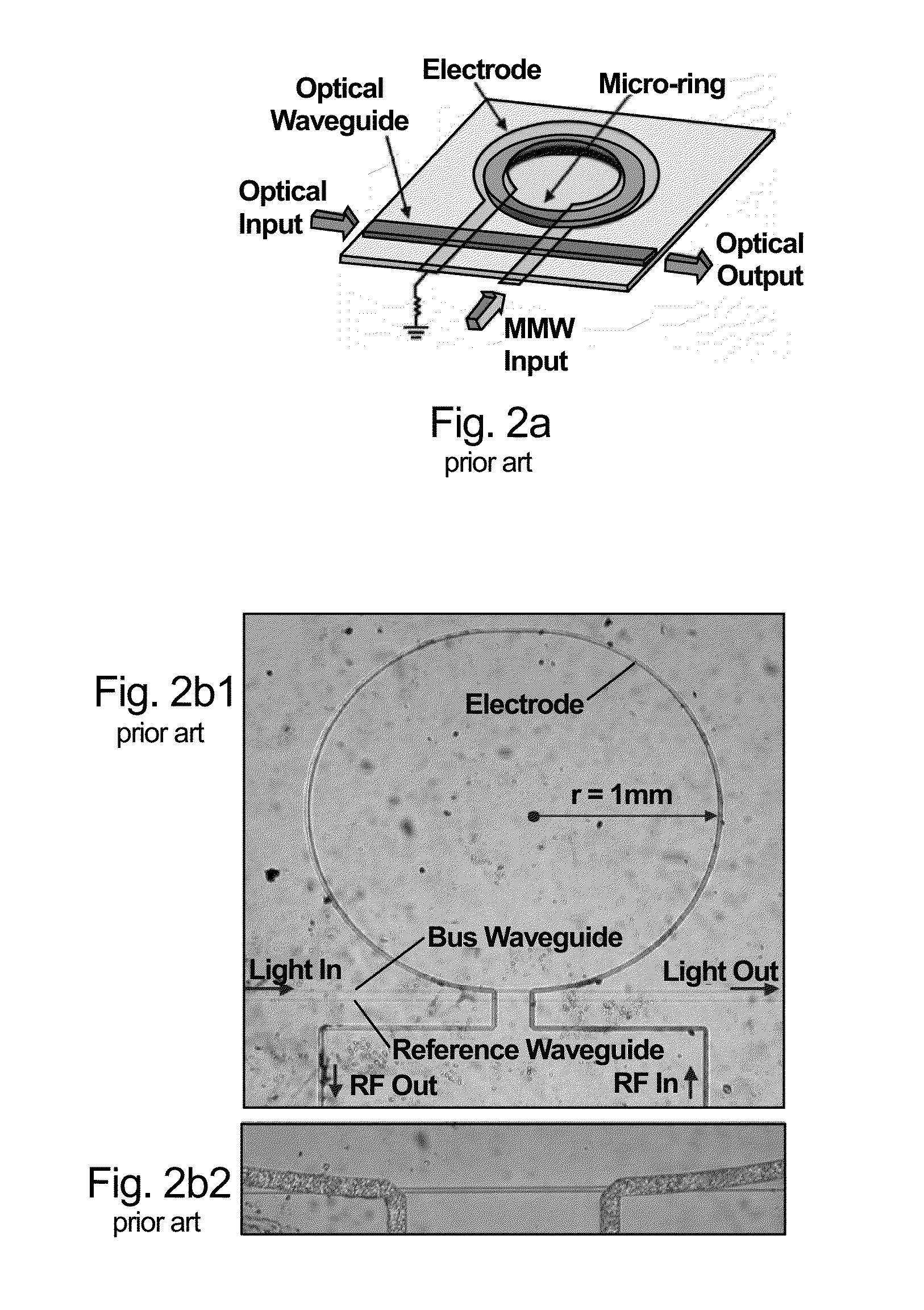
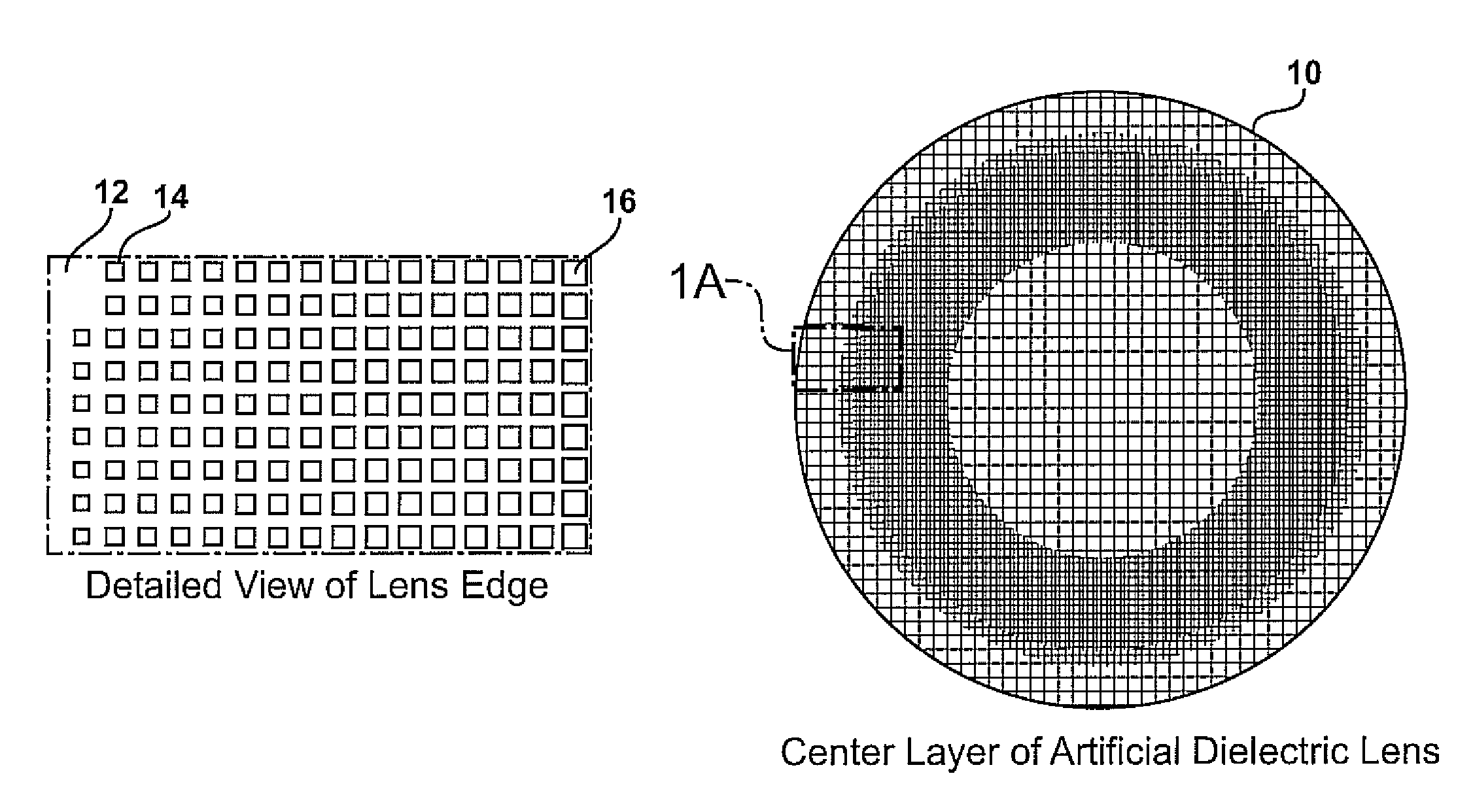
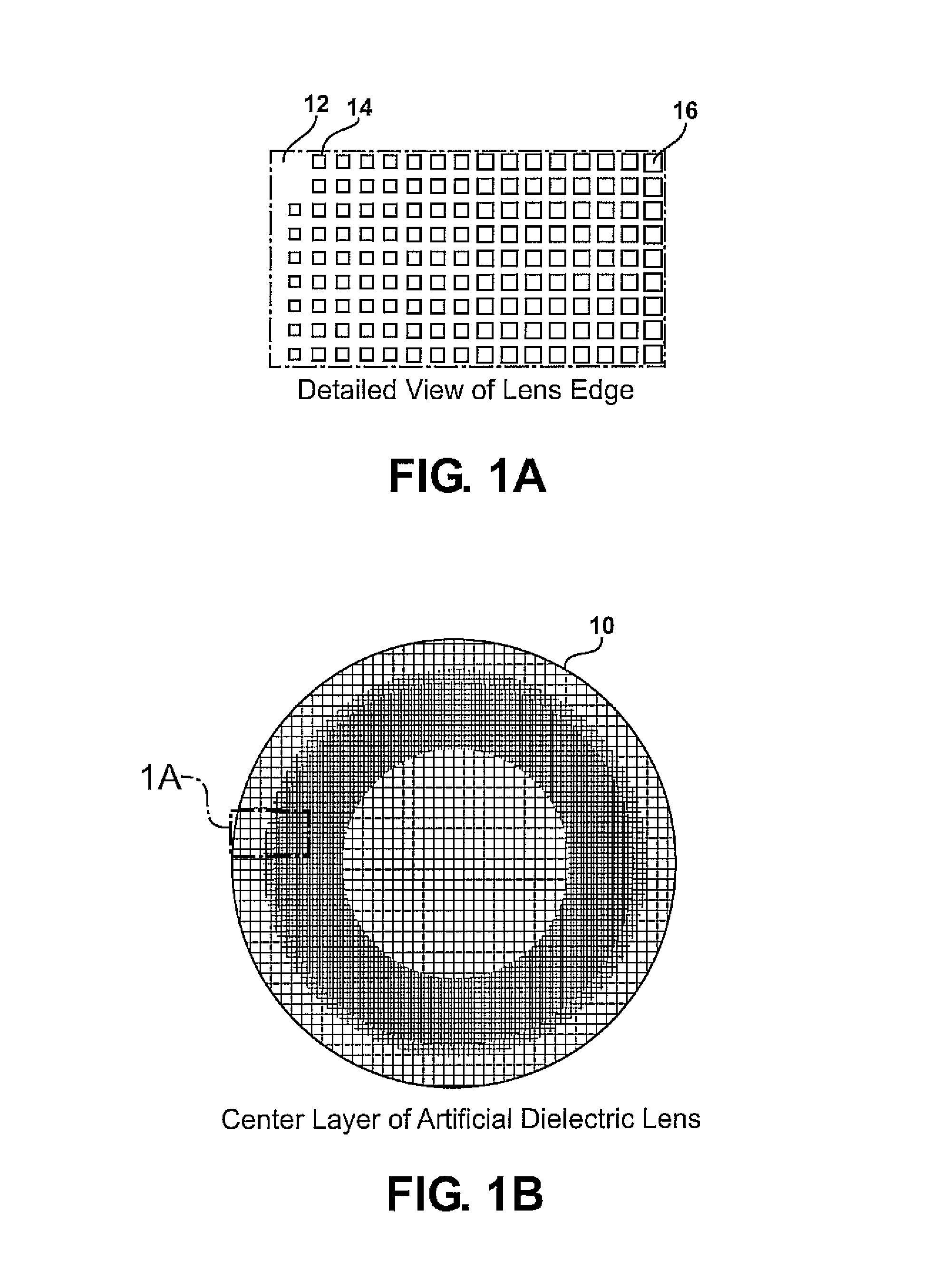
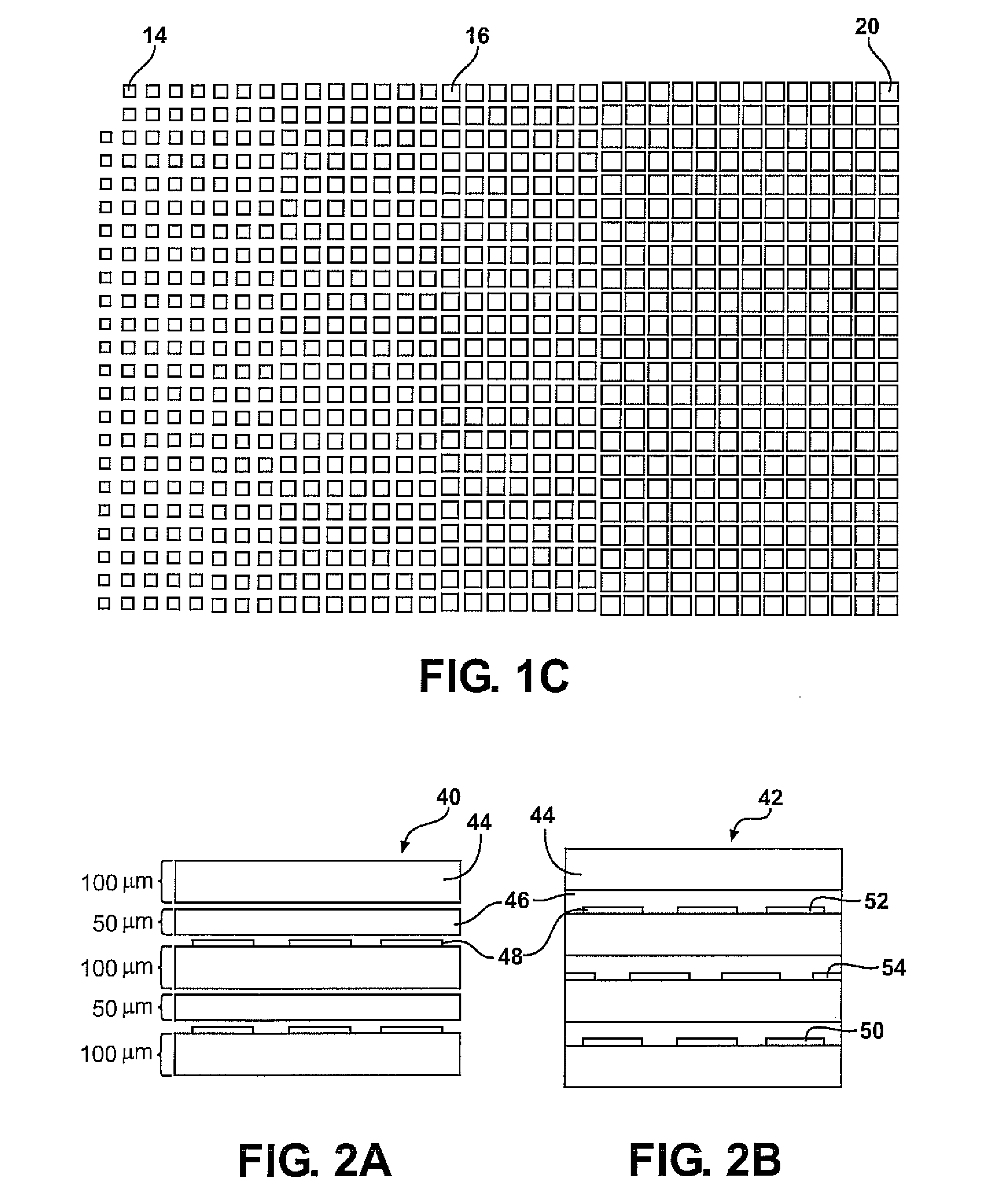
Planar gradient-index artificial dielectric lens and method for manufacture
A gradient index lens for electromagnetic radiation includes a dielectric substrate, a plurality of conducting patches supported by the dielectric substrate, the conducting patches preferably being generally square shaped and having an edge length, the edge length of the conducting patches varying with position on the dielectric substrate so as to provide a gradient index for the electromagnetic radiation. Examples include gradient index lenses for millimeter wave radiation, and use with antenna systems.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Silicon-based electro-optic device
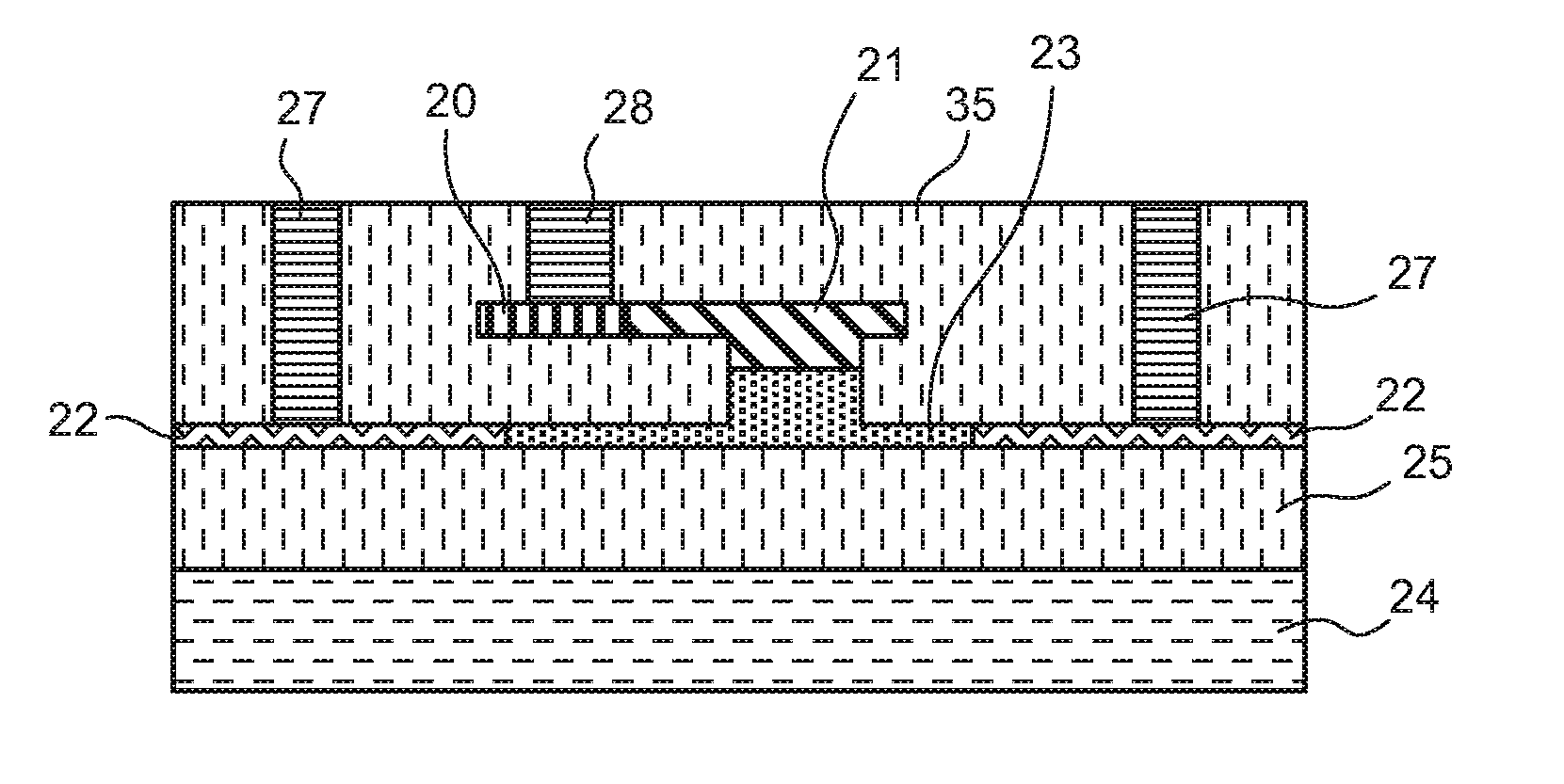
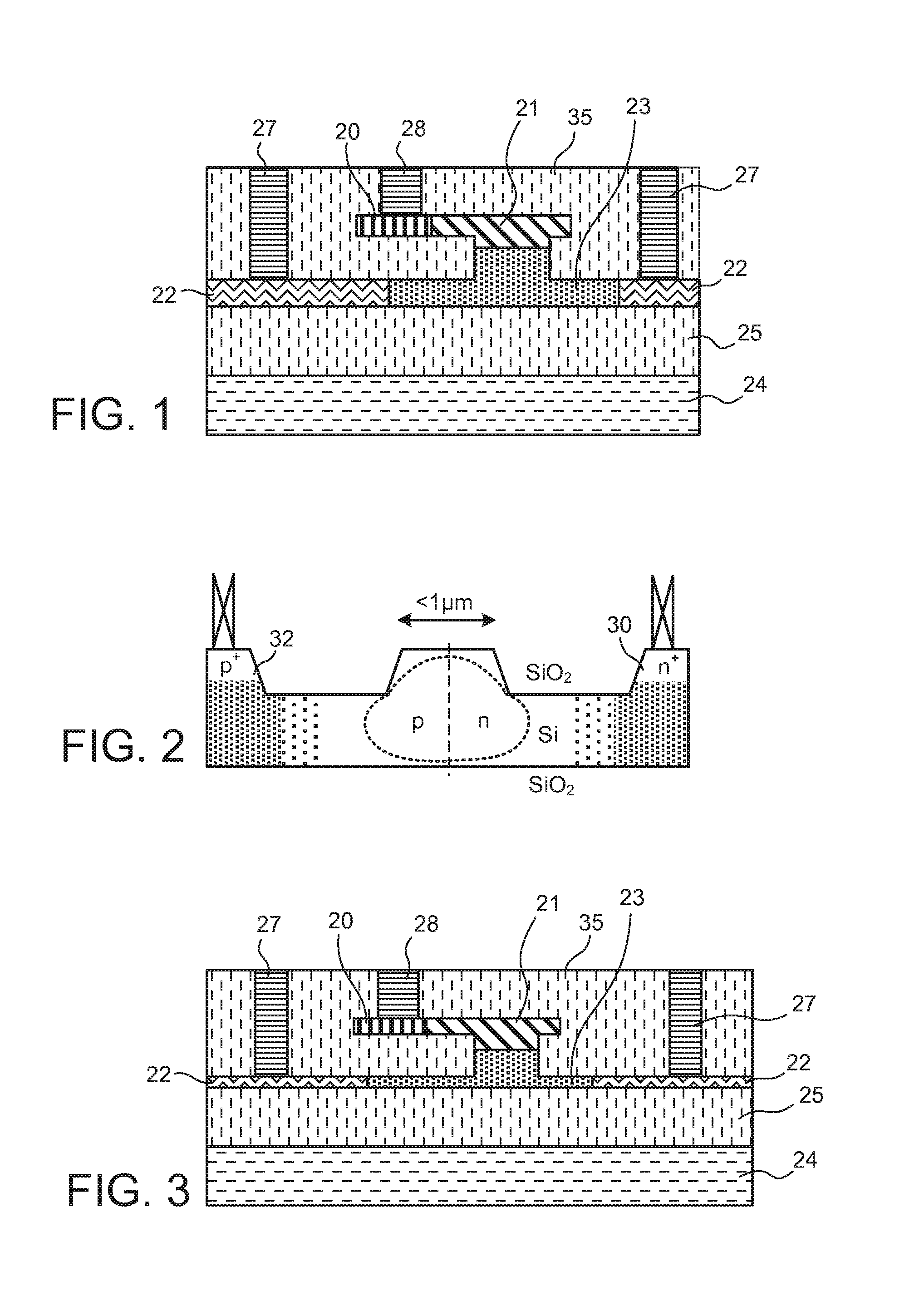
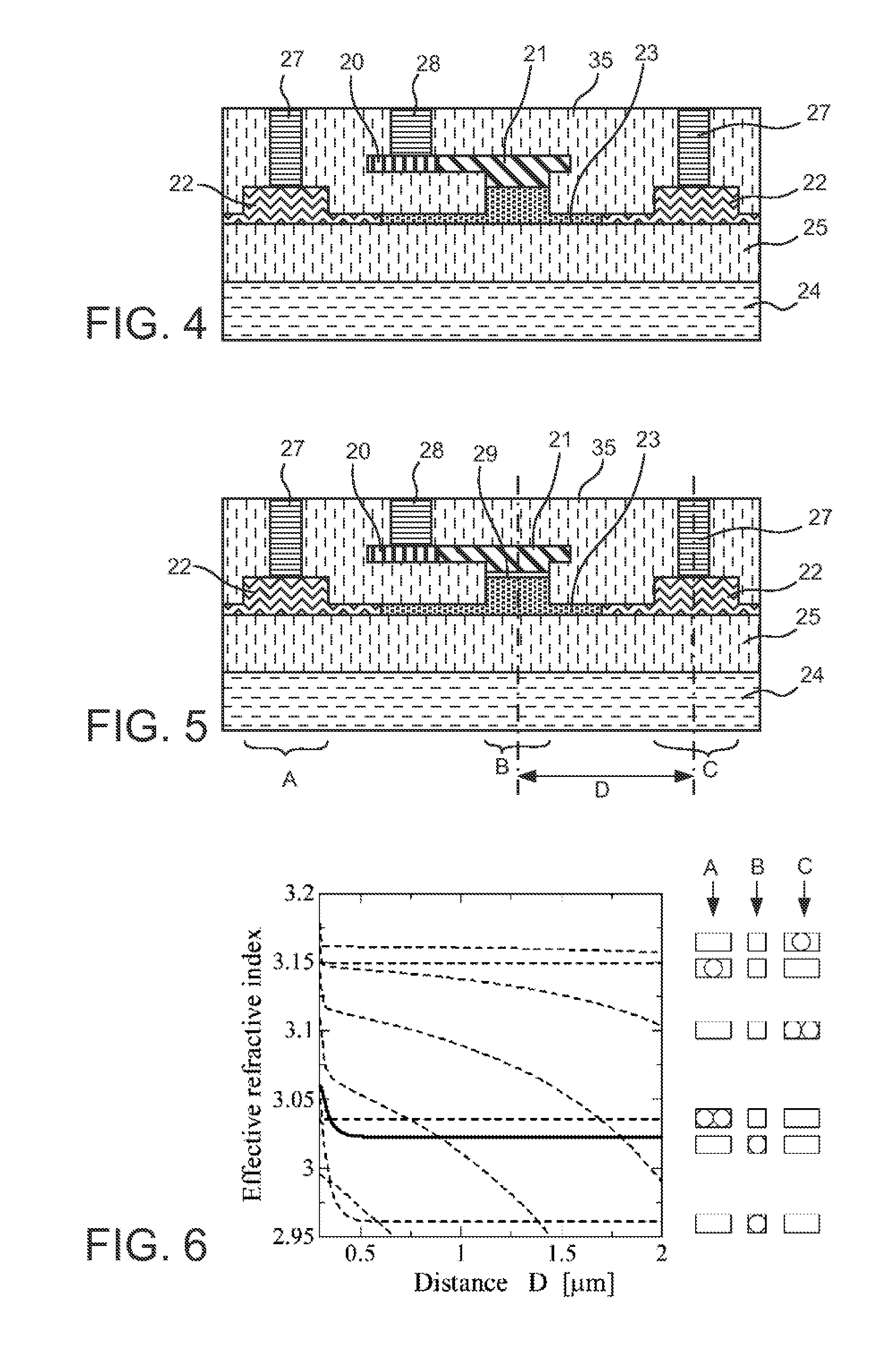
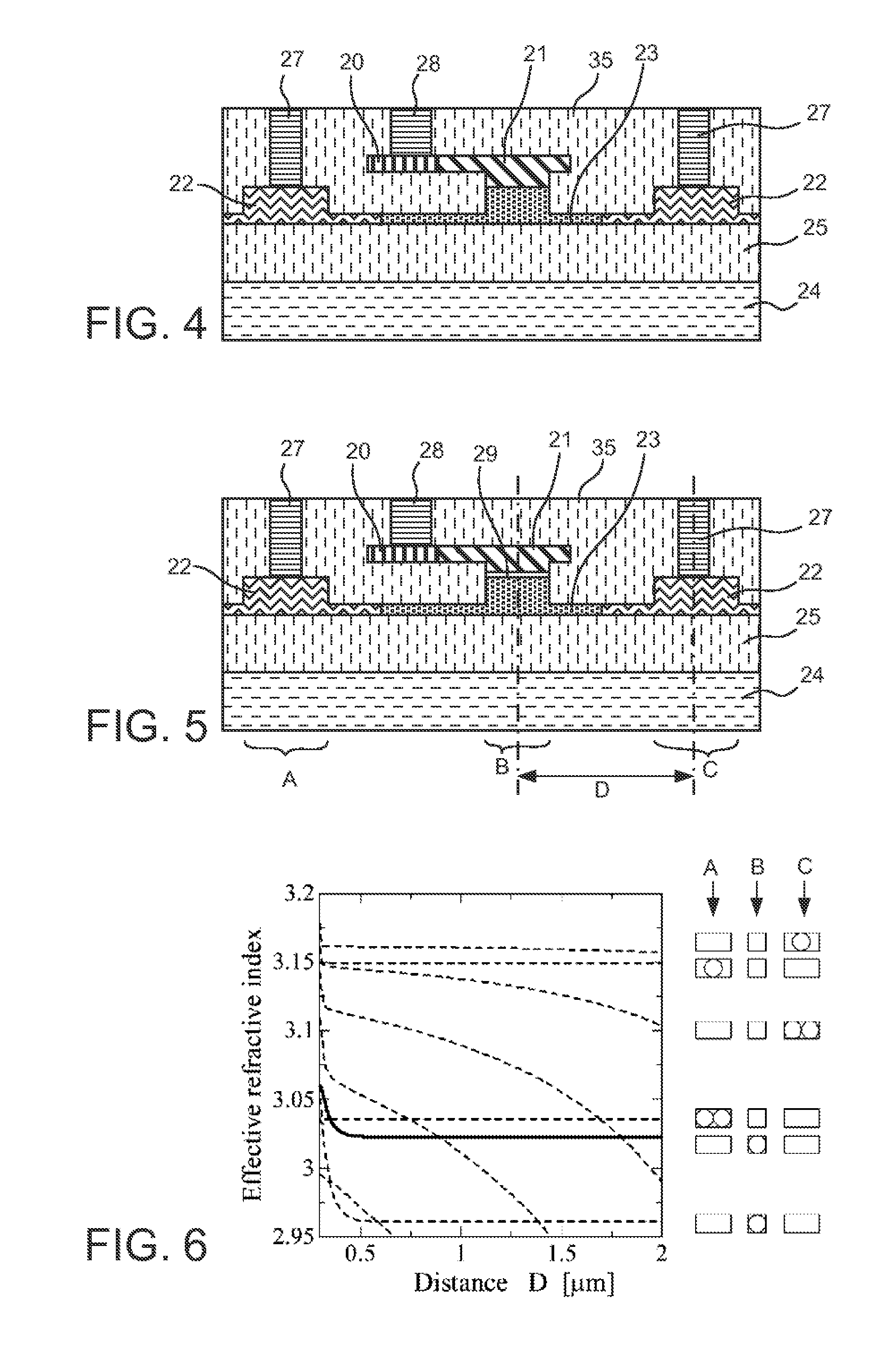
ActiveUS20110211786A1Efficient connectionReduced propagation lossOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsMetal electrodesMaterials science
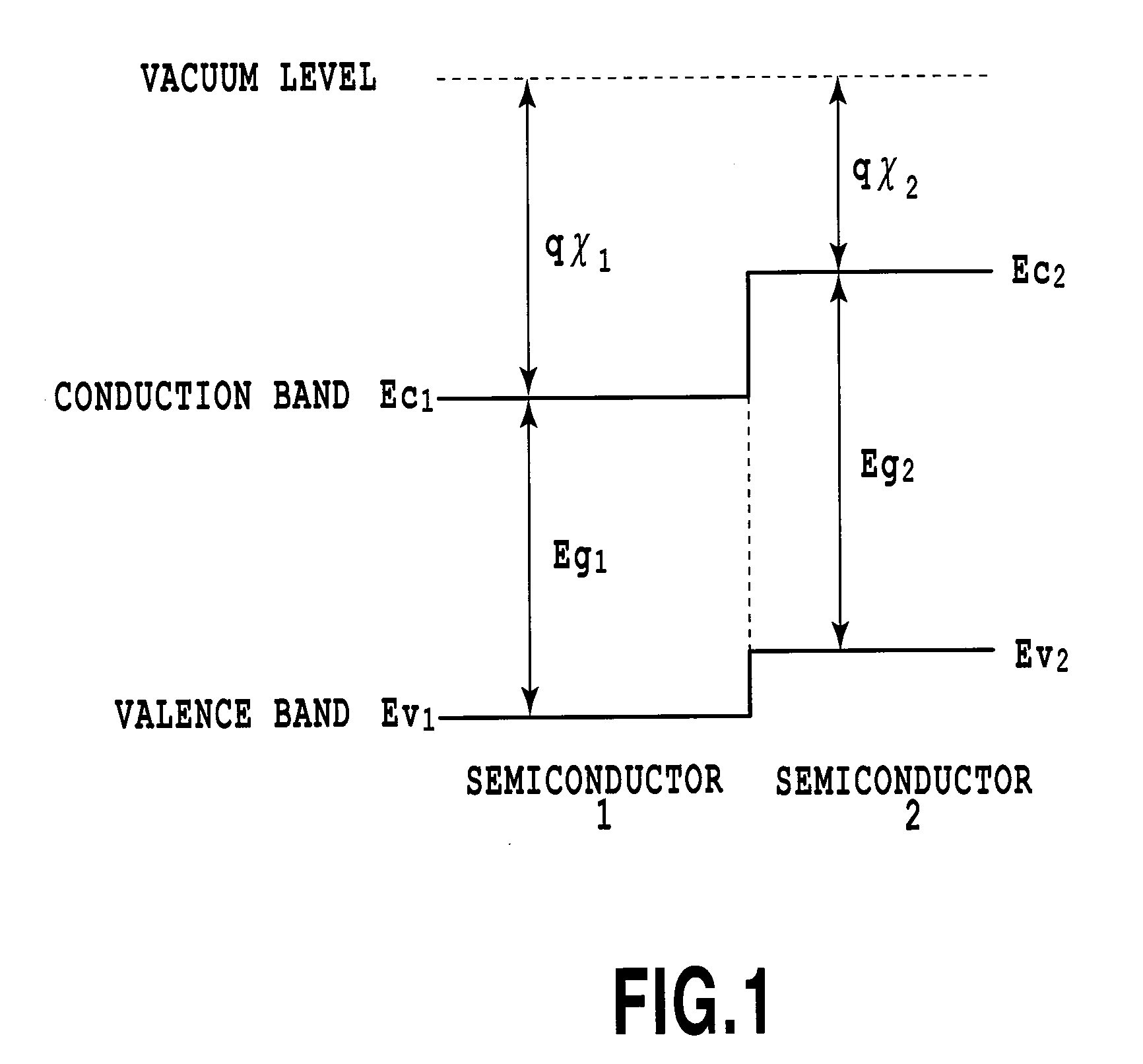
In an electro-optic device, a stack structure including a first silicon layer of a first conductivity type and a second silicon layer of a second conductivity type has a rib waveguide shape so as to form an optical confinement area, and a slab portion of a rib waveguide includes an area to which a metal electrode is connected. The slab portion in the area to which the metal electrode is connected is thicker than a surrounding slab portion. The area to which the metal electrode is connected is set so that a range of a distance from the rib waveguide to the area to which the metal electrode is connected is such that when the distance is changed, an effective refractive index of the rib waveguide in a zeroth-order mode does not change.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FOUNDRY PTE LTD +1
Near-field light generating element comprising surface plasmon antenna with surface or edge opposed to waveguide
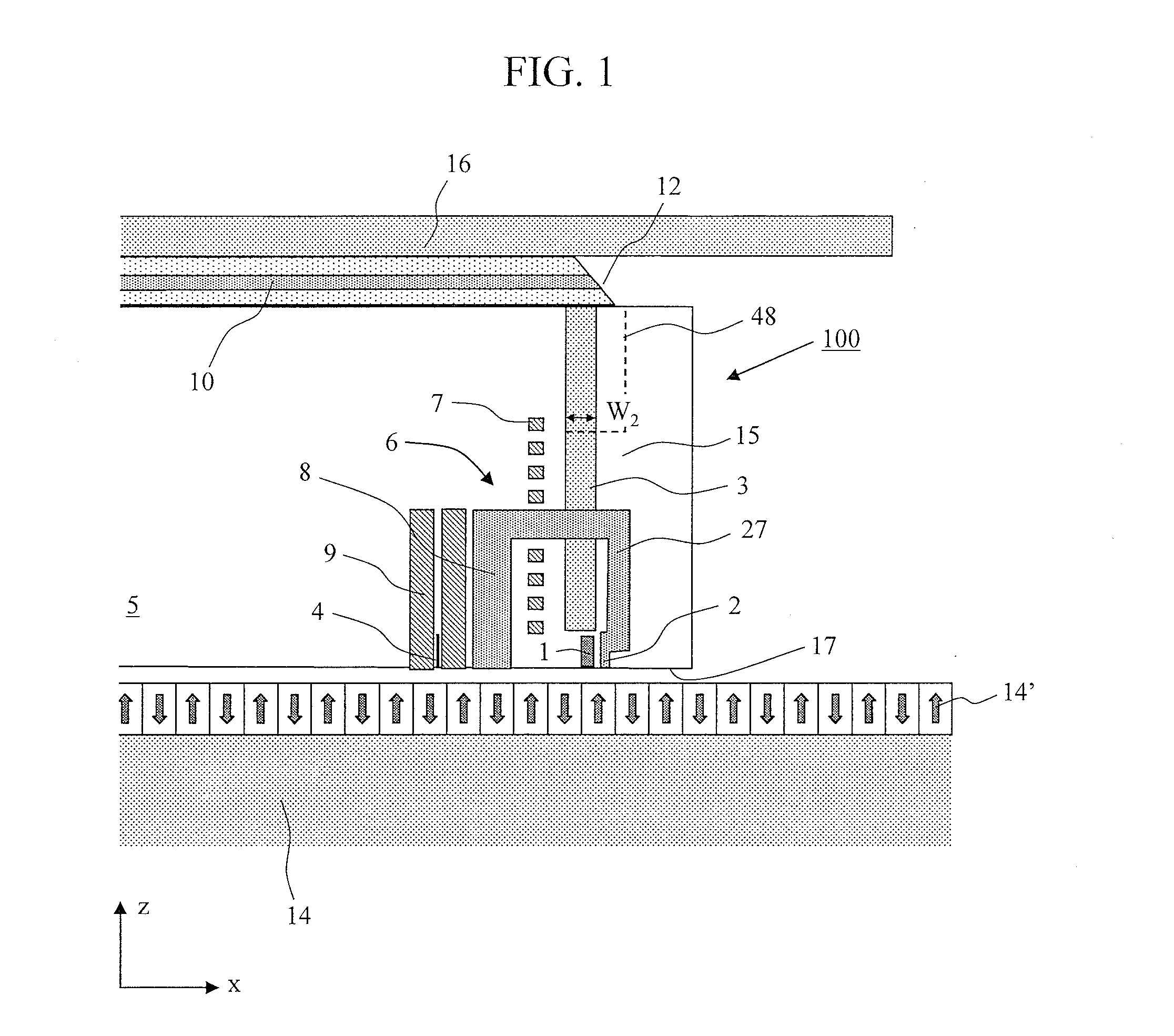
ActiveUS20100149930A1Improve light use efficiencyReduced propagation lossCombination recordingArm with optical waveguideWavenumberWaveguide
Provided is a near-field light generating element in which reduced is the propagation loss of excited surface plasmon that propagates to the near-field light generating end. The element comprises: a waveguide through which light for exciting surface plasmon propagates; and a plasmon antenna comprising a near-field light generating end and a propagation surface or edge. The propagation surface or edge extends to the near-field light generating end, and causes surface plasmon excited by the light to propagate thereon. Further, a portion of the side surface on the near-field light generating end side is opposed to the propagation surface or edge with a predetermined distance so as for the light to be coupled with the plasmon antenna in a surface plasmon mode. In this configuration, surface plasmon can propagates without significantly changing its wavenumber, which leads to a less propagation loss, and to an improved light use efficiency.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
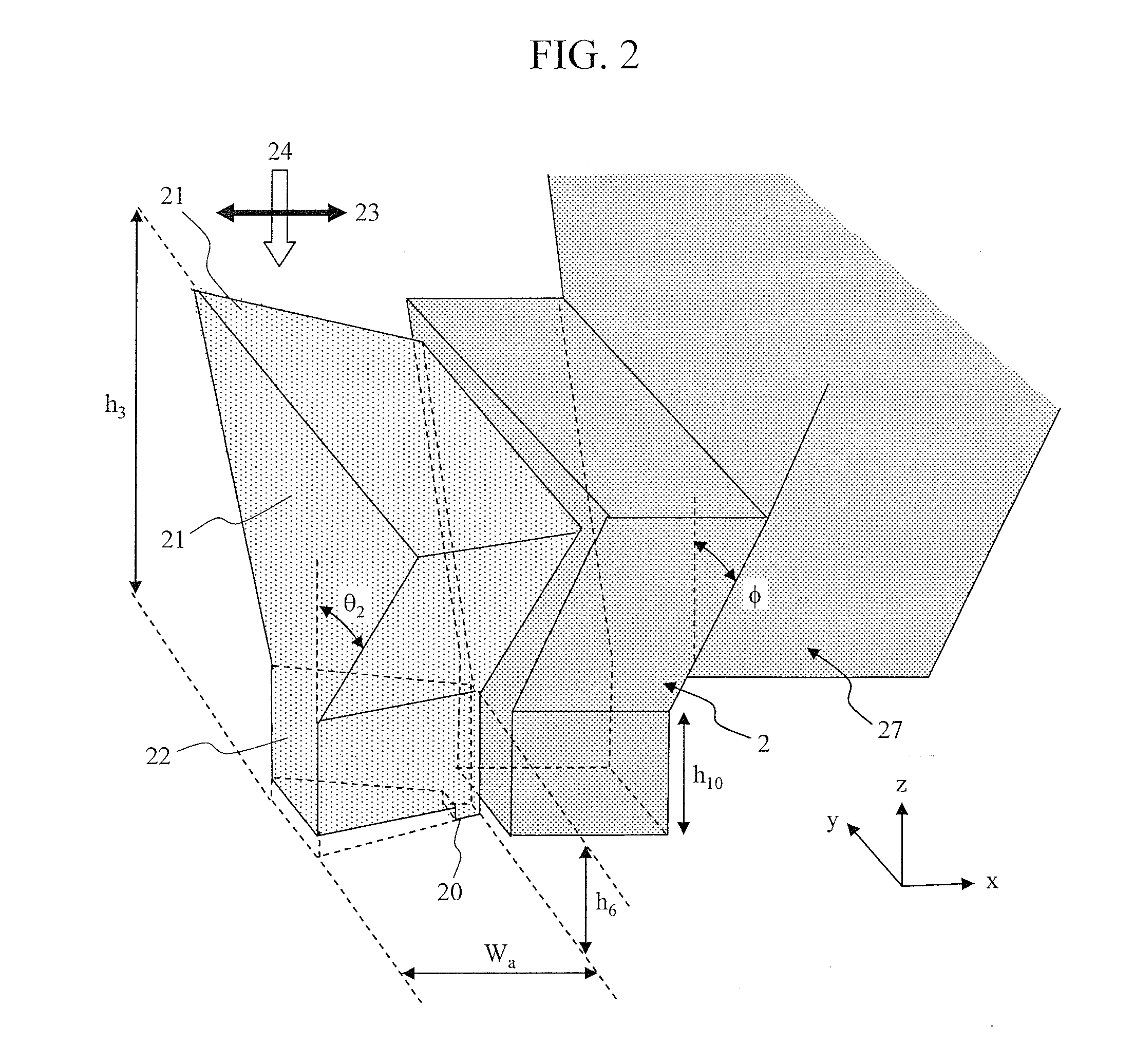
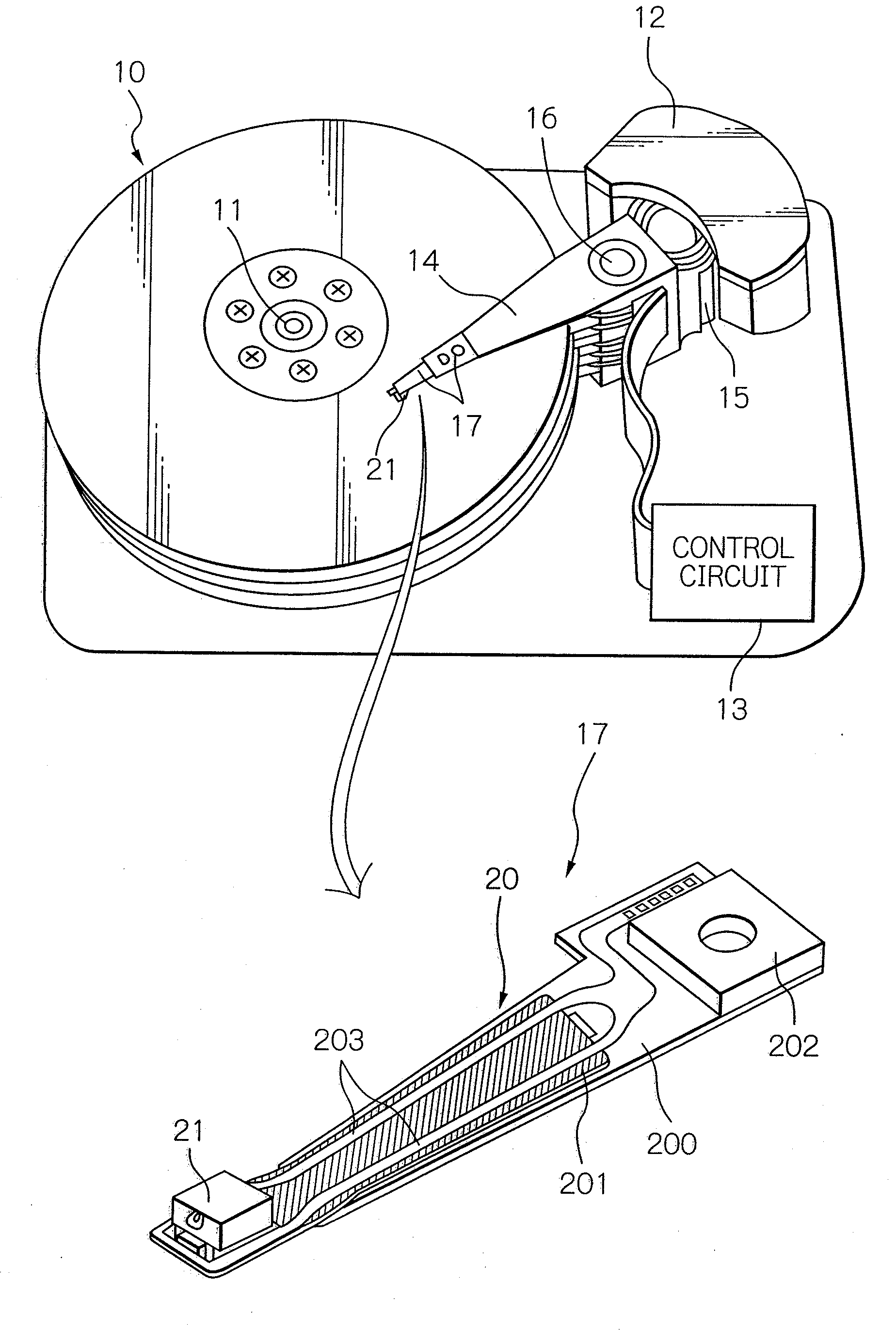
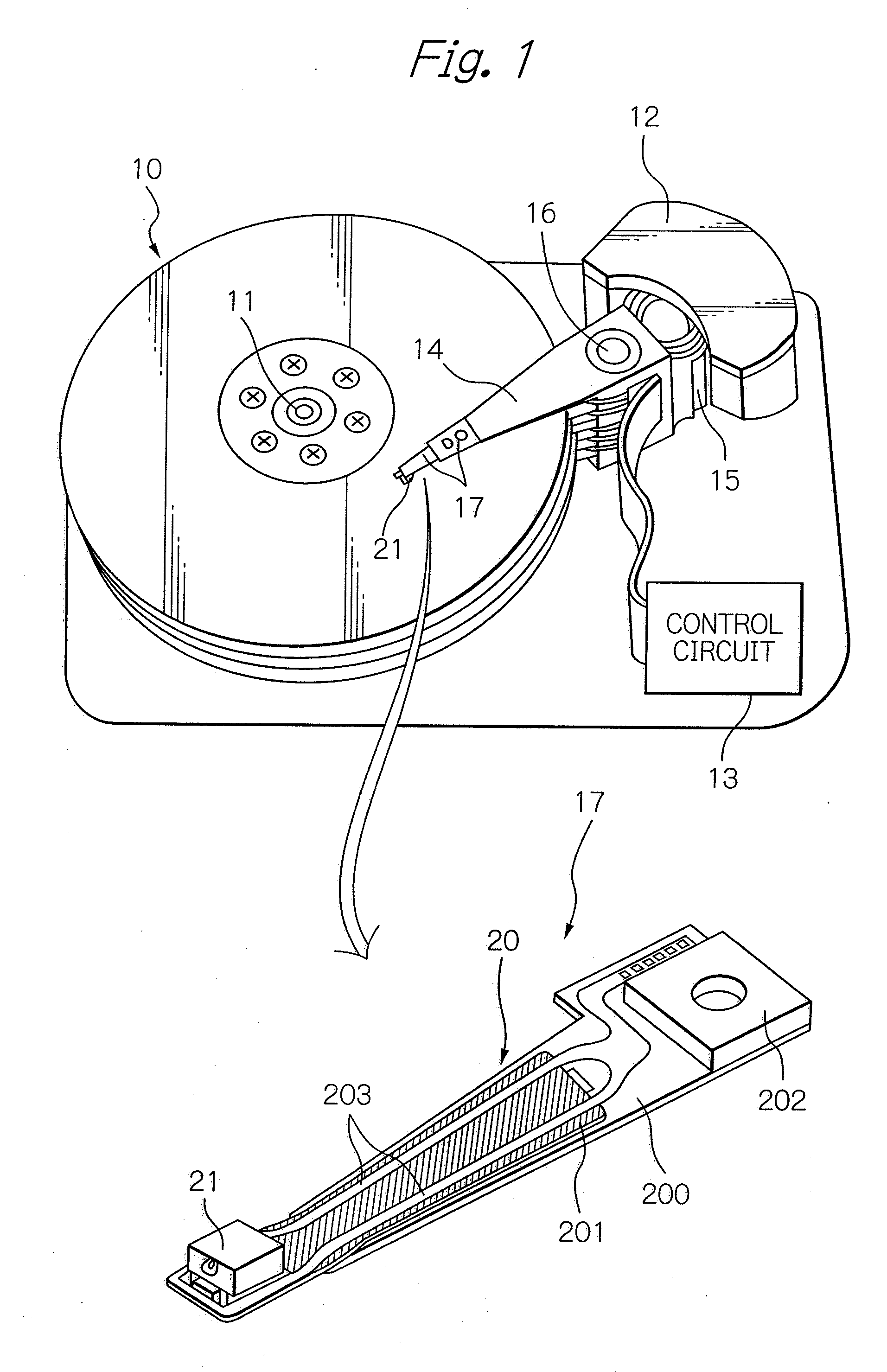
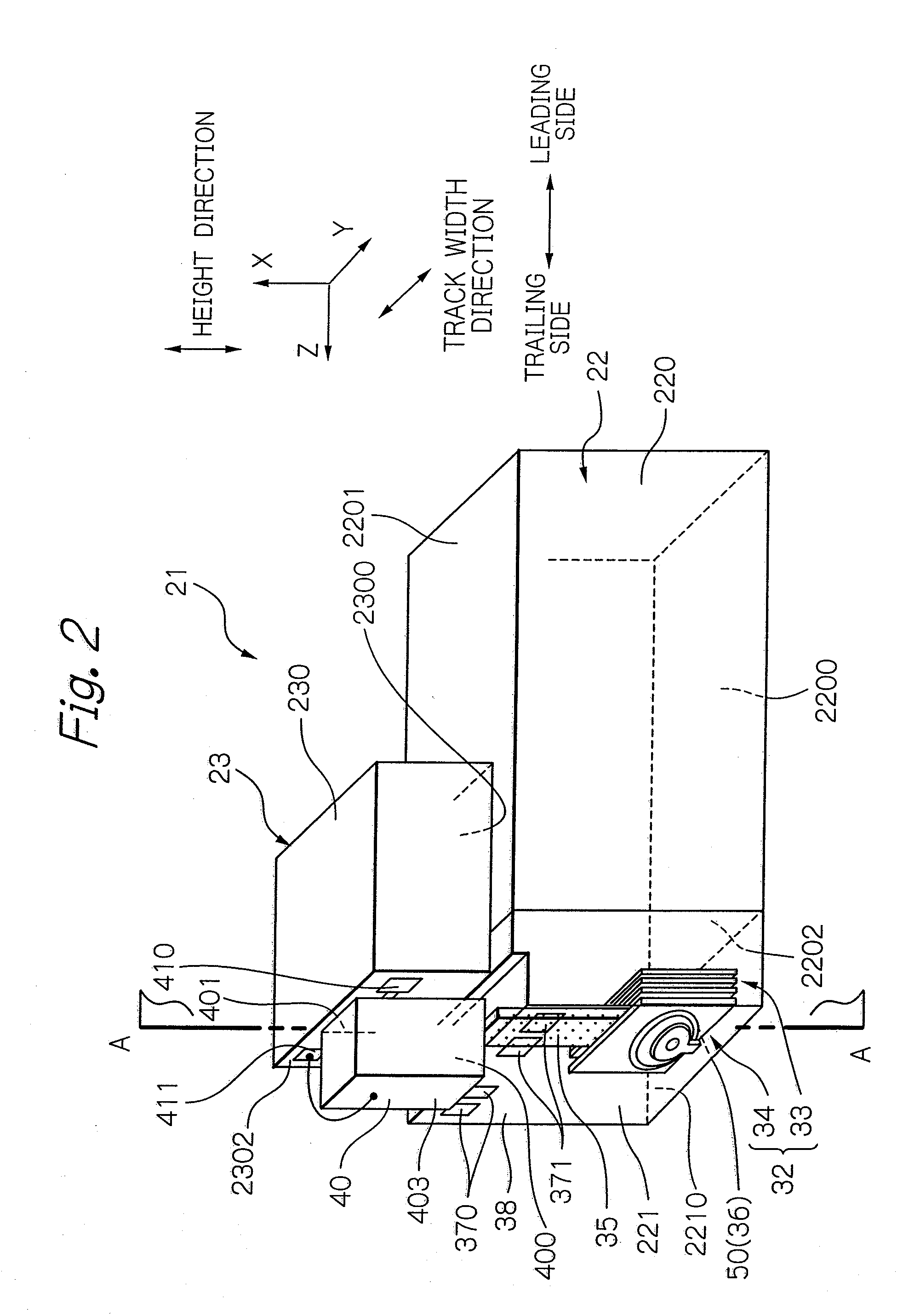
Head for thermal assisted magnetic recording device, and thermal assisted magnetic recording device
InactiveUS20110096639A1High strengthAvoid temperature riseCombination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingField intensity
The present invention suppresses temperature rise of an optical near-field generator while increasing optical near-field intensity in a thermally assisted magnetic recording head using a conductive scatterer as the optical near-field generator. The present invention uses a conductive scatterer having a cross-sectional shape in which its width is gradually reduced toward an apex where an optical near-field is generated, and also has a shape in which its width is reduced gradually or in a stepwise fashion toward the apex where the optical near-field is generated in a traveling direction of incident light.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Near-field light generating element comprising surface plasmon antenna with surface or edge opposed to waveguide
ActiveUS8107325B2Improve light utilization efficiencyReduced propagation lossCombination recordingArm with optical waveguideSurface plasmonWaveguide
Provided is a near-field light generating element in which reduced is the propagation loss of excited surface plasmon that propagates to the near-field light generating end. The element comprises: a waveguide through which light for exciting surface plasmon propagates; and a plasmon antenna comprising a near-field light generating end and a propagation surface or edge. The propagation surface or edge extends to the near-field light generating end, and causes surface plasmon excited by the light to propagate thereon. Further, a portion of the side surface on the near-field light generating end side is opposed to the propagation surface or edge with a predetermined distance so as for the light to be coupled with the plasmon antenna in a surface plasmon mode. In this configuration, surface plasmon can propagates without significantly changing its wavenumber, which leads to a less propagation loss, and to an improved light use efficiency.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
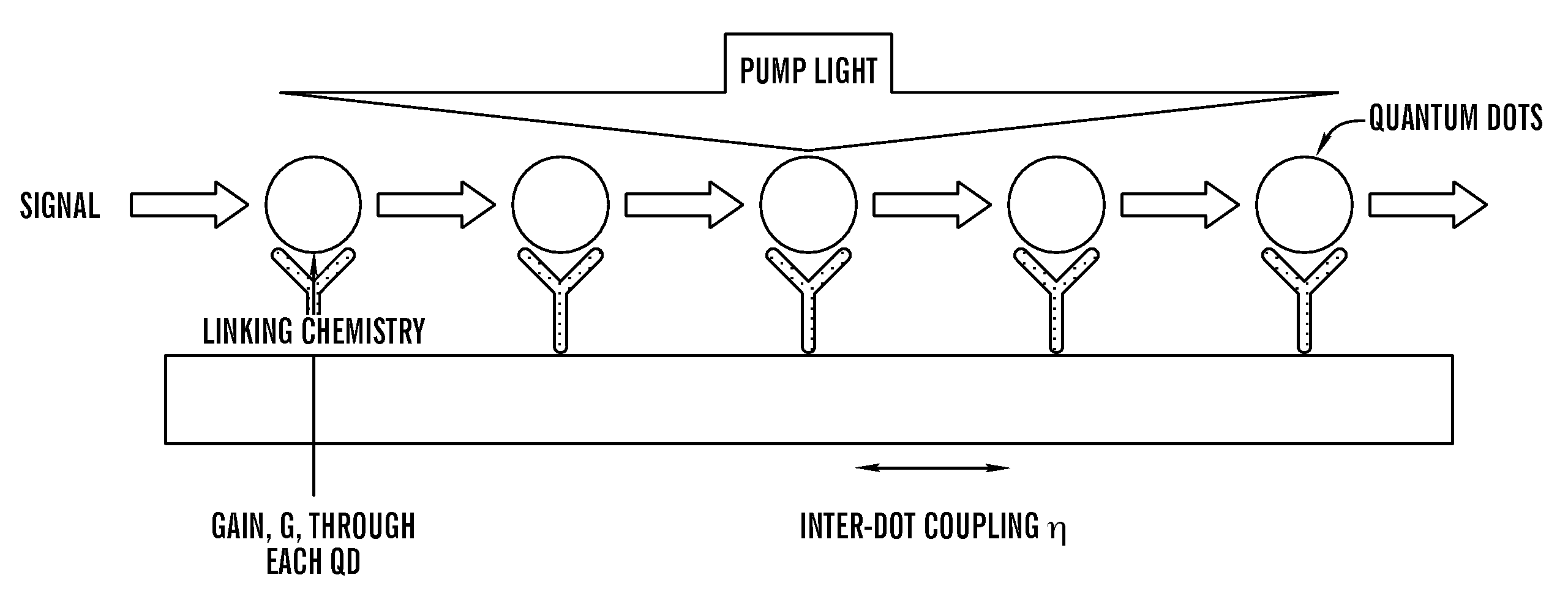
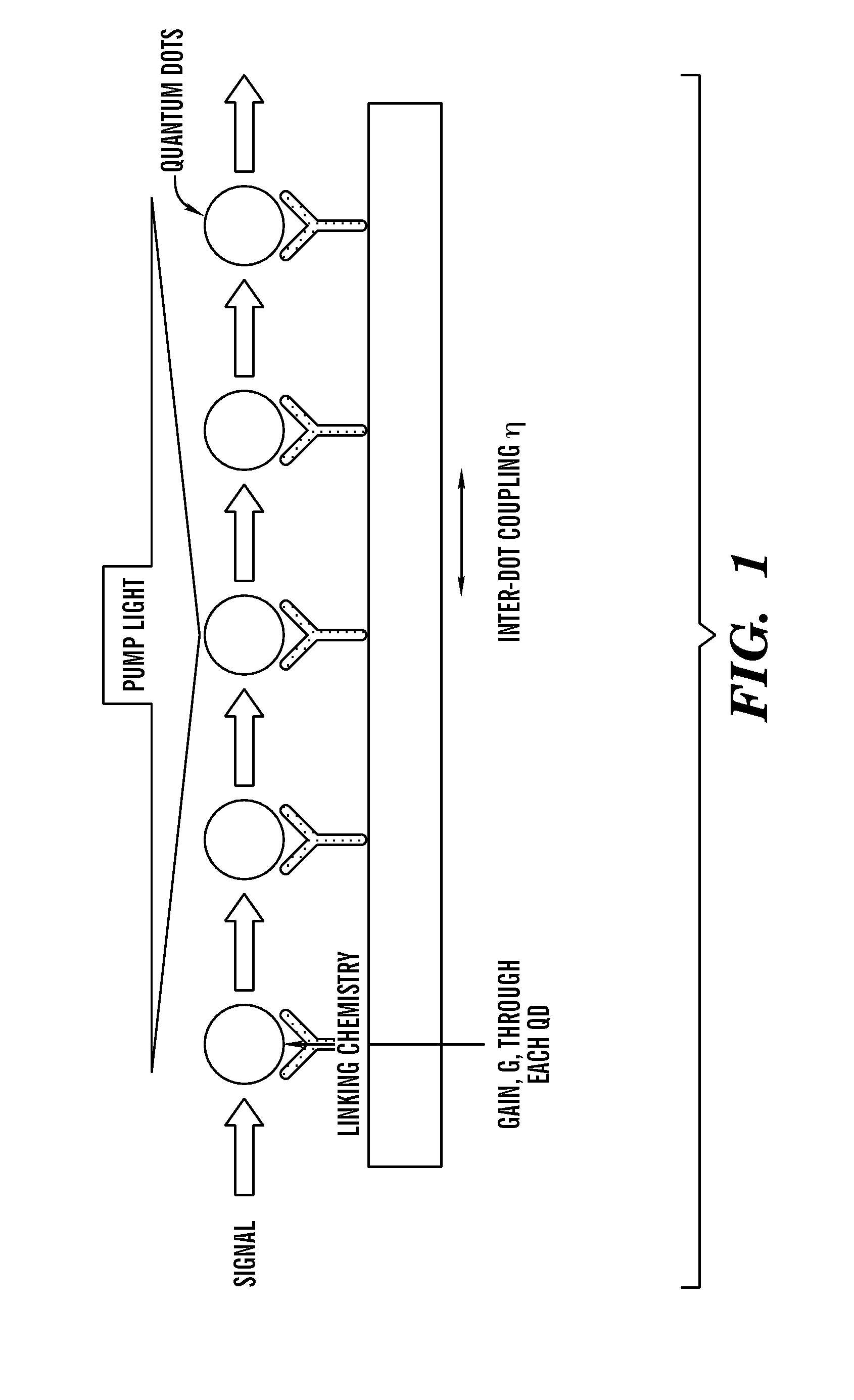
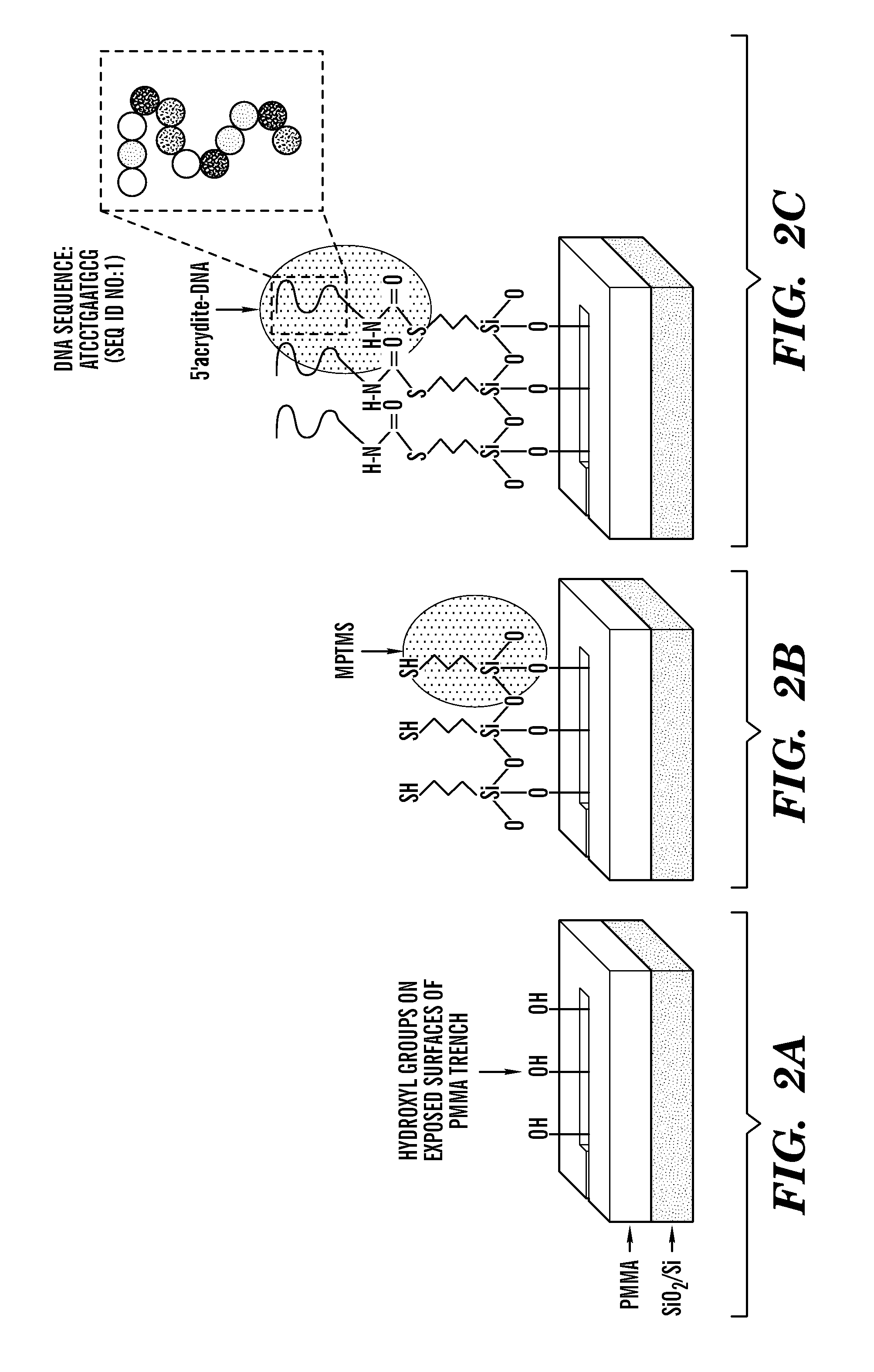
Multiple quantum dot waveguides
InactiveUS20080085088A1Threshold current densityReduced propagation lossLaser detailsNanoopticsSignal lightGain
The present invention relates to an assembly of multiple waveguides which includes a substrate and a plurality of waveguides positioned on said substrate at locations effective to suppress cross-talk between different waveguides. The plurality of waveguides each comprise an elongate array of quantum dots extending between sets of first and second locations on the substrate. The waveguides are positioned to receive: (1) pumped light uniformly applied to the array to produce electron-hole pairs and to enable optical gain and (2) signal light at the first location to trigger an emission from the quantum dot at the first location and transmission of photons along the array to the second location. A light transmission system which includes this assembly as well as methods of making and using the assembly are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Semiconductor optical modulator
ActiveUS20090034904A1Excellent characteristicOperates stablyOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsOptical modulatorVoltage
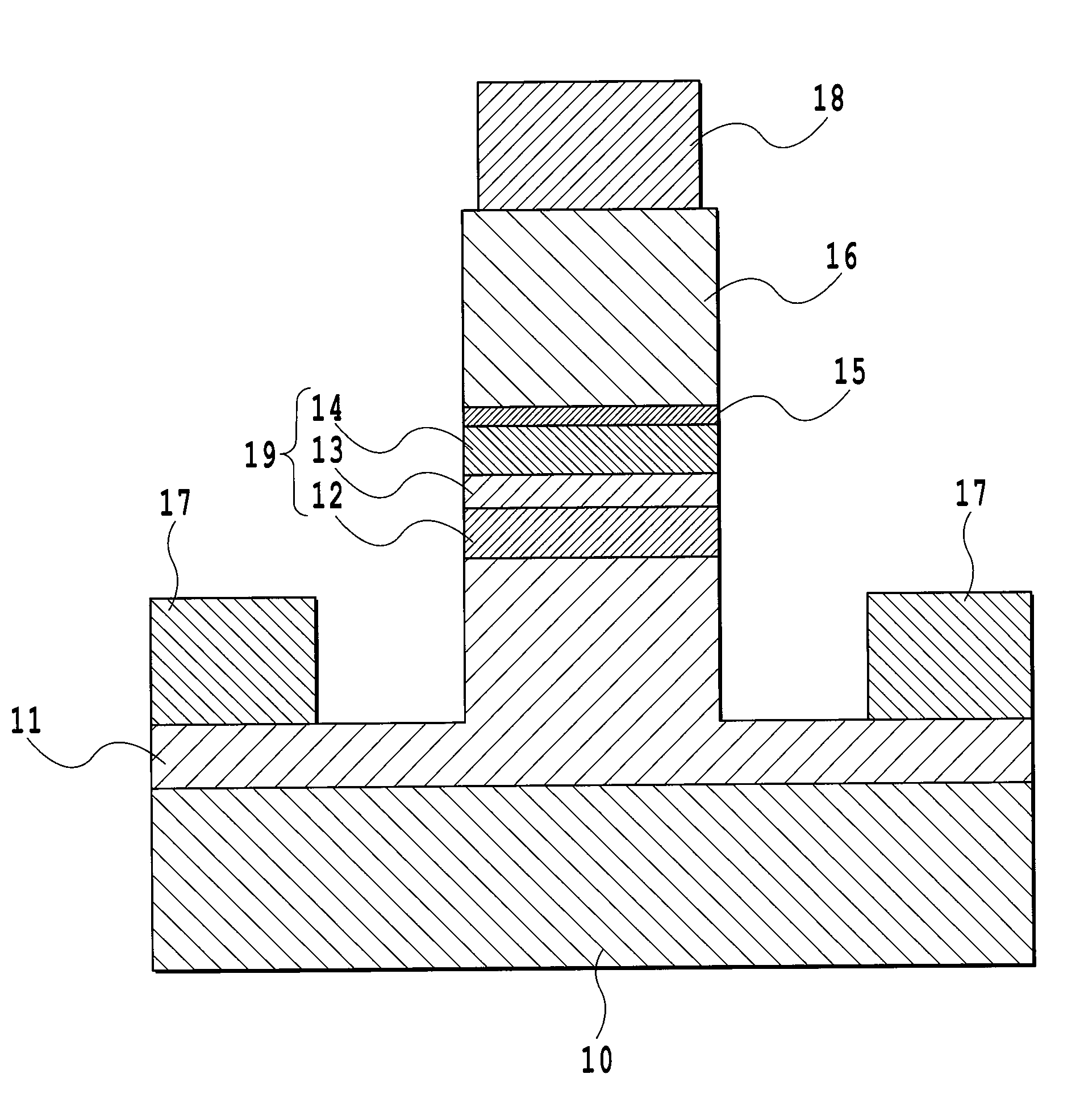
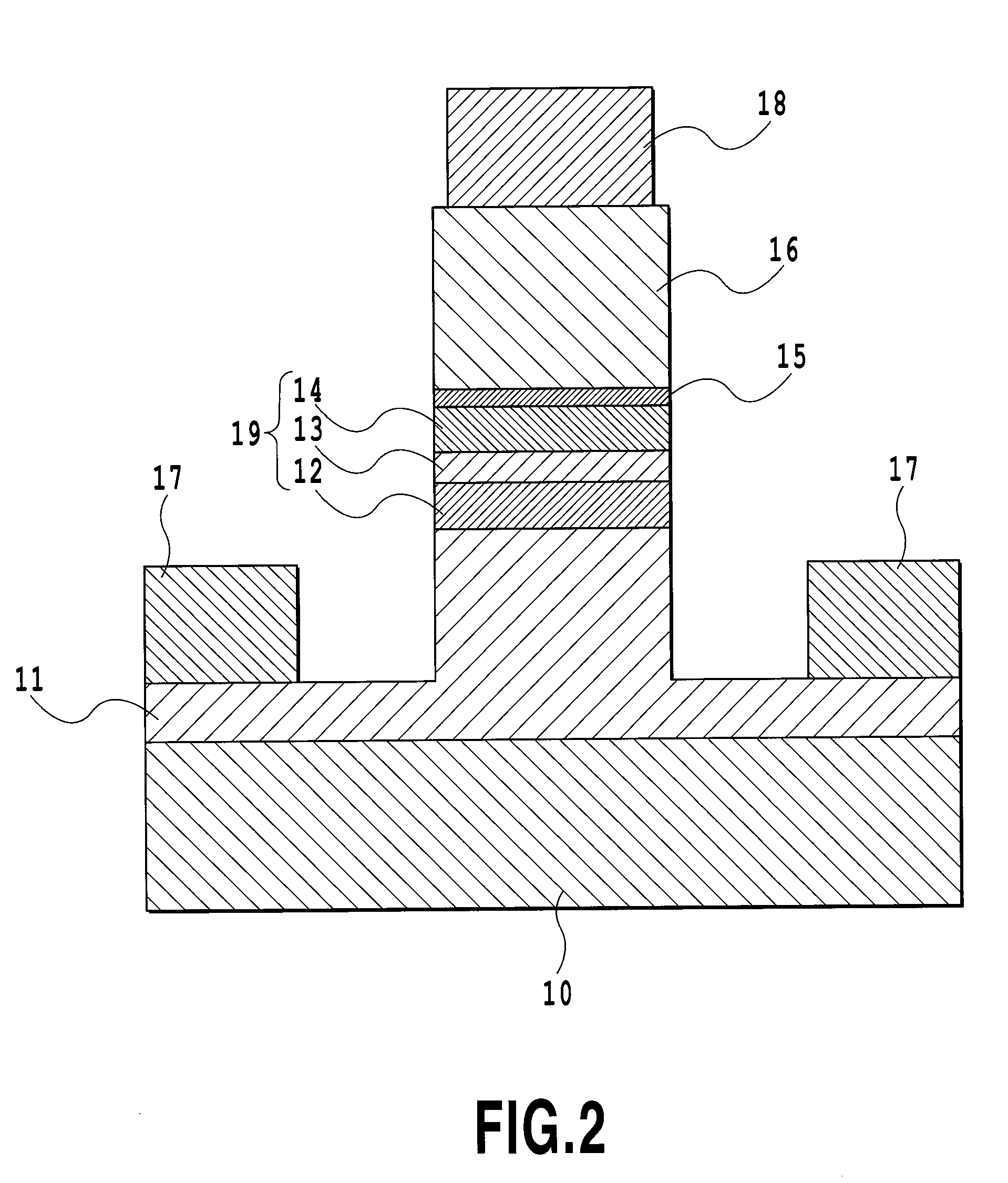
There is provided a semiconductor optical modulator capable of performing a stable operation and having an excellent voltage-current characteristic to an electric field while exhibiting the characteristic of a semiconductor optical modulator with an n-i-n structure. The semiconductor optical modulator includes a waveguide structure that is formed by sequentially growing an n-type InP clad layer (11), a semiconductor core layer (13) having an electro-optic effect, a p-InAlAs layer (15), and an n-type InP clad layer (16). An electron affinity of the p-InAlAs layer (15) is smaller than an electron affinity of the n-type InP clad layer (16). In the waveguide structure having such a configuration, a non-dope InP clad layer (12) and a non-dope InP clad layer (14) may be respectively provided between the n-type InP clad layer (11) and the semiconductor core layer (13), and between the semiconductor core layer (13) and the p-InAlAs layer (15).
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method of producing polymer optical waveguide
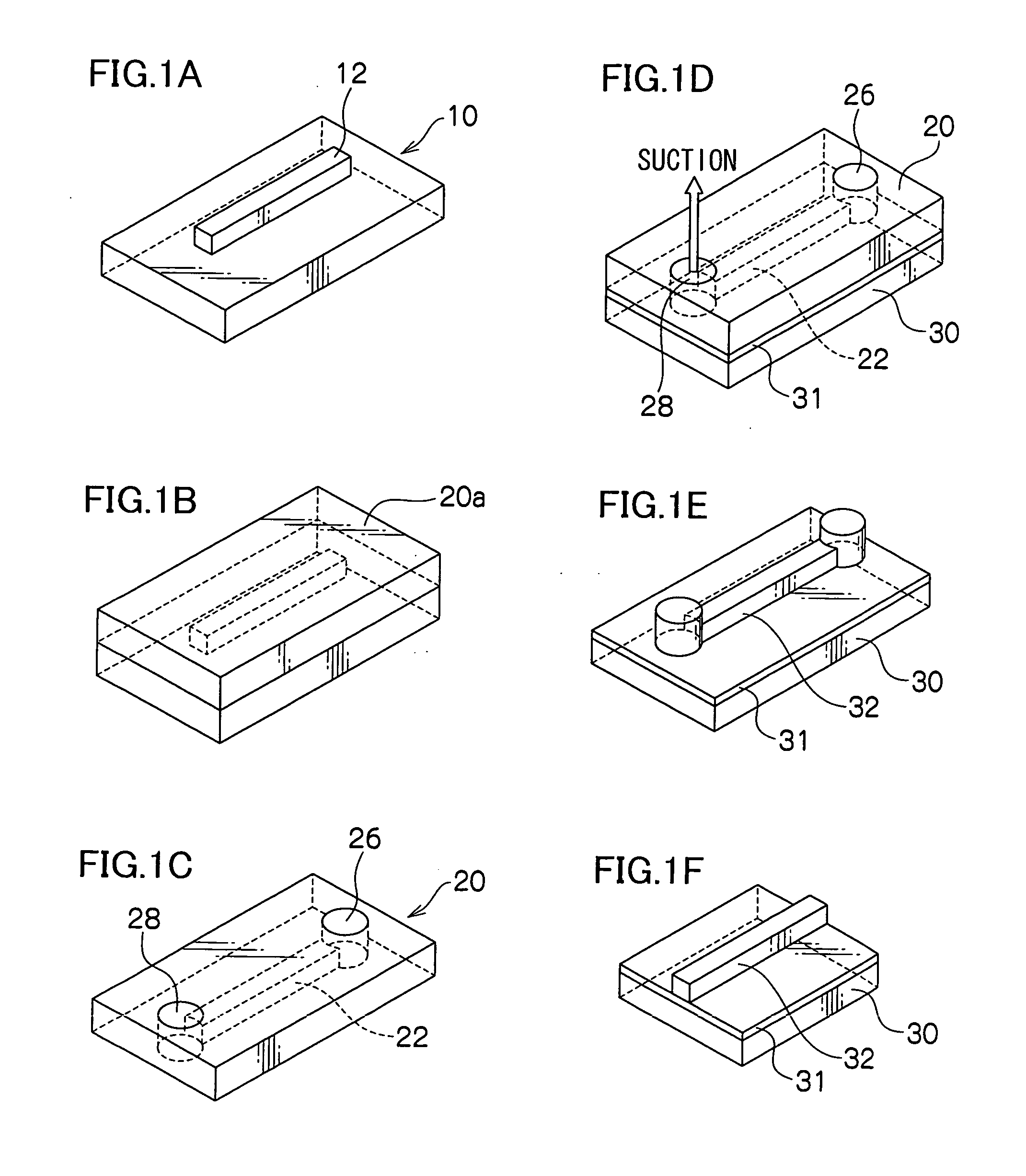
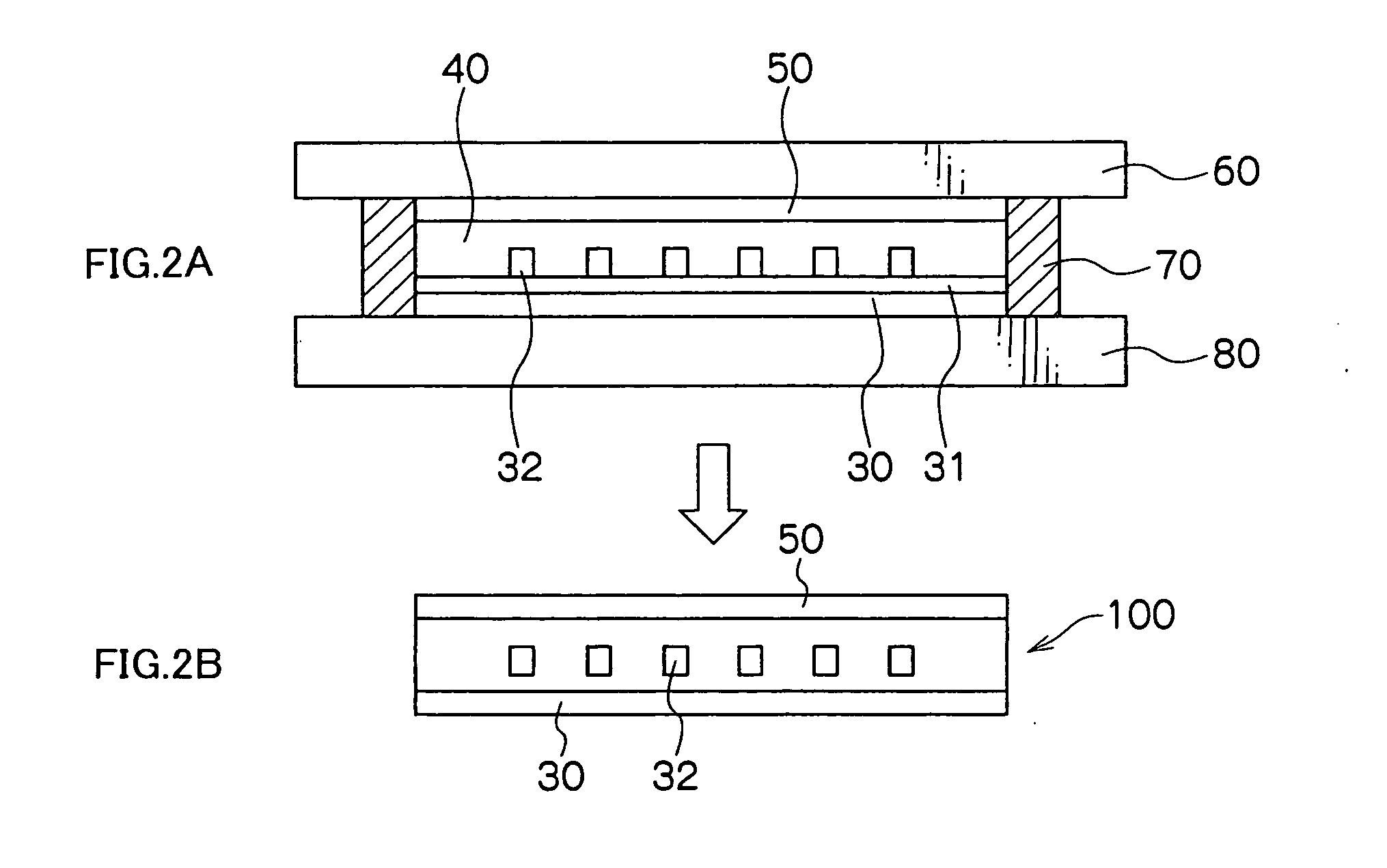
InactiveUS20050158003A1Low costModest loss in propagationOptical articlesOptical waveguide light guideFilm basePolymer optical waveguide
A method of producing a polymer optical waveguide, including: preparing a mold; preparing a lower film base material; introducing a core-forming curable resin into a first through-hole of the mold with which the lower film base material is brought into close contact while sucking the concave portion of the mold from a second through-hole under reduced pressure to introduce the core-forming curable resin into the concave portion of the mold; curing the core-forming curable resin which has been introduced; removing the mold from the lower film base material; providing a clad-forming curable resin layer and an upper film base material, the clad-forming curable resin layer being sandwiched between the lower film base material, on which the core is formed, and the upper film base material; and curing the clad-forming curable resin layer to fix the lower film base material and the upper film base material.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Opto-electric hybrid module and manufacturing method thereof
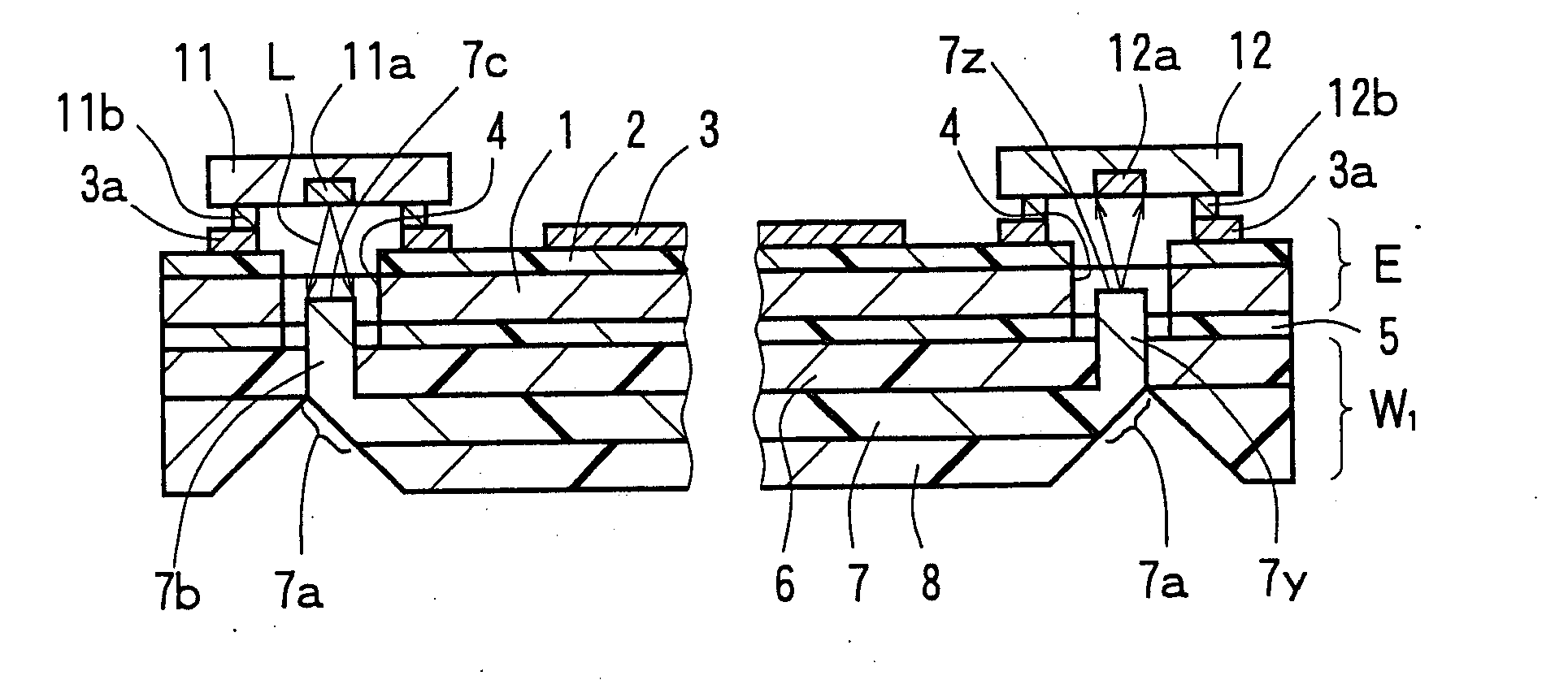
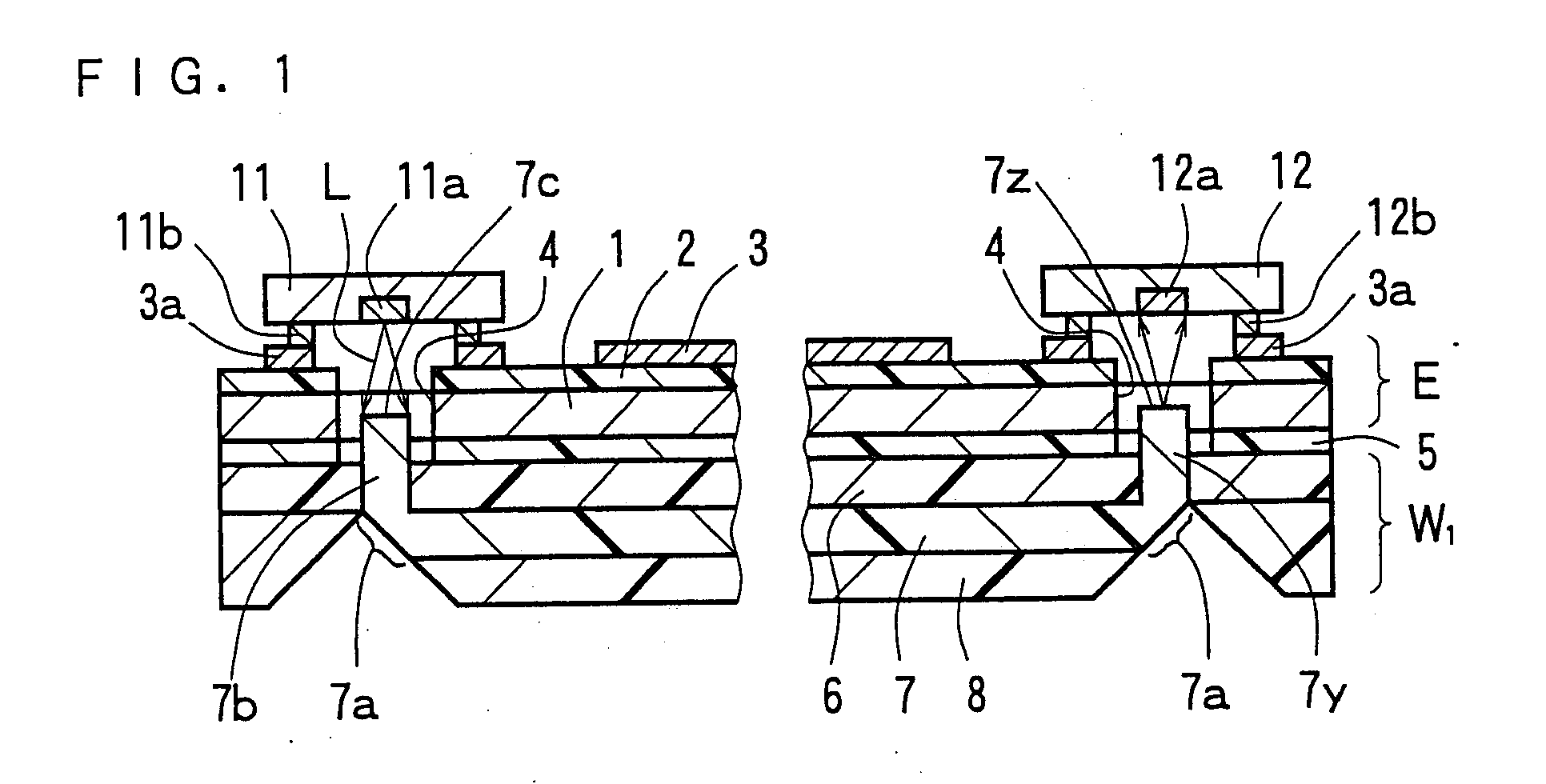
ActiveUS20090297096A1Reduced propagation lossDistanceCircuit optical detailsSolid-state devicesLight reflectionLight beam
An opto-electric hybrid module capable of reducing the propagation loss of light beams, and a manufacturing method thereof. An opto-electric hybrid module in which a light-emitting element and a light-receiving element are mounted on the front surface side of an electric circuit board E, and an optical waveguide W1 is bonded to the back surface side thereof. The optical waveguide W1 includes a core having opposite end portions formed as light reflection portions. Portions of the core near the opposite end portions are formed as extensions extending from the light reflection portions toward the light-emitting element and the light-receiving element. The extensions and are positioned in through holes for light propagation formed in the electric circuit board E, and have distal end surfaces and in face-to-face relationship with a light-emitting portion of the light-emitting element and a light-receiving portion of the light-receiving element, respectively.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
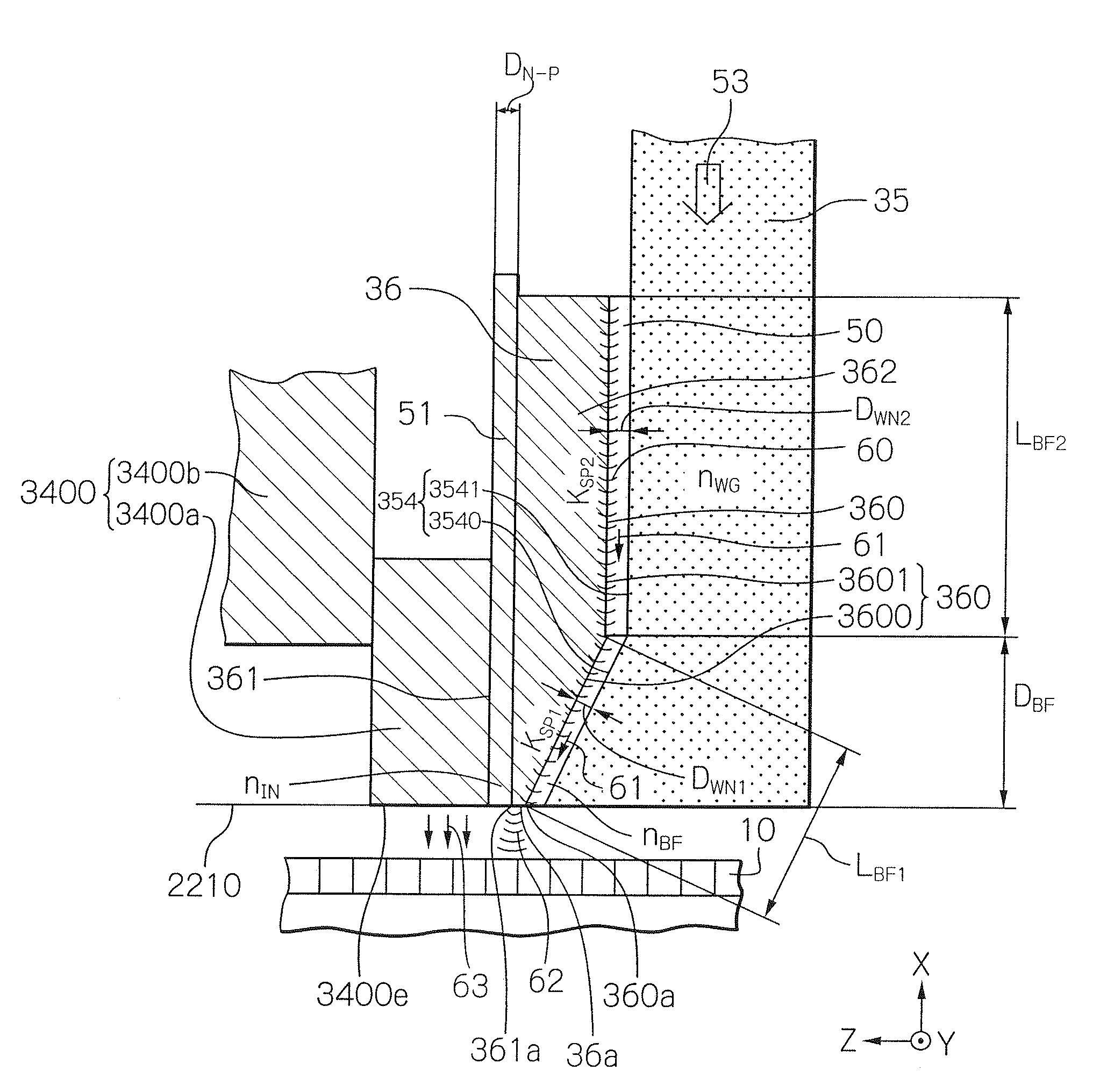
Near-Field Light Generating Element And Method For Forming The Element
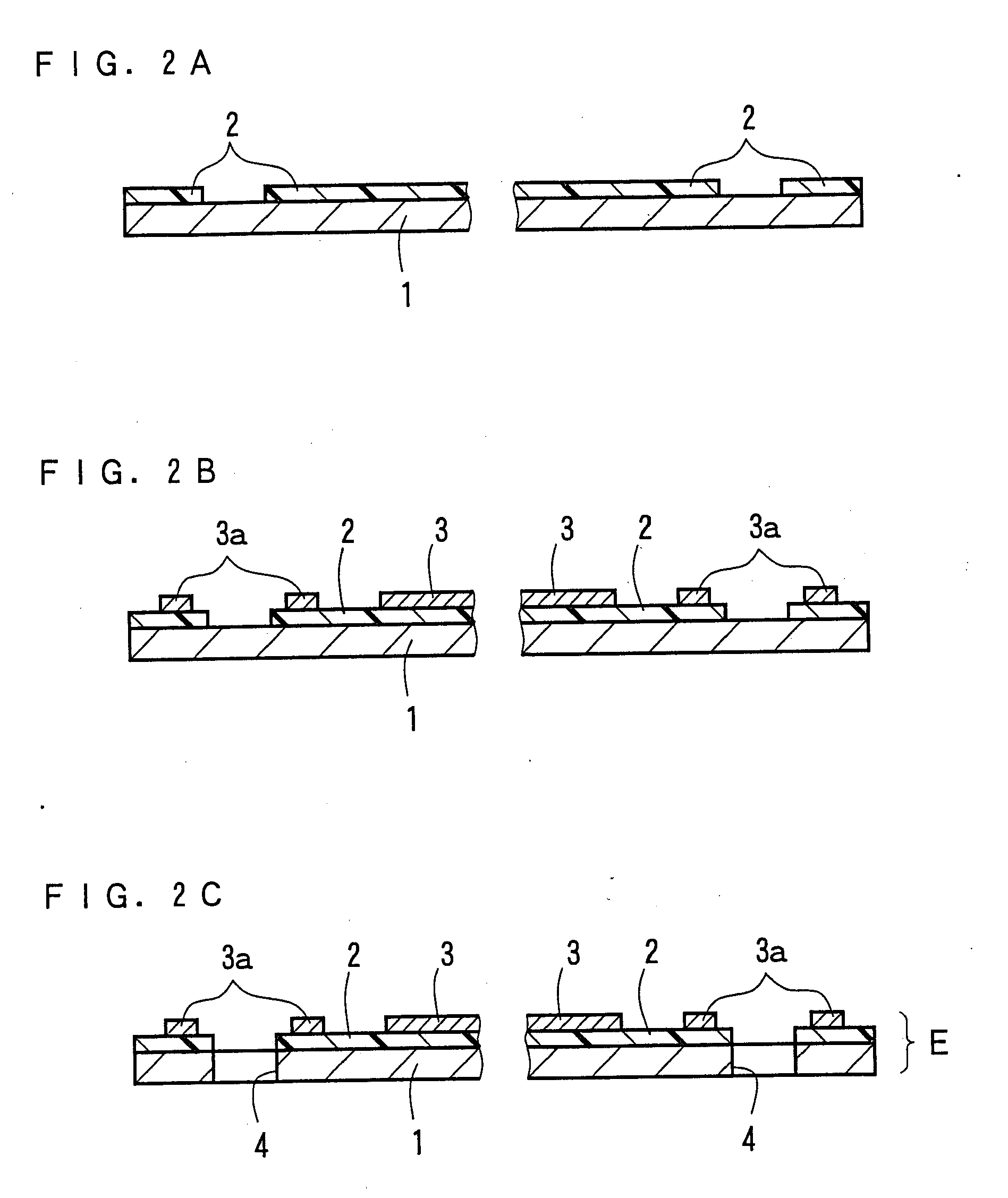
ActiveUS20100142079A1Suppression of distortionSuppress unevennessDecorative surface effectsRecord information storageDistortionPhysics
Provided is a method for forming a near-field light generating element, which is capable of sufficiently suppressing the unevenness of a waveguide surface and the distortion within the waveguide. The forming method comprises the steps of: forming a first etching stopper layer on a lower waveguide layer; forming a second etching stopper layer; forming, on the second etching stopper layer, a plasmon antenna material layer; performing etching with the second etching stopper layer used as a stopper, to form a first side surface of plasmon antenna; forming a side-surface protecting mask so as to cover the first side surface; and performing etching with the first and second etching stopper layers used as stoppers, to form the second side surface. By providing the first and second etching stopper layer, over-etching can be prevented even when each etching process takes enough etch time, which allows easy management of etching endpoints.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical functional devices
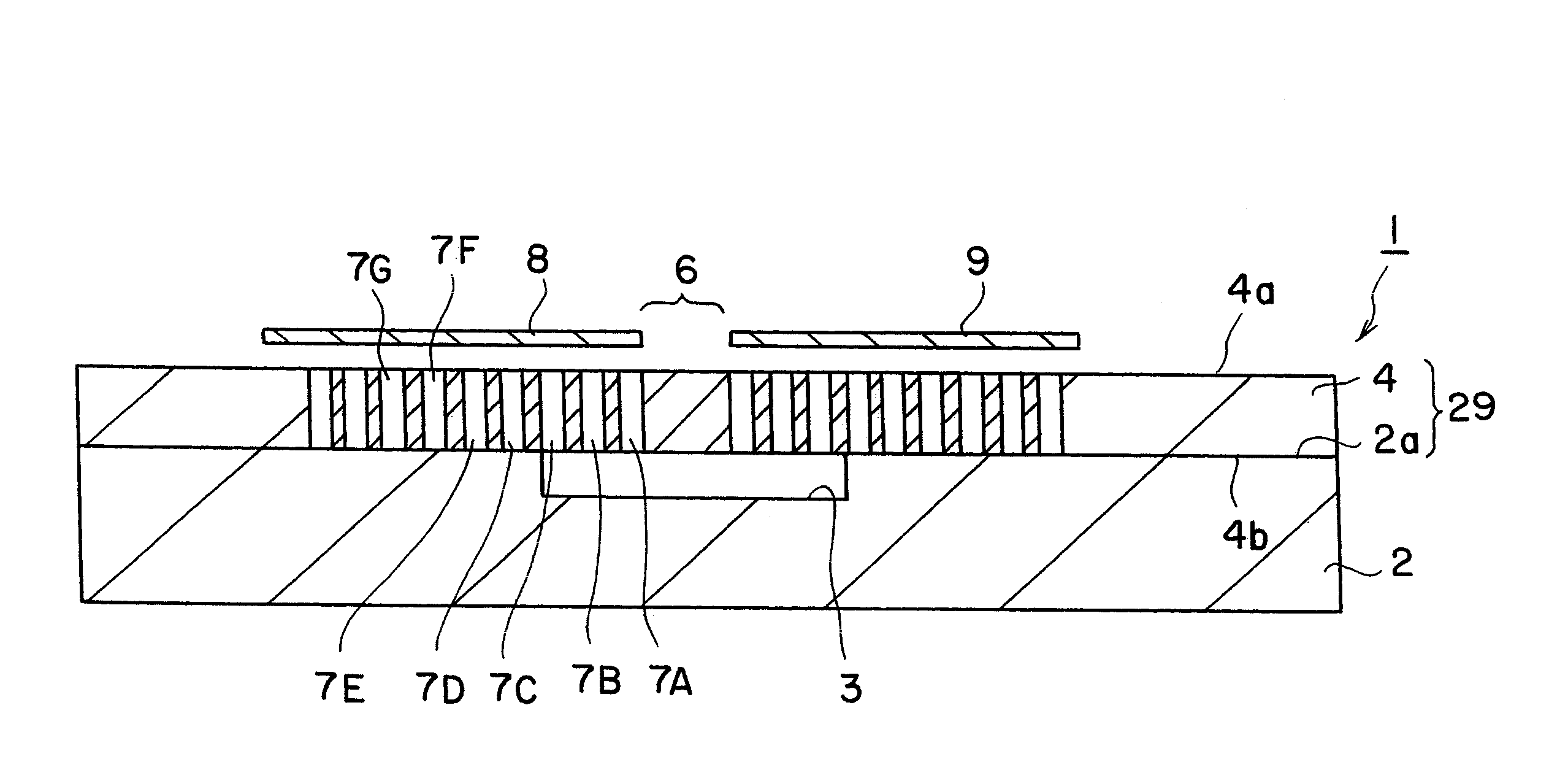
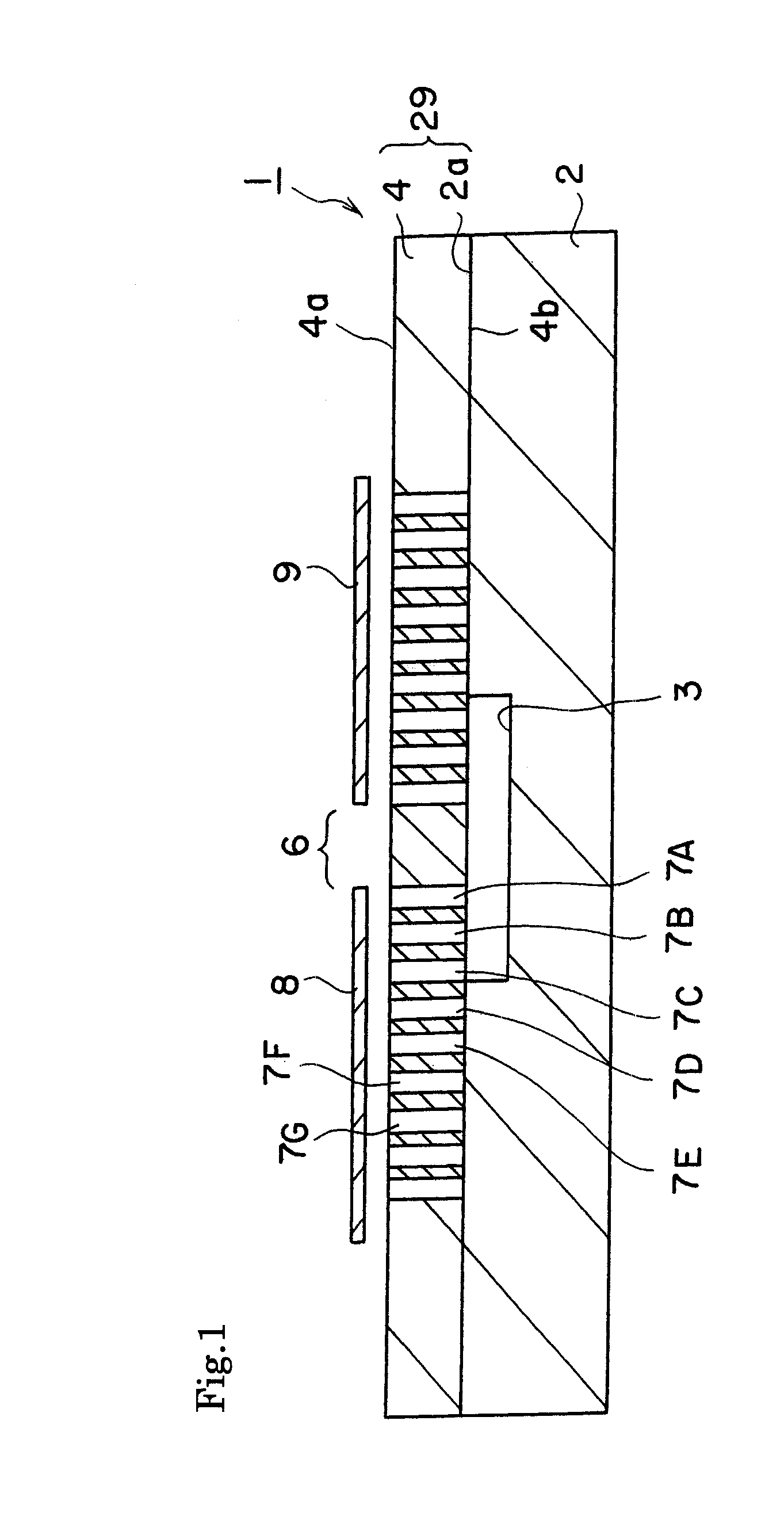
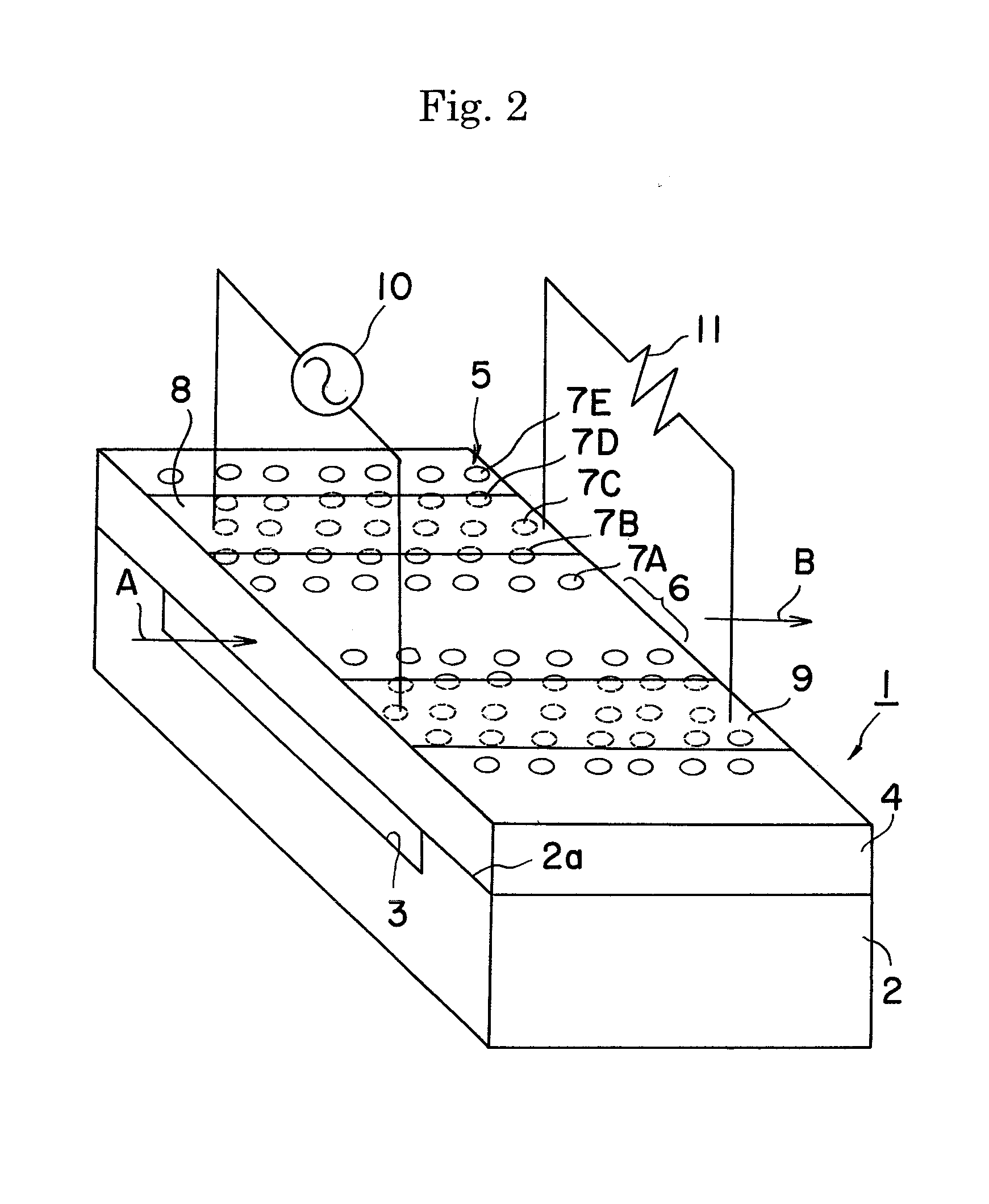
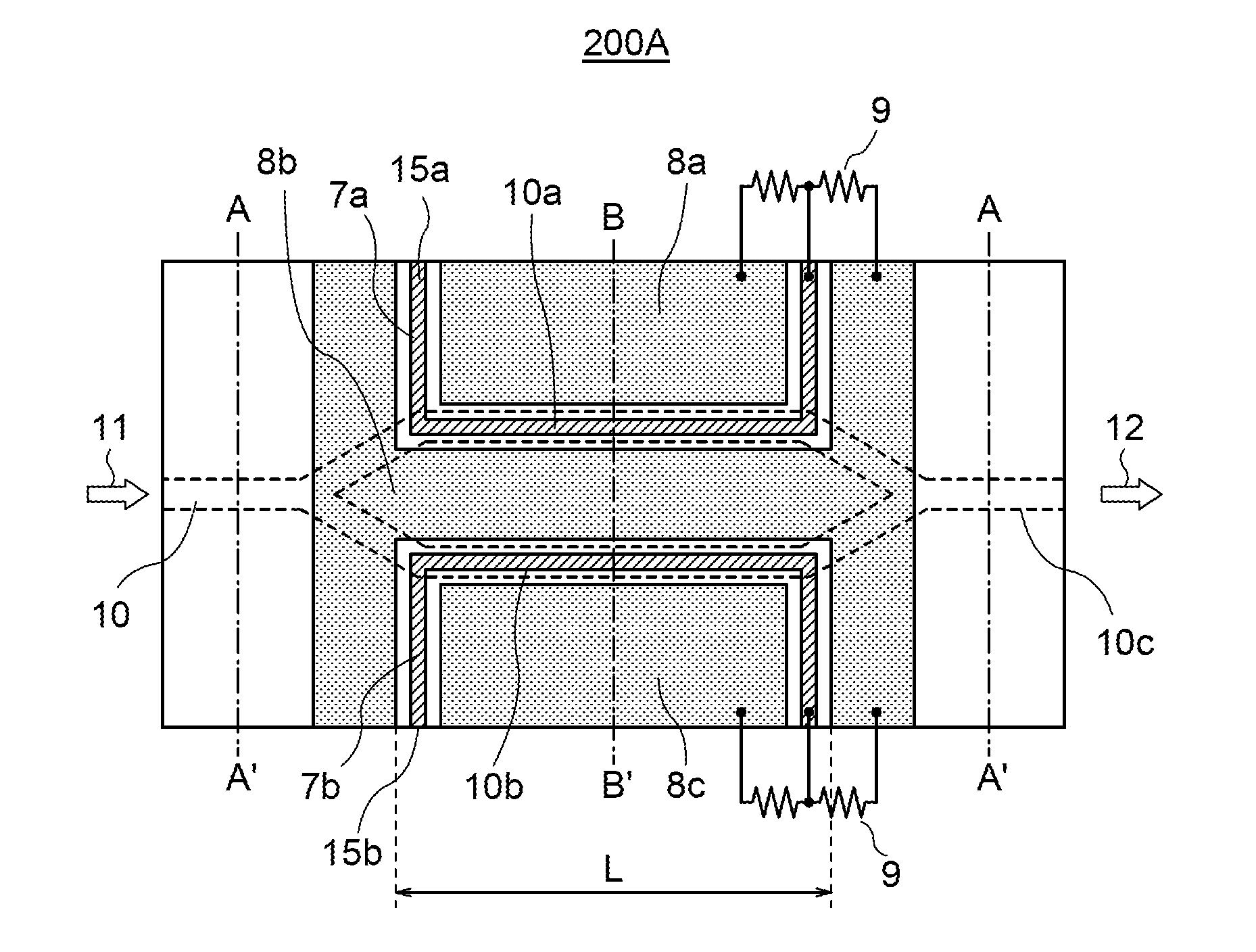
ActiveUS20080050082A1Raises effective refractive index NmPrevent leakageOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsPhotonic crystalDielectric layer
An optical functional device 1 has a slab type two-dimensional photonic crystal layer 29. The layer 29 has a dielectric layer 4 and a plurality of lattice columns 5 each comprising dielectric pillars. A waveguide portion 6 is provided in the photonic crystal layer 29. A ground electrode 8 and a signal electrode 9 are formed on the dielectric layer 4 for applying a modulating voltage on light propagating in the waveguide portion 6. A layer 2 of a high dielectric constant is laminated on the dielectric layer 4. A low dielectric portion is formed direct under the waveguide portion 6 and the lattice columns 7a, 7B and 7C of at least first, second and third orders in distance with respect to said waveguide portion.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
High efficiency wavelength converters
InactiveUS7170671B2Efficiently obtainedAvoid surface damageAfter-treatment detailsBy pulling from meltEnergy transferHigh rate
A method is provided for forming a waveguide region within a periodically domain reversed ferroelectric crystal wherein the waveguide region has a refractive index profile that is vertically and horizontally symmetric. The symmetric profile produces effective overlapping between quasi-phasematched waves, a corresponding high rate of energy transfer between the waves and a symmetric cross-section of the radiated wave. The symmetric refractive index profile is produced by a method that combines the use of a diluted proton exchange medium at a high temperature which produces a region of high index relatively deeply beneath the crystal surface, followed by a reversed proton exchange which restores the original crystal index of refraction immediately beneath the crystal surface.
Owner:HC PHOTONICS
Silicon-based electro-optic device
ActiveUS8532440B2Efficient connectionReduced propagation lossOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsZeroth orderMetal electrodes
In an electro-optic device, a stack structure including a first silicon layer of a first conductivity type and a second silicon layer of a second conductivity type has a rib waveguide shape so as to form an optical confinement area, and a slab portion of a rib waveguide includes an area to which a metal electrode is connected. The slab portion in the area to which the metal electrode is connected is thicker than a surrounding slab portion. The area to which the metal electrode is connected is set so that a range of a distance from the rib waveguide to the area to which the metal electrode is connected is such that when the distance is changed, an effective refractive index of the rib waveguide in a zeroth-order mode does not change.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FOUNDRY PTE LTD +1
Slot Waveguide with Structural Modulation
ActiveUS20190067830A1Reduced propagation lossLarge mode overlapIndividually energised antenna arraysElectromagnetic transmittersSlot-waveguideElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
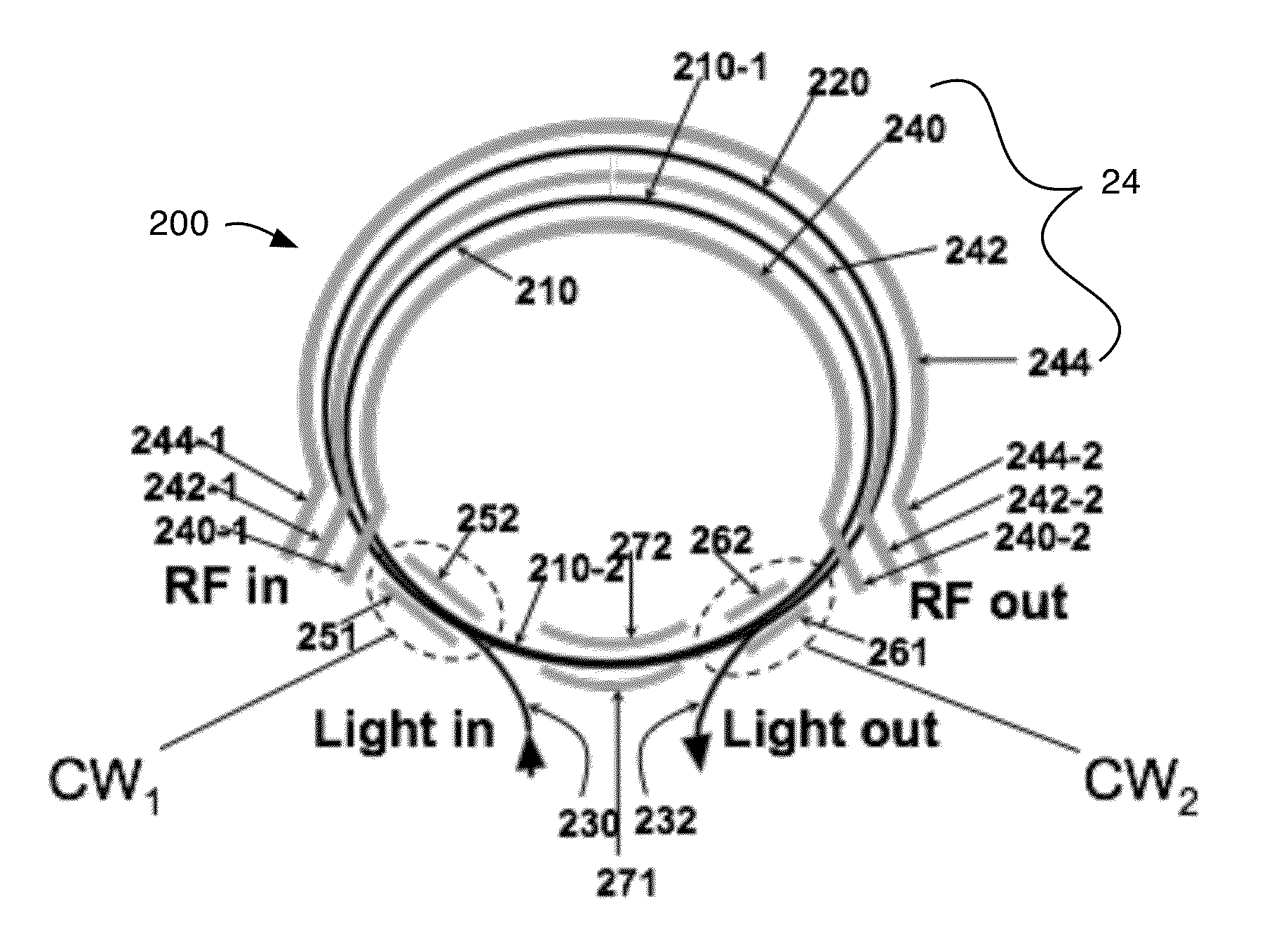
Re-circulation enhanced electro-optic modulator
ActiveUS9291837B1Wide modulation bandwidthImprove efficiencyNon-linear opticsMach–Zehnder interferometerEngineering
An optical modulator includes a waveguide Mach-Zehnder interferometer having a first and a second input and a first and a second output, a feedback waveguide segment connecting the second output with the second input, and a traveling-wave electrode; wherein the Mach-Zehnder interferometer, feedback waveguide segment and traveling-wave electrode are substantially arranged at or adjacent the perimeter of a smooth curve defining a closed geometric figure, the traveling-wave electrode extending along at least 50% of the length of the perimeter of the smooth curve.
Owner:HRL LAB
Optical device integrated head
InactiveUS7921436B2Decreasing the former optical lossSmall sizeCombination recordingRecord information storageWaveguideLaser
An optical device integrated head having high light utilizing efficiency by decreasing the propagation loss caused from an optical source to a recording medium, conducting by mounting according to compact active alignment method for efficiently guiding a light generated from a laser device to the top end of a head, in which a light source device mounted on a submount has a mirror portion having an inclinated surface to at least a portion of one edge thereof for reflecting an output light from the optical source device at the inclinated surface, a structural member including a lens structure for further allowing a light to pass through the submount, and an optical waveguide disposed passing through a slider for mounting the submount, and the optical source and the slider are positioned by using active alignment of light in a chip-on carrier structure having the optical source device mounted on the submount.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical waveguide element and optical modulator using the same
ActiveUS20170052424A1Effective refractive indexReduced propagation lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideLength waveLithium niobate
Disclosed herein is an optical waveguide element that includes a substrate and a waveguide layer formed on the substrate and comprising lithium niobate. The waveguide layer has a slab part having a predetermined thickness and a ridge part protruding from the slab part. The maximum thickness of the slab part is 0.05 times or more and less than 0.4 times a wavelength of a light propagating in the ridge part.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Photonic bandgap fiber
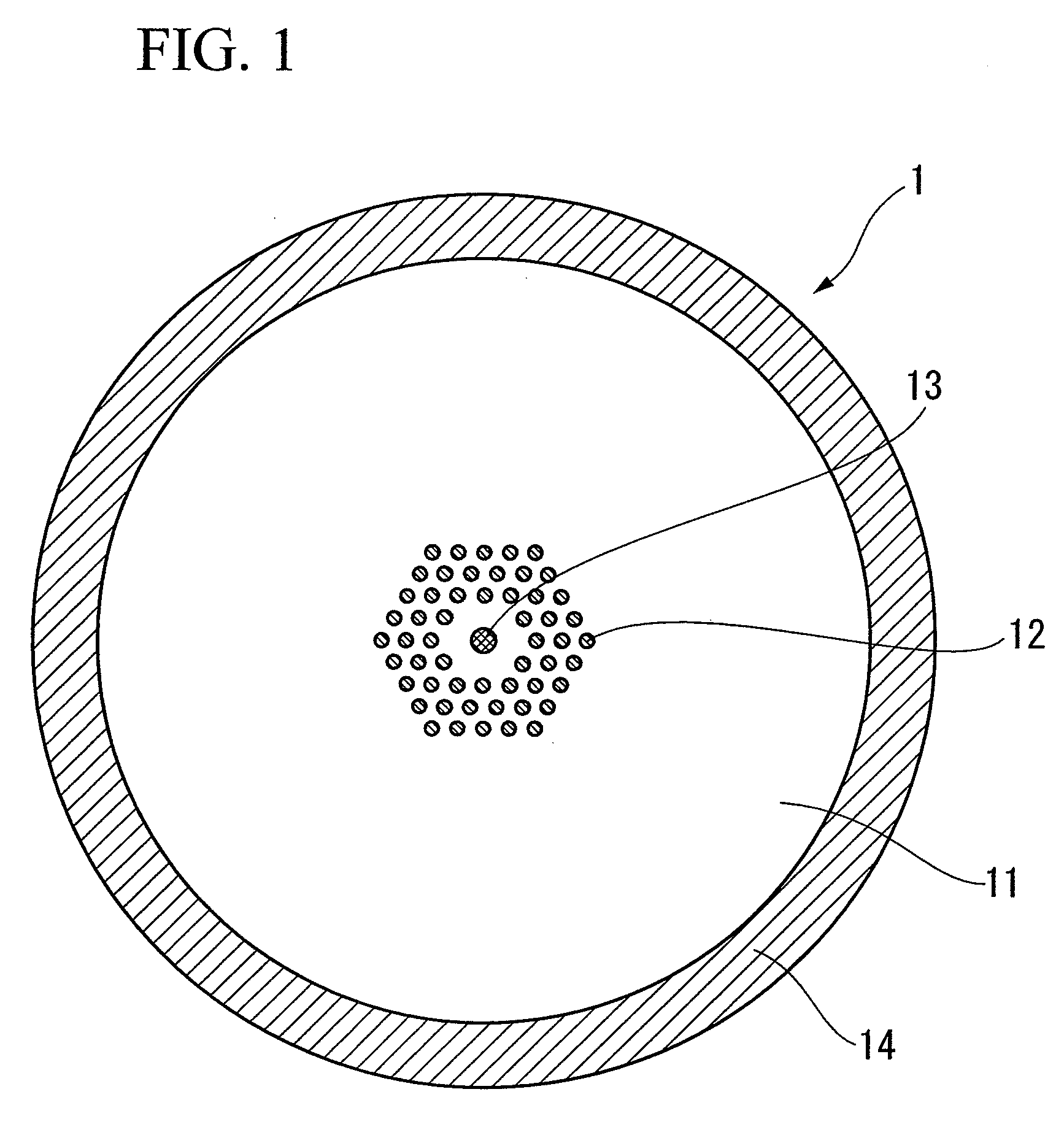
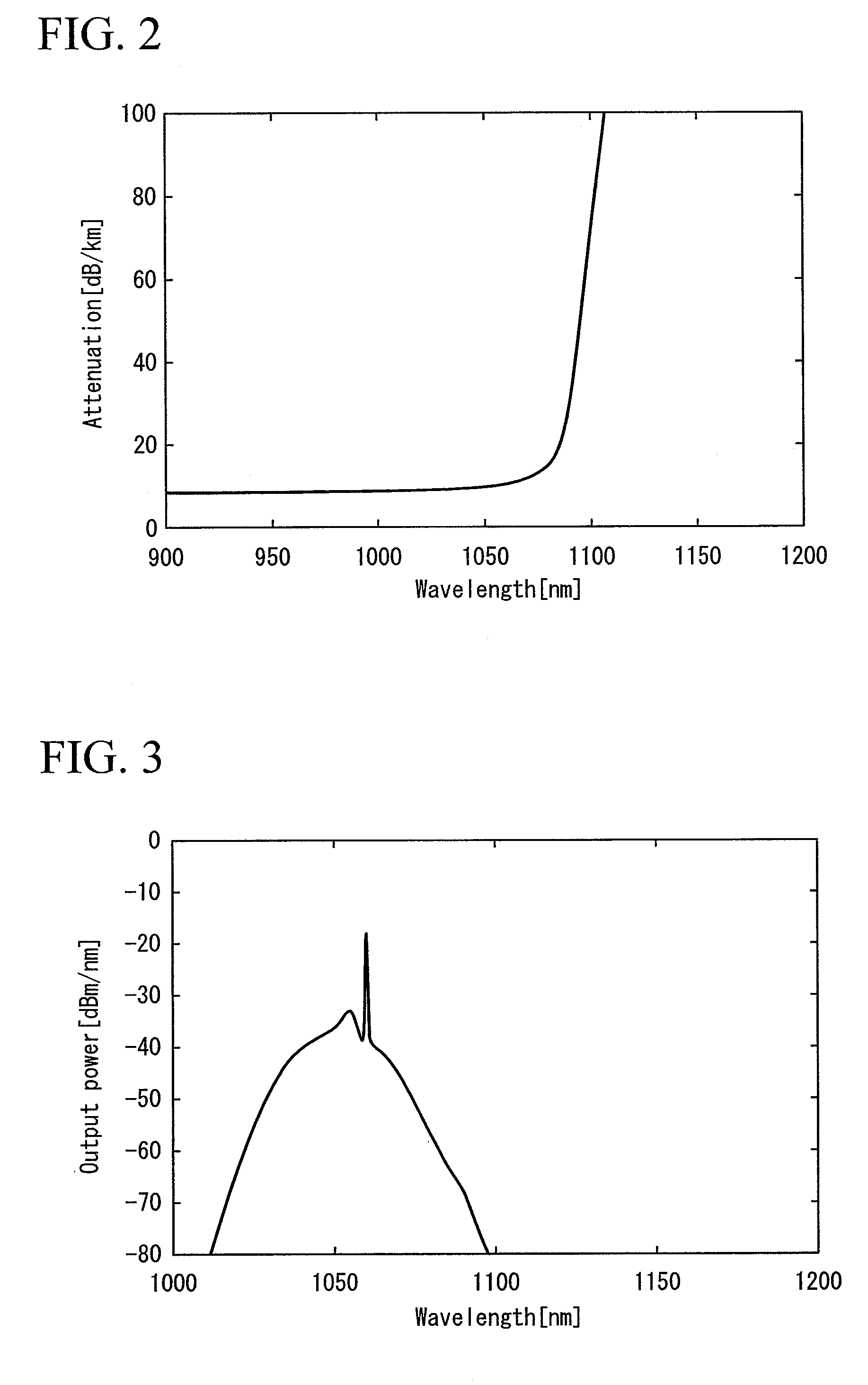
ActiveUS8035891B2Suppressing propagation of lightAccelerate emissionsLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
A photonic bandgap fiber includes a core and a cladding that surrounds the core. In this photonic bandgap fiber, high refractive index portions which have a refractive index higher than that of a medium of the cladding are provided in the cladding so as to form a triangular lattice structure with a lattice constant Λ, and the refractive index of the core is higher than the refractive index of the medium of the cladding and lower than the refractive index of the high refractive index portion. The coupling length between the core and the high refractive index portion that is closest to the core is longer than the coupling length between adjacent high refractive index portions, or a periodic structure formed by the high refractive index portions is not provided around the entirely of the area along the circumference of the core.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Image sensing device
InactiveCN101364261AAvoid diffractionAvoid crosstalkSolid-state devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer scienceImage sensing
An image sensing device is disclosed. The image sensing device comprises a plurality of image sensor units disposed separately and a plurality of wave guiding units. Each wave guiding unit is disposed on each corresponding image sensor unit. The image sensing device can avoid diffraction and crosstalk. In addition, since each interlayer distance is short, the effect to isolate beams and reduce propagation loss is reached to some degree.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
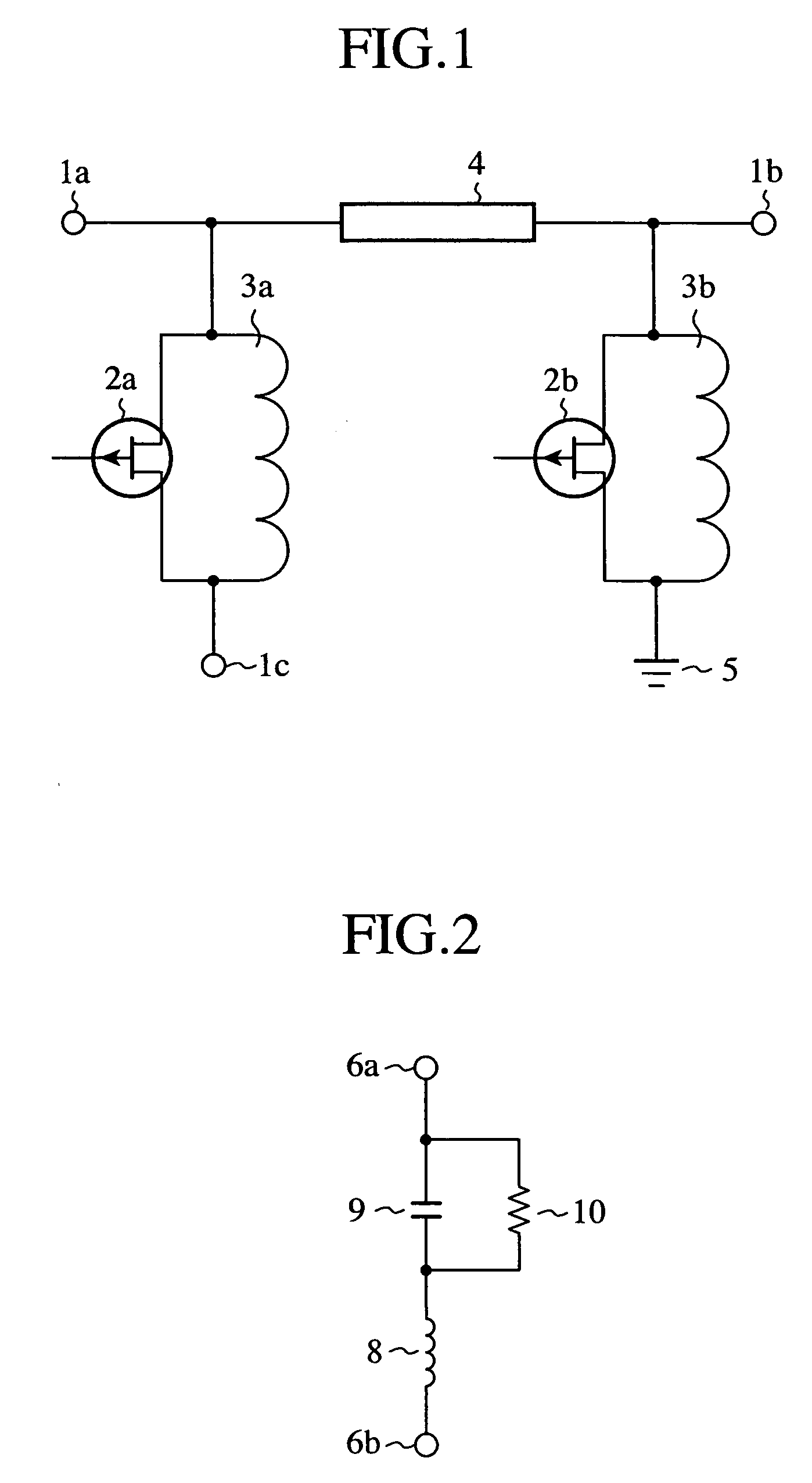
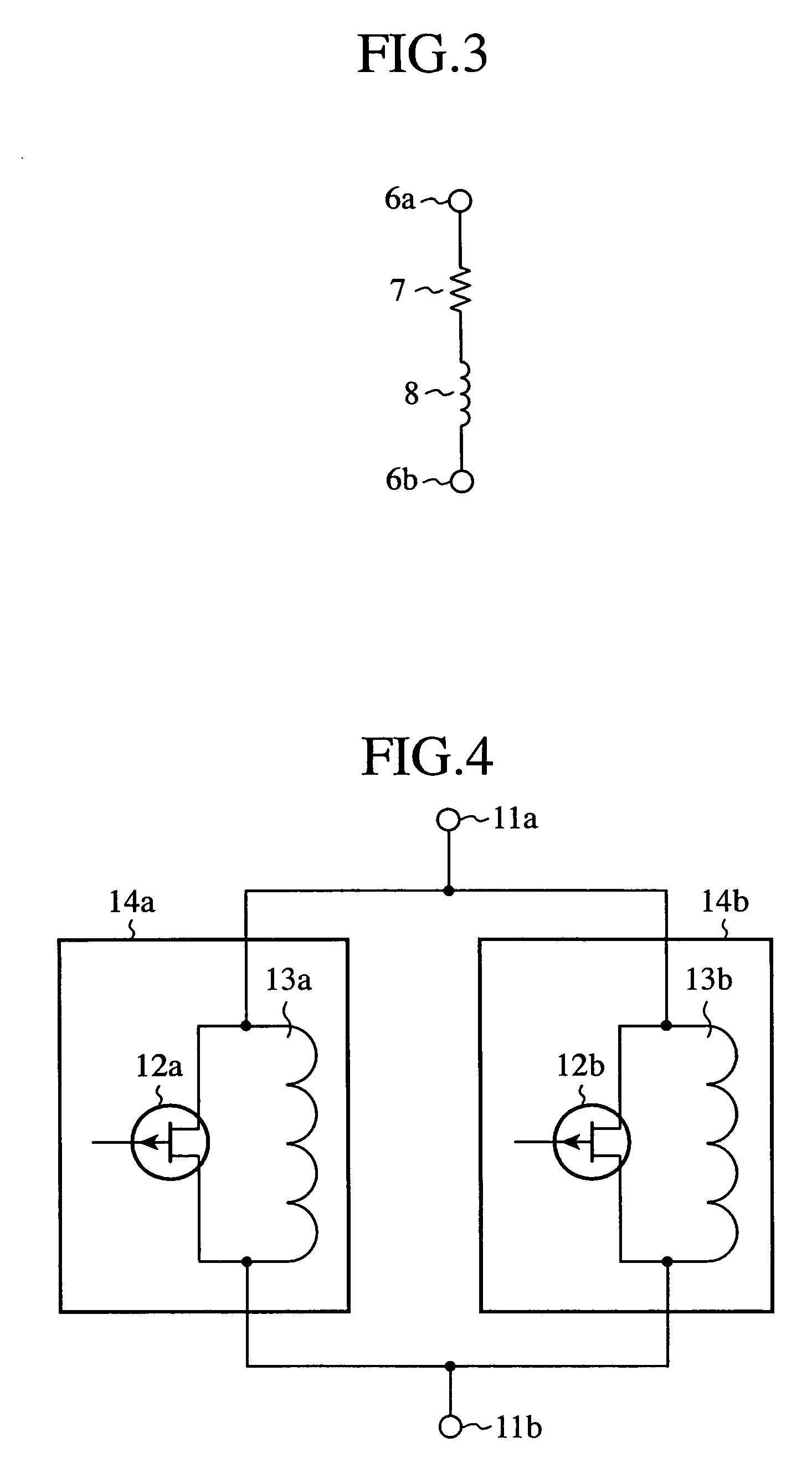
SPST switch, SPDT switch and MPMT switch
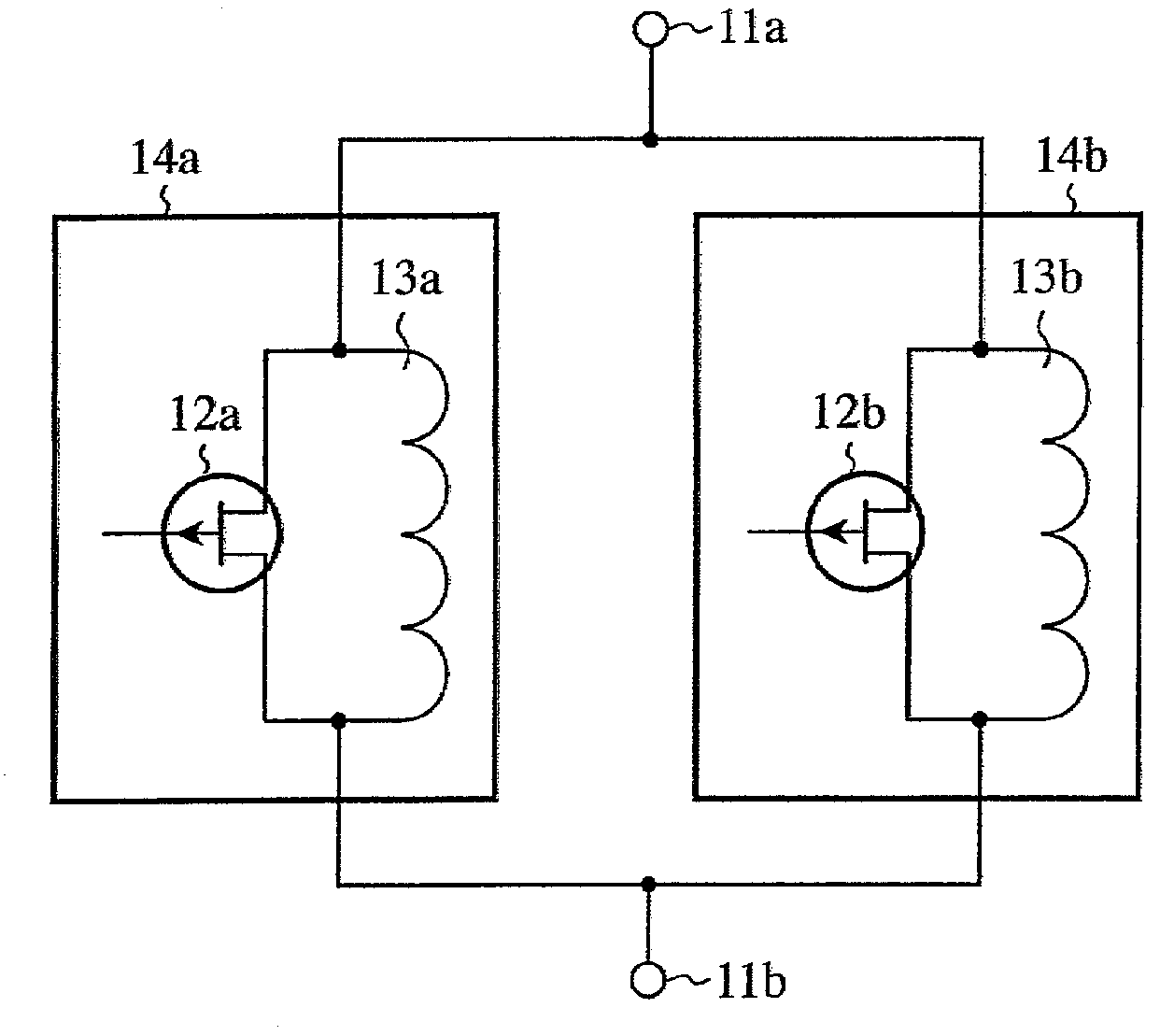
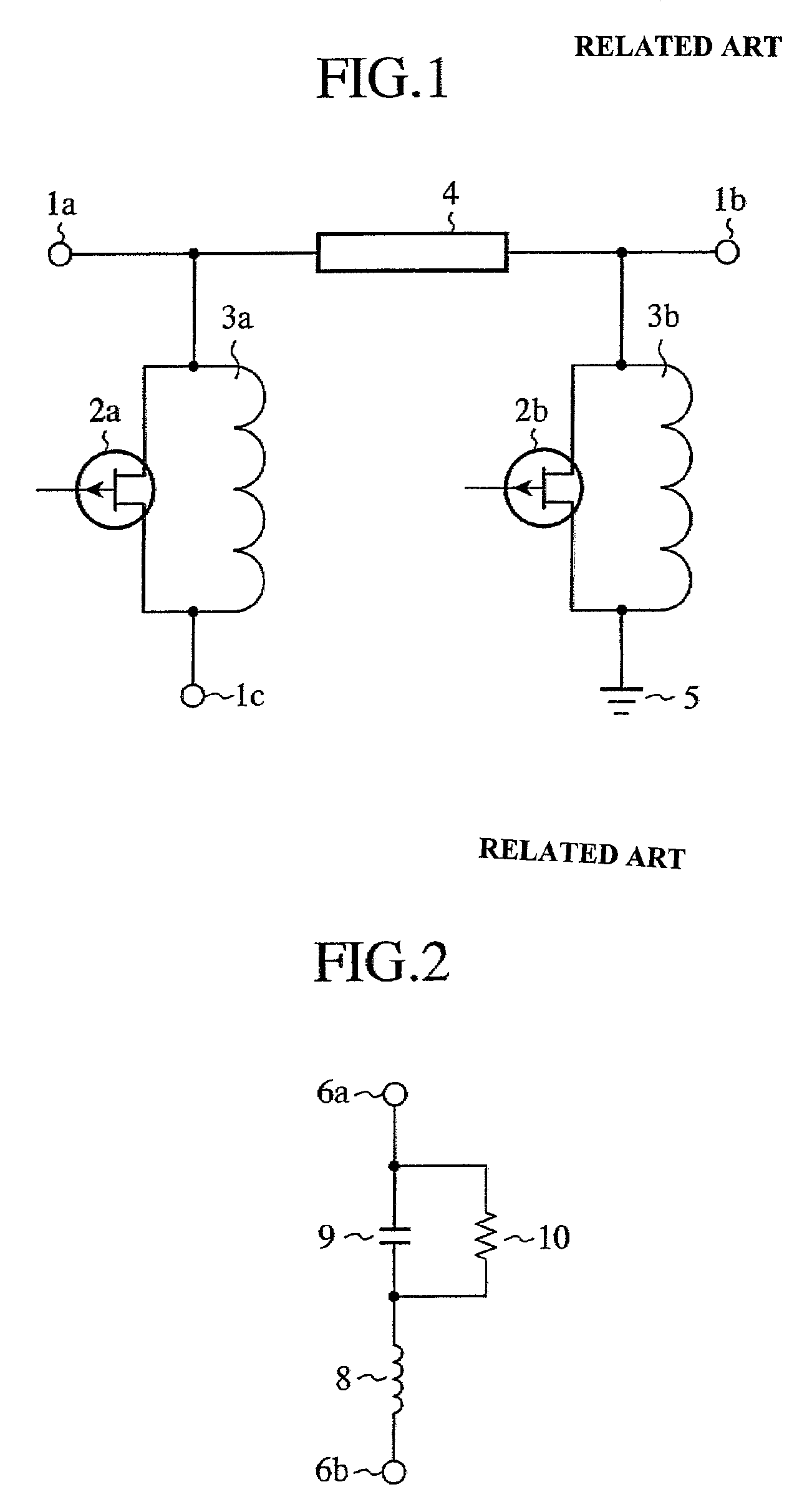
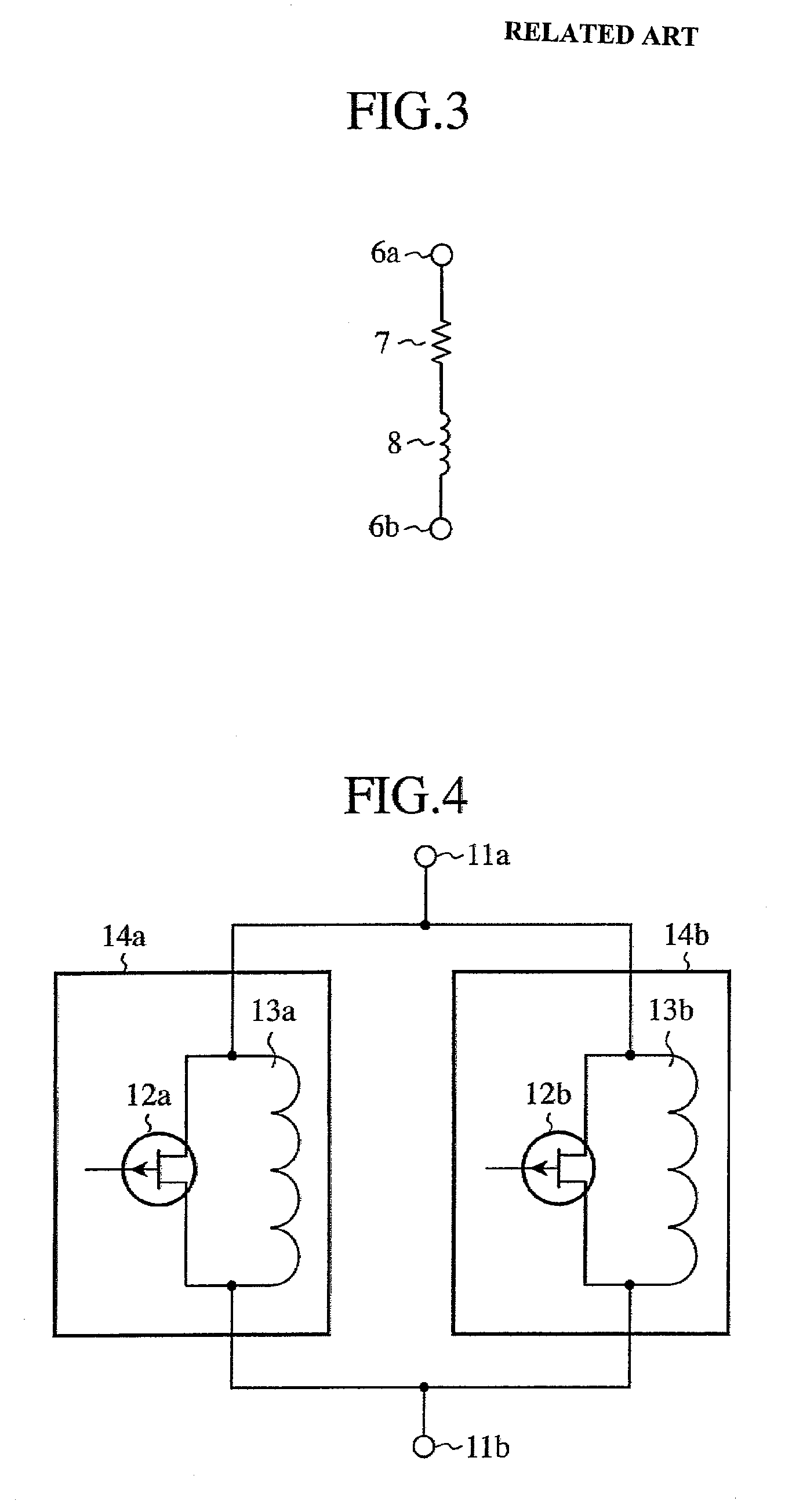
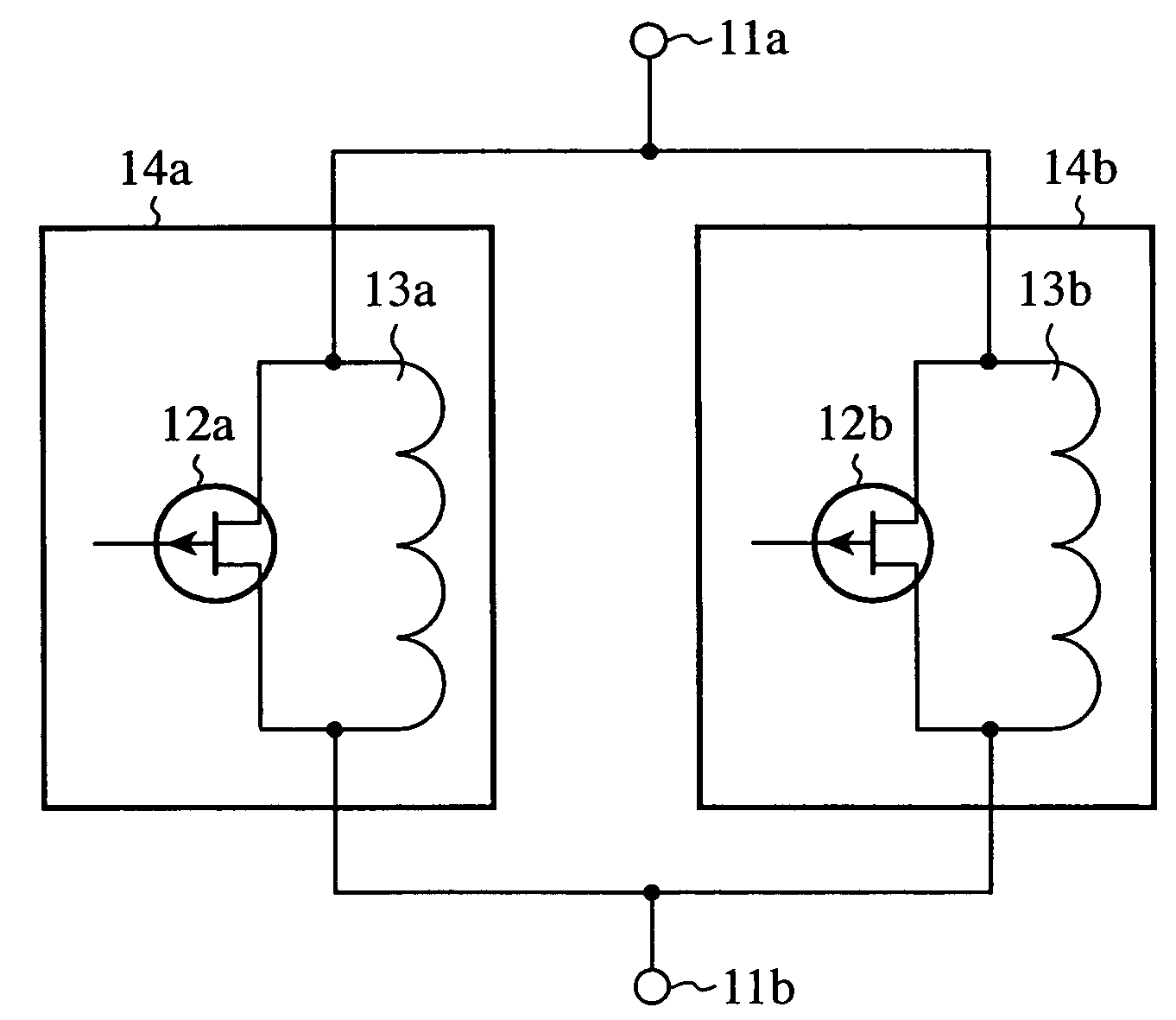
InactiveUS7633357B2Reduced propagation lossAvoid attenuationElectronic switchingCoupling devicesEngineeringInductor
A single pole single throw switch for controlling propagation of a high frequency signal between an input terminal (11a) and an output terminal (11b). First FET switches (14a, 14b) in which drains and sources of FETs (12a, 12b) are connected in parallel with inductors (13a, 13b) are connected in parallel. Each FET (12a, 12b) is switched between on state and off state by a voltage being applied to the gate thereof. At the frequency of the high frequency signal, each inductor (13a, 13b) connected with off capacitor of each FET (12a, 12b) resonates in parallel.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Optical device and fabrication method and apparatus for the same
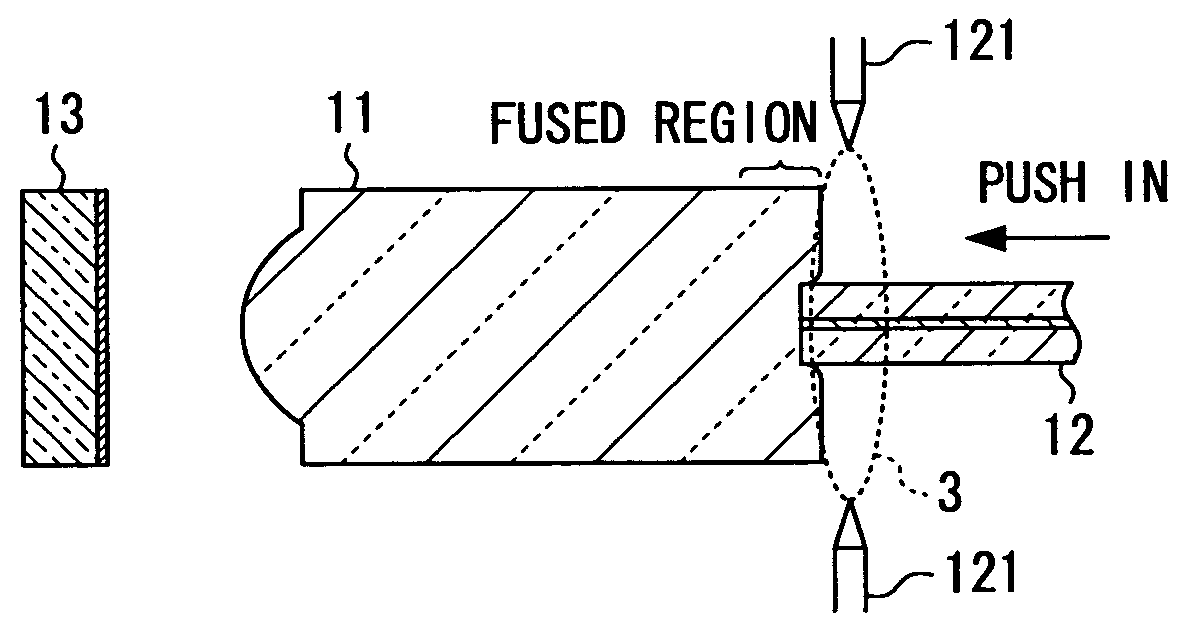
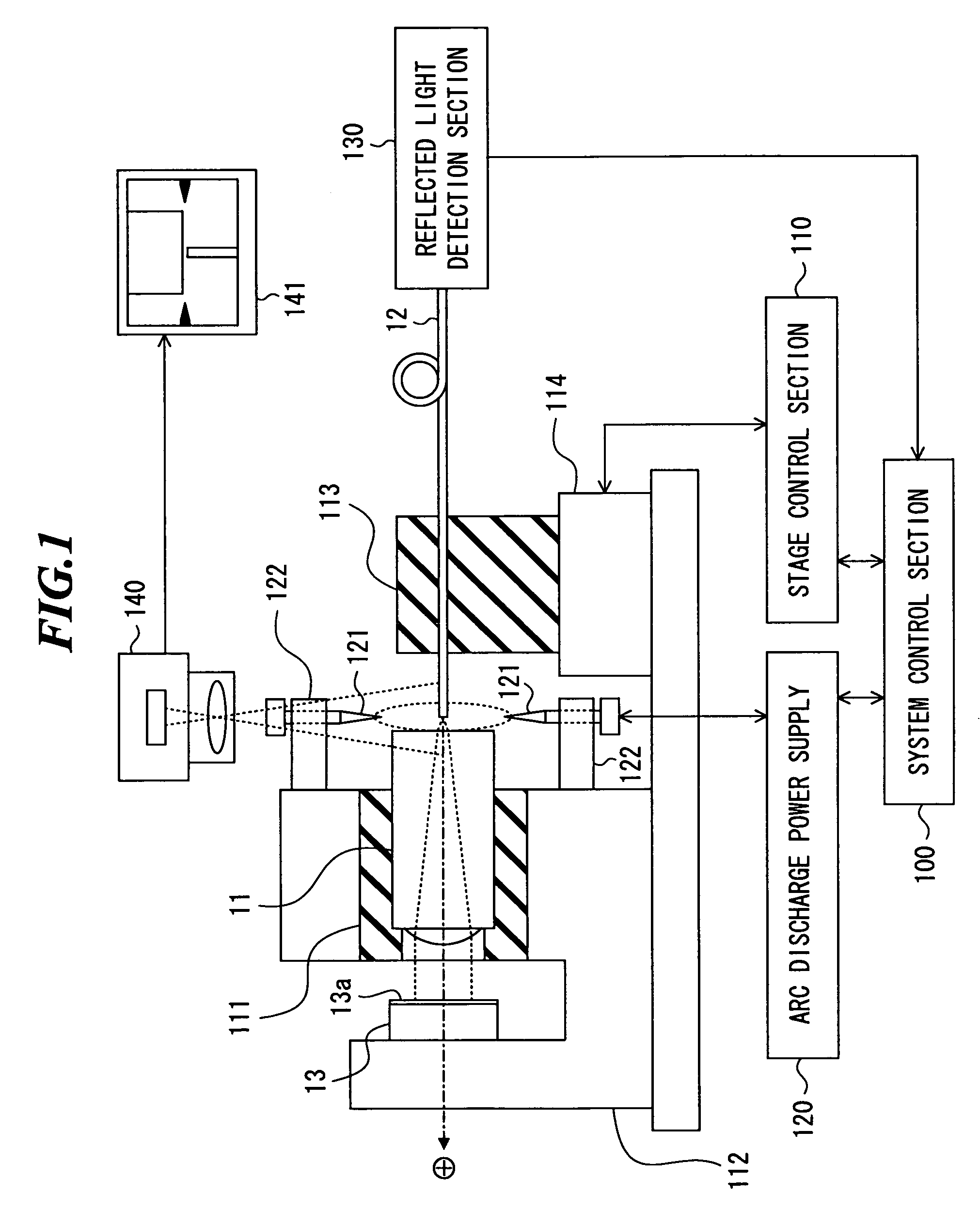
InactiveUS7400799B2High precision and reliabilitySimple processCoupling light guidesEngineeringJoint surface
An optical device fabrication method capable of fabricating optical devices with high precision and reliability in a simple process and at a low cost. The method of splicing a first optical device and a second optical device to fabricate a third optical device includes the steps of: (a) starting heating of an end surface of the first optical device to soften the end surface; (b) pushing the second optical device into the softened end surface to splice the first optical device and a joint surface of the second optical device to each other; (c) pulling back the second optical device to arrange the joint surface of the second optical device onto or outside of the end surface of the first optical device; and (d) terminating heating of the end surface to fix the first and second optical device spliced to each other.
Owner:PRECISE GAUCO
Planar gradient-index artificial dielectric lens and method for manufacture
InactiveUS8803738B2Easy to getLow propagation lossSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateRefractive index
A gradient index lens for electromagnetic radiation includes a dielectric substrate, a plurality of conducting patches supported by the dielectric substrate, the conducting patches preferably being generally square shaped and having an edge length, the edge length of the conducting patches varying with position on the dielectric substrate so as to provide a gradient index for the electromagnetic radiation. Examples include gradient index lenses for millimeter wave radiation, and use with antenna systems.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
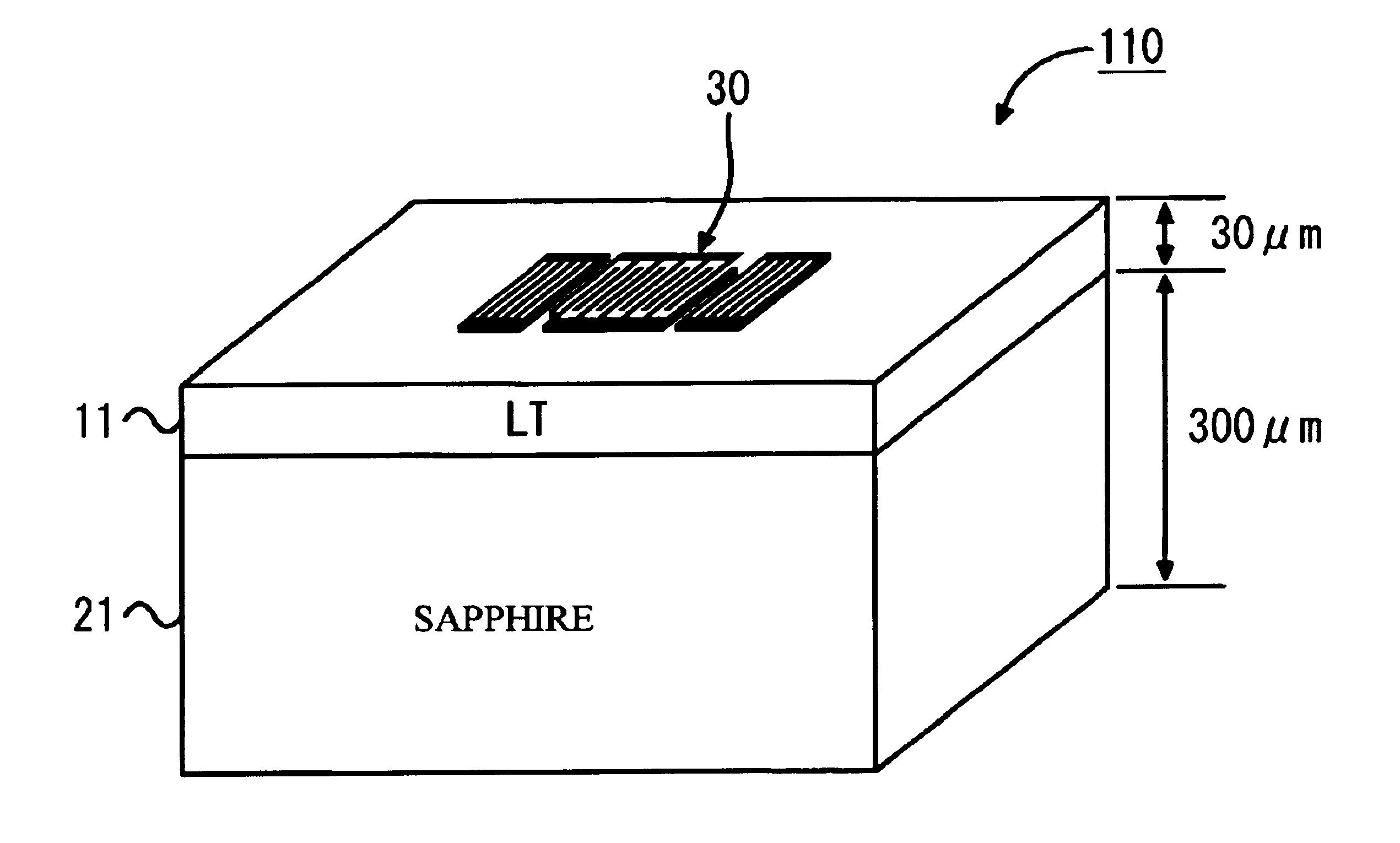
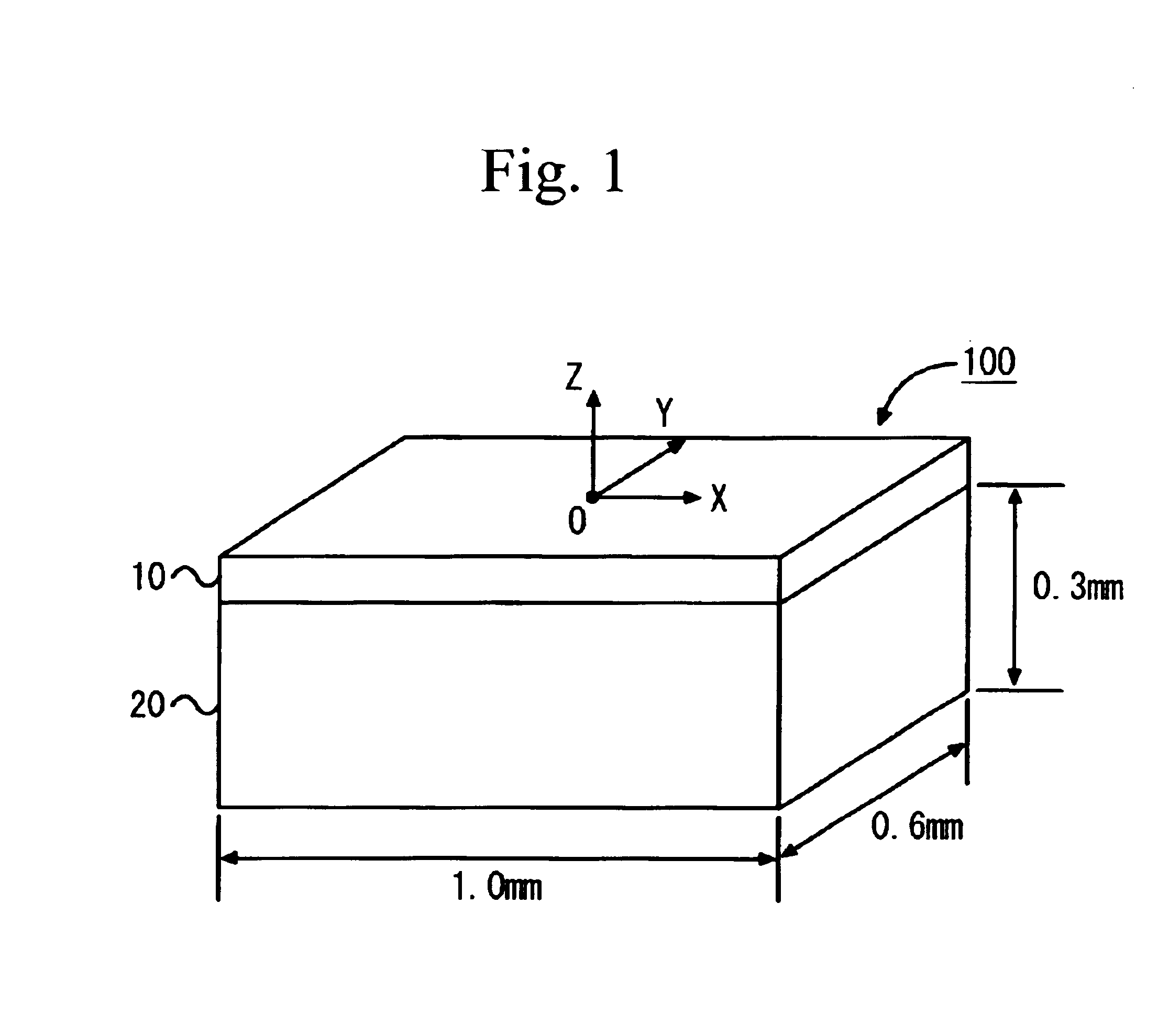
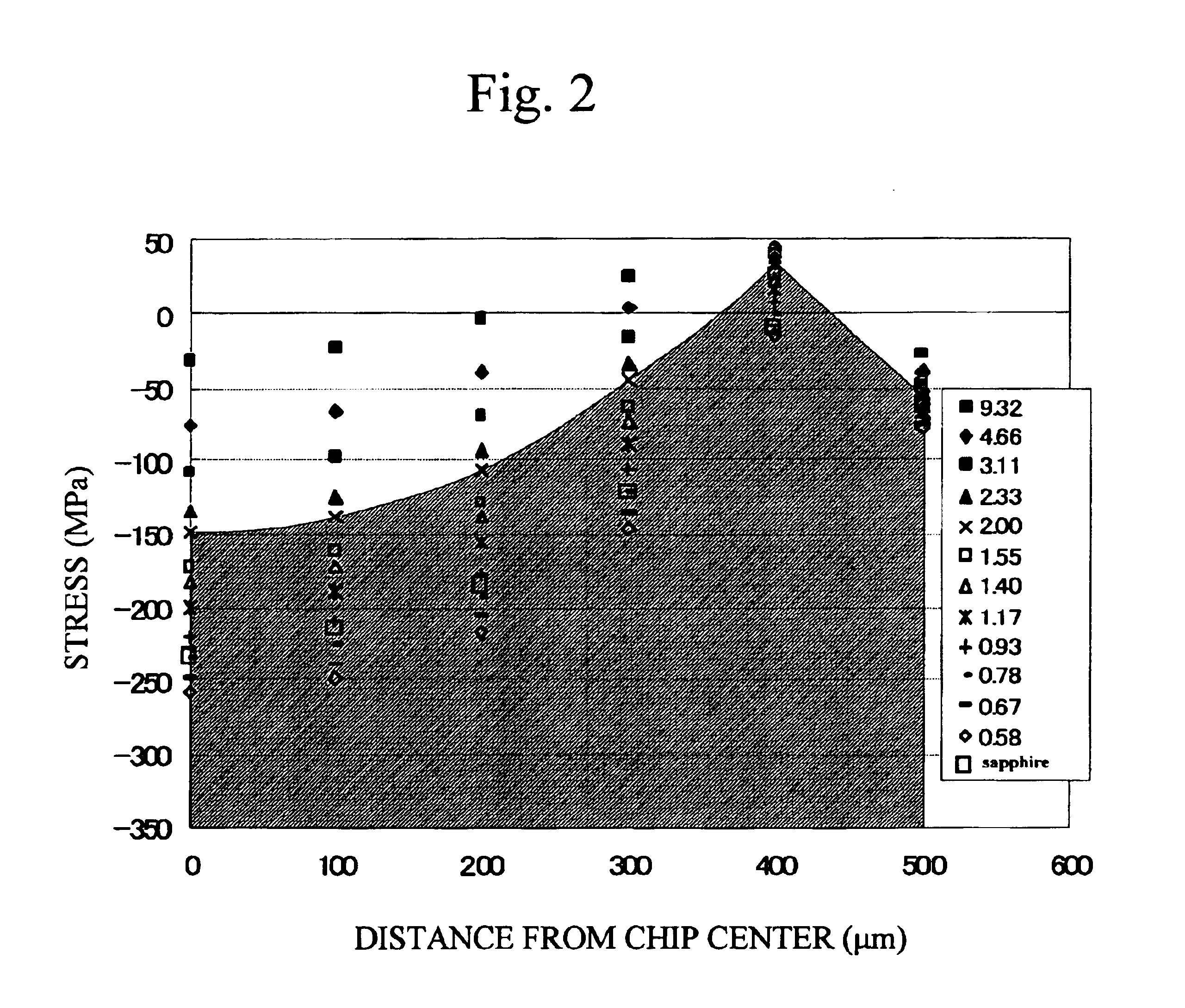
Surface acoustic wave device with lithium tantalate on a sapphire substrate and filter using the same
InactiveUS6933810B2Reduce frequency differenceImprove featuresImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLithiumAcoustic wave
A surface acoustic wave device includes a piezoelectric substrate having a first surface on which comb-like electrodes are formed, and a second surface, and a support substrate joined to the second surface of the piezoelectric substrate. The piezoelectric substrate is made of lithium, tantalate, and the support substrate is made of sapphire. The following expressions being satisfied:T / t<⅓ (1)T / λ>10 (2)where T is a thickness of the piezoelectric substrate, t is a thickness of the support substrate, and λ is a wavelength of a surface acoustic filter, propagated along the first surface of the piezoelectric substrate.
Owner:FUJITSU MEDIA DEVICES +1
Photonic bandgap fiber
ActiveUS20090207485A1Suppressing propagation of lightAccelerate emissionsLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
A photonic bandgap fiber includes a core and a cladding that surrounds the core. In this photonic bandgap fiber, high refractive index portions which have a refractive index higher than that of a medium of the cladding are provided in the cladding so as to form a triangular lattice structure with a lattice constant Λ, and the refractive index of the core is higher than the refractive index of the medium of the cladding and lower than the refractive index of the high refractive index portion. The coupling length between the core and the high refractive index portion that is closest to the core is longer than the coupling length between adjacent high refractive index portions, or a periodic structure formed by the high refractive index portions is not provided around the entirely of the area along the circumference of the core.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
High-frequency line structure on resin substrate and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100308941A1Reduced propagation lossMultiple-port networksWaveguidesEngineeringLine structure
A high-frequency line structure includes a multi-layered resin substrate in which insulating layers of a resin are laminated. A high-frequency-signal input part is arranged on the resin substrate to input a high-frequency signal and supply the high-frequency signal to the resin substrate. A high-frequency-signal output part is arranged in the resin substrate to receive the high-frequency signal from the input part and output the received high-frequency signal. A first metal layer is arranged to encircle the input and output pads and electrically insulated from the input and output parts. A second metal layer is arranged on the resin substrate. A plurality of penetration vias are arranged in the resin substrate to encircle the input part and the output part, and each penetration via being connected to the first and second metal layers.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Heat-assisted recording head and heat-assisted recording device
InactiveUS8406094B2Reduced propagation lossCombination recordingArm with optical waveguideTransducerWaveguide
In a thermally assisted recording head using a conductive scatterer as an optical near-field transducer, a propagation loss in a waveguide for guiding light to the scatterer is reduced. An optical near-field is generated by using the conductive scatterer having a width that gradually becomes smaller toward a vertex at which the optical near-field is generated. At the same time, a height of the conductive scatterer for generating the optical near-field is made substantially equal to a height of a main pole or longer than the height of the main pole.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
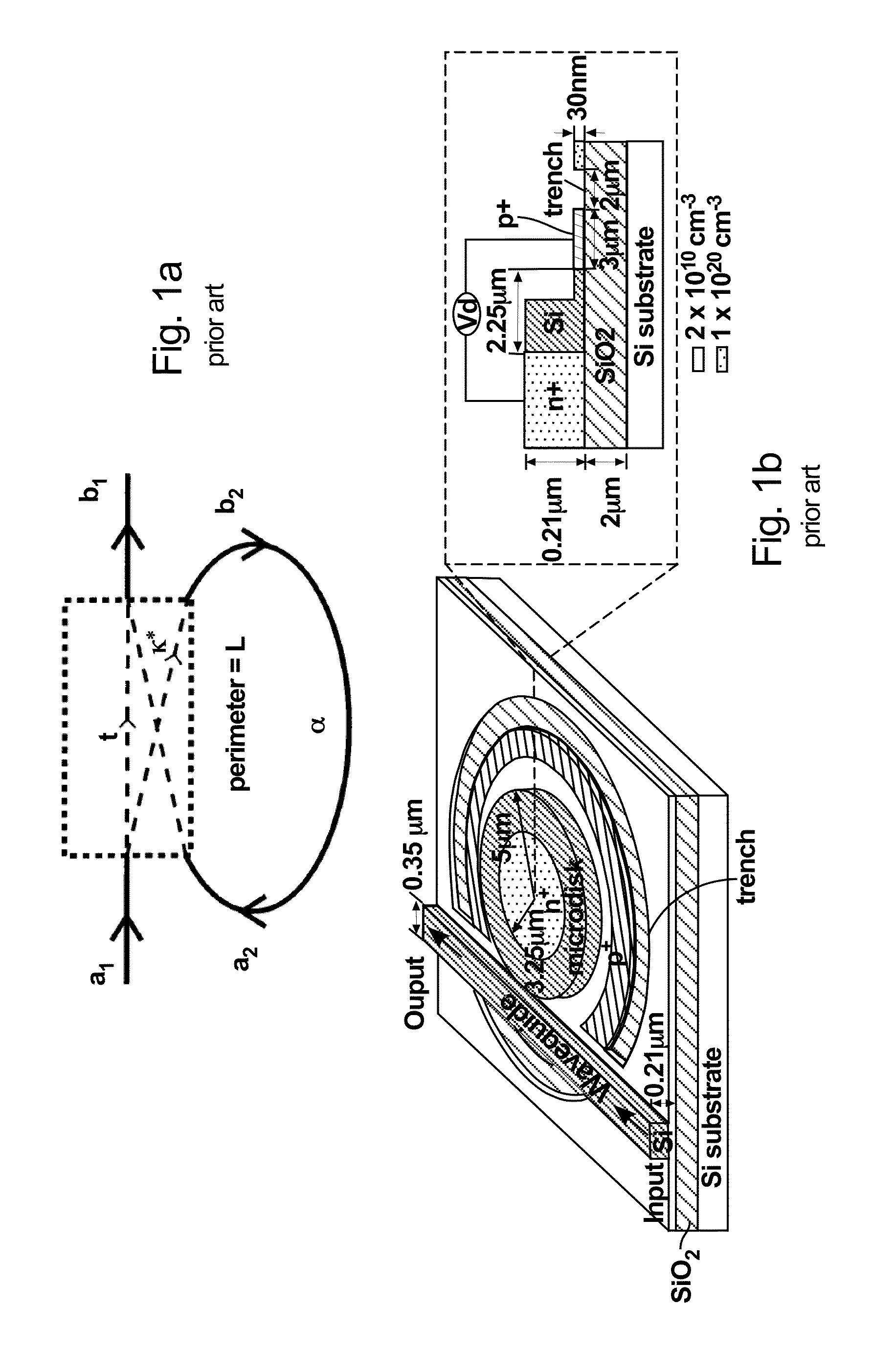
Low loss microring resonator device
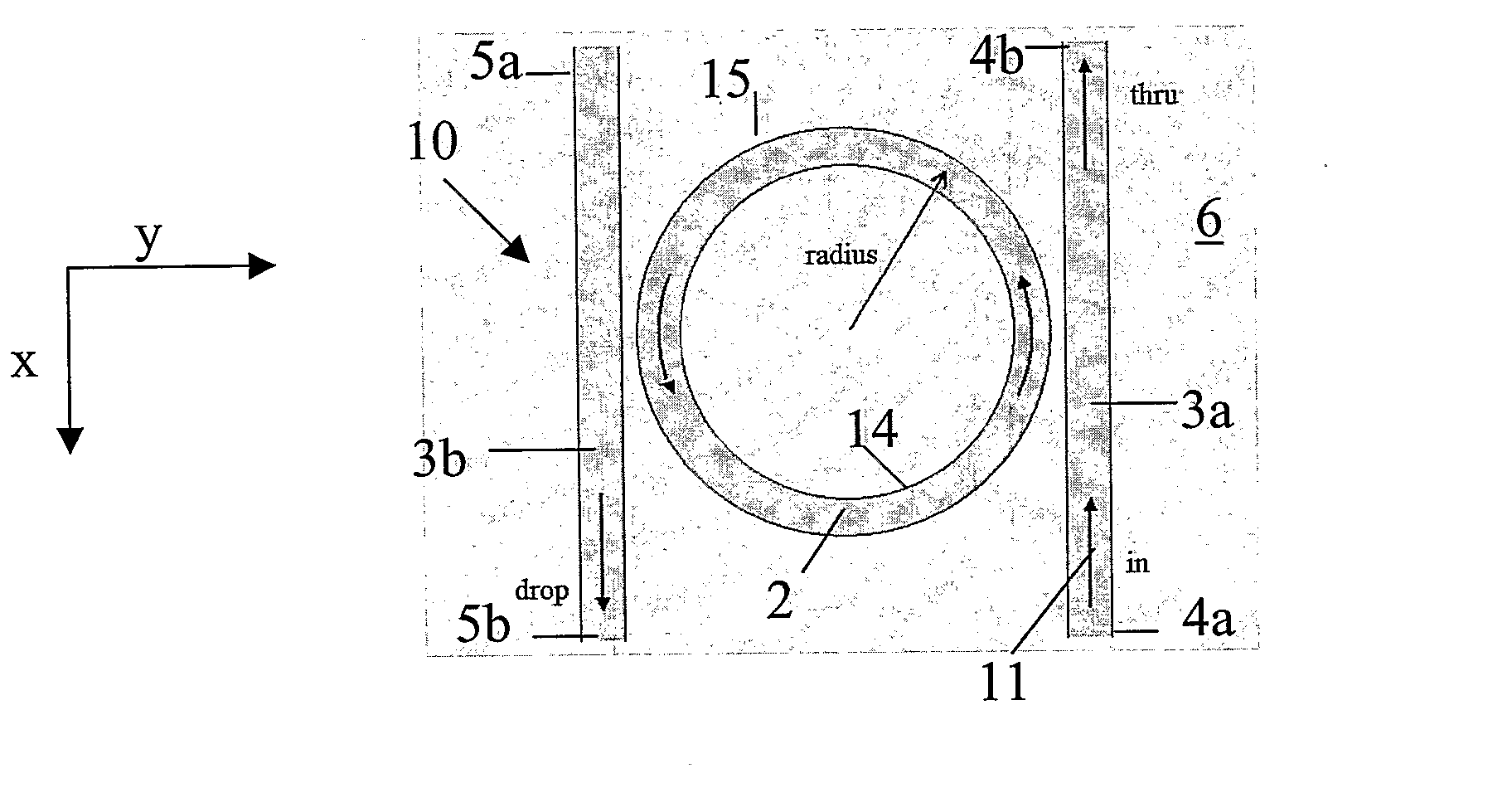
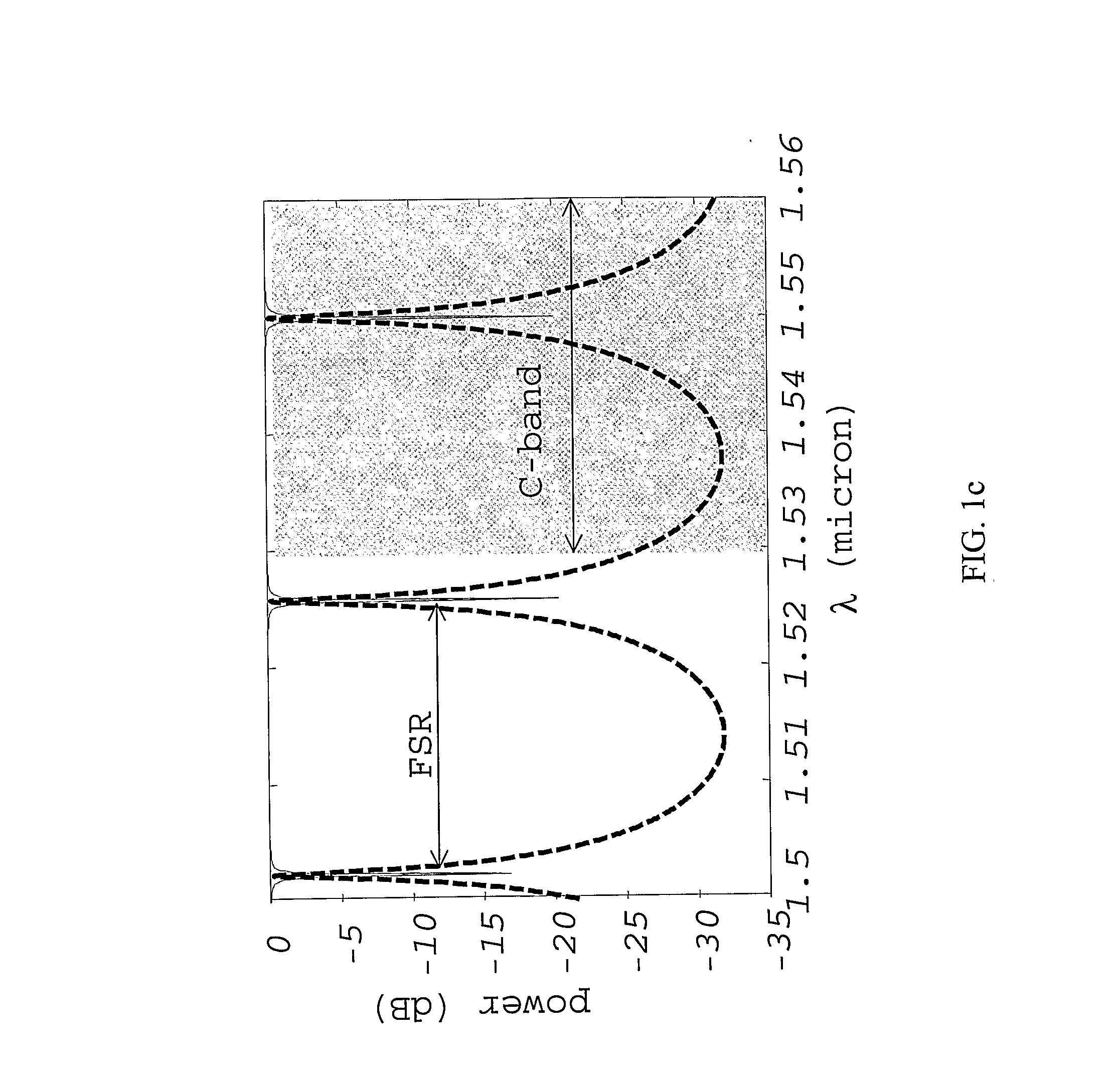
InactiveUS20070071394A1Reduced propagation lossMinimizing propagation lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexClosed loop
A low loss micro-ring resonator device which has a closed-loop resonator waveguide having a first refractive index, the resonator waveguide defining an inner and an outer region by an outer curved edge of the waveguide. The resonator waveguide is arranged on a substrate having a second refractive index, the refractive index difference between the first refractive index and the second refractive index is greater than 0.3. The device also has an upper cladding covering the inner region of the resonator waveguide having a third refractive index and a lateral cladding in contact with the outer curved edge and extending in the outer region, the lateral cladding having a fourth refractive index, the fourth refractive index being lower than the third refractive index. A method for reducing propagation losses of a resonator device is also described.
Owner:PIRELLI & C
Spst Switch, Spdt Switch and Mpmt Switch
InactiveUS20080238570A1Reduced propagation lossAvoid attenuationElectronic switchingCoupling devicesInductorCapacitor
A single pole single throw switch for controlling propagation of a high frequency signal between an input terminal (11a) and an output terminal (11b). First FET switches (14a, 14b) in which drains and sources of FETs (12a, 12b) are connected in parallel with inductors (13a, 13b) are connected in parallel. Each FET (12a, 12b) is switched between on state and off state by a voltage being applied to the gate thereof. At the frequency of the high frequency signal, each inductor (13a, 13b) connected with off capacitor of each FET (12a, 12b) resonates in parallel.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com